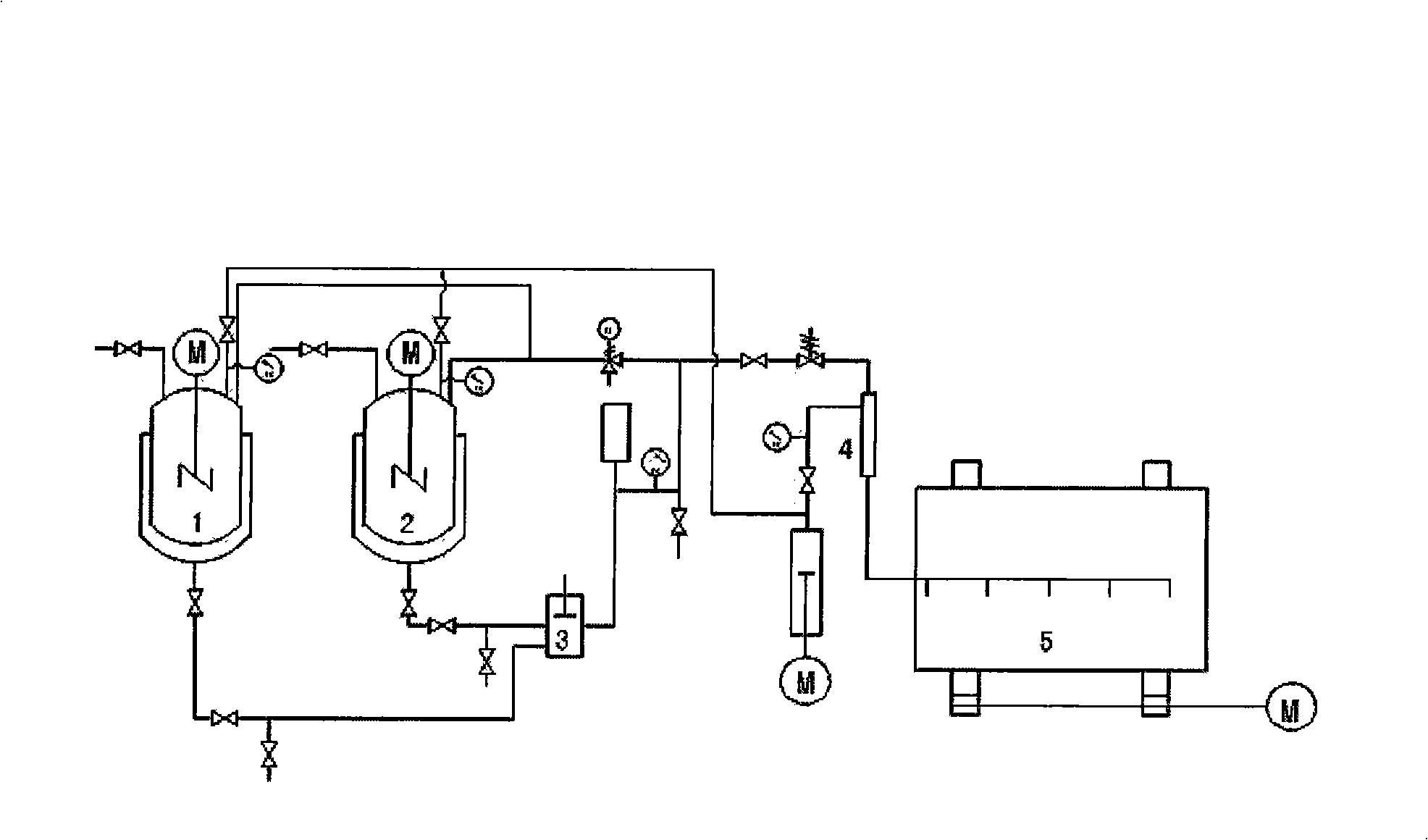
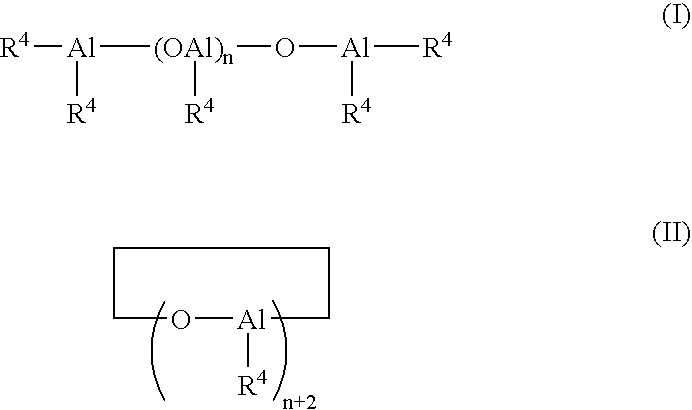
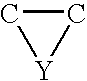
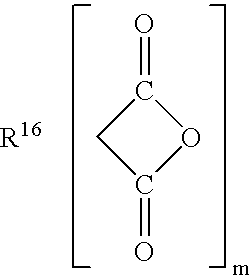
Patents
Literature
7183 results about "Isocyanate compound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
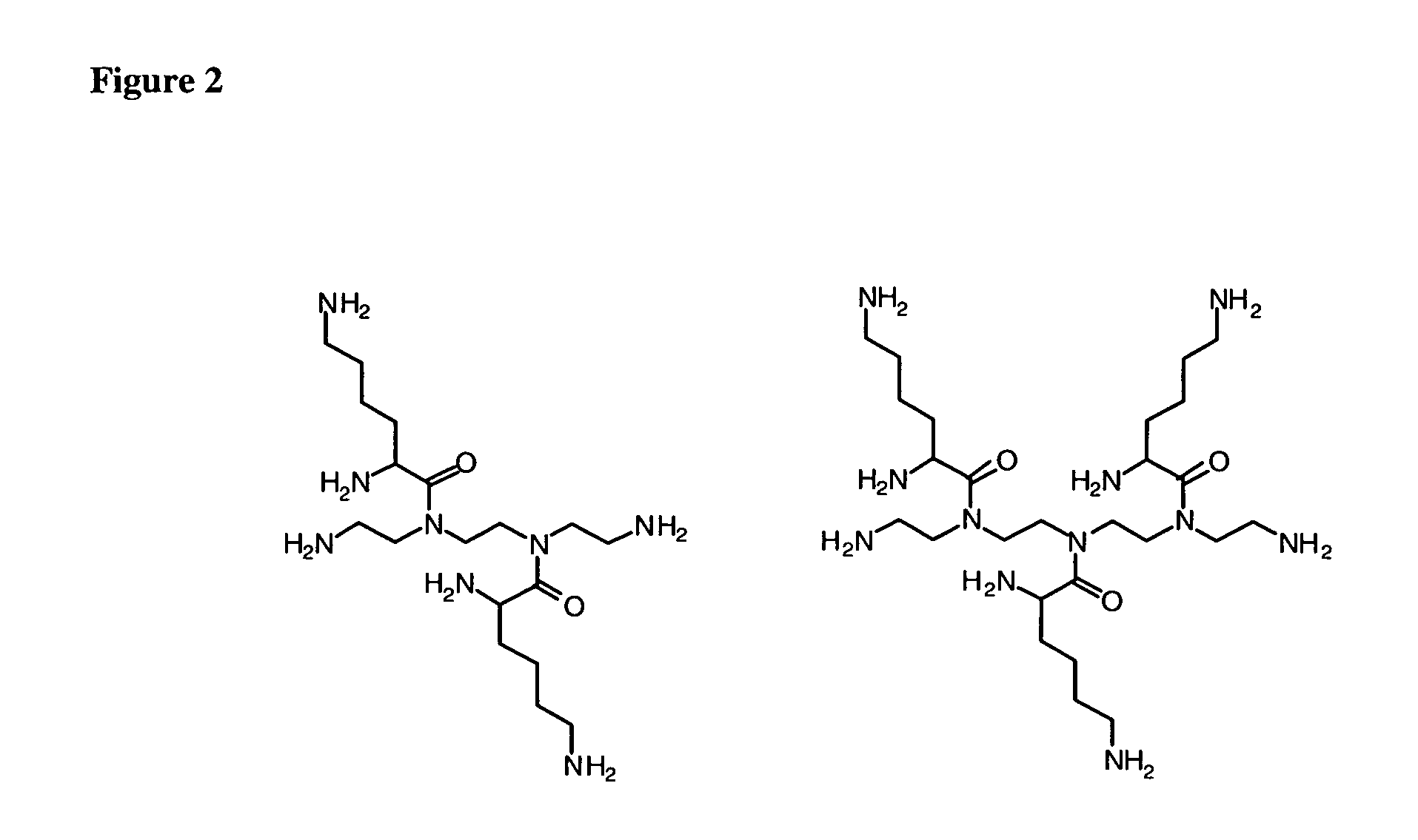
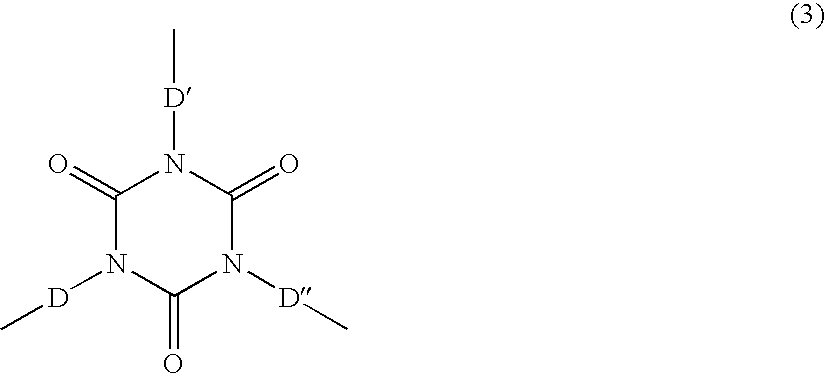
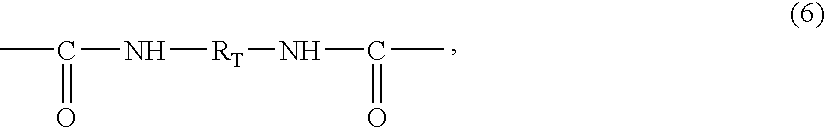
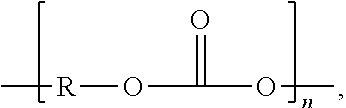
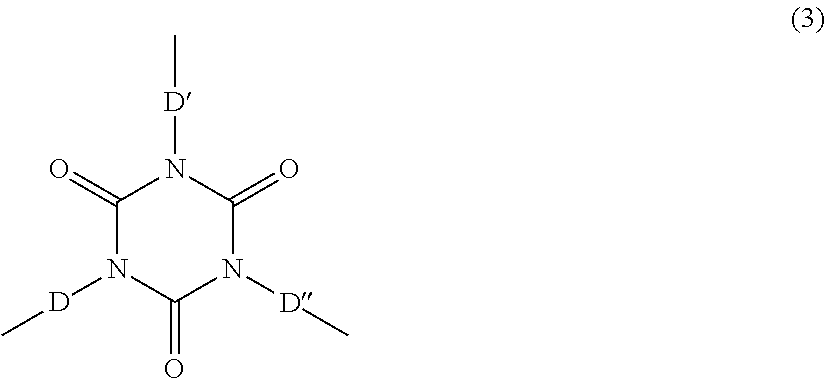
Isocyanate is the functional group with the formula R–N=C=O. Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An isocyanate that has two isocyanate groups is known as a di-isocyanate.
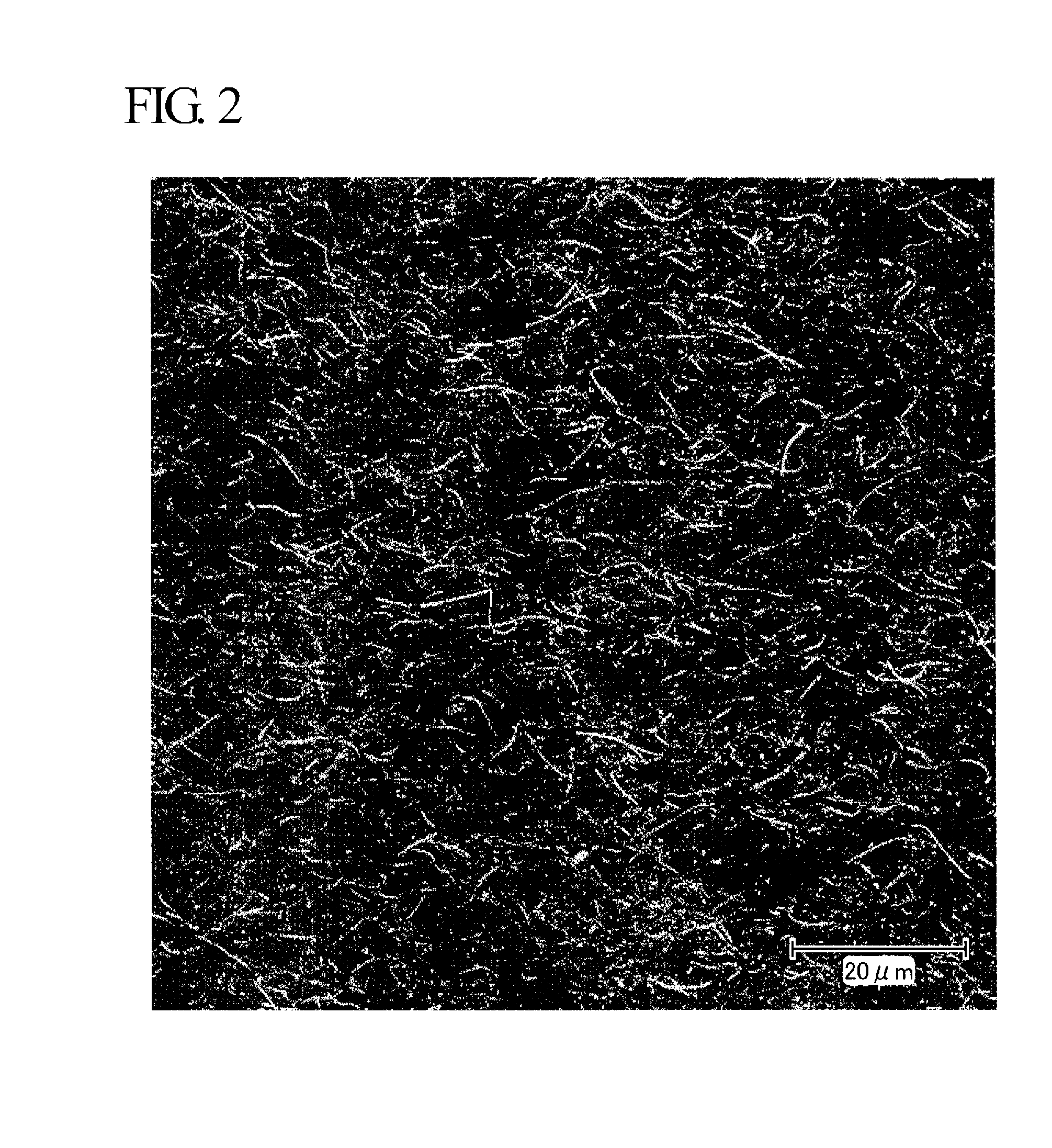
Biodegradable polyurethanes and use thereof
InactiveUS20050013793A1Improve responseIncrease ratingsCell culture supports/coatingSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPolymer scienceDrug biological activity
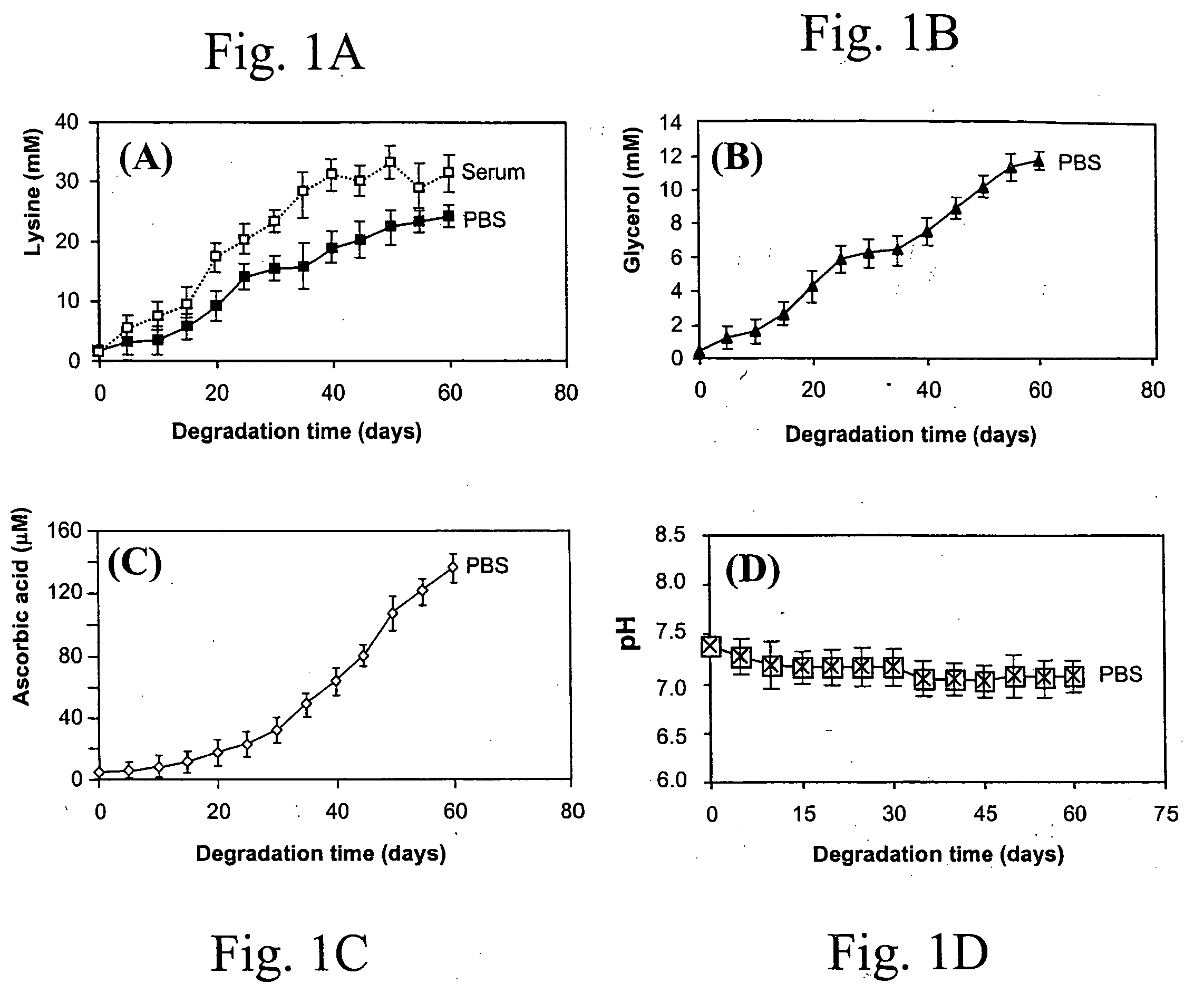
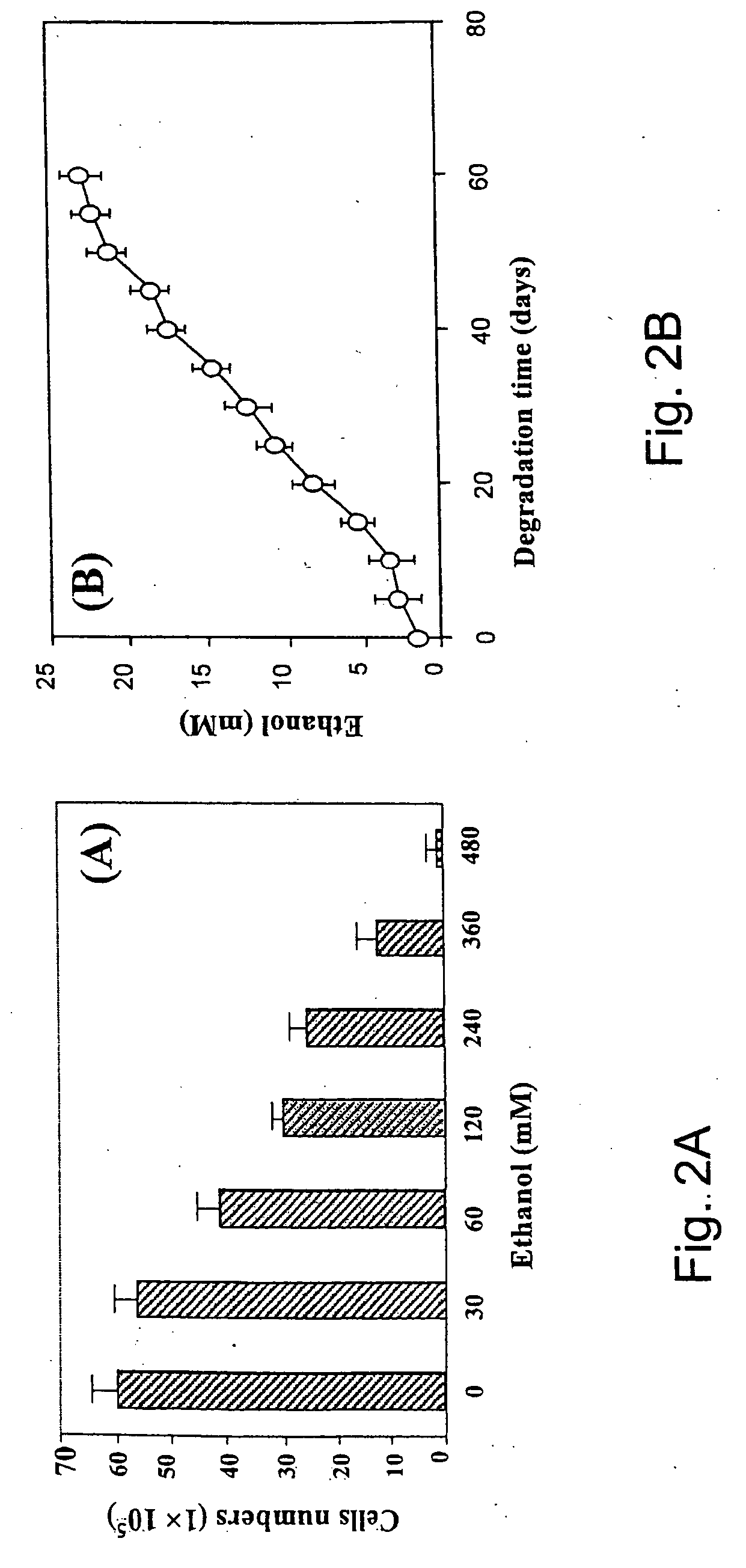
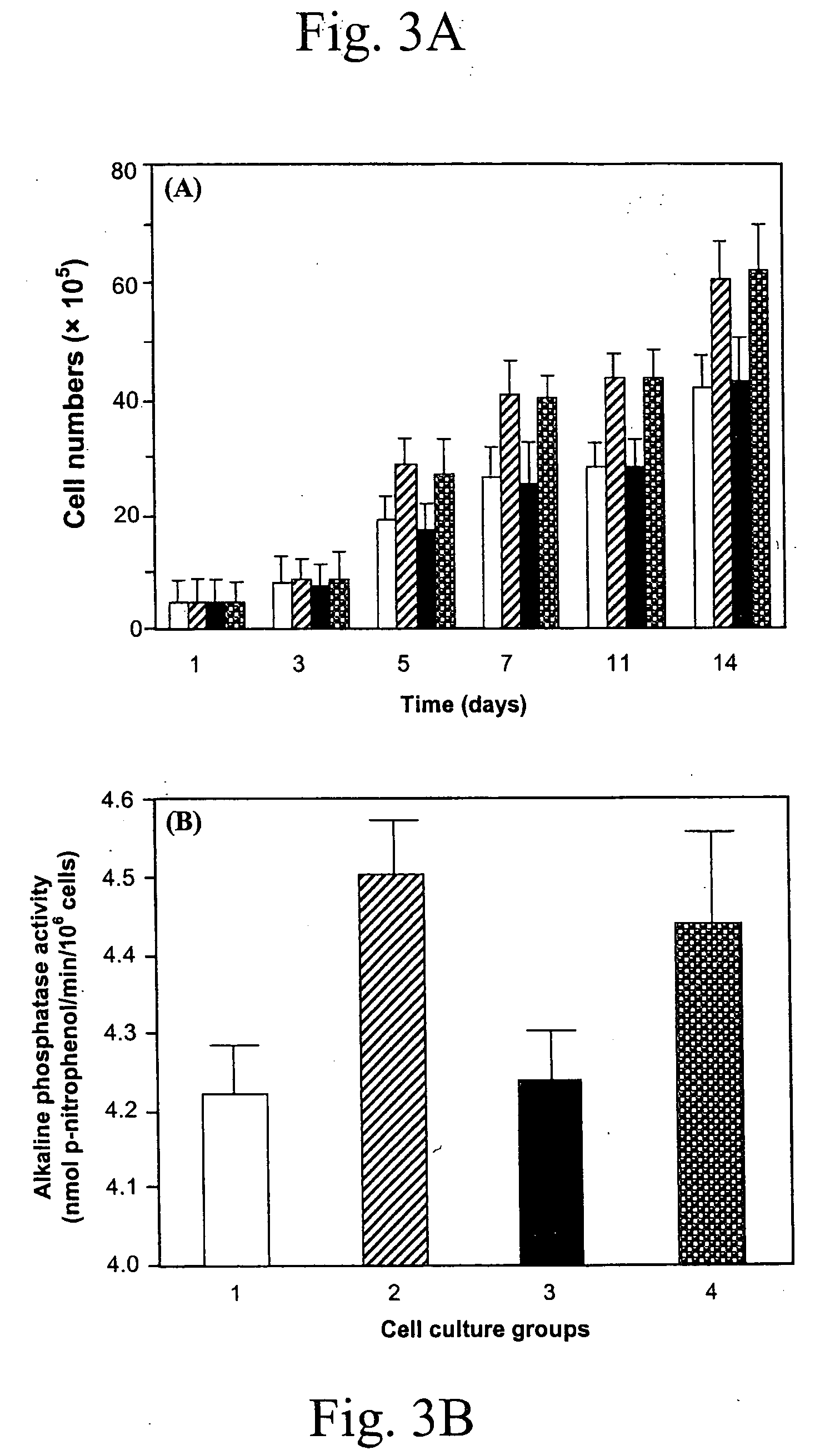
A biodegradable and biocompatible polyurethane composition synthesized by reacting isocyanate groups of at least one multifunctional isocyanate compound with at least one bioactive agent having at least one reactive group —X which is a hydroxyl group (—OH) or an amine group (—NH2). The polyurethane composition is biodegradable within a living organism to biocompatible degradation products including the bioactive agent. Preferably, the released bioactive agent affects at least one of biological activity or chemical activity in the host organism. A biodegradable polyurethane composition includes hard segments and soft segments. Each of the hard segments is preferably derived from a diurea diol or a diester diol and is preferably biodegradable into biomolecule degradation products or into biomolecule degradation products and a biocompatible diol. Another biodegradable polyurethane composition includes hard segments and soft segments. Each of the hard segments is derived from a diurethane diol and is biodegradable into biomolecule degradation products.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Cellular plastic material
An improved cellular plastic material comprises a urethane foam that is the reaction product of soy oil, an isocyanate, and a cross linker. The soy oil replaces the polyol typically generally required in the production of urethanes. Because the replaced polyol is a petrochemical, use of a renewable and environmentally friendly material such as soy oil is most advantageous. Further, plastic materials of many final qualities may be formed using a single vegetable oil. In addition to cellular foams, solid plastic elastomers may be formed.
Owner:URETHANE SOY SYST +1
Crosslinked gels comprising polyalkyleneimines, and their uses as medical devices
ActiveUS20070196454A1Promote cell growthSoft tissue growthIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSurgical adhesivesCross-linkCysteine thiolate
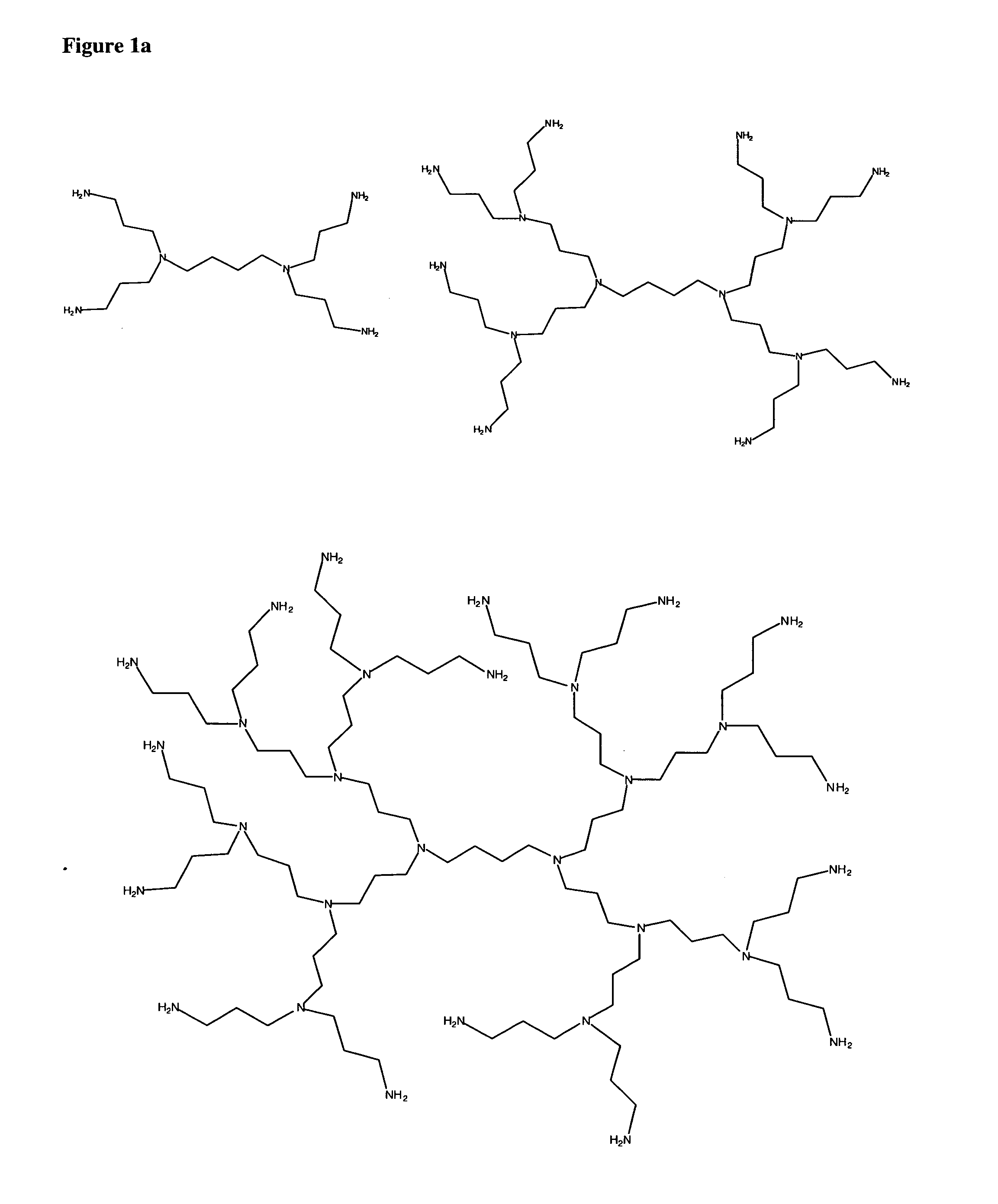
One aspect of the present invention generally relates to methods of sealing a wound or tissue plane or filling a void splace. In a preferred embodiment, the wound is an ophthalmic, pleural or dural wound. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane comprises a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Treatment of the polyethyleneimine with a cross-linking reagent causes the polyethyleneimine polymers to polymerize forming a seal. In certain instances, the cross-linking reagent is a polyethylene glycol having reactive terminal groups. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are isocyanates. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine has a lysine, cysteine, isocysteine or other nucleophilic group attached to the periphery of the polymer. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine is mixed with a second polymer, such as a polyethylene glycol containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing electrophilic groups with a cross-linking reagent containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the electrophilic groups on the polyalkyleneamine are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing photopolymerizable groups with ultraviolet or visibile light. Compositions used to seal the wound which contain PEI or a derivative of PEI are found to adhere tightly to the tissue. Other aspects of the present invention relate to methods of filling a void of a patient or adhering tissue. In certain instances, the methods use a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a polymeric composition formed by exposing a polyalkyleneamine to an activated polyalkylene glycol. In certain instances, the composition is attached to mammalian tissue.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
Reactive oligomers for isocyanate coatings
InactiveUS6221494B1Extended shelf lifeHigh glossAluminium compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxyOligomer
The invention is directed to a two-pack solvent-based ambient curable coating composition comprising a binder of a hydroxyl and crosslinking components. The hydroxyl component includes a linear or branched cycloaliphatic moiety-containing reactive oligomer or blend of oligomers with a weight average molecular weight not exceeding 3,000, a polydispersity not exceeding about 1.7 with at least 2 hydroxyl groups, at least 1, on average, being a primary hydroxyl group. The reactive oligomer is formed by the reaction of an oligomeric acid with monofunctional epoxy. The crosslinking component includes one or more of an oligomeric crosslinker containing at least 2 isocyanate groups. The coating composition of the invention is particularly suited in automotive refinish coatings.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Crosslinkable polyurea prepolymers
The present invention provides a water-soluble crosslinkable polyurea prepolymer. The crosslinkable polyurea prepolymer of the invention is prepared by reacting an amine- or isocyanate-capped polyurea with a multifunctional compound having at least one one ethylenically unsaturated group and a function group coreactive with the capping amine or isocyanate groups of the amine- or isocyanate-capped polyurea. The amine- or isocyanate-capped polyurea is a copolymerization production of: (a) at least one poly(oxyalkylene)diamine, (b) optionally at least one organic di- or poly-amine, (c) optionally at least one diisocyanate, and (d) at least one polyisocyanate. The crosslinkable polyurea prepolymer of the invention can find use in economically producing contact lenses which have durable, highly elastic soft contact lenses with desired physical properties. In addition, the present invention provides method for making a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method of preparing an aliphatic polyurea spray elastomer system
This invention concerns a method for the preparation of polyurea elastomers, comprising: (a) reacting an amine chain extender with dialkyl maleate to form an aspartic ester, wherein the chain extender has a molar amount of amine groups that is less than the moles of dialkyl maleate; (b) blending the aspartic ester with one or more polyoxyalkyleneamines to prepare a resin blend; (c) contacting the resin blend with an isocyanate under conditions effective to form a polyurea elastomer. This invention also concerns a a polyurea elastomer, comprising the reaction product of (a) a resin blend containing one or more polyoxyalkyleneamine and an aspartic ester and (b) an isocyanate, wherein the aspartic ester in the resin blend comprises a reaction product of an amine chain extender and a dialkyl maleate, wherein the mole ratio of amine functionality in the amine chain extender to dialkyl maleate or fumarate is greater than 1:1.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK N A AS COLLATERAL AGENT +1
Biodegradable polyurethane and polyurethane ureas
ActiveUS20060051394A1Fast formingEasily degradableOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryPolyolInsertion stent
This invention relates to biocompatible, biodegradable thermoplastic polyurethane or polyurethane / ureas comprising isocyanate, polyol and a conventional chain extender and / or a chain extender having a hydrolysable linking group and their use in tissue engineering and repair applications, particularly as stents and stent coating.
Owner:POLYNOVO BIOMATERIALS PTY LTD
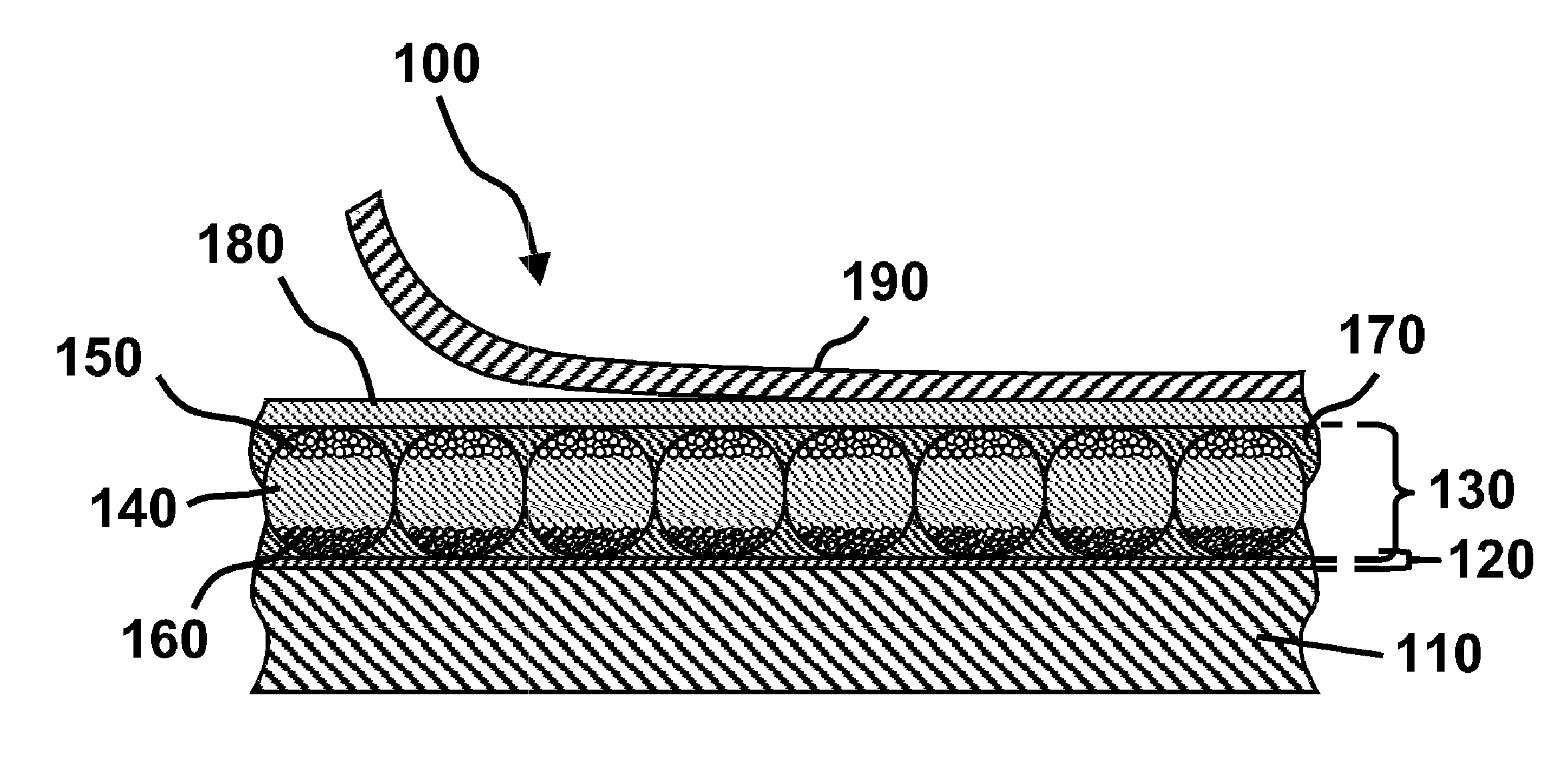
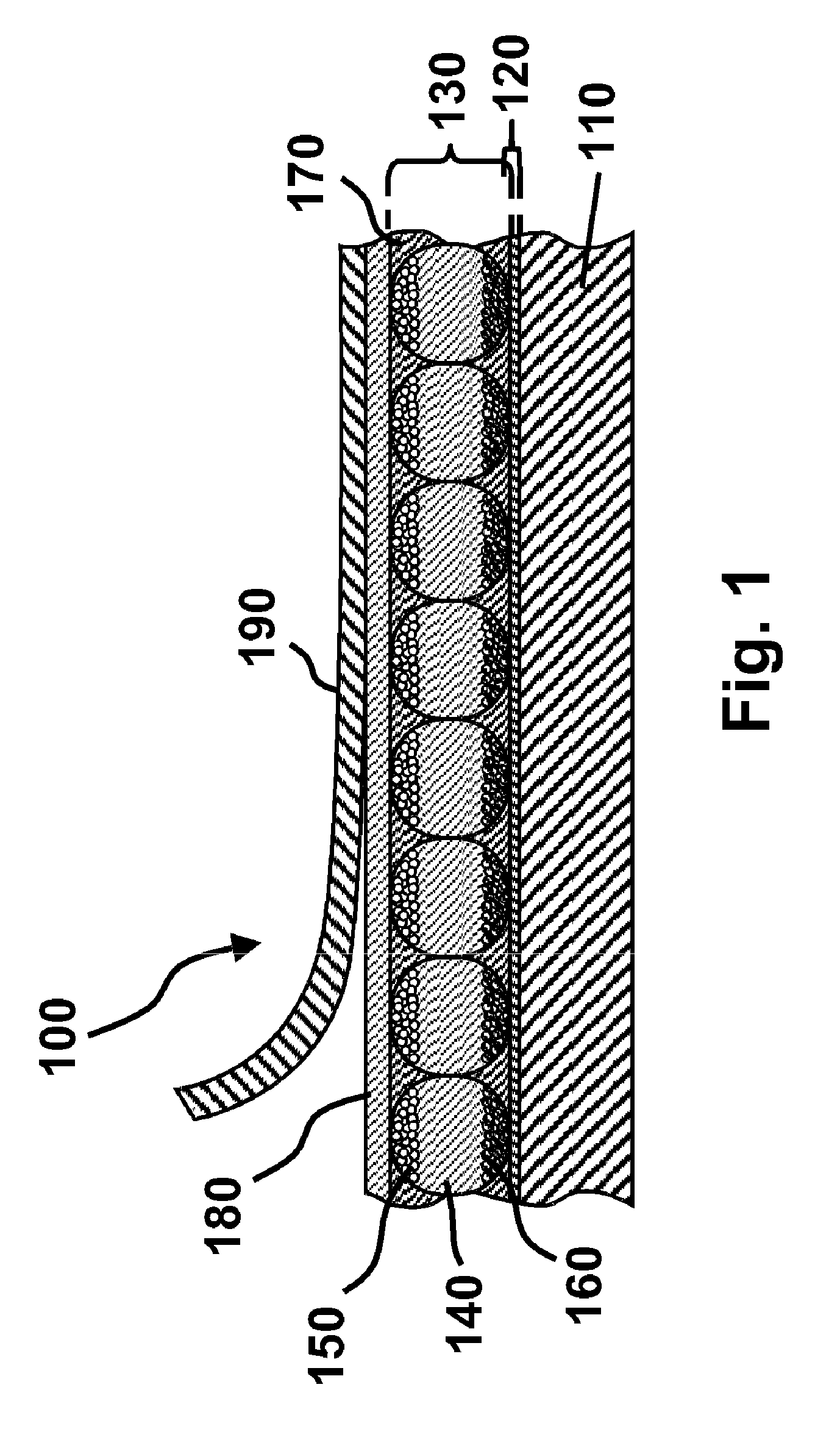
Electro-optic display and materials for use therein
A polyurethane is formed from an isocyanate and a polyester diol having a molecular weight less than about 2000, or a polyester diol comprising two polyester diol segments connected by a steric hindrance group, each of the polyester diol segments having a molecular weight less than about 2000. The polyurethane is useful as a binder in electro-optic displays, and in components used to form such displays.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC +1
Bioabsorbable adhesive compounds and compositions
Bioabsorbable compounds which include a polyalkylene oxide backbone with two or more isocyanate substituents are useful as one component adhesives. Absorbable compositions useful as a two component adhesive contain a) a polyethylene oxide having two or more amine substituents with b) a bioabsorbable diisocyanate compound, or alternatively contain a) a polyethylene oxide having two or more isocyanate substituents with b) a bioabsorbable diamine compound, or, alternatively contain a) a bioabsorbable diisocyanate compound and b) a bioabsorbable diamine compound.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Degradable polymer filmcoated controlled release fertilizer, preparation thereof and special filmcoated material
ActiveCN101323545AHas the ability to degradeAchieve friendlyFertilizer mixturesControl releasePolyol
The invention discloses a polymer coated released fertilizer and a preparation method thereof and a special coating material thereof. The coating material comprises isocyanate, polyol, degradable functional monomer, an aid agent of coating and a chain extender, wherein, the mol ratio between the isocyano group in the isocyanate and the hydroxyl group in the polyol is 1:2 to 2:1 and the mass of the degradable functional monomer is 1 percent to 20 percent of the mass of the coating material. The coated released fertilizer provided by the invention consists of a core and a karyotheca, wherein, the core is granule fertilizer and the karyotheca is prepared from the coating material, and the mass of the karyotheca is 2 percent to 10 percent of the mass of the core. The coating material has good film forming and water resisting performance and can be degraded in nature. The hardness and the elasticity of the material can be adjusted by changing the mixure ratio of the coating material so as to prepare released fertilizers with different releasing periods.
Owner:CNSG ANHUI HONG SIFANG FERTILIZER IND CO LTD
Solid golf ball
InactiveUS20080312008A1Improve spin performanceIncrease distanceGolf ballsSolid ballsOrganosulphur compoundPolymer science
The invention provides a solid golf ball having a solid core and a cover layer that encases the core and has an outermost layer on an outside surface of which are formed a plurality of dimples. The solid core is formed of a rubber composition composed of 100 parts by weight of a base rubber that includes 60 to 100 parts by weight of a polybutadiene rubber having a cis-1,4 bond content of at least 60% and synthesized using a rare-earth catalyst, 0.1 to 5 parts by weight of an organosulfur compound, an unsaturated carboxylic acid or a metal salt thereof, and an inorganic filler. The solid core has a deformation, when compressed under a final load of 130 kgf from an initial load of 10 kgf, of 2.0 to 4.0 mm, and has a specific hardness distribution. The cover layer is formed by injection molding a single resin blend composed primarily of (A) a thermoplastic polyurethane and (B) a polyisocyanate compound, which resin blend contains a polyisocyanate compound in at least some portion of which all the isocyanate groups on the molecule remain in an unreacted state, and has a thickness of 0.5 to 2.5 mm, a Shore D hardness at the surface of 50 to 70. The golf ball has a deformation, when compressed under a final load of 130 kgf from an initial load of 10 kgf, of 2.0 to 3.8 mm. The solid golf ball is advantageous overall in competitive use.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
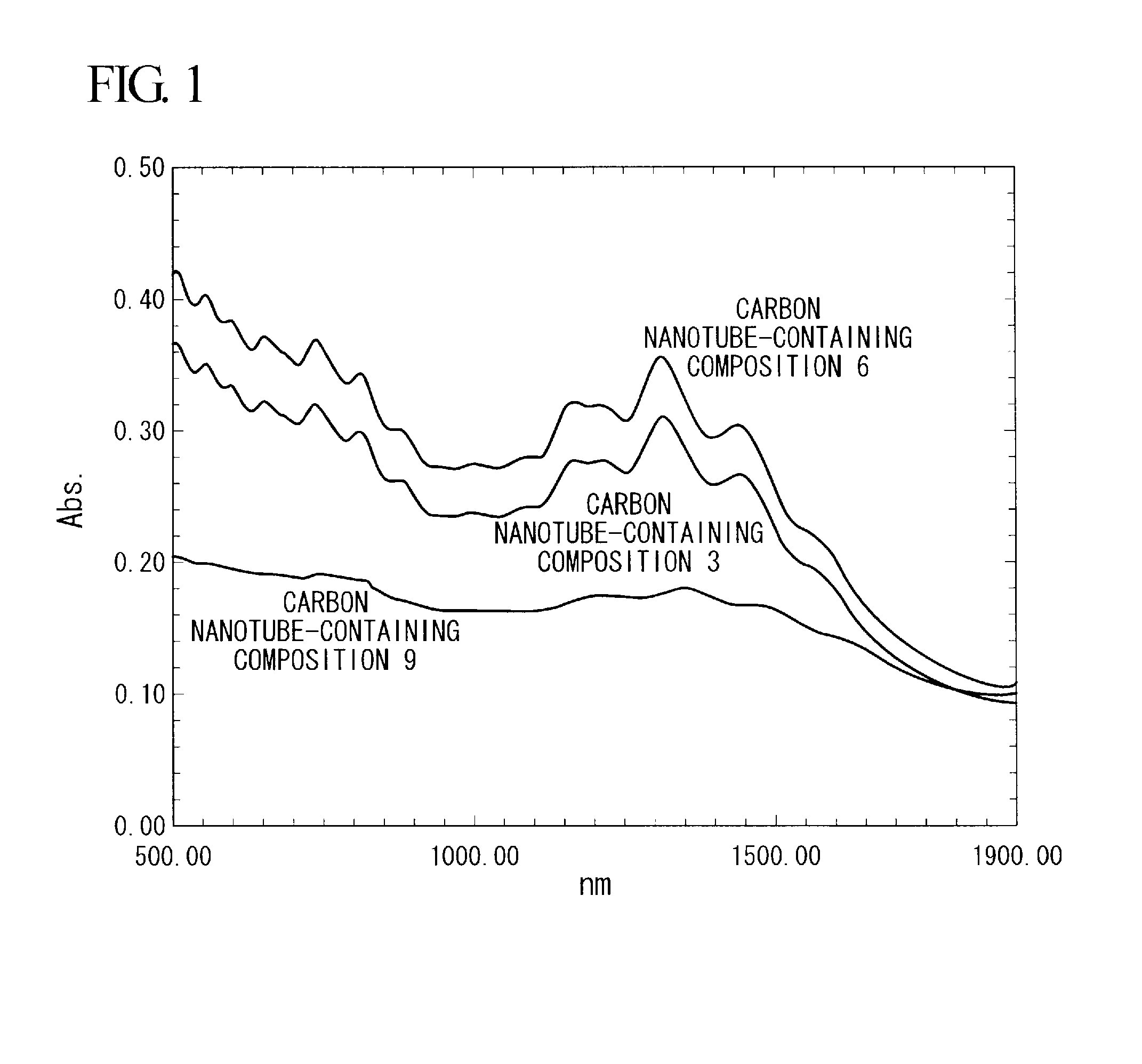
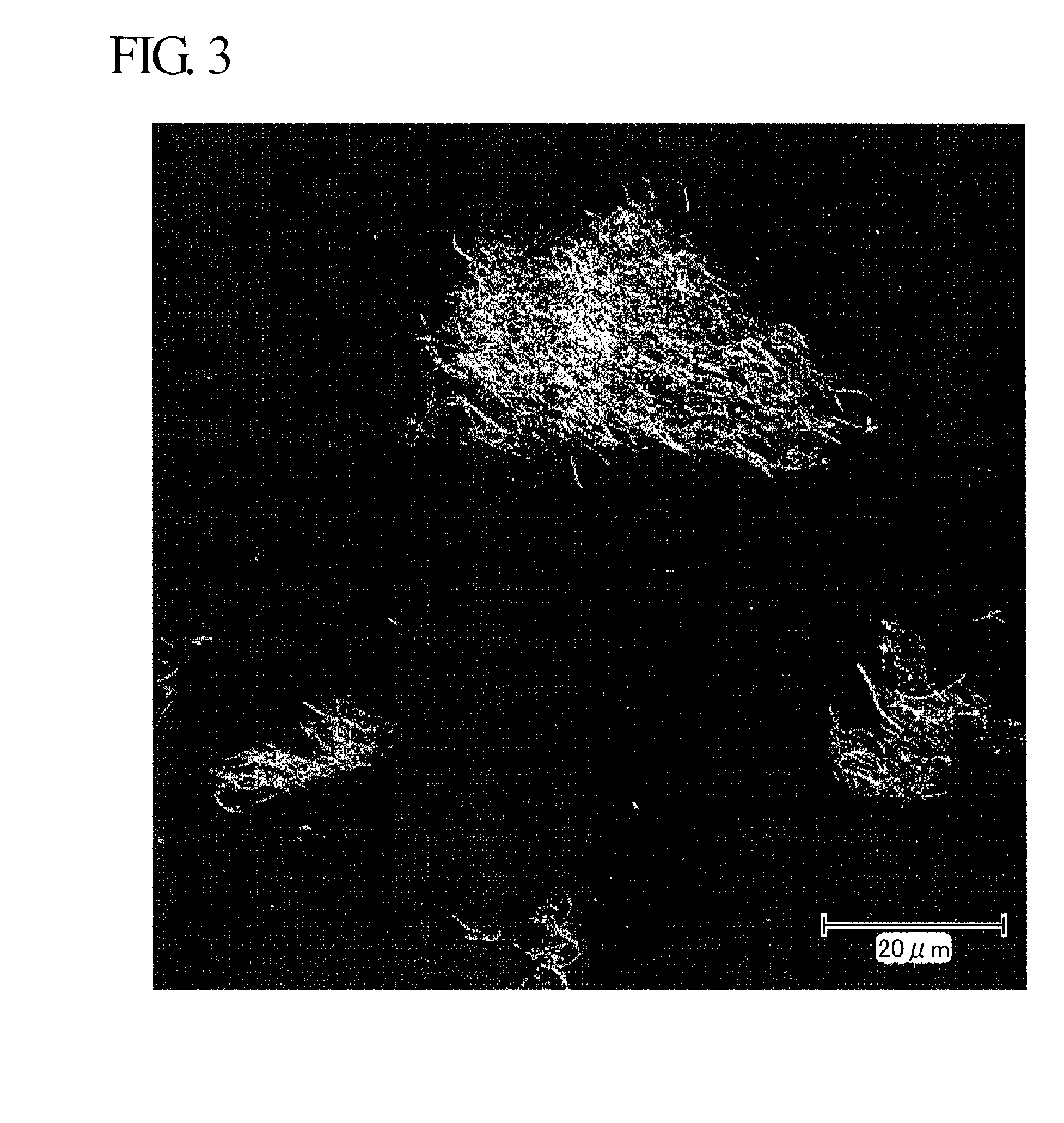
Carbon nanotube-containing composition, composite, and methods for producing them
ActiveUS20100065788A1Improve conductivityInhibit coloringMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialMeth-Carbon nanotube
Disclosed is a carbon nanotube-containing composition which contains a carbon nanotube and a urethane compound obtained by a reaction between a hydroxyl group-containing (meth)acrylate and a isocyanate compound. Also disclosed is a composite having a coating film or a cured film composed of the carbon nanotube-containing composition on at least one surface of a base material. The carbon nanotube-containing composition and the composite are excellent in electrical conductivity, film-formability, moldability, and transparency without deteriorating the characteristic properties of the carbon nanotube itself.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Electro-optic display and materials for use therein
ActiveUS7986450B2Lamination ancillary operationsMagnetic materials for record carriersPolyesterAdhesive
A polyurethane formed from an isocyanate, a polyether diol and a polyester diol, the polyester diol having a molecular weight less than about 2000, or comprising two polyester diol segments connected by a steric hindrance group, each of the polyester diol segments having a molecular weight less than about 2000, the molar ratio of polyether diol to polyester diol being in the range of from about 1:9 to about 9:1. The polyurethane is useful as a lamination adhesive in electro-optic displays, and in components used to form such displays.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION +1
Polyurethane composite thermal insulation board, manufacturing method and application of the same
InactiveCN101220614AImprove thermal insulation performanceImprove fire and flame retardant performanceCovering/liningsLaminationProduction lineAlcohol
The invention provides a polyurethane compound heated board and a manufacturing method and application, which relates to a heated board and supplies a polyurethane compound heated board that has good heat-insulating effect, high fire-fighting and flame-retardant performance, convenient using performance and high constructing efficiency and the manufacturing method and the application. The invention includes a polyurethane rigid foam insulating layer, a bonding layer and an inorganic material composite board; the bonding layer is arranged between the polyurethane rigid foam insulating layer and the inorganic material composite board; the thickness of the polyurethane rigid foam insulating layer is 20-80mm and the thickness of the inorganic material composite plate is 3-10mm. The inorganic material composite board can be continuously produced for further use; an adhesive treatment agent is coated on the inorganic material composite board; polyhydric alcohol combination material and isocyanate combination material are added into the continuous production line for mixed foaming and curing to obtain the polyurethane compound heated board; the mass ratio of the polyhydric alcohol combination material and the isocyanate is 100:95-160.
Owner:厦门高特高新材料有限公司
Modified hydrophilic polyurethane memory foam, application and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070032561A1Broaden applicationImprove temperature resistancePolymer scienceCelsius Degree
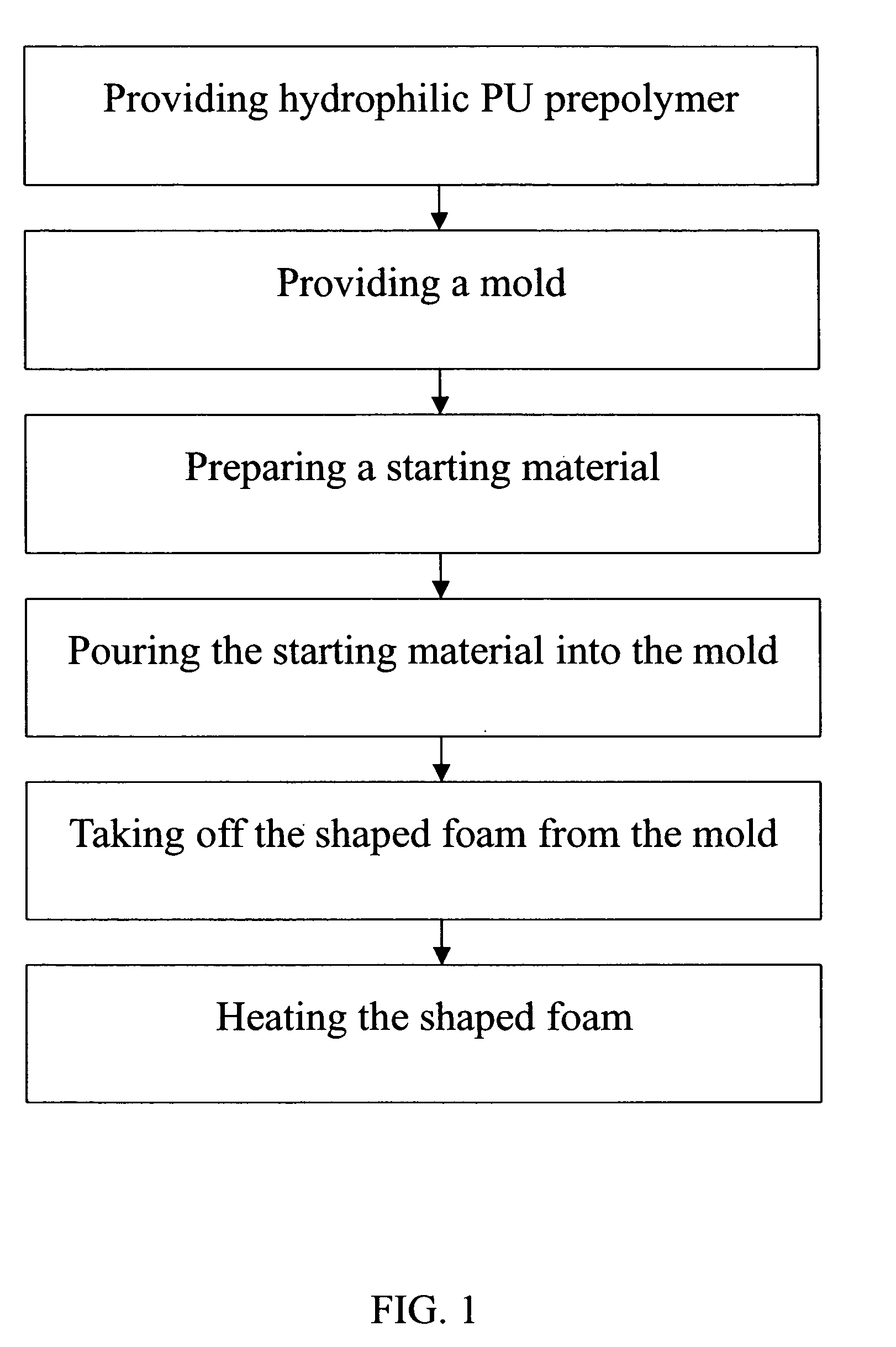
A manufacturing method of modified hydrophilic Polyurethane memory foam and products thereof are disclosed. The starting material of the foam includes hydrophilic PU prepolymer, acrylic emulsion polymer and second polyether polyol. The hydrophilic PU prepolymer consists of a first polyether polyol and isocyanate. The molecular weight of the first polyether polyol ranges from 600 to 2000 and the first polyether polyol contains at least 40 mole % of -EO— where the content of the -EO— ranges from 20 to 99.9 wt %. The foaming agent is carbon dioxide produced by the reaction of isocyanate and the water. After foaming process, there is a heating step for dehydration. The foam has specific high hydrophilic polymer structure with features of shock absorbing, uniform pressure relief, moisture absorbency and heat absorbing so as to provide users dry and cool feelings. It wouldn't become rigid below 10 degrees Celsius.
Owner:LIN I SIOUN
Polyurethanes obtained from hydroxyalkanoates and isocyanates
A polyurethane is described which is a reaction product of at least one isocyanate containing material having at least two isocyanate groups and at least one compound having at least two hydrogen atoms capable of reacting with the isocyanate. The compound having the at least two hydrogen atoms contains a hydroxyalkanoate, which is preferably a thermally decomposable or a biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate. The polyurethane of the present invention can be used in a number of applications and preferably has improved properties such as, but not limited to, improved flexibility and / or improved hydrophobicity. The polyurethanes of the present invention are preferably biodegradable and easily recycled.
Owner:METABOLIX
Vegetable oil-based coating and method for application
A vegetable oil-based coating and a method for applying the coating to a substrate where the coating includes the reaction product of a transesterified vegetable oil-based polyol, a catalyst, and an isocyanate; the reaction product of a vegetable oil based polyol, a cross-linker, a catalyst, and an isocyanate where the vegetable-oil based polyol may optionally be oxylated and / or neutralized.
Owner:URETHANE SOY SYST +1
Water dispersions of non-uniform polyurethane particles
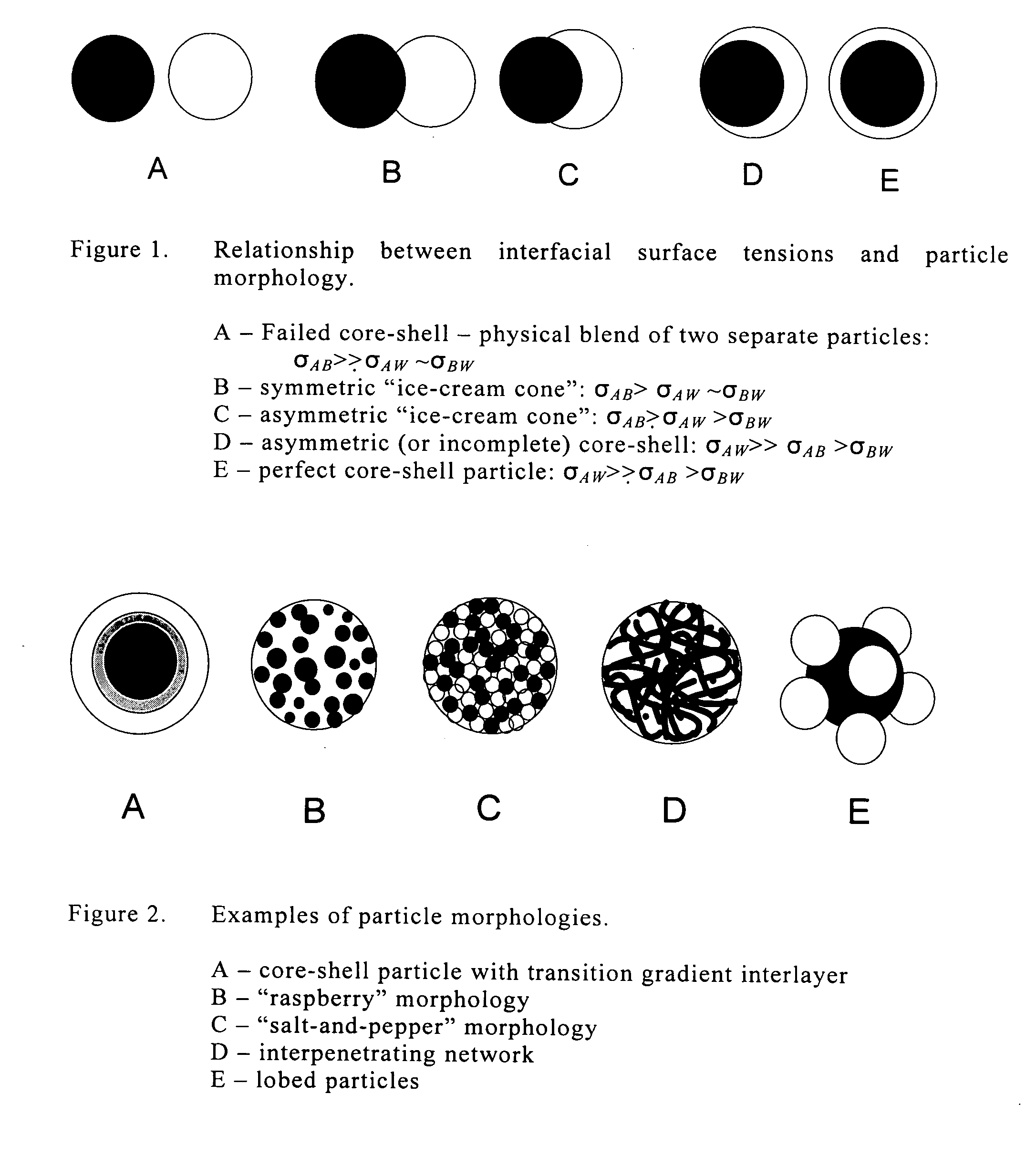
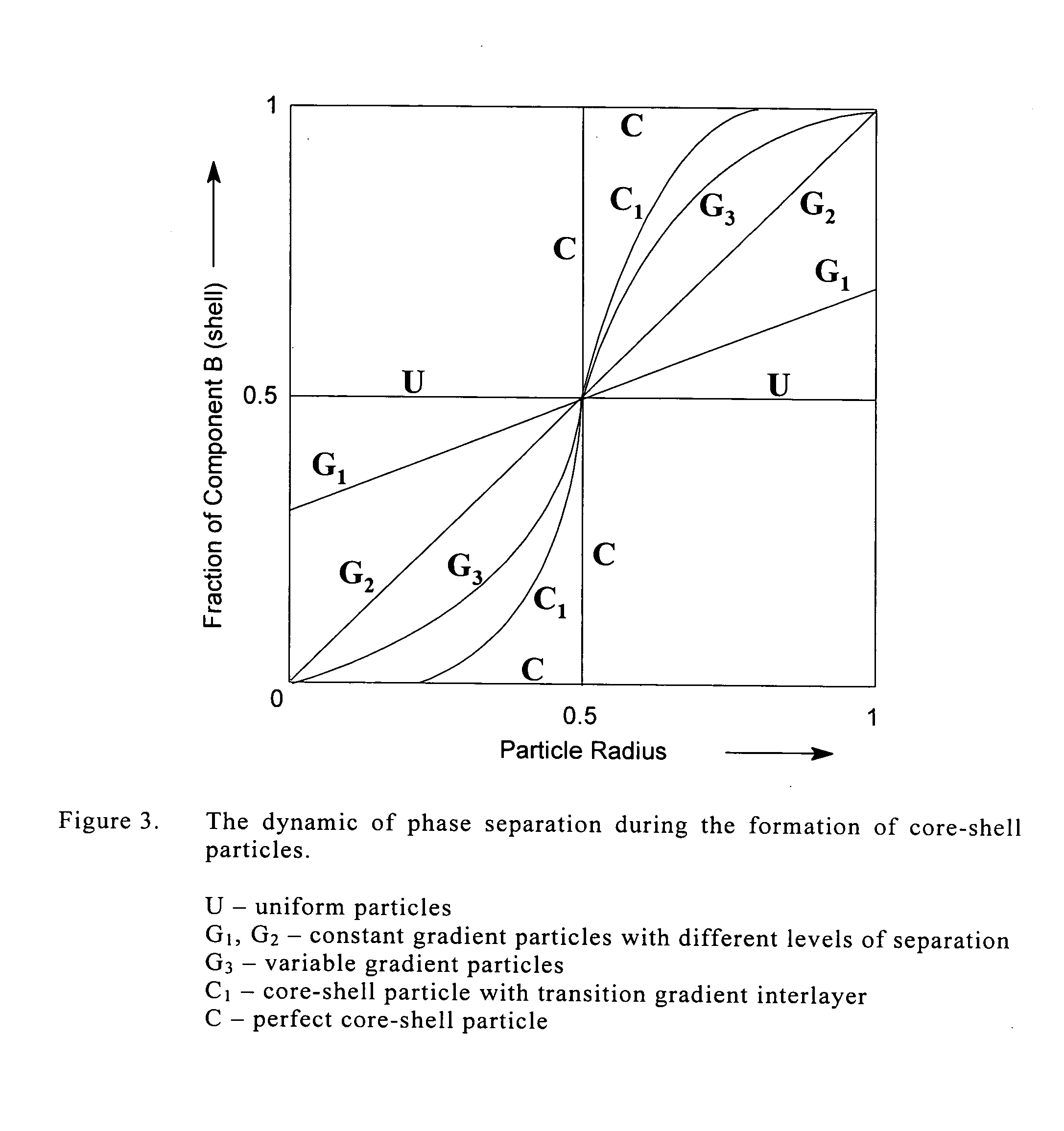
A novel method of preparing an aqueous dispersion of non-uniform polyurethane particles which comprises (a) preparing at least two isocyanate-terminated polyurethane prepolymers having different hydrophilicities; (b) preparing a uniform mixture of said prepolymers; and (c) dispersing the mixed prepolymers in an aqueous medium. The resulting dispersion of the prepolymers may optionally be chain extended. This method enables the preparation of core-shell particles as well as particles of other morphologies, including “raspberry”, interpenetrating network, “salt-and-pepper”, “ice-cream cone” and particles of gradient composition. Similarly, an aqueous dispersion of two different polyurethane polymers may be obtained by first preparing at least two different isocyanate-terminated polyurethane prepolymers, preparing a uniform mixture of such prepolymers and thereafter dispersing the mixture in an aqueous medium.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Lignin polyurethane and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing lignin polyurethane, which comprises the following steps of: using an organic solvent to dissolve the lignin which is extracted and separated from residues after producing ethanol from straws by sodium hydroxide; removing the residues, and depositing the mixture with water; separating the lignin; modifying the lignin with an epoxide; dissolving the lignin into a polylol; and finally compounding the lignin with raw materials of isocyanate and the like to obtain a polyurethane material. The lignin used in the method has high reactivity which can be further enhanced through modification so as to obtain a lignin polyurethane material; the polylol used in the method not only can be used as a solvent but also can take part in a synthetic reaction, has good dissolvability to the lignin, and ensures that undissolved lignin particles cannot appear in a polyurethane foam material; and the link for polyurethane synthesis uses no volatile organic solvents, so the production process causes no pollution to the environment, and simultaneously the cost of a polyurethane product is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Polyisobutylene urethane, urea and urethane/urea copolymers and medical devices containing the same
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
UV curable coating composition
The present invention is directed to a non-aqueous composition curable by UV radiation broadly comprising a mixture of two UV curable urethane acrylates. The invention is also directed to a coating process using such composition. One of the urethane acrylates is the reaction product of an isocyanate and a specific OH functional lactone ester (meth)acrylate. The other urethane acrylate is the reaction product of an isocyanate and a specific hydroxy functional (meth)acrylate.
Owner:ALLNEX NETHERLANDS BV
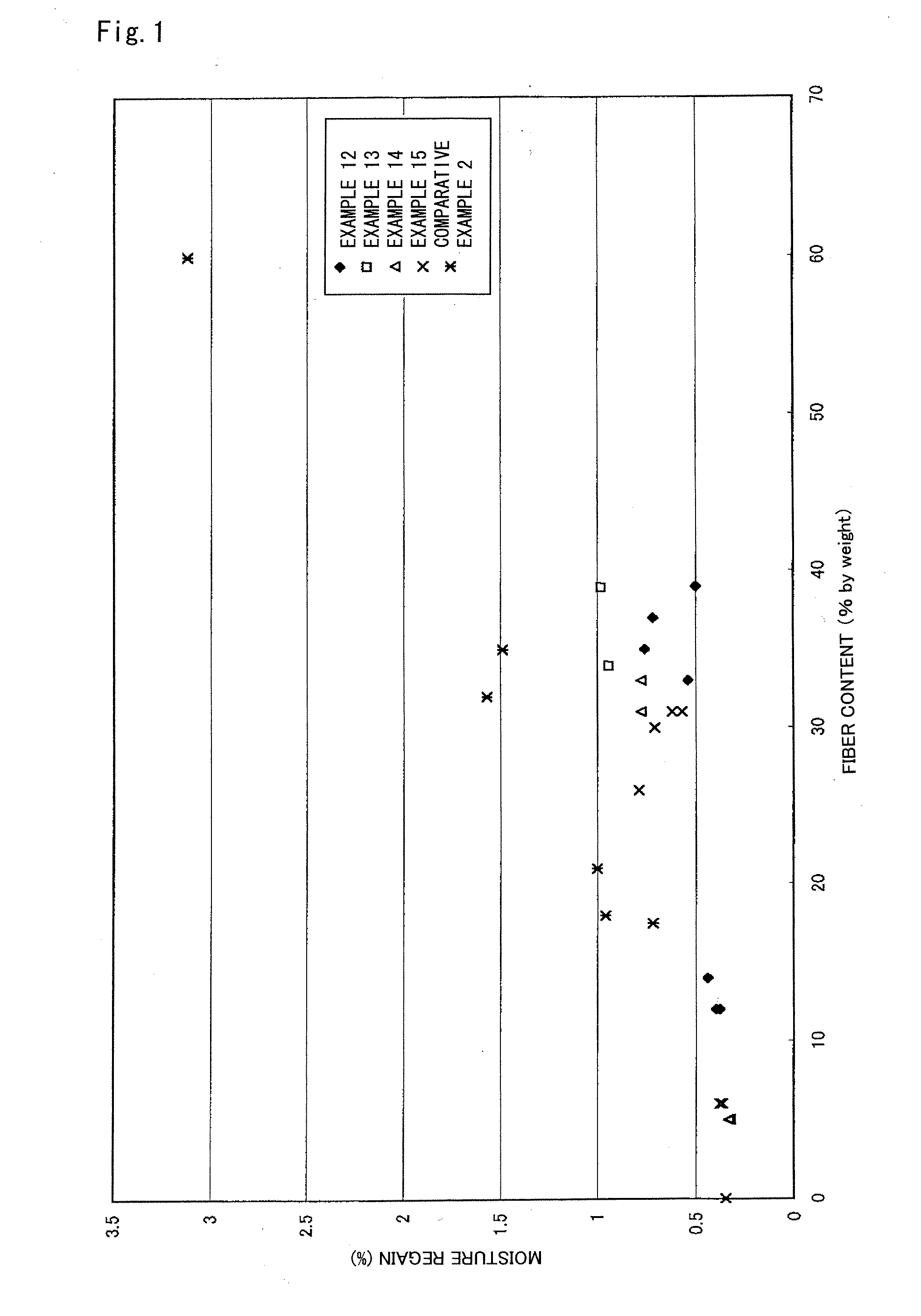
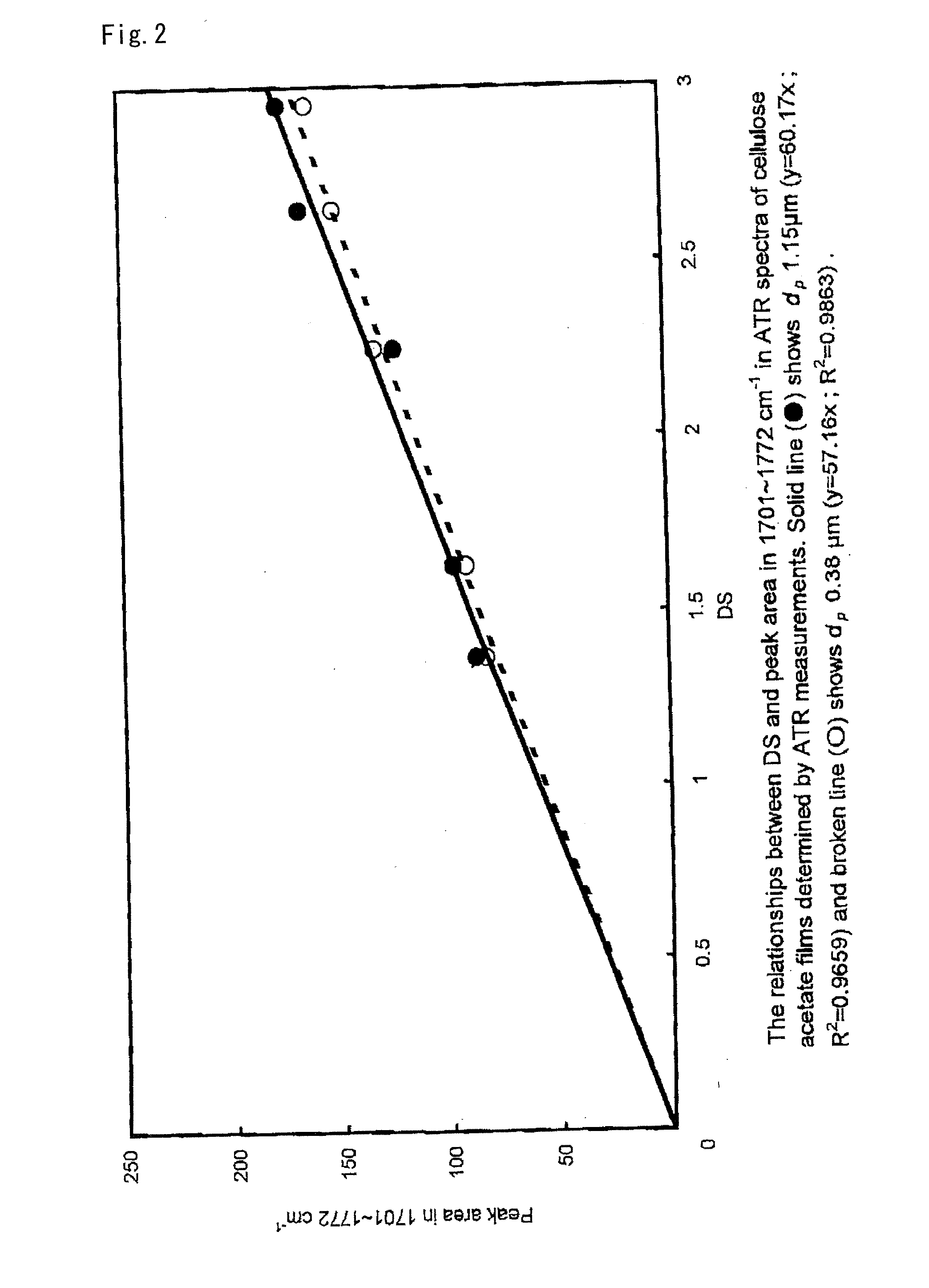
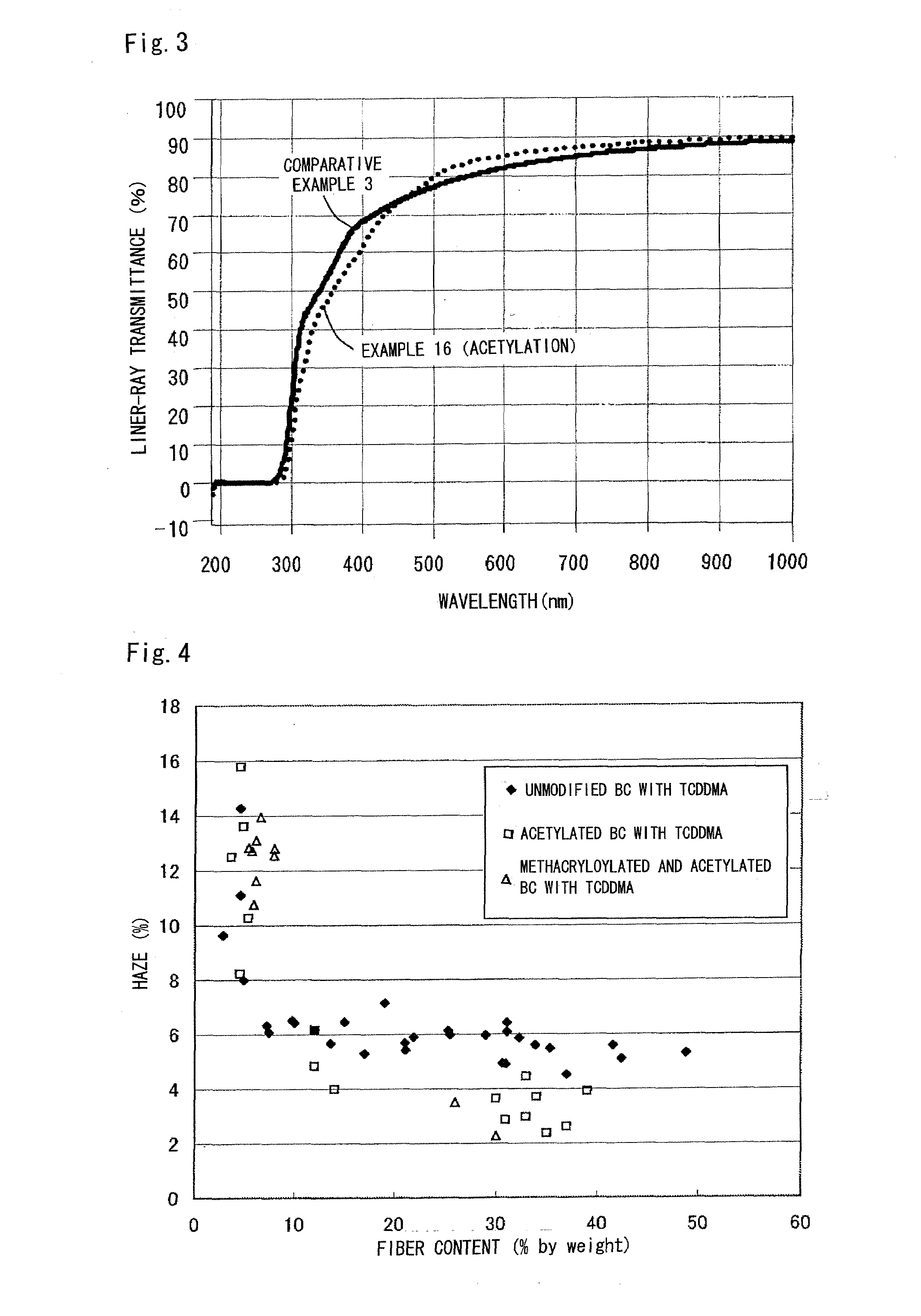
Fiber-reinforced composite material and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20090054552A1Moisture absorptivity and transparencySolid-state devicesThin material handlingAlcoholFiber-reinforced composite
Disclosed is a highly transparent fiber-reinforced composite material including an assembly of cellulose fibers of 4 to 200 nm average fiber diameter impregnated with a matrix material so as to not only remedy the moisture absorbency attributed to cellulose fibers but also further improve transparency. There is provided a fiber-reinforced composite material including an assembly of cellulose fibers impregnated with a matrix material. In the fiber-reinforced composite material, hydroxyl groups of cellulose fibers are chemically modified through a reaction with one or more chemical modifiers selected from the group consisting of an acid, an alcohol, a halogenating reagent, an acid anhydride, and an isocyanate so that the ratio of a functional group introduced by the chemical modification is 5 to 40 percent by mole based on the hydroxyl groups of cellulose fibers before the chemical modification. The chemical modification of hydroxyl groups of cellulose fibers can reduce the hydrophilicity of cellulose fibers to thereby reduce the moisture absorbency of fiber-reinforced composite material. Further, the affinity between cellulose fibers and matrix material can be enhanced to thereby further improve transparency.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +2
Preparation method and application of modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of polyisocyanate curing agents
InactiveCN101696262ASimple processEasy to operatePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsLeather surface finishingPolyesterSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of polyisocyanate curing agents. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out prepolymerization reaction by using polyester polyol, vulcabond monomer and a polyisocyanate curing agent; reacting with a hydrophilic chain-extending agent and a micro-molecule chain-extending agent to obtain polyurethane prepolymer containing hydrophilic groups (carboxyl or sulfonic groups) and isocyanate(NCO)-terminated groups; neutralizing the polymer into salt, and then dispersing the salt into water; and preparing the modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of the polyisocyanate curing agents by the chain extending of a polyamine chain-extending agent. The modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of the polyisocyanate curing agents have self-crosslinking function at room temperature, and the self-crosslinking density is over 85%. Compared with non-modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions prepared under the same condition, the modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions have superior film forming property, water resistance, alcohol resistance, pollution resistance, cold resistance, dry / wet rubbing resistance and chemical solvent resistance; and coating films have especially high drying speed, high hardness increment speed and high final hardness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Coating composition, process for preparing coating composition and process for preparing dispersing component of inorganic oxide sol
InactiveUS6022919AGood weather resistanceLow appearance requirementsSpecial tyresMixingMeth-Acrylonitrile
A coating composition which comprises (A) a resin having a glass transition temperature of 50 to 120 DEG C., a number average molecular weight of 2,000 to 100,000, a hydroxyl value of 50 to 150 mgKOH / g and an acid value of 1 to 25 mgKOH / g, which is produced by copolymerizing 10 to 90 percent by weight of (a) a (meth)acrylic acid ester of a C1 to C12 alkyl alcohol, 10 to 50 weight % of (b) a first polymerizable double bond-containing and hydroxyl group-containing monomer, 0.1 to 10 weight % of (c) a polymerizable double bond-containing and carboxyl group-containing monomer, 0 to 20 weight % of (d) styrene, 0 to 20 weight % of (e) acrylonitrile and 0 to 10 weight of (f) a second polymerizable double bond-containing monomer, (B) at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a polyisocyanate compound having two or more unblocked isocyanate groups and / or blocked isocyanate groups in the molecule and an aminoplast resin, (C) a dispersing component of at least one inorganic oxide sol selected from the group consisting of an aluminum oxide sol, a silica sol, a zirconium oxide sol and an antimony oxide sol, wherein an amount of a nonvolatile matter of component (C) is 5 to 60 percent by weight based on a total amount of nonvolatile matter of resin (A), compound (B) and component (C). The coating composition provides cured films having excellent weathering resistance, light resistance, stain resistance, stain-removing property, chemical resistance, moisture resistance and appearance and is environmentally friendly and safe.
Owner:BASF NOF COATINGS CO LTD
Electro-optic display and materials for use therein
ActiveUS7477444B2Magnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storagePolyesterDisplay device
A polyurethane is formed from an isocyanate and a polyester diol having a molecular weight less than about 2000, or a polyester diol comprising two polyester diol segments connected by a steric hindrance group, each of the polyester diol segments having a molecular weight less than about 2000. The polyurethane is useful as a binder in electro-optic displays, and in components used to form such displays.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC +1
Crosslinkable polyurea prepolymers
The present invention provides a water-soluble crosslinkable polyurea prepolymer. The crosslinkable polyurea prepolymer of the invention is prepared by reacting an amine- or isocyanate-capped polyurea with a multifunctional compound having at least one one ethylenically unsaturated group and a function group coreactive with the capping amine or isocyanate groups of the amine- or isocyanate-capped polyurea. The amine- or isocyanate-capped polyurea is a copolymerization production of: (a) at least one poly(oxyalkylene)diamine, (b) optionally at least one organic di- or poly-amine, (c) optionally at least one diisocyanate, and (d) at least one polyisocyanate. The crosslinkable polyurea prepolymer of the invention can find use in economically producing contact lenses which have durable, highly elastic soft contact lenses with desired physical properties. In addition, the present invention provides method for making a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Elastic body, method for manufacturing the same and mattress including the same
InactiveUS6704962B2Promote absorptionLow elastic modulusStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesElastomerAlcohol
Disclosed are an elastic body having a good elasticity and an impact absorbing efficiency, a method of manufacturing the same and a mattress employing the same. The elastic body is a foamed polyurethane body including polystyrene and has a plurality of foams in which air is contained. The elastic body is prepared by a method comprising the steps of preparing polyether polyol by mixing poly alcohol and a polyether compound in a mixing ratio of 3-5 to 5-7 by weight, obtaining a polyol mixture by adding 2-20 parts by weight of polystyrene and a trace amount of a catalyst and water to 30-50 parts by weight of the obtained polyether polyol, adding and stirring 20-60 parts by weight of an isocyanate compound to 40-80 parts by weight of the polyol mixture at 20-80° C., and pouring the resulting product into a mold to foam cast. A mattress manufactured by using such elastic bodies has a good elasticity and is capable of absorbing pressure, thereby providing comfort for users.
Owner:CHOI YOUN SOO
Biocidal polyurethane compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS7459167B1Improve adhesionImprove hydrolytic resistanceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMicroorganismAmmonium compounds
Polymeric compositions that include polyurethane polymers derived from a polyisocyanate compound and a polyactive hydrogen compound. The polyurethane compound is at least partially endcapped with a group including at least one antimicrobial quaternary ammonium compound. The polymeric composition of the present invention is capable of forming a self-supporting film. The polymeric compositions are suitable for coating substrates to effectively kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, mold, mildew, algae fungi and the like. The polymeric compositions are particularly useful for protecting construction materials used in moist, outdoor environments to prevent discoloration or decay from microorganisms and for surfaces in health care facilities to mitigate the spread of pathogens.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Plastic material
An improved material comprising the reaction product of an A-side having a prepolymer isocyanate and a B-side having a cross-linker comprising a multifunctional alcohol, a first vegetable oil, preferably a blown / oxidized vegetable oil, most preferably a blown / oxidized soybean oil, and a catalyst and the method of producing the same.
Owner:RHINO LININGS CORP
Process for producing polyurethane foam
InactiveUS6777455B2Get stableFine and uniform cellsAbrasion apparatusLapping toolsHydrogenReactive gas
A process for producing a finely cellular polyurethane foam by mixing a first ingredient comprising an isocyanate compound and a second ingredient comprising a compound containing an active hydrogen group, characterized by comprising adding a nonionic silicone surfactant containing no hydroxyl group to at least one of the first ingredient and the second ingredient in an amount of 0.1 to 5 wt %, excluding 5 wt %, based on the total amount of the first ingredient and the second ingredient, subsequently agitating the surfactant containing ingredient together with an unreactive gas, which has no reactivity to isocyanate group or active hydrogen group, to disperse the unreactive gas as fine bubbles to prepare a bubble dispersion and then mixing the bubble dispersion with the remaining ingredient to cure the resultant mixture and forming finely cellular structure into the resultant polyurethane foam by the fine bubbles of the bubble dispersion.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com