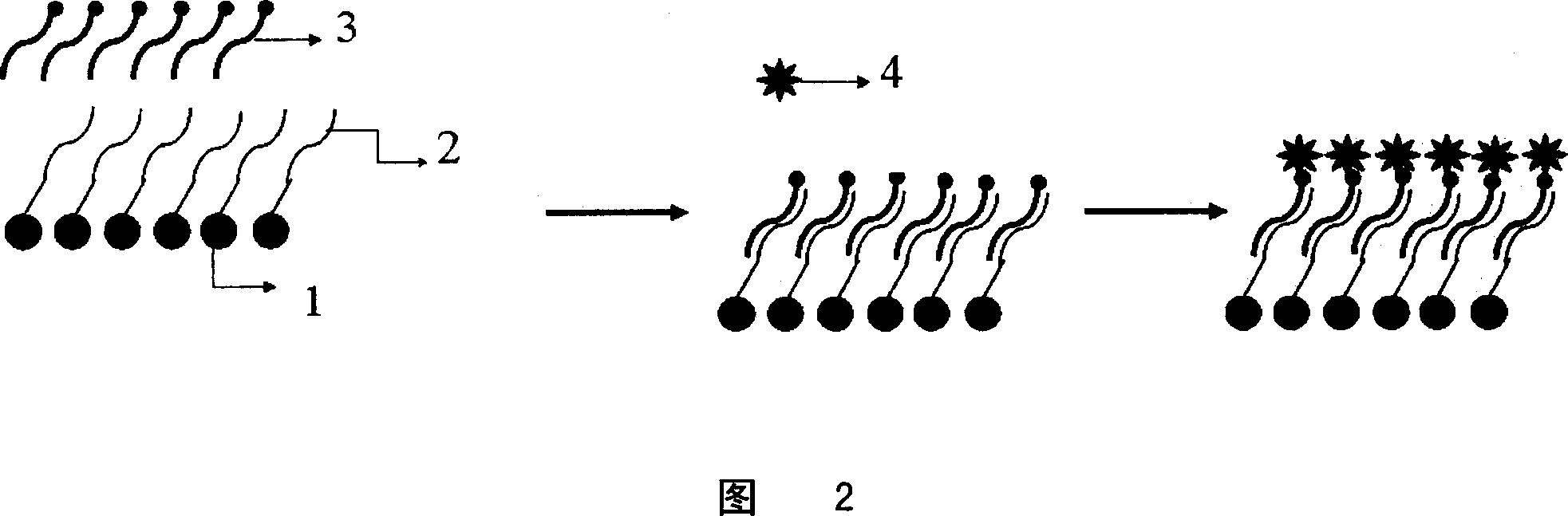
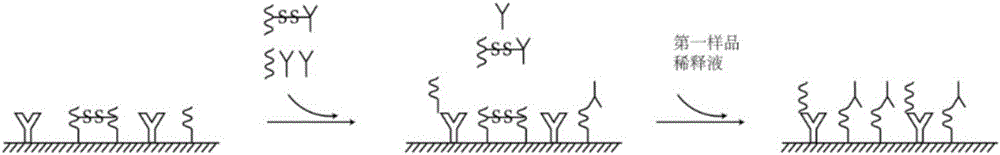
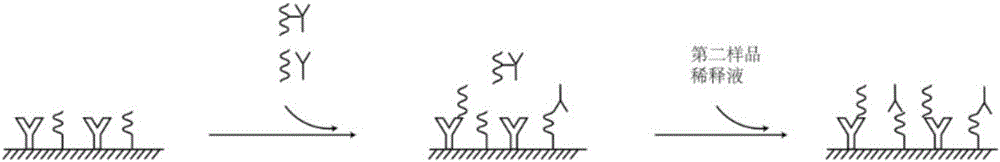
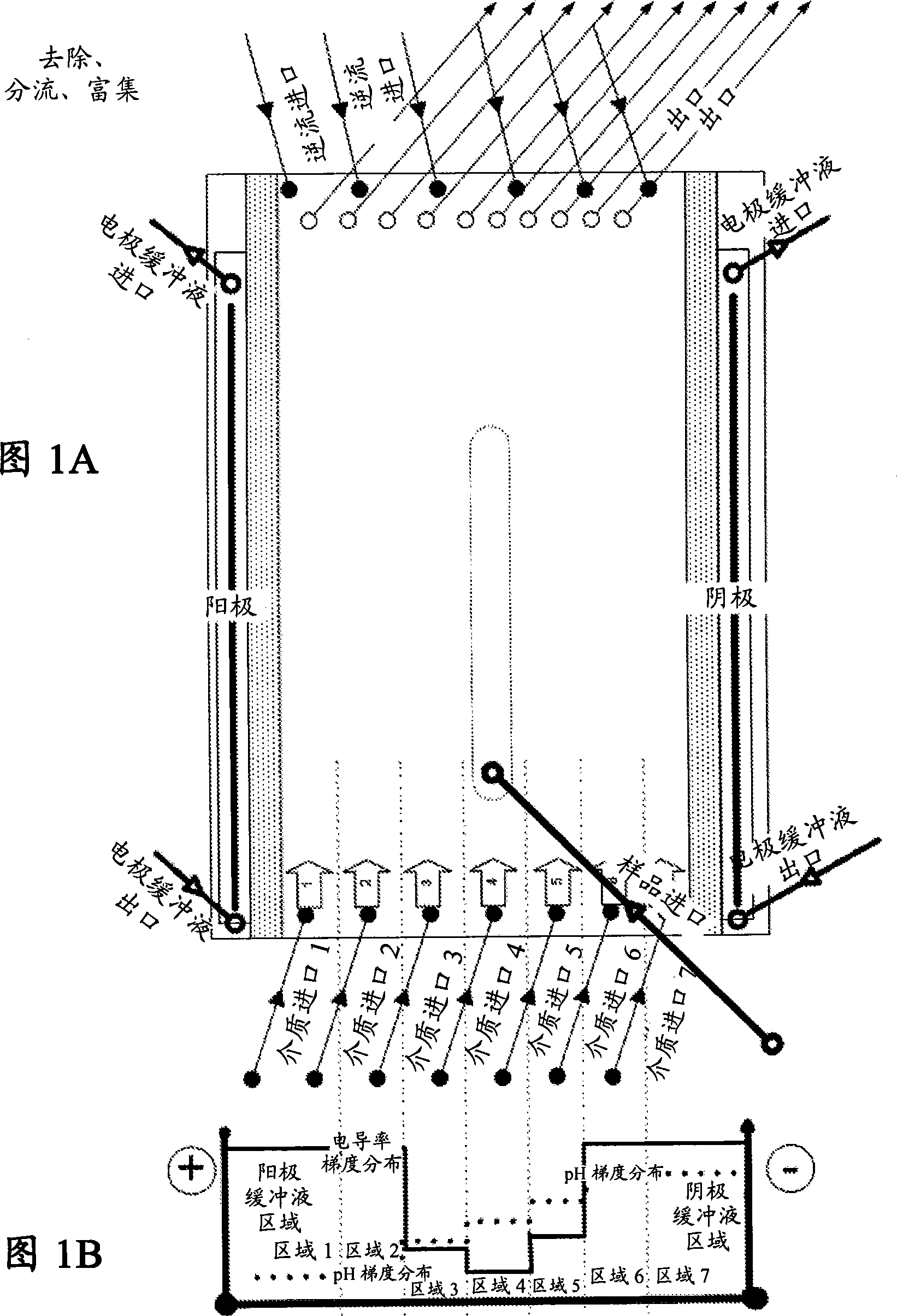
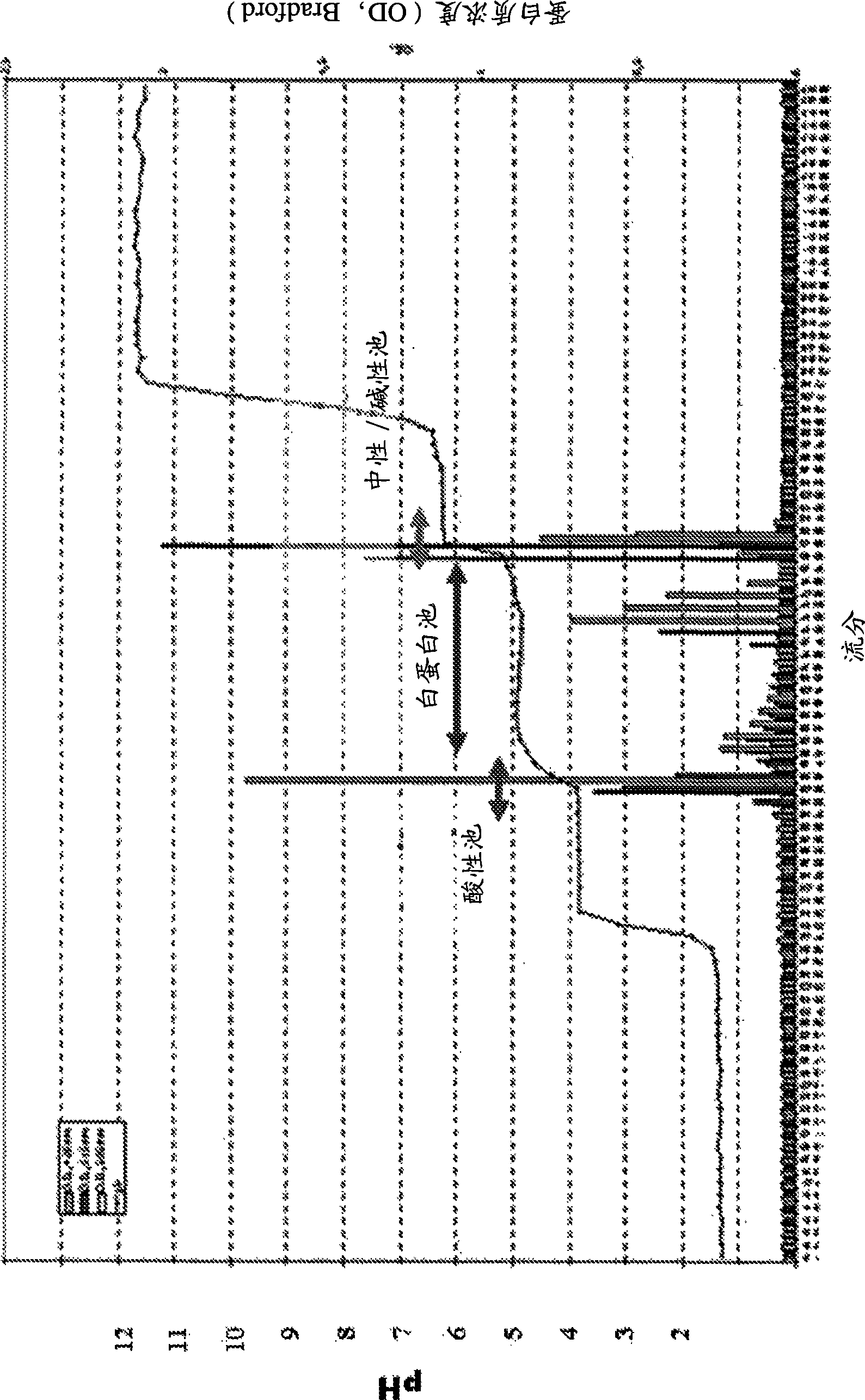
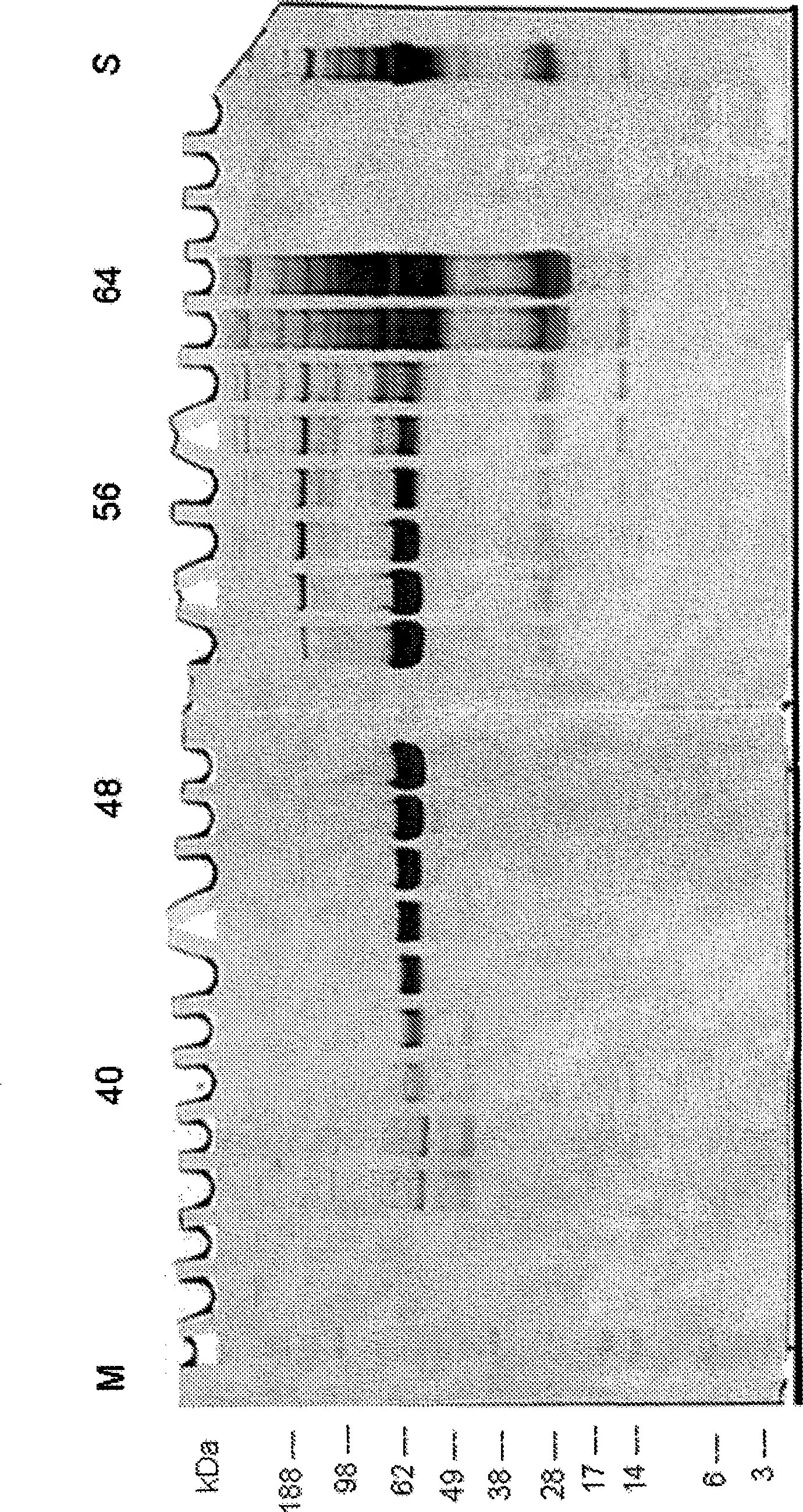
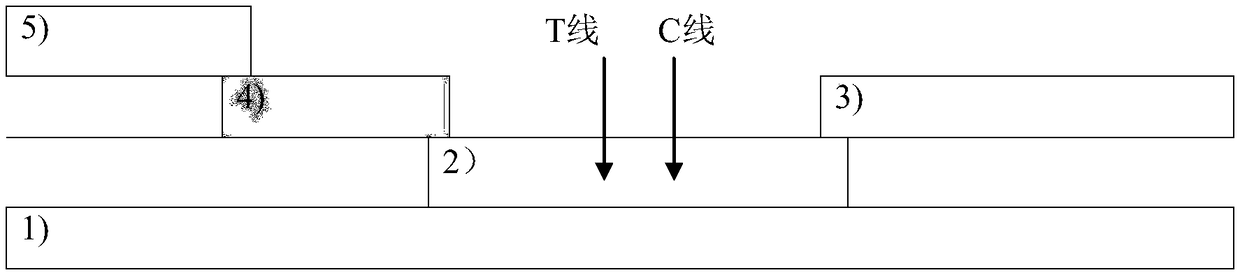
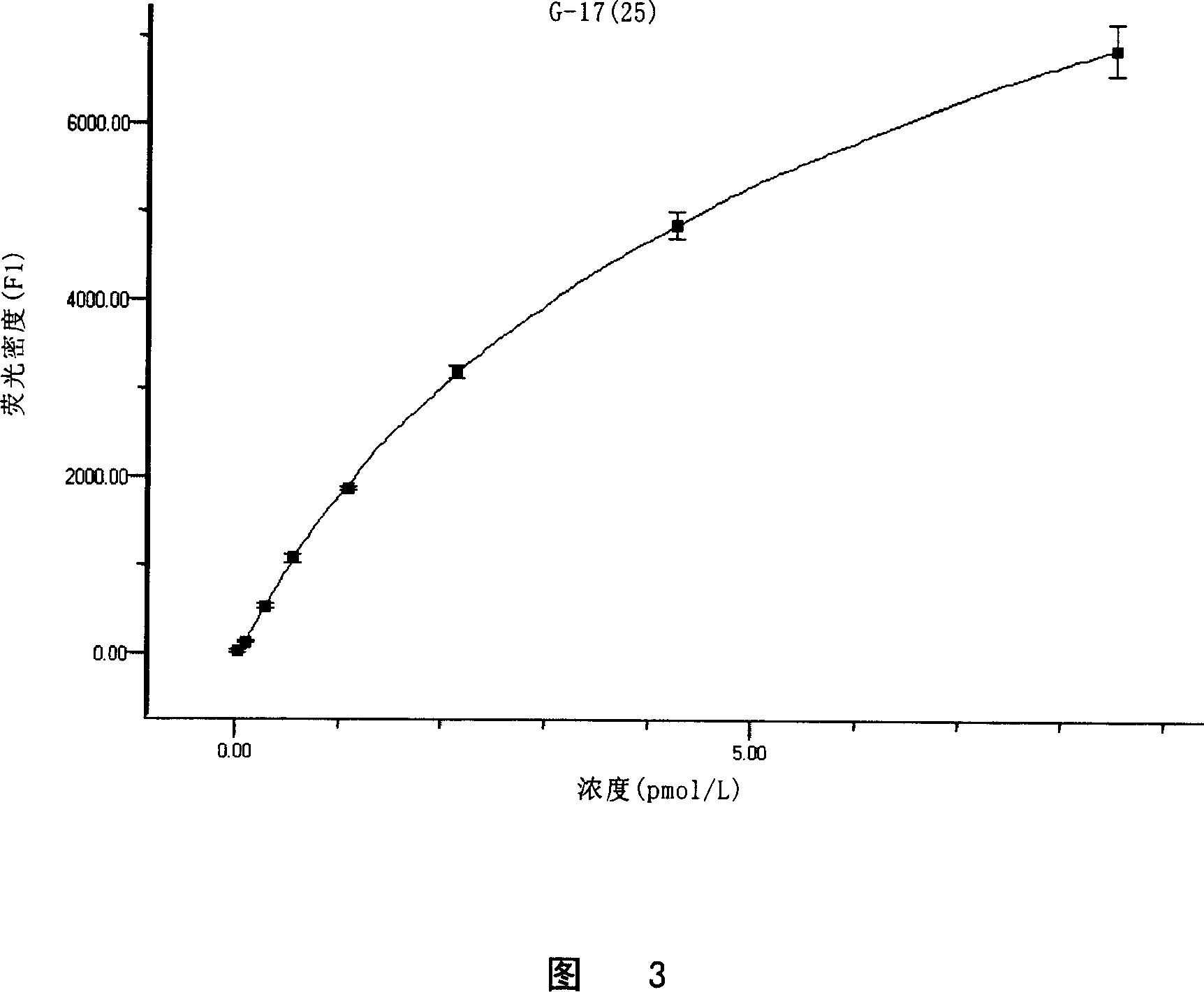Patents
Literature
131results about How to "Reduce non-specific binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Kit for detecting trypanosoma cruzi antibody as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN105548565AAccurate measurementSensitive assayChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingAntigenMedicine
The invention provides a kit for detecting a trypanosoma cruzi antibody and a preparation method of the kit. The kit comprises a component A and a component B, wherein the component A is a chagas antigen which is marked by a tracking marker or coated with a magnetic ball; the component B is a chagas second antibody which is coated with the magnetic ball or marked by the tracking marker; and any one of the component A and the component B is marked by the tracking marker and the other one is coated with the magnetic ball. The invention further provides a method for detecting the chagas antibody. By utilizing the kit provided by the invention, the concentration of chagas in a sample can be accurately and flexibly determined. On the basis, a pre-treatment solution is used for carrying out pre-treatment optimization so that the background interference can be reduced and the detection flexibility is improved. Meanwhile, detection of the full-automatic chemiluminiscence method can be realized with the help of a chemiluminiscence immunoassay analyzer, so that the operation time is shortened and manual operation errors are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEW INDS BIOMEDICAL ENG
Detection kit for glycocholic acid for eliminating chyle interference
InactiveCN106124439AEliminate distractionsPrevention of missing elimination agentColor/spectral properties measurementsPreservativeMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a detection kit for glycocholic acid for eliminating chyle interference. The detection kit comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2 and a calibrator. The reagent R1 contains buffer solution a, chyle elimination agent, stabilizer a, surfactant a, reaction promoter a and preservative a; the reagent R2 contains buffer solution b, latex particles of antihuman glycocholic acid monoclonal antibody, stabilizer b, surfactant b, preservative b and reaction promoter b; the calibrator contains buffer solution c, glycocholic acid standard, stabilizer c, surfactant c, reaction promoter c and preservative c. The detection kit is short in detection time, strong in anti-interference capacity, good in stability and repeatability and high in accuracy and detection sensitivity.
Owner:山东康华生物医疗科技股份有限公司
Preparation method of polystyrene fluorescent microsphere coupled with antibody
InactiveCN104530459AHigh coupling rateGood dispersionFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntiendomysial antibodiesPolystyrene
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polystyrene fluorescent microsphere coupled with an antibody, which comprises the following steps: 1. activating a carboxyl group on the surface of a fluorescent microsphere; 2. coupling an amino group of a monoclonal antibody with the carboxyl group on the surface of the fluorescent microsphere; 3. blocking activated groups not subjected to complete reaction on the surface of the fluorescent microsphere; and 4. preserving the polystyrene fluorescent microsphere coupled with the antibody. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, easy to implement, low in cost and suitable for industrialization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Targeting molecular imaging probe and living molecular imaging method
InactiveCN102743770AGuaranteed accuracyTarget-specificGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsRadioactive preparation carriersMolecular imagingDistribution characteristic
Owner:申宝忠
Cystatin C detection kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108107201AIncrease absorbanceHigh blank absorbanceBiological material analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrosphereCentrifugation
The invention provides a cystatin C detection kit and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2 and a cystatin C calibration product, wherein the reagent R1 comprisesa preservative, a surfactant, an emulsifier and a buffer solution; the reagent R2 comprises a cystatin C antibody, polystyrene latex microspheres, a latex microsphere activating agent, a sealing agent, an emulsifier, a preservative, a surfactant and a buffer solution. The cystatin C antibody is slowly dropwise added to an activated polystyrene latex microsphere solution, a polystyrene latex microsphere suspension coupled with the cystatin C antibody is obtained after a stirring reaction, sealing is performed, the antibody and latex microspheres are coupled together in a chemical crosslinking manner, and centrifugation, cleaning and ultrasonic resuspension processes in conventional methods are omitted. The production process is simplified, and the kit has the advantages of low blank absorbency, high sensitivity and precision and large linear range.
Owner:QINGDAO HIGHTOP BIOTECH
Binding solution, kit and method for purifying nucleic acid by magnetic bead method as well as application
InactiveCN110923228AImprove bindingAccelerated precipitationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSodium acetateLithium chloride
The invention provides a binding solution, kit and method for purifying nucleic acid by magnetic bead method as well as application. The binding solution comprises a citrate buffer solution, EDTA, sodium acetate, lithium chloride and isopropyl alcohol but does not comprise guanidine salt. The binding solution contains no guanidine salt, can coexist with magnetic beads for a long time and can fullypromote precipitation of nucleic acid and binding with magnetic beads, the low isopropyl alcohol content contributes to increase of the nucleic acid purity, and nonspecific binding of impurities withmagnetic beads is reduced.
Owner:广州高盛生物科技有限公司
Chip and detecting reagent kit for detecting gastricism relevant indication marks object
InactiveCN101063684AReduce non-specific bindingReduce generationMaterial analysisGastritisTest agent
This invention discloses one protein chip, which comprises more than two kinds of micro ball fixed with different anti-gastritis label first antibody. This invention also discloses one method for test of the label. This invention also discloses one test agent case with protein chip. This invention protein chip has first antibody volume match design for accurate test.
Owner:上海华冠生物芯片有限公司
Combined detection kit for hepatitis c virus (HCV) antigen-antibody
InactiveCN106093402AImprove specific recognition abilityReduce non-specific bindingMaterial analysisHCV AntibodyHcv core antigen
The invention discloses a combined detection kit for HCV antigen-antibody. The kit comprises a first monoclonal antibody against HCV core, a first HCV recombinant chimeric antigen, a first diluted sample solution, a second diluted sample solution, a first enzyme-labeled second monoclonal antibody against HCV core antigen, a first ligand-labeled second HCV recombinant chimeric antigen, a second enzyme-labeled second ligand, a developer and a stopping solution, wherein the first diluted sample solution comprises a reducing agent, a first surfactant and a first denaturant; and the second diluted sample solution comprises a second surfactant and a second denaturant. The combined detection kit for the HCV antigen-antibody opens mismatched disulfide bonds in coating antigen and in an antigen-antibody complex of a sample in virtue of the first diluted sample solution, and destroys HCV core antigen and HCV antibody compounds in virtue of the second diluted sample solution, so more antigen is released; and thus, detection sensitivity is improved.
Owner:HUNAN KANGRUN PHARMA
Myoglobin enzymatic chemiluminescence immunodetection method and kit
InactiveCN103033627AAvoid influenceStrong specificityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingTrue positive rateImmuno detection
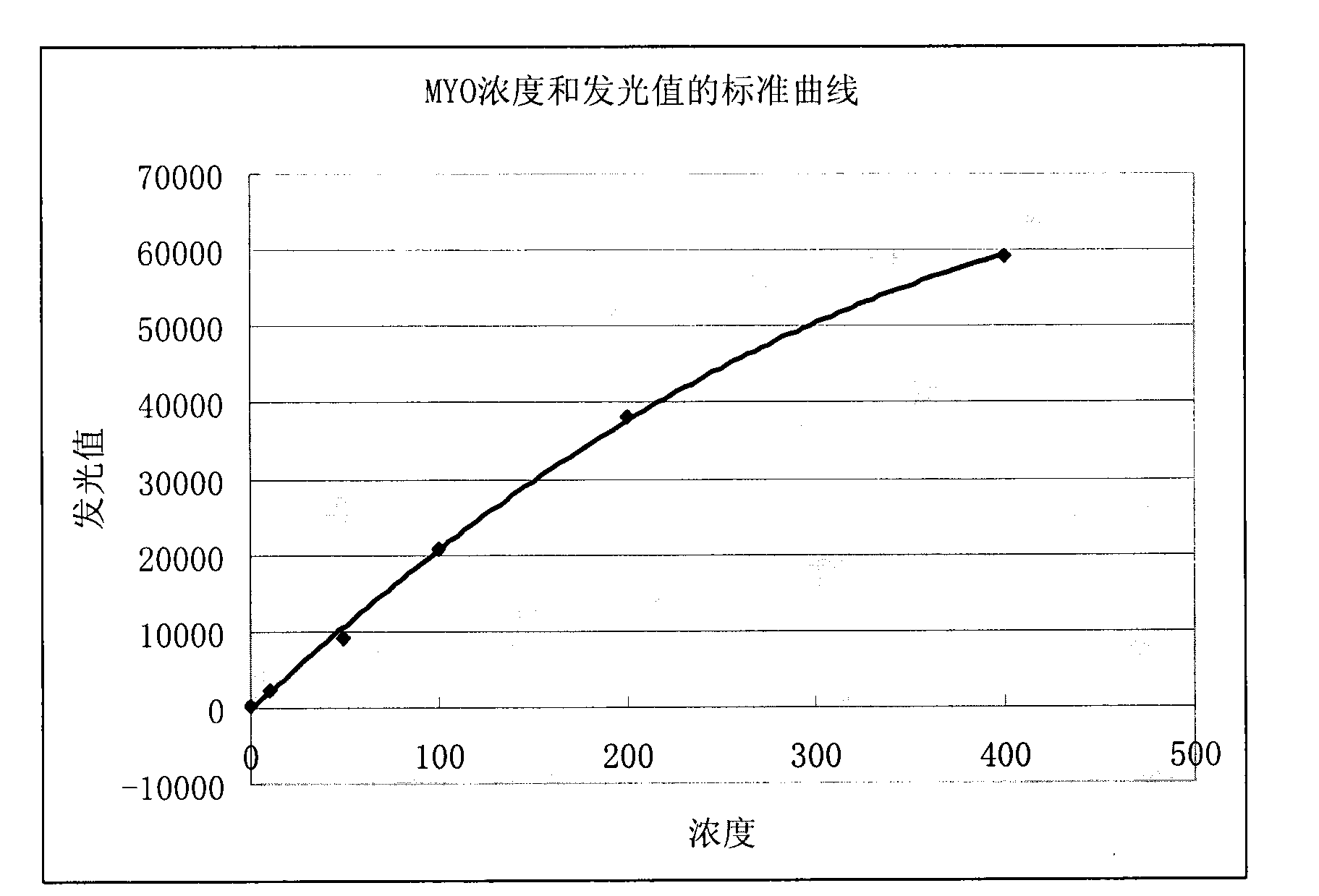
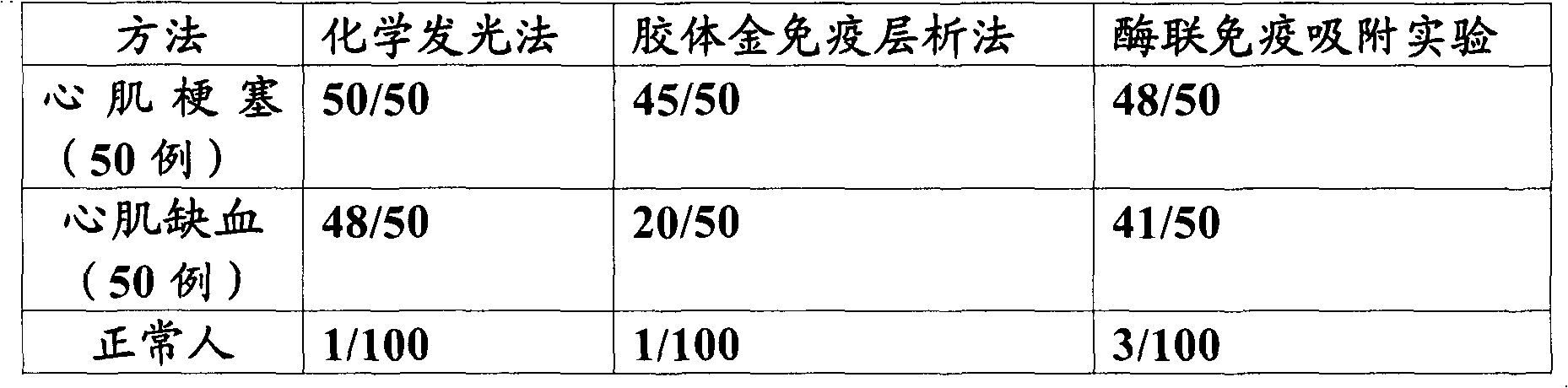
Belonging to the technical field of immunodetection and analysis, the invention specifically provides a myoglobin enzymatic chemiluminescence immunodetection method. The method includes the steps of: forming a solid phase-antibody-antigen-enzyme-labeled secondary antibody immune sandwich composite and detecting the immune sandwich composite by means of chemiluminescence. The invention also provides a myoglobin enzymatic chemiluminescence immunodetection kit. The detection method and the detection kit provided in the invention are suitable for detection and analysis of myoglobin, and have the advantages of large detection range, and high sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:BEIJING YUANDE BIO MEDICAL ENG
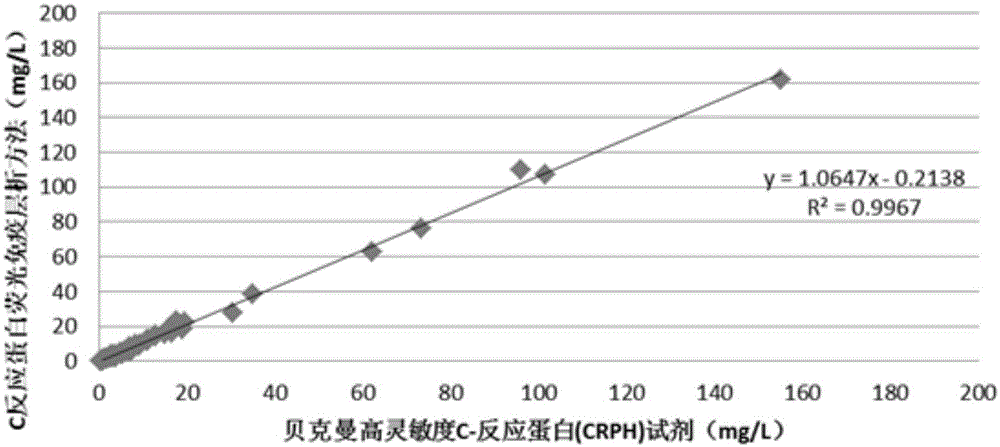
Kit for detecting C-reactive protein through fluorescent immunochromatography
PendingCN105158482AEffective filteringReduce mistakesBiological material analysisBiological testingFluoresceinMonoclonal antibody
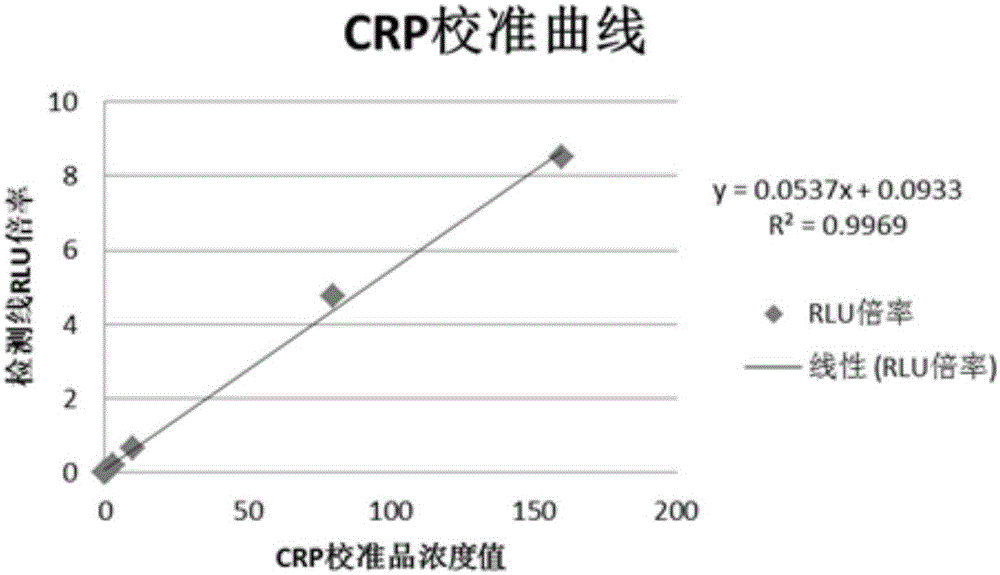
The invention discloses a kit for detecting C-reactive protein through fluorescent immunochromatography. In the kit, a mouse anti-human CRP (C-reactive protein) monoclonal antibody with a fluorescent label and a rabbit IgG (immunoglobulin G) with a fluorescent label are made by subjecting the mouse anti-human CRP monoclonal antibody and the rabbit IgG to fluorescein labeling; in labeling the mouse anti-human CRP monoclonal antibody and the rabbit IgG with fluorescein, the mouse anti-human CRP monoclonal antibody and the rabbit IgG are added into activated fluorescein storage liquid; the concentration of fluorescein in the fluorescein storage liquid is 5-10mg / mL. The kit is high in sensitivity and good in detection stability, enables reduction in nonspecific binding, has a wider linear range, takes only 3 minutes for detection and enables great improvement in diagnostic efficiency.
Owner:NINGBO RUI BIO TECH
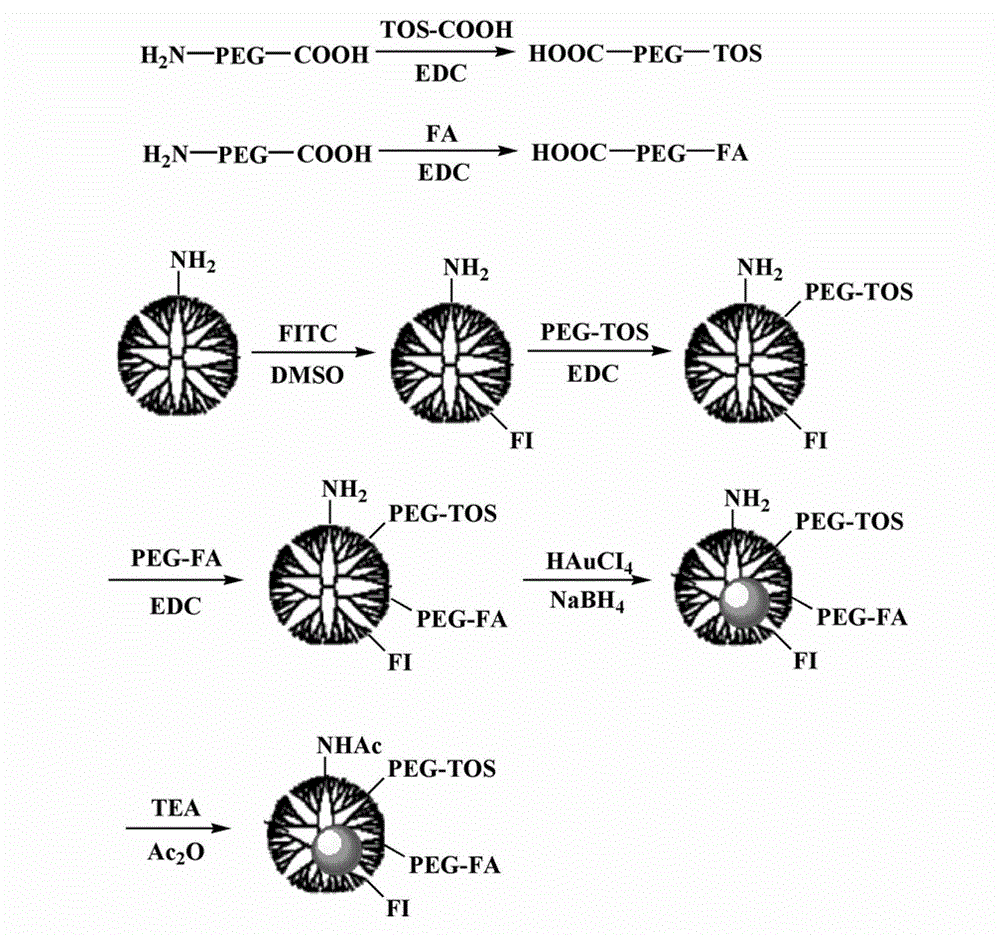
Preparation method for alpha-TOS-loaded and dendrimer-wrapped gold nanoparticles
InactiveCN102973949AGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsDendrimerAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a preparation method for alpha-TOS-loaded and dendrimer-wrapped gold nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding EDC and an NH2-PEG-COOH solution into an alpha-TOS solution and reacting to obtain TOS-PEG-COOH; (2) adding the EDC and the NH2-PEG-COOH solution into folic acid and reacting to obtain FA-PEG-COOH; (3) adding a poly amidoamine dendrimer solution into an FI solution and reacting to obtain G5.NH2-FI; (4) adding the TOS-PEG-COOH and FA-PEG-COOH solution into the EDC for activation, adding into the G5.NH2-F1 water solution, and reacting to obtain a dendrimer solution; and (5) adding chloroauric acid, NaBH4, N(C2H5)3 and acetic anhydride into the above solution, and reacting to obtain the gold nanoparticles. The method is simple in preparation process, and is easy to implement.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Zwitterion-containing acridinium compounds
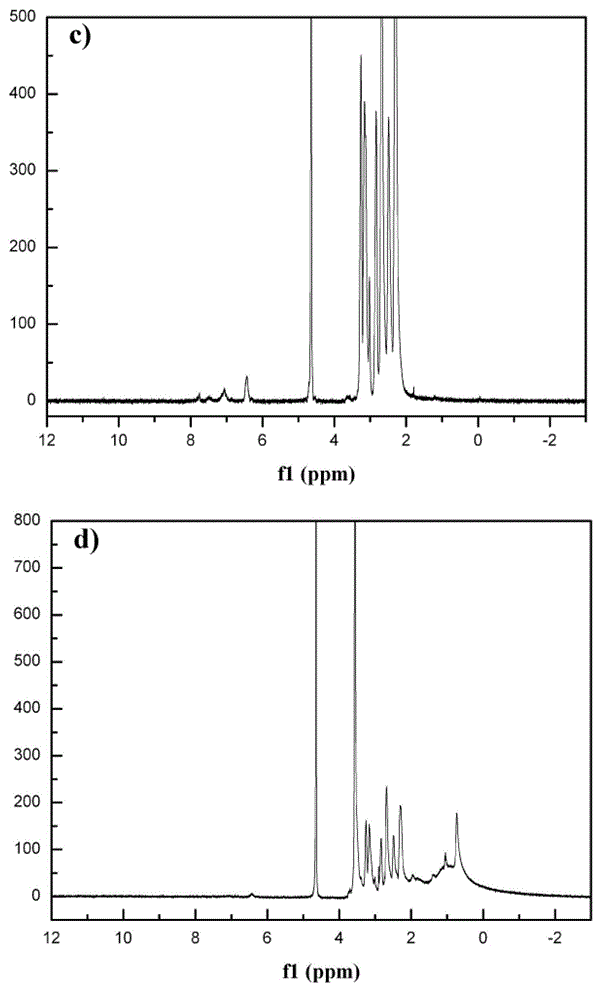
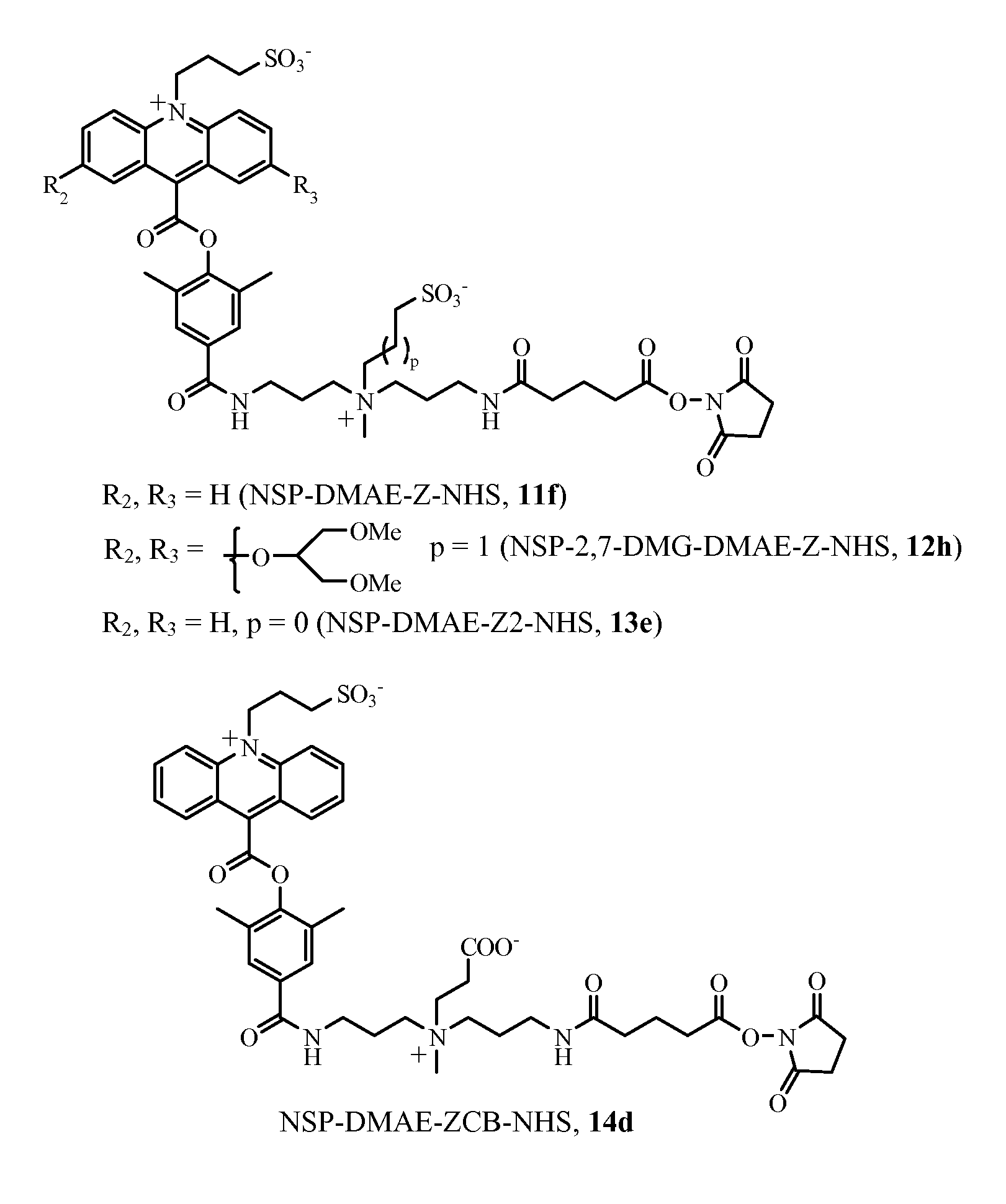
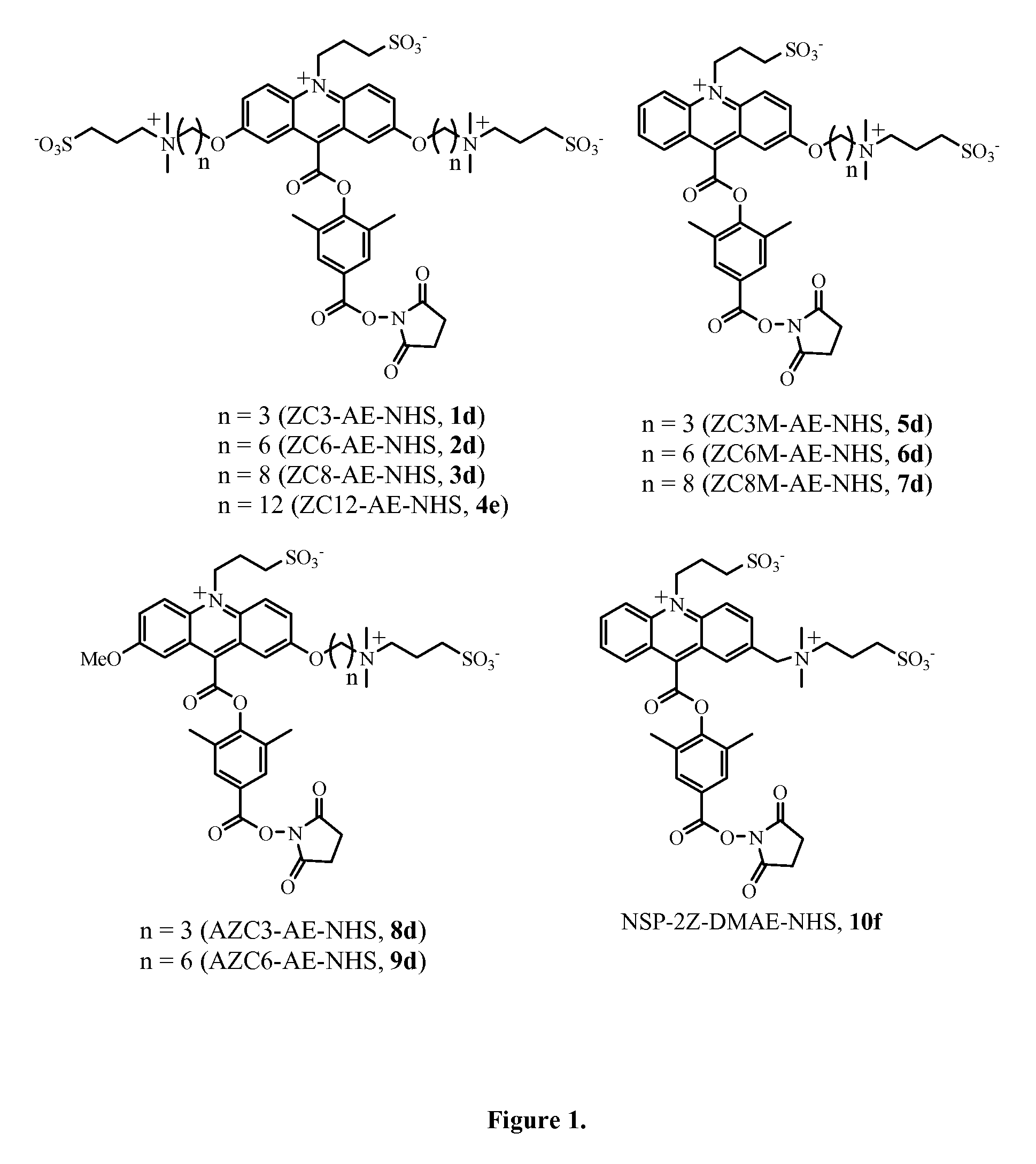
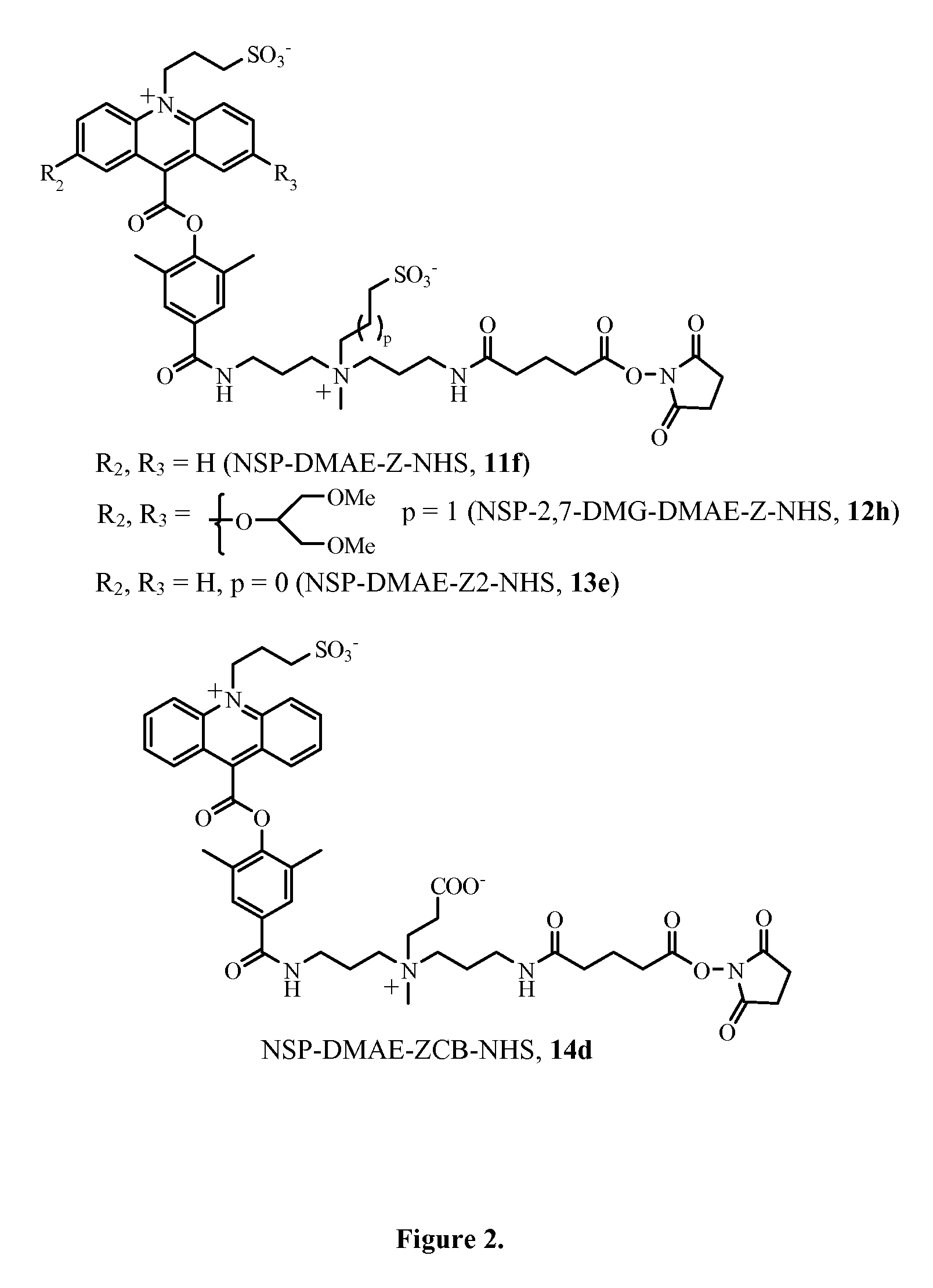
ActiveUS8778624B2Reduce non-specific bindingImprove hydrophilicityOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAssay sensitivityOnium
Hydrophilic, chemiluminescent acridinium compounds containing zwitterions are disclosed. These acridinium compounds, when used as chemiluminescent labels in immunochemistry assays and the like, exhibit decreased non-specific binding to solid phases and provide increased assay sensitivity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
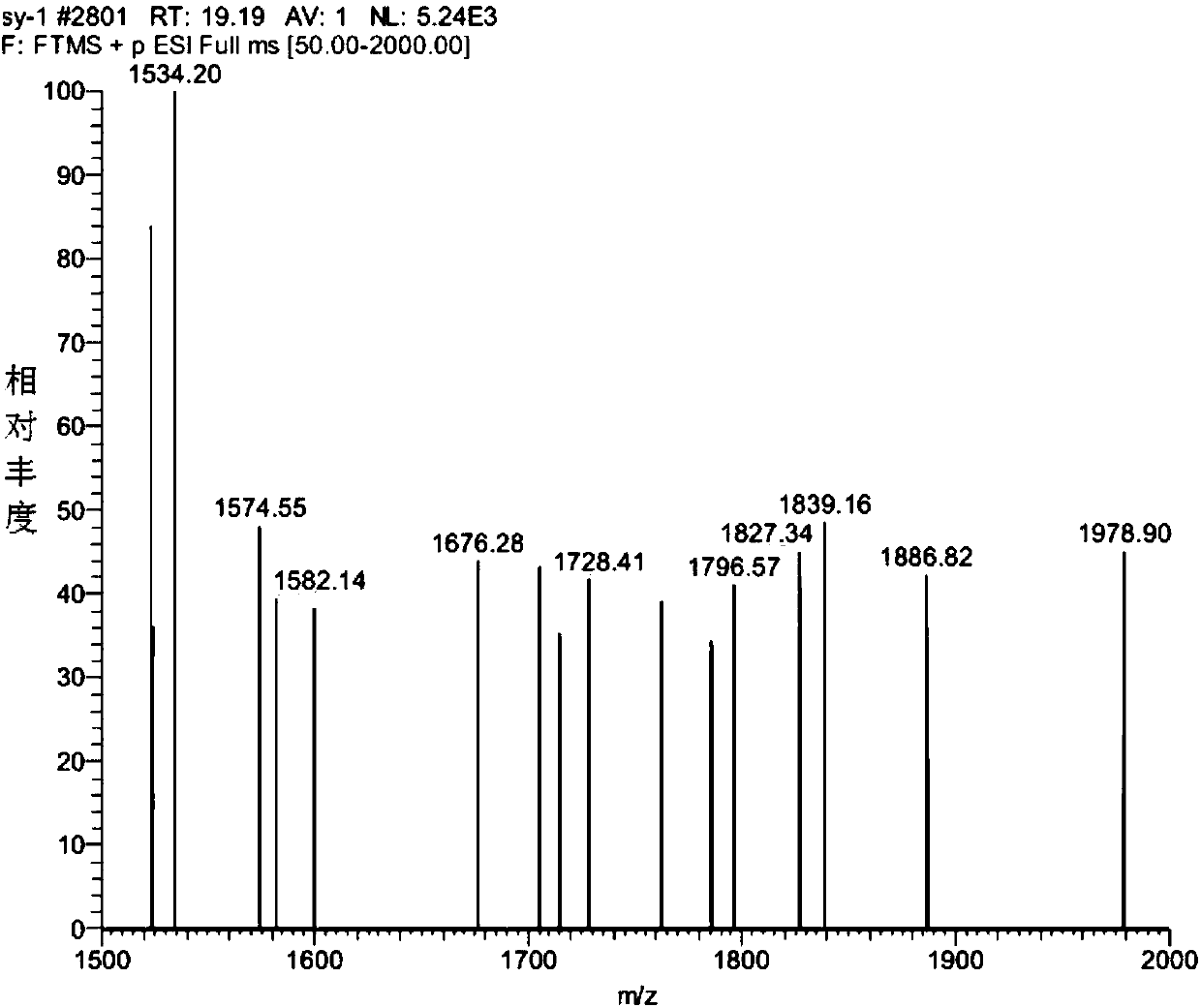
uPAR (urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor) targeted peptides, probe and living molecular imaging method
PendingCN107652358AImprove stabilityShort sequence lengthGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsMedicineMolecular imaging
The invention discloses uPAR (urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor) targeted peptides with the amino acid sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO. 1. The uPAR targeted peptides is linear peptides formed by 13 amino acids, the peptides are easy to synthesize and can form a stable conformation and be combined with uPARs with specific target. The invention discloses a uPAR targeted probe comprisinga single unit and the above uPAR targeted peptides. The uPAR targeted probe is subjected to specific identification of the peptides and is combined with the uPARs, signals for detection of imaging equipment are transmitted through the signal unit, living visual detection of the uPARs is achieved, and distribution and number of the uPARs are displayed visually and are used for disease detection foruPAR expression abnormalities. The invention further discloses a living molecular imaging method. The uPAR targeted probe is utilized, and the living molecular imaging method has the advantages of being safe, non-invasive, dynamic, visual and the like and is suitable for direct detection of human body.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
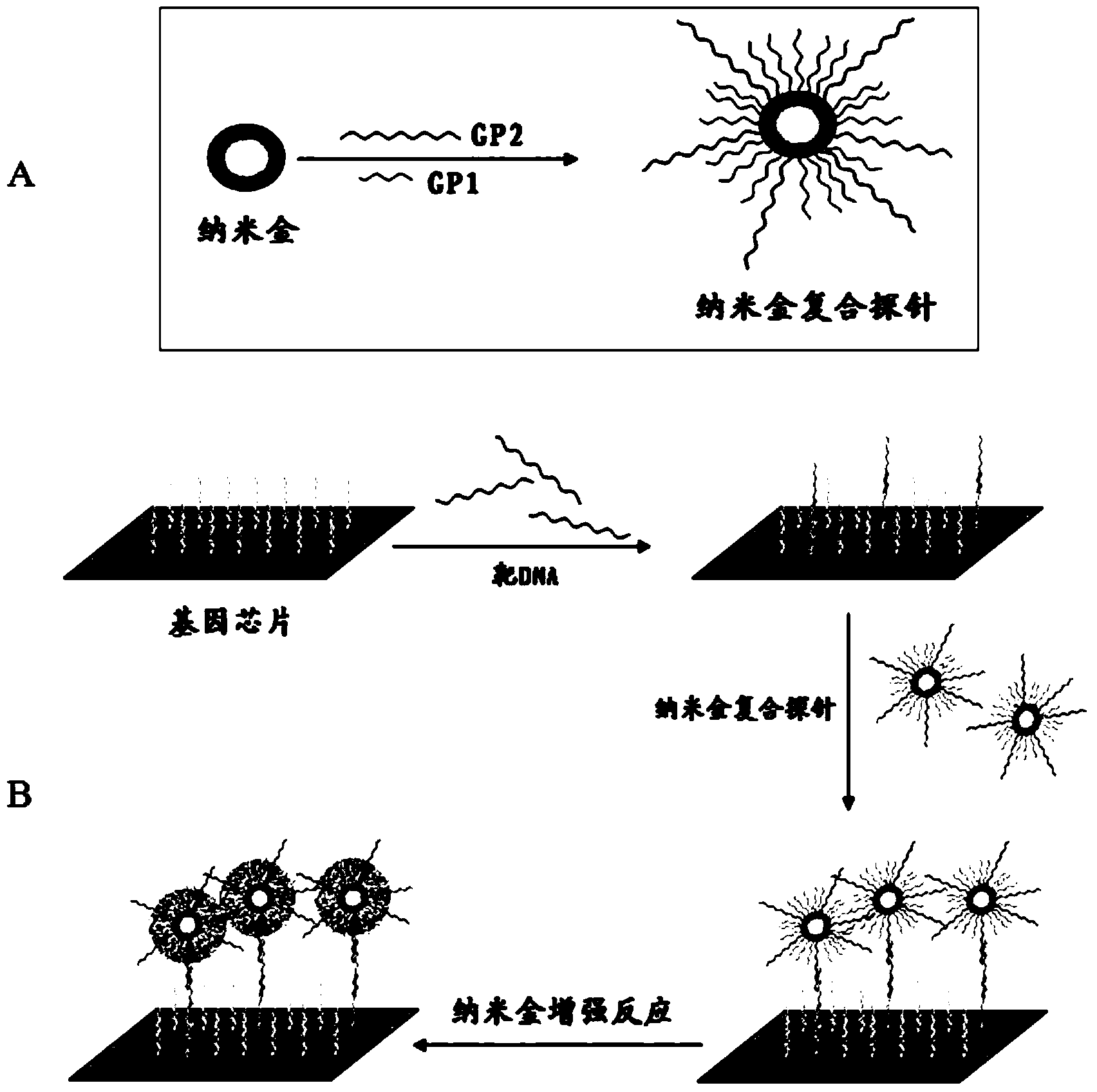
Gold deposition detection method for gene chip
ActiveCN103451313AHigh sensitivityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological macromoleculeHydrogen peroxide
The invention provides a gold deposition detection method for a gene chip. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of carrying out sample application on an existing DNA sequence to a micro array to prepare the gene chip, previously decorating a biological macromolecule at the 5' end of nucleic acid to be detected, marking the other biological macromolecule matched with a decorative molecule on the nucleic acid to be detected on nanogold to establish a nanogold composite probe, then mixing the decorated nucleic acid to be detected, the marked nanogold composite probe and the gene chip, incubating, washing the unreacted nanogold composite proble and adding hydrogen peroxide gold to enhance reaction liquid observation. The gold deposition detection method for the gene chip has the advantages of being high in flexible, convenient to detect, simple to operate, short in consumed time, low in cost, visual in detection and low in relying degree on detecting and signal reading equipment.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
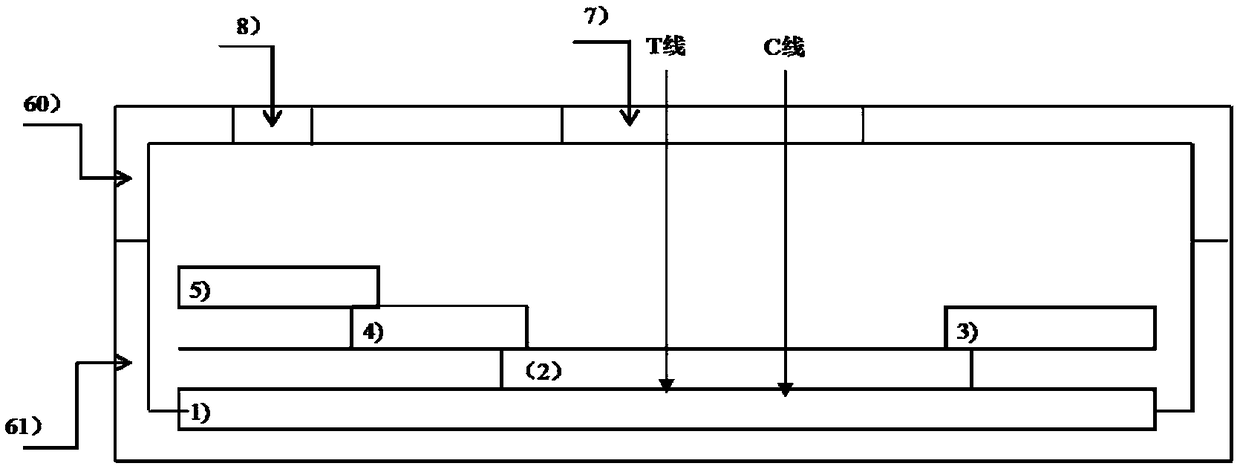
IL-6 biotin-streptavidin immunochromatographic detection card
PendingCN110596404AHigh affinityHigh detection sensitivityBiological testingDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses an IL-6 biotin-streptavidin immunochromatographic detection card, which belongs to the technical field of disease detection. The IL-6 biotin-streptavidin immunochromatographicdetection card comprises a PVC bottom plate, a sample pad, a combination pad, a coating film and water absorbing paper, wherein the sample pad, the combination pad, the coating film and the water absorbing paper are sequentially arranged on the PVC bottom plate from front to back, a detection T line and a quality control C line are arranged on the coating film, and an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodycoupled with a tracing marker and an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody coupled with biotin are arranged on the combination pad; and the detection T line is coated with streptavidin, and the quality control C line is coated with a polyclonal antibody. The IL-6 biotin-streptavidin immunochromatographic detection card quantitatively detects the content of IL-6 in human serum, blood plasma and whole blood samples by utilizing an immunochromatographic technology according to the principle of a double-antibody sandwich method, can obtain the concentration of IL-6 in the samples precisely, and improvesthe detection sensitivity, particularly the detection sensitivity of a low-end value.
Owner:CHENGDU RENZHI TECH
Reduction of non-specific adsorption of biological agents on surfaces
InactiveUS20060134656A1Reduced non-specific adsorptionReduce non-specific bindingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlycol synthesisBiochip
The present invention relates to surface-modified substrates that demonstrate reduced non-specific adsorption of biological agents. The substrates are silicon or carbon substrates having ethylene glycol oligomers covalently bound to at least one substrate surface. The substrates may be used in sensor devices, such as biochips, and in implantable medical devices in order to reduce the non-specific binding of biological agents.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Reduction of non-specific binding in immunoassays
InactiveUS20080108147A1Reduce non-specific bindingImmunoglobulins against hormonesBiological testingThiolAnalyte
Methods and compositions are disclosed for reducing non-specific binding in a binding assay for the determination of an analyte in a sample wherein one of the reagents for conducting the binding assay is an antibody reagent. The methods comprise treating the antibody reagent at a pH of about 2.0 to about 3.5. The method may further comprise treating the antibody reagent with a reducing agent in an amount sufficient to reduce non-specific binding of the antibody reagent. In some embodiments the reducing agent may be a thiol-containing reducing agent or a combination of two or more thiol-containing reducing agents.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Radioactive C-MET-targeted affinity micromolecular compound and application thereof
ActiveCN106008339AGood pharmacokinetic profileGood biological distribution characteristicsIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersNuclear medicineLung cancer
The invention especially relates to a radioactive C-MET-targeted affinity micromolecular compound and application thereof, belonging to the field of medical diagnosis and treatment. According to the invention, in-vivo tracking and imaging of diseases like tumors is realized through radiolabeling of a C-MET receptor antagonist. The radioactive C-MET-targeted affinity micromolecular compound can be used for monitoring the characteristics of biochemical changes of a hepatocyte growth factor receptor, visually displays the distribution and quantity of C-MET and is applicable to specific detection of a plurality of cancers including glioma, lung cancer, prostatic cancer, breast cancer, esophagus cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, pancreas cancer, ovarian cancer, rectal cancer and cervical cancer. The radioactive C-MET-targeted affinity micromolecular compound also has certain anticancer activity and has wide clinical application prospect.
Owner:上海准视生物科技有限公司
Chip for protein detection, method for manufacturing the same, and method for detecting protein by using the same
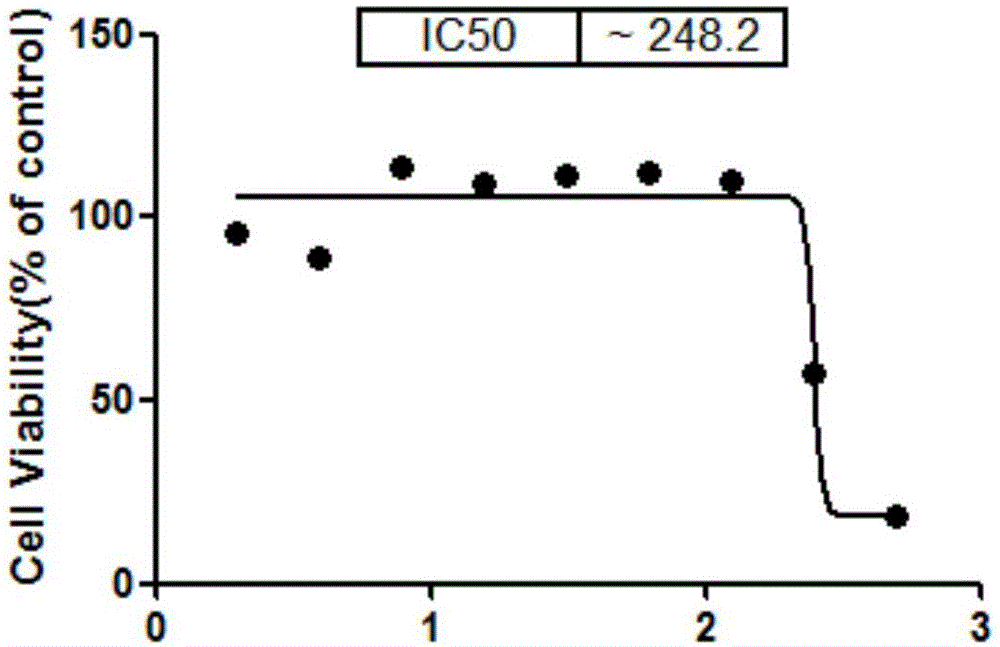
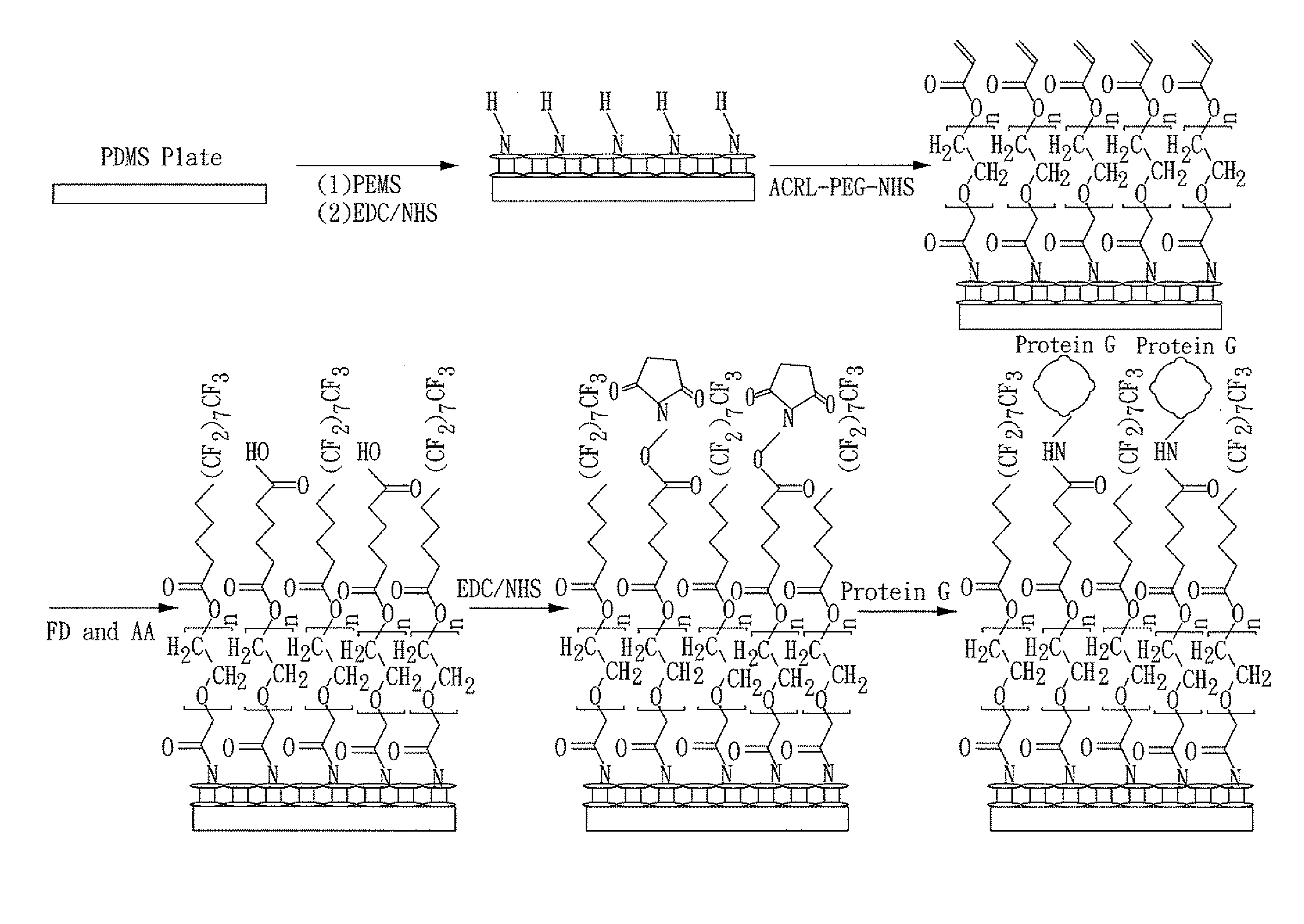
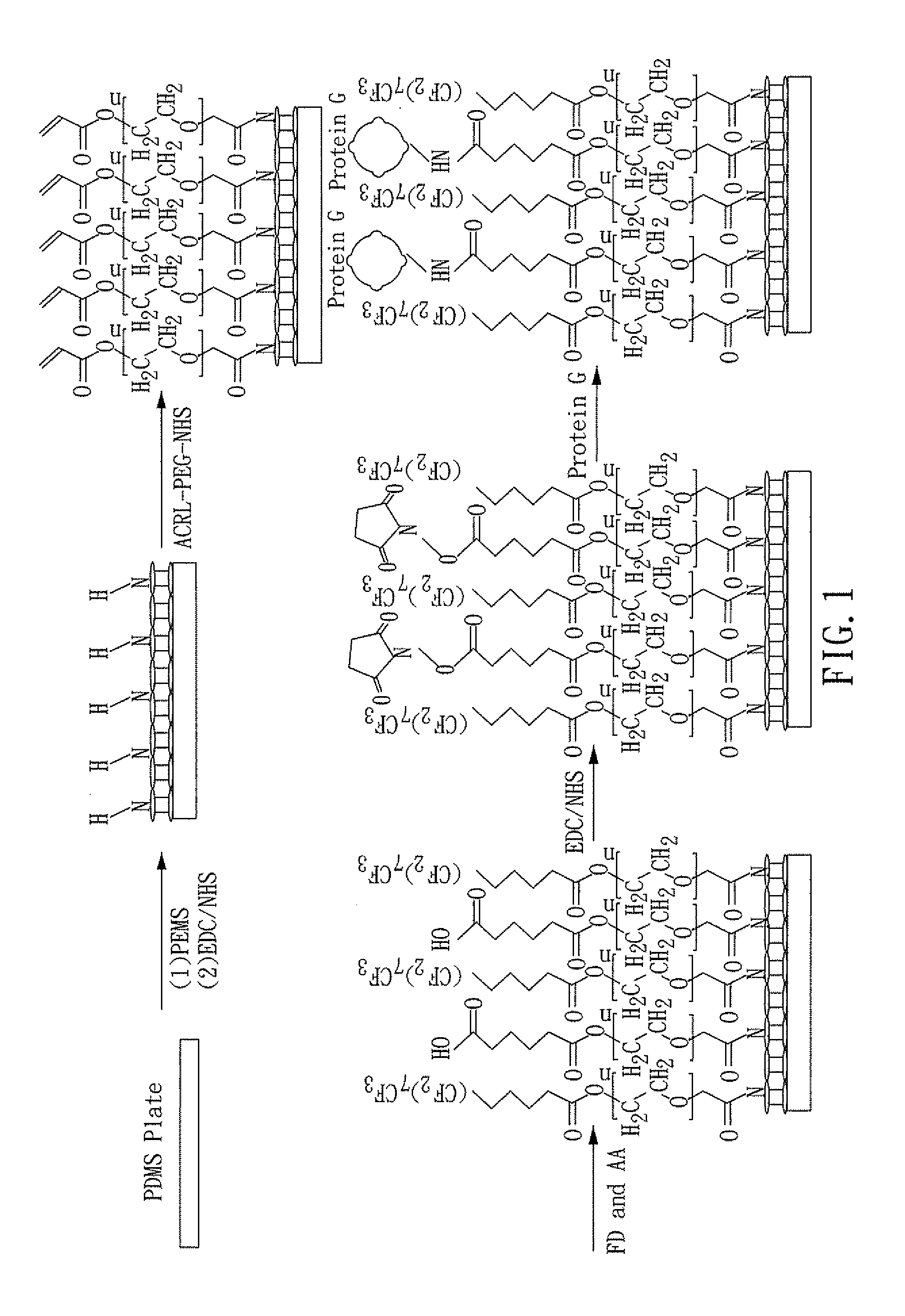
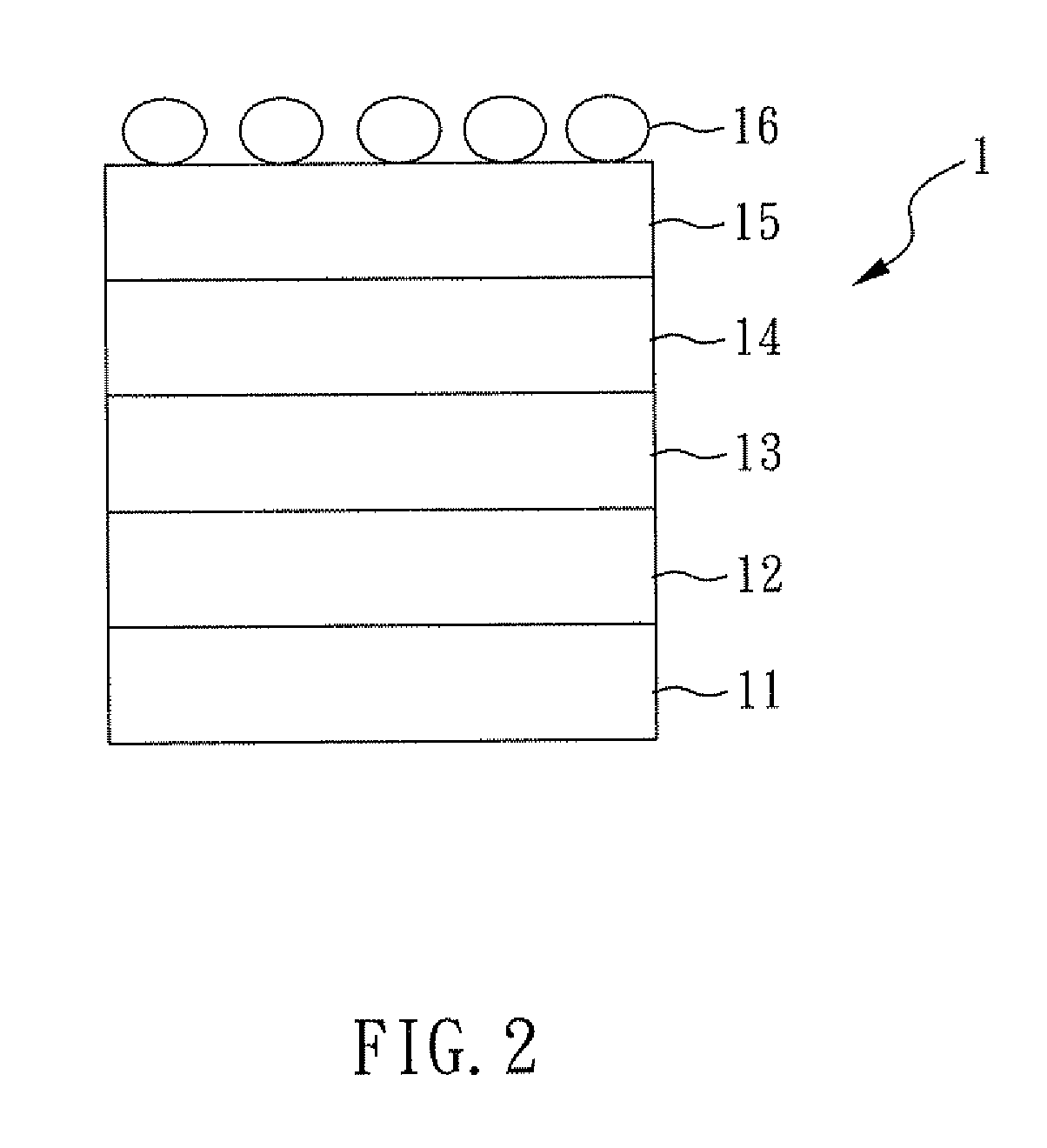
InactiveUS20130053260A1Reduce non-specific bindingBlocking phenomenonPreparing sample for investigationLibrary screeningProtein detectionMolecular binding
A chip for protein detection, a method for manufacturing the same, and a method for detecting protein by using the chip are provided in the present invention. The chip for protein detection of the present invention comprises: a substrate; a covalent modification layer disposed on the substrate; a fluorinated layer disposed on the covalent modification layer, wherein the fluorinated layer comprises fluorinated functional groups and bio-molecular binding groups; and antibody-binding molecules connecting to the bio-molecular binding groups.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Kit for quantitatively detecting heart-type fatty acid binding protein, and preparation method thereof
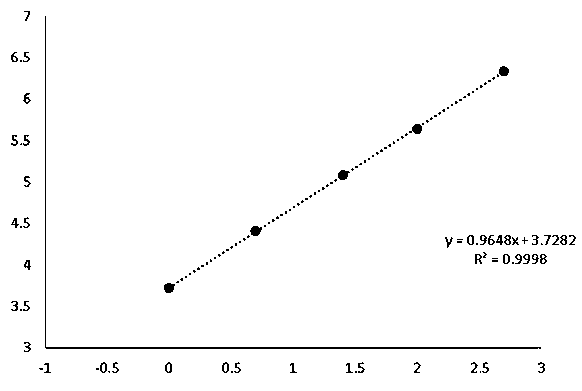
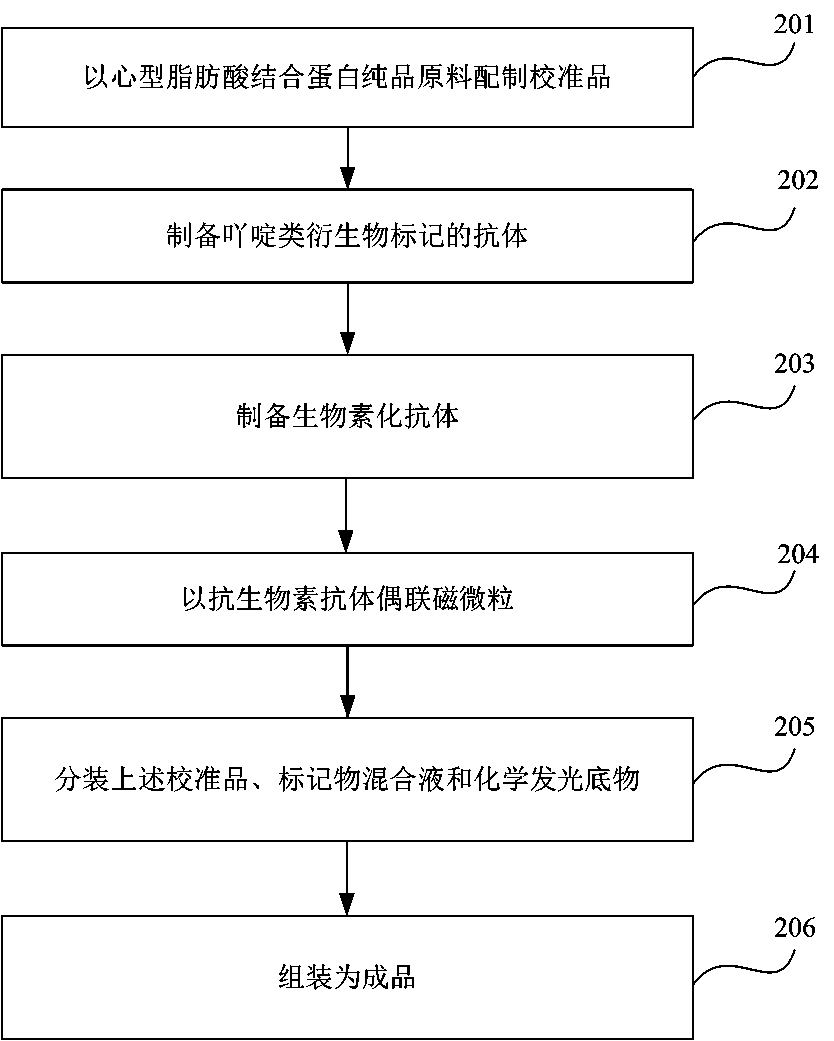
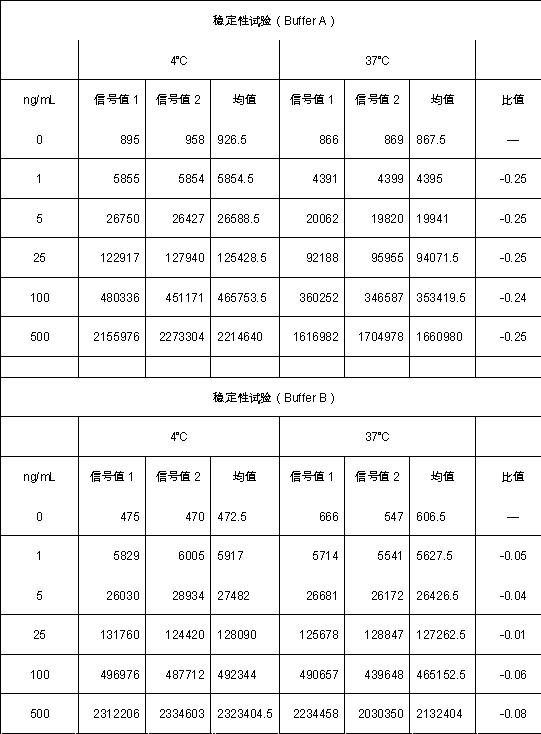
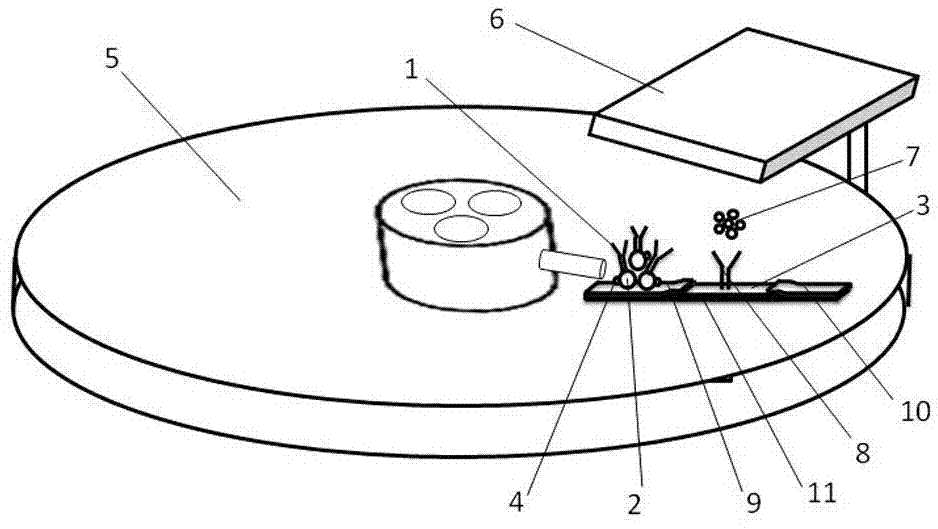
The invention provides a kit for quantitatively detecting a heart-type fatty acid binding protein. The kit comprises a heart-type fatty acid binding protein calibrator, a magnetic particle coupled with an anti-biotin antibody, an acridine derivative-labeled heart-type fatty acid binding protein monoclonal antibody, a biotin-labeled heart-type fatty acid binding protein monoclonal antibody, a chemiluminescent substrate and a quality control substance. A preparation method of the kit comprises the following steps: preparing the calibrator from a pure heart-type fatty acid binding protein raw material; preparing the acridine derivative-labeled antibody; preparing a biotinylated antibody; coupling a magnetic particle with the anti-biotin antibody; sub-packaging the calibrator, a marker mixturesolution and the chemiluminescent substrate; and performing assembling to obtain the finished product. The kit has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, high accuracy of a quantitative detection result, low use cost, and easiness in promotion and application.
Owner:浙江艾明德生物科技有限公司
Paper-chromatography chemiluminescent detection method
InactiveCN107449906AImprove capture binding capacityReduce background noise distractionsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSolid phasesBinding ability
The invention discloses a combined chemiluminescent detection kit and a detection method. The combined chemiluminescent detection kit comprises a specific conjugate of a to-be-detected substance, a microparticle, a solid-phase film, a chemiluminescent reagent, a centrifugal device and a luminescent detector, wherein the chemiluminescent reagent comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of a chemiluminescent enzyme, a chemiluminescent substance, a chemiluminescent enzyme reaction substrate and a starting luminescent reagent; the microparticle is a particle capable of specifically binding to a protein and / or the chemiluminescent reagent in a direct binding and / or chemically crosslinking way and maintaining stable; the solid-phase membrane is a membranous substance having the characteristic of non-specific binding to a protein; the centrifugal device is a structure capable of centrifugally driving chromatographic flowing of a liquid phase on the solid-phase membrane; and the specific conjugate of the to-be-detected substance is at least one selected from a group consisting of antigen, antibody, avidin, biotin and analogue thereof with specific binding ability. The combined chemiluminescent detection kit and the detection method in the invention have the characteristics of high sensitivity and short detection time, and have good application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING KANGHUAYUAN SCI TECH CO LTD
Reagent systems for biological assays
InactiveUS20050136413A1Avoid smearingEasy to storeMicrobiological testing/measurementChemistryCyclic amines
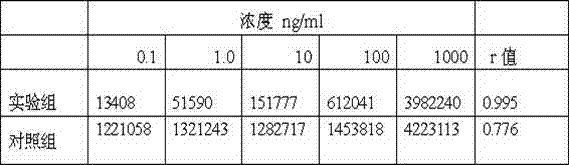
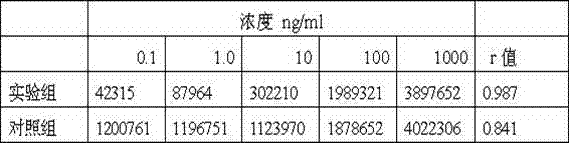
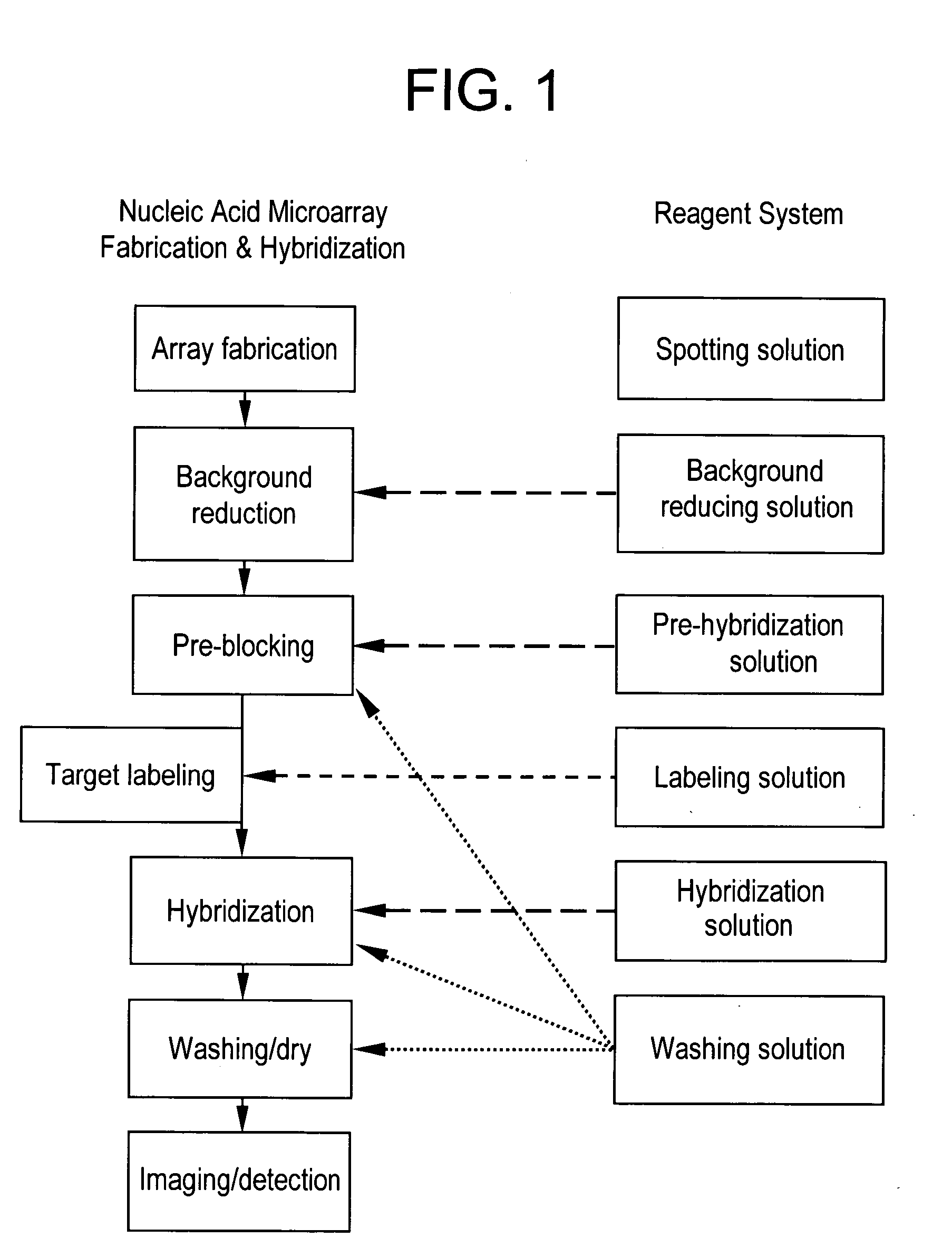
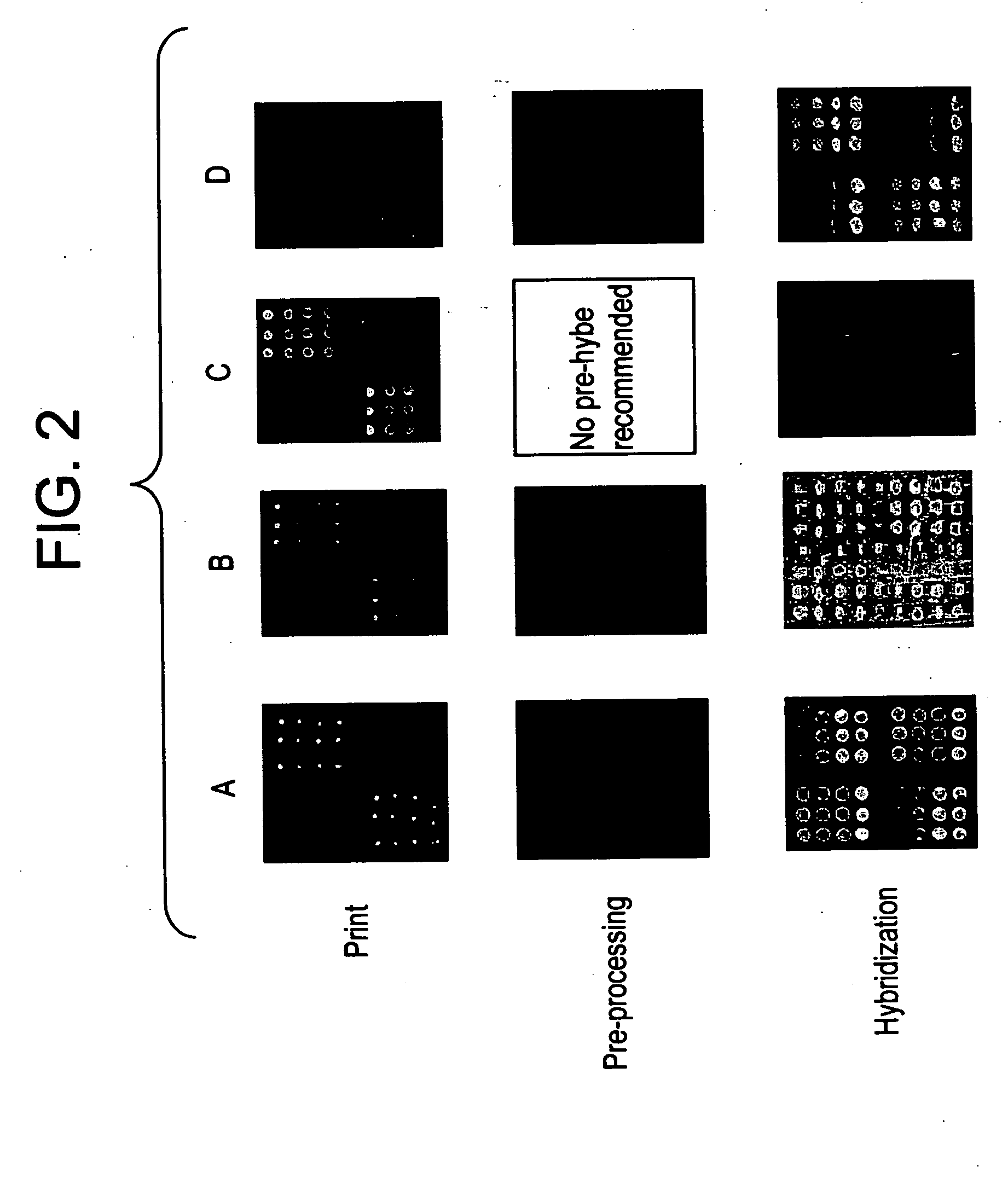
A reagent system for printing, assaying, and processing nucleic acid microarrays is provided. The system comprises: a printing kit, which includes a nucleic acid spotting solution; and a hybridization kit, which includes a nucleic acid pre-hybridization solution, a nucleic acid hybridization solution, and first, second, and third wash reagents, wherein the respective constituent components of the printing and hybridization kits are stable and retain functional performance, when stored together at a temperature between about 10° C. to about 50° C. A background reducing agent or solution is also included. The present reagent solutions are optimized for use with glass substrates having preferably an amine-coating, such as GAPS.
Owner:CORNING INC
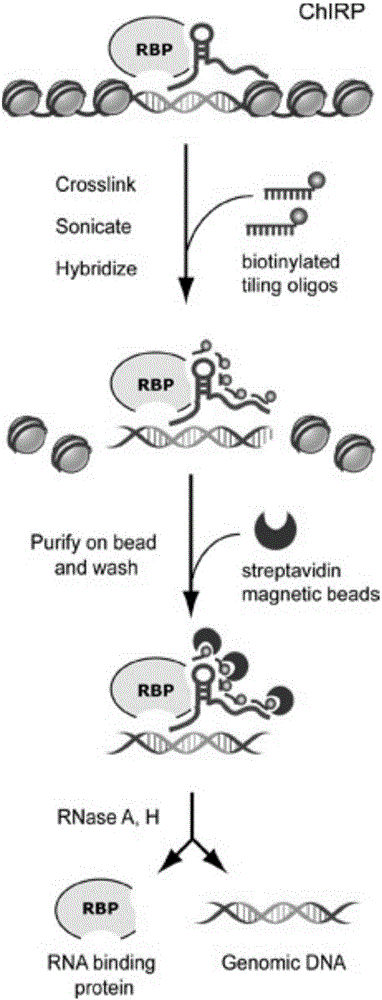
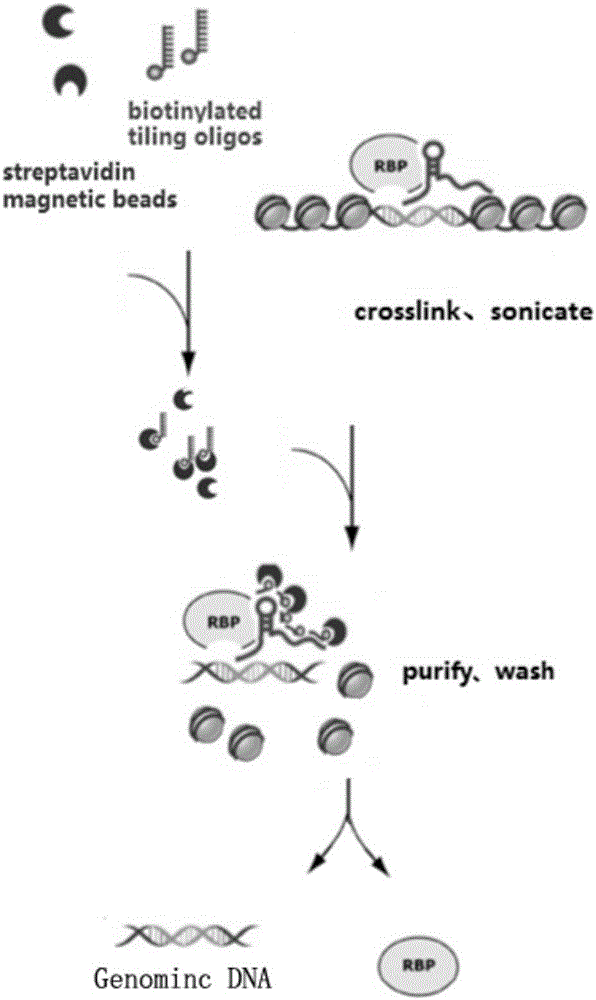
DNA pulldown method and kit
ActiveCN106093437AReduce non-specific bindingImprove non-specificityBiological testingMagnetic beadGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a DNA pulldown method and a kit. The method includes the following steps of pretreating magnetic beads, wherein the magnetic beads marked by BSA(bovine serum albumin) and oligonucleotide random primer closed streptavidin are used; preparing a probe-magnetic bead compound; extracting and pretreating cell nucleus protein, wherein deoxyribonuclease is added into an extracting nucleoprotein sample for incubation, the magnetic beads are added for incubation and then removed, and supernatant is collected; carrying out pulldown; collecting the protein sample. The DNA pulldown method has the following advantages that BSA and an oligonucleotide random primer are used for closing the magnetic beads in advance, and nonspecific binding between the magnetic beads, protein and genomic DNA is reduced. Nuclease contamination is prevented through systemic nuclease protection, stability and reliability of experiments are improved, repeatability is high, and the experiment process is simplified.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIOSENSE BIOSCI
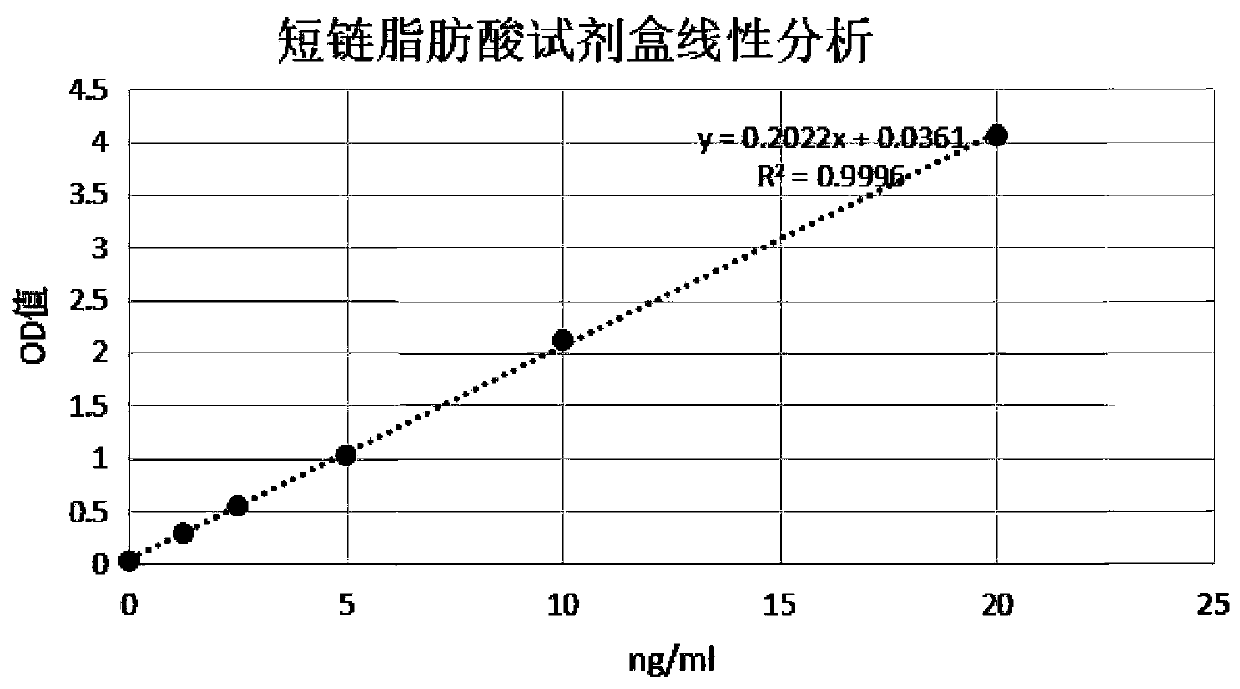
Kit for detecting short-chain fatty acid and application thereof
PendingCN110907649AStrong specificityReduce non-specific bindingMaterial analysisAntiendomysial antibodiesMedicine
The invention discloses a kit for detecting short-chain fatty acid. The kit comprises a kit body, an elisa plate arranged in the kit body, a short-chain fatty acid standard substance gradient solution, a sample diluent, an alkaline phosphatase labeled antibody for detecting an anti-short-chain fatty acid conjugate, a 20* concentrated washing solution, a color developing agent, a stop solution, a plate sealing film, a sealing bag and an instruction book, wherein the elisa plate is a transparent polystyrene 96 or 48-hole elisa plate, and each hole of the elisa plate is coated with an anti-short-chain fatty acid monoclonal antibody Mab1 with the concentration of 5mu g / mL. The short-chain fatty acid standard substance gradient solution has six concentrations, separately 20 ng / mL, 10 ng / mL, 5 ng / mL, 2.5 ng / mL, 1.25 ng / mL and 0 ng / mL. The detection kit provided by the invention provides an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody labeled by alkaline phosphatase (ALP), so that the stability and sensitivity of the kit are remarkably improved.
Owner:山东莱博生物科技有限公司
Method and device for separation and depletion of certain proteins and particles using electrophoresis
ActiveCN101512334AEasy to recycleHigh separation resolutionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteElectrophoresis
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Test strip capable of quantificationally detecting content of c-reactive protein in peripheral blood and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109270274AImprove stabilityHigh luminous intensityBiological testingQuality controlMonoclonal antibody
The invention relates to a test strip capable of quantificationally detecting content of c-reactive protein in peripheral blood. The test strip comprises a sample cushion, a quantum cushion, a nitrocellulose membrane, water absorbing paper and a lining plate, the quantum cushion wraps c-reactive protein antibodies marked by carbon quantum dots, and a detecting line and a quality control line are successively arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane from the sample cushion side to the water absorbing paper side; the detecting line wraps c-reactive protein recognizing monoclonal antibodies, and the quality control line wraps goat anti mouse IgG. The test strip is simple in structure and can quickly and accurately detect CRP in the peripheral blood quantificationally, the detection of the teststrip is high in sensitivity and stability and good in specificity, the detecting time is shorter than 15 min, and the diagnostic efficiency and the work efficiency of detecting operators can be greatly improved.
Owner:重庆新赛亚生物科技有限公司
RNA (ribonucleic acid)purification chromatin separation technique
PendingCN106191296AReduce non-specificityReduce non-specific bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementLysisMagnetic bead
The invention relates to an RNA (ribonucleic acid) purification chromatin separation technique. The technique includes the following steps: binding probes with magnetic beads prior to hybridizing with chromatin lysis solution, and then performing washing for multiple times via gradient temperature. The magnetic beads are closed with BSA and random oligonucleotide primers in advance, and accordingly nonspecific binding of the magnetic beads with proteins and RNA is reduced. The magnetic beads are incubated with the probes firstly prior to being incubated with the proteins after excessive probes are removed, gradient temperature washing is performed after hybridization to assure that the magnetic beads fully bind with the probes and bind with target RNA, and hybridization efficiency is increased.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIOSENSE BIOSCI
Use of Nucleic Acid Probes to Detect Nucleotide Sequences of Interest in a Sample
InactiveUS20090203017A1Reduce signalingHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid hybridisation
The invention relates to methods for the determination and detection of nucleic acids sequences in a sample. The nucleic acid may be RNA or DNA or both. The invention also relates to methods for the determination of the presence and species of various microorganisms in a sample. We have also identified a set of oligonucleotide nucleic acid sequences within the rRNAs of Gram-negative organisms that facilitates both the broad identification of Gram-negative organisms as a class when used as a pool, or in combination, for example in a hybridization assay. This set of oligonucleotides may detect sequences that are indicative of the presence of organisms of the broad class of Gram-negative organisms while exhibiting little or no false identification of Gram-positive organisms, and fungi, or other microorganisms. The assay includes concurrent incubation with at least one nucleotide sequence of interest, at least one nucleic acid probe, a fluorosurfactant, and a nuclease. The assay may further be employed to detect the presence of bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms by use of additional specific probes, or to detect and / or identify target nucleic acid sequences in a sample. Further, the invention also relates to methods of reducing non-specific binding and facilitating complex formation in a binding assay. The binding assay may be, but is not limited to, a nucleic acid hybridization assay or an immunoassay. The invention also relates to methods of detection that employ at least one target of interest, which may be a nucleotide sequence, at least one probe, which may be a nucleic acid probe and a nuclease.
Owner:BIOVENTURES INC
Mesothelin immunohistochemical detection kit
ActiveCN110531077AReduce non-specific bindingImprove detection efficiencyBiological material analysisBiological testingMonoclonal antibodyMesothelin
The application relates to a mesothelin (MSLN) immunohistochemical detection kit, which contains a MSLN monoclonal antibody 3-2G6.
Owner:REMEGEN CO LTD
Chitosan-based fluorescence probe suitable for long circulation of blood and preparing method thereof
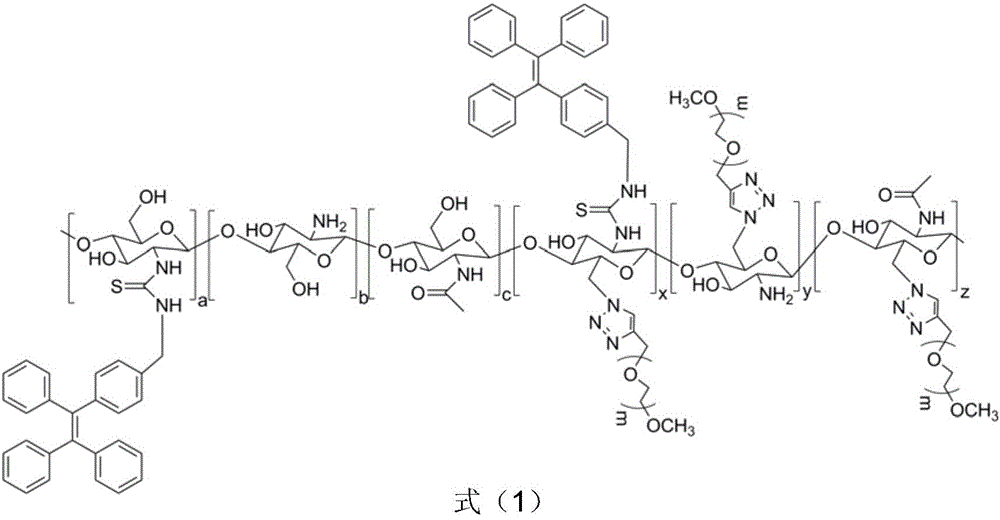
InactiveCN106010503AHas aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesHigh sensitivityLuminescent compositionsDrug metabolismAggregation-induced emission
The invention discloses a chitosan-based fluorescence probe suitable for long circulation of blood. The chitosan-based fluorescence probe has a structure as shown in formula (1). A preparing method for the chitosan-based fluorescence probe comprises the steps of grafting polyethylene glycol onto chitosan to obtain polyethylene glycol-chitosan suitable for long circulation of blood, and then marking tetraphenyl ethylene fluorescent molecules on a chitosan link to obtain the chitosan-based fluorescence probe which has an aggregation-induced emission property and is suitable for long circulation of blood. The prepared fluorescence probe has the advantages that sensitivity and light stability are high, quenching is avoided when concentration is high, and fluorescence spectrum shift is avoided, is suitable for long circulation of blood, and has broad application prospects in the fields including cell tracing, tumor diagnosis and drug metabolism detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com