Patents
Literature
76 results about "Photoacoustic microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
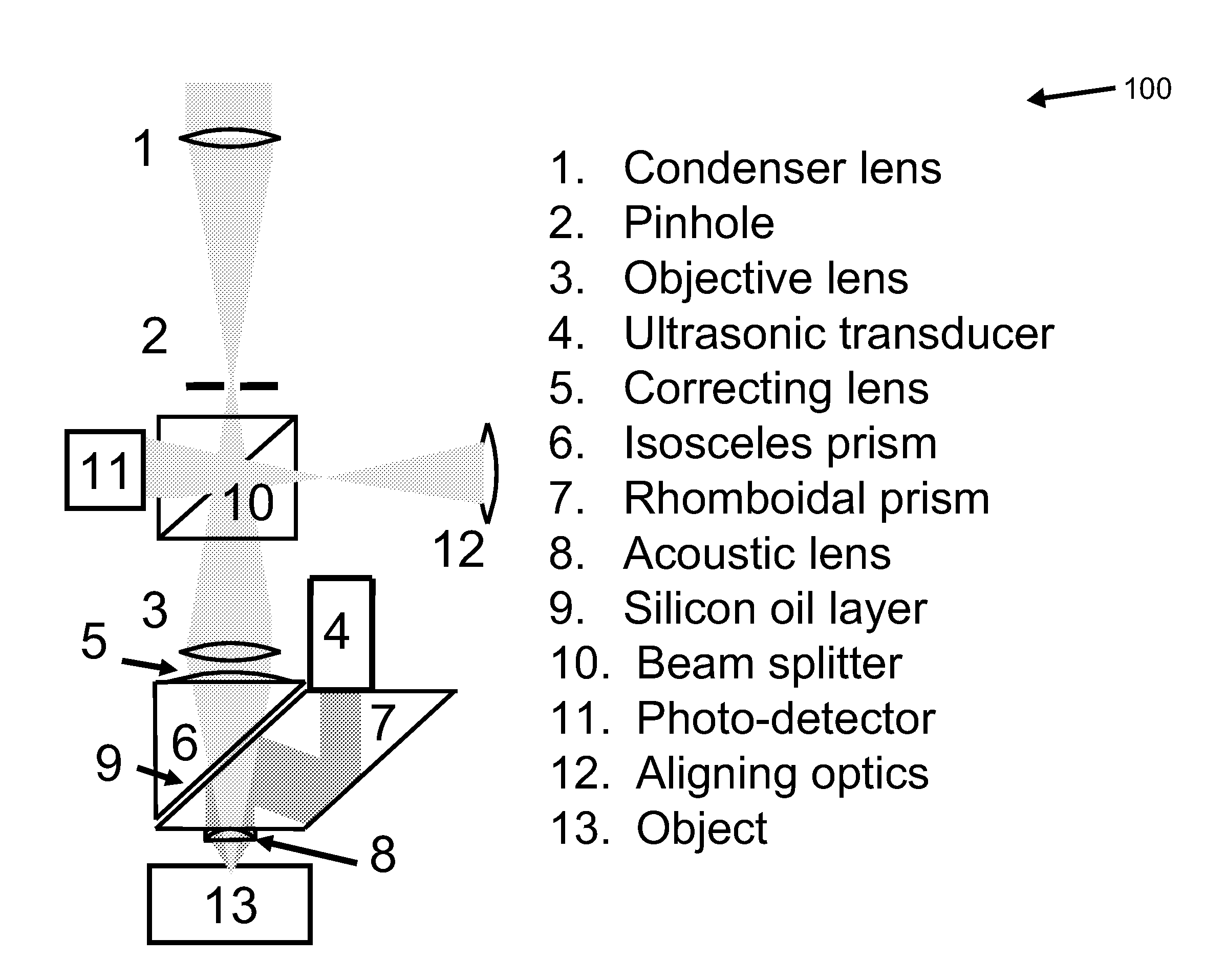
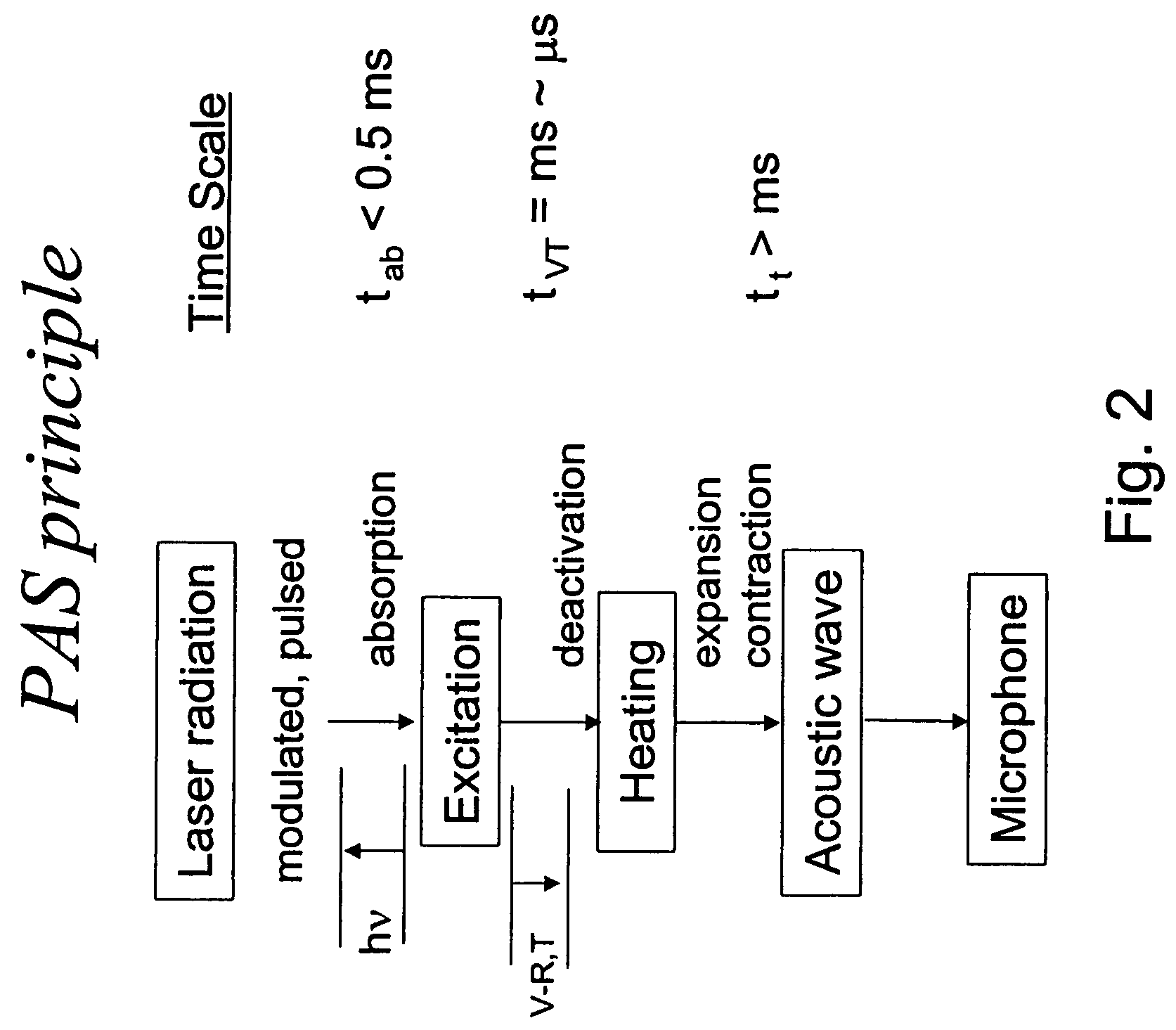
Photoacoustic microscopy is an imaging method based on the photoacoustic effect and is a subset of photoacoustic tomography. Photoacoustic microscopy takes advantage of the local temperature rise that occurs as a result of light absorption in tissue.
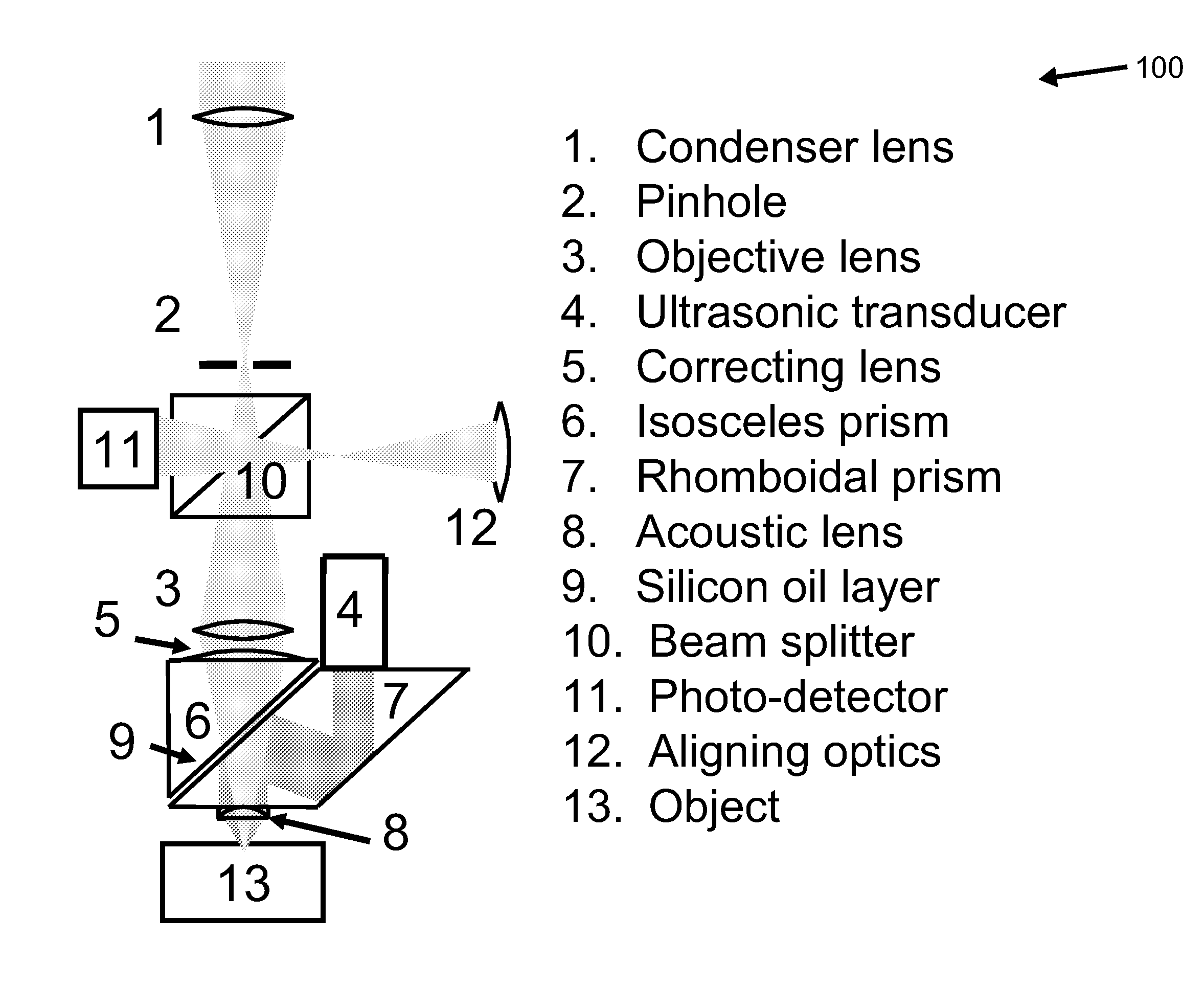
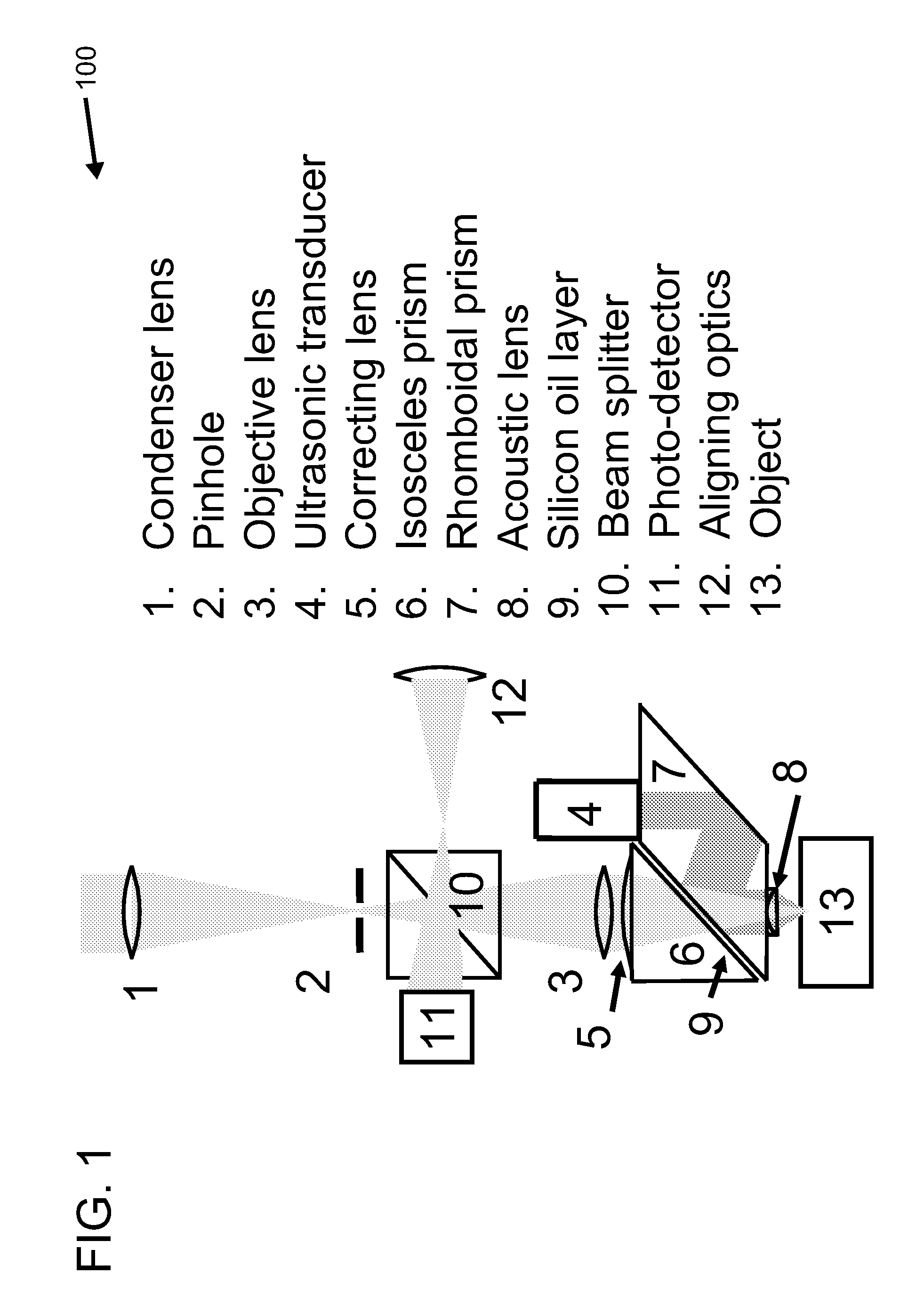
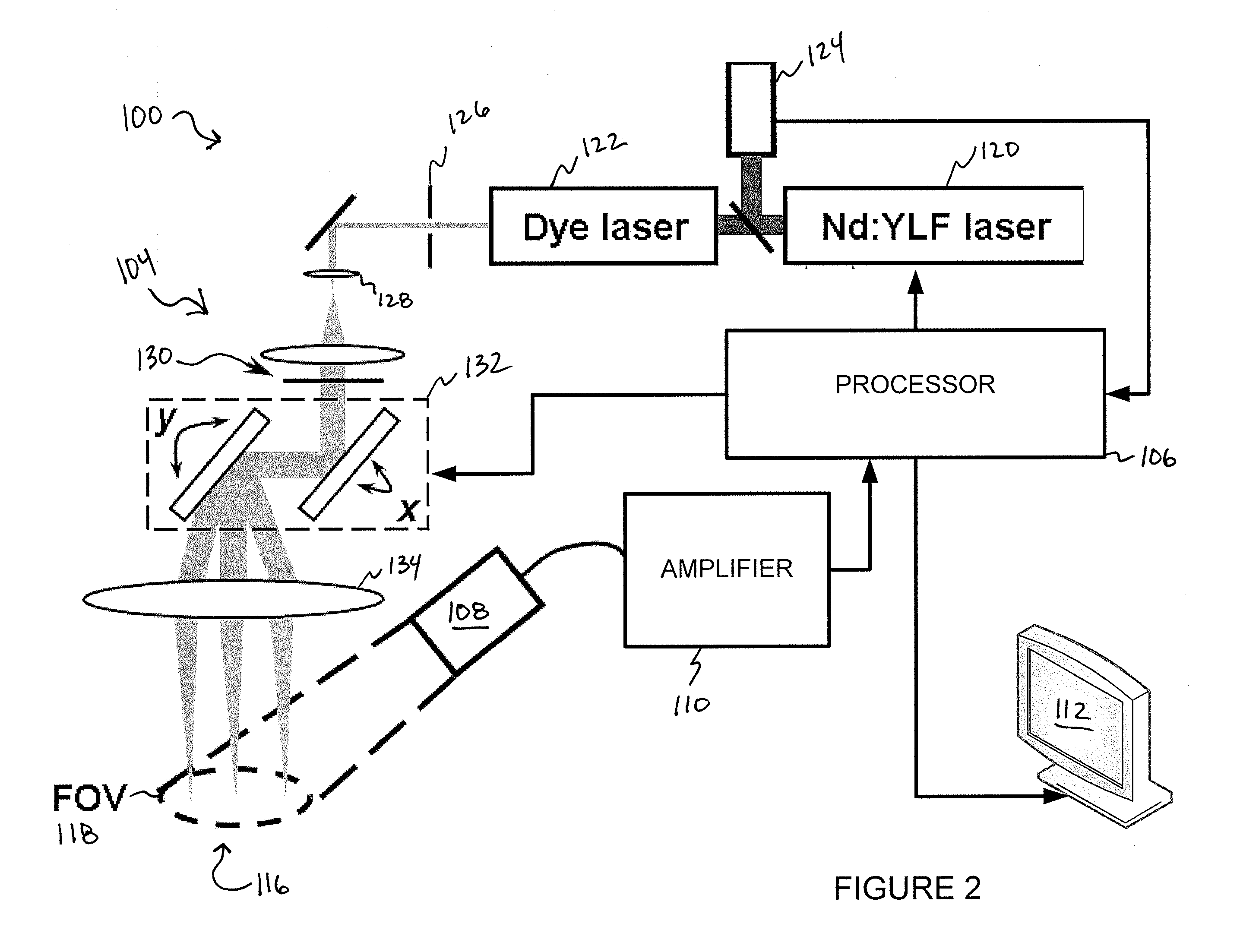
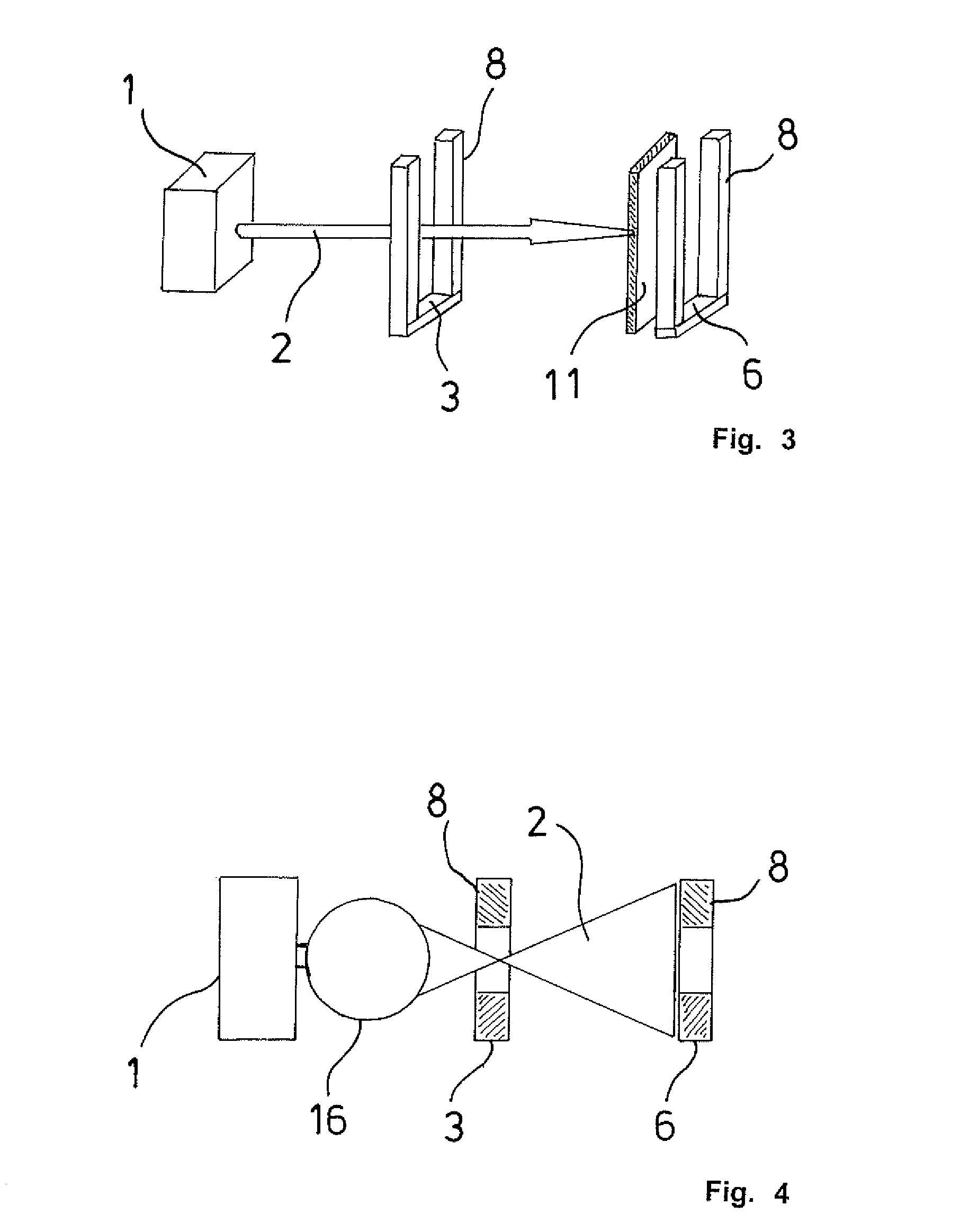
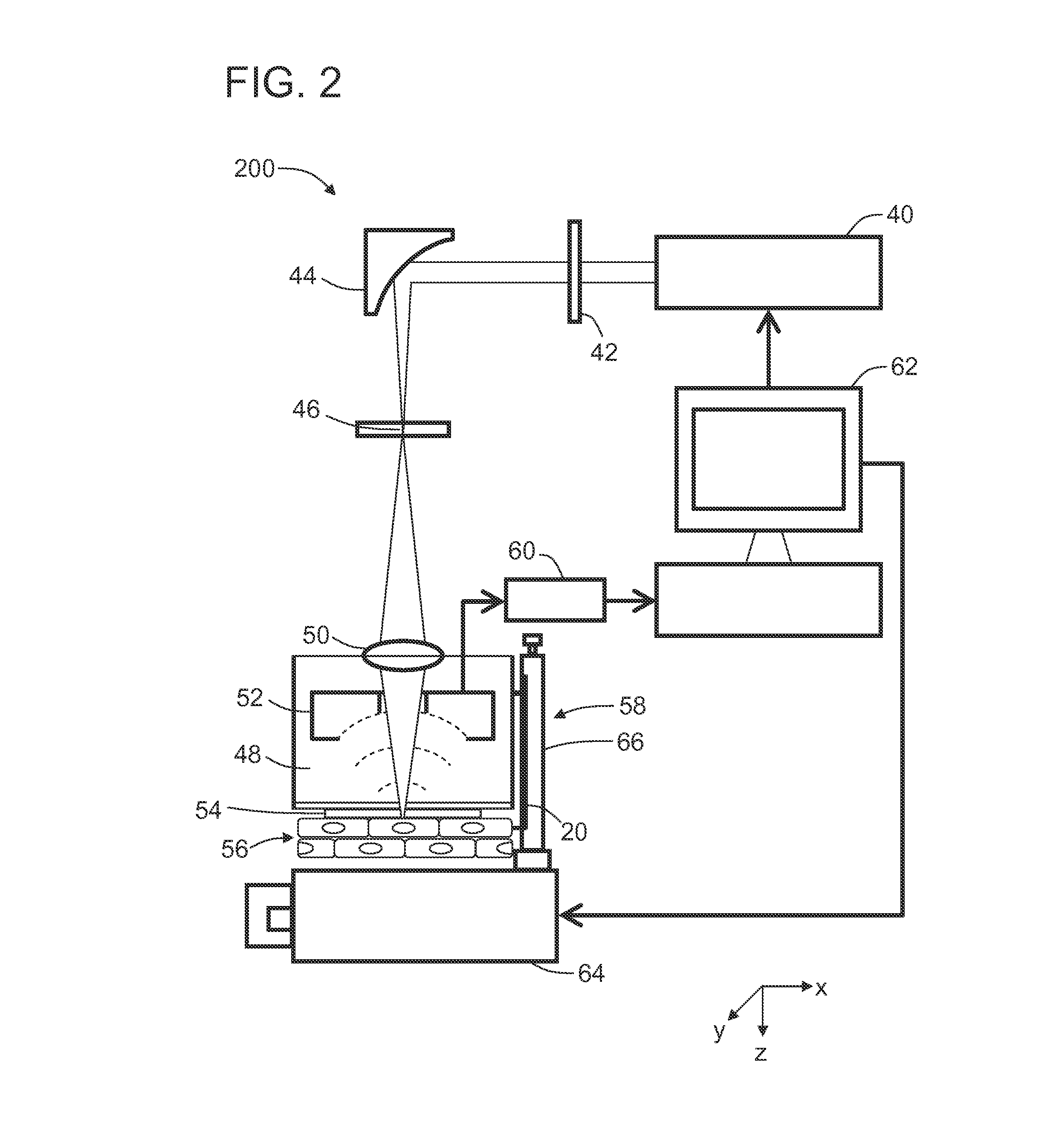
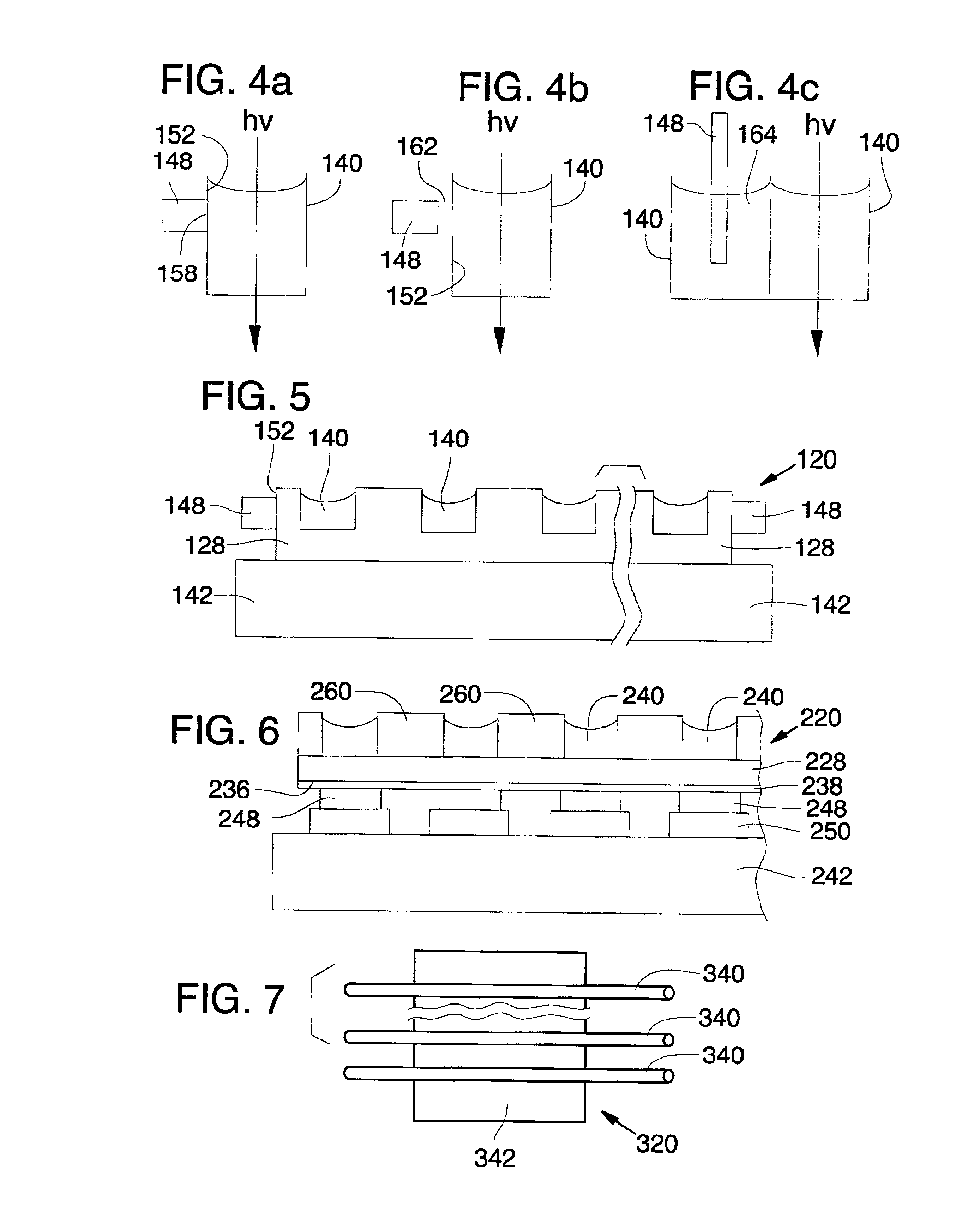
Confocal photoacoustic microscopy with optical lateral resolution
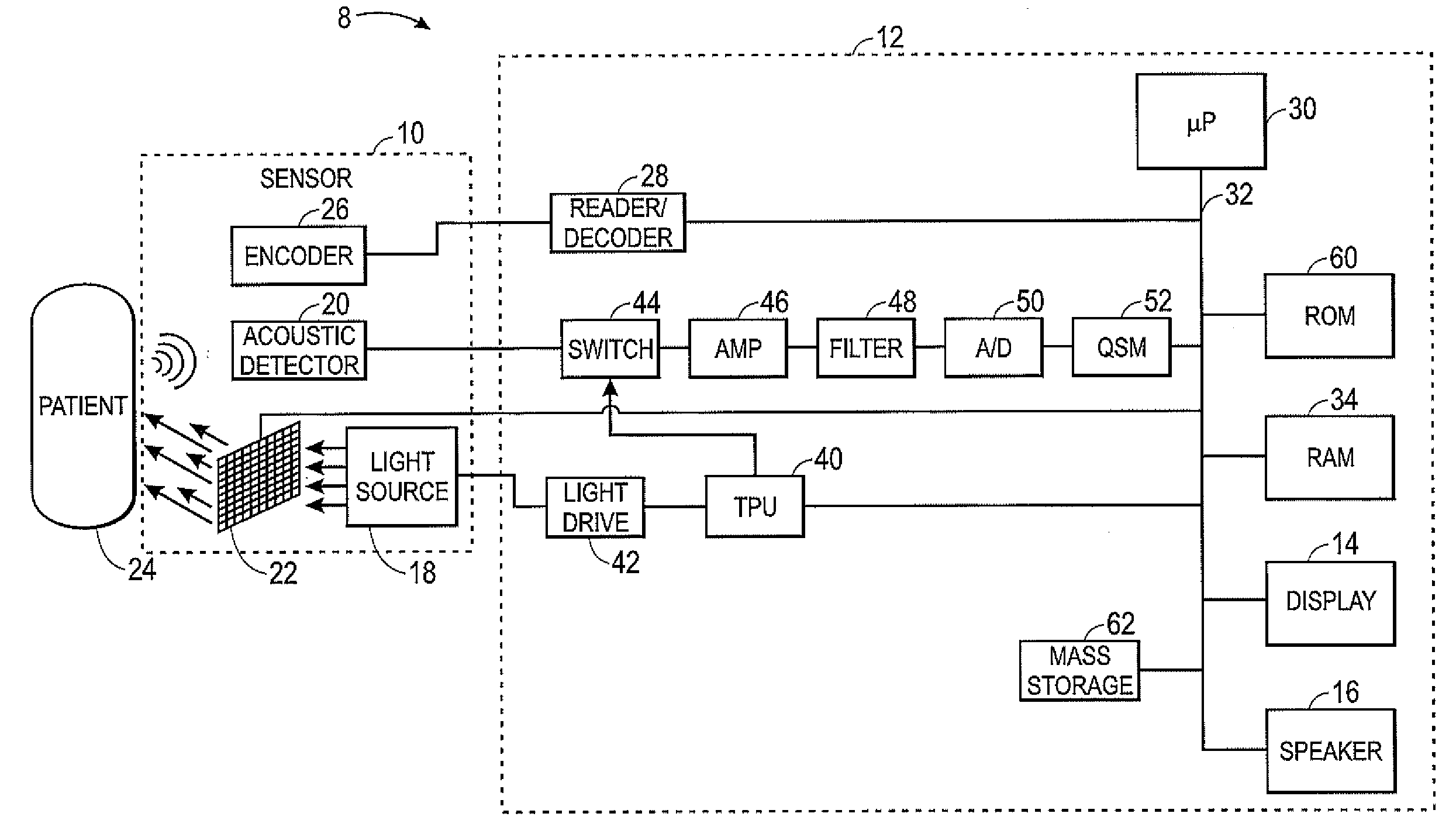
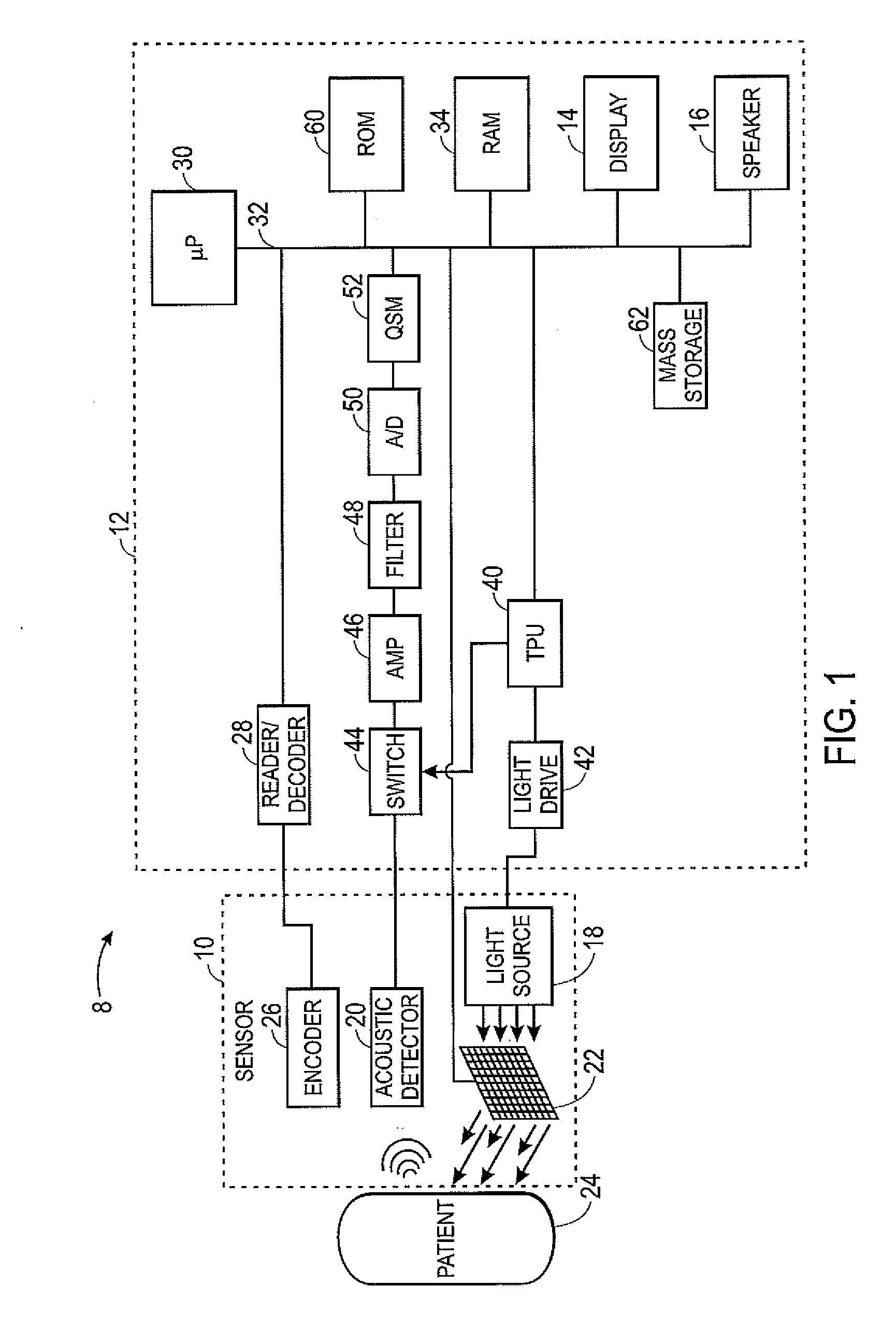
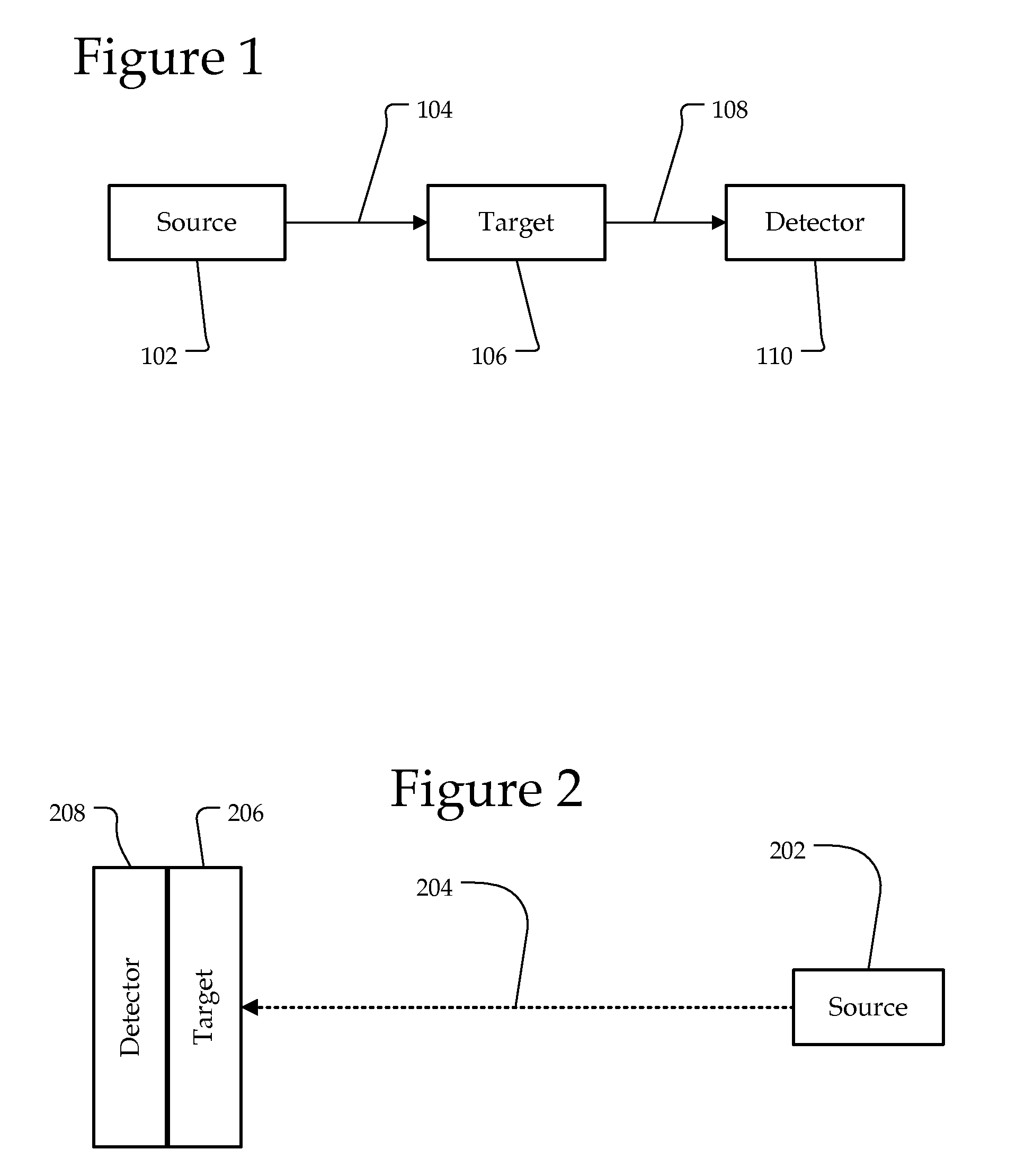
ActiveUS20100268042A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotoacoustic microscopyUltrasonic sensor
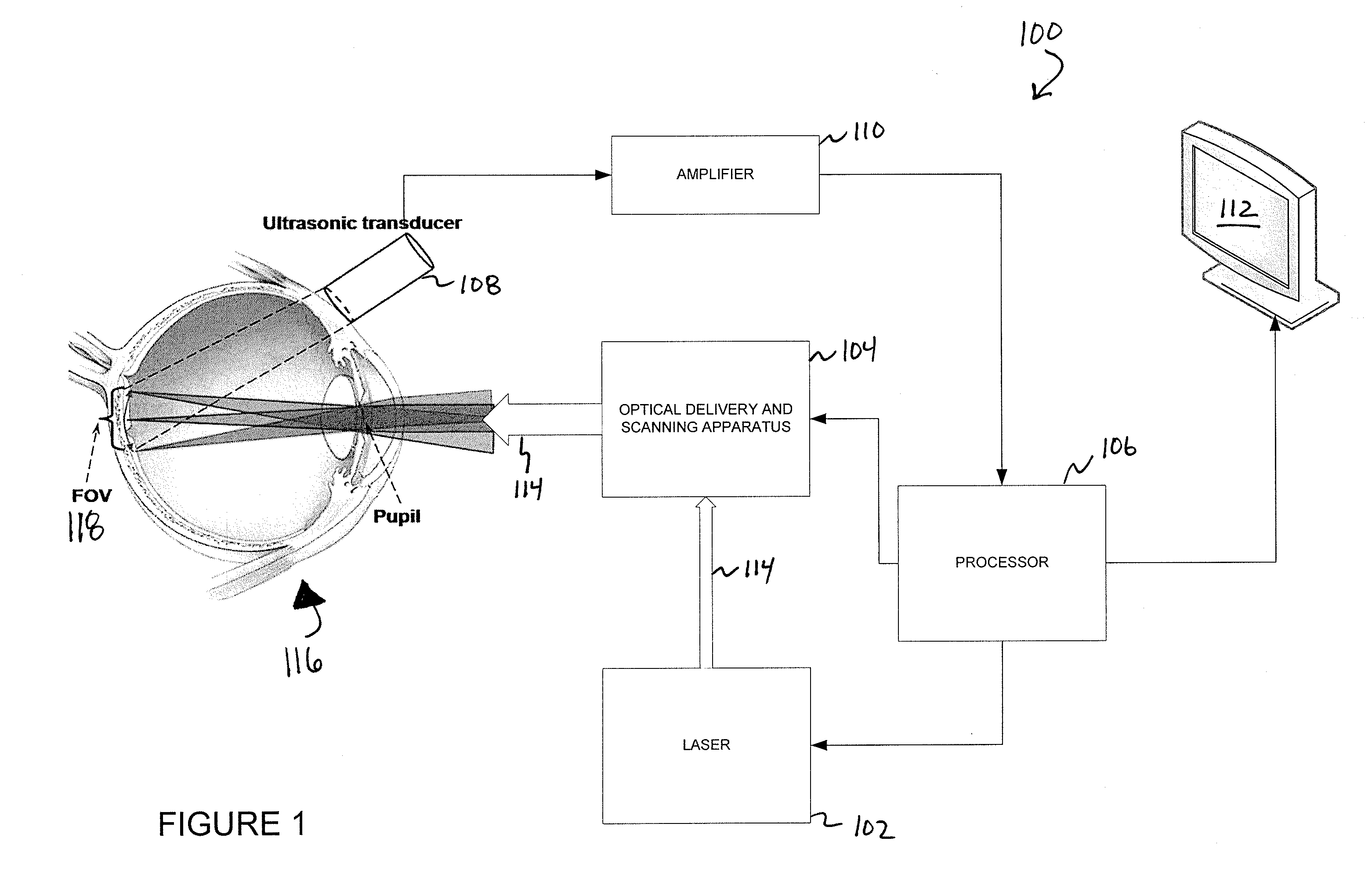
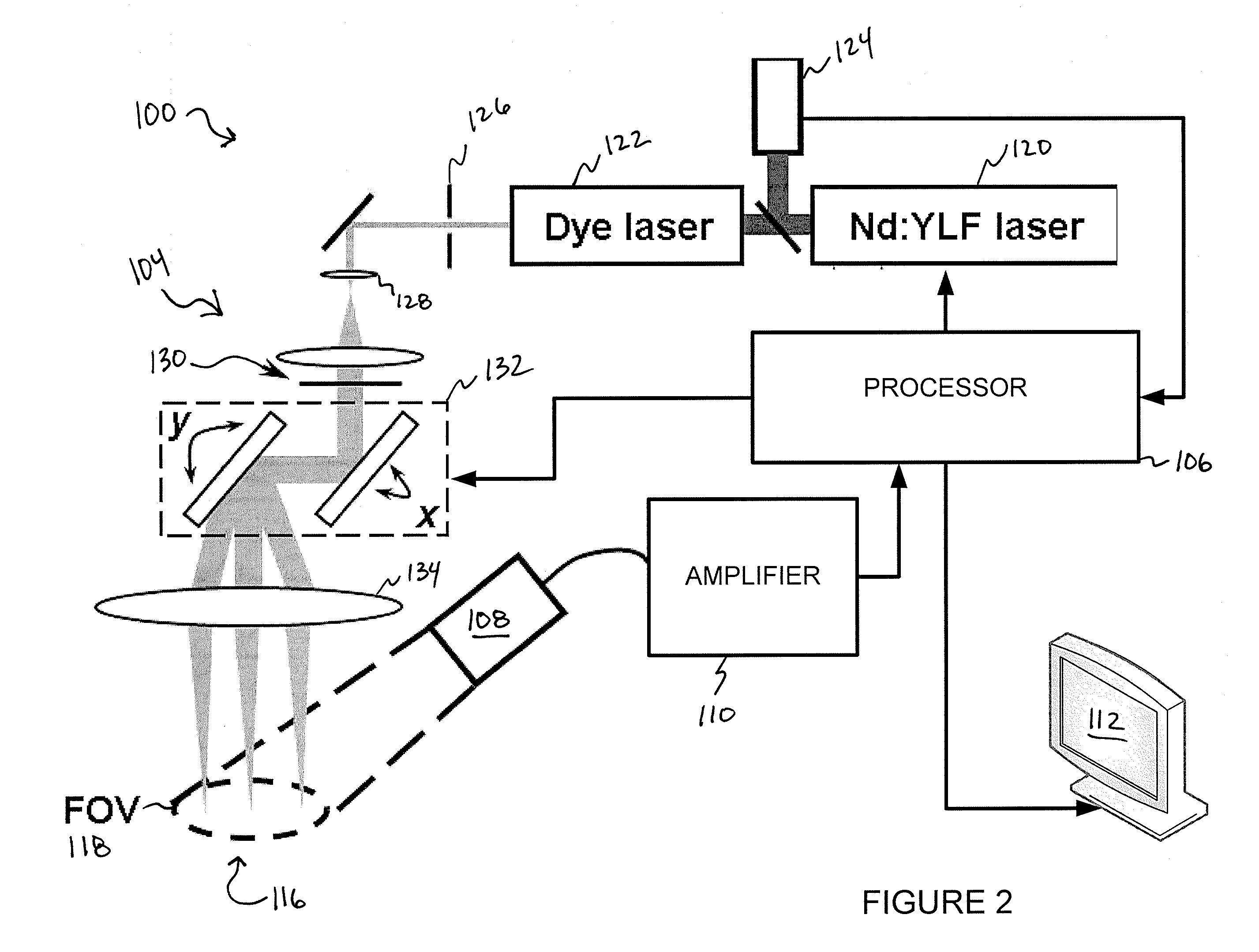
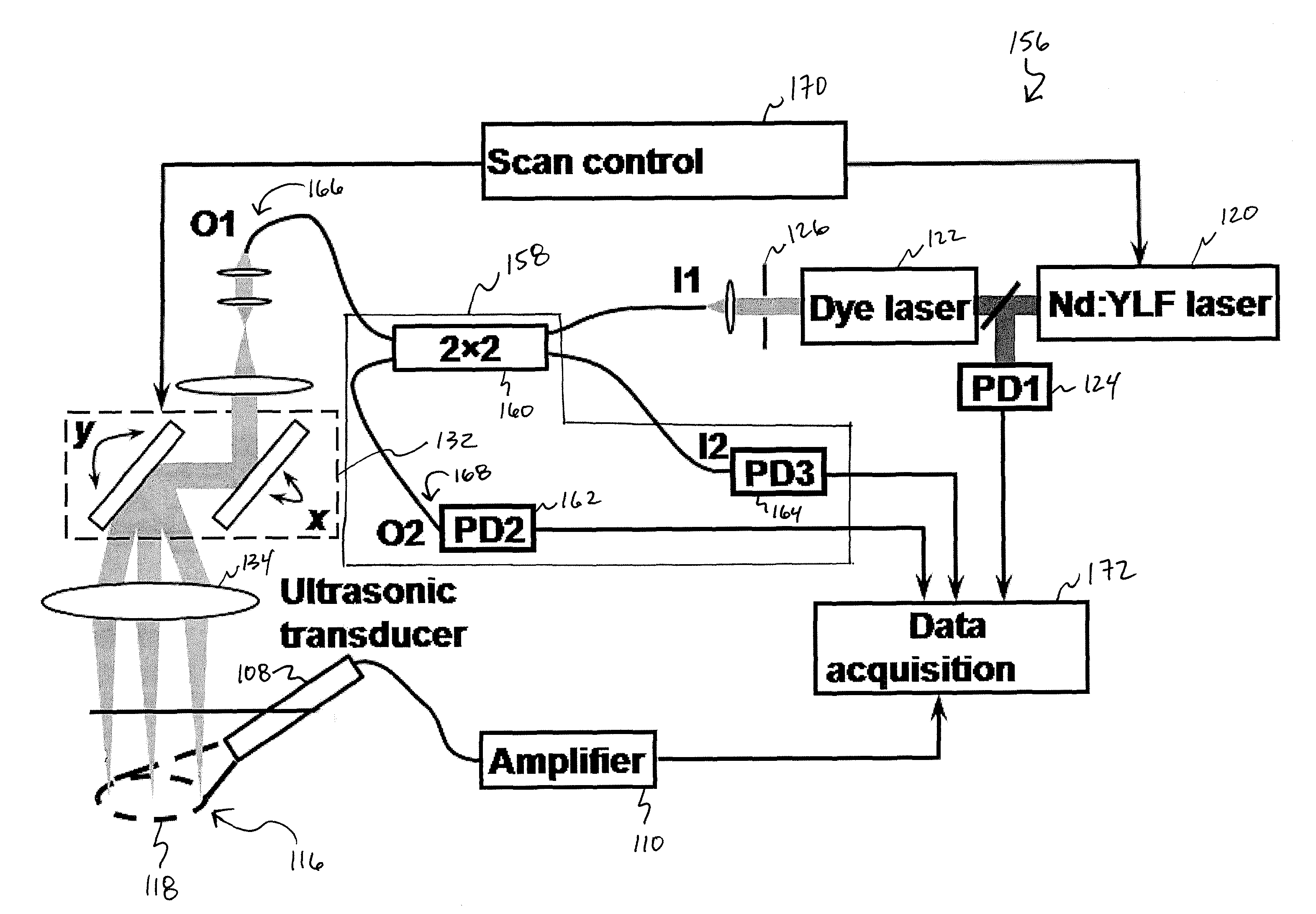
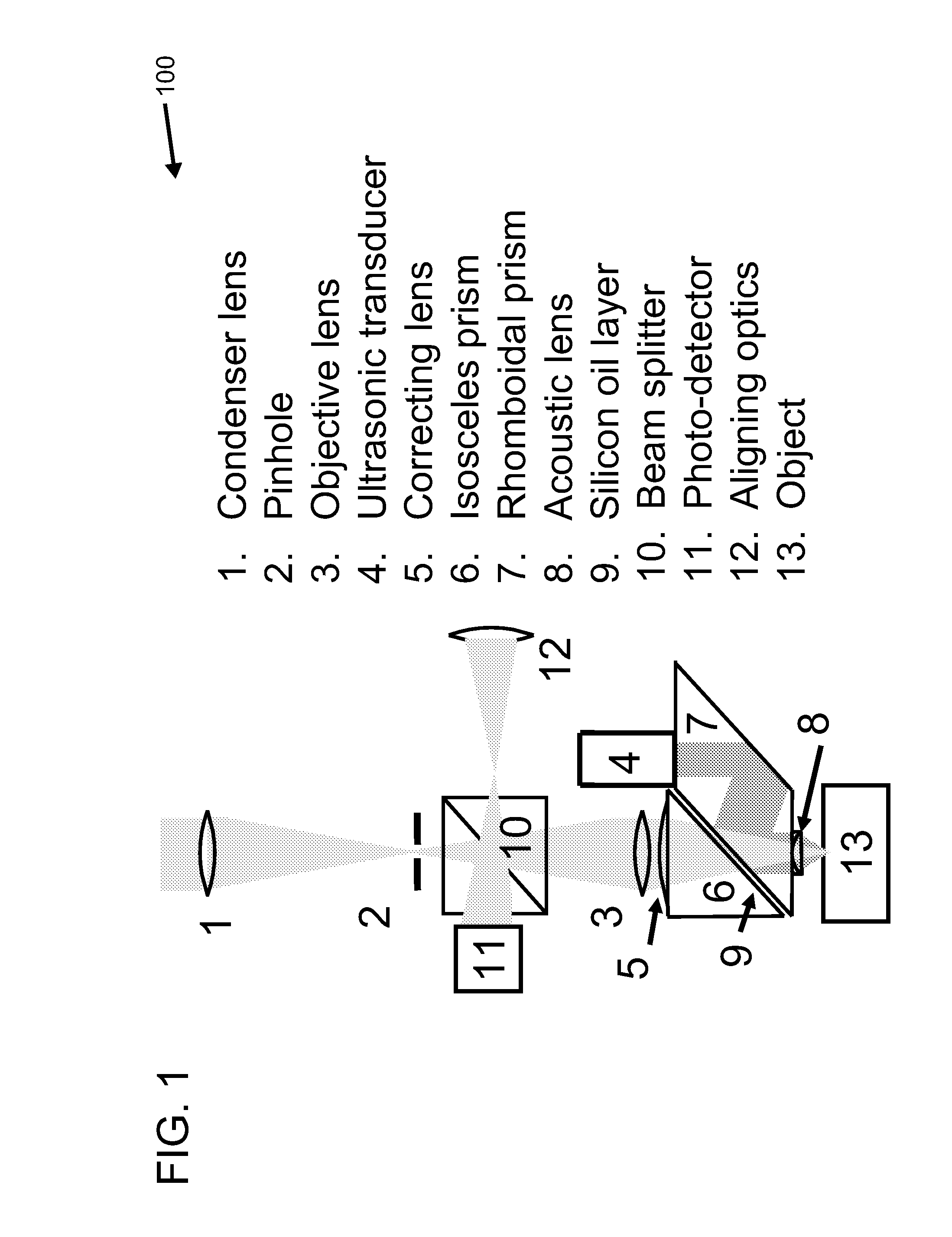
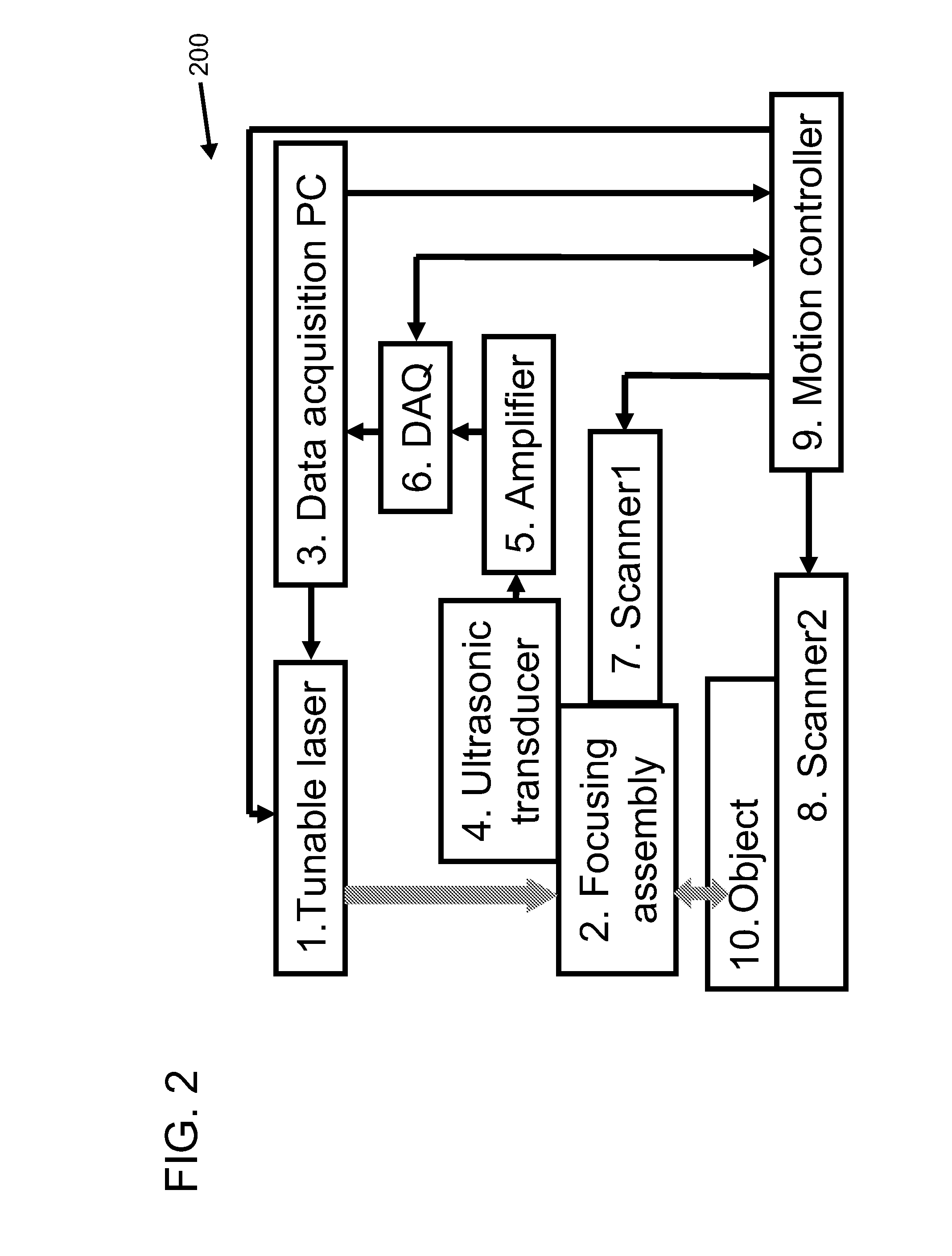
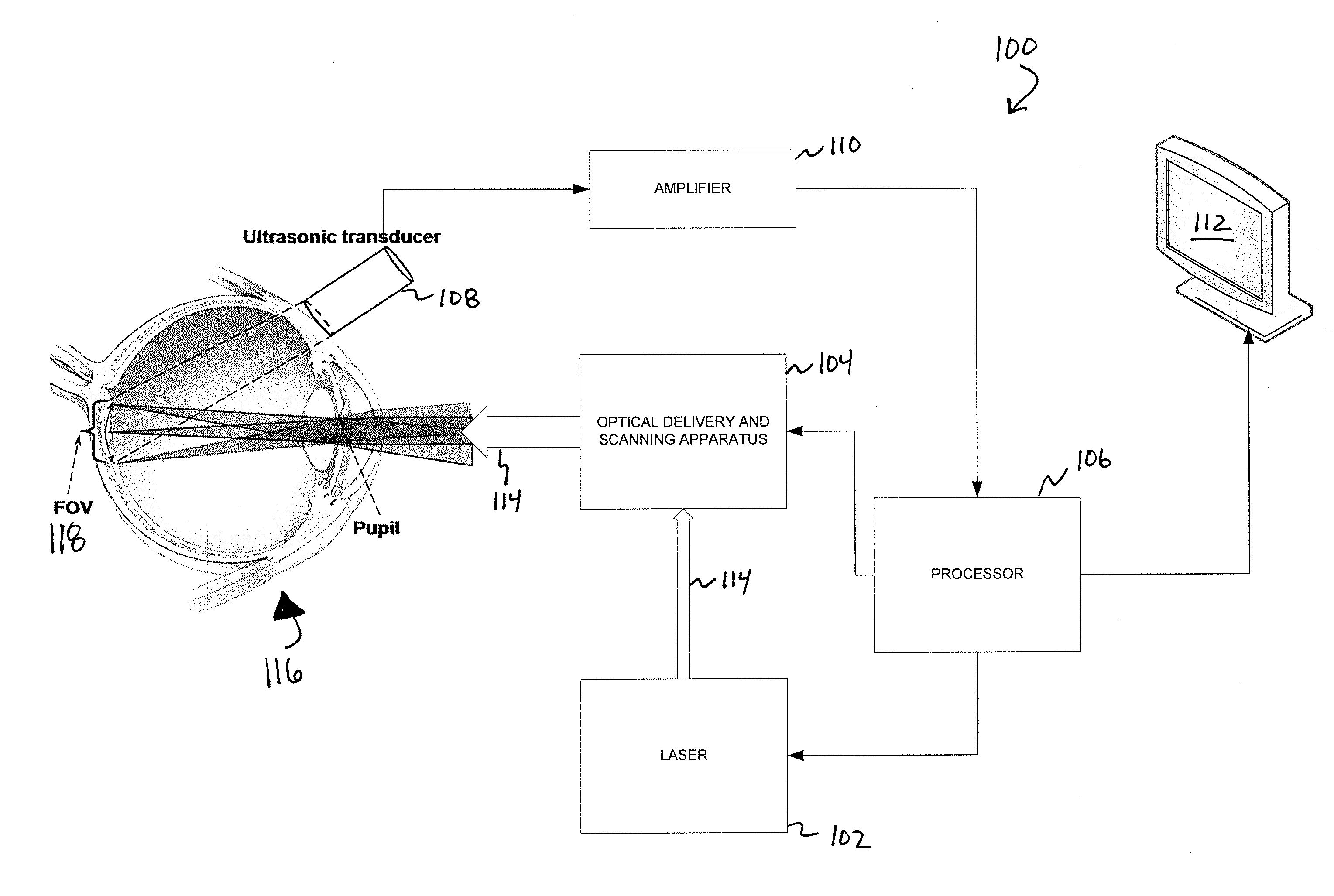
A confocal photoacoustic microscopy system includes a laser configured to emit a light pulse, a focusing assembly configured to receive the light pulse and to focus the light pulse into an area inside an object, an ultrasonic transducer configured to receive acoustic waves emitted by the object in response to the light pulse, and an electronic system configured to process the acoustic waves and to generate an image of the area inside the object. The focusing assembly is further configured to focus the light pulse on the object in such a way that a focal point of the focusing assembly coincides with a focal point of the at least one ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Ultrasonic imaging device
InactiveUS20100249562A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostics using lightPhotoacoustic microscopyDiagnostic Radiology Modality
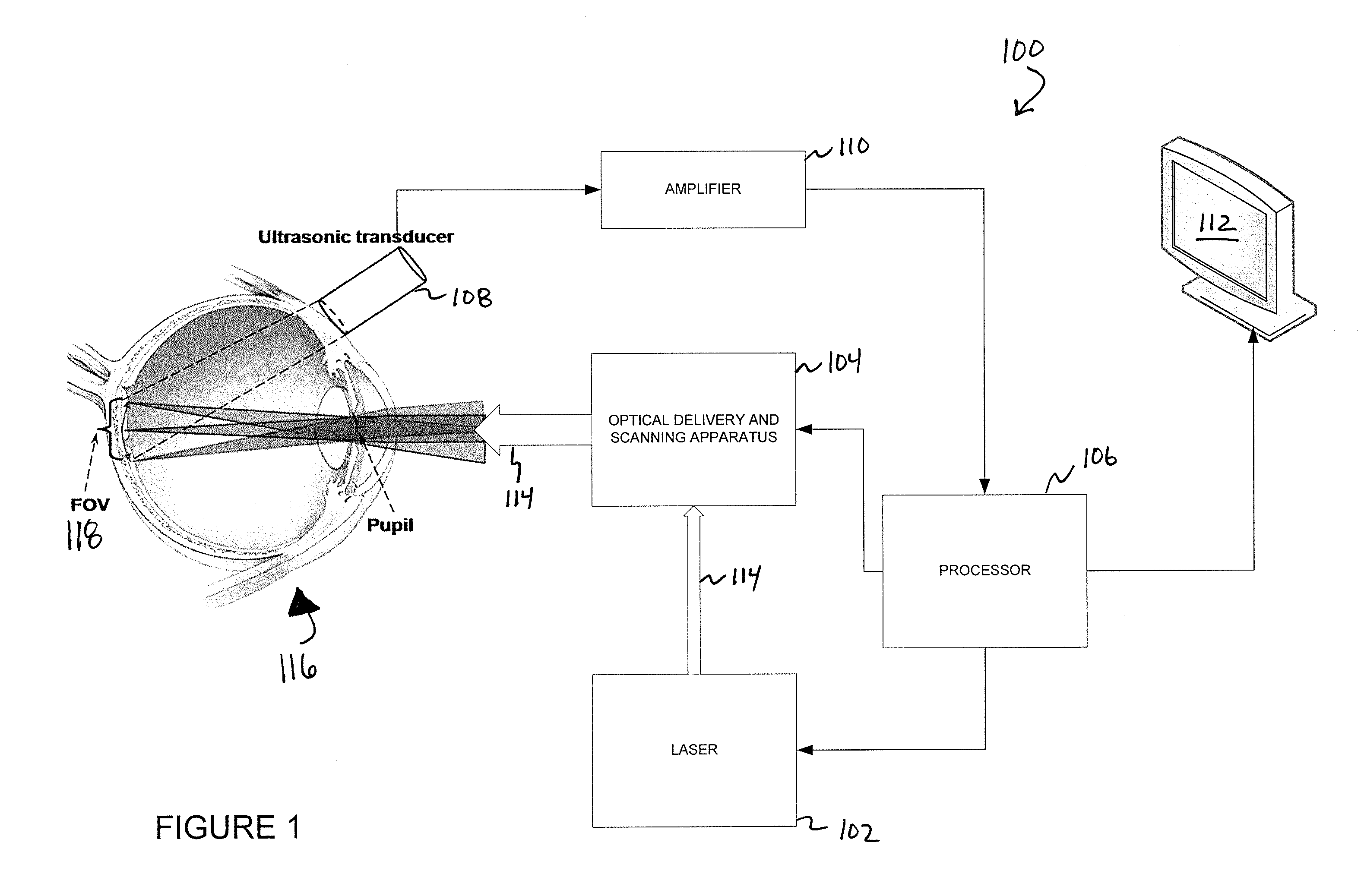
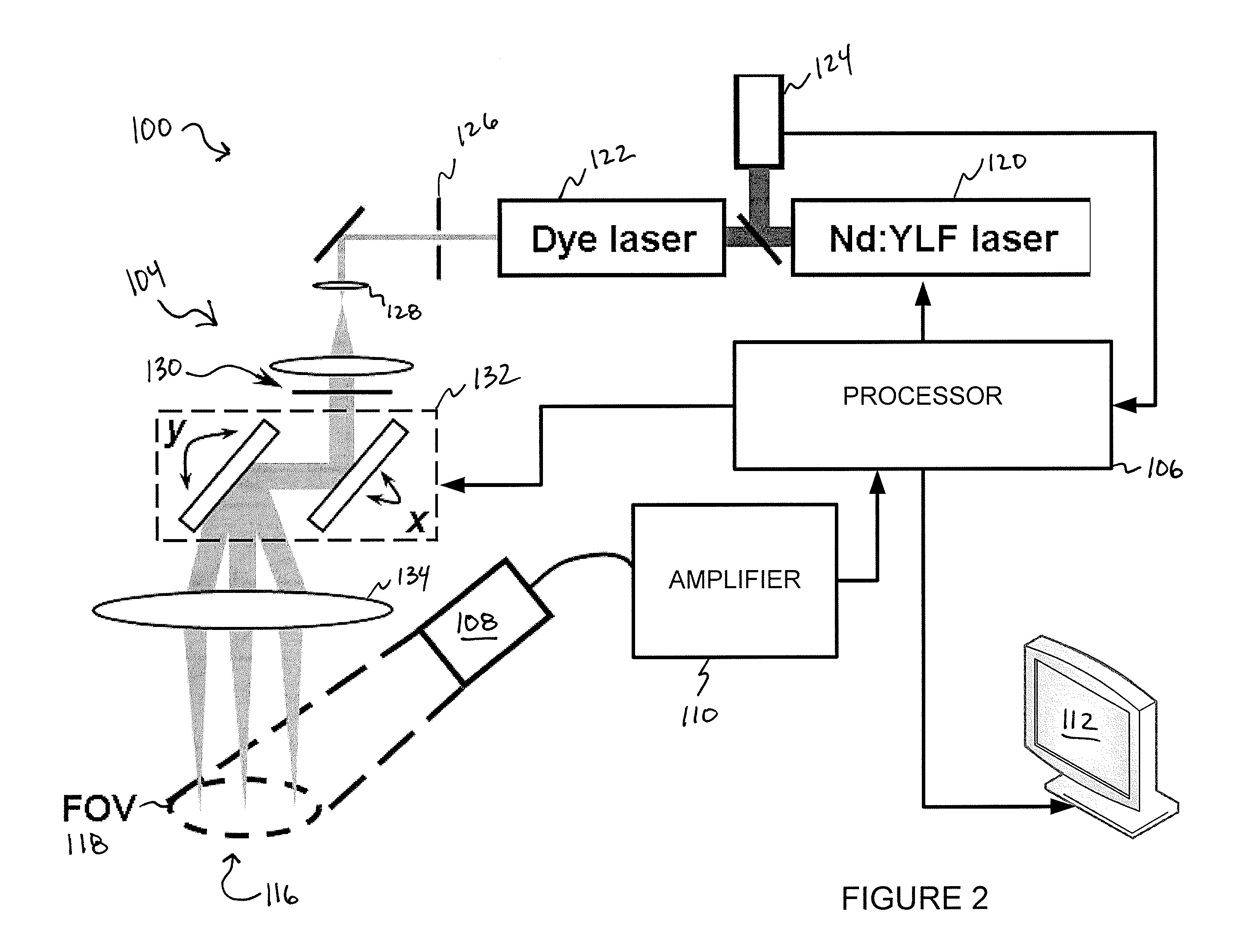
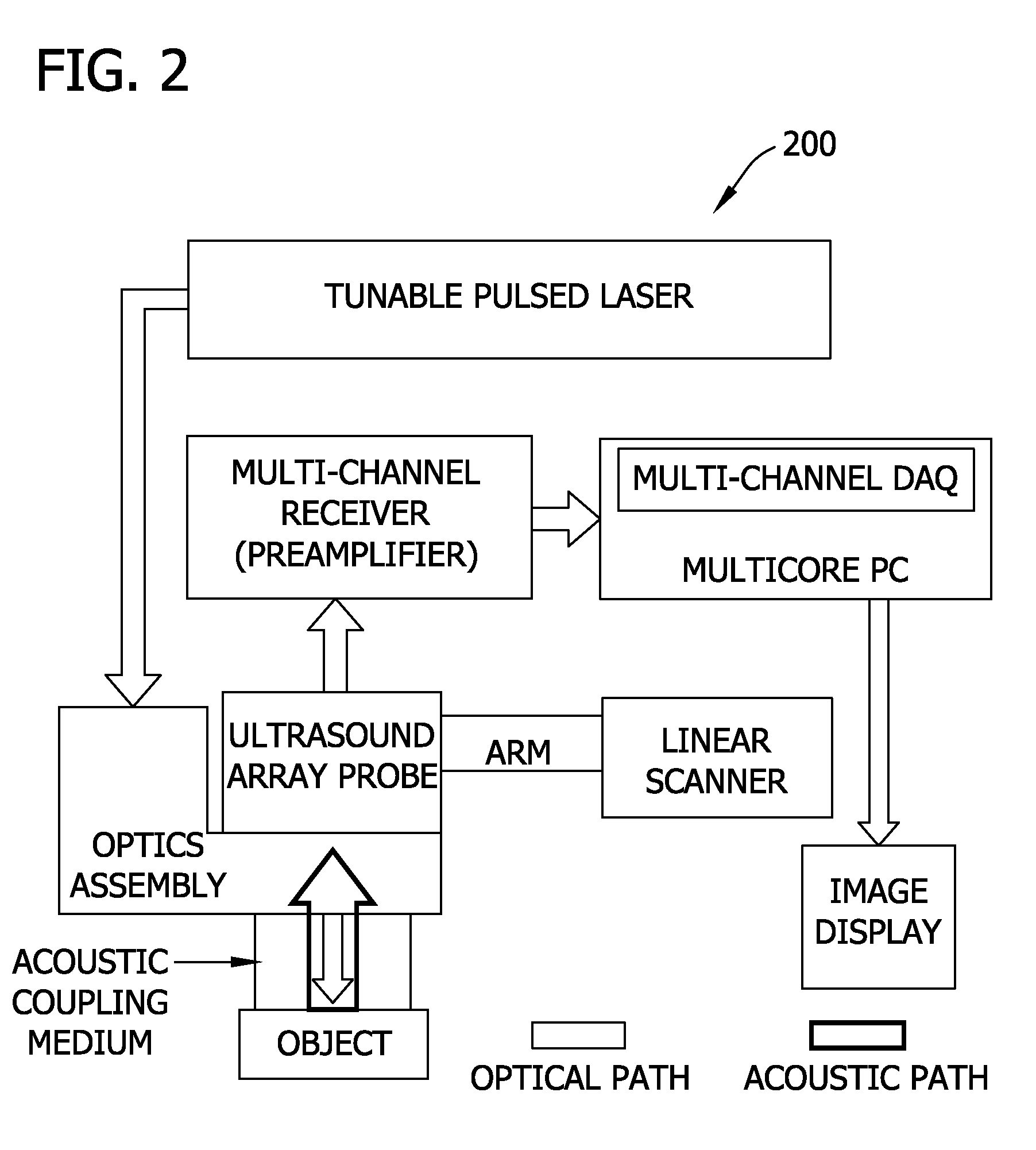
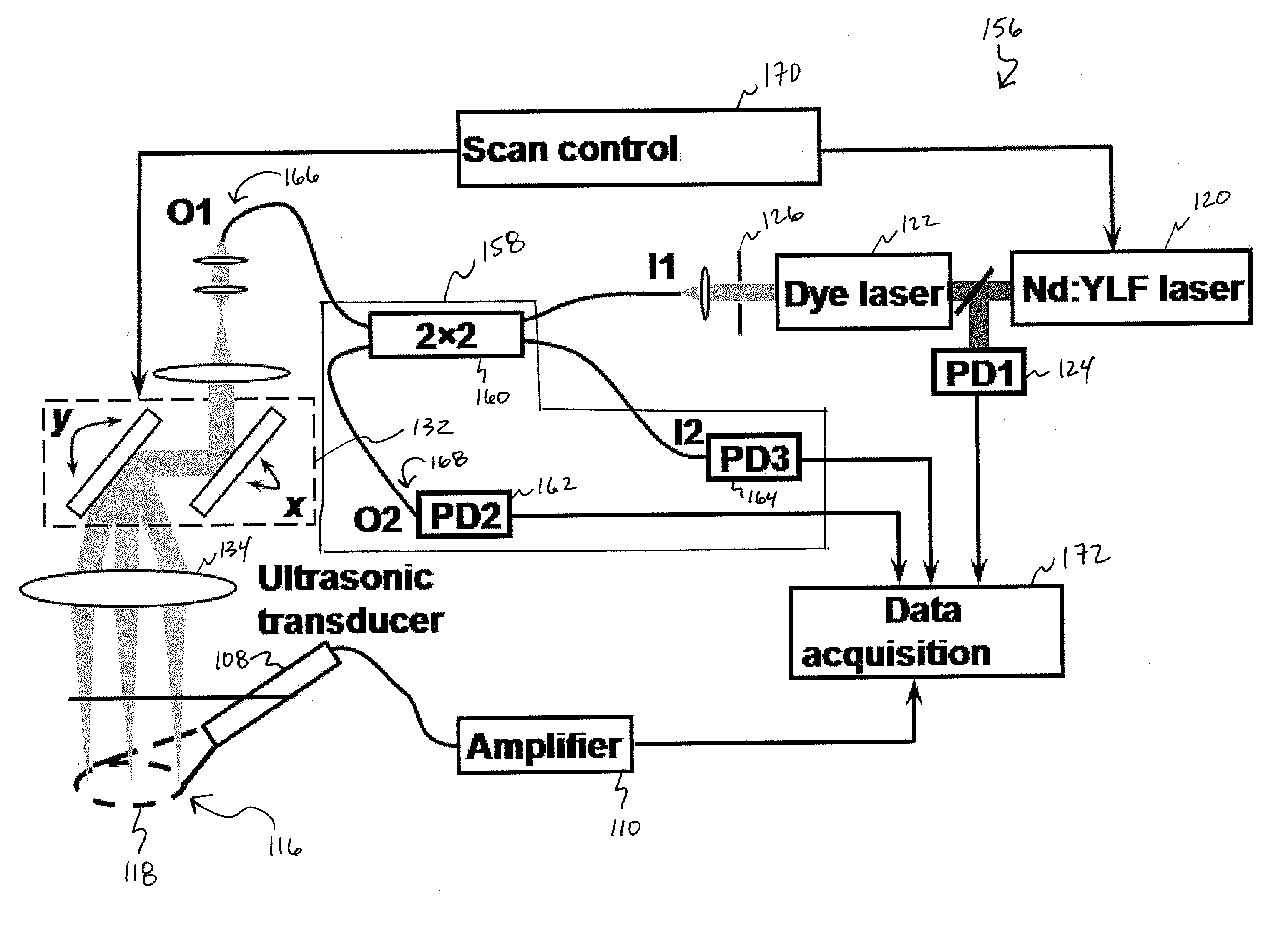
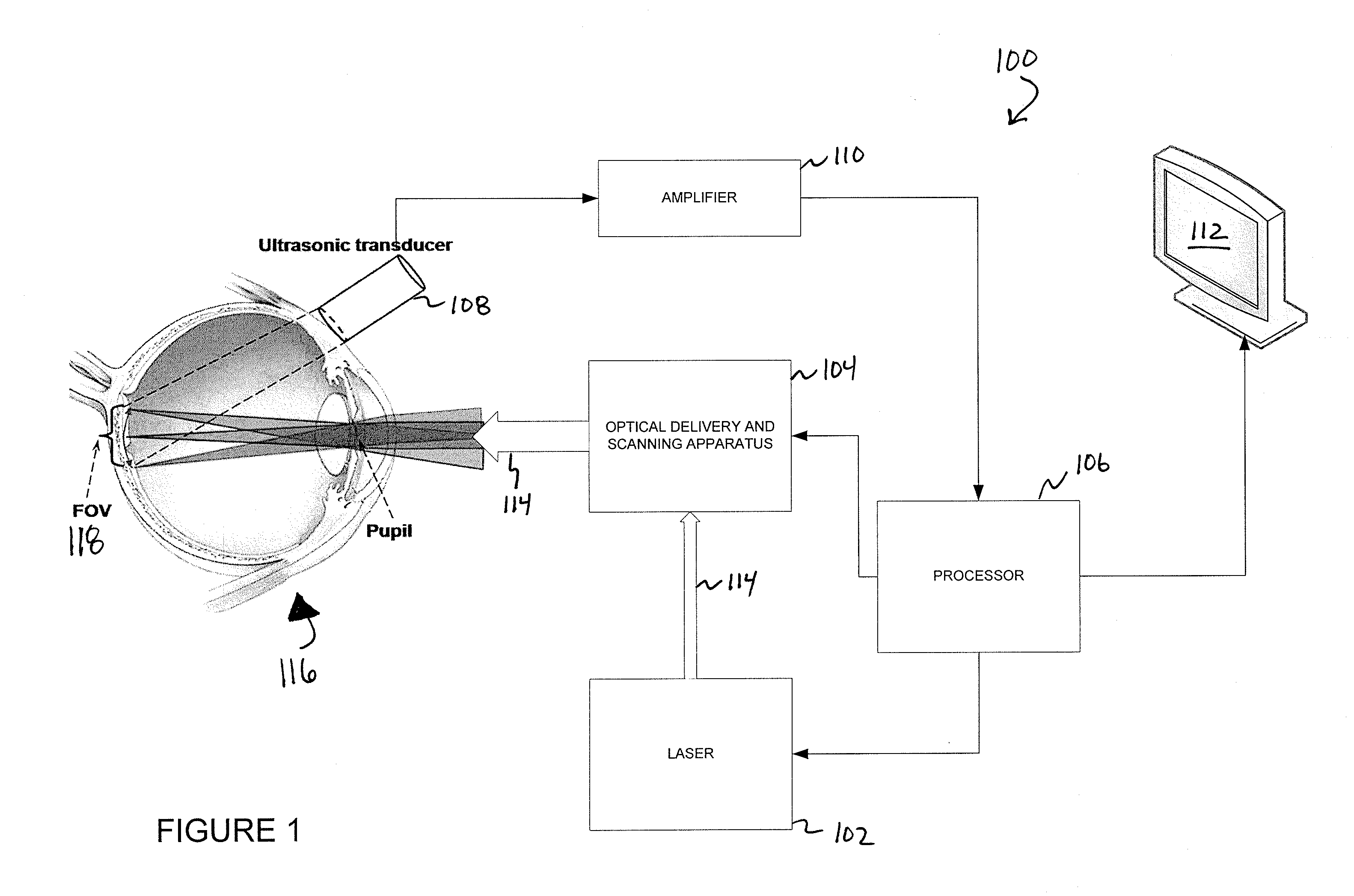
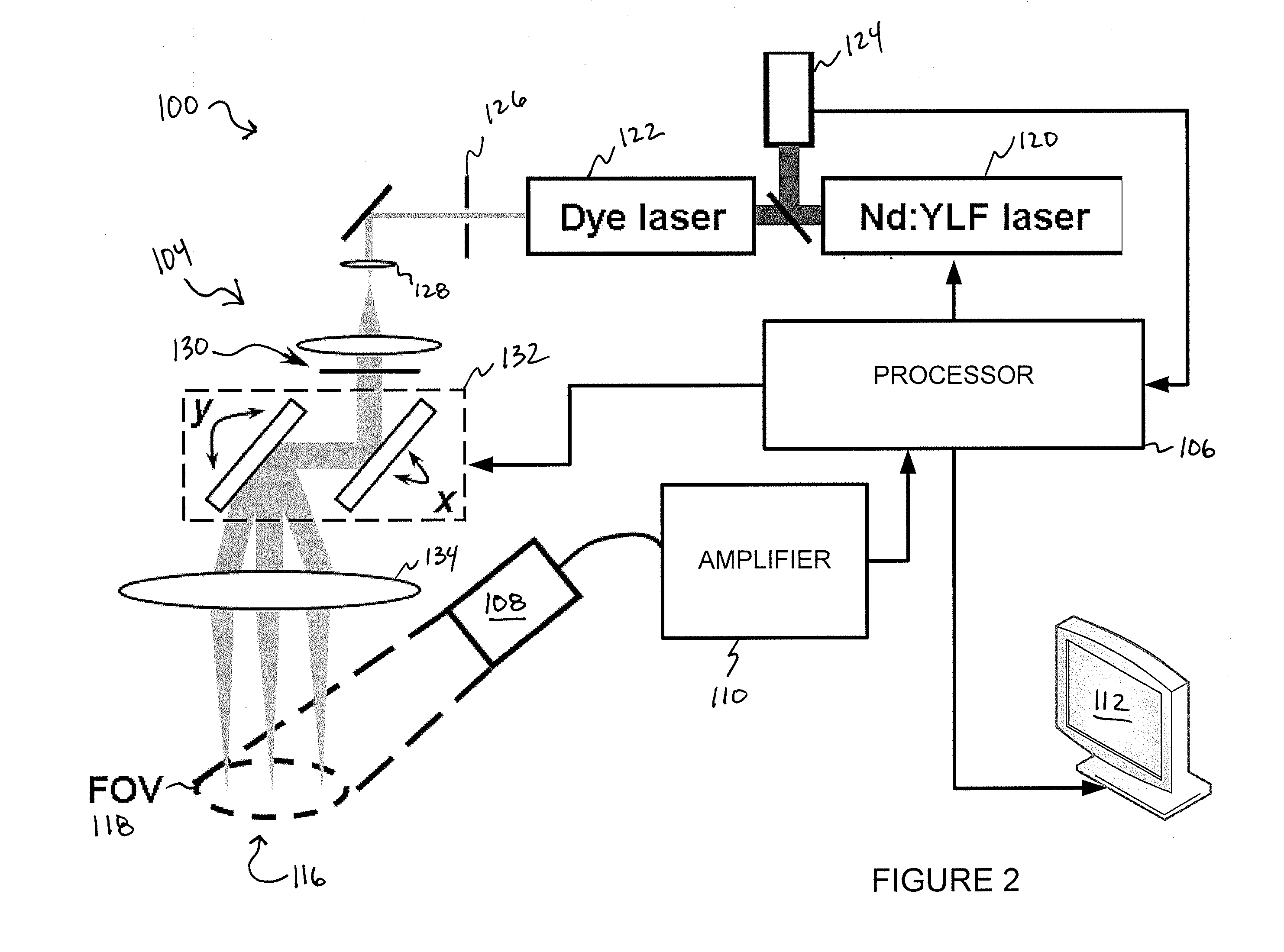
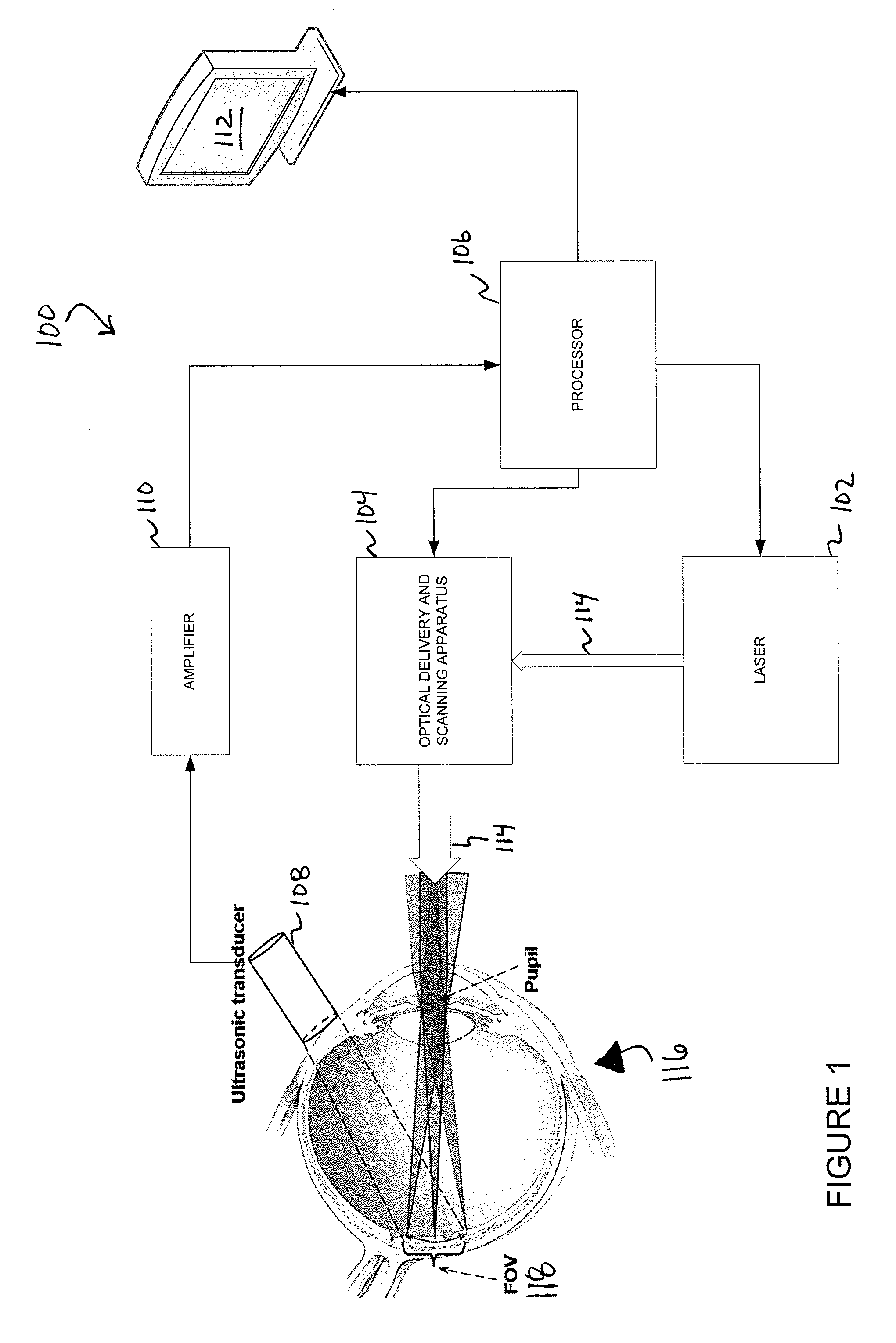
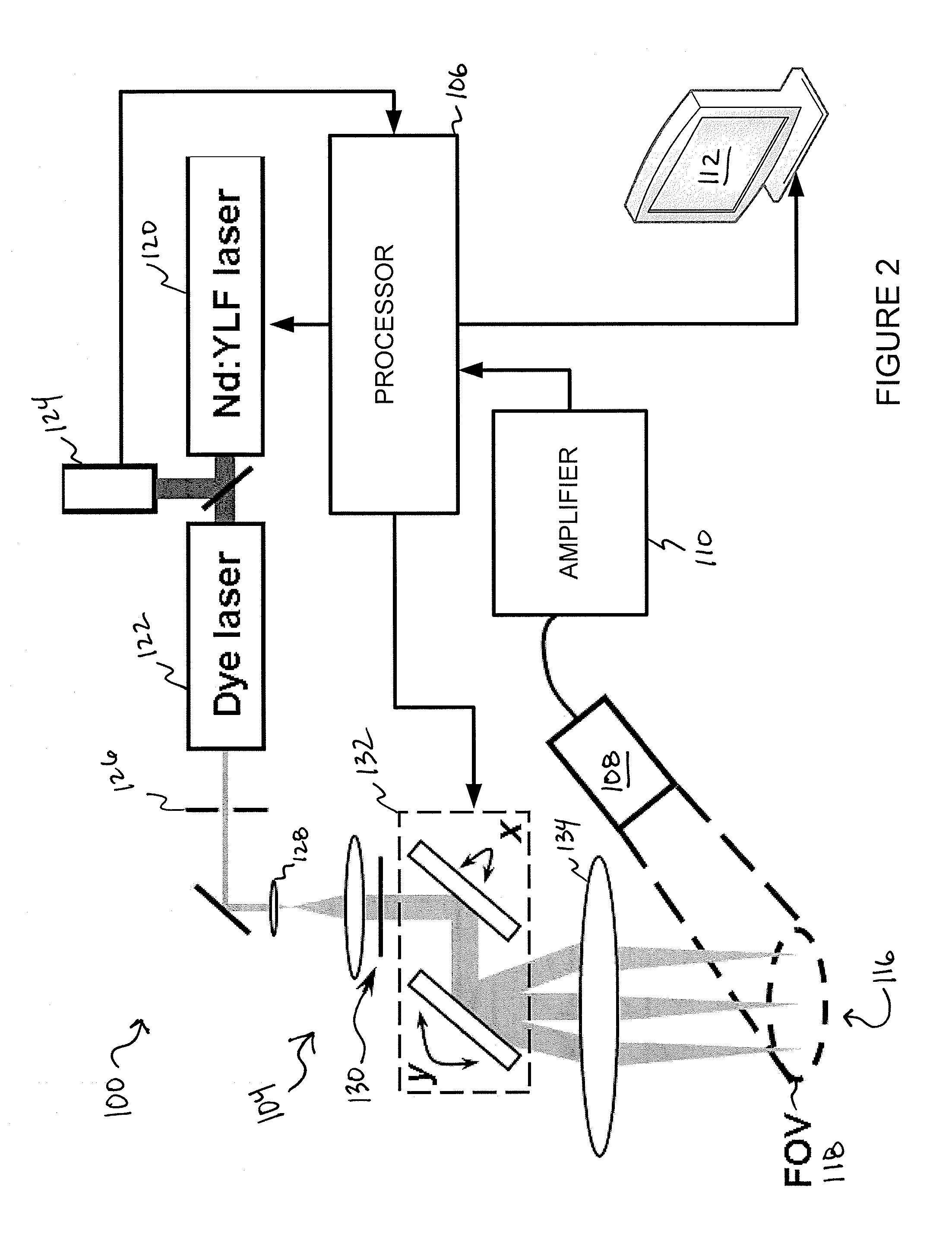
Various embodiments of the present invention include systems and methods for multimodal functional imaging based upon photoacoustic and laser optical scanning microscopy. In particular, at least one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a contact lens in combination with an ultrasound transducer for purposes of acquiring photoacoustic microscopy data. Traditionally divergent imaging modalities such as confocal scanning laser opthalmoscopy and photoacoustic microscopy are combined within a single laser system. Functional imaging of biological samples can be utilized for various medical and biological purposes.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC +1
Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS7245380B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRadiation pyrometryPhotoacoustic microscopyTuning fork
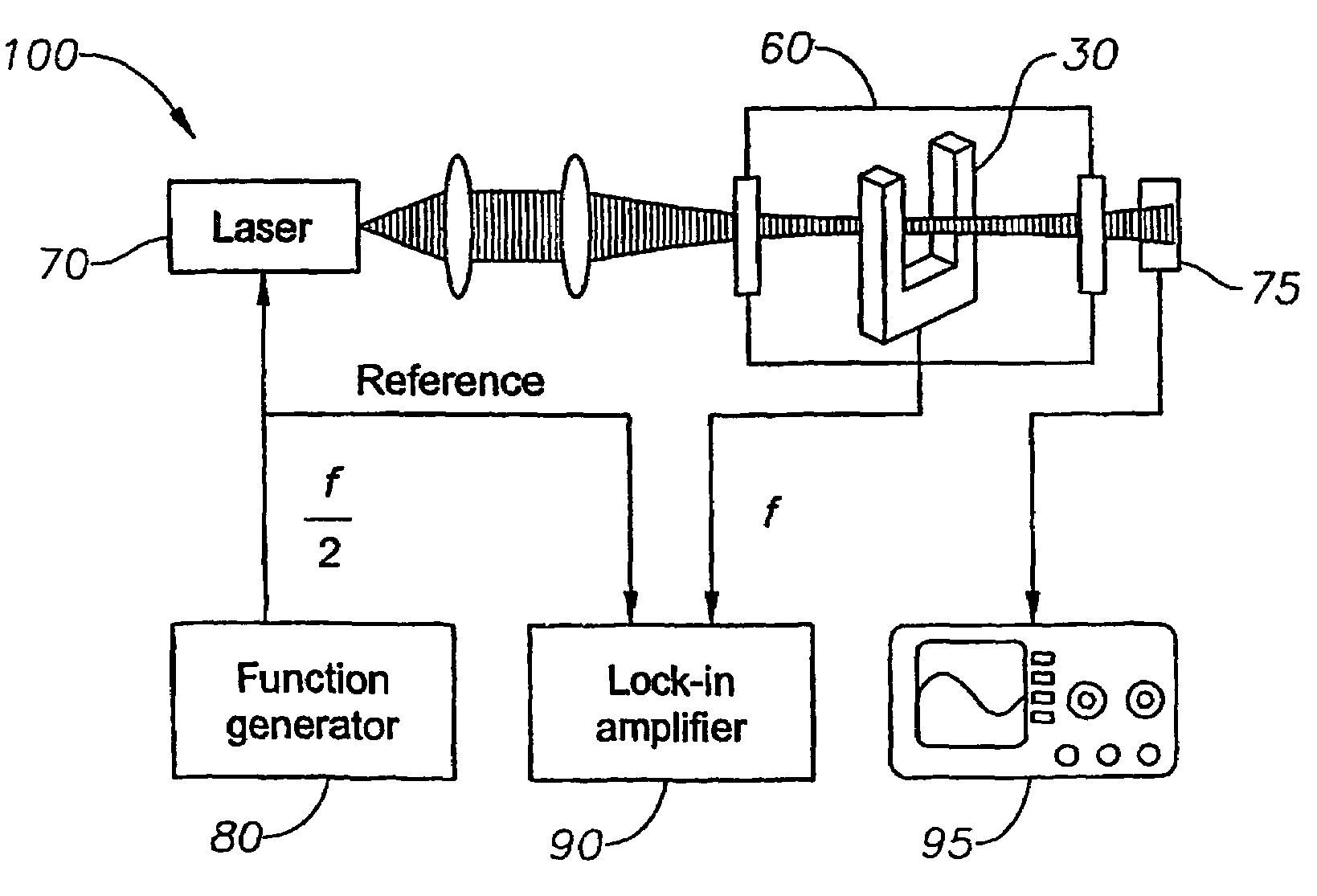
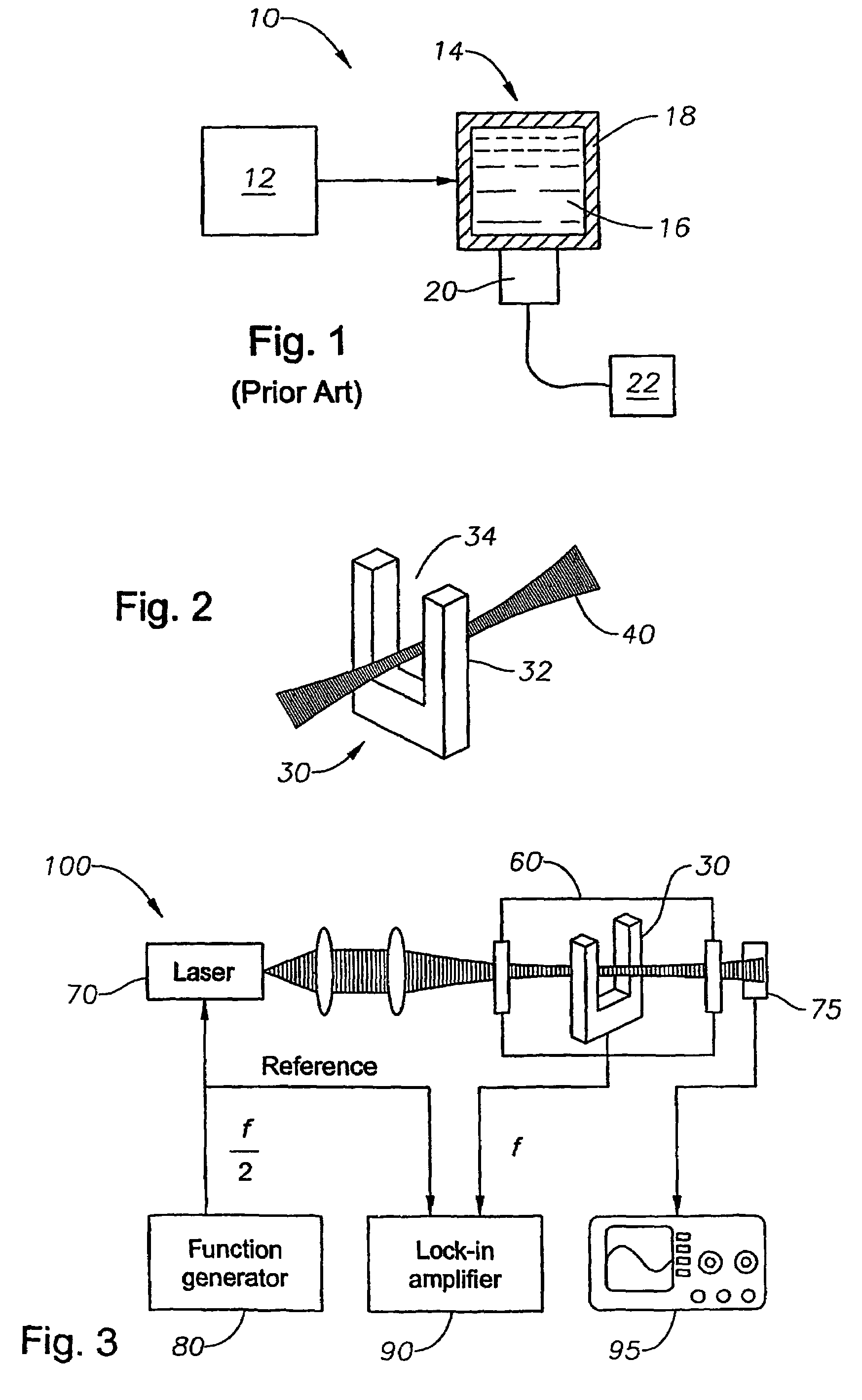
Methods and apparatus for detecting photoacoustic signals in fluid media are described. The present invention differs from conventional photoacoustic spectroscopy in that rather than accumulating the absorbed energy in the fluid of a sample cell, the absorbed energy is accumulated in an acoustic detector or sensitive element. In a preferred embodiment, the acoustic detector comprises piezoelectric crystal quartz. The quartz is preferably in the shape of a tuning fork.
Owner:RICE UNIV
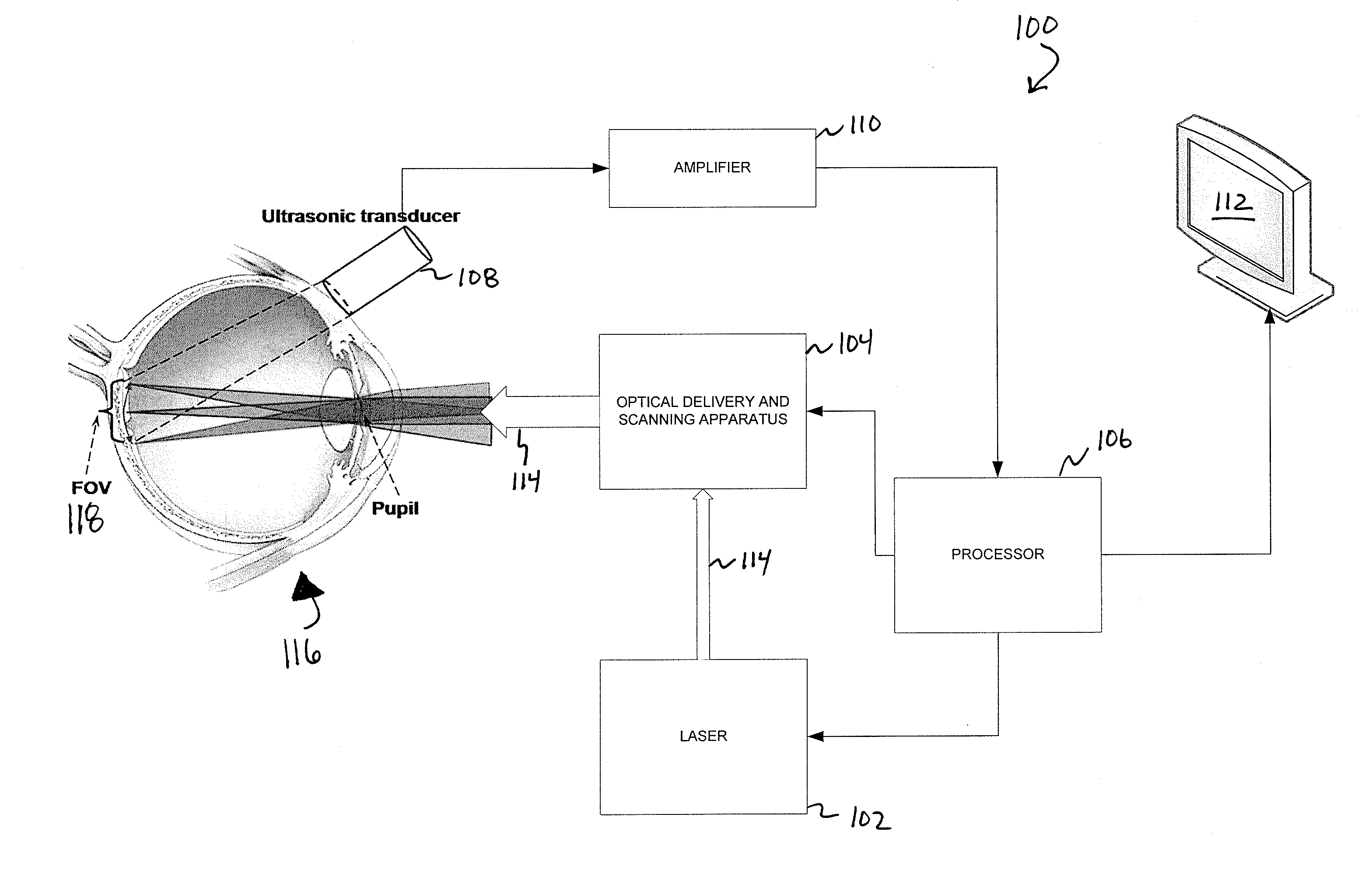
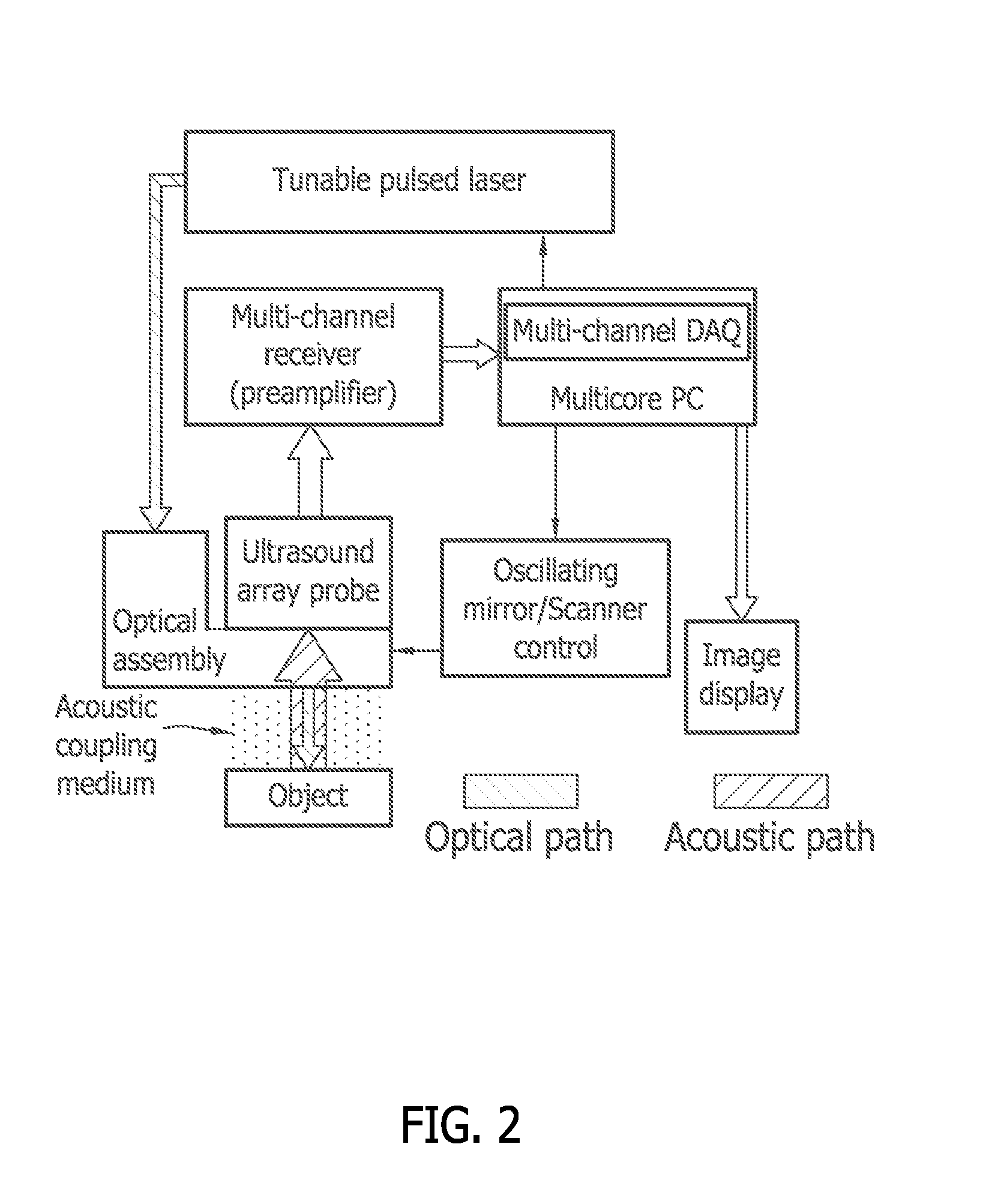
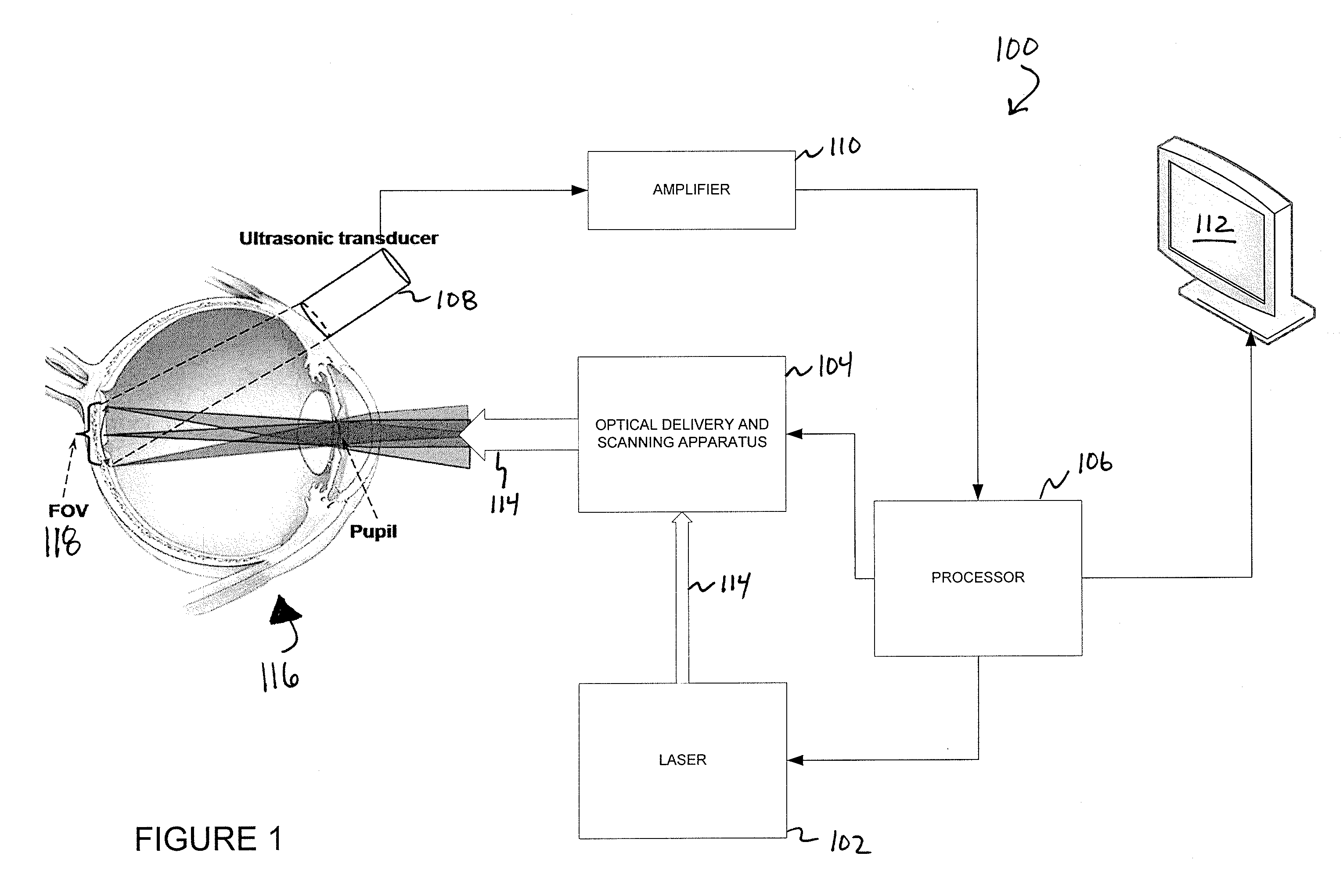
Systems and methods for photoacoustic opthalmoscopy
InactiveUS20100245766A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostics using lightDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhotoacoustic microscopy
Various embodiments of the present invention include systems and methods for multimodal functional imaging based upon photoacoustic and laser optical scanning microscopy. In particular, at least one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a contact lens in combination with an ultrasound transducer for purposes of acquiring photoacoustic microscopy data. Traditionally divergent imaging modalities such as confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy and photoacoustic microscopy are combined within a single laser system. Functional imaging of biological samples can be utilized for various medical and biological purposes.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC +1
Systems and methods for photoacoustic opthalmoscopy
InactiveUS8016419B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostics using lightDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhotoacoustic microscopy
Various embodiments of the present invention include systems and methods for multimodal functional imaging based upon photoacoustic and laser optical scanning microscopy. In particular, at least one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a contact lens in combination with an ultrasound transducer for purposes of acquiring photoacoustic microscopy data. Traditionally divergent imaging modalities such as confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy and photoacoustic microscopy are combined within a single laser system. Functional imaging of biological samples can be utilized for various medical and biological purposes.
Owner:UMW RES FOUND INC +1
Confocal photoacoustic microscopy with optical lateral resolution
ActiveUS8454512B2Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotoacoustic microscopyElectronic systems
A confocal photoacoustic microscopy system includes a laser configured to emit a light pulse, a focusing assembly configured to receive the light pulse and to focus the light pulse into an area inside an object, an ultrasonic transducer configured to receive acoustic waves emitted by the object in response to the light pulse, and an electronic system configured to process the acoustic waves and to generate an image of the area inside the object. The focusing assembly is further configured to focus the light pulse on the object in such a way that a focal point of the focusing assembly coincides with a focal point of the at least one ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
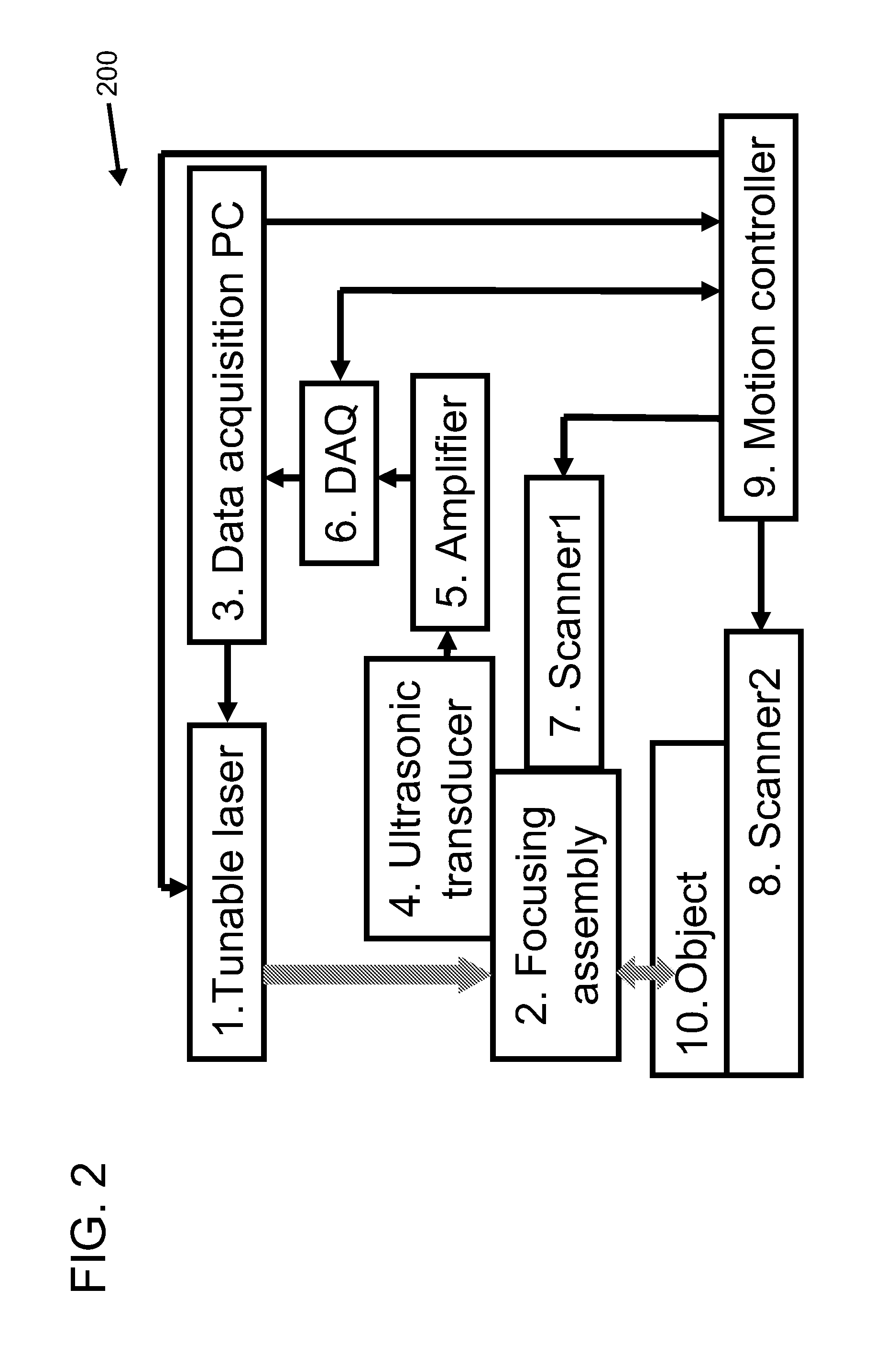
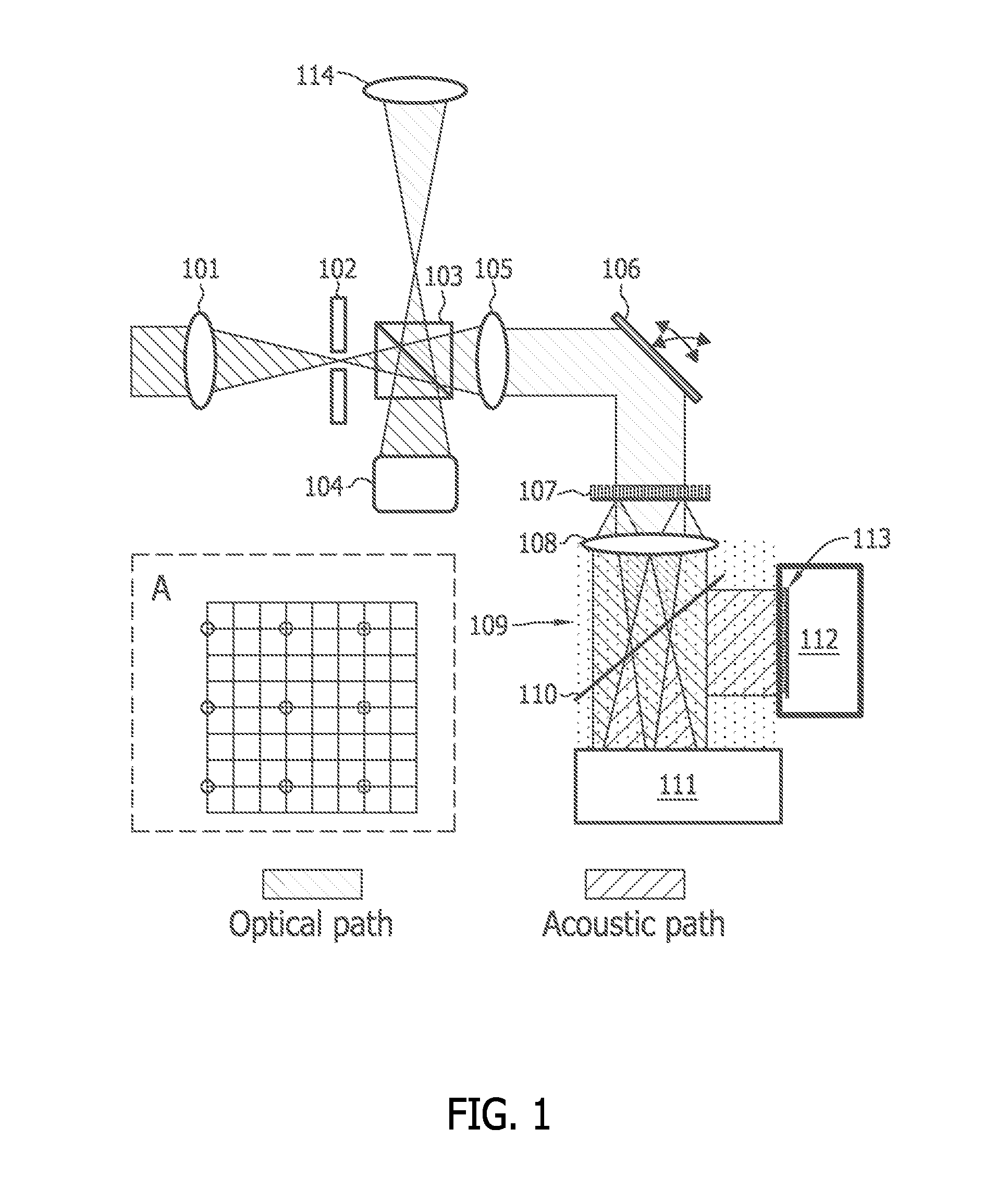
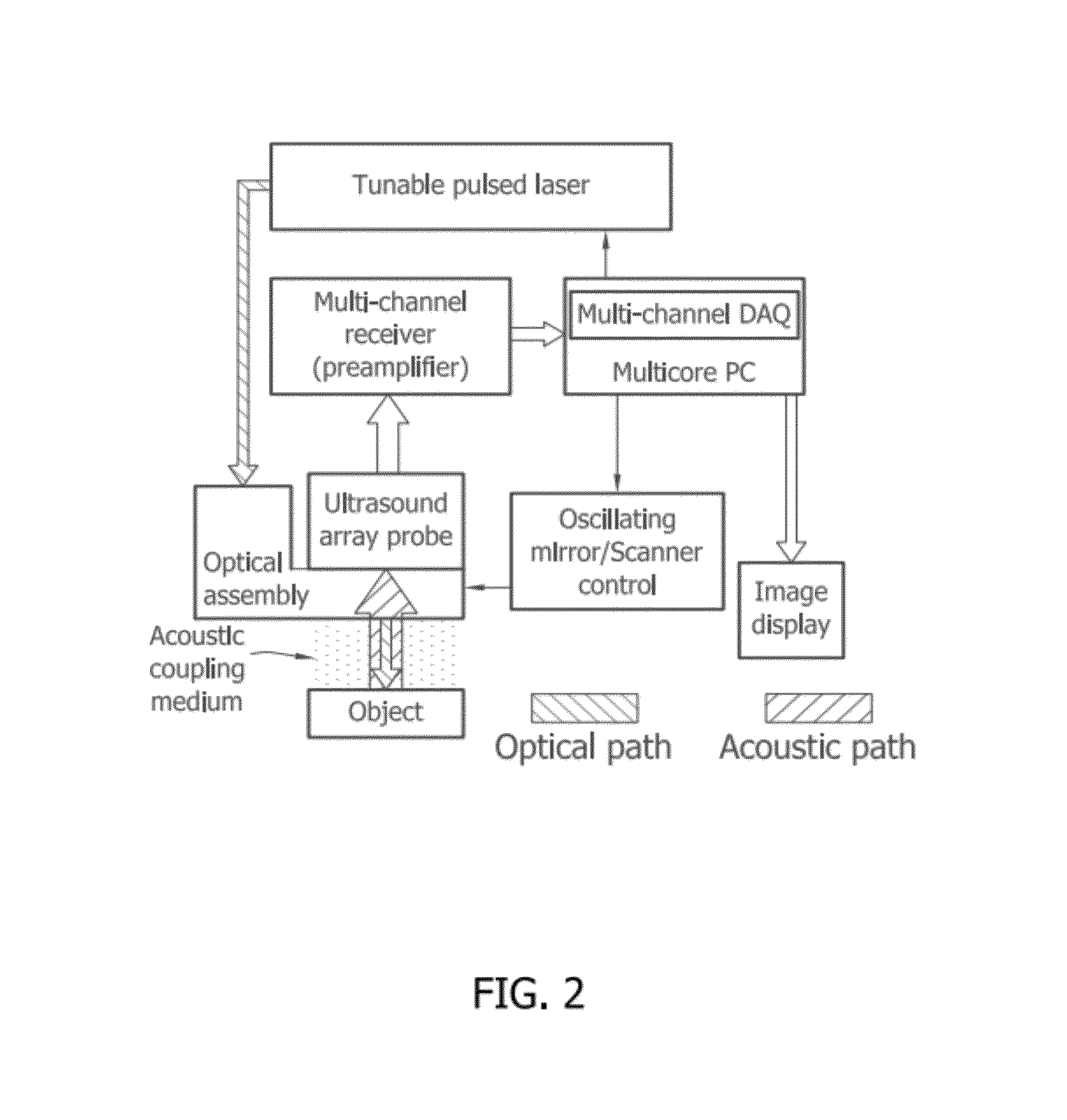
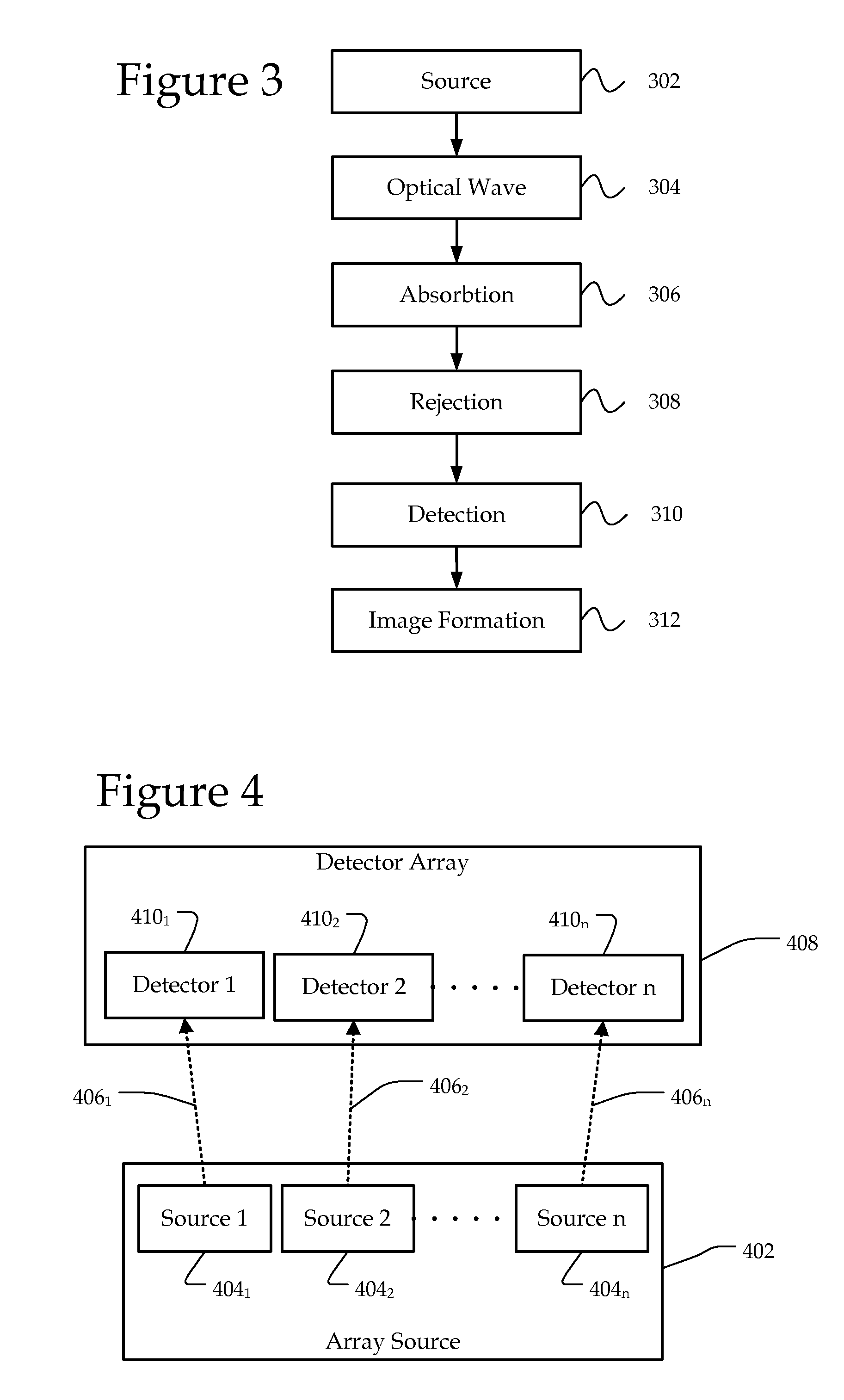
Section-illumination photoacoustic microscopy with ultrasonic array detection
InactiveUS20120275262A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotoacoustic microscopySonification
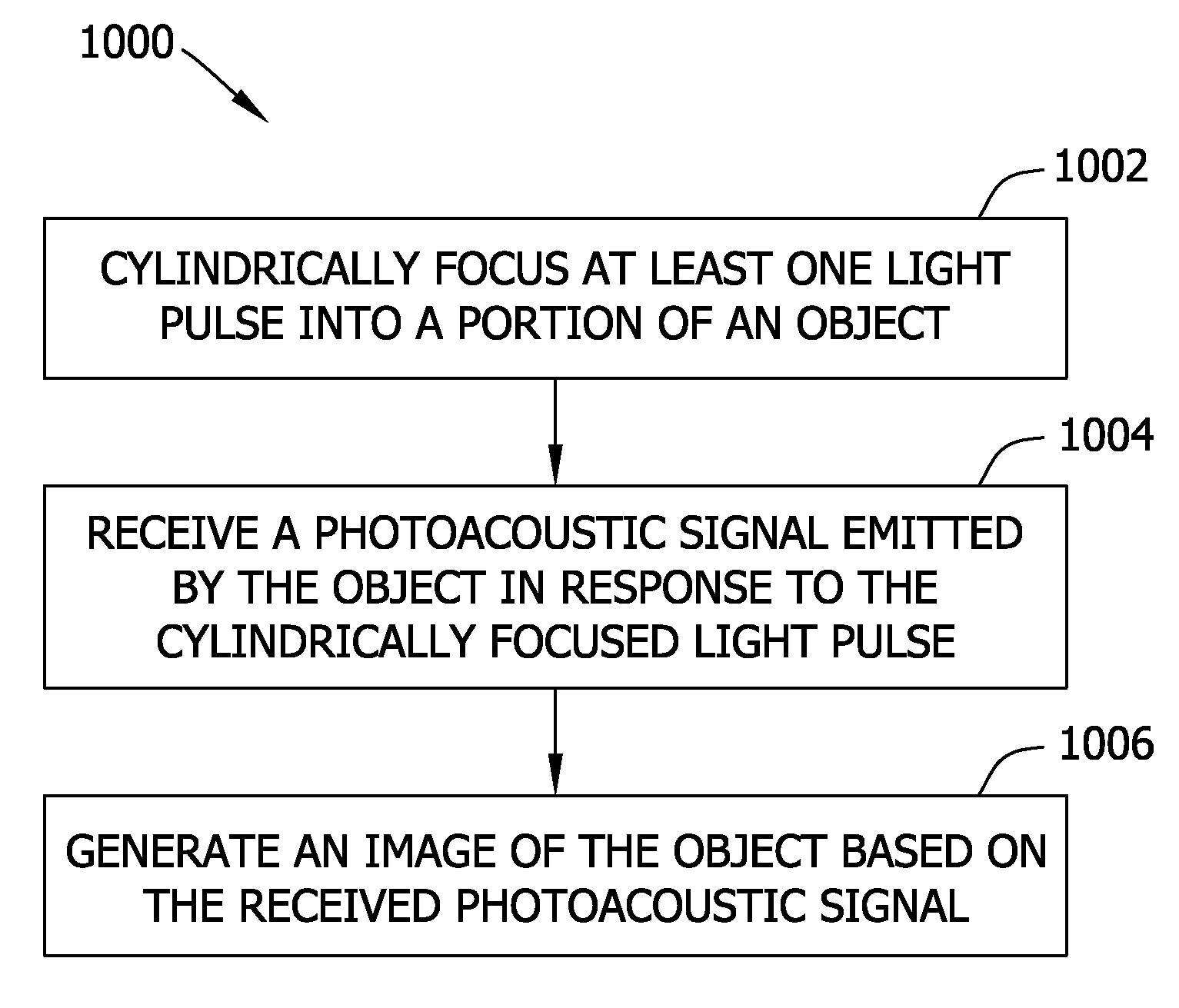
Imaging systems, probes for imaging systems, and methods for noninvasive imaging are disclosed. In one example, a probe for use with an imaging system includes a slit configured to spatially filter a light beam from a light source. The probe includes a focusing device configured to cylindrically focus the spatially filtered light beam into an object, and an ultrasound transducer array configured to detect a photoacoustic signal emitted by the object in response to the cylindrically focused light beam.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Systems and methods for photoacoustic opthalmoscopy
InactiveUS20100245770A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInterferometric spectrometryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhotoacoustic microscopy
Various embodiments of the present invention include systems and methods for multimodal functional imaging based upon photoacoustic and laser optical scanning microscopy. In particular, at least one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a contact lens in combination with an ultrasound transducer for purposes of acquiring photoacoustic microscopy data. Traditionally divergent imaging modalities such as confocal scanning laser opthalmoscopy and photoacoustic microscopy are combined within a single laser system. Functional imaging of biological samples can be utilized for various medical and biological purposes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Systems and methods for photoacoustic opthalmoscopy
InactiveUS8025406B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotoacoustic microscopyDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Various embodiments of the present invention include systems and methods for multimodal functional imaging based upon photoacoustic and laser optical scanning microscopy. In particular, at least one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a contact lens in combination with an ultrasound transducer for purposes of acquiring photoacoustic microscopy data. Traditionally divergent imaging modalities such as confocal scanning laser opthalmoscopy and photoacoustic microscopy are combined within a single laser system. Functional imaging of biological samples can be utilized for various medical and biological purposes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
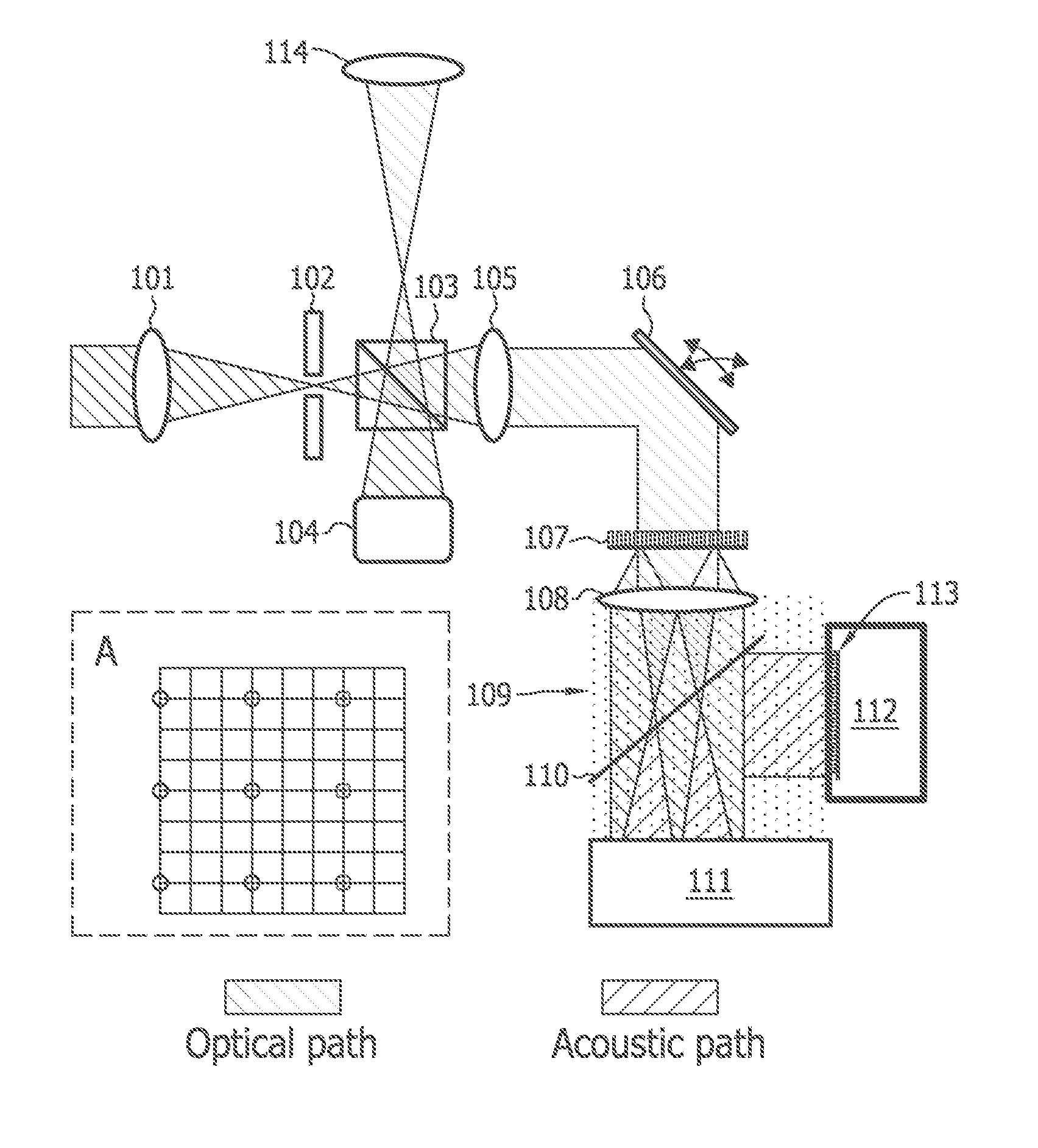
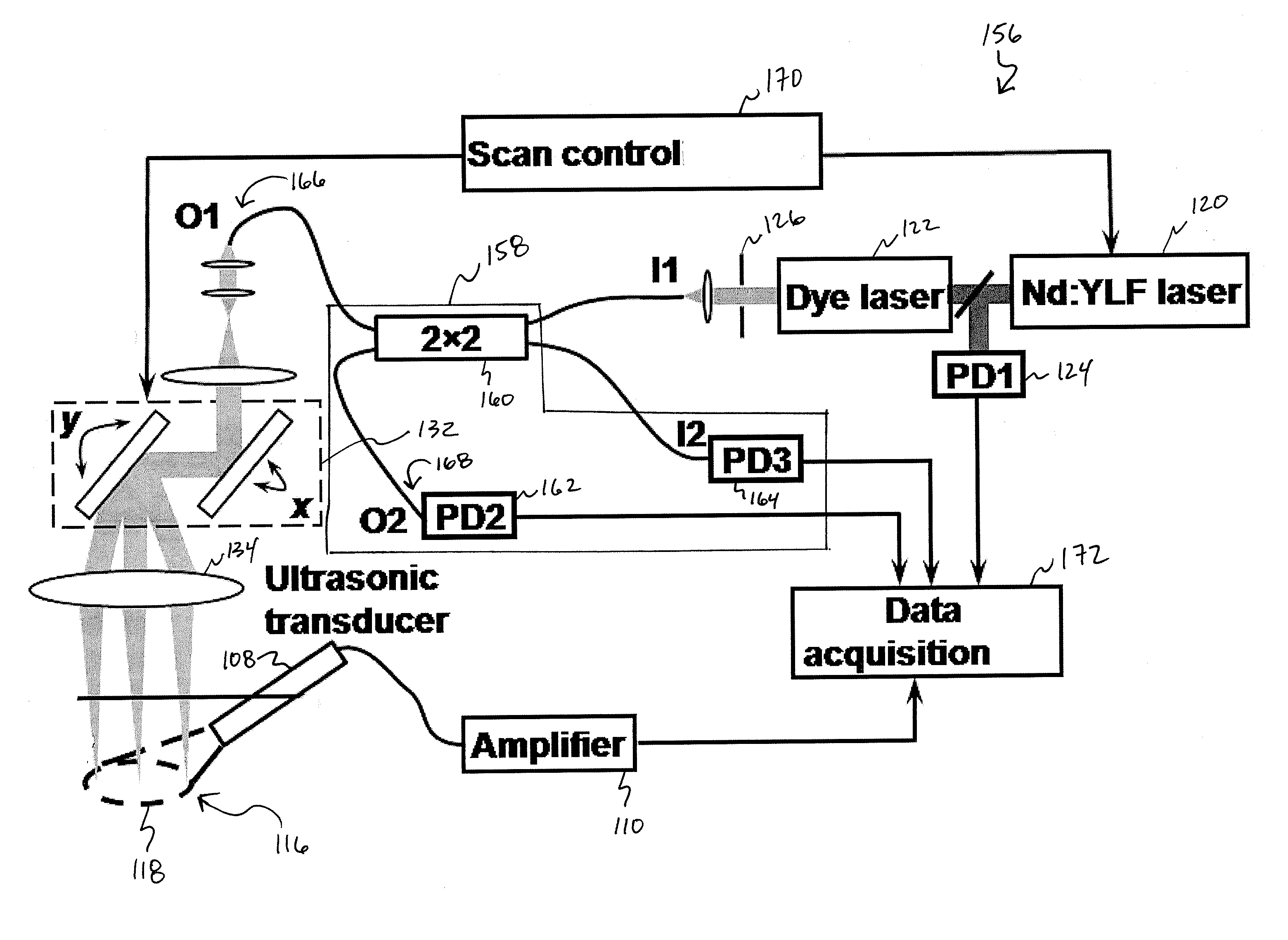
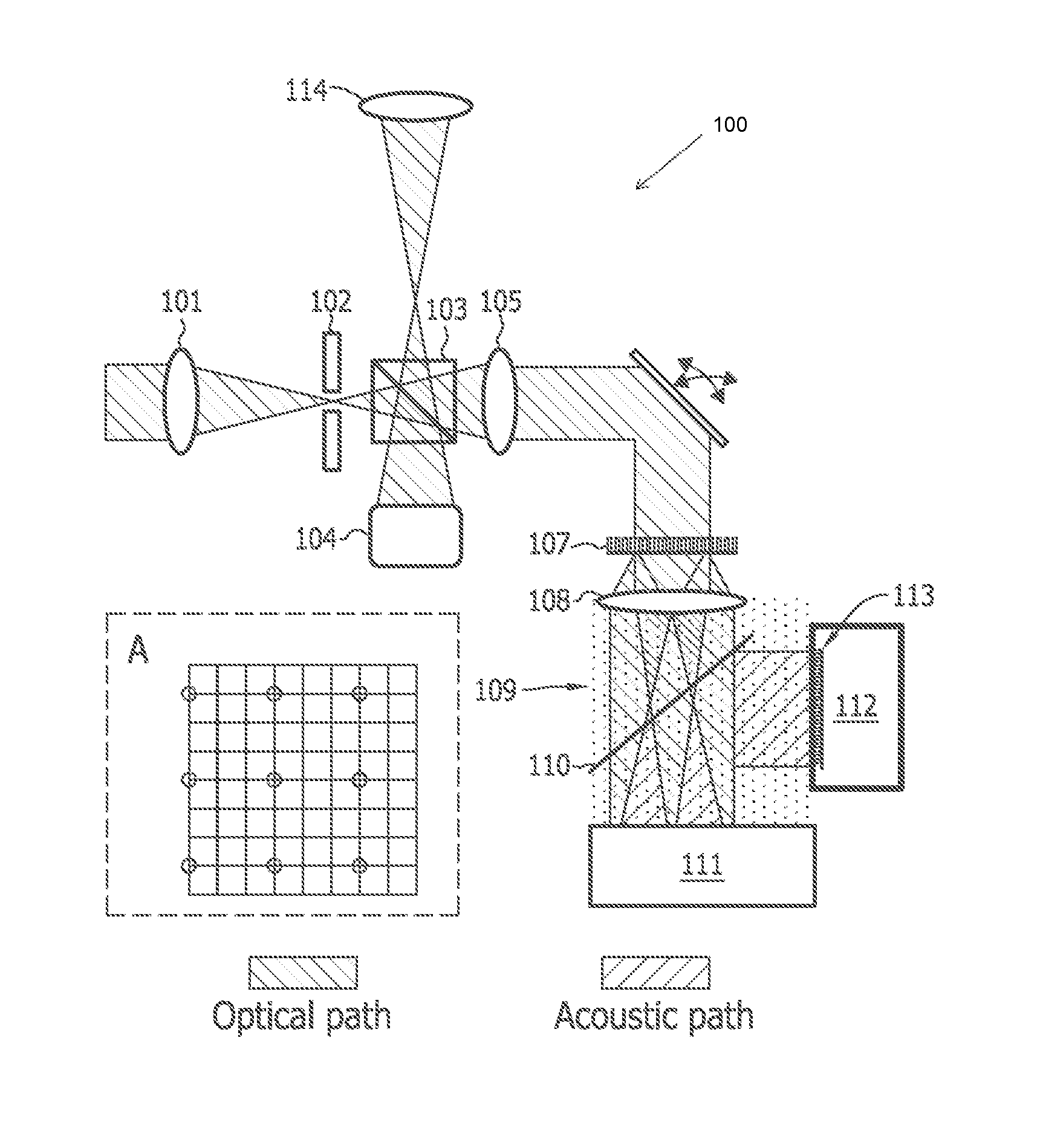
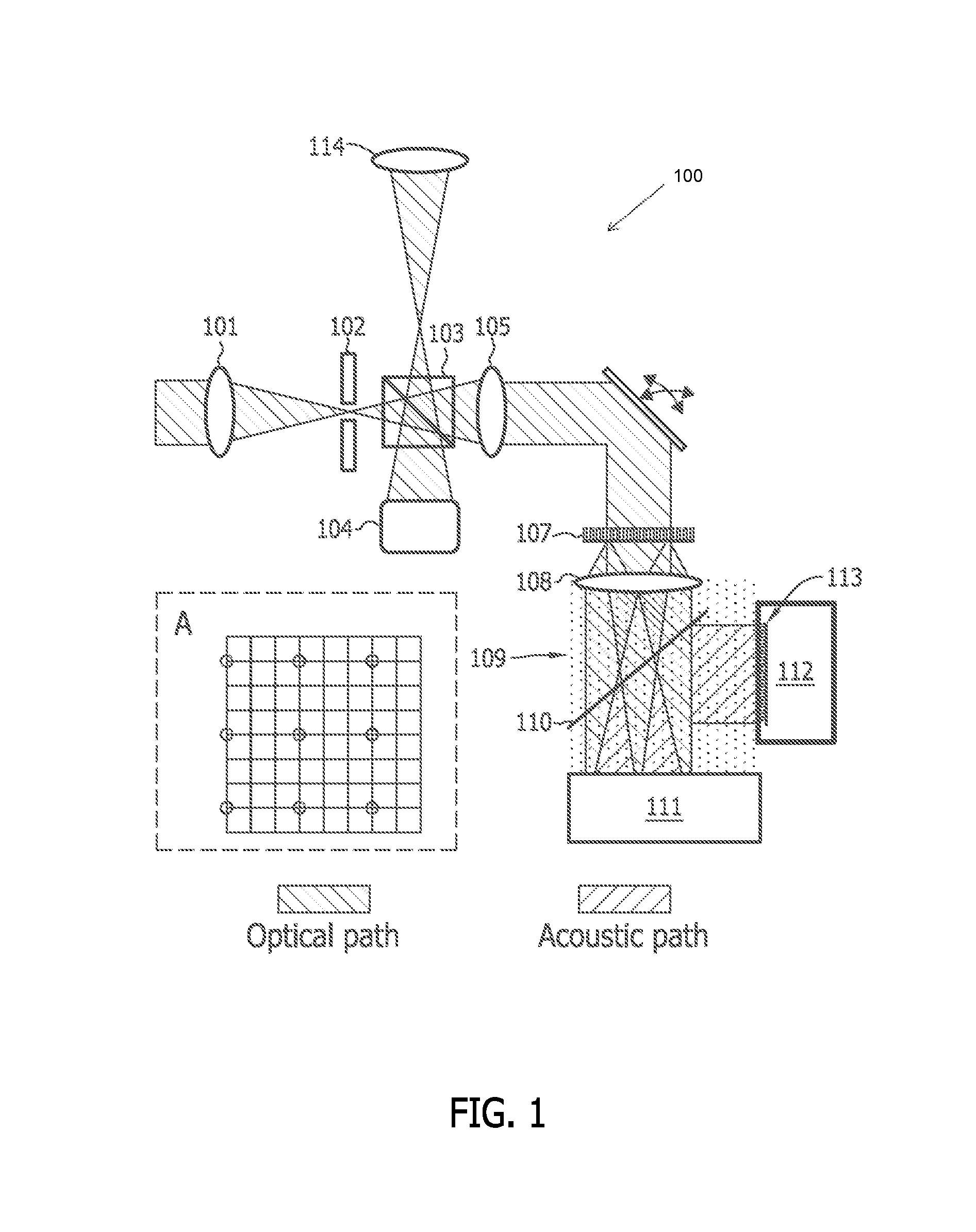
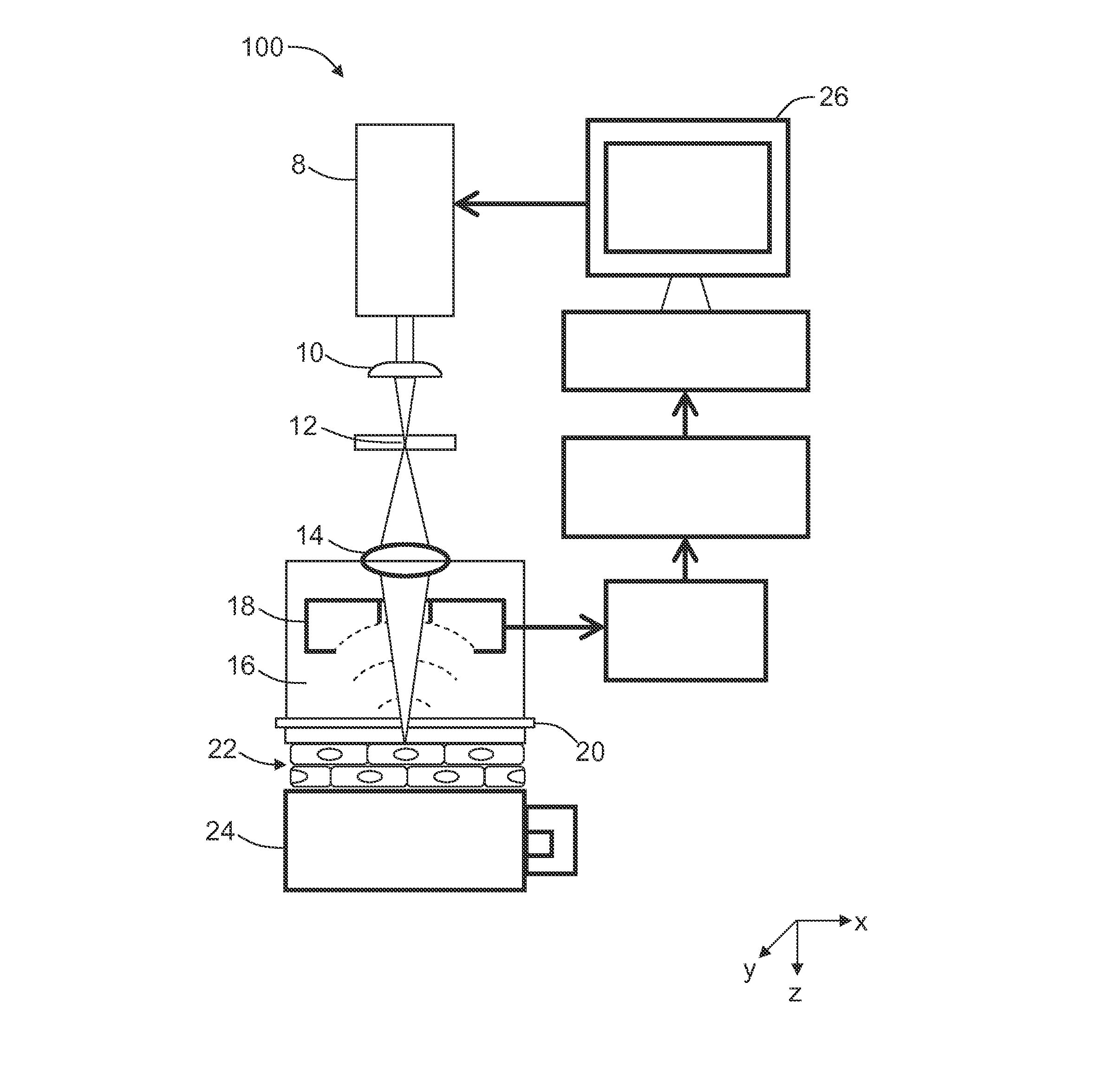
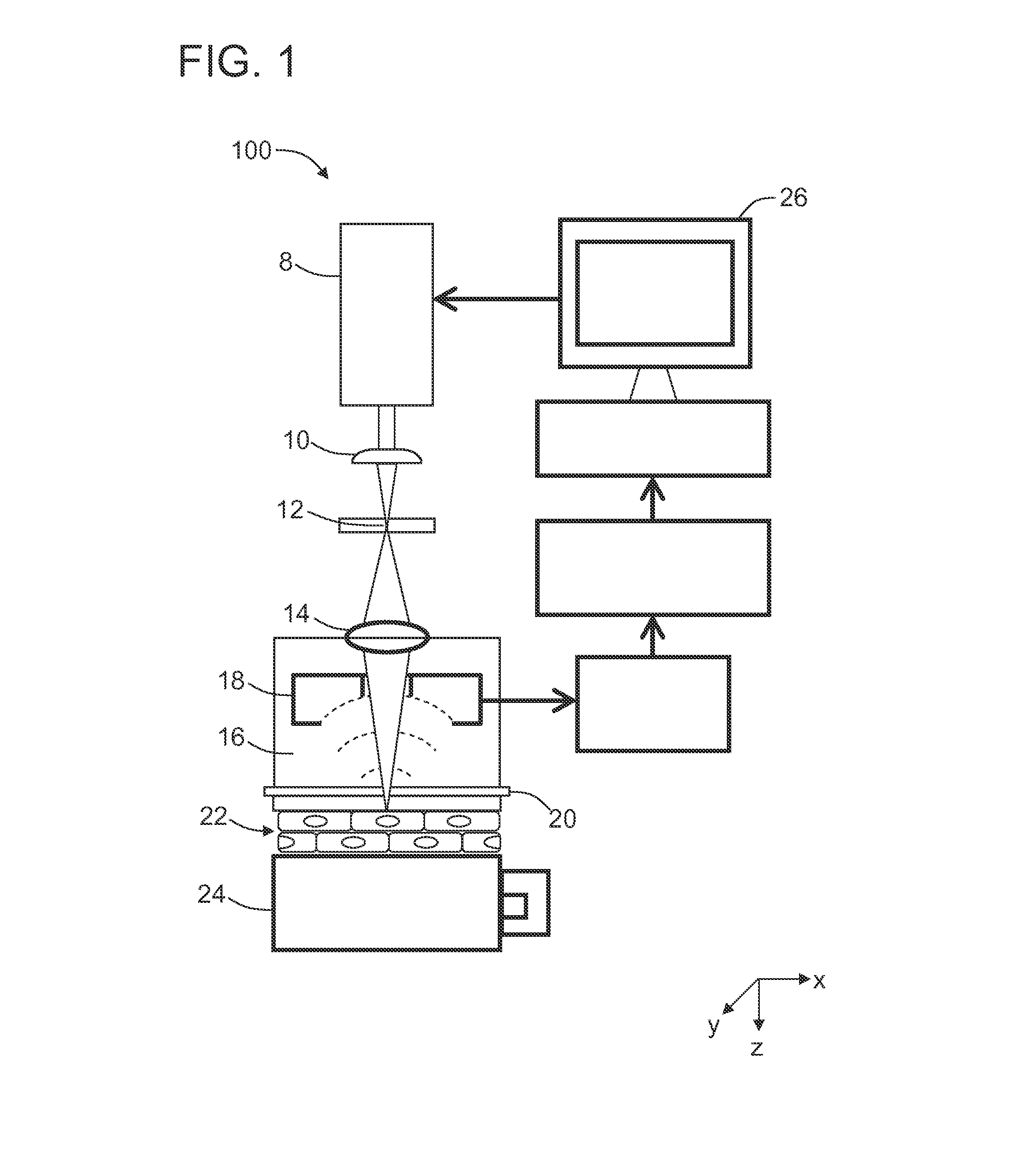
Multi-focus optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy with ultrasonic array detection
ActiveUS20120204648A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotoacoustic microscopyImage resolution
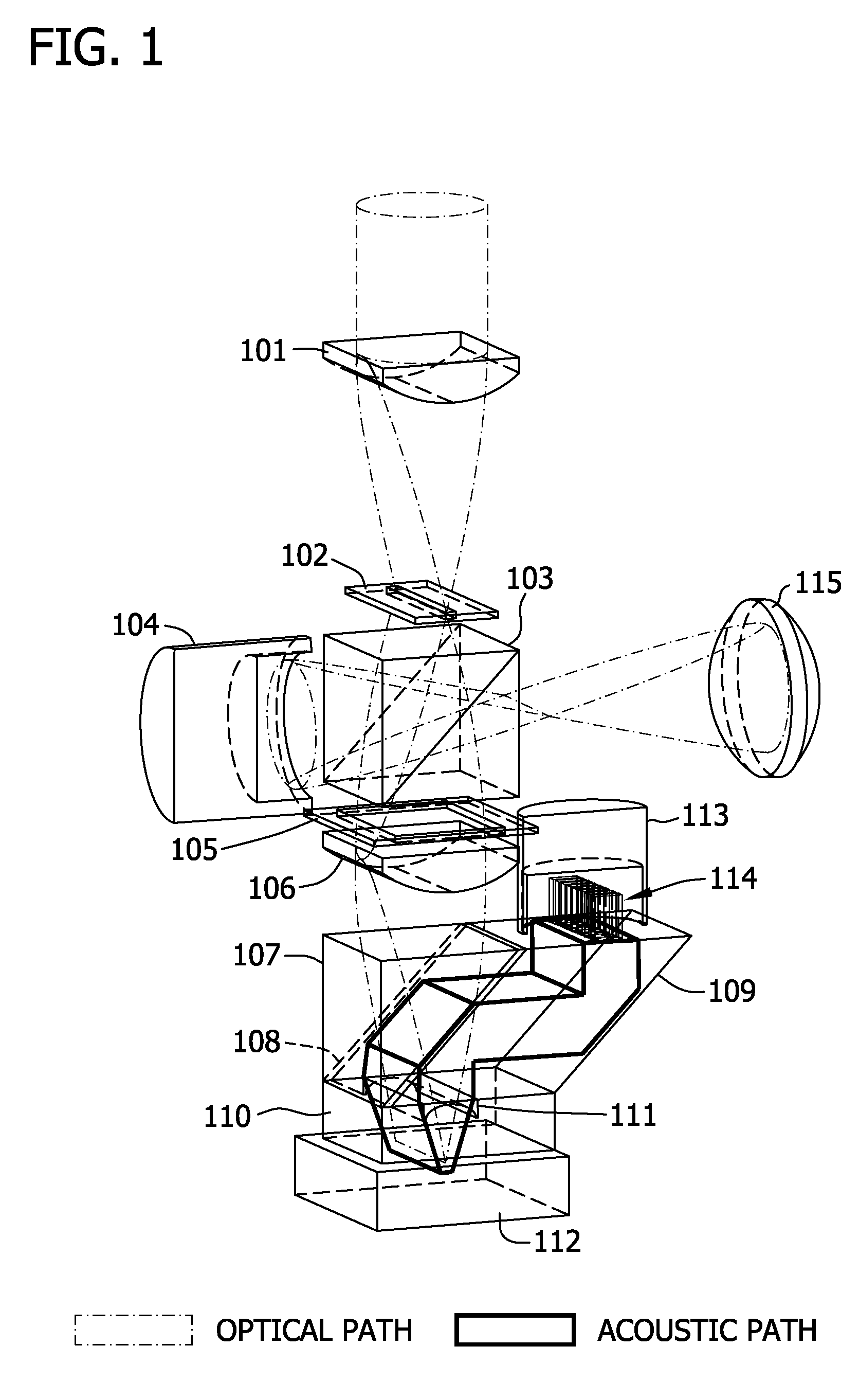
A probe for use with an imaging system, including a scanning device configured to receive a first light beam from a light source, a beam-divider configured to split the first light beam into a plurality of second light beams, and a focusing device configured to focus each of the second light beams on respective locations in an object of interest.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for photoacoustic opthalmoscopy
InactiveUS20100245769A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhotoacoustic microscopy
Various embodiments of the present invention include systems and methods for multimodal functional imaging based upon photoacoustic and laser optical scanning microscopy. In particular, at least one embodiment of the present invention utilizes a contact lens in combination with an ultrasound transducer for purposes of acquiring photoacoustic microscopy data. Traditionally divergent imaging modalities such as confocal scanning laser opthalmoscopy and photoacoustic microscopy are combined within a single laser system. Functional imaging of biological samples can be utilized for various medical and biological purposes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
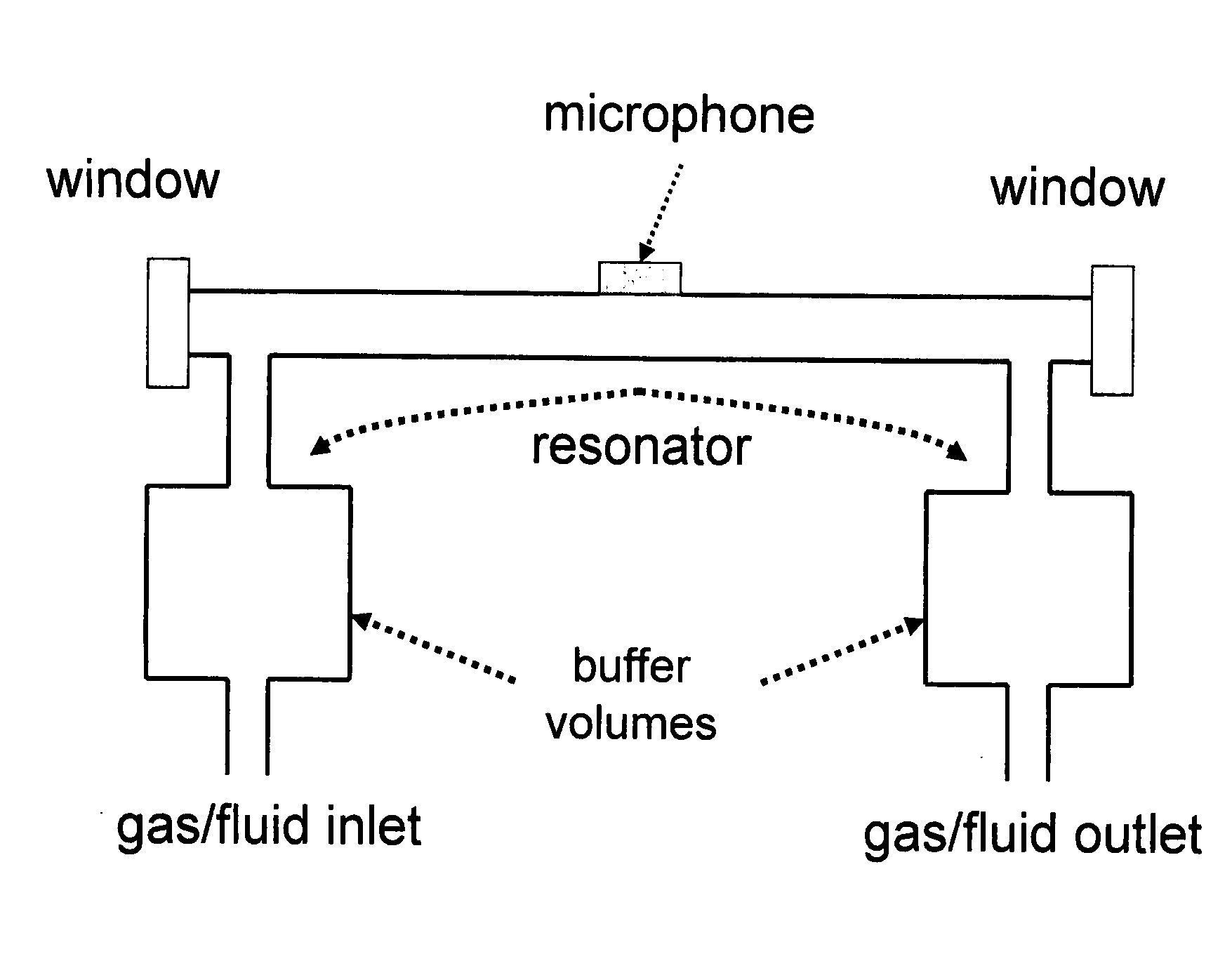
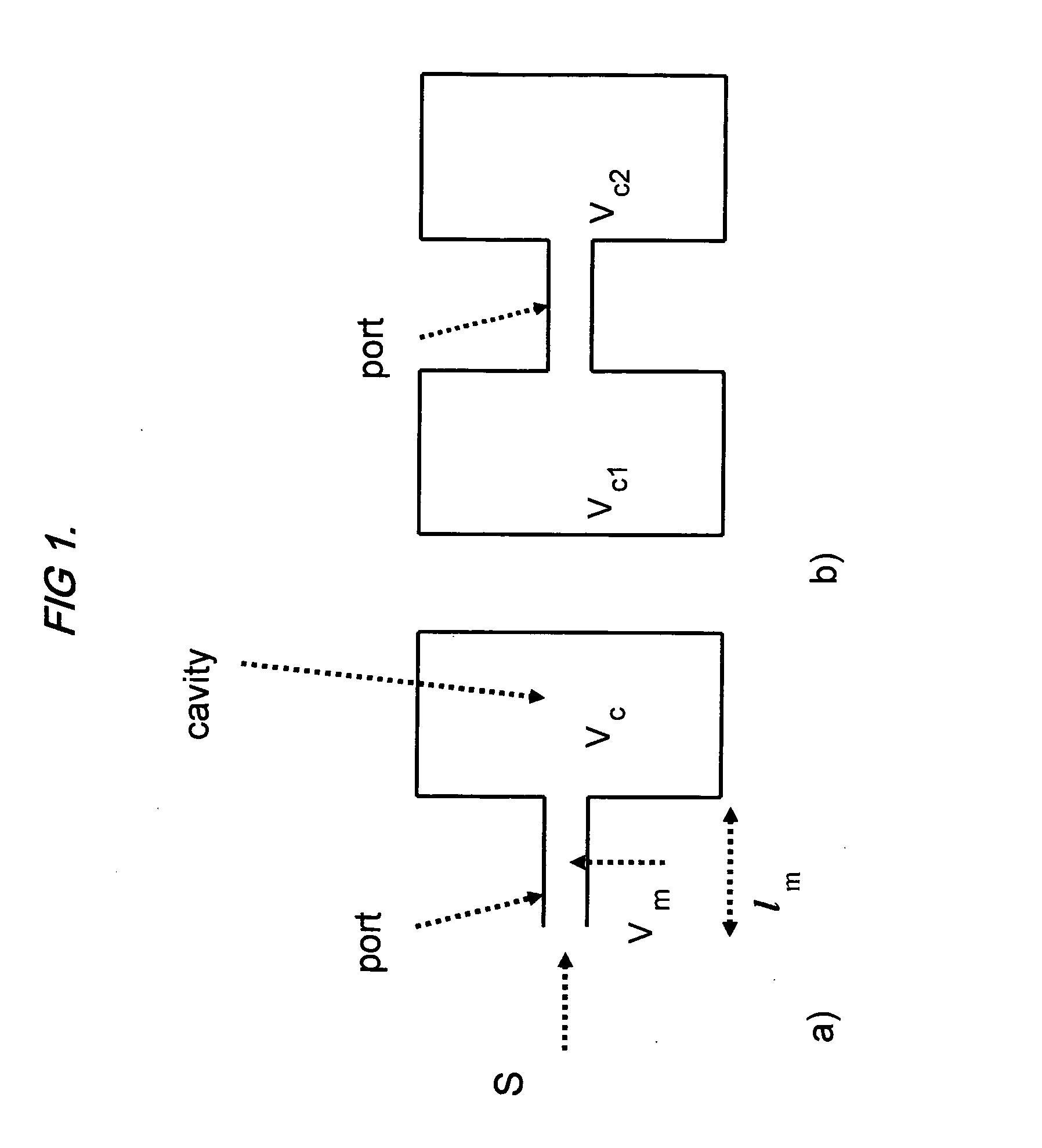
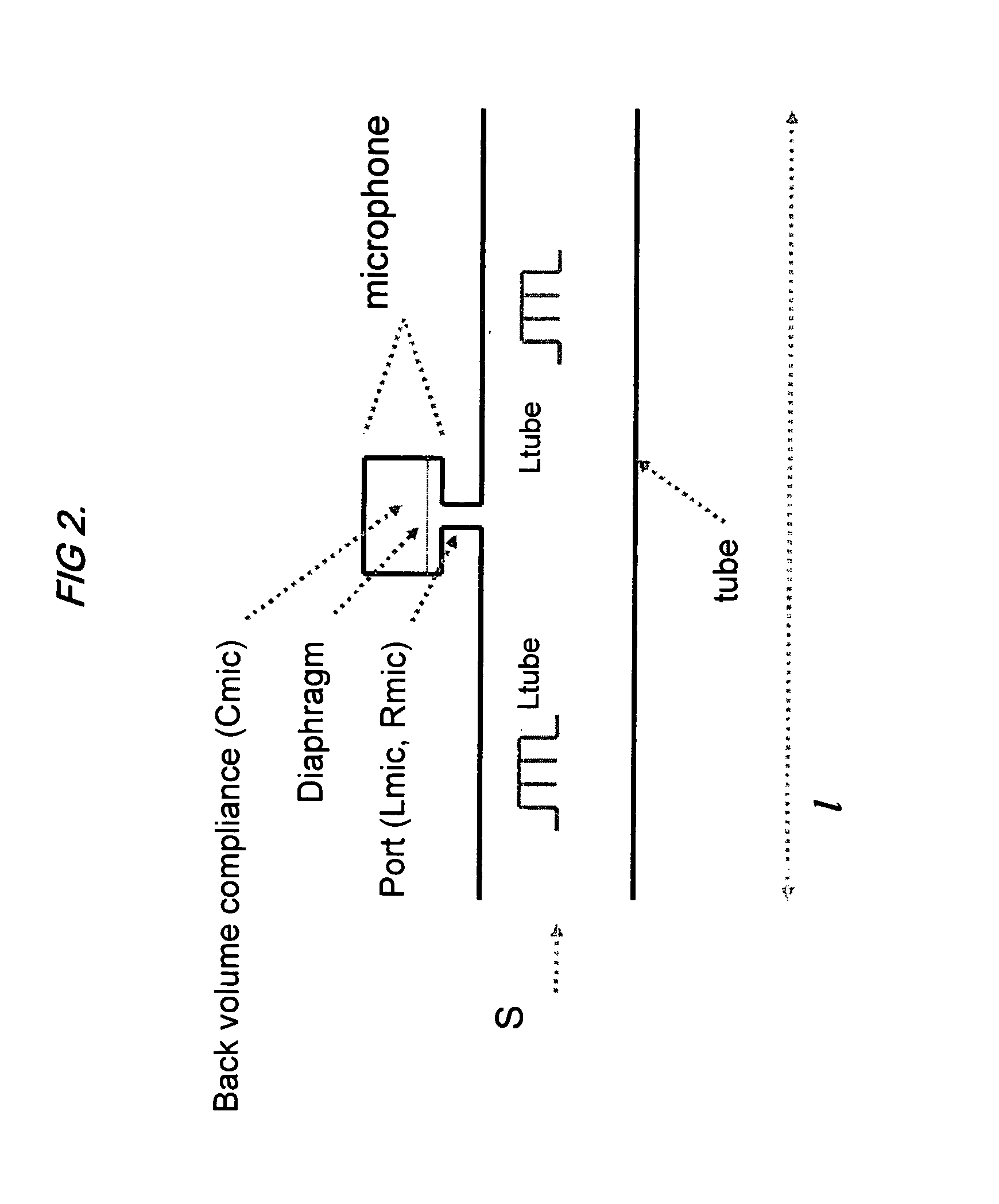
System and method for gas analysis using photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS20080134756A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGas analysisPhotoacoustic microscopy
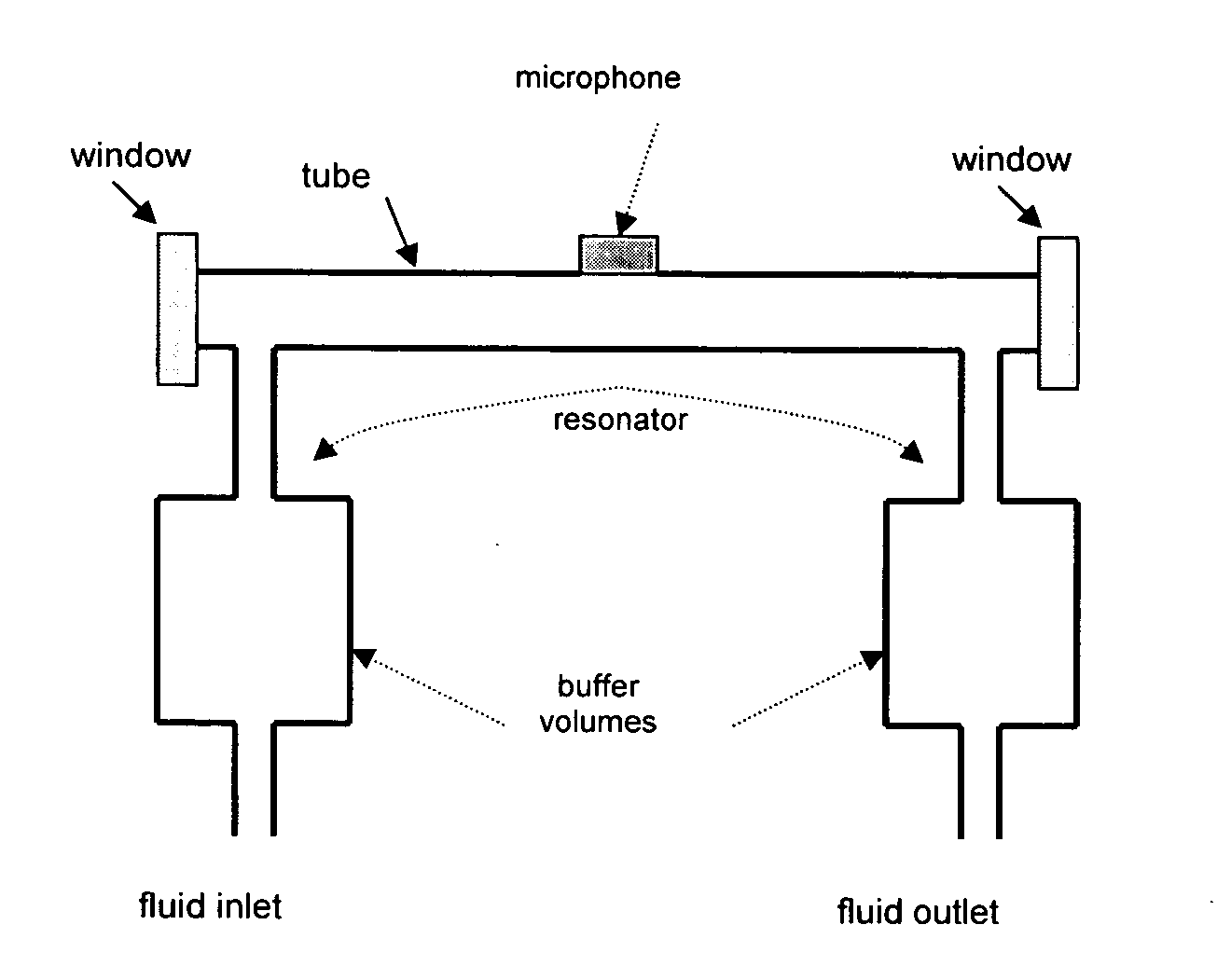
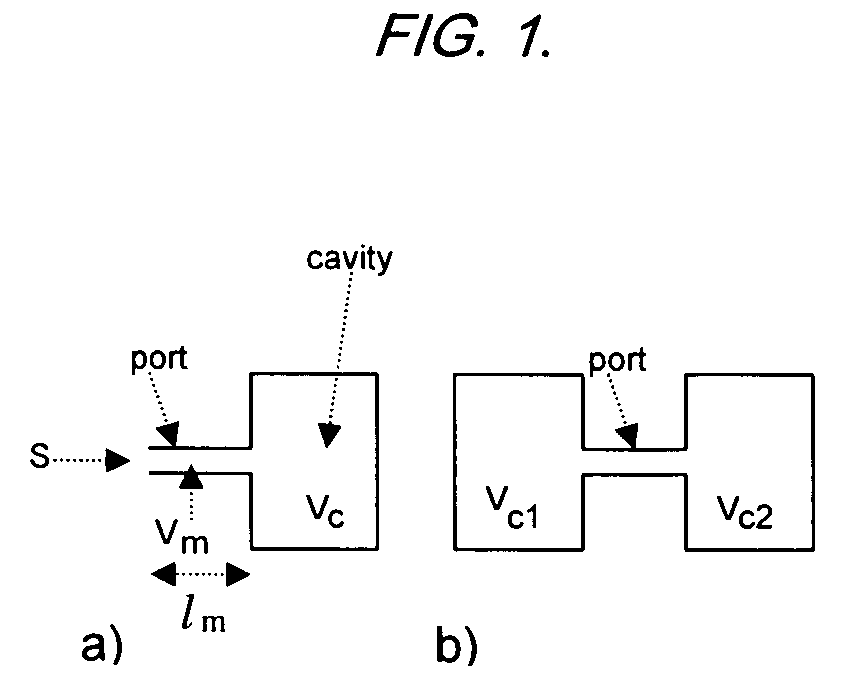
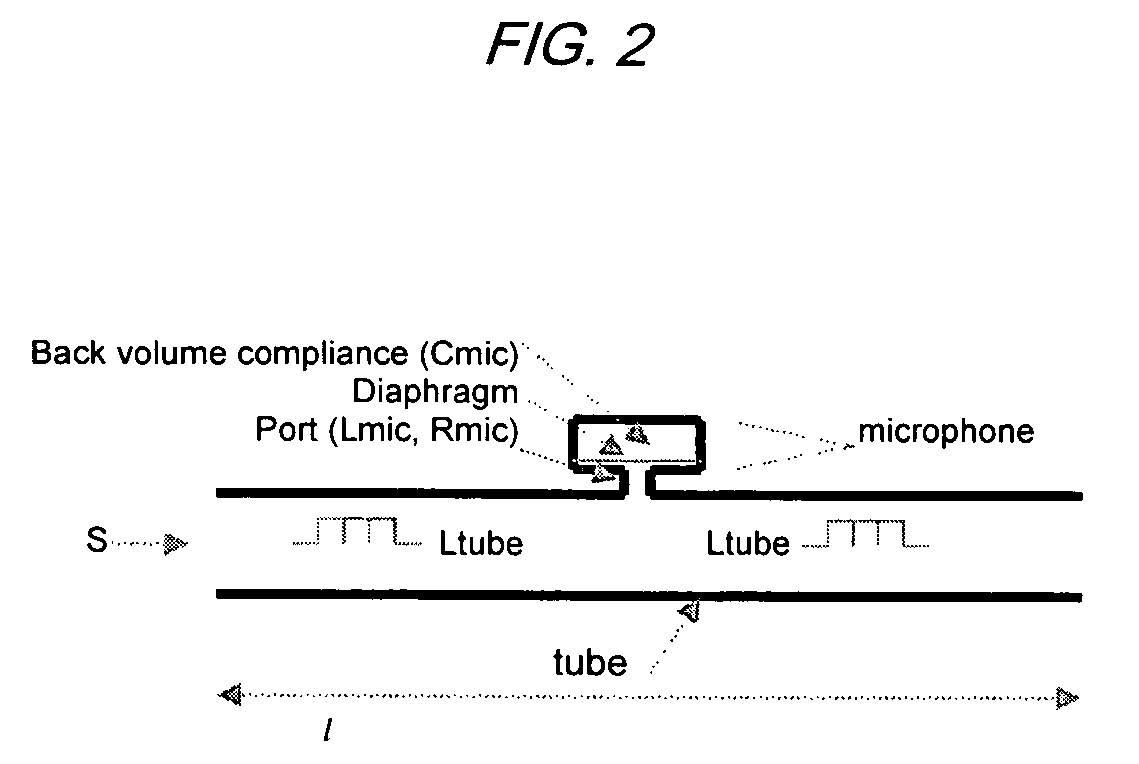
A system and method for analyzing a target analyte gas concentration using a photoacoustic spectroscopy cell comprising:i) a modulatable light source which provides optical radiation at an absorption wavelength of a target analyte;ii) a resonant acoustic chamber for containing said analyte;iii) a microphone positioned within said chamber whereby the acoustic reactance of the microphone is a substantial factor in determining the acoustic resonant frequency of the acoustic chamber and where the magnitude of the acoustic reactance of the microphone is at least two times the acoustic resistance of the microphone.
Owner:LI COR
System and method for gas analysis using photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080011055A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical radiationGas analysis
A method for analyzing a target analyte gas concentration using a photoacoustic spectroscopy cell comprising:i) a modulatable light source which provides optical radiation at an absorption wavelength of a target analyte;ii) a resonant acoustic chamber for containing said analyte;iii) a microphone positioned within said chamber whereby the acoustic reactance of the microphone is substantially equal but opposite in value to the acoustic reactance of the chamber at a selected cell resonance frequency.
Owner:FINESSE +1
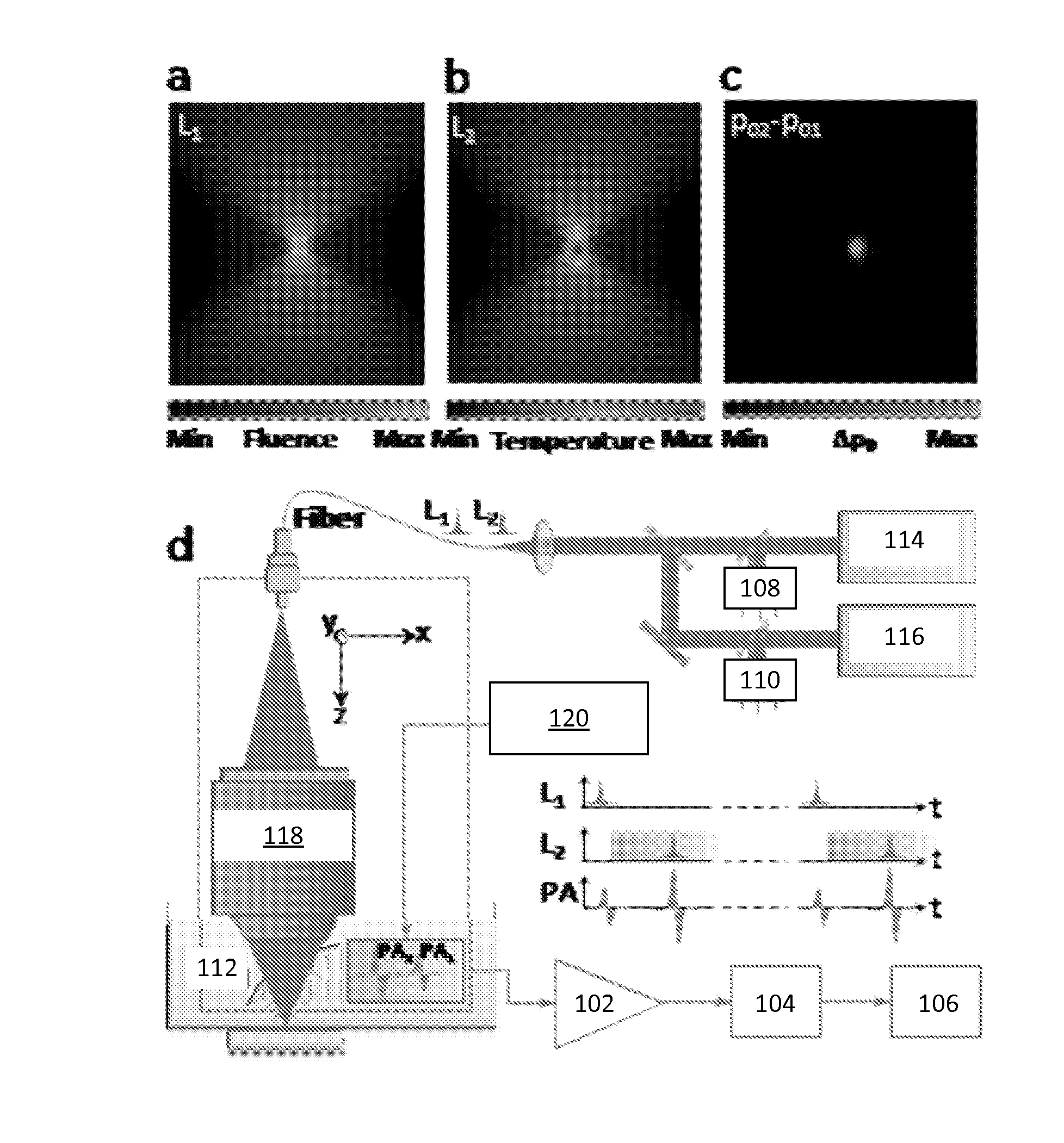
Systems and methods of grueneisen-relaxation photoacoustic microscopy and photoacoustic wavefront shaping
ActiveUS20160305914A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicroscopesPhotoacoustic microscopyWavefront
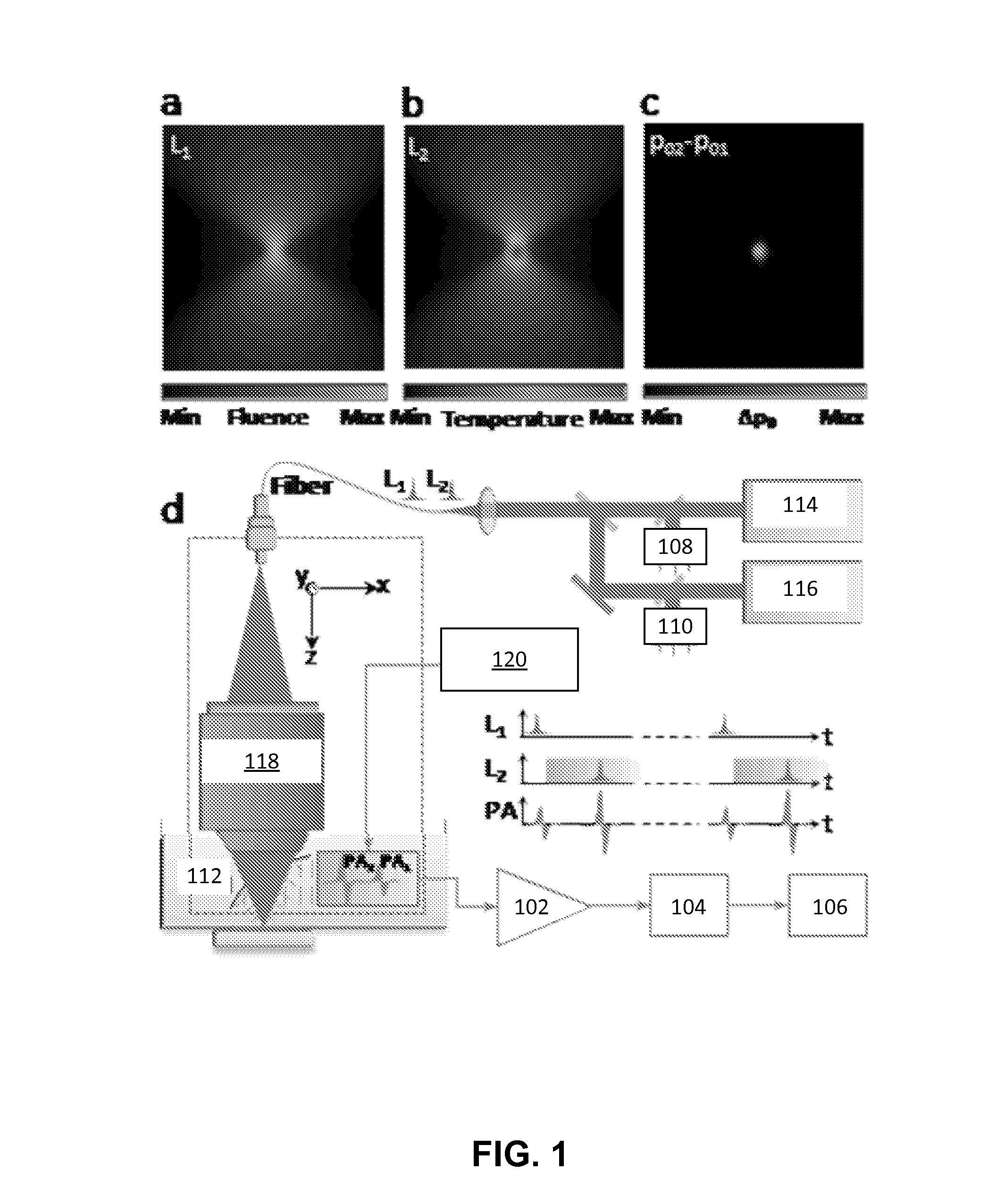
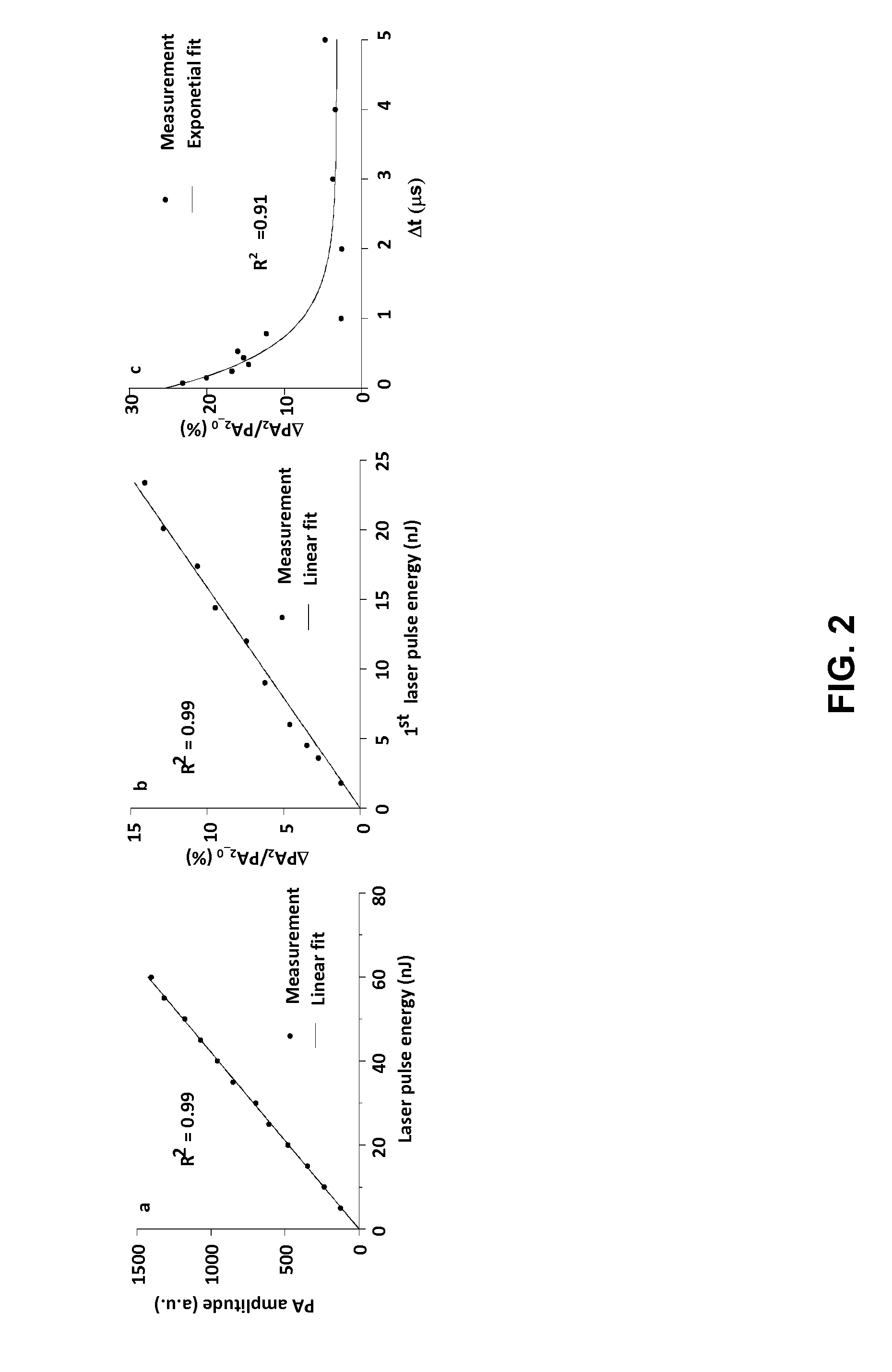
Systems and methods for focusing a light pulse within a focus area using nonlinear photoacoustic wavefront shaping (PAWS) are disclosed herein. The method includes modulating a spatial phase pattern of a light pulse's waveform based on a Grueneisen-relaxation photoacoustic (GR-PA) feedback signal. In addition, systems and methods for performing Grueneisen-relaxation photoacoustic microscopy (GR-PAM) are disclosed herein that include analyzing photoacoustic signals resulting from illumination of a focus region by two closely spaced light pulses. A method of obtaining an absorption coefficient of a sample using Grueneisen-relaxation photoacoustic microscopy (GR-PAM) is also disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and gas sensor for performing quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS7605922B2Reduce contributionLow costRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotoacoustic microscopyLaser intensity
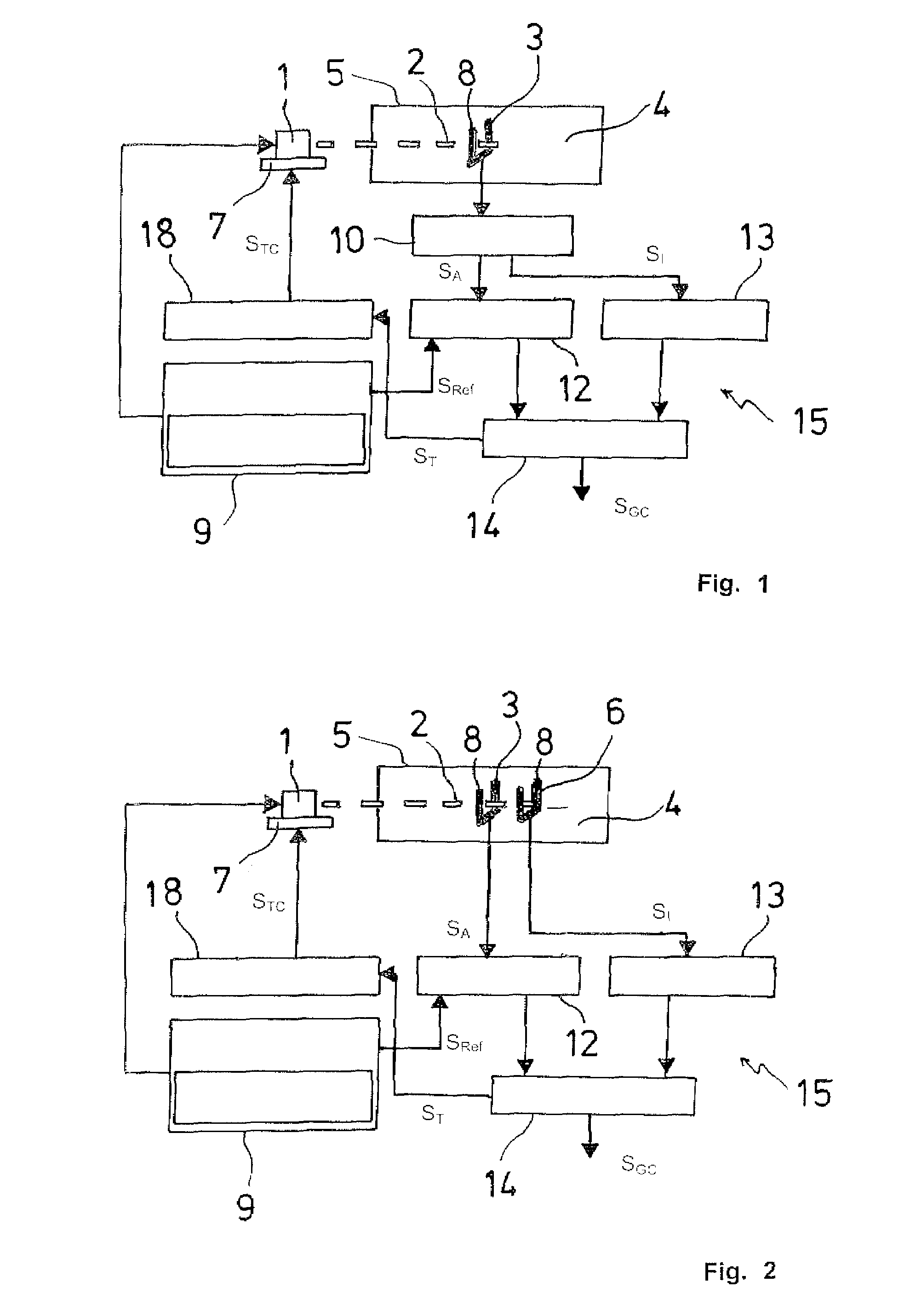
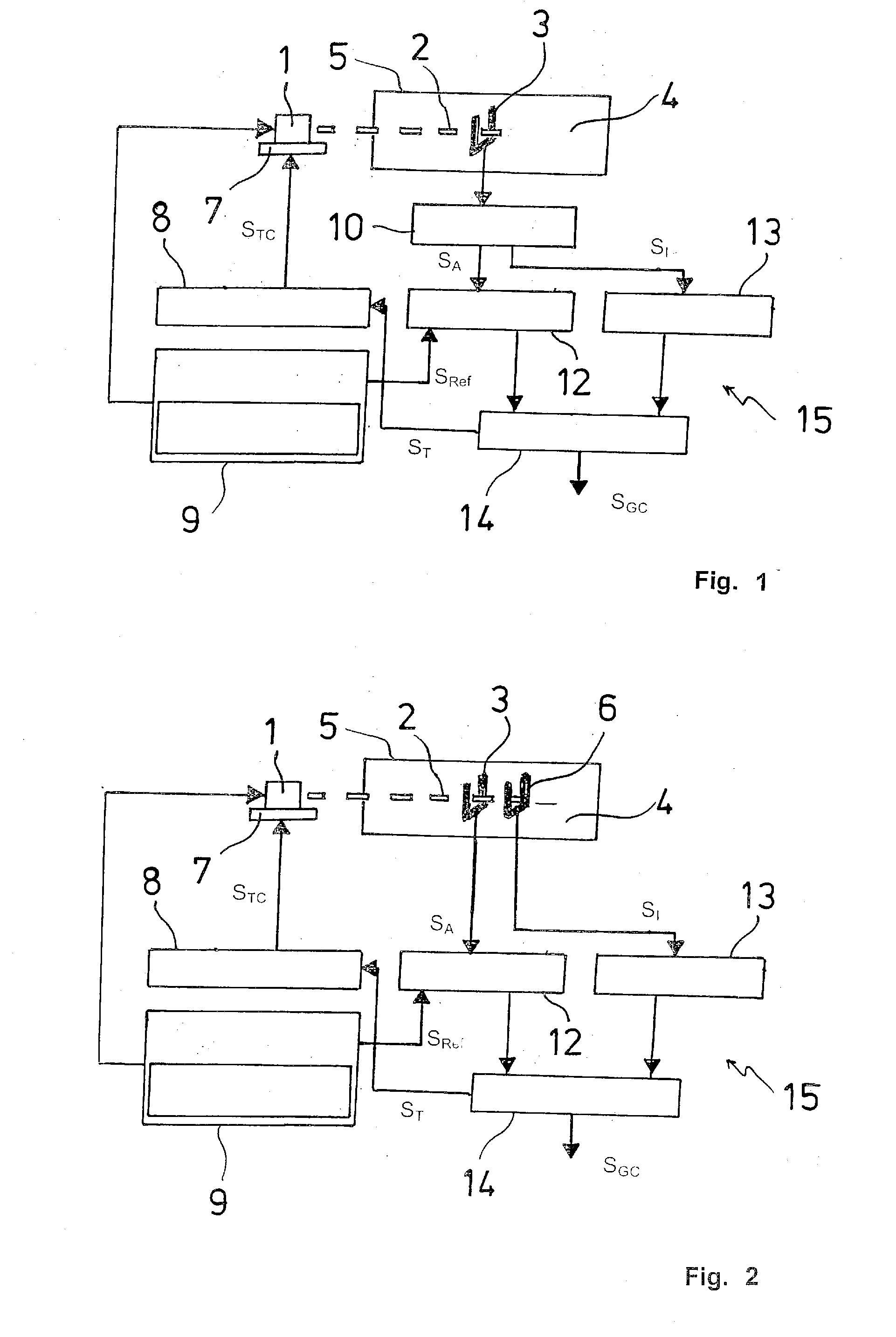
A method for performing quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy of a gas, includes providing a light source configured to introduce a laser beam having at least one wavelength into the gas such said at least one molecule within in the gas is stimulated generating an acoustic signal, accumulating the acoustic signal in a resonant acoustic detector, generating a resonant absorption signal (SA) relative to the gas concentration by at least one tuning fork serving as resonant acoustic detector, generating additionally a resonant intensity signal (SI) proportional to the intensity of the laser beam travelling through the gas, and providing an output signal (SGC) from said absorption signal (SA) and said intensity signal (SI) being independent of the intensity of the light relative to the presence or concentration of the gas.
Owner:AXETRIS AG
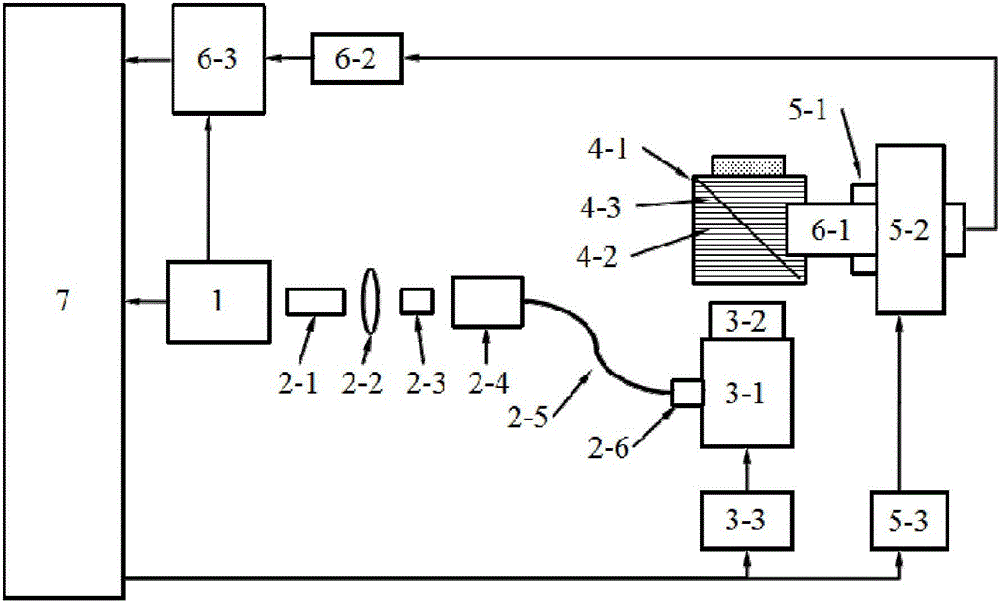
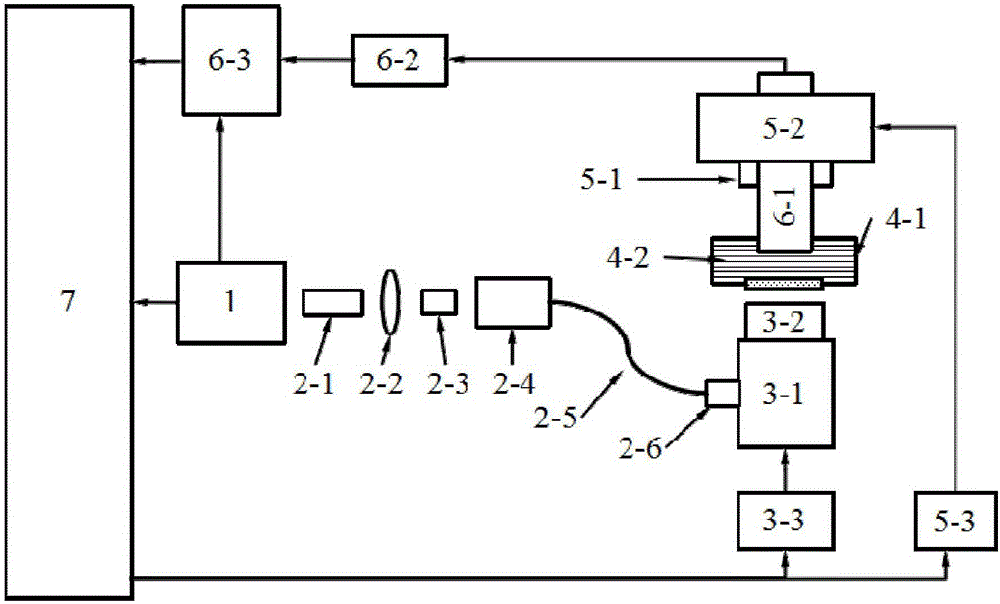
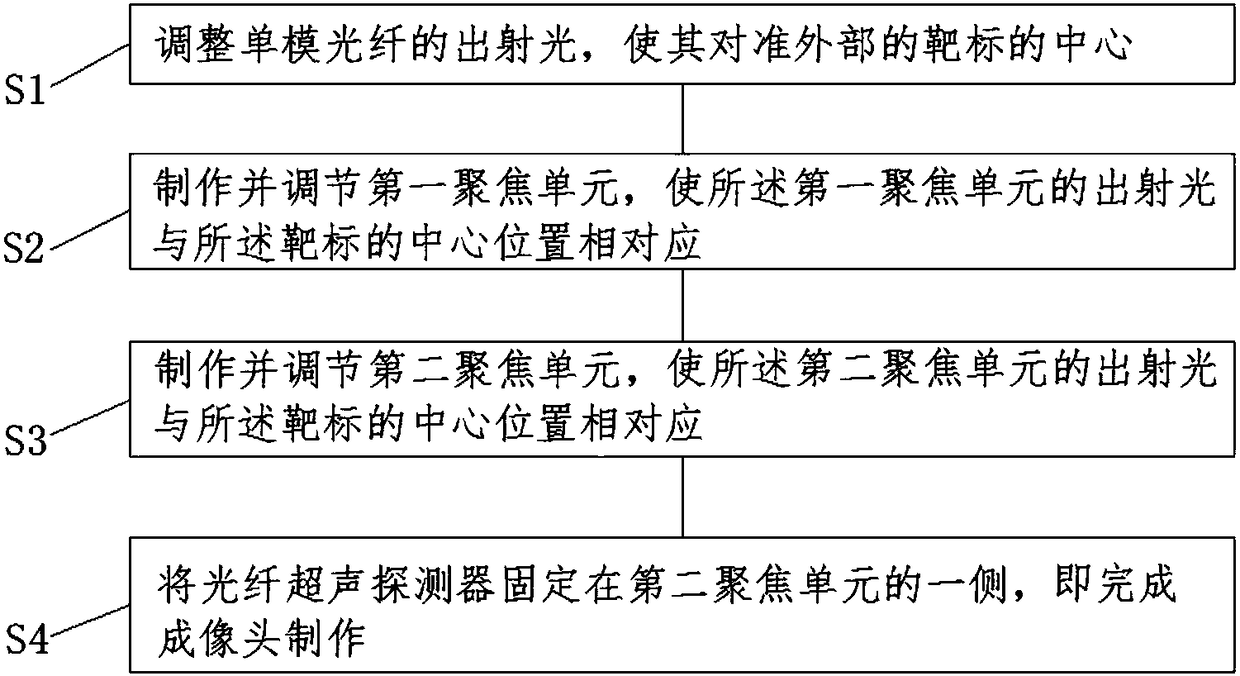
Novel scanning method and novel scanning device of optical resolution photo-acoustic microscope
InactiveCN106769876AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEliminate the effects ofMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoacoustic microscopySonification
The invention discloses a novel scanning method and a novel scanning device of an optical resolution photo-acoustic microscope, belonging to the technical field of photo-acoustic imaging. The device disclosed by the invention has the working process and working principle that after being collimated by using a single mold optical fiber coupling component, pulse laser emitted from a laser emitter is input into a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer system; the two-dimensional scanning galvanometer system focuses the laser onto a target object to generate a photo-acoustic signal, and a linear area corresponding to a focusing area of a linear focusing ultrasonic detector is scanned; photo-acoustic signals generated in different scanning positions are transmitted to the linear focusing ultrasonic detector through a water tank full of an ultrasonic coupling liquid, and are converted into piezoelectric signals; after being amplified by using an amplifier, the piezoelectric signals are acquired by using a data acquisition card, and are stored in a computer for data processing. The optical resolution photo-acoustic microscope and the target object do not need to move relative to each other, the requirements of the optical resolution photo-acoustic microscope on a signal to noise ratio can be met, and meanwhile, a large view field range and a high resolution can be met.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Photoacoustic Spectroscopy With Focused Light
InactiveUS20110083509A1Reduce and eliminate effect of light diffusionReducing the ultrasonic waves generatedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVibration measurement in solidsPhotoacoustic microscopyPhotoacoustic spectroscopy
Photoacoustic measurements utilize emitted light to generate an acoustic response in tissue, with the acoustic response being proportional to the presence of an absorber of the light in the tissue. The present disclosure relates the use of focused light to acquire photoacoustic measurements. In one embodiment, the light is modulated, such as spatially modulated, such that the light may be focused within an otherwise scattering medium, such as tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and gas sensor for performing quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS20090027677A1Reduce contributionLow costRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotoacoustic microscopyGas concentration
A method for performing quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy of a gas, includes providing a light source configured to introduce a laser beam having at least one wavelength into the gas such said at least one molecule within in the gas is stimulated generating an acoustic signal, accumulating the acoustic signal in a resonant acoustic detector, generating a resonant absorption signal (SA) relative to the gas concentration by at least one tuning fork serving as resonant acoustic detector, generating additionally a resonant intensity signal (SI) proportional to the intensity of the laser beam travelling through the gas, and providing an output signal (SGC) from said absorption signal (SA) and said intensity signal (SI) being independent of the intensity of the light relative to the presence or concentration of the gas.
Owner:AXETRIS AG
Multi-focus optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy with ultrasonic array detection
ActiveUS8997572B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotoacoustic microscopyImage resolution
A probe for use with an imaging system, including a scanning device configured to receive a first light beam from a light source, a beam-divider configured to split the first light beam into a plurality of second light beams, and a focusing device configured to focus each of the second light beams on respective locations in an object of interest.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
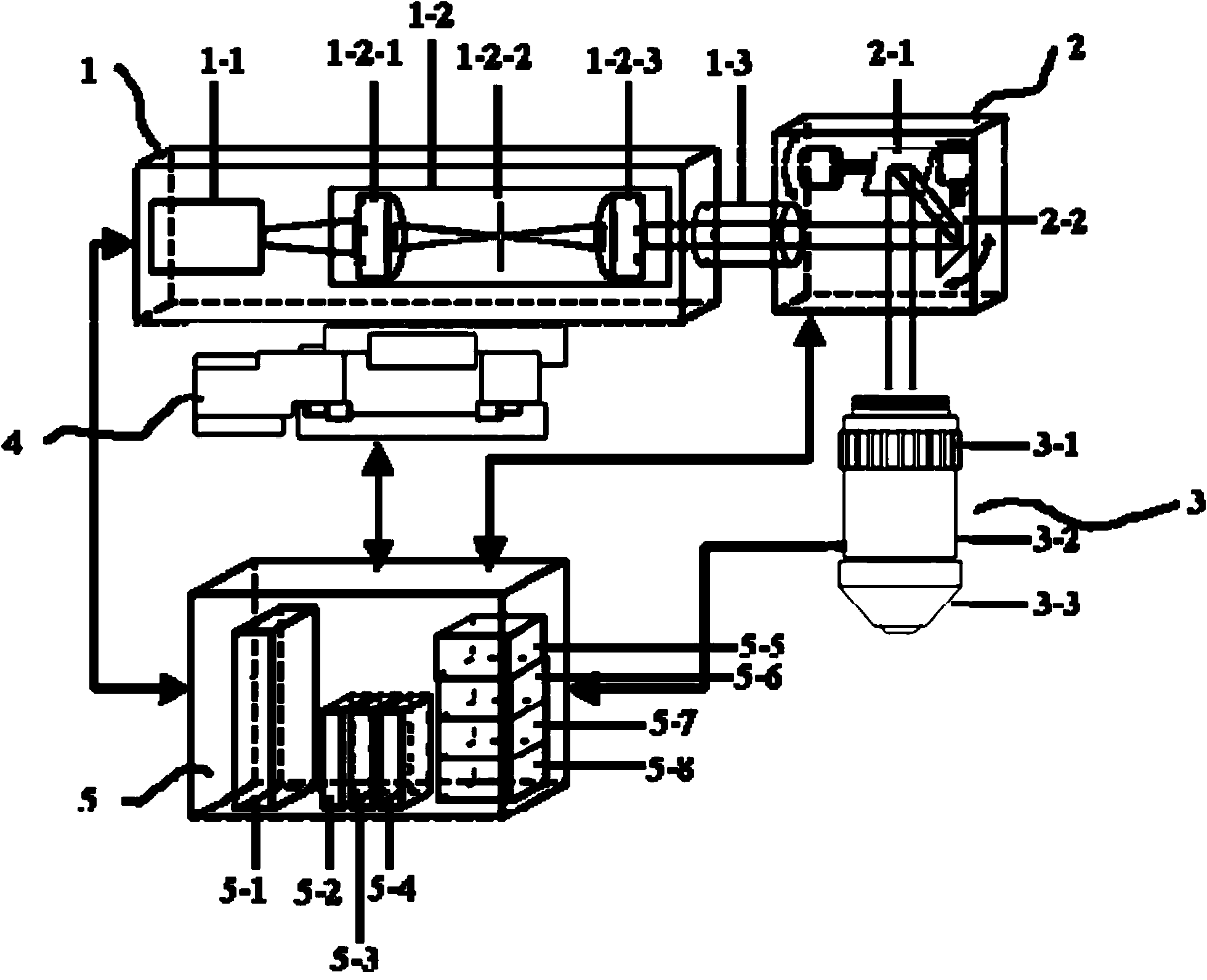
Optical resolution type photoacoustic microscope based on optical beam scanning
InactiveCN102854142AReduce volumeLow priceMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoacoustic microscopyRapid imaging
The invention provides an optical resolution type photoacoustic microscope based on optical beam scanning. The photoacoustic microscope comprises a laser diode, a collimating lens, a multidimensional laser galvanometer, a focusing lens, a rectangular prism, a coupling liquid box, an ultrasonic coupling liquid, a film, a shell, a lifting platform, an ultrasonic sensor, a signal processing circuit, a data acquisition circuit, a computer, a galvanometer driving circuit, a clock circuit and a driving power circuit. According to the invention, miniature, inexpensive and easily maintained laser diode is applied to the field of optical resolution forward photoacoustic microscopy excitation, and the laser galvanometer is used to realize substitution of mechanical scanning by beam scanning to achieve fast imaging. The photoacoustic microscope has the advantages of portable volume, high resolution and fast imaging, and can be widely applied to photoacoustic microimaging in the fields of material detection, industrial inspection and medical image.
Owner:曾吕明
In vivo label-free histology by photoacoustic microscopy of cell nuclei
InactiveUS20140356897A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotoacoustic microscopyUltraviolet lights
The present disclosure is directed to methods of non-invasively imaging cell nuclei. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to methods of imaging cell nuclei in vivo using ultraviolet photoacoustic microscopy (UV-PAM), in which ultraviolet light is used to excite unlabeled DNA and RNA in cell nuclei to produce photoacoustic waves.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
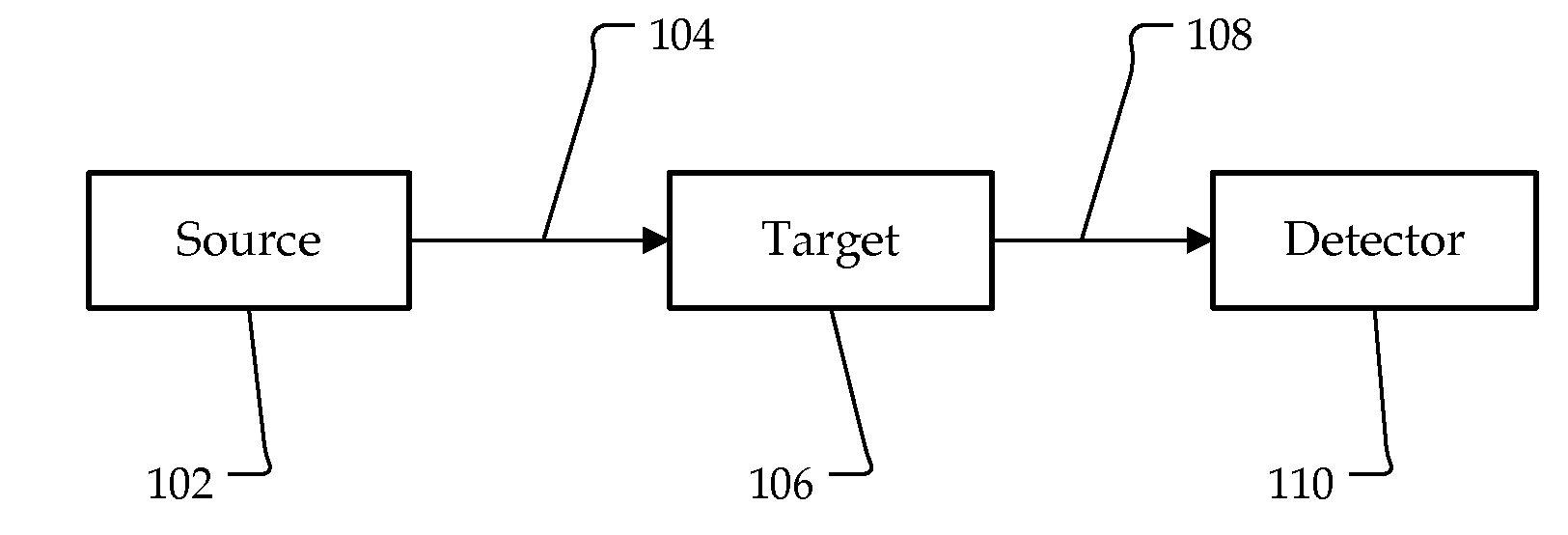
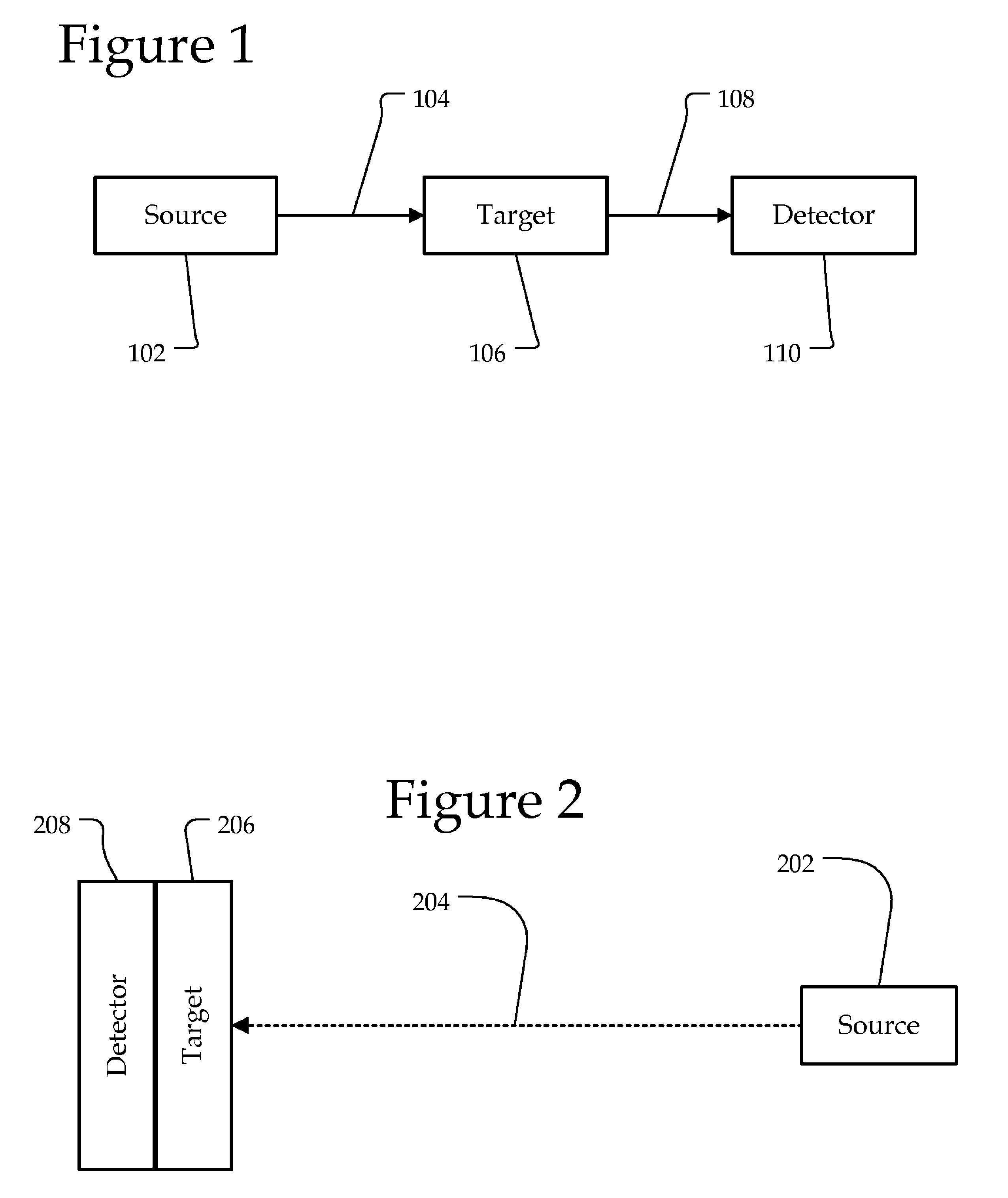
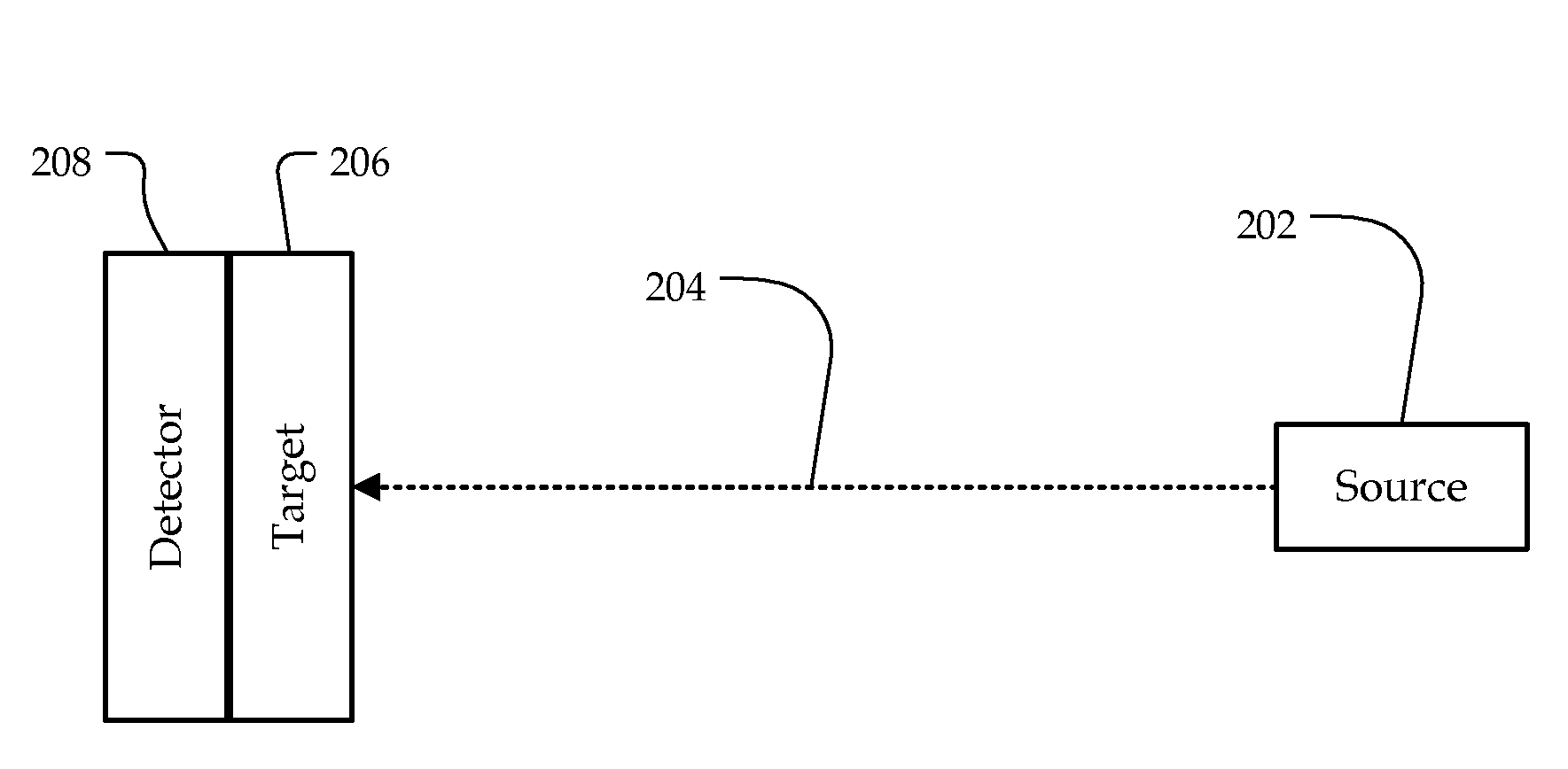
Photoacoustic point spectroscopy
InactiveUS7961313B2Emission spectroscopyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotoacoustic microscopyAbsorption ratio
A system and method are disclosed for generating a photoacoustic spectrum in an open or closed environment with reduced noise. A source may emit a beam to a target substance coated on a detector that measures acoustic waves generated as a result of a light beam being absorbed by the target substance. By emitting a chopped / pulsed light beam to the target substance on the detector, it may be possible to determine the target's optical absorbance as the wavelength of light is changed. Rejection may decrease the intensity of the acoustic waves on the detector while absorption may increase the intensity. Accordingly, an identifying spectrum of the target may be made with the intensity variation of the detector as a function of illuminating wavelength.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
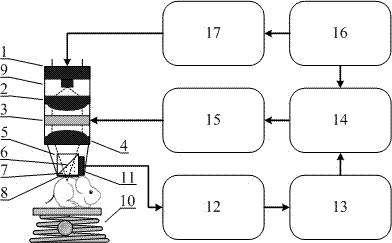
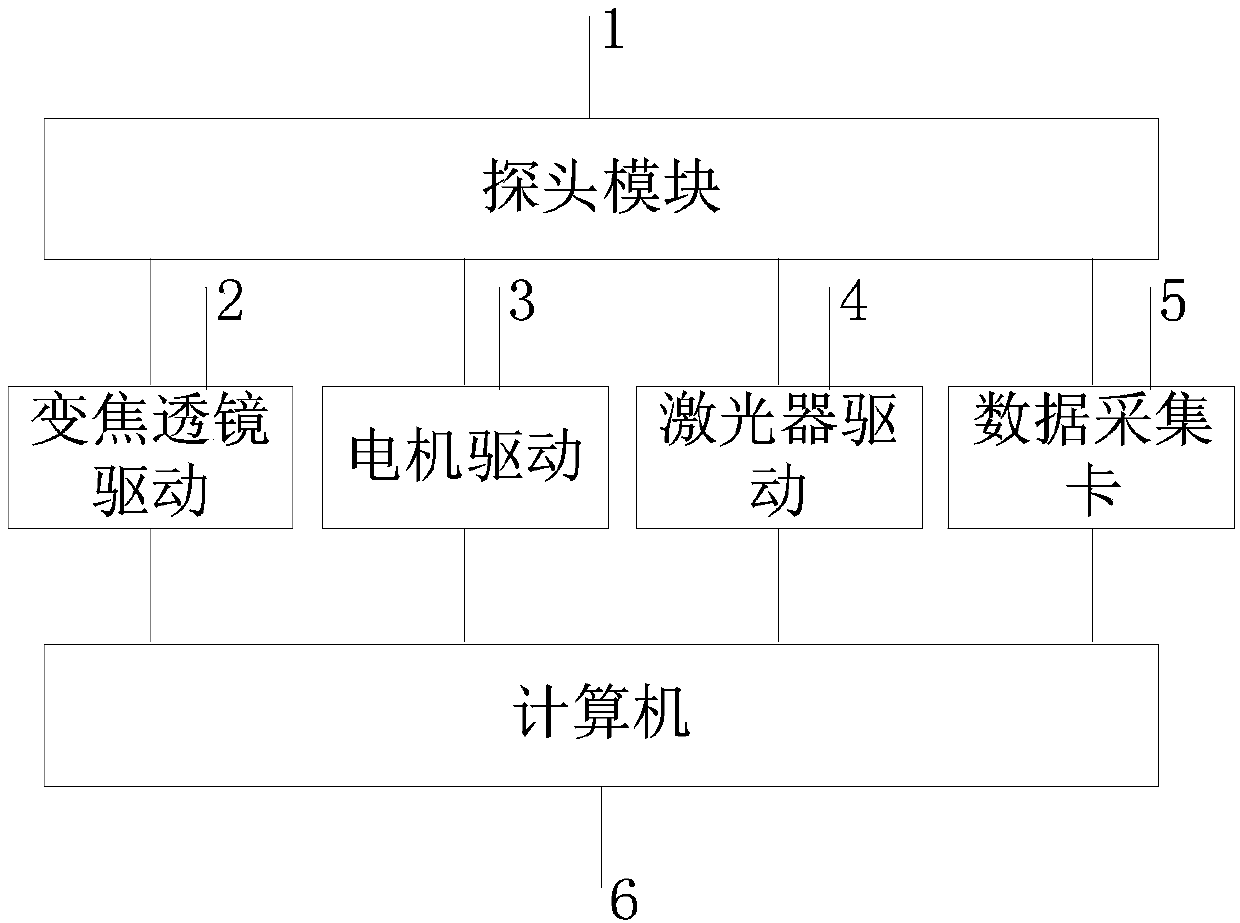
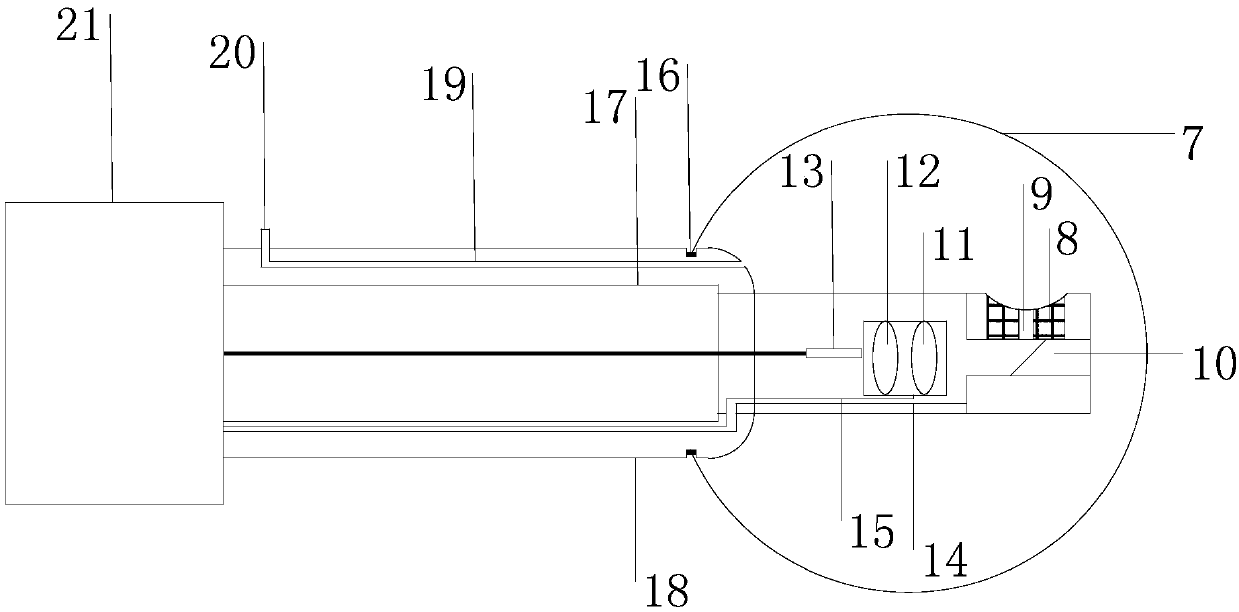
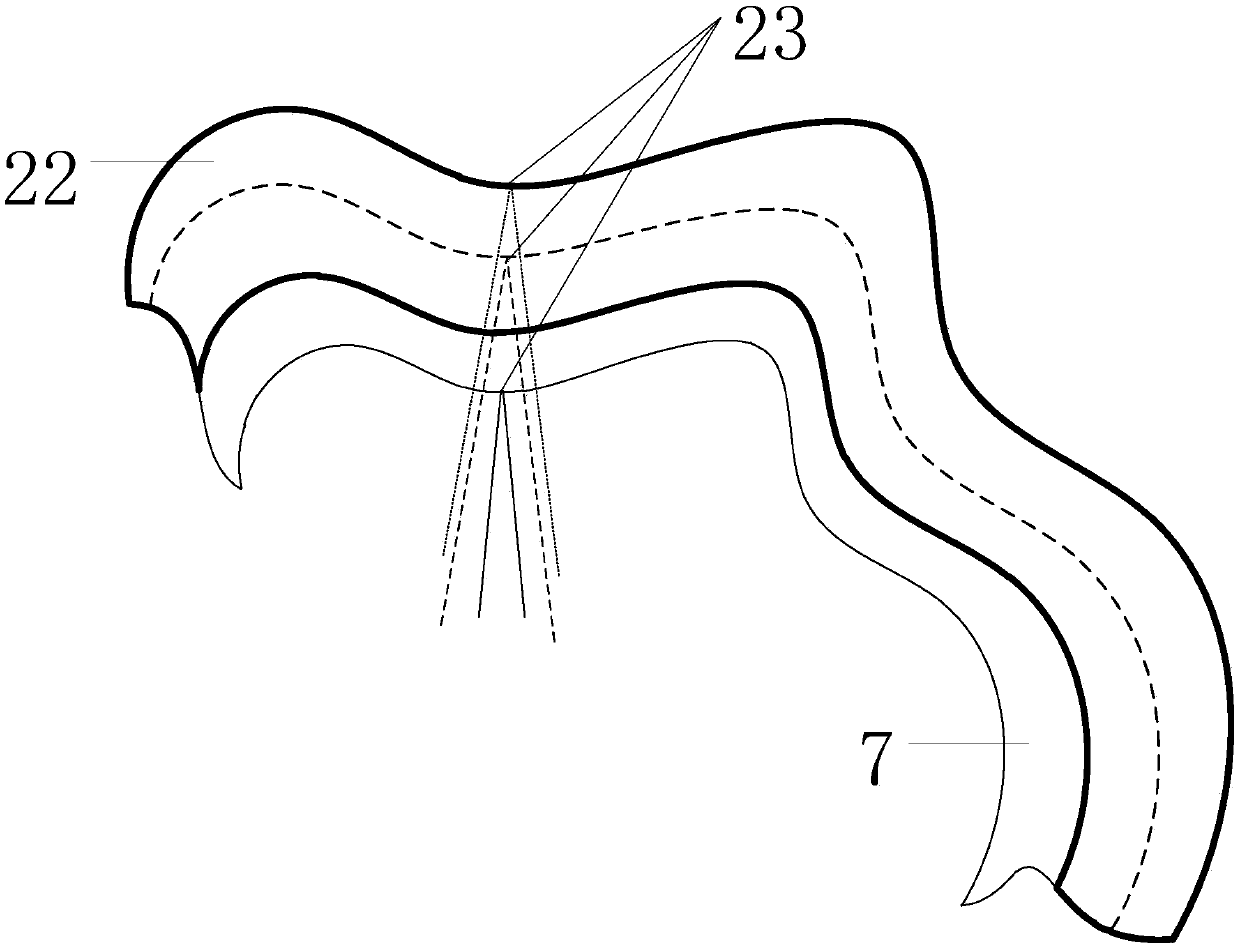
Self-adaptive focusing photoacoustic endoscope based on light-transmittable sound-transmittable water sac and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN107638168AHigh resolutionIncrease contrastEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringPhotoacoustic microscopyUltrasonic sensor
The invention discloses a self-adaptive focusing photoacoustic endoscope based on a light-transmittable sound-transmittable water sac and an implementation method thereof. The endoscope comprises a probe module, a control module and a display module; the probe module comprises the water sac, an annular hollow ultrasonic transducer, an optical component, a rotary shaft, an outer sleeve pipe and a handle, wherein the optical component comprises a glass column, a reflector with the angle of 45 degrees, a varifocal lens, a collimating lens and an optical fiber, the outer sleeve pipe injects waterinto the water sac through a water injection channel, and the probe is controlled to rotate by a motor and an electric slip ring contained in the handle; the control module comprises a motor drive, alaser drive, a varifocal lens drive and a data acquisition card; the display module comprises a computer. According to the self-adaptive focusing photoacoustic endoscope based on the light-transmittable sound-transmittable water sac and the implementation method, through flexible matching of the water sac and an enteric cavity in an irregular shape, by means of the photoacoustic signals of the water sac itself, the border of the enteric cavity is precisely determined, so that the multilayer structures of each circle of the intestinal wall at different angles are on the focus when the probe scans all around at 360 degrees, and an image with high resolution and high contrast is obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
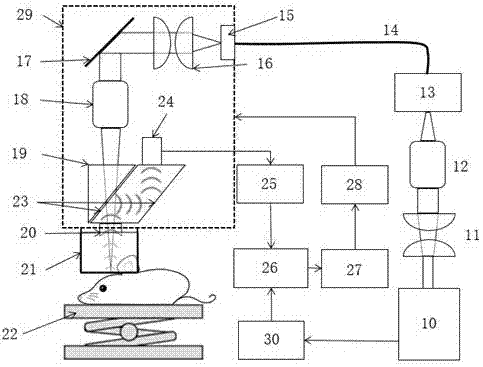
Photoacoustic microscopy imaging-based quantitative detection device for nevus flammeus blood vessel
ActiveCN104323762AResolution resolutionIncrease contrastDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhotoacoustic microscopyFiltered backprojection
The invention discloses a photoacoustic microscopy imaging-based quantitative detection device for a nevus flammeus blood vessel. The device comprises two parts, namely hardware and software, wherein the hardware comprises a light emitting system, an optical rapid scanning system, a photoacoustic detection system, an X, Y and Z-axis motor positioning system and a host computer system; the software comprises driving, deconvolution and filter back-projection algorithms of various hardware, and three scanning imaging modes; the imaging depth of the device is 2mm; the transverse resolution is 3.8mu m; the axial resolution is 40mu m; the imaging range is 0.5mm or 1mm; the problem that a pure optical method cannot reach the imaging depth, and ultrasound cannot reach the resolution are solved; two-dimensional and three-dimensional structure imaging is adopted, so that the parameters such as pipe diameter and depth of the blood vessel, and relative blood volume percentage distributed along the depth direction can be quantitatively counted; the defects and disadvantages in an existing clinical PWS detection technology are solved; and a non-destructive real-time multi-mode detection method is provided for PWS pathological study.
Owner:广州佰奥廷电子科技有限公司
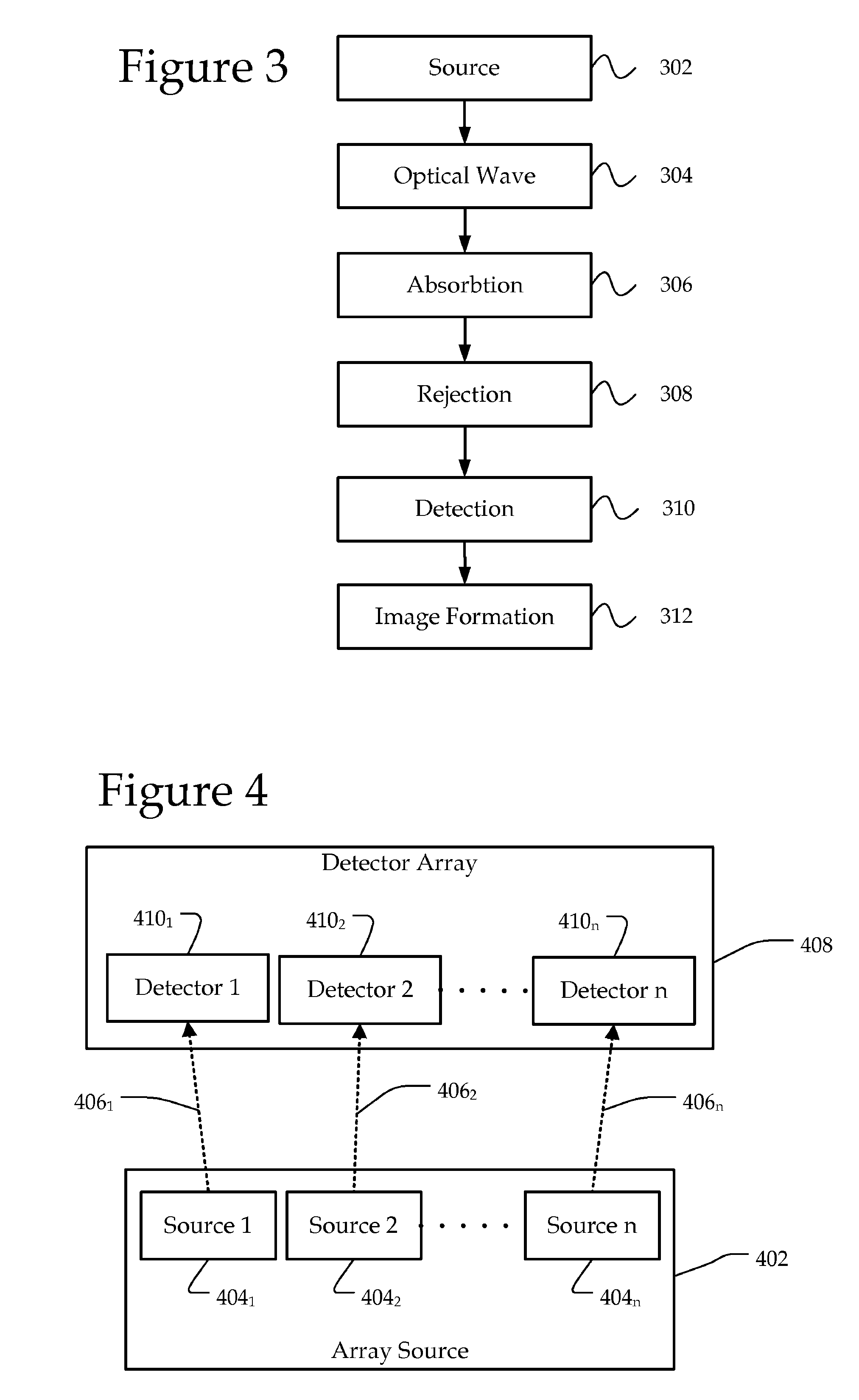
Array-based photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS6870626B2Transmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotoacoustic microscopyCombined use
Methods and apparatus for simultaneous or sequential, rapid analysis of multiple samples by photoacoustic spectroscopy are disclosed. A photoacoustic spectroscopy sample array including a body having at least three recesses or affinity masses connected thereto is used in conjunction with a photoacoustic spectroscopy system. At least one acoustic detector is positioned near the recesses or affinity masses for detection of acoustic waves emitted from species of interest within the recesses or affinity masses.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST +1
Photoacoustic microscope and method for monitoring breaking of microvesicles in biological tissue
PendingCN106943120AIncrease contrastHigh resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterPhotoacoustic microscopyMicro imaging
The invention discloses a photoacoustic microscope. The photoacoustic microscope comprises a microscope system, a signal collection control system and a driving system. The invention further discloses a method for monitoring breaking of microvesicles in biological tissue with the use of the photoacoustic microscope. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with features of high contrast ratio of optical imaging and high resolution ratio of acoustic imaging. Due to low scattering properties of acoustic signal transmission in tissue, deeper penetration degree is obtained compared with a conventional optical imaging method. There is no need to slicing tissue and the method is non-invasive so that long-term monitoring is achieved. Photoacoustic microscope imaging equipment helps achieve imaging of multiple anatomical positions.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
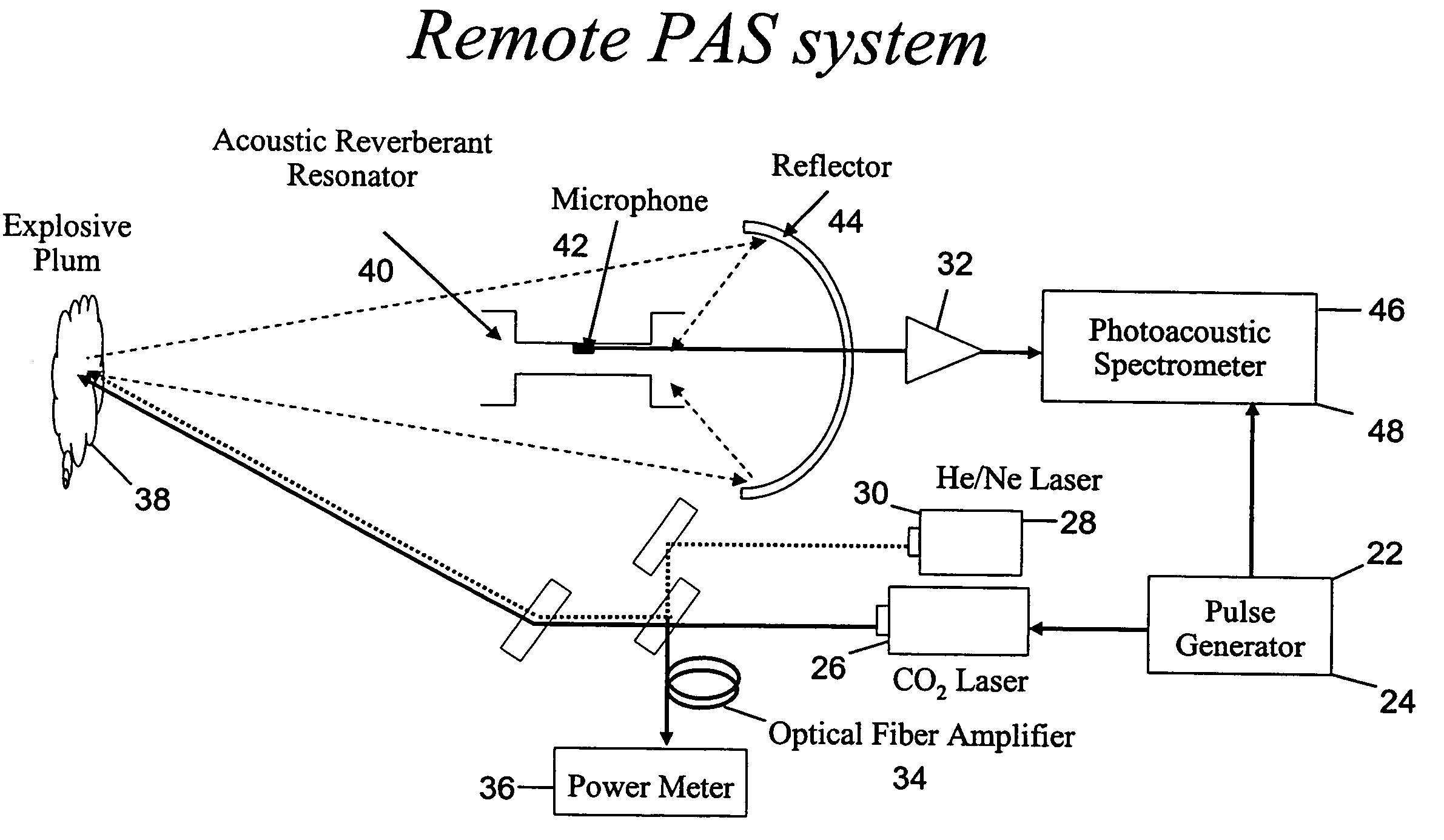
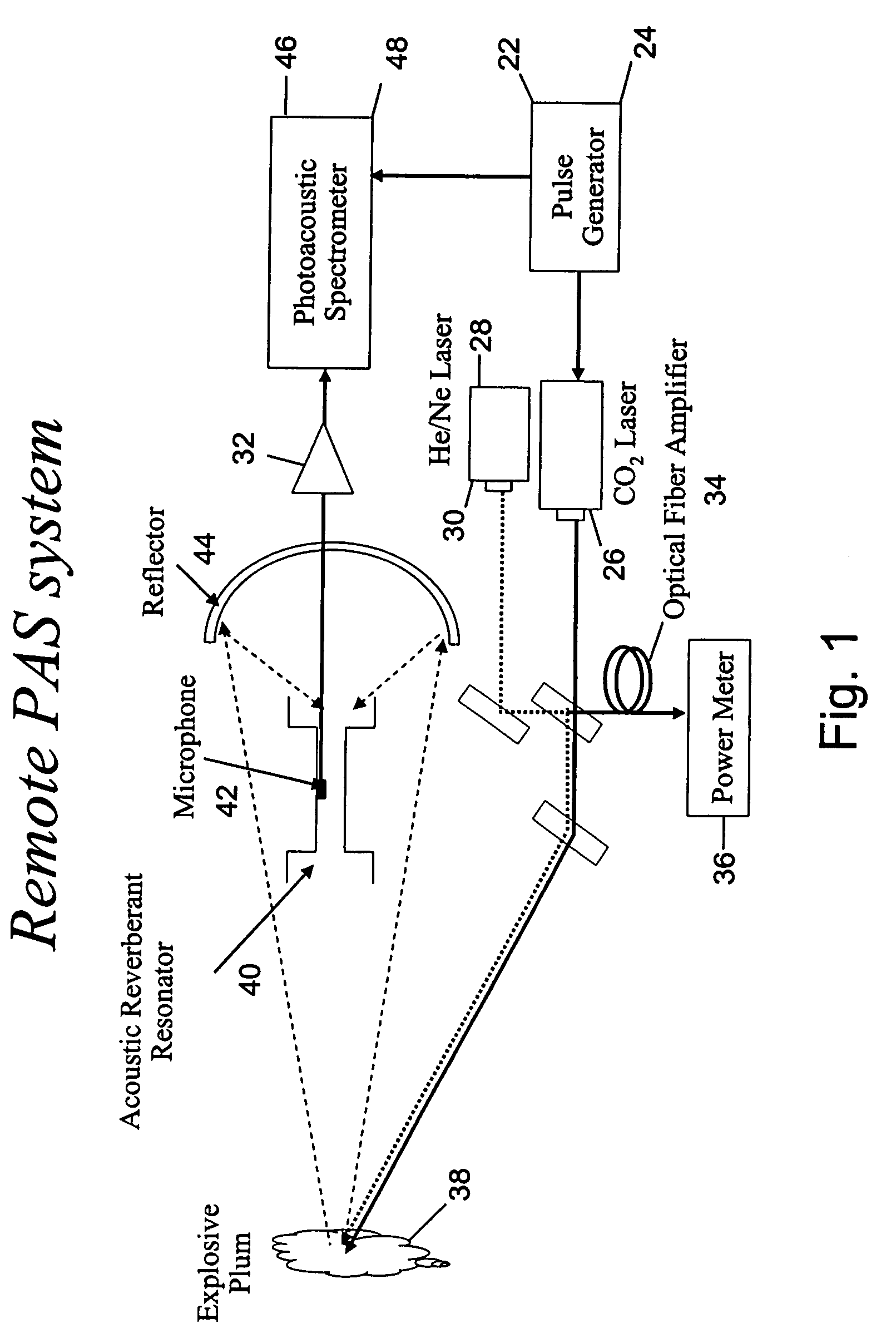
Photoacoustic spectroscopy system and technique for remote sensing of explosives and toxic chemicals
InactiveUS7644606B2Easy to useReduce sound distractionAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoacoustic microscopyData acquisition
A user-friendly photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS) system and process (technique) provides an open-field PAS instrument, unit and device to remotely sense explosives, chemicals and biological agents. The PAS system and process can include: a pulsed tunable laser, such as a CO2 laser, a reflector, such as a parabolic reflector, an acoustic reverberant resonator in which a microphone is installed, and a data acquisition and analysis system.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Photoacoustic point spectroscopy
InactiveUS20100033722A1Emission spectroscopyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotoacoustic microscopyLight beam
A system and method are disclosed for generating a photoacoustic spectrum in an open or closed environment with reduced noise. A source may emit a beam to a target substance coated on a detector that measures acoustic waves generated as a result of a light beam being absorbed by the target substance. By emitting a chopped / pulsed light beam to the target substance on the detector, it may be possible to determine the target's optical absorbance as the wavelength of light is changed. Rejection may decrease the intensity of the acoustic waves on the detector while absorption may increase the intensity. Accordingly, an identifying spectrum of the target may be made with the intensity variation of the detector as a function of illuminating wavelength.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
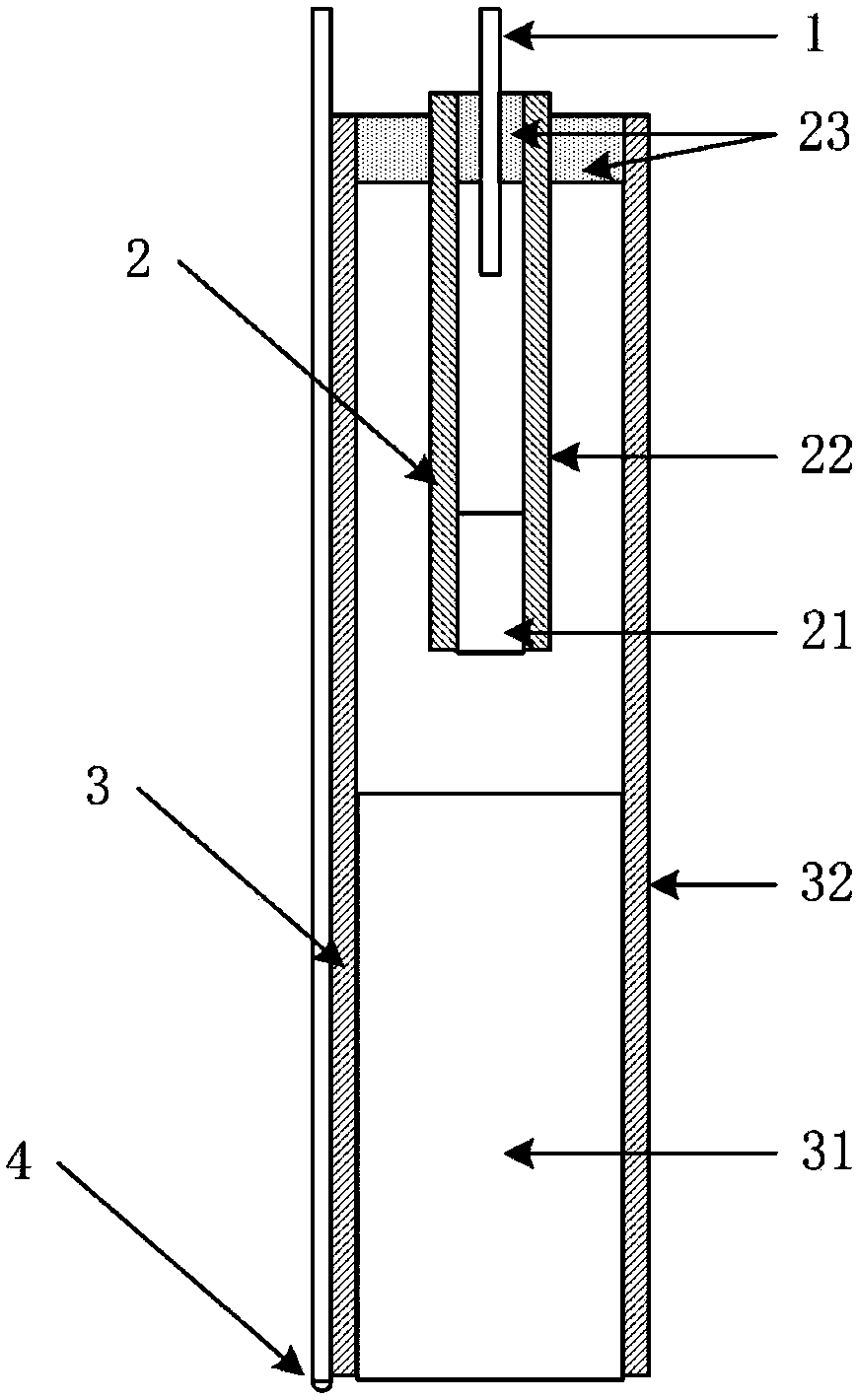
Micro photoacoustic microscopic imaging head, production method and system consisting of micro photoacoustic microscopic imaging head
InactiveCN108362646AImprove image qualityEasy to makeMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringMicroscopic imagePhotoacoustic microscopy
The invention discloses a micro photoacoustic microscopic imaging head, a production method and a system consisting of the micro photoacoustic microscopic imaging head. The microscopic imaging head comprises a single mode fiber, a first focusing unit, a second focusing unit and a fiber ultrasonic detector, wherein the first focusing unit comprises a first gradient refractive index lens and a glasstube, the first gradient refractive index lens is arranged in one end of the glass tube, the single mode fiber penetrates through the other end of the glass tube, and emergent light of the single mode fiber corresponds to the center of an outer target after being transmitted by the first gradient refractive index lens; the second focusing unit comprises a second gradient refractive index lens anda steel tube, the second gradient refractive index lens is arranged in one end of the steel tube, and the other end of the steel tube sleeves the first focusing unit; the fiber ultrasonic detector isarranged on the outer side of the steel tube. The micro photoacoustic microscopic imaging head is high in resolution, long in working distance, low in cost and simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Sound signal detector based on surface wave, and reflection type photoacoustic microscope
ActiveCN106092901ARealize imaging detectionImplement point detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoacoustic microscopyImage detection
The present invention belongs to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging sound pressure detection, and provides a sound signal detector based on surface wave, and a reflection type photoacoustic microscope. The sound signal detector comprises a prism having two planes parallel to each other, wherein one of the two planes is plated with a thin film, and the thin film is used for detecting a photoacoustic signal transmitted through a medium. According to the present invention, the sound signal detector uses the optical sensing refractive index, such that the object to be measured has the characteristic of the non-marking and non-contact sensing detection, and the advantages of bandwidth detection and sensitive detection can be achieved; and with the application of the sound signal detector based on the surface wave in the reflection type photoacoustic microscope, the imaging detection of the biological living body can be achieved.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN SHEN GUANG SU TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com