Patents
Literature
44 results about "Program proving" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
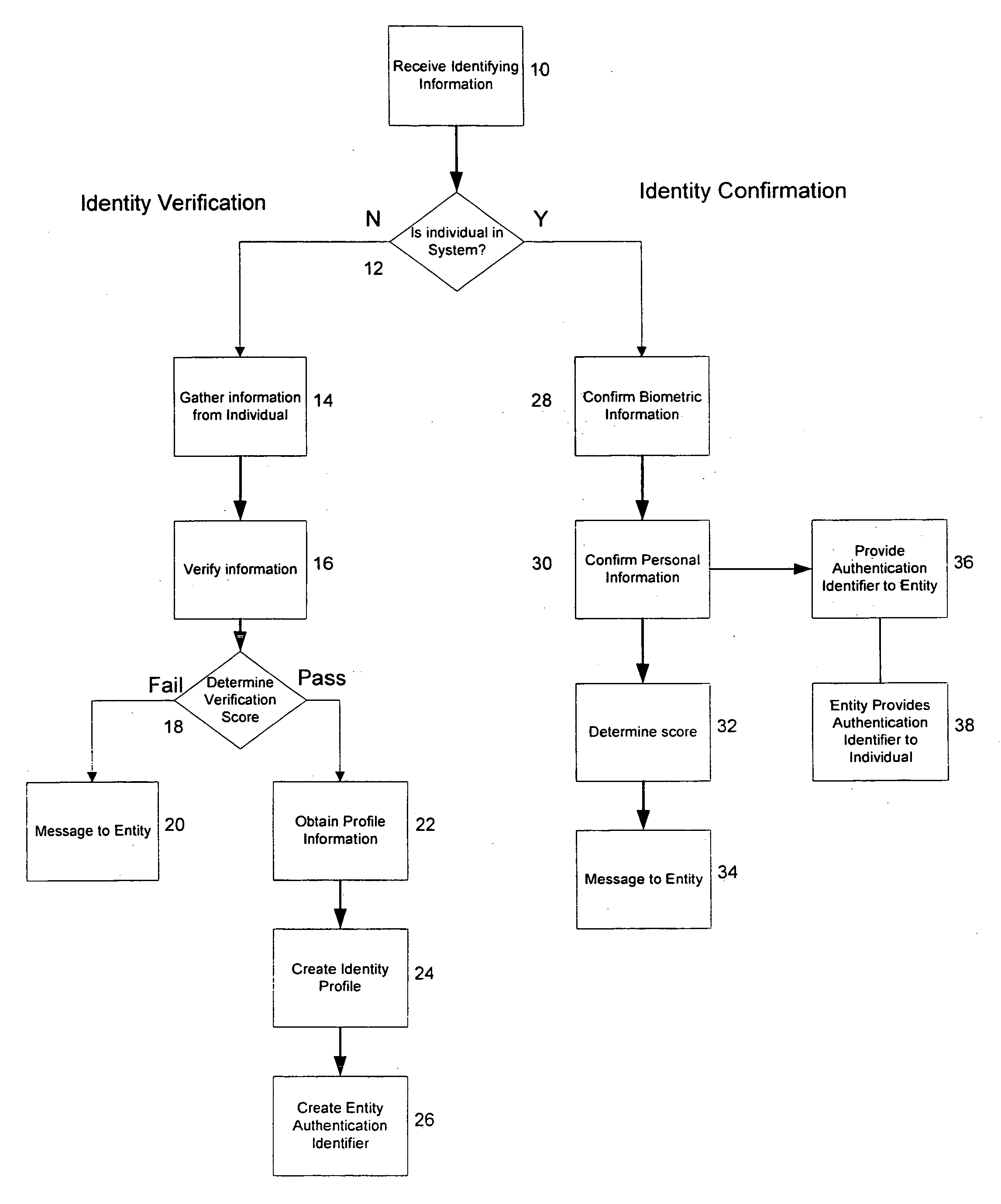
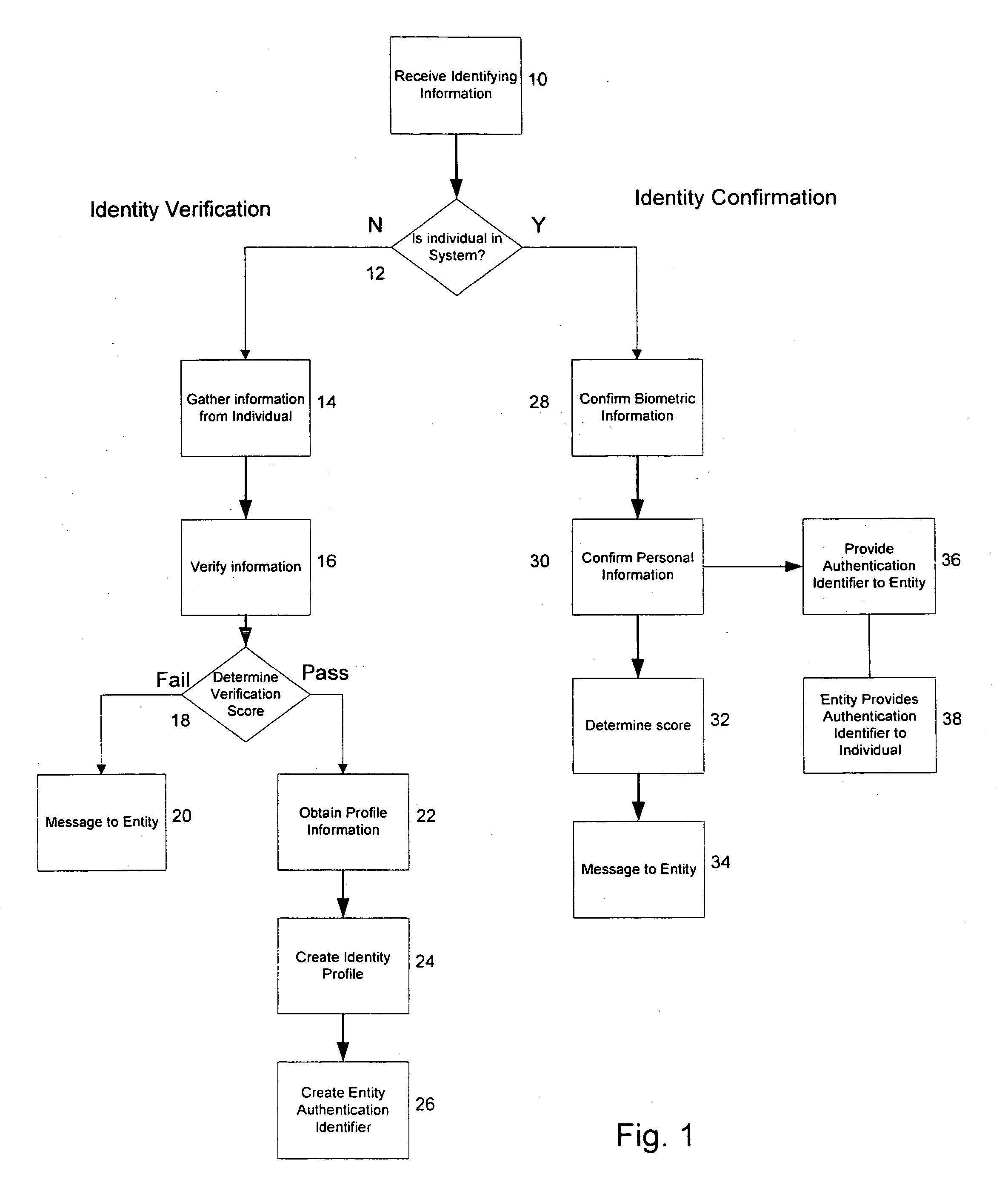
Method and system for confirming personal identity
ActiveUS20070177768A1Confirm the accuracyValidityCharacter and pattern recognitionCommerceProgram provingInternet privacy
An authentication utility may be provided to entities, such as businesses, organizations or even individuals, that require the identification, verification and control of the identity of another entity, for example, an individual, such as a consumer, employee, etc. The authentication utility may also determine and provide the financial and non-financial characteristics of an individual. Before entering into a relationship or transaction, an entity could verify the other party's identity with the authentication utility.
Owner:INTERSECTIONS LLC +1
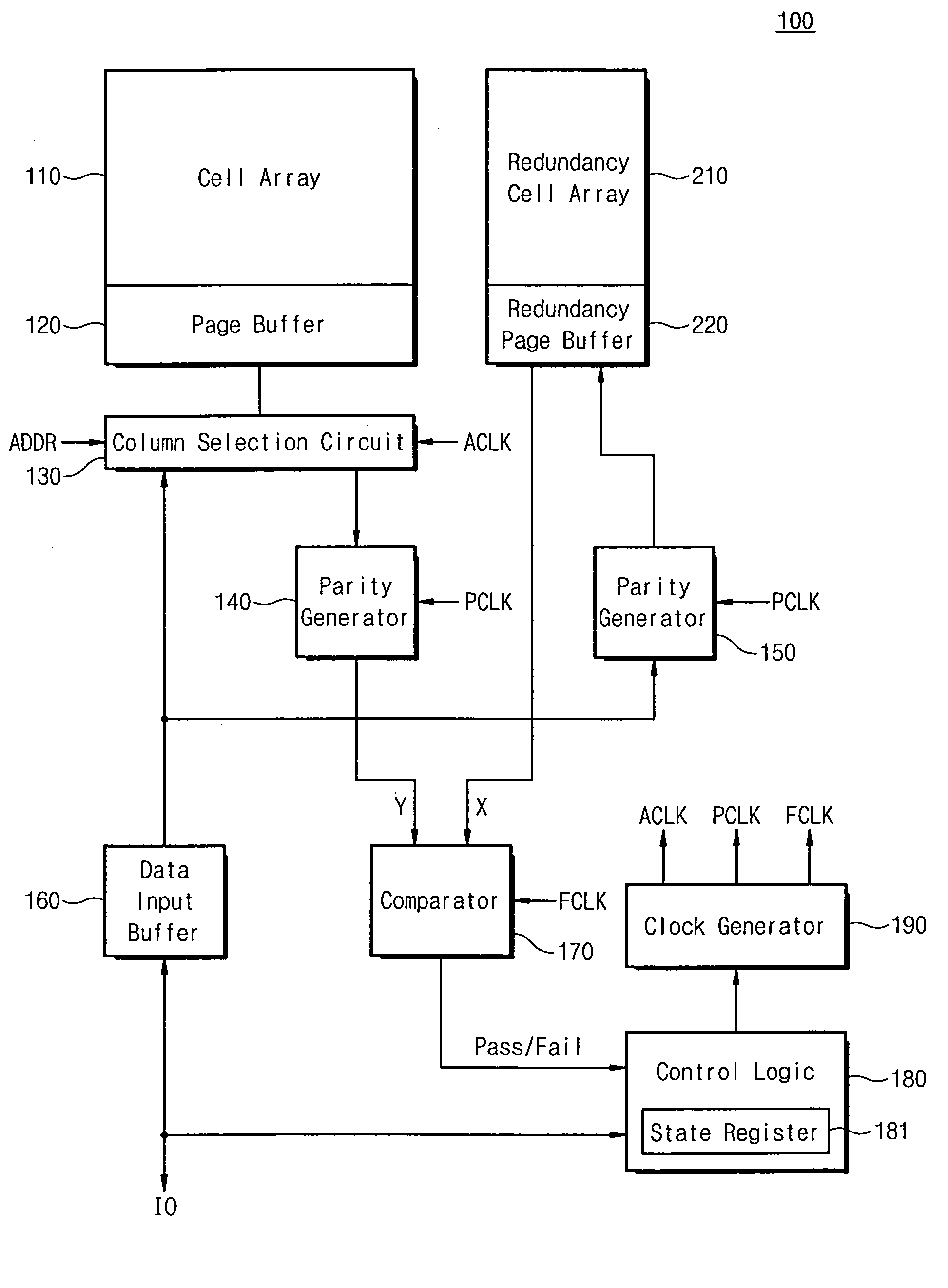
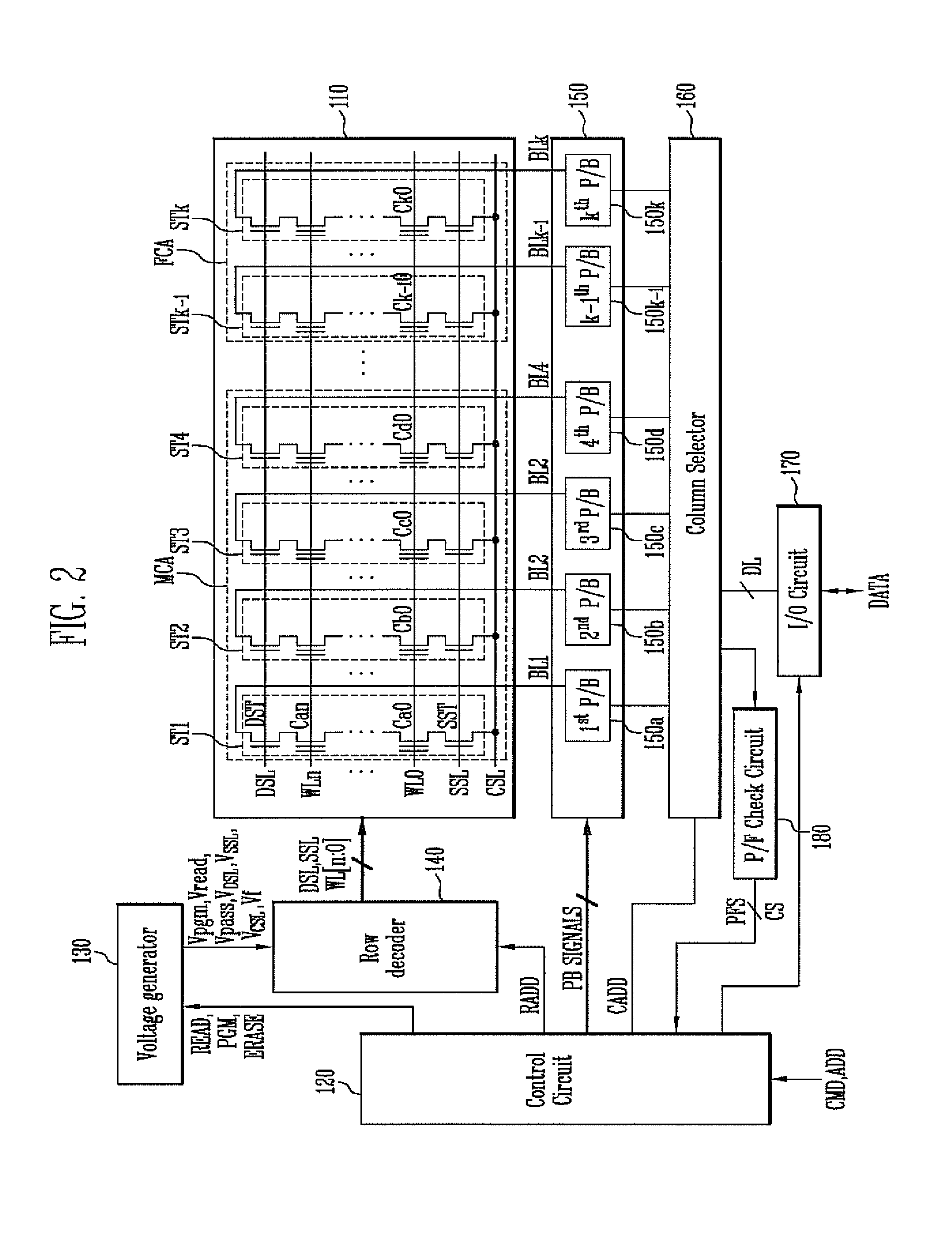
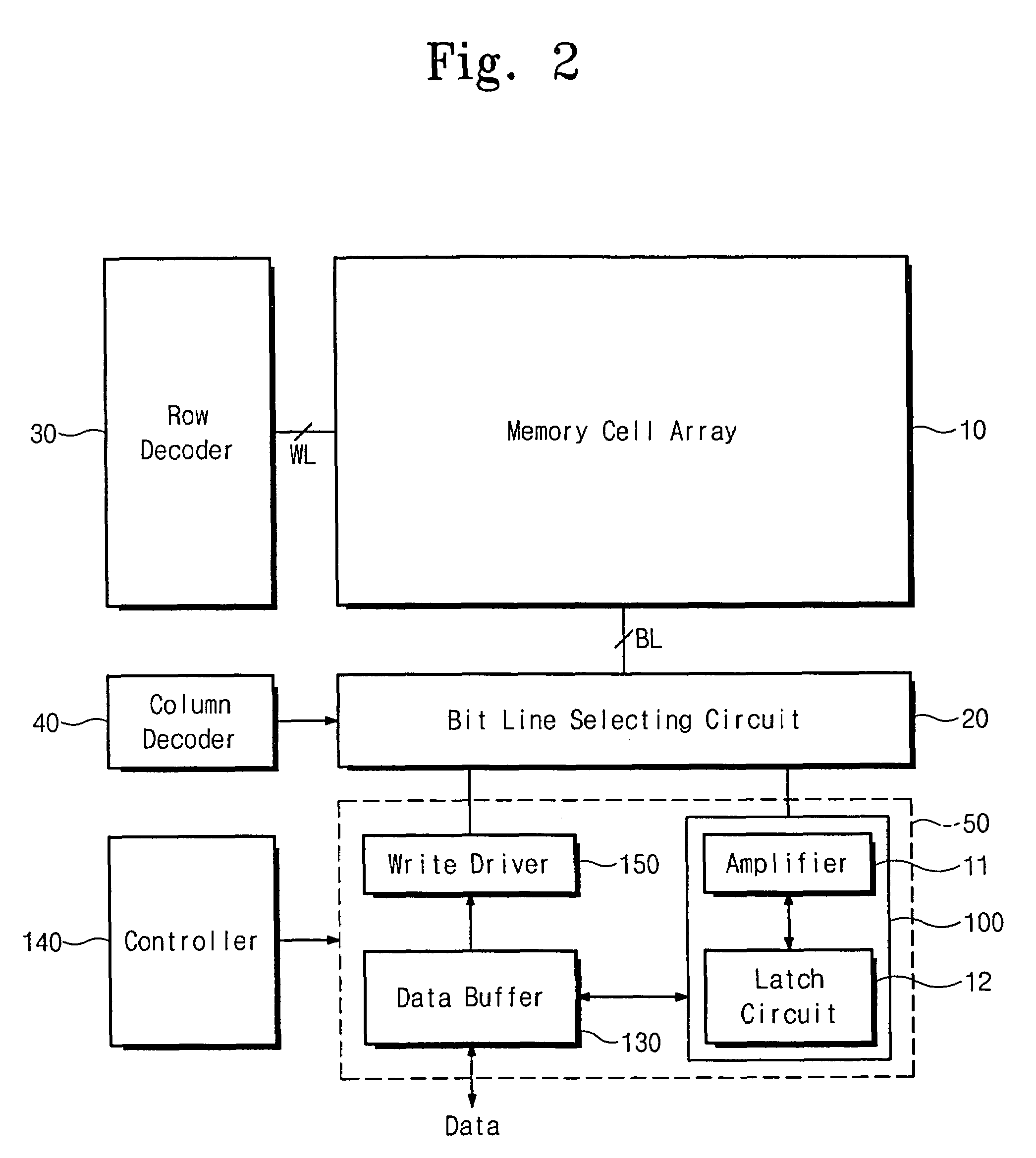
NAND flash memory device and copyback program method for same
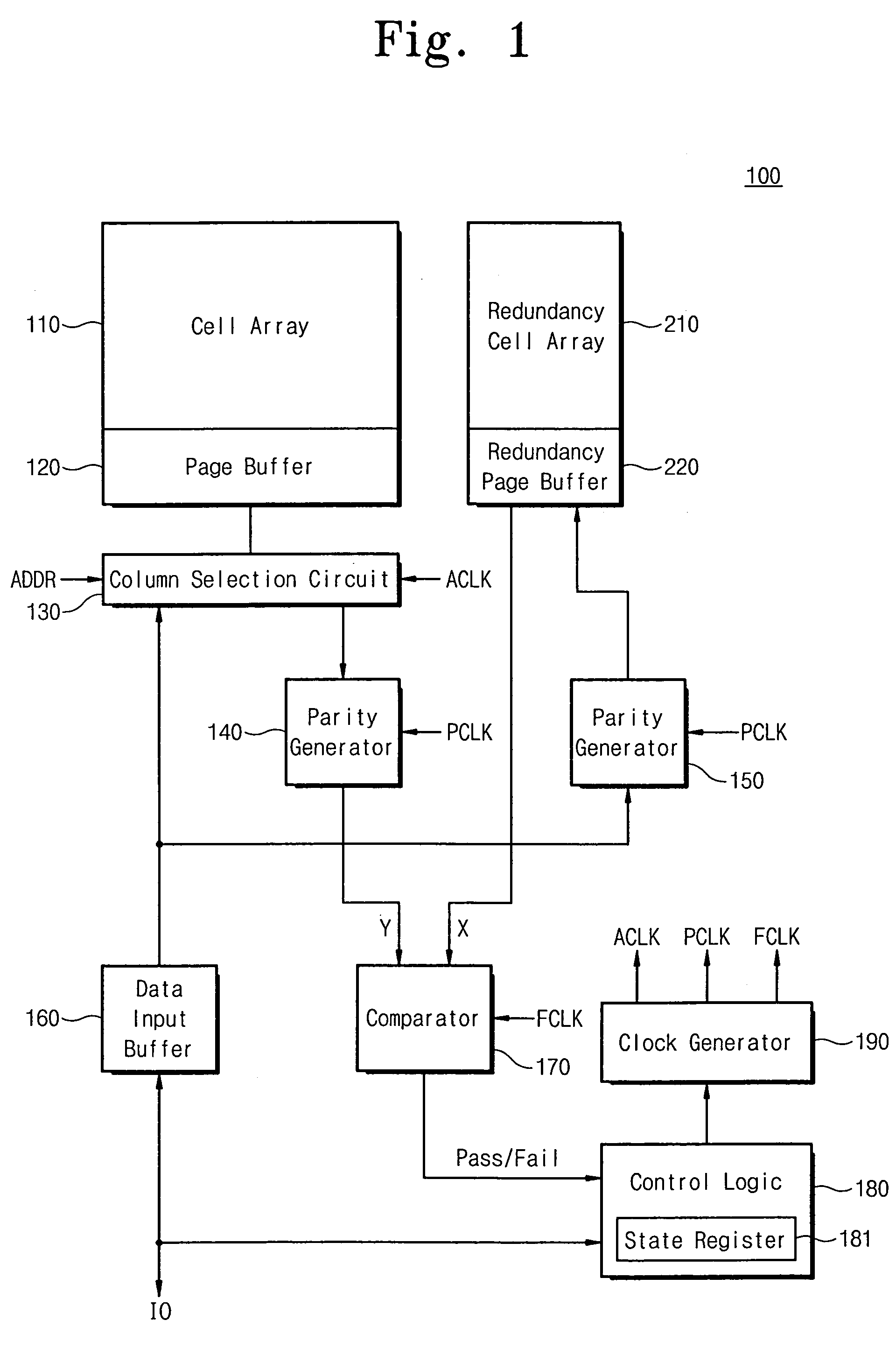
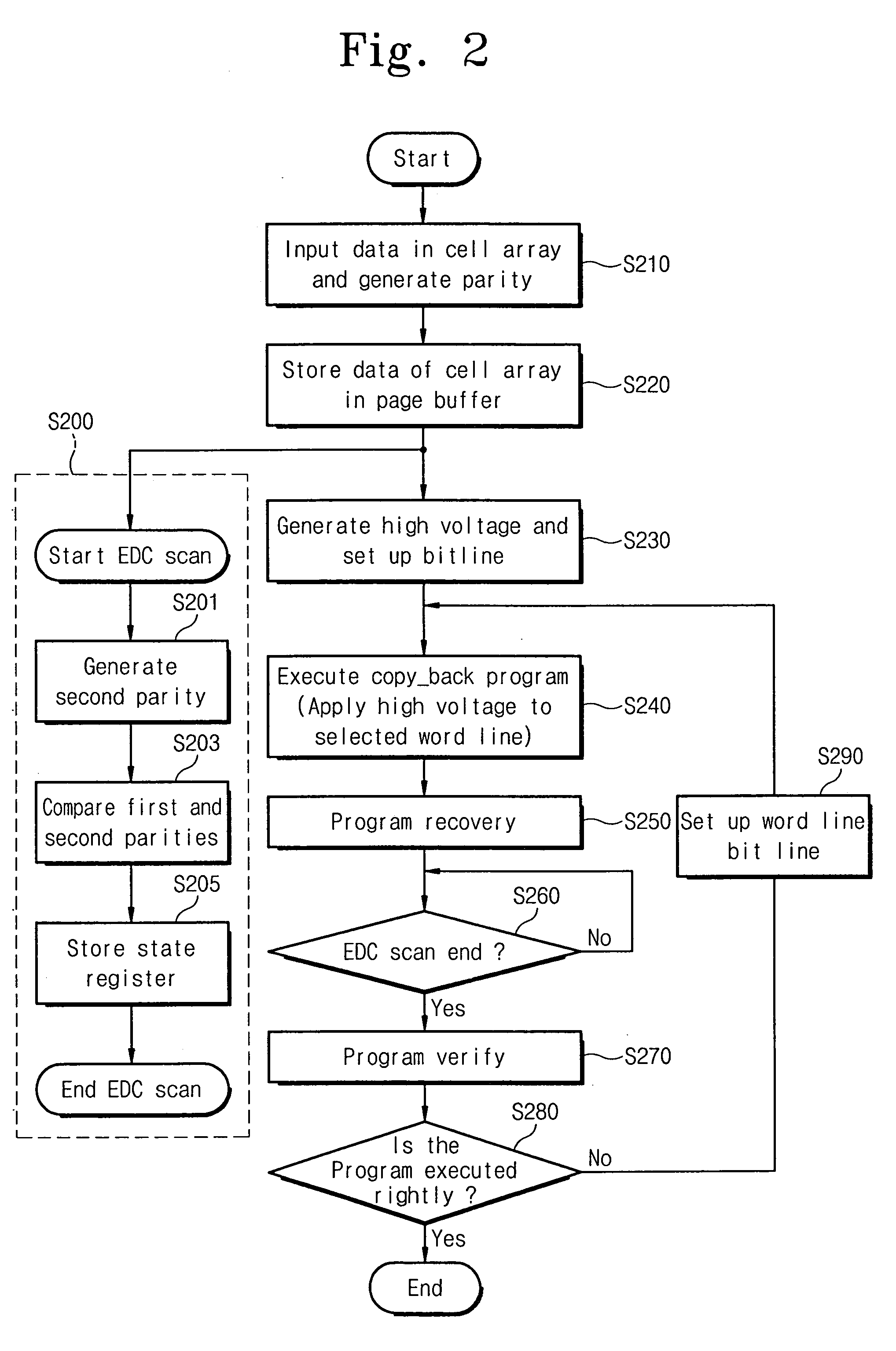
ActiveUS20060050576A1Avoid mistakesError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesProgram provingTime delays
A NAND flash memory device according to some embodiments includes a cell array, a page buffer configured to copyback read the data in the cell array, and an error detector for detecting errors that occur during the copyback reading and for generating a detection signal. Detecting errors is performed concurrently with a copyback program operation and completes before finishing a copyback program verify operation. The data stored in the page buffer may be copyback programmed when the detection signal is a pass signal. The copyback operation may end without executing the copyback program operation when the detection signal is a fail signal. Since the copyback program operation and the error detection operation are performed concurrently, the errors occurring during the copyback operation may be detected without additional time delay. Additionally, occurrence of two-bit error may be prevented because the copyback program is not executed when the fail signal is generated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
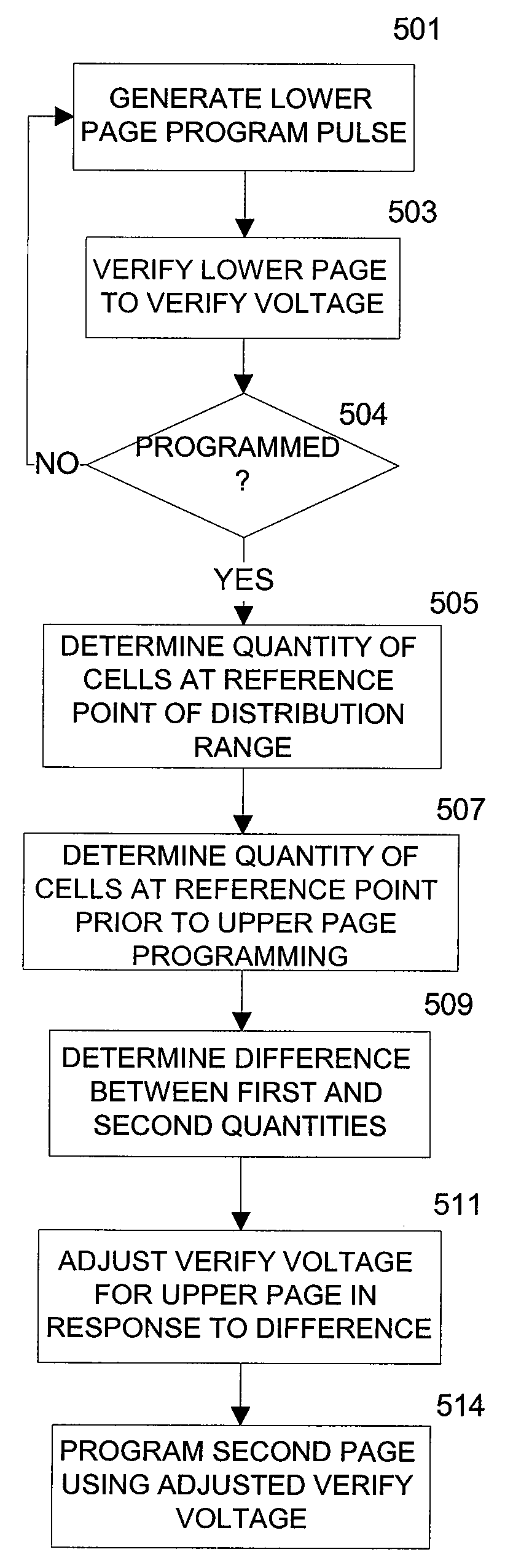
Charge loss compensation during programming of a memory device
In programming a selected word line of memory cells, a first program verify or read operation is performed, after one page of a selected word line is programmed, in order to determine a first quantity of memory cells that have been programmed to a predetermined reference point in the programmed first page distribution. Prior to programming the second page of the selected word line, a second program verify or read operation is performed to determine a second quantity of cells that are still at the reference point. The difference between the first and second quantities is an indication of the quantity of cells that experienced quick charge loss. The difference is used to determine an adjustment voltage for the second page verification operation after programming of the second page.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
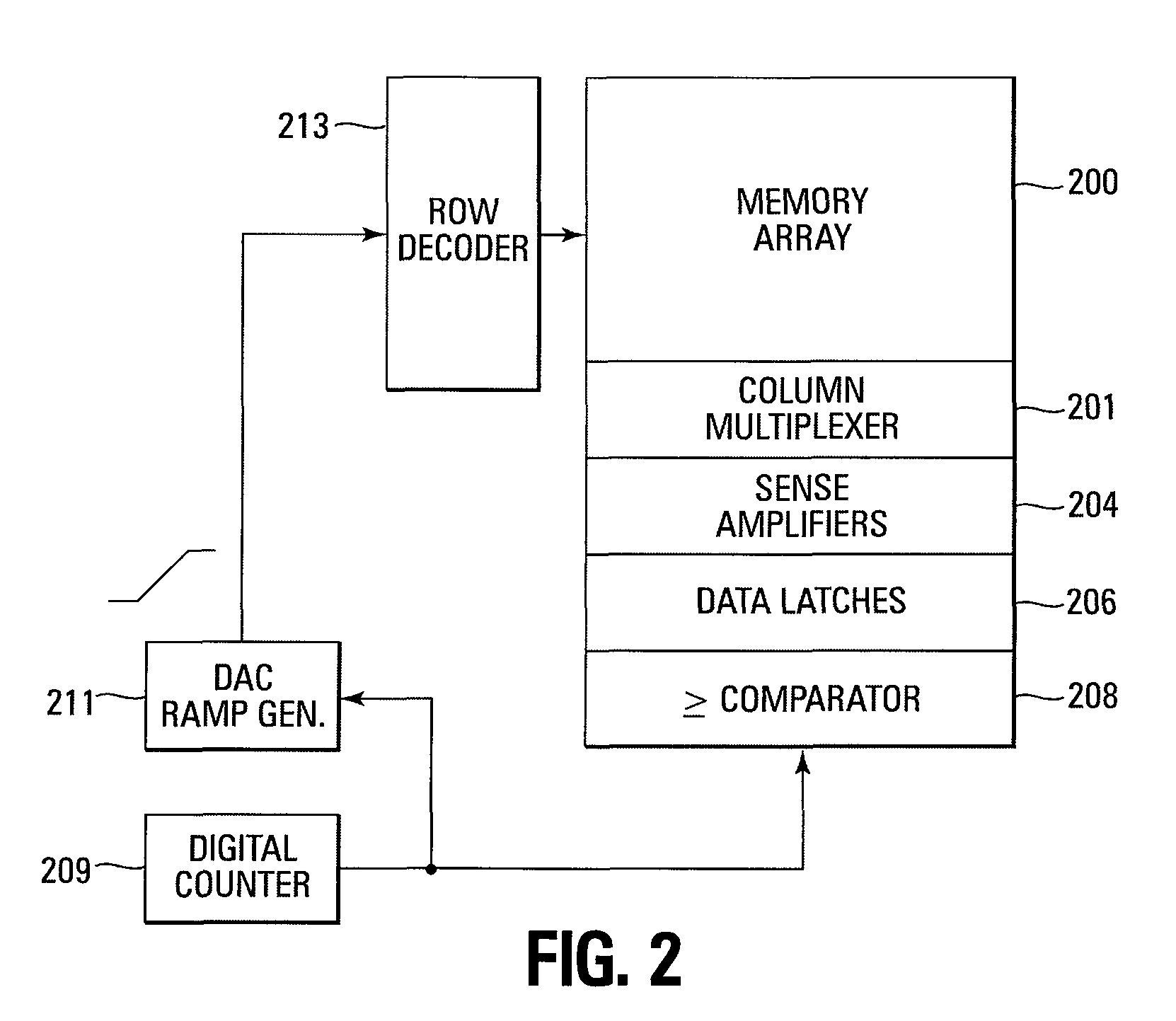
Mitigation of runaway programming of a memory device
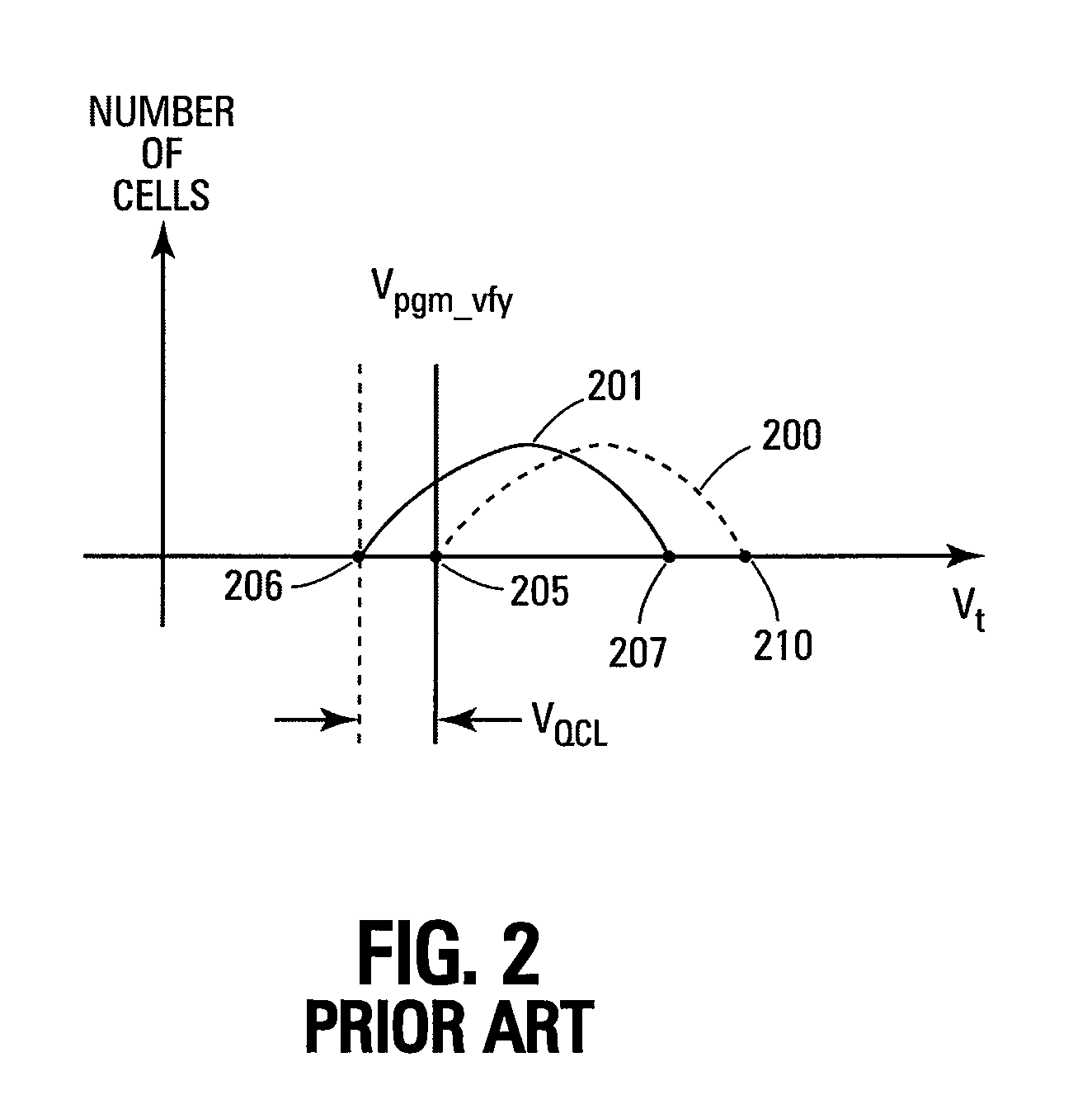
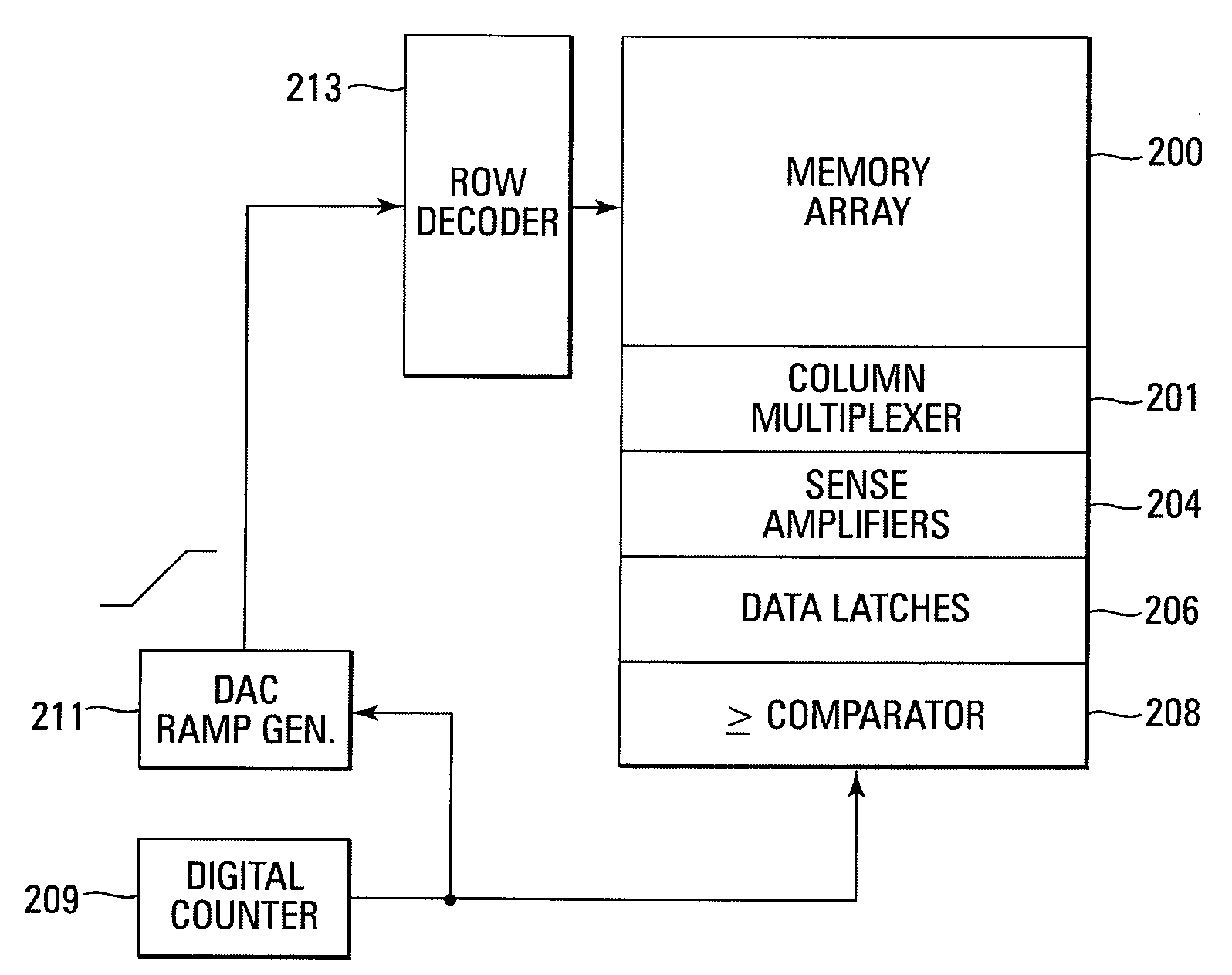
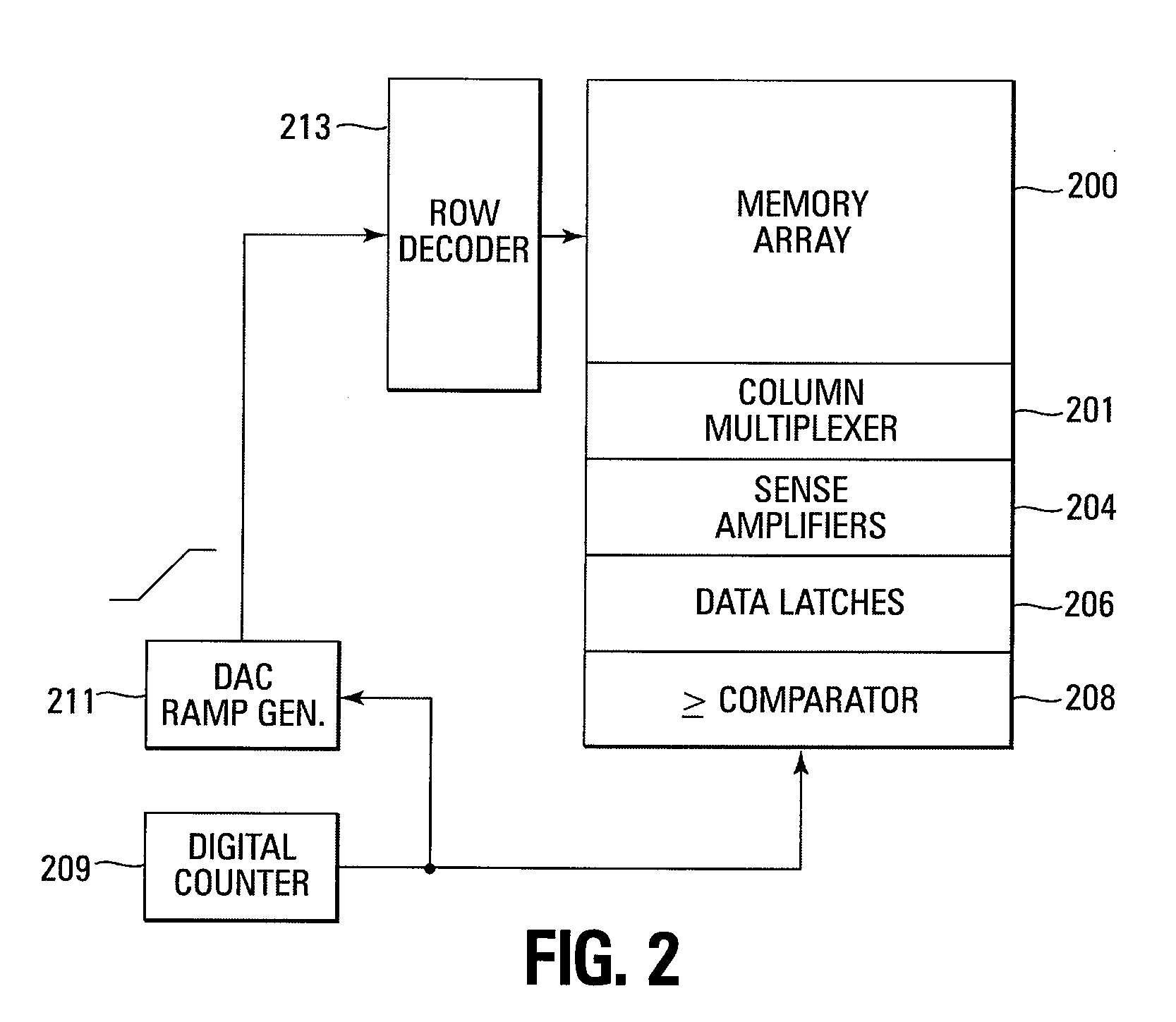
Methods for mitigating runaway programming in a memory device, methods for program verifying a memory device, a memory device, and a memory system are provided. In one such method, a ramp voltage signal is generated by a digital count signal. A memory cell being program verified is turned on by a particular verify voltage of the ramp voltage signal in response to a digital count of the digital count signal. The memory cell turning on generates a bit line indication that causes the digital count to be compared to a representation of the target data to be programmed in the memory cell. The comparator circuit generates an indication when the digital count is greater than or equal to the target data.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
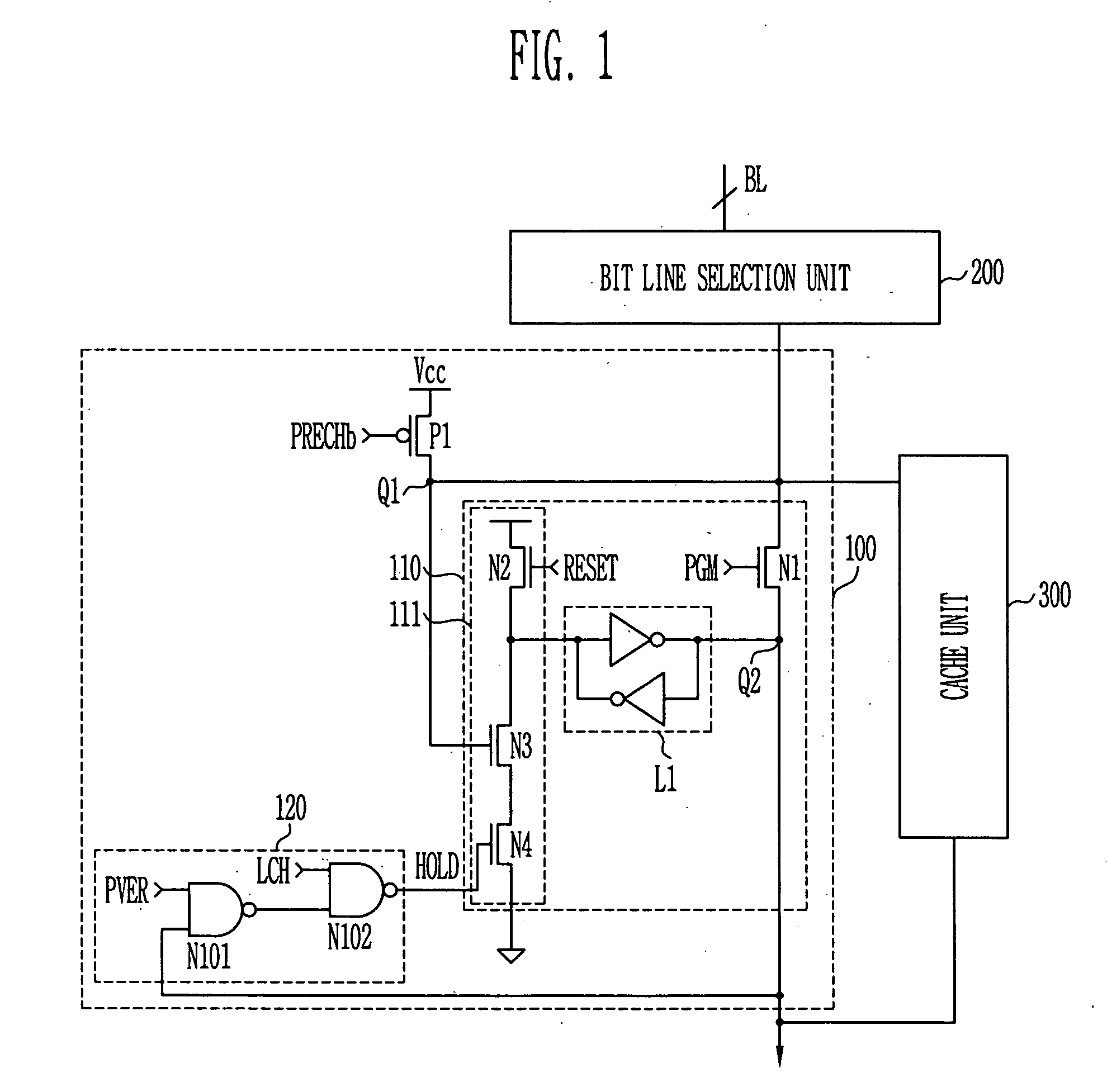
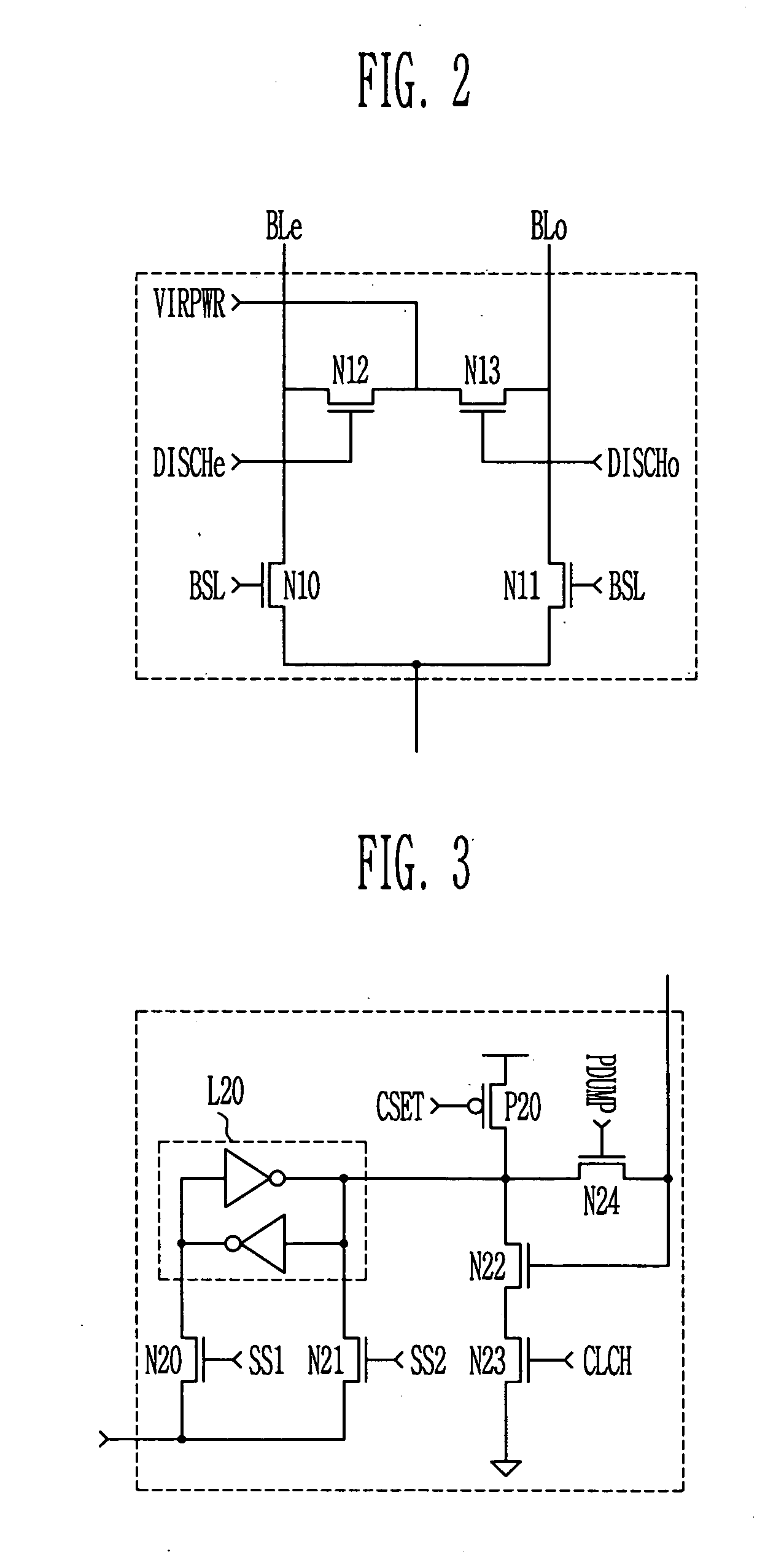
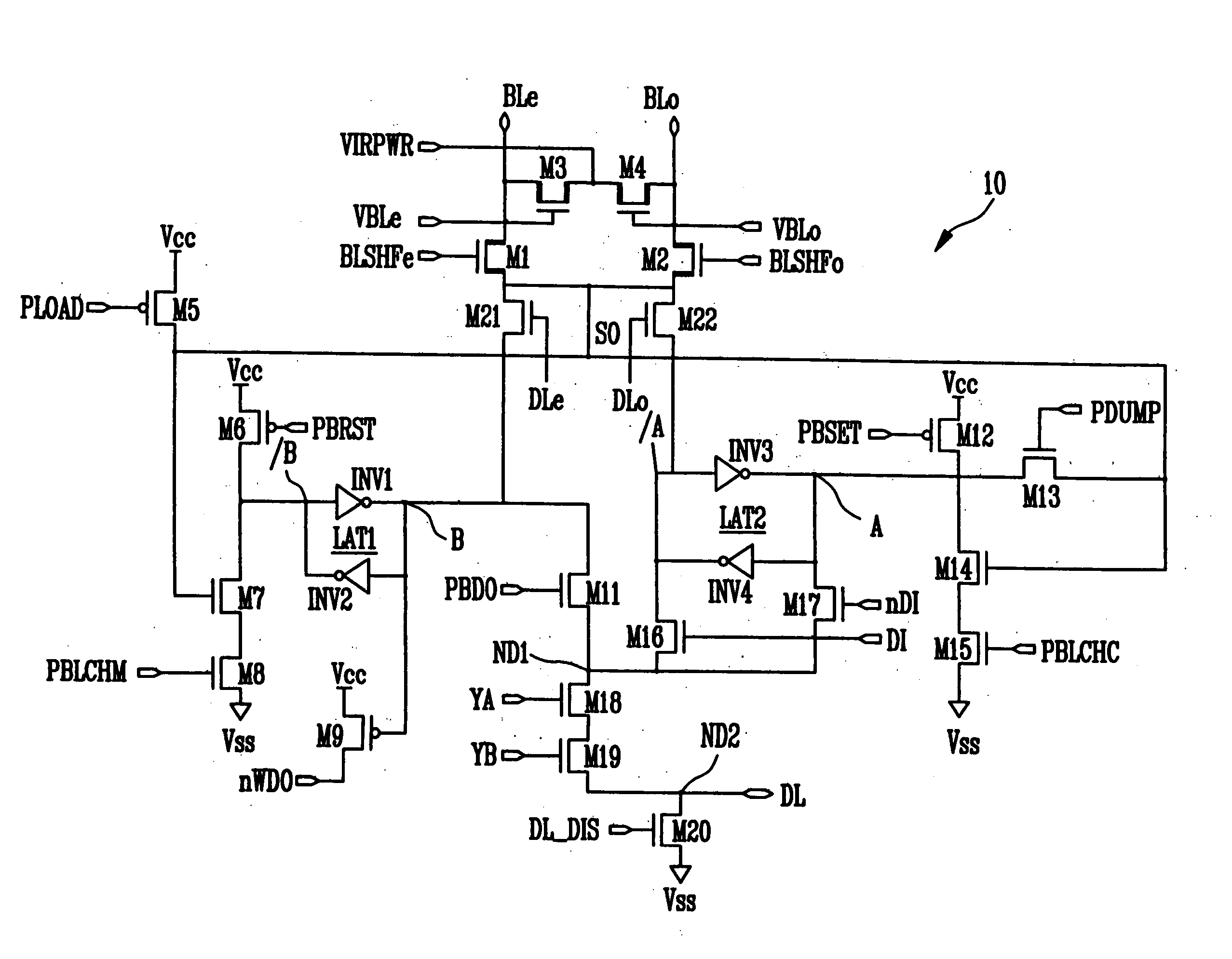
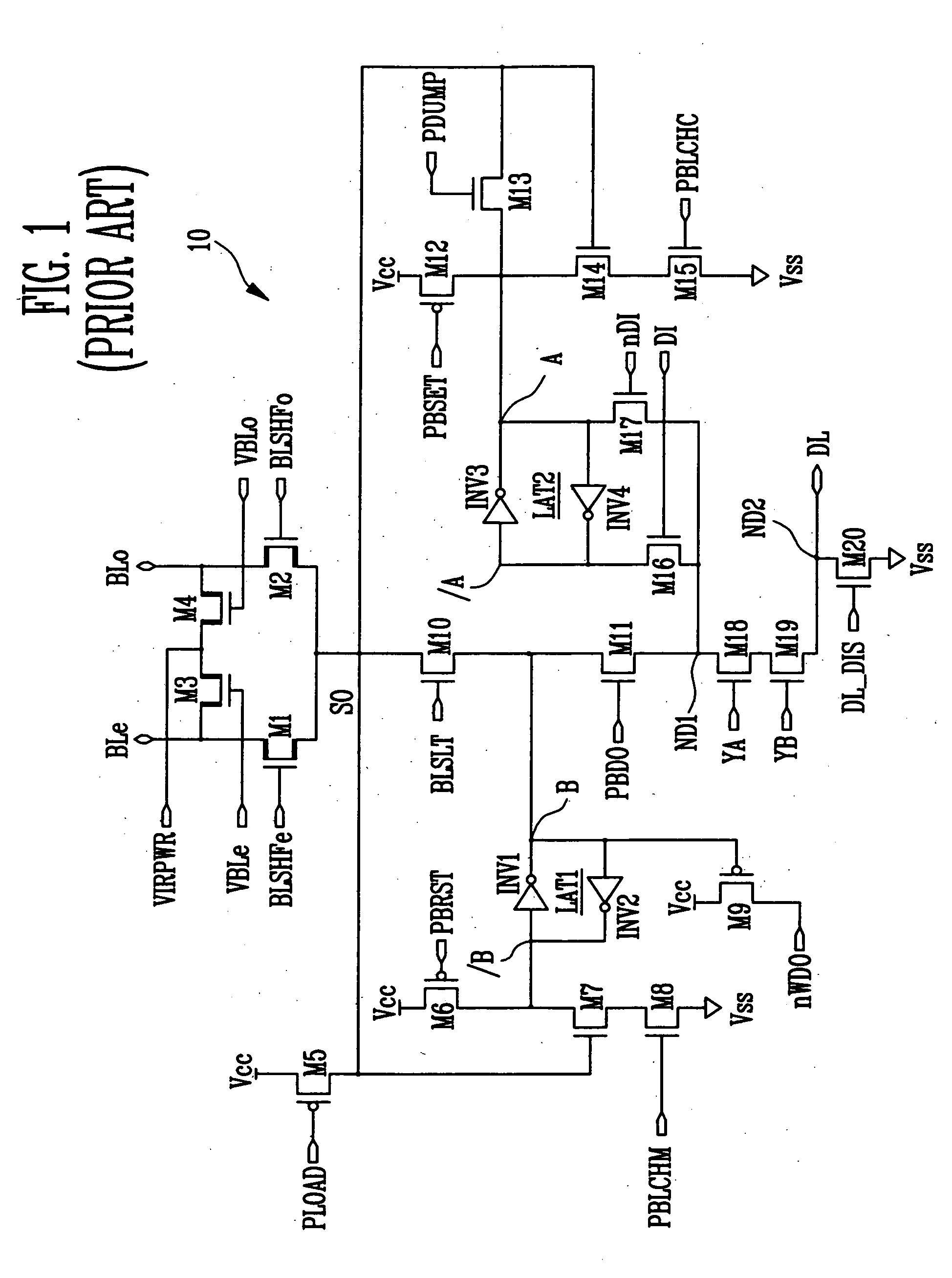
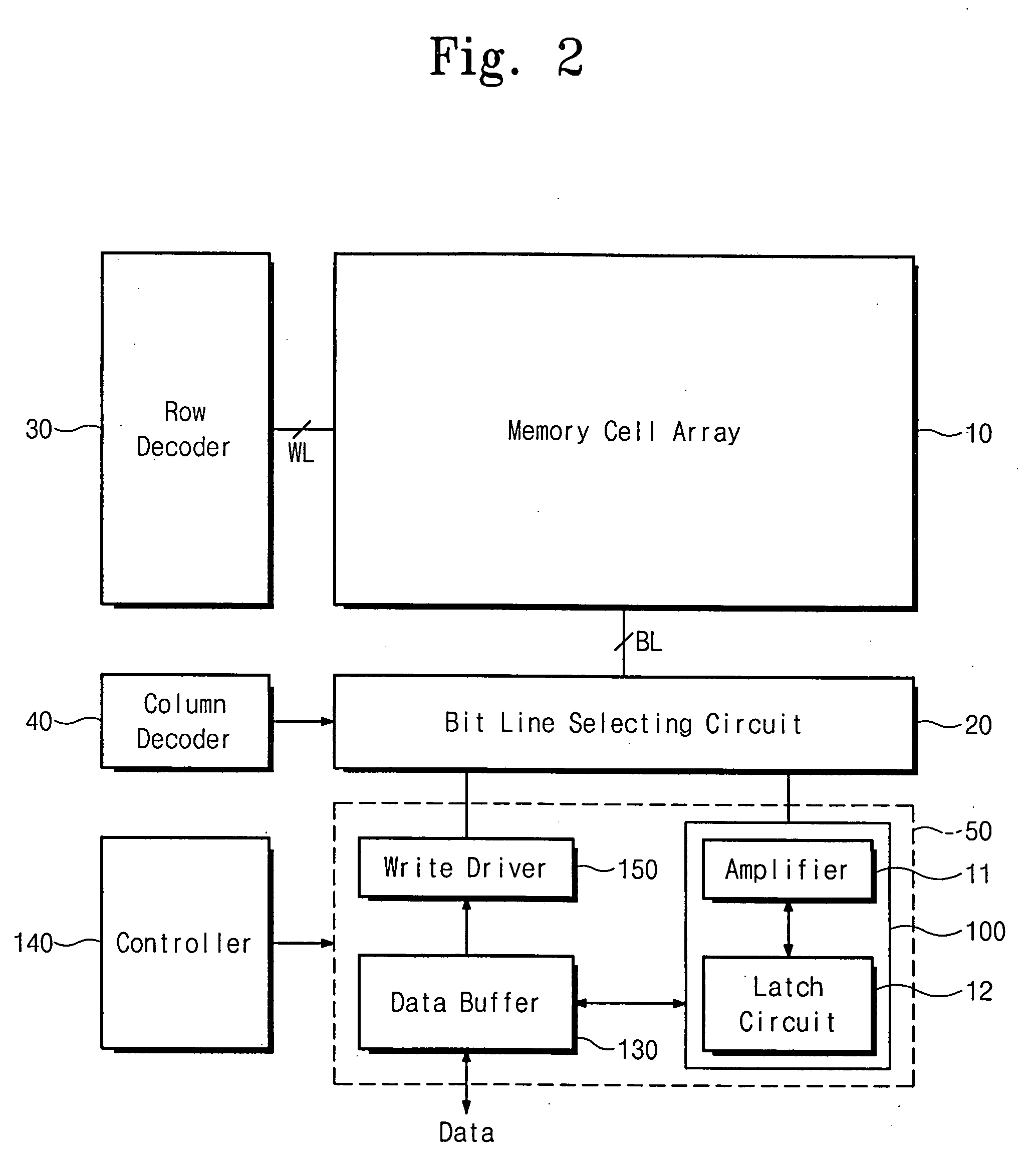
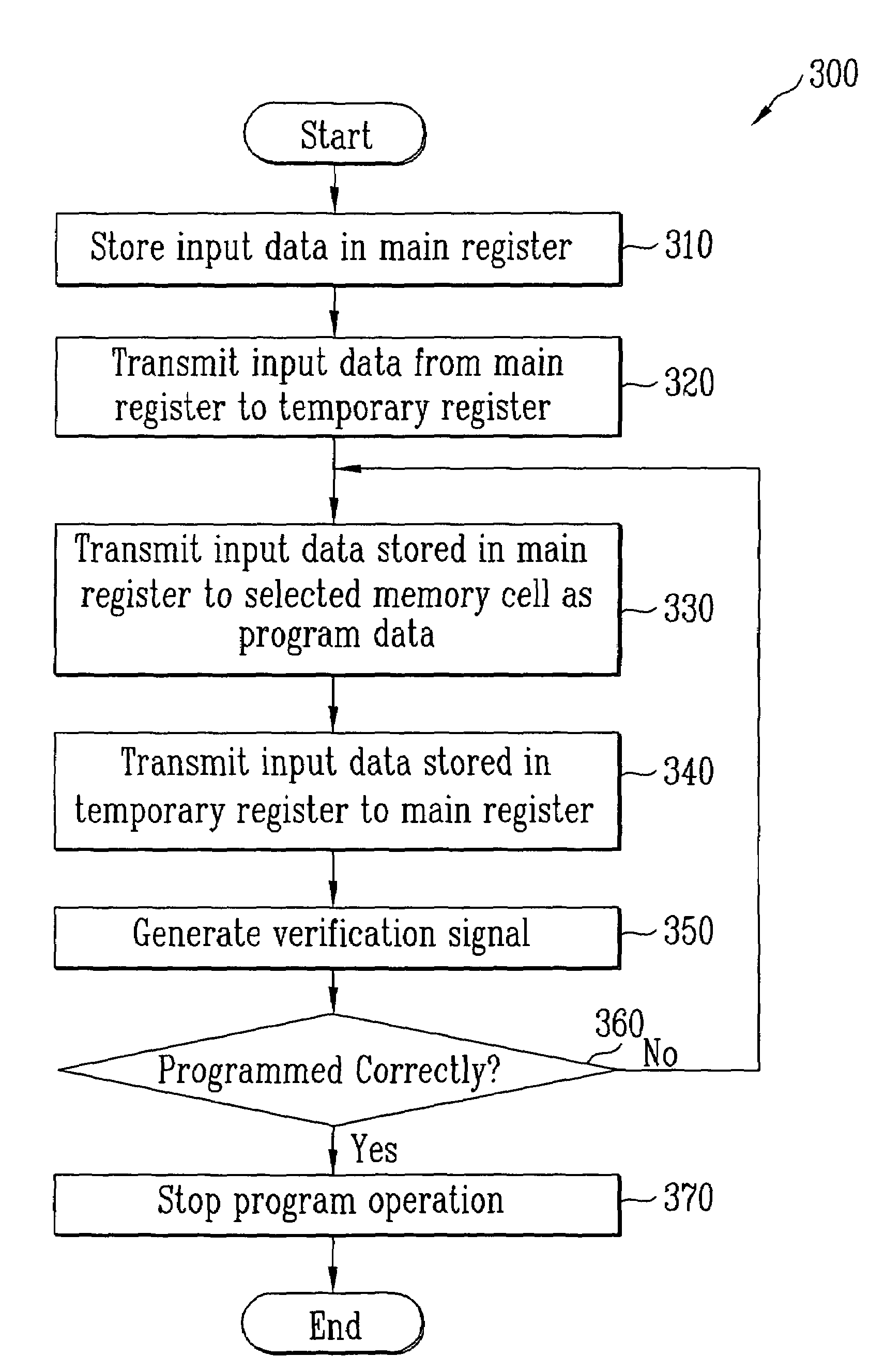
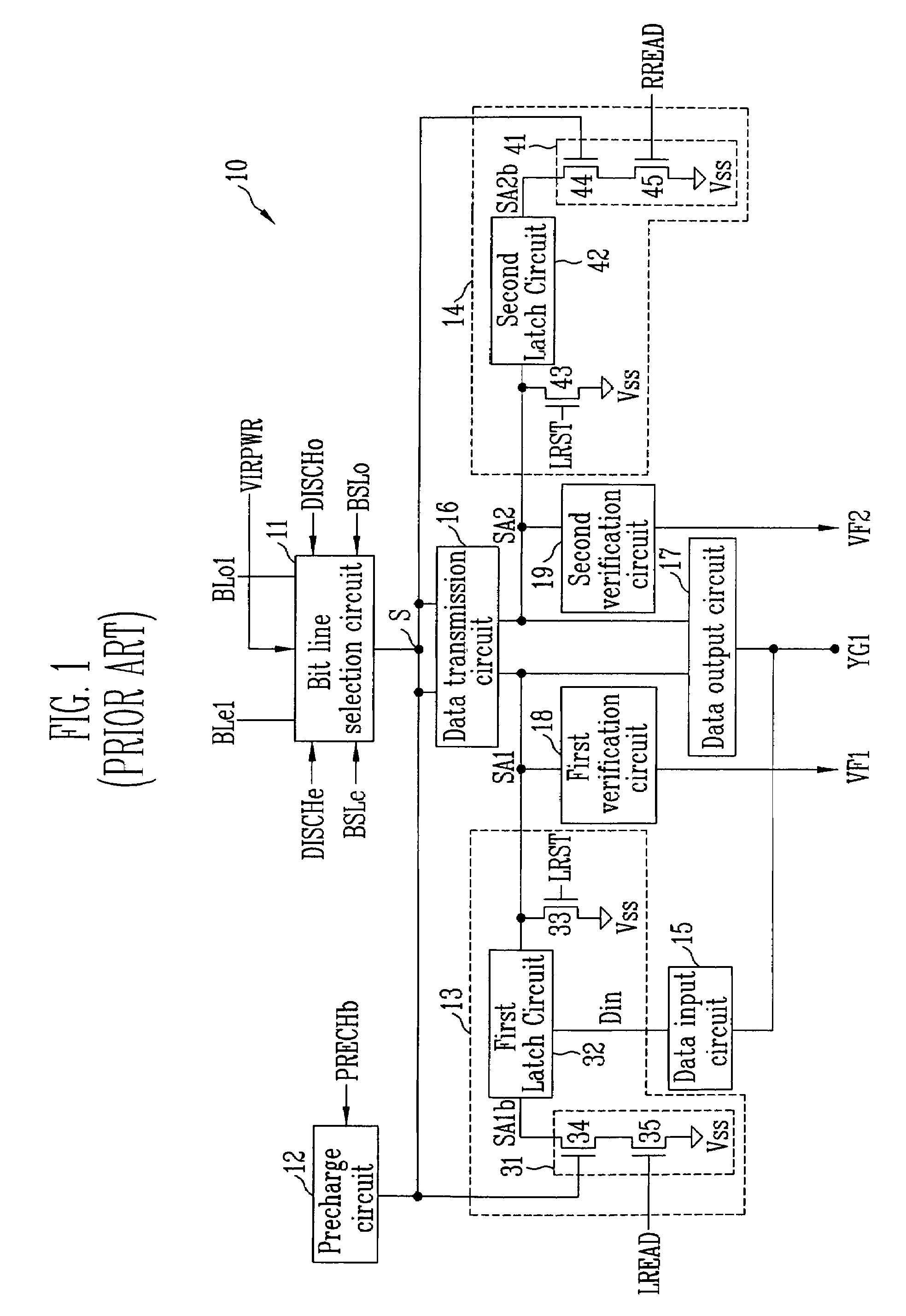
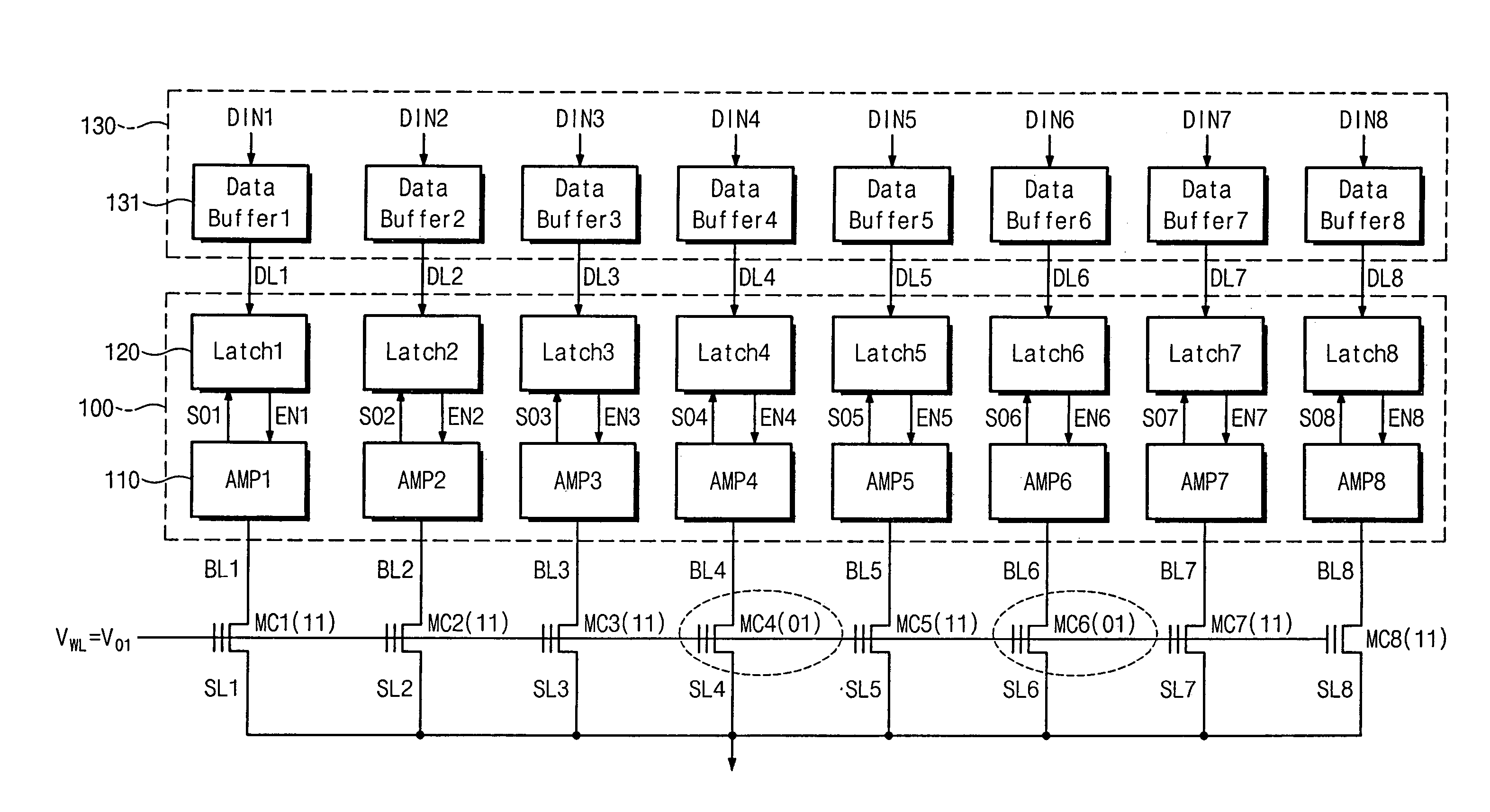
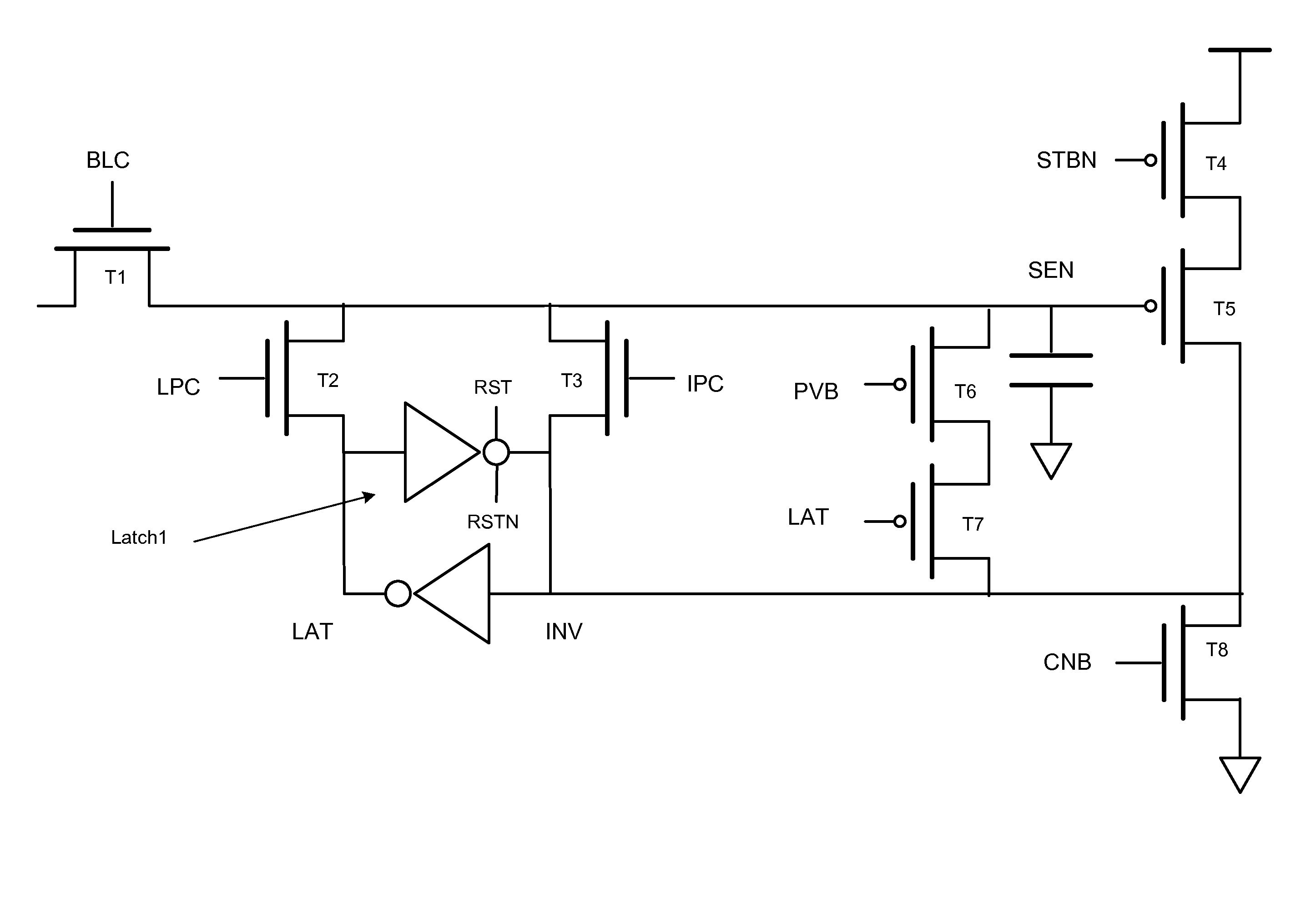
Page buffer of flash memory device and data program method using the same
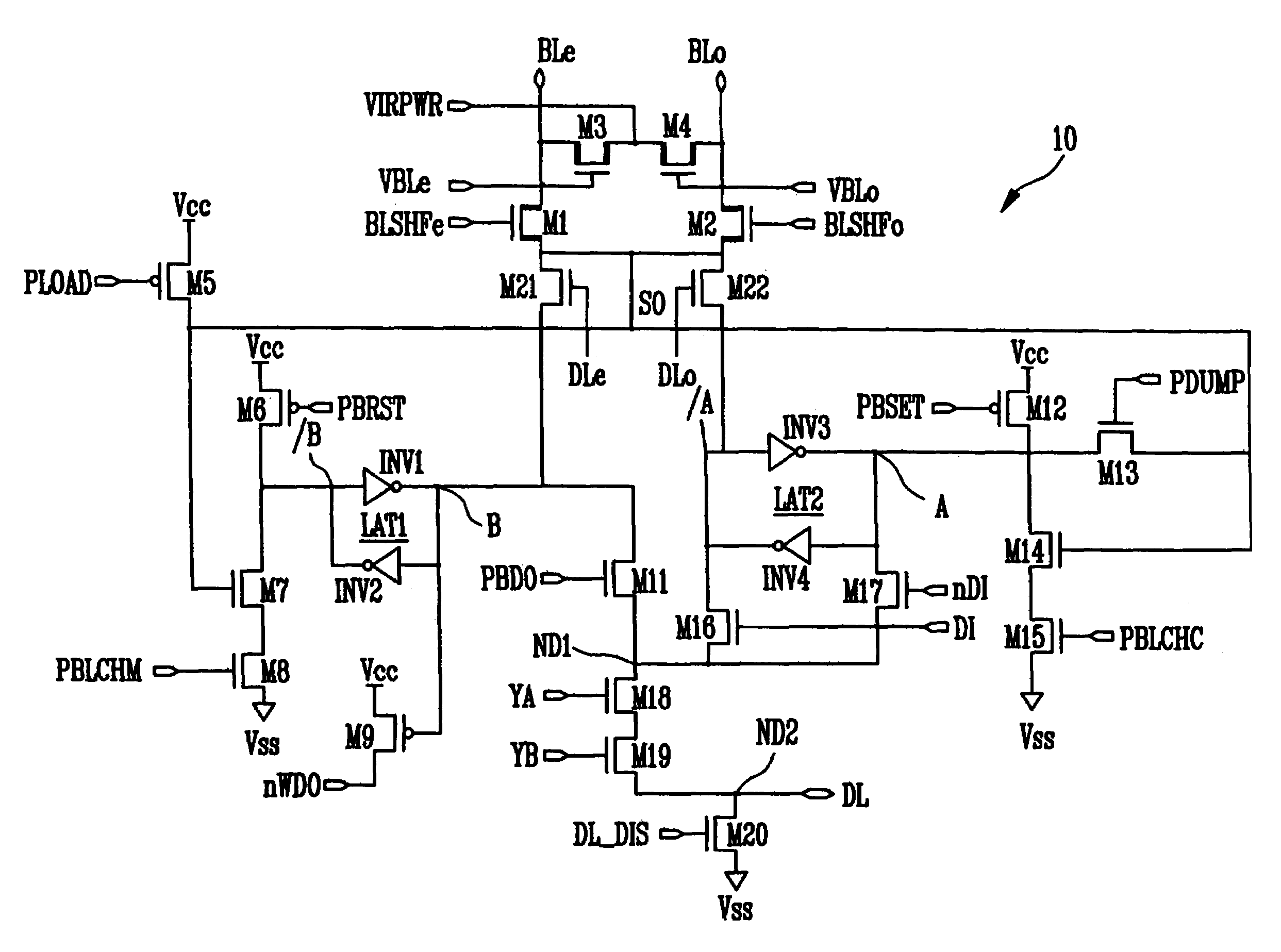
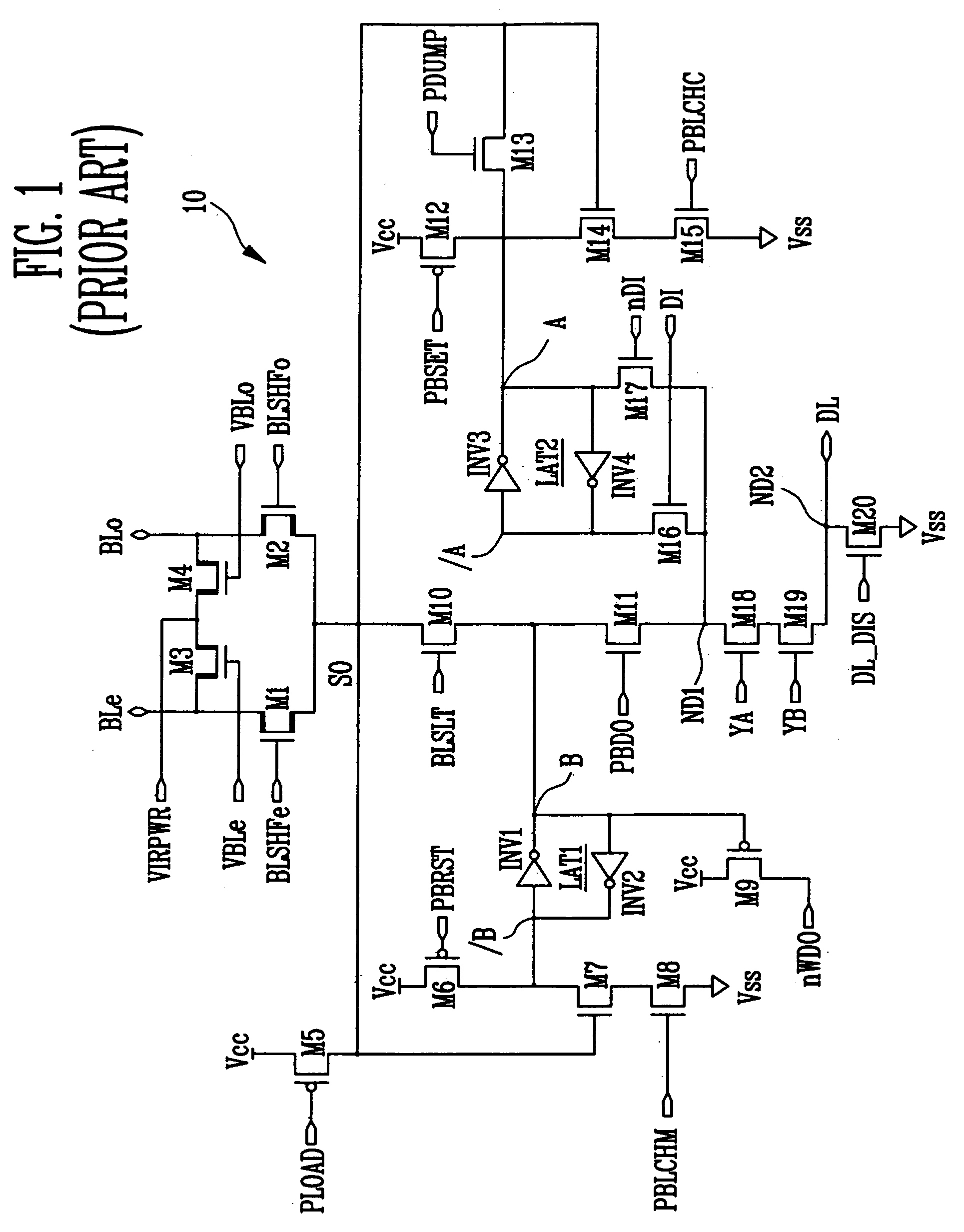
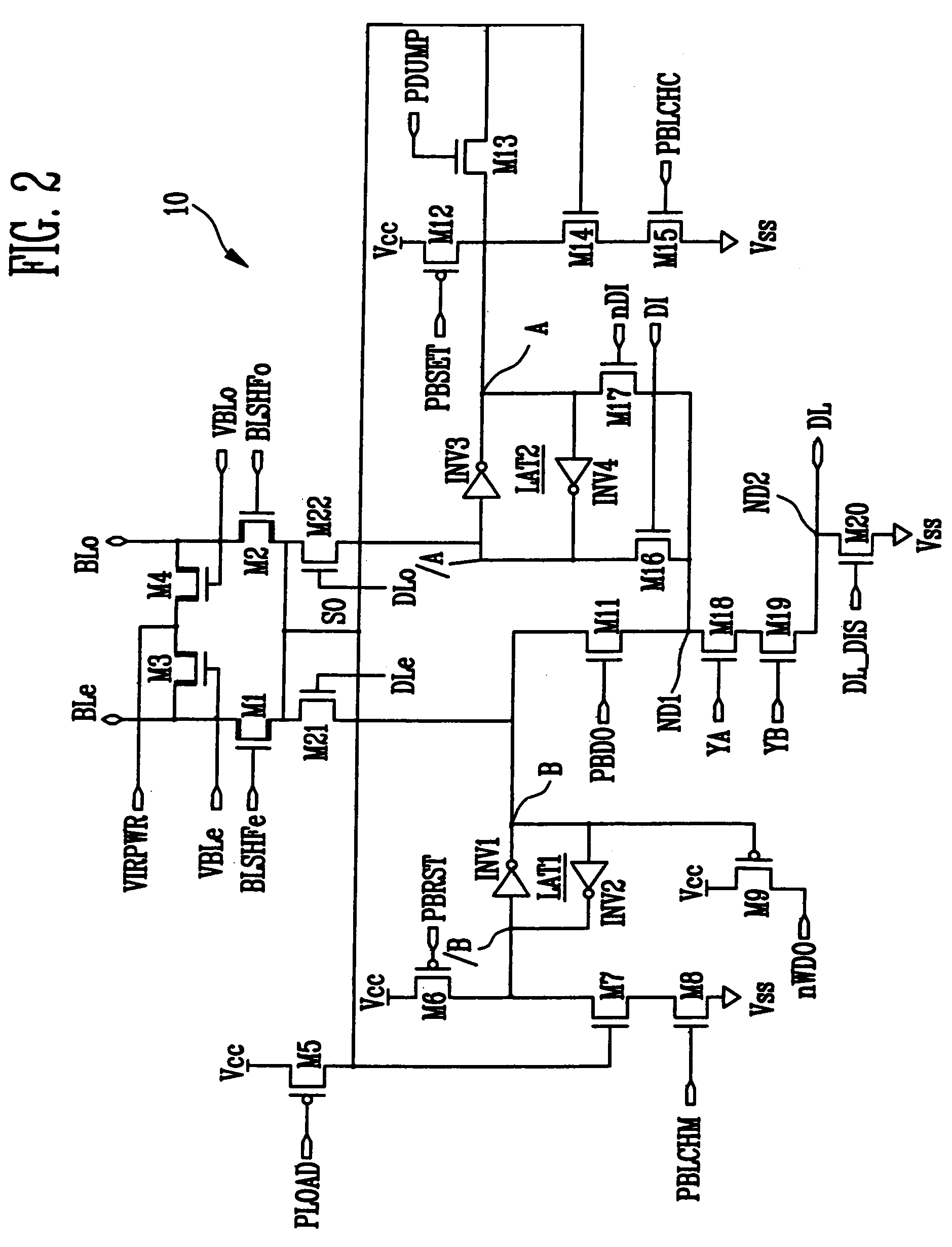
Disclosed are a page buffer of a flash memory device and data program method using the same. After two data are sequentially stored in a main register (first latch) and a cache register (second latch) provided in a page buffer, they are respectively transferred to an even bit line and an odd bit line at the same time, and a bias needed for a program is applied to cells connected to the even bit line and the odd bit line, respectively, whereby the program is performed at the same time. Therefore, the number and time of operations for data loading, program operation and program verification can be reduced by half and the operating speed of the device can be improved.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Page buffer for flash memory device
InactiveUS20050152188A1Solve the real problemRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingPage buffers
The disclosed is a page buffer of a flash memory device. In accordance with the present invention, a latch is controlled through a program verification signal, a latch signal, and latch data in a page buffer during a program verification. As a result, there are many advantages. First, in the event that the program verification is performed after programming once more, a passed cell is not sensed again and maintains its value. Second, it is possible to prevent a problem caused by a sensing operation as well as a verification error due to an external factor. As a result, program operation errors can be prevented.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Program verify method for otp memories
A method for executing a program verify operation in a non-volatile memory. A data register having master and slave latching circuits is used for concurrently storing two different words of data. In a program operation, the master latch stores program data which is used for programming selected memory cells. In a program verify operation, the data programmed to the memory cells are read out and stored in the slave latches. In each data register stage, the logic states of both latches are compared to each other, and a status signal corresponding to a program pass condition is generated if opposite logic states are stored in both latches. The master latch in each stage is inverted if programming was successful, in order to prevent re-programming of that bit of data.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Program verifying system, program verifying method, and storage medium for storing software of program verifying method
InactiveUS6772410B1Accurate acquisitionEasy to useError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram provingData type
A storage area managing system using a system for virtually executing a program code before really executing the program code, the storage area managing system, that comprises virtual executing means for verifying only a data type restriction of the program code before really executing the program code, data valid range deciding means for deciding the final use position of each data and storing it during the process of said virtual executing means, and storage area unallocating means for unallocating a storage area for data that exceeds the data valid range corresponding to the data validity range information designated by said data valid range deciding means during the real execution of the program code.
Owner:NEC CORP
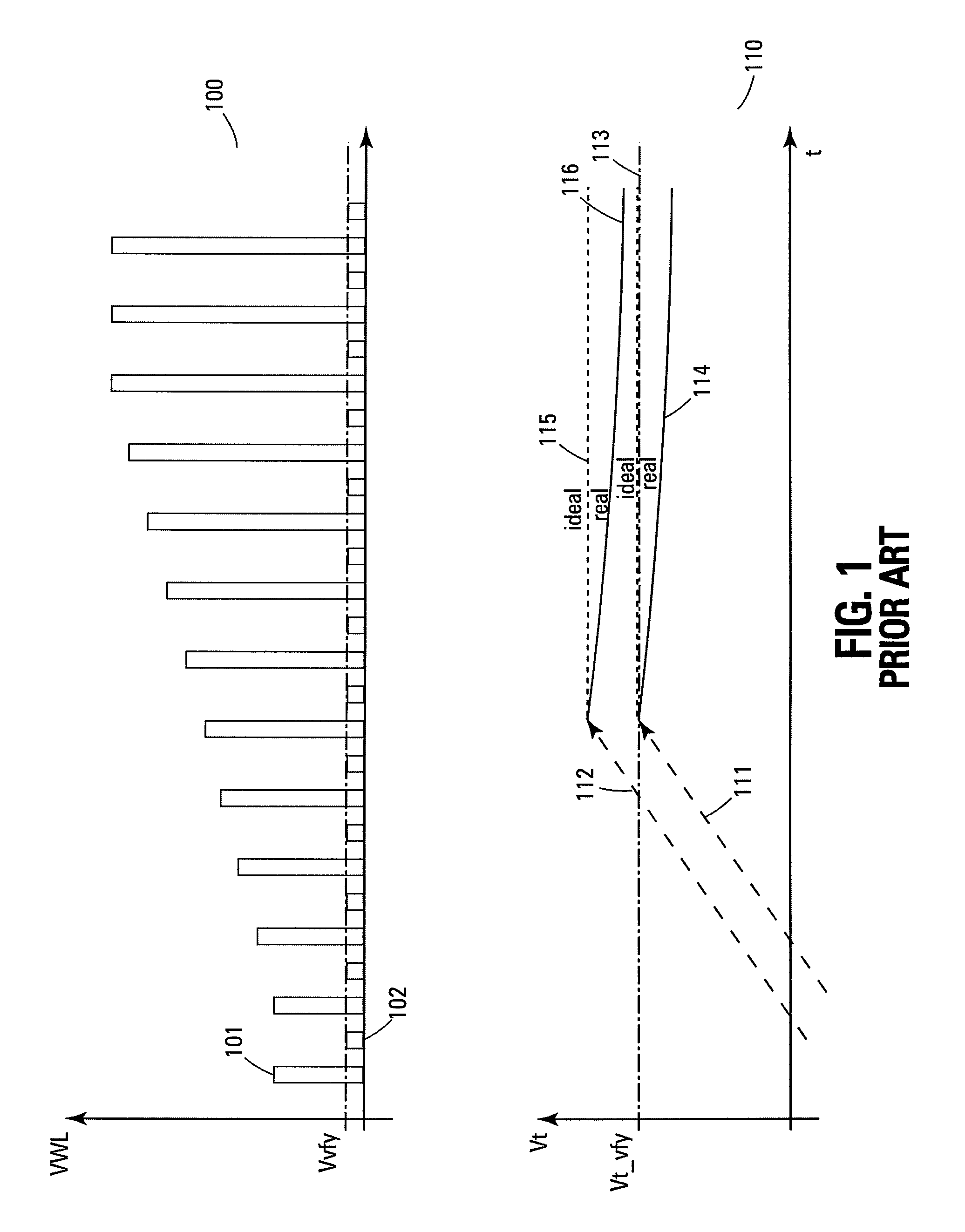
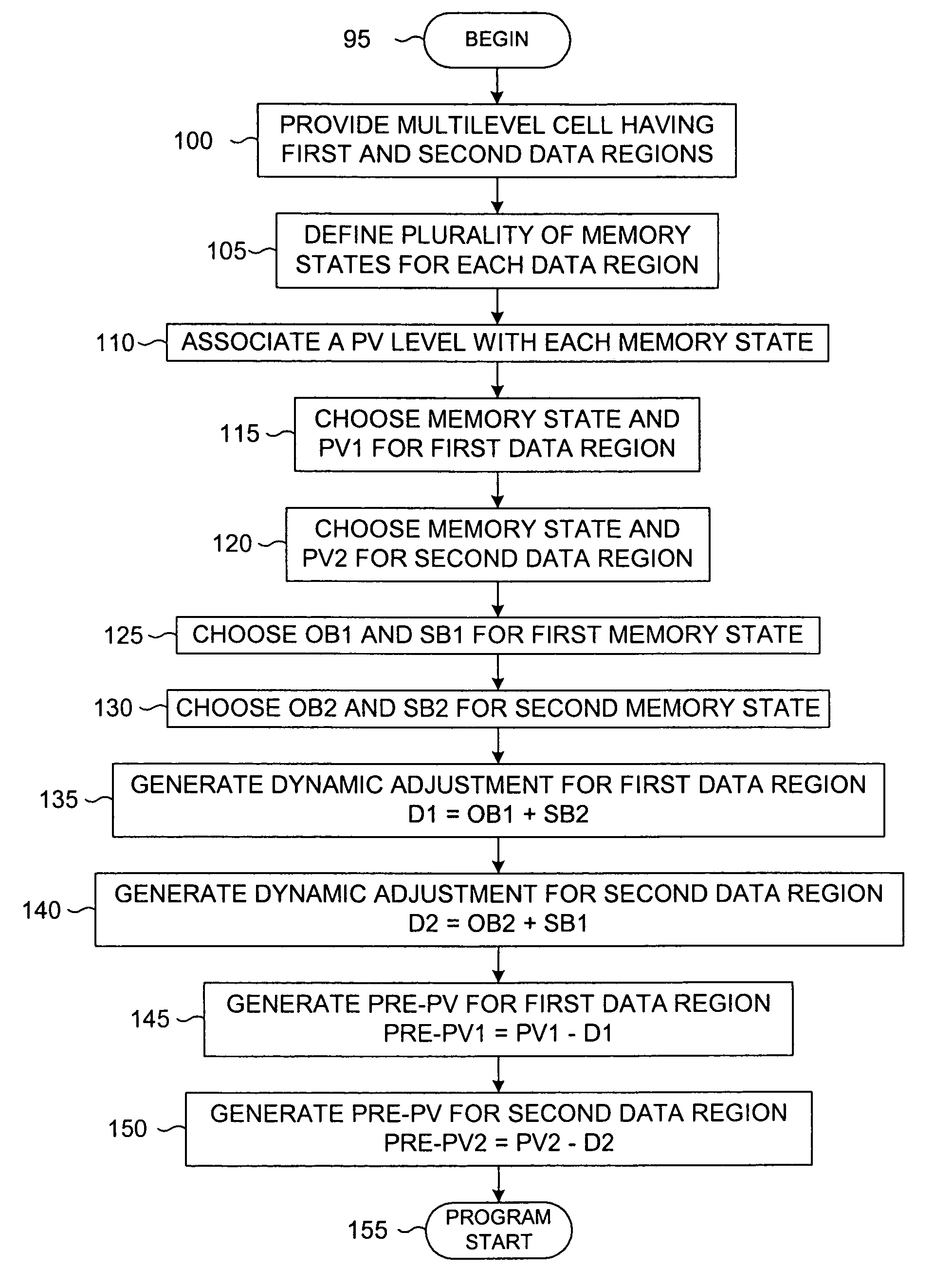
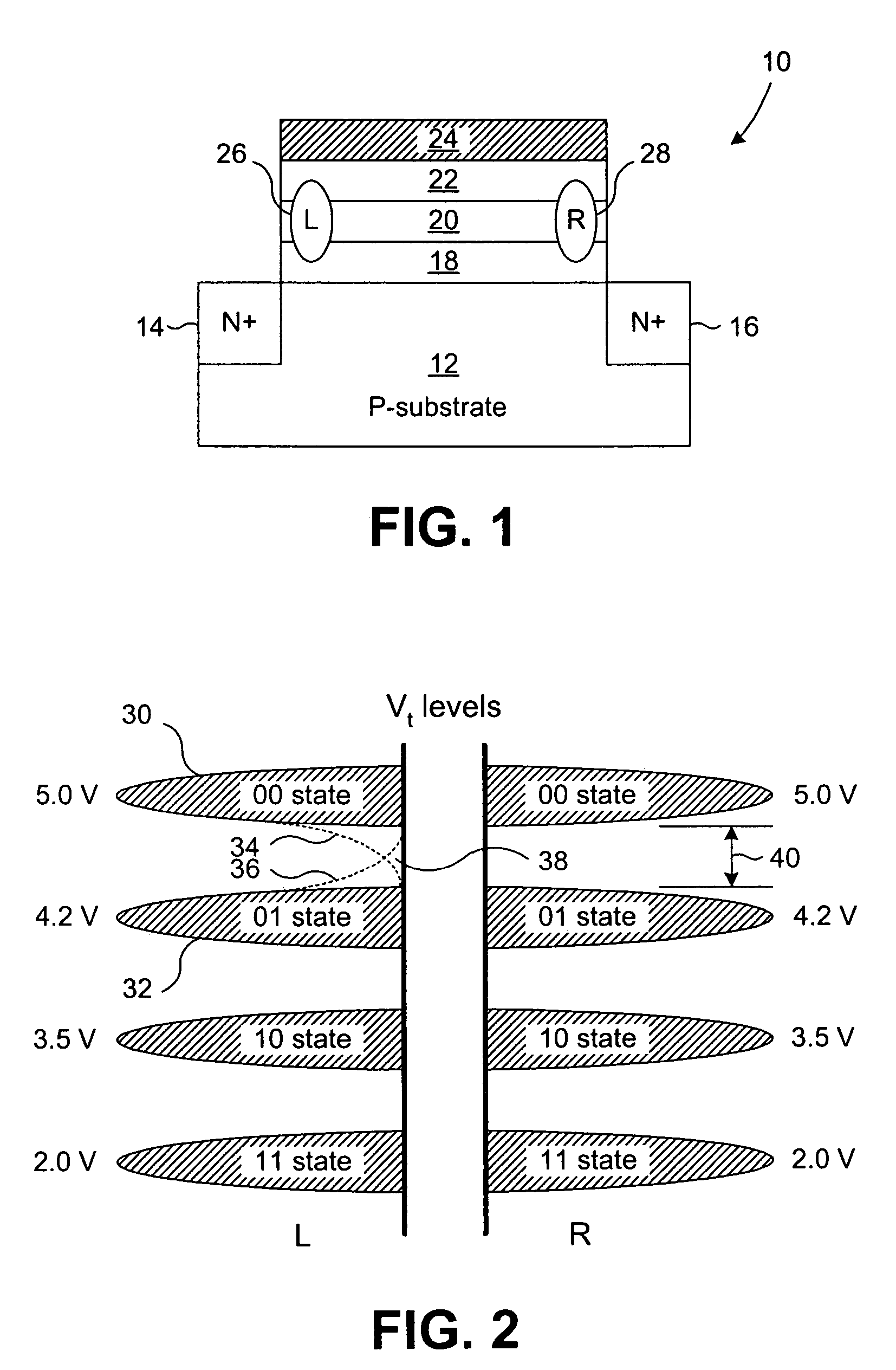
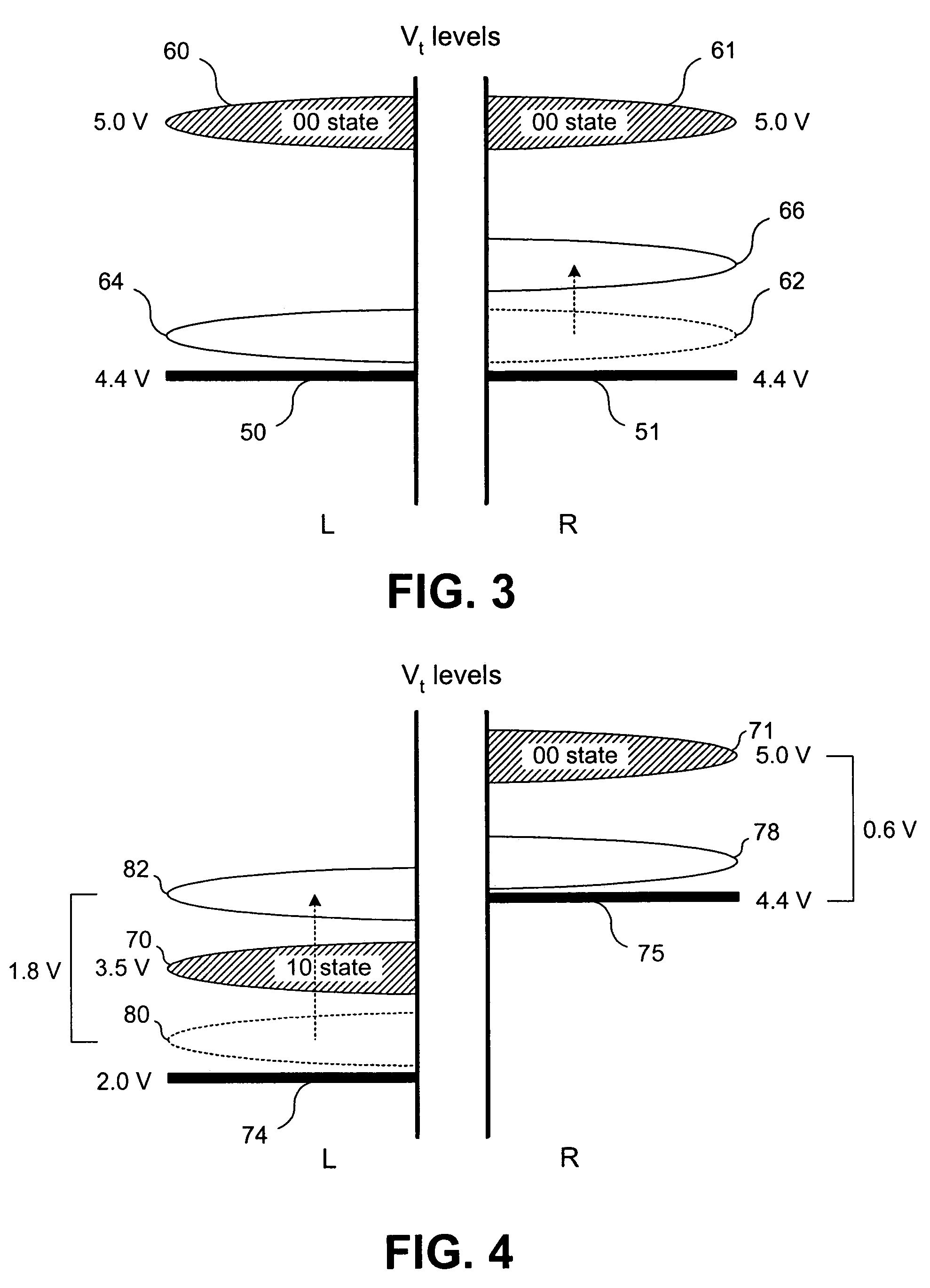
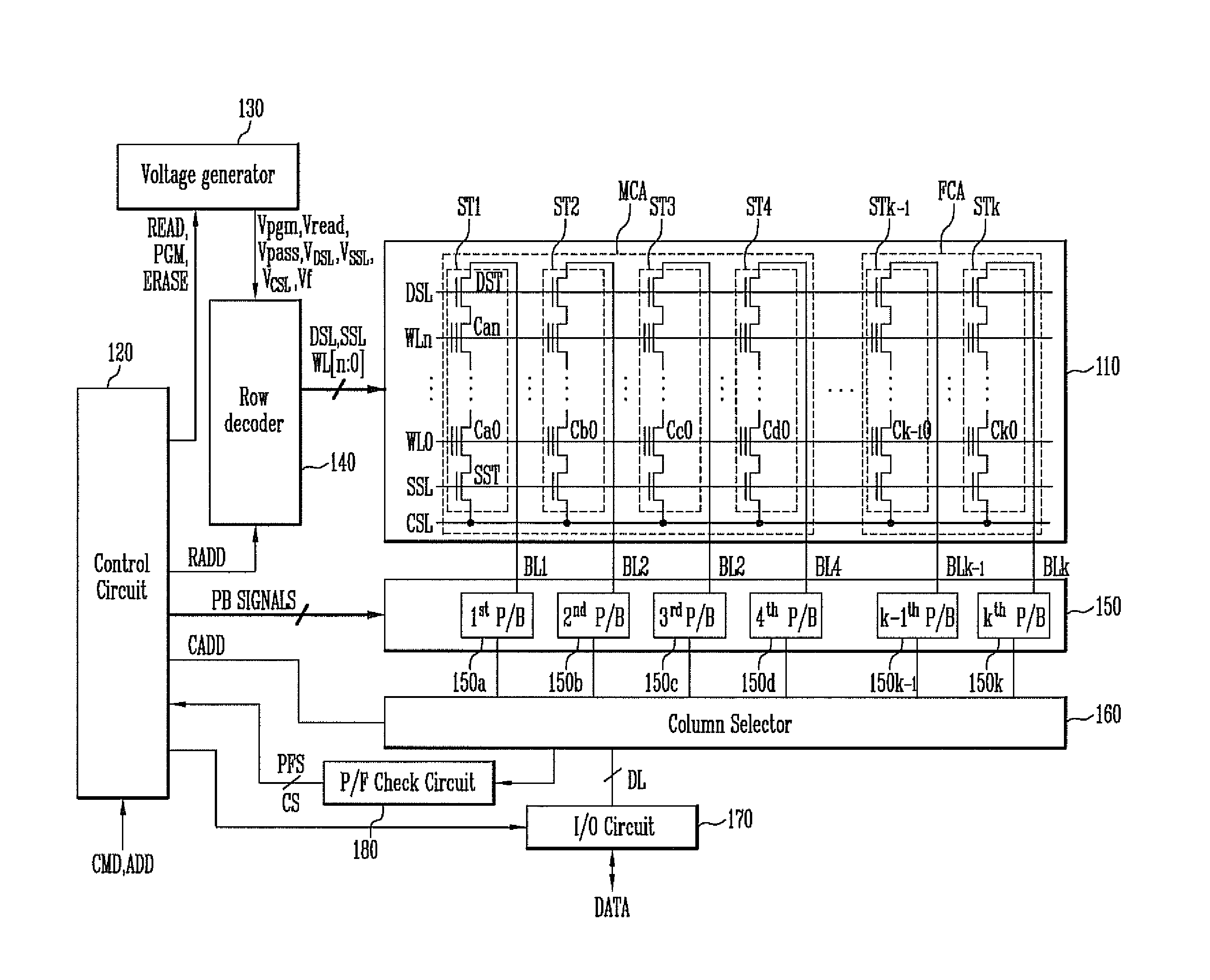
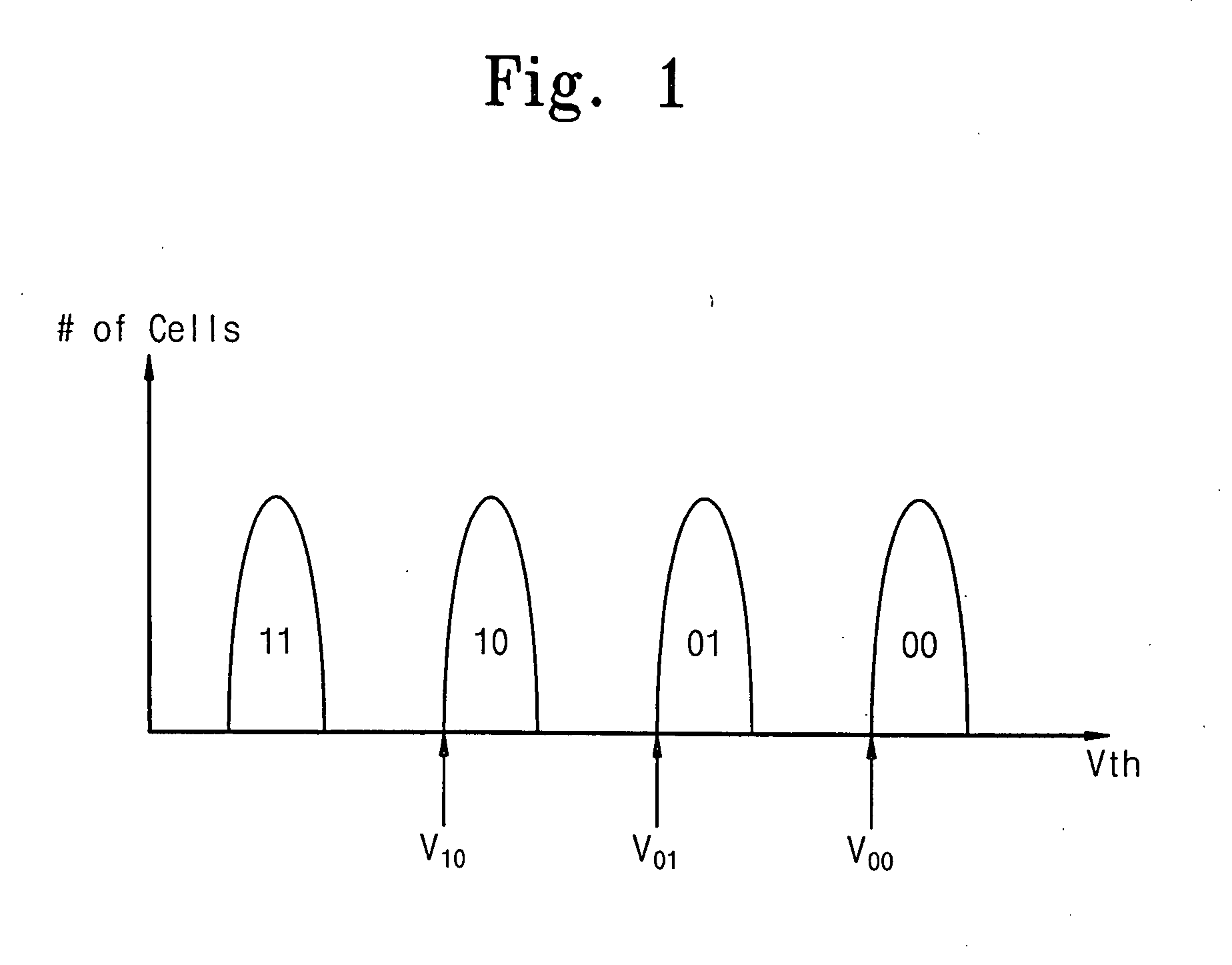
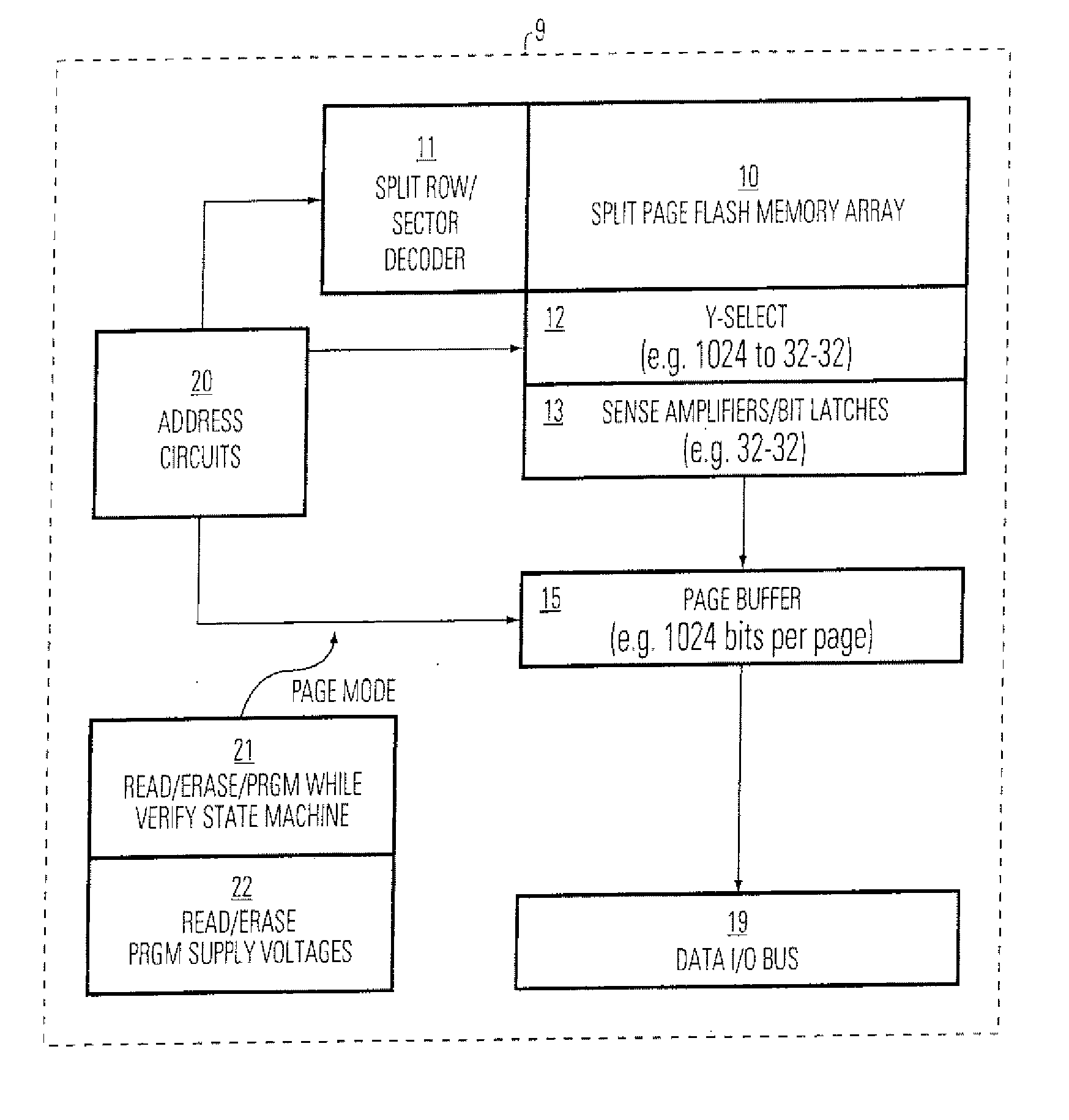
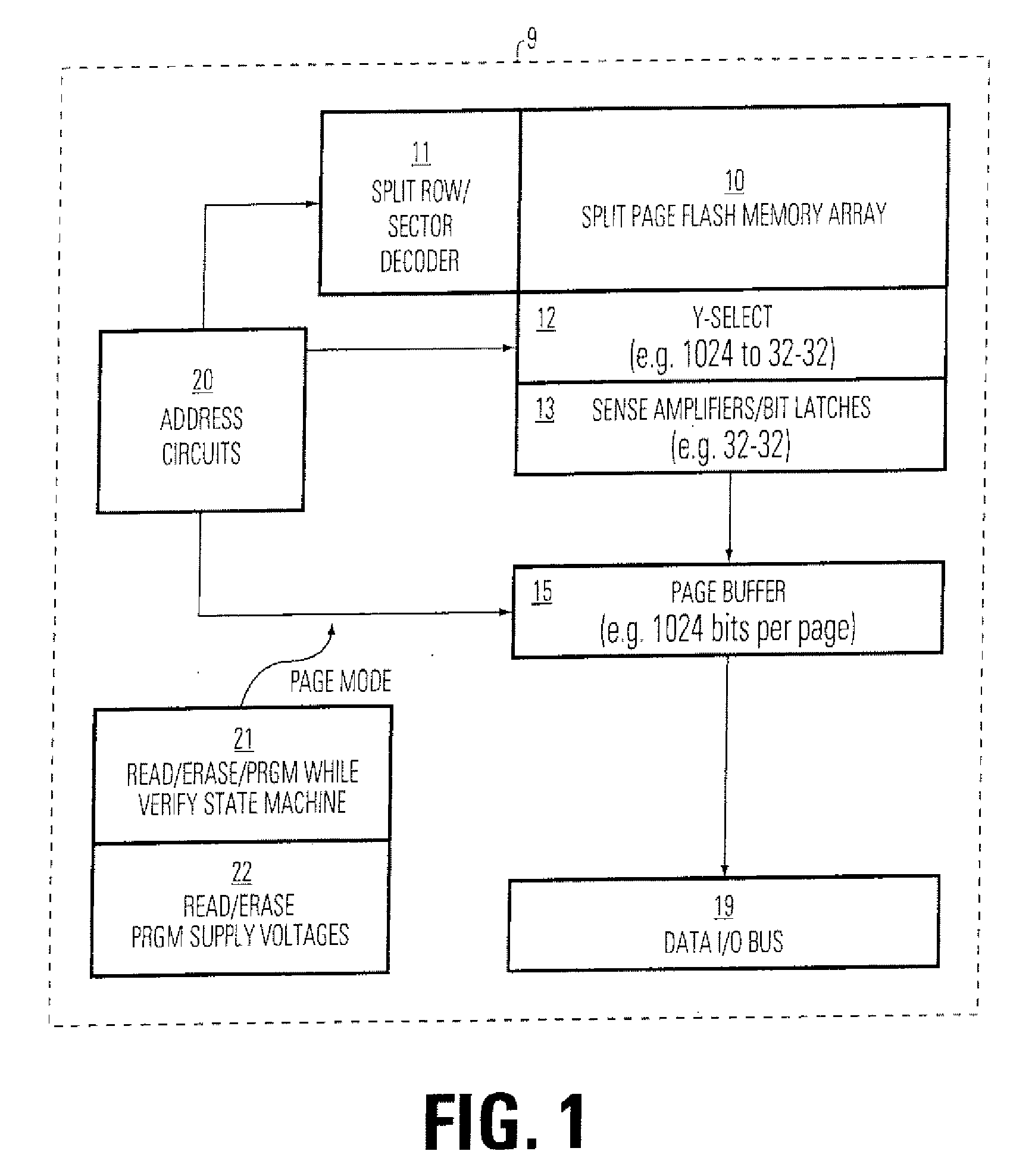
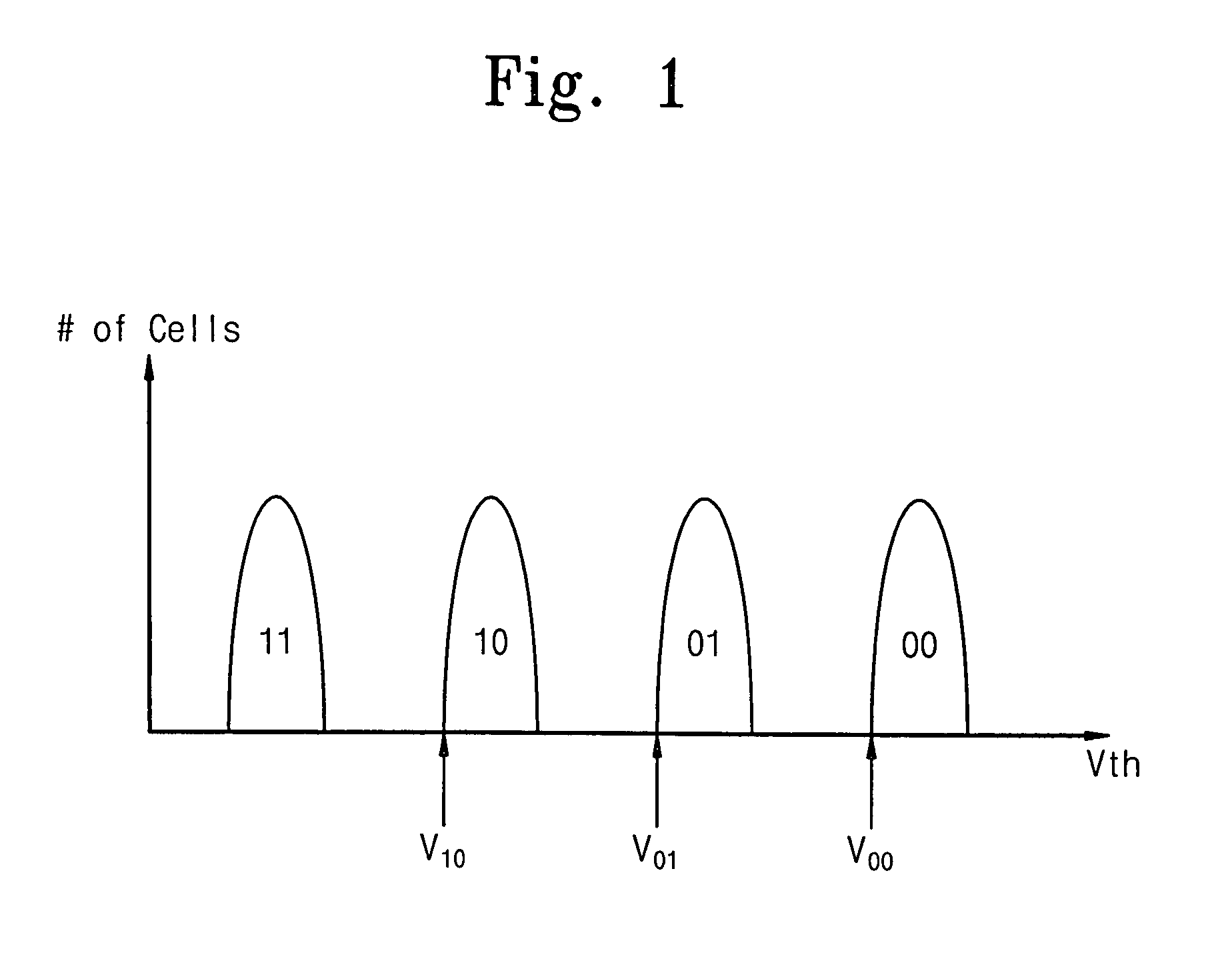
Method of dynamically controlling program verify levels in multilevel memory cells
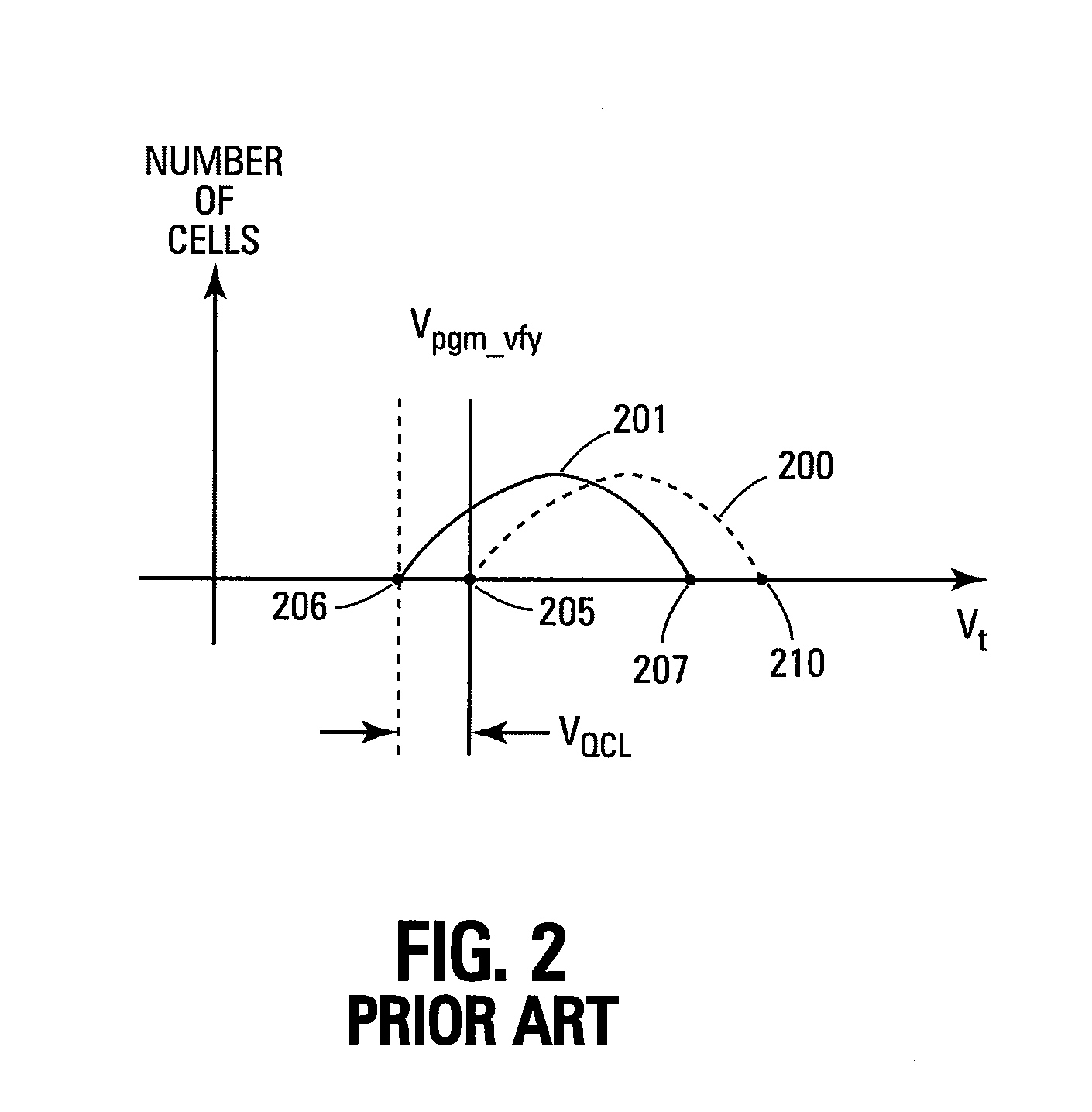
Pre-program verify levels for a multilevel read-only memory cell are generated dynamically. A determination takes into account a program verify level, an over-program budget, and a second-bit effect budget to generate pre-program verify levels. The generated pre-program verify levels mitigate issues of over-programming, hard-to-program, and second-bit effect.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Method of programming nonvolatile memory device
ActiveUS20100329021A1Improve reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingError checking
A method of programming a nonvolatile memory device includes inputting program data to page buffers; performing a program operation and a program verification operation until threshold voltages of memory cells included in a selected page reach a target level according to the program data; when the threshold voltages of the memory cells reach the target level, performing an over-program verification operation to determine over-programmed memory cells in the memory cells; and making a determination of whether error checking and correction (ECC) processing for the over-programmed memory cells is feasible.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
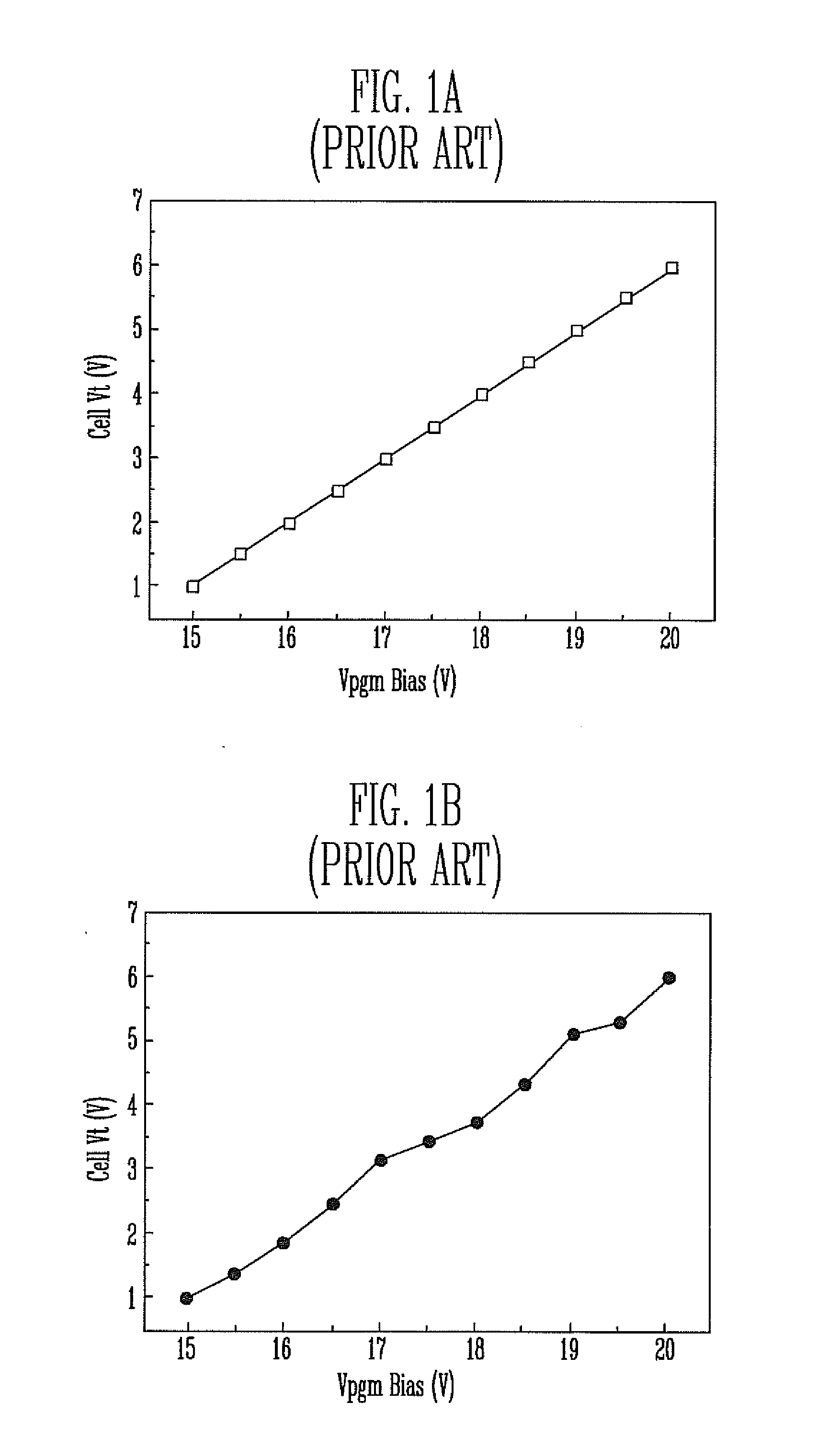
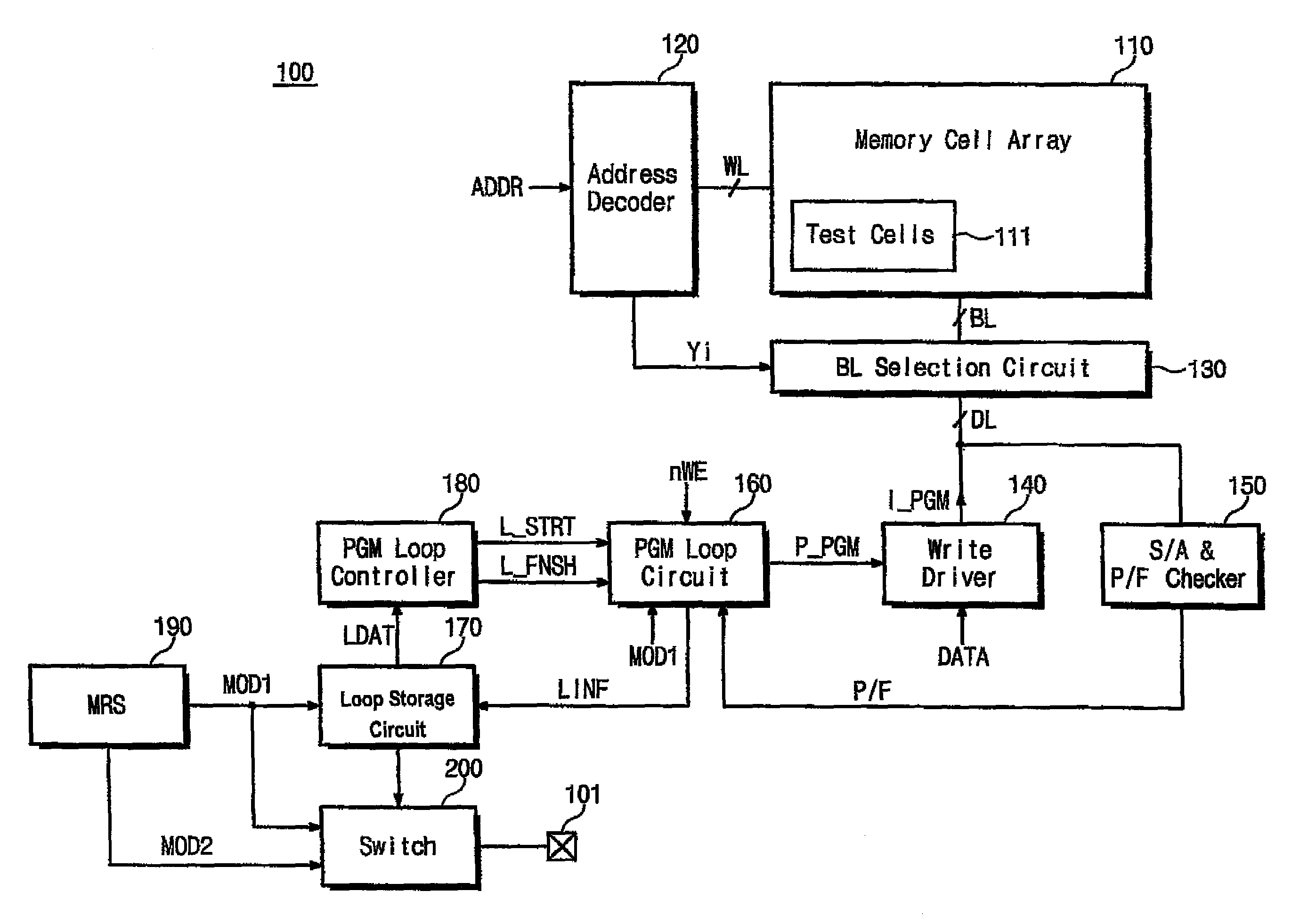
Phase-change random access memory (PRAM) performing program loop operation and method of programming the same
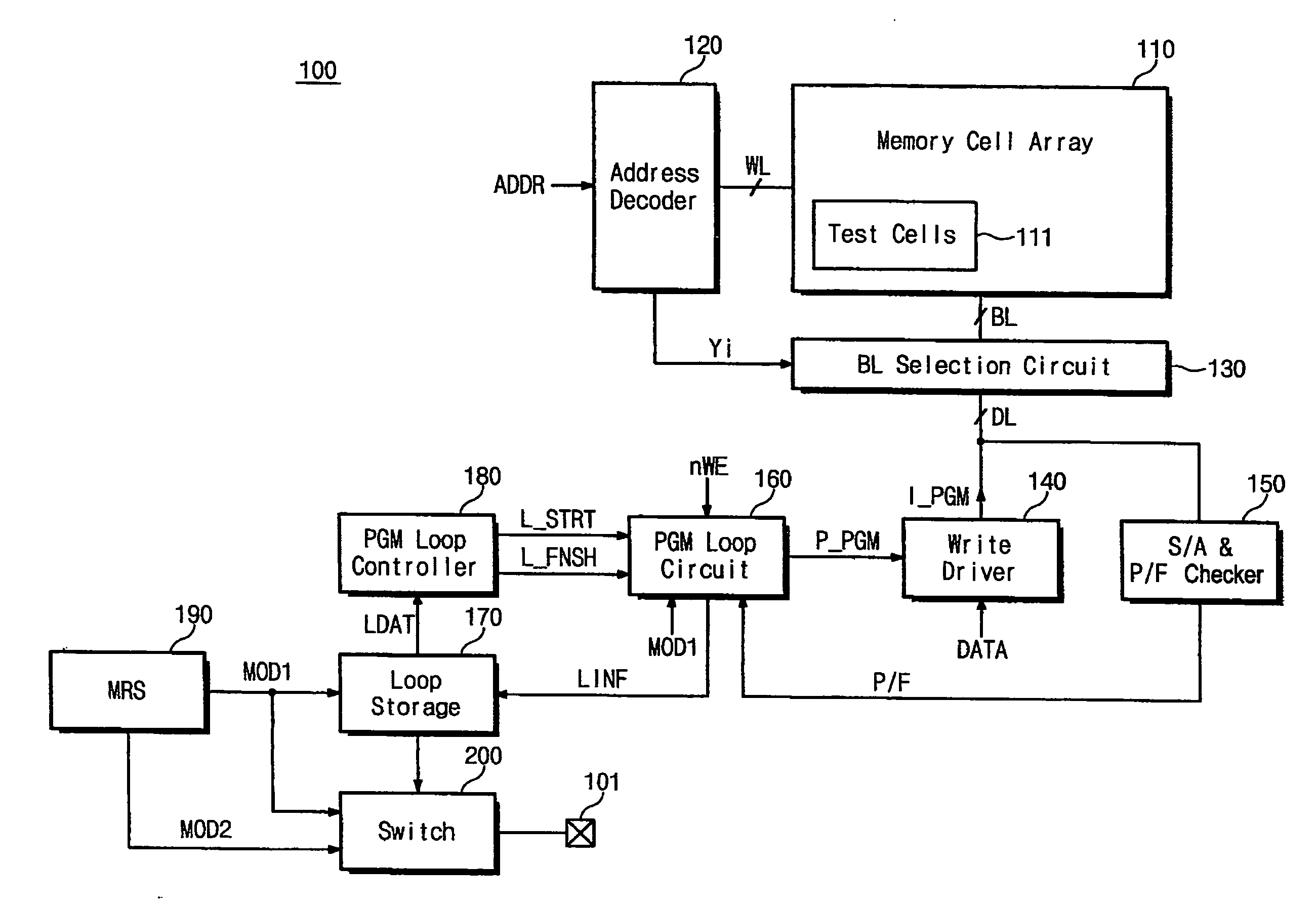
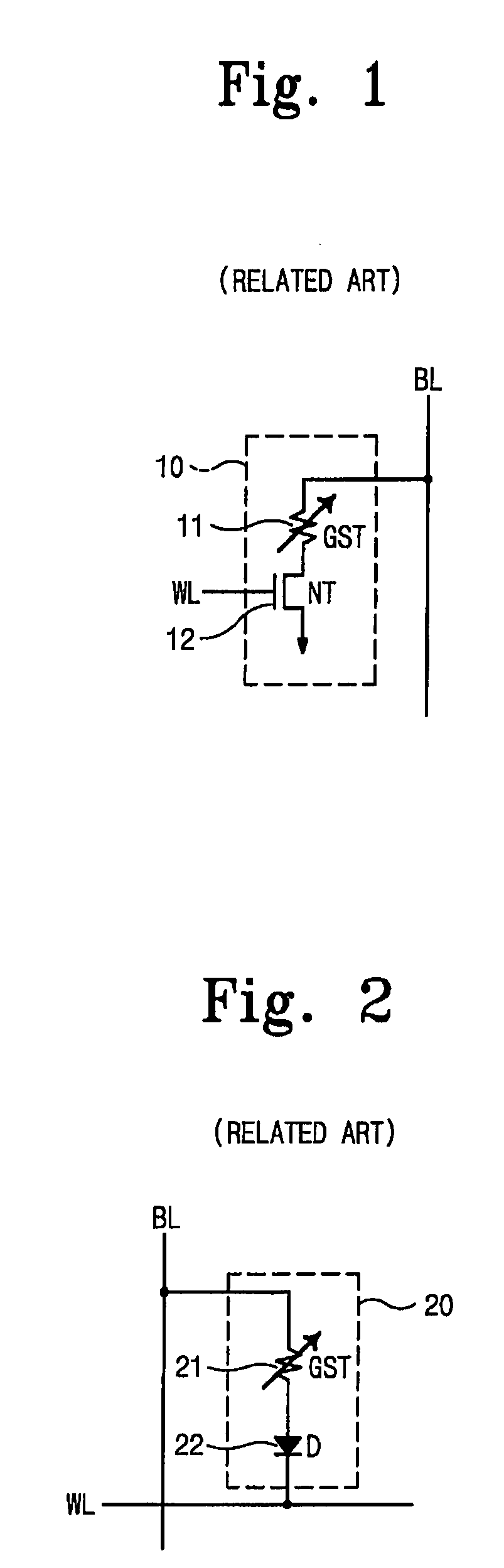
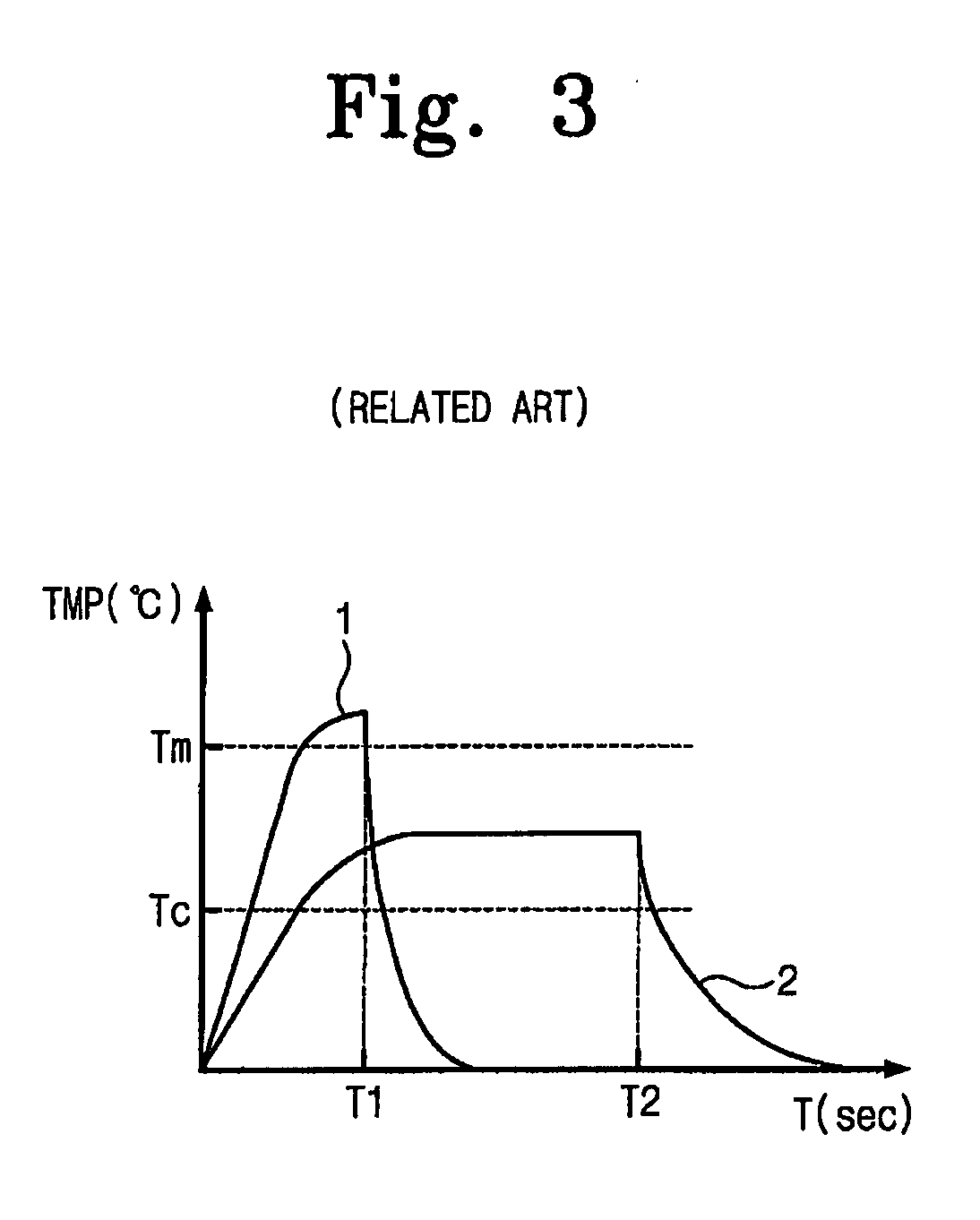
ActiveUS7573758B2Shorten programming timeTotal current dropRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingLoop control
A PRAM and programming method are disclosed. The PRAM includes a memory cell array including a test cell, a write driver applying a program pulse and providing a program current to the memory cell array, a sense amplification and verification circuit reading data programmed in the memory cell array and performing a program verify operation on the data, and a program loop control unit storing program verification result for the test cell at each program loop during test operation and generating the program pulse according to the program verification result to control the start of the program loop during normal operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flash memory device and program verification method thereof
ActiveUS7099196B2Avoid misjudgmentEvenly distributedRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage generatorProgram proving
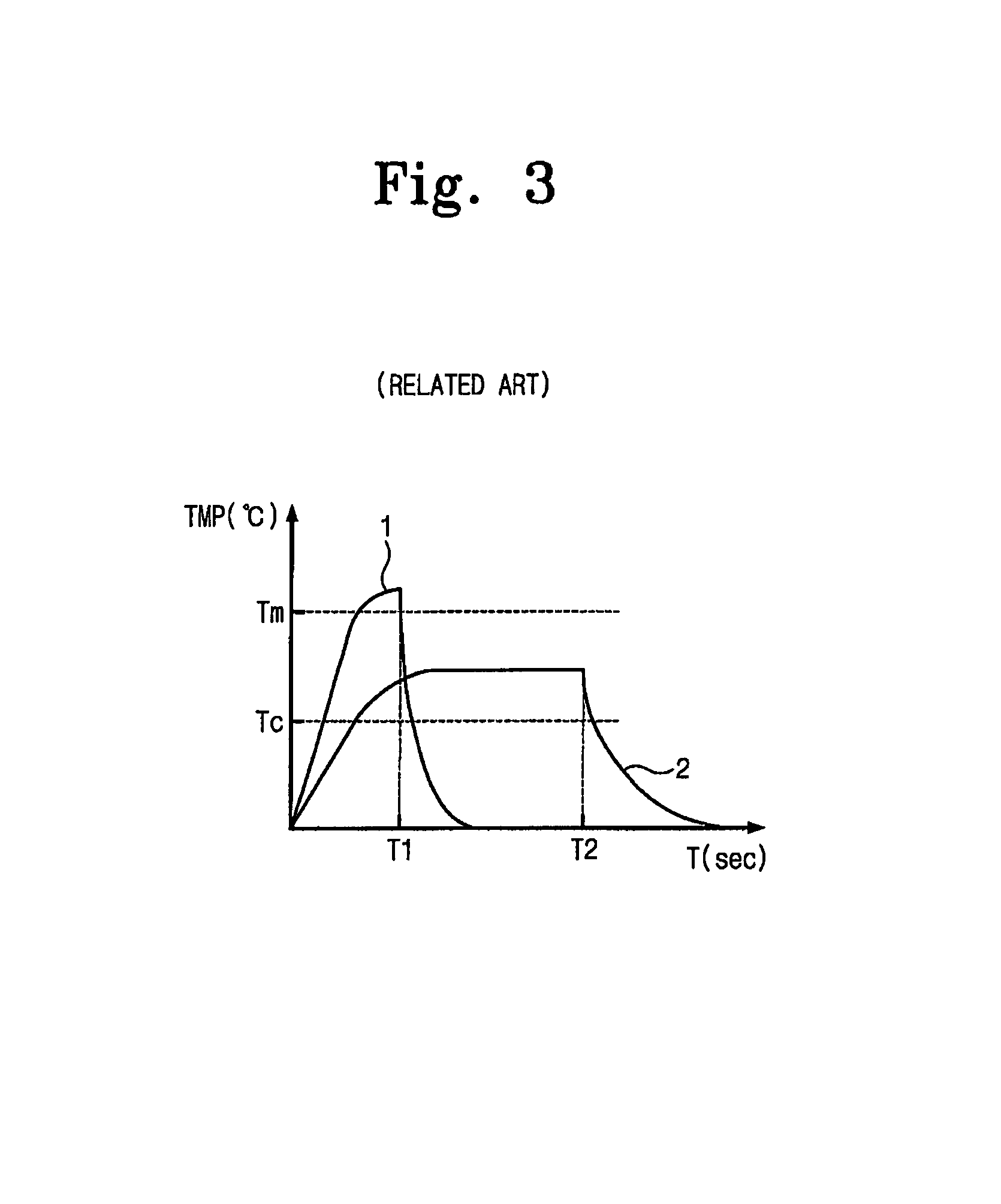
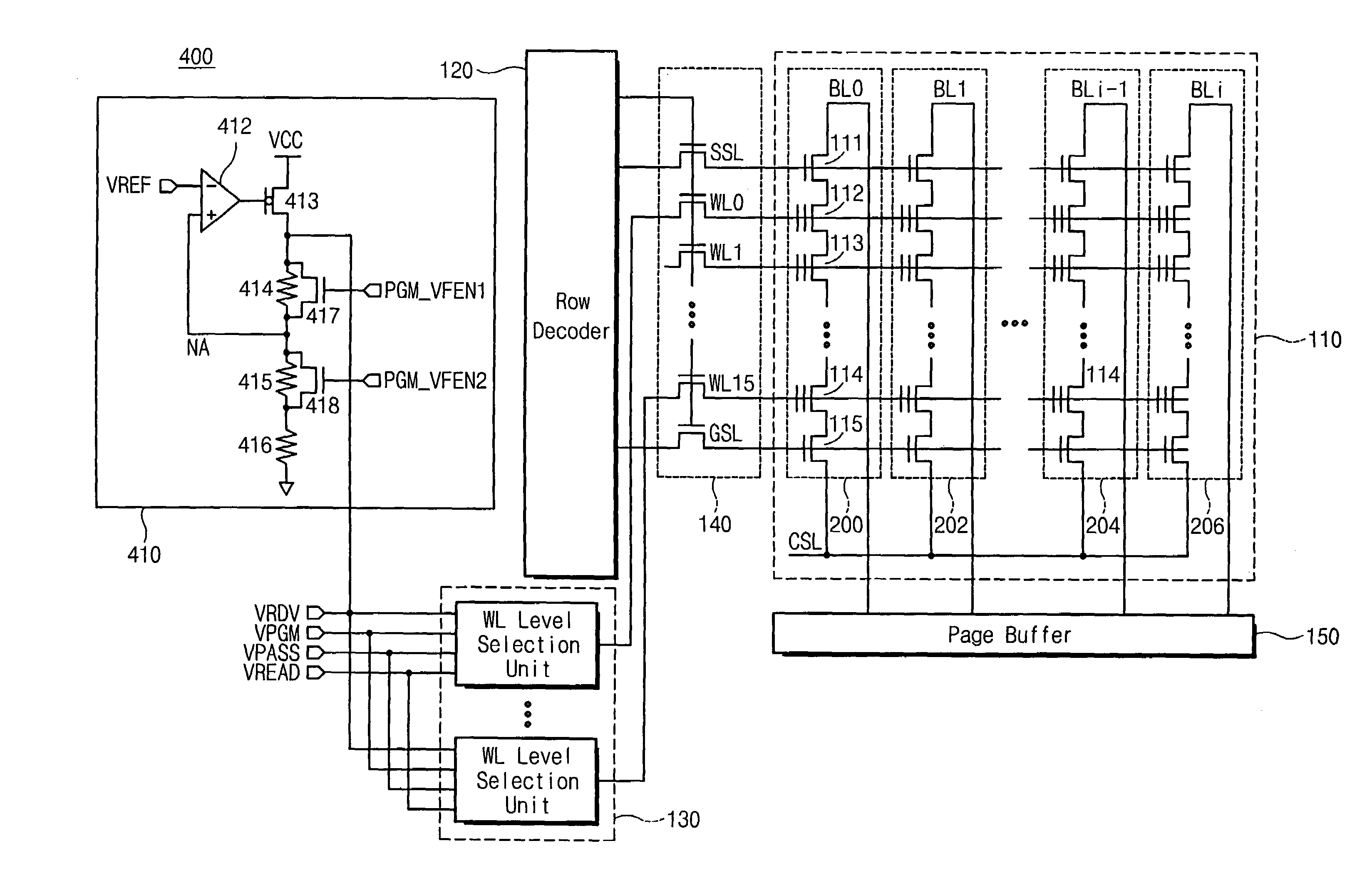
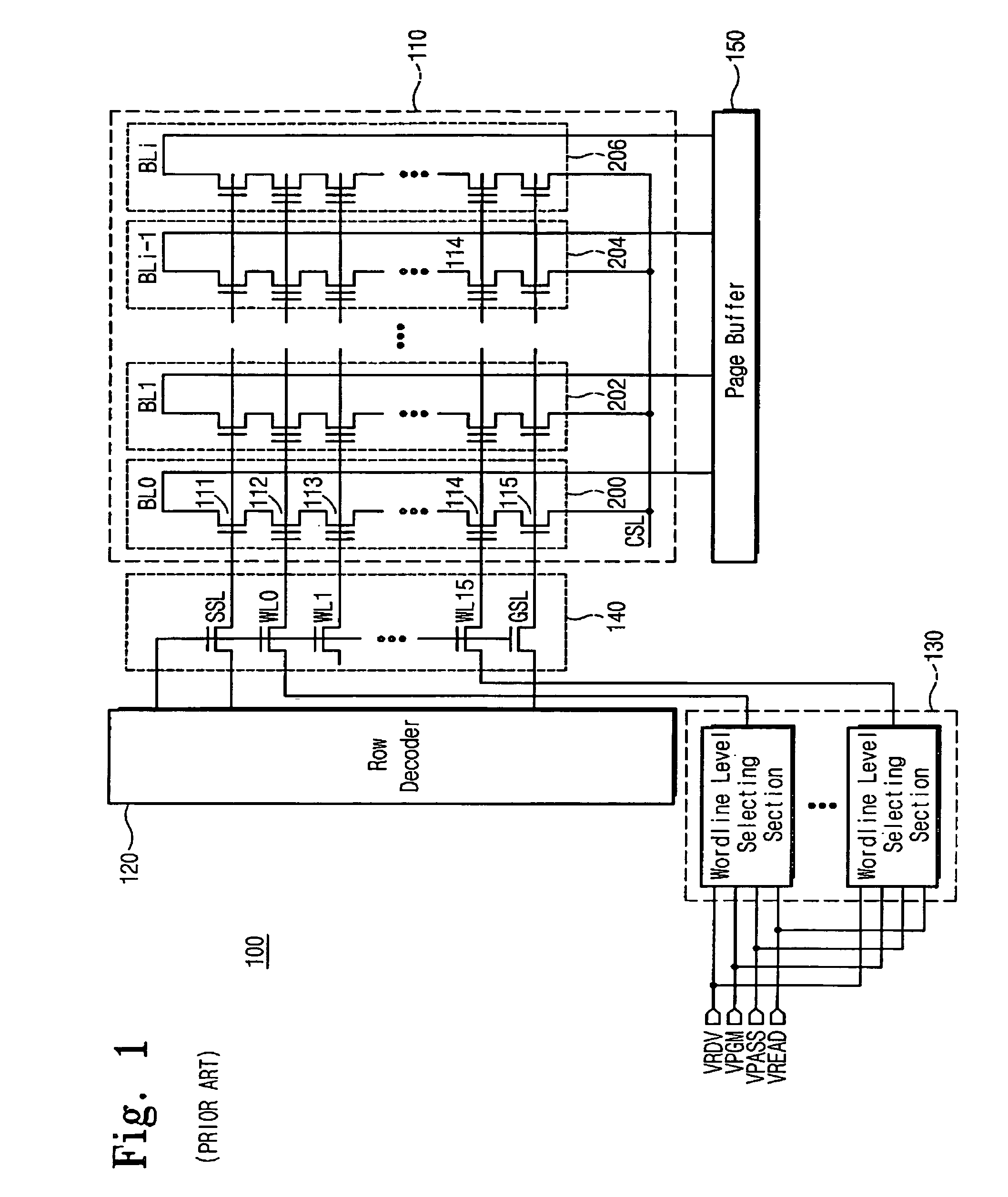
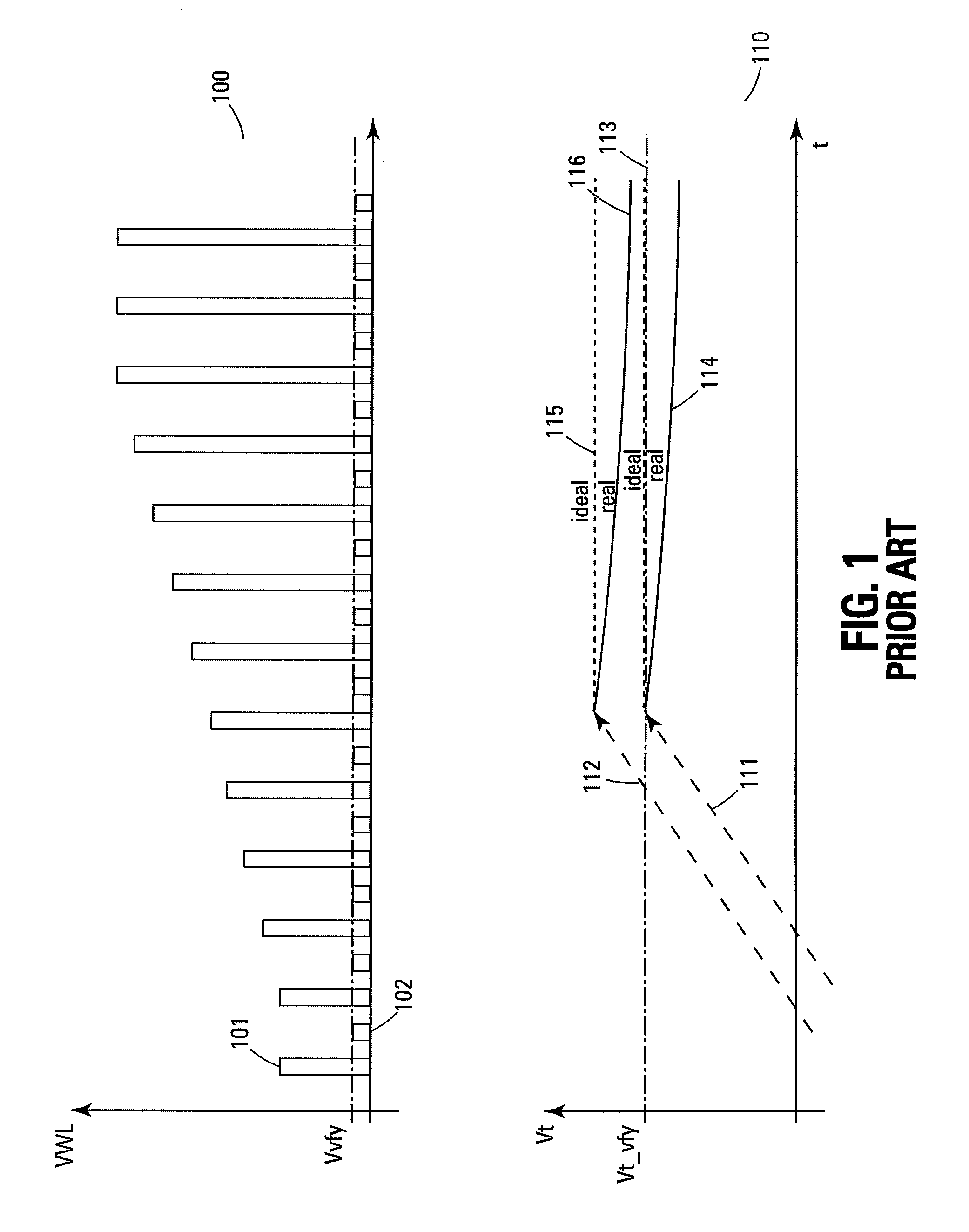
Disclosed is a flash memory device and a program verification method thereof which can prevent a misjudgment as to whether flash memory cells are programmed or not. The flash memory device includes: a program verification voltage generator for variably generating program verification voltages used to verify whether the flash memory cells are programmed or not and a word line level selector for transferring the program verification voltages to word lines connected to control gates of the flash memory cells. The flash memory cells that are verified as uncertain as to whether the flash memory cells are programmed or not can be completely programmed since the program verification operation is carried out with program verification voltage levels that are changed according to the selective activations of the program verification control signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
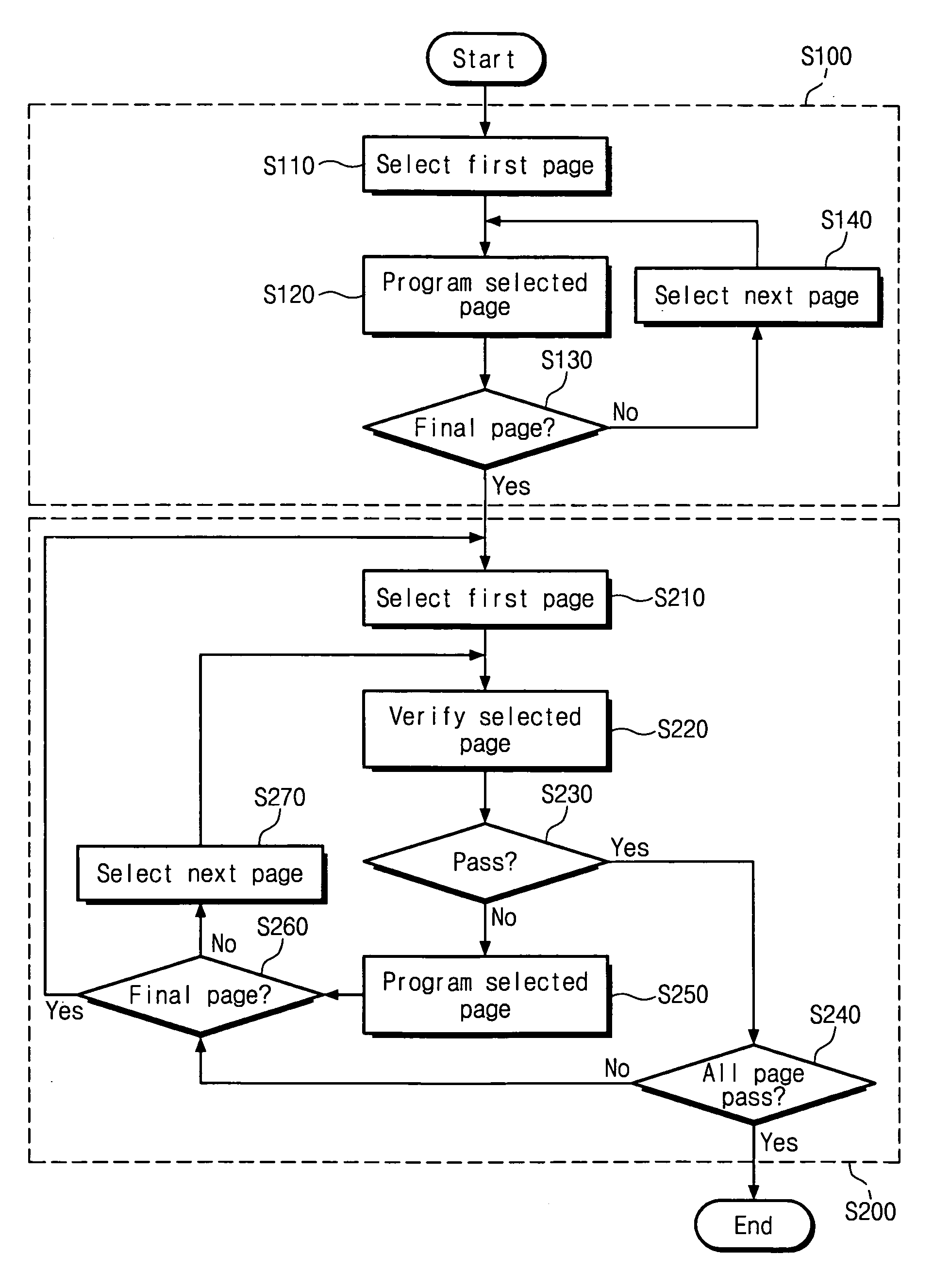
Program and program verify operations for flash memory
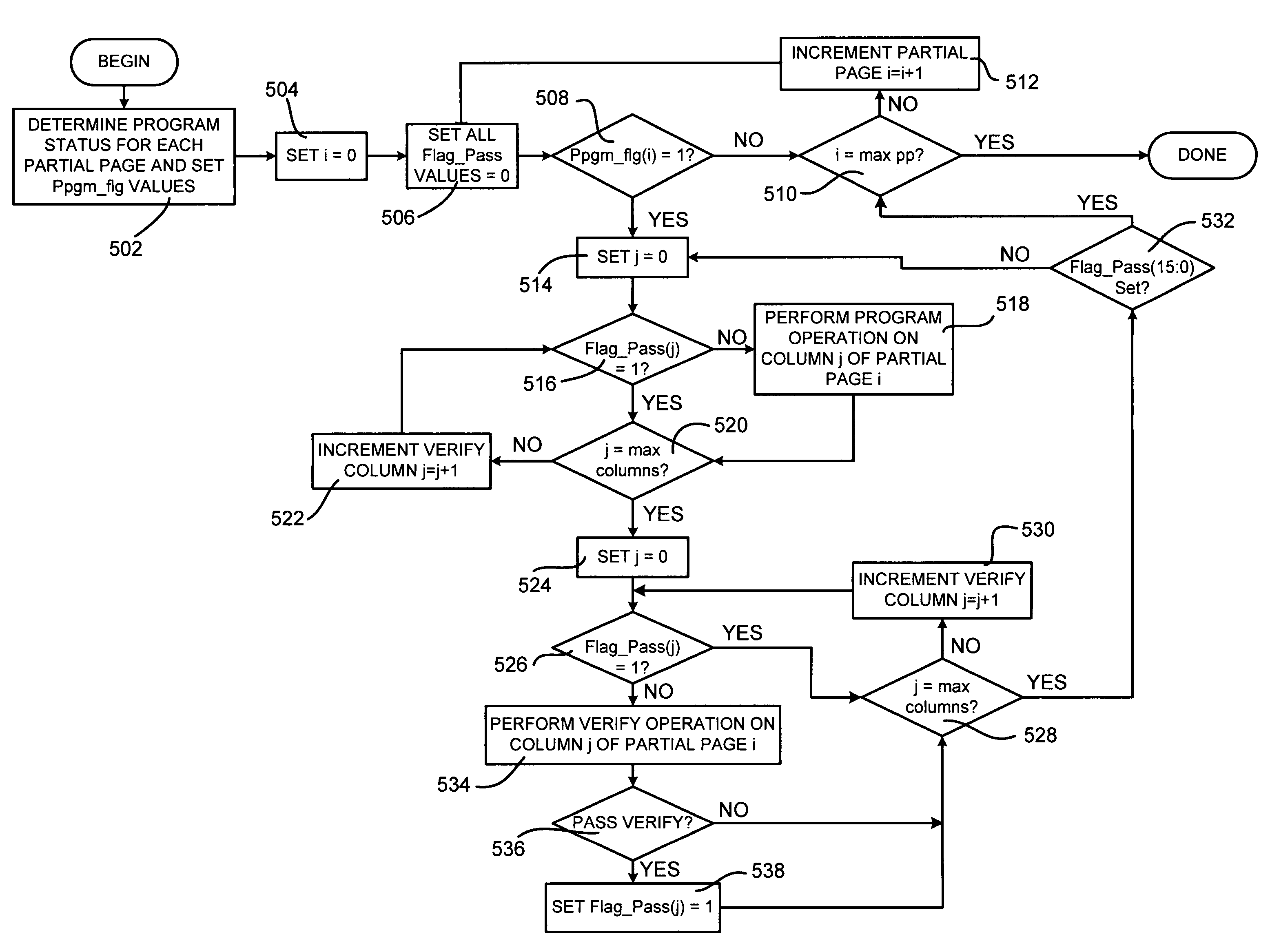
A method for programming a nonvolatile memory array including an array of memory cells, each memory cell including a substrate, a control gate, a charge storage element, a source region and a drain region, includes performing a program operation on a group of memory cells, where the group of memory cells includes a plurality of subgroups. A verify status value is stored for each subgroup, the verify status value indicating a verify status of each subgroup, wherein the verify status value indicates whether an associated subgroup has been program verified. A program verify operation is performed on a selected subgroup when the verify status value associated with the selected subgroup indicates that the selected verify subgroup has not been program verified.
Owner:VALLEY DEVICE MANAGEMENT
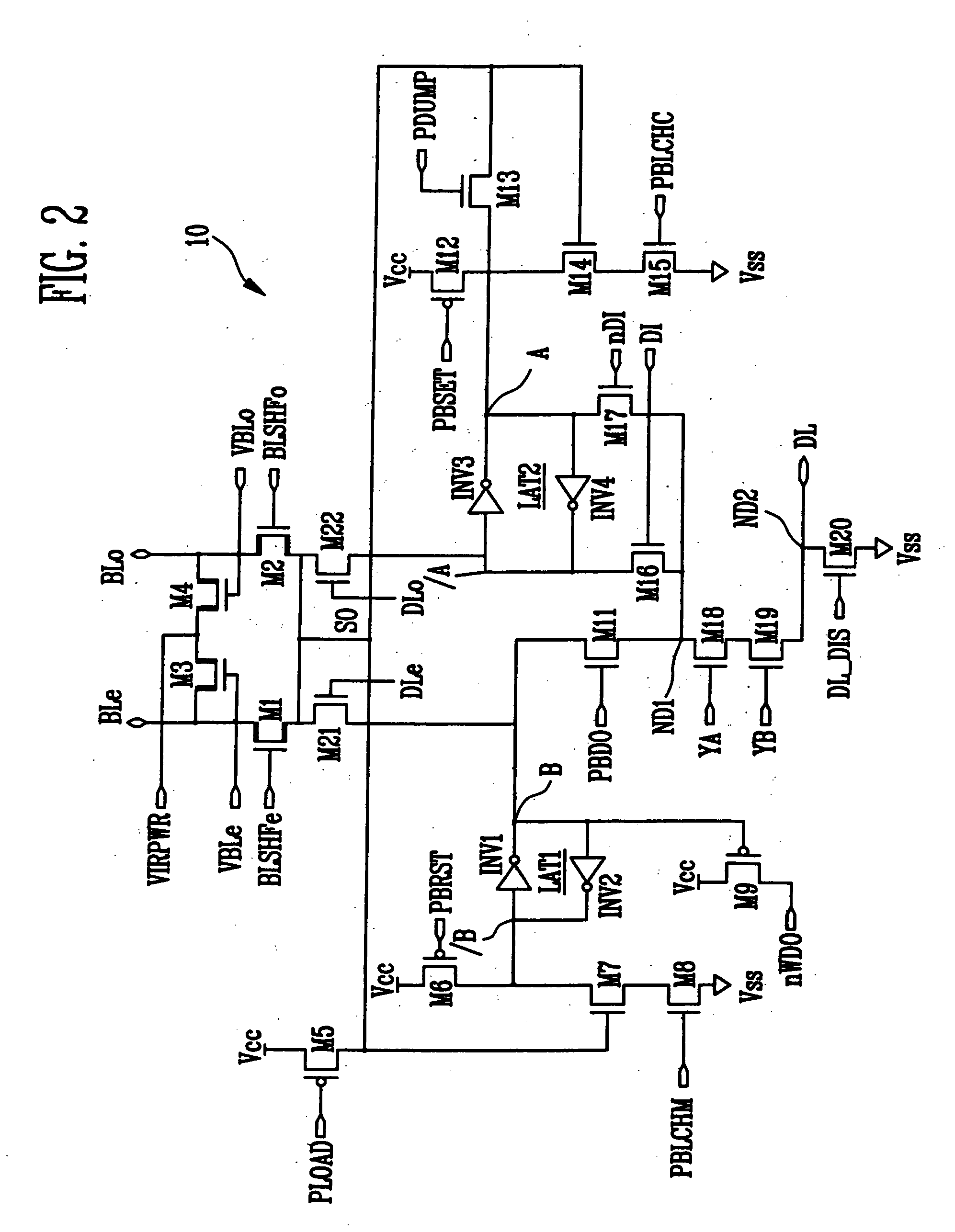
Page buffer of flash memory device and data program method using the same
ActiveUS20050265078A1Increase speedHigh speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingBit plane
Disclosed are a page buffer of a flash memory device and data program method using the same. After two data are sequentially stored in a main register (first latch) and a cache register (second latch) provided in a page buffer, they are respectively transferred to an even bit line and an odd bit line at the same time, and a bias needed for a program is applied to cells connected to the even bit line and the odd bit line, respectively, whereby the program is performed at the same time. Therefore, the number and time of operations for data loading, program operation and program verification can be reduced by half and the operating speed of the device can be improved.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Semiconductor memory device and related programming method
A NOR flash memory device and related programming method are disclosed. The programming method includes programming data in a memory cell and, during a program verification operation, controlling the supply of current from a sense amplifier to the memory cell in relation to the value of the programmed data. Wherein a program verification operation is indicated, current is provided from the sense amplifier to the memory cell. Where a program verification operation is not indicated, current is cut off from the sense amplifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory with program while program verify
ActiveUS20070070704A1Save a lot of timeIncrease speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingOperating system
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Pram performing program loop operation and method of programming the same
ActiveUS20080068903A1Shorten programming timeImprove programming speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgram provingLoop control
A PRAM and programming method are disclosed. The PRAM includes a memory cell array including a test cell, a write driver applying a program pulse and providing a program current to the memory cell array, a sense amplification and verification circuit reading data programmed in the memory cell array and performing a program verify operation on the data, and a program loop control unit storing program verification result for the test cell at each program loop during test operation and generating the program pulse according to the program verification result to control the start of the program loop during normal operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reachability analysis for program verification
InactiveUS7926039B2High precisionSimplified representationSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsStatic timing analysisProgram proving
An improved method for automatically improving the precision of an extrapolation operator used, for example, in software program verification in connection with the static analysis and model checking of the software programs which rely on fix-point computation. In particular, a new extrapolation-with-care-set operator, together with a method for gradually increasing the precision of this operation by tightening the care set.
Owner:NEC CORP
Mitigation of runaway programming of a memory device
Methods for mitigating runaway programming in a memory device, methods for program verifying a memory device, a memory device, and a memory system are provided. In one such method, a ramp voltage signal is generated by a digital count signal. A memory cell being program verified is turned on by a particular verify voltage of the ramp voltage signal in response to a digital count of the digital count signal. The memory cell turning on generates a bit line indication that causes the digital count to be compared to a representation of the target data to be programmed in the memory cell. The comparator circuit generates an indication when the digital count is greater than or equal to the target data.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
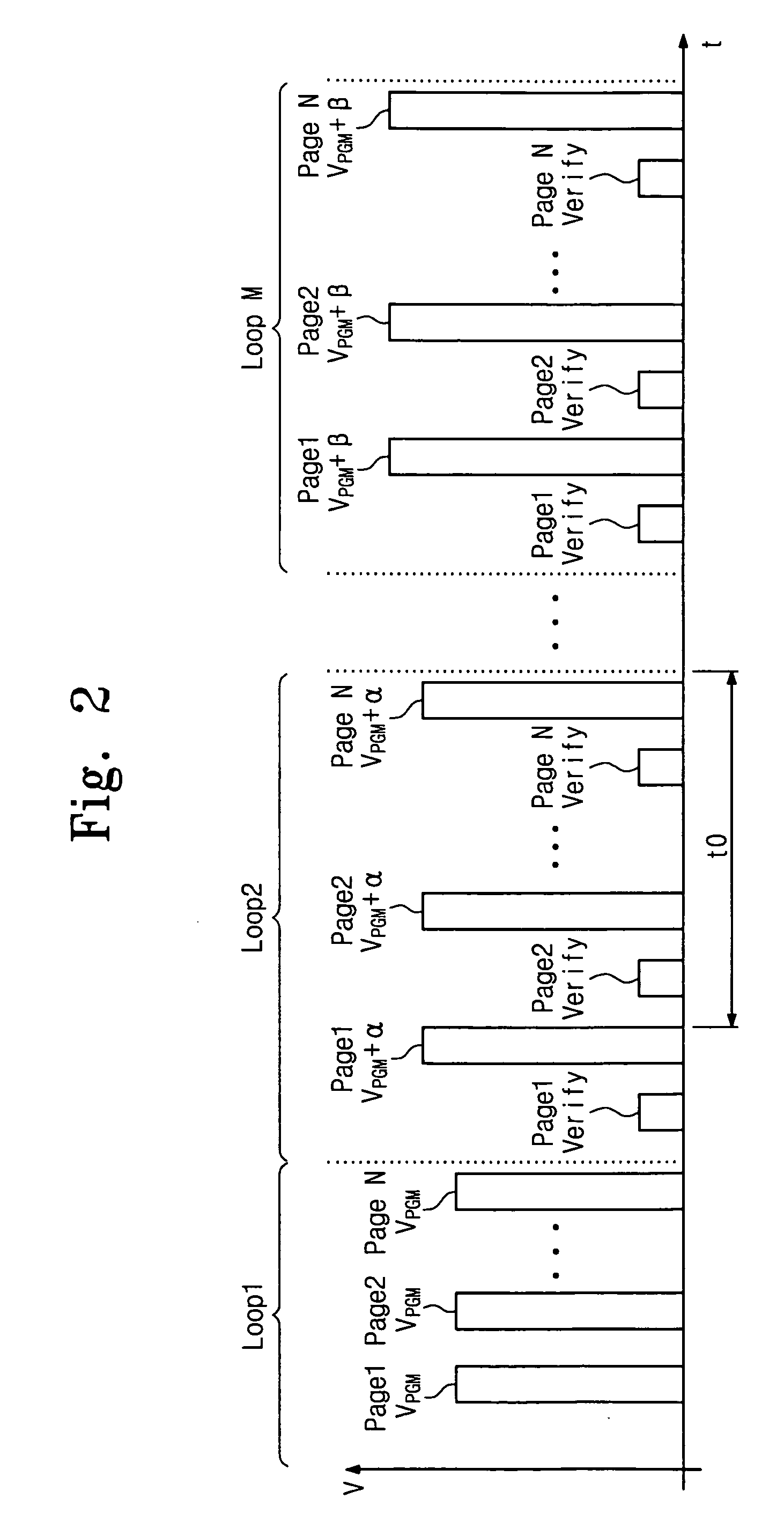
NAND flash memory device and method of programming the same
Provided are a NAND flash memory device and a method of programming the same. The NAND flash memory device may include a cell array including a plurality of pages; a page buffer storing program data of the pages; a data storage circuit providing program verification data to the page buffer; and a control unit. The control unit may program the pages and verify the pages using the program verification data following the programming of at least two of the pages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reachability analysis for program verification
InactiveUS20080016497A1High precisionSimplified representationSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsProgram provingReachability
An improved method for automatically improving the precision of an extrapolation operator used, for example, in software program verification in connection with the static analysis and model checking of the software programs which rely on fix-point computation. In particular, a new extrapolation-with-care-set operator, together with a method for gradually increasing the precision of this operation by tightening the care set.
Owner:NEC CORP
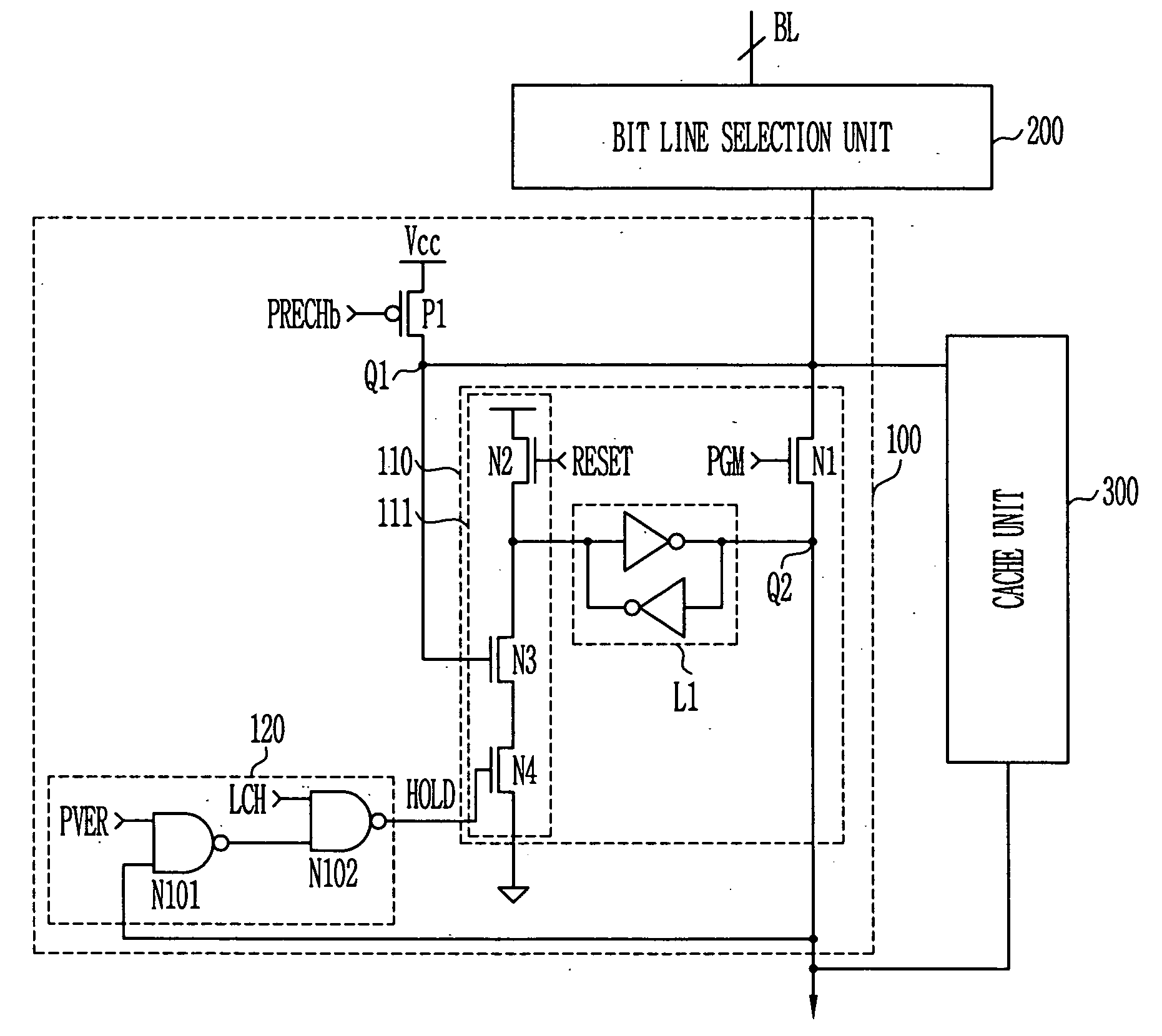
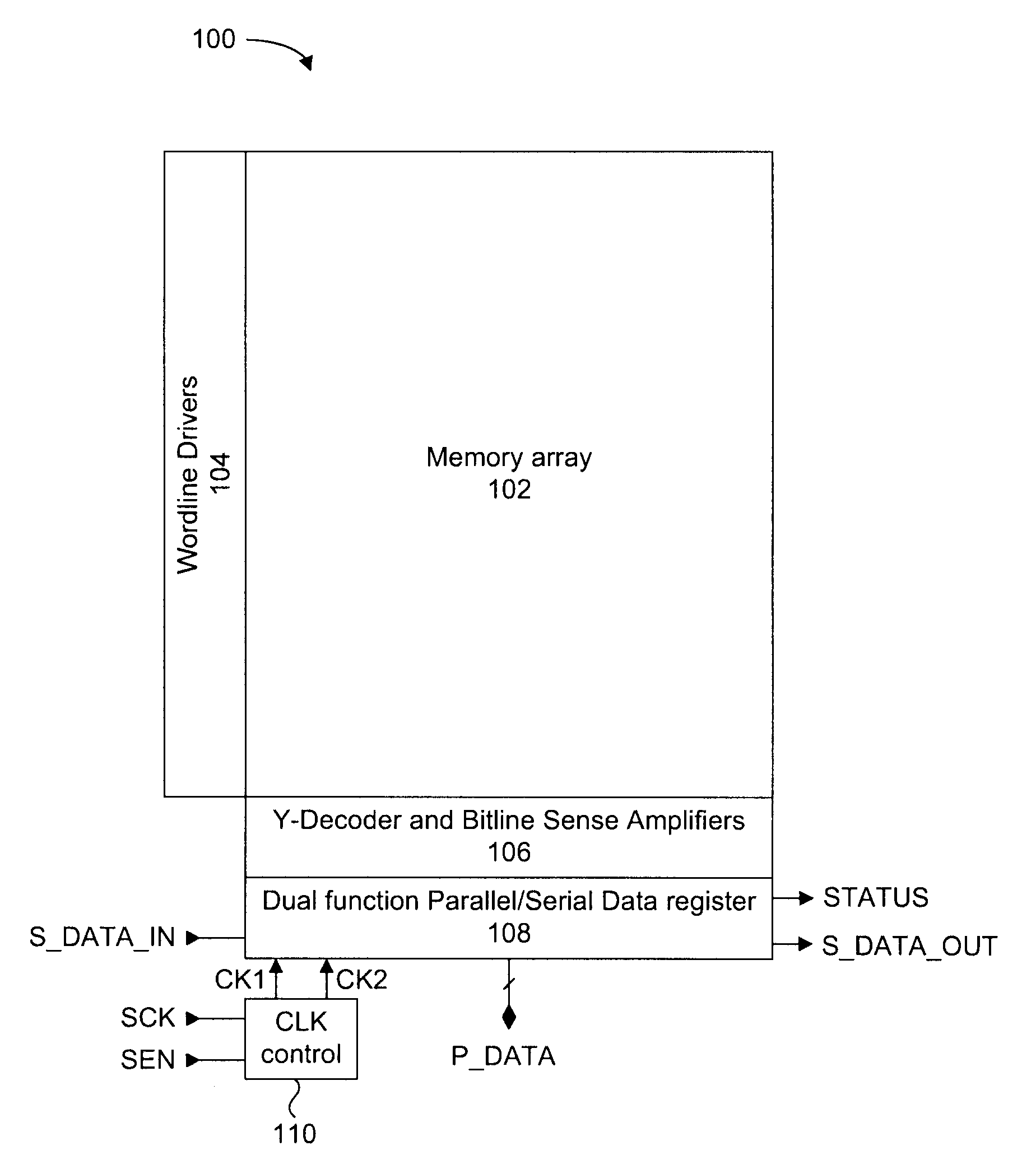
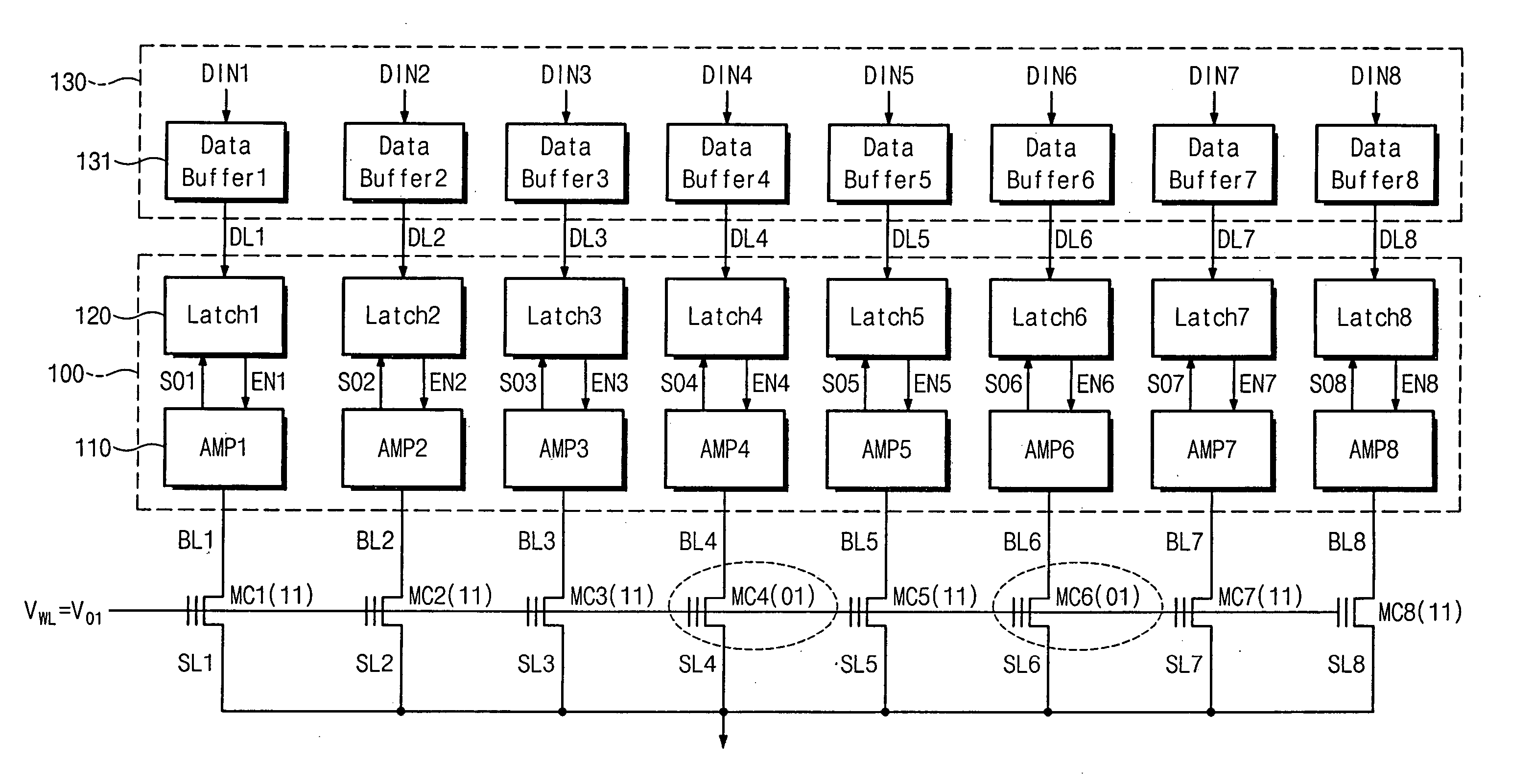
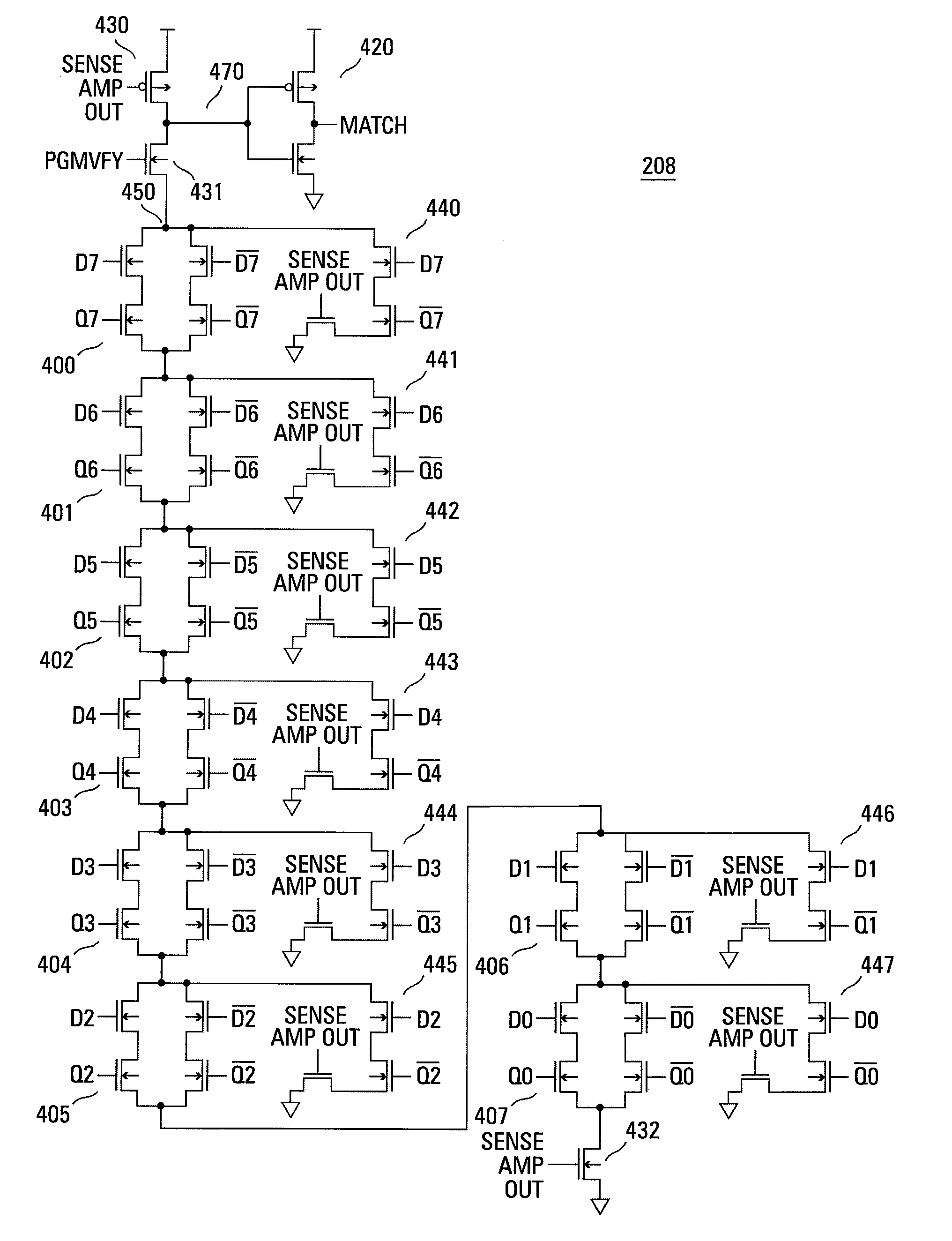
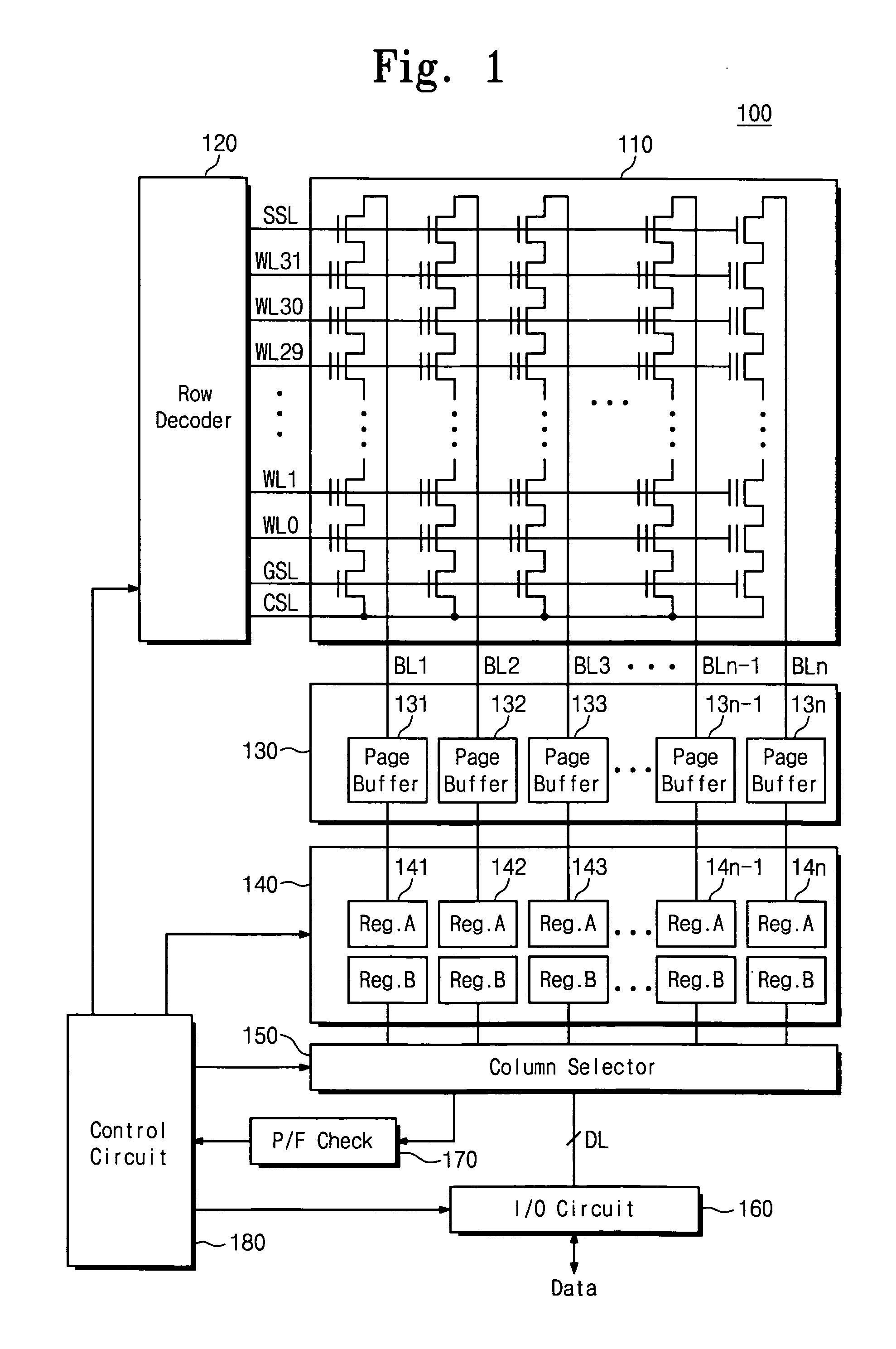
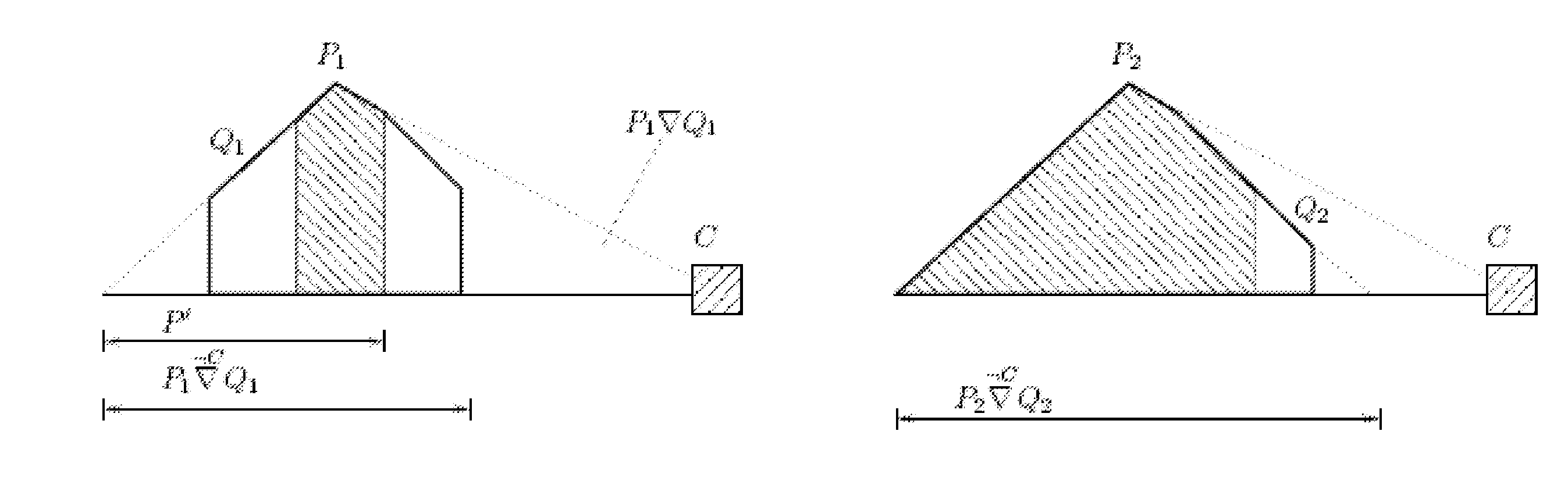
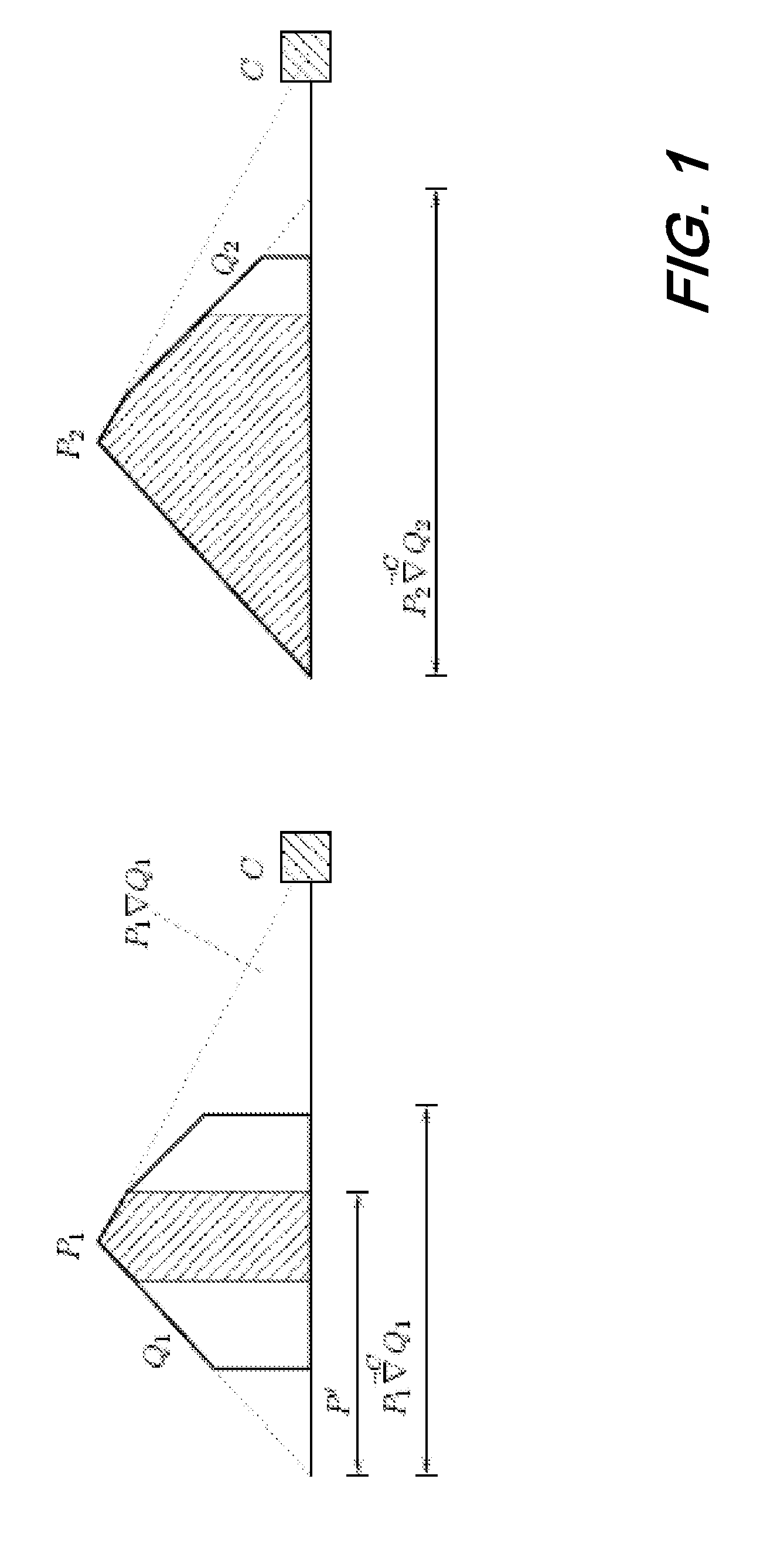
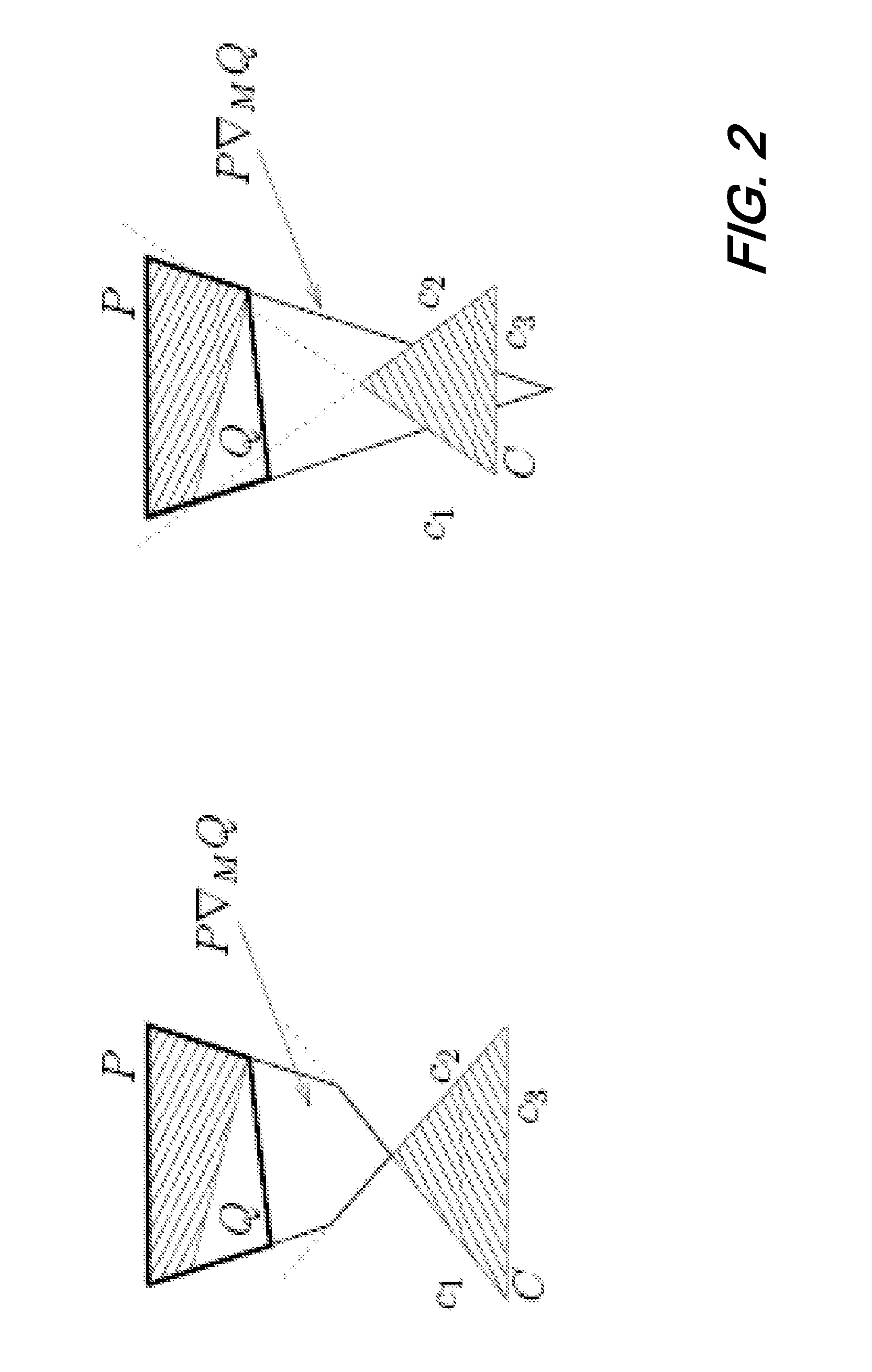
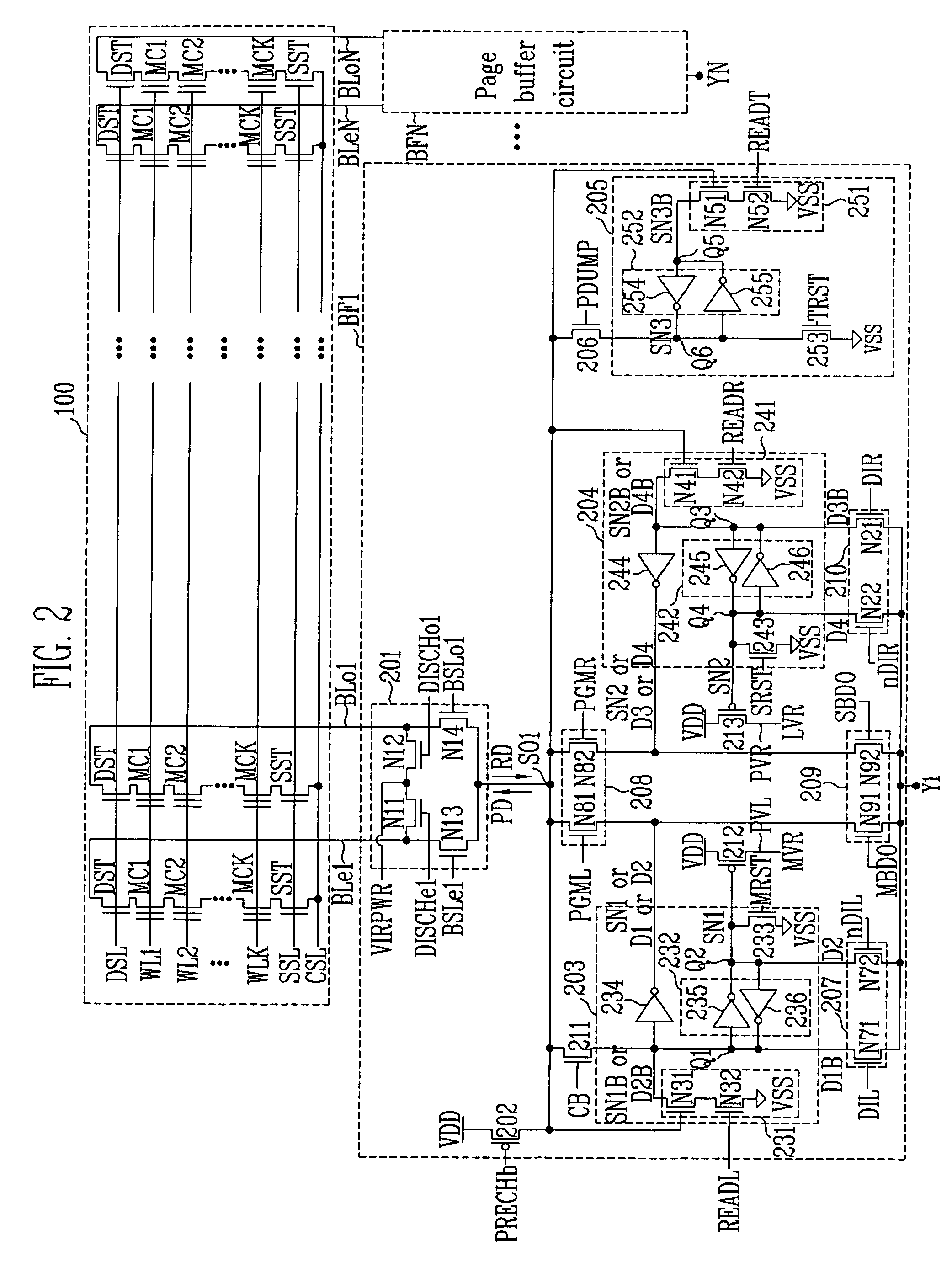
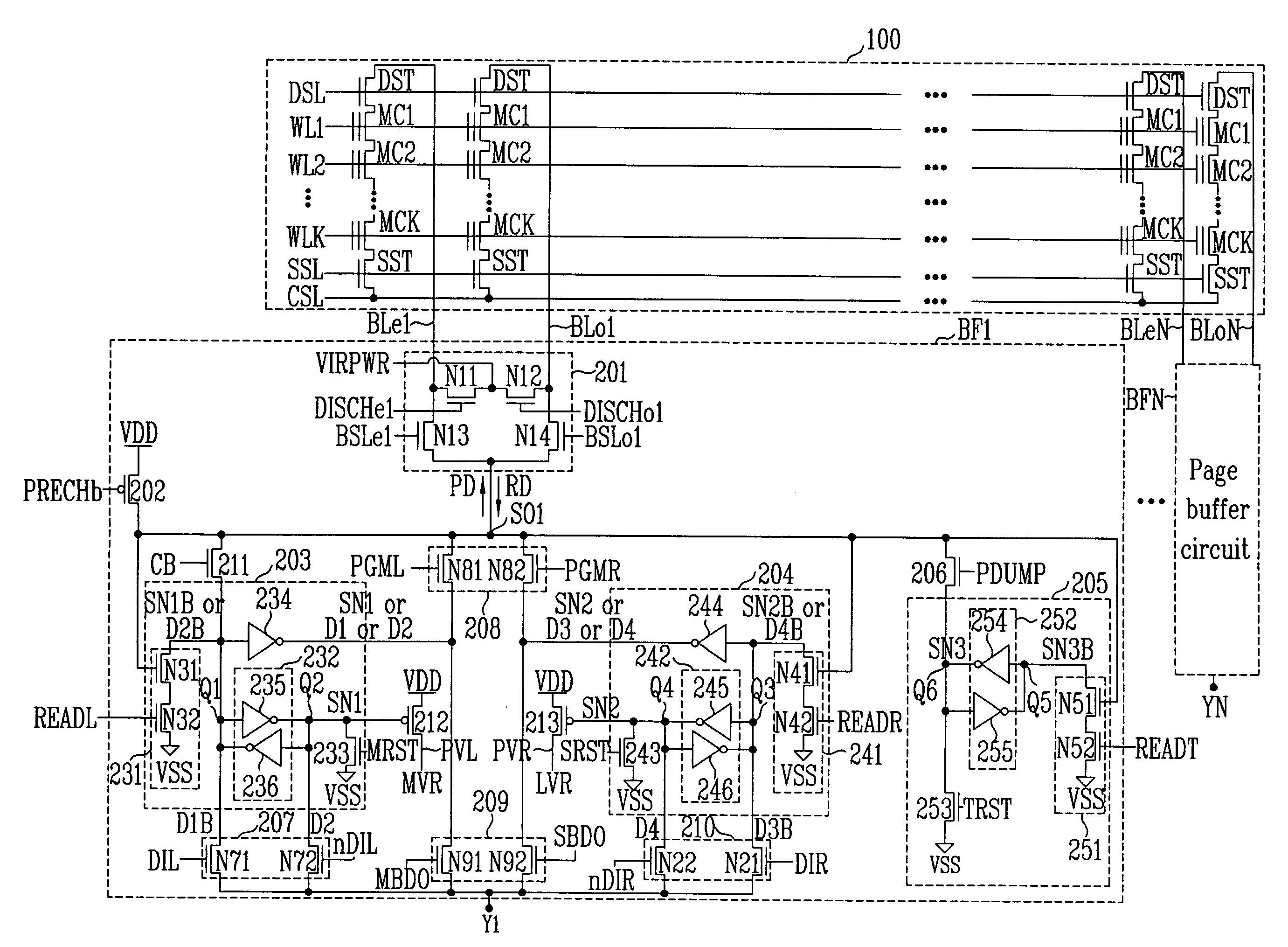
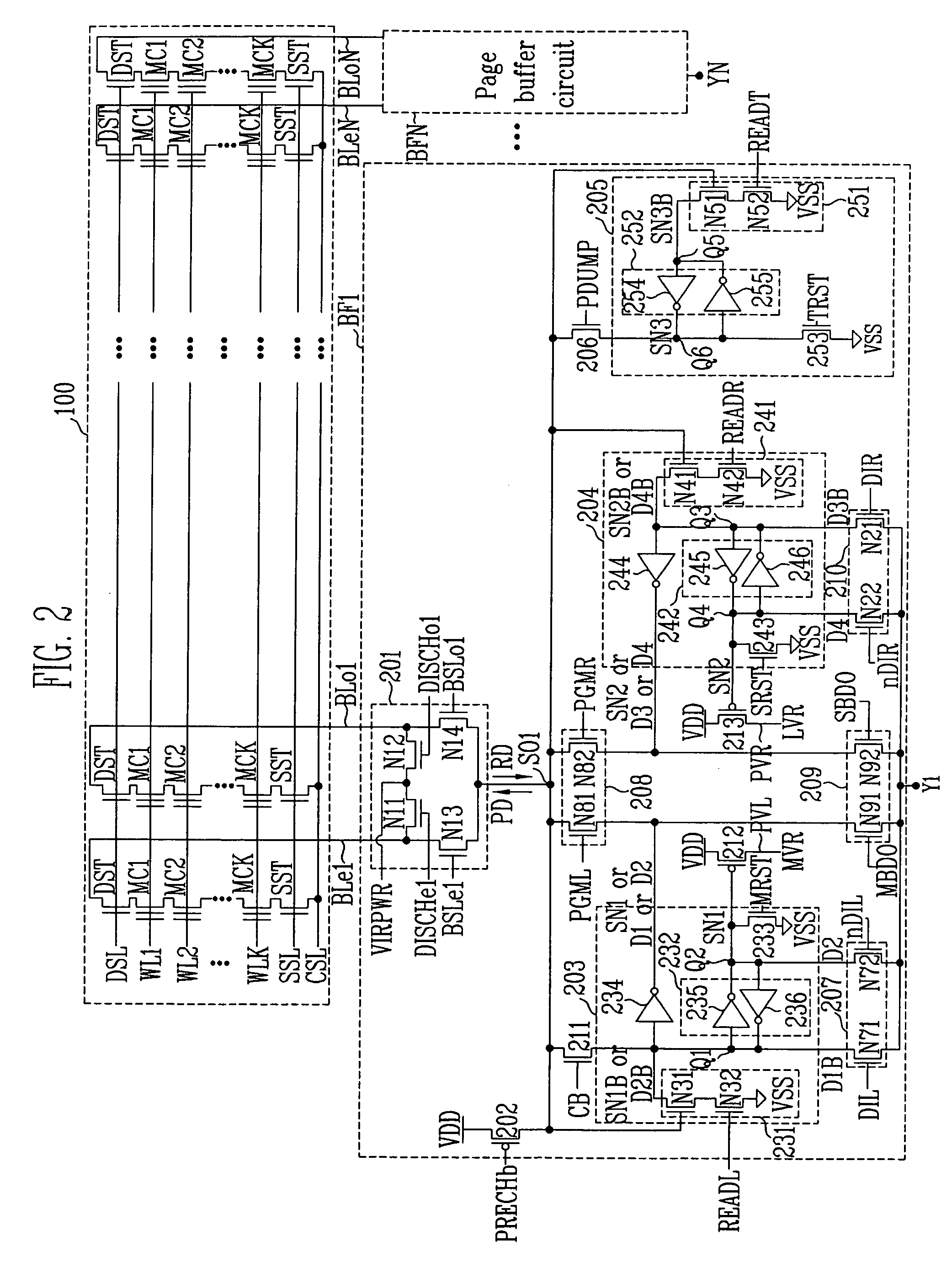
Page buffer circuit of flash memory device and program operation method thereof
A page buffer circuit includes a bit line selection circuit, a main register, a program transmission circuit, a temporary register, and a verification transmission circuit. The verification transmission circuit transmits data stored in the temporary register to the main register through a sensing node in response to a transmission control signal during a program verification operation. A memory cell that has been determined to be programmed in a previous program verification process is verified again in a next program verification process.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
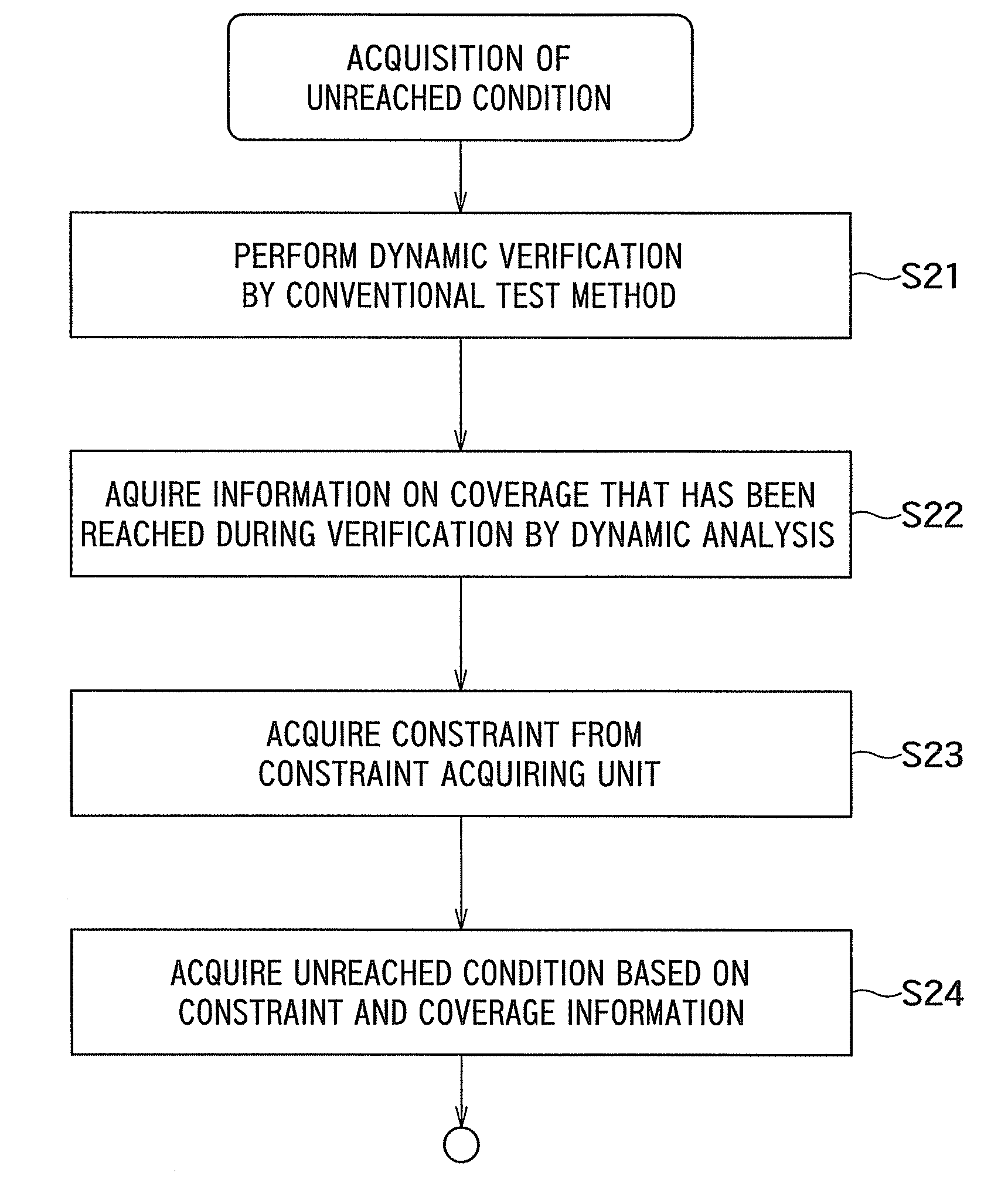
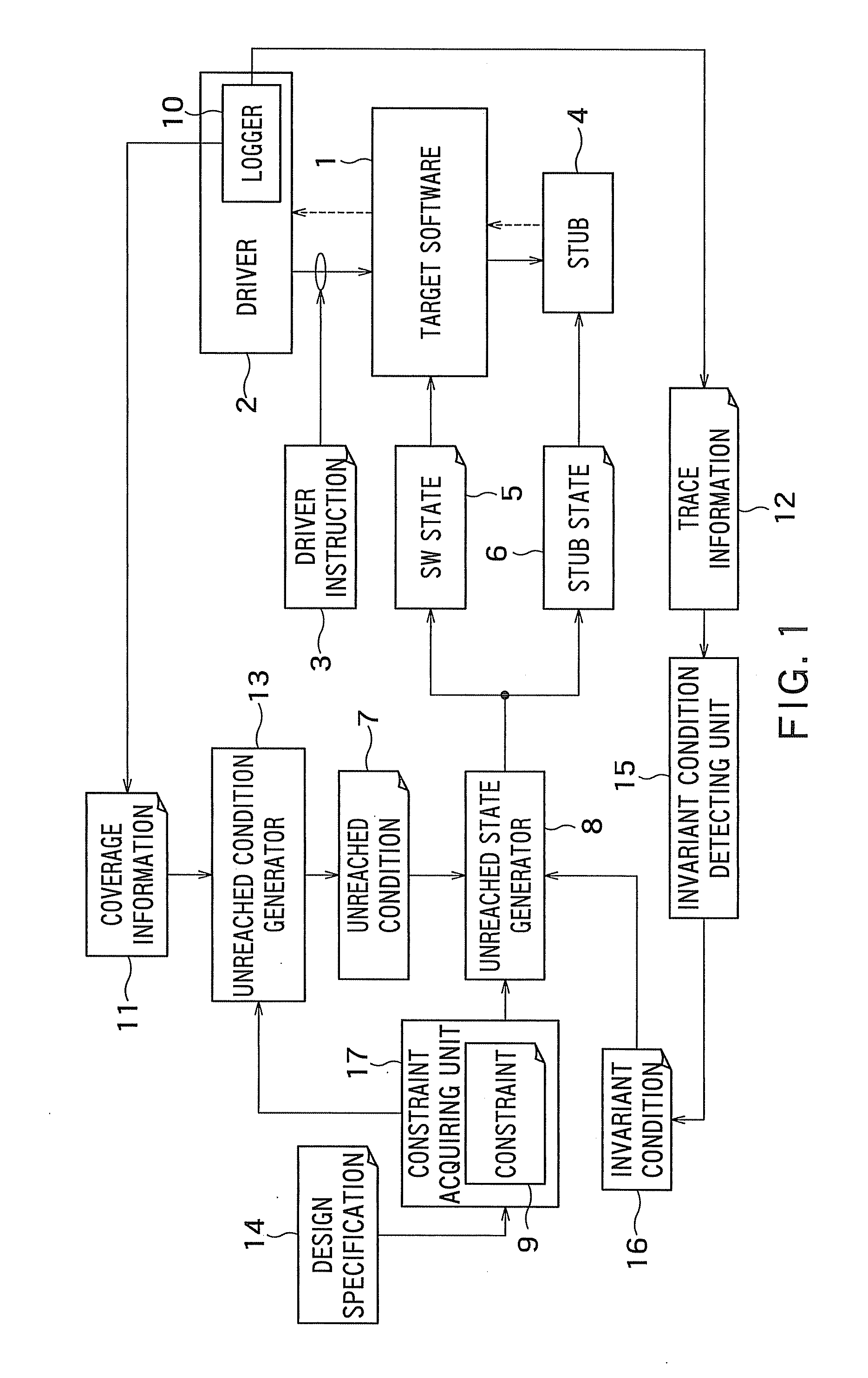
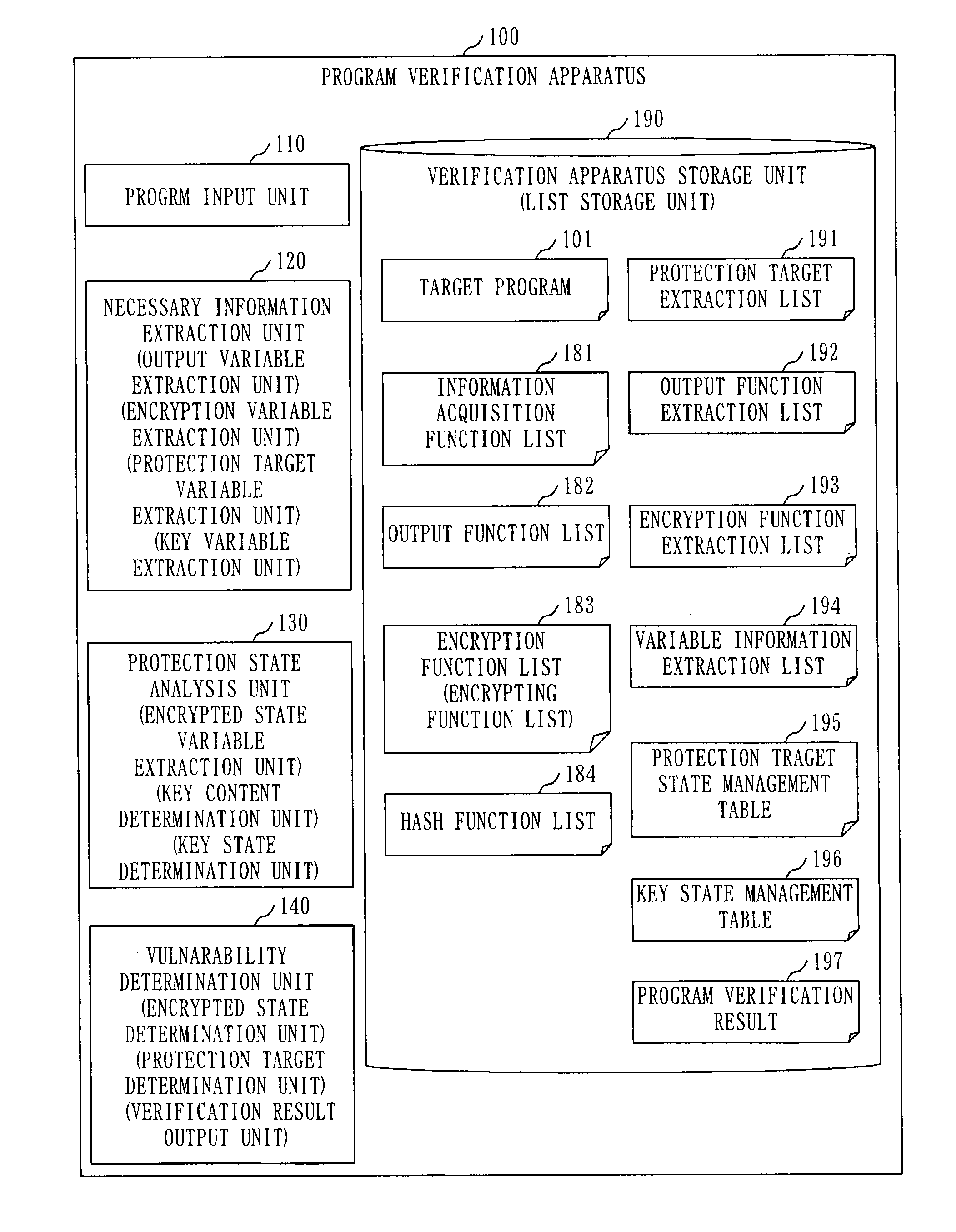
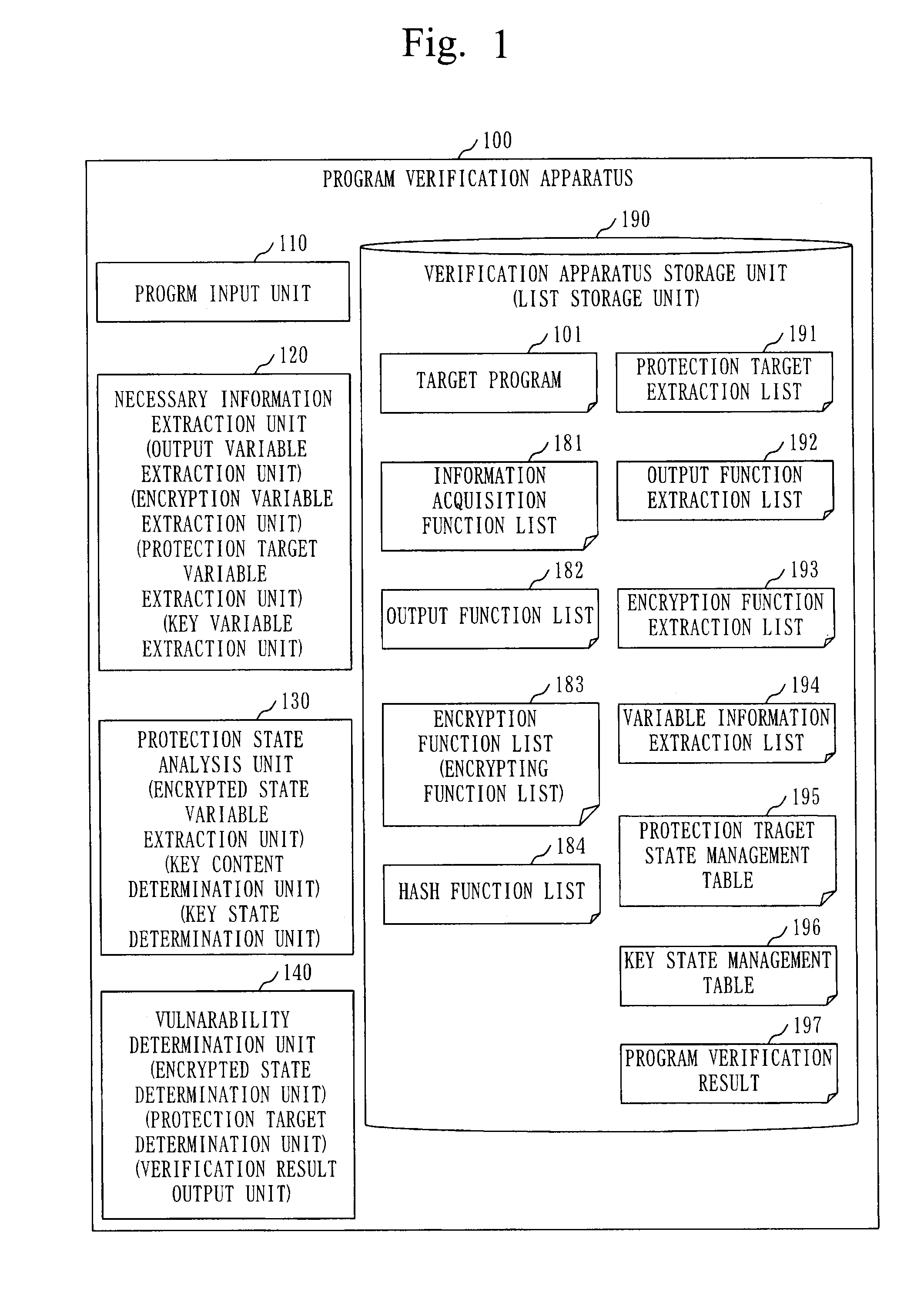
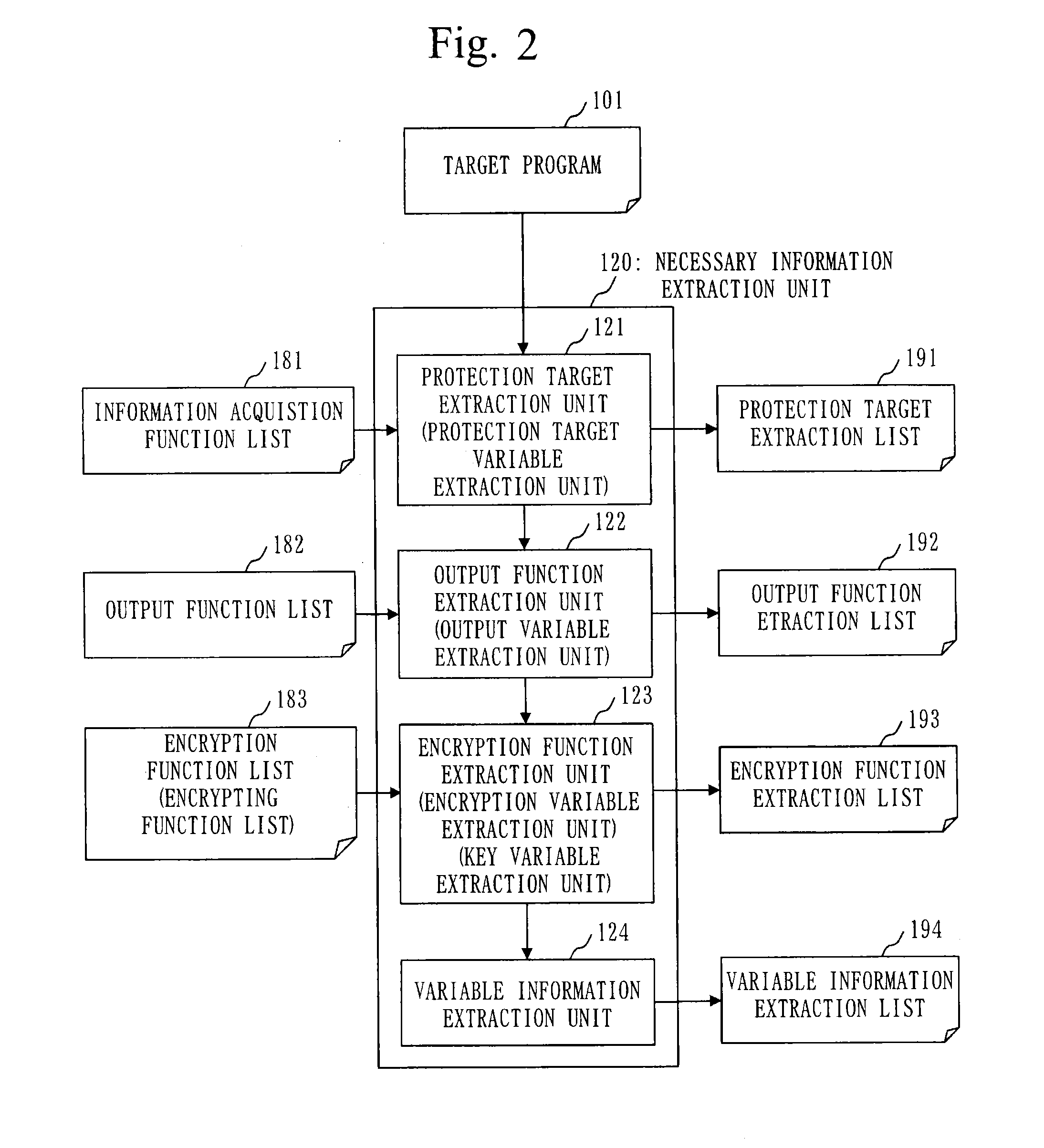
Program verification apparatus, program verification method, and program storage medium
InactiveUS20090172643A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram provingTheoretical computer science
A program verification apparatus includes: a program executing unit executing a program; a variable monitoring unit monitoring a plurality of variables in the program to obtain monitor values of the variables; a target variable determiner determining one or more target variables out of the variables; a constraint condition storage storing a first constraint condition that defines a constraint to be satisfied for each of the target variables and a second constraint condition that defines a constraint to be satisfied among the target variables; a state acquiring unit sequentially acquiring target program state each of which is a combination of monitor values of the target variables at same time respectively; a state generating unit generating an unreached target program state which has not been acquired yet and satisfies the first and second constraint conditions; and a state setting unit setting the unreached target program state to the program.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Charge loss compensation during programming of a memory device
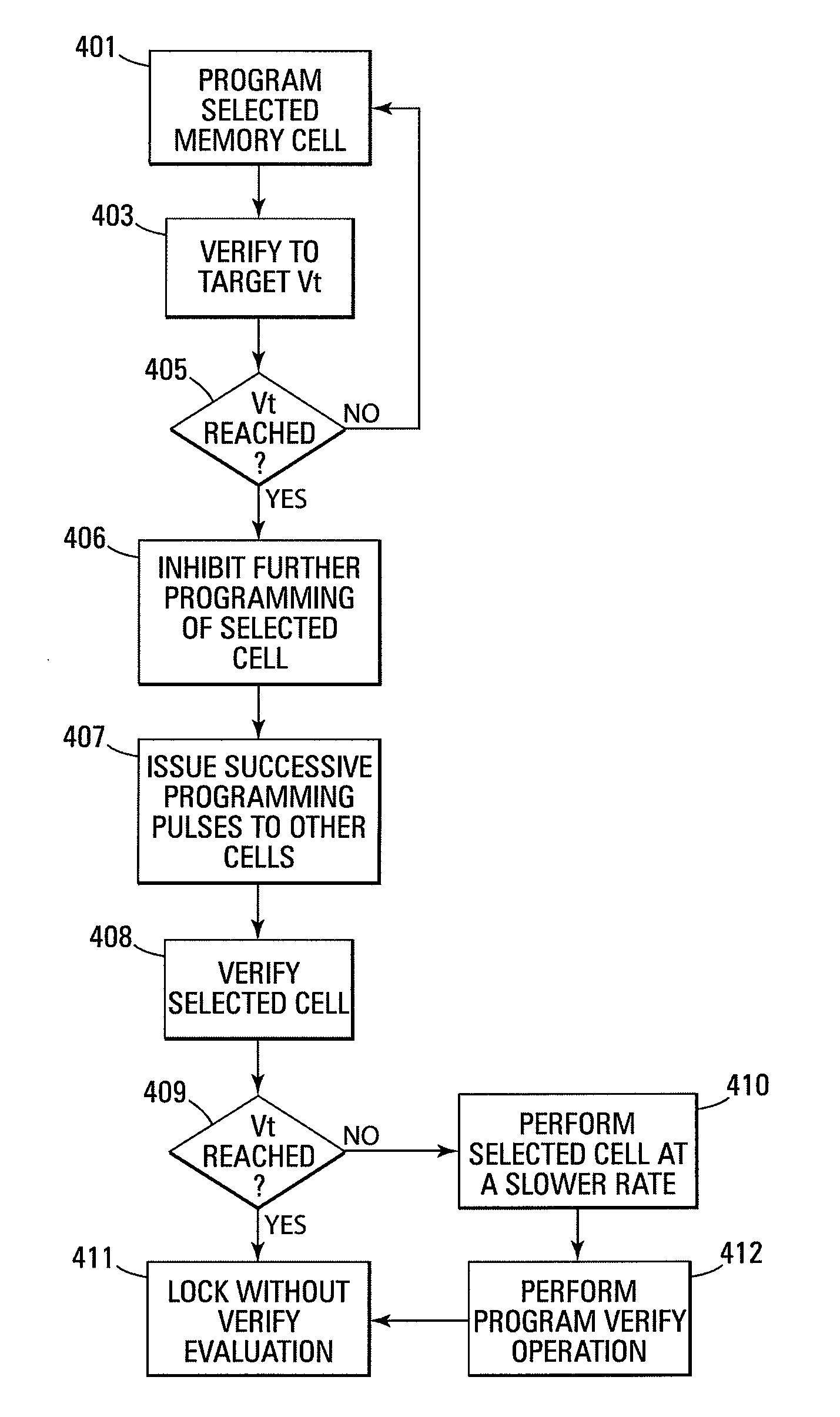
A selected memory cell on a selected word line is programmed through a plurality of programming pulses that are incremented by a step voltage. After a successful program verify operation, programming of the selected memory cell is inhibited while other memory cells of the selected word line are being programmed. Another program verify operation is performed on the selected memory cell. If the program verify operation fails, a bit line coupled to the selected cell is biased at the step voltage and a final programming pulse is issued to the selected word line. The selected memory cell is then locked from further programming without evaluating the final program verify operation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor memory device and related programming method
A NOR flash memory device and related programming method are disclosed. The programming method includes programming data in a memory cell and, during a program verification operation, controlling the supply of current from a sense amplifier to the memory cell in relation to the value of the programmed data. Wherein a program verification operation is indicated, current is provided from the sense amplifier to the memory cell. Where a program verification operation is not indicated, current is cut off from the sense amplifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
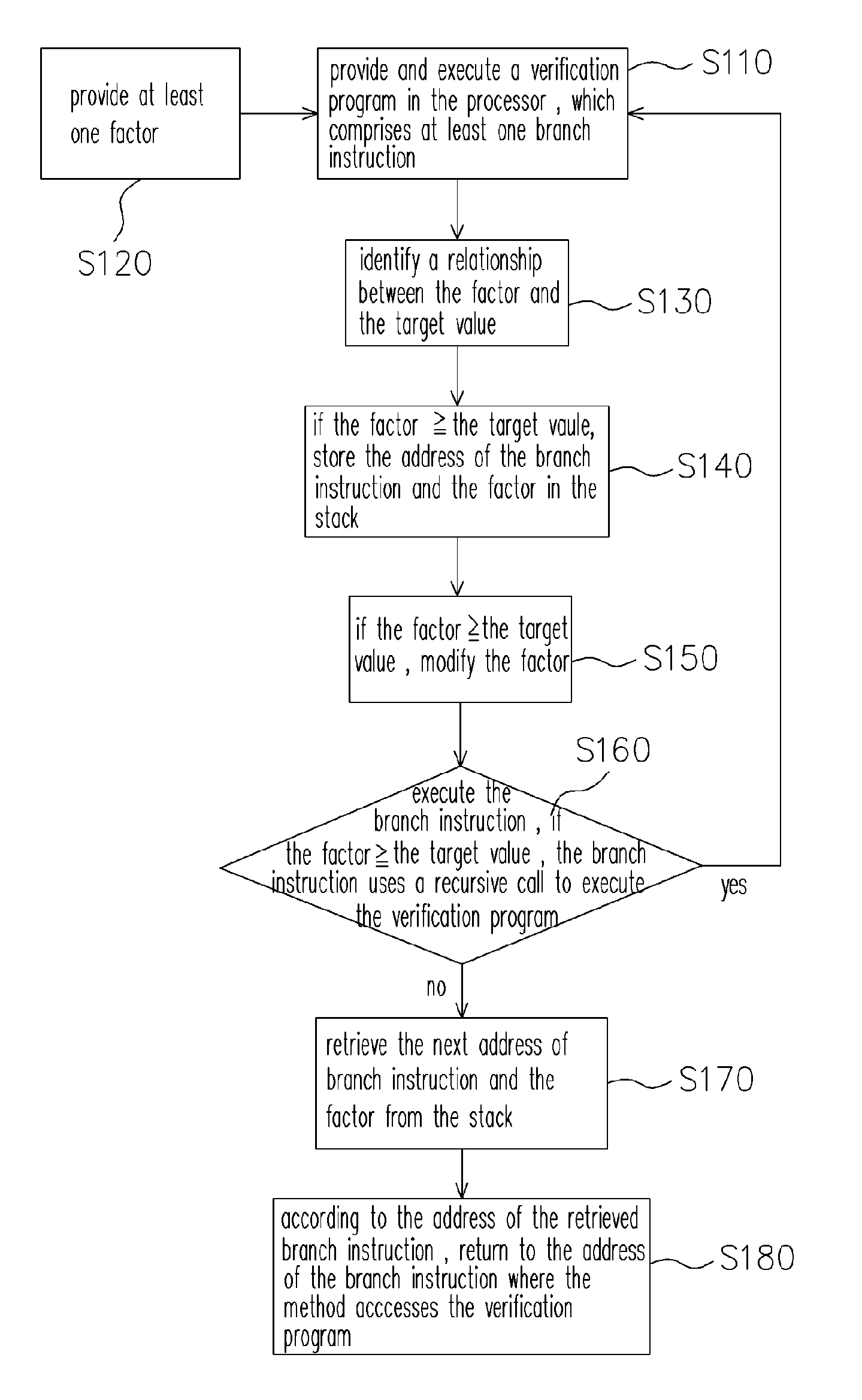
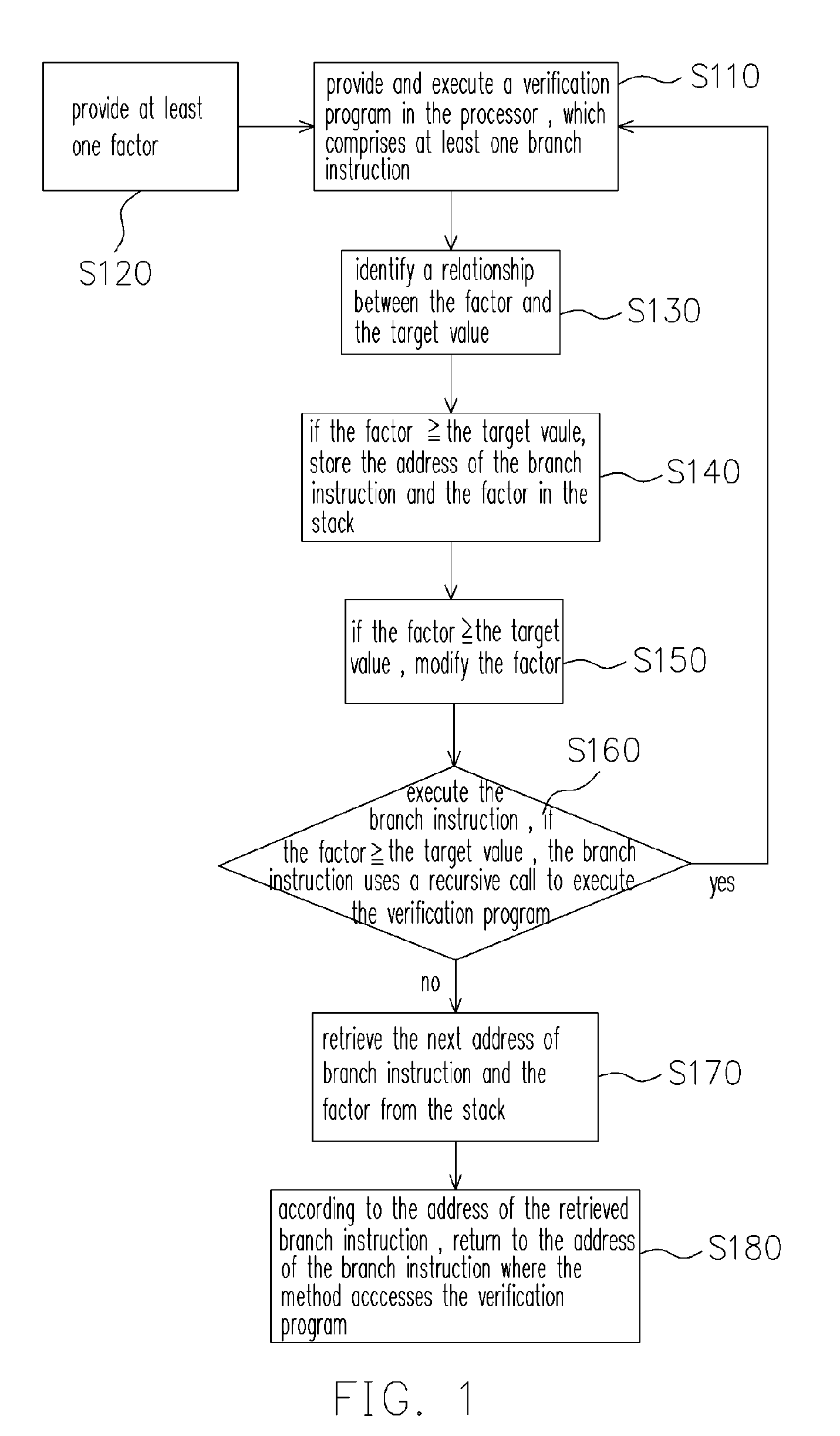
Method for verifying branch prediction mechanism and accessible recording medium for storing program thereof
InactiveUS20060041868A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram provingVerified procedure
A method for verifying a branch prediction mechanism and an accessible recording medium for storing a verification program are provided. The method is used for verifying the branch prediction mechanism, such as a branch target buffer (BTB), in a processor. The method comprises providing and executing a verification program in the processor. The verification program comprises at least one branch instruction, which determines whether to use a recursive call and execute the verification program according to a given condition.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
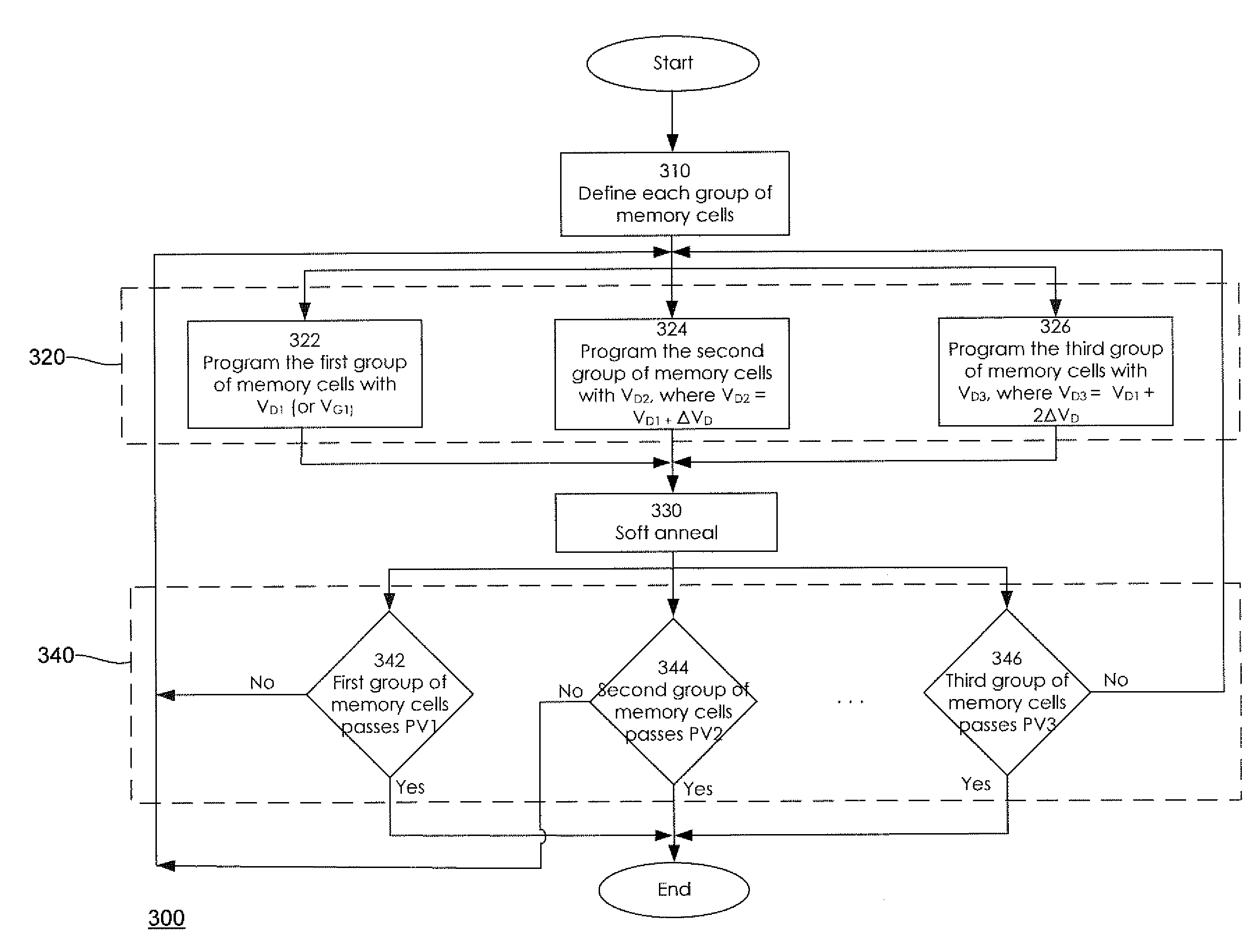
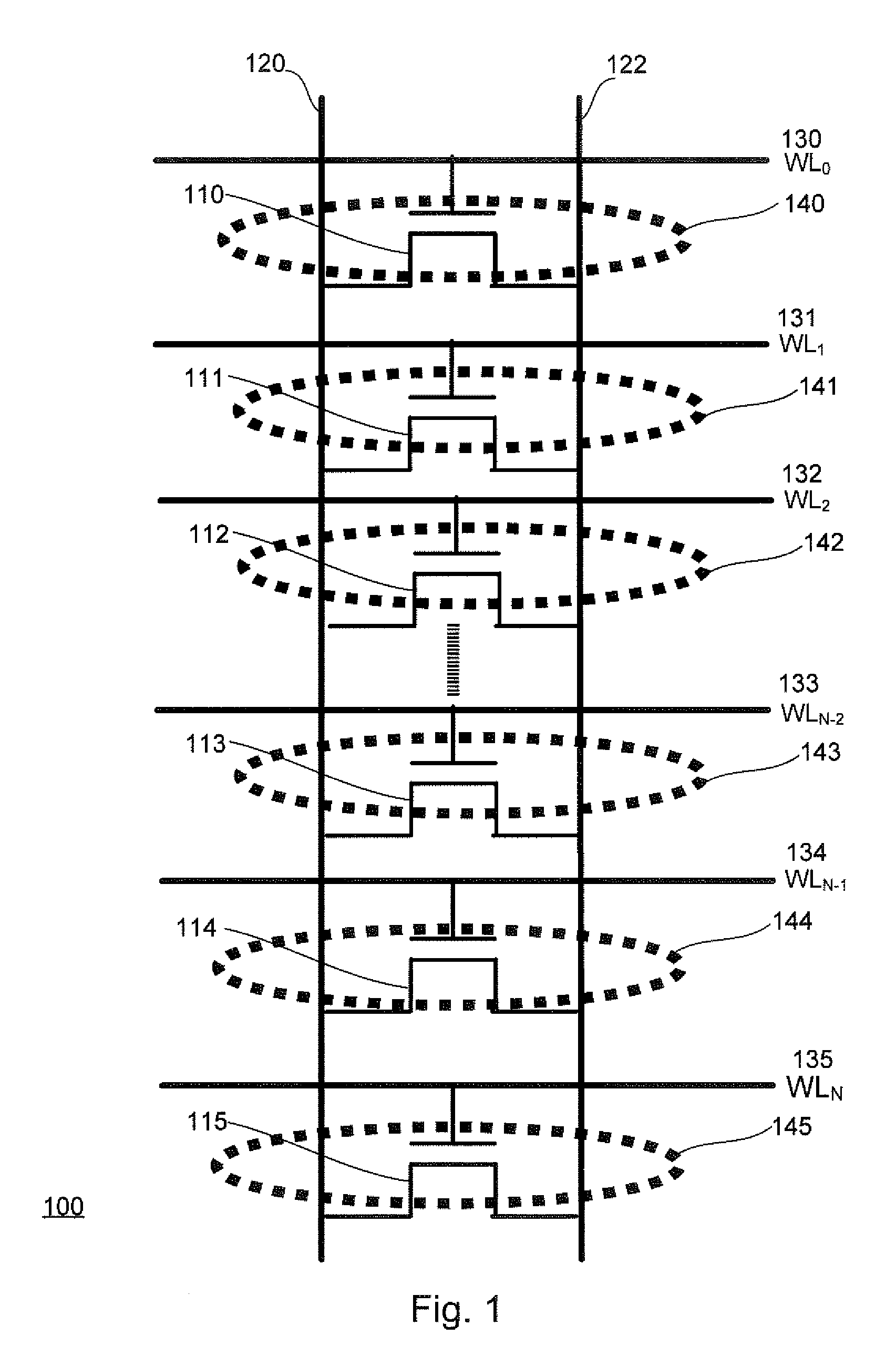
Variable Program and Program Verification Methods for a Virtual Ground Memory in Easing Buried Drain Contacts
ActiveUS20080158966A1Eases buried drain contact induced operationHigh retention rateRead-only memoriesDigital storageVirtual memoryProgram proving
Methods for programming and program verification of a flash memory are described that ease the buried drain contact induced operation and increase the retention window. In a first aspect of the invention, a program operation method provides varying program biases which are applied to different groups of memory cells. The program biases can be supplied as drain bias voltages or gate bias voltages. The program biases vary depending on which group of memory cells is programmed. In one embodiment, a first drain voltage VD1 is applied to the first group of memory cells M0 and Mn. A second drain voltage VD2 is applied to the second group of memory cells M1 and Mn-1, where VD2=VD1+ΔVD. In a second aspect of the invention, a plurality of program verification voltage levels are selected to verify that the memory cells pass the program voltage levels.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Page buffer circuit of flash memory device and program operation method thereof
A page buffer circuit includes a bit line selection circuit, a main register, a program transmission circuit, a temporary register, and a verification transmission circuit. The verification transmission circuit transmits data stored in the temporary register to the main register through a sensing node in response to a transmission control signal during a program verification operation. A memory cell that has been determined to be programmed in a previous program verification process is verified again in a next program verification process.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Program verification apparatus, program verification method, and program verification program
InactiveUS20150302202A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionProgram provingState variable
A necessary information extraction unit extracts, from variables used in a target program, an output variable to which output information to be output by an output function defined in an output function list is set. The necessary information extraction unit extracts, from the variables used in the target program, an encryption variable to which encrypted information encrypted by an encrypting function defined in an encryption function list is set. A protected state analysis unit refers to an assignment statement included in the target program, and extracts an encrypted state variable to which the encrypted information is assigned. A vulnerability determination unit determines whether or not the encrypted state variable and the output variable are the same variable, and outputs a program verification result based on a result of determination.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Page buffer circuit
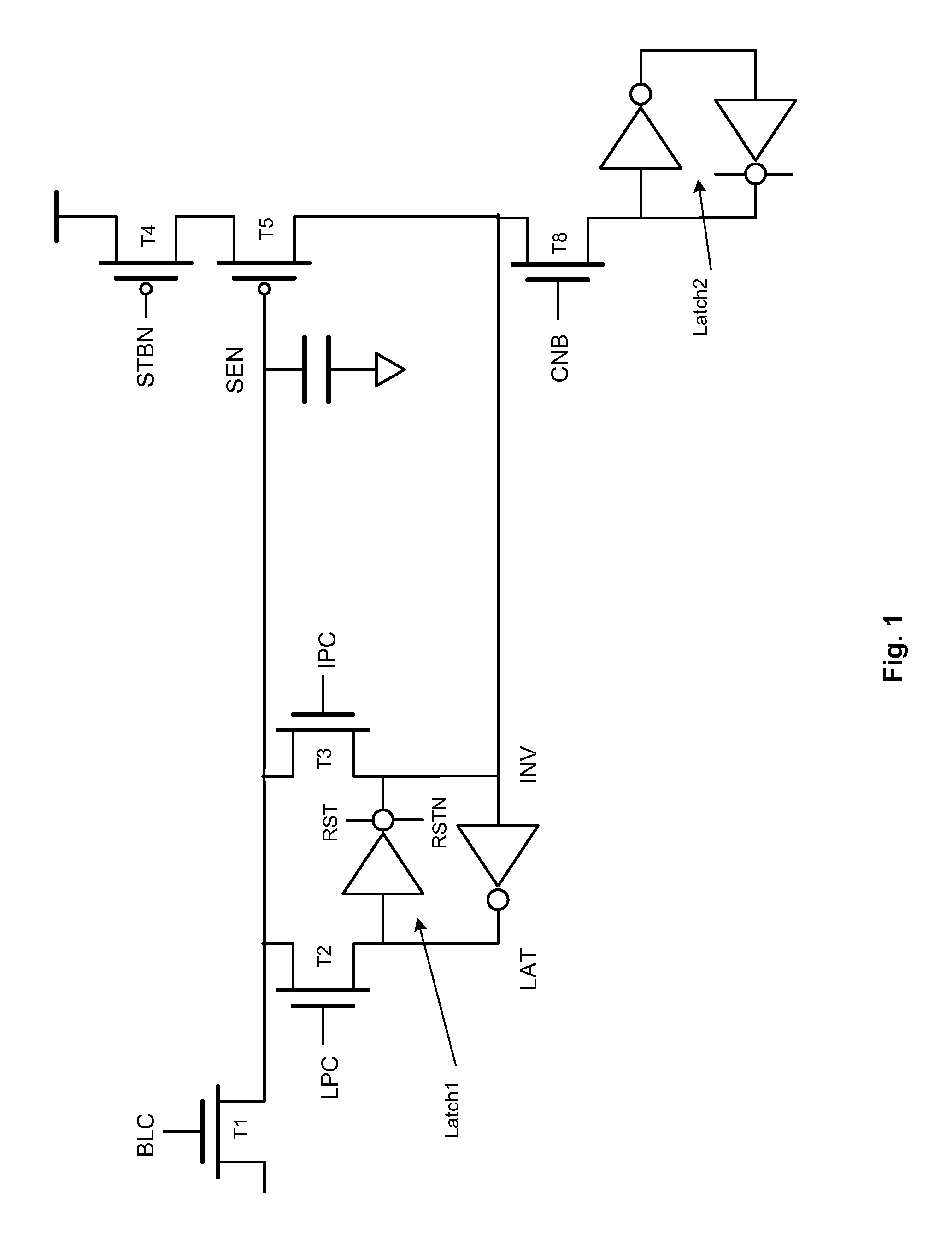
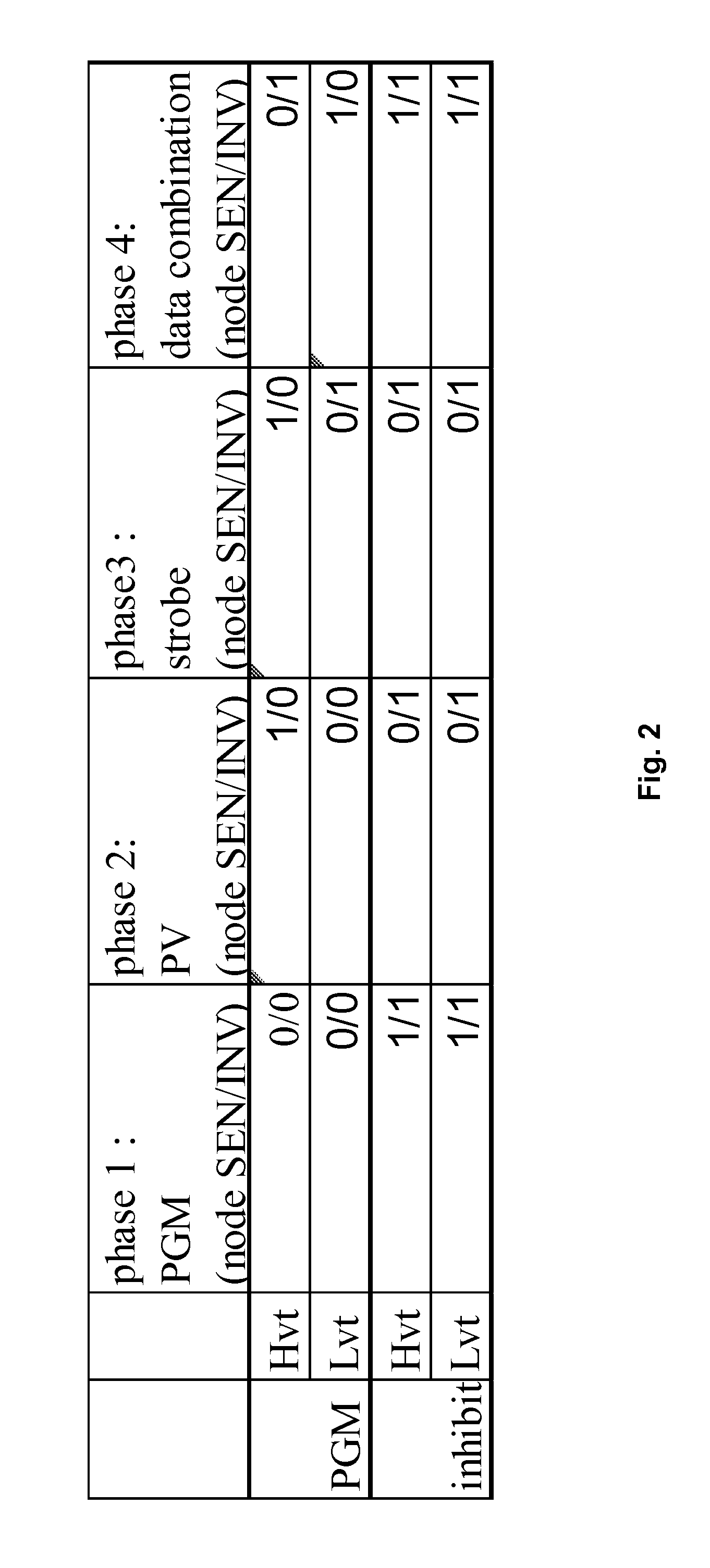
A page buffer circuit is coupled to a bit line of a memory array. The page buffer circuit includes a latch storing different data during different phases of a multi-phase program operation. A preparation phase is after the program phase and after the program verify phase of the present multi-phase program operation. For the preparation phase, the control circuitry causes the latch to store the preparation data indicating whether to program the memory cell in a subsequent multi-phase program operation following the present multi-phase program operation. Results of the program verify phase, and contents of the latch at a start of the present multi-phase program operation, are sufficient to determine the preparation data.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com