Patents
Literature
213results about How to "High light sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
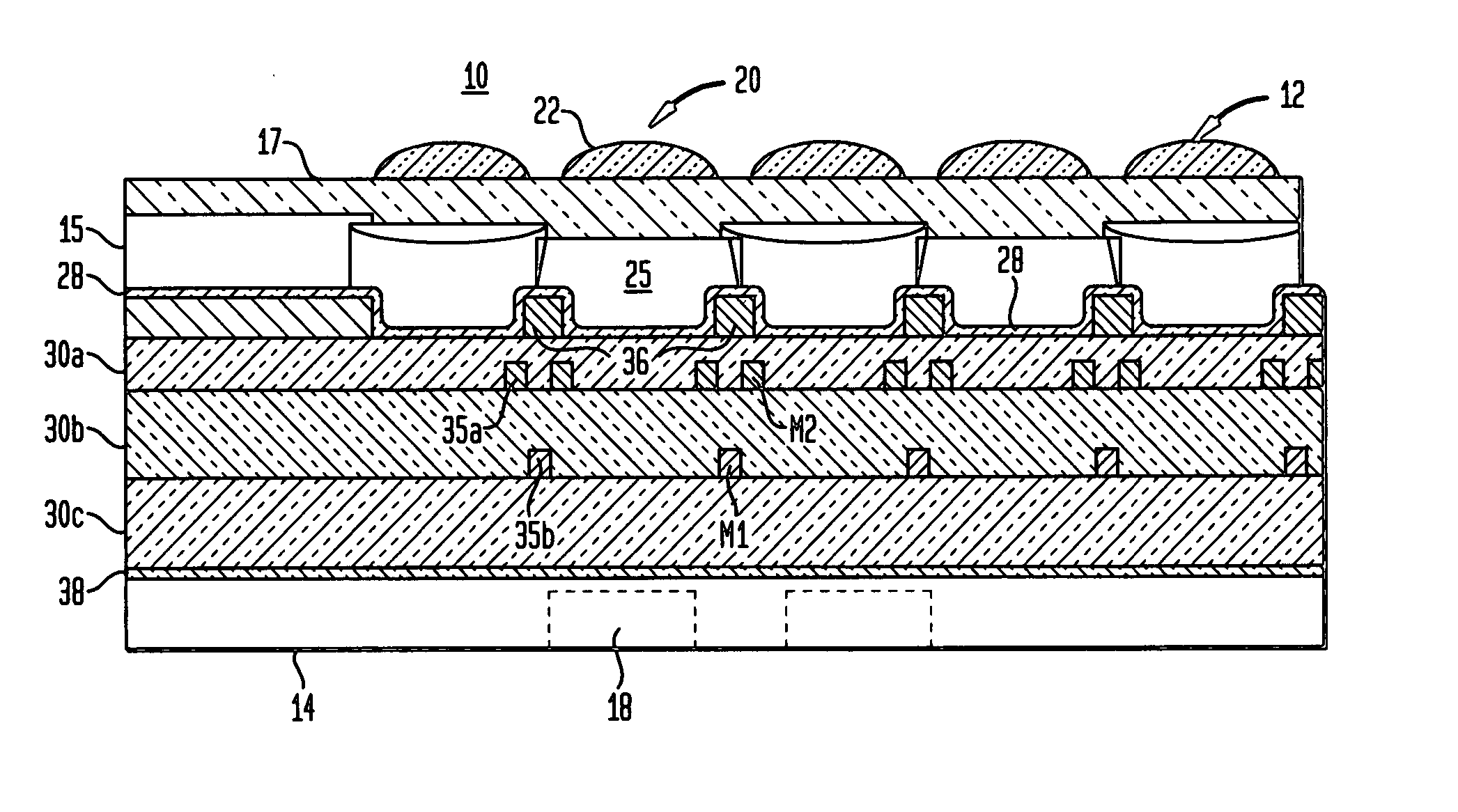
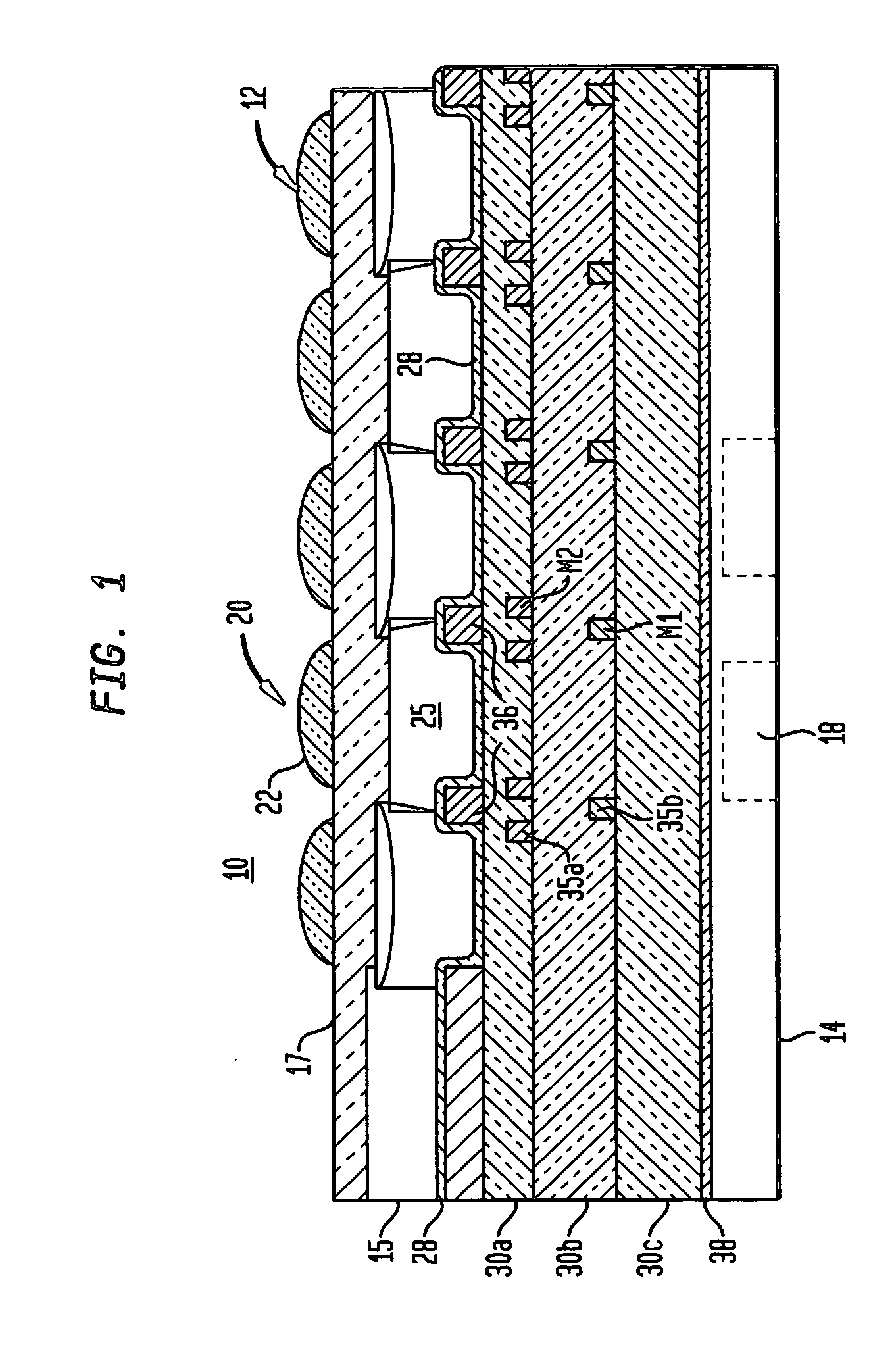
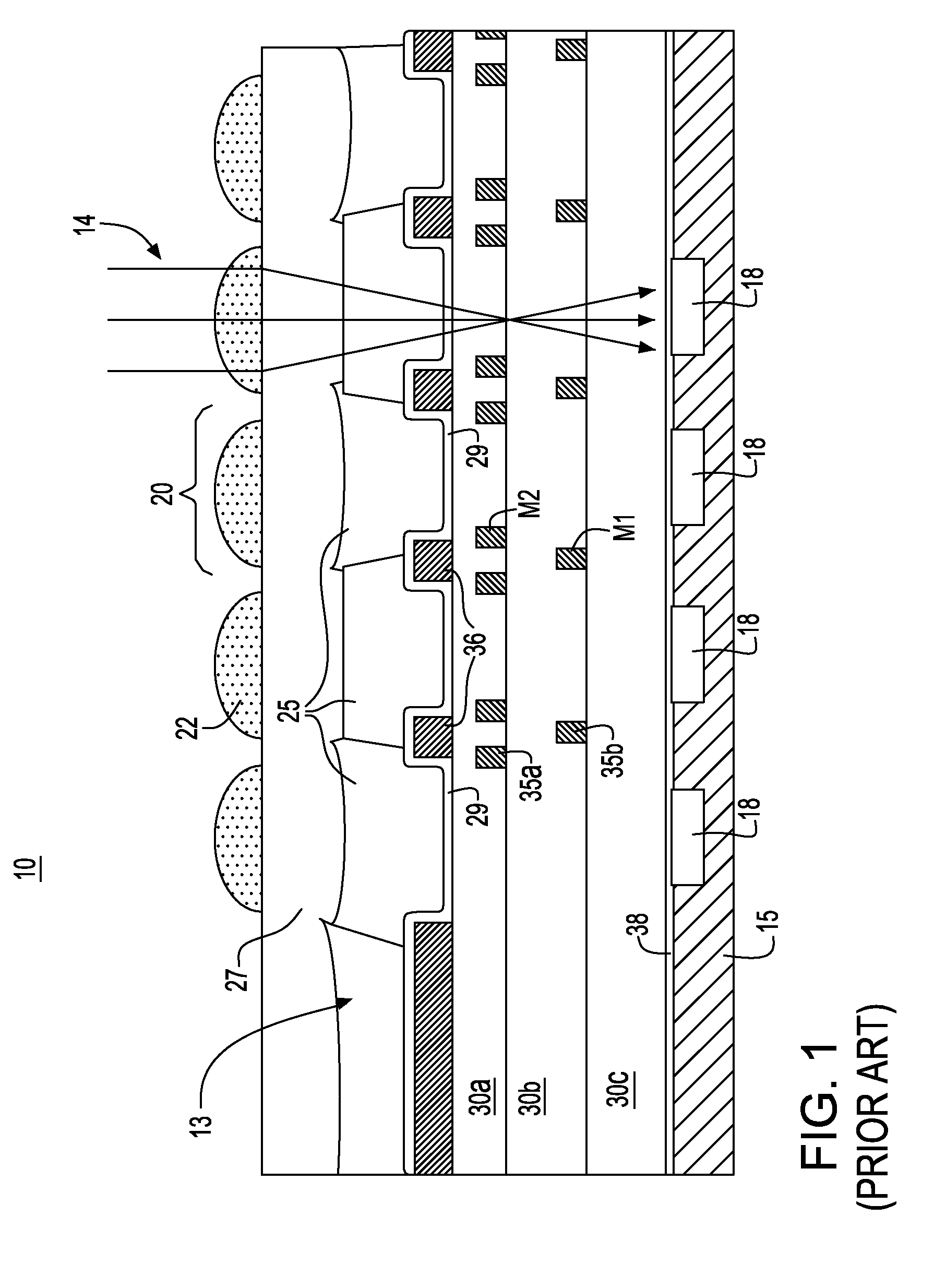
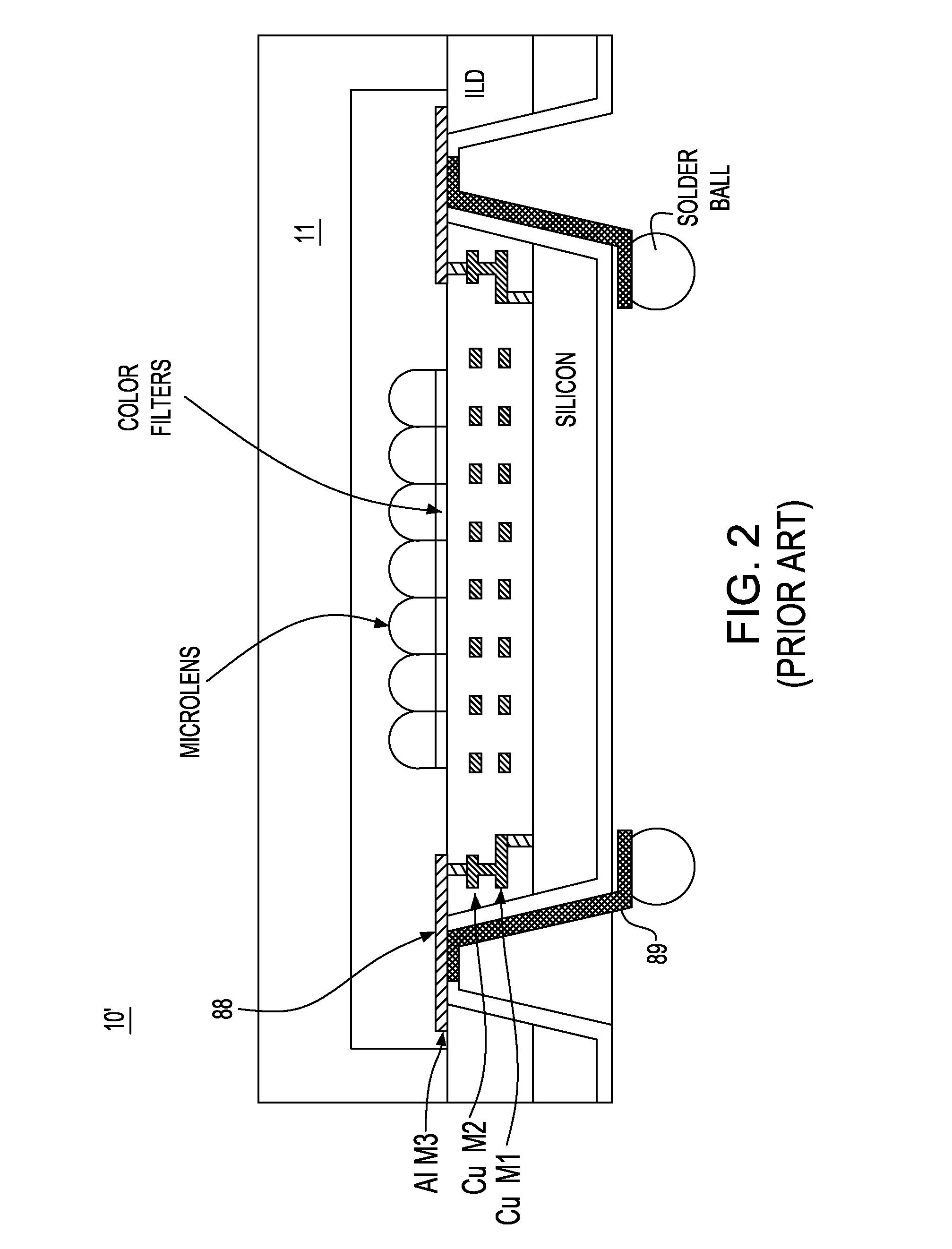
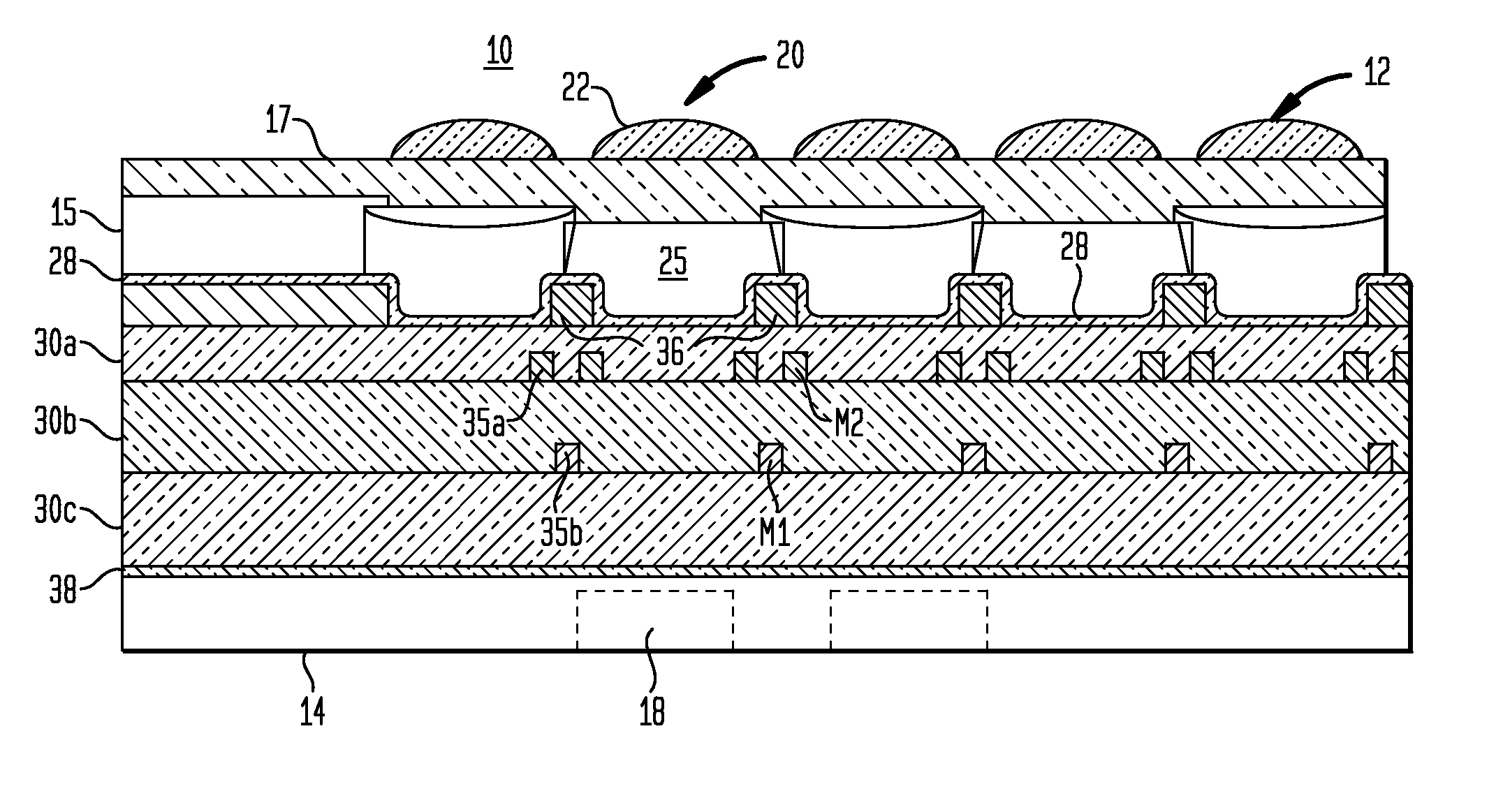
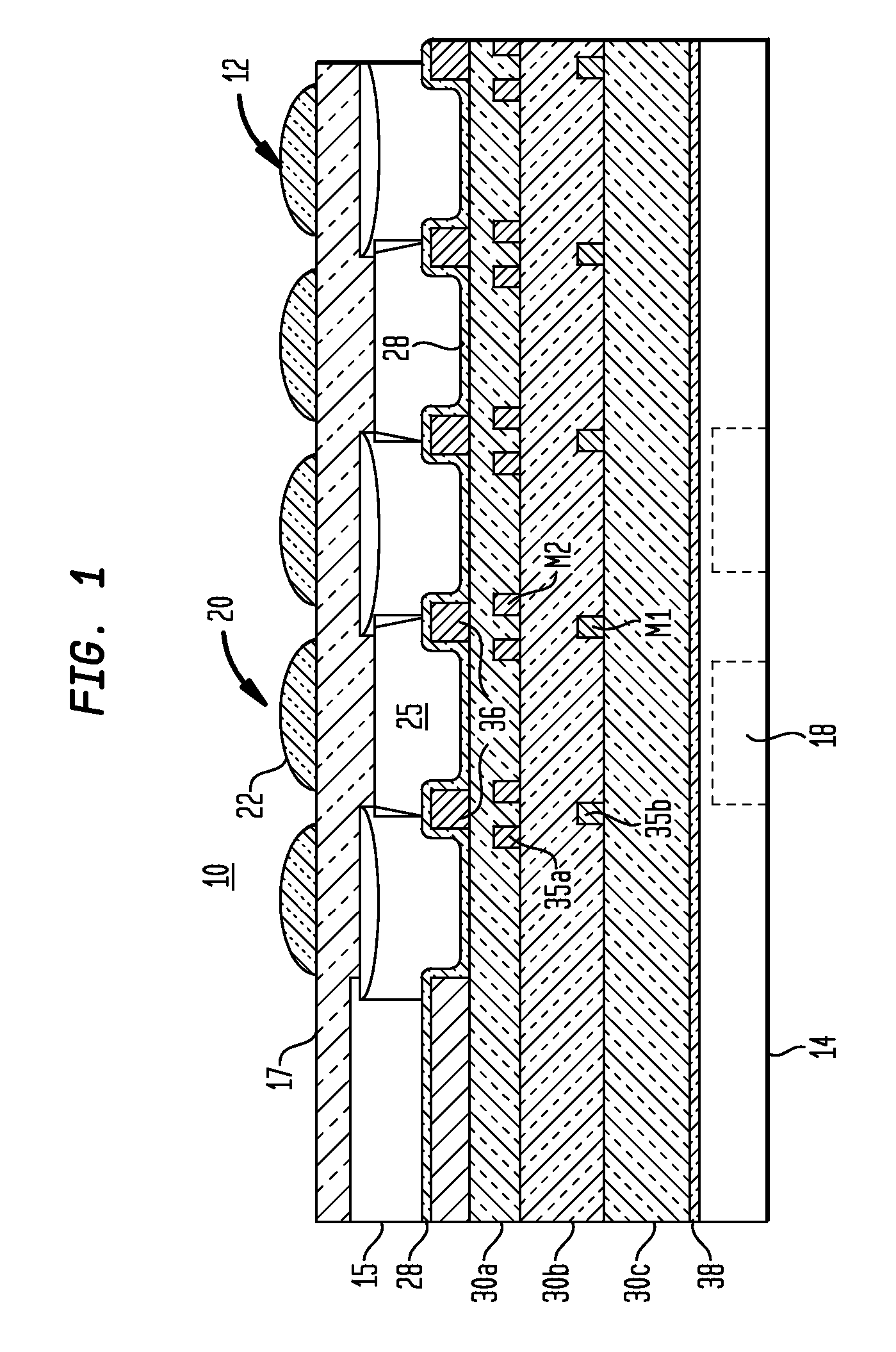
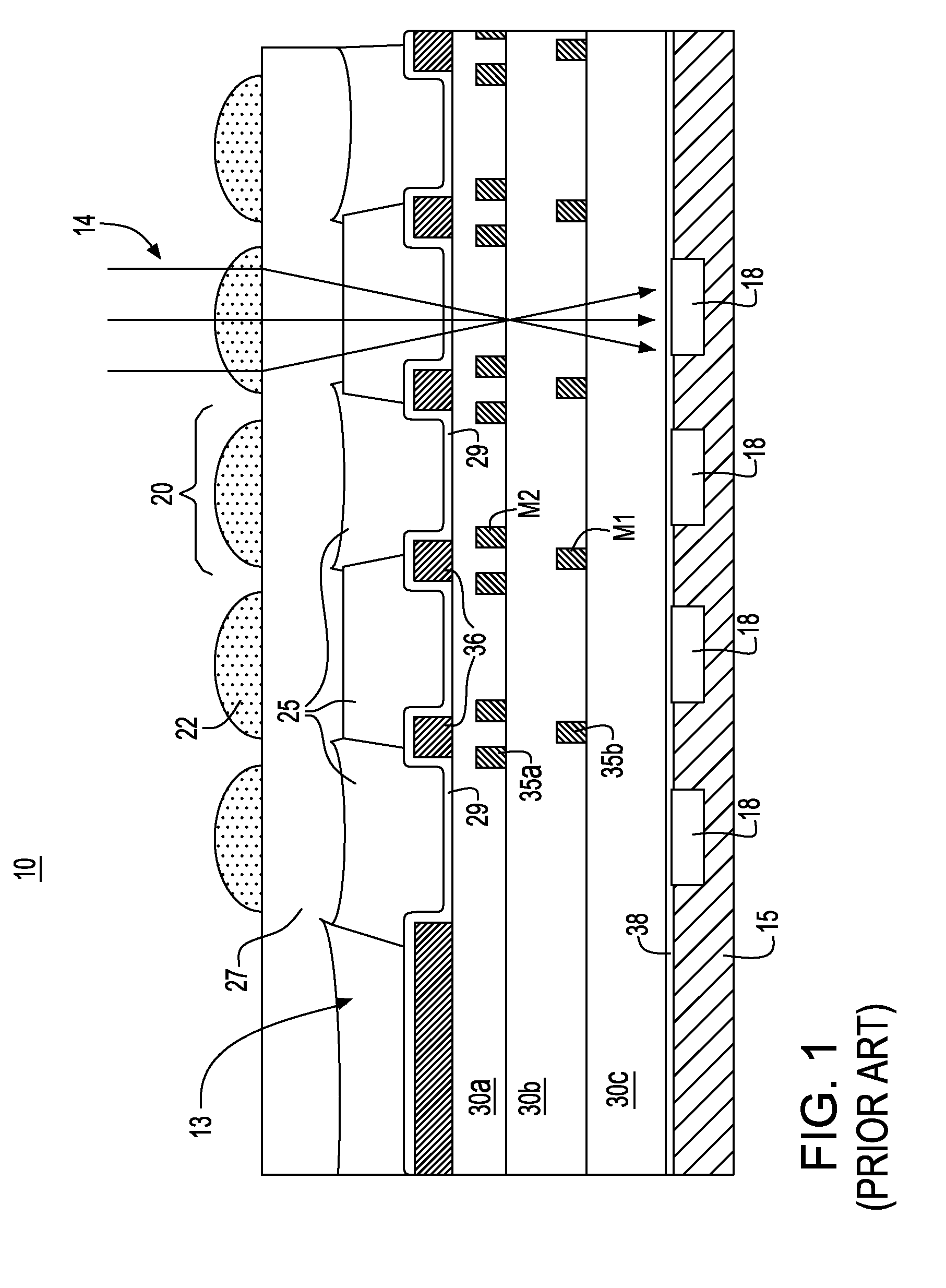
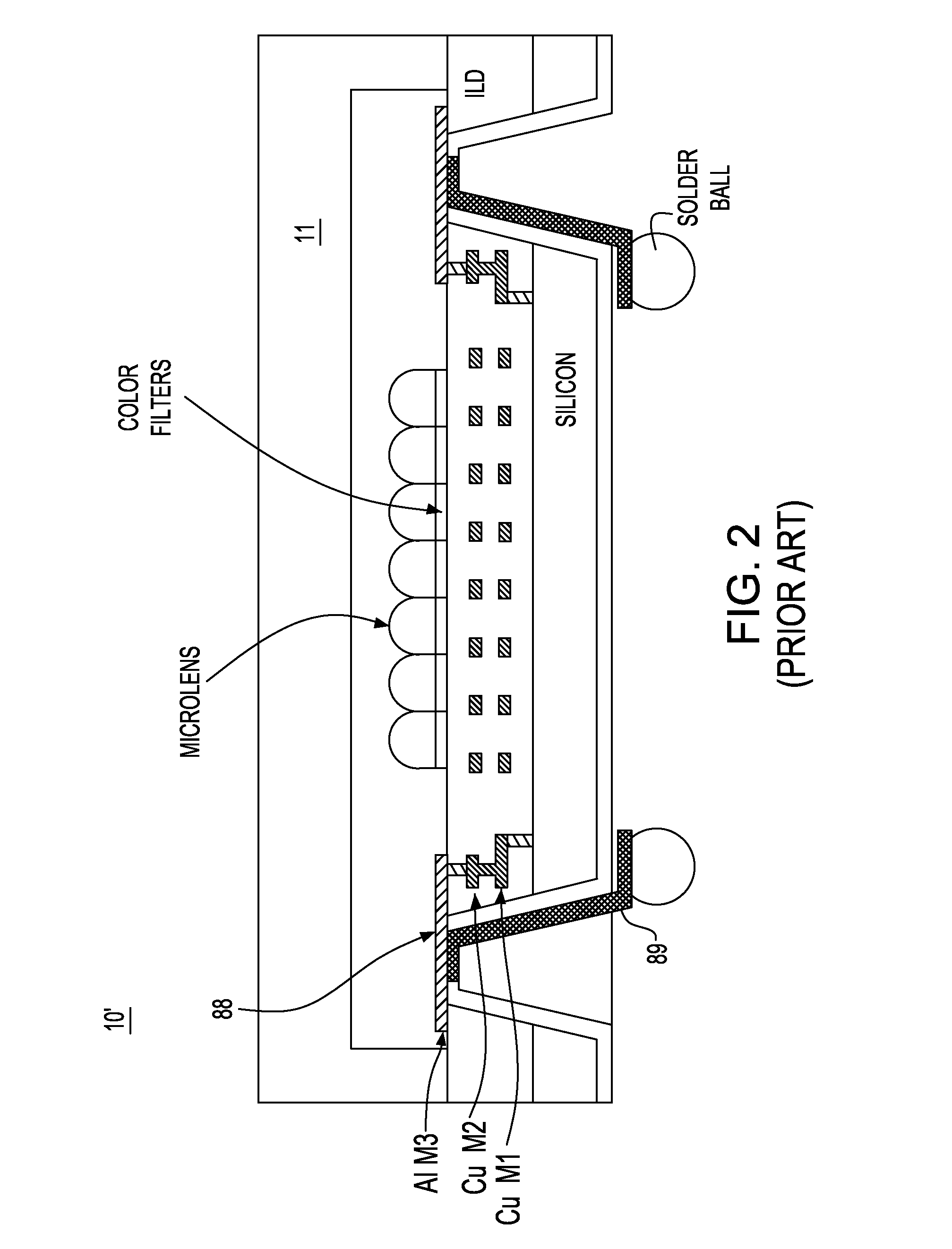
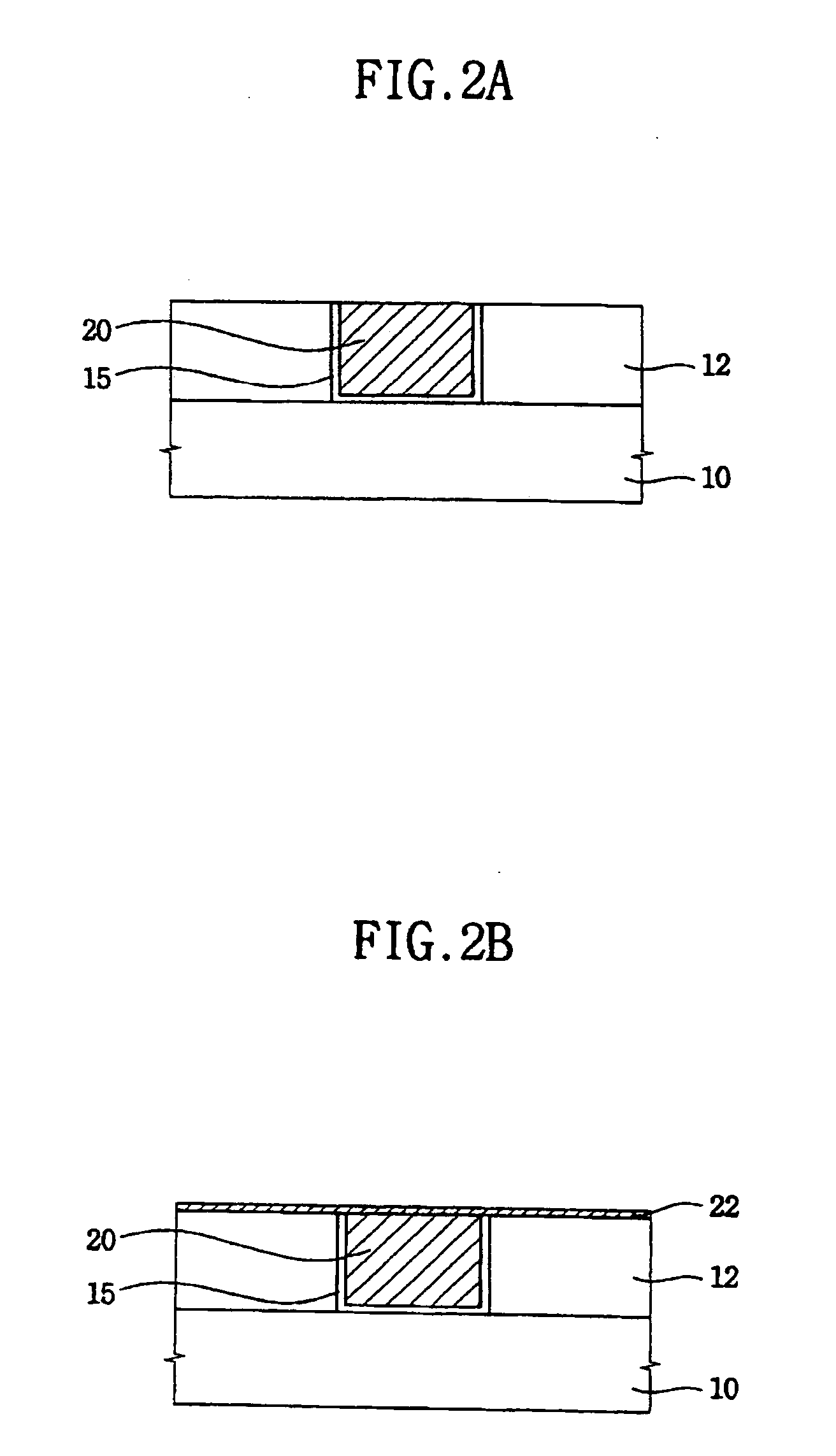
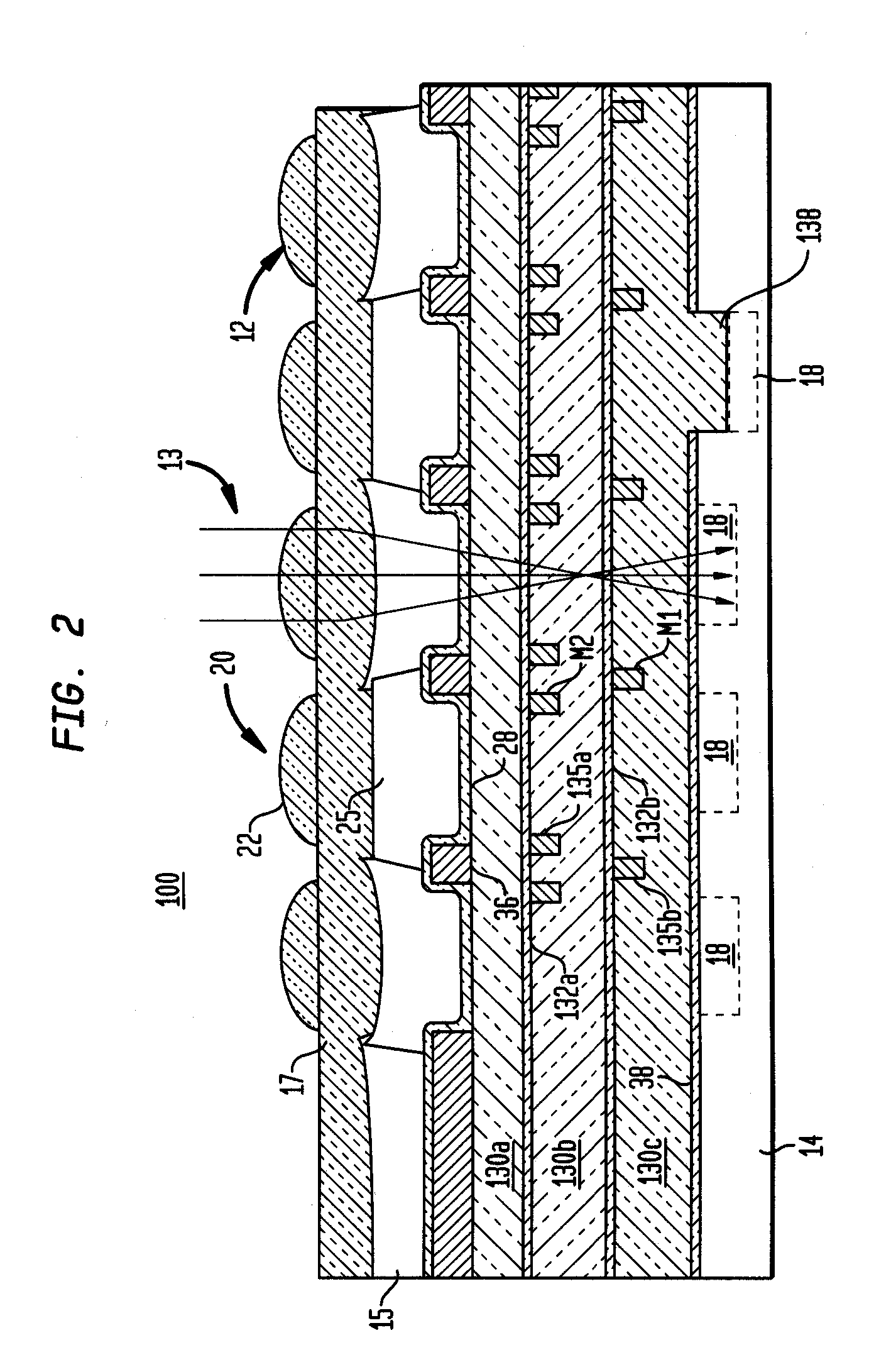
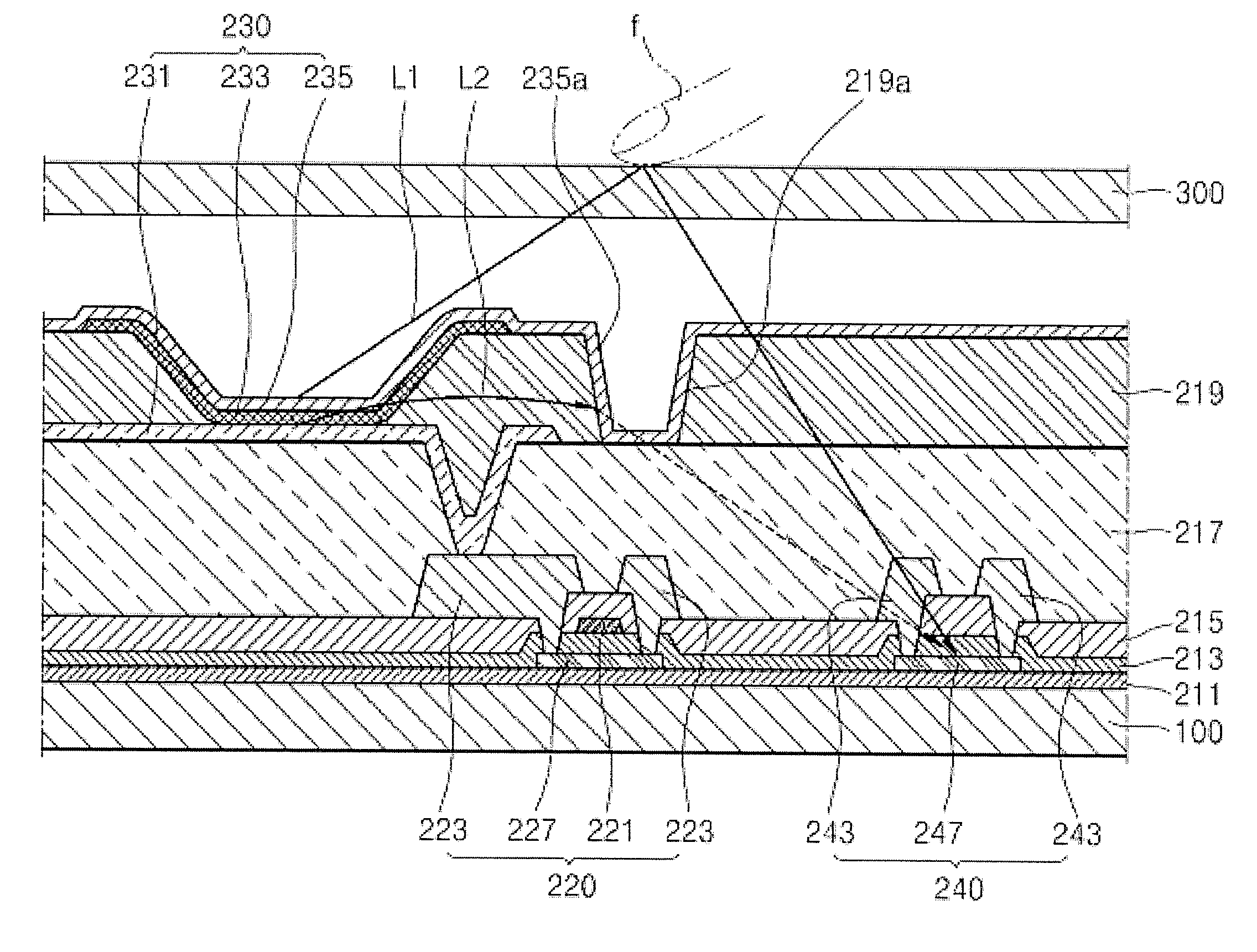
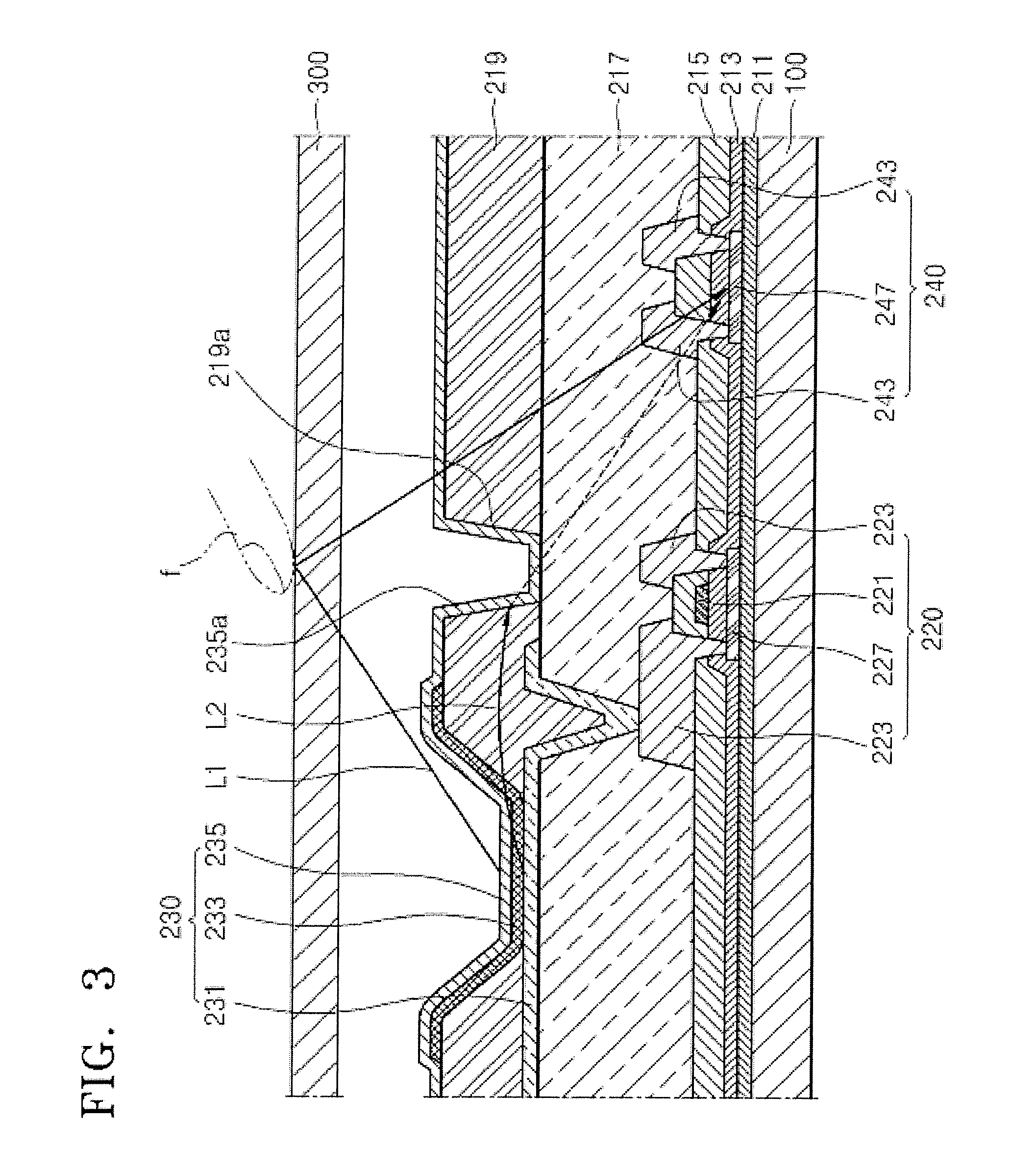
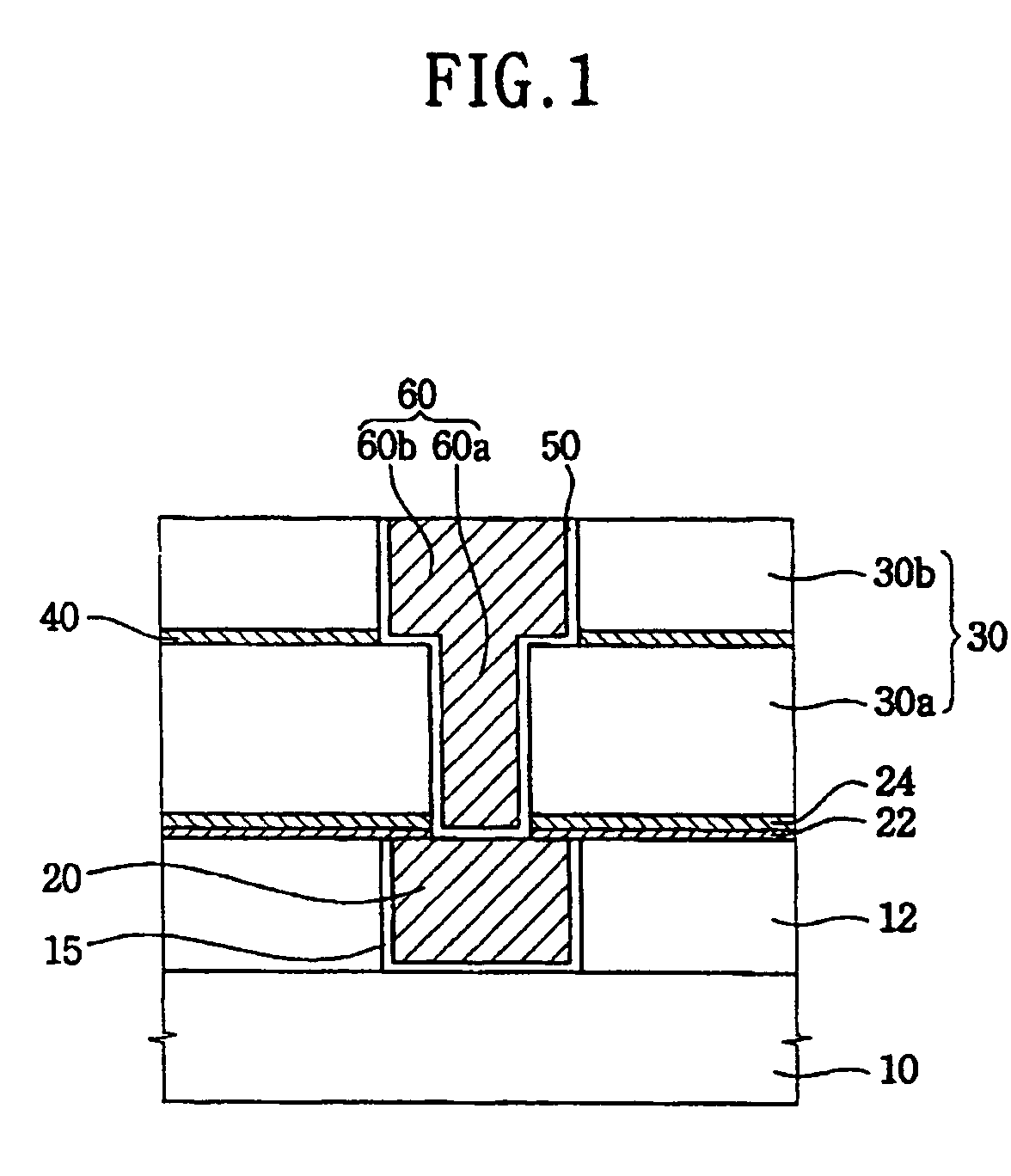
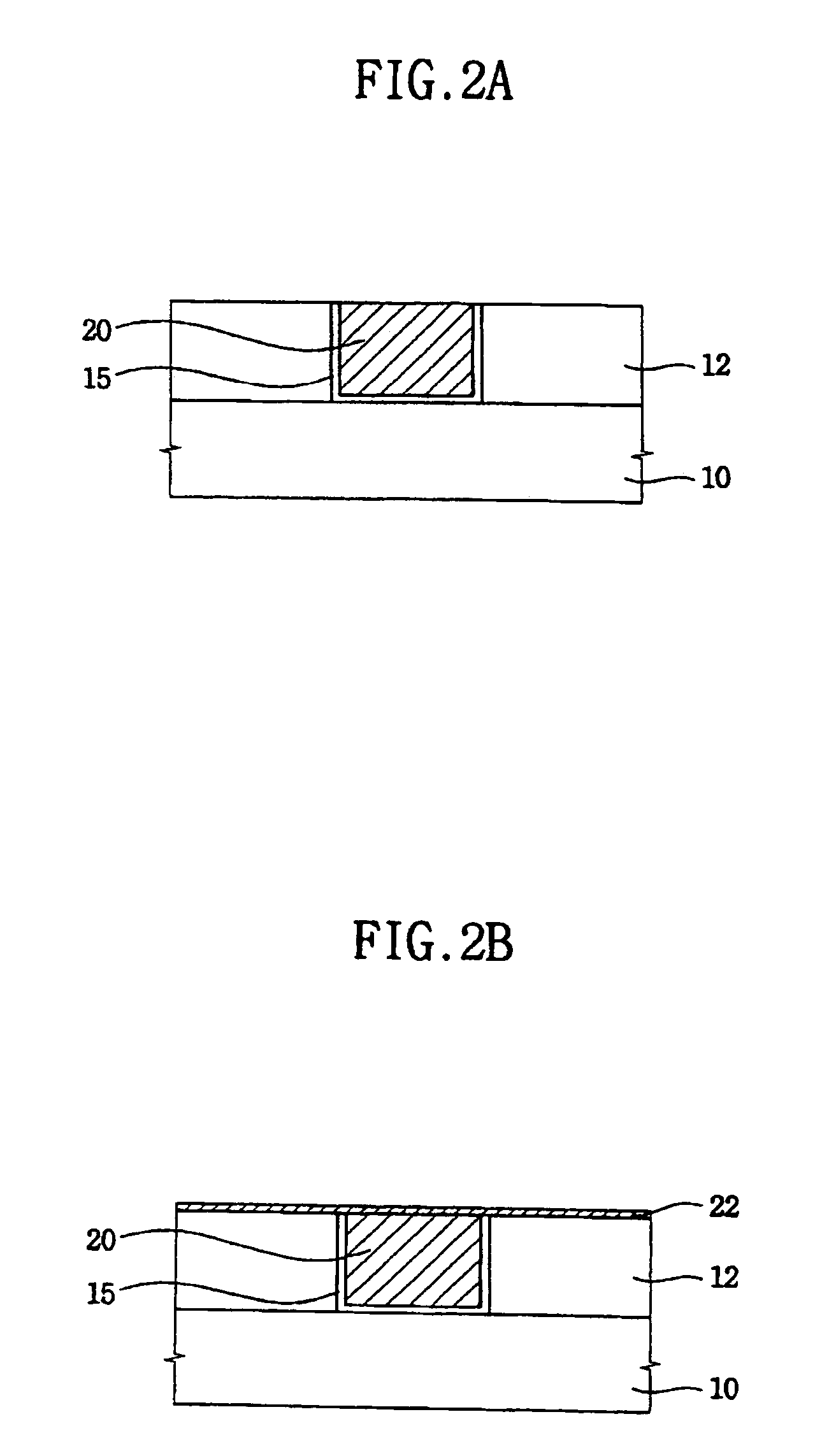
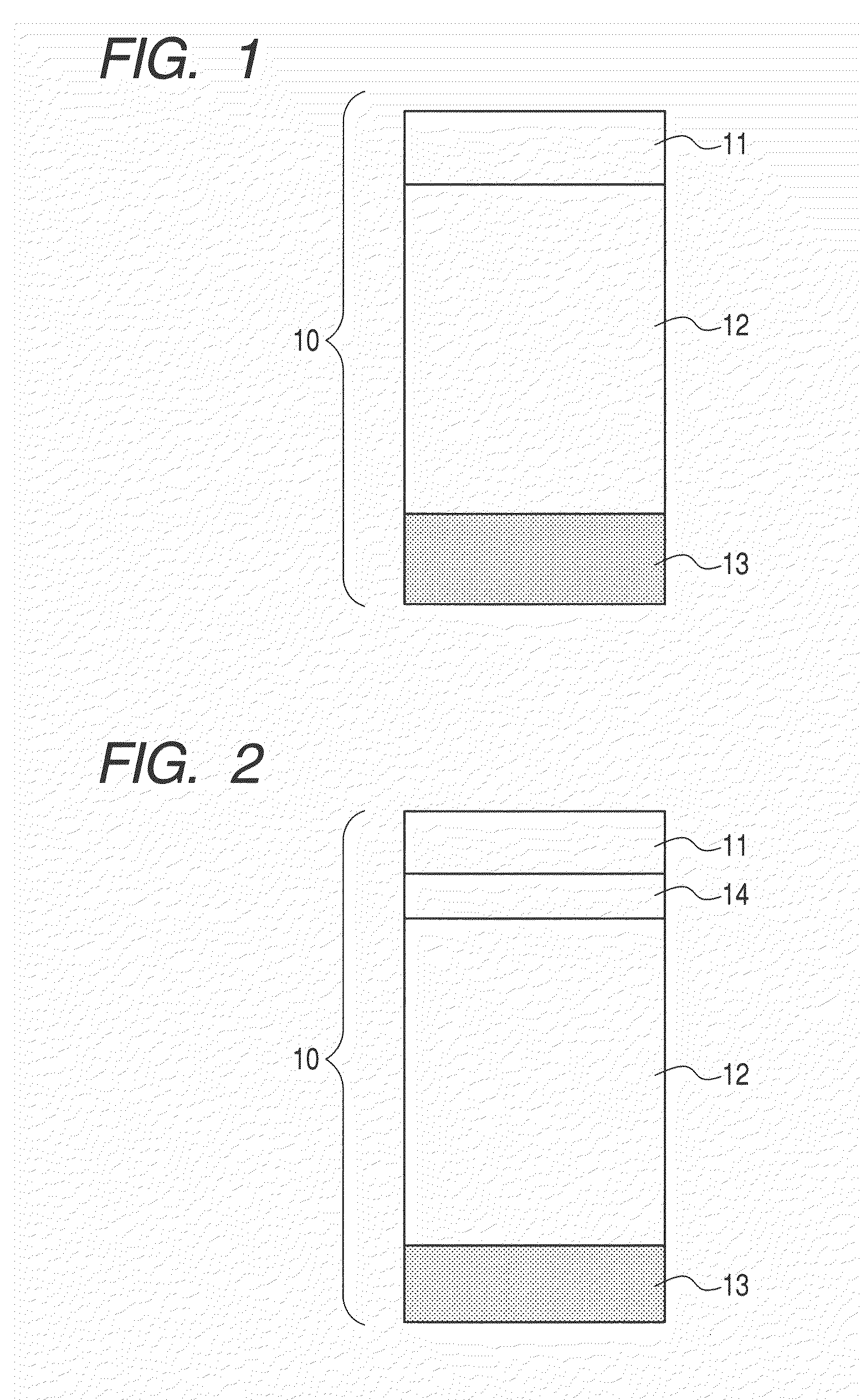
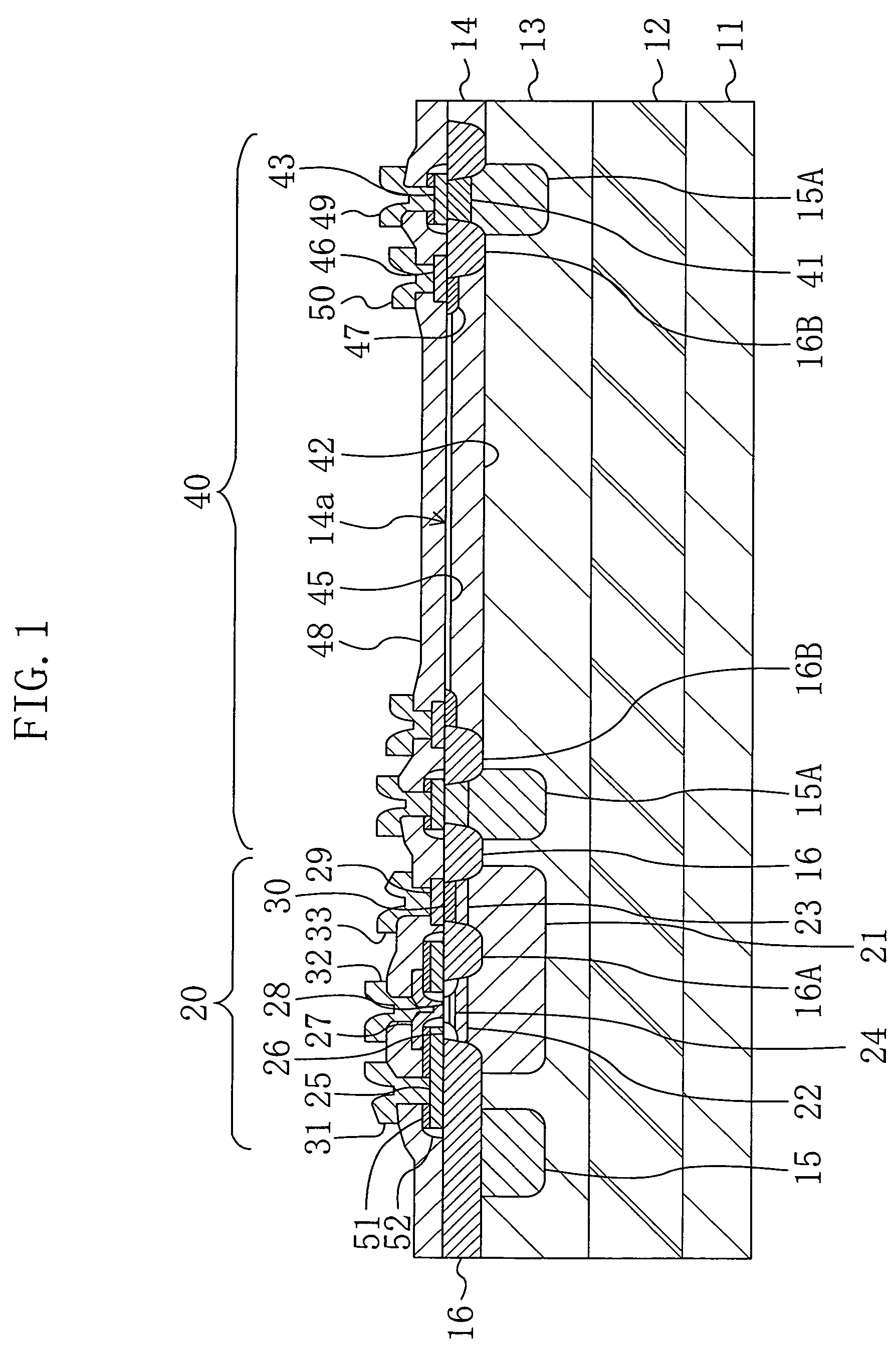
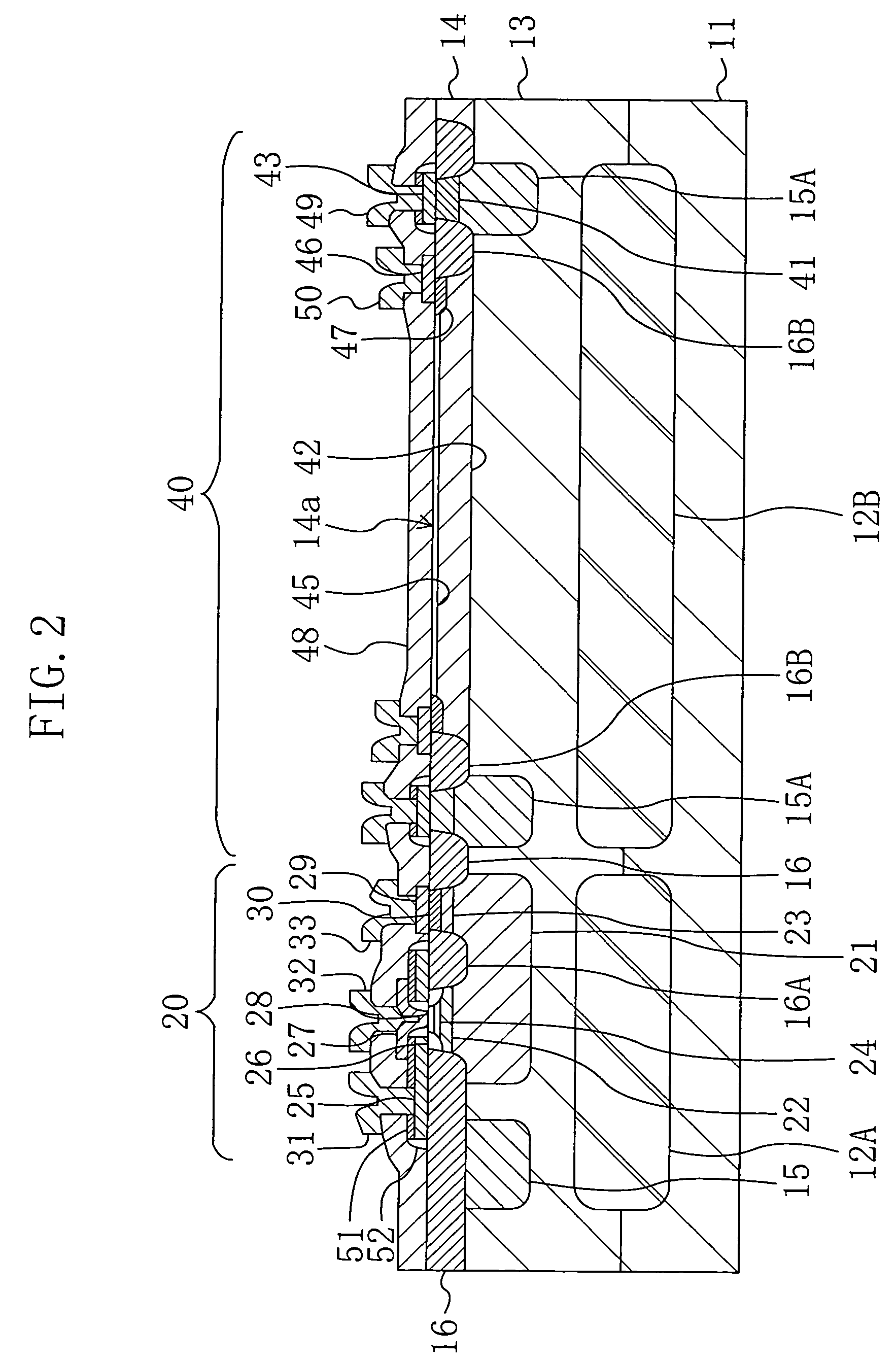
A damascene copper wiring image sensor
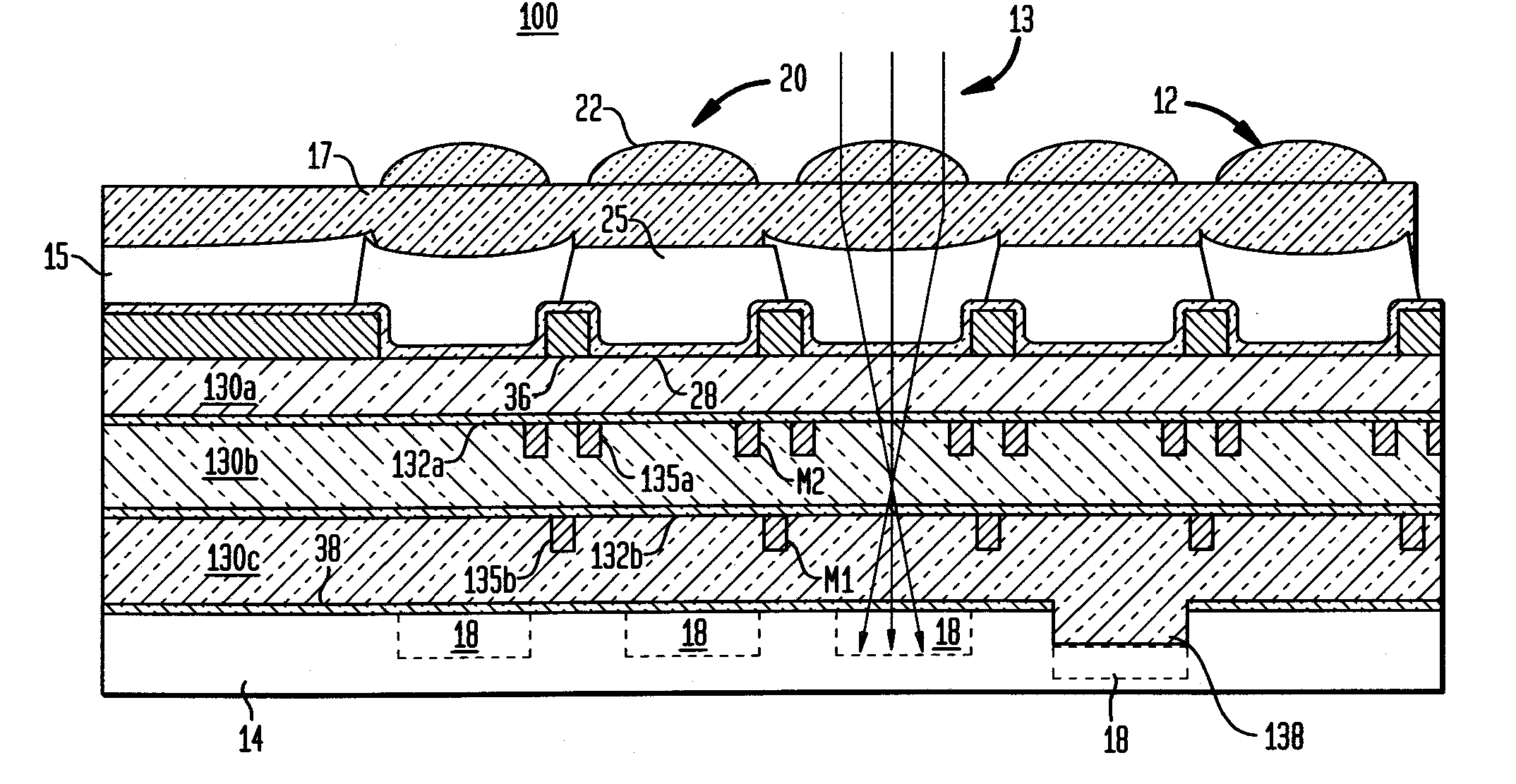
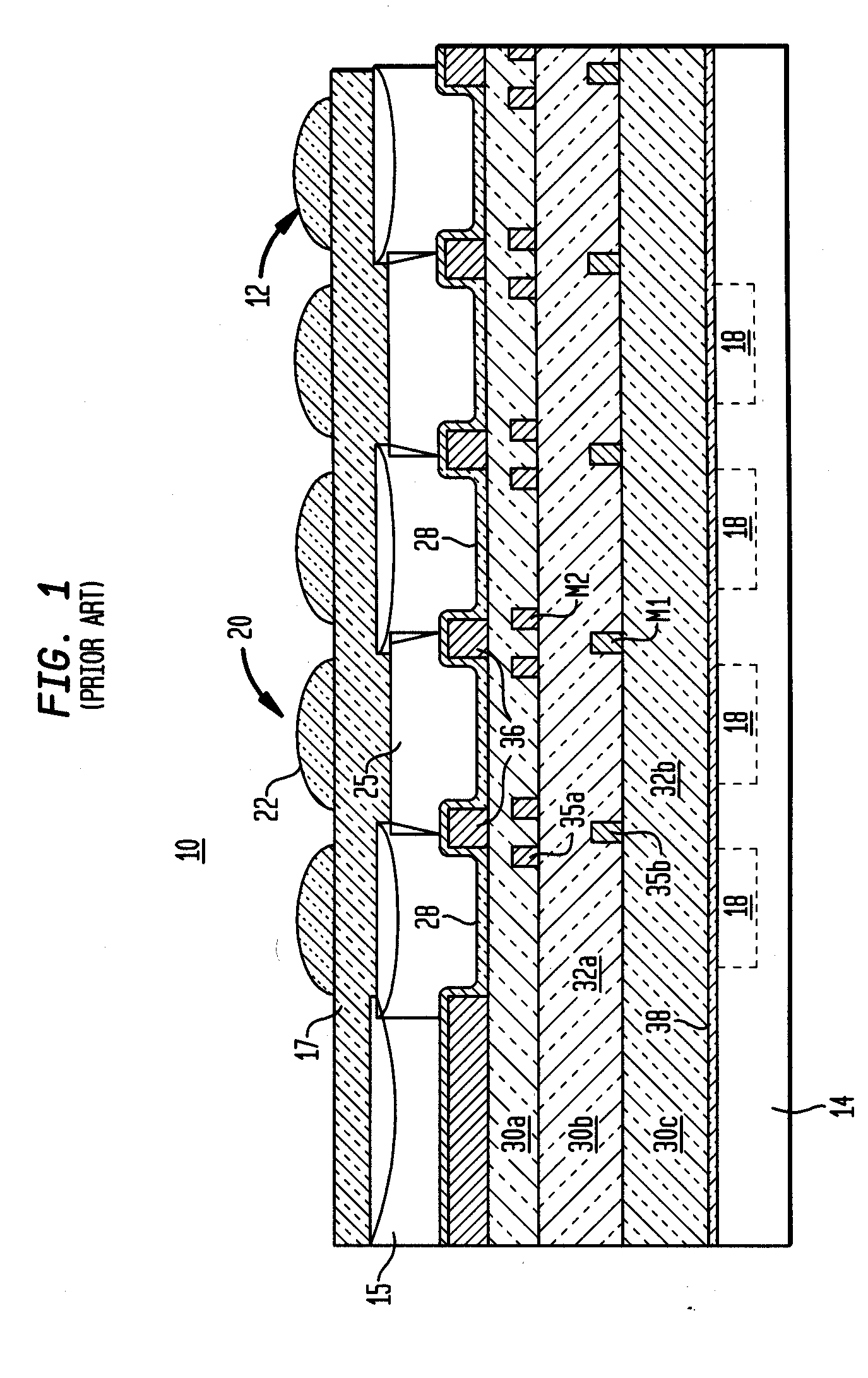
ActiveUS20060113622A1High sensitivityEliminate contaminationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical pathPixel array
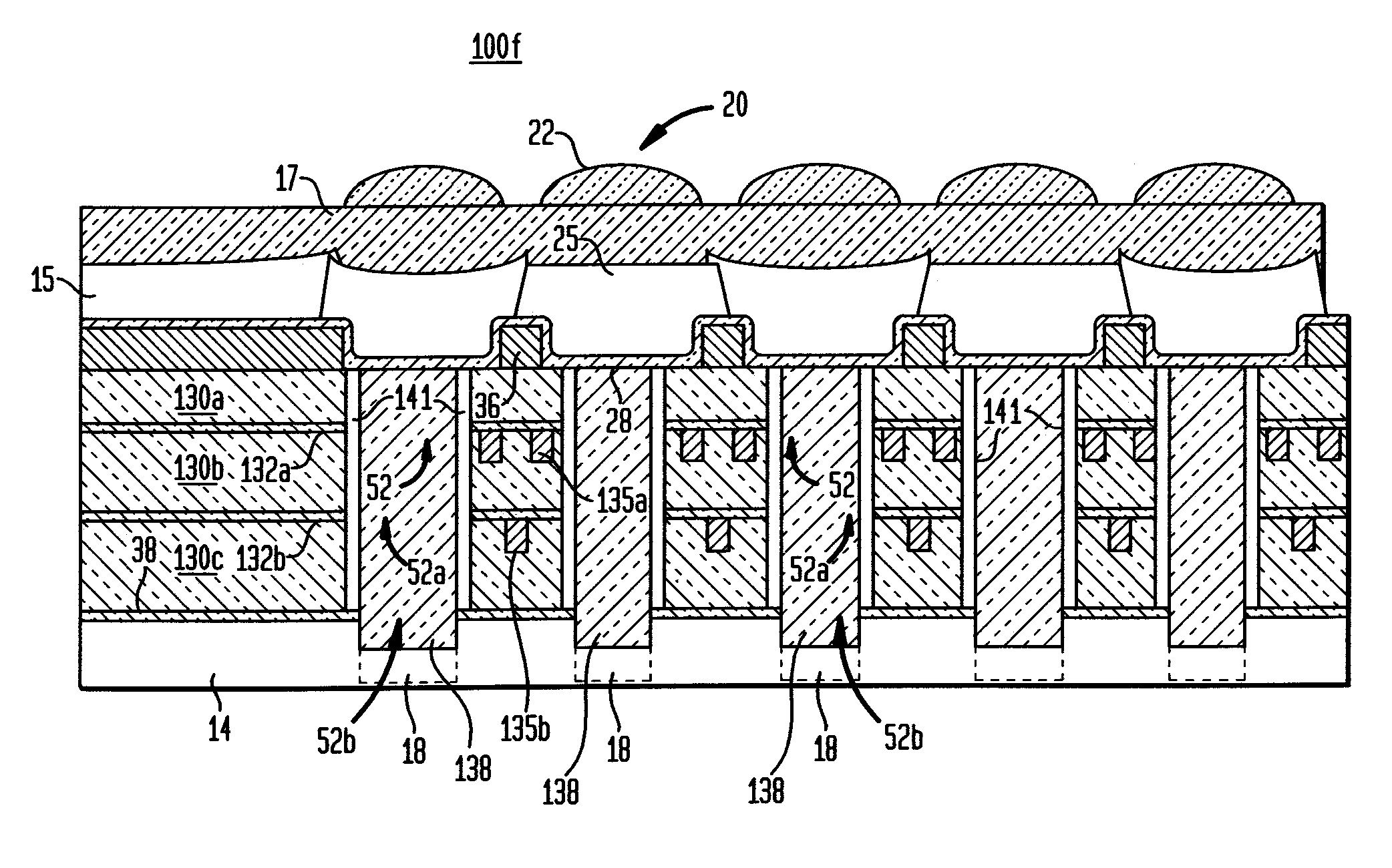
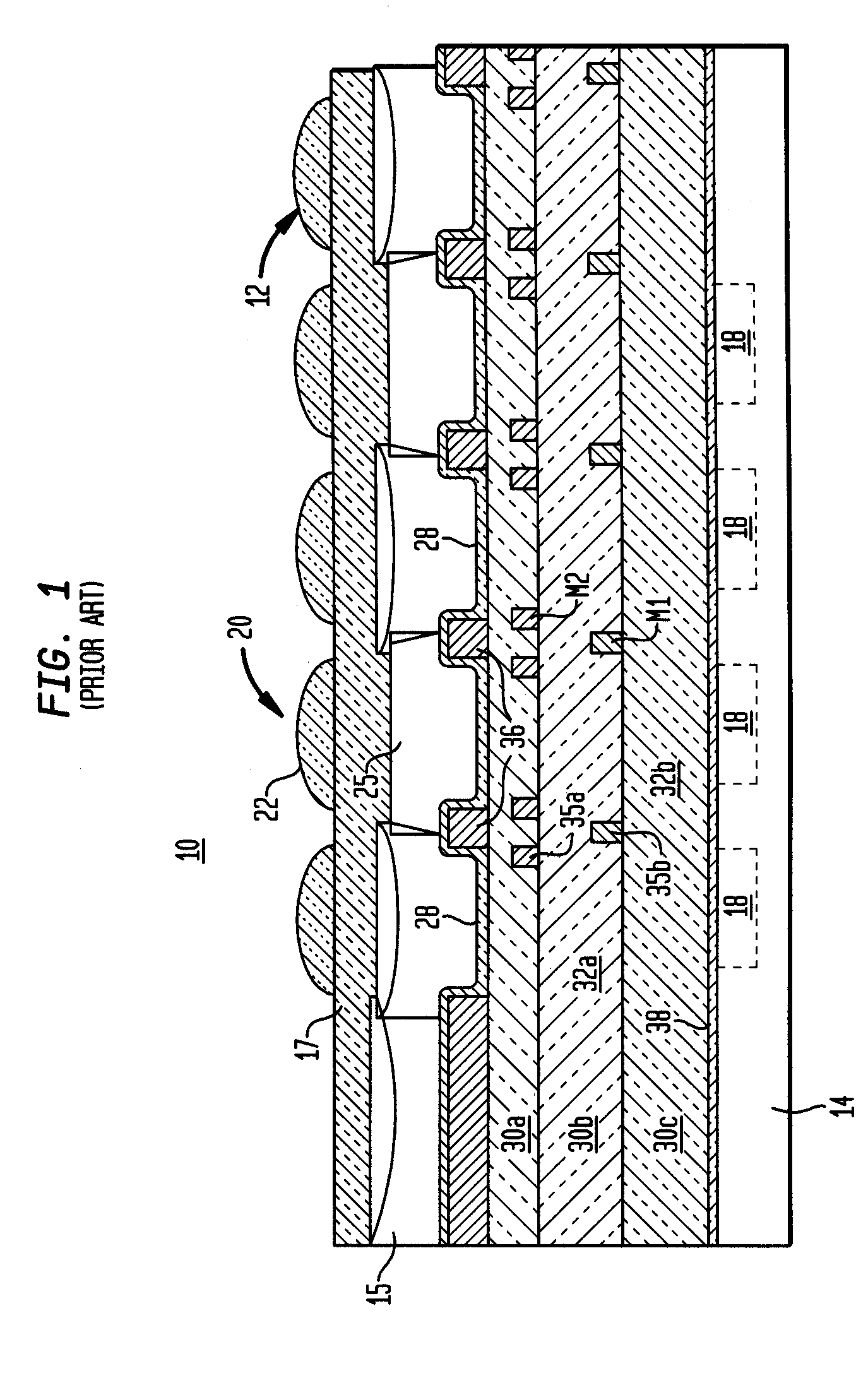
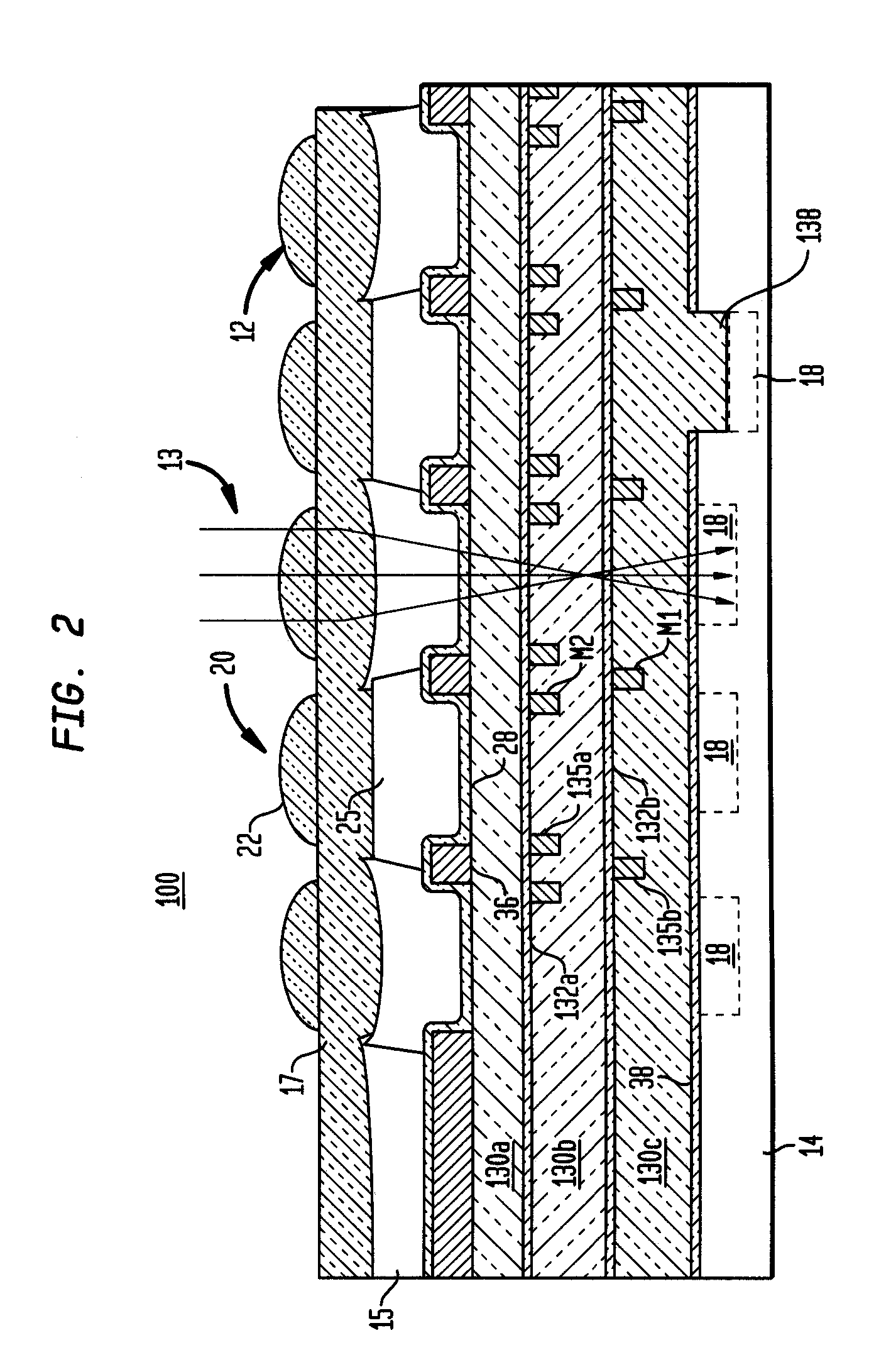
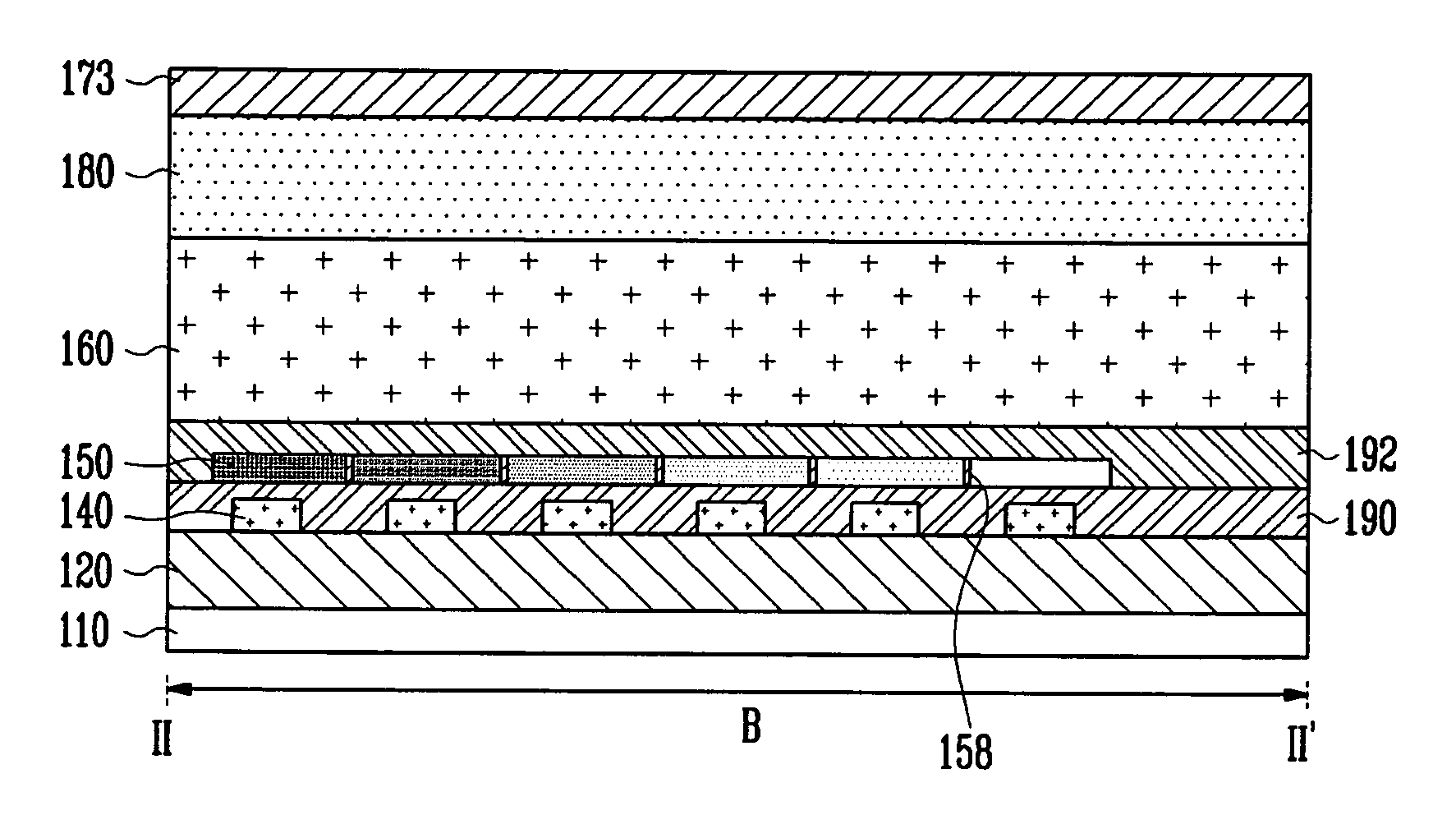
An image sensor array and method of fabrication wherein the sensor includes Copper (Cu) metallization levels allowing for incorporation of a thinner interlevel dielectric stack with improved thickness uniformity to result in a pixel array exhibiting increased light sensitivity. In the sensor array, each Cu metallization level includes a Cu metal wire structure formed at locations between each array pixel and, a barrier material layer is formed on top each Cu metal wire structure that traverses the pixel optical path. By implementing a single mask or self-aligned mask methodology, a single etch is conducted to completely remove the interlevel dielectric and barrier layers that traverse the optical path. The etched opening is then refilled with dielectric material. Prior to depositing the refill dielectric, a layer of either reflective or absorptive material is formed along the sidewalls of the etched opening to improve sensitivity of the pixels by either reflecting light to the underlying photodiode or by eliminating light reflections.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
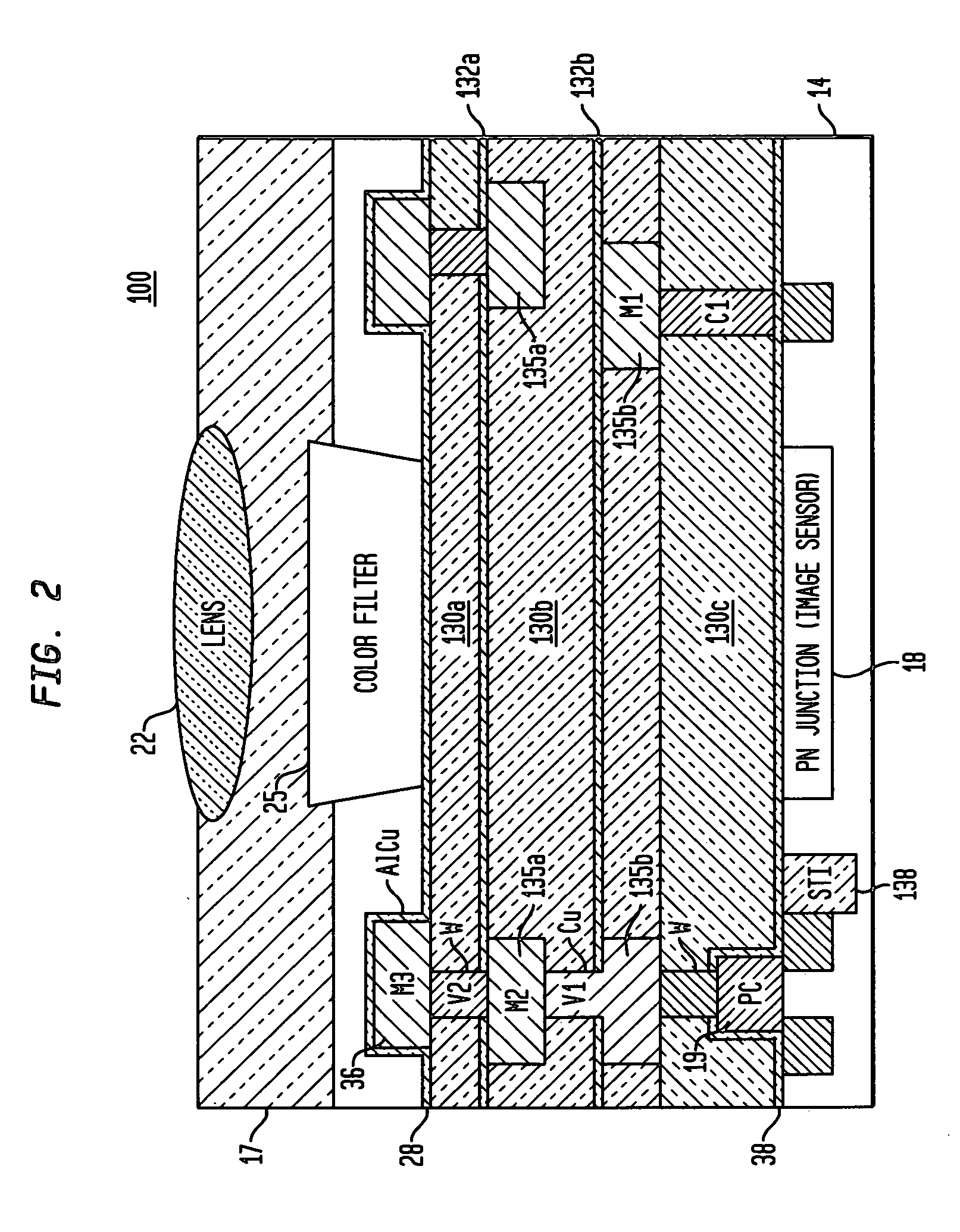
CMOS imager array with recessed dielectric
ActiveUS20080116537A1Thin dielectric stackHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSensor arrayCMOS
A CMOS image sensor array and method of fabrication. The CMOS imager sensor array comprises a substrate; an array of light receiving pixel structures formed above the substrate, the array having formed therein “m” levels of conductive structures, each level formed in a corresponding interlevel dielectric material layer; a dense logic wiring region formed adjacent to the array of light receiving pixel structures having “n” levels of conductive structures, each level formed in a corresponding interlevel dielectric material layer, where n>m. A microlens array having microlenses and color filters formed above the interlevel dielectric material layer, a microlens and respective color filter in alignment with a respective light receiving structure formed at a surface of the substrate. A top surface of the interlevel dielectric material layer beneath the microlens array is recessed from a top surface of the interlevel dielectric material layers of the dense logic wiring region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
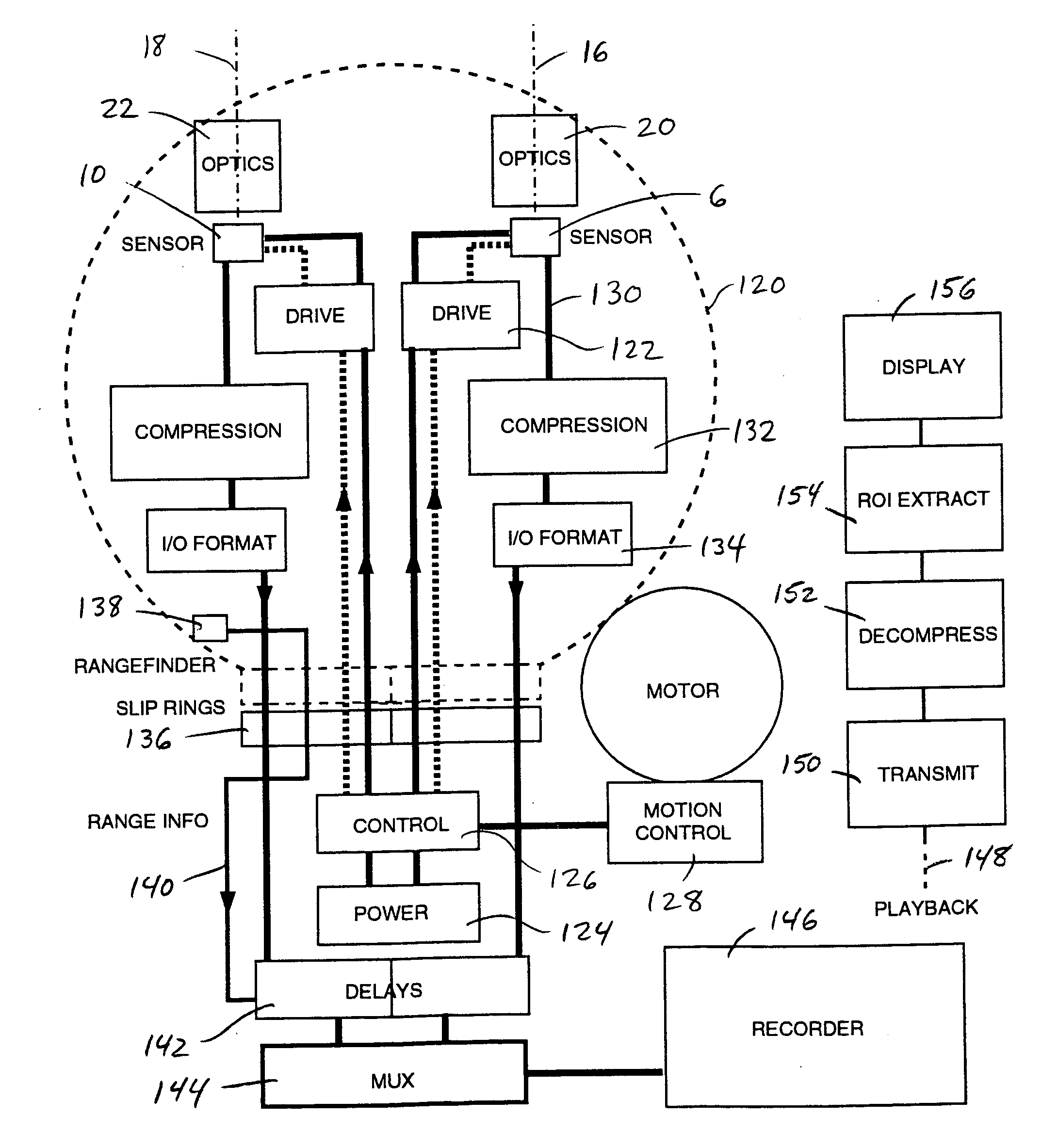
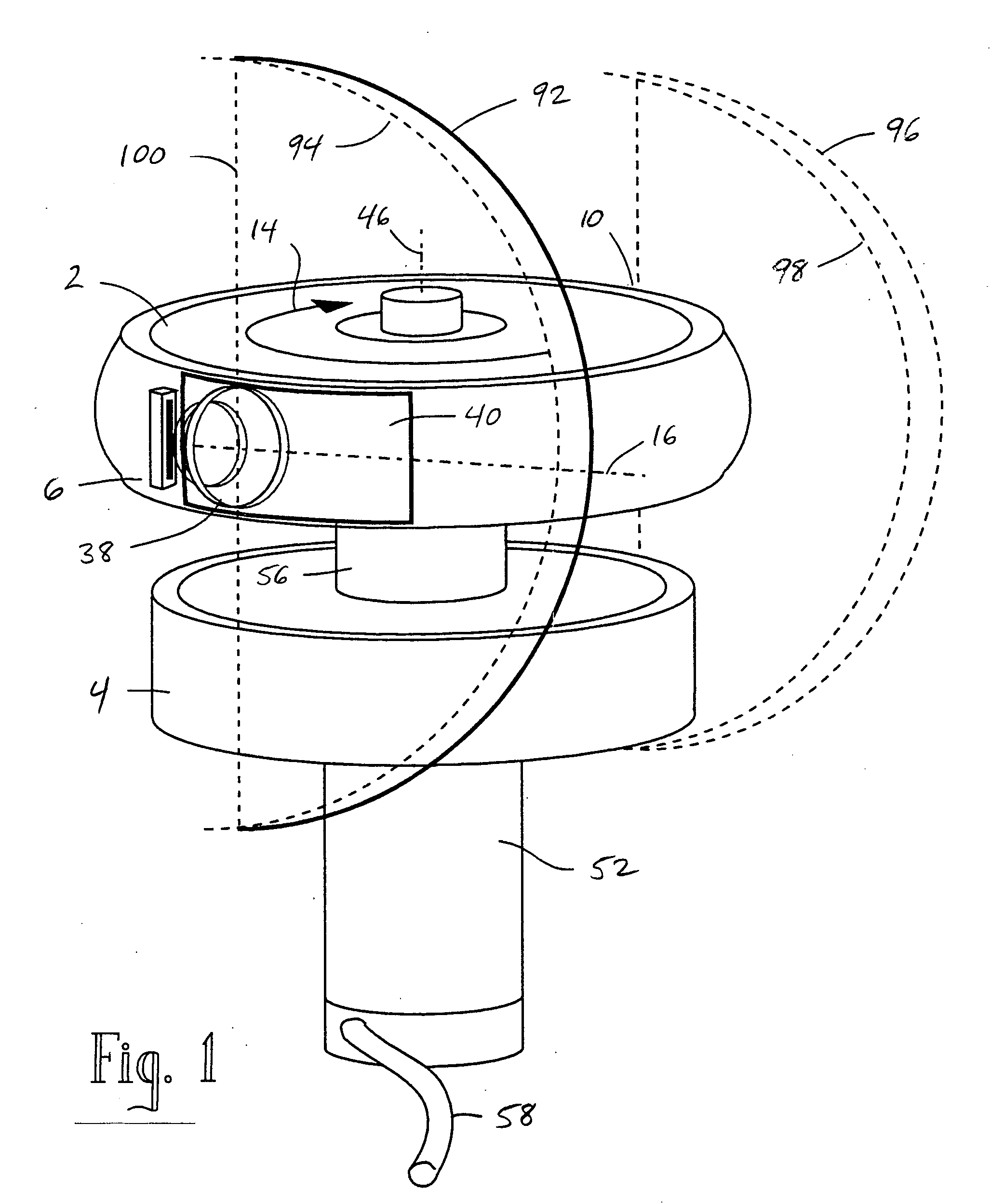
Rotating scan camera
InactiveUS20060072020A1High resolutionHigh light sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsViewpointsRapid rotation
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. The adjustment of convergence between stereoscopic viewpoints is described that improves the viewing and interpretation of stereoscopic images. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially full-sphere field of view. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution and light sensitivity through multiplexed or additive recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
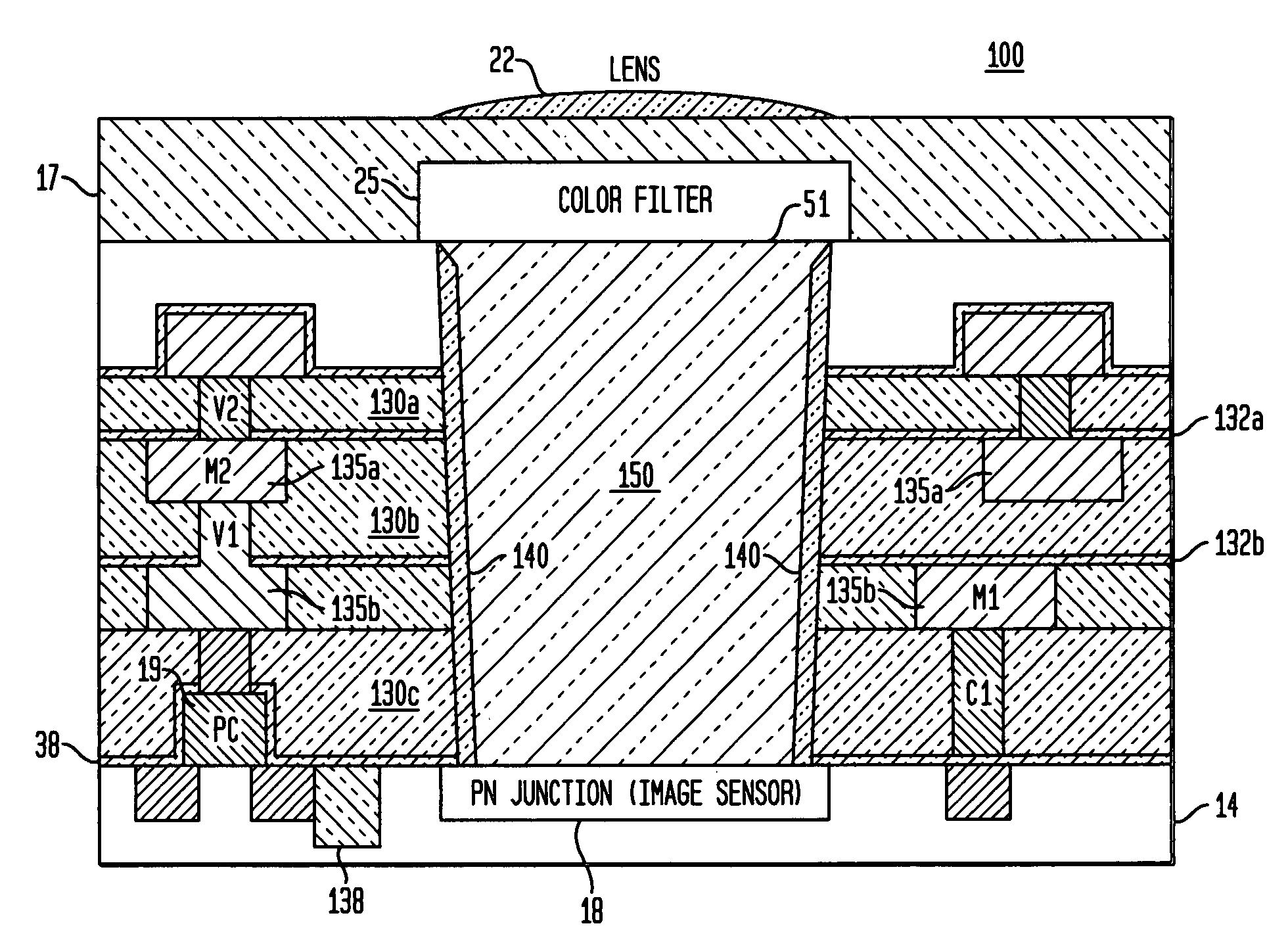
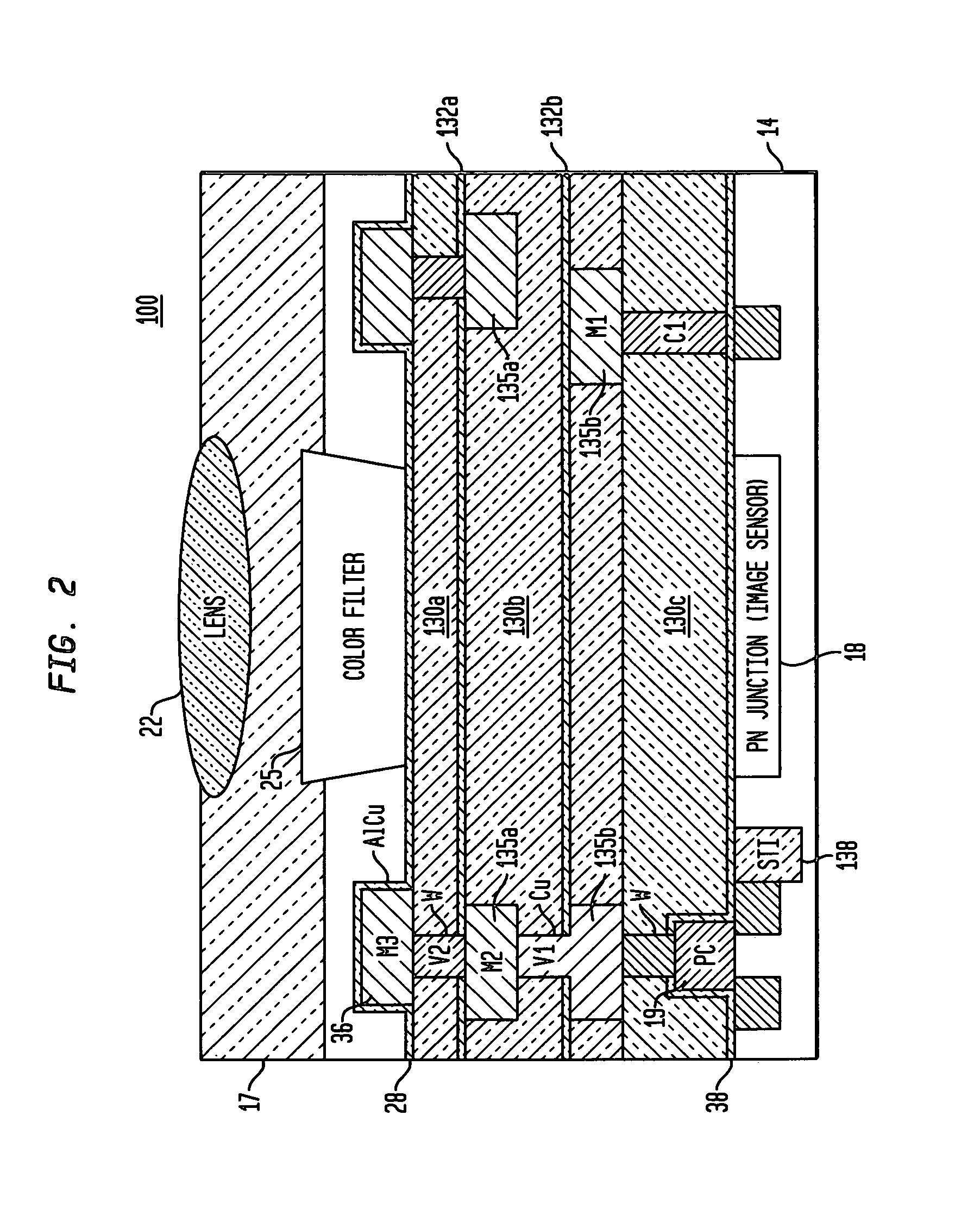
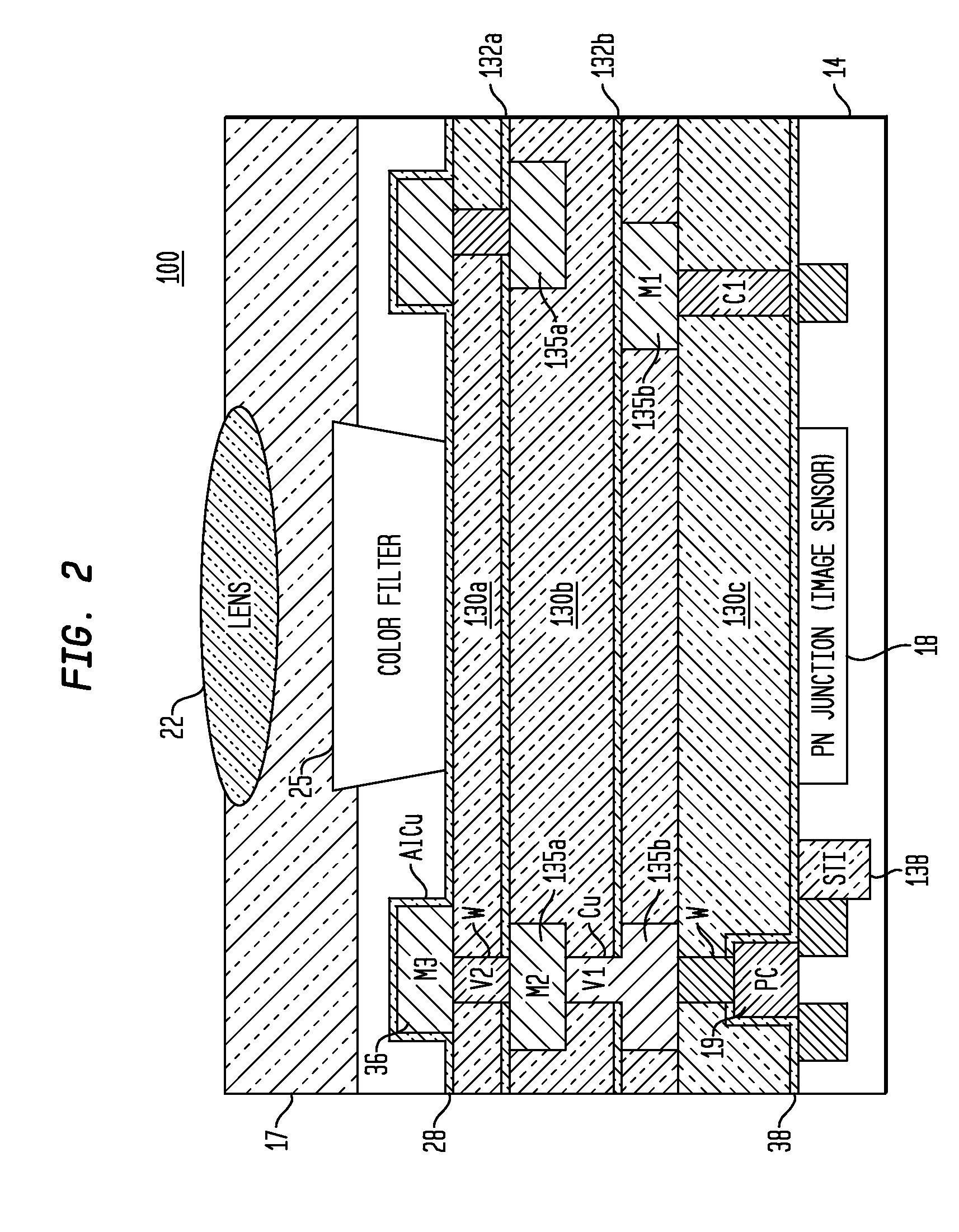
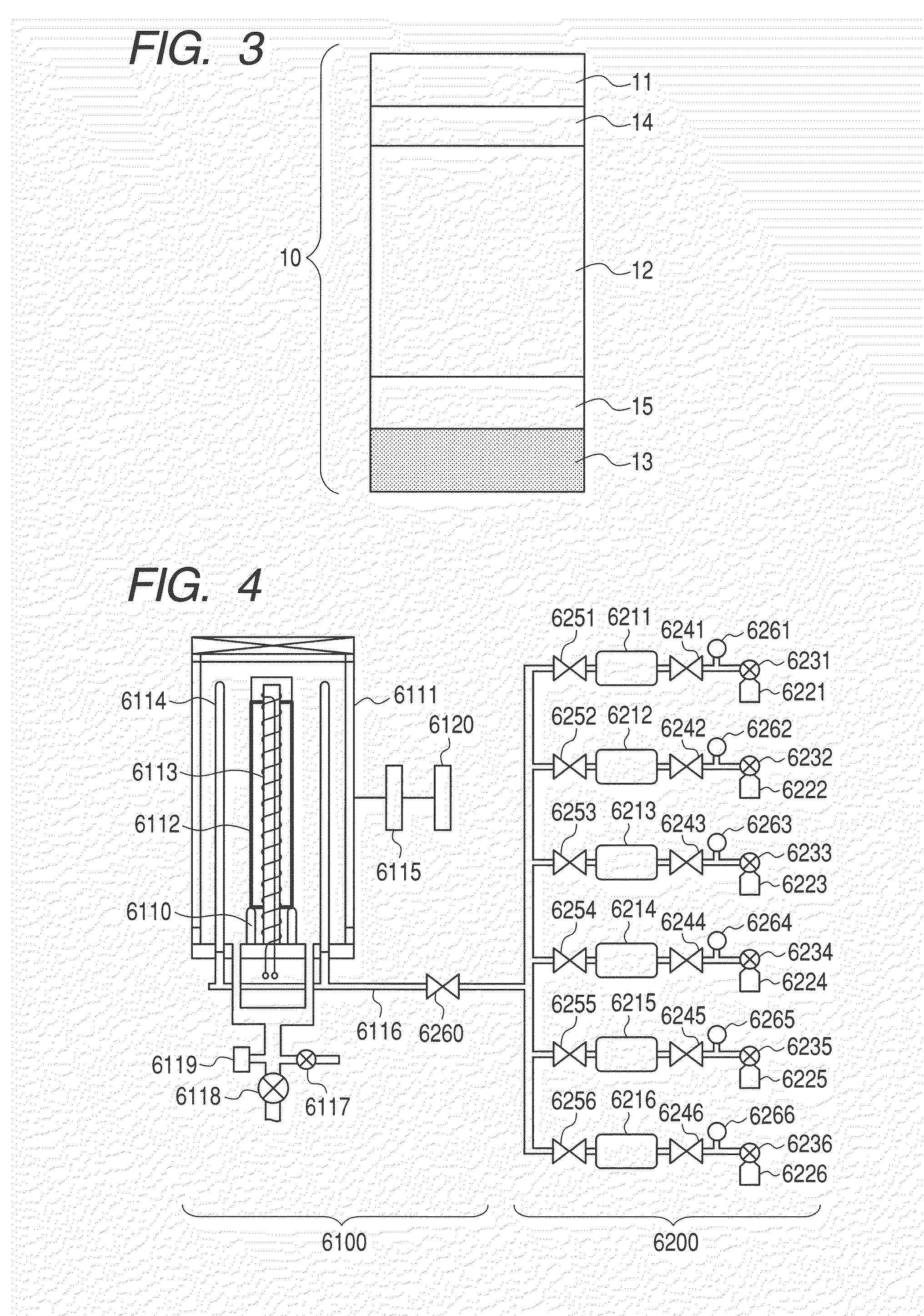
Damascene copper wiring image sensor
ActiveUS7193289B2Eliminate contaminationHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSensor arrayLight reflection
An image sensor array and method of fabrication wherein the sensor includes Copper (Cu) metallization levels allowing for incorporation of a thinner interlevel dielectric stack with improved thickness uniformity to result in a pixel array exhibiting increased light sensitivity. In the sensor array, each Cu metallization level includes a Cu metal wire structure formed at locations between each array pixel and, a barrier material layer is formed on top each Cu metal wire structure that traverses the pixel optical path. By implementing a single mask or self-aligned mask methodology, a single etch is conducted to completely remove the interlevel dielectric and barrier layers that traverse the optical path. The etched opening is then refilled with dielectric material. Prior to depositing the refill dielectric, a layer of either reflective or absorptive material is formed along the sidewalls of the etched opening to improve sensitivity of the pixels by either reflecting light to the underlying photodiode or by eliminating light reflections.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
Damascene copper wiring optical image sensor
ActiveUS20070114622A1Eliminate contaminationHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricCopper-wiring
A CMOS image sensor array and method of fabrication wherein the sensor includes Copper (Cu) metallization levels allowing for incorporation of a inner interlevel dielectric stack with improved thickness uniformity to result in a pixel array exhibiting increased light sensitivity. In the sensor array, each Cu metallization level includes a Cu metal wire structure formed at locations between each array pixel and, a barrier material layer is formed on top each Cu metal wire structure that traverses the pixel optical path. By implementing a single mask or self-aligned mask methodology, a single etch is conducted to completely remove the interlevel dielectric and barrier layers that traverse the optical path. The etched opening is then refilled with dielectric material. Prior to depositing the refill dielectric, a layer of either reflective or absorptive material is formed along the sidewalls of the etched opening to improve sensitivity of the pixels by either reflecting light to the underlying photodiode or by eliminating light reflections.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
CMOS imager array with recessed dielectric
ActiveUS7781781B2Thin dielectric stackHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSensor arrayDielectric
A CMOS image sensor array and method of fabrication. The CMOS imager sensor array comprises a substrate; an array of light receiving pixel structures formed above the substrate, the array having formed therein “m” levels of conductive structures, each level formed in a corresponding interlevel dielectric material layer; a dense logic wiring region formed adjacent to the array of light receiving pixel structures having “n” levels of conductive structures, each level formed in a corresponding interlevel dielectric material layer, where n>m. A microlens array having microlenses and color filters formed above the interlevel dielectric material layer, a microlens and respective color filter in alignment with a respective light receiving structure formed at a surface of the substrate. A top surface of the interlevel dielectric material layer beneath the microlens array is recessed from a top surface of the interlevel dielectric material layers of the dense logic wiring region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
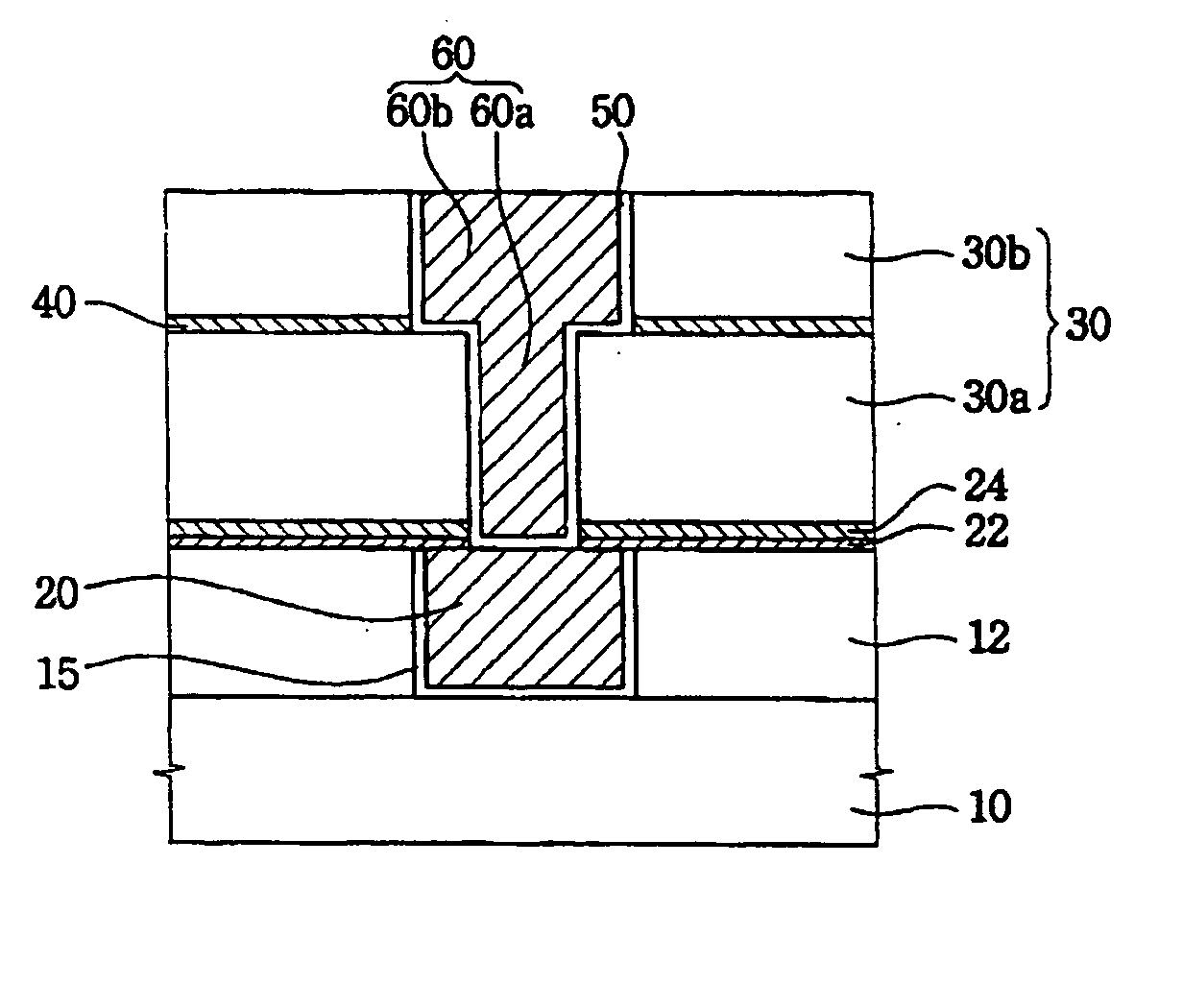
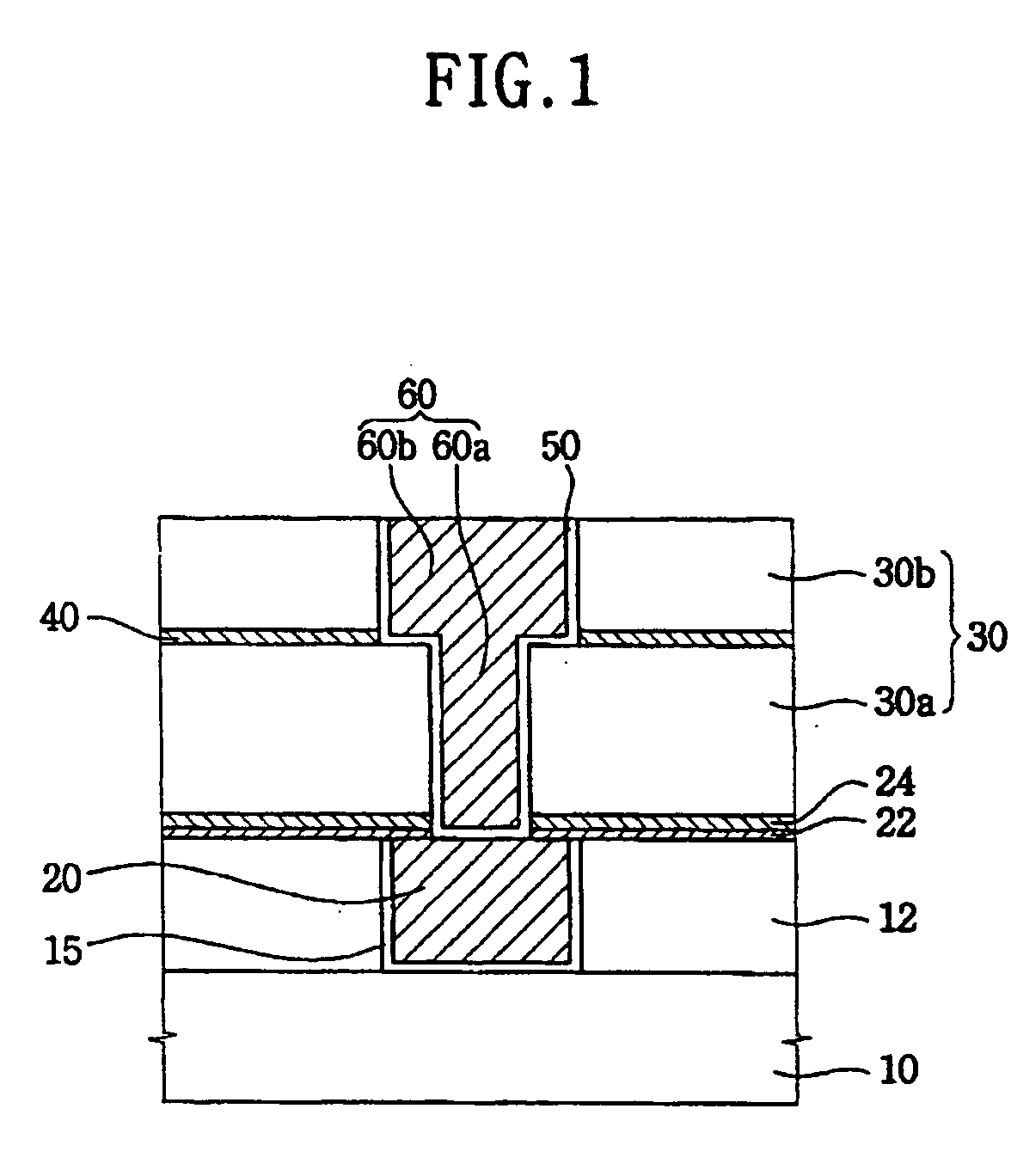
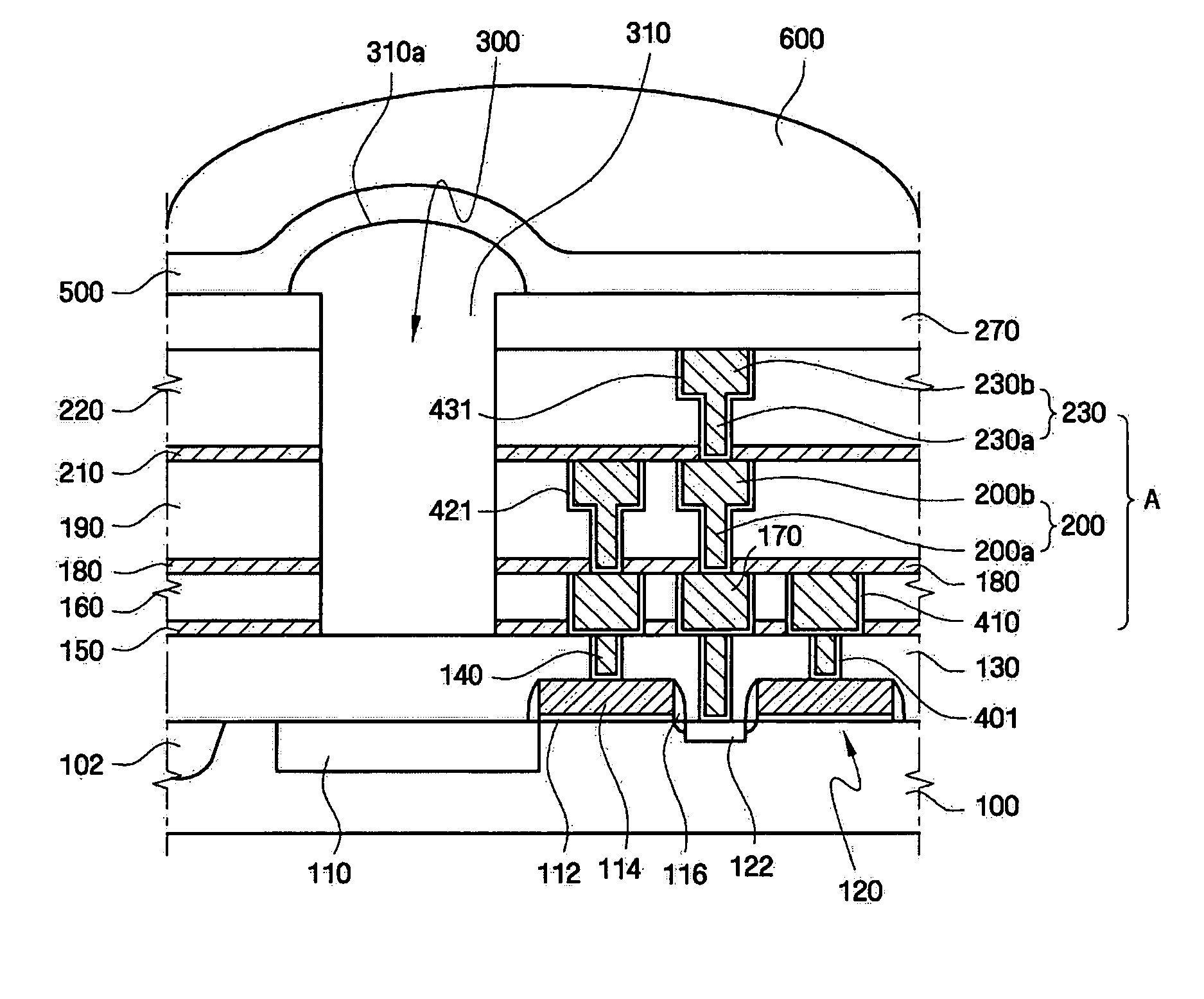
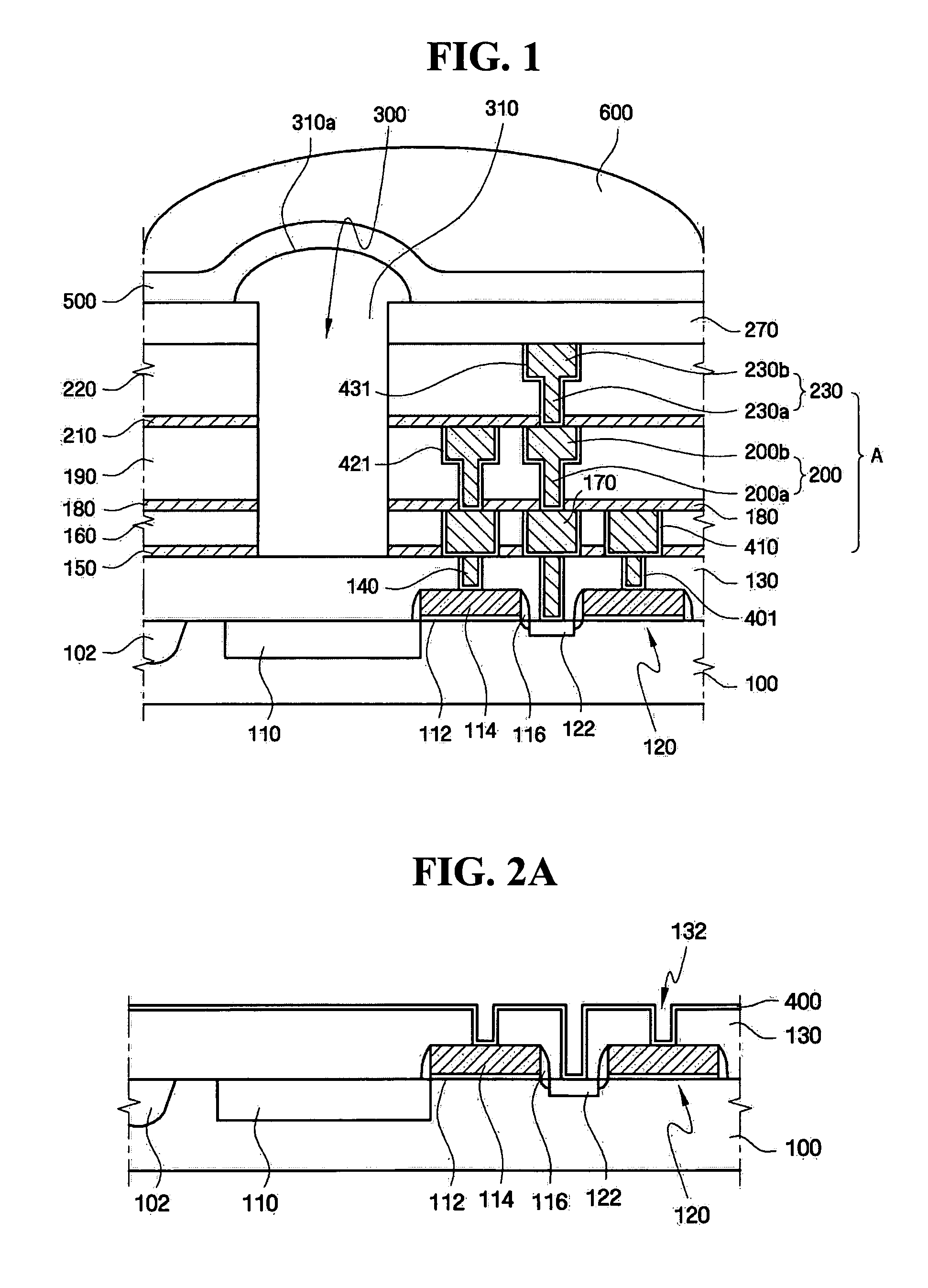
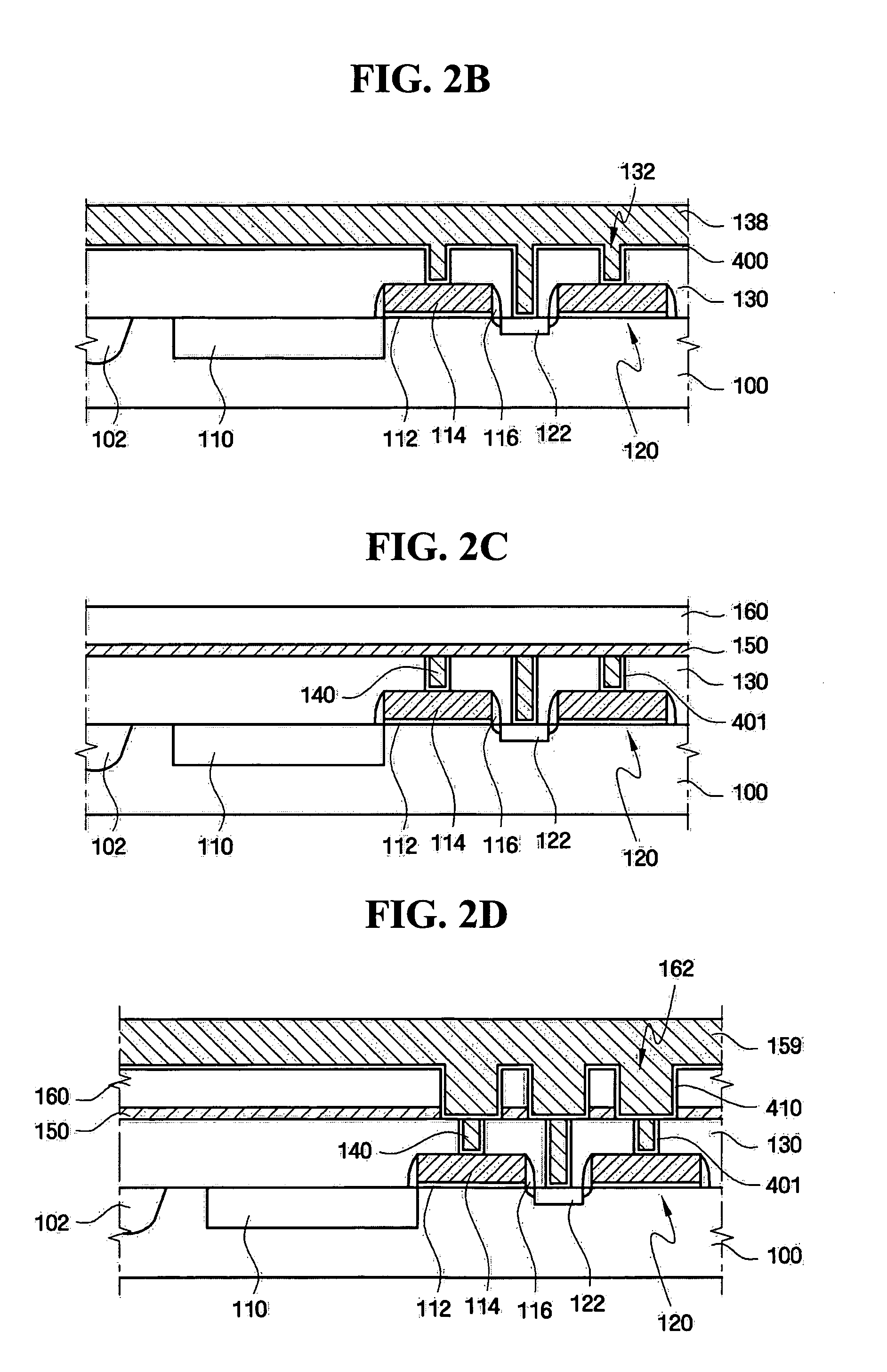
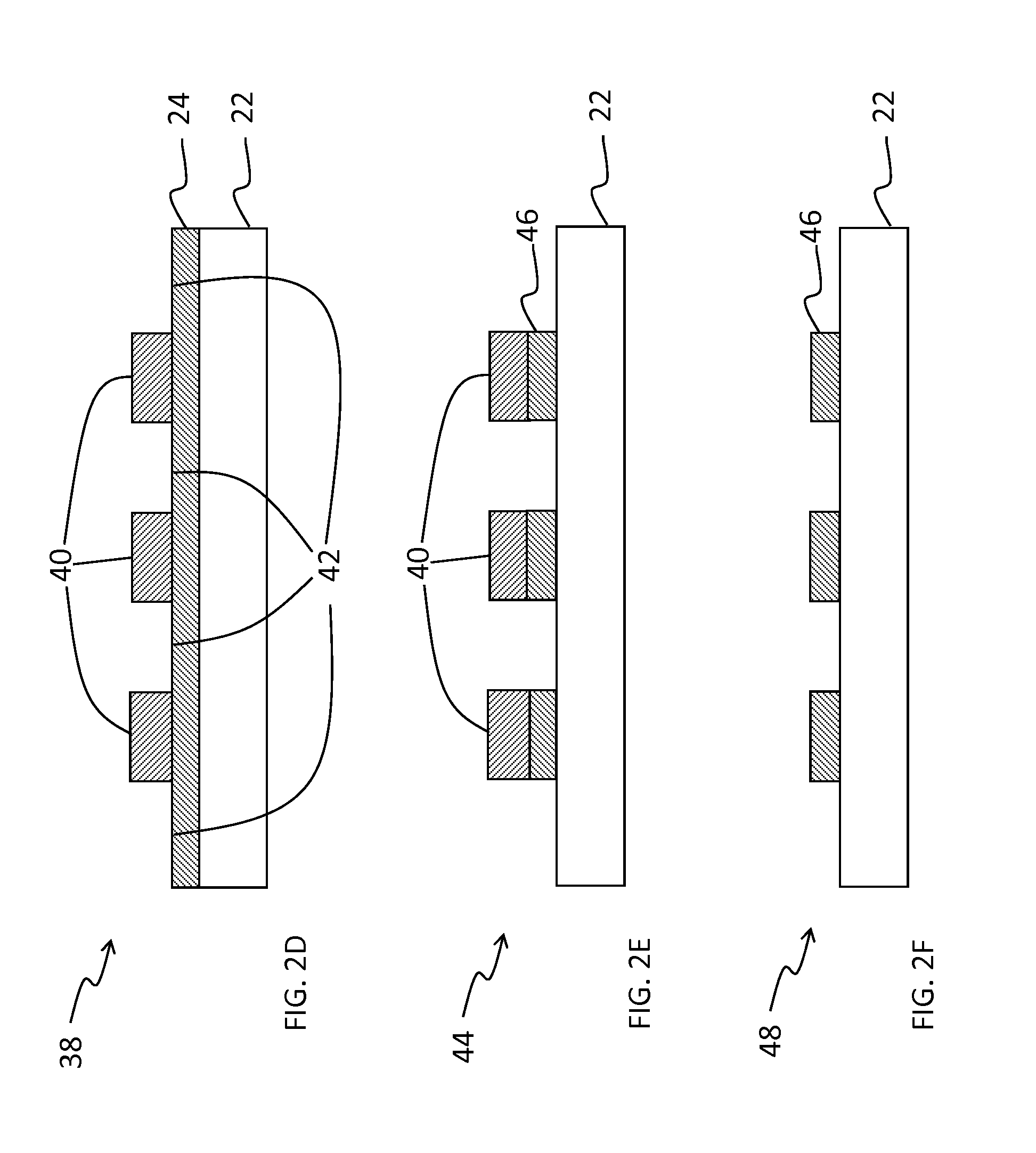
Electrical interconnection, method of forming the electrical interconnection, image sensor having the electrical interconnection and method of manufacturing the image sensor
InactiveUS20050001318A1Inhibited DiffusionGood diffusion preventionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransmittanceImage sensor
An electrical interconnection for a highly integrated semiconductor device includes a first insulation layer having at least a first recessed portion on a substrate. The first recessed portion is filled with metal to form a first metal pattern. A diffusion barrier layer including aluminum oxide of high light transmittance is provided on the first insulation layer and the first metal pattern for preventing metal from diffusing. An insulating interlayer including a second recessed portion for exposing an upper surface of the first metal pattern is provided on the diffusion barrier layer. The second recessed portion is filled with metal to form a second metal pattern. The electrical interconnection may be used with an image sensor. The metal may be copper. High light transmittance of the diffusion barrier layer ensures external light reaches the photodetector. The aluminum oxide of the diffusion barrier layer reduces parasitic capacitance of the electrical interconnections.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Commissioning Coded Light Sources
ActiveUS20120200226A1Easy to debugReduced risk of collisionElectric light circuit arrangementClose-range type systemsLighting systemLight emission
Commissioning a coded light source in a lighting system is accomplished by using a remote controller. When an identification of a light source is successful, a control message is sent to that light source to at least partly switch off its light emission. Thus the light contribution of the identified light source is suppressed. Thereby the chance of coded light from an already identified light source colliding with identifiers comprised in coded light emitted by other light sources is reduced. When no more coded light is detectable, a sensitivity of the remote controller can be increased until coded light again is detectable. Further light sources can then be identified and commissioned.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Image sensor with embedded photodiode region and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS7417273B2Raise the ratioHigh light sensitivityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringFloating diffusion
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
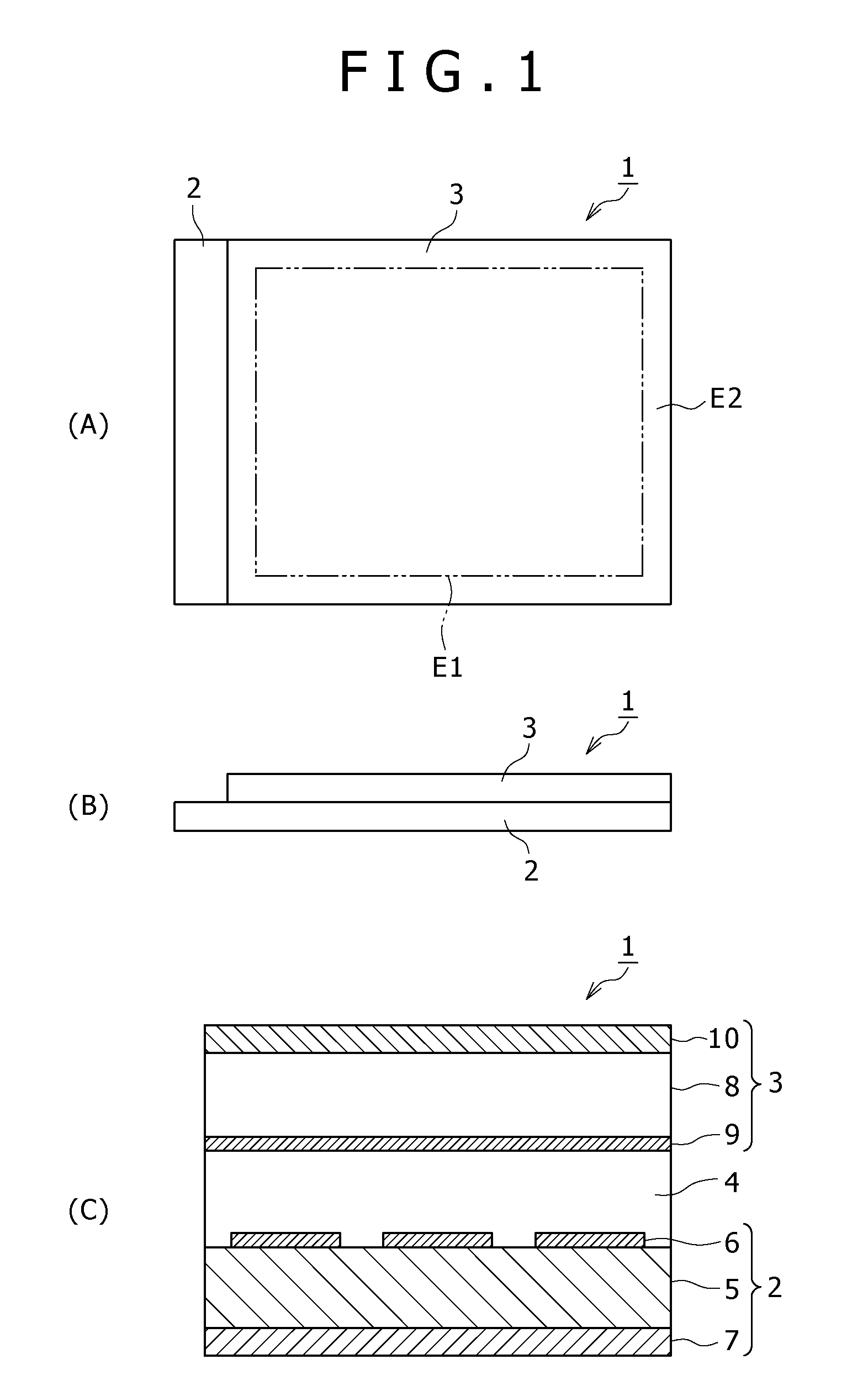
Display and method for manufacturing display
ActiveUS20100171120A1High light sensitivityHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay devicePhotoelectric conversion
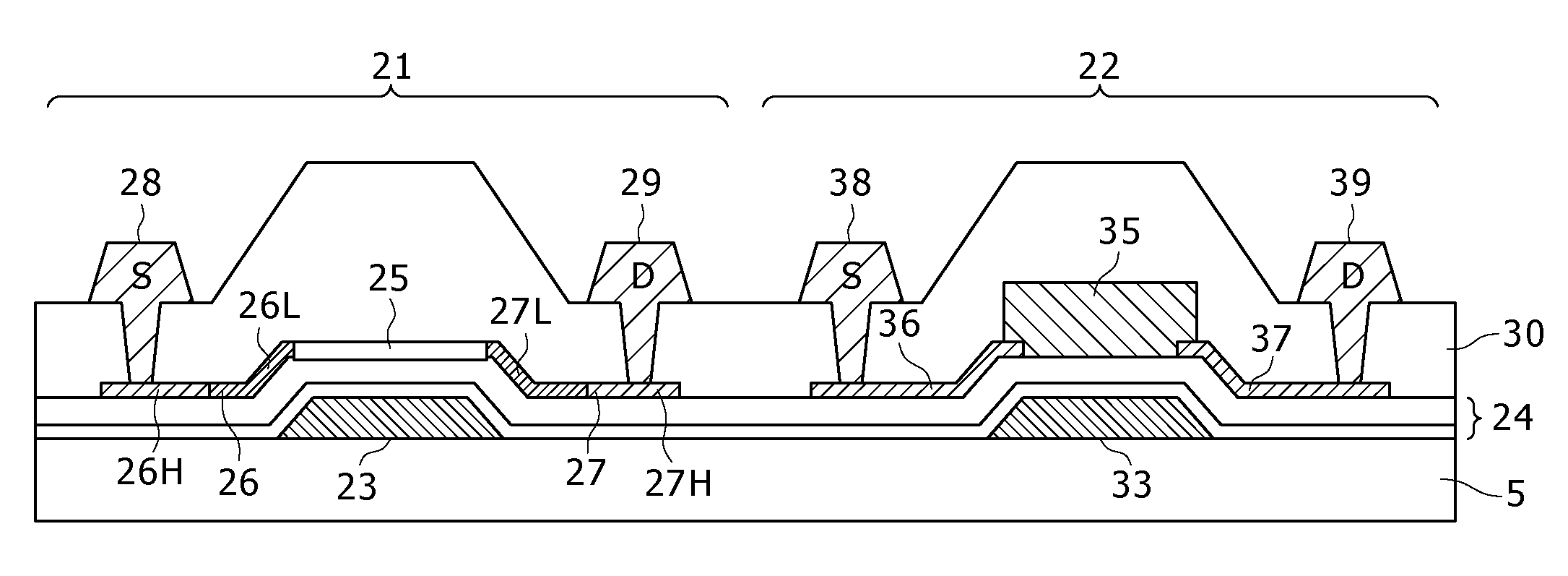
In the case of forming switching elements and light sensor elements over the same substrate, an increase in the film thickness of active layers in an attempt to enhance the sensitivity of the light sensor elements would adversely affect the characteristics of the switching elements (TFTs). In a configuration of a display in which a channel layer 25 for constituting thin film transistors to form the switching elements for pixels and a photoelectric conversion layer 35 for constituting the light sensor elements are provided over a gate insulating film 24 on a glass substrate 5 to be provided with a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix pattern, the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is formed to be thicker than the channel layer 25, and / or the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is formed of a material different from the material for the channel layer 25, whereby the light absorption coefficient of the photoelectric conversion layer 35 is made to be higher than that of the channel layer 25.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
A CMOS imager with cu wiring and method of eliminating high reflectivity interfaces therefrom
ActiveUS20060138480A1Increase volumeHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSensor array
An image sensor and method of fabrication wherein the sensor includes Copper (Cu) metallization levels allowing for incorporation of a thinner interlevel dielectric stack to result in a pixel array exhibiting increased light sensitivity. The image sensor includes structures having a minimum thickness of barrier layer metal that traverses the optical path of each pixel in the sensor array or, that have portions of barrier layer metal selectively removed from the optical paths of each pixel, thereby minimizing reflectance. That is, by implementing various block or single mask methodologies, portions of the barrier layer metal are completely removed at locations of the optical path for each pixel in the array. In a further embodiment, the barrier metal layer may be formed atop the Cu metallization by a self-aligned deposition.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
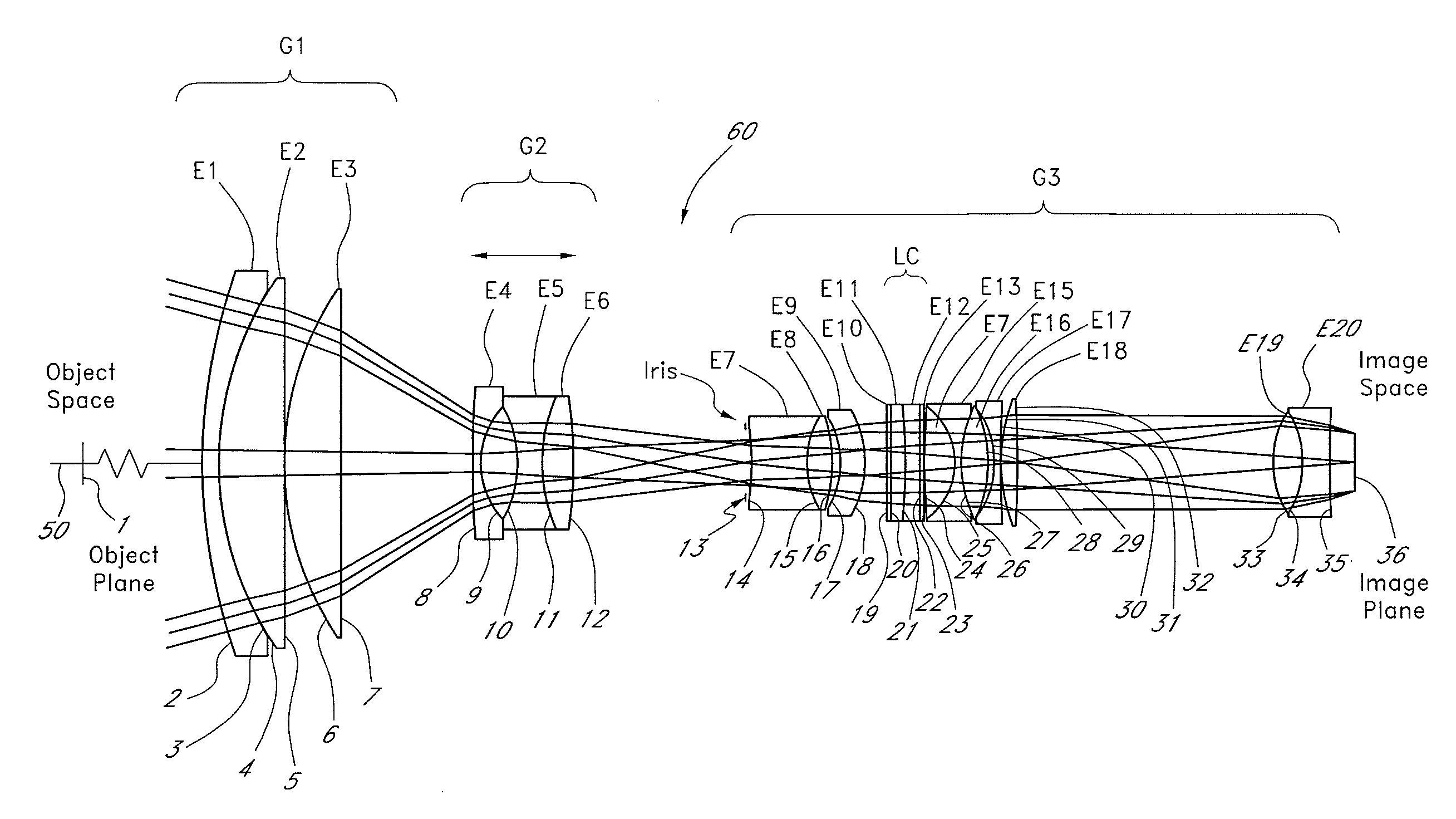
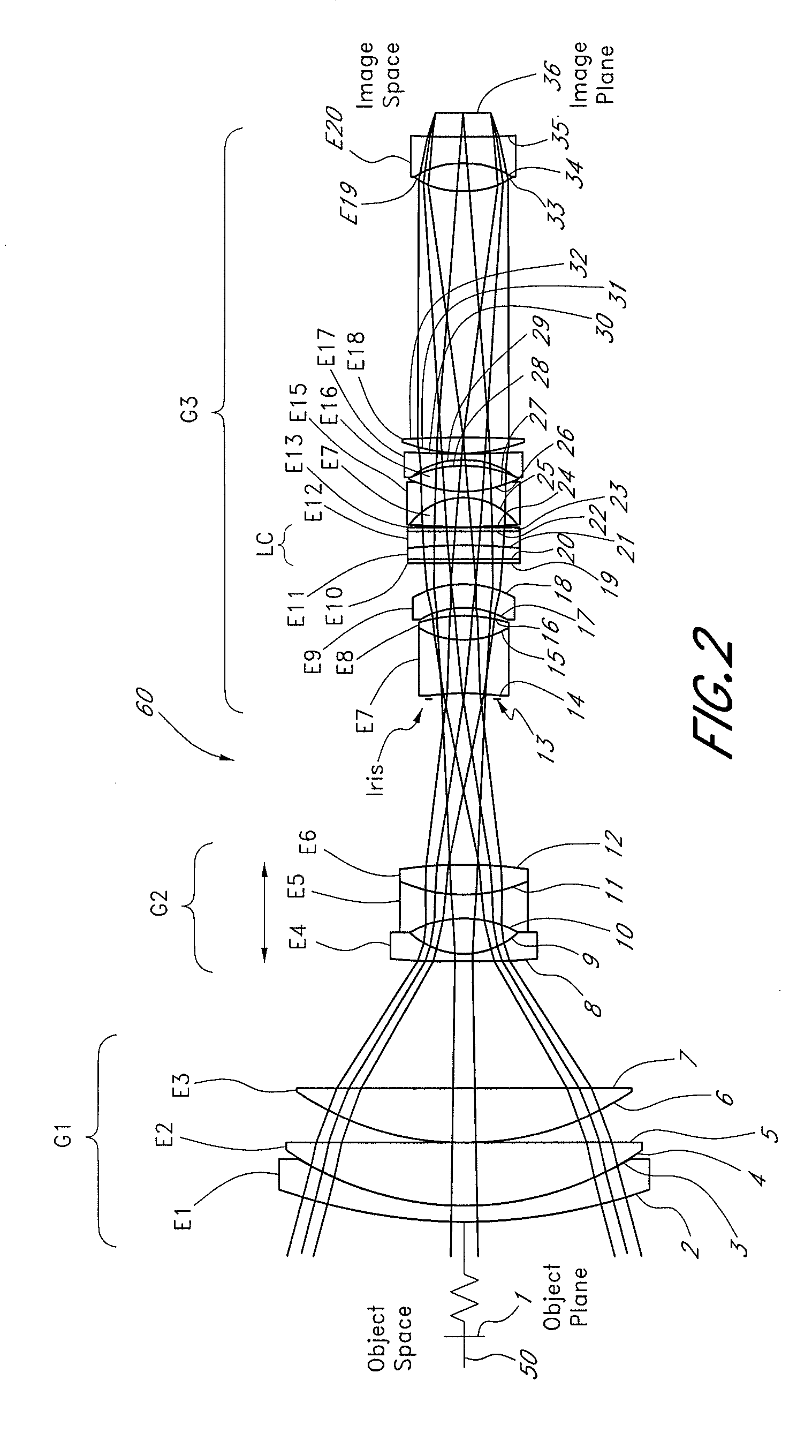
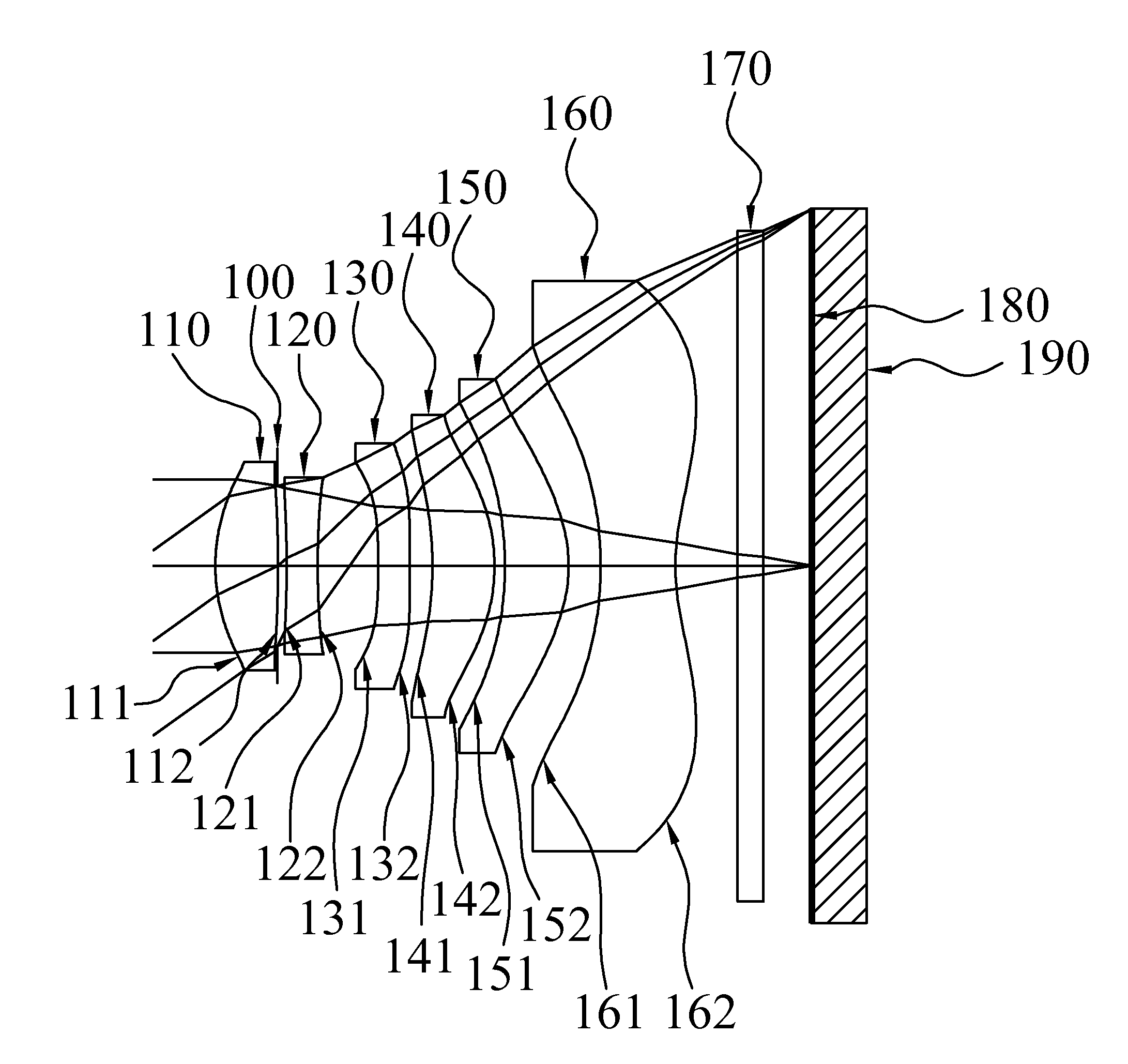
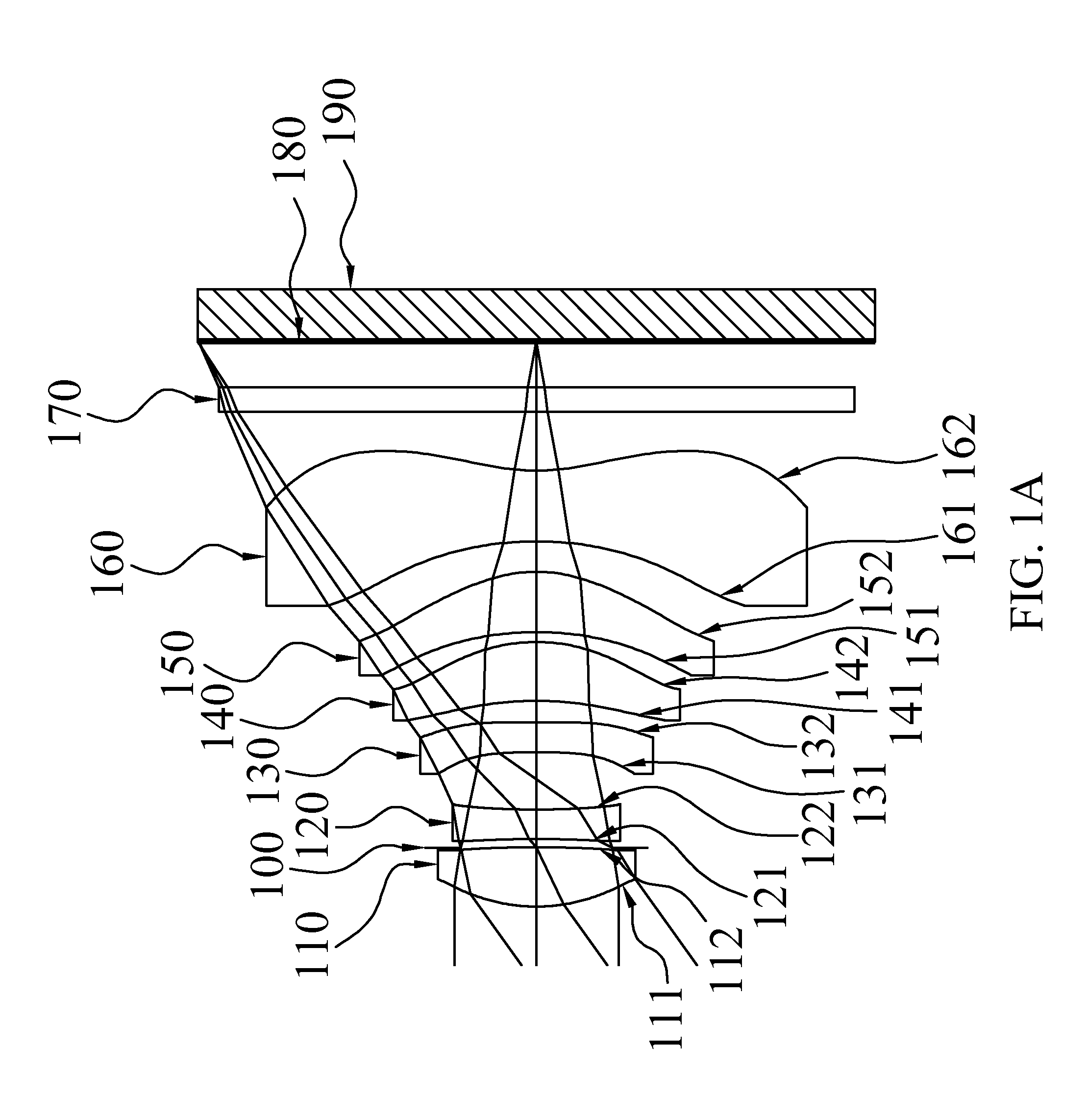
Liquid optics zoom lens and imaging apparatus
A high performance zoom lens system suitable for use with a camera is disclosed. The zoom lens systems employs liquid optics and a movable lens group to provide optical performance over the zoom focal length range at focus distances from close to infinity. The system also provides compensation for undesirable thermally induced effects by adjustments of the zoom group and the variably shaped optical surface in the liquid lens cell.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Image device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060049439A1Prevents scattering and irregular reflection of lightHigh light sensitivityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsDielectric structure
An image device includes a substrate in which a light receiving element is formed, an interlayer dielectric structure which is formed on the substrate and has a cavity over the light receiving element, a transparent dielectric layer which fills the cavity and has a lens-shaped portion protruding beyond an upper portion of the interlayer dielectric structure, and a color filter which is formed on the transparent dielectric layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radiation curable thiol-ene composition
InactiveUS20070043205A1High light sensitivityLow shrinkagePhotomechanical apparatusPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsChemistryPhotoinitiator
The invention relates to a curable thiol-ene composition comprising either compound A and compound B, or a compound B further comprising polythiol functionality as defined under (A), wherein (A) a polythiol, (B) a compound having a plurality of cyclic ene groups thereon, wherein said compound (B) comprises a carbonyl group directly attached to at least one cyclic ene group and comprises at least one hydrogen donating group, wherein the distance between at least one of said cyclic ene groups and at least one of said hydrogen donating groups is at least two skeletal bonds, wherein compound (B) does not contain a (meth)acrylate group, and 0-10 wt. % of a (free-radical) photoinitiator. The invention further relates to the use of such composition fiber optical coating, stereolithography resin, medical coating and adhesive.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
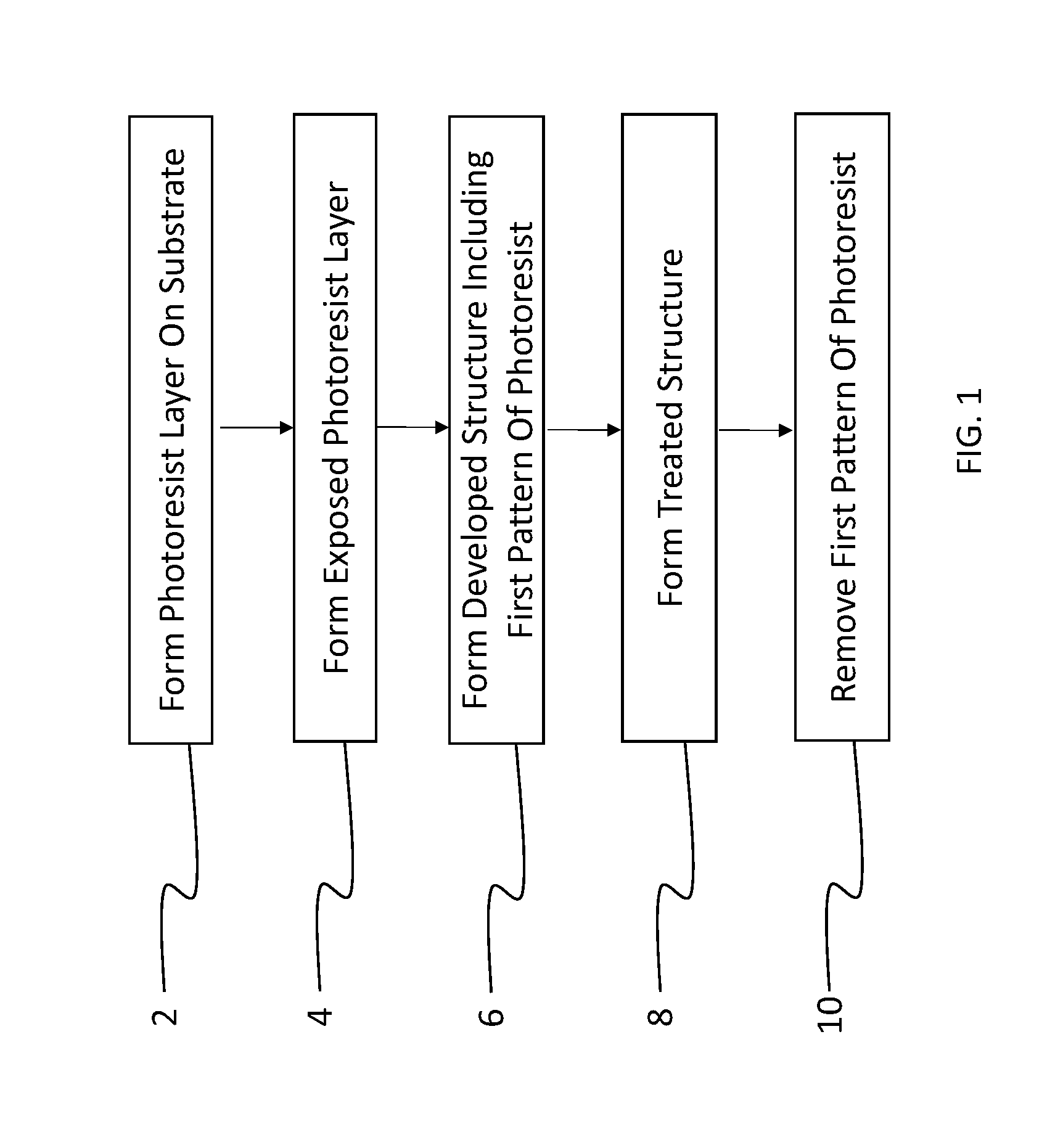
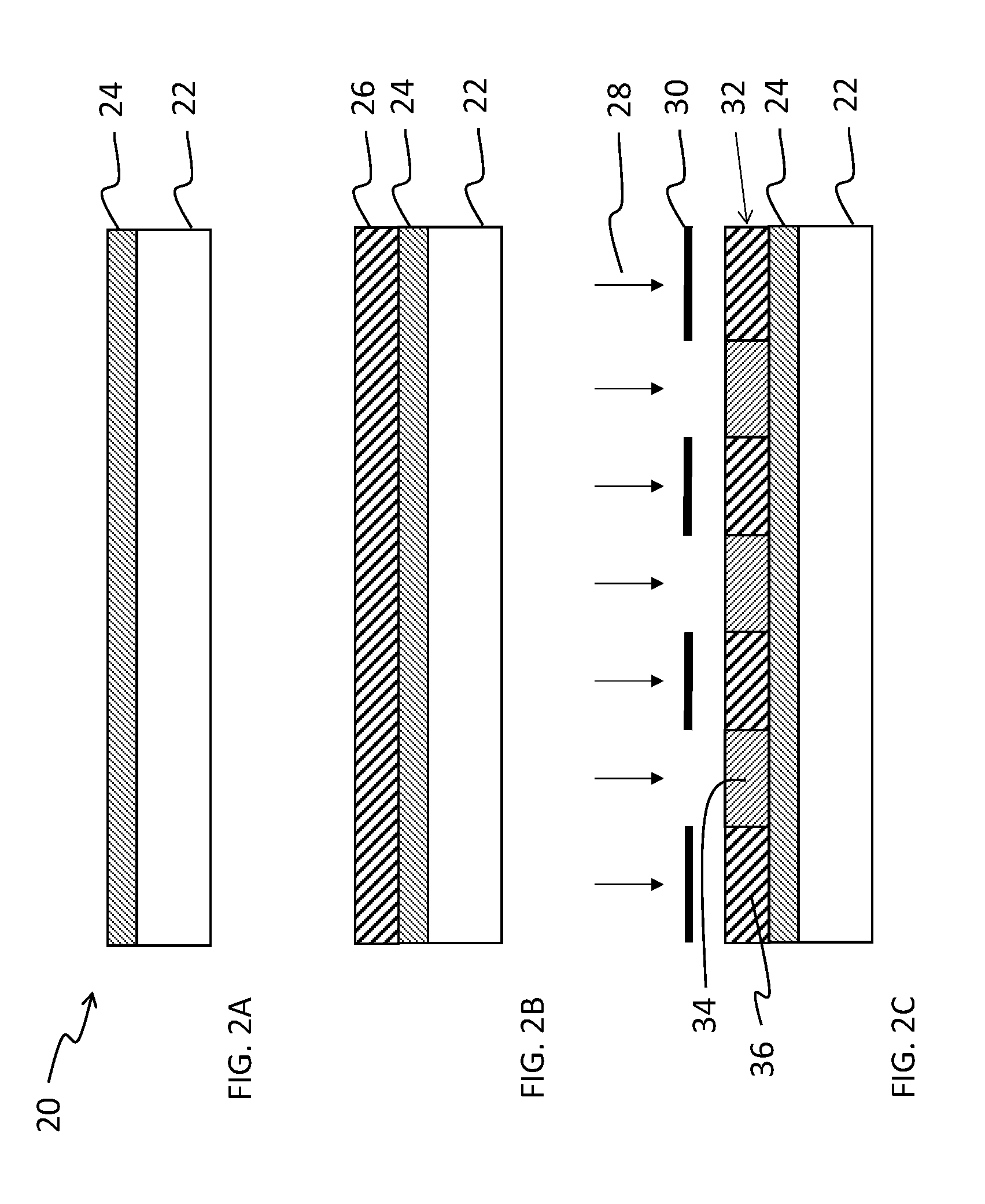
Fluorinated photopolymer with integrated anthracene sensitizer
InactiveUS20140356789A1High light sensitivityLess exposure energyPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAnthraceneAlcohol
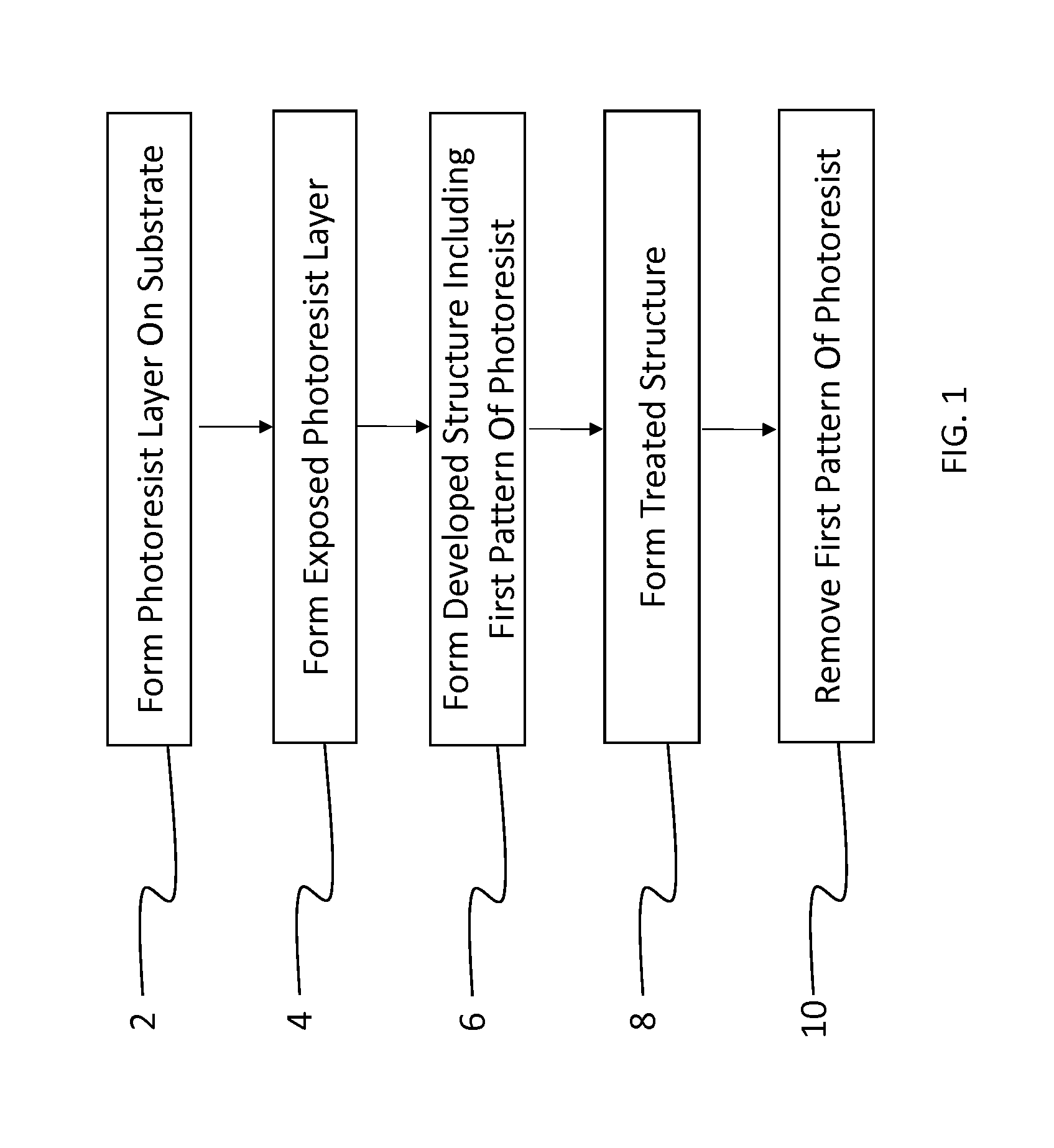
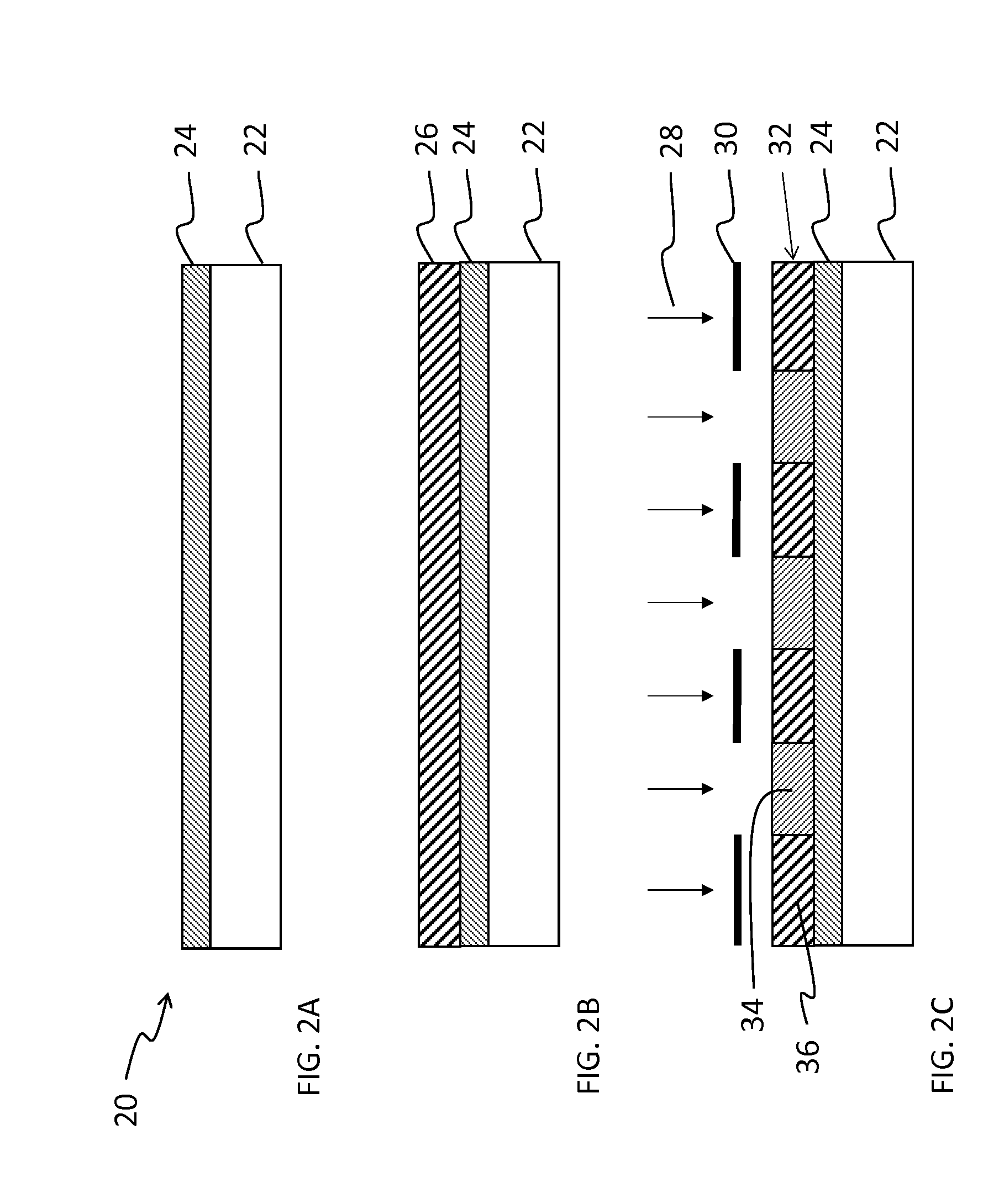
A method of patterning a device comprises providing on a device substrate a layer of a fluorinated photopolymer comprising at least three distinct repeating units including a first repeating unit having a fluorine-containing group, a second repeating unit having an acid- or alcohol-forming precursor group, and a third repeating unit having an anthracene-based sensitizing dye. The photopolymer has a total fluorine content in a range of 15 to 60% by weight. The photopolymer layer is exposed to patterned light and contacted with a developing agent to remove a portion of exposed photopolymer layer in accordance with the patterned light, thereby forming a developed structure having a first pattern of photopolymer covering the substrate and a complementary second pattern of uncovered substrate corresponding to the removed portion of photopolymer. The developing agent comprises at least 50% by volume of a fluorinated solvent.
Owner:ORTHOGONAL
Organic light emitting display apparatus
ActiveUS20100148163A1High light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight-emitting diodeOLED
An organic light emitting display apparatus includes an organic light emitting diode, a photo sensor, and a light blocking portion. The light blocking portion is at at least a side of the photo sensor so that light emitted from the organic light emitting diode is not directly incident on the photo sensor.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
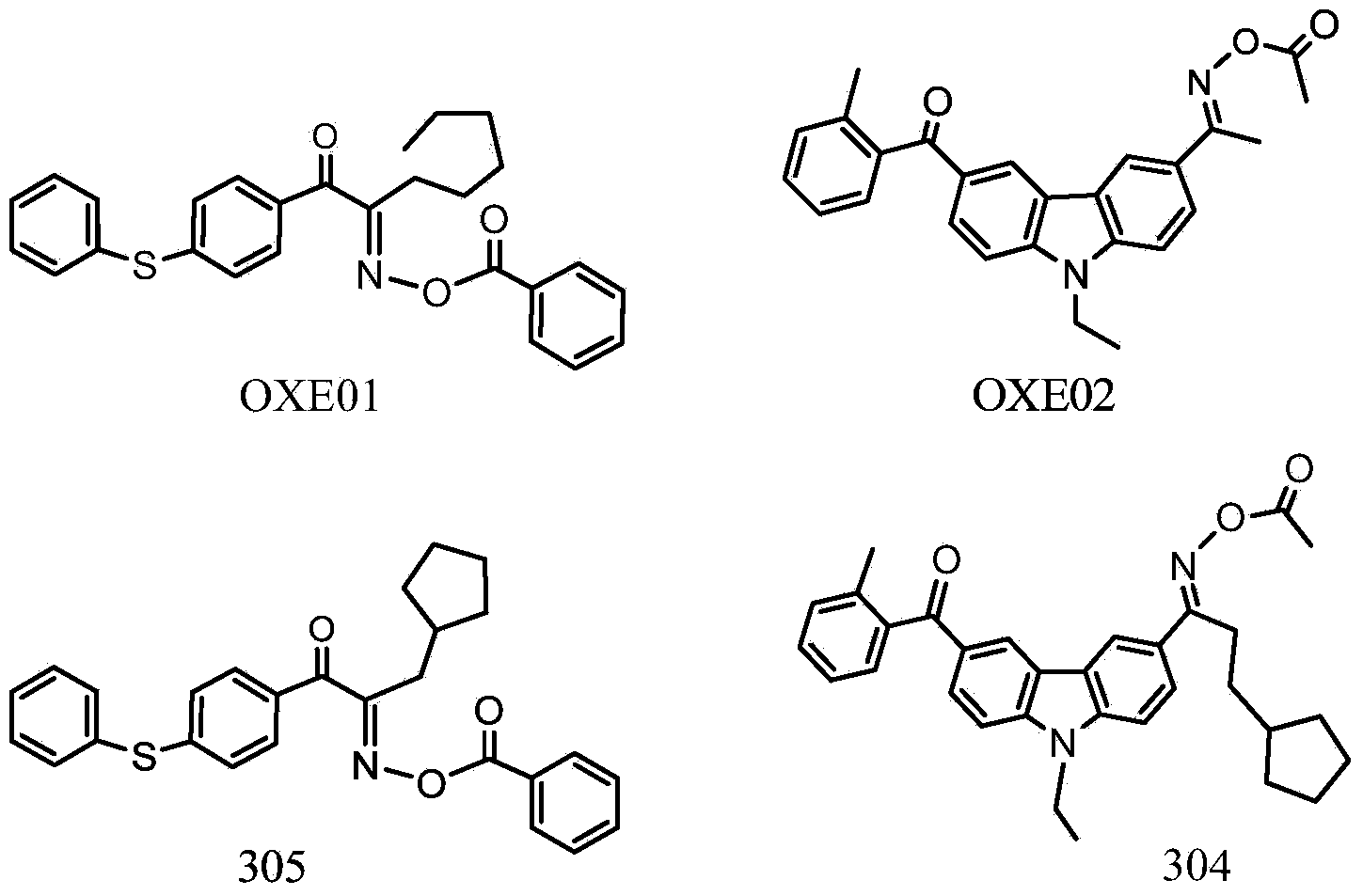
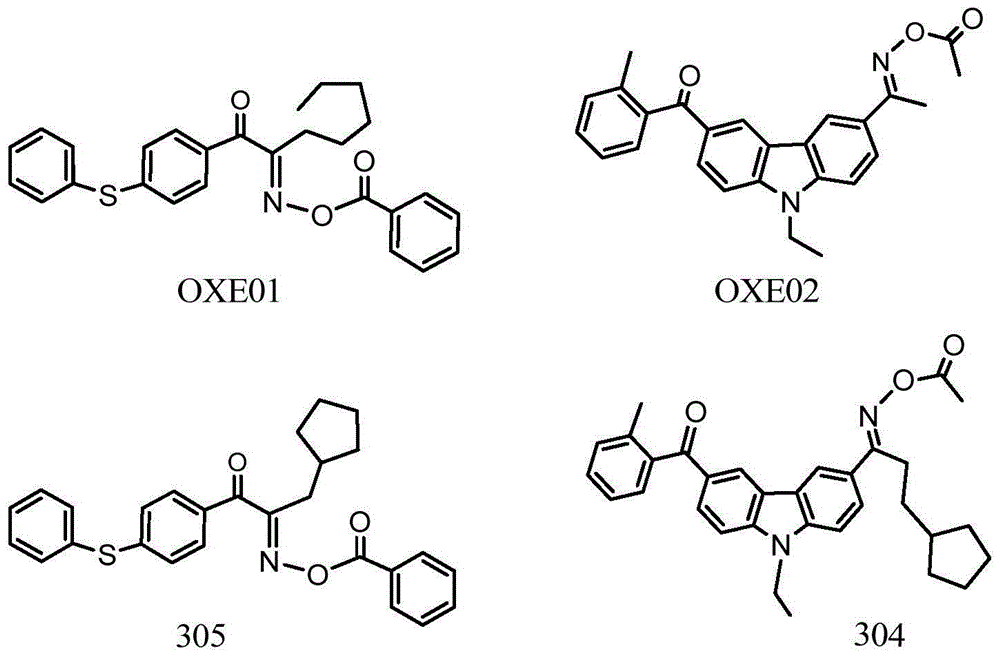
Cyclopentadiketoxime ester and applications thereof
ActiveCN103998422AHigh light sensitivityThe imaging effect is clearGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesColor gelMedicinal chemistry
Owner:INSIGHT HIGH TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Electrical interconnection, method of forming the electrical interconnection, image sensor having the electrical interconnection and method of manufacturing the image sensor
InactiveUS7084056B2Inhibited DiffusionReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerPhotodetector
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fluorinated photoresist with integrated sensitizer
ActiveUS20140356788A1Reduce photo degradationImprove light sensitivityPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSolventChemistry
A method of patterning a device comprises providing on a device substrate a layer of a fluorinated photopolymer comprising at least three distinct repeating units including a first repeating unit having a fluorine-containing group, a second repeating unit having an acid- or alcohol-forming precursor group, and a third repeating unit having a sensitizing dye. The photopolymer has a total fluorine content in a range of 15 to 60% by weight. The photopolymer layer is exposed to patterned light and contacted with a developing agent to remove a portion of exposed photopolymer layer in accordance with the patterned light, thereby forming a developed structure having a first pattern of photopolymer covering the substrate and a complementary second pattern of uncovered substrate corresponding to the removed portion of photopolymer. The developing agent comprises at least 50% by volume of a fluorinated solvent.
Owner:ORTHOGONAL
Optical Imaging System for Pickup
An optical imaging system for pickup, sequentially arranged from an object side to an image side, including: the first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, the second lens element with refractive power, the third lens element with refractive power, the fourth lens element with refractive power, the fifth lens element with refractive power; the sixth lens element made of plastic, the sixth lens with refractive power having a concave image-side surface with both being aspheric, and the image-side surface having at least one inflection point.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
CMOS imager with Cu wiring and method of eliminating high reflectivity interfaces therefrom
ActiveUS7342268B2High light sensitivityIncrease photosensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSensor arrayCMOS
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
Electrophotographic photosensitive member and electrophotographic apparatus
InactiveUS20100021835A1Superior in abrasionGood adhesivenessElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeSurface layerMedicine
The present invention provides an electrophotographic photosensitive member in which a photoconductive layer is an amorphous layer that contains a silicon atom as a main component, and a surface layer contains an aluminum atom, a zinc atom and an oxygen atom so as to satisfy Expression (1) and Expression (2):3.0≦100 {y / (x+y)}≦7.0 (1), and1.05≦z / (1.50x+y)≦1.20 (2),in Expression (1) and Expression (2), x represents atom % of the aluminum atom contained in the surface layer, y represents atom % of the zinc atom contained in the surface layer, and z represents atom % of the oxygen atom contained in the surface layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Solid state imaging device, method of producing the same and camera relating to same
InactiveUS20070064137A1Improve imaging characteristicImprove sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSolid-stateVoltage
A solid state imaging device improving and stabilizing imaging characteristic by optimizing a location of a positive hole accumulation layer to an electrode at the periphery of a light receiving portion, and having light receiving portions formed on a substrate and electrodes formed on the substrate at the periphery of the light receiving portion, each electrode including at least a first electrode to which a positive voltage is applied and a second electrode to which only 0 volt or a negative polarity voltage is applied, each light receiving portion having a signal charge accumulation region formed on the substrate and a positive hole accumulation region formed in a surface layer portion of the signal charge accumulation region, each positive hole accumulation region arranged at a distance from the first electrode and arranged so as to overlap the second electrode, and method of producing the same and a camera.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor photodetector device
InactiveUS20050189546A1Reduce capacitanceImprove frequency characteristicSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesPhotodetectorHigh concentration
A semiconductor photodetector device includes: a first semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type; and a second semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type formed on the first semiconductor layer and having a light-receiving region. The first semiconductor layer includes a first region containing an impurity of the first conductivity type at a high concentration and a second region formed on the first region and containing an impurity of the first conductivity type at a concentration lower than that of the first region. The second semiconductor layer includes a third region containing an impurity of the second conductivity type at a concentration higher than that of the second region and a fourth region formed on the third region and containing an impurity of the second conductivity type at a concentration higher than that of the third region.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Photo sensor and light emitting display having the same
ActiveUS20090032823A1High light sensitivitySolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsTransmittanceDisplay device
A photo sensor includes a light incidence unit including a plurality of light incidence layers, the light incidence unit having a varying light transmittance with respect to external light, and a photo sensing unit including a plurality of photo sensing elements, the photo sensing unit being configured to output electrical signals in accordance with an amount of light transmitted through the light incidence unit to determine intensity of the external light, each of the photo sensing elements being configured to output electrical signals in accordance with light transmitted through a respective light incidence layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
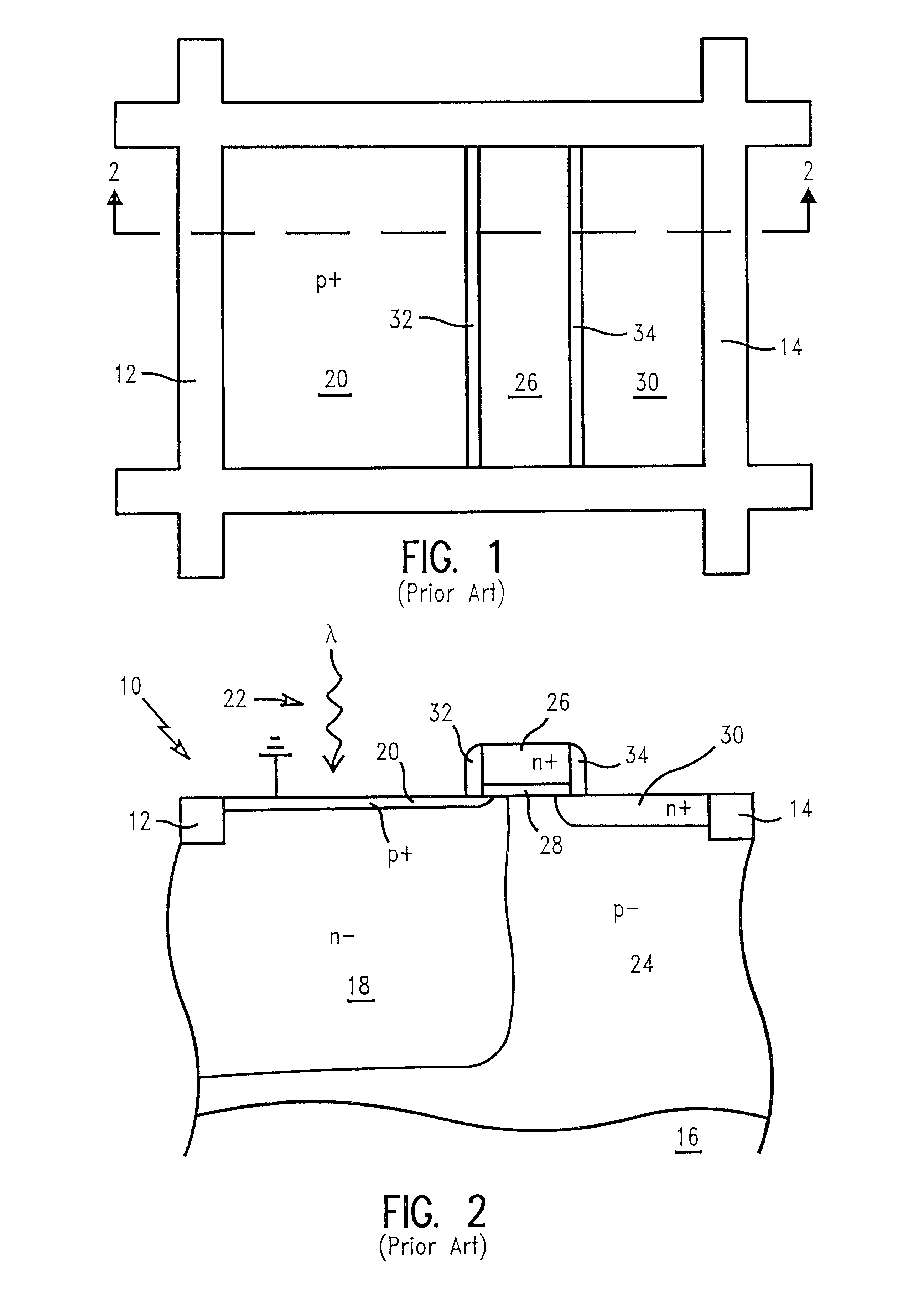
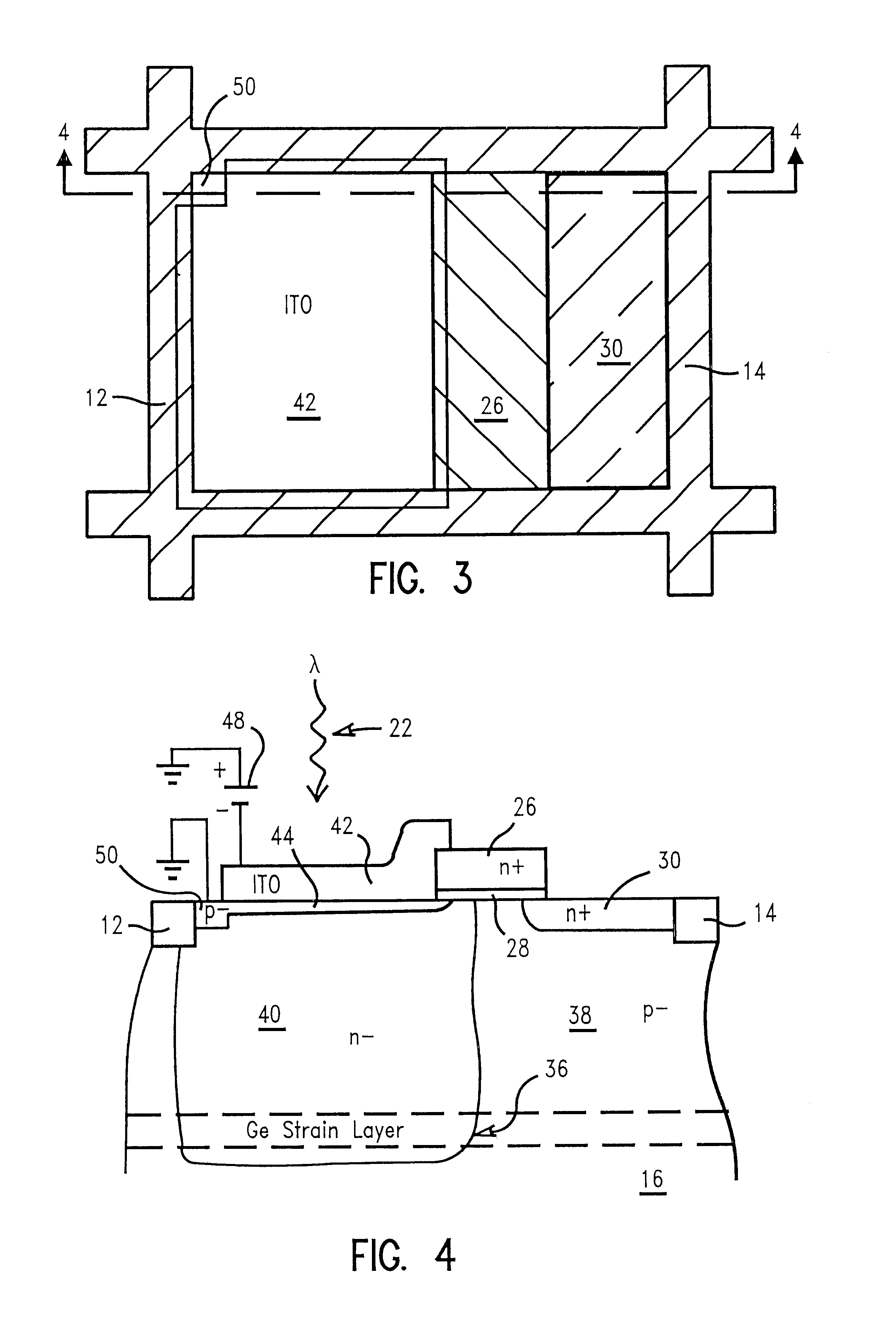
Method of detecting electromagnetic radiation with bandgap engineered active pixel cell design
InactiveUS6278102B1High light sensitivityReduce thicknessSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOS sensorSemiconductor materials
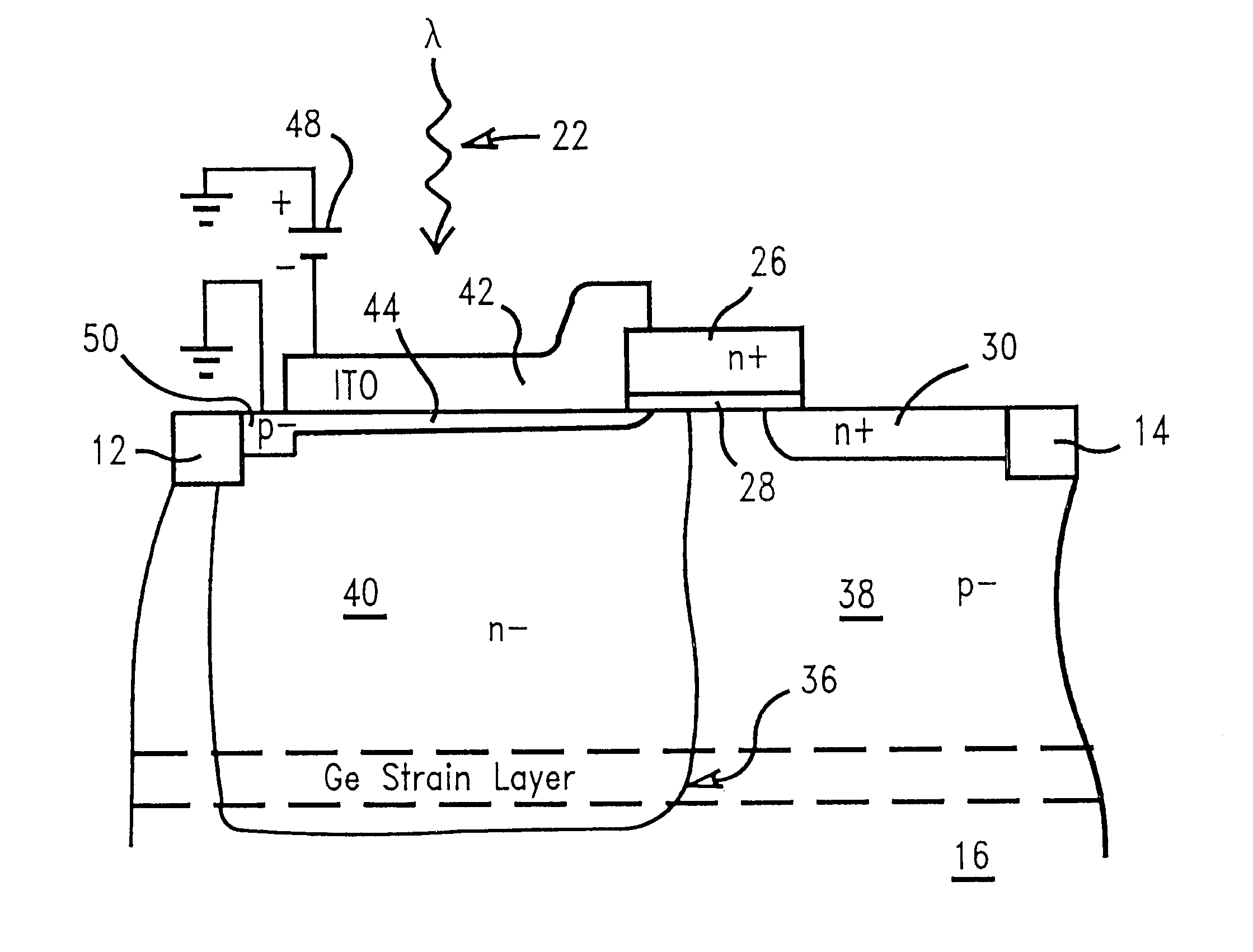
A method of detecting electromagnetic radiation with an active pixel sensor photosensitive device having an extremely thin virtual pinning layer formed by inverting semiconductor material at the surface of a photosensitive region. The thin pinning layer improves blue light response. The inverted pinning layer is produced by connecting a negative potential source to a transparent conductive layer, preferably made of indium-tin-oxide positioned over most of the photosensitive region. The conductive layer is insulated from the photosensitive region by a thin insulating layer. Connection to the pinning layer is through a coupling region formed in an area not covered by the conductive and insulating layers. Red light response is improved and the depth of the photosensitive region reduced by creating a strained layer, preferably of germanium silicon, deep within the photosensitive region. The strained layer has a modified bandgap which increases the absorption rate of red light.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
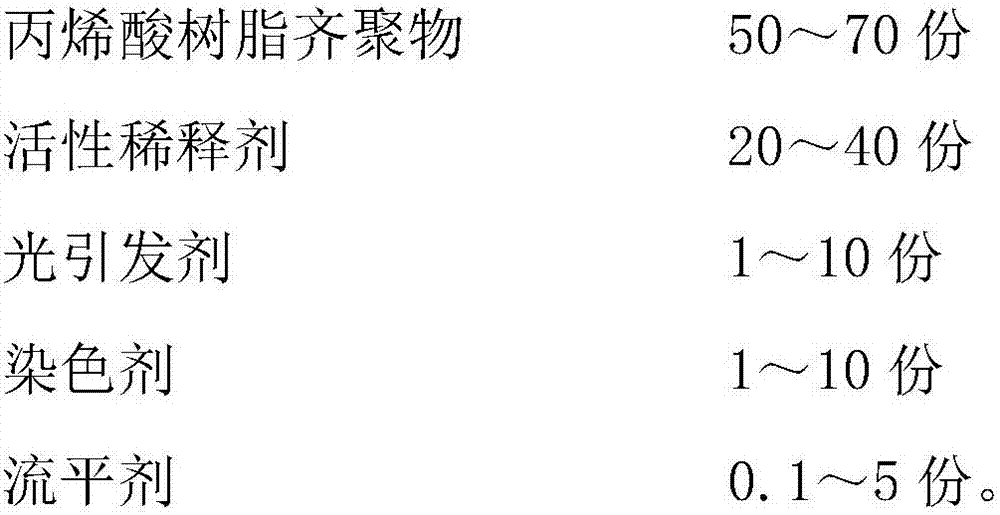
3D (three-dimensional) printing light-cured resin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106977658AHigh light sensitivityFast molding speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusOligomerAcrylic resin
The invention discloses a 3D (three-dimensional) printing light-cured resin and a preparation method thereof. The 3D printing light-cured resin is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 50 to 70 parts of acrylic resin oligomers, 20 to 40 parts of a reactive diluent, 1 to 10 parts of a photoinitiator, 1 to 10 parts of a coloring agent and 0.1 to 5 parts of a flatting agent. The 3D printing light-cured resin disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high light sensitivity and fast forming speed; the purpose of enabling resin monolayer curing time to be within 0.5s can be realized; 3D printing equipment can achieve a forming speed of 220 to 360mm / h; and the processing efficiency of the 3D printing equipment is greatly improved.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
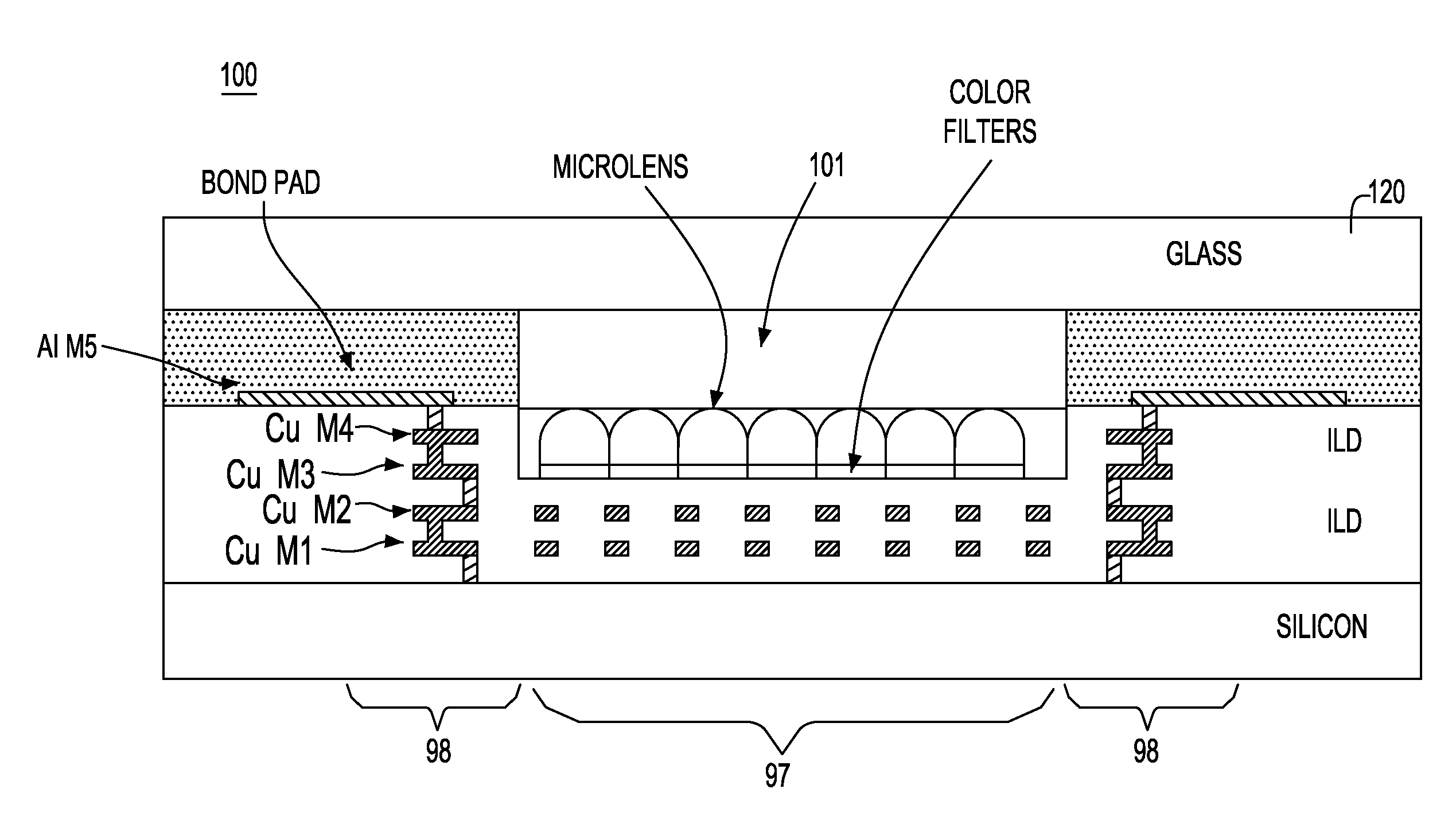
Biochip Having Image Sensor with Back Side Illumination Photodiode
ActiveUS20110172129A1High light sensitivityAvoiding characteristicBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLight sensingPhotodiode
A biochip having an image sensor with a back side illumination photodiode structure includes: a biochip layer; and an image sensor layer attached to one surface of the biochip layer and configured to sense light with biochemical reaction information, which is emitted from the biochip layer, wherein the image sensor layer includes a plurality of light sensing parts which receive the light directed toward a back side of a wafer.
Owner:OPTOLANE TECH
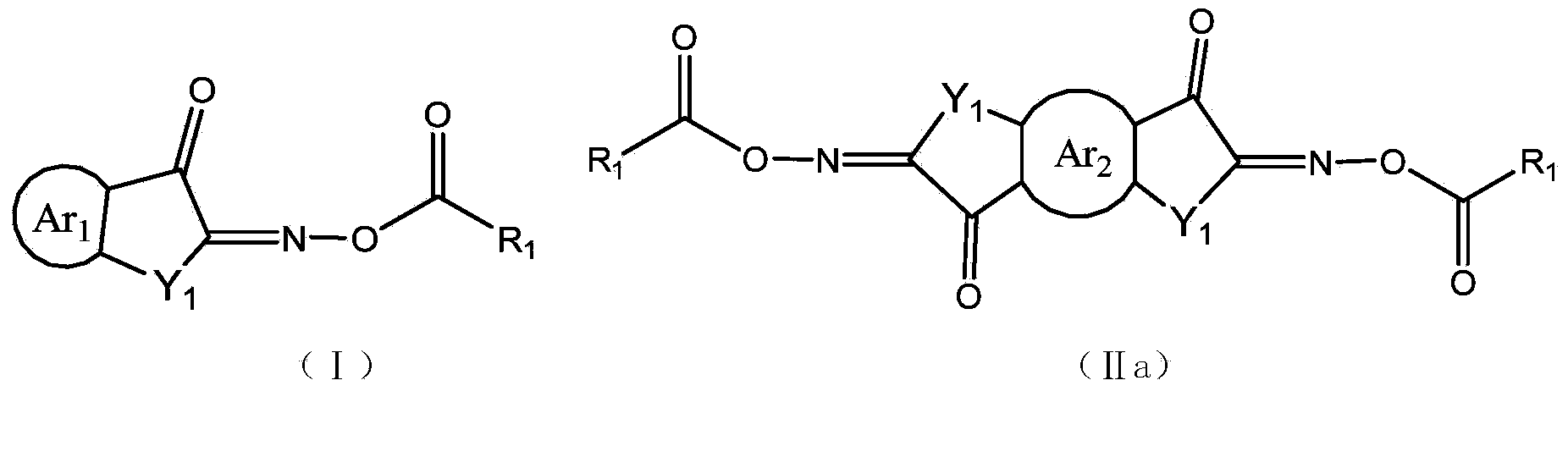
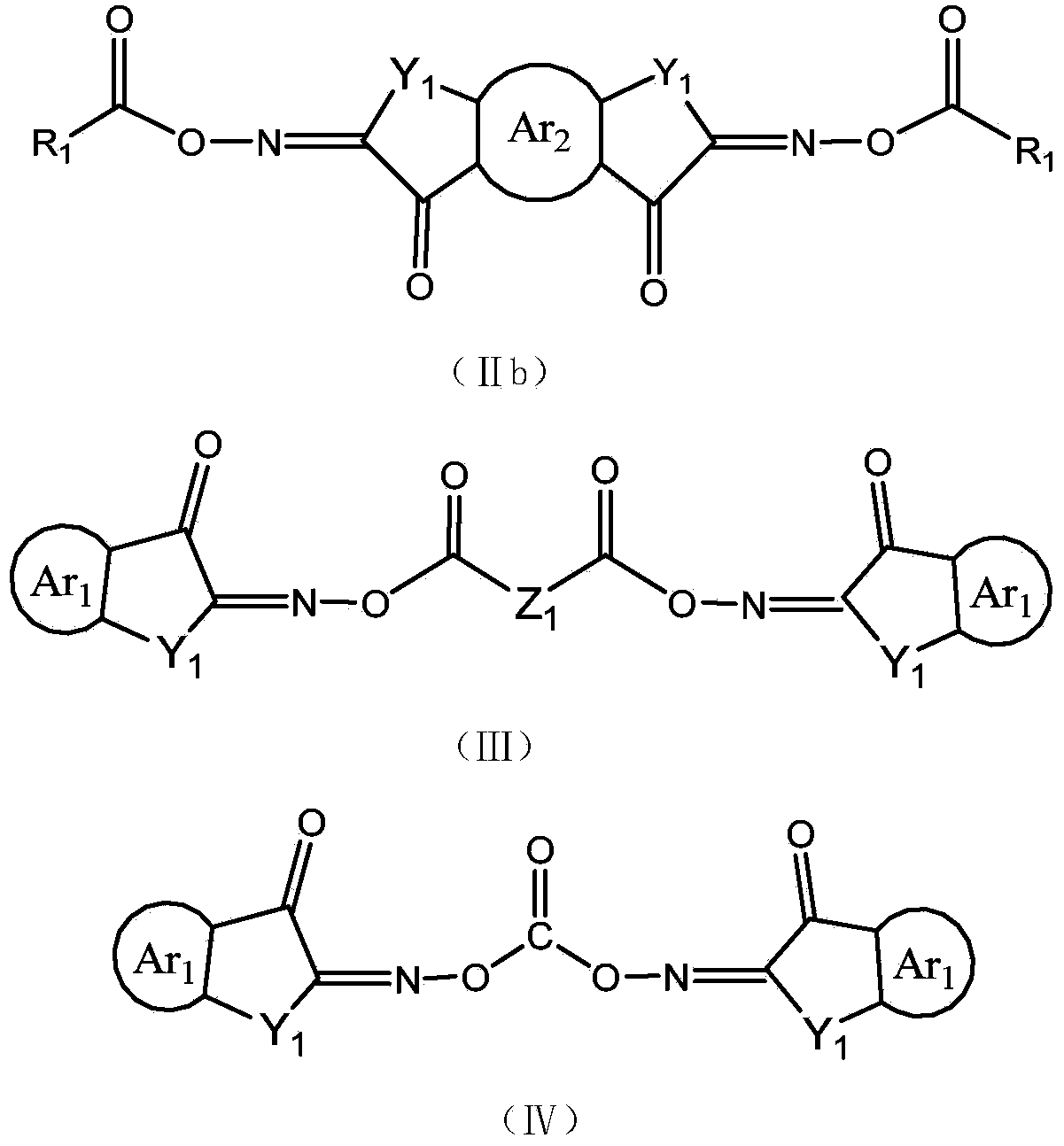
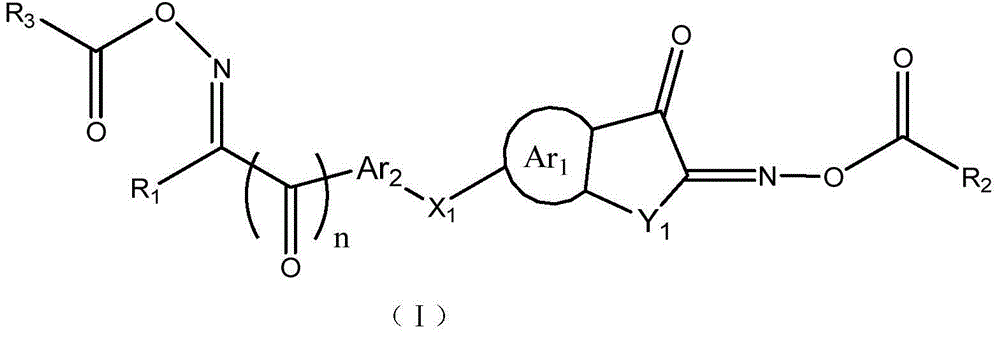
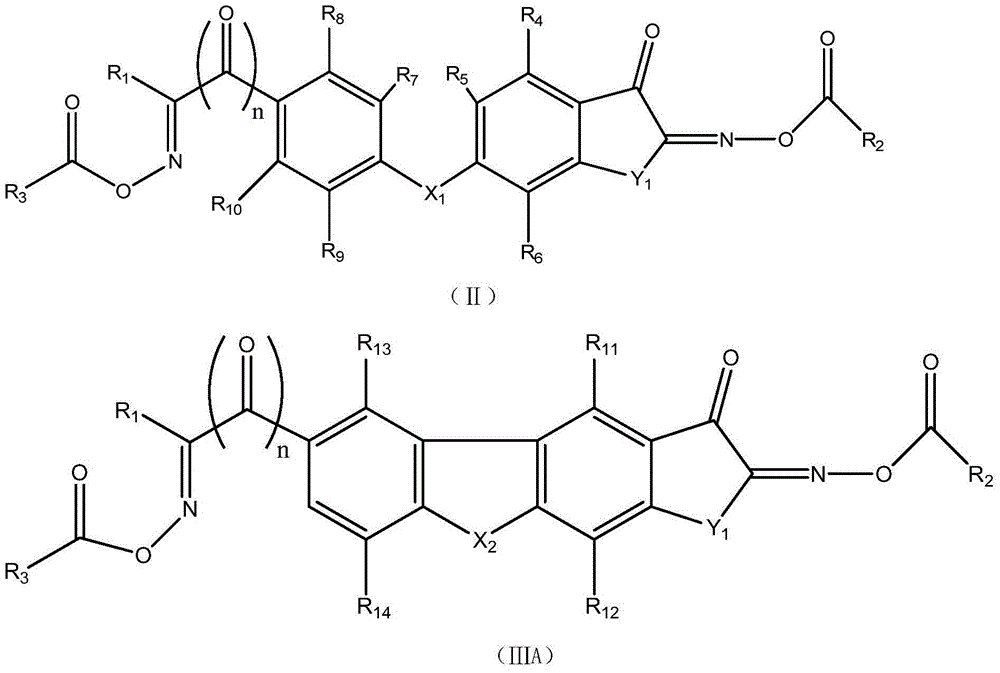
Asymmetric dioxime ester compound, making method and application thereof
ActiveCN104910053AHigh light sensitivityThe imaging effect is clearOptical filtersInksChemical compoundPhotoinitiator
The invention relates to an asymmetric dioxime ester compound shown as general formula I and a making method thereof. In the general formula I, Ar1 is X1 substituted C6-C20 o-arylene or C3-C20 o-heteroarylene; Ar2 is C6-C20 arylene or C3-C20 heteroarylene, is connected to Ar1 through X1, or at the same time of connection to Ar1 through X1, the Ar2 carbon atom adjacent to the substituent group X1 is in connection with Ar1 through an axial bond, carbon atom, carbonyl, O, S and NR18 to form a cyclic structure; n is 0 or 1; X1 is NR18, O, S, C=O or S=O; Y1 is (CH2)mCR15R16, NR19, O(CR15R16)m, S(CR15R16)m, (CR15R16)m C=O, S=O; m is 0 or 1; R1, R2 and R3 are respectively hydrogen atom, alkyl or alkoxy, arbitrary group substituted alkyl or alkoxy, cycloalkyl, arbitrary group substituted aryl, and acyl. The invention also relates to a photocurable composition with the general formula I compound as the photoinitiator. The composition is used for preparation of photoresist devices like color filters for display screens, and shows very high curing sensitivity. (formula I as shown in the specification).
Owner:INSIGHT HIGH TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Semiconductor photodetector device
InactiveUS7211829B2High light sensitivityIncreased sensitivitySolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesHigh concentrationElectrical conductor
A semiconductor photodetector device includes: a first semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type; and a second semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type formed on the first semiconductor layer and having a light-receiving region. The first semiconductor layer includes a first region containing an impurity of the first conductivity type at a high concentration and a second region formed on the first region and containing an impurity of the first conductivity type at a concentration lower than that of the first region. The second semiconductor layer includes a third region containing an impurity of the second conductivity type at a concentration higher than that of the second region and a fourth region formed on the third region and containing an impurity of the second conductivity type at a concentration higher than that of the third region.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com