Patents
Literature
43 results about "Agglutination assay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
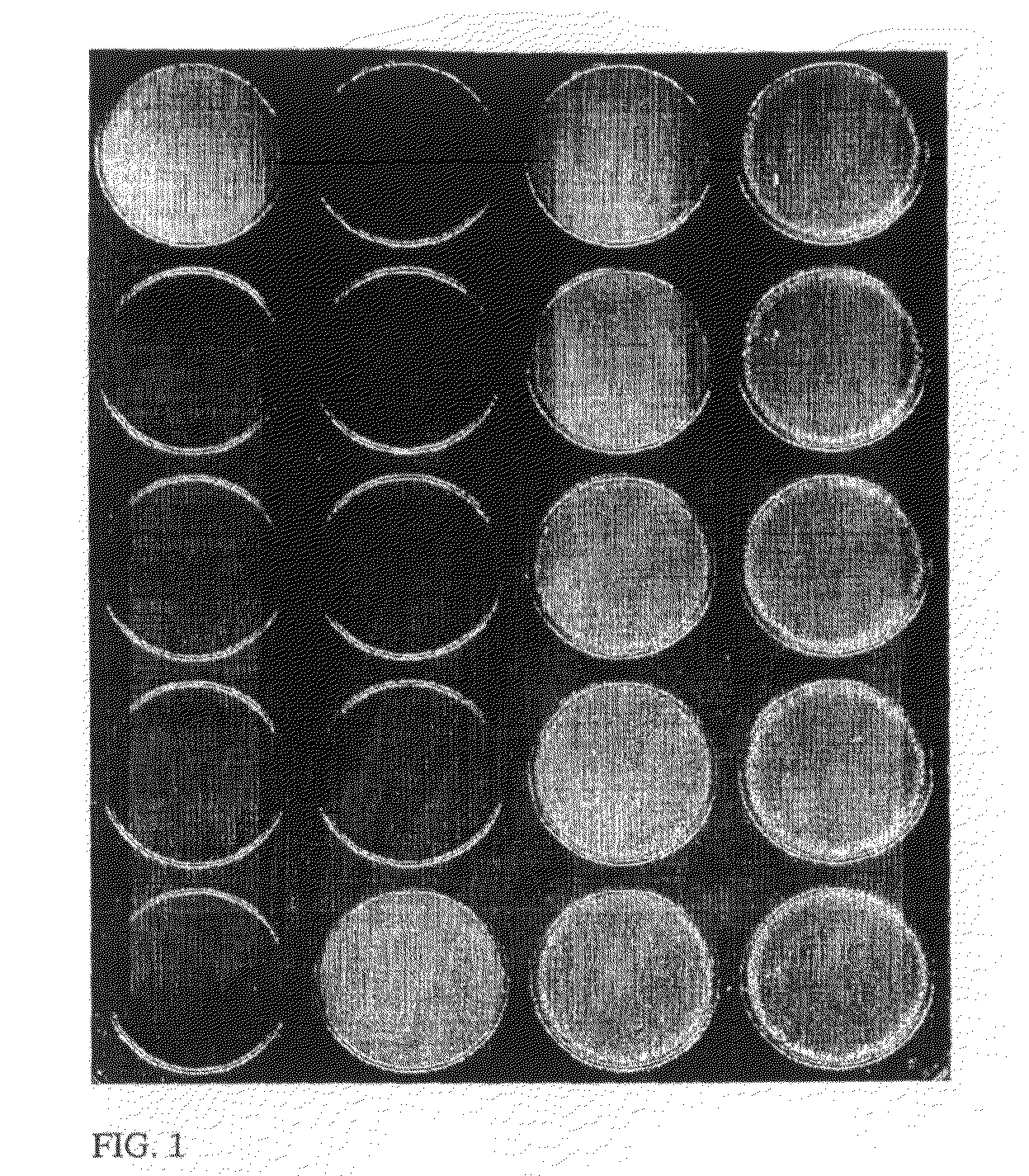
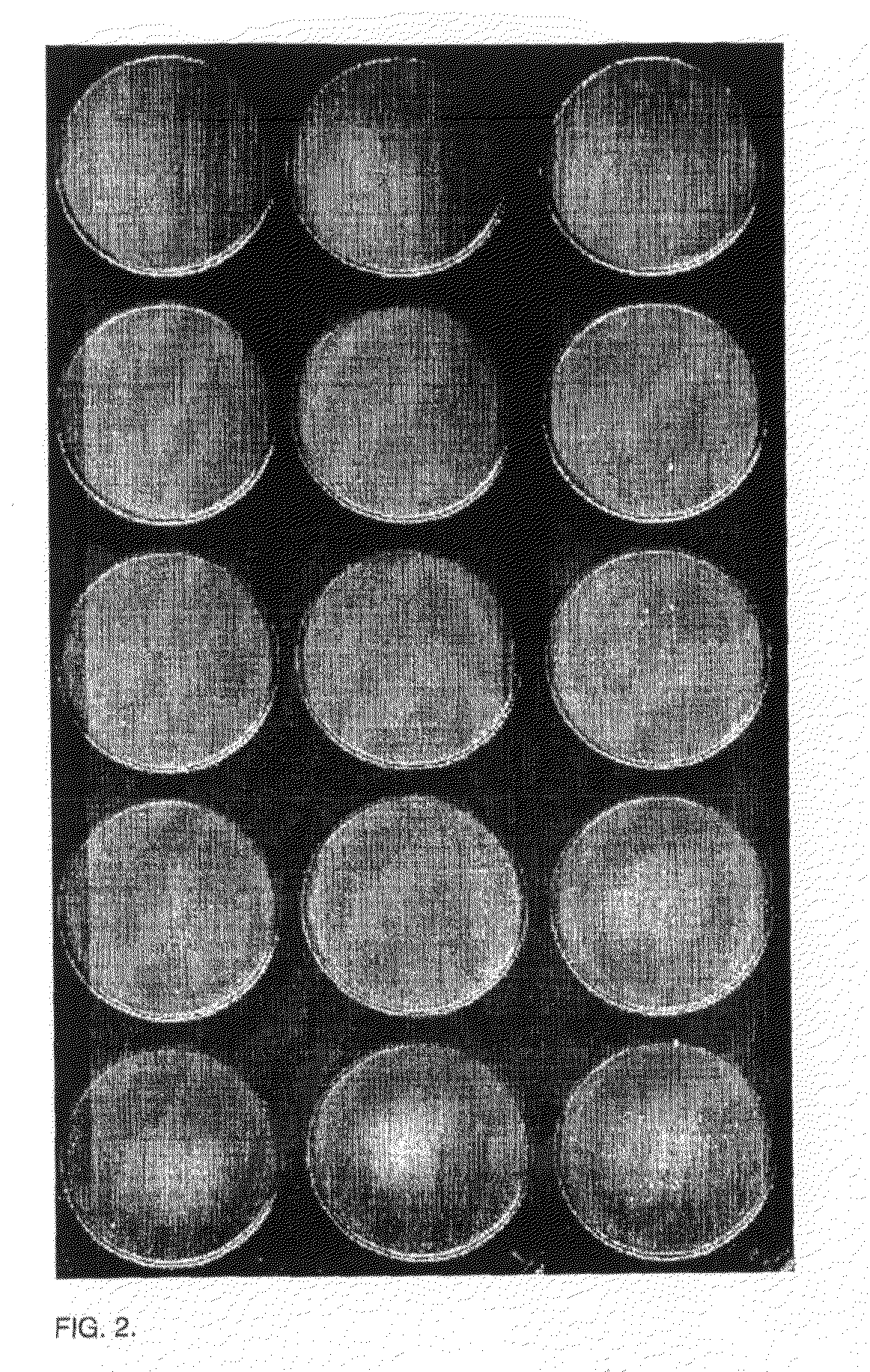
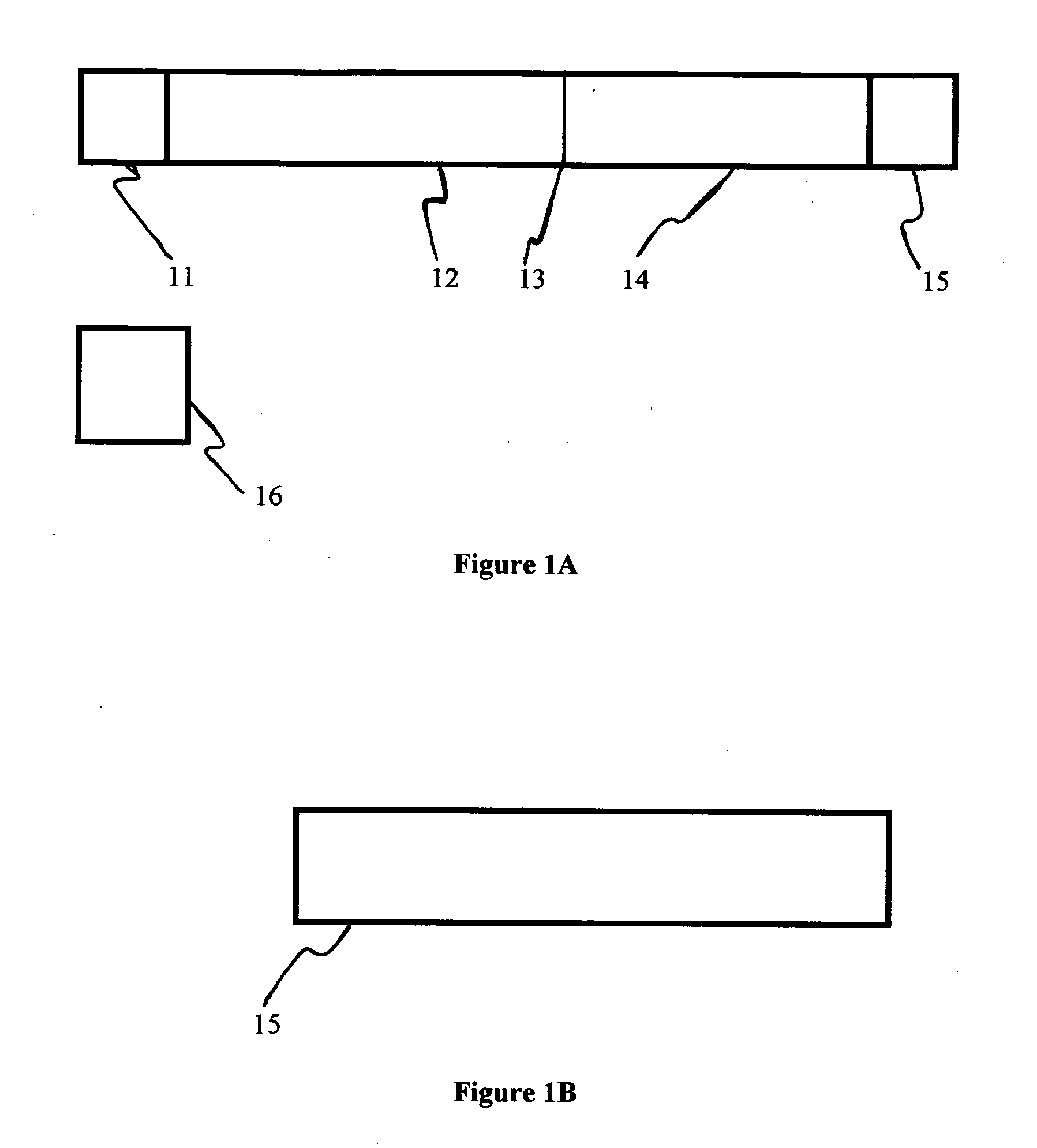
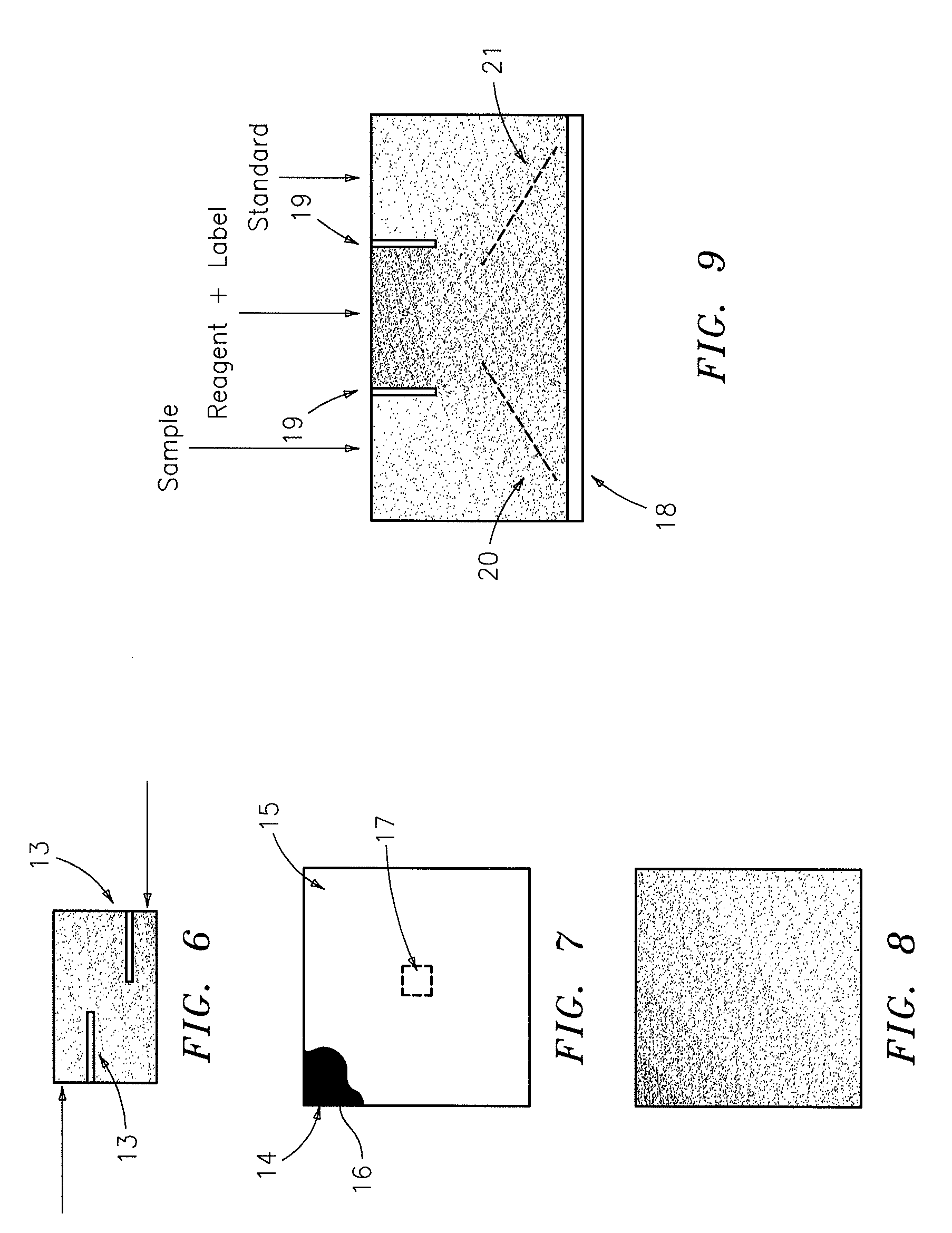
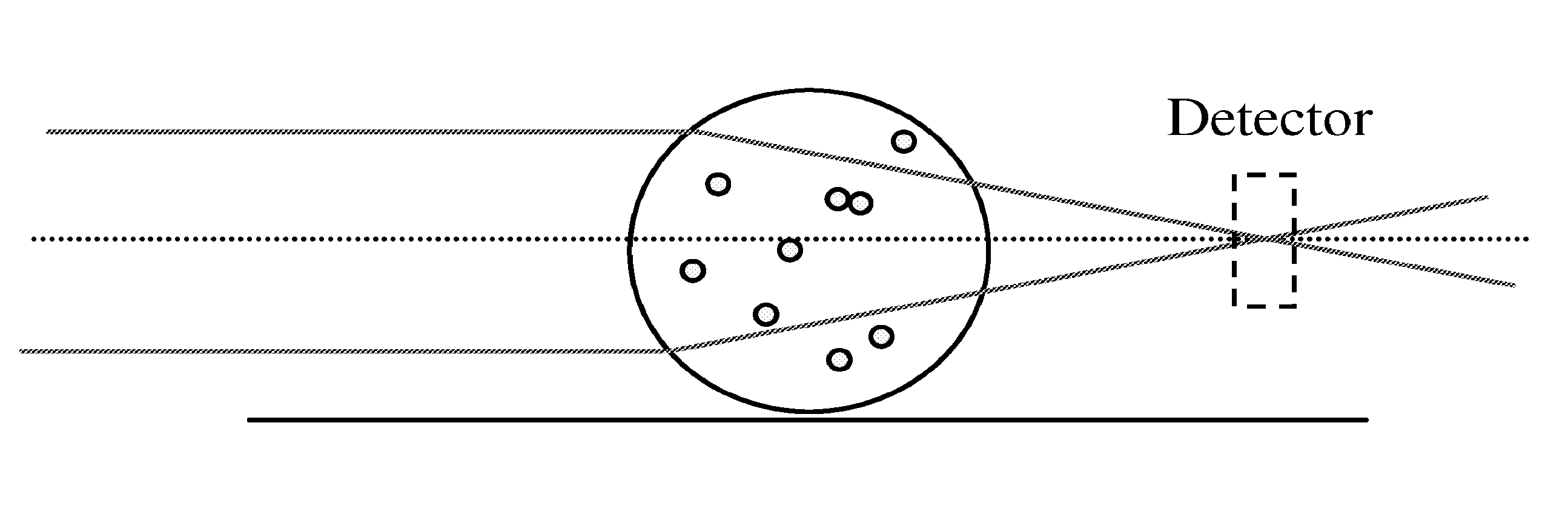
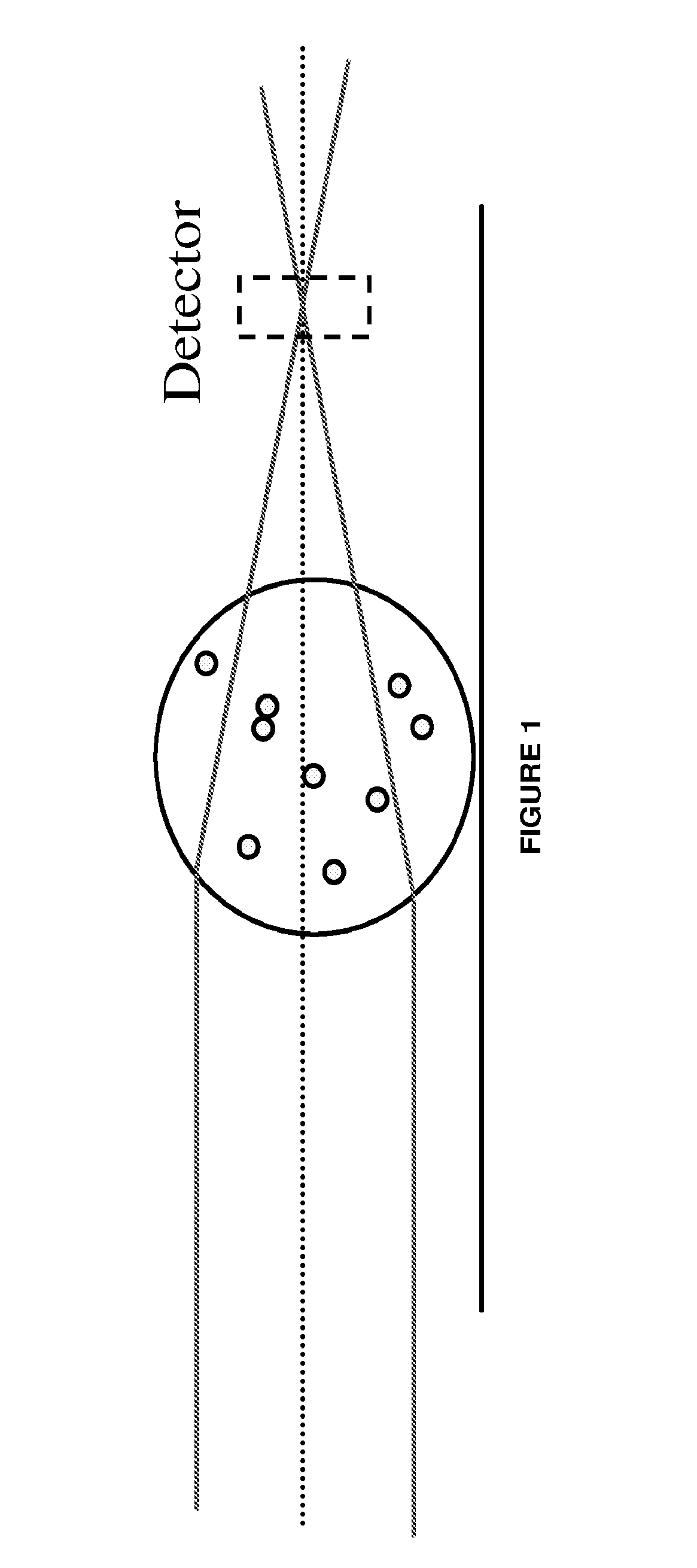
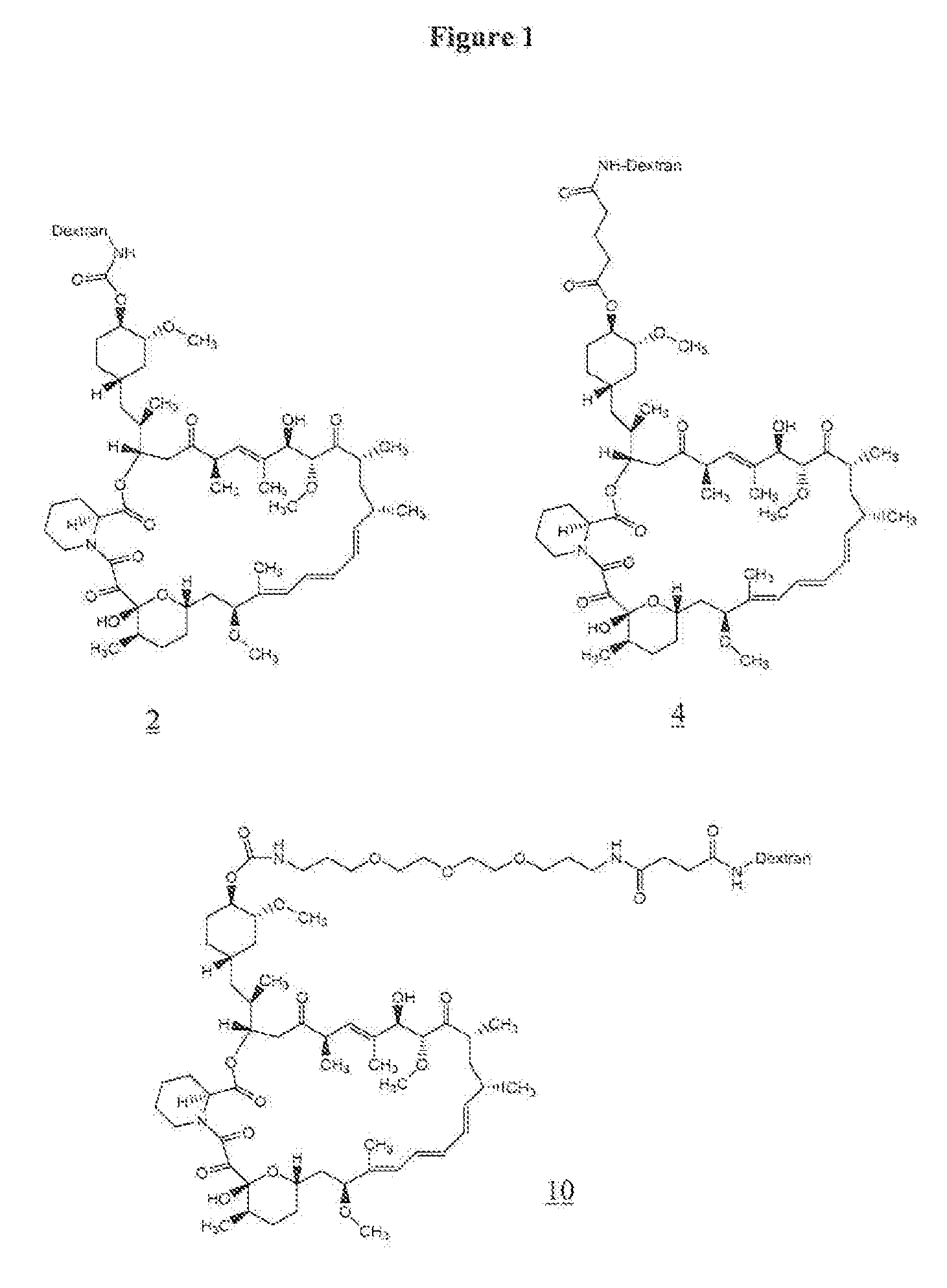
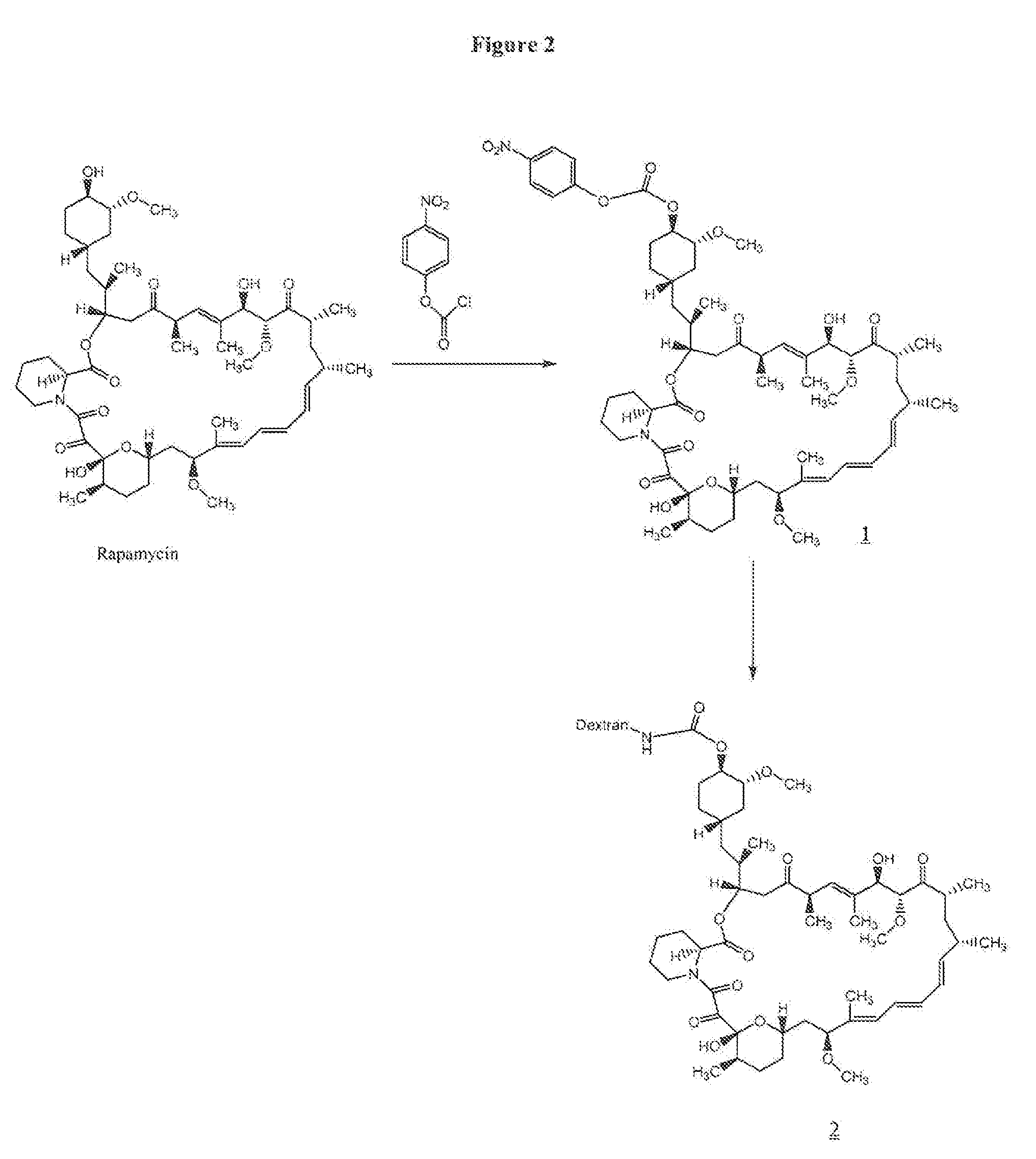
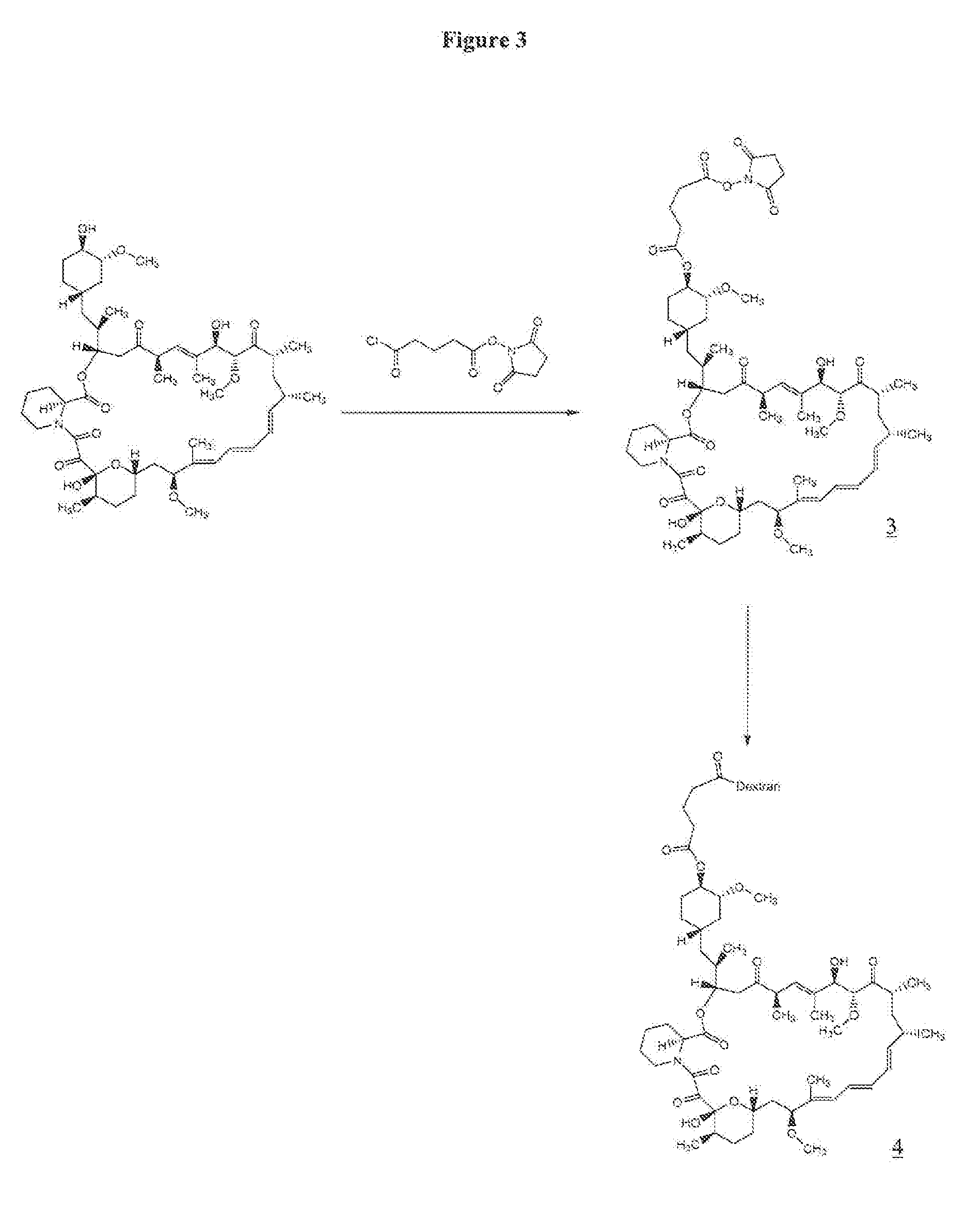
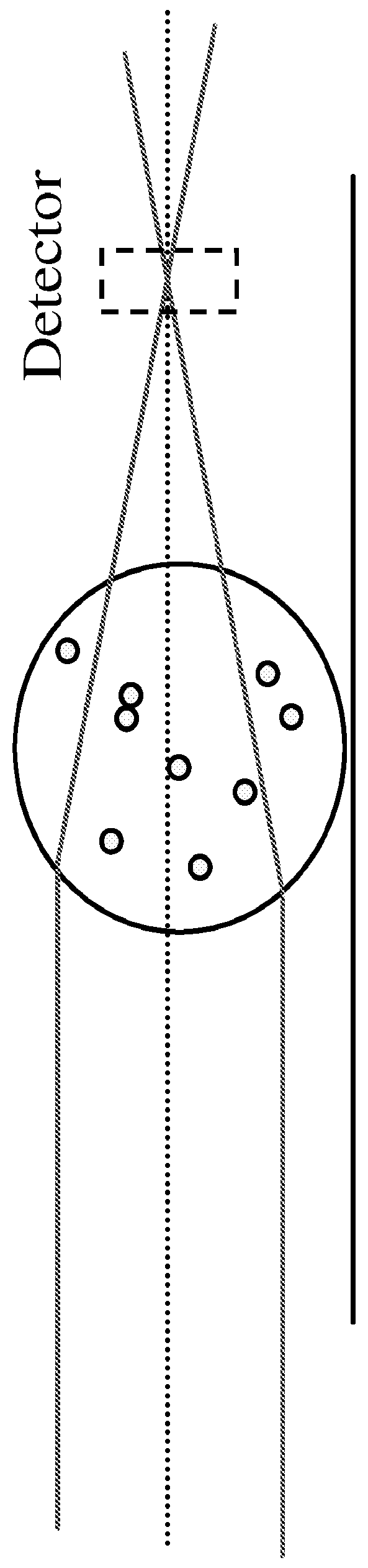
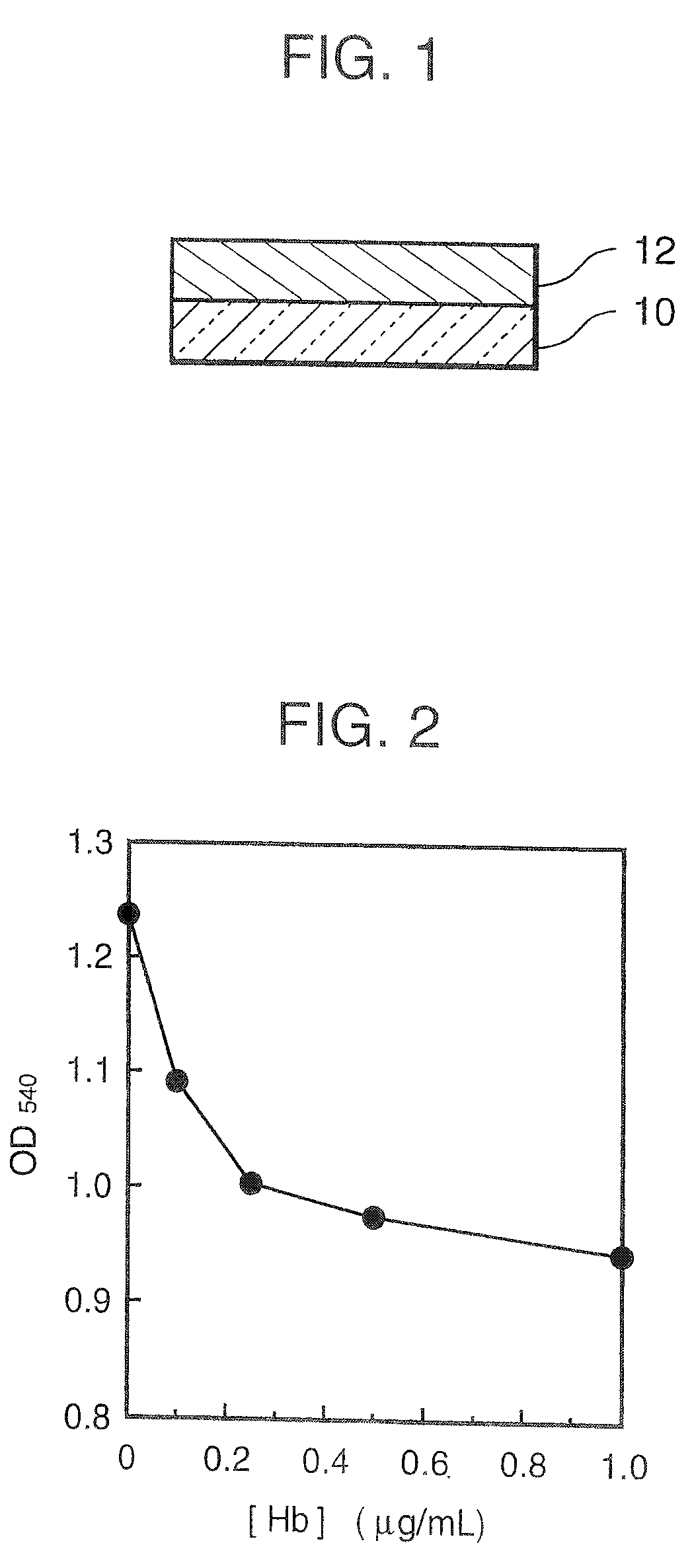
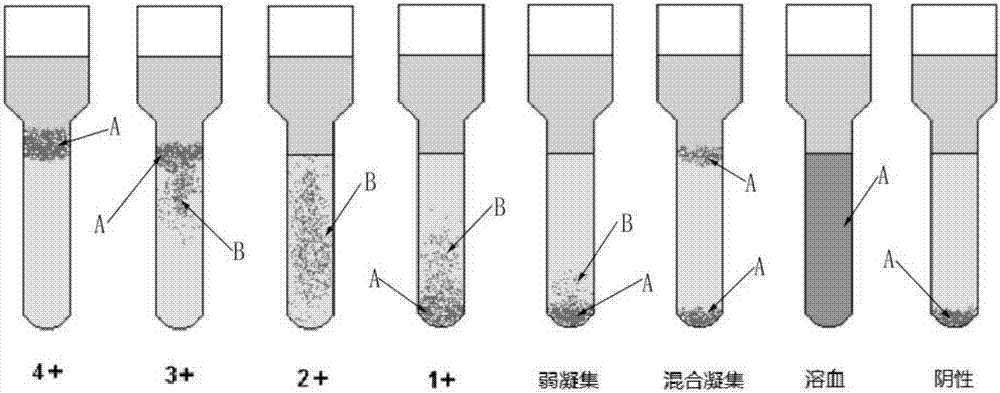
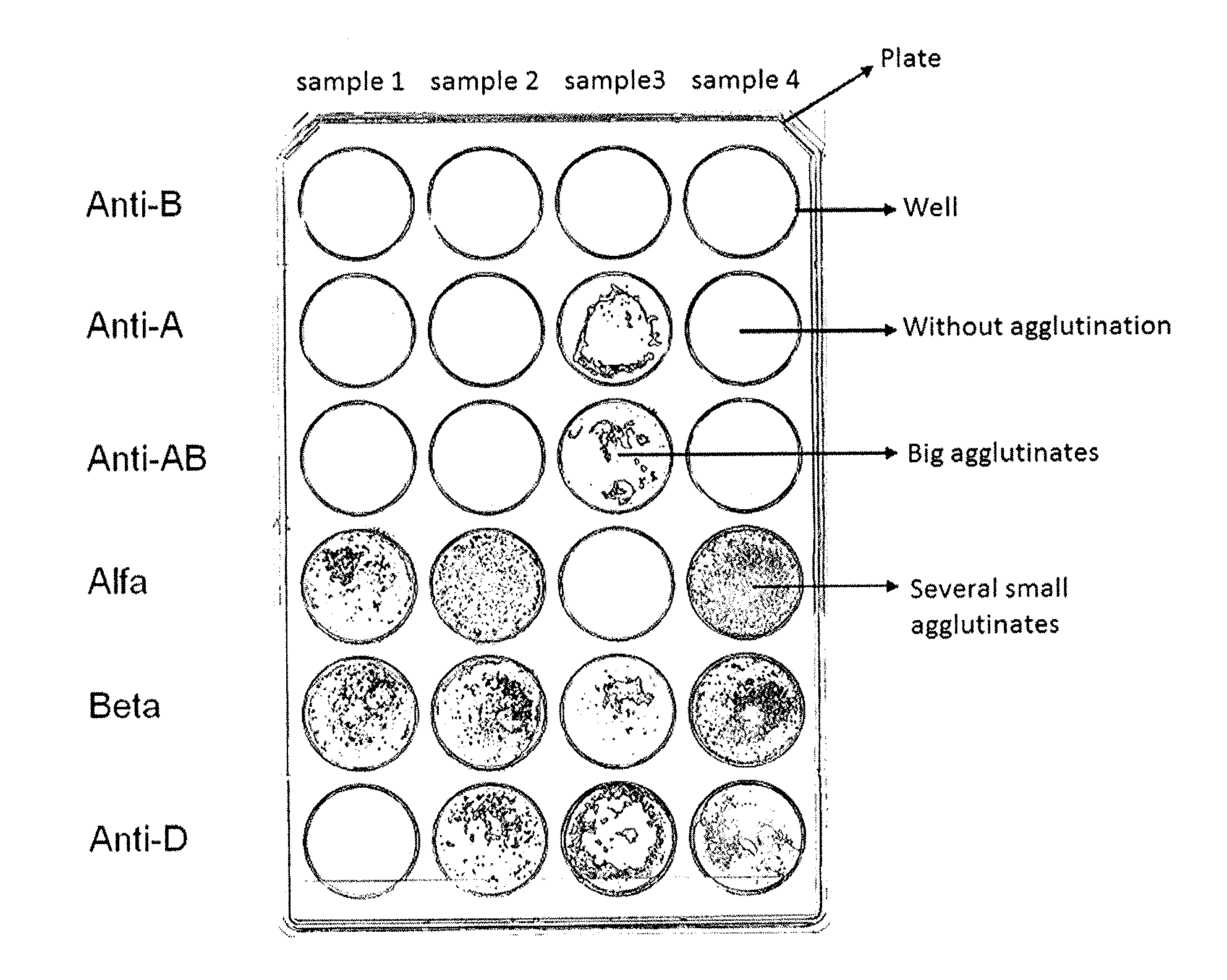
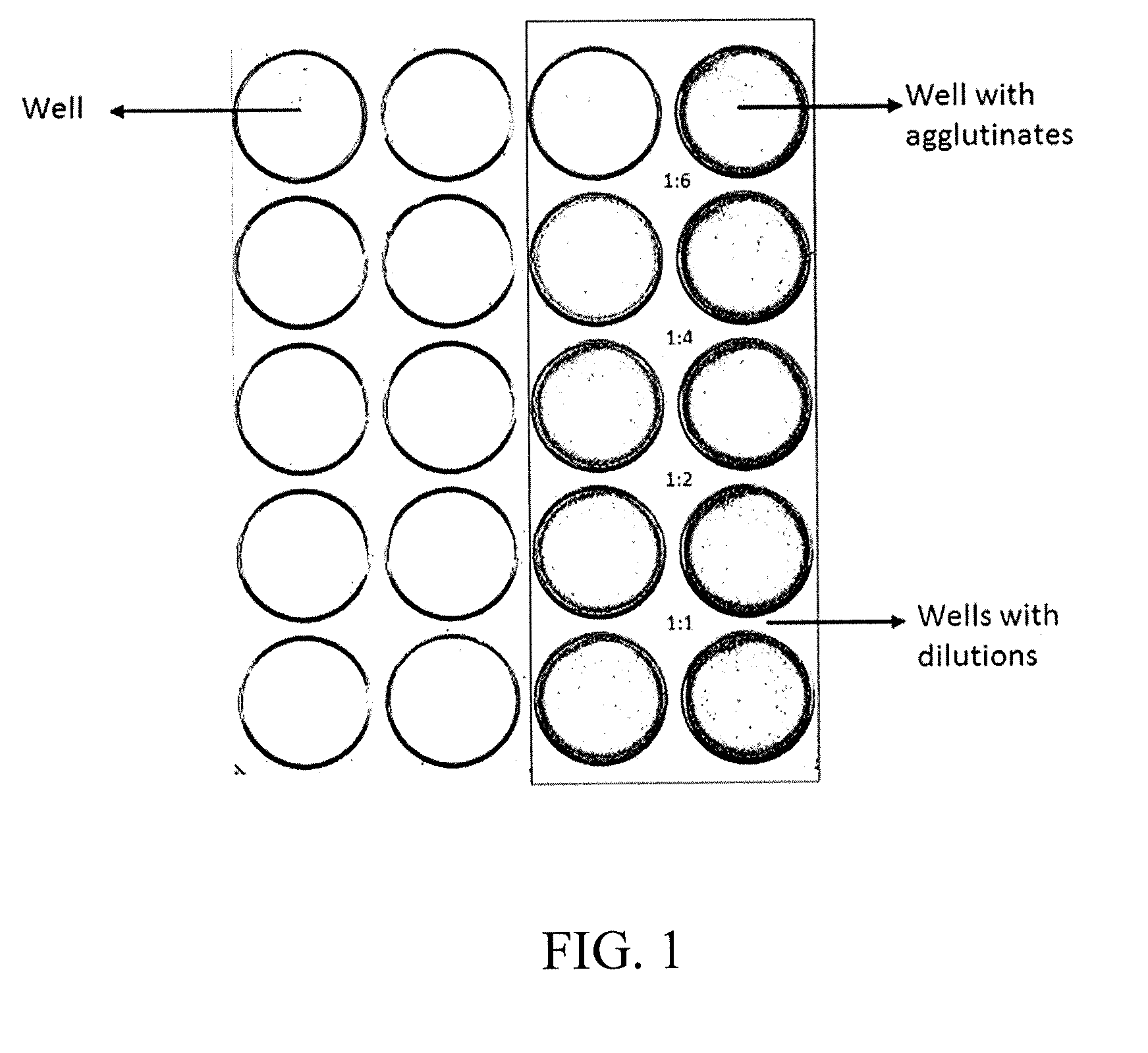
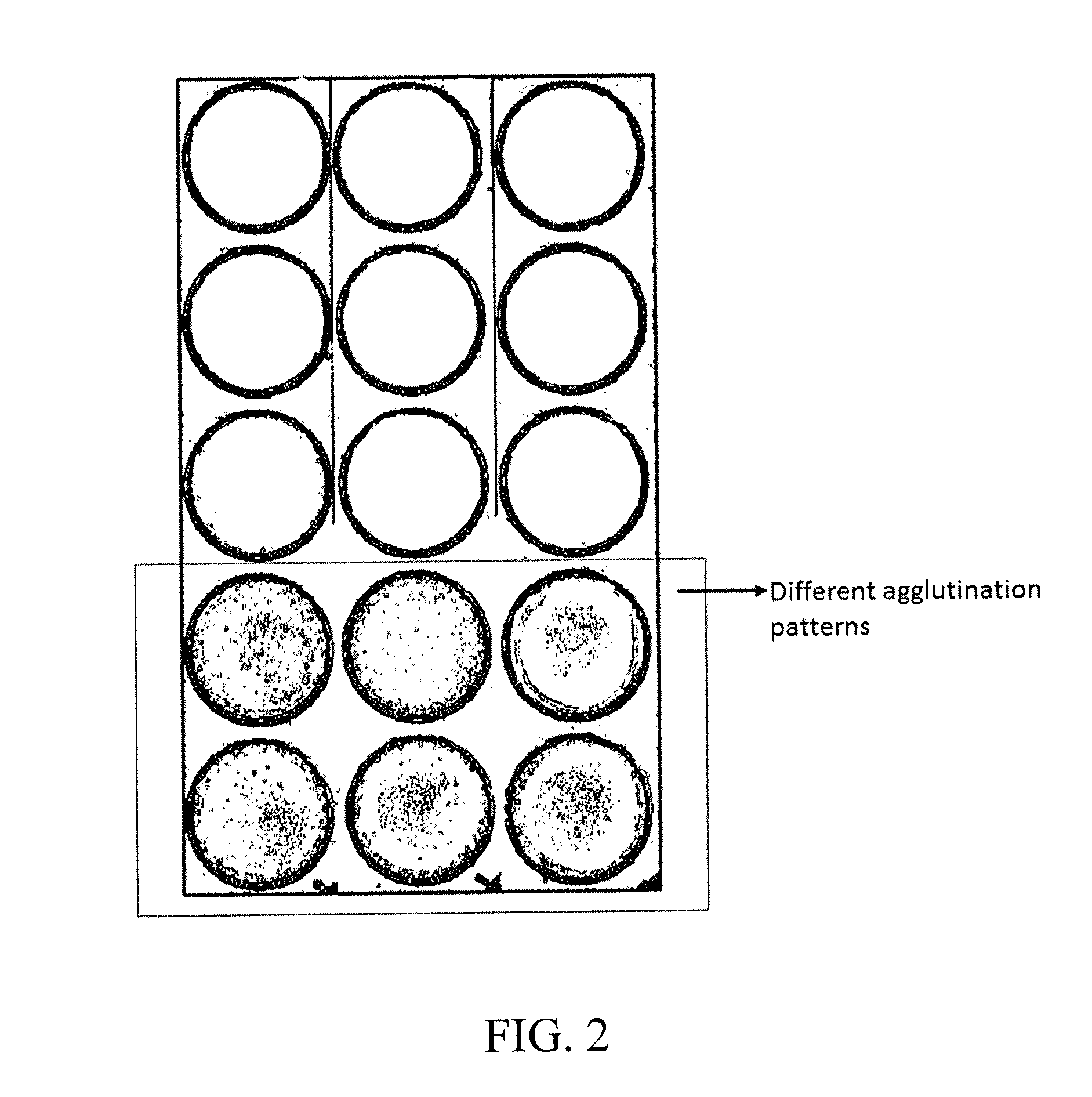
Agglutination can be used as an indicator of the presence of antibodies against bacteria or red blood cells. Agglutination assays are usually quick and easy to perform on a glass slide or microtiter plate (Figure 1).
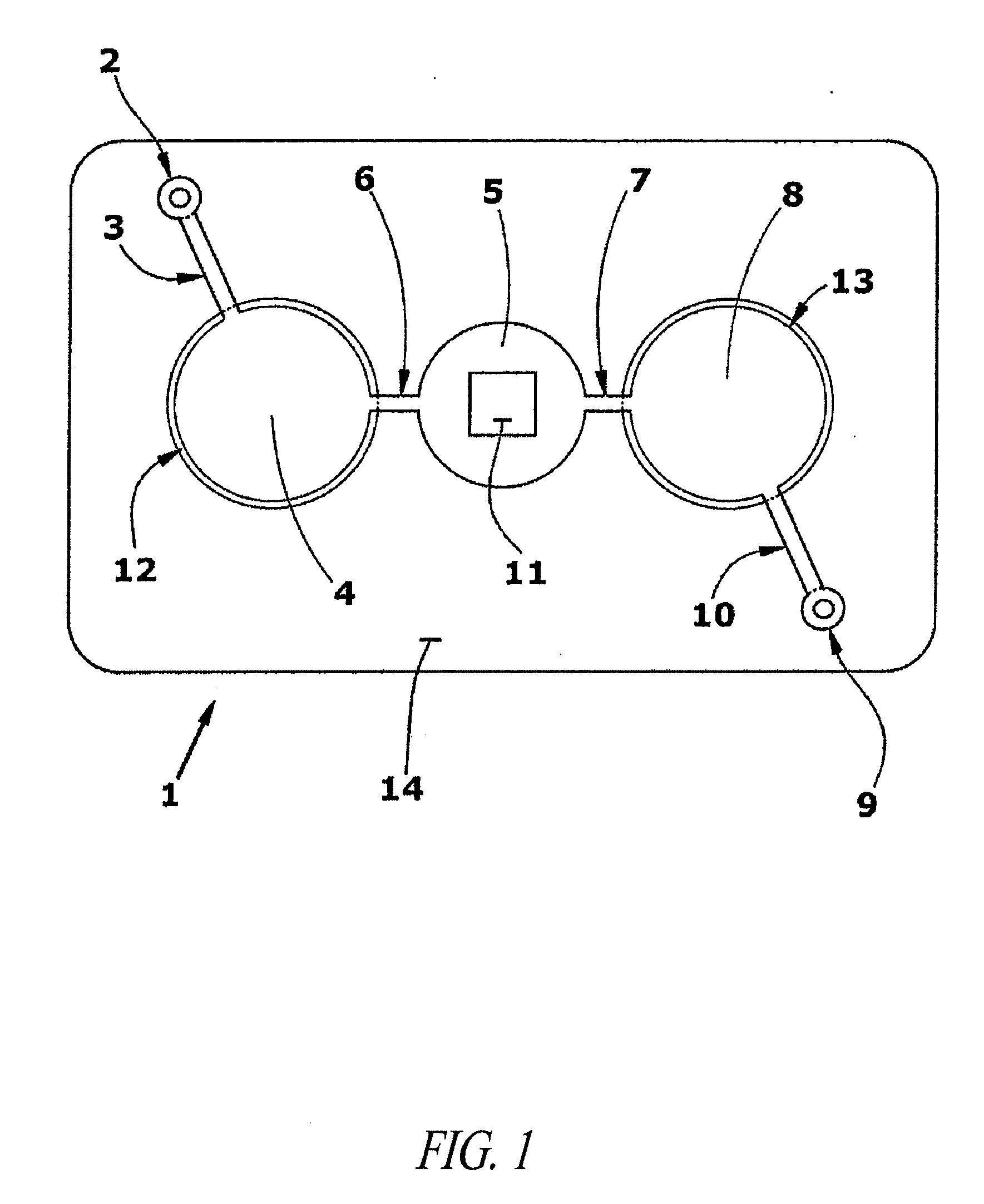
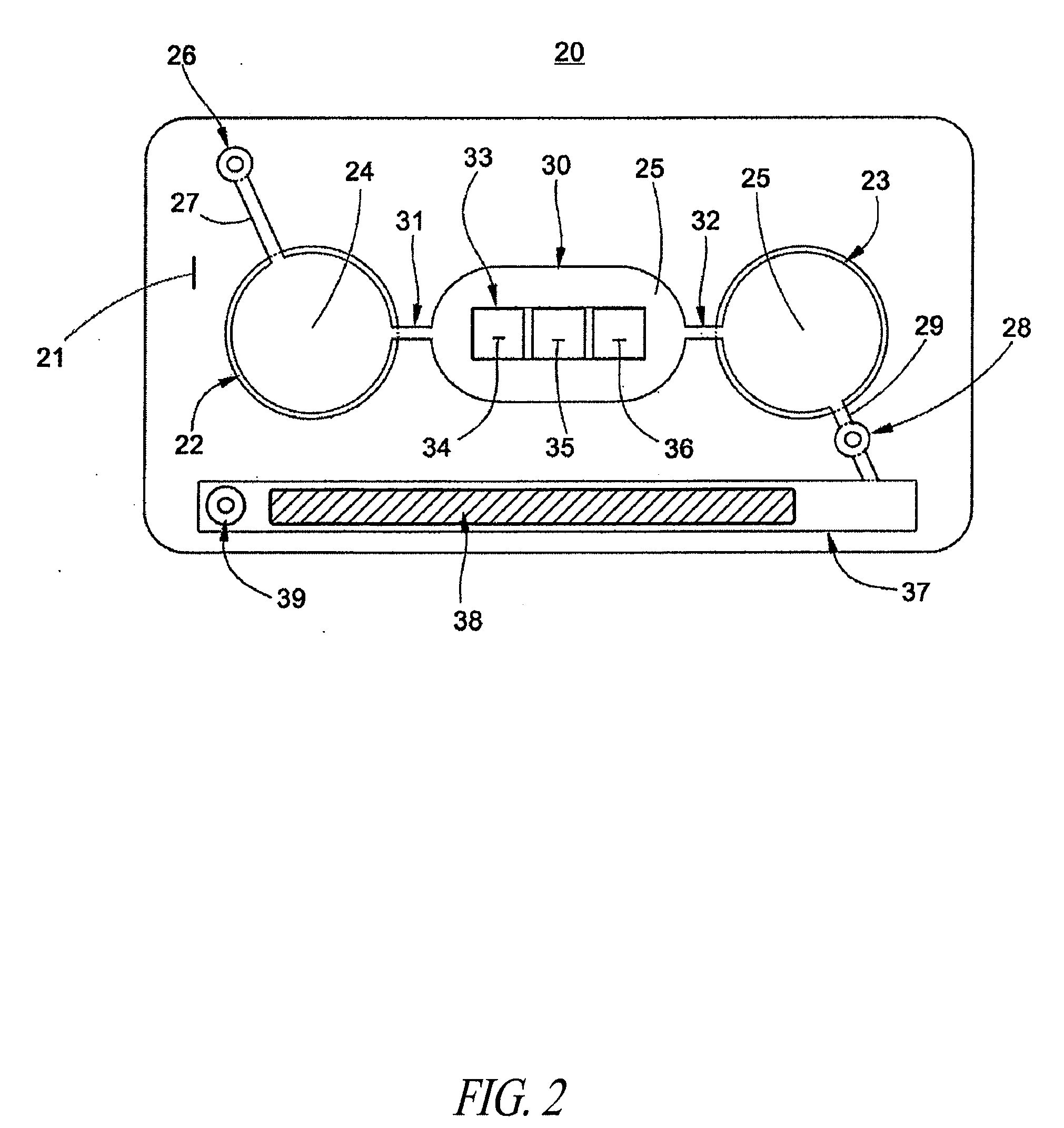
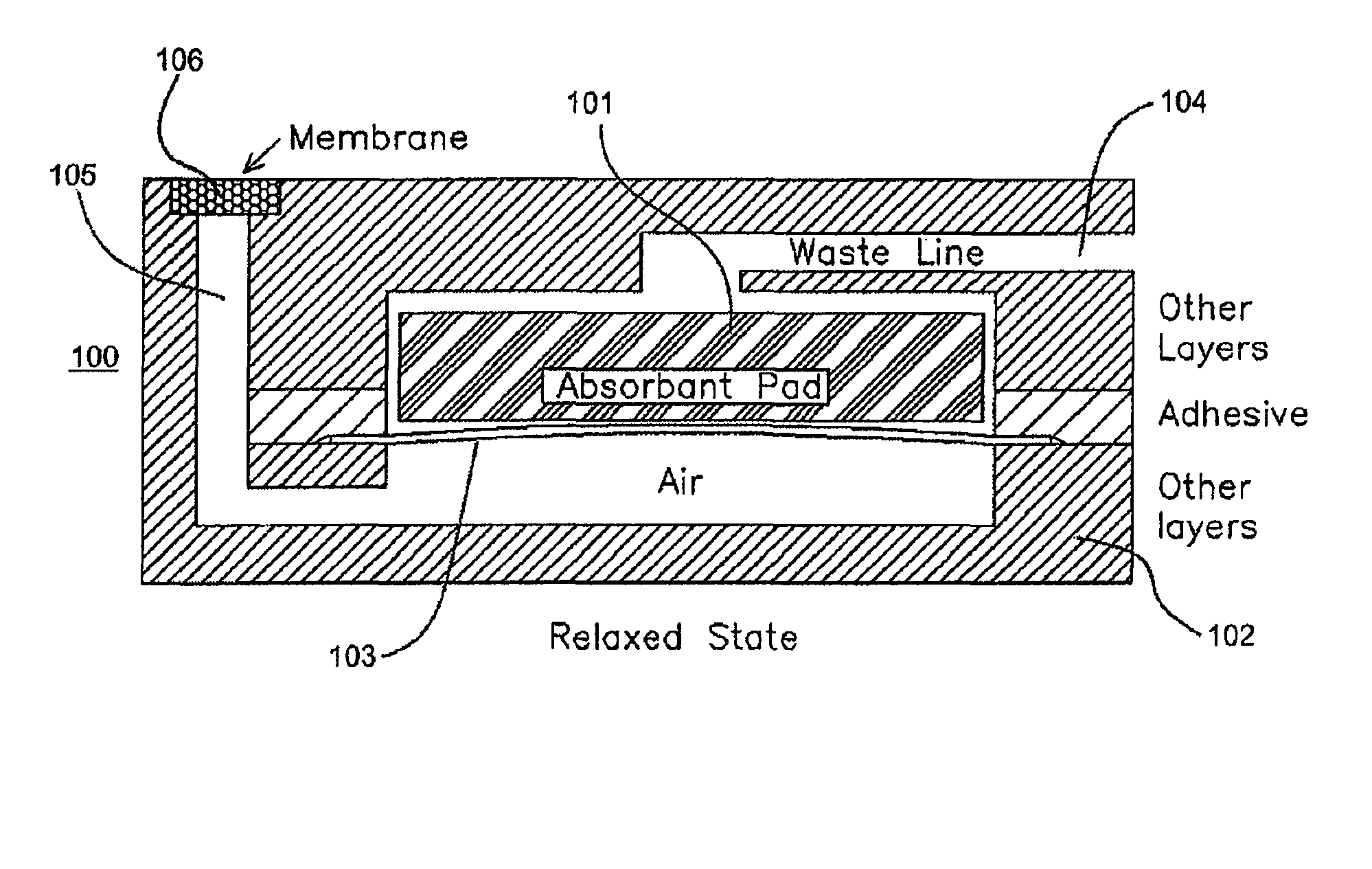
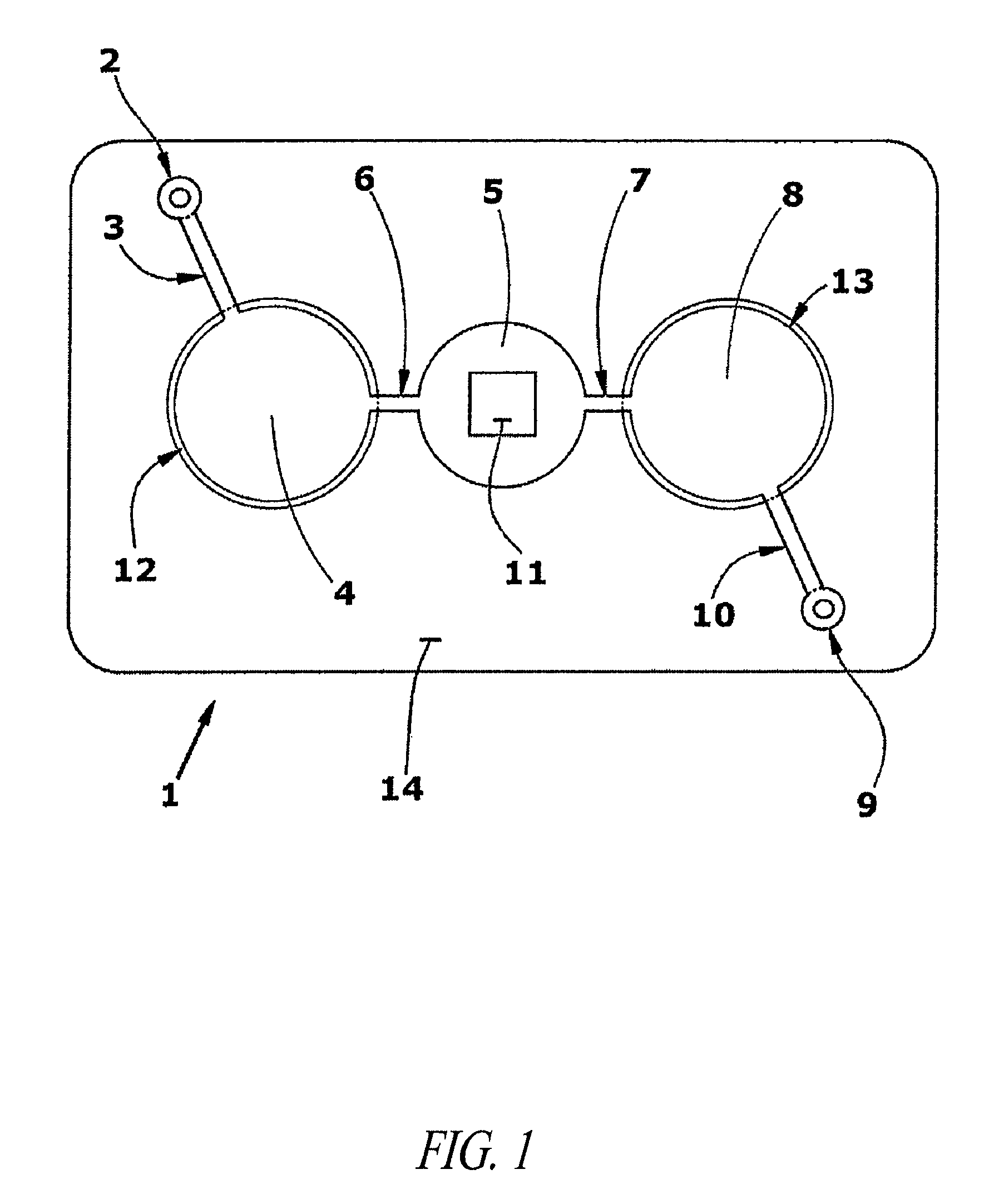
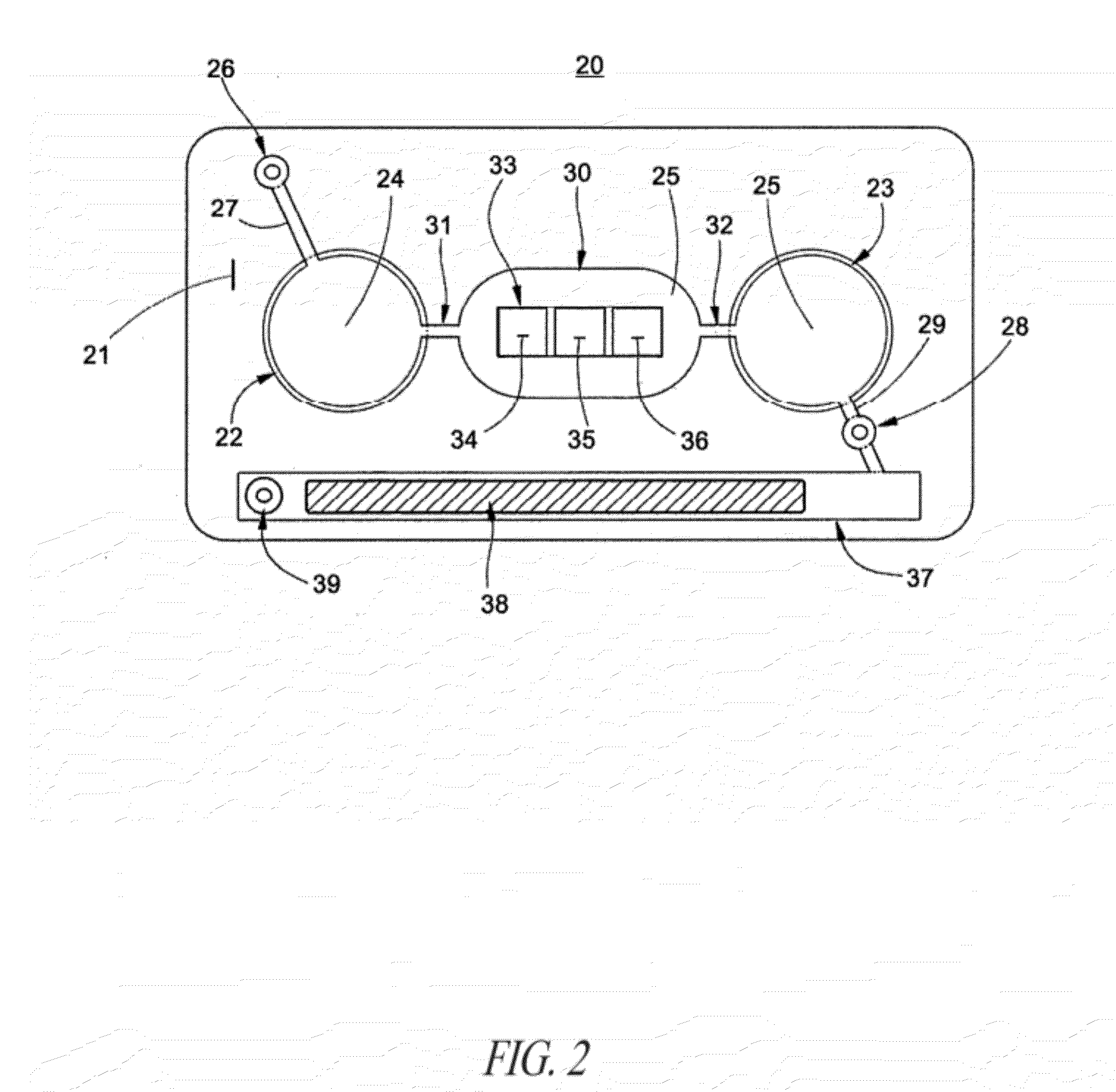
Methods and devices for microfluidic point-of-care immunoassays
ActiveUS20090181411A1Endpoint detectionReduce incubation timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careSystems design
Microfluidic methods and devices for heterogeneous binding and agglutination assays are disclosed, with improvements relating to mixing and to reagent and sample manipulation in systems designed for safe handling of clinical test samples.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
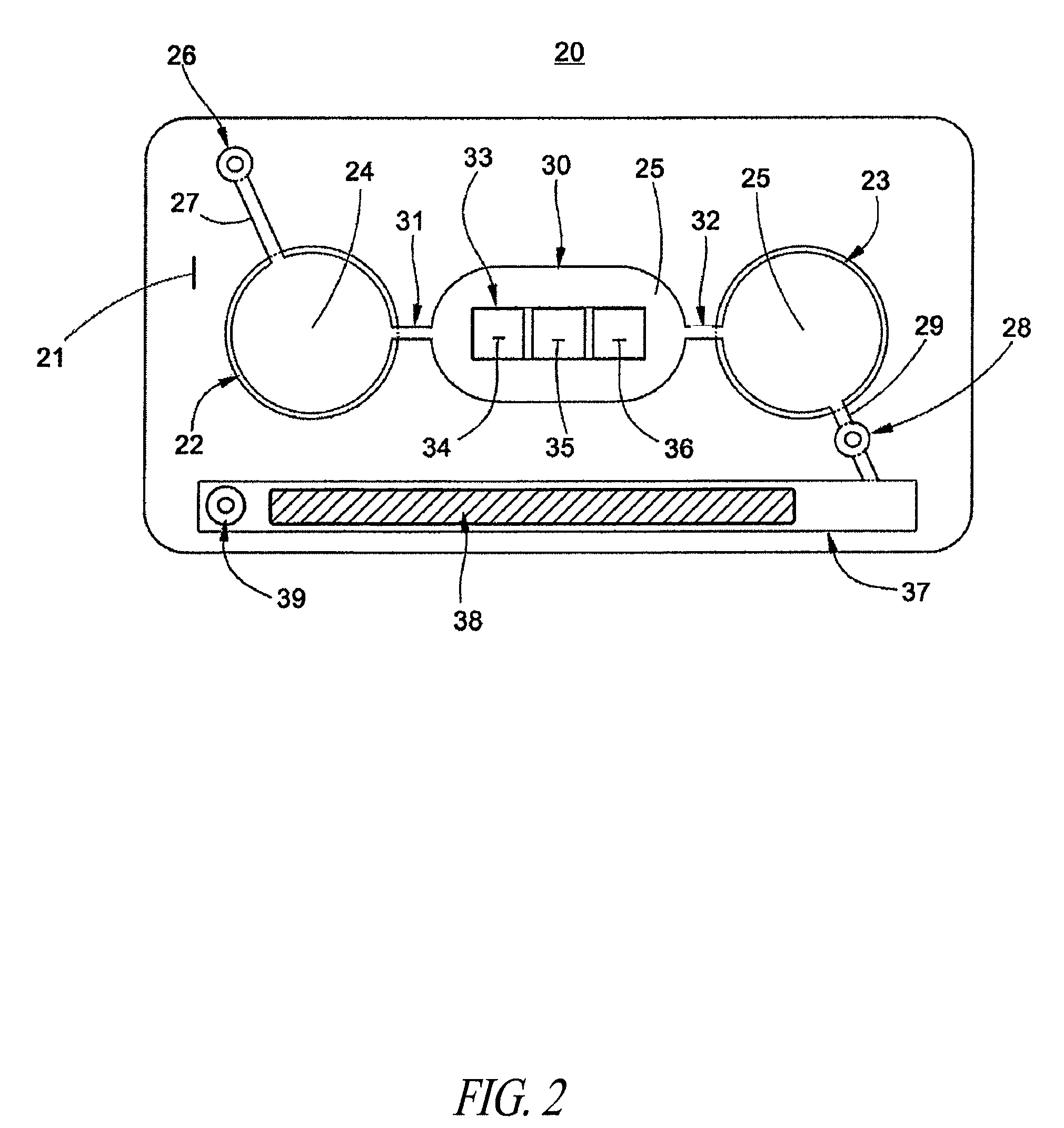
Methods and devices for microfluidic point-of-care immunoassays
ActiveUS8110392B2Reduce incubation timeMean flow velocityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersPoint of careSystems design
Microfluidic methods and devices for heterogeneous binding and agglutination assays are disclosed, with improvements relating to mixing and to reagent and sample manipulation in systems designed for safe handling of clinical test samples.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
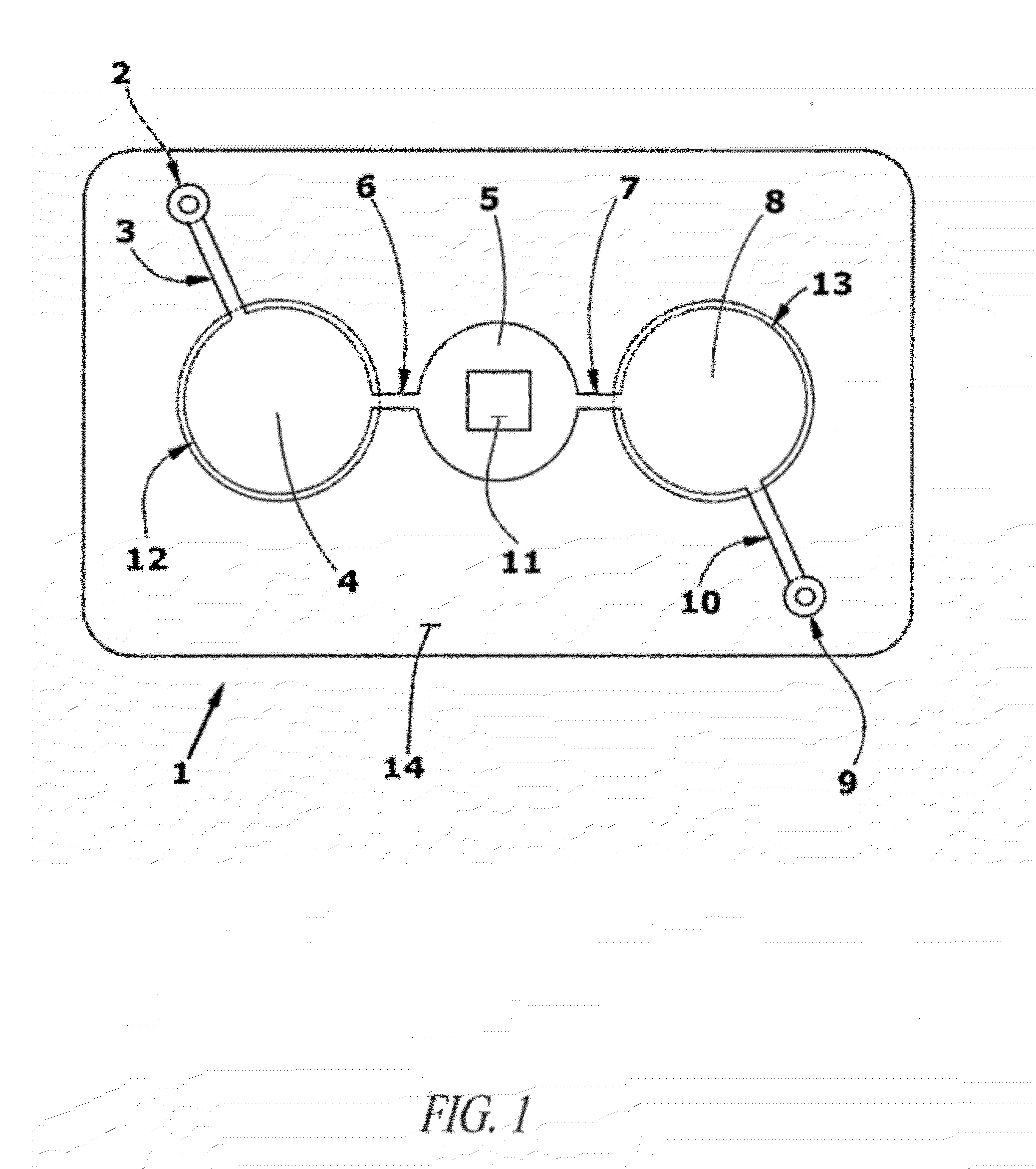
Methods and devices for microfluidic point-of-care immunoassays
InactiveUS20120164627A1Reduce incubation timeMean flow velocityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersPoint of careSystems design
Microfluidic methods and devices for heterogeneous binding and agglutination assays are disclosed, with improvements relating to mixing and to reagent and sample manipulation in systems designed for safe handling of clinical test samples.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
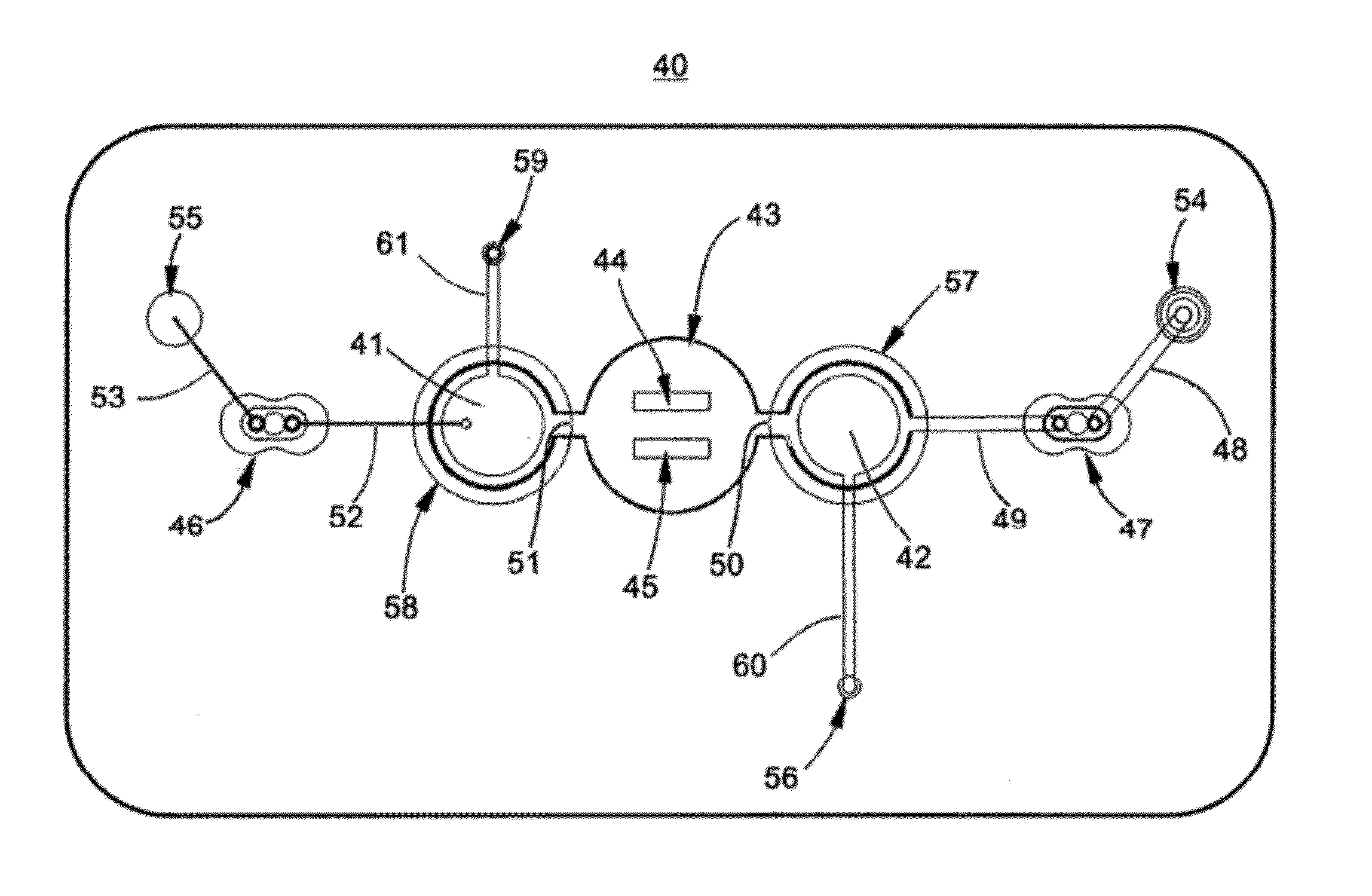
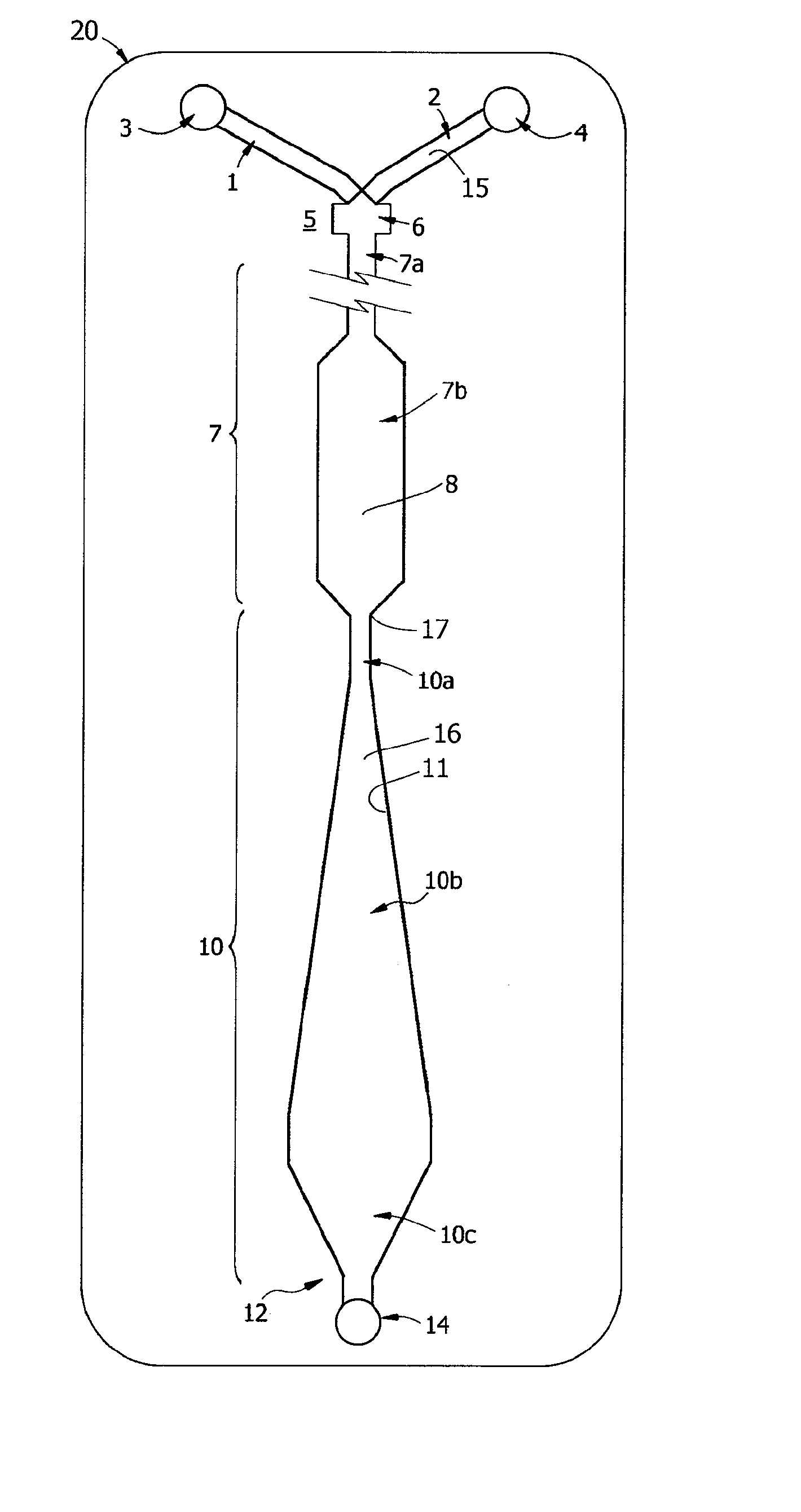
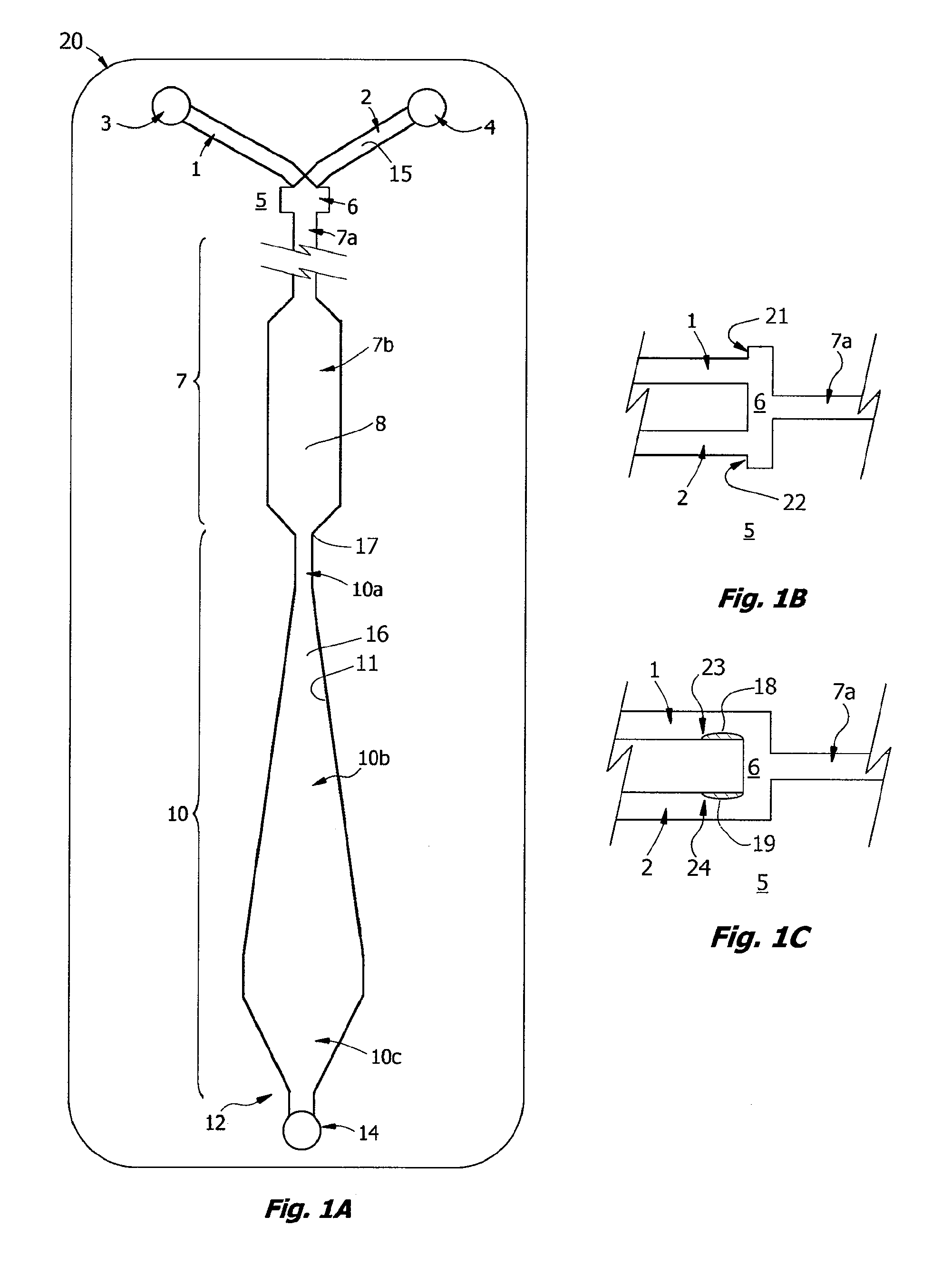
Microfluidic apparatus and methods for performing blood typing and crossmatching
ActiveUS8318439B2Increase ratingsEasy to distinguishBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideAntigenAntibody-mediated agglutination
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Method and device for ultrasound assisted particle agglutination assay
InactiveUS20090053688A1Accurate assessmentSensitive detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActive matterAgglutination assay
Ultrasound-assisted particle agglutination assay methods and apparatuses are described based on first providing a standing wave ultrasound field at a resonance frequency of a test liquid in a resonator cell containing microparticles covered with a binding agent with high affinity to an analyte sought to be detected by the assay test. Formation of the specifically-bound and nonspecifically-bound aggregates of these microparticles is then followed by effective stirring of the liquid with swept-frequency sonication causing disintegration of nonspecifically-bound aggregates and leaving specifically-bound aggregates in place for further detection and measurement. The methods and devices of the invention allow significant improvement in the sensitivity and specificity of agglutination tests and are advantageously applicable to detecting various proteins, DNA, RNA and other biologically active substances. Specific examples are provided.
Owner:ALLIED INNOVATIVE SYST
Measuring agglutination parameters
ActiveUS20100033158A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or moreImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismAgglutination assayAgglutination
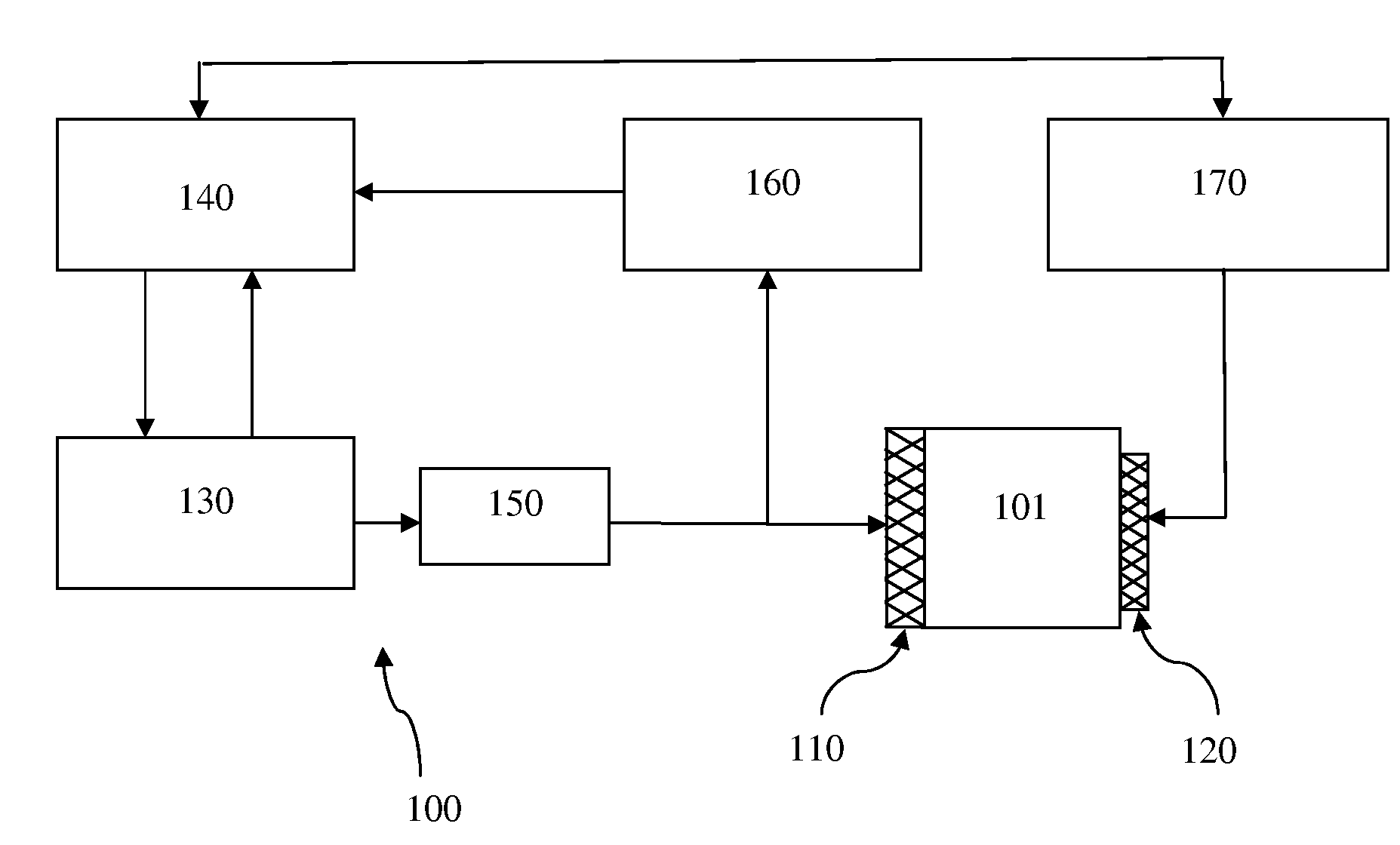
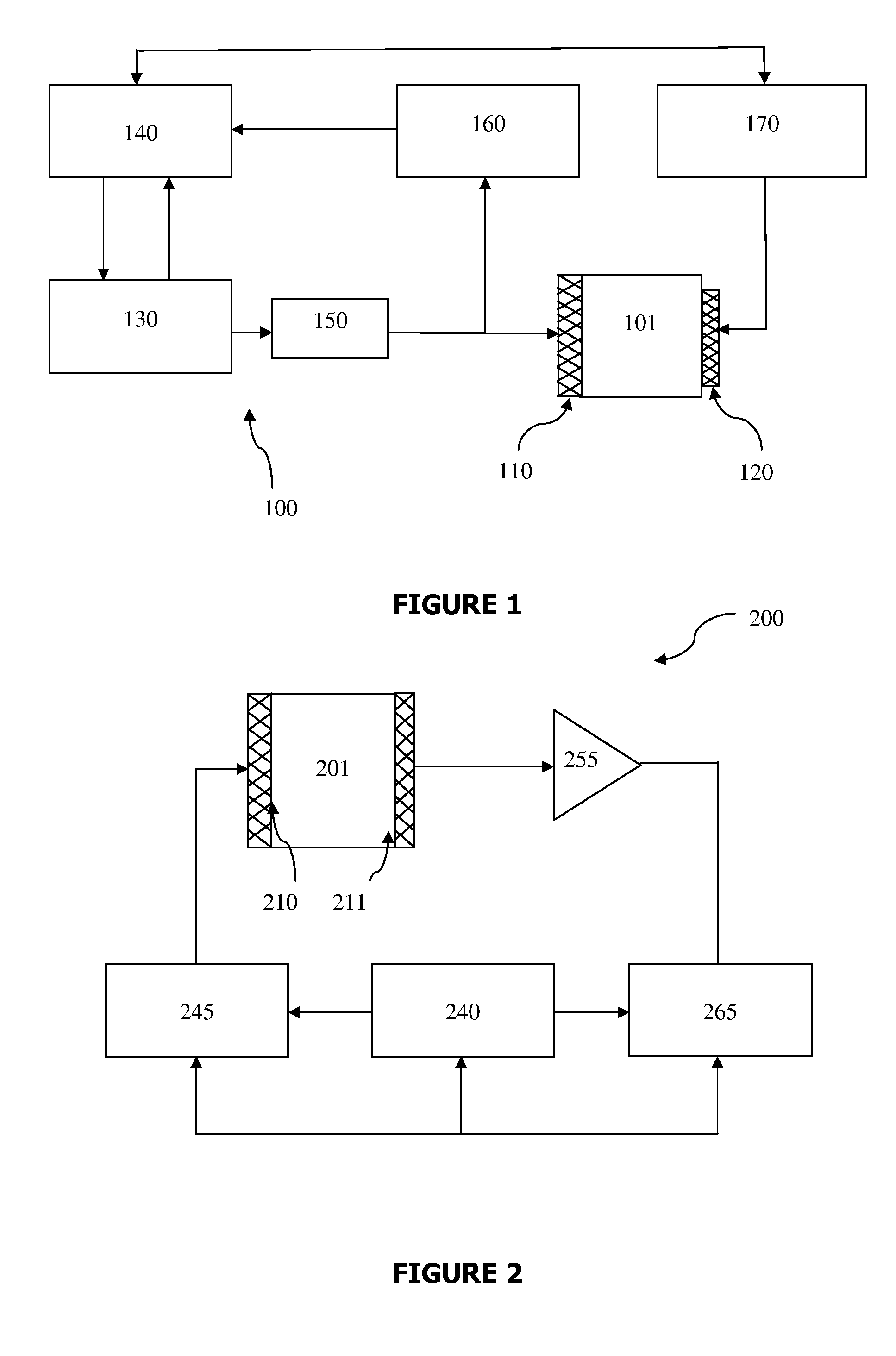
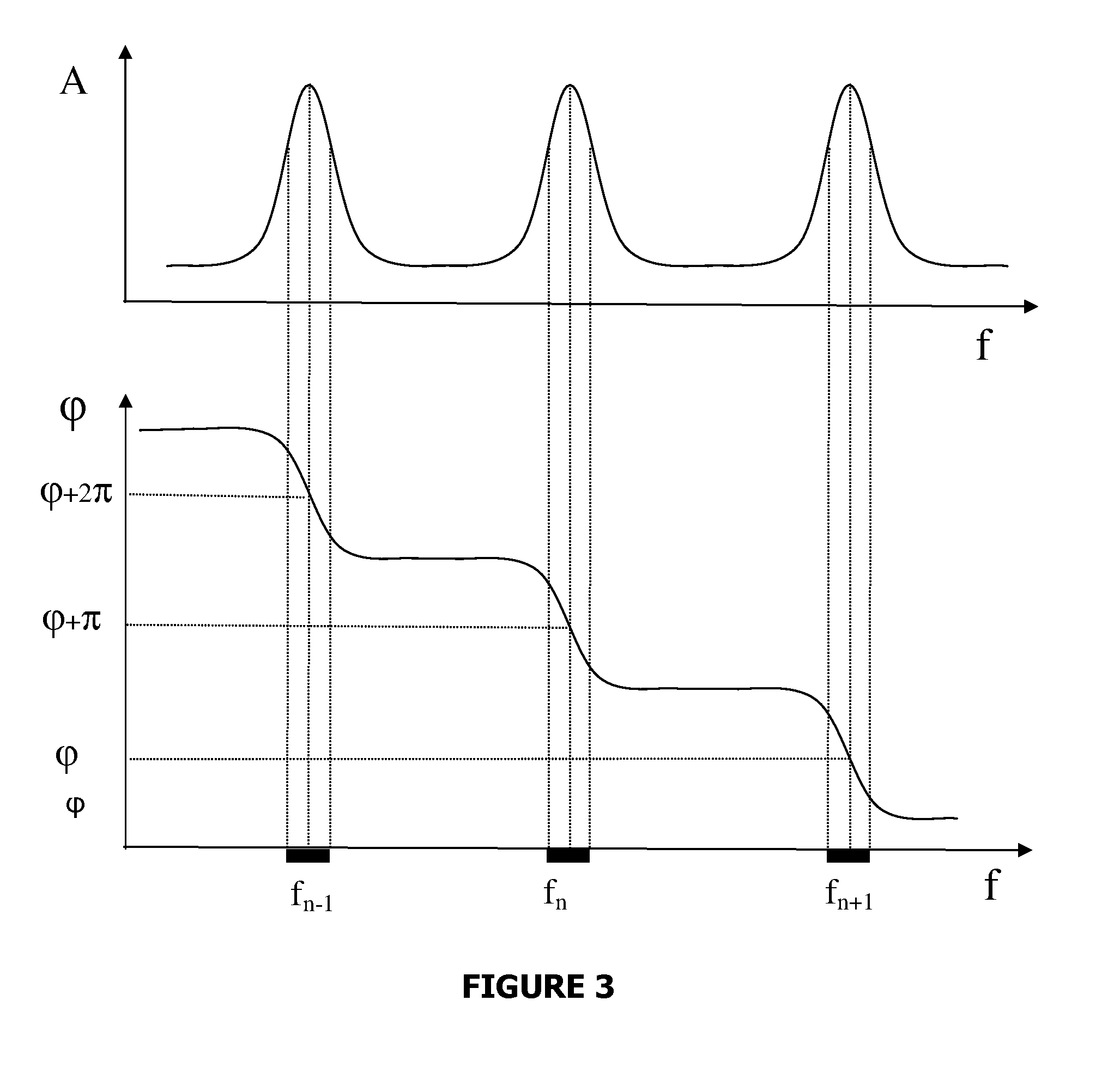
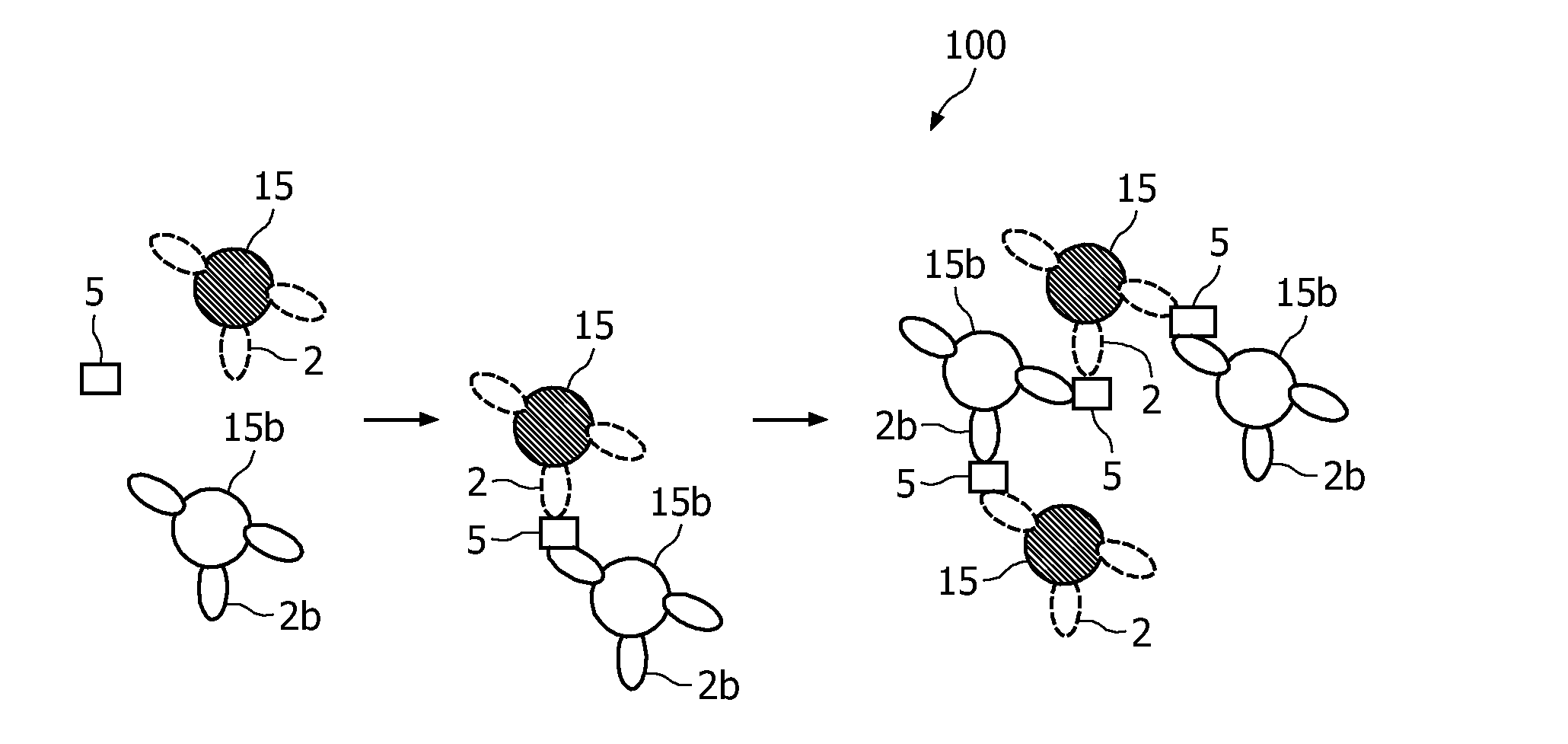
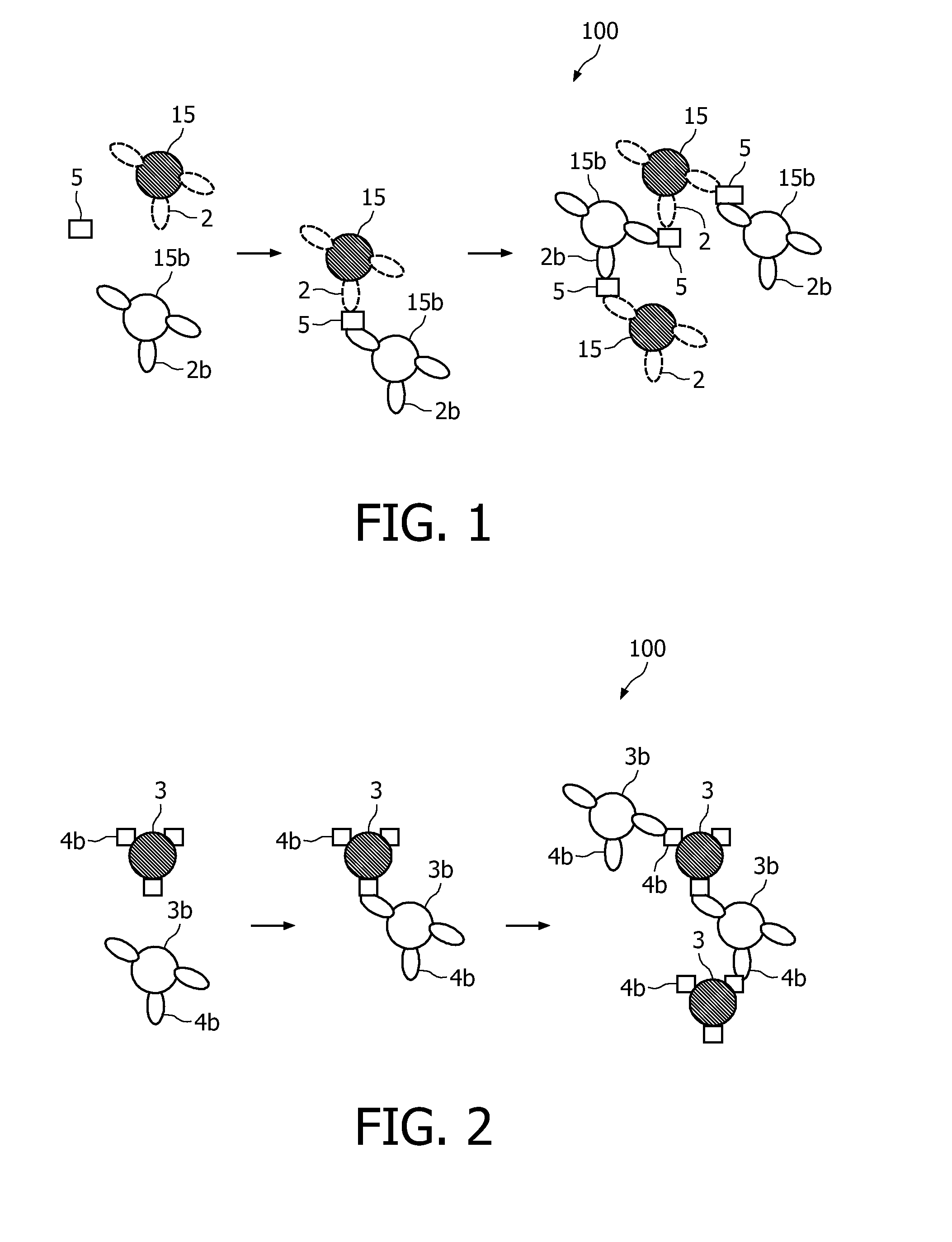
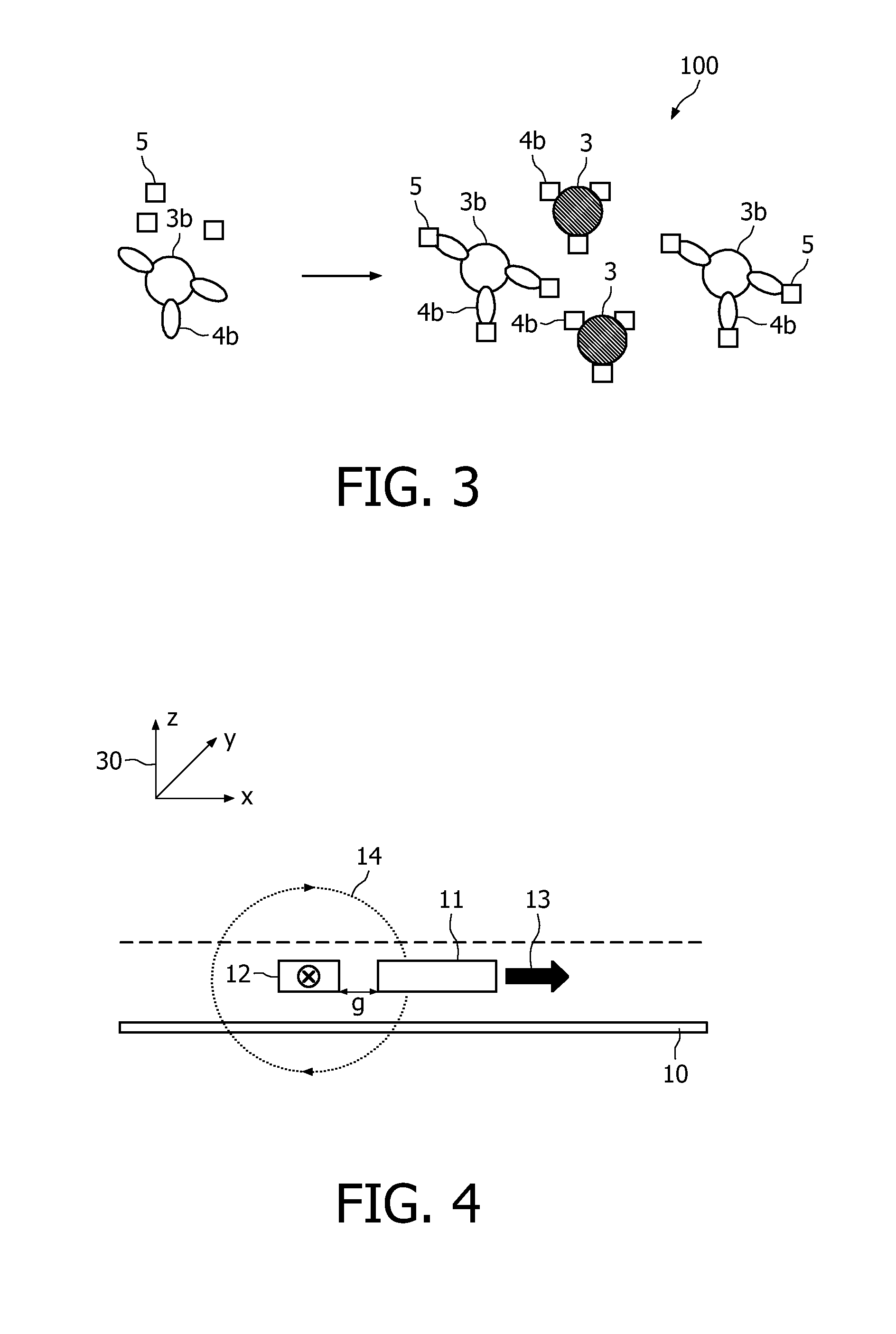
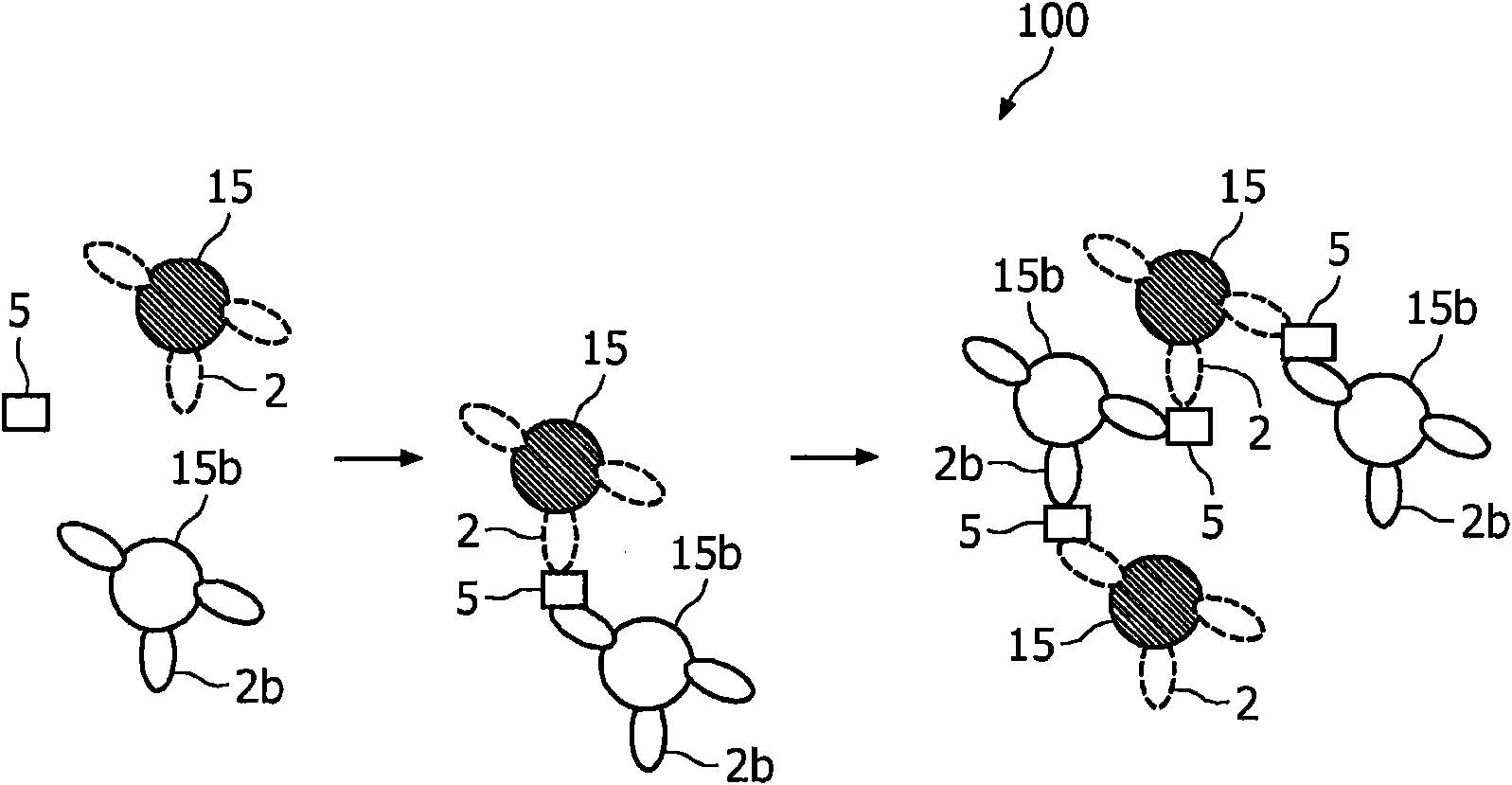
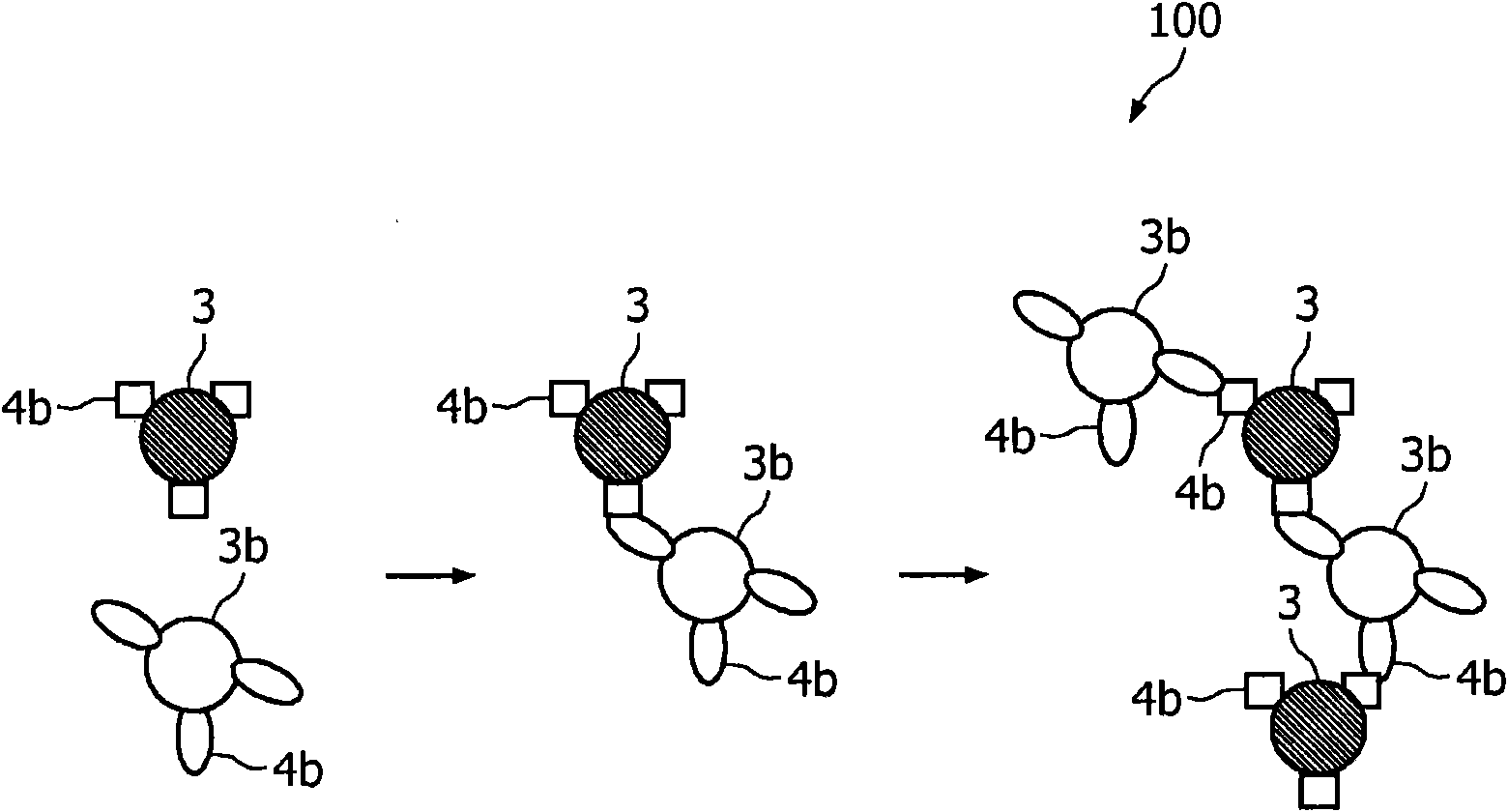
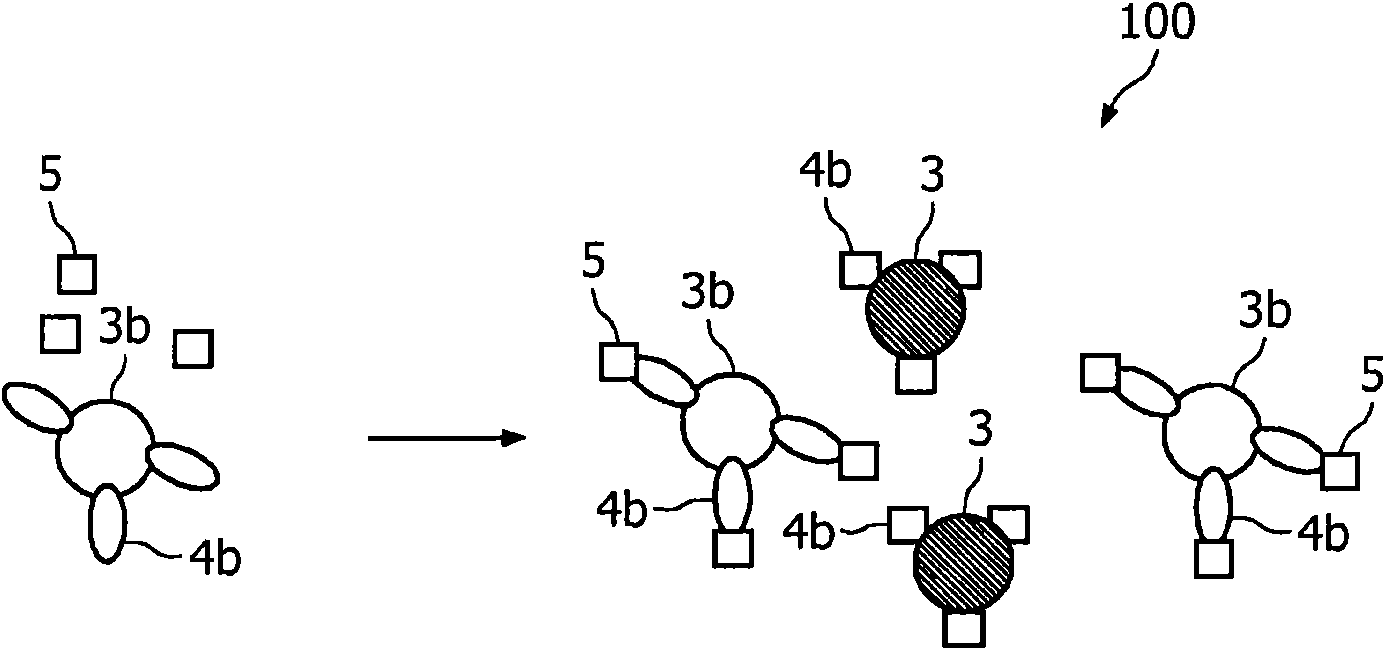
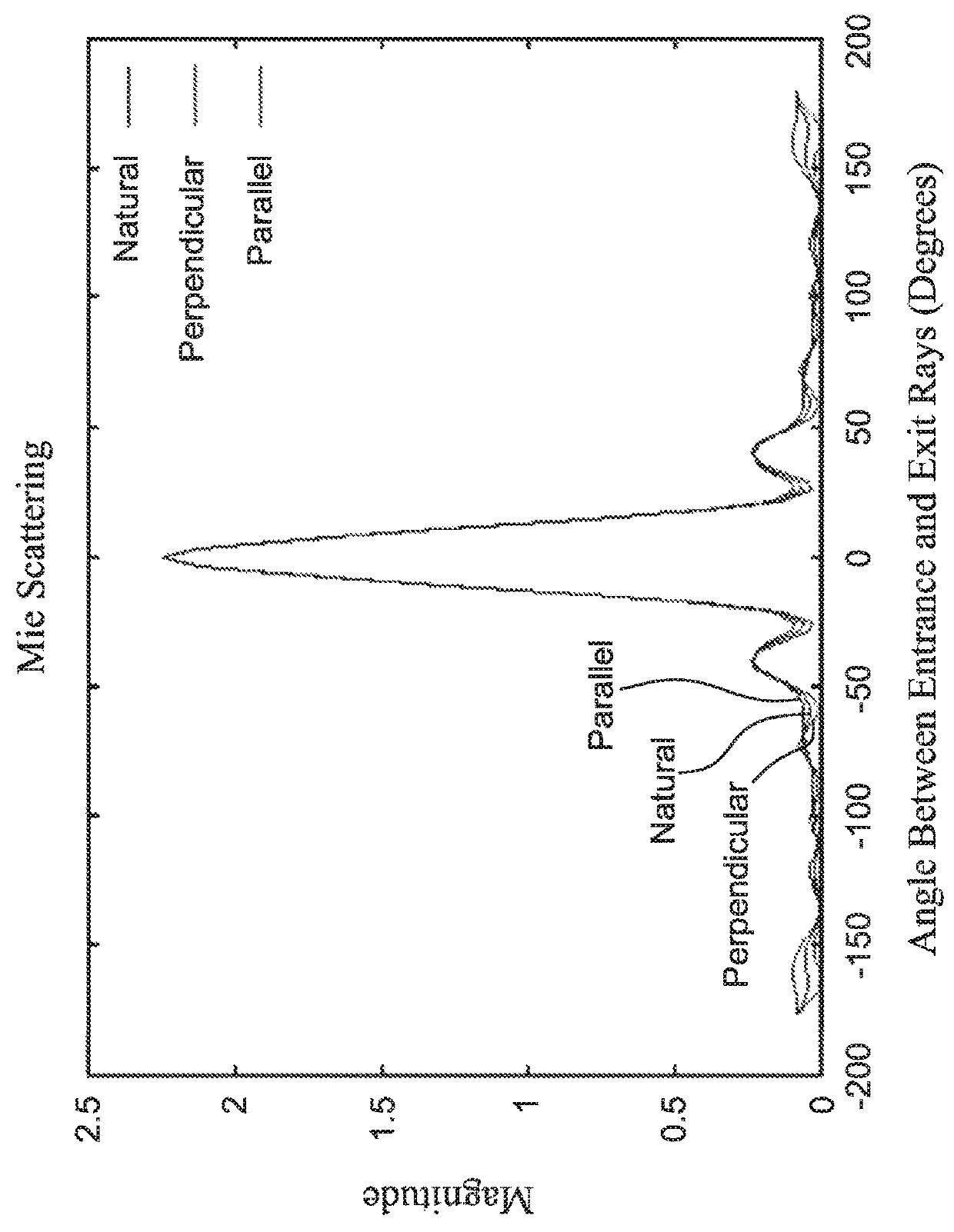
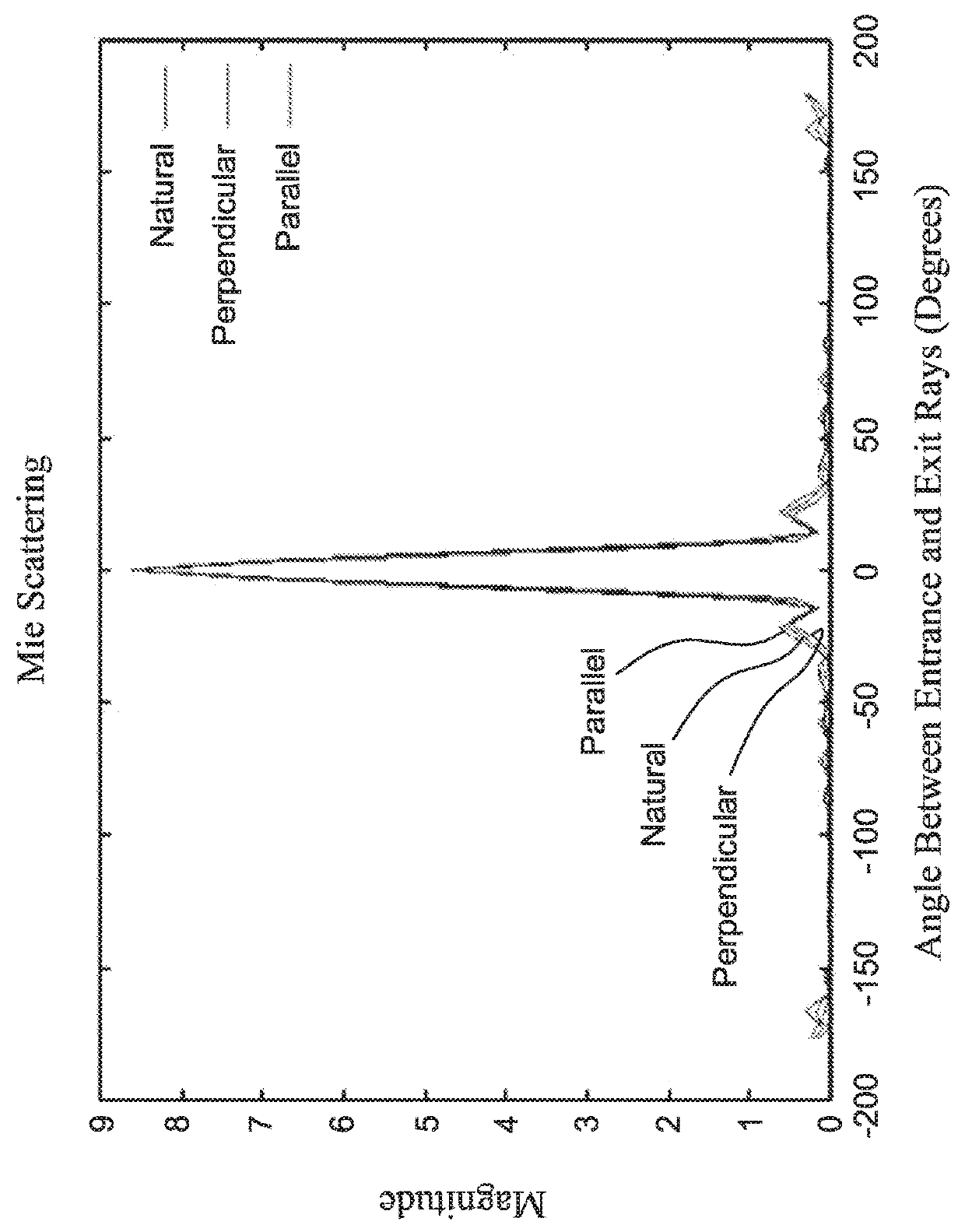
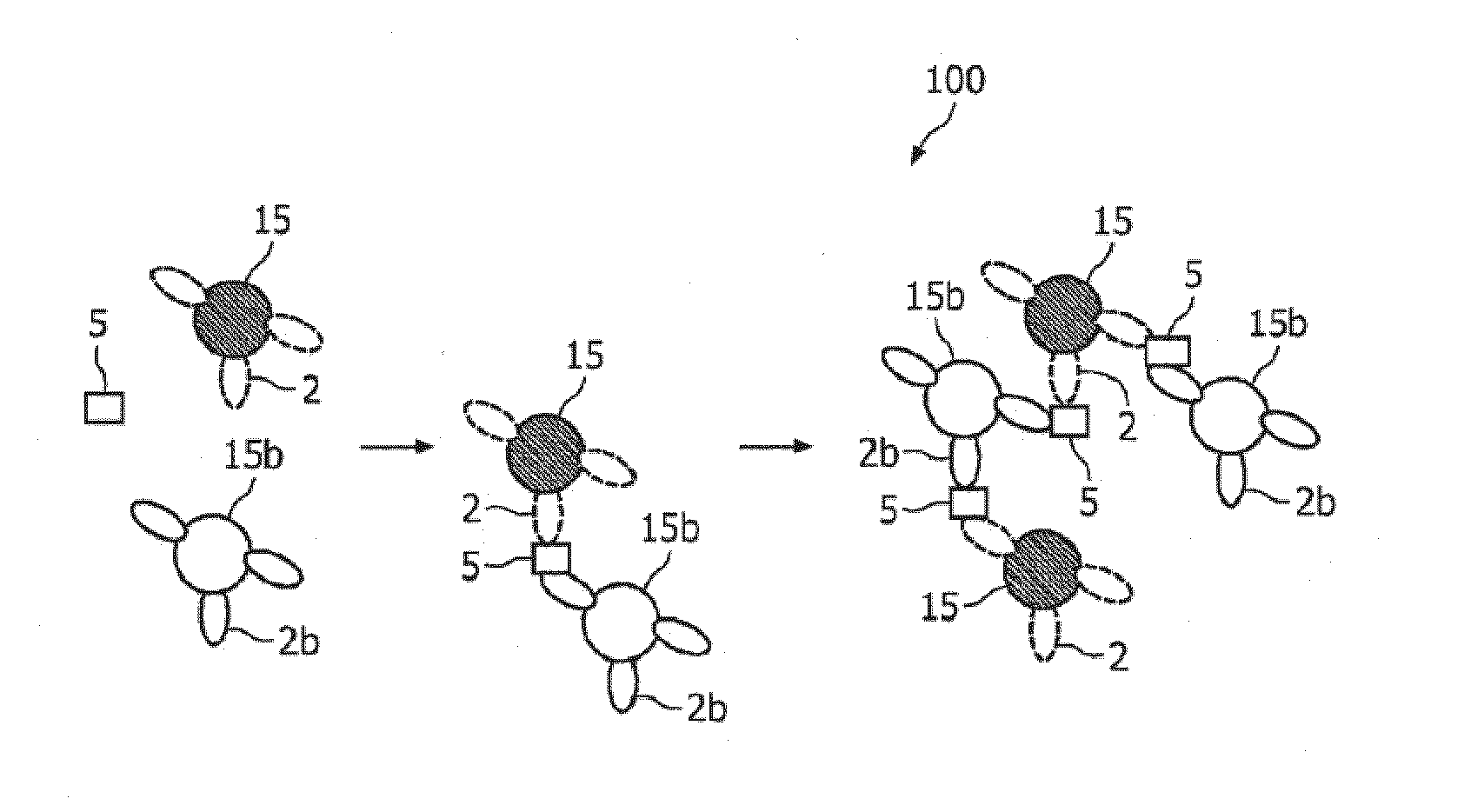
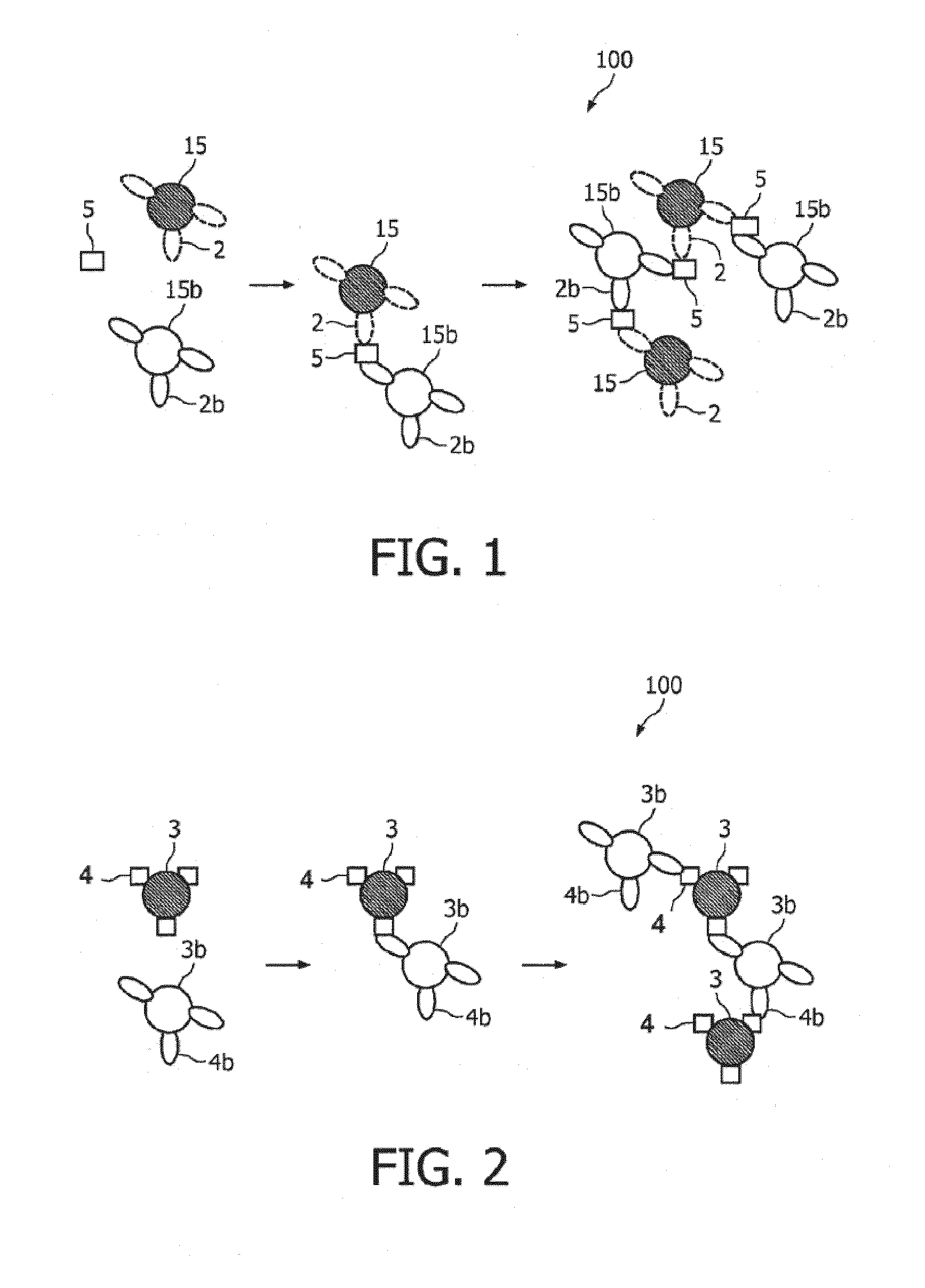
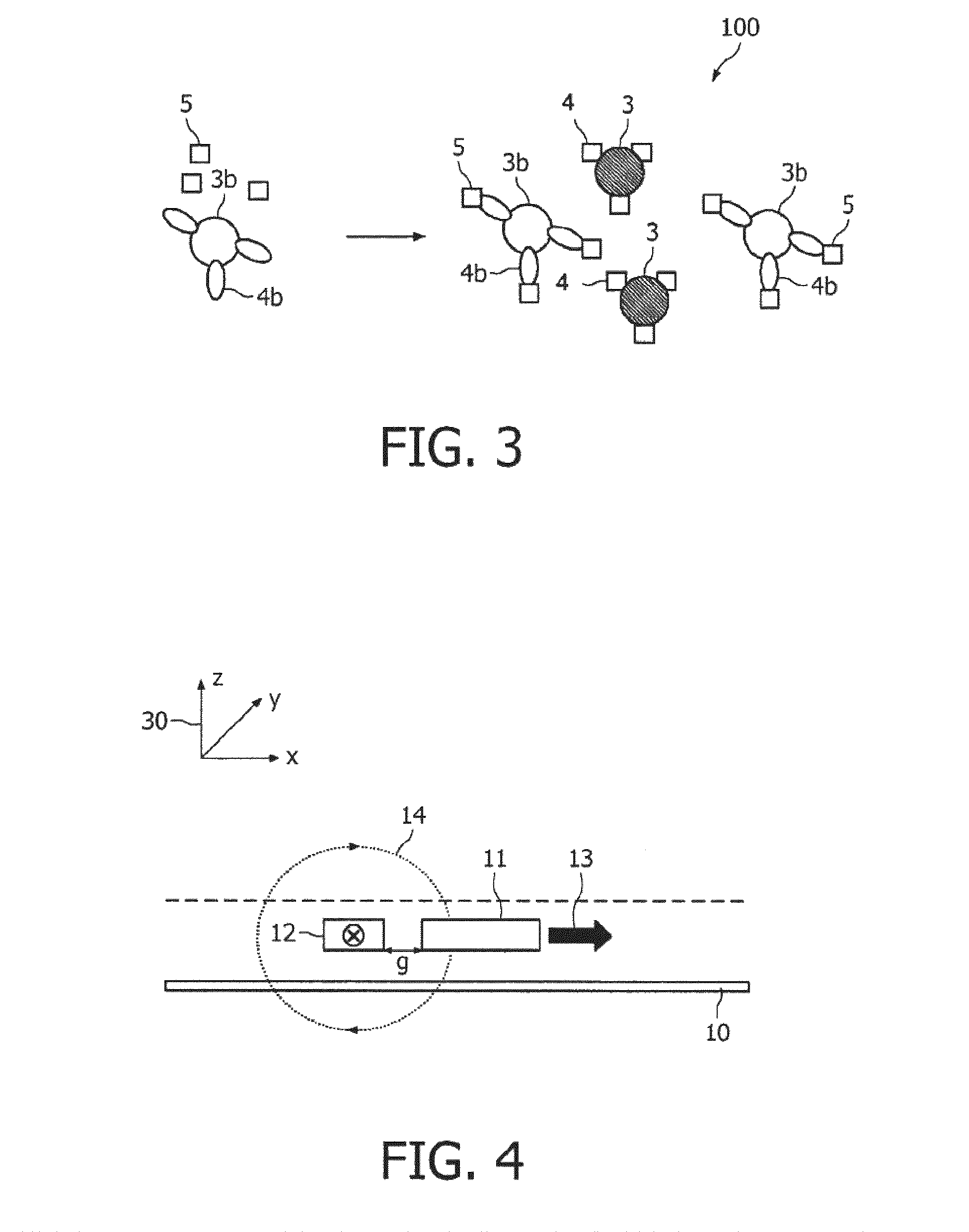
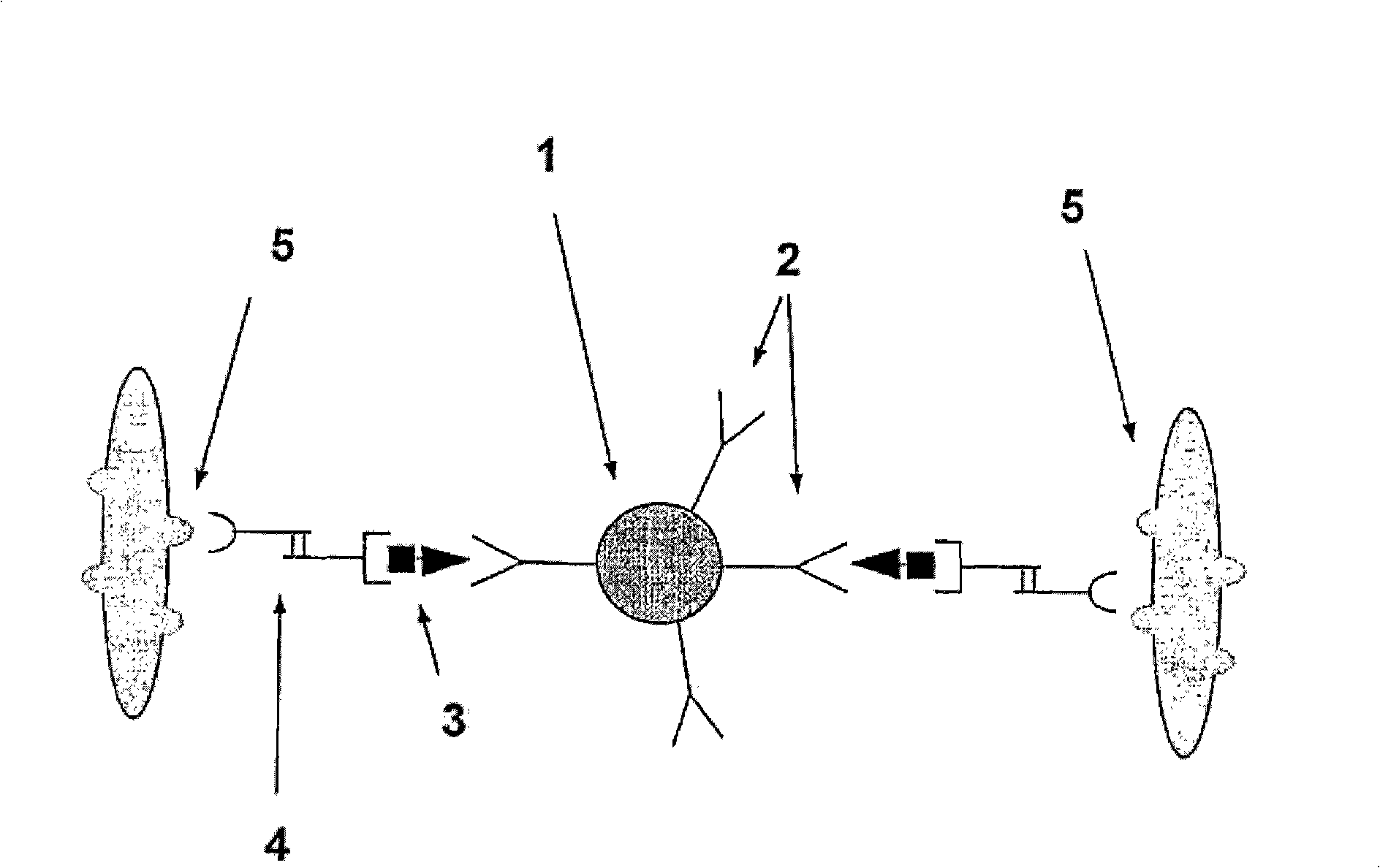
A method and system are described for measuring agglutination in a target-induced agglutination assay with one or more magnetic particles performed in a reaction chamber. After the magnetic particles (3, 15), which are capable of binding to a target (5) are provided in the assay, an agglutination process resulting in agglutinated particles (100) comprising at least one magnetic particle is performed. The method then further comprises applying an alternating current magnetic field (HAC) to the assay and—measuring an effect of the HAC on the one or more magnetic particles (3,15) unattached to any surface. The measured effect is indicative of one or more agglutination parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
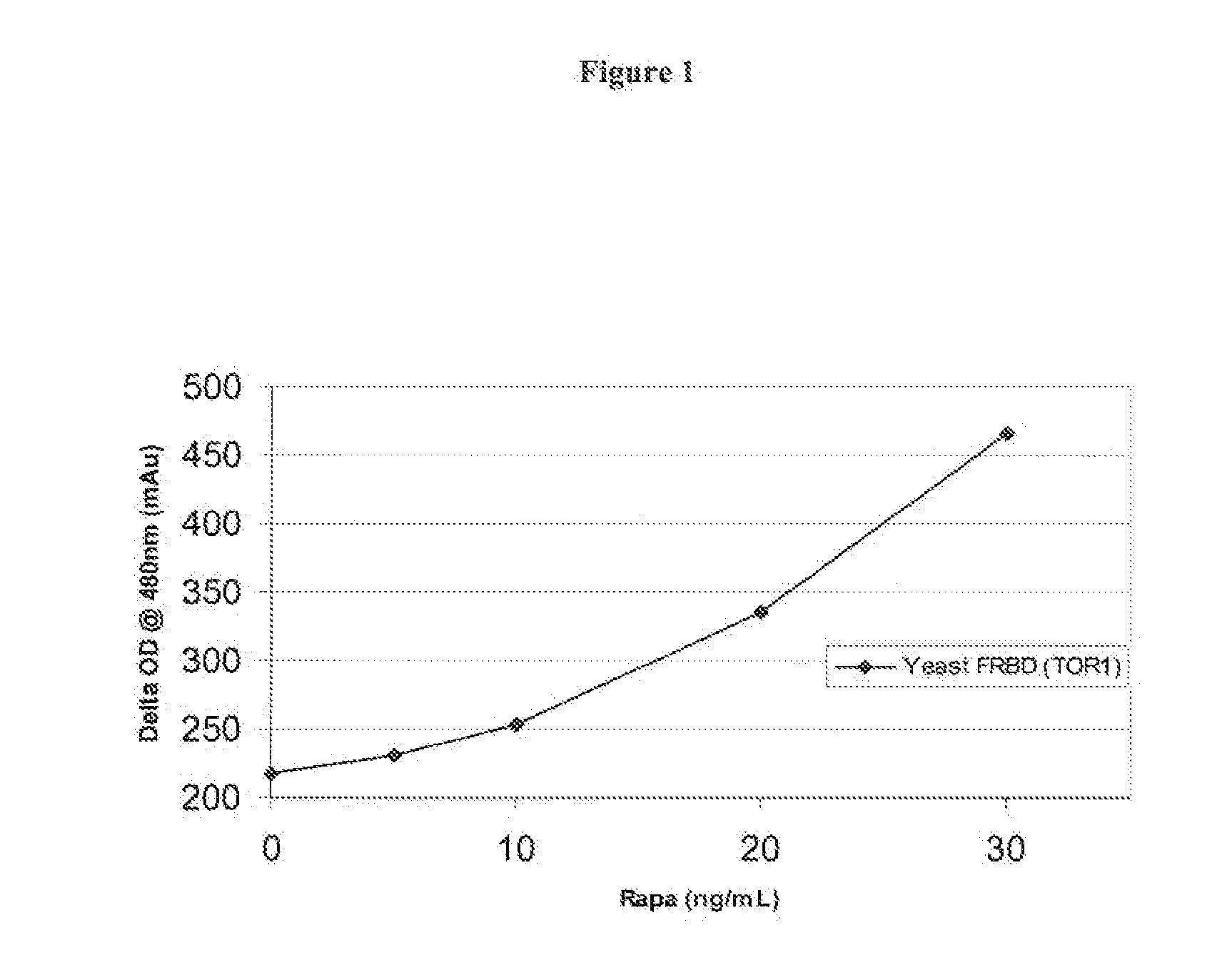
Homogeneous double receptor agglutination assay for immunosuppressant drugs
A homogeneous, non-competitive, double receptor agglutination assay for measuring immunosuppressant drugs is described. The assay employs at least two receptors wherein each receptor is specific for a separate binding site on the drug and wherein each receptor is bound to a detection particle. The immunosuppressant drug binds to the receptors and causes particle agglutination, which can be measured and correlated with the presence or amount of immunosuppressant drug in a sample.
Owner:SIGLER GERALD F +5
Method for analyzing image data relating to agglutination assays
InactiveUS20090324036A1Maximize signal to noiseEnhances agglutinatesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method for acquiring a digital image of an agglutination result comprising performing an agglutination assay on a reaction substrate having a set of dimensions and characteristics which permit a pattern of agglutination in a result of said assay. The image of the result is developed. The image has a colored background which maximizes a signal to noise ratio. Further, the image has been passed through a filter that complements an action of the colored background and enhances the agglutinates in the image while additionally increasing the signal to noise ratio.
Owner:LAB CELSIUS
Reagent for Measuring Agglutination and Method of Measuring Agglutination
ActiveUS20100167310A1Reduced measurement timeEffective calculationMaterial analysisAgglutinationReagent
[PROBLEMS] To provide a reagent for measuring agglutination by using a reaction accelerator, which causes no spontaneous agglutination of receptor-sensitized carrier particles in the coexistence of these carrier particles, and a measurement method.[MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] A reagent for measuring agglutination by using a specific amine compound, whereby aggregation based on a specific reaction can be accelerated without causing spontaneous agglutination of carrier particles, and measurement method.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Chromatographic exclusion agglutination assay and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050221386A1Easy to distinguishEasily differentiatedMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingDiseaseAnalyte
The present invention relates to agglutination assays and in particular to chromatographic exclusion assays and methods of use thereof The present invention includes a novel strategy for determining the presence of one or more analytes on interest in a test sample by using chromatographic exclusion of aggregates of bound detectable specific binding reagents that are accumulated at a particular and non-random location on the test device. In the absence of analytes of interest in the sample under test, the specific detectable binding reagent aggregates are not formed, and hence not excluded from the chromatographic media creating a distinct and readily differentiating event. The present invention is particularly adaptable as a simple test device for detection of diseases or monitoring of treatments at a doctor's office or in the home.
Owner:BINAX INC
Method Of Pretreating Specimen And Immunoassay Using The Same
InactiveUS20080008992A1Preventing non-specific reactionImprove simplicityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlkaline proteasePretreatment method
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Method for serologic agglutination and other immunoassays performed in a thin film fluid sample
InactiveUS20090253218A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingAgglutination assayAgglutination
A method and system for performing a serological agglutination assay in a liquid sample. The system provides a simple method for creating an in-situ sample / reagent admixture within a sample analysis chamber without the use of any precision fluid-handling components.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Latex particles for agglutination assay
A latex particle for high-sensitive agglutination assay and a reagent for agglutination assay including the particle are provided. The latex particle barely initiates non-specific reactions and can readily prepare diagnostic agents. A latex particle for agglutination assay including a polymerizable monomer having a phenyl group, a polymerizable monomer having a phenyl group and a salt of sulfonic acid, and a polymerizable monomer represented by Formula (1): €ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒCH 2 =CR 1 -COO (CH 2 CH 2 O) n -R 2 €ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒ€ƒ(1) where R 1 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group; R 2 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group; and n is 1‰¤n<20, wherein the density of functional groups derived from the polymerizable monomer represented by Formula (1) on the surface of the particle is 0.05 to 0.5 µmol / m 2 .
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Inert carrier Escherichia coli and its potential application
ActiveCN110257276AImprove and refine specificity bottlenecksBacteriaBiological material analysisEscherichia coliAgglutination assay
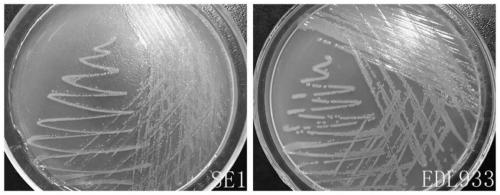
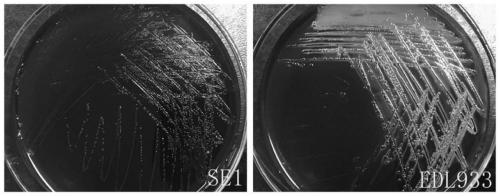
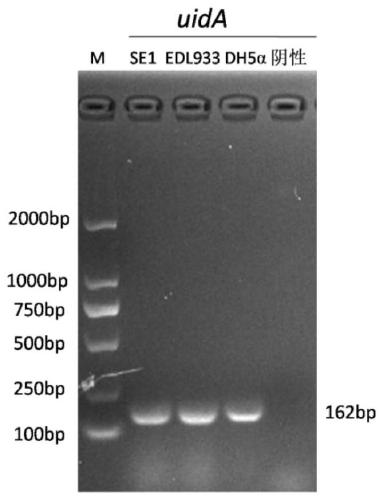
The present invention relates to an inert carrier Escherichia coli and its potential application, the Escherichia coli isolated strain has the inert carrier property, and is expected to be developed into a carrier strain for an indirect agglutination test. The inert carrier Escherichia coli is preserved in the China General Microorganisms Collection and Management Center (CGMCC), and a preservation address is Beijing, China, a preservation number is CGMCC No. 17339, a preservation date is March 18, 2019, a classification name is Escherichia coli, and a strain code is SE1. The Escherichia coli isolated strain is from a healthy flock, the bacteria number at a higher working concentration does not cause any macroscopic agglutination reaction with various chicken serums of different genetic backgrounds, and does not generate non-specific agglutination reaction with chicken source serum, so that the Escherichia coli is called as an inert carrier Escherichia coli. The application provides an inert carrier strain and its potential application for developing a simple and rapid indirect agglutination assay.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Use of superhydrophobic surfaces for liquid agglutination assays
ActiveUS20120264113A1Wide detection rangeFast aggregationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsThermal energyAnalyte
This invention relates to the use of thermodynamically incompatible surfaces in agglutination assays for the express purpose of using the sample as a key component of the detection instrument. Specifically, the invention relates to formation of a lense and a virtual container for rapid mixing via thermal energy by a sample liquid disposed on a superhydrophobic surfaces, and a subsequent specific analyte or overall protein concentration assay using particles agglutination for use in the industrial, environmental, and clinical laboratory test fields.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Measuring agglutination parameters
ActiveCN101627297AEasy to separateIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticle size analysisAgglutination assayAgglutination
A method and system are described for measuring agglutination in a target- induced agglutination assay with one or more magnetic particles performed in a reaction chamber. After the magnetic particles (3, 15), which are capable of binding to a target (5) are provided in the assay, an agglutination process resulting in agglutinated particles (100) comprising at least one magnetic particle is performed. The method then further comprises applying an alternating current magnetic field (HAC) to the assay and- measuring an effect of the HAC on the one or more magnetic particles (3,15) unattached to any surface. The measured effect is indicative of one or more agglutination parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Single receptor assays for immunosuppressive drugs
InactiveUS20070054338A1Hinder and reduce bindingReduce non-specific bindingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaintainance of heating chambersImmunosuppressive drugBinding site
A highly specific homogeneous assay method for an immunosuppressive drug using an immunophilin in a single receptor format is provided. In the simplest format, a single receptor is utilized analogous to a competitive immunoassay whereby an immunophilin is substituted for an antibody, and a competition results between a drug conjugate and the drug analyte for a limited number of immunophilin binding sites. In a microparticle agglutination assay format, an immunophilin is either bound to a particle or in solution. In the case where an immunophilin is bound to a particle, a polyvalent conjugate of the drug analyte is present in solution.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Use of superhydrophobic surfaces for liquid agglutination assays
ActiveUS9995688B2Wide detection rangeFast aggregationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsThermal energyAnalyte
This invention relates to the use of thermodynamically incompatible surfaces in agglutination assays for the express purpose of using the sample as a key component of the detection instrument. Specifically, the invention relates to formation of a lense and a virtual container for rapid mixing via thermal energy by a sample liquid disposed on a superhydrophobic surfaces, and a subsequent specific analyte or overall protein concentration assay using particles agglutination for use in the industrial, environmental, and clinical laboratory test fields.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Measuring agglutination parameters
ActiveUS8217647B2Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or moreImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismAgglutination assayAgglutination
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Agglutination assay method in binder medium
InactiveUS20050153460A1High sensitive analysisEasy to operateBiological testingAnalyteWater insoluble
An agglutination assay method for quantitatively determination of an analyte in a liquid sample using particles bearing an anti-analyte. The agglutination is conducted in a reagent layer composed of at least one binder selected from the group consisting of: a water-soluble polymer having a solution viscosity of 6 cP or less; a water-insoluble and water-swellable polymer; and gelatin having a molecular weight of 20,000 or less. A speedy quantitative determination of the analyte can be conveniently attained with high sensitivity. When the particle-labeled anti-analyte is contained in the reagent layer medium, the anti-analyte can be stored with higher stability in the dry state. A dry analysis element for enabling such analysis method is also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
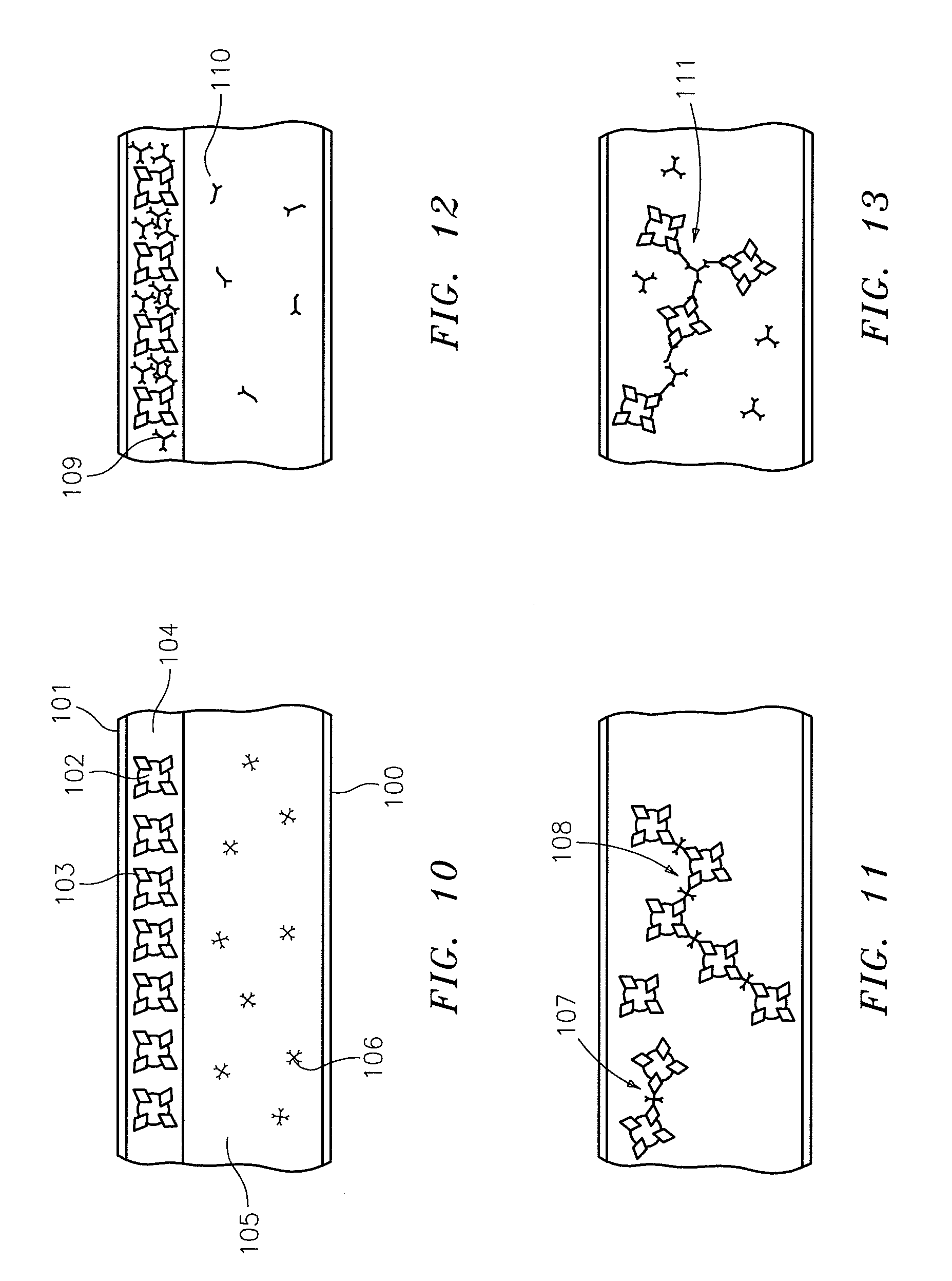
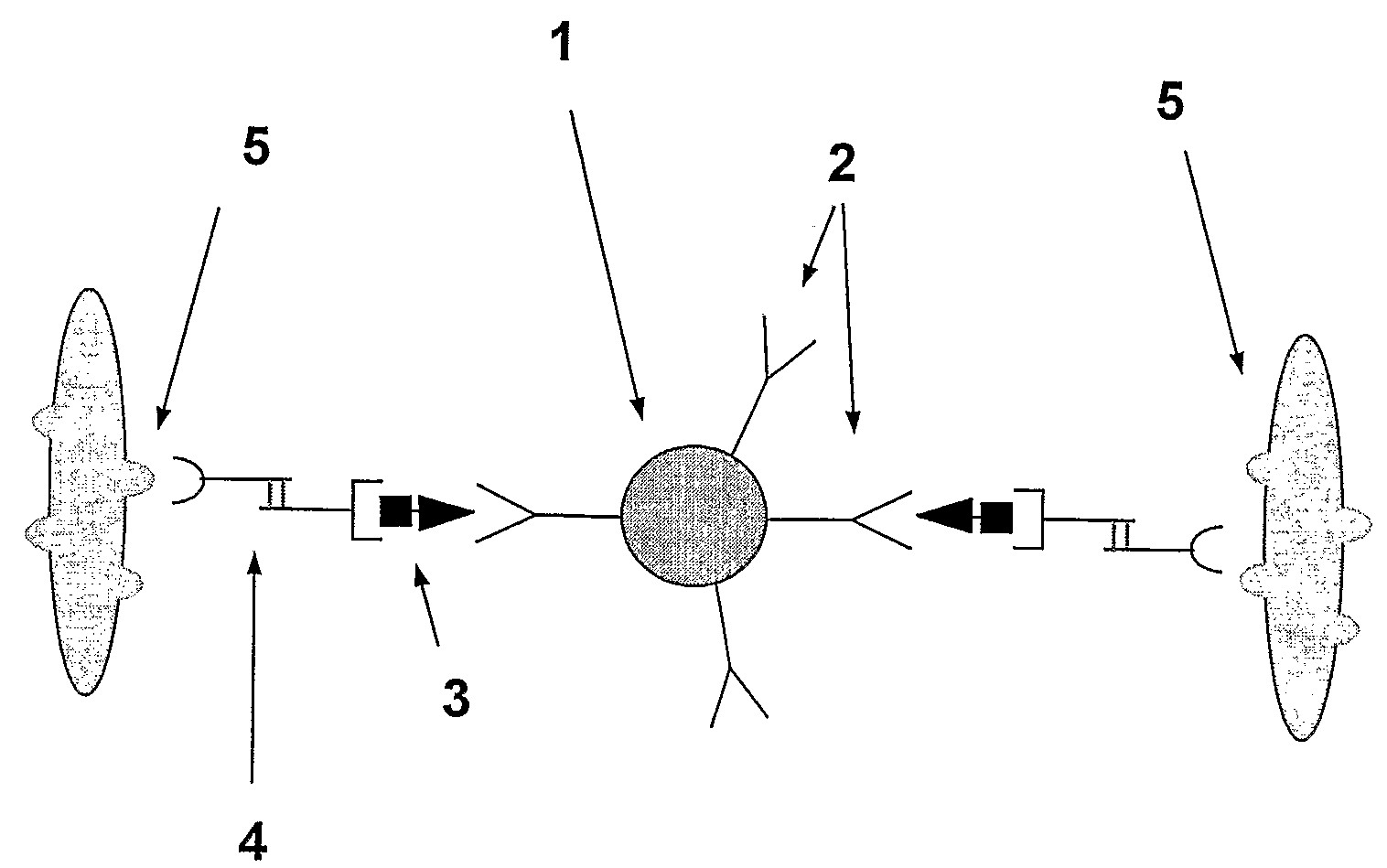
Agglutination Assay
The invention relates to agglutination assays and related kits, reagents and devices. In particular methods of assaying small analytes having few epitopes are disclosed, by means of using hub moieties to which multiple analytes may be bound by a first epitope, together with a further moiety capable of binding a second analyte epitope and which is also capable of binding to a detectable particle. Stable agglutinated complexes may be so formed, which may used as the basis for various assay formats.
Owner:PLATFORM DIAGNOSTICS LTD
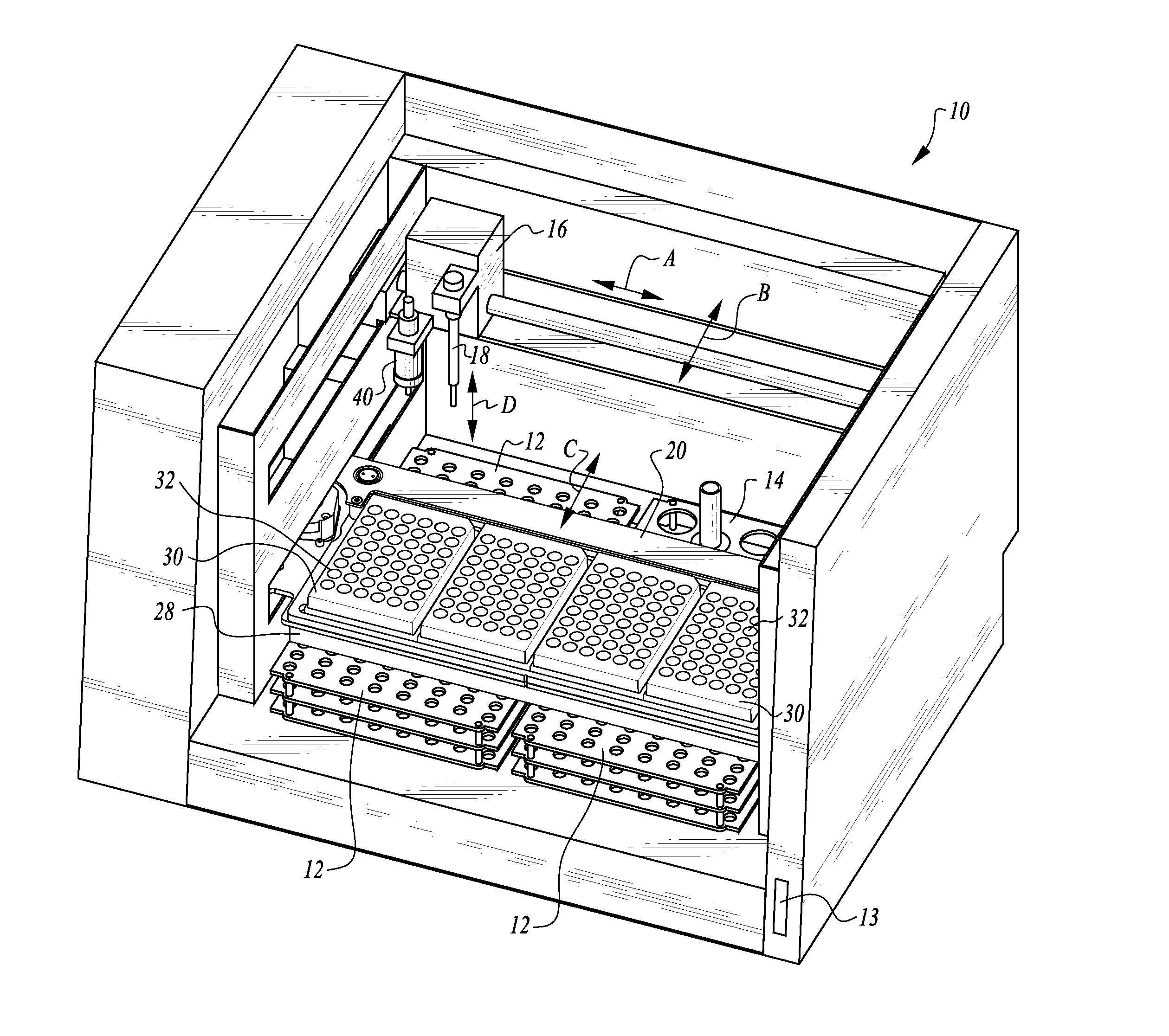
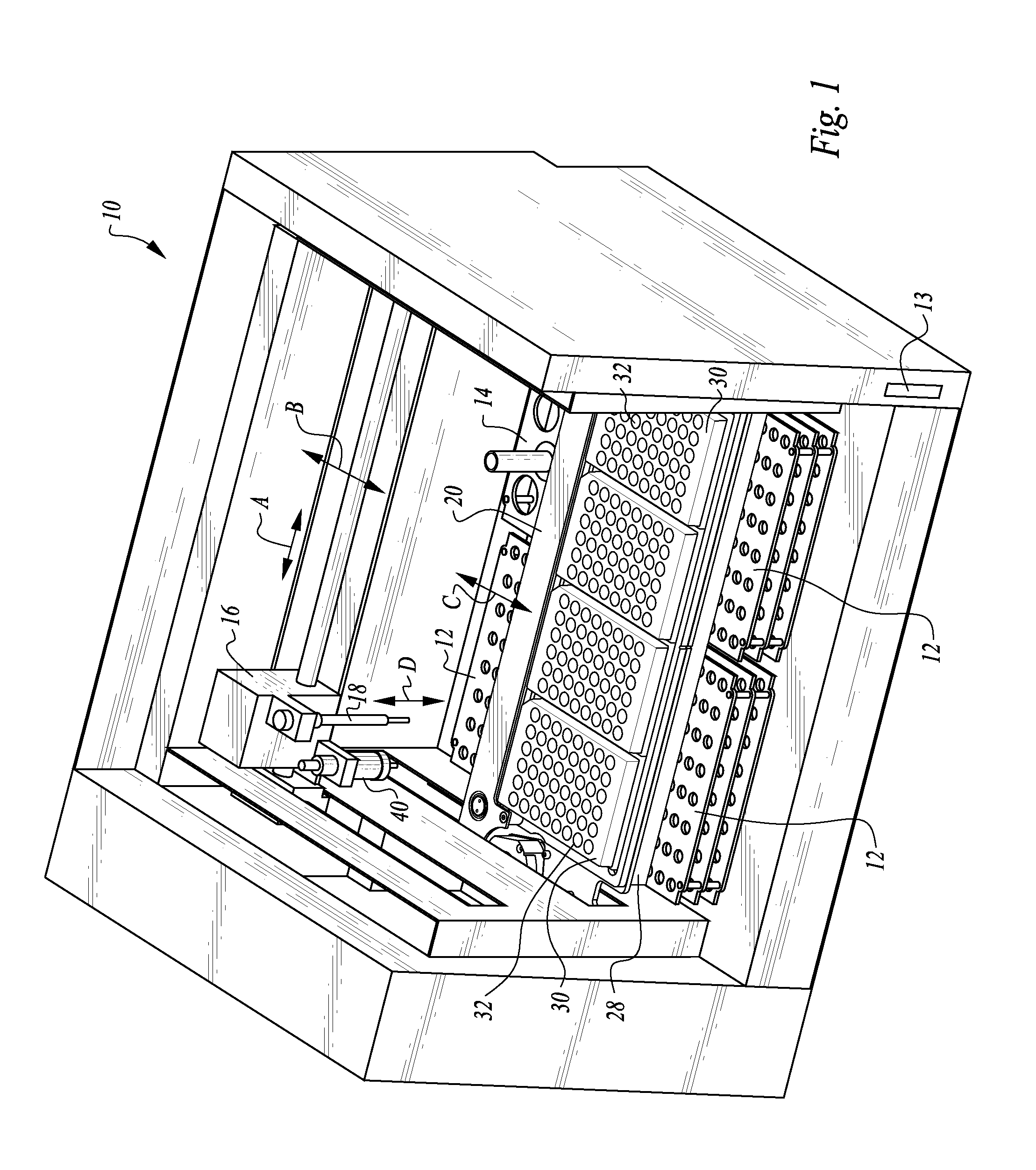
Process and machine for automated agglutination assays
InactiveUS20150309025A1Minimize potentialMaximize efficacyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrotiter plateAgglutination assay
The machine is configured to perform an automated rapid plasma reagent (RPR) agglutination test or other agglutination test. The machine includes a sample rack with multiple sample locations thereon and a reagent rack for storing of reagent. A shaker assembly supports at least one microtiter plate or other well supporting structure thereon with a plurality of wells in the plate. An automated syringe or other aspirator and dispenser accesses samples and reagent and deposits them within wells of the microtiter plate. The shaker assembly shakes multiple samples within the wells of the microtiter plate according to the RPR or other agglutination test. Finally, a camera photographs the wells of the plate, preferably from above with a light source below and the plate at least partially transparent, to evaluate whether the specimen is reactive or non-reactive. Test results and photographic evidence of the test results are preferably archived within a database.
Owner:GOLD STANDARD DIAGNOSTICS
Agglutination Assay Method in Porous Medium Layer
An agglutination assay method for quantitatively determination of an analyte in an aqueous liquid sample using particles bearing an anti-analyte. The agglutination is conducted in the porous medium layer of the analysis element A speedy quantitative analysis of the analyte can be conveniently attained with high sensitivity. When the particle-labeled anti-analyte is contained in the porous medium layer, the anti-analyte can be stored with higher stability in the dry state A dry analysis element for enabling such analysis method is also provided.
Owner:NAKAMURA KENTARO +4
Agglutination assay
The invention relates to agglutination assays and related kits, reagents and devices. In particular methods of assaying small analytes having few epitopes are disclosed, by means of using hub moieties to which multiple analytes may be bound by a first epitope, together with a further moiety capable of binding a second analyte epitope and which is also capable of binding to a detectable particle. Stable agglutinated complexes may be so formed, which may used as the basis for various assay formats.
Owner:PLATFORM DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Microtube column agglutinatior agglutination assay result identification system and blood grouping analyzer
ActiveCN107389957AAvoid Interfering with Analysis and JudgmentImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingTarget analysisBlood grouping
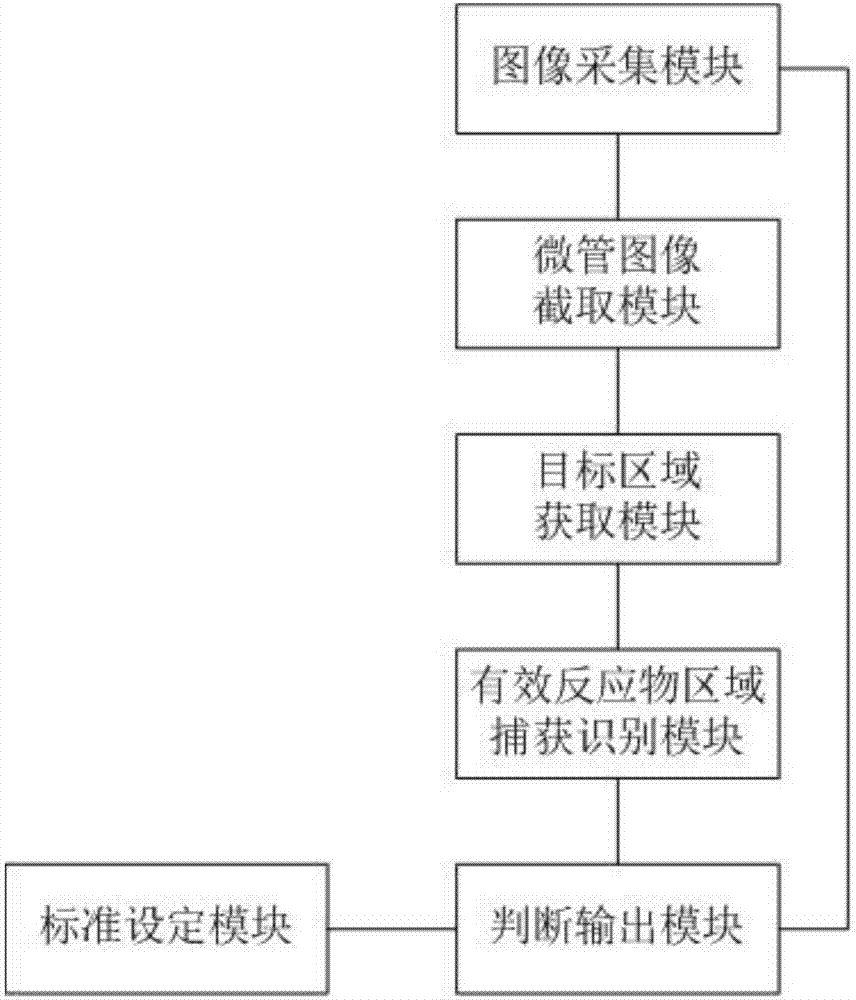
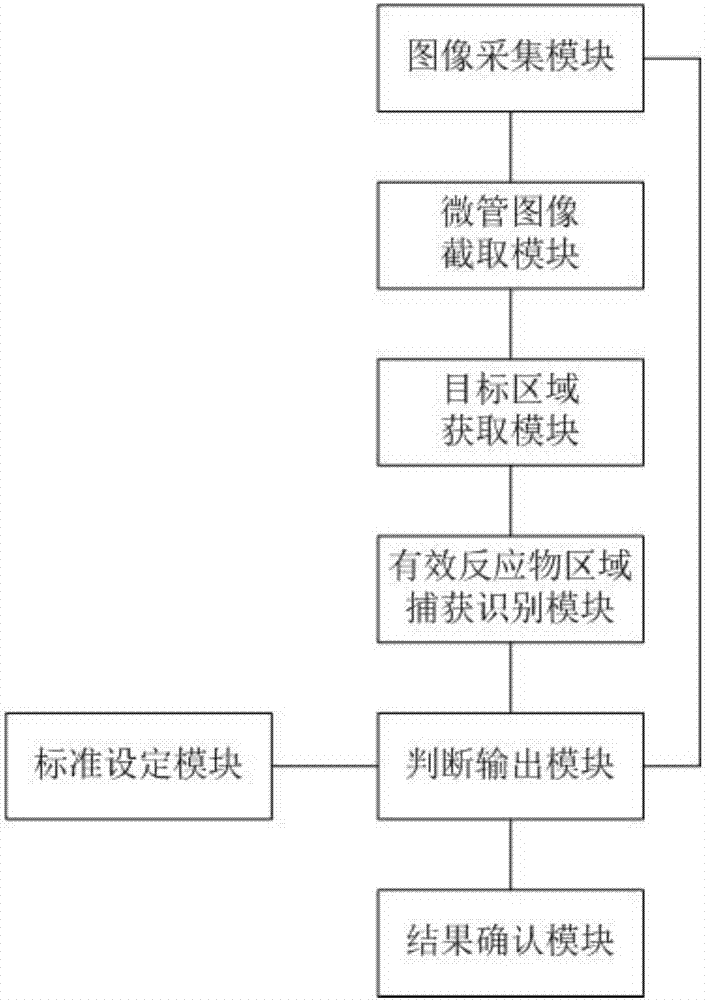
The invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment and discloses a microtube column agglutinatior agglutination assay result identification system. The microtube column agglutinatior agglutination assay result identification system comprises an image acquisition module, a microtube image capture module, a target area acquisition module, an effective reactant area capture and identification module, a standard setting module and a judgment output module. Boundary lines on the inner wall of a microtube are automatically fit out through a binarization processing unit and a fitting tracing unit, a reaction area within the boundary lines on the inner wall of the microtube are acquired to serve as a target analysis area, so that analytical judgment cannot be interfered by the image part beyond the area, and the identification accuracy is effectively improved; meanwhile, the microtube column agglutinatior agglutination assay result identification system is suitable for various microtube column agglutinatiors with different specifications, and the university of the microtube column agglutinatior agglutination assay result identification system in analyzers with different specifications is improved; and brightness position and relative area combined classified judgment is performed on the effective reactant area in the target analysis area, and contrast analysis is performed on rough classification and fine classification, so that the result identification accuracy is further improved.
Owner:SUZHOU HYBIOME BIOMEDICAL ENG CO LTD
Agglutination reaction and separation vessel
InactiveCN1544948AAvoid displacementPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingAgglutination assayAgglutination
A vessel for conducting blood cell agglutination assays is disclosed. A barrier retains reactants in an upper chamber during incubation, then, in response to a force, permits reagents to enter a lower chamber containing a matrix for separating agglutination.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Method for analyzing image data relating to agglutination assays
InactiveUS8417002B2Enhances agglutinatesMaximize signal to noiseMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCharacter and pattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Assay
A method for analyzing a digital image containing the result of an agglutination assay to generate a quantitative result value representative of the degree of agglutination of the sample is provided. The method for analyzing the digital image includes: applying a filter to extract a component of the image or portion of a spectrum where a signal to noise ratio between agglutinated and background is maximized; extracting a set of features that characterize the agglutination pattern, obtaining a quantification function which maps measured features to the actual concentration of the sample and computing a quantitative result for each sample in the assay.
Owner:LAB CELSIUS
Process and machine for automated agglutination assays with image automated evaluation
ActiveUS20170192002A1Maximize efficacyImprove performanceImage analysisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPipetteAgglutination assay
The machine is configured to perform an automated rapid plasma reagent (RPR) agglutination test or other agglutination test. The machine includes a sample rack with multiple sample locations thereon and a reagent rack for storing of reagent. A shaker assembly supports at least one microtiter plate or other well supporting structure thereon with a plurality of wells in the plate. An automated pipette accesses samples and reagent and deposits them within wells of the microtiter plate. The shaker assembly shakes multiple samples within the wells of the microtiter plate. Finally, a camera photographs the wells of the plate, preferably from above with a light source below and the plate at least partially transparent. The image is then analyzed in an automated fashion to determine whether a ring of contrast material has remained smooth indicative of a non-reactive sample or has agglutinated / clumped together indicative of a reactive sample.
Owner:GOLD STANDARD DIAGNOSTICS
Agglutination assay
The invention relates to agglutination assays and related kits, reagents and devices. In particular methods of assaying small analytes having few epitopes are disclosed, by means of using hub moieties to which multiple analytes may be bound by a first epitope, together with a further moiety capable of binding a second analyte epitope and which is also capable of binding to a detectable particle. Stable agglutinated complexes may be so formed, which may used as the basis for various assay formats.
Owner:PLATFORM DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Chromatographic exclusion agglutination assay and methods of use thereof
InactiveCN101019023AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingDiseaseAnalyte
The present invention relates to agglutination assays and in particular to chromatographic exclusion assays and methods of use thereof. The present invention includes a novel strategy for determining the presence of one or more analytes on interest in a test sample by using chromatographic exclusion of aggregates of bound detectable specific binding reagents that are accumulated at a particular and non-random location on the test device. In the absence of analytes of interest in the sample under test, the specific detectable binding reagent aggregates are not formed, and hence not excluded from the chromatographic media creating a distinct and readily differentiating event. The present invention is particularly adaptable as a simple test device for detection of diseases or monitoring of treatments at a doctor's office or in the home.
Owner:BINAX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com