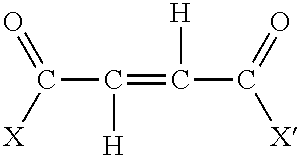
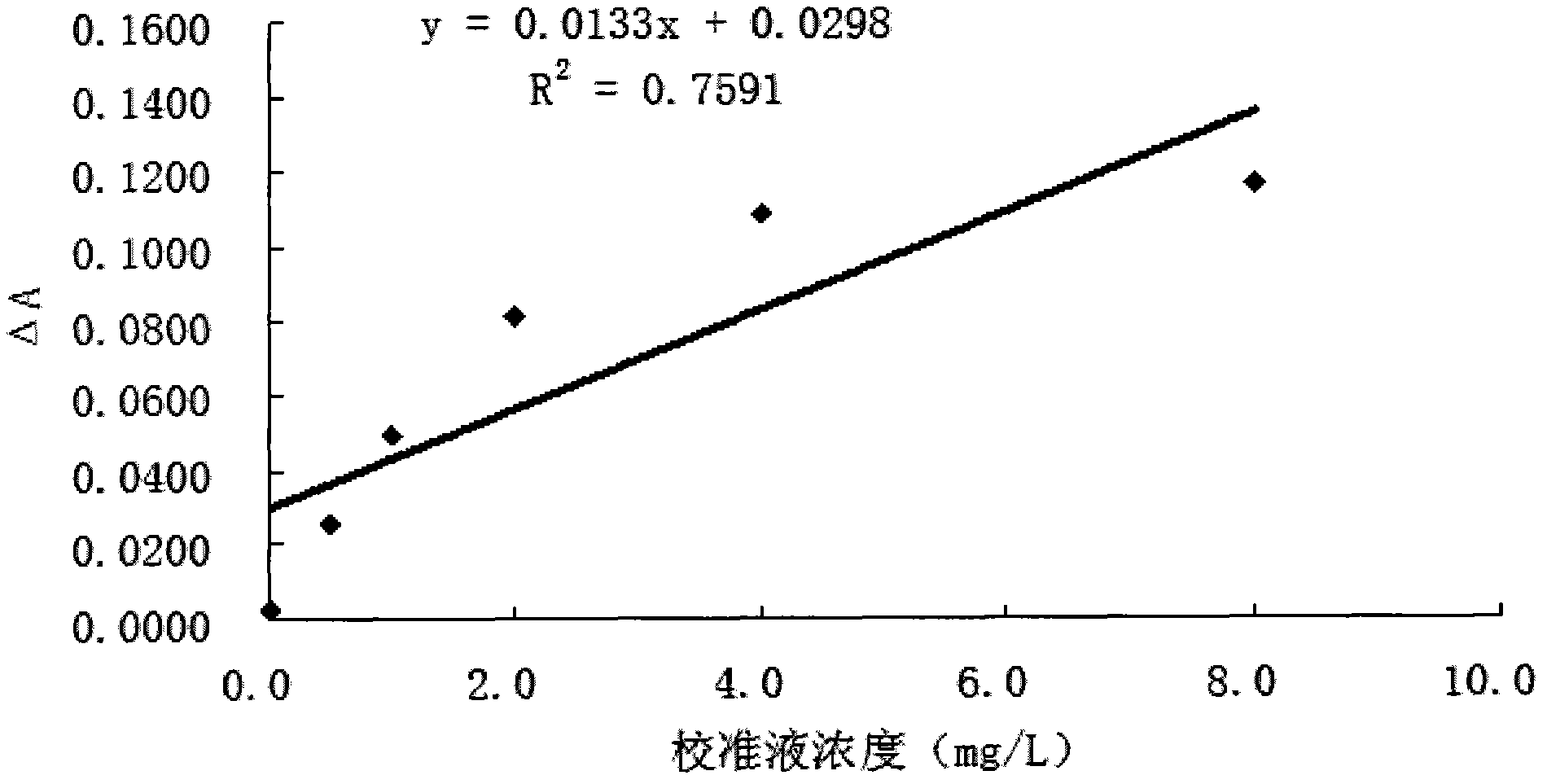
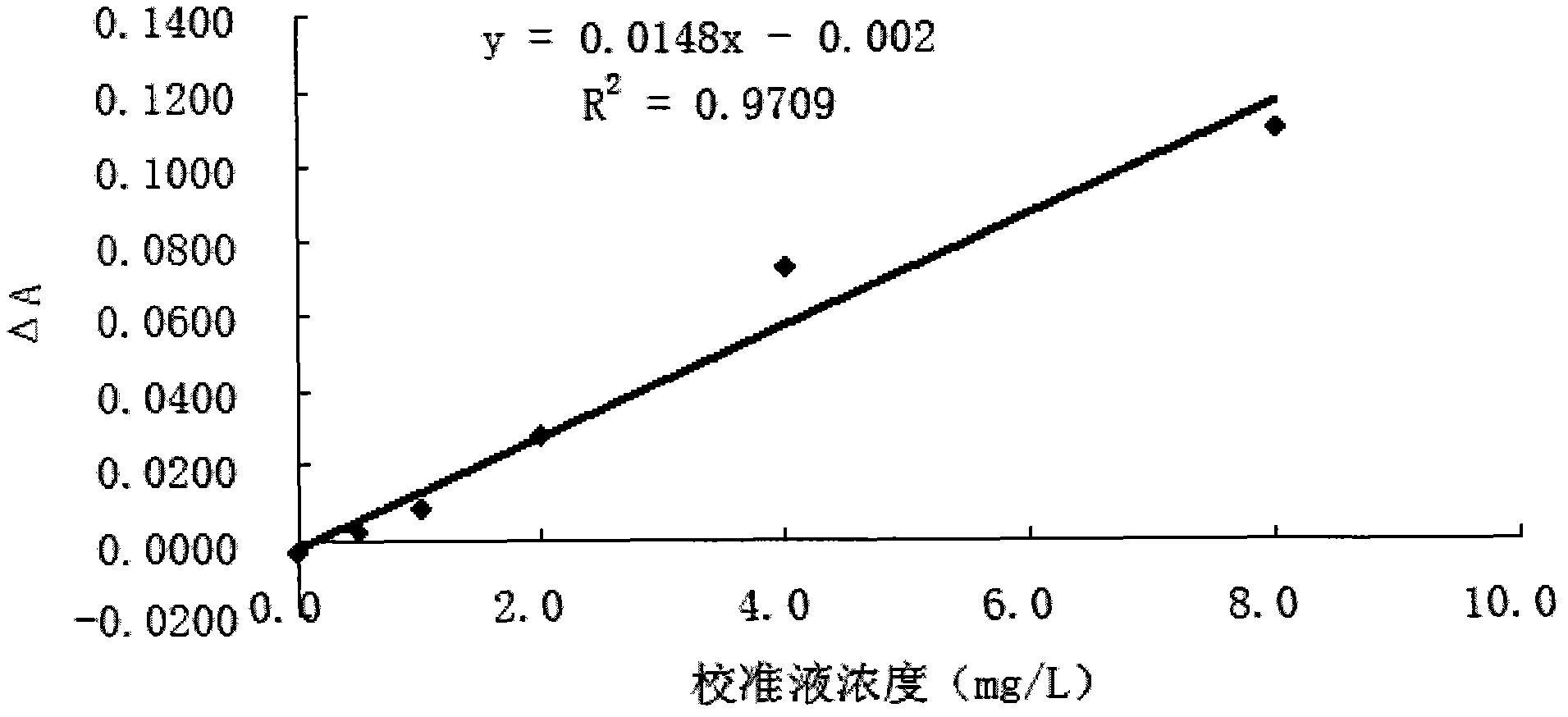
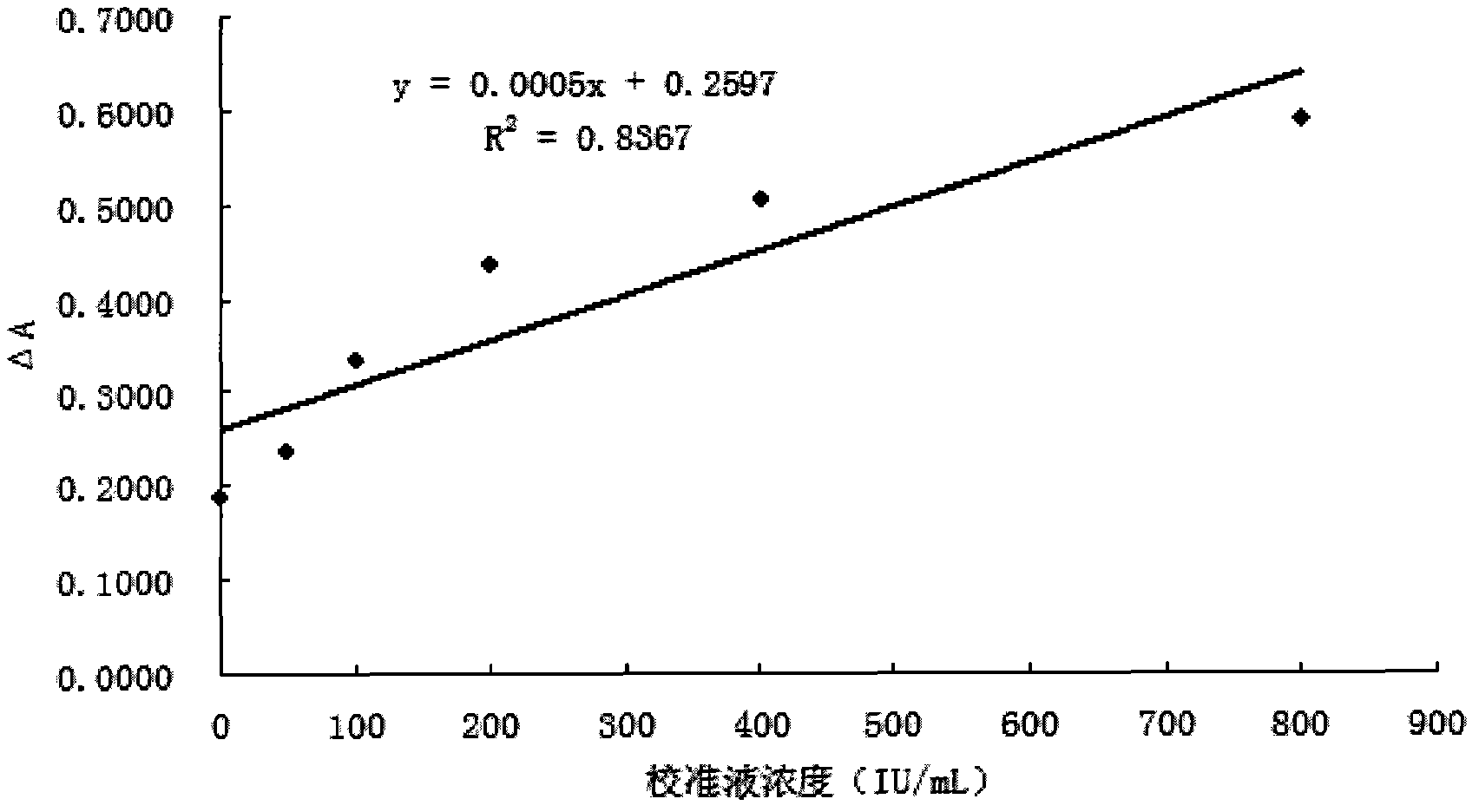
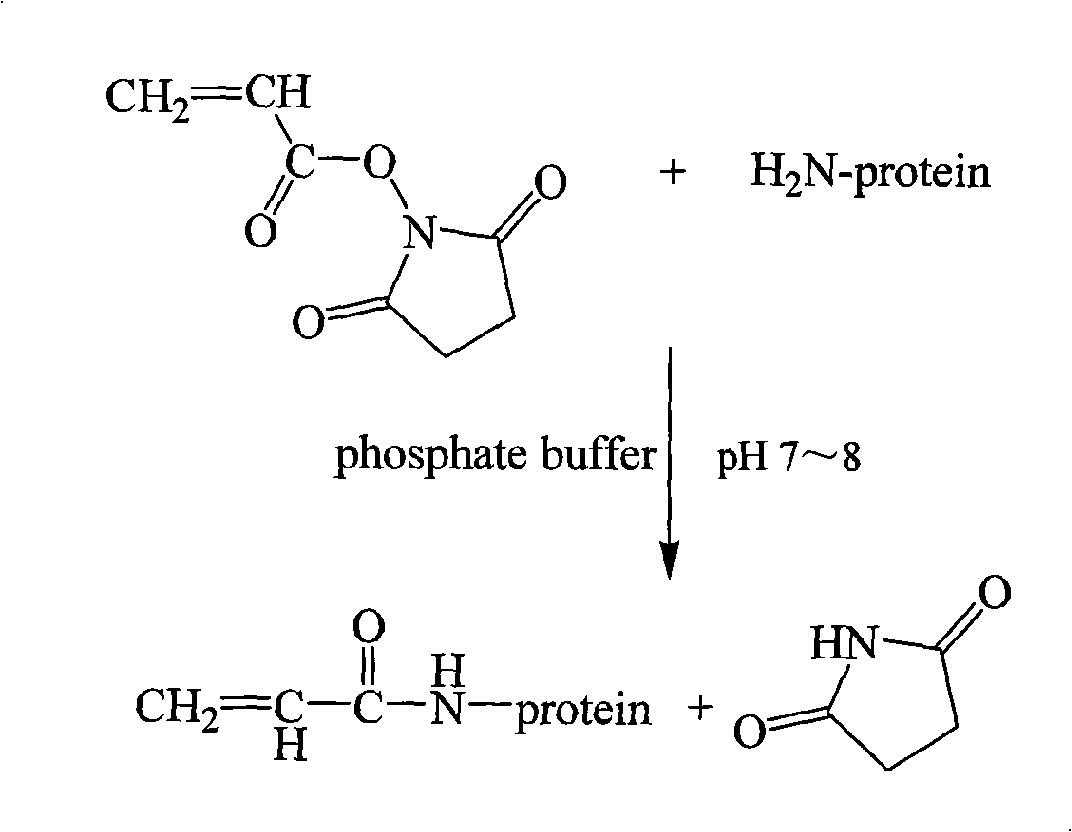
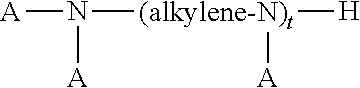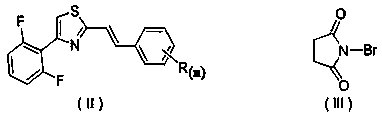Patents
Literature
399 results about "Succinimides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A subclass of IMIDES with the general structure of pyrrolidinedione. They are prepared by the distillation of ammonium succinate. They are sweet-tasting compounds that are used as chemical intermediates and plant growth stimulants.
Process for the preparation of polyalkenyl succinic anhydrides
A polyalkenyl succinic anhydride is prepared with low amounts of resinous or chlorinated byproducts in a two-step process whereby a polyalkene is first reacted with an unsaturated organic acid in a thermal ene reaction, followed with exposure to a gaseous halogen in presence of an additional amount of the unsaturated organic acidic reagent. The foregoing process produces a polyisobutenyl succinic anhydride having a high ratio of succinic anhydride functional groups to polyisobutenyl backbone groups. Such a polyisobutenyl succinic anhydride is particular suitable for the production of oil-soluble hydrocarbyl succinimides that have good dispersant properties when added to lubricating oil compositions.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Crosslinked gels comprising polyalkyleneimines, and their uses as medical devices
ActiveUS20070196454A1Promote cell growthSoft tissue growthIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSurgical adhesivesCross-linkCysteine thiolate
One aspect of the present invention generally relates to methods of sealing a wound or tissue plane or filling a void splace. In a preferred embodiment, the wound is an ophthalmic, pleural or dural wound. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane comprises a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Treatment of the polyethyleneimine with a cross-linking reagent causes the polyethyleneimine polymers to polymerize forming a seal. In certain instances, the cross-linking reagent is a polyethylene glycol having reactive terminal groups. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are isocyanates. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine has a lysine, cysteine, isocysteine or other nucleophilic group attached to the periphery of the polymer. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine is mixed with a second polymer, such as a polyethylene glycol containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing electrophilic groups with a cross-linking reagent containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the electrophilic groups on the polyalkyleneamine are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing photopolymerizable groups with ultraviolet or visibile light. Compositions used to seal the wound which contain PEI or a derivative of PEI are found to adhere tightly to the tissue. Other aspects of the present invention relate to methods of filling a void of a patient or adhering tissue. In certain instances, the methods use a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a polymeric composition formed by exposing a polyalkyleneamine to an activated polyalkylene glycol. In certain instances, the composition is attached to mammalian tissue.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
Lubricating oil composition
ActiveUS20070287643A1Improve wear resistanceEasy to keepOrganic compound preparationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAniline pointAutomatic transmission
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
Ethers of polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides and fuel compositions containing the same
Ethers of polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides having the formula: or a fuel soluble salt thereof. The compounds of formula I are useful as fuel additives for the prevention and control of engine deposits.
Owner:CHEVRON CHEM
Production process of cross-linked polysuccinimide resin
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Novel bio-medical adhesive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105477678AGood biocompatibilityStrong adhesionSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPhosphateFreeze-drying
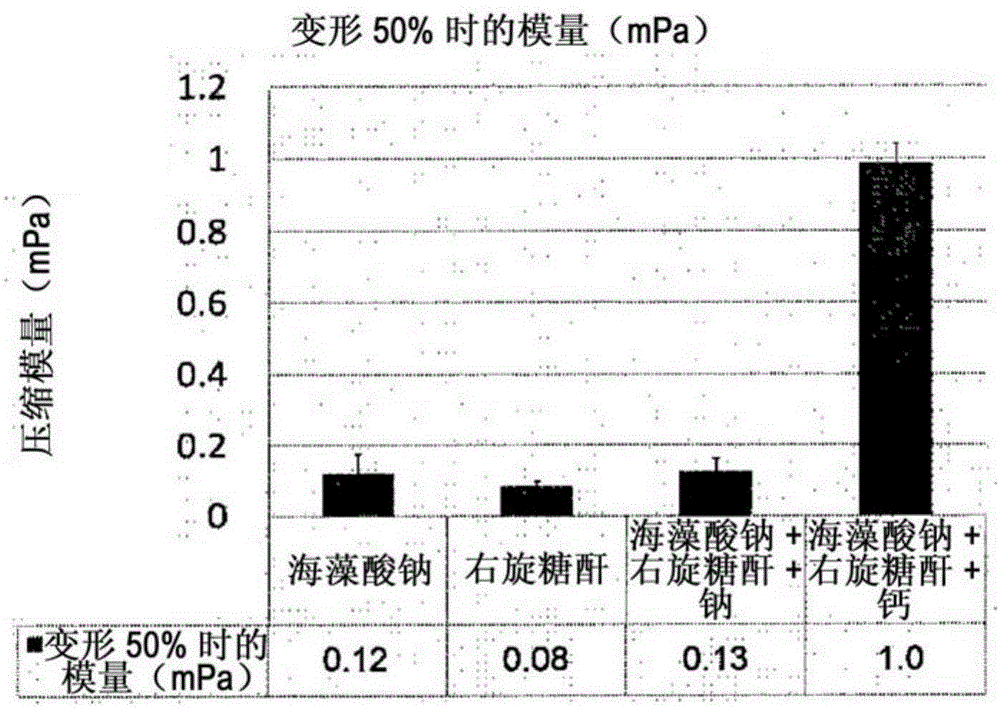
The invention discloses a bio-medical adhesive, which can be cross-linked with a wound in situ, and a preparation method of the bio-medical adhesive. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the steps of first, preparing oxidized sodium alginate by using sodium periodate to oxidize sodium alginate; dissolving the oxidized sodium alginate in an MES (Methyl Ester Sulfonate) buffer solution, dissolving 1-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxyl succinimide in the MES buffer solution as well under nitrogen protection, continuously adding dopamine, carrying out dialyzing and freeze-drying after reacting for 8 to 24 hours, and obtaining A liquid by dissolving a reaction product in a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) or a sodium borate solution; then, dissolving I-shaped collagen in an acid solution, and obtaining B liquid by neutralizing the solution pH (potential of Hydrogen) to be 5 to 8; firstly pre-treating the wound by using hydrogen peroxide or HRP (Horse Radish Peroxidase) before the bio-medical adhesive is used, then immediately coating the wound with the bio-medical adhesive after mixing the A liquid with the B liquid, and forming gel in 30 to 120 s, wherein the gel is firmly adhered to the surface of the wound. The bio-medical adhesive disclosed by the invention has a stronger adhesive force under a moist environment in vivo, integrates filling, sealing and bleeding stopping functions, is good in biocompatibility, is bio-degradable and can be used for promoting wound healing.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Power transmission fluid with enhanced friction characteristics
InactiveUS20070293406A1Minimize equipmentMinimize performance problemAdditivesBase-materialsElectric power transmissionBase oil
A power transmission fluid composition, a power transmission containing the fluid, a method of operating a power transmission with the fluid and method of improving friction durability for a power transmission fluid. The power transmission fluid includes (a) a base oil and (b) an additive composition having therein (i) at least one ashless dispersant; (ii) a metal detergent providing greater than about 100 ppm metal in the power transmission fluid composition; (iii) a friction modifying amount of an imidazoline; (iv) a succinimide friction modifier; and (v) a non-hydroxy tertiary amine friction modifier other than (iii).
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Preparation of CT/MRI dual-modality imaging contrast agent based on dendrimer
InactiveCN102294038AShorten the relaxation timeNarrow size distributionX-ray constrast preparationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAcetic anhydride
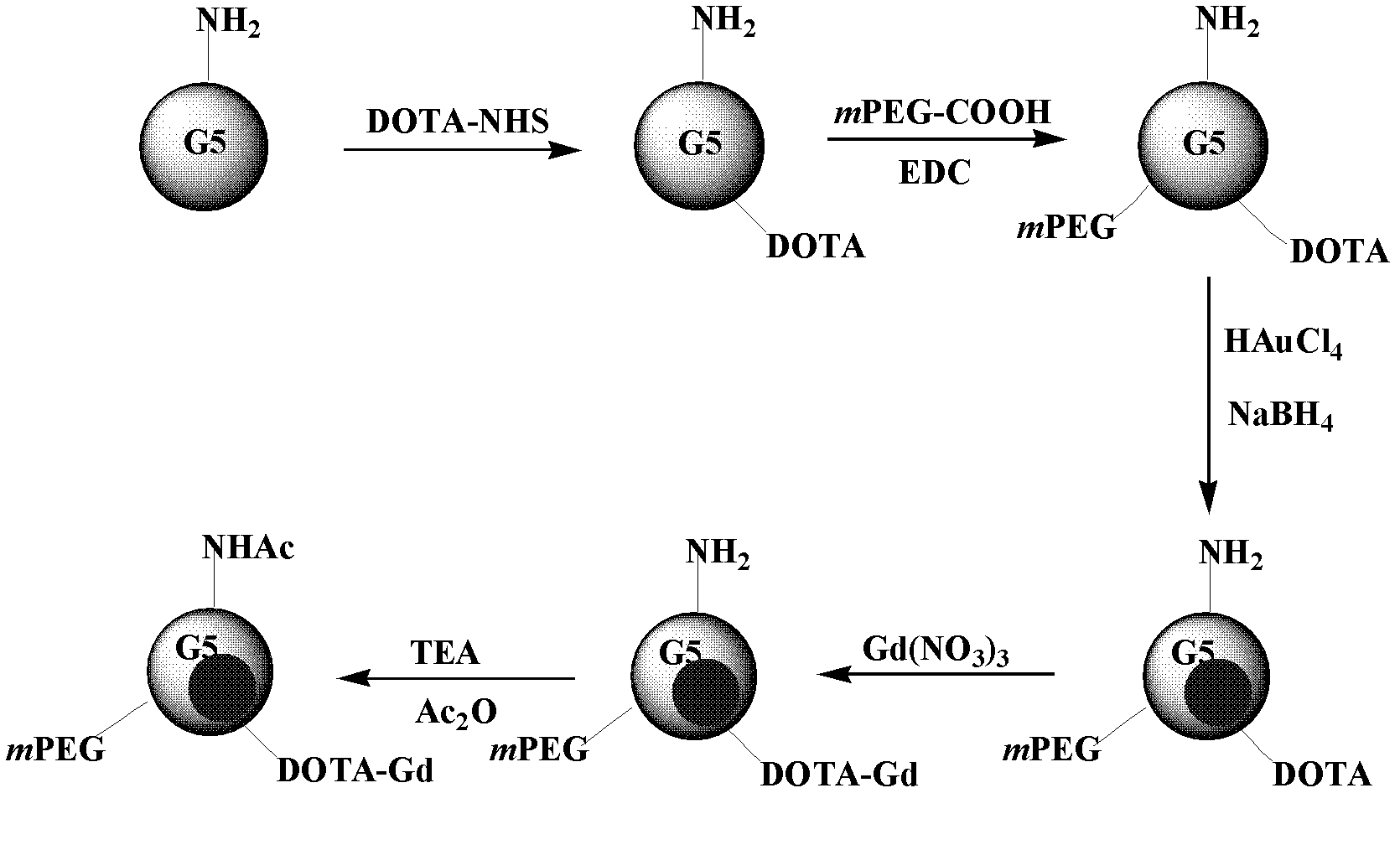
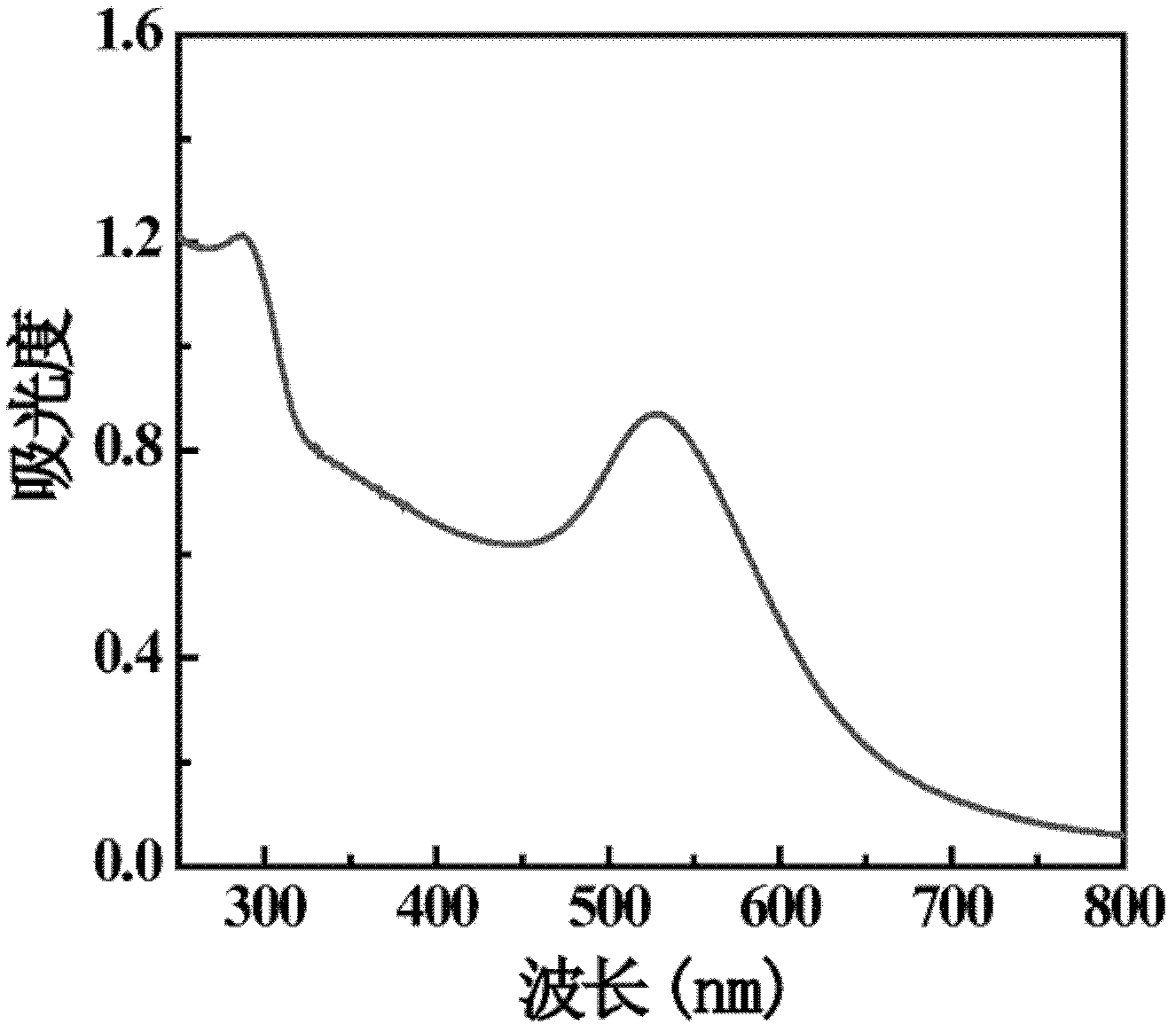
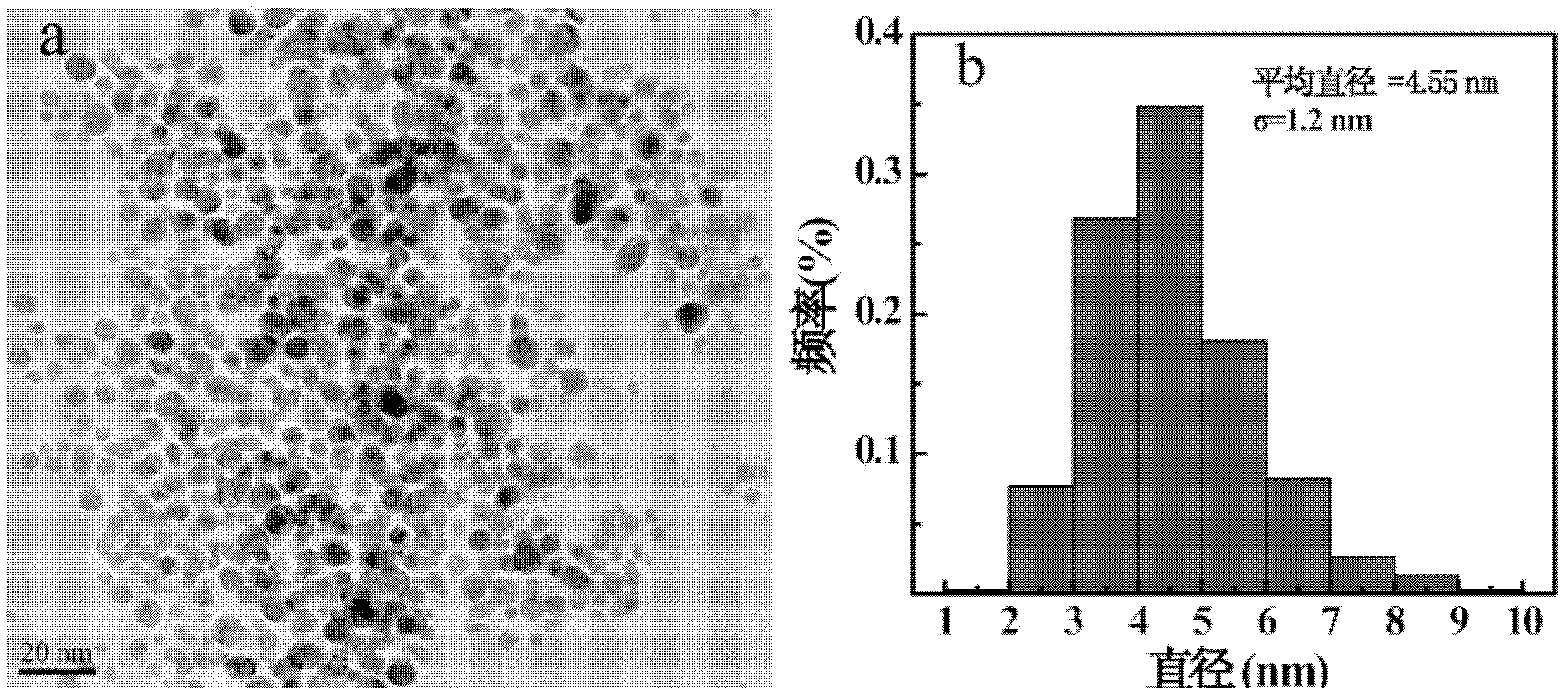
The invention relates to a method for preparing a computed tomography (CT) / magnatic resonance imaging (MRI) bimodal imaging contrast agent based on dendrimers. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding DOTA-N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS) solution into the fifth generation of poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimer solution, adding methoxy poly(ethylene glycol) (mPEG)-COOH solution which is subjected to 1-ethy 1-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl] carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) activation, reacting with stirring, and thus obtaining functionalized dendrimer solution; (2) adding chloroauric acid solution and sodium borohydride solution into the functionalized dendrimer solution, reacting with stirring, adding gadolinium nitrate solution, stirring, adding triethylamine and acetic anhydride, andreacting with stirring for 8 to 24 hours; and (3) dialyzing the solution obtained in the step (2), performing freeze drying treatment, and thus obtaining the contrast agent. The method has a simple preparation process, and experimental conditions are realized at normal temperature and under normal pressure; and the CT / MRI bimodal imaging contrast agent prepared by the method has a good CT / MRI effect, and a favorable foundation is laid for the development of a novel multifunctional contrast agent.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Formulations comprising an asphaltene-dispersing/inhibiting additive based on oxazolidines derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides
The present invention relates to formulations of asphaltenes' inhibitor-dispersant additives based on oxazolidine derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides. Said formulations can contain inert organic solvents, preferably including: toluene, mixtures of xylene, o-xylene, p-xylene, kerosene, turbo-fuel; or inert hydrocarbon solvents having boiling points within the range of gasoline and diesel; or inert hydrocarbon or organic solvents having a boiling point within a range from 75 to 300° C. The ratio in weight of inert organic solvents to additive that prevents and controls the precipitation and deposition of asphaltenes ranges from 1:9 to 9:1, preferably from 1:3 to 3:1.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
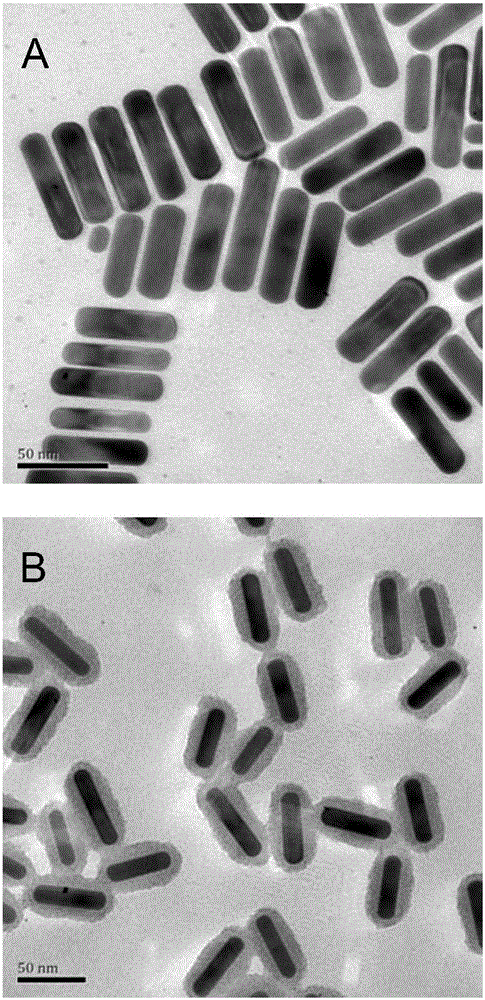
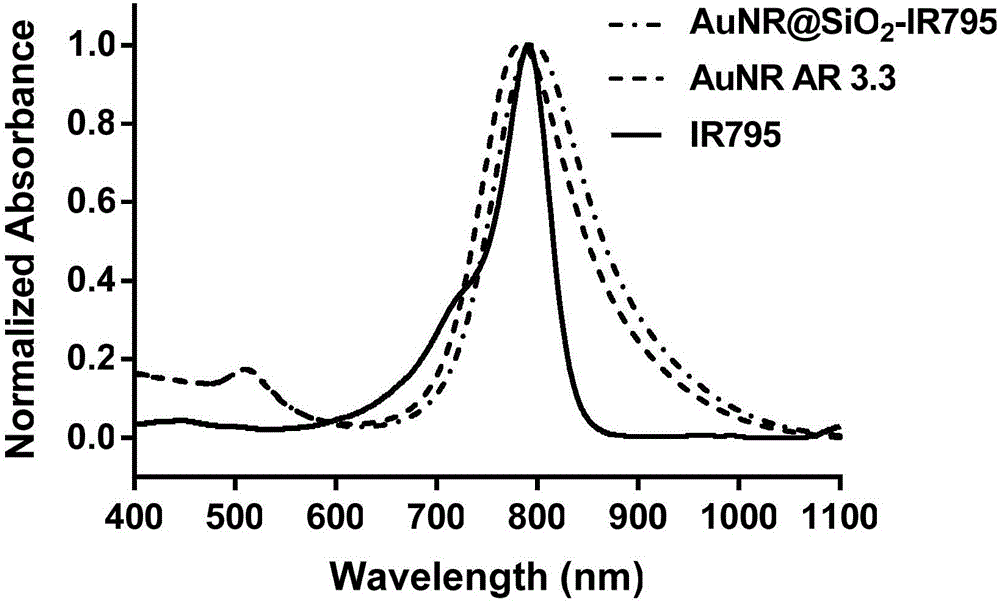
Composite gold nanorod carrier having photo-thermal/photodynamic therapy treatment performance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106267202AImprove the effect of photodynamic therapyAchieve synergyPowder deliveryPhotodynamic therapyFluorescenceSilanes
The invention provides a composite gold nanorod carrier having photo-thermal / photodynamic therapy treatment performance and a preparation method thereof. The composite gold nanorod carrier uses a gold nanorod as a core and uses silicon dioxide as a shell layer, a near infrared fluorescent dye for photodynamic therapy is modified on the outer surface of the shell layer. The preparation method comprises the steps that a chloroauric acid solution and a cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide solution are mixed, a sodium borohydride ice water mixed solution is added to obtain a nano gold seed solution A; a silver nitrate solution and a chloroauric acid solution are added to a binary surface active agent solution, a hydrochloric acid is added after reaction to obtain a solution B, then ascorbic acid and the solution A are added, and a gold nanorod is obtained after reaction; a tetraethoxysilane methanol solution and an aminopropyl trimethoxy silane methanol solution are added to a gold nanorod solution to obtain composite nanoparticles; 1-(3-dimethyl amino propyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride is added to the near infrared fluorescent dye, then N-hydroxyl succinimide is added to obtain a solution C; the composite nanoparticle solution is mixed with the solution C to obtain a product.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method of Operating an Engine Using an Ashless Consumable Lubricant
ActiveUS20110297122A1Reduced deposit formationReduce wearElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSulfateEngineering
The present invention relates to methods of using a low sulfur, low phosphorus, low-ash, zinc free consumable lubricating composition in an internal combustion engine equipped with a pilot ignition system, where the composition comprises: an oil of lubricating viscosity; a high TBN succinimide dispersant and where the lubricant composition overall has a sulfated ash value of up to about 0.2, a phosphorus content of up to about 50 to about 800 ppm and a sulfur content of up to about 0.4 percent by weight.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Magnetic biological probe and test strip for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) and preparation method and using method of biological probe
InactiveCN103293295ASignal sensitiveImprove stabilityMaterial analysisMagnetite NanoparticlesHepatitis B virus
The invention discloses a magnetic nanoparticle biological probe and a test strip for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) and a preparation method and a using method of the biological probe. The method for preparing the biological probe comprises the following steps of: performing surface amino functionlization treatment on magnetic nanoparticles with the particle size of 50-300nm, performing carboxylation treatment, mixing and reacting the magnetic nanoparticles subjected to surface carboxylation, carbodiimide and N-hydroxy succinimide in a buffer solution, and washing to obtain a reactant A; mixing and reacting the reactant A and an antibody for a HBV marker in a coupled buffer solution to obtain a reactant B; mixing and reacting the reactant B and a solution of a compound containing amino, and washing to obtain the product. The biological probe is high in specificity, sensitive in signal and high in stability and is suitable for detecting multiple hepatitis B markers according to the selected targeting markers and matched antibodies. According to the test strip, an obtained magnetic signal can be subjected to secondary determination through visual inspection and MAR detection, the personal error can be greatly reduced, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:上海爱纳玛斯医药科技有限公司
Macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, gelatin film thereof and preparation method
InactiveCN105237645ADirect connectionImprove light blocking performanceFlexible coversWrappersCross-linkPhosphate
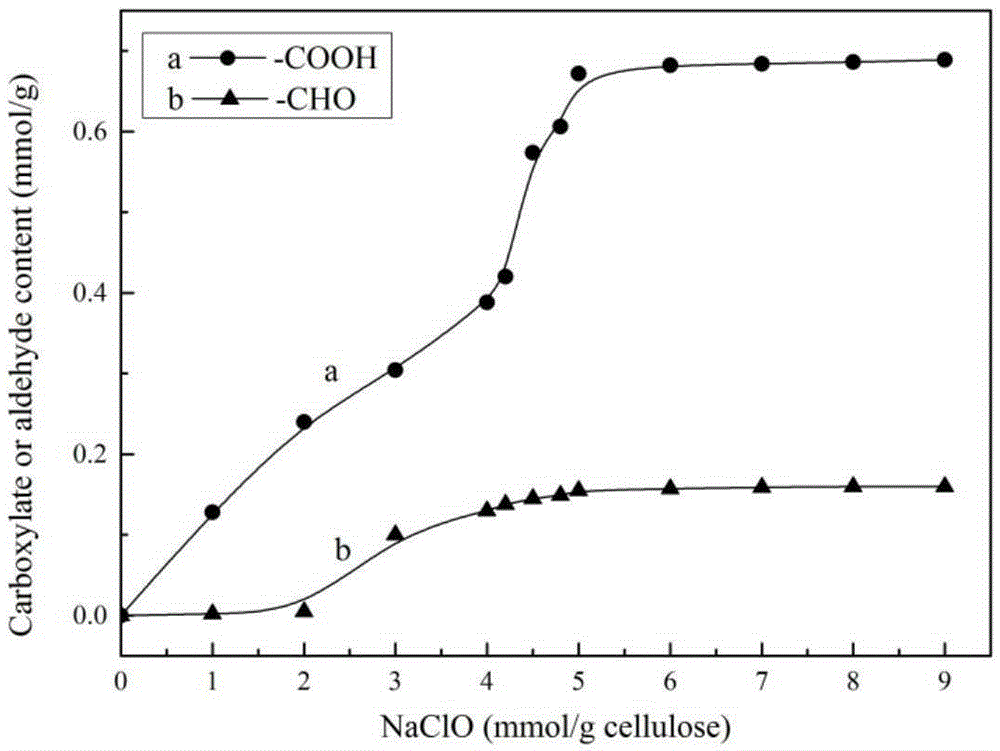
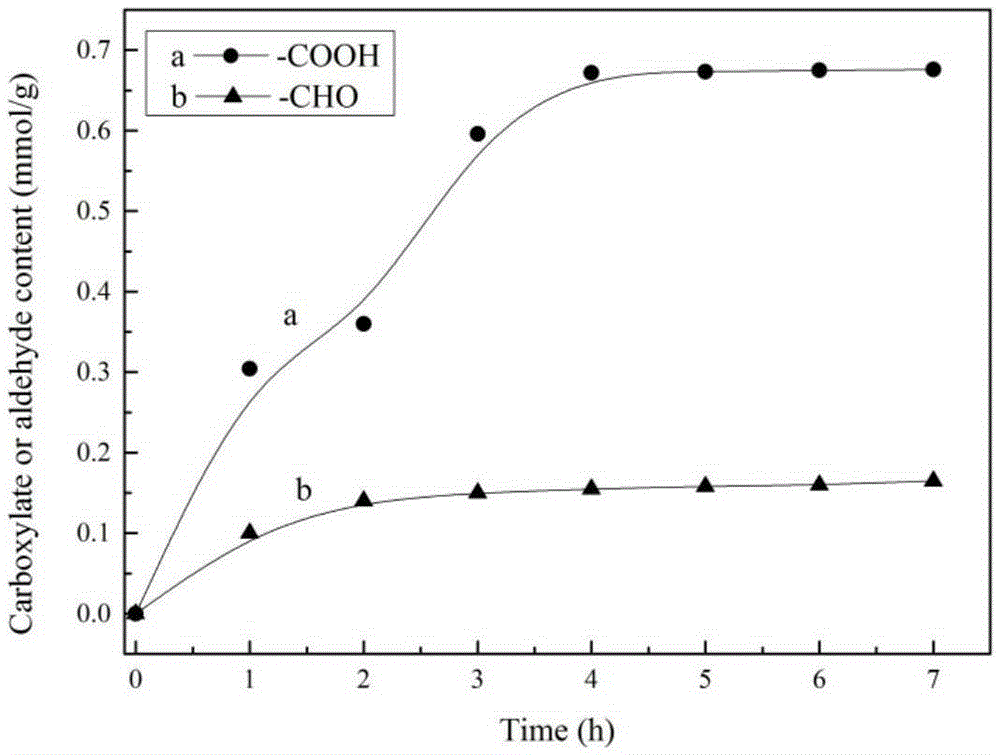
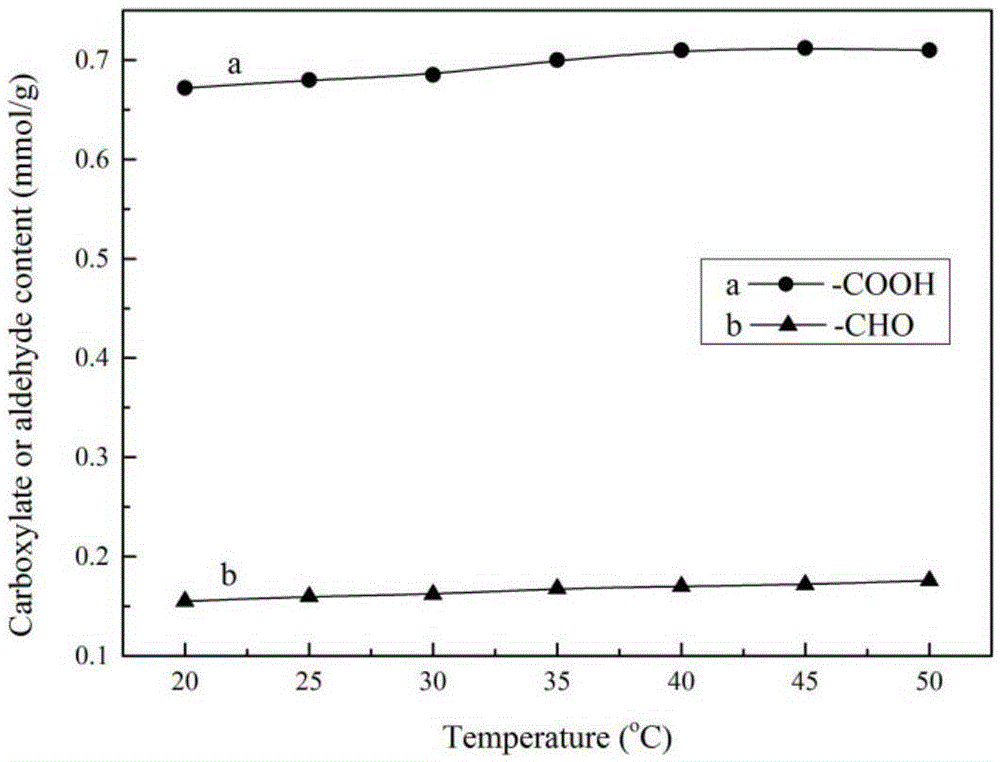
The invention discloses a macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, a gelatin film thereof and a preparation method. The preparation method of the gelatin film comprises the following steps: 1, oxidizing a primary amino group on the C6 position of cellulose into carboxyl through a TEMPO / NaBr / NaClO system, and obtaining oxidized cellulose TOMCC; 2, treating N-hydroxy succinimide and TOMCC obtained in step 1 as raw materials, and manufacturing a macromolecule cross-linking agent TMN; 3, making the macromolecule cross-linking agent TMN be subjected to chemical cross-linking with a gelatin film, and obtaining the food package gelatin film based on oxidized cellulose chemical cross-linking. Light-blocking performance, thermal stability, anti-biodegradation capability, the mechanical property (elasticity) and hydrophobicity of the gelatin film are all improved to a large extent, and a favorable condition is provided for application of the gelatin film to the food package field. In addition, biodegradation mechanisms of a modified gelatin film and a pure gelatin film in a phosphate buffered solution (PBS) and lysozyme are explored and analyzed as well.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Environment-friendly water-based synthetic cutting fluid
InactiveCN103031197AIncreased durabilityFree from corrosionLubricant compositionWater basedTetrafluoroborate
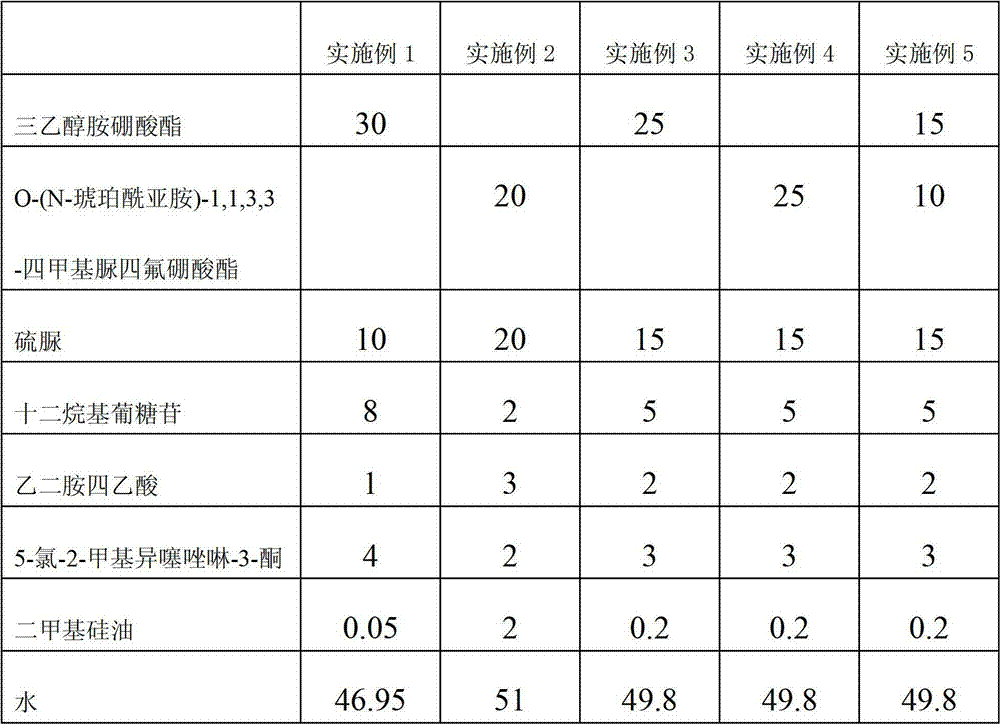
The invention discloses an environment-friendly water-based synthetic cutting fluid. The environment-friendly water-based synthetic cutting fluid contains the following components in percentage by weight: 20-30% of antirust agent, 10-20% of lubricating agent, 2-8% of surfactant, 1-3% of chelating agent, 2-4% of bactericide, 0.05-0.2% of defoamer and the balance of water, wherein the antirust agent is one or a mixture of triethanolamine borate and O-(N-succinimide)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate. The environment-friendly water-based synthetic cutting fluid disclosed by the invention has favorable lubricating, cooling and cleaning effects and a particularly favorable antirust effect, and can form a protective film on the surface of metal so as to prevent a machine took, a workpiece and a cutter from being corroded by surrounding mediums.
Owner:SHENZHEN FRANCOOL TECH
Method for covalently coupling amino-containing molecules to microspheres
The invention relates to a method for covalently coupling amino-containing molecules to microspheres. According to the method, a reaction mixture is simultaneously in contact with carbodiimide and N-hydroxy succinimide (or N-hydroxy thiosuccimide)to carry out a covalent coupling reaction. A reagent prepared by utilizing the method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively improving the self polymerization of the amino-containing molecules in a coupling process and has better linearity when a standard curve is drawn.
Owner:BEIJING BEIJIAN XINCHUANGYUAN BIOLOGICAL TECH
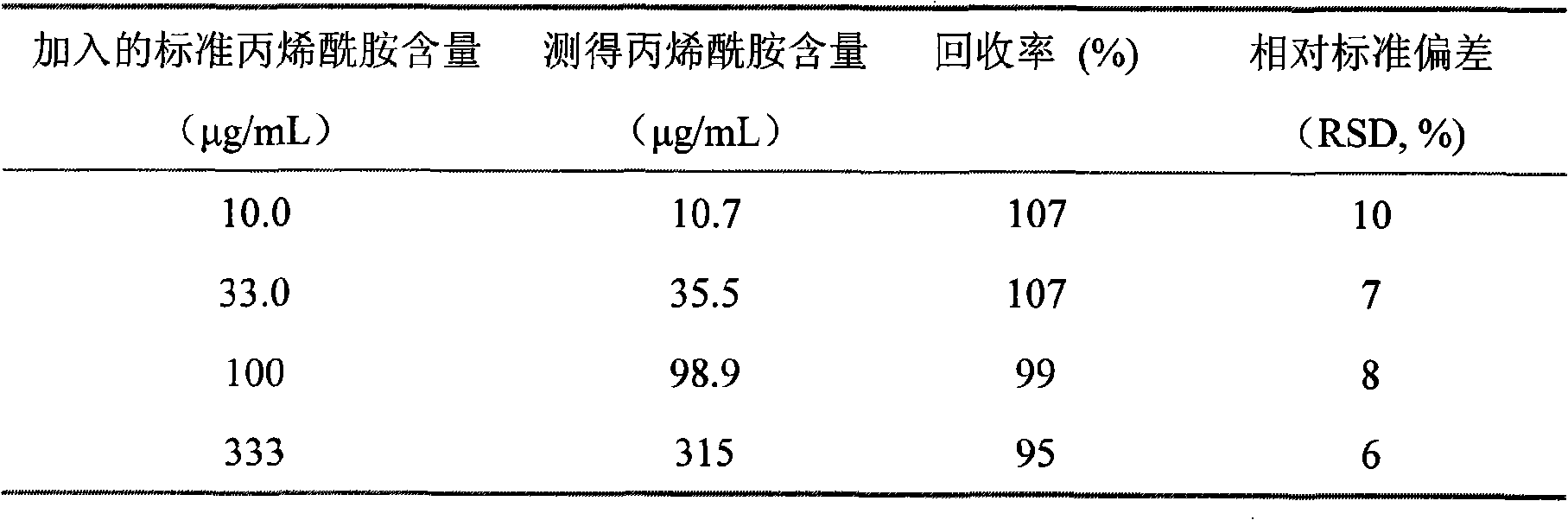
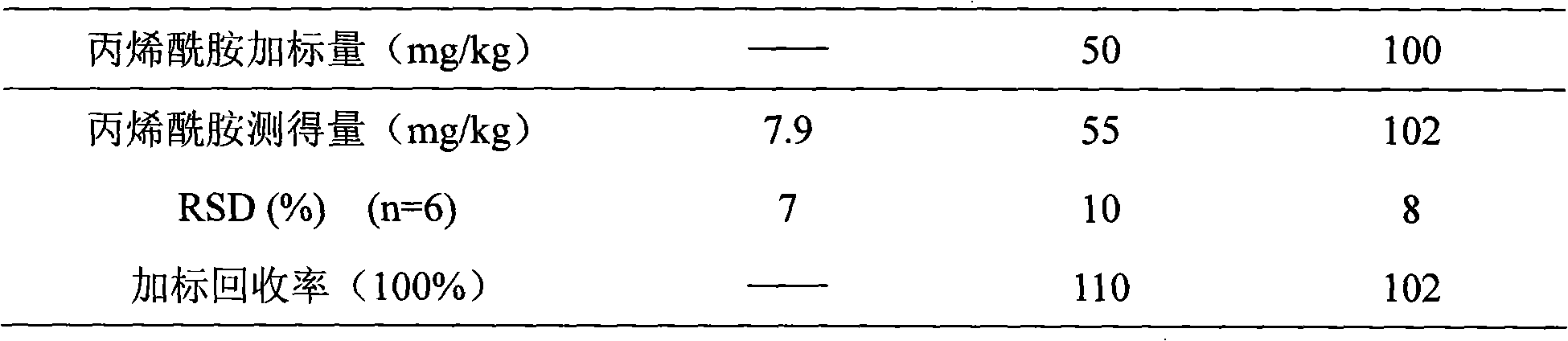
Acrylic amide complete antigen preparation and its ELISA quantitative determination method
The invention provides a method for preparing acrylamide complete antigen. The method is as follows: amine uncoupling reaction is directly carried out between N-acryloyloxy succinimide and the surface amino group of carrier protein molecule in a neutral or weakly alkaline phosphate buffer solution, thereby forming acrylamide complete antigen. Polyclonal antibody capable of realizing specificity identification of acrylamide is obtained through a complete antigen immune animal, so as to establish an enzyme immunoassay method suitable for measuring the content of acrylamide in an aqueous solution or food and to provide a corresponding reagent box. The method has simple operation and does not need other reaction reagent, thereby furthest maintaining the structural integrity of acrylamide; moreover, the method ensures that a coupling position is at a maximum distance from a feature group so as to fully expose the feature structure of acrylamide molecule. The established enzyme immunoassay method of acrylamide and the reagent box have strong specificity, high sensitivity and convenient operation, and are suitable to realize massive sample detection which has low cost and is quick and simple.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Lubricant composition
ActiveUS20130005624A1Excellent in deposition resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceOrganic chemistryAdditivesWear resistanceSulfur containing
A lubricant oil composition which is excellent in deposition resistance, corrosion resistance and wear resistance, despite its low phosphorus content and low sulfuric acid ash content, is provided by using a succinimide compound in combination with at least one selected from specific sulfur-containing compounds, specific heterocyclic compounds and reaction products thereof.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Vehicle fuel oil environmentally-friendly and energy-saving agent
The invention discloses a vehicle fuel oil environmentally-friendly and energy-saving agent which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 10-12 parts of solvent oil; 8-10 parts of oil calcium sulfonate; 5-7 parts of ethyl acetate; 5-6 parts of C9 alkylphenol polyoxyethylene ether; 10-15 parts of isooctyl nitrate; 15-17 parts of sulfonated fatty acid isooctyl sodium salt; 10-15 parts of naphthenate; 8-12 parts of diesel / petrol; 15-17 parts of sodium bis-(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate, 3-5 parts of dicyclopentadiene; and 3-5 parts of succinimide. The environmentally-friendly and energy-saving agent can improve the vehicle dynamic property, reduce the oil consumption and the vehicle operation cost and also reduce the emission of pollutants in motor vehicle waste gas, effectively improve the gasoline quality, gasoline octane number and the flammability, and completely combust along with the fuel without generating sediments or residues and has oil saving ratio, no side effects and no adverse effects on other properties of fuel oil.
Owner:王政银
Ultrasonic cyanogen-free fast silver coating method
InactiveCN101235523AImprove solubilityEliminate passivation film on cathode surfaceCleaning using liquidsStrong bindingMaterials science
An ultraphonic non-cyanide rapid silver plating method belongs to the metal material technology field, which comprises the following steps: preparing compound electrolyte, removing oil by acetone ultraphonic, removing oxydic films by acid pickling, and carrying out ultraphonic electroplating, wherein the electrolyte comprises 0.05-0.5M / L methanesulfonic acid, 0.05-0.5M / L silver nitrate, 0.15-1.5M / L succinimide and 0.1-0.5M / L boric acid, wherein the ultraphonic electroplating has the following parameters: ultrasonic frequency is 20kHz-45kHz, ultrasonic power is 5W / cm2-250W / cm2, range of current density is 0-6A / dm2, temperature is 35-80 DGE C, pH value is 8-11 and electroplating time is10-60min. The method has the advantages of improving the dissolving of the anode white substance by high temperature, eliminating passivating film of the surface of the cathode by the ultraphonic function, enlarging current density, without pre-plating silver or soaking the silver and the method has the advantages of simple technology, safety and poison free, bright mirror face of the obtained silver layer, high hardness and high abradability and a strong binding force with the basal body of the bright silver coating.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of in-tube solid-phase micro-extraction column
InactiveCN103638693ARealize analysis and detectionSimplify the experimental stepsSolid sorbent liquid separationWater bathsMechanical property
The invention discloses an in-tube solid-phase micro-extraction column and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analytic chemistry sample pretreatment. The in-tube solid-phase micro extraction column is composed of a quartz capillary tube and a graphene oxide coating layer, wherein the graphene oxide coating layer is fixed on the inner wall of the quartz capillary tube through chemical bonding. During preparation, the inner wall of the quartz capillary tube is successively washed with an acid, washed with an alkali and blown to dry by nitrogen, a toluene solution containing 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) is poured into the capillary tube, the capillary tube has both ends sealed and is placed in a water bath for reaction, then a graphene oxide aqueous solution activated by 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbide diimine / N-hydroxy succinimide (EDC / NHS) is poured into the capillary tube, the capillary tube has the both ends sealed and is subjected to a reaction in the water bath, the graphene oxide is allowed to be bonded to the quartz capillary tube wall, and the in-tube solid-phase micro-extraction column is obtained. The in-tube solid-phase micro-extraction column has simple and rapid preparation method, allows the graphene coating layer to have good chemical property, mechanical property and thermal stability, has high extraction capacity and long service life, and has broad application prospects in the analytic chemistry and environmental analysis fields.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Human glucagon-like peptide-1 compound and its preparing method
InactiveCN1676163AImprove biostabilityImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMonomethoxypolyethylene glycolGlucagon-like peptide-1
The present invention relates to a human pancreatic glucagons sample peptide-1 compound and its preparation method. The human pancreatic glucagons sample peptide-1 in said compound is human pancreatic glucagons sample peptide-1(7-37) or human pancreatic glucagons sample peptide-1(7-36)Nh2. Said compound is formed from human pancreatic glucagons sample peptide-1 and monomethoxy polyglycol containing active group activated by succinimide, namely said compound is mPEG-GLP-1.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
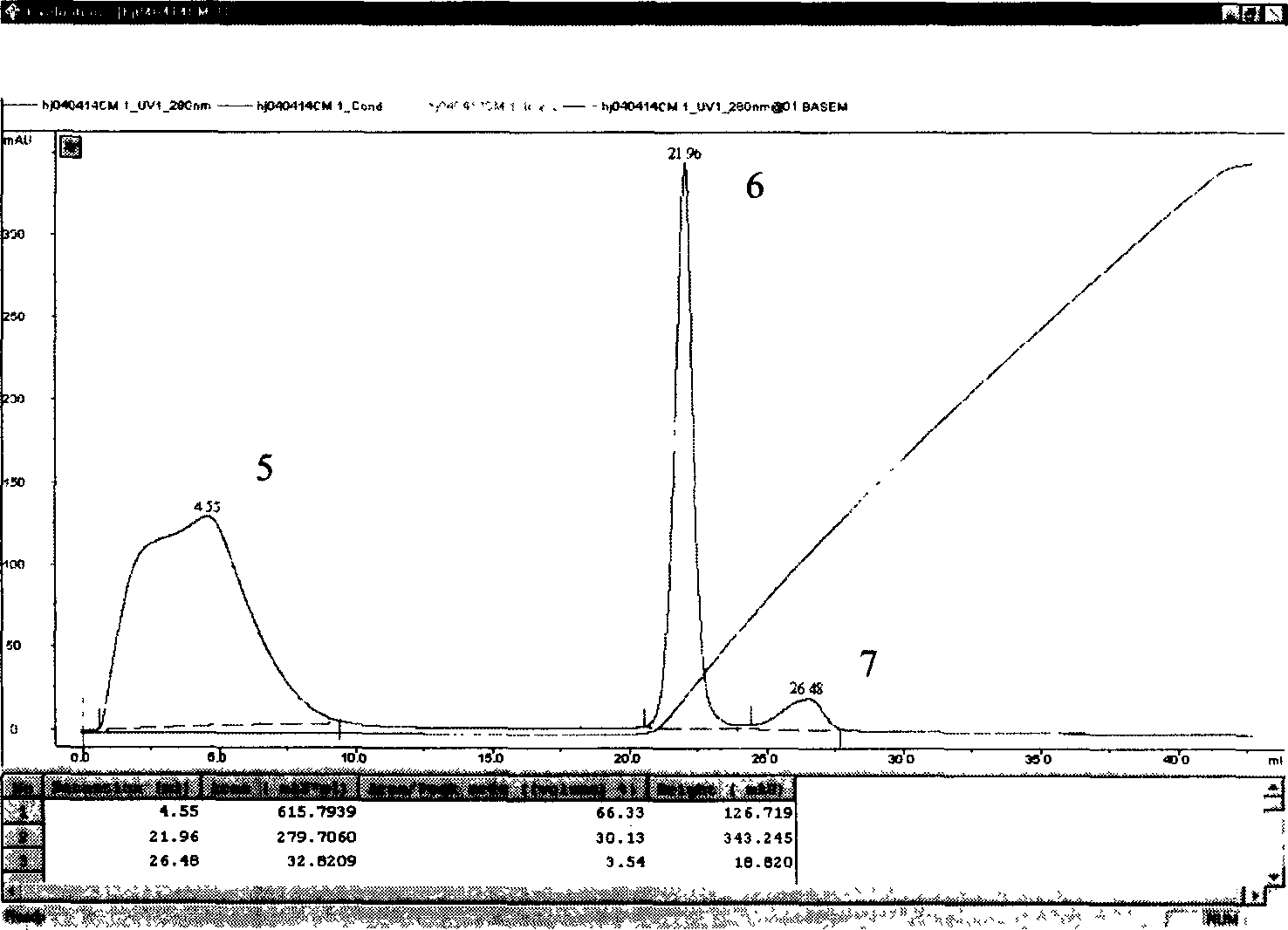
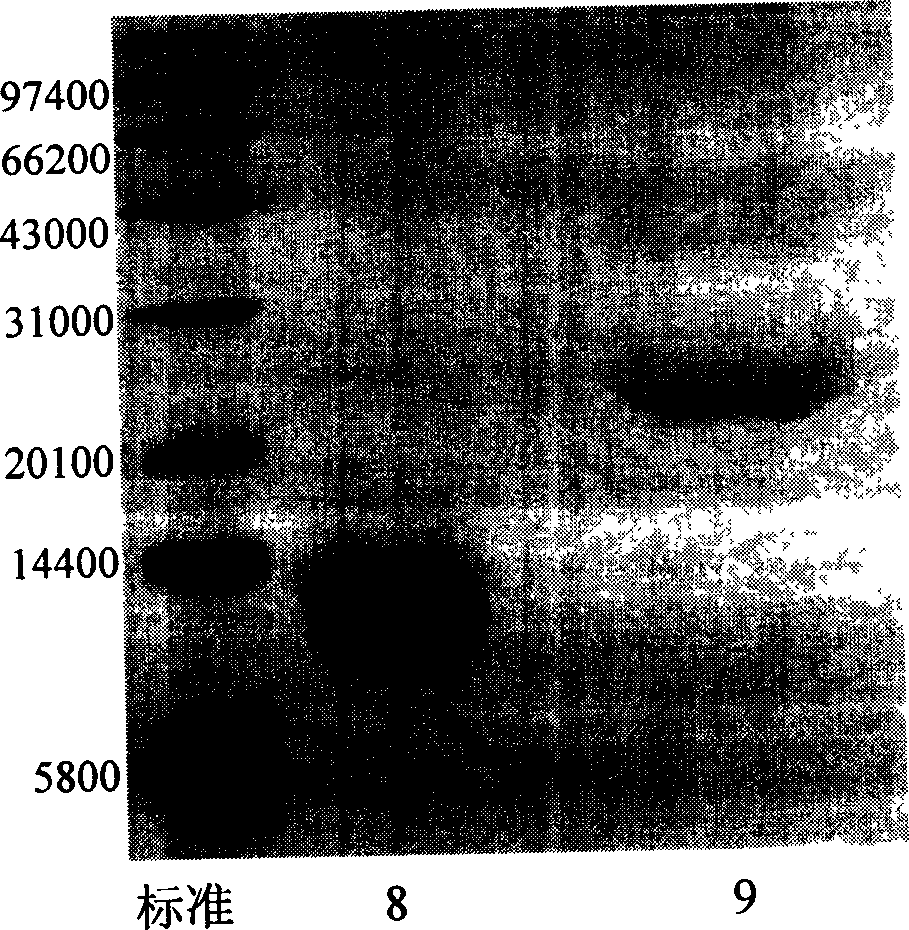
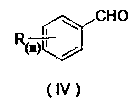
Distyrene compound containing bromothiazole ring as well as synthesis method and application thereof
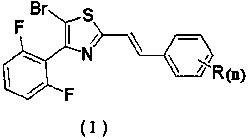
ActiveCN108863977AEasy to makeModerate inhibitory activityBiocideAntimycoticsTriethylphosphiteThiazole
The invention discloses a distyrene compound containing a bromothiazole ring as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. The compound has the following synthesis process that firstly, 2-(brome methyl)-4-(2,6-difluorophenyl) thiazole and triethyl phosphite react in a backflow state; TLC monitoring is performed till reaction completion; concentration is performed to remove excessive triethyl phosphite; solvents DMF, sodium hydroxide and substituted benzaldehyde are added into the obtained concentrated solution; reaction is performed at room temperature; after the reaction is completed, post treatment is performed to obtain a distyrene compound containing a thiazole ring; next, the distyrene compound containing the thiazole ring and N-bromo-succinimide take bromo reaction in acetonitrile solvents at 0 to 100 DEG C; the distyrene compound containing the bromothiazole ring is obtained. By using the technology, a kind of novel (E)-5-brome-4-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-2-substituted styryl thiazole compounds can be obtained through synthesis. The preparation of the compound is simple; certain anticancer and anti-fungus activity is shown.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Fuel additive to control deposit formation
The present disclosure is directed to a fuel composition comprising a deposit-modifying effective amount of a hydrocarbyl-substituted succinimide; a detergent; and a fuel. A method for reducing deposit formation is also disclosed.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Copolymer based on environmental response and preparation method thereof
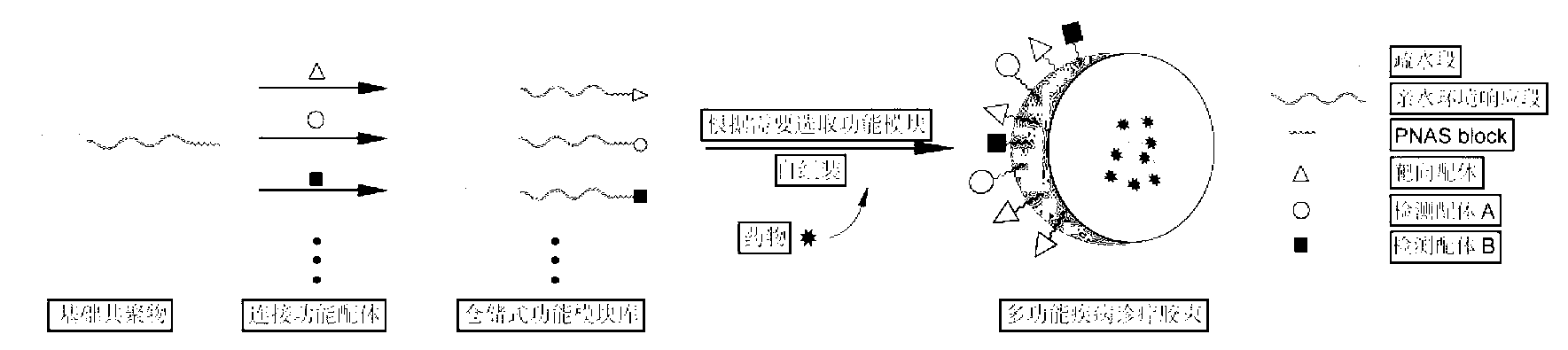
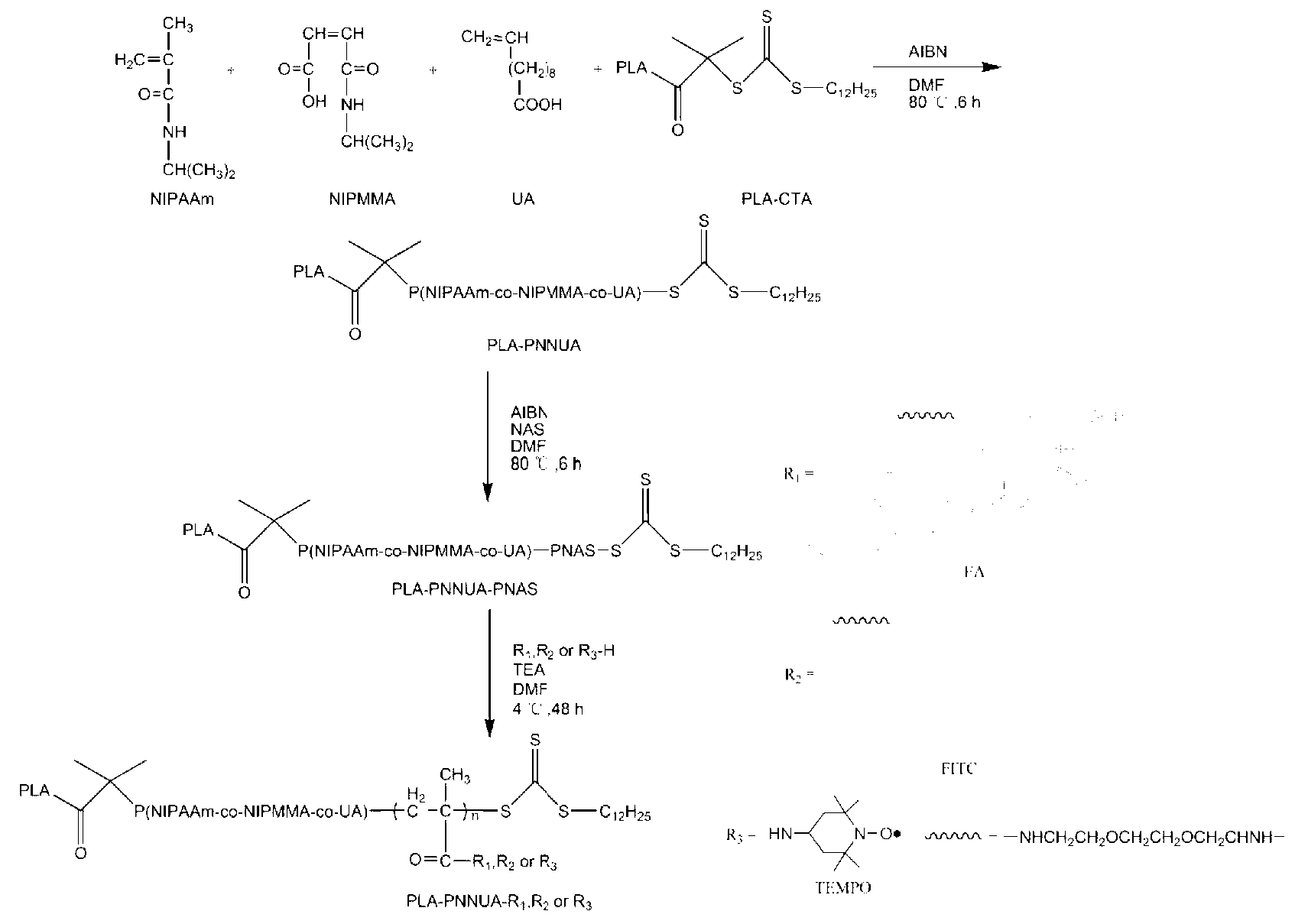
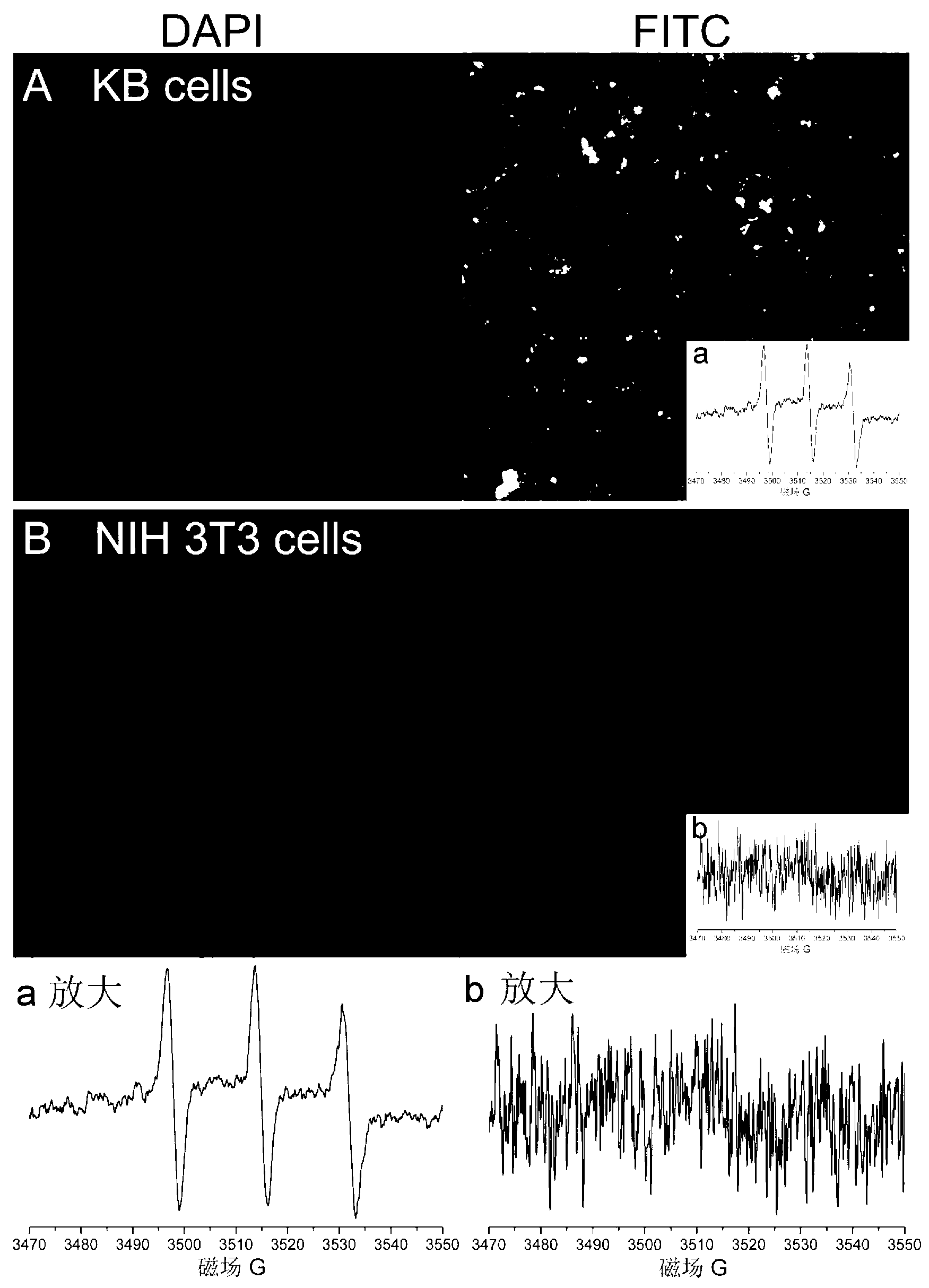
InactiveCN102796235AImprove scalabilityEasy to manufactureOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMonomerSuccinimides
The invention relates to a copolymer based on environmental response and a preparation method thereof, wherein the copolymer has specific three blocks which are sequentially a hydrophobic block, a hydrophilic environmental response block and a ploy-N-methylacryloyl succinimide (PNAS) chain with reactivity. The preparation method of the copolymer comprises the following steps of: connecting the hydrophobic block with a micromolecular chain transfer agent to prepare a macroinitiator; performing primary polymerization on the hydrophilic environmental response block and the macroinitiator; and performing secondary polymerization on an N-methylacryloyl succinimide (NAS) monomer and a product of the first step, so as to obtain the copolymer based on environmental response. The copolymer has the advantages that the copolymer based on environmental response has a controllable structure, and the hydrophobic block, the hydrophilic environmental response block and the PNAS chain are independent from one another; and the copolymer based on environmental response has a clear specific structure, and can fully play the performances of all the chain segments.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Special lubricating oil for mechanical gears
InactiveCN106635323AExtended service lifeImprove adhesionLubricant compositionGlycerolPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a special lubricating oil for mechanical gears. The special lubricating oil for mechanical gears is composed of phosphite, talcum powder, phosphoric acid, sorbitol, p-hydroxy benzyl aldehyde, methyl citrate, monomethyl citrate, tetrahydropalmatine, mesembryanthemoidigenic acid, isodehydrocostus lactone, lupeol palmitate, oleanonic acid, naphthenic oil, butter, tetrahydroxyethyl ammonium swelling oily agent, aluminum disulfide, aromatic hydrocarbon, paraffin base, succimide succinate, boron nitride, fish gallbladder, fatty soap, glycerol, polyalkenyl succinimide, graphite, amino monothioester and molybdenum dialkyldithiocarbamate. Compared with the prior art, the special lubricating oil for mechanical gears can lower the loss of engine oil, increases the environment-friendly effect of the original special engine oil, enhances the adhesion of lubricating oil, increases the lubricating effect of the engine oil, and lowers the friction, so that the mechanical gears can well operate, thereby enhancing the service life of the machine. Thus, the special lubricating oil for mechanical gears has popularization and application value.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Biocompatible in situ hydrogel
ActiveCN105209075APharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsQuinonePolymer modified
The present invention provides compositions, and related kits and methods, for formation of hydrogels. The compositions comprise one or more chemically crosslinkable agents dissolved in an aqueous solution to form a precursor solution. The chemically crosslinkable agents useful in the present invention are selected from polymers modified with a molecule selected from acrylate, maleimide, vinylsulfone, N-hydroxy succinimide, aldehyde, ketone, carbodiimide, carbonate, iodoacetyl, mercaptonicotinamide, quinone, thiol, amine, and combinations thereof. The precursor solution is characterized as being in an aqueous form at a non-physiologic physical-chemical condition and undergoing gelation when in contact with another fluid or body at a physiologic physical-chemical condition.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Kit for detecting interleukin-6 and method for detecting interleukin-6 for non-diagnostic purpose
ActiveCN103941021AIncrease coating surface areaIncreased sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological material analysisInterleukin 6White blood cell
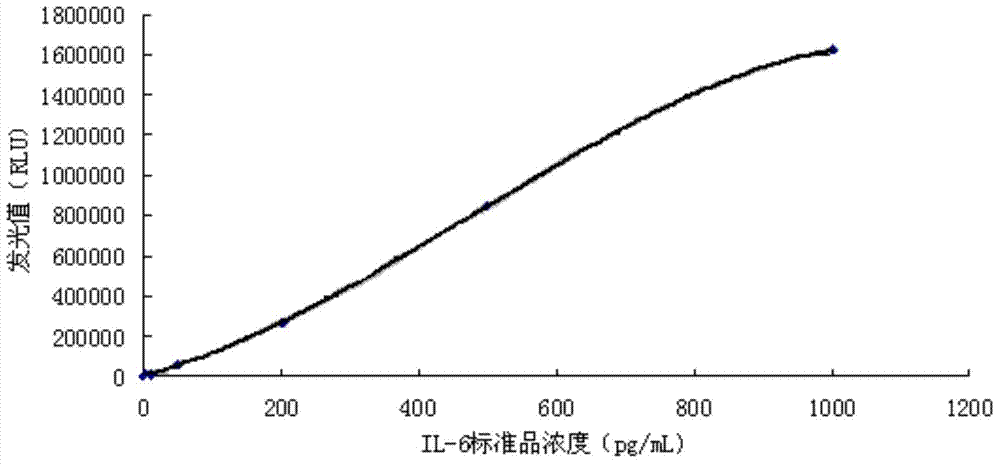
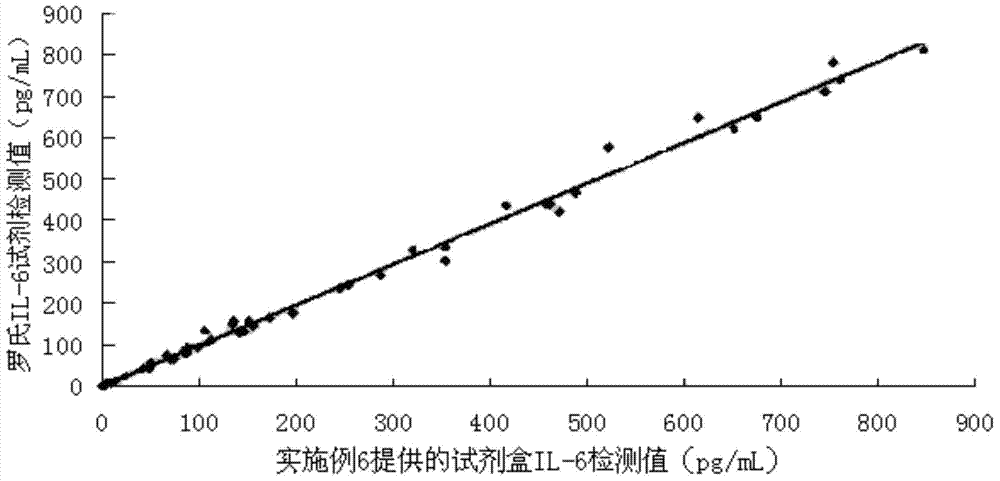
The invention relates to the field of immunoassay and in particular relates to a kit for detecting interleukin-6 and a method for detecting interleukin-6 for non-diagnostic purpose. The kit comprises a biotinylation antibody, an enzyme-labeled antibody, a chemiluminescence substrate and avidin conjugated superparamagnetic particles, wherein the biotinylation antibody is a product of conjugating biotin N-hydroxy succinimide and an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody A; the enzyme-labeled antibody is a product of conjugating an enzyme and an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody B. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, high specificity, short detection time and simple detection process and can be conveniently used for full-automatic detection instruments.
Owner:SHENZHEN GOLDSITE DIAGNOSTICS
Hydrophobic nanoparticle compositions for crude oil collection
InactiveUS10131556B1Achieve recyclabilityHigh mechanical strengthMaterial nanotechnologyFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSilica nanoparticlesHydrophobic silica
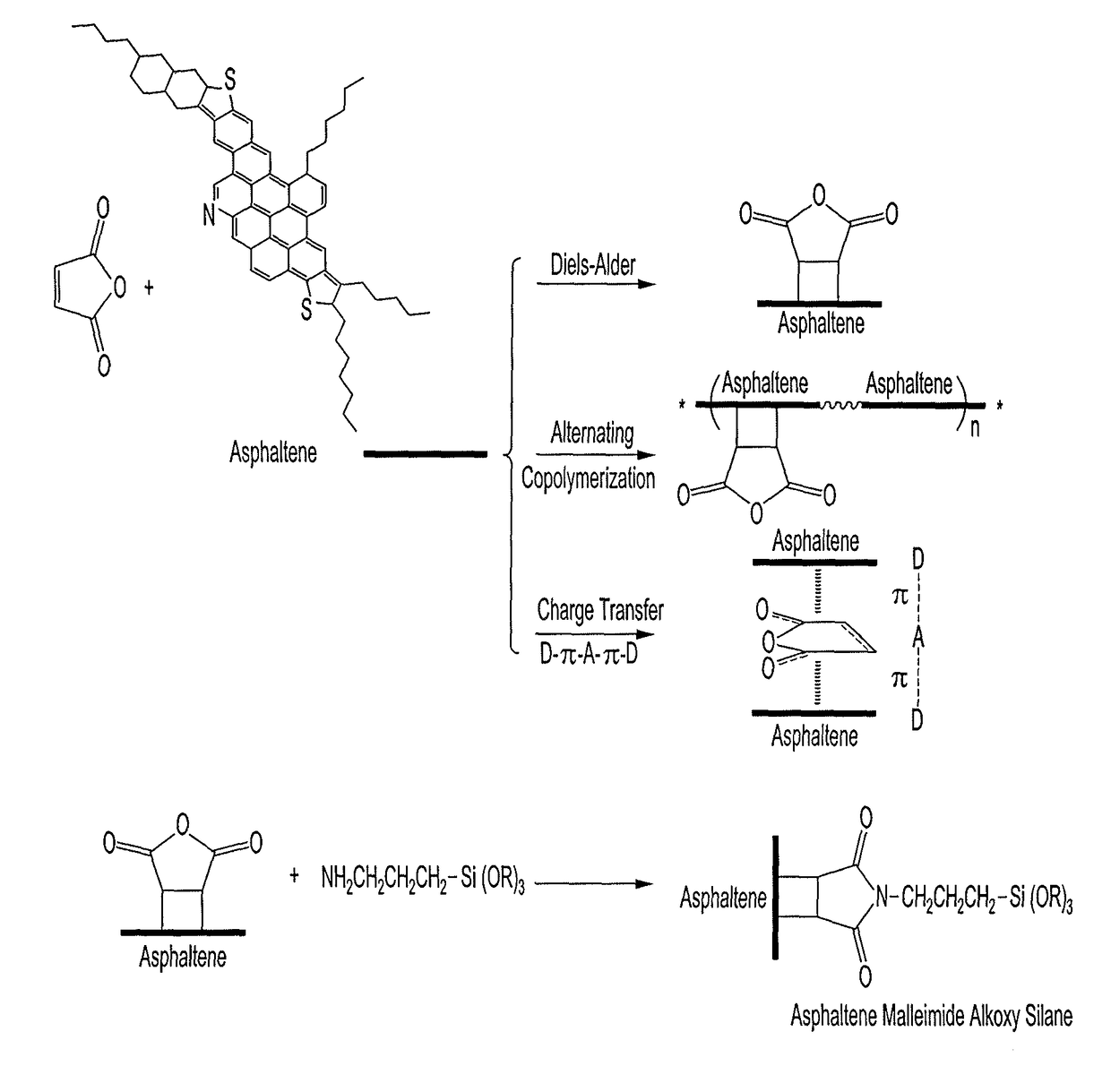
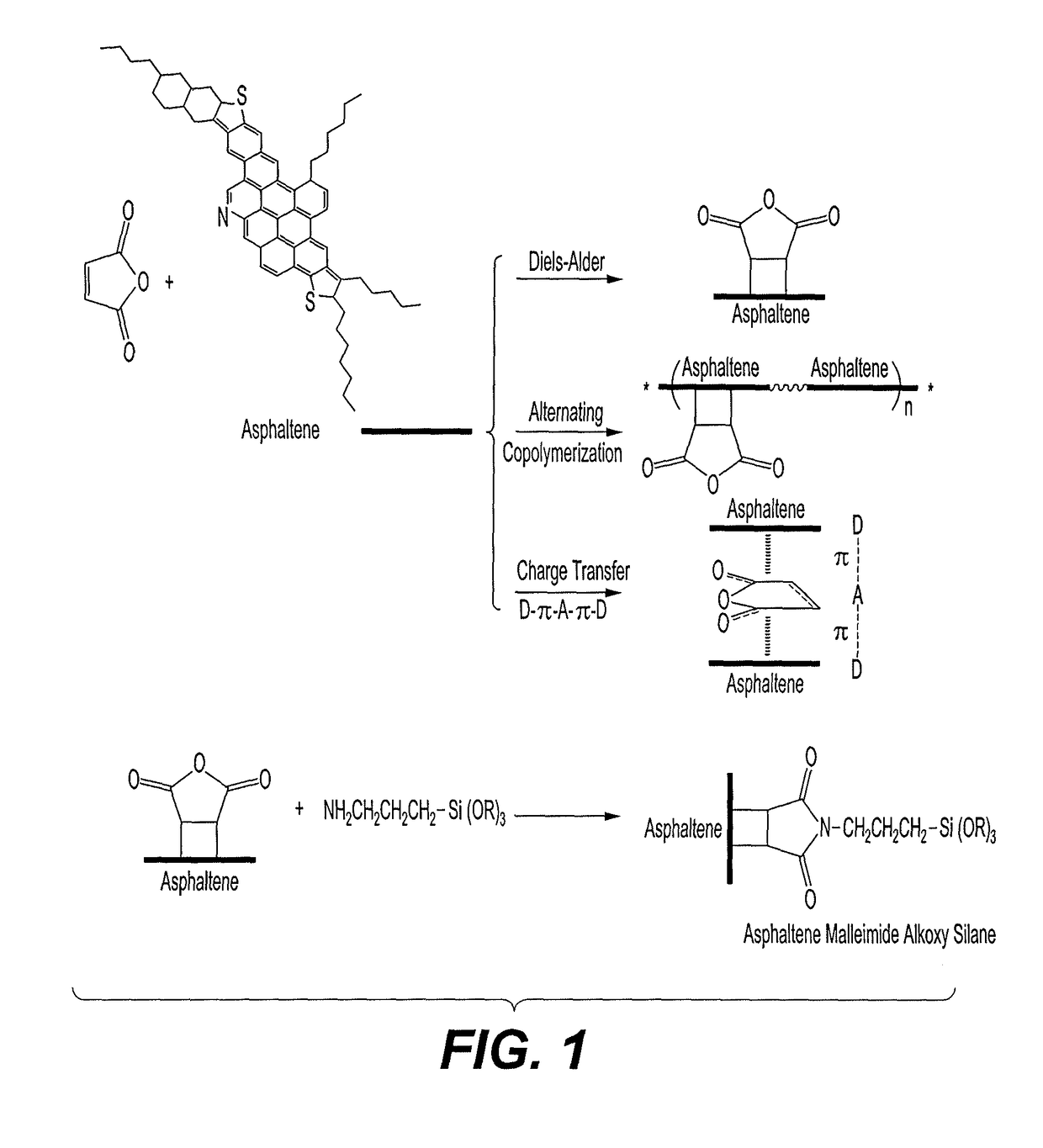
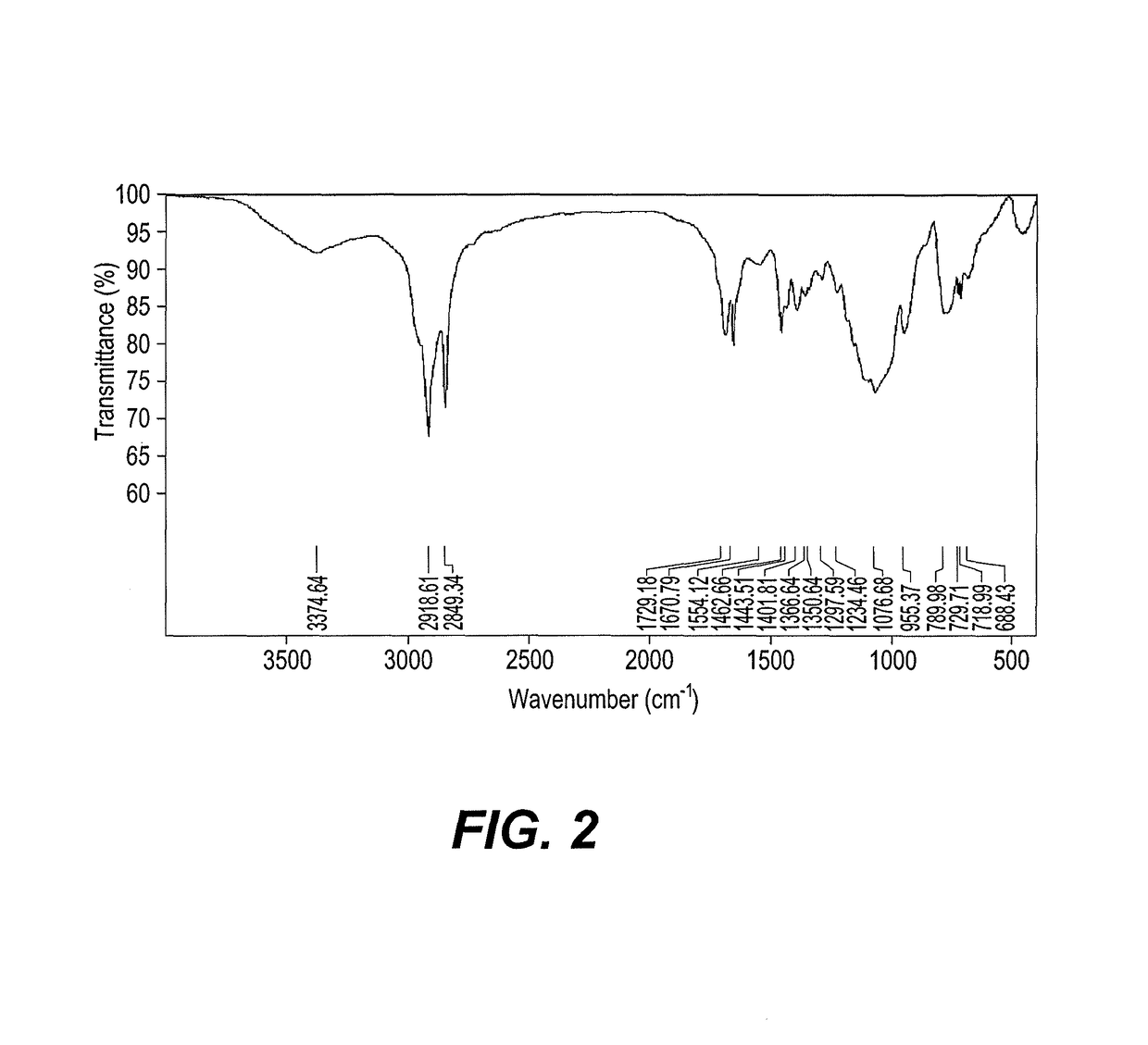
Hydrophobic nanoparticle compositions include silica nanoparticles capped with asphaltene succinimide alkoxy silane (ASAS). The nanoparticles can have a particle size ranging from about 20 nm to about 10000 μm. The nanoparticle compositions can be used as a coating for raw sand to provide a super-hydrophobic sand. The nanoparticle compositions can be used as a coating for a polyurethane (PU) sponge to provide a super-hydrophobic sponge. The super-hydrophobic sand and / or super-hydrophobic sponge can be used to collect crude oil deposited in aquatic environments as a result of petroleum crude oil spills.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Microalbuminuria detection kit and preparation thereof
The invention provides a microalbuminuria (mAlb) detection kit, which is based on a latex enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay method, is a liquid double reagent, namely reagent R1 and reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 is a reactant and the reagent R2 is a solution containing albumin immuno latex particles, and the detection kit is characterized by crosslinking by applying a chemical process, and covalently crosslinking a goat anti-human albumin antibody (also called goat anti-human mAlb antibody) with carboxylated polystyrene latex through water-soluble carbodiimide (EDC) and H-hydroxy succinimide (NHS), so as to form an mAlb antibody latex reagent. The reagent has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity and simple preparation, and is worthy of further promotion.
Owner:王贤俊
Lubricating oil composition
ActiveCN101522873AImprove anti-friction performanceImprove oxidation stabilityAdditivesBase-materialsInternal combustion engineFatty acid
The present invention provides a lubricating oil composition comprising a base oil for a lubricating oil, (A) a fatty acid partial ester compound, 0.5 to 1.5 % by mass of (B) (b1) an aliphatic amine compound and / or (b2) an acid amide compound, 0.01 to 0.1 % by mass of (C) a specific benzotriazole derivative and a specific amount of (D) a specific succinimide compound. It is a lubricating oil composition of an environmental regulation compliant type which is used for internal combustion engines such as gasoline engines, diesel engines, engines using dimethyl ether for fuel, gas engines and thelike, which does not contain Mo base friction reducing agents and is reduced in ash, phosphorus and sulfur and in which a friction reducing effect, an oxidation stability and a corrosion inhibiting effect are enhanced.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com