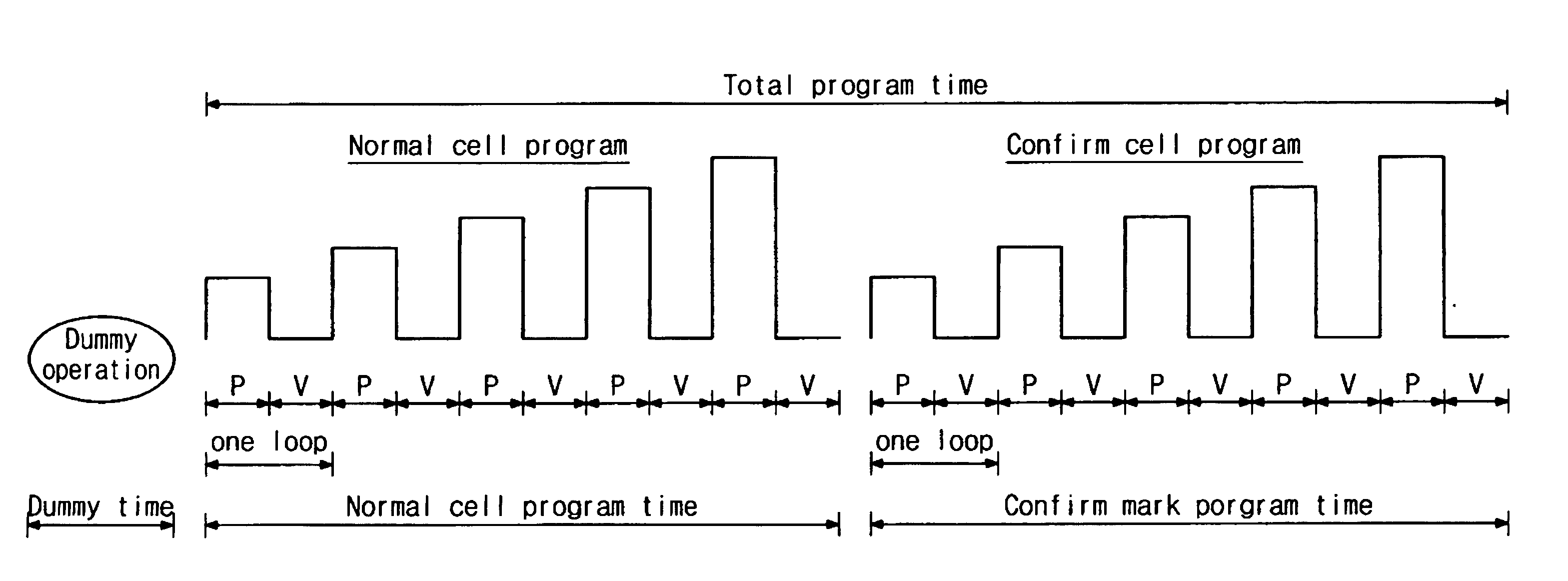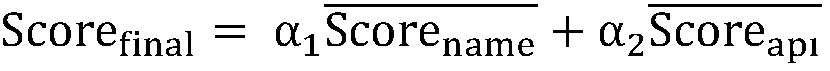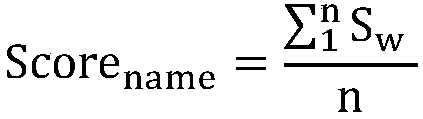Patents
Literature
267results about How to "Shorten programming time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
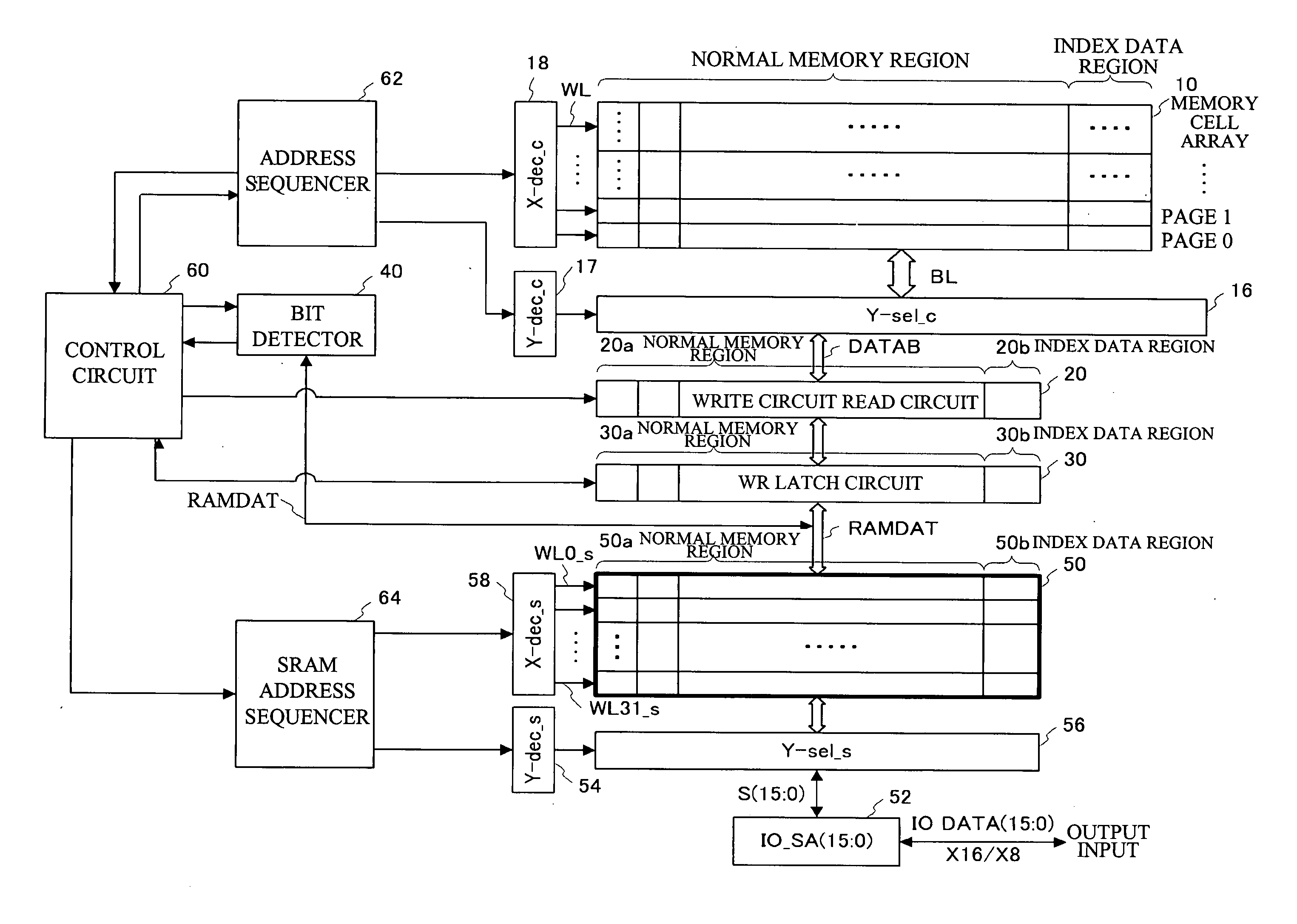
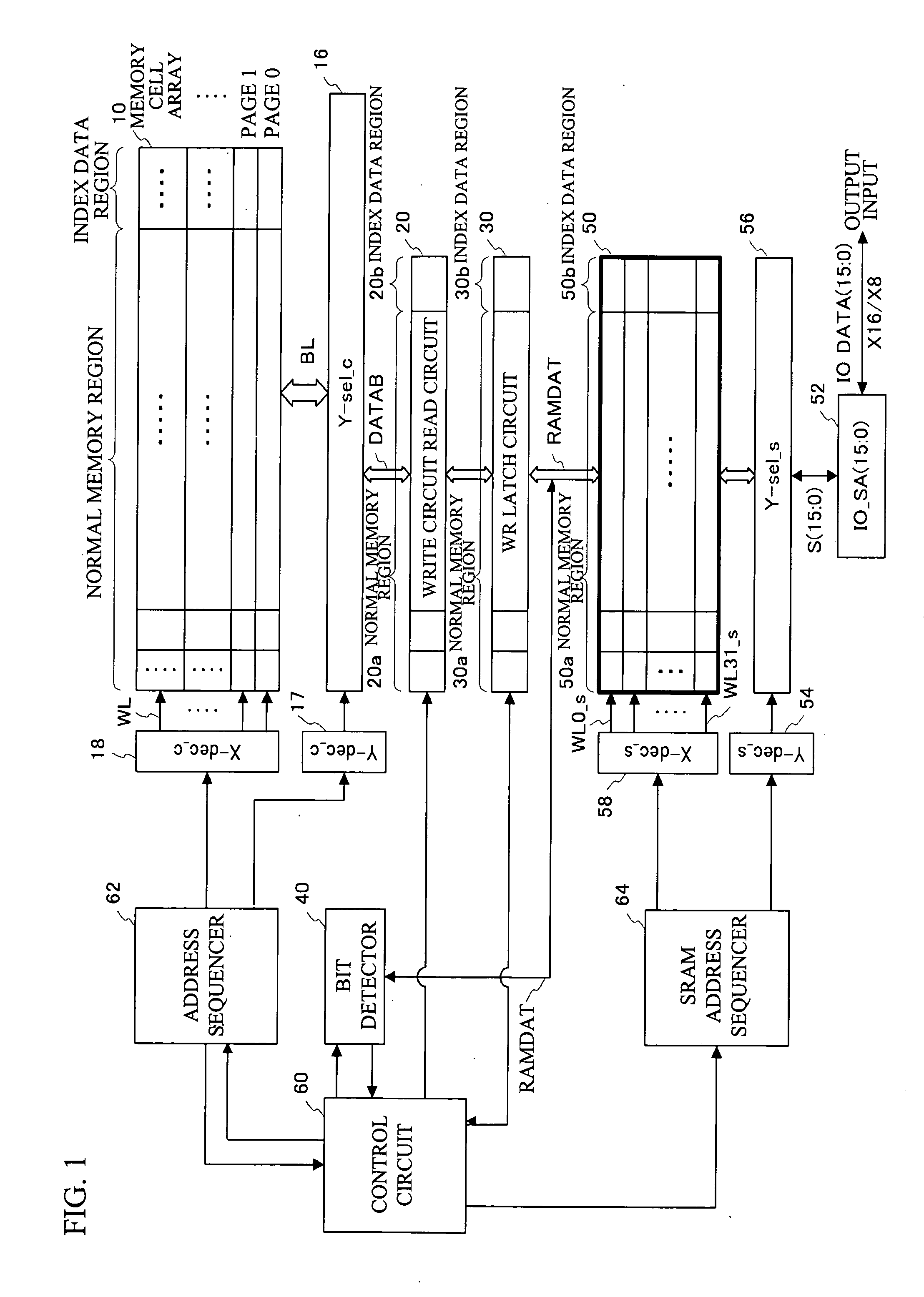
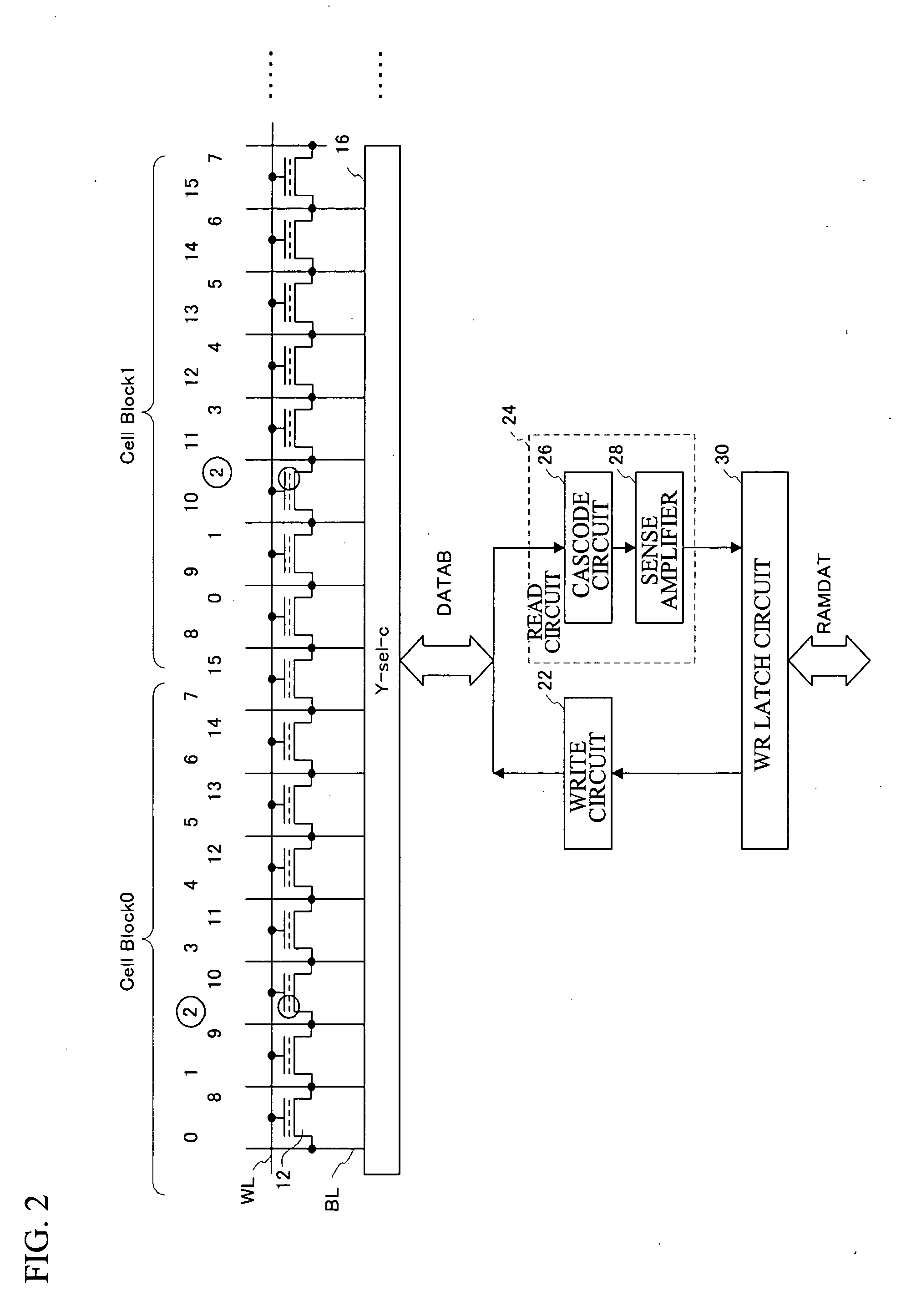
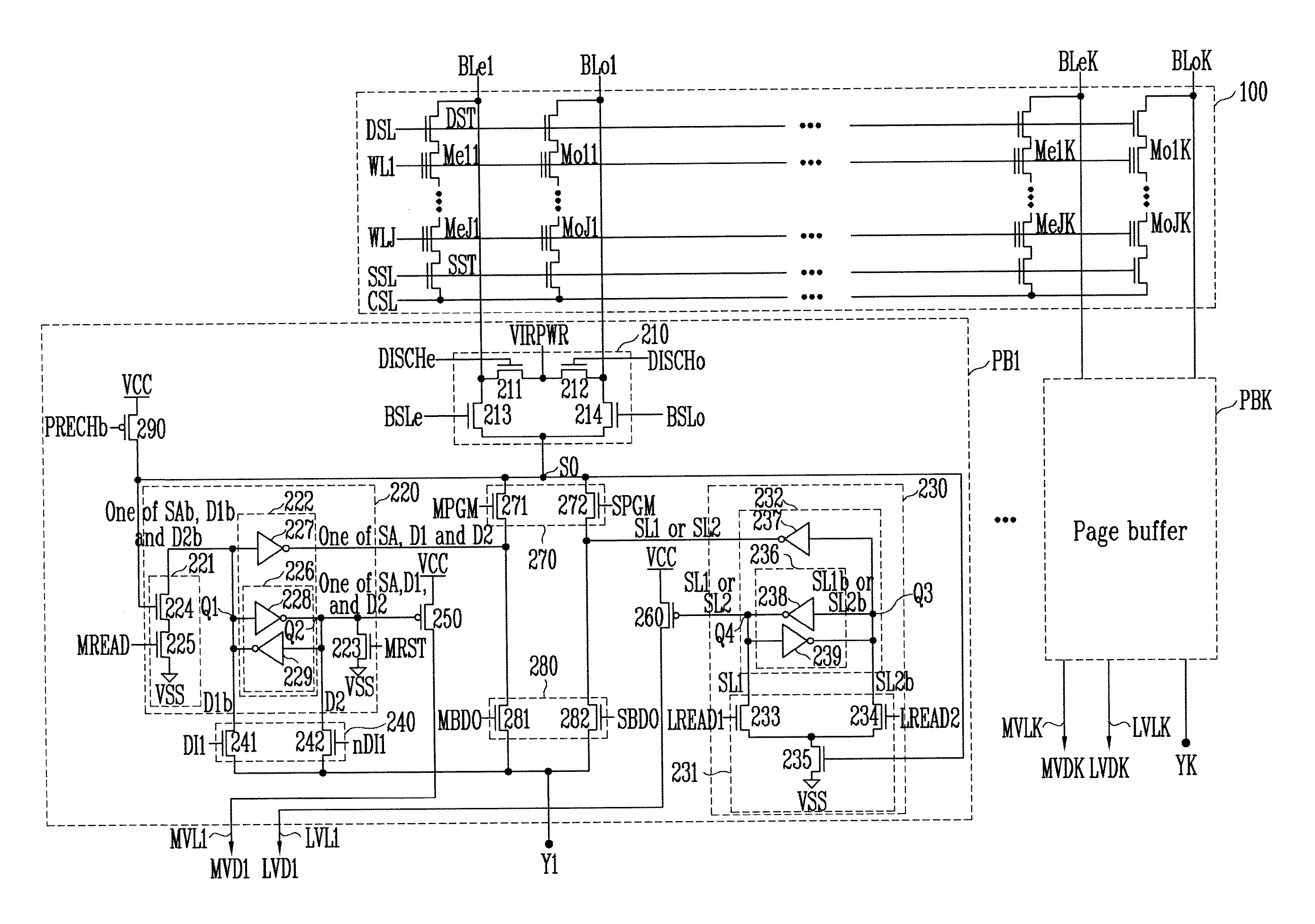
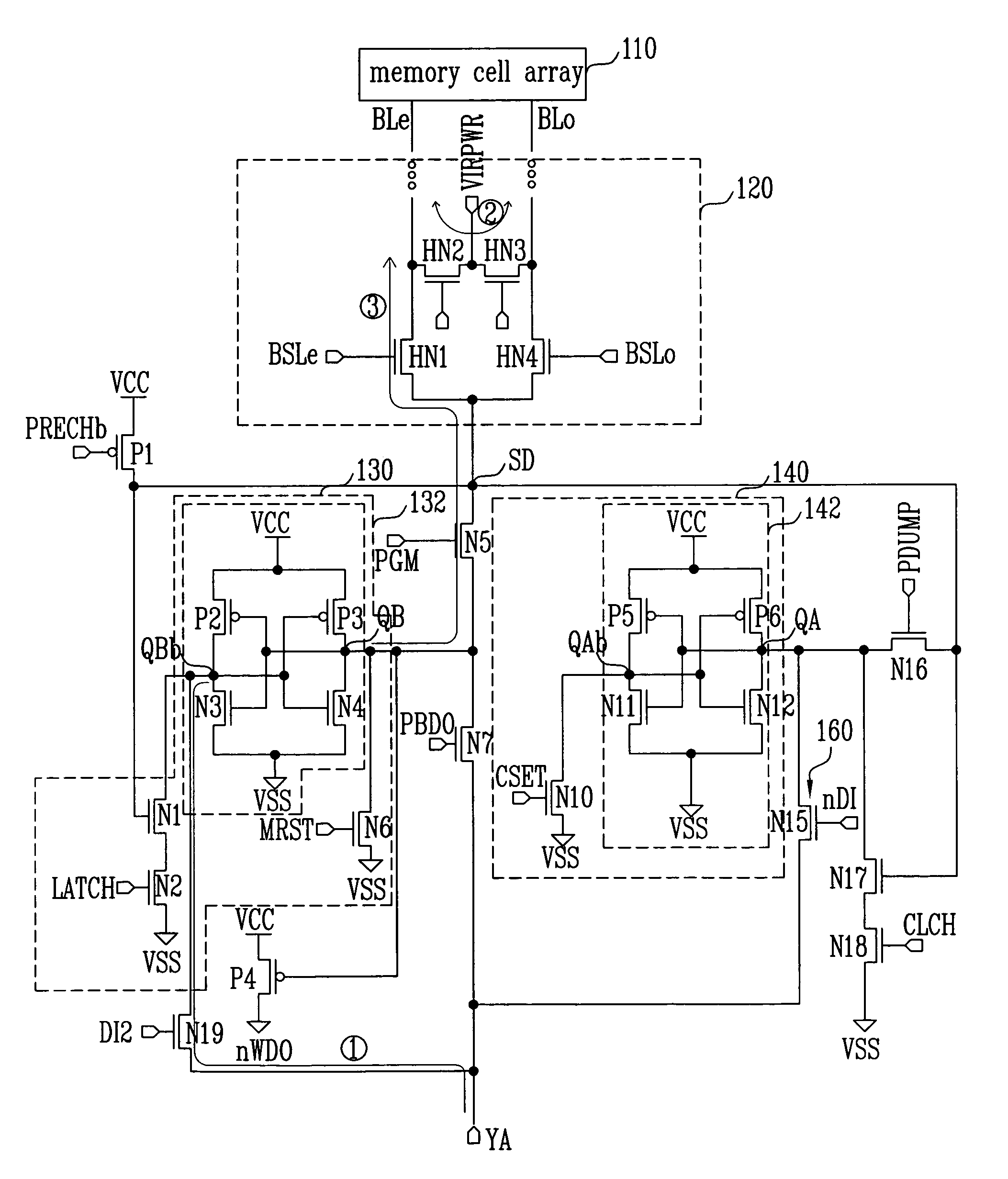
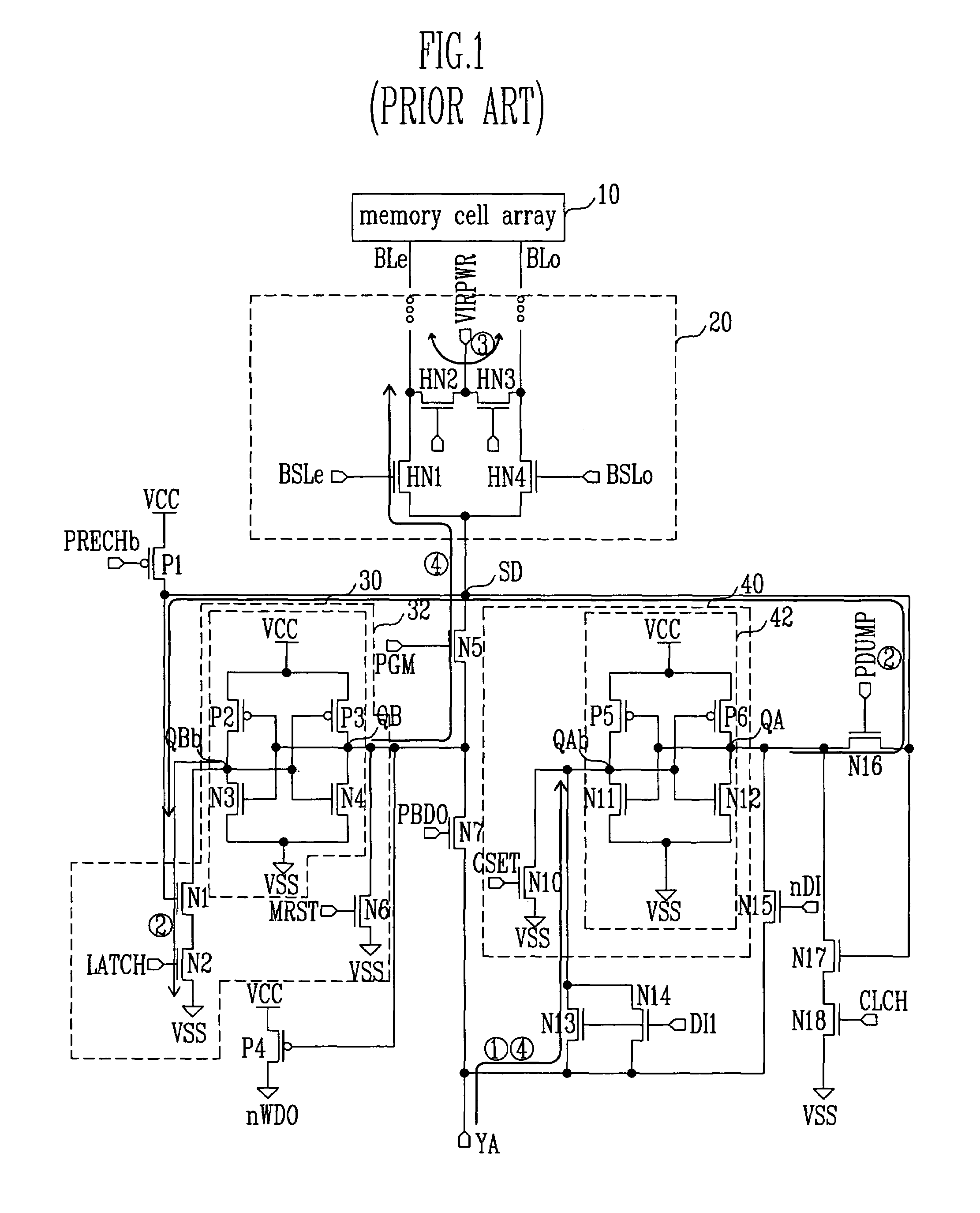
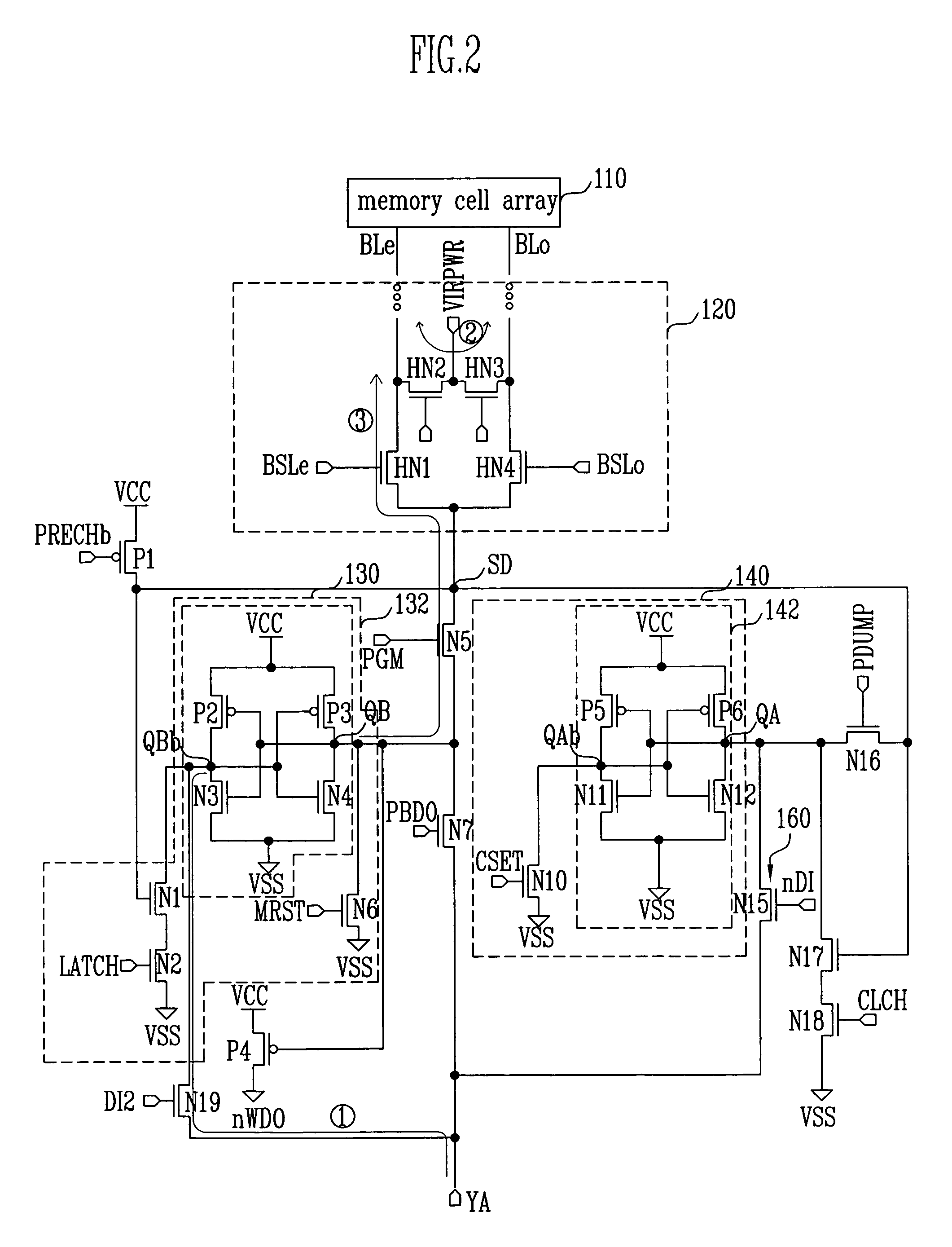
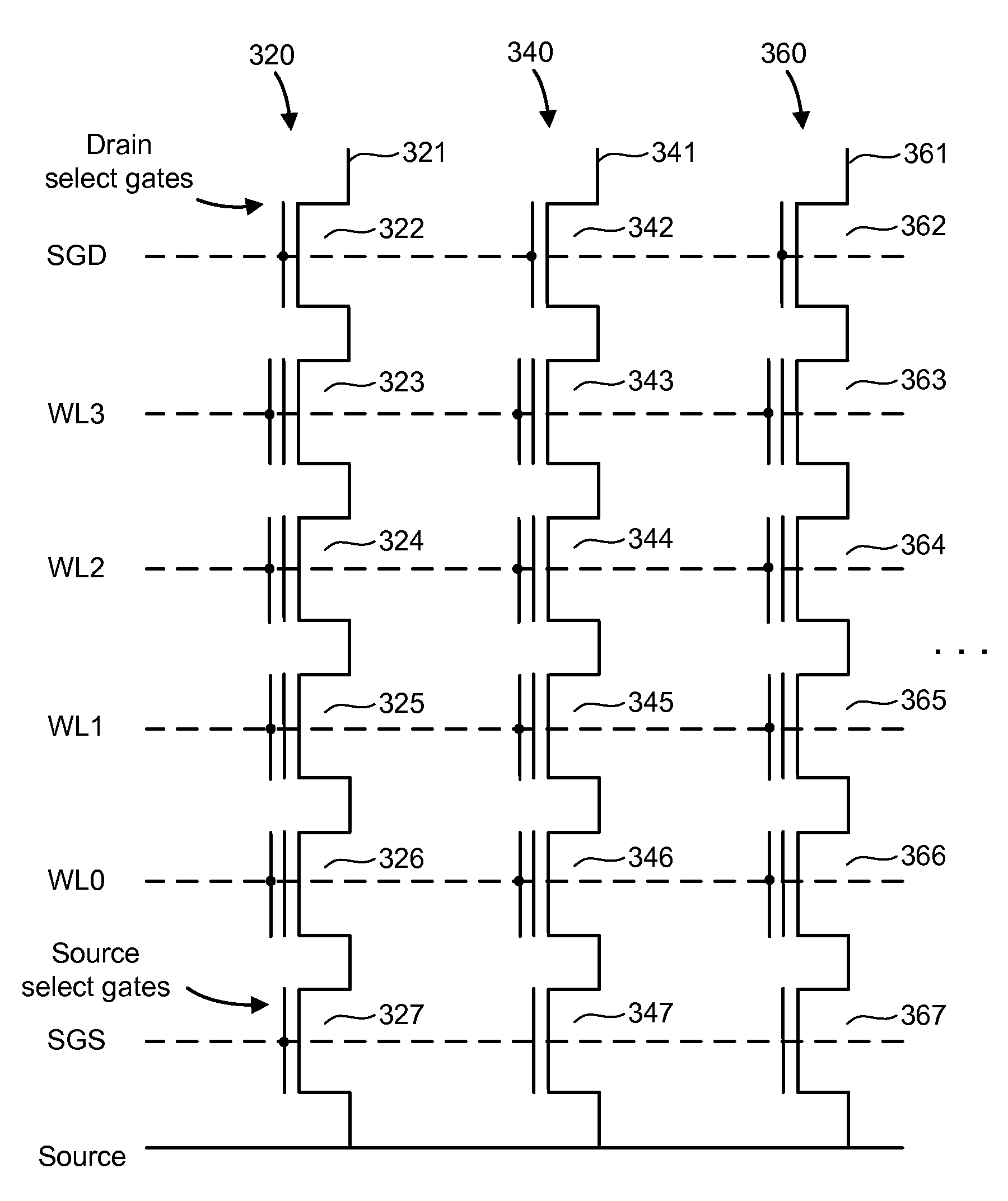
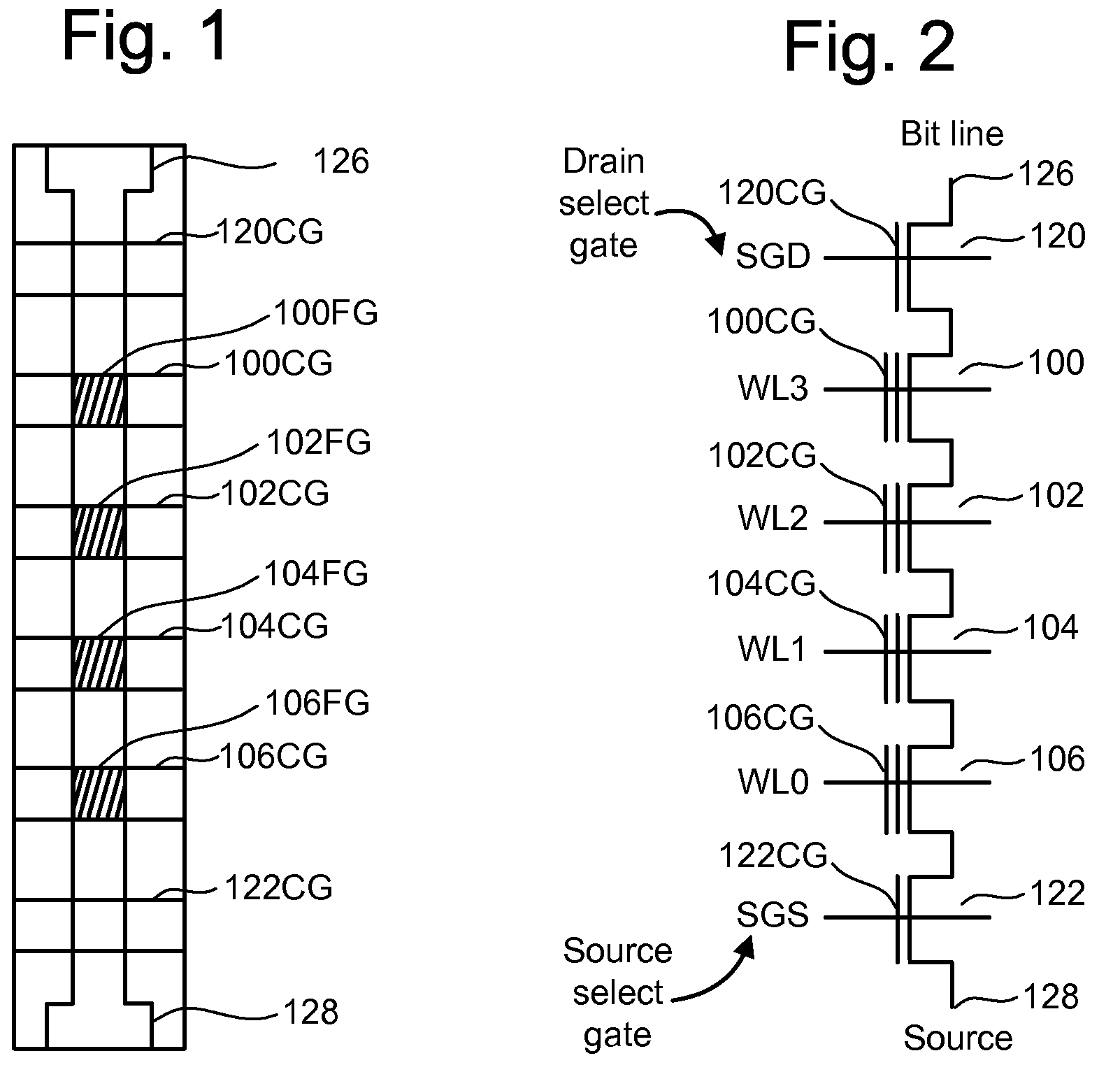
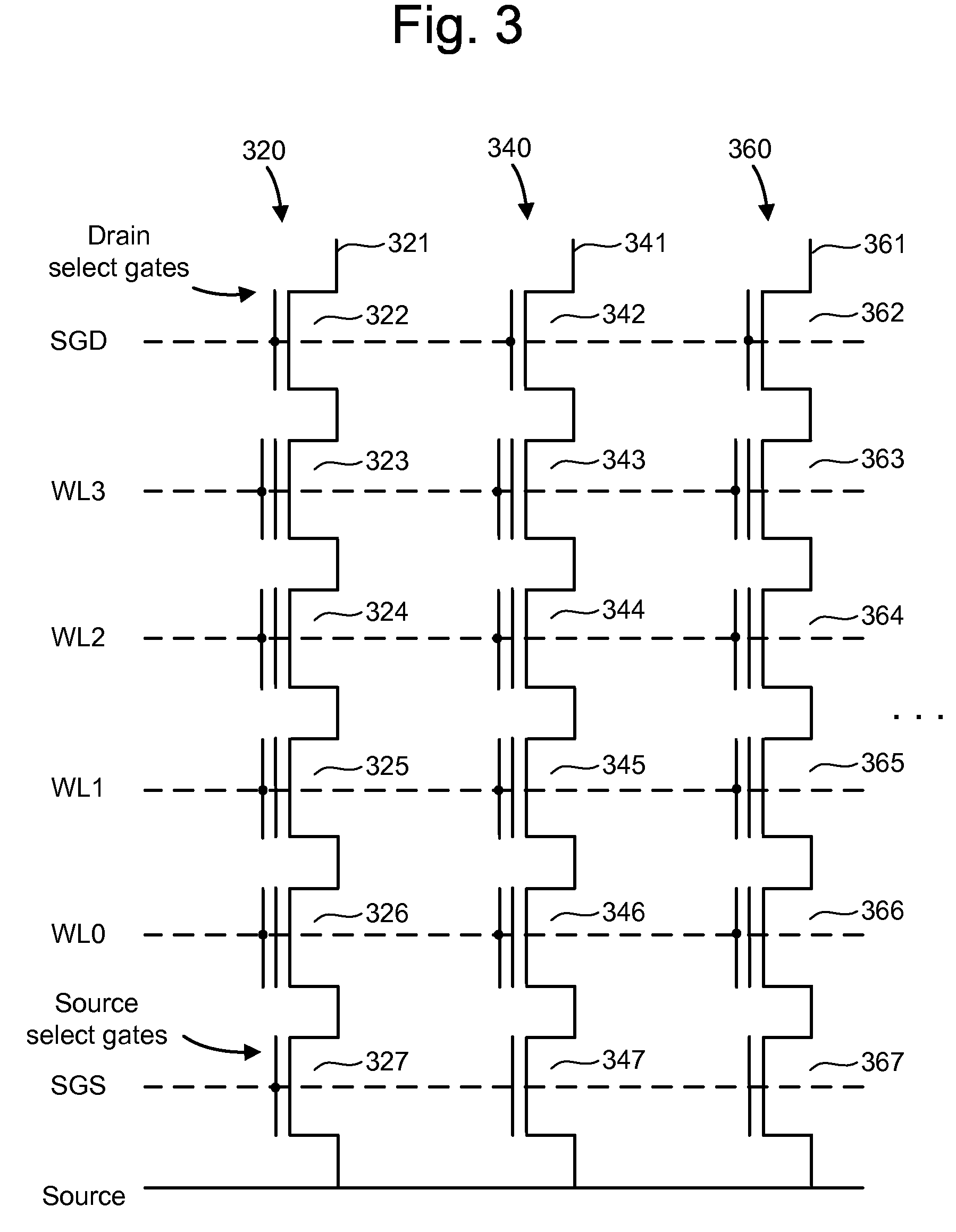
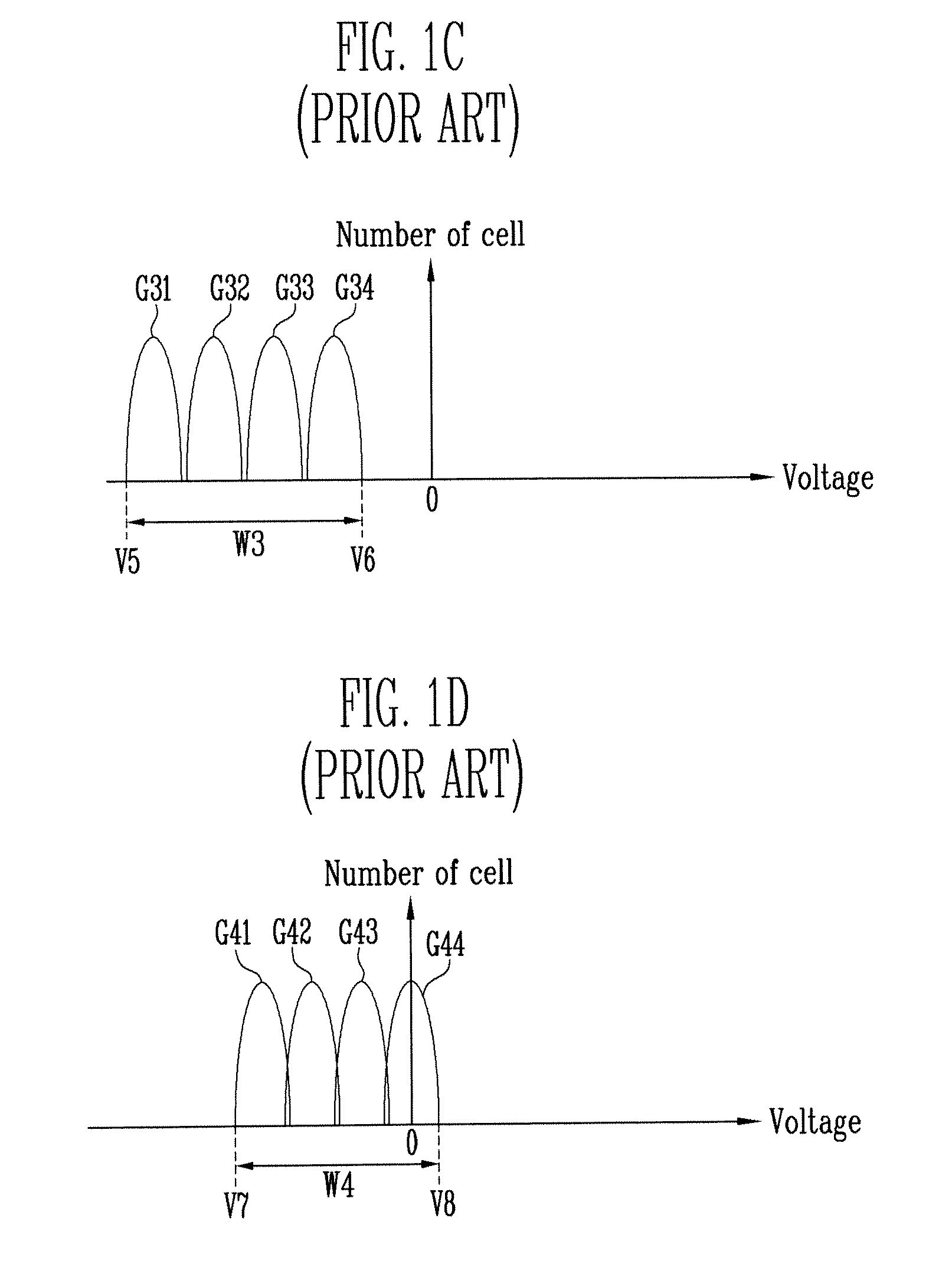
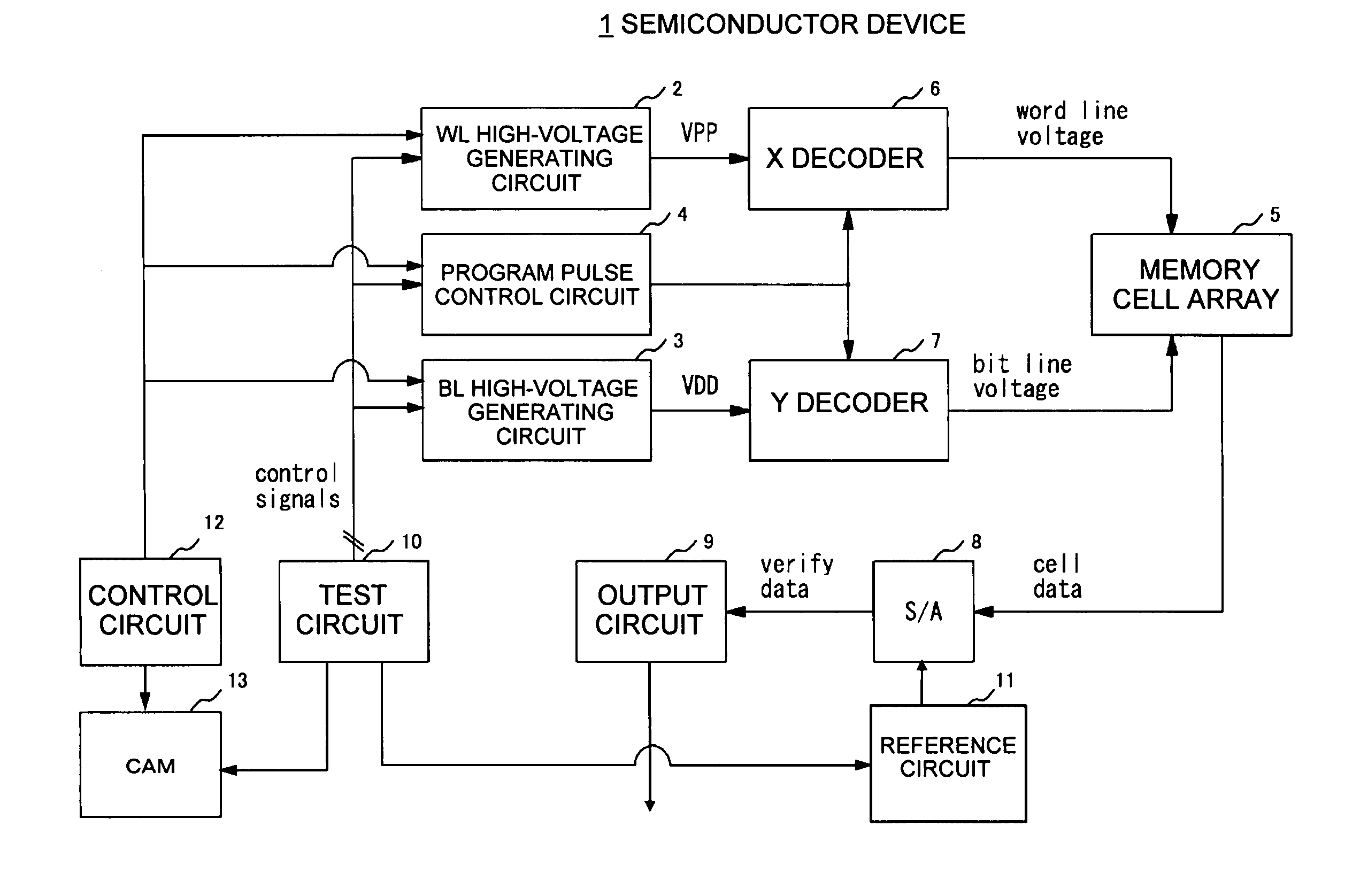
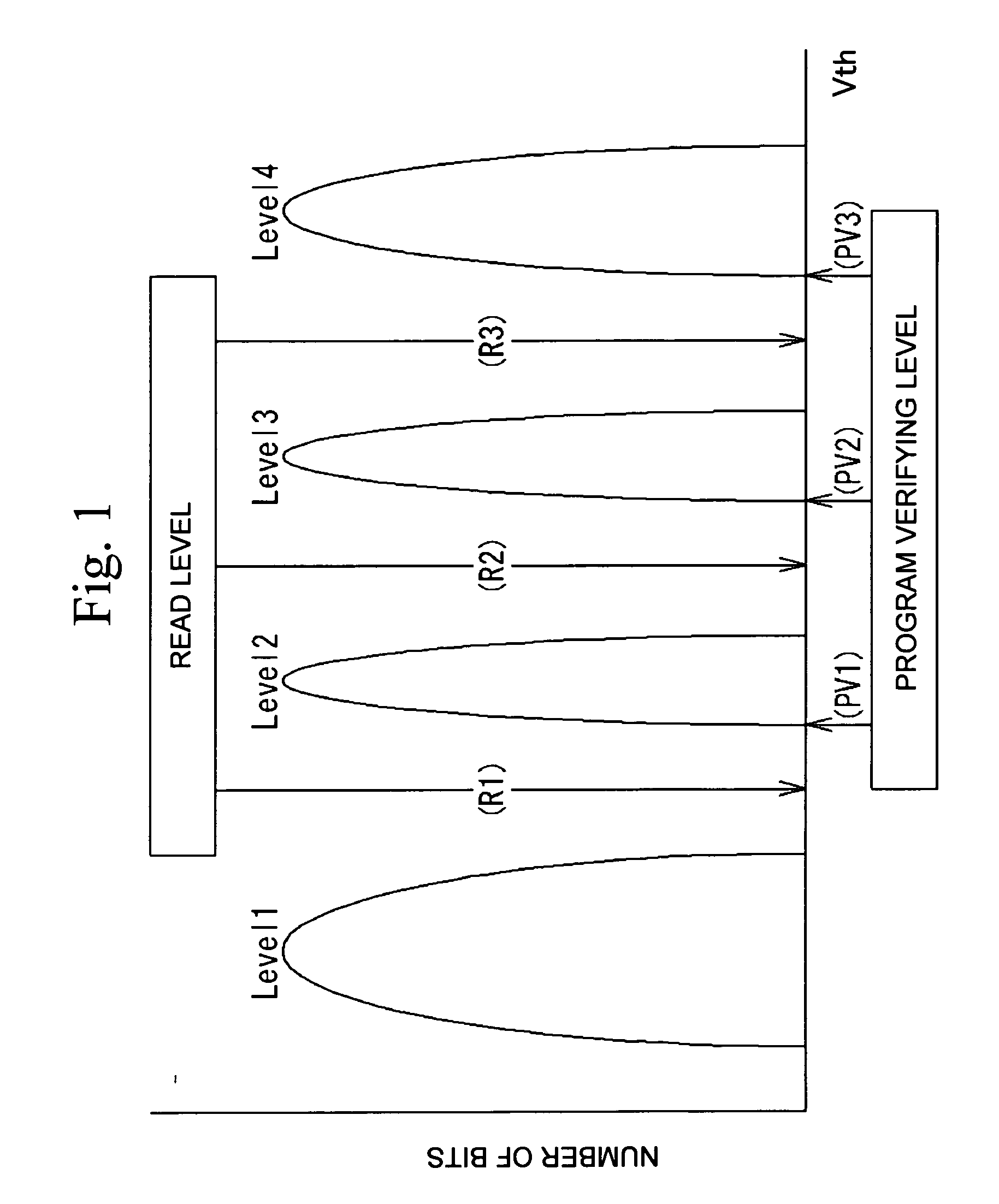
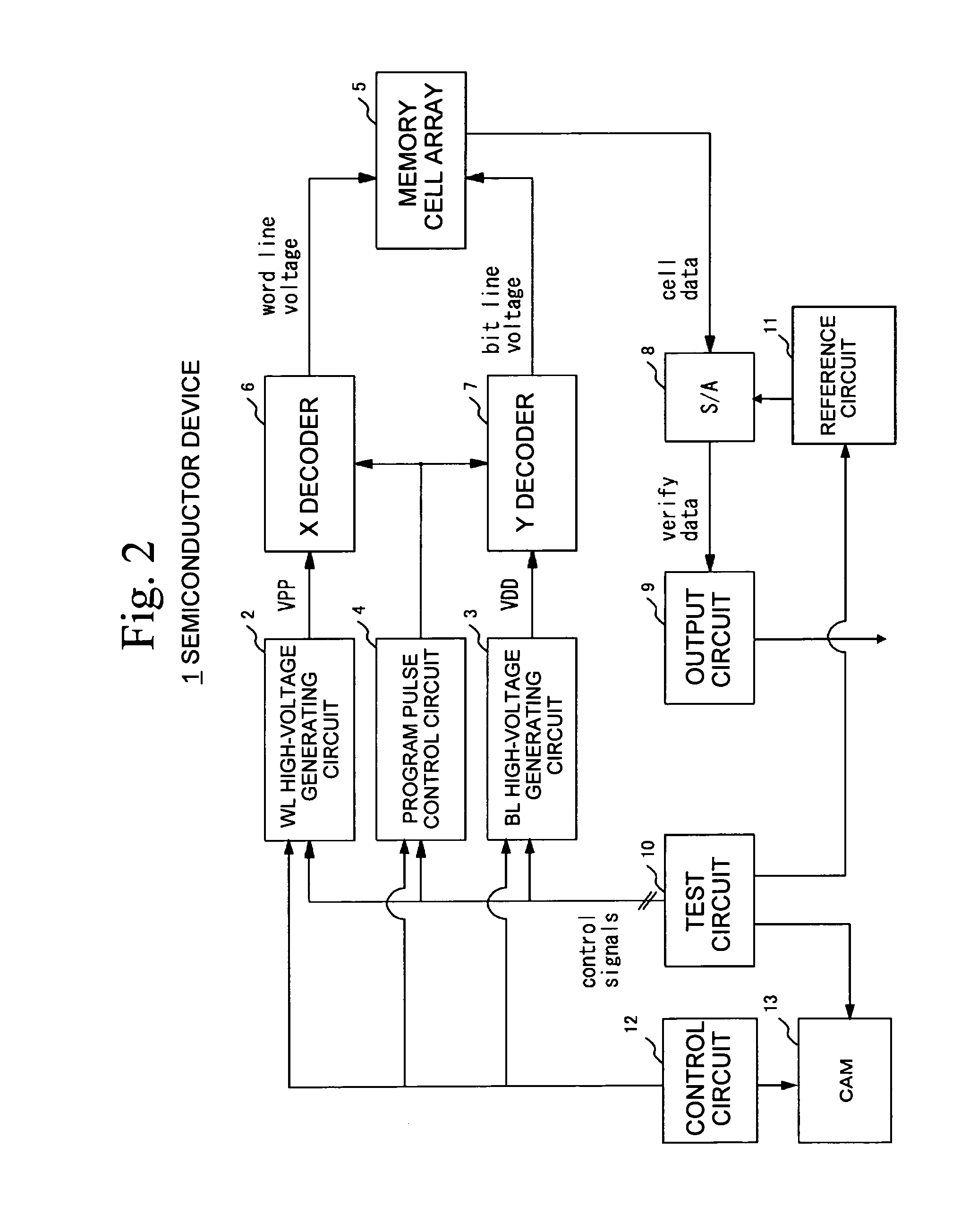
Semiconductor device and control method therefor
ActiveUS20070180184A1Shorten programming timeLonger programming timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageStorage cellSemiconductor
The present invention provides a semiconductor device and a method for controlling a semiconductor device having a memory cell array having a plurality of nonvolatile memory cells, the method including detecting the number of bits to be written as division data that is divided from data to be programmed into the memory cell array, comparing the number of bits with a predetermined number of bits, inverting or not inverting the division data to produce inversion data in accordance with a result of comparing the number of bits with the predetermined number of bits, and programming the inversion data into the memory cell array. The method further includes detecting the number of bits to be written as next division data and comparing the number of bits of next division data with the predetermined number of bits, while concurrently programming the inversion data into the memory cell array.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
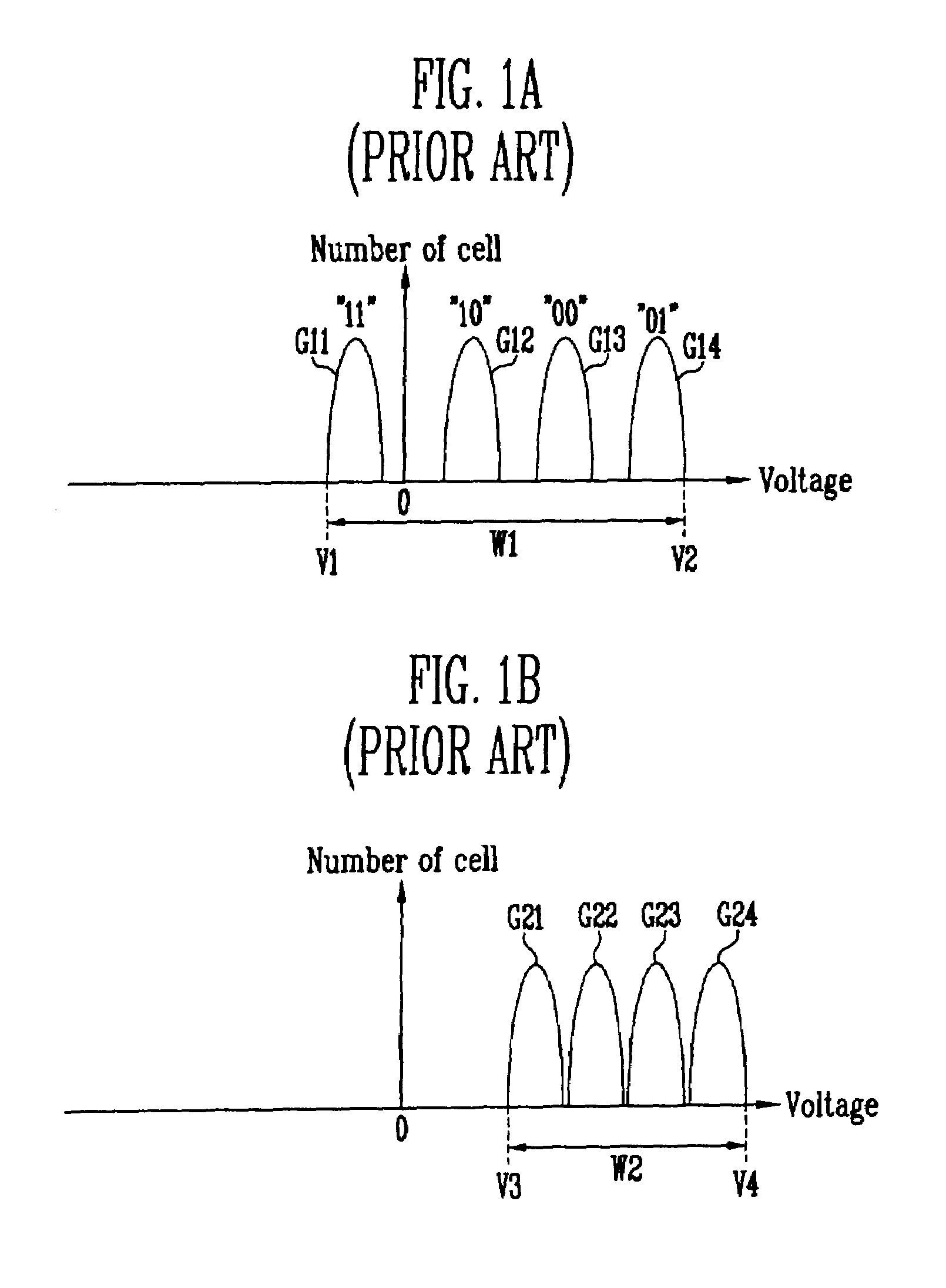
Erase and Program Method of Flash Memory Device for Increasing Program Speed of Flash Memory Device
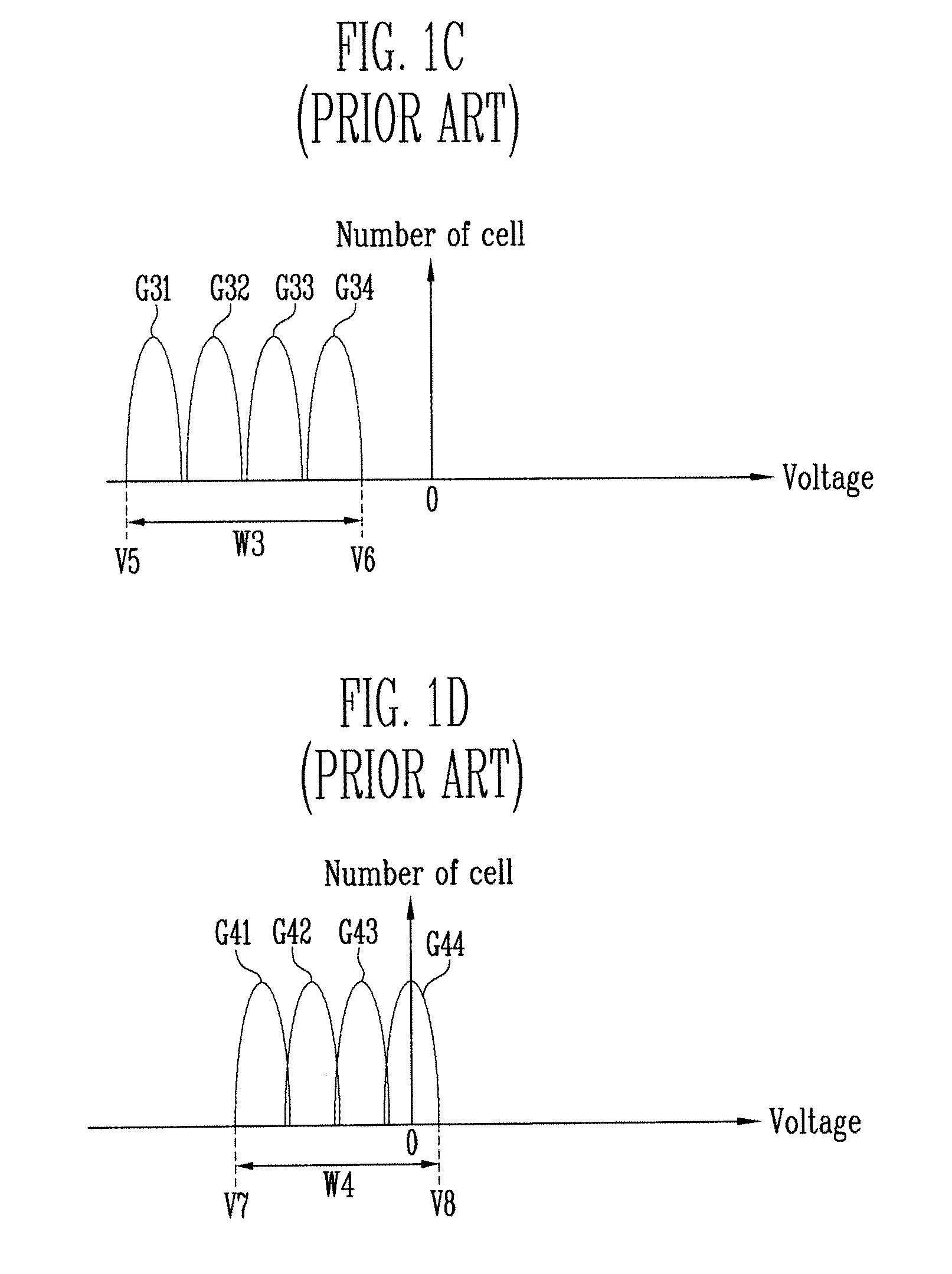
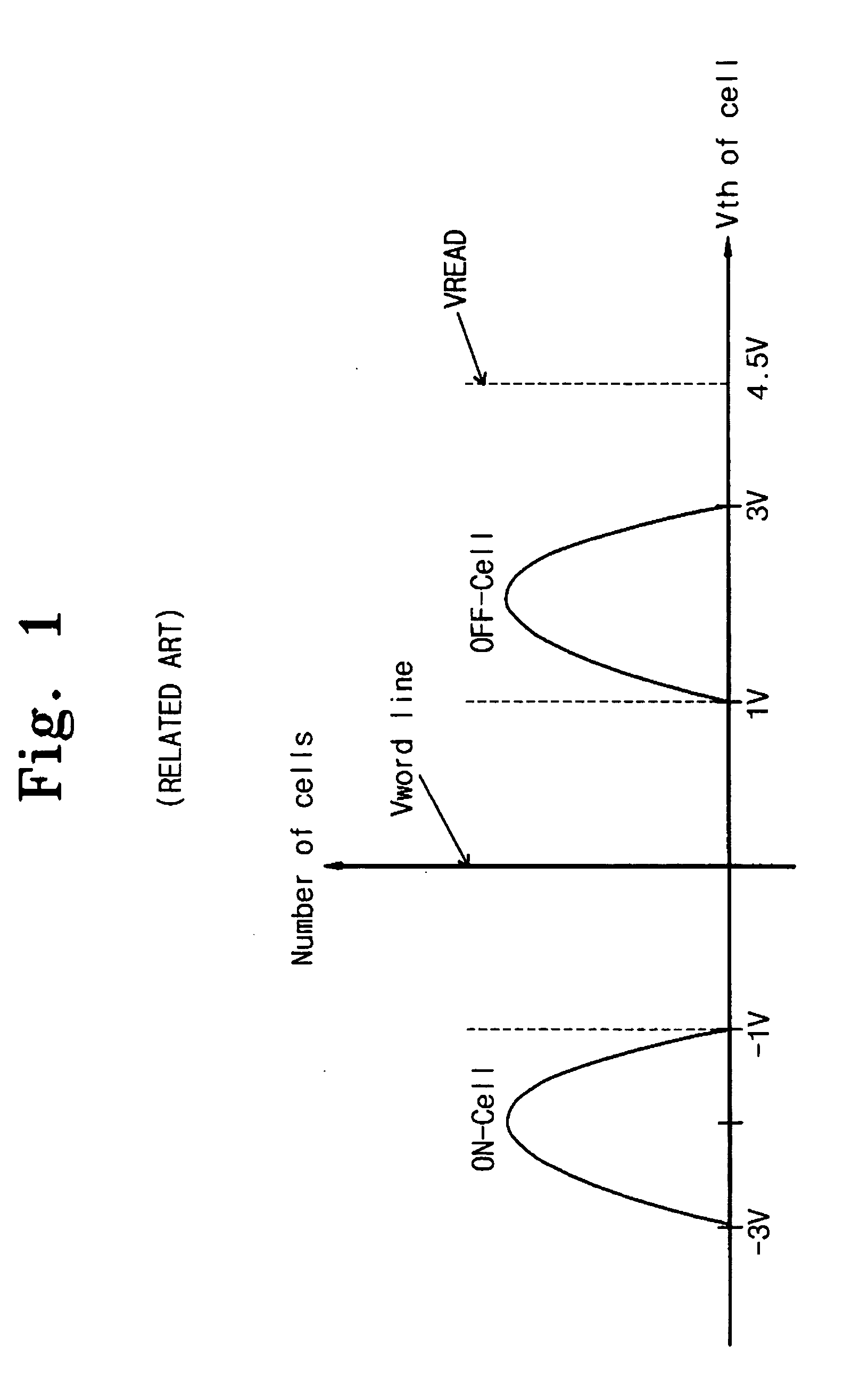
ActiveUS20070058446A1Fail occurrence ratioImproved Threshold Voltage DistributionRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage rangeThreshold voltage
The present invention relates to erase and program methods of a flash memory device including MLCs for increasing the program speed. In the erase method according to the present invention, MLCs are pre-programmed so that a voltage range in which threshold voltages of MLCs are distributed can be reduced. Therefore, a fail occurrence ratio can be reduced when erasing MLCs, the threshold voltage distribution of MLCs can be improved and an overall program time can be shortened in a subsequent program operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
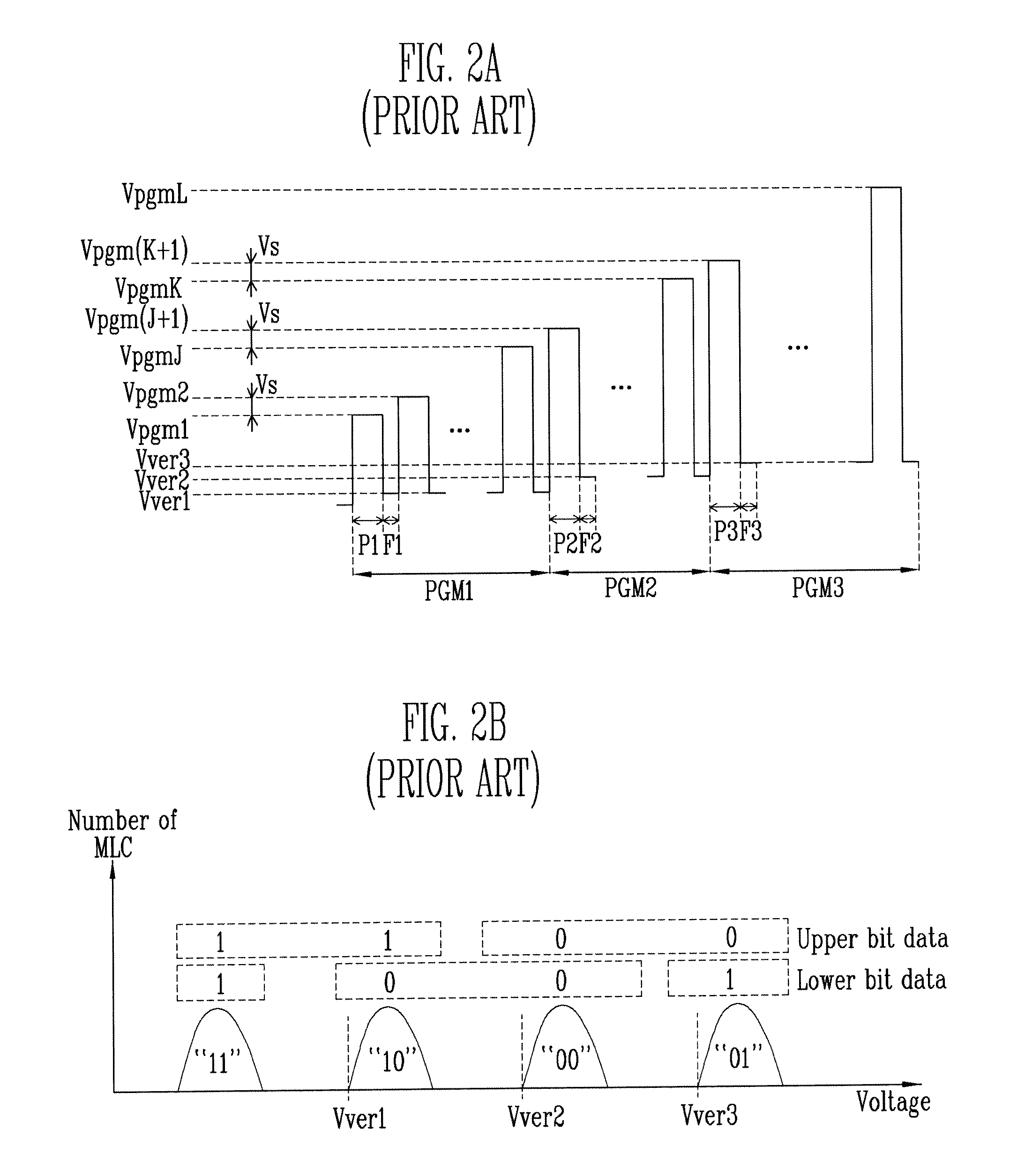
Faster programming of higher level states in multi-level cell flash memory
A program voltage signal implemented as a series of increasing program voltage pulses is applied to a set of non-volatile storage elements. Different increment values can be used when programming memory cells to different memory states. A smaller increment value can be used when programming memory cells to lower threshold voltage memory states and a larger increment value used when programming memory cells to higher threshold voltage memory states such as the highest memory state in an implementation. When non-volatile storage elements of a set are programmed to different memory states under simultaneous application of a single program voltage signal, programming can be monitored to determine when lower state programming is complete. The increment value can then be increased to complete programming to the highest memory state. Coarse / fine programming methodology can be incorporated for the highest memory state when the increment value is increased to maintain the threshold distribution within a reasonable range.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Situation sensitive memory performance
ActiveUS20070033581A1Avoid timeoutImprove programming speedEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTerm memoryComputer science
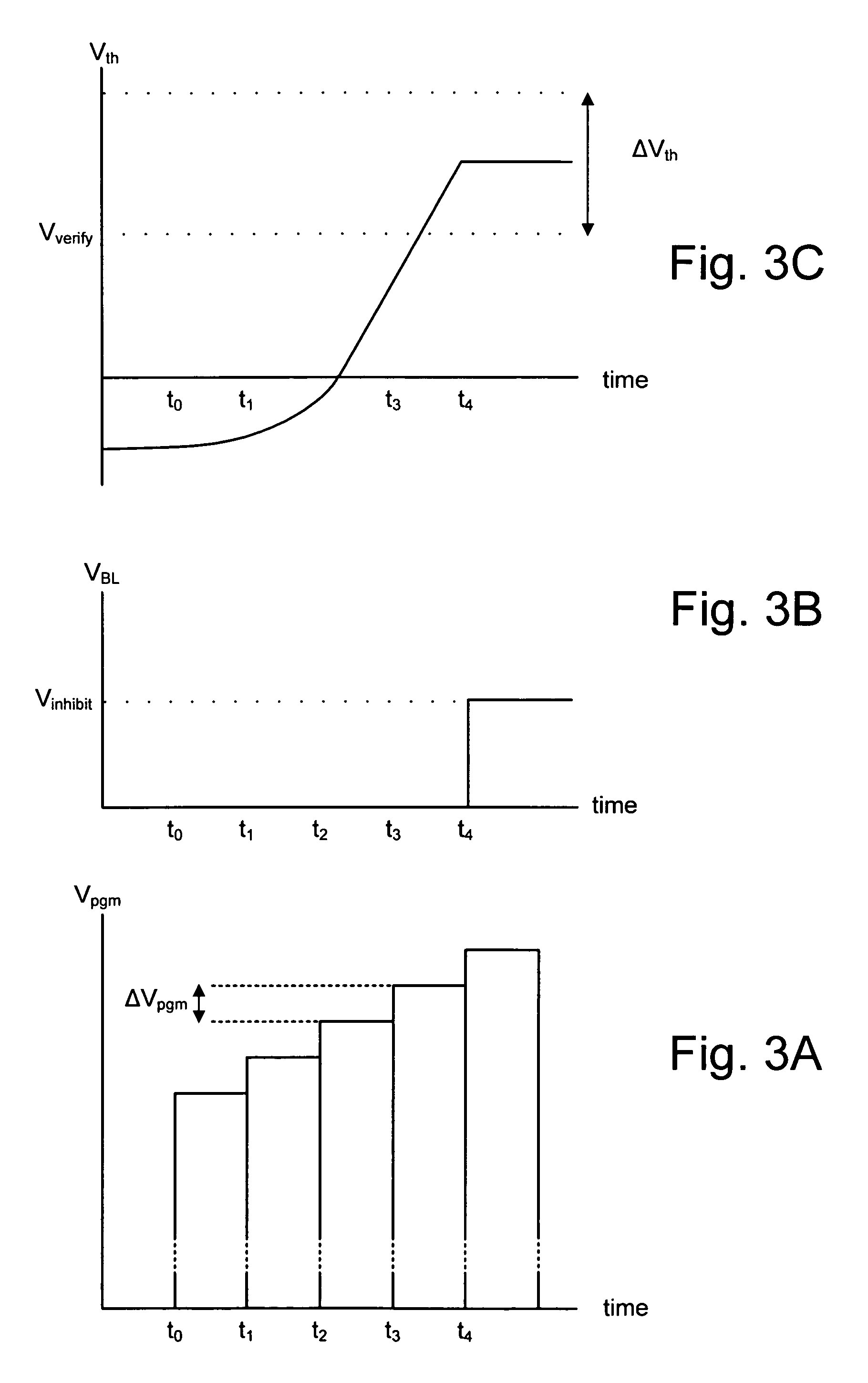
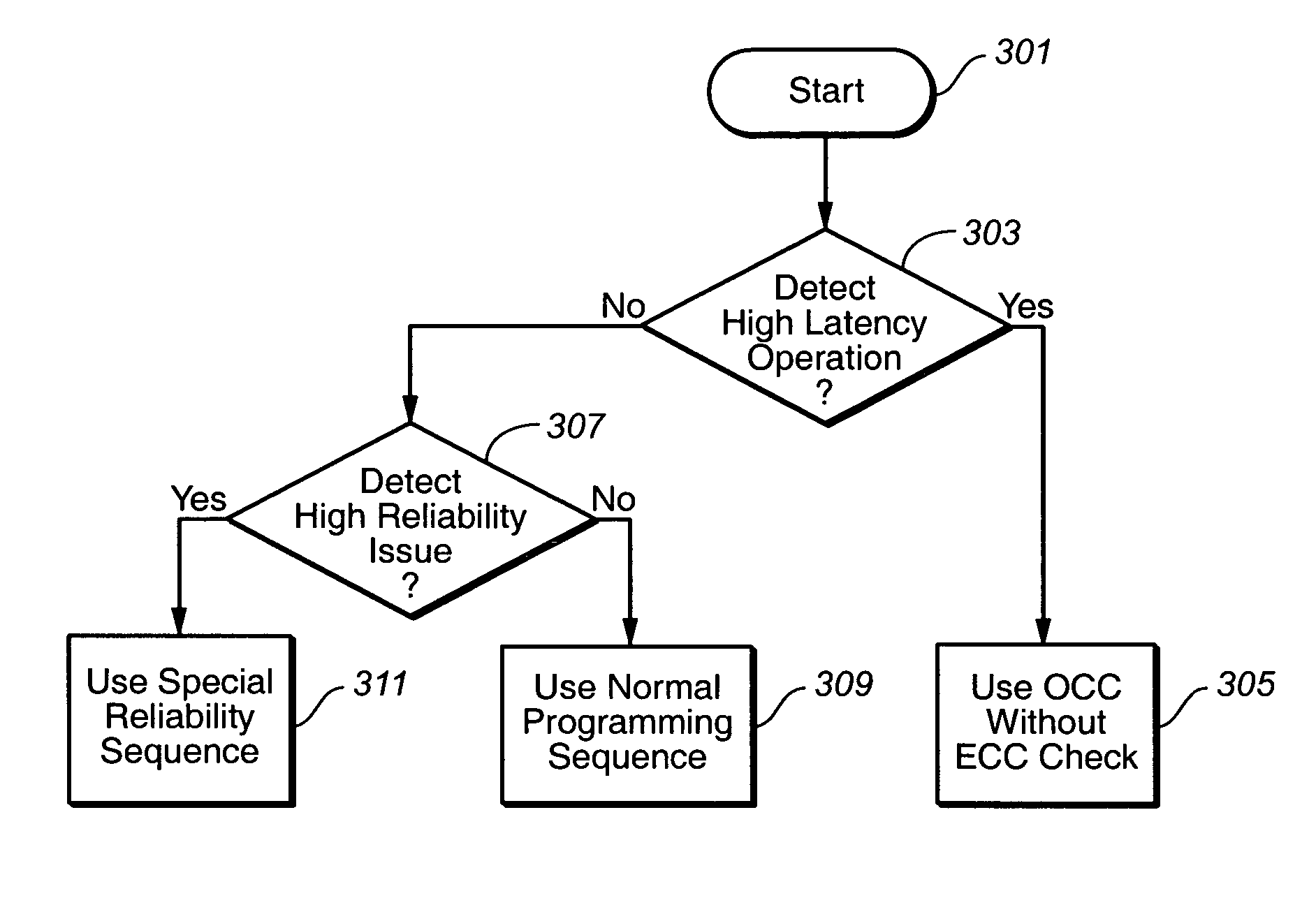
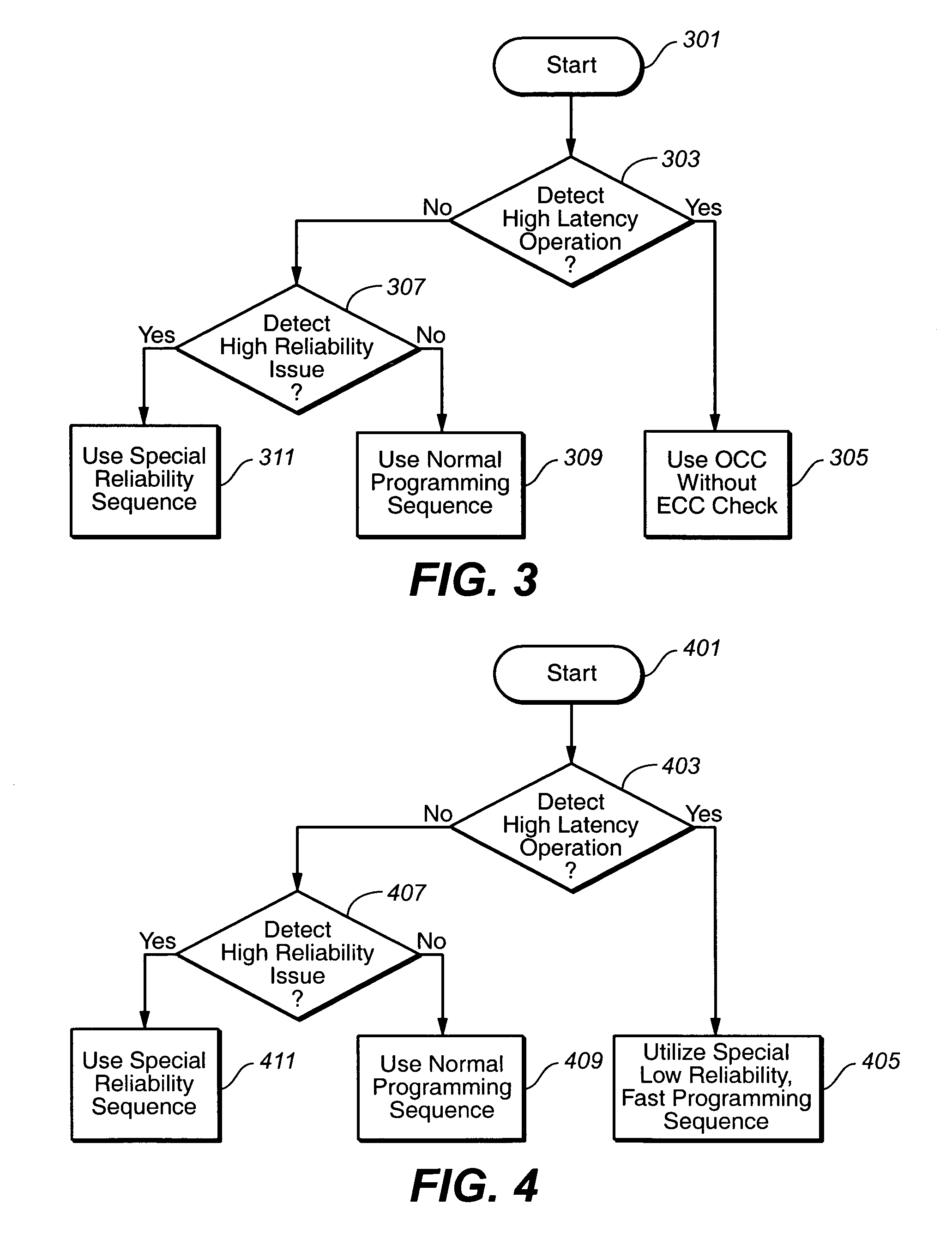
The present invention presents a non-volatile memory system that adapts its performance to one or more system related situation. If a situation occurs where the memory will require more than the allotted time for completing an operation, the memory can switch from its normal operating mode to a high performance mode in order to complete the operation quickly enough. Conversely, if a situation arises where reliability could be an issue (such as partial page programming), the controller could switch to a high reliability mode. In either case, once the trigging system situation has returned to normal, the memory reverts to the normal operation. The detection of such situations can be used both for programming and data relocation operations. An exemplary embodiment is based on firmware programmable performance.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
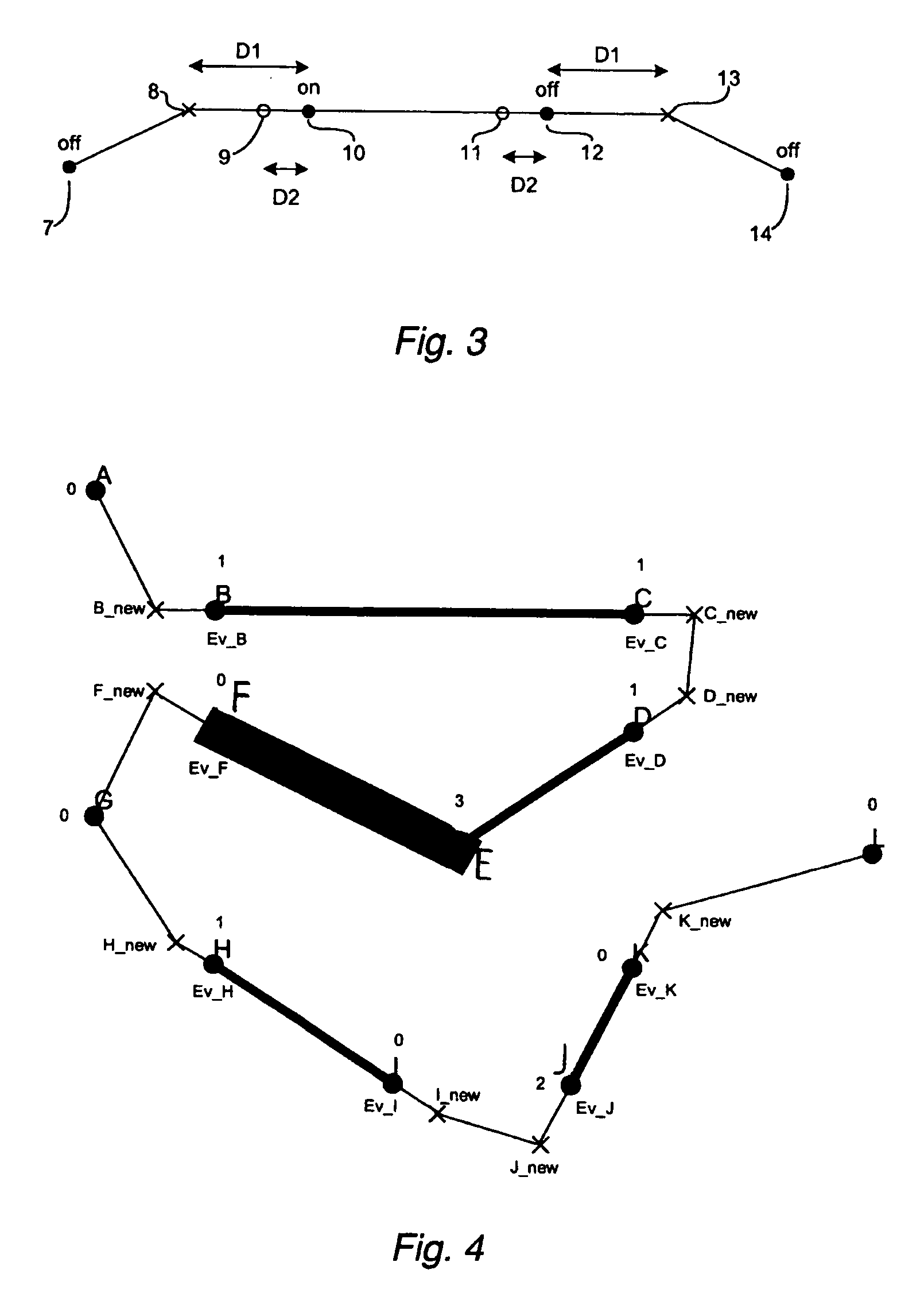
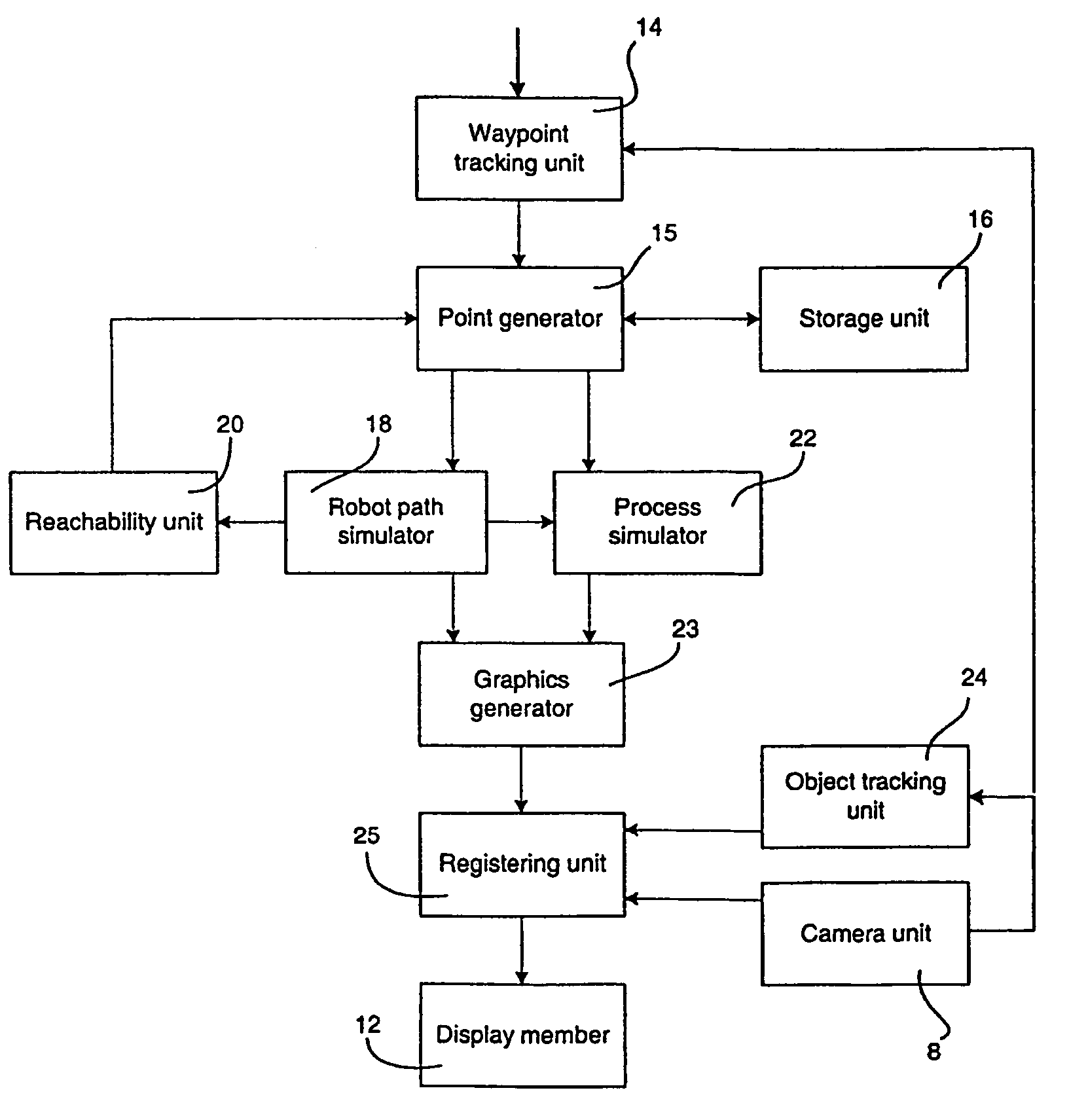
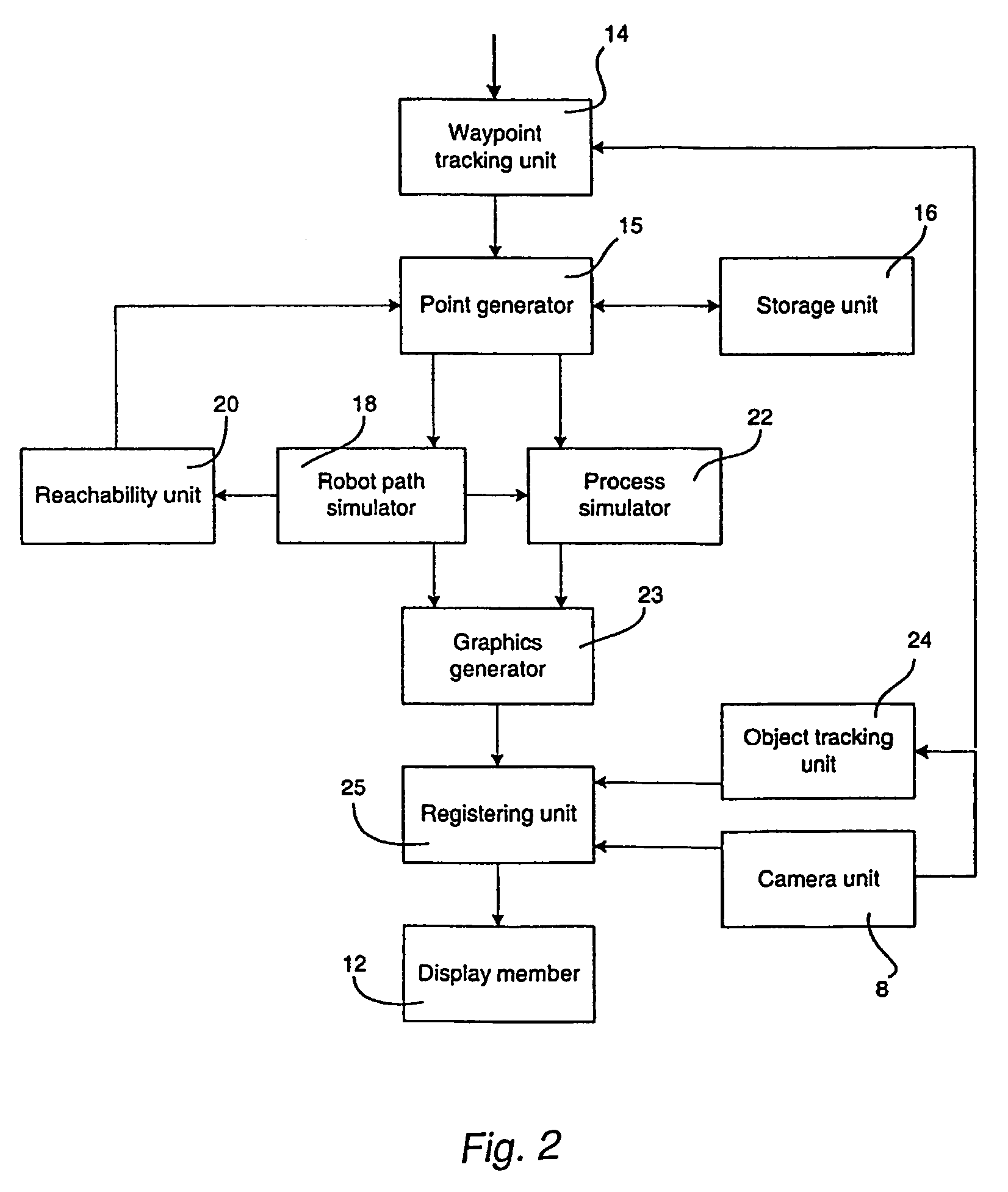
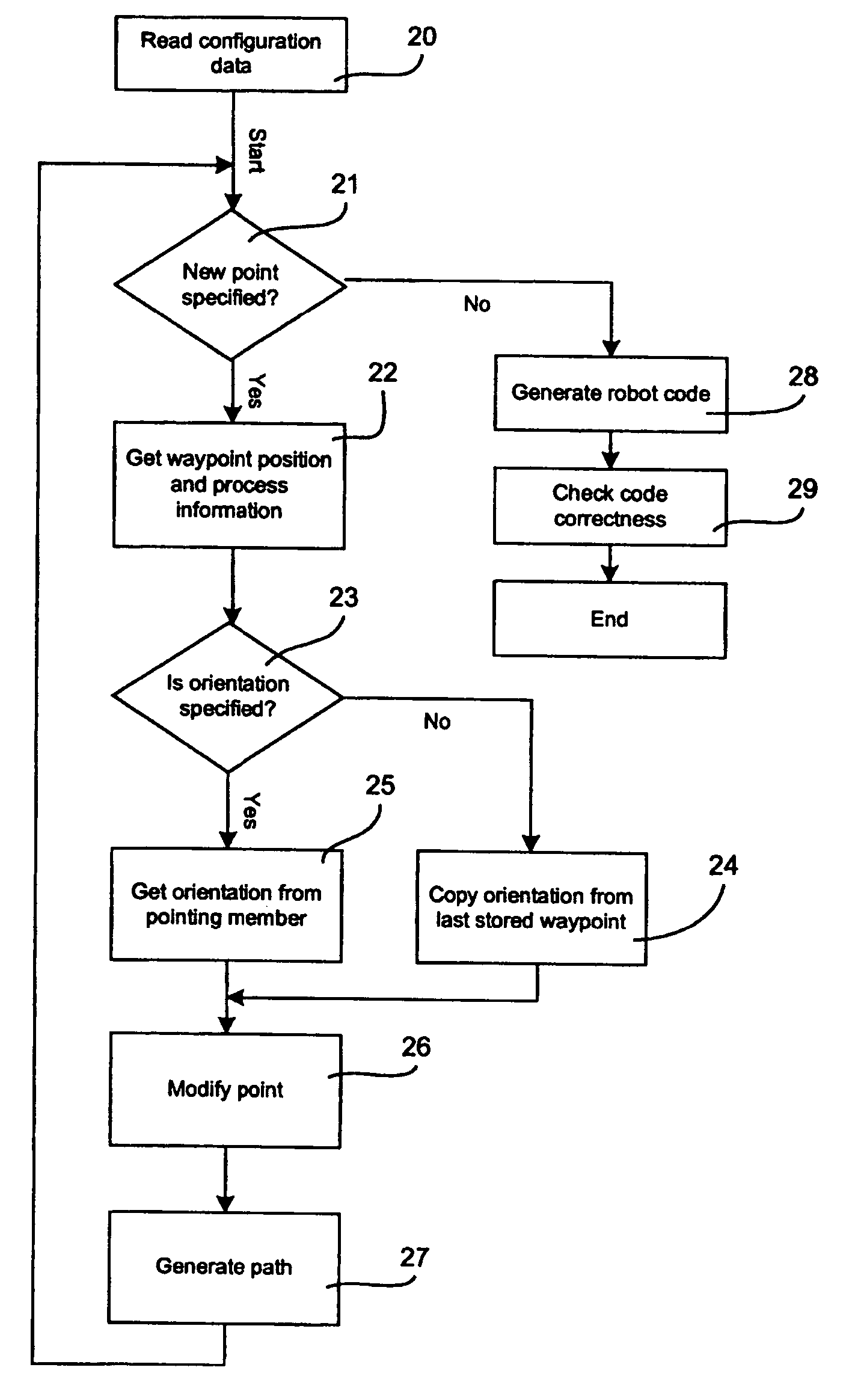
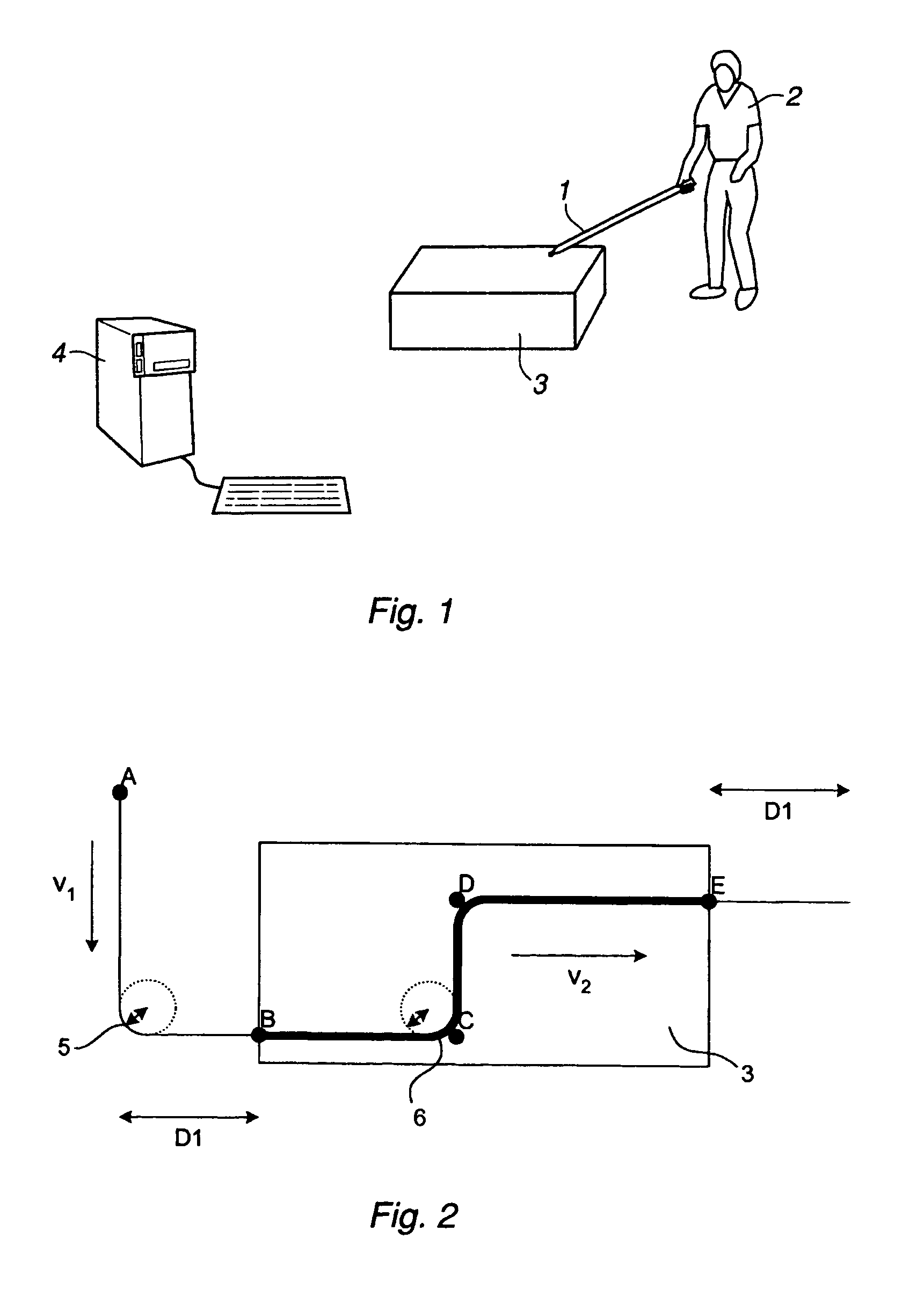
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
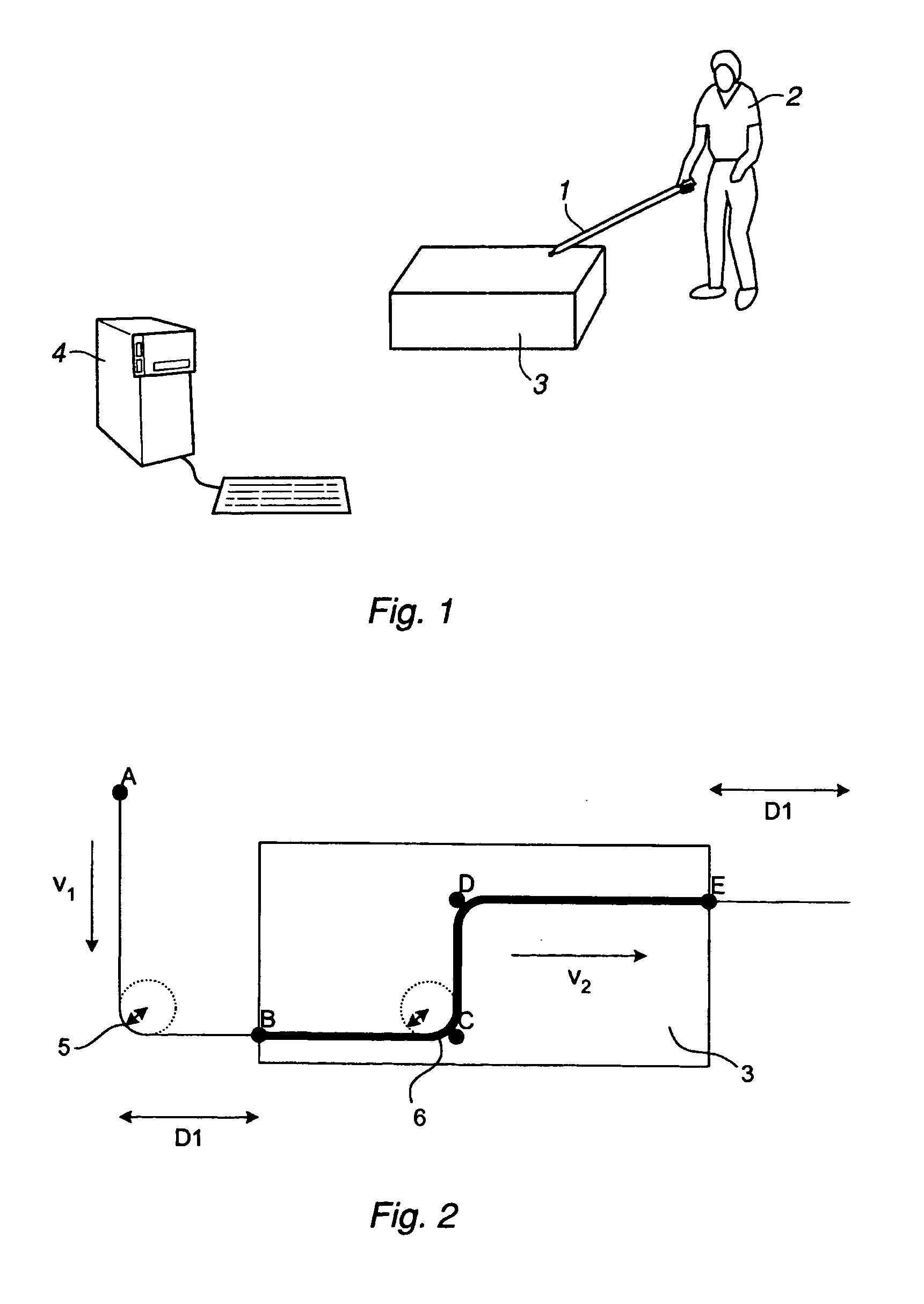
ActiveUS20050149231A1Shorten teaching timeQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsAnalog robot
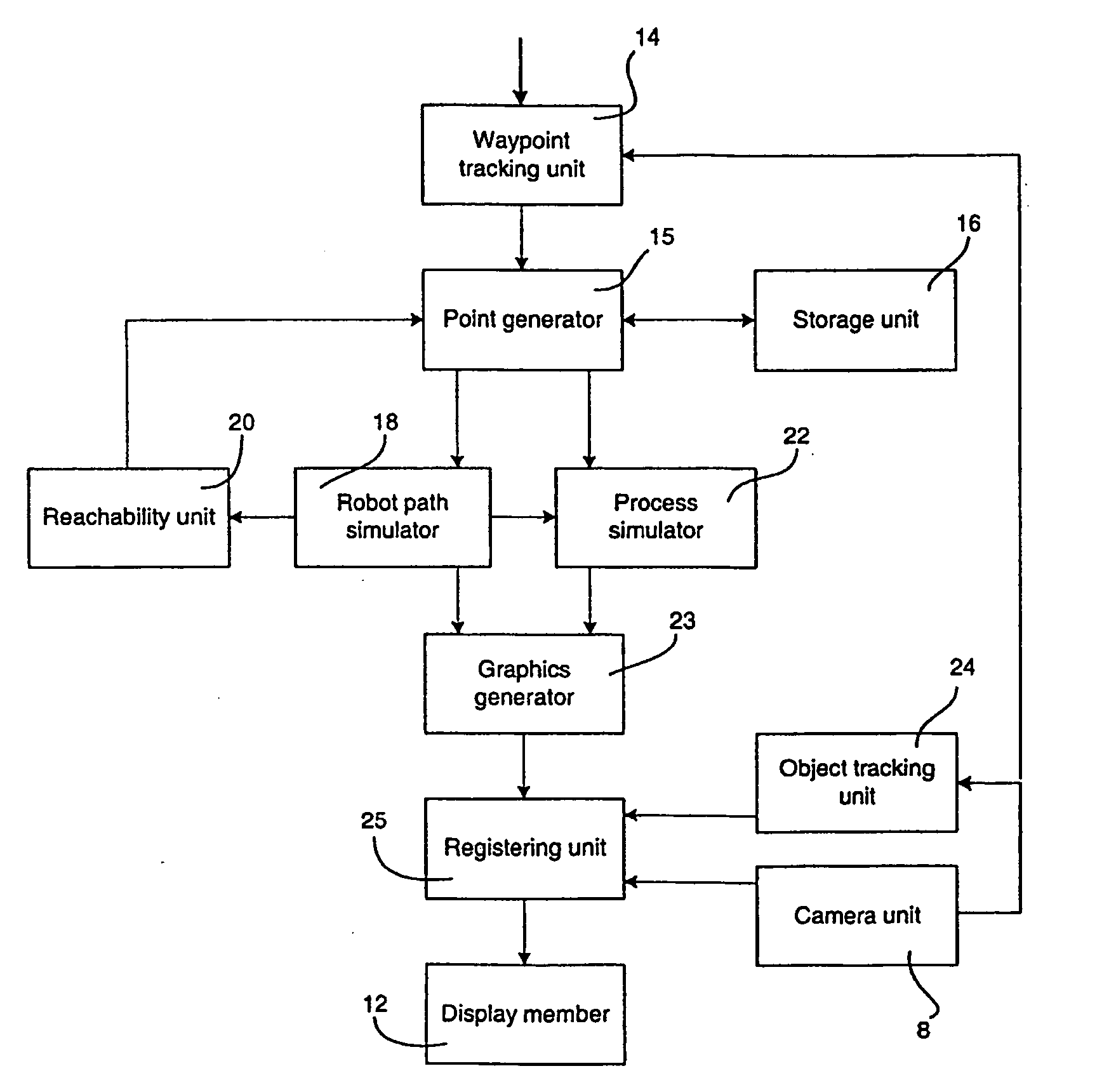
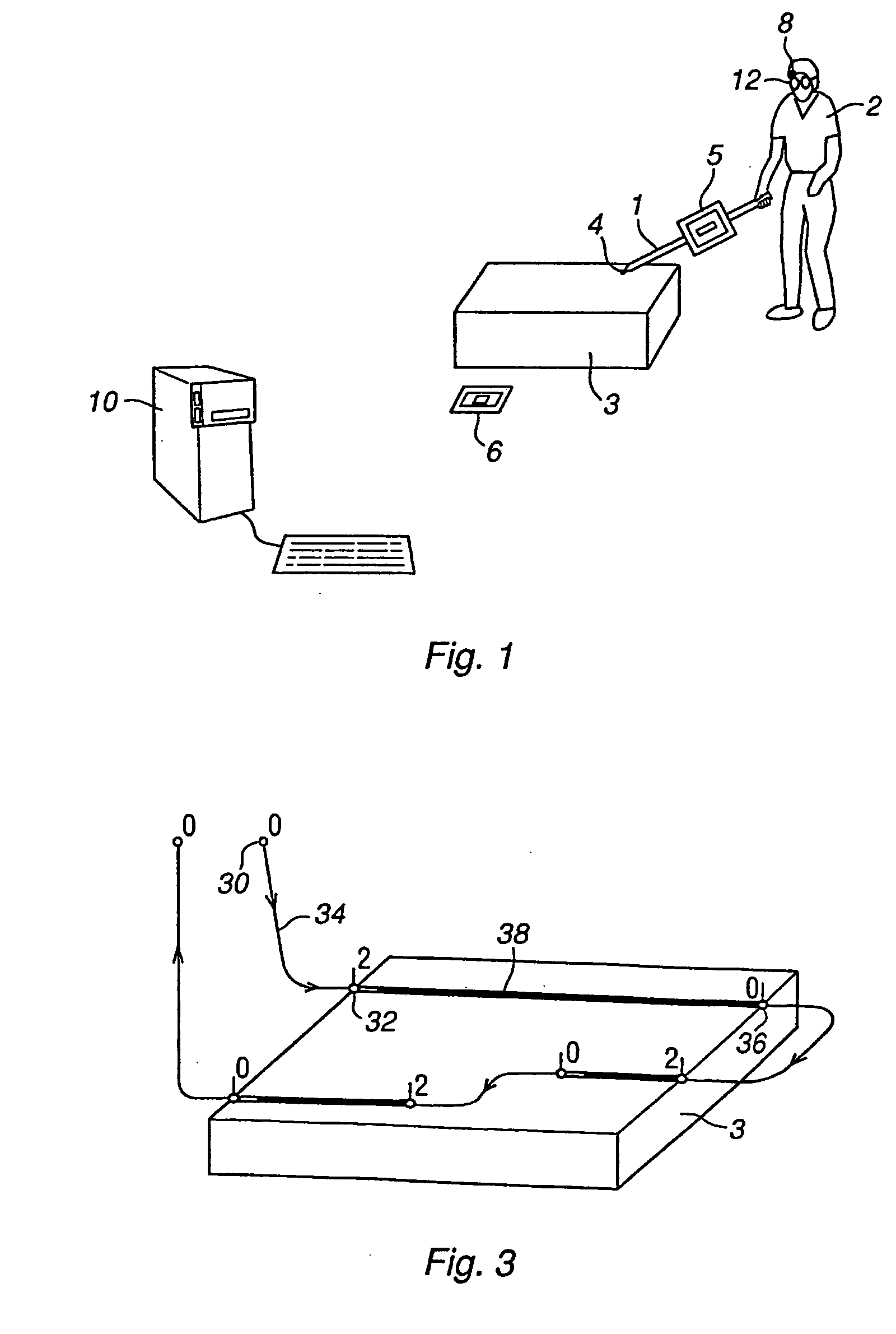
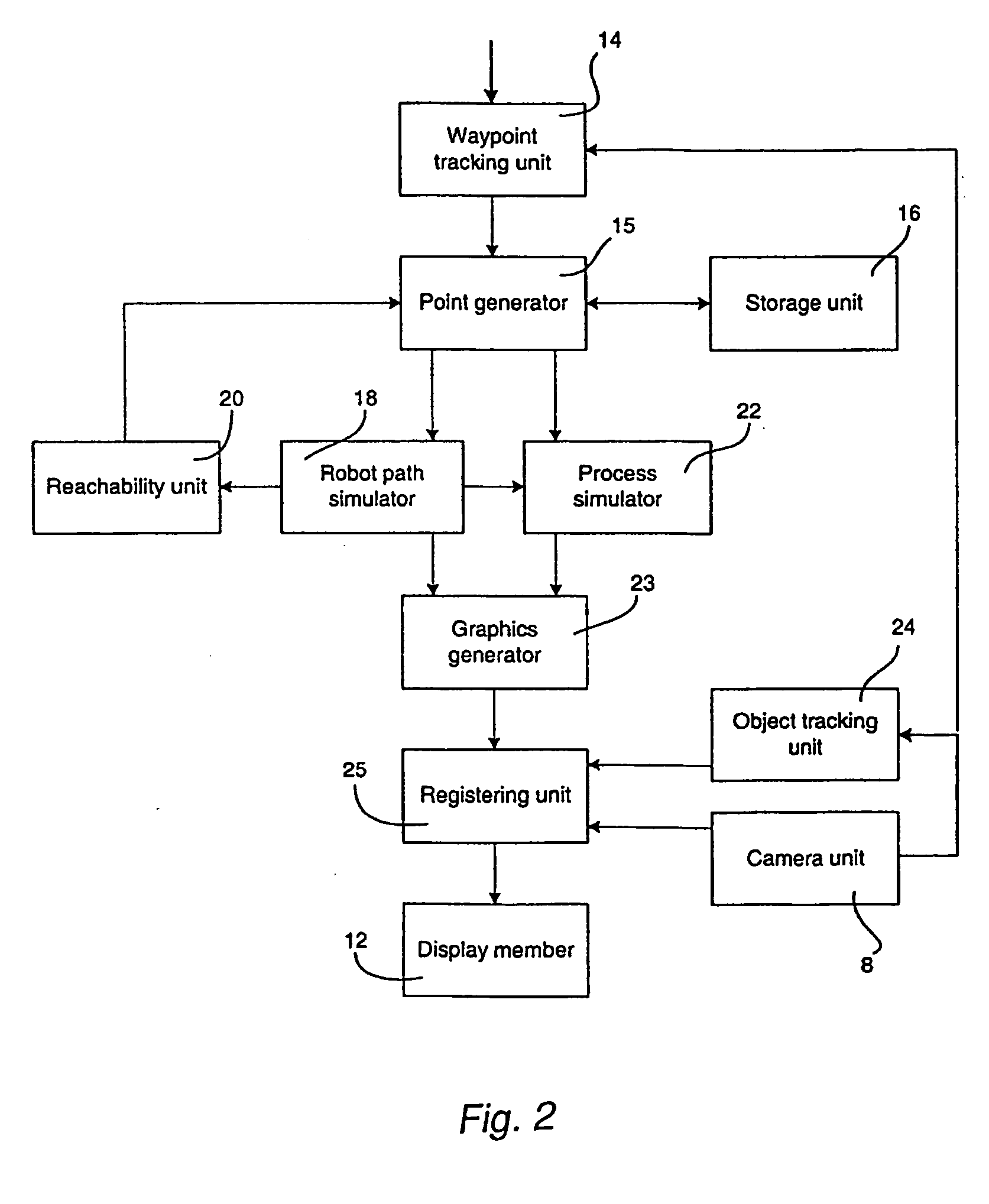
A method and a system for use in connection with programming of an industrial robot, the programming comprises teaching the robot a path having a number of waypoints located on or in the vicinity of an object to be processed by the robot. The system comprises: means for obtaining information about the waypoints of the path in relation to the object, a storage unit (16), for storing the obtained information, a simulation unit (18), simulating the robot path based on the obtained information about the waypoints and a model of the robot, a graphics generator (23), generating a graphical representation of the simulated robot path, and a display member (12) displaying a view comprising the object and said graphical representation of the robot path projected on the object.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method and device for programming control information
InactiveUS20050248992A1Shorten programming timeRead-only memoriesTemporary pavingsProgramming languageLow speed
Method and device for programming control information, such as a flag, a control flag, a mark, or a control mark. The method and device may perform a lower-speed programming of a given cell type in a first area of memory array, confirm a result of the lower-speed programming of the given cell type in the first area of memory array, and perform a higher-speed programming of the given cell type in a second area of memory array after confirming the result of the lower-speed programming, wherein an initial programming voltage of the higher-speed programming may be different from that of the lower-speed programming. The first and second programming may be different, for example, the first programming may be a lower-speed operation, such as the writing of data, and the second programming may be a higher-speed operation, such as the writing of control information. The first and second programming methods may also be different, for example, the first programming method may be a programming method that does not permit over-programming and the second programming method may be a programming method that does permit over-programming.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
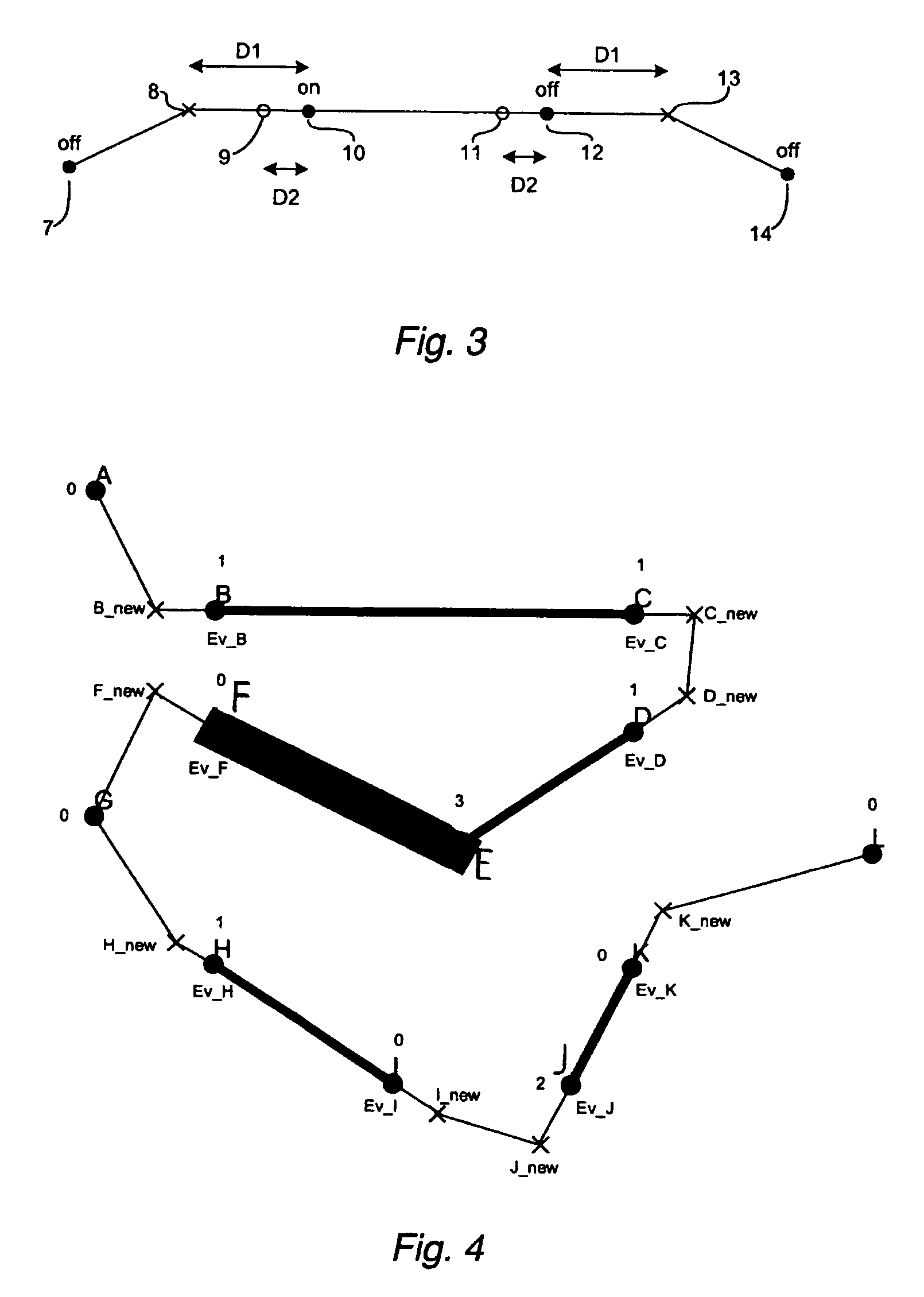
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
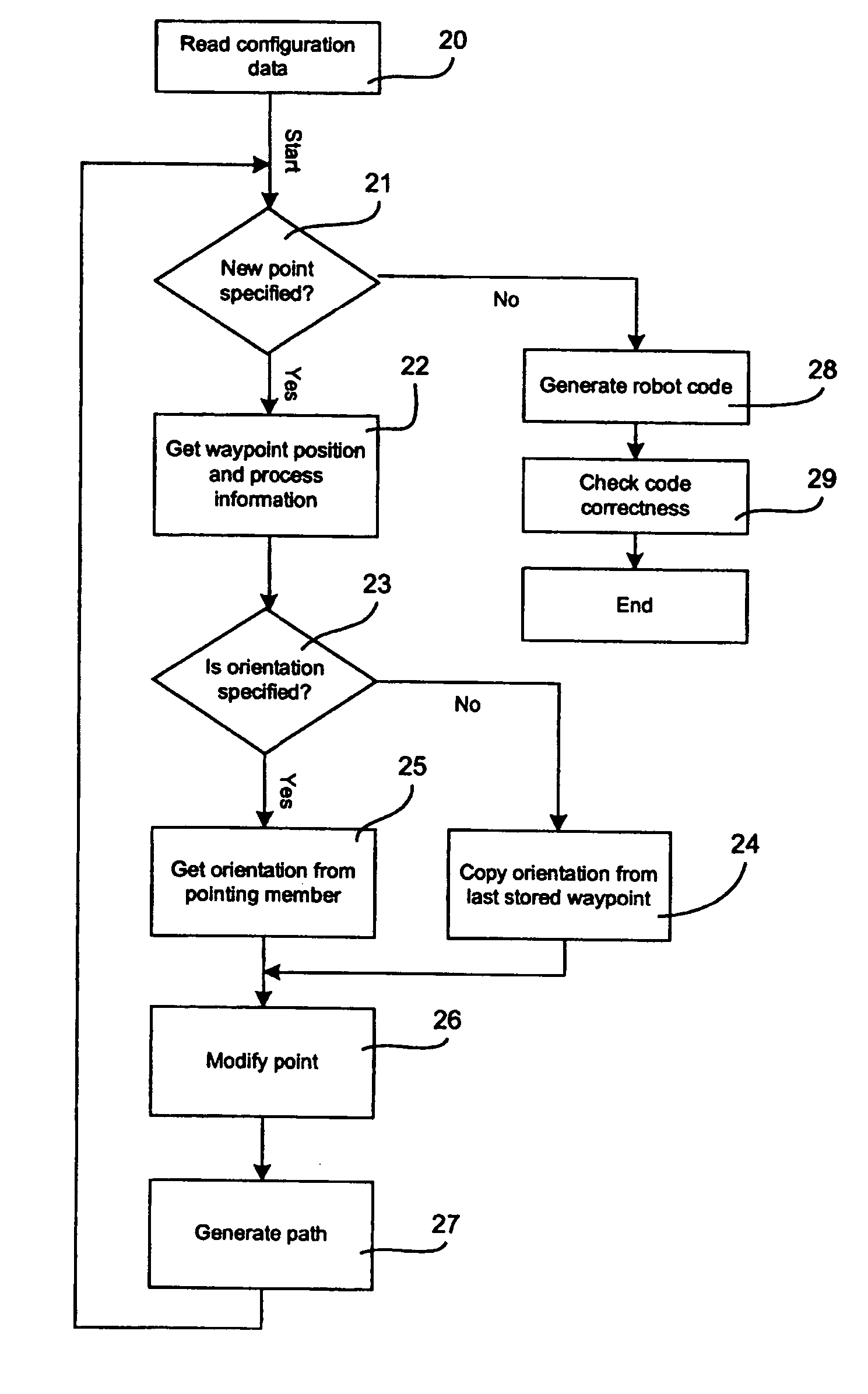
ActiveUS20040193321A1Shorten programming timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlComputer visionAlgorithm
A method for programming an industrial robot having a tool, to perform a process on an object while following a robot path defined by a number of waypoints. The method comprises: obtaining configuration data including configuration data for the tool, configuration data for the robot path and information about the position and orientation of the object in relation to the robot, obtaining a sequence of waypoints, which defines the process in relation to the object, the waypoints comprises information about desired positions of the tool in relation to the object and desired positions of process events in relation to the object, obtaining at least one distance for adjusting the position of a waypoint, deciding whether an obtained waypoint should be modified or not, based on the obtained information about the waypoints, generating a modified sequence of waypoints by modifying the waypoints in the obtained sequence of waypoints, based on said decision, the obtained distance and the obtained information about the waypoints and generating the actual robot path based on the modified sequence of waypoints and the obtained configuration data.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
ActiveUS7236854B2Shorten teaching timeQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsAnalog robot
A method and a system for use in connection with programming of an industrial robot. The programming includes teaching the robot a path having a number of waypoints located on or in the vicinity of an object to be processed by the robot. The system includes elements for obtaining information about the waypoints of the path in relation to the object, a storage unit for storing the obtained information, a simulation unit for simulating the robot path based on the obtained information about the waypoints and a model of the robot, a graphics generator for generating a graphical representation of the simulated robot path, and a display member for displaying a view comprising the object and the graphical representation of the robot path projected on the object.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
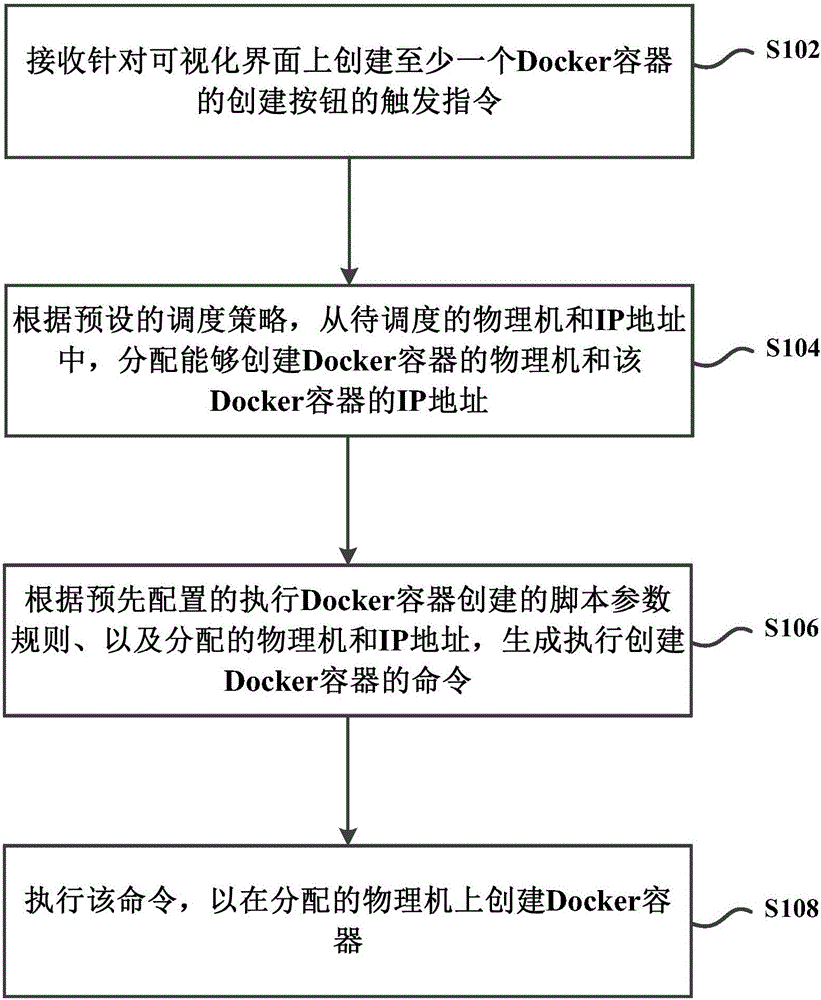
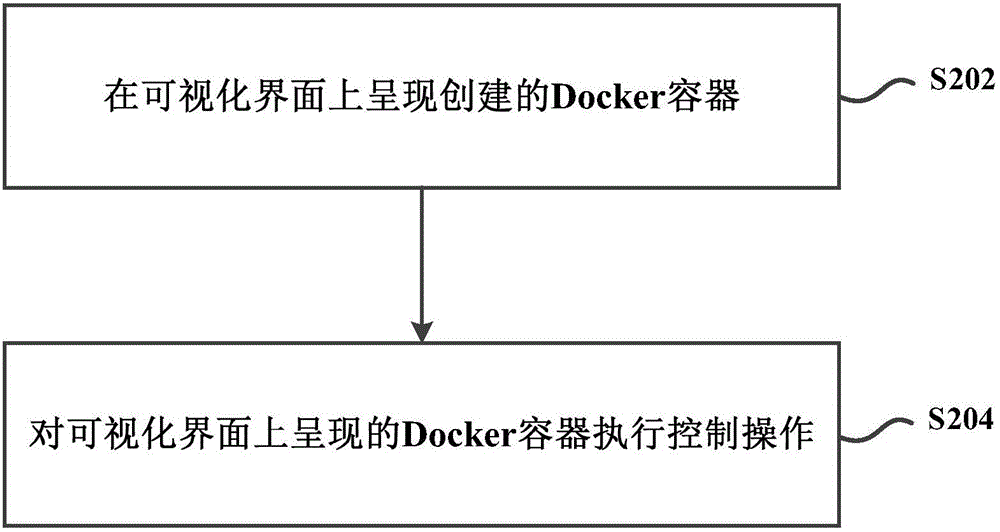
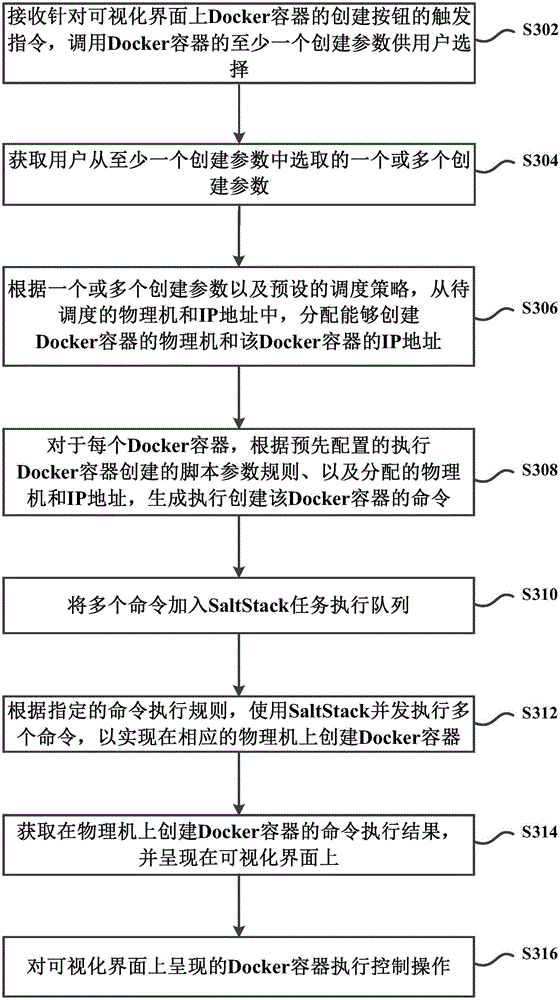
Docker container management method and system
ActiveCN104991815AEasy to operateImprove creation efficiencyMultiprogramming arrangementsIp addressOperability
The present invention provides a Docker container management method and system. The method comprises: receiving a trigger instruction of a create button for creating at least one Docker container on a visual interface; according to a preset scheduling policy, assigning a physical machine capable of creating the Docker container and an IP address of the Docker container from physical machines and IP addresses to be scheduled; according a preconfigured script parameter rule on execution of Docker container creation, and the assigned physical machine and IP address, generating a command of executing the creation of the Docker container; and executing the command to create the Docker container on the physical machine. According to the present invention, the utilization of a visual interface to create a Docker container is more intuitive, simpler, and higher in operability, and also can provide an automated creation process with no need of manual involvement and with high efficiency.
Owner:北京鸿享技术服务有限公司
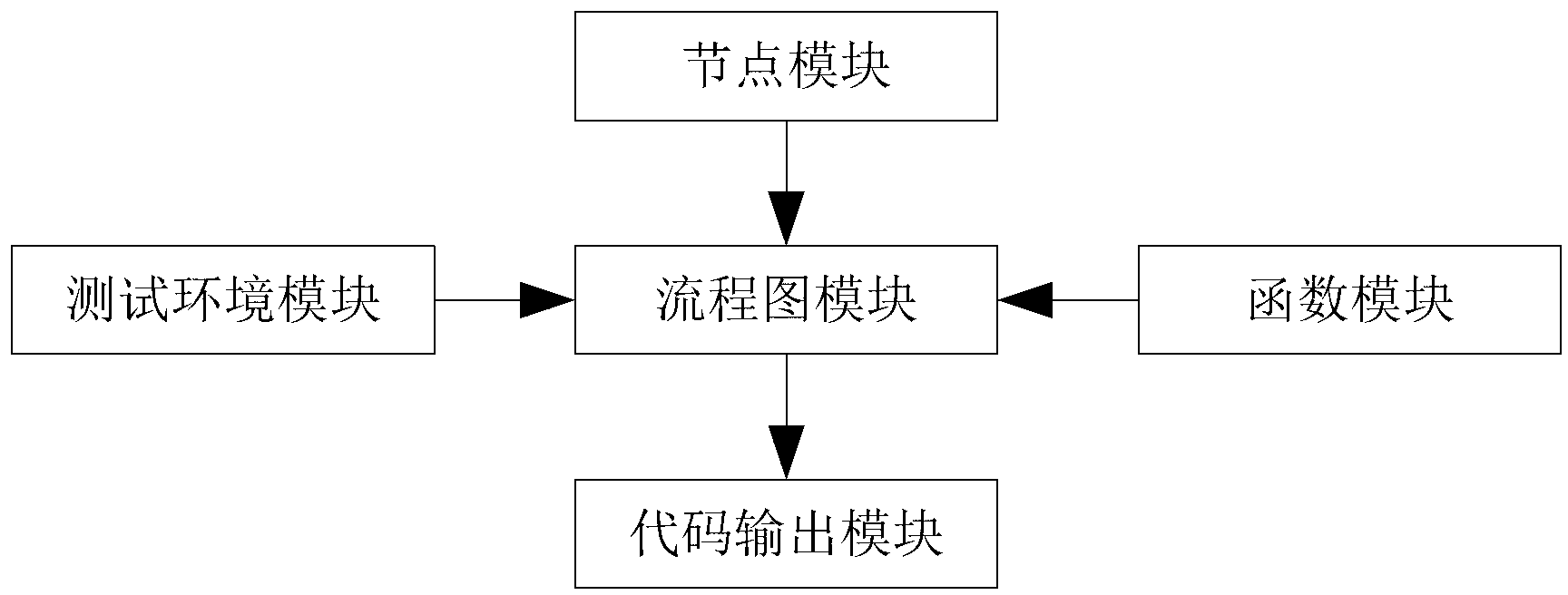
Method for implementing code programming by graphical operations
ActiveCN102915242AShorten programming timeAvoid cumbersomenessSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemOperating environment
The invention discloses a method for implementing code programming by graphical operations. The method is involved with a node module, a testing environment module, a flow chart module, a function module and a code output module. The node module is used for establishing test nodes corresponding to test programs according to different devices to be tested, related test devices and the corresponding test programs. The testing environment module is used for establishing a current operating environment for the flow chart module according to information of the device to tested, selected by a user. The flow chart module is used by the user to sequentially establish graphic flow charts formed by the test nodes according to the devices predicted for testing and the test nodes selected in correspondence to the corresponding test devices. The function module is used for storing and recording new functions and for supporting function calls regarding to the node module and the flow chart module. The code output module is used for converting the generated graphic flow charts into executable files formed by codes and outputting the files. The method is compatible with various testing environments (operating systems and CPU (central processing unit) environments) and is capable of providing graphical interface editing and testing logics to users and visually displaying the operating process and testing implication of function modules.
Owner:CHINA TECHENERGY +1
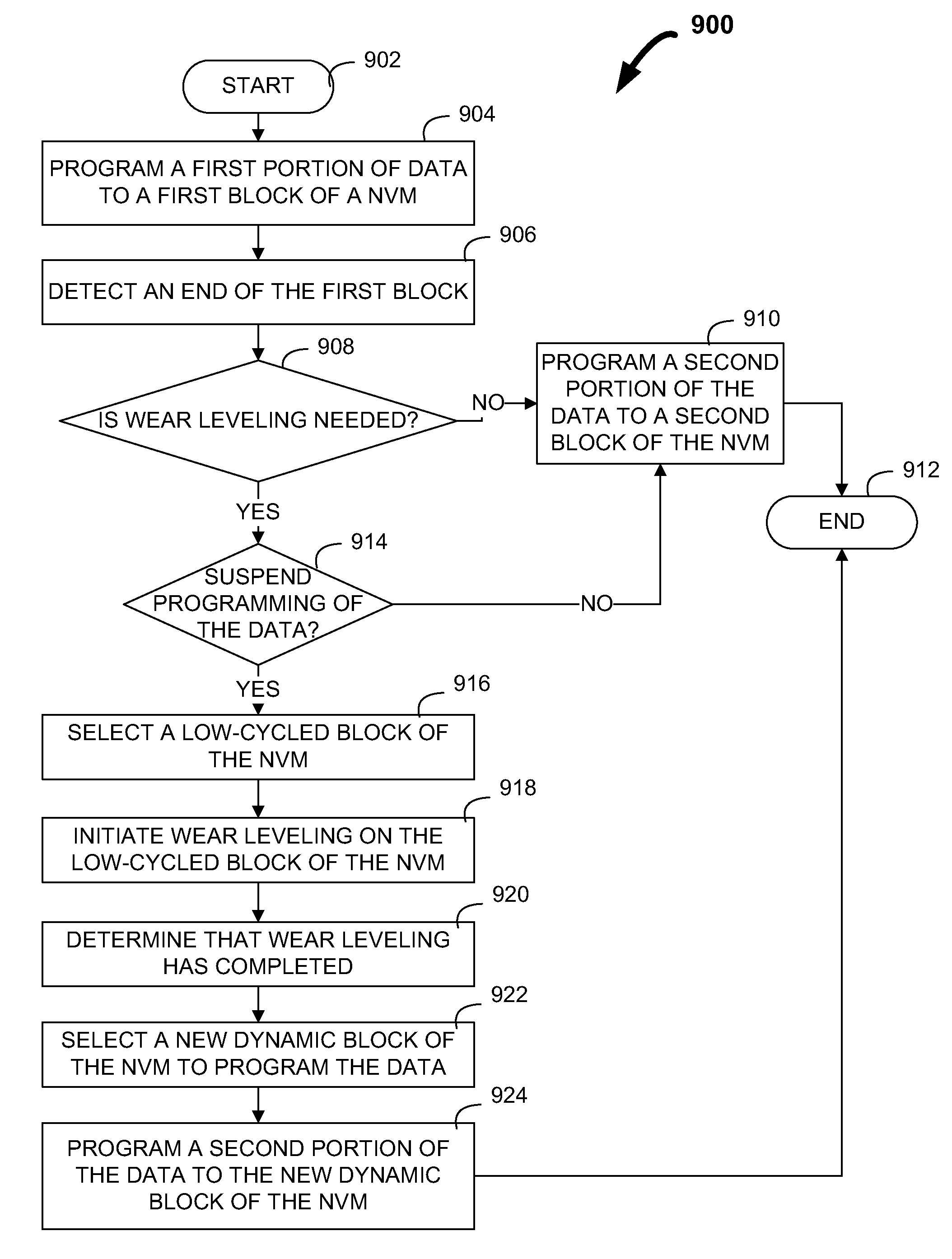
Initiating wear leveling for a non-volatile memory
ActiveUS20120030409A1Improve system performanceImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMemory interfaceWaste collection
Systems and methods are provided for initiating wear leveling on block-aligned boundaries for non-volatile memories (“NVMs”), such as flash memory. In some embodiments, an electronic device including the NVM may suspend the programming of data upon reaching the end of a dynamic block. The electronic device may then perform wear leveling on a low-cycled block of the NVM. The electronic device may thus be configured to copy static data from the low-cycled block to another block of the NVM. After wear leveling has completed, the memory interface can program a second portion of the data to a new dynamic block of the NVM. This way, the electronic device can improve the efficiency of garbage collection. In addition, the electronic device can decrease the programming time for user generated writes, the wearing of the NVM, and overall power consumption.
Owner:APPLE INC
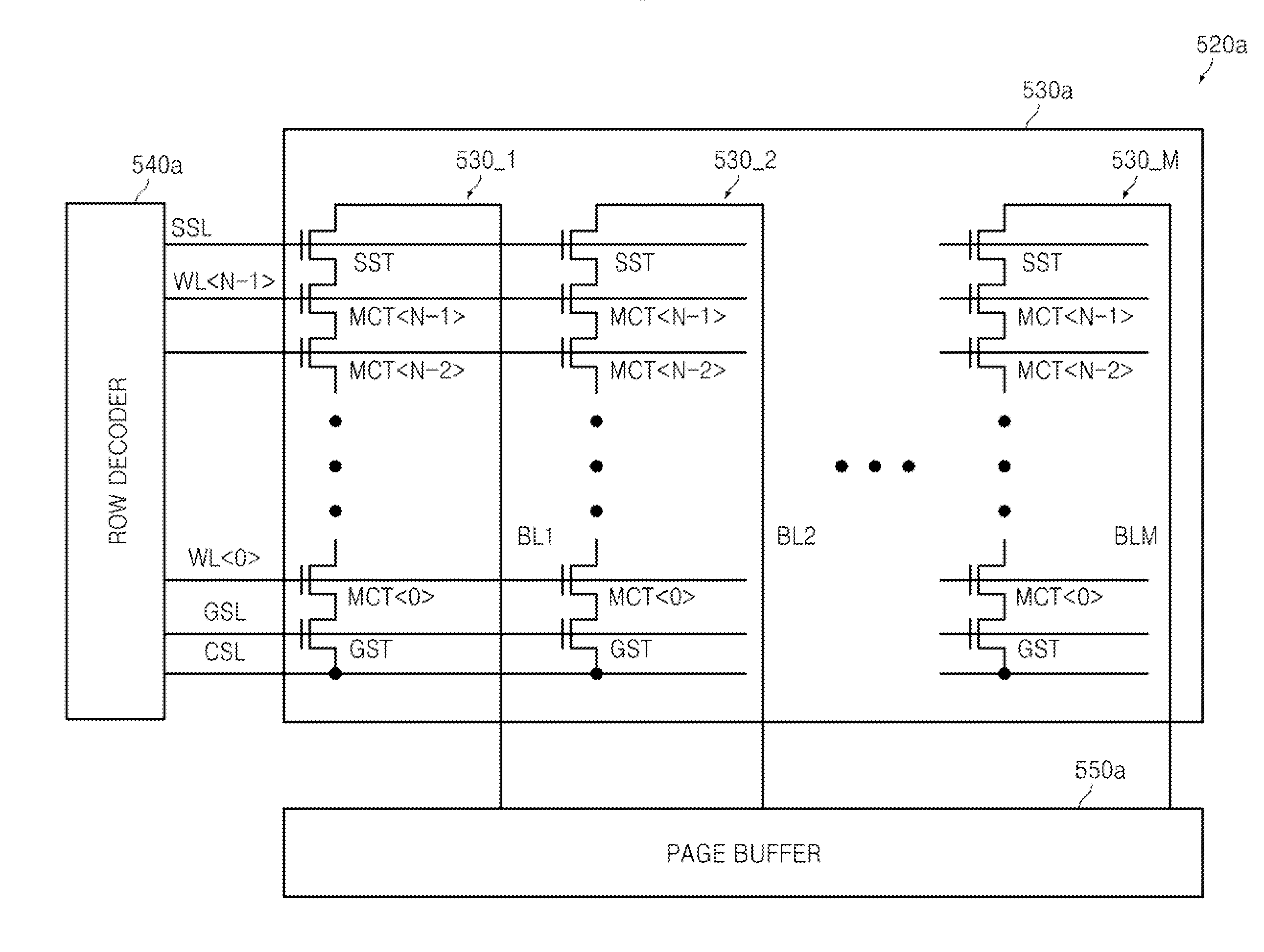
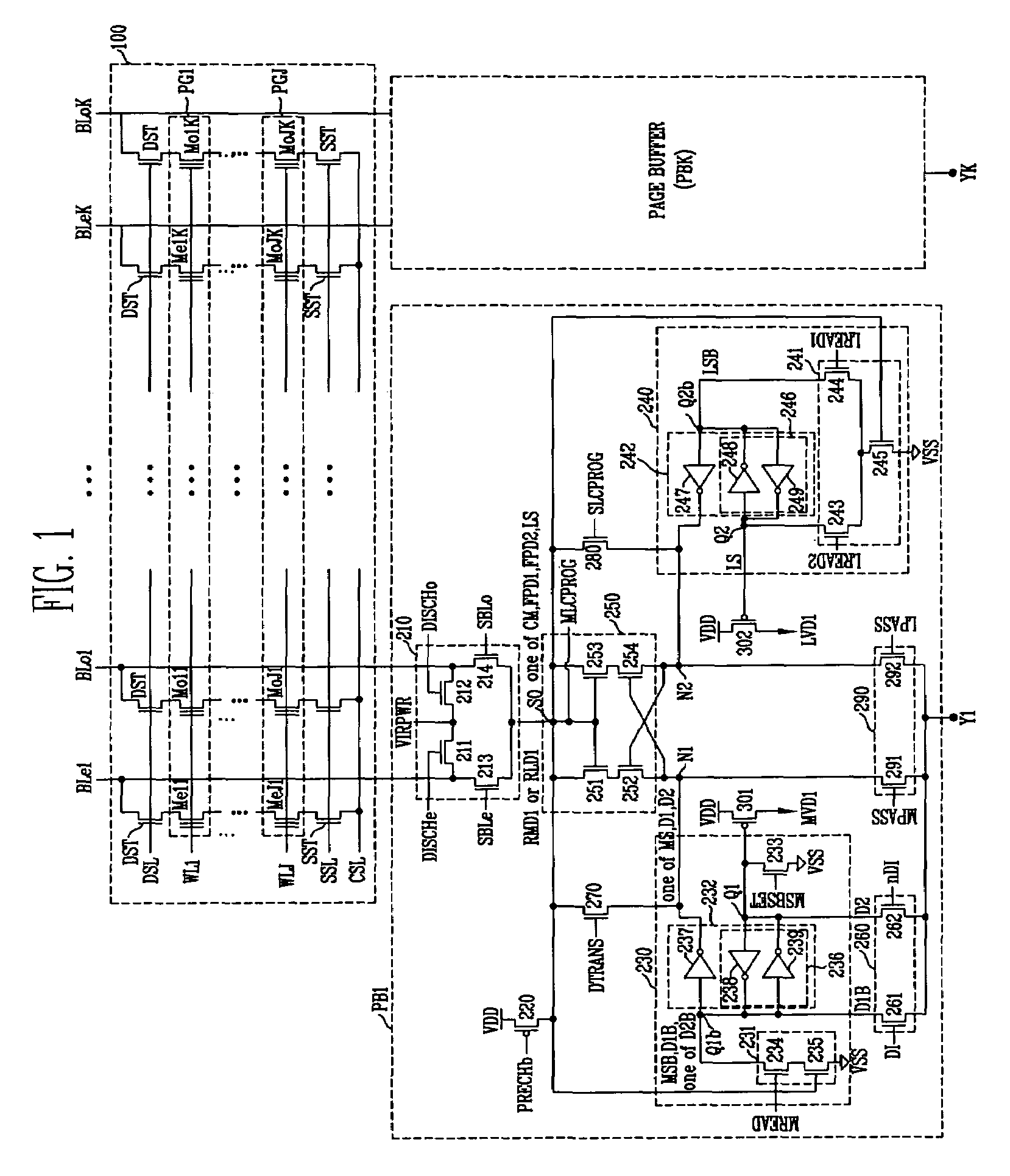
Page buffer having dual register, semiconductor memory device having the same, and program method thereof
InactiveUS6963509B1Shorten programming timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingData transmission
The present invention discloses a page buffer having a dual register, a semiconductor memory device having the same, and a program method thereof. A data transmission path is formed by installing switching units so that a main register as well as a cache register can be directly provided with a data. Therefore, a program operation is performed directly by using the main register in a normal program operation, and by using the cache register in a cache program operation. Accordingly, a process for transmitting the data from the cache register to the main register is omitted in the normal program operation, to reduce a transmission time (about 3 μs). As a result, the program time can be reduced in the whole program operation. Because the process for transmitting the data from the cache register to the main register is omitted in the normal program operation, the circuit control operation can be simplified.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
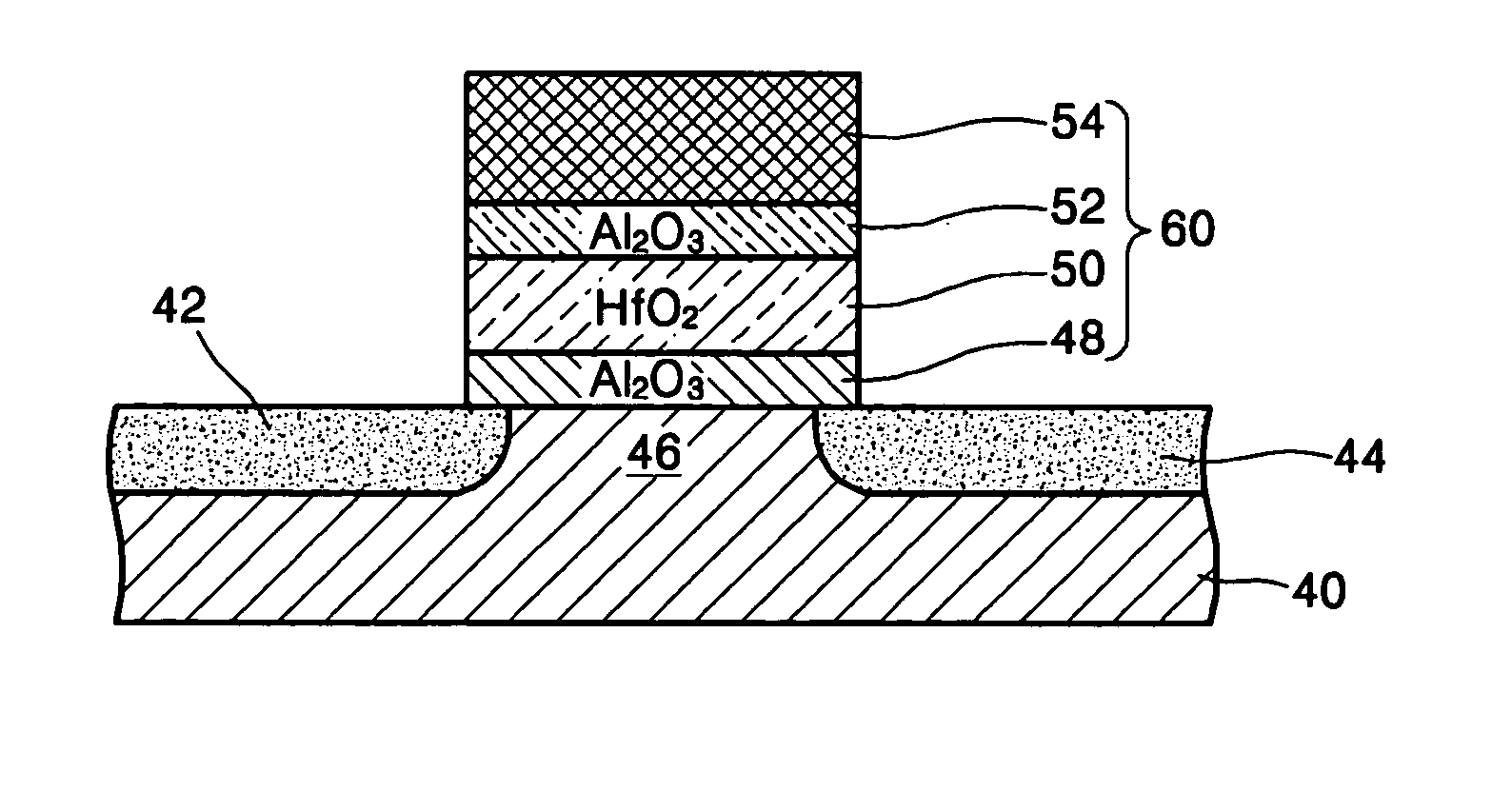
SONOS type memory device
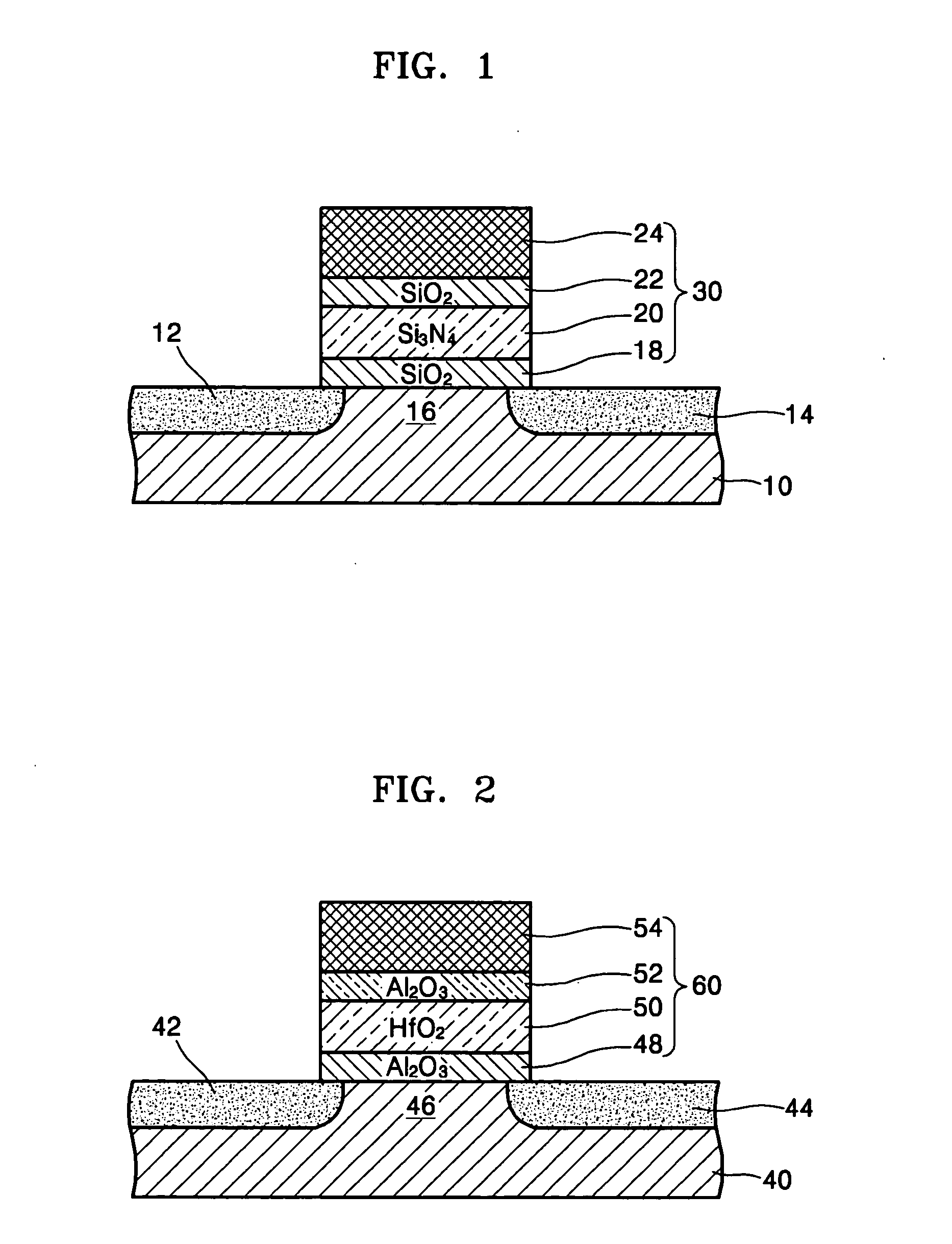
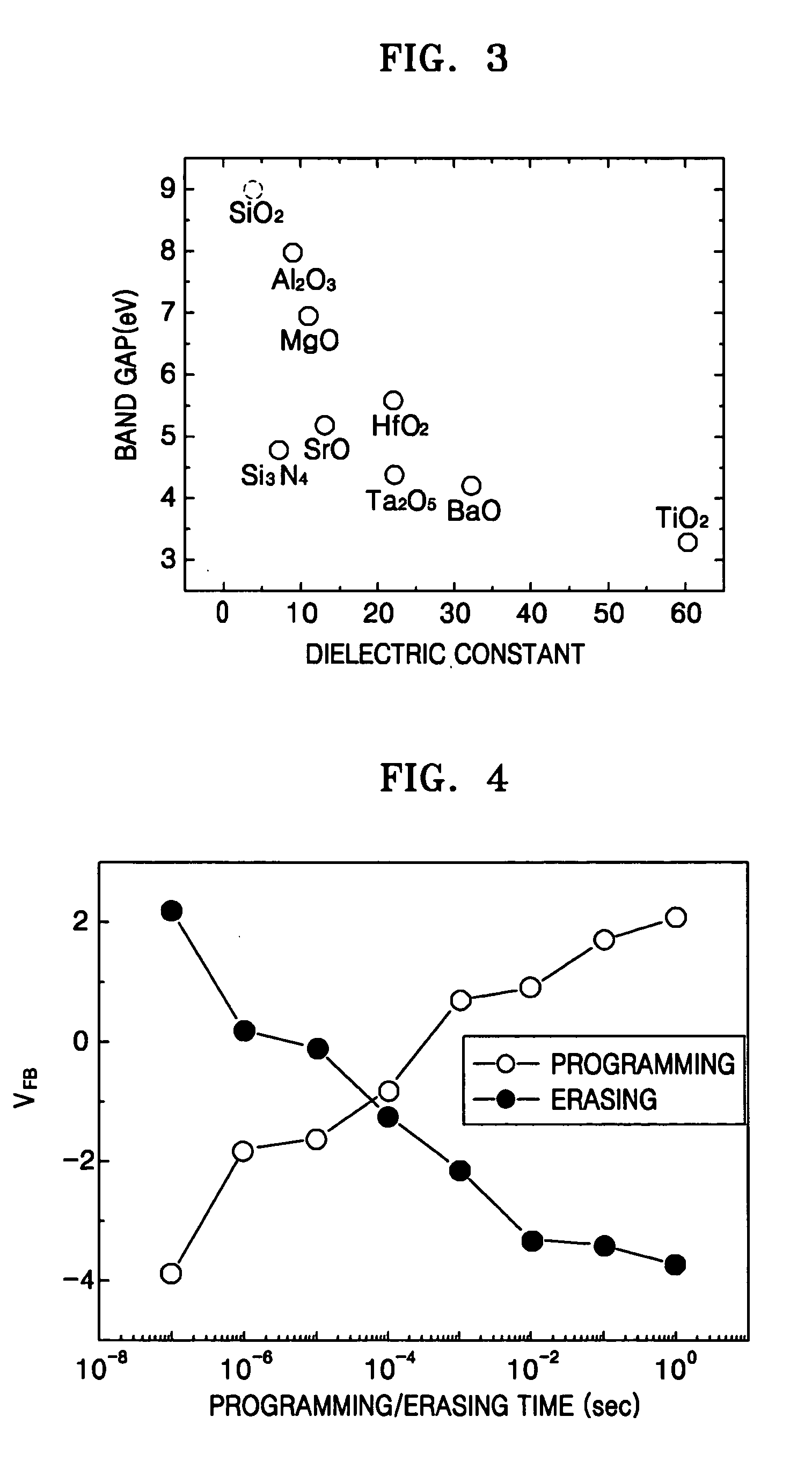
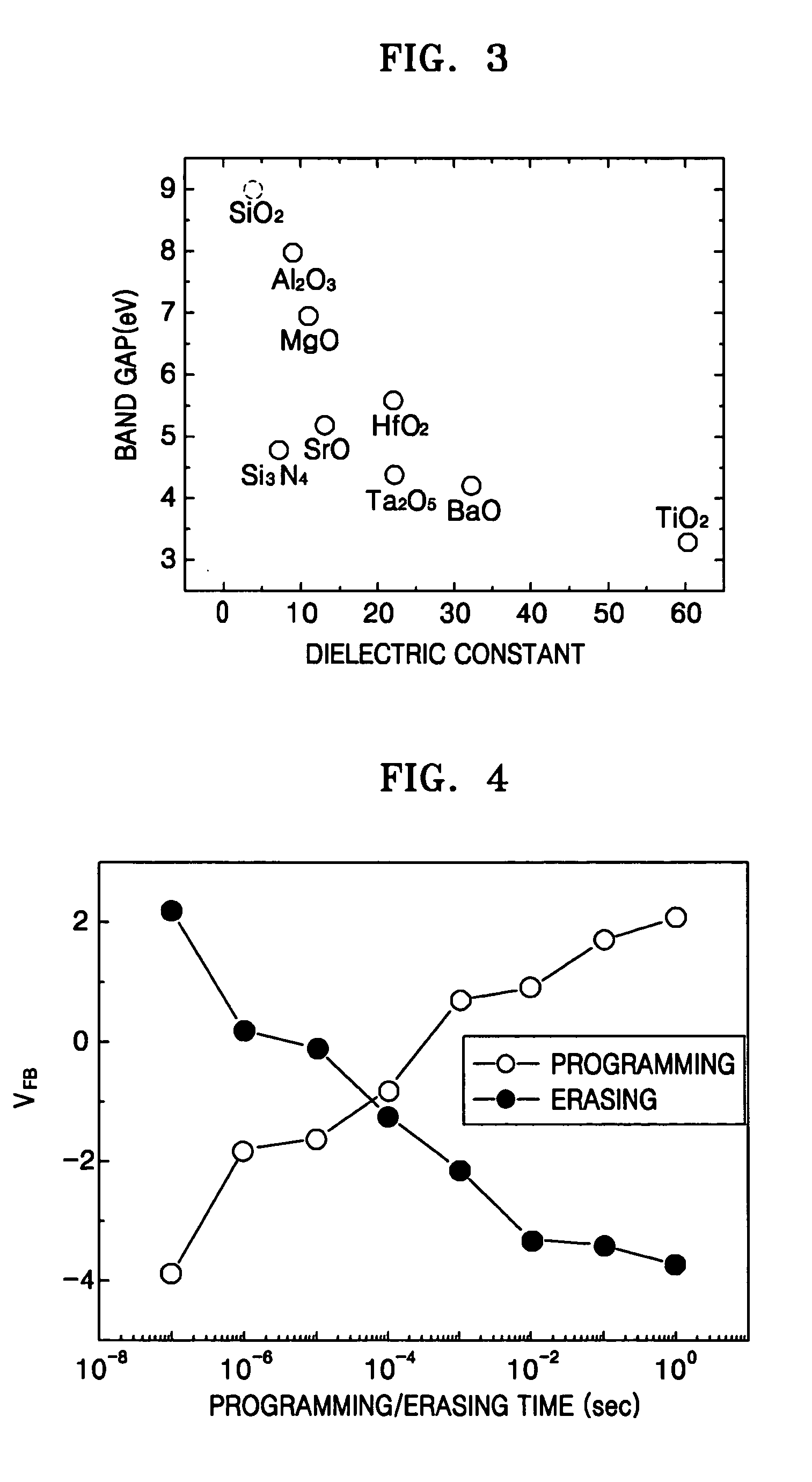
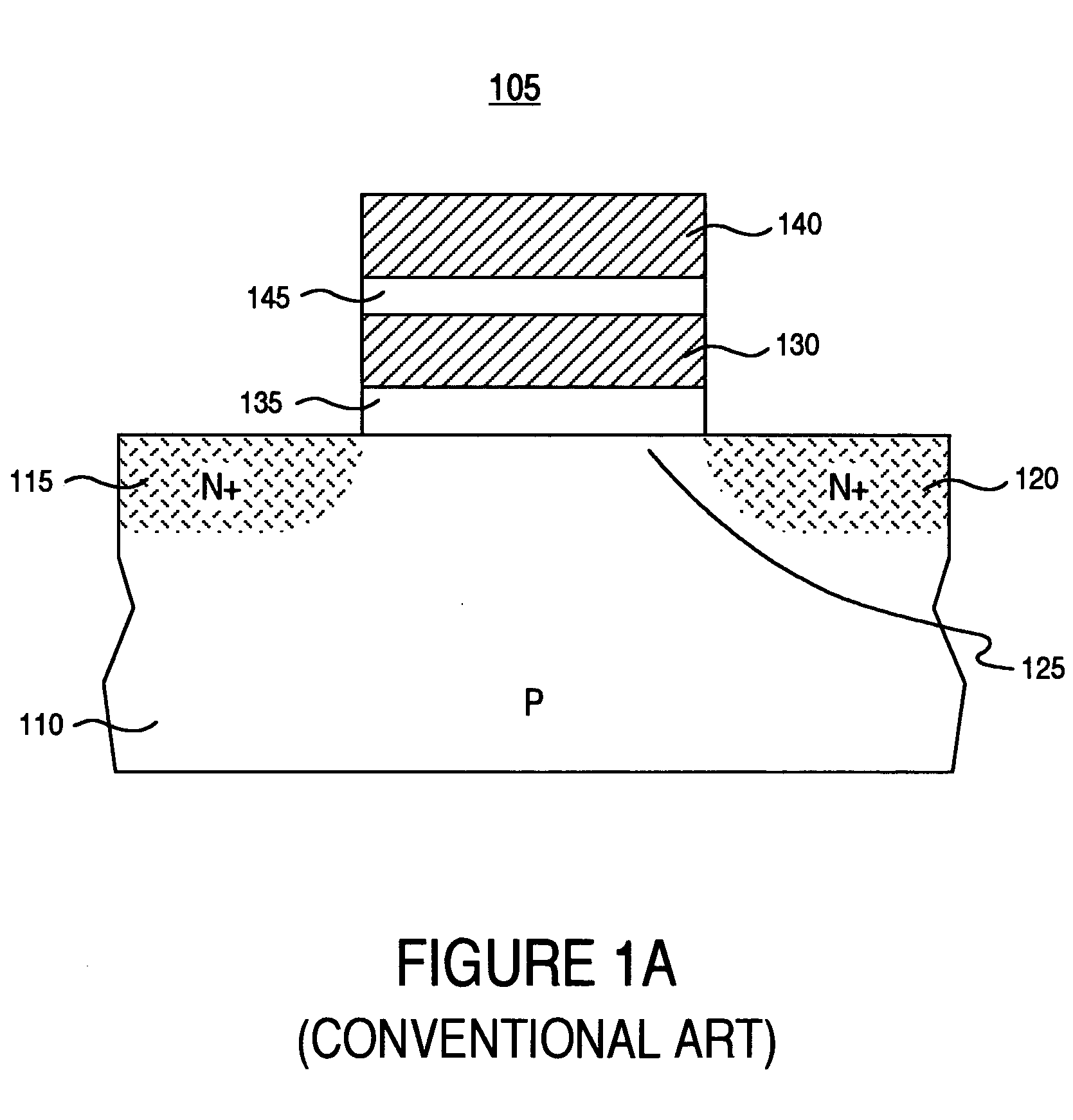
InactiveUS20050205920A1Shorten programming timeImproving data processing speedTransistorSolid-state devicesBand offsetData memory
A SONOS type memory includes a semiconductor substrate, first and second impurity regions in the semiconductor substrate doped with impurity ions of a predetermined conductivity, separated a predetermined distance from each other, a channel region between the first and second impurity regions, and a data storage type stack on the semiconductor substrate between the first and second impurity regions. The data storage type stack includes a tunneling oxide layer, a memory node layer for storing data, a blocking oxide layer, and an electrode layer, which are sequentially formed. A dielectric constant of the memory node layer is higher than dielectric constants of the tunneling and the blocking oxide layers, and a band offset of the memory node layer is lower than band offsets of the tunneling and the blocking oxide layers. The tunneling oxide layer and the blocking oxide layer are high dielectric insulating layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Programming method of non-volatile memory device having multi-plane structure
InactiveUS20070061538A1Shorten programming timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesDatabasePage buffers
A method for performing a program operation of a non-volatile memory device includes loading first, second, third, and fourth data to first, second, third, and fourth page buffers, respectively, in sequence; programming the first data loaded onto the first page buffer into a first page while loading the second data to the second buffer; and programming the second data loaded onto the second page buffer into a second page while programming the first data into the first page.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
SONOS type memory device
InactiveUS7053448B2Shorten programming timeErasing timeTransistorSolid-state devicesData memoryImpurity ions
A SONOS type memory includes a semiconductor substrate, first and second impurity regions in the semiconductor substrate doped with impurity ions of a predetermined conductivity, separated a predetermined distance from each other, a channel region between the first and second impurity regions, and a data storage type stack on the semiconductor substrate between the first and second impurity regions. The data storage type stack includes a tunneling oxide layer, a memory node layer for storing data, a blocking oxide layer, and an electrode layer, which are sequentially formed. A dielectric constant of the memory node layer is higher than dielectric constants of the tunneling and the blocking oxide layers, and a band offset of the memory node layer is lower than band offsets of the tunneling and the blocking oxide layers. The tunneling oxide layer and the blocking oxide layer are high dielectric insulating layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
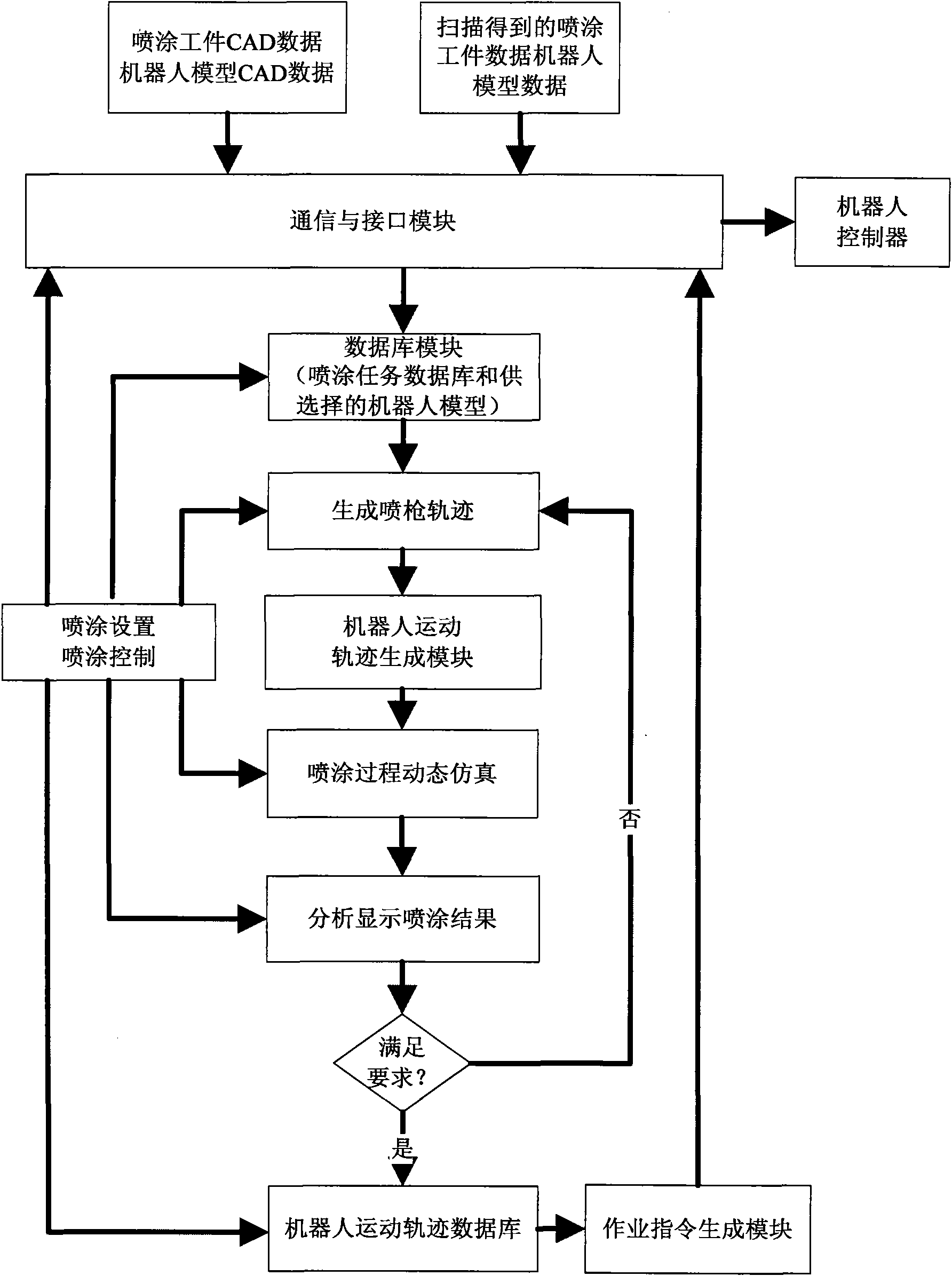
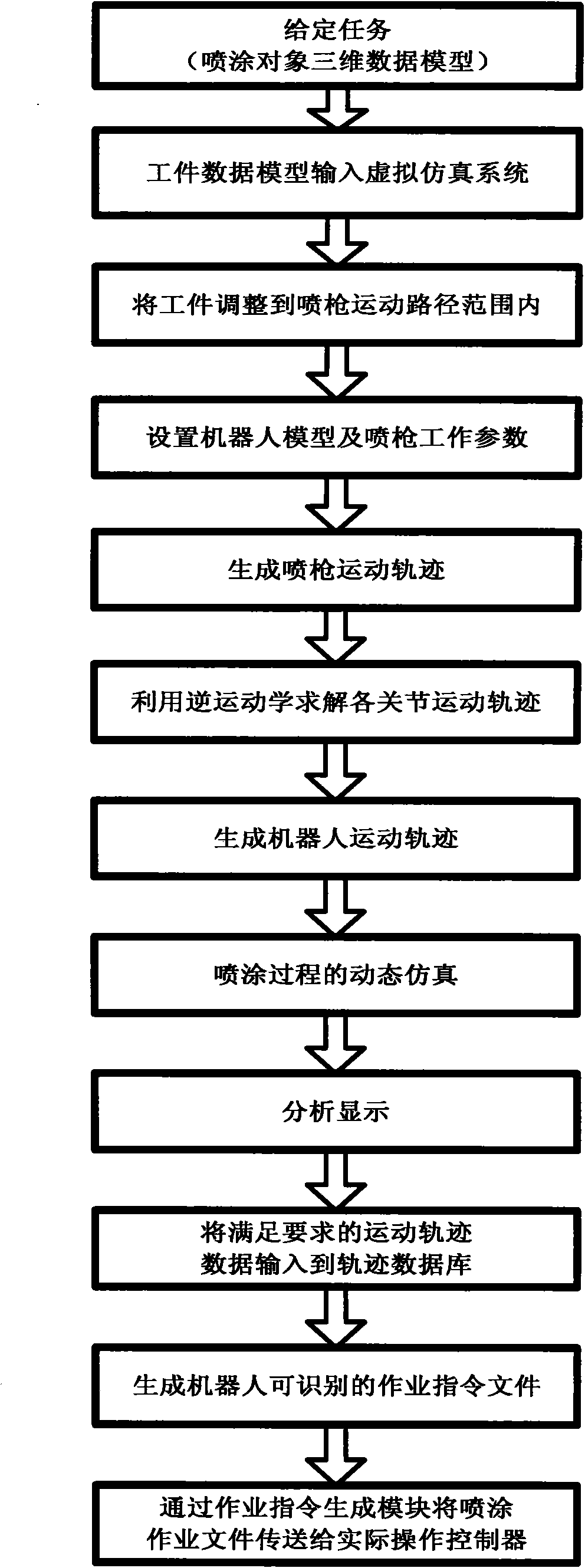
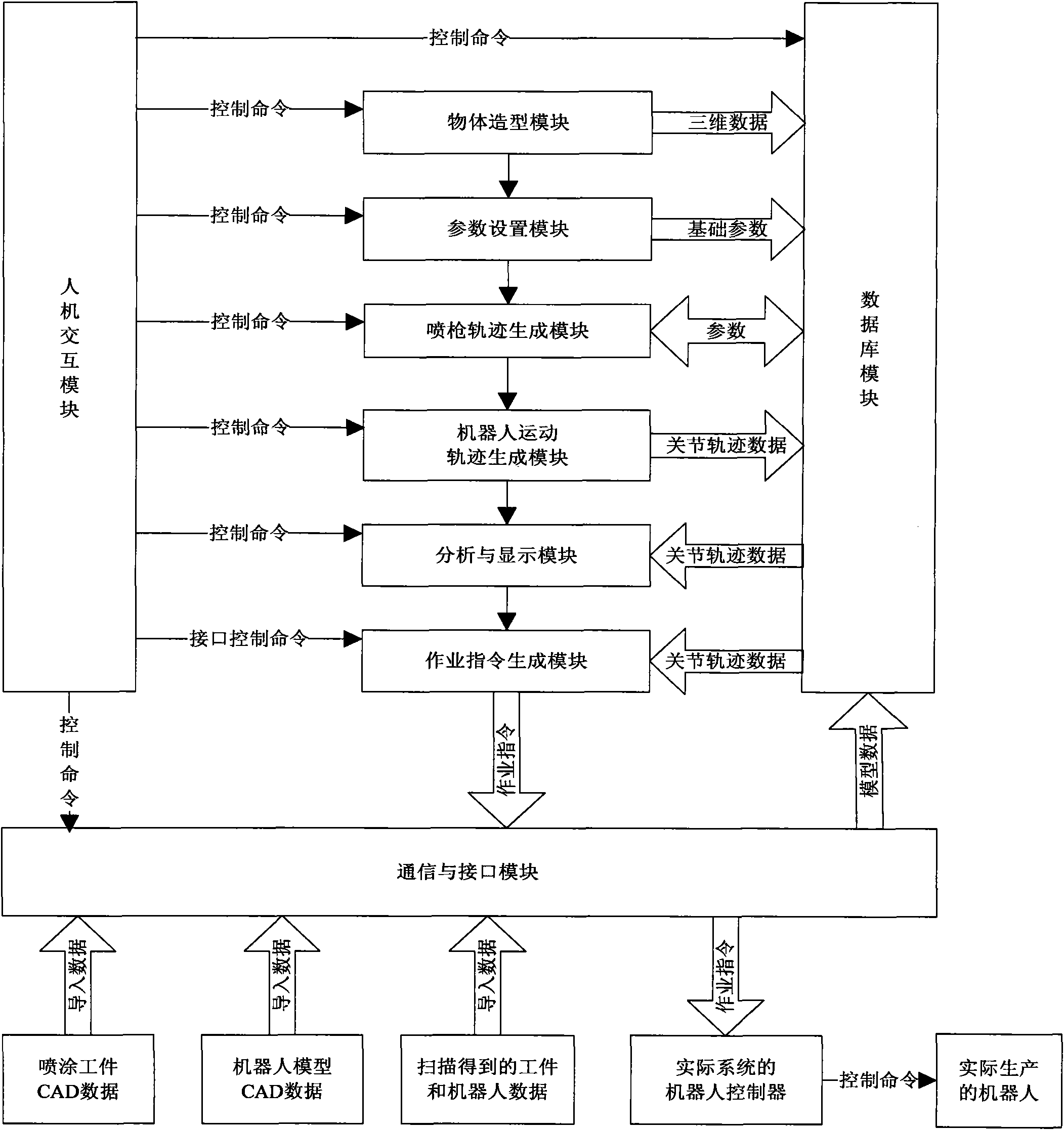
Industrial robot comprehensive control platform and control method thereof
InactiveCN101850552AReduce in-circuit debugging timeDoes not take up working timeManipulatorProduction ratePath generation
The invention relates to an industrial robot comprehensive control platform and a control method thereof. The industrial robot comprehensive control platform comprises an object modeling module, a parameter setting module, a database module, a spray gun path generation module, a robot motion path generation module, a man-machine interaction module, an analysis and display module, an operation command generation module and a communication and interface module. The invention has the advantages that the functions are complete, the commonality is high, the robot program development cycle is shortened, the painting accuracy of the system is improved, the production cost is reduced, the production efficiency is improved, the requirements on the technical capability of operators are reduced, the economic benefit is high and the platform can be easily accepted by users.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
ActiveUS7209801B2Easy and intuitive to useShorten teaching timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAlgorithmComputer vision
A method for programming an industrial robot having a tool. The method includes obtaining configuration data for the tool and for the robot path and information about the position and orientation of the object in relation to the robot, obtaining a sequence of waypoints, which defines the process in relation to the object, obtaining at least one distance for adjusting the position of a waypoint, deciding whether an obtained waypoint should be modified or not, based on the obtained information about the waypoints, generating a modified sequence of waypoints by modifying the waypoints in the obtained sequence of waypoints, based on the decision, the obtained distance and the obtained information about the waypoints and generating the actual robot path based on the modified sequence of waypoints and the obtained configuration data.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
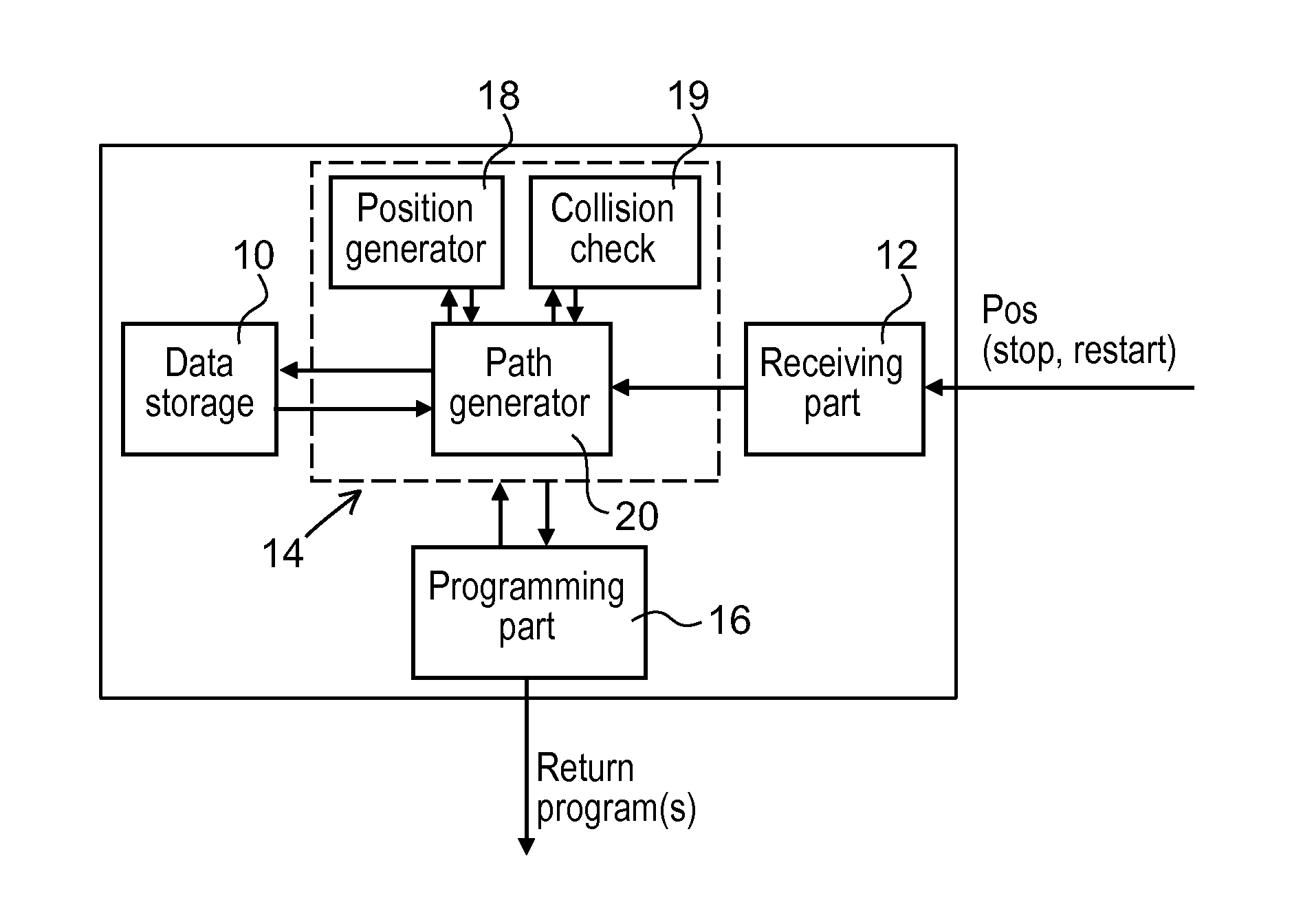
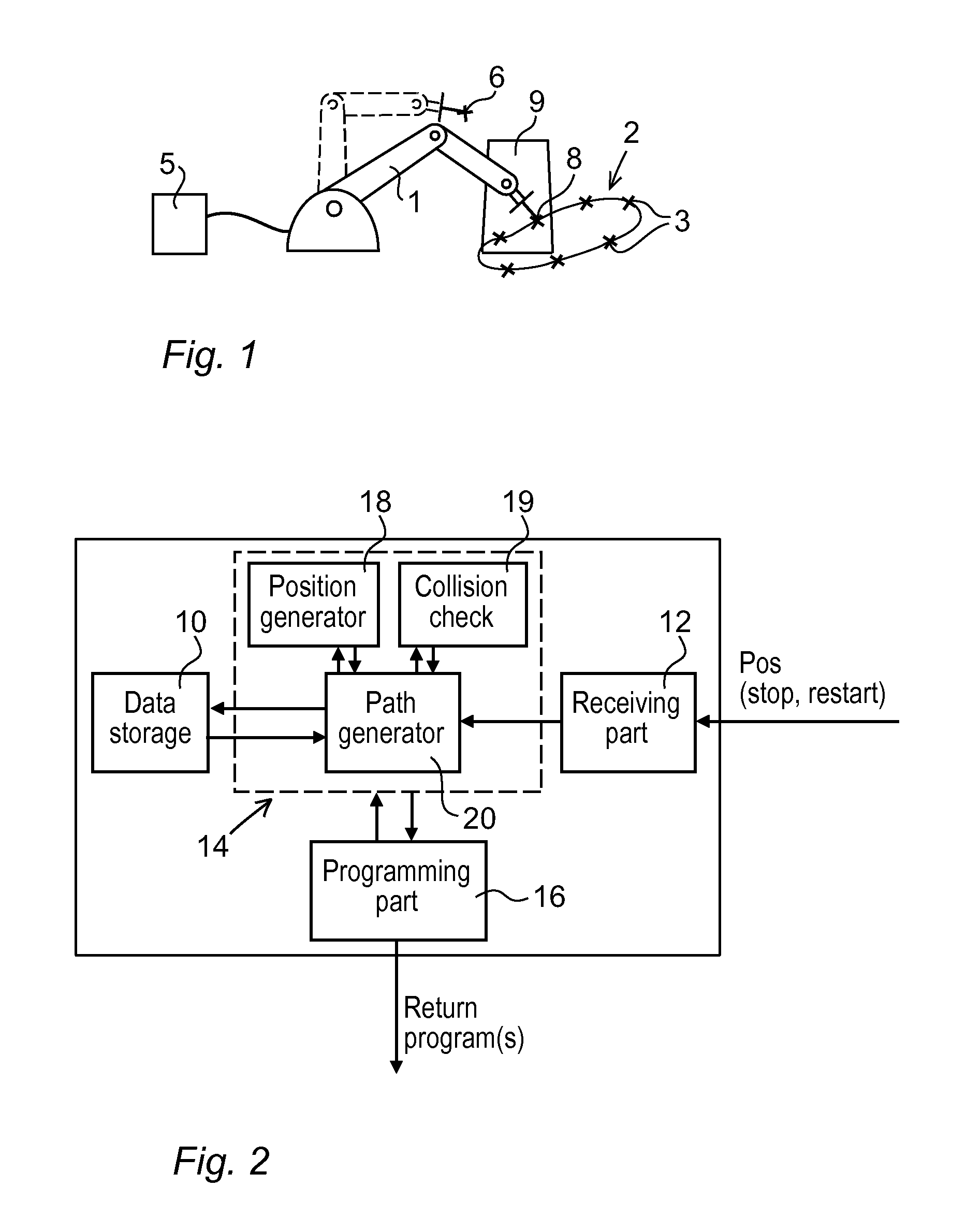
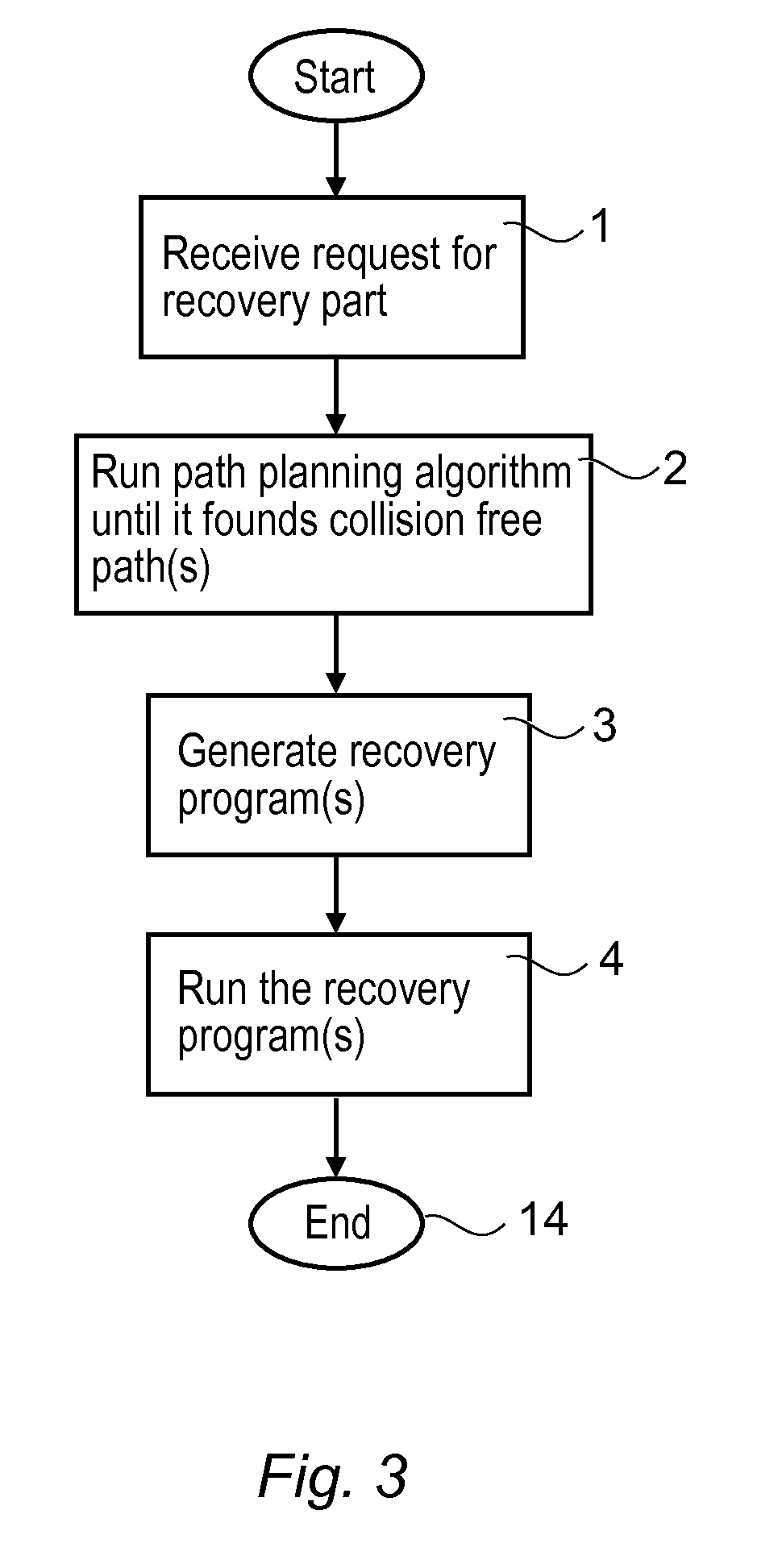
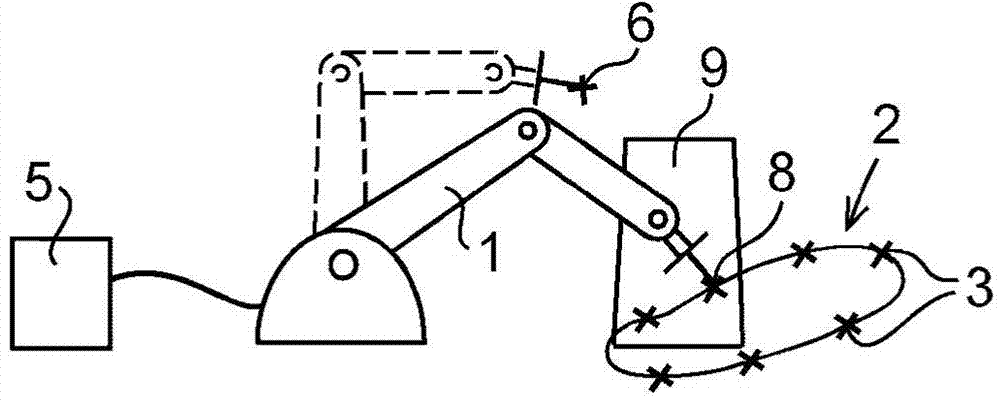
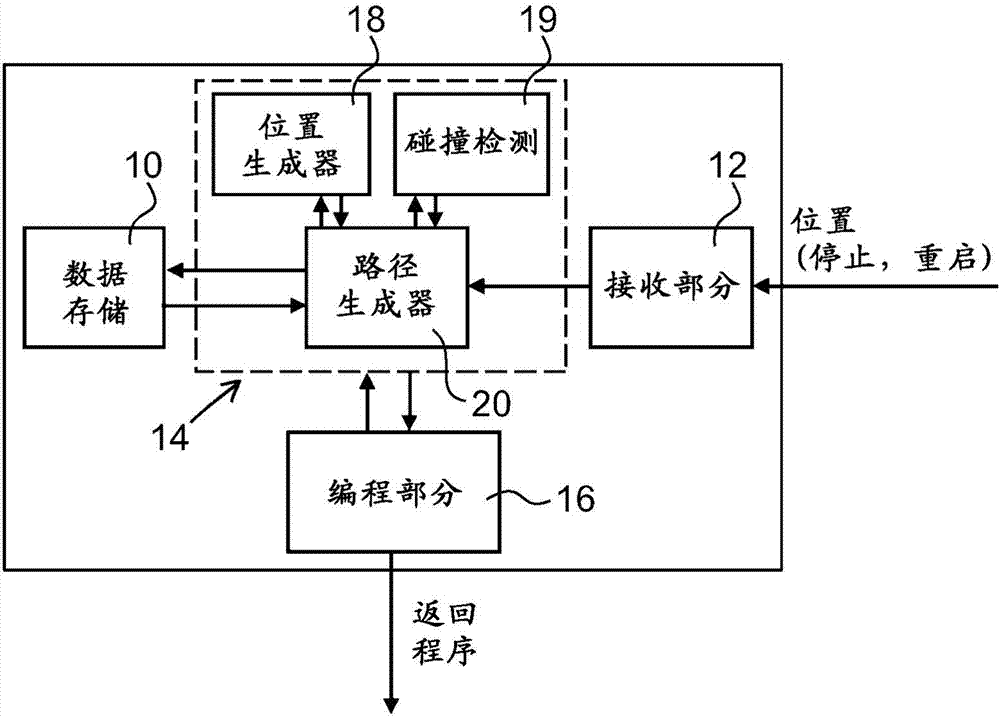
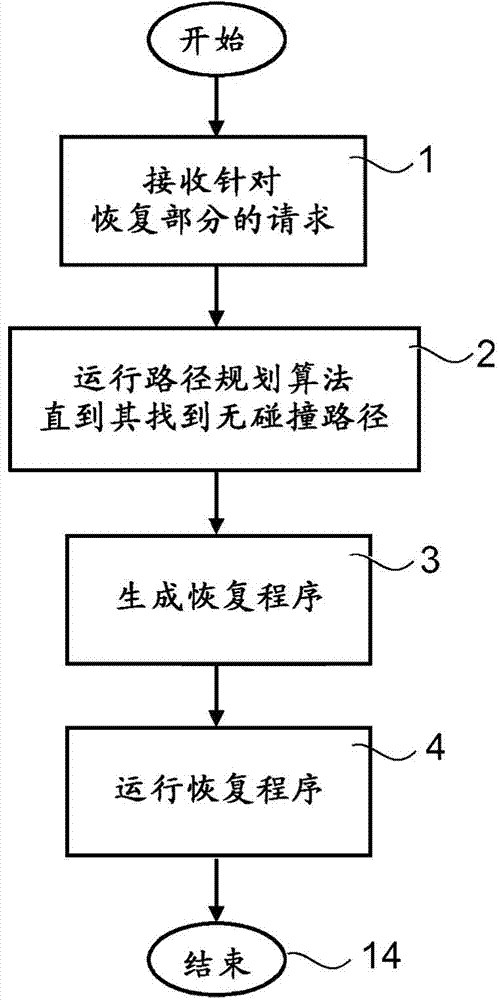
Method And An Apparatus For Automatically Generating A Collision Free Return Program For Returning A Robot From A Stop Position To A Predefined Restart Position
InactiveUS20150266182A1Shorten programming timeEasy to understandProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobot positionPath generation
A method and an apparatus for automatically generating a collision free return program for returning a robot from a stop position to a predefined restart position when the robot has been stopped during operation due to an error. The apparatus includes a receiving part adapted to receive a request for a recovery path and information on the stop position of the robot. A path generating part is adapted to generate a collision free recovery path for the robot upon receiving the request, based on the predefined restart position and the stop position of the robot using a path planning algorithm that generates robot positions connected by collision free path segments. A programming part is adapted to generate the return program based on the generated return path.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
A method and an apparatus for automatically generating a collision free return program for returning a robot from a stop position to a predefined restart position
InactiveCN104812535AEasy to understandShorten programming timeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot positionSimulation
Owner:ABB TECH AG
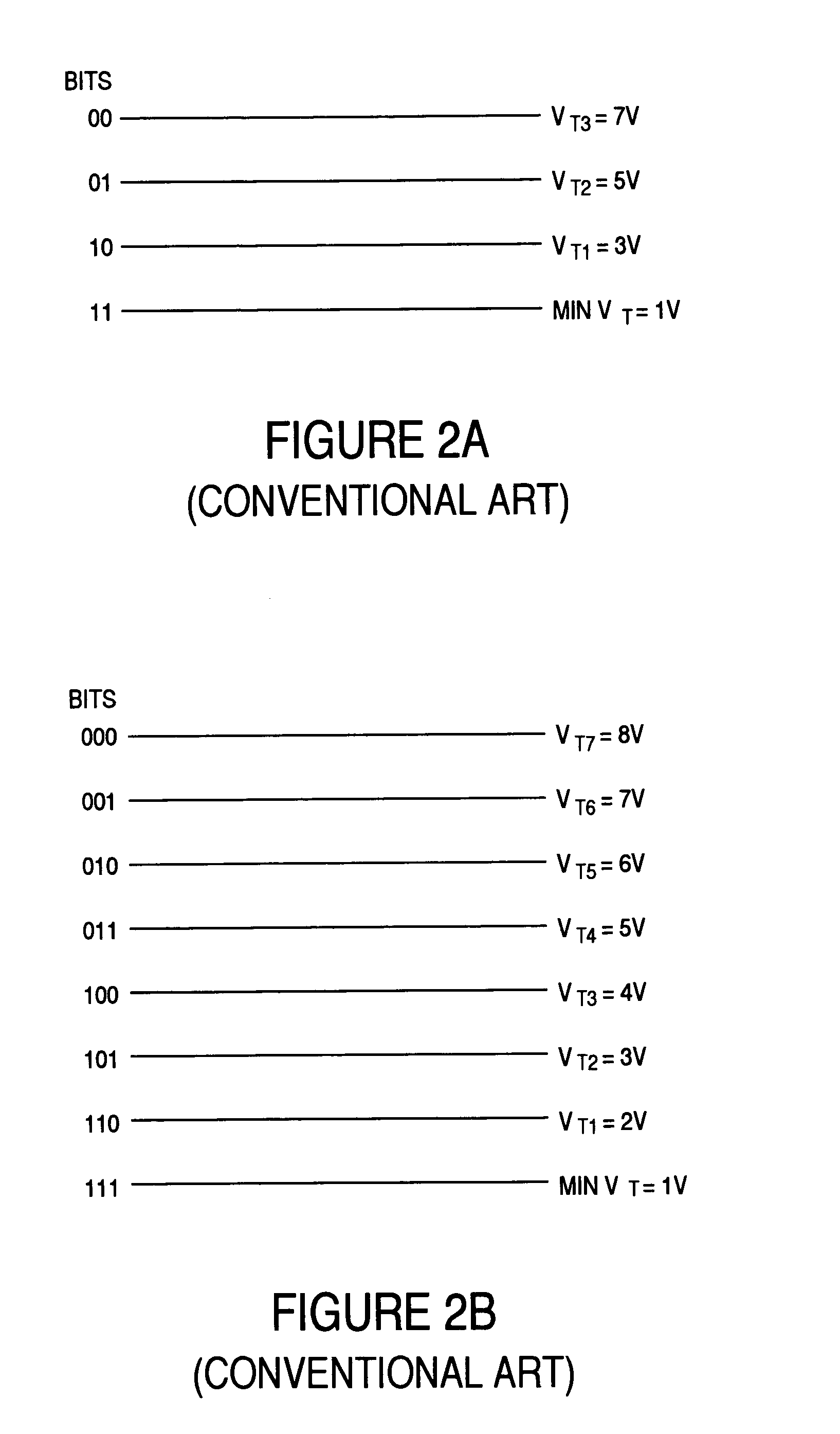
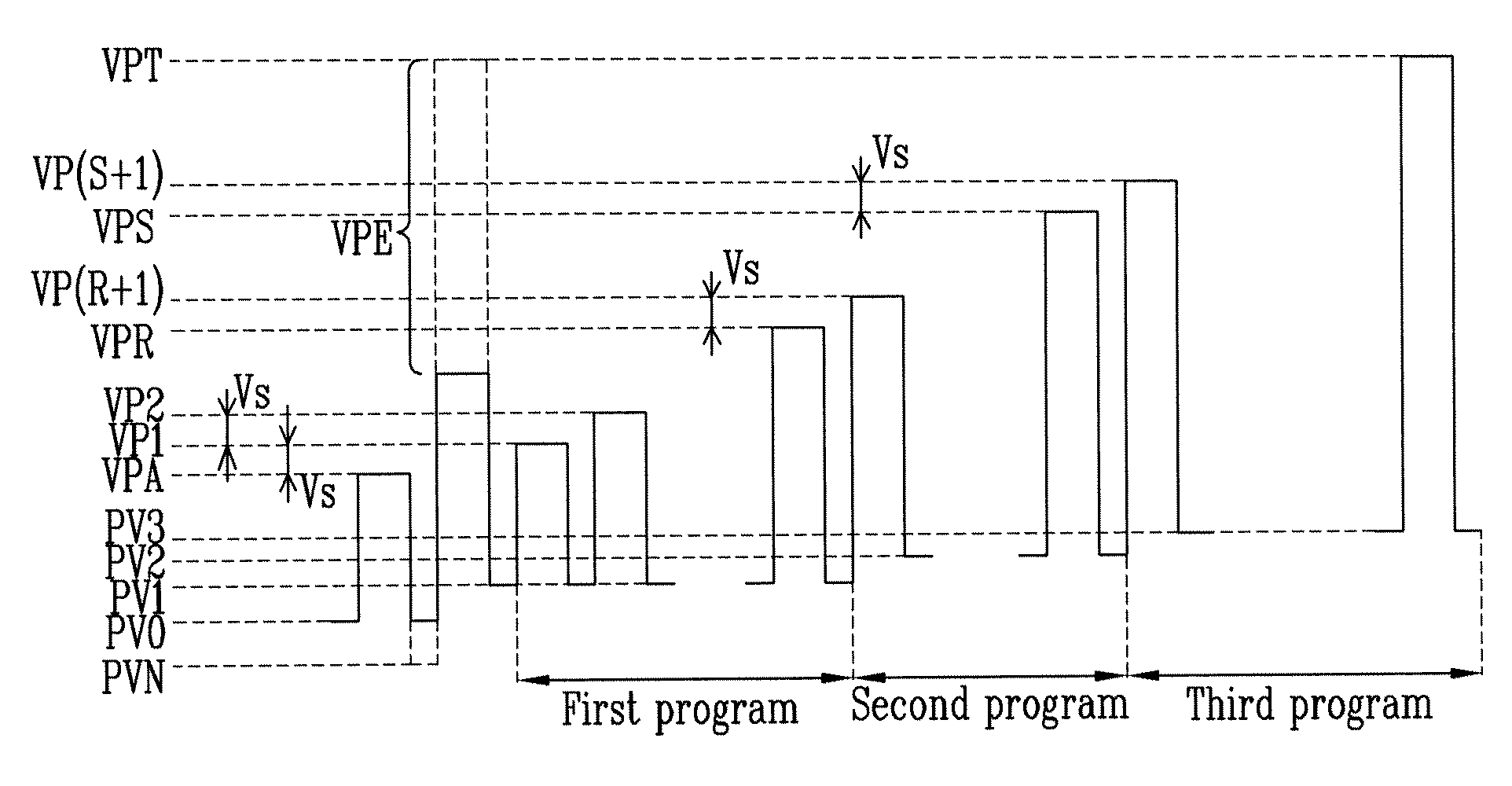
Nonvolatile Memory Device with Incremental Step Pulse Programming
ActiveUS20100124123A1Shorten programming timeShorten the timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineDriver circuit
A nonvolatile memory device includes a sense amplifier circuit sensing first data from a memory cell via a bit line and outputting the sensed first data, in response to a read command. A write driver circuit programs the memory cell and stores second data indicating a programming state of the memory cell, in response to a program command. A verification block outputs a result of a comparison between the first and second data in response to a first read command. The second data is updated based on the determination on the programming of the memory cell in response to a second read command applied following the first read command.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
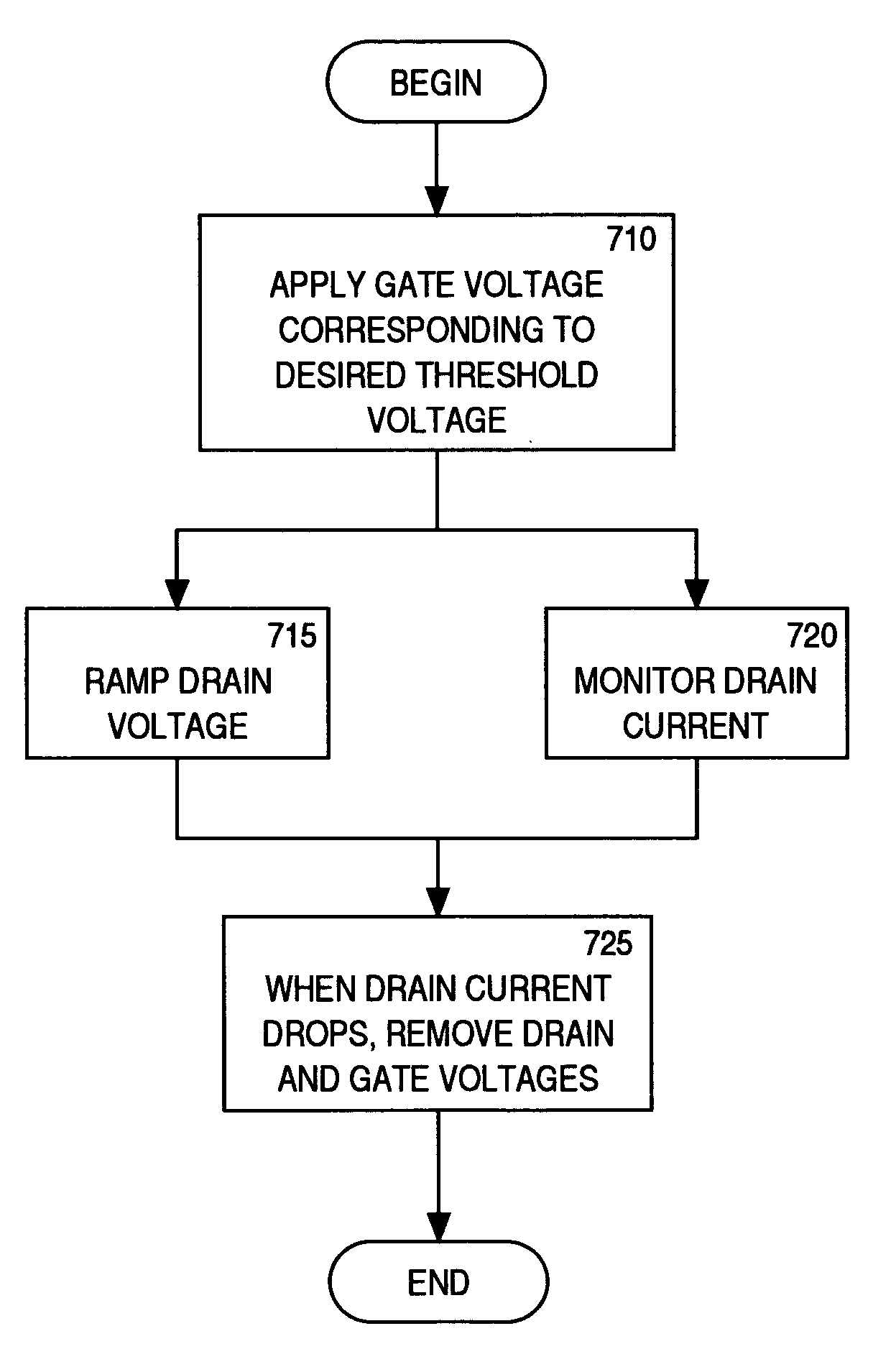
Programming of a flash memory cell
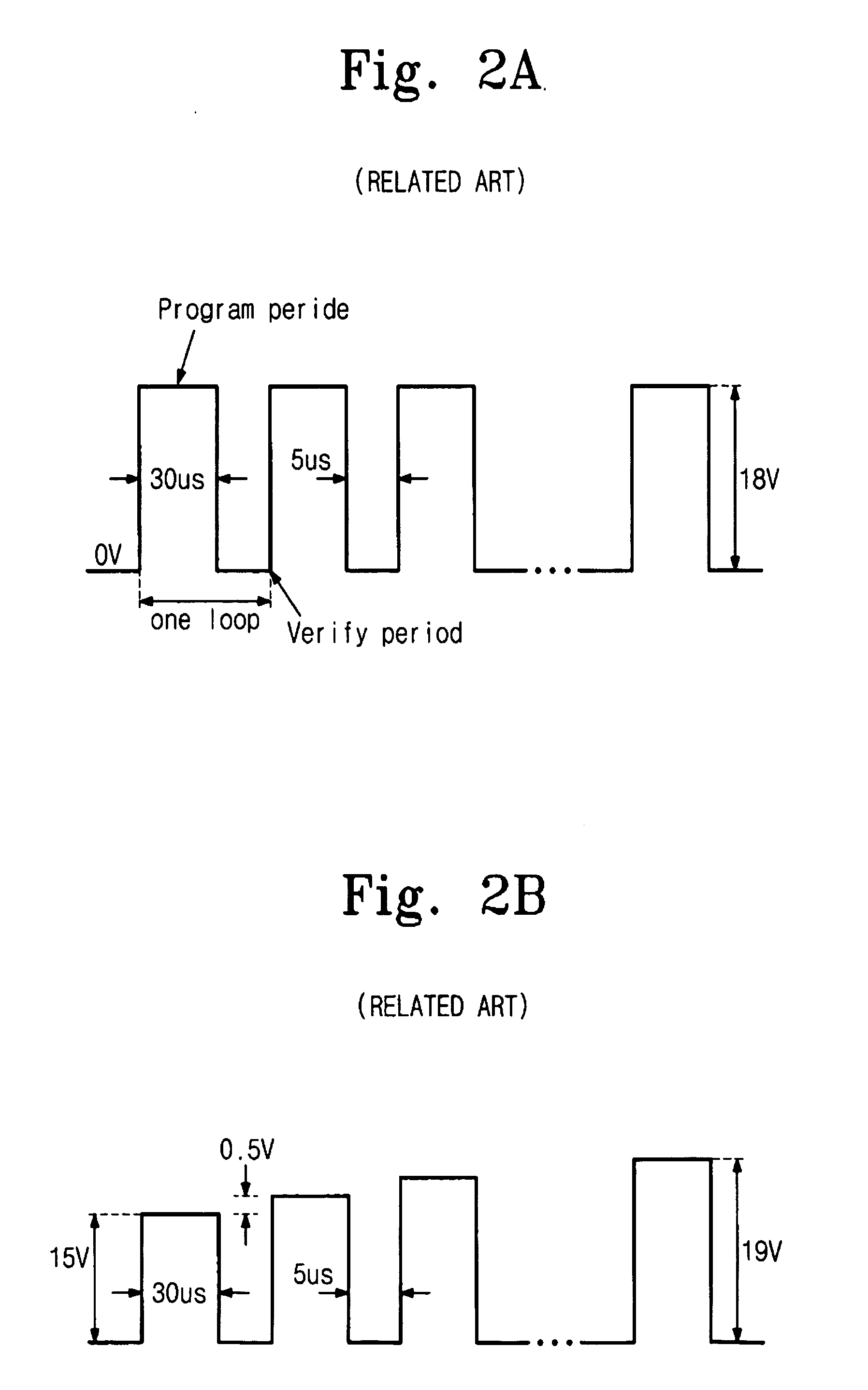
ActiveUS6937518B1Reduce programming timeIncrease reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltageEngineering
A method of programming a memory device comprises applying a first programming voltage to one of a plurality of wordlines, corresponding to a cell to be programmed. The first programming voltage is substantially equal to the desired threshold voltage. A second programming voltage is also applied to one of a plurality of bitlines, corresponding to the cell to be programmed. The second programming voltage gradually increases from a low level toward a high level. The first programming voltage and second programming voltage are removed when the corresponding bitline current begins to decrease.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
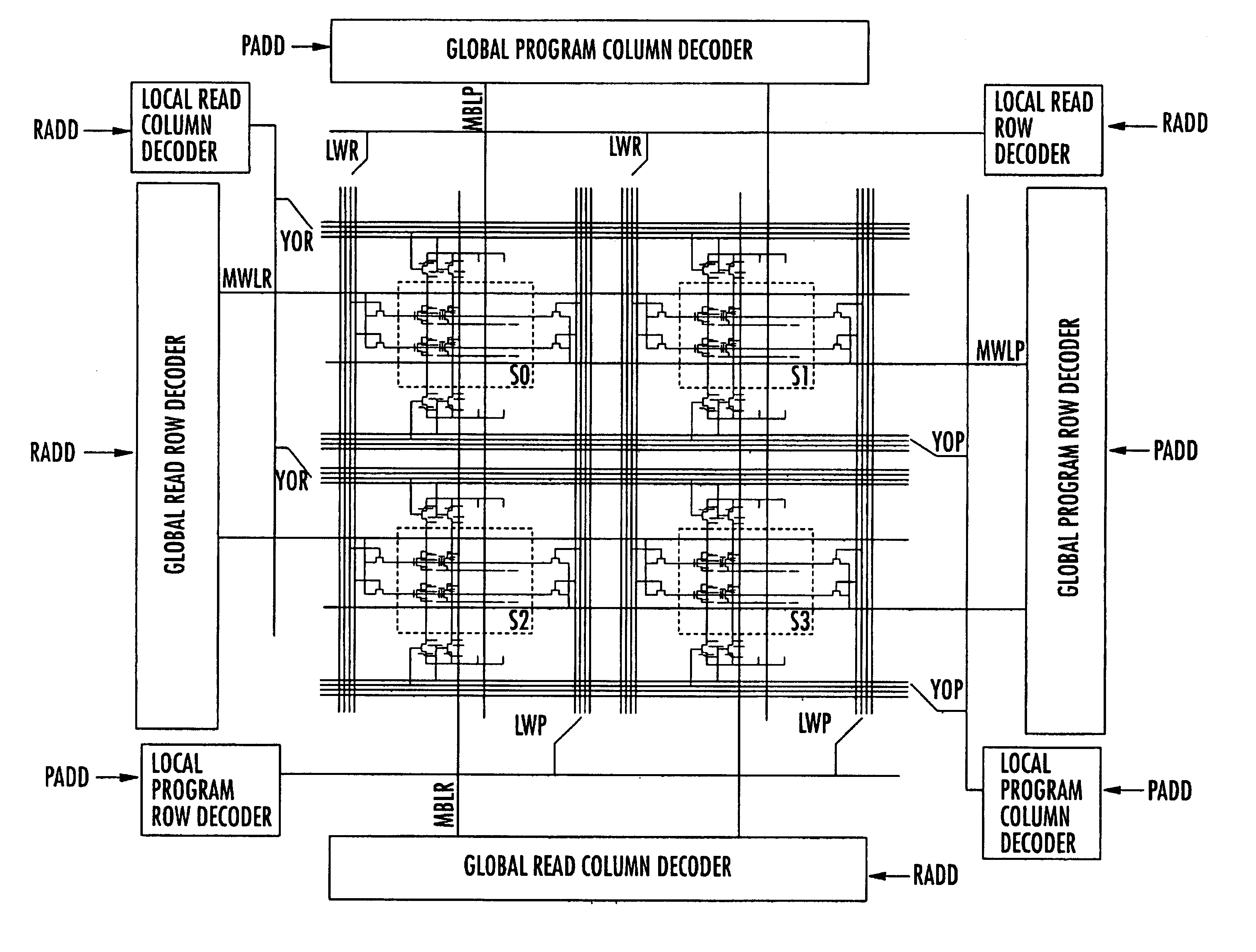
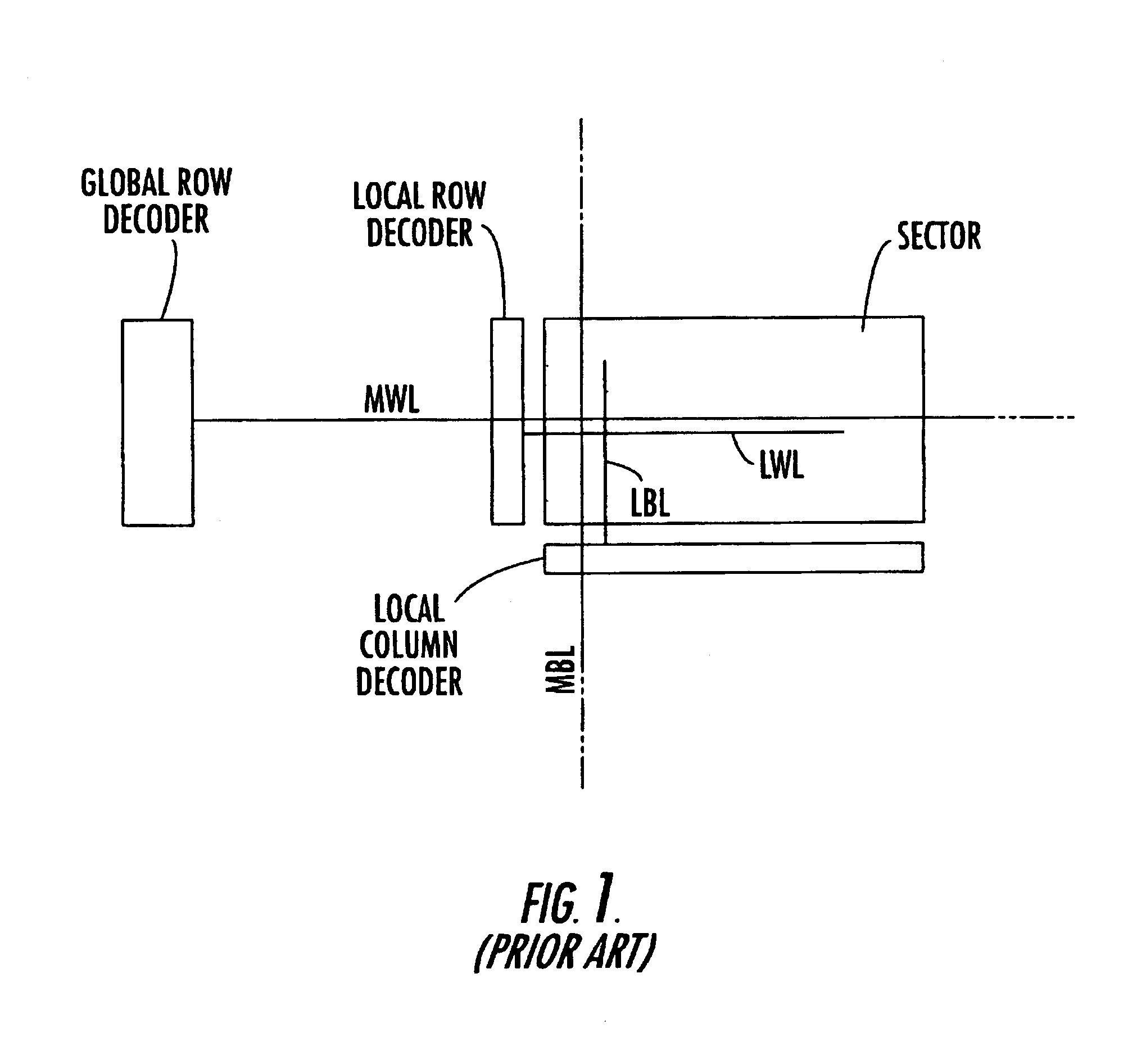
Architecture for a flash-EEPROM simultaneously readable in other sectors while erasing and/or programming one or more sectors
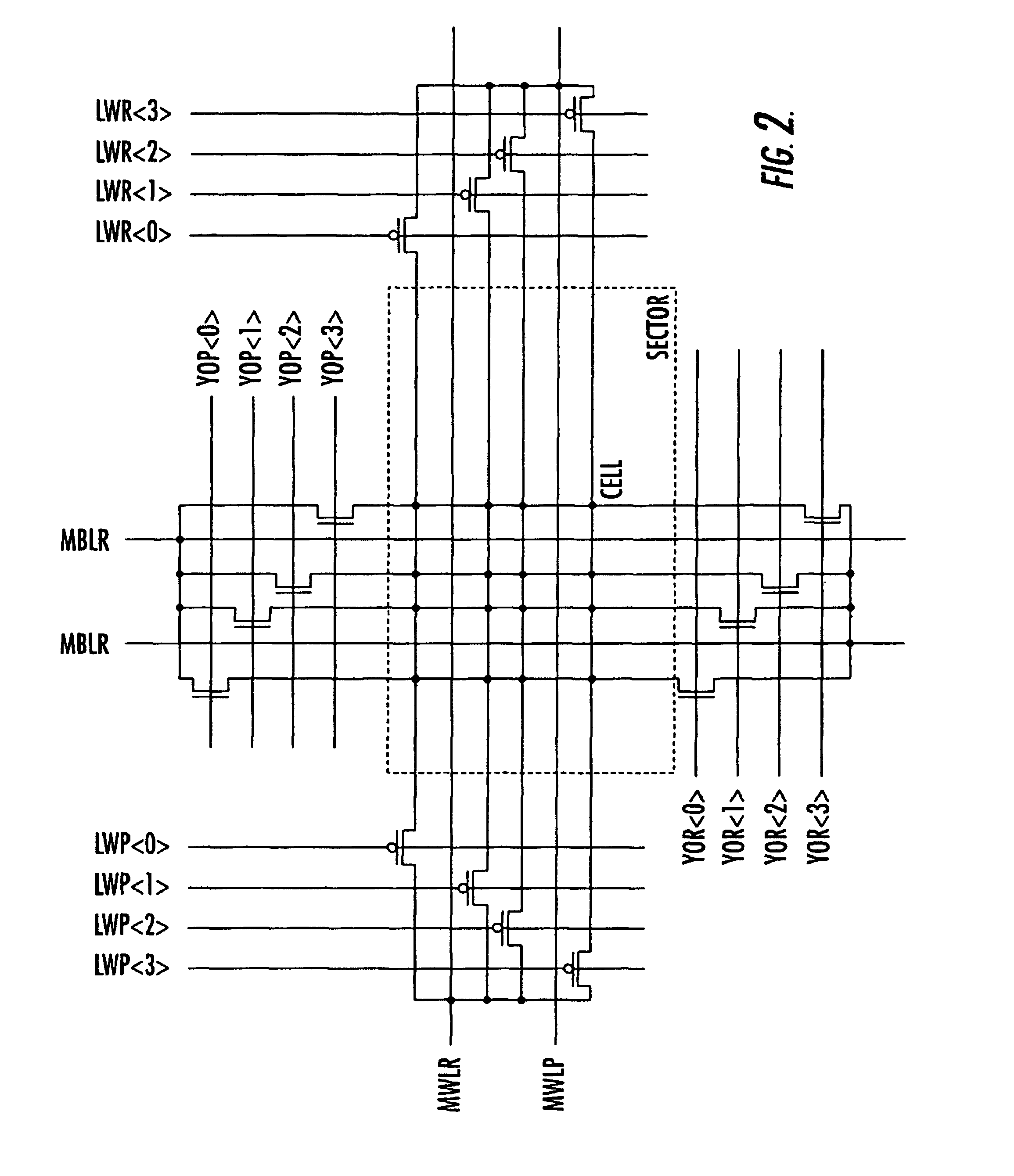
InactiveUS6891755B2Reduced silicon integration areaMinimize required areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureAddress bus
A memory device includes an array of memory cells organized into a plurality of sectors, and local wordlines and local bitlines are connected to the memory cells in each respective sector. Main read wordlines and main program wordlines are connected to the local wordlines in each sector. A main read row decoder is connected to the main read wordlines, and a main program row decoder connected to the main program wordlines. Main read bitlines and main program bitlines are connected to the local bitlines in each sector. A main read column decoder is connected to the main read bitlines, and a main program column decoder is connected to the main program wordlines. A read address bus is connected to the main read row decoder and to the main read column decoder for providing an address thereto. A program address bus is connected to the main read column decoder and to the main program row decoder for providing an address thereto.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Programming algorithm to reduce disturb with minimal extra time penalty
ActiveUS7800956B2Reduces program disturbShorten programming timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgramming processComputer science
Programming time is reduced in a non-volatile memory in a multi-pass programming process. In a first programming pass, high state cells are programmed by a sequence of program pulses to identify fast and slow high state cells, while lower state cells are locked out from programming. Once identified, the fast high state cells are temporarily locked out from programming while the slow high state cells continue being programmed to their final intended state. Further, the program pulses are sharply stepped up to program the slow high state cells. In a second programming pass, the fast high state cells are programmed along with the other, lower state cells, until they all reach their respective intended states. A time savings is realized compared to approaches in which all high state cells are programmed in the first programming pass.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method for improving programming speed and precision of soldering robot by using computer-aided design (CAD) file
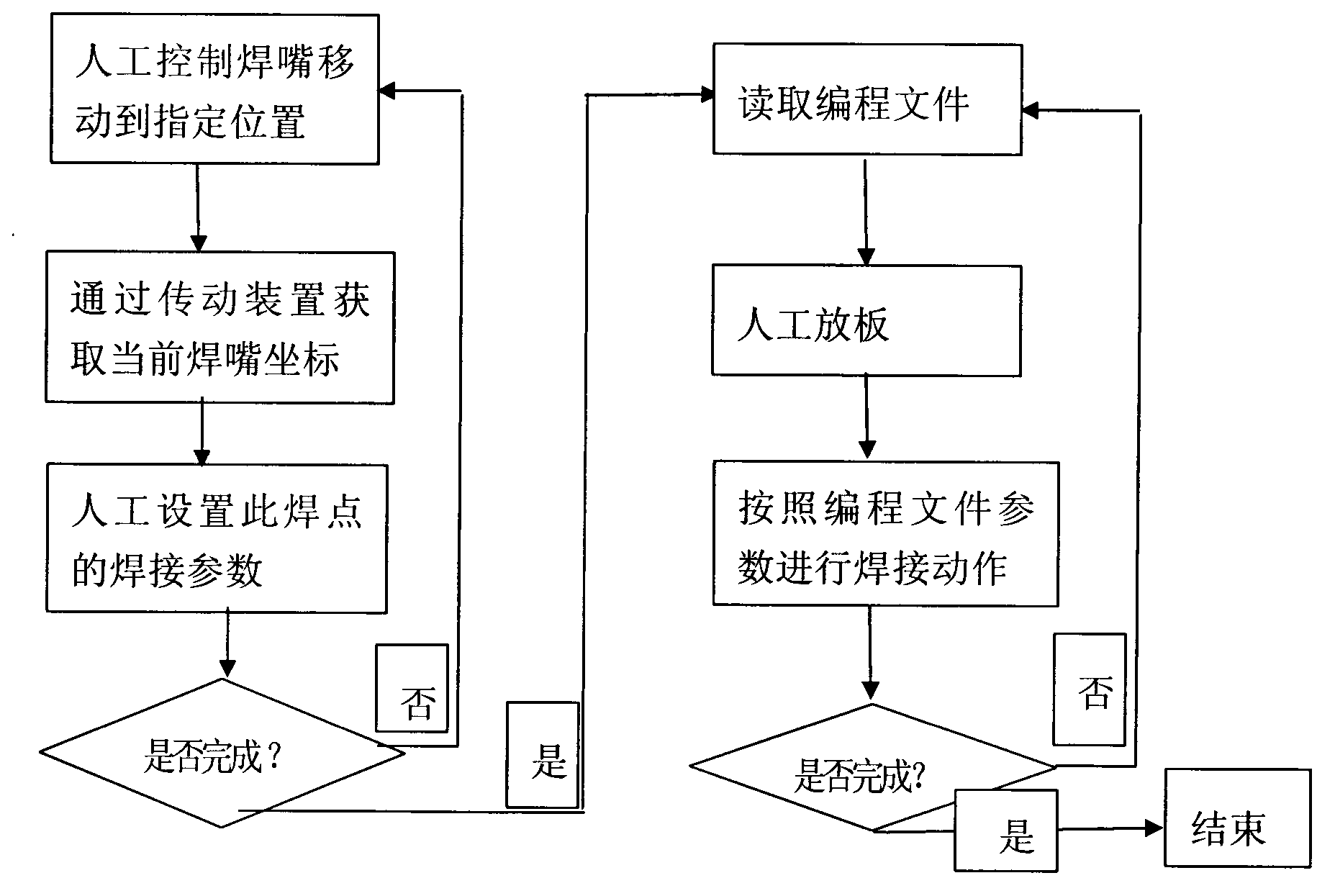
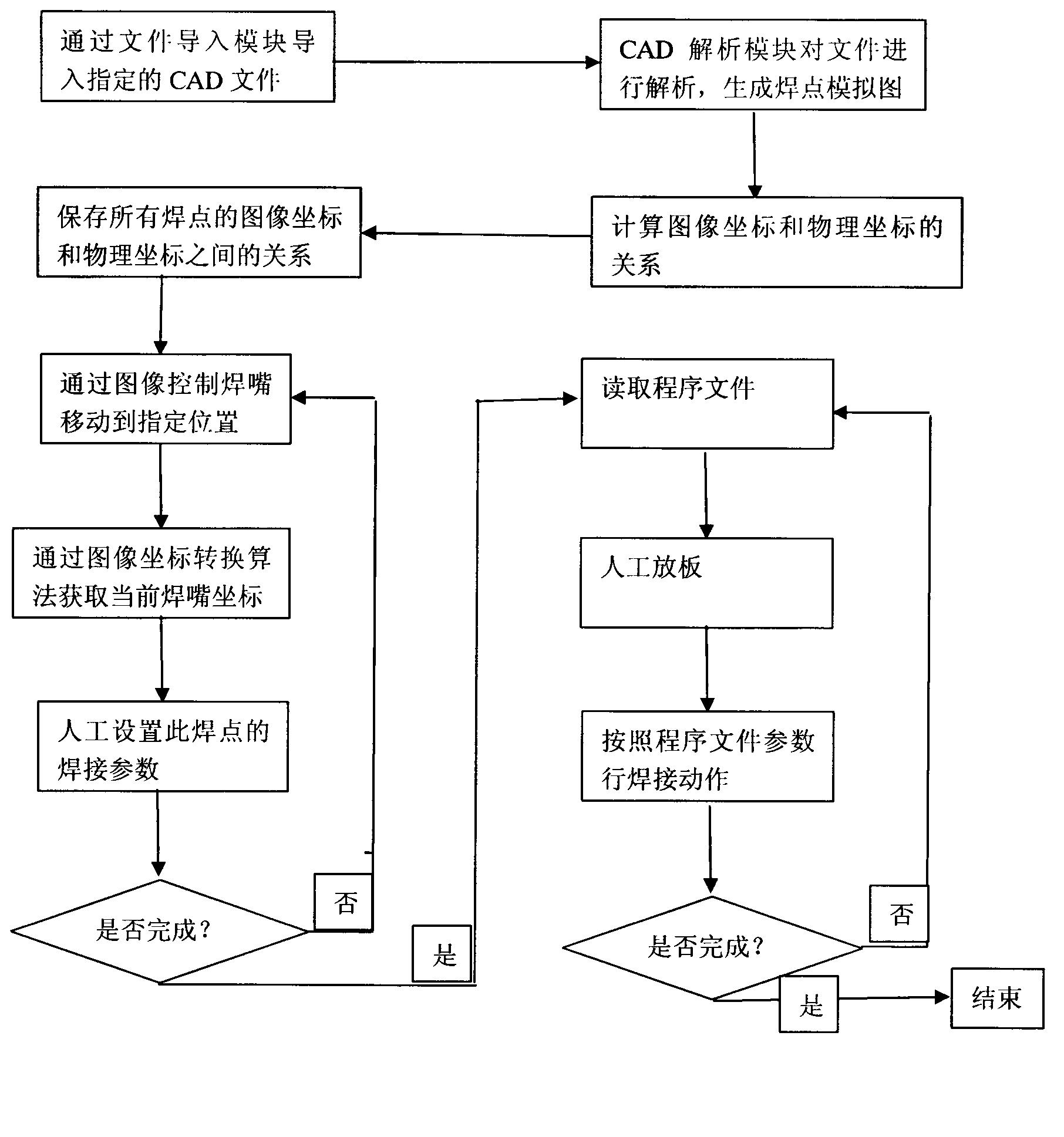
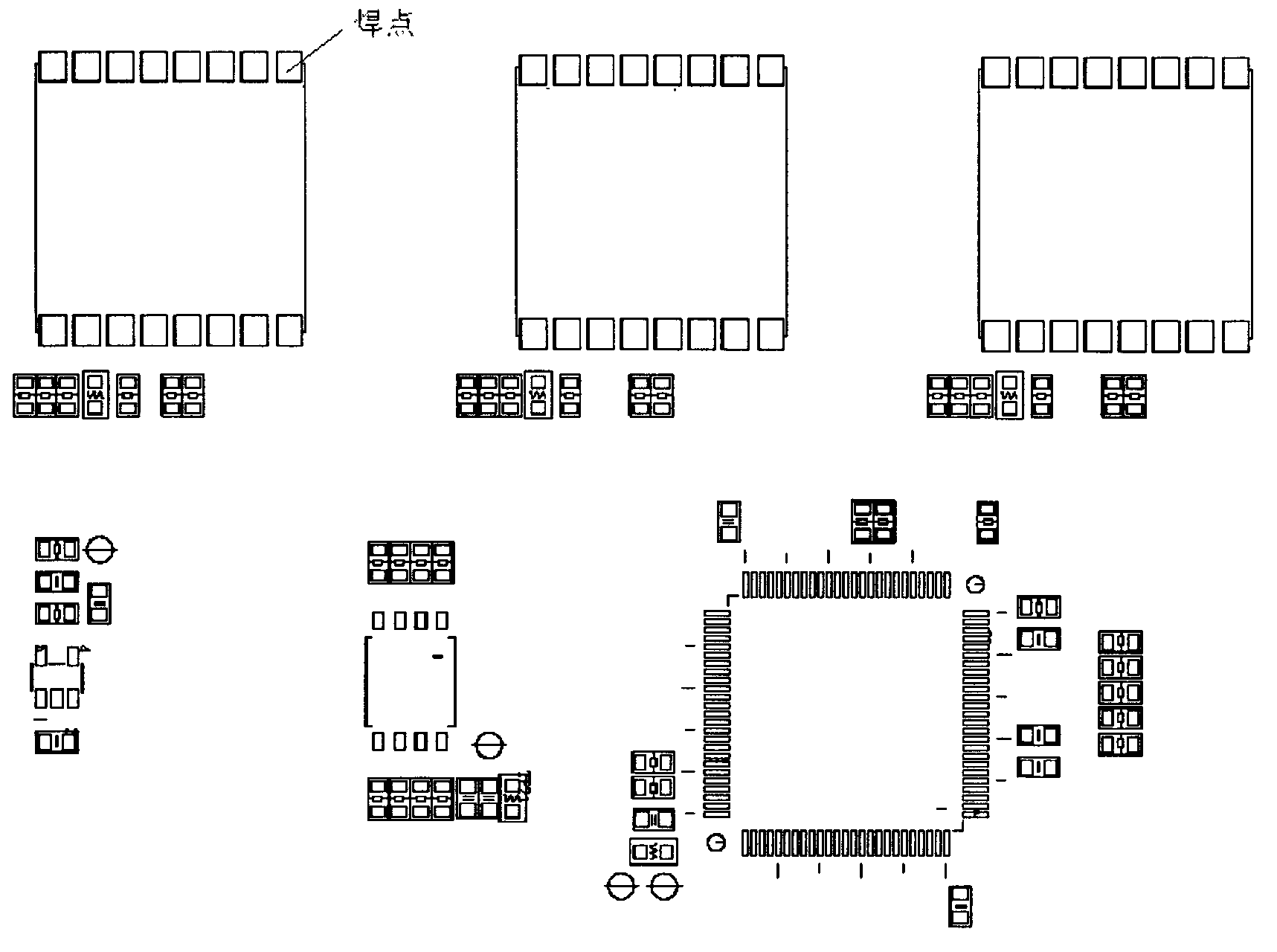
ActiveCN102990179APrecise angle of rotationAccurate compensationMetal working apparatusGraphicsComputer Aided Design
The invention discloses a method for improving programming speed and precision of a soldering robot by using a computer-aided design (CAD) file. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) introducing the CAD file comprising a printed circuit board (PCB) into a programming file; (2) analyzing the CAD file, and converting the programming file into a supportable file format; (3) generating a corresponding CAD graph in the programming file, wherein the graph comprises precise position information of all the welding disks; (4) processing the generated CAD graph, and constructing a relation between graph coordinates and object coordinates; (5) selecting a welding point to be welded on the processed CAD graph, obtaining actual physical coordinates according to the coordinate conversion relation obtained in step (4), and moving a welding nozzle to a position with the actual physical coordinates so as to perform parameter setting and welding; and (6) finding other welding points by the method in step (5), and welding. By adopting the method, a camera is not required to shoot a thumbnail, and the programming time is shortened; the rotating angle of the PCB can be accurately calculated and can be compensated; and the welding precision is improved.
Owner:廖怀宝
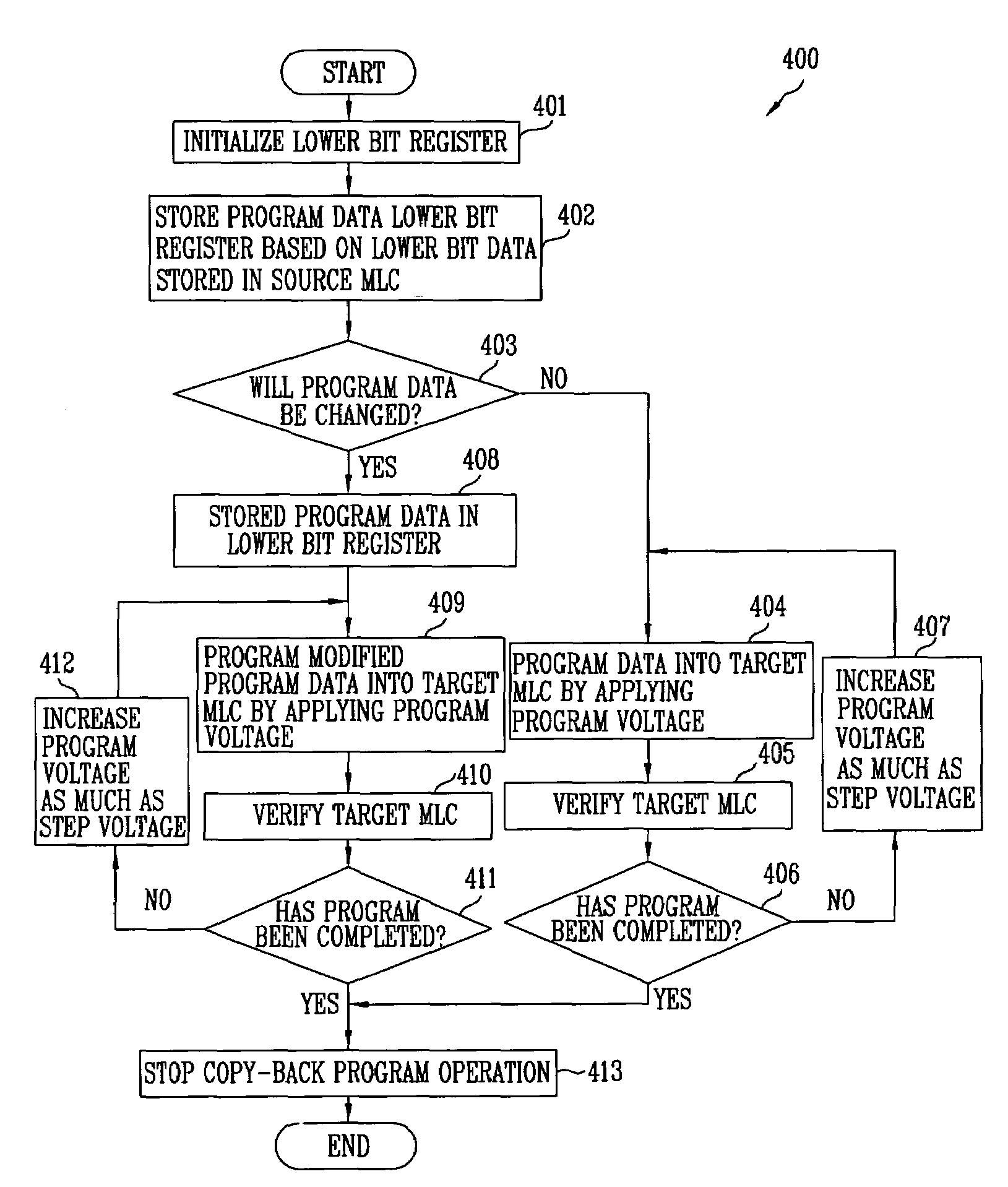
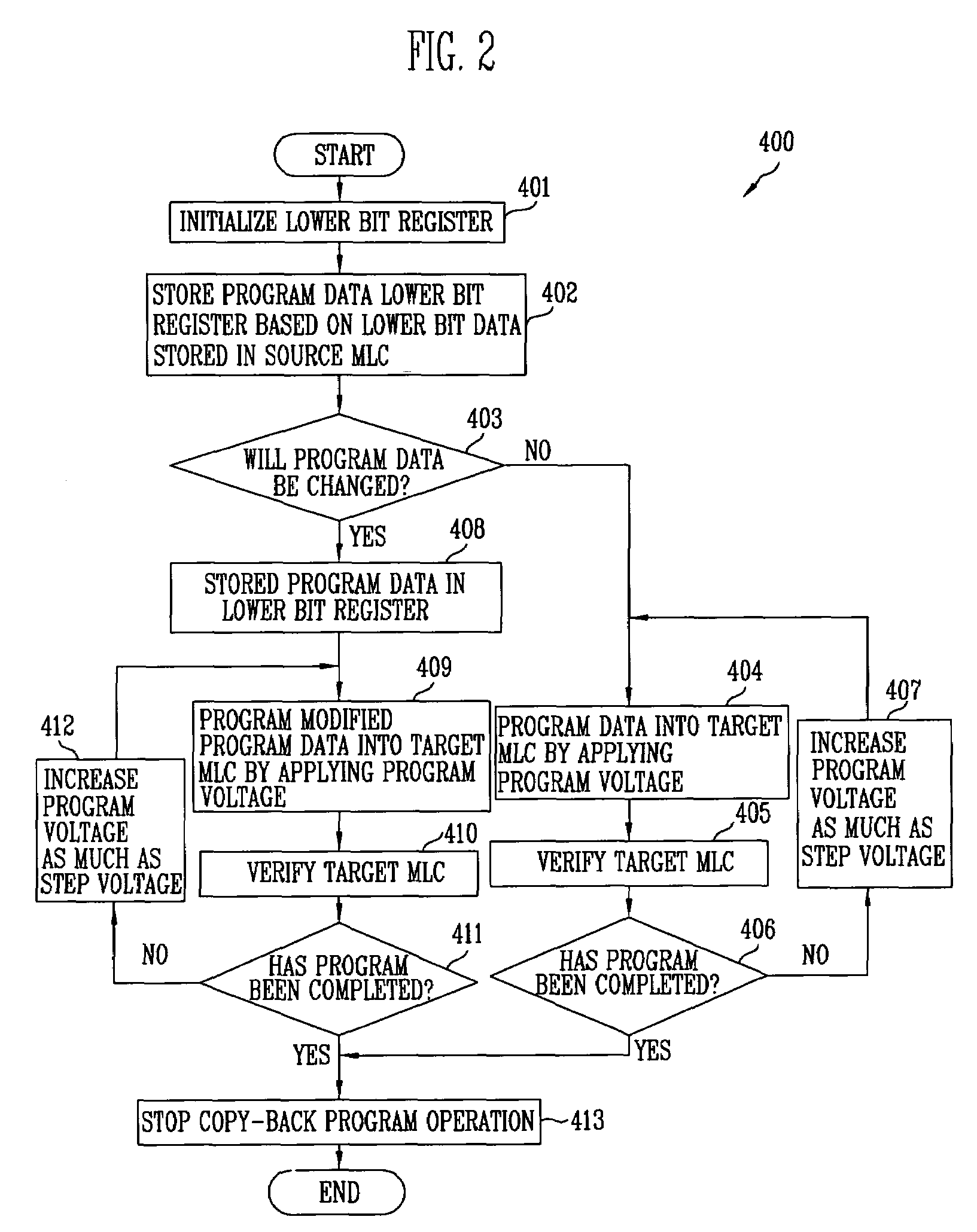
Method of controlling copy-back operation of flash memory device including multi-level cells
ActiveUS7301825B2Improve business performanceShorten programming timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageMulti-level cellComputer science
A method of controlling a copy-back operation of a flash memory device including multi-level cells. In the method, the copy-back operation can be executed even without an additional storage space. Accordingly, a program time can be shortened and operational performance of a flash memory device can be improved.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Erase and program method of flash memory device for increasing program speed of flash memory device
ActiveUS7539057B2Improved Threshold Voltage DistributionFail occurrence ratioRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage rangeComputer science
Erase and program methods of a flash memory device including MLCs for increasing the program speed are described. In the erase method, MLCs are pre-programmed so that a voltage range in which threshold voltages of MLCs are distributed can be reduced. Therefore, a fail occurrence ratio can be reduced when erasing MLCs, the threshold voltage distribution of MLCs can be improved and an overall program time can be shortened in a subsequent program operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor device, semiconductor device testing method, and programming method
InactiveUS20060077736A1Increase the pulse widthShorten programming timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageDevice materialSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes: a latch circuit that latches a given signal in a test mode; and a generating circuit that generates a signal that defines a program voltage used for programming of a memory cell in accordance with the signal latched in the latch circuit. The generating circuit includes: a circuit that generates the signal that defines an initial voltage of the program voltage; a circuit that generates the signal that defines a pulse width of the program voltage; and a circuit that generates the signal that defines a step width of the program voltage when the program voltage is a voltage that increases stepwise.
Owner:VALLEY DEVICE MANAGEMENT
A semantic similarity-based Java application program interface use mode recommendation method
ActiveCN109670022AImprove development efficiencyVersatileDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsHierarchical cluster algorithmApplication programming interface
The invention discloses a semantic similarity-based Java application program interface use mode recommendation method, which comprises the following steps of extracting the annotation information, anapplication program interface calling sequence and a method signature in a Java file in a project to form a metadata structure; using a hierarchical clustering algorithm for the metadata structure, and extracting an application program interface use mode; and based on the semantic similarity, carrying out the application program interface use mode recommendation. According to the method, the Javaapplication program interface use mode is recommended through the semantic similarity, the recommendation accuracy of the Java application program interface use mode is improved, the programming timeof developers is shortened, and the development efficiency of the developers is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High-speed high-precision flexible electronic gear box control method
ActiveCN103294007AShorten programming timeImprove programming efficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlGear grindingGrating
The invention discloses a high-speed high-precision flexible electronic gear box control method based on an open numerical control system. An electronic gear box is a core part of a gear processing numerical control system, and by parameter setting, requirements, on multi-axis linkage strict speed ratio relationships, of different machine tools for gear hobbing, gear grinding and the like can be met. Each axis servo motor and a spindle motor are connected with the system through motor interfaces, main movement signals are fed back through a motor encoder or a grating ruler, processed by the numerical control system and distinguished and computed through the flexible electronic gear box, and follow-up numerical control shafts are controlled to complete master-slave electronic gear ratio movement.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
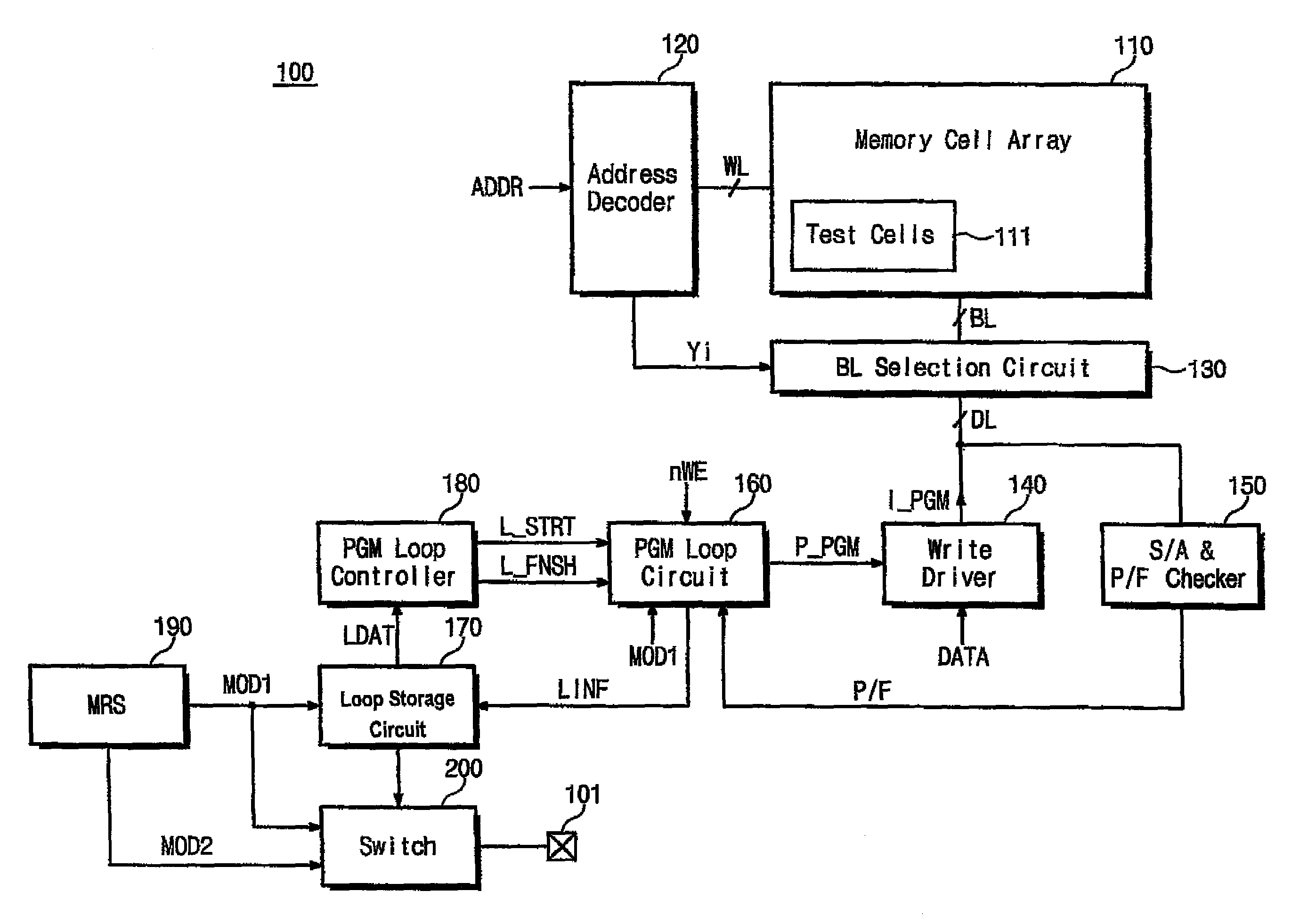
Phase-change random access memory (PRAM) performing program loop operation and method of programming the same
ActiveUS7573758B2Shorten programming timeTotal current dropRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingLoop control
A PRAM and programming method are disclosed. The PRAM includes a memory cell array including a test cell, a write driver applying a program pulse and providing a program current to the memory cell array, a sense amplification and verification circuit reading data programmed in the memory cell array and performing a program verify operation on the data, and a program loop control unit storing program verification result for the test cell at each program loop during test operation and generating the program pulse according to the program verification result to control the start of the program loop during normal operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com