Binding solution, kit and method for purifying nucleic acid by magnetic bead method as well as application
The technology of a kit and magnetic bead method is applied in the field of binding solution for nucleic acid purification by magnetic beads, which can solve the problems of increasing the workload of production personnel, increasing the difficulty of the operator's work, and particularly troublesome reagent production. Better effect, longer storage time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] The assembly of embodiment 1 kit
[0093] Prepare according to the formula of each liquid below:
[0094]1. Lysis solution (pH7.0-8.0): Tris-Cl (50-150mM), EDTA (1-10mM), hydrochloric acid stock (2-4M), guanidine isothiocyanate (2-4M), SDS (0.5 -1%, m / v), TritonX-100 (1-2%, v / v), Tween-20 (1-2%, v / v), NaCl (50-100mM), choose to add according to different samples DTT (1-10mM), proteinase K (1-2mg / mL);
[0095] 2. Binding solution (pH5.0-6.0): citrate buffer (50-100mM), EDTA (1-10mM), sodium acetate (100-300mM), lithium chloride (100-200mM), isopropanol (10-30%, v / v);
[0096] 3. Rinse solution I (pH7.5-8.5): Tris-Cl (1-10mM), NaCl (50-100mM), EDTA (1-5mM), guanidine hydrochloride (1-2M);
[0097] 4. Wash solution II (pH7.5-8.5): Tris-Cl (1-10mM), EDTA (1-5mM), ethanol (75-85%, v / v);
[0098] 5. Eluent (pH7.5-8.5): Tris-Cl (1-10mM), EDTA (1-5mM), glycerol (1-5%, v / v), SDS (0.01-0.05%, m / v), sodium fluoride (0.01-0.02%, m / v);
[0099] The above-mentioned lysate, bi...
Embodiment 2
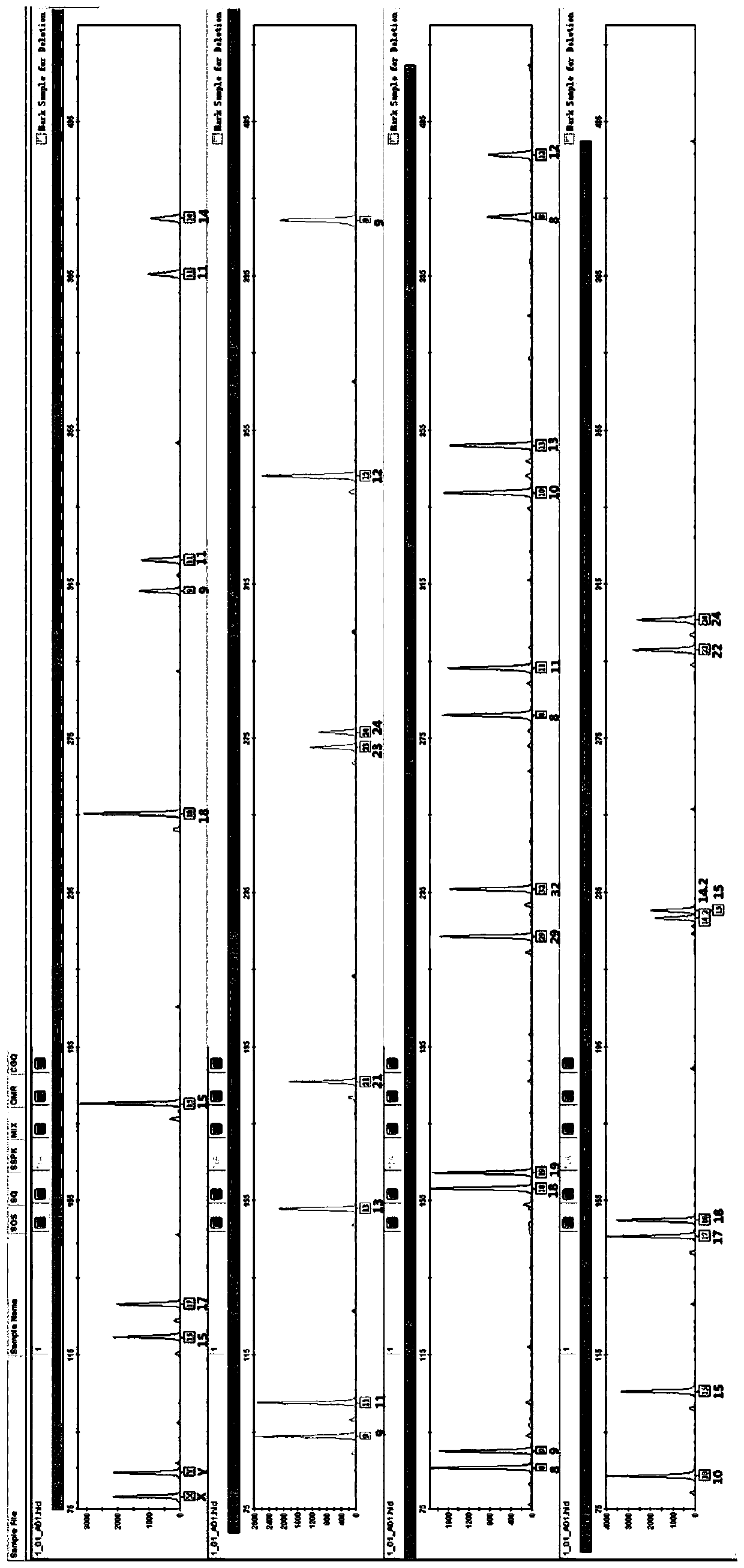
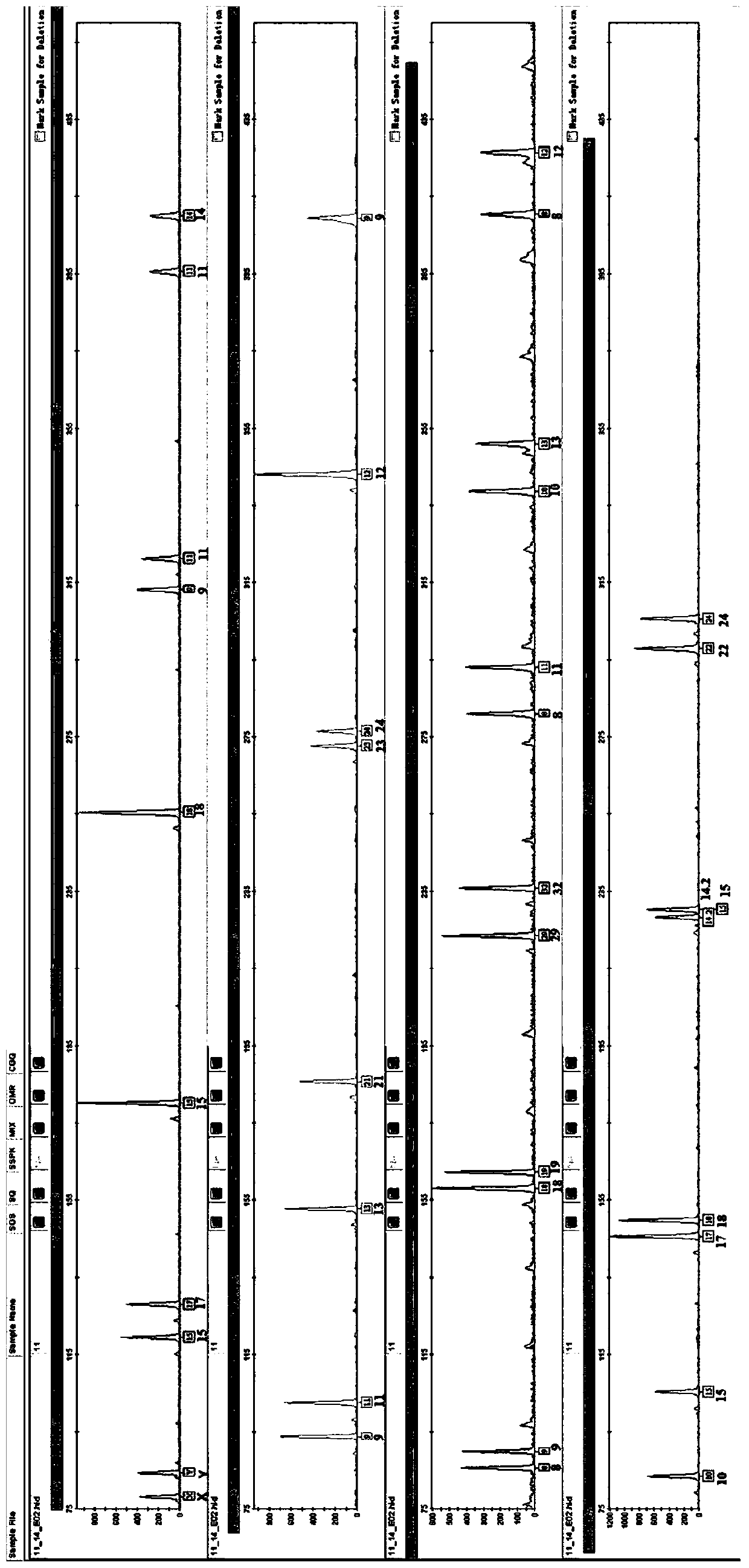
[0100] Example 2 Calculation of DNA recovery rate
[0101] Using the kit described in Example 1 to calculate the DNA recovery rate, the specific steps are as follows: take 5ng, 10ng, and 20ng standard genomic DNA respectively, repeat 3 samples for each gradient, and carry out DNA extraction through the subordinate extraction process, and extract the DNA with Qubit3 .0 for quantification, calculate the DNA recovery rate before and after extraction, the quantitative results are shown in Table 1.
[0102] (1) Take the standard DNA corresponding to the above content, dilute it into 10 μl aqueous solution, add 100-150 μl lysis solution, add 100-300 μl binding solution and 10 μl magnetic beads, and incubate in a centrifuge tube at room temperature for 10 minutes (pure DNA does not go through the lysis step) ;
[0103] (2) Place the centrifuge tube on the magnetic stand for 1 min, and remove the supernatant;
[0104] (3) Remove the centrifuge tube from the magnetic stand, add 300 μ...
Embodiment 3
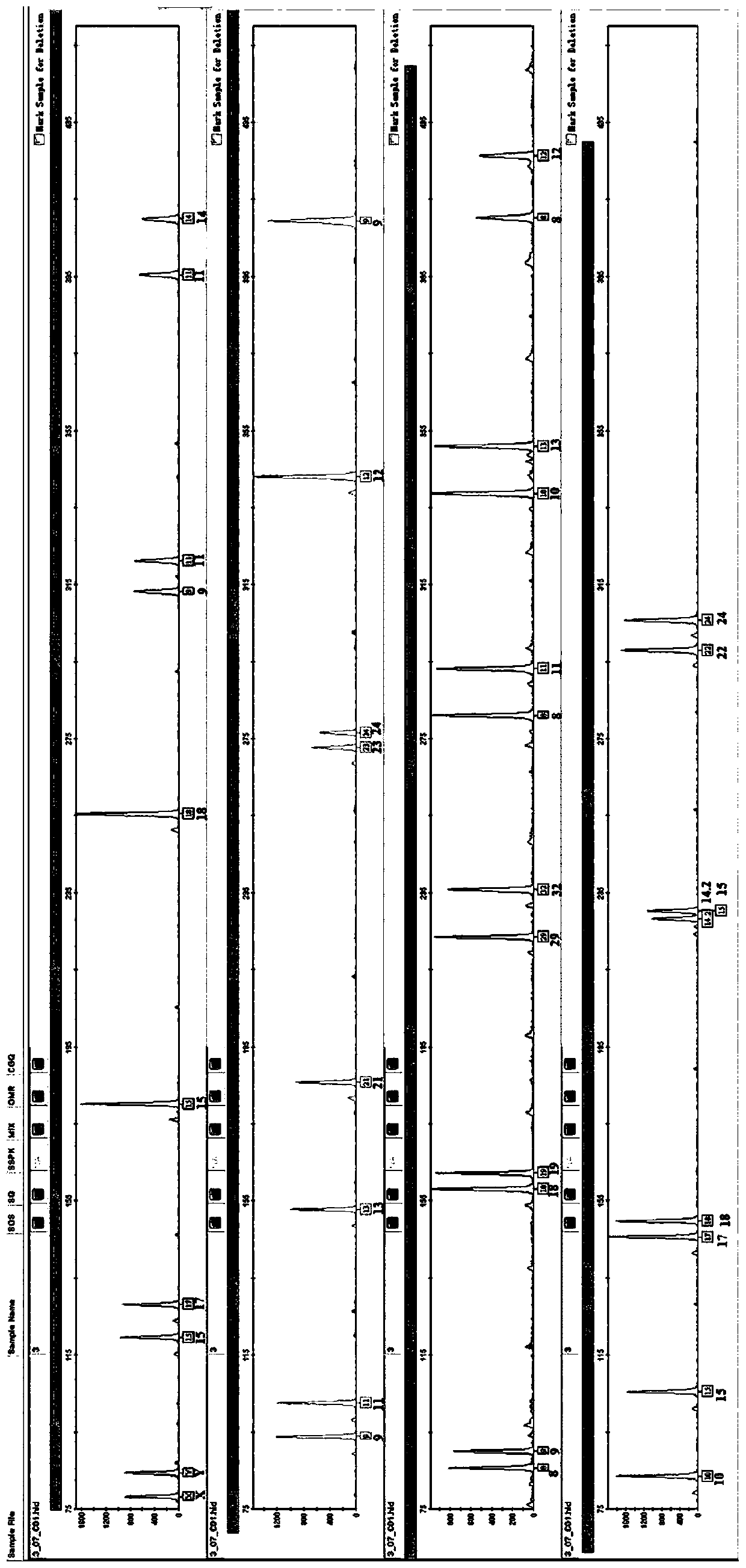
[0113] Example 3 Different Carrier Blood DNA Extraction
[0114] The kit in Example 1 was used to extract DNA from different carriers, and the specific steps were as follows: Take 2 μl of whole blood, dilute it with 200 μl of ultrapure water, and drop it evenly on the FTA card, qualitative filter paper and gauze, and take 3 replicates for each carrier sample. Among them, FTA card, qualitative filter paper, and gauze are all cut into samples of 0.2cm×0.2cm size for extraction:
[0115] (1) Take the above sample in a centrifuge tube, add 200-400 μl lysate, add 2 mg / mL proteinase K, and incubate at 56°C for 20 minutes;
[0116] (2) Collect the supernatant after centrifugation at 10000rpm, add 200-600μl of binding solution and 15μl of magnetic beads, incubate at room temperature for 10min, shake and mix well during the period;
[0117] (3) Place the centrifuge tube on the magnetic stand for 1 min, and remove the supernatant;
[0118] (4) Remove the centrifuge tube from the magn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com