Patents
Literature
209results about How to "Improve programming speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
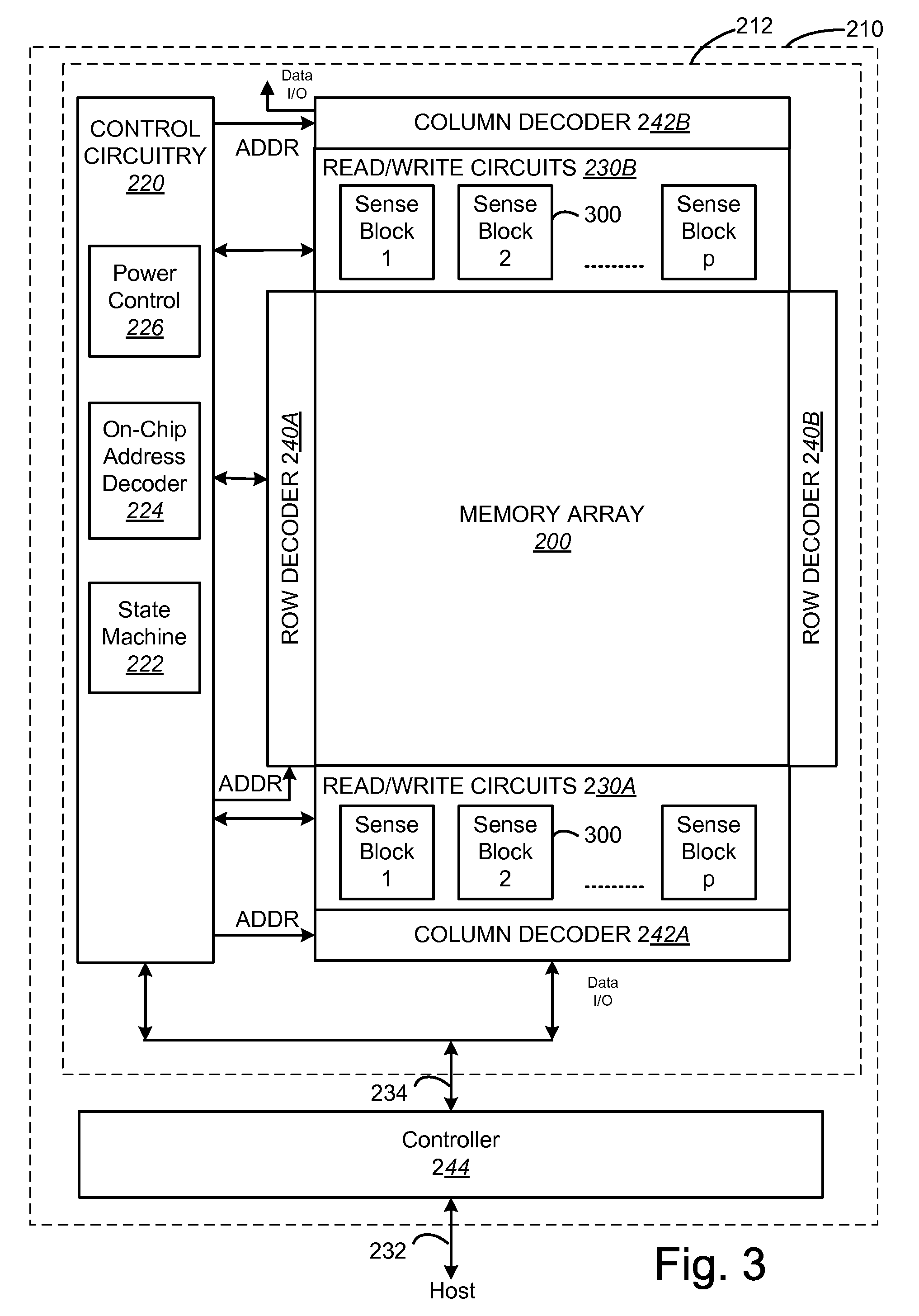
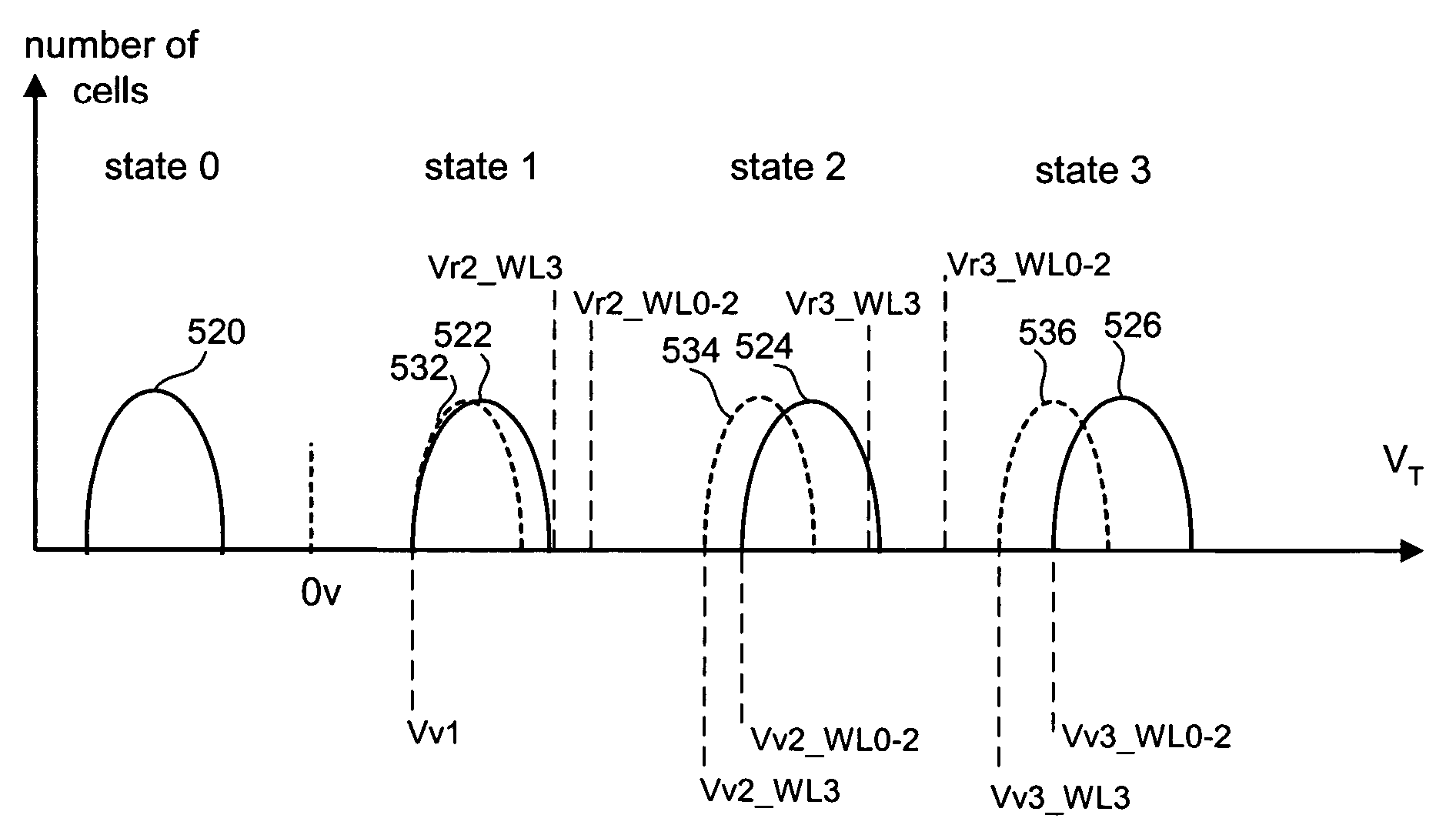
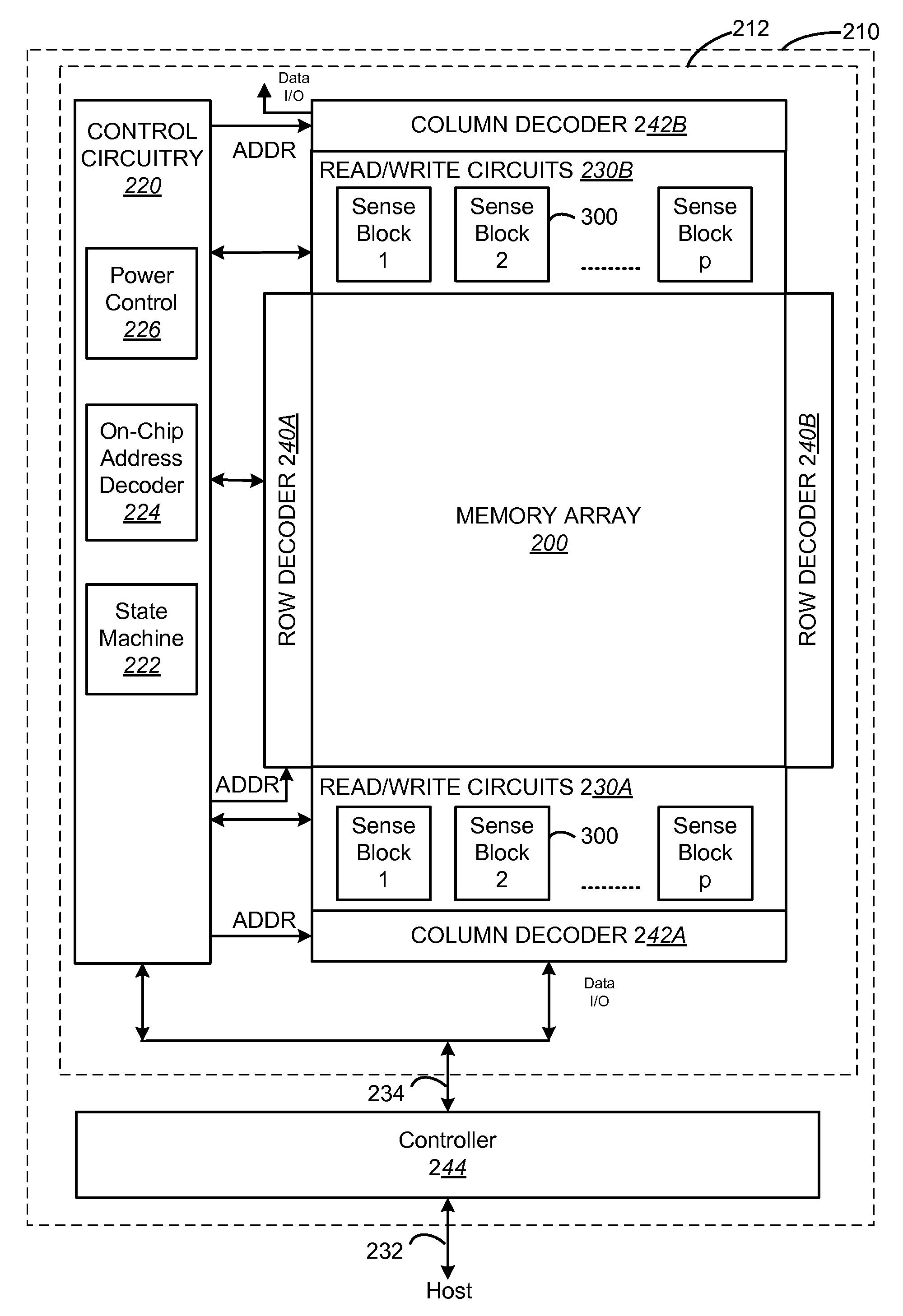
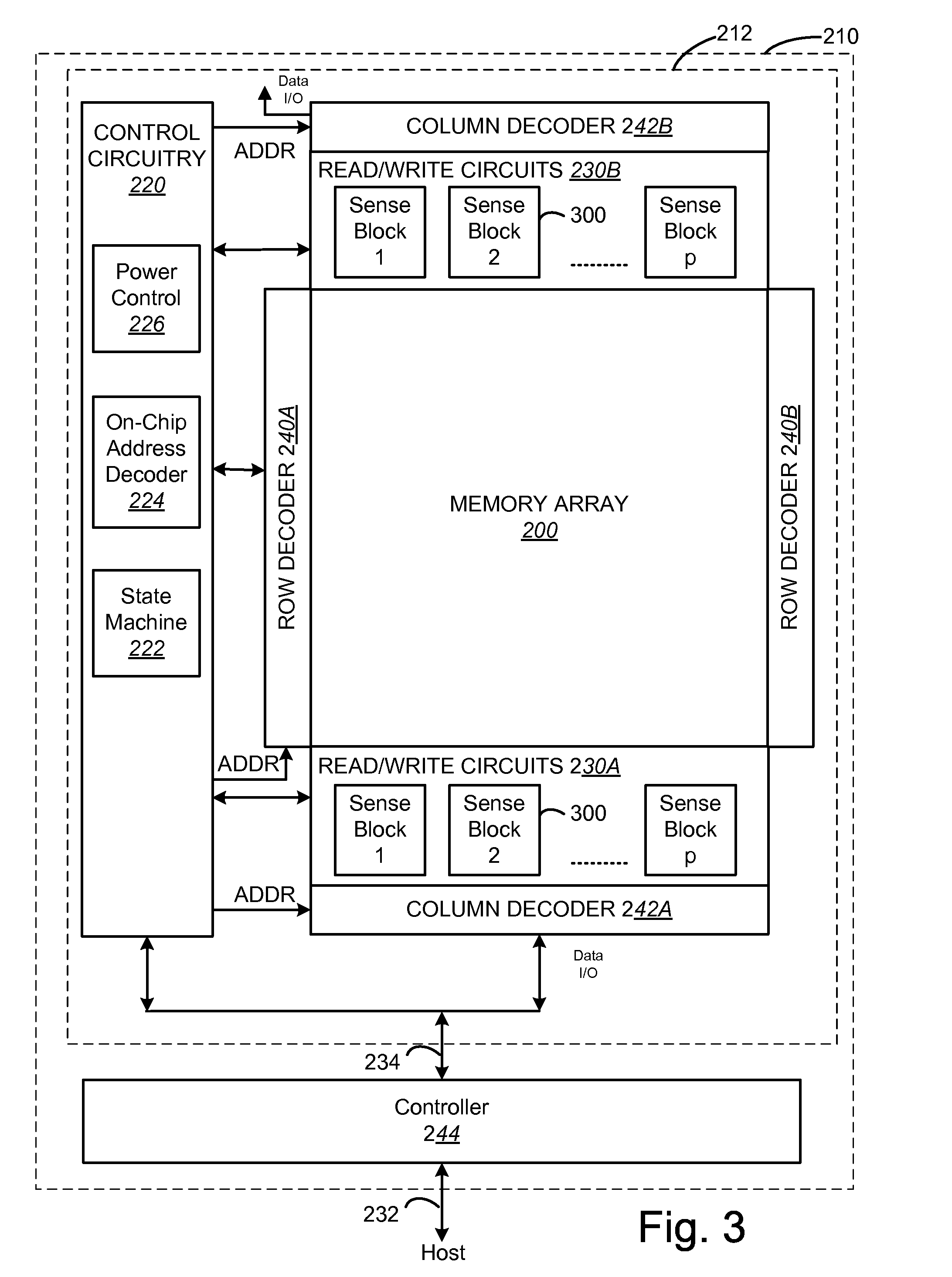
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
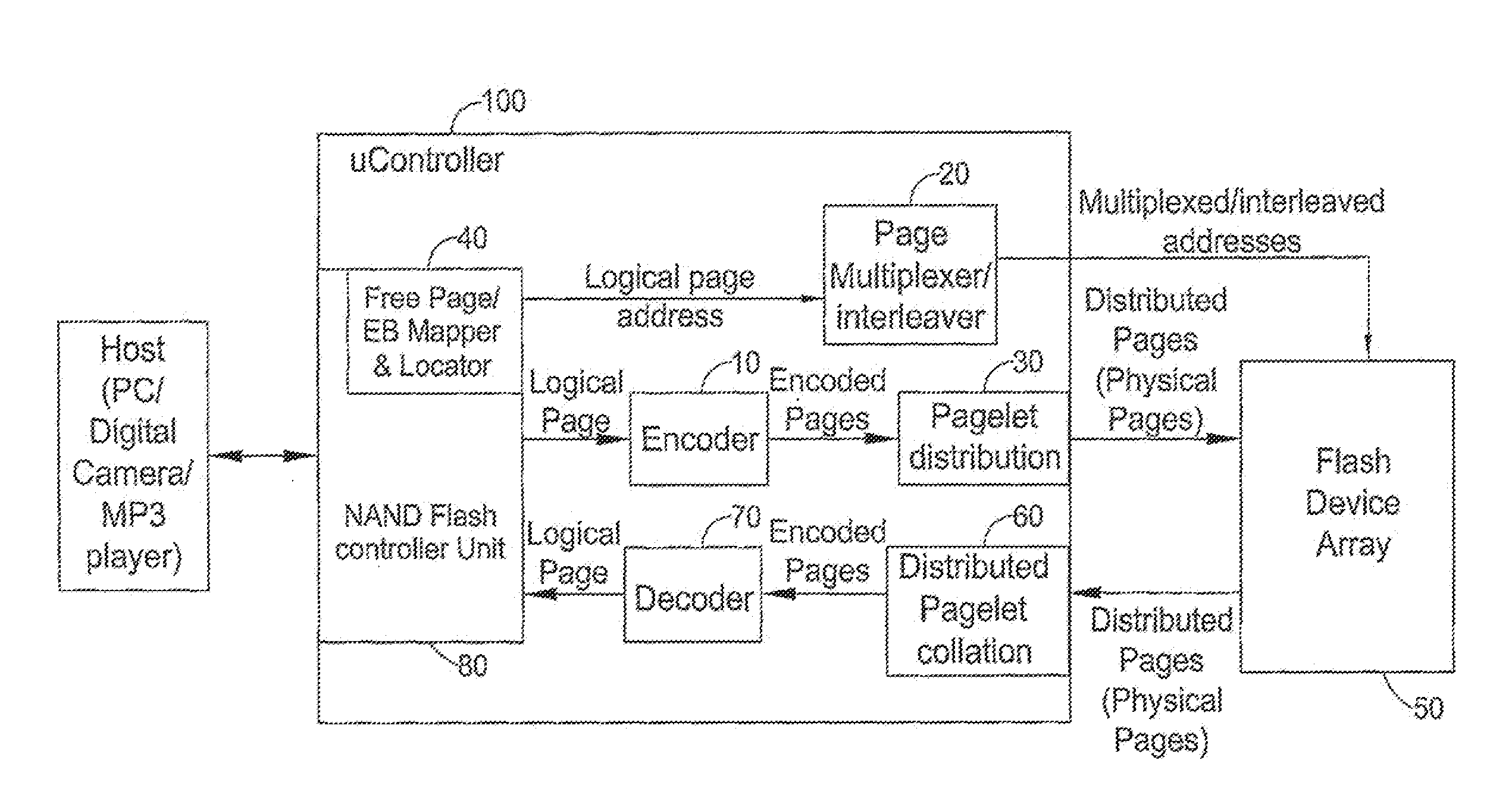
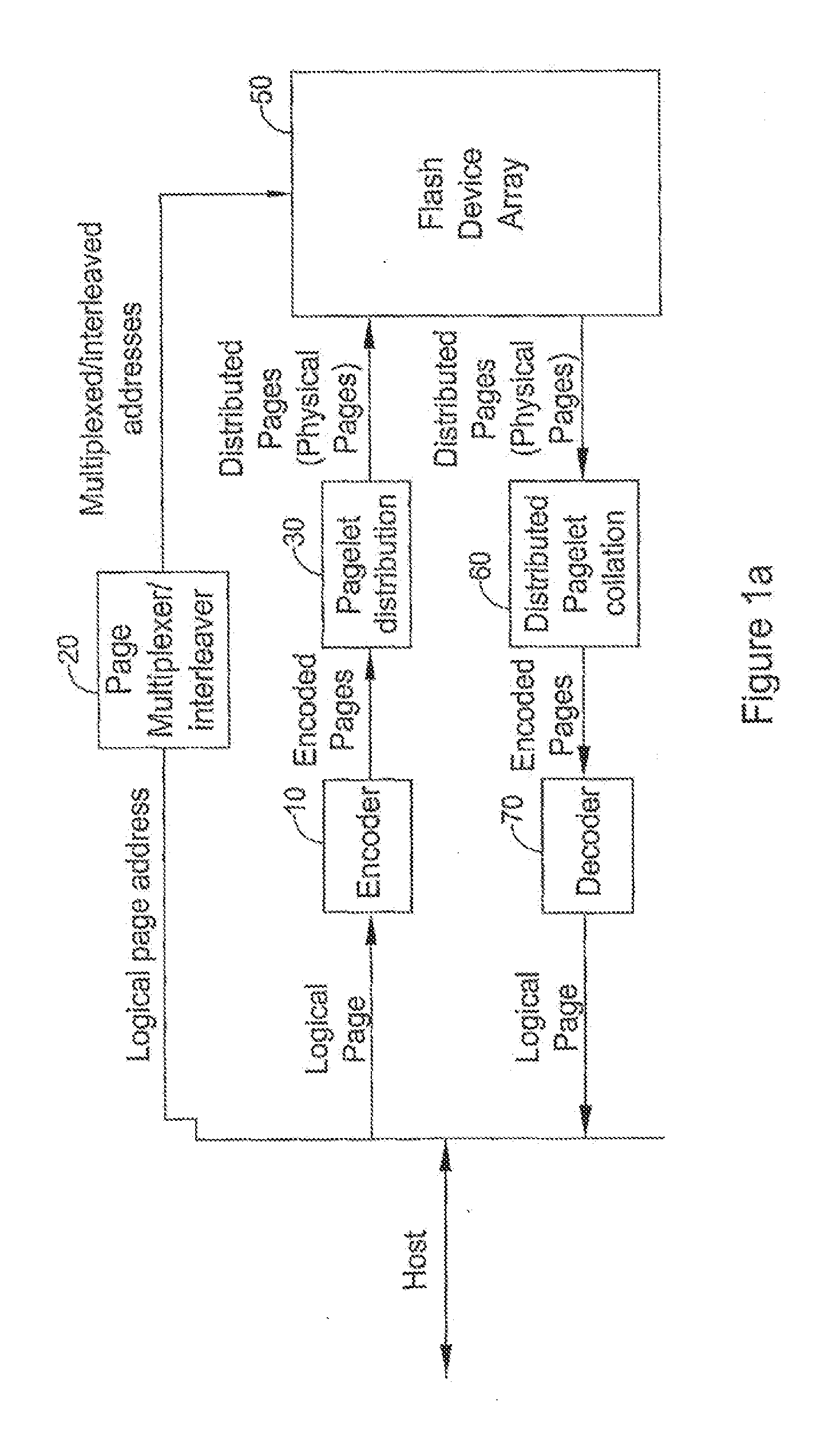
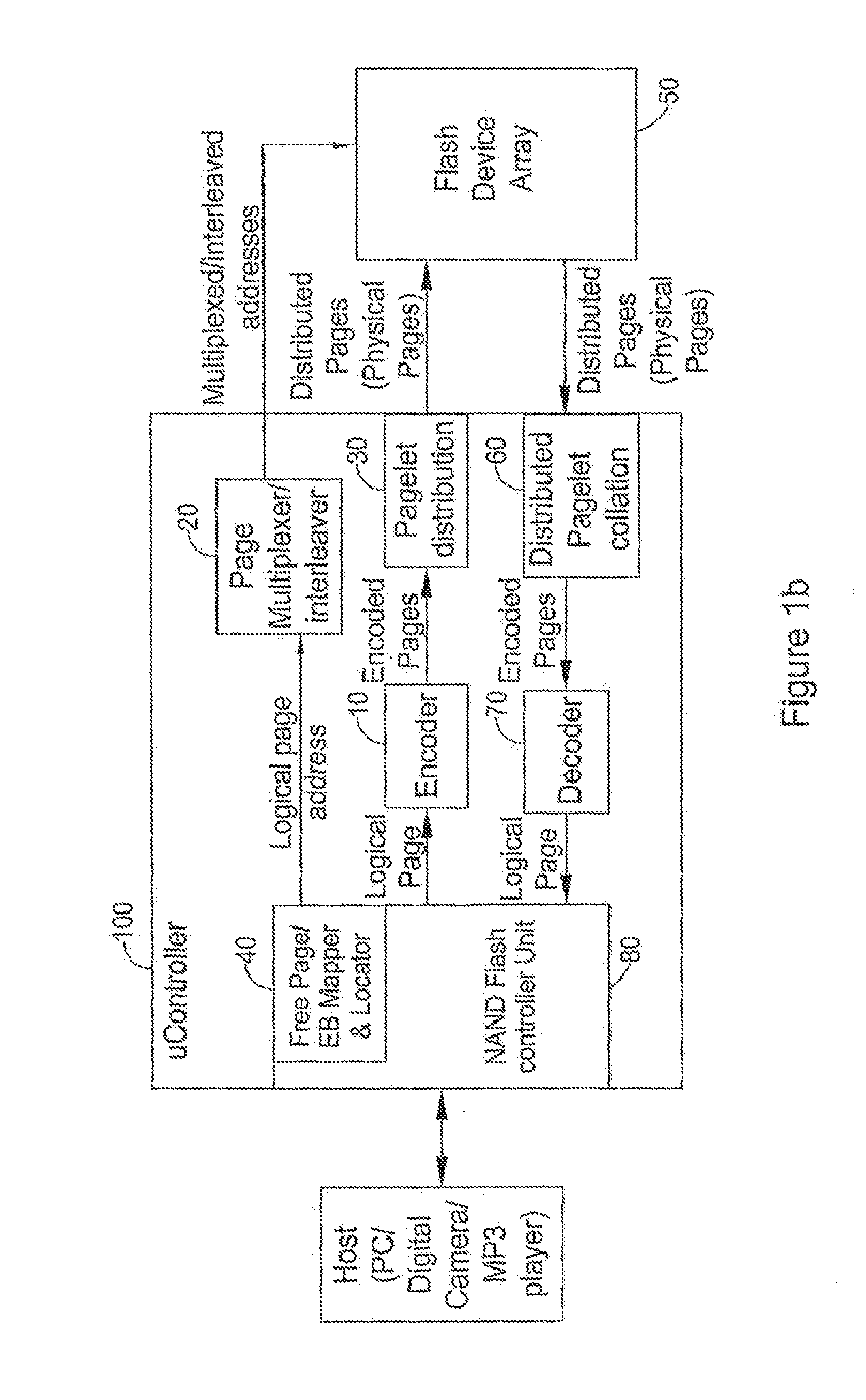
Systems and methods for averaging error rates in non-volatile devices and storage systems
ActiveUS20120066441A1Improve programming speedReduce probabilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationError preventionInformation storageFlash memory
A system for storing a plurality of logical pages in a set of at least one flash device, each flash device including a set of at least one erase block, the system comprising apparatus for distributing at least one of the plurality of logical pages over substantially all of the erase blocks in substantially all of the flash devices, thereby to define, for at least one logical page, a sequence of pagelets thereof together including all information on the logical page and each being stored within a different erase block in the set of erase blocks; and apparatus for reading each individual page from among the plurality of logical pages including apparatus for calling and ordering the sequence of pagelets from different erase blocks in the set of erase blocks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
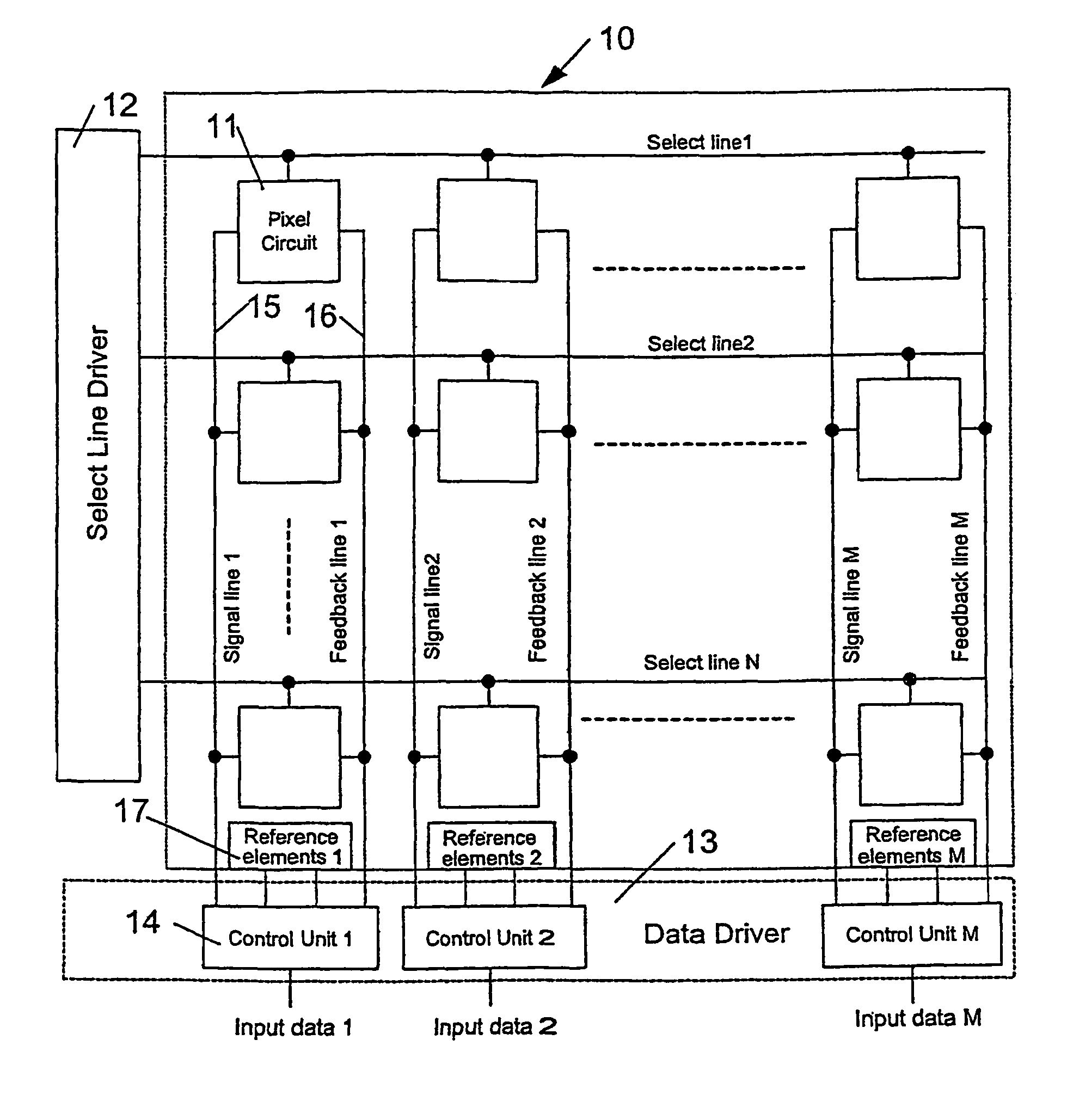
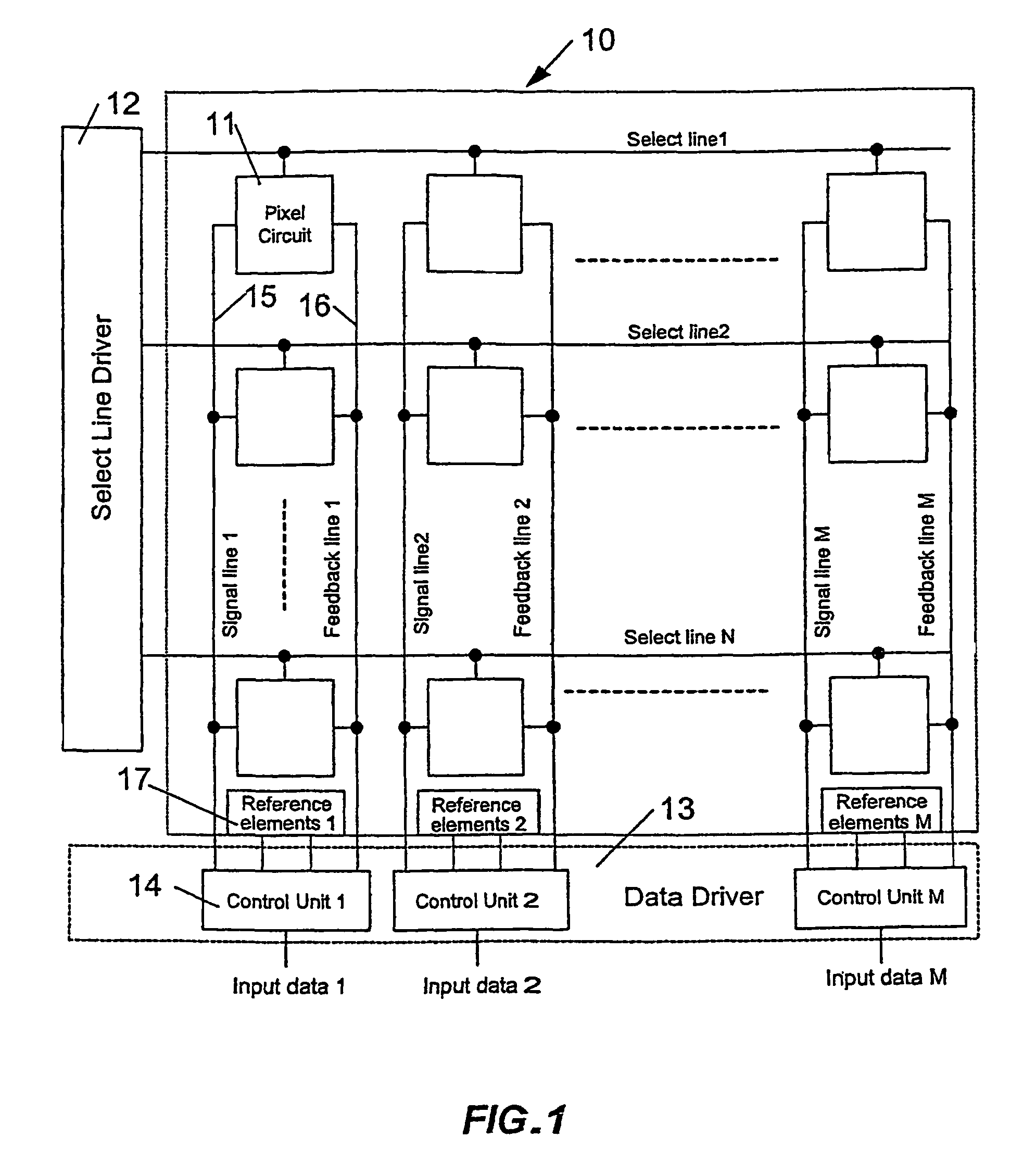
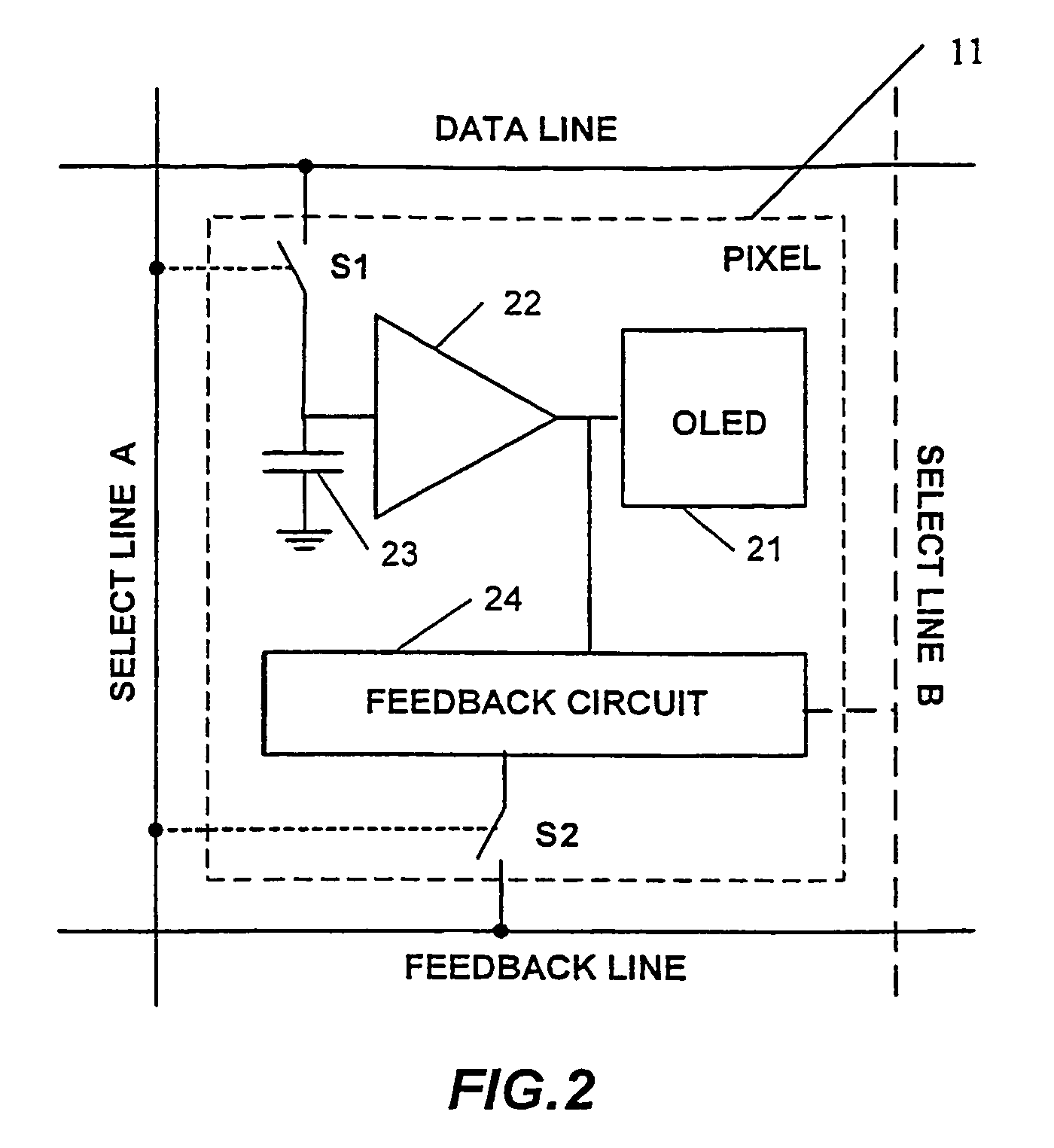
Circuit and method for driving an array of light emitting pixels
ActiveUS7978187B2Stable currentMaintain image qualityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSignal correctionData source
A technique for driving a column of pixels that include light emitting elements. The technique incorporates feedback data provided from feedback data sources connected to the data line and to feedback line of the array, pixel driving circuit with feedback path. The technique can also include block of the reference elements for input signal corrections.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
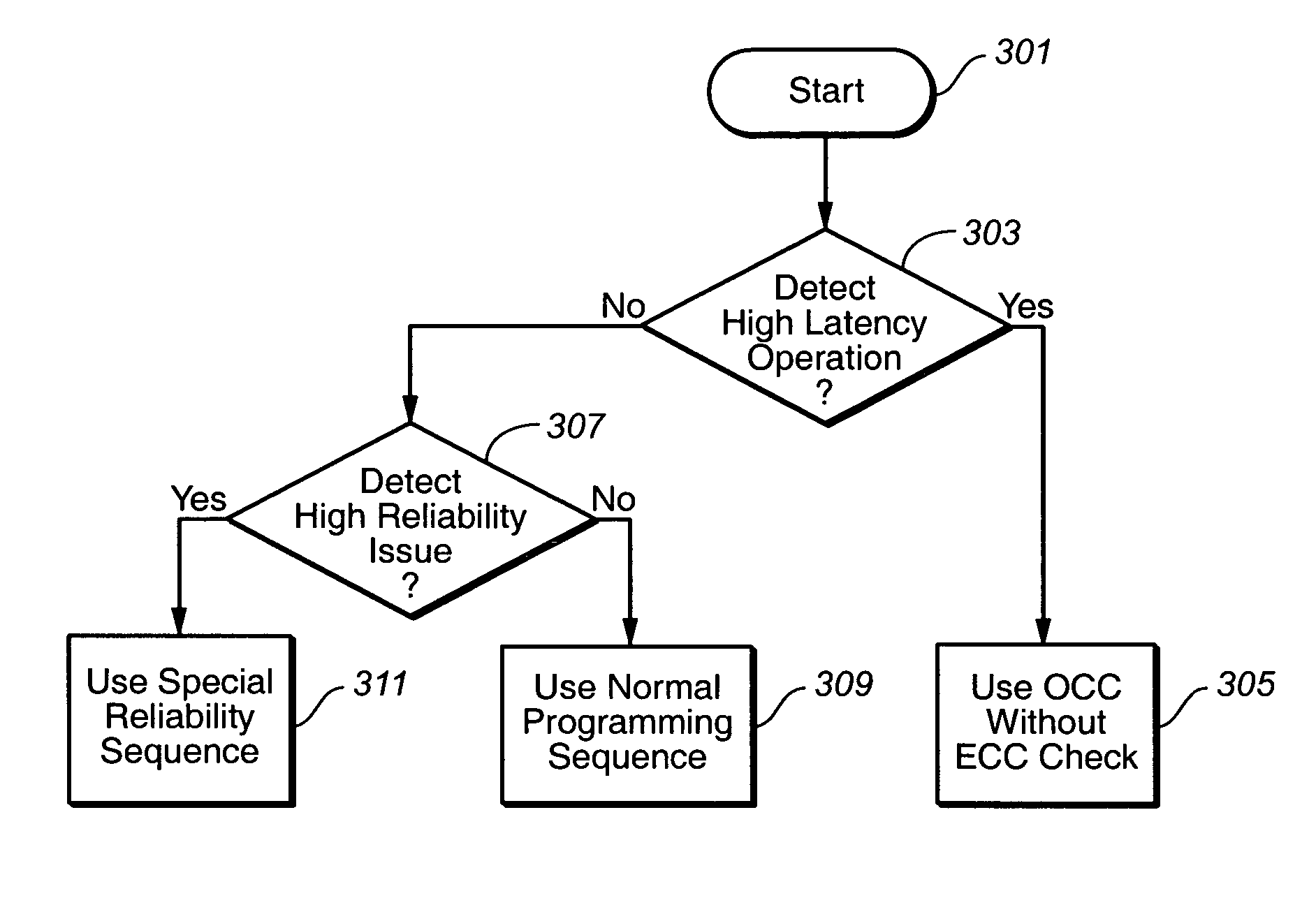
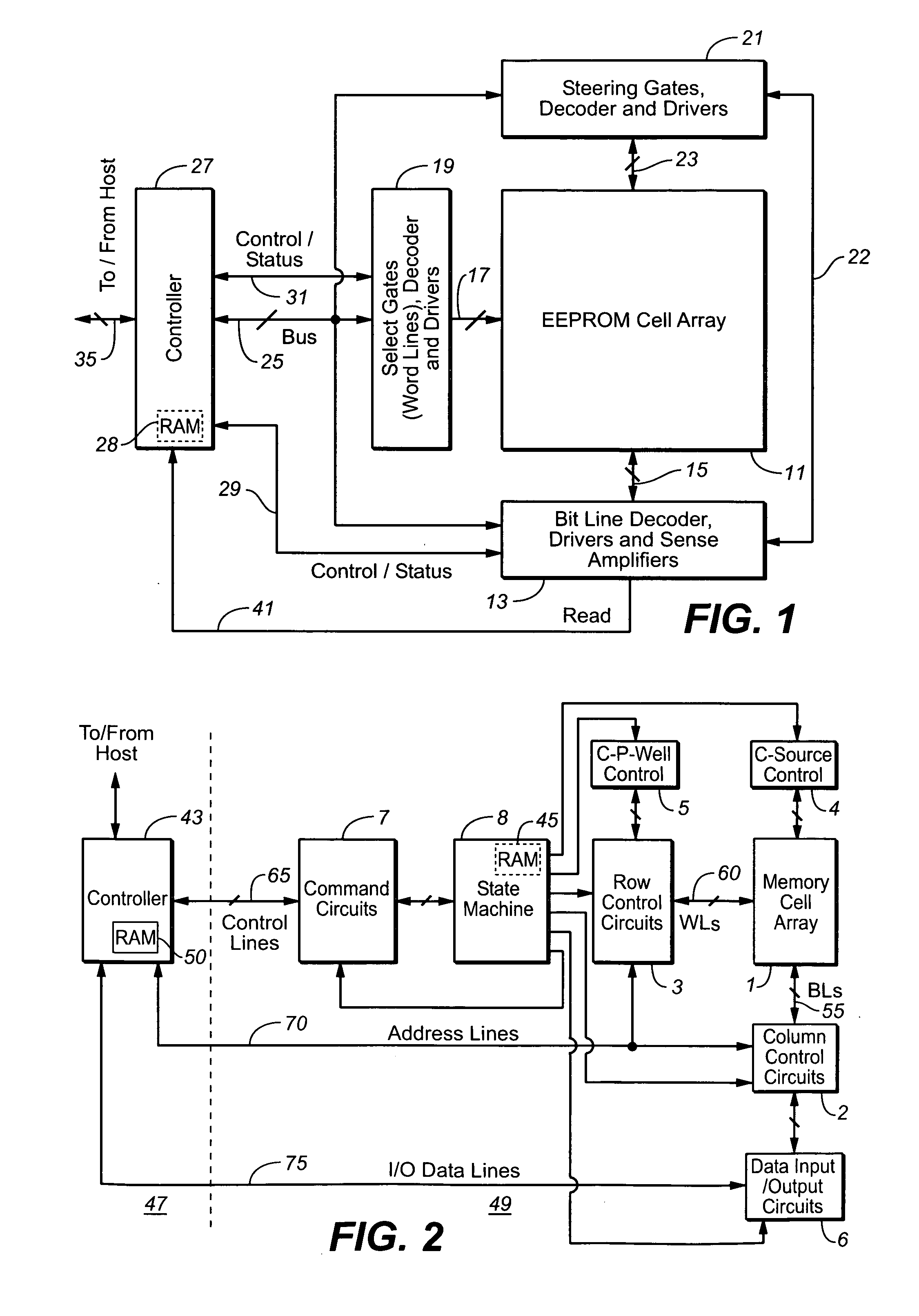
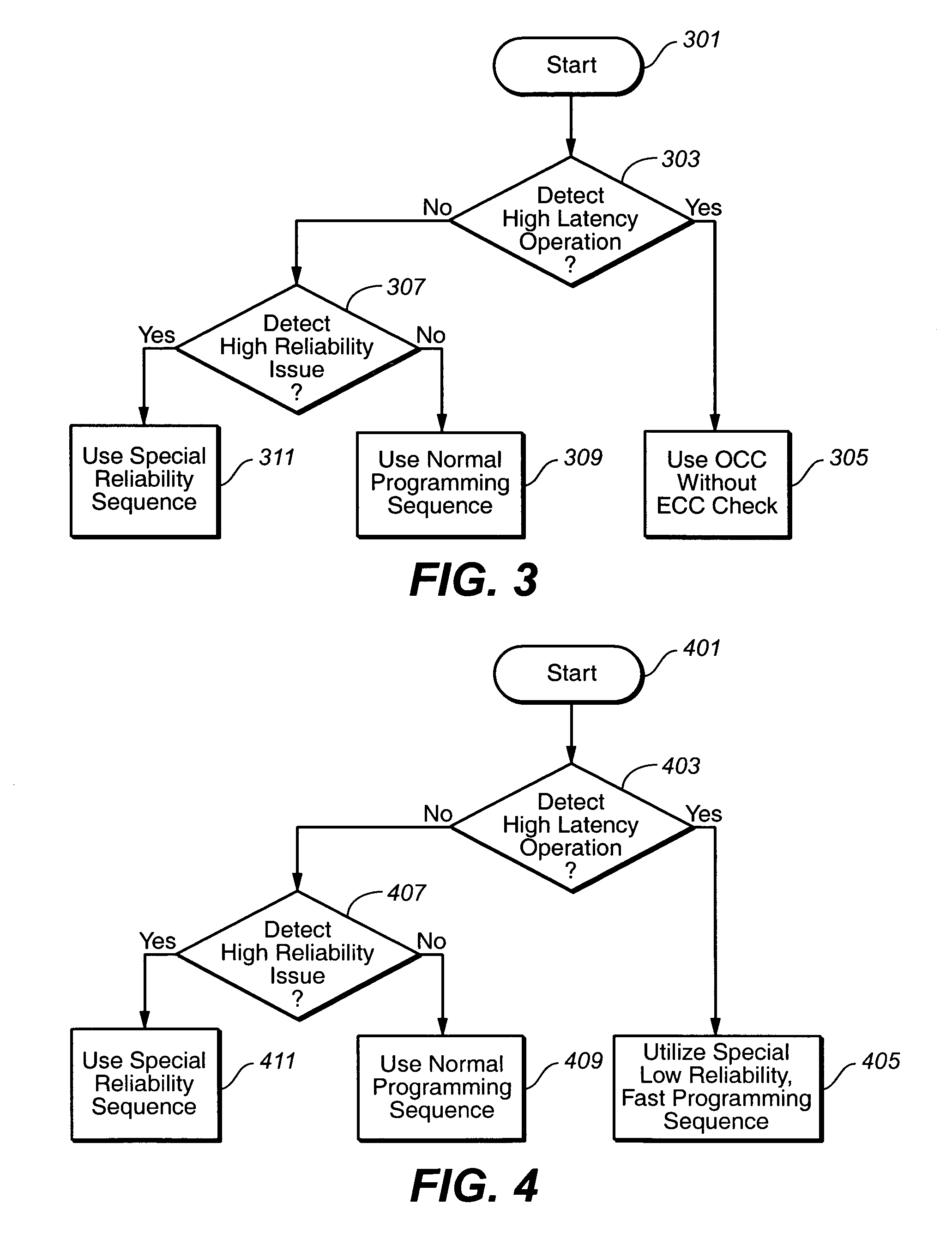
Situation sensitive memory performance
ActiveUS20070033581A1Avoid timeoutImprove programming speedEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTerm memoryComputer science
The present invention presents a non-volatile memory system that adapts its performance to one or more system related situation. If a situation occurs where the memory will require more than the allotted time for completing an operation, the memory can switch from its normal operating mode to a high performance mode in order to complete the operation quickly enough. Conversely, if a situation arises where reliability could be an issue (such as partial page programming), the controller could switch to a high reliability mode. In either case, once the trigging system situation has returned to normal, the memory reverts to the normal operation. The detection of such situations can be used both for programming and data relocation operations. An exemplary embodiment is based on firmware programmable performance.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
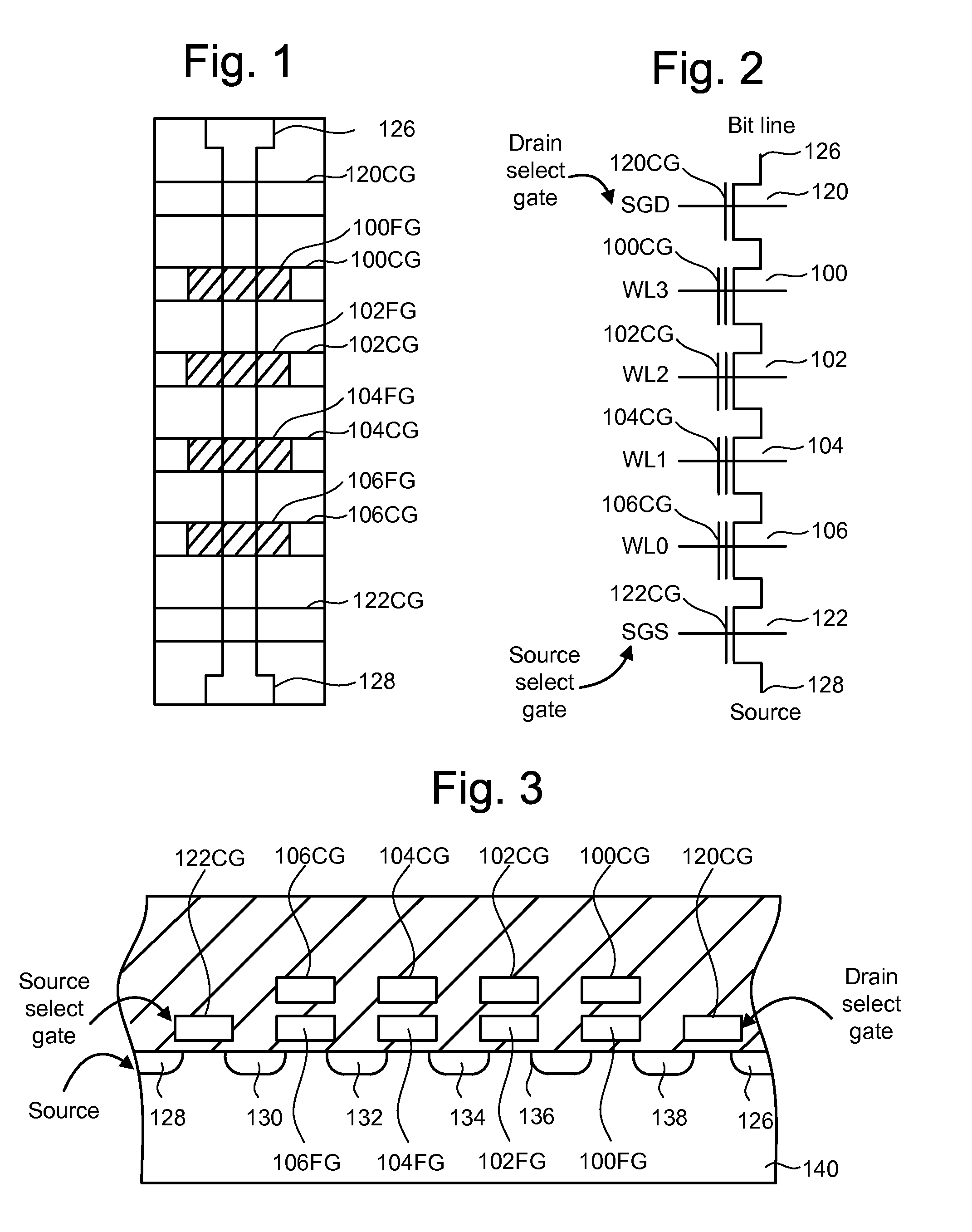
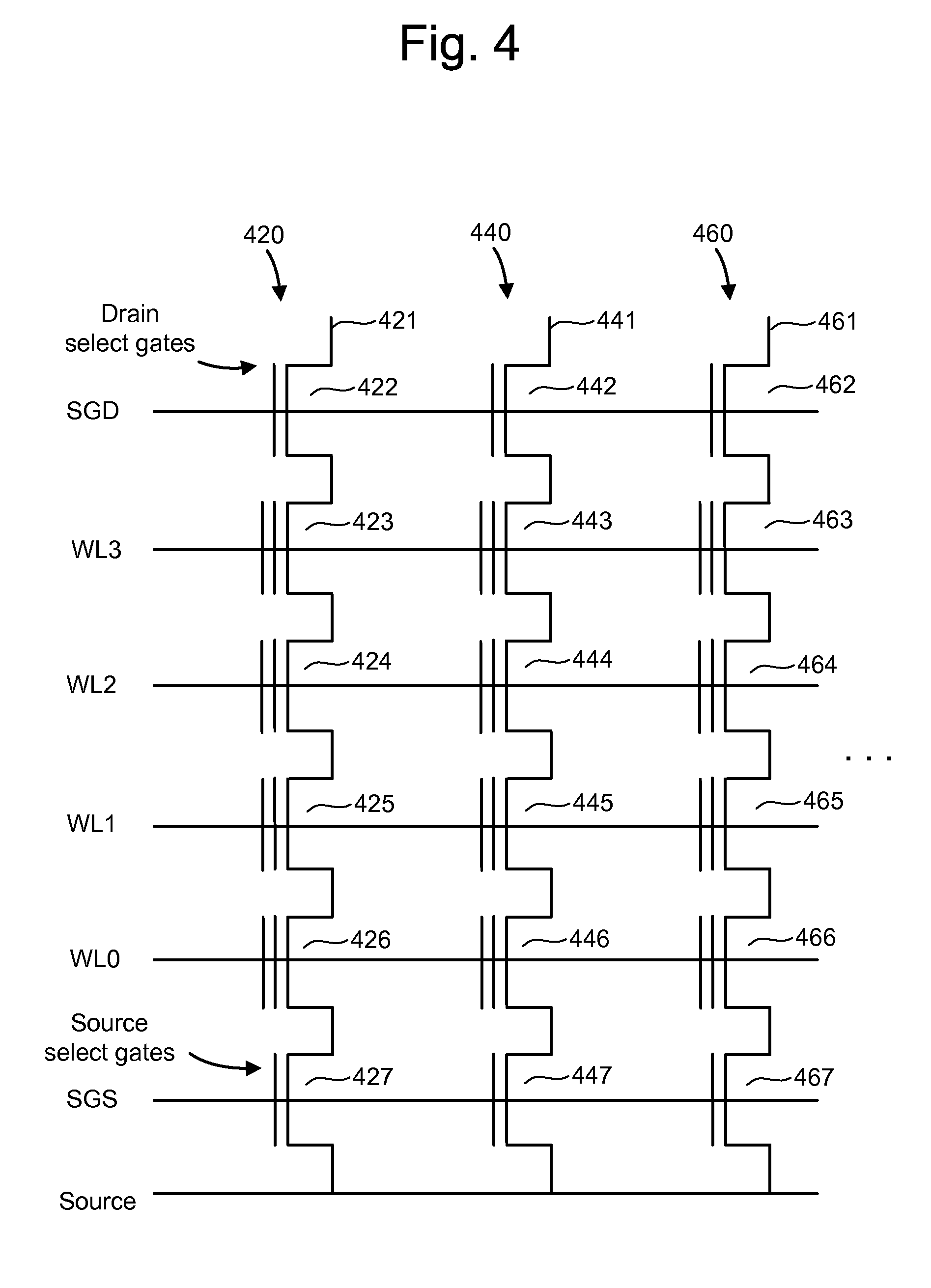
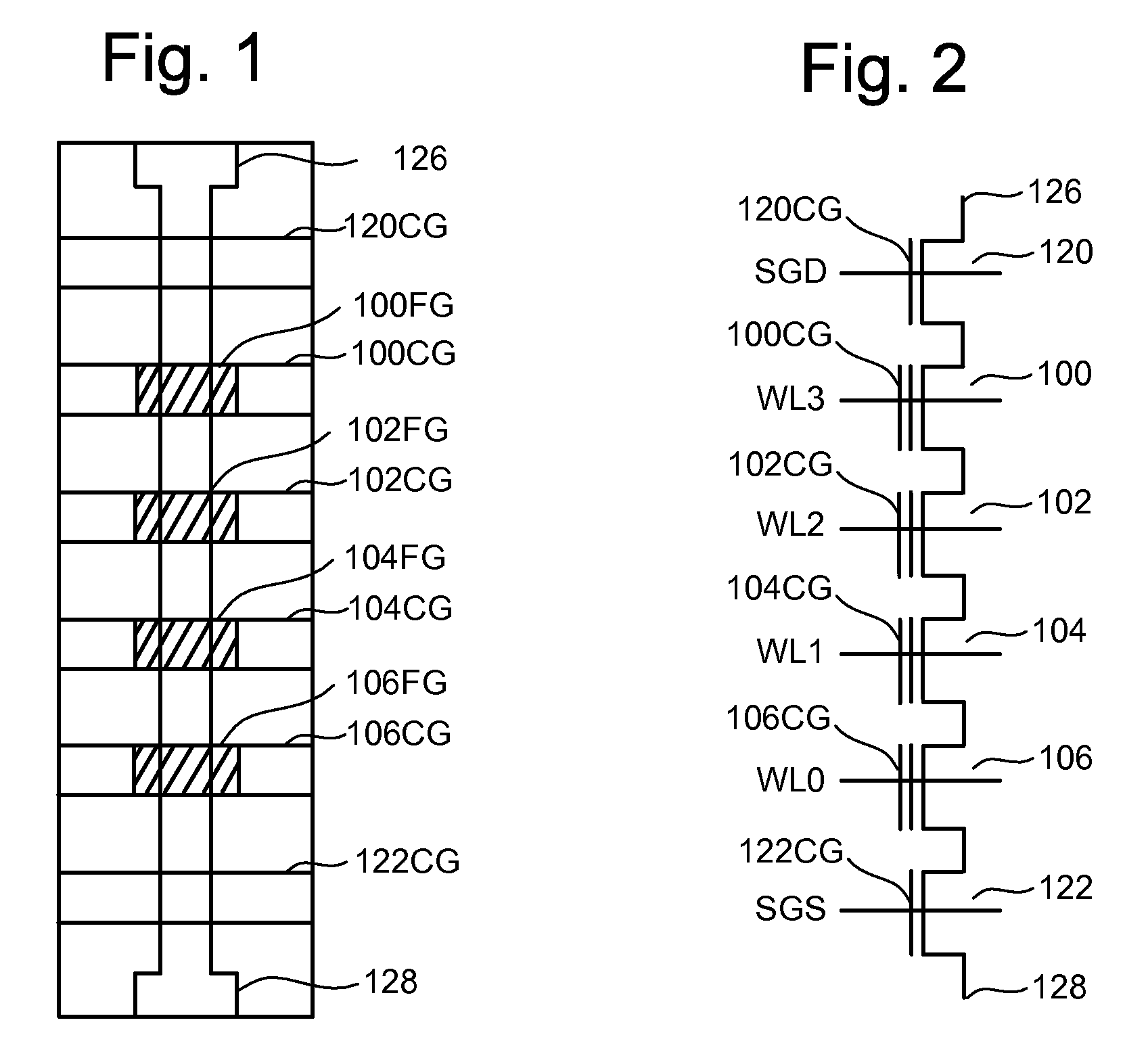
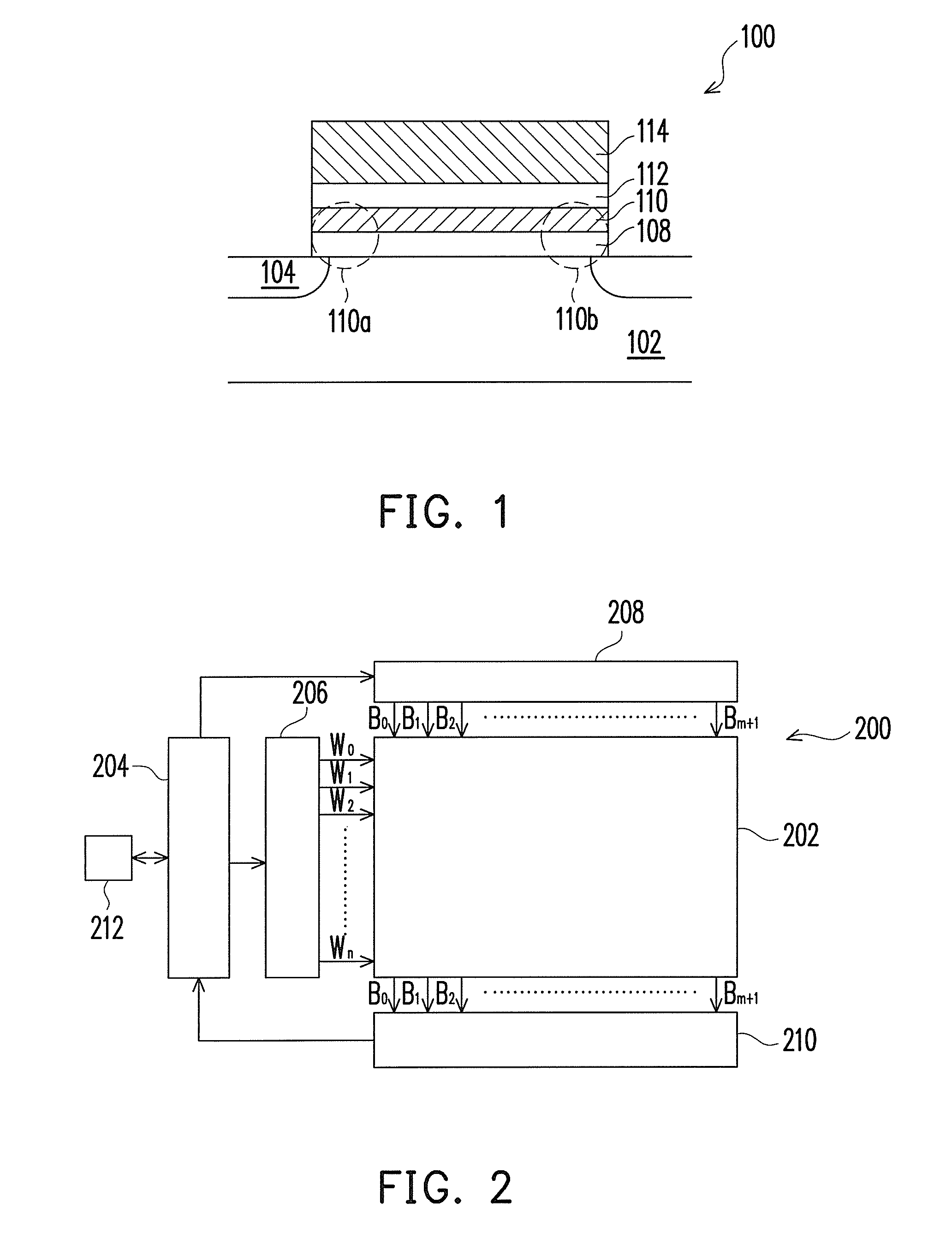
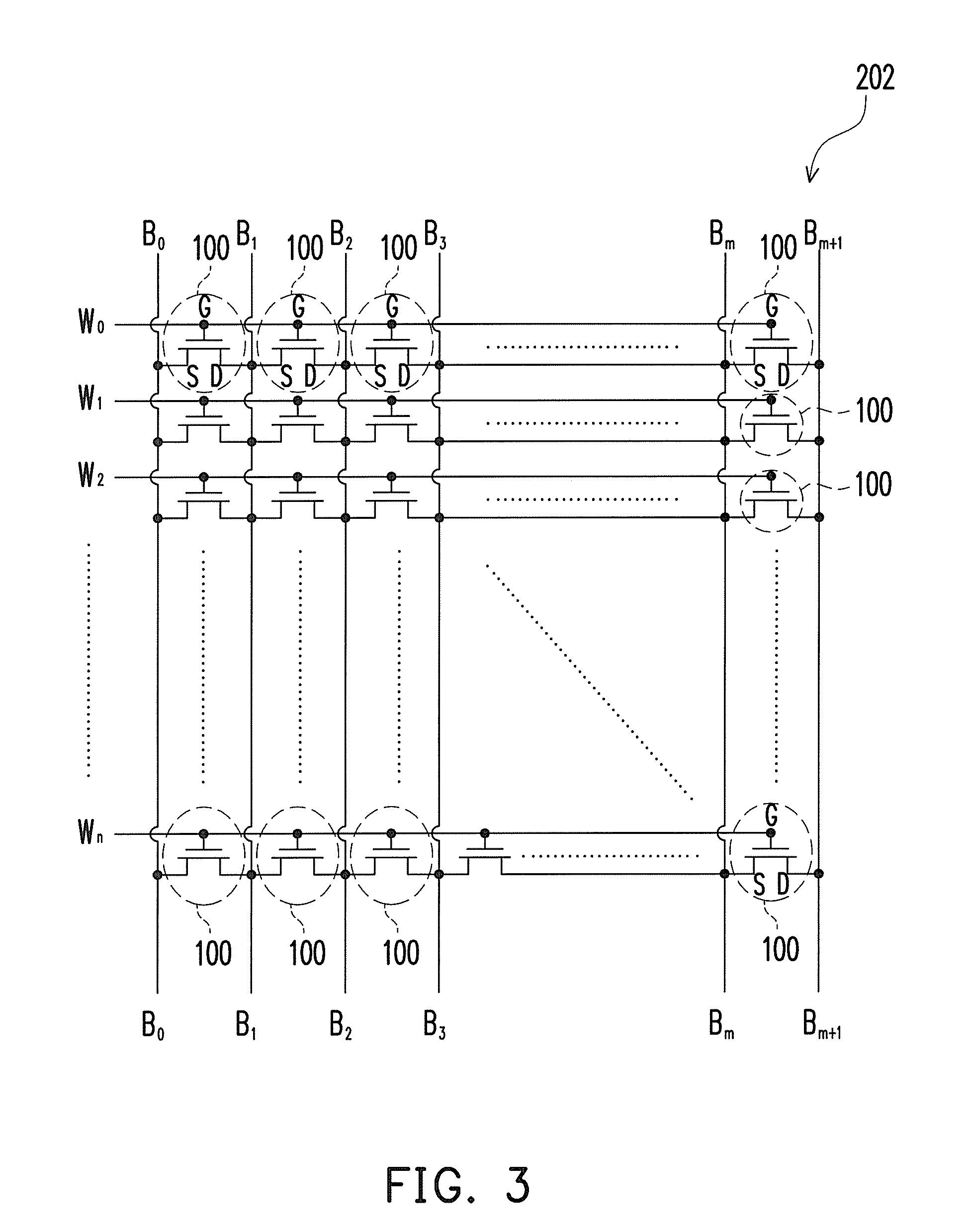
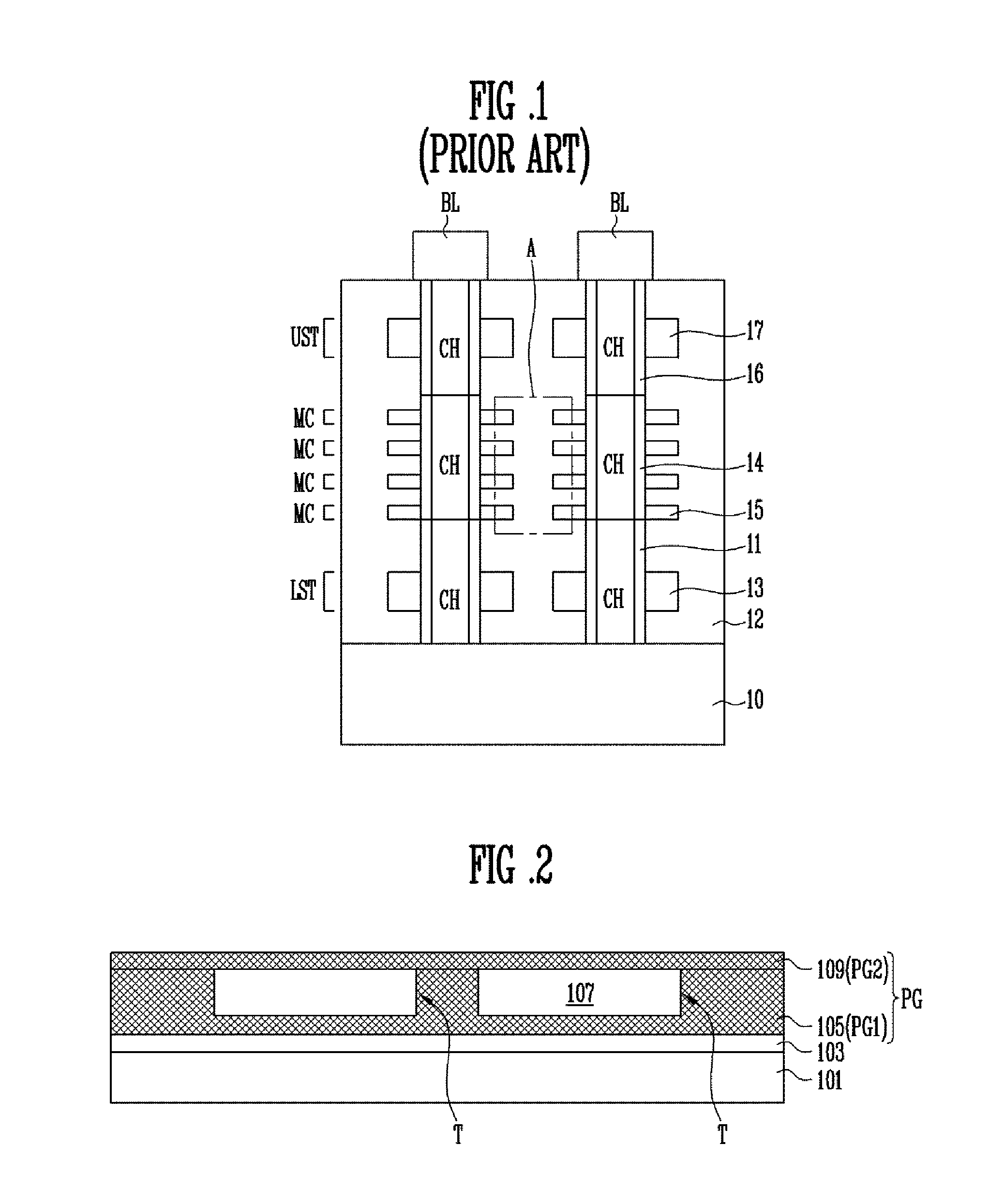
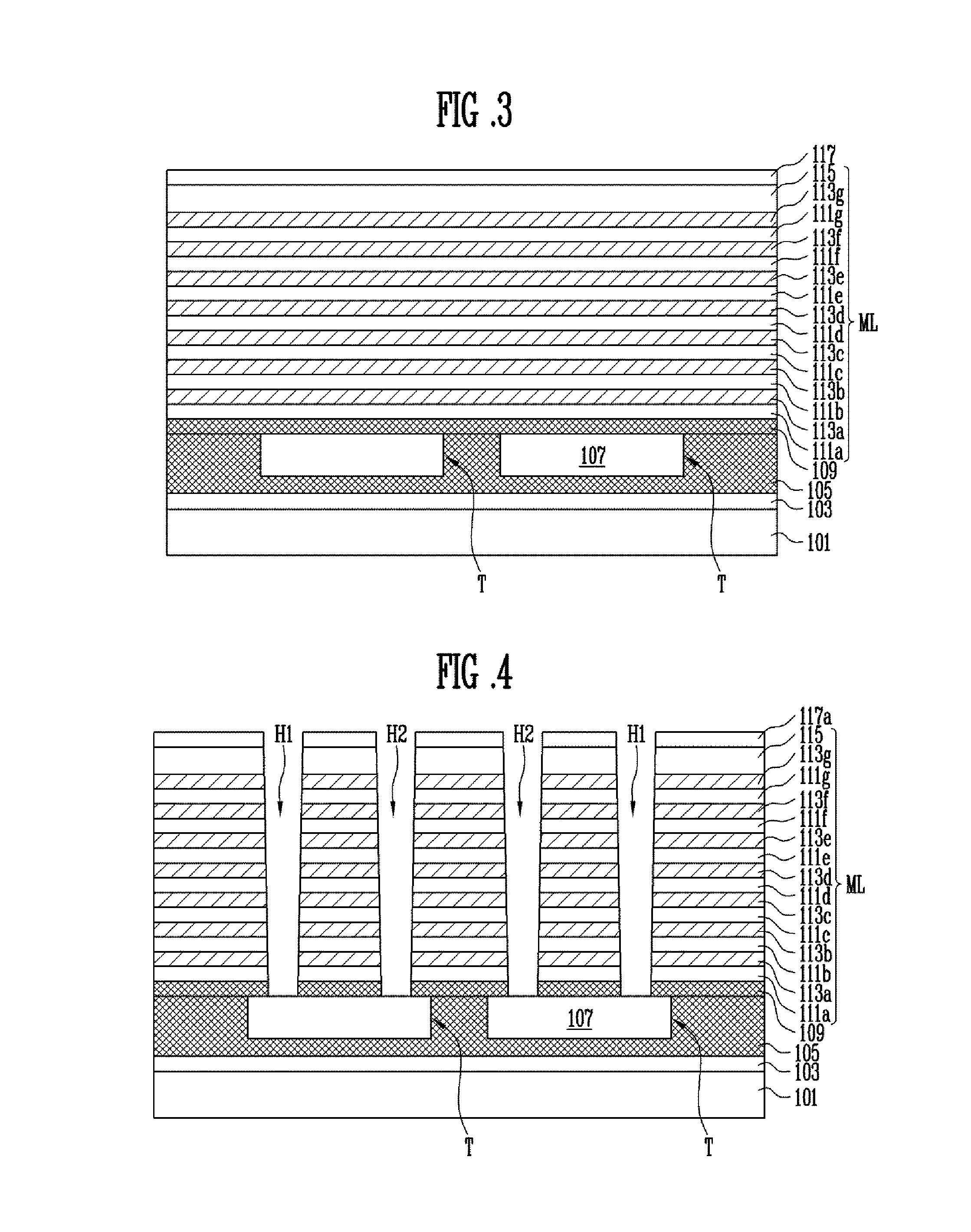
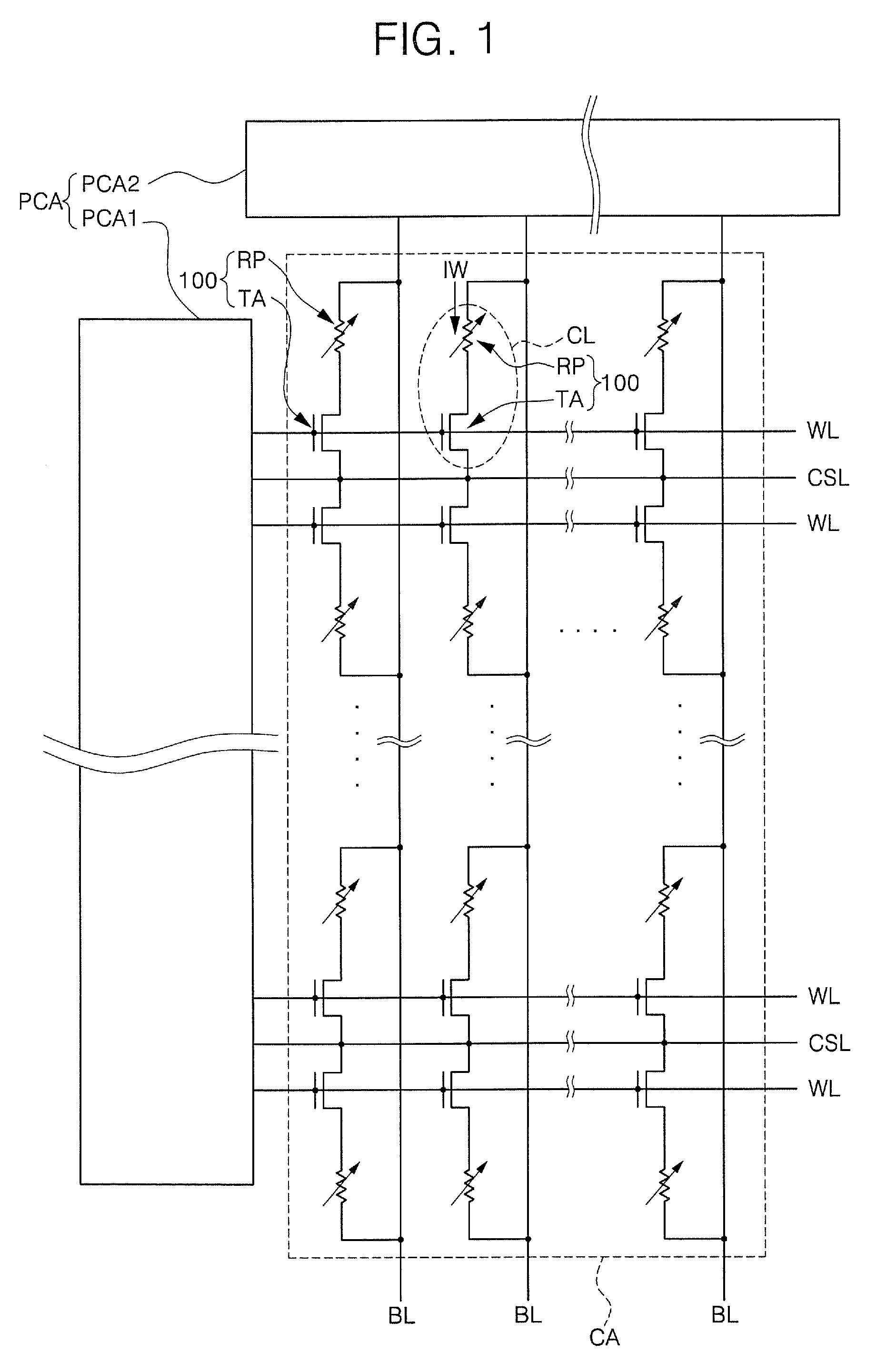
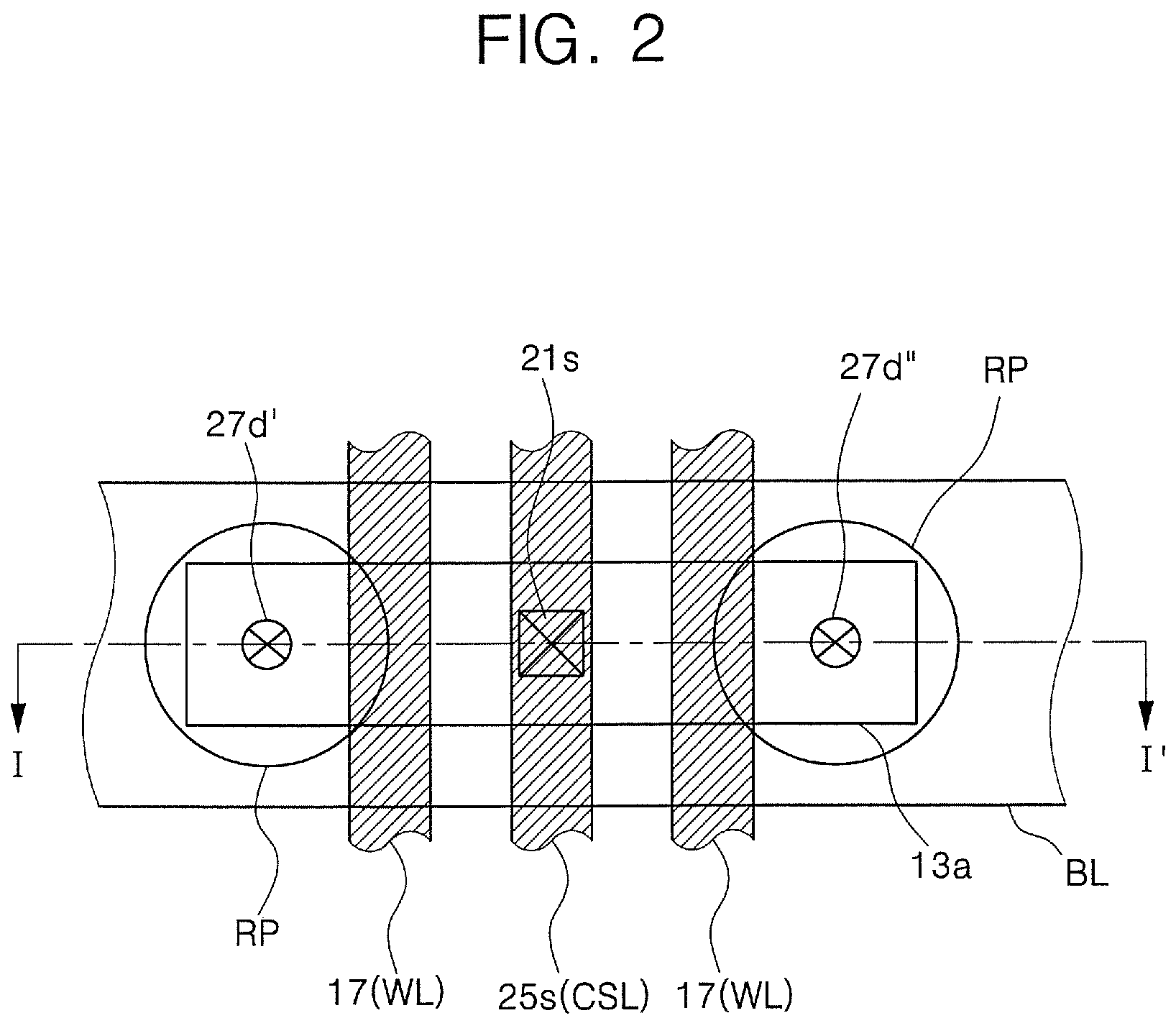
[NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof]
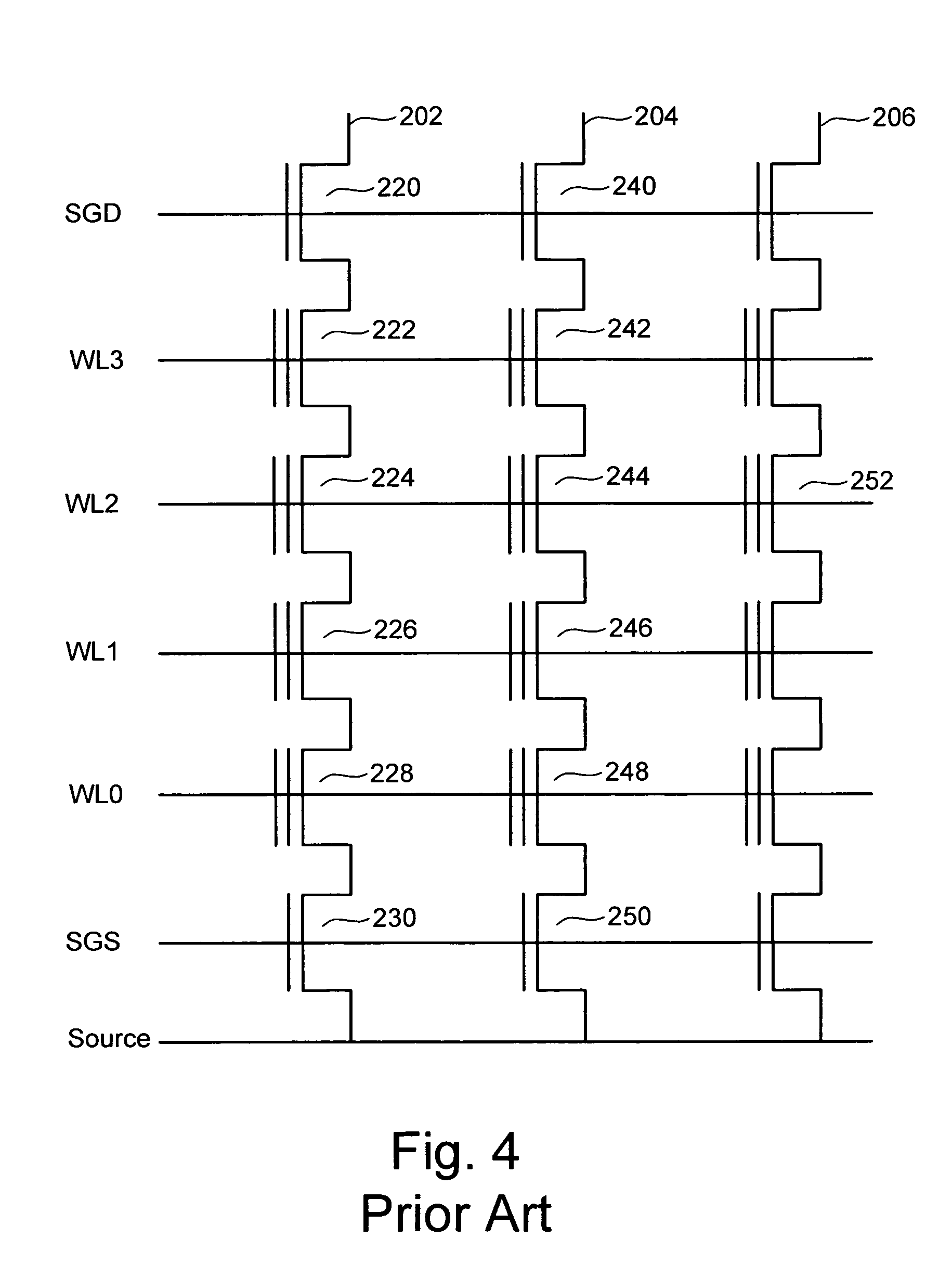
InactiveUS20050087892A1Simplify the manufacturing processIncrease speedTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineComputer architecture
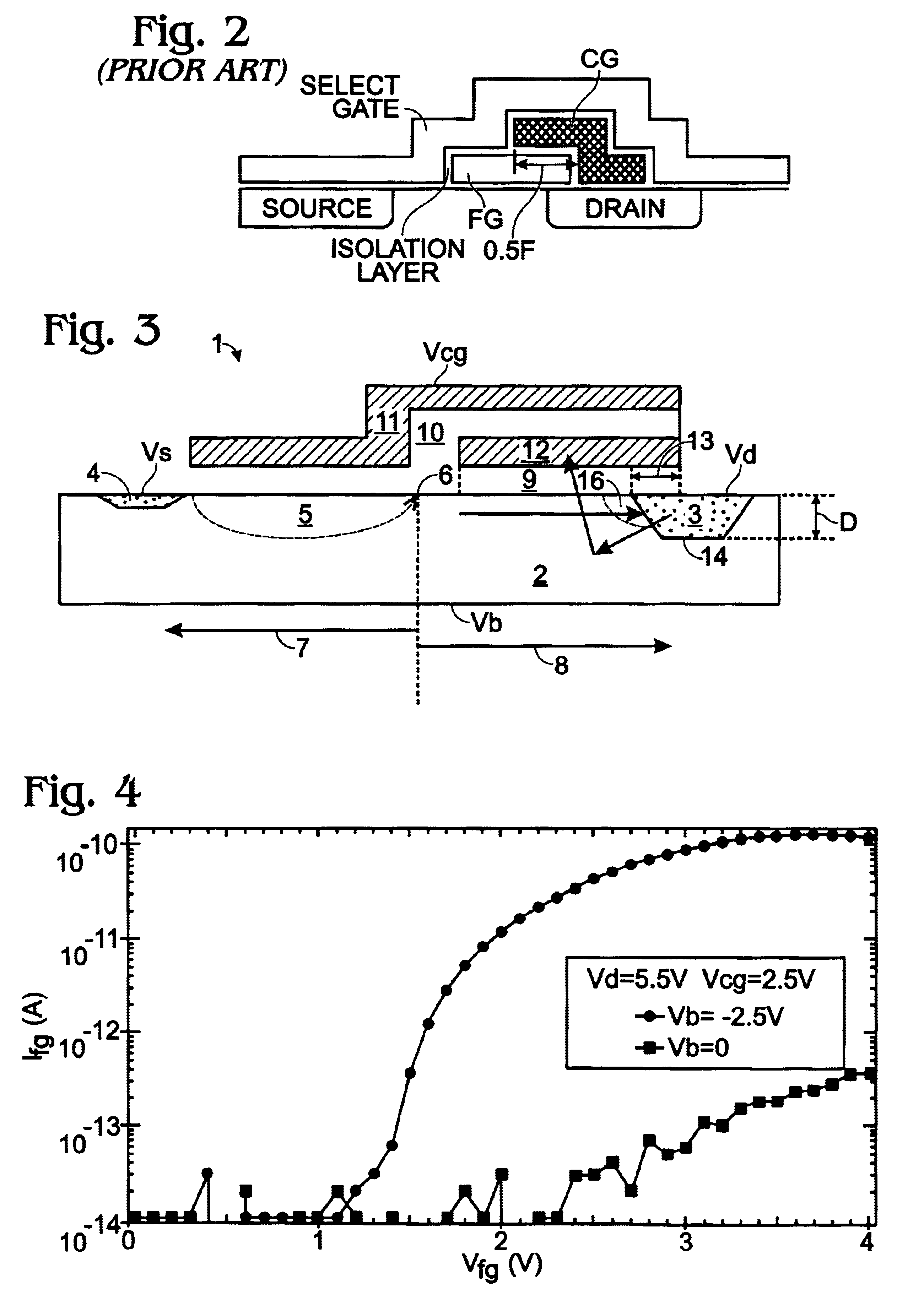
A NAND flash memory cell array including a plurality of memory cell row is provided. Each of memory cell row includes a plurality of memory cells disposed between first selecting transistor and second selecting transistor connected in series. Each memory cell has a tunneling dielectric layer, a floating gate, an inter-gate dielectric, a control gate and source / drain regions. An erase gate is disposed between two adjacent memory cells. A plurality of word lines serve to connect the memory cells in rows. A source line serves to connect the source region of the first transistor in a row, whereas a plurality of bit lines serve to connect the drain region of second transistor in a row. A first selecting gate line and a second selecting gate line serve to connect the gate of the first transistor in a row and the gate of second transistor in a row respectively. A plurality of erase gate lines is connected to the erase gates in a row.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
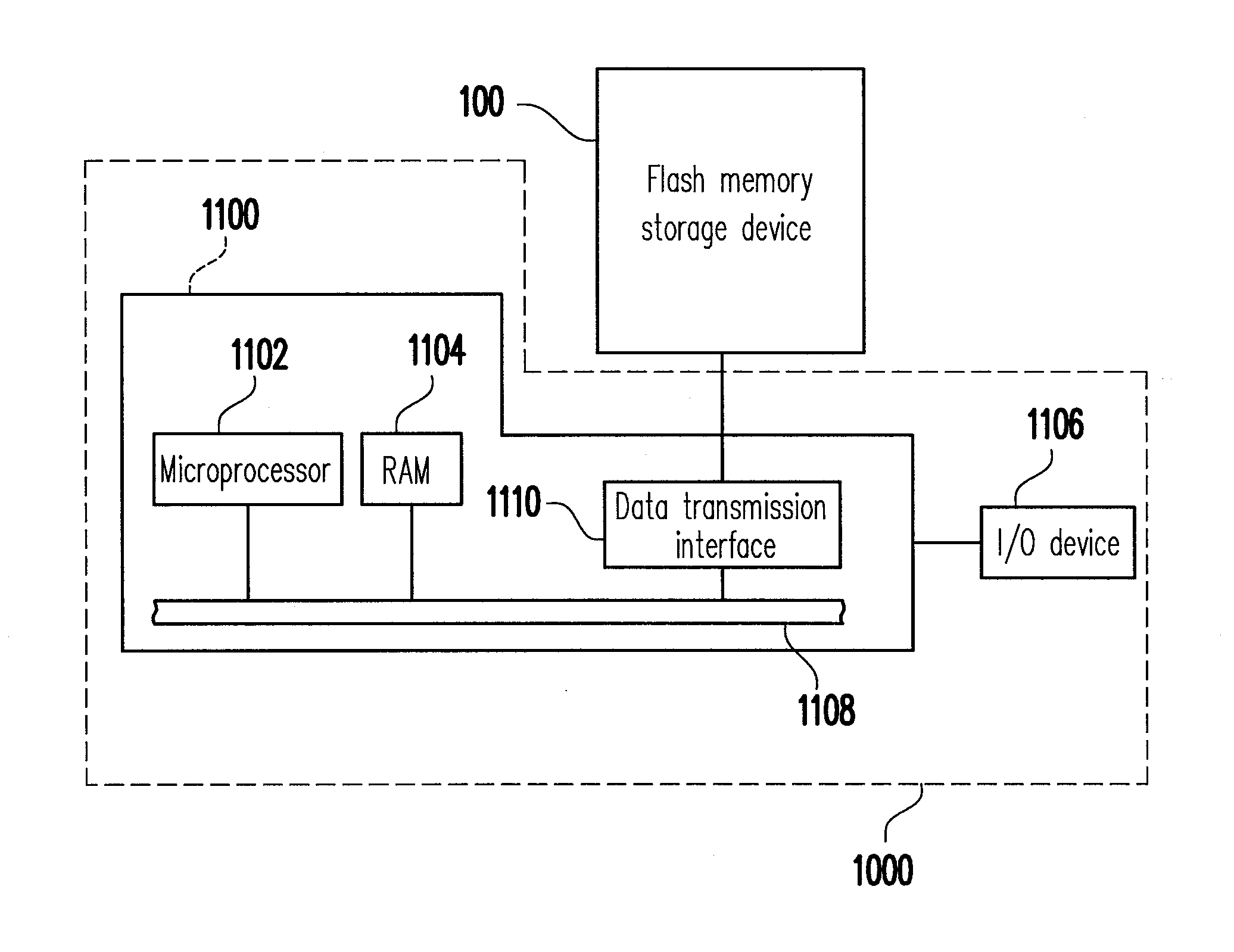
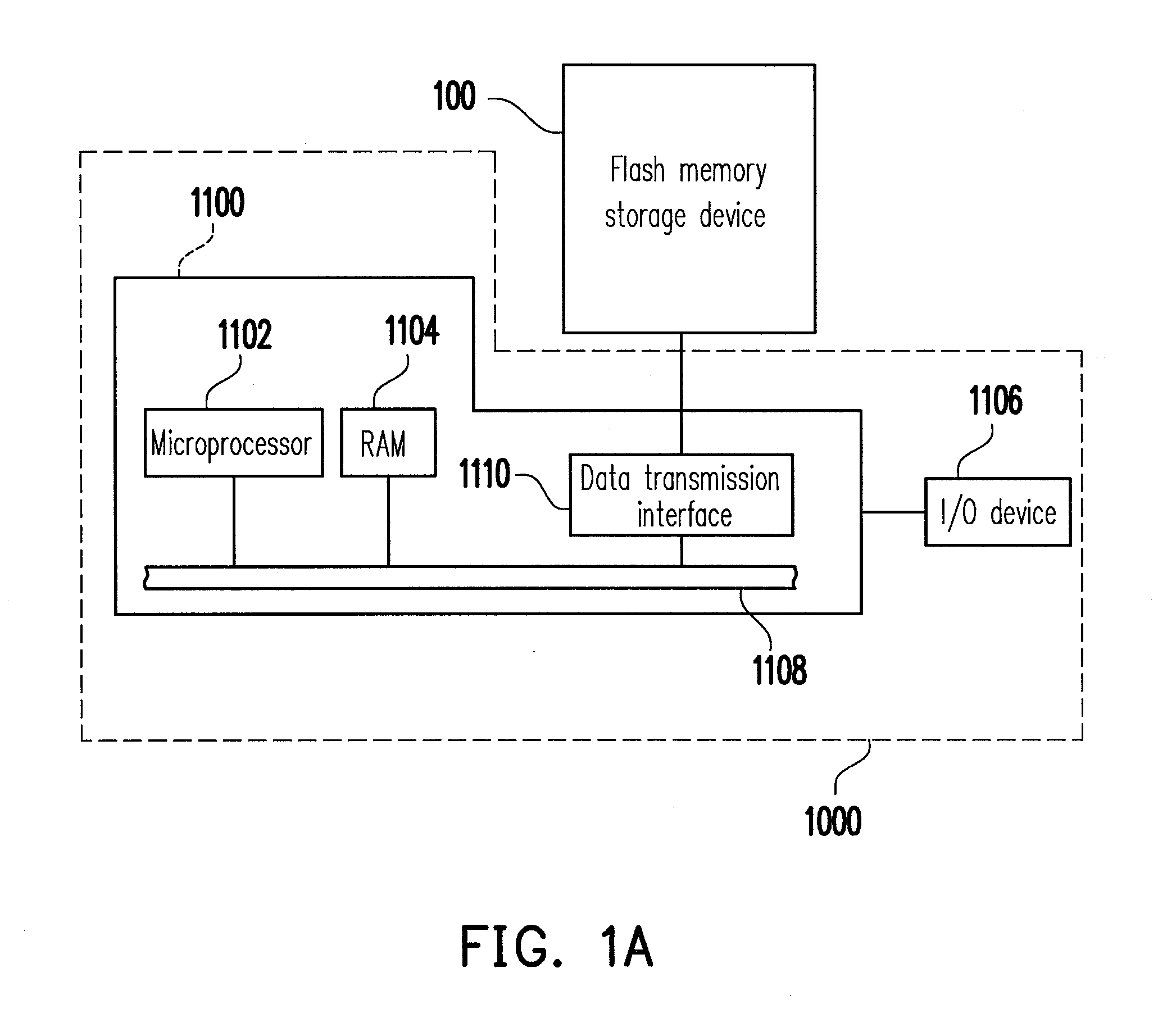
Flash memory storage device, controller thereof, and data programming method thereof
ActiveUS20110191525A1Improve programming speedAvoid negative influenceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData bufferLogical address
A flash memory storage device, a controller thereof, and a data programming method are provided. The flash memory storage device has a flash memory comprising a plurality of physical blocks, each physical block includes a plurality of physical addresses, and the physical addresses comprises at least one fast physical address and at least one slow physical address. The method comprises at least grouping the physical blocks into a data area and a spare area; setting a predetermined block number; obtaining m physical blocks from the spare area, receiving a write command comprising a write data and a logical address, determining a logical address range of a buffer according to the logical address and the predetermined block number. When all logical addresses to be programmed with the write data are within the logical address range of the buffer, using a fast mode to program the data into the m physical blocks.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
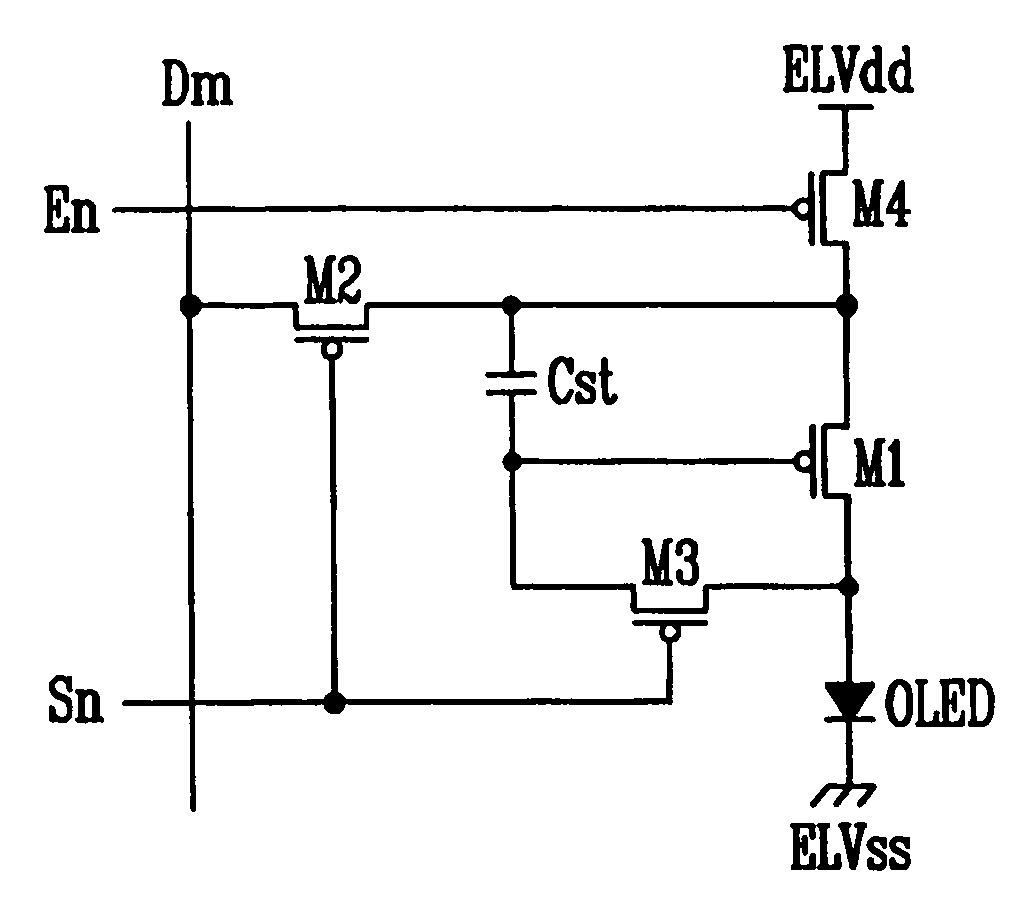
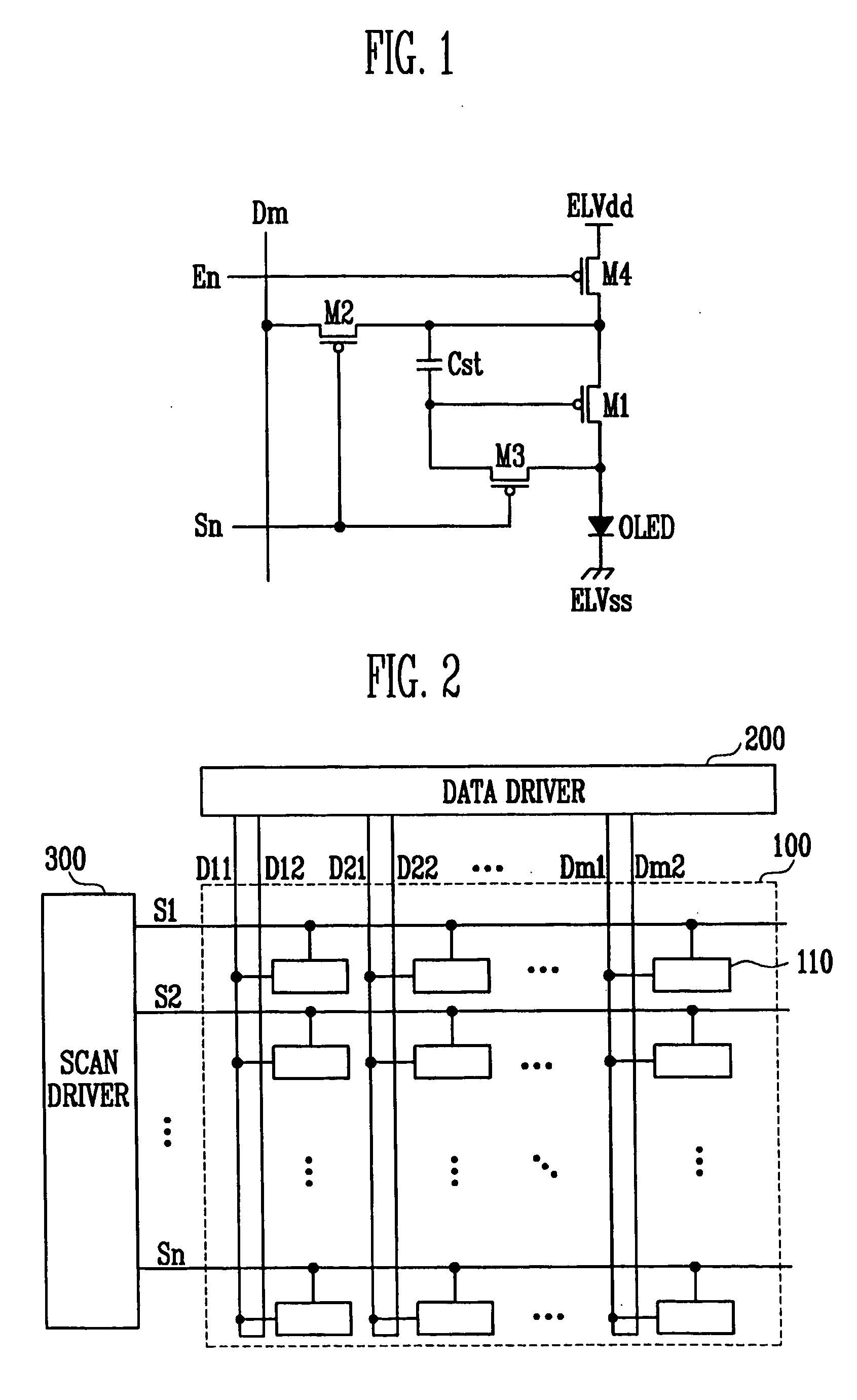
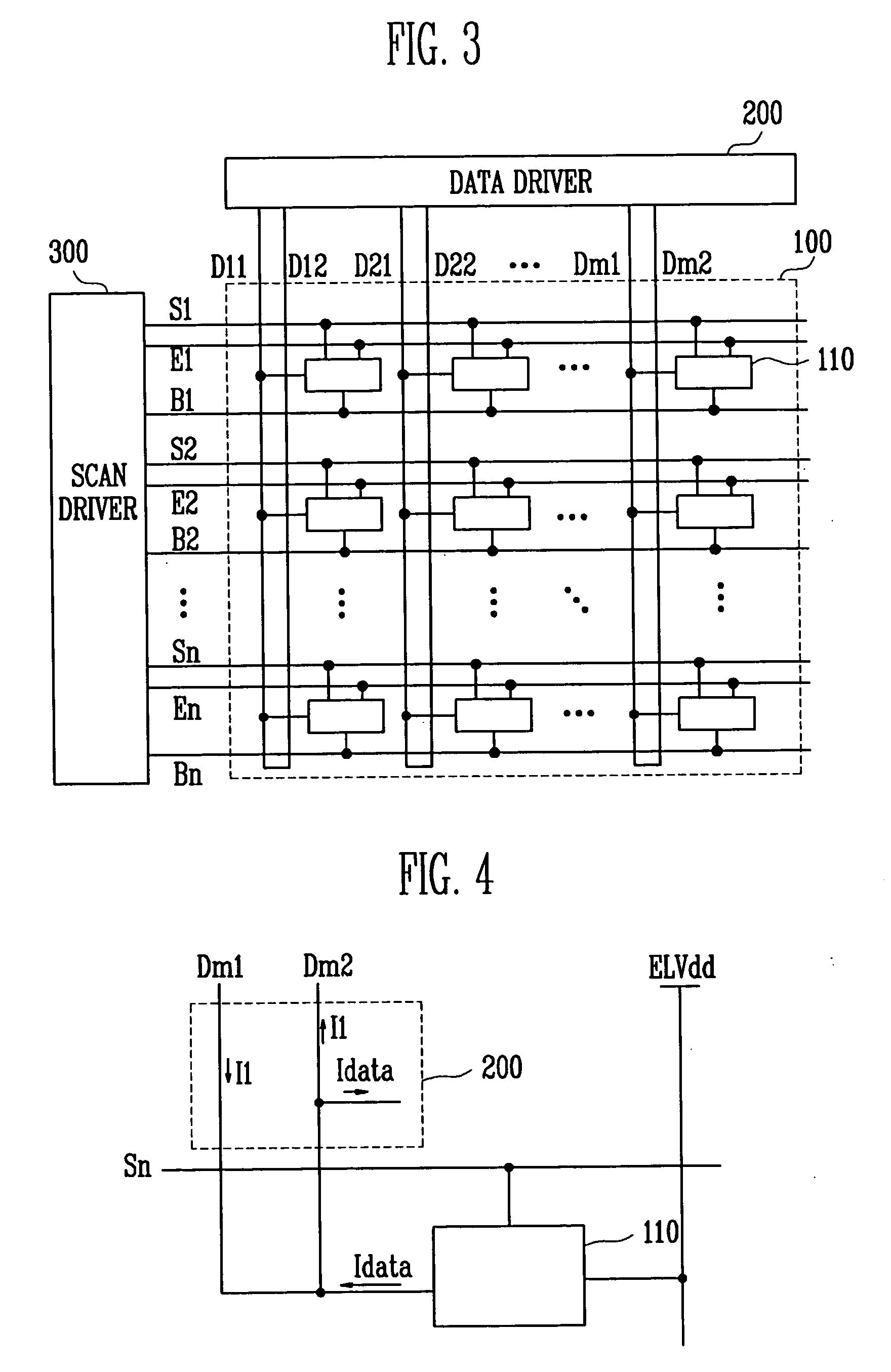
Light emitting display
ActiveUS20060139259A1Simple designImprove programming speedStatic indicating devicesControl signalDisplay device
A light emitting display that includes a pixel portion having a plurality of pixels to display an image, a scan driver to supply a scan signal and an emission control signal to the pixel portion, and a data driver connected to a plurality of data lines each divided into a first data line through which a first current is supplied to the pixel, and a second data line through which a current having the same magnitude as the first current and a data current are induced from the pixel, wherein the data driver includes a current applying circuit to generate the first current, supply the first current to the pixel through the first data line, and receive the first current from the pixel through the second data line; and a data driving integrated circuit to induce the data current in the pixel through the second data line.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Branch prediction apparatus and process for restoring replaced branch history for use in future branch predictions for an executing program
InactiveUS6877089B2Saving and fast utilizationImprove programming speedDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingSemiconductor
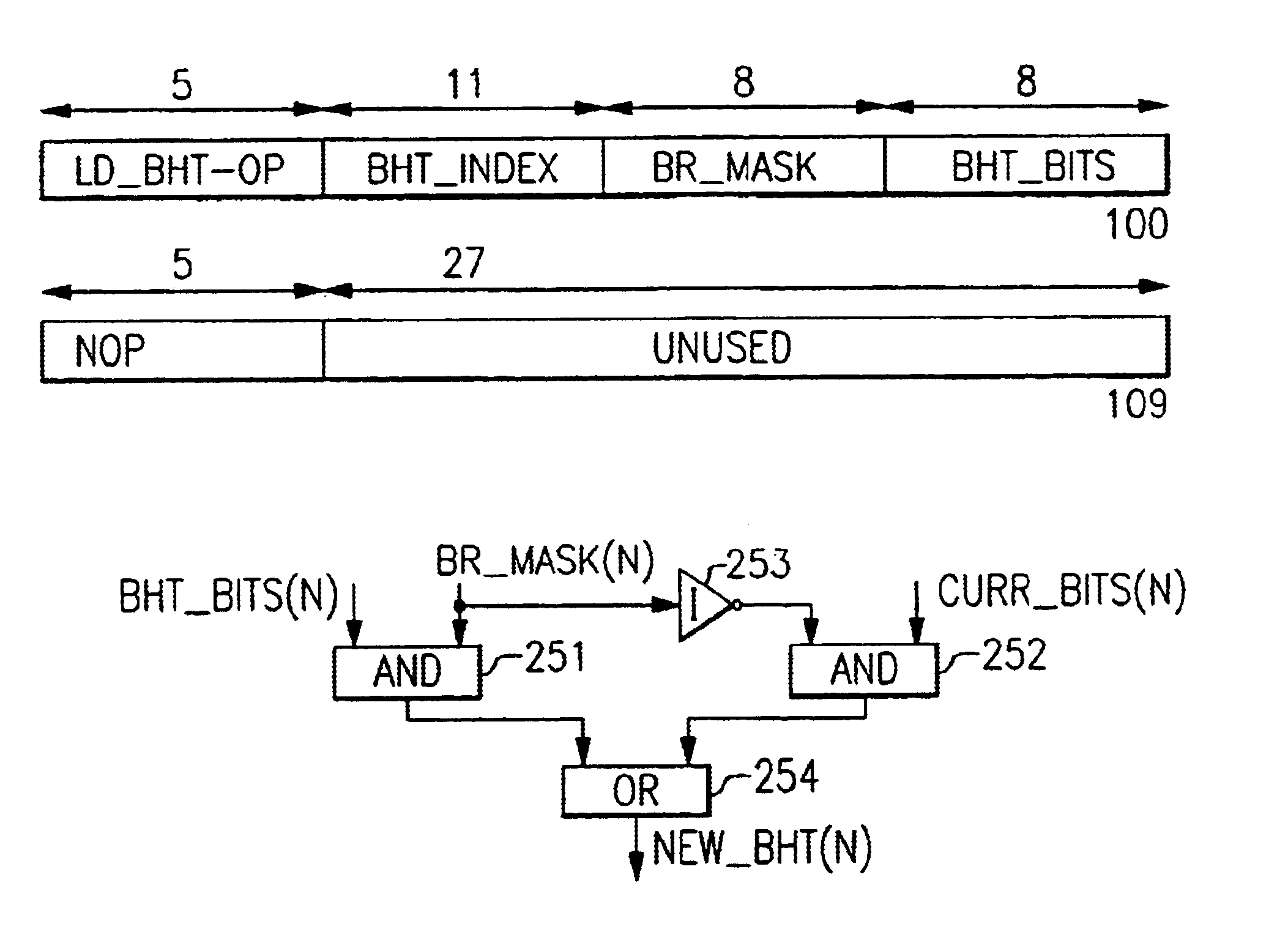
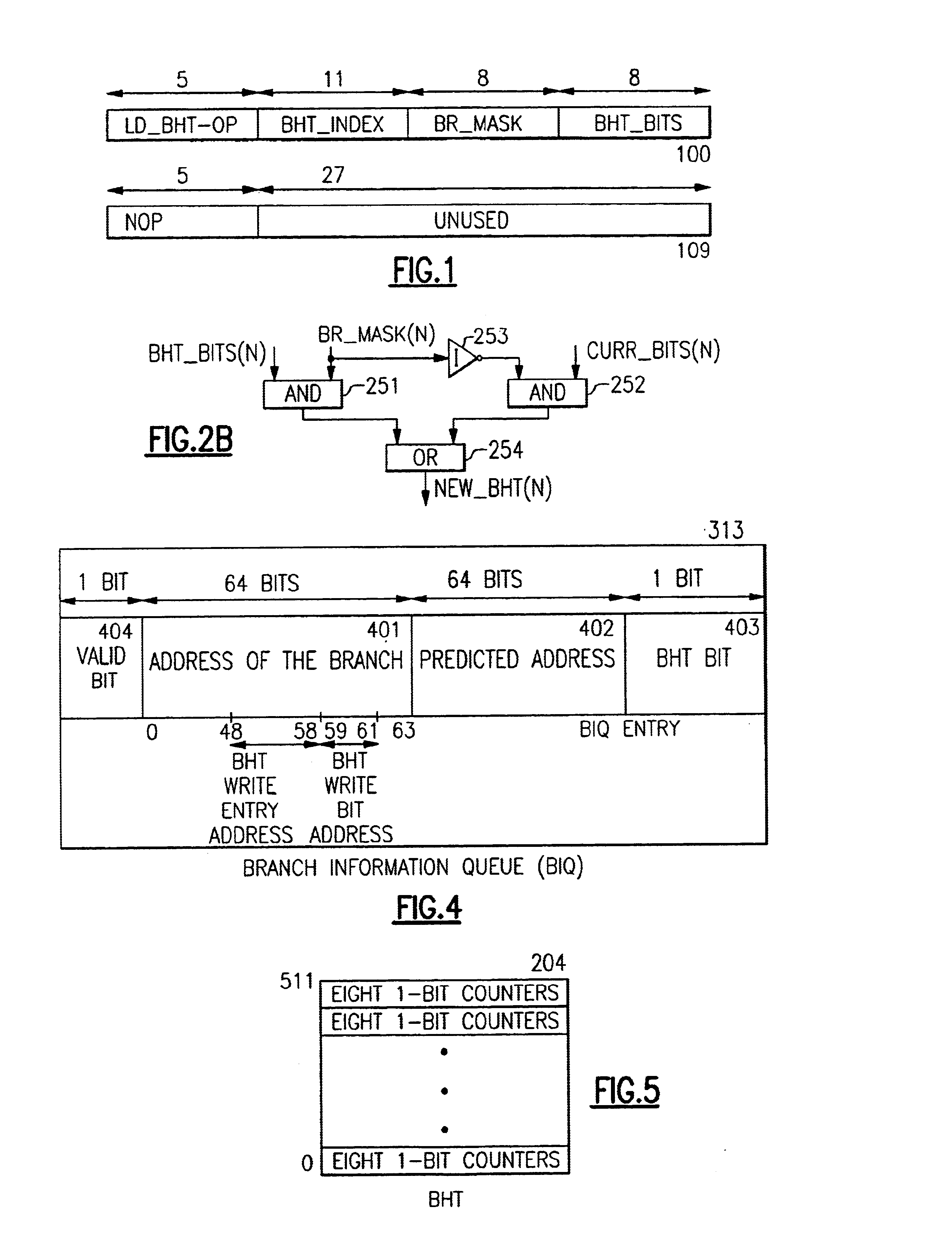
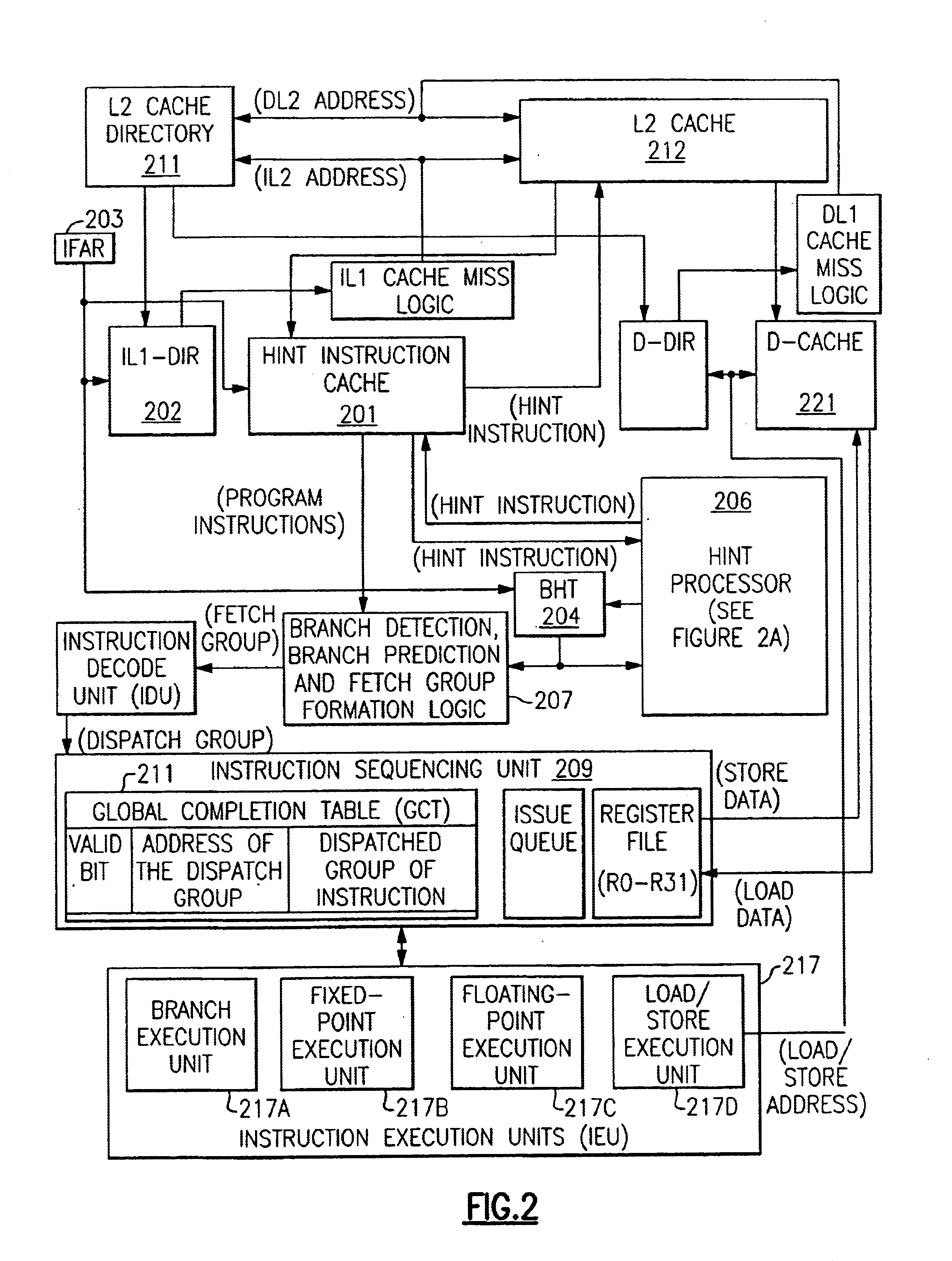
Apparatus and methods implemented in a processor semiconductor logic chip for providing novel “hint instructions” that uniquely preserve and reuse branch predictions replaced in a branch history table (BHT). A branch prediction is lost in the BHT after its associated instruction is replaced in an instruction cache. The unique “hint instructions” are generated and stored in a unique instruction cache which associates each hint instruction with a line of instructions. The hint instructions contains the latest branch history for all branch instructions executed in an associated line of instructions, and they are stored in the instruction cache during instruction cache hits in the associated line. During an instruction cache miss in an instruction line, the associated hint instruction is stored in a second level cache with a copy of the associated instruction line being replaced in the instruction cache. In the second level cache, the copy of the line is located through the instruction cache directory entry associated with the line being replaced in the instruction cache. Later, the hint instruction can be retrieved into the instruction cache when its associated instruction line is fetched from the second level cache, and then its associated hint instruction is also retrieved and used to restore the latest branch predictions for that instruction line. In the prior art this branch prediction would have been lost. It is estimated that this invention improves program performance for each replaced branch prediction by about 80%, due to increasing the probability of BHT bits correctly predicting the branch paths in the program from about 50% to over 90%. Each incorrect BHT branch prediction may result in the loss of many execution cycles, resulting in additional instruction re-execution overhead when incorrect branch paths are belatedly discovered.
Owner:IBM CORP
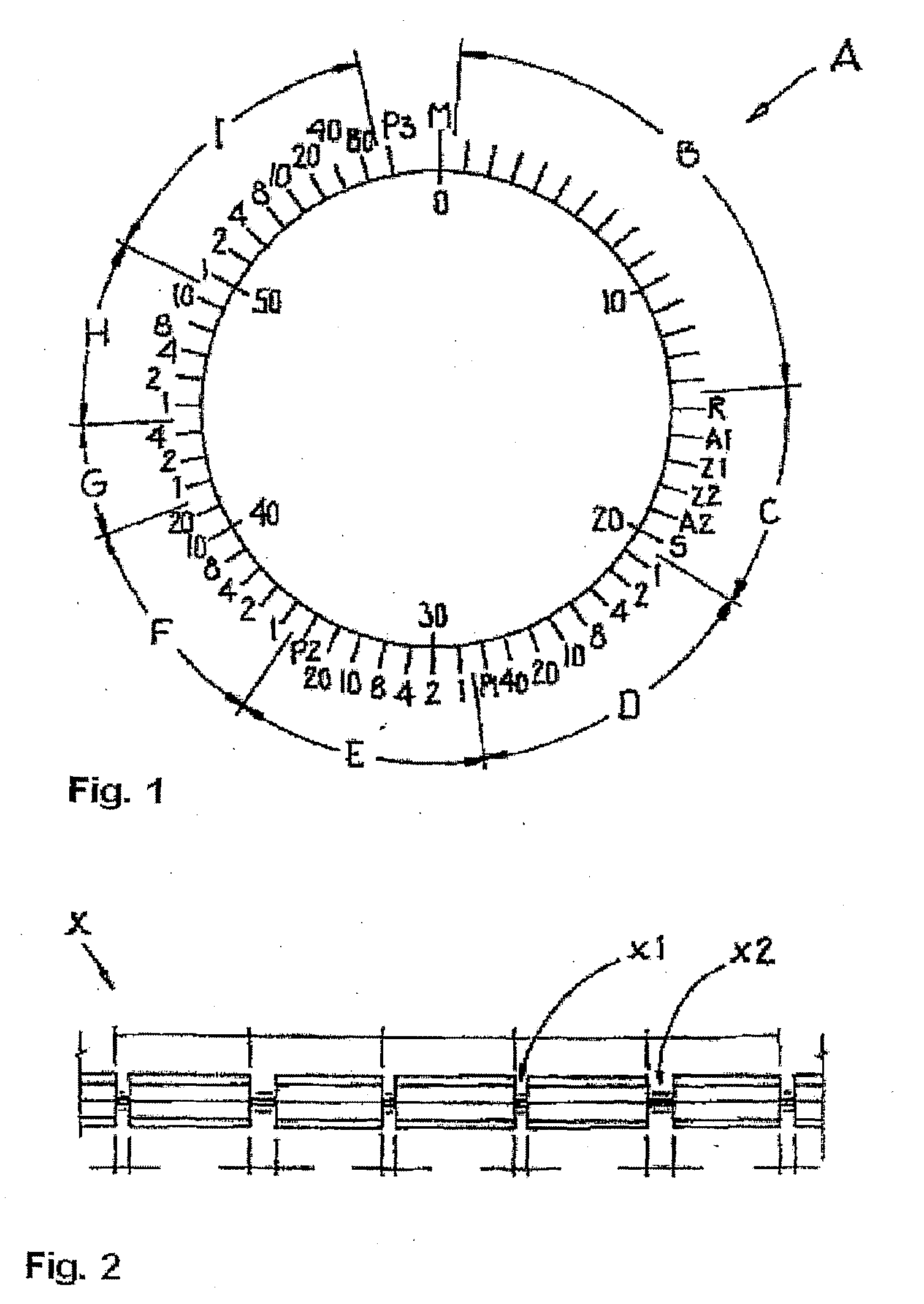
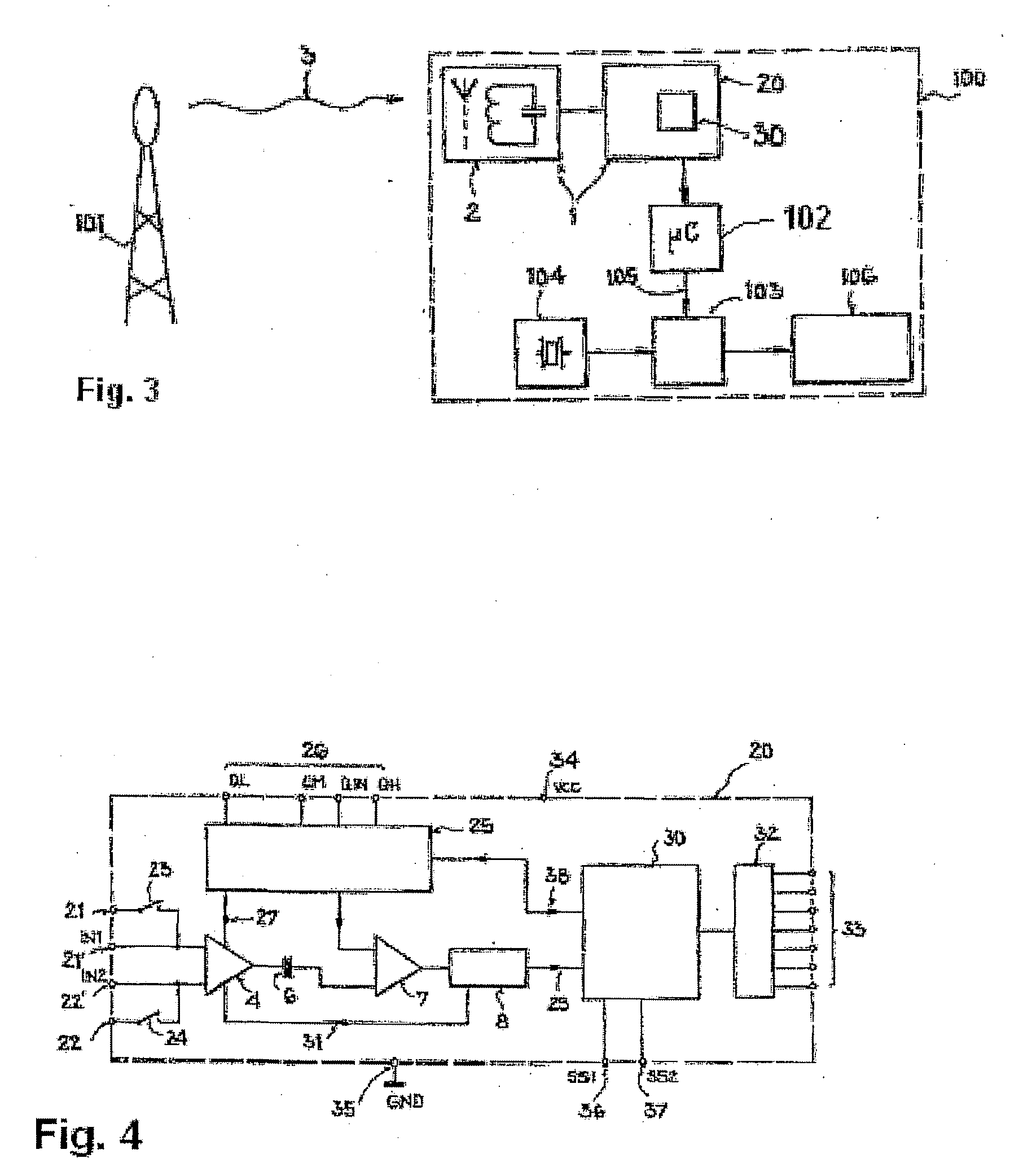
Notification device and method for programming a notification device
InactiveUS20080212416A1Halving of programming timeReduce power consumptionAcoustic time signalsElectric indicationOutput deviceComputer science
A notification device with a time signal receiver is provided that has a receiver for receiving an electromagnetic time signal and processor for processing the time signal and is assigned a signal output device to generate a warning signal, and to a method for programming a notification device comprising a time signal receiver. In the notification device the time signal receiver and / or the signal output device can be set up to generate a warning signal when there is at least one piece of additional information transmitted with the time signal.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY +1
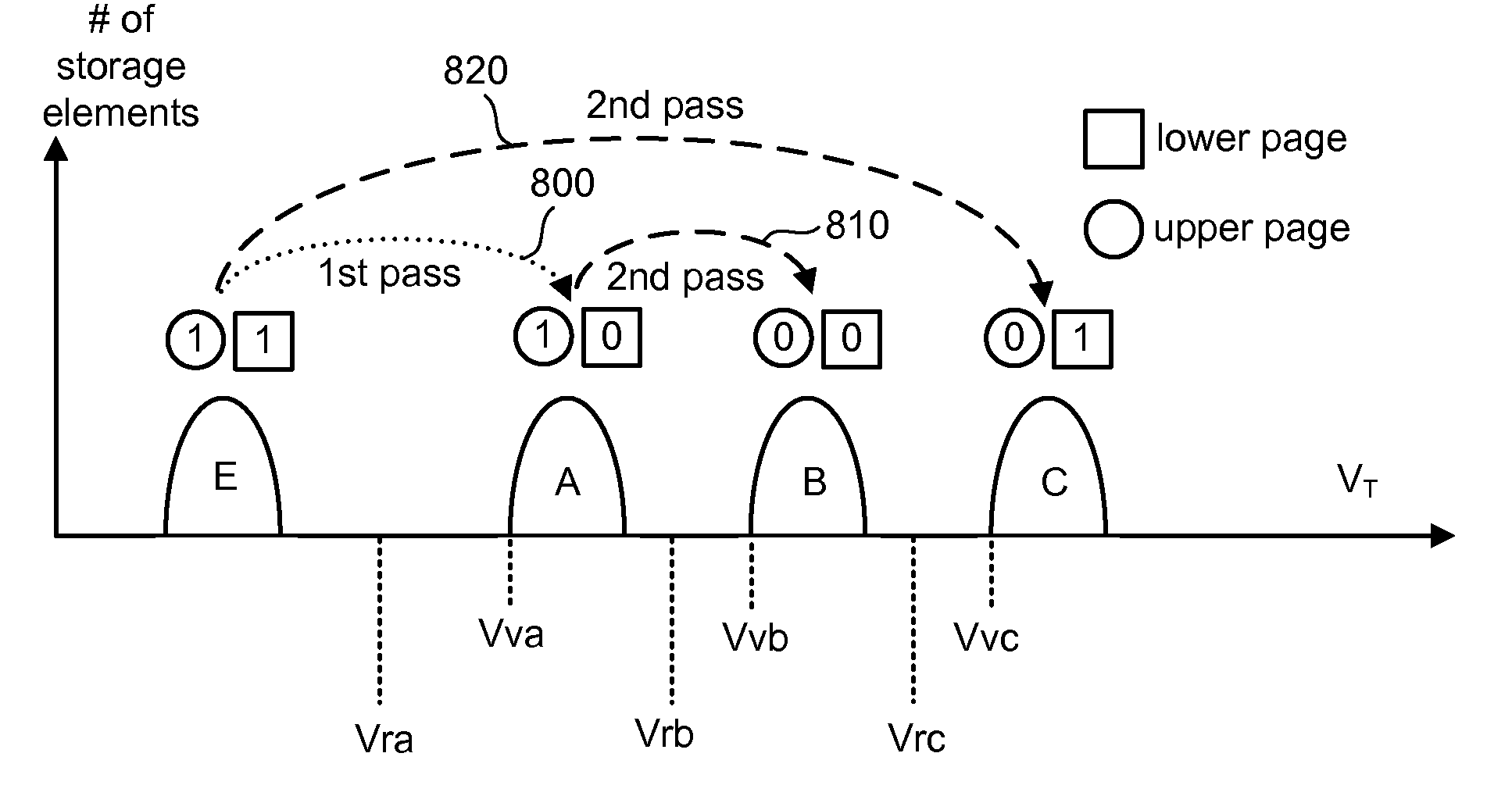
Multiple pass write sequence for non-volatile storage
ActiveUS20080198660A1Improve programming speedMaintains reasonably tight threshold voltage distributionRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgramming processVoltage
A set of non-volatile storage elements are erased to an erased threshold voltage distribution. A multi-pass programming process is performed that programs the set of non-volatile storage elements from the erased threshold voltage distribution to a set valid data threshold voltage distributions. Each programming pass has one or more starting threshold voltage distributions and programs non-volatile storage elements to at least two ending threshold voltage distributions.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
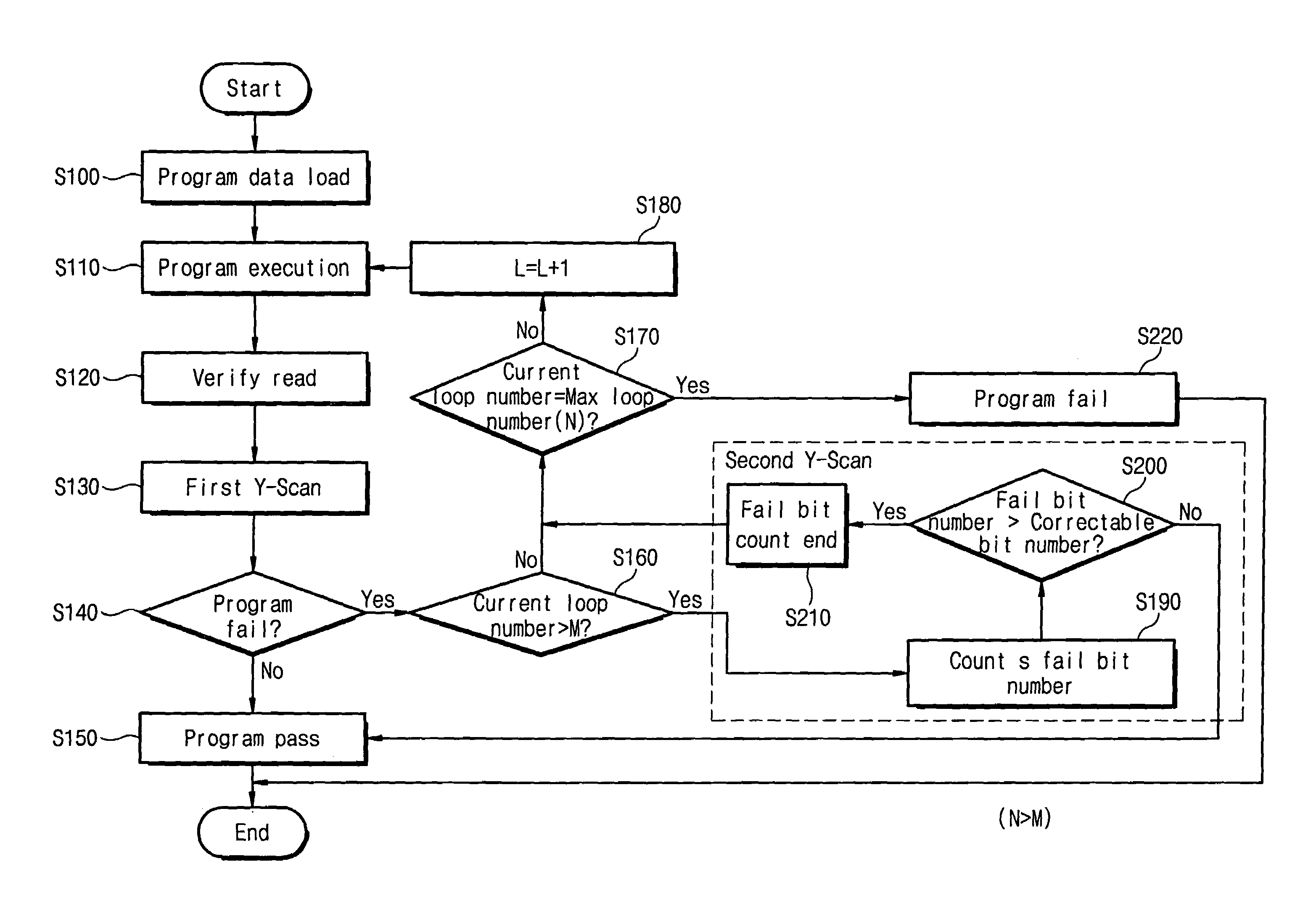
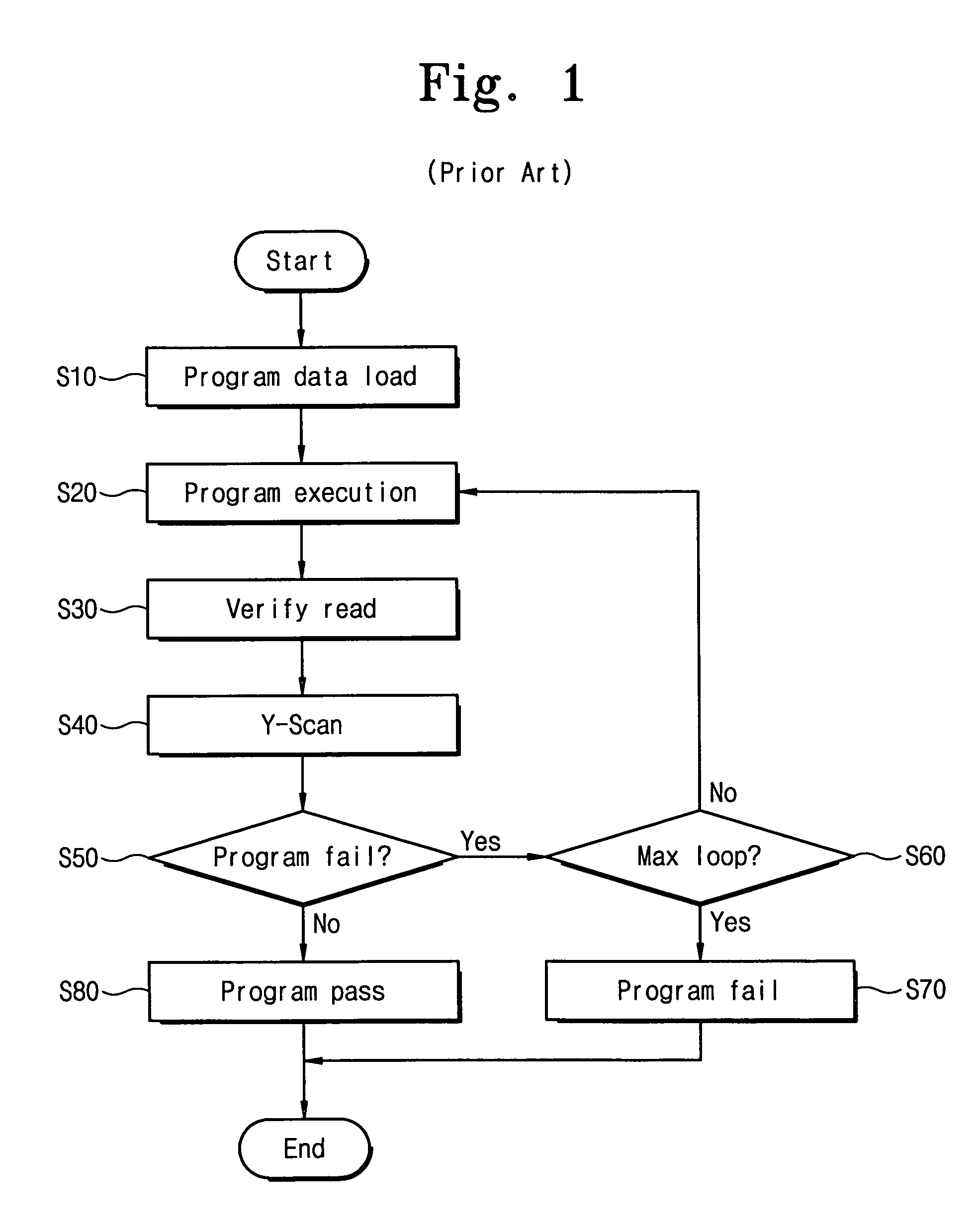
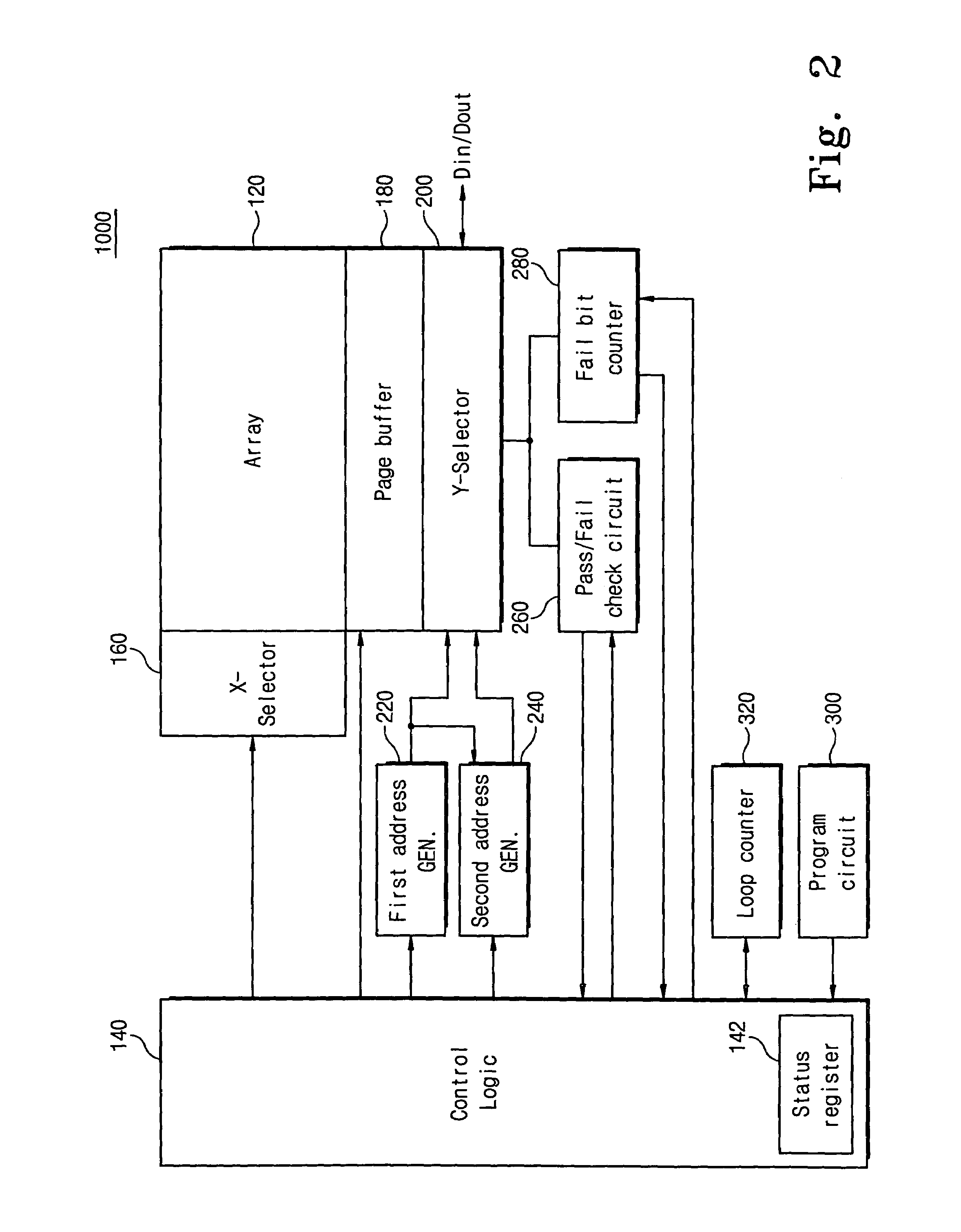
Non-volatile memory device having improved program speed and associated programming method
ActiveUS7352630B2Improve programming speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageError correctingOperating system
A non-volatile memory device comprises a memory cell array having a plurality of non-volatile memory cells arranged in rows and columns. Selected memory cells are programmed by applying program voltages thereto. Next, data bits stored in the selected cells are read. Then, a first column scan operation is performed to determine whether any of the selected memory cells is inadequately programmed. Upon determining that at least one of the selected memory cells is inadequately programmed, a second column scan operation is performed to detect a total number of the selected memory cells that are inadequately programmed. Upon determining that the total number of the selected memory cells that are inadequately programmed is less than a number that can be corrected by an error correcting circuit, the program operation terminates with a program pass status.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
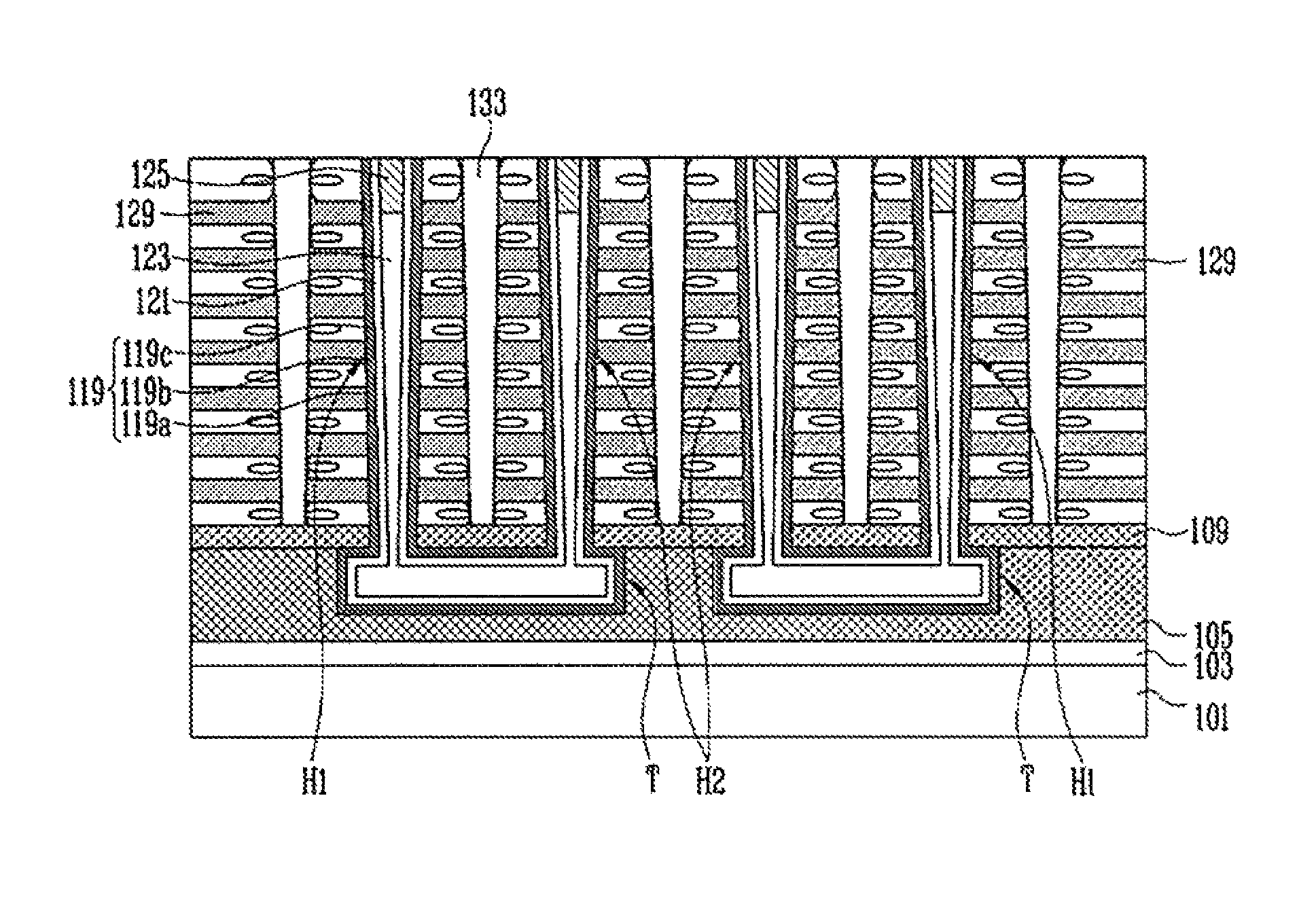
Three-dimensional non-volatile memory device, memory system including the same and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8912591B2Improve programming speedReduce capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
A three-dimensional (3-D) non-volatile memory device includes a plurality of vertical channel layers protruding from a substrate, a plurality of interlayer insulating layers and a plurality of memory cells stacked alternately along the plurality of vertical channel layers, and an air gap formed in the plurality of interlayer insulating layers disposed between the plurality of memory cells, so that capacitance between word lines is reduced to thus improve a program speed.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
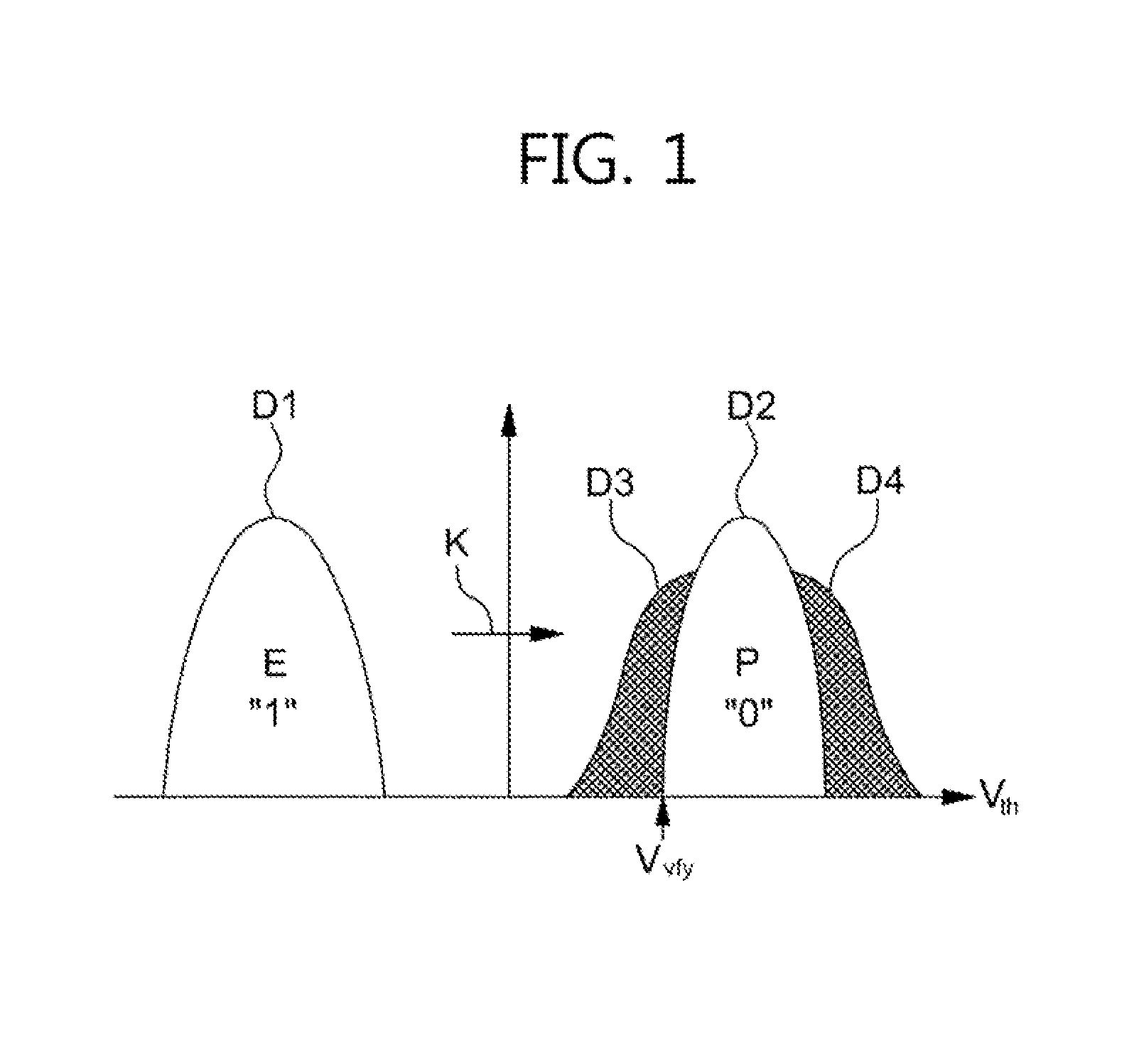
Phase change memory cell employing a GeBiTe layer as a phase change material layer, phase change memory device including the same, electronic system including the same and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7817464B2Improve programming speedTotal current dropSolid-state devicesDigital storagePhase-change memoryElectronic systems
A phase change memory cell includes an interlayer insulating layer formed on a semiconductor substrate, and a first electrode and a second electrode disposed in the interlayer insulating layer. A phase change material layer is disposed between the first and second electrodes. The phase change material layer may be an undoped GeBiTe layer, a doped GeBiTe layer containing an impurity or a doped GeTe layer containing an impurity. The undoped GeBiTe layer has a composition ratio within a range surrounded by four points (A1(Ge21.43, Bi16.67, Te61.9), A2(Ge44.51, Bi0.35, Te55.14), A3(Ge59.33, Bi0.5, Te40.17) and A4(Ge38.71, Bi16.13, Te45.16)) represented by coordinates on a triangular composition diagram having vertices of germanium (Ge), bismuth (Bi) and tellurium (Te). The doped GeBiTe layer contains an impurity and has a composition ratio within a range surrounded by four points (D1(Ge10, Bi20, Te70), D2(Ge30, Bi0, Te70), D3(Ge70, Bi0, Te30) and D4(Ge50, Bi20, Te30)) represented by coordinates on the triangular composition diagram.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
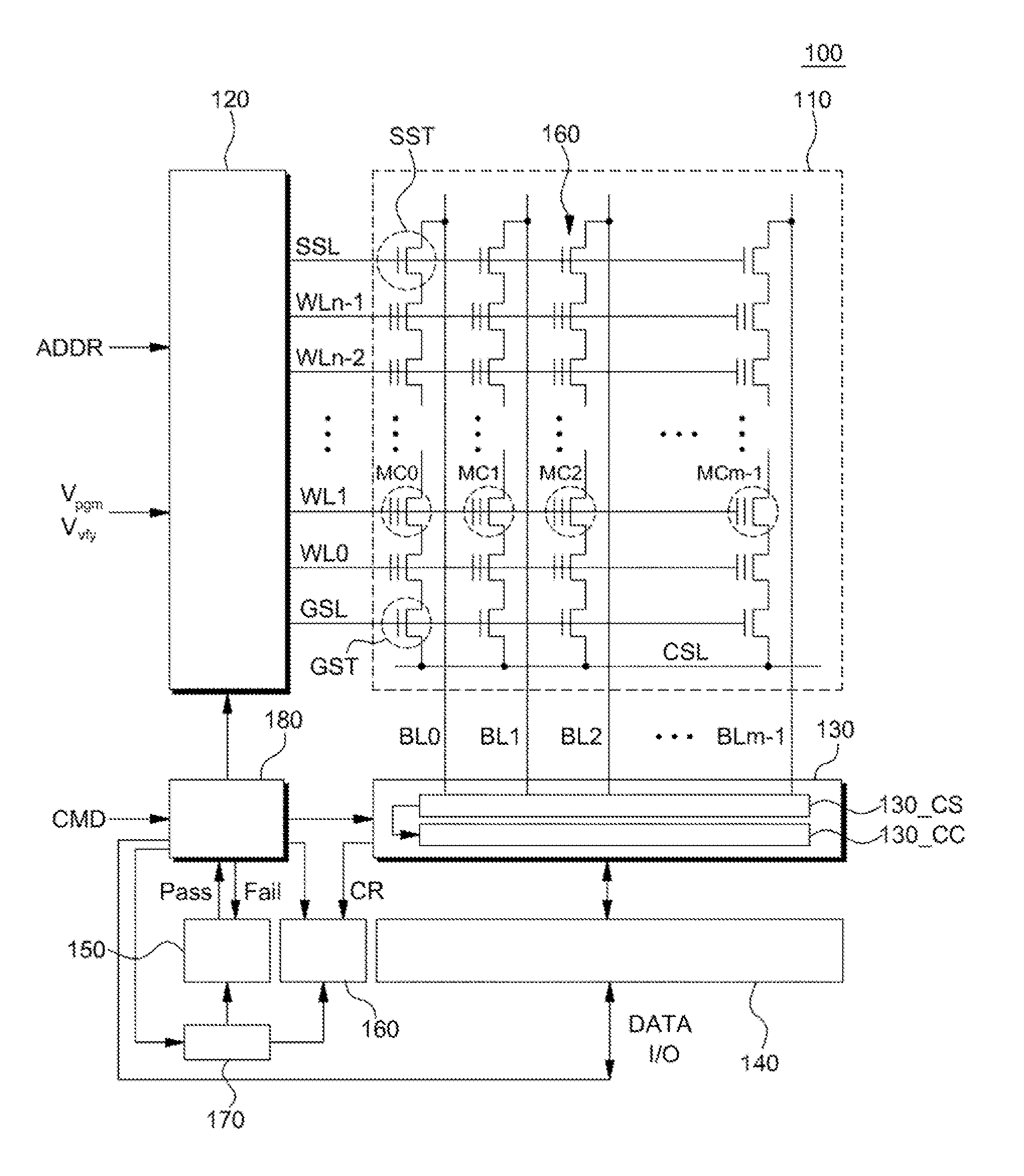
Data storage device and method of programming memory cells
ActiveUS20160148695A1Improve programming speedHigh data reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer architectureStorage cell
A method of programming a non-volatile memory device includes programming memory cells selected from the plurality of memory cells by increasing turn values of program loops based on an incremental step pulse program (ISPP) algorithm; detecting a first turn value of a first program loop wherein, in the first program loop, a first number or a first ratio of first unprogrammed memory cells is smaller than or equal to a first set value; calculating a second turn value of a second program loop based on the first turn value wherein, in the second program loop, a second number or a second ratio of second unprogrammed memory cells is expected to be smaller than or equal to a second set value, the second set value being smaller than the first set value; executing subsequent program loops on the unprogrammed memory cells up to the second program loop; detecting a third number or a third ratio of third unprogrammed memory cells in the second program loop; comparing the third number or the third ratio of the third unprogrammed memory cells to the second set value; determining a program pass when the third number or the third ratio of the third unprogrammed memory cells is smaller than or equal to the second set value; and determining a program fail when the third number or the third ratio of the unprogrammed memory cell exceeds the second set value.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Program conversion device and program conversion method
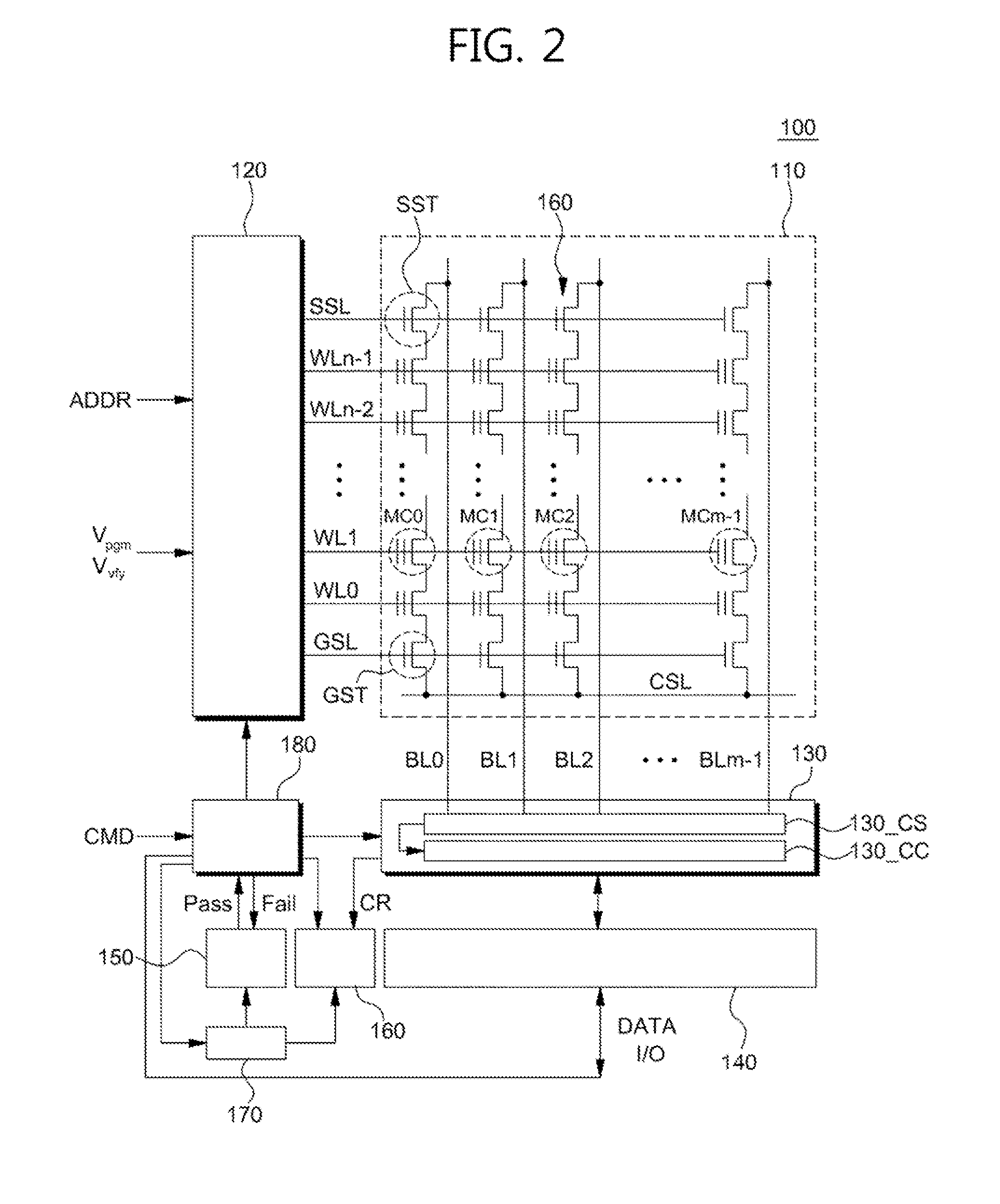
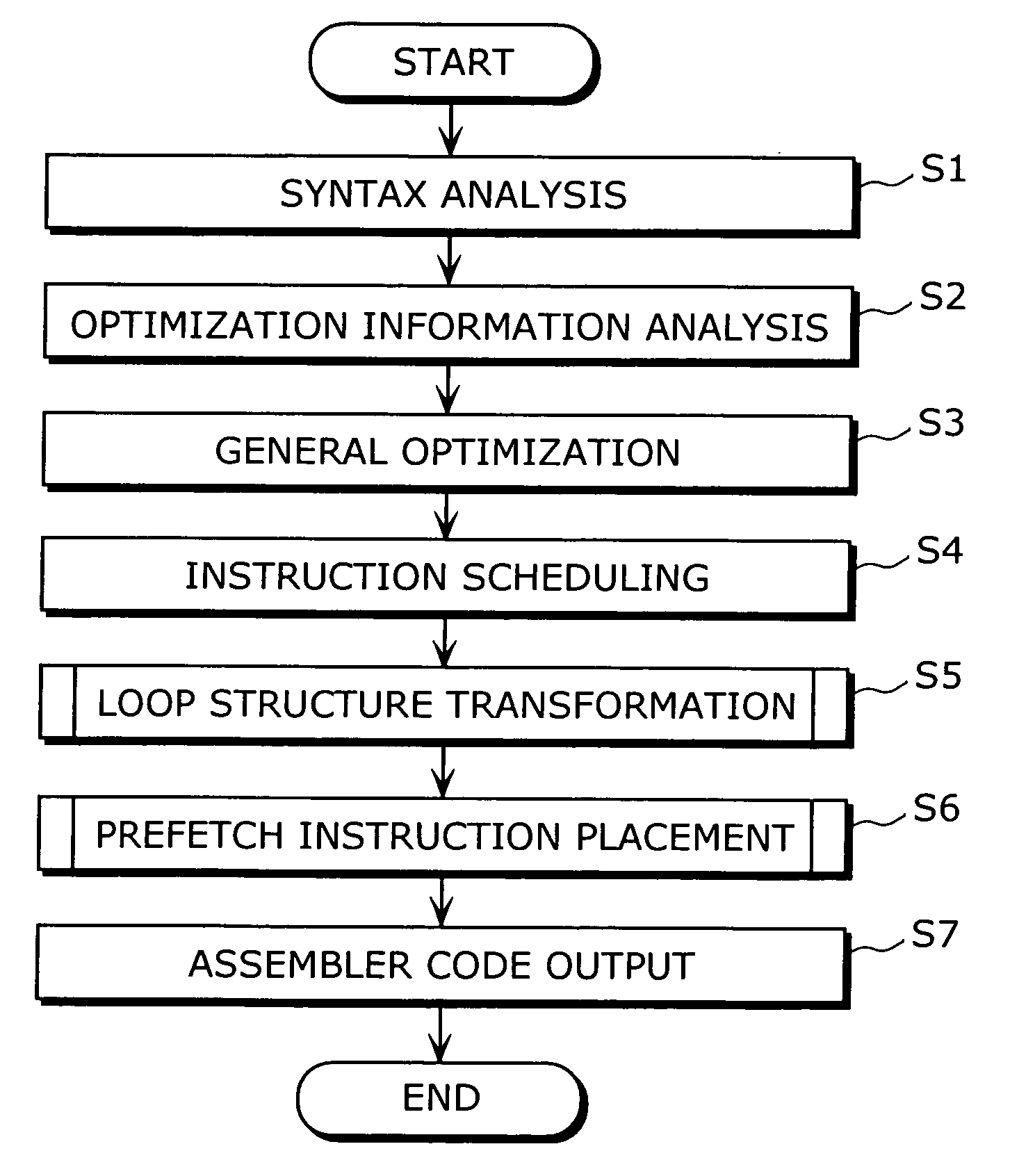
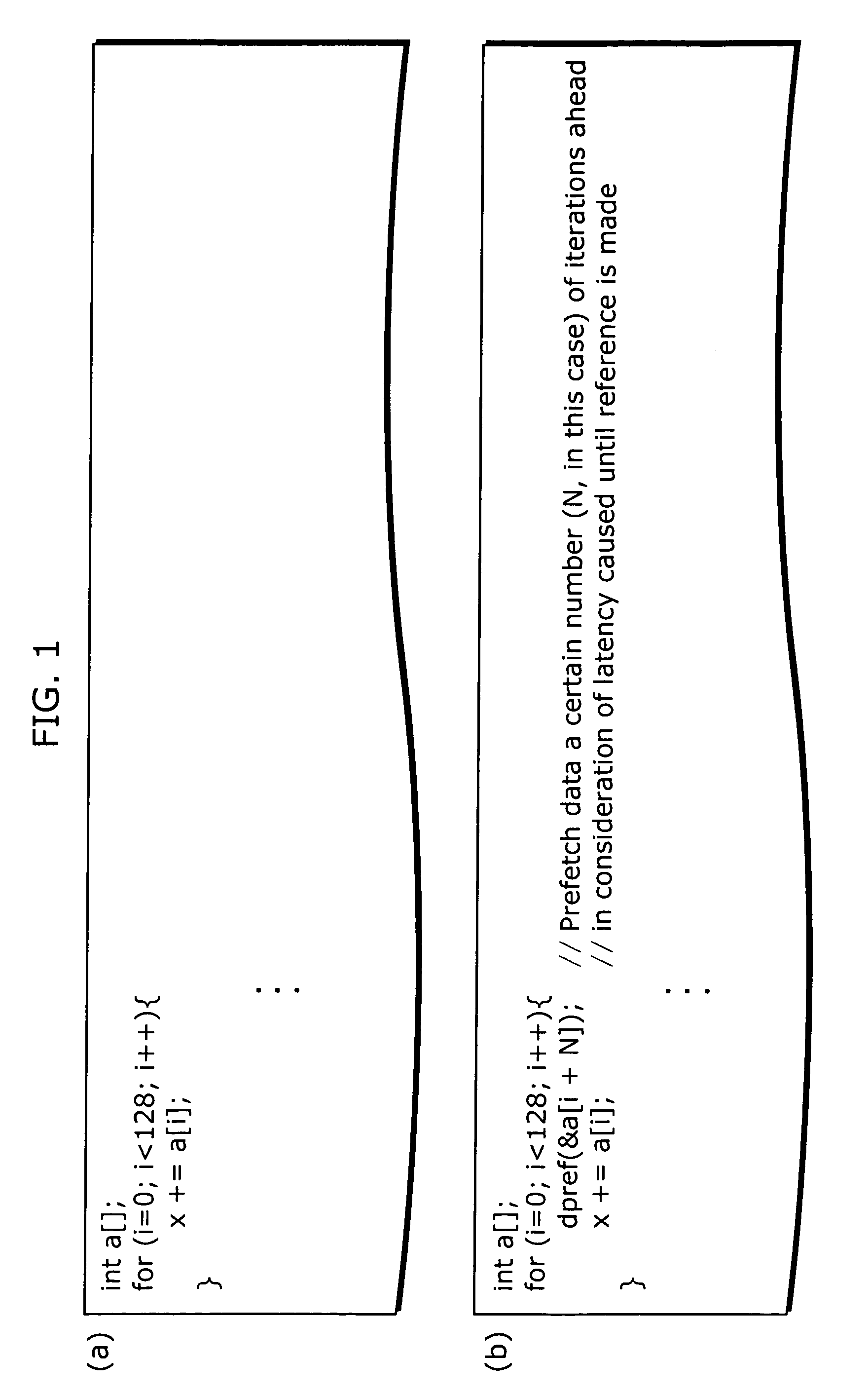
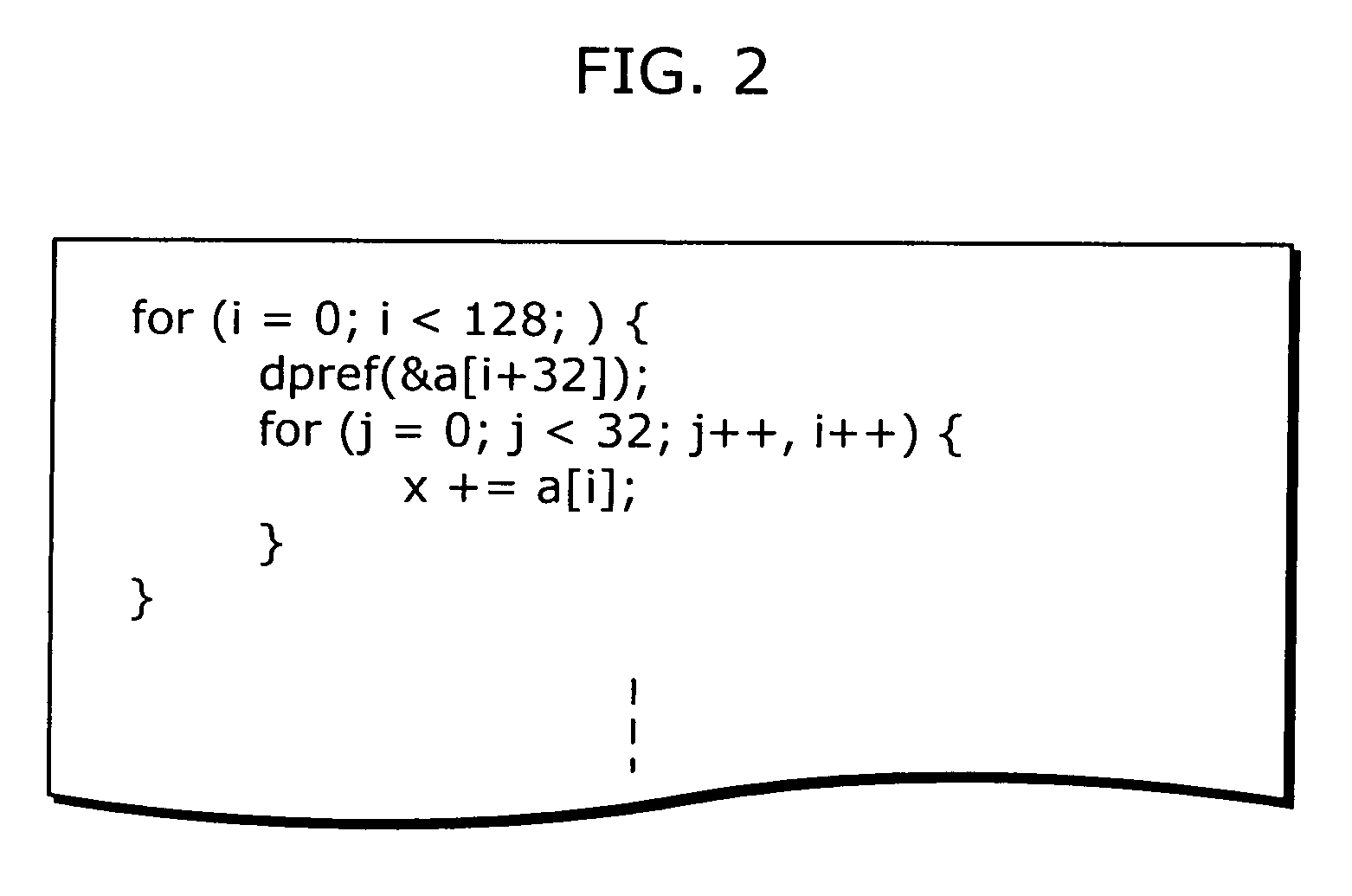
InactiveUS20060248520A1Improve programming speedSoftware engineeringProgram controlInner loopParallel computing
A compiler which improves the processing speed of a program execution without needlessly issuing an instruction that has a possibility of causing an interlock is targeted at a processor having an instruction that has a possibility of causing an interlock when the instruction is executed, the compiler causing a computer to function as: a loop structure transforming unit (186) which performs double looping transformation on an input program so that a loop whose iteration count is y is split off from a loop whose loop count is x and the loop whose iteration count is y is an inner loop whereas a loop whose iteration count is x / y is an outer loop; and an instruction optimum placing unit (187) which places an instruction that has a possibility of causing an interlock in the program on which the double looping transformation has been performed.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
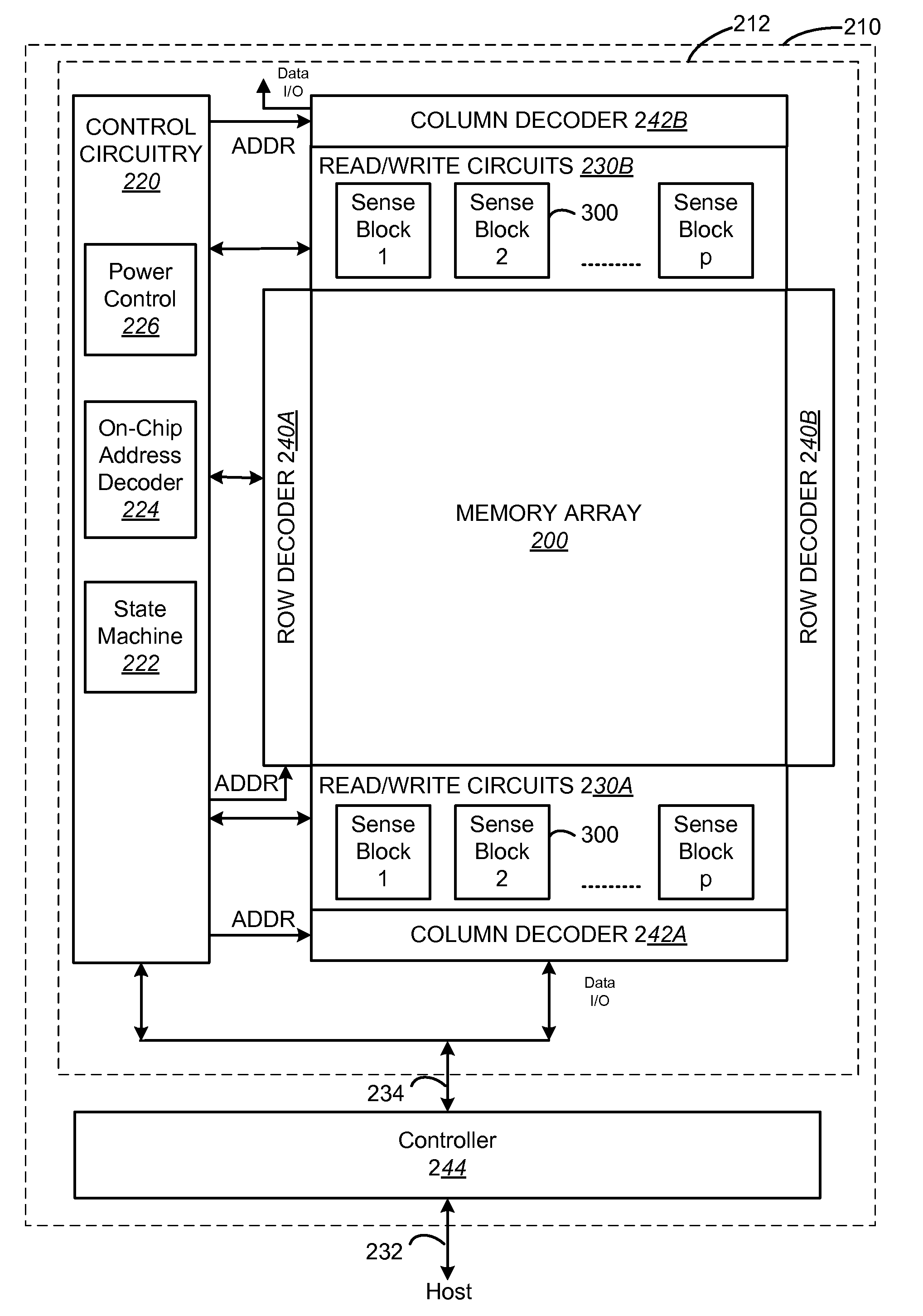
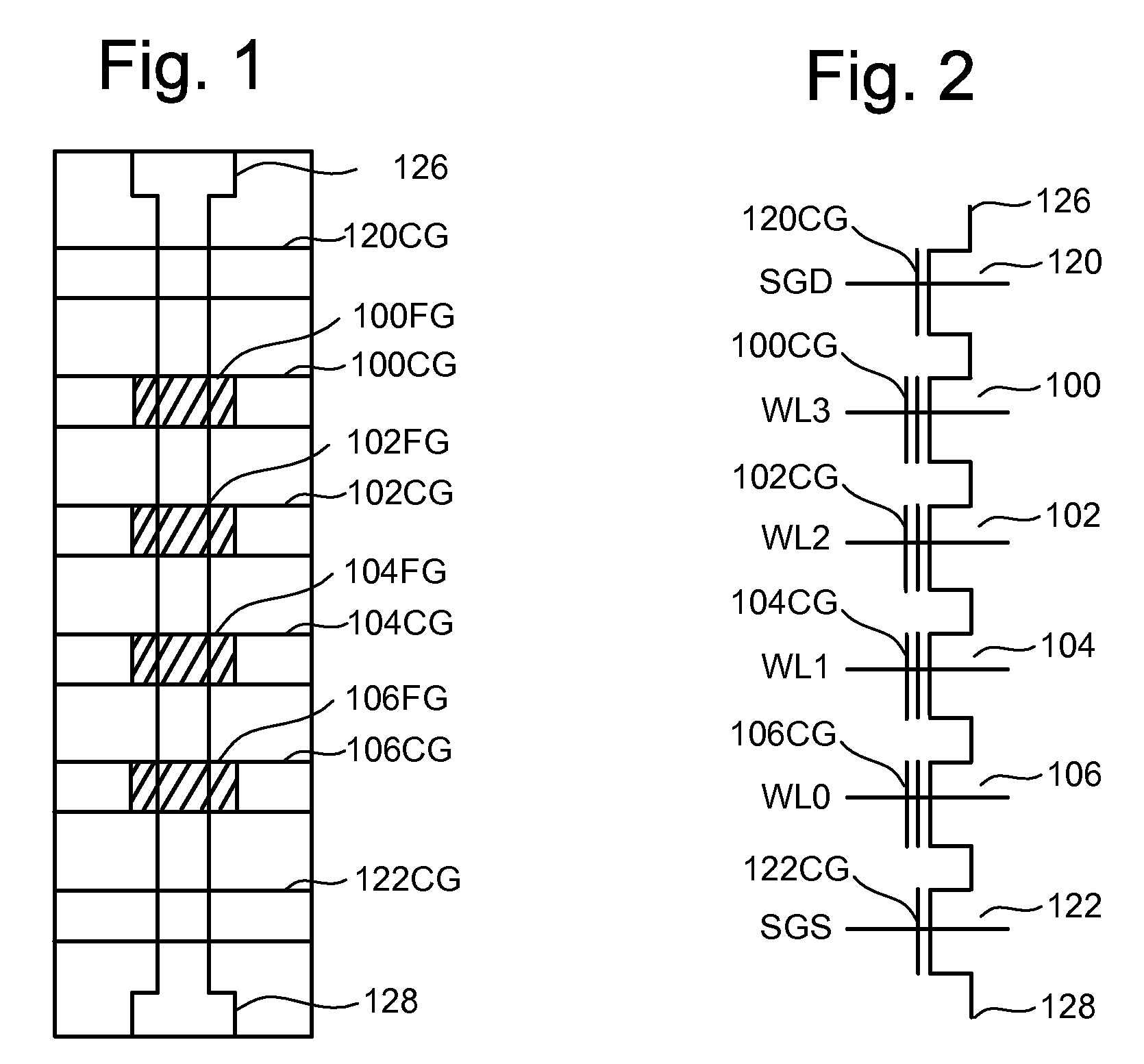
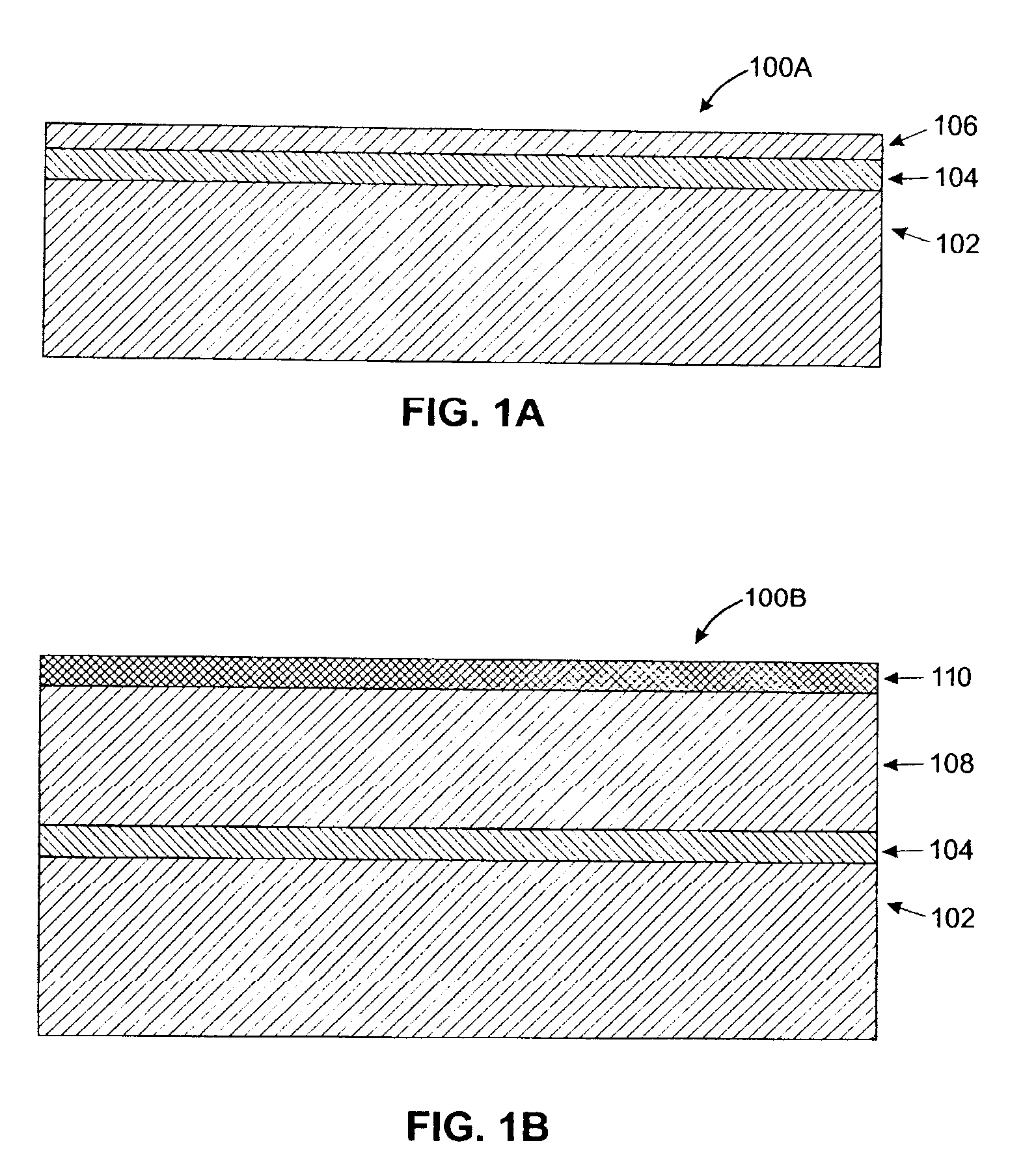
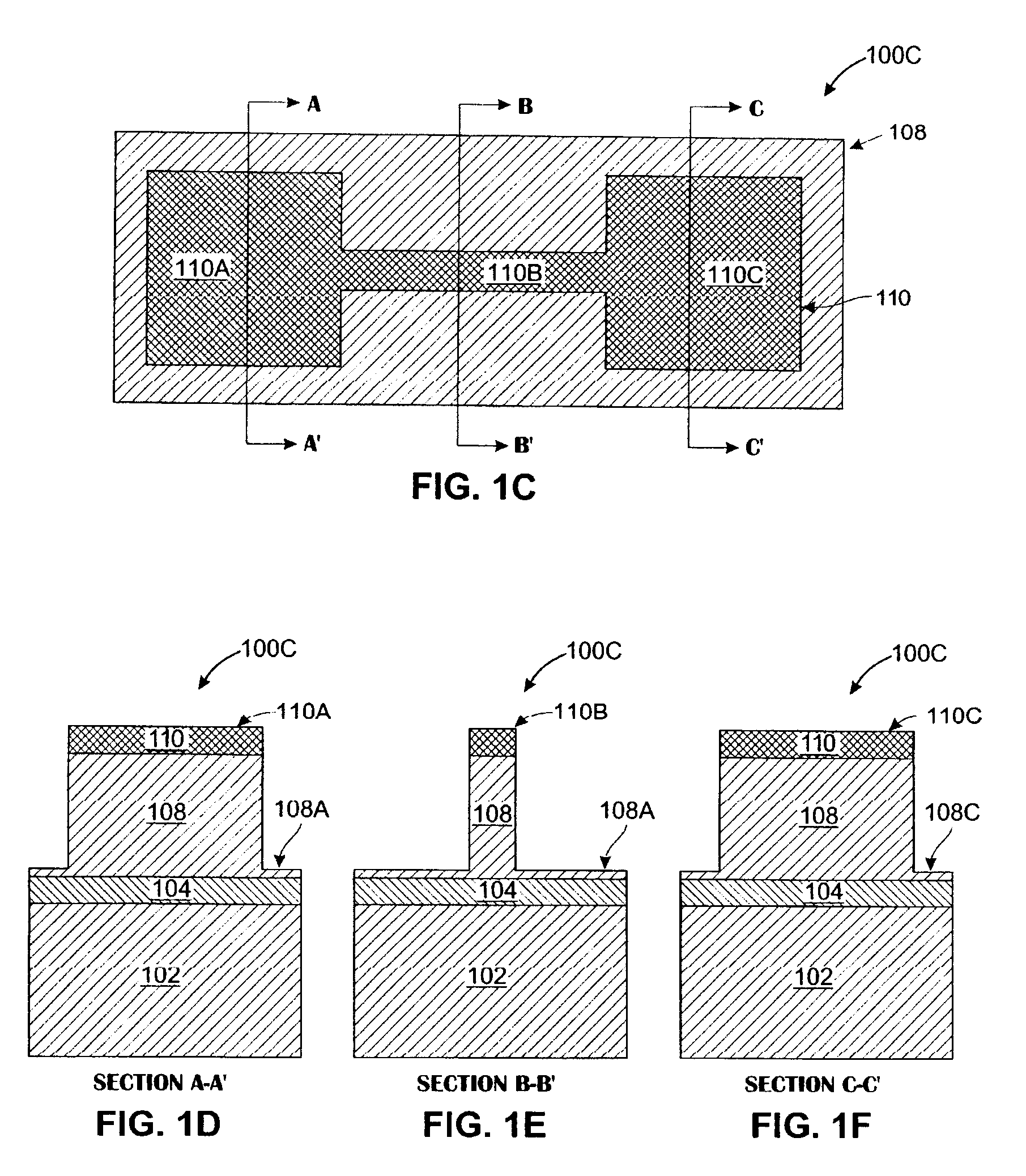
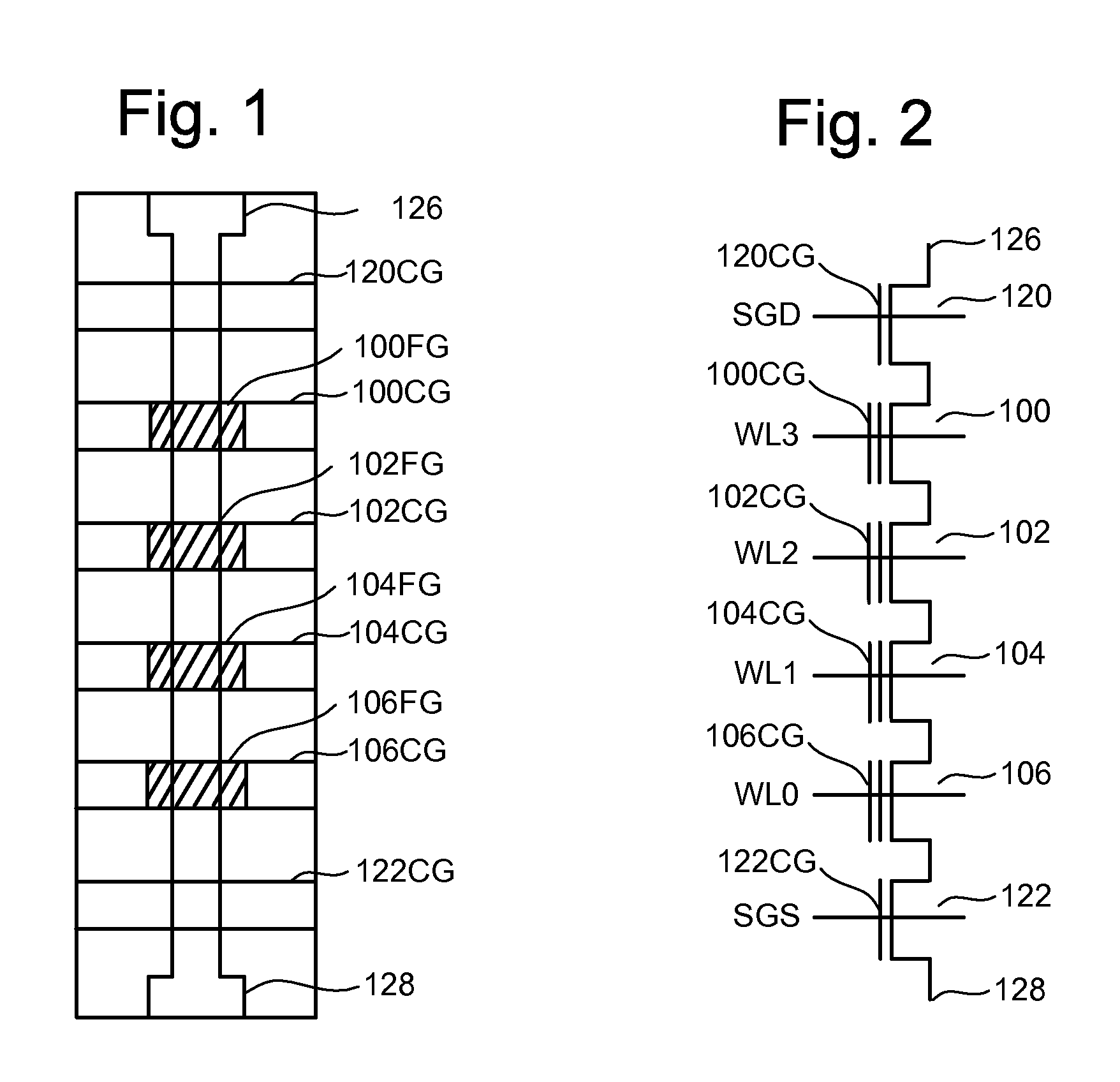
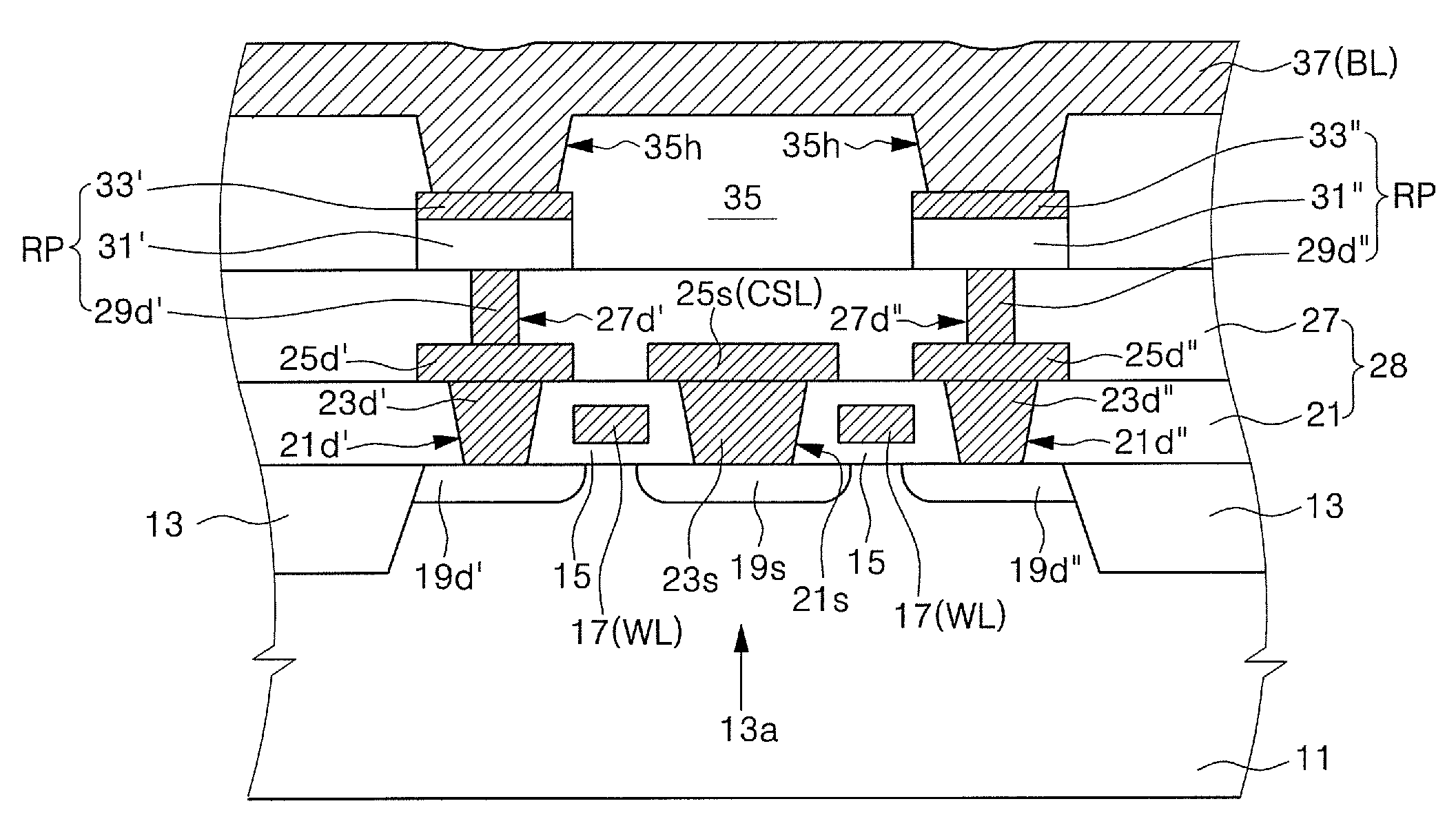
[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]
InactiveUS20050224858A1Easy to manufactureImprove programming speedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesGate dielectricDielectric layer
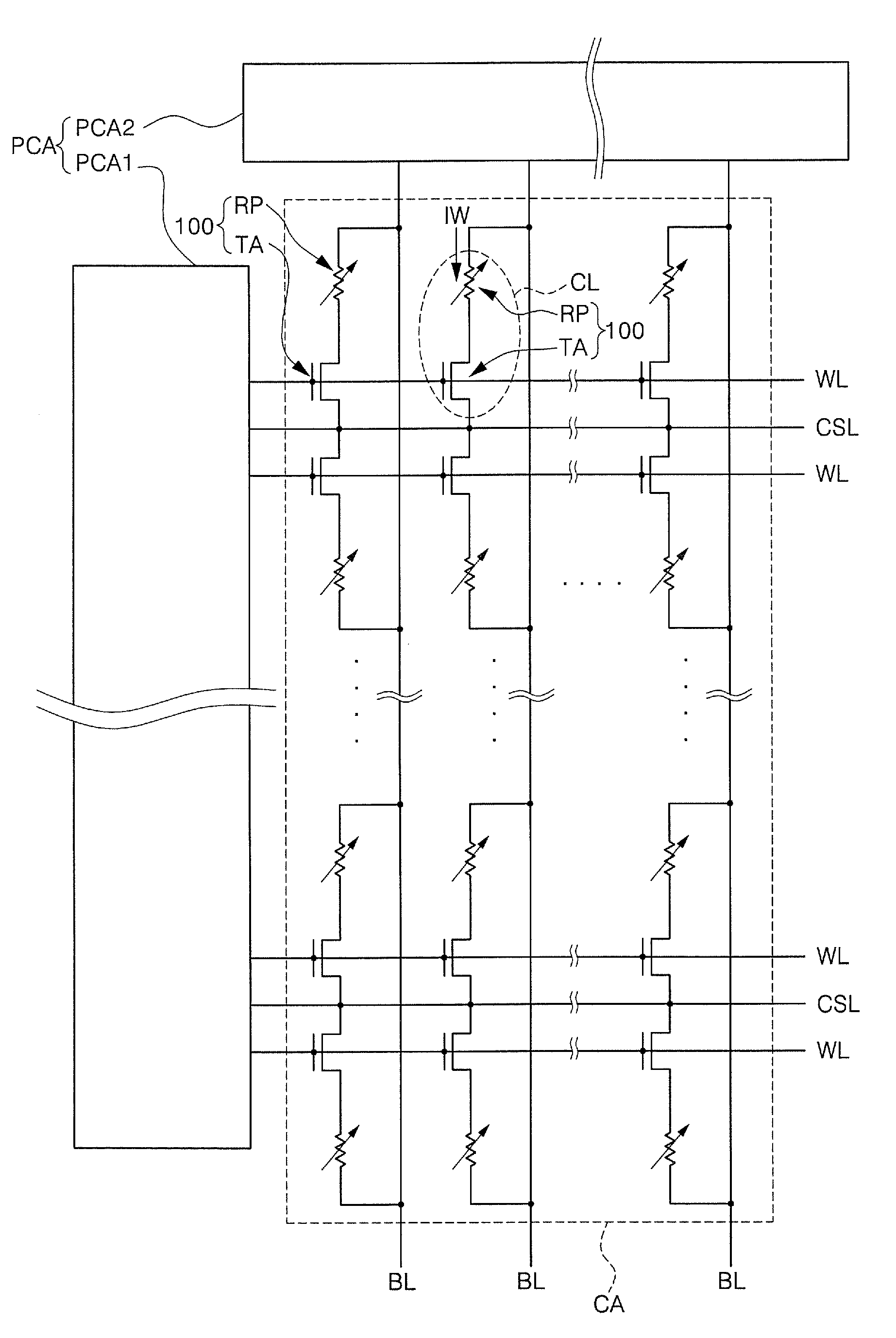
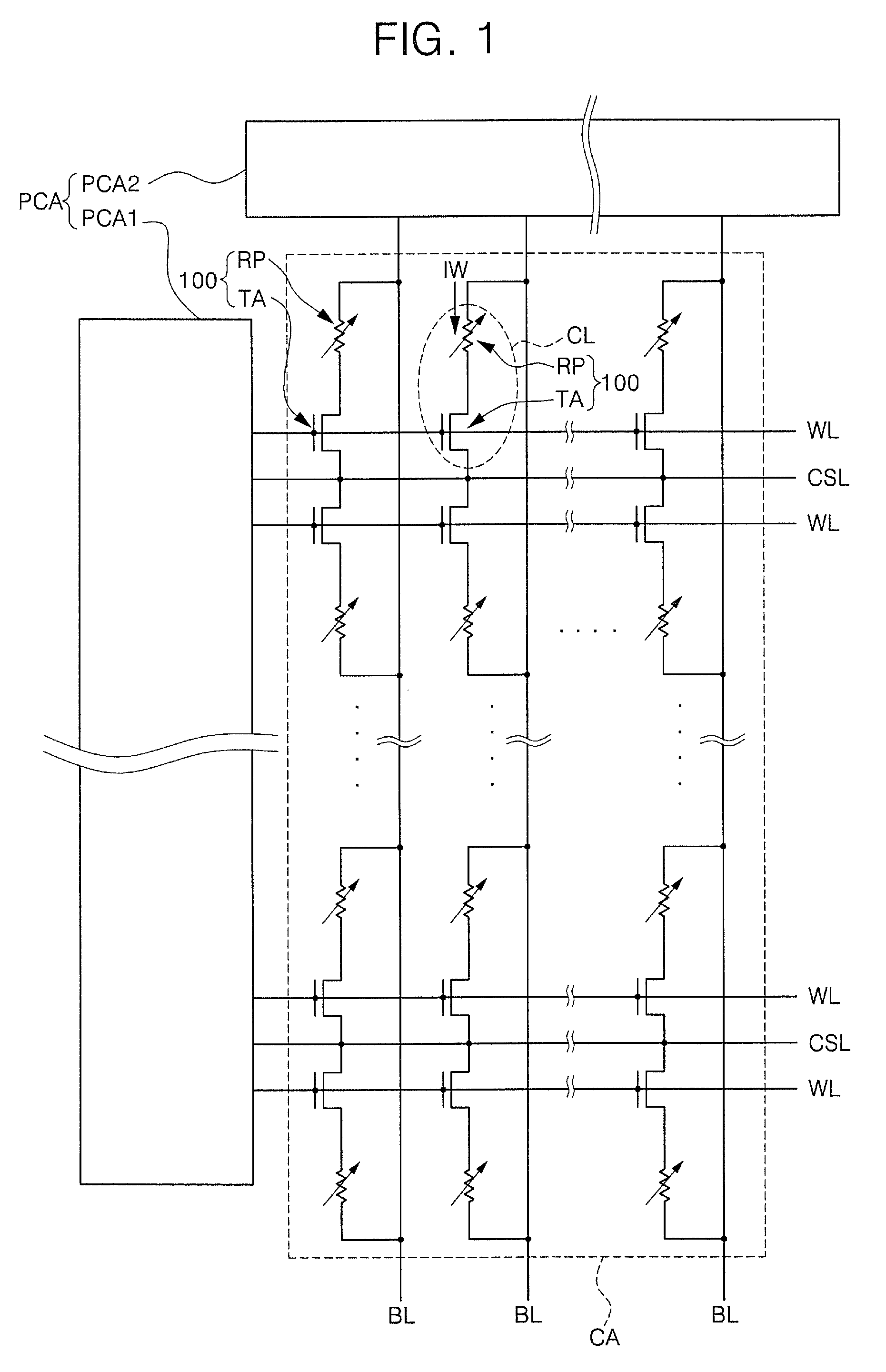
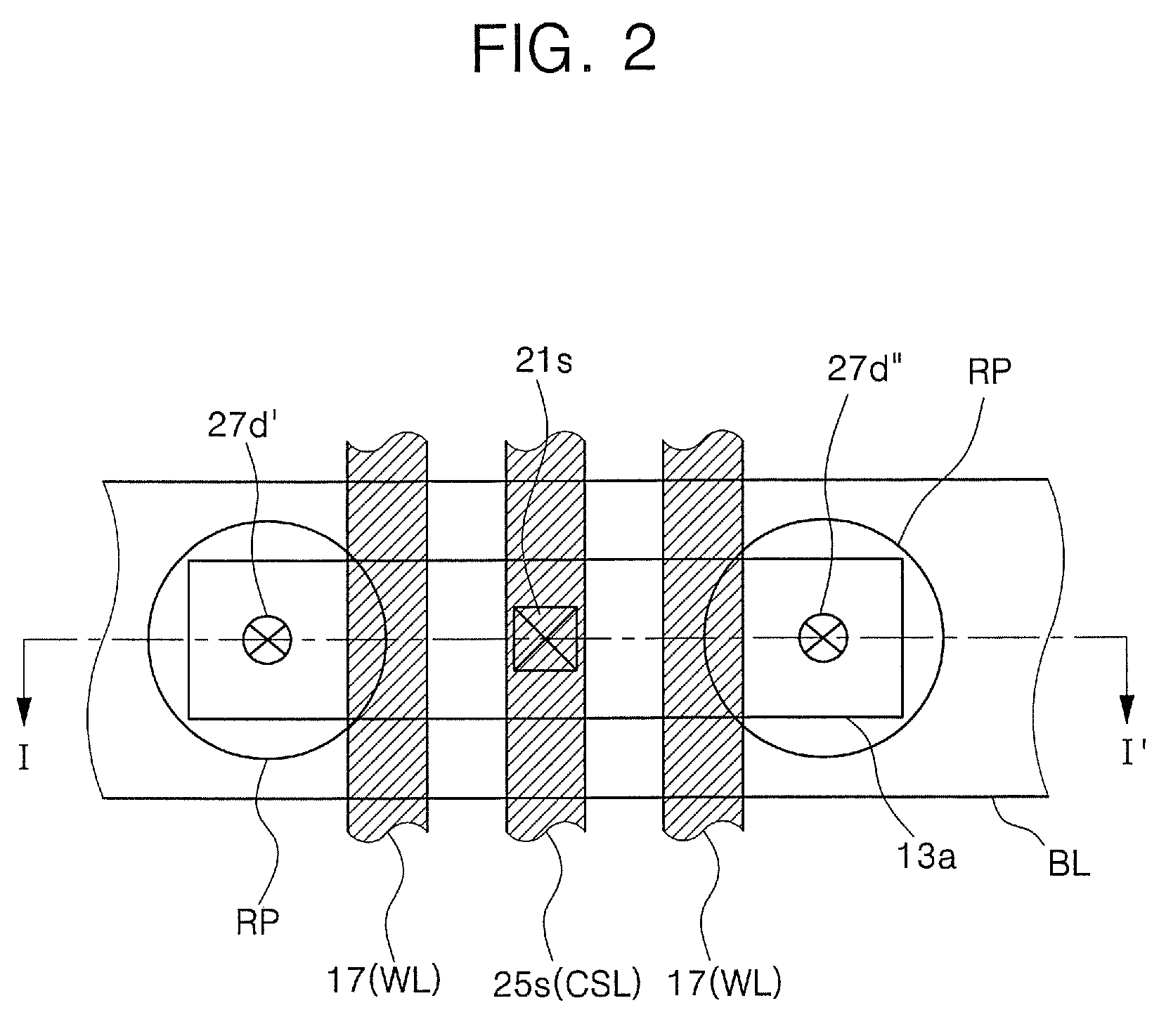
A non-volatile memory including a substrate, a plurality of gate structures, a plurality of select gate structures, spacers and source region / drain region is provided. Each gate structure on the substrate further includes a bottom dielectric layer, an electron trapping layer, an upper dielectric layer, a control gate and a cap layer. The select gate structures are disposed on one side of the respective each gate structure. Each select gate structure includes a select gate dielectric layer and a select gate. The select gate structures and the gate structures are connected in series to form a memory cell row. The spacers are disposed between the select gate structures and the gate structures. The source region and the drain region are disposed in the substrate on each side of the memory cell row.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
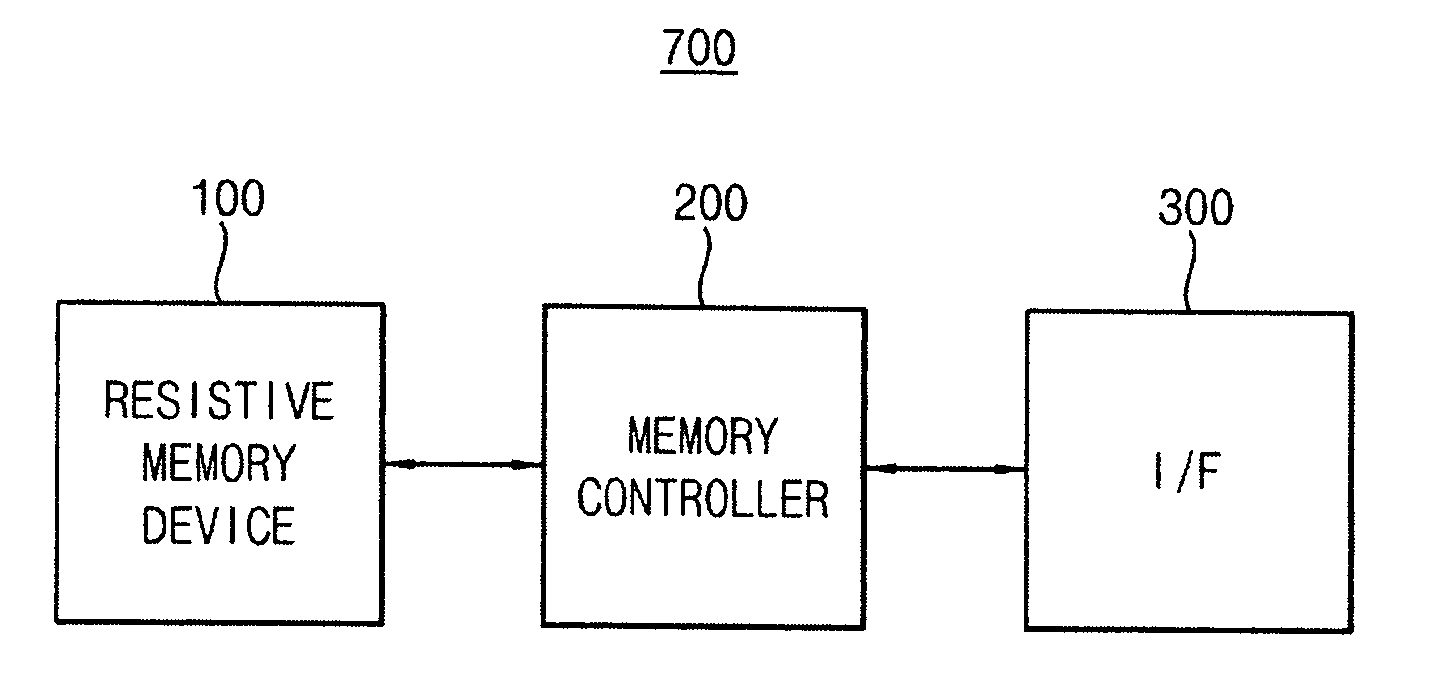
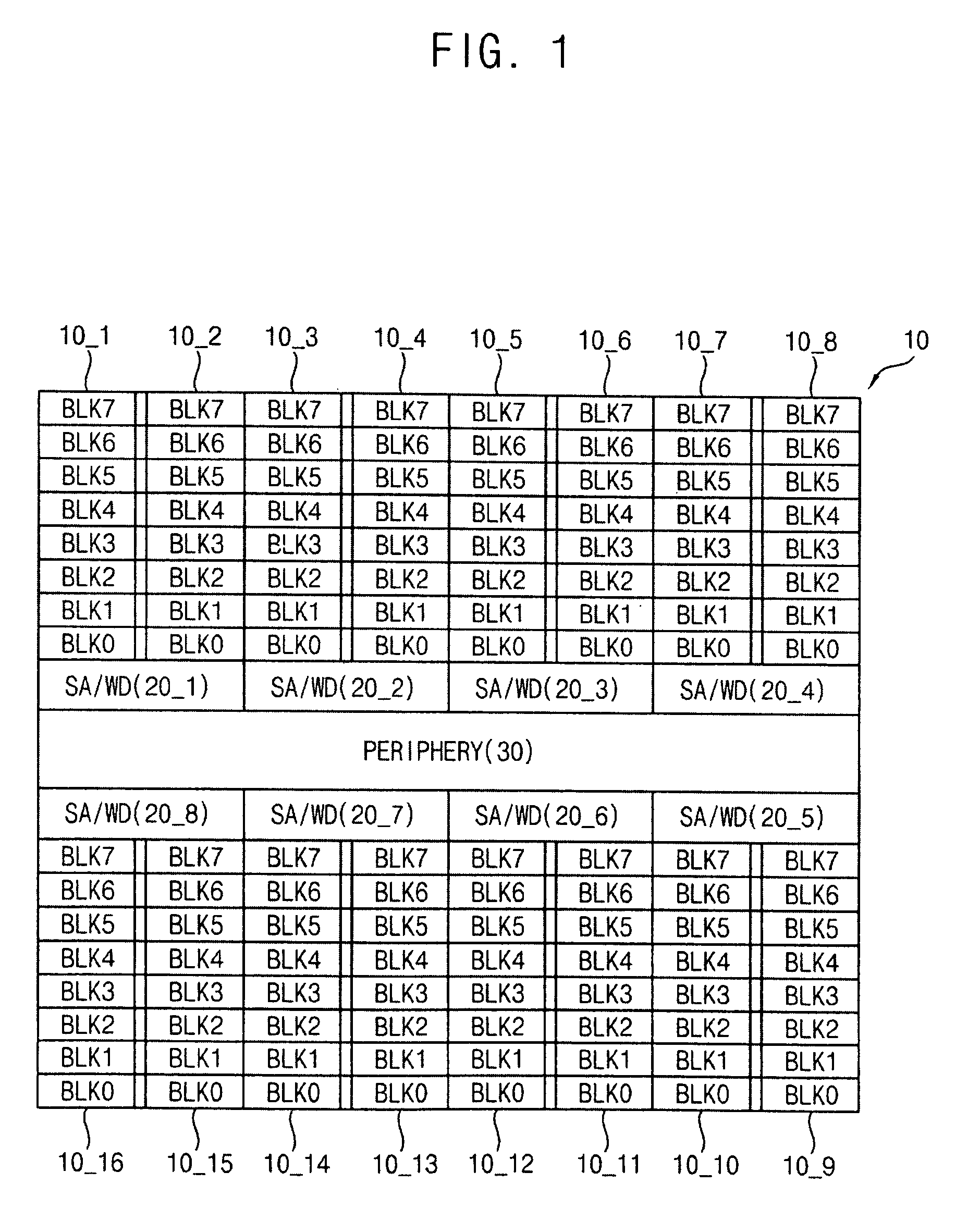
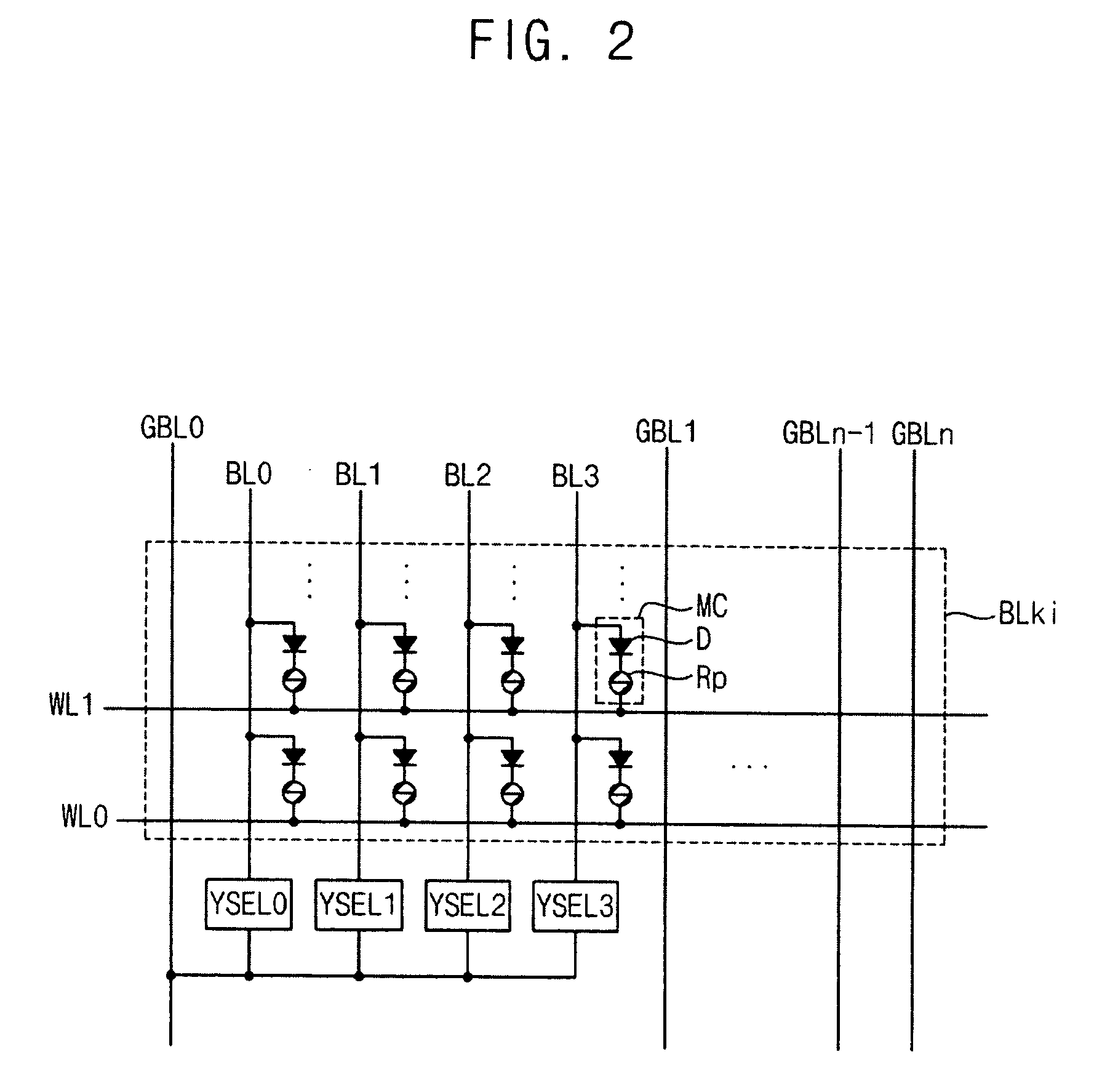
Memory device, memory system having the same, and programming method of a memory cell
InactiveUS20100214831A1Improve programming speedIncrease speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingStorage cell
A memory device includes an array of resistance change memory cells divided into a first memory block including a first selected memory cell of a first plurality of memory cells and a second memory block including a second selected memory cell of a second plurality of memory cells, and sensing and writing circuitry configured to simultaneously activate a line connected with the first and second selected memory cells. The first and second selected memory cells may be written by iteratively applying a level-controlled write signal to memory cells not having a programmed state equal to the write data until a verify-read operation indicates respective programmed states for the first and second selected memory cells are equal to the write data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
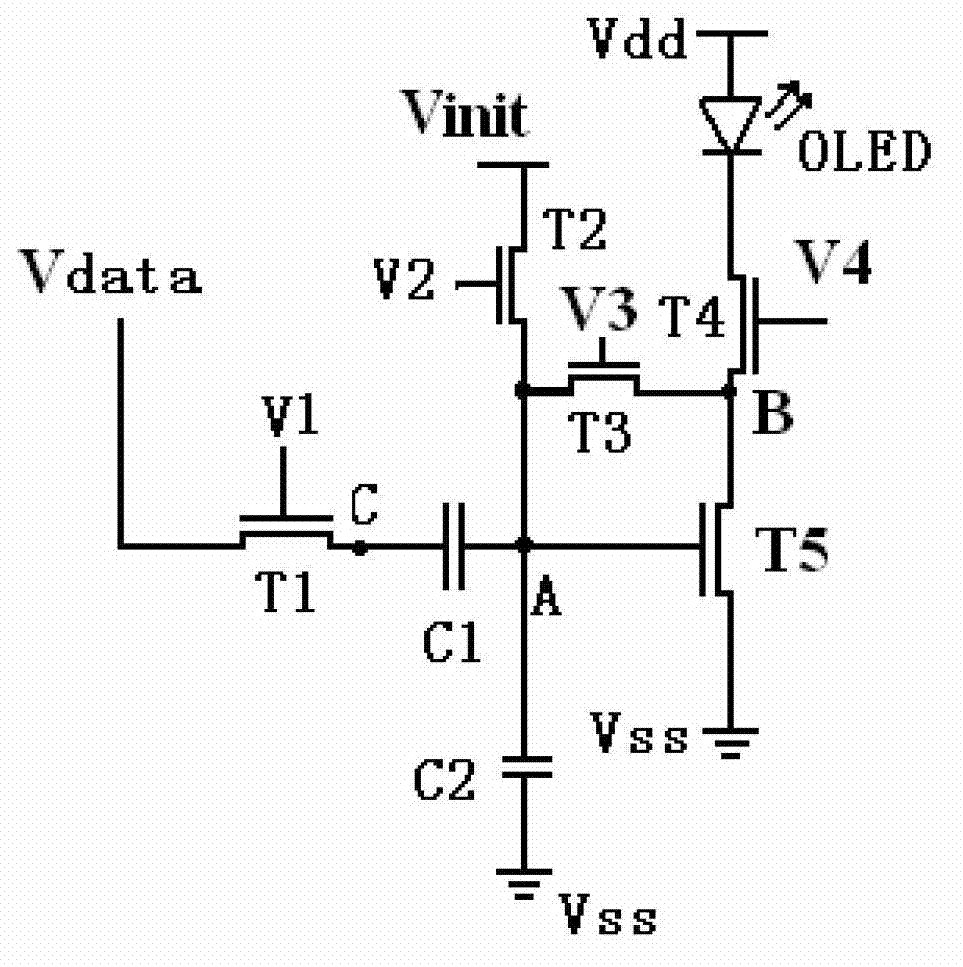
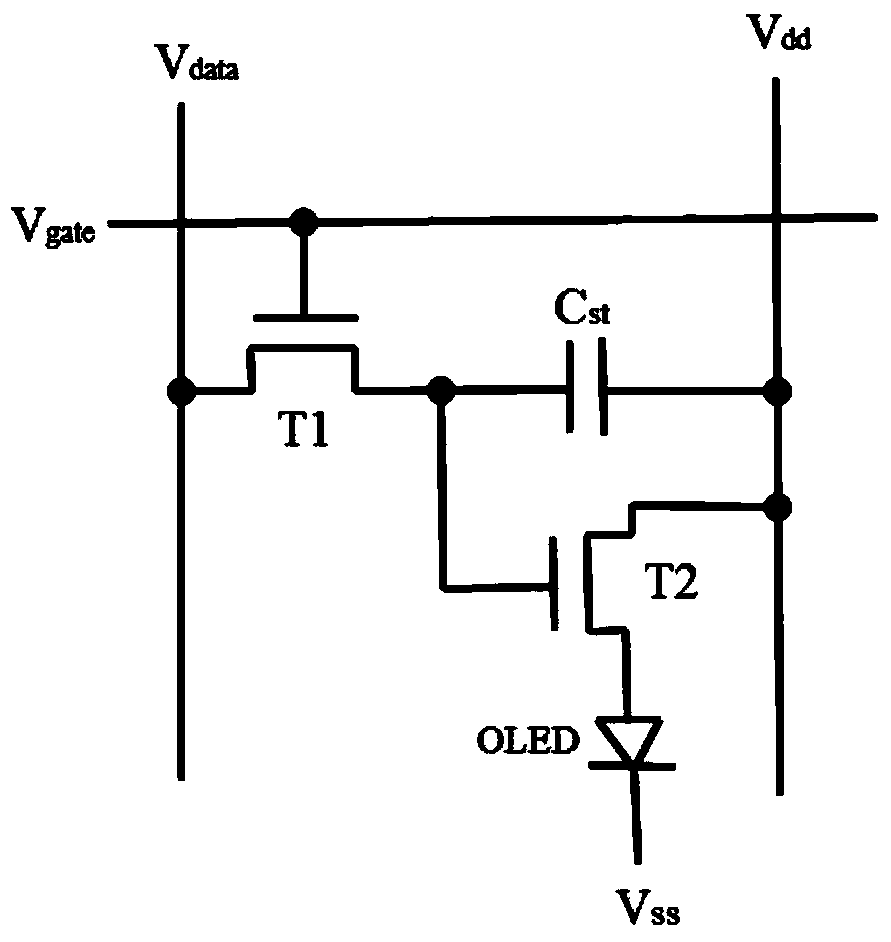
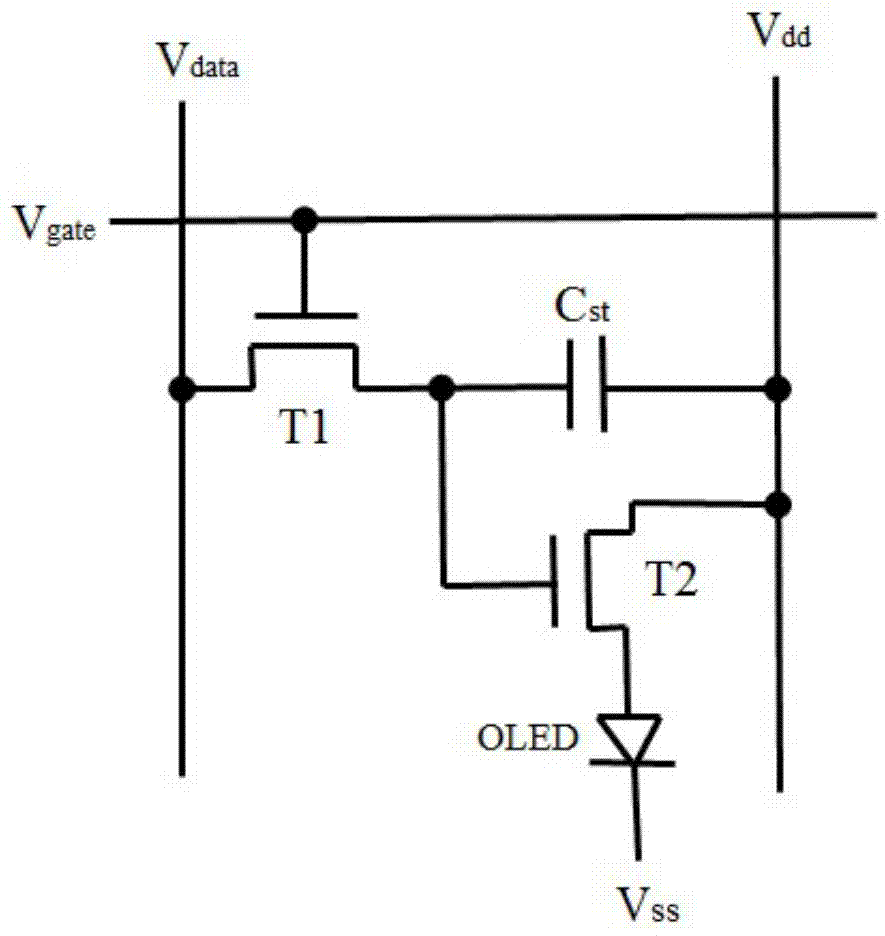
Pixel circuit of active organic electroluminescent display and programming method of pixel circuit
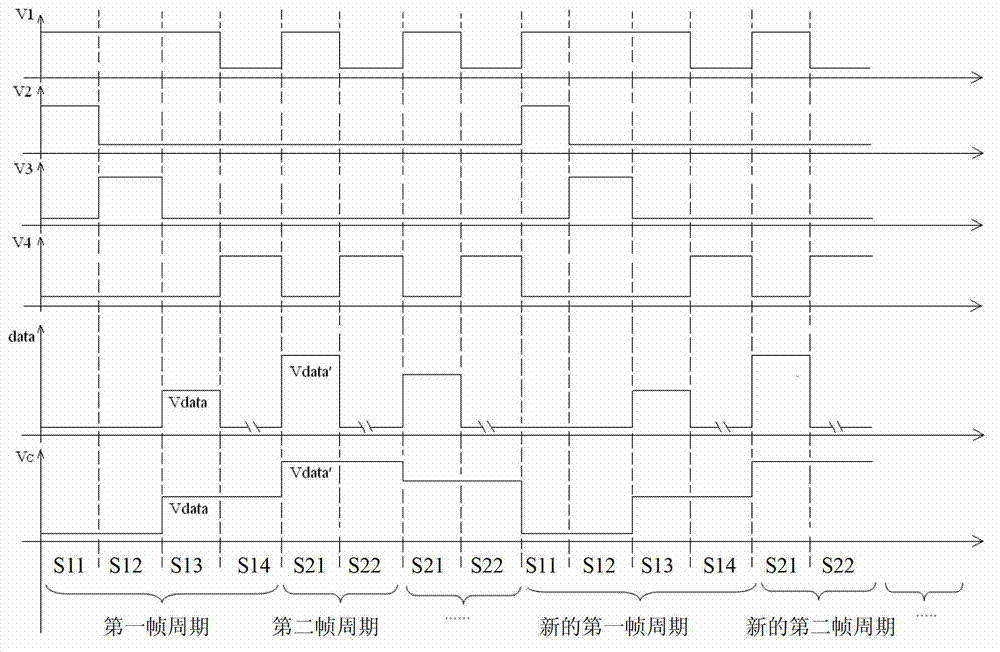
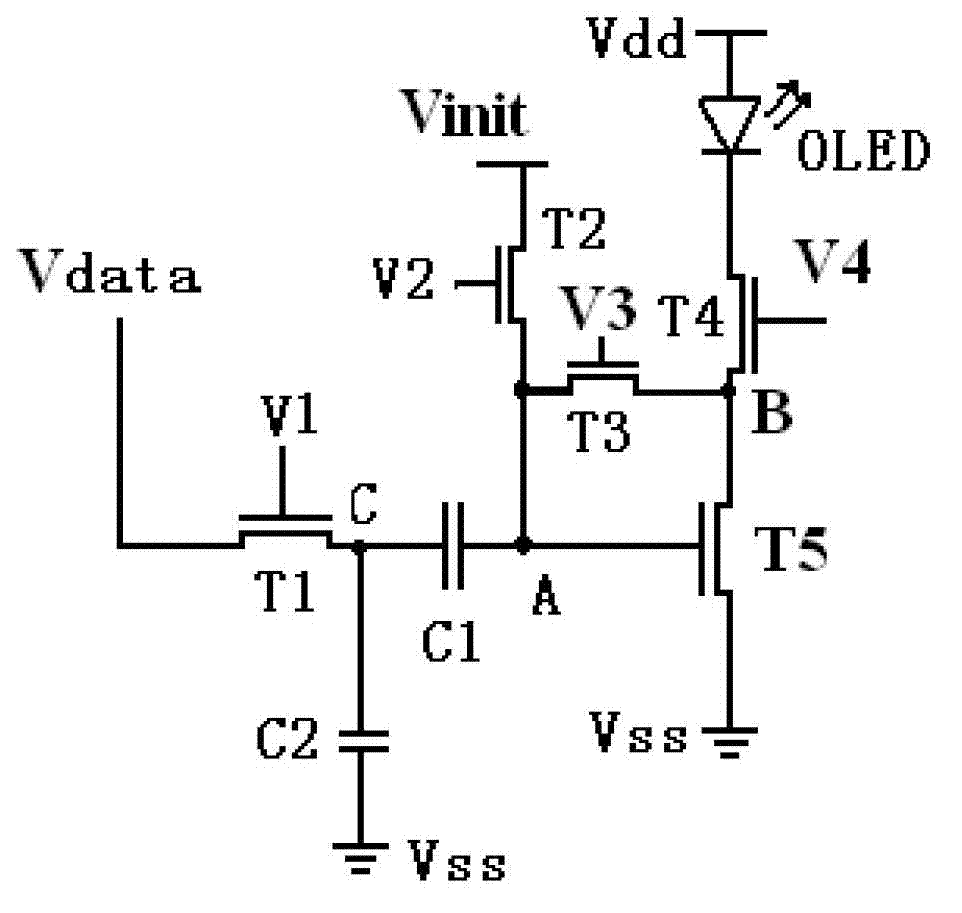
InactiveCN103117041AImprove programming speedConstant currentStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention discloses a pixel circuit of an active organic electroluminescent display. The pixel circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a third transistor, a fourth transistor, a fifth transistor, an organic lighting emitting diode, a first capacitor and a second capacitor. The invention further discloses a programming method of the pixel circuit of the active organic electroluminescent display. The programming method includes that in the first frame period, programming includes stages of initializing, threshold voltage latch, data loading and lighting of the organic light emitting diode; in continuous N frame periods from the second frame, programming only includes stages of data loading and lighting of the organic light emitting diode; and repeating the above process consecutively and circularly. In case of threshold voltage drift of the driving transistor and ageing of the organic light emitting diode, current of the organic light emitting diode is always kept constant, and programming speed of the pixel circuit is effectively increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
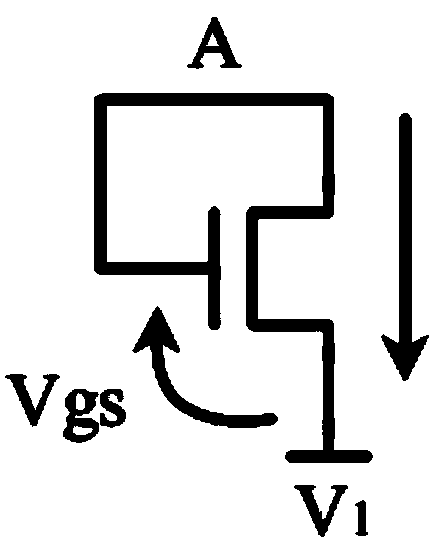
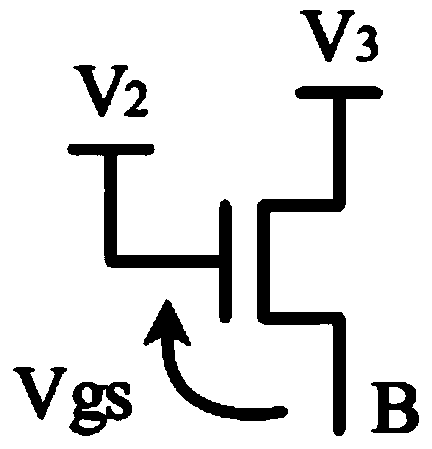
Non-volatile electrically alterable semiconductor memory device
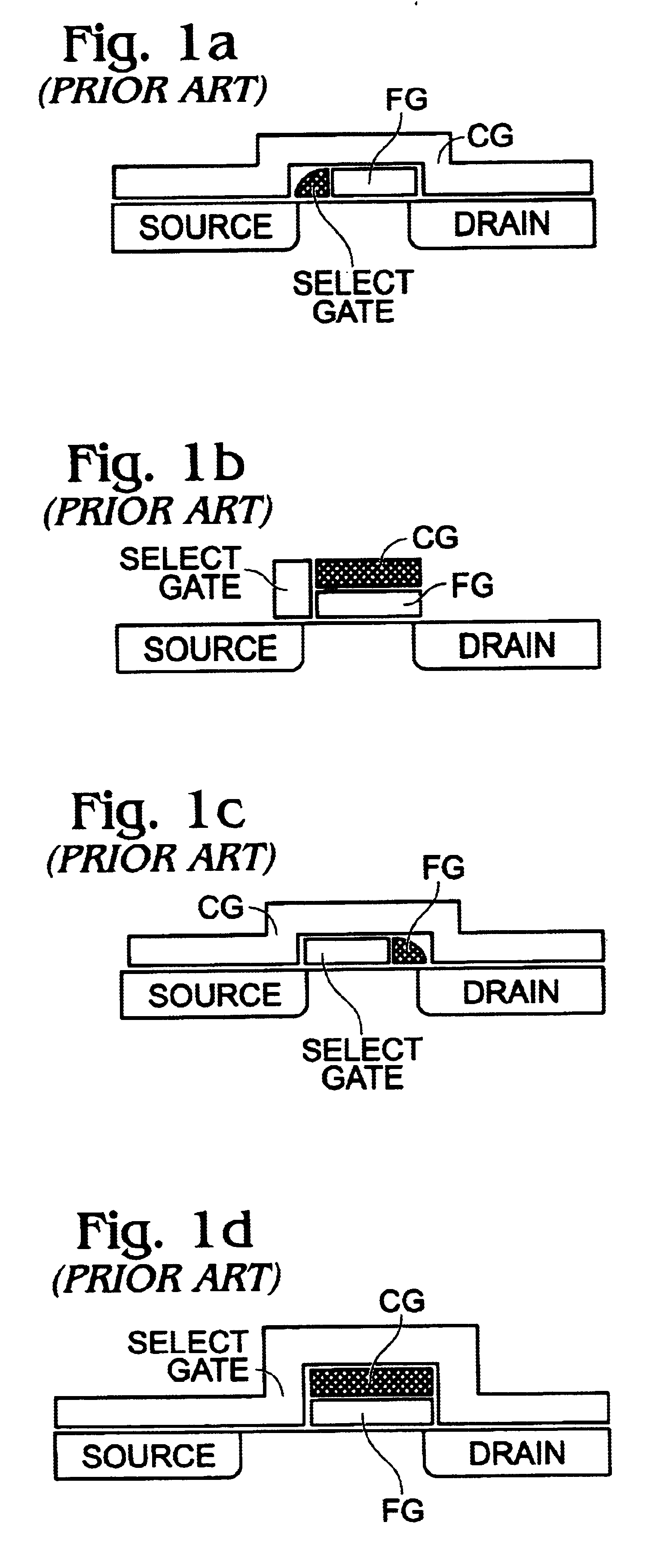
InactiveUS6653682B1Fast programming capabilityReduce voltageTransistorRead-only memoriesCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
Apparatus for an electrically programmable and erasable memory device and methods for programming, erasing and reading the device. The device has a single transistor including a source, a drain, a control gate and a floating gate positioned between the control gate, the source and the drain, where the floating gate is capacitively coupled to the drain. At least one part of the floating gate is partly positioned between the control gate, the drain and the source, and the other part of the floating gate overlaps with the drain. Further, the single transistor of the device includes means for injecting hot electrons generated by the drain induced secondary impact ionization onto the floating gate. Additionally, the means are arranged to induce Fowler-Nordheim tunnelling of charges from the floating gate to the drain.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Phase Change Memory Cell Employing a GeBiTe Layer as a Phase Change Material Layer, Phase Change Memory Device Including the Same, Electronic System Including the Same and Method of Fabricating the Same
ActiveUS20070267721A1Improve programming speedTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryElectronic systems
A phase change memory cell includes an interlayer insulating layer formed on a semiconductor substrate, and a first electrode and a second electrode disposed in the interlayer insulating layer. A phase change material layer is disposed between the first and second electrodes. The phase change material layer may be an undoped GeBiTe layer, a doped GeBiTe layer containing an impurity or a doped GeTe layer containing an impurity. The undoped GeBiTe layer has a composition ratio within a range surrounded by four points (A1(Ge21.43, Bi16.67, Te61.9), A2(Ge44.51, Bi0.35, Te55.14), A3(Ge59.33, Bi0.5, Te40.17) and A4(Ge38.71, Bi16.13, Te45.16)) represented by coordinates on a triangular composition diagram having vertices of germanium (Ge), bismuth (Bi) and tellurium (Te). The doped GeBiTe layer contains an impurity and has a composition ratio within a range surrounded by four points (D1(Ge10, Bi20, Te70), D2(Ge30, Bi0, Te70), D3(Ge70, Bi0, Te30) and D4(Ge50, Bi20, Te30)) represented by coordinates on the triangular composition diagram.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
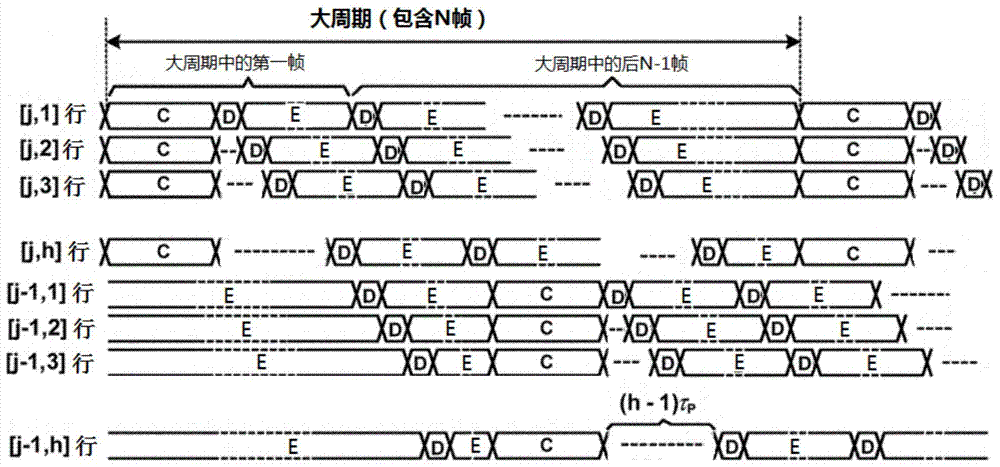
Pixel circuit of active organic electroluminescence displayer and driving method of pixel circuit
ActiveCN104008726AConstant currentImprove programming speedStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceControl signal
The invention discloses a pixel circuit of an active organic electroluminescence displayer and a driving method of the pixel circuit. The pixel circuit is arranged at the crossing part of a scanning line which provides the row form of control signals and a signal line which provides the column form of data signals. The pixel circuit comprises a first switch transistor, a second switch transistor, a third switch transistor, a fourth switch transistor, a driving transistor, an organic light-emitting diode, a first capacitor and a second capacitor. The pixel circuit can compensate the threshold voltage drift (including positive threshold voltage and negative threshold voltage) of the transistors, control signal multiplexing is carried out on several adjacent pixel rows, accordingly, the number of control signal lines is reduced, and the requirement for periphery driving is lowered. Therefore, cost is lowered, a high-speed programming mode can be achieved, and the active organic electroluminescence displayer is suitable for large-size and high-resolution displaying.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
System for increasing programming speed for non-volatile memory by applying counter-transitioning waveforms to word lines
ActiveUS20070291545A1Improve programming speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceTelecommunications
Non-volatile storage elements are programmed using counter-transitioning waveform portions on neighboring word lines which reduce capacitive coupling to a selected word line. In one approach, the waveform portions extend between pass or isolation voltages of a boosting mode, which are applied during a programming pulse on the selected word line, and read voltages, which are applied when verify pulses are applied to the selected word line to verify whether the storage elements have been programmed to a desired programming state. The waveform portions reduce the net voltage change which is coupled to the selected word line. The selected word line can reach a reduced, steady state level sooner so that the verify pulses can be applied sooner, thus reducing the overall programming time. In another aspect, a pass voltage transitions directly to a read voltage on an unselected word line, thereby reducing programming time.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile storage apparatus with variable initial program voltage magnitude
InactiveUS20080198661A1Improve programming speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage amplitudeProgramming language
Multiple programming processes are performed for a plurality of non-volatile storage elements. Each of the programming process operates to program at least a subset of said non-volatile storage elements to a set of target conditions using program pulses. In one embodiment, a first programming pass includes soft programming and additional programming passes include the programming of data. In another embodiment, all of the programming process include programming data. For at least a subset of said programming processes, a program pulse associated with achieving a particular result for a respective programming process is identified. The identified program pulse is used to adjust programming for a subsequent programming process.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Variable initial program voltage magnitude for non-volatile storage
ActiveUS7564715B2Improve programming speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage amplitudeProgramming language
Multiple programming processes are performed for a plurality of non-volatile storage elements. Each of the programming process operates to program at least a subset of said non-volatile storage elements to a set of target conditions using program pulses. In one embodiment, a first programming pass includes soft programming and additional programming passes include the programming of data. In another embodiment, all of the programming process include programming data. For at least a subset of said programming processes, a program pulse associated with achieving a particular result for a respective programming process is identified. The identified program pulse is used to adjust programming for a subsequent programming process.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
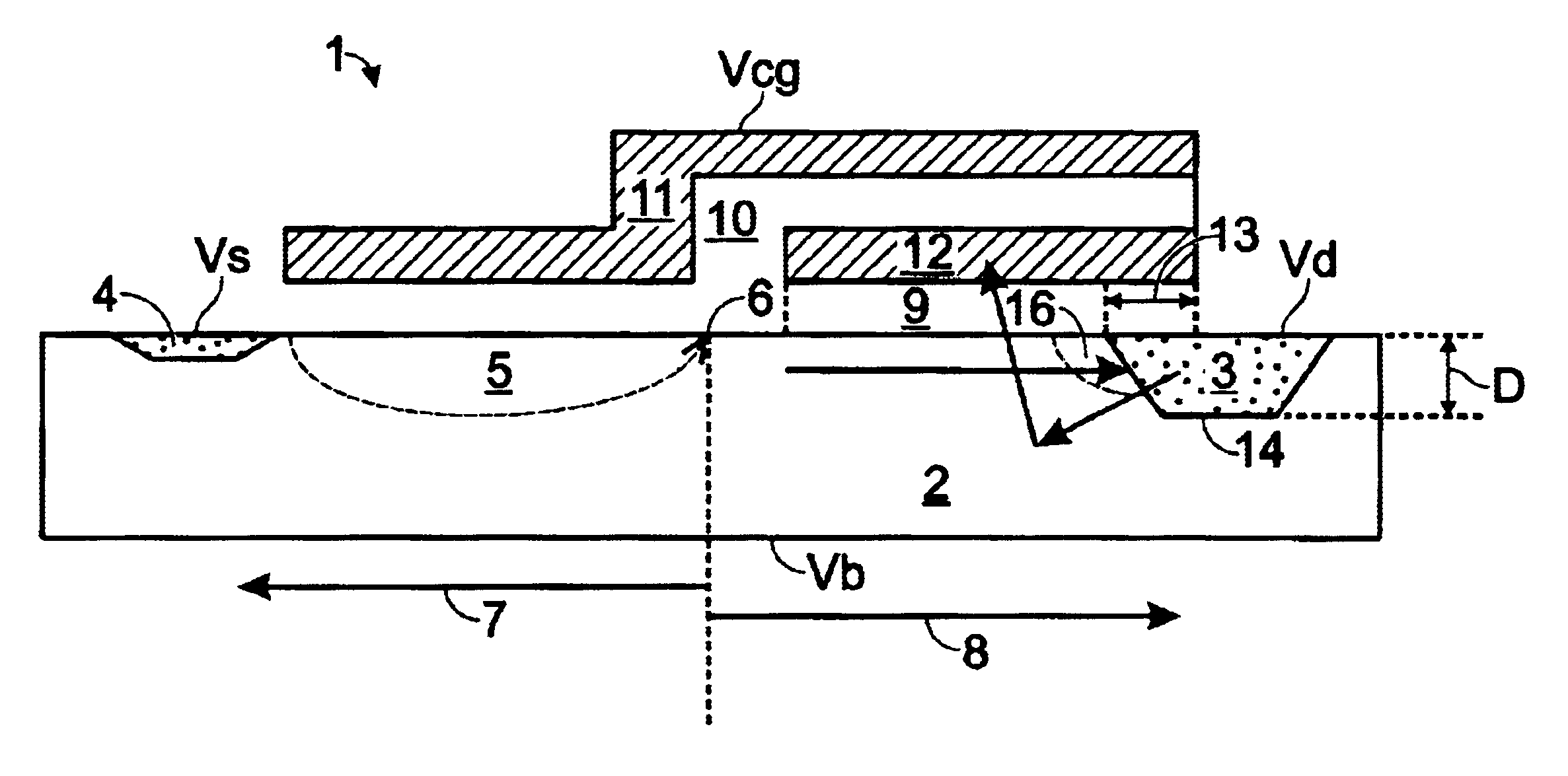
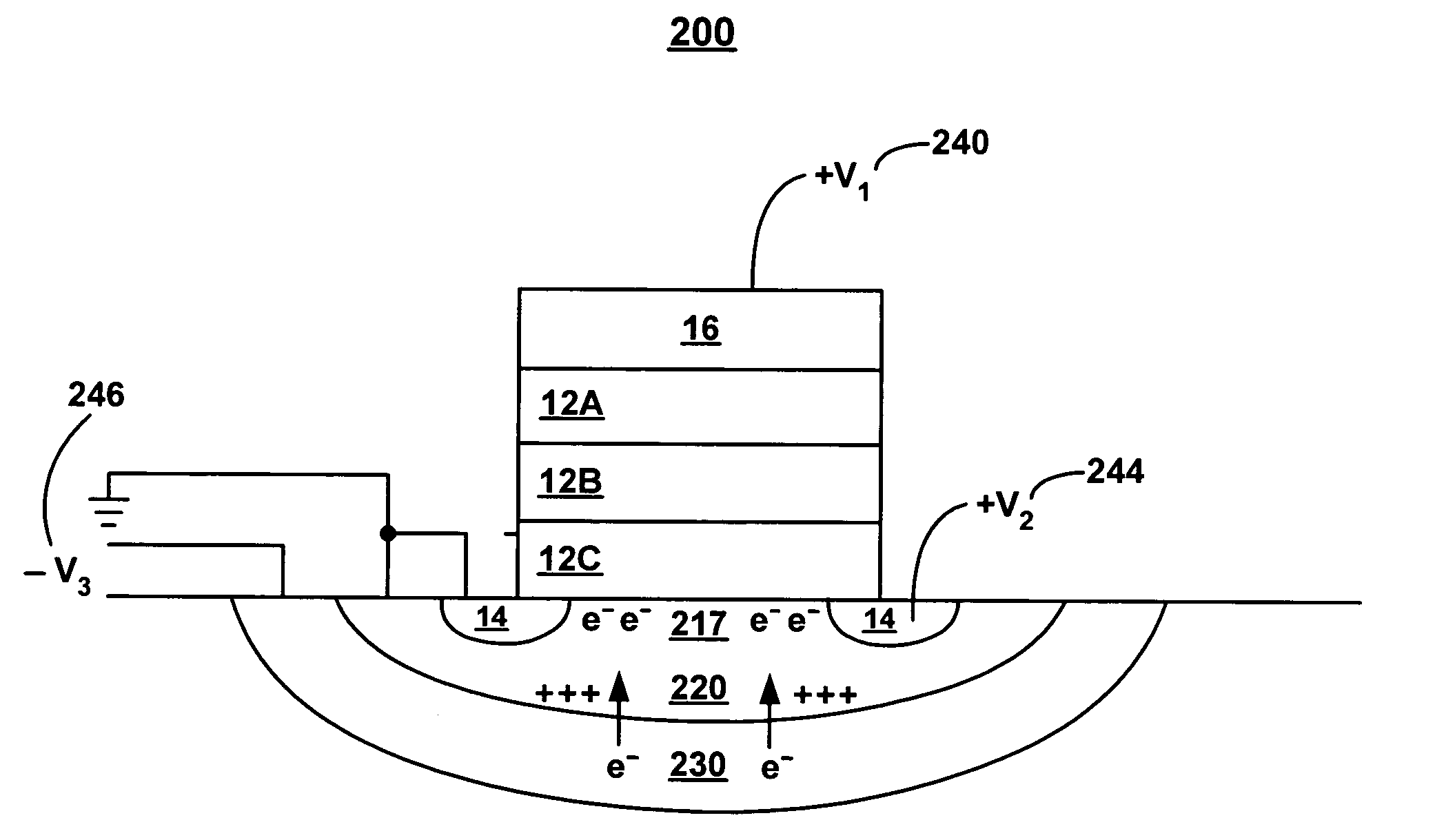
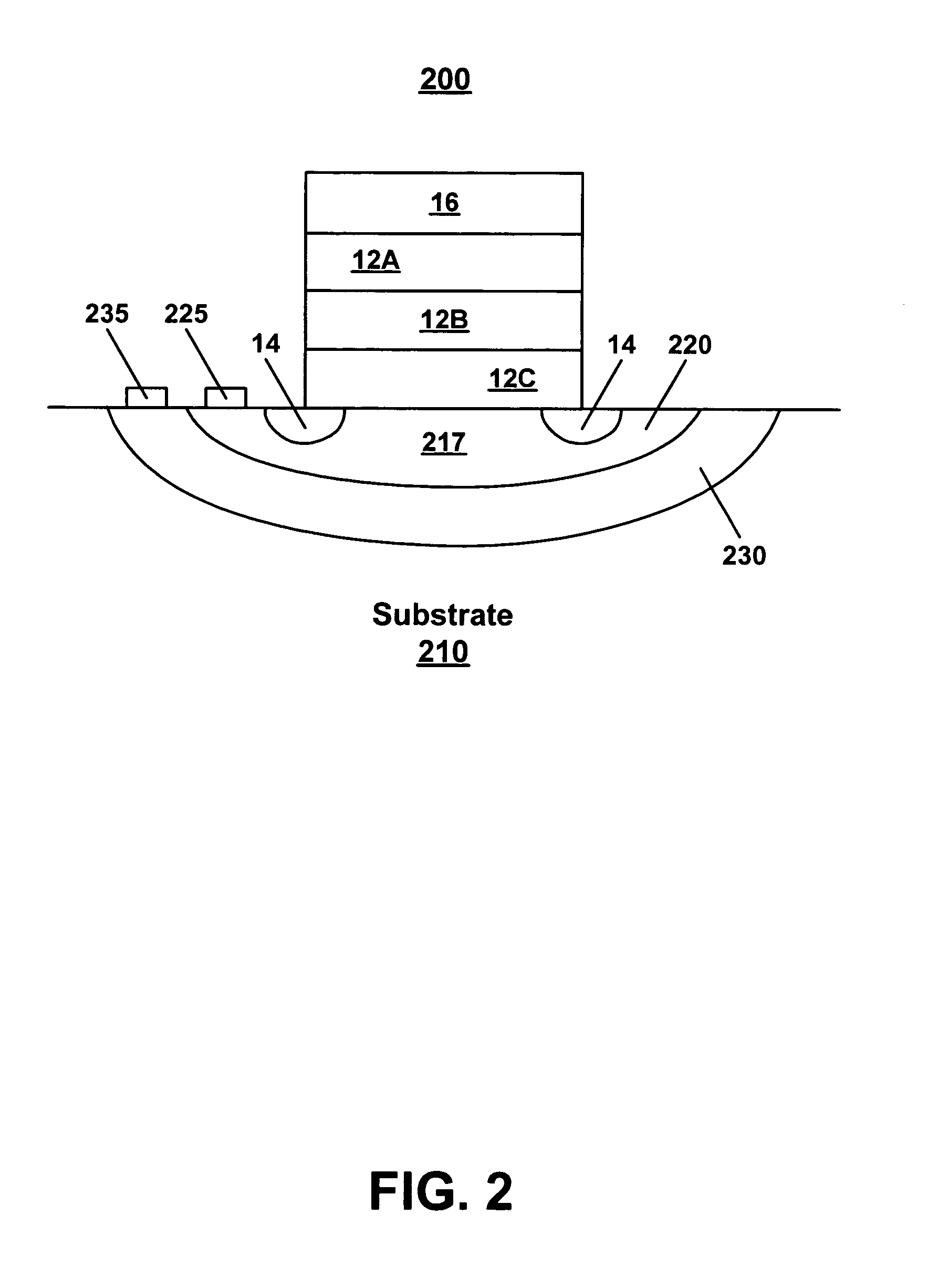
Substrate bias for programming non-volatile memory
A method and system for substrate bias for programming non-volatile memory. A bias voltage is applied to a deep well structure under a well comprising a channel region for a non-volatile memory cell. During programming, a negative bias applied to the deep well beneficially creates a non-uniform distribution of electrons within the channel region, with an abundance of electrons at the surface of the channel region. The application of additional bias voltages to a control gate and a drain may cause electrons to migrate from the channel region to a storage layer of the non-volatile memory cell. Advantageously, due to the increased supply of electrons at the surface of the channel region, programming of the non-volatile cell takes place faster than under the conventional art.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Memory apparatus and method for operating the same
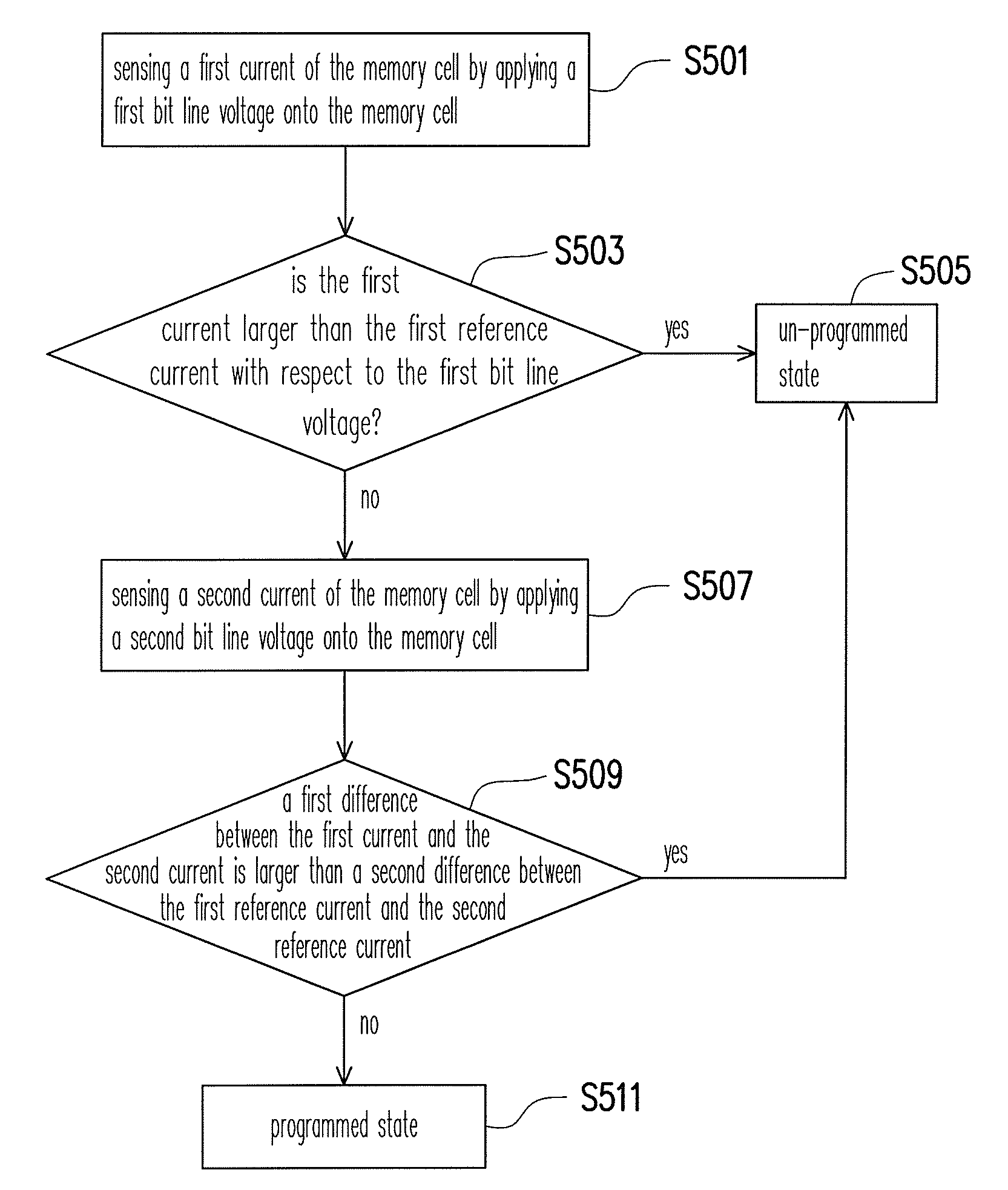
ActiveUS20100254194A1Reduce stepsReduce impactRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineReference current
The invention provides a method for reading a first data storage of a memory cell. The method comprises sensing a first current of the memory cell by applying a first bit line voltage on the memory cell. When the first current is larger than a first reference current with respect to the first bit line voltage, the first data storage is determined to be at an un-programmed state. Otherwise, a second current of the memory cell is sensed by applying a second bit line voltage on the memory cell. When the difference between the first current and the second current is larger than the difference between the first reference current and the second reference current, the first data storage is determined to be at the un-programmed state. Otherwise, the first data storage is determined to be at a programmed state
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Multiple pass write sequence for non-volatile storage
ActiveUS7564711B2Improve programming speedTight distribution of threshold voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageMultiple passProgramming process
A set of non-volatile storage elements are erased to an erased threshold voltage distribution. A multi-pass programming process is performed that programs the set of non-volatile storage elements from the erased threshold voltage distribution to a set valid data threshold voltage distributions. Each programming pass has one or more starting threshold voltage distributions and programs non-volatile storage elements to at least two ending threshold voltage distributions.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
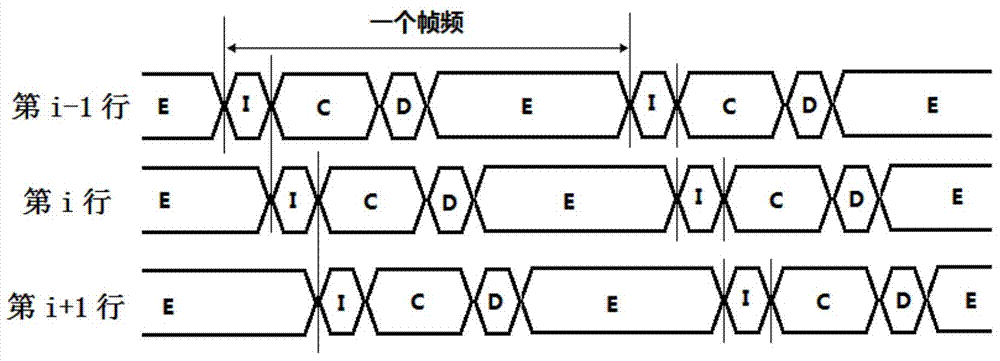
Method for driving pixel circuit of active organic electroluminescence displayer
ActiveCN103578428AReduce power consumptionImprove programming speedStatic indicating devicesEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
The invention discloses a method for driving a pixel circuit of an active organic electroluminescence displayer. The method comprises a plurality of major cycles and each major cycle comprises N frames. In the first frame, programming is conducted through an initialization stage, a threshold voltage latching stage, a data loading stage and an organic light-emitting diode lighting stage, wherein the threshold voltage latching stage is separated from a signal scanning stage; in the second frame to the Nth frame, programming is conducted only through an data loading stage and an organic light-emitting diode lighting stage. In terms of a whole pixel array, when an initialization step of pixels on the ith row is completed, the initialization step of pixels on the i+1th row is conducted. According to the method for driving the pixel circuit of the active organic electroluminescence displayer, threshold voltage drift of a driving transistor and degeneration of an organic light-emitting diode can be made up, the display quality is guaranteed, the power consumption can also be reduced, and the programming speed is effectively improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
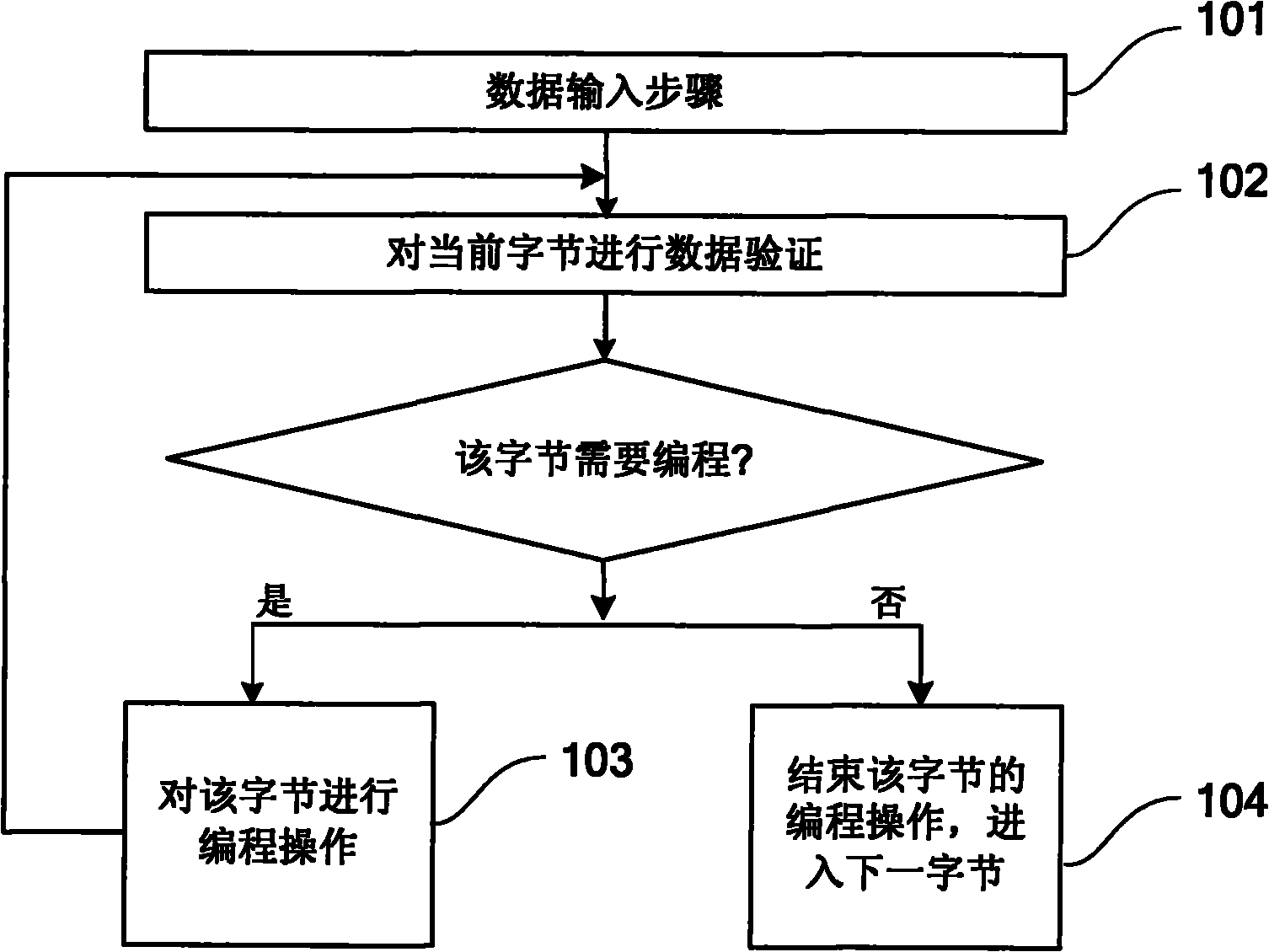
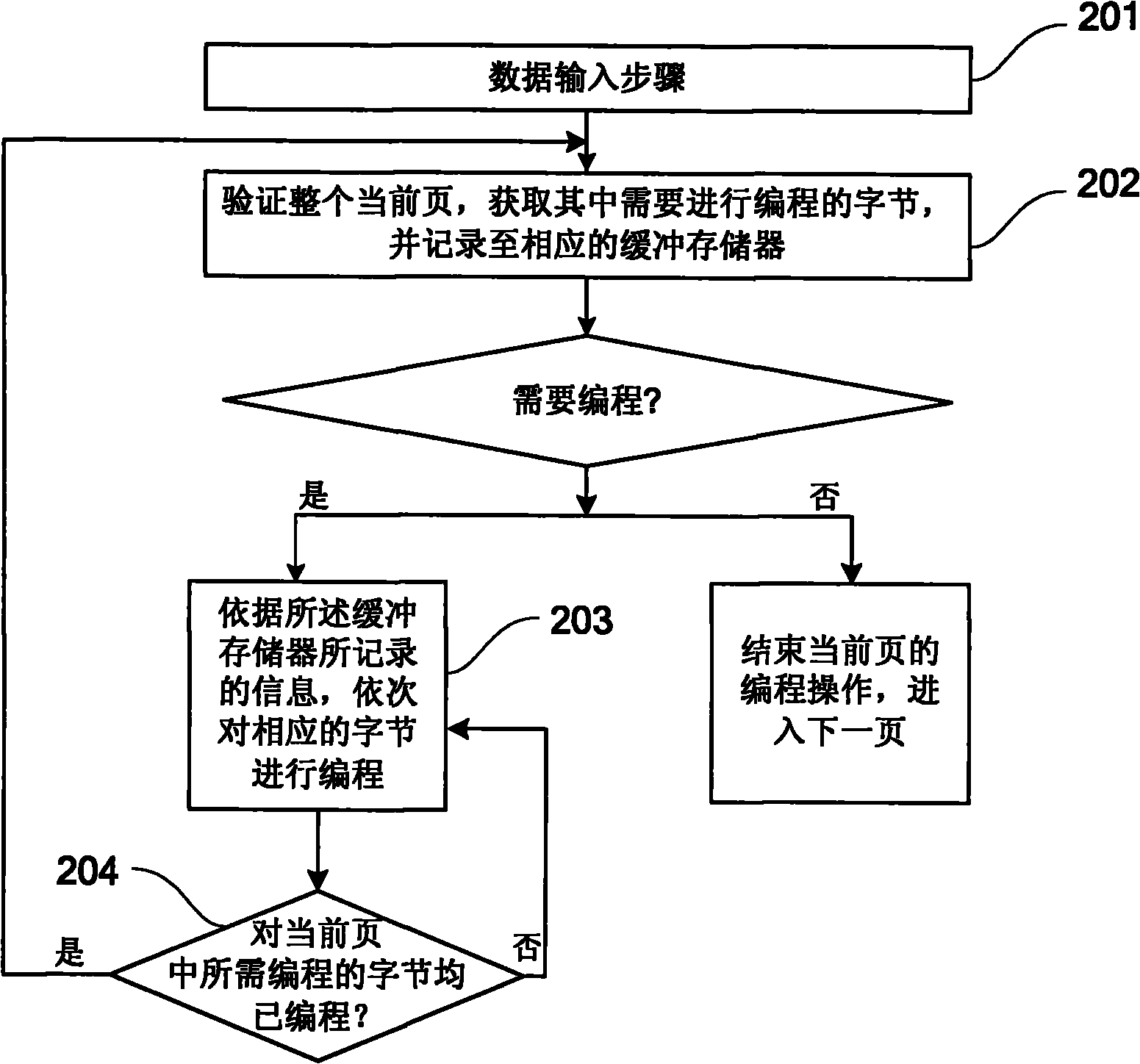
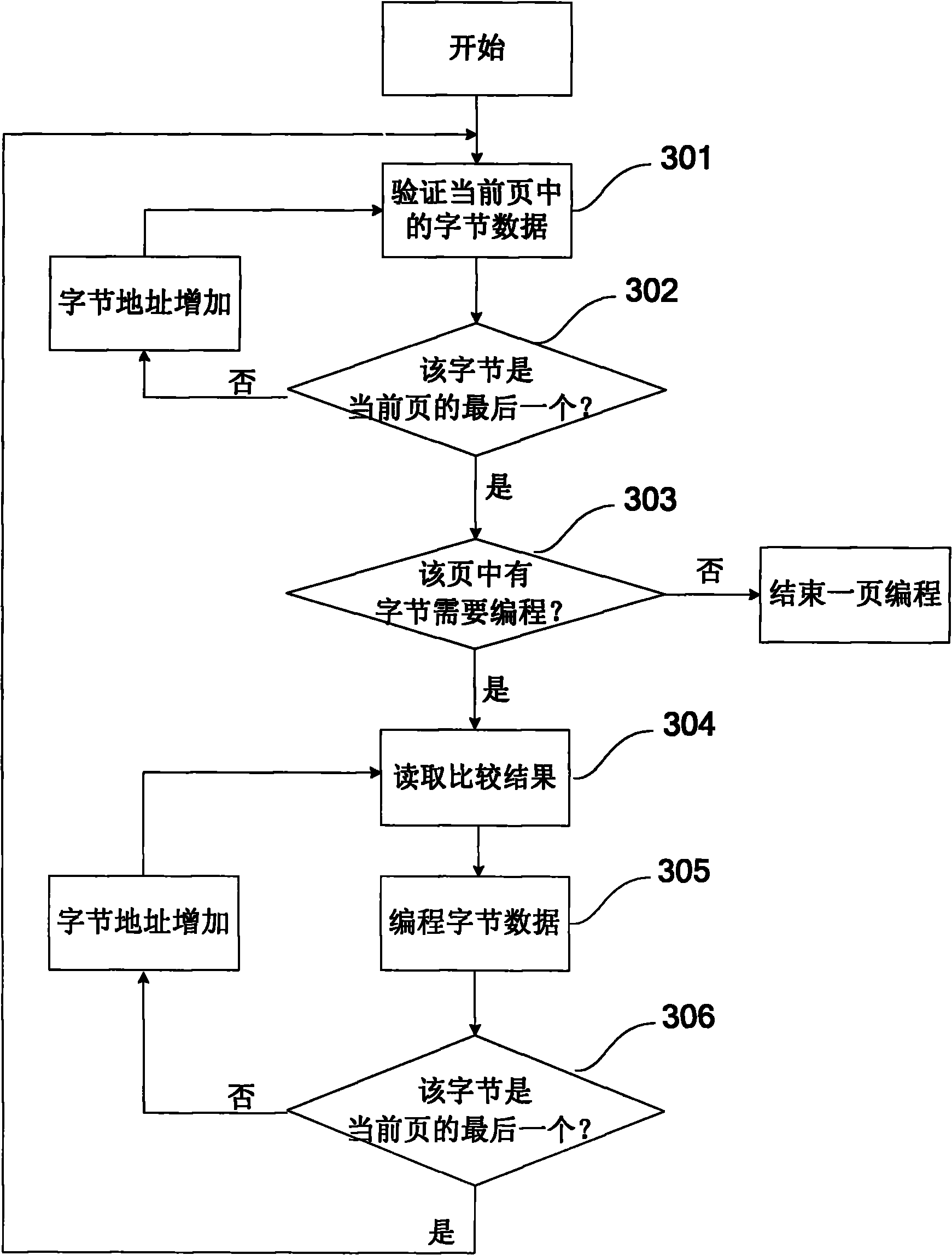
Method and device for carrying out data programming on flash
ActiveCN101800077AImprove programming speedShort charge and discharge timeRead-only memoriesData validationSource Data Verification
The invention discloses a method for carrying out data programming on flash, comprising the following steps: a. inputting data; b. verifying the current whole page, obtaining the bytes needing to be programmed in the page and recording the bytes into a corresponding buffer storage unit, and completing data programming in the current page if the current page contains no bytes needing to be programmed; and c. programming the corresponding bytes in sequence according to the information recorded in the buffer storage unit, and if the bytes needing to be programmed in the current page have been programmed, returning to the step b, or continuing the step c and operating the next byte. In the invention, the step of data verification and the step of data writing in the process of programming operation are carried out on the whole page, thus greatly reducing the switching times of different voltage on loading grid and drain, saving the charge and discharge time of the grid and drain voltage pumps and then improving the programming speed of flash.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON SHANGHAI INC +1
Single crystal fuse on air in bulk silicon
ActiveUS20090090993A1Raise the temperature gradientImprove programming speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceSalicide
An integrated eFUSE device is formed by forming a silicon “floating beam” on air, whereupon the fusible portion of the eFUSE device resides. This beam extends between two larger, supporting terminal structures. “Undercutting” techniques are employed whereby a structure is formed atop a buried layer, and that buried layer is removed by selective etching. Whereby a “floating” silicide eFUSE conductor is formed on a silicon beam structure. In its initial state, the eFUSE silicide is highly conductive, exhibiting low electrical resistance (the “unblown state of the eFUSE). When a sufficiently large current is passed through the eFUSE conductor, localized heating occurs. This heating causes electromigration of the silicide into the silicon beam (and into surrounding silicon, thereby diffusing the silicide and greatly increasing its electrical resistance. When the current source is removed, the silicide remains permanently in this diffused state, the “blown” state of the eFUSE.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof] [NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fd24ad20-241c-499a-ae01-18d1c3524bcb/US20050087892A1-20050428-D00000.png)
![[NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof] [NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fd24ad20-241c-499a-ae01-18d1c3524bcb/US20050087892A1-20050428-D00001.png)
![[NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof] [NAND flash memory cell row, NAND flash memory cell array, operation and fabrication method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fd24ad20-241c-499a-ae01-18d1c3524bcb/US20050087892A1-20050428-D00002.png)
![[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof] [non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/754b3ed3-8dc8-4ae1-afef-ef843bfb71df/US20050224858A1-20051013-D00000.png)
![[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof] [non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/754b3ed3-8dc8-4ae1-afef-ef843bfb71df/US20050224858A1-20051013-D00001.png)
![[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof] [non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/754b3ed3-8dc8-4ae1-afef-ef843bfb71df/US20050224858A1-20051013-D00002.png)