Patents
Literature
183results about "Monitoring particle agglomeration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
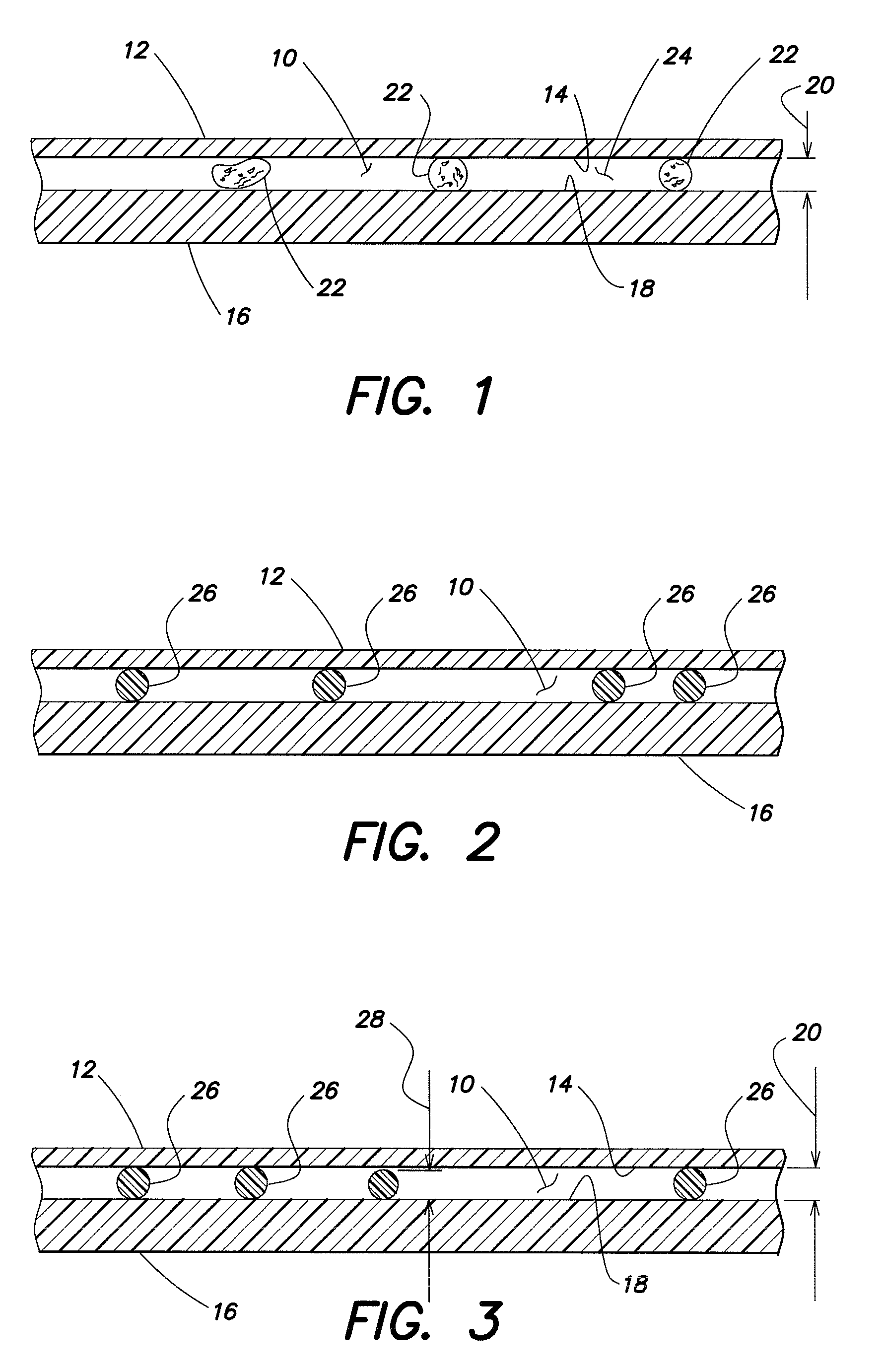
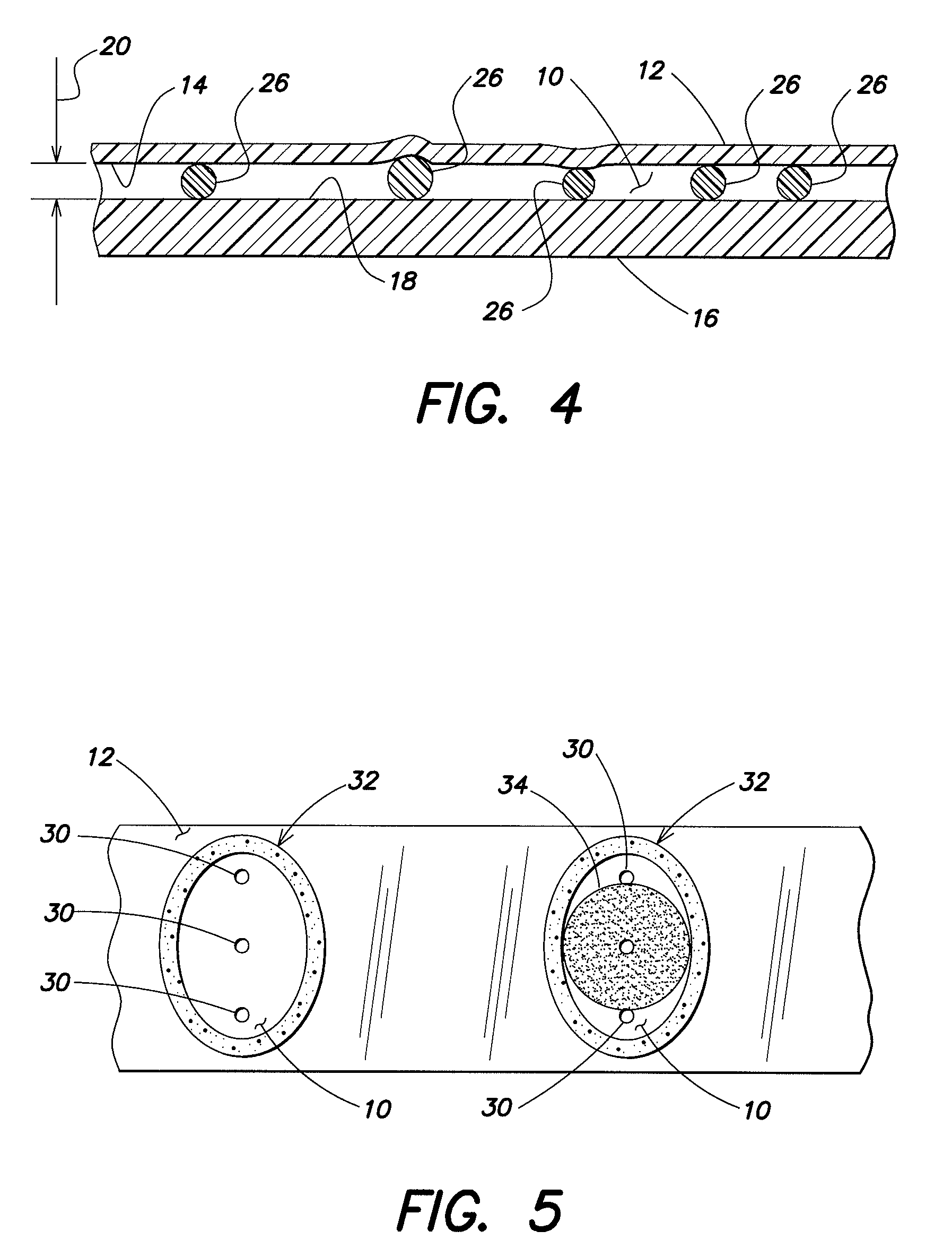
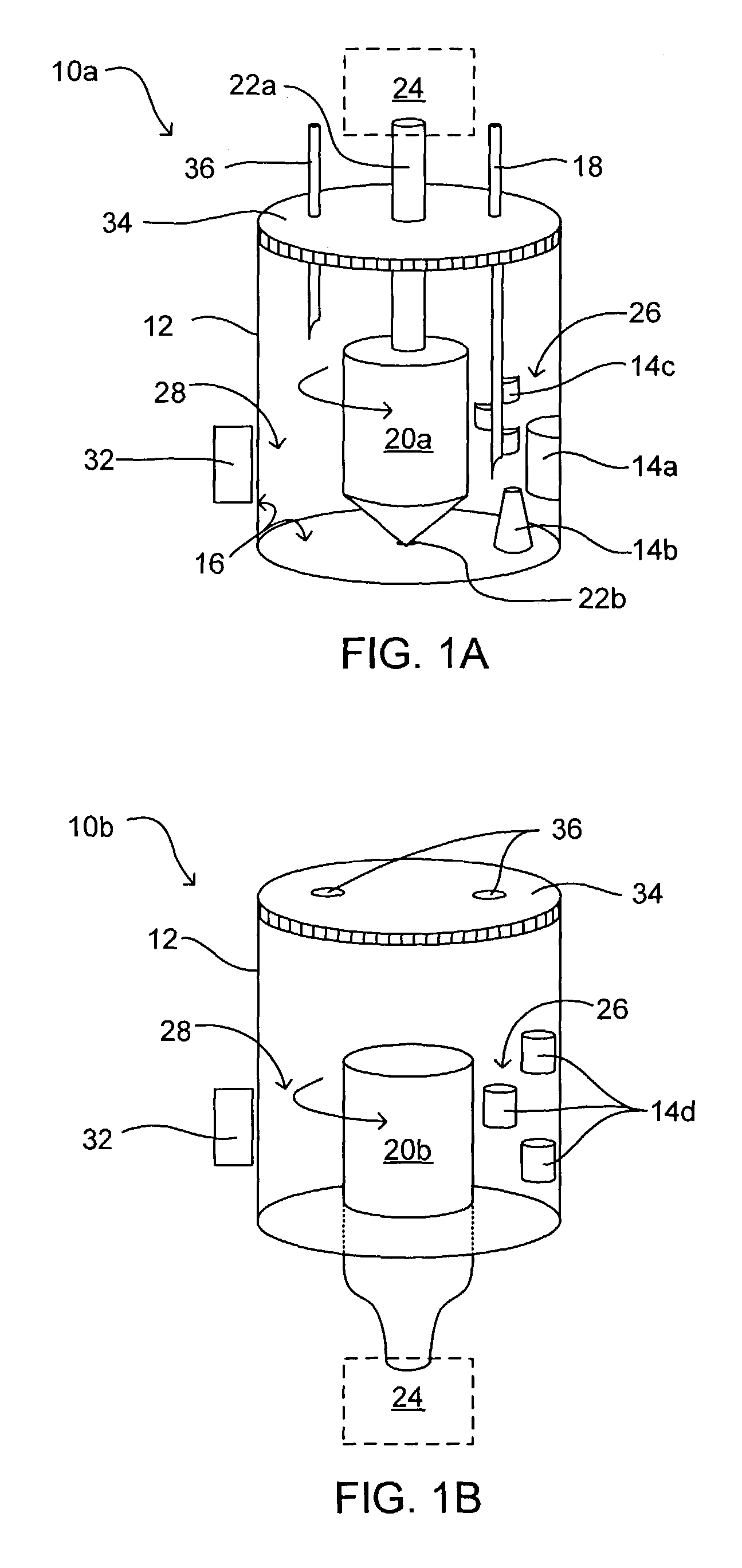
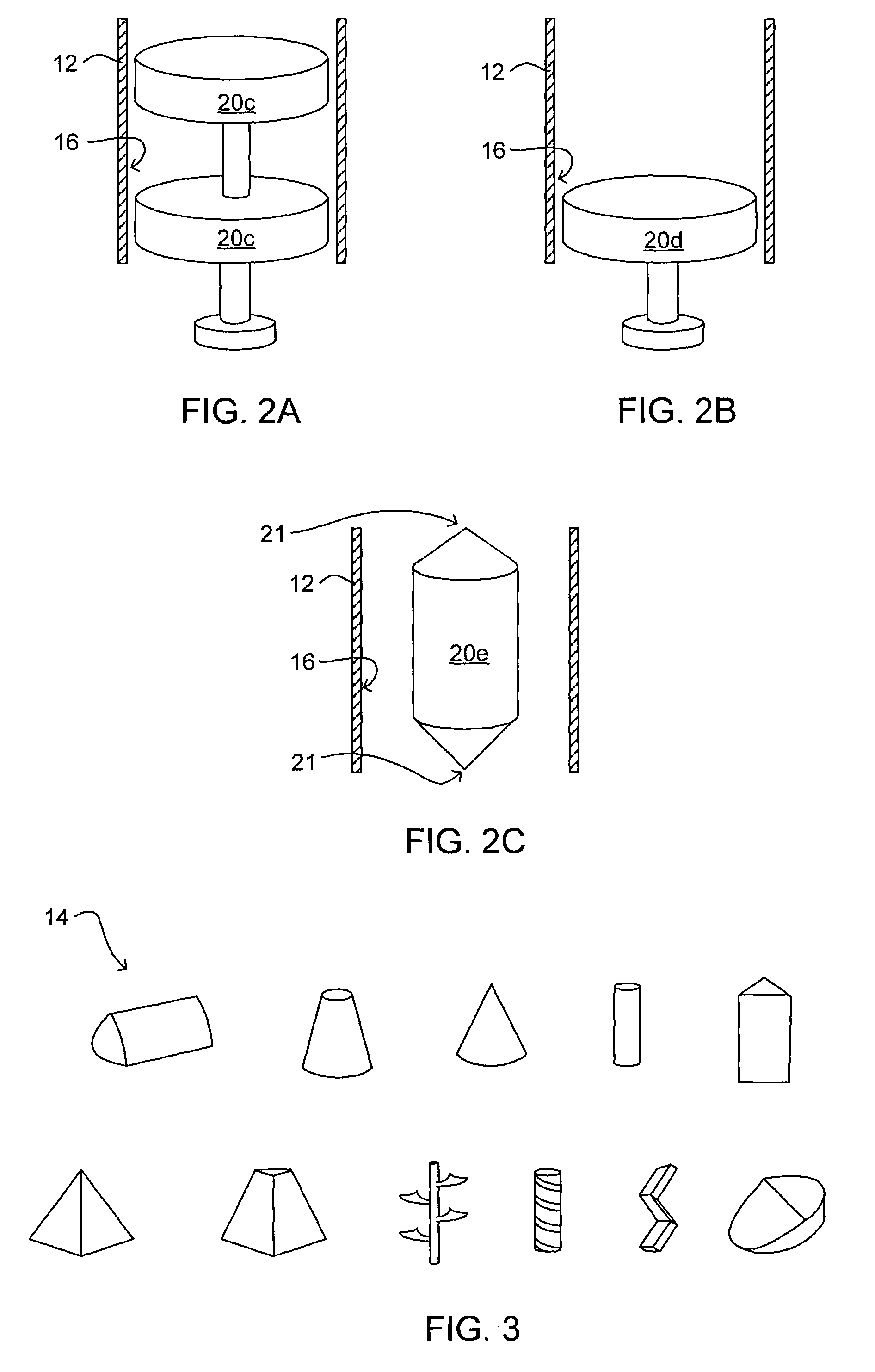
Reinforcing aluminum-based filler and rubber composition comprising such a filter
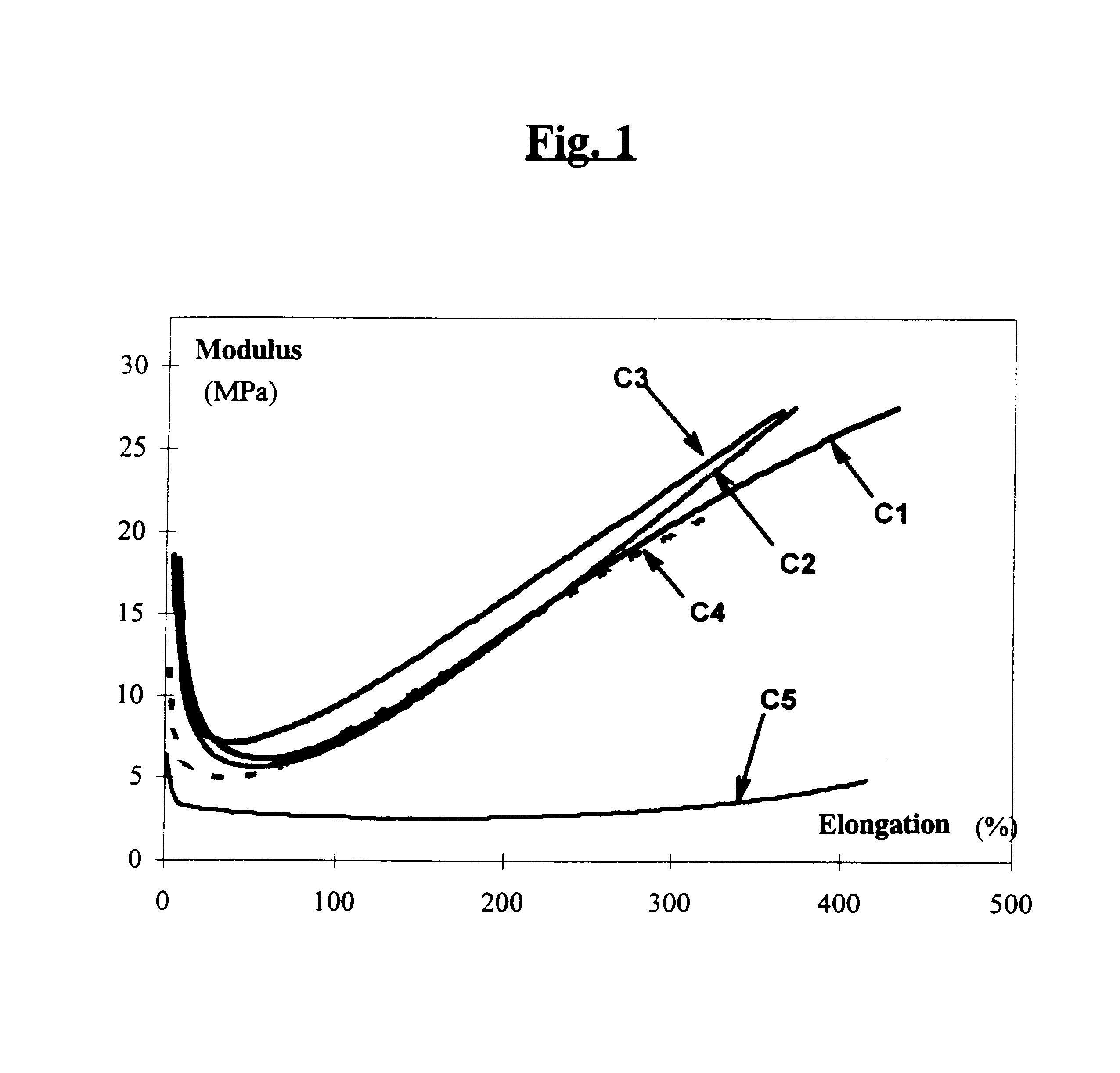
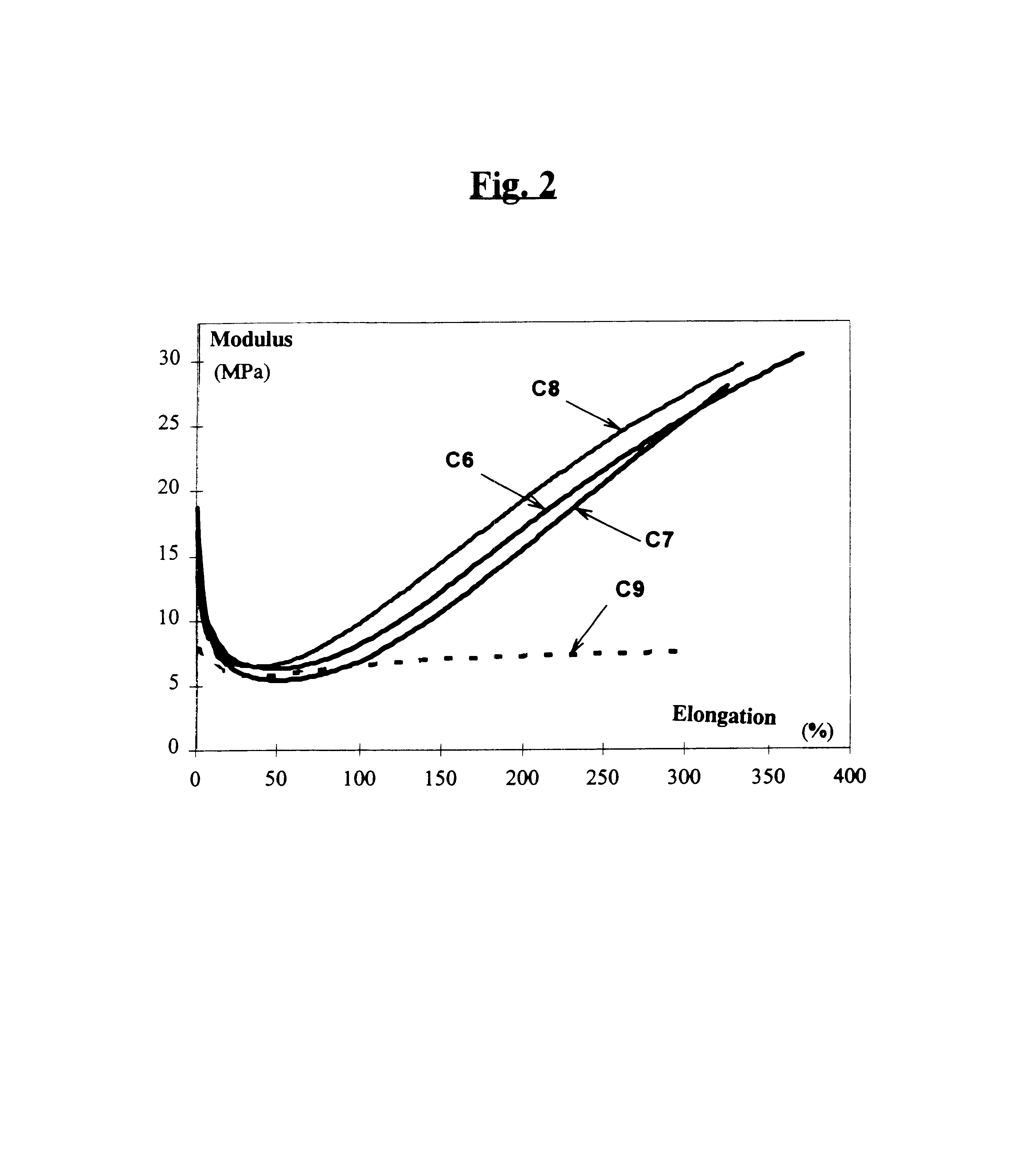
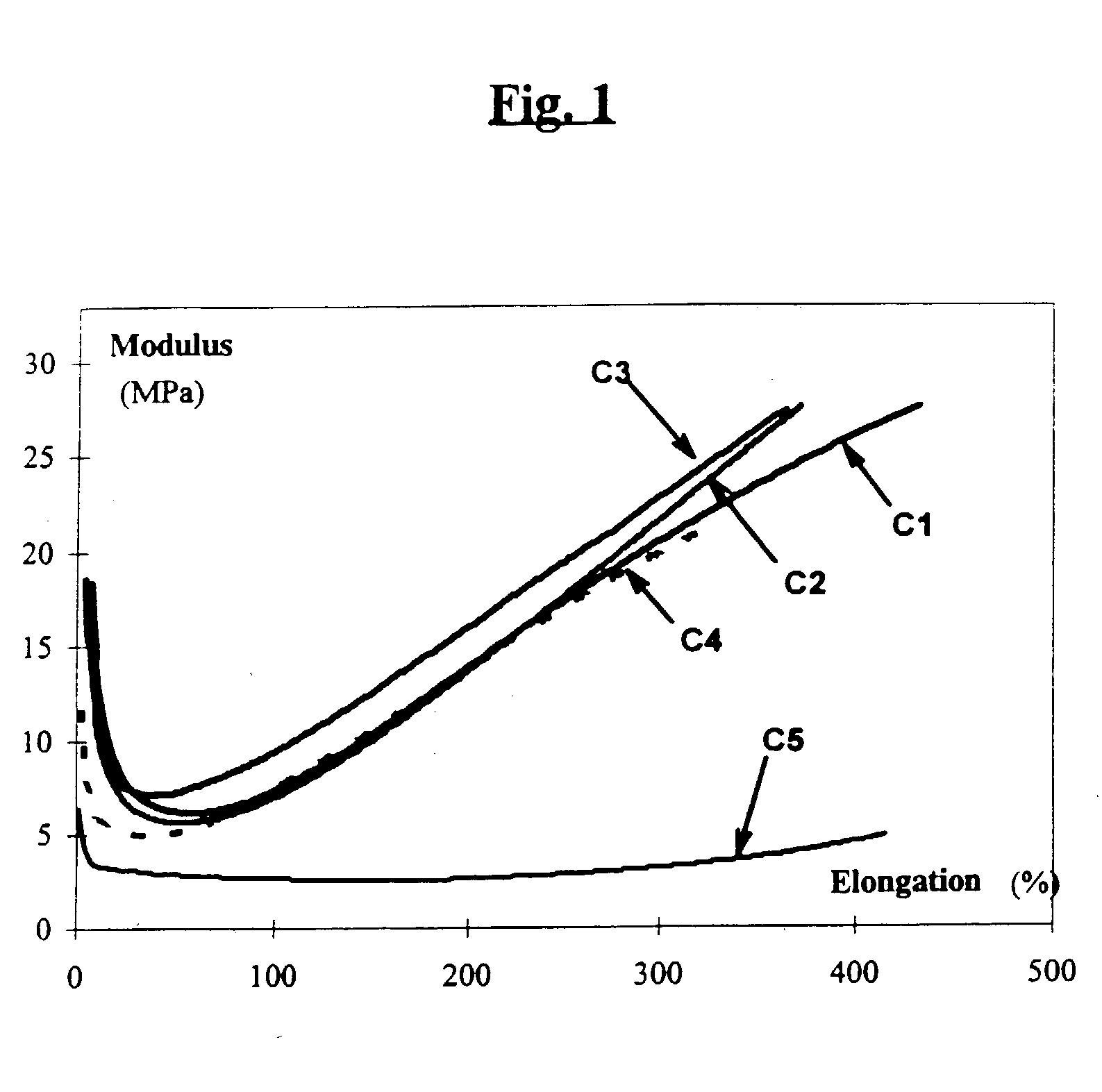
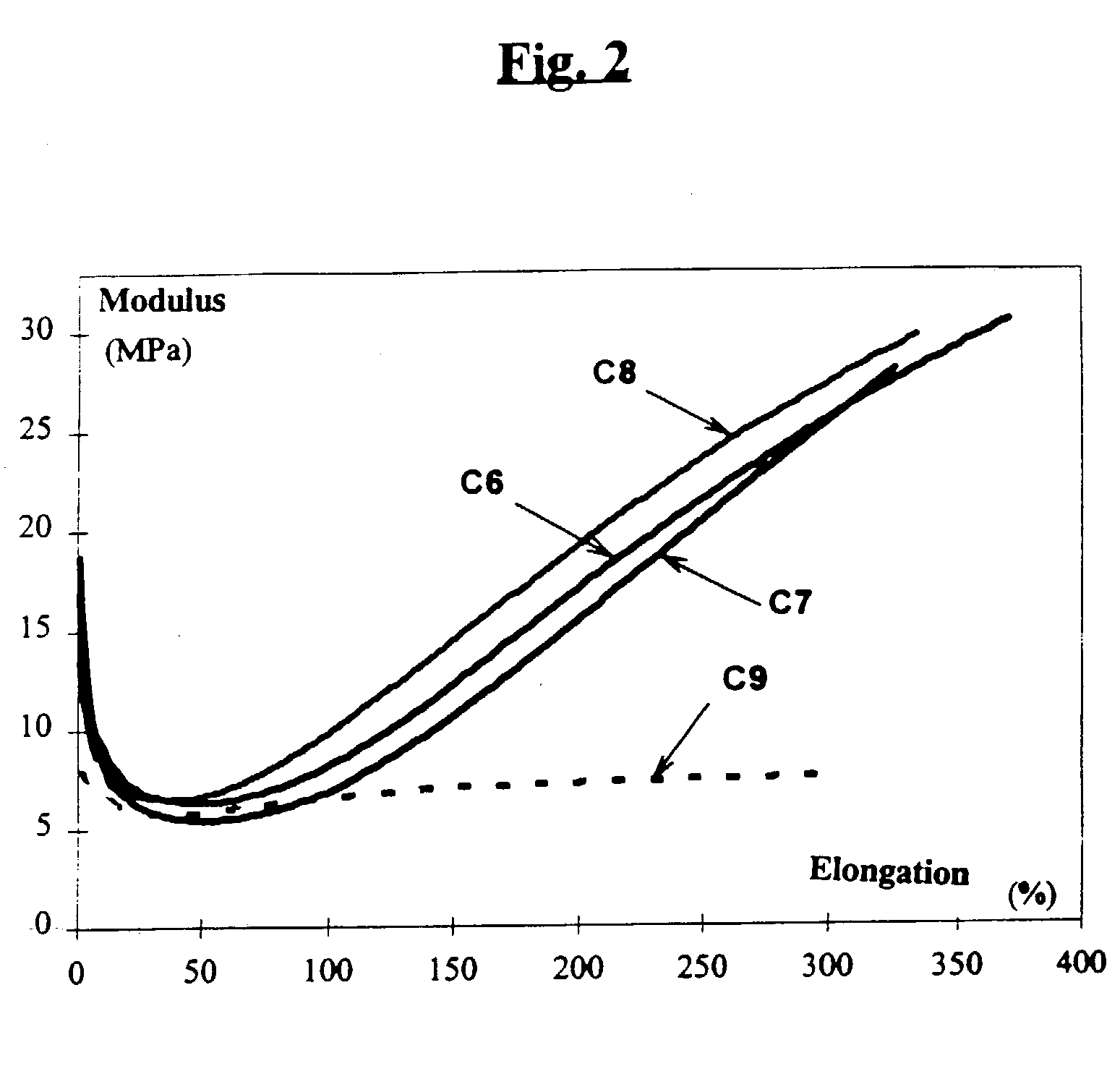
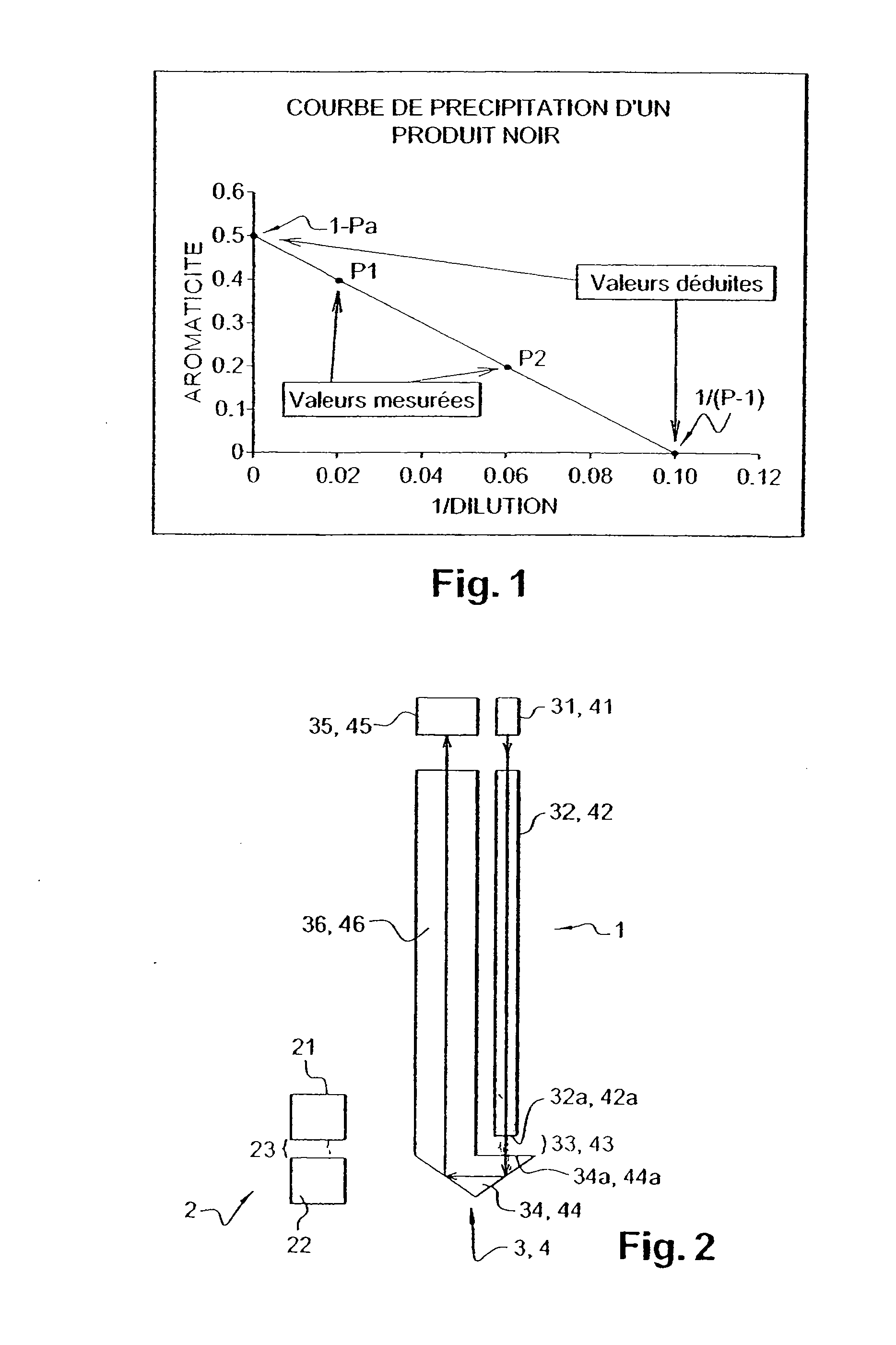
A reinforcing aluminum-based filler which can be used for reinforcing diene rubber compositions intended for the manufacture of tires, comprising an aluminum (oxide-)hydroxide corresponding, with the exception of any impurities and the water of hydration, to the general formula (a and b being real numbers):the specific BET surface area of which is between 30 and 400 m2 / g, the average particle size (by mass) dw of which is between 20 and 400 nm and the disagglomeration rate, alpha, of which, measured via an ultrasound disagglomeration test at 100% power of a 600-watt ultrasonic probe, is greater than 5x10-3 mum-1 / s is provided. A rubber composition suitable for the manufacture of tires comprising said aluminum-based filler as reinforcing filler.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
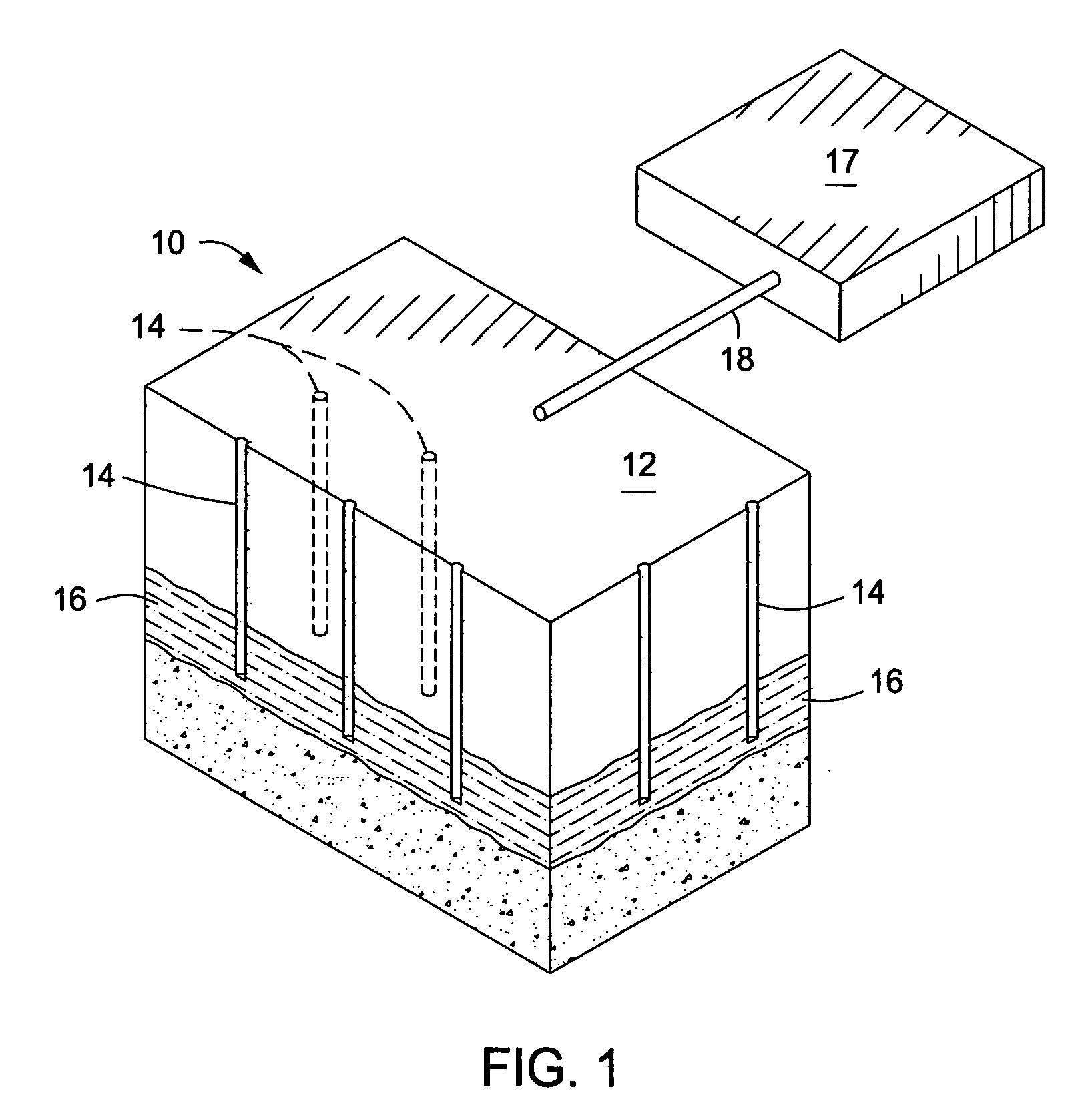
Downhole burner wells for in situ conversion of organic-rich rock formations
A method for in situ heating of an organic-rich rock formation is provided. Preferably the organic-rich rock formation comprises kerogen. The method may include the steps of providing a first wellbore extending at least to a depth of the organic-rich rock formation, and providing a second wellbore also extending to a depth of the organic-rich rock formation and intersecting the first wellbore. The method may also include injecting air and a combustible fuel into the first wellbore, and providing a downhole burner in the wellbore so as to cause the air and the combustible fuel to mix and to combust at substantially the depth of the organic-rich rock formation. The method may further include, circulating combustion products into and up the second wellbore such that a pyrolysis zone is created from the first wellbore and second wellbores that provides substantially complete pyrolysis of the organic-rich rock formation between the first wellbore and the second wellbore. Operating conditions may be set or controlled so that the pyrolysis zones surrounding the first and second wellbore mate so to minimize underheated and overheated regions.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
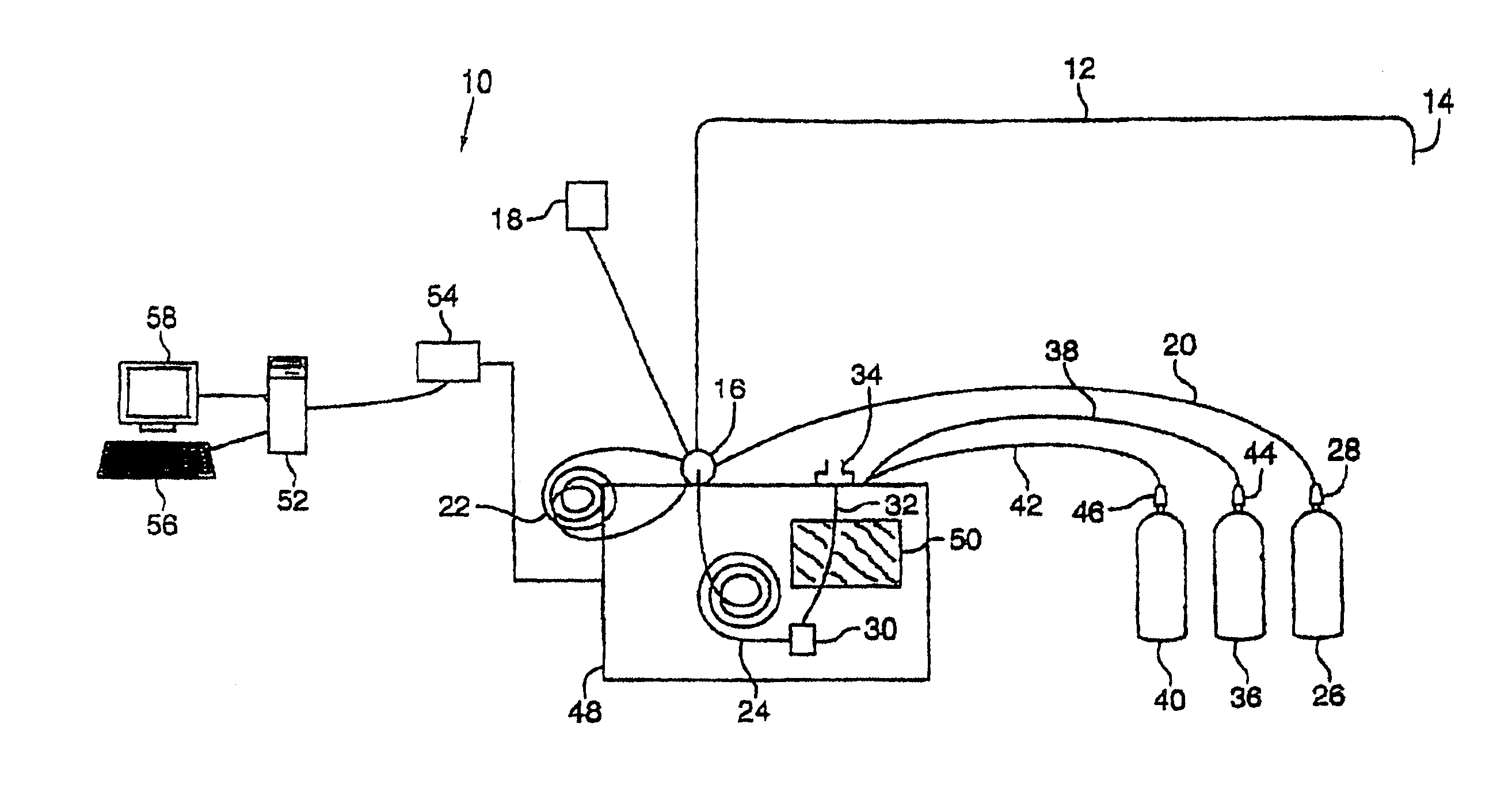
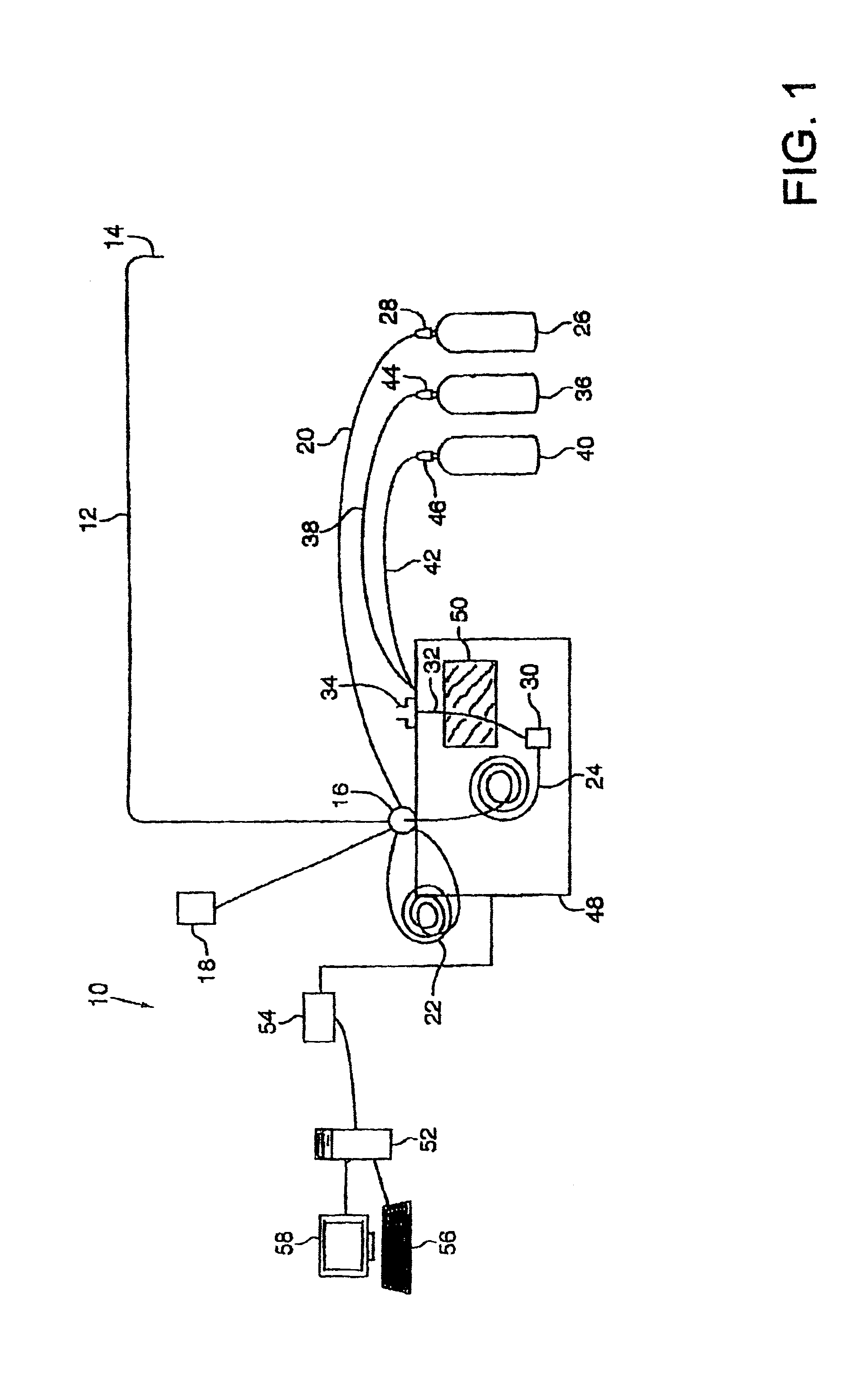
Method and apparatus for sample analysis
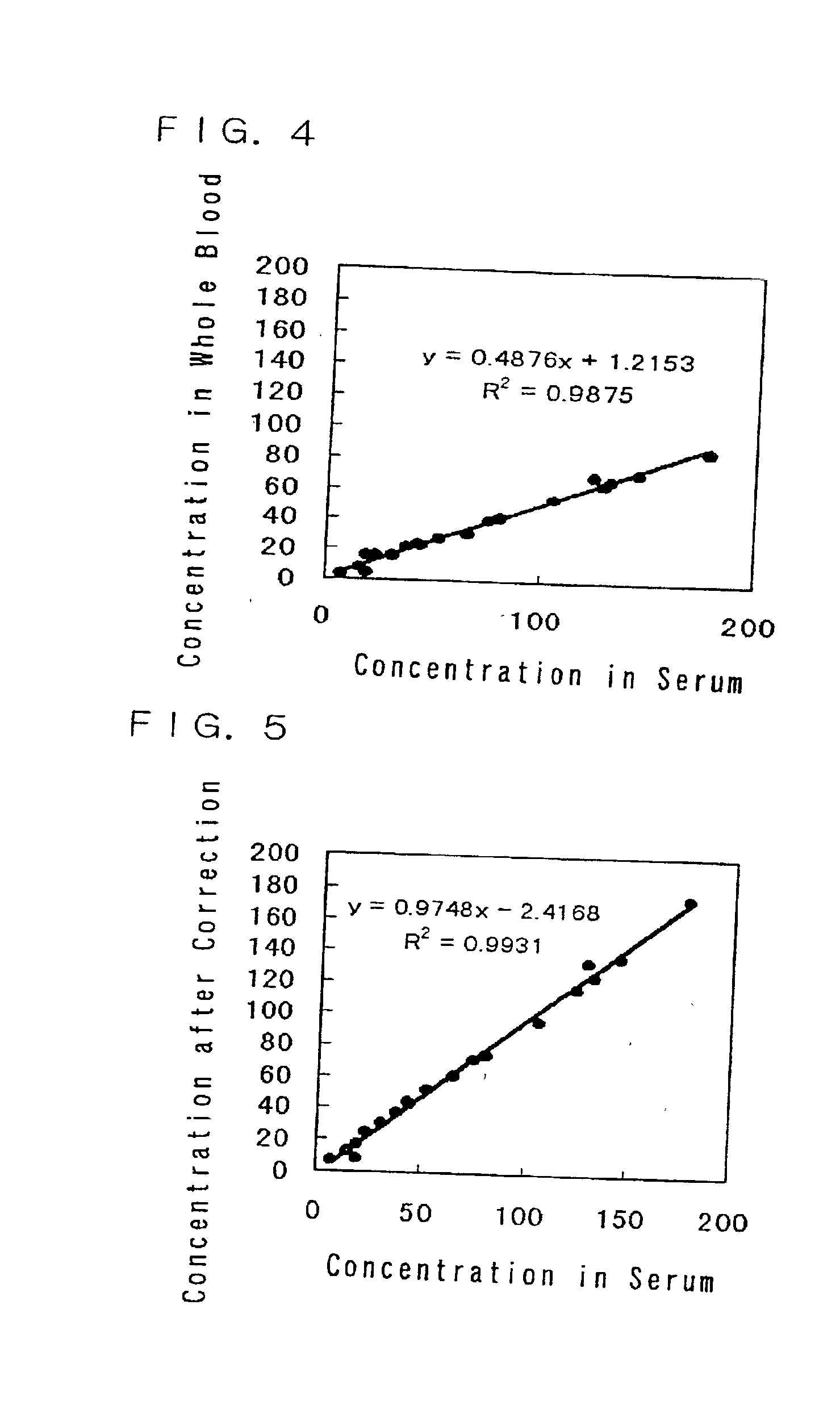
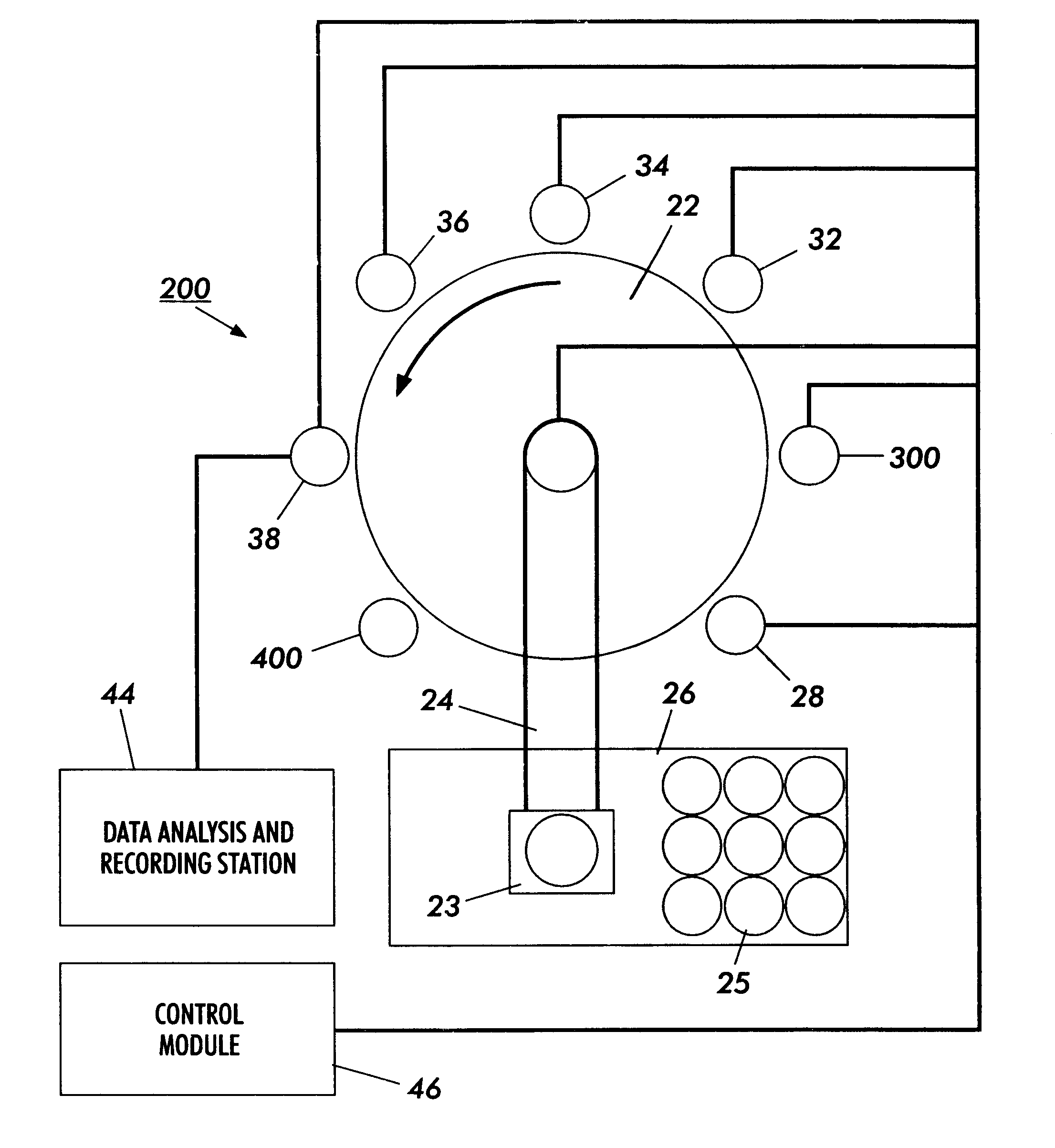
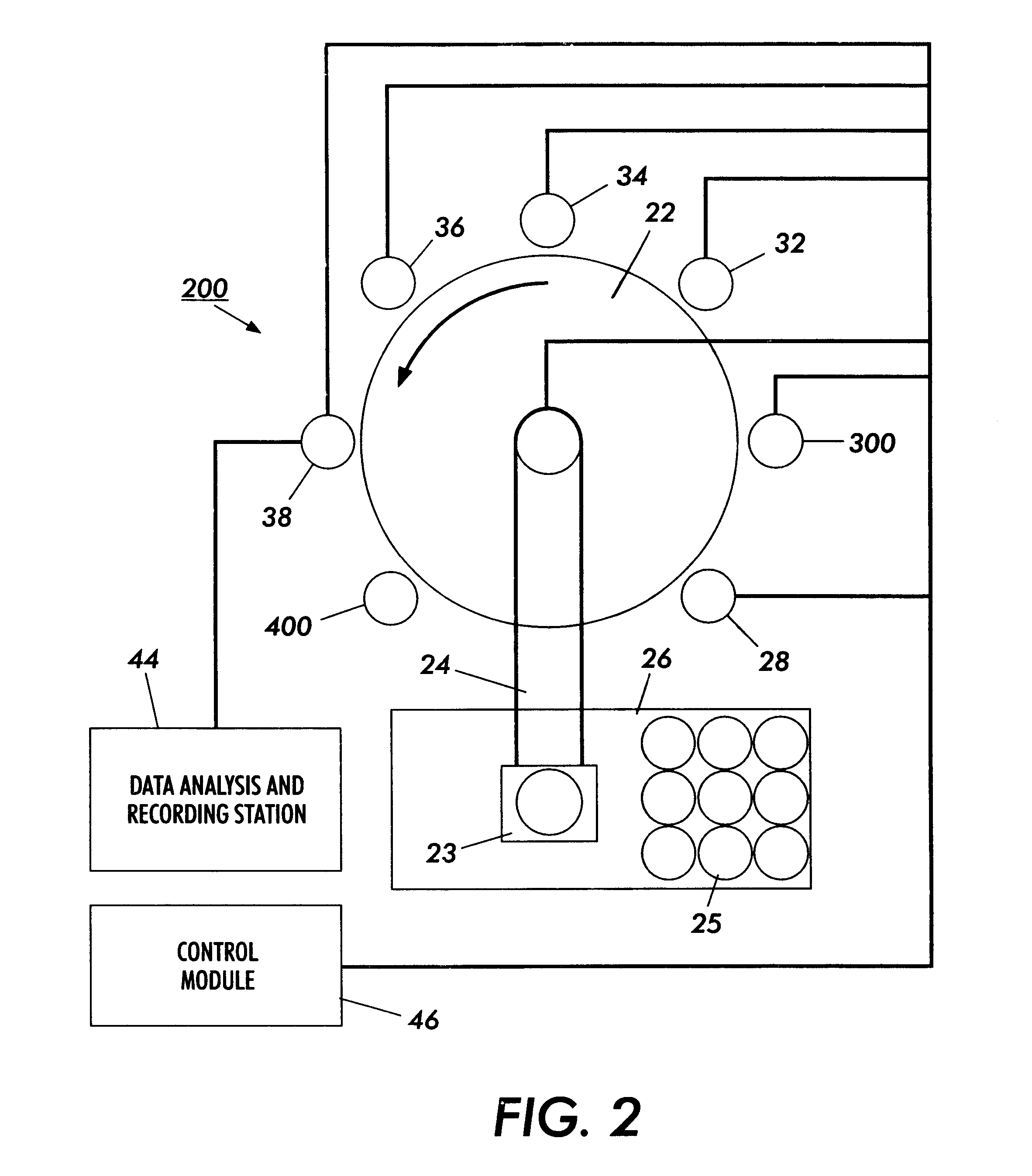
InactiveUS6865926B2Easy to operateAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationParticulatesGas analysis
Methods and systems for analyzing samples, such as gas samples, are described. One method comprises providing a gas sample, increasing pressure applied to the gas sample to compress the sample to a smaller volume and provide a pneumatically focused gas sample, and analyzing the pneumatically focused gas sample using any of a variety of analytical techniques. Also disclosed are systems for gas analysis, including systems for analysis of pneumatically focused, and thereby concentrated, gas samples and for analysis of particulate matter in gas samples. Analytical systems constructed within personal computer cases also are disclosed.
Owner:PORTLAND STATE UNIV
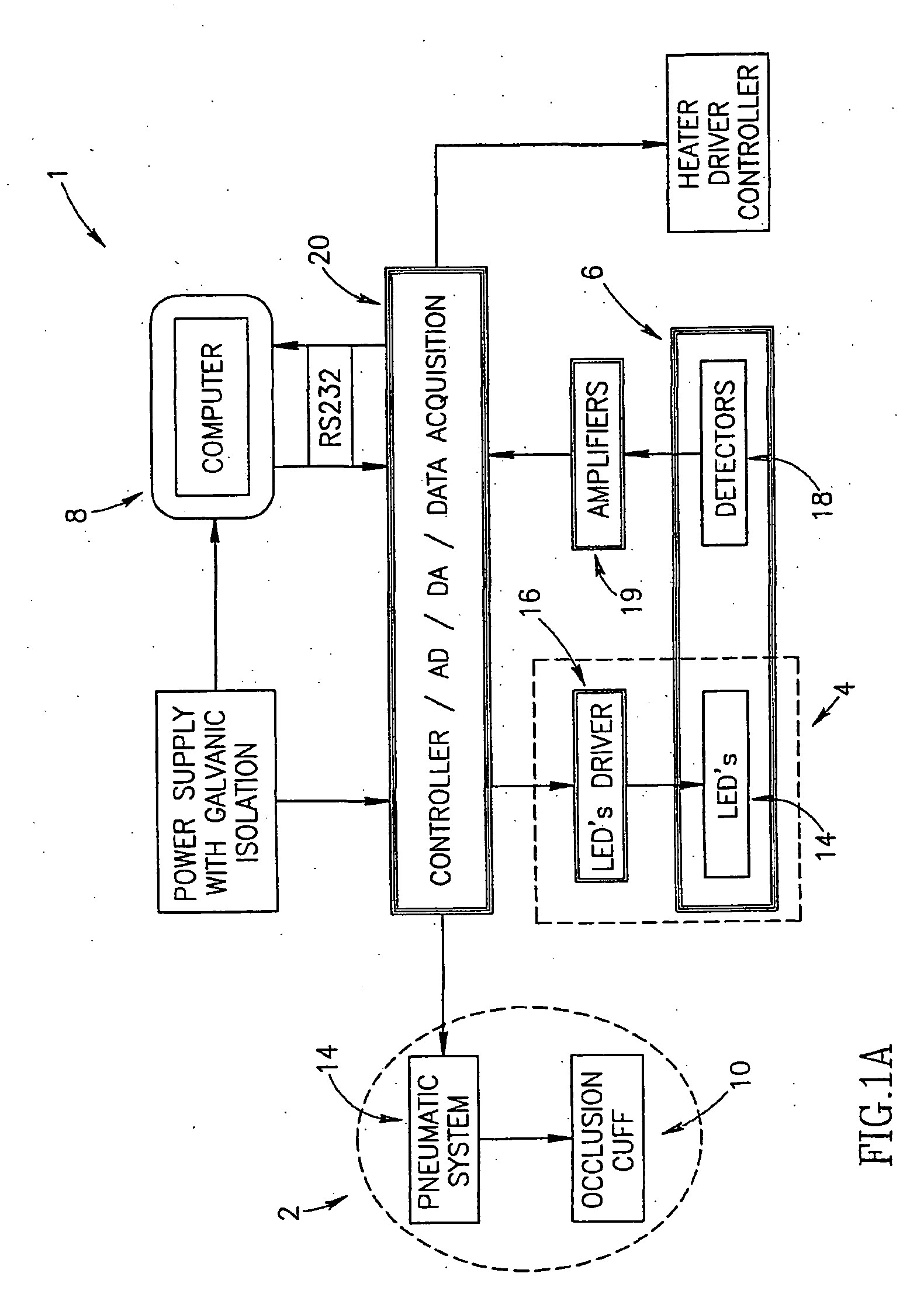
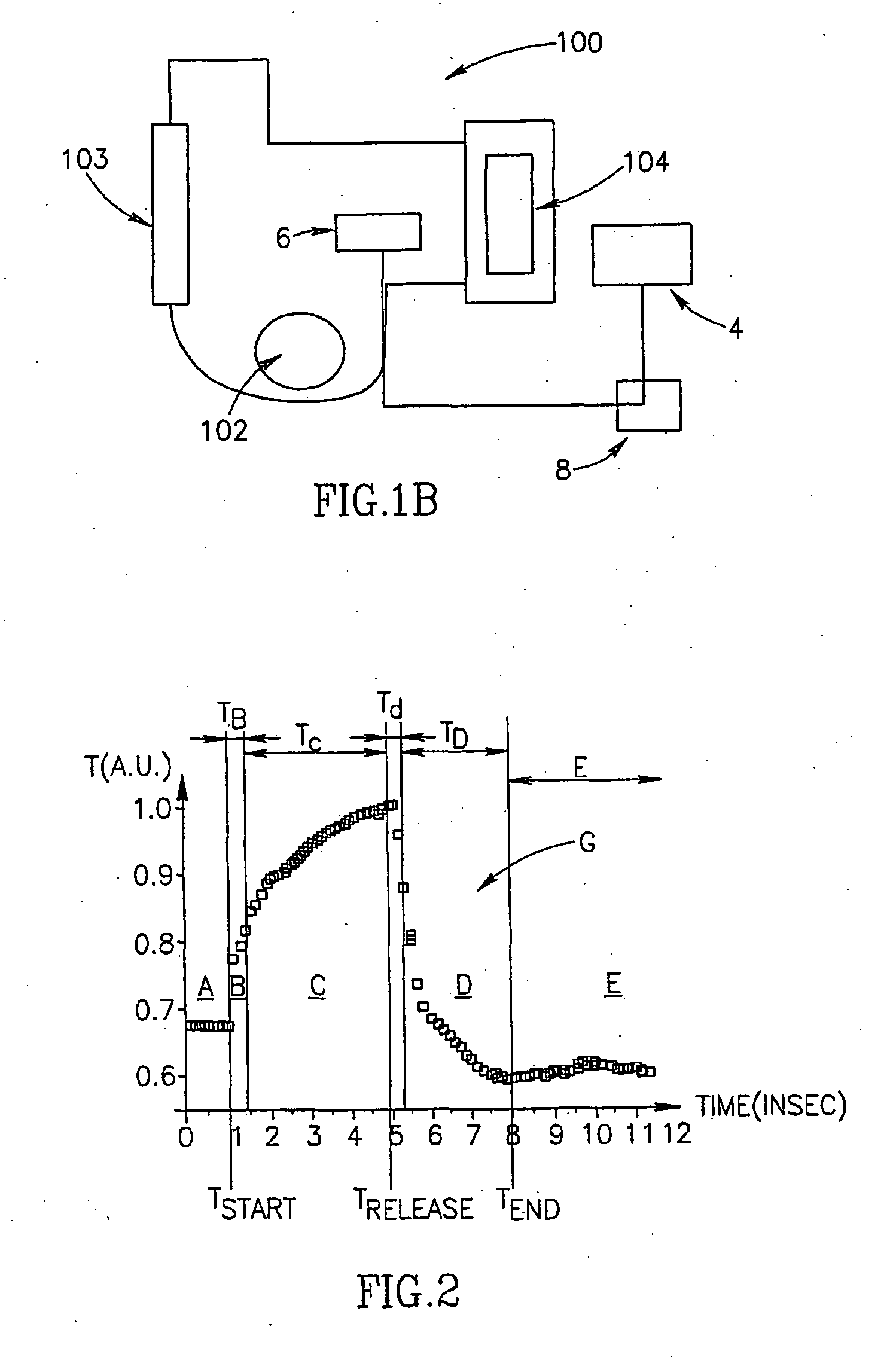
Method of optical measurements for determining various parameters of the patient's blood
InactiveUS7043289B2Improve accuracyAccurate informationEvaluation of blood vesselsMonitoring particle agglomerationRed blood cellMedicine
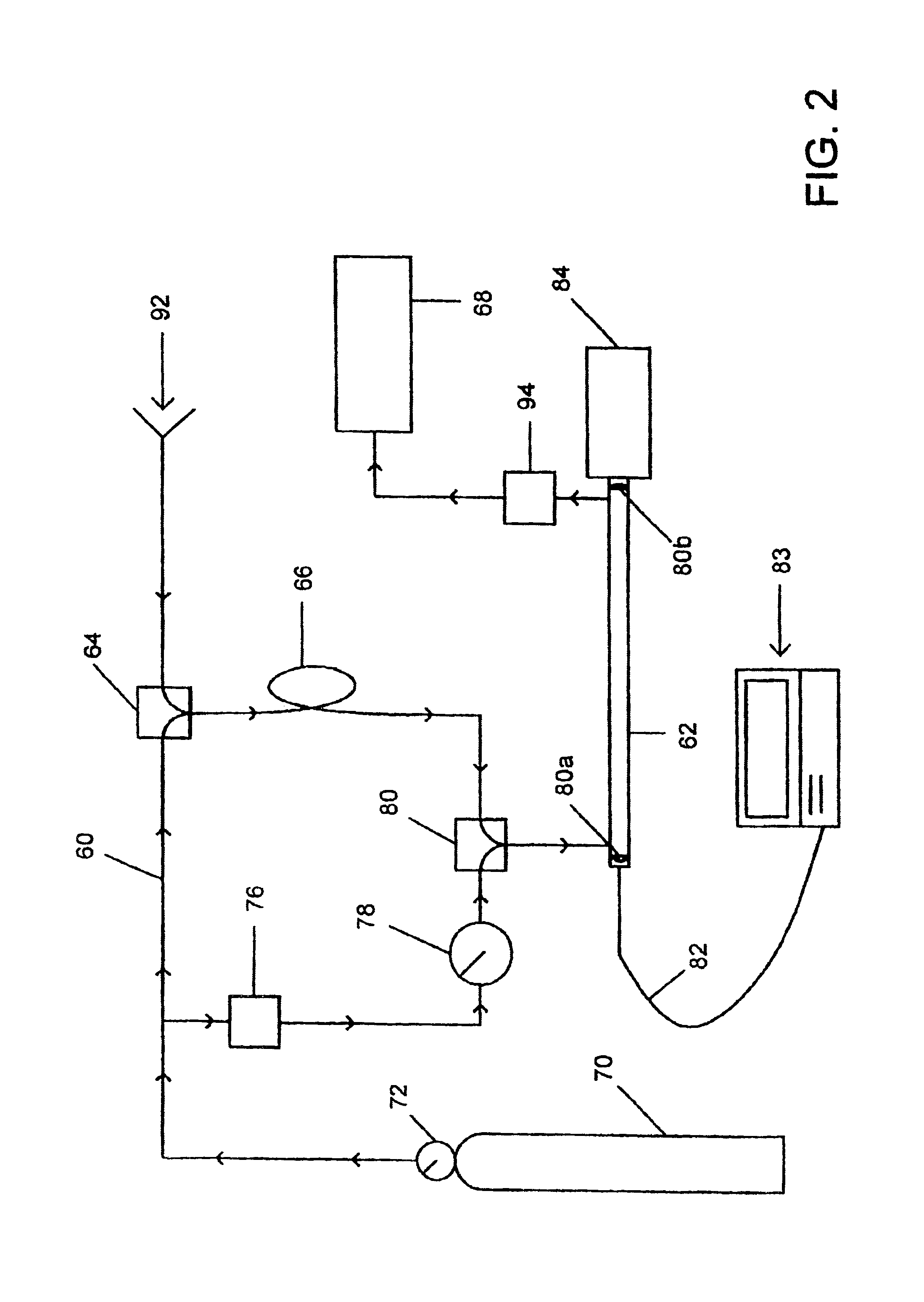
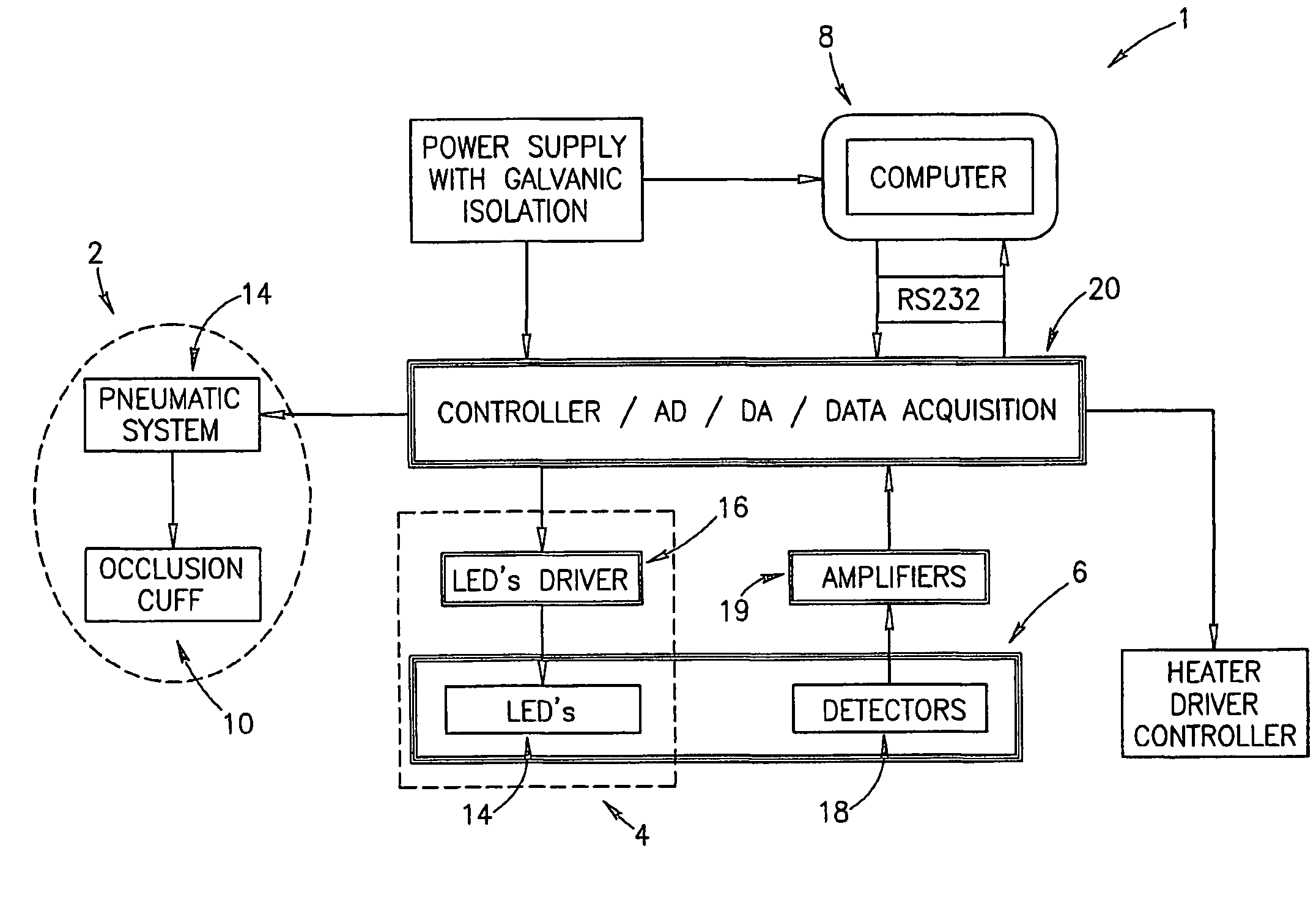
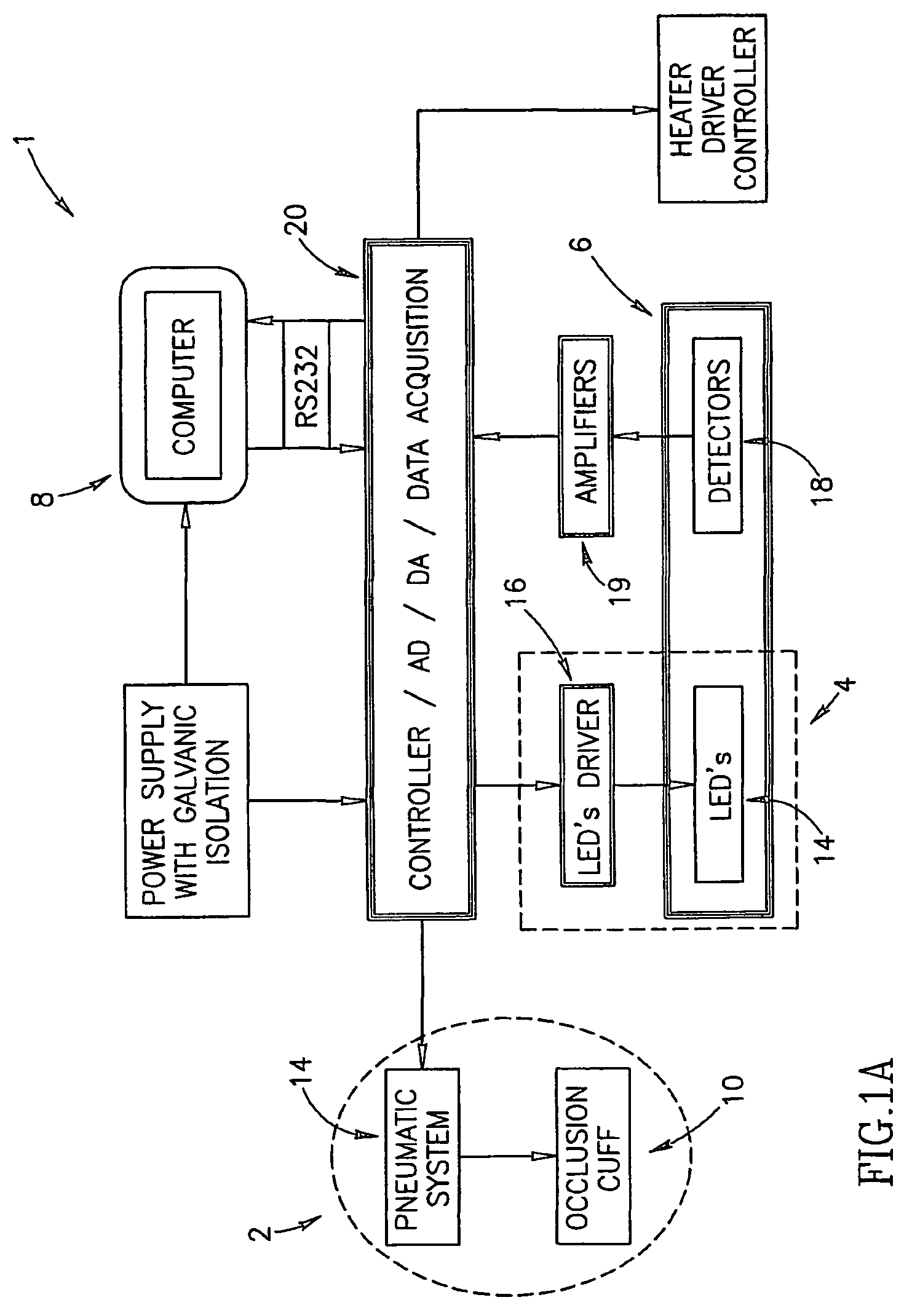
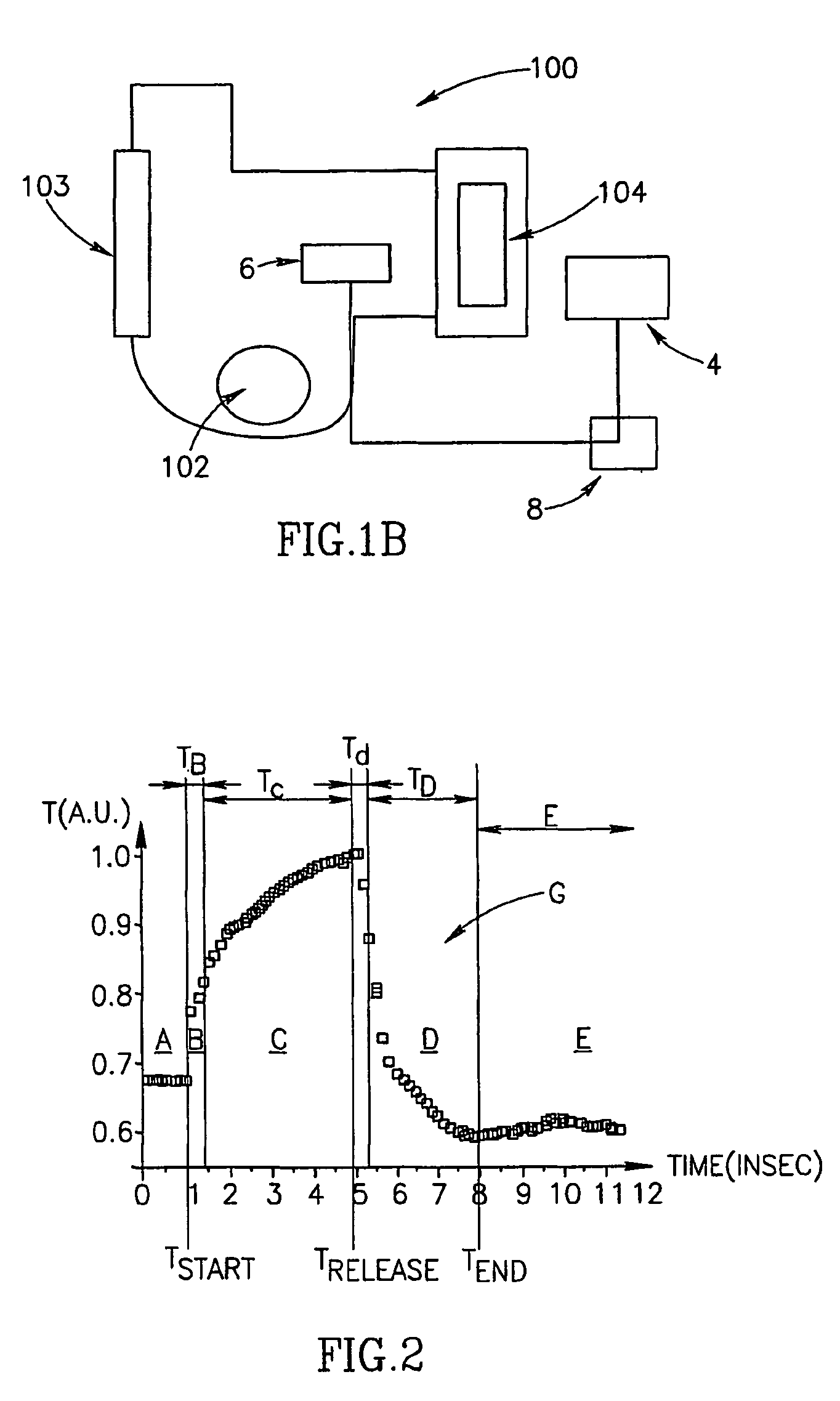
A method for optical measurements of desired parameters of the patient's blood is presented. A state of the blood flow cessation is provided within a measurement region and maintained during a predetermined time period. Measurement sessions are performed within this predetermined time period. Each measurement session includes at least two measurements with different wavelengths of incident light. Obtained measured data is representative of the time dependence of light response of the blood in the measurement region. The analyses of the measured data enables the determination of the desired blood parameters extracted from optical characteristics associated with the erythrocytes aggregation process during the state of the blood flow cessation.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
Method and apparatus for detecting and counting platelets individually and in aggregate clumps
ActiveUS7929121B2Accurate countShorten the counting processBiological particle analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescenceGranularity
A method for enumerating platelets within a blood sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: 1) depositing the sample into an analysis chamber adapted to quiescently hold the sample for analysis, the chamber defined by a first panel and a second panel, both of which panels are transparent; 2) admixing a colorant with the sample, which colorant is operative to cause the platelets to fluoresce upon exposure to one or more predetermined first wavelengths of light; 3) illuminating at least a portion of the sample containing the platelets at the first wavelengths; 4) imaging the sample, including producing image signals indicative of fluorescent emissions from the platelets, which fluorescent emissions have an intensity; 5) identifying the platelets by their fluorescent emissions, using the image signals; 6) determining an average fluorescent emission intensity value for the individual platelets identified within the sample; 7) identifying clumps of platelets within the sample using one or more of their fluorescent emissions, area, shape, and granularity; and 8) enumerating platelets within each platelet clump using the average fluorescent emission intensity value determined for the individual platelets within the sample.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Method and device for reading an emulsion
ActiveUS20110188717A1Character and pattern recognitionMonitoring particle agglomerationMicroreactorComputer science
A method for reading an emulsion (3) including droplets and a continuous phase surrounding the droplets, the method includes:two-dimensional scanning of the emulsion (3), andconstruction of a two-dimensional image of the emulsion (3) based on the scanning. Preferably, the droplets do not move during scanning, for example by solidifying the continuous phase or by using a two-dimensional compact or semi-compact network of droplets. The method can further include time-based monitoring of a chemical or biological reaction taking place in at least one of the droplets. A device implementing this method is also described. The method is applicable for the detection and / or sorting of microdroplets performing the role of microreactors or containing specific cells or molecules, in fields such as gene expression or diagnosis.
Owner:ECOLE SUPERIEURE DE PHYSIQUE & DE CHIM IND DE LA VILLE DE PARIS +1
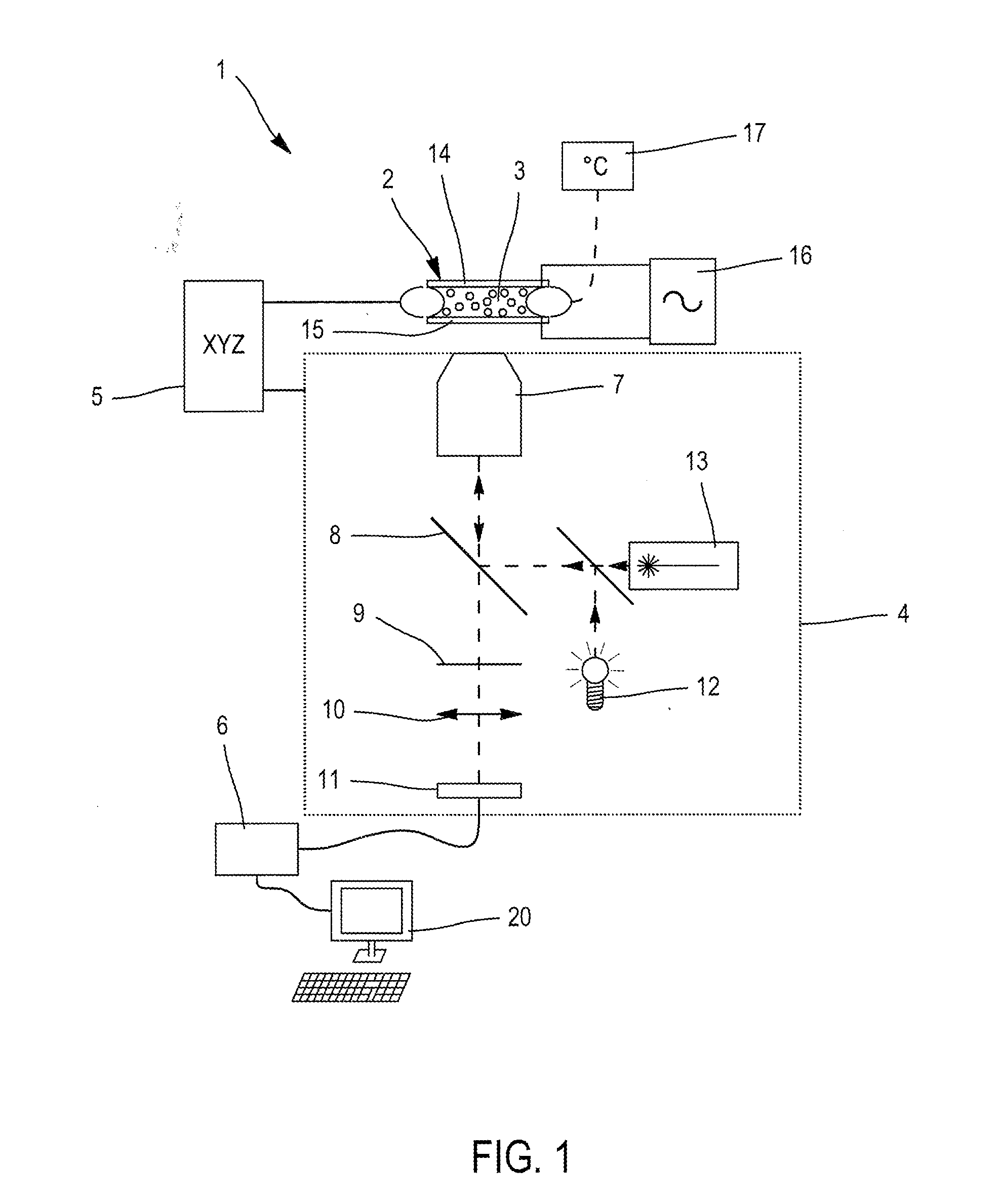
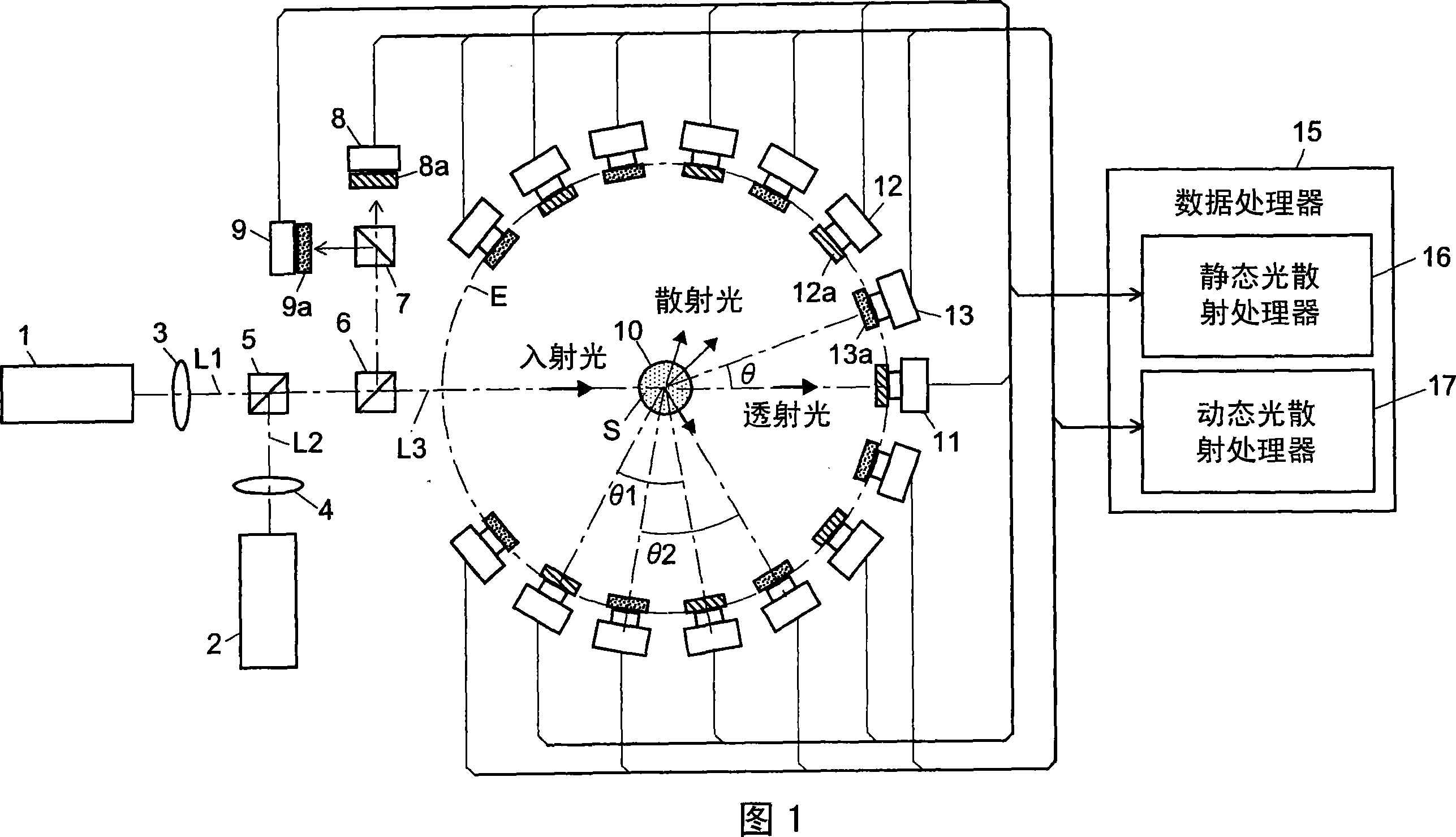
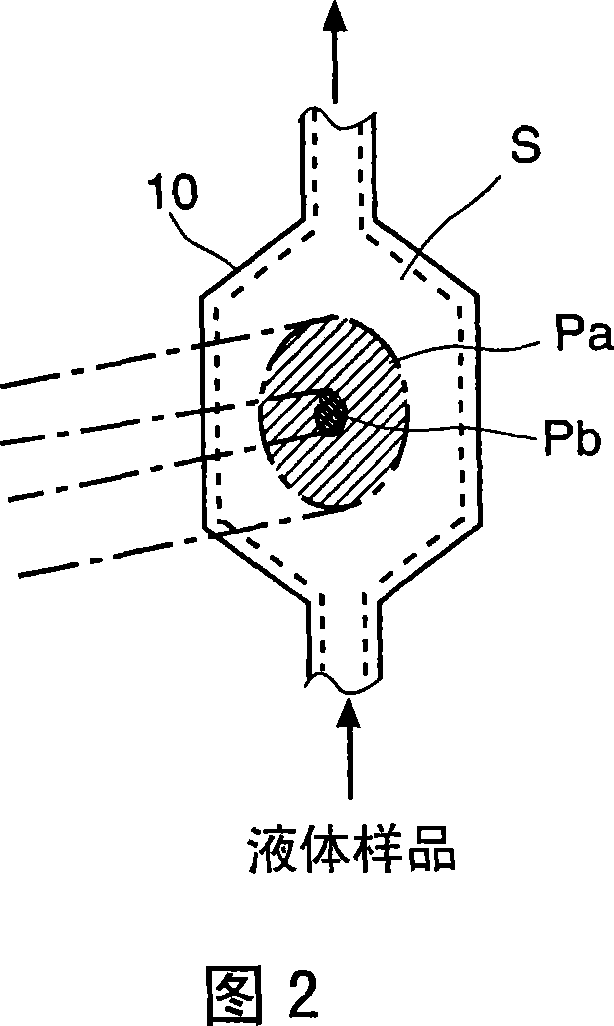
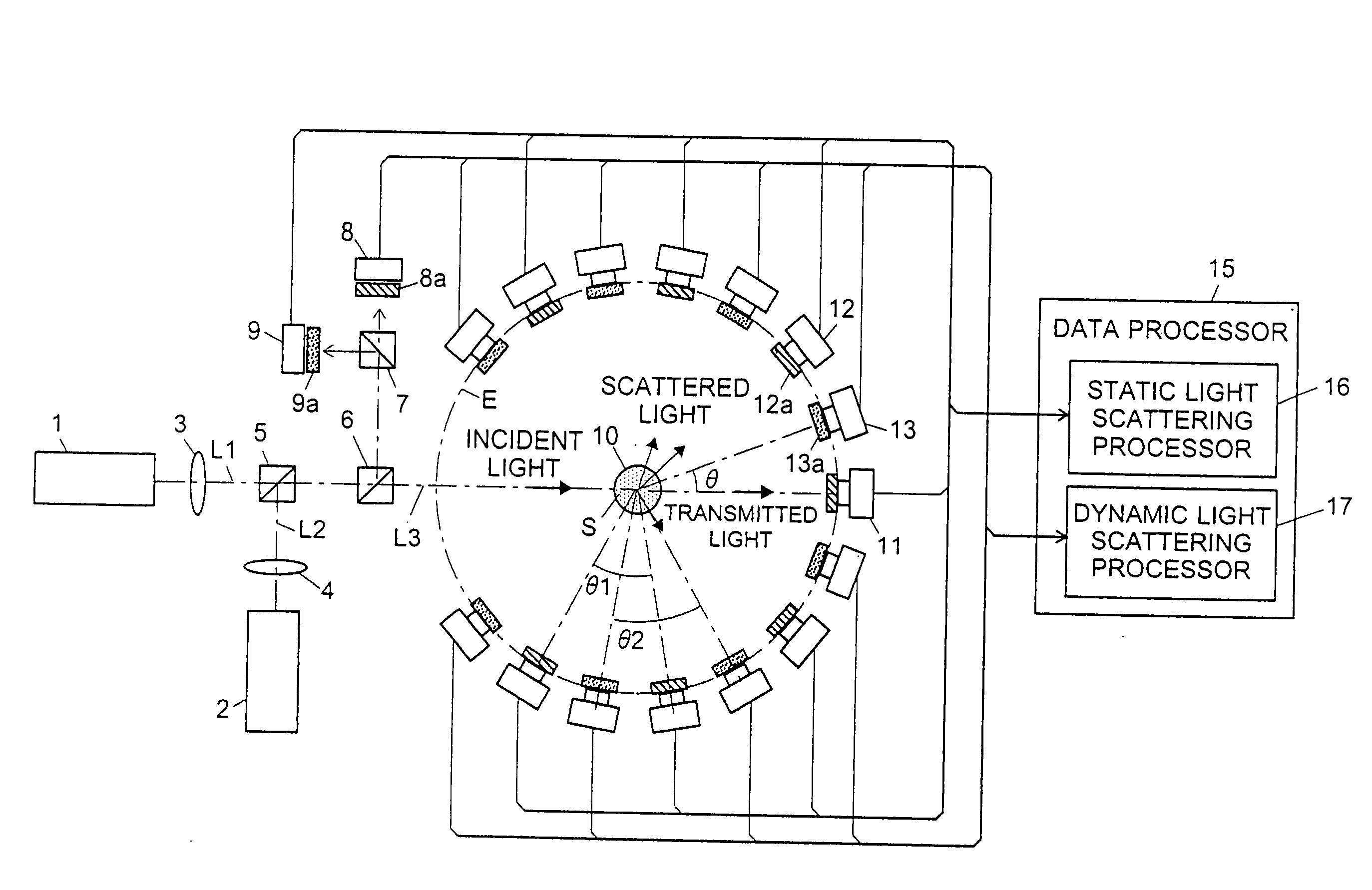
Light scattering detector
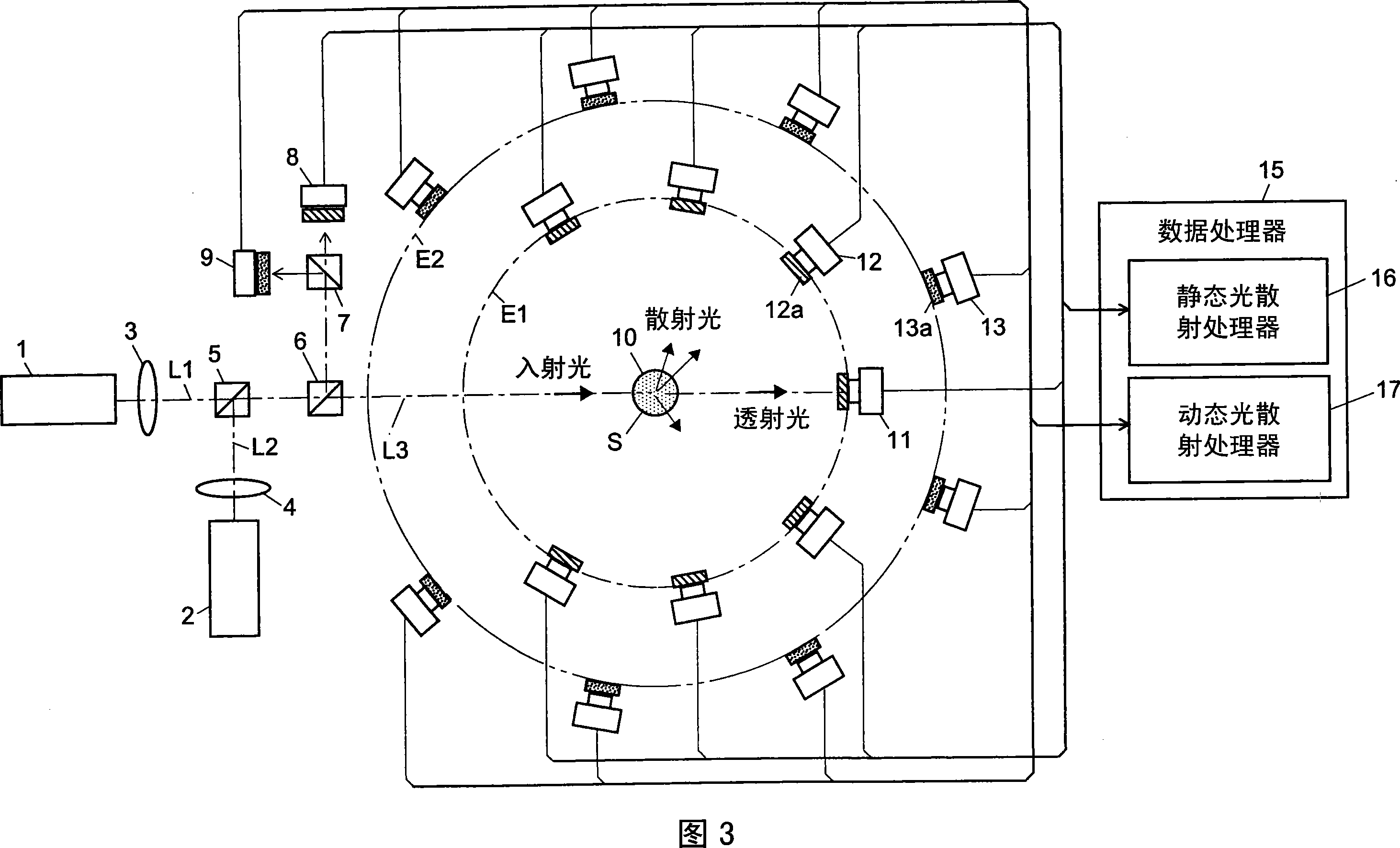
InactiveCN101118210AEasy to measureEliminates the problem of missed detectionsScattering properties measurementsMonitoring particle agglomerationChemical physicsBeam splitter
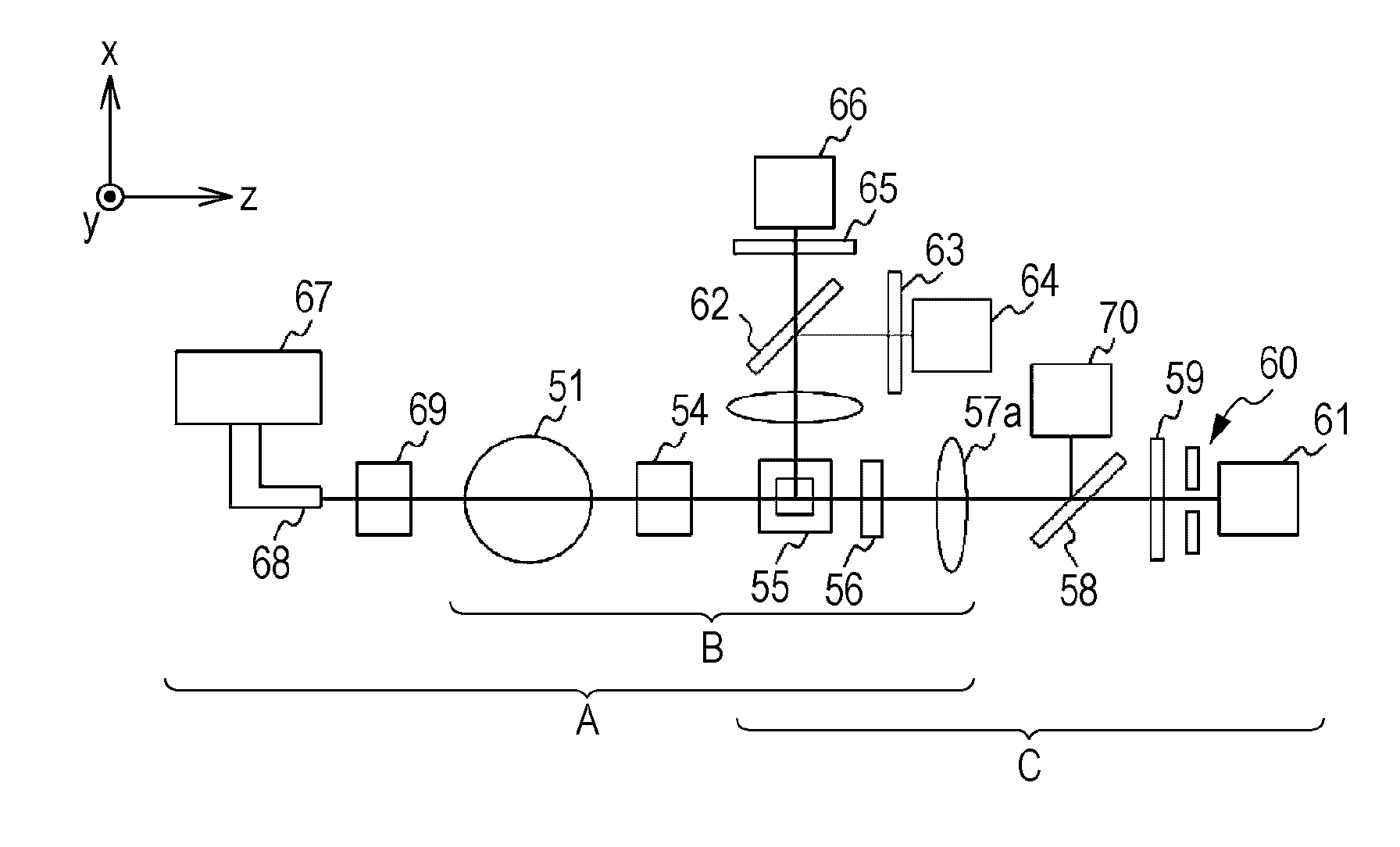
The light scattering detector according to the present invention aims at simultaneously measuring the molecular weight and size of particles having varieties of diameters. This detector facilitates the measurement operation and knowing how particles associate or dissociate as time progresses. In this detector, the emitted light (static light scattering measurement light) having a first wavelength by the first light source and the emitted light (dynamic light scattering measurement light) having a second wavelength which is different from the first wavelength by the second light source are combined by a beam splitter 5 and coaxially directed onto the sample sell 10 to which a liquid sample S is supplied. While the irradiated area by the static light scattering measurement light is large, the irradiated area by the dynamic light scattering measurement light, which is coherent light, is narrow. Detectors 12 which selectively detect the first wavelength and detectors 13 which selectively detect the second wavelength are placed so as to encircle the sample cell 10. The detection signals by the detectors 11, 12 and the detection signals by the detectors 13 are separately mathematically-operated by a data processor 15 to calculate the molecule weight and size of the particles in the sample S.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
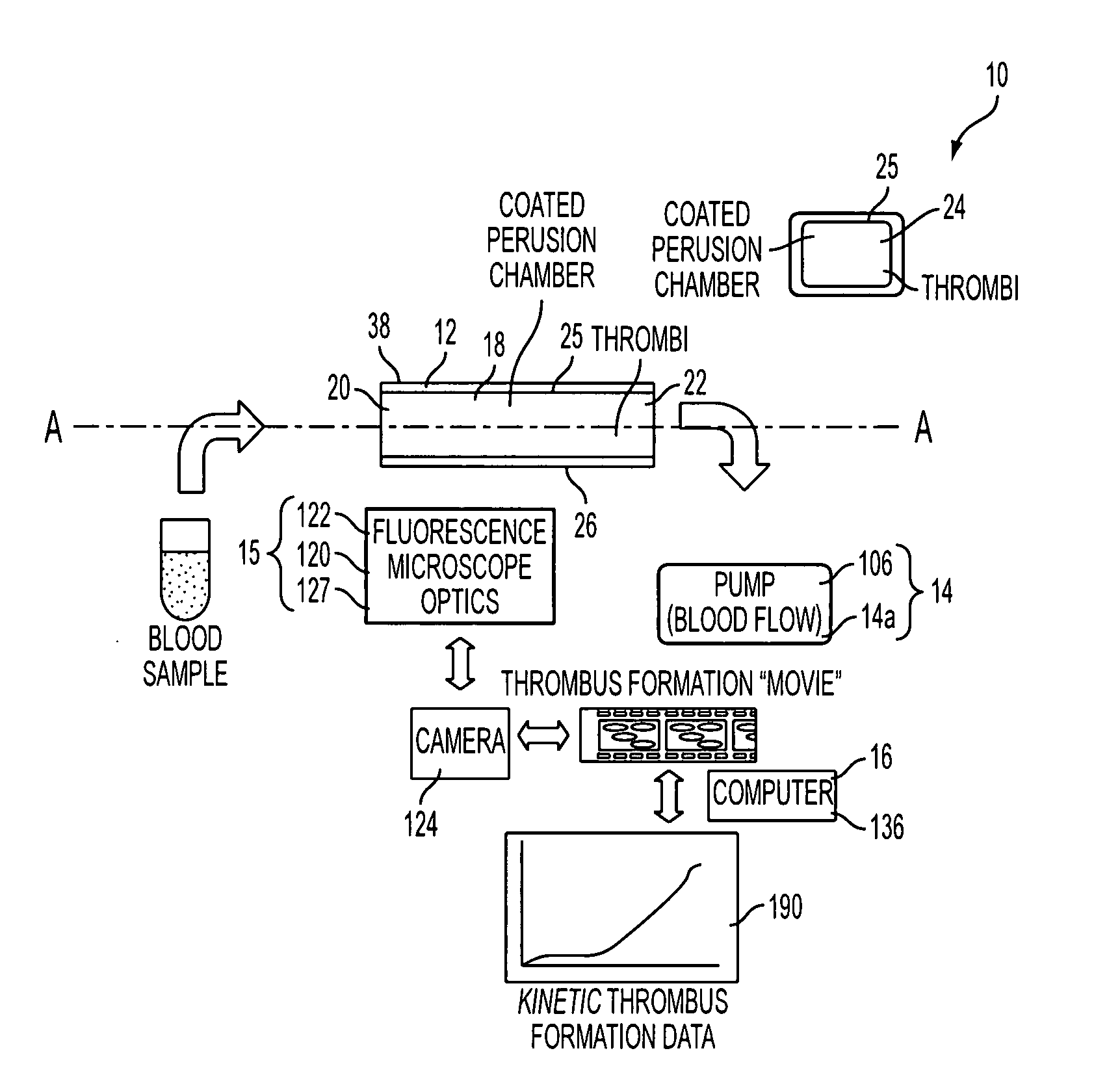
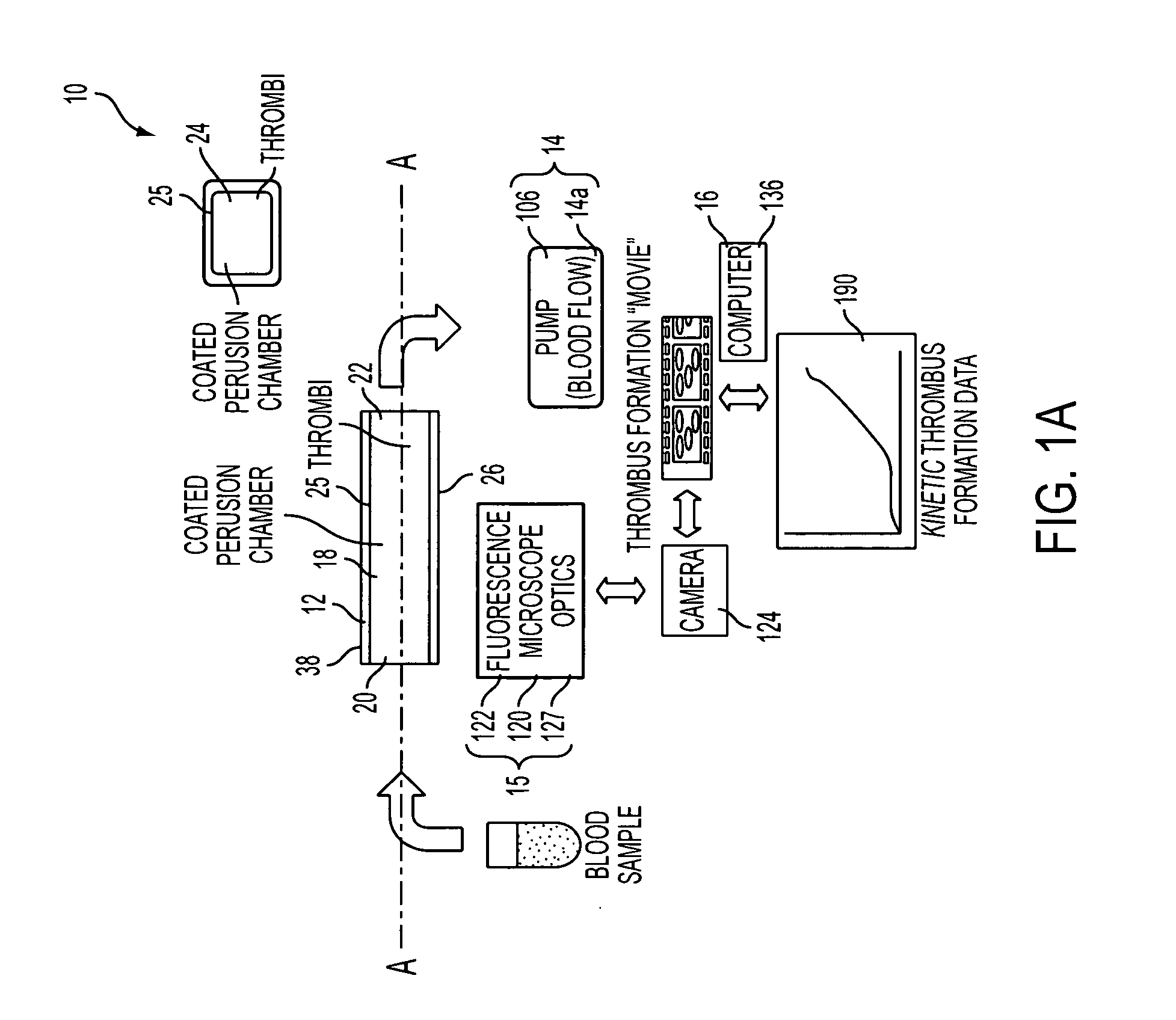
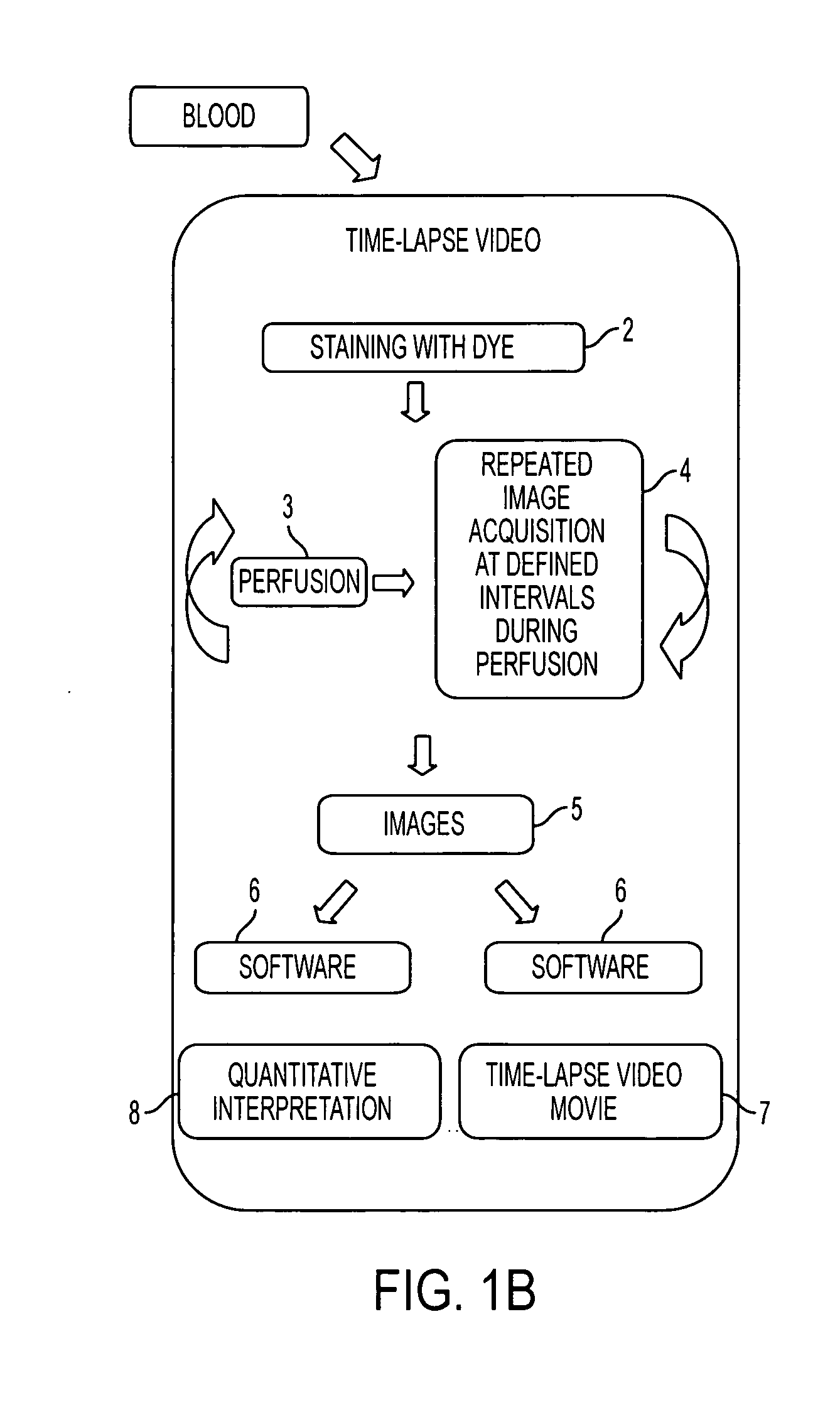
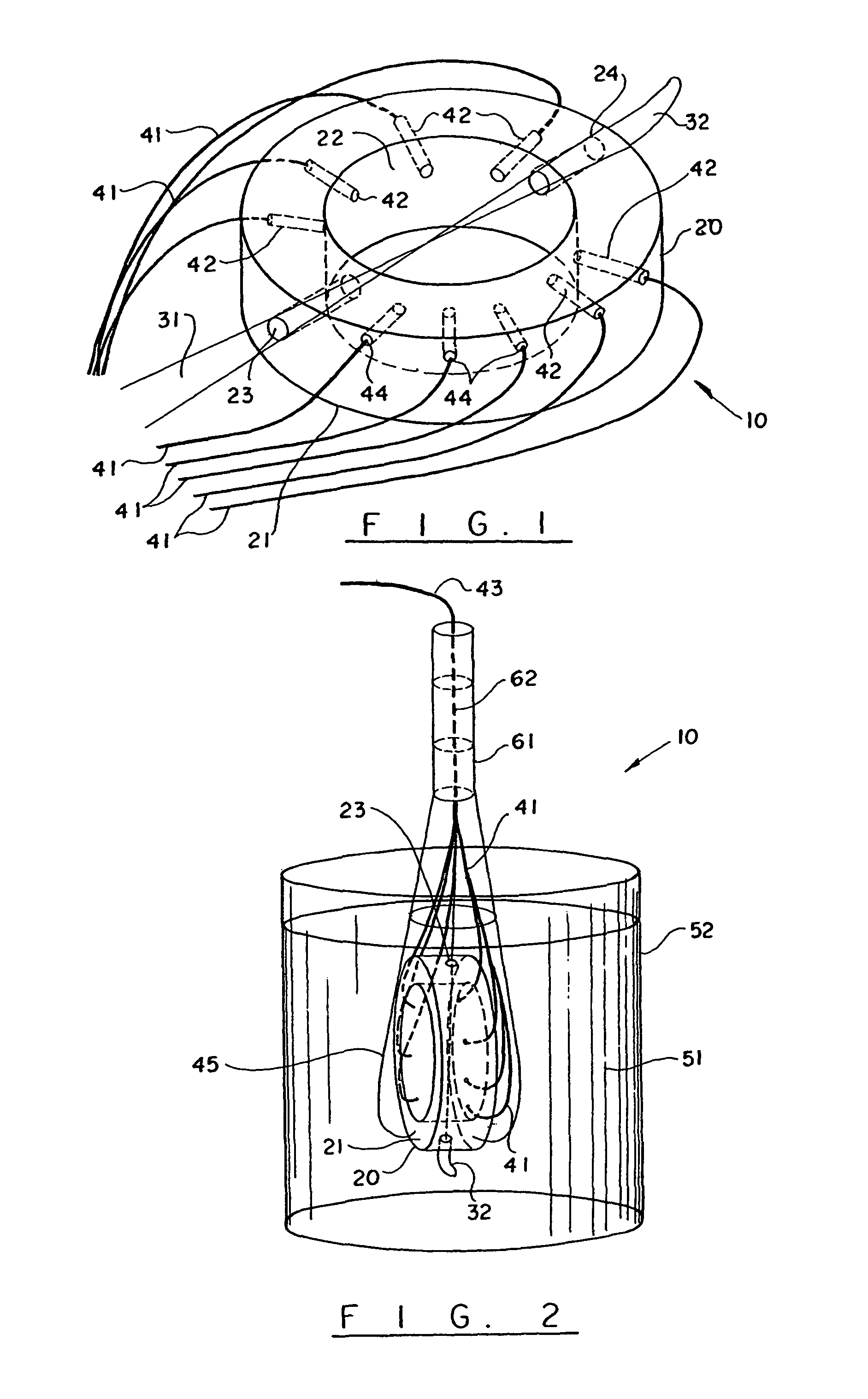
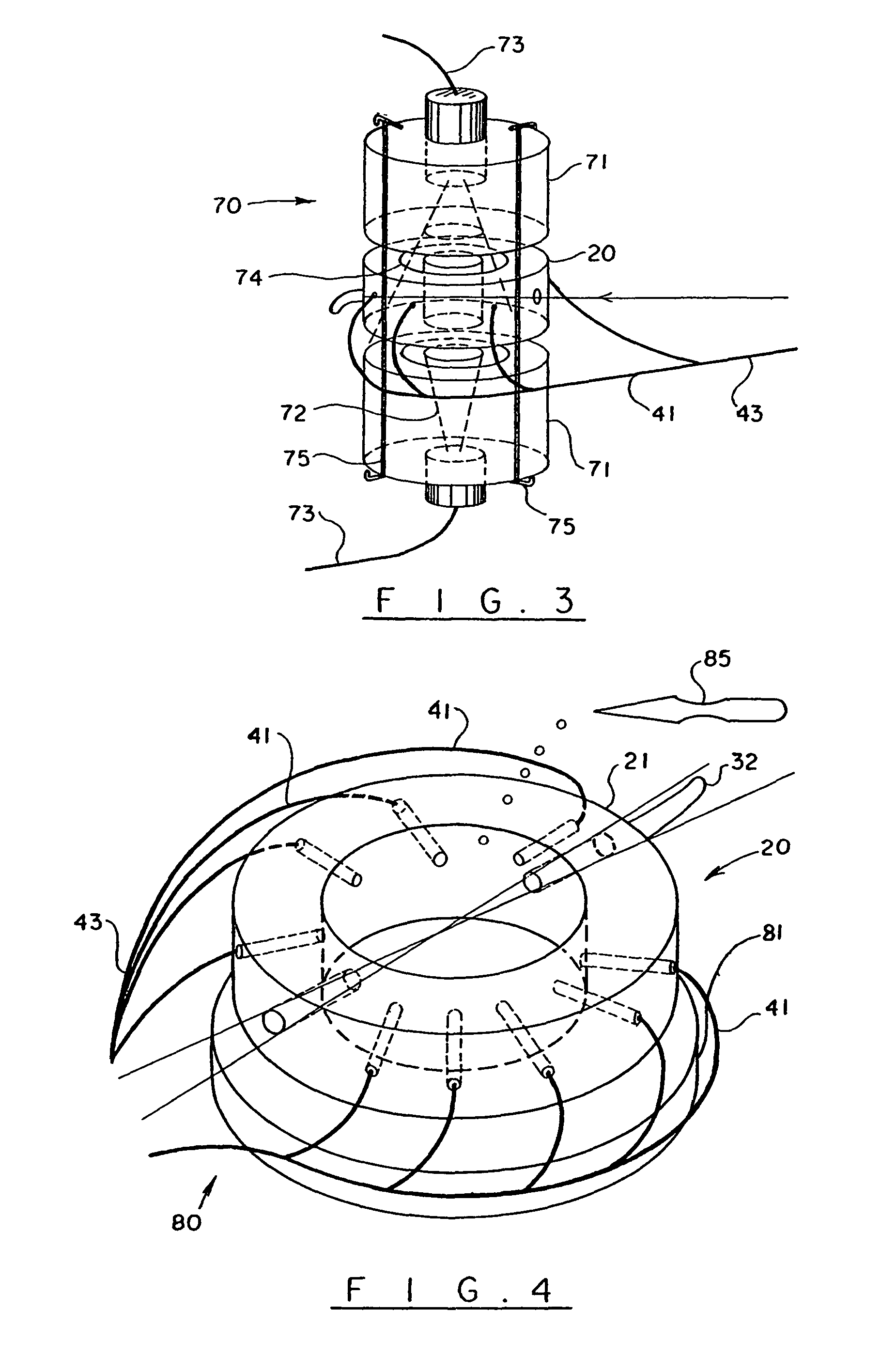
Device for aggregating, imaging and analyzing thrombi and a method of use
An instrument for capturing an image of thrombus formation, blood coagulation, recruitment of circulating inflammatory or tumour cells in a blood sample. The instrument comprises a member defining a channel therethrough, a fluid handling assembly that permits the blood sample to move through the channel at a flow rate, and an imaging assembly including a microscopy device. The imaging assembly is disposed relative to the channel so as to capture light rays defining the image of thrombus formation in the channel.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
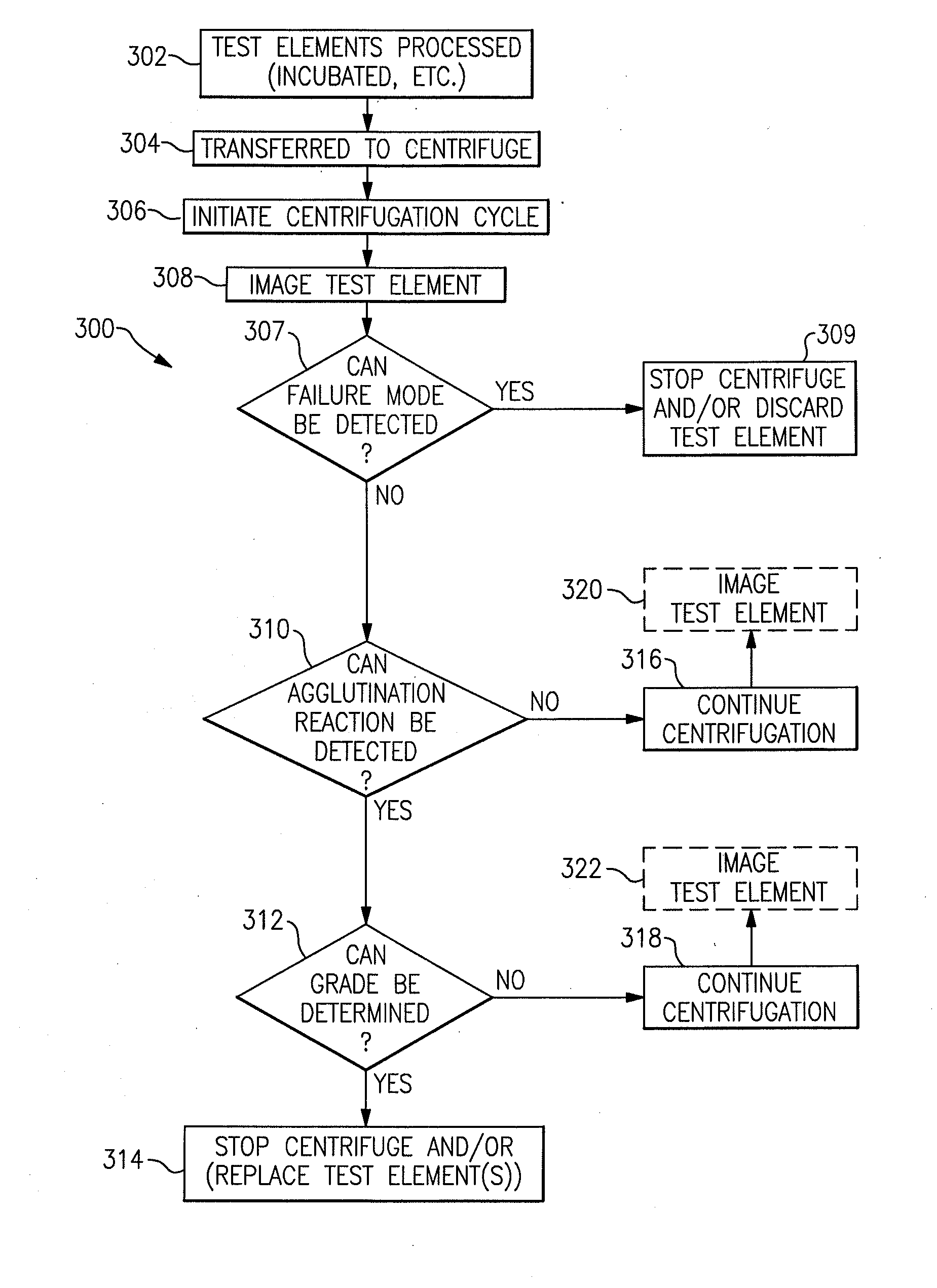
Immunodiagnostic test apparatus having at least one imager to provide agglutination evaluations during centrifugration cycle
InactiveUS20090274348A1Save a lot of timeSimple designCharacter and pattern recognitionMonitoring particle agglomerationCentrifugationEngineering
An immunodiagnostic testing apparatus includes a centrifuge and an imager disposed in relation to the centrifuge wherein at least one image is captured of at least one test element in advance of a complete centrifugation period in order to provide predictive data concerning the presence of an agglutination reaction or failure mode of the apparatus or test element.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
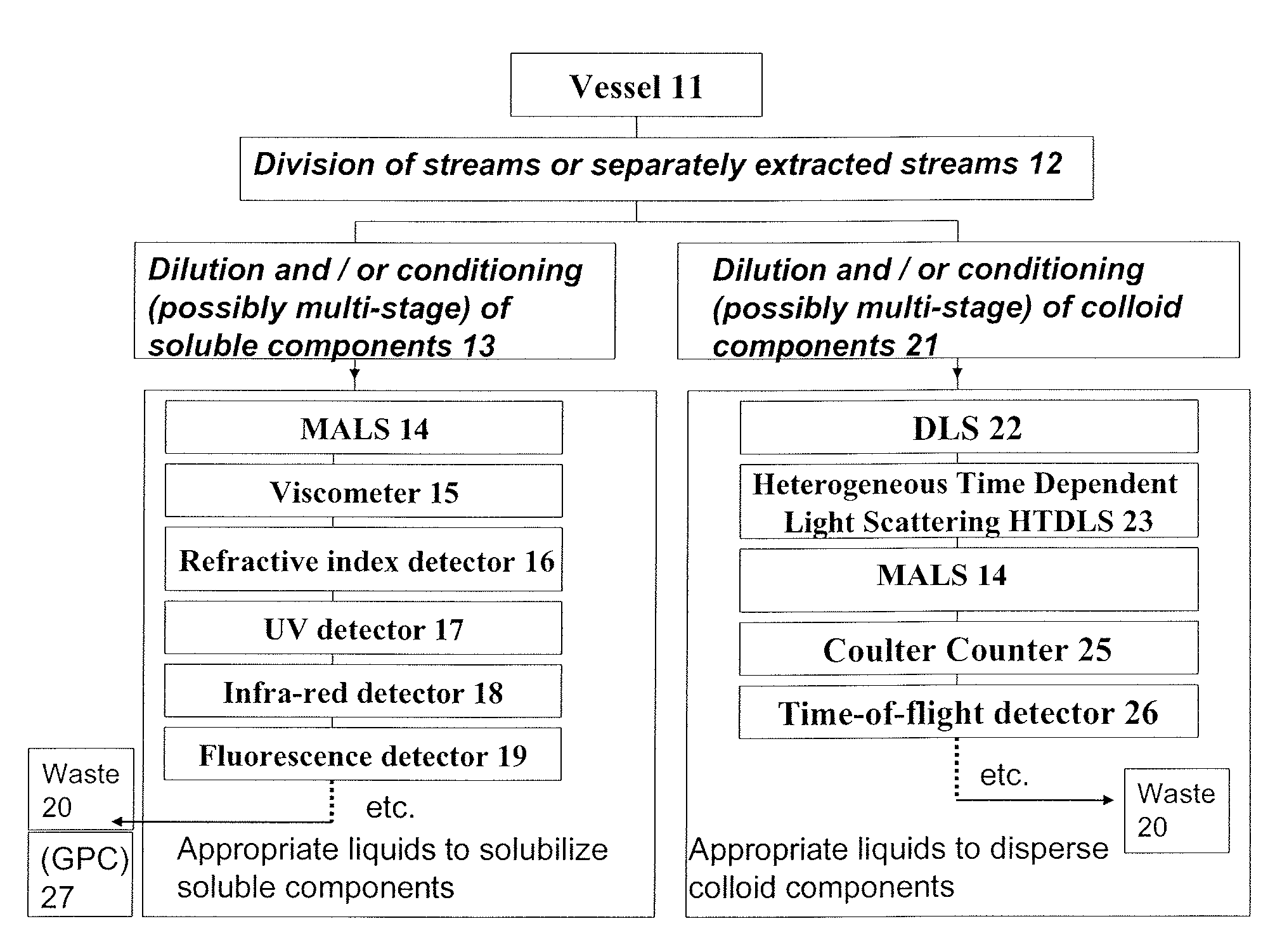
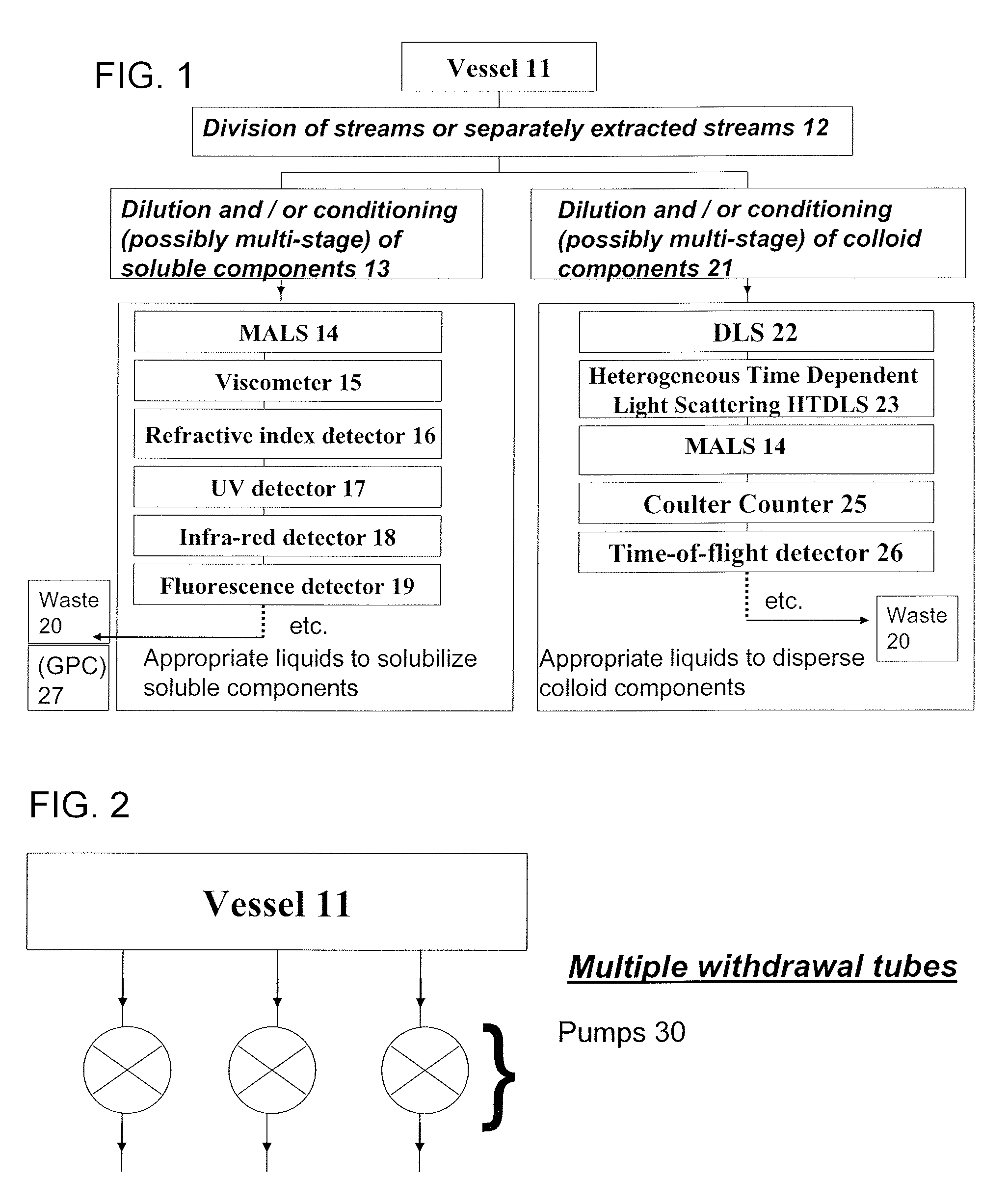
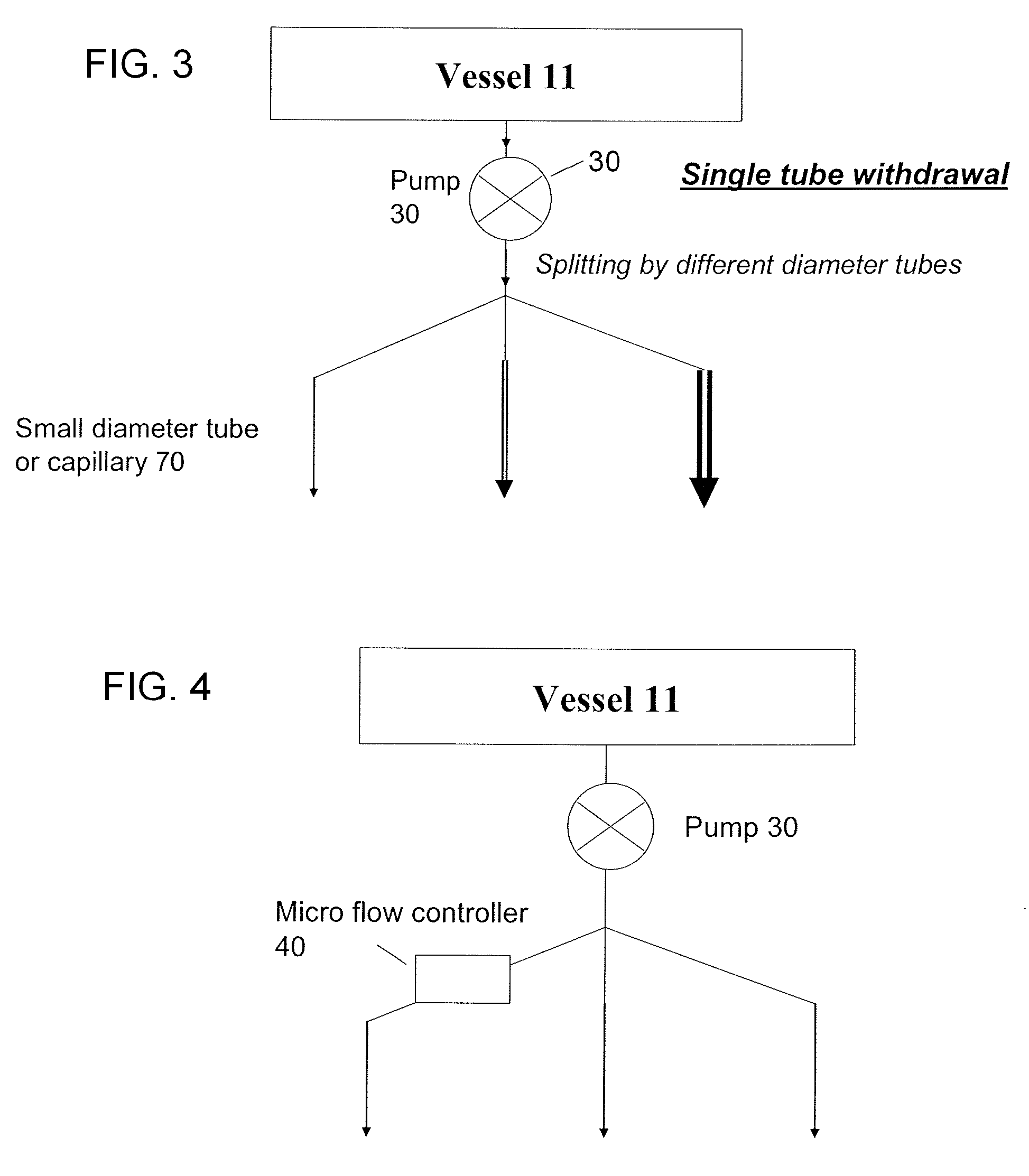
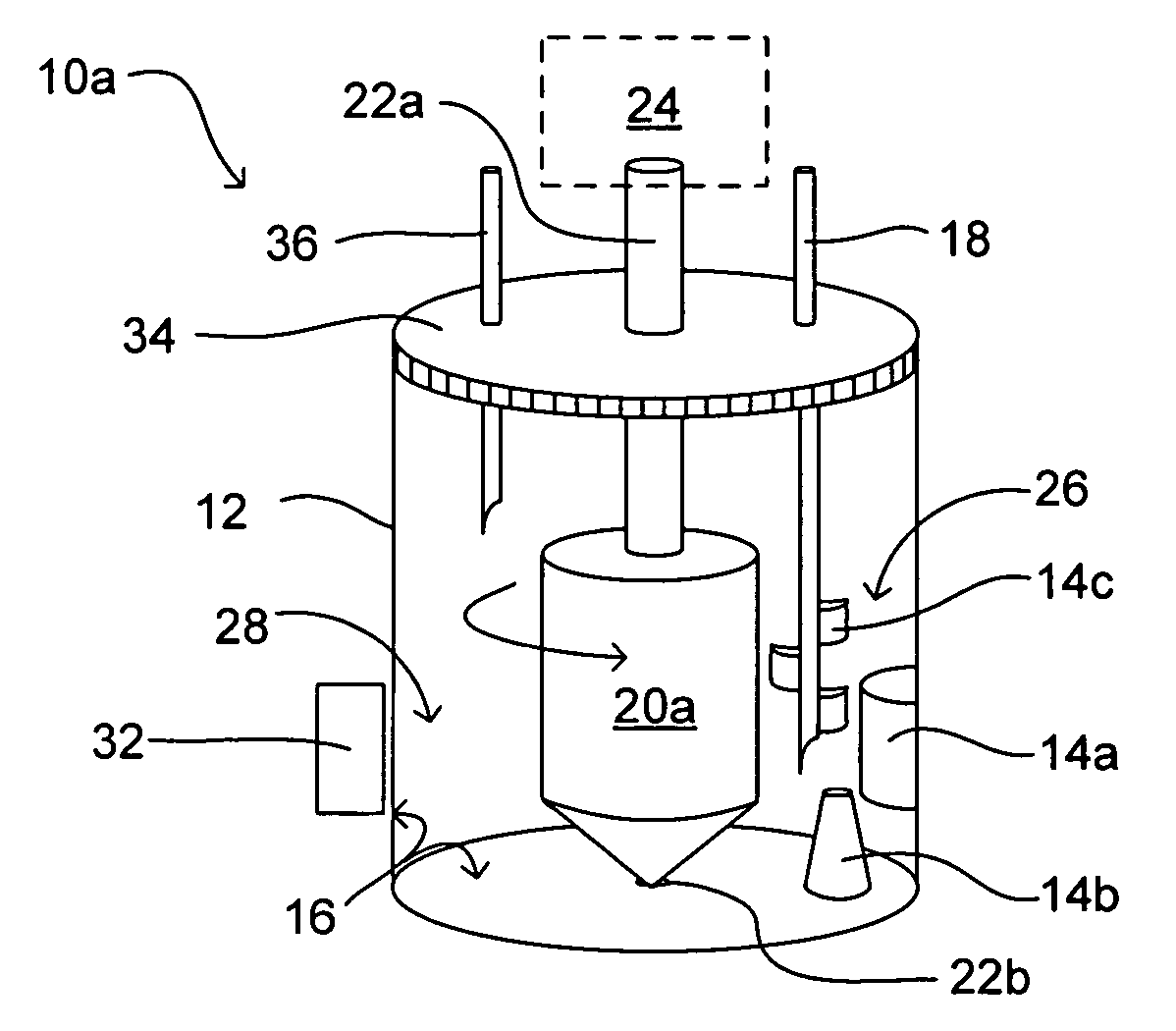
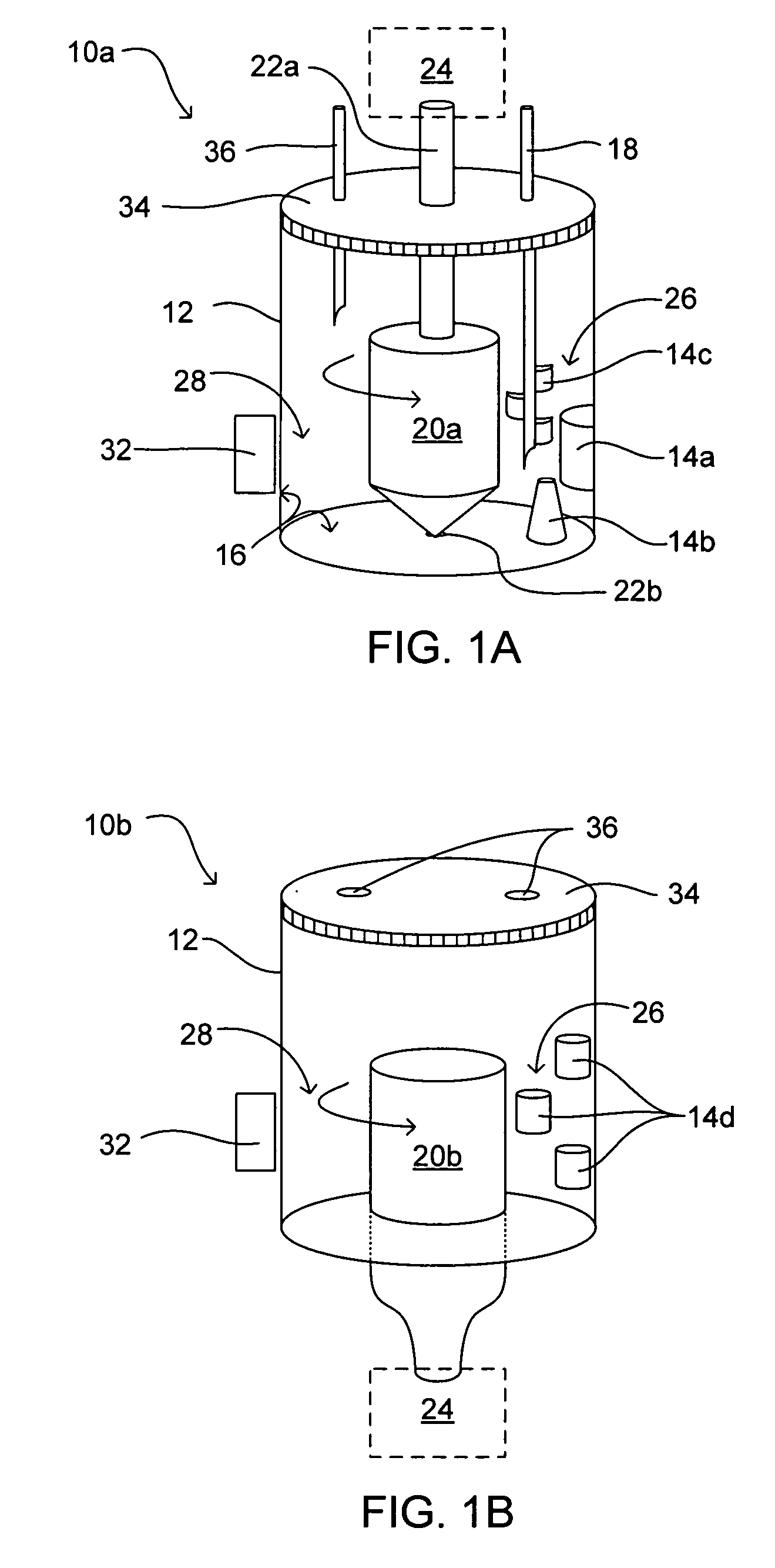
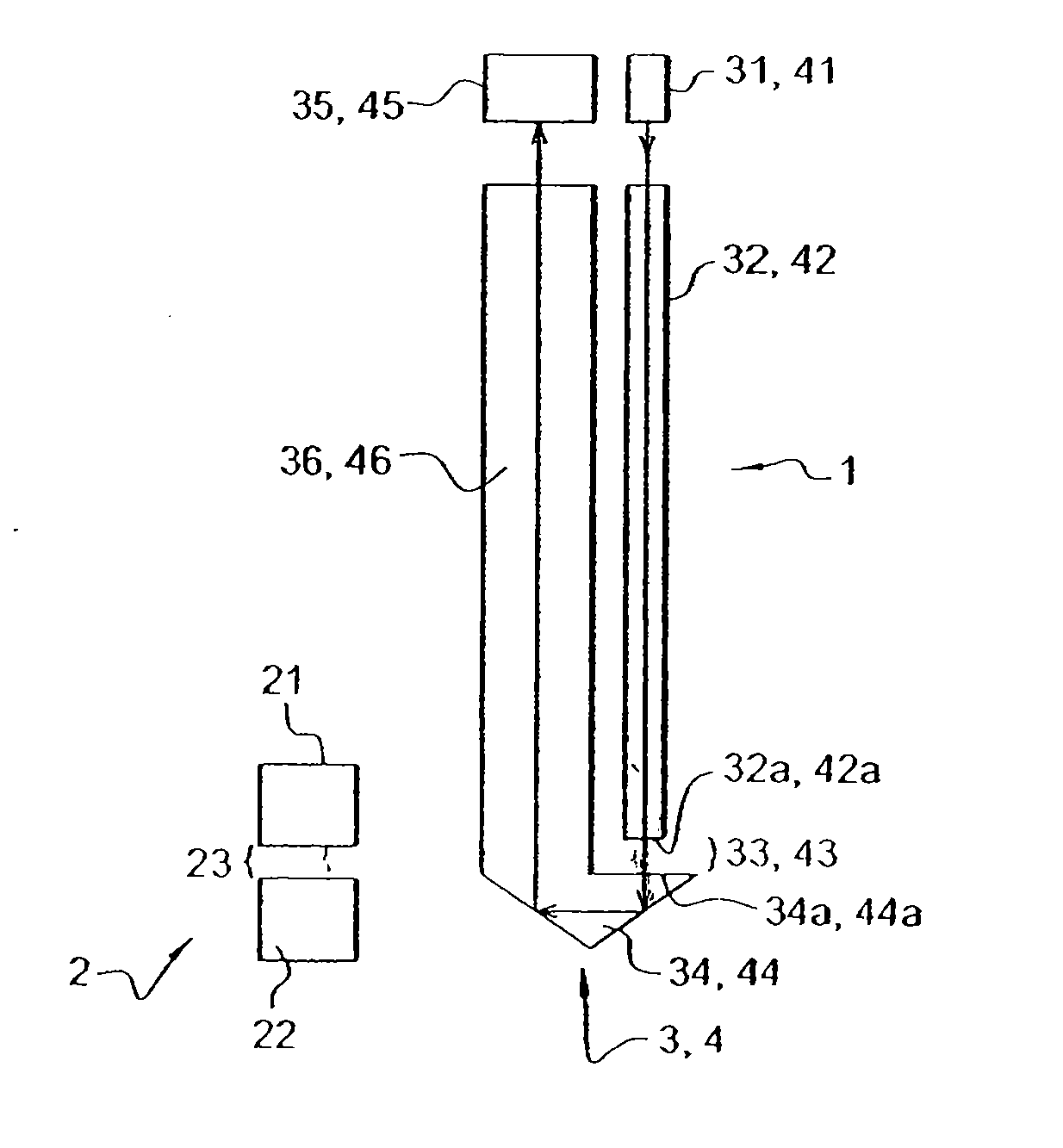
Methods and devices for simultaneously monitoring the characteristics of microscopic particles in suspension and the characteristics of soluble components during reactions
A method and apparatus for continuously extracting liquid in at least two separate streams from a vessel, continuously diluting and / or conditioning a first stream in one or more stages, producing, as a result of the extraction, dilution and / or conditioning, the first stream consisting of a dispersion of particles to be characterized, and diluting and / or conditioning a second stream, the second stream consisting of soluble components; and subjecting the first and second streams to various characterizing measurements.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Portable contaminant sampling system
InactiveUS7100461B2High microbial recoveryEfficient and non-destructiveWithdrawing sample devicesMonitoring particle agglomerationParticulatesMicroorganism
The invention is a portable sampling system for sampling various media for contaminants. The media sample can include gases, liquids, and dry powders. The contaminant sample can include gaseous components, particulates of various kinds, and microorganisms. The system can be used to sample the surfaces of fruits and vegetables, meat carcasses, the interior of envelopes of other containers, gases in rooms or containers, and surfaces such as countertops, a vehicle exterior, skin, and clothing.
Owner:MICROBIAL VAC SYST
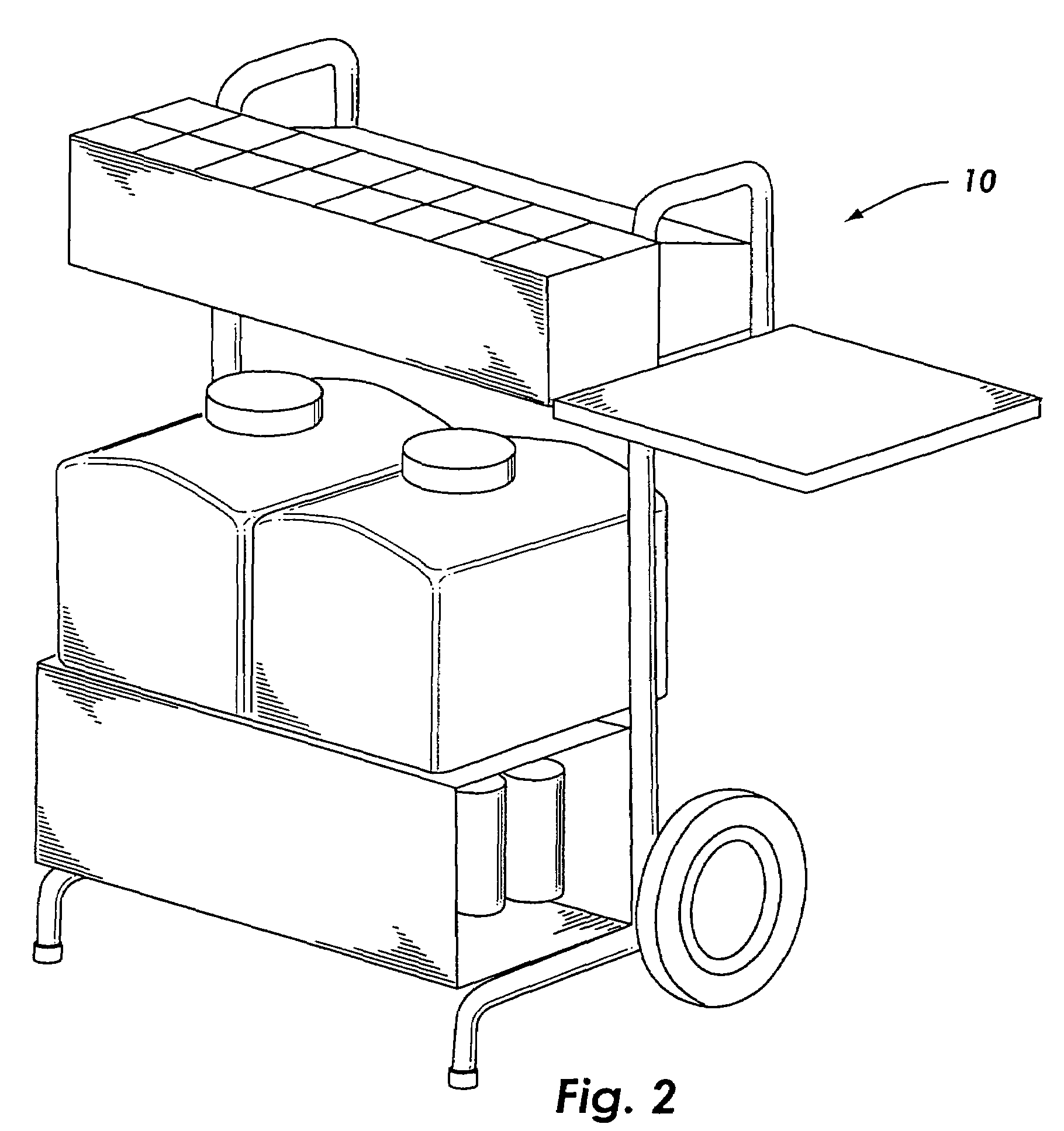
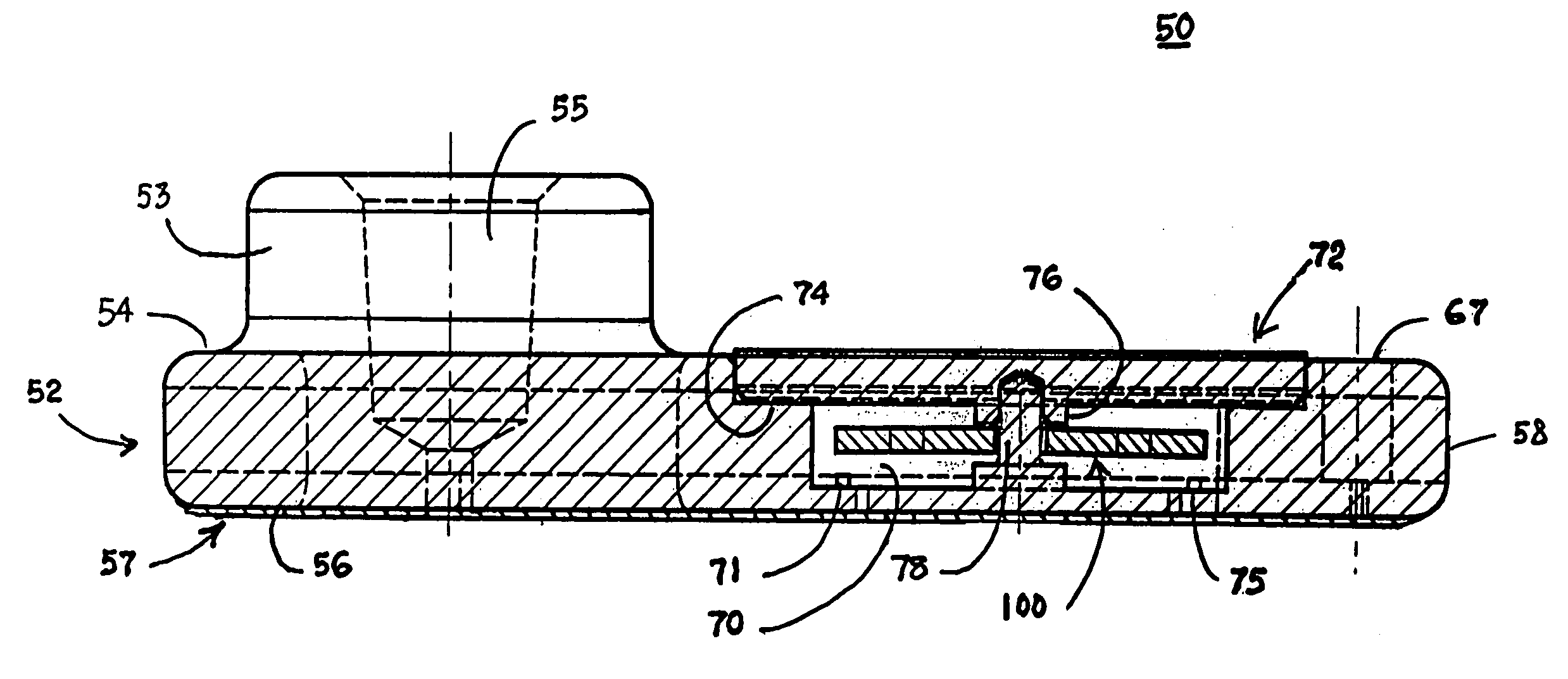
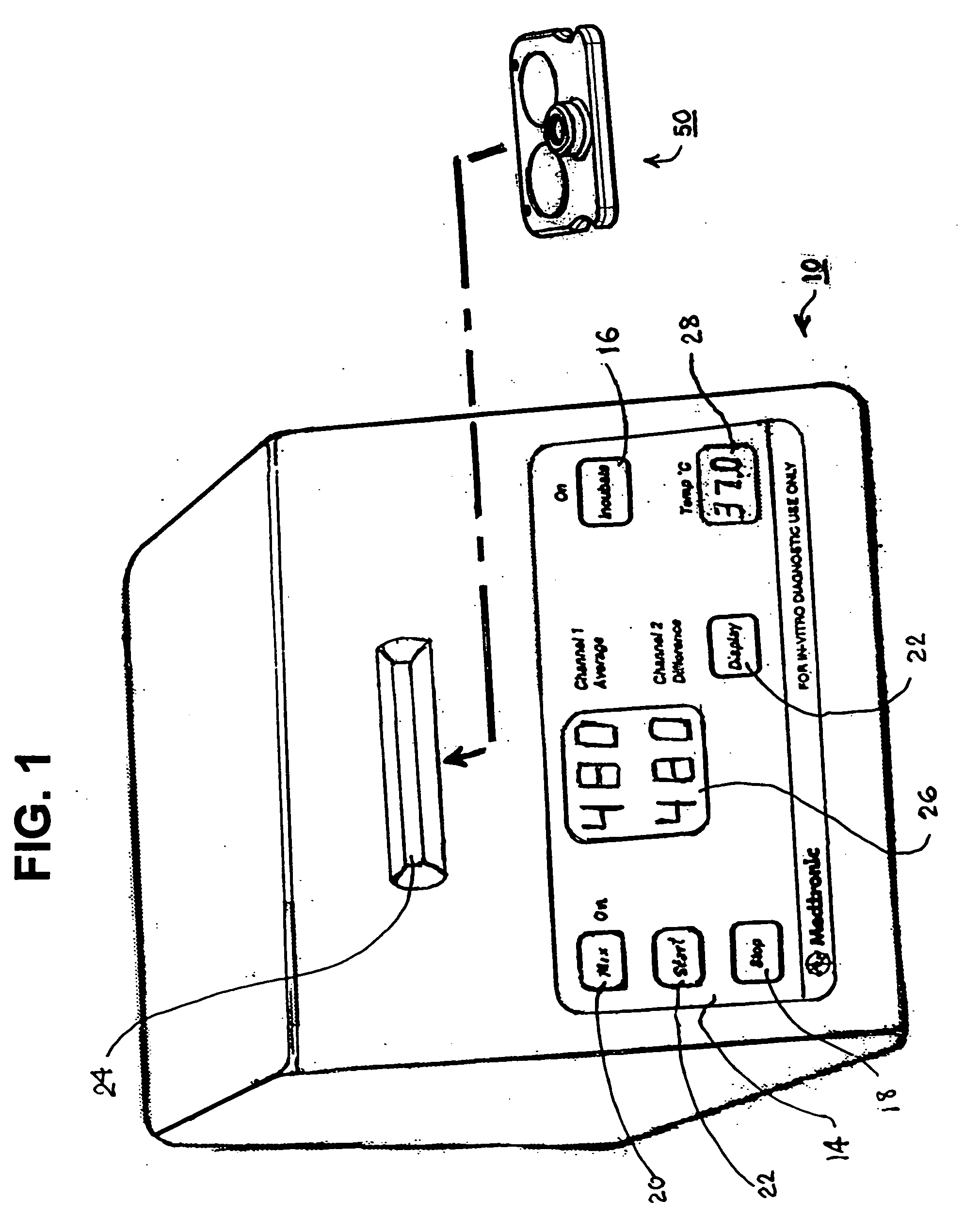
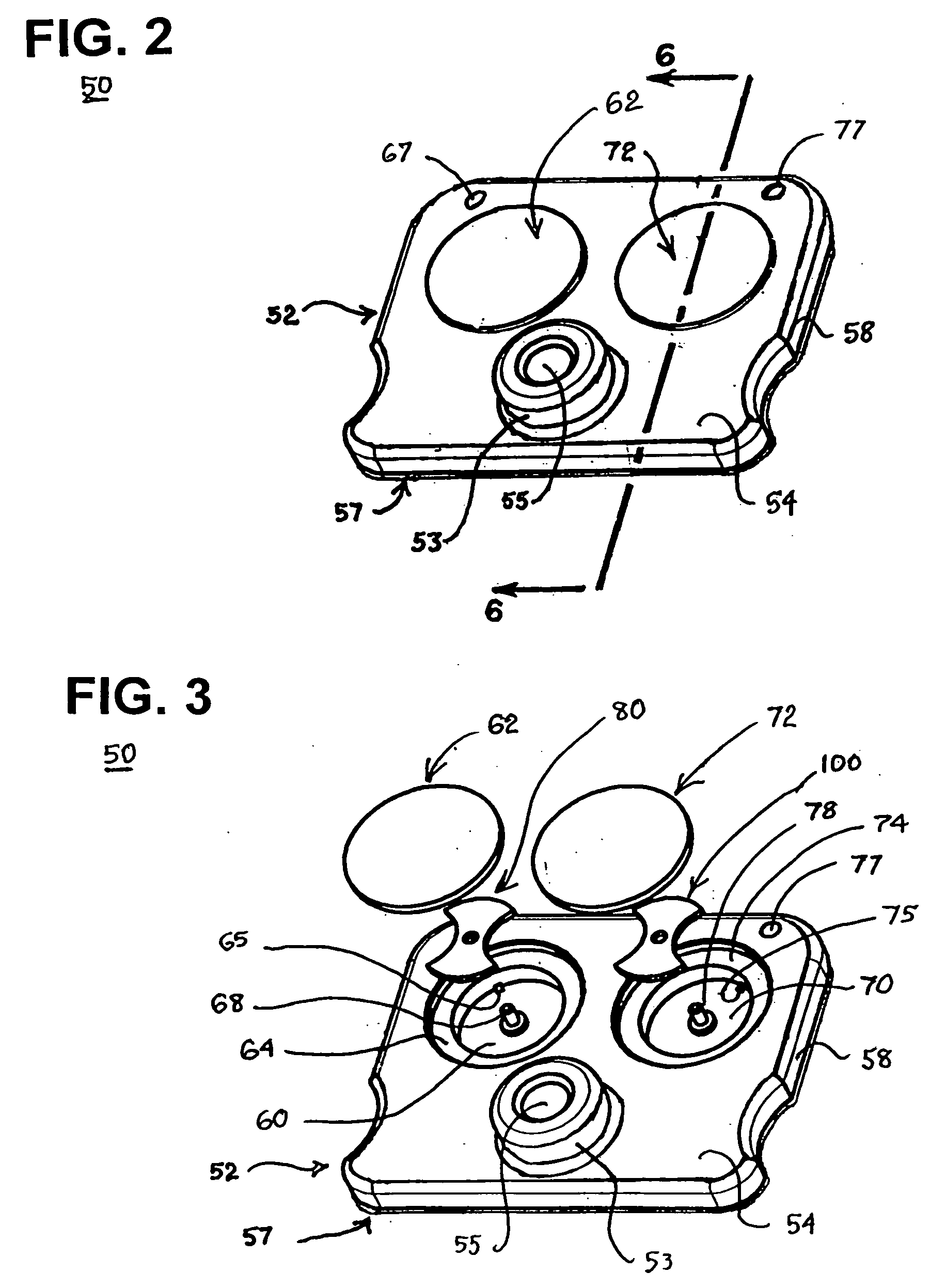
Blood coagulation test cartridge, system, and method
ActiveUS20050233460A1Practical and convenientRapid and reliableAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTest sampleEngineering
A system and method for determining a coagulation time, e.g., TT, PT, aPTT, and ACT, of a test sample deposited in a test cartridge is disclosed. A cartridge housing having upper and lower major sides and a minor sidewall encloses a test chamber having a test chamber pivot element and is provided with a cartridge port for introducing a test sample into the test chamber,. Ferromagnetic agitator vane leaflets extend from an agitator pivot element supported by the test chamber pivot element intermediate the upper and lower major sides for rotational motion. The agitator vane leaflets can be swept, in response to an external magnetic field, through the test sample in the absence of coagulation. A timer is started when the agitator movement is commenced whereupon the agitator moves freely. Resistance to agitator movement due to coagulation is detected, and the coagulation time is measured.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
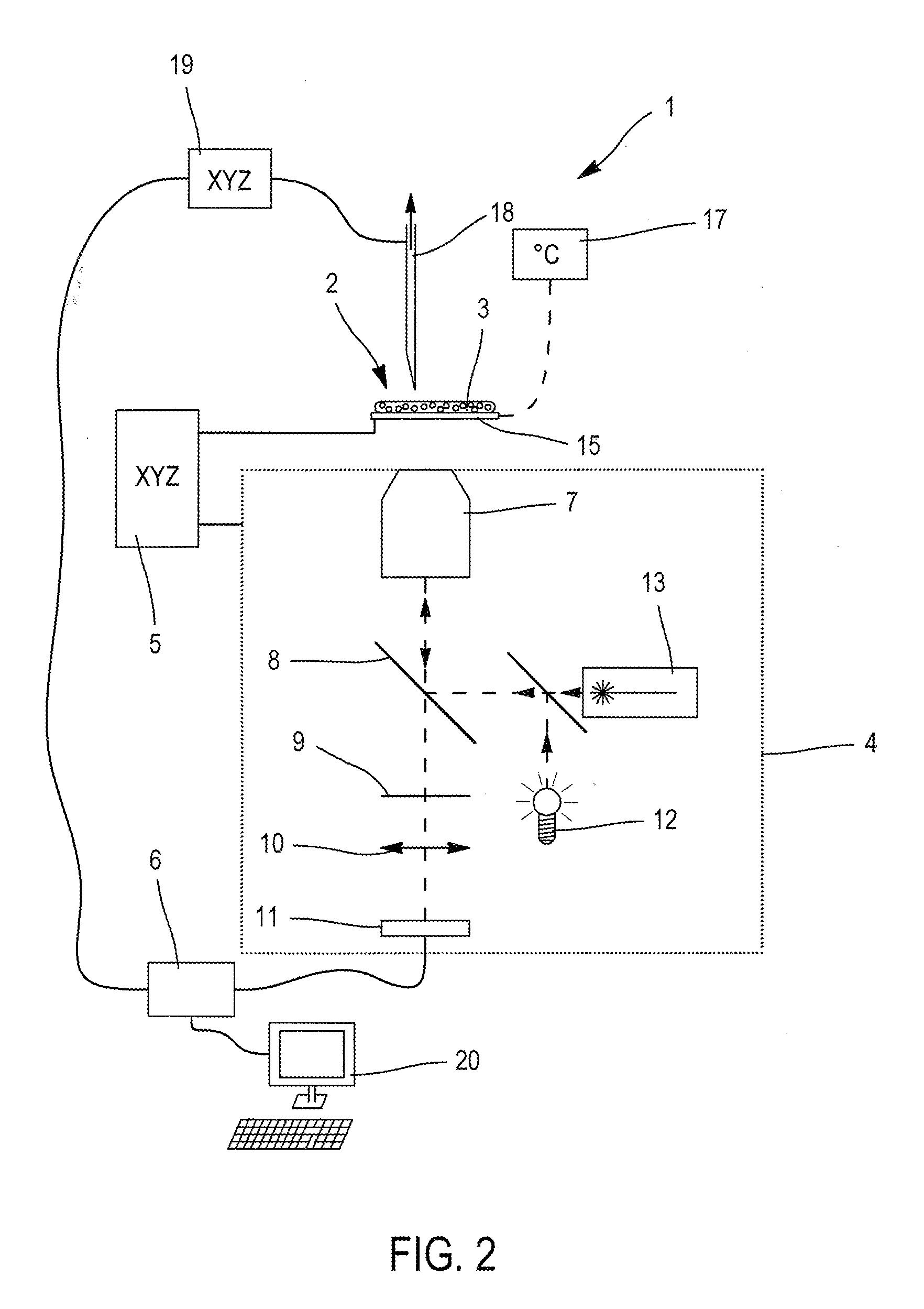
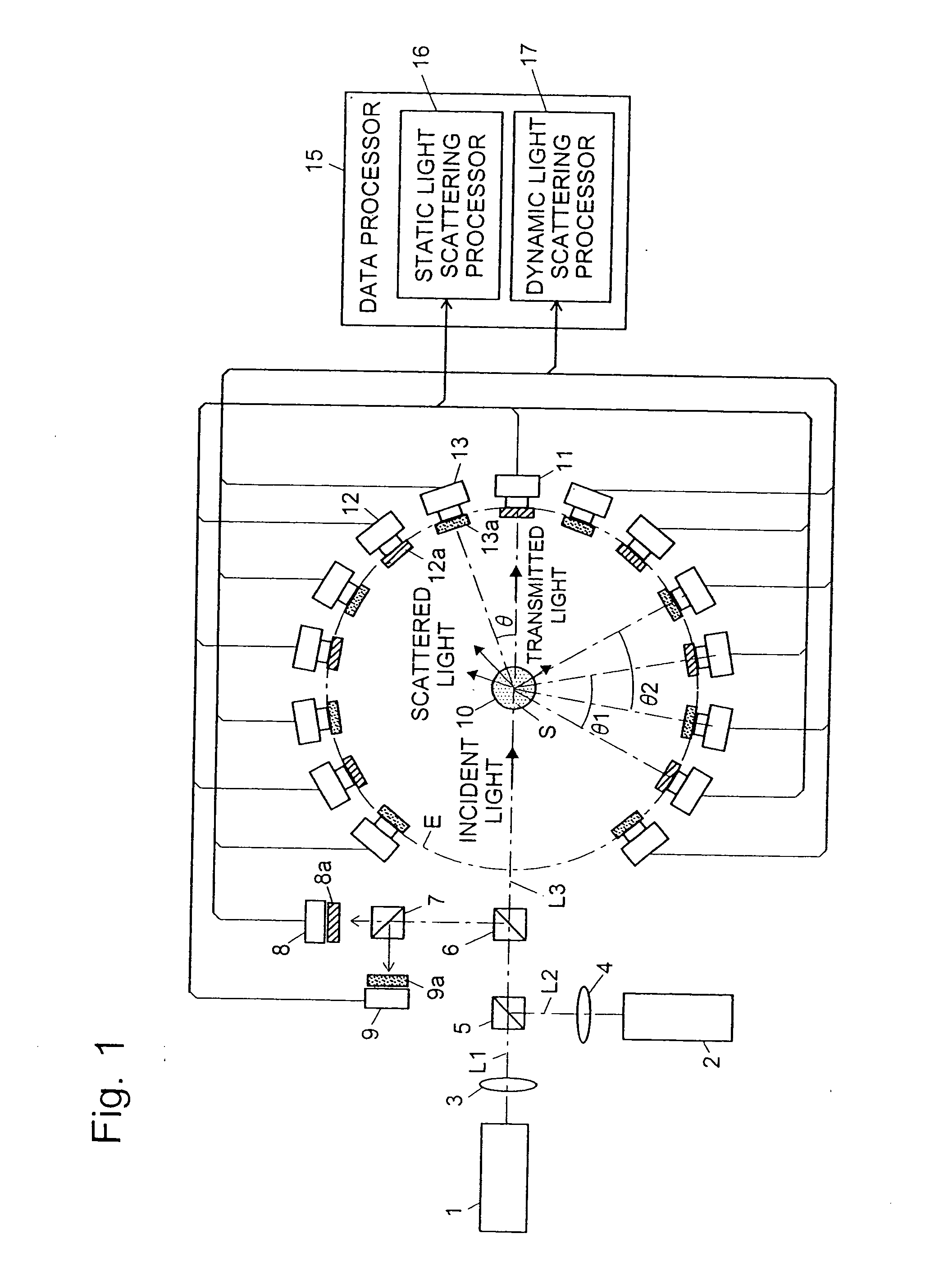
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20080285032A1Dynamic light scattering measurement result can be eliminatedEasy to operateScattering properties measurementsMonitoring particle agglomerationBeam splitterChemical physics
The light scattering detector according to the present invention aims at simultaneously measuring the molecular weight and size of particles having varieties of diameters. This detector facilitates the measurement operation and knowing how particles associate or dissociate as time progresses. In this detector, the emitted light (static light scattering measurement light) having a first wavelength by the first light source and the emitted light (dynamic light scattering measurement light) having a second wavelength which is different from the first wavelength by the second light source are combined by a beam splitter 5 and coaxially directed onto the sample sell 10 to which a liquid sample S is supplied. While the irradiated area by the static light scattering measurement light is large, the irradiated area by the dynamic light scattering measurement light, which is coherent light, is narrow. Detectors 12 which selectively detect the first wavelength and detectors 13 which selectively detect the second wavelength are placed so as to encircle the sample cell 10. The detection signals by the detectors 11, 12 and the detection signals by the detectors 13 are separately mathematically-operated by a data processor 15 to calculate the molecule weight and size of the particles in the sample S.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method of optical measurements for determining various parameters of the patient's blood
InactiveUS20060200014A1Improve accuracyAccurate informationEvaluation of blood vesselsMonitoring particle agglomerationMedicineRed blood cell
A method for optical measurements of desired parameters of the patient's blood is presented. A state of the blood flow cessation is provided within a measurement region and maintained during a predetermined time period. Measurement sessions are performed within this predetermined time period. Each measurement session includes at least two measurements with different wavelengths of incident light. Obtained measured data is representative of the time dependence of light response of the blood in the measurement region. The analyses of the measured data enables the determination of the desired blood parameters extracted from optical characteristics associated with the erythrocytes aggregation process during the state of the blood flow cessation.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
Method and apparatus for detecting and counting platelets individually and in aggregate clumps
ActiveUS20090238439A1Accurate platelet countShorten the counting processBiological particle analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescenceGranularity
A method for enumerating platelets within a blood sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: 1) depositing the sample into an analysis chamber adapted to quiescently hold the sample for analysis, the chamber defined by a first panel and a second panel, both of which panels are transparent; 2) admixing a colorant with the sample, which colorant is operative to cause the platelets to fluoresce upon exposure to one or more predetermined first wavelengths of light; 3) illuminating at least a portion of the sample containing the platelets at the first wavelengths; 4) imaging the sample, including producing image signals indicative of fluorescent emissions from the platelets, which fluorescent emissions have an intensity; 5) identifying the platelets by their fluorescent emissions, using the image signals; 6) determining an average fluorescent emission intensity value for the individual platelets identified within the sample; 7) identifying clumps of platelets within the sample using one or more of their fluorescent emissions, area, shape, and granularity; and 8) enumerating platelets within each platelet clump using the average fluorescent emission intensity value determined for the individual platelets within the sample.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
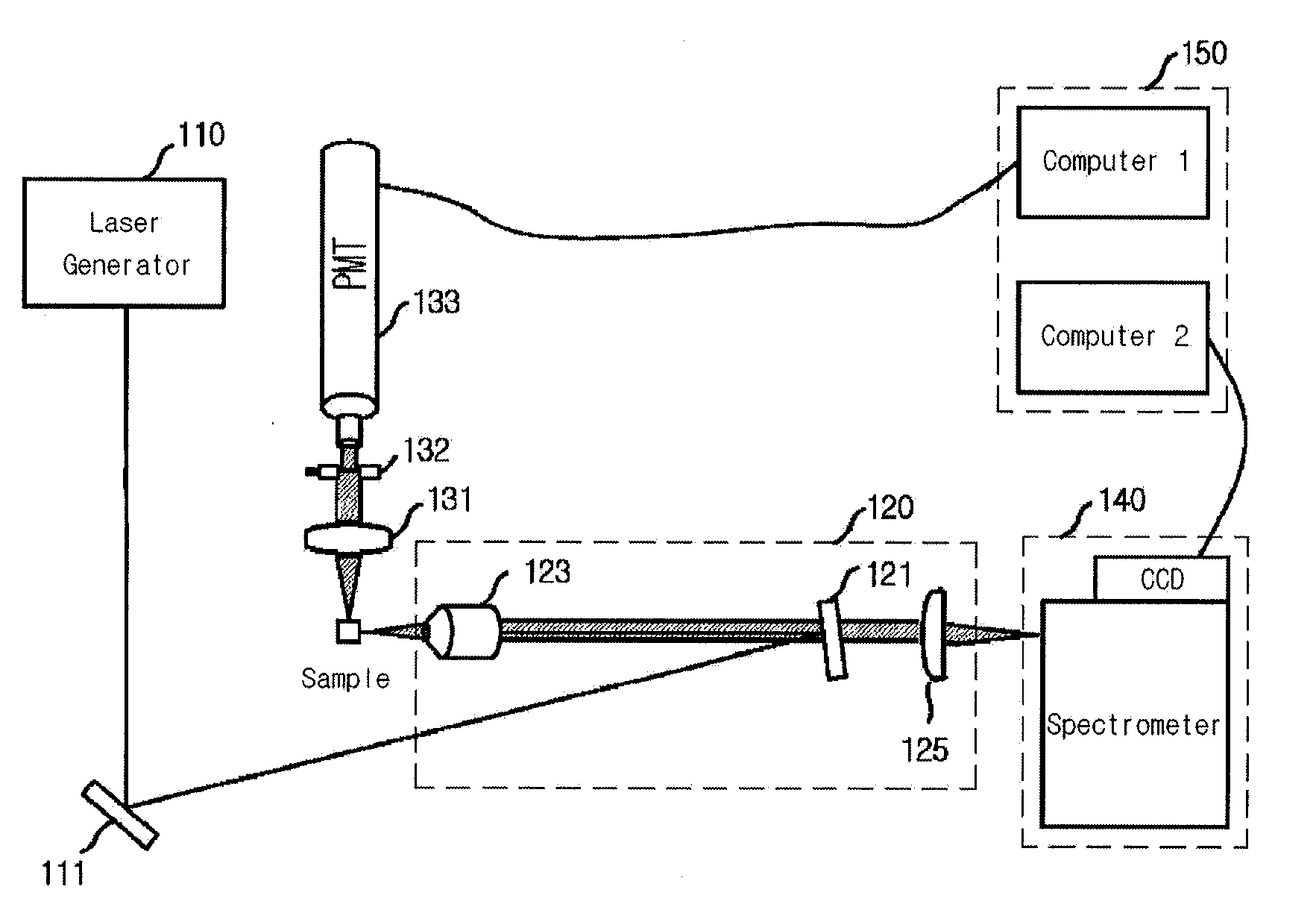
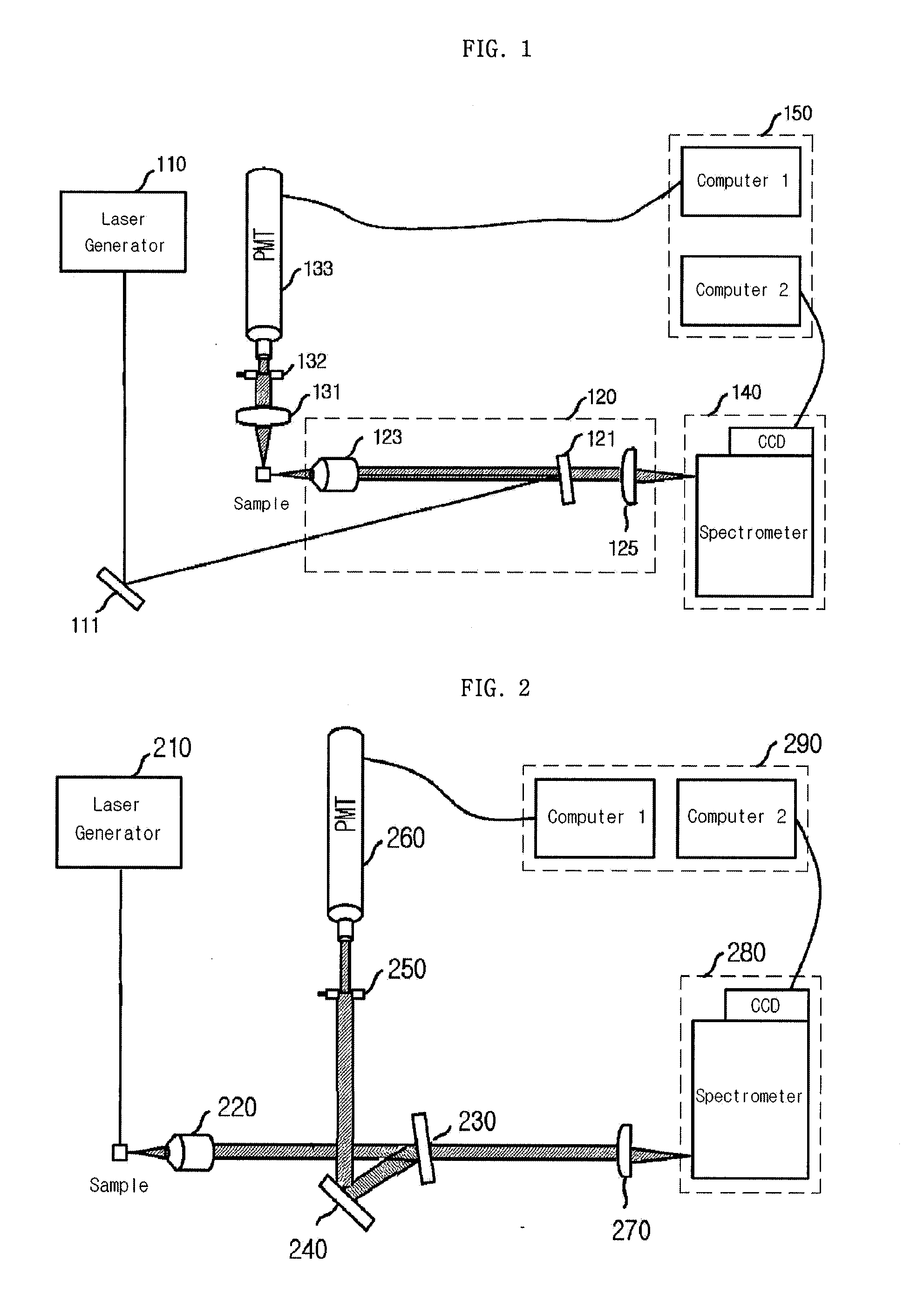
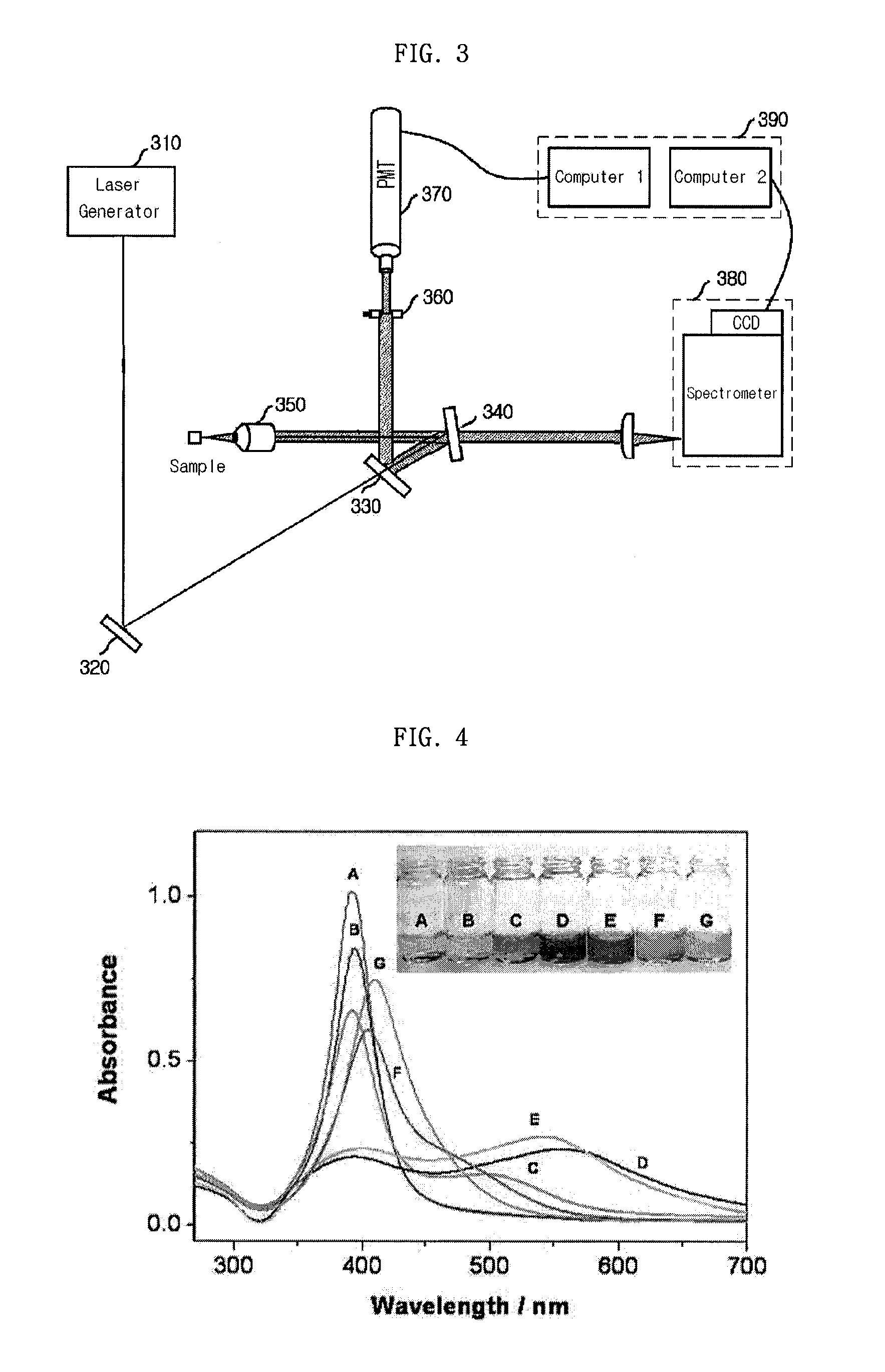
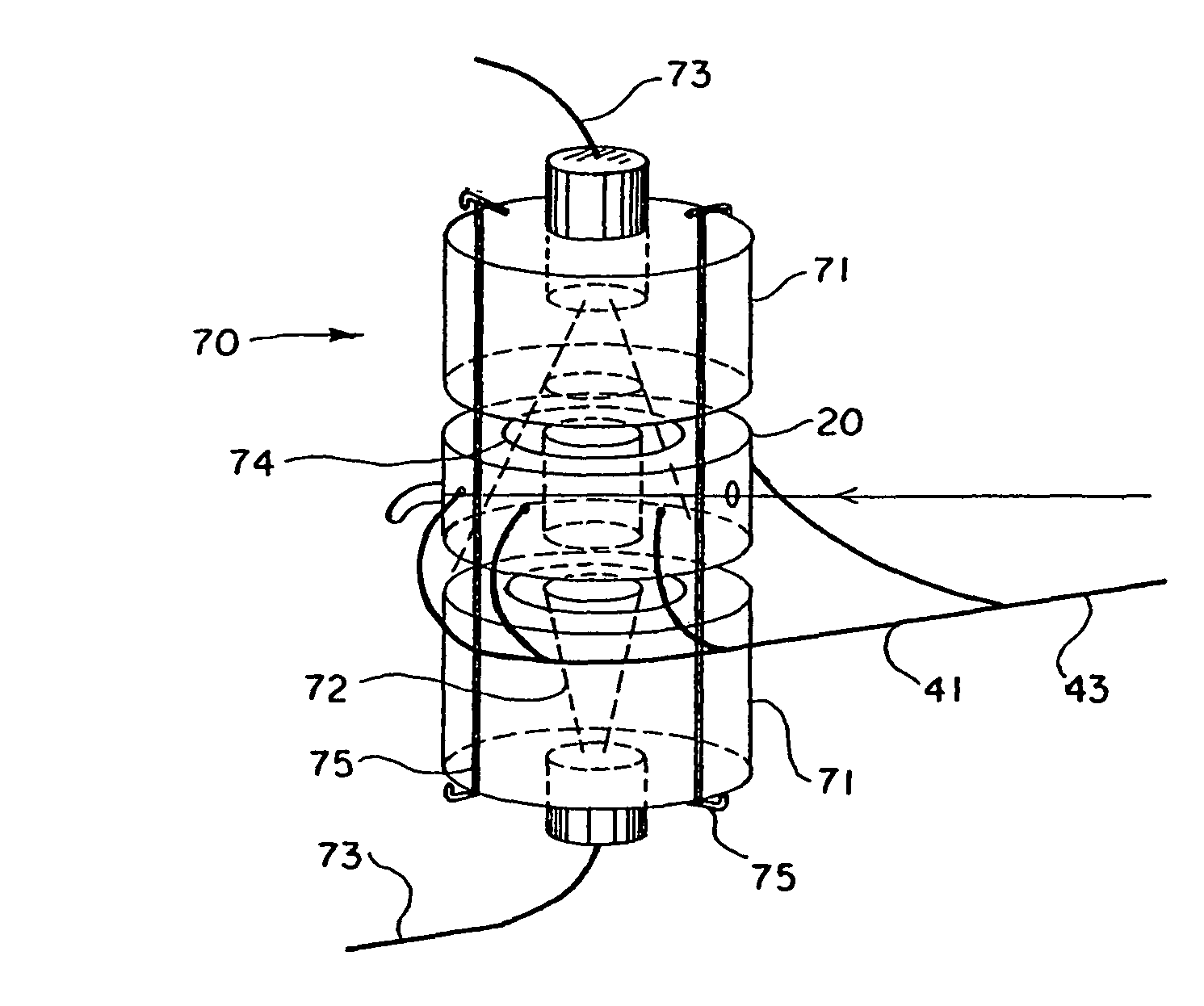
Simultaneous detection apparatus of raman and light scattering
ActiveUS20100020312A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDynamic light scatteringProtein antigen
Provided is a detection apparatus of Raman scattering and light scattering, and more particularly, a simultaneous detection apparatus of Raman scattering and dynamic light scattering and a detection method using the same. The simultaneous detection apparatus of Raman scattering and light scattering includes: a detection unit for applying incident light to a sample, and detecting Raman scattering in 90° or 180° geometry and light scattering in 90° or 180° geometry in order to simultaneously collect Raman scattering and light scattering; and a computer connected to the detection unit to obtain at least one of the size and distribution of particles from the detected light scattering, and to obtain information of the molecular structure from the detected Raman scattering. This apparatus may simultaneously observe the size of nano-sized or larger material and molecular information thereof, and phenomena accompanying changes in molecular environment according to material variation and changes of the material in size and distribution, and thus is very useful for studying nano materials and protein antigens and antibodies.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Reinforcing aluminum-based filler and rubber composition Comprising such a filler
A reinforcing aluminum-based filler which can be used for reinforcing diene rubber compositions intended for the manufacture of tires, comprising an aluminum (oxide-)hydroxide corresponding, with the exception of any impurities and the water of hydration, to the general formula (a and b being real numbers): Al(OH)aOb, with 0<a<=3 and b=(3-a) / 2, (I) the specific BET surface area of which is between 30 and 400 nm<2> / g, the average particle size (by mass) dw of which is between 20 and 400 nm and the disagglomeration rate, alpha, of which, measured via an ultrasound disagglomeration test at 100% power of a 600-watt ultrasonic probe, is greater than 5x10<-3 >mum<-1> / s is provided. A rubber composition suitable for the manufacture of tires comprising said aluminum-based filler as reinforcing filler.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
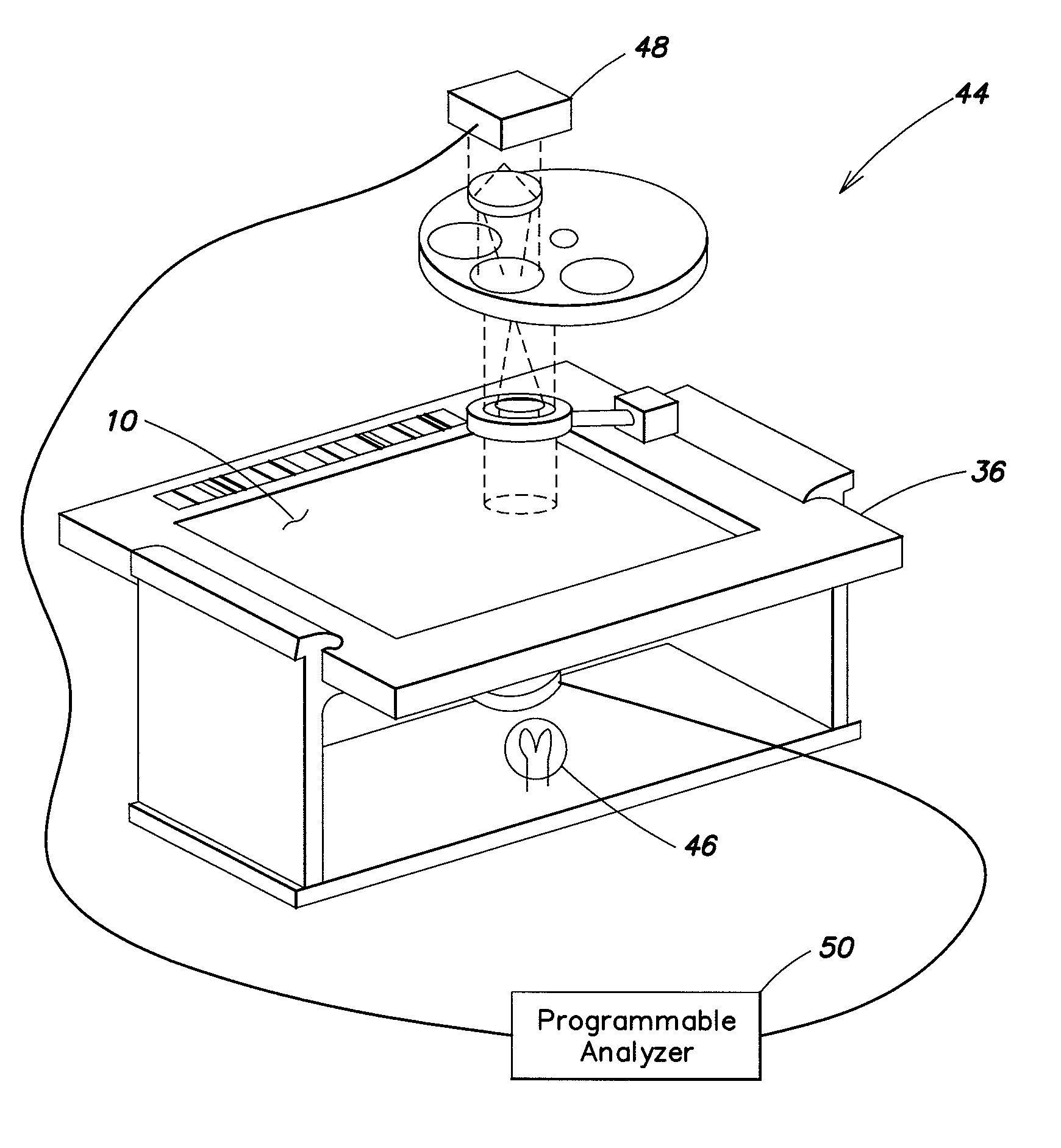
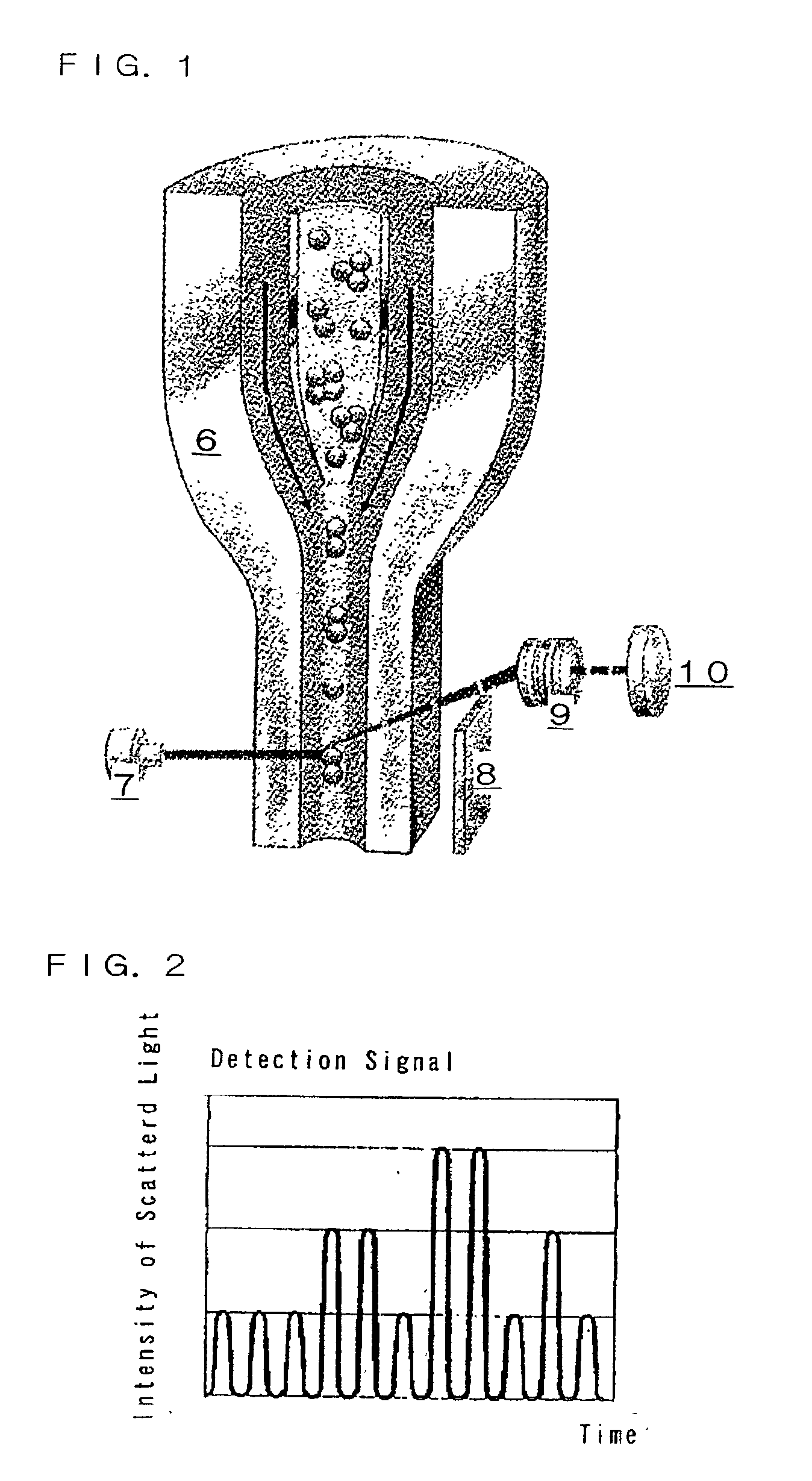
Particle analyzing apparatus and particle imaging method
A particle analyzing apparatus, comprising: a flow cell which forms a specimen flow including particles; first and second light sources; an irradiation optical system which applies lights emitted from the first and second light sources so that the lights are applied to the specimen flow; a detector which detects forward scattered light, the forward scattered light being emitted from the first light and scattered by the particle in the specimen flow, and generates a signal according to the detected scattered light; a light blocking member disposed between the flow cell and the detector; a controller which obtains characteristic parameters of the particle based on the signal from the detector; and an imaging device which captures an image of the particle in the specimen flow using the light from the second light source is disclosed. Particle imaging method is also disclosed.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Use of focused light scattering techniques in biological applications
ActiveUS20100035235A1Large particle sizeHigh throughput screeningCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLiquid mediumParticle density
Methods for using focused light scattering techniques for the optical sensing of biological particles suspended in a liquid medium are disclosed. The optical sensing enables one to characterize particles size and / or distribution in a given sample. This, in turn, allows one to identify the biological particles, determine their relative particle density, detect particle shedding, and identify particle aggregation. The methods are also useful in screening and optimizing drug candidates, evaluating the efficacy and dosage levels of such drugs, and in personalized medicine applications.
Owner:INVITROX
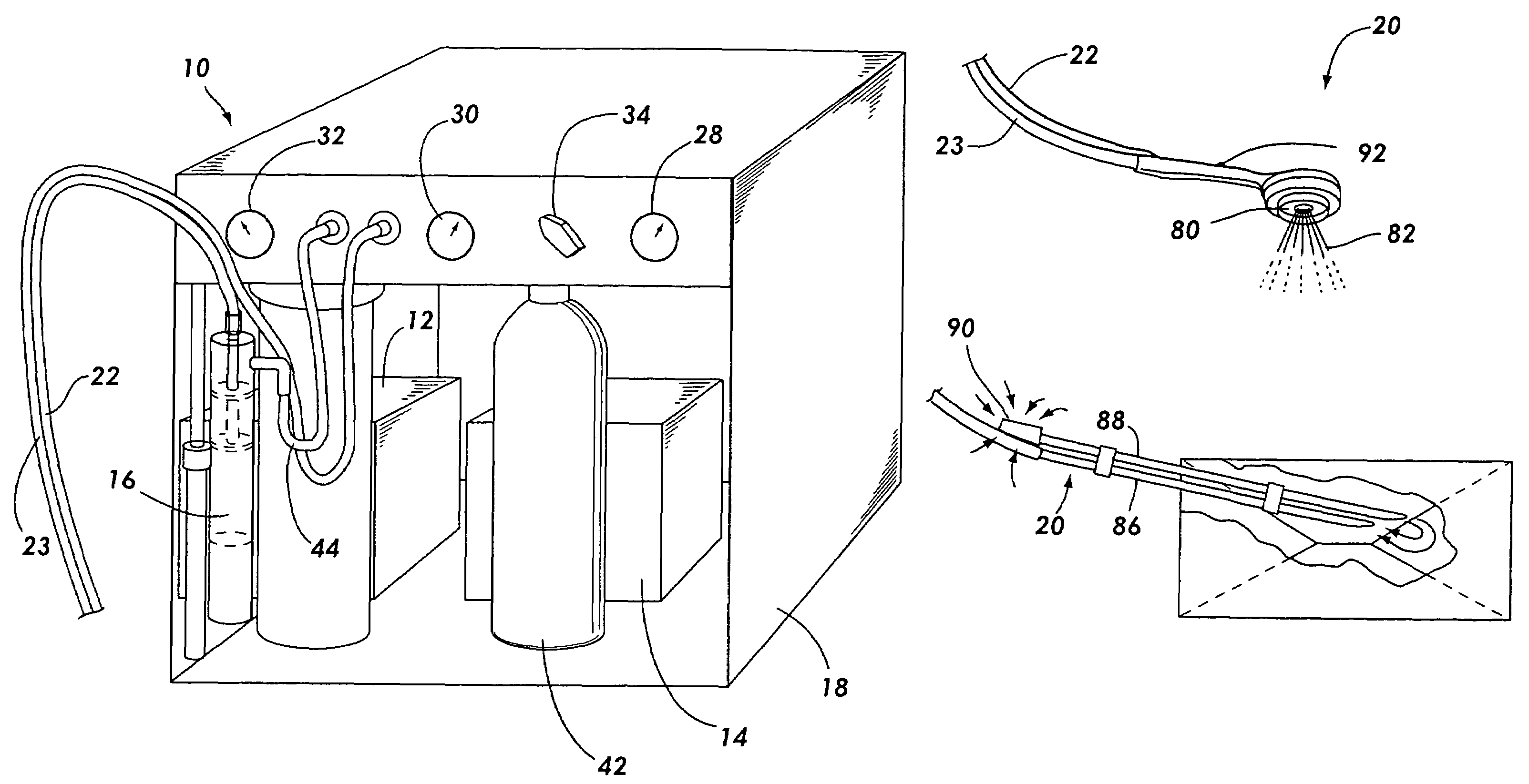
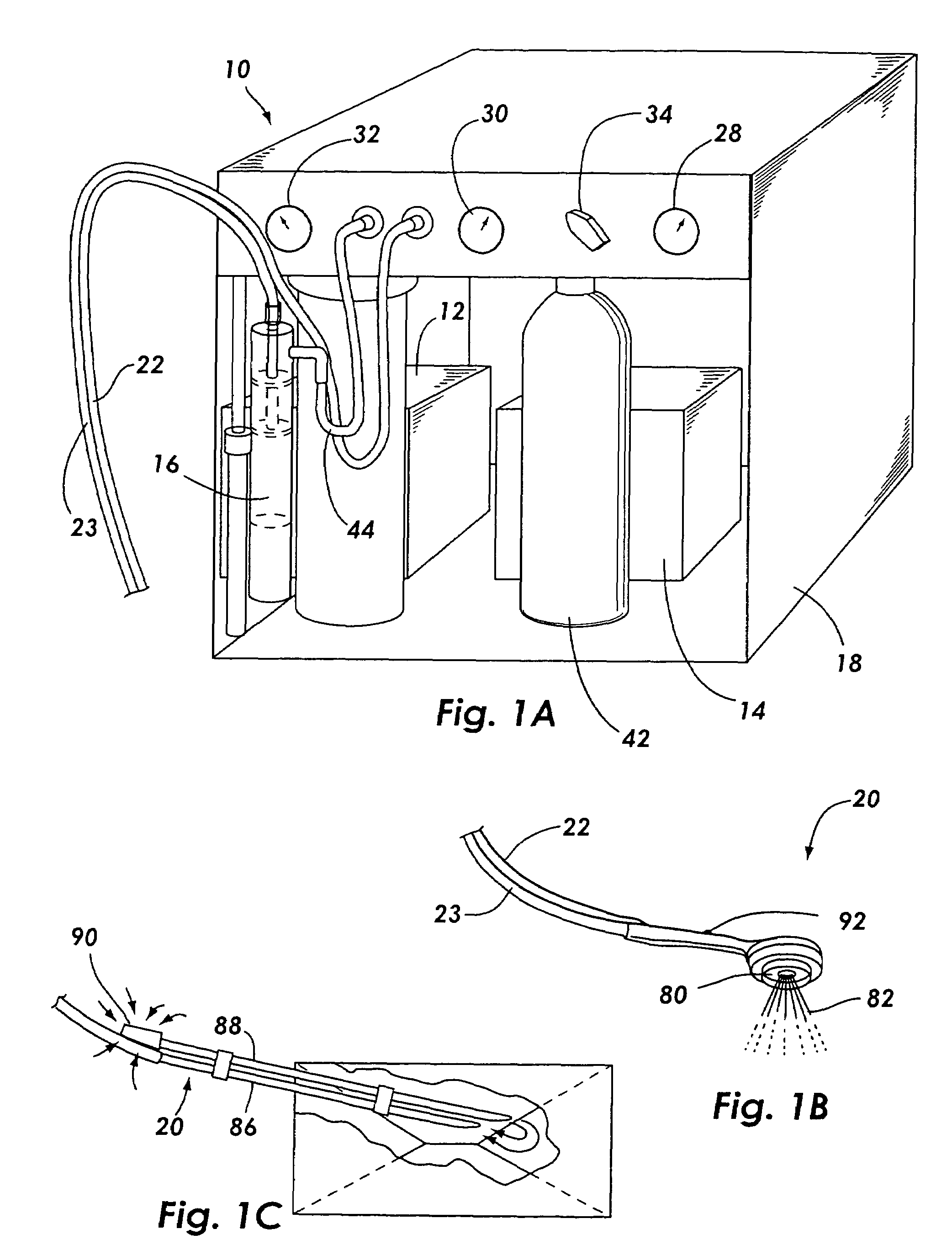
Image Recognition and Analysis System and Software
InactiveUS20080166037A1Sure easyEnhanced informationImage enhancementImage analysisMean diameterColor changes
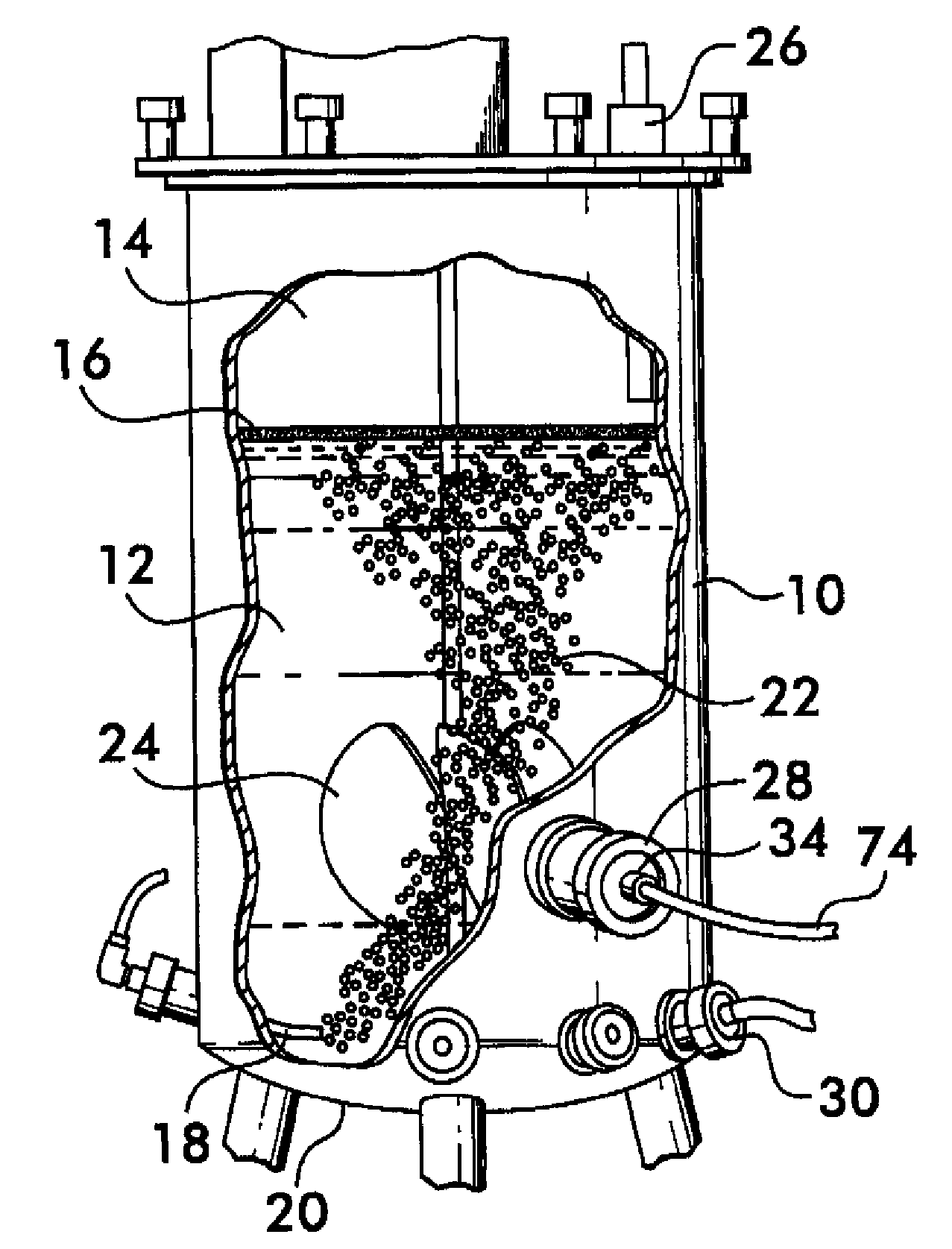
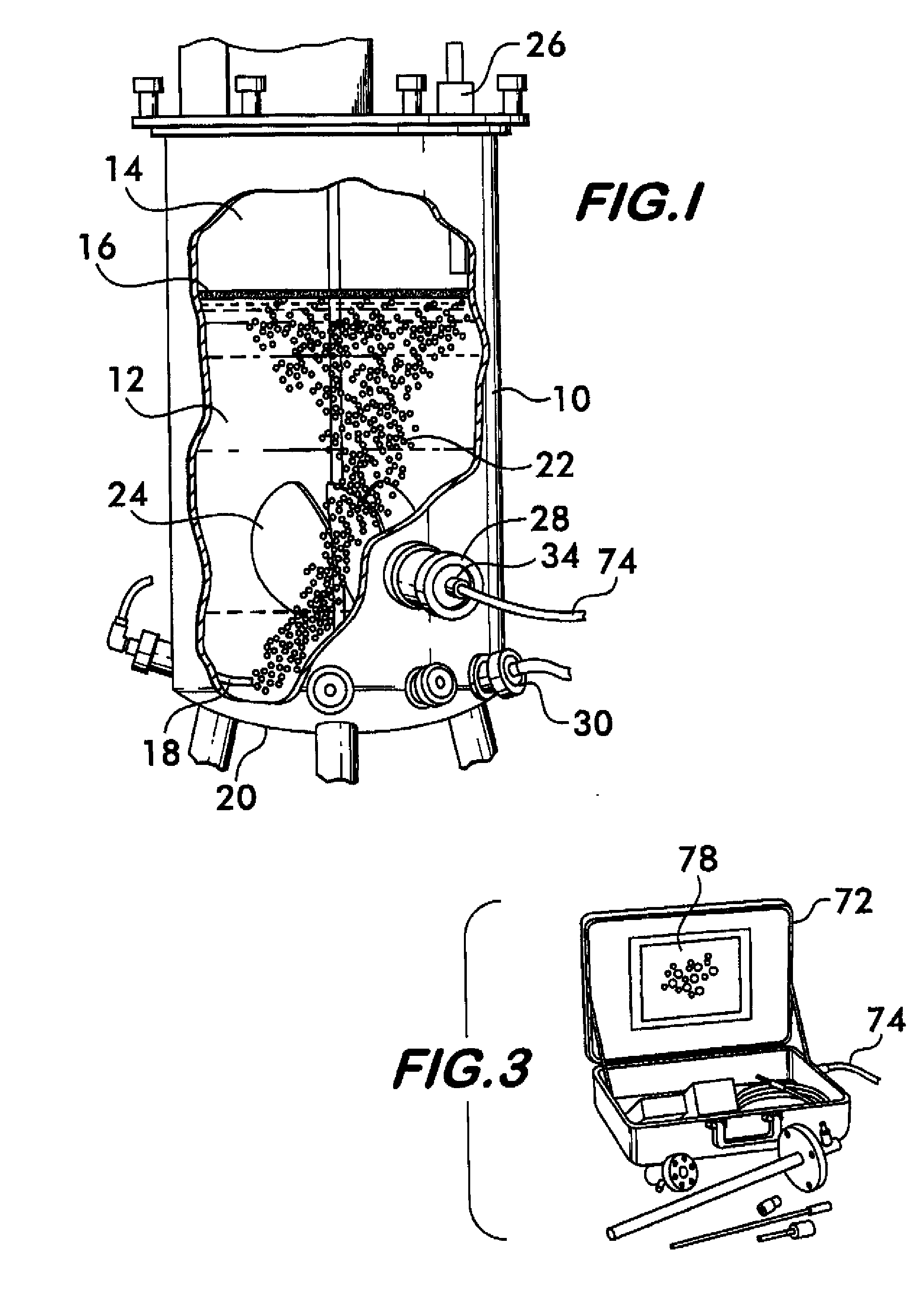
A method of analyzing bubbles, cells, cell viability, or other particles or agglomerates in a process liquid contained in a vessel is provided. Images of bubbles, cells or other particles in the liquid are obtained in-situ with a vision probe extending through a wall of the vessel. The images are analyzed with image recognition software. The software measures at lease one of bubble, cell or particle size, mean diameter, surface area, flow rate, flow pattern, population distribution, viability, agglomerates or clumping, color change, viscosity, Sauter mean, ratio of surface area of bubbles relative to volume of bubbles, gas hold-up ratio of gas volume to volume of liquid, or interfacial area. The software distinguishes valid or viable bubbles, cells or particles that should be included in an analysis from invalid or non-viable bubbles, cells or particles that should not be included. The software can be configured to provide an analysis of the valid bubbles, cells or particles that fall within pre-set size and shape or viability parameters.
Owner:POLLACK LAB
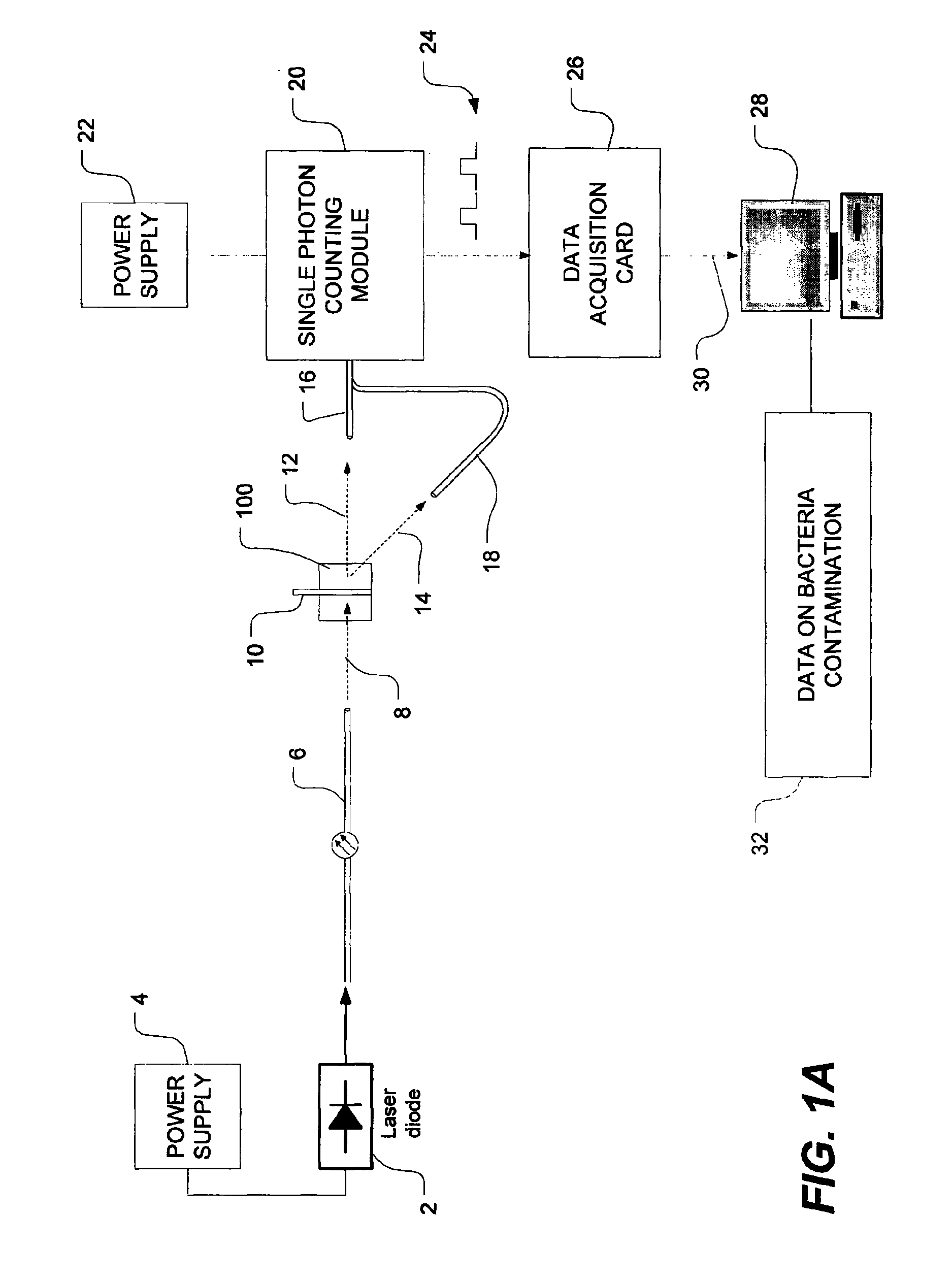
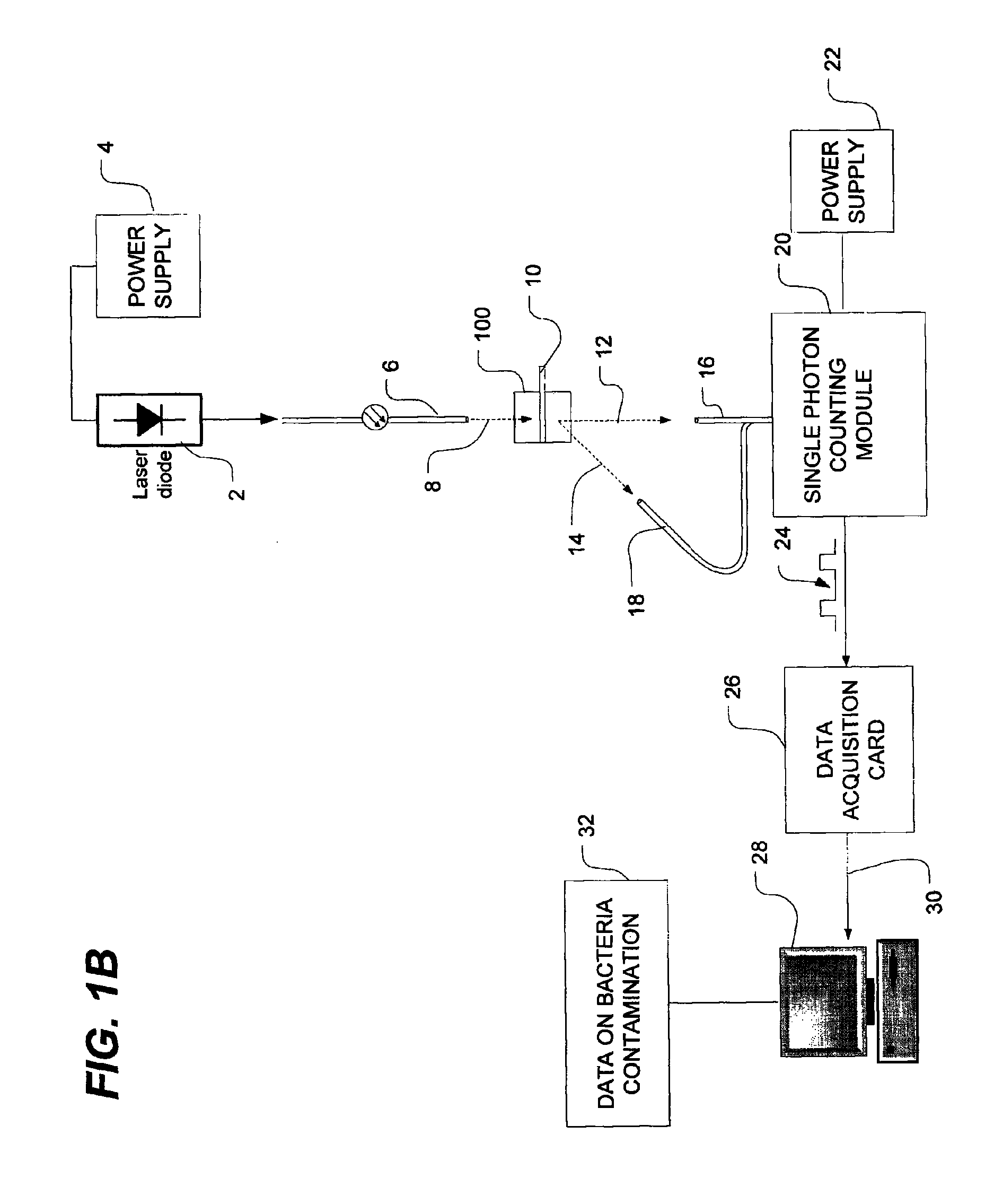
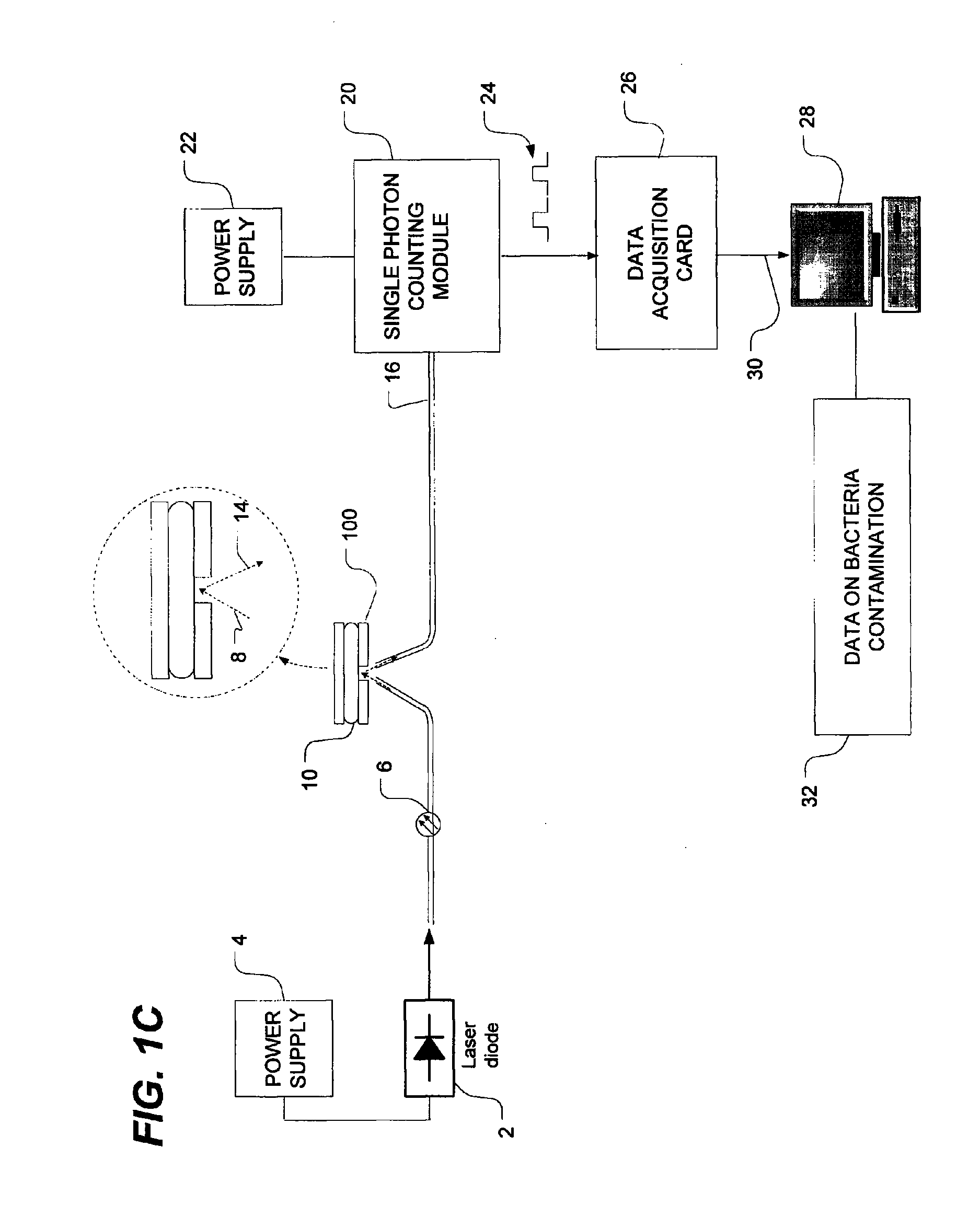
Method of detecting bacterial contamination using dynamic light scattering
InactiveUS8877458B2High strengthReduce intensityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDynamic light scatteringMicroparticle
Methods of detecting bacterial contamination in a platelet concentrate are performed using a dynamic light scattering (DLS) instrument and a sample holder. A sample of platelet concentrate can be held vertically or horizontally in a capillary in the sample holder. Alternatively, novel platelet storage bags modified to include an optically translucent window can be held within another variant of the sample holder. Still alternatively, platelet storage bags having one or more tubes detachably appended to the bag can be used. A sample is drawn off into an appended tube for placement directly into the sample holder. This method provides a number of related, non-invasive techniques for detecting whether bacteria has contaminated a platelet concentrate. Contamination indicators include a population of particles different from platelets, microparticles or proteins, bad-quality platelets, i.e. low DLS score, and very high or very low scattering intensity.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Systems and methods for measuring fluid properties
InactiveUS20070041874A1Accurate measurementImprove the mixing effectShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFlow propertiesParticulatesBlood component
A method for measuring properties of a fluid including placing a quantity of fluid in a container; inducing flow in the fluid wherein the flow is substantially streamlined in at least a measuring region of the container by constricting flow, and wherein the fluid is recirculated through the measuring region. A mixing region can be created separate from the measuring region sufficient to substantially mix the fluid. Free stream particulates in the fluid can be measured in the streamlined region. The invention is of particular interest in the assessment of blood platelet function. The method provides specific localized regions of thorough mixing that enable reproducible platelet aggregation, and also provides specific localized regions of streamlined flow that enable certain modalities of assessing aggregation. Both of these regions of flow are induced such that damage to platelet aggregates and other blood components as well as undesirable agglomeration on device surfaces is minimized.
Owner:THROMBODYNE INC
Assay particle concentration and imaging apparatus and method
InactiveUS20100060893A1Quantity minimizationImproved accuracy in placing the magnetic particlesRadiation pyrometryNanomagnetismImaging equipmentAcoustics
An assay apparatus having a sample vessel within which an assay may be performed. The apparatus further includes a holder having a receptacle, socket or other device configured to operatively receive the sample vessel in a precise and easily repeated location with respect to the holder. A magnet may be operatively associated with the holder such that a magnetic field generated by the magnet intersects a portion of the sample vessel defining a magnetic concentration region within the sample vessel. A separate or integrated detection or interrogation instrument, typically a spectrometer, may be provided.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Measuring agglutination parameters
ActiveUS20100033158A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or moreImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismAgglutination assayAgglutination
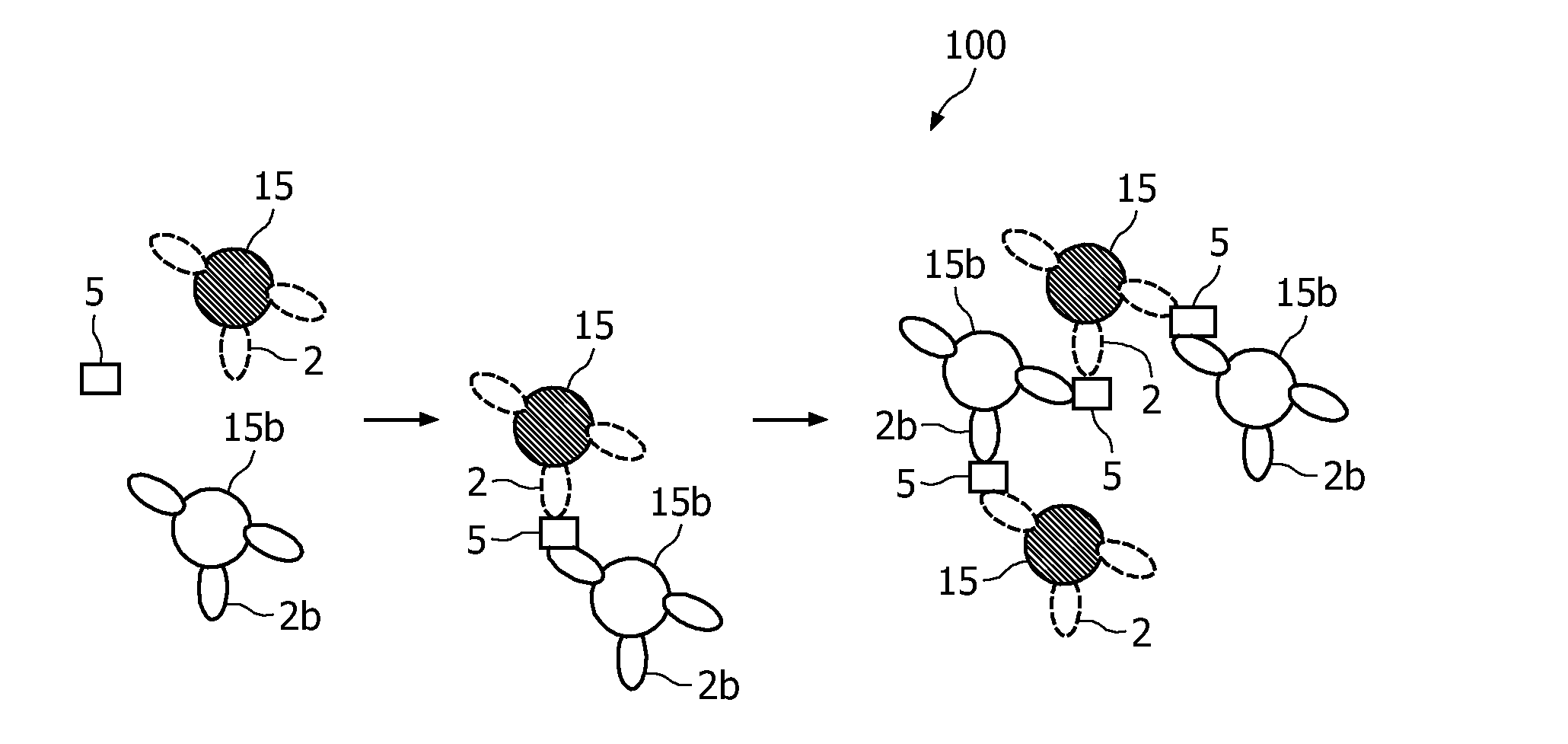
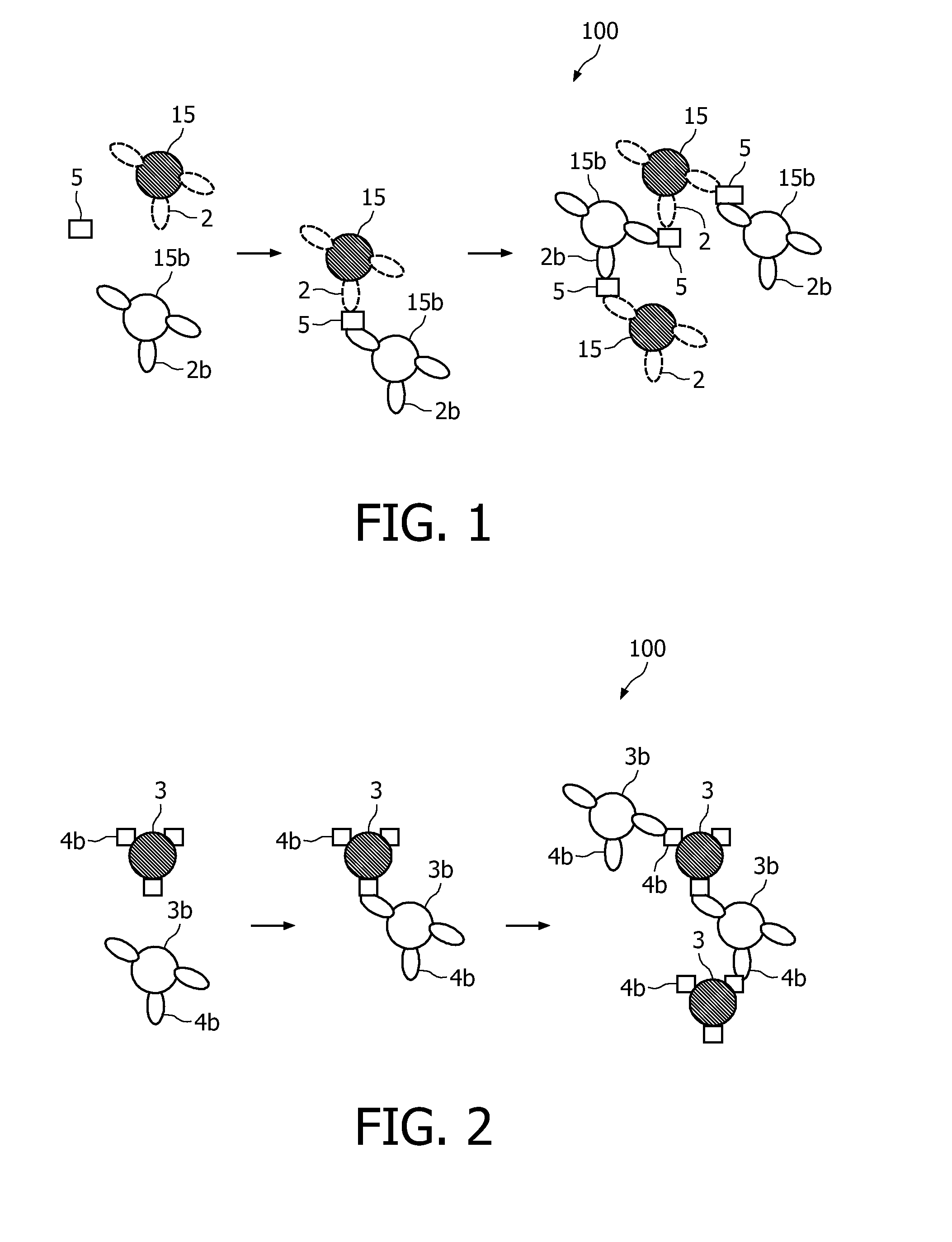
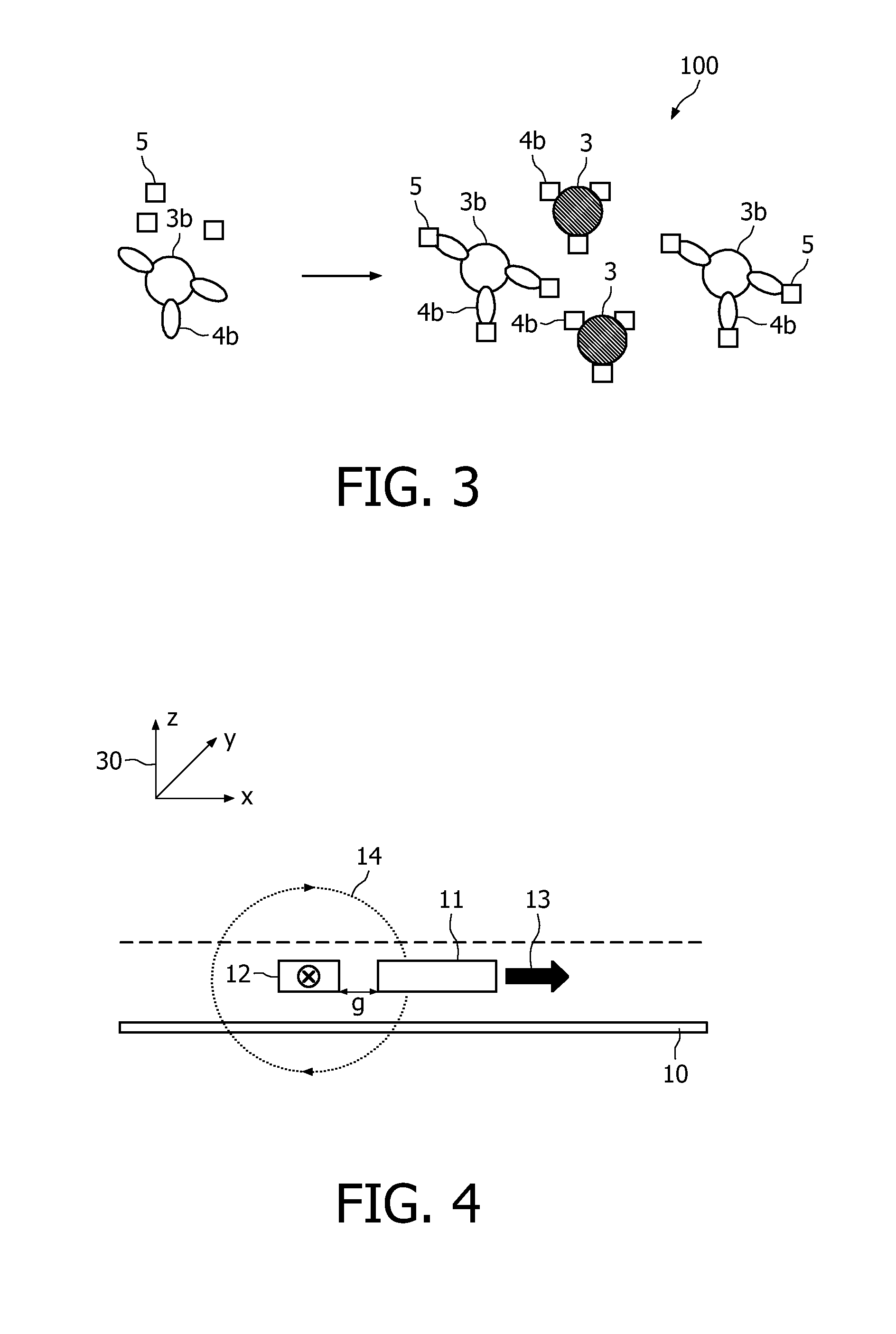
A method and system are described for measuring agglutination in a target-induced agglutination assay with one or more magnetic particles performed in a reaction chamber. After the magnetic particles (3, 15), which are capable of binding to a target (5) are provided in the assay, an agglutination process resulting in agglutinated particles (100) comprising at least one magnetic particle is performed. The method then further comprises applying an alternating current magnetic field (HAC) to the assay and—measuring an effect of the HAC on the one or more magnetic particles (3,15) unattached to any surface. The measured effect is indicative of one or more agglutination parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Systems and methods for measuring fluid properties
ActiveUS7262059B2Accurate measurementImprove the mixing effectShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingBlood componentPlatelet aggregation
A method for measuring properties of a fluid including placing a quantity of fluid in a container; inducing flow in the fluid wherein the flow is substantially streamlined in at least a measuring region of the container, and wherein the fluid is recirculated through the measuring region; creating a mixing region separate from the measuring region sufficient to substantially mix the fluid; and measuring a property of the fluid in the streamlined region. The invention is of particular interest in the assessment of blood platelet function. The method provides specific localized regions of thorough mixing that enable reproducible platelet aggregation, and also provides specific localized regions of streamlined flow that enable certain modalities of assessing aggregation. Both of these regions of flow are induced such that damage to platelet aggregates and other blood components is minimized.
Owner:THROMBODYNE INC
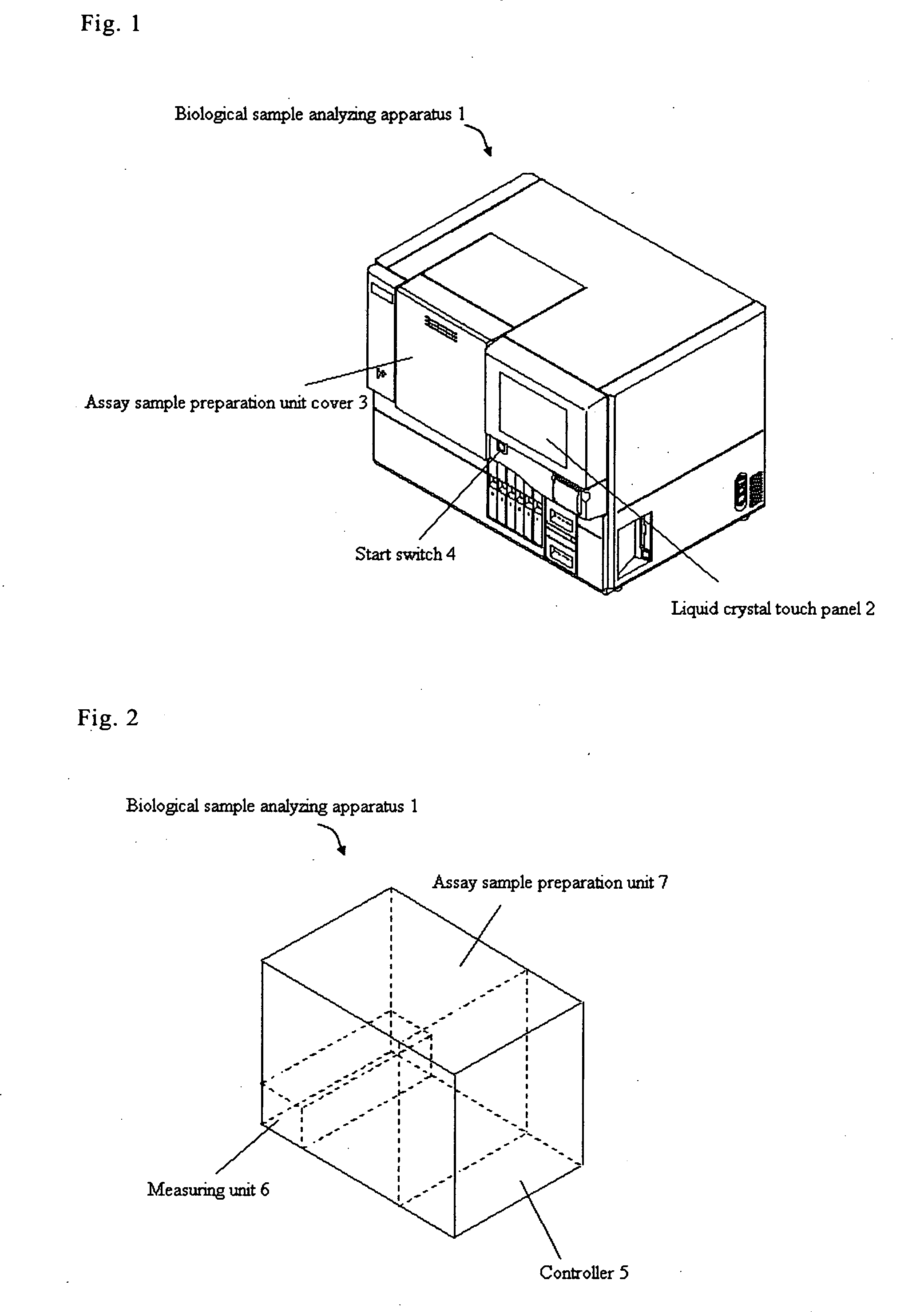
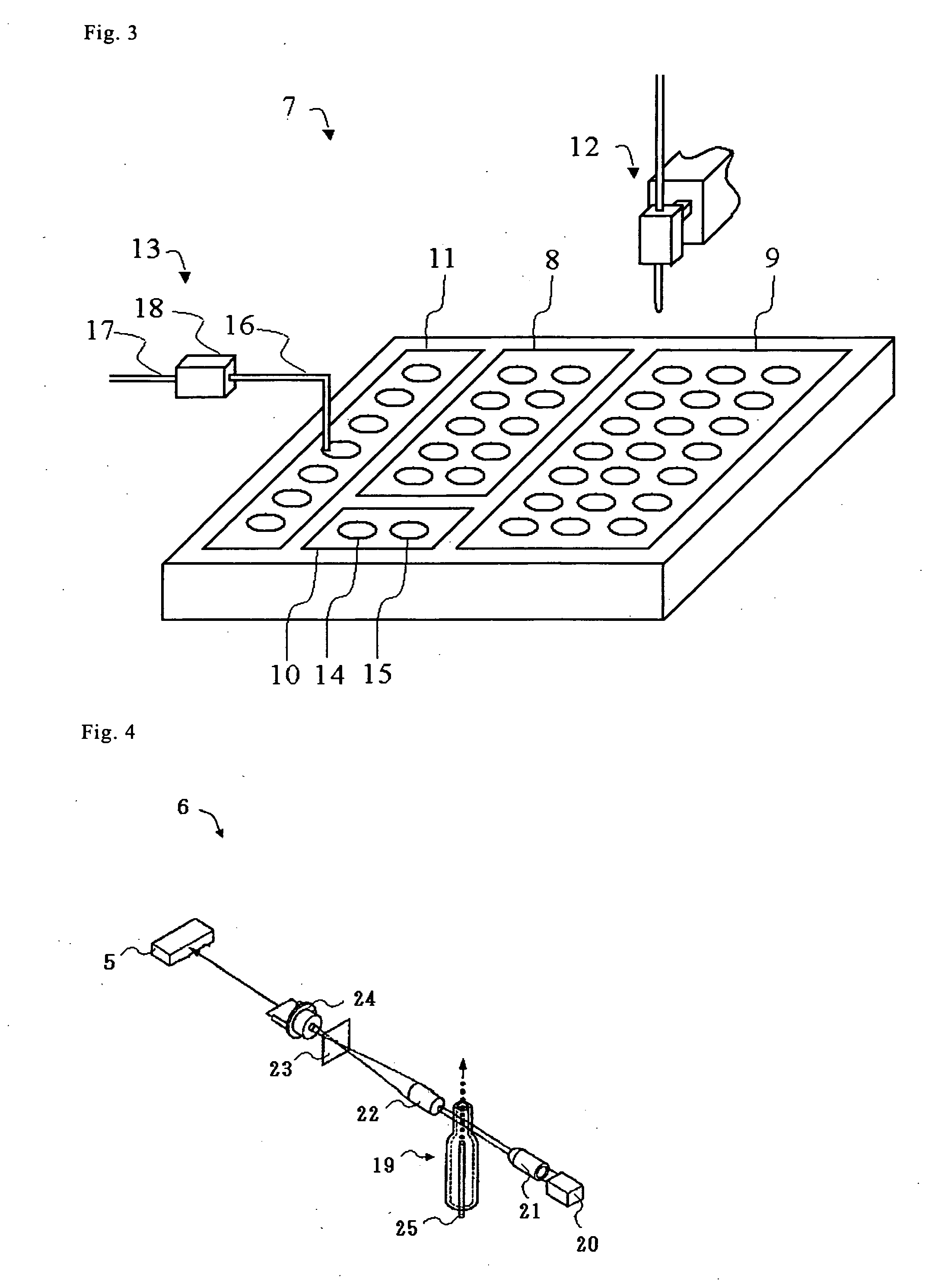
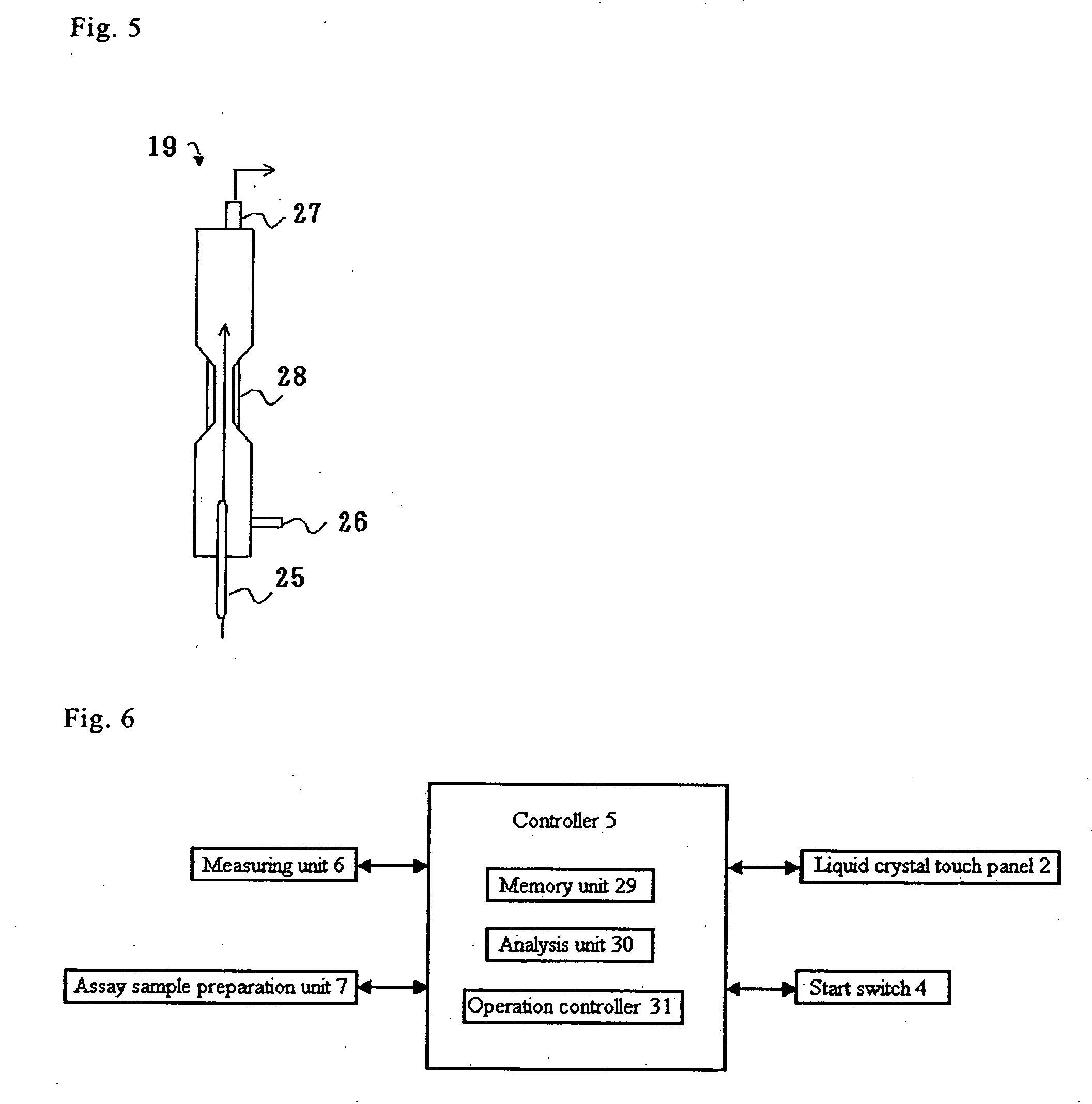
Biological sample analyzing apparatus and biological sample analyzing method
ActiveUS20060089810A1Improve efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalysis methodBiology
In a biological sample analyzing apparatus and method, an assay sample is prepared by mixing a reagent with a biological sample which may contain assay material. Then, a first information relating to the assay material is collected from the assay sample, and when the first information satisfies predetermined condition, the assay material is analyzed based on the first information. However, when the first information does not satisfy the predetermined condition, a second information related to the assay material is collected from the assay sample, and the assay material is analyzed based on the second information.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Automatic sampling and dilution apparatus for use in a polymer analysis system
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
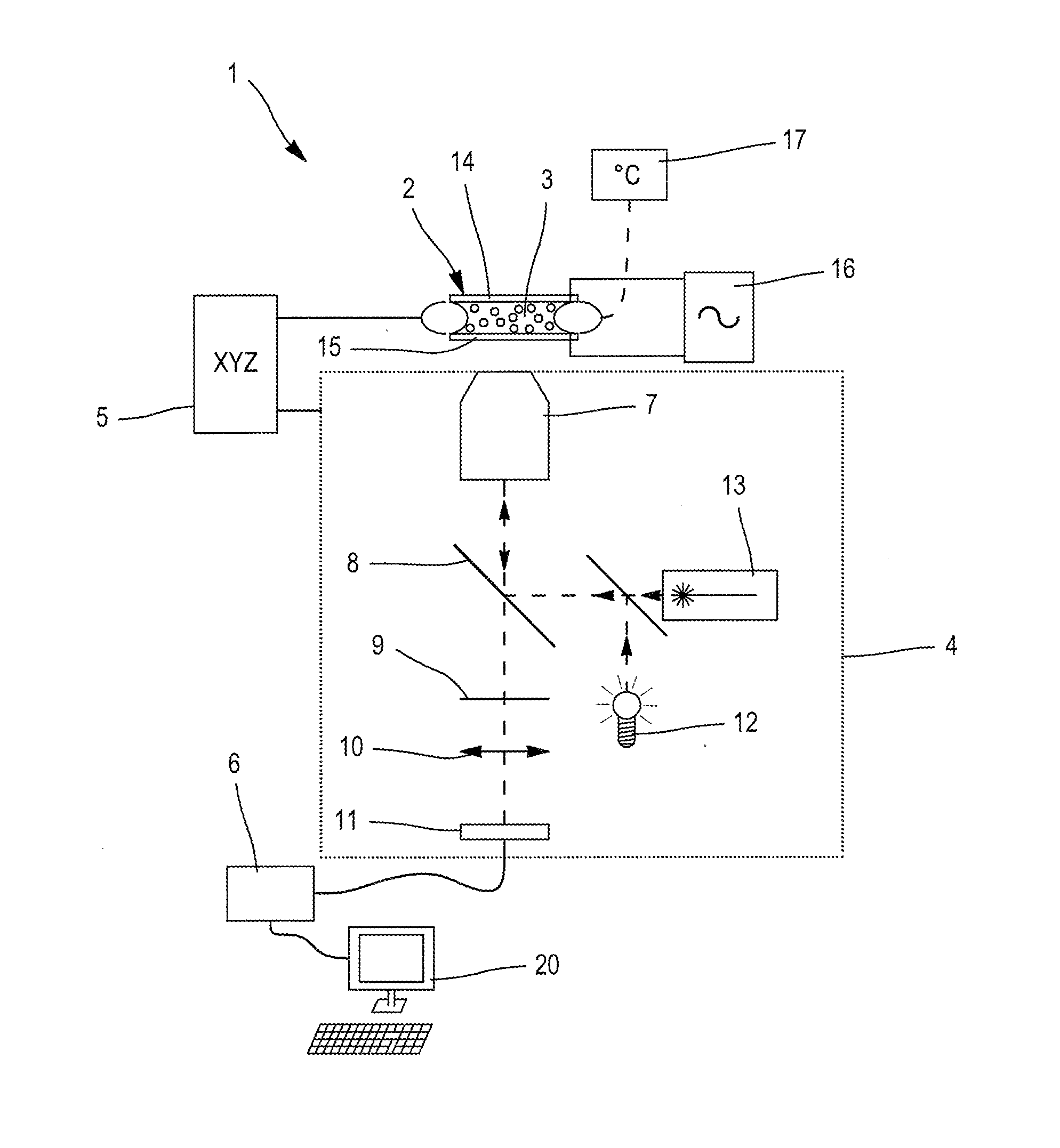
Probe for Measuring Light in a Liquid, Probe for Detecting the Flocculation Threshold of a Colloidal Medium, Related Detection Method and Use for Determining the Flocculation of Asphaltenes
ActiveUS20080043240A1Different dilution rateRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsFlocculationCompound (substance)
The invention concerns a device for measuring light in a liquid by introducing in said medium at least one emitting probe comprising: a transmitter connected to a first waveguide; a second waveguide; and included in said second waveguide, at least one reflecting surface. The invention also concerns a method for measuring the flocculation threshold of a colloidal medium by gradually adding apolar solvent using the inventive device, comprising a step which consists in determining, using at least one probe of said device, flocculation after adding the amount of apolar solvent required for flocculation. The invention is applicable to asphaltenes. The invention also concerns the use of said device for measuring physico-chemical properties in opaque media.
Owner:TOTAL RAFFINAGE MARKETING
Immunoassay and immunoassay apparatus
InactiveUS20030082662A1Highly accurate immunoassaySimple correctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsValue setAgglutination
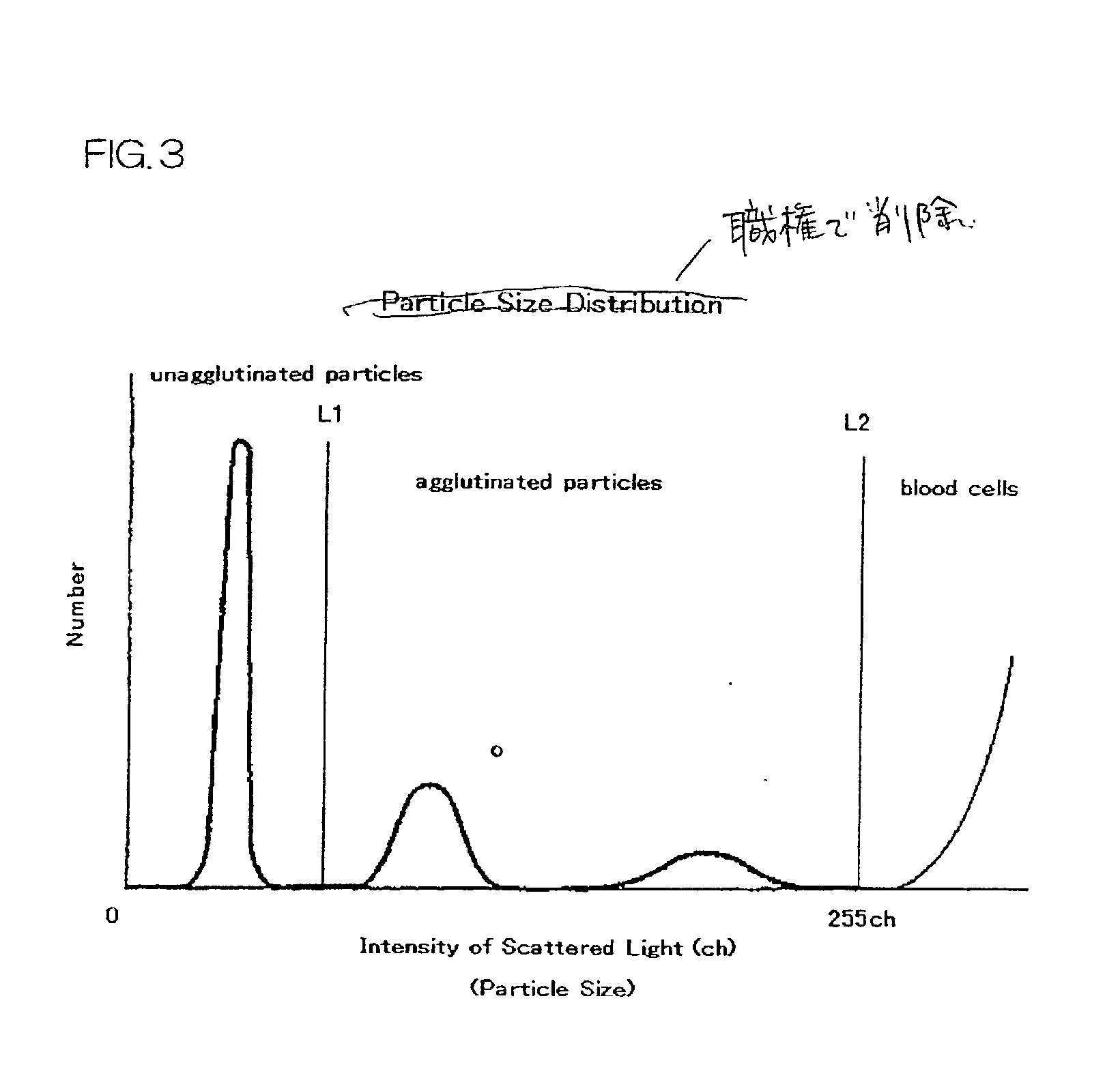
An immunoassay comprises the steps of: (a) mixing a whole blood sample with sensitized insoluble carrier particles smaller than erythrocytes to cause an immune agglutination reaction; (b) introducing the resulting immune agglutination reaction mixture including agglutinated particles and unagglutinated particles to a flow cell, irradiating the particles passing through the flow cell with laser light, and detecting scattered lights generated thereby; (c) setting a threshold value for distinguishing unagglutinated particles from agglutinated particles and a threshold value for distinguishing the agglutinated particles from blood cells with regard to intensity of the scattered light; and (d) distinguishing and counting the unagglutinated particles, the agglutinated particles and the blood cells from the scattered lights detected in the step (b), in reference to the threshold values set in the step (c).
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Method for additive adhesion force particle analysis and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS6598466B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationAdhesion forceEngineering
A method including: sonicating a liquid suspension of first particles; and analyzing the liquid phase for second particles. An apparatus including: a sonicator adapted to sonicate a liquid suspension of first particles; and a first analyzer adapted to analyze the sonicated liquid phase for second particles. The method and apparatus can be used to analyze the adhesion force relationships between the main or host first particles and guest or surface additive second particles.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com