Method and device for carrying out data programming on flash
A data programming and data technology, which is applied in the field of memory, can solve problems affecting programming speed, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing programming speed, reducing switching times, and saving charging and discharging time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
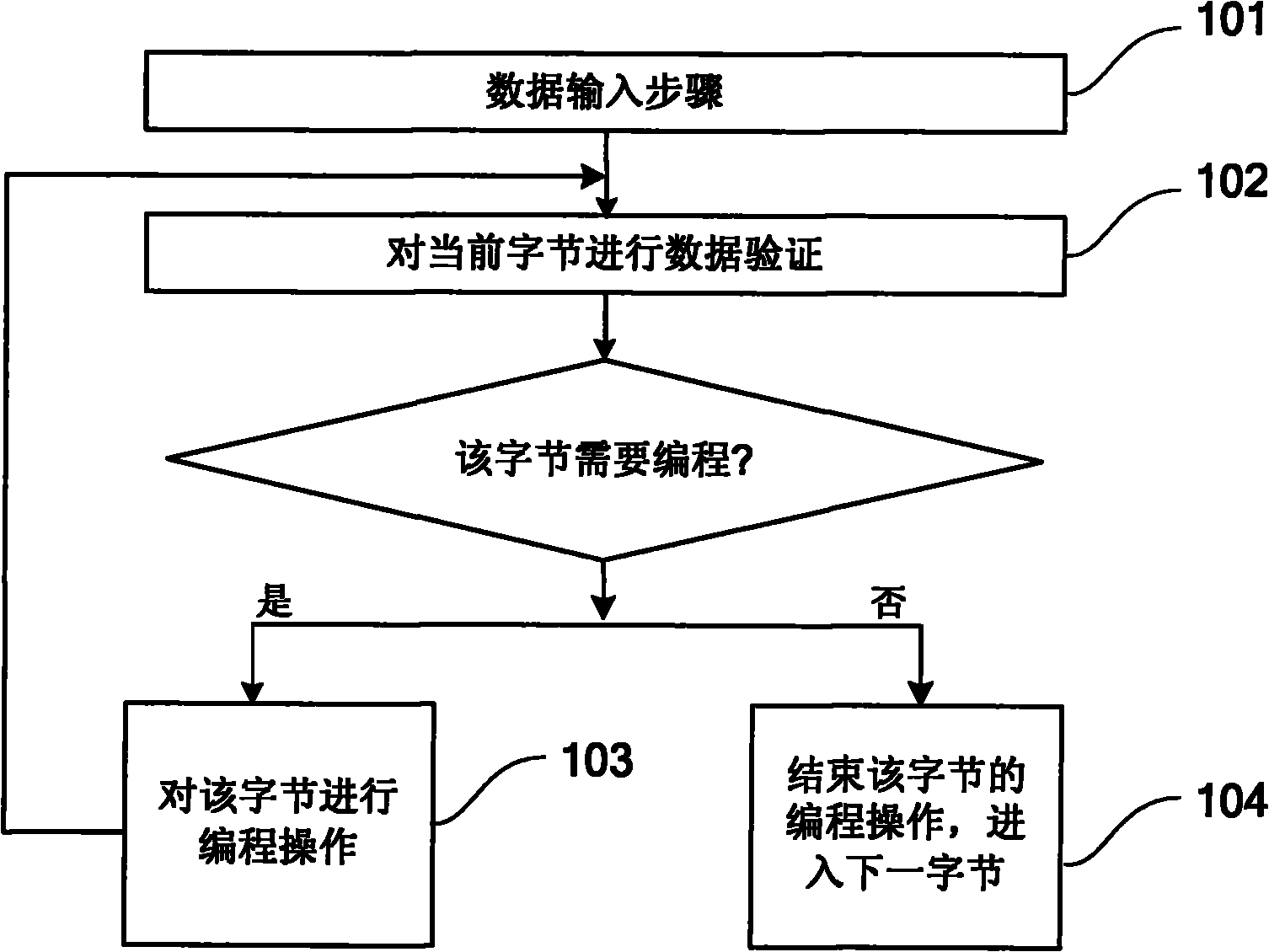
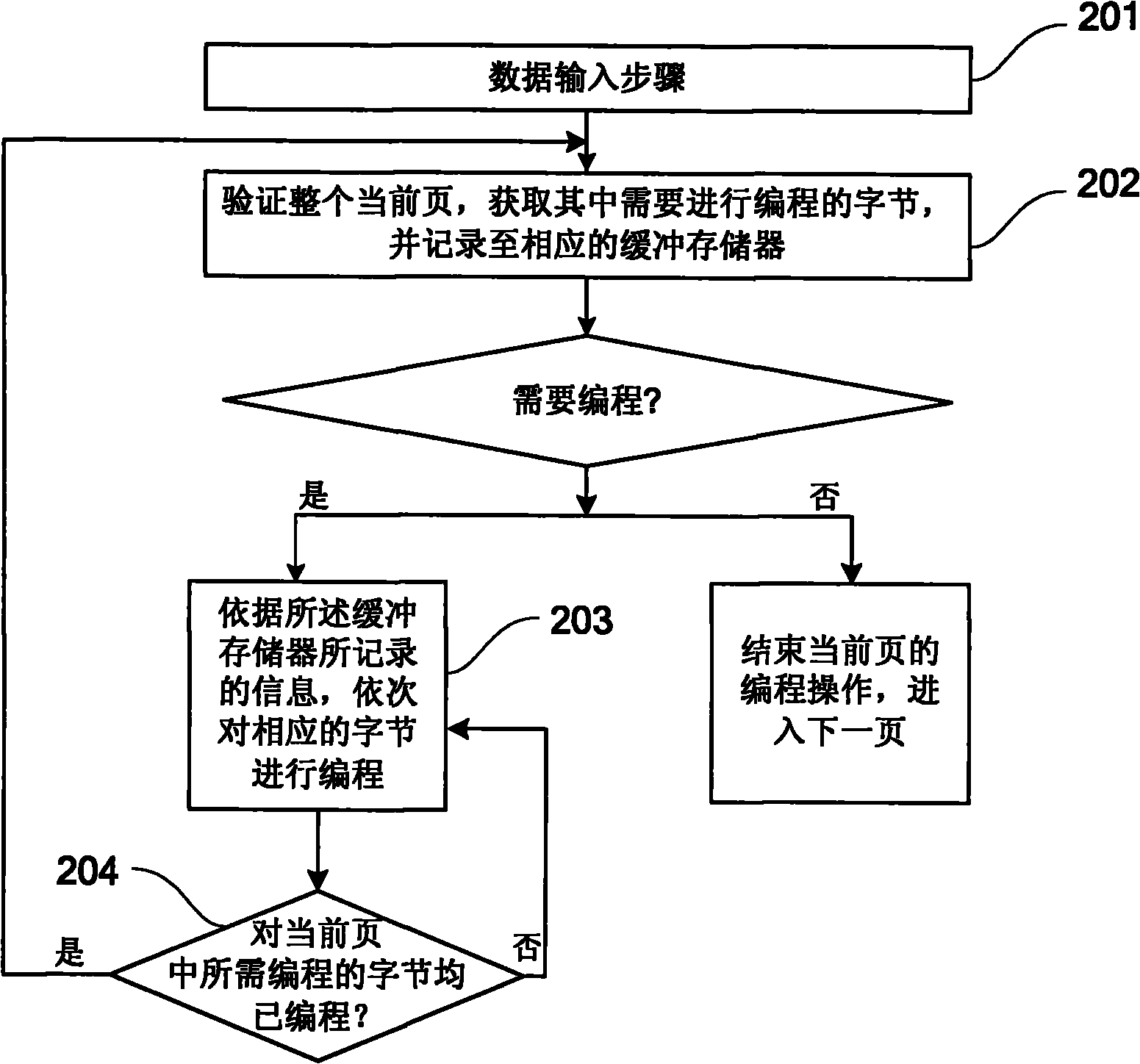
[0046] refer to figure 2 , showing a method embodiment 1 for performing data programming on a flash memory, which is characterized in that it includes:
[0047] Step 201, the data input step; more specifically, the received data (that is, the data to be written) can be stored in the page buffer of the flash memory, so as to be acquired in the subsequent programming step;
[0048] Step 202, verify the entire current page, obtain the bytes that need to be programmed, and record them into the corresponding buffer memory; if there are no bytes that need to be programmed in the current page, then end the data programming operation of the current page, and enter the next page. one page;
[0049] Of course, it should be noted that when all the input data has been programmed, there is no need to enter the verification and programming process on the next page, and the entire programming operation can be ended directly.
[0050] Step 203, according to the information recorded in the bu...
Embodiment 2
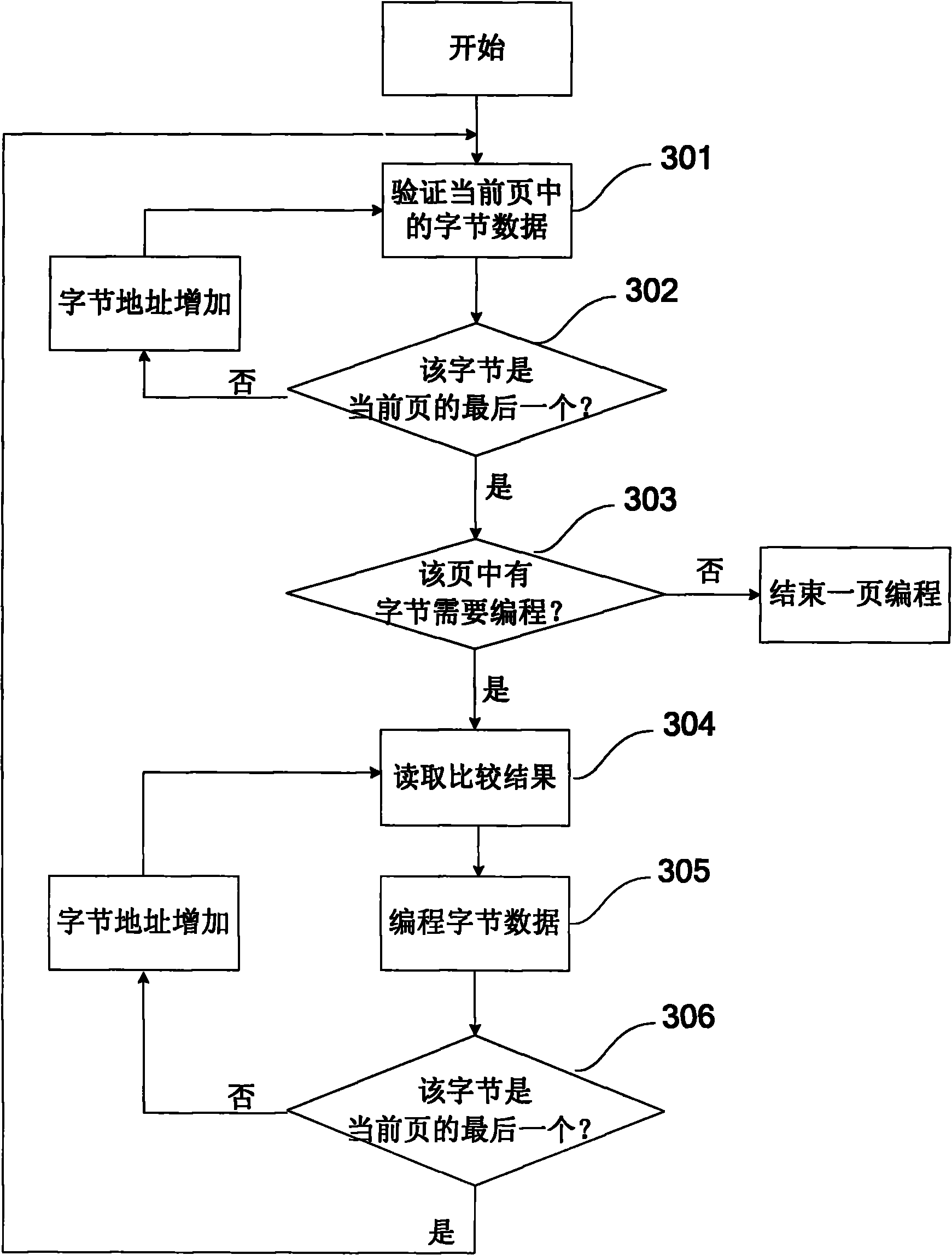
[0060] refer to image 3 , shows an embodiment 2 of the present invention for performing data programming on a flash memory, which may specifically include:
[0061] Step 301, starting from the start address of a page, verifying in units of bytes, comparing whether the data stored in the byte is consistent with the data to be written; writing the result into the buffer memory corresponding to the byte address ; Of course, generally, a byte does not correspond to a buffer memory, and the comparison result of the byte can be stored in the buffer memory corresponding to the address of the byte.
[0062] Step 302 , after verifying the current byte, increase the byte address, and verify the byte at the next address until the entire page is verified. Specifically, it can be judged whether the currently verified byte is the last byte of the page, and if yes, the next step is performed; otherwise, the byte address is increased to continue the verification.
[0063] Step 303 , confir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com