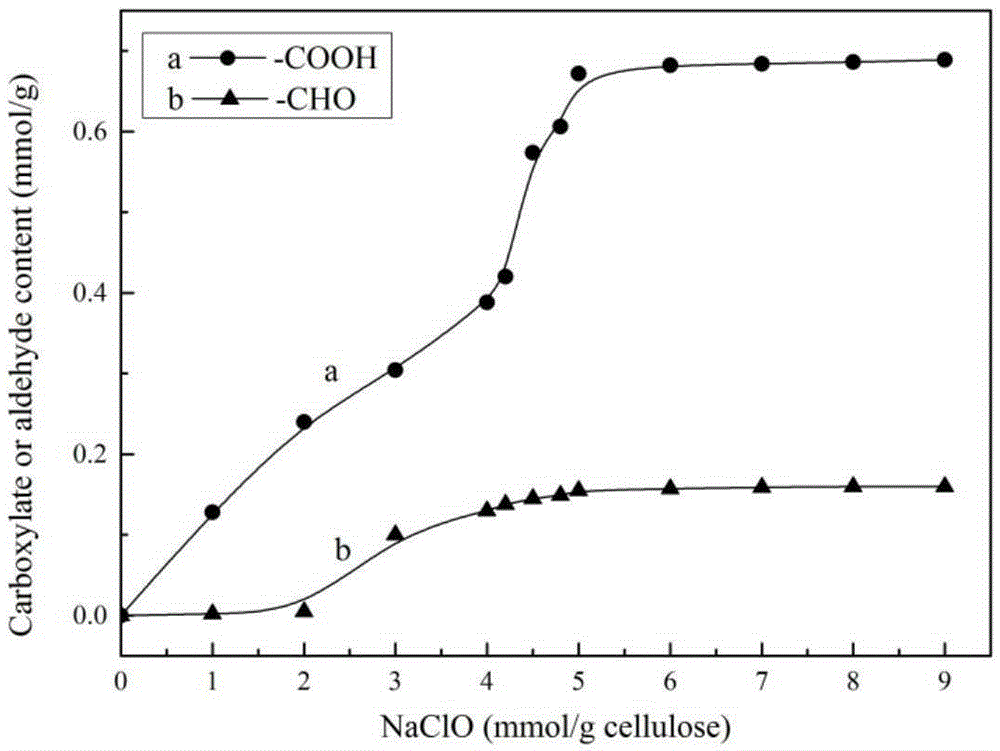
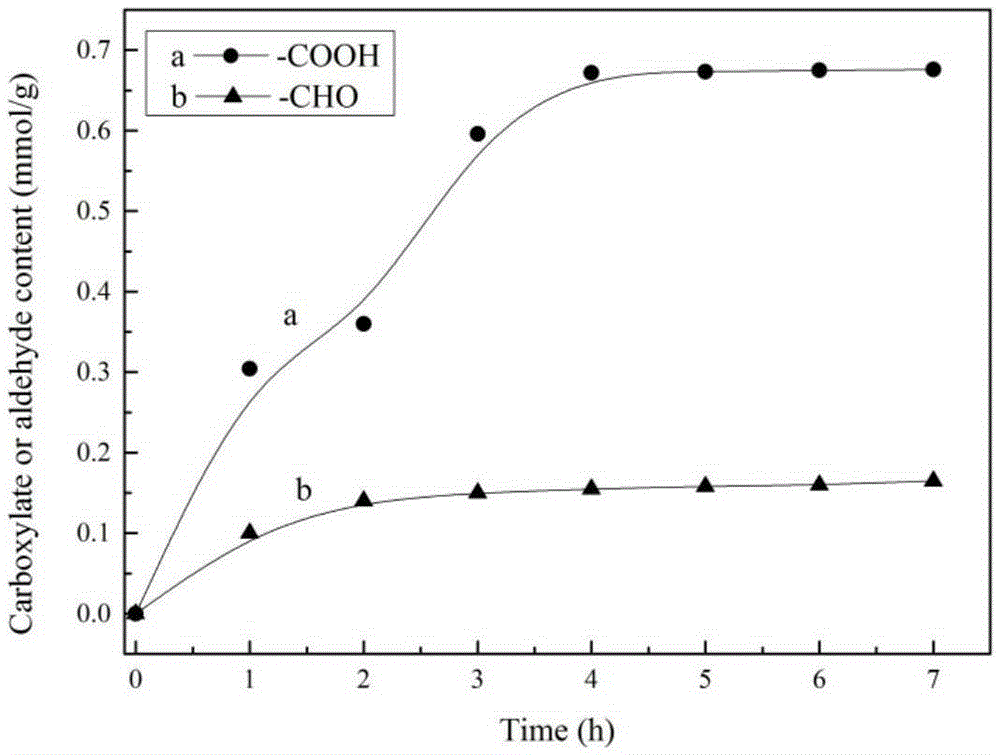
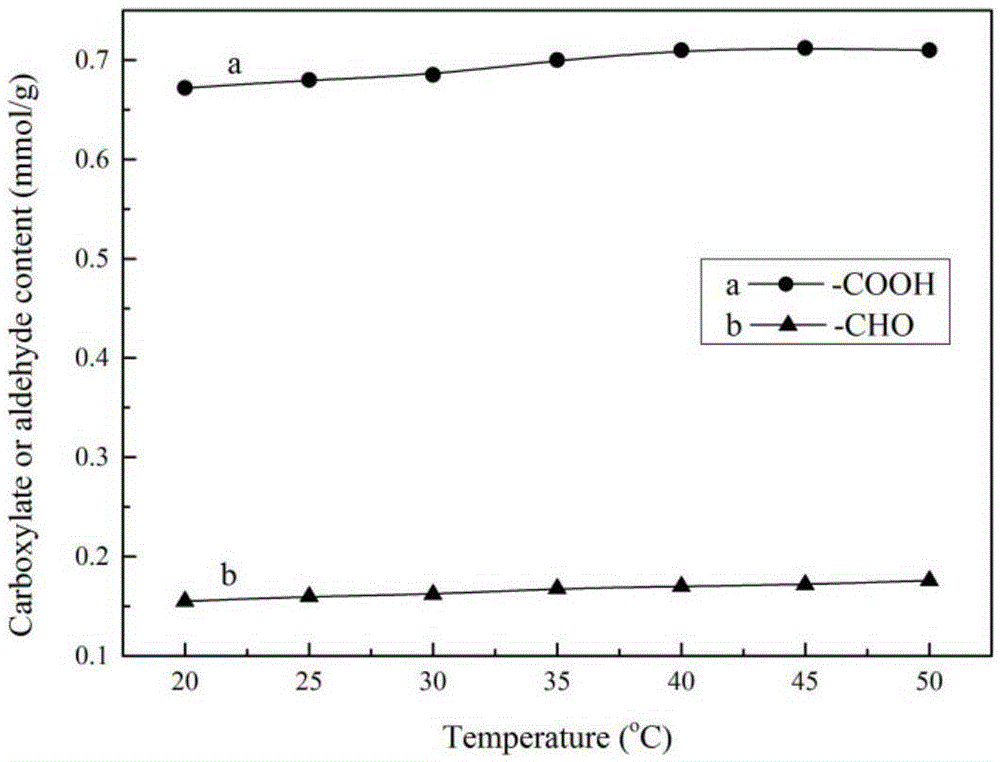
Macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, gelatin film thereof and preparation method
A macromolecular cross-linking agent, oxidized cellulose technology, used in climate change adaptation, sustainable manufacturing/processing, flexible coverings, etc., can solve the problems of low transparency and low light transmittance of gelatin films, and achieve mechanical properties. Good, improved hydrophobicity, and the effect of maintaining light blocking properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] A kind of synthetic method of novel macromolecular cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose:
[0066] (1) Preparation of oxidized cellulose (TOMCC) and determination of carboxyl aldehyde content:
[0067] Weigh microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy free radical (TEMPO) and NaBr of corresponding quality by mass ratio 400:1:10 in water (80ml / gMCC), During the stirring process, add 5 mmol / g MCC NaClO solution (5% available chlorine) drop by drop, adjust the pH to 10.5, stir magnetically in a water bath at 20°C for 4 hours, centrifuge to collect the precipitate after the reaction, wash with water three times, wash with ethanol once, and vacuum dry at 40°C , to obtain white powdery solid oxidized cellulose TOMCC. 10% (w / v) suspension of TOMCC in water and 0.9g / gTOMCC in NaClO 2 Mixed for secondary oxidation of TOMCC, 5MCH 3 Adjust the pH to 4.2 with COOH, and oxidize for 48 hours. After the oxidation, the precipitate was collected by c...
Embodiment 2
[0114] (1) Preparation of oxidized cellulose (TOMCC) and determination of carboxyl aldehyde content:
[0115] Weigh microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy free radical (TEMPO) and NaBr of corresponding quality by mass ratio 400:0.7:8 in water (80ml / gMCC), Add 5 mmol / g MCC NaClO solution (5% available chlorine) drop by drop during stirring, adjust the pH to 10, stir magnetically in a water bath at 20°C for 2 hours, centrifuge to collect the precipitate after the reaction, wash with water three times, wash with ethanol once, and dry in vacuum at 40°C , to obtain white powdery solid oxidized cellulose TOMCC. 10% (w / v) suspension of TOMCC in water and 0.8g / gTOMCC in NaClO 2 Mixed for secondary oxidation of TOMCC, 5MCH 3 Adjust the pH to 4.5 with COOH, and oxidize for 40 hours. After the oxidation, the precipitate was collected by centrifugation, washed three times with water and once with ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 40°C to obtain secondary oxidi...
Embodiment 3
[0125] (1) Preparation of oxidized cellulose (TOMCC) and determination of carboxyl aldehyde content:
[0126] Take microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy free radical (TEMPO) and NaBr of corresponding quality by mass ratio 350:1:9 in water (80ml / gMCC), Add 2 mmol / g MCC NaClO solution (available chlorine 5%) drop by drop during the stirring process, adjust the pH to 11, stir magnetically in a water bath at 20°C for 4 hours, centrifuge to collect the precipitate after the reaction, wash with water three times, wash with ethanol once, and vacuum dry at 40°C , to obtain white powdery solid oxidized cellulose TOMCC. 10% (w / v) suspension of TOMCC in water and 0.9g / gTOMCC in NaClO 2 Mixed for secondary oxidation of TOMCC, 5MCH 3 Adjust the pH to 5 with COOH, and oxidize for 48 hours. After the oxidation, the precipitate was collected by centrifugation, washed three times with water and once with ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 40°C to obtain secondary o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com