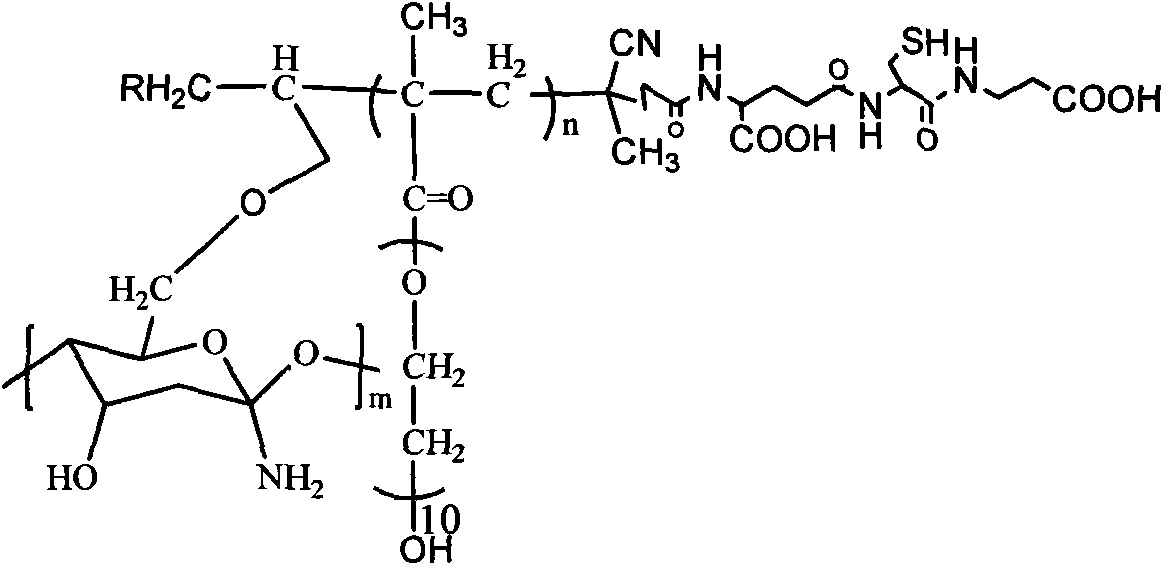
Glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer serving as non-viral gene carrier material and preparation and application thereof
A technology of chitosan copolymer and glutathione is applied in the field of preparation of non-viral gene carriers, which can solve the problems of low transfection rate of active genes, low-efficiency intracellular operation, unfavorable biological distribution, etc., and reduce cytotoxicity. , low immune rejection, good protective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1) Weigh 10.0g chitosan and dissolve it in deionized water, then add appropriate amount of sodium hydroxide and sodium borohydride, dissolve evenly, then add 10ml allyl bromide at 40°C, heat up to 60°C and stir for 3 After that, it was neutralized with acetic acid, and the product was repeatedly precipitated and extracted in ethanol, then vacuum-dried to constant weight to obtain allyl chitosan.
[0041] 2) Weigh 2.104g of polyethylene glycol methacrylate macromonomer (MPEG), dissolve 5.6mg of ACVA and 27.9mg of CPADB in methanol, and then, after three times of liquid nitrogen freezing-evacuation-thawing cycle degassing, at 60°C Under reaction for 24 hours. Then, the reaction was terminated with ice water, and viscous active polymer PMPEG was obtained through repeated precipitation in cold ether and vacuum drying.
[0042] 3) Weigh 0.2g of allyl chitosan obtained in step 1), and 0.25g of PMPEG and initiator ACVA obtained in step 2) are dissolved in dimethylformamide (D...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The cell transfection steps of copolymer (CS-PMPEG-GSH) are:
[0046] 1) Preparation of CS-PMPEG-GSH / pDNA complex:
[0047] Dissolve the polymer in sodium acetate solution at pH 5.5 to prepare a CS-PMPEG-GSH solution, then add the prepared plasmid DNA solution labeled with green fluorescent protein at a concentration of 0.5 μg / μL to the polymer in equal volume Add 2.5 μg pDNA to each complex, mix, let stand at room temperature for 30 minutes, and then stand still to obtain CS-PMPEG-GSH / pDNA complex solution.
[0048] 2) In vitro cell transfection experiments:
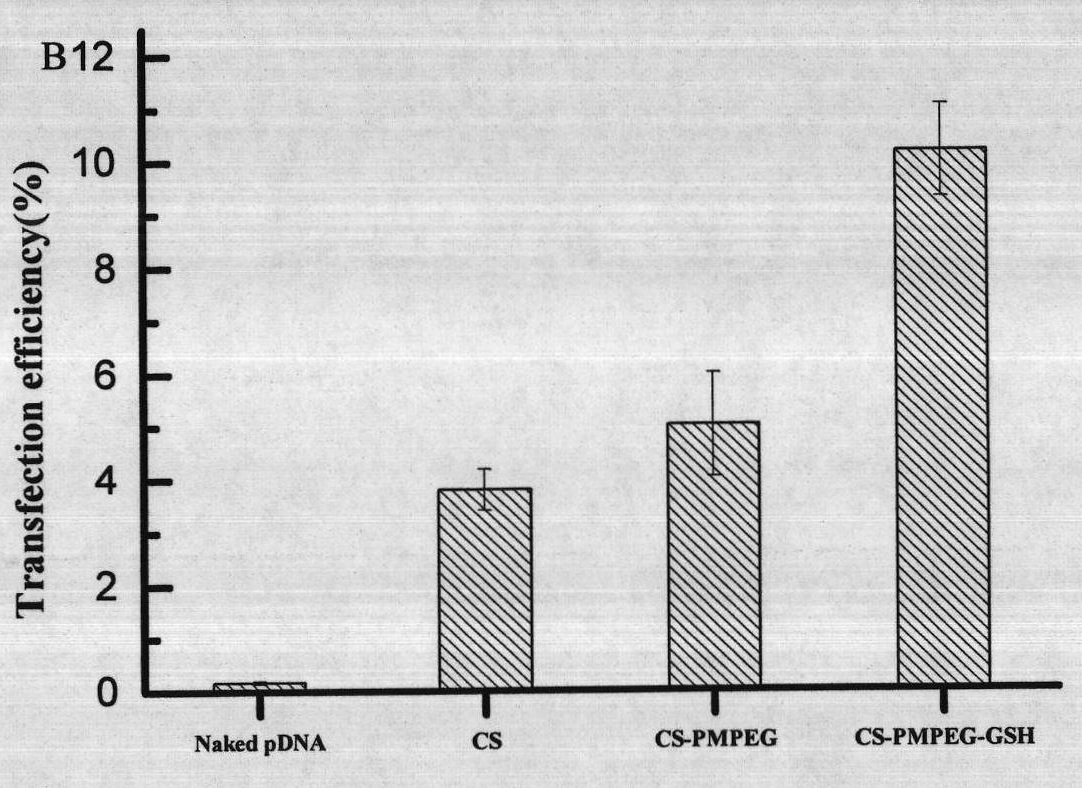
[0049] NIH3T3 cells at 1×10 per well 5 Several kinds of cells were put into 24-well culture plate and cultivated for 24 hours, then replaced with new medium containing glutathione-grafted chitosan copolymer CS-PMPEG-GSH / pDNA complex, continued to cultivate for 48 hours, and flow cytometry The transfection efficiency was quantified by cytometer. The result is as figure 2 shown.
[0050] figure 2It was sho...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: gel retardation experiment:
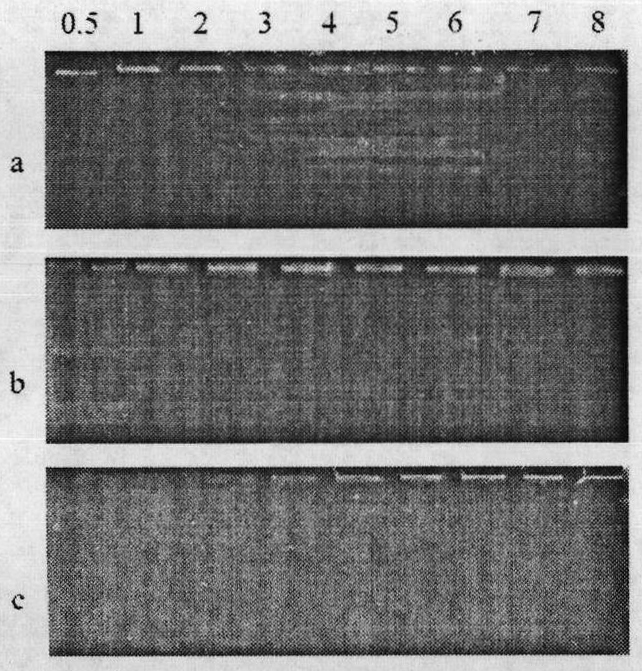
[0052] First, prepare electrophoresis gel after dissolving agarose with a concentration of 1%, then CS-PMPEG-GSH / pDNA complex solutions with different N / P ratios, in which each sample contains 0.066 μg of pDNA, and finally electrophoresis at a constant voltage of 100V After electrophoresis, place the gel plate in EB solution for staining, soak for 30 minutes, and observe the pDNA band under ultraviolet light. The result is as image 3 shown.
[0053] image 3 Agar gel electrophoresis images of different N / P ratios, (a) chitosan / pDNA; (b) copolymer CS-PMPEG / pDNA and (c) graft copolymer CS-PMPEG-GSH / pDNA. It can be seen that the glutathione-grafted chitosan copolymer can wrap pDNA well when the N / P ratio is above 4.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of deacetylation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com