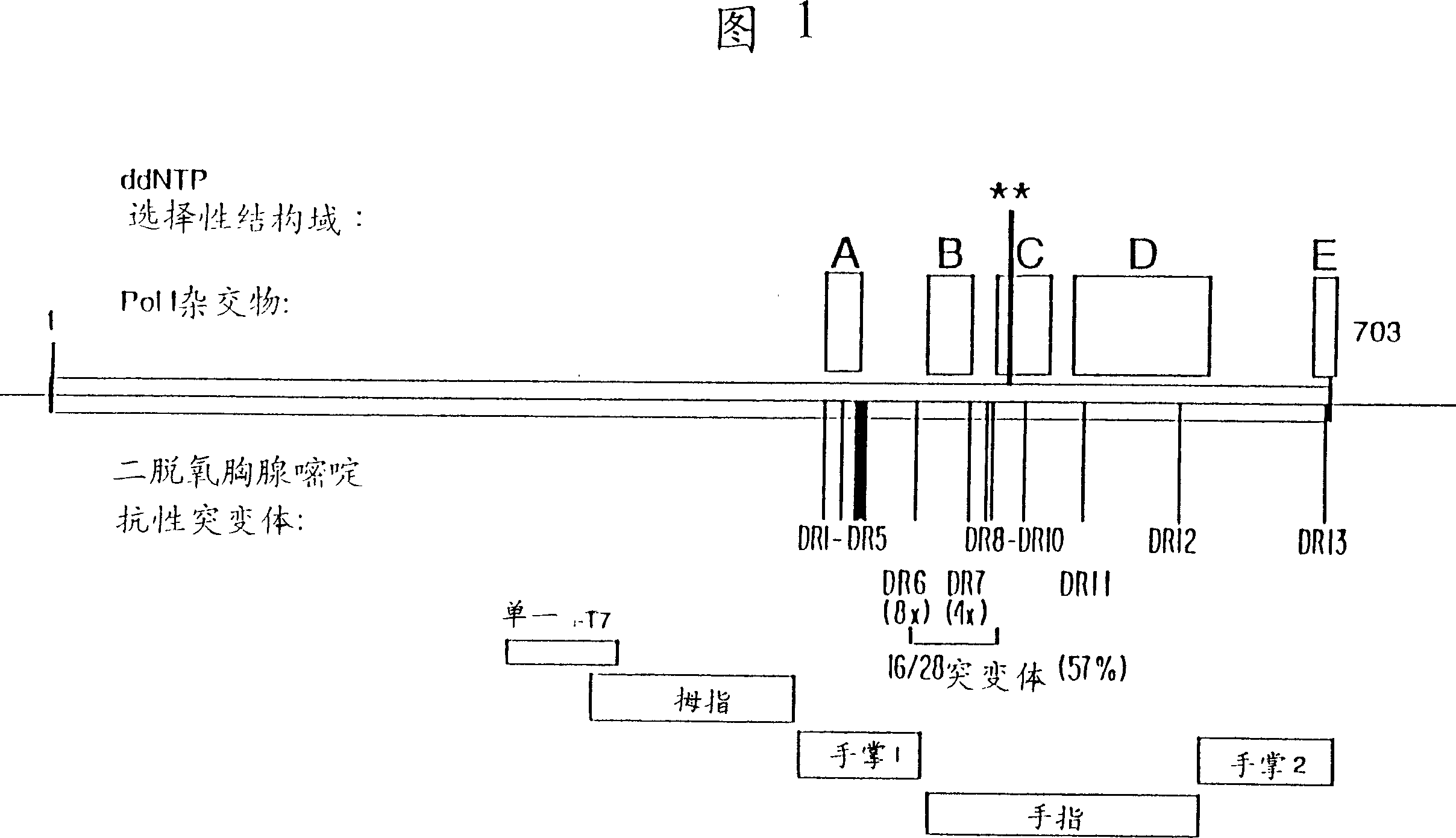
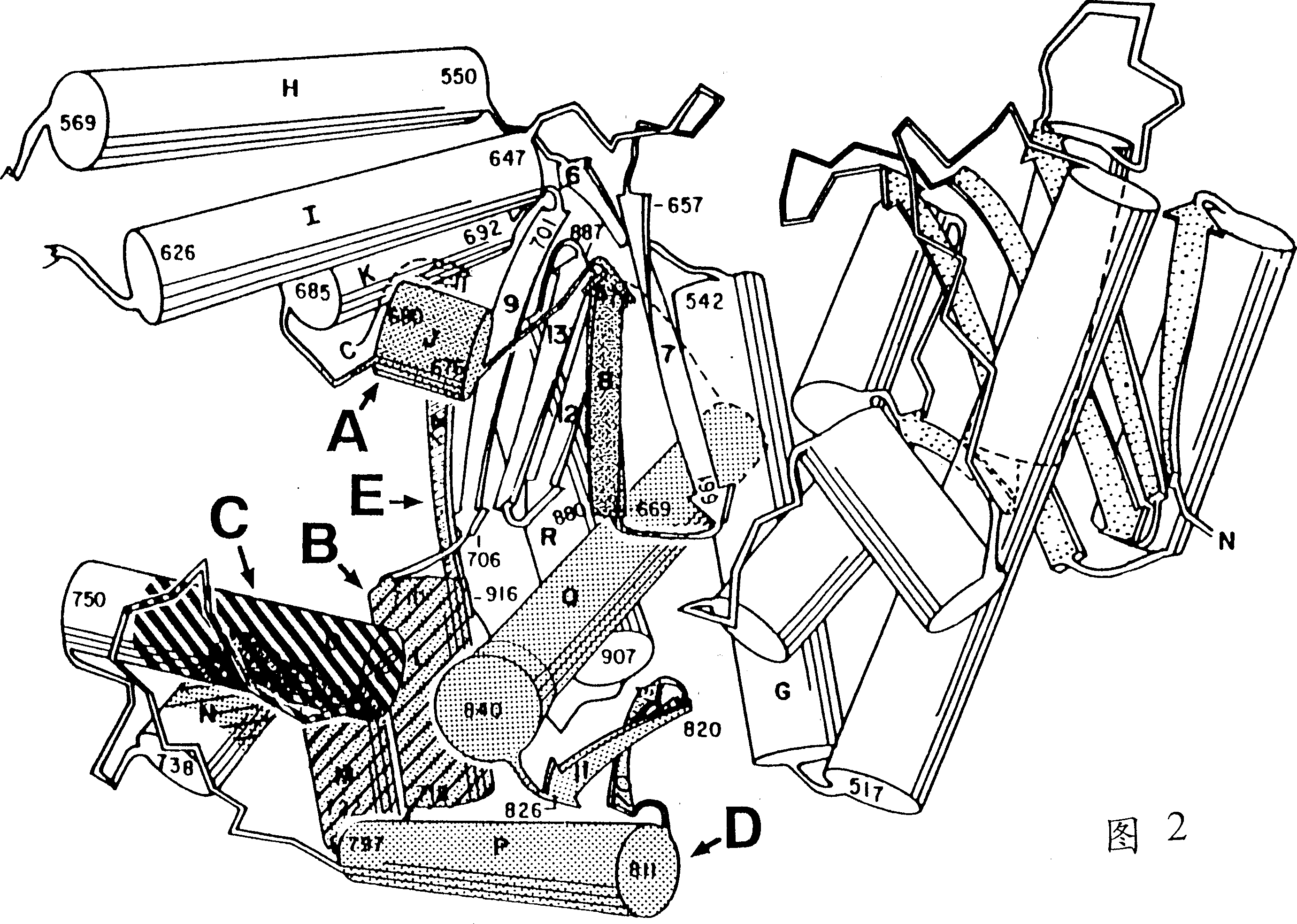
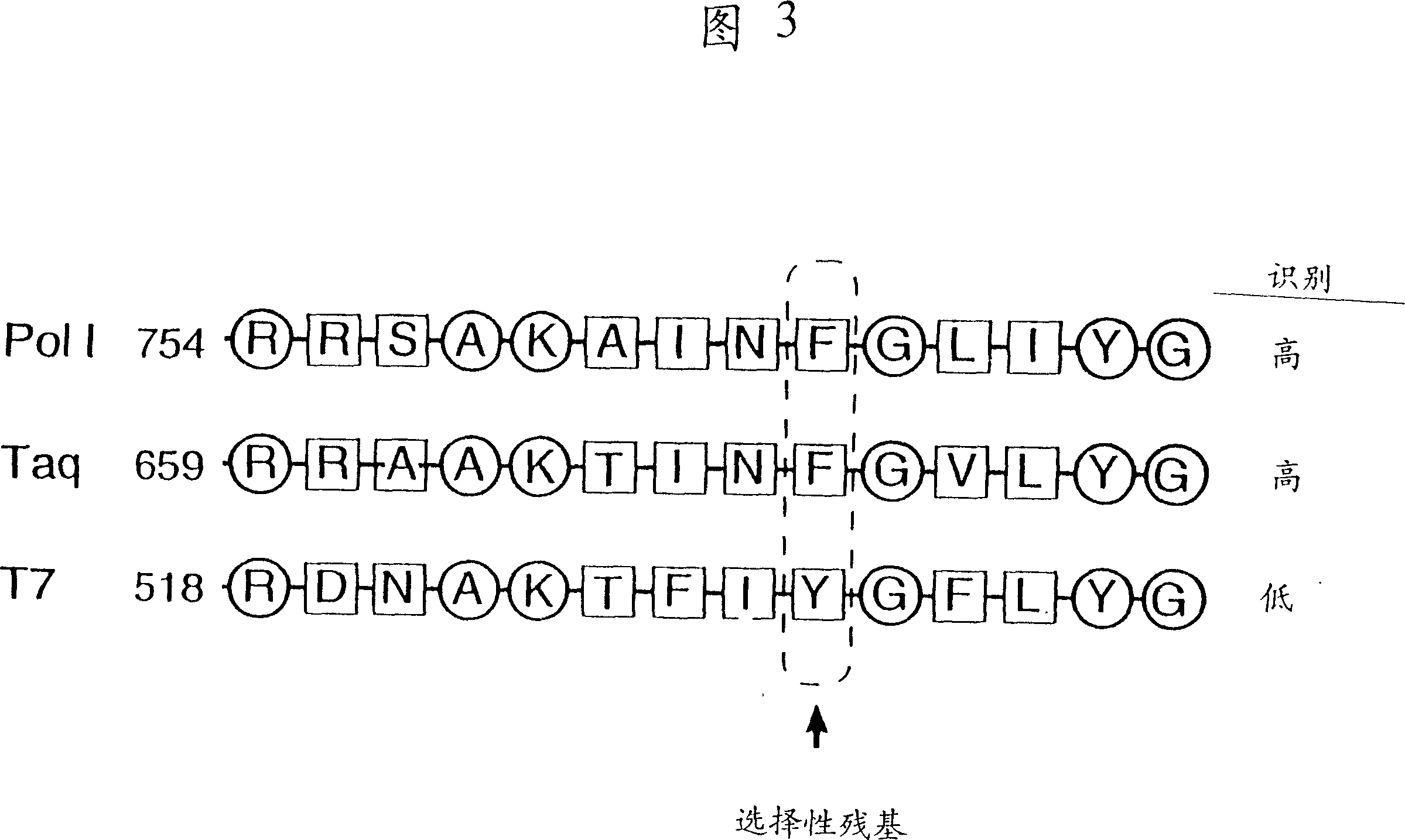
DNA polymerases having modified nucleotide binding site for DNA sequencing
A technology of polymerase and DNA molecules, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the accuracy of DNA sequences, reducing sensitivity, and difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1D
[0222] Mutagenesis and Mutants of Example 1 DNA Polymerase Gene
[0223] Overproduction of DNA polymerase
[0224] The mutant DNA polymerase gene is cloned and expressed using standard techniques. Starting material for generating mutants of E. coli DNA polymerase I and Taq DNA polymerase - encoding a large fragment of E. coli DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment) and a large fragment of Taq DNA polymerase (KlenTaq or Taq DNA polymerase, See Barnes 112 Gene 29, 1992 or Stoffel Fragment, see Lawyer et al. 2 PCR Methods Applied 275, 1993) the gene is expressed under the control of the T7 RNA polymerase promoter. Starting material for generation of mutants of T7 DNA polymerase - the gene encoding the 28 amino acid deletion of T7 DNA polymerase (see Tabor and Richardson, 264 J. Biol. Chem. 6447, 1989) is essential for the production of T7 DNA polymerase for sustained DNA synthesis. The factor E. coli thioredoxin (Tabor and Richardson, supra) was expressed under the control of...
Embodiment 2
[0227] Example 2 Quickly screen out the efficiency of incorporation of dideoxynucleotides from DNA polymerase
[0228] Mutants with increased efficiency of incorporation of deoxynucleotides
[0229] The mutant DNA polymerases were screened for their ability to incorporate dideoxynucleotides by SDS activity gel assay. This procedure is a modification of the method described in Spanos and Hübscher 91 Enzymology and Karawya et al 135 Analytical Biochem 318,1983. Briefly, 10 ml of cells were induced for 4 to 6 hours and then pelleted. Cell pellets were resuspended in 0.3ml 25mM Tris Hcl, pH7.0, 5mM EDTA. Mix 20μl of resuspended cells with 40μl of 1% SDS (sodium dodecylsulfonate), 2% mercaptoethanol, 30% glycerol, 0.04 % bromophenol blue and 100 mM Tris HCl, pH 6.8 solution were mixed. The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 5 minutes, and two 20 μl aliquots were applied to two SDS polyacrylamide gels. The separation gel of SDS polyacrylamide contains 8% polyacrylamide, 0.27...
Embodiment 3
[0236] Example 3 Single-stranded M13 DNA-5' 32 P-labeled 40mer
[0237] Preparation and purification of primer complexes
[0238] The template was 9950 nucleotides long M13 mGP1-2 single-stranded DNA as described in US Patent 4,795,699 (Figure 9). The deposit number of phage M13 mGP1-2 in ATCC is 40303. M13 mGP1-2 single-stranded DNA was purified as described by Tabor et al. 262 J Biol Chem., 16212, 1987 . Briefly, phage were purified by twice CsCl gradient centrifugation, dialyzed to remove CsCl, and DNA (human phage) was extracted with phenol:chloroform and 0.1% sodium dodecylsulfate. HCl, pH 7.5, dialyzed fully with 2mM EDTA, store at 4°C. Determine the concentration of M13 mGP1-2 single-stranded DNA with a photometer, the extinction coefficient is 8.1, and the A260 unit is equal to 1 mg / ml or 0.3 pmol per microliter M13 mGP1-2 template molecular.
[0239] The primer was a 40-mer synthesized by standard methods with the sequence 5'd(TTTTCCCAGTCACGACGTTGTAAAACGAC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com