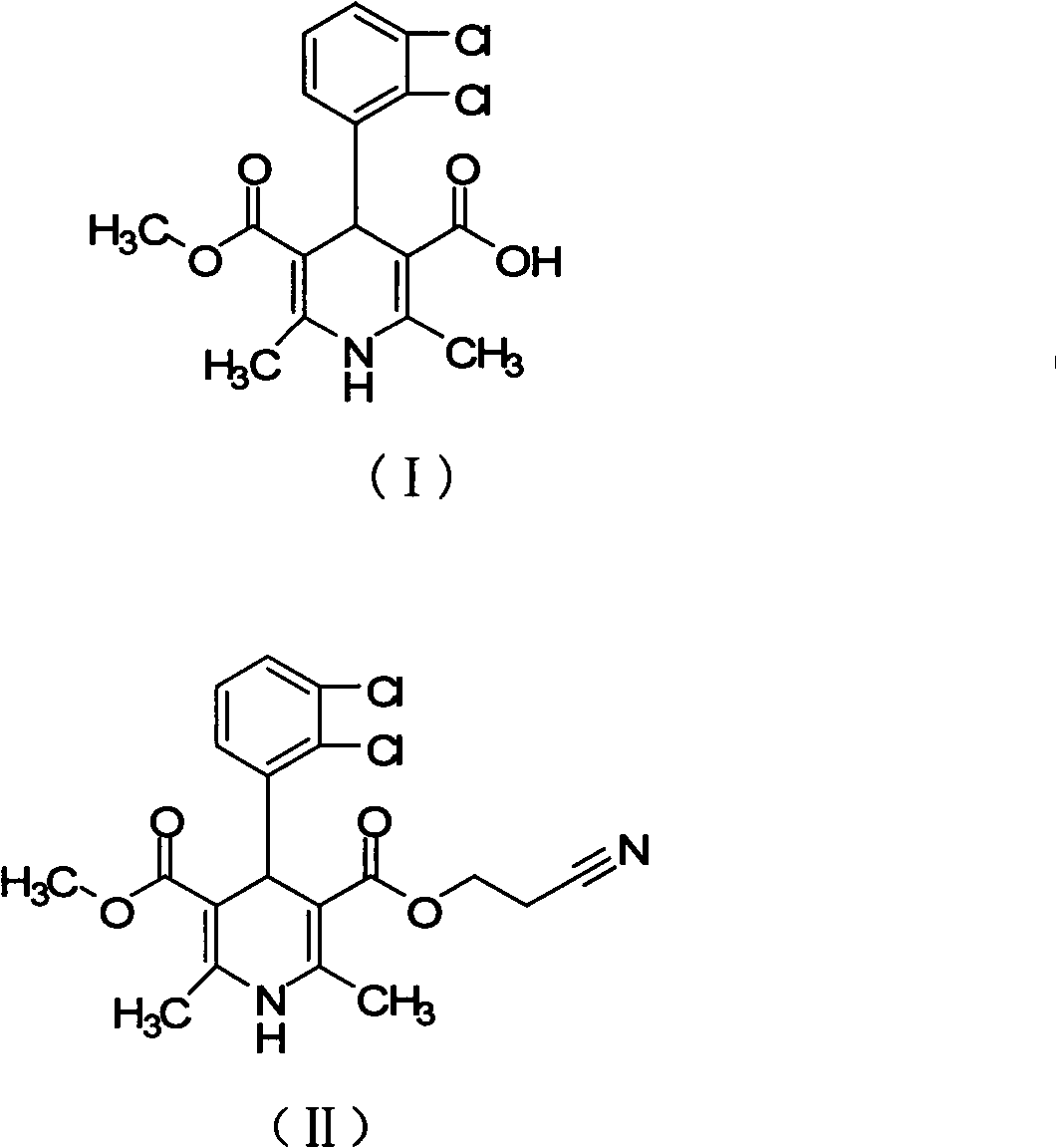
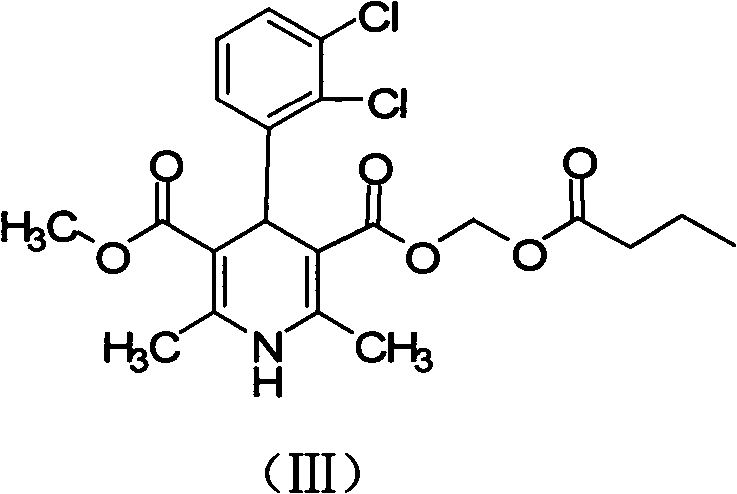
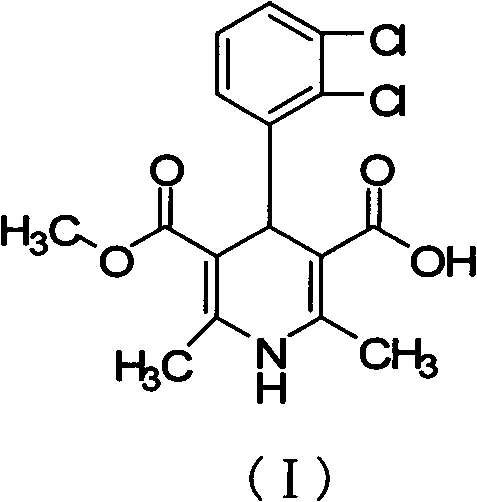
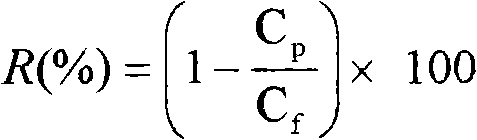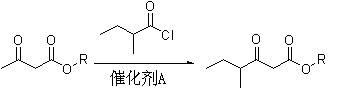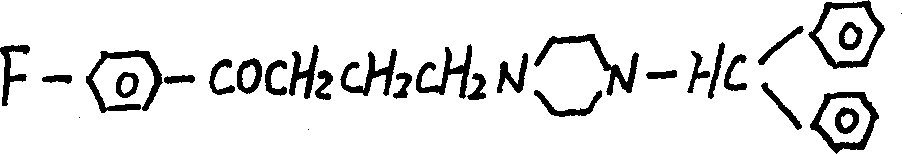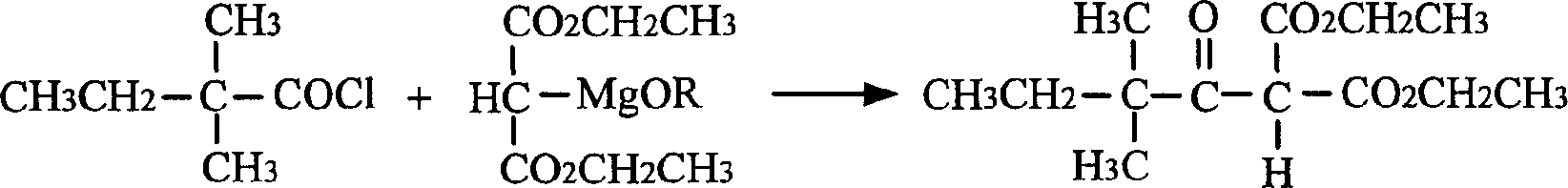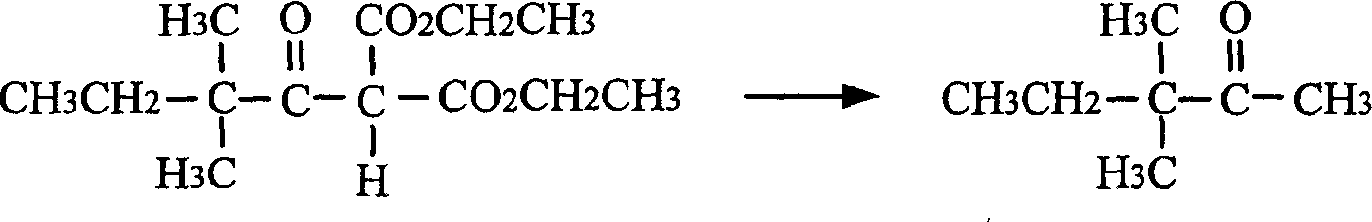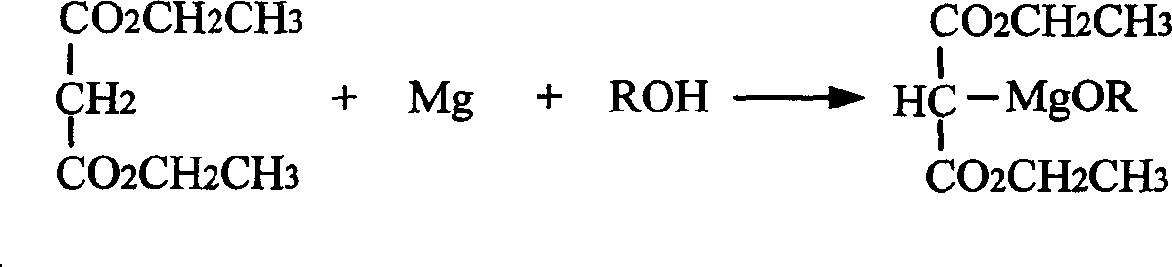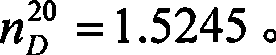Patents
Literature
114 results about "Butyryl chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Butyryl chloride (also known as n-butyryl chloride, butanoyl chloride, or C-4 acyl halide) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C₄H₇ClO. Butyryl chloride is liquid at room temperature, has a colorless to light yellowish appearance and has an extremely strong pungent odor. Butyryl chloride is soluble in almost all aprotic organic solvents, but it decomposes violently by heating and spontaneously decomposes when exposed to moist air or water to form pure hydrogen chloride gas. It also reacts violently when mixed with strong oxidants, metals (especially iron), alkali metals, alkali earth metals, bases and wide range of organic substances such as amines, dimethyl sulfoxide, and alcohols. These reactions tend to result in explosions and fire; hence extreme caution must be taken when mixing with other substances. Butyryl Chloride belongs in the group of acyl halides which are involved in acylation process that introduce an acyl group (RCO-) into compounds.
Synthesis method of photoinitiator 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone
ActiveCN103613492AReduce consumptionQuick responseOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationKetone synthesisCatalytic effect
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a photoinitiator 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone, which comprises the following steps: reacting high-purity gas phosgene with isobutyric acid to synthesize isobutyryl chloride; and carrying out chlorine substitution reaction by a cascade technique: exhaust of a first reaction kettle after chlorine introduction is connected into a second reaction kettle in cascade, and hydrogen chloride and chlorine in the exhaust released by the first reaction enter the second reaction kettle to catalyze the absorption and utilization. The method can well enhance the purity of isobutyryl chloride and further enhance the purity and yield of the product 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propyl ketone; and the catalytic action of hydrogen chloride in the exhaust is utilized to increase the reaction speed, lower the chlorine consumption and enhance the product content. The generated exhaust is recycled after innocent treatment, thereby solving the problem of environmental pollution of the exhaust.
Owner:岳阳市国发植物用药工程技术研究中心有限公司
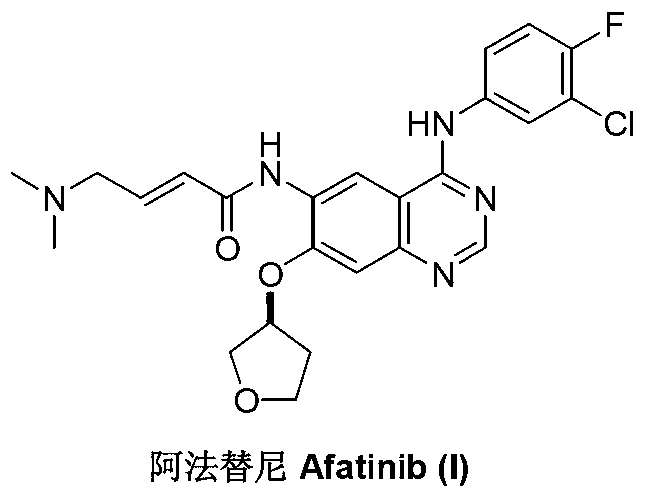
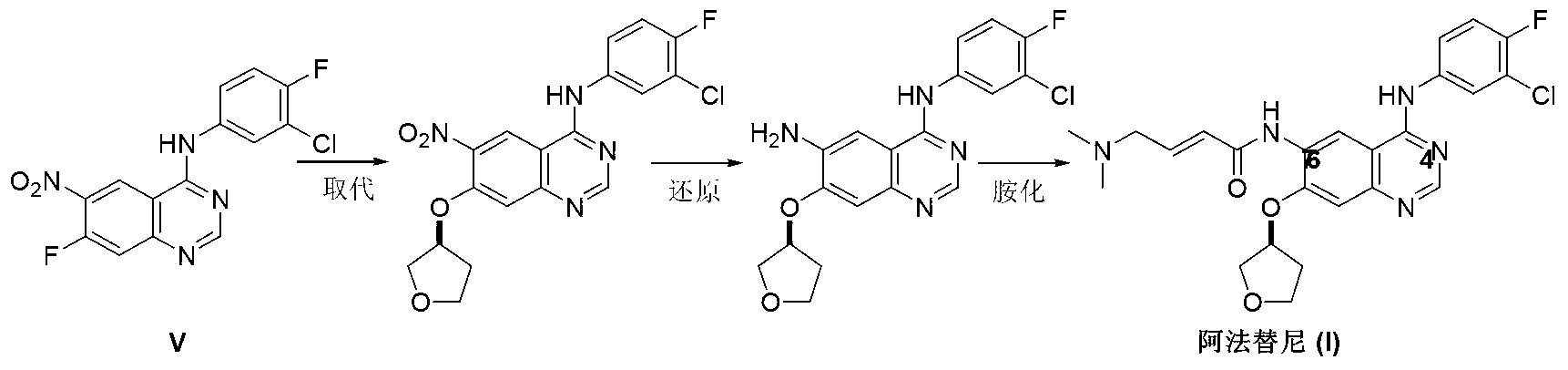
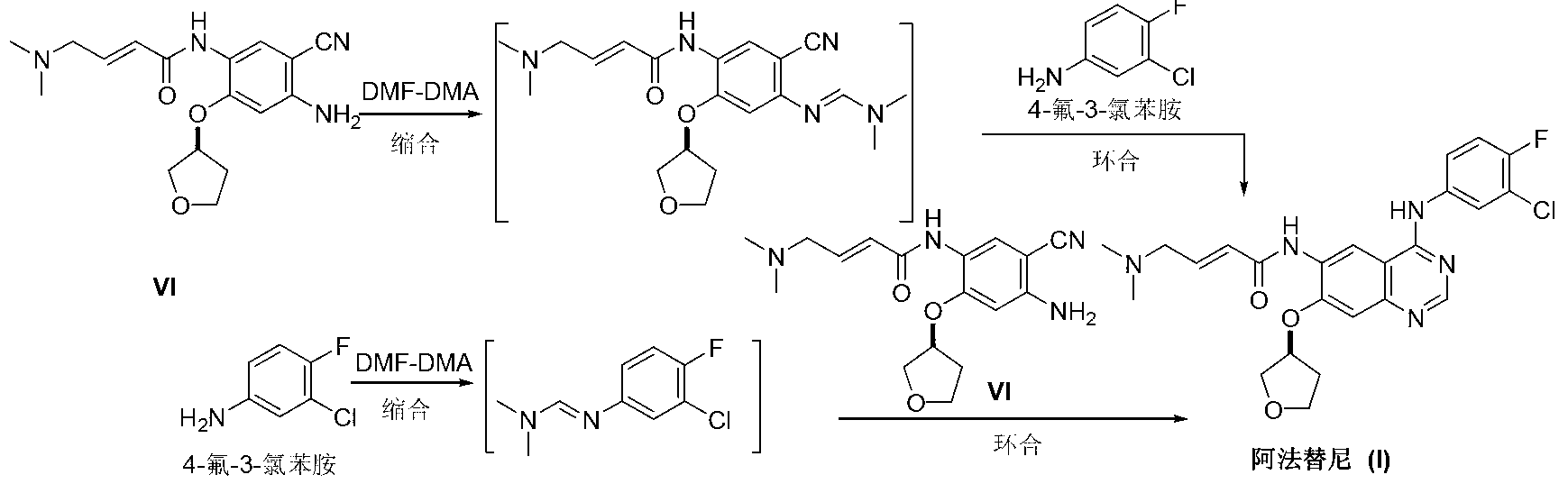
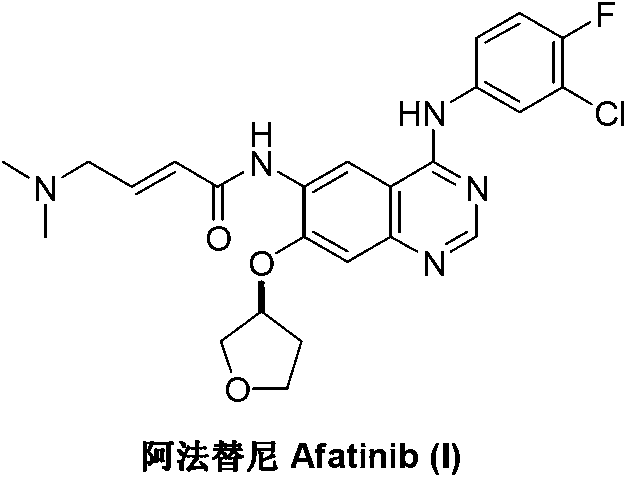
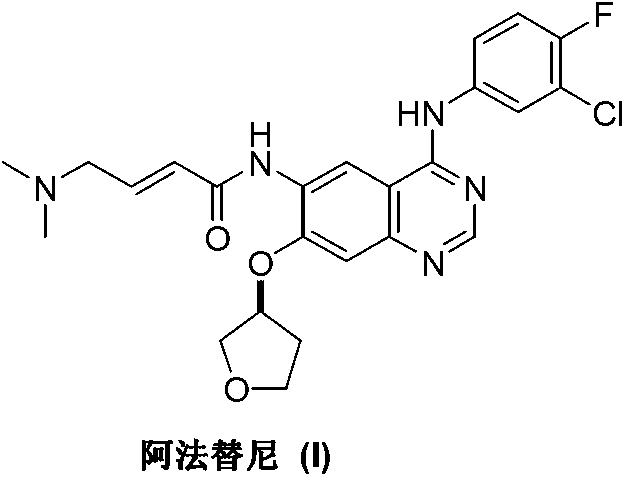
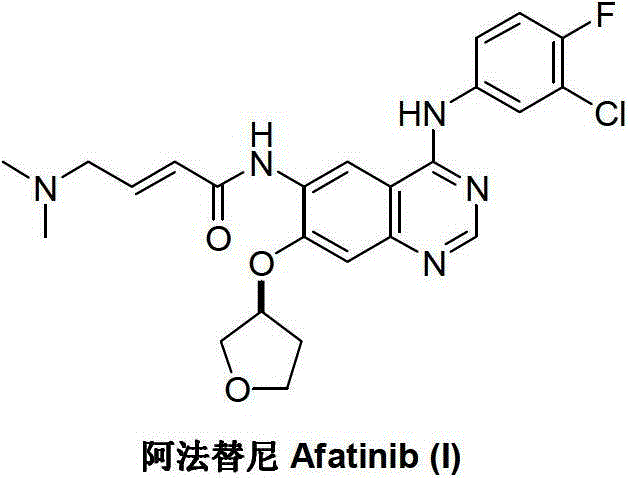
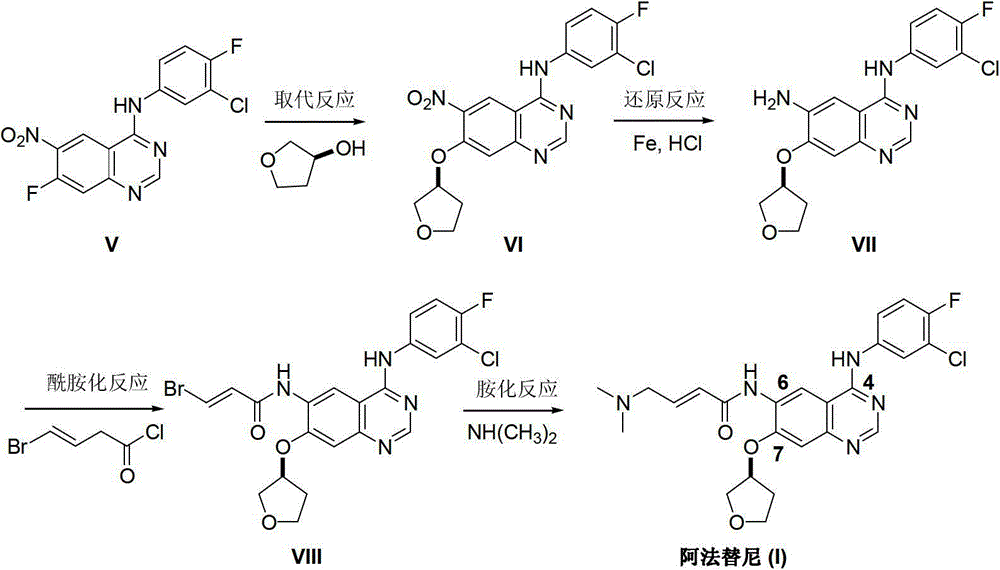
Preparation method of afatinib (I)
InactiveCN103288808AEase of industrial productionPromote the development of economy and technologyOrganic chemistry3-HydroxytetrahydrofuranKetone
The invention discloses a preparation method of afatinib (I). The preparation method comprises the following steps that 6-amino-7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-ketone (II) and (S)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran carry out etherification reaction to generate 6-amino-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-ketone (III), the compound (III) and 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-2-ene-butyryl chloride carry out acylation reaction to generate 6-{[4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-butene-1-yl]amino}-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-ketone (IV), and the compound (IV) and 4-fluoro-3-chloroaniline carry out condensation reaction to prepare the afatinib (I). The preparation method is concise, economical and environment-friendly in process and is suitable for the requirement of industrial amplification.
Owner:鄄城县人民医院
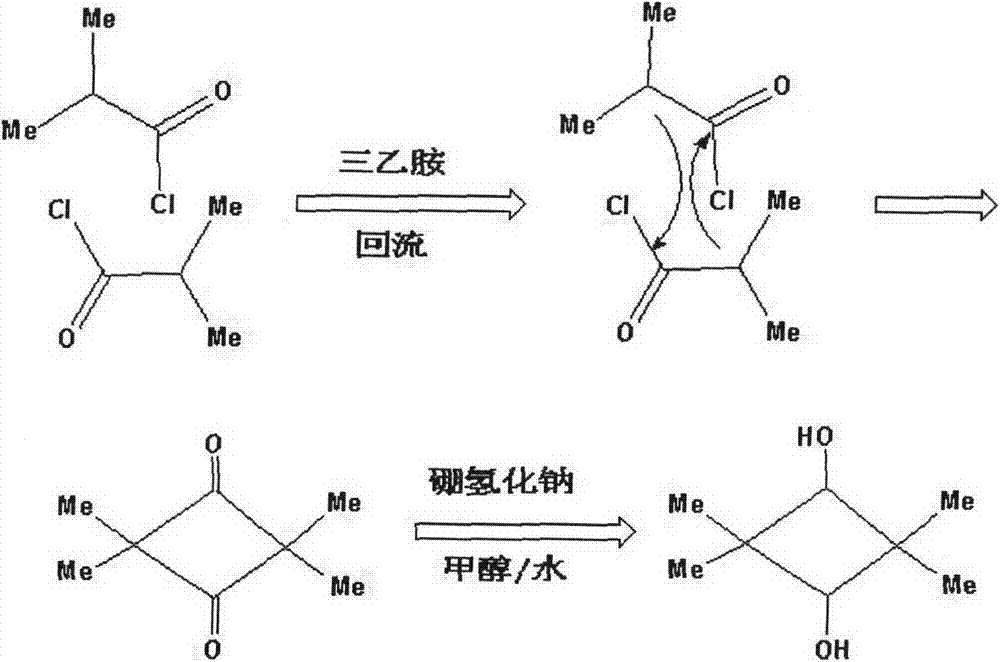
Method for synthesizing 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol
InactiveCN103694083ALow costMild operating conditionsOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationEvaporationMethyl group
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol. Iso-butyryl chloride used as a raw material is stirred evenly in ether solvent, triethylamine is added, reflux reaction is carried out for 13-16h, diluted hydrochloric acid is used for washing, pressure is reduced to remove solvent to obtain intermediate 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanedione, the intermediate is dissolved in mixed solvent of methyl alcohol and water, NaOH is used for regulating pH value to be alkaline, quantitative NaBH4 is added in batches under an ice-bath condition, the reaction is performed for 3-5h at normal temperature, diluted hydrochloric acid is used for quenching, solvent is removed, absolute ethyl alcohol is used for extraction, after ethyl alcohol is removed through rotary evaporation, water is used for extraction, and finally, the water is removed to obtain 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol. The method has simple equipment requirement, mild operation condition, low cost and high product purity, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING NANOEAST BIOTECH +1
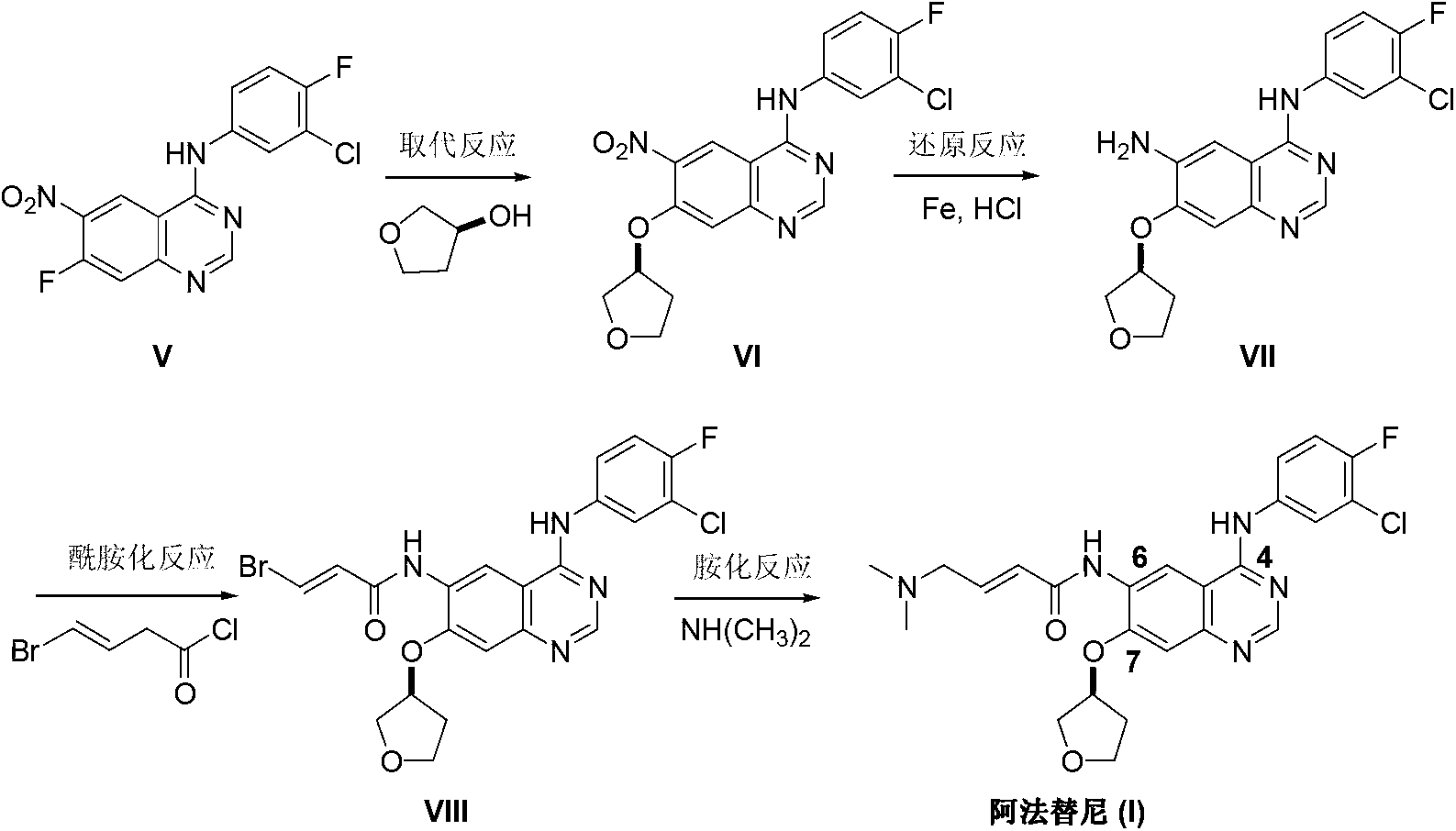
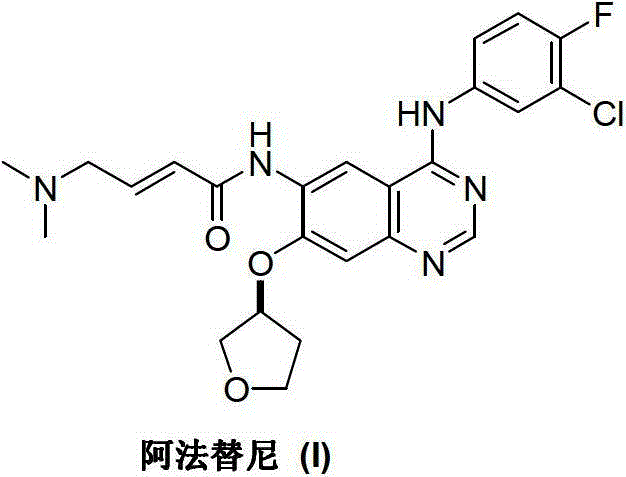
Afatinib preparation method
ActiveCN103242303AEase of industrial productionPromote the development of economy and technologyOrganic chemistry3-Hydroxytetrahydrofuran2-Butene
The invention discloses an Afatinib (I) preparation method which comprises the following steps: performing etherification reaction on 4-chloro-6-amino-7-hydroxyquinazoline (II) and (S)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran to generate 4-chloro-6-amino-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]quinazoline (III); performing acylation reaction on the compound (III) and 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-2-ene-butyryl chloride to generate 4-chloro-6-{[4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-butene-1-yl]amino}-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]quinazoline (IV); and performing condensation reaction on the compound (IV) and 4-fluoro-3-chloroaniline to obtain Afatinib (I). The preparation method is simple, economic and environment-friendly in process, and meets the requirements for large-scale industrialization.
Owner:铜陵尚东高新科创有限公司
Method for preparing tributyrin
ActiveCN104045556AAchieve the purpose of separationPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesGlycerolVaporization
The invention provides a method for preparing tributyrin. The method comprises the following steps: reacting glycerinum with butyryl chloride by taking organic alkali as a acid-binding agent, thereby obtaining a mixture containing tributyrin, wherein the mole ratio of the three materials, namely, glycerinum, butyryl chloride and organic alkali, is 1:(3-3.3):3.3. The method further comprises the following steps: extracting a mixture containing tributyrin by using water, collecting an organic phase, and performing reduction vaporization to remove a solvent in the organic phase, thereby obtaining tributyrin. In the method, the mole ratio of butyryl chloride to glycerinum is kept at (3-3.3):1 during reaction, and massive over amount is not needed. In addition, after the reaction is completed, residual trace butyryl chloride can be hydrated into butyric acid and hydrochloric acid in the following water washing process and can be carried away by a water phase together with residual glycerinum, thus a purpose that butyryl chloride is separated from a target object is achieved.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Polypiperazine-amide nanofiltration membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101352659AImprove performanceBroaden your optionsSemi-permeable membranesNanofiltrationAqueous solution
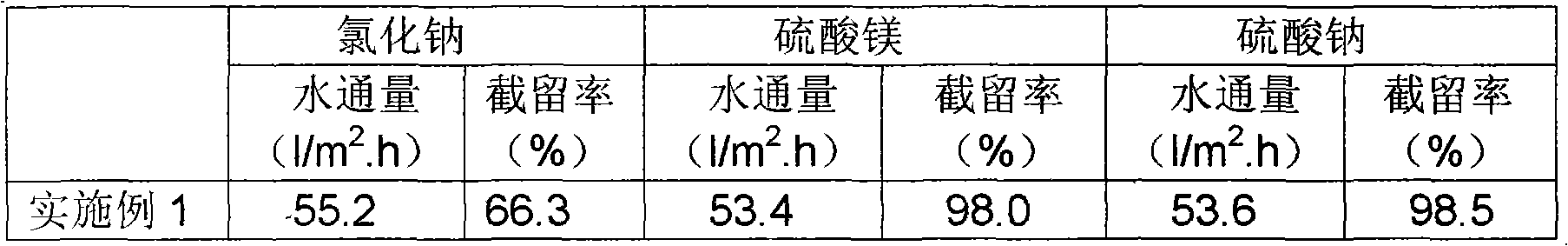
The invention relates to a novel poly piperazine amide nanofiltration membrane and a preparation method thereof. The poly piperazine amide nanofiltration membrane provided by the invention consists of a polysulfone supporting layer and a poly piperazine amide functional layer which is prepared by interfacial polycondensation of the aromatic multi acyl chloride with biphenyl structure or compounds thereof and piperazine. The novel poly piperazine amide nanofiltration membrane is prepared by utilizing the interfacial polycondensation of the organic solution of the novel butyryl chloride with biphenyl structure or compounds thereof and the aqueous solution of piperazine on the polysulfone porous supporting layer. The nanofiltration membrane prepared by the method has high water flux (more than 60l / m<2>.h) and high desalinization ratio (above 98%) of dianion and comparatively high desalinization ratio of single valence anion (60%-70%) under the operation pressure of 0.5Mpa.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
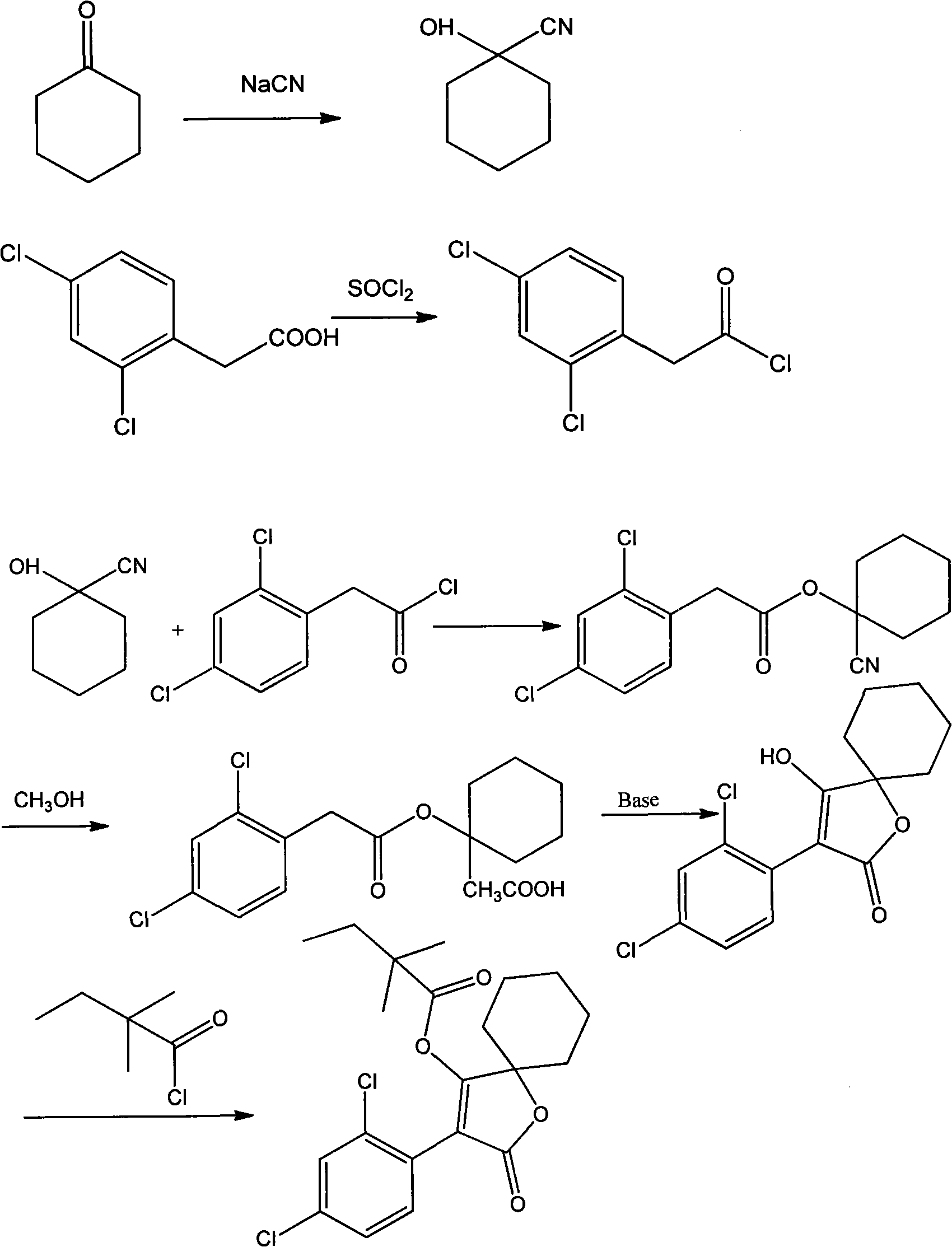
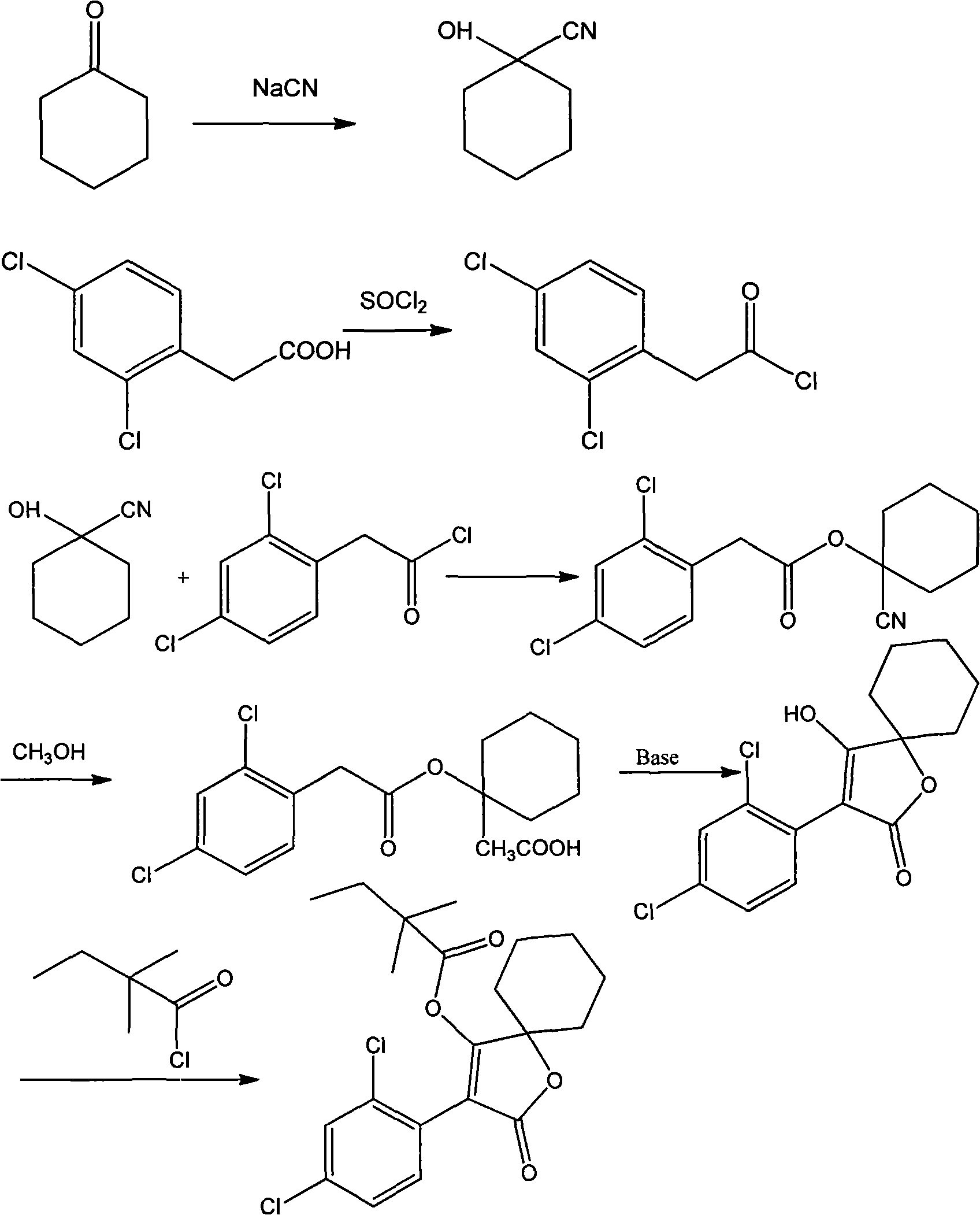
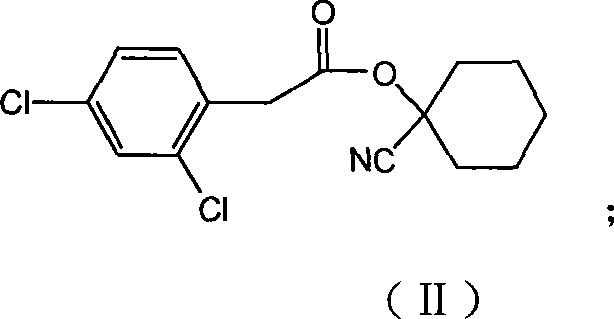
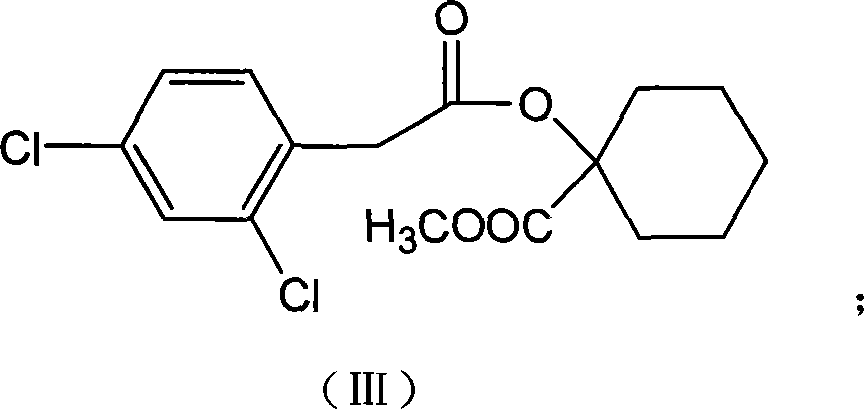
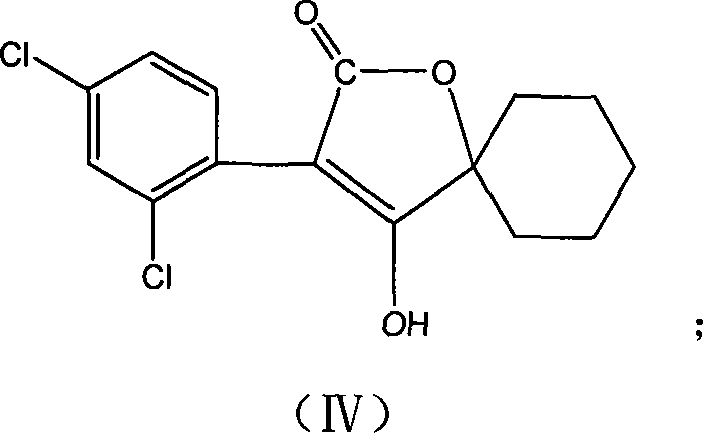
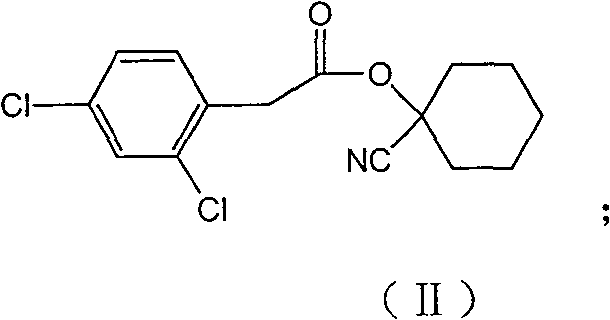
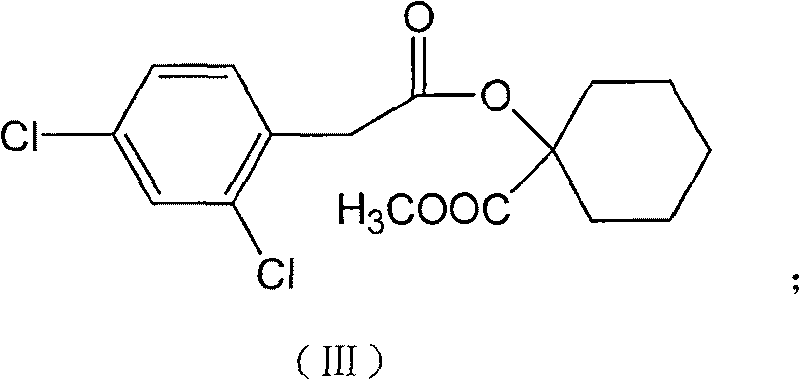
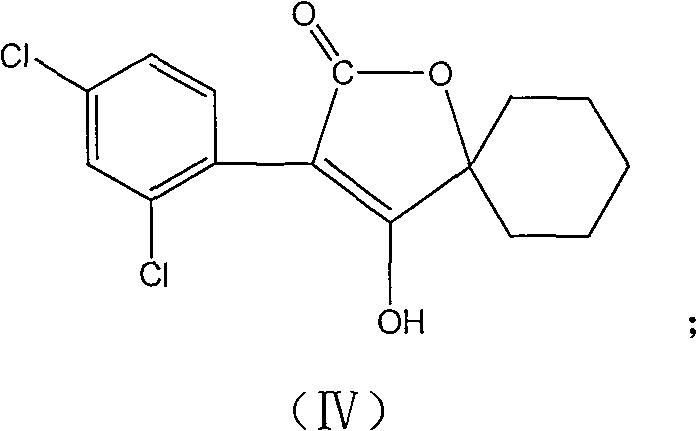
Production method for spirodiclofen
InactiveCN102372687ASimple processRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryCyclohexanoneSpirodiclofen
The present invention discloses a production method for spirodiclofen. According to the production method, cyclohexanone is adopted as a starting raw material, and is subjected to reactions of addition, acylation, esterification, cyclization and the like to obtain a spirodiclofen intermediate 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro[4.5]-dec-3-en-4-ol; then the 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro[4.5]-dec-3-en-4-ol reacts with 2,2-dimethyl butyryl chloride to prepare 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro[4.5]-dec-3-en-4-yl-2,2-dimethyl butyrate, which is the spirodiclofen. The production method of the present invention has characteristics of simple process, available raw materials and easy operation, and is suitable for industrial production of the spirodiclofen. With the present invention, the total yield of the five-step reaction is 36.6%, and is increased by nearly 17% than the yield in the prior art.
Owner:南通德益化工有限公司
Method for synthesizing spirodiclofen
InactiveCN101235023ASimple processAdapt to industrial productionOrganic chemistryAcaricidesAcetic acidAlcohol
The invention discloses a synthesis method of spirodiclofen which uses 1-cyano cyclohexanol, 2, 4-dichlorobenzene acetyl chloride and 2, 2-dimethyl butyryl chloride as main materials. The synthesis method comprises (1) generating compound II as 2, 4-dichlorobenzene acetic acid-1-cyano cyclohexyl, (2) generating compound III as 1-[2-(2, 4-dichloro-phenyl)-acetoxy]-cyclohexane methyl formate, (3) generating compound IV as 3-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro [4. 5]-sebacic-3-ene 4-alcohol, (4), generating compound I as 3-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro [4. 5]-sebacic-3-ene 4-radical-2, 2-dimethyl butyl. The spirodiclofen synthesis method has high yield and support for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
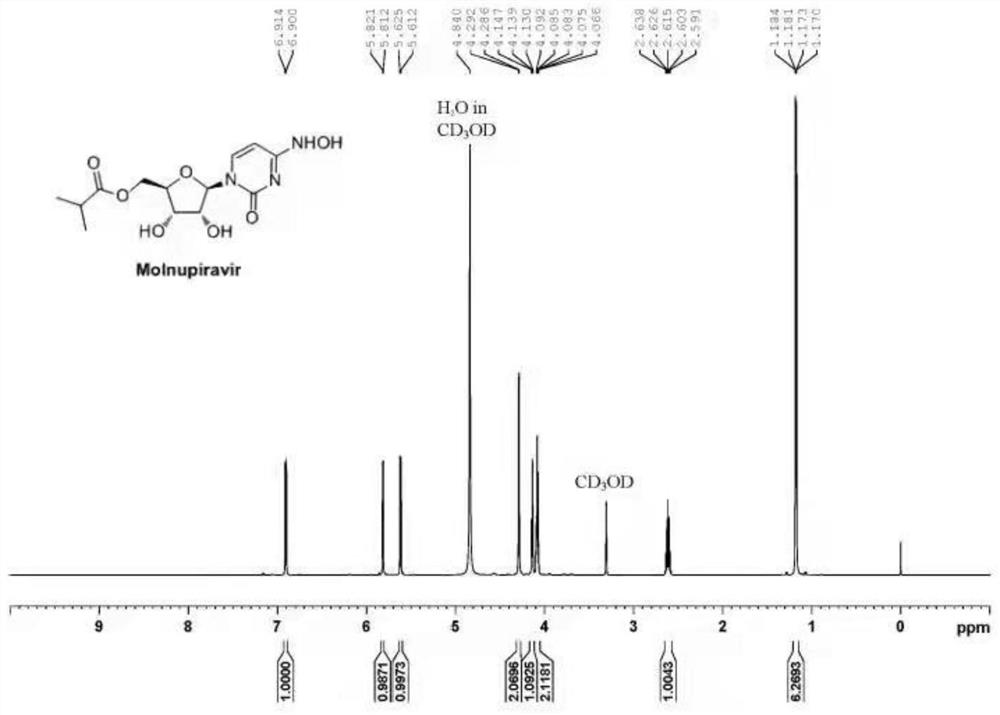
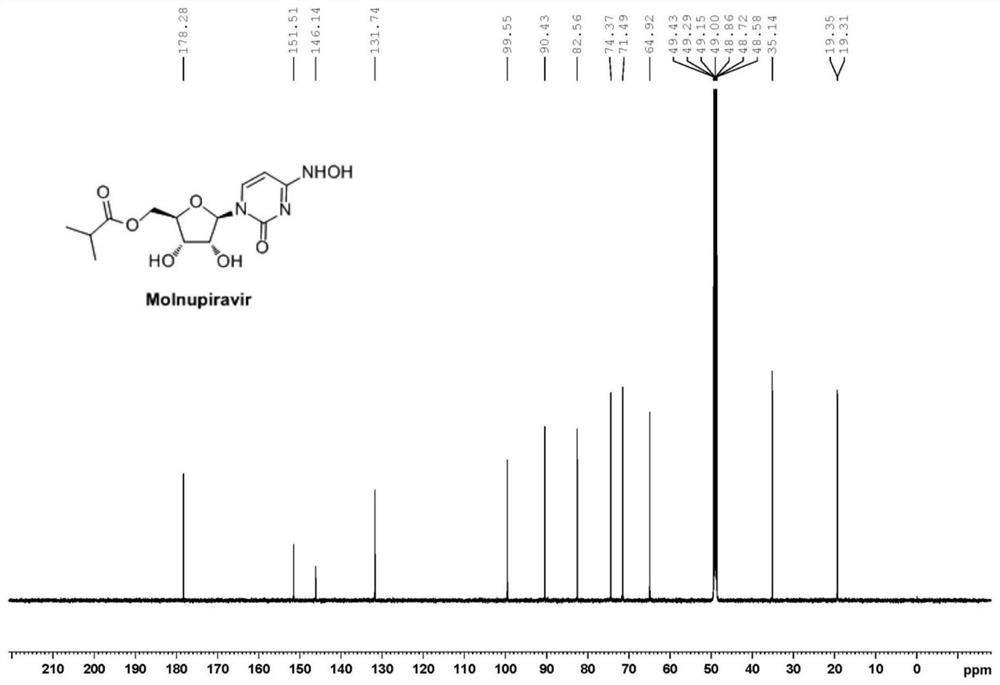
Preparation method of Molnupiravir
PendingCN113880903AEasy to operateHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydroxylamineRegioselectivity
The invention discloses a preparation method of Molnupiravir, and relates to the technical field of medicines. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking cytidine (1) as a starting material, and carrying out hydroxyl protection to obtain a compound 2; carrying out acylation on a compound 2 through isobutyryl chloride to obtain a diacylation intermediate 3; carrying out regioselective deacylation and hydroxyamination cascade reaction on the compound 3 to obtain a compound 4; and carrying out deprotection and refining on the compound 4 to obtain the finished product Molnupiravir (5). The process route is as follows.
Owner:厦门蔚嘉制药有限公司
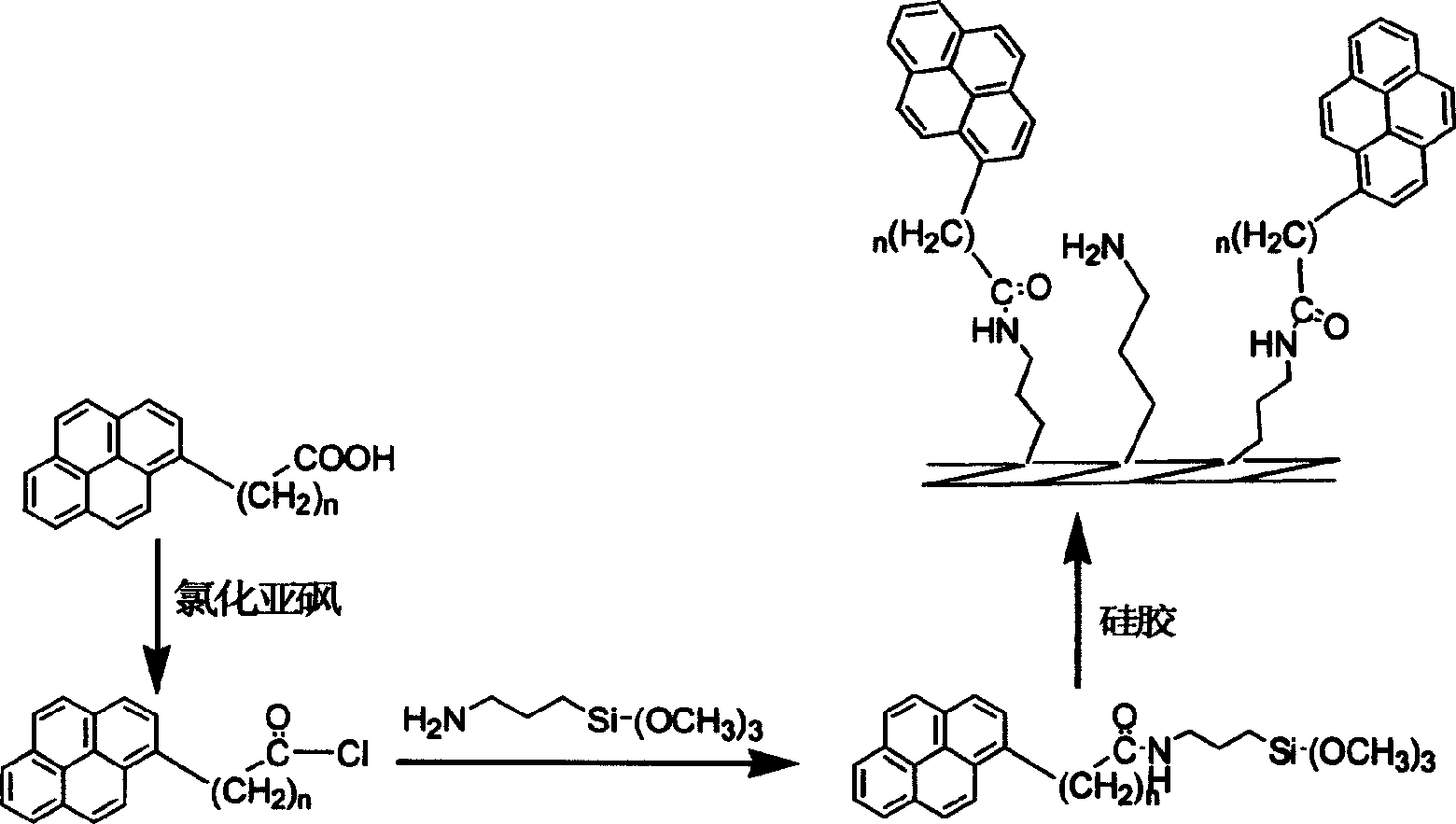
Method for preparing pyrenly bonded silicagel fixed phase
The present invention relates to a preparation mthod of pyrenyl bonded silica gel fixed phase. Said method includes the following steps; heating pyrenyl butyric acid and sulfur oxychloride according to the mole ratio of 1:1.2-1.5, making reflux reaction for 8-24 hr., reduced pressure distilling out sulfur oxychloride to obtain pyrenyl butyryl chloride, then using coupling agent 3-aminopropyl trimethoxysilane as intermediate adaptor for connecting pyrenyl butyryl chloride and silica gel, making bonding reaction so as to obtain the invented pyrenyl bonded silica gel fixed phase, in which the weight ratio of pyrenyl butyryl chloride, silica gel and coupling agent is 1:0.15-0.55:0.25-0.85. Said invented product can be used for separating fullerence, perchlorinated aromatic hydrocarbon, nitro-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbon with condensed rings.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
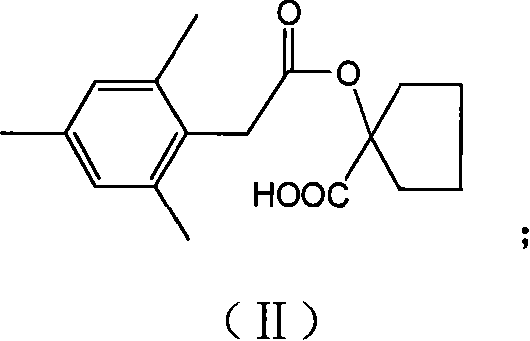
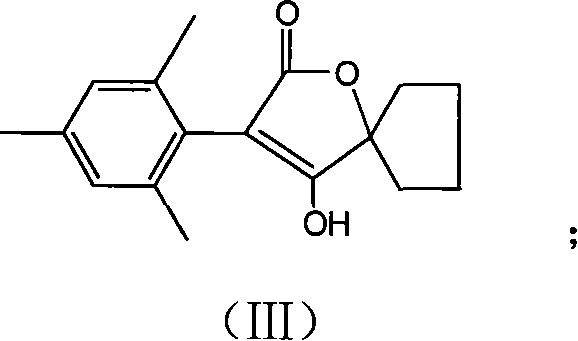
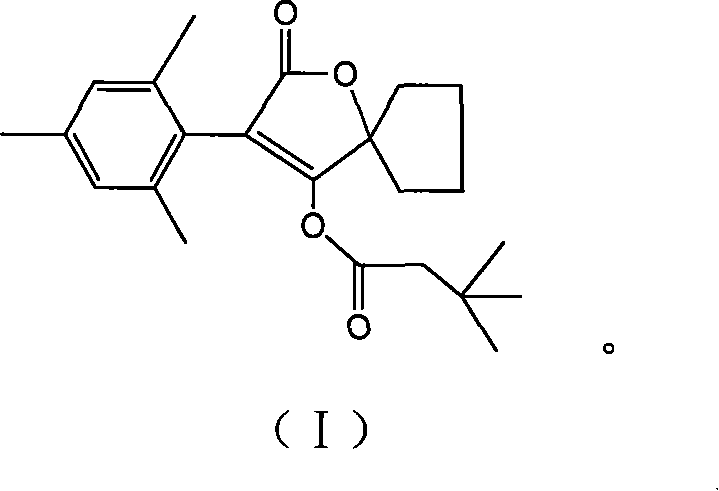
Preparation method of spiromesifen
The invention discloses a preparation method of spiromesifen, which uses 1-carboxyl cyclopentanol, 2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzene dichloroacetyl chloride and 3, 3-dimethyl butyryl chloride as main materials. The preparation method comprises (1), generating compound II: reacting 1-carboxyl cyclopentanol and 2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzene dichloroacetyl chloride in the presence of catalyst and in organic solvent, (2), generating compound III by heating the compound II and strong alkali in alcohol solution or in aprotic strong polar solvent to process reflux reaction, (3), generating spiromesifen by reacting the compound III and 3, 3-dimethyl butyryl chloride in the presence of catalyst and in organic solvent, wherein the prepared spiromesifen is represented as above. The preparation method of spiromesifen is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
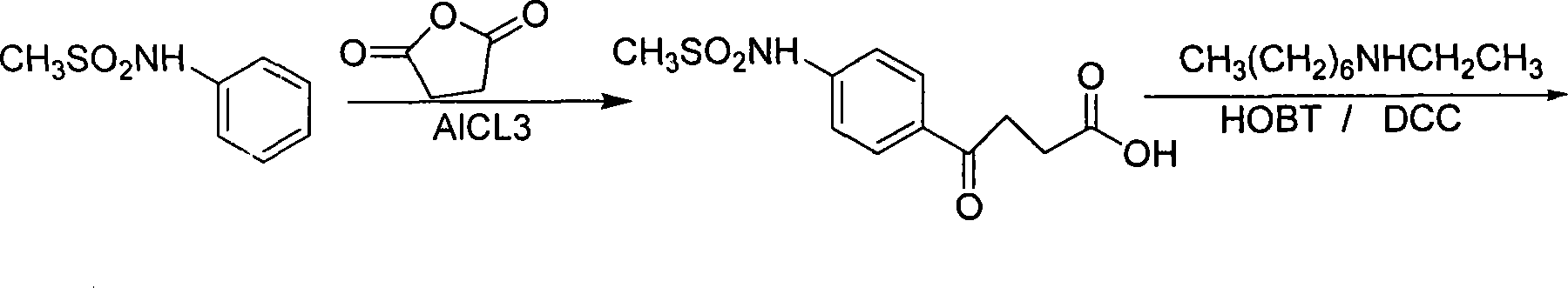
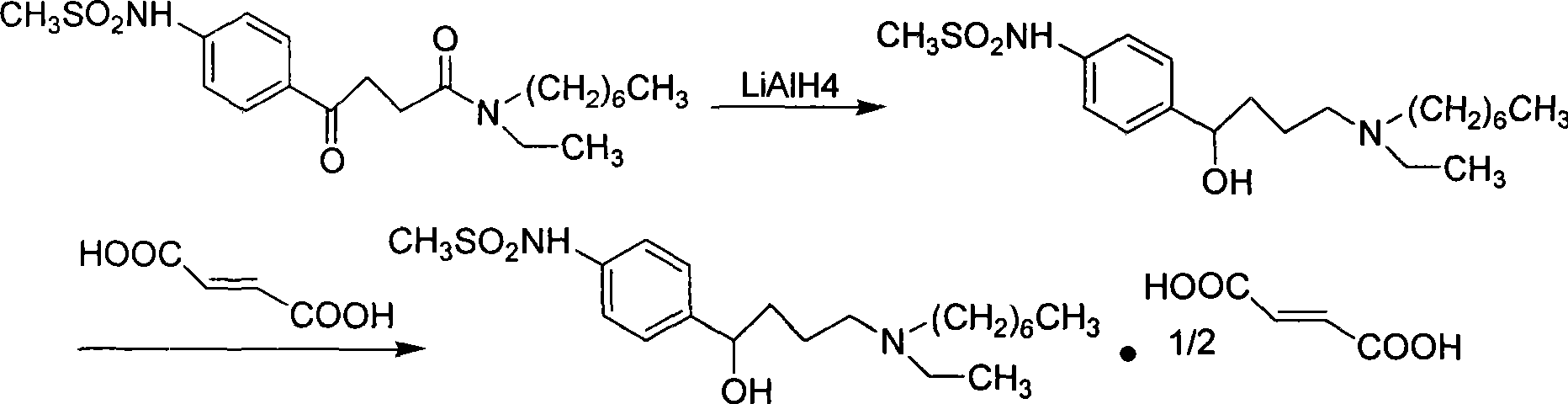
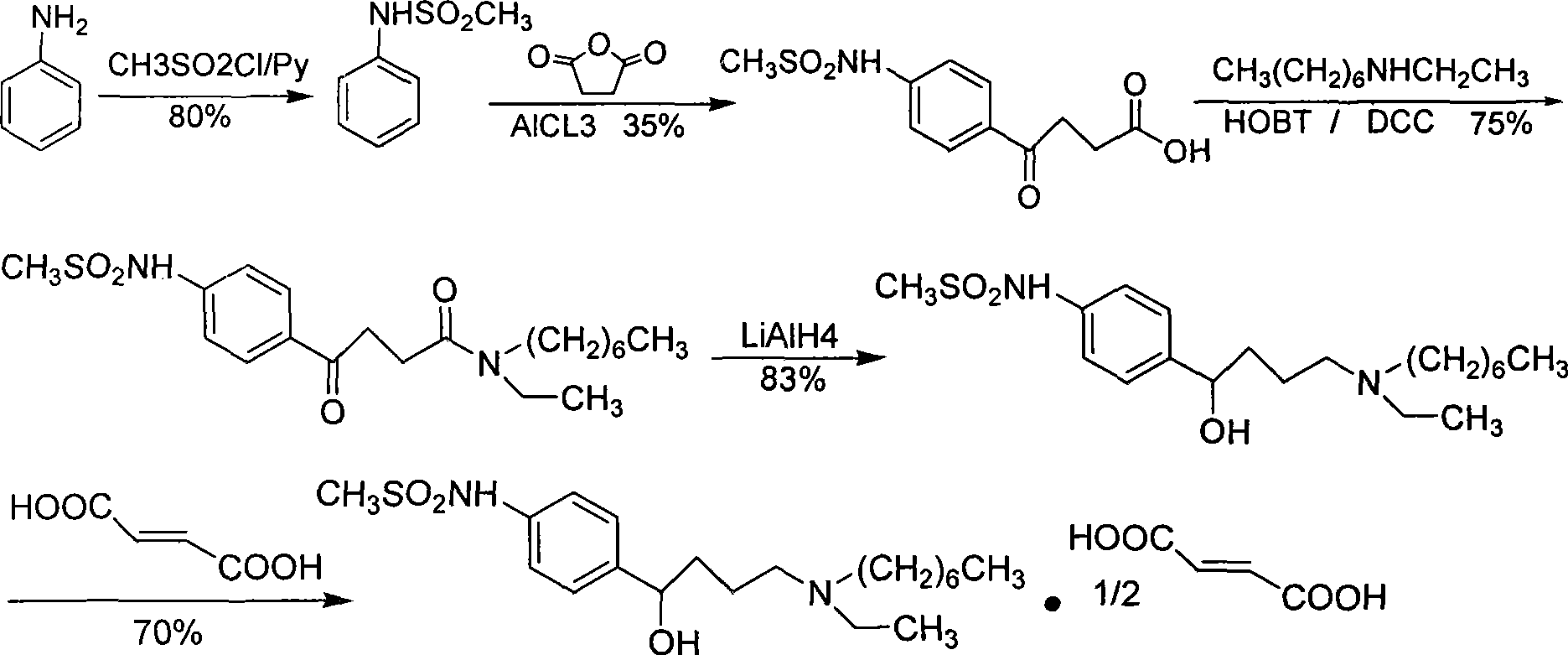
Ibutilide fumarate synthetic process
InactiveCN101381332AHigh synthesis costHigh yieldSulfonic acid amide preparationCardiovascular disorderAluminateFumaric acid
The invention relates to a process for synthesizing ibutilide fumarate. 2-pyrrolidone is taken as an initial raw material, DMF is taken as a solvent, and the 2-pyrrolidone and the DMF are N-alkylated with halogen ethane to obtain N-ethyl-butyrolactam under the catalysis; then 4-ethylamino-ethyl acetic acid is obtained through acid hydrolysis; the 4-ethylamino-ethyl acetic acid reacts with chloroheptane under the catalysis to obtain 4-ethylheptylamino-ethyl acetic acid; 4-ethylheptylamino-n-butyryl chloride is obtained through the acidylation; and the 4-ethylheptylamino-n-butyryl chloride is subjected to friedel-crafts reaction with N-phenylmethanesulfonamide to obtain (+ / -)-N-[4-[4-(ethylheptylamino)-1-ketonebutyl]phenyl] methanesulfonamide, (+ / -)-N-[4-[4-(ethylheptylamino)-1-hydroxybutyl]phenyl] methanesulfonamide is obtained by reducing sodium borohydride and / or tetrahydro-aluminate lithium, and then a target compound, namely the tetrahydro-aluminate lithium is obtained by salifying with fumaric acid. The process is more reasonable and is more convenient for industrialized production.
Owner:重庆医科大学医药研究所
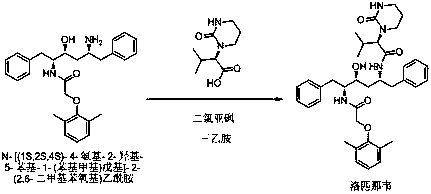
Method used for preparing Lopinavir using one-pot method
InactiveCN108218791ASimple processShorten the production cycleOrganic chemistryOrganic solventReaction system
The invention discloses a method used for preparing lopinavir using one-pot method. According to the method, under certain organic solvent conditions, (2S)-(1-Tetrahydropyramid-2-one)-3-methylbutanoicacid is reacted with thionyl chloride so as to obtain (2S)-(1-Tetrahydropyramid-2-one)-3-methyl butyryl chloride; a weak base acid binding agent and N-[(1S,2S,4S)-4-amino-2-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1-(phenylmethyl)pentyl]-2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)acetamide are added into an obtained reaction system for amidation reaction; after amidation reaction, an obtained product is subjected to post-treatment so as toobtain lopinavir finished product. According to the method, on-pot method is adopted, the process is simple, production period is short, the finial products can be separated and purified easily, synthesis yield is high, the method is economical and is high in feasibility, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:YANCHENG DESANO PHARMA CO LTD
Process method for synthesizing and purifying 4-chlorobutyryl chloride
InactiveCN104592001AHigh activityHigh selectivityChemical recyclingCarboxylic acid halides preparationPtru catalystSulfite salt
The invention discloses a process method for synthesizing and purifying 4-chlorobutyryl chloride. The process method comprises the following steps of reacting gamma-butyrolactone and thionyl chloride in the presence of a mixed catalyst to synthesize a 4-chlorobutyryl chloride crude product and purifying the 4-chlorobutyryl chloride crude product to obtain the 4-chlorobutyryl chloride finished product of which the purity is equal to or greater than 99%, the individual impurity is less than 0.30% and the yield is equal to or greater than 90%. In the process method, exhaust gas generated in the production of 4-chlorobutyryl chloride is comprehensively utilized to produce a 30% hydrochloric acid and sodium sulfite solution and the tail material is used for producing 4-chlorobutyric acid ester. The process method is simple, convenient to operate, high in yield and purity of a product and almost free of emission of three wastes and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:HUBEI BIOCHEM PHARMA TECH
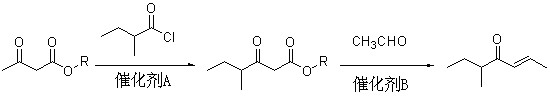
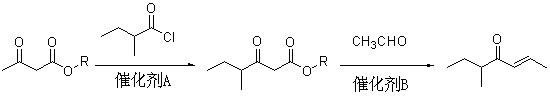
Method for preparing 5-methyl-2-hepten-4-one
InactiveCN102030626AReaction raw materials are readily availablePrevent oxidationOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAcetoacetatesBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing spice 5-methyl-2-hepten-4-one with nutty aroma. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting acetoacetate serving as a raw material with 2-methylbutyryl chloride to obtain an intermediate of 2-methylbutyryl acetate; and condensing the intermediate with acetaldehyde to prepare the product of 5-methyl-2-hepten-4-one. The used acetoacetate, 2-methylbutyryl chloride and acetaldehyde are commercial products, and the reaction raw materials are readily available, namely the raw materials are low in cost. In addition, the method avoids a Grignard reaction and stoichiometric oxidation, and is environmentally-friendly, easy to operate and suitable for industrialization.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Process for preparing bis-phenyl fluorozine and its use as medicine in treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
InactiveCN1654461ASimple processHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseDiphenylmethanol
The present invention relates to the preparation process of diphenyl ofloxacin and its application in preparing medicine for treating cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases. The preparation process includes the following steps: A) preparing gamma-chloro-4-fluorobenzene-1-butanone through the reaction between gamma-butyrolactone and sulfoxide chloride to obtain gamma-butyryl chloride and the subsequent reaction in mixed solvent with catalyst; B) preparing benzhydryl piperazine through the reaction between diphenylcaabinol and concentrated hydrochloric acid to obtain diphenyl chloromethane, the subsequent reaction in mixed solvent with catalyst and filtering; and C) preparing the product diphenyl ofloxacin with proper amount of benzhydryl piperazine, gamma-chloro-4-fluorobenzene-1-butanone, solvent methyl isobutyl ketone and catalyst potassium iodide and potassium carbonate, and through mixing and reaction.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Purification method of saccharose-6-acetate
InactiveCN109593107ANot muchLower reaction conditionsEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesAcetic acidPurification methods
The invention relates to a purification method of saccharose-6-acetate. The purification method comprises the following steps: (1) distilling a saccharose-6-acetate solution dissolved in an organic solvent DMF at a reduced pressure at 45-65 DEG C, raising the temperature to 50-70 DEG C when the pressure is reduced till the volume of the solution is 25% of the original volume, then adding one of ora combination of more of the following solvents: trimethylpentane, butyryl chloride, trichloro ethylene and chloroform, wherein the volume ratio of the solvents and saccharose-6-acetate is 1.5: 1 to8: 1, and reducing the temperature to 25-40 DEG C; and after analyzing saccharose-6-acetate crystals, filtering the crystals and drying the same to obtain purified saccharose-6-acetate. The solvent ispreferably trimethylpentane. The purification method has the advantages that the amount of needed trimethylpentane is small, the reaction conditions are relatively low, and the purity of the obtainedsaccharose-6-acetate reaches 95-97% or above.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
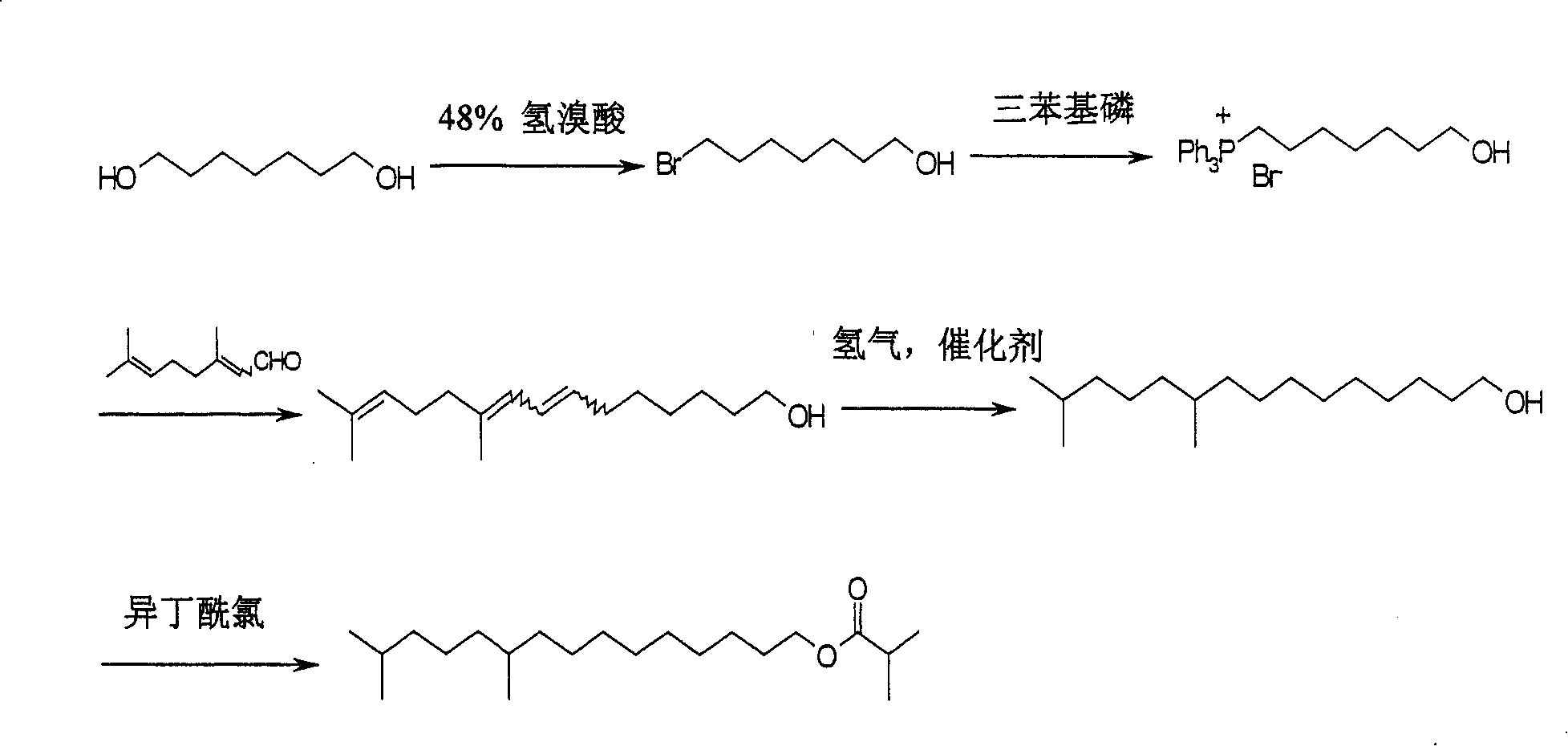
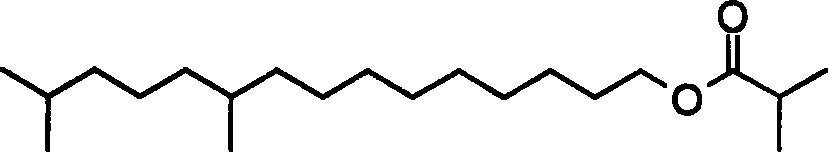
Improved synthesis method for tea caterpillar sex pheromone
ActiveCN101209968AMaterials are readily availableFew synthetic stepsPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesOrganic base1-Heptanol
The invention relates to an improved synthesis method for sex pheromone of euproctis pseudoconspersa, which is characterized in that 1, 7-heptanediol and 30-70 percent of hydrobromic acid solution react at the temperature of 50-130 DEG C and monobromide product 7-bromine-1-heptanol is obtained; the monobromide product 7-bromine-1-heptanol reacts with triphenyl phosphine in organic solvent I at the temperature of 50-130 DEG C, thus obtaining quaternary ammonium salt of triphenyl phosphine; with the function of organic base I or inorganic base, the obtained quaternary ammonium salt of triphenyl phosphine carries out Witting reaction with citral in organic solvent II and at the temperature of -20 DEG C-80 DEG C, and 10, 14-dimethyl-7, 9, 13-pentadec-1-triethylenic alcohols is produced; the triethylenic alcohols produced is reduced into 10, 14- dimethyl-1-pentadecanol in organic solvent III through catalysis and hydrogenation; finally, the 10, 14-dimethyl-1-pentadecanol obtained reacts with iso-butyryl chloride in the existence of the organic base II, so that 10, 14-dimethyl pentadec isobutyl is obtained. The invention has the advantages of easily obtained raw material, low cost, moderate reaction, suitability for scale production and high yield.
Owner:宁波纽康生物技术有限公司
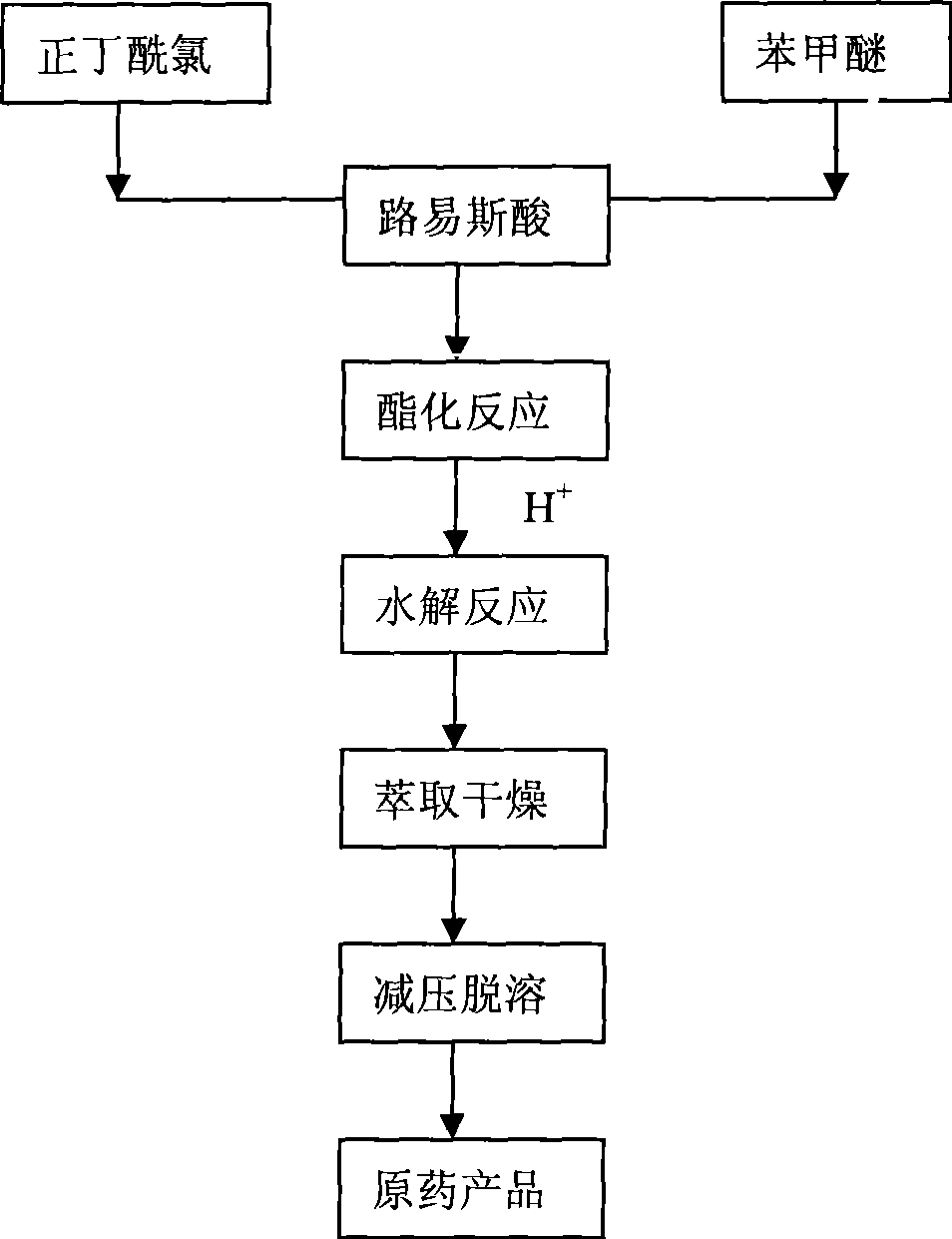
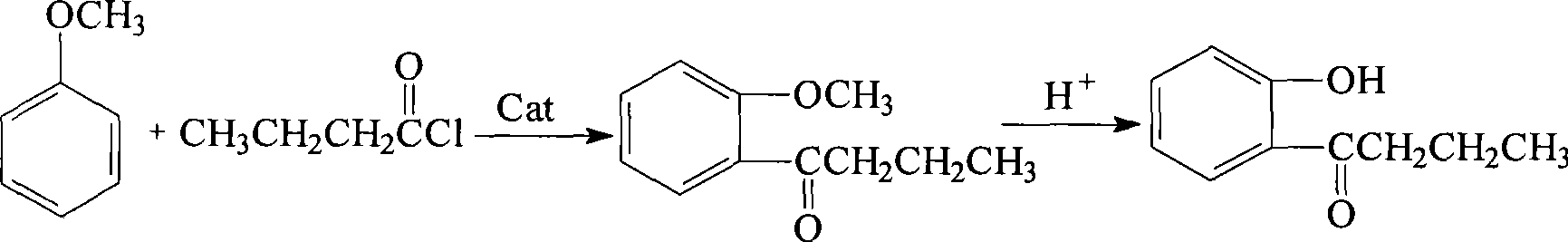
Method for preparing 1-o-hydroxyphenyl butanone
InactiveCN101386573AShort processHigh purityCarbonyl compound preparation by condensationOrganic solventDistillation
The present invention relates to a method for preparing 1-ortho-hydroxy phenyl butanone. In the presence of a catalyst of Lewis acid, anisole and butyryl chloride are reacted with an organic solvent as the reaction media at a circumfluence temperature for 2 to 3 hours. The reaction liquid is hydrolyzed by hydrochloric acid. A hydrolysate is separated from the reaction liquid so as to obtain an organic phase. The organic phase is dried by anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and then an organic solvent in the organic phase is removed through reduced pressure distillation so as to obtain 1-ortho-hydroxy phenyl butanone. The removed organic solvent can be recycled. The method is short in process flow, and high in product yield that usually reaches up to more than 90 percent. The obtained 1-ortho-hydroxy phenyl butanone is high in purity that reaches up to more than 95 percent usually. The reaction condition is mild and the three wastes are not discharged.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Afatinib preparation method
ActiveCN103242303BEase of industrial productionPromote the development of economy and technologyOrganic chemistry3-Hydroxytetrahydrofuran2-Butene
The invention discloses an Afatinib (I) preparation method which comprises the following steps: performing etherification reaction on 4-chloro-6-amino-7-hydroxyquinazoline (II) and (S)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran to generate 4-chloro-6-amino-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]quinazoline (III); performing acylation reaction on the compound (III) and 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-2-ene-butyryl chloride to generate 4-chloro-6-{[4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1-oxo-2-butene-1-yl]amino}-7-[(S)-(tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy]quinazoline (IV); and performing condensation reaction on the compound (IV) and 4-fluoro-3-chloroaniline to obtain Afatinib (I). The preparation method is simple, economic and environment-friendly in process, and meets the requirements for large-scale industrialization.
Owner:铜陵尚东高新科创有限公司
Preparation method of clevidipine butyrate intermediate
InactiveCN102391174AMild reaction conditionsPost-processing is simpleOrganic chemistryEthyl esterBenzene
The invention relates to a preparation method of a clevidipine butyrate intermediate, namely 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3 ,5- dipicolinic acid monomethyl ester (I). The preparation method is characterized by taking 3-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2-acetyl benzene gadoleic acid methyl ester and 3-amino-2-butenoic acid (2-cyano) ethyl ester as materials, cyclizing the materials to obtain 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid methyl (2-cyano) ethyl ester (II), and hydrolyzing the II under alkaline conndition, thus obtaining the product 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3 ,5- dipicolinic acid monomethyl ester (I). The preparation method has the advantages as follows: the starting material is cheap and easy to obtain, the production cost is reduced, the reaction operation is simple, industrialization is easy, the purity of the obtained material is high and byproducts are few; the byproducts in the preparation method are fewer than that in the preparation of the clevidipine butyrate by butyl chloride methyl ester; the purity is high and the crude product can achieve 99.5%; and medicinal standard requirements can be met.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF PHARMA IND
Process for preparing 3, 3-dimethyl -2-pentanone
InactiveCN1781894ASimple processRelaxed reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationMalonateMedicinal chemistry
The present invention relates to a process of preparing 3, 3-dimethyil-2-pentanone. The preparation process includes the following steps: reaction of magnesium alkoxyl ethyl malonate and 2-dimethyl butyryl chloride to prepare 2, 2-dimethyl butyryl ethyl malonate; and converting 2, 2-dimethyl butyryl ethyl malonate into 3, 3-dimethyil-2-pentanone. The preparation process of the present invention adopts cheap and facile material, and is simple, suitable for industry use and high in reaction yield.
Owner:LYNCHEM
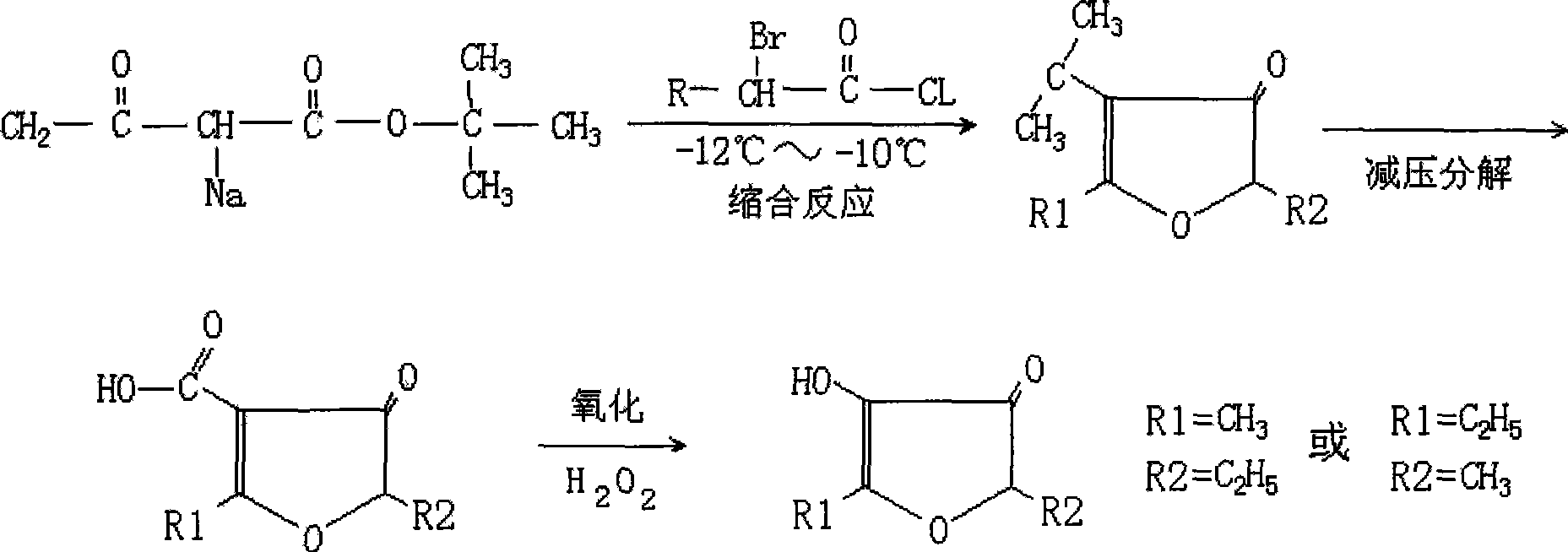
Method for preparing alkyl furanone by low-temperature condensation method
InactiveCN101397285ARaw materials are easy to getReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryAcetic acidState of art
The invention relates to a method adopting a low-temperature condensation method to prepare alkyl furanone. The method firstly adopts active hydrogen atoms in the t-butyl acetoacetate to react with sodium metal to prepare sodio-t-butyl acetoacetate; then the sodio-t-butyl acetoacetate and alpha-bromo-butyryl-chloride are condensed under the low temperature to form the furan nucleus with the alkyl, then the furan nucleus is decomposed under decompression and finally the outcome of decomposing under decompression is oxidated to prepare the required product. Compared with the prior art, the method has more advantages that not only the material is more available, the process cycle is comparatively short, the operation is easy and the yield is satisfying, but also the obtained alkyl furanone is better in color, odor and flavor, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN CHEM REAGENT RES INST
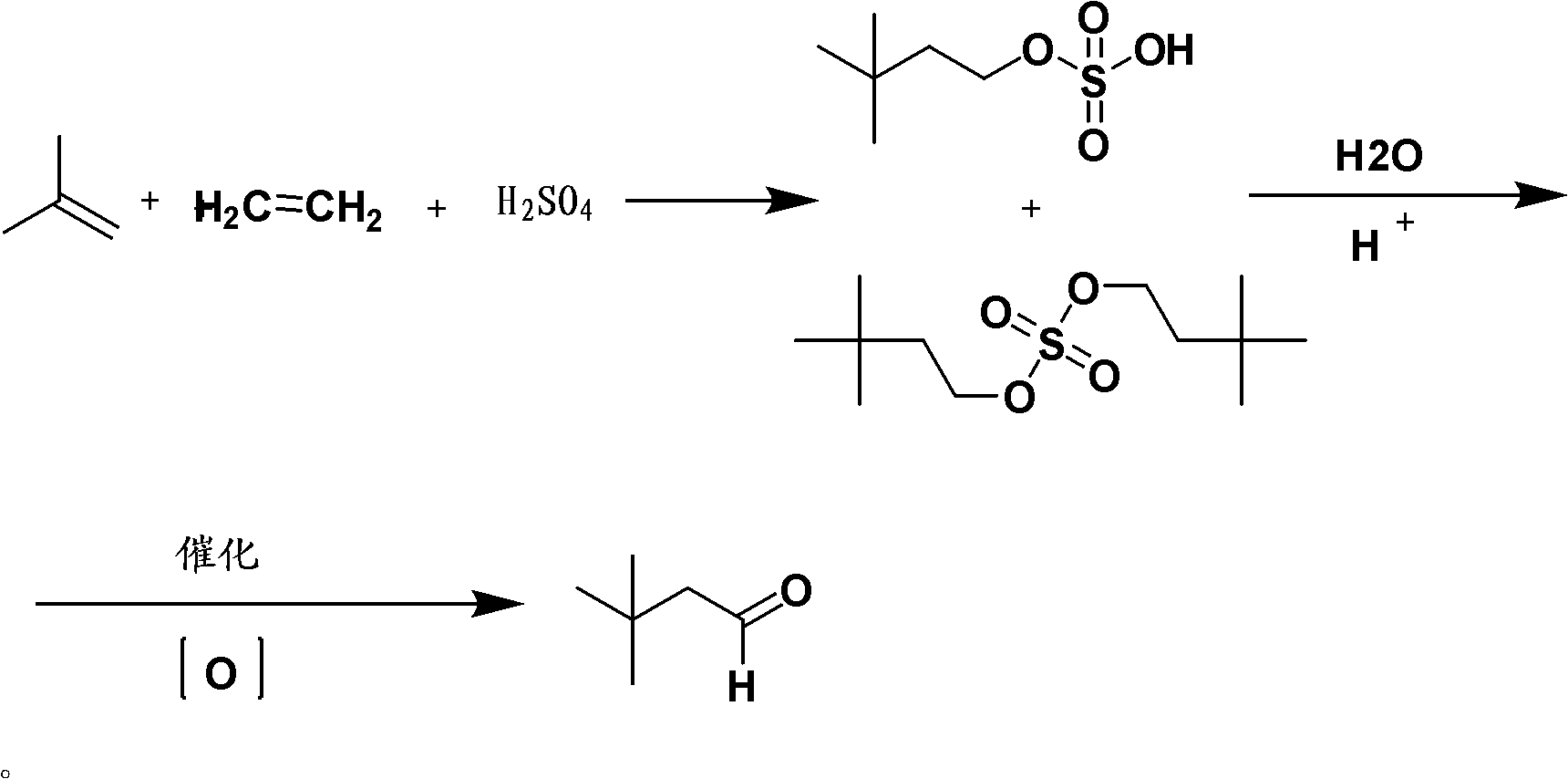
Method for preparing 3,3-dimethyl butyraldehyde
The invention provides a method for preparing 3,3-dimethyl butyraldehyde, which comprises the following steps of: adding an acid-binding agent, a catalyst, an auxiliary catalyst and a solvent into 3,3-dimethyl butyryl chloride, and reacting under a certain pressure of H2 to obtain the 3,3-dimethyl butyraldehyde, wherein the acid-binding agent is from inorganic base or organic base; the catalyst is selected from recyclable precious metals; and the auxiliary catalyst is a metal salt. The method is suitable for the large-scale industrial production of the 3,3-dimethyl butyraldehyde; in the method, the raw materials used are cheap and readily available, the drawback that a large amount of hydrogen is discharged into the atmosphere in a normal-pressure reaction is overcome; and the method is environmentally-friendly; the reaction is compete, the product yield and product purity are high, the post treatment is simple and the production cost is low.
Owner:太仓浦源医药原料有限公司
Method for preparing gamma-tertiary butyl-chlorobenzene butanone
InactiveCN101700996AEasy to absorb moistureReaction is easy to controlOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationChlorobenzeneButyl chloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing gamma-tertiary butyl-chlorobenzene butanone. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) acylation reaction: sucking butyrolactone into a clean and dry reaction kettle and strring, and then adding zinc chloride into the reaction kettle for reaction to generate semi-finished butyl chloride; (b) hydrolysis reaction: adding dichloroethane and aluminium choride into a clean and dry reaction kettle, dropwise adding the butyl chloride into the reaction kettle while stirring; then continuing to dropwise adding tedin benzene , and steaming off dichloroethane to generate the gamma-tertiary butyl-chlorobenzene butanone. 3gamma-tertiary butyl-chlorobenzene butanone products prepared by the method are pale yellow granules, wherein the content of the 3gamma-tertiary butyl-chlorobenzene butanone is more than or equal to 90 percent, and the pH value is larger than or equal to 3.85. The reaction process of the method is easy to control, the utilization rate of raw materials and the yield of the products are improved, and the method conforms to the requirements on environmental protection and cleaner production and improves the economic benefits of enterprises.
Owner:扬州市天平化工厂有限公司
Adsorbent, preparation method thereof, and resin containing long-chain quaternary ammonium salt
InactiveCN105126785AHigh yieldOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesQuaternary ammonium cationIon exchange
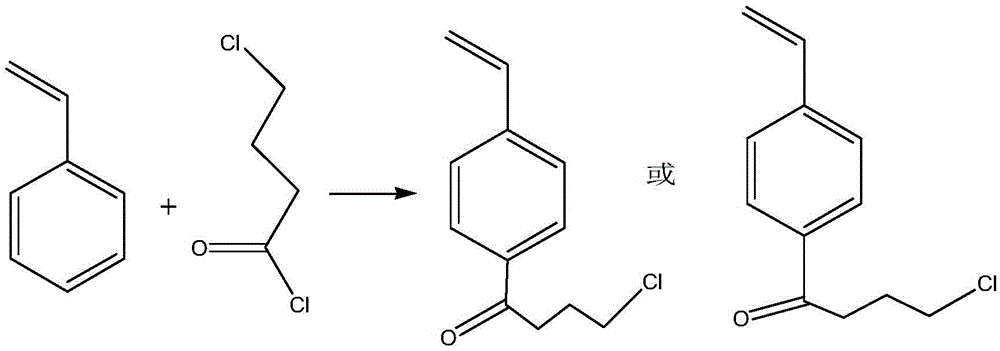
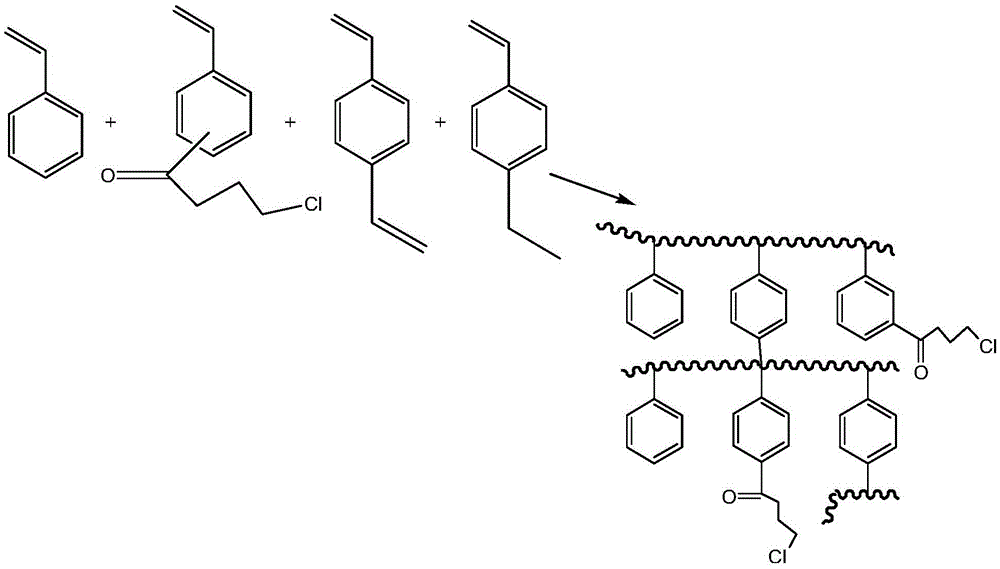
The invention provides an adsorbent, a preparation method thereof, and resin containing long-chain quaternary ammonium salt. The adsorbent is used to adsorb bilirubin in blood purification. The adsorbent comprises strong-basic anion exchange resin containing long-chain quaternary ammonium salt. The exchange resin comprises at least one quaternary ammonium salt group and polystyryl macroporous resin matrix, and the quaternary ammonium salt group and polystyryl macroporous resin matrix are connected through a butyryl substituted group. The resin has the advantages of high thermal stability and good absorbing performance. The preparation method of adsorbent comprises the following steps in sequence: preparing 4-butyryl chloride substituted styrene, preparing polystyryl macroporous resin matrix, preparing strong-basic anion exchange resin containing long-chain quaternary ammonium salt, and preparing adsorbent. The preparation method is more environment-friendly, and moreover, the ion exchange capacity can be precisely controlled by controlling the weight ratio of 4-butyryl chloride substituted styrene to other monomers.
Owner:JAFRON BIOMEDICAL
Chemical synthetic method for n-butyryl chloride
InactiveCN102199083AAdvanced process routeReasonable process conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationChemical synthesisOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a green chemical synthetic method for n-butyryl chloride, in particular to a chemical synthetic method for preparing n-butyryl chloride by utilizing the reaction between bis (trichloromethyl) carbonate and n-butyric acid. The method comprises the steps of: with n-butyric acid and bis (trichloromethyl) carbonate as the raw materials, reacting in organic solvent at the temperature of 50 DEG C to 100 DEG C for 1 to 10 hours under the action of an organic amine catalyst, and then distilling to obtain the n-butyryl chloride. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of advanced process route, reasonable process conditions, simplicity and safety in operation, high reaction yield rate, low production cost, and less 'three wastes' (waste gas, waste water and waste residues); and the method has greater implementation value and social and economical benefits.
Owner:湖州沙龙化工有限公司
Method for synthesizing spirodiclofen
InactiveCN101235023BSimple processAdapt to industrial productionOrganic chemistryAcaricidesSynthesis methodsPhenyl group
The invention discloses a synthesis method of spirodiclofen which uses 1-cyano cyclohexanol, 2, 4-dichlorobenzene acetyl chloride and 2, 2-dimethyl butyryl chloride as main raw materials. The synthesis method comprises (1) generating a compound II as 2, 4-dichlorobenzene acetic acid-1-cyano cyclohexyl, (2) generating a compound III as 1-[2-(2, 4-dichloro-phenyl)-acetoxy]-cyclohexane methyl formate, (3) generating a compound IV as 3-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro [4. 5]-sebacic-3-ene 4-alcohol, (4), generating a compound I as 3-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-oxaspiro [4. 5]-sebacic-3-ene4-radical-2, 2-dimethyl butyl. The spirodiclofen synthesis method has high yield and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for continuously producing diisobutyryl peroxide through multipoint feeding and reinforced mixing
InactiveCN111072542ARealize mixing in secondsIncrease the molar ratioOrganic compound preparationPeroxy compound preparationSide reactionHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for continuously producing diisobutyryl peroxide by multi-point feeding and enhanced mixing. The method comprises the following steps: (1) continuously feeding a hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution and an alkaline aqueous solution stream 1 into a first flow reactor to carry out salt forming reaction; (2) reacting the reaction solution obtained in the step (1) and acontinuously added isobutyryl chloride solution stream 1 for generating IBP in a second flow reactor; (3) feeding the reaction solution obtained in the step (2) and a continuously added aqueous alkalistream 2 into a third flow reactor for salt forming reaction; and (4) reacting the reaction solution obtained in the step (3) and the continuously added isobutyryl chloride solution stream 2 for generating IBP in a fourth flow reactor; wherein the IBP is abbreviation of diisobutyryl peroxide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, side reactions such as acyl chloride hydrolysis can be obviously reduced, the IBP yield is improved, and reaction heat is removed in time, so that the whole reaction is carried out under safe and environment-friendly continuous conditions.
Owner:YUNNAN ZHENGBANG SCI & TECH
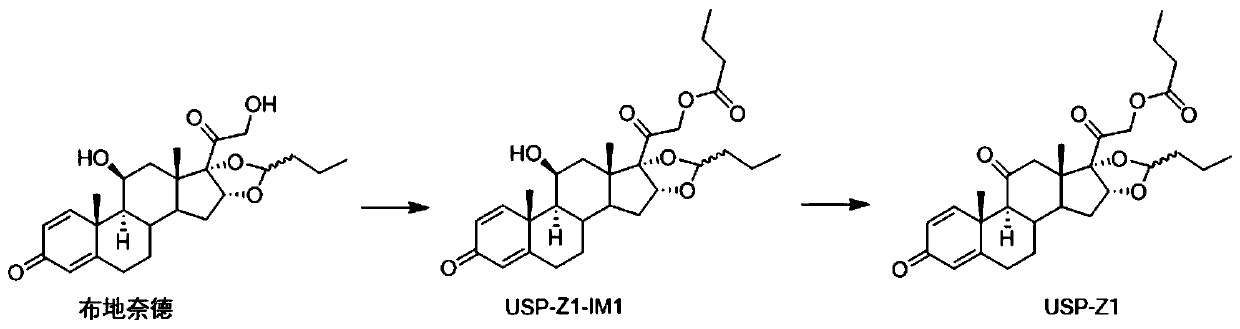
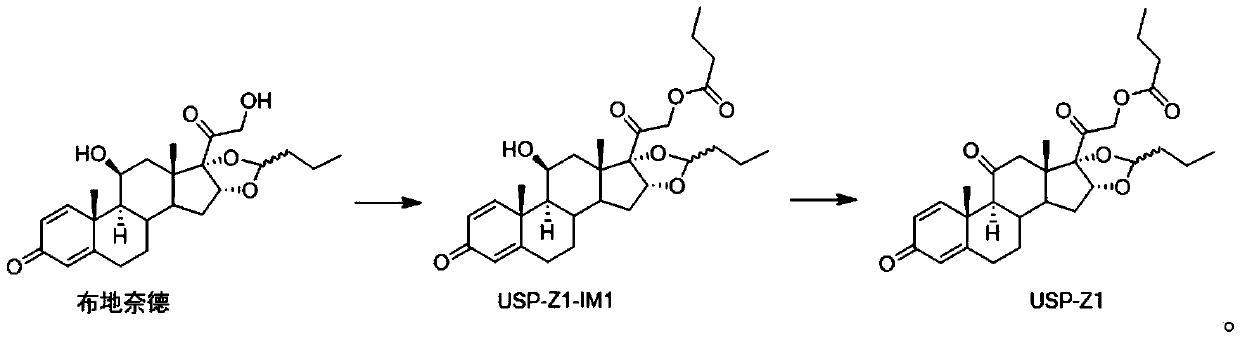
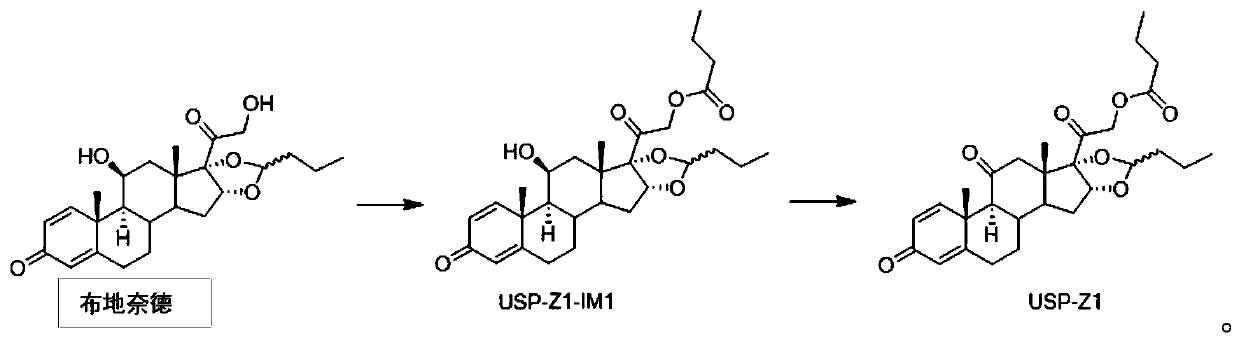
Synthesis method of budesonide impurity USP-Z1
The invention provides a synthesis method of a budesonide impurity USP-Z1. According to the synthesis method, firstly, budesonide is taken as a raw material and subjected to a reaction with butyryl chloride or butyric anhydride under the condition of an organic solvent and an acid-binding agent to produce a compound USP-Z1-IM1; then, the compound USP-Z1-IM1 is dissolved in the organic solvent, anoxidant is added, oxidation is performed, and the impurity USP-Z1 is produced. The synthesis method adopts a simple process route and is convenient to operate, good in selectivity and high in yield; the synthesized budesonide impurity USP-Z1 can serve as a reference substance for detection and study of budesonide and is applied to quality control of budesonide and related preparations to control the purity of raw materials or preparations of budesonide.
Owner:BIONNA (BEIJING) MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com