Patents
Literature
581 results about "N-Hydroxysuccinimide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
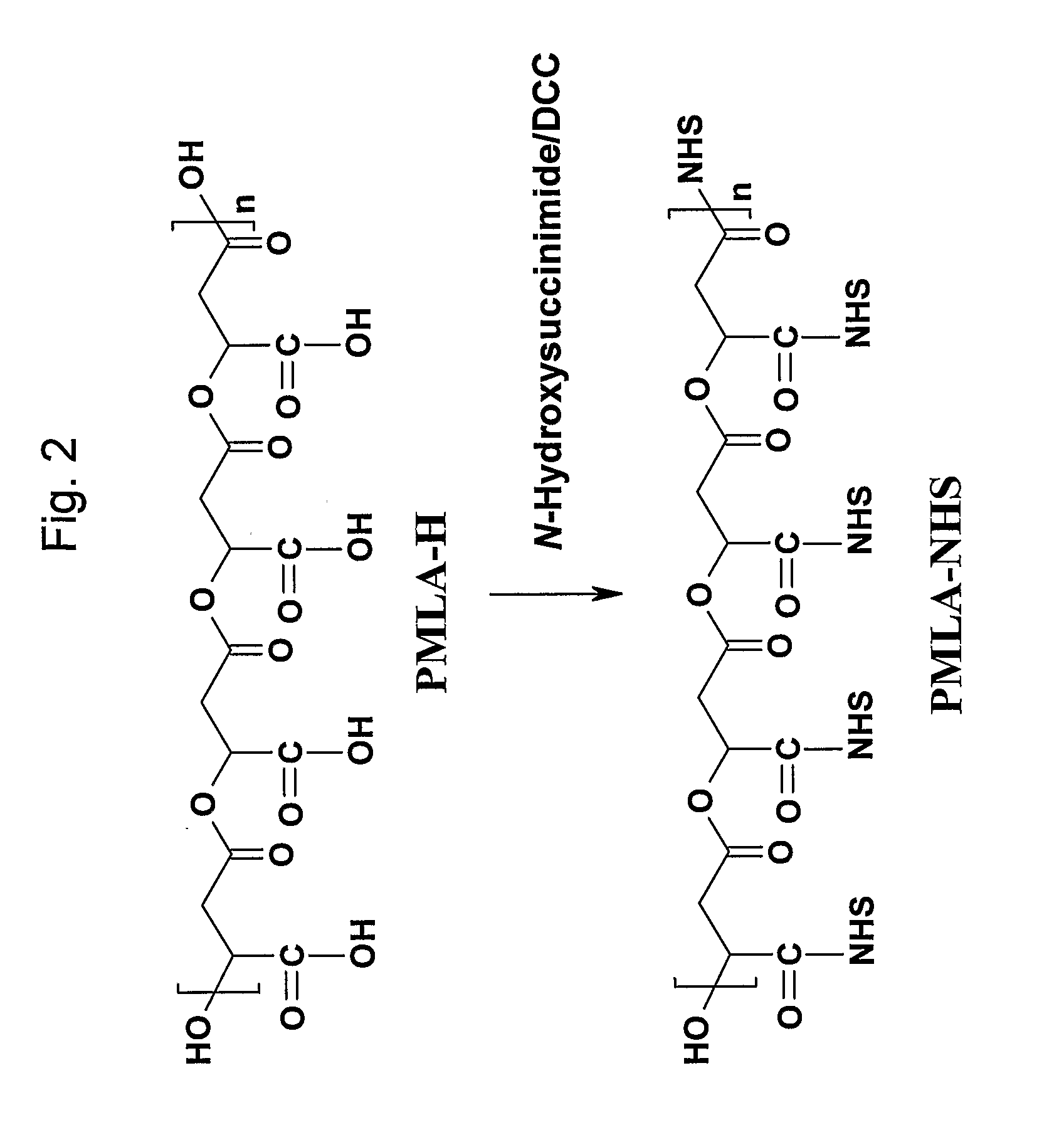
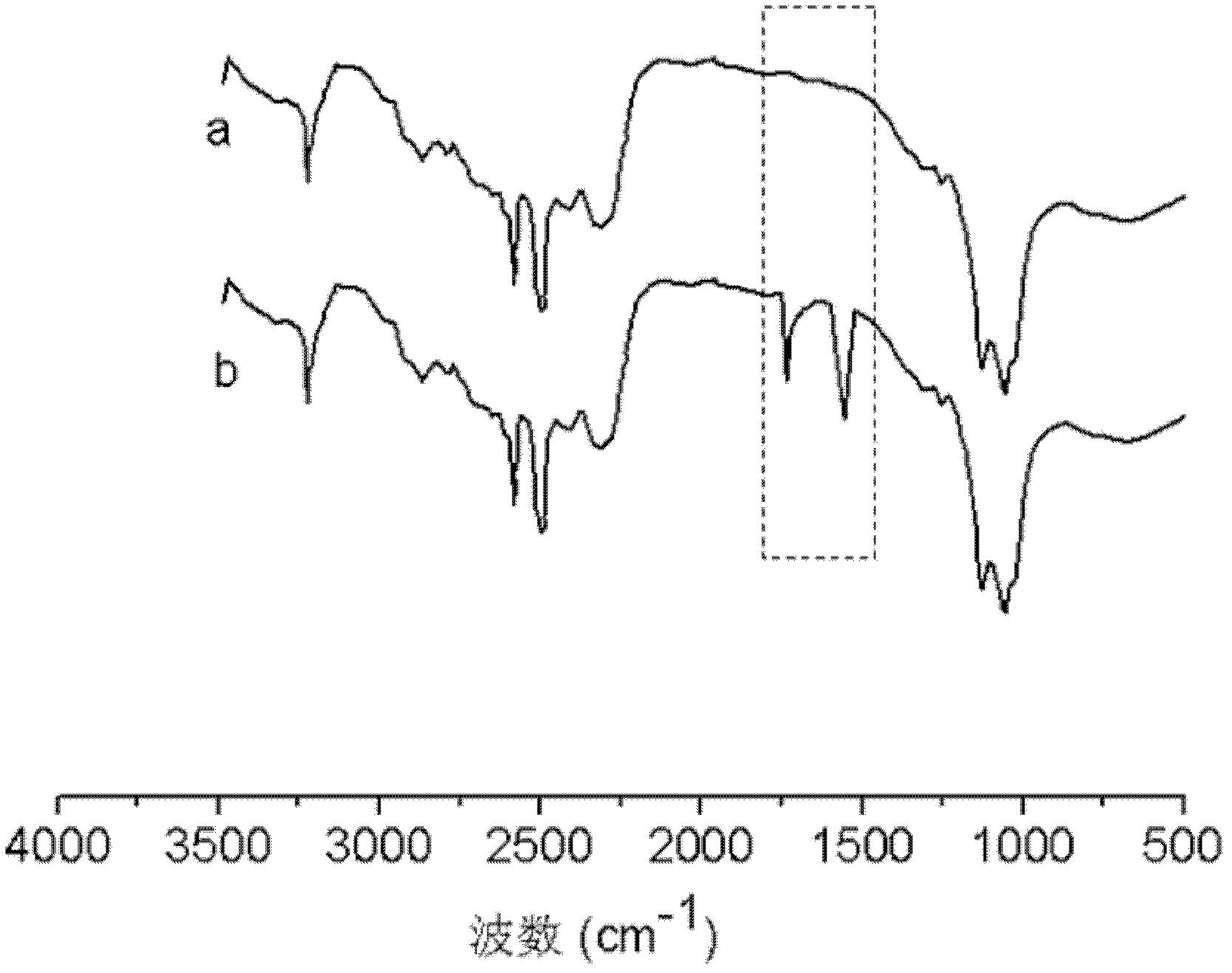
N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) is an organic compound with the formula (CH₂CO)₂NOH. It is a white solid that is used as a reagent for preparing active esters in peptide synthesis.
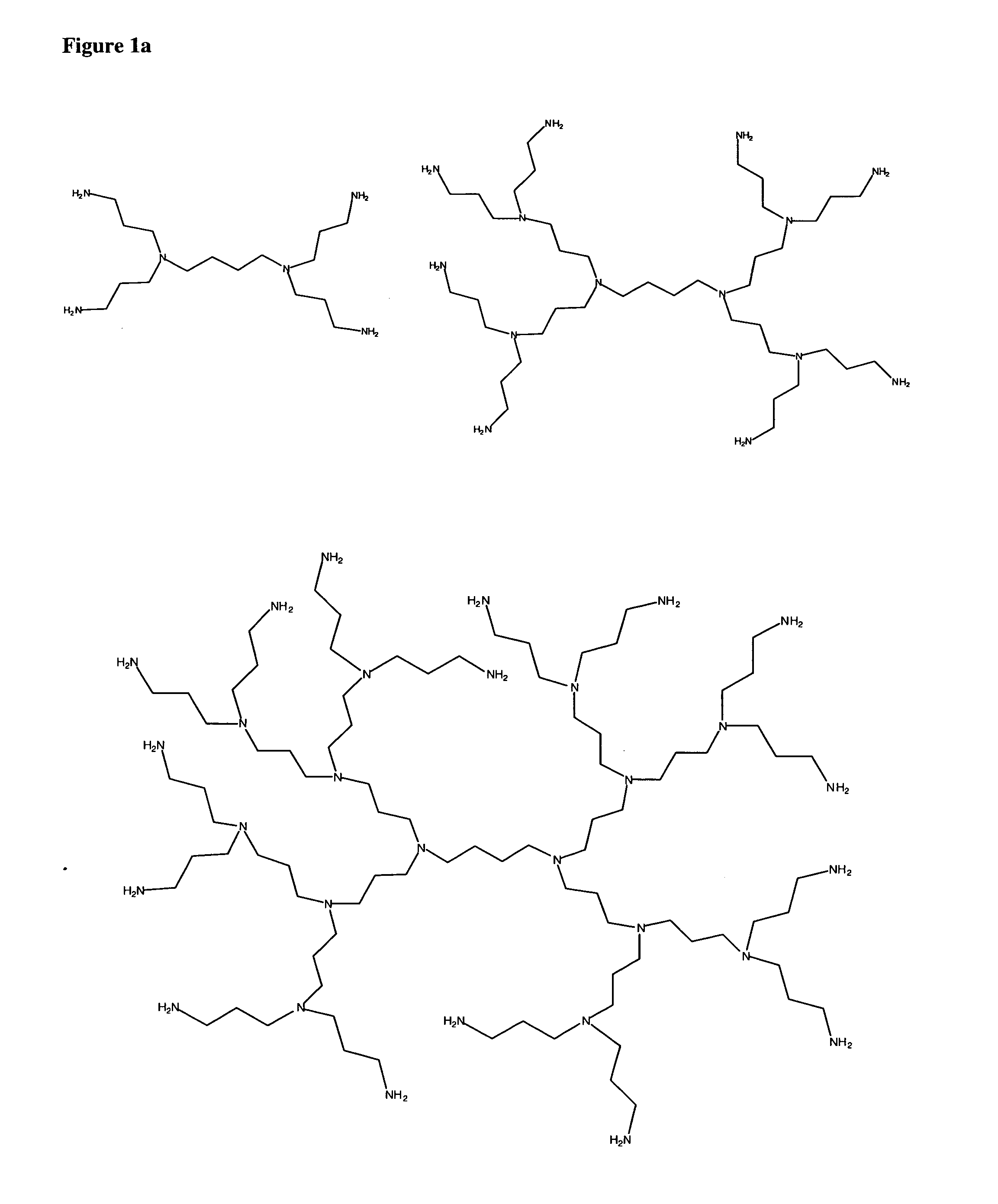
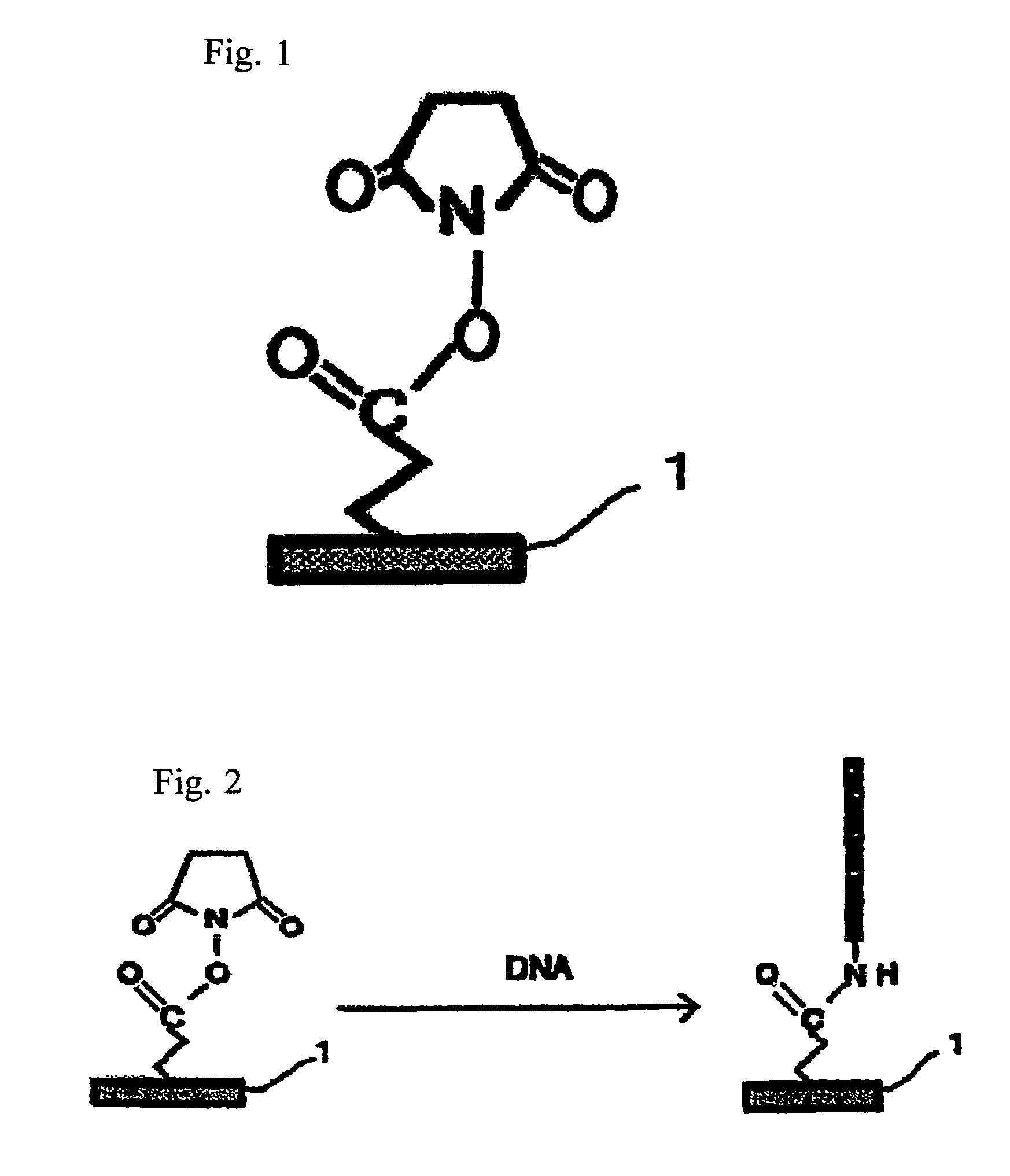
Crosslinked gels comprising polyalkyleneimines, and their uses as medical devices
ActiveUS20070196454A1Promote cell growthSoft tissue growthIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSurgical adhesivesCross-linkCysteine thiolate
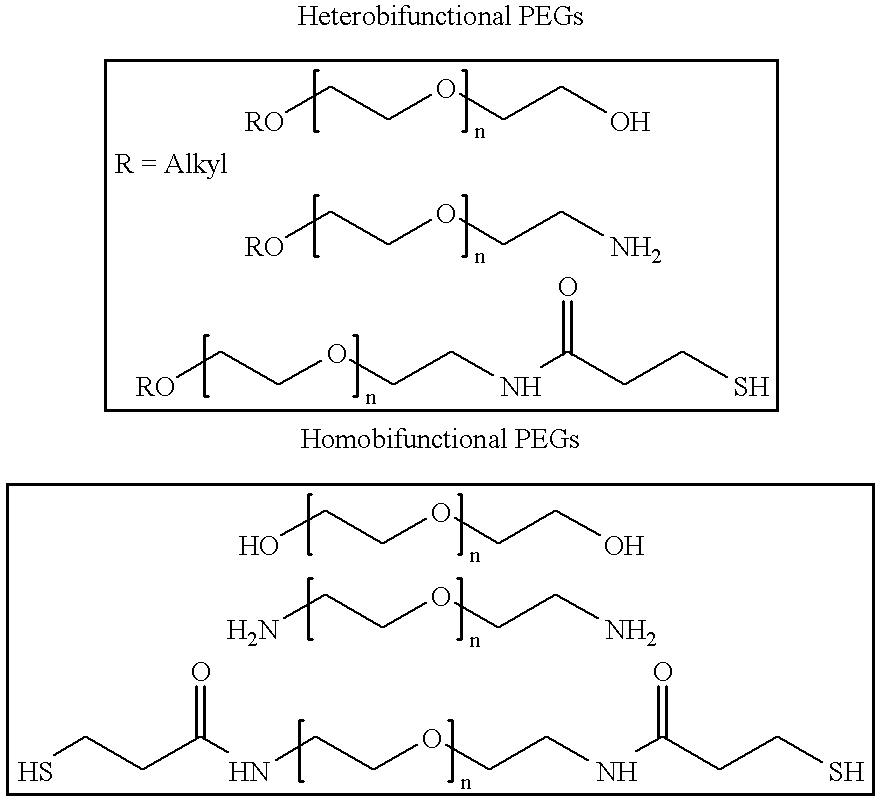
One aspect of the present invention generally relates to methods of sealing a wound or tissue plane or filling a void splace. In a preferred embodiment, the wound is an ophthalmic, pleural or dural wound. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane comprises a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Treatment of the polyethyleneimine with a cross-linking reagent causes the polyethyleneimine polymers to polymerize forming a seal. In certain instances, the cross-linking reagent is a polyethylene glycol having reactive terminal groups. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are isocyanates. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine has a lysine, cysteine, isocysteine or other nucleophilic group attached to the periphery of the polymer. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine is mixed with a second polymer, such as a polyethylene glycol containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing electrophilic groups with a cross-linking reagent containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the electrophilic groups on the polyalkyleneamine are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing photopolymerizable groups with ultraviolet or visibile light. Compositions used to seal the wound which contain PEI or a derivative of PEI are found to adhere tightly to the tissue. Other aspects of the present invention relate to methods of filling a void of a patient or adhering tissue. In certain instances, the methods use a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a polymeric composition formed by exposing a polyalkyleneamine to an activated polyalkylene glycol. In certain instances, the composition is attached to mammalian tissue.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
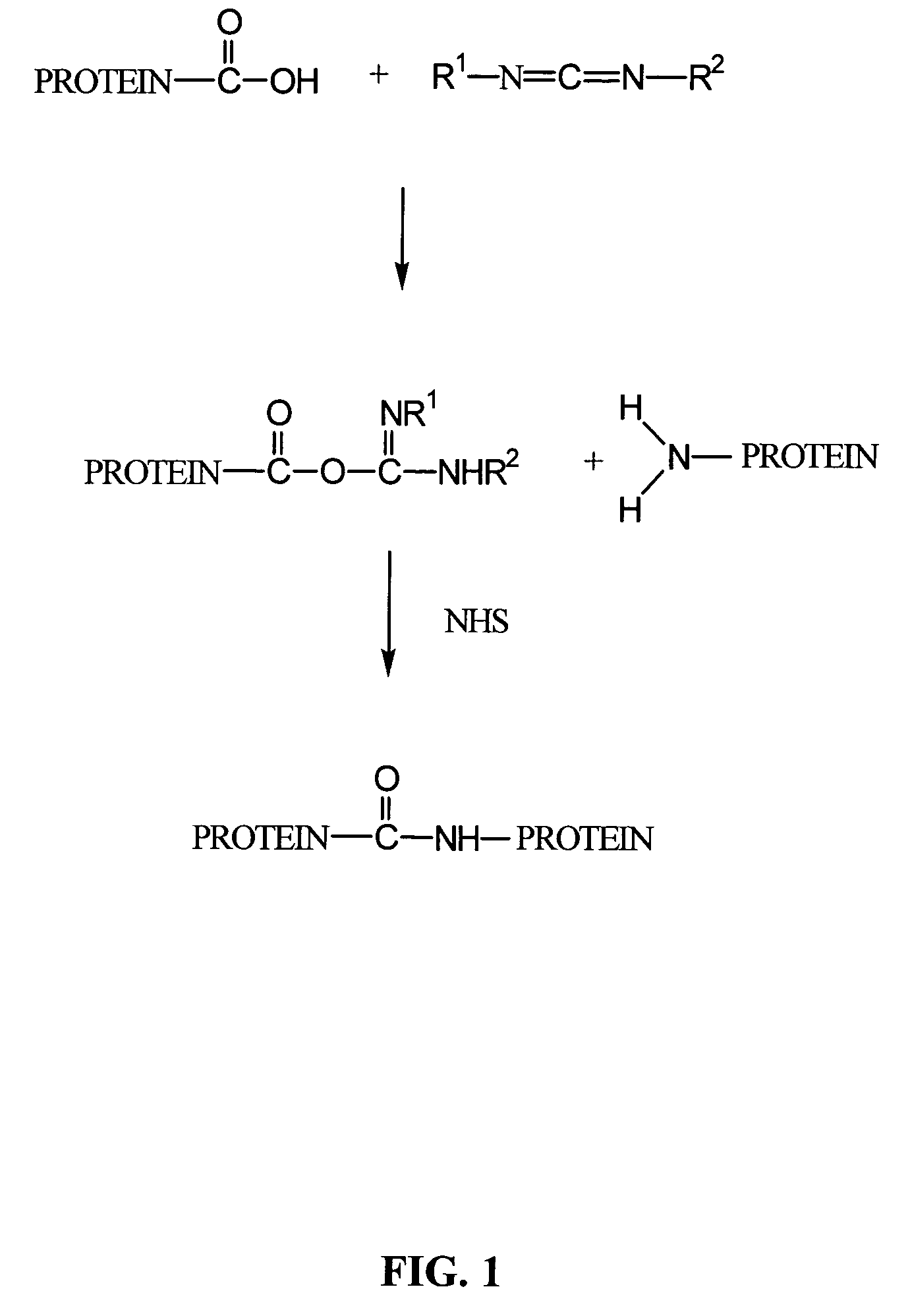
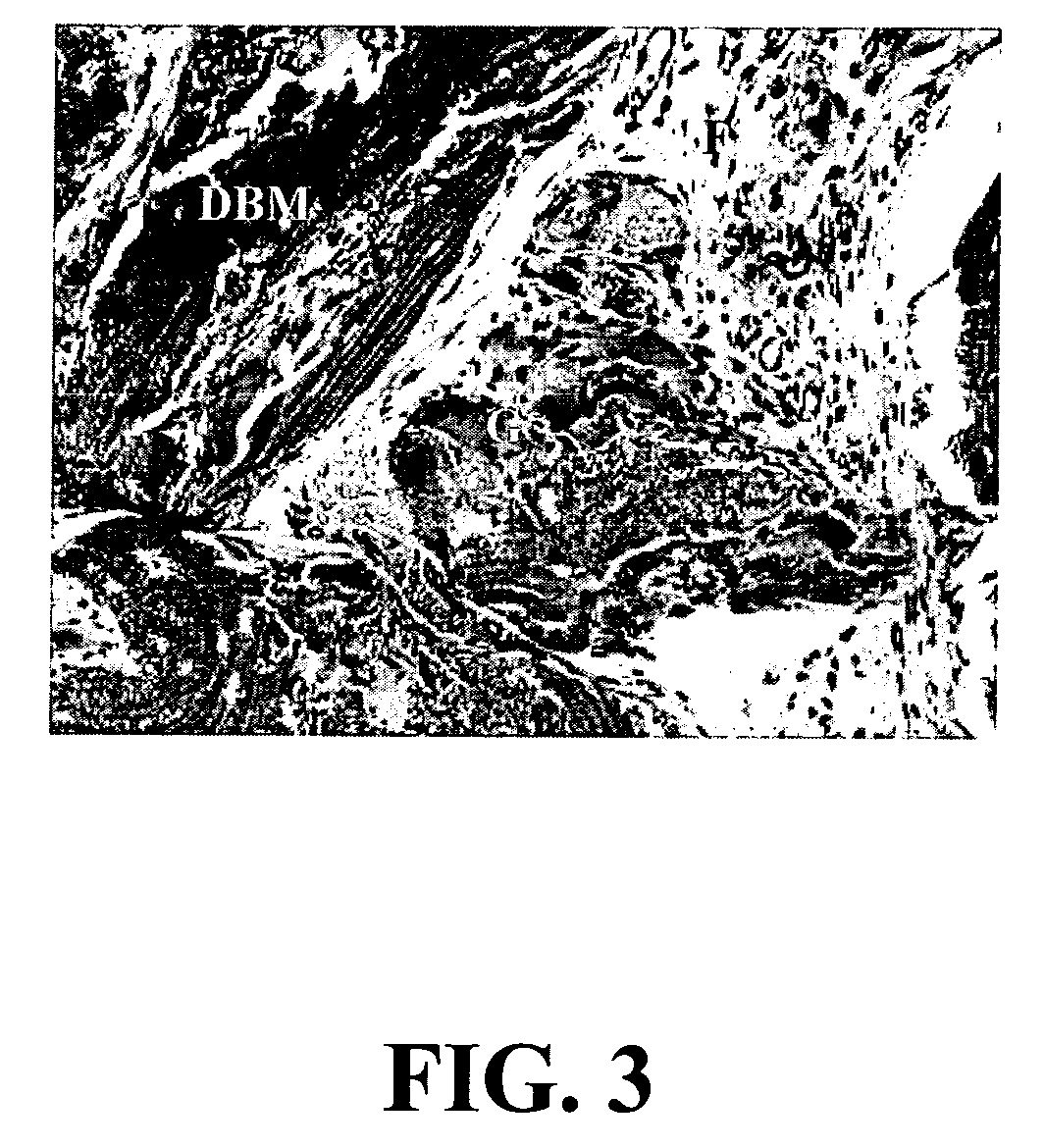
Crosslinked compositions comprising collagen and demineralized bone matrix, methods of making and methods of use
A composition comprising a collagen protein and demineralized bone matrix is described wherein the composition is chemically cross-linked with a carbodiimide such as N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC). The crosslinking reaction can be conducted in the presence of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). The collagen can be in a porous matrix or scaffolding. The DBM can be in the form of particles dispersed in the collagen. A method of making the composition is also described wherein a collagen slurry is cast into the desired shape, freeze dried to form a porous scaffolding and infitrated with a solution comprising the cross-linking agent. The composition can be used as an implant for tissue (e.g., soft tissue or bone) engineering.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Antineoplastic conjugates of transferrin, albumin and polyethylene glycol
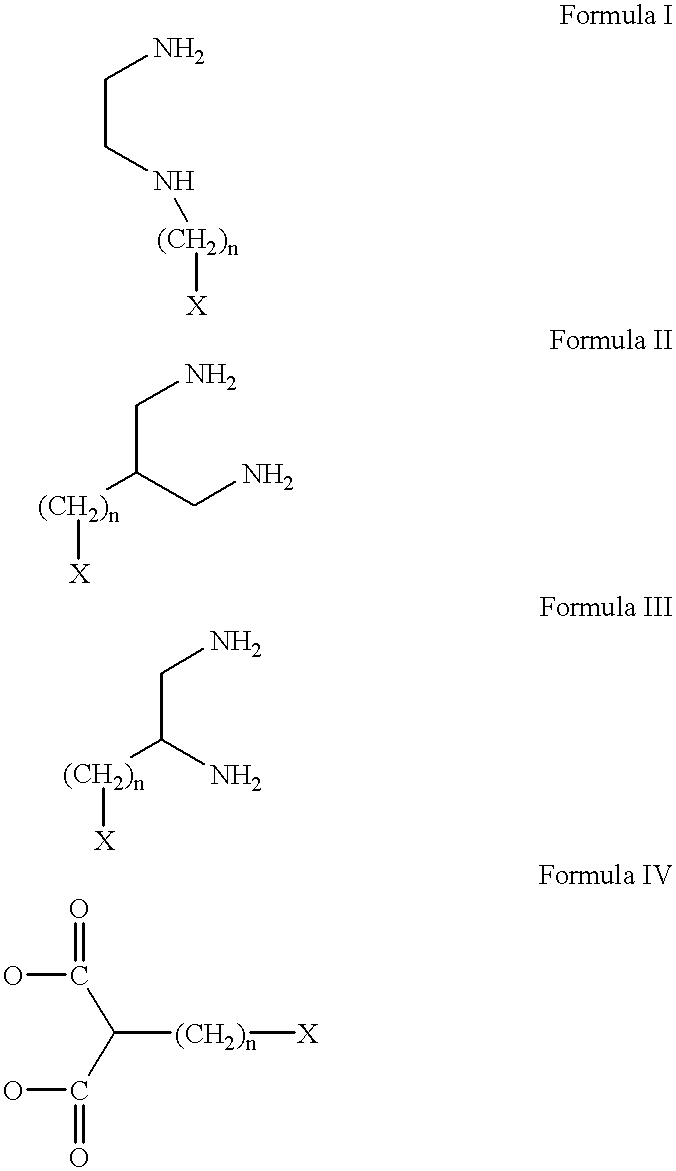
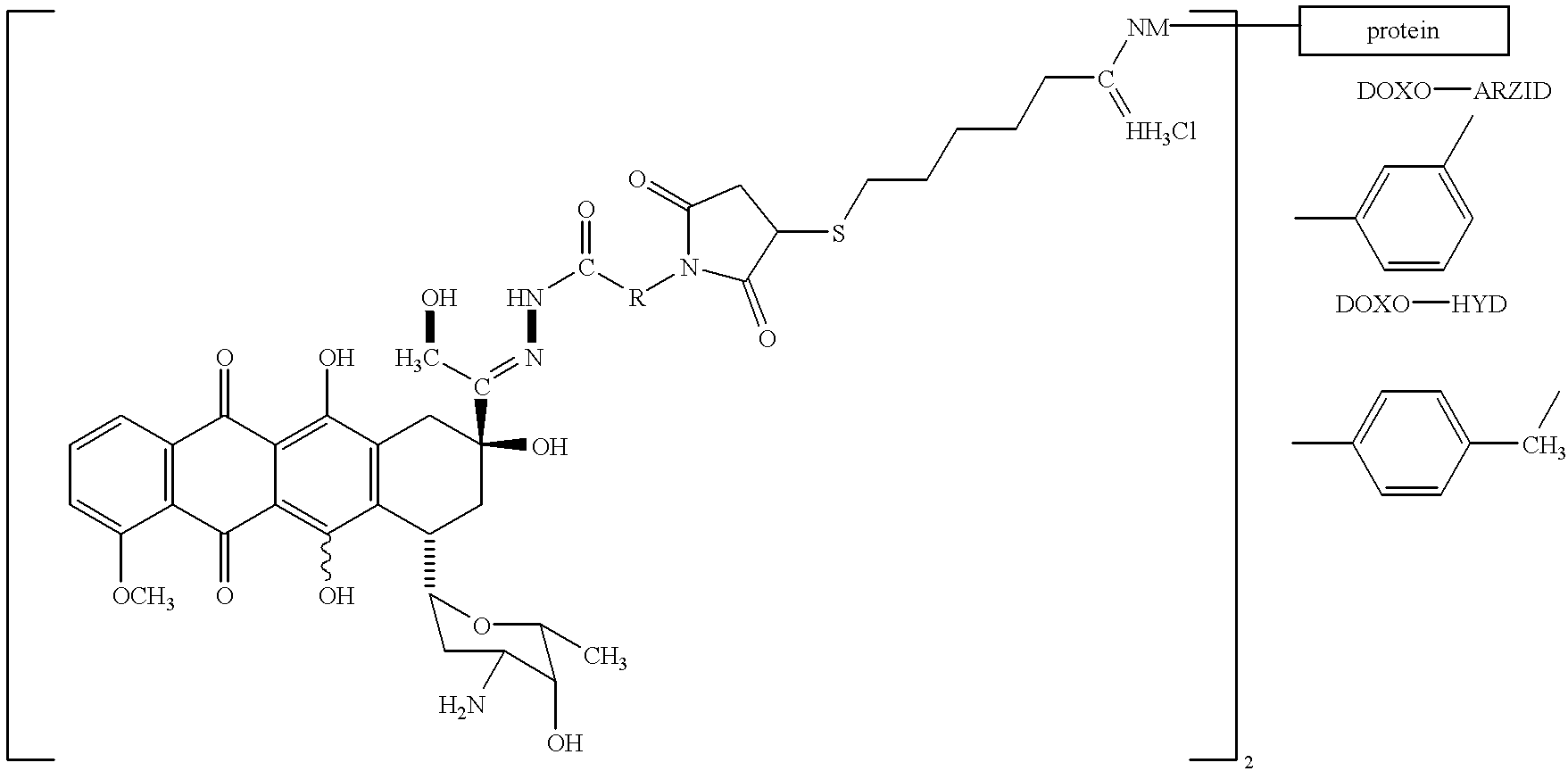
Conjugates of transferrin, albumin and polyethylence glycol consisting of native or thiolated transferrin or albumin or of polyethylene glycol (MW between approximately 5,000 and 20,0000) with at least one HS-, HO- or H2N group and cytostatic compounds derived through maleinimide or N-hydroxysuccinimide ester compounds, such as doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin, mitoxandrone, chloroambucil, melphalan, 5-fluorouracyl, 5'-desoxy-5-fluorouridine, thioguanine, methotrexate, paclitaxel, docetaxel, topotecan, 9-aminocamptothecin, etoposide, teniposide, mitopodoside, vinblastine, vincristine, vindesine, vinorelbine or a compound of general formula A, B, C or D, where n=0-6, X=-NH2, -OH, -COOH, -O-CO-R-COR*, -NH-CO-R-COR*, where R is an aliphatic carbon chain with 1-6 carbon atoms or a substituted or unsubstituted phenylene group and R* H, phenyl, alkyl with 1-6 carbon atoms.
Owner:KRATZ FELIX
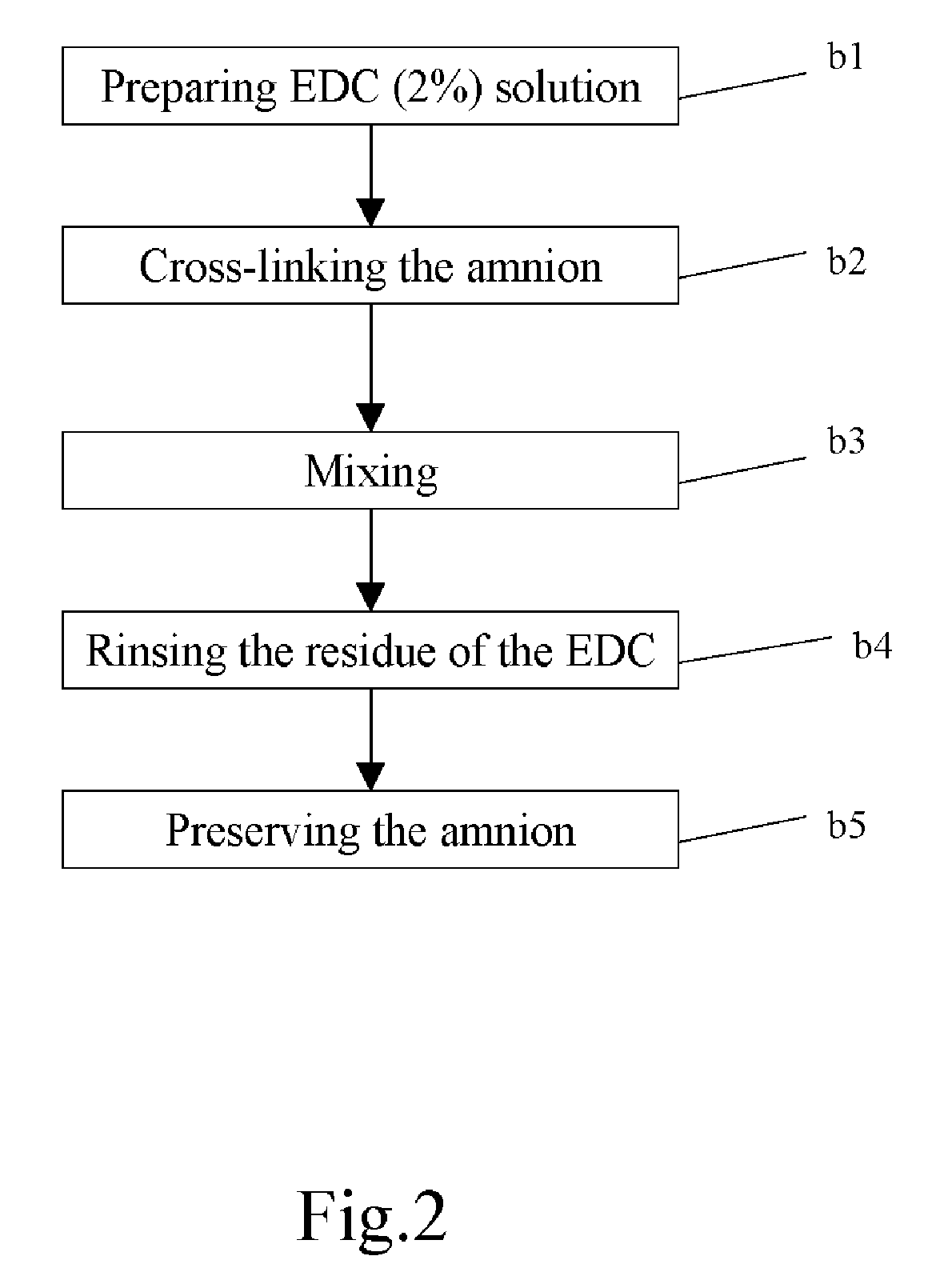
Method of cross-linking amnion to be an improved biomedical material
InactiveUS20080233552A1Reduce cell proliferationMore resistantMammal material medical ingredientsDead animal preservationCross-linkDisease
The present invention discloses a method of cross-linking amnion to be an improved biomedical material. The present invention adopts the amnion cross-linked by EDC (N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethyl-carbodiimide HCI) or NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide), and the cross-linked amnion not only has more resistance to protease, but also binds specific extracellular matrix (ECM) such as heparin by using cross-linked functional group. Further, by using the affinity of the ECM with specific growth factors, the amnion can be an efficient carrier for specific growth factor. Hence, some specific diseases may be treated.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
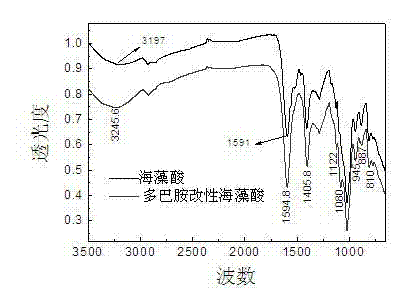
Polysaccharide-dopamine composite biogel and application thereof
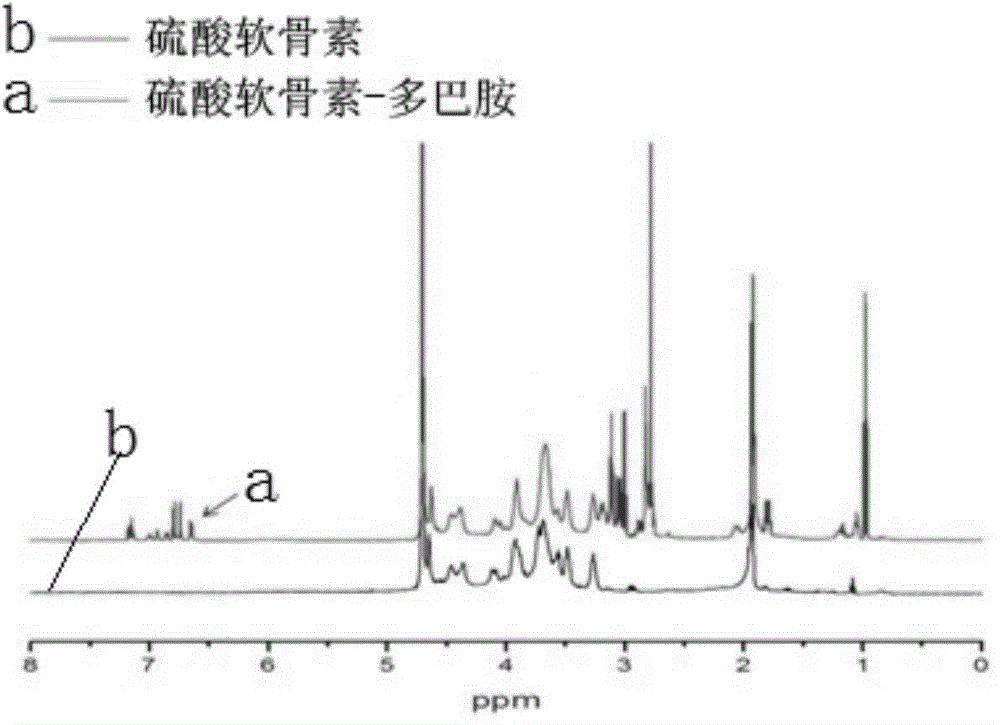
The invention discloses a polysaccharide-dopamine composite biogel and application of the biogel. A preparation method of the biogel comprises the following steps: dissolving 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxy succinimide sodium in an MES (Methyl Ester Sulfonate) buffer solution with a pH value being 5-6 in an inert gas atmosphere so as to prepare an EDC (ethylcarbodiimide) mixed solution, subsequently adding the EDC mixed solution into a polysaccharide solution for reacting at 20-30 DEG C for 0.5-1 hour, then adding a dopamine solution for further reacting at 20-30 DEG C for 1-4 hours, dialyzing a reactant by taking distilled water as a dialyzate, taking trapped fluid for freezing and drying to obtain the polysaccharide-dopamine composite biogel. The polysaccharide-dopamine composite biogel is simple and effective in modification method and capable of increasing the surface viscidity of the cartilage tissue, reducing loss of therapeutic drugs or implanted cells and facilitating the repairing of the cartilage injury.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of biocompatible gamma-polyglutamic-acid hydrogel
The invention discloses a preparation method of biocompatible gamma-polyglutamic-acid hydrogel, which comprises the following steps of: by using polyglutamic acid as a main raw material and a biological-source material chitosan oligosaccharide as a cross-linking agent, carrying out preparation reaction in an aqueous solution, and activating a gamma-polyglutamic-acid carboxyl group by utilizing activating agents diamine carbide and N-hydroxysuccinimide ester to enable the polyglutamic acid and the free amino group of the chitosan oligosaccharide to form an amido bond to further form the hydrogel in a three-dimensional netted structure. After the prepared gel is swelled and balanced, drying is carried out by adopting a freeze-drying, vacuum-drying or microwave-drying mode. The biological-source material chitosan oligosaccharide is selected as the cross-linking agent, so that the biocompatibility of an obtained hydrogel system can be markedly improved; and a reaction system is an aqueous-solution system, reaction regulating and controlling properties are good, and the gel is stable. Because the hydrogel prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has good biocompatibility, the hydrogel can be widely applied to medicament carriers, auxiliary wound materials, medical and sanitary articles and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Chemiluminescence quantitative detection kit for procalcitonin, and preparation method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103901203ALow cross-reactivityImprove accuracyChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexN-Hydroxysuccinimide
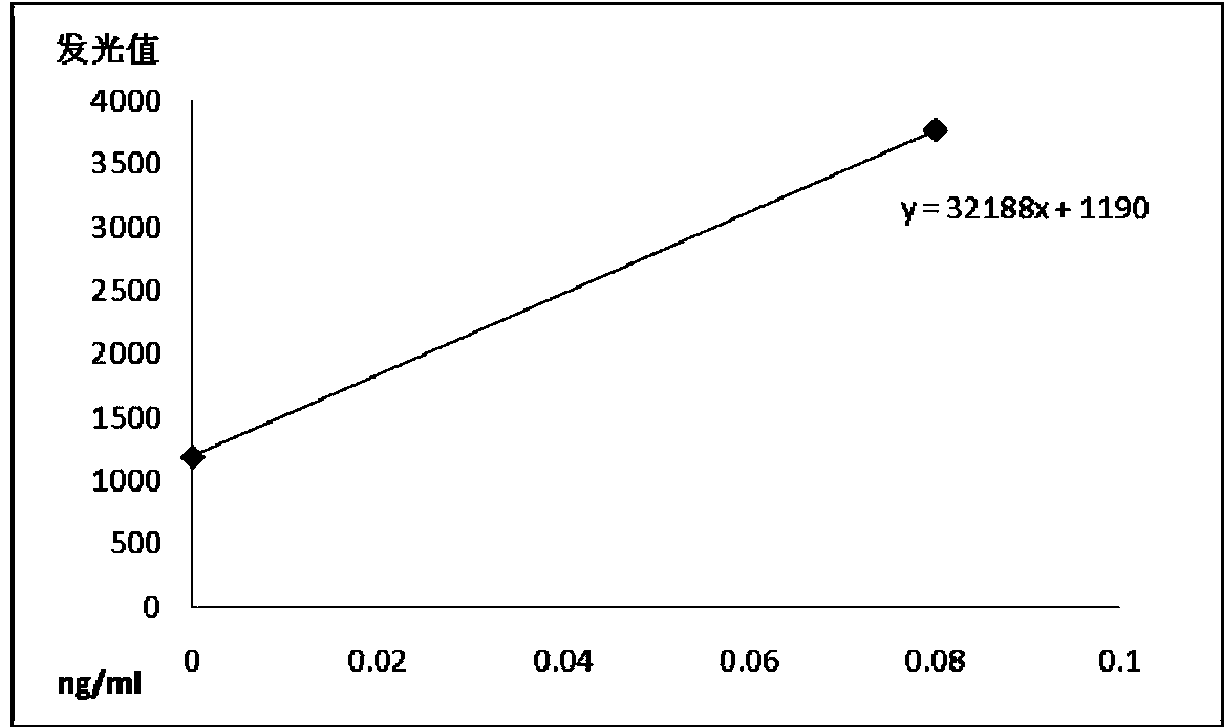
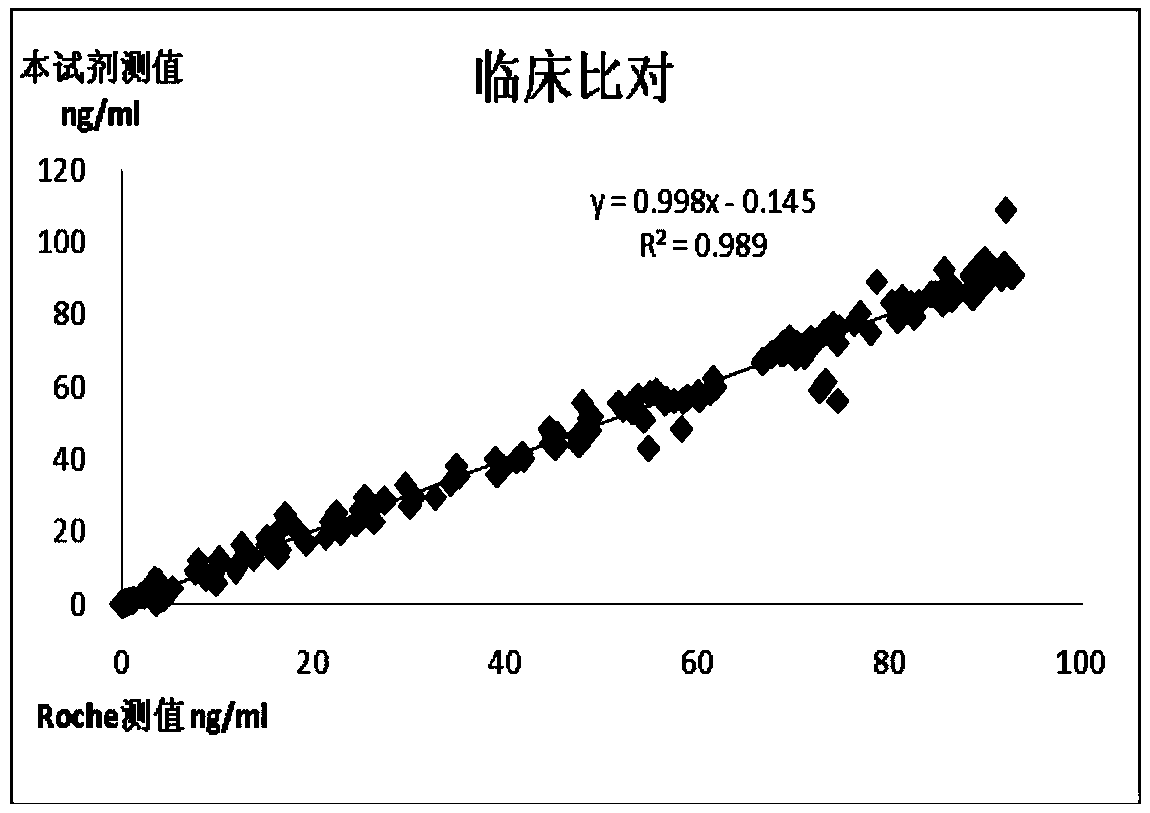
The invention relates to a chemiluminescence quantitative detection kit for procalcitonin, and a preparation method and detection method thereof. The kit comprises a procalcitonin series standard substance, a magnetic separation reagent (magnetic particle suspension coupled with streptavidin), a first reagent (anti-procalcitonin monoclonal antibody solution containing biotin N-hydroxysuccinimide ester label) and a second reagent (anti-procalcitonin monoclonal antibody solution containing alkaline phosphatase label). The sensitivity of the kit prepared from the magnetic particle suspension coupled with streptavidin, anti-procalcitonin monoclonal antibody solution containing biotin N-hydroxysuccinimide ester label and anti-procalcitonin monoclonal antibody solution containing alkaline phosphatase label is up to 0.008ng / ml; and the kit has the advantages of high accuracy, high precision, no need of prediluting the sample, and wide detection range, and is simple and time-saving to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Novel bio-medical adhesive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105477678AGood biocompatibilityStrong adhesionSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPhosphateFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a bio-medical adhesive, which can be cross-linked with a wound in situ, and a preparation method of the bio-medical adhesive. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the steps of first, preparing oxidized sodium alginate by using sodium periodate to oxidize sodium alginate; dissolving the oxidized sodium alginate in an MES (Methyl Ester Sulfonate) buffer solution, dissolving 1-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxyl succinimide in the MES buffer solution as well under nitrogen protection, continuously adding dopamine, carrying out dialyzing and freeze-drying after reacting for 8 to 24 hours, and obtaining A liquid by dissolving a reaction product in a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) or a sodium borate solution; then, dissolving I-shaped collagen in an acid solution, and obtaining B liquid by neutralizing the solution pH (potential of Hydrogen) to be 5 to 8; firstly pre-treating the wound by using hydrogen peroxide or HRP (Horse Radish Peroxidase) before the bio-medical adhesive is used, then immediately coating the wound with the bio-medical adhesive after mixing the A liquid with the B liquid, and forming gel in 30 to 120 s, wherein the gel is firmly adhered to the surface of the wound. The bio-medical adhesive disclosed by the invention has a stronger adhesive force under a moist environment in vivo, integrates filling, sealing and bleeding stopping functions, is good in biocompatibility, is bio-degradable and can be used for promoting wound healing.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
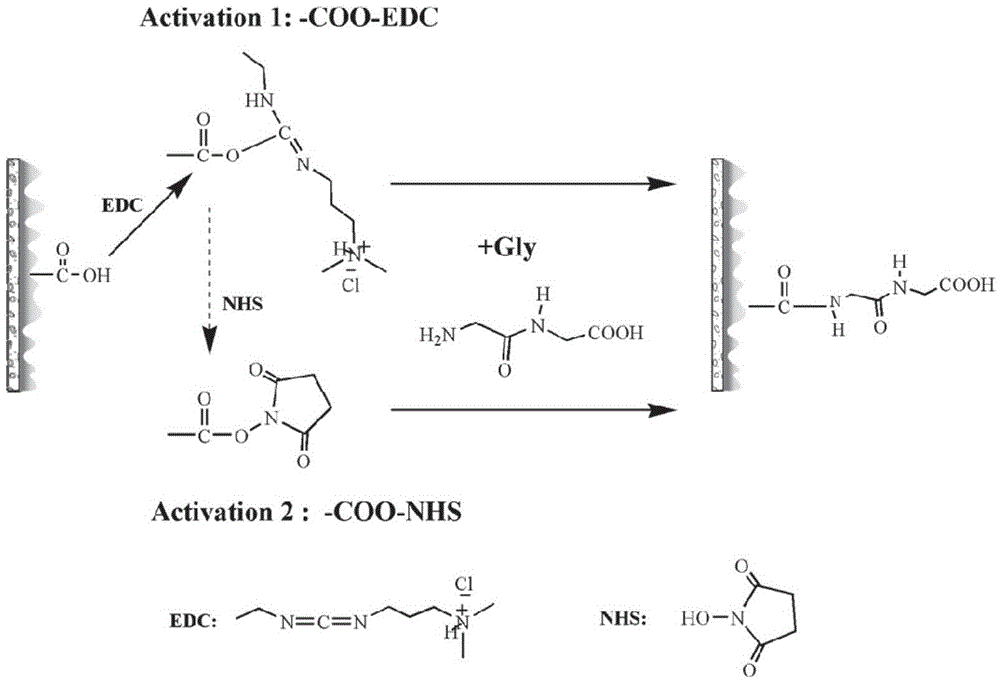
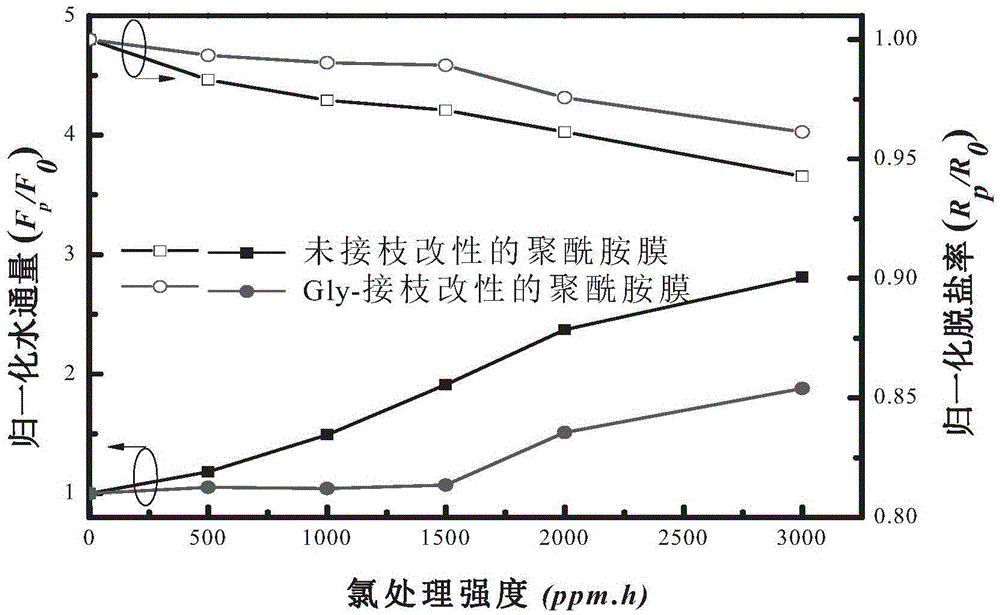
Polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane having renewable chlorine resistance and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane having renewable chlorine resistance and a preparation method thereof, wherein the preparation method comprises the steps: (1) a polyamide reverse osmosis original membrane having the surface with carboxyl is soaked in a catalyst and is subjected to surface activation; and (2) the membrane obtained after surface activation is soaked in a solution containing a graft material and is subjected to surface grafting, wherein the catalyst contains 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, and the graft material is at least one of glycylglycine, glutamine and tyrosine. According to the preparation method, the surface of the polyamide reverse osmosis original membrane is introduced with aliphatic amide small molecules with the tail end being carboxyl, amide N-H in a structure is used as an sacrificial-layer functional group for preferentially undergoing a reaction with active chlorine, a body polyamide layer is protected, the chlorine resistance of the polyamide reverse osmosis composite membrane is strengthened, and at the same time, the chlorine resistance can be regenerated through reduction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
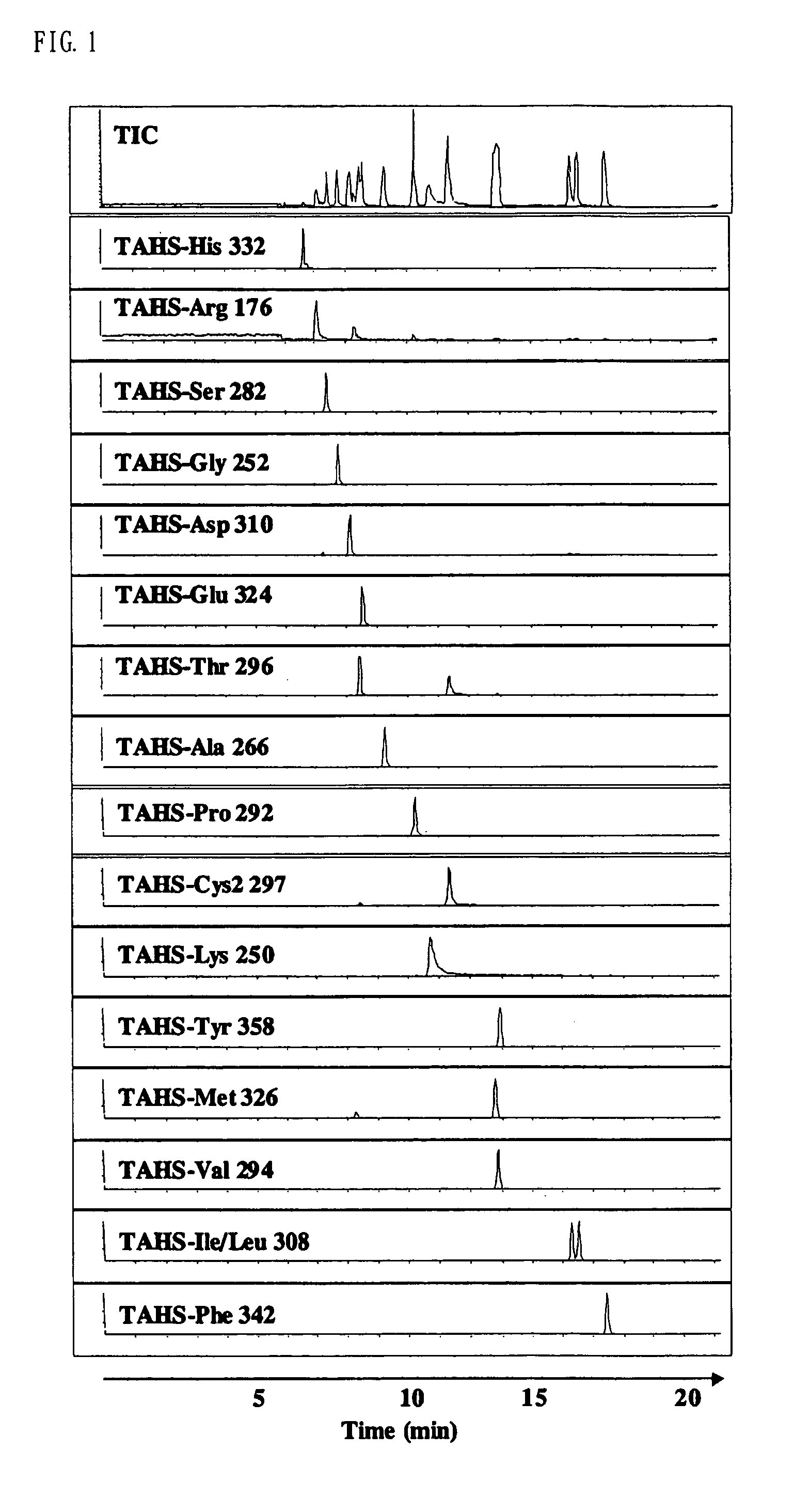
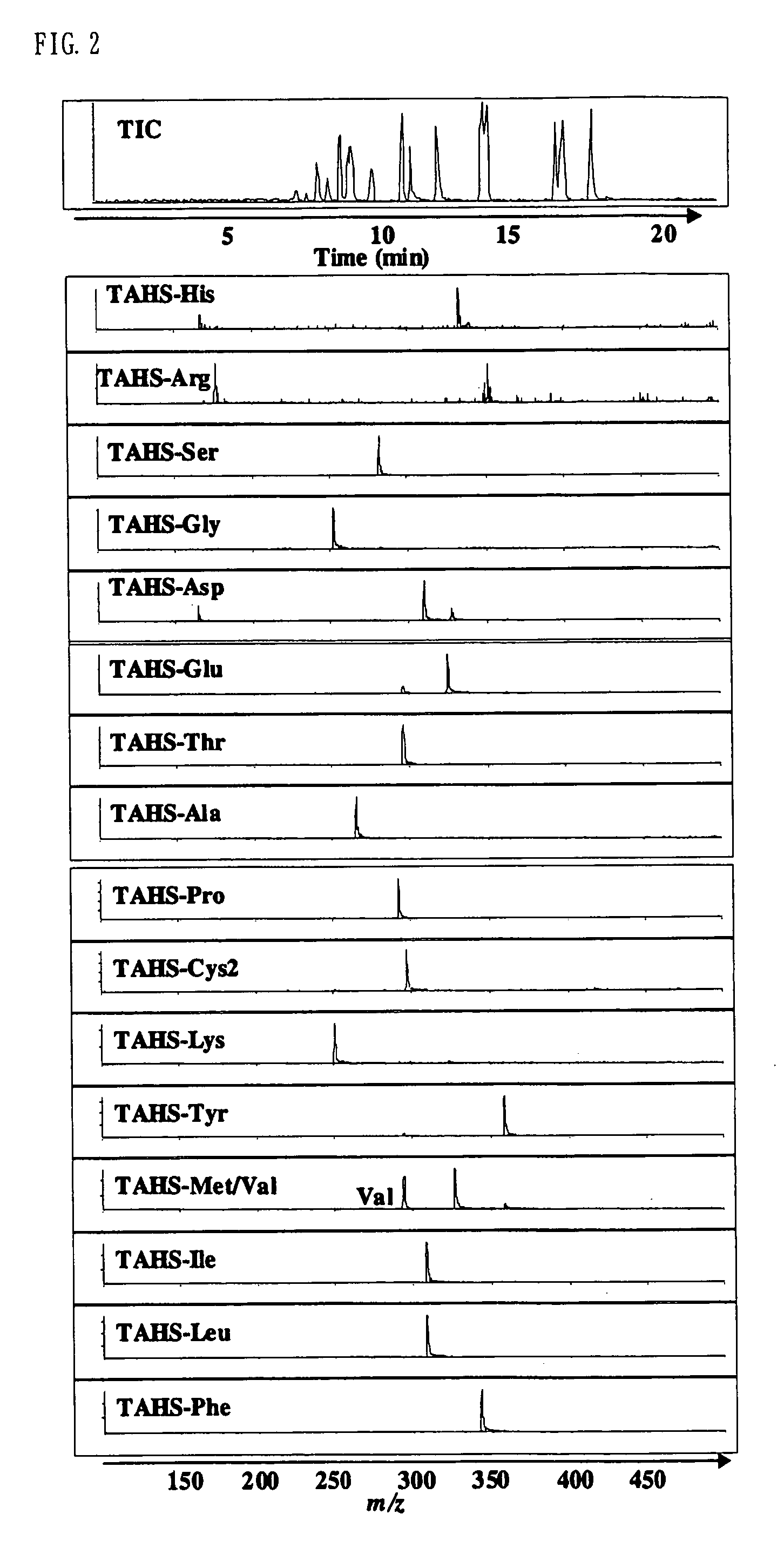
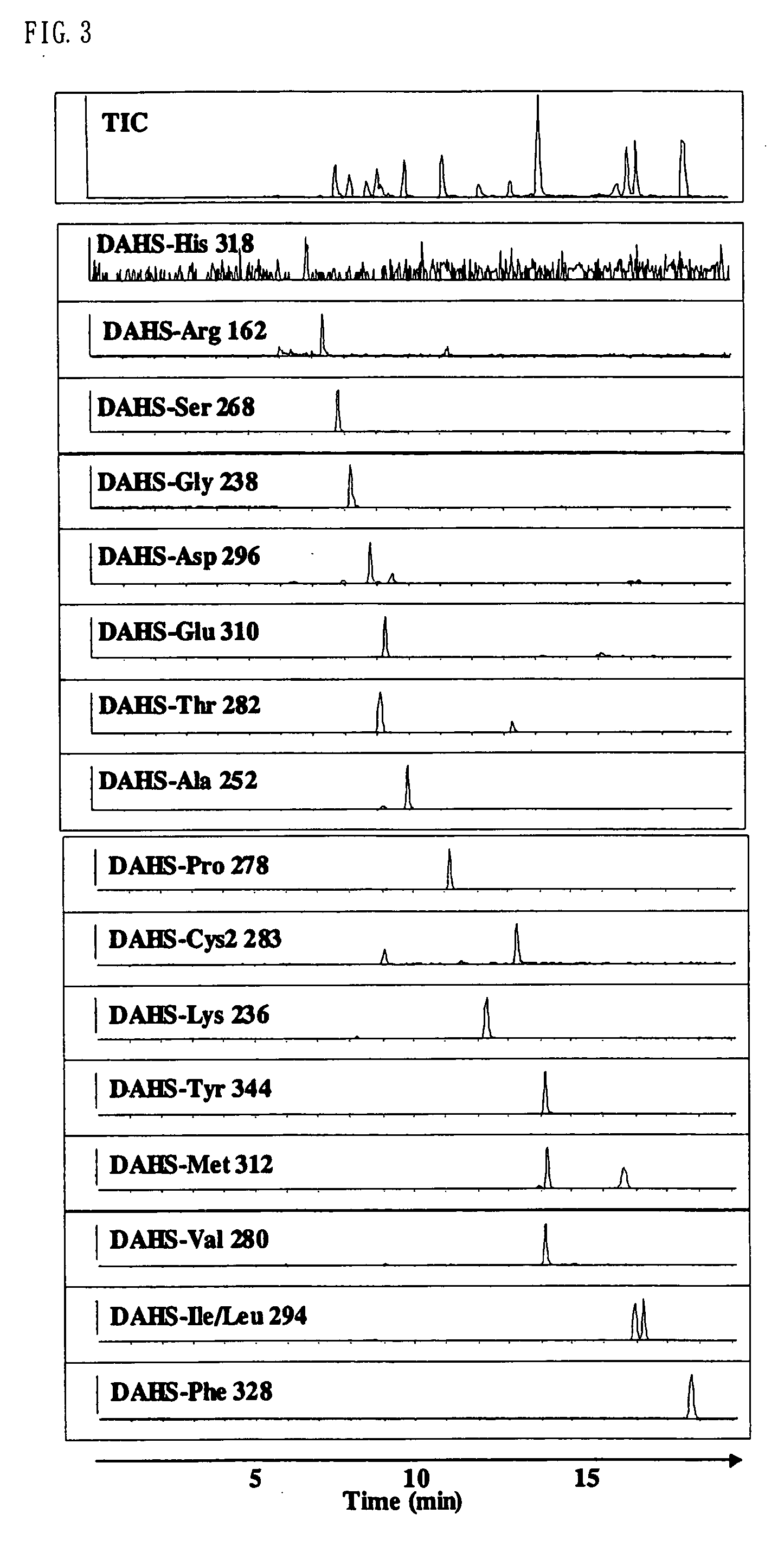
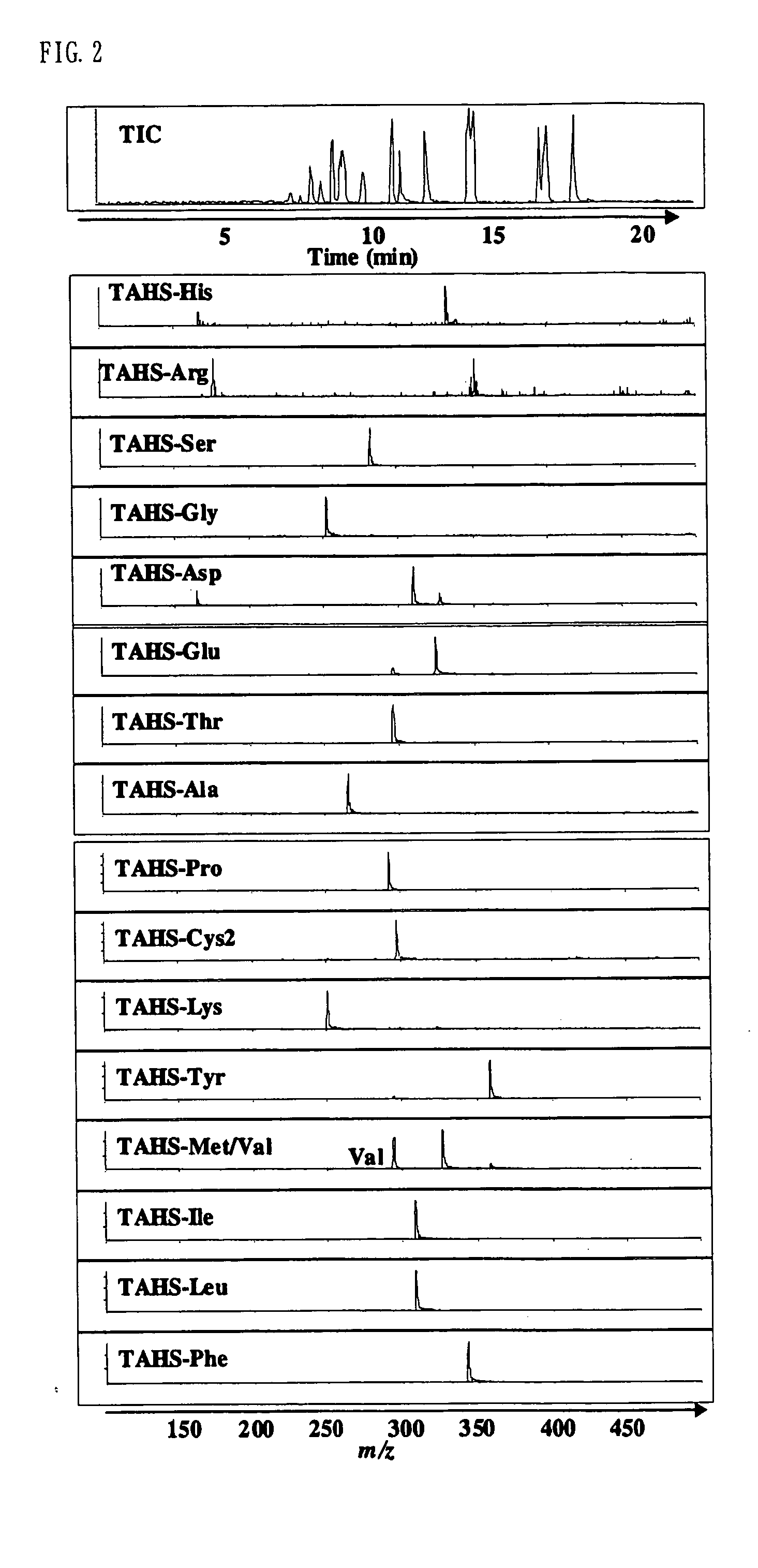
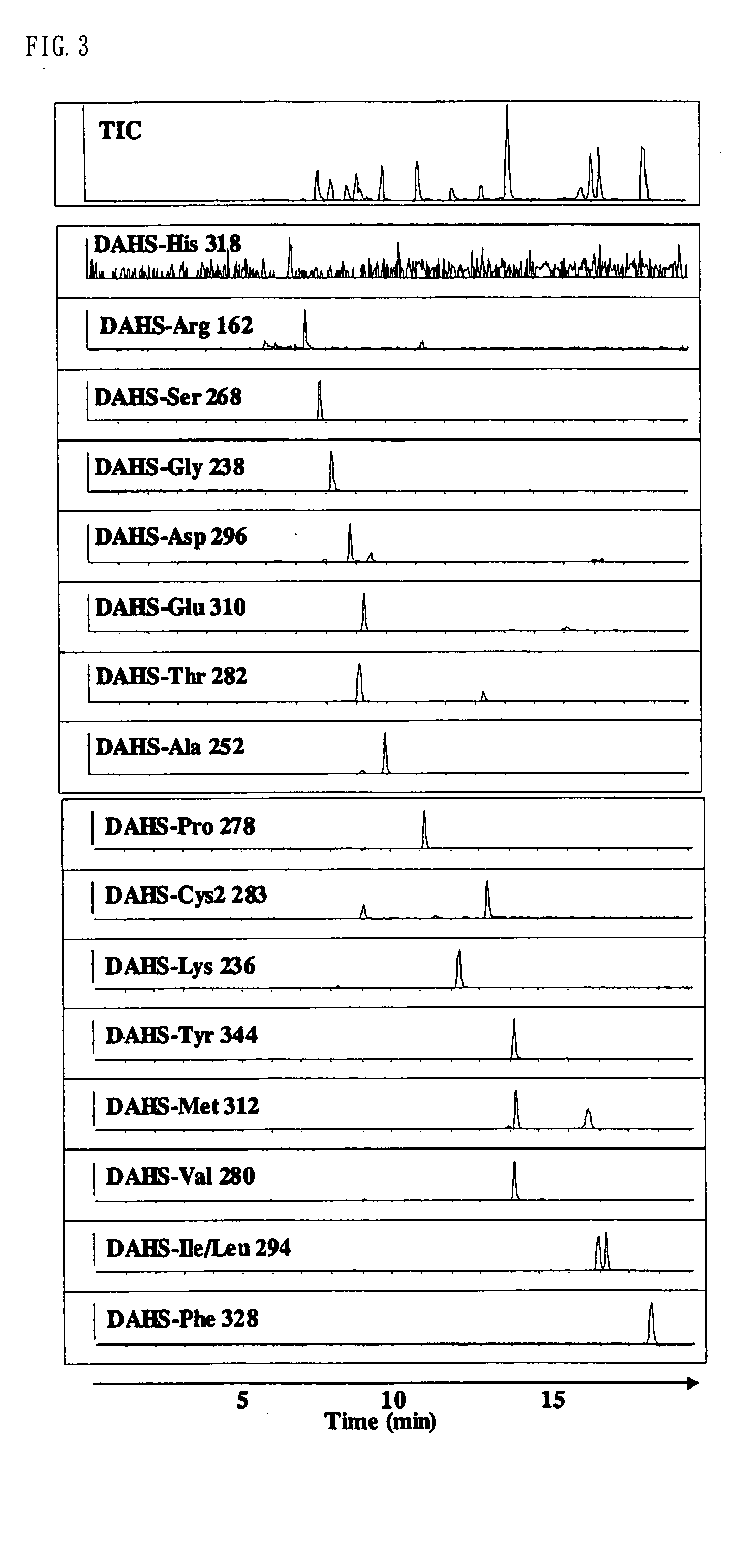
Method for analysis of compounds with amino group and analytical reagent therefor
InactiveUS7148069B2Convenient and highly and selectiveMass spectrometric analysisPeptide preparation methodsCarbamateChemical compound
The present invention provides a method for the analysis of a compound with amino group (e.g., an amino acid or peptide) contained in a sample and convenient manner with a high sensitivity. The compound with amino group in a sample containing the compound with amino group is labeled with a specific carbamate compound such as p-trimethylammonium anilyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate iodide to enhance the selectivity and sensitivity. The present invention is preferably used in conjunction with mass spectrometry such as MS / MS method to facilitate quantitative analysis. The present invention further provides labeling reagents for mass spectrometry.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Preparation method of polydopamine modified alginic acid microspheres
InactiveCN102964610AImprove mechanical propertiesGood anti-swelling performanceMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMicrosphereN-Hydroxysuccinimide
The invention discloses a preparation method of polydopamine modified alginic acid microspheres, which comprises the following steps of: under the protection of nitrogen, grafting dopamine to alginic acid by use of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride; polymerizing the synthesized dopamine modified alginic acid under the slight alkaline condition to obtain a polydopamine modified alginic acid solution; dropwise adding the polydopamine modified alginic acid solution into a CaCl2 solution by a syringe; and aging to obtain polydopamine modified alginic acid microspheres. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, and the prepared modified alginic acid microspheres have higher swelling resistance and good mechanical properties.
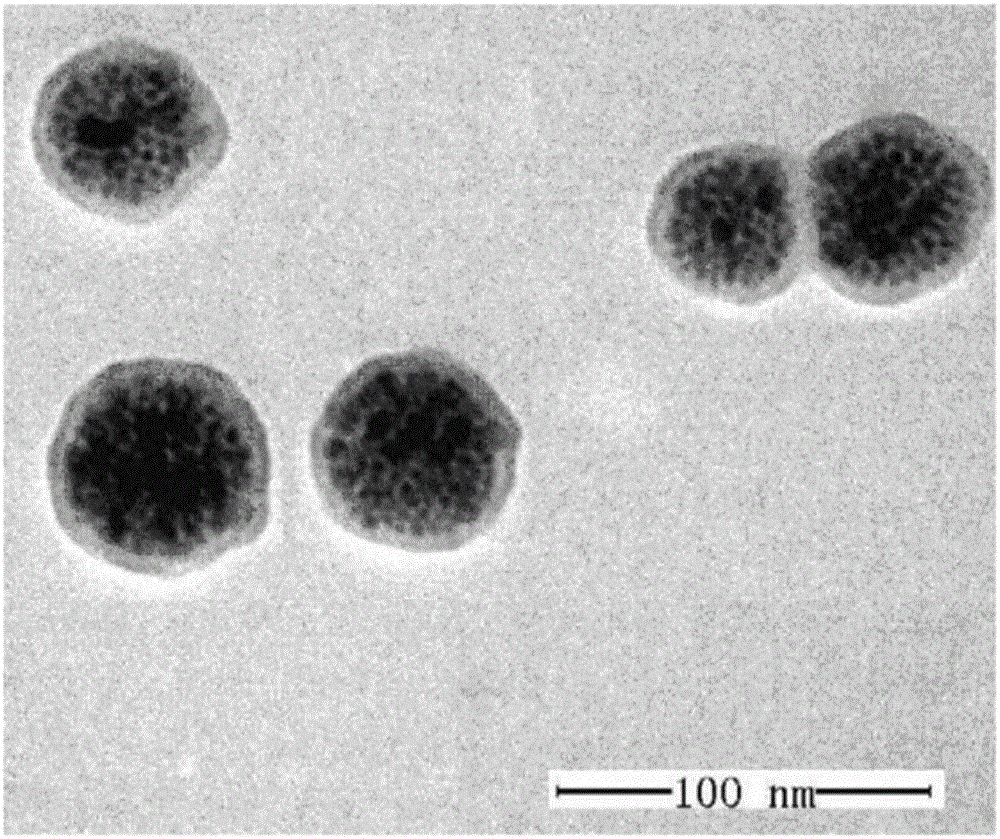
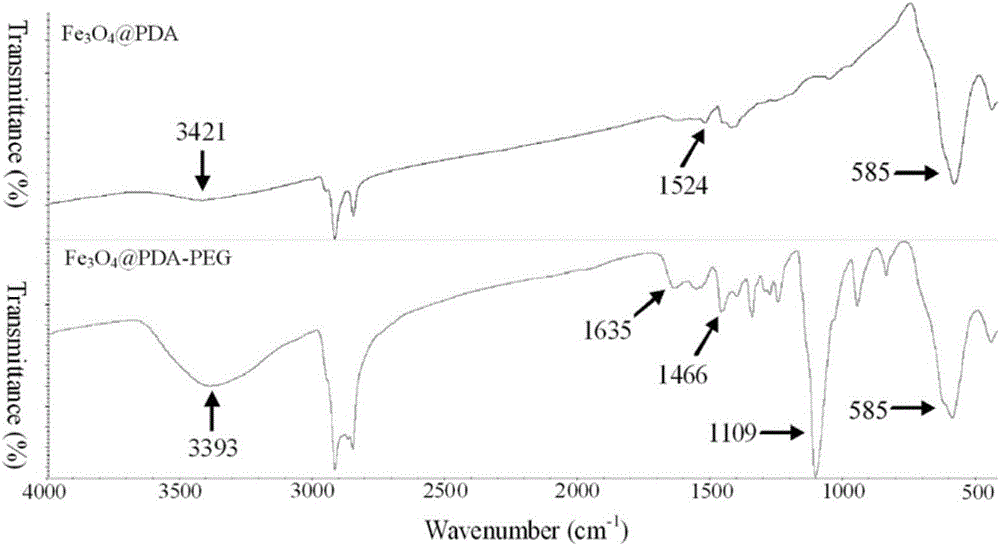
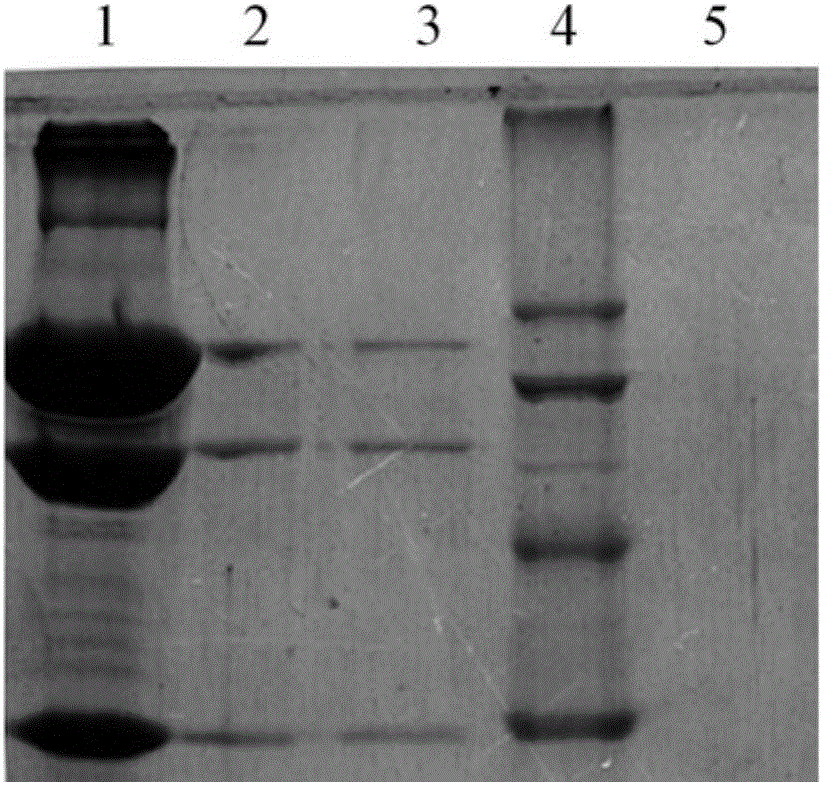
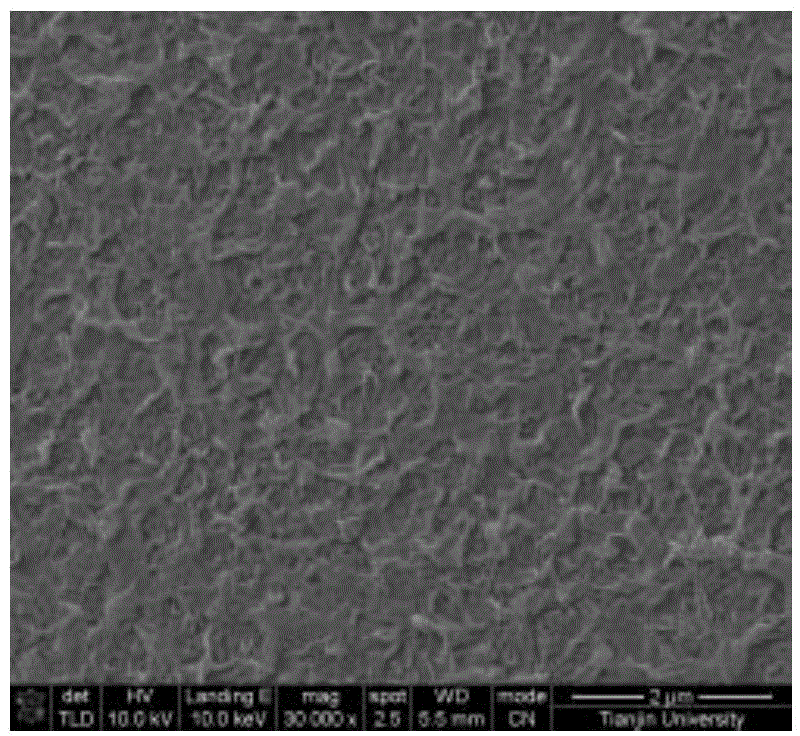
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
In-situ crosslinked alginate hydrogels and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102408496AGood biocompatibilityGood water solubilityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryNitrogen gasOxygen
The invention relates to in-situ crosslinked alginate hydrogels with an active ingredient of disulfide bond disulfide bond alginate derivative. The preparation method thereof is as follows: the organic liquids of carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide eater are added into the alginate aqueous liquid of the alginate to activate the carboxyl of the alginate aqueous liquid; then the organic liquid of 4-aminothiolphenol is added under the conditions of keeping in dark place under 10 DEG C and nitrogen protection, so that the amino of the 4-aminothiolphenol and the carboxyl of the alginate aqueous liquid form an amido bond. The proportions of each matter adjusted and the pH value of muriatic acid is adjusted to 6.0, ethanol is deposited, frozen and dried to obtain sulfhydrylation alginates of different sulfydryl contents. The alginate aqueous liquid of the alginate oxidizes the sulfydryl thorugh the oxygen in the liquid under a room temperature to crosslink and form a disulfide bond, thus obtaining the crosslinked alginate hydrogels. The hydrogels prepared through the method has pH sensitivity and reduction responsiveness, and has potential application values in drug delivery field.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
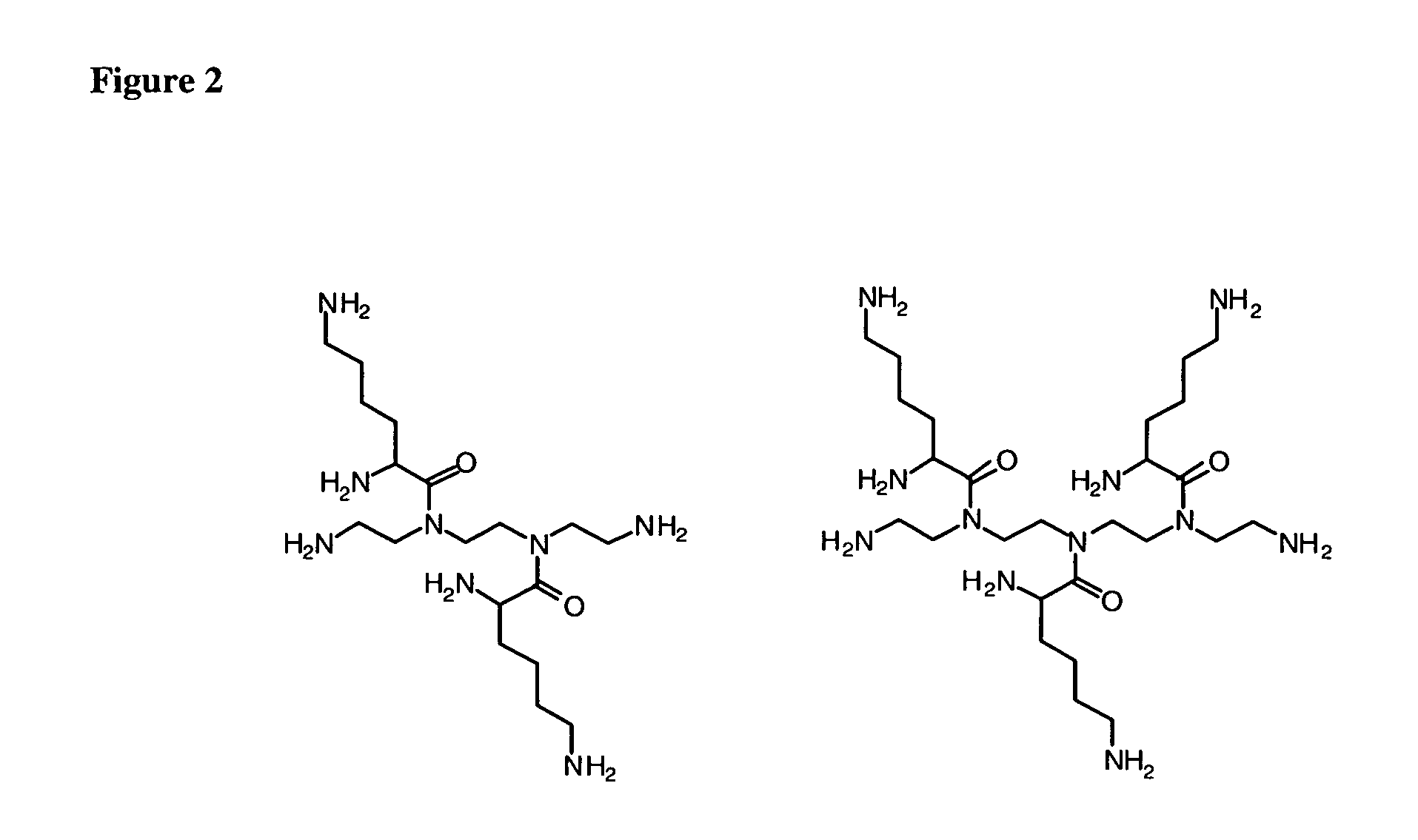
Methods for preparing multivalent constructs for therapeutic and diagnostic applications and methods of preparing the same
InactiveUS7666979B2Increase flexibilityNovel methodUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryGlutaric acidN-Hydroxysuccinimide
Methods for the preparation of multivalent constructs for therapeutic and diagnostic applications are provided. More specifically, novel methods for preparing multivalent constructs comprising the formula A-B-C-D-E-B′-F for therapeutic and diagnostic applications are provided which use a novel linker D comprising, in various embodiments, a dicarboxylic acid derivative such as, e.g., a glutaric acid bis N-hydroxysuccinimidyl ester or a derivative thereof; or a diamine derivative.The remaining components in the multivalent construct A-B-C-D-E-B′-F are defined as follows: A is a first peptide, B is a first branching group, C is an optional first spacer, E is an optional second spacer which may be the same as or different from said first spacer C, B′ is an optional second branching group which may be the same as or different from said first branching group B, and F is a second peptide which may be the same as or different from said first peptide A.
Owner:DYAX CORP +1
Carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt/PAMAM(Polyamidoamine) core-shell nanoparticles and preparation method
The invention discloses carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt / PAMAM(Polyamidoamine) core-shell nanoparticles and a preparation method. The nanoparticles are chitosan derivatives which are formed in a way that amino-terminated polyamidoamine dendritic macromolecule is grafted with carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, and the chitosan derivatives are self-aggregated to form core-shell nanoparticles in water solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing quaterisation decoration to amino at a second position of chitosan by CTA (3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride); performing carboxymethyl decoration to hydroxy at a sixth position of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt to synthetize carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt; activating carboxyl of the carboxymethyl chitosan quaternary ammonium salt by using NHS(N-Hydroxysuccinimide) / EDC(carbodiimide) to link the amino-terminated polyamidoamine dendritic macromolecule to synthetize the dendritic chitosan derivatives. The preparation process condition is simple and mild, and the product is easy to purify; and the core-shell nanoparticles of the prepared dendritic chitosan derivatives have the advantages of excellent water-solubility and functionality and has the attractive application prospect in the fields of antibiosis, gene transfer and drug controlled release.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
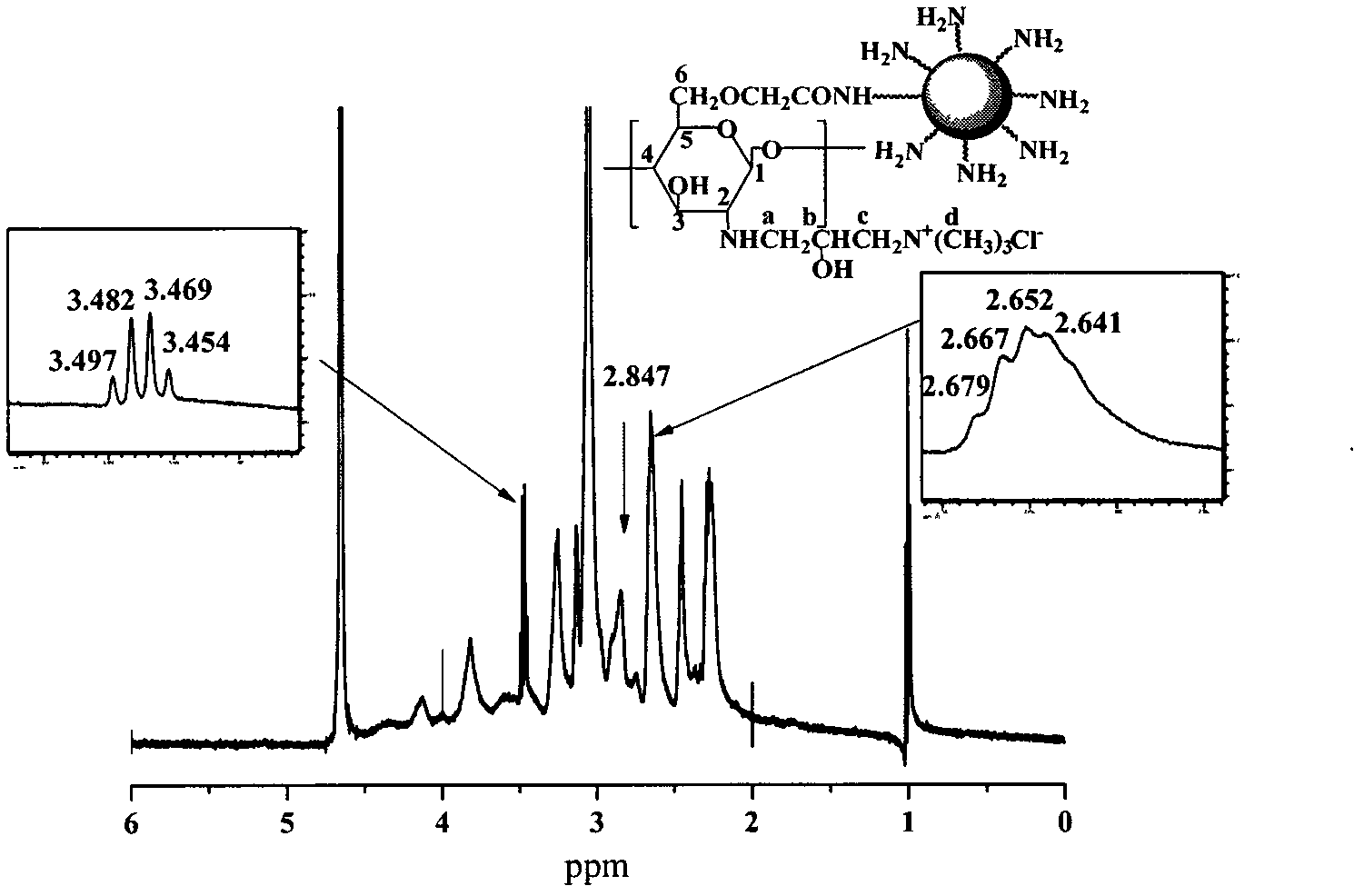
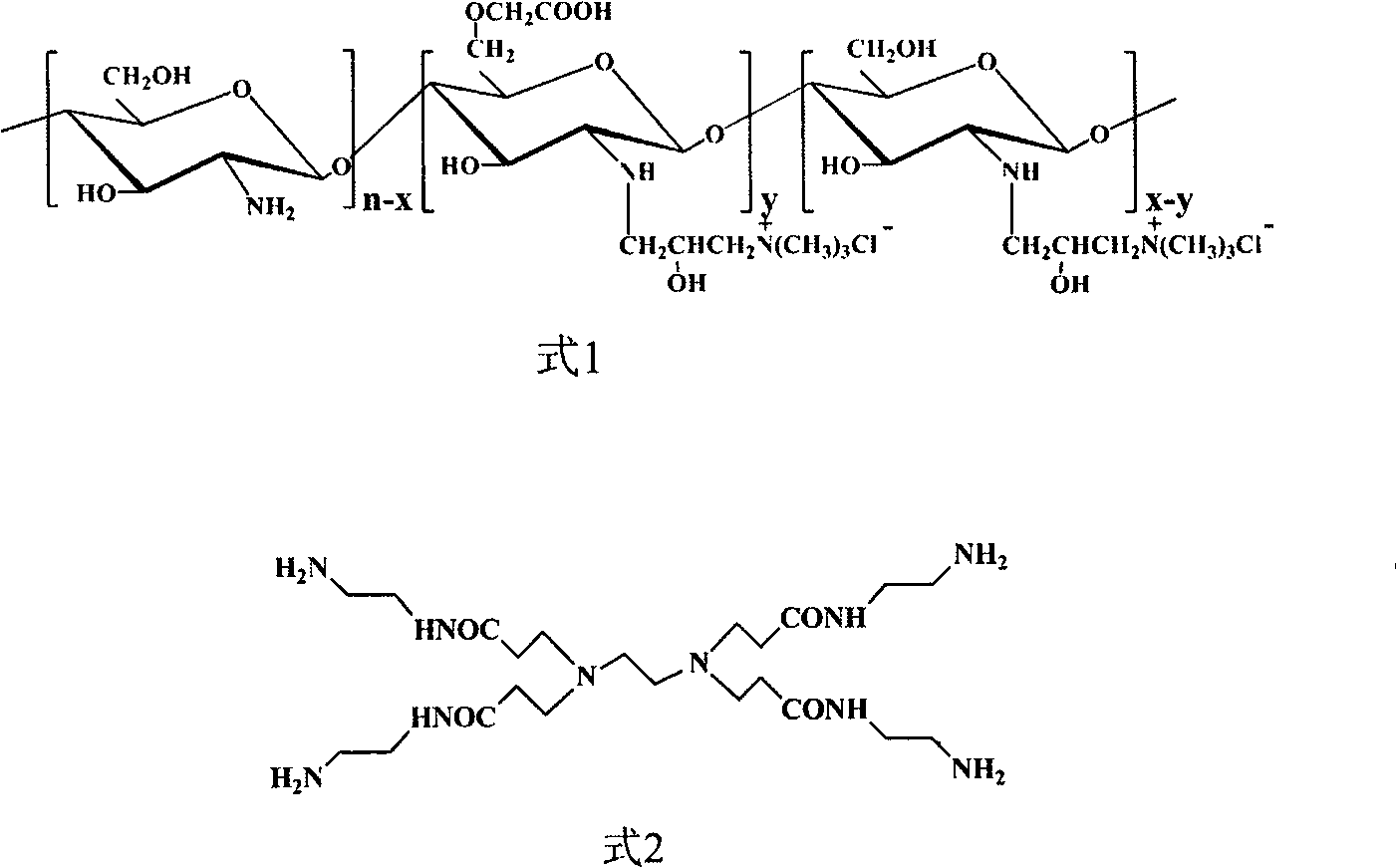
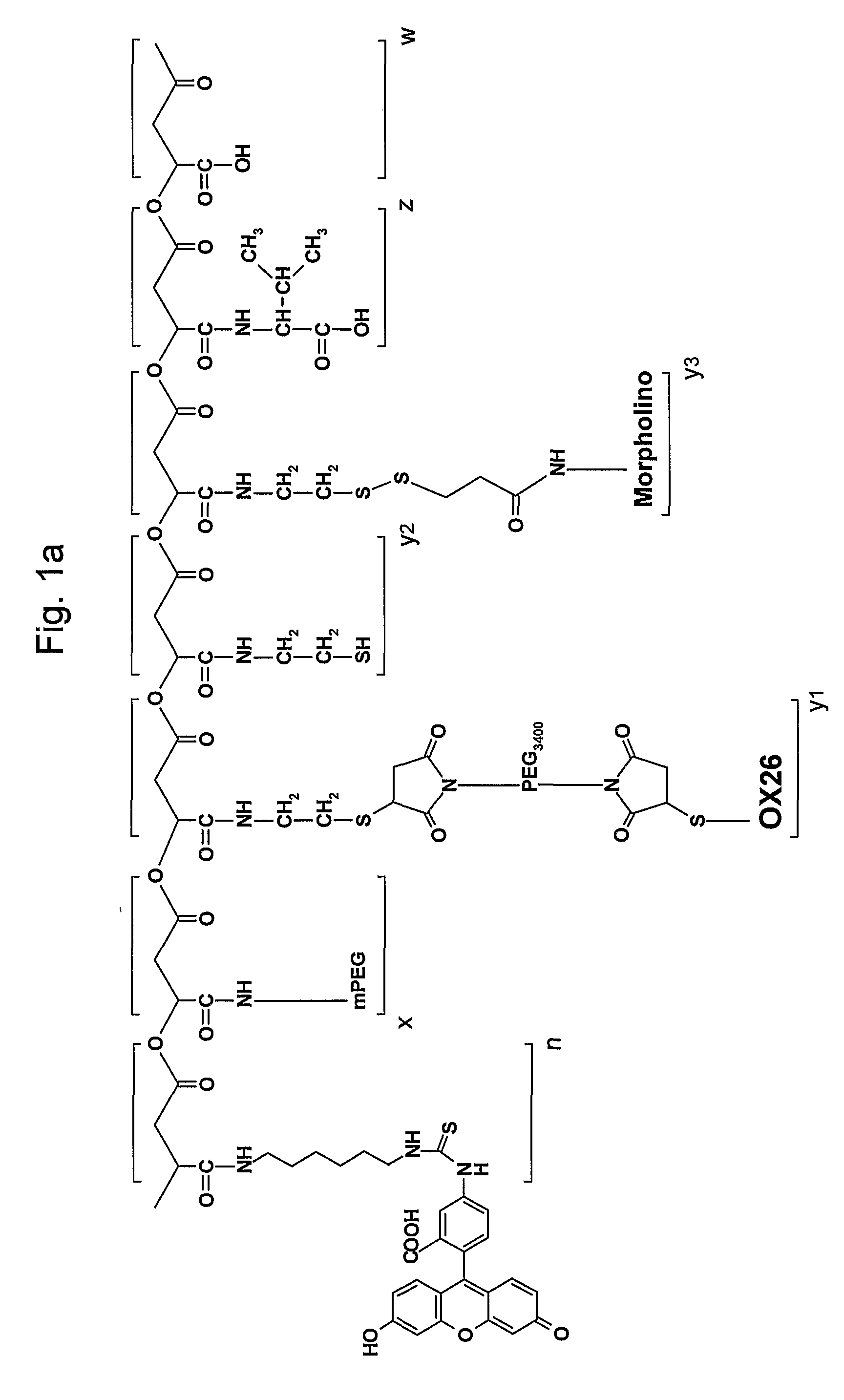
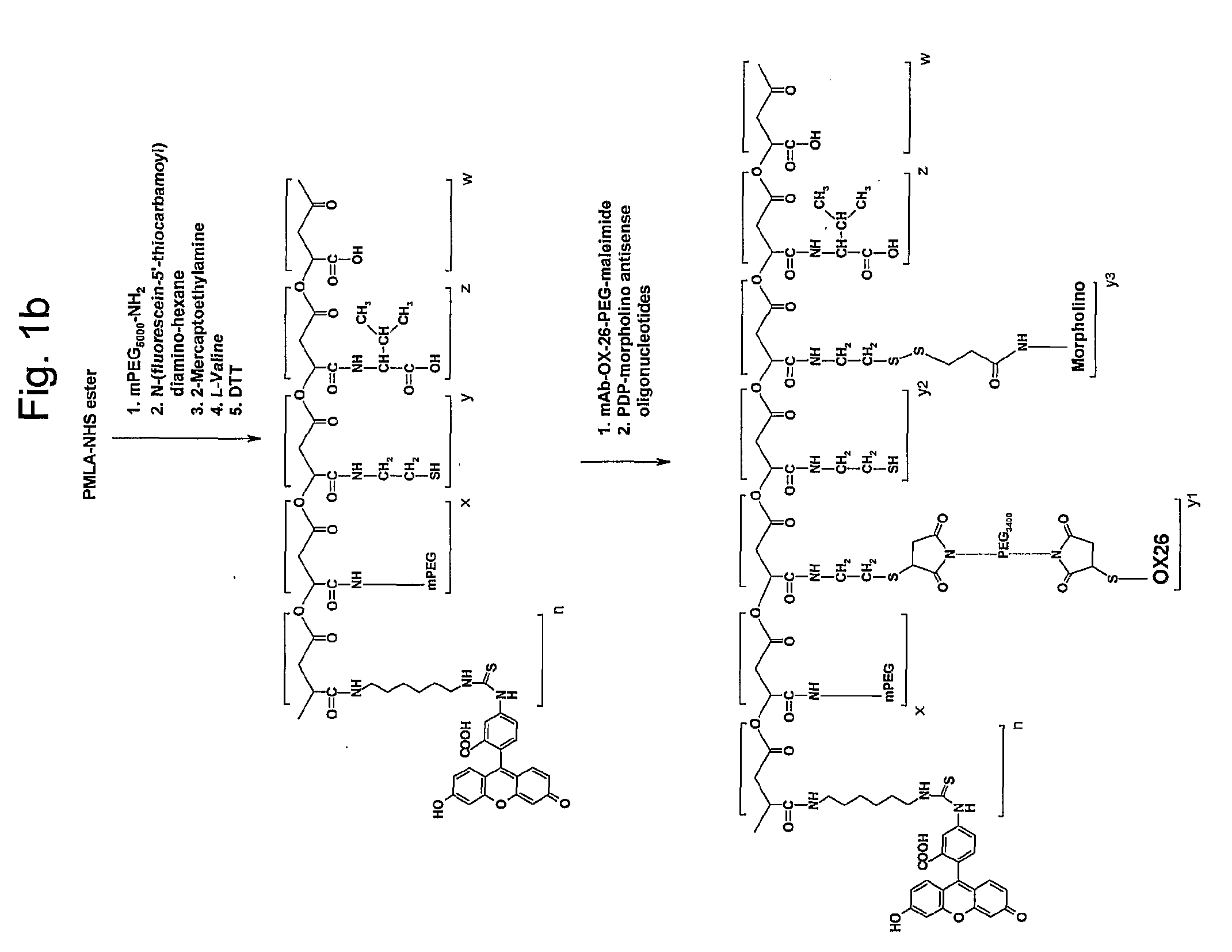
Polymalic Acid-Based Multi-Functional Drug Delivery System
ActiveUS20070259008A1Low toxicityReadily availableOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNatural sourceFluorescence
A structured drug system that is useful for delivering a drug payload to a specific tissue or cell type is disclosed. The system is based on purified polymalic acid. This polymer isolated from natural sources is biocompatible, biodegradable and of very low toxicity. The polymer is extremely water soluble and contains a large number of free carboxyl groups which can used to attach a number of different active molecules. In the examples disclosed N-hydroxysuccinimide esters of the carboxyl groups are used to attach such molecules. The active molecules include monoclonal antibodies to promote specific cellular uptake and specific pro-drugs such as antisense nucleic acids designed to modify the cellular metabolism of a target cell. The pro-drugs are advantageously linked by a somewhat labile bond so that they will be released under specific conditions. In addition, the system contains amide-linked valine to encourage membrane disruption under lysosomal conditions. Polyethylene glycol groups are attached to extend the drug system's circulation half-life. In addition, fluorescent reported groups can be readily included to aid in visualizing and confirming drug system targeting. The drug system can deliver treatments for a wide range of diseases and is specially advantageous for treatment of neoplasms.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
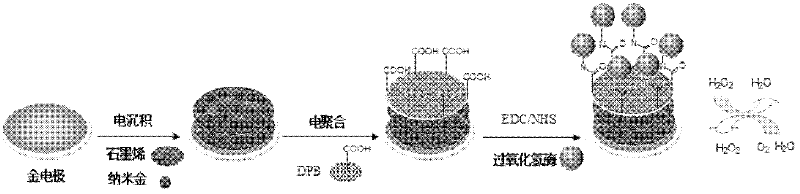
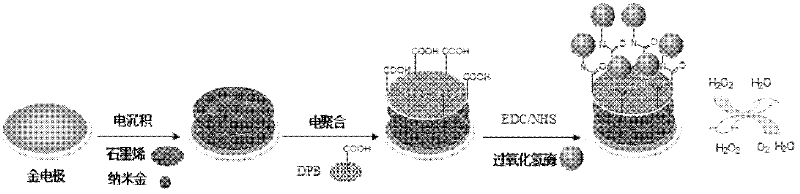
Method for preparing graphene biosensor
ActiveCN102520038ASensitive electrochemical responsePrecise size controlMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSupporting electrolyteConductive polymer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene biosensor, belonging to the technical field of electrochemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: immersing a processed gold electrode into graphene oxide and a sodium sulphate solution, electrically depositing the electrode through a control electric potential, taking out the electrode, washing the electrode by using water, after drying the electrode at room temperature, putting the electrode in a chloroauric acid solution, electrically depositing the electrode through the control electric potential, taking out the electrode, washing the electrode by using water, and drying the electrode at room temperature; putting a modified electrode in a conductive polymer monomer and a supporting electrolyte solution, polymerizing the electrode through the control electric potential by adopting a cyclic voltammetry, taking out the electrode, washing the electrode by using water, and drying the electrode at room temperature; and activating the modified electrode in an EDC / NHS (Dichloroethane / N-Hydroxysuccinimide) solution, and immersing the modified electrode in a vomiting toxin antibody. The method disclosed by the invention is used for fixing graphene, gold nanoparticles and conducting polymers through electro-deposition; therefore, the method is very green and environment-friendly; furthermore, the thickness of a coating and sizes and distribution densities of the gold nanoparticles can be precisely controlled, thus, the batch production repeatability of the modified electrode is good.
Owner:盐城福万家保温板有限公司
Preparation method of bionic coating carrying bioactive factors
InactiveCN102327645AImprove long-term stabilityImprove stabilityImpression capsDentistry preparationsOsseointegrationArg-Gly-Asp
The invention provides a preparation method of bionic coating carrying bioactive factors, which is characterized in that: under a catalyzing system of carbodiimide and N-hydroxy-succinamide, Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) polypeptide chain containing a disulfide bond is grafted onto polyelectrolyte and then is prepared into RGD grafted polyanion electrolyte solution and RGD grafted bioactive-factor-loaded polycation electrolyte solution, the polyanion electrolyte solution is combined with the polycation electrolyte solution carrying the bioactive factors to establish an organic composite coating carrying the bioactive factors on the surface of planting body through a static self-assembling technology. The composite coating solves the bottleneck problem of bioactive factors used surrounding the planting body, can promote the early growth of osteogenesis surrounding the planting body so as to realize the early osseointegration, and facilitates the long-term stability of the planting body. The method is simple to operate, has moderate preparation conditions, is convenient to control and can realize the continuous production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for analysis of compounds with amino group and analytical reagent therefor
InactiveUS20050079624A1Convenient and highly and selectiveMass spectrometric analysisPeptide preparation methodsCarbamateN-Hydroxysuccinimide
The present invention provides a method for the analysis of a compound with amino group (e.g., an amino acid or peptide) contained in a sample and convenient manner with a high sensitivity. The compound with amino group in a sample containing the compound with amino group is labeled with a specific carbamate compound such as p-trimethylammonium anilyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate iodide to enhance the selectivity and sensitivity. The present invention is preferably used in conjunction with mass spectrometry such as MS / MS method to facilitate quantitative analysis. The present invention further provides labeling reagents for mass spectrometry.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
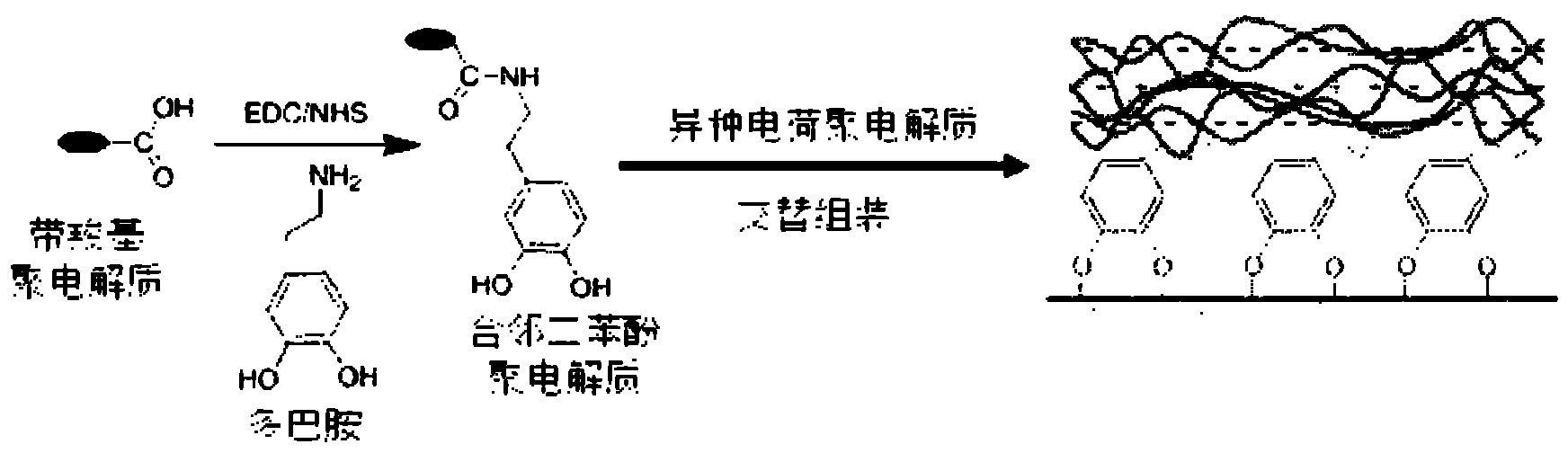
Layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembling method based on dopamine-modified polyelectrolyte and application
InactiveCN102634792ARealize the loadHigh bonding strengthMetallic material coating processesPolyelectrolyteN-Hydroxysuccinimide
The invention discloses a layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembling method based on dopamine-modified polyelectrolyte and application. Dopamine and polyelectrolyte with carboxyl are subjected to dark reaction through carbodiimide / N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDS / NHS) so as to generate the polyelectrolyte of which a carboxyl part of a main chain is substituted by a pyrocatechol functional group; two hydroxyl groups on a benzene ring of pyrocatechol form tight combination with the material surface; and the obtained polyelectrolyte is alternatively deposited together with the polyelectrolyte with opposite charges so as to be assembled into a multi-layer film. Compared with other layer-by-layer assembling techniques, the layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembling method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that being simple in operation, not affected by material and shape of a substrate, free of surface pretreatment, high in binding strength with the substrate and better in popularization and application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
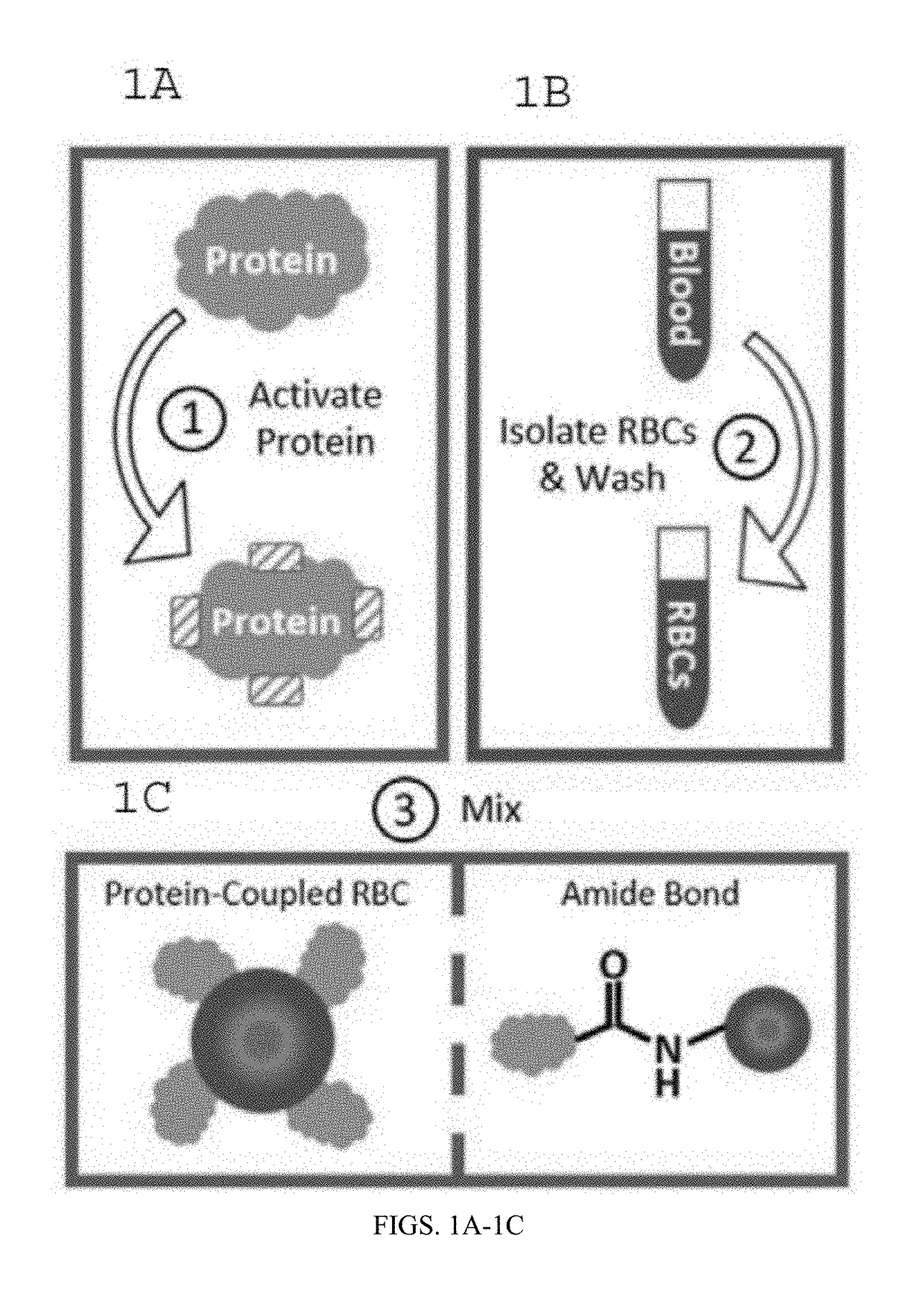
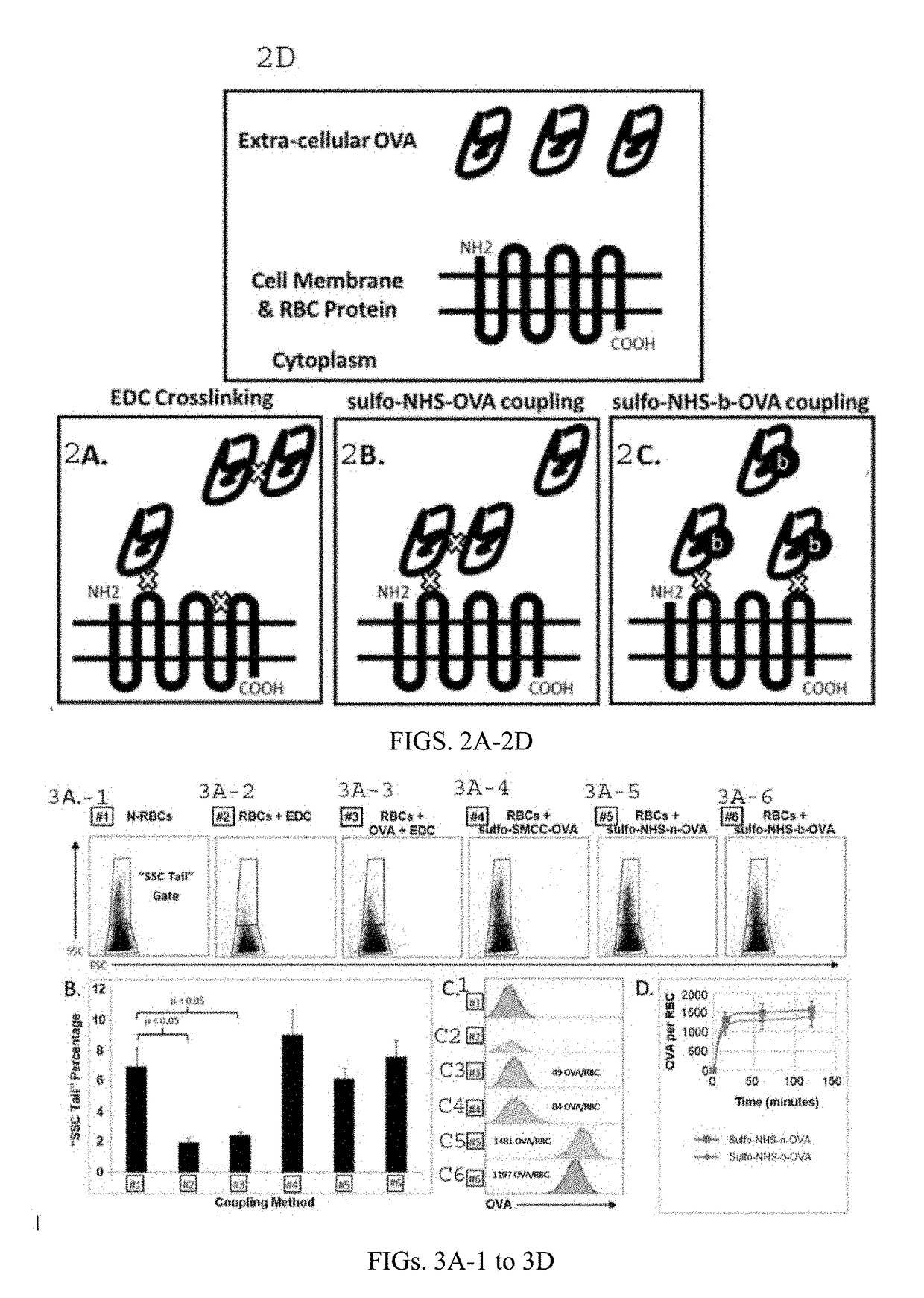
Protein-Coupled Red Blood Cell Compositions and Methods of Their Use
InactiveUS20170326213A1Extended half-lifeLimited half-lifePowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsN-hydroxysulfosuccinimideConjugated protein
Methods and compositions for using N-hydroxysuccinimide and N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide to covalently couple protein(s) to the surface of red blood cells universally, rapidly and conveniently are provided. In one embodiment, the compositions promote immune tolerance in a subject. One embodiment provides autologous or allogenic red blood cells having whole protein(s) of interests conjugated to proteins on or within the plasma membrane of the red blood cells, wherein the conjugated proteins display at least one antigen to which immune tolerance is desired. The proteins are conjugated to the RBCs using carbodiimide chemistry. In a preferred embodiment, the whole proteins are conjugated using EDC in combination with NHS or sulfo-NHS.
Owner:AUGUSTA UNIV RES INST INC
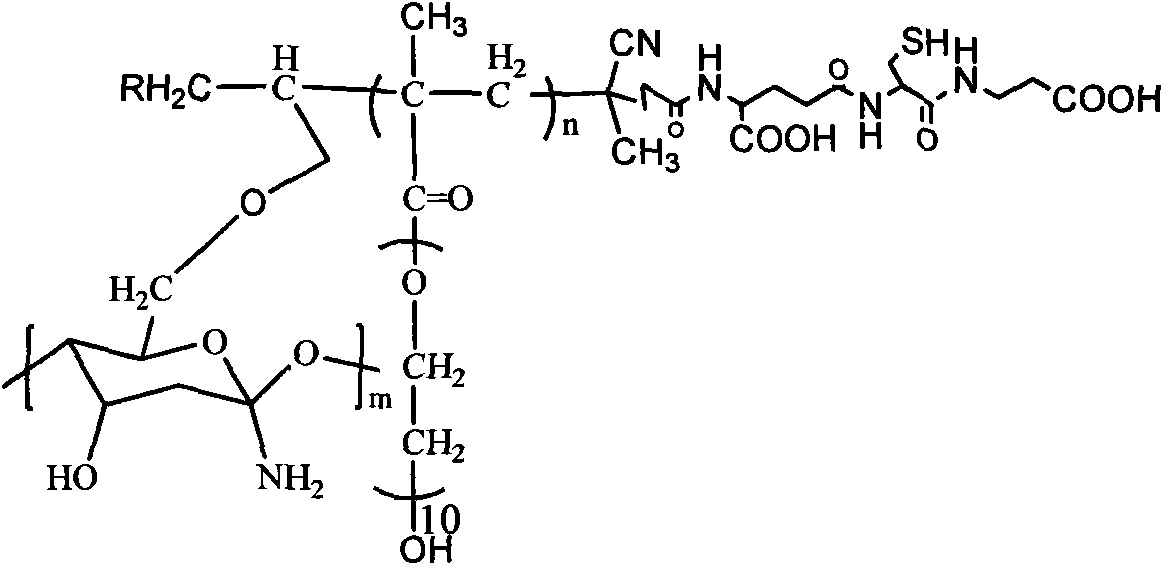
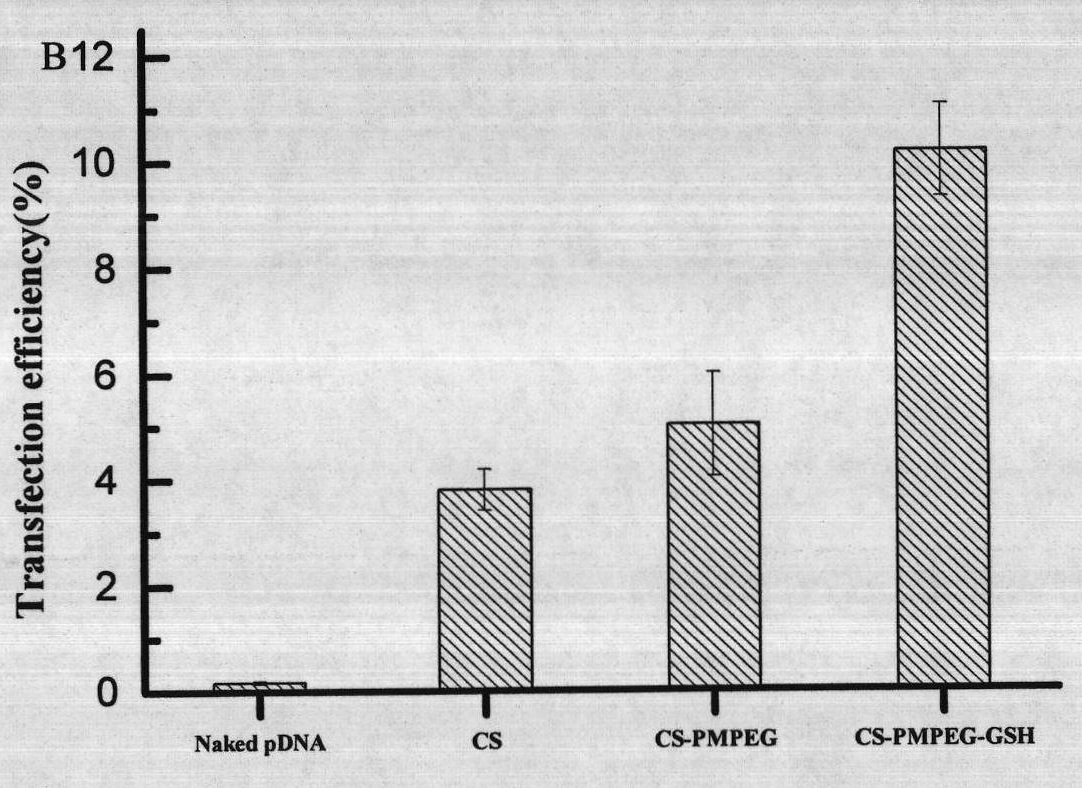
Glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer serving as non-viral gene carrier material and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN102140171AGood biocompatibilityReduce immune rejectionVector-based foreign material introductionActivation methodPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer serving as a non-viral gene carrier material and preparation and application thereof, which belong to the fields of gene therapy and novel materials. A preparation method of the copolymer comprises the following steps of: (1) synthesizing an allyl-modified chitosan derivative; (2) synthesizing brush-like PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) polymer chains with different molecular weights through RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer); (3) grafting the brush-like PEG onto a chitosan framework by adopting a free radical coupling method; and (4) linking glutathione to the chain end of the brush-like PEG by adopting an EDC (1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethyllaminopropyl) Carbodiimide hydrochloride) / NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide) activation method to obtain a glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer carrier material. The glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer obtained by adopting the technology serves as the non-viral gene carrier material. By adopting the copolymer, the endocytosis function of a composite nanoparticle formed from the copolymer and DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) can be remarkably enhanced, the releasing mechanism of DNA from a composite particle after cell entrance is improved, and the non-viral gene carrier material with a high transfection efficiency is further obtained.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Low-toxicity functionalized quantum dot modified by amination beta-cyclodextrin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102220128AGood low toxicityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSolubilityFluorescence
The invention relates to a low-toxicity functionalized quantum dot modified by amination beta-cyclodextrin and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of a special molecular recognition and diagnosis reagent. The method comprises the following steps that functional-group amino is connected on beta-cyclodextrin by a chemical modification method to obtain amino-group-beta-cyclodextrin;under the action of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl propylamine) carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, amino-group-beta-cyclodextrin is coupled with folic acid to obtain folic acid-beta-cyclodextrin; and by taking silver, zinc and other low-toxicity elements as raw materials, an oil-solubility near-infrared quantum dot is prepared, and folic acid-Beta-cyclodextrin is used to carry out water-solubility modification to the oil-solubility near-infrared quantum dot so as to obtain the low-toxicity functionalized quantum dot modified by amination beta-cyclodextrin. The quantum dot has good water-solubility and low-toxicity; and as emission spectrum is in a near-infrared area, and the folic acid is coupled, the quantum dot can be used for special fluorescence detection of tumors.
Owner:江苏迈健生物科技发展股份有限公司
Substrate activation kit and method for detecting DNA and the like using the same
InactiveUS7078172B1Accurate detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityFluorescence
It is intended to provide a method whereby DNA can be conveniently and rigidly immobilized on a substrate at such a high density as achieved by the conventional methods and a method of accurately detecting DNA. A substrate activation kit comprising a phosphate buffer (pH6), a solution A (an aqueous solution) of N-hydroxysuccinimide and a solution B (a dioxide solution) of 1-[3-(dimethylamino) propyl]3-ethylcarbodiimide; and a method of detecting DNA characterized by comprising spotting DNA on a substrate having been activated by using the above activation kit and then hybridizing the spotted DNA with fluorescence labeled DNA.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
Lipoprotein capillary coating and the preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101750449ARetain activityGood biocompatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEthyl groupNon-covalent interactions
The invention relates to a lipoprotein capillary coating and the preparation method thereof. The coating can be prepared with the physisorphtion and chemical bonding methods. In the physisorphtion, a noncovalent interaction between lipoprotein solution with a concentration ranging from 0.01 to 10mg / ml and the internal wall of a capillary is performed and the lipoprotein solution is self-assembled to the internal surface to form the coating. In the chemical bonding method, the capillary is modified with aminopropyl siloxane and the amino is introduced and then the glutaraldehyde or N, N-DSS or 1-ethide-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)-carbodiimide / N-hydroxysuccinimide is used as the resin acceptor to covalently connect the amino on the capillary wall with the amino acid residues on the lipoprotein on the conditions of buffer solution with a pH ranging from 4 to 9 and lipoprotein with a concentration ranging from 0.1 to 10mg / ml for the purpose of obtain the lipoprotein coating. The coating preserves the biological activity, can be used for suppressing the absorption and electroosmotic adjustment on the surface of the capillary and also can be used for biochemical separation analysis.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Labeling reactants and their use
InactiveUS6080839AEasy to markSimple methodCarbamic acid derivatives preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrogen atomLanthanide
The invention relates to a novel labeling reactant, suitable for labeling of a biospecific binding reactant using solid-phase synthesis. The invention further concerns new labeling methods. The novel labeling reactant has the formula (I) wherein -A- is a bivalent aromatic structure capable of absorbing light or energy and transferring the excitation energy to a lanthanide ion after the product made by the said solid-phase synthesis has been released from the used solid support, deprotected and converted to a lanthanide chelate; -G- is a bridge replacing a hydrogen atom in A; R is a protected amino acid residue -CH(NHX)COOH, where X is a transient protecting group, or its active ester, where said ester is e.g. an N-hydroxysuccinimido, p-nitrophenol or pentafluorophenol ester; and R' is -COOR''' where R''' is an alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl or benzyl, which phenyl or benzyl can be substituted or unsubstituted.
Owner:WALLAC
Targeted adriamycin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles and preparation method and application
InactiveCN106729773AGood target recognition abilityExcellent photothermal killing functionOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsEGFR AntibodyMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention provides a targeted adriamycin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles and a preparation method and application, and belongs to the magnetic nanoparticles and preparation thereof. The targeted adriamycin-loaded magnetic nanoparticles are formed by taking the magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles formed by using dopamine to wrap as a core, and an EGFR antibody covalently coupled on the surface of the magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles through 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride or N-hydroxysuccinimide, and adriamycin non-covalently coupled to the surface of the nanoparticles. The nanoparticles provided by the invention have good target recognition capacity to the colon cancer cell DLD-1, can effectively enter the internal of the DLD-1 cell, has excellent photo-thermal killing ability on the DLD-1 cell, can be used for the photo-thermal treatment and medicine chemotherapy of the colon cancer cell, and has a good magnetic resonance imaging function.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Reverse osmosis membrane with polyvinylamine grafted on surface, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104815567AWide variety of sourcesReduced surface negative charge densityReverse osmosisActivation methodReverse osmosis
The present invention relates to a reverse osmosis membrane with polyvinylamine grafted on the surface, and a preparation method thereof. According to the reverse osmosis membrane with polyvinylamine grafted on the surface, the carboxy on the surface of an aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane and the primary amine group of polyvinylamine are connected, the high cation density hydrophilic polymer polyvinylamine is grafted on the surface of the aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane by using a carboxy activation method using 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, and the primary amine of the polyvinylamine reacts with the carboxy on the membrane surface so as to form the firm amide bond. The reverse osmosis membrane of the present invention has characteristics of surface negative charge density reducing and hydrophilicity increasing, and provides anti-pollution performances for proteins, surfactants and other contaminants. After the reverse osmosis composite membrane of the present invention is polluted, the flux decline rate is low, and the flux recovery rate is high after cleaning, such that the good anti-pollution performance is provided. In addition, the preparation method has characteristics of wide raw material source, mild reaction condition, and simple method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing protein stuffing for tanning with chrome-containing scrap leather from tanning
ActiveCN102559952AEase of useAchieve self-digestionTanning treatmentRecycling and recovery technologiesN-HydroxysuccinimideRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing protein stuffing for tanning with chrome-containing scrap leather from tanning, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: rubbing the chrome-containing scrap leather from tanning and taking 100 parts, then immersing the chrome-containing scrap leather into 0.3-1.5 wt% of alkaline compound solution that at least can submerse the scrap leather for 15-45 hours, and draining; putting the pre-treated chrome-containing scrap leather into a reaction kettle equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, and a reflux condenser; adding 8-18 parts of alkaline compound and water that at least can submerse the chrome-containing scrap leather, raising the temperature to 55-90 DEG C, and keeping for 3-18 hours to obtain thick liquid with deep color; cooling the liquid and adjusting the pH value with inorganic acid to 6-7, then filtering to obtain collagen polypeptide-rich filtrate with a solid content of 10-20%; adding 0.2-0.5 wt% of polycarboxylic acid-N-hydroxysuccinimide based on the weight of the dry basis of collagen polypeptide, and reacting at room temperature under continuously stirring for 1-3 hours; and concentrating and drying to obtain the protein stuffing for tanning.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
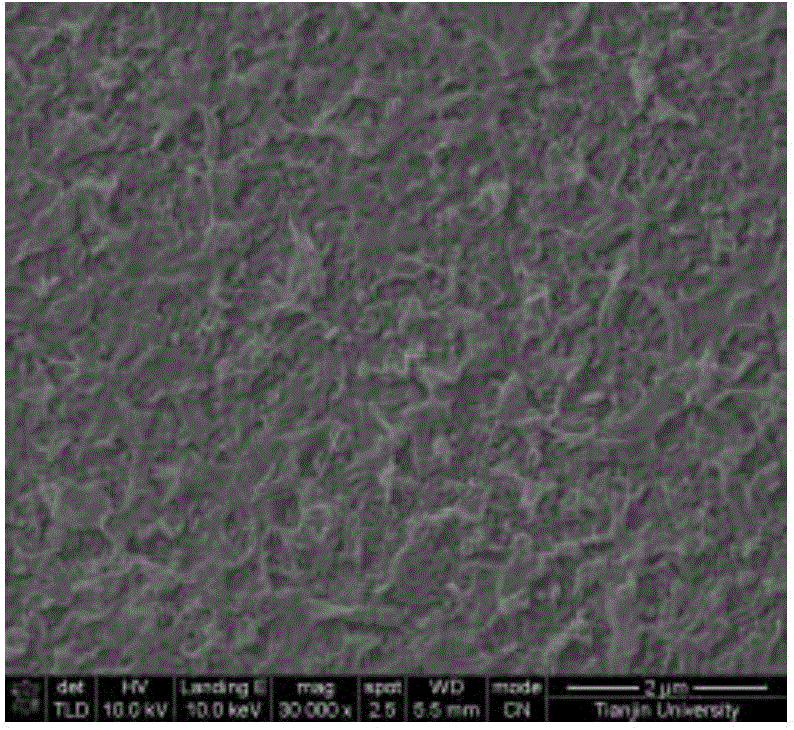
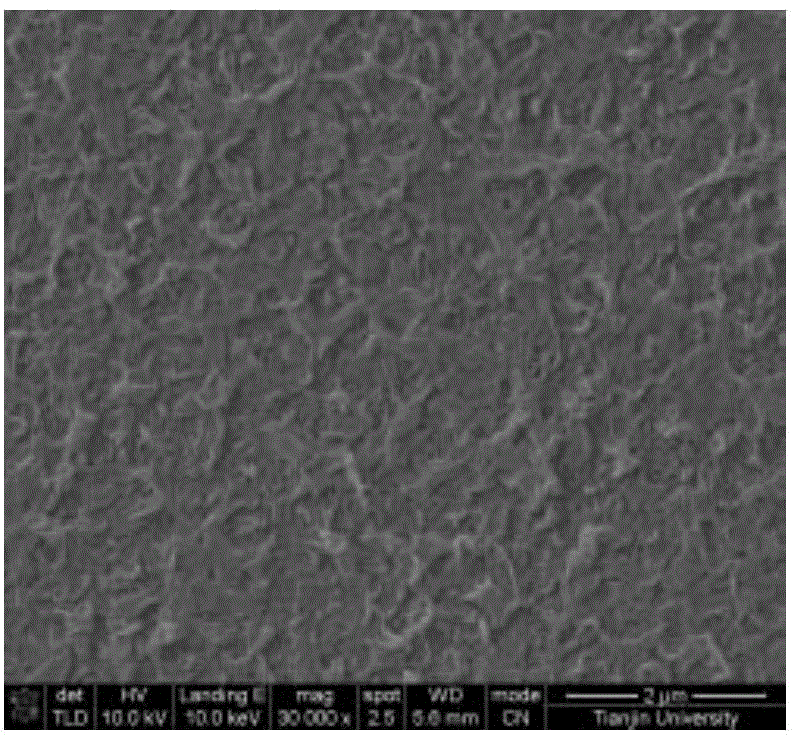
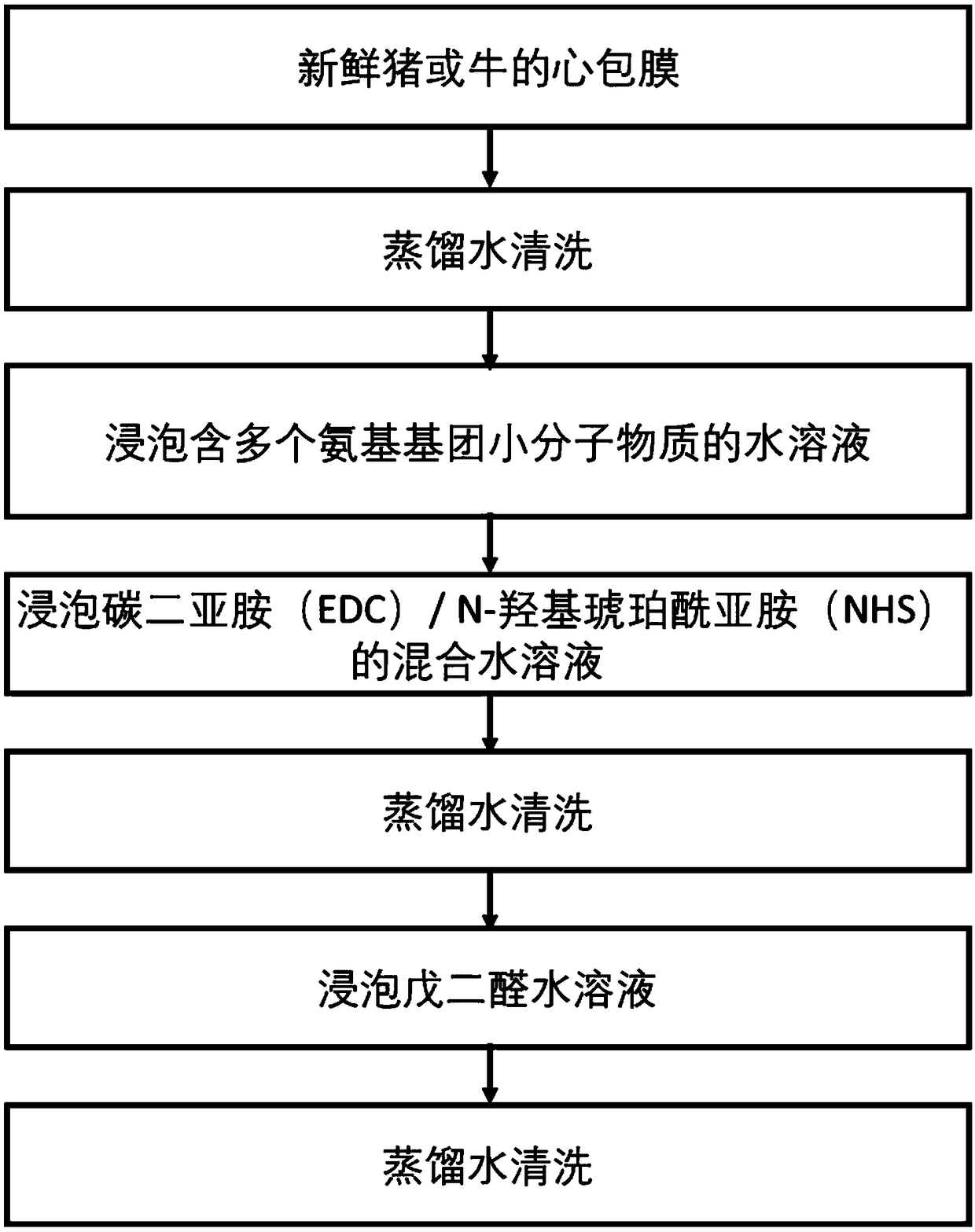
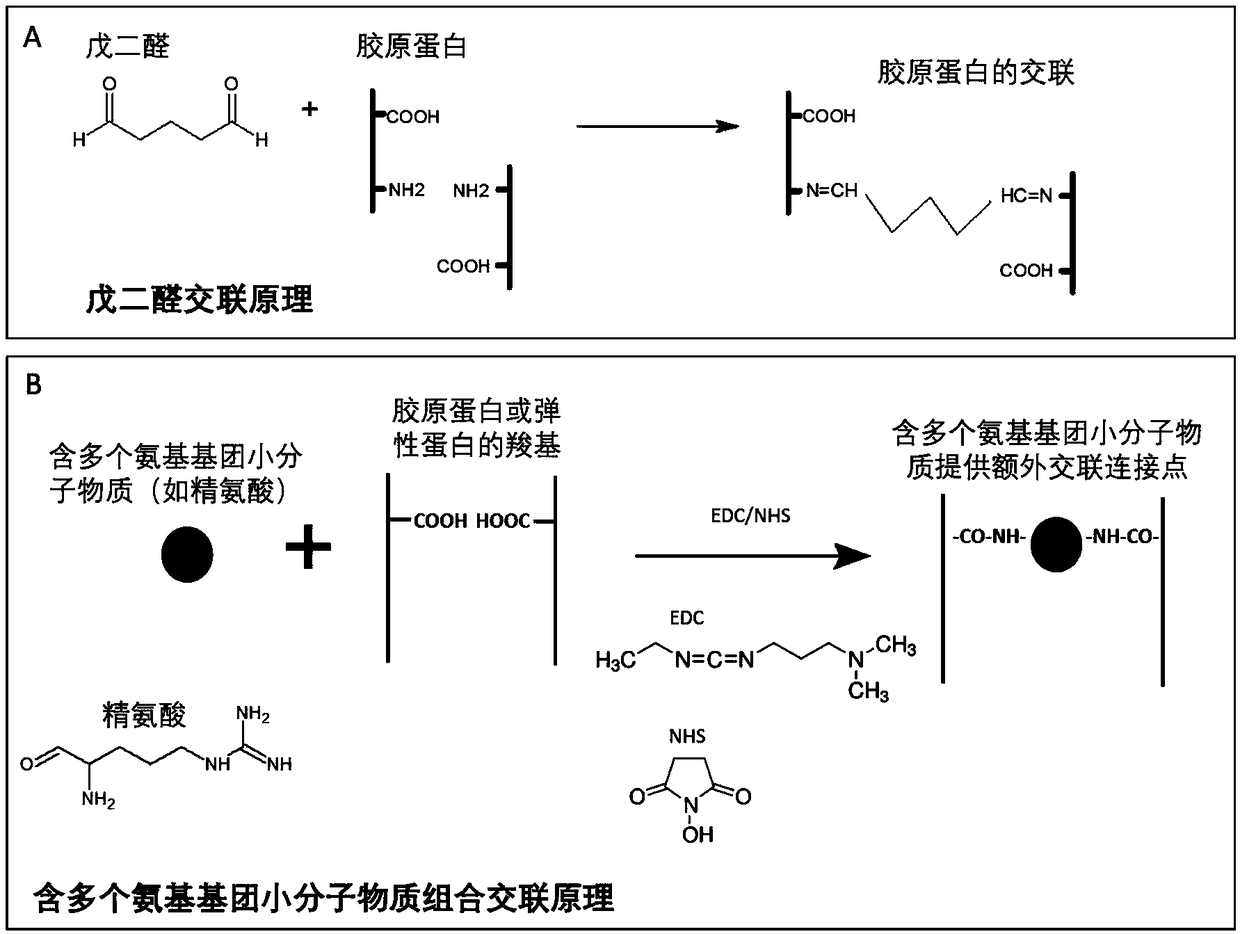
Treatment method for improving anti-calcification performance of biological material, and biological material
InactiveCN108785747AImprove anti-calcification propertiesImprove stabilityTissue regenerationProsthesisCalcificationN-Hydroxysuccinimide
The invention discloses a treatment method for improving the anti-calcification performance of biological materials, and the biological materials. The method comprises the steps of soaking the biological materials in an aqueous solution containing a plurality of amino group small molecule substances, wherein small amino molecules permeate into a pericardium material; then, enabling the biologicalmaterials and the plurality of amino group small molecule substances to be subjected to a chemical crosslinking reaction by means of carboxyl on pericardium under the catalytic action of a mixed solution of carbodiimide (EDC) / N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). The plurality of amino group small molecule substances are used as an exogenous amino donor, so that more cross-linking points are provided for the biological materials, and the structural stability of the biological materials is further improved. The method provided by the invention can improve the structural stability, mechanical strength andanti-calcification performance of the biological materials, so that the service lives of the biological materials are potentially prolonged.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing silk-fibroin-based water-absorbing material by grafting vinyl monomer
ActiveCN105924596AImprove the efficiency of graft copolymerization reactionHigh graft copolymerization efficiencyFermentationN-HydroxysuccinimideCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing a silk-fibroin-based water-absorbing material by grafting a vinyl monomer. Vinyl-containing carboxylic acid is grafted on the silk fibroin surface by the aid of EDC / NHS (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide / N-hydroxysuccinimide), acrylamide (AM) and acrylic acid (AA) monomers are added, and a horseradish peroxidase / oxydol / acetylacetonate system is utilized to catalyze the silk fibroin-vinyl monomer graft copolymerization, thereby preparing the silk-fibroin-based water-absorbing material by a bioenzyme process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a silk fibroin solution; (2) grafting vinyl onto the silk fibroin surface by an EDC / NHS process; (3) catalyzing the silk fibroin-AM-AA graft copolymerization by using the horseradish peroxidase; and (4) forming the silk-fibroin-based water-absorbing material. Compared with the traditional process, the method has the advantages of high graft copolymerization efficiency and mild enzyme treatment conditions. The silk-fibroin-based composite water-absorbing material has the advantages of favorable water absorptivity, favorable water retention property and favorable biodegradability.
Owner:无锡市奥菲超细织物有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com