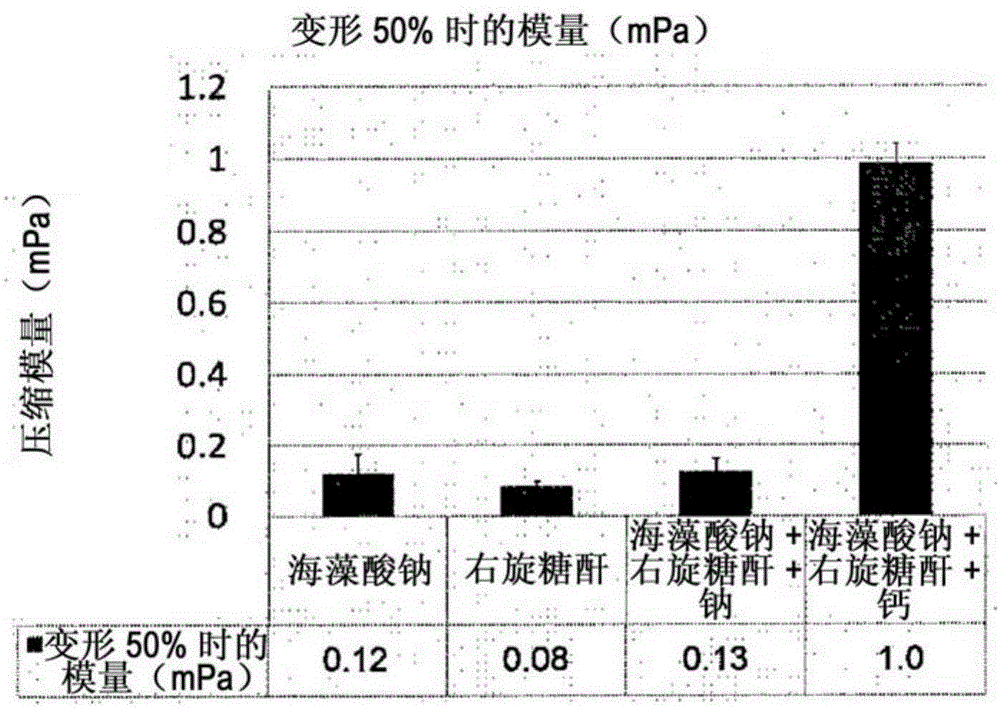
Biocompatible in situ hydrogel
一种水凝胶、生理性的技术,应用在生物相容性原位水凝胶领域,能够解决医疗费用增加、操作困难、风险高等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0115] Example 1: Chemical condensation of polymers containing multiple vinylsulfones and polymers containing multiple nucleophiles gelation trigger
[0116] Vinylsulfonated dextran (dex-VS) with a molecular weight (MW) of 70 kDa and a degree of modification (DM) of 8% (dex-VS) and sulfylated dextran with a MW of 70 kDa and a DM of 8% (dex-SH) were dissolved at a concentration of 25% in water or saline. The pH of the water or saline in this area (Hong Kong) is about 5.3 to 5.5. The polymer solution was mixed and loaded into a syringe. A 30-gauge needle was attached to the syringe, and the solution was injected into PBS. A gel formed shortly after the polymer solution was exposed to PBS.
example 2
[0117] Example 2: Chemical condensation of polymers containing multiple vinylsulfones and polymers containing multiple nucleophiles gelation trigger
[0118] dex-VS with MW of 70 kDa and DM of 8% and dex-SH with MW of 70 kDa and DM of 8% were dissolved in water or saline at a concentration of 25%. The pH of the water or saline in this area (Hong Kong) is about 5.3 to 5.5. The polymer solution was mixed and loaded into a syringe. A 30-gauge needle was attached to the syringe, and the solution was injected into 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB). Hydrogels formed shortly after the polymer solution came into contact with PB.
[0119] In another example, HA-VS with a MW of 29 kDa and a DM of 20% was dissolved in a pH 7 buffer at a concentration of 10% w / v, and HA-VS with a MW of 29 kDa, 20% DM of HA-SH was dissolved in a pH 7.8 buffer. The two polymers were cooled on ice and mixed on ice. The solution was injected into PBS at 37°C. A gel formed shortly after the solution came i...
example 3
[0120] Example 3: Chemical condensation of polymers containing multiple vinylsulfones and polymers containing multiple nucleophiles gelation trigger
[0121] dex-VS with MW of 70 kDa and DM of 8% and dex-SH with MW of 70 kDa and DM of 8% were dissolved in water or saline at a concentration of 25%. The pH of the water or saline in this area (Hong Kong) is about 5.3 to 5.5. The polymer solution was mixed and loaded into a syringe. A 30-gauge needle was attached to the syringe, and the solution was injected into rabbit blood. A gel formed shortly after the polymer solution came into contact with blood.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com