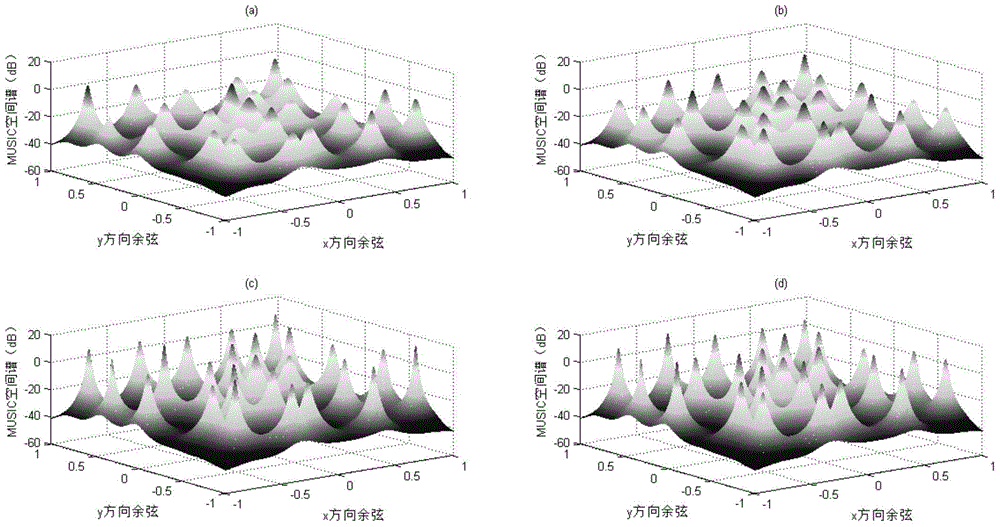
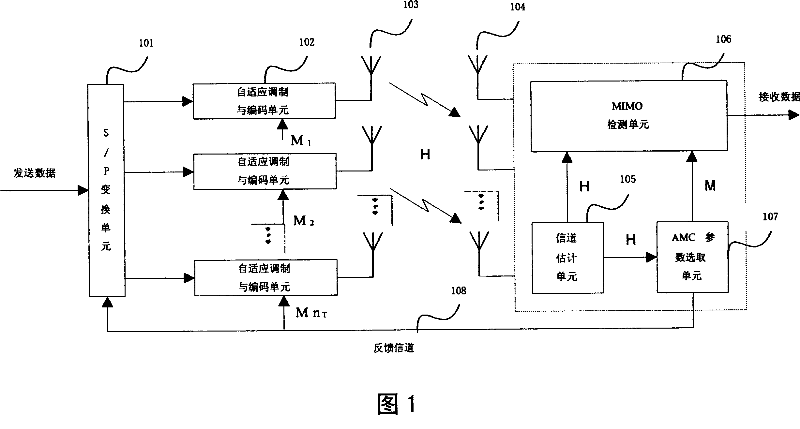
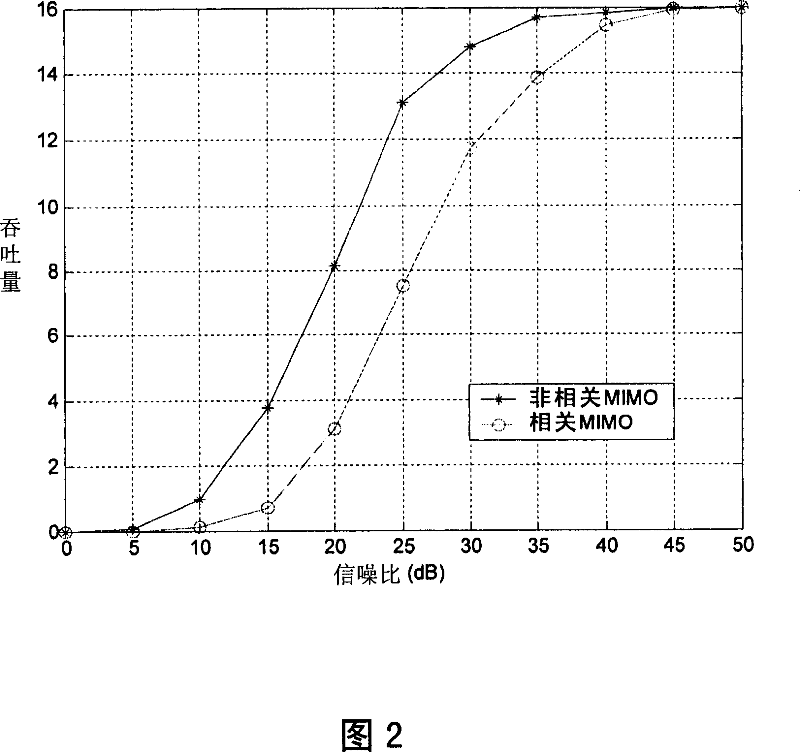
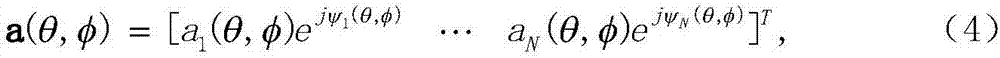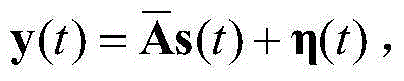Patents
Literature
146 results about "Second order statistics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
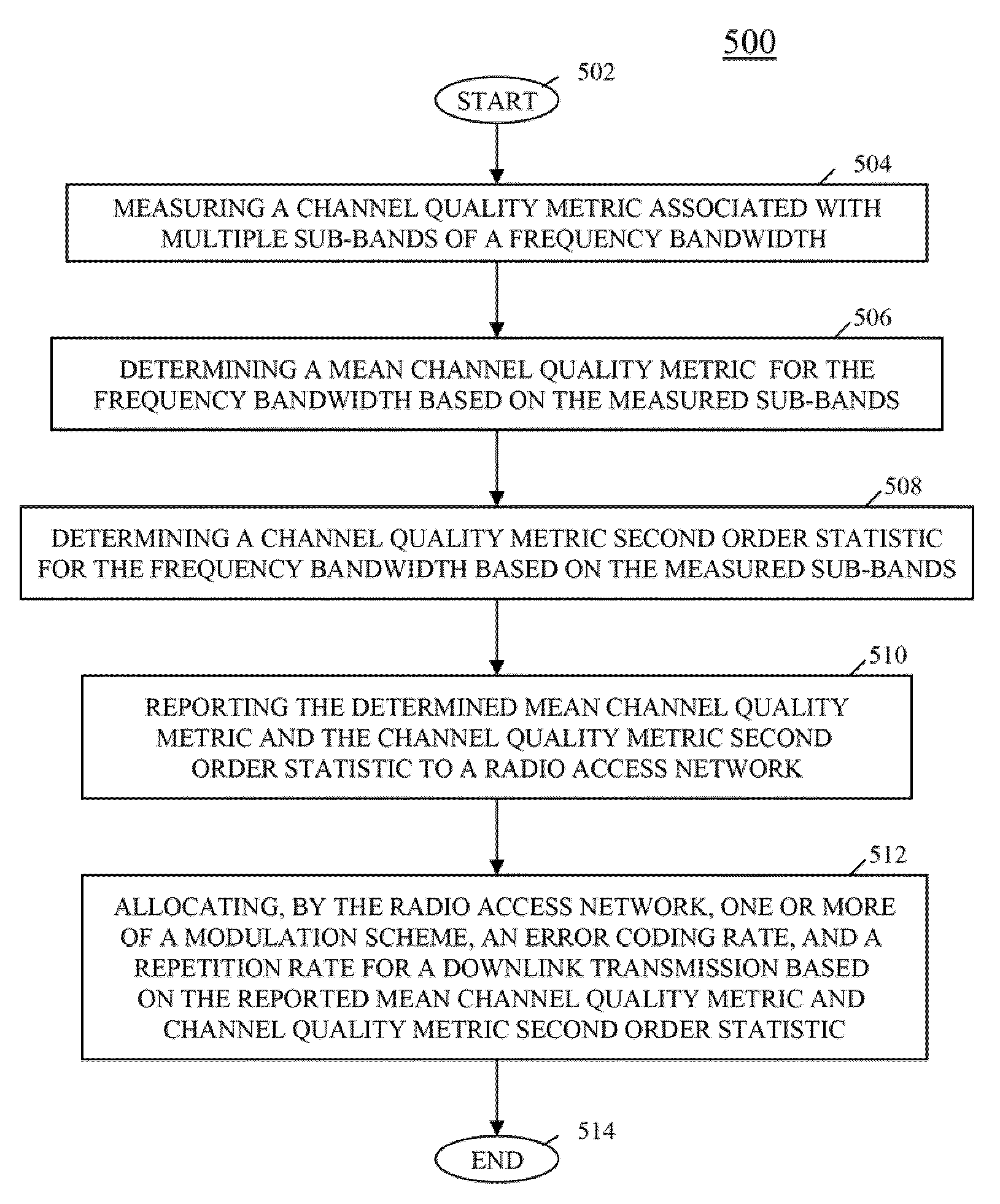
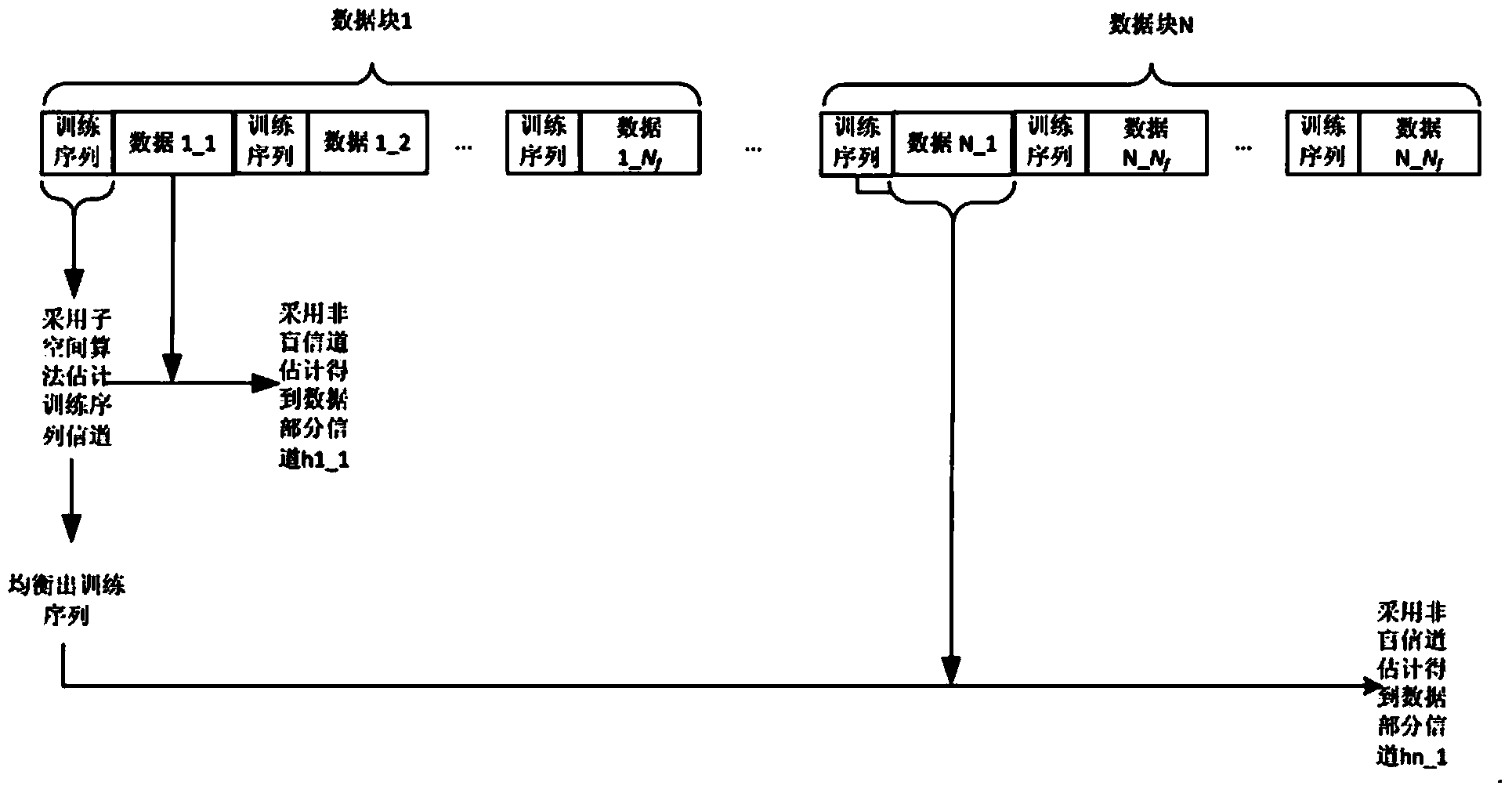
The first order statistic is the smallest sample value (i.e. the minimum), once the values have been placed in order. For example, in the sample 9, 2, 11, 5, 7, 4 the first order statistic is 2.
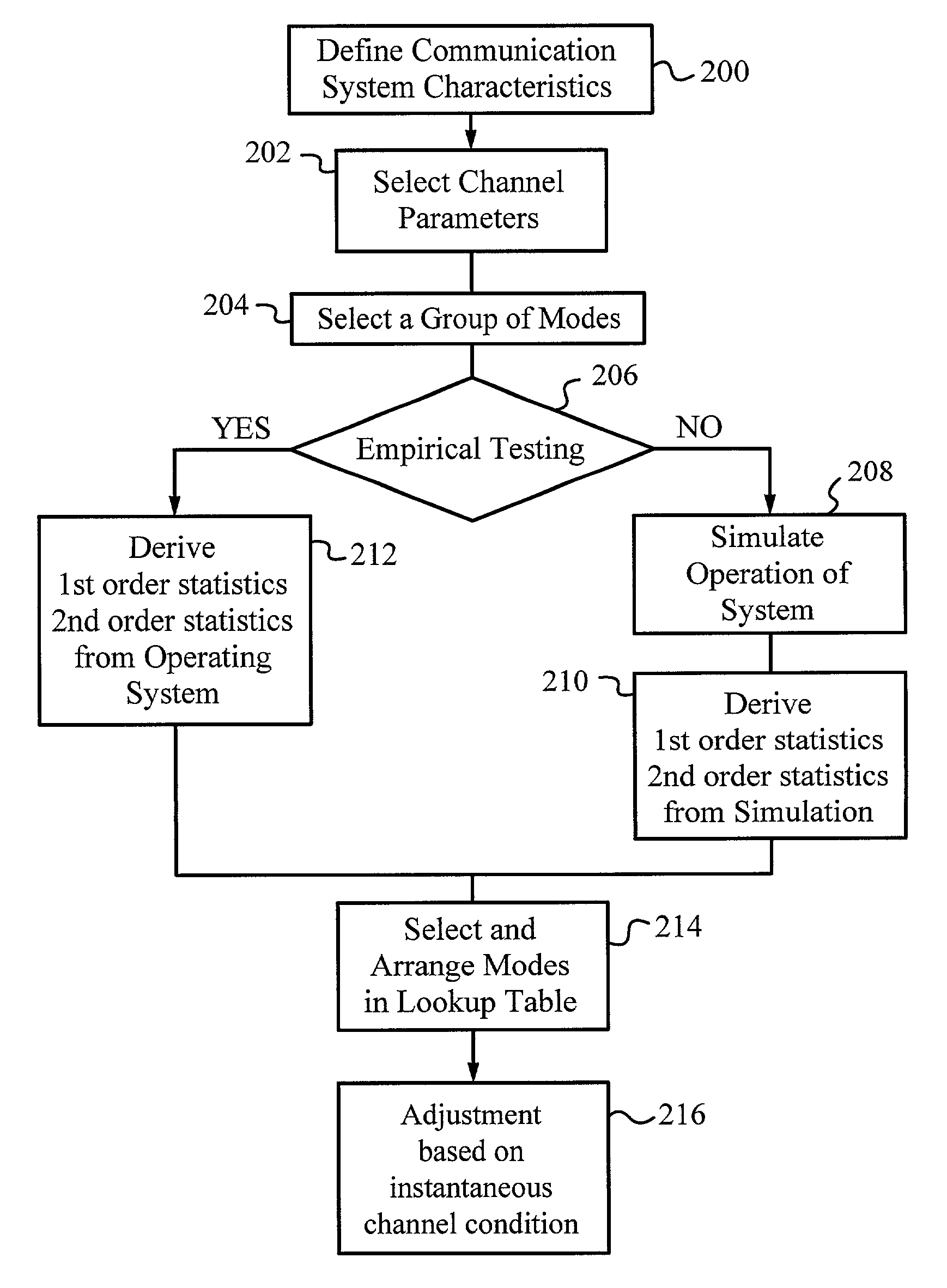
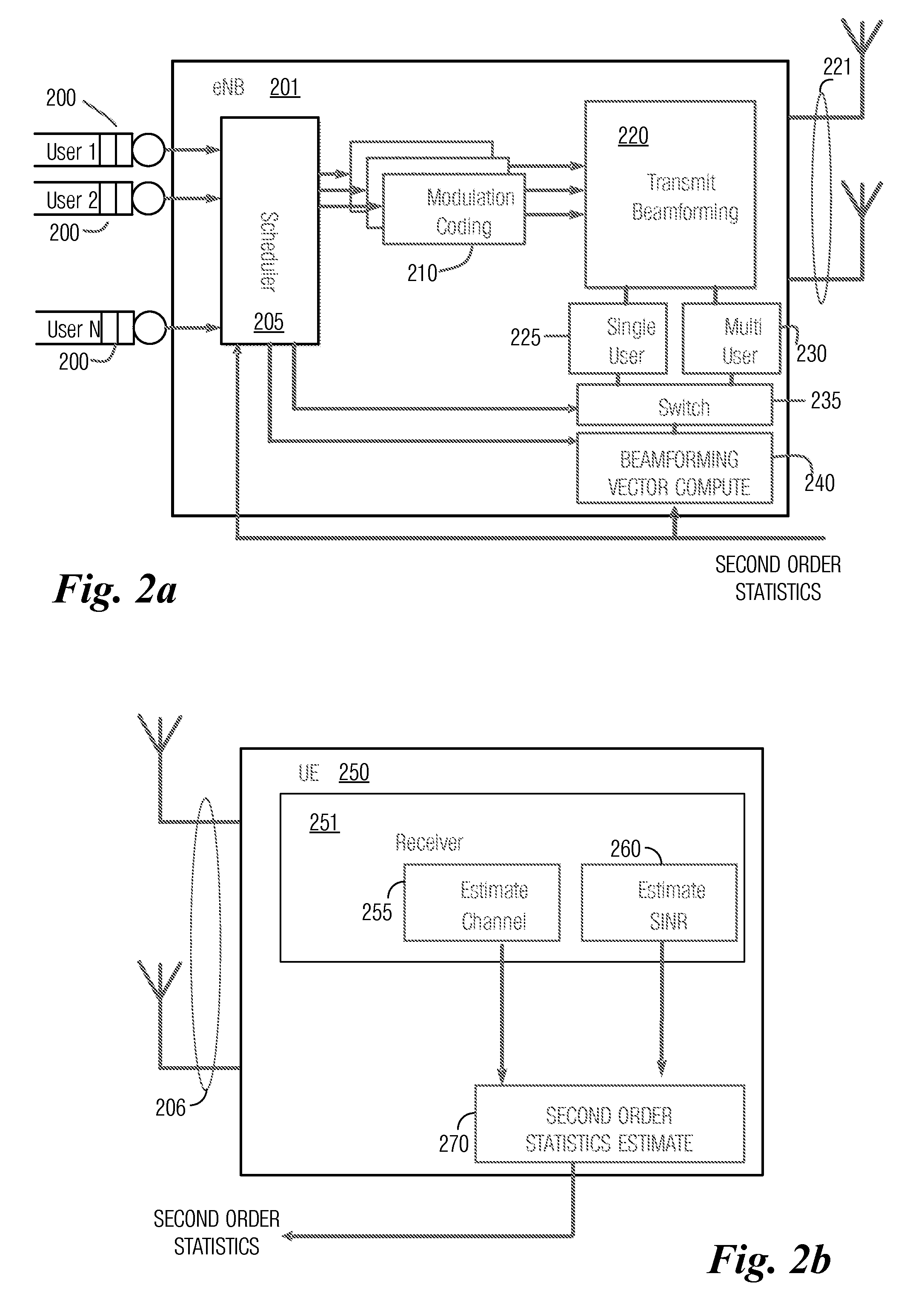
Mode lookup tables for data transmission in wireless communication channels based on statistical parameters
InactiveUS7191381B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceSignal quality
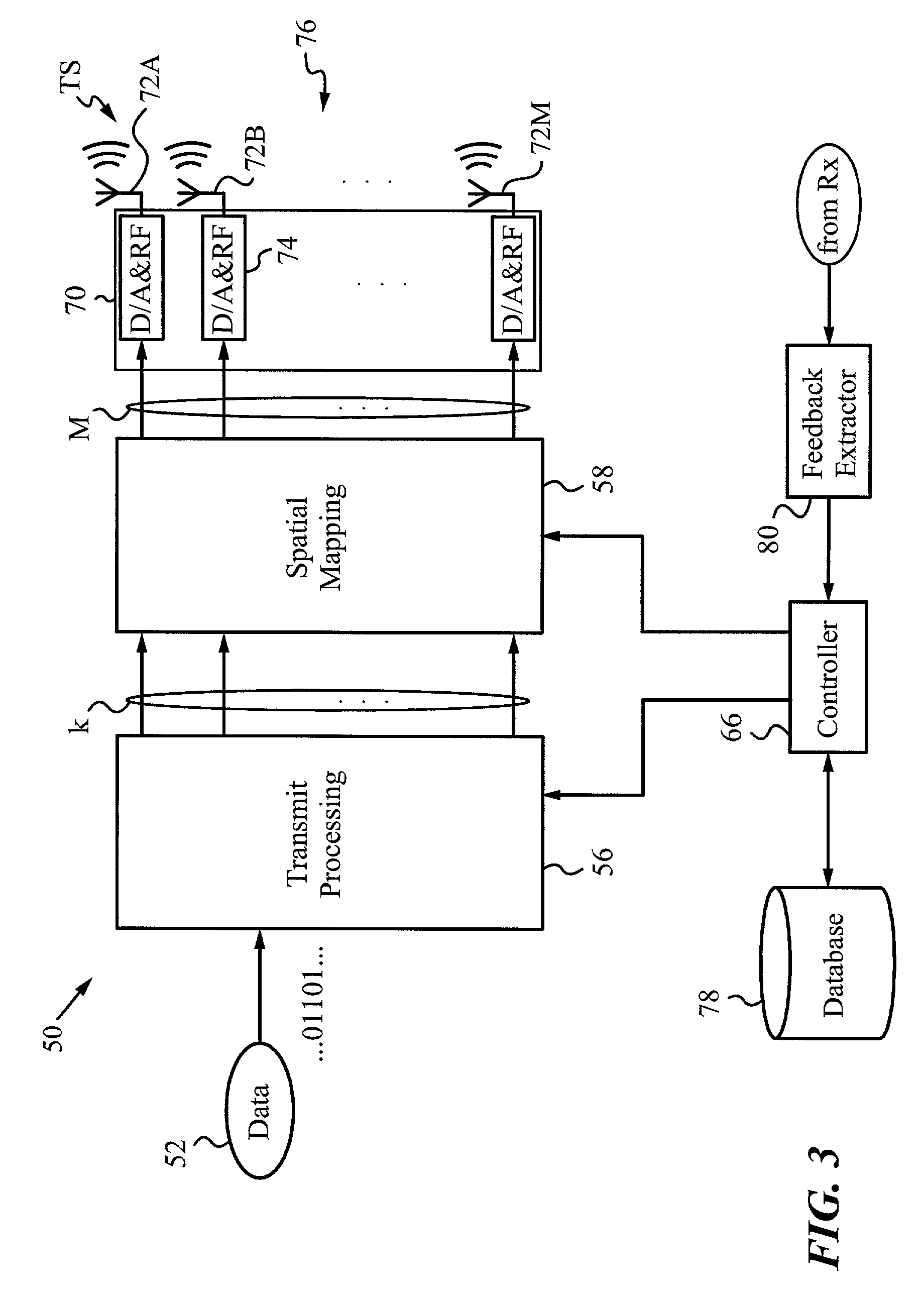
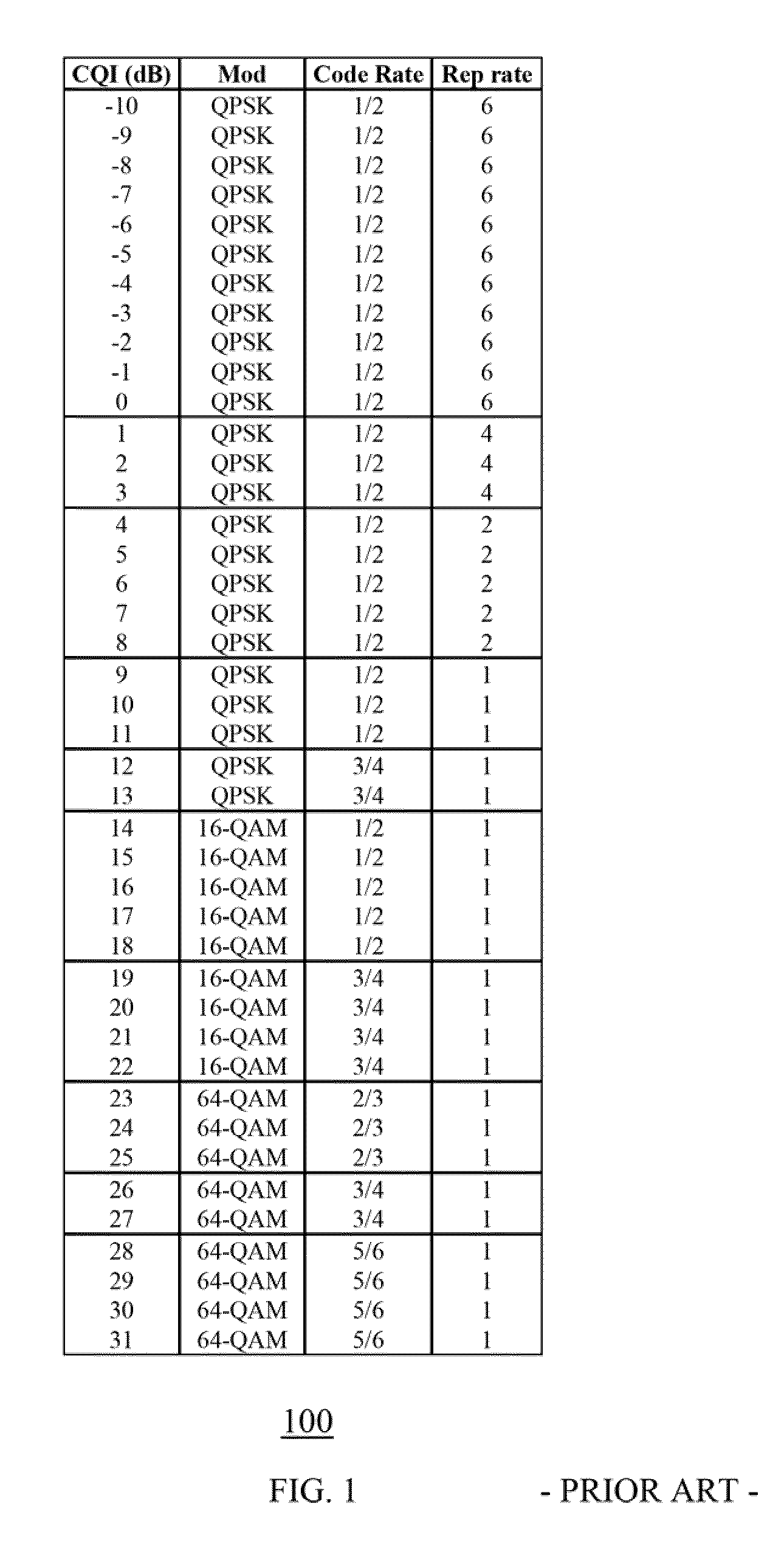
A method and medium tangibly embodying the method of constructing a lookup table of modes for encoding data for transmission in a wireless communication channel from a transmit unit to a receive unit by using at least one quality parameter of the data and its first-order and second-order statistical parameters to arrange the modes in the lookup table. The first-order and second-order statistical parameters can be determined from a simulation of the wireless communication channel or from field measurements of the wireless communication channel. The modes in the lookup table are ordered by a target value of a communication parameter such as PER, BER, data capacity, signal quality, spectral efficiency, throughput or another suitable communication parameter set to achieve a desired quality of service. The quality parameter selected is conveniently a short-term quality parameter such as signal-to-interference and noise ratio (SINR), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) or power level. During use adjustments depending on the instantaneous condition of the channel can be used to tune the lookup table.
Owner:INTEL CORP
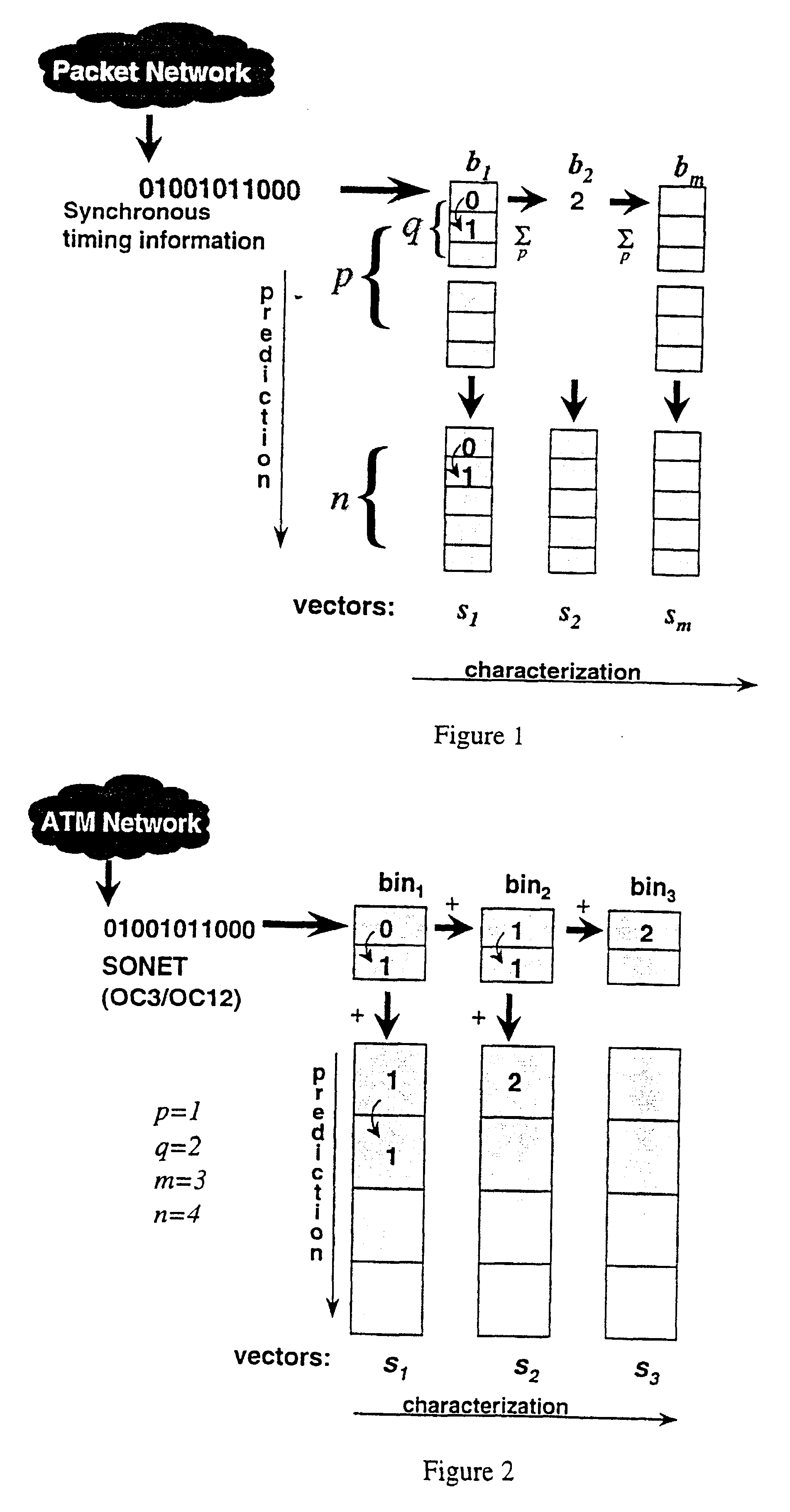
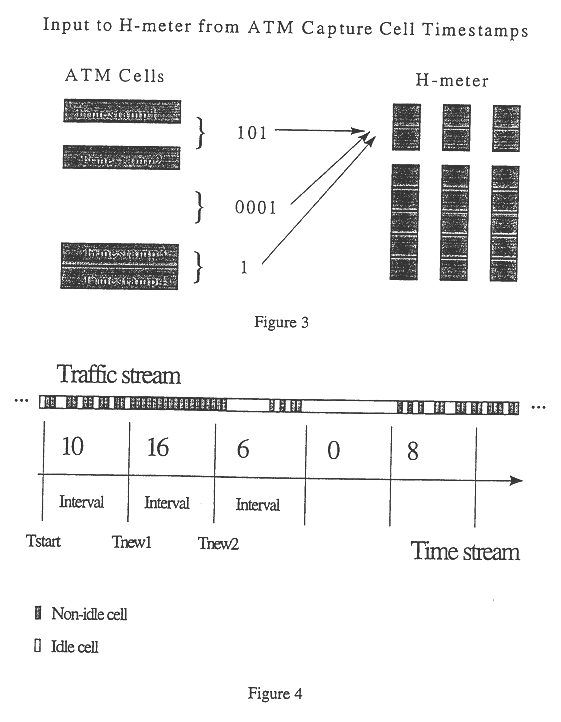
Method for real-time traffic analysis on packet networks
An architecture for capture and generation, and a set of methods for characterization, prediction, and classification of traffic in packet networks are disclosed. The architecture consists of a device that stores packet timing information and processes the data so that characterization, prediction, and classification algorithms can perform operations in real-time. A methodology is disclosed for real-time traffic analysis, characterization, prediction, and classification in packet networks. The methodology is based on the simultaneous aggregation of packet arrival times at different times scales. The traffic is represented at the synchronous carrier level by the arrival or non-arrival of a packet. The invention does not require knowledge about the information source, nor needs to decode the information contents of the packets. Only the arrival timing information is required. The invention provides a characterization of the traffic on packet networks suitable for a real-time implementation. The methodology can be applied in real-time traffic classification by training a neural network from calculated second order statistics of the traffic of several known sources. Performance descriptors for the network can also be obtained by calculating the deviation of the traffic distribution from calculated models. Traffic prediction can also be done by training a neural network from a vector of the results of a given processing against a vector of results of the subsequent processing unit; noticing that the latter vector contains information at a larger time scale than the previous. The invention also provides a method of estimating an effective bandwidth measure in real time which can be used for connection admission control and dynamic routing in packet networks. The invention provides appropriate traffic descriptors that can be applied in more efficient traffic control on packet networks.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Semantic segmentation method with second-order pooling
InactiveUS20150104102A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFree formFeature coding
Feature extraction, coding and pooling, are important components on many contemporary object recognition paradigms. This method explores pooling techniques that encode the second-order statistics of local descriptors inside a region. To achieve this effect, it introduces multiplicative second-order analogues of average and max pooling that together with appropriate non-linearities that lead to exceptional performance on free-form region recognition, without any type of feature coding. Instead of coding, it was found that enriching local descriptors with additional image information leads to large performance gains, especially in conjunction with the proposed pooling methodology. Thus, second-order pooling over free-form regions produces results superior to those of the winning systems in the Pascal VOC 2011 semantic segmentation challenge, with models that are 20,000 times faster.
Owner:UNIV DE COIMBRA OF REITORIA DA UNIV DE COIMBRA
Method and apparatus for providing channel quality feedback in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
ActiveUS20090274204A1Receivers monitoringError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Communications system
In an OFDM communication system, a mobile station provides a radio access network (RAN) a channel quality metric second order statistic, in one embodiment a signal to noise plus interference power ratio (SINR) second order statistic and in particular an SINR standard deviation and / or variance, along with a mean channel quality metric, that is, a mean SINR. By providing both a mean channel quality metric and a channel quality metric second order statistic, the communication system permits the RAN to create a more accurate fading profile of an associated air interface, and in particular a downlink of the air interface, thereby facilitating an improved scheduling decision over the prior art and assuring that a packet has a higher probability to go through a downlink channel without too many retransmissions.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
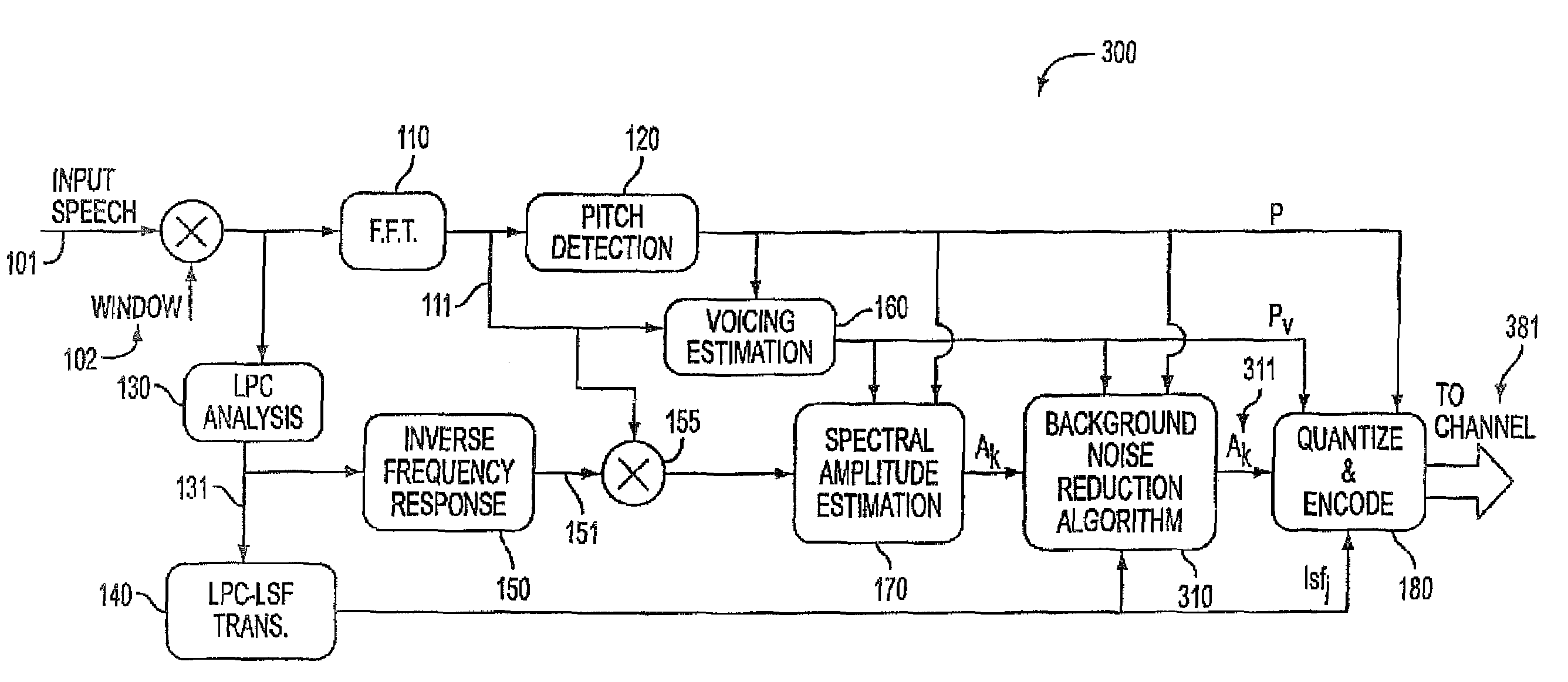
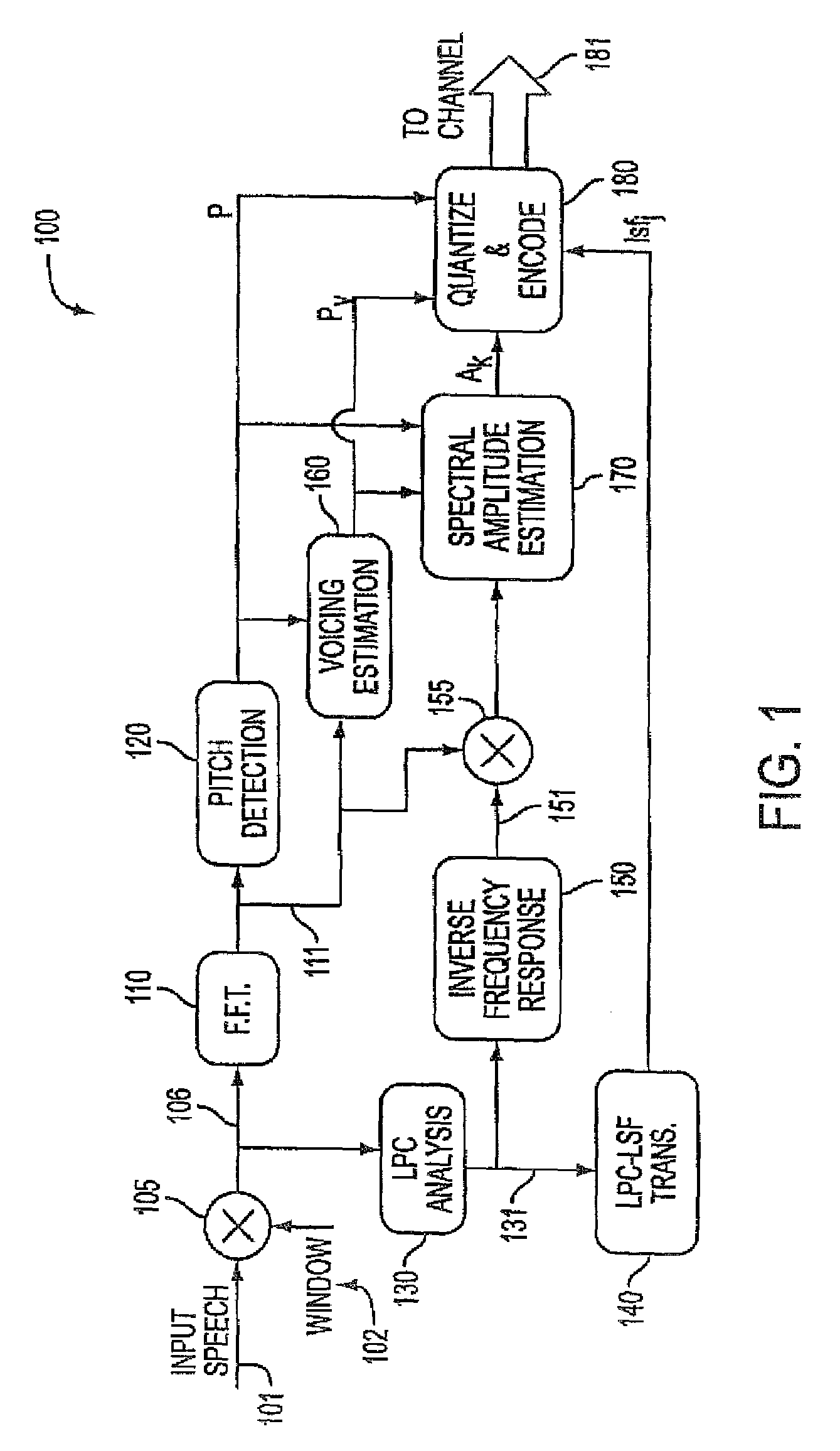
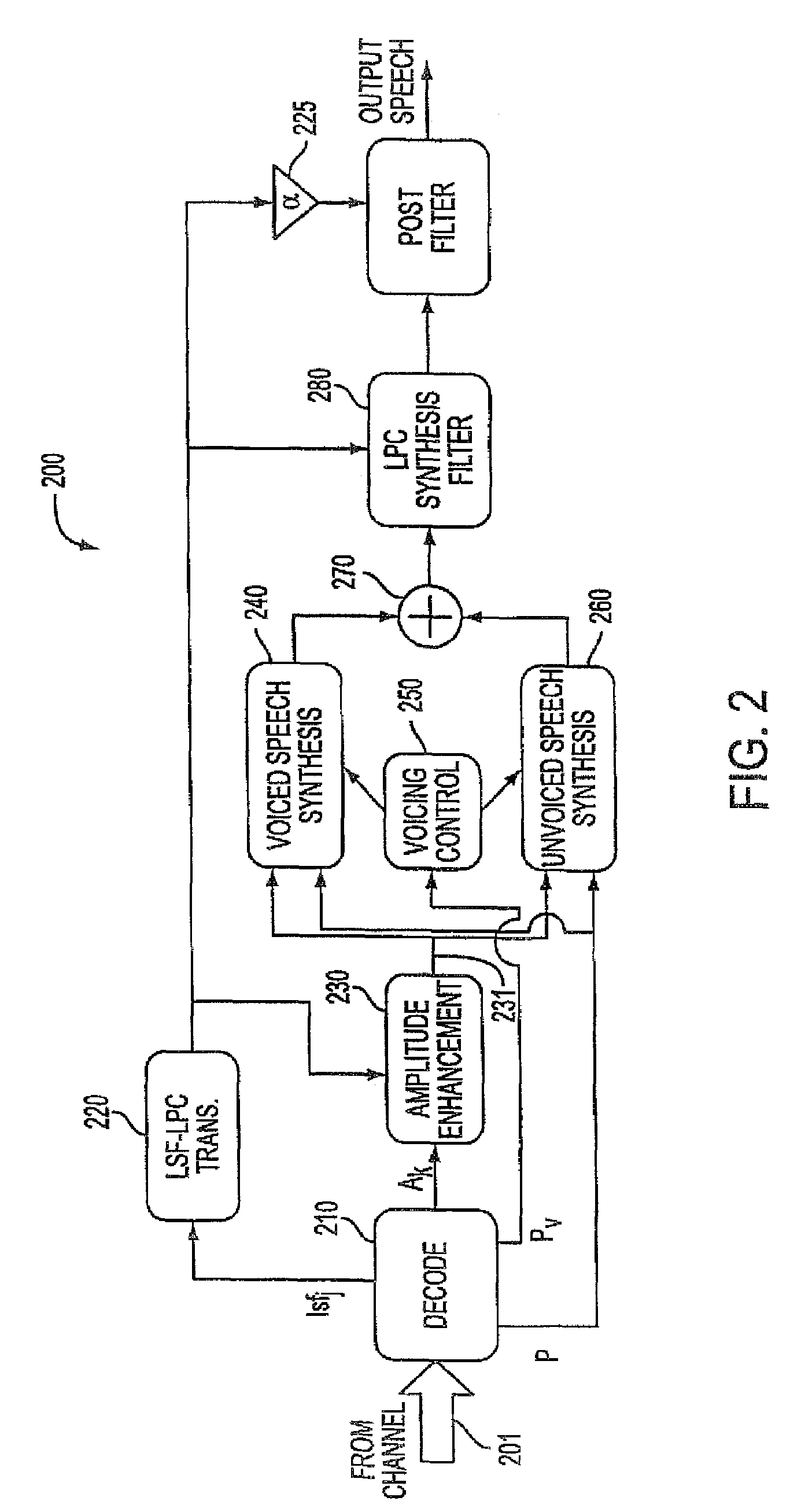
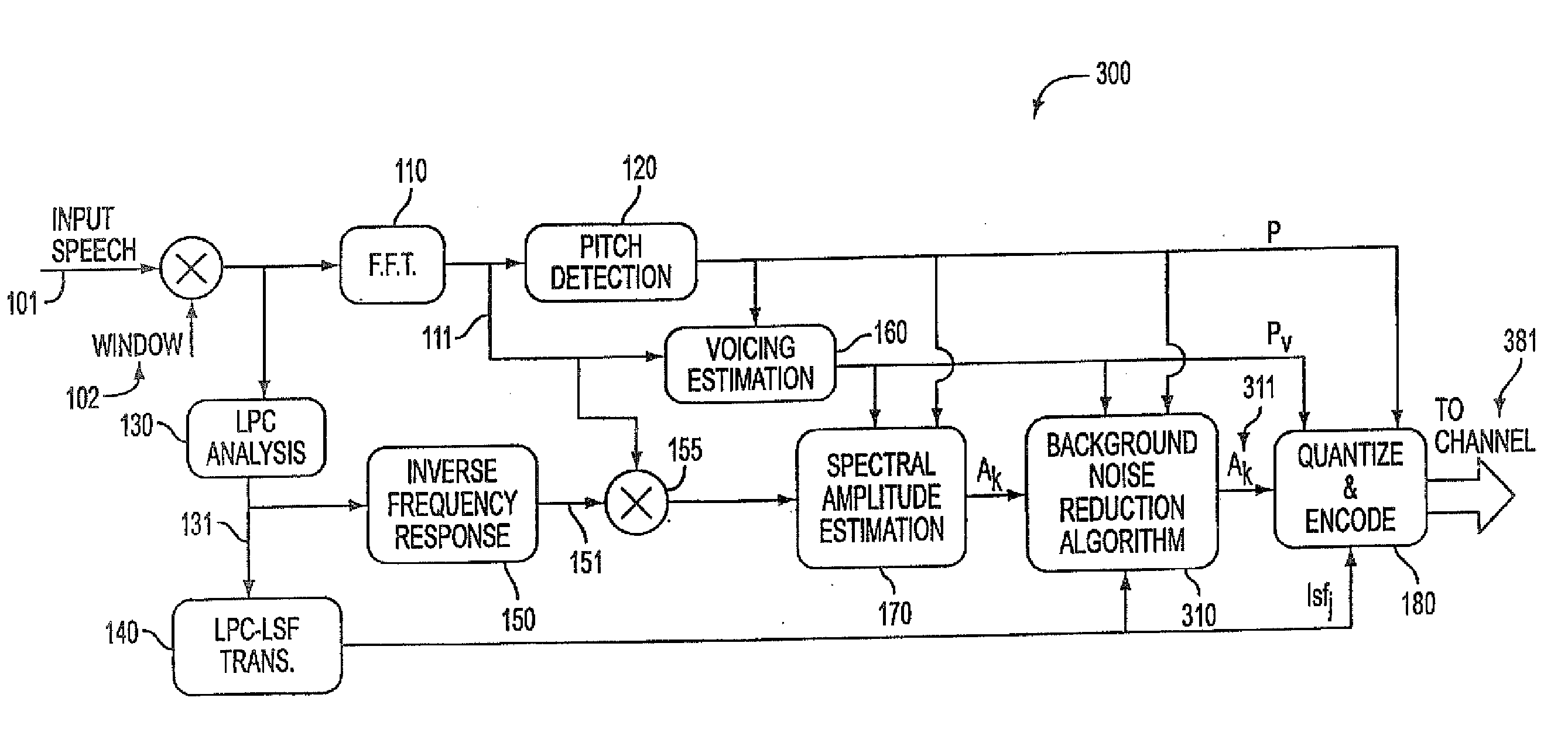
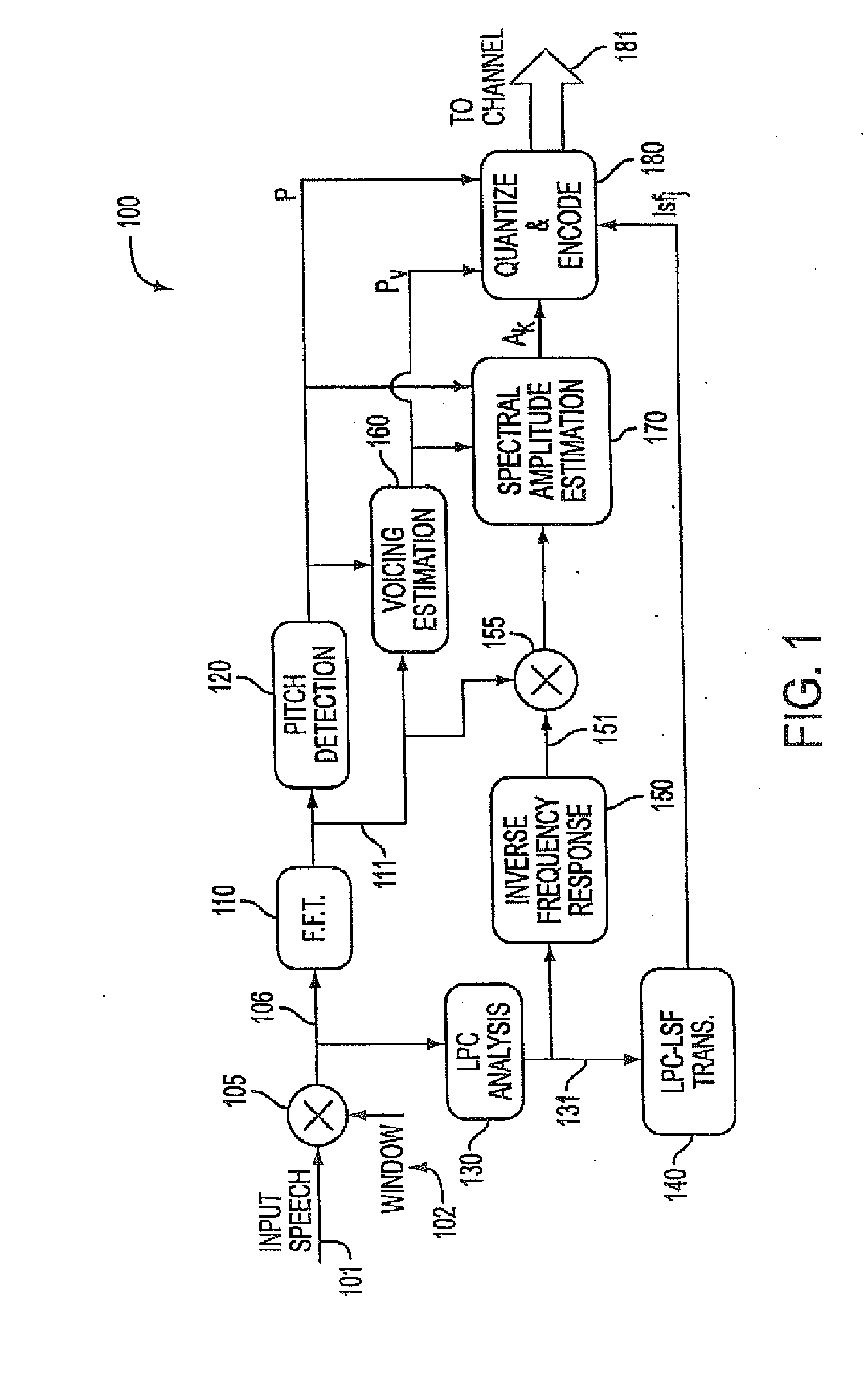
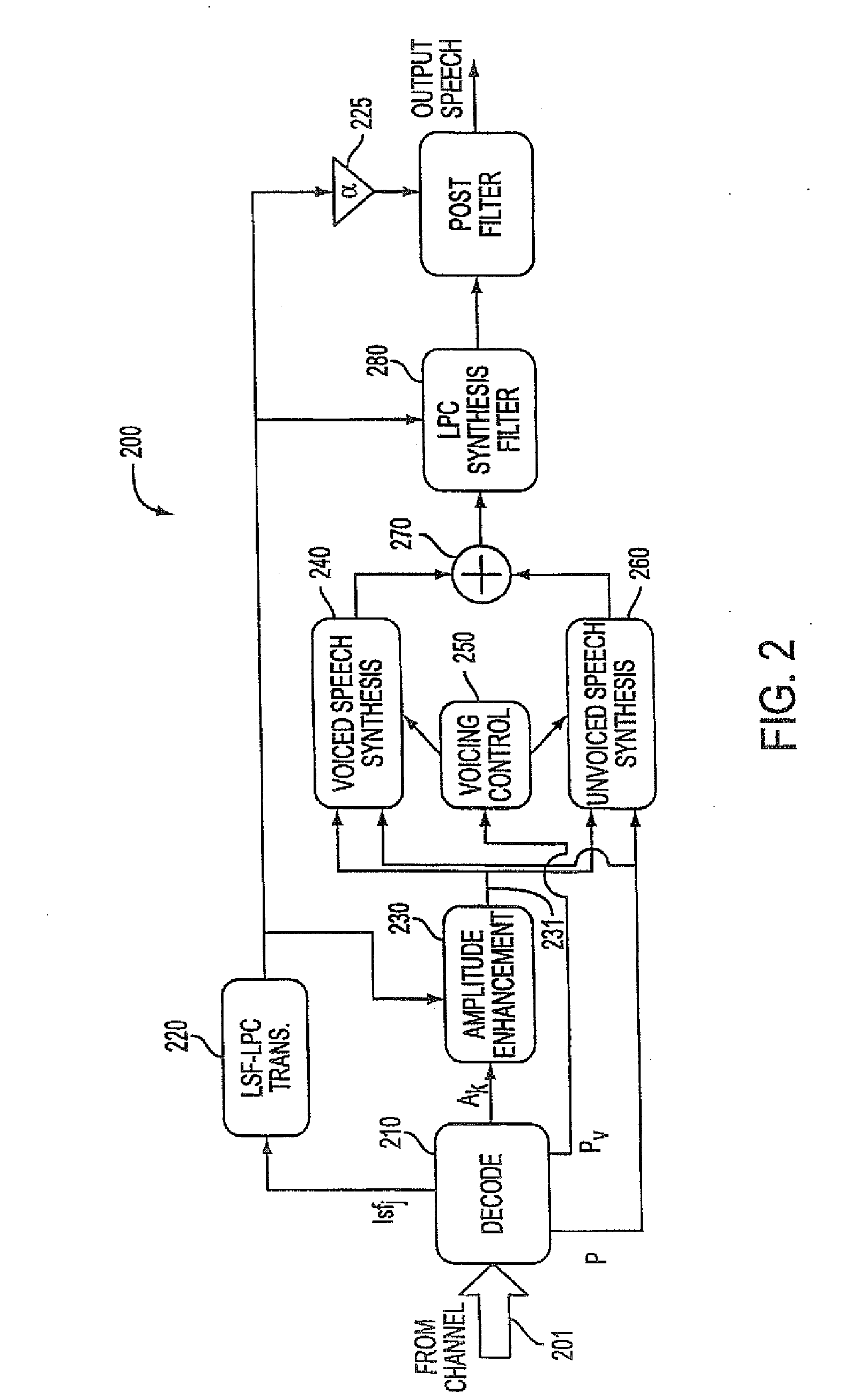
Background noise reduction in sinusoidal based speech coding systems
A method and apparatus to reduce background noise in speech signals in order to improve the quality and intelligibility of processed speech. In mobile communications environment, speech signals are degraded by additive random noise. A randomness of the noise, which is often described in terms of its first and second order statistics, make it difficult to remove much of the noise without introducing background artifacts. This is particularly true for lower signal to background noise ratios. The method and apparatus provides noise reduction without any knowledge of the signal to background noise ratio.
Owner:COMSAT
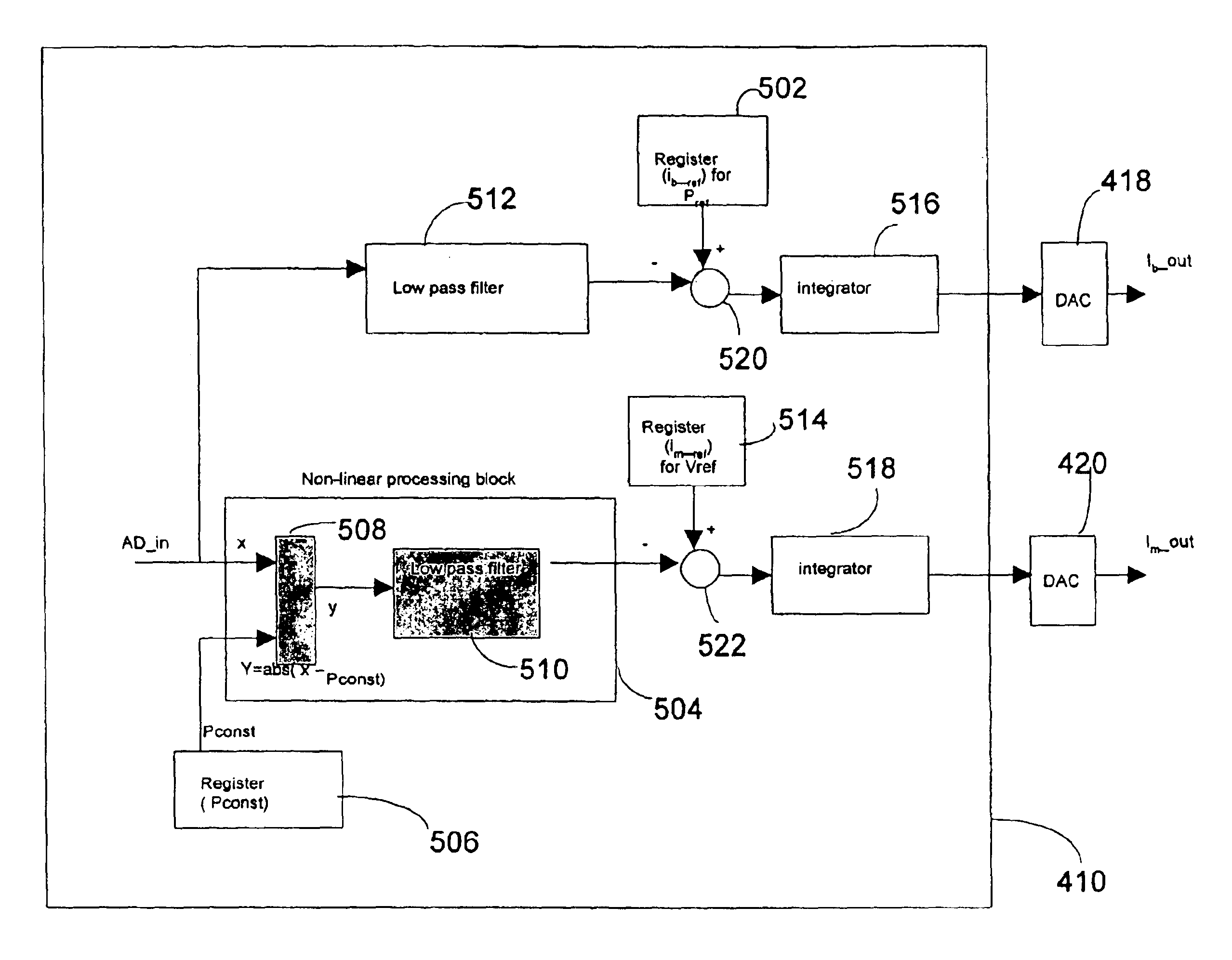
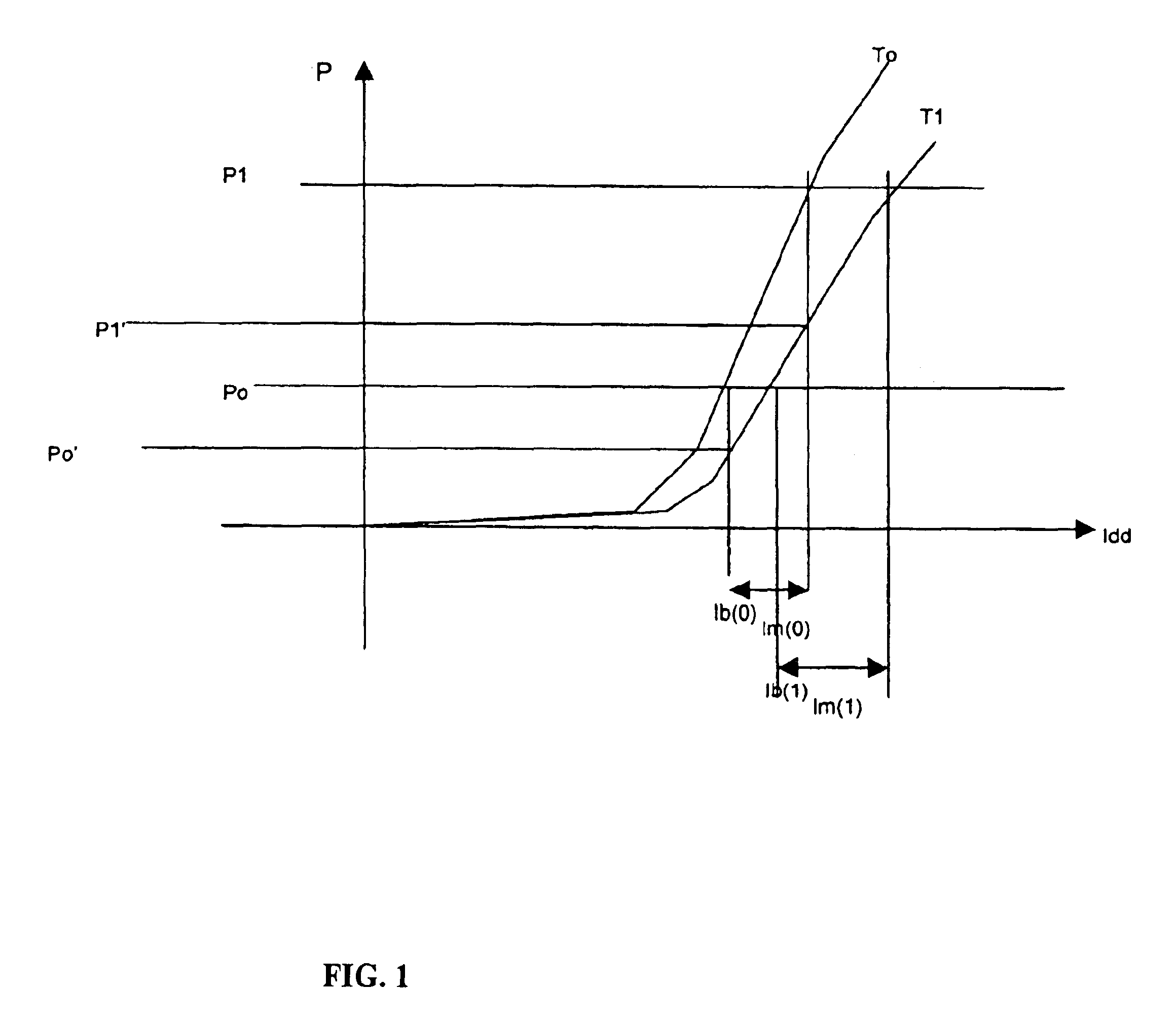
Statistic parameterized control loop for compensating power and extinction ratio of a laser diode
InactiveUS6909731B2Minimizes of extinction ratioMinimizes fluctuationLaser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmissionDriving currentPower control system
An automatic closed loop power control system is described for simultaneously adjusting an output power and an extinction ratio P1 / P0 of a laser diode in order to maintain a desired average output power and a desired extinction ratio. The bias current component of a laser diode drive current is adjusted to compensate for changes in the average output power caused by ambient characteristics such as temperature and aging. Simultaneously, a modulation current component of the laser diode drive current is adjusted to maintain an extinction ratio of the laser diode output signal. The bias current and modulation current adjustments are based on the second order statistics of an average output power of the laser diode and a variance in the power output of the laser diode.
Owner:CENTILLIUM COMM
Co-channel interference rejection in a digital receiver
InactiveUS7107031B2Increase the number ofIncreased rejectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringCo-channel interference
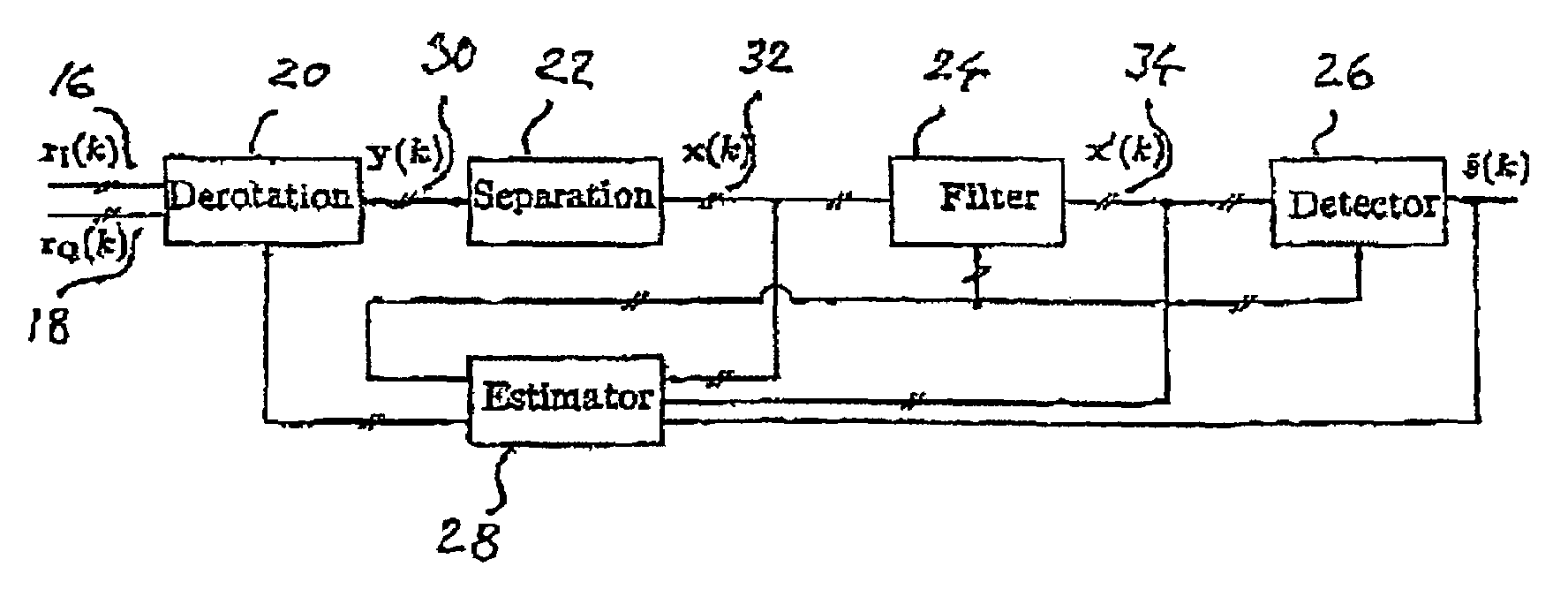
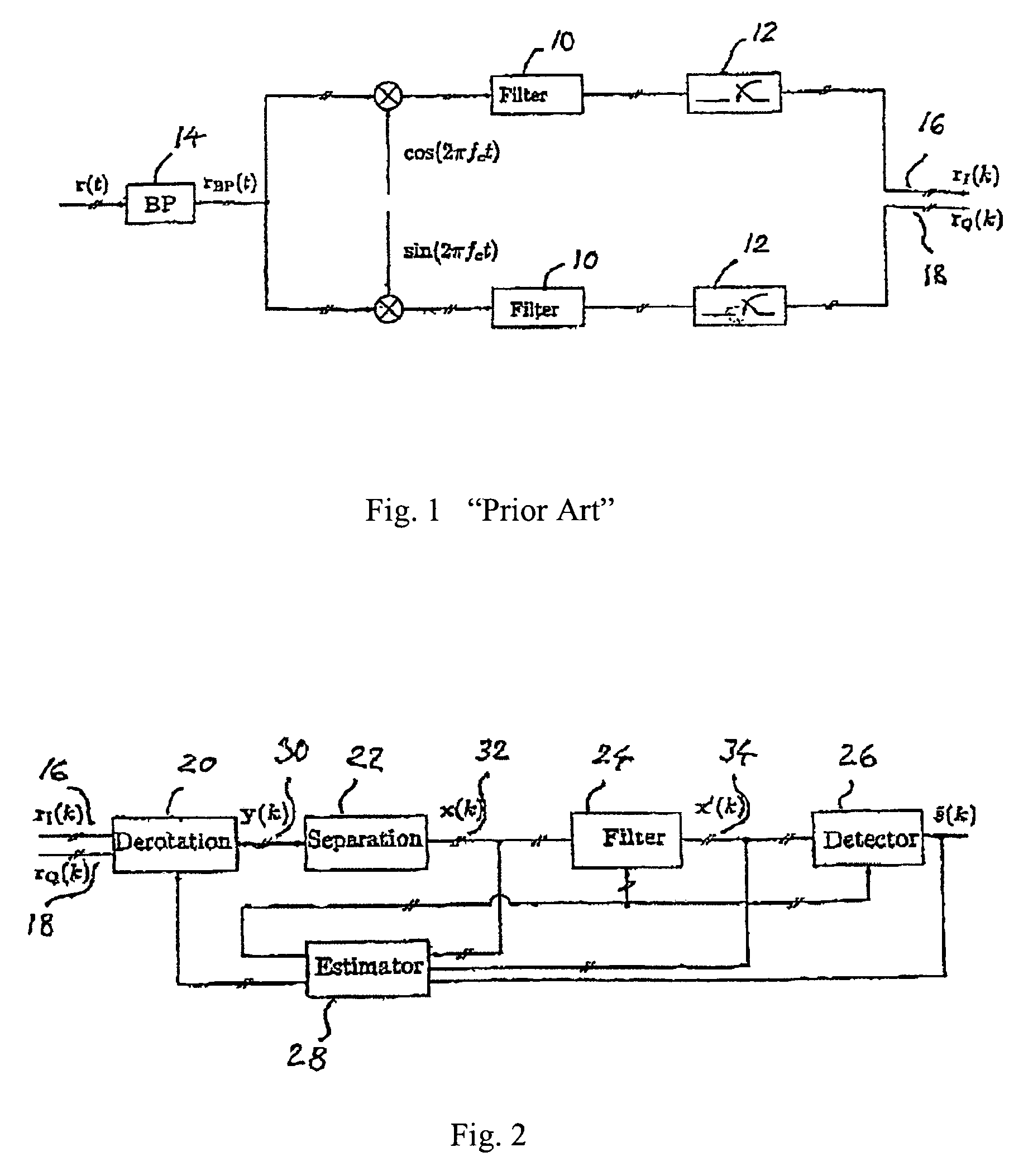
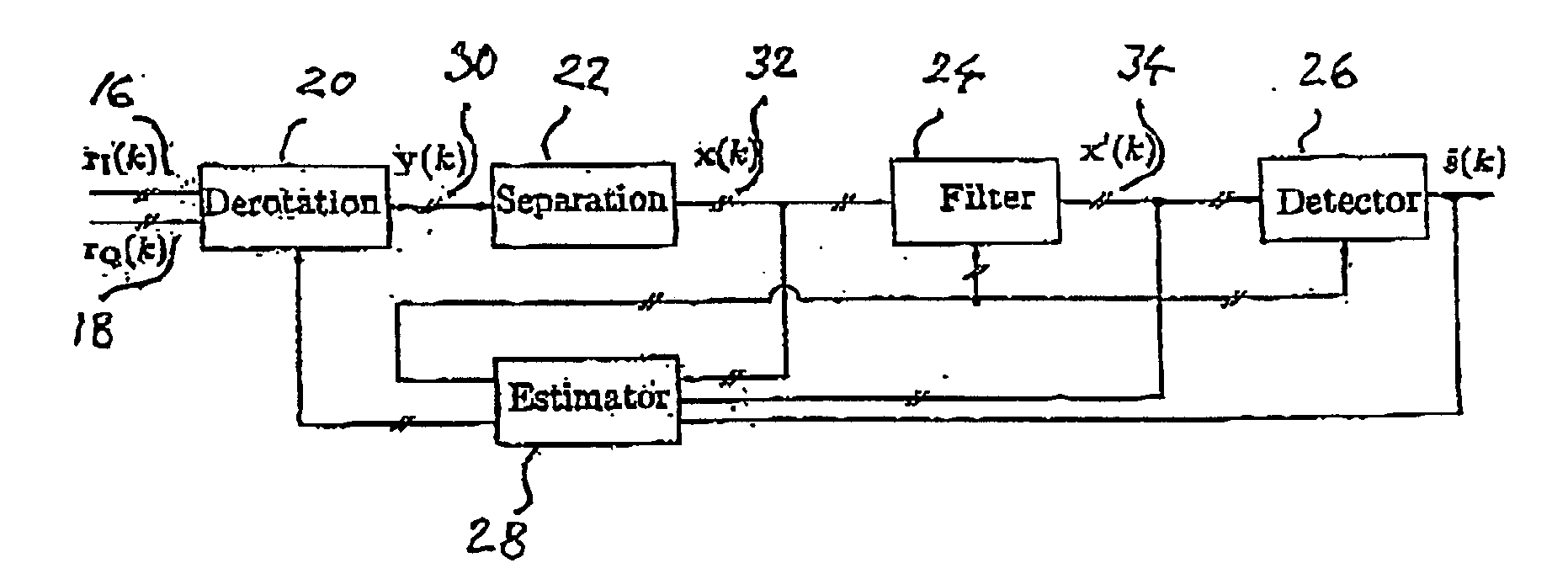
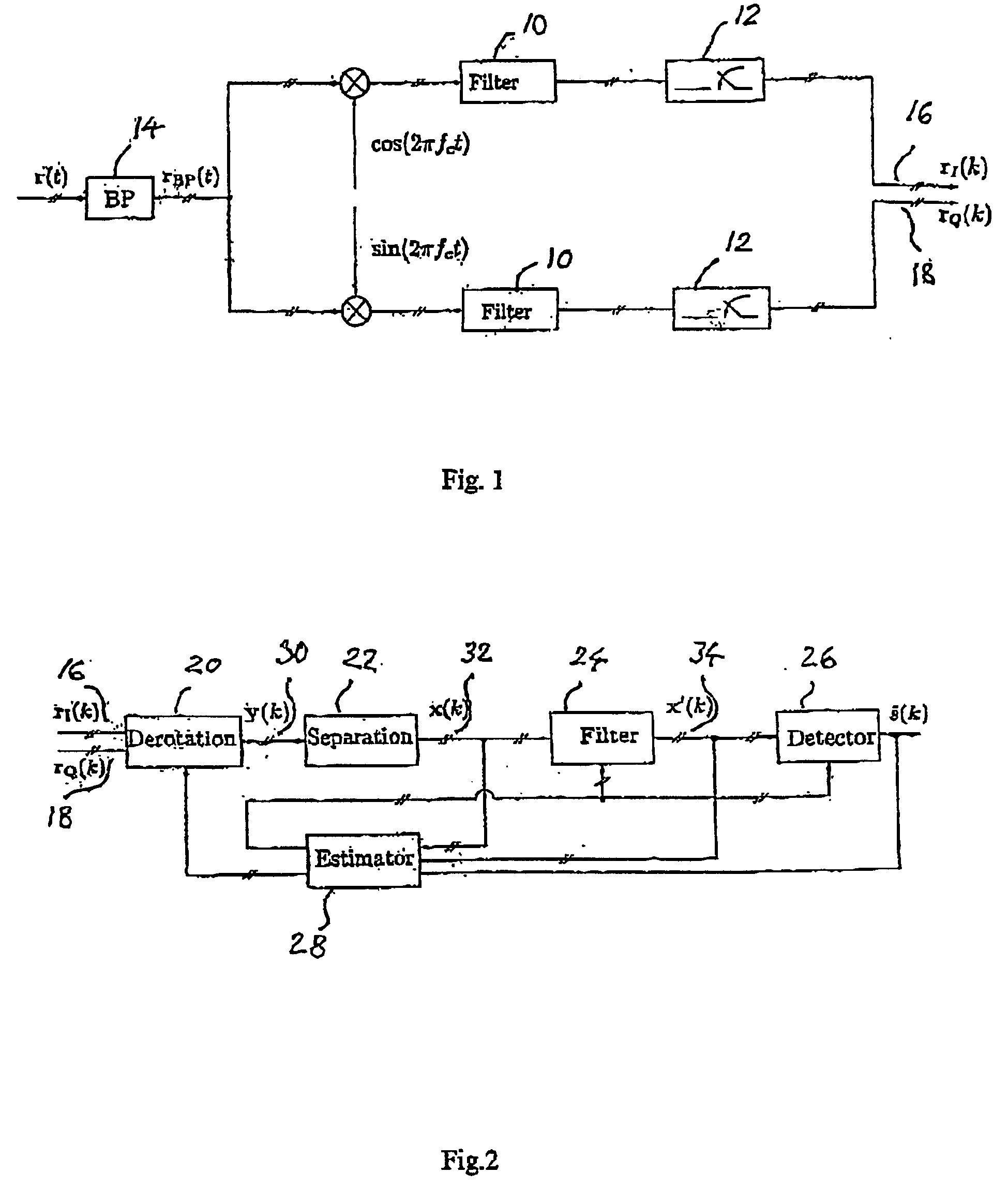
The present invention relates to a method for a digital receiver and a receiver exploiting second order statistics for adaptive co-channel interference rejection in wireless communication. It uses digitally I, in phase, and Q, quadrature, branches of a received transmitted signal as input to the receiver, a coarse synchronization and a coarse frequency offset compensation have being performed on the signal. It comprises a means for derotation, means for separation, means for filtering, means for estimating and means for detecting transmitted symbols in the received signal. The invention thereby improving co-channel rejection in wireless communication, thus making it possible to increase the number of communication channels for frequencies used.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Reverse link outer loop power control with adaptive compensation
InactiveUS6965780B1Power managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
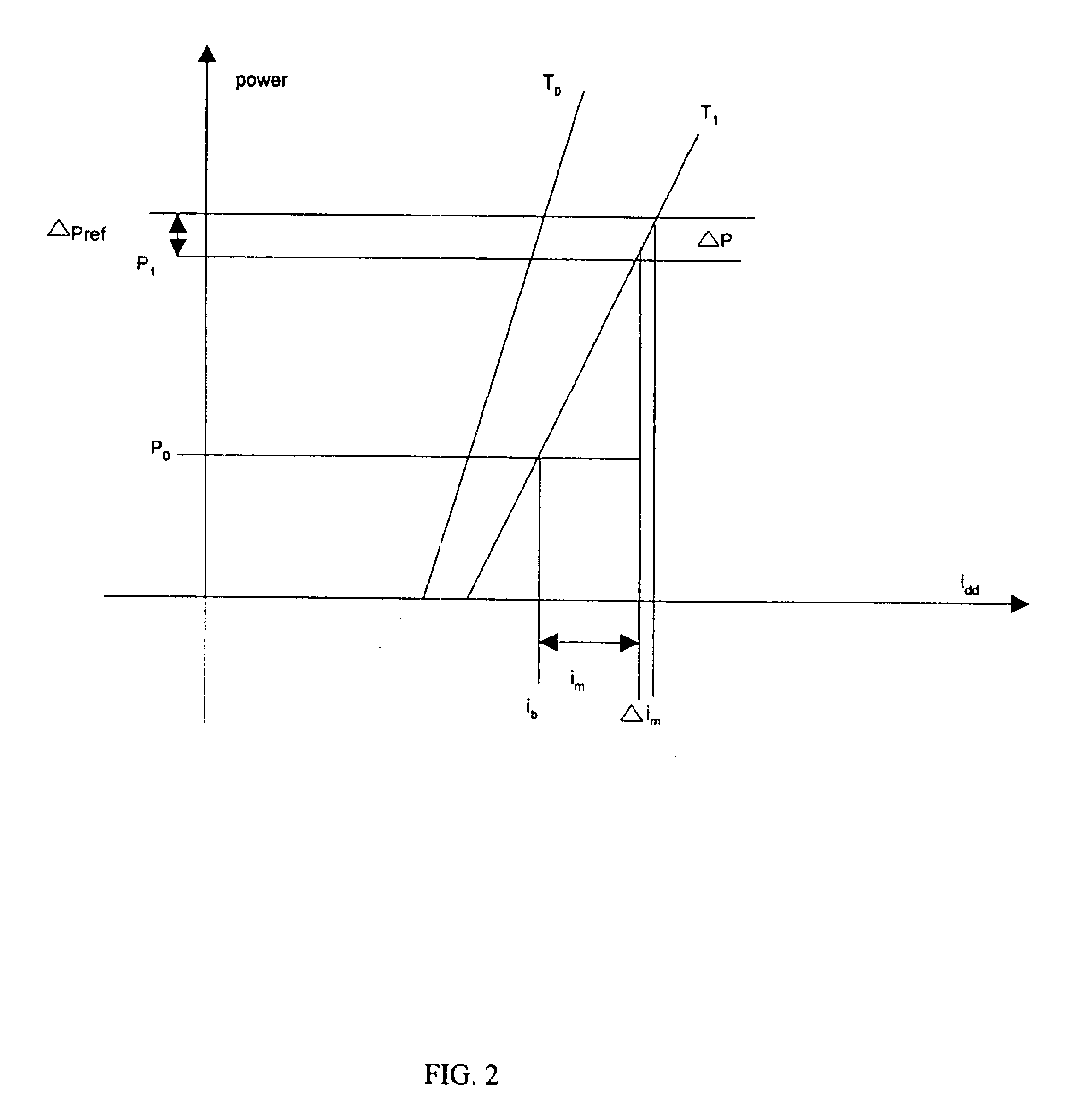
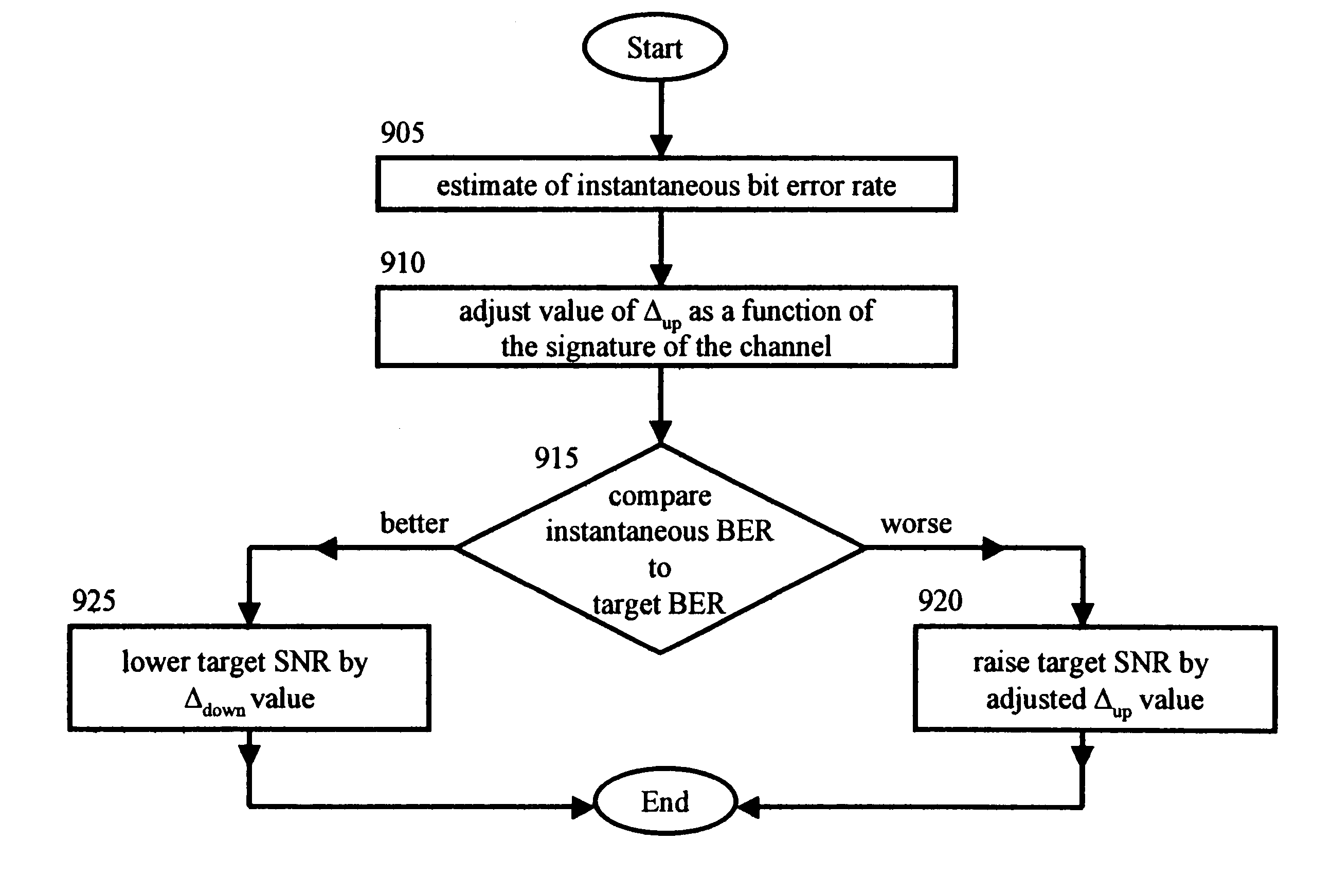
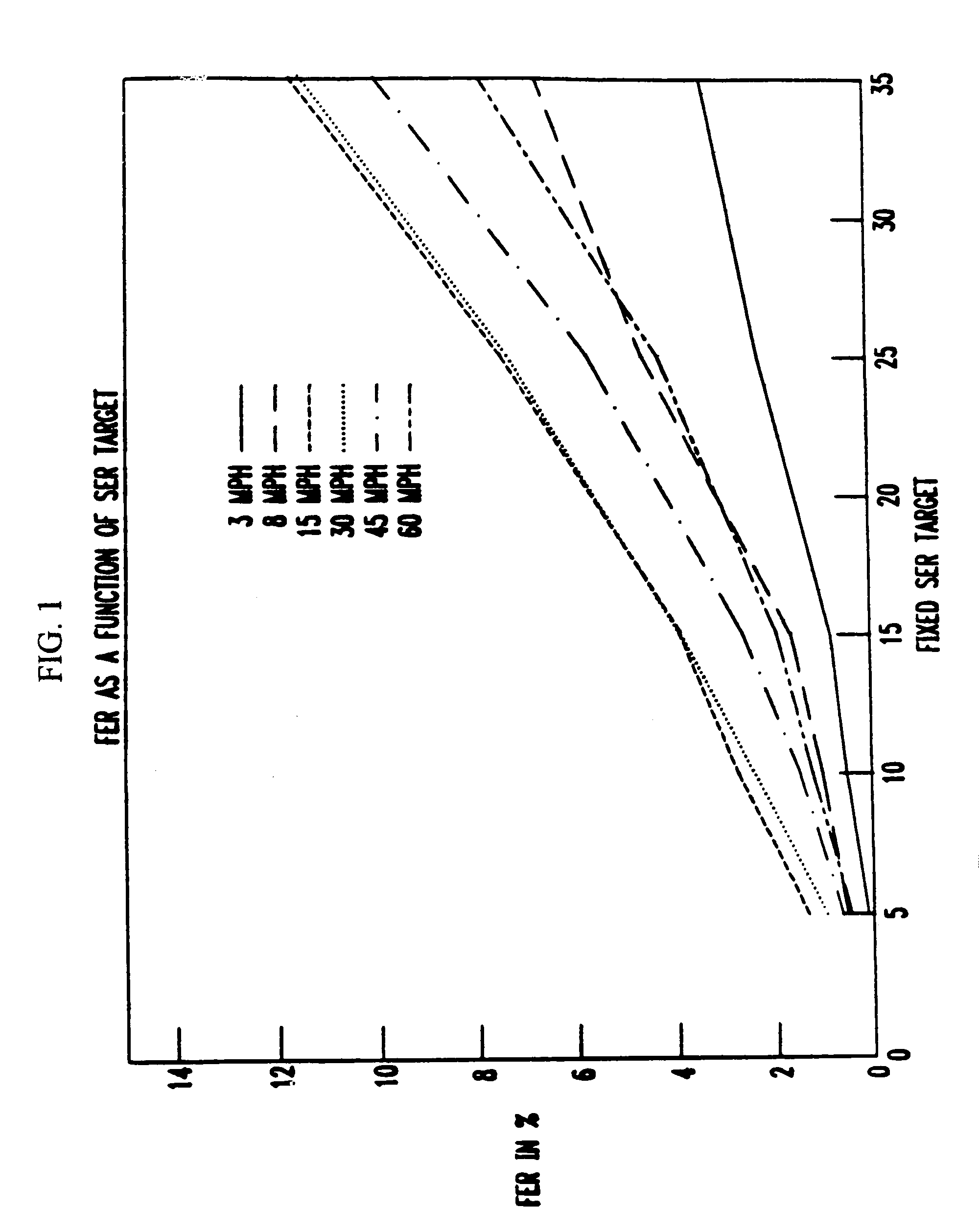
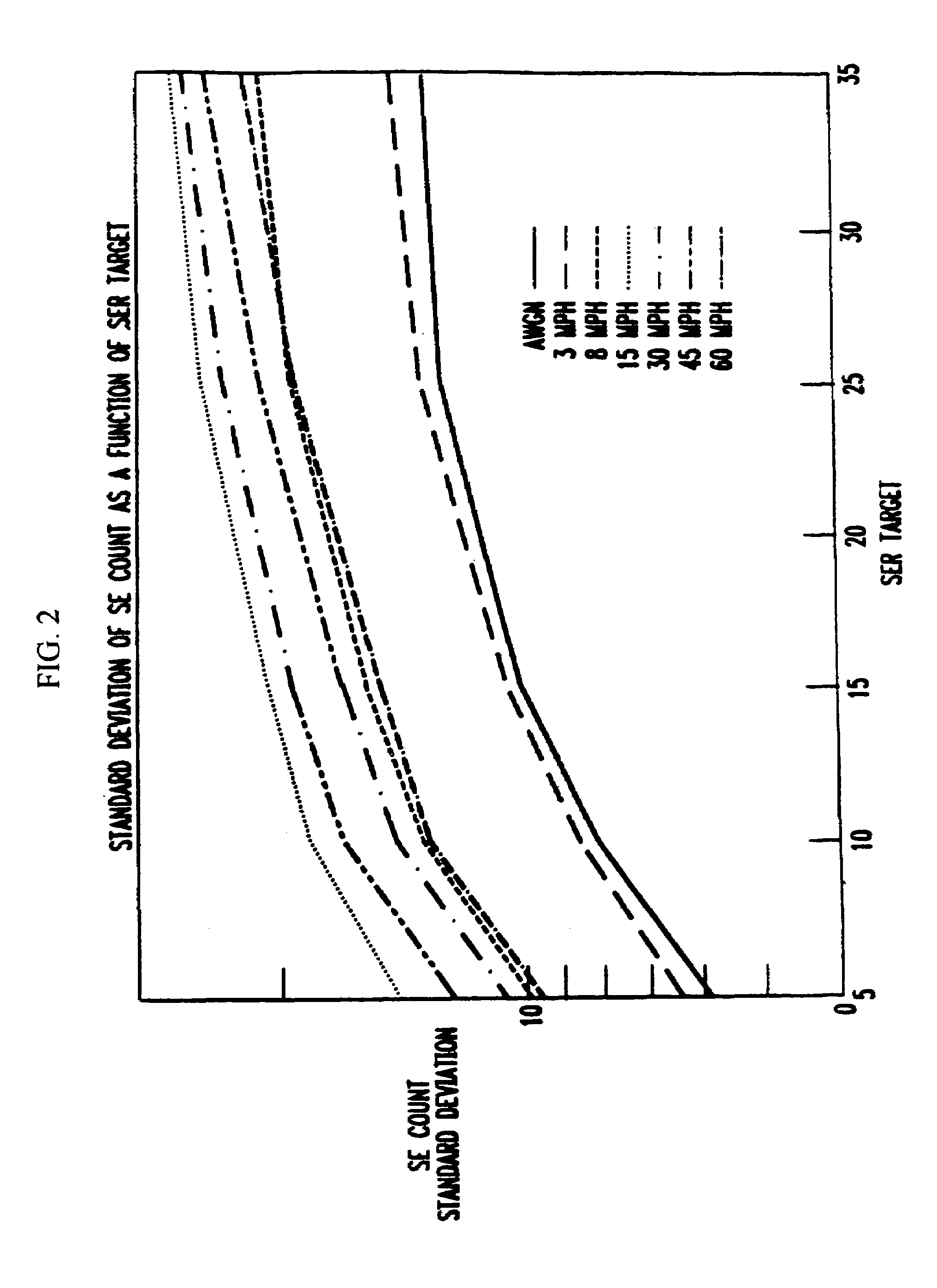
In a wireless communications system, a base station employs a bit error rate (BER) based Reverse Outer Loop Power Control (ROLPC) technique. The ROLPC technique uses either instantaneous or weakly filtered values of the BER for comparison with a BER target value for adjusting a target signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The BER target value is varied as a function of a second order statistic (e.g. variance, standard deviation) of the received SNR. In another embodiment, a symbol error count based ROLPC technique uses adaptive SER targets. In particular, a base station uses a 2nd order statistic, e.g., standard deviation (variance), to identify, or act as a signature of, a particular cellular (wireless) communications environment. The base station monitors the standard deviation of the symbol error count of a received signal (transmitted from a mobile station). The target signal-to-noise ratio ((Eb / N0)T) of this received signal is adjusted as a function of the value of the standard deviation and the adjusted (Eb / N0)T target is used to provide power control.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Receiver
InactiveUS20040014424A1Increase the number ofIncreased rejectMultiplex communicationTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringCo-channel interference
The present invention relates to a method for a digital receiver and a receiver exploiting second order statistics for adaptive co-channel interference rejection in wireless communication. It uses digitally I, in phase, and Q, quadrature, branches of a received transmitted signal as input to the receiver, a coarse synchronization and a coarse frequency offset compensation have being performed on the signal. It comprises a means for derotation, means for separation, means for filtering, means for estimating and means for detecting transmitted symbols in the received signal. The invention thereby improving co-channel rejection in wireless communication, thus making it possible to increase the number of communication channels for frequencies used.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
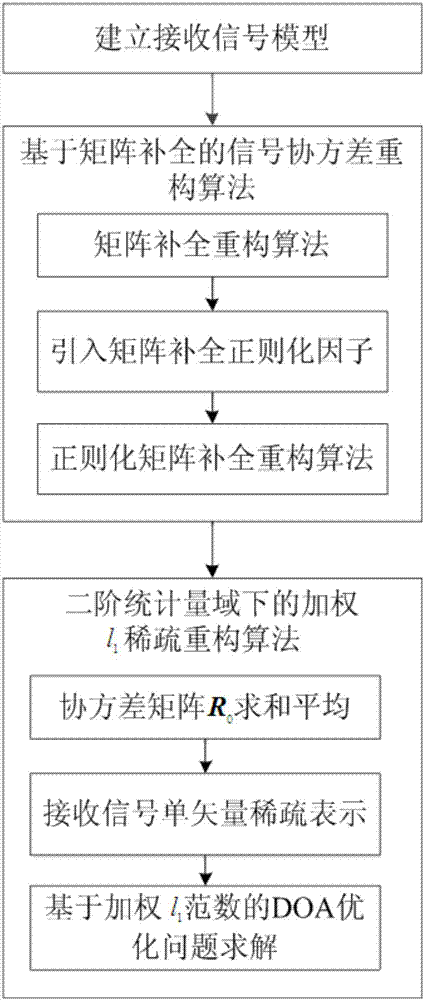
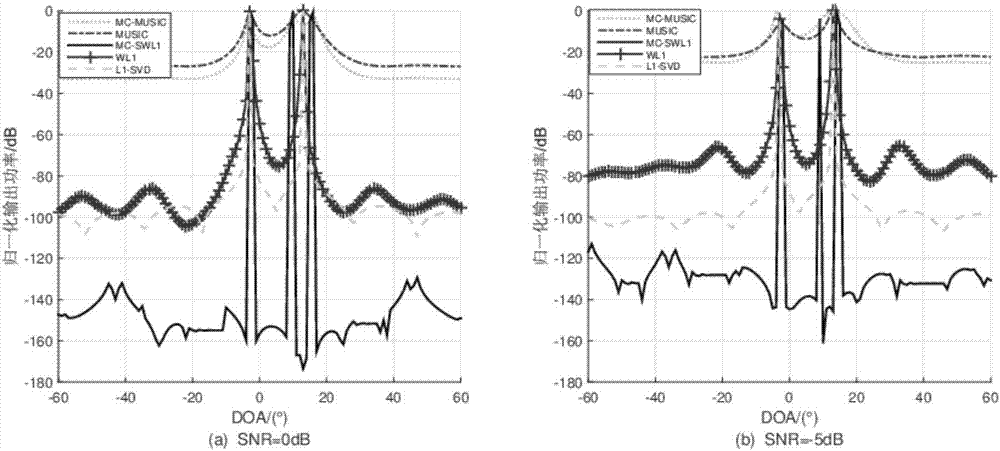
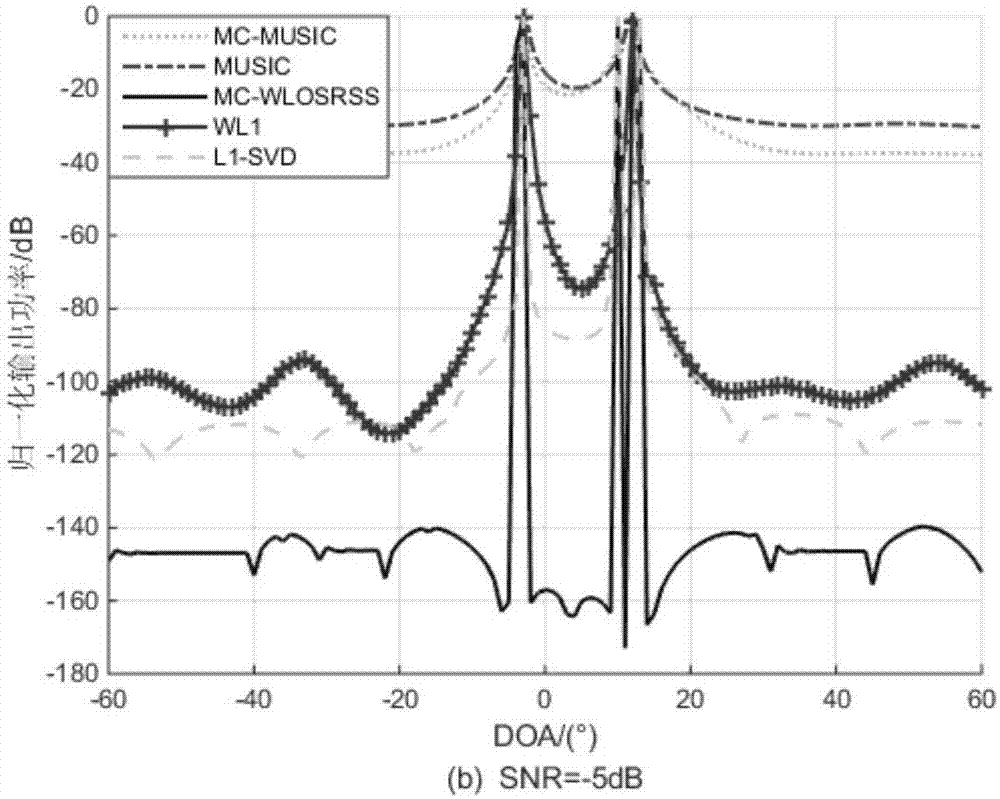
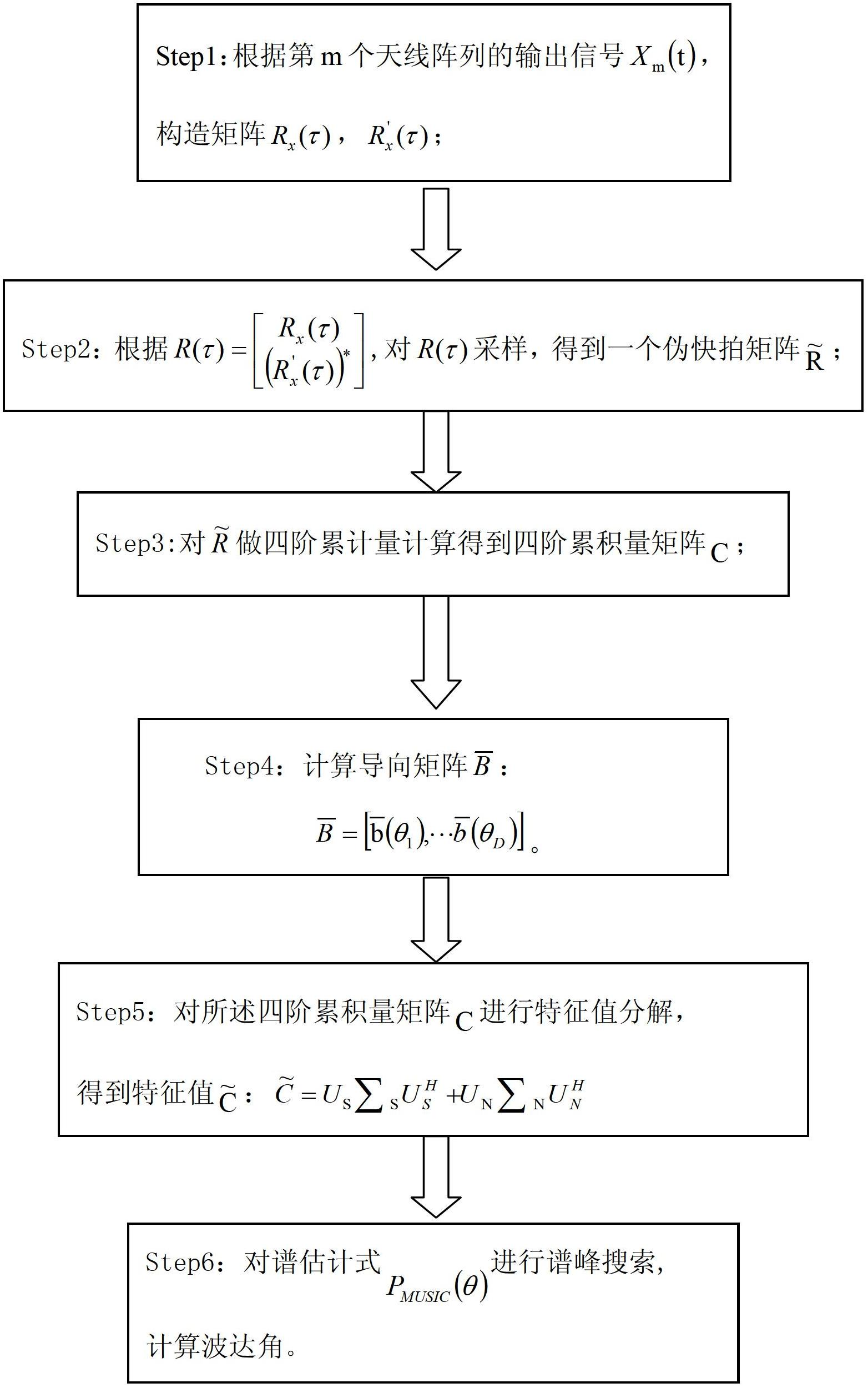
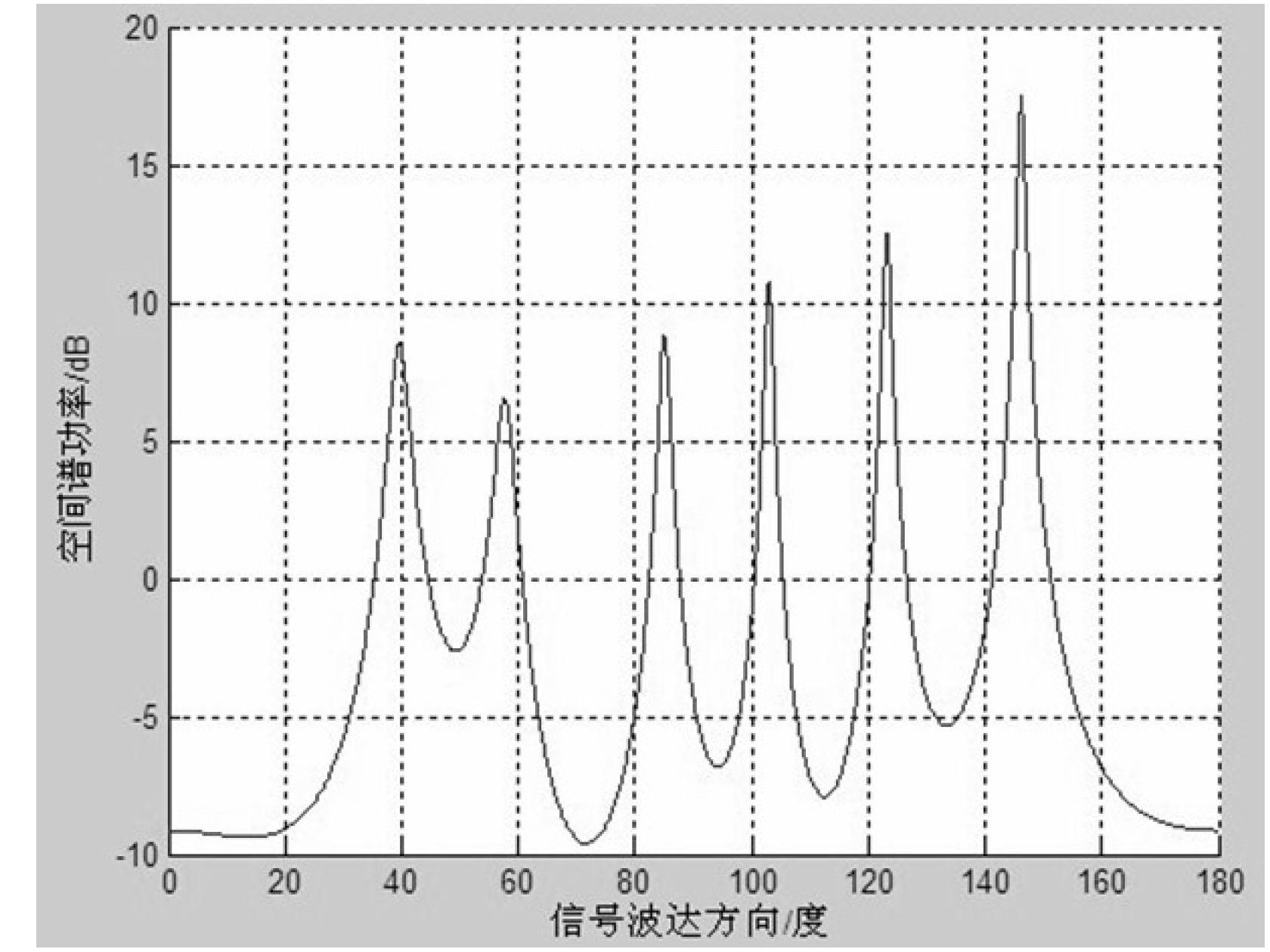
DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method through second-order statistics reconstruction based on matrix completion
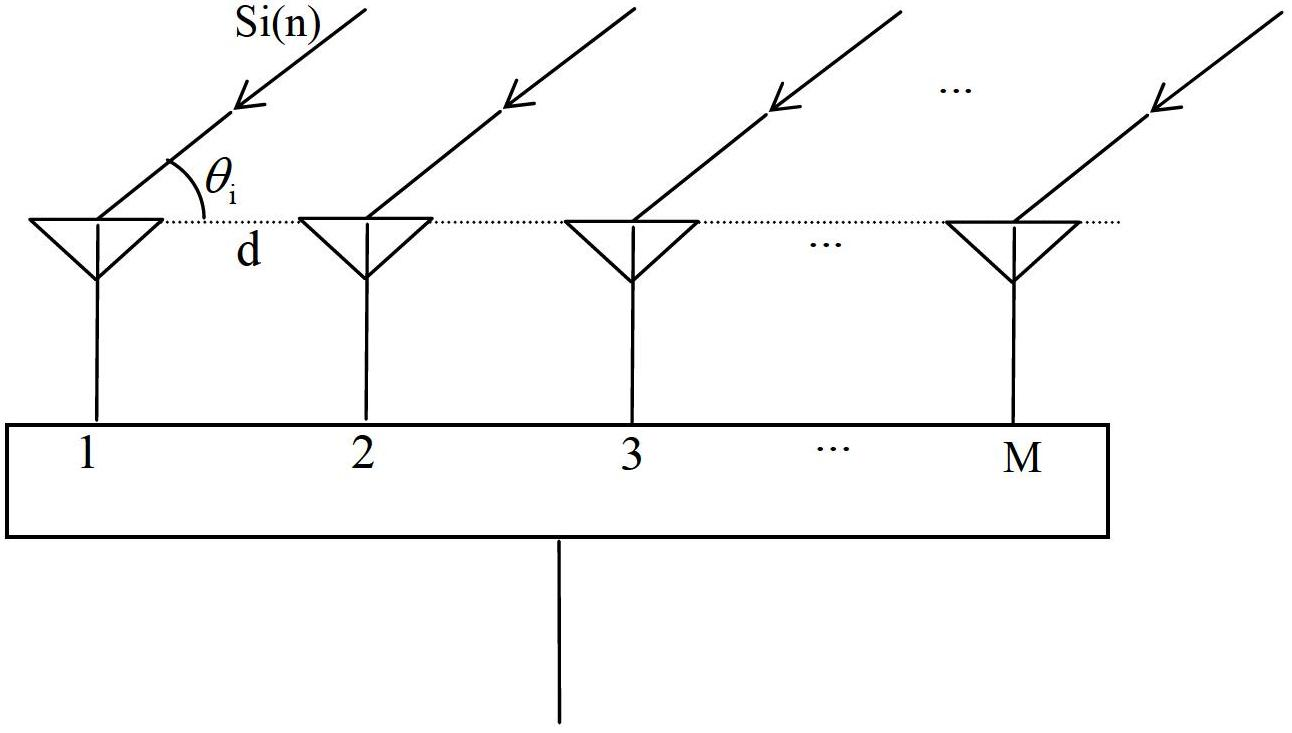
ActiveCN107544052AImprove numerical stabilityImprove estimation performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Estimation methods
The invention belongs to the field of signal processing, and particularly relates to a DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method through second-order statistics reconstruction based on matrix completion. Based on the matrix completion theory, the DOA estimation method through second-order statistics reconstruction based on matrix completion is put forward. Firstly, based on the matrix completion method, an elastic regularization factor is introduced to reconstruct a received signal covariance matrix to a noise-free covariance matrix; under the second-order statistics domain, through matrixsummation averaging, a multi-vector problem of the noise-free covariance matrix is converted to a single-vector problem; and finally, a sparse reconstructed weighted l1 norm is used to realize DOA parameter estimation. Non-uniform noise influences can be significantly suppressed, the DOA parameter estimation performance is good, and in a condition of a low signal-to-noise ratio, the provided algorithm has high angle estimation precision and high resolution.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
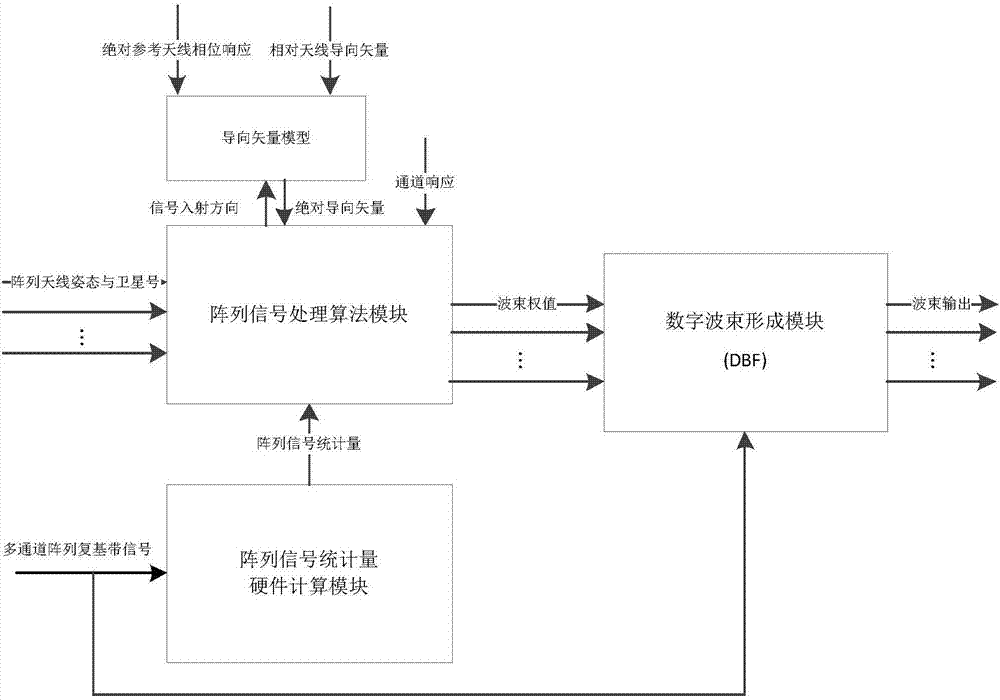
Digital beam forming and phase fitting method
ActiveCN107356943AAchieve stabilizationSuppress interferenceSatellite radio beaconingPhase fittingModel parameters
The invention provides a digital beam forming and phase fitting method, and aims to provide a method capable of suppressing interference, improving the signal to interference and noise ratio and accurately controlling the phase of a beam forming signal. The method is implemented according to the technical scheme that a steering vector model obtains relative steering vectors by using online calibration, accurate absolute steering vectors are acquired by combining absolute phase responses, which are measured in a darkroom, of a reference array element, model parameters of the steering vector are fitted out by combining the existing absolute steering vectors, and an accurate spare steering vector of an antenna array in any direction is acquired; the second-order statistic of the array signal is iteratively calculated through an array signal statistic hardware calculation module, and sent to an array signal processing algorithm module together with an antenna array steering vector and a channel response to calculate an optimal beam weight; and finally, the array signal processing algorithm module imbeds the optimal beam weight into the digital beam forming module to perform real-time digital beam forming and phase fitting and process multi-channel array data and beam output in real time.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
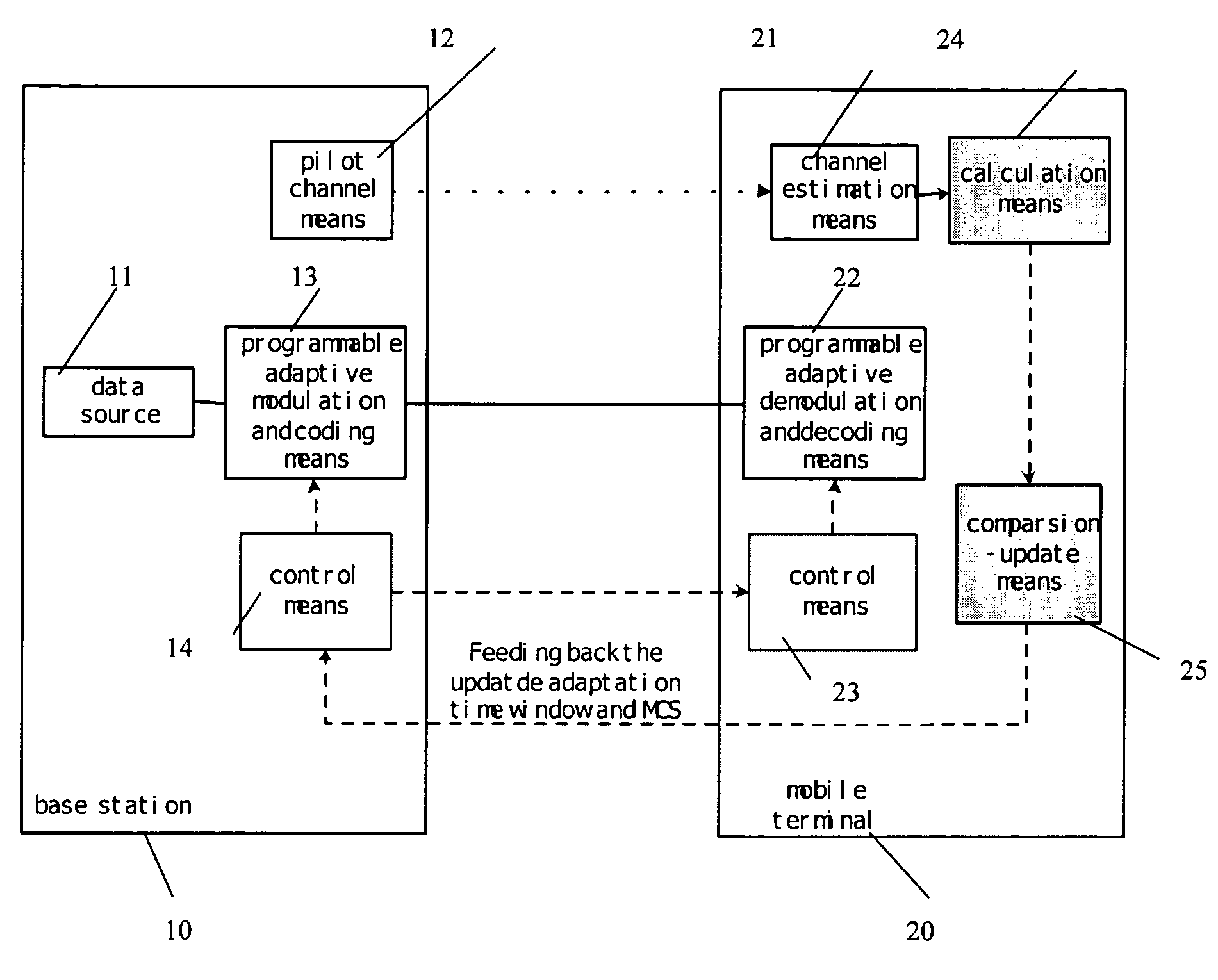
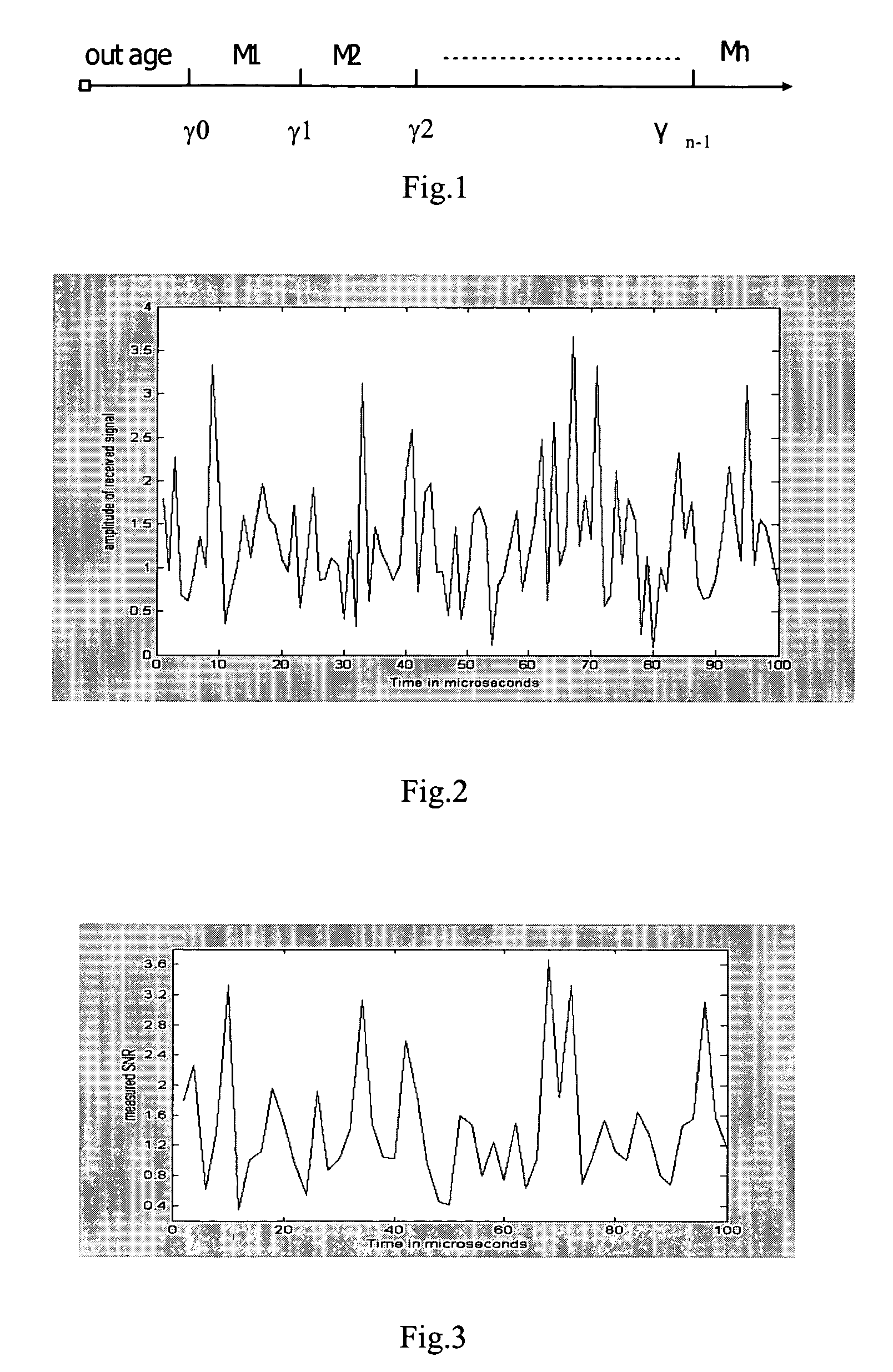
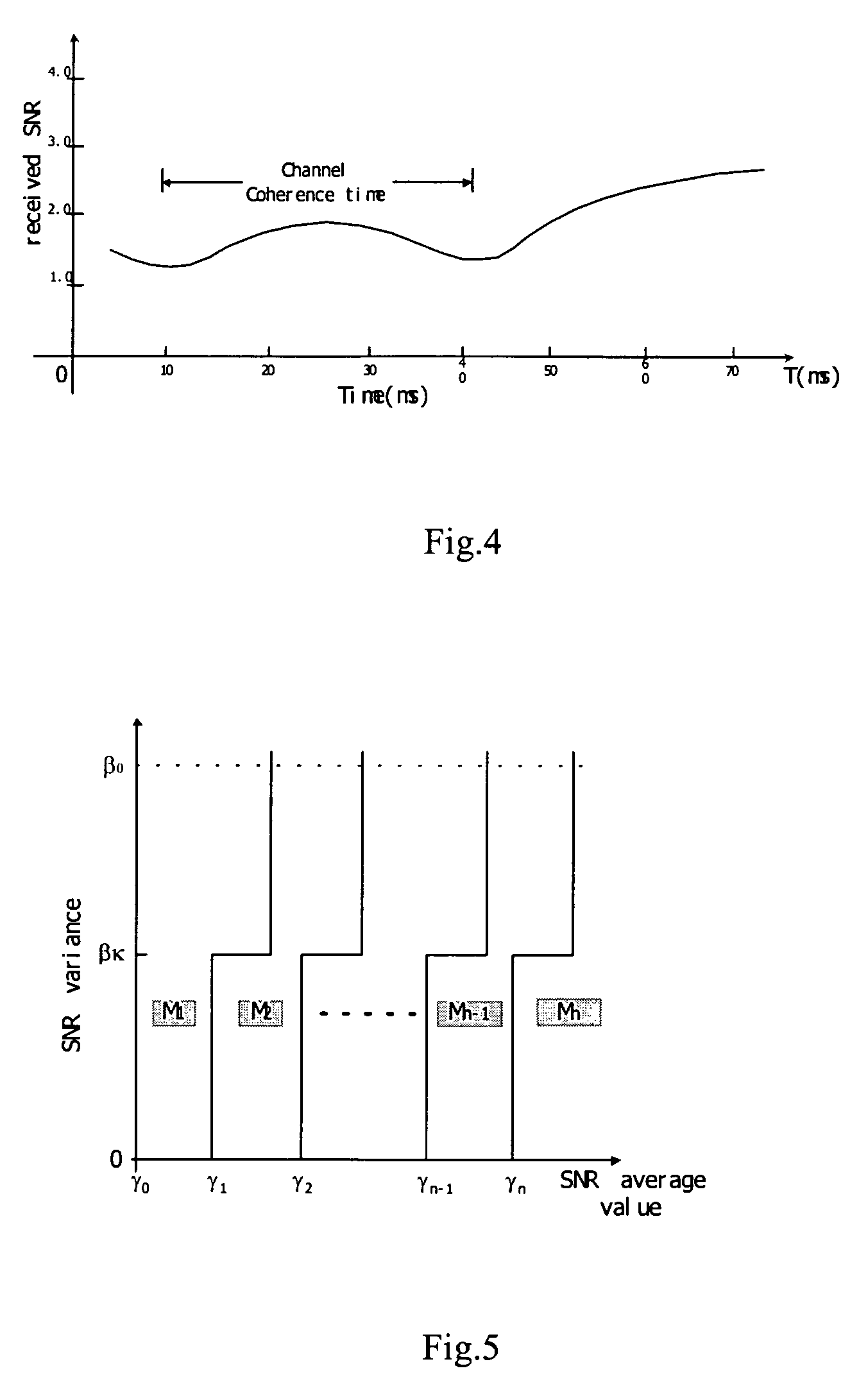
Self-adaptive modulating and coding method and device based on channel information second order statistics
InactiveCN1567758AEasy to trackImprove usabilityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplexSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention provides a self-adapting modulating and encoding method and device based on channel second-order statistics in OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplex) system, and its characteristic: by character signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) variance, dynamically selecting suitable adapting time window; and using a two-grade moment criterion, i.e. according to SNR average value and variance, selecting suitable modulating and coding style (MCS) to accurately convert SNR to MCS, thus enhancing the applicability of self-adapting modulation and coding and reducing the possibility of system interruption, and therefore, bringing about better error bit rate property.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SHANGHAI BELL CO LTD
Method and system for automatically detecting an edge and width of a document utilizing a scanning system
A method and system automatically determines the width (i.e., left and right edges) of a document when it is loaded for scanning or copying. When a document is staged, the scanner collects a predetermined number scanlines of the leadedge of the document. Both first order and second order statistics of the scanner and document are then calculated based on the scanned data. The auto-width detection process is adaptive to CCD sensor output variation, document variation, and scanner variation, thus making it robust against dust in the sensor path and random fluctuations of the scanner.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and device for adaptive modulation and coding based on second order statistics of channel information
ActiveUS7542514B2Easy to trackAccurate mappingError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Algorithm
The present invention discloses a method and device for adaptive modulation and coding based on second order statistics of channel information in OFDM system, characterized in that, by means of variance of Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) an appropriate adaptation time window is selected dynamically to trace time-varying channel better; and in that a decision criterion of second order, namely selecting an appropriate modulation and coding schemes (MCS) according to average value of SNR and variance of SNR, is employed to obtain accurate mapping from SNR to MCS. The mapping enhances practicability of the adaptive modulation and coding, decreases probability of system outage, and thus results in better performance of bit error rate.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Frequency characteristic-based nondestructive detection method of stress waves of wood
InactiveCN102928514AThe test result is accurateEasy to detectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalFourier transform on finite groupsData acquisition
The invention discloses a frequency characteristic-based nondestructive detection method of stress waves of wood. The frequency characteristic-based nondestructive detection method comprises the following steps of: mounting piezoelectric type acceleration sensors around raw wood uniformly, knocking the No. 0 sensor by using a pulse hammer, and acquiring and storing output signals of the sensors by using a data acquisition card; carrying out K-point fast Fourier transform on the acquired signals and then solving an actual measurement frequency response function; establishing an observation matrix according to the actual measurement frequency response function and a frequency response function of healthy wood; carrying out blind source separation on the basis of second order statistic and establishing a frequency response function between a defect point and an observation point; and finally, judging whether the interior of the wood has defects as well as defect quantity and defect sizes according to a clustering result. The nondestructive detection method of the stress waves based on the frequency response function of the wood is not subject to interference from reflected wave and refracted wave signals and is more accurate in detection result, capable of automatically detecting information, such as whether the interior of the wood has defects as well as the defect sizes, and simple and convenient in detection process and strong in practicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Blind channel equalizers and methods of blind channel equalization
InactiveUS6463099B1Less sensitive to channel order estimatesMultiple-port networksEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemEngineering
Blind channel equalization methods, receivers and systems incorporating the same for use in a multiple-input, multiple-output, (MIMO) wireless communication system are described. Signal equalization is achieved by devising a characteristic system convolution matrix and algebraically operating on said convolution matrix by equalizing functions generated from second order statistics of the received signals. Such equalization is done with an aim to removing or suppressing inter-symbol interference elements from the received signals to enable satisfactory signal recovery. The described methods, systems and receivers, have the benefits of retaining the speed and processing power efficiency of equalization algorithms based on second order statistics while substantially insensitive to the accuracy of channel order estimates.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV FOR SCI & TECH THE
Method of Estimating the Frequency Response of Multipath Channels
ActiveUS20170180063A1High resolutionTransmission monitoringChannel estimationDOCSISFrequency response
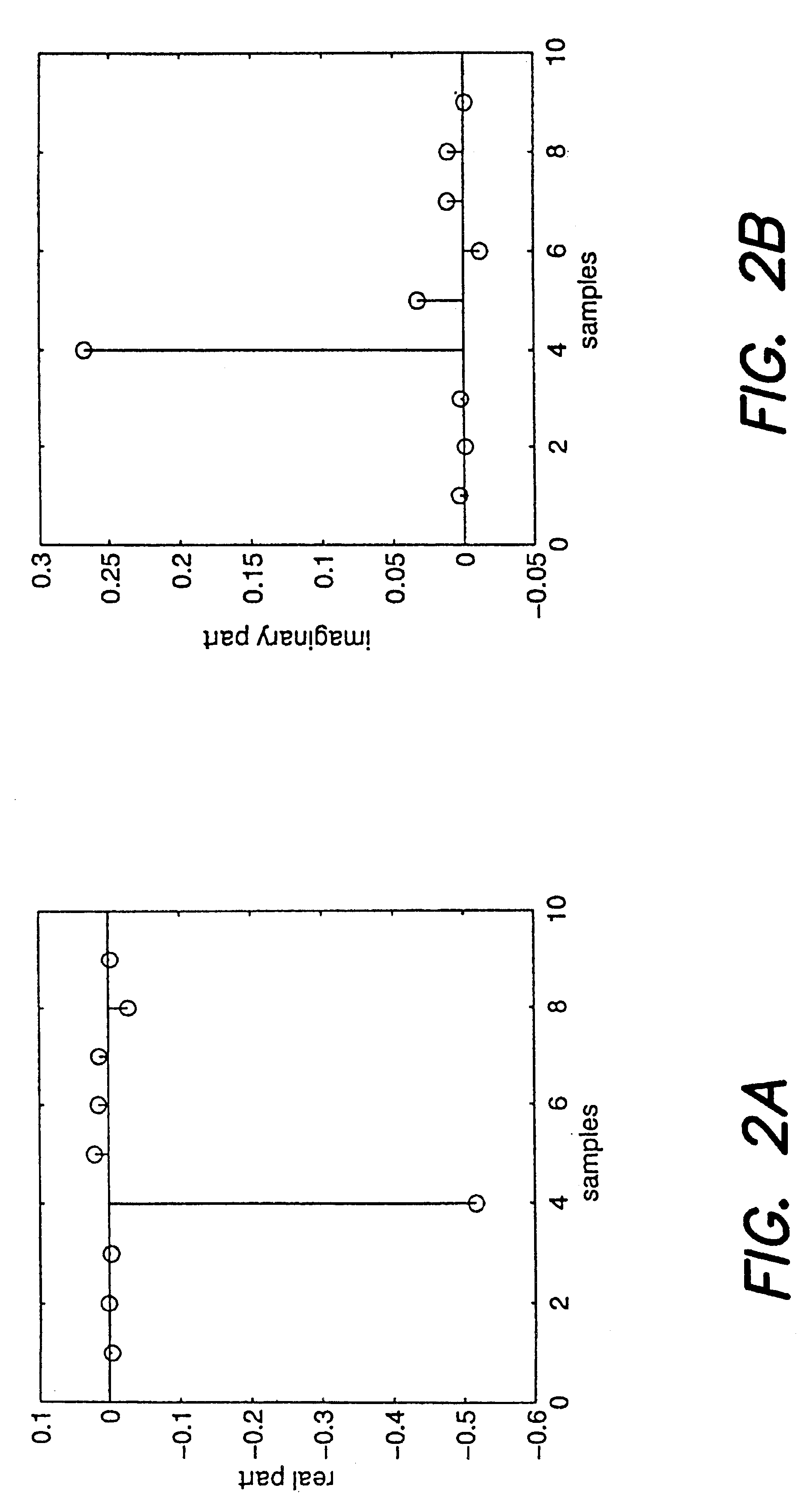
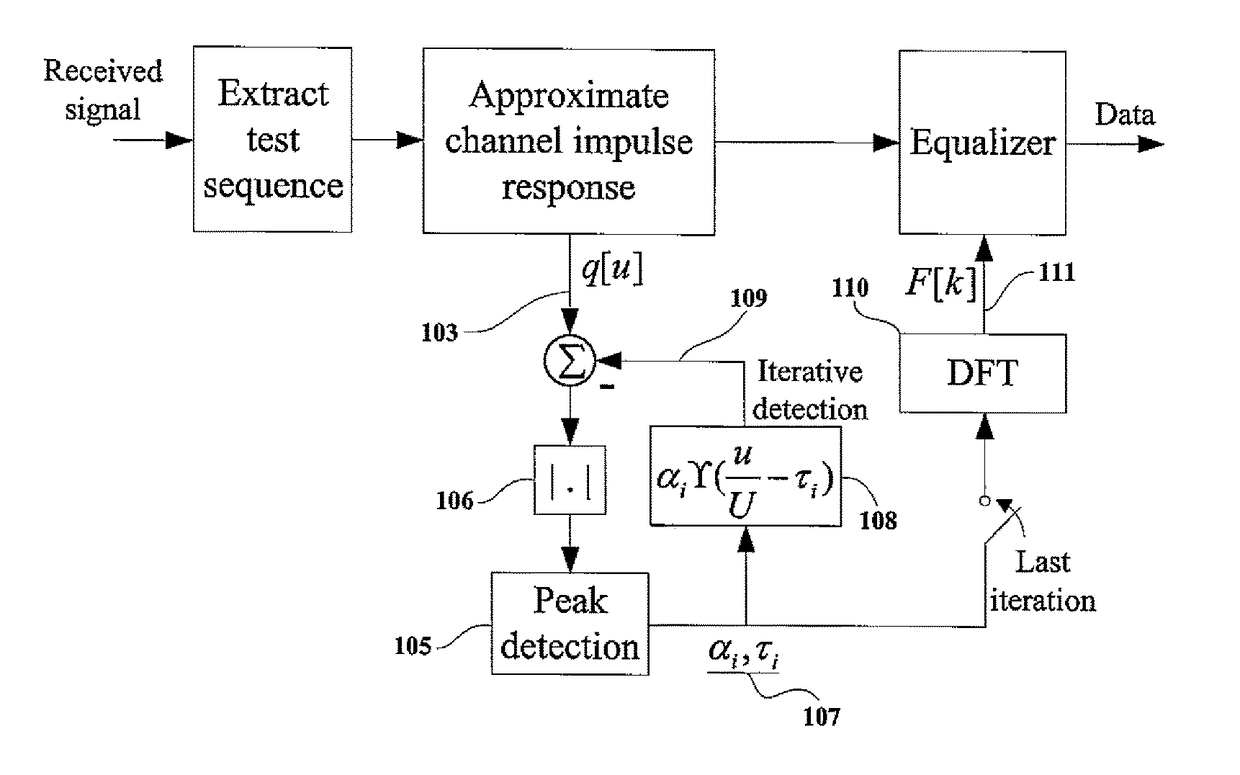
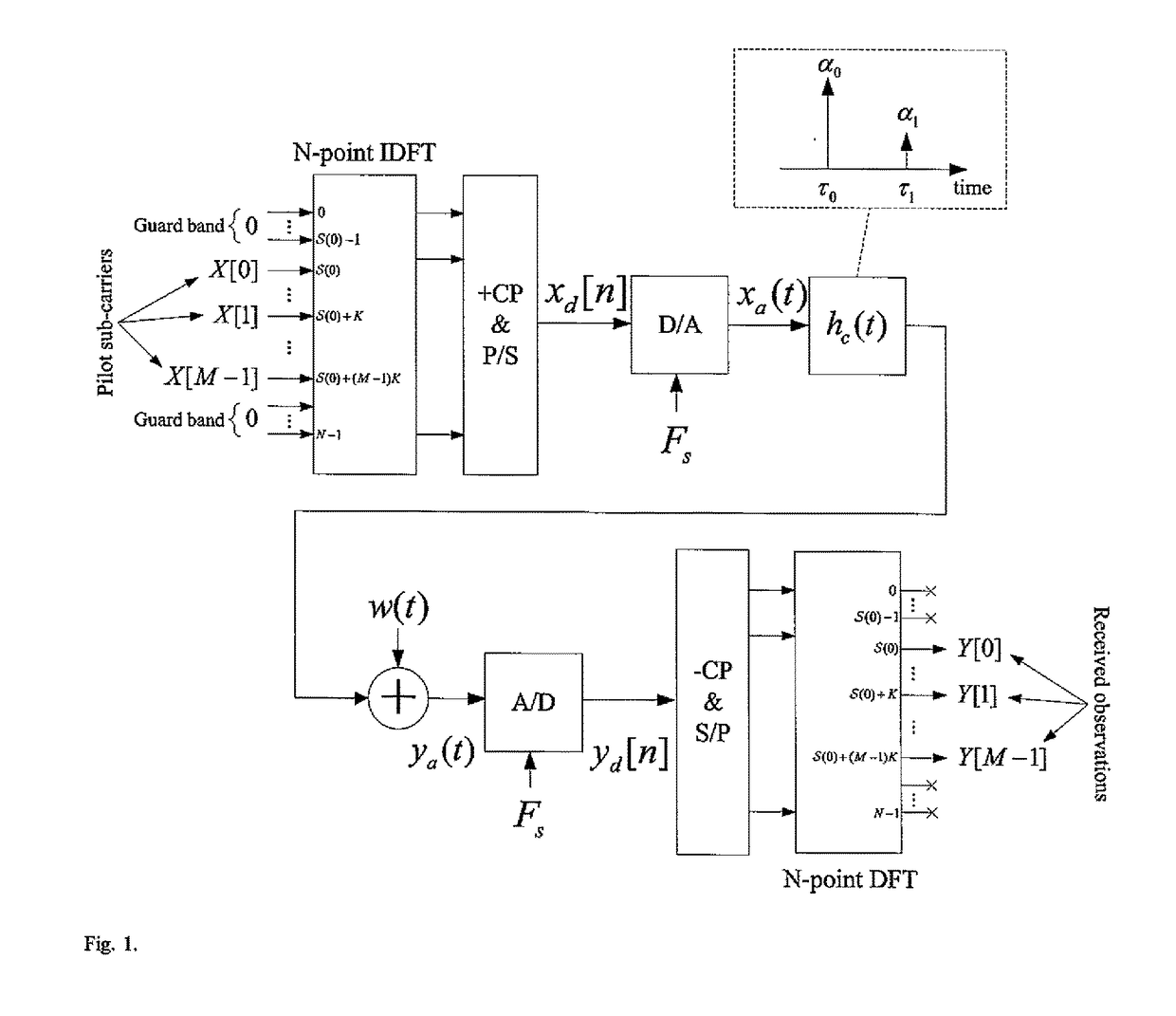
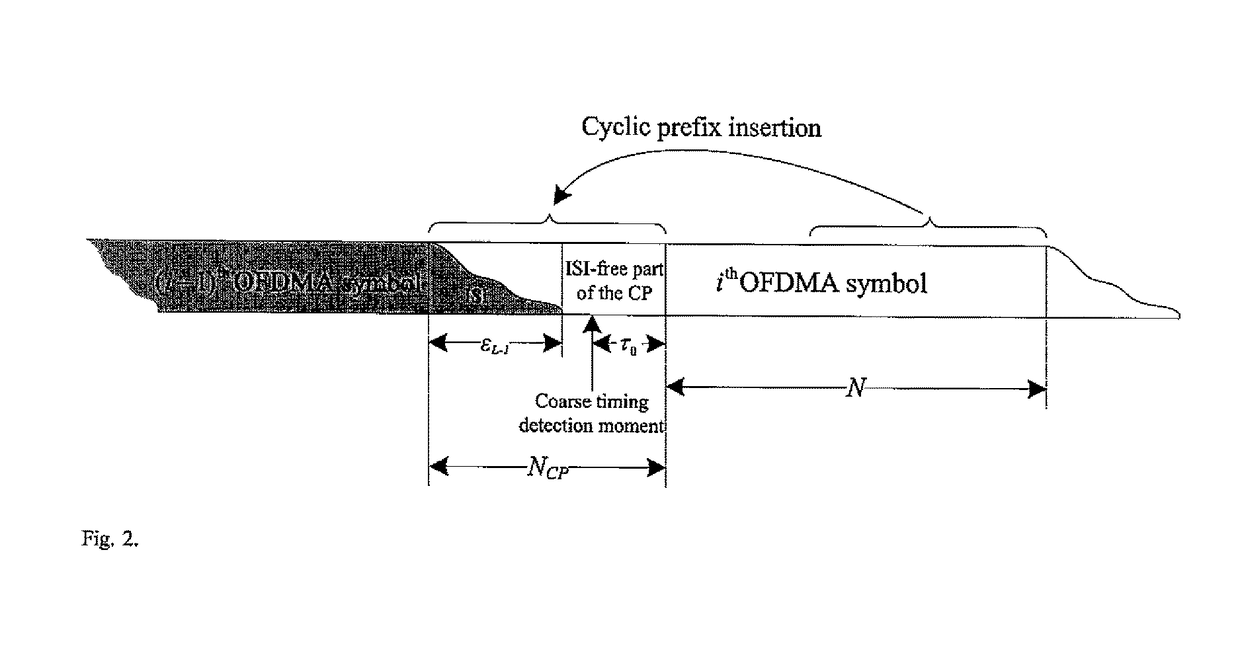
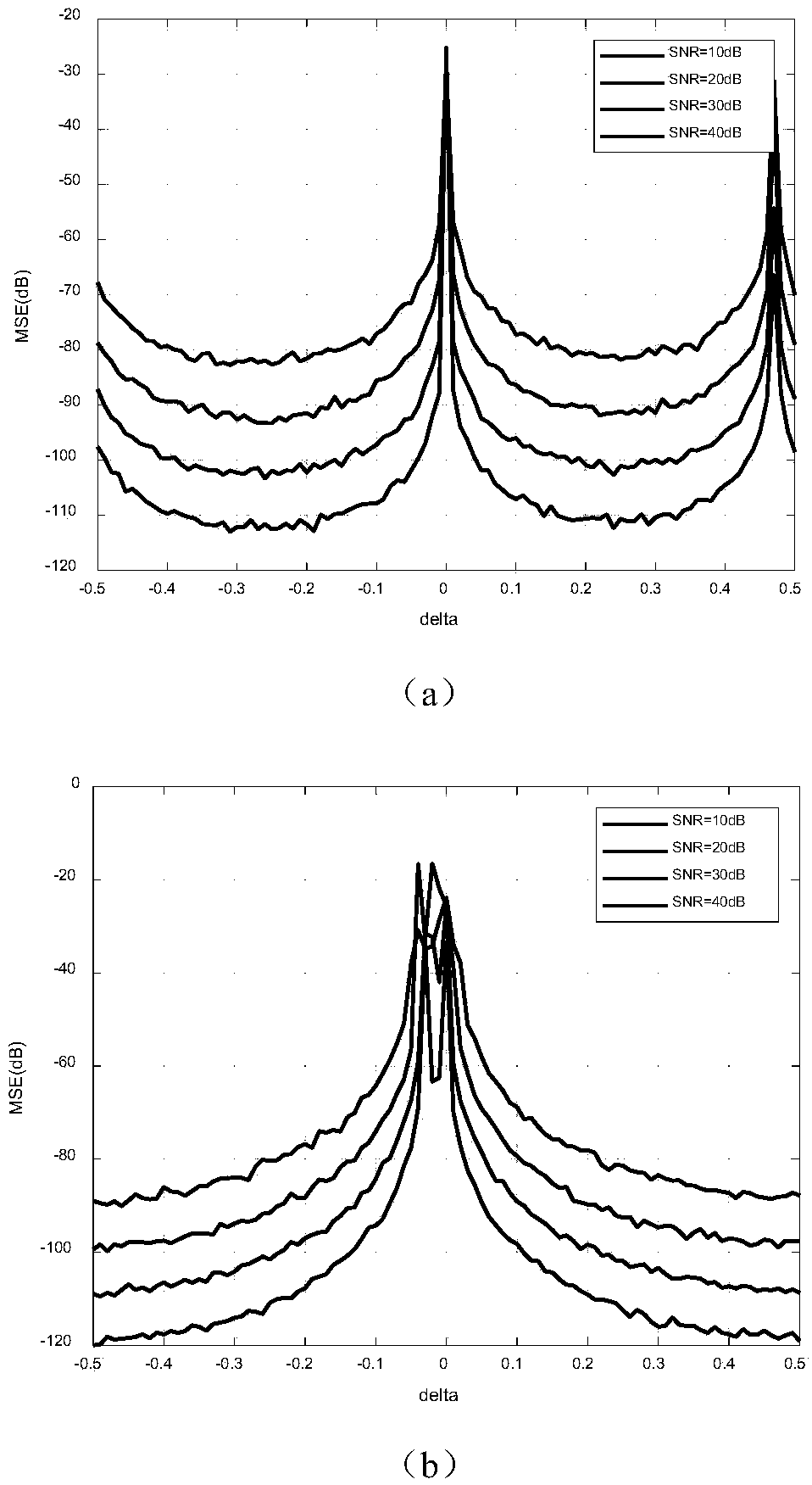
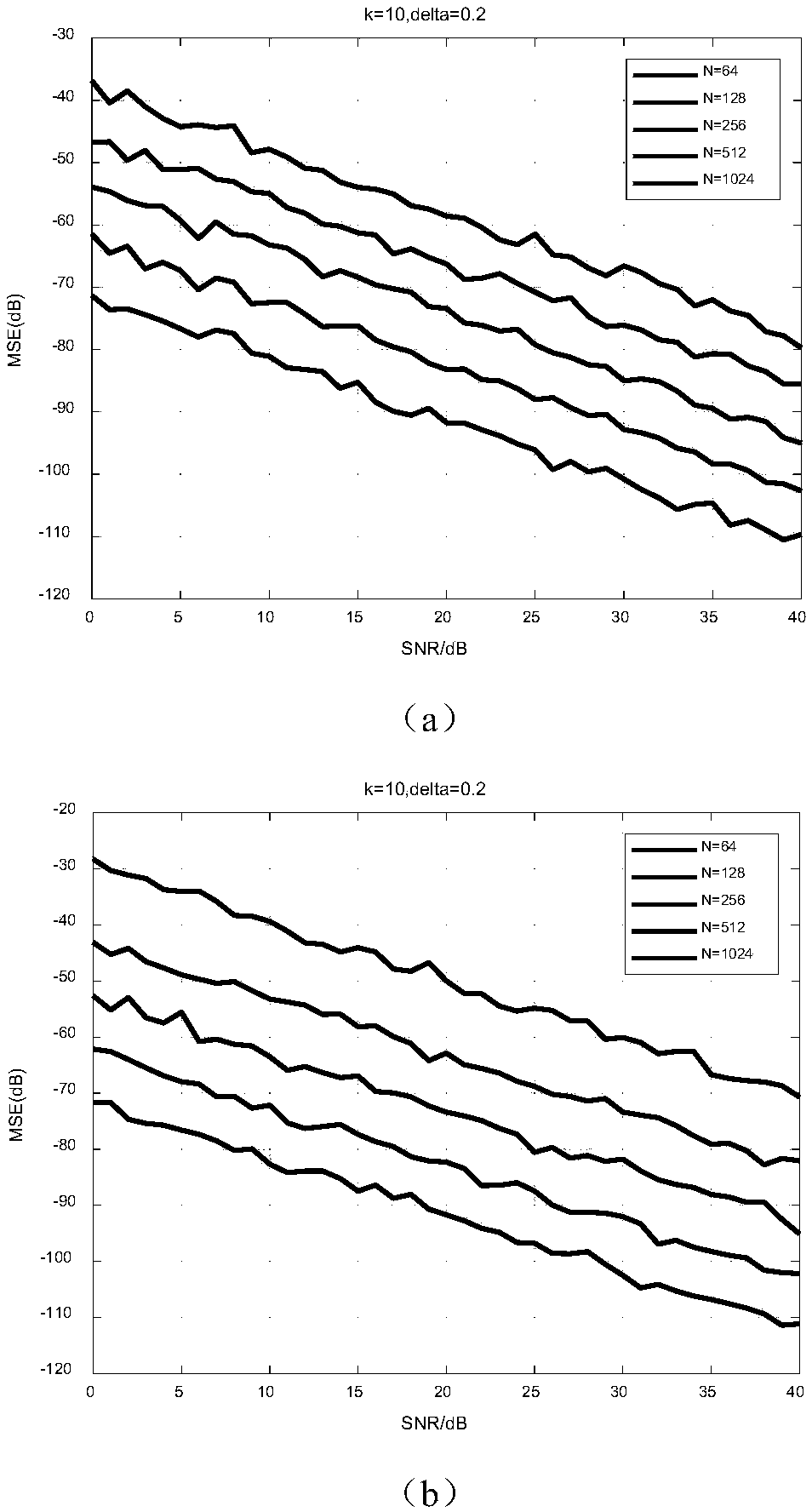
In a digital communication system there is provided a method for OFDM channel estimation that jointly considers the effects of coarse timing error and multipath propagation. The method uses an iterative channel estimation technique, which considers the practical scenario of fractional timing error and non-sample space echo delays. The method does not require channel state information such as second-order statistic of the channel impulse responses or the noise power. Moreover, timing error can be conveniently obtained with the proposed technique. Simulation shows that, when comparing OFDM channel estimation techniques under DOCSIS 3.1 realistic channel conditions, the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms conventional methods.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
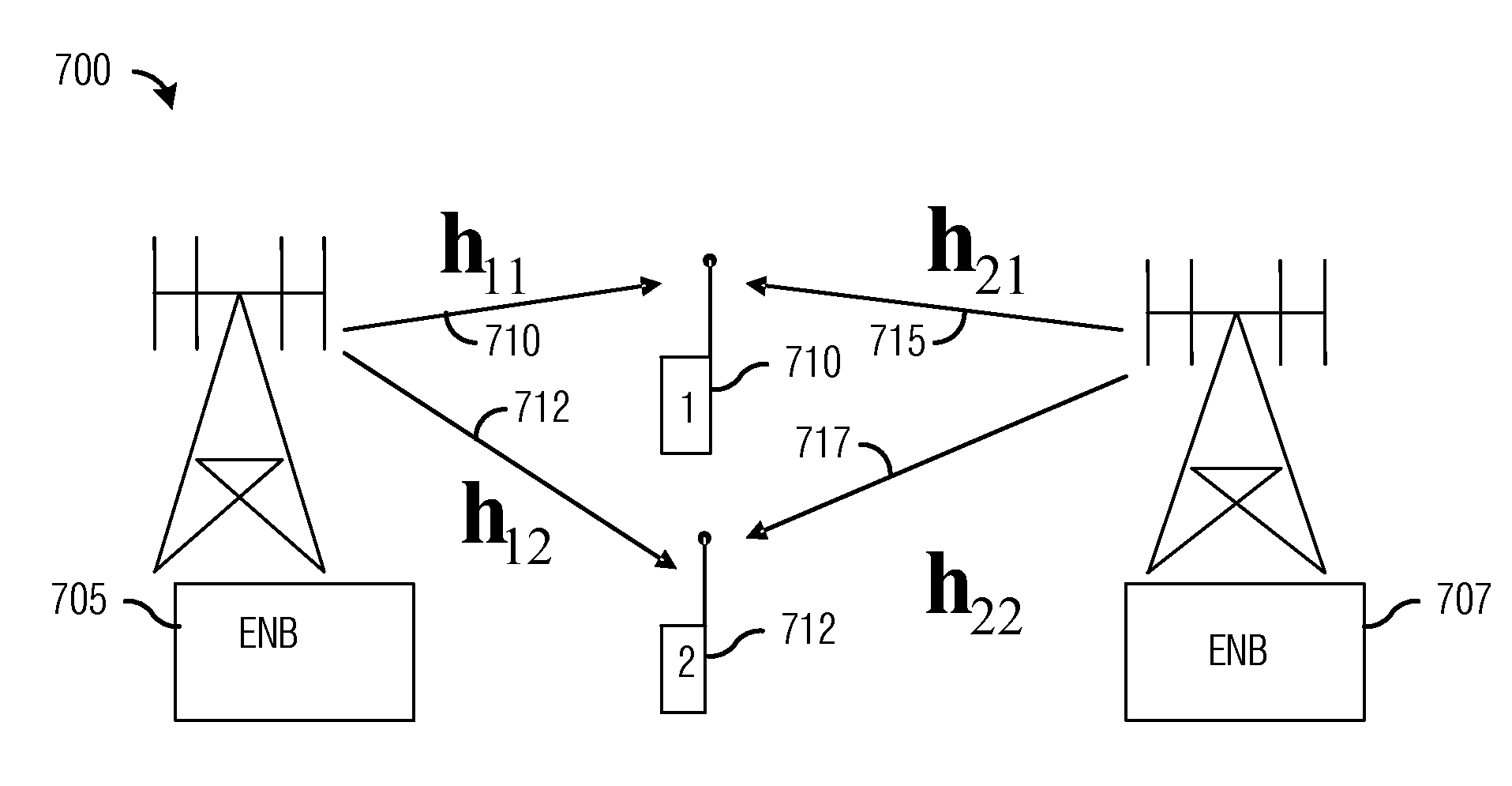
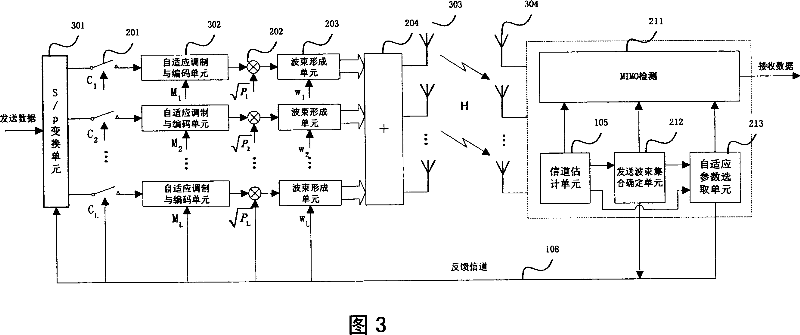
System and Method for Coordinated Spatial Multiplexing Using Second Order Statistical Information
ActiveUS20110115675A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce frequencyDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSubstation equipmentSpatial multiplexingCommunication device
A system and method for coordinated spatial multiplexing using second order statistical information is provided. A method for controller operations includes receiving second order statistics from a plurality of communications devices, computing a beamforming vector for each communications device in the plurality of communications devices, selecting a subset of communications devices from the plurality of communications devices to receive transmissions, and transmitting transmissions to the subset of selected communications devices. The beamforming vector for a communications device is based on the second order statistics provided by the communications device, and the transmitting uses the computed beamforming vector for each selected communications device to transmit the transmissions to the selected communications device.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Background noise reduction in sinusoidal based speech coding systems
A method and apparatus to reduce background noise in speech signals in order to improve the quality and intelligibility of processed speech. In mobile communications environment, speech signals are degraded by additive random noise. A randomness of the noise, which is often described in terms of its first and second order statistics, make it difficult to remove much of the noise without introducing background artifacts. This is particularly true for lower signal to background noise ratios. The method and apparatus provides noise reduction without any knowledge of the signal to background noise ratio.
Owner:COMSAT
Channel ambiguity removing method in MIMO signal blind detection process
InactiveCN103763222AEliminate sorting ambiguity issuesImprove reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsCommunications systemAmbiguity
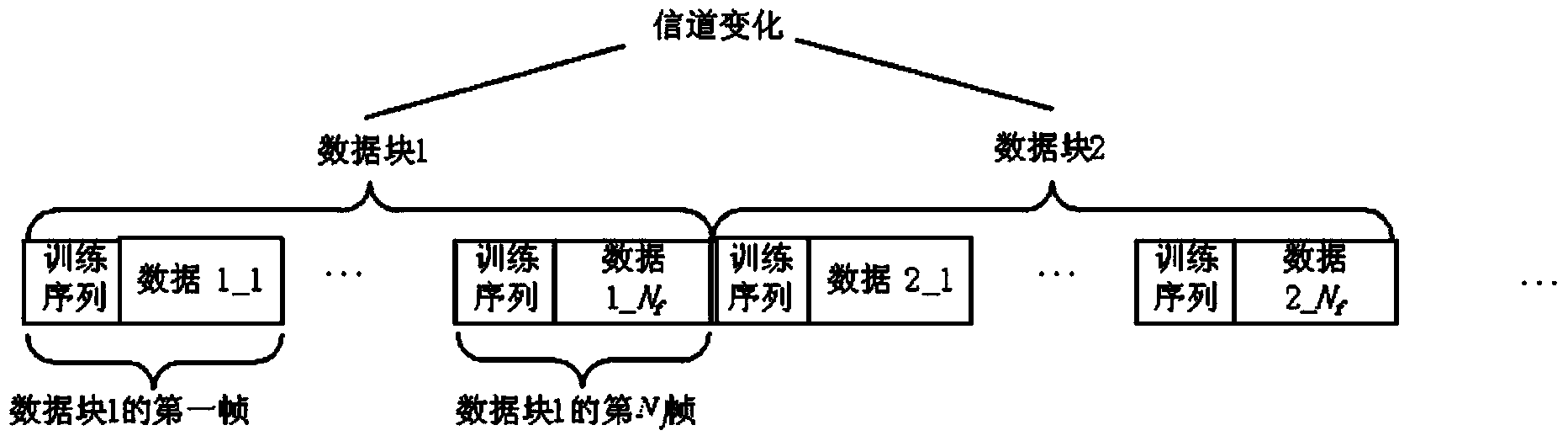
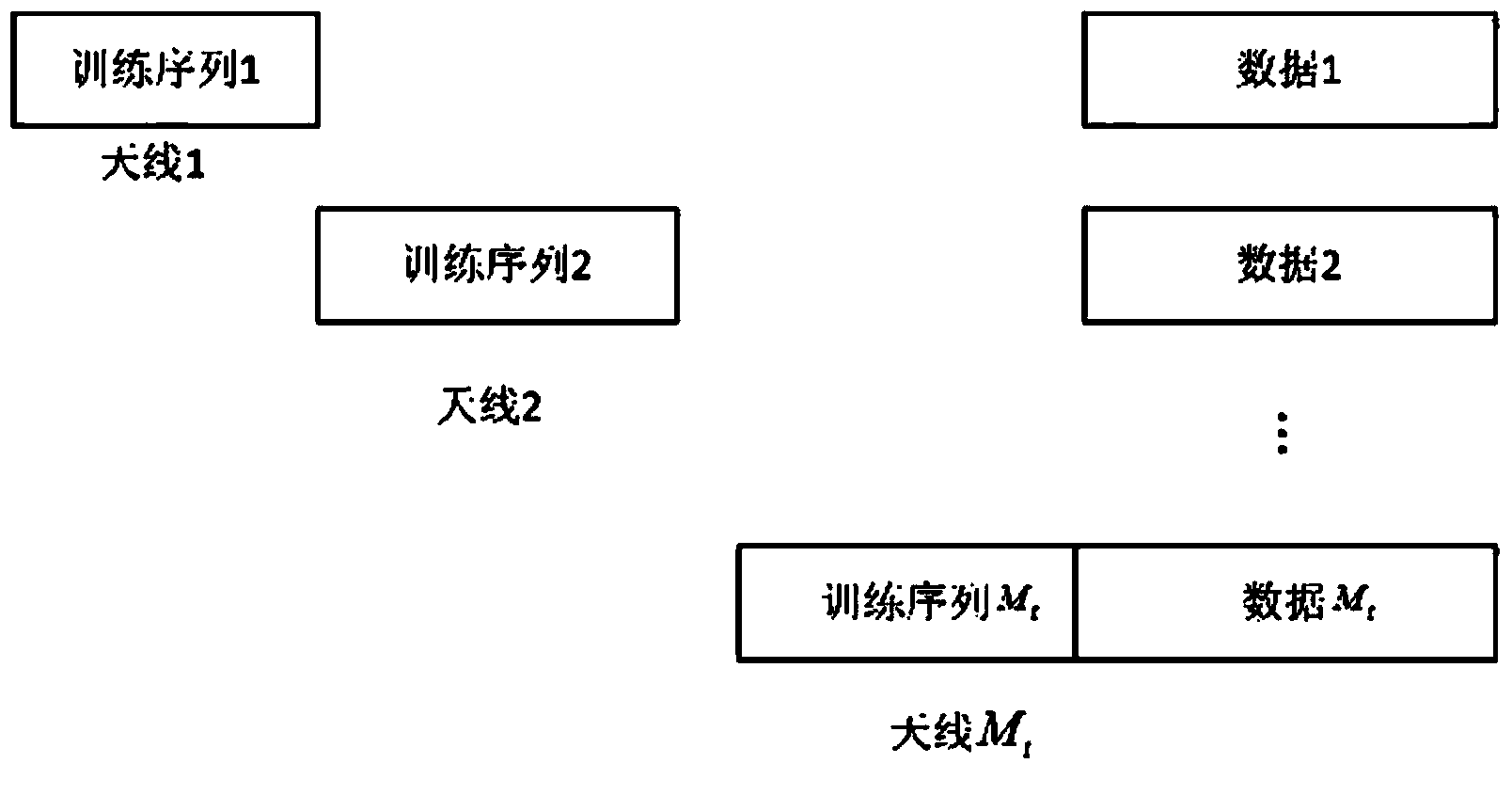
The invention discloses a channel ambiguity removing method in the MIMO signal blind detection process. The method is characterized by including the first step of dividing a channel matrix of an MIMO system into channels of Mt SIMO systems, the second step of intercepting received signals of each SIMO system, the third step of estimating the channels of each SIMO system through a subspace blind channel estimation algorithm based on second-order statistics according to the intercepted received signals, the fourth step of estimating the obtained channels and the received signals of each SIMO system and balancing out a training sequence of each transmitting antenna through a zero-forcing mode, and the fifth step of utilizing the training sequence obtained through balancing in a first frame and the intercepted signals to carry out channel estimation on subsequent data blocks, enabling the channels of the Mt SIMO systems to form the channel matrix of the MIMO system and obtaining the channel estimation value of the MIMO system. The channel ambiguity removing method has the advantages of being fewer in calculated quantity and low in complexity, eliminating sorting ambiguity, reducing normalization root-mean-square errors and the error rate of the system and improving the reliability of a non-cooperative communication system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
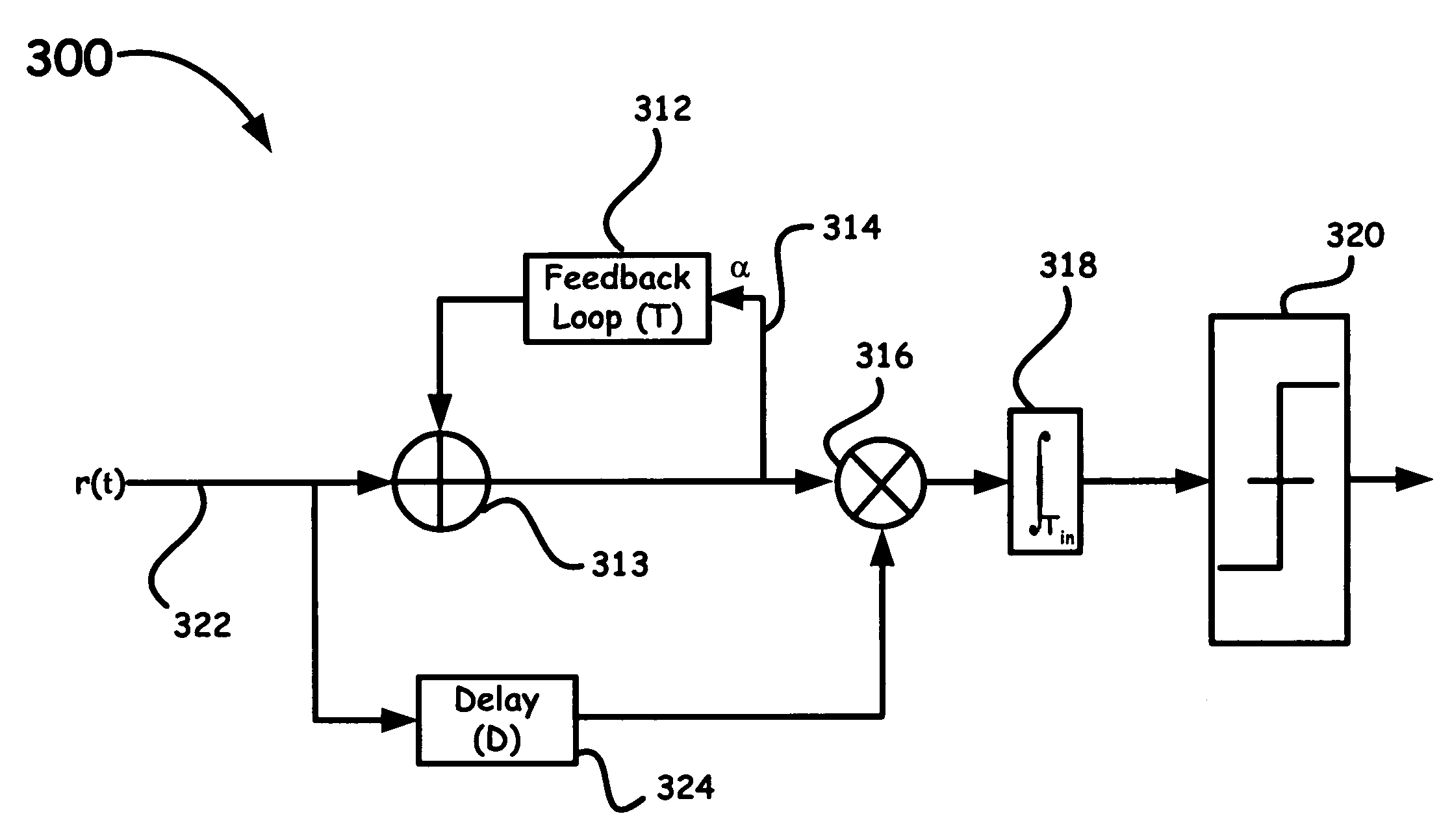
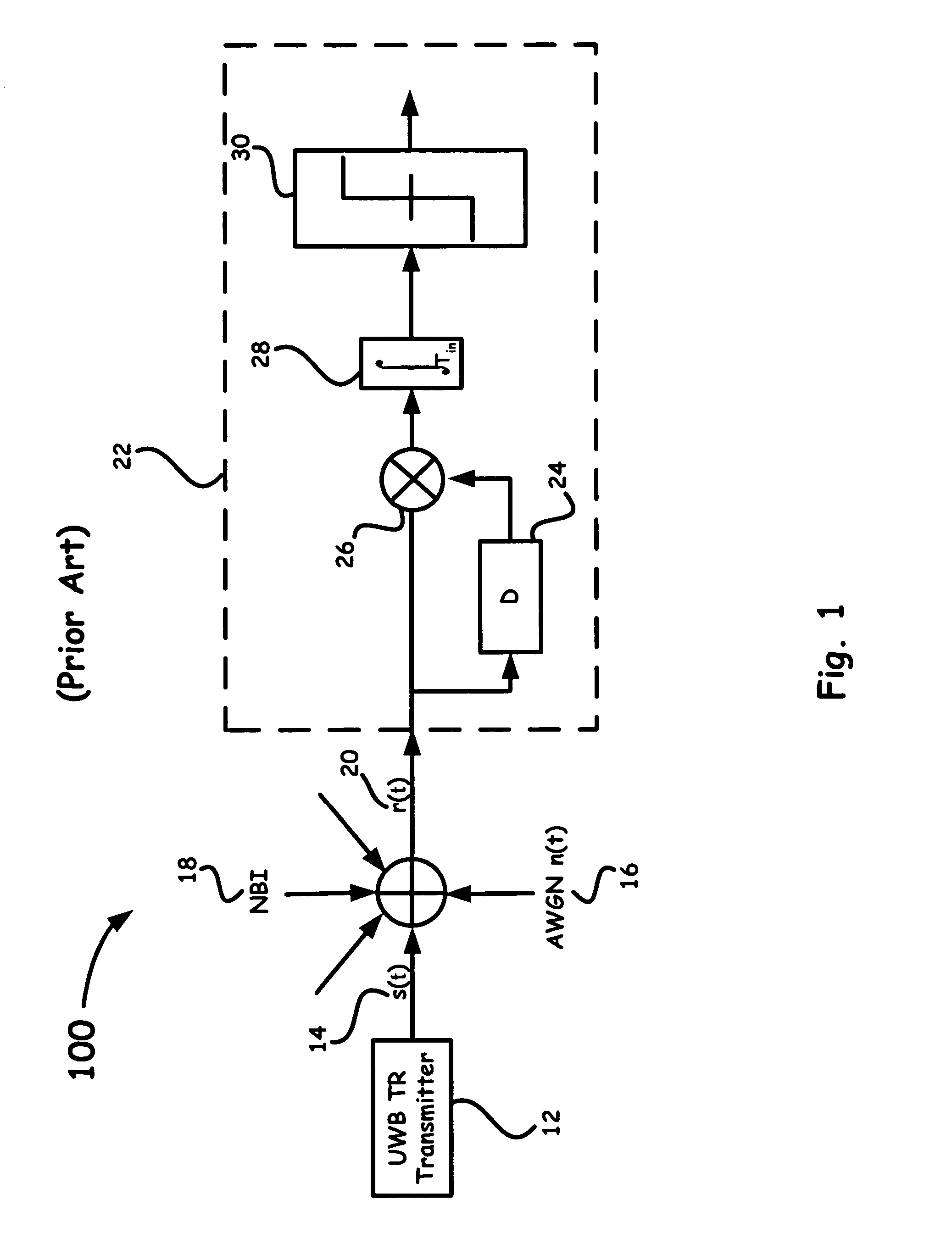
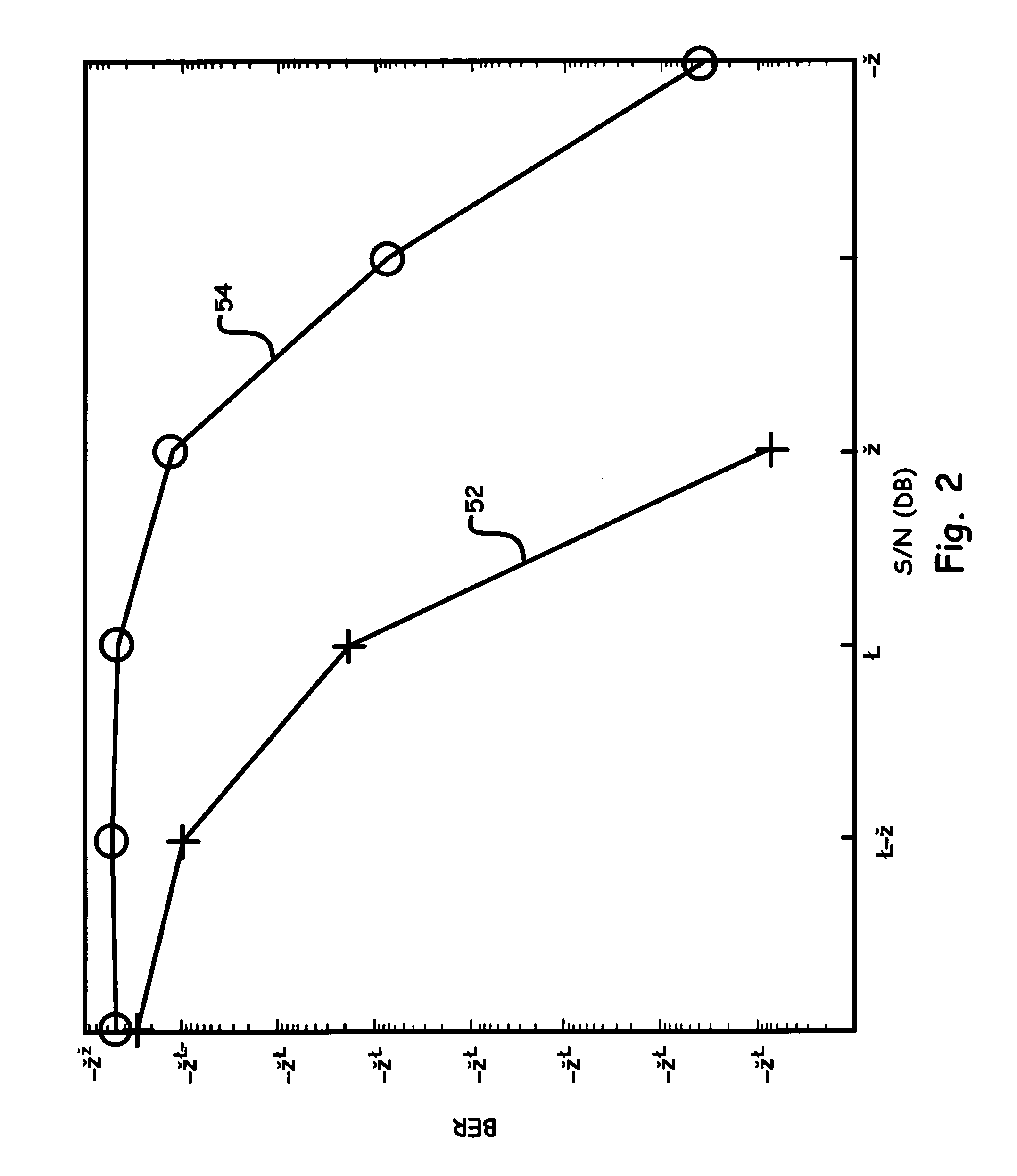
UWB communication receiver feedback loop
InactiveUS7305052B2Increased signal noiseA large amountResonant long antennasAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
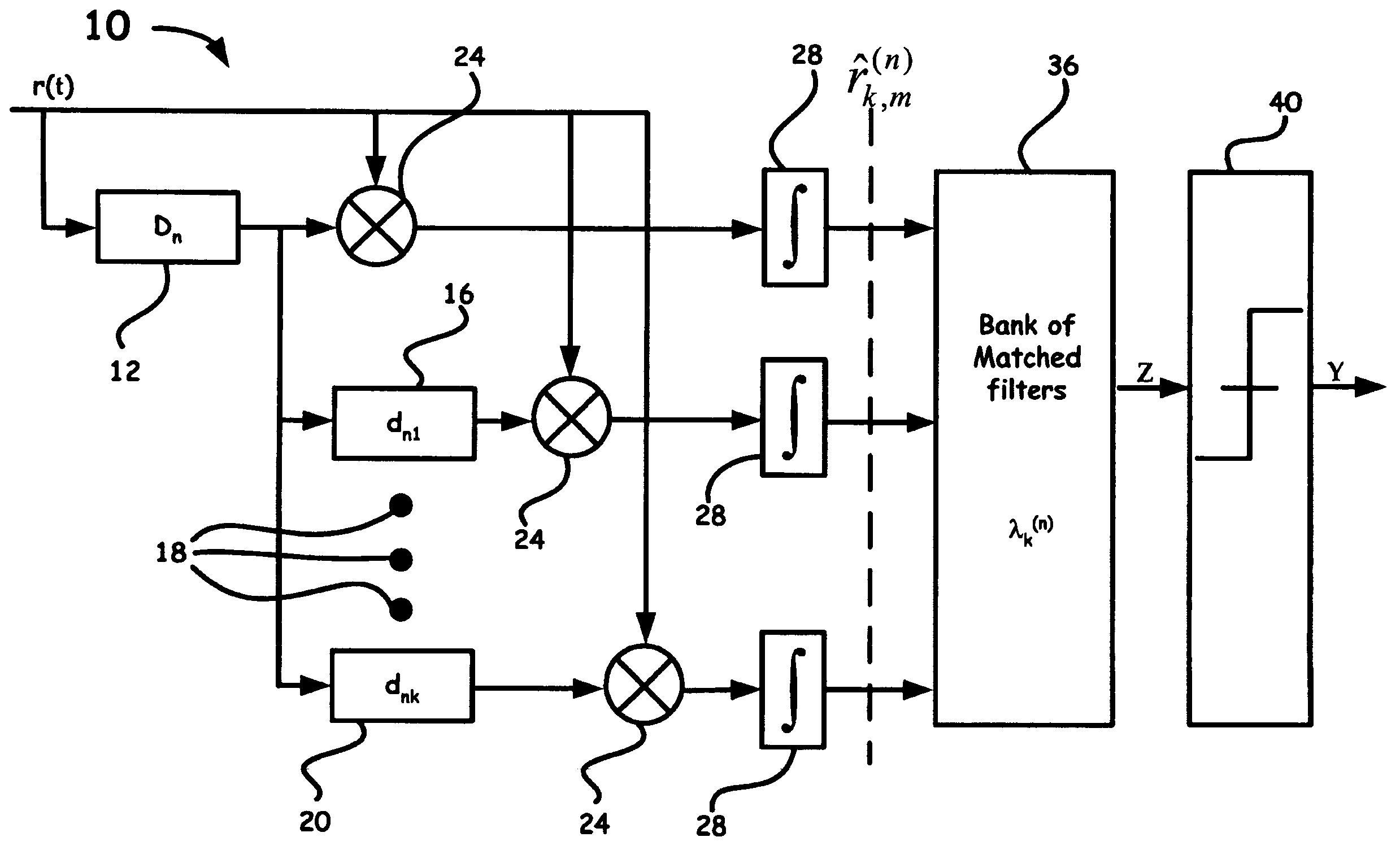
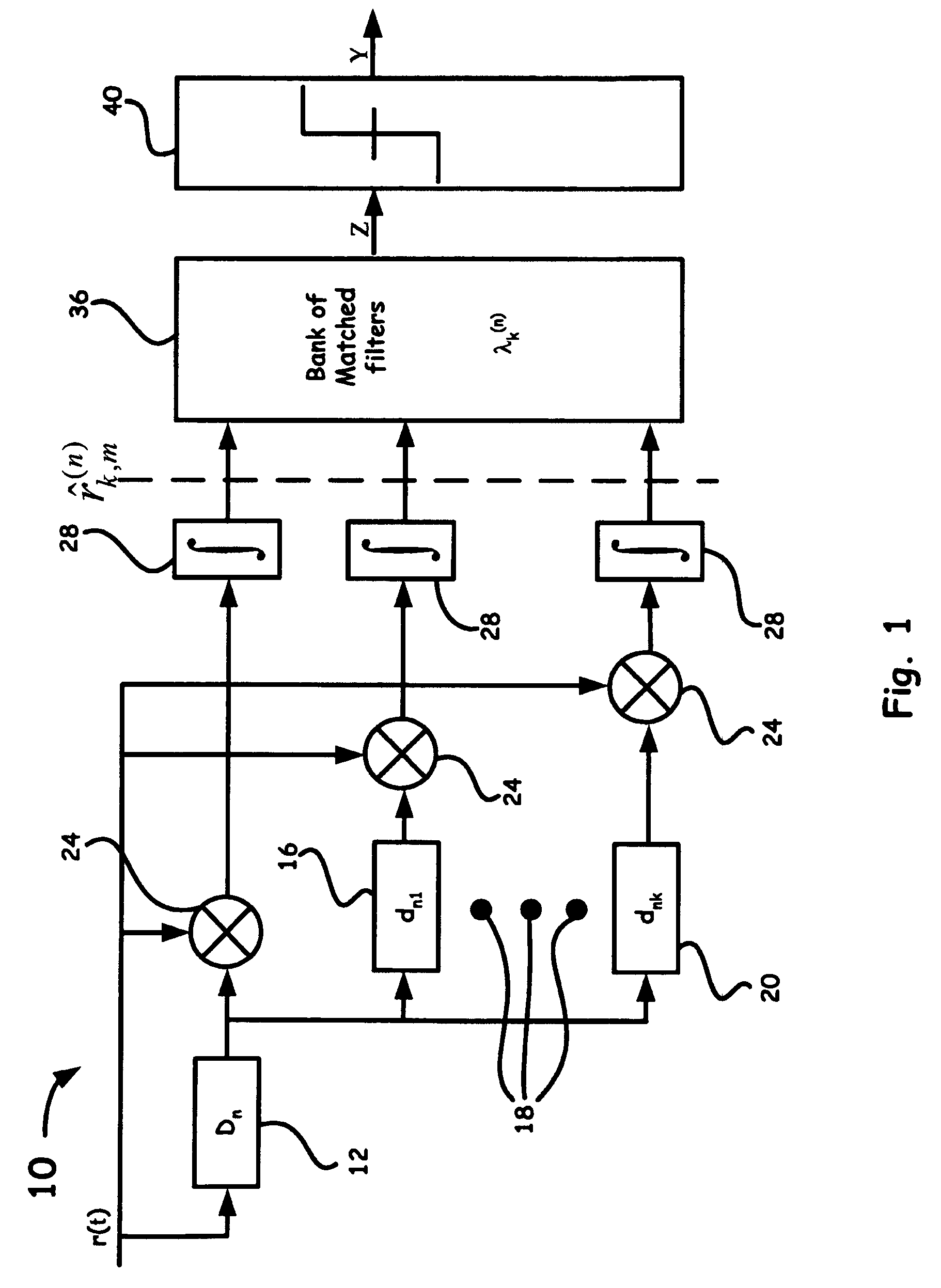
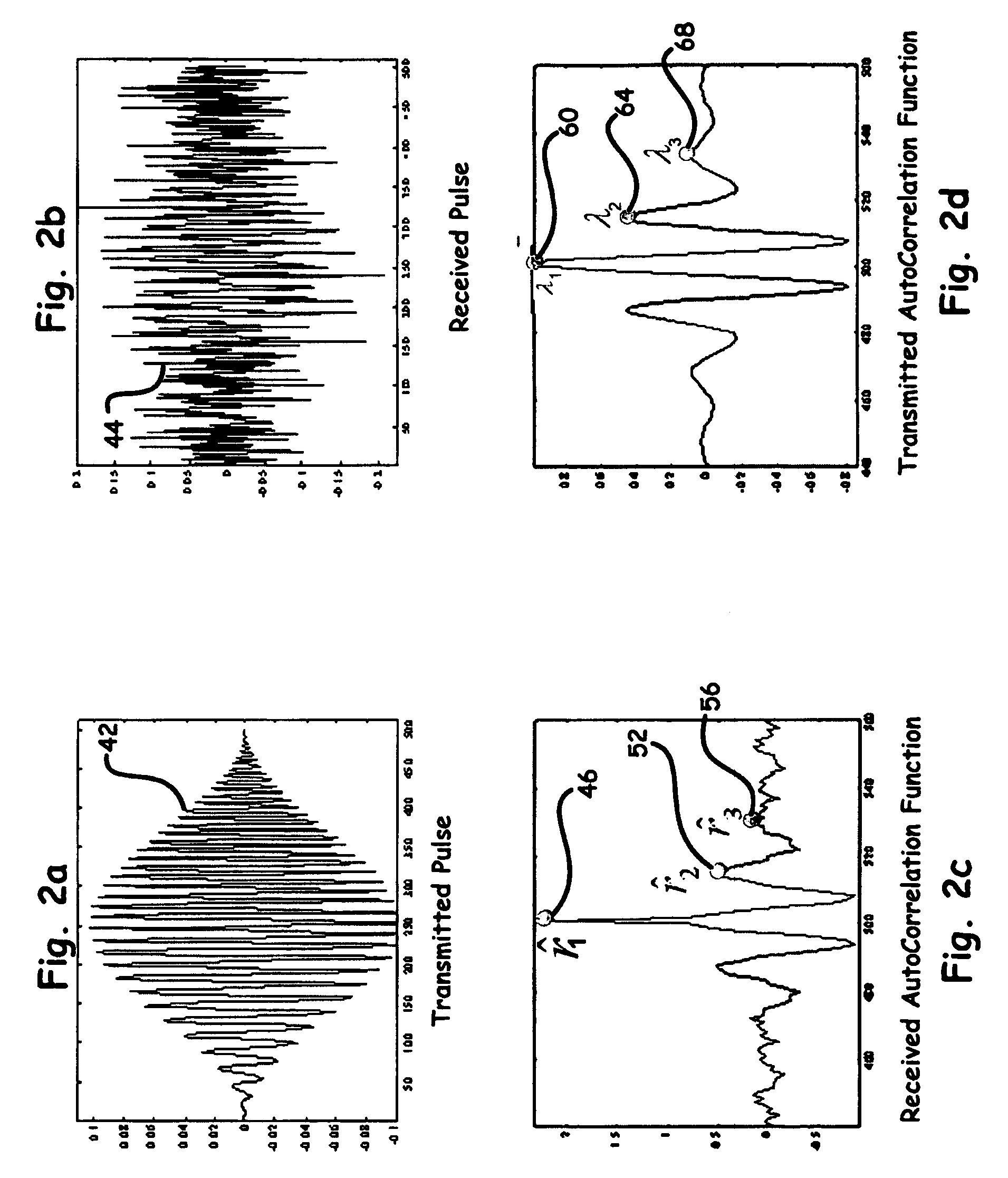
A novel technique and structure that maximizes the extraction of information from reference pulses for UWB-TR receivers is introduced. The scheme efficiently processes an incoming signal to suppress different types of UWB as well as non-UWB interference prior to signal detection. Such a method and system adds a feedback loop mechanism to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of reference pulses in a conventional TR receiver. Moreover, sampling the second order statistical function such as, for example, the autocorrelation function (ACF) of the received signal and matching it to the ACF samples of the original pulses for each transmitted bit provides a more robust UWB communications method and system in the presence of channel distortions.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Multi-pulse multi-delay (MPMD) multiple access modulation for UWB
A new modulation scheme in UWB communications is introduced. This modulation technique utilizes multiple orthogonal transmitted-reference pulses for UWB channelization. The proposed UWB receiver samples the second order statistical function at both zero and non-zero lags and matches the samples to stored second order statistical functions, thus sampling and matching the shape of second order statistical functions rather than just the shape of the received pulses.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
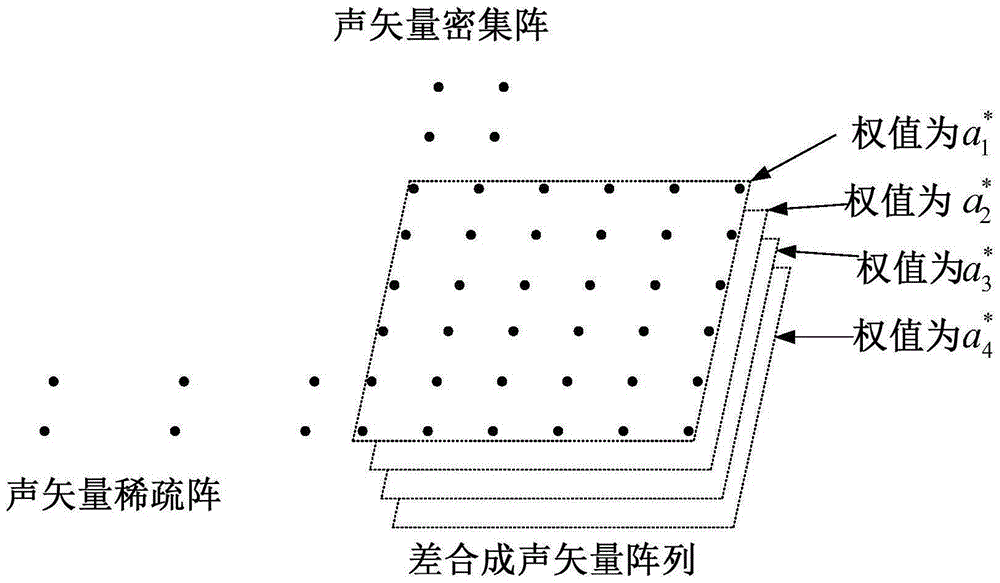
Target direction-finding method based on acoustic vector two-dimensional nested array
InactiveCN105182285AIncrease freedomRealize high precision direction findingDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesNested arraysSparse grid
The invention discloses a target direction-finding method based on an acoustic vector two-dimensional nested array, and is used for direction and pitching measurement of an underwater target. The method includes building a new acoustic vector two-dimensional nested array which is formed by two two-dimensional acoustic vector subarrays nested in geometric position, array elements of the subarray 1 are distributed in sparse grids, array elements of the subarray 2 are distributed in dense grids, two grids can be selected arbitrarily, that a matrix that associate the grids is an integer matrix is required only, the integer matrix can also be selected freely, then an autocorrelation matrix of signals output by the array are utilized to build a difference synthesis acoustic vector two-dimensional array, and finally a three-dimensional smooth DOA algorithm is utilized to obtain second-order statistics of received signals of the difference synthesis acoustic vector array.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Method and system for selecting and transmitting self-adaptive wave velocity in related multi-input multi-output system
InactiveCN101039163AImprove transmission performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMulti inputBit allocation
The invention discloses a self-adaptive beam selection and transmission method in the relative MIMO system. In the method, according to the second order characteristics statistical of the signal channel in the relative MIMO system, a receiver determines to send beam set and feed backs it to an inchoation. At each moment of transmission, according to current signal channel characteristics, the receiver chooses some beams form the beam set as sending beam which is used at present, at the same time, determines the power and bit allocation of each beam, and feedbacks the result to a sender. According to the result feed backed by the receiver, the sender chooses the corresponding beam from the sending beam set, and carries out the corresponding power and bit allocation, and then sends out. In the method, self-adaptive transmission method which is based on the beam selection, beam power and bit allocation is used, and multiplexing signal correlation is removed, at the same time, the transmission performance of MIMO system is improved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
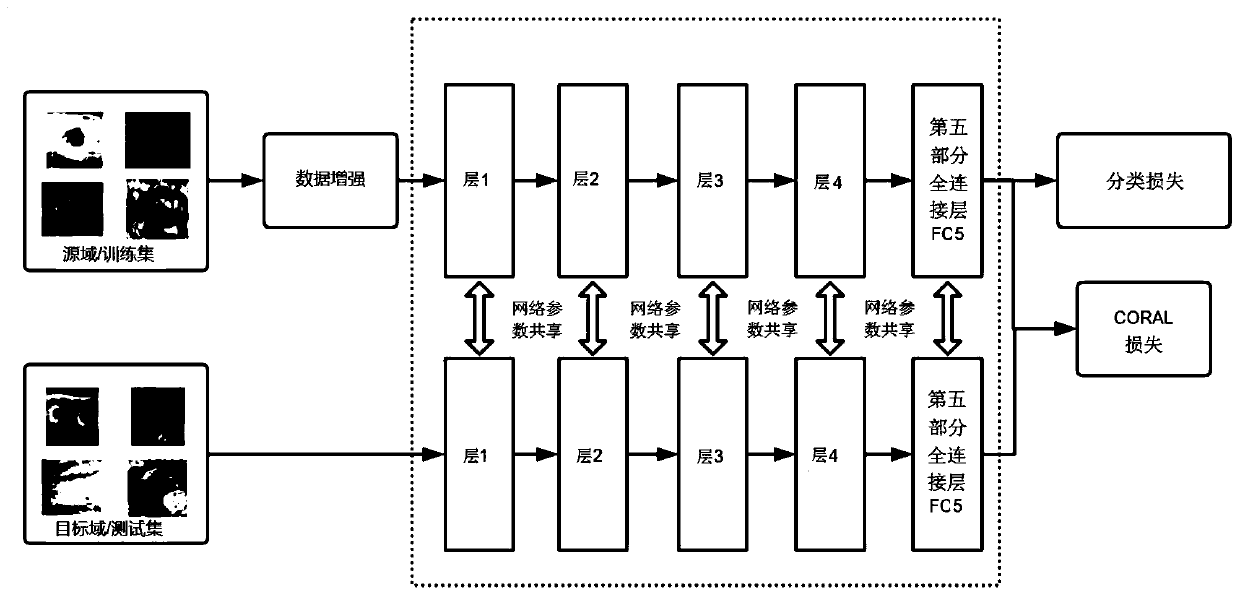
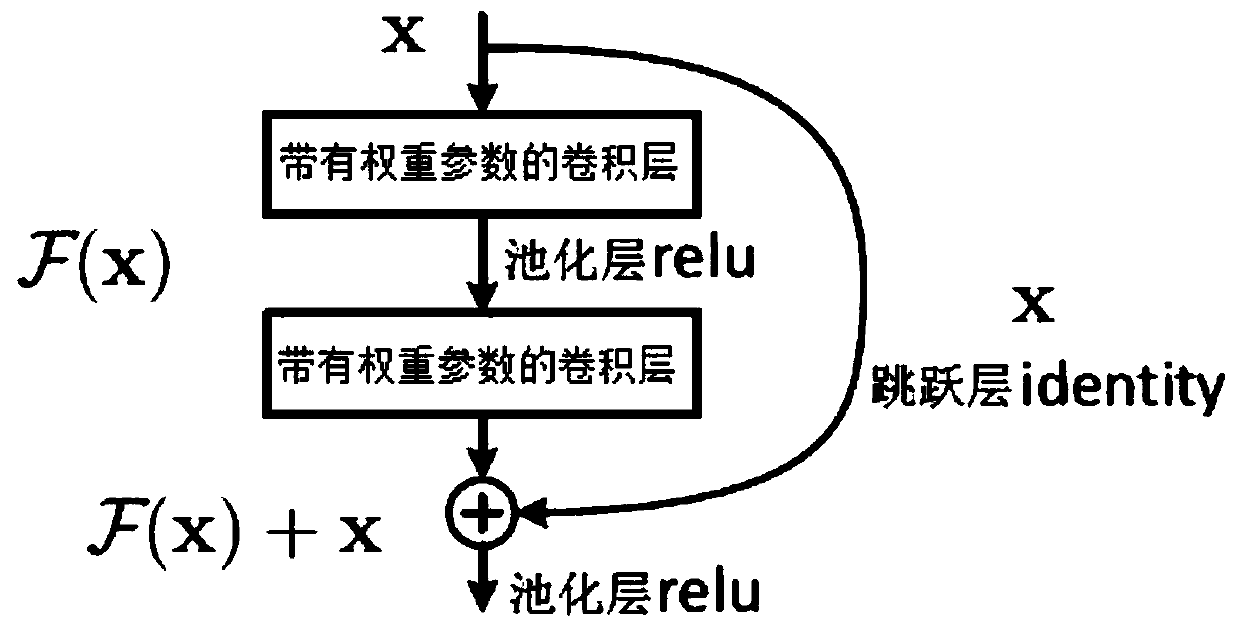
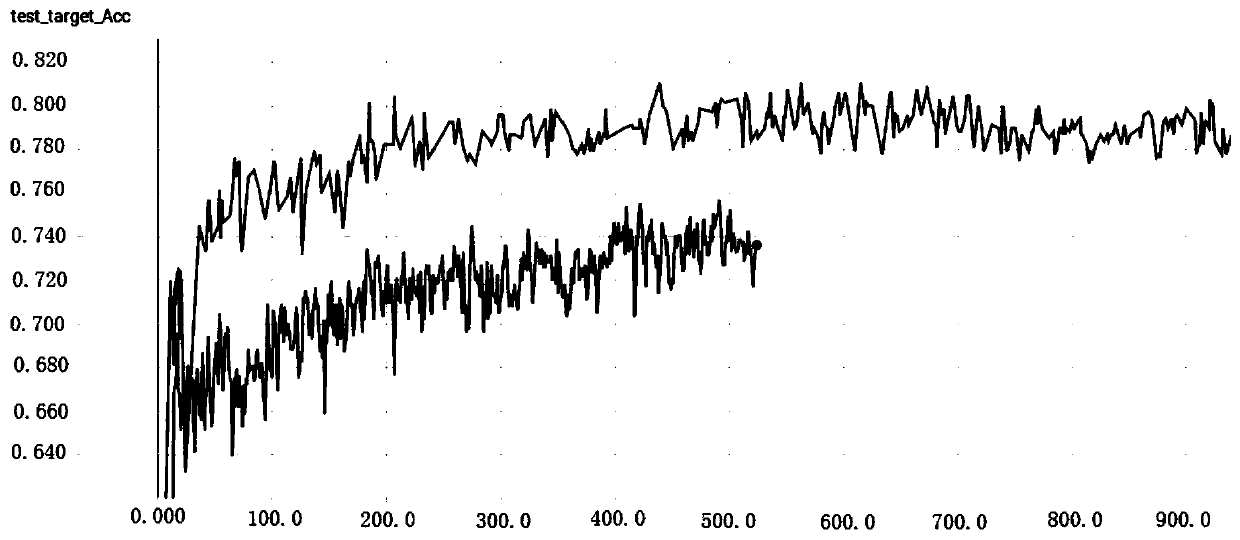
Industrial data classification method based on model migration
ActiveCN110555467AReduce manpowerReduce lossesCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCovarianceModel migration
The invention relates to an industrial data classification method based on model migration. The method comprises: collecting source domain data and target domain data respectively; performing data enhancement on the source domain data; constructing a convolutional neural network with a residual structure; establishing a loss function to minimize the difference of cross-domain learning feature covariances, and minimizing domain displacement by aligning second-order statistics of distribution of source domain data and target domain data on a feature level; and training and predicting the model.According to the method, other similar data are used for learning to carry out feature migration under the conditions that the target data are few and the data are difficult to obtain, and then the target domains are classified, so that the method has a relatively high application value.
Owner:青岛奥利普奇智智能工业技术有限公司
Speed detection method in communication system, receiver, network element and processor
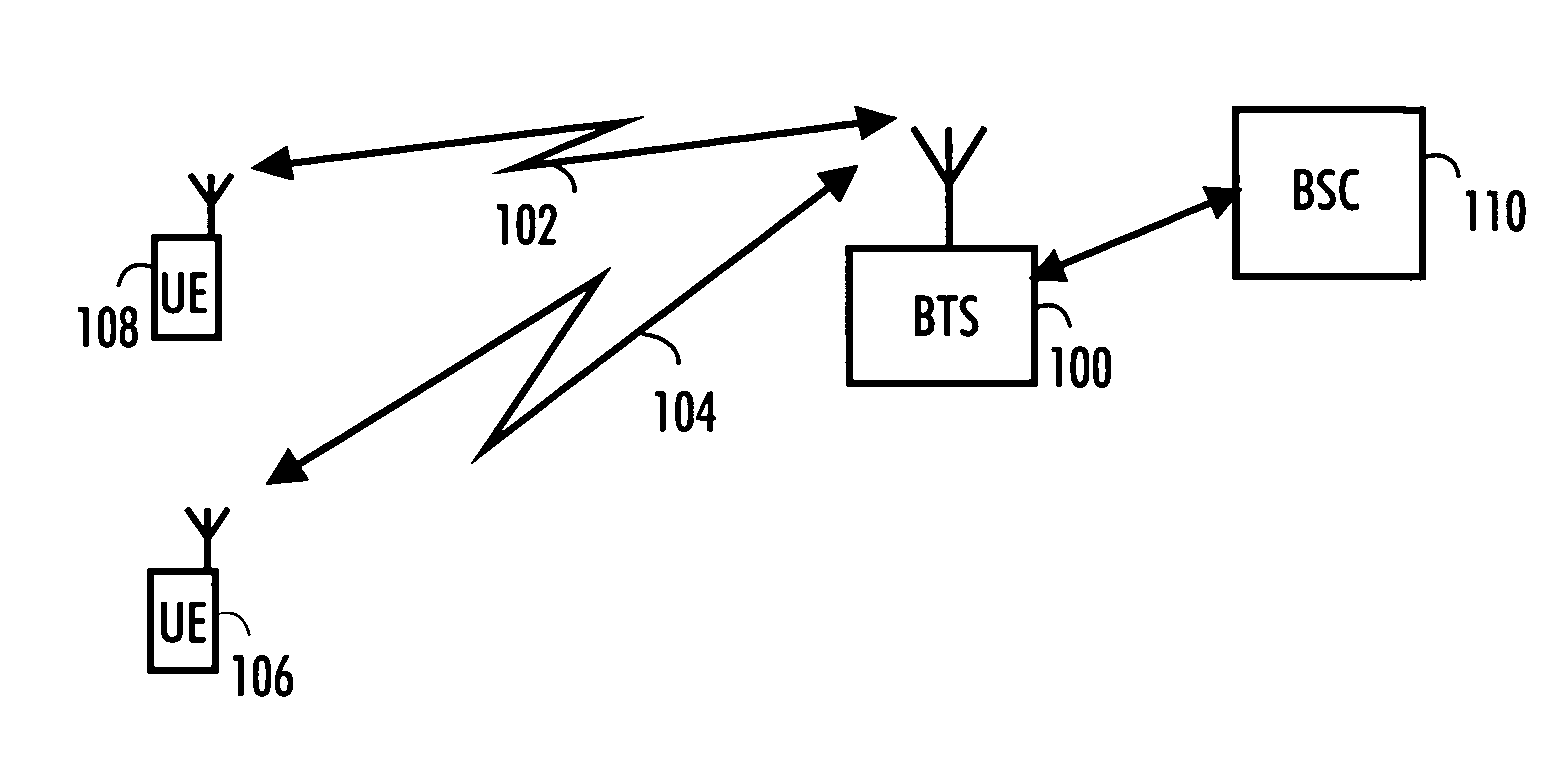
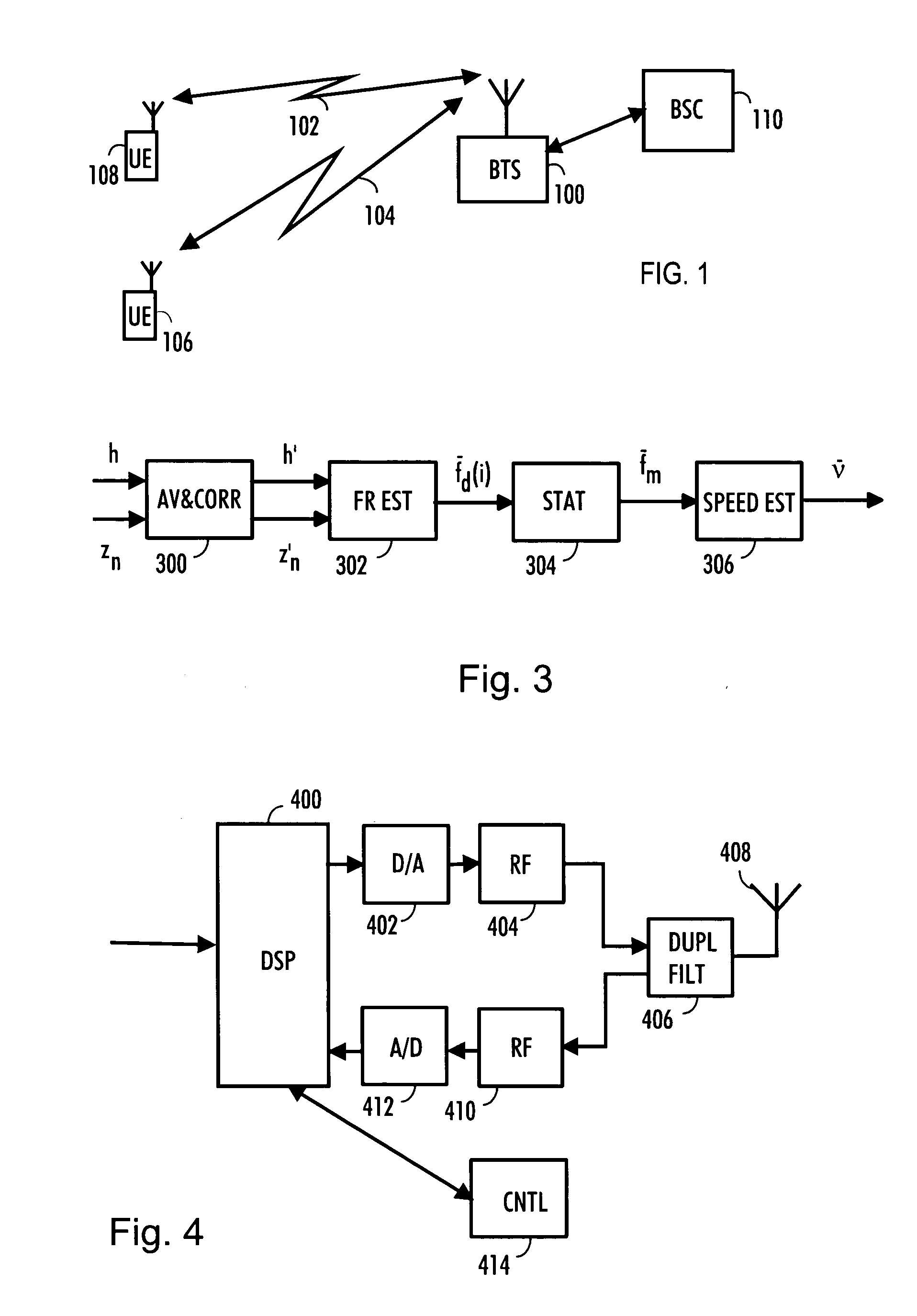
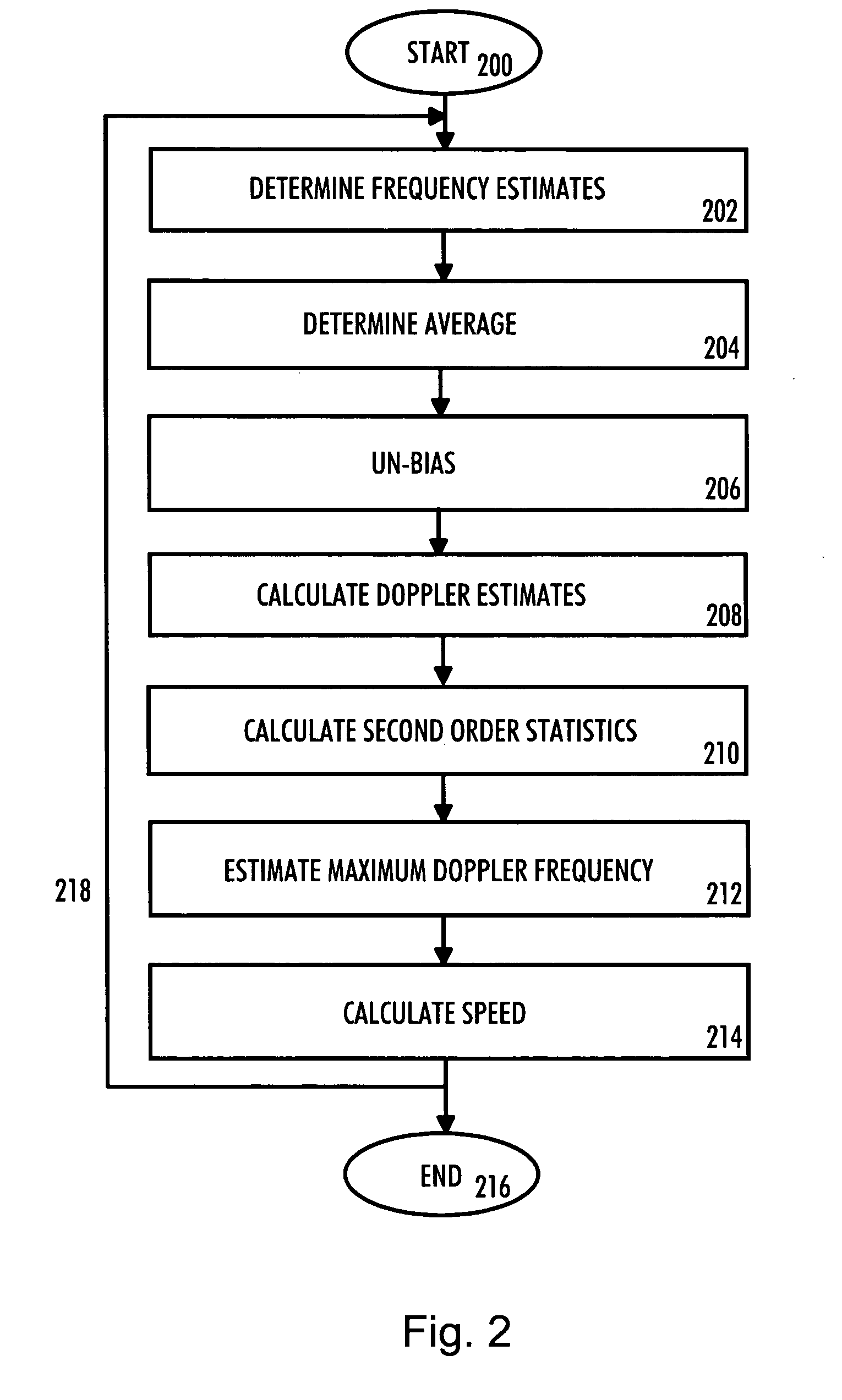
InactiveUS20070046527A1Increase speedGood suitSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionCommunications systemImpulse response
The embodiment of the invention is related to a processor comprising, for example, means for determining a predetermined number of frequency estimates, means for determining an average of the frequency estimates for obtaining an averaged frequency offset, means for unbiasing received samples and / or impulse response values using the averaged frequency offset, means for calculating Doppler frequency estimates using the unbiased received samples and / or impulse response values and means for calculating selected second order statistics of the Doppler frequency estimates over a predetermined period.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Arrival direction estimation method based on conjugation expansion
ActiveCN102694588ALower requirementIncreased number of signal directionsSpatial transmit diversitySignal onEstimation methods
The invention discloses an arrival direction estimation method based on conjugation expansion. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly calculating and receiving a second order statistic between signals, obtaining a conjugation matrix of an oriented matrix by utilizing the property of a delay self-correlation function, then constructing a new pseudo snapshot matrix by utilizing delay sampling of an extensible vector, and finally estimating an arrival direction of a signal on the matrix by adopting a fourth-order cumulant method. By virtue of a signal arrival direction estimation method based on array extension, the number of estimated signal arrival directions is greatly increased and signal arrival direction estimation accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pilot frequency optimization and allocation combined pre-coding method for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output
ActiveCN105681009AReduce pollutionGood estimateSpatial transmit diversityPilot signal allocationPrecodingCell based
The invention discloses a pilot frequency optimization and allocation combined pre-coding method for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output. A base station averagely divides all pilot frequencies into two pilot frequency subgroups; the pilot frequency subgroups are allocated to two kinds of cells; DOAs of terminals are obtained; intra-cell pilot frequency allocation is carried out; the terminals send pilot frequency information to cell base stations to which the terminals belong; the cell base stations obtain the channel information of terminals containing pilot frequency pollutions through channel estimation; the channel information is obtained according to the time division duplexing channel reciprocity; through estimating the DOAs of the terminals, the DOAs of the terminals are searched; the channel information of the terminals containing the pilot frequency pollutions are recalculated according to the DOAs, thus obtaining optimized channel information of the terminals; G terminals with relatively good channel quality are selected as user group centers; the distances between other terminals and the user group centers are calculated; the rest terminals are allocated according to the distance values; the user group centers are updated; all users are iterated and grouped; and data are sent after calculating the second-order statistics of the channels of the user groups. According to the method provided by the invention, the channel design is optimized; and the system performance is promoted.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
IpDFT-based frequency estimation method of non-equilibrium electric power system
ActiveCN108020721AImprove estimation accuracyImprove stabilitySpectral/fourier analysisFrequency measurement arrangementComputation complexityElectric power system
The present invention discloses an IpDFT(Interpolation Discrete Fourier Transform)-based frequency estimation method of a non-equilibrium electric power system. The problem of non-circular signal employed frequency estimation in a non-equilibrium condition is solved based on modeling of complex-valued signals deduced from a three-phase voltage through orthogonal [Alpha][Beta]transformation. The newest progress obtained through enhanced complex-valued second-order statistics is employed, and in a non-equilibrium condition, the complex-valued signals are second-order non-circular signals. In theinvention, interpolation Fourier transform is employed to estimate frequency of the signals, the non-circular signals are converted to sinusoidal signals through simple calculation, positive and negative frequency components are considered, and therefore, the estimation accuracy of the frequency is improved and the calculation is simple. Compared to traditional linear adaptive estimation, the method is more suitable for the non-equilibrium system, gives out unbiased frequency estimation, and is not sensitive to frequency change. The method is more stable and low in calculation complexity, andis improved in robustness anti-noise performance and estimation precision.
Owner:南京福致通电气自动化有限公司 +1
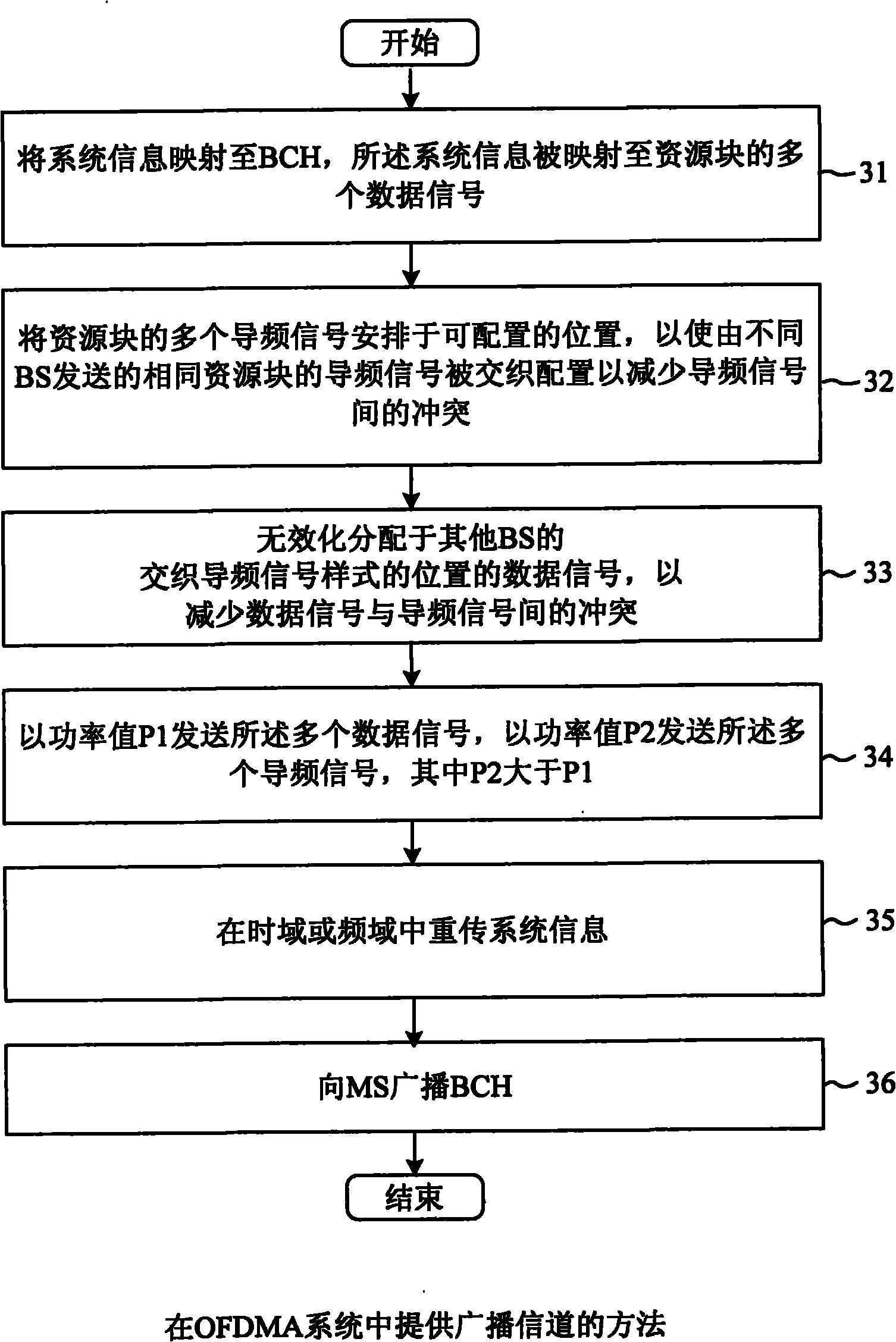
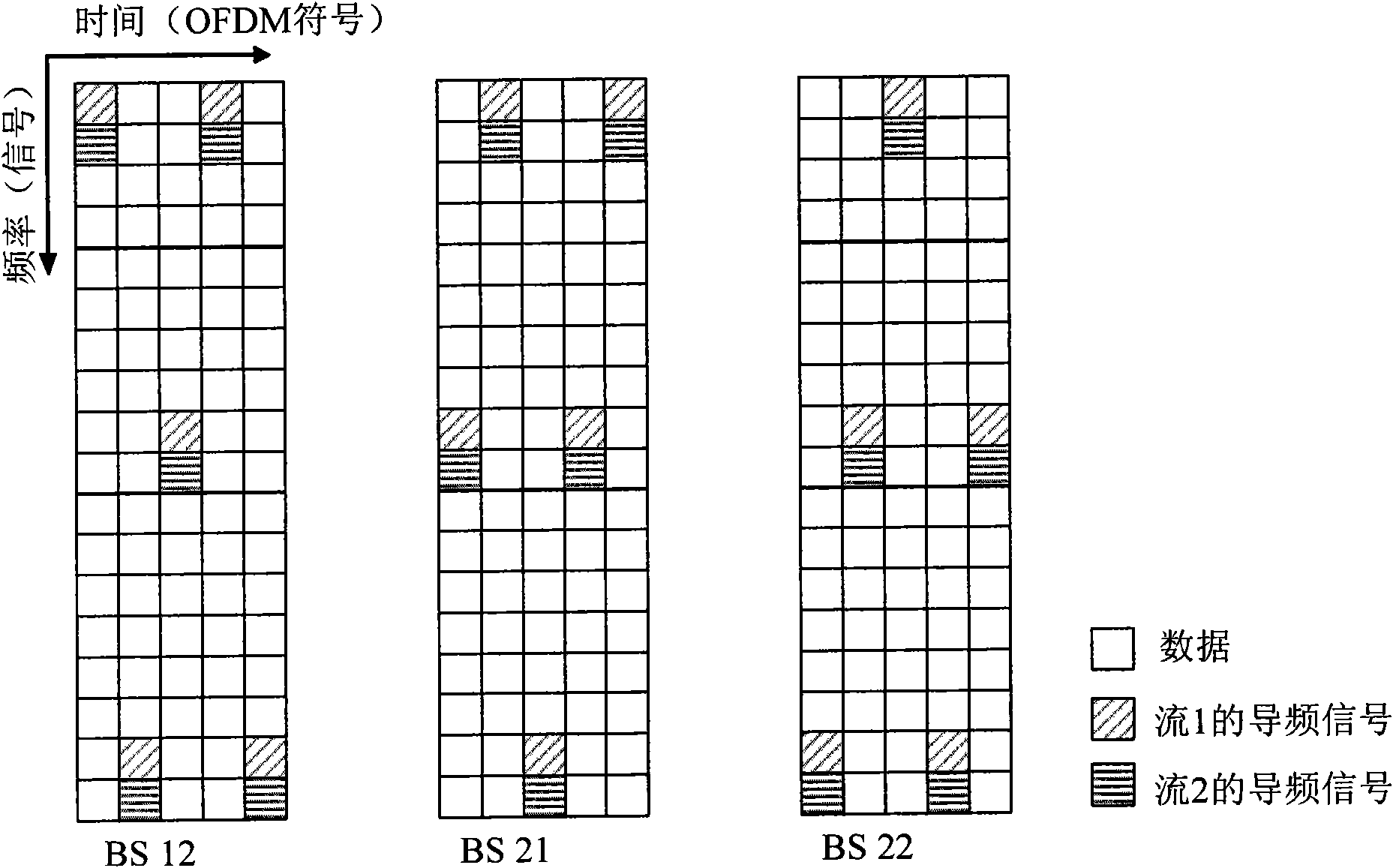
Method and apparatus for broadcasting and receiving system information in ofdma systems
InactiveCN101933303AImprove detection reliabilityTransmission path divisionAssess restrictionBroadcast channelsResource block
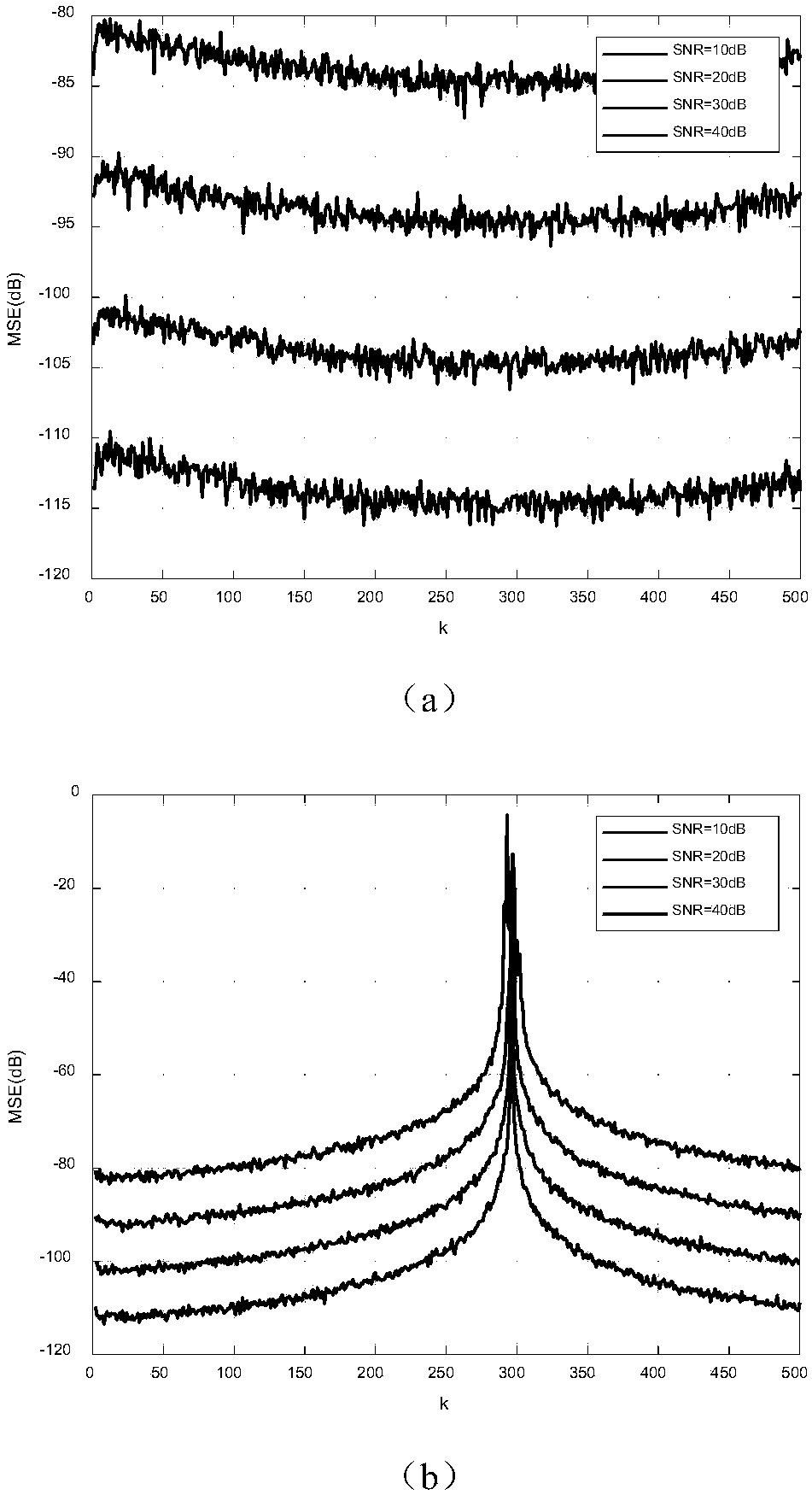
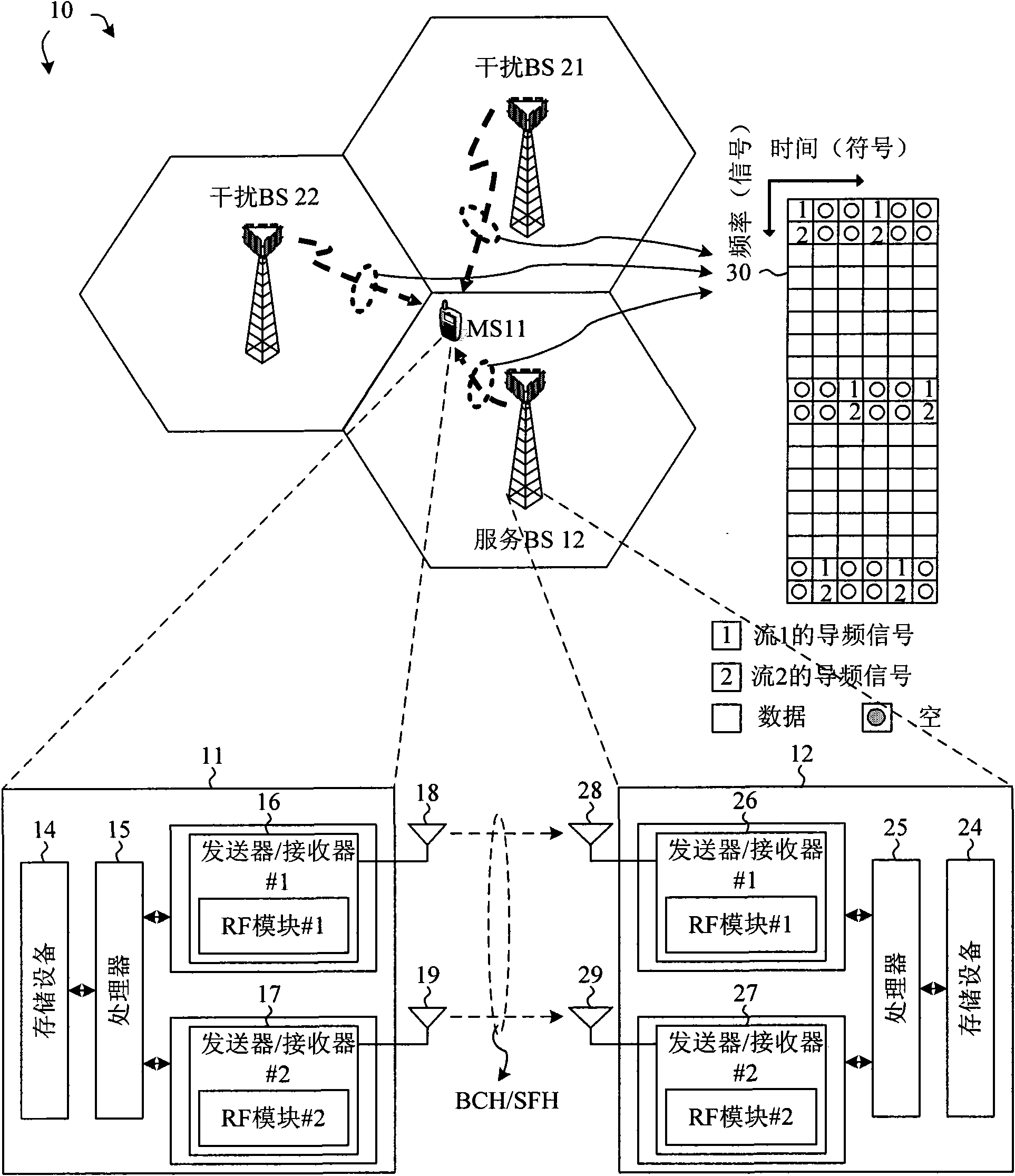
A method for broadcasting system information via a broadcast channel (BCH) in an OFDMA system is provided. The BCH comprises one or more two-dimensional resource blocks. A plurality of pilot tones and a plurality of data tones are positioned within each resource block. The system information is mapped onto the plurality of data tones. In one embodiment, the plurality of pilot tones are located in configurable positions such that pilot tones of the same resource blocks transmitted by different base stations in the OFDMA system are interlaced to reduce pilot-to-pilot collision. In another embodiment, data tones that are located in pilot positions of other adjacent cells are nullified to reduce data-to-pilot collision. In one novel aspect, the property of interlaced pilot patterns and tone nullification is leveraged to estimate interference second-order statistics, which facilitates receiver implementation and improves receiver performance.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com