Single receptor assays for immunosuppressive drugs
a single receptor and immunosuppressive technology, applied in the field of immunosuppressive drug detection and quantification assays, to achieve the effects of reducing the sensitivity of the assay, reducing the binding or reducing the binding, and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific embodiments
EXAMPLE 1
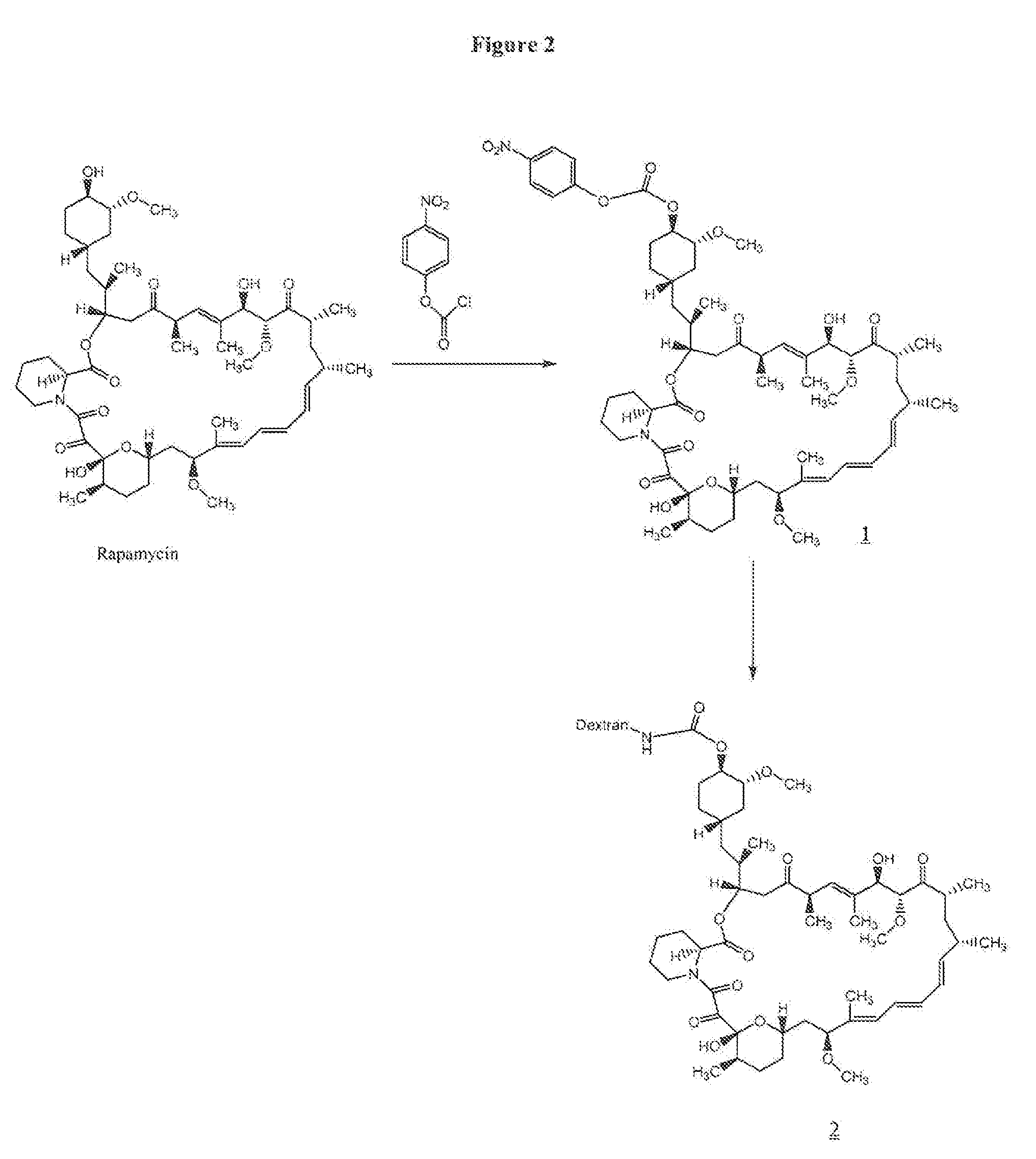
Preparation of rapamycin 40-O-p-nitrophenyl carbonate (1)
[0064] To 100 mg (0.109 mmol) of rapamycin was added 2.5 mL of freshly distilled dichloromethane (distilled over CaH2), 33 μL (0.40 mmol) of anhydrous pyridine and 33 mg (0.16 mmol) of p-nitrophenylchloroformate at −78° C. The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at −78° C. for 1 h and at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction was quenched with 50 mL of water at room temperature, and the resulting mixture was extracted with 4×50 mL of dichloromethane. The organic part was dried (anhydrous Na2SO4) and concentrated. The residue was purified by preparative HPLC using a gradient run of acetonitrile and water containing 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid. The fractions containing product were combined, concentrated in the rotary evaporator, and then lyophilized to give 82 mg (0.074 mmol, 69%) of rapamycin p-nitrophenyl carbonate (1) as a white solid. LC-MS: M+H 1101.5.
example 2
Preparation of 40-O-urethane Linked Rapamycin-Aminodextran Conjugate (2)
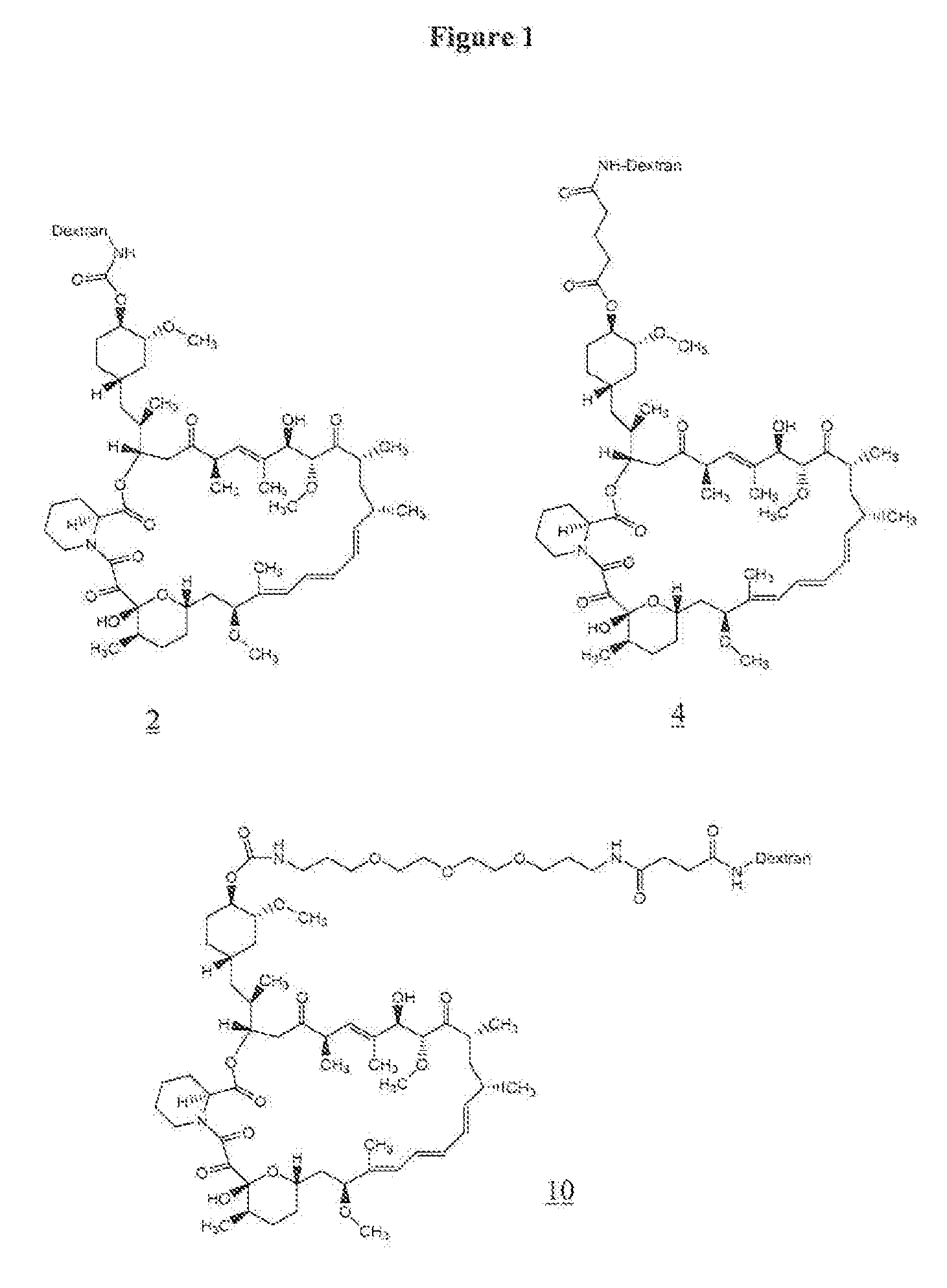
[0065] To 50 mg (1.25×10−3 mmol) of aminodextran (40,000) (prepared as in U.S. Pat. No. 6,653,456) was added 2 mL of anhydrous DMSO, and the mixture was allowed to stir for 5 minutes at room temperature. To the reaction mixture 10.7 mg (0.087 mmol) of 4-dimethylaminopyridine was added followed by a solution of 20 mg (0.018 mmol) of rapamycin p-nitrophenyl carbonate in 0.5 mL of anhydrous DMF. The reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature for 2 days. The resulting yellow solution was placed in a Spectrapor dialysis tubing (mw cut-off 2000) and dialyzed against 90% DMSO in DI water (2×3 h), 70% DMSO in DI water (1×3 hr), 50% DMSO in DI water (1×3 h), 30% DMSO in DI water (1×3 h), and 10% DMSO in DI water (1×3 h). This was followed by dialysis against DI water (6×6 h), and the resulting solution was lyophilized to give 39 mg of rapamycin-aminodextran conjugate (2) as a white solid. The incorporation of rapa...
example 3
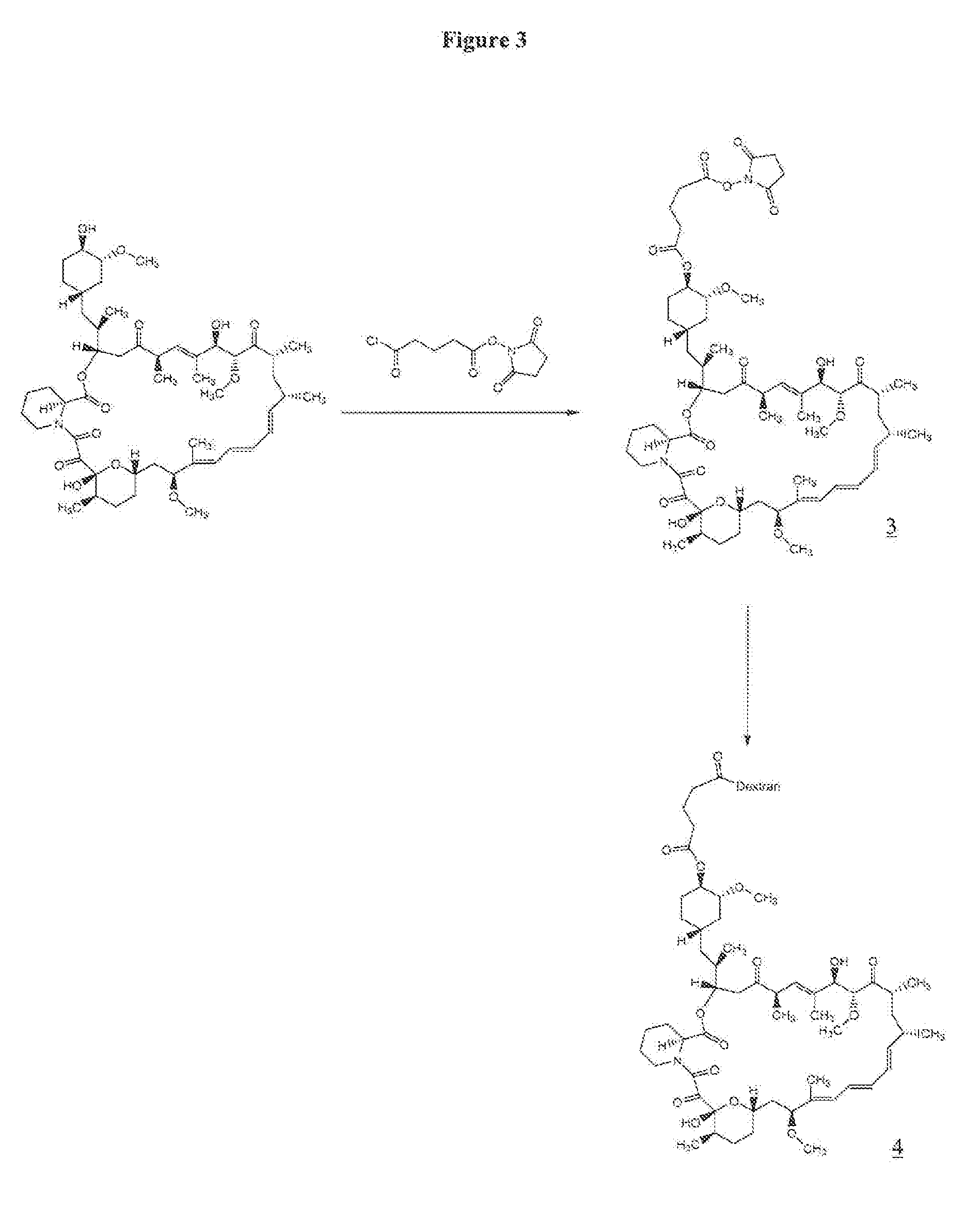
Perparation of Rapamycin 40-O-glutarate NHS Ester (3)
[0066] A solution of 150 mg (0.164 mmol) of rapamycin in 4 mL of dichloromethane (freshly distilled over CaH2) was cooled to −78° C. To the reaction mixture was added 61 mg (0.25 mmol) of succinimido-oxycarbonyl-butyryl chloride, 15 mg (0.12 mmol) of 4-dimethylaminopyridine and 50 μL of pyridine. Succinimido-oxycarbonyl-butyryl chloride, i.e., 5-(2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl-oxy)-5-oxo-pentanoyl chloride, was prepared according to Antonian et al., EP 0 503 454. The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at −78° C. for 2 h and LC-MS of the crude reaction mixture indicated incomplete reaction. To the reaction mixture an additional 61 mg (0.25 mmol) of succinimido oxycarbonyl butyryl chloride and 50 μL (0.60 mmol) of pyridine were added at −78° C. The resulting reaction mixture was allowed to stir at −78° C. for 2 h and then quenched with 50 mL of water. The aqueous layer was extracted with 5×50 mL of dichloromethane, and the organic laye...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com