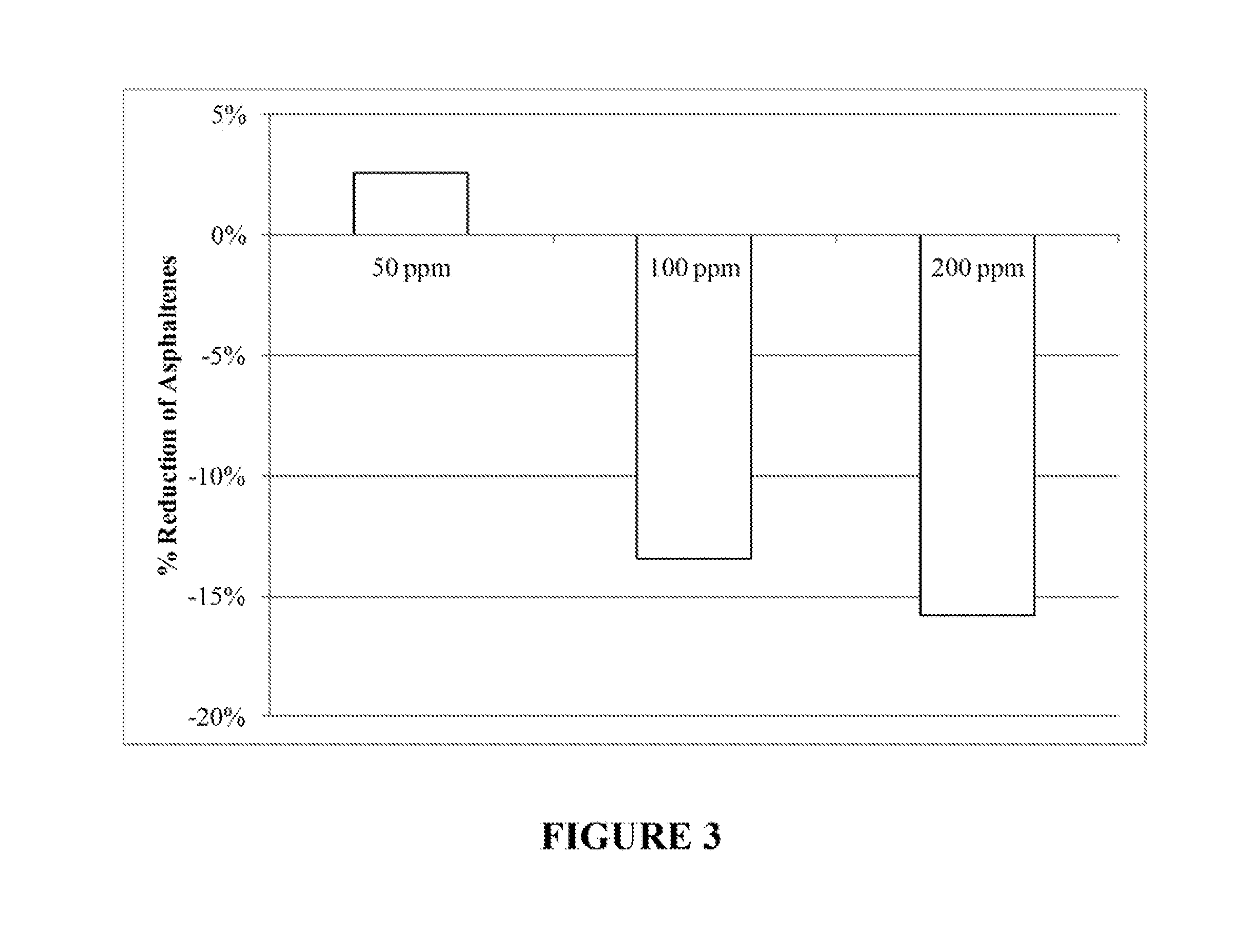
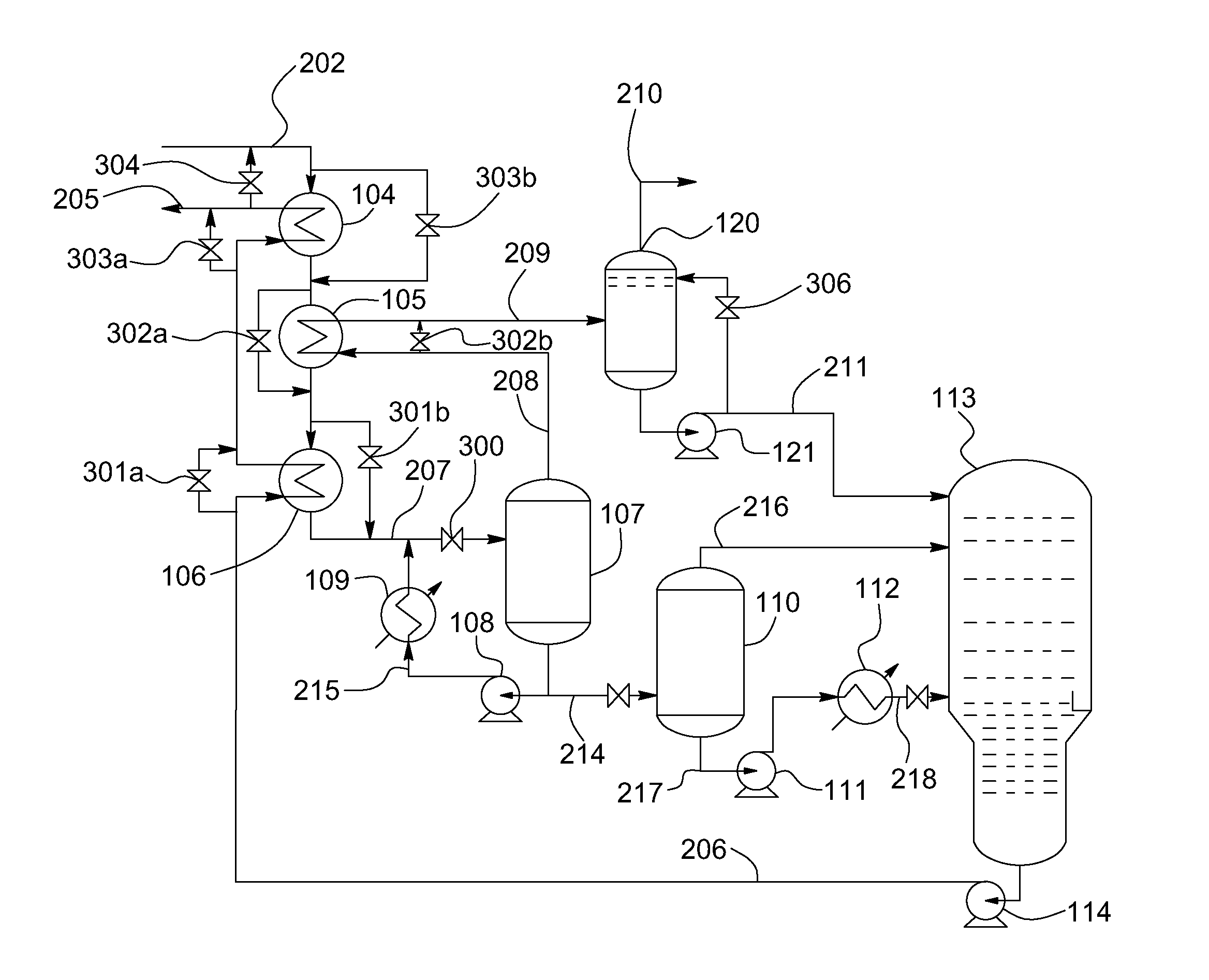
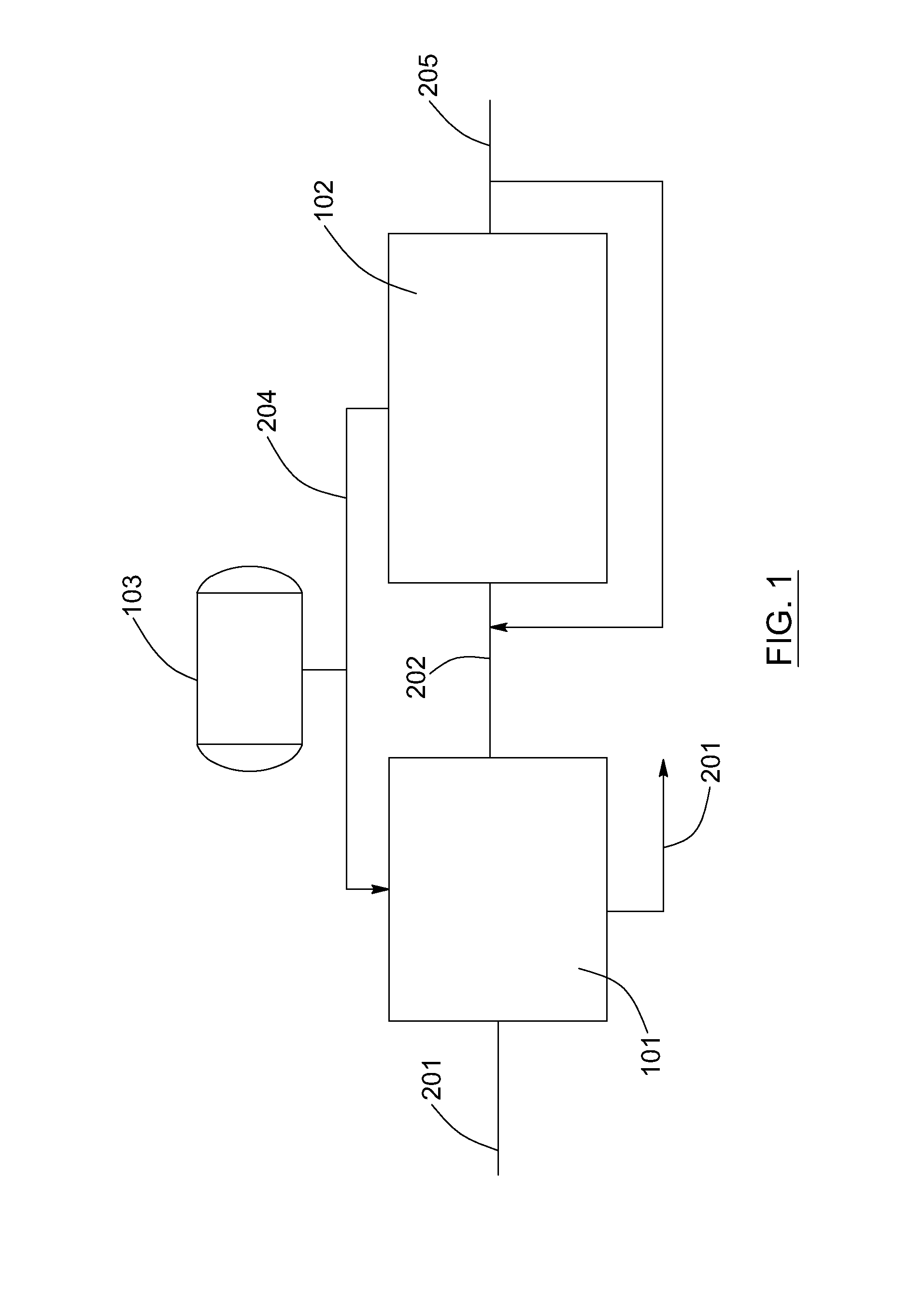
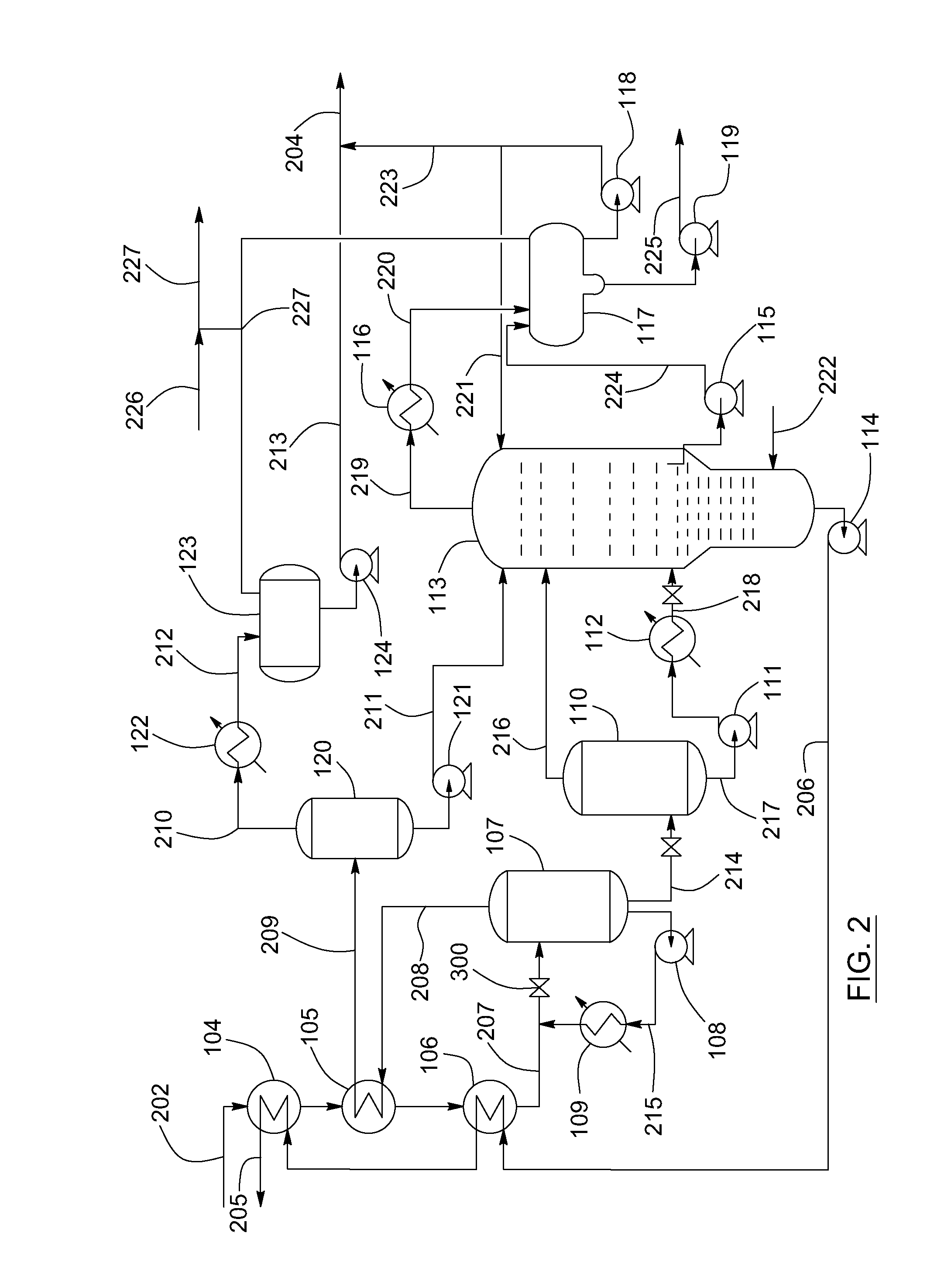
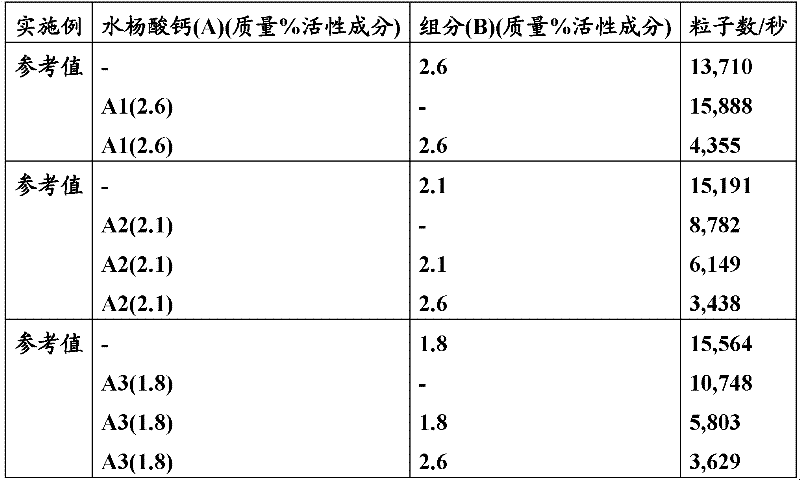
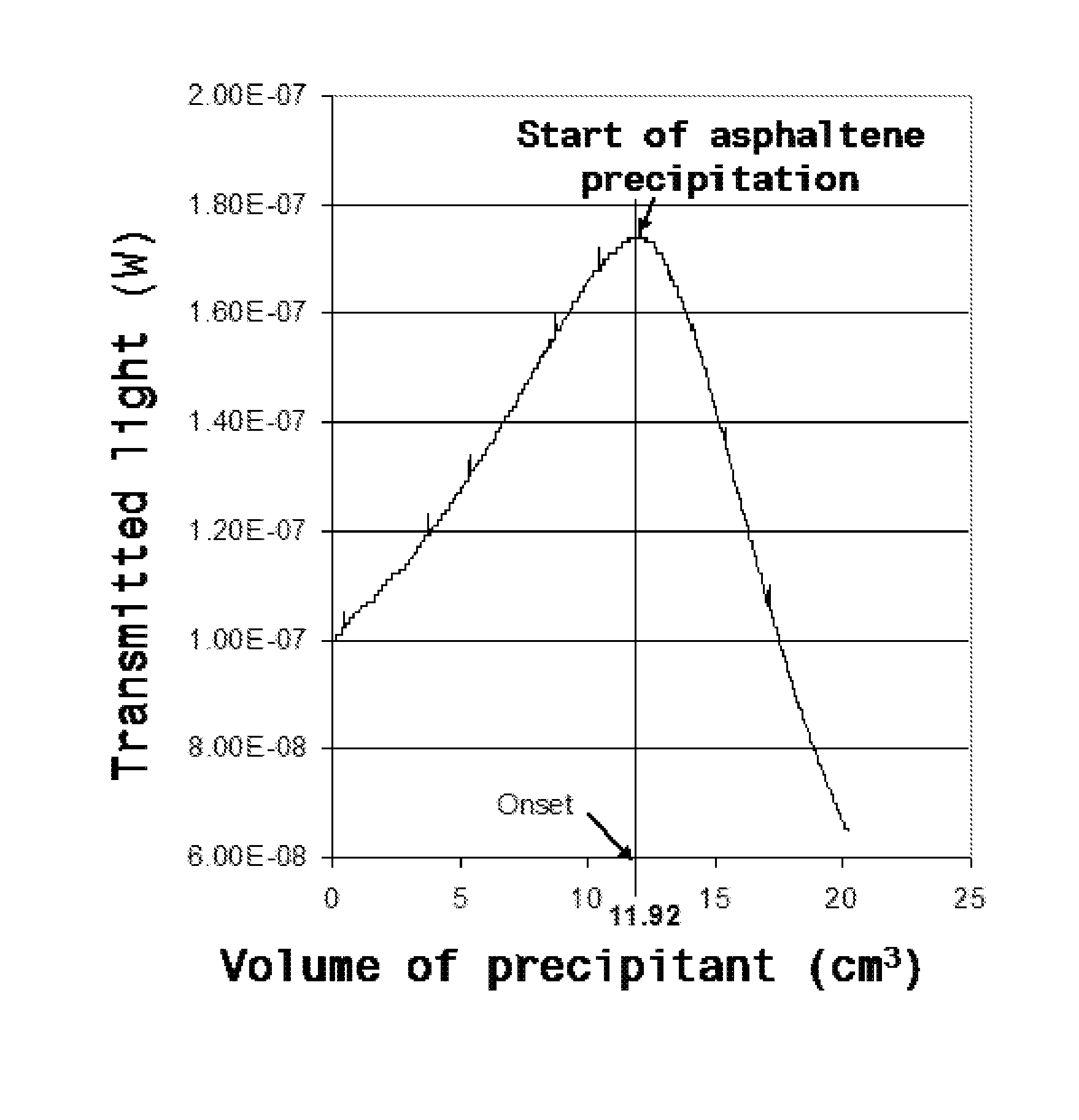
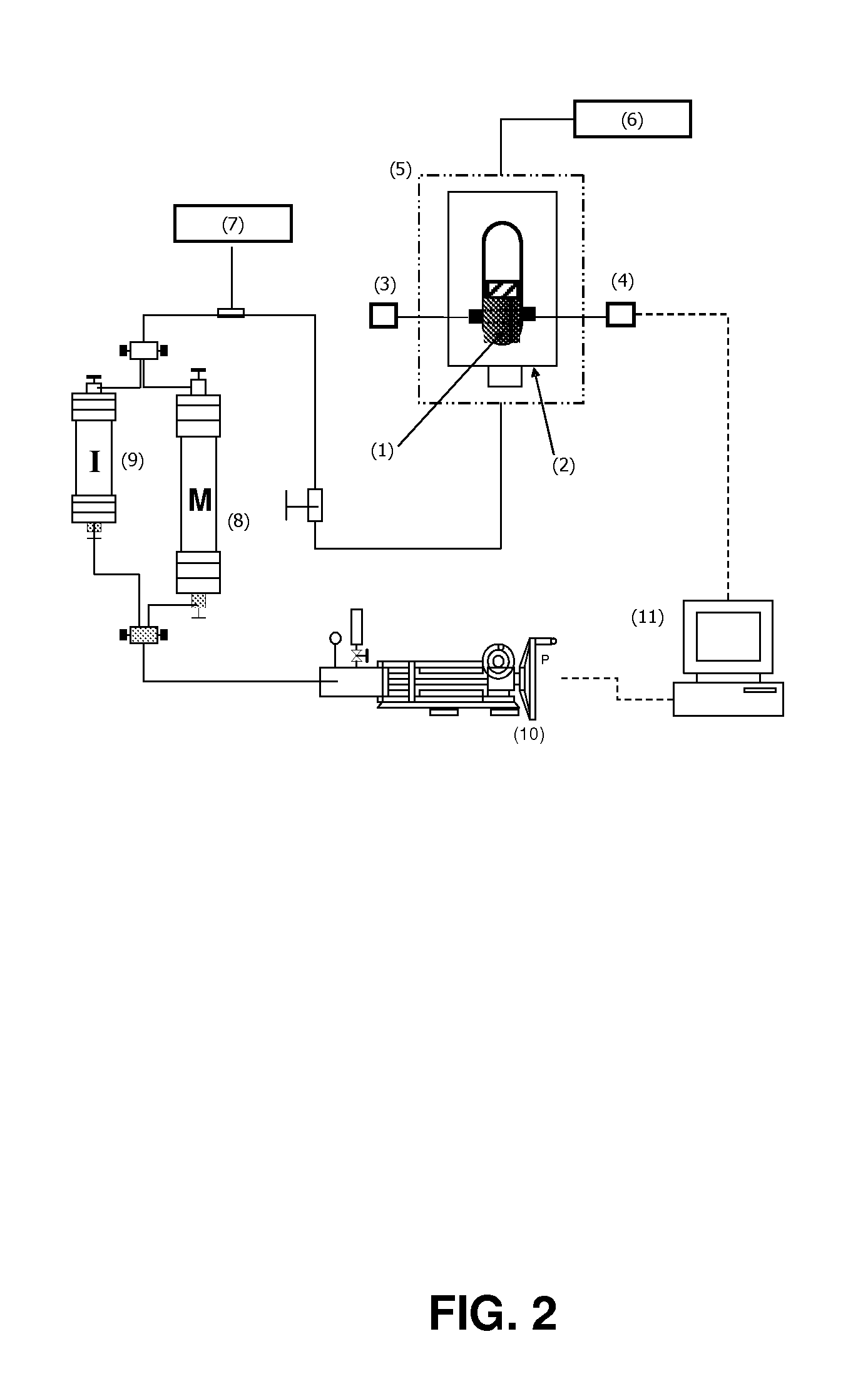
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Asphaltene precipitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Asphaltene precipitation. Asphaltene precipitation is caused by a number of factors including changes in pressure, temperature, and composition. The two most prevalent causes of asphaltene precipitation in the reservoir are decreasing pressure and mixing of oil with injected solvent in improved oil recovery (IOR) processes.
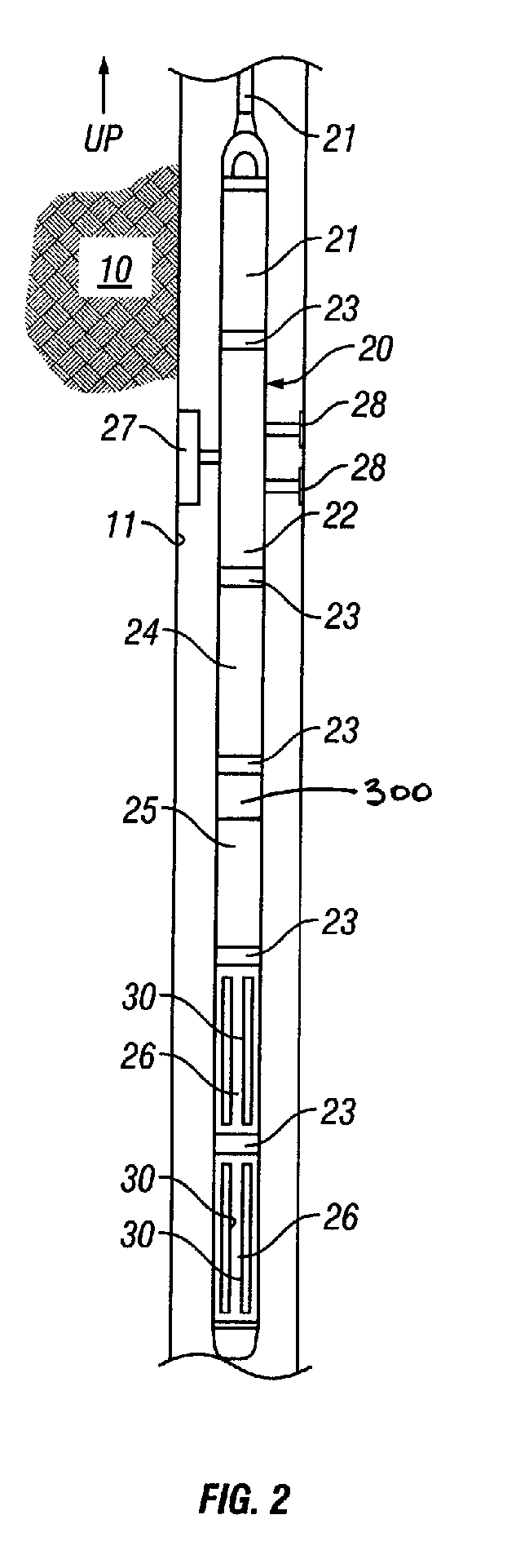
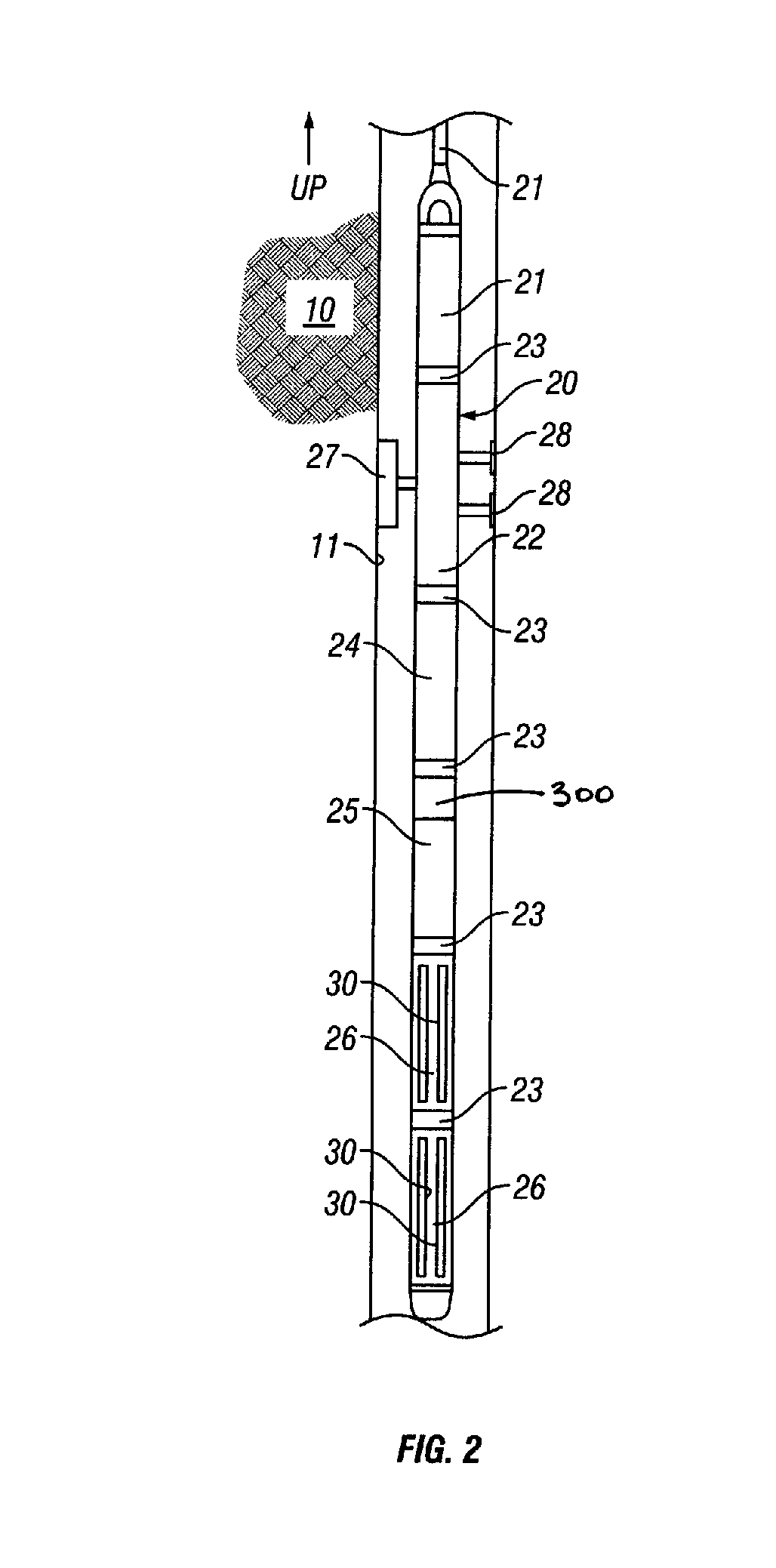
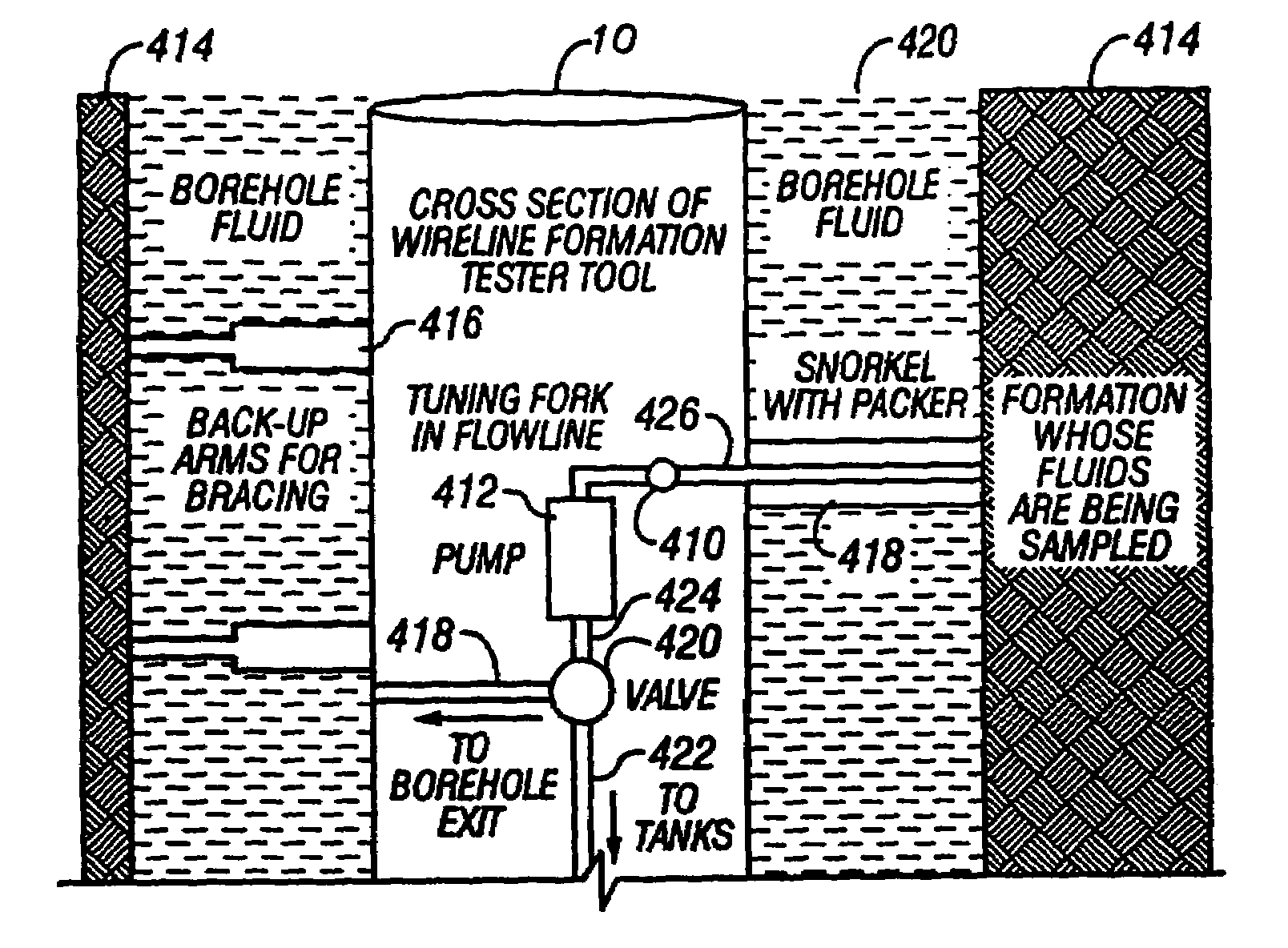
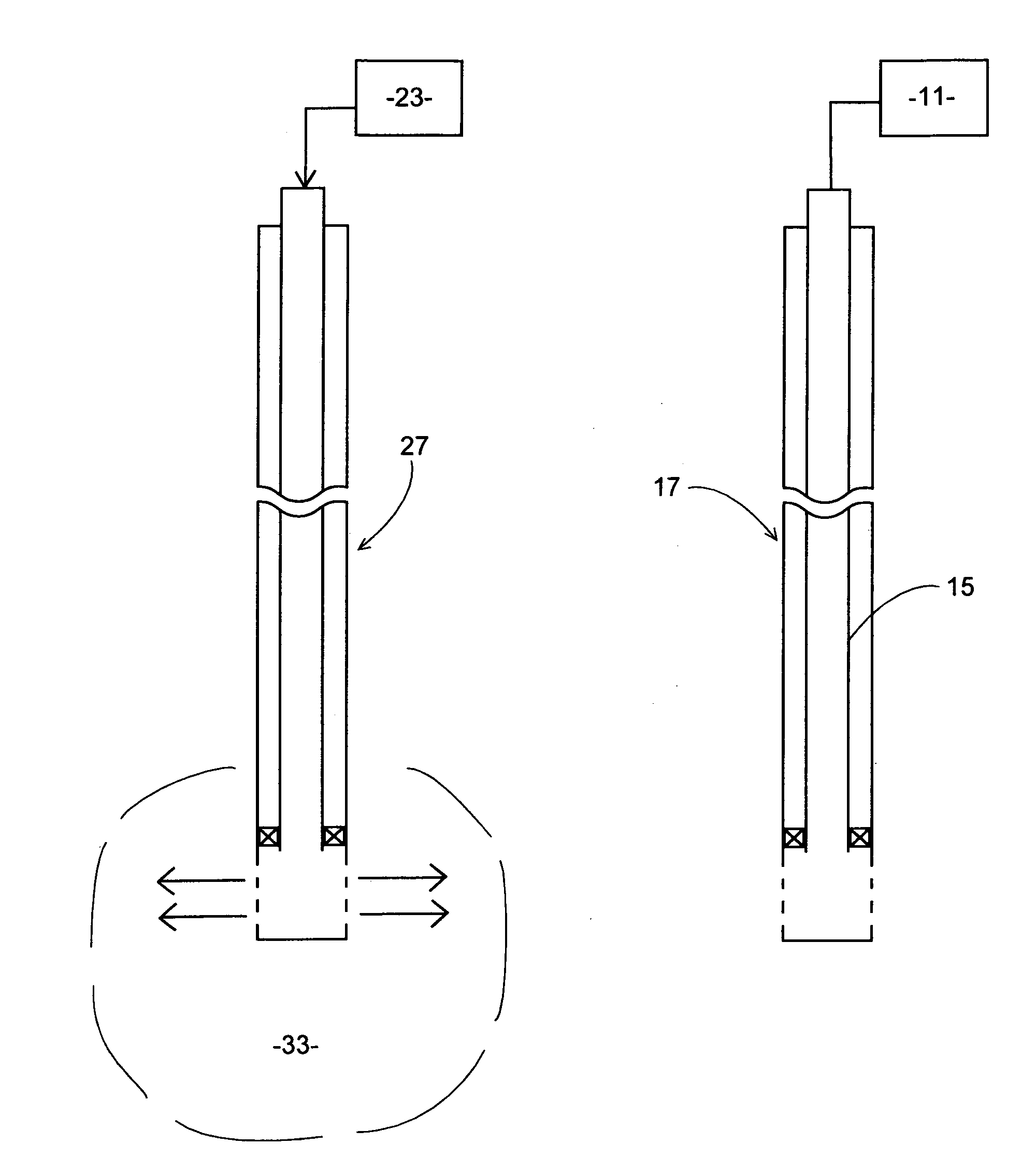
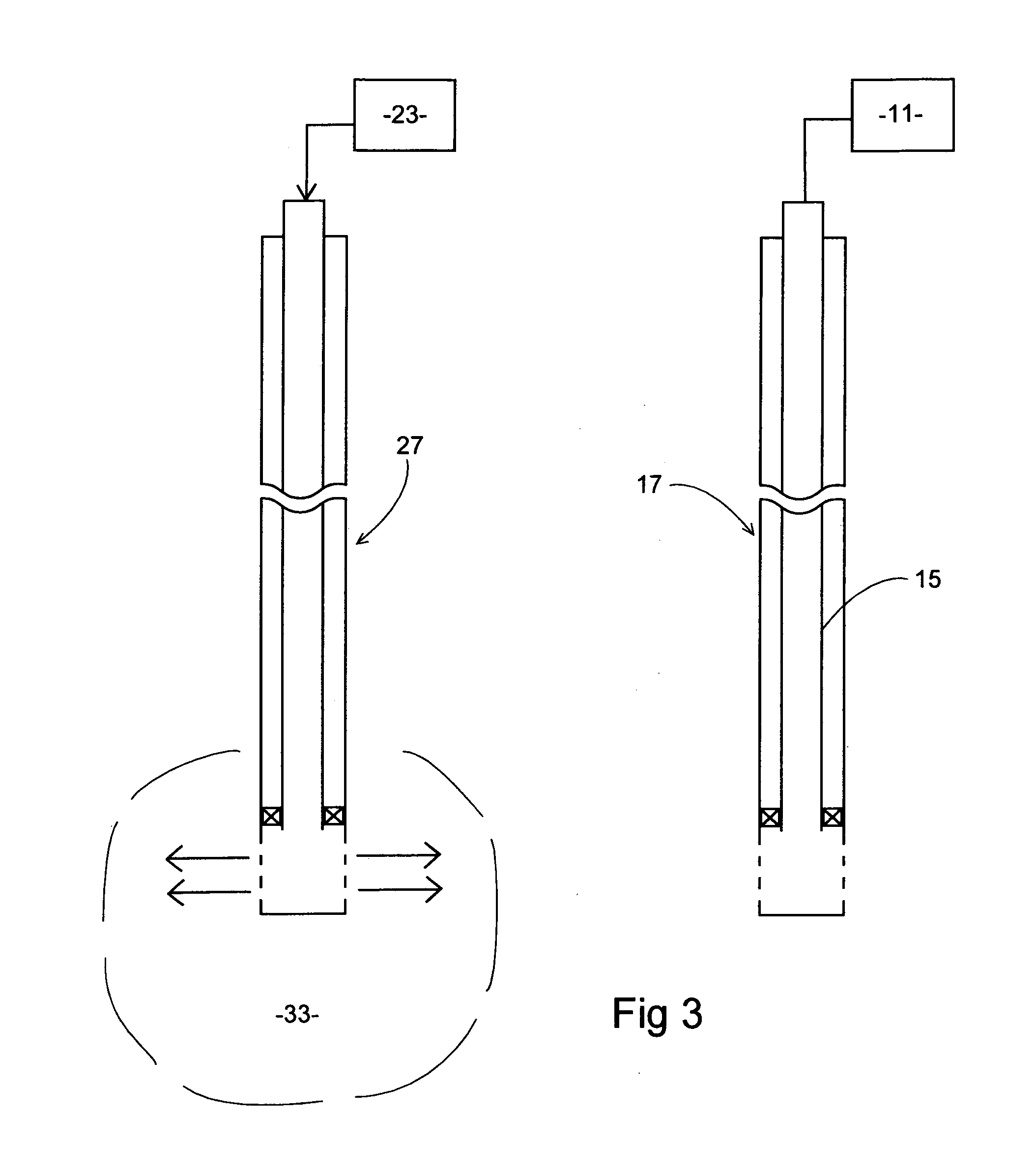
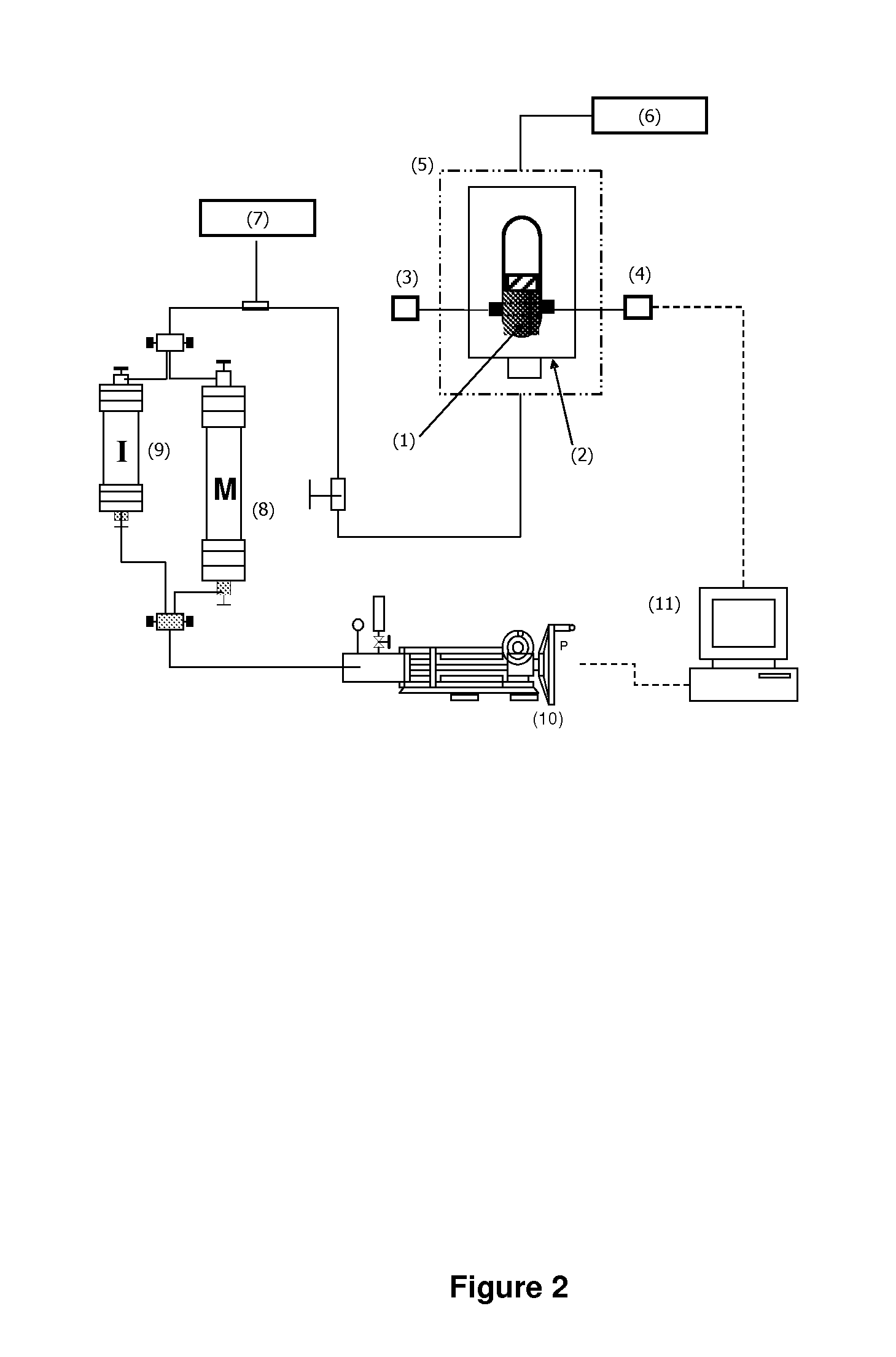
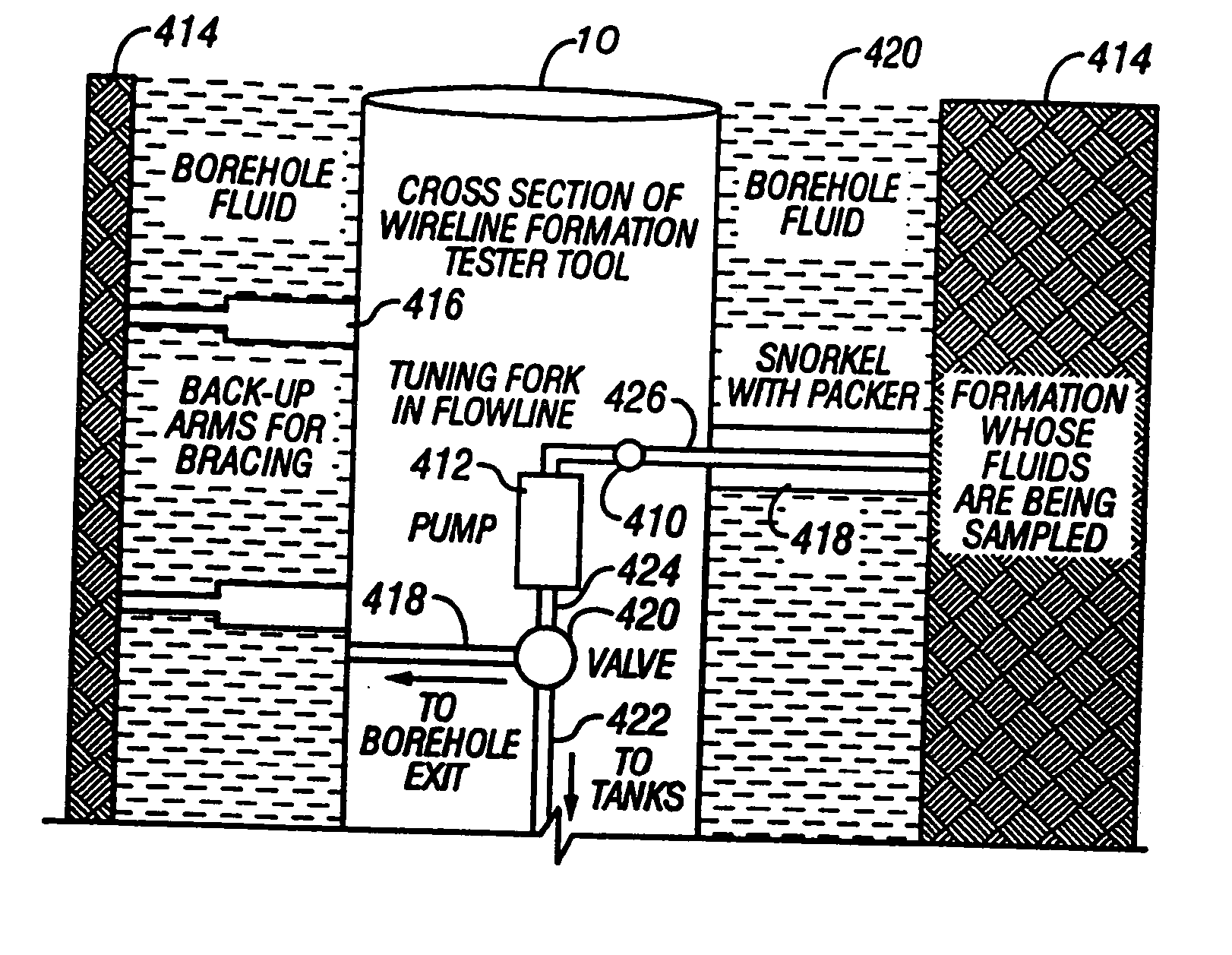
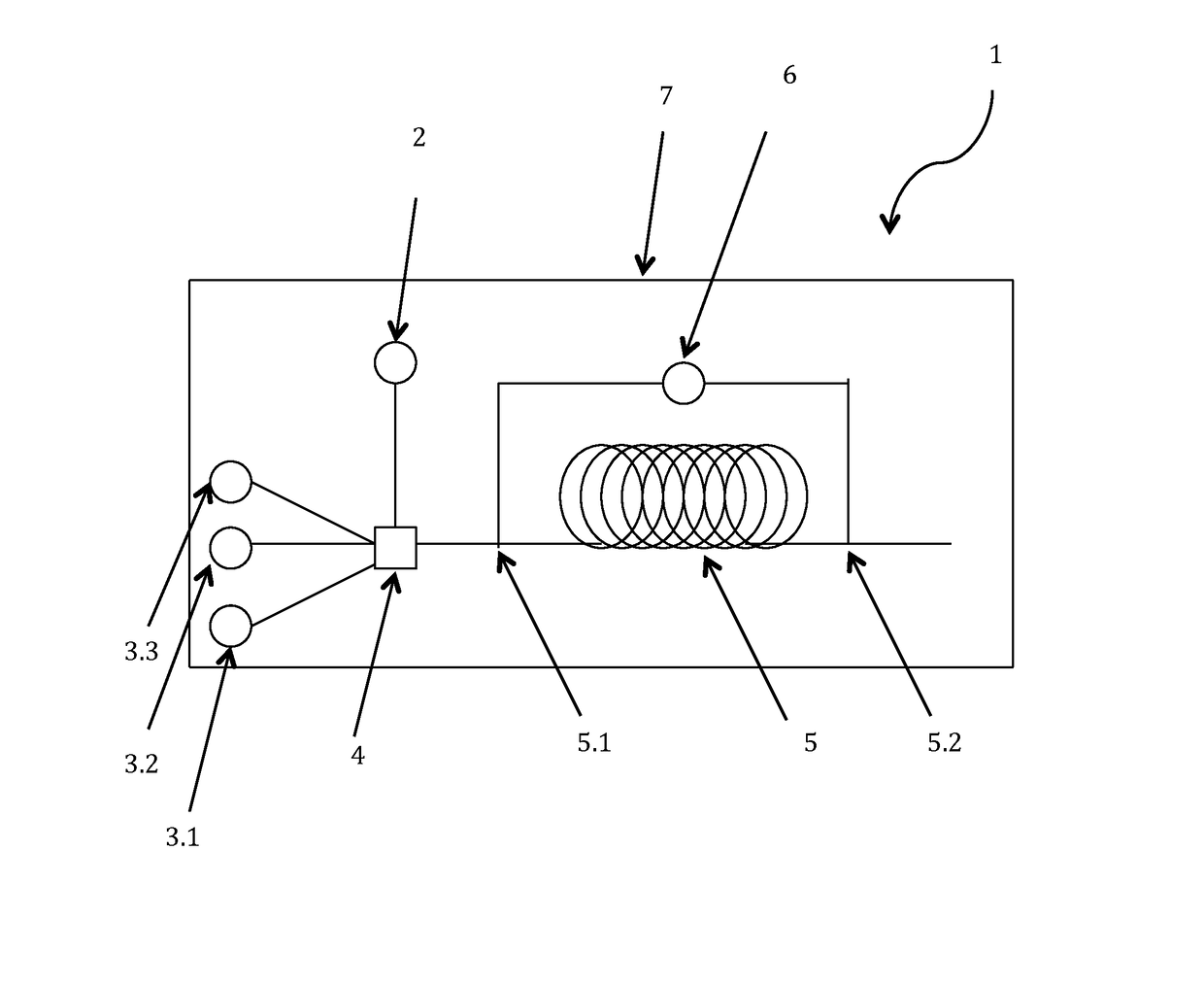
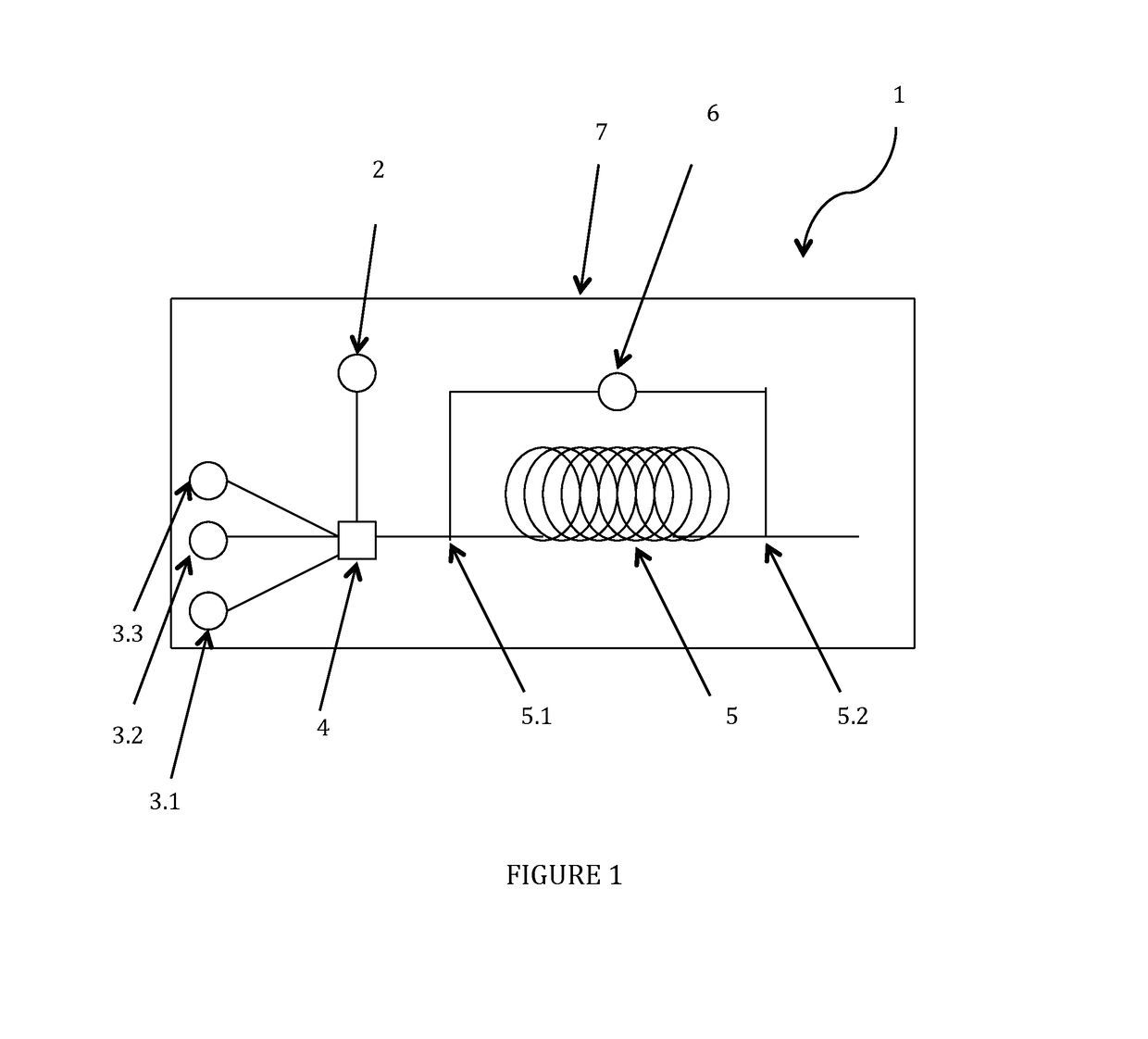
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
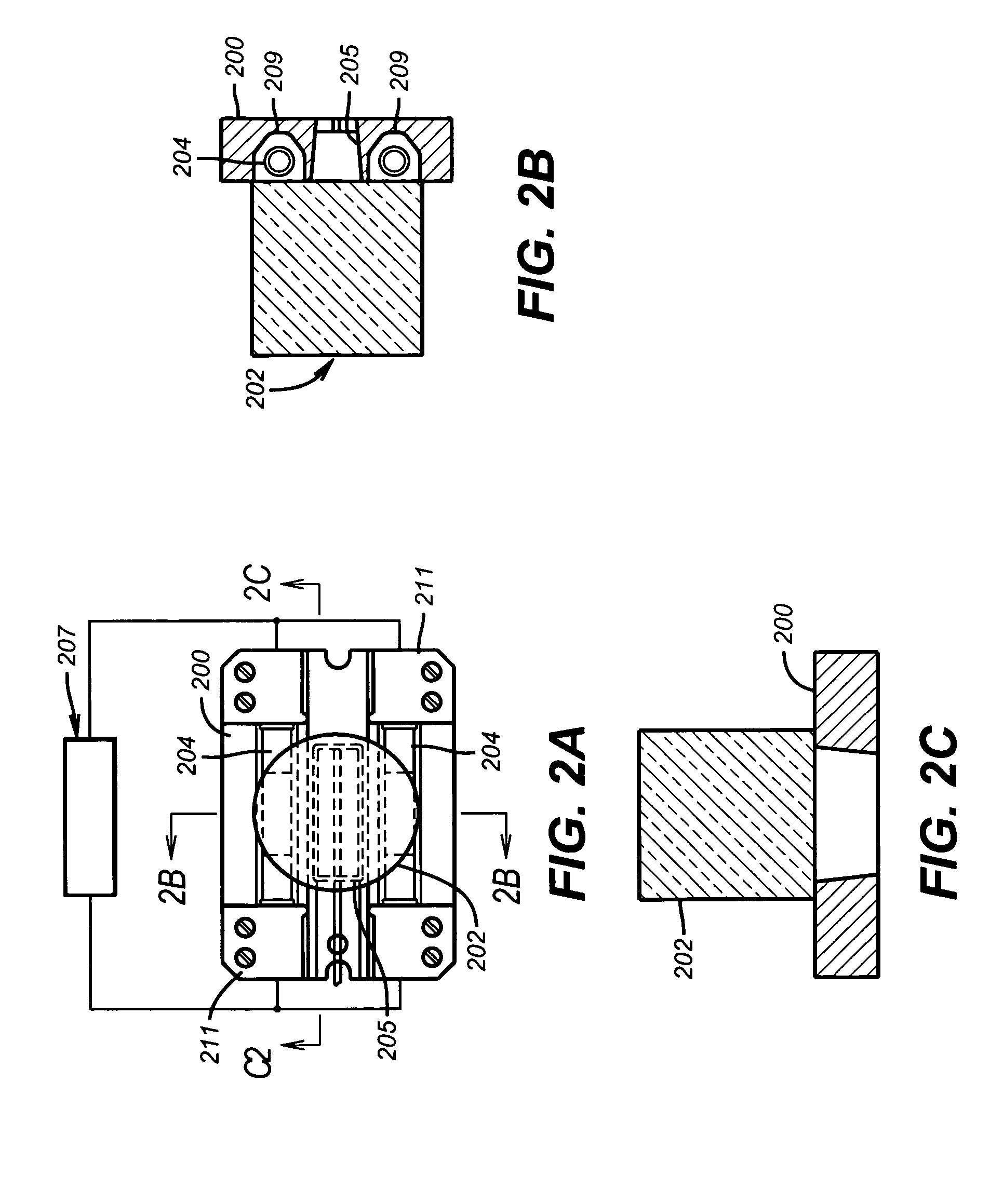
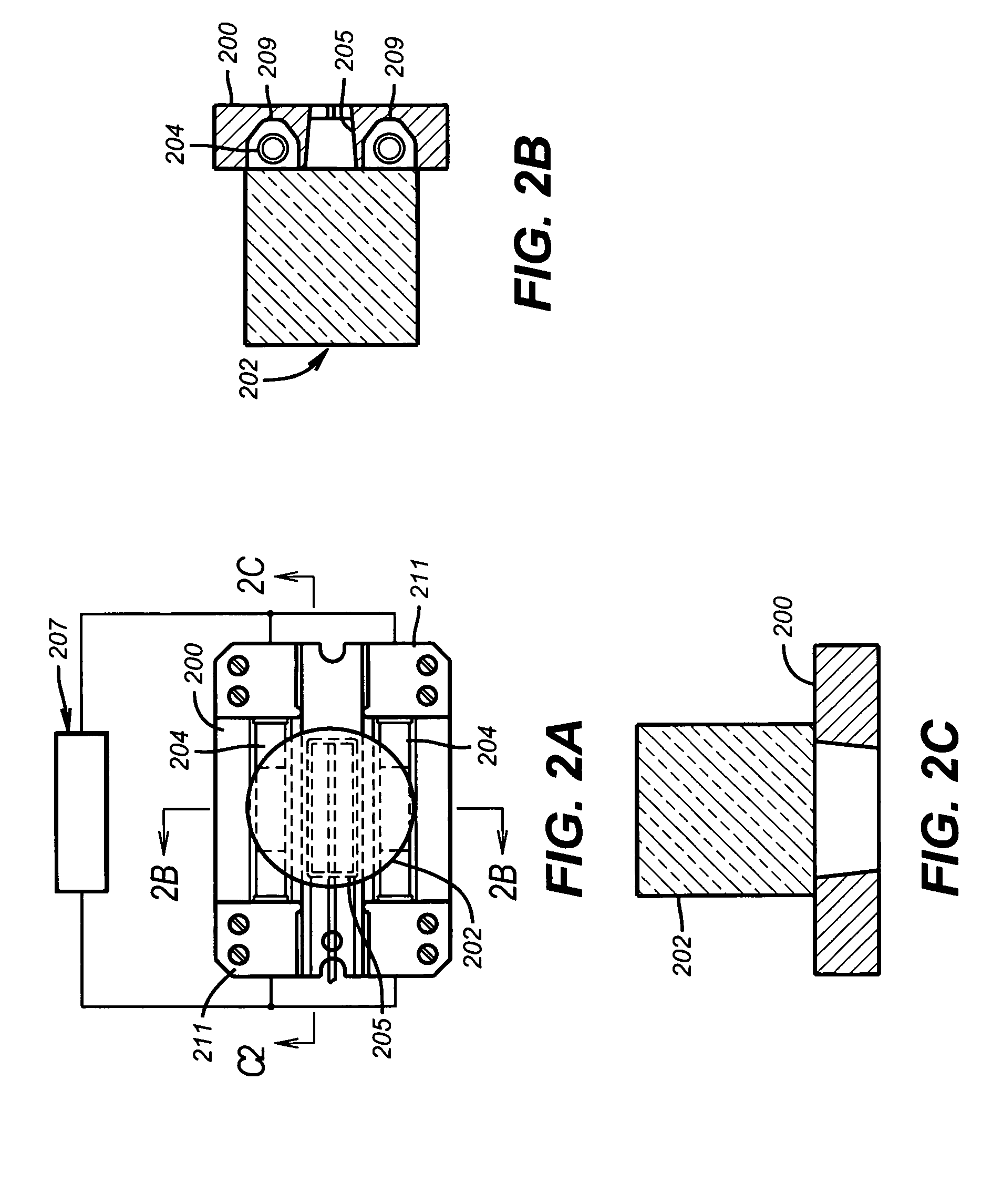
InactiveUS20020178805A1Avoid contact corrosionProtection from damageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkFormation fluid
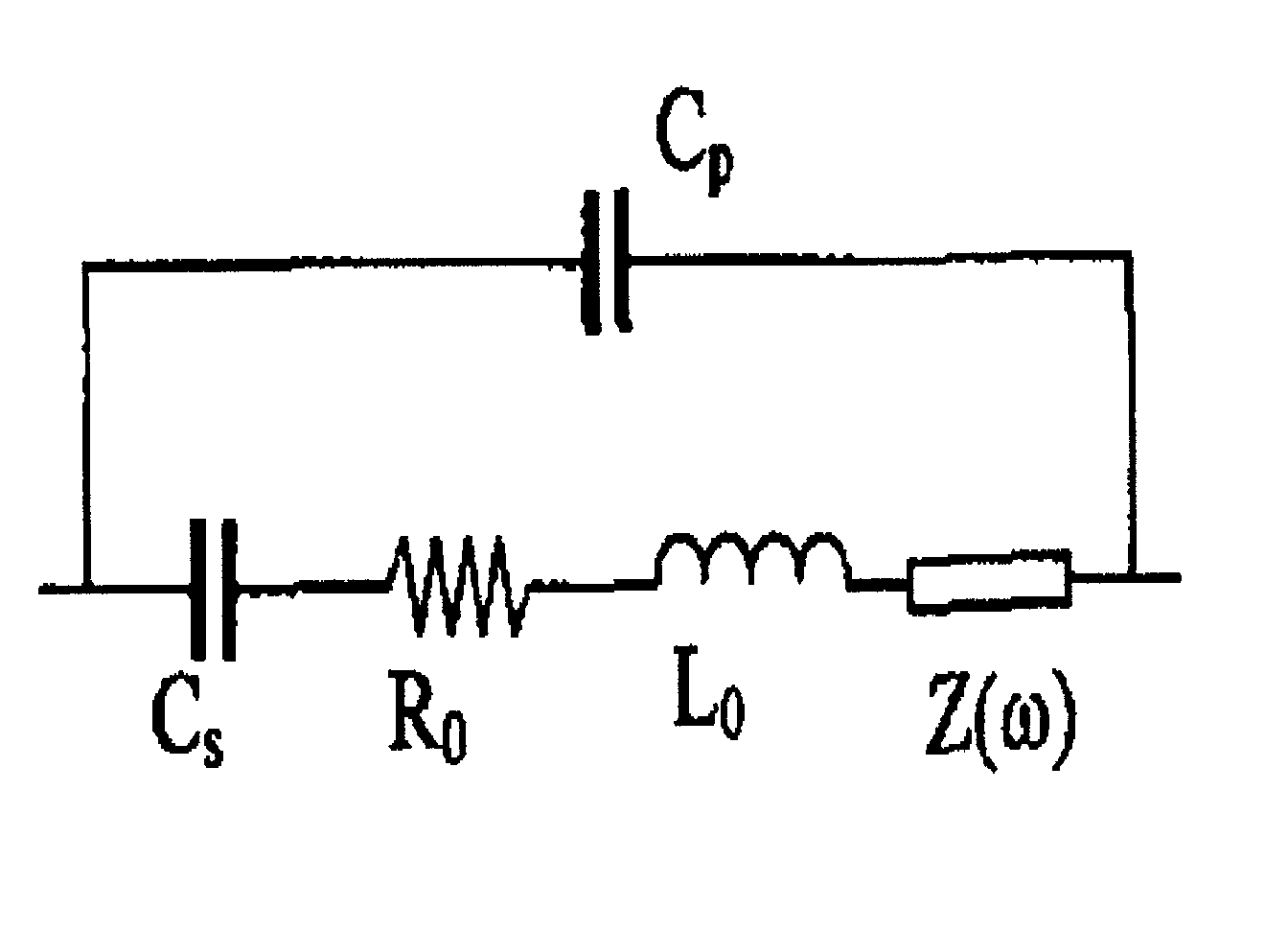
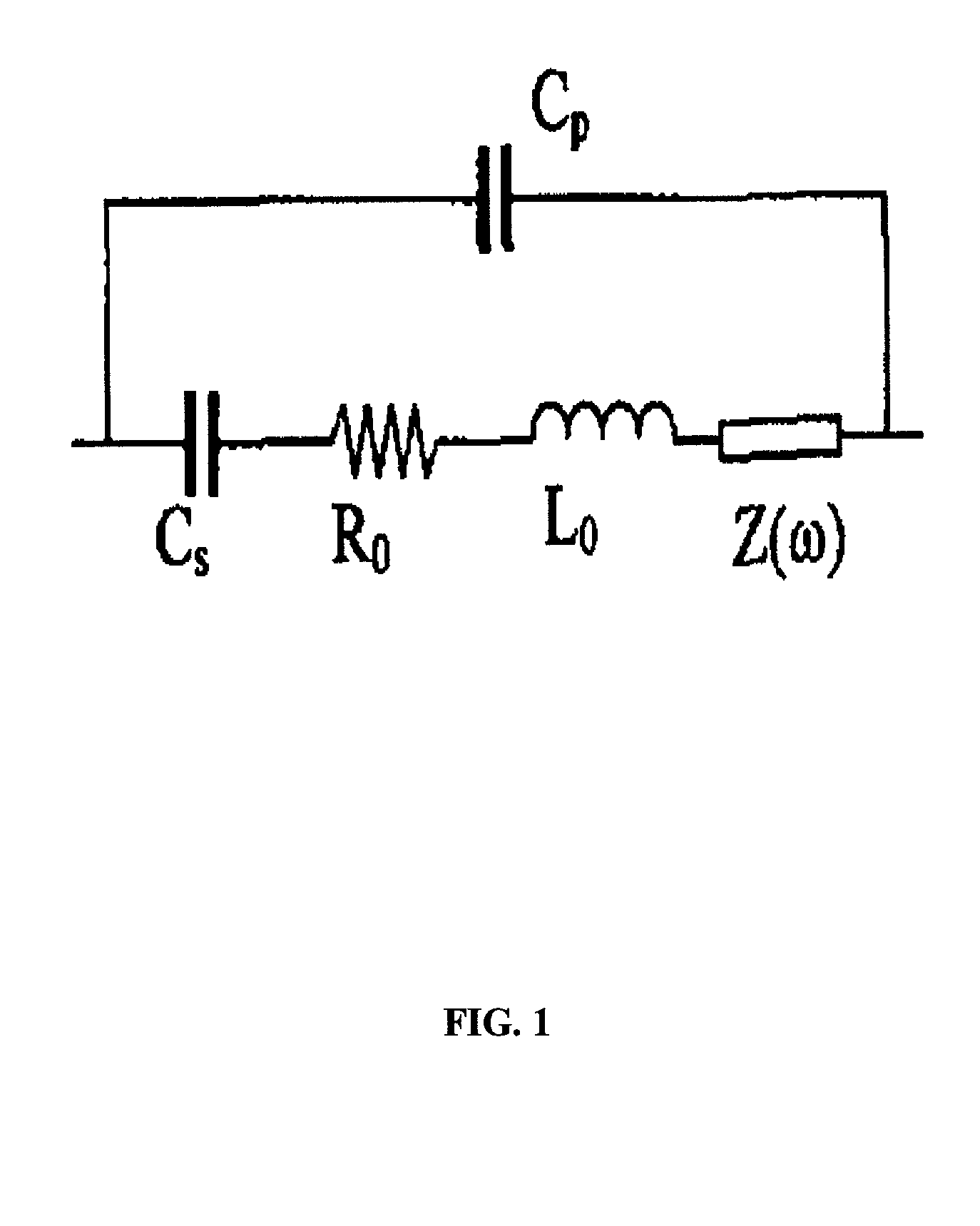
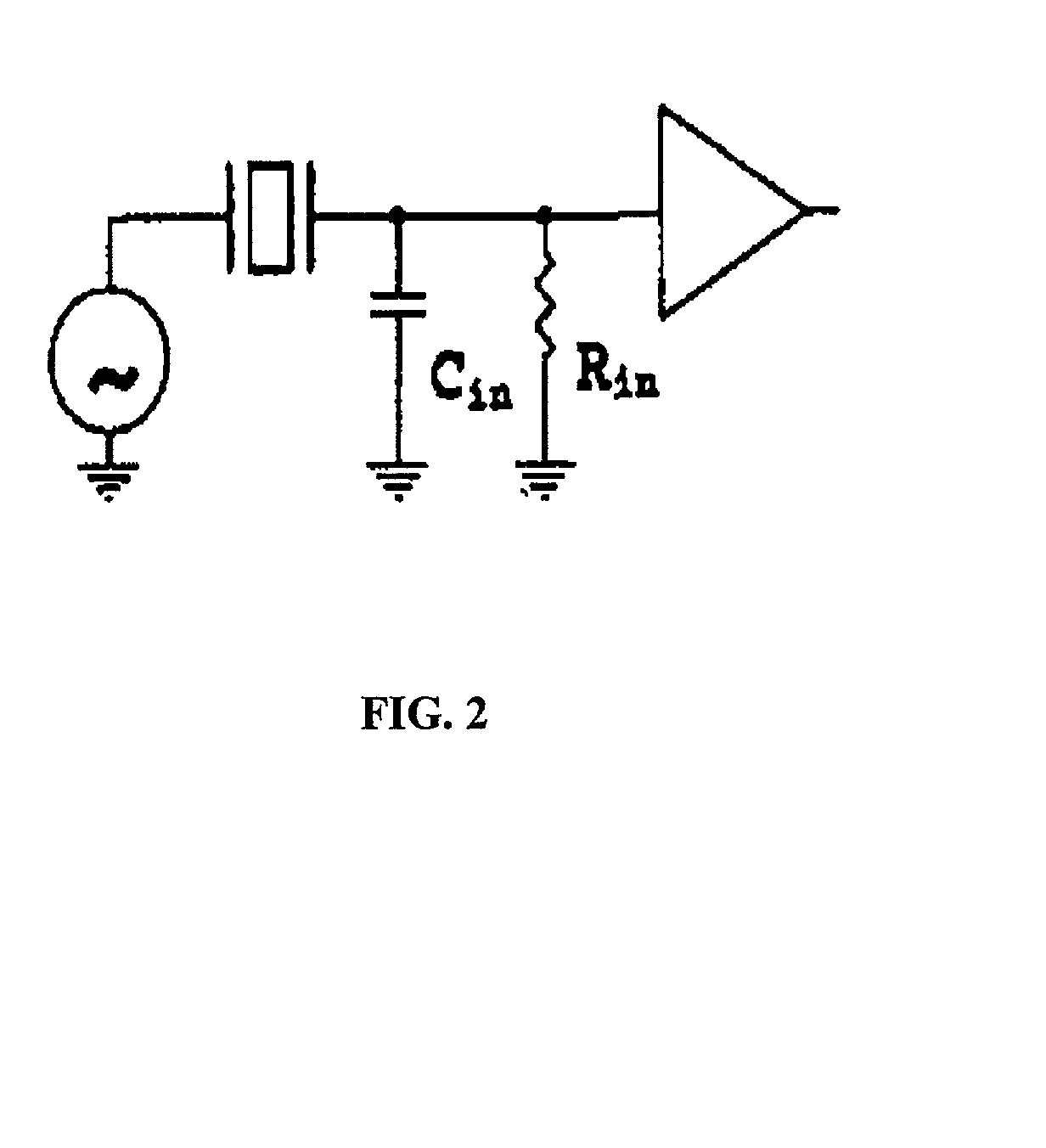
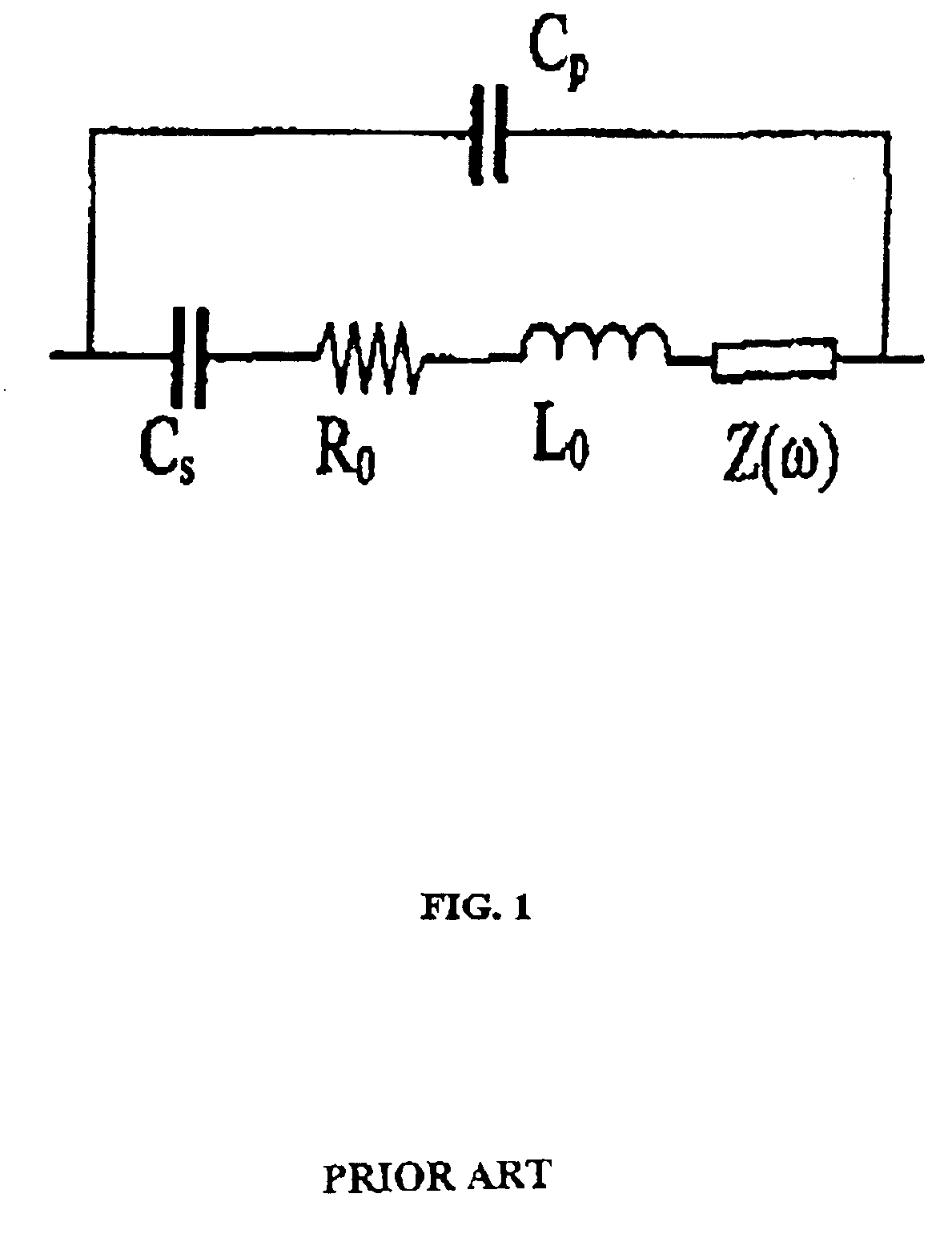
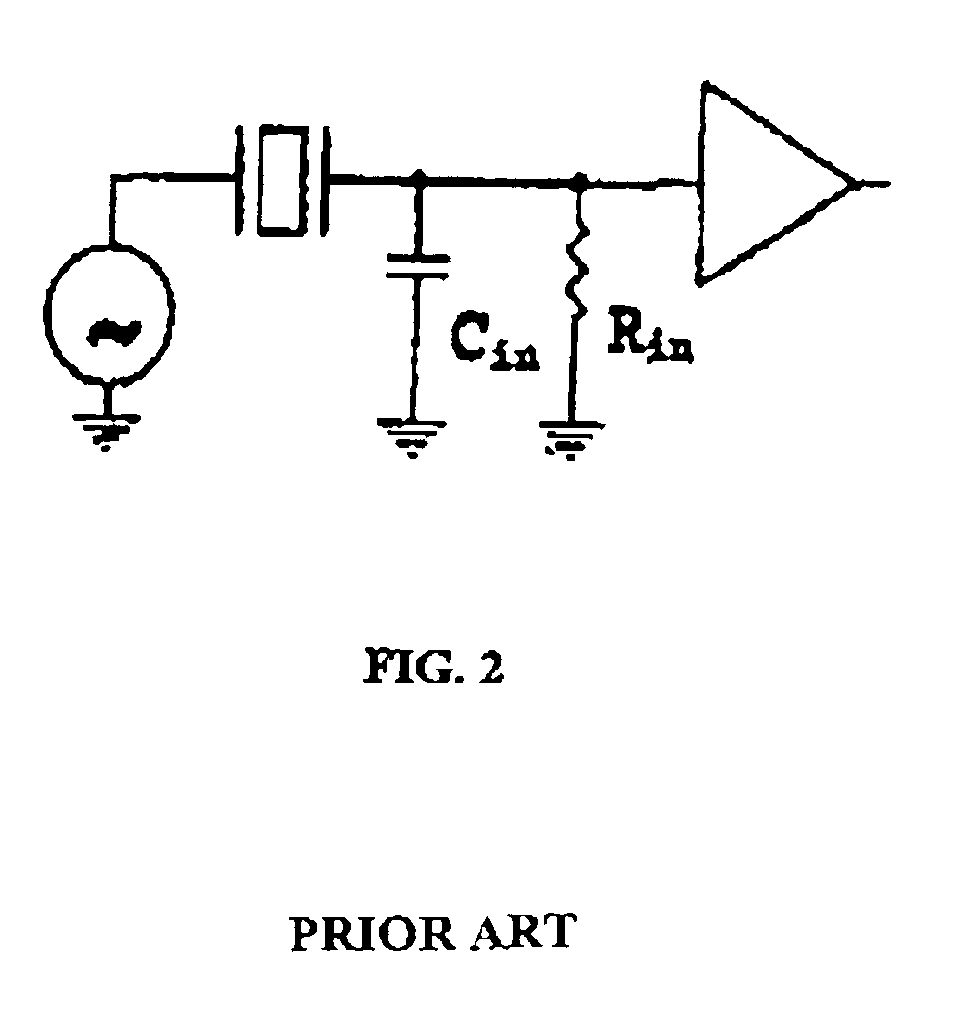
The present invention provides a downhole method and apparatus using a flexural mechanical resonator, for example, a tuning fork to provide real-time direct measurements and estimates of the viscosity, density and dielectric constant of formation fluid or filtrate in a hydrocarbon producing well. The present invention additionally provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cleanup from a leveling off of viscosity or density over time, measuring or estimating bubble point for formation fluid, measuring or estimating dew point for formation fluid, and determining the onset of asphaltene precipitation. The present invention also provides for intercalibration of plural pressure gauges used to determine a pressure differential downhole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS6938470B2Avoid contact corrosionInversely to viscosityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkFormation fluid
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
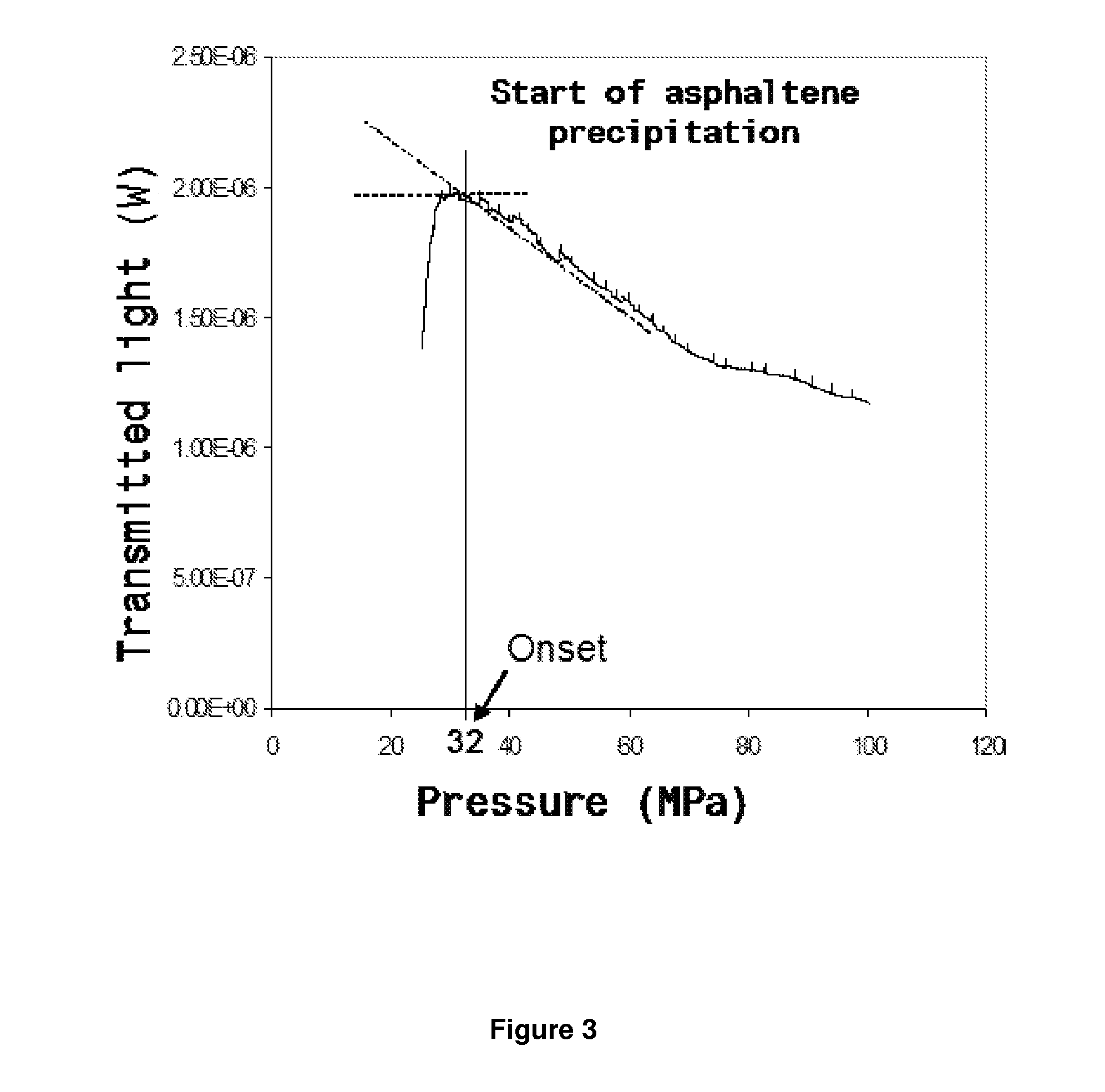
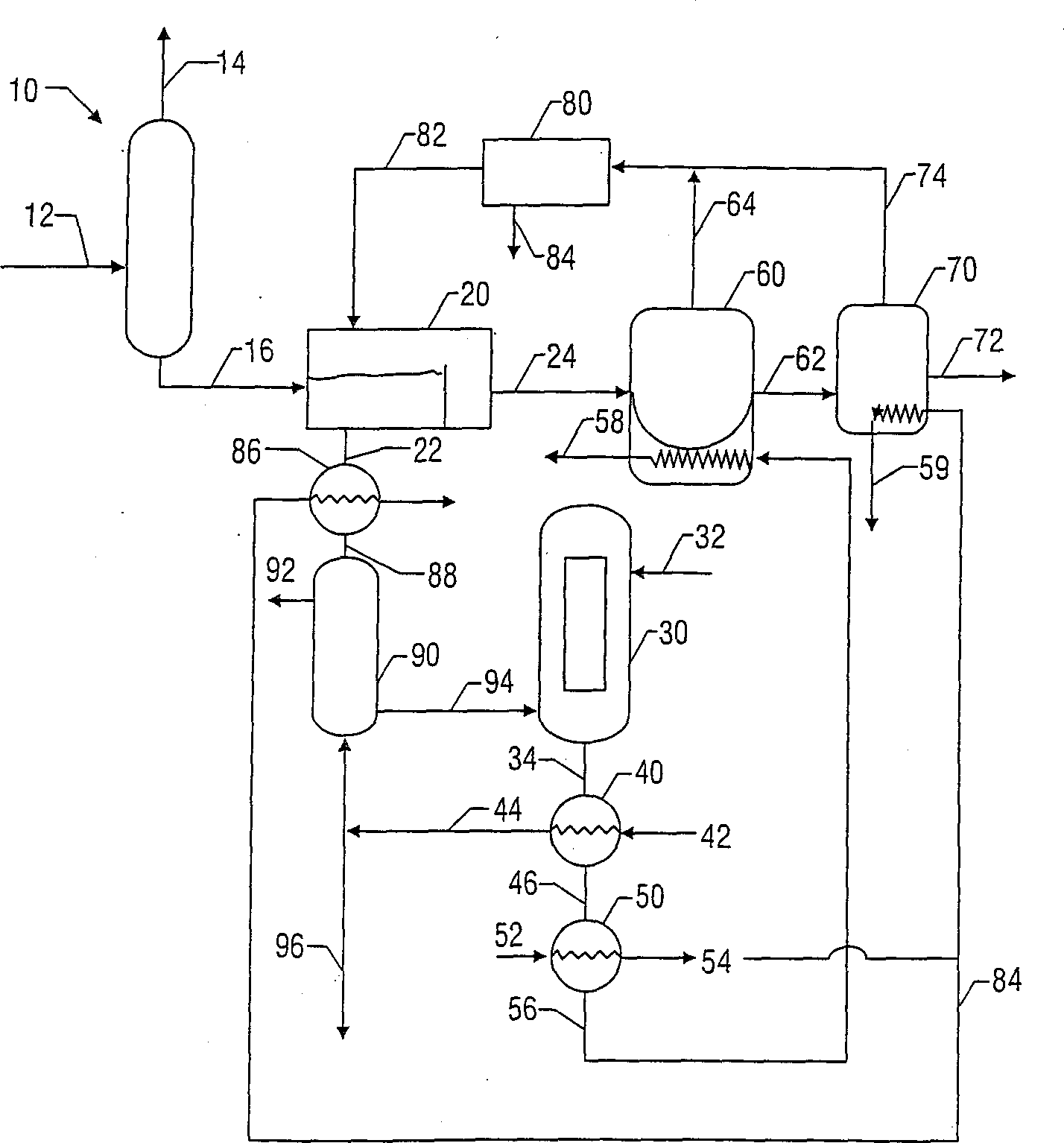
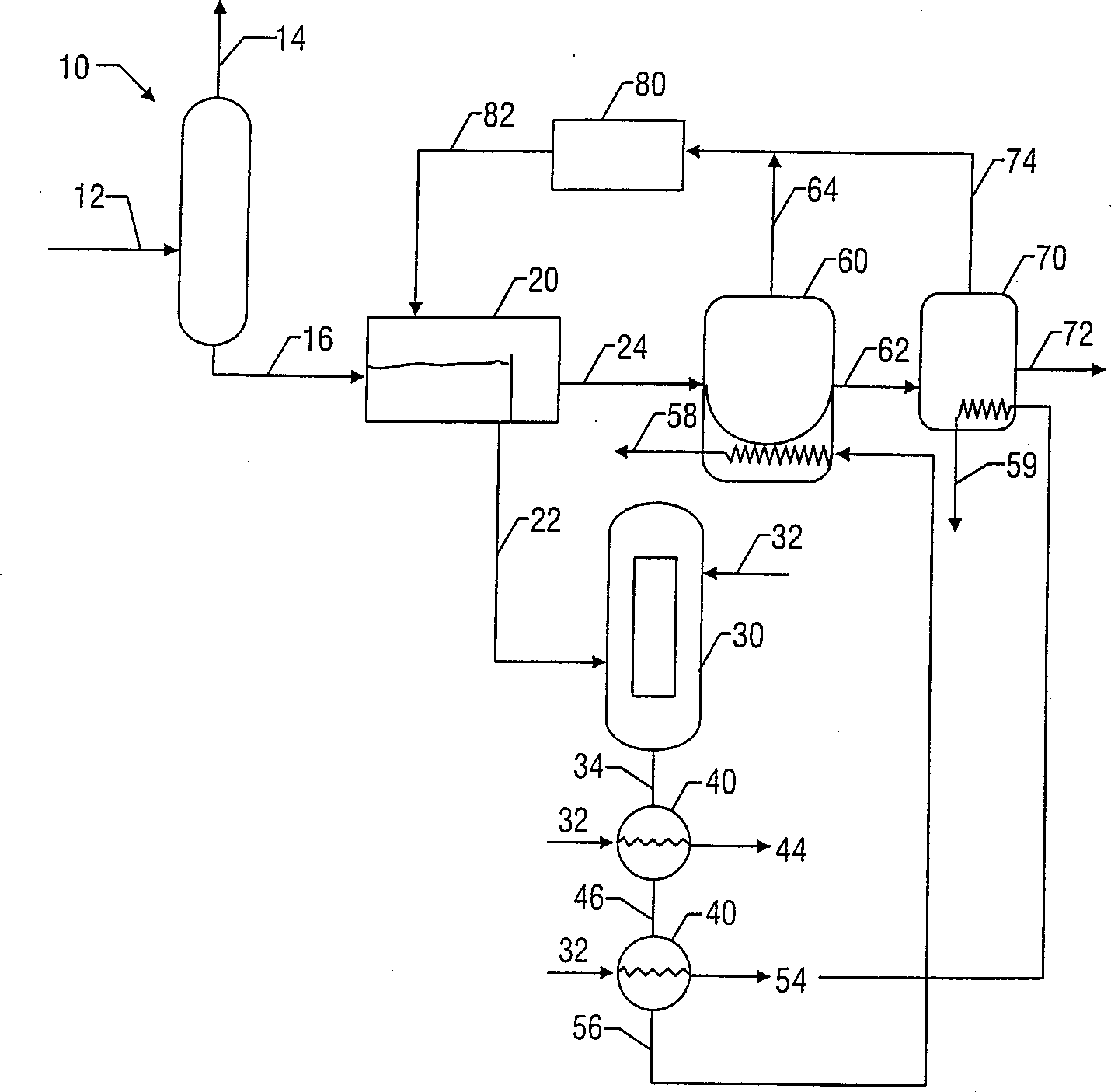
Method and apparatus for determining an optimal pumping rate based on a downhole dew point pressure determination
ActiveUS20040231408A1Reduce capacityReduce pressureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsLight energyDew
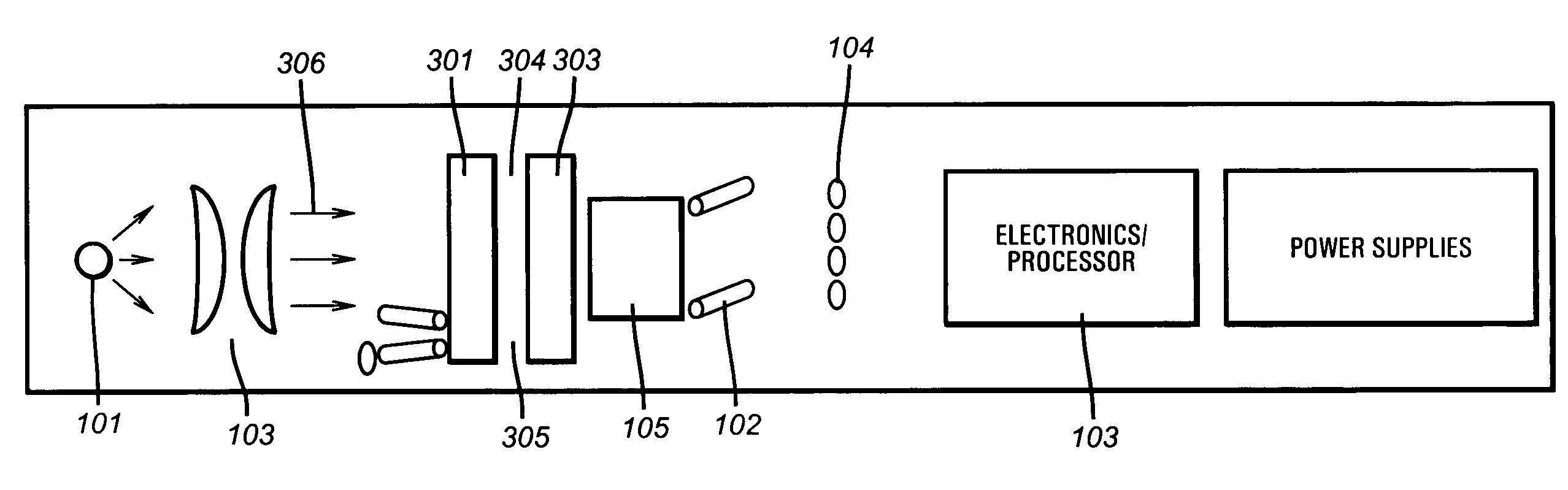
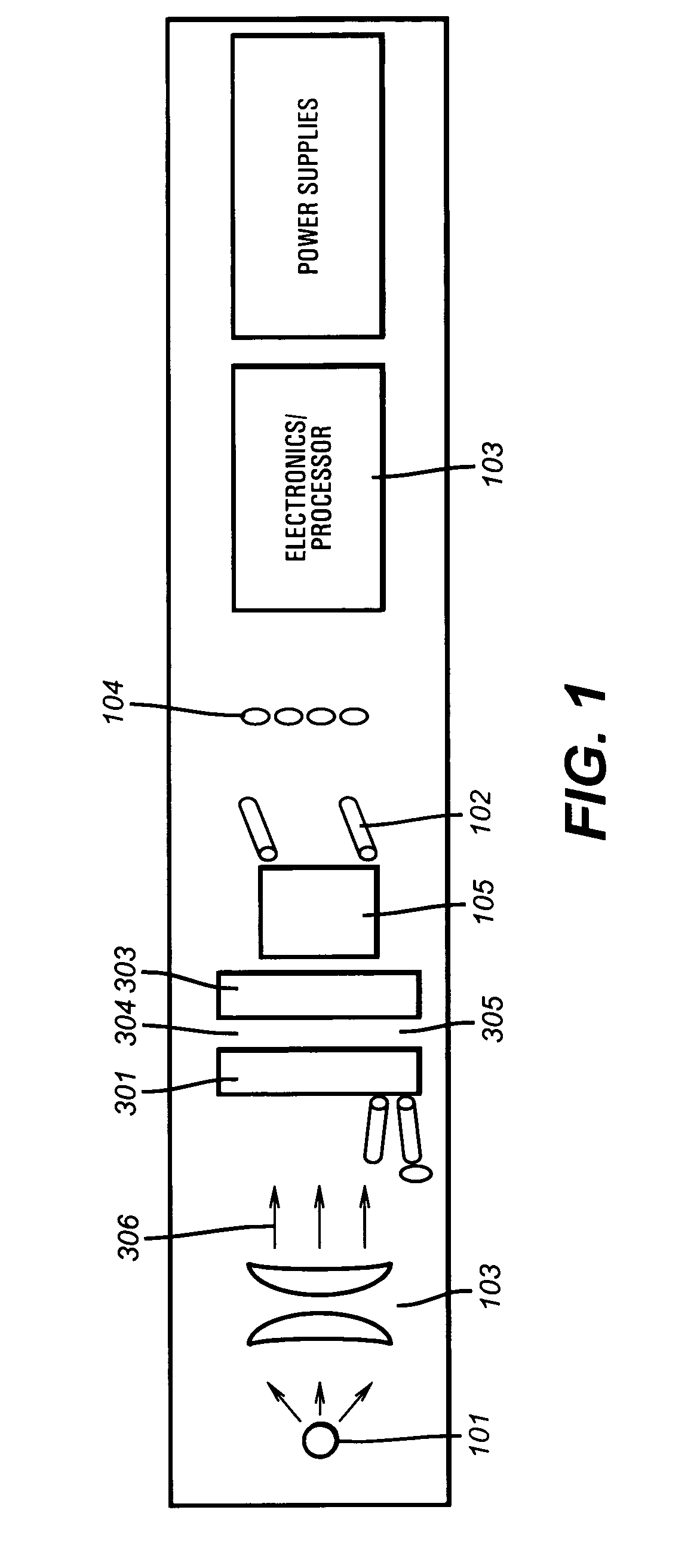
The present invention provides a down hole spectrometer for determination of dew point pressure to determine an associated optimal pumping rate during sampling to avoid precipitation of asphaltenes in a formation sample. A sample is captured at formation pressure in a controlled volume. The pressure in the controlled volume is reduced. Initially the formation fluid sample appears dark and allows less light energy to pass through a sample under test. The sample under test, however, becomes lighter and allows more light energy to pass through the sample as the pressure is reduced and the formation fluid sample becomes thinner or less dense under the reduced pressure. At the dew point pressure, however, the sample begins to darken and allows less light energy to pass through it as apshaltenes begin to precipitate out of the sample. Thus, the dew point is that pressure at which peak light energy passes through the sample. The dew point pressure is plugged into an equation to determine the optimum pumping rate for a known mobility, during sampling to avoid dropping the pressure down to the dew point pressure to avoid asphaltene precipitation or dew forming in the sample. The bubble point can be plugged into an equation to determine the optimum pumping rate for a known mobility, during sampling to avoid dropping the pressure down to the bubble point pressure to avoid bubbles forming in the sample.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Marine engine lubrication
InactiveUS20120028522A1Easy to handlePropulsion power plantsOutboard propulsion unitsEngineeringFuel oil
Trunk piston marine engine lubrication, when the engine is fueled by heavy fuel oil, is effected by a composition comprising a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity containing at least 50 mass % of a basestock containing greater than or equal to 90% saturates and less than or equal to 0.03% sulphur or a mixture thereof, and respective minor amounts of an over-based metal hydrocarbyl-substituted hydroxybenzoate detergent other than such a detergent having a basicity index of less than two and a degree of carbonation of 80% or greater and at least 1 mass % of a hydrocarbyl-substituted carboxylic acid, anhydride, ester or amide thereof. Asphaltene precipitation in the lubricant, caused by the presence of contaminant heavy fuel oil, is prevented or inhibited.
Owner:INFINEUM INT LTD
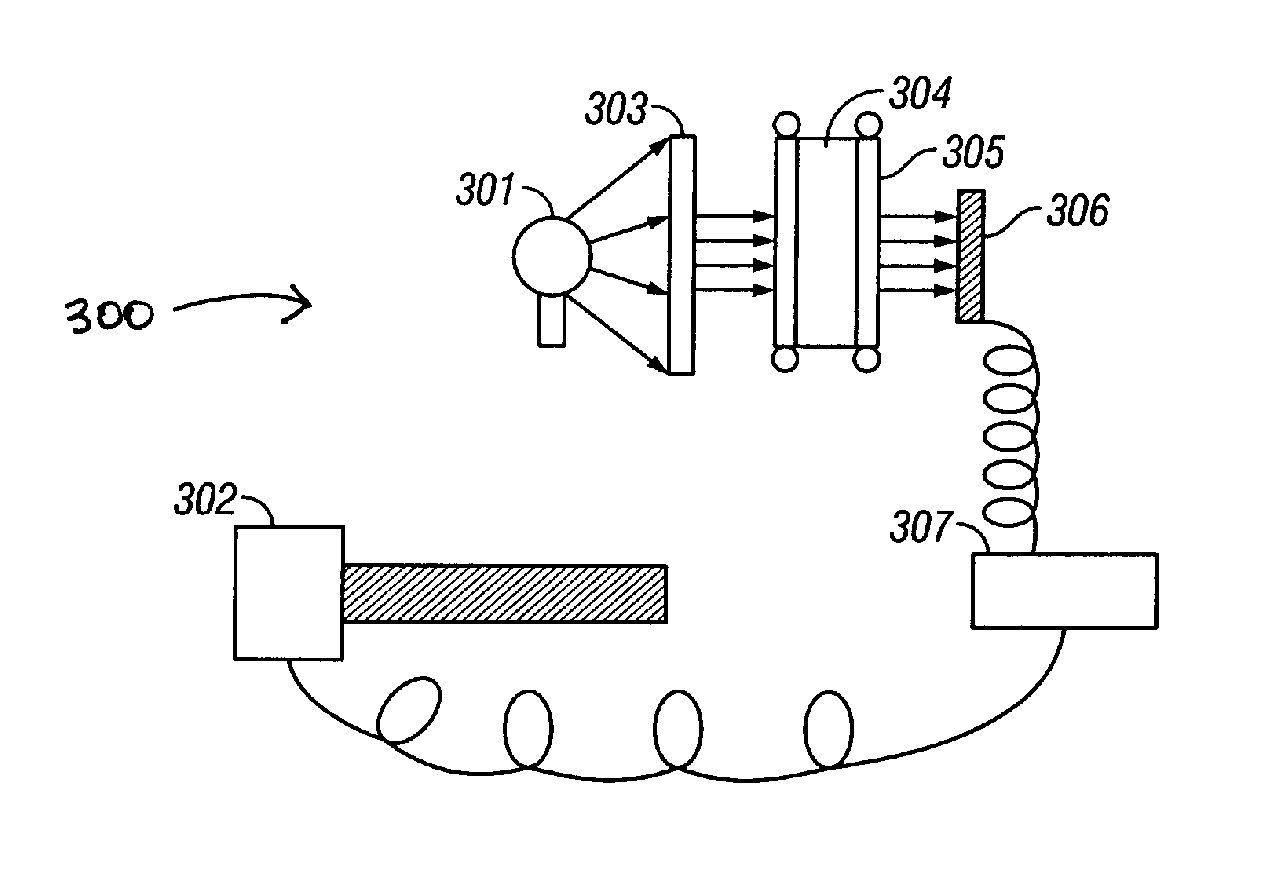
Method and apparatus for a downhole fluorescence spectrometer
ActiveUS20040104355A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryAPI gravityFluorescence spectrometry
The invention comprises an apparatus and method for simple fluorescence spectrometry in a downhole environment using a UV light source and UV fluorescence to determine a parameter of interest for a sample downhole. The UV light source illuminates the fluid, which in turn fluoresces light. The fluoresced light is transmitted back towards the UV light source and through the pathway towards an optical spectrum analyzer. API gravity is determined by correlation the wavelength of peak fluorescence and brightness of fluorescent emission of the sample. Asphaltene precipitation pressure is determined by monitoring the blue green content ratio for a sample under going depressurization.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for a downhole fluorescence spectrometer
InactiveUS7084392B2Easy to measureQuantify OBM filtrate contaminationRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyAPI gravityFluorescence spectrometry
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method for removing asphaltene deposits
InactiveUS20080020949A1Reduce and prevent formationPreventing and reducing precipitationWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansFlushingKeroseneFuel oil
Compositions comprising at least one C4-C30 olefin or oxidation product thereof and kerosene or an aromatic solvent are particularly effective for use in removing asphaltene and asphaltene-containing organic deposits and in preventing or reducing the precipitation and deposition of asphaltenes from hydrocarbon fluids. When added to heavy oils comprising asphaltenes, alone or in combination with dispersants and further inhibitors, the invented compositions lower viscosity and pour point, and aid in preventing asphaltene precipitation during transport and in combustion.
Owner:INEOS USA LLC
Solids Management in Slurry Hydroprocessing
InactiveUS20100122939A1EfficiencyPromote precipitationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbon oil crackingLiquid productParticulates
The recovery of solids, and particularly solid particulates used as catalysts in slurry hydroprocessing, from asphaltene containing hydrocarbons is improved by controlling asphaltene precipitation. The formation of agglomerates of the solid particulates, having an increased diameter, results in the presence of precipitated asphaltenes, possibly due to flocculation. Asphaltene precipitation is controlled by varying process parameters or introducing additional diluent or flush streams that change the polarity of an asphaltene containing liquid product recovered from an effluent of a slurry hydroprocessing reaction zone.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method and apparatus for an optimal pumping rate based on a downhole dew point pressure determination
InactiveUS20070214877A1Reduce pressureLess-light energyBorehole/well accessoriesLight energyFormation fluid
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for determining an optimal pumping rate based on a downhole dew point pressure determination
ActiveUS7222524B2Reduce pressureLess-light energyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsLight energyDew
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method of Reducing Asphaltene Precipitation in an Engine
ActiveUS20100062957A1Good dispersionOrganic compound preparationWork treatment devicesAlkaline earth metalBlack paint
A method of reducing asphaltene precipitation or ‘black paint’ in an engine is disclosed. The method includes the step of lubricating the engine with a lubricating oil composition comprising: an oil of lubricating viscosity in a major amount; and, a salicylate detergent system in a minor amount comprising one or more neutral or overbased alkaline earth metal C22 hydrocarbyl substituted salicylates.
Owner:INFINEUM INT LTD
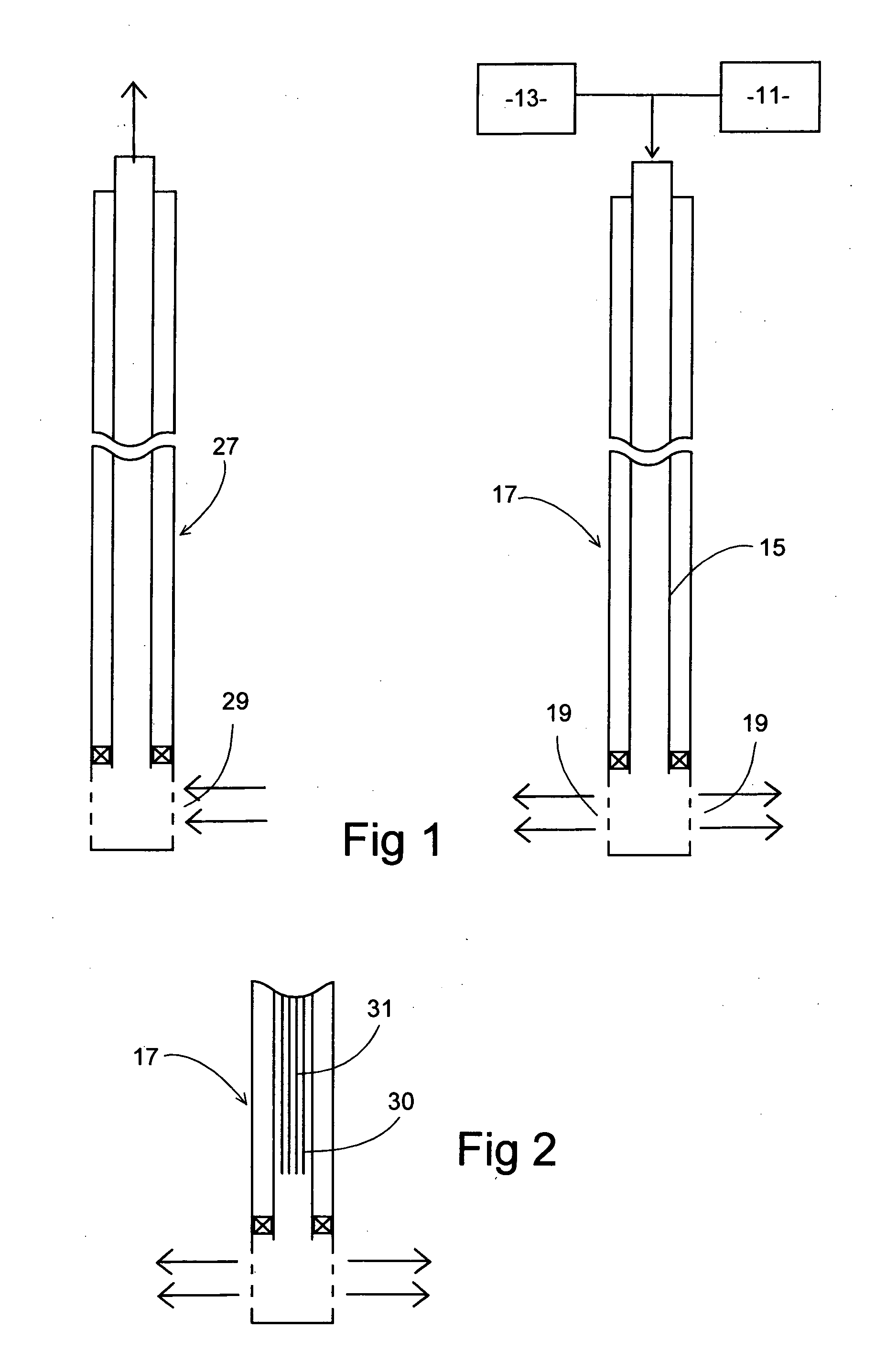
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS7162918B2Avoid contact corrosionInversely to viscosityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyTuning forkFormation fluid
The present invention provides a downhole method and apparatus using a flexural mechanical resonator, for example, a tuning fork to provide real-time direct measurements and estimates of the viscosity, density and dielectric constant of formation fluid or filtrate in a hydrocarbon producing well. The present invention additionally provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cleanup from a leveling off of viscosity or density over time, measuring or estimating bubble point for formation fluid, measuring or estimating dew point for formation fluid, and determining the onset of asphaltene precipitation. The present invention also provides for intercalibration of plural pressure gauges used to determine a pressure differential downhole. A hard or inorganic coating is placed on the flexural mechanical resonator (such as a tuning fork) to reduce the effects of abrasion from sand particles suspended in the flowing fluid in which the flexural mechanical resonator is immersed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Solvent assisted oil recovery
InactiveUS20110152136A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce precipitationFlushingDrilling compositionEtherDiluent
The recovery of oil from a reservoir is assisted by injecting a diluent into the reservoir formation to reduce the viscosity of the crude oil. This diluent is a mixture of a material which is an asphaltene precipitant, especially supercritical carbon dioxide, and a more polar material which comprises at least one aliphatic compound which includes at least one of a cycloaliphatic ring, an olefinic unsaturation, an ester or ether group. The inclusion of such an aliphatic compound which is more polar than the asphaltene precipitant reduces asphaltene precipitation and can enhance the efficiency of oil recovery when the precipitant is by supercritical carbon dioxide.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Formulations comprising an asphaltene-dispersing/inhibiting additive based on oxazolidines derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides
The present invention relates to formulations of asphaltenes' inhibitor-dispersant additives based on oxazolidine derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides. Said formulations can contain inert organic solvents, preferably including: toluene, mixtures of xylene, o-xylene, p-xylene, kerosene, turbo-fuel; or inert hydrocarbon solvents having boiling points within the range of gasoline and diesel; or inert hydrocarbon or organic solvents having a boiling point within a range from 75 to 300° C. The ratio in weight of inert organic solvents to additive that prevents and controls the precipitation and deposition of asphaltenes ranges from 1:9 to 9:1, preferably from 1:3 to 3:1.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS20050247119A1Avoid contact corrosionProtection from damageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyTuning forkFormation fluid
The present invention provides a downhole method and apparatus using a flexural mechanical resonator, for example, a tuning fork to provide real-time direct measurements and estimates of the viscosity, density and dielectric constant of formation fluid or filtrate in a hydrocarbon producing well. The present invention additionally provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cleanup from a leveling off of viscosity or density over time, measuring or estimating bubble point for formation fluid, measuring or estimating dew point for formation fluid, and determining the onset of asphaltene precipitation. The present invention also provides for intercalibration of plural pressure gauges used to determine a pressure differential downhole. A hard or inorganic coating is placed on the flexural mechanical resonator (such as a tuning fork) to reduce the effects of abrasion from sand particles suspended in the flowing fluid in which the flexural mechanical resonator is immersed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Marine engine lubrication
ActiveUS20120103303A1Not effectiveEasy to handleCombustion enginesEngine controllersEngineeringFuel oil
Trunk piston marine engine lubrication, when the engine is fueled by heavy fuel oil, is effected by a composition comprising a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity and a minor amount of one or more phenolic compounds comprising distilled cashew nut shell liquid or hydrogenated distilled cashew nut shell liquid. Asphaltene precipitation in the lubricant, caused by the presence of contaminant heavy fuel oil, is prevented or inhibited.
Owner:INFINEUM INT LTD
Method for removing asphaltene deposits
InactiveUS7754657B2Reduce and prevent formationPreventing and reducing and depositionWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansFlushingKeroseneFuel oil
Compositions comprising at least one C4-C30 olefin or oxidation product thereof and kerosene or an aromatic solvent are particularly effective for use in removing asphaltene and asphaltene-containing organic deposits and in preventing or reducing the precipitation and deposition of asphaltenes from hydrocarbon fluids. When added to heavy oils comprising asphaltenes, alone or in combination with dispersants and further inhibitors, the invented compositions lower viscosity and pour point, and aid in preventing asphaltene precipitation during transport and in combustion.
Owner:INEOS USA LLC
Method for determining the effectiveness of asphaltene dispersant additives for inhibiting or preventing asphaltene precipitation in a hydrocarbon-containing material subjected to elevated temperature and pressure conditions
ActiveUS20140130581A1High trafficReduce dirtRefining with non-metalsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionAsphaltene precipitationHigh pressure
Disclosed herein is a method for determining the effectiveness of one or more asphaltene dispersant additives for inhibiting or preventing asphaltene precipitation in a hydrocarbon-containing material subjected to elevated temperature and pressure conditions.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Asphaltene deposition solid inhibitor for light oil exploitation
InactiveCN101235280AAvoid depositionPrevent depreciationDrilling compositionAgglutinationHigh pressure
The invention relates to asphaltene deposition solid inhibitor in the exploitation of light oil which can effectively reduce and control asphaltene to gather and deposit in the light oil exploitation process, which is used on the crude oil exploitation, and can solve the problems of asphaltene deposition and precipitation in the light oil exploitation process. The technical scheme is that the inhibitor is formed by high-pressure polyethylene, diesel fuel and other auxiliary agent, and the product of asphaltene deposition solid inhibitor can be obtained through conducting molten agglutination reaction for 20-60% high-pressure polyethylene, 10-40% diesel fuel and 20-40% other auxiliary agent which comprises three medicaments of polyoxyethylene ether, sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate and 2,6-ditrertiarybutyl p-methyl phenyl under the temperature of 100-130 DEG C to form even mixture before molding. The product can be direct thrown into drug-carrying container or be thrown by means of a drug-adding pipe, is slowly released as the scouring of bottom hole oil stream, which can effectively inhibit the gathering and growth of asphaltene, solves the problem of pipe column plugging-up problem in well, and has the advantages of high inhibiting efficiency, long cycle, small additive dose and low cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Process for treating high paraffin diluted bitumen
ActiveUS20140083911A1Reduce pollutant loadLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbon oils refiningParaffin waxAsphaltene precipitation
A paraffinic solvent recovery process for treating high paraffin diluted bitumen includes supplying the latter to flashing apparatus; separating into flashed paraffinic solvent and diluted bitumen underflow; and returning a portion of the underflow as returned diluted bitumen into the high paraffin diluted bitumen prior to introduction into the flashing apparatus, at temperature and amount to shift asphaltene precipitation equilibrium to reduce asphaltene precipitation. The process includes pre-heating the high paraffin diluted bitumen by transferring heat from hot dry bitumen, flashed paraffinic solvent and / or a portion of diluted bitumen underflow. Flashed paraffinic solvent may contain residual light end bitumen contaminants that increase asphaltenes solubility and the process may include removing contaminants to produce reusable paraffinic solvent at given solvent-to-bitumen ratio range to maintain given asphaltene precipitation. The process may also include a bitumen fractionation column producing hot dry bitumen underflow containing at most 0.5 wt % paraffinic solvent.
Owner:TRUENORTH ENERGY CORP
Dispersing additive for asphaltenes and its uses
ActiveUS20180079976A1Reduce the temperatureMaintain mechanical propertiesDrilling compositionBuilding insulationsAlkylphenolAsphaltene
Use of an alkylphenol-aldehyde resin modified by at least one alkylamine in a composition of crude oils or in a product derived from a composition of crude oils as dispersing additive for asphaltenes. Process for the treatment of a composition of crude oils or a derived product which makes it possible to prevent the precipitation of asphaltenes, in particular in crude oils and the products which result therefrom by refining and / or extraction processes. Bituminous compositions including an alkylphenol-aldehyde resin modified by at least one alkylamine.
Owner:TOTAL MARKETING SERVICES SA
Marine engine lubrication
InactiveUS20120028521A1Propulsion power plantsOutboard propulsion unitsFuel oilAsphaltene precipitation
Trunk piston marine engine lubrication, when the engine is fueled by heavy fuel oil, is effected by a composition comprising a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity containing at least 50 mass % of a Group II basestock, and respective minor amounts of an overbased metal hydrocarbyl-substituted hydroxybenzoate detergent other than such a detergent having a basicity index of less than two and a degree of carbonation of 80% or greater and at least 1 mass % of a hydrocarbyl-substituted carboxylic acid, anhydride, ester or amide thereof. Asphaltene precipitation in the lubricant, caused by the presence of contaminant heavy fuel oil, is prevented or inhibited.
Owner:INFINEUM INT LTD
Method for storing and transporting crude oil
Disclosed is a method for transporting blended crude oils comprising the steps of; (a) admixing a first crude oil with a second, different crude oil to form a crude oil admixture; (b) determining a first value representing the content of unprecipitated asphaltenes in the admixture; (c) holding the admixture for a period of time at standard conditions; (d) determining a second value representing the content of unprecipitated asphaltenes in the admixture; and (e) either: (i) transporting the admixture if the second value is the same as or within a predetermined range of the first value; or (ii) taking remedial action to prevent asphaltene precipitation prior to transporting if the second value is outside a predetermined range from the first value. Also disclosed is a method for estimating the storage stability of stored crude oils and crude oil admixtures.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Focused beam reflectance measurement to optimized desalter performance and reduce downstream fouling
InactiveUS20100038286A1Improve performanceLiquid separation by electricityElectrostatic separationEngineeringDesalter
Performance of equipment, such as a desalter, in a refinery is monitored in real-time and on-line to minimize fouling of downstream equipment. Using an instrument to measure particles and droplets in-process allows monitoring of the various operations to optimize performance. Such measurement can also be used during crude oil blending to detect asphaltene precipitates that can cause fouling and can be used for monitoring other fouling streams.
Owner:GREANEY MARK A +3
Marine engine lubrication
Trunk piston marine engine lubrication, when the engine is fueled by heavy fuel oil, is effected by a composition comprising a major amount of an oil of lubricating viscosity containing at least 50 mass % of a basestock containing greater than or equal to 90% saturates and less than or equal to 0.03% sulphur or a mixture thereof, and respective minor amounts of an overbased metal hydrocarbyl-substituted hydroxybenzoate detergent other than such a detergent having a basicity index of less than two and a degree of carbonation of 80% or greater and at least 1 mass % of a hydrocarbyl-substituted carboxylic acid, anhydride, ester or amide thereof. Asphaltene precipitation in the lubricant, caused by the presence of contaminant heavy fuel oil, is prevented or inhibited.
Owner:INFINEUM INT LTD
Asphaltene inhibition
ActiveUS20170306215A1Improved asphaltene dispersing propertyLow viscosityLiquid carbonaceous fuelsDrilling compositionPolyesterPolyol
A method of inhibiting asphaltene precipitation and / or deposition in a hydrocarbon, preferably crude oil, by adding to the hydrocarbon a polyester asphaltene dispersing agent which is the reaction product of an alk(en)yl substituted succinic anhydride wherein the average number of succinic groups per alk(en)yl group is less than 2.0, and at least one polyol.
Owner:CRODA
Asphaltene-dispersing/inhibiting additive based on oxazolidines derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides
The present invention relates to formulations of asphaltenes' inhibitor-dispersant additives based on oxazolidine derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides. Said formulations can contain inert organic solvents, preferably including: toluene, mixtures of xylene, o-xylene, p-xylene, kerosene, turbo-fuel; or inert hydrocarbon solvents having boiling points within the range of gasoline and diesel; or inert hydrocarbon or organic solvents having a boiling point within a range from 75 to 300° C. The ratio in weight of inert organic solvents to additive that prevents and controls the precipitation and deposition of asphaltenes ranges from 1:9 to 9:1, preferably from 1:3 to 3:1.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Integration of solvent deasphalting and gasification
InactiveCN1330696AGaseous fuelsRefining by solvent de-asphaltingPartial oxidationAsphaltene precipitation
The invention is the integration of a process of gasifying asphaltenes in a gasification zone by partial oxidation and the process of asphaltene extraction with a solvent. The integration allows low level heat from the gasification reaction to be utilized in the recovery of solvent that was used to extract asphaltenes from an asphaltene-containing hydrocarbon material. Asphaltenes are extracted from an asphaltene-containing hydrocarbon material by mixing a solvent in quantities sufficient to precipitate at least a fraction of the asphaltenes. The precipitated asphaltenes are then gasified in a gasification zone to synthesis gas. The gasification process is very exothermic. The low level heat in the synthesis gas, either directly, or via an intermediate step of low pressure steam, is used to remove and recover the solvent from the deasphalted hydrocarbon material and from the asphaltenes prior to gasification.
Owner:GE ENERGY USA
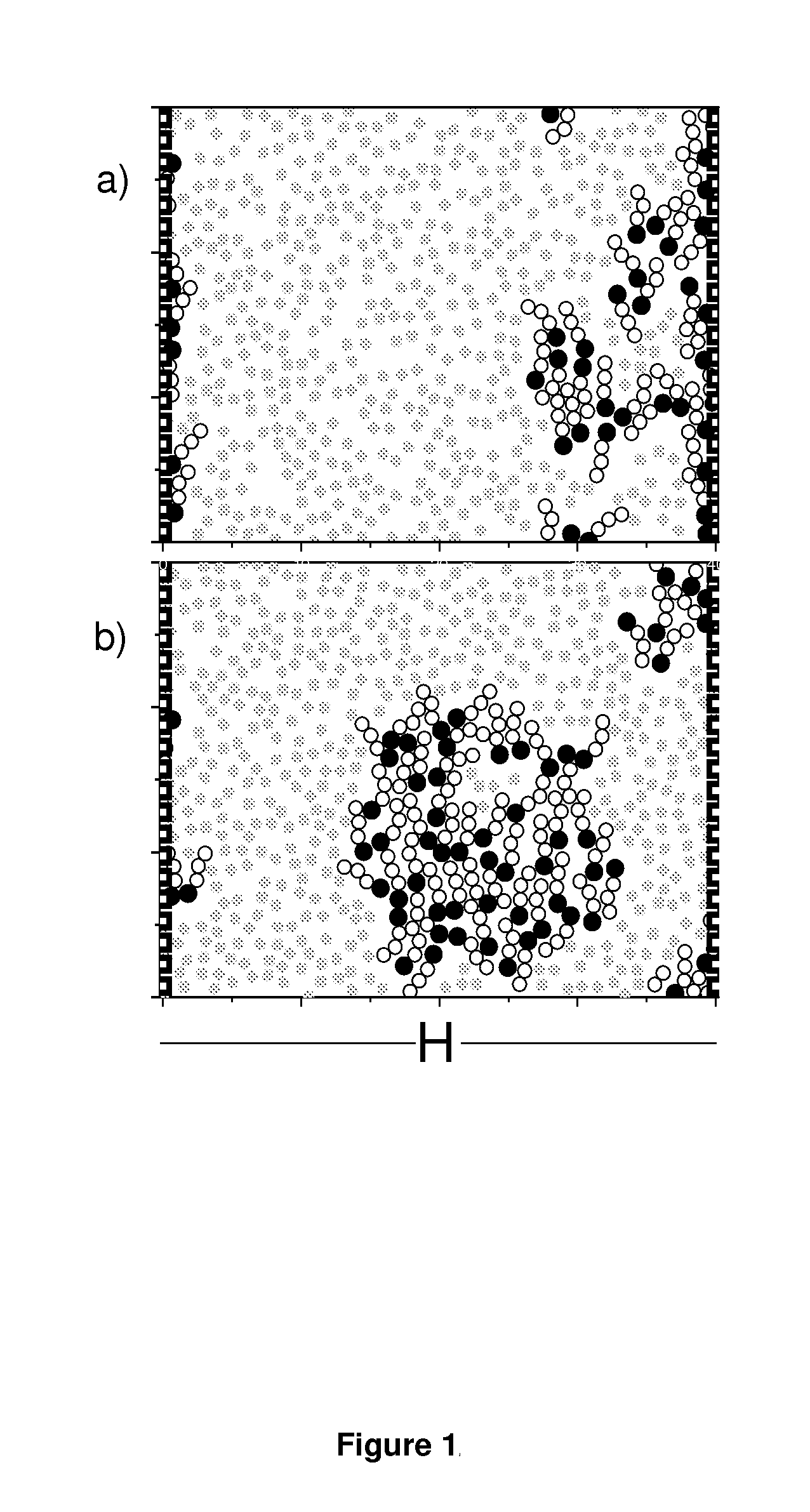
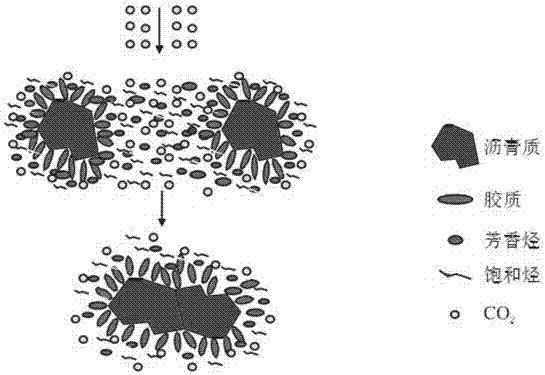
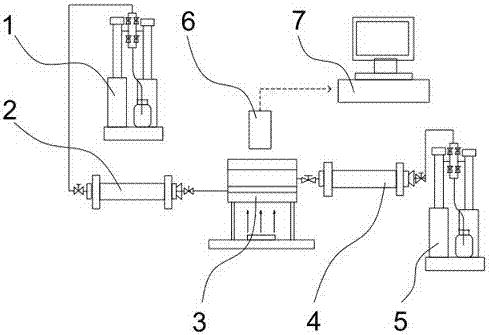
Method or dynamically measuring precipitation amount of asphaltene generated through CO2-crude oil action
InactiveCN107219322ALow costEasy to operateMonitoring particle agglomerationParticle size analysisCoverage ratioImaging analysis
The invention provides a method or dynamically measuring the precipitation amount of asphaltene generated through CO2-crude oil action. The method comprises the steps of injecting crude oil into a reaction kettle through a crude oil piston container by using a first ISCO pump; introducing CO2 into the reaction kettle through a CO2 piston container by using a second ISCO pump and controlling the pressure intensity of the CO2 by using the second ISCO pump; observing an image of a crude oil-CO2 layer in real time through a CCD camera and a computer and measuring the area of asphaltene precipitation and the size distribution of particles by using image analysis software, measuring the precipitation amount under the condition of a small amount of reservoir through an indirect measurement method of the asphaltene precipitation amount; and calibrating an asphaltene precipitation image obtained in a previous experiment through the measured values and building a linear relationship between the precipitation coverage ratio and the asphaltene precipitation amount in the image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
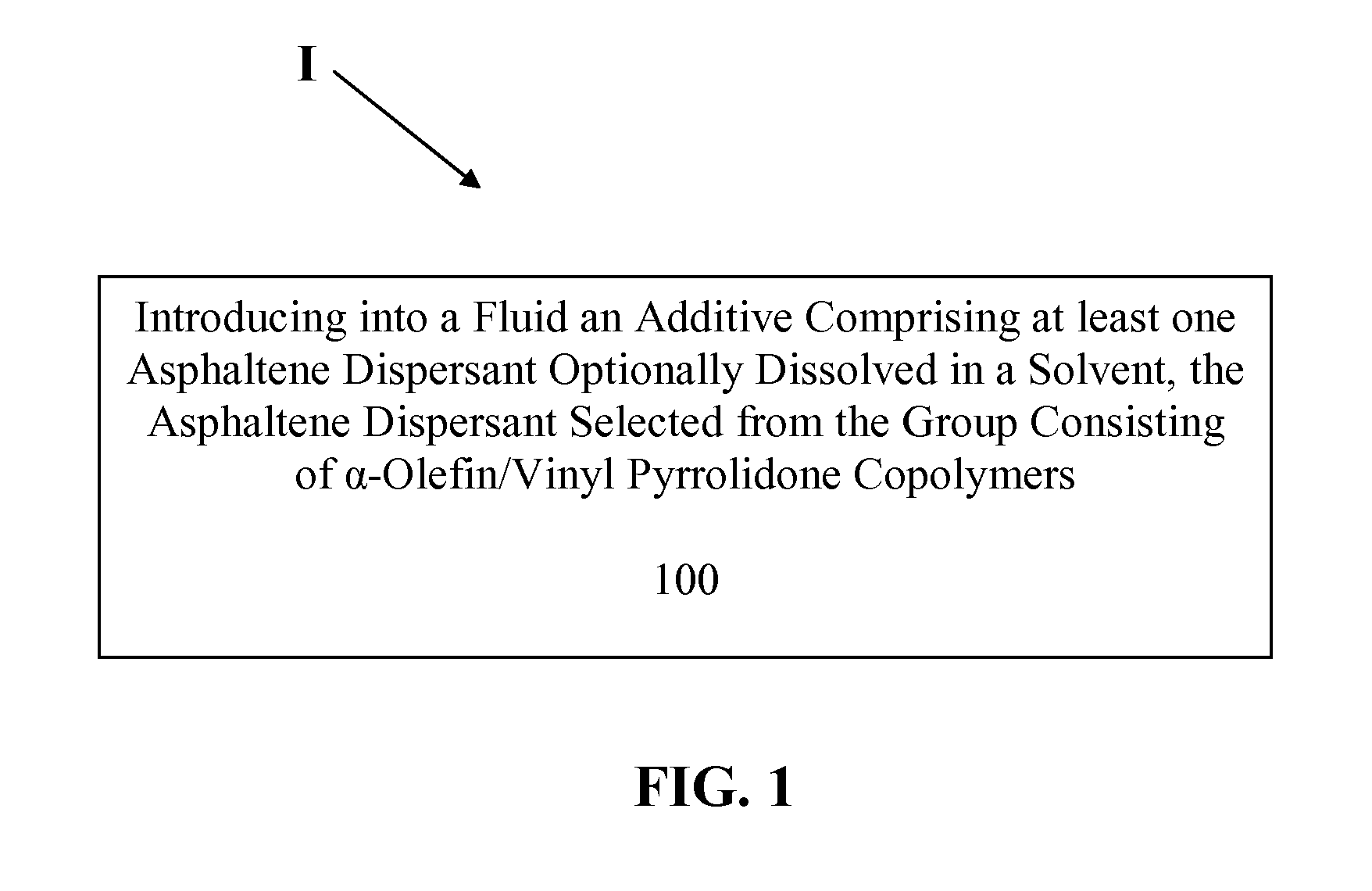
a-OLEFIN / VINYL PYRROLIDINONE COPOLYMERS AS ASPHALTENE DISPERSANTS
InactiveUS20120220807A1Prevent precipitationDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsPyrrolidinones1-hexadecene
An additive comprising, dissolved in a solvent, an asphaltene dispersant selected from the group consisting of α-olefin / vinyl pyrrolidinone copolymers. The copolymer can comprise at least one α-olefin selected from the group consisting of mono-α-olefins, at least one α-olefin selected from the group consisting of linear α-olefins and / or at least one α-olefin is selected from the group consisting of 1-hexadecene, 1-octadecene, 1-eicosene, 1-docosene, 1-tetracosene, 1-hexacosene, 1-octacosene and 1-triacontene. The additive can comprise a copolymer of 2-pyrrolidinone, 1-ethenyl monomer. The copolymer can have a Hansen Solubility Parameter (HSP), δ, of greater than 16, 17 or 18 MPa1 / 2. The solvent can be selected from the group consisting of aromatic solvents, such as 1-methyl naphthalene, bis-(m-phenoxyphenyl)ether, o-xylene, toluene and heavy aromatic solvents. Also provided is a method of inhibiting asphaltene precipitation in a fluid by introducing into the fluid an asphaltene dispersant selected from the group consisting of α-olefin / vinyl pyrrolidinone copolymers.
Owner:SHRIEVE CHEM PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com