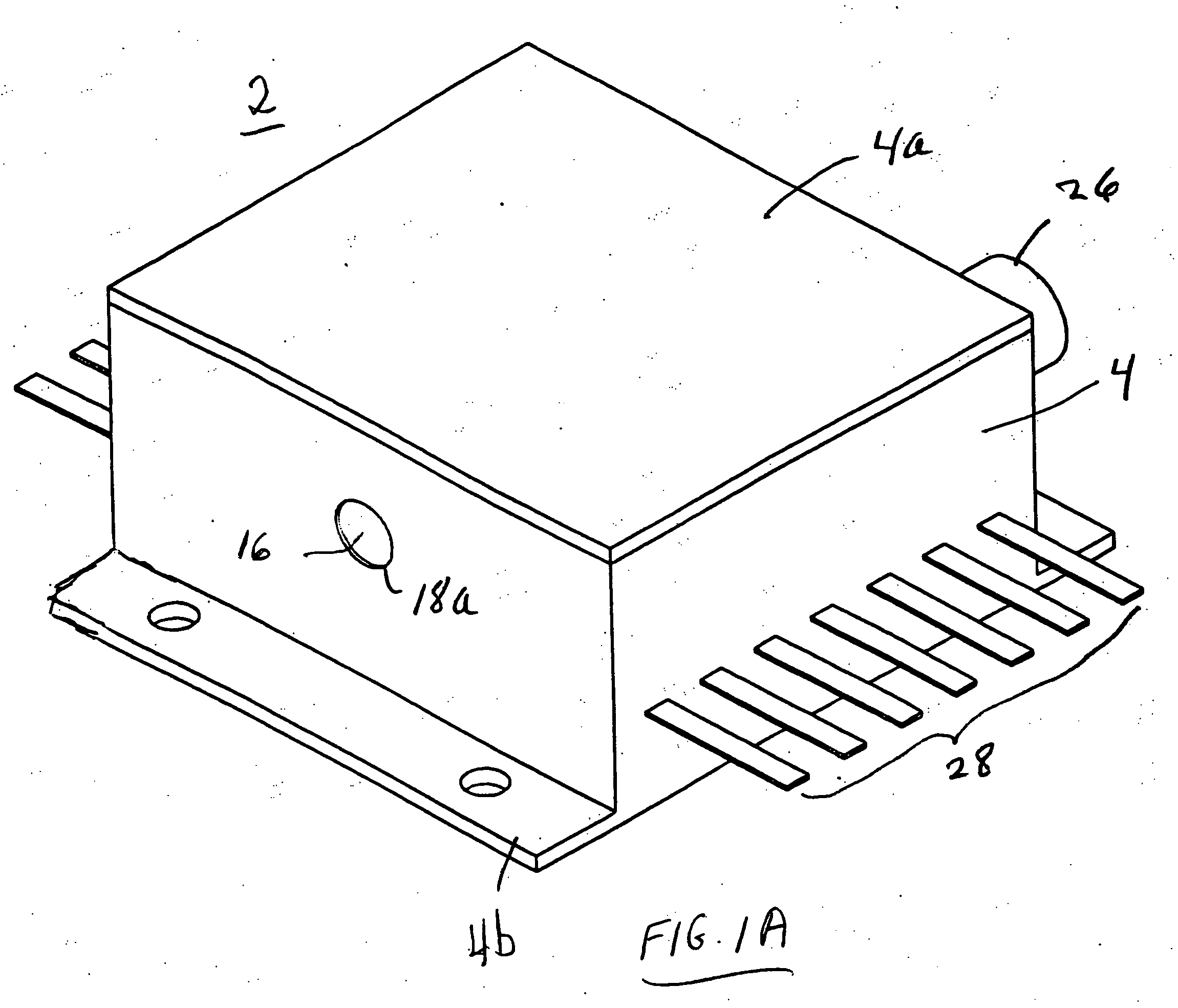
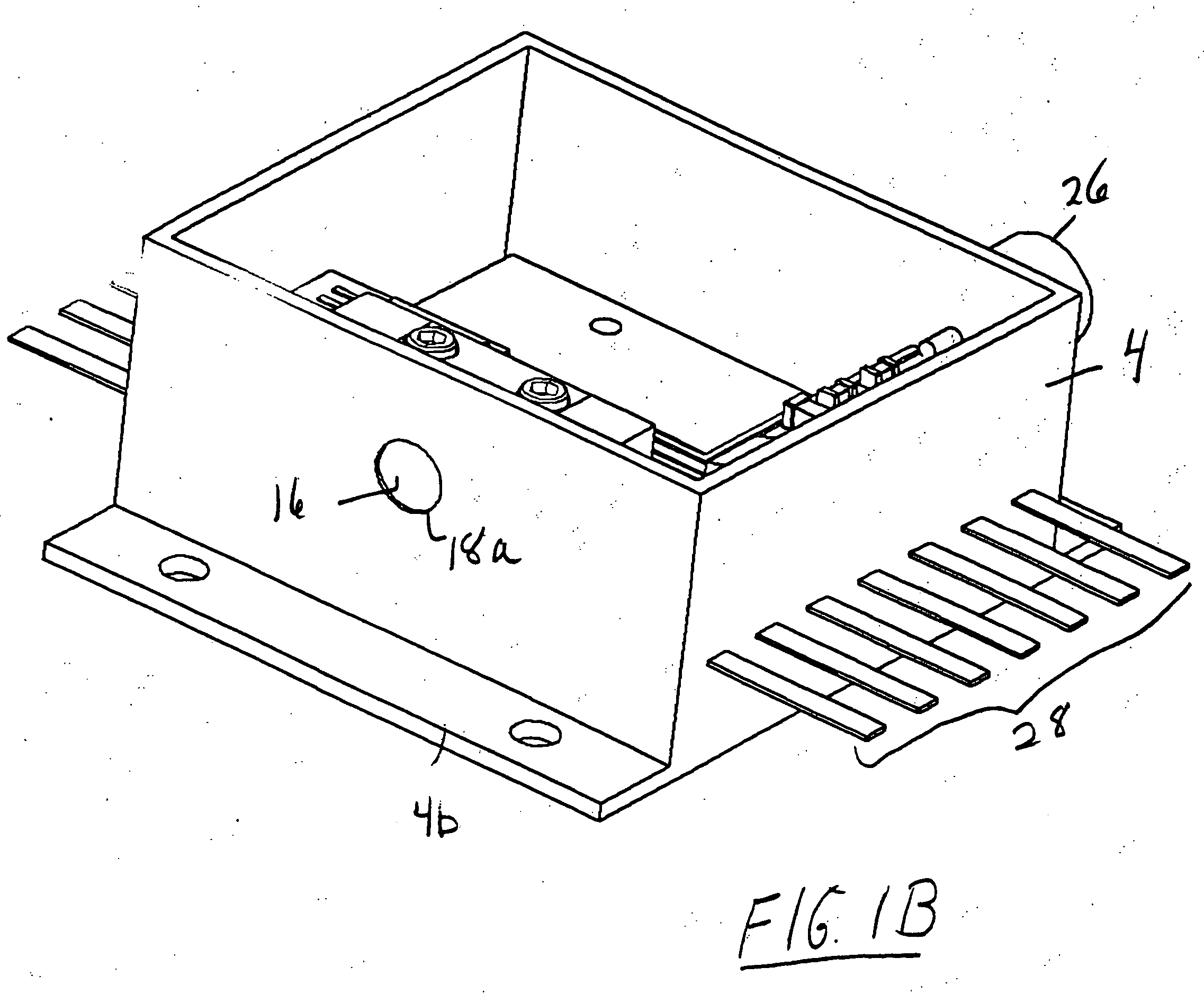
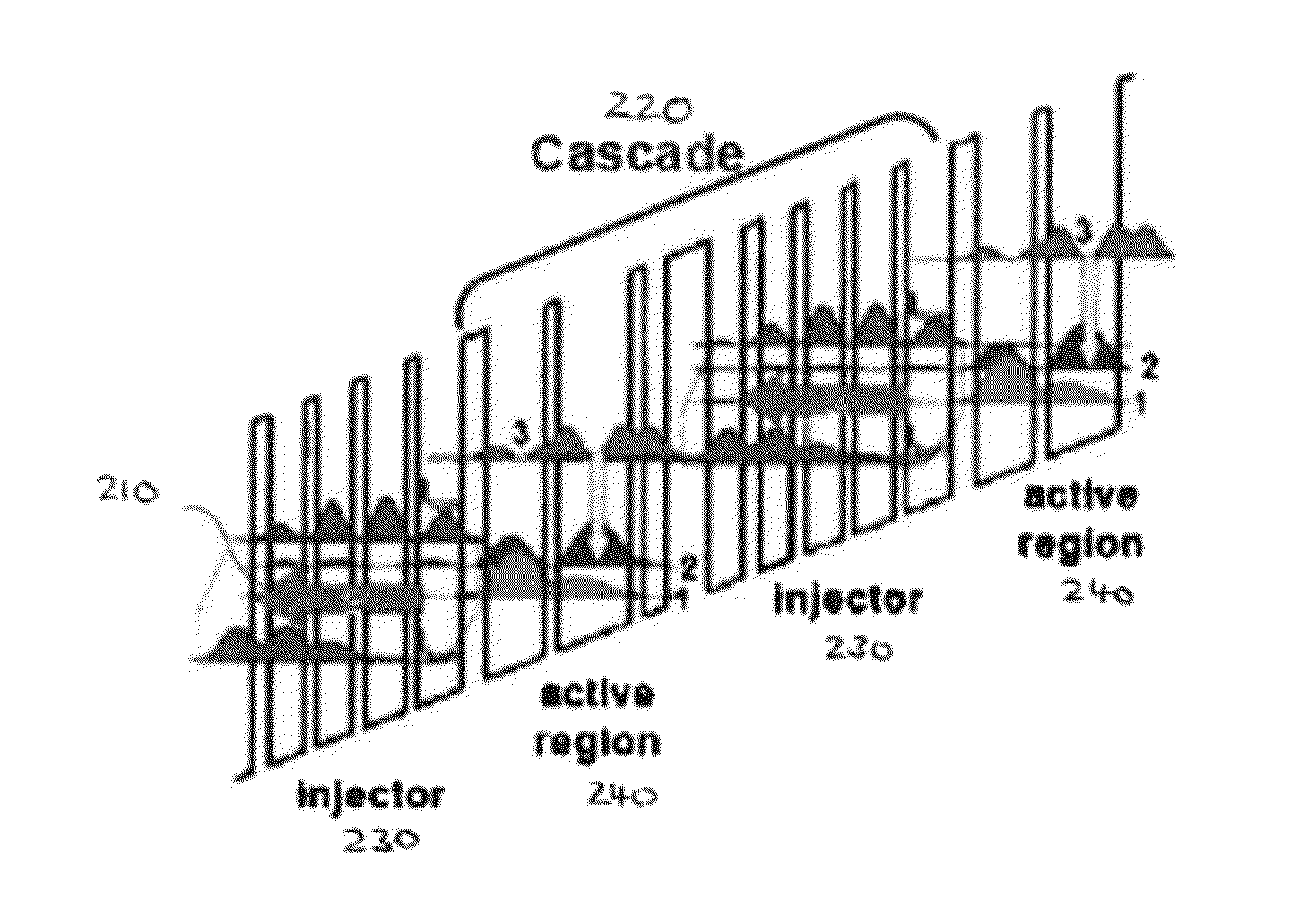
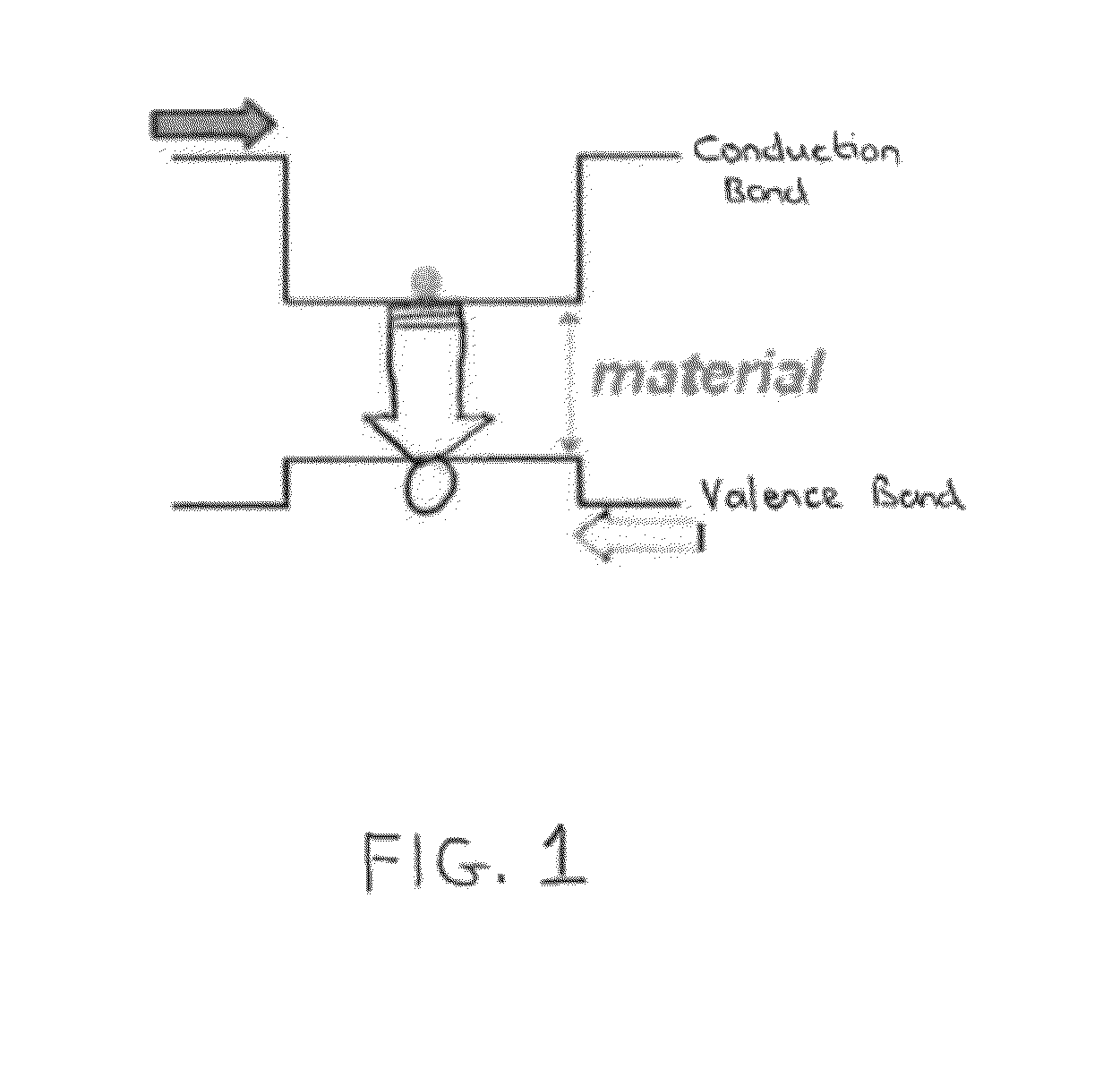
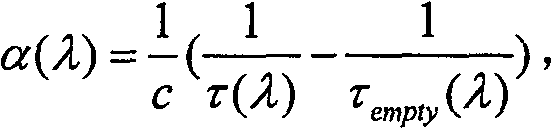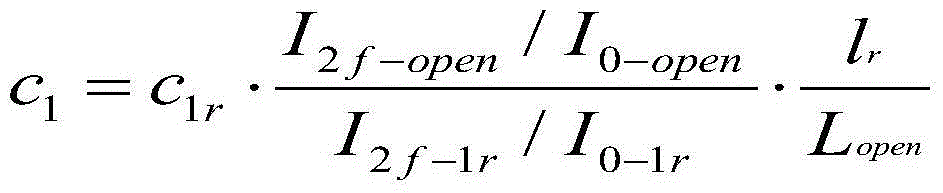Patents
Literature
410 results about "Quantum cascade laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
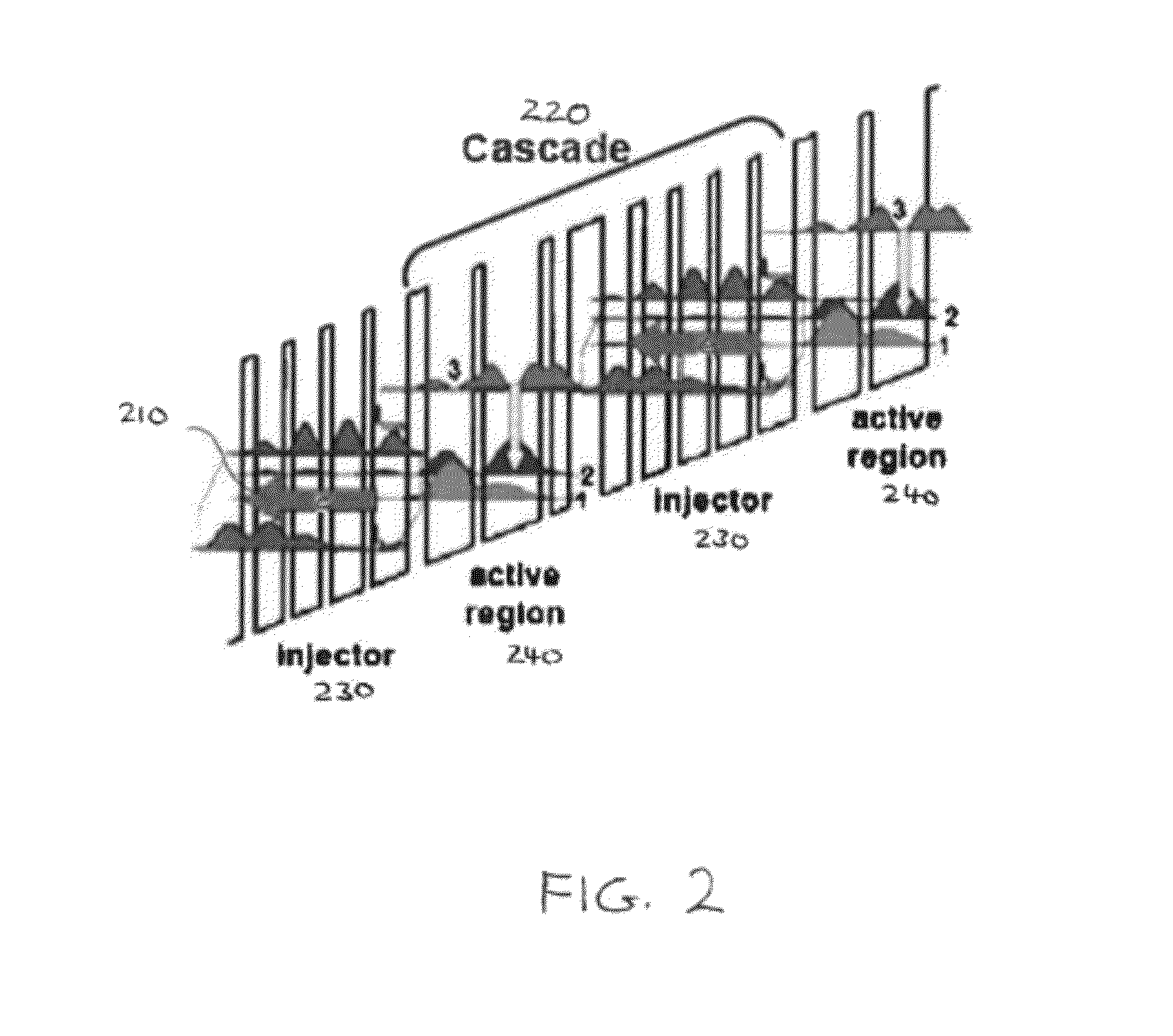
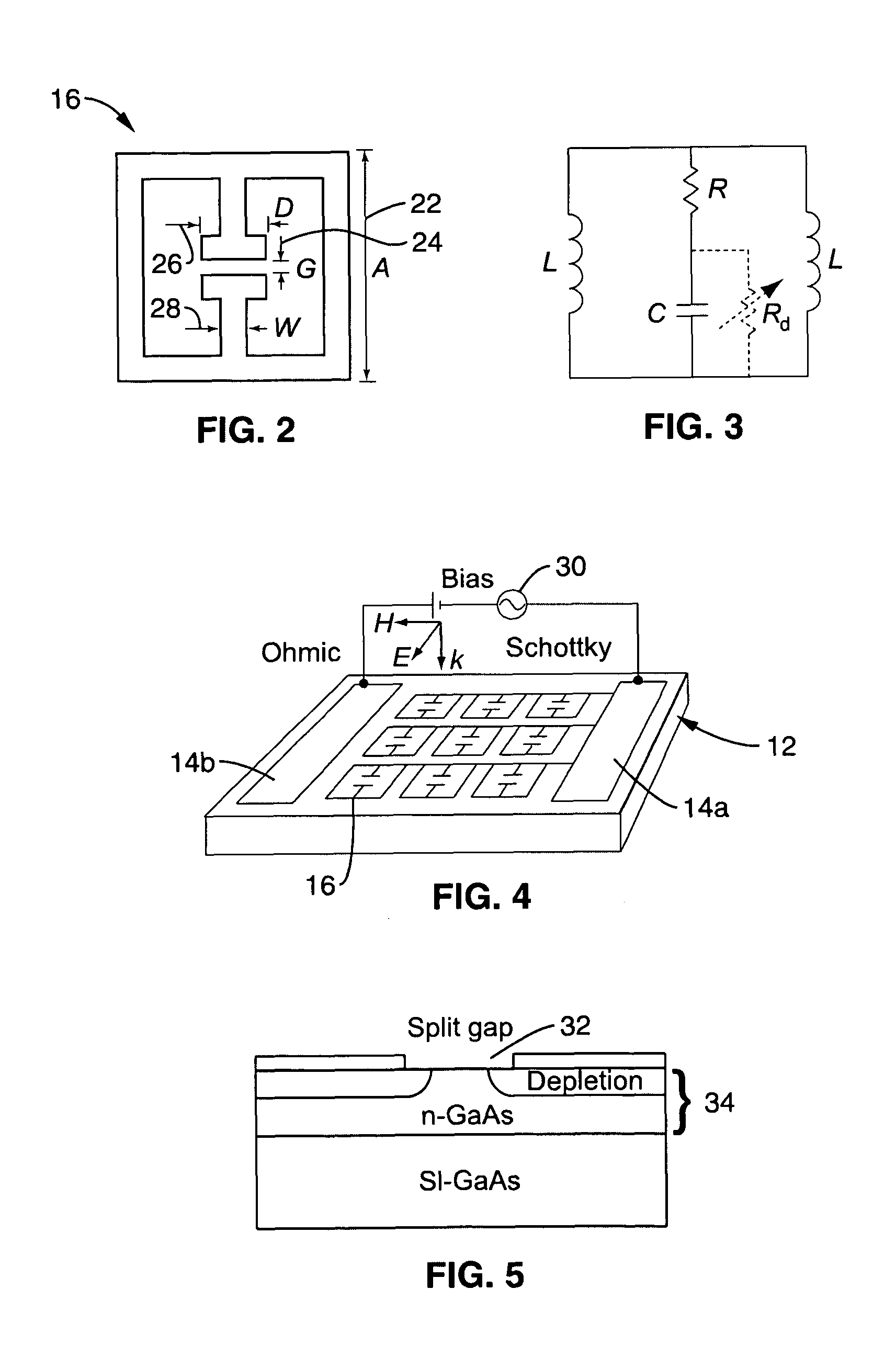
Quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) are semiconductor lasers that emit in the mid- to far-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and were first demonstrated by Jerome Faist, Federico Capasso, Deborah Sivco, Carlo Sirtori, Albert Hutchinson, and Alfred Cho at Bell Laboratories in 1994.
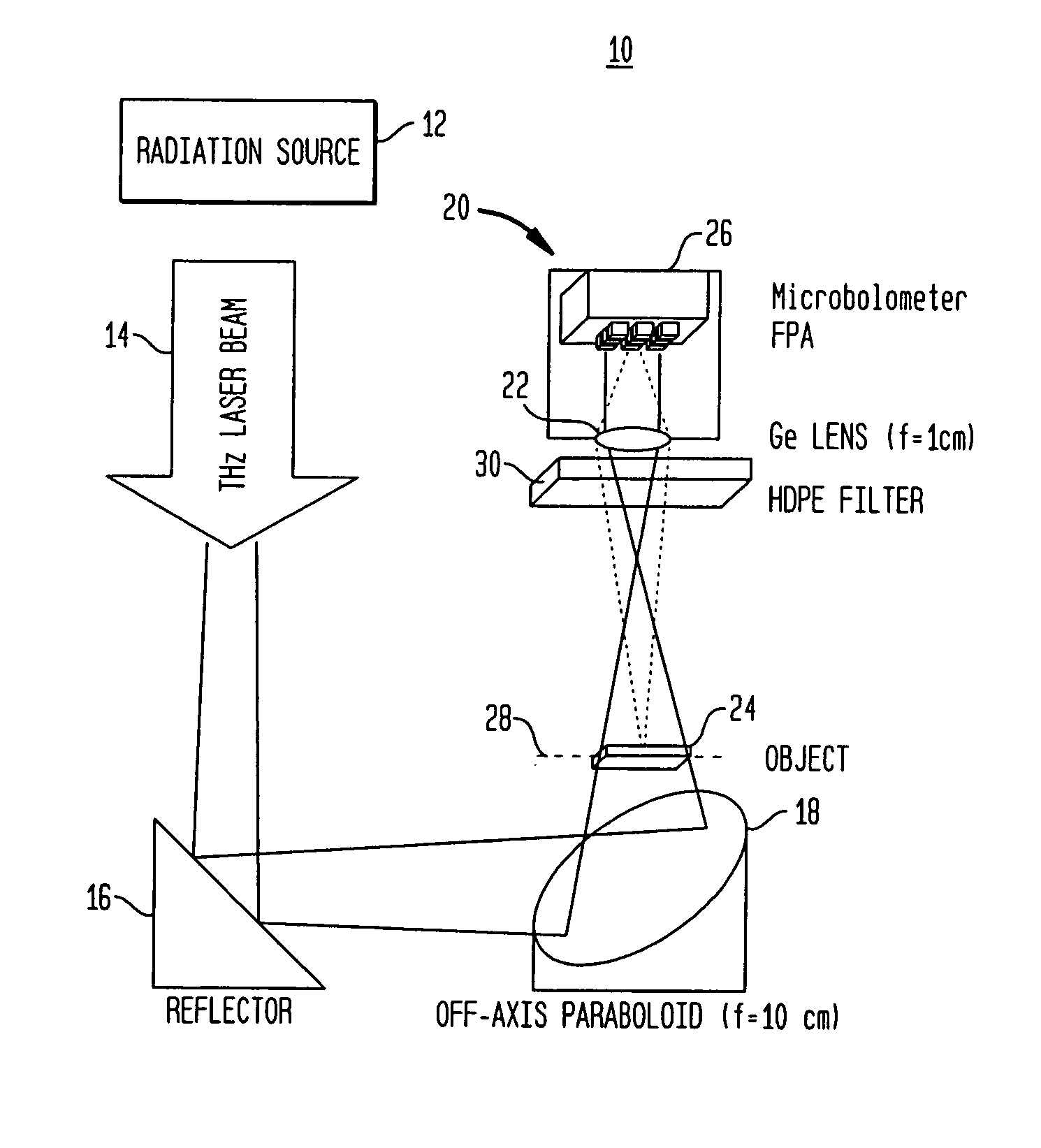
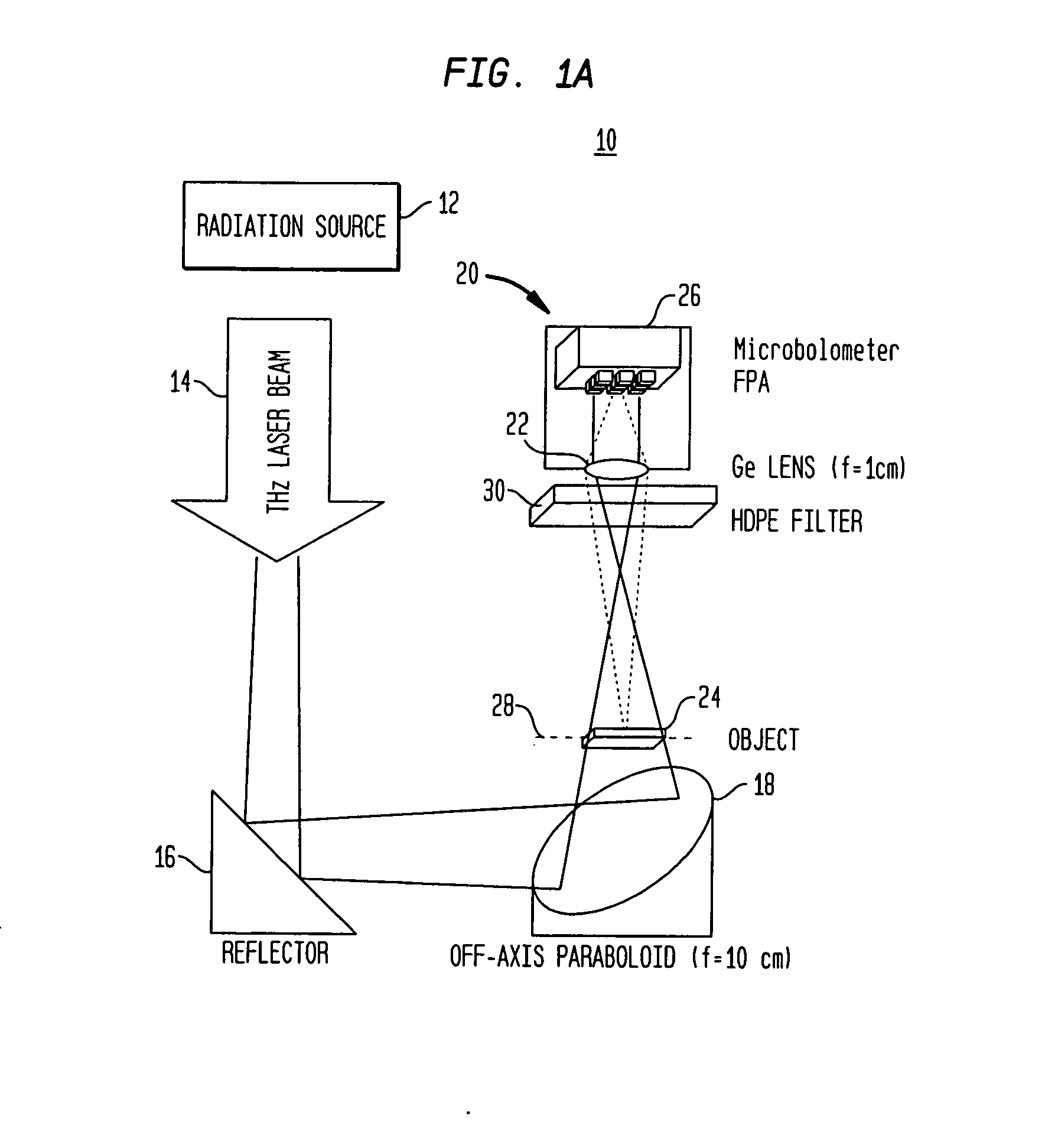
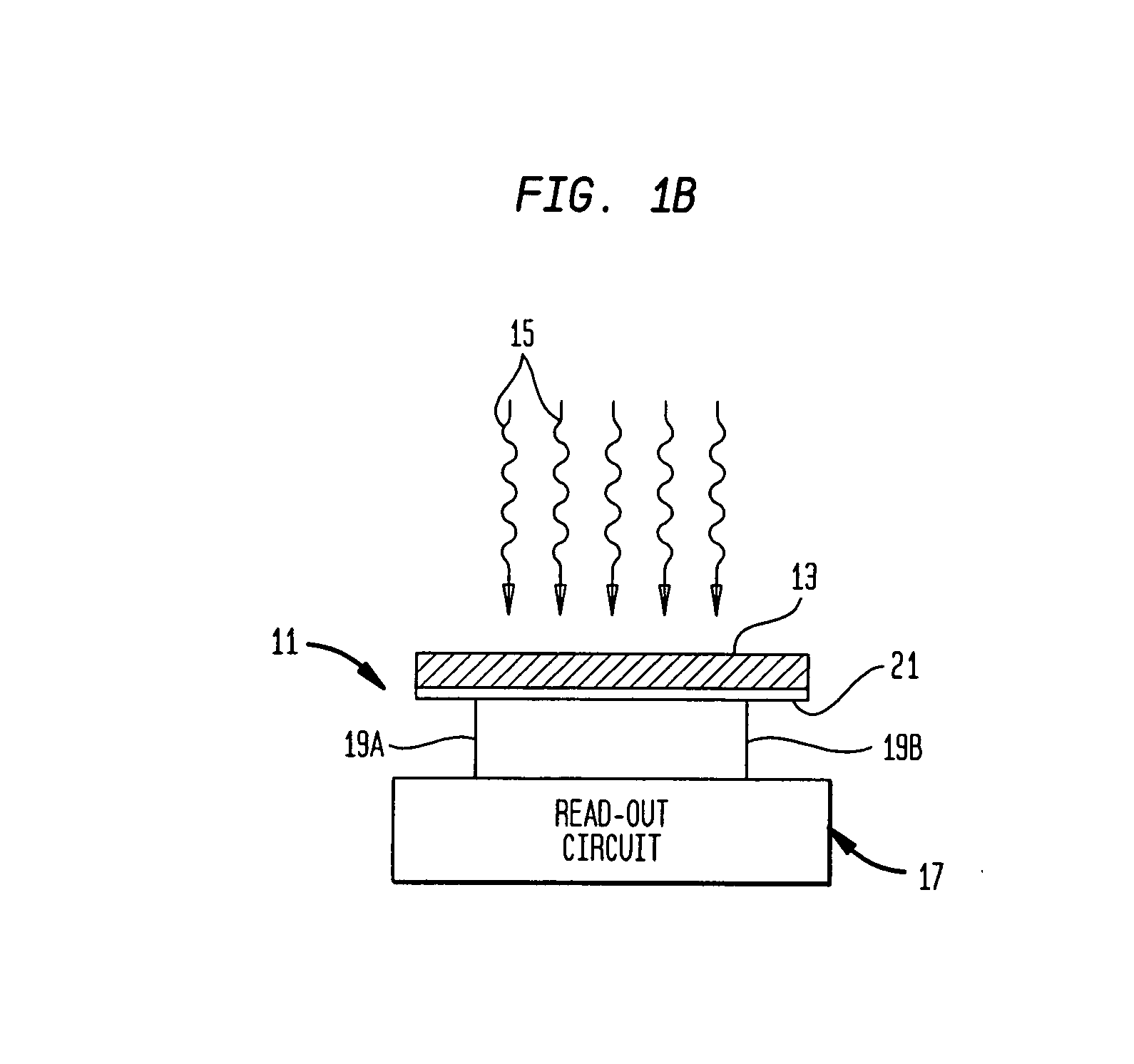
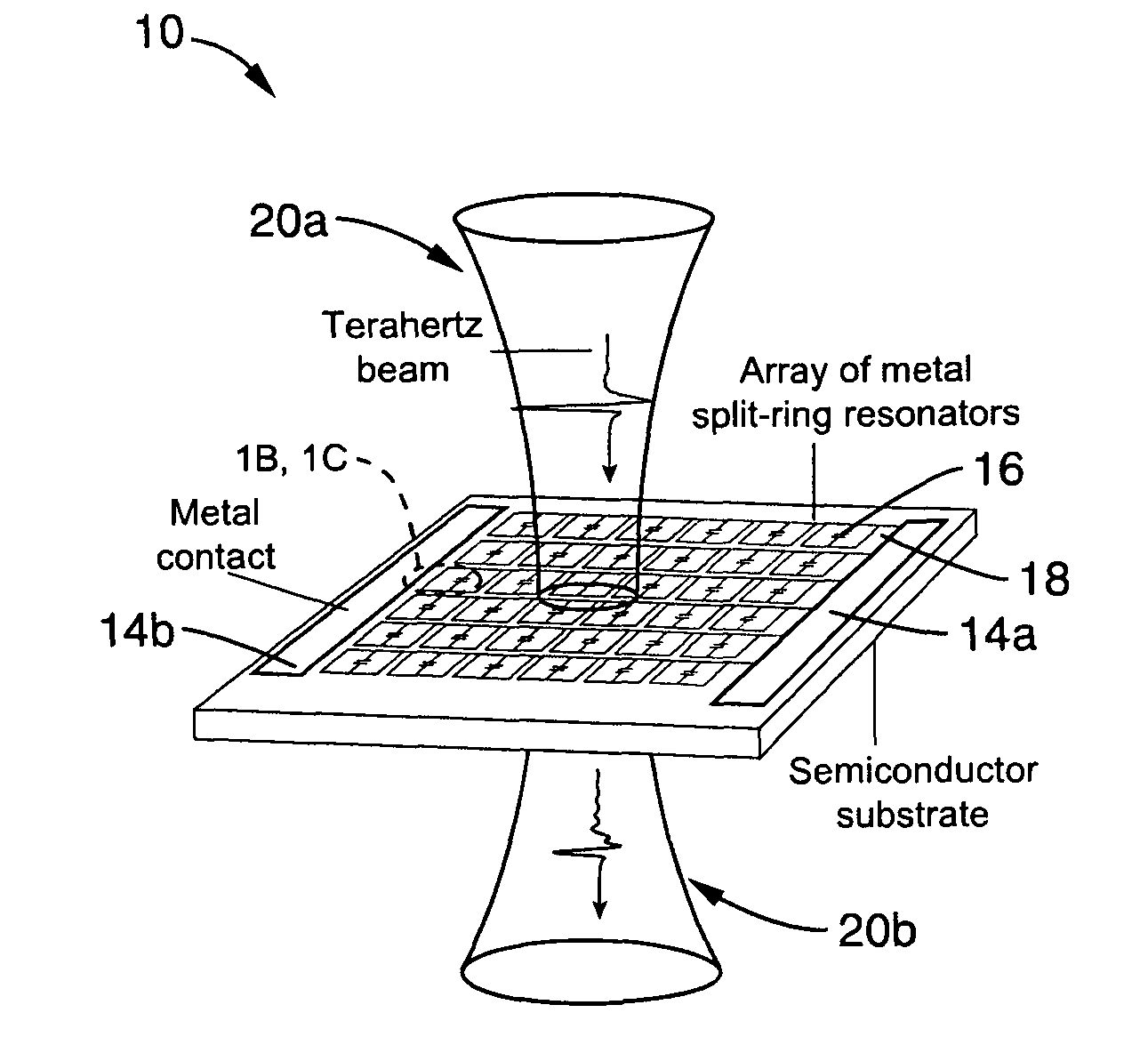
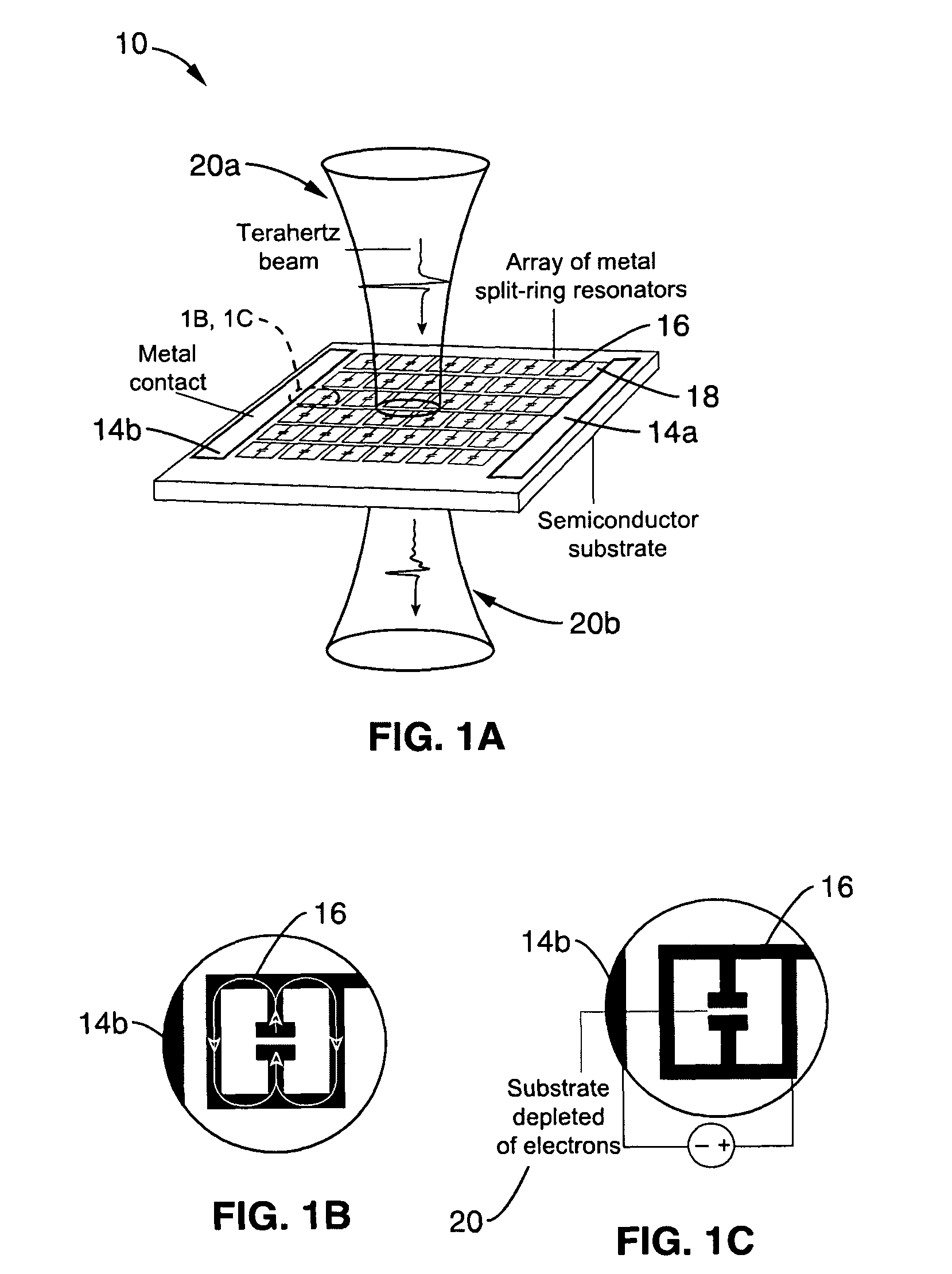
Real-time, continuous-wave terahertz imaging using a microbolometer focal-plane array
InactiveUS20080156991A1Improve image qualityReduce noiseRadiation pyrometryPhotometryTwo dimensional detectorMicrobolometer
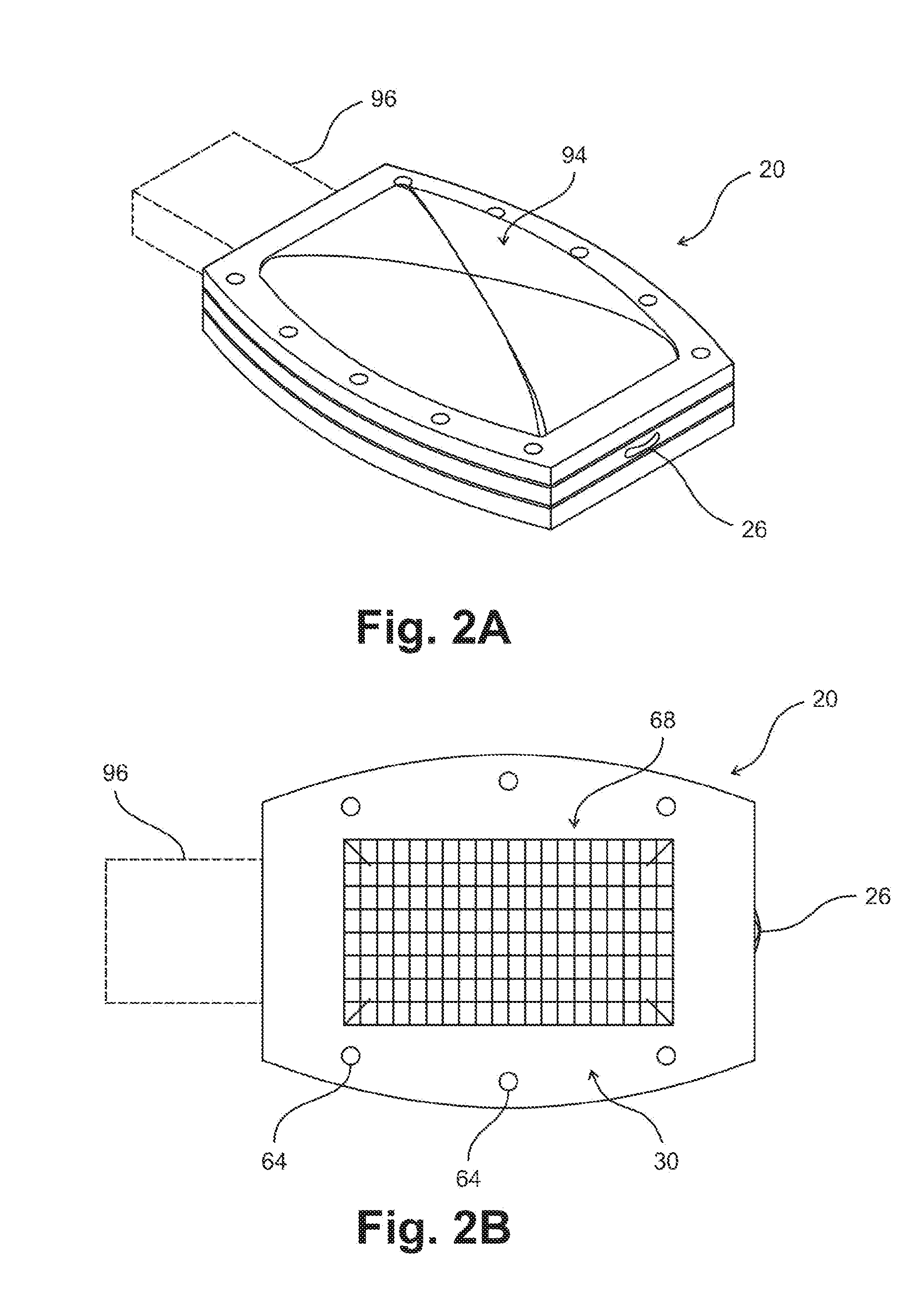
The present invention generally provides a terahertz (THz) imaging system that includes a source for generating radiation (e.g., a quantum cascade laser) having one or more frequencies in a range of about 0.1 THz to about 10 THz, and a two-dimensional detector array comprising a plurality of radiation detecting elements that are capable of detecting radiation in that frequency range. An optical system directs radiation from the source to an object to be imaged. The detector array detects at least a portion of the radiation transmitted through the object (or reflected by the object) so as to form a THz image of that object.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
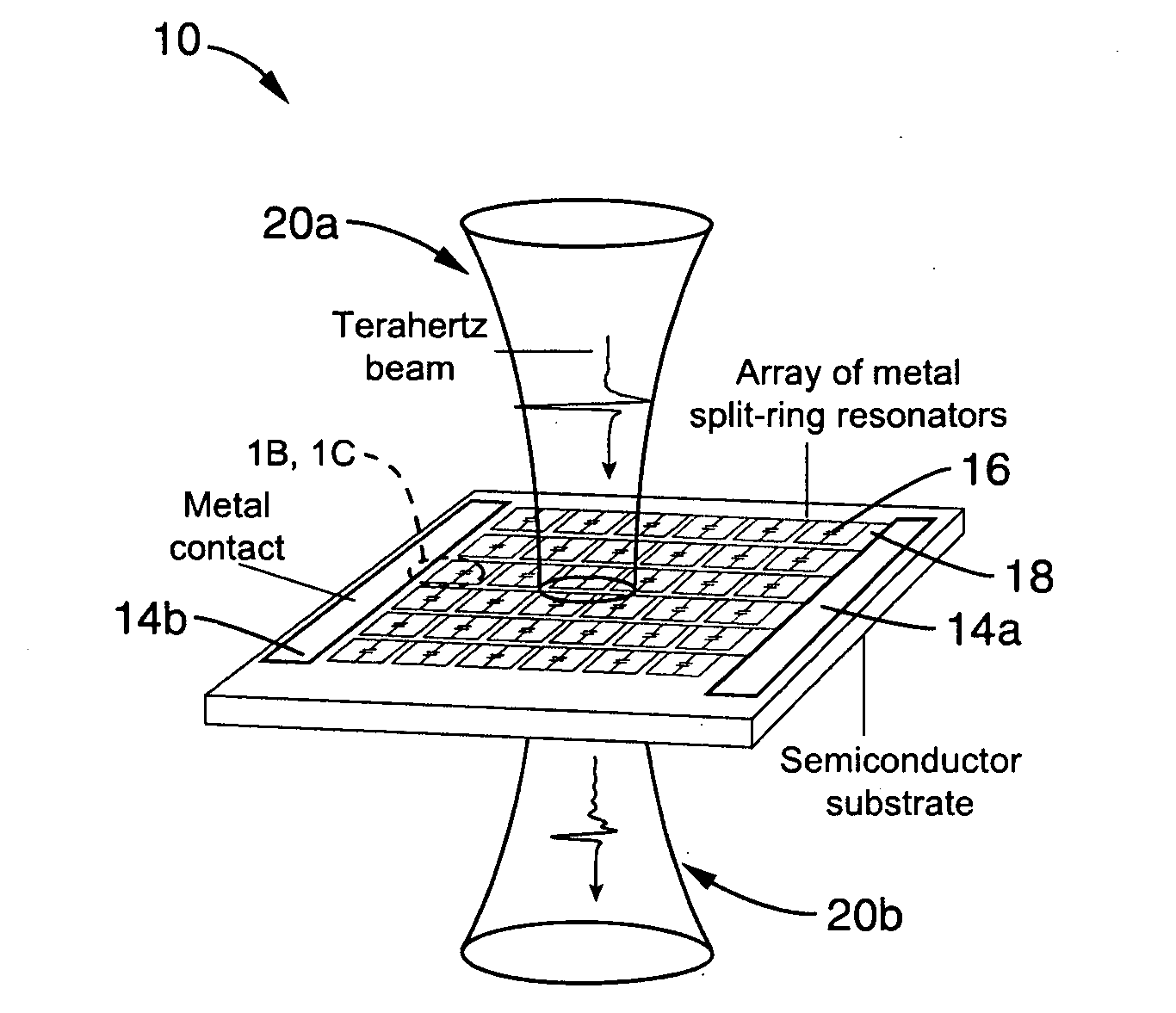
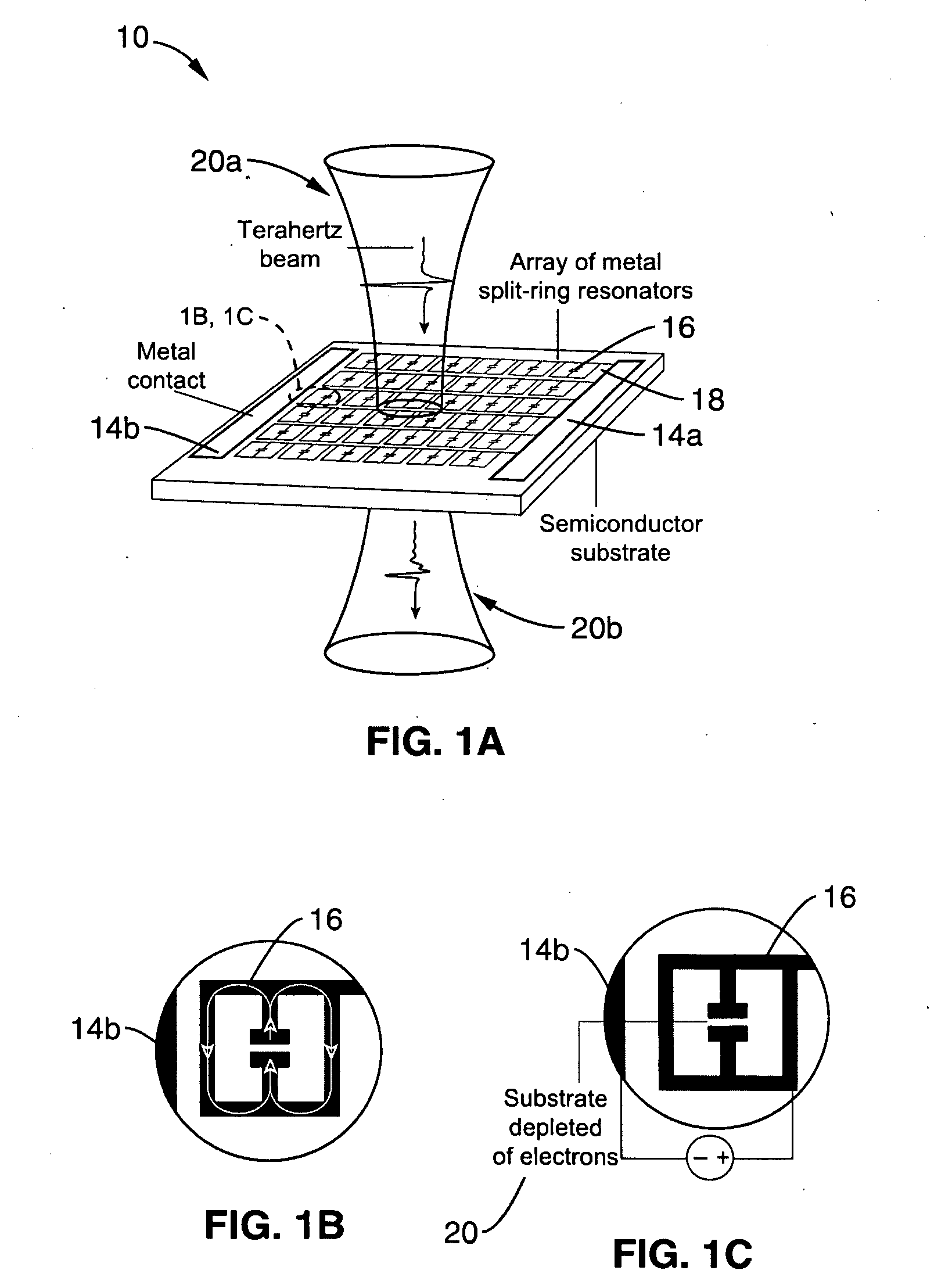
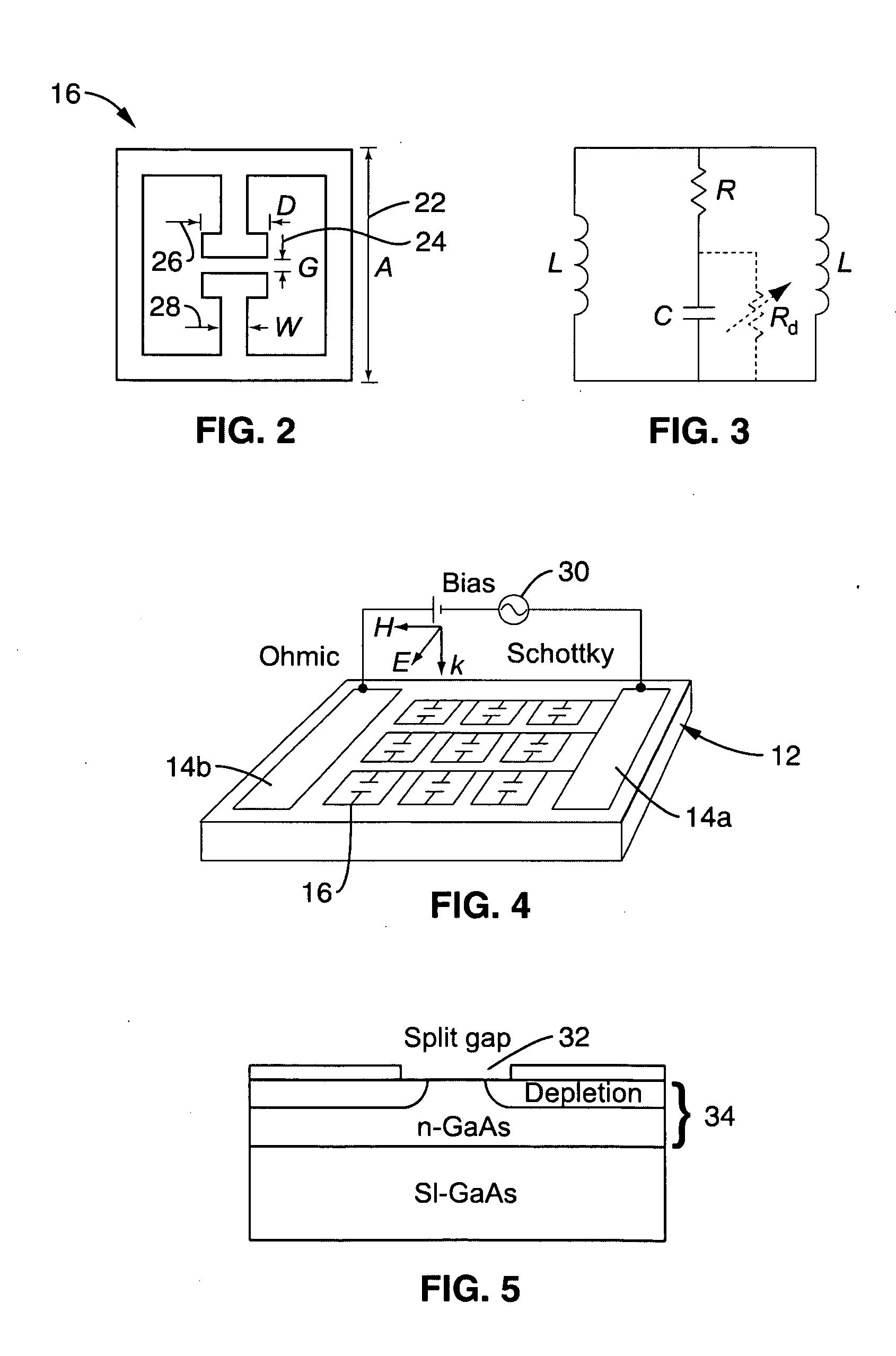
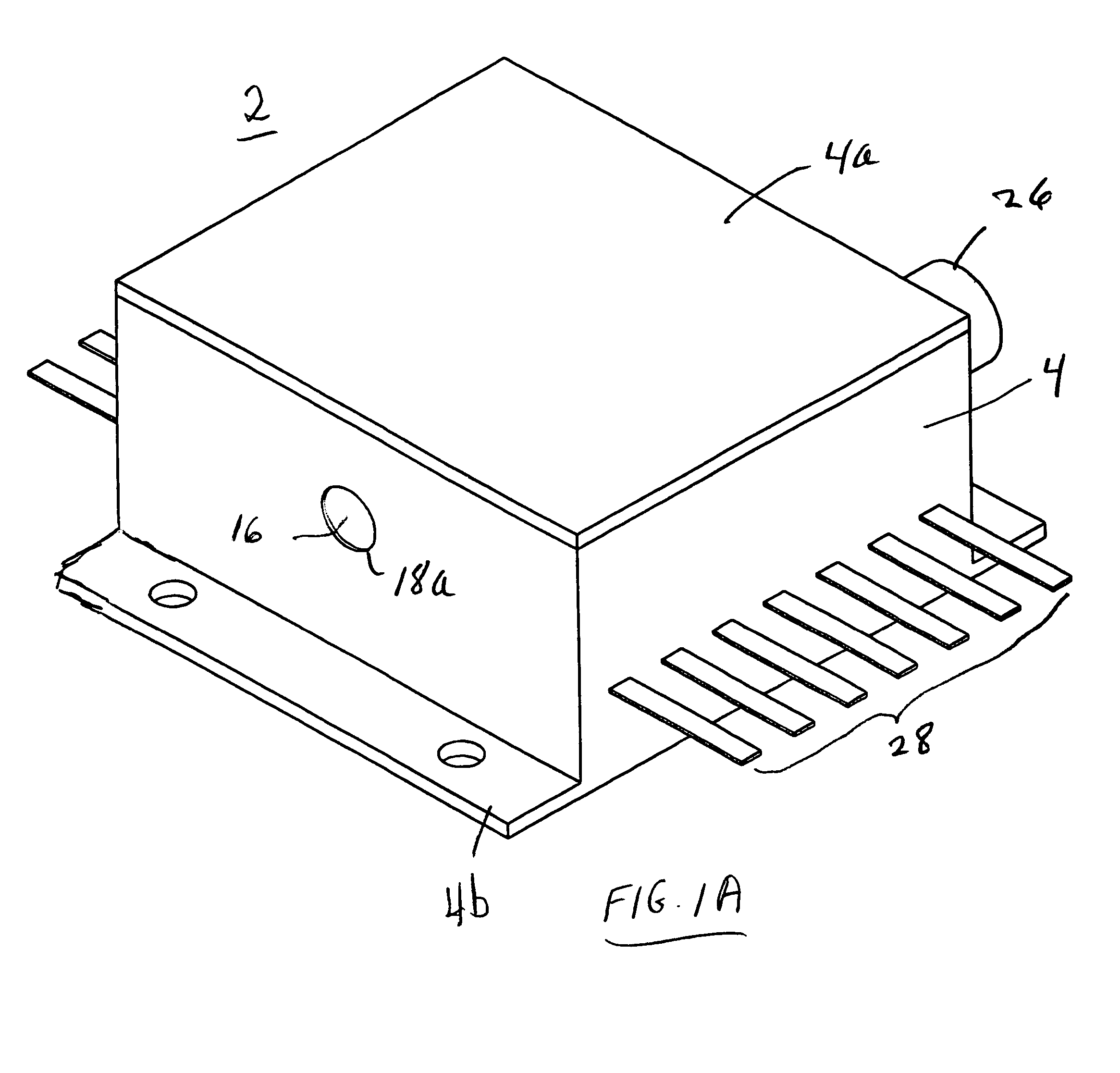
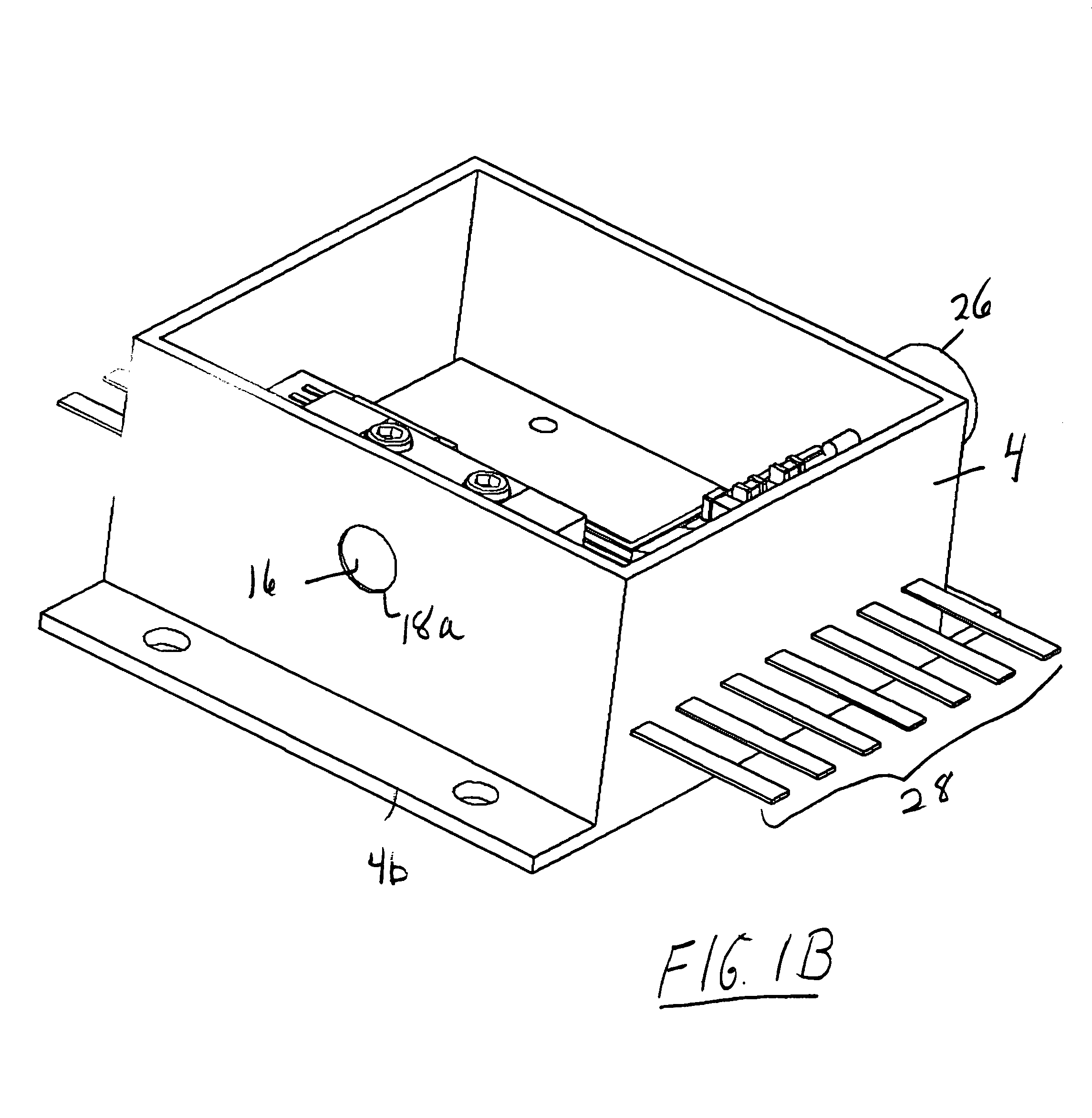
Active terahertz metamaterial devices
ActiveUS20090262766A1Dampens resonant responseIncrease capacitanceResonant long antennasLaser detailsTerahertz metamaterialsTransmittance
Metamaterial structures are taught which provide for the modulation of terahertz frequency signals. Each element within an array of metamaterial (MM) elements comprises multiple loops and at least one gap. The MM elements may comprise resonators with conductive loops and insulated gaps, or the inverse in which insulated loops are present with conductive gaps; each providing useful transmissive control properties. The metamaterial elements are fabricated on a semiconducting substrate configured with a means of enhancing or depleting electrons from near the gaps of the MM elements. An on to off transmissivity ratio of about 0.5 is achieved with this approach. Embodiments are described in which the MM elements incorporated within a Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) to provide surface emitting (SE) properties.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Non-invasive, in vivo substance measurement systems
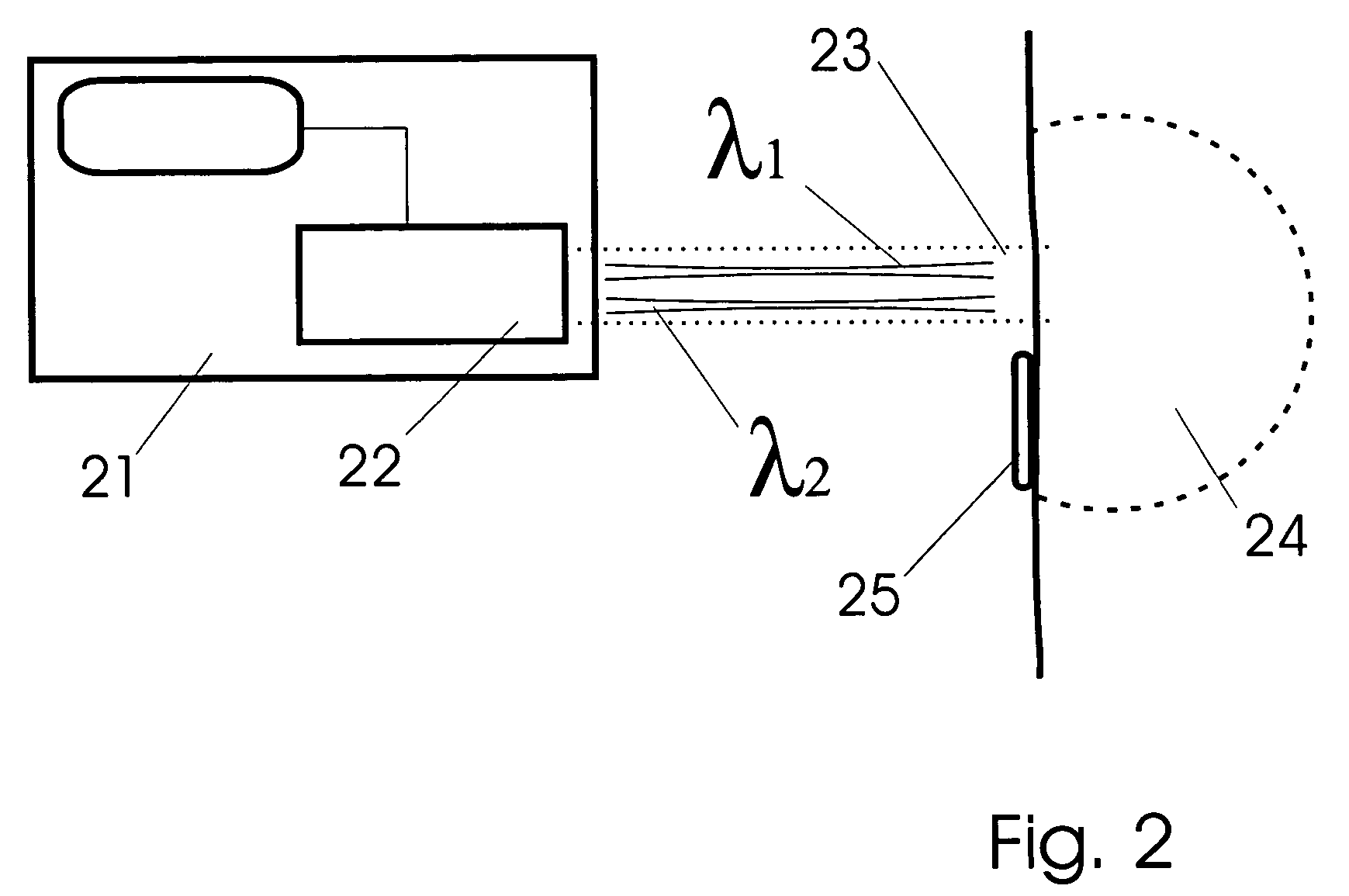
Tissue substance measurement systems are arranged with highly specialized optical sources. Quantum cascade lasers are high power semiconductor lasers which are tiny in size and highly tunable with respect to wavelength. When deployed in non-invasive tissue substance measurement systems, quantum cascade lasers offer system advantages such as high accuracy, small size, convenience, efficiency, among others. These specialized semiconductors may be used with systems based upon photoacoustic principles. Systems may be formed of a plurality of quantum cascade laser in an optical source, mechanism to couple light into tissue, an acoustic detector and a signal processor. In some versions, user interfaces provide a reporting and feedback function to a user.
Owner:HEFTI JOHN +2
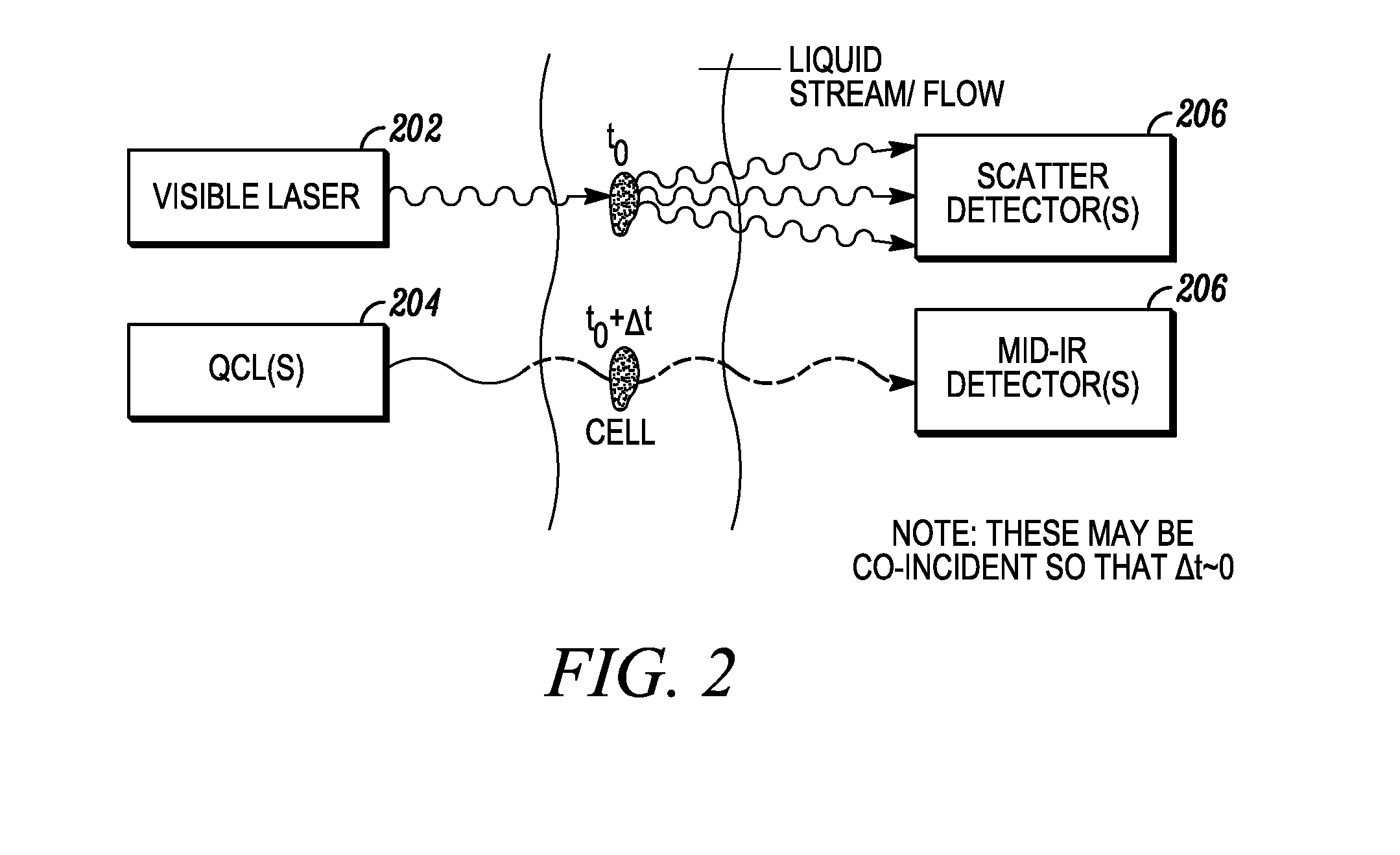
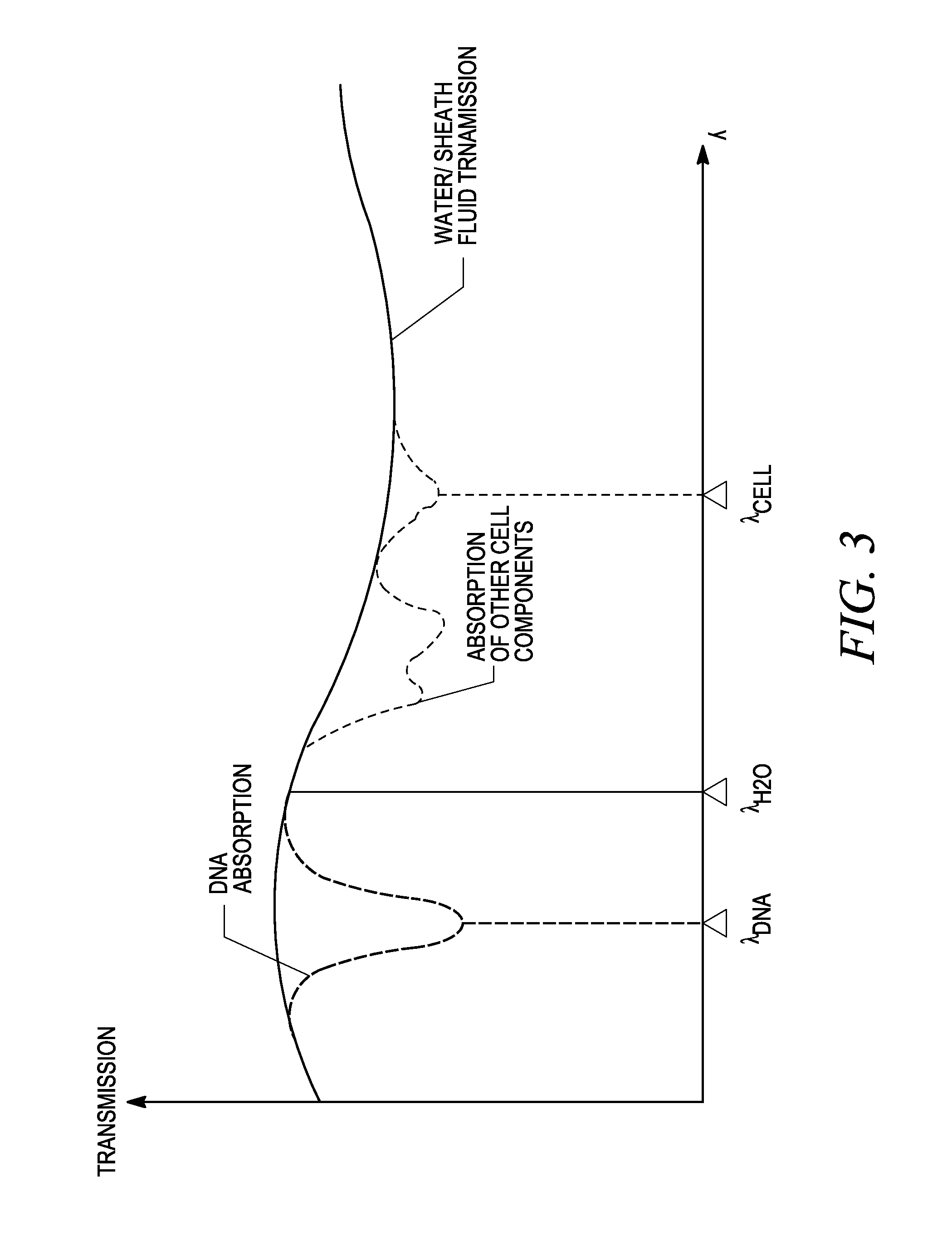
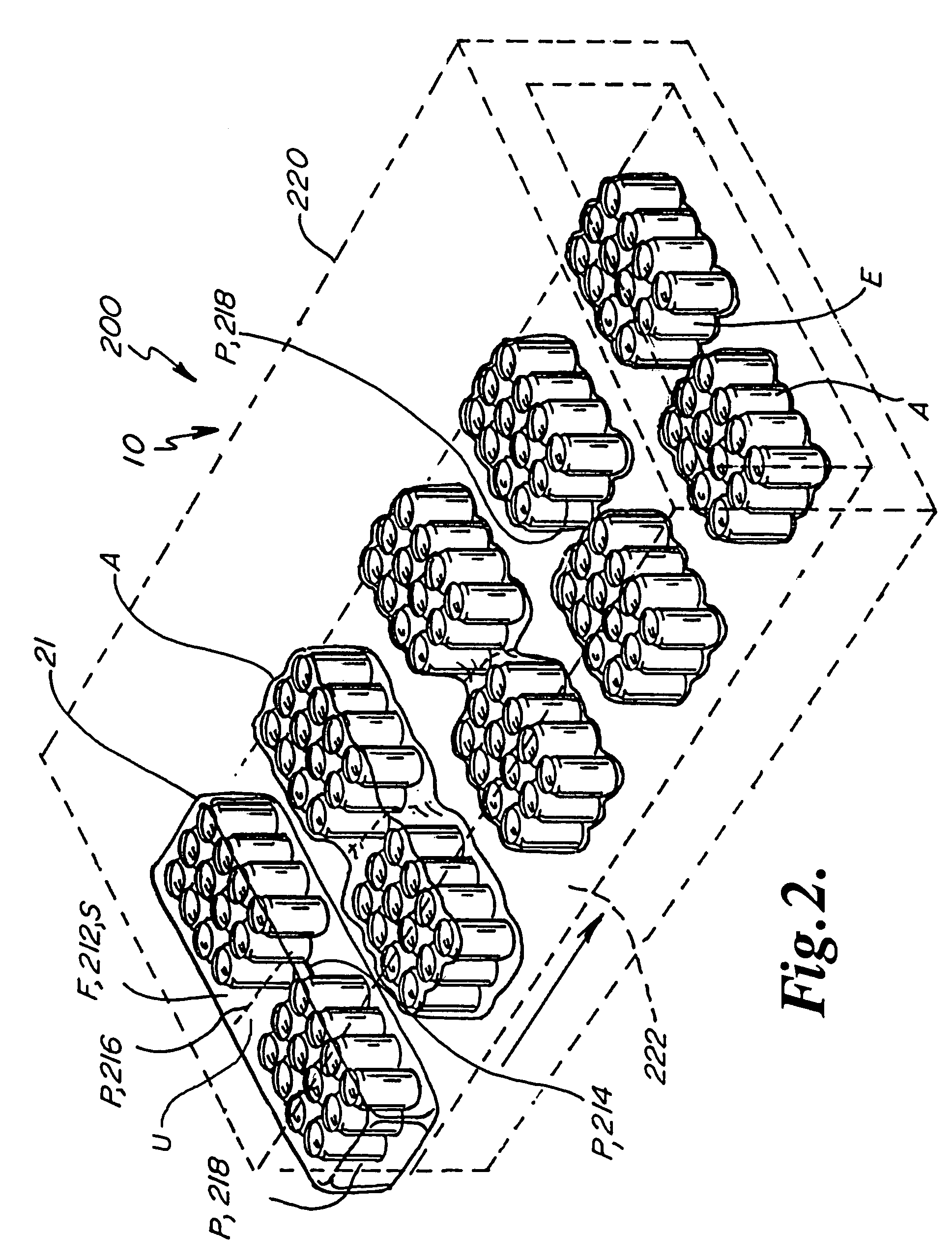
Cytometry system with quantum cascade laser source, acoustic detector, and micro-fluidic cell handling system configured for inspection of individual cells
InactiveUS20120225475A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteCell handling
This disclosure concerns a cytometry system including a handling system that presents single cells to at least one quantum cascade laser (QCL) source. The QCL laser source is configured to deliver light to a cell within the cells in order to induce resonant mid-IR vibrational absorption by one or more analytes, leading to local heating that results in thermal expansion and an associated shockwave. An acoustic detection facility that detects the shockwave emitted by the single cell.
Owner:1087 SYST
Highly portable and wearable blood analyte measurement system
InactiveUS20050054907A1Encourages better and more complete use of the instrumentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsContinuous measurementNon invasive
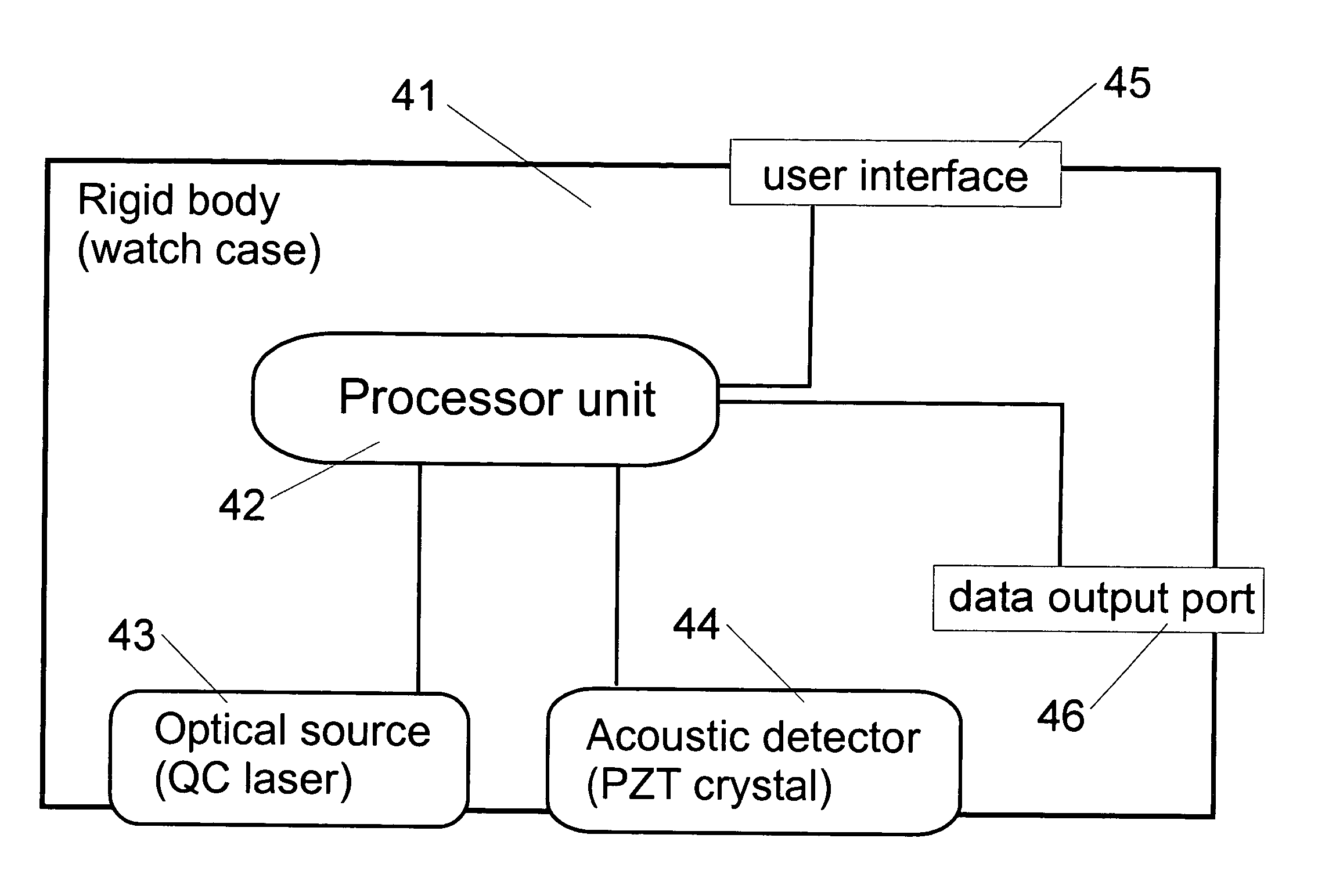
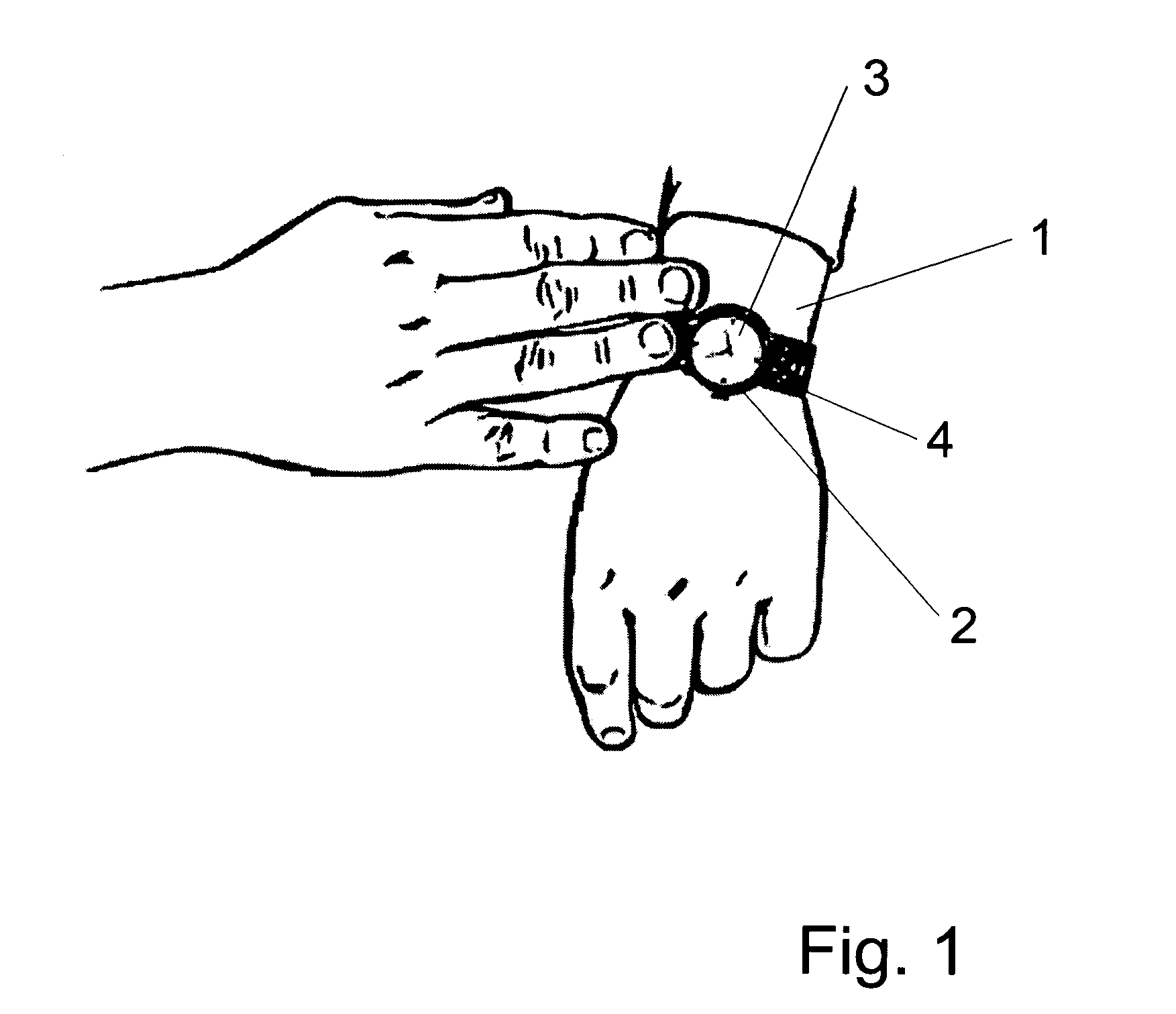
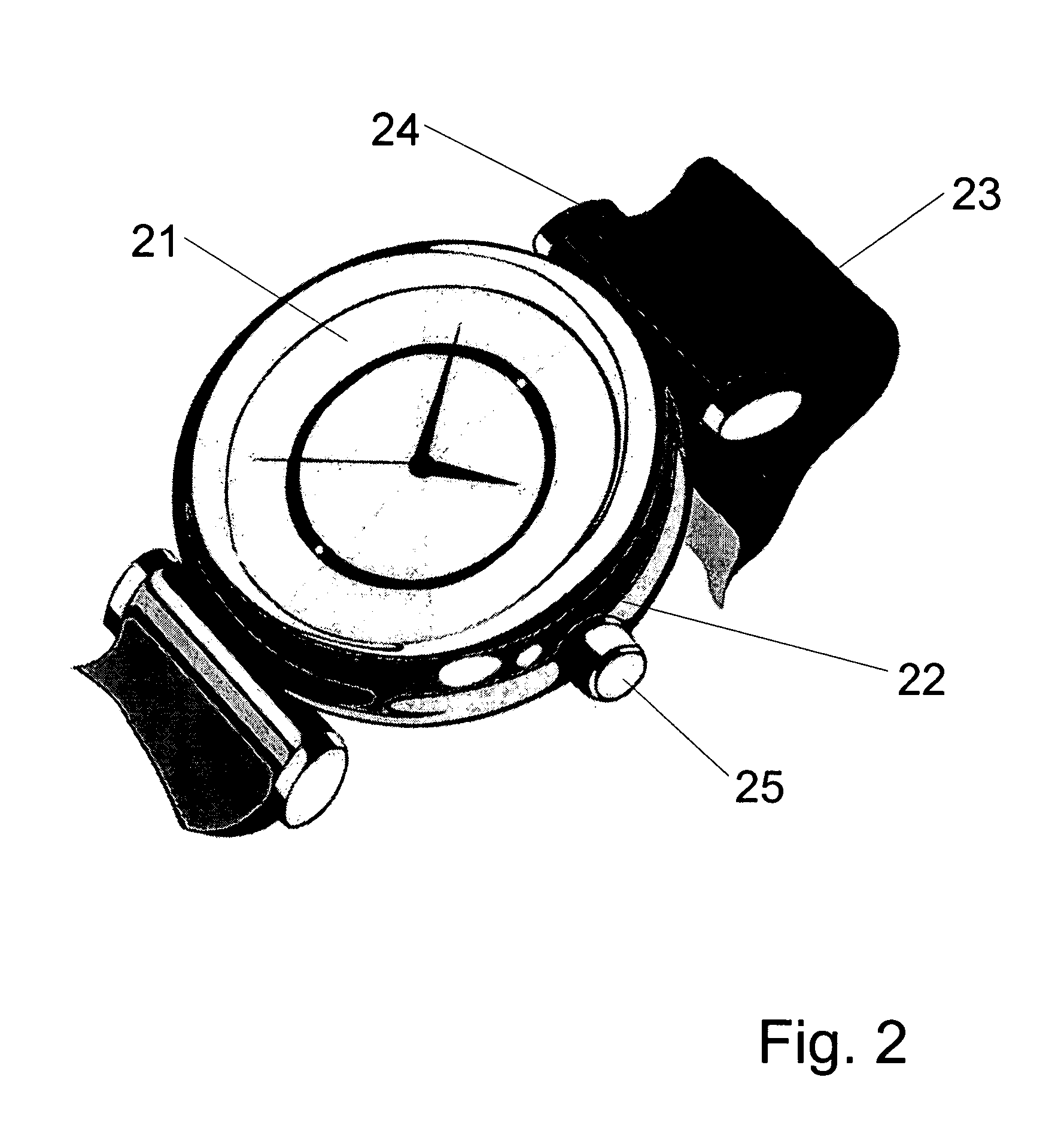
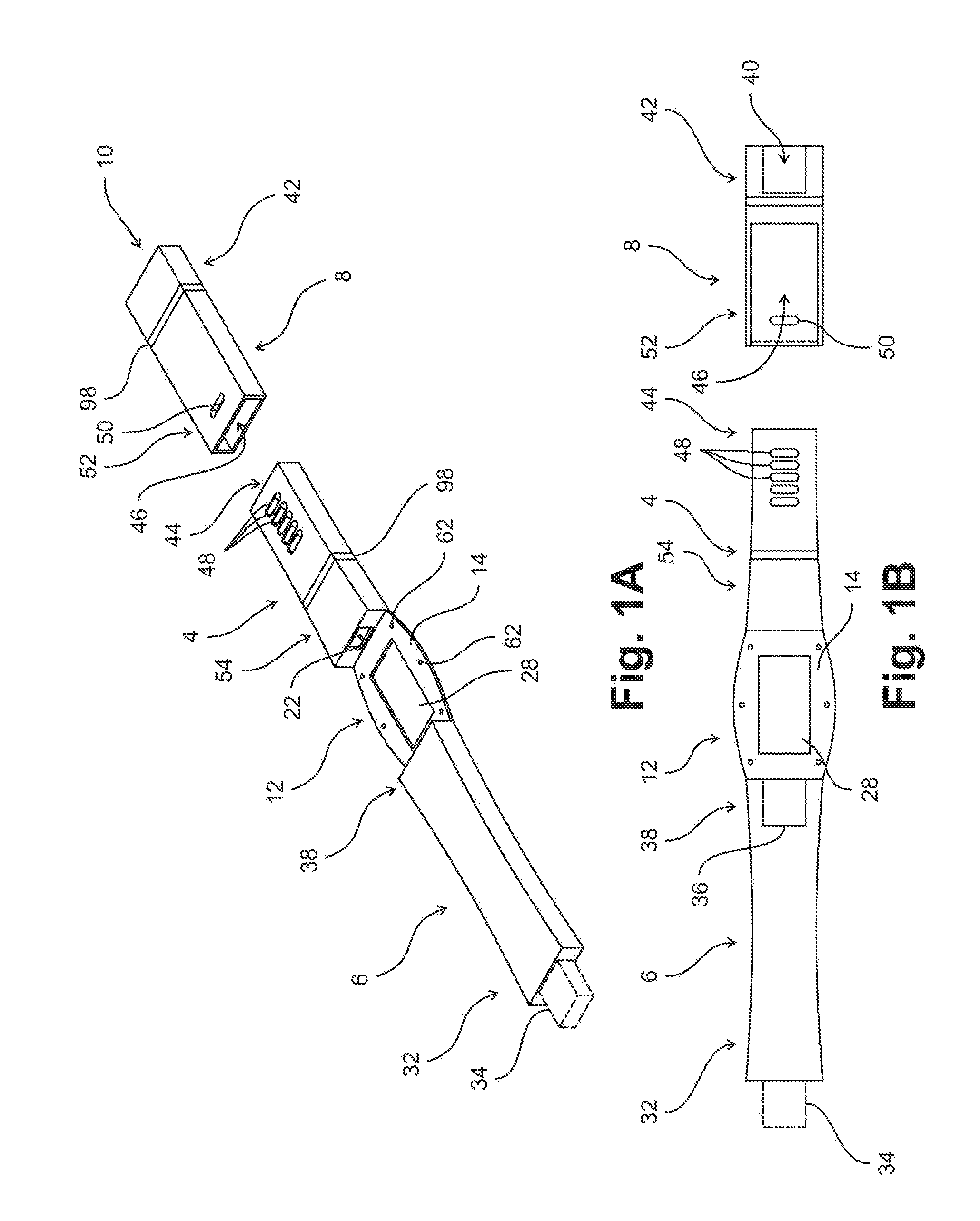
Non-invasive wearable systems for continuous measurement of blood glucose concentrations help diabetics maintain best awareness and control. A wearable article such as a wristwatch includes elements integrated therewith to provide for biometric measurements. Specifically, both optical and acoustic transducers are arranged within an article such that they are coupled to tissue in a manner which permits blood analytes measurements to be made. In best versions, a quantum cascade laser is arranged with crystalline acoustic detectors in a photoacoustic effect measurement scheme. Laser pulses stimulate special vibrational states of glucose molecules to produce an acoustic return signal to be received at a piezoelectric detector. A wristwatch case may include a back member which supports arrangements and coupling between the back of the watch, elements contained therein, and tissue in contact with the device.
Owner:PAGE JOSEPH +1
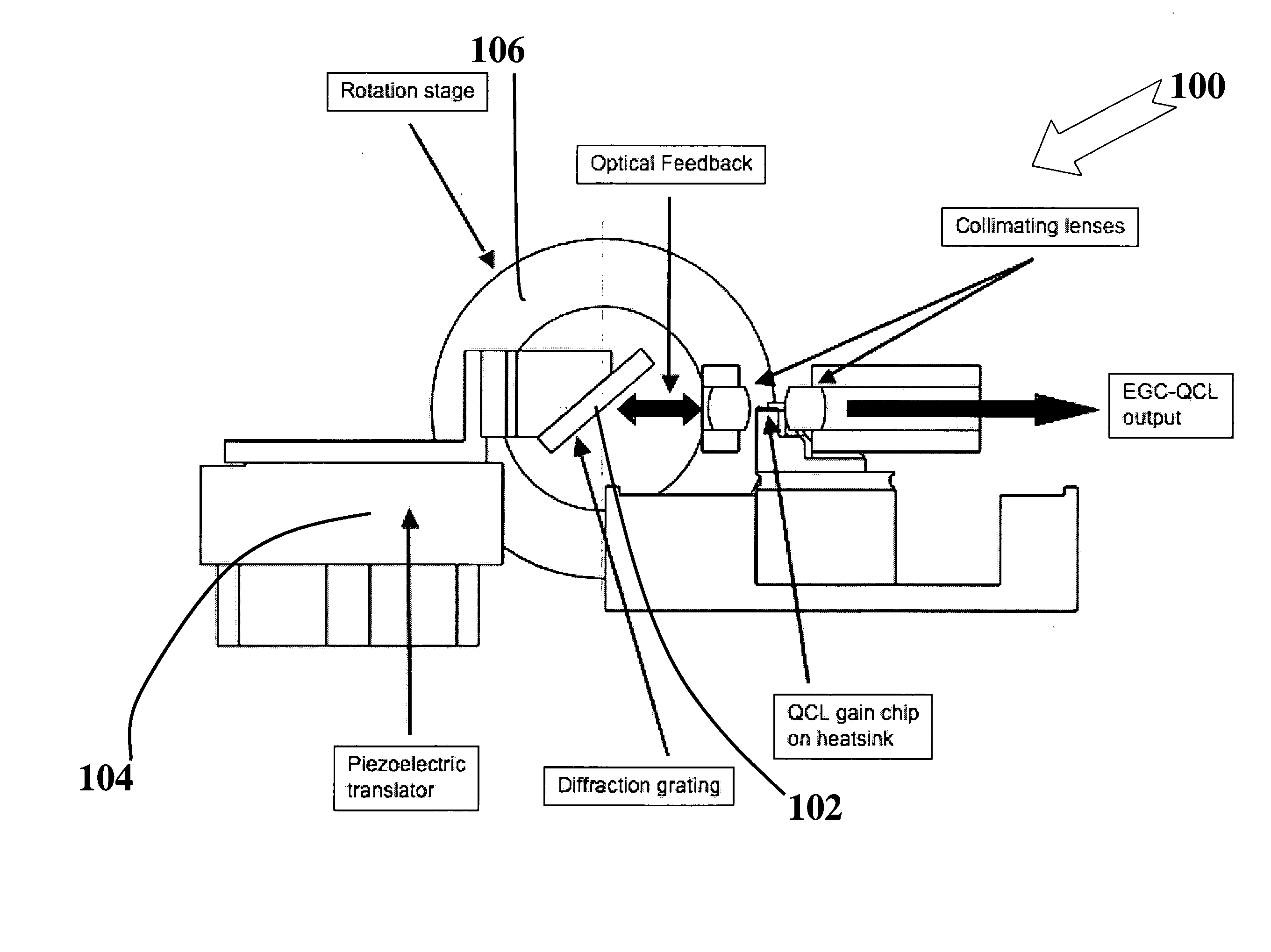
External cavity tunable compact mid-IR laser
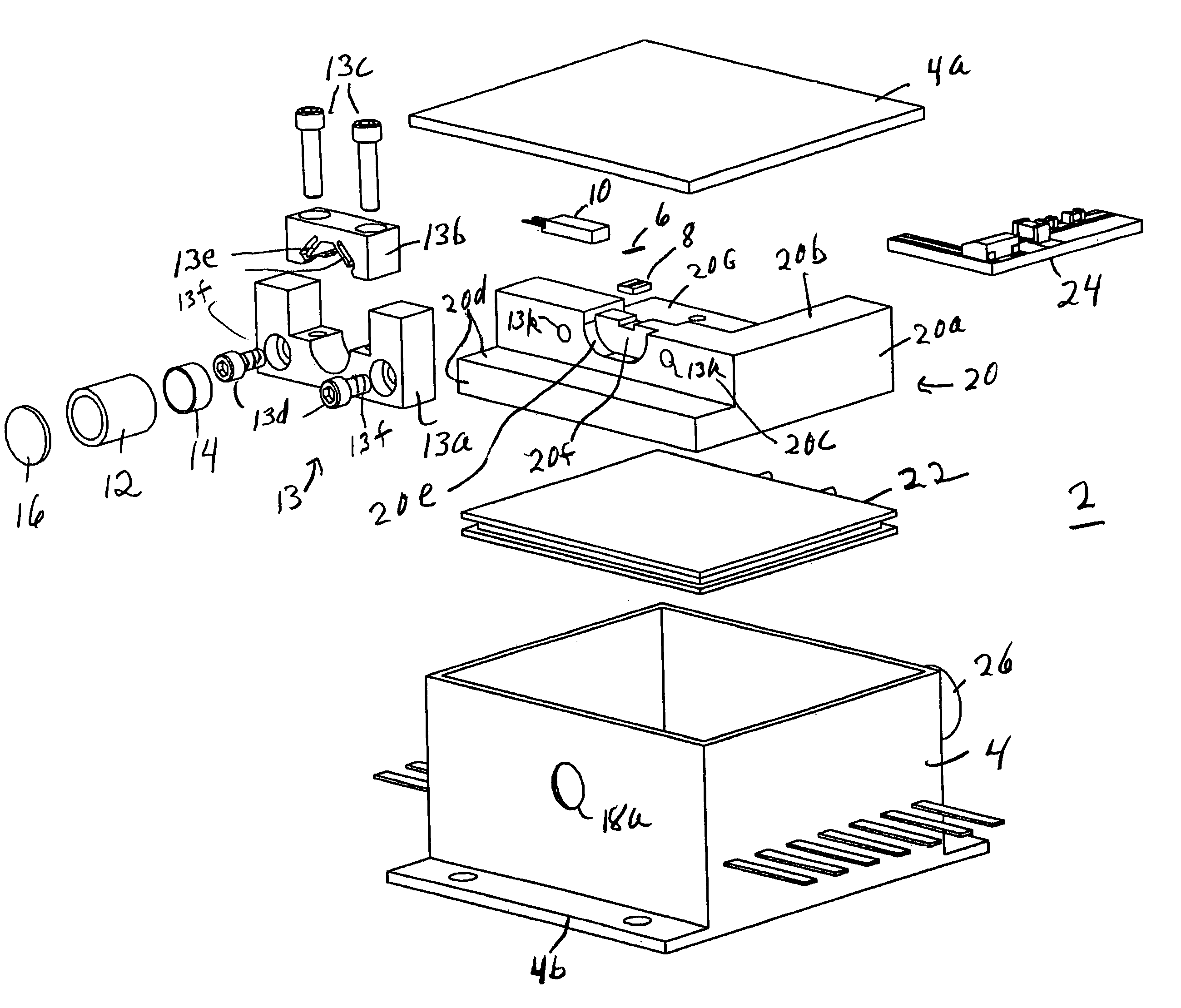
ActiveUS20070030865A1Reduce usageImprove cooling effectLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
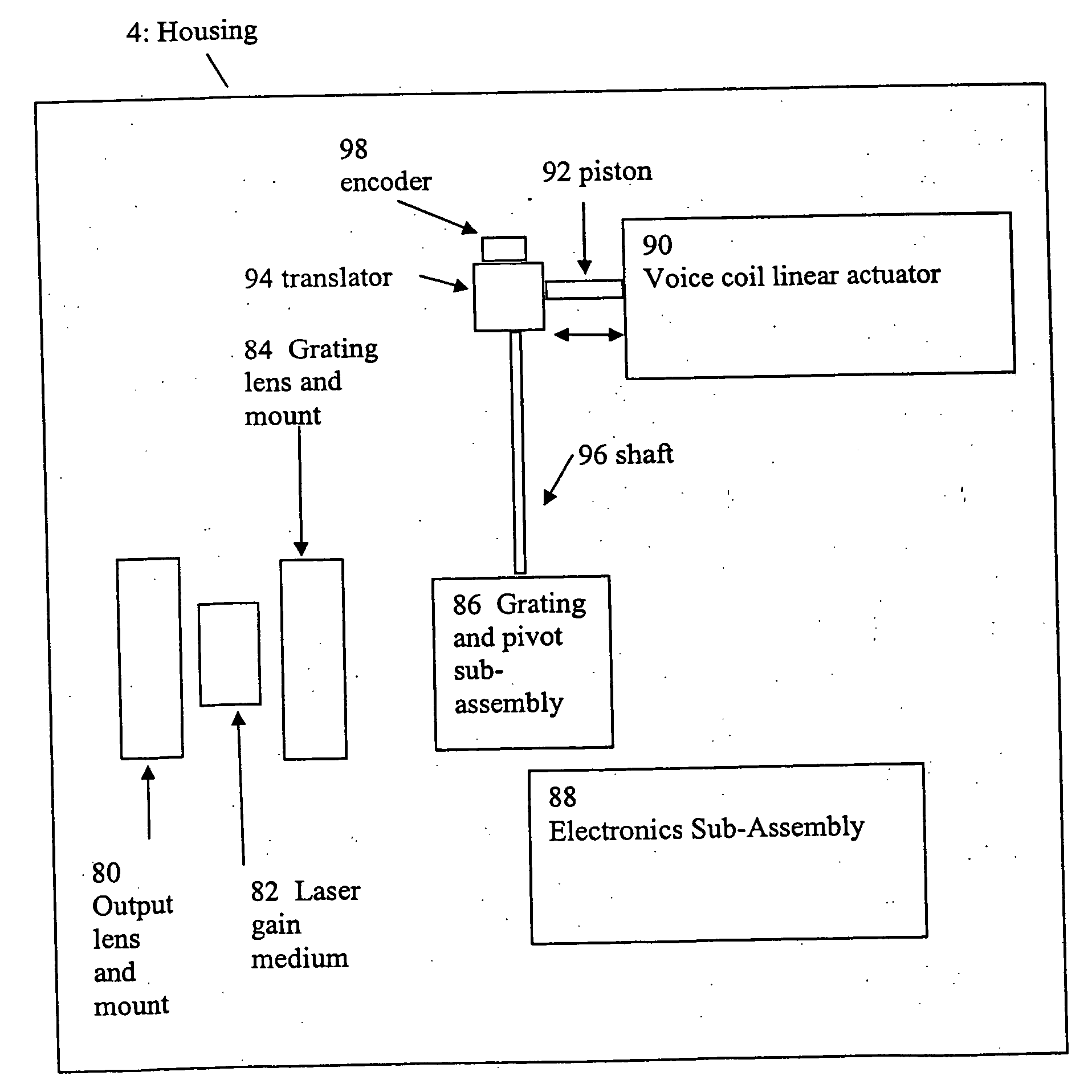
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Wavelength beam combining of quantum cascade laser arrays
ActiveUS20120033697A1Increase overlapLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser arrayLight beam
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Tunable quantum cascade lasers and photoacoustic detection of trace gases, TNT, TATP and precursors acetone and hydrogen peroxide
ActiveUS20080159341A1High rejectionShorten the timeMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical resonator shape and constructionQuantum cascade laserPeroxide
Methods and apparatus for broad tuning of single wavelength quantum cascade lasers and the use of light output from such lasers for highly sensitive detection of trace gases such as nitrogen dioxide, acetylene, and vapors of explosives such as trinitrotoluene (TNT) and triacetone triperoxide (TATP) and TATP's precursors including acetone and hydrogen peroxide. These methods and apparatus are also suitable for high sensitivity, high selectivity detection of other chemical compounds including chemical warfare agents and toxic industrial chemicals. A quantum cascade laser (QCL) system that better achieves single mode, continuous, mode-hop free tuning for use in L-PAS (laser photoacoustic spectroscopy) by independently coordinating gain chip current, diffraction grating angle and external cavity length is described. An all mechanical method that achieves similar performance is also described. Additionally, methods for improving the sensor performance by critical selection of wavelengths are presented.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070291804A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7492806B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Active terahertz metamaterial devices
ActiveUS7826504B2Dampens resonant responseIncrease capacitanceResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsTerahertz metamaterialsTransmittance
Metamaterial structures are taught which provide for the modulation of terahertz frequency signals. Each element within an array of metamaterial (MM) elements comprises multiple loops and at least one gap. The MM elements may comprise resonators with conductive loops and insulated gaps, or the inverse in which insulated loops are present with conductive gaps; each providing useful transmissive control properties. The metamaterial elements are fabricated on a semiconducting substrate configured with a means of enhancing or depleting electrons from near the gaps of the MM elements. An on to off transmissivity ratio of about 0.5 is achieved with this approach. Embodiments are described in which the MM elements incorporated within a Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) to provide surface emitting (SE) properties.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Continuous whole blood glucose monitor
InactiveUS20110009720A1Improve fitOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationPeristaltic pumpPhotoconductive detector
A portable continuous whole blood glucose monitor comprising, a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser and driver in optical communication with a transmission cell and a photo-conductive detector and pre-amplifier. The monitor further comprises a peristaltic pump connected to a single lumen catheter peripherally inserted into a patient's vein. The single lumen catheter, in combination with the peristaltic pump, is operable to automatically withdraw a fixed and metered amount of whole blood from a patient, then a tube delivers a fixed and metered amount of the saline / surfactant supply to the whole blood. Methods of enhancing measurement sensitivity are also provided.
Owner:CASCADE METRIX LLC
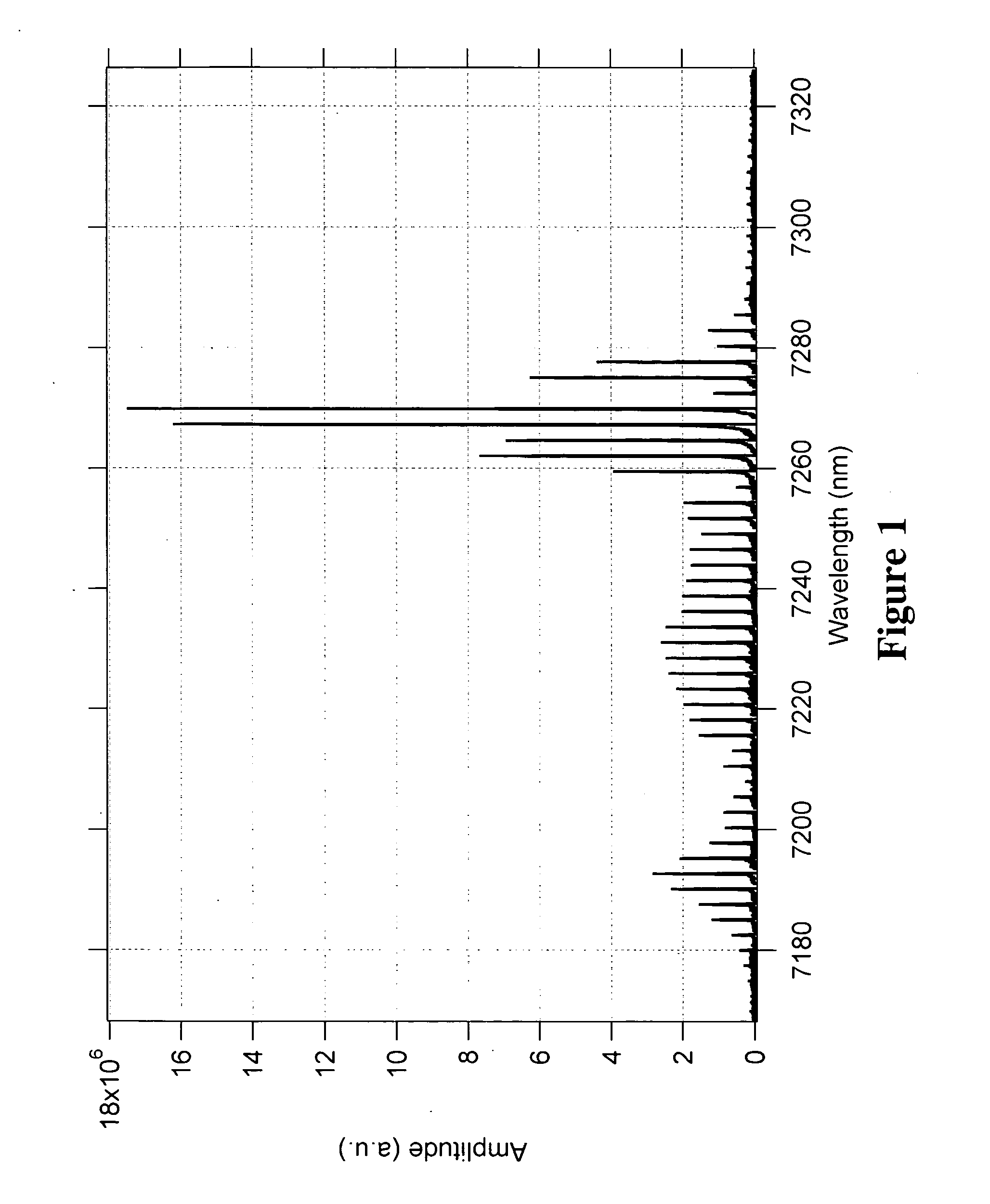
Broadly tunable single-mode quantum cascade laser sources and sensors
ActiveUS20080144677A1Easy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingLine width
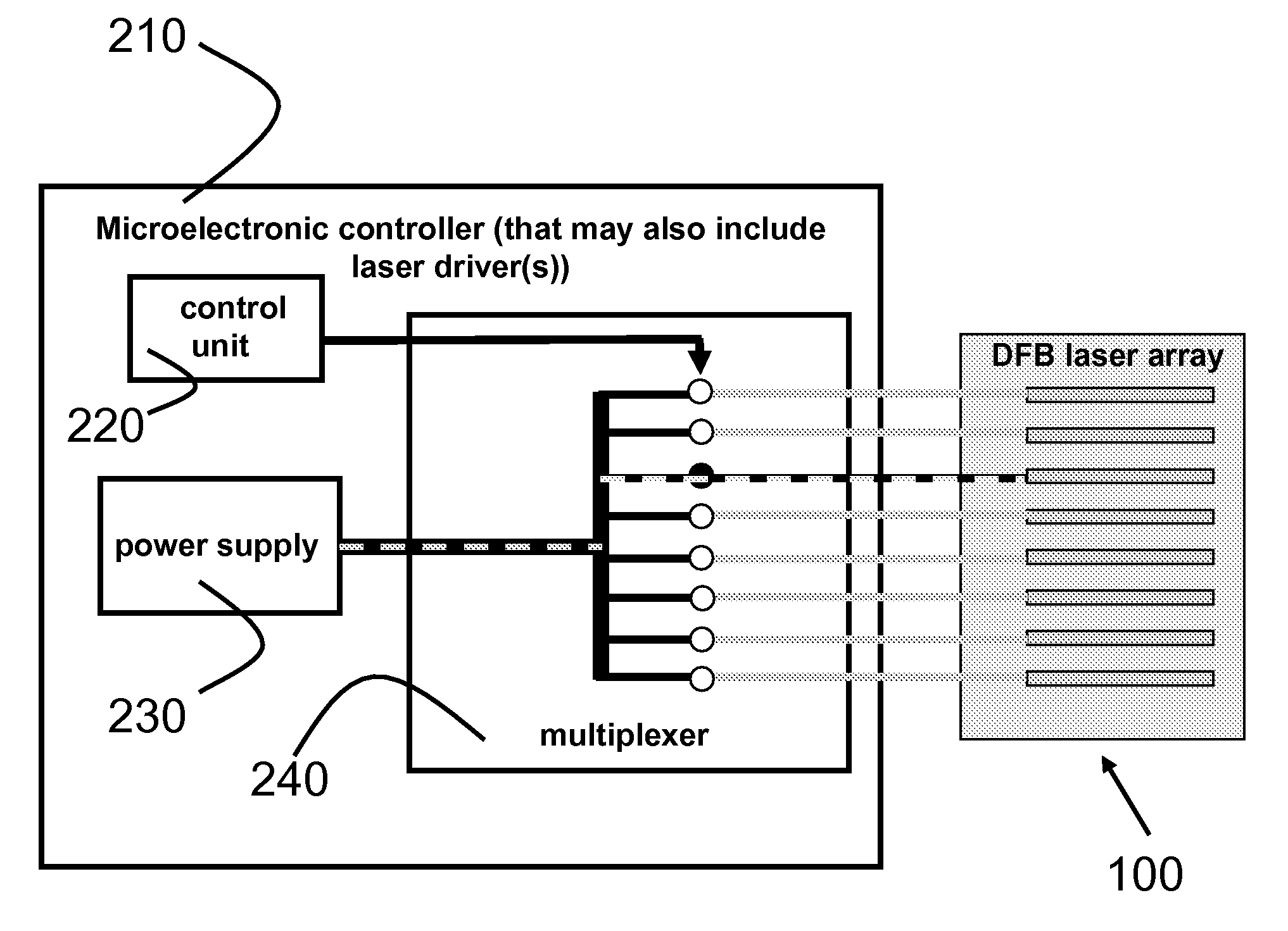
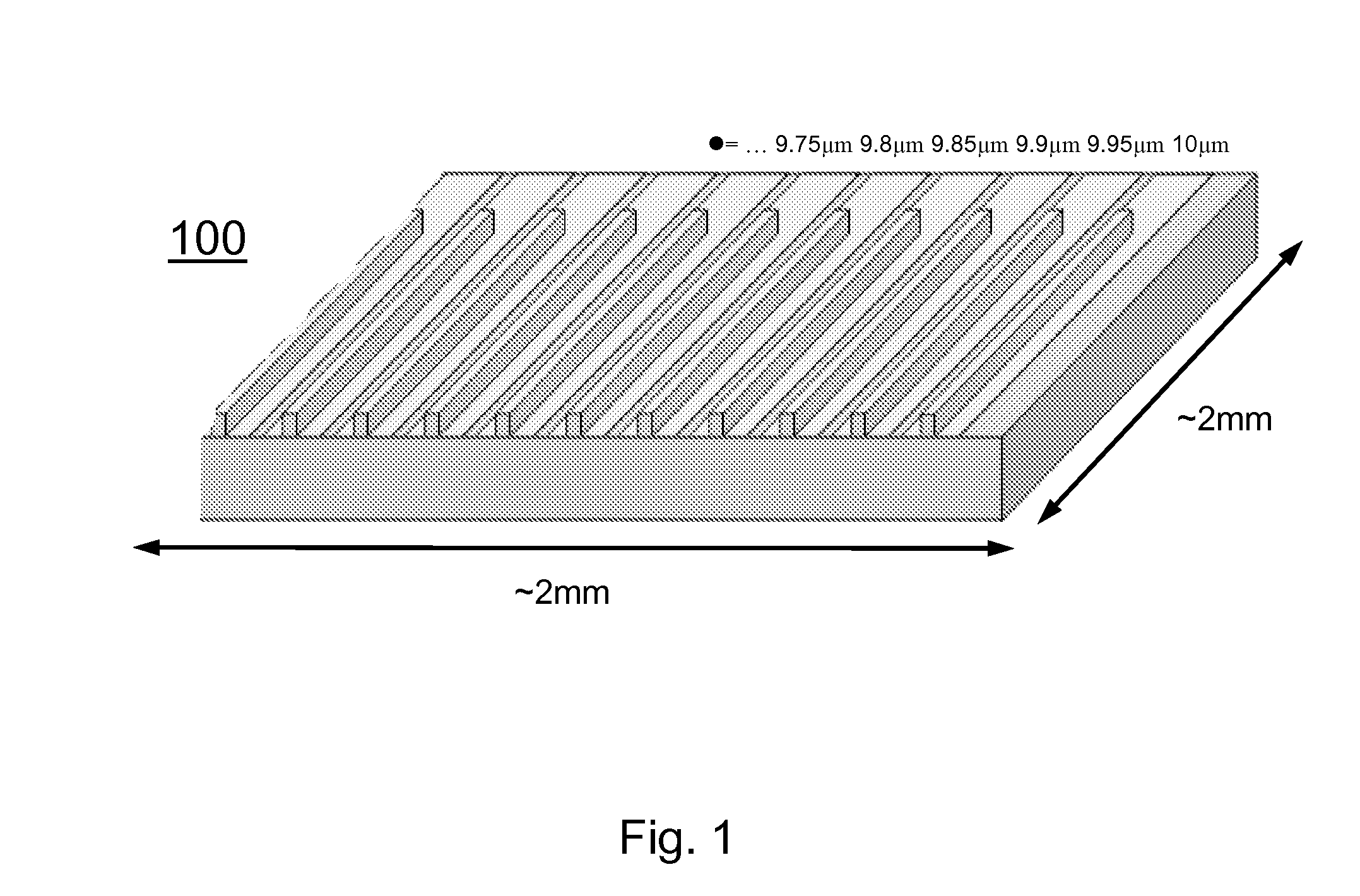
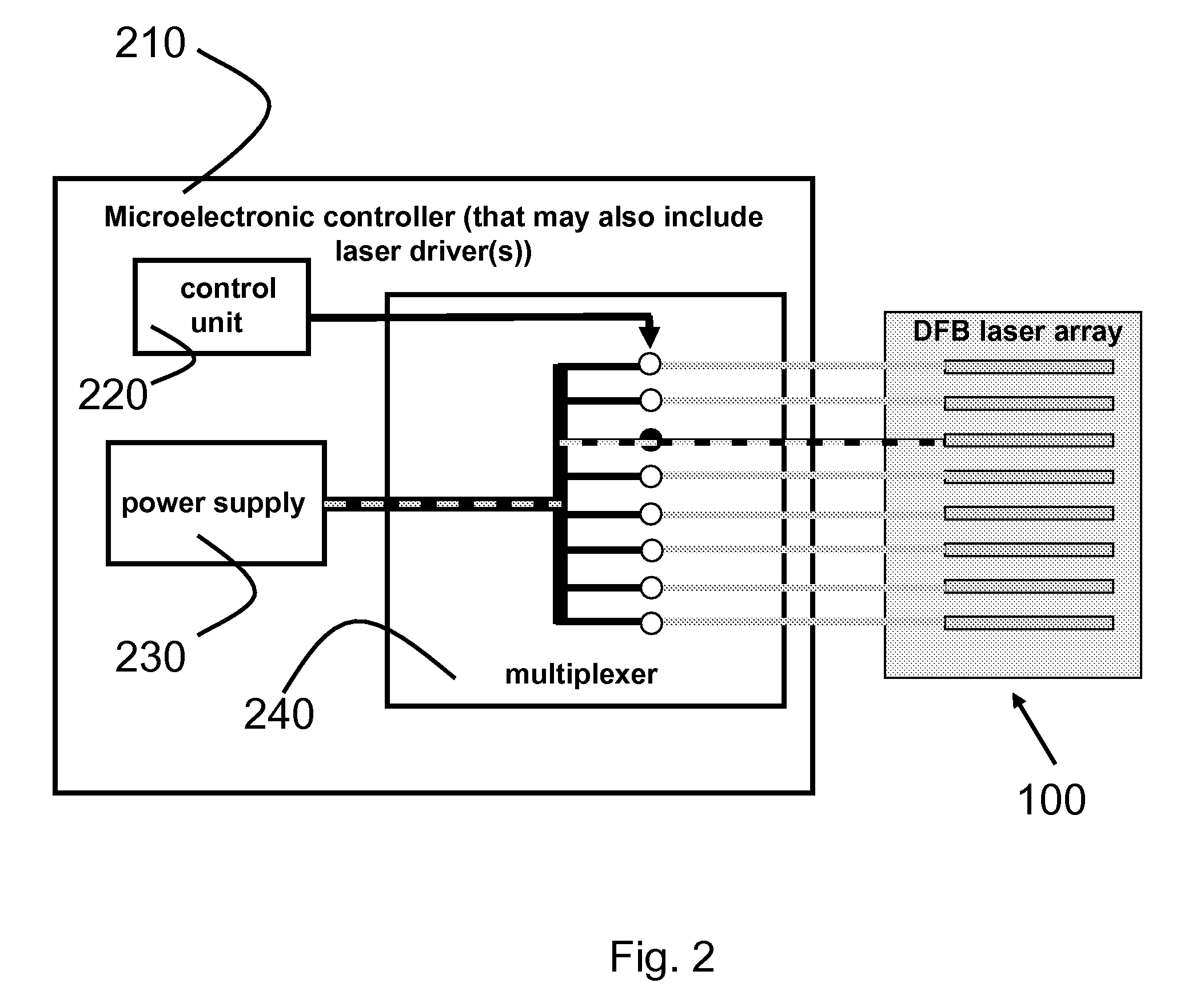
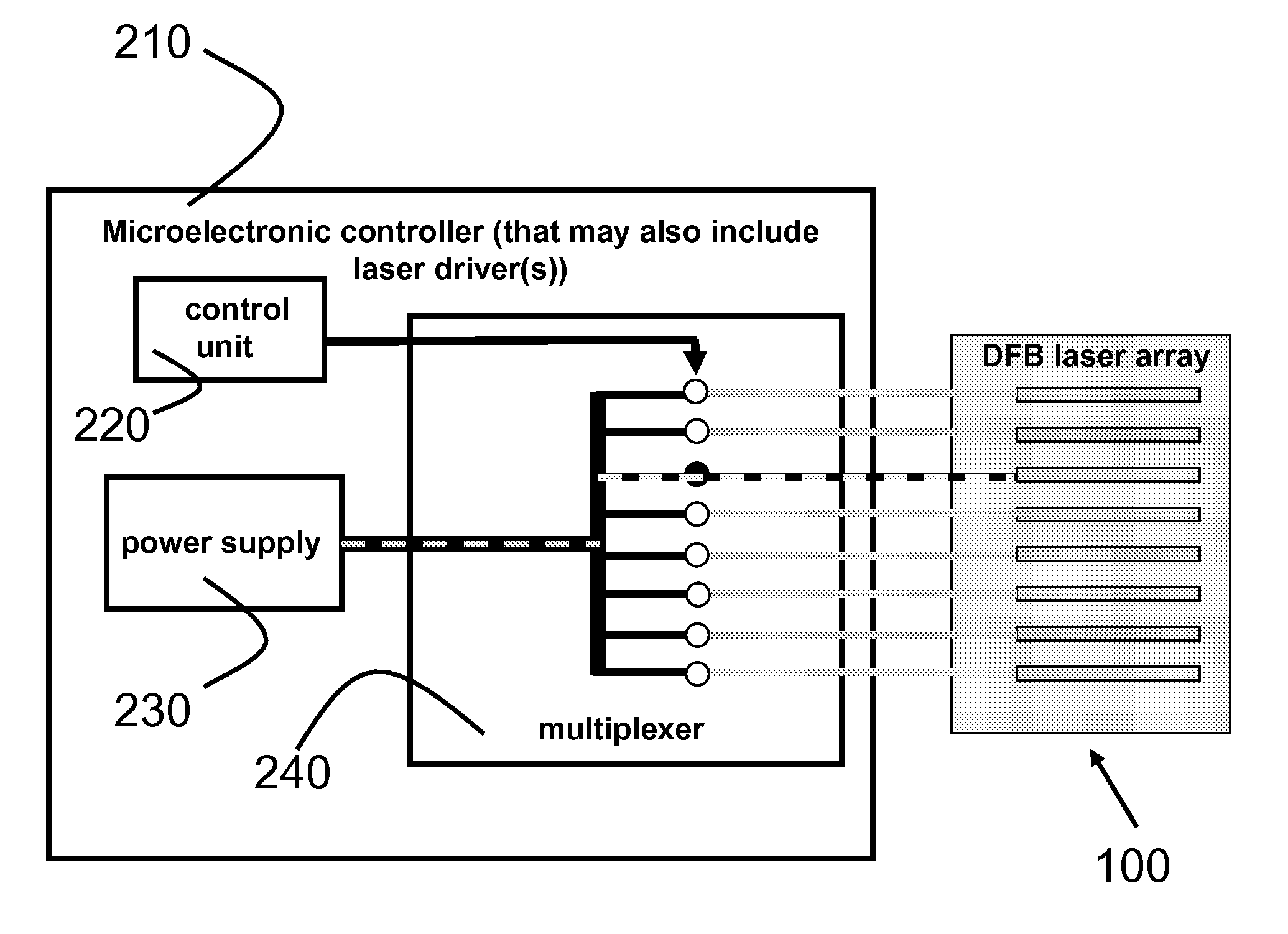
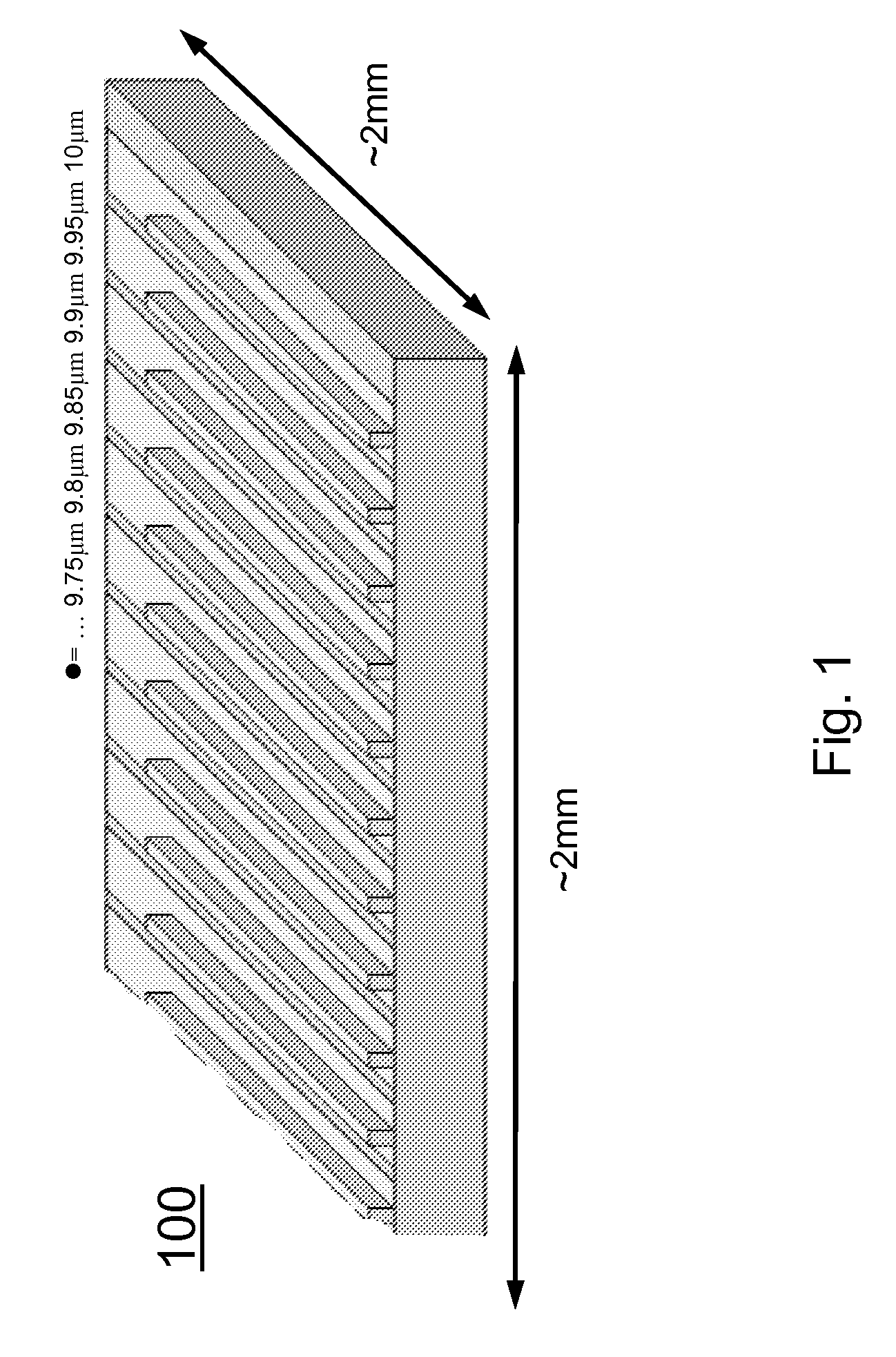
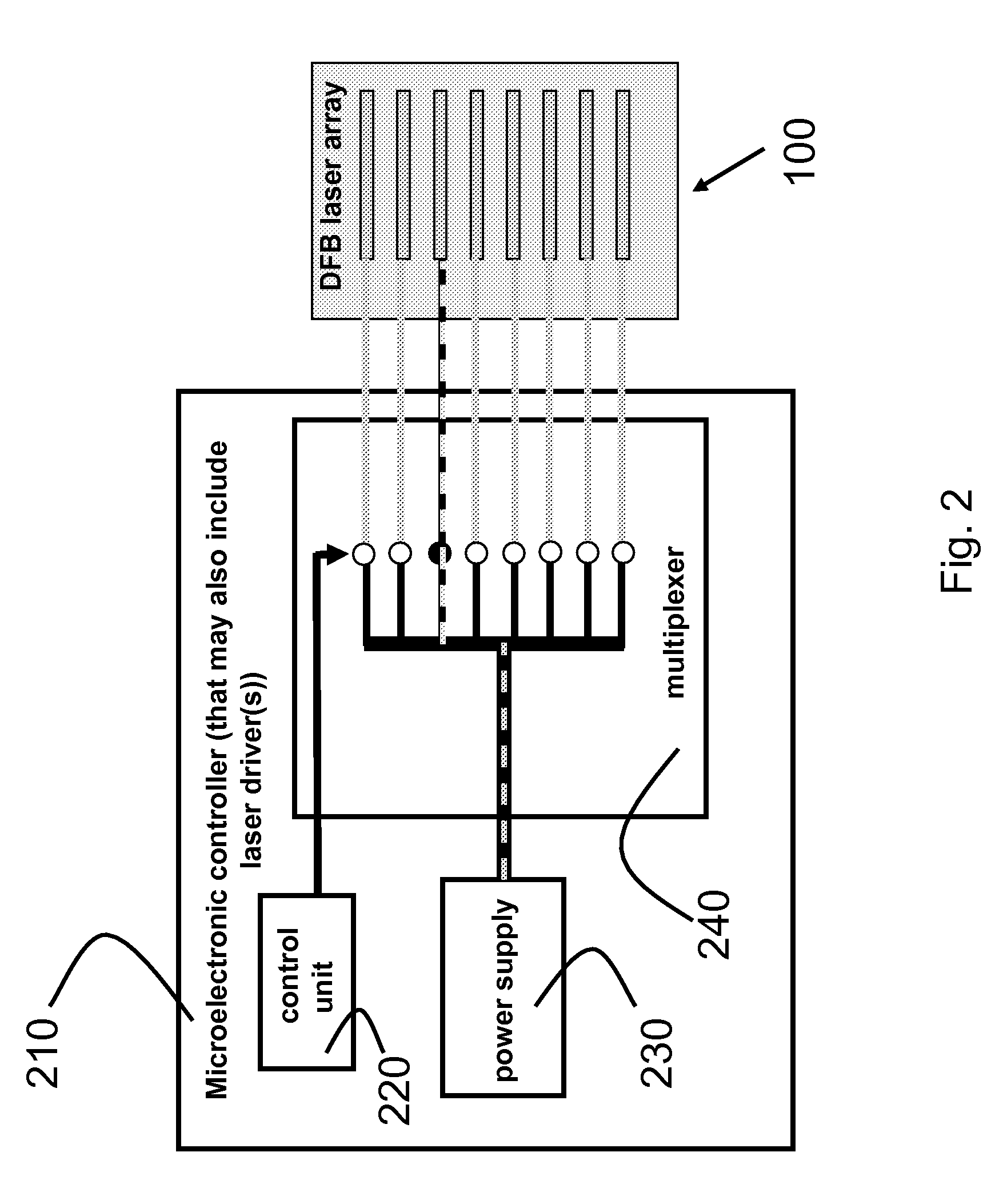
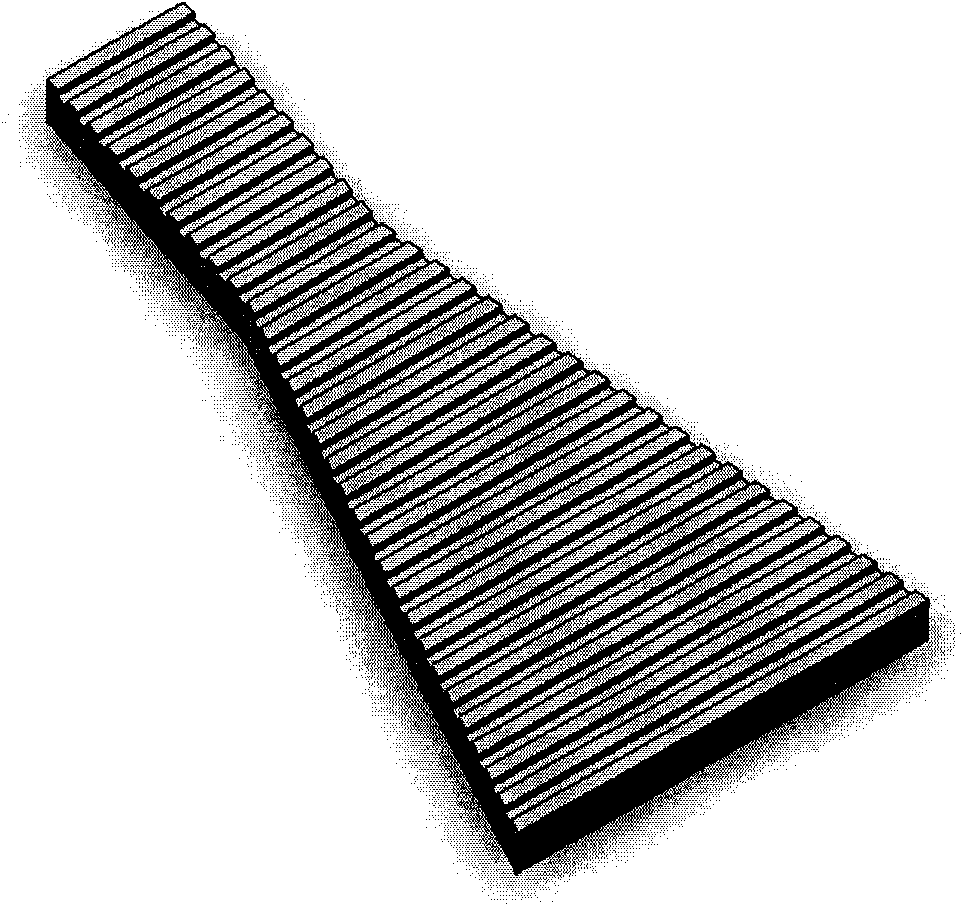
A broadly tunable single-mode infrared laser source based on semiconductor lasers. The laser source has two parts: an array of closely-spaced DFB QCLs (or other semiconductor lasers) and a controller that can switch each of the individual lasers in the array on and off, set current for each of the lasers and, and control the temperature of the lasers in the array. The device can be used in portable broadband sensors to simultaneously detect a large number of compounds including chemical and biological agents. A microelectronic controller is combined with an array of individually-addressed DFB QCLs with slightly different DFB grating periods fabricated on the same broadband (or multiple wavelengths) QCL material. This allows building a compact source providing narrow-line broadly-tunable coherent radiation in the Infrared or Terahertz spectral range (as well as in the Ultraviolet and Visible spectral ranges, using semiconductor lasers with different active region design). The performance (tuning range, line width, power level) is comparable to that of external grating tunable semiconductor lasers, but the proposed design is much smaller and much easier to manufacture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
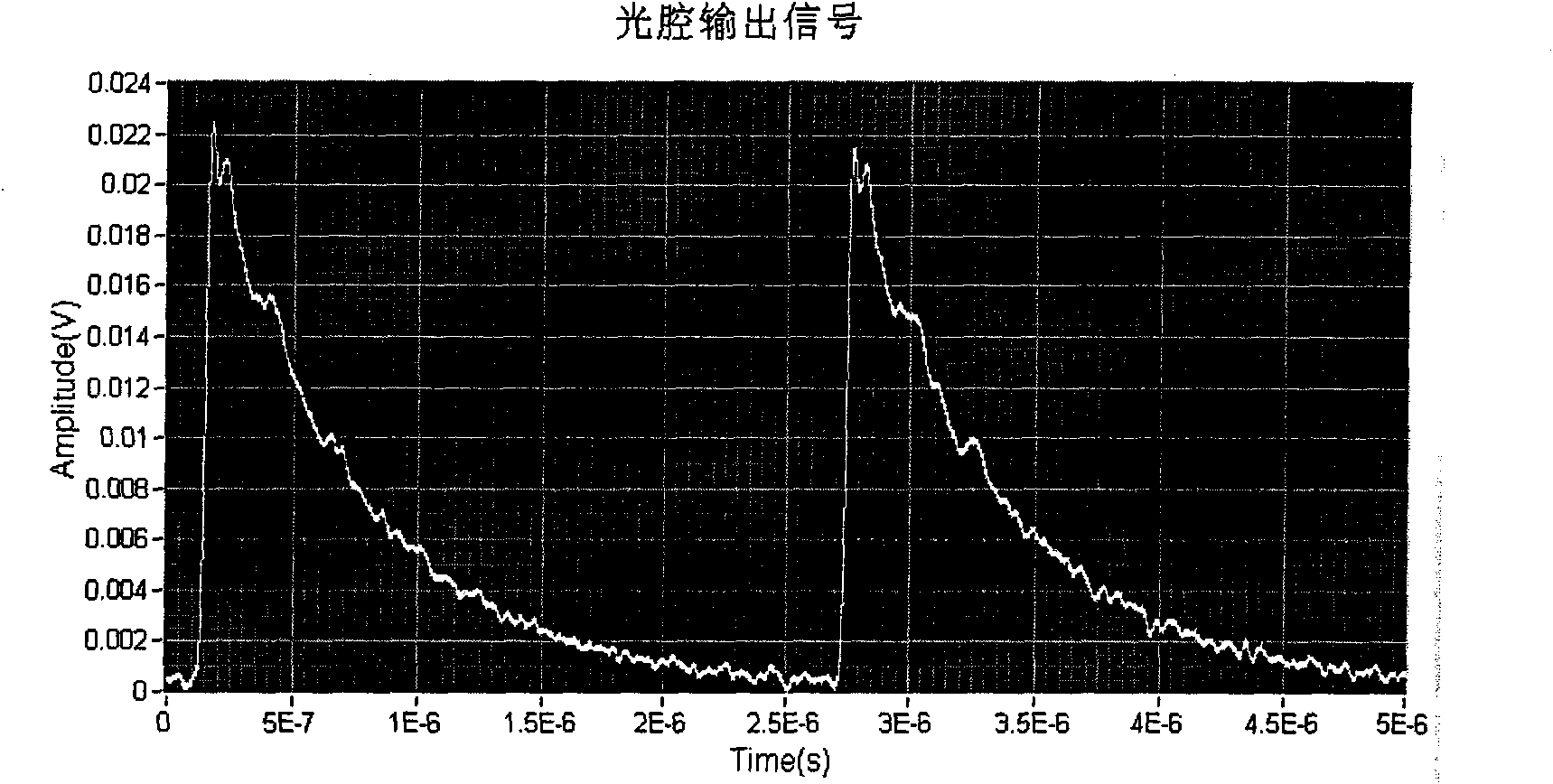
Infrared cavity ring-down spectroscopy trace gas detection method based on quantum cascade laser
InactiveCN101644673AEquivalent absorption lengthGood choiceColor/spectral properties measurementsAction spectrumPeak value
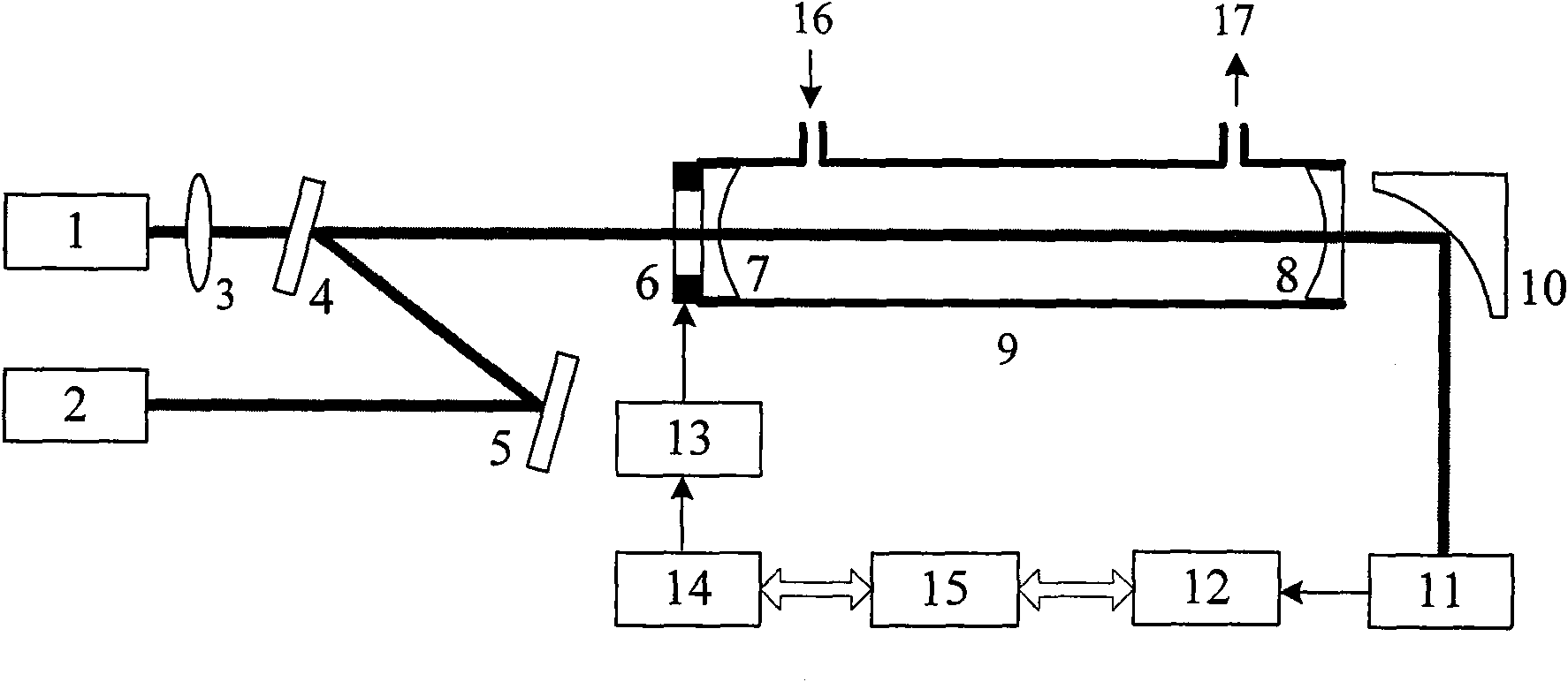
The invention discloses an infrared cavity ring-down spectroscopy trace gas detection method based on quantum cascade laser; comprising the following steps: using a tunable quantum cascade laser as alight source, and selecting measuring waveband and wavelength scan step length aiming at spectrum line characteristic of the gas to be detected; respectively measuring the cavity ring-down time of each wavelength in the cavity with absorption or without absorption by cavity ring-down technique, and calculating the gas absorption coefficient of corresponding wavelength so as to obtain a relation curve that is an absorption spectrogram of the measured gas absorption coefficient and toned laser wavelength. The spectrogram is contrasted with spectrum line characteristic of corresponding gas in HITRAN database, thereby being capable of analyzing and determining weather the measured gas contains the predetermined gas component; the absolute concentration of the gas to be measured can be calculated and obtained and the absolute concentration of the gas to be measured can be measured through scaling measurement by using absorption peak wavelength of the absorption spectrum as the best detection wavelength and the relation among the gas absorption coefficient of the wavelength, the absorption cross section and concentration. The method has high measuring sensitivity and high property of resisting interference so that the fast and exact on-line analysis and detection of multiple trace gases are easily realized.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
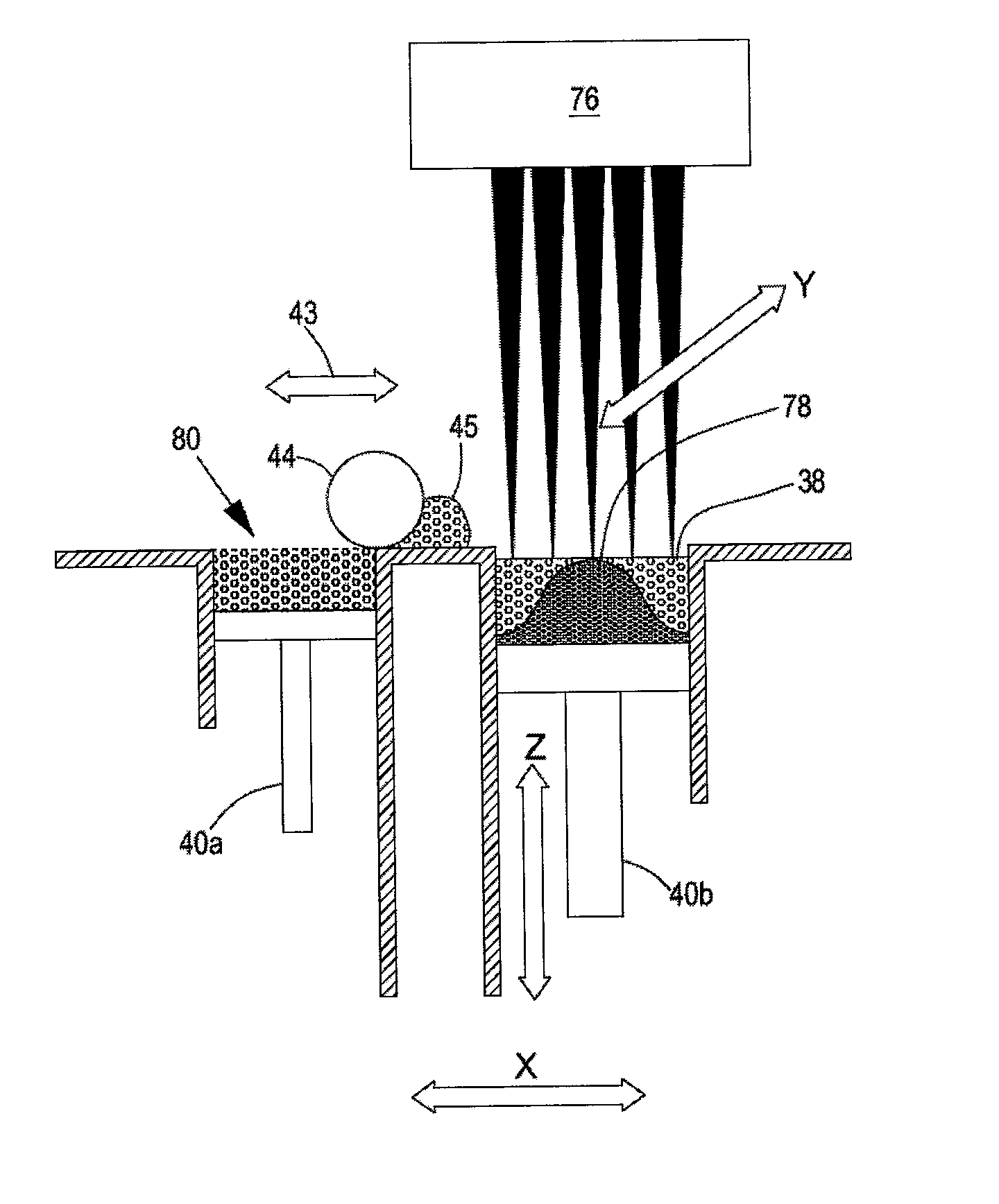
Apparatus and method for selective processing of materials with radiant energy
InactiveUS7823366B2Maximize contactReduce capacityWrappers shrinkageMechanical working/deformationControl systemDna testing
Apparatus selectively processes a substrate using radiant energy. The substrate can consist of any target material having a portion to be processed using the radiant energy and a larger portion to be unprocessed. The apparatus includes a source of radiant energy (preferably a quantum cascade laser) that has a customizable spectrum that can be configured to be specifically absorbed only by the portion to be processed, and a control system for targeting the radiant energy only at the portion to be processed. Specific examples of the use of the apparatus and method are in the technologies of heat-shrinking polyethylene film, fusing toner to paper in a laser printer, heating reaction vessels in DNA testing, and temperature profiling bottle pre-forms.
Owner:DOUGLAS MACHINE LIABILITY
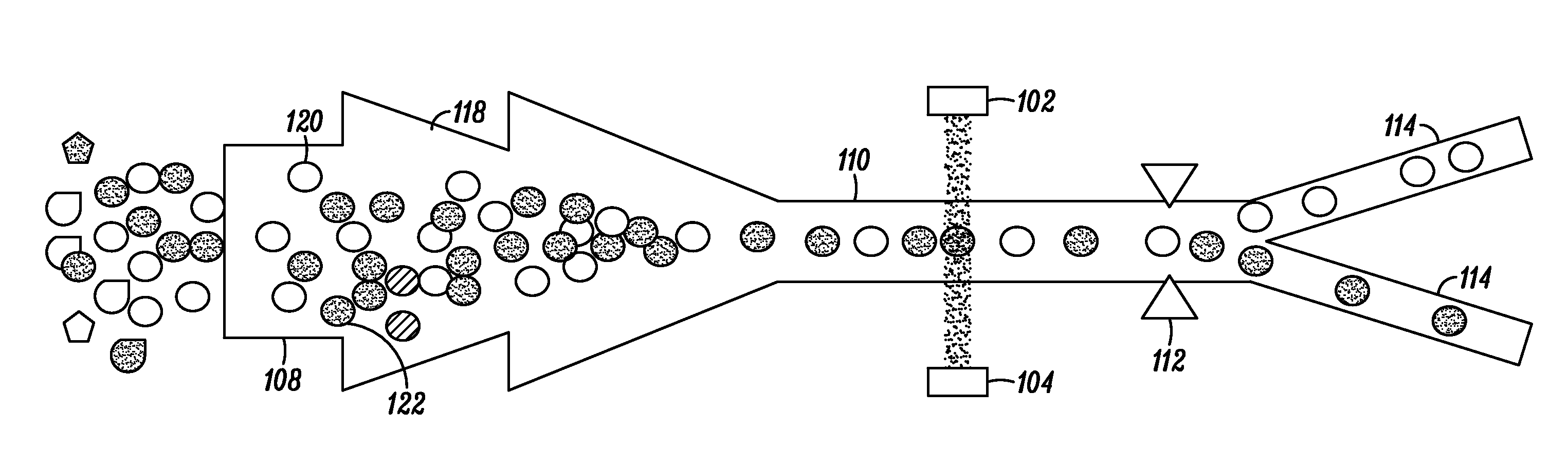
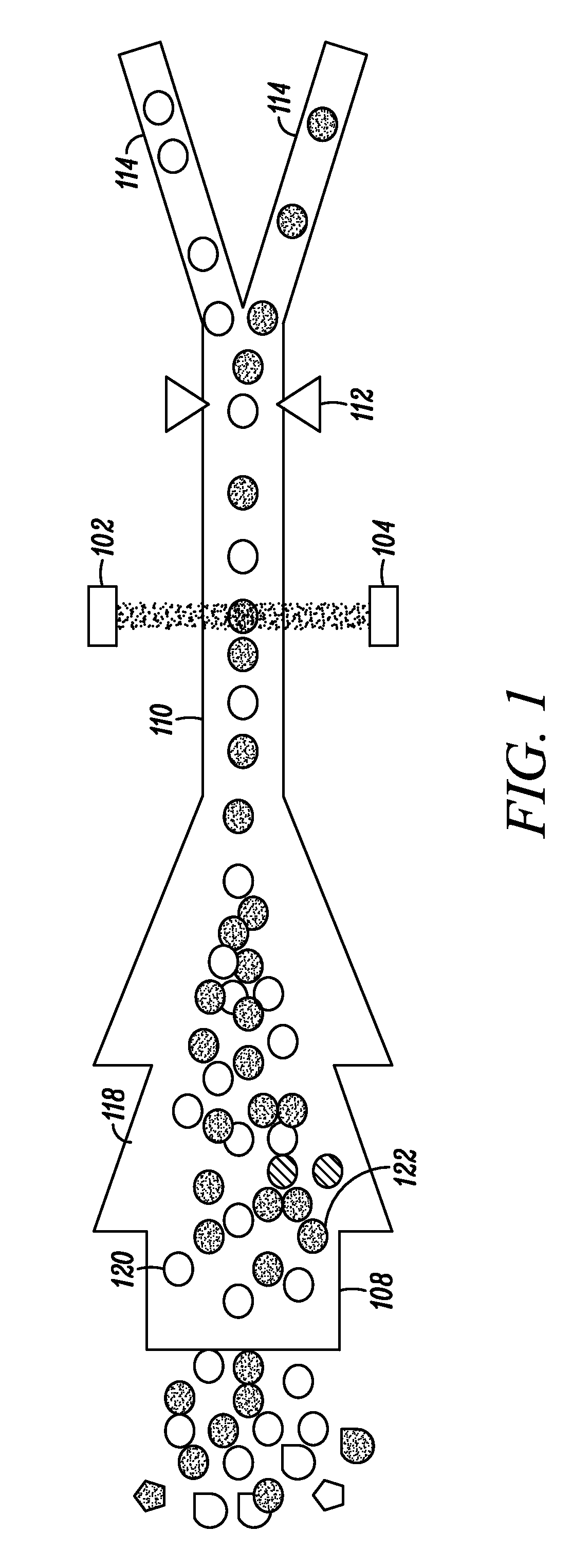
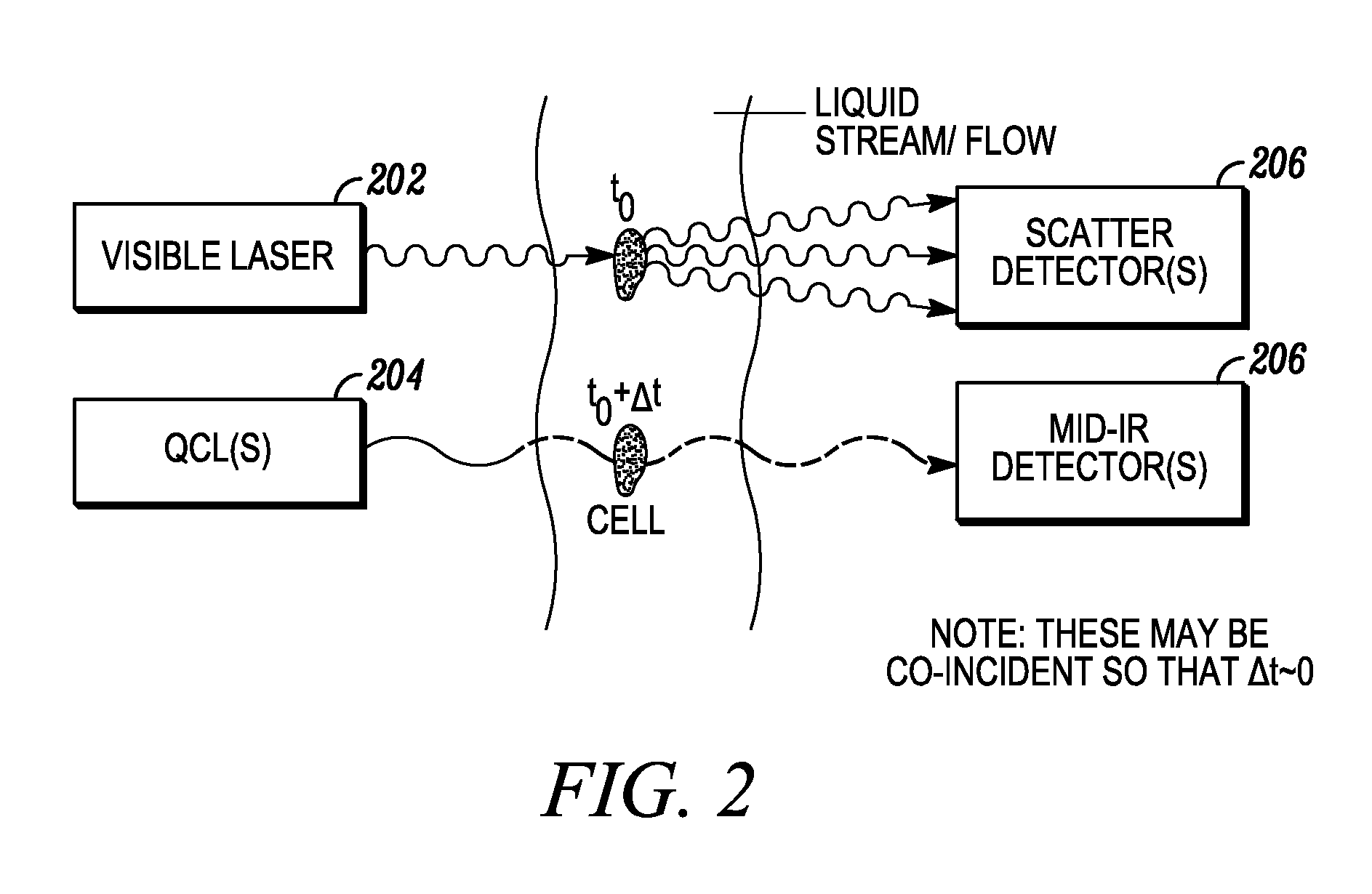
Combined inspection system including mid-ir vibrational spectroscopy and a fluorescent cytometry facility
InactiveUS20120196356A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalyteSpectroscopy
This disclosure concerns a cytometry system including a handling system that presents single cells to at least one quantum cascade laser (QCL) source. The QCL laser source configured to deliver light to a cell within the cells in order to induce resonant mid-infrared absorption by one or more analytes of the cell. The system includes a laser source that excites at least one fluorophore present in the cell or on the surface of the cell and a fluorescence detector that measures the fluorescence intensity of the fluorophore. A mid-infrared detection facility detects the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light and the fluorescence intensity are used to identify at least one cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
External cavity tunable compact Mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7535936B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
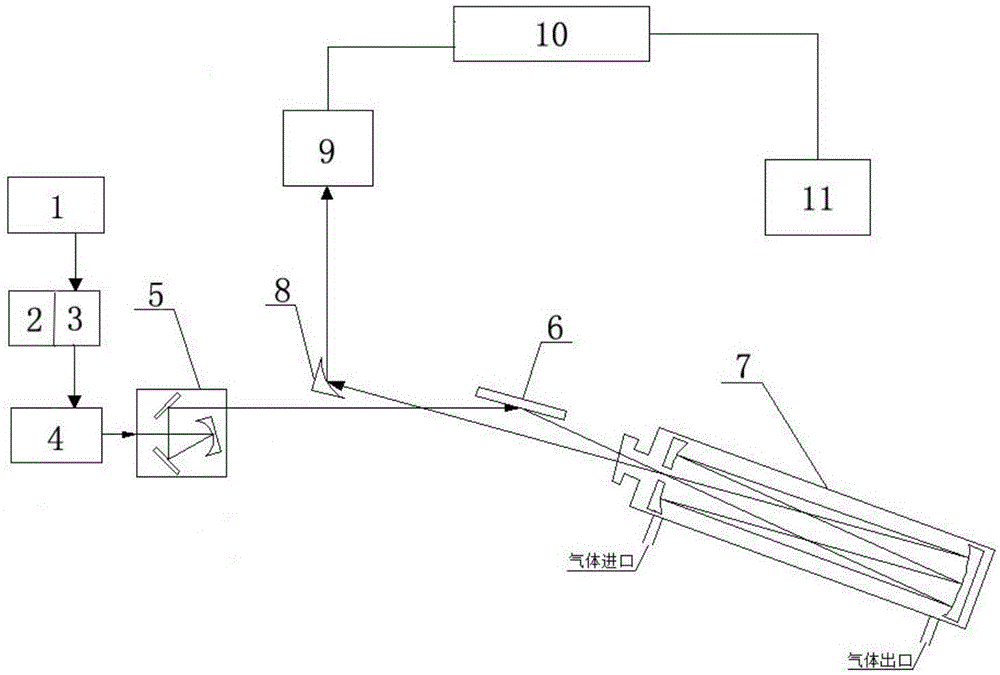
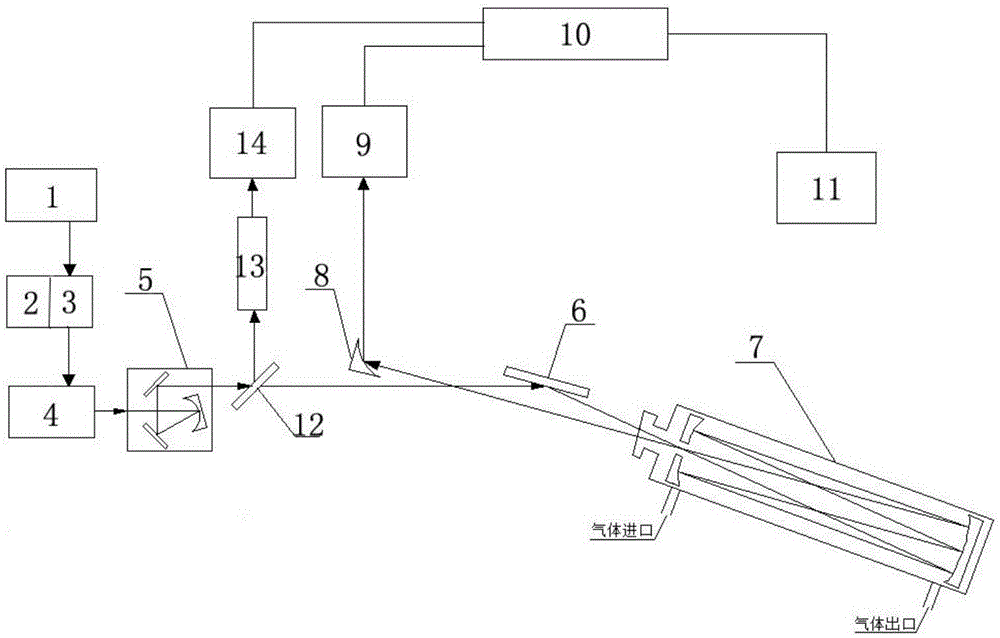
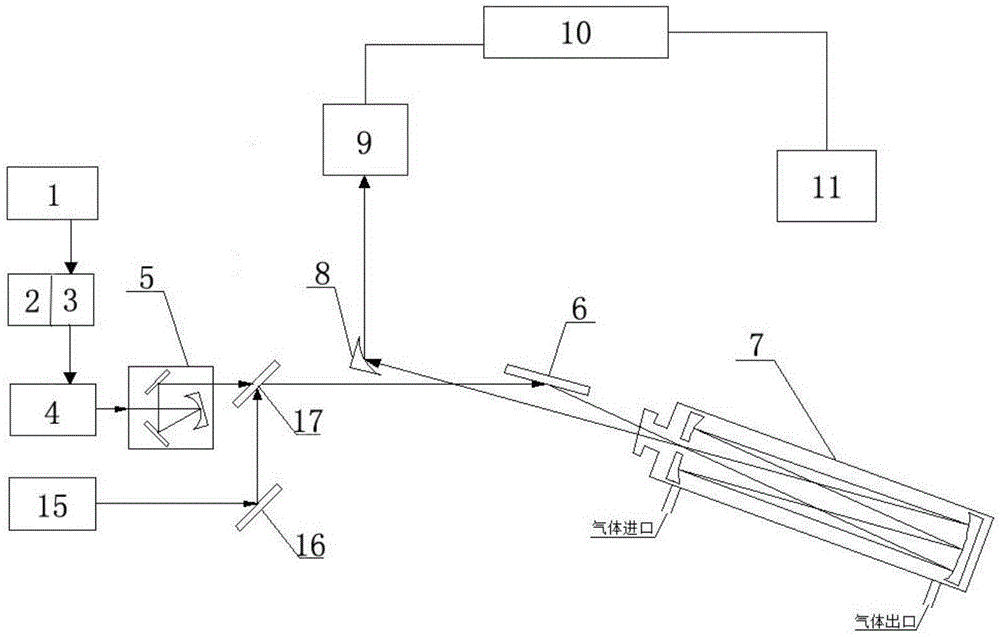
Two quantum cascade laser spectrum-based multicomponent gas simultaneous detection device and method
ActiveCN105277503AEfficient detectionAvoid absorbing interference effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsQuantum cascade laser
The present invention relates to the technical field of laser spectrum detection and gas detection, and in particular relates to a two quantum cascade laser spectrum-based multicomponent gas simultaneous detection device and method. An arbitrary waveform function generator outputs a periodic signal which only superposes high-frequency modulation signals in any half period to be used as a laser current signal, a room temperature continuous mode mid-infrared quantum cascade laser is driven by a current control unit, the laser emits a laser signal, the laser signal passes sequentially through a focusing collimating three-dimensional adjustment system, a first mirror, a sample absorption pool and a off-axis parabolic mirror to be reflected to a first detector, the first detector passes the laser signal through a data acquisition unit to convert into an electrical signal and transmit to a computer, and information of the gas to be measured can be obtained by analysis and processing of the electrical signal by the computer. The devices simultaneously utilizes two spectrums for gas detection, and has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, high detection accuracy, no need of external standard gas calibration, simple optical path adjustment, fast response, and stability, and the like.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
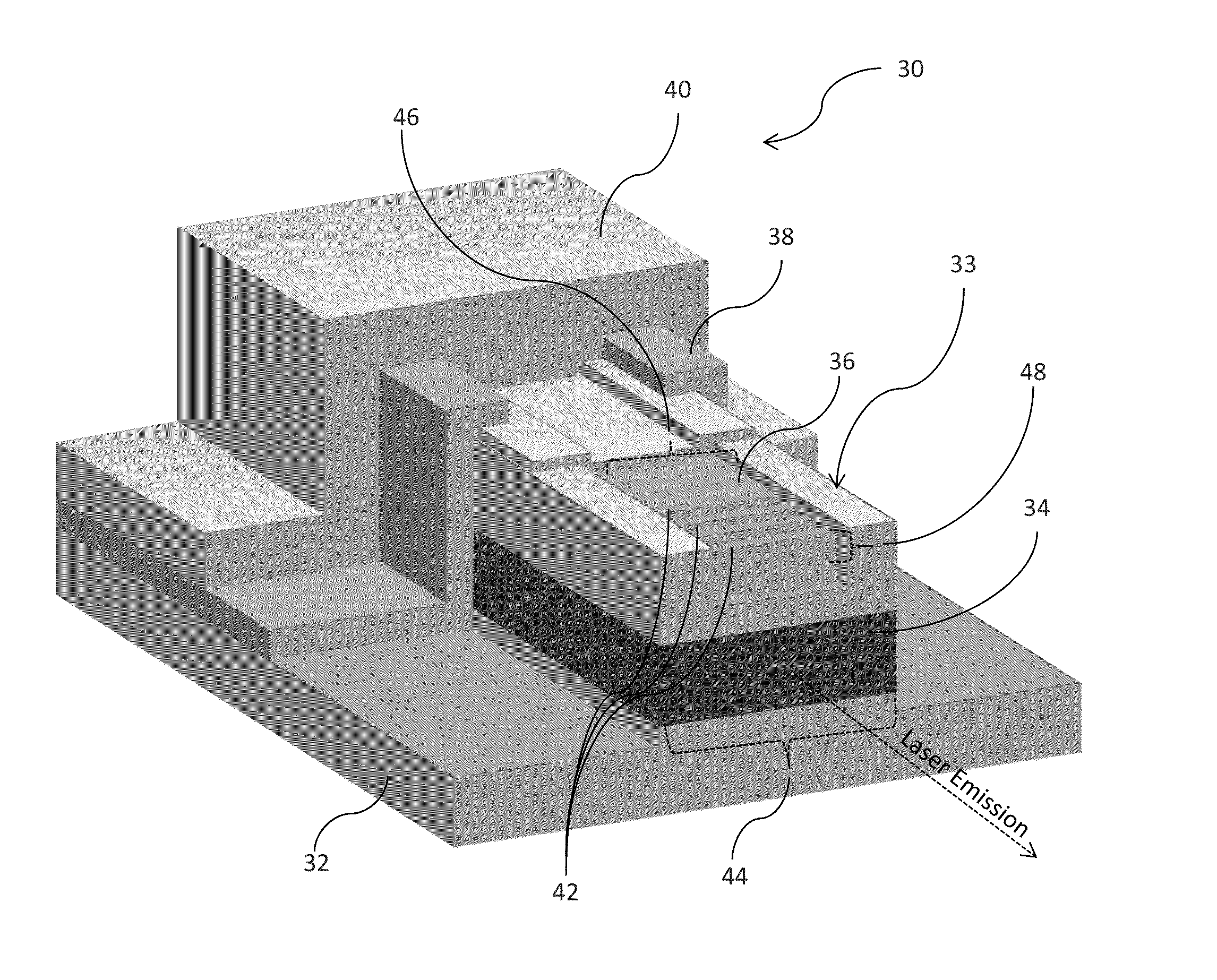
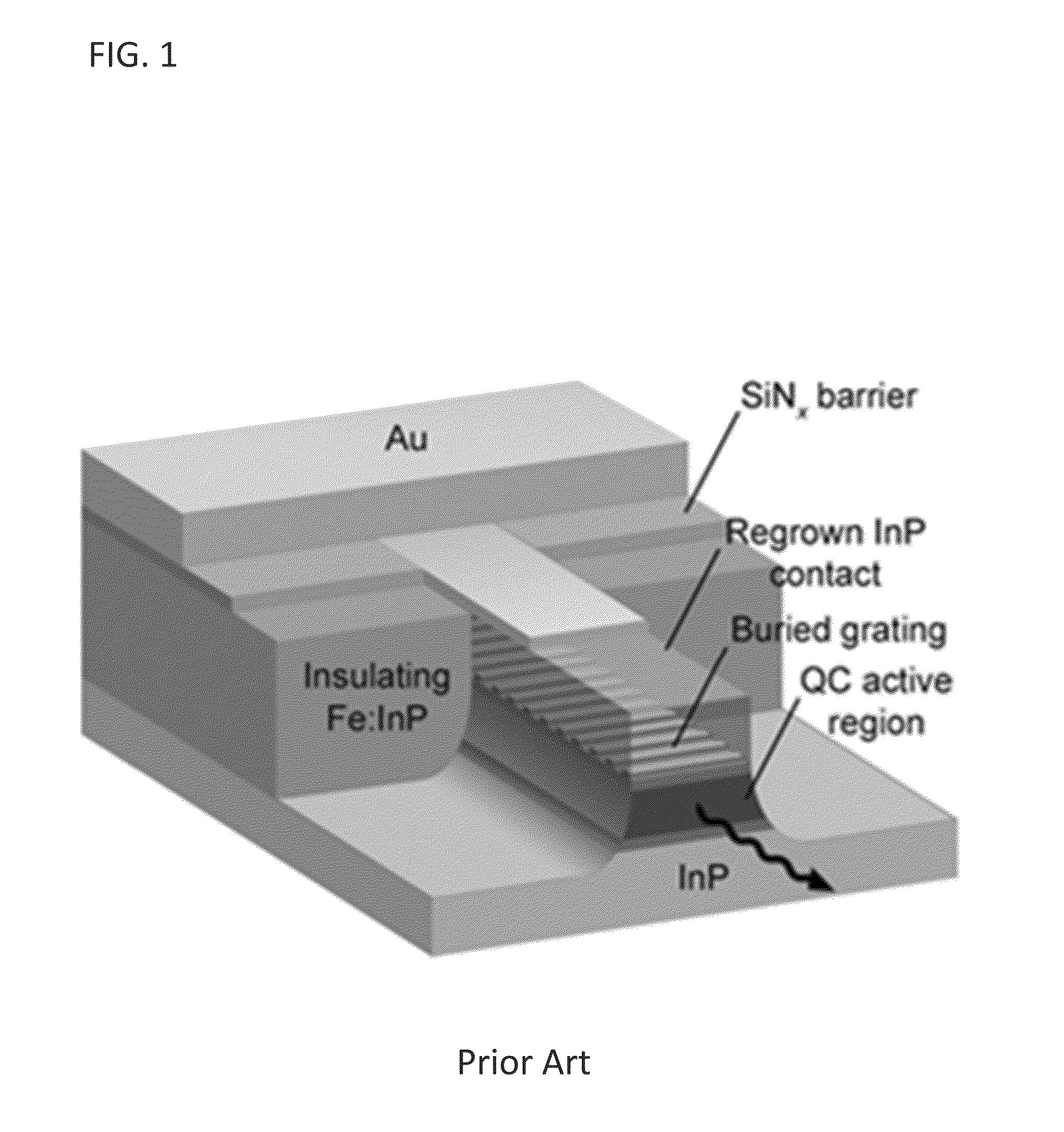
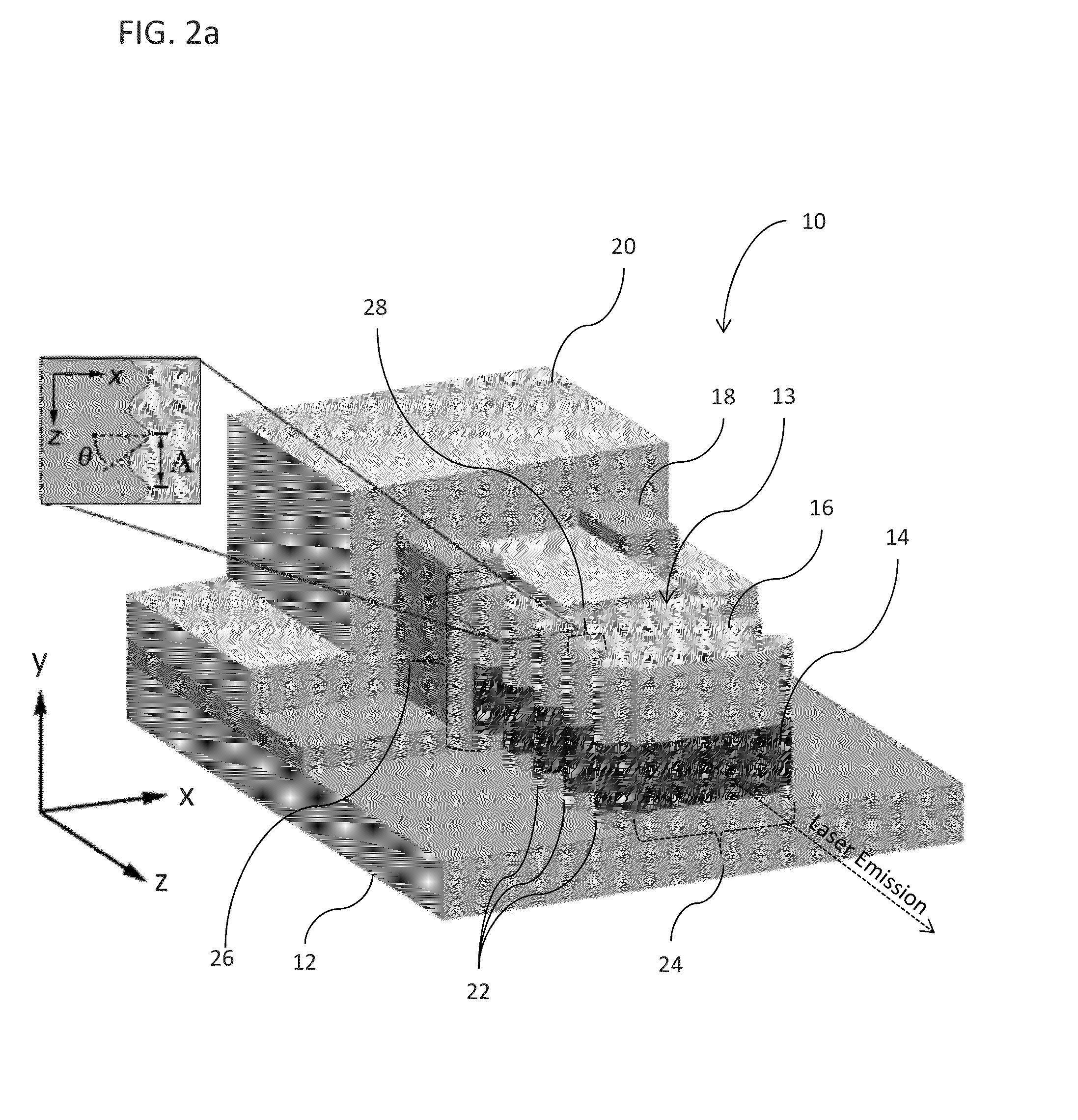
Index-coupled distributed-feedback semiconductor quantum cascade lasers fabricated without epitaxial regrowth
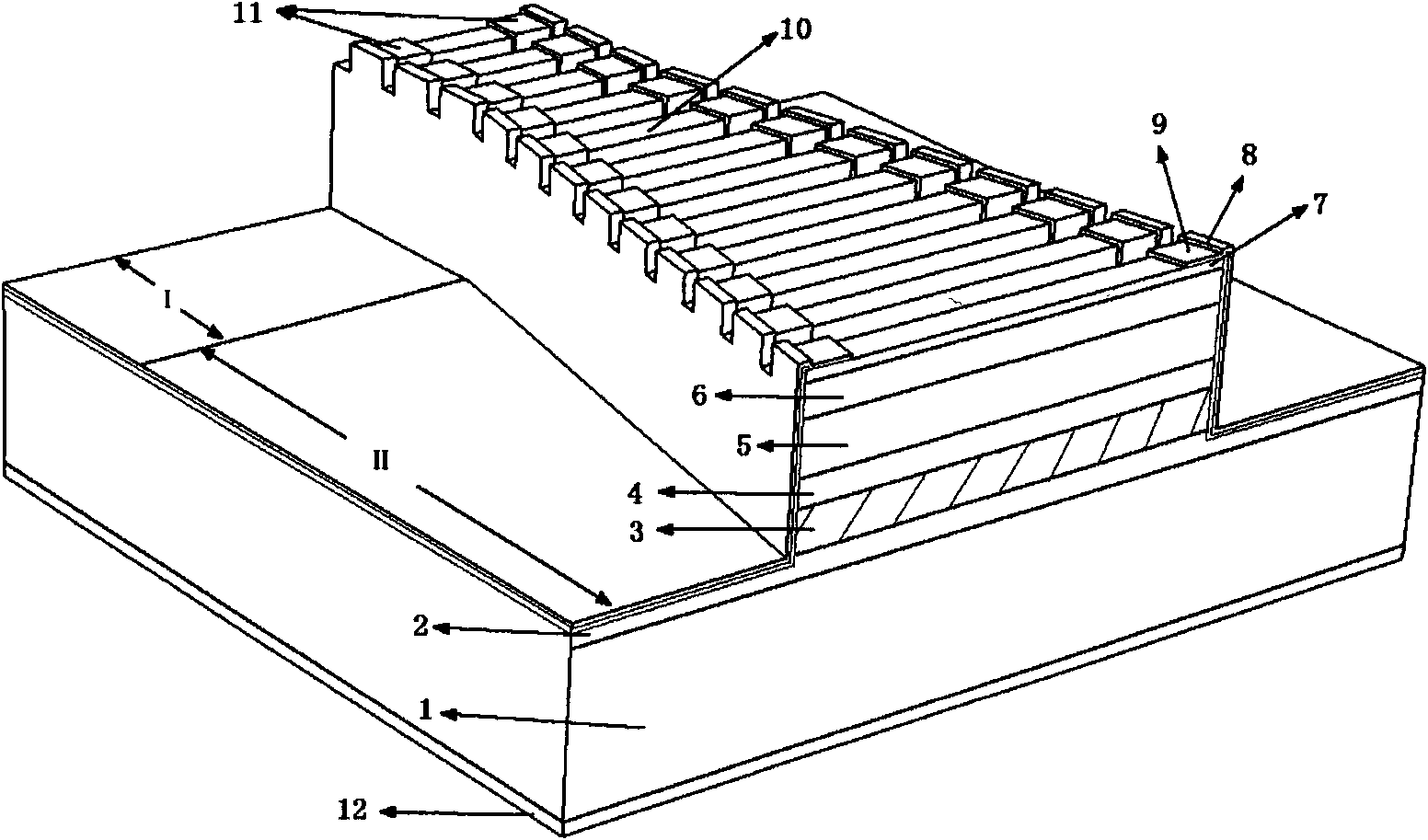
Quantum cascade (QC) lasers and methods of fabricating such QC lasers are provided. The QC lasers incorporate a DFB grating without requiring the use of relying on epitaxial regrowth processes. The DFB gratings are formed as sidewall gratings along the lateral length of the QC active region, or the DFB gratings are formed atop the lateral length of the QC active region, and wherein the top DFB grating is planarized with a polymeric material.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Device and a method for 3D printing and manufacturing of materials using quantum cascade lasers
ActiveUS20160082662A1More compact in sizeAbsorption of radiant energyAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor laser arrangementsChannel powerEngineering
A 3D printer device utilizing at least one Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) image head having at least one beam focused in a focal plane of the device for building on a surface of the device a 3D model of a target object from a digital image. The inventive 3D printer is more compact in size due to the use of QCL image heads, which provides focused wavelengths of QCLs matching the absorption properties in plastics for more efficient absorption of the radiant energy. Each QCL channel power in the inventive 3D printer can be doubled by combining two lasers with a polarization beam splitter. The QCL image head is provided with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) for compensating for imaging speed. The invention includes a method for scaling up the building speed of 3D printing regardless of detail level. The invention discloses an affordable 3D printer using QCL technology while maintaining high standards of resolution, use of quality materials, and rapid building speeds.
Owner:3DM DIGITAL MFG LTD
Broadly tunable single-mode quantum cascade laser sources and sensors
ActiveUS7826509B2Easy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingLine width
A broadly tunable single-mode infrared laser source based on semiconductor lasers. The laser source has two parts: an array of closely-spaced DFB QCLs (or other semiconductor lasers) and a controller that can switch each of the individual lasers in the array on and off, set current for each of the lasers and, and control the temperature of the lasers in the array. The device can be used in portable broadband sensors to simultaneously detect a large number of compounds including chemical and biological agents. A microelectronic controller is combined with an array of individually-addressed DFB QCLs with slightly different DFB grating periods fabricated on the same broadband (or multiple wavelengths) QCL material. This allows building a compact source providing narrow-line broadly-tunable coherent radiation in the Infrared or Terahertz spectral range (as well as in the Ultraviolet and Visible spectral ranges, using semiconductor lasers with different active region design). The performance (tuning range, line width, power level) is comparable to that of external grating tunable semiconductor lasers, but the proposed design is much smaller and much easier to manufacture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Trace gas detection device and method based on intermediate infrared quantum cascade laser direct absorption spectrum method
ActiveCN102175641AFull absorption lineIncreased absorption pathlengthColor/spectral properties measurementsAnti jammingLight spot
The invention discloses a trace gas detection device and a trace gas detection method based on an intermediate infrared quantum cascade laser direct absorption spectrum method. A tunable quantum cascade laser serves as a light source, and concentration information of gas molecules to be measured is acquired by utilizing fundamental frequency fingerprint absorption characteristics of the gas molecules in an intermediate infrared wave band; the measured result is slightly influenced by light-intensity variation of the laser and has higher signal to noise ratio and certain anti-jamming capability by utilizing a direct absorption spectrum technology; and whether the measured gas contain expected gas components can be analyzed and determined by contrasting the measured spectrum with spectral line characteristics of corresponding gas in a HITRAN database, and concentration inversion is performed by utilizing spectral line parameters provided by the HITRAN database. The system is simple and compact in structure and convenient to use and maintain, has the characteristics of high measuring sensitivity, high accuracy and high response speed, can rapidly and accurately analyze and detect a plurality of trace gases and isotope ratios on line, and can be used for indicating and rapidly and accurately positioning intermediate infrared light spots.
Owner:合肥中科环境监测技术国家工程实验室有限公司
Mid-infrared spectroscopy-based trace gas detection method and device combining long-optical-path open light path with wavelength modulation technique
InactiveCN104596987AReal-time concentration change informationOnline Concentration Change InformationColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterPlane mirror
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
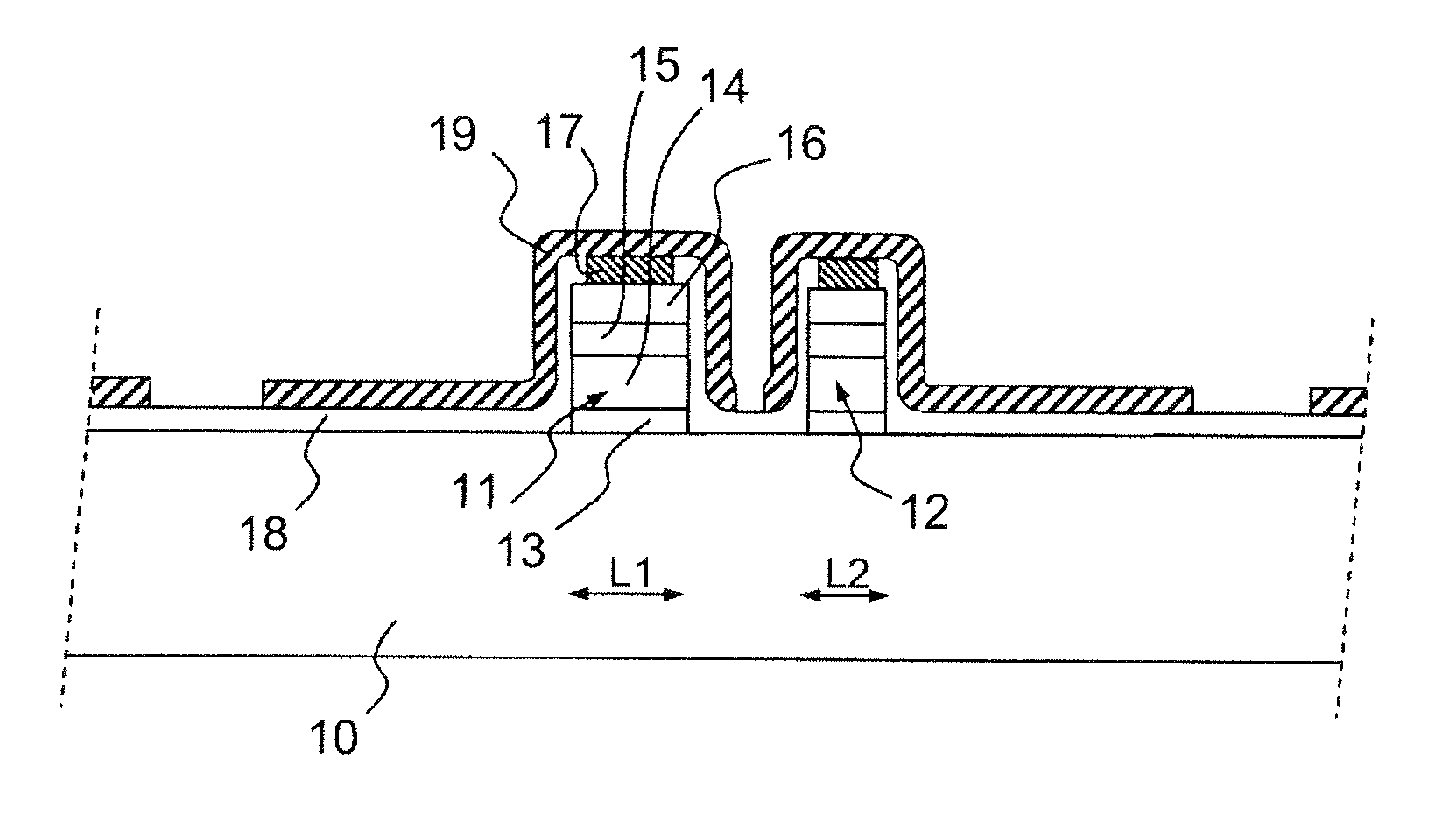
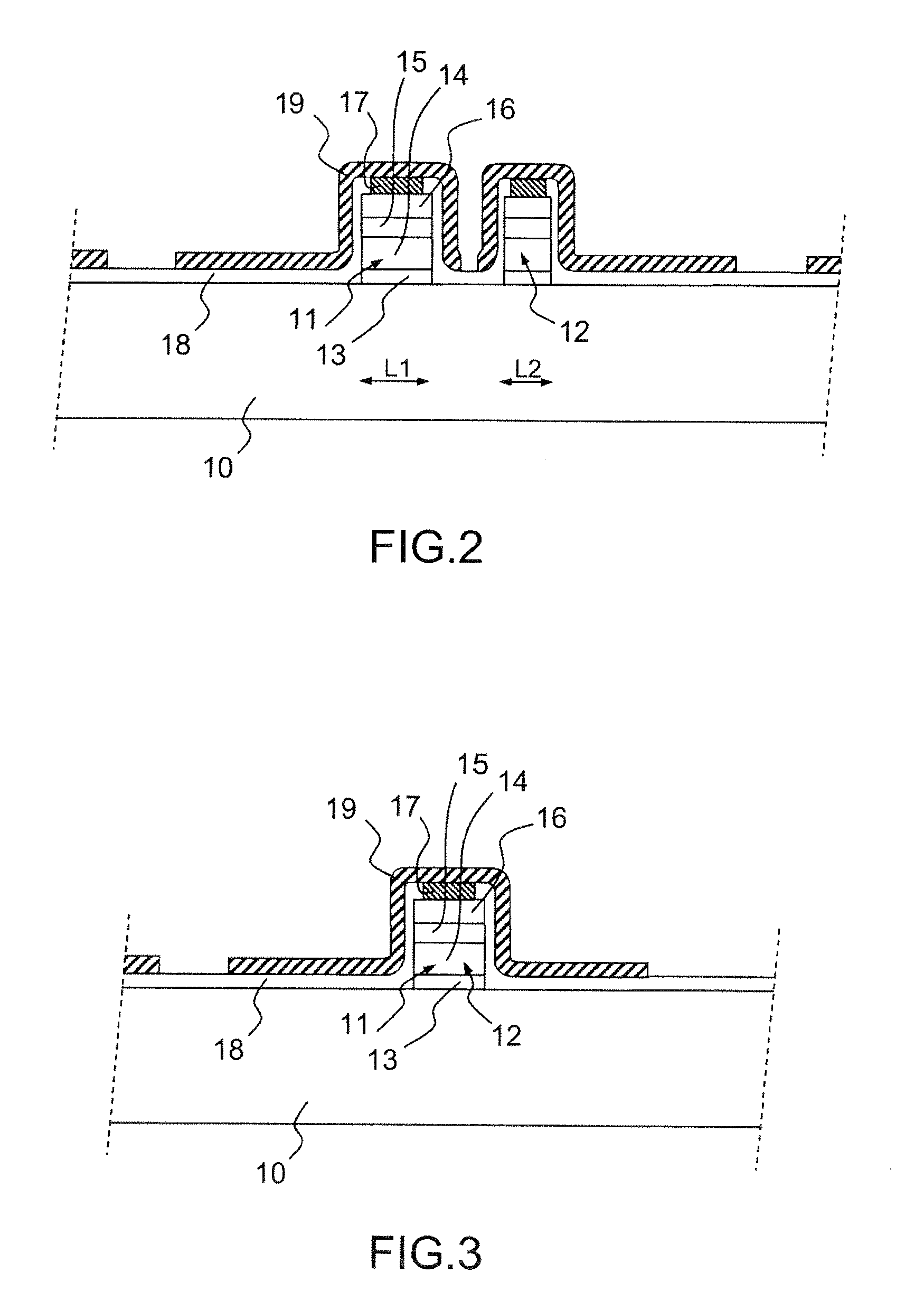
Method of fabricating an optical analysis device comprising a quantum cascade laser and a quantum detector
InactiveUS20100029026A1Wave based measurement systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMid infraredLight beam
The invention relates to a method of fabricating an optical device for analysing a scene, comprising an emitter and a detector in the mid-infrared or far-infrared, characterized in that it comprises:the production of a stack of semiconductor layers grown epitaxially on the surface of a semiconductor substrate, certain layers of which are doped;the production of a first, quantum cascade laser emission device (L) emitting an analysis beam in the mid-infrared or far-infrared, from a first level called the emission level, into the stack of semiconductor layers; andthe production of a second, quantum detector device (D) capable of detecting a beam backscattered by the scene to be analysed, at the same level in the stack as the emission level.
Owner:THALES SA
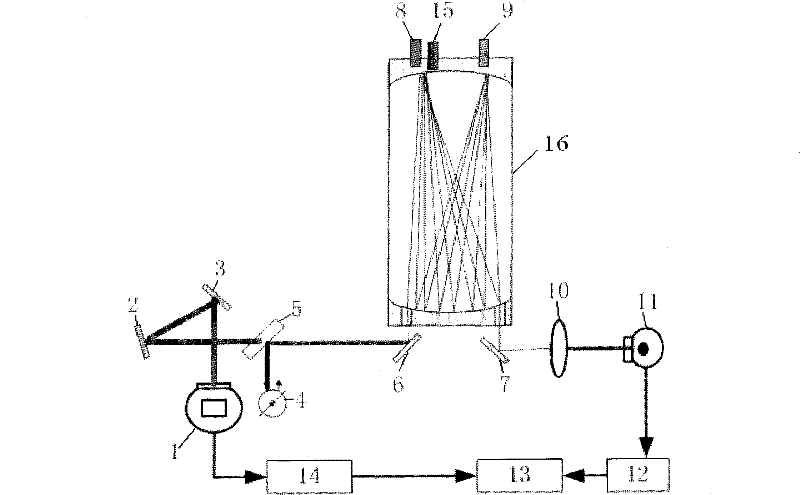
Method and Apparatus for the Detection of Trace Gas Species Using Multiple Line Integrated Absorption Spectroscopy
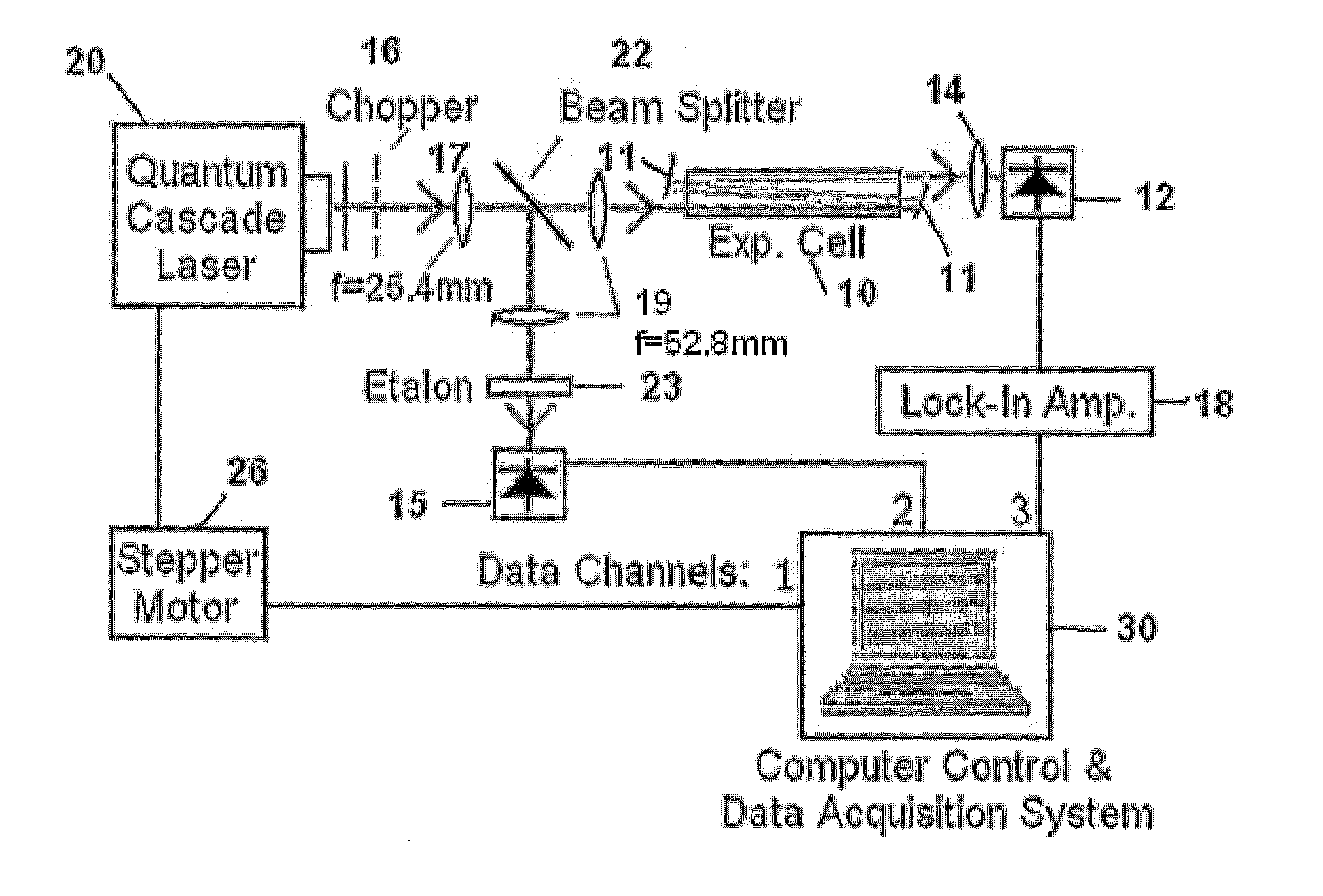
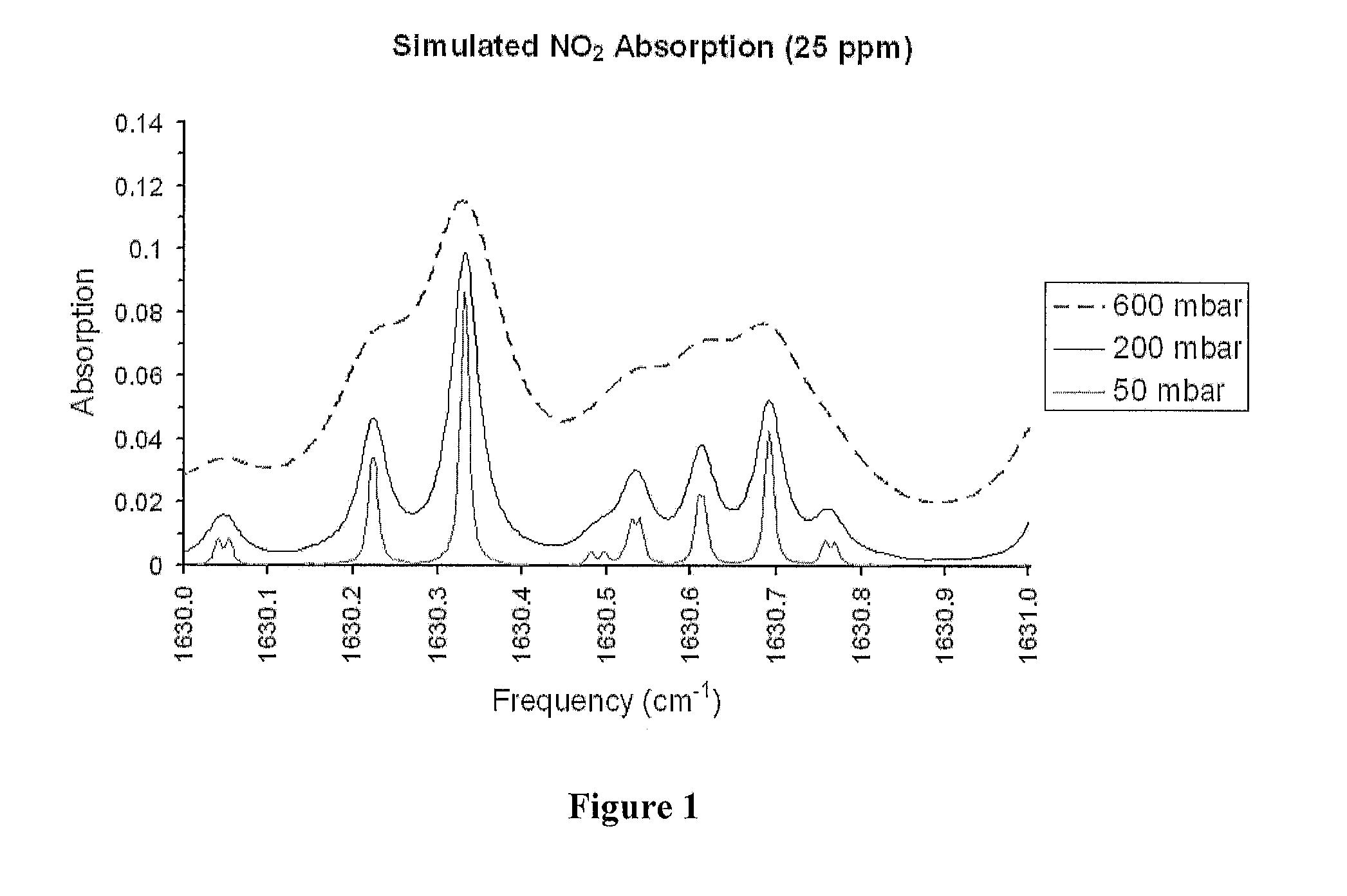
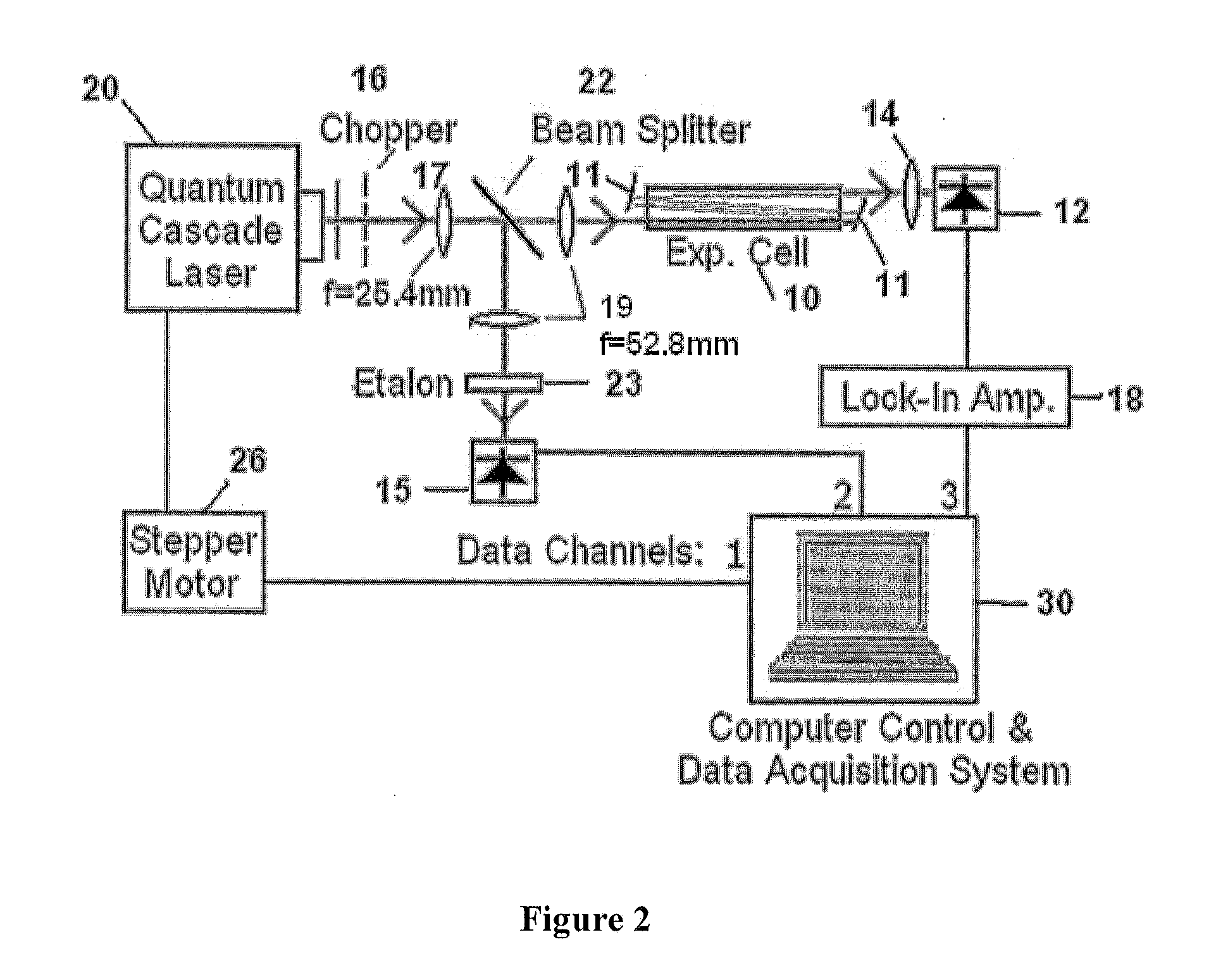
InactiveUS20120062895A1Improve accuracyHigh detection sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsAir quality improvementData acquisitionQuantum cascade laser
An apparatus and method are used to enhance the sensitivity of a spectrometer (sensor) for trace gas species detection by employing an external cavity continuously tunable CW quantum cascade laser and integrating the absorption spectra across multiple lines of the species. With this method the absorption spectra of NO2 is continuously recorded across the R-branch from 1628.8 cm−1 to 1634.5 cm−1. By integrating the resulting spectra, the detection sensitivity for NO2 is improved by a factor of 15 compared to the sensitivity achieved using single line laser absorption spectroscopy with the same apparatus. This procedure offers much shorter data acquisition times for the real-time monitoring of trace gas species compared with adding repeated scans of the spectra to improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:ADELPHI UNIVERSITY
Device and method for non-invasive glucose monitoring
InactiveUS20150112170A1Avoid mistakesReduce exposureSensorsBlood characterising devicesFiberDisplay device
A device and method for non-invasively measuring analytes and physiological parameters by measuring terahertz radiation emitted though biological tissue. Terahertz pulses are emitted from a miniaturized quantum cascade laser to a fiber optic array into the wrist of the user. A corresponding sensor on the opposite side of the wrist receives the terahertz signals that have been modified by interacting with organic molecules. The data from the sensor is compiled and analyzed on a RAM chip and logic chip, where a program uses an algorithm to compare measurements to a library of existing measurements and topographic maps generated when the user first dons the device. Once the algorithm has parsed all the data points, a value, such as blood glucose level, appears on a display of the device. The device may be equipped with a gasket to reduce ambient light from contacting the sensor.
Owner:AMERSON
Tapered photonic crystal quantum cascade laser and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN102055135ANovel structureSimple structureOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsInsulation layerOhmic contact
The invention discloses a tapered photonic crystal quantum cascade laser for outputting near-diffraction-limited beams and the manufacture method thereof. The laser comprises a substrate, as well as a lower waveguide layer, an active area, an upper waveguide layer, an upper cover layer, an upper contact layer, an ohmic contact layer, an electrical insulation layer, a front side electrode and a rear side electrode on the substrate. The laser has the ridge-shaped mesa double-grooved waveguide structure, wherein the ridge-shaped mesa structure includes a main control oscillation area with a uniform ridge width and a gain amplification area with a tapered structure. The photonic crystal structure is used for providing a distributed feedback waveguide manufactured between the upper contact layer and the ohmic contact layer. The tapered photonic crystal quantum cascade laser can acquire singe-mode near-diffraction-limited beam output. The waveguide structure with the combination of the ridge-shaped mesa and the tapered gain amplification area can greatly reduce the far-field divergence angle, thereby improving the output power while obviating the heat dissipation problem that is difficult to avoid for the similar wide-ridge large-power devices.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
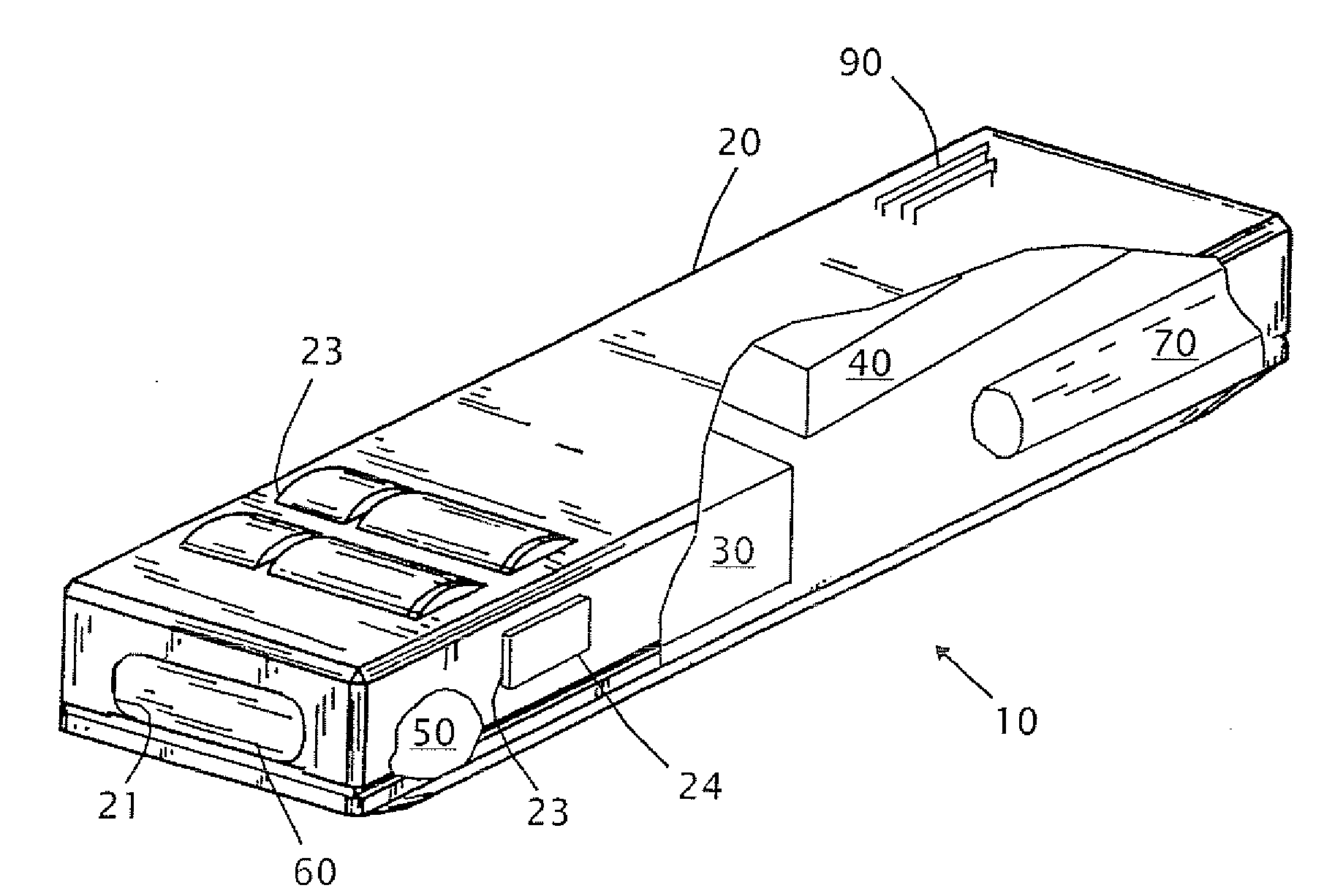
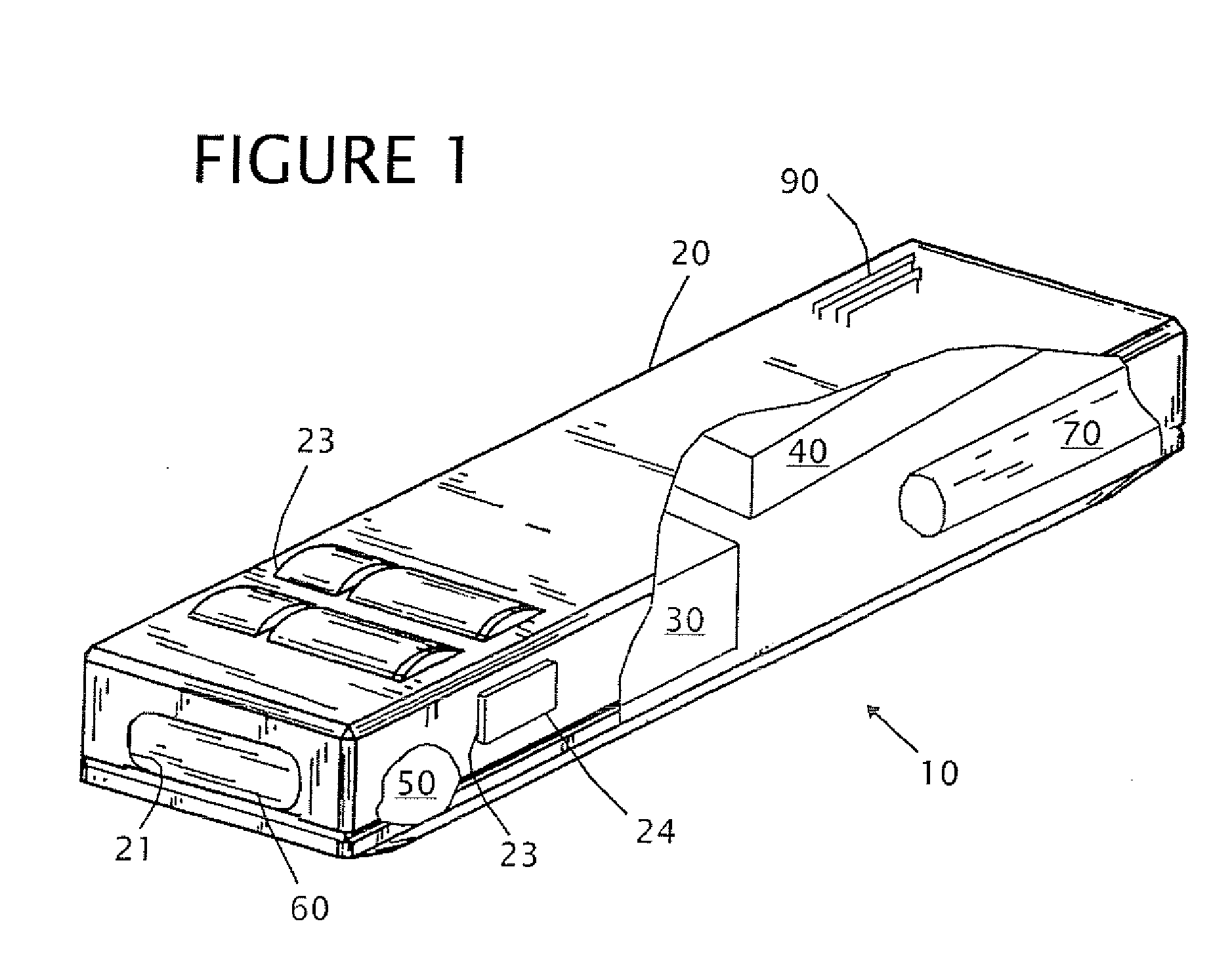
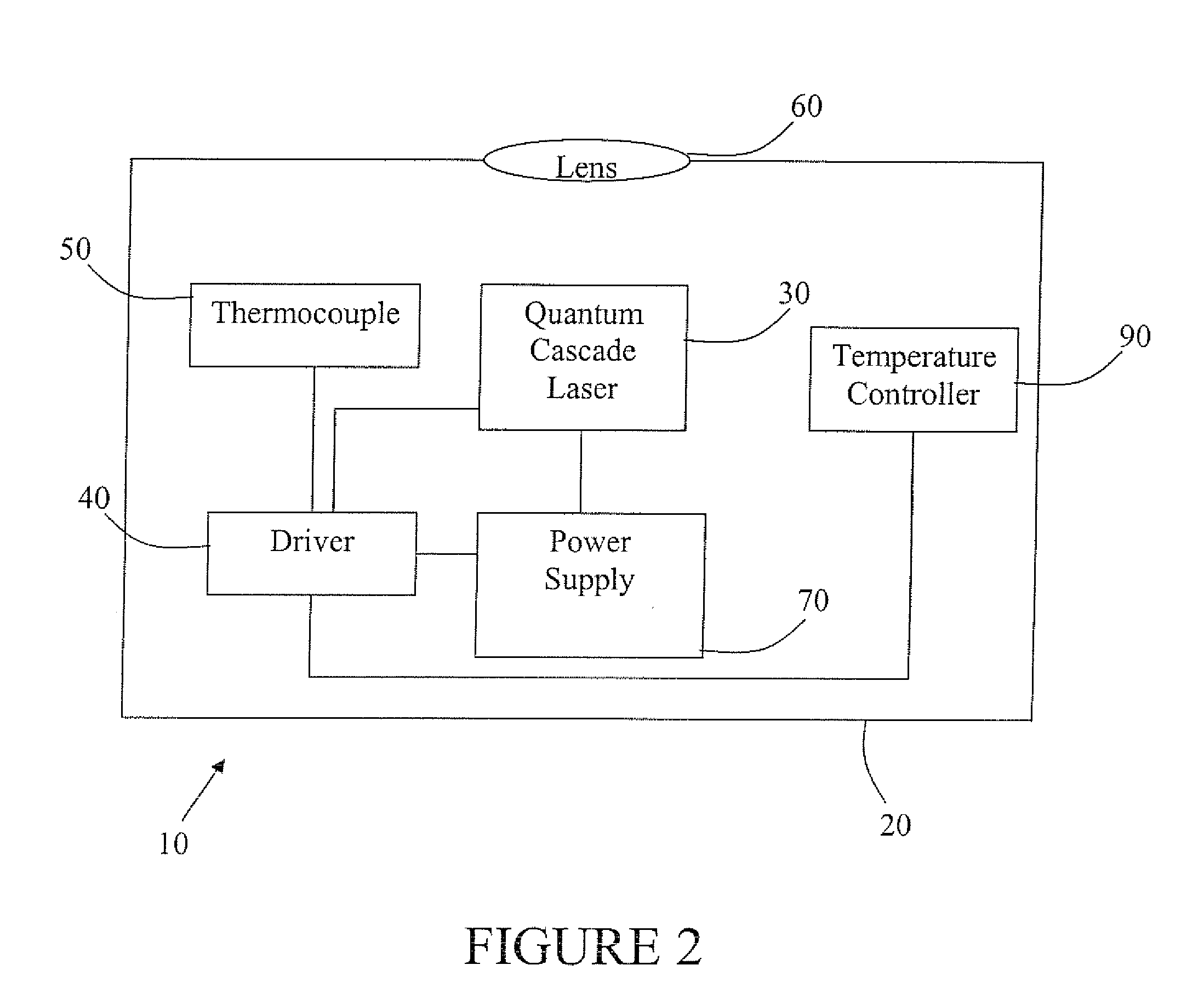
Target Marker having Quantum Cascade Laser for Thermally Marking a Target
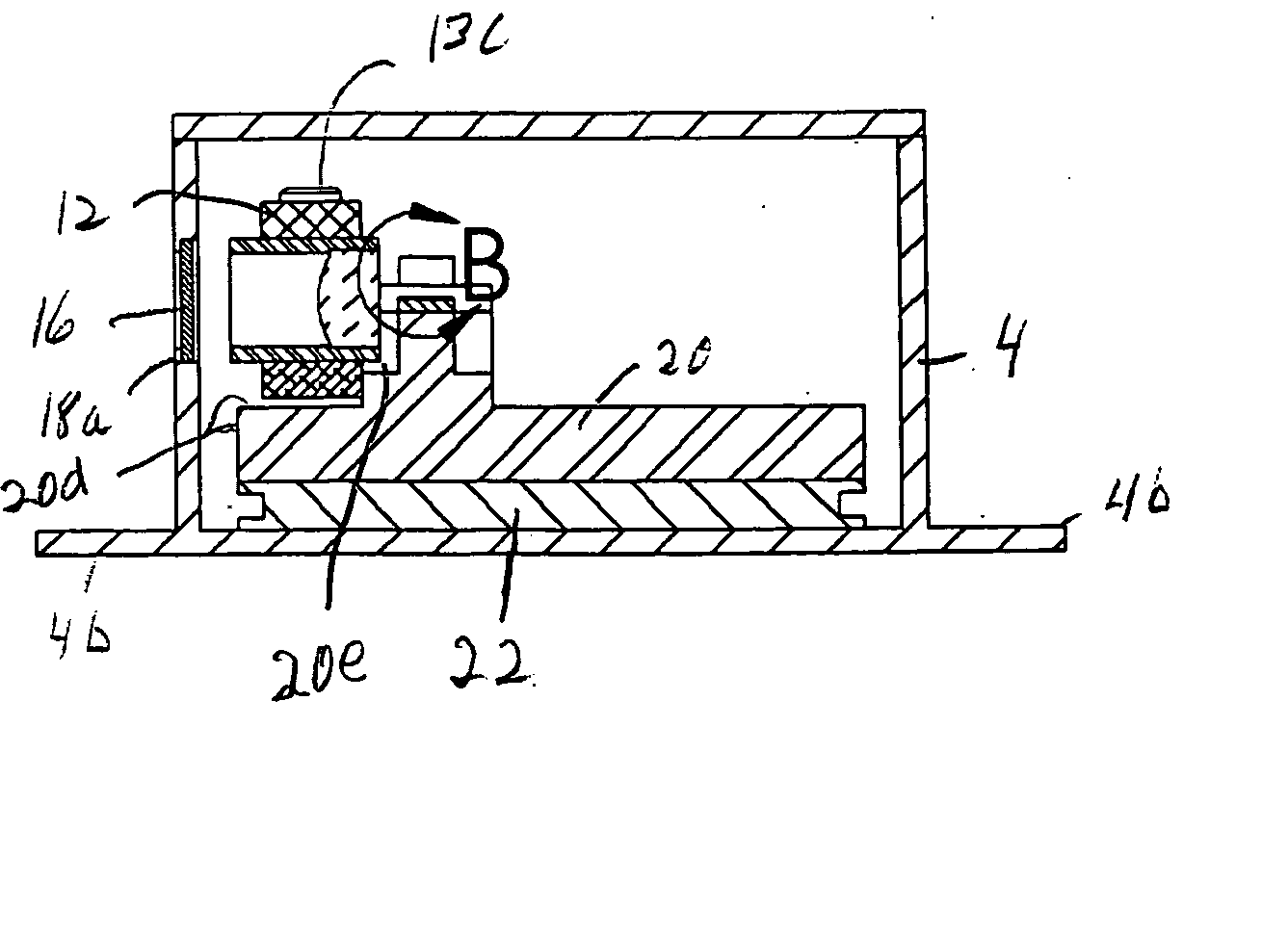
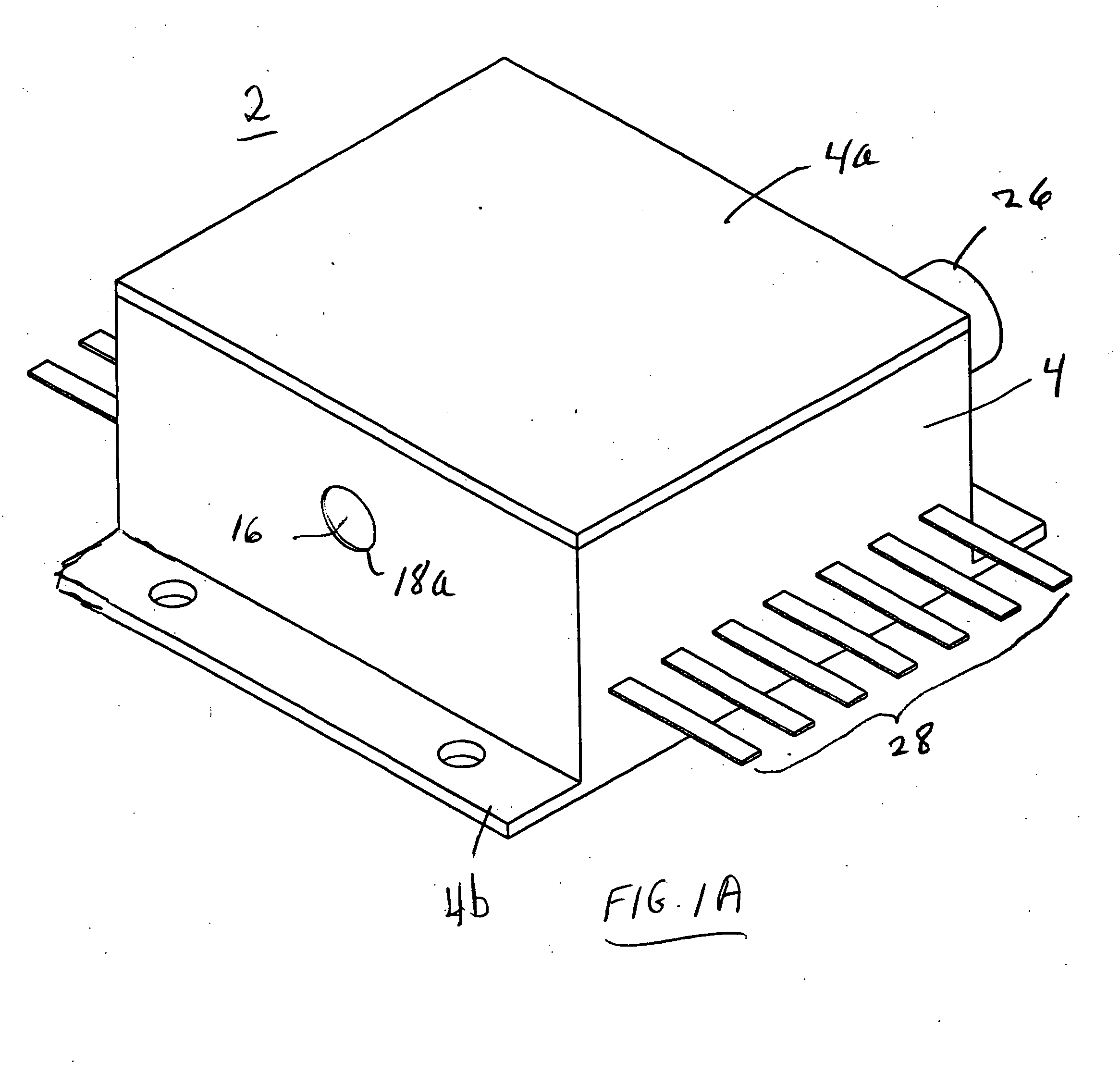
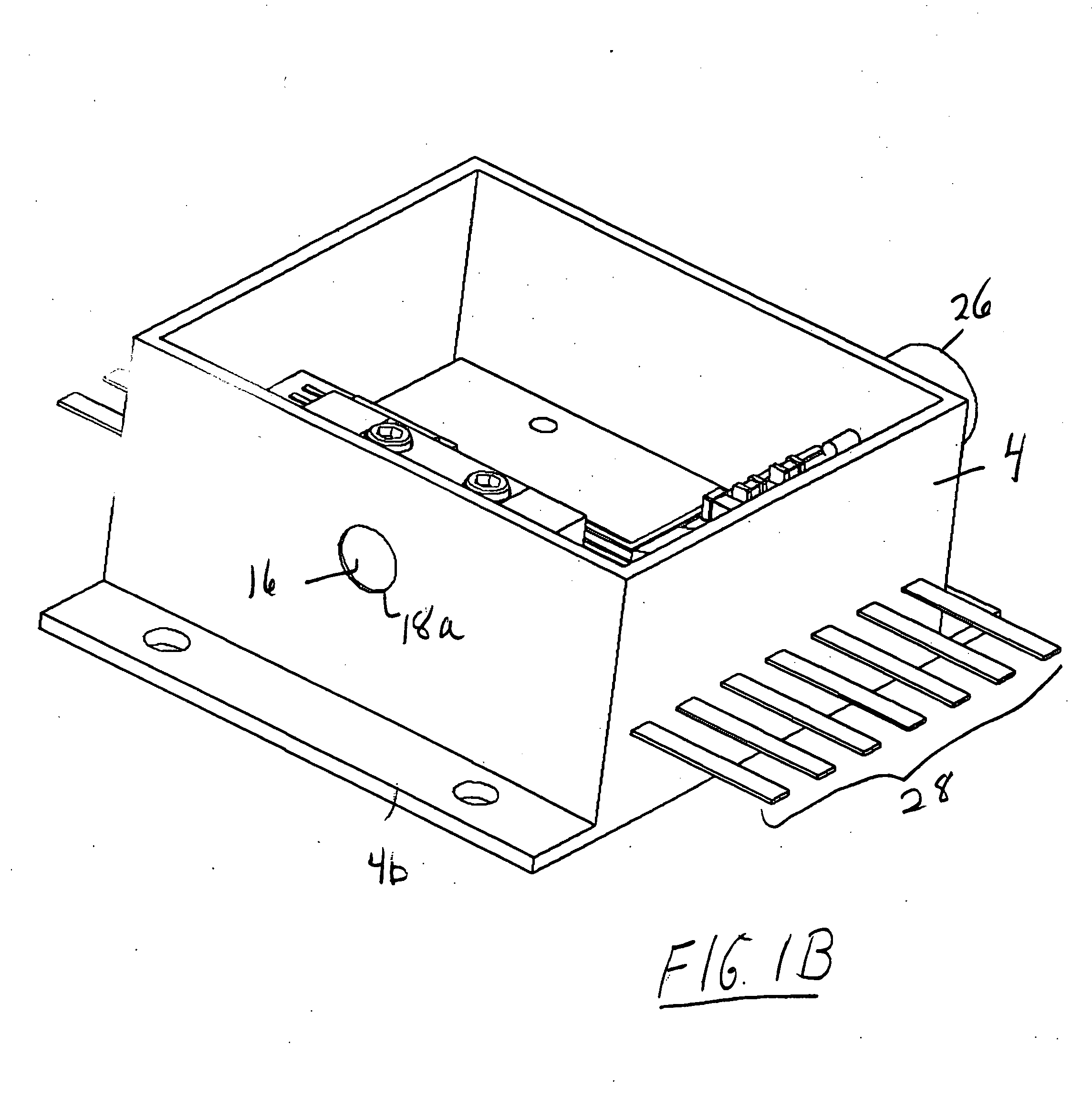
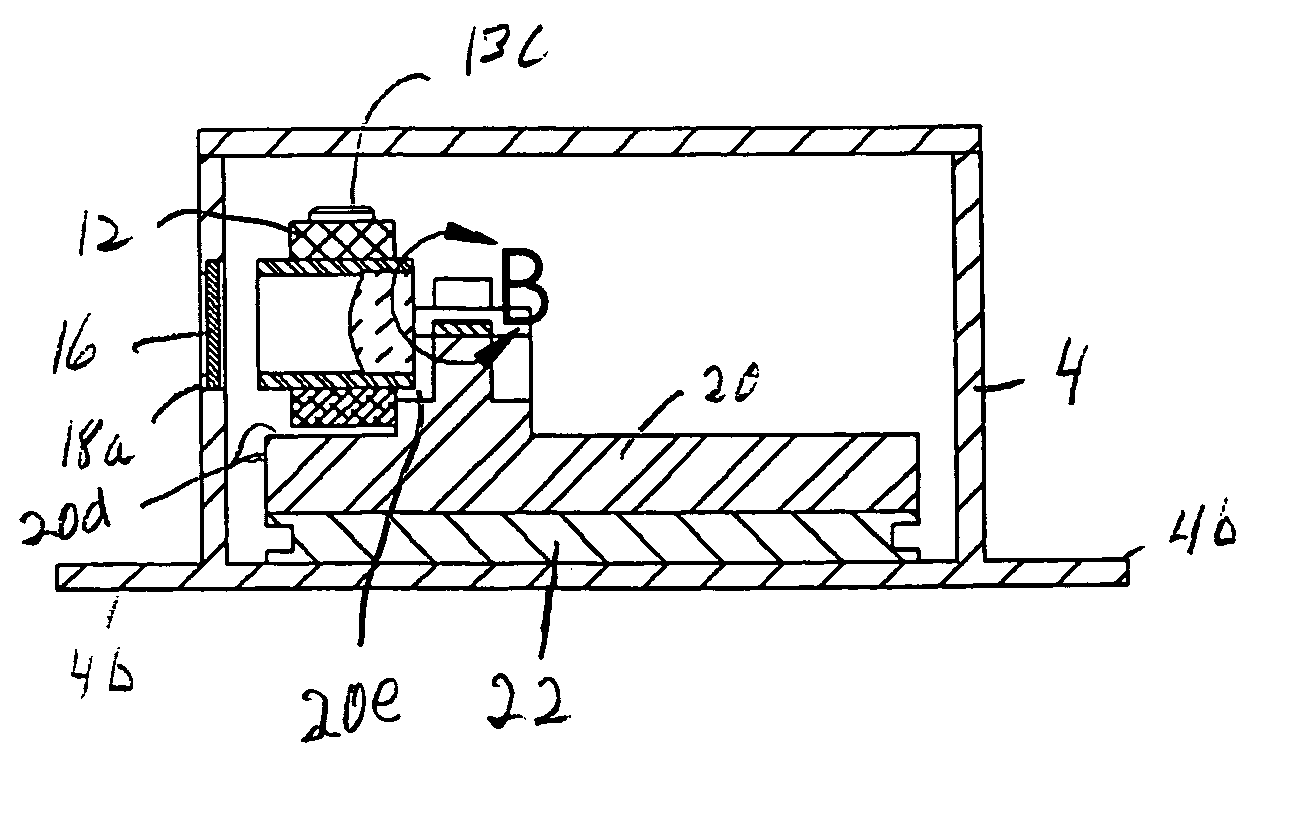
ActiveUS20090224153A1Robust configurationMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamThermographic camera
A handheld target marker is provided, wherein the target marker includes a housing retaining a quantum cascade laser, a collimating or focusing lens, a driver and a power supply. The quantum cascade laser produces a thermal infrared beam which can be selectively directed to impinge upon a target. The impinging beam is viewable by a thermal imager. The handheld target marker operates at ambient temperatures and incorporates the driver and power supply necessary for operation of the quantum cascade laser.
Owner:LMD APPL SCI LLC
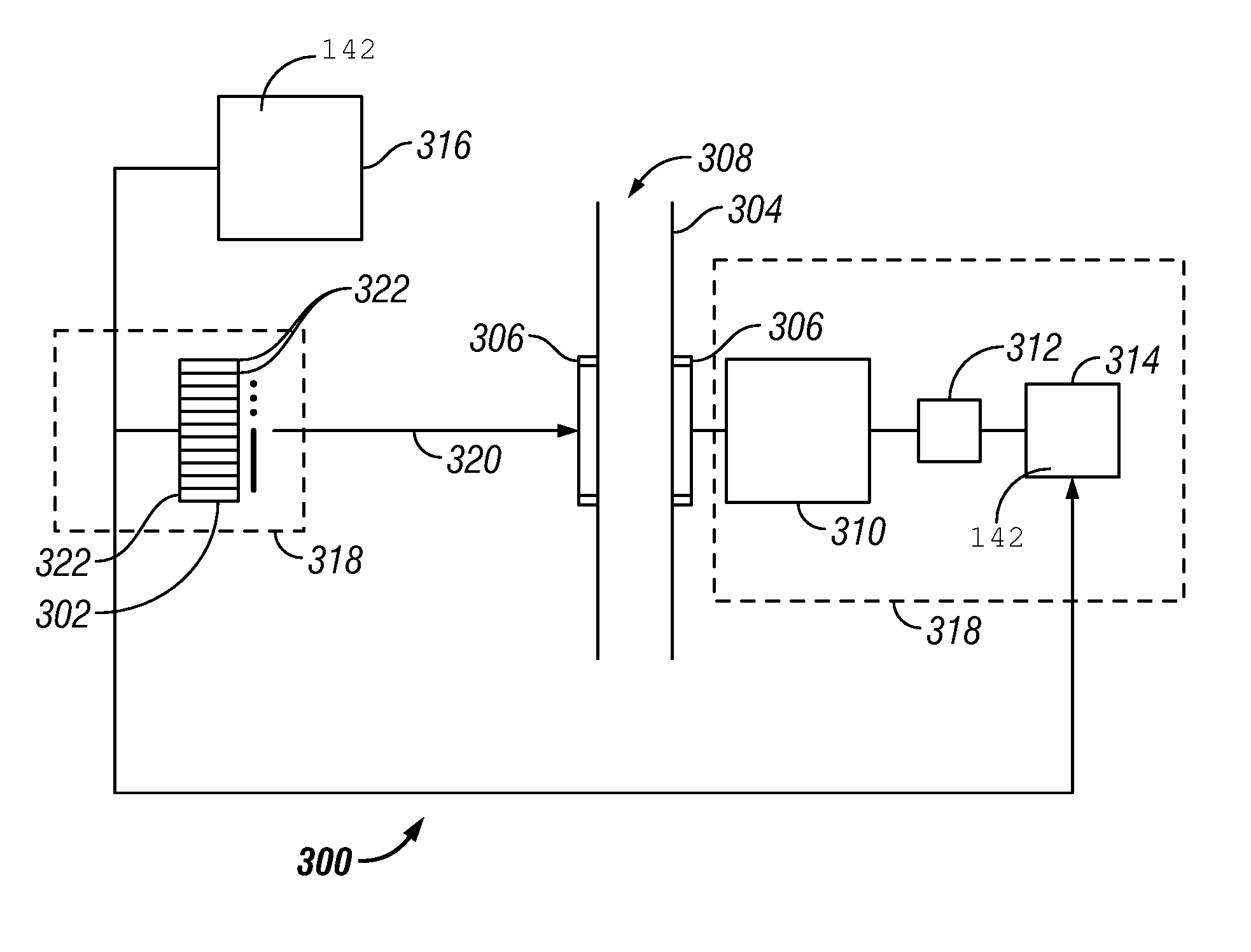
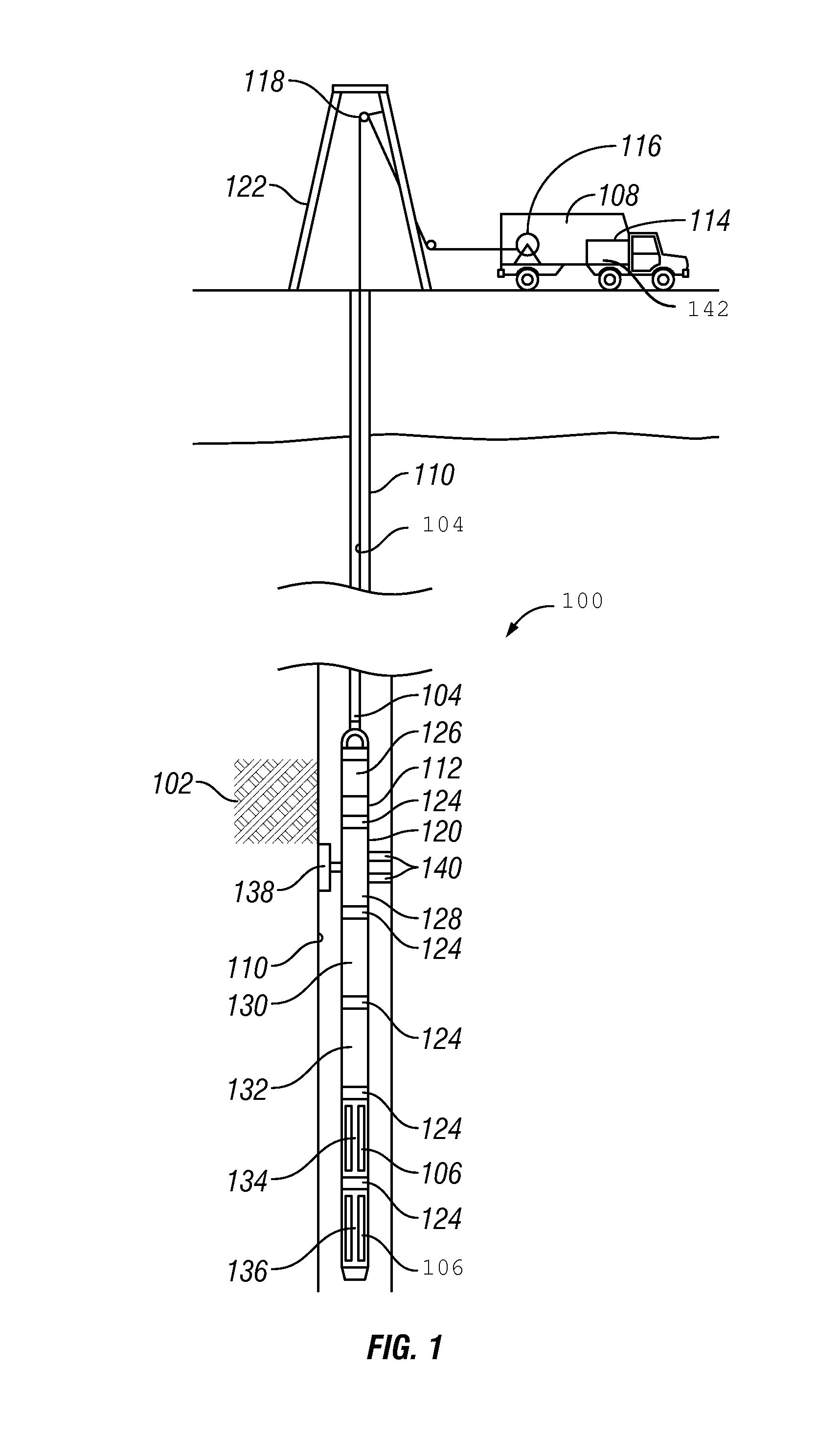
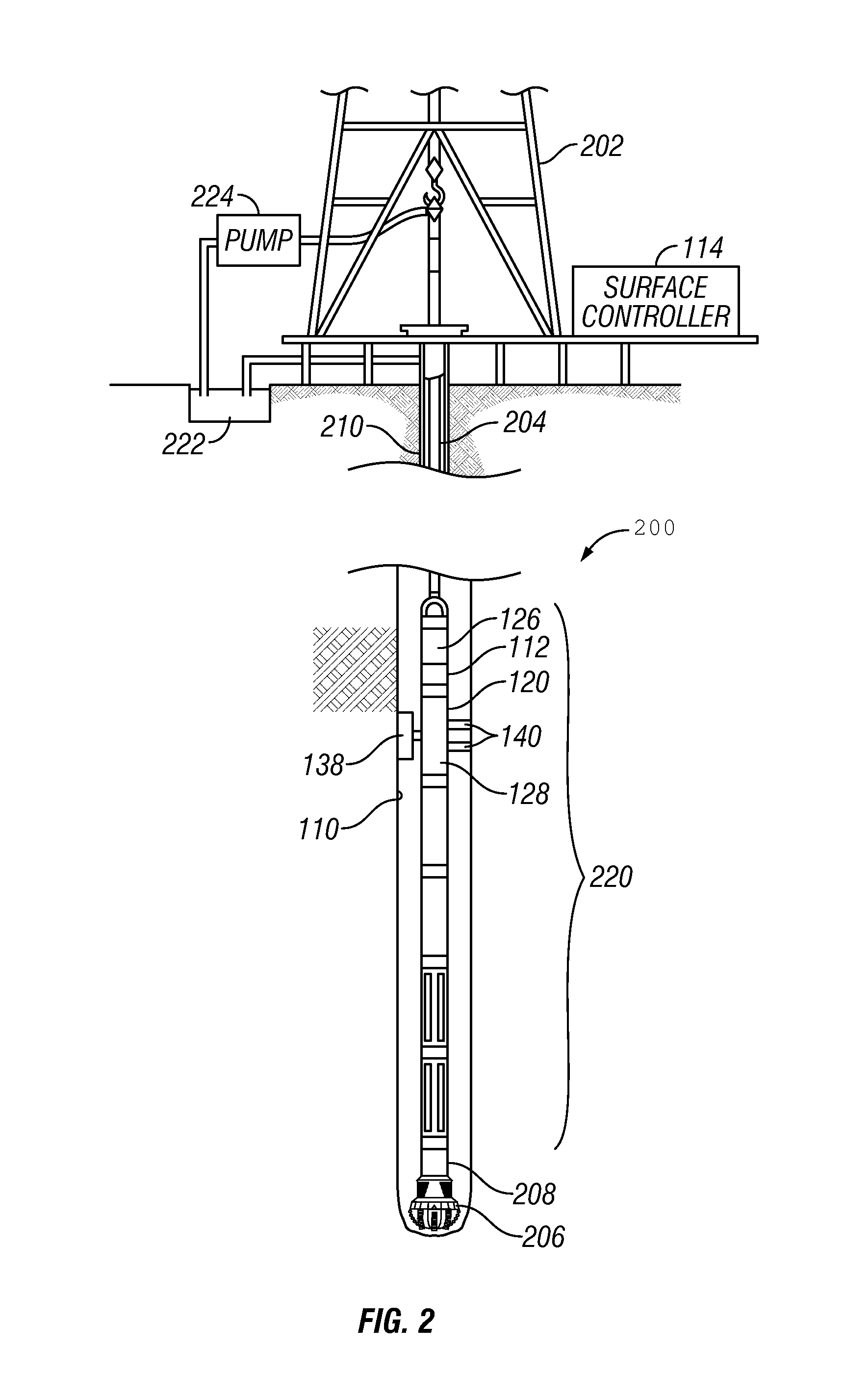
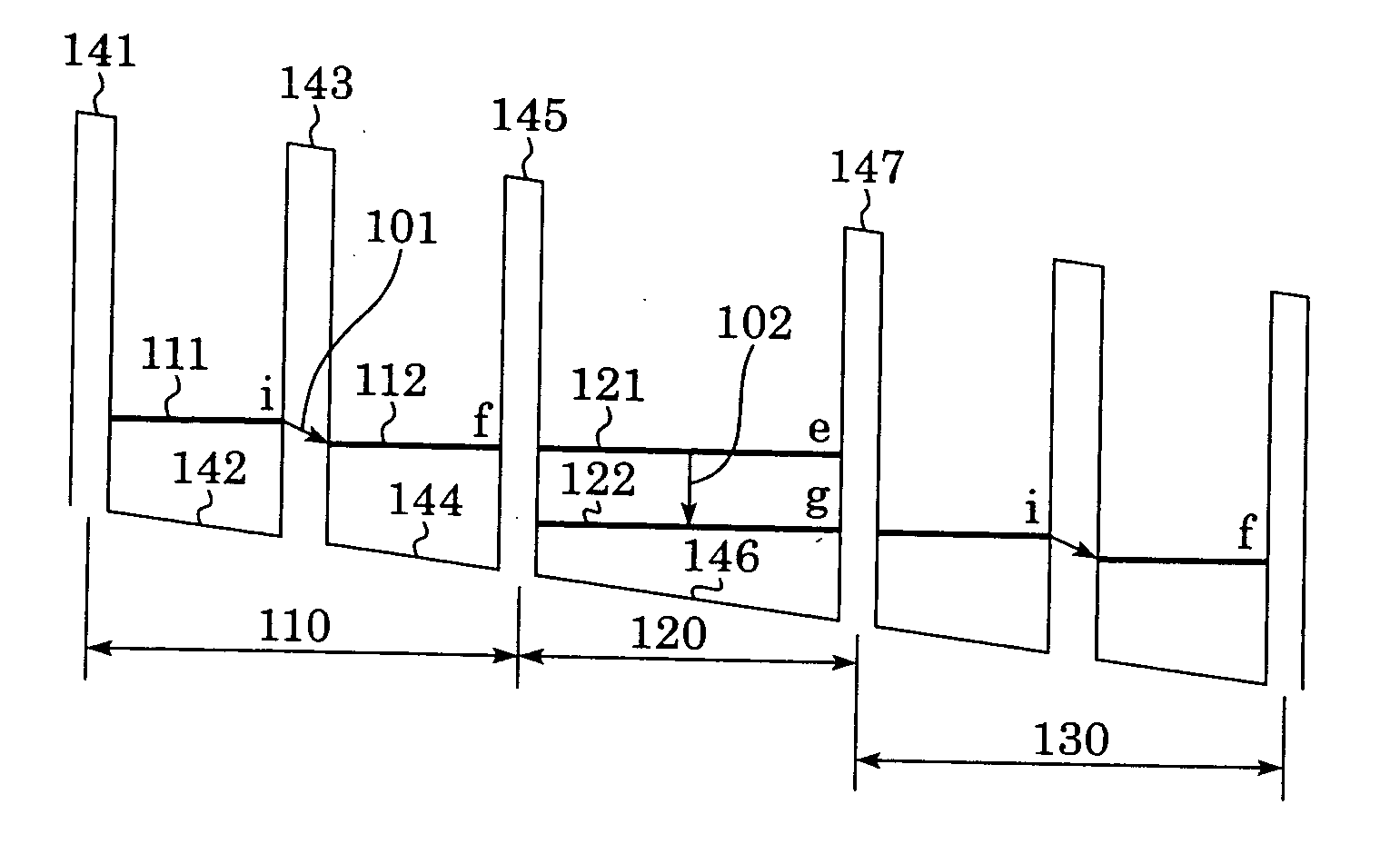
Methods and apparatus for estimating a downhole fluid property
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
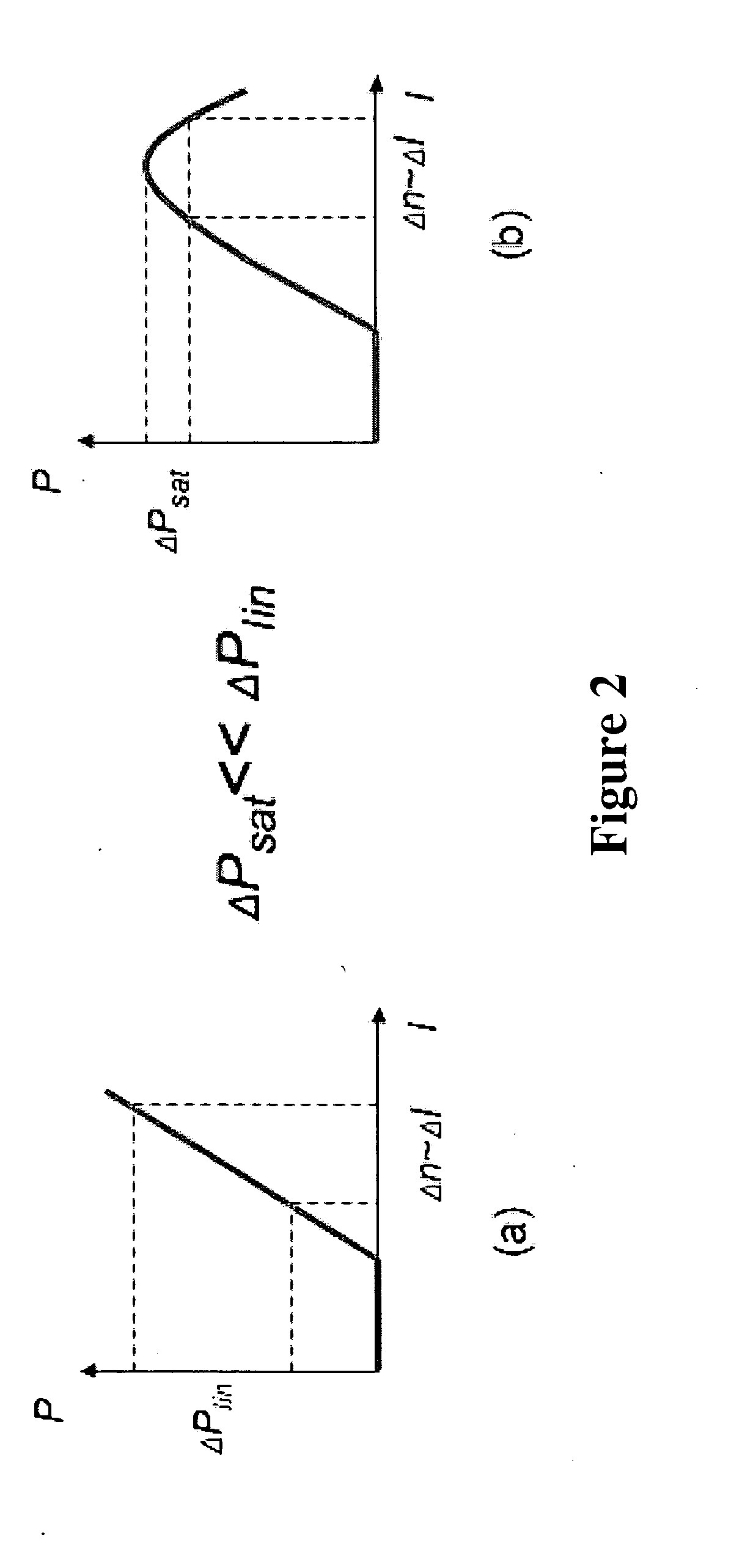
Quantum cascade laser device
InactiveUS20060039431A1Total current dropTransit-time limitedOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsQuantum cascade laserCondensed matter physics
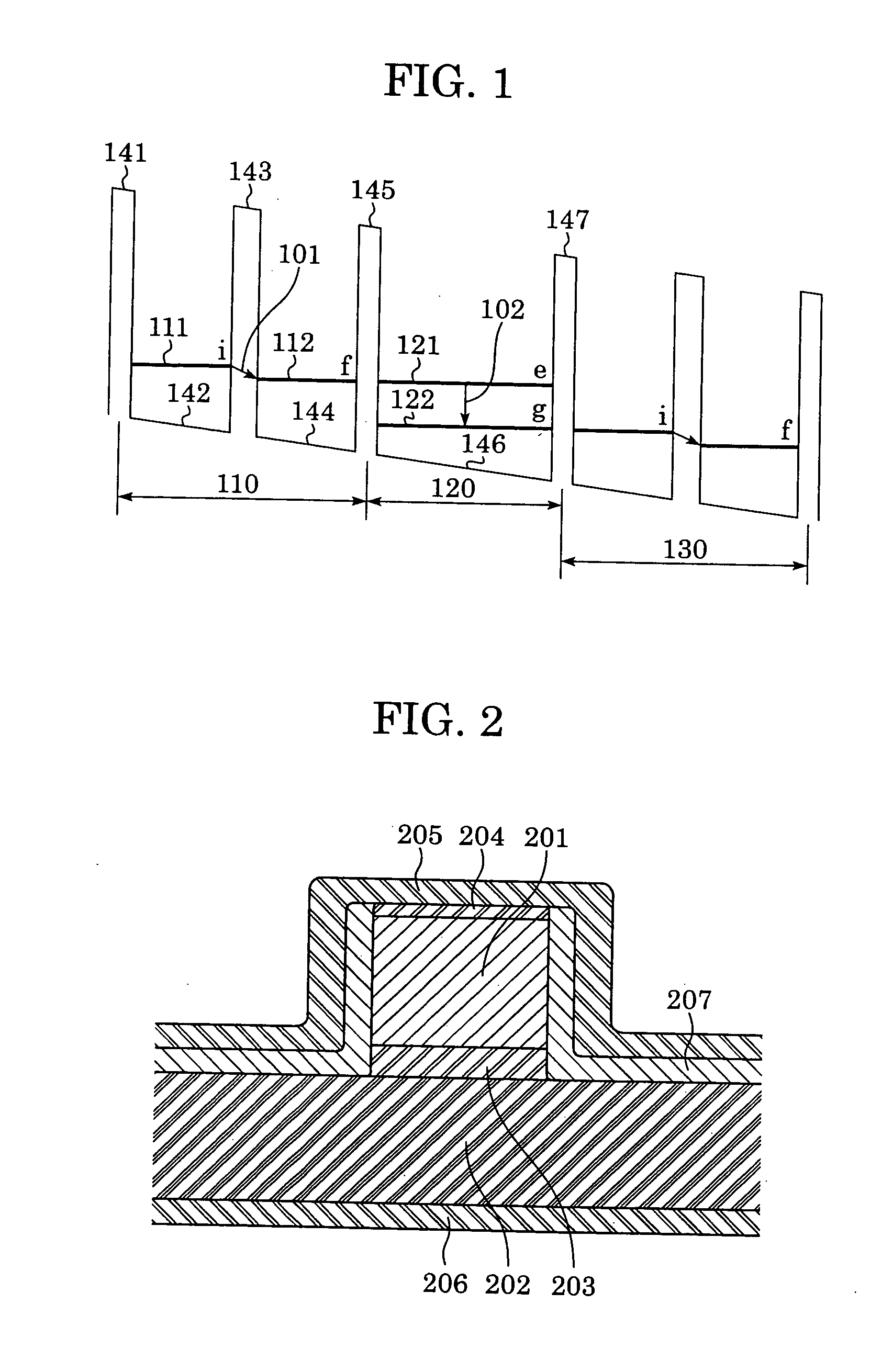
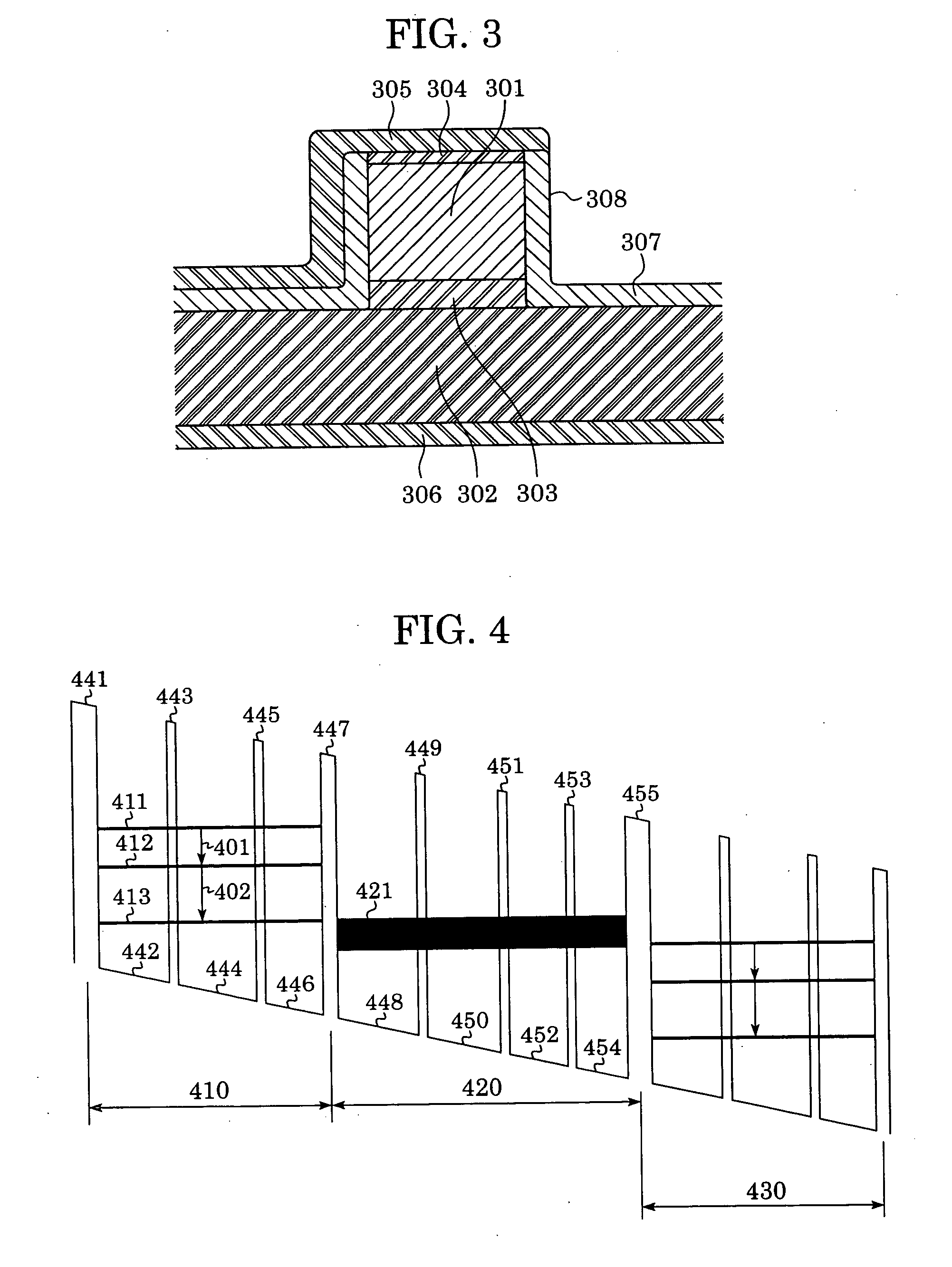
A device includes a multiple quantum well with potential barriers and quantum wells, and an electric field element for applying an electric field thereto. The multiple quantum well includes at least two regions A and a region B disposed therebetween. The region A includes a plurality of energy levels, and a carrier is transported from a specific energy level i to a specific energy level f in the region A through one of the potential barriers by photon-assisted tunneling. The region B includes a plurality of energy levels, and an energy relaxation is performed with a relaxation time shorter than a transit time of the carrier in the region A from a specific energy level e to a specific energy level g in the region B. When an electric field is applied, electric current flows through the multiple quantum well and light is emitted or absorbed in the region A.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com