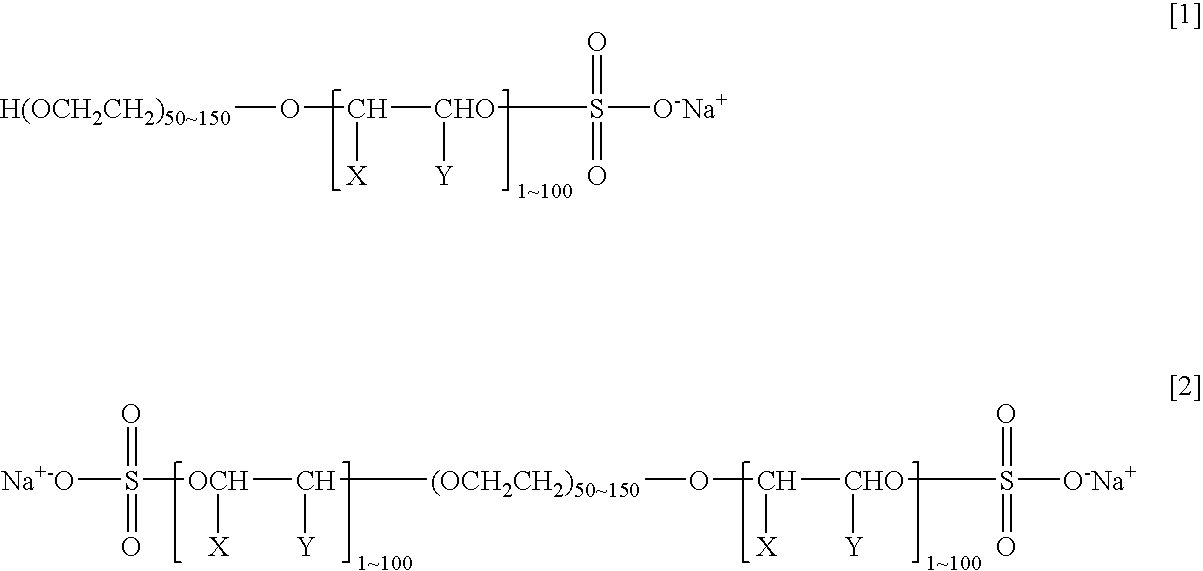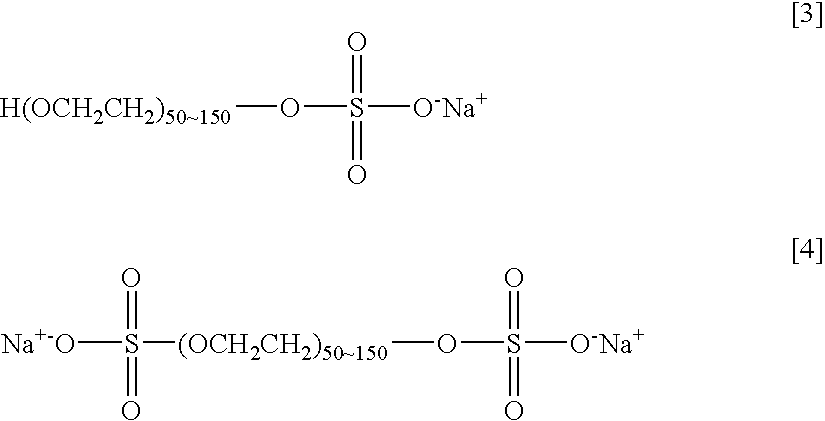Patents
Literature
93results about How to "Increased reject" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
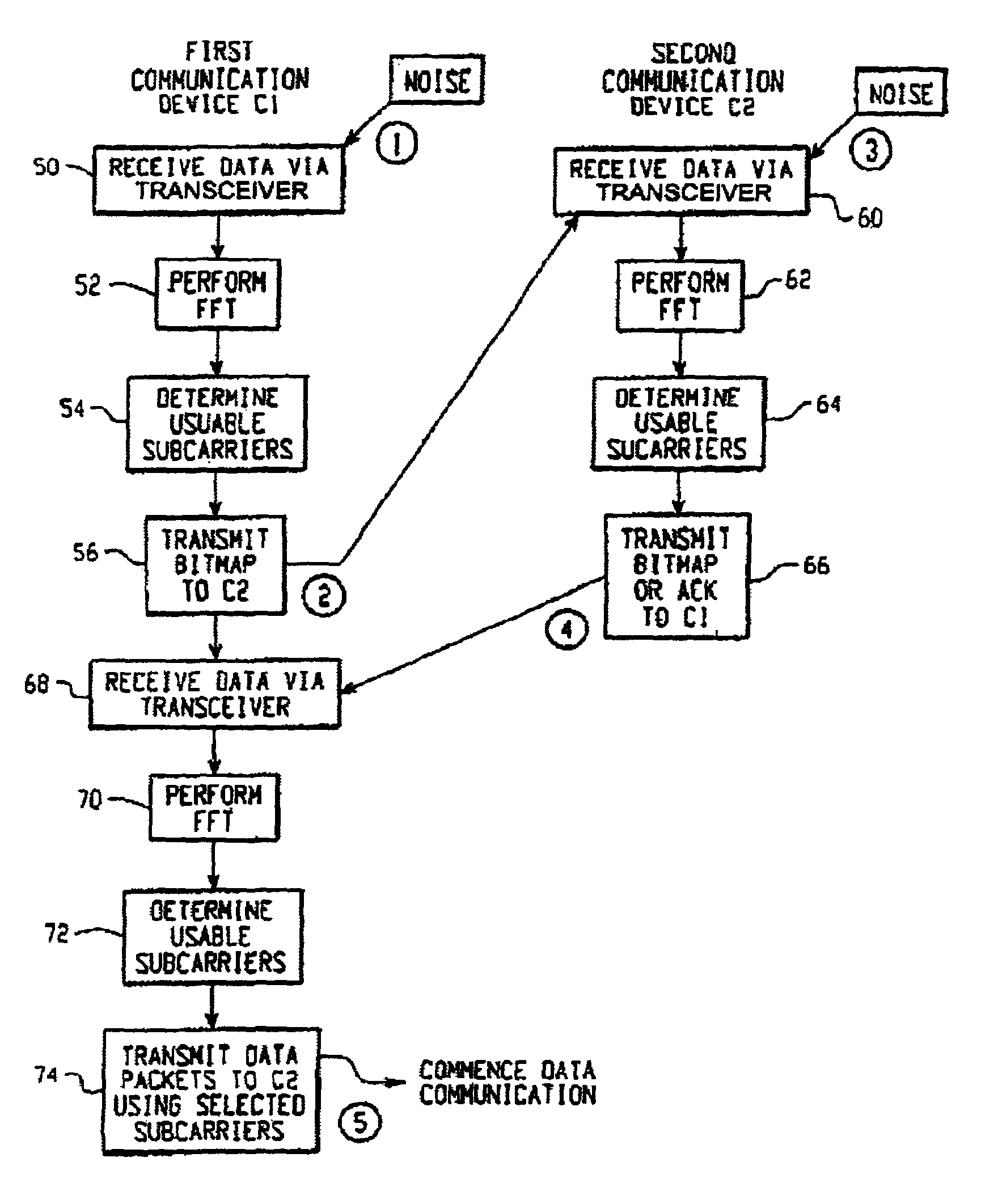
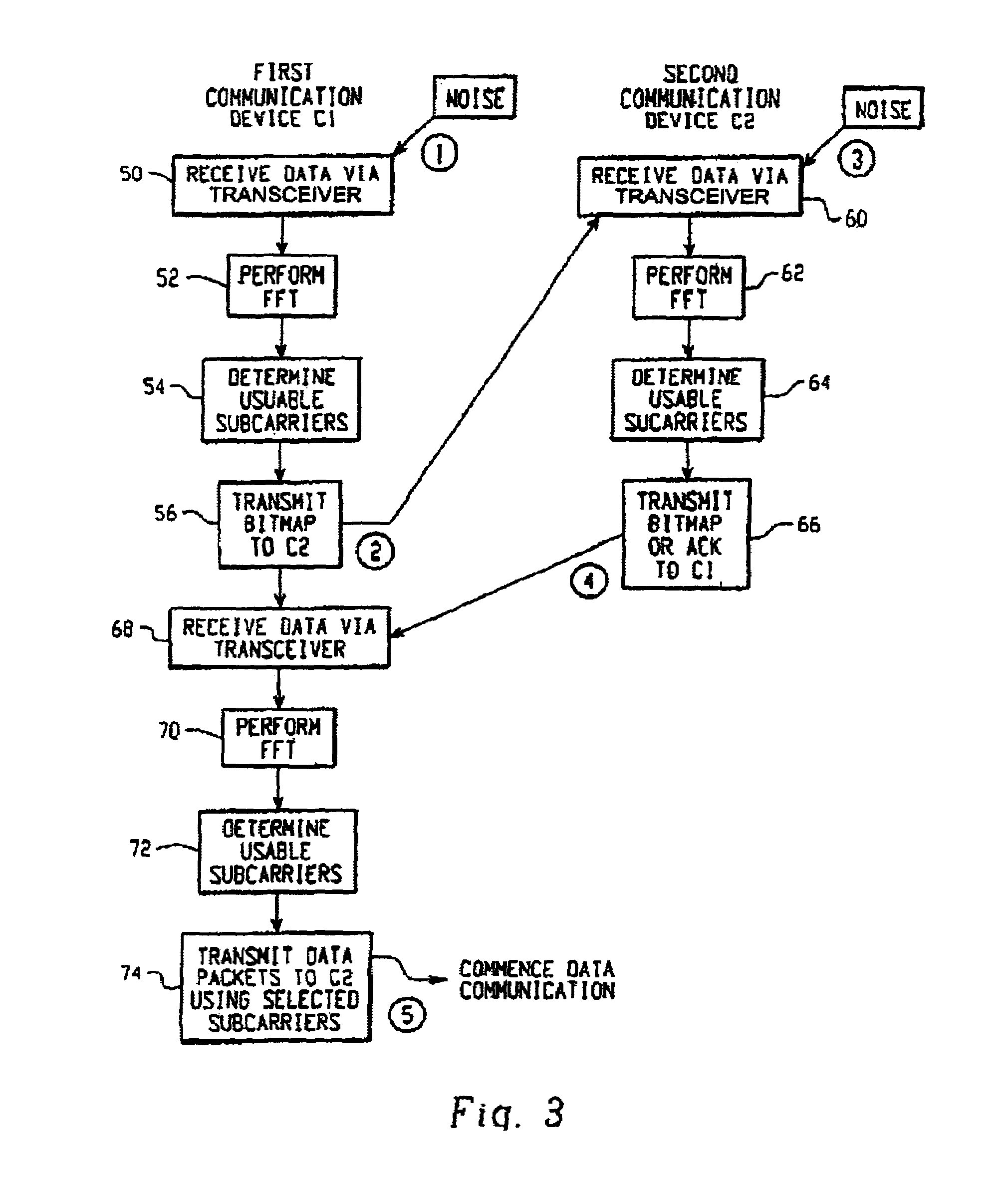
Adaptive control system for interference rejections in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS6934340B1Improved interference rejectionImprove robustnessSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemControl system
An adaptive control system for controlling the effects of narrow to medium bandwidth interferers in a wireless communications system (e.g., wireless LAN devices) by identifying which sub-carriers in a multi-carrier system are located on frequencies that are subject to interfering signals, and using only those sub-carriers that are not subject to interference for communications between wireless communications devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
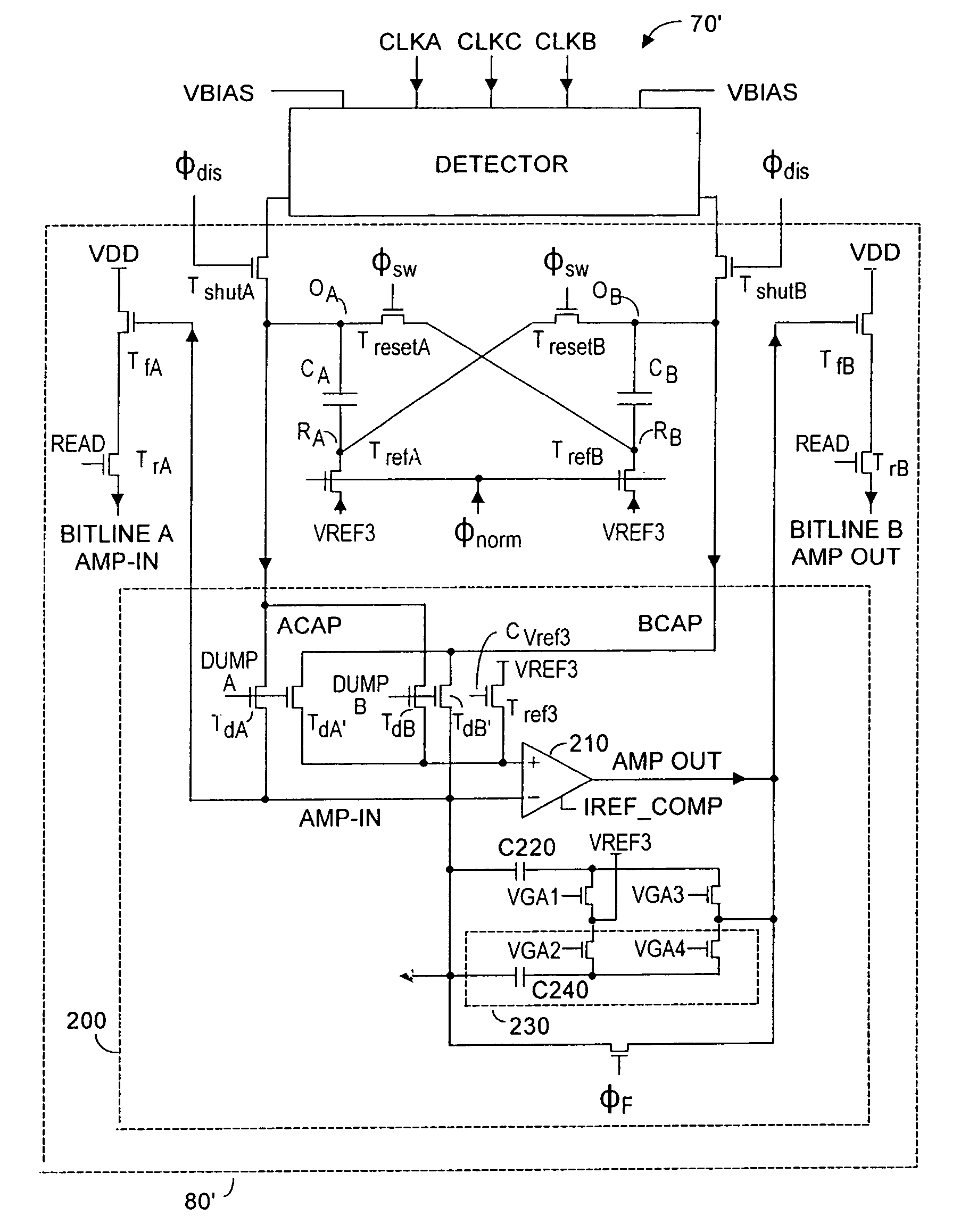
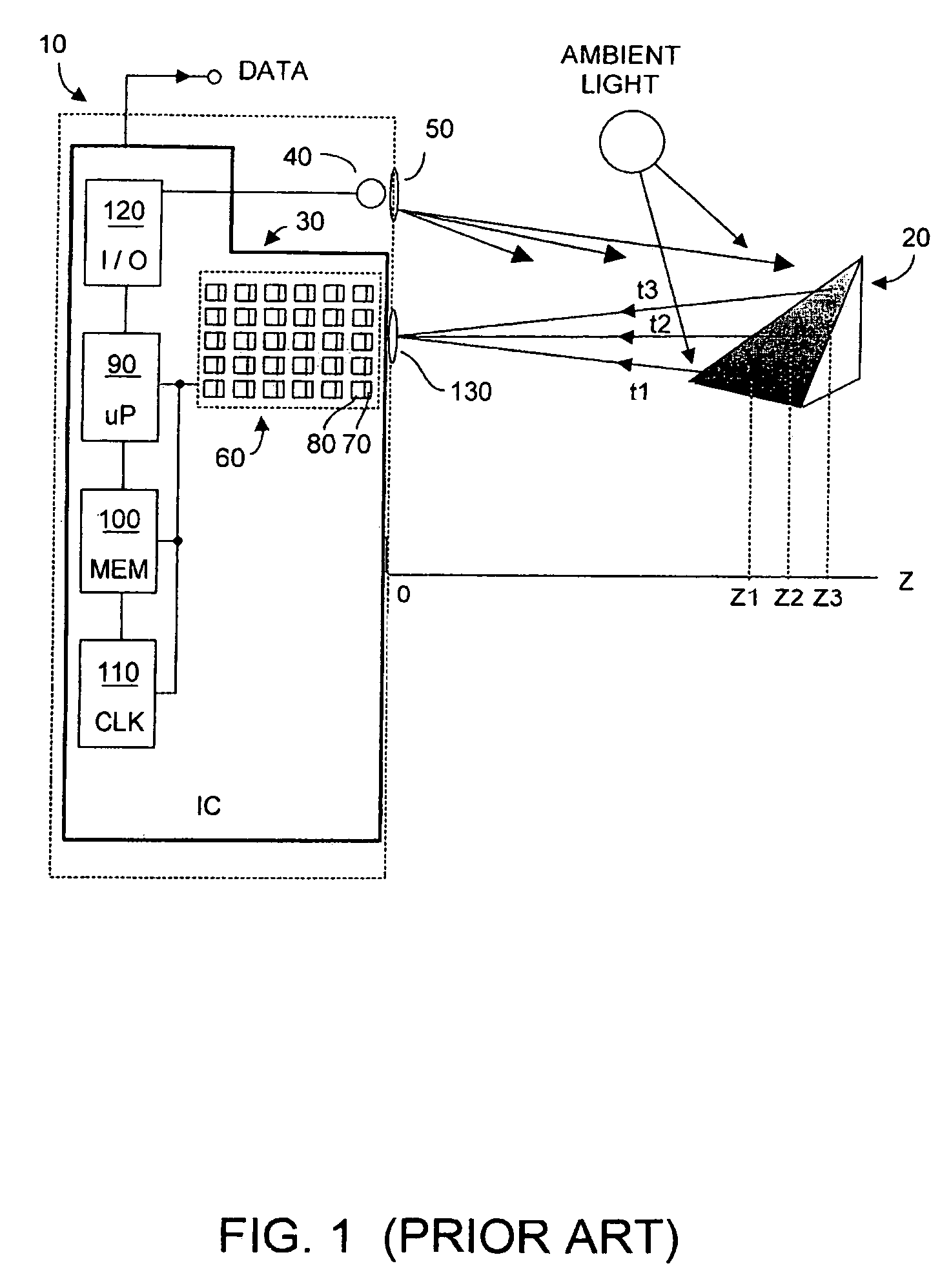
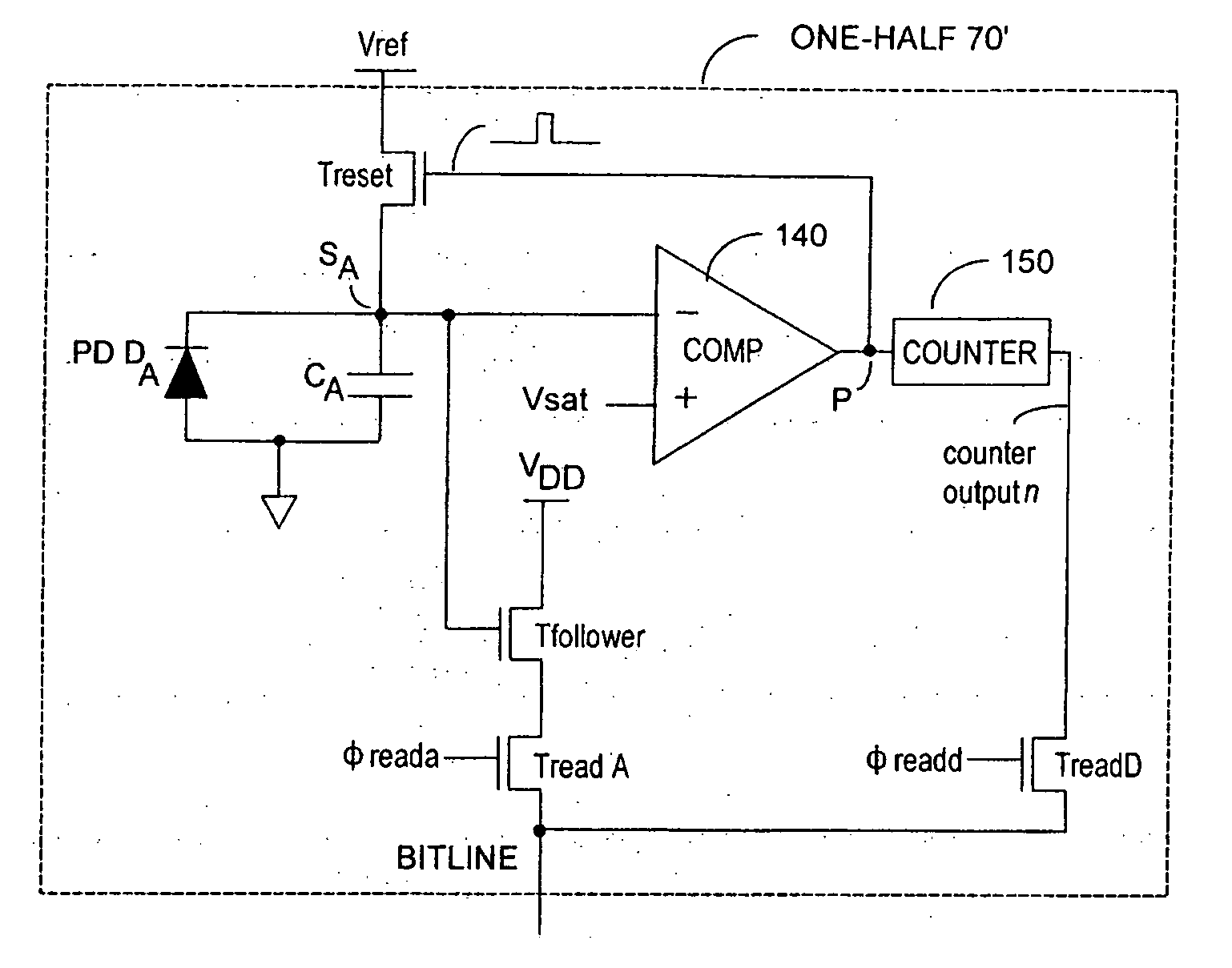
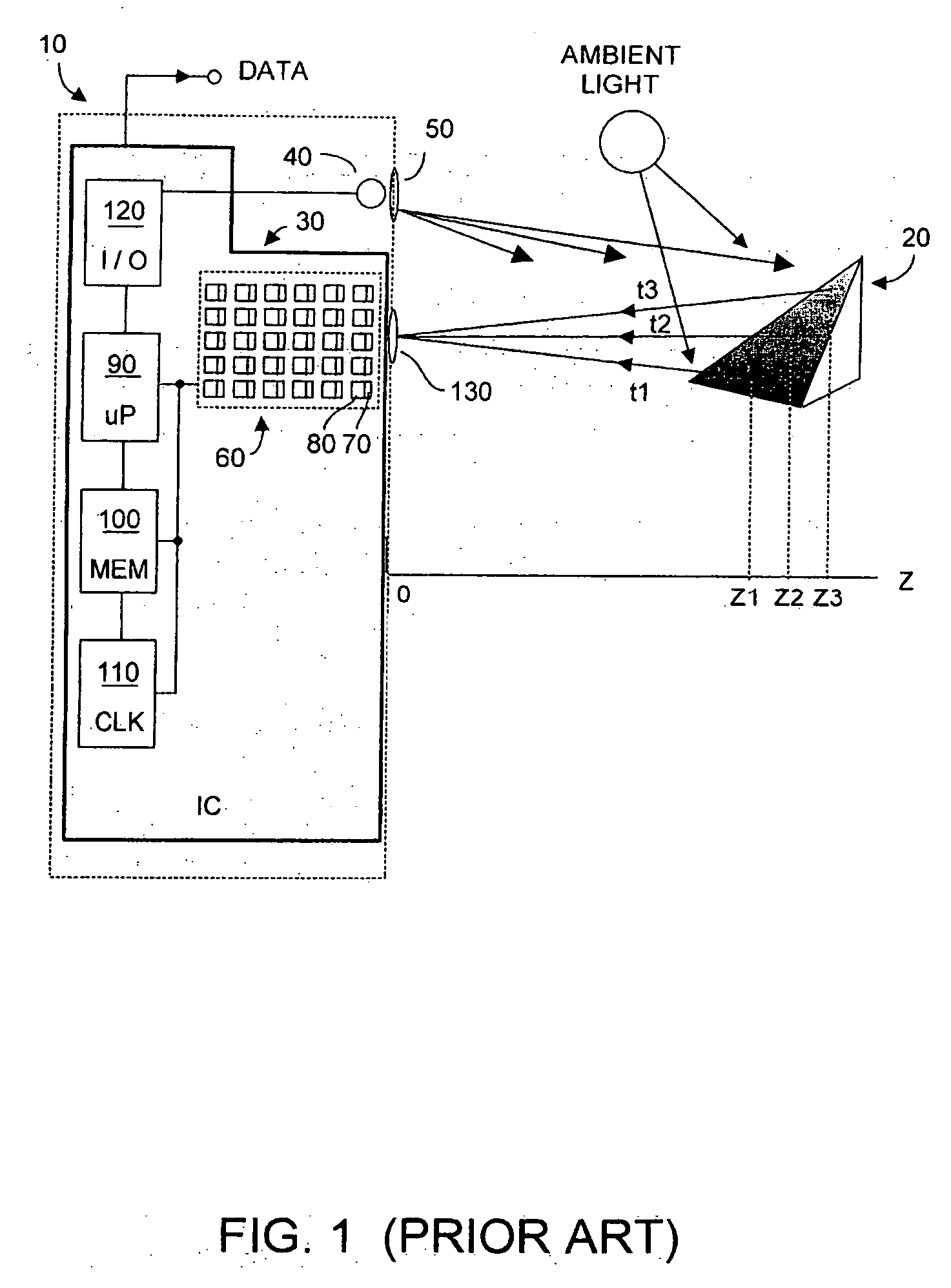
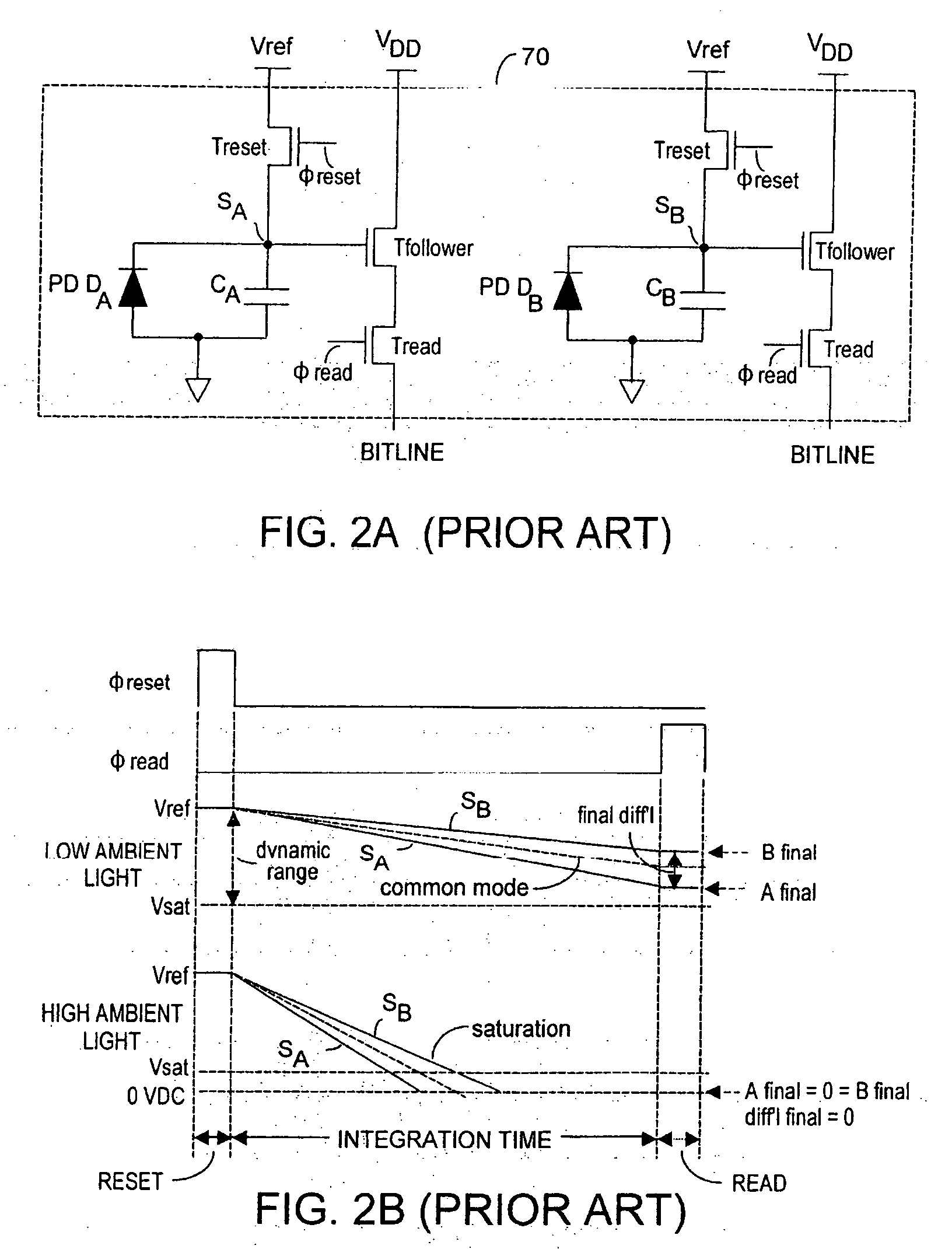
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range using enhanced common mode reset
ActiveUS7176438B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotodetector
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
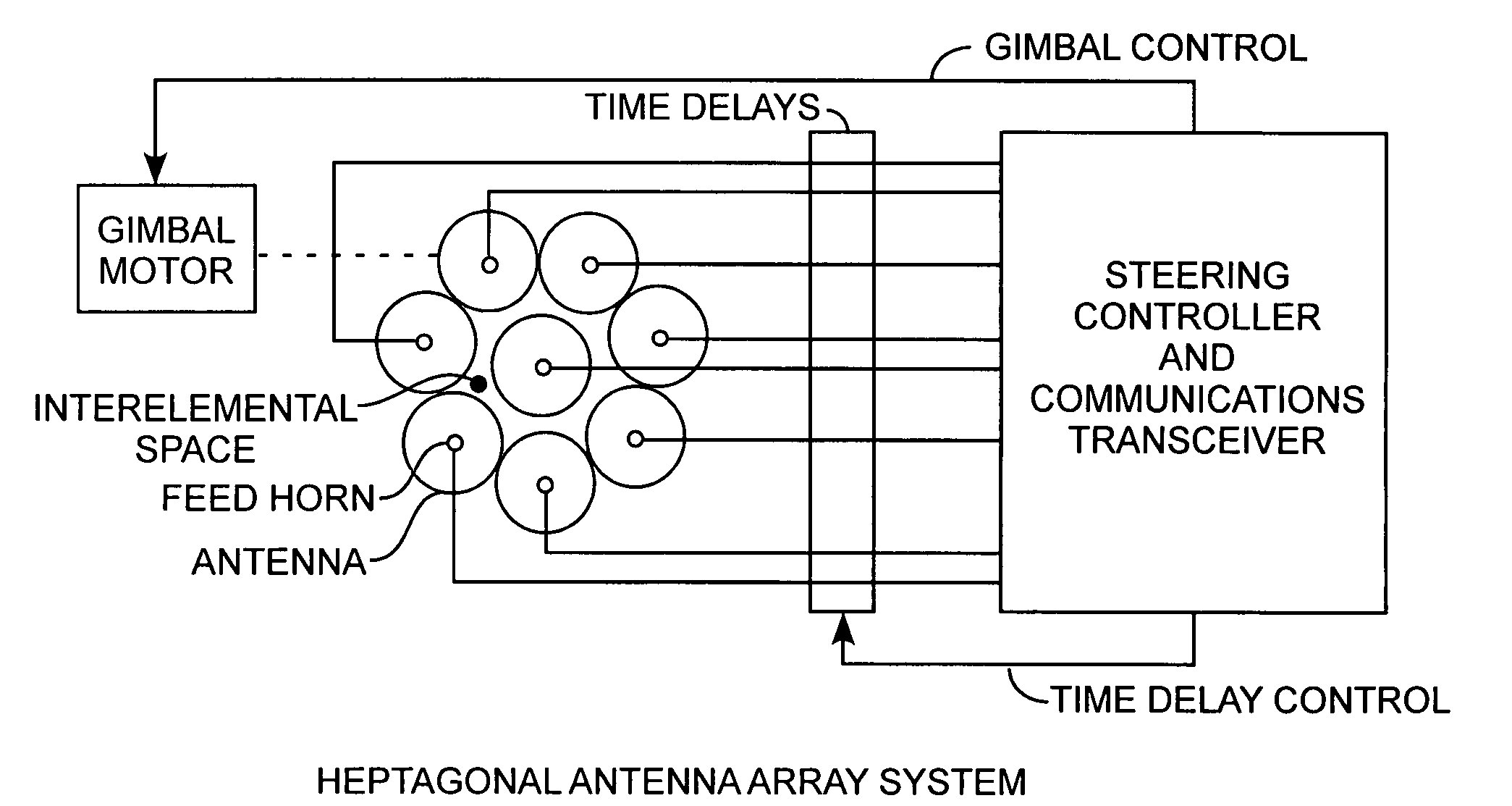
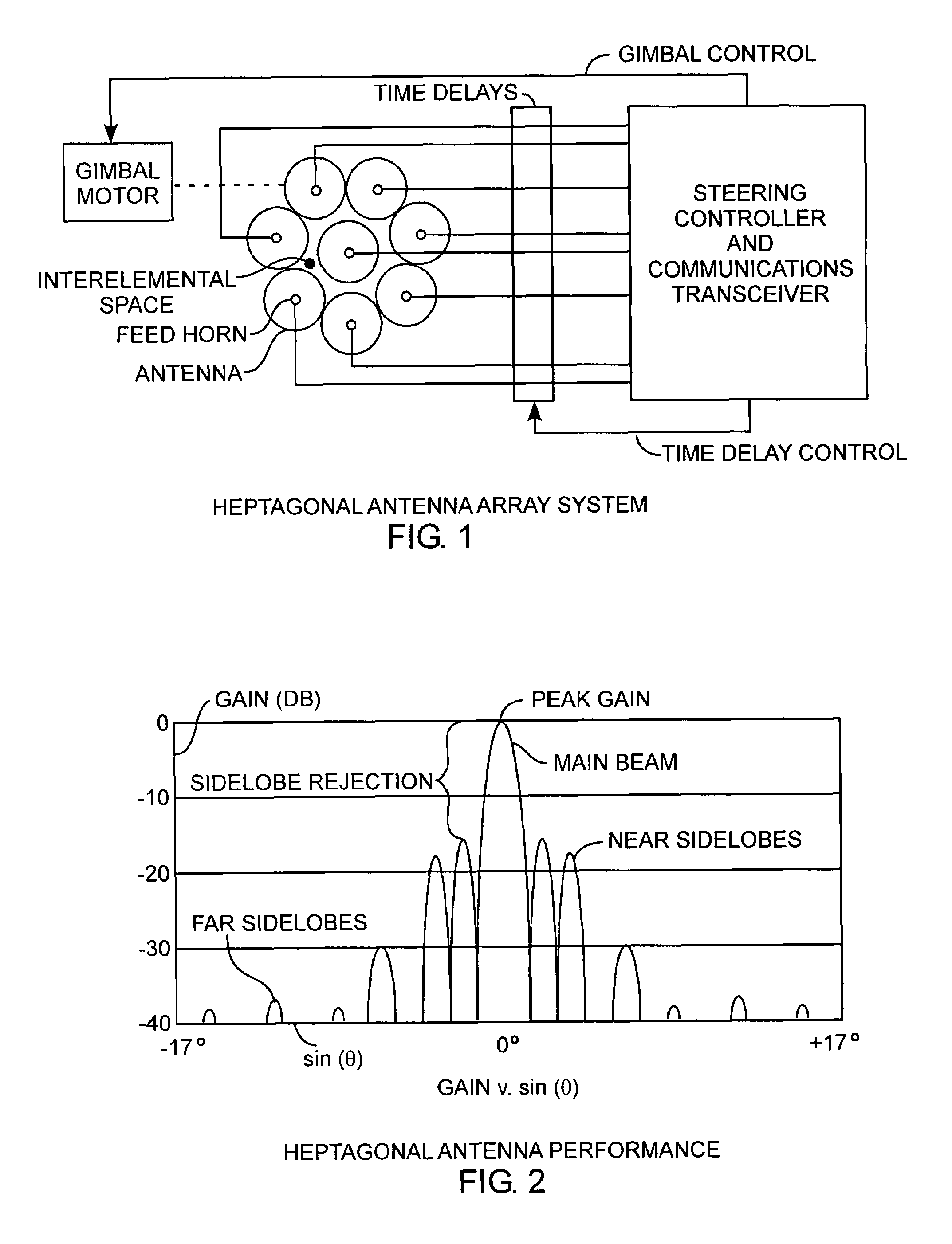
Heptagonal antenna array system
InactiveUS7710346B2Increased sidelobe rejectionIncreased rejectIndividually energised antenna arraysTime delaysSide lobe
An antenna system includes a heptagonal antenna array having one center antenna element and seven circumferentially surrounding antenna elements offering improved near and far sidelobe rejection, which is well suited for mechanically-gimbaled and time delayed electrical steering antenna applications.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
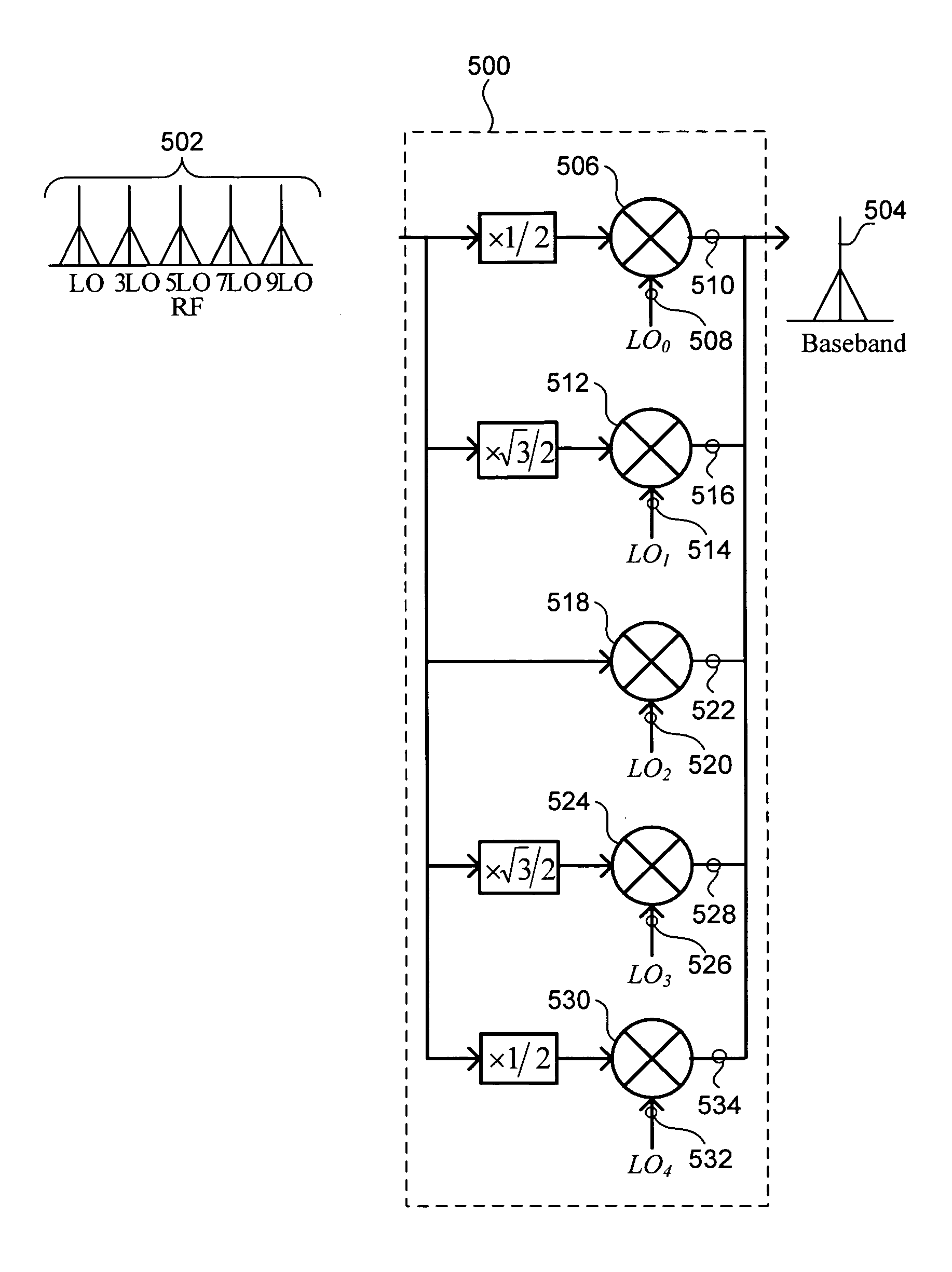
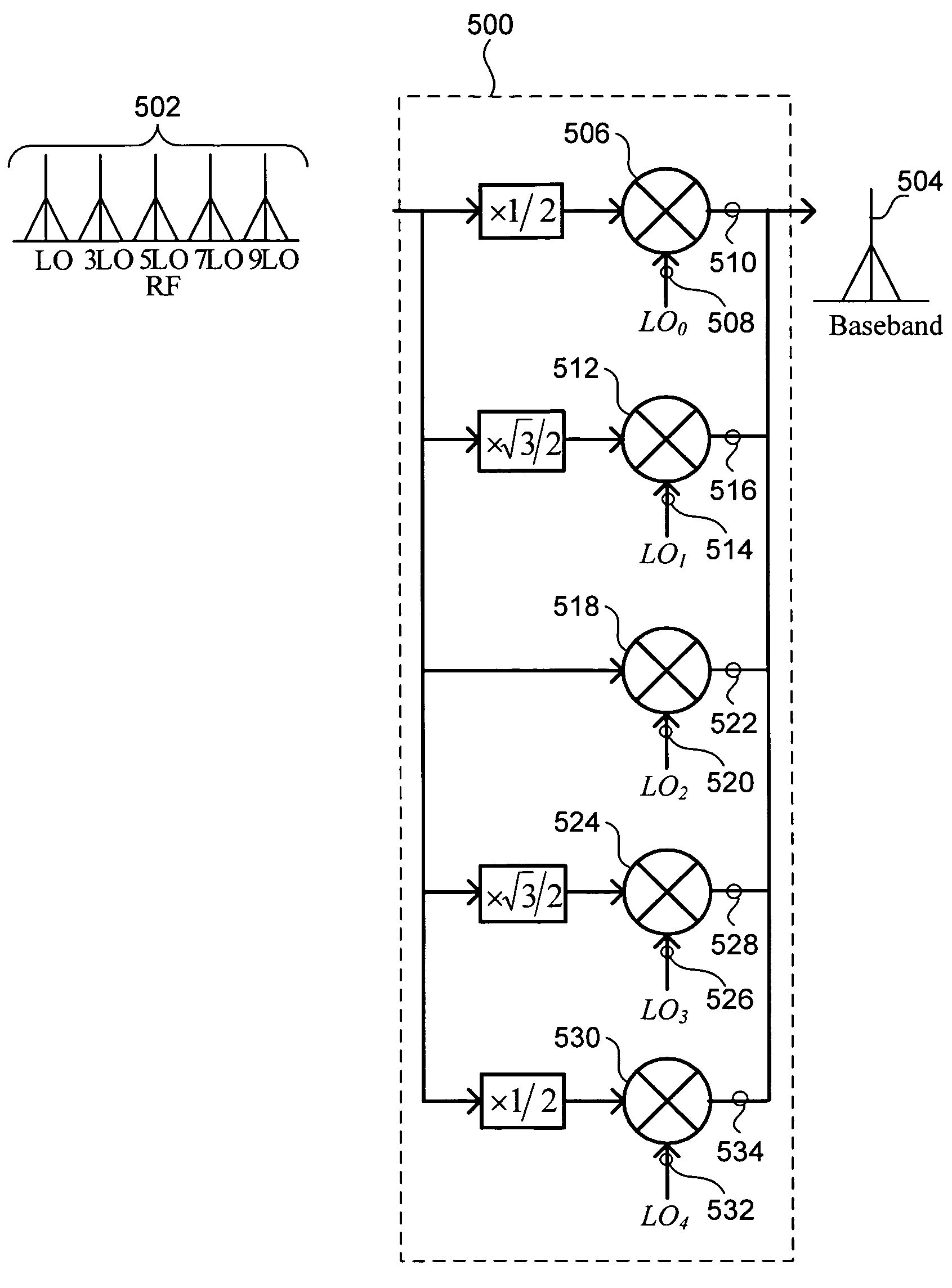
High-order harmonic rejection mixer using multiple LO phases
InactiveUS20060205370A1Improve rejectionIncreased rejectModulation transferenceTransmissionPhase shiftedPhysics
A mixer produces an improved output signal during frequency translation of an input signal using a local oscillator (LO) signal. The mixer includes five component mixers connected in parallel. Each component mixer uses a phase-shifted version of the LO signal for frequency translation to produce a component output signal from the input signal. The component output signals are scaled according to corresponding gain factors and combined to form the output signal. When the mixer is used in a receiver, the phases of the component LO signals and the gain factors are configured to substantially cancel overlapping baseband versions of component input signals located at the third, fifth, seventh and ninth harmonics of the LO frequency. When used in a transmitter, the same phase and gain factor configurations substantially cancel third, fifth, seventh and ninth harmonics within the output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
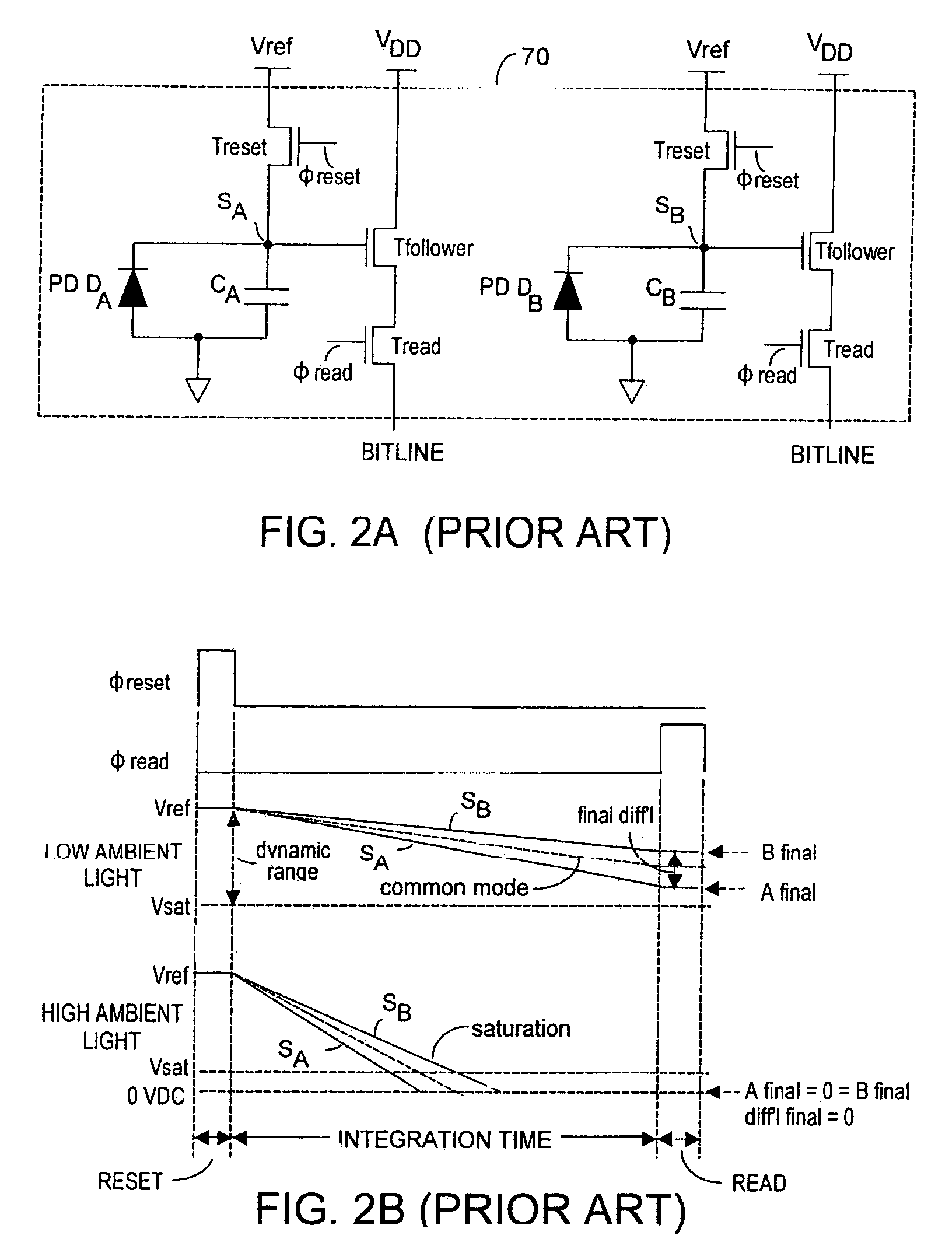
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range using enhanced common mode reset
ActiveUS20060027730A1Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibition effectTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotovoltaic detectors
Effective differential dynamic range and common mode rejection in a differential pixel detector are enhanced by capturing and isolating differential detector charge output before using common mode reset to avoid detector saturation due to common mode components of optical energy to be detected. Differential charge is stored into an integration capacitor associated with an operational amplifier coupled to receive as input the differential detector outputs. Common mode reset is achieved by resetting storage capacitors coupled to the outputs of the differential detector at least once within an integration time T before storage potential exceeds a saturation voltage Vsat for the photodetector.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
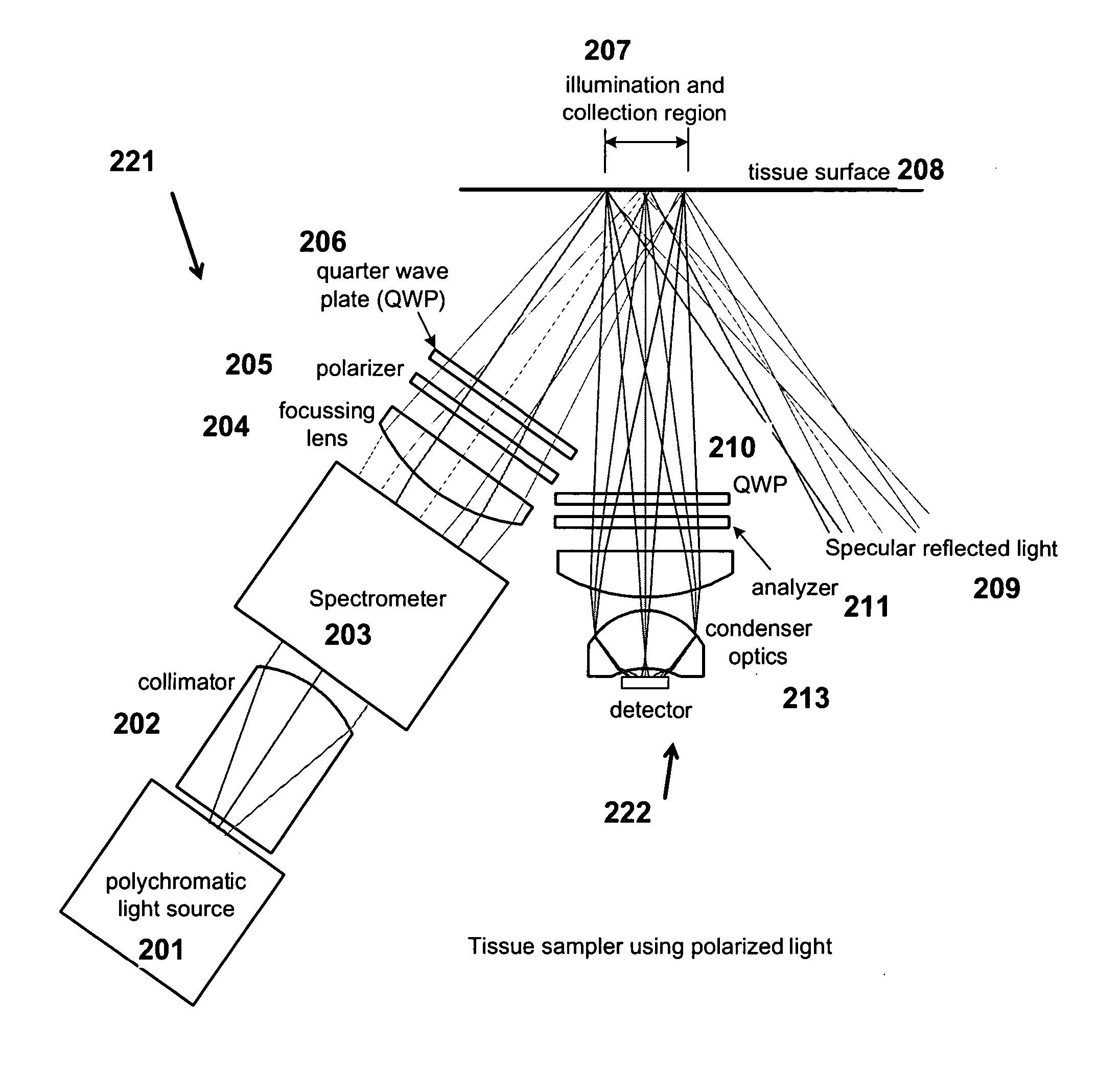
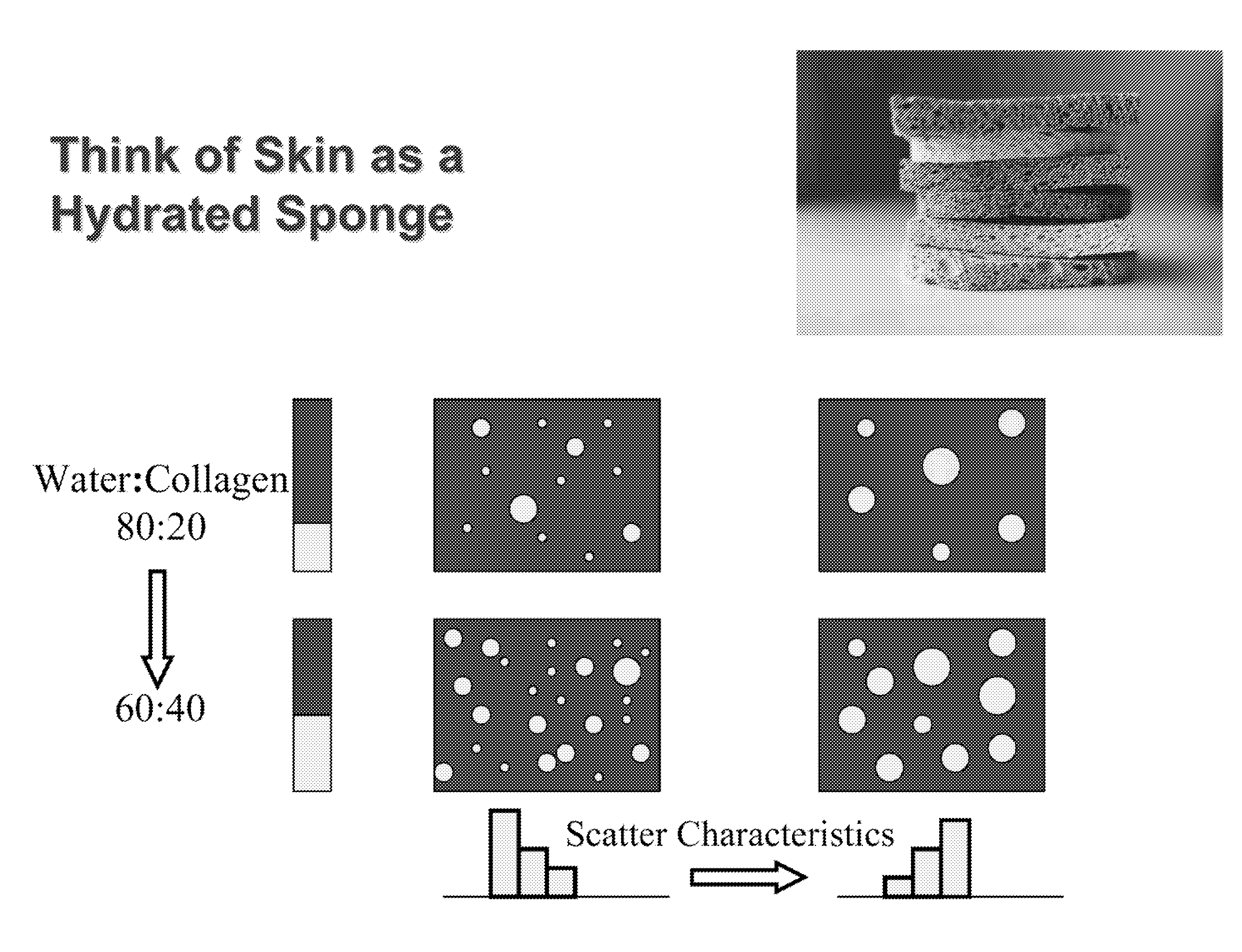
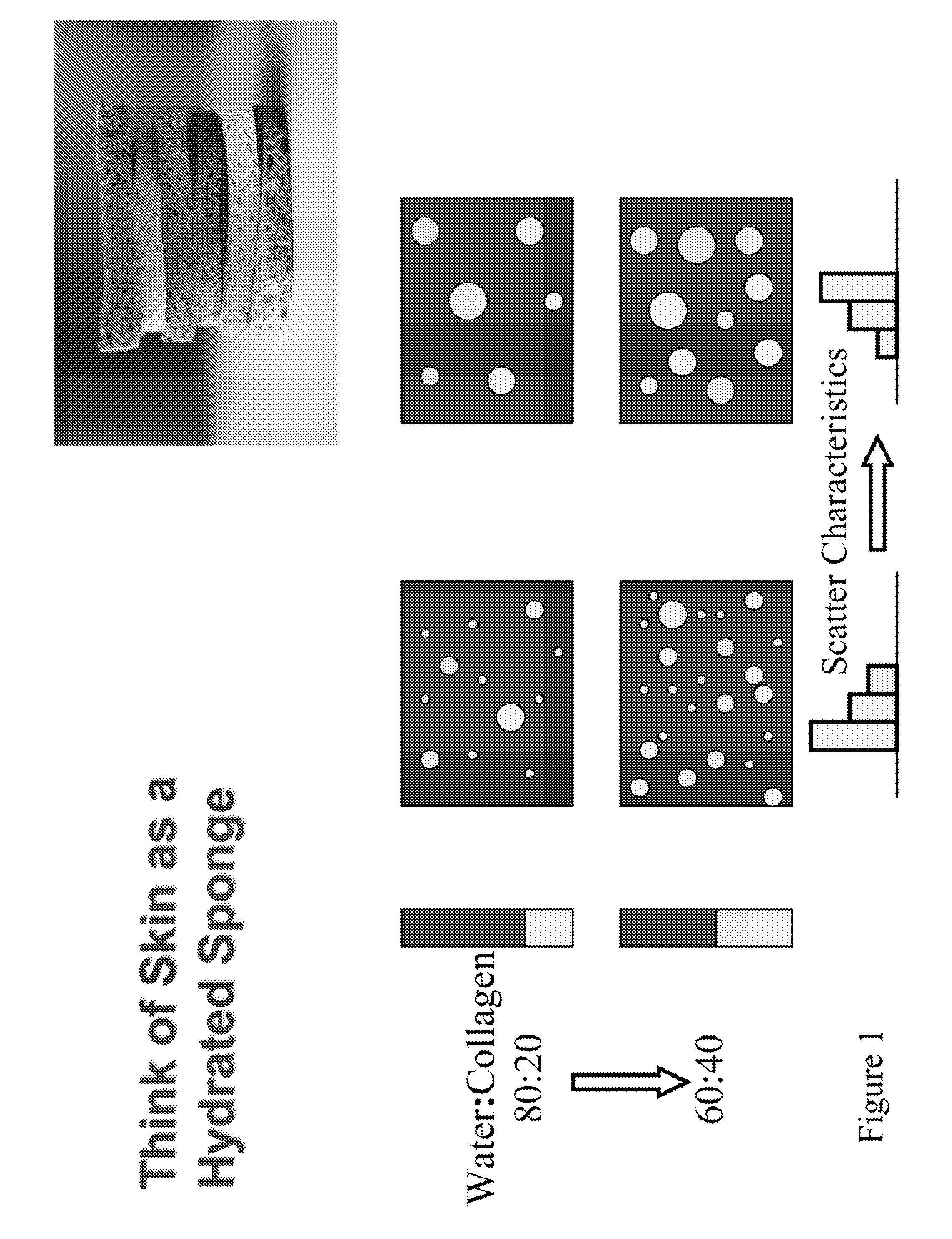
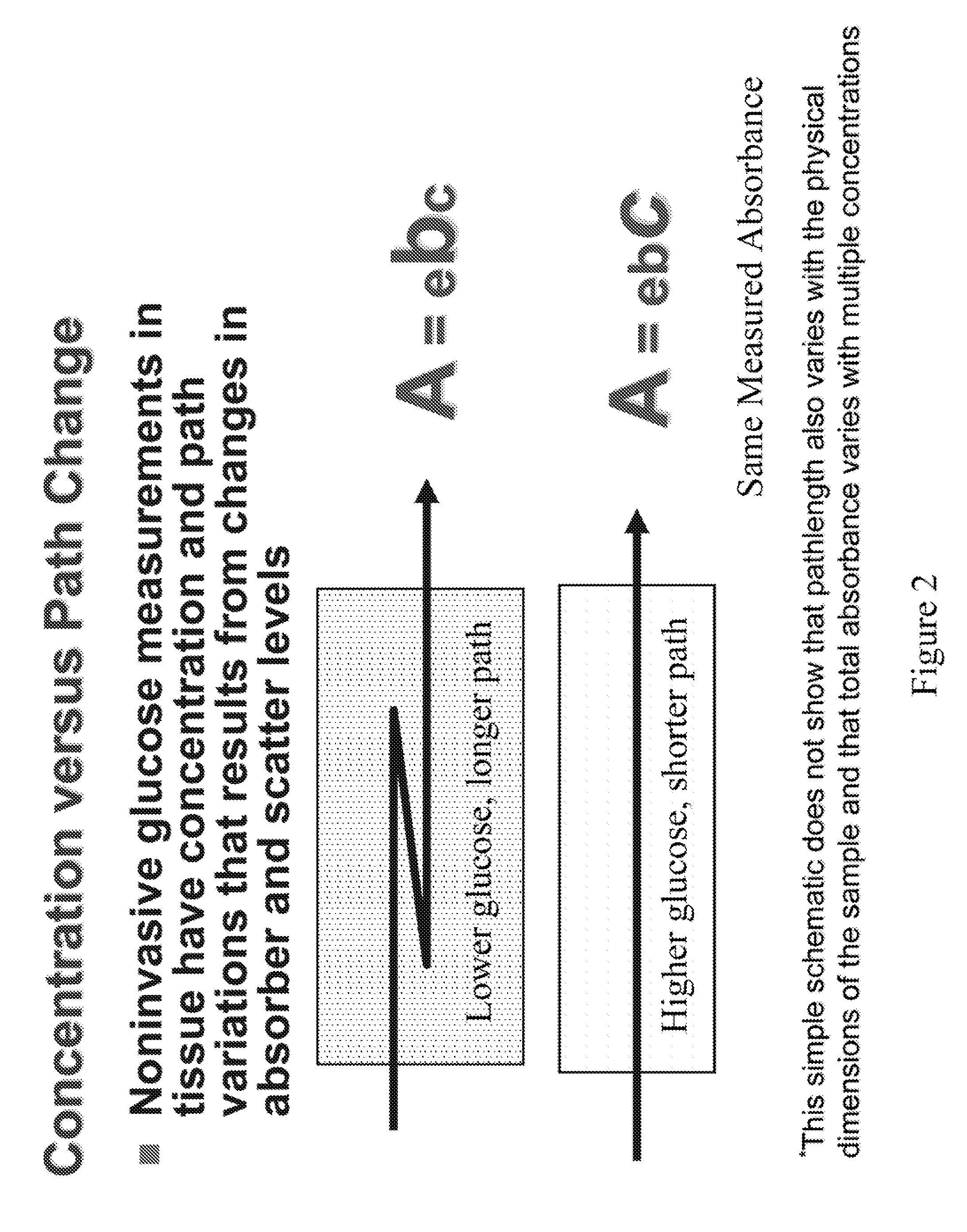
Methods and apparatuses for noninvasive determinations of analytes
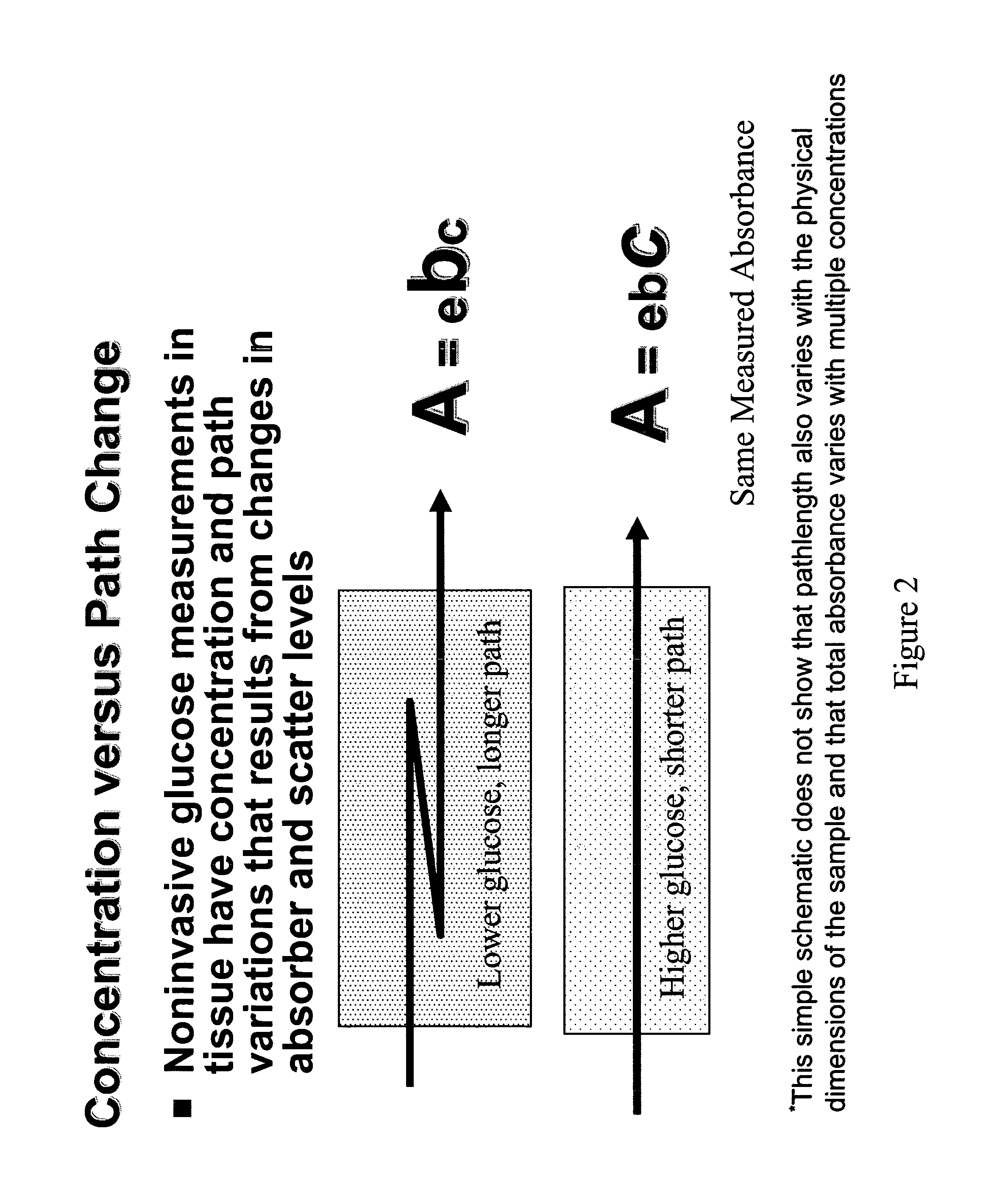
InactiveUS20060178570A1Accurate noninvasive determinationDiscourage collection of lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsPath lengthAnalyte
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for accurate noninvasive determination of tissue properties. Some embodiments of the present invention comprise an optical sampler having an illumination subsystem, adapted to communicate light having a first polarization to a tissue surface; a collection subsystem, adapted to collect light having a second polarization communicated from the tissue after interaction with the tissue; wherein the first polarization is different from the second polarization. The difference in the polarizations can discourage collection of light specularly reflected from the tissue surface, and can encourage preferential collection of light that has interacted with a desired depth of penetration or path length distribution in the tissue. The different polarizations can, as examples, be linear polarizations with an angle between, or elliptical polarizations of different handedness.
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
High-order harmonic rejection mixer using multiple LO phases
InactiveUS7509110B2Increased rejectEliminate needModulation transferenceTransmissionPhase shiftedFrequency mixer
A mixer produces an improved output signal during frequency translation of an input signal using a local oscillator (LO) signal. The mixer includes five component mixers connected in parallel. Each component mixer uses a phase-shifted version of the LO signal for frequency translation to produce a component output signal from the input signal. The component output signals are scaled according to corresponding gain factors and combined to form the output signal. When the mixer is used in a receiver, the phases of the component LO signals and the gain factors are configured to substantially cancel overlapping baseband versions of component input signals located at the third, fifth, seventh and ninth harmonics of the LO frequency. When used in a transmitter, the same phase and gain factor configurations substantially cancel third, fifth, seventh and ninth harmonics within the output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Lowpass filter formed in a multi-layer ceramic
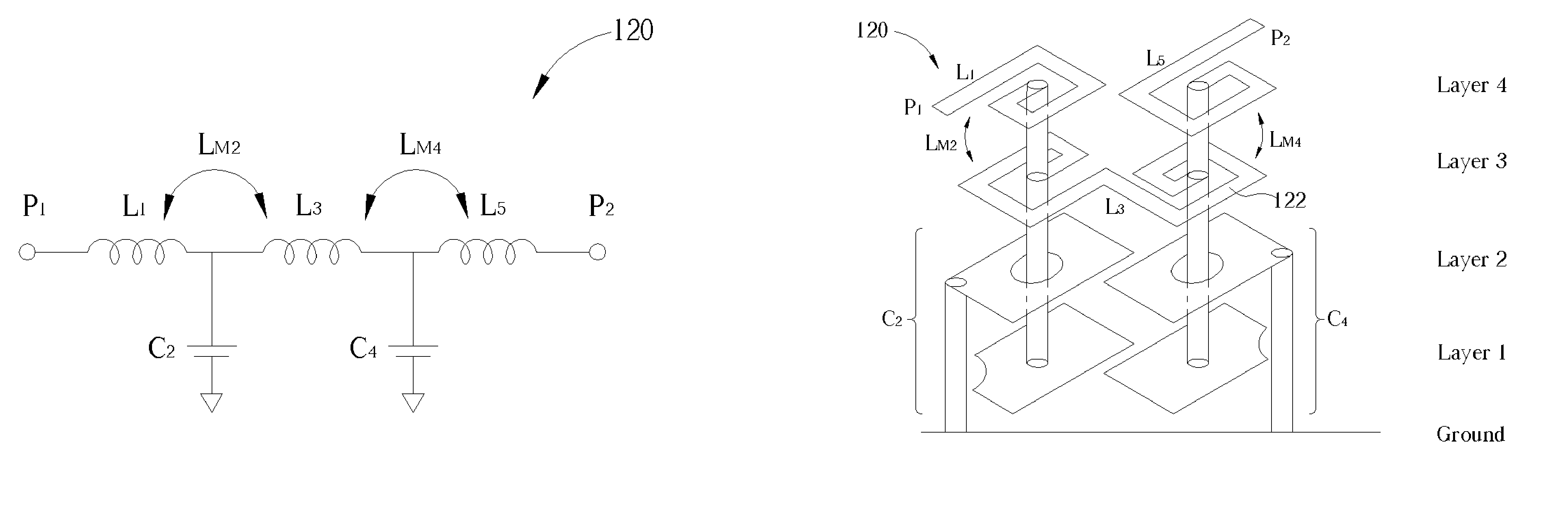
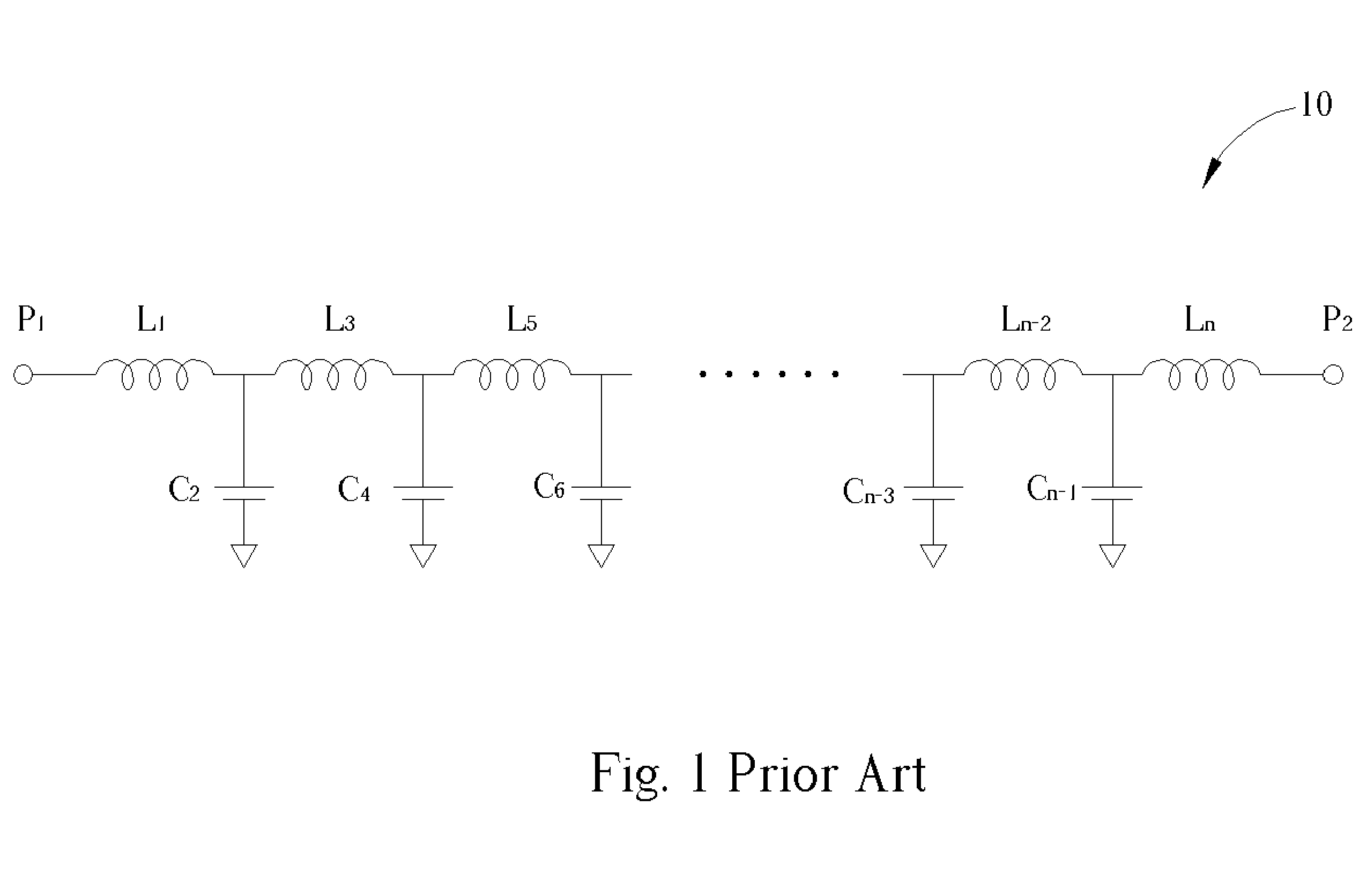
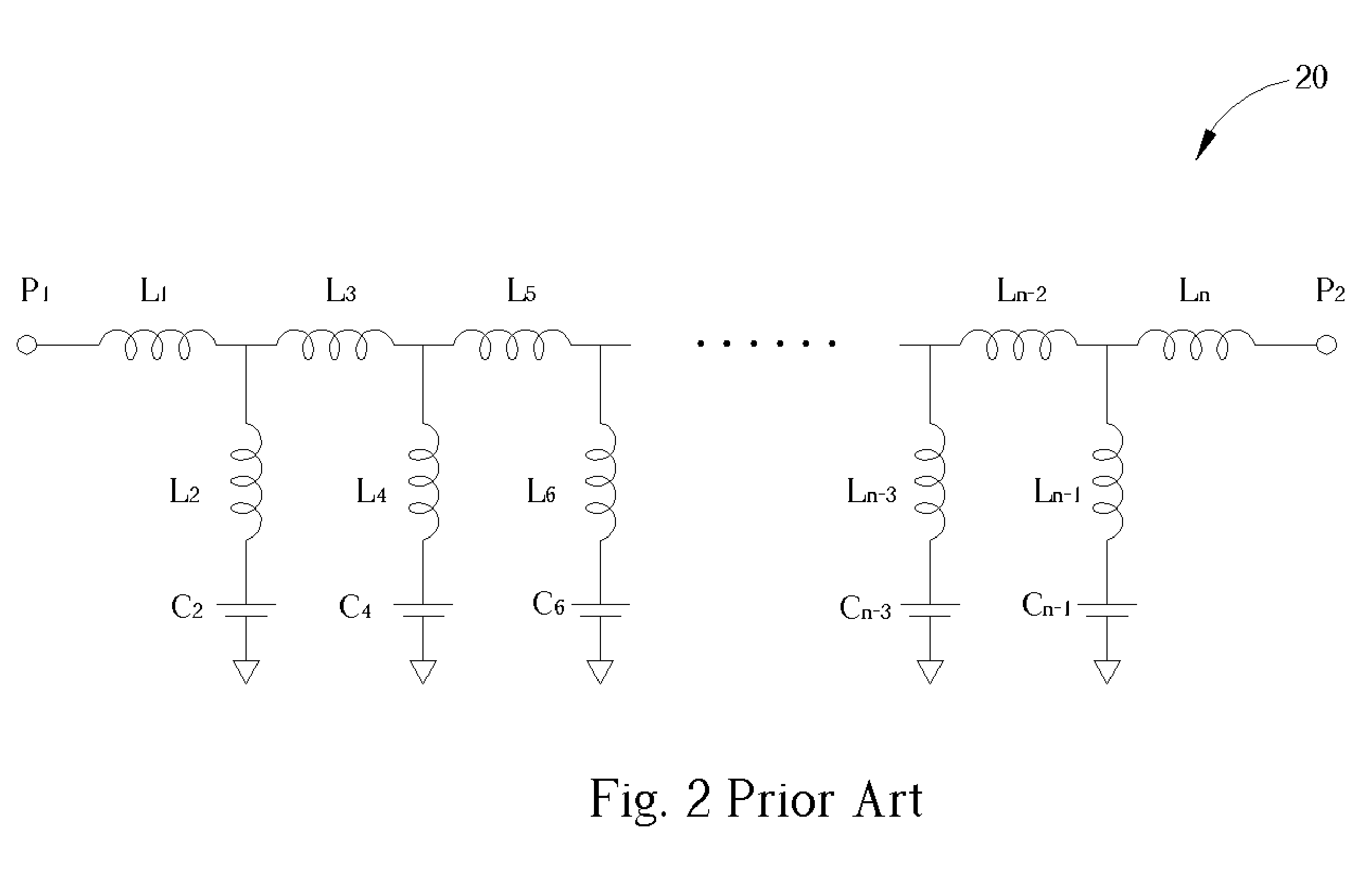
InactiveUS6970057B2Reduce areaIncreased rejectMultiple-port networksPrinted capacitor incorporationLow-pass filterInductor
A lowpass filter formed in a multi-layered substrate includes a first capacitor formed on at least one layer of the multi-layered substrate and being electrically connected to a first node, a first inductor being electrically connected to the first capacitor at the first node, and a second inductor being electrically connected to the first inductor and the first capacitor at the first node. In the lowpass filter, negative mutual inductance exists between the first inductor and the second inductor.
Owner:CHI MEI COMM SYST INC
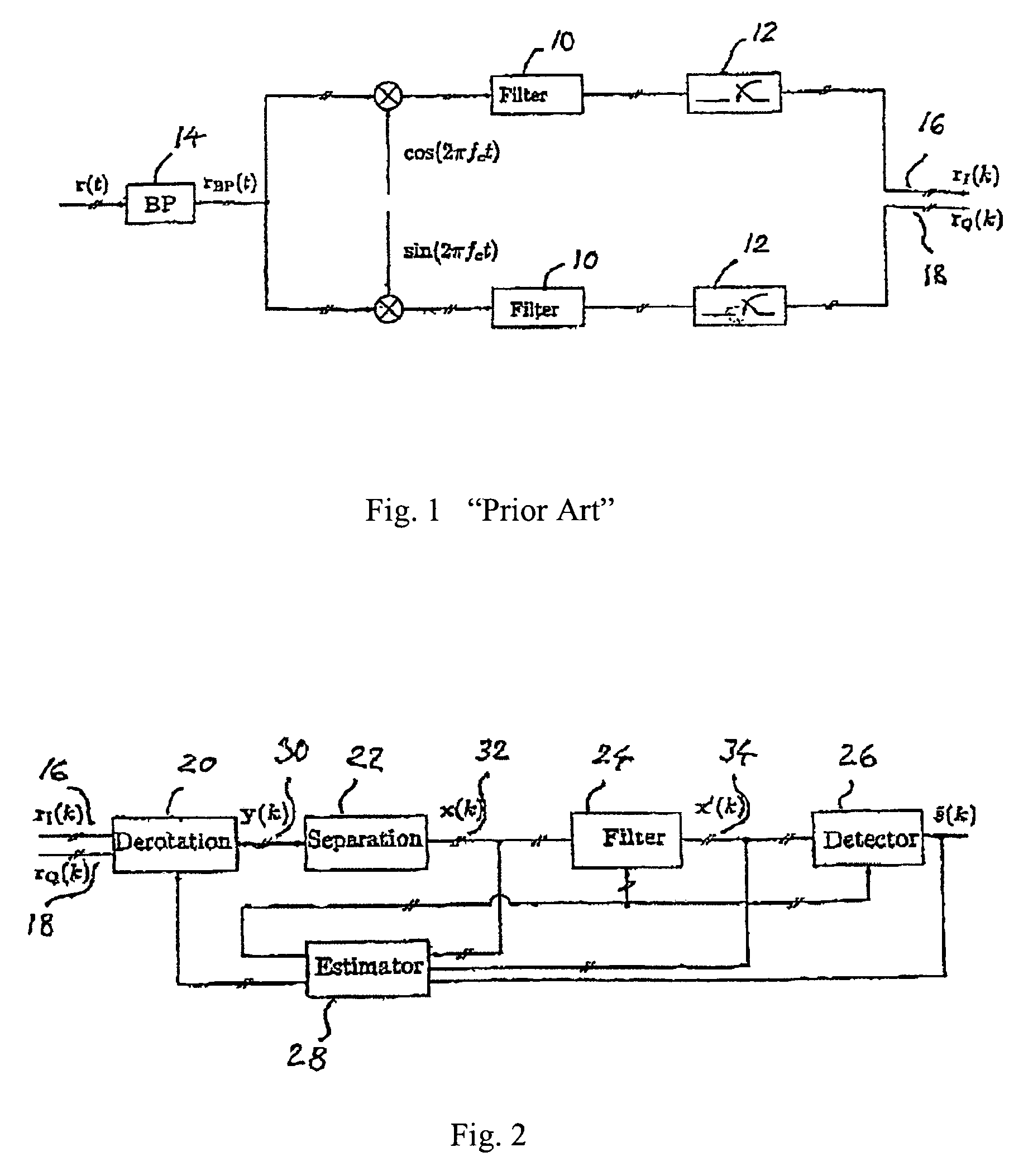
Co-channel interference rejection in a digital receiver
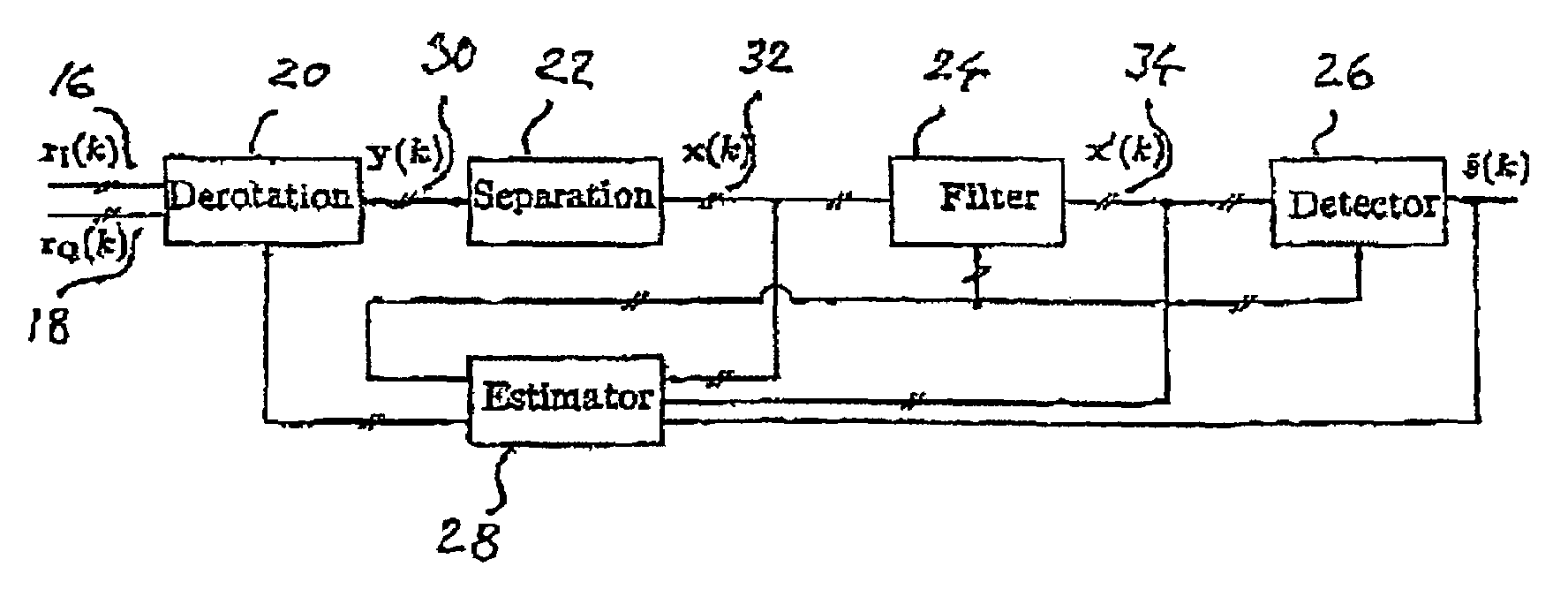
InactiveUS7107031B2Increase the number ofIncreased rejectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringCo-channel interference
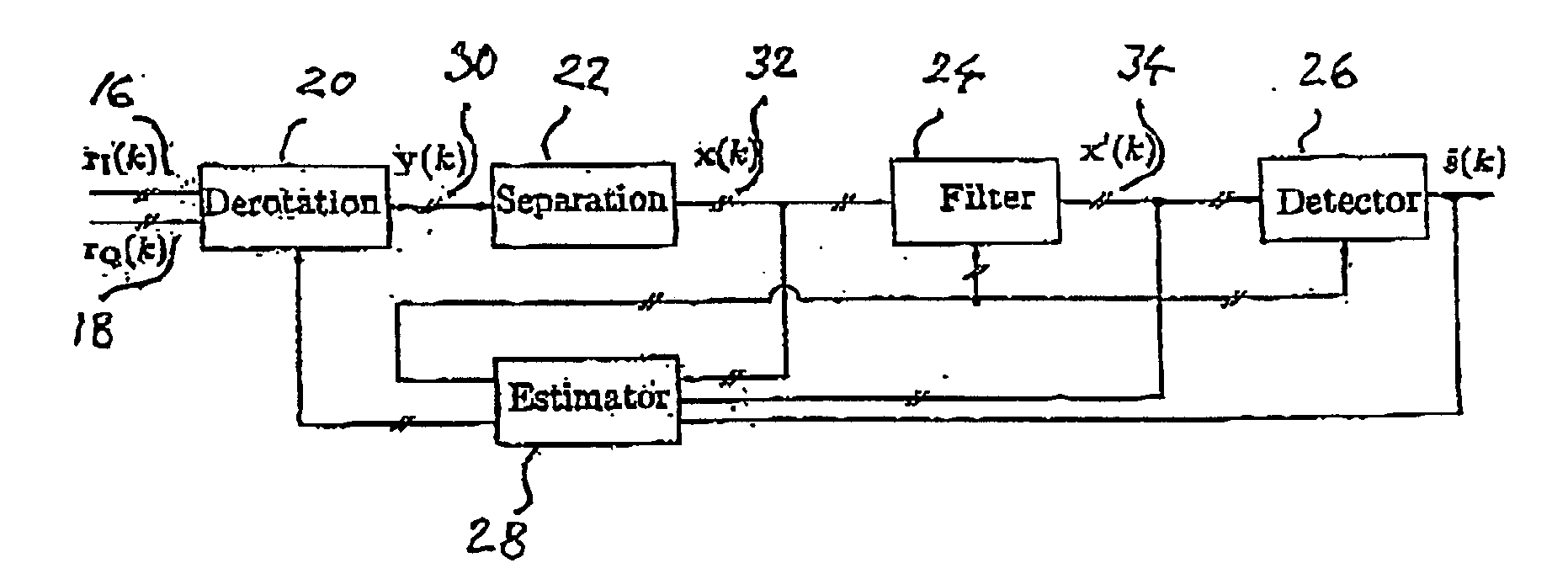
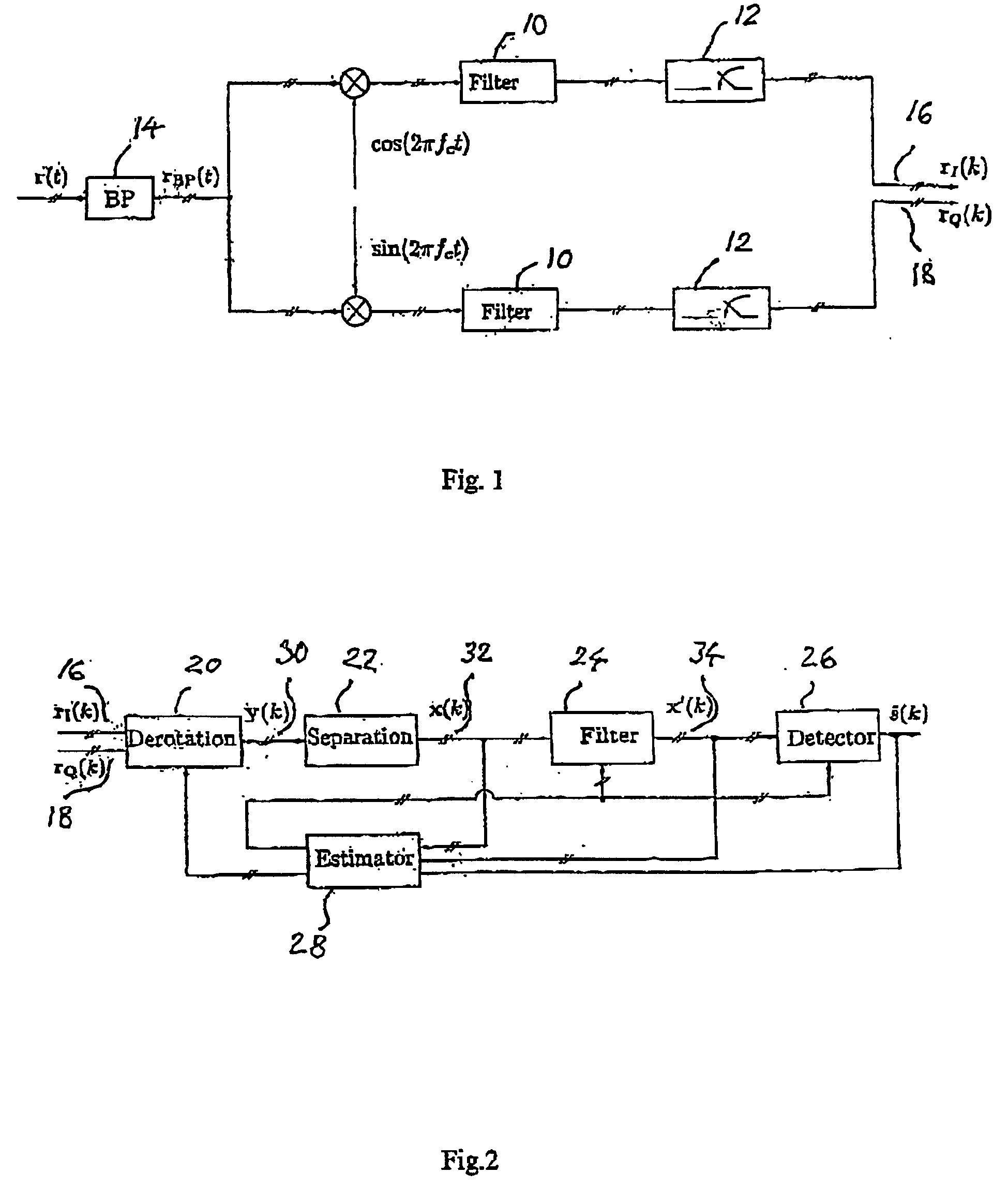
The present invention relates to a method for a digital receiver and a receiver exploiting second order statistics for adaptive co-channel interference rejection in wireless communication. It uses digitally I, in phase, and Q, quadrature, branches of a received transmitted signal as input to the receiver, a coarse synchronization and a coarse frequency offset compensation have being performed on the signal. It comprises a means for derotation, means for separation, means for filtering, means for estimating and means for detecting transmitted symbols in the received signal. The invention thereby improving co-channel rejection in wireless communication, thus making it possible to increase the number of communication channels for frequencies used.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
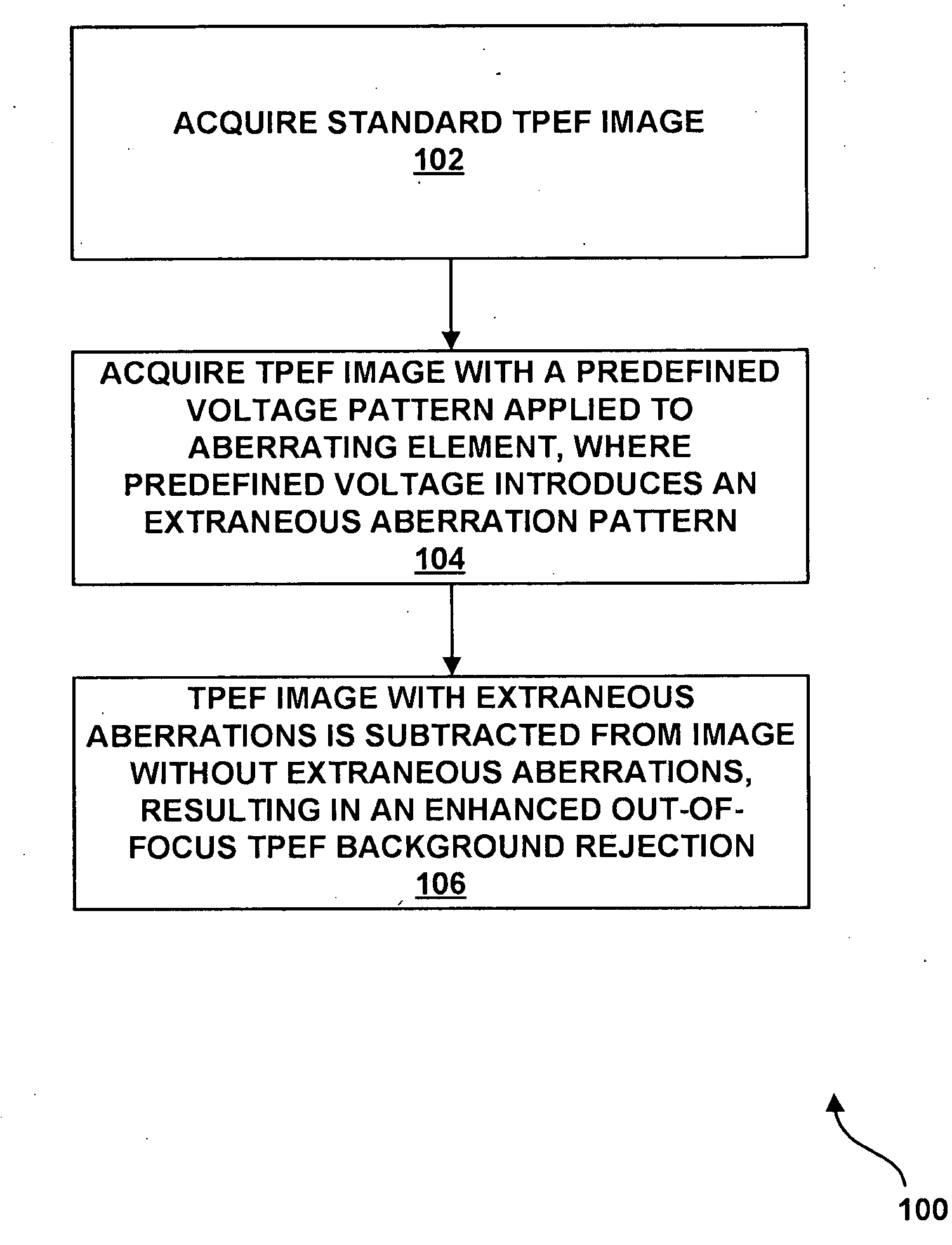
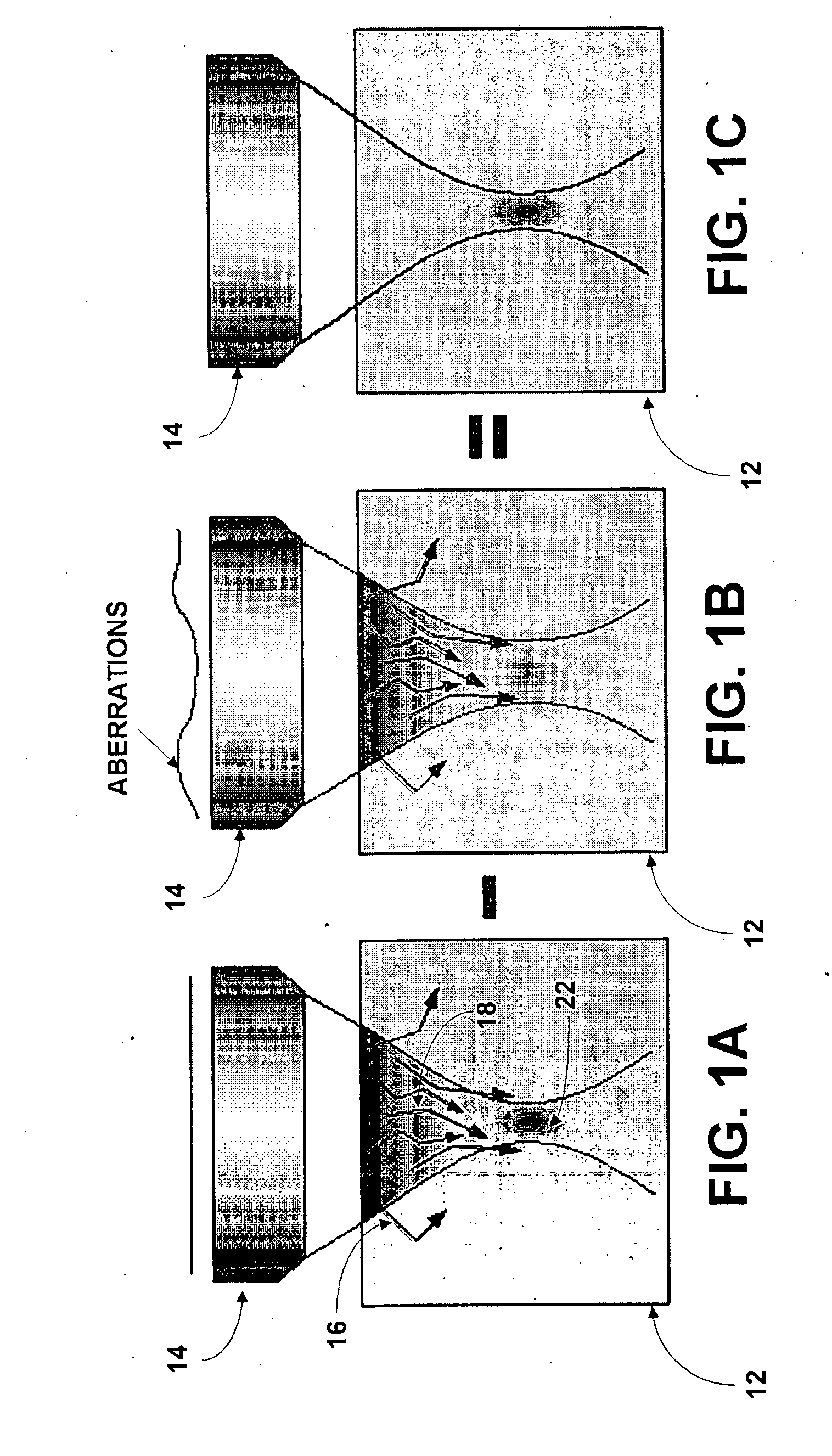
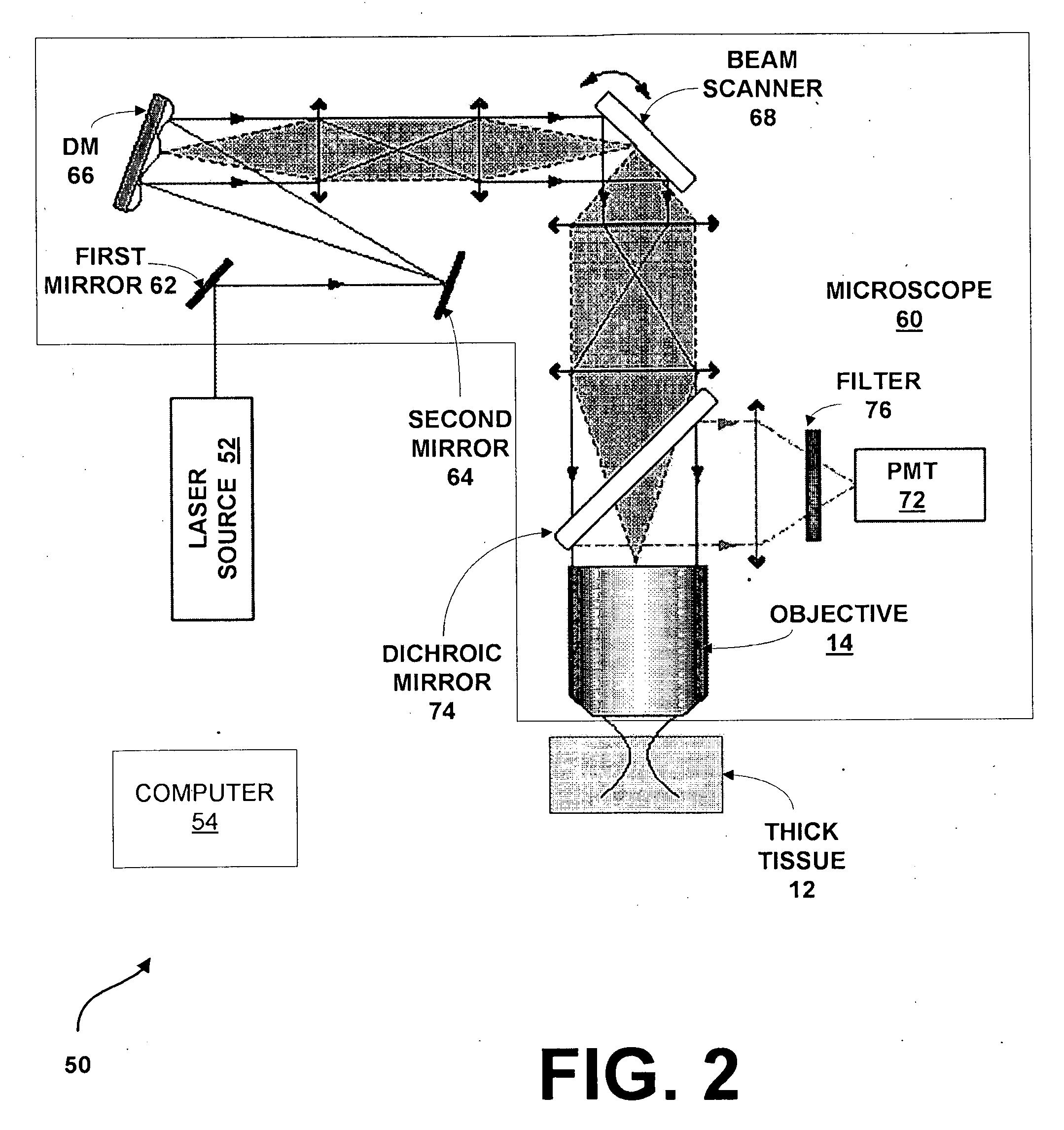
System and method for providing enhanced background rejection in thick tissue with differential-aberration two-photon microscopy
InactiveUS20090084980A1Enhance rejectionGood discriminationPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersPhysicsMicroscopy
A system for providing enhanced background rejection in thick tissue contains an aberrating element for introducing controllable extraneous spatial aberrations in an excitation beam path; at least one mirror capable of directing received laser pulses to the aberrating element; an objective; a beam scanner imaged onto a back aperture of the objective so that the beam scanner steers beam focus within the thick tissue; and a detector for recording signals produced by the tissue. An associated method comprises the steps of acquiring two-photon excited fluorescence of thick tissue without extraneous aberrations; introducing an extraneous aberration pattern in an excitation beam path; acquiring two-photon excited fluorescence of the thick tissue having the introduced extraneous aberration pattern; and subtracting the two-photon excited fluorescence with extraneous aberrations from the acquired standard two-photon excited fluorescence of the thick tissue without extraneous aberrations.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Receiver
InactiveUS20040014424A1Increase the number ofIncreased rejectMultiplex communicationTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringCo-channel interference
The present invention relates to a method for a digital receiver and a receiver exploiting second order statistics for adaptive co-channel interference rejection in wireless communication. It uses digitally I, in phase, and Q, quadrature, branches of a received transmitted signal as input to the receiver, a coarse synchronization and a coarse frequency offset compensation have being performed on the signal. It comprises a means for derotation, means for separation, means for filtering, means for estimating and means for detecting transmitted symbols in the received signal. The invention thereby improving co-channel rejection in wireless communication, thus making it possible to increase the number of communication channels for frequencies used.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Process and equipment for rejuvenation treatment of photoresist development waste
InactiveUS6083670AIncreased rejectEfficient removalIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic anion exchangersElectrolysisWastewater
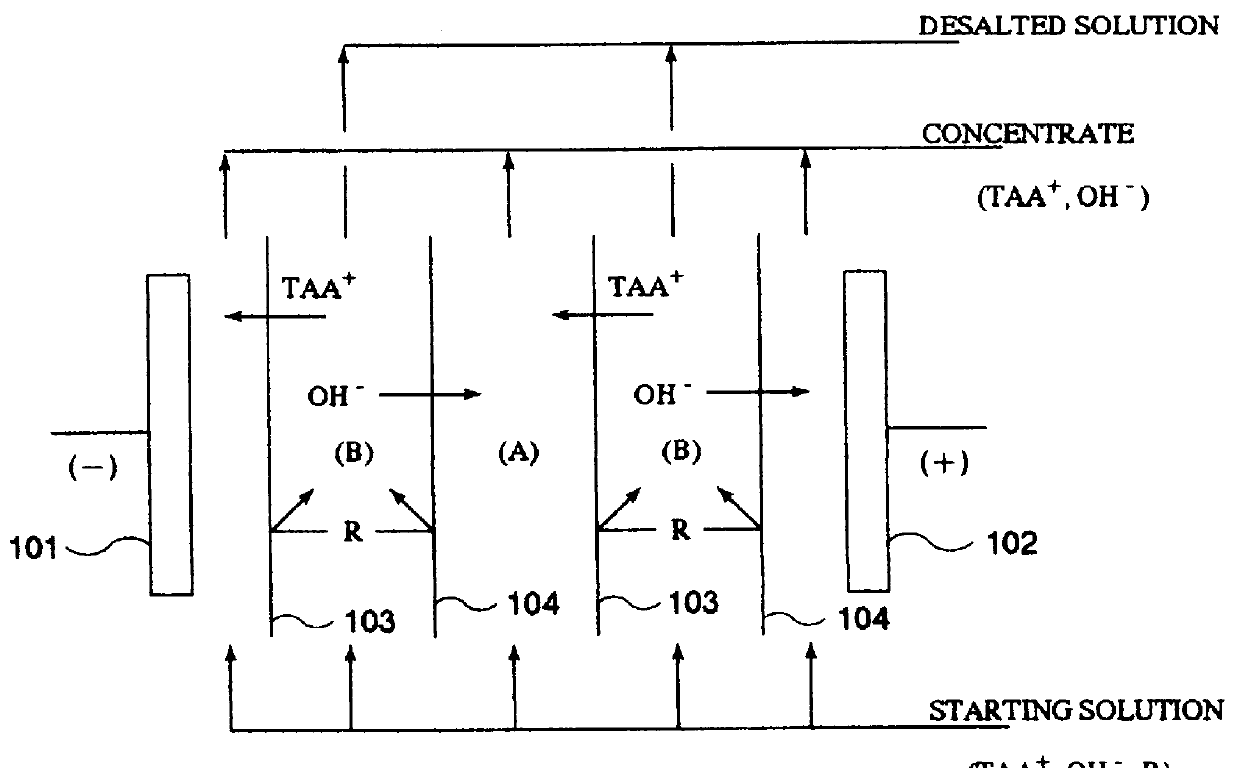
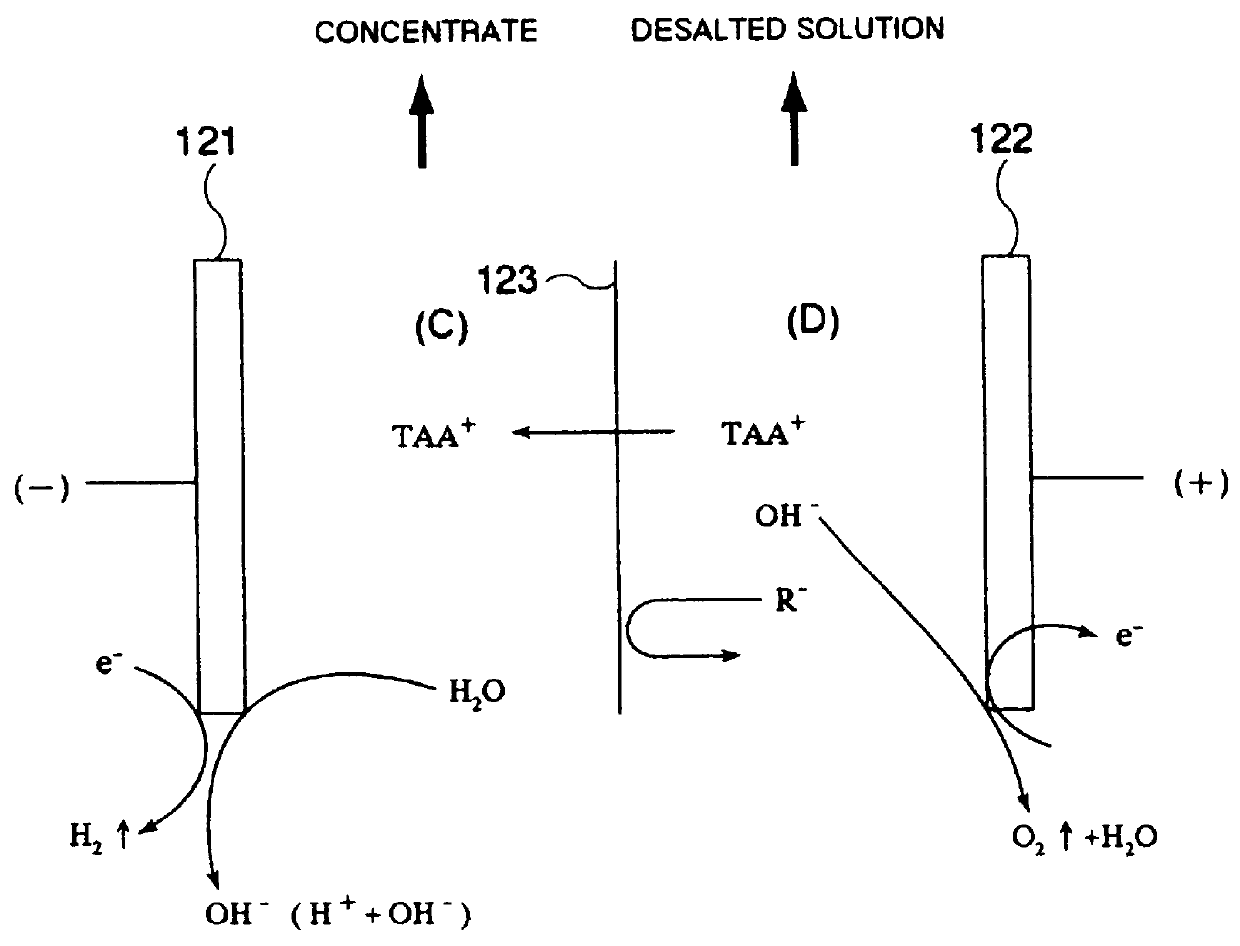
The disclosed process for rejuvenation treatment of a photoresist development waste mainly containing a photoresist and tetraalkylammonium (TAA) ions comprises at least a simple membrane separation step of treating the photoresist development waste or a treated solution derived from the photoresist development waste with a nanofiltration membrane (NF membrane) to obtain a concentrate (NF concentrate) mainly containing impurities such as the photoresist and a higher-purity permeate (NF permeate) mainly containing TAA ions. The NF concentrate and / or the NF permeate, preferably the NF permeate, is desirably subjected to a step of concentration and refining by electrodialysis or electrolysis and / or a step of refining by ion exchange treatment, for example, with an anion exchange resin and / or a cation exchange resin in one of the H form and the TAA form. The NF permeate may advantageously be passed through the concentrating cells of an electrodialysis unit while passing the NF concentrate through the desalting cells of the electrodialysis unit to further recover TAA ions remaining in the NF concentrate, whereby the amount of wastewater discharged as the desalted waste can be decreased. The NF membrane separation step is preferably effected in multiple stages.
Owner:ORGANO CORP
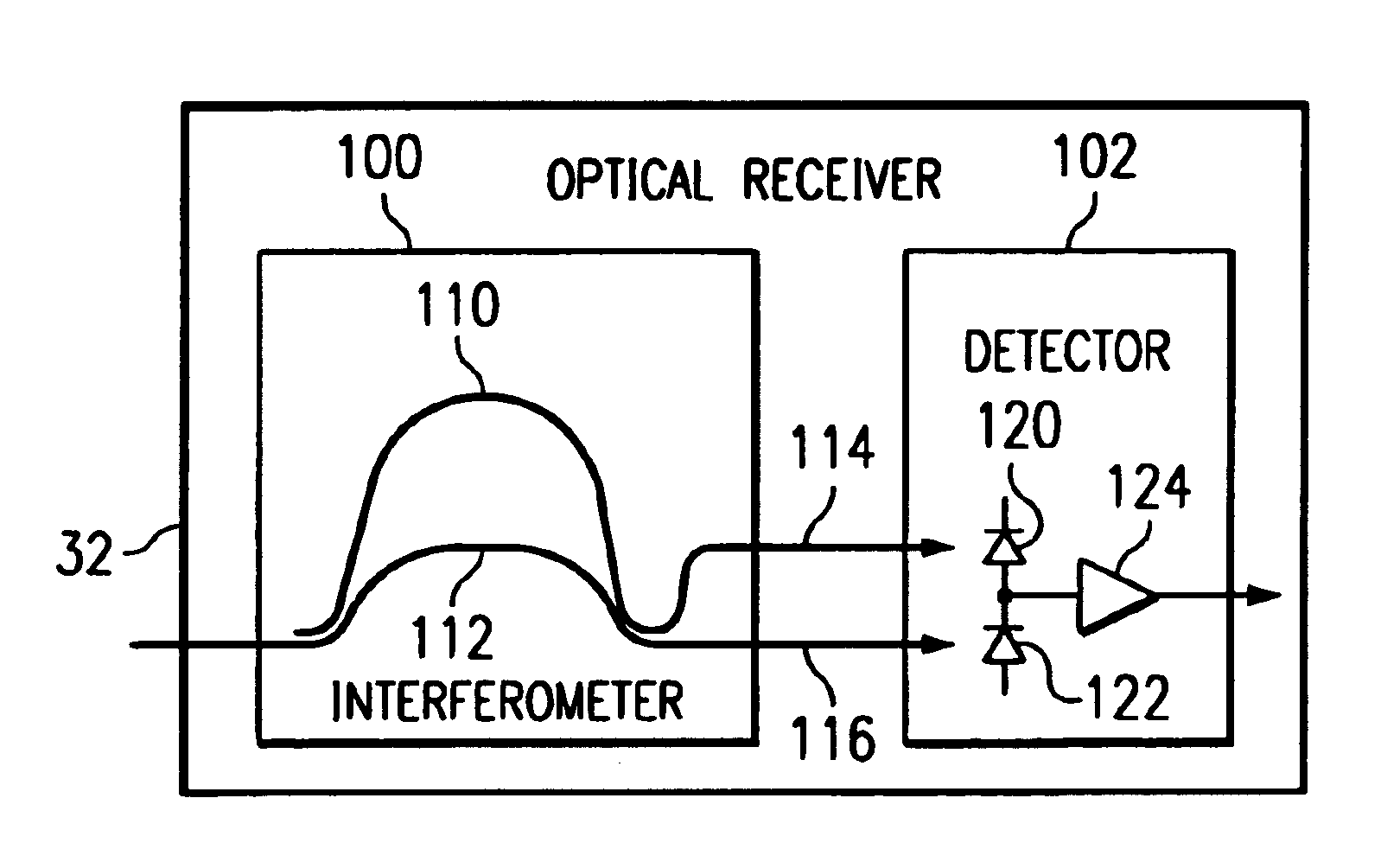
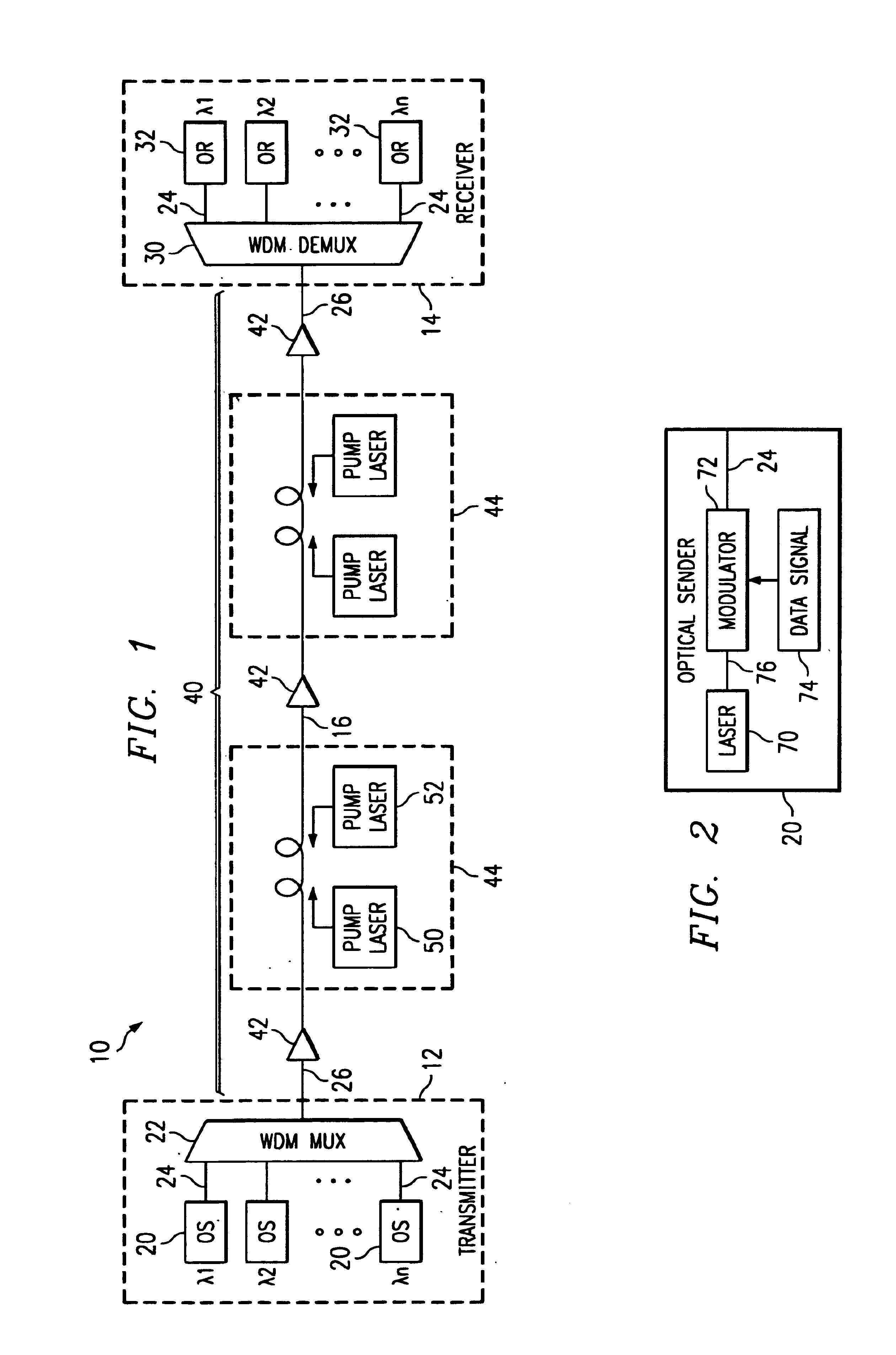
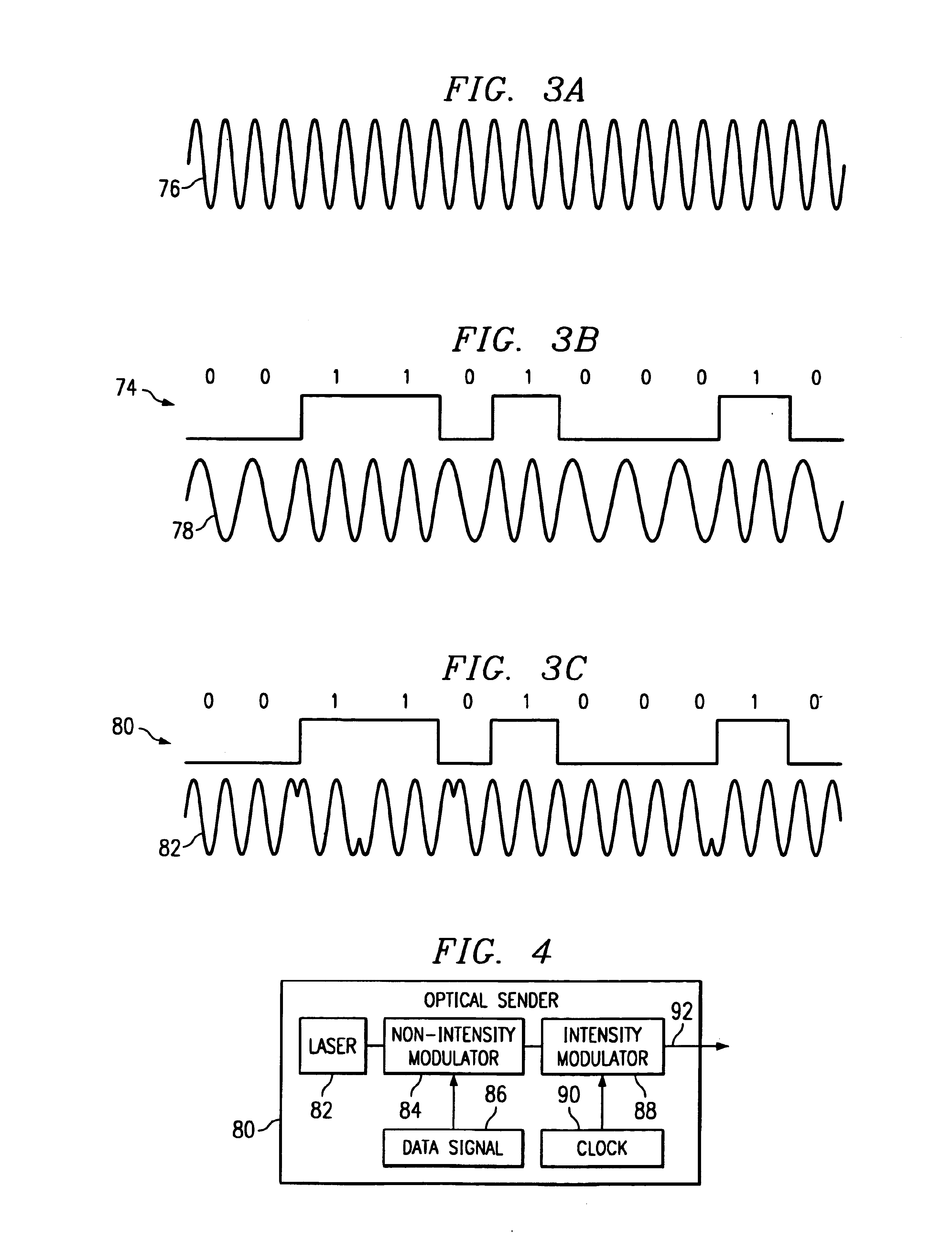
Receiver and method for a multichannel optical communication system
InactiveUS7200344B1Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersCommunications systemData signal
A method and system for transmitting information in a wavelength division multiplex (WDM) or other suitable multichannel optical communication system includes receiving a multichannel signal having a symbol rate and comprising a plurality of non-intensity modulated optical information signals. The non-intensity modulated optical information signals have a minimum channel spacing comprising a multiple of the symbol rate within 0.4 to 0.6 of an integer. The non-intensity modulated optical information signals are separated from the multichannel signal and each converted into an intensity modulated optical information signal using an asymmetric interferometer. A data signal is recovered from the intensity modulated optical information signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Active balun circuit for single-ended to differential RF signal conversion with enhanced common-mode rejection
InactiveUS6922108B2Increased rejectBalance-unbalance networksDifferential amplifiersBalanced mixerDBc
An active balun circuit is provided for single-ended to differential RF signal conversion with enhanced common-mode rejection which suppresses common mode signal and which achieves phase and amplitude balance without sophisticated tuning or compensation methods. The circuit has a single-ended input and balanced output with phase and amplitude balance error less than 2° and 1.2 dB, respectively, measured from 1.5 GHz to 1.8 GHz at 5V supply. When supply voltage drops down to 1.5V, its phase and amplitude balance error remains within 5° and 2 dB, respectively. The circuit achieves a balanced output via an output network which behaves as an impedance matching network for differential mode signal and is grounded for common mode signal. As a result, common mode signal is suppressed and 180-degree phase balance at output is achieved. The circuit has high-linearity (P1 dBin=5 dBm, IIP3=16.6 dBm) and low residual phase noise (<−155 dBc / Hz at 100 kHz and above) which make it suitable as an active balun / buffer amplifier between LO and balanced mixer for base station receiver applications.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
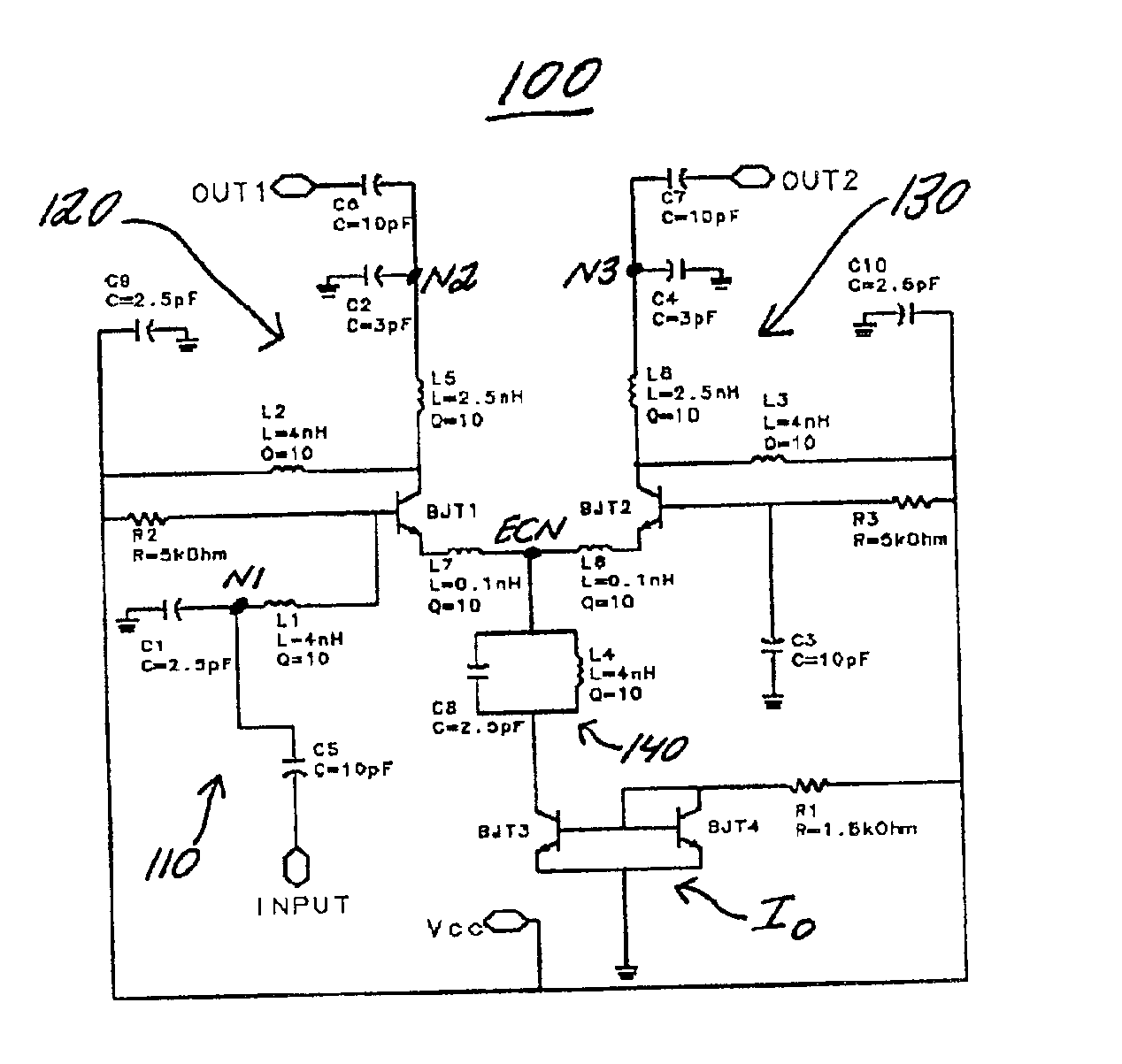
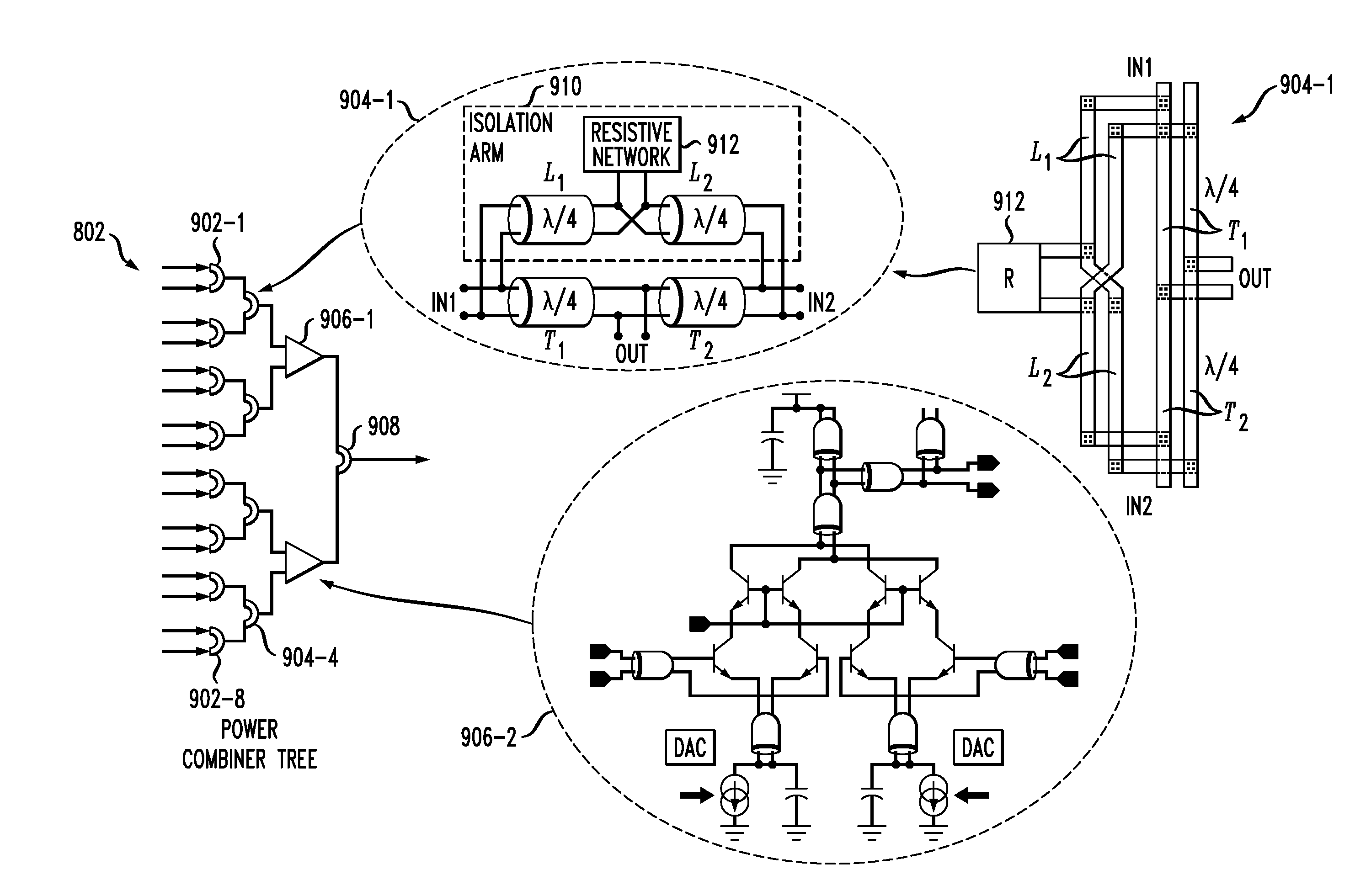
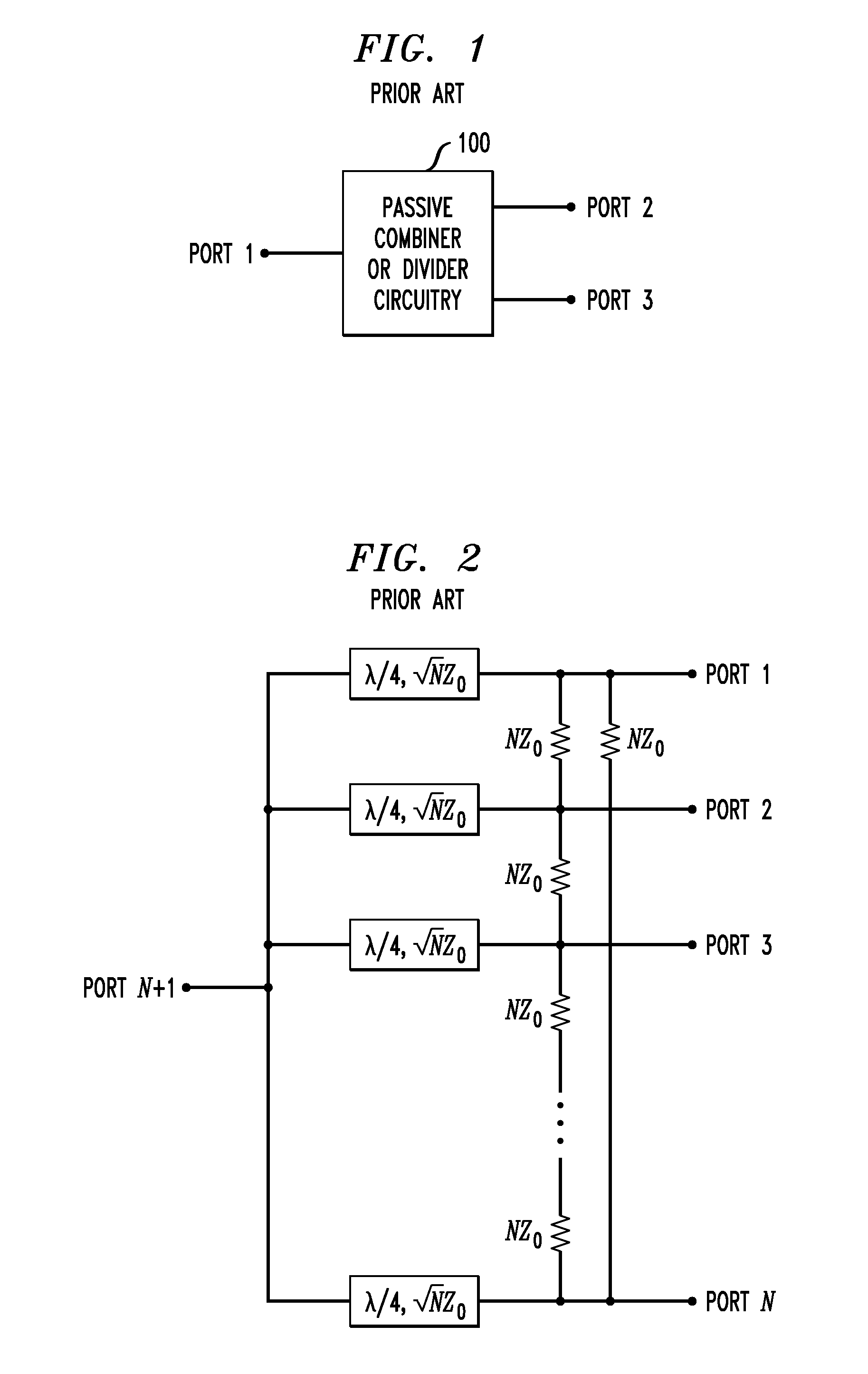
Differential Cross-Coupled Power Combiner or Divider
ActiveUS20110063048A1Improve rejectionSmall physical sizeAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCoupling devicesIntegrated circuitPower combiner
A differential cross-coupled power combiner in one aspect comprises a plurality of inputs, an output, a plurality of differential transmission lines each coupled between a corresponding one of the inputs and the output, and at least one set of additional differential transmission lines arranged in series between any two of the inputs. First and second ones of the additional differential transmission lines in the set are coupled to one another using a cross-coupling arrangement. Other aspects of the invention provide a differential cross-coupled power divider, communication system receivers and transmitters incorporating respective power combiners and dividers, and integrated circuit implementations of power combiners and dividers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Mixer circuit and method of operation
InactiveUS8140044B2Increases IIPGood rejectionResonant long antennasModulation transferenceFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
A mixer circuit to mix a RF (Radio Frequency) signal with a LO (Local Oscillator) signal to generate an IF (Intermediate Frequency) signal including a dummy branch connected in parallel of a mixing branch, the dummy branch including a transconductance stage having an input connected to a reference potential independent from the RF signal, to transform the reference potential into a current signal, and a current switching core to switch the current signal according to LO and signals, and chopping switches to connect in series the transconductance stage of the mixing branch to the current switching core of the mixing branch and, in the alternative, to the current switching core of the dummy branch under the control of a chopping signal.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Digital-to-analogue converter circuits
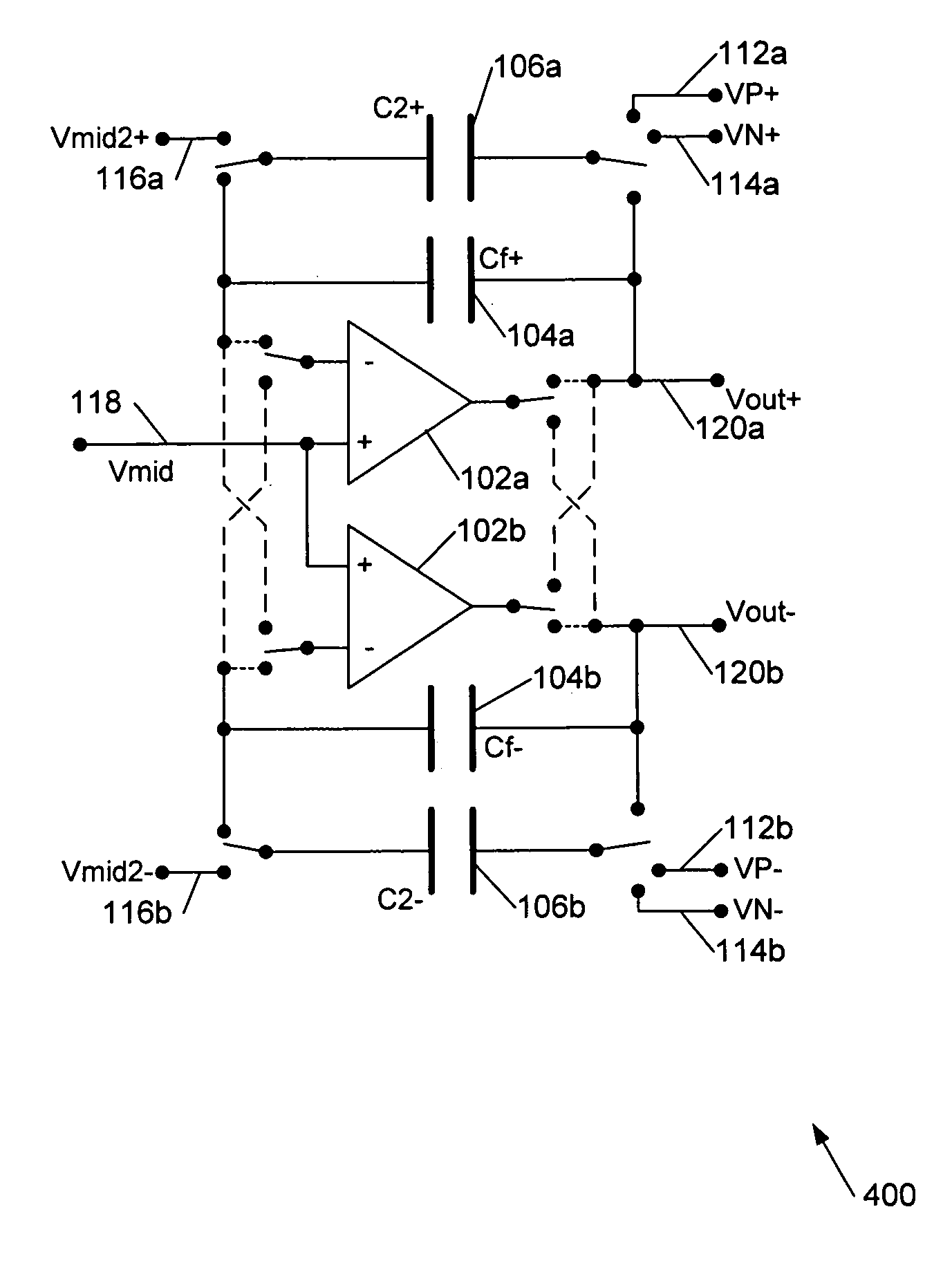
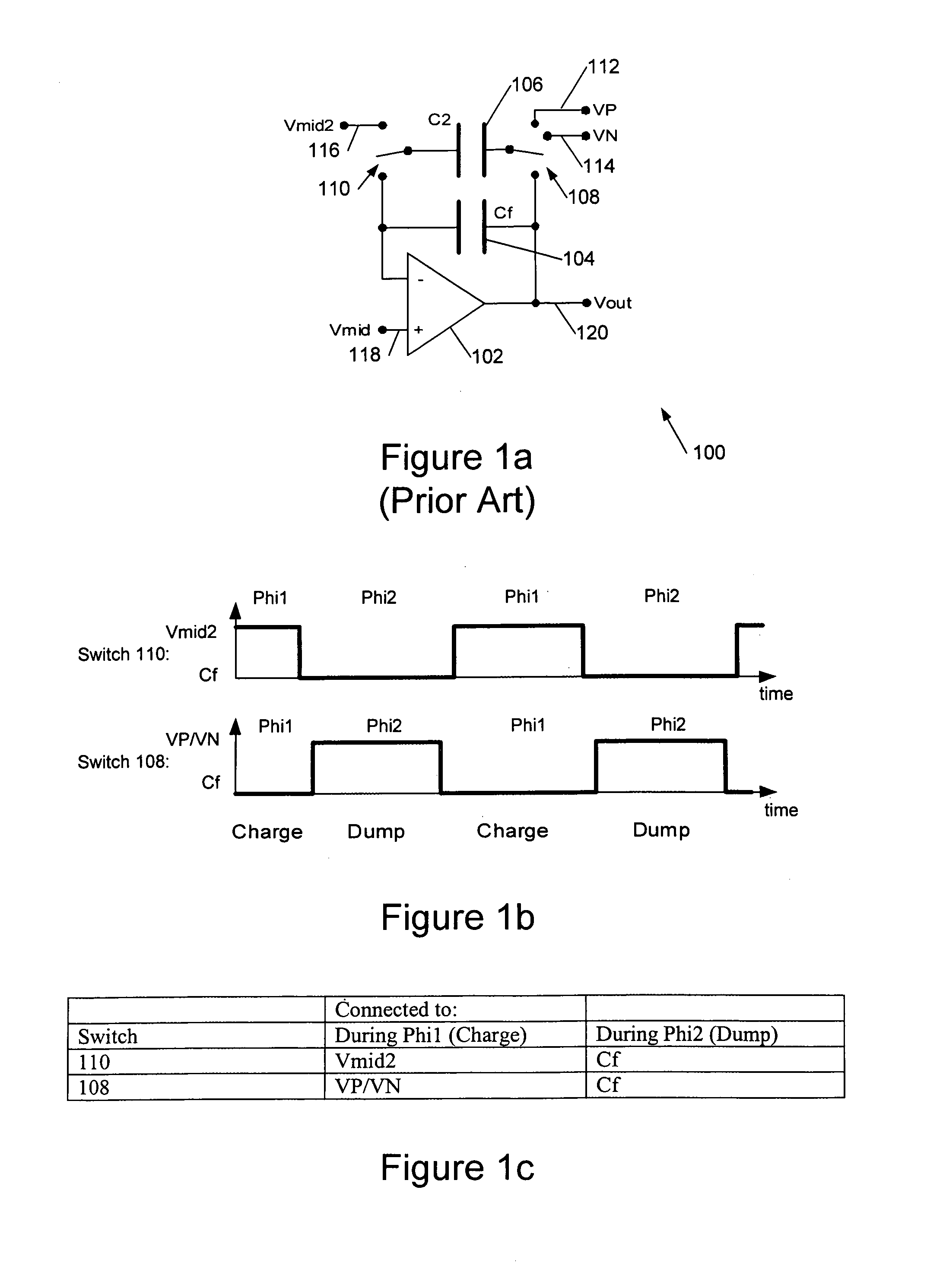
ActiveUS6952176B2Reduce loadIncreased rejectElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationDigital analog converterAudio power amplifier
This invention is generally concerned with digital-to-analogue converters and more particularly relates to techniques for reducing signal dependent loading of reference voltage sources used by these converters.A differential switched capacitor digital-to-analogue (DAC) circuit (500) comprises first and second differential signal circuit portions (500a,b) for providing respective positive and negative signal outputs with respect to a reference level, and has first and second reference voltage inputs (112,114) for receiving respective positive and negative references. Each of said first and second circuit portions comprises an amplifier (102a,b) with a feedback capacitor (104a,b), a second capacitor (106a,b), and a switch (108a,b, 110a,b) to switchably couple said second capacitor to a selected one of said reference voltage inputs to charge the second capacitor and to said feedback capacitor to share charge with the feedback capacitor. The switch of said first circuit portion is further configured to connect said second capacitor (106a) of said first circuit portion to share charge with said feedback capacitor (104b) of said second circuit portion; and the switch of said second circuit portion is further configured to connect said second capacitor (106b) of said second circuit portion to share charge with said feedback capacitor (104a) of said first circuit portion. This enables the second capacitors to in effect be alternately pre-charged to positive and negative signal-dependent nodes so that, on average, signal dependent loading of the references is approximately constant.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
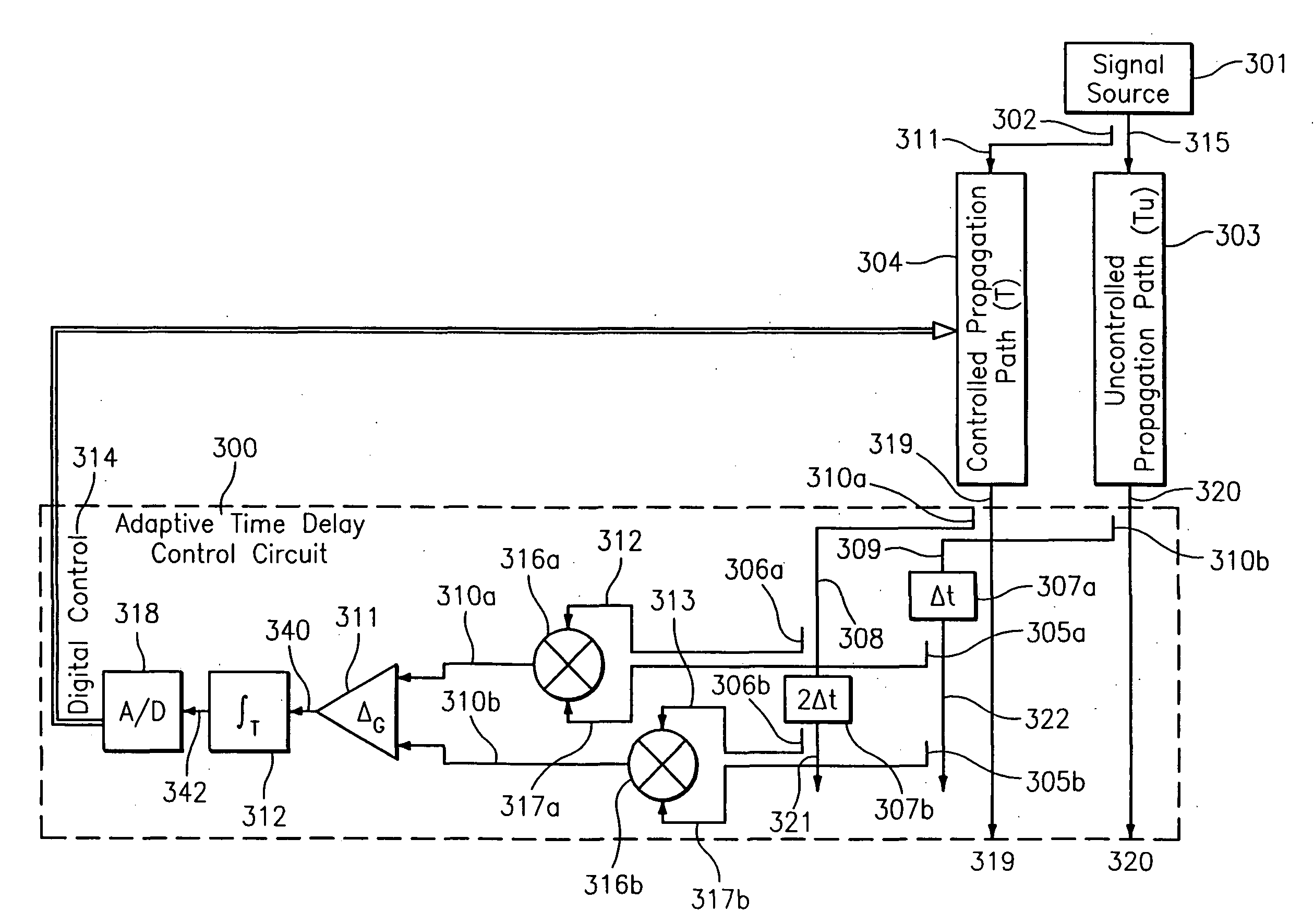
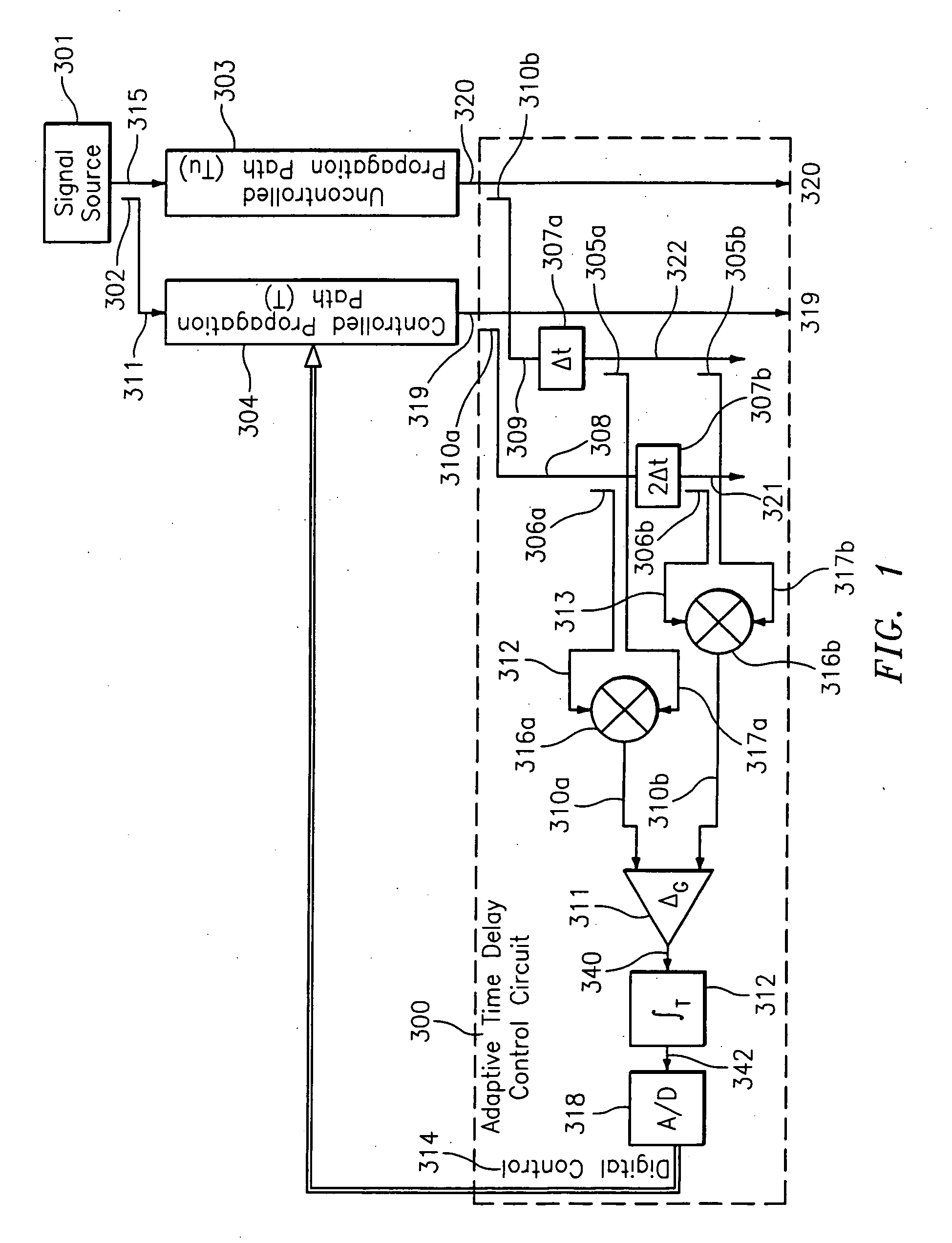
Variable time delay control structure for channel matching
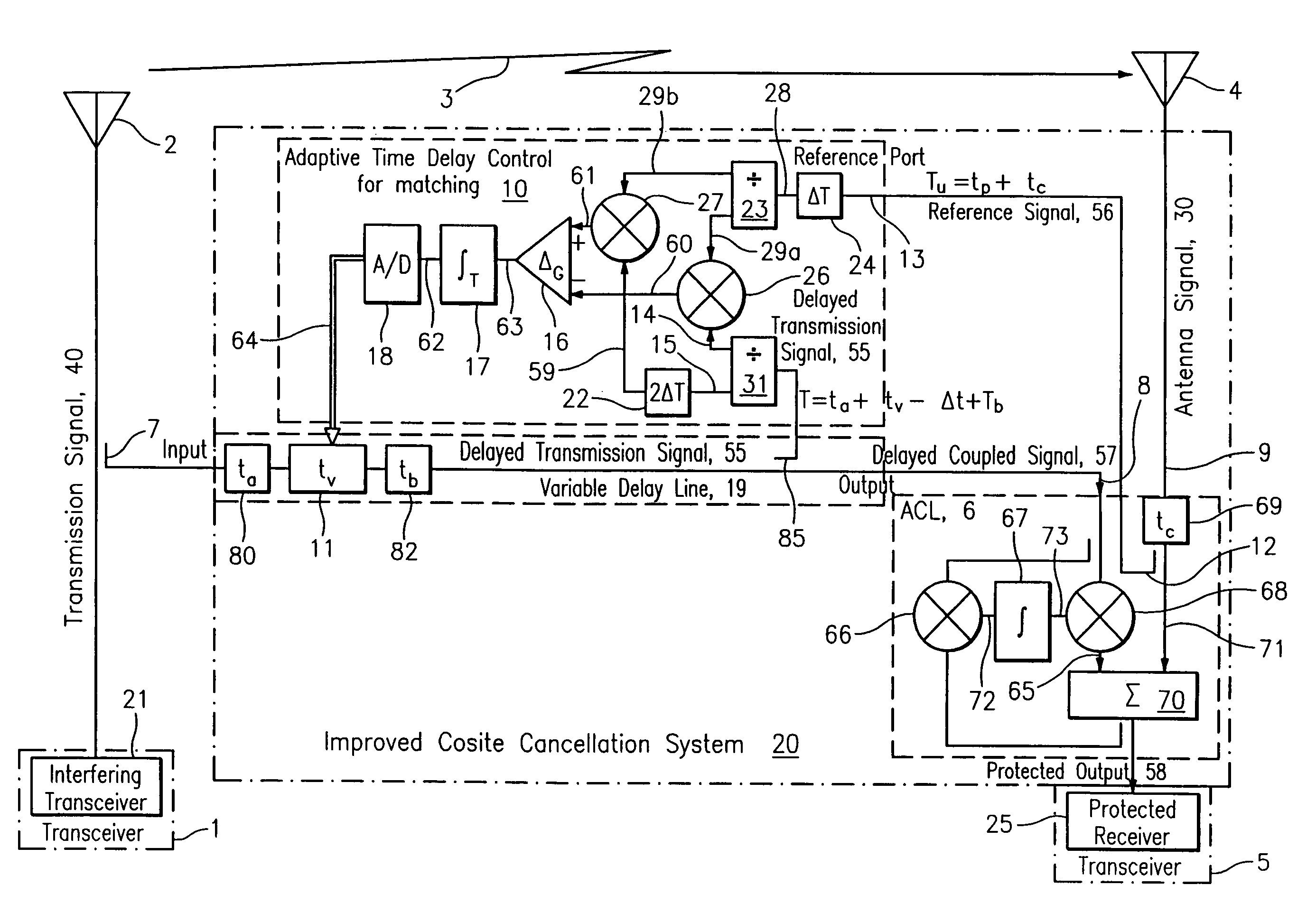
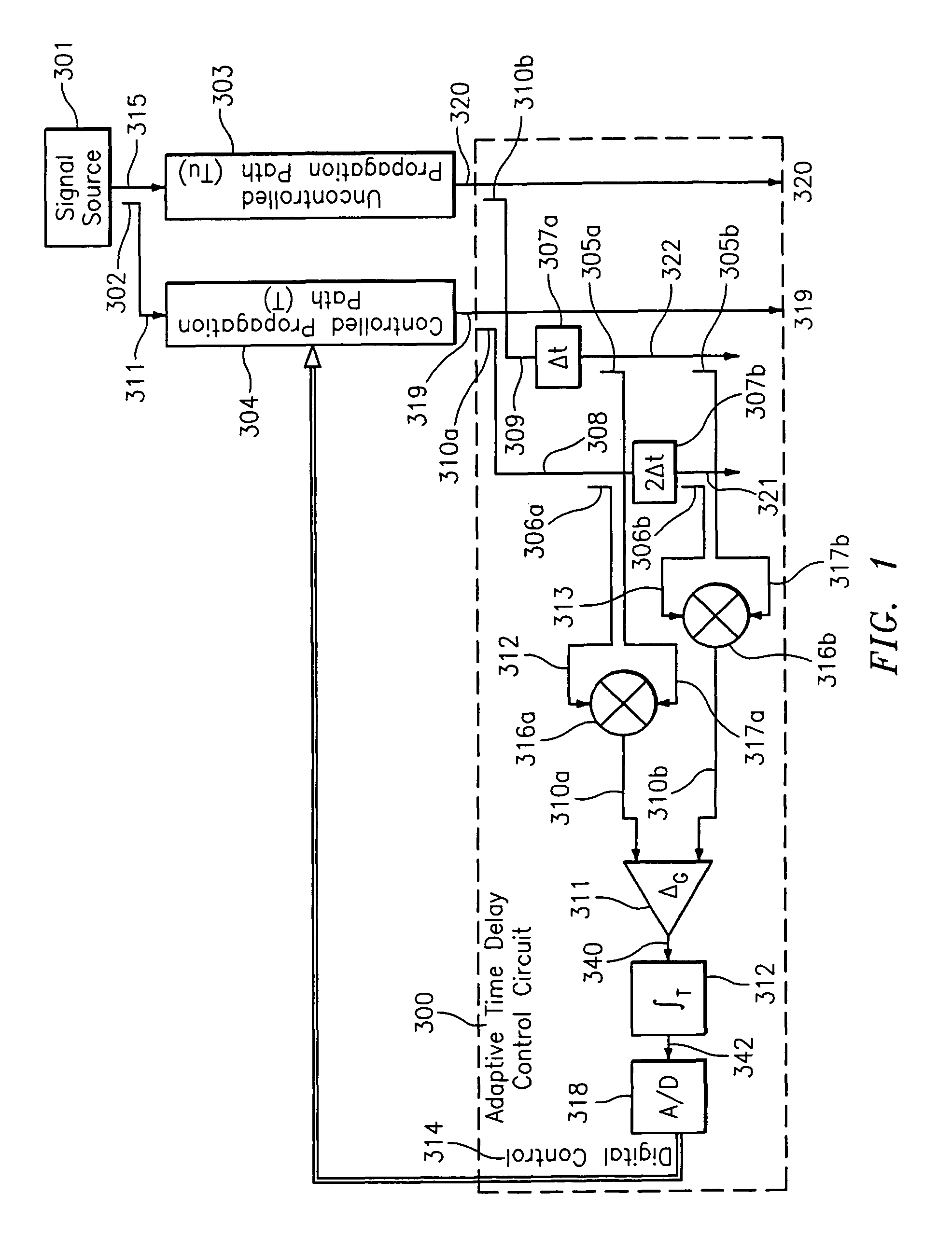
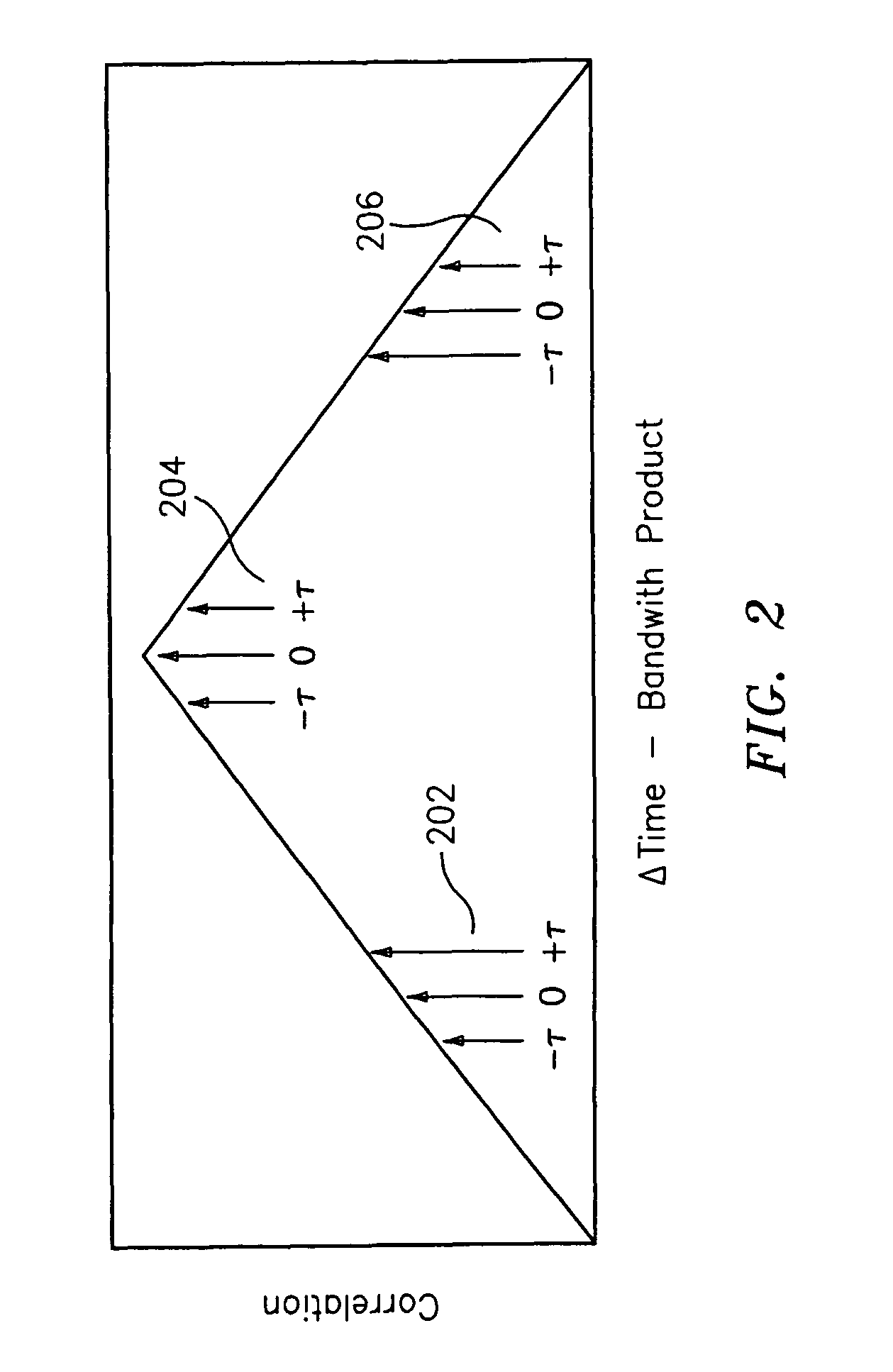
ActiveUS8094764B2Reduce impactAffect qualityError preventionModulated-carrier systemsSignal RepressionTime delays
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
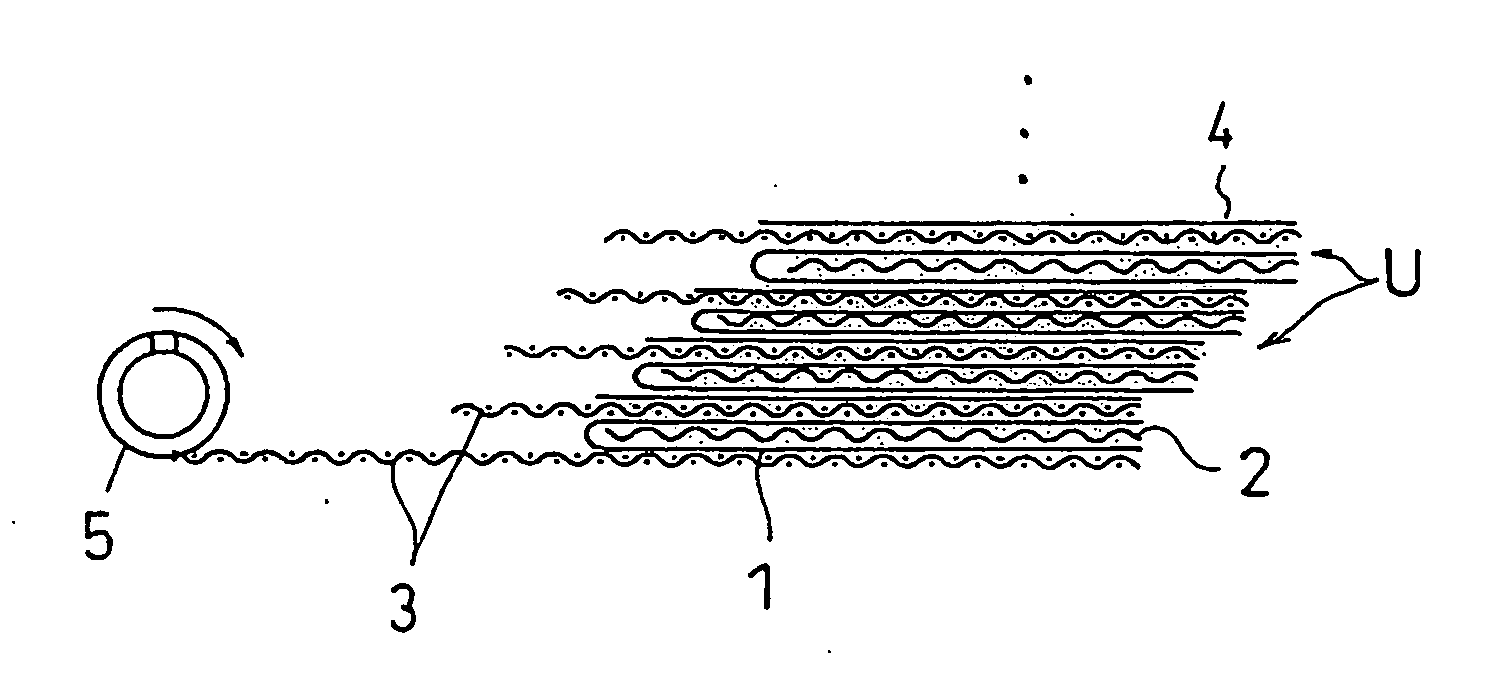
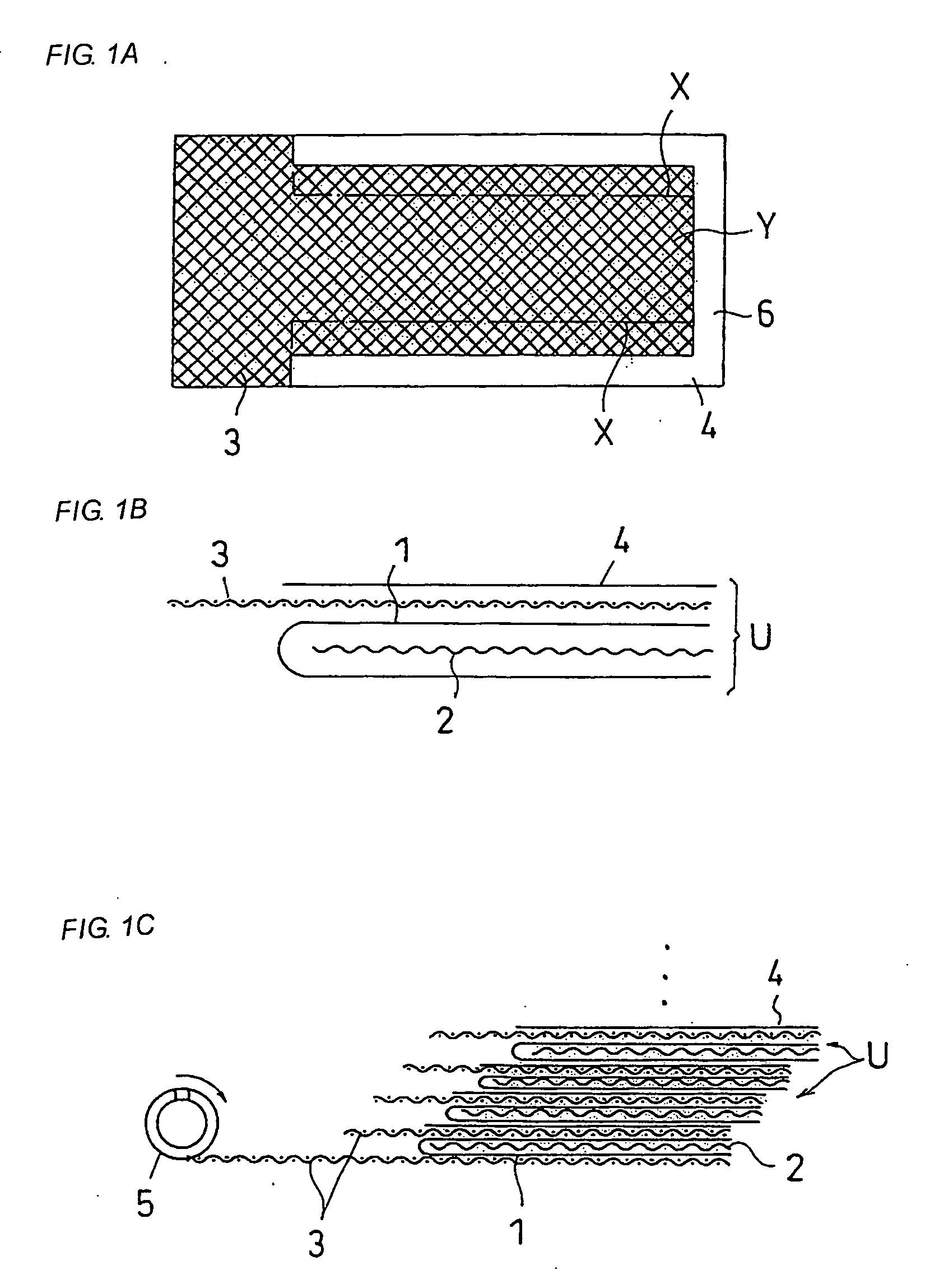
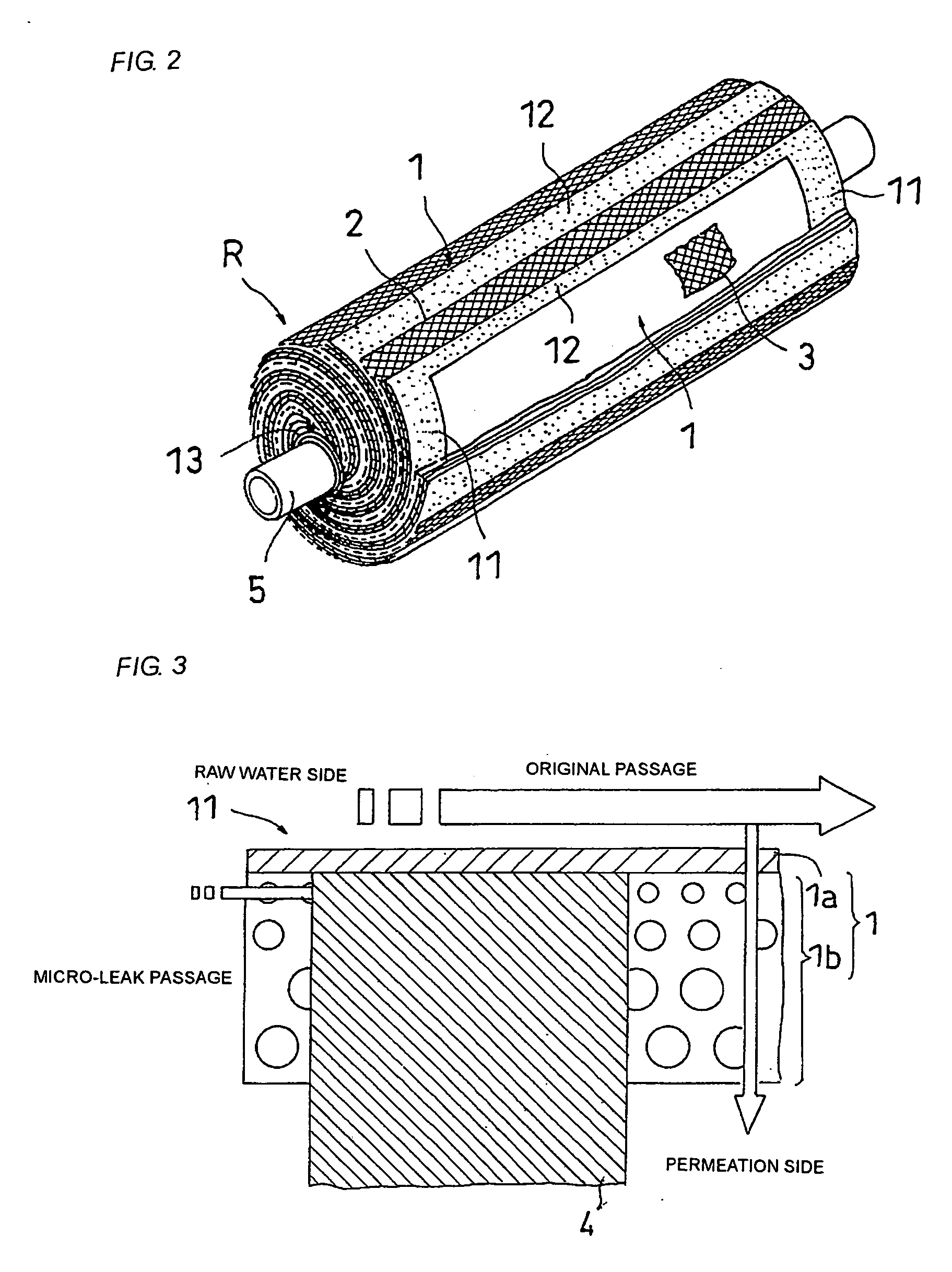
Spiral reverse osmosis membrane element, method of manufacturing the same, and its use method
ActiveUS20060043013A1Avoid dippingEasy to separateSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisReverse osmosisPermeation
A spiral reverse osmosis membrane element that improves impregnation property of a sealing resin at edges of a membrane leaf and can effectively prevent micro-leaks, by using, for example, a porous support having a structure capable of sufficiently impregnating therein a sealing resin, a method for manufacturing the same, and a use method of the same are disclosed. The spiral reverse osmosis membrane element comprises a cylindrically wound body comprising a perforated core tube and, spirally wound therearound, a separation membrane, a feed-side passage material and a permeation-side passage material in a laminated state, and a sealing portion for preventing a feed-side liquid and a permeation-side liquid from being mixed together, wherein the separation membrane facing through the permeation-side passage material has a structure that a porous support and a skin layer are successively laminated on a non-woven fabric layer, and the sealing portion sealed with a sealing resin is provided at the edges of the separation membrane, wherein the separation membrane is impregnated with the sealing resin at least up to the vicinity of the skin layer through the porous support.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Variable time delay control structure for channel matching
ActiveUS20100135443A1Reduce effectEliminate effectError preventionModulated-carrier systemsTime delaysSingle antenna interference cancellation
A cosite interference cancellation system is provided for improved rejection of a signal coupled from a transmission antenna into a local receive antenna in the presence of local multipath. The cosite interference cancellation system and associated method advantageously provide improved signal rejection by continuously controlling (adjusting) a matching time delay to reduce cosite interference.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Methods and Apparatuses for Noninvasive Determinations of Analytes using Parallel Optical Paths
InactiveUS20090018415A1Accurate noninvasive determinationAvoid collectingSamplingPolarisation-affecting propertiesAnalyteOptical polarization
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for accurate noninvasive determination of tissue properties. Some embodiments of the present invention comprise an optical sampler having an illumination subsystem, adapted to communicate light having a first polarization along a first path to a tissue surface; a collection subsystem, adapted to collect light having a second polarization communicated from the tissue along a second path after interaction with the tissue; wherein the first polarization is different from the second polarization; and wherein the first path and the second path are substantially parallel for at least of portion of each path.
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Gyroscope with temperature compensation
InactiveUS7801694B1Improve reliabilityIncreased durabilityTesting/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsVibrating structure gyroscopeEngineering
A method for compensating for bias and scale factor errors in vibrating structure gyroscopes. Certain embodiments utilize the functional relationship that bias and scale factor errors have with resonant frequency of vibration in the main vibrating body. Other embodiments utilize the functional relationships that other drive parameters of vibrating structure gyroscopes, such as drive voltage, have with bias and scale factor errors. The various methods may be used repeatedly during normal gyroscope operation in order to continually compensate for the bias and scale factor errors.
Owner:WATSON INDUSRIES
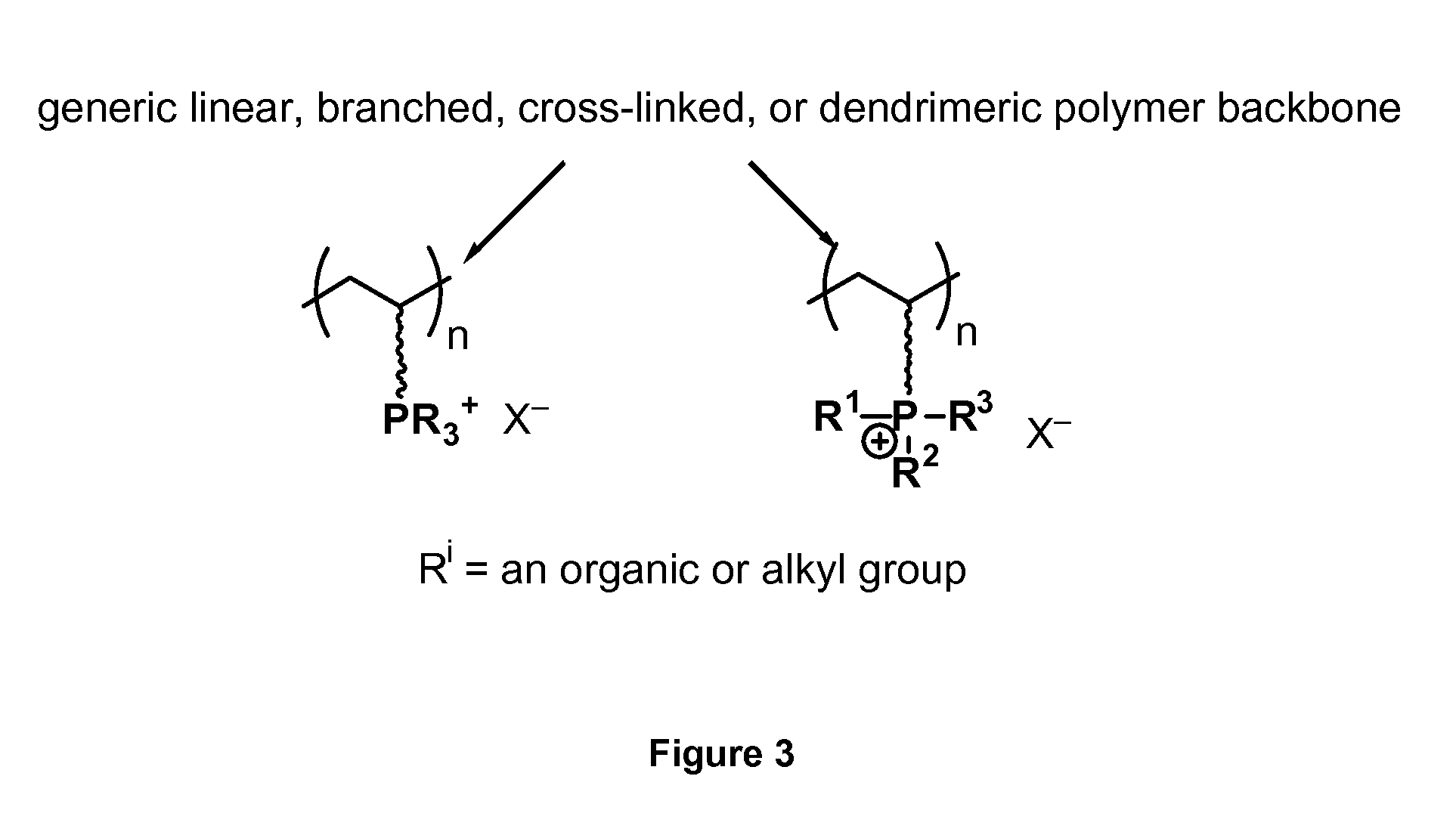
Polymer coatings that resist adsorption of proteins
InactiveUS20100096327A1Easy to synthesizeOxidation stabilityMembranesUltrafiltrationPhosphoniumFiltration
The invention provides membranes useful for filtration of water and other liquids. The membrane may be a composite membrane having a polymer layer incorporating quaternary phosphonium or ammonium groups. The polymer layer may be resistant to protein adsorption in an aqueous environment. The membrane may also be a surface-modified membrane in which a polymer having quaternary phosphonium or ammonium groups is covalently attached to the membrane surface. Methods for making and using the membranes of the invention are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Agent and Process for Increasing Rejection of Nanofiltration Membrane or Reverse Osmosis Membrane, Nanofiltration Membrane or Reverse Osmosis Membrane, Process for Water Treatment and Apparatus for Water Treatment
InactiveUS20090266764A1Reduce fluxIncreased rejectMembranesOrganic chemistryReverse osmosisBiochemistry
An agent for increasing the rejection of a nanofiltration membrane or a reverse osmosis membrane which comprises a compound having a polyalkylene glycol chain having a weight-average molecular weight of 2,000 to 6,000; a process for increasing the rejection of a nanofiltration membrane or a reverse osmosis membrane which comprises bringing the nanofiltration membrane or the reverse osmosis membrane into contact with an aqueous solution of a compound having a polyalkylene glycol chain which is obtained by diluting the agent for increasing the rejection of a nanofiltration membrane or a reverse osmosis membrane described above with water; a nanofiltration membrane or a reverse osmosis membrane exhibiting a rejection increased in accordance with the process; and a process and an apparatus for water treatment using the nanofiltration membrane or the reverse osmosis membrane. The rejection and, in particular, the rejection to nonionic solutes, of a nanofiltration membrane or a reverse osmosis membrane can be increased while the flux is kept at a great value.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Lowpass filter formed in a multi-layer ceramic
InactiveUS20050219011A1Improved stopband rejectionReduce circuit areaMultiple-port networksPrinted capacitor incorporationLow-pass filterInductor
A lowpass filter formed in a multi-layered substrate includes a first capacitor formed on at least one layer of the multi-layered substrate and being electrically connected to a first node, a first inductor being electrically connected to the first capacitor at the first node, and a second inductor being electrically connected to the first inductor and the first capacitor at the first node. In the lowpass filter, negative mutual inductance exists between the first inductor and the second inductor.
Owner:CHI MEI COMM SYST INC
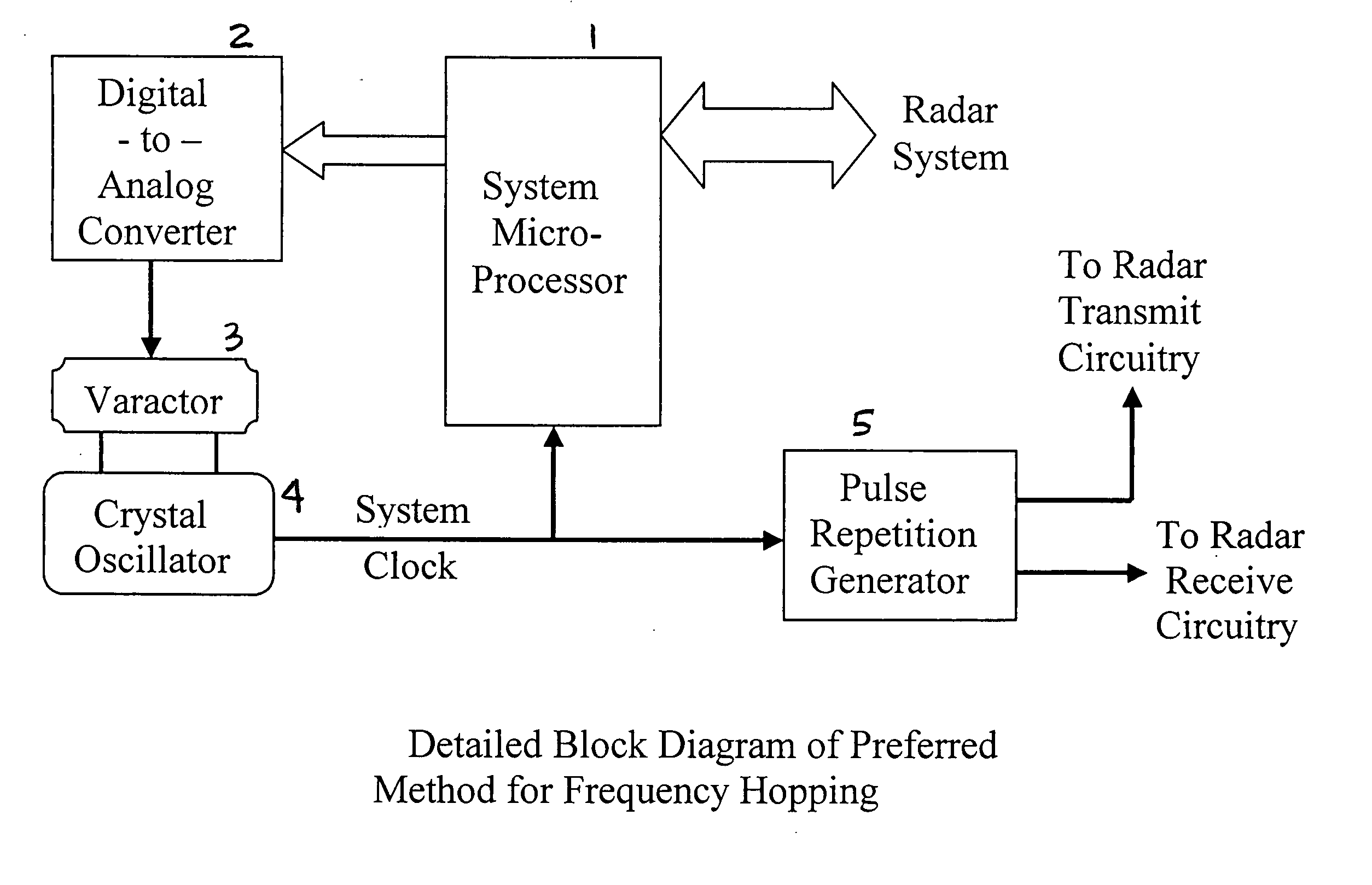
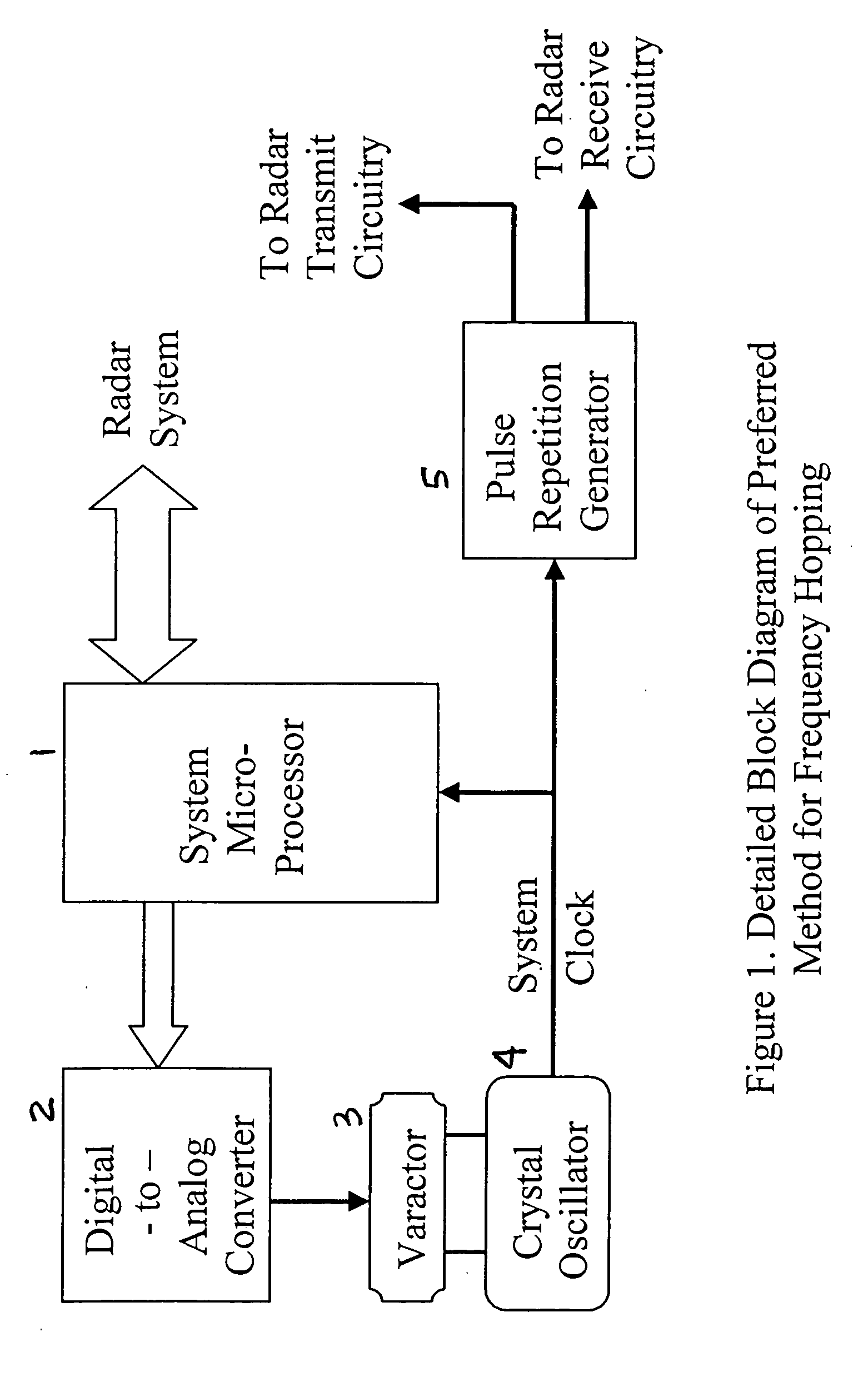
Radar frequency hopping
ActiveUS20050104765A1Avoiding extended reception of interfering signalMaximize receiver sensitivityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandTime domain
Apparatus and methods for adjusting or “hopping” the center frequency or the pulse repetition frequency of a radar system improve the co-locatability of multiple radars commonly located in a region. In a Time Domain Downconversion (TDDC) or Ultra-Wideband (UWB) radar system having a display update period between range sweeps, the preferred device comprises a frequency variable oscillator for adjusting the radar's internal timing reference frequency during a plurality of the display update periods. Radar frequency hopping methods and apparatus may result in improvements in interference immunity compared to other interference reduction techniques and may achieve cost reduction. In frequency hopping radar, if an actual target is present, the receiver waveform will repeat at the newly adjusted center frequency. Confirmation of a target is realized as an ongoing reflection and not interference.
Owner:PRECO ELECTRONICS
Optical filtering structure in the visible and/or infrared domain
ActiveUS20140034835A1Reduce in quantityReduce sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMirrorsComputational physics
An optical filtering structure comprising a stack of layers forming a first filter letting pass a first spectral band, and a second filter adjacent to the first filter and which lets pass a second spectral band comprising:a plurality of dielectric layers common to the two filters and of different refractive indices;n first metal layers common to the two filters;m second metal layers arranged only in the second filter;and wherein at least one of said dielectric layers comprises, in the first filter, a thickness different to that in the second filter, and / or wherein at least one dielectric layer is arranged only in the second filter;n being an integer greater than or equal to 0, and m being an integer greater than or equal to 1.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
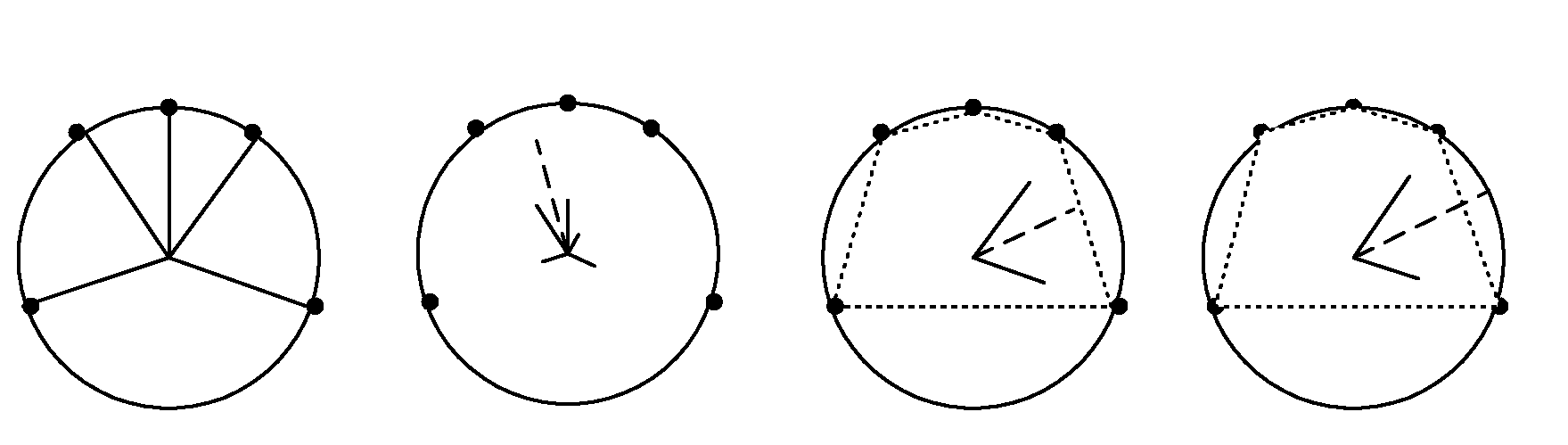
Microphone Array Processor Based on Spatial Analysis
ActiveUS20090103749A1Increase spatial selectivityIncrease heightSignal processingMicrophones signal combinationLight beamSpatial analysis
An array processing system improves the spatial selectivity by forming multiple steered beams and carrying out a spatial analysis of the acoustic scene. The analysis derives a time-frequency mask that, when applied to a reference look-direction beam (or other reference signal), enhances target sources and substantially improves rejection of interferers that are outside of the specified region.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Radio-frequency mixer arrangement
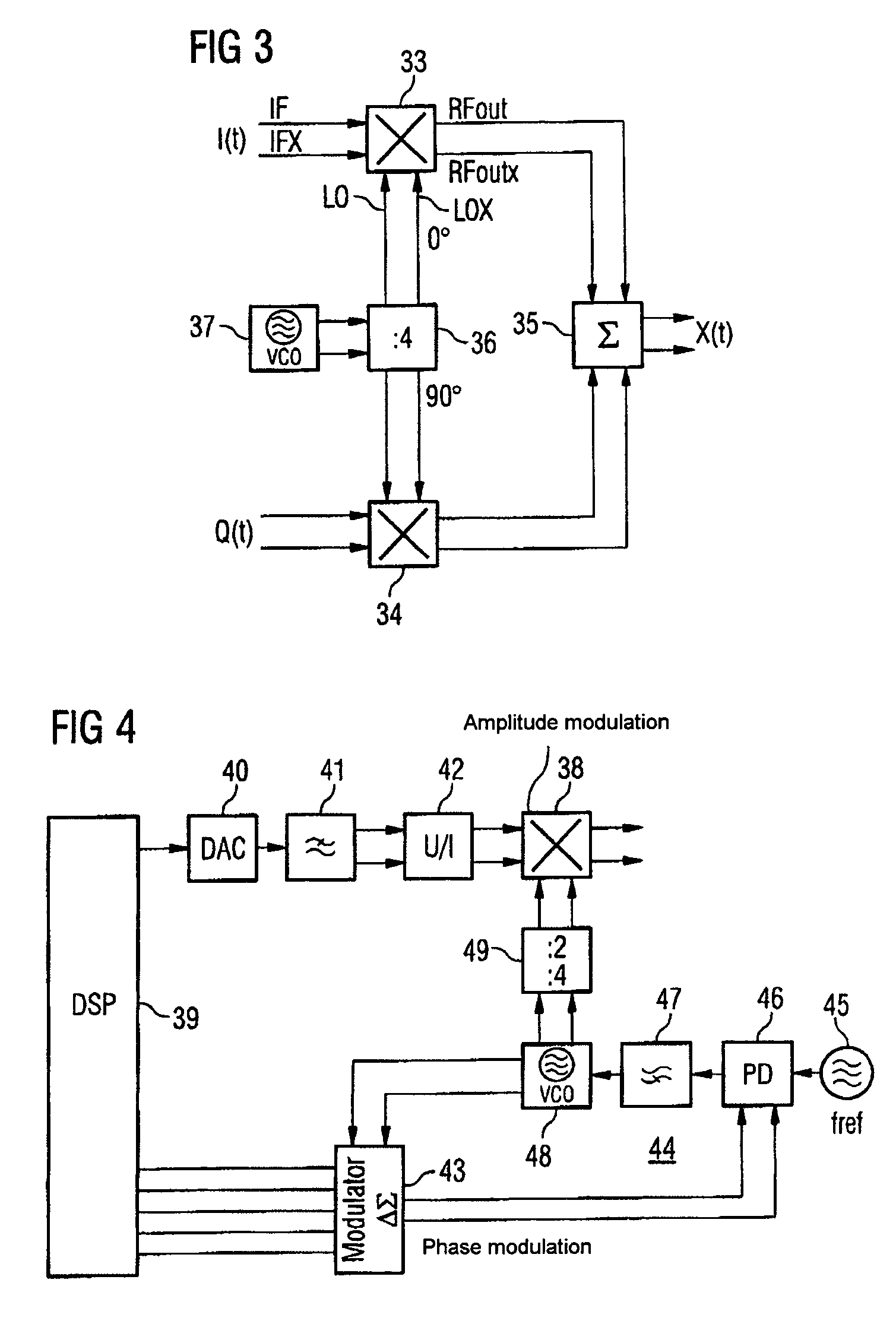
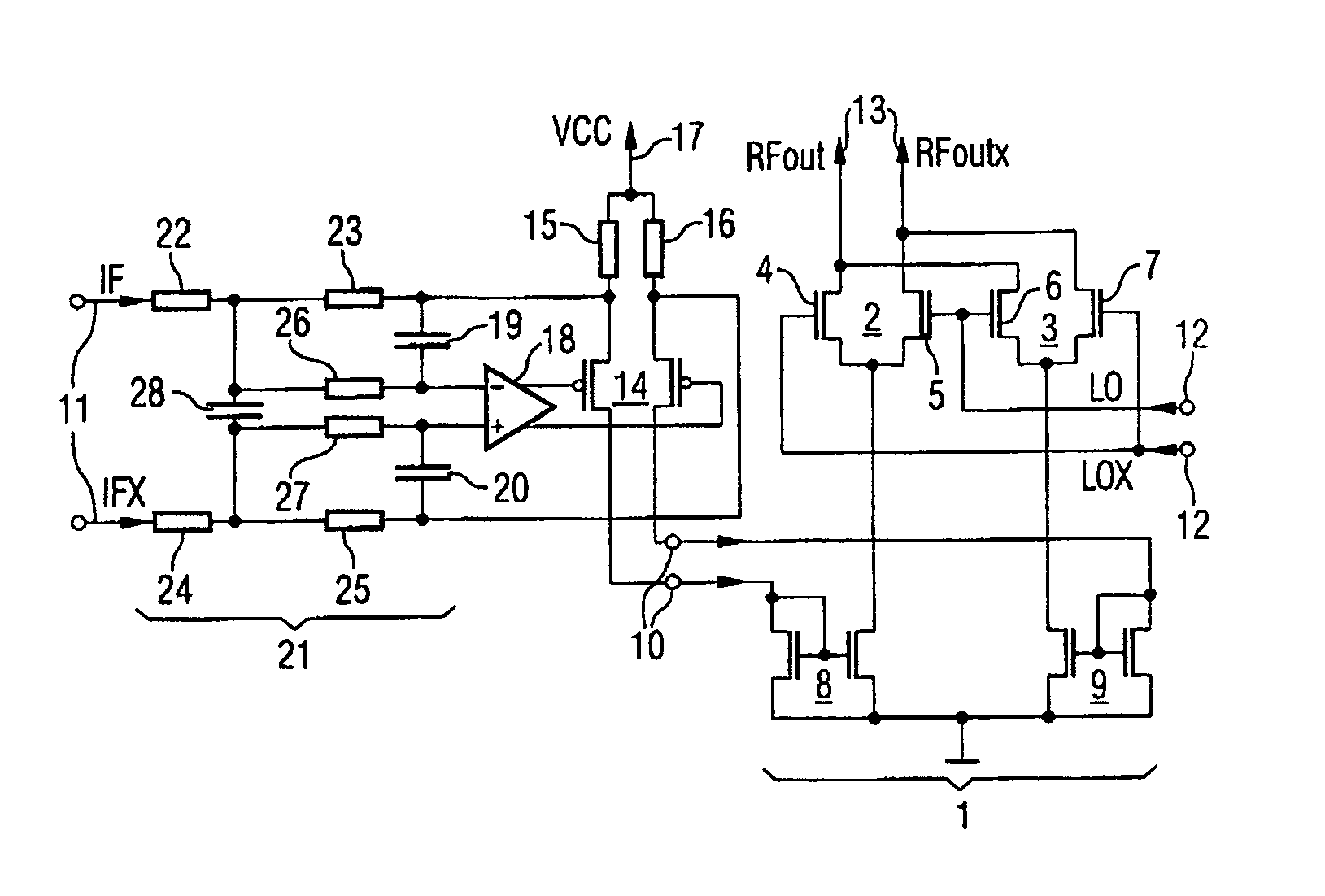
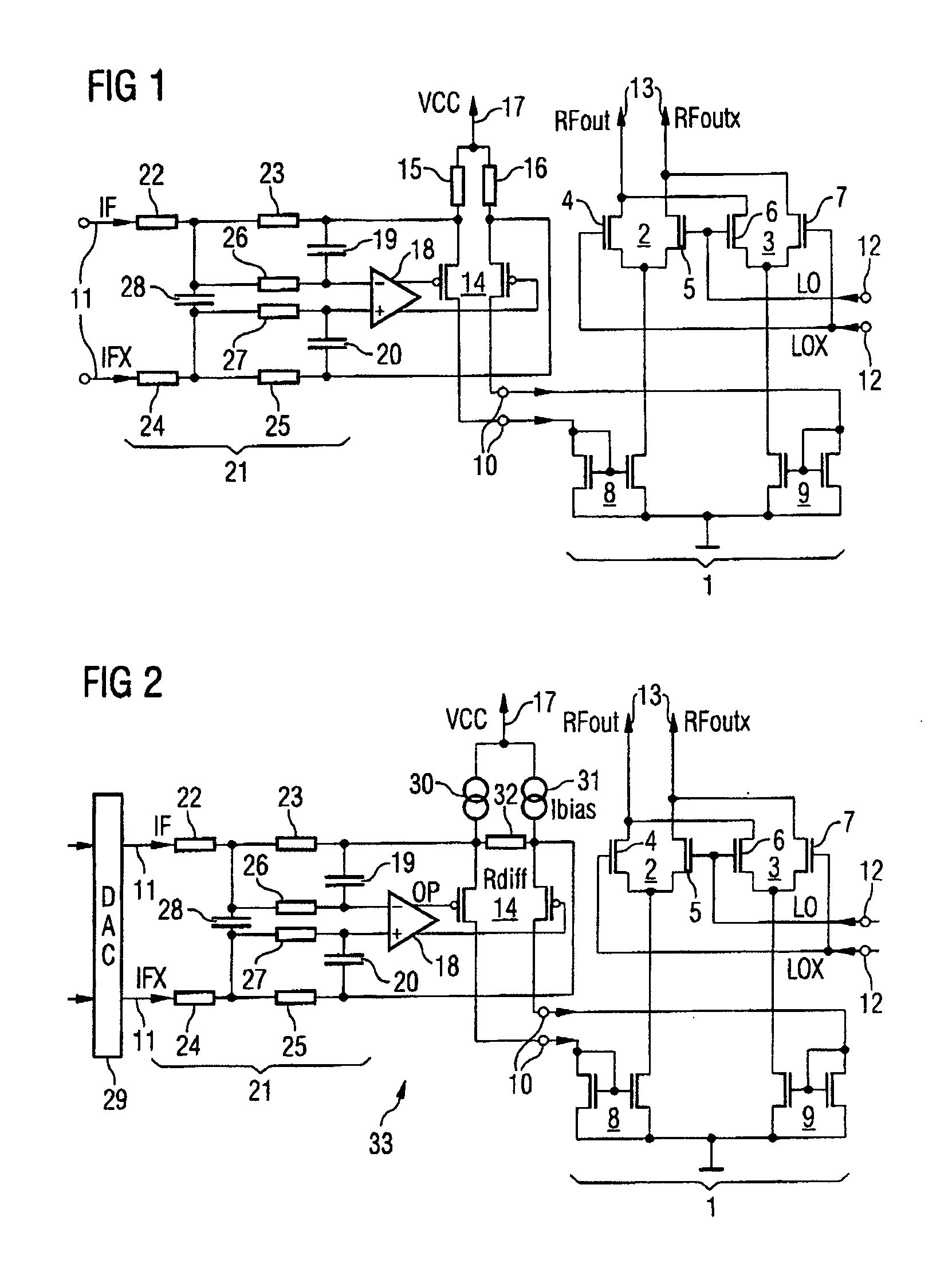
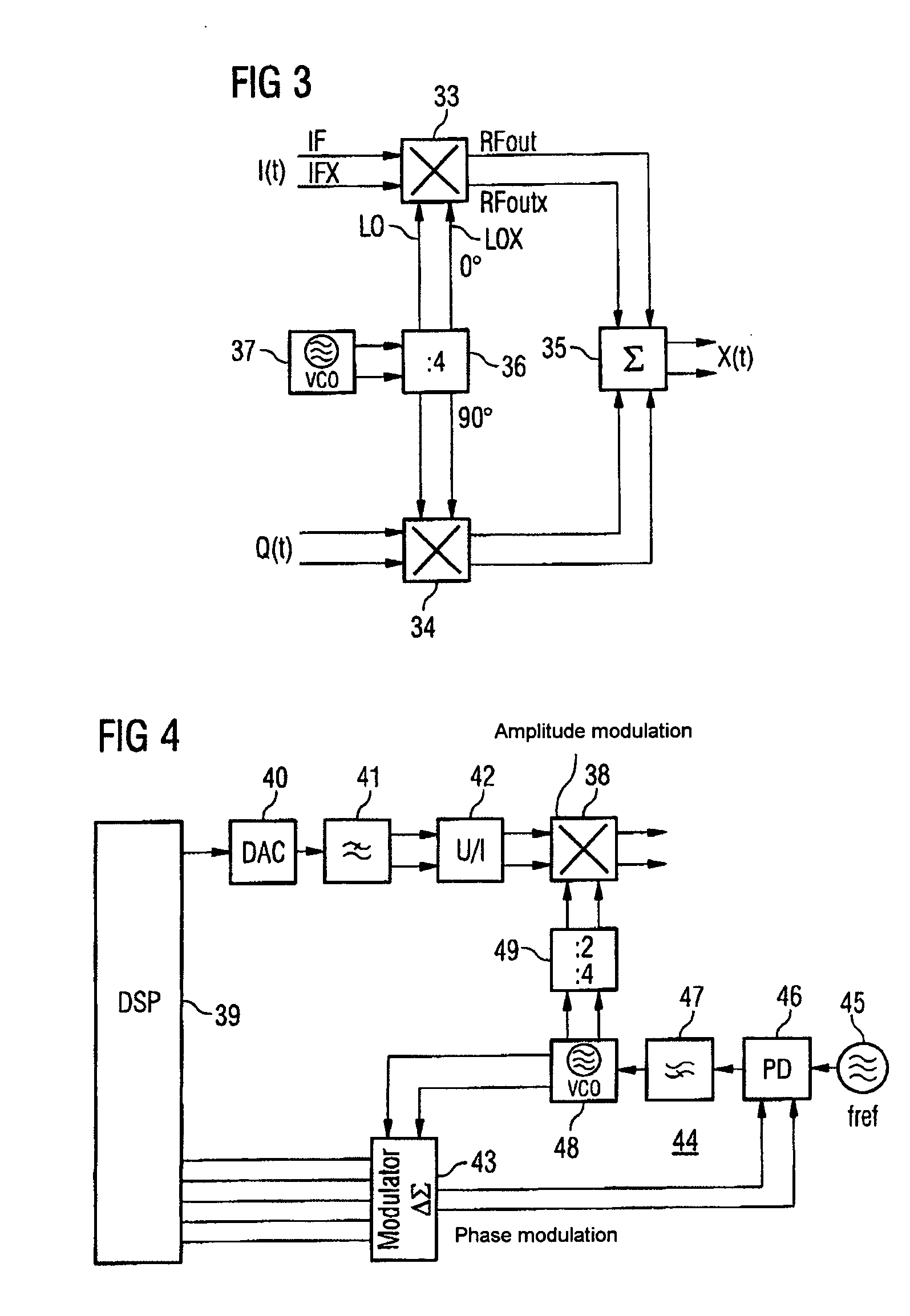
InactiveUS7218163B2Increased rejectSimple designModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a radio-frequency mixer arrangement in which a differential amplifier is connected to an input on a multiplier. The differential amplifier is arranged together with at least one capacitance in the feedback path of an operational amplifier. The at least one capacitance performs the function of an antialiasing filter. The feedback operational amplifier with the design described results in a highly linear output signal given low output noise and a low current requirement. The mixer proposed is particularly suitable for use in vector modulators or polar modulators in transmission paths in mobile radios.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Radio-frequency mixer arrangement
InactiveUS20050130619A1Increased rejectSimple designModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a radio-frequency mixer arrangement in which a differential amplifier is connected to an input on a multiplier. The differential amplifier is arranged together with at least one capacitance in the feedback path of an operational amplifier. The at least one capacitance performs the function of an antialiasing filter. The feedback operational amplifier with the design described results in a highly linear output signal given low output noise and a low current requirement. The mixer proposed is particularly suitable for use in vector modulators or polar modulators in transmission paths in mobile radios.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com