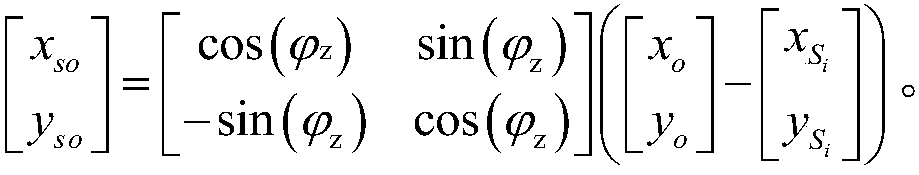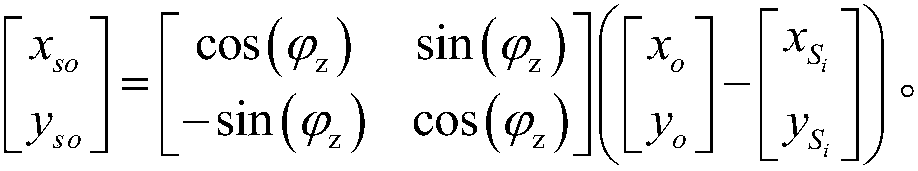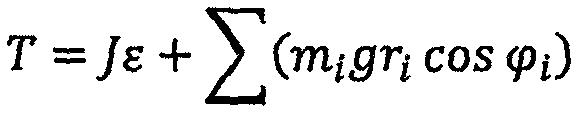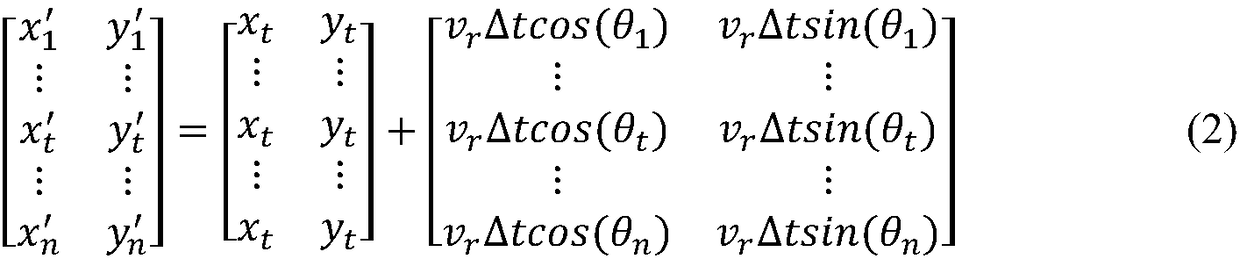Patents
Literature
102 results about "Analog robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An analog robot is a type of robot which uses analog circuitry to go toward a simple goal such as finding more light or responding to sound. The first real analog robot was invented in the 1940s by William Grey Walter. The name of these robots were ELSIE and ELMER (Electro Mechanical Robot). The original circuitry was developed using two vacuum tubes and a photocell to search and follow a light. Recently a kind of analog robots was developed by Mark Tilden.
Automated bot development system
ActiveUS7039654B1Increases scale and scopeProlong lifeResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsAnalog robotProgram instruction
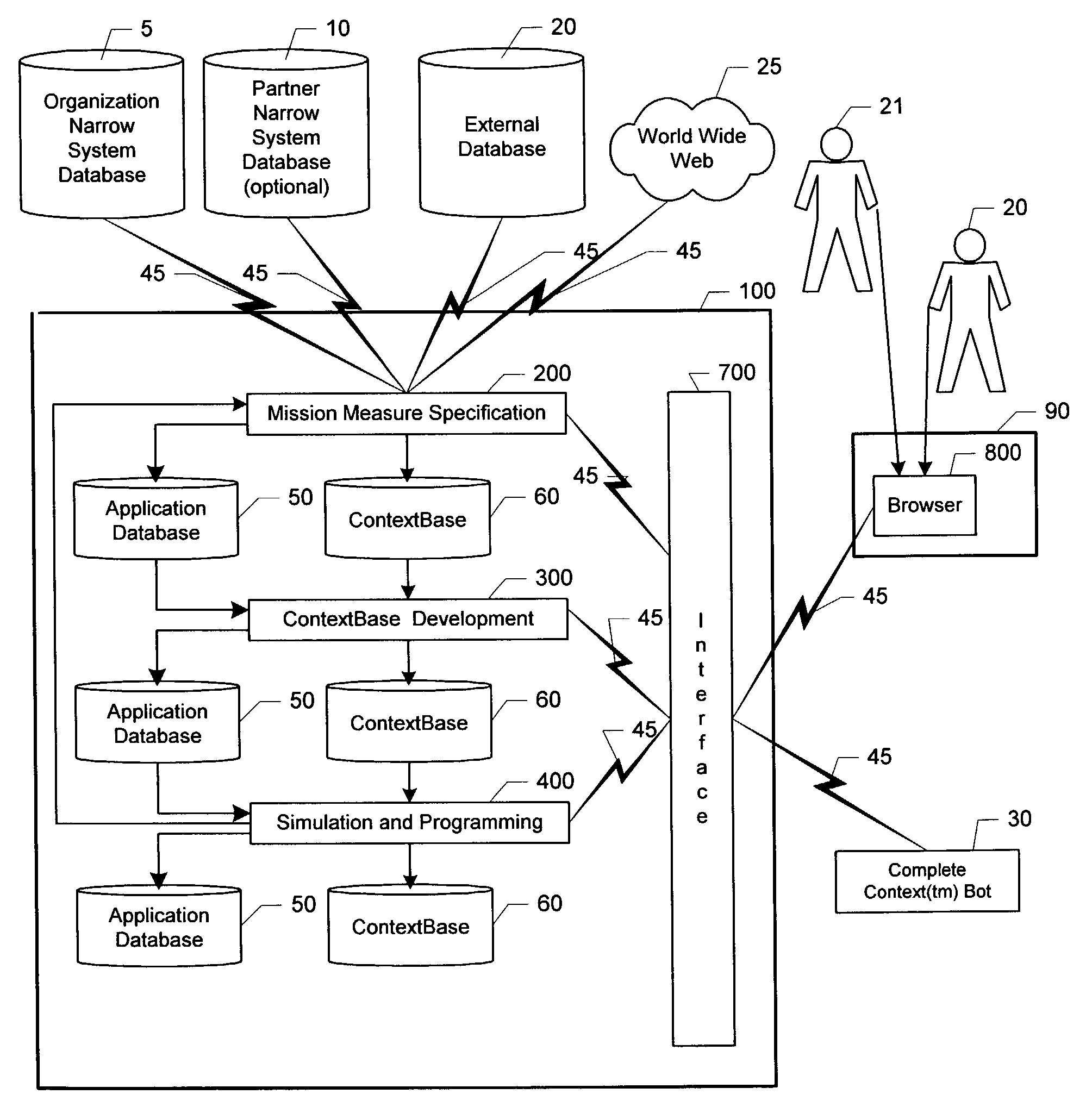
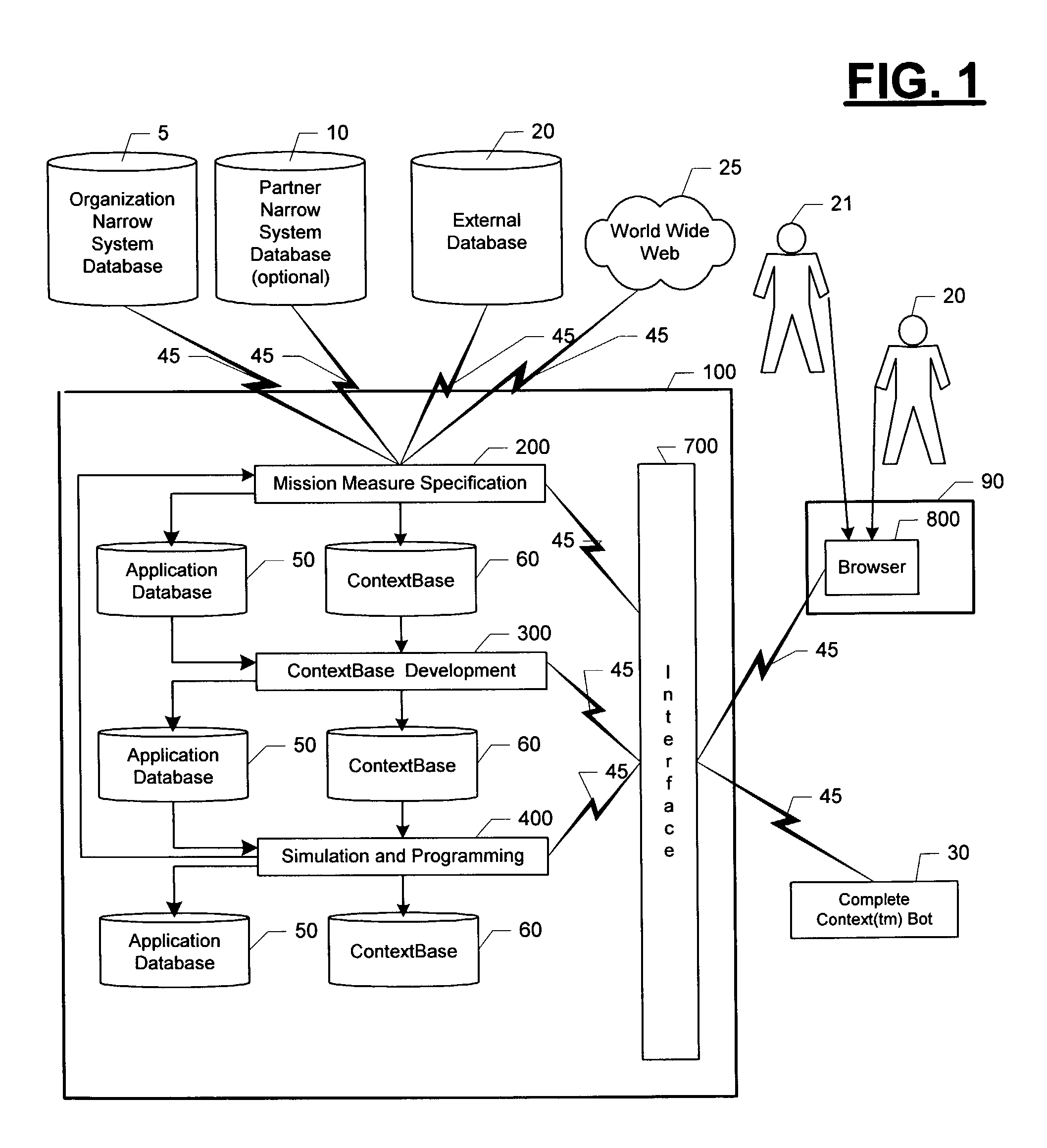
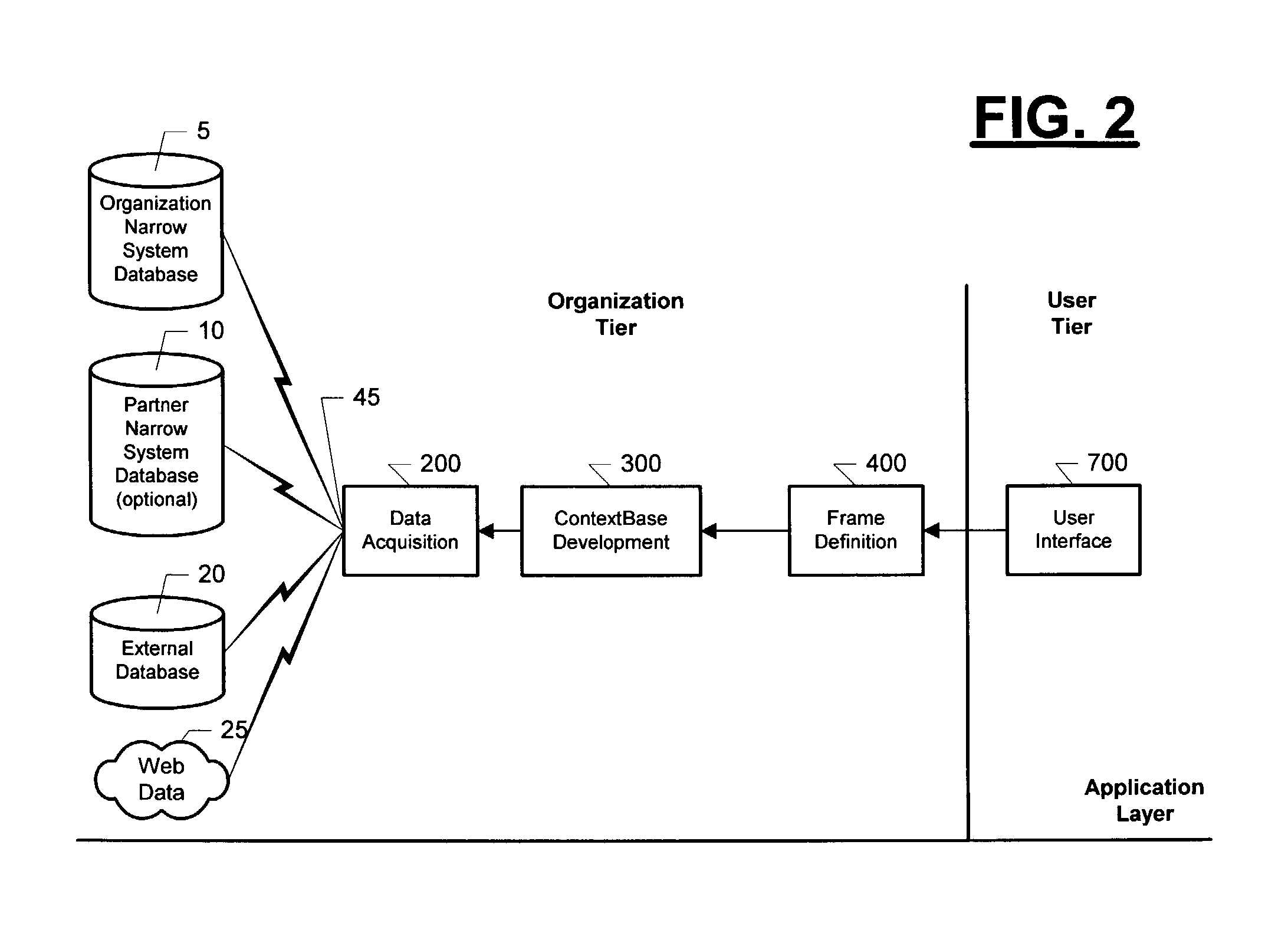
An automated system (100) and method for developing Complete Context™ Bots (30) for an organization. After extracting data from existing narrowly focused systems, mission measures and organization levels are defined for one or more organizations. The elements, factors and risks that contribute to mission measure performance by organization level and organization are systematically defined and stored in a ContextBase (60) using up to six context layers. ContextBase (60) information is extracted for specified combinations of context layers, organization levels and organizations as required to produce complete context frames that are used to support simulations of bot performance under a variety of scenarios. The program instructions that will maximize bot performance under the forecast scenarios are identified. After this programming is transferred to the Complete Context™ Bot (30), it is activated.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
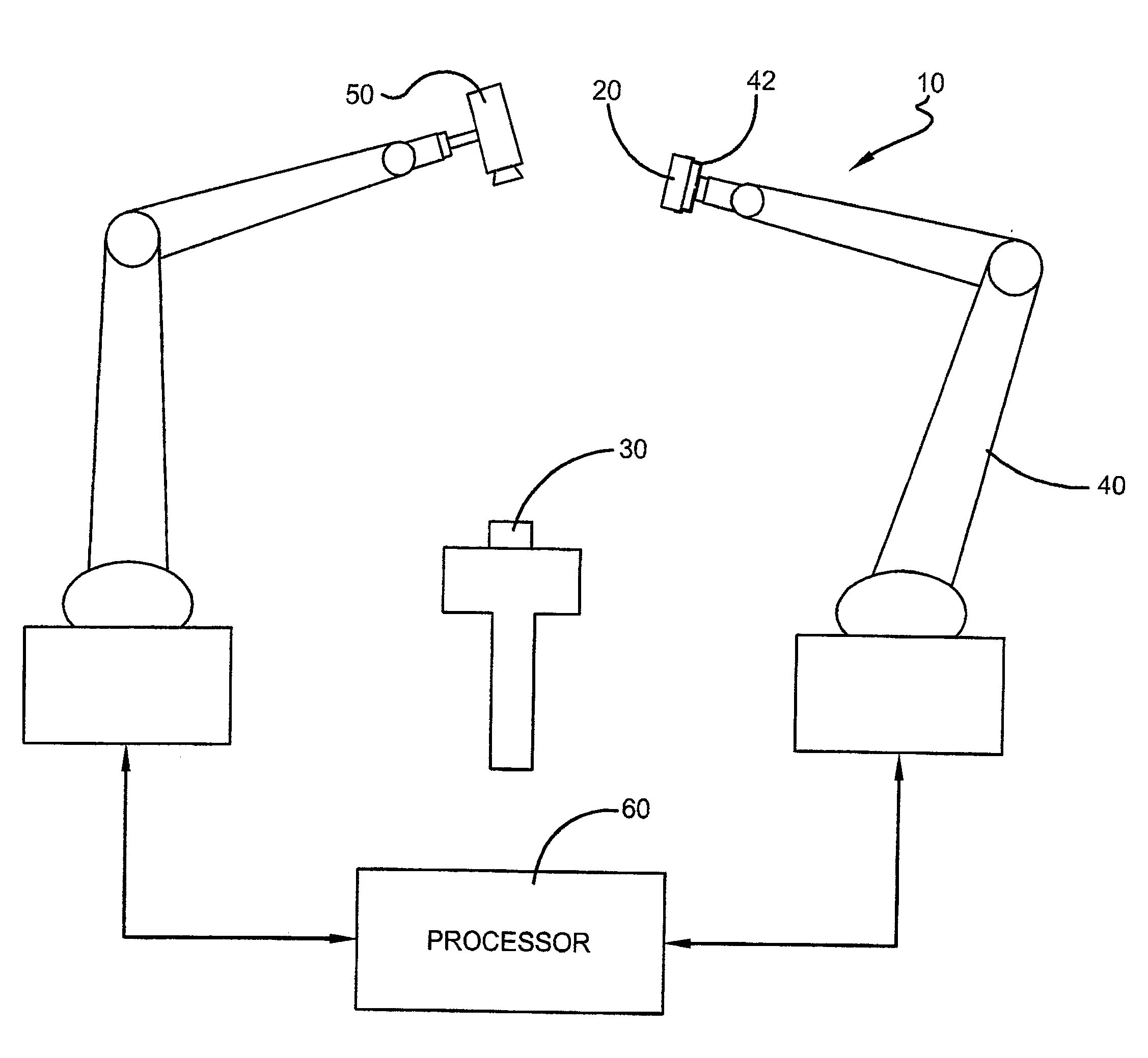
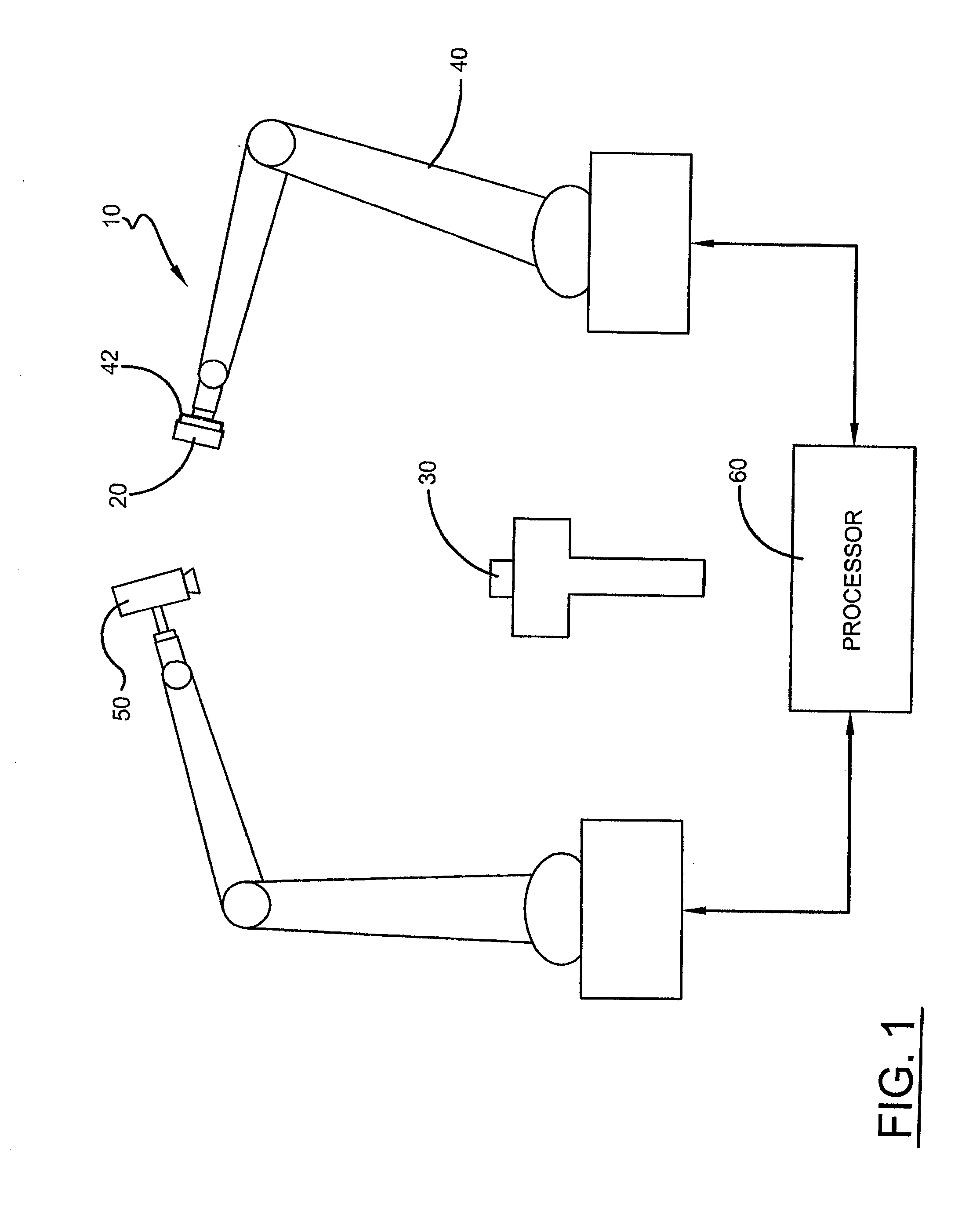
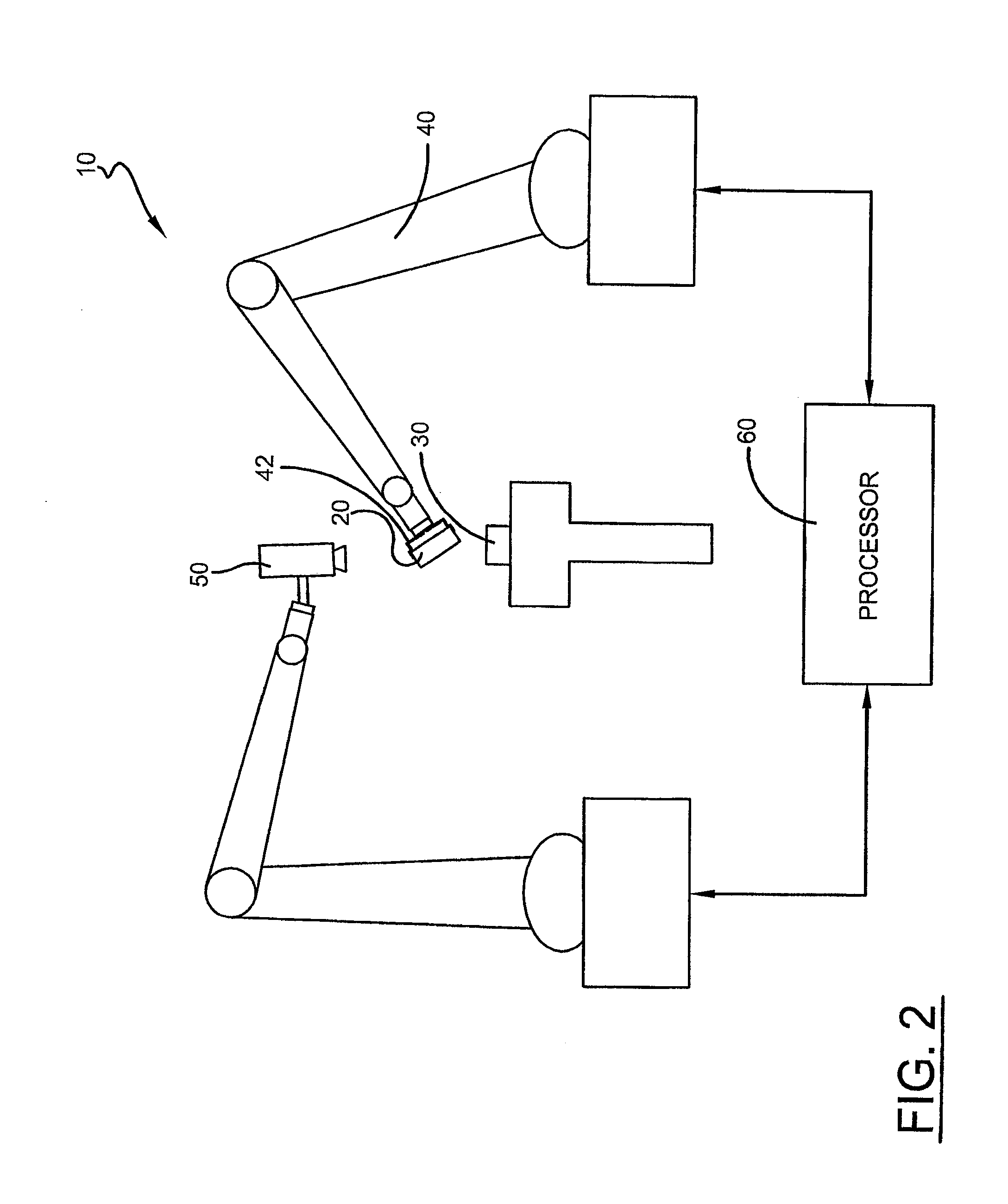
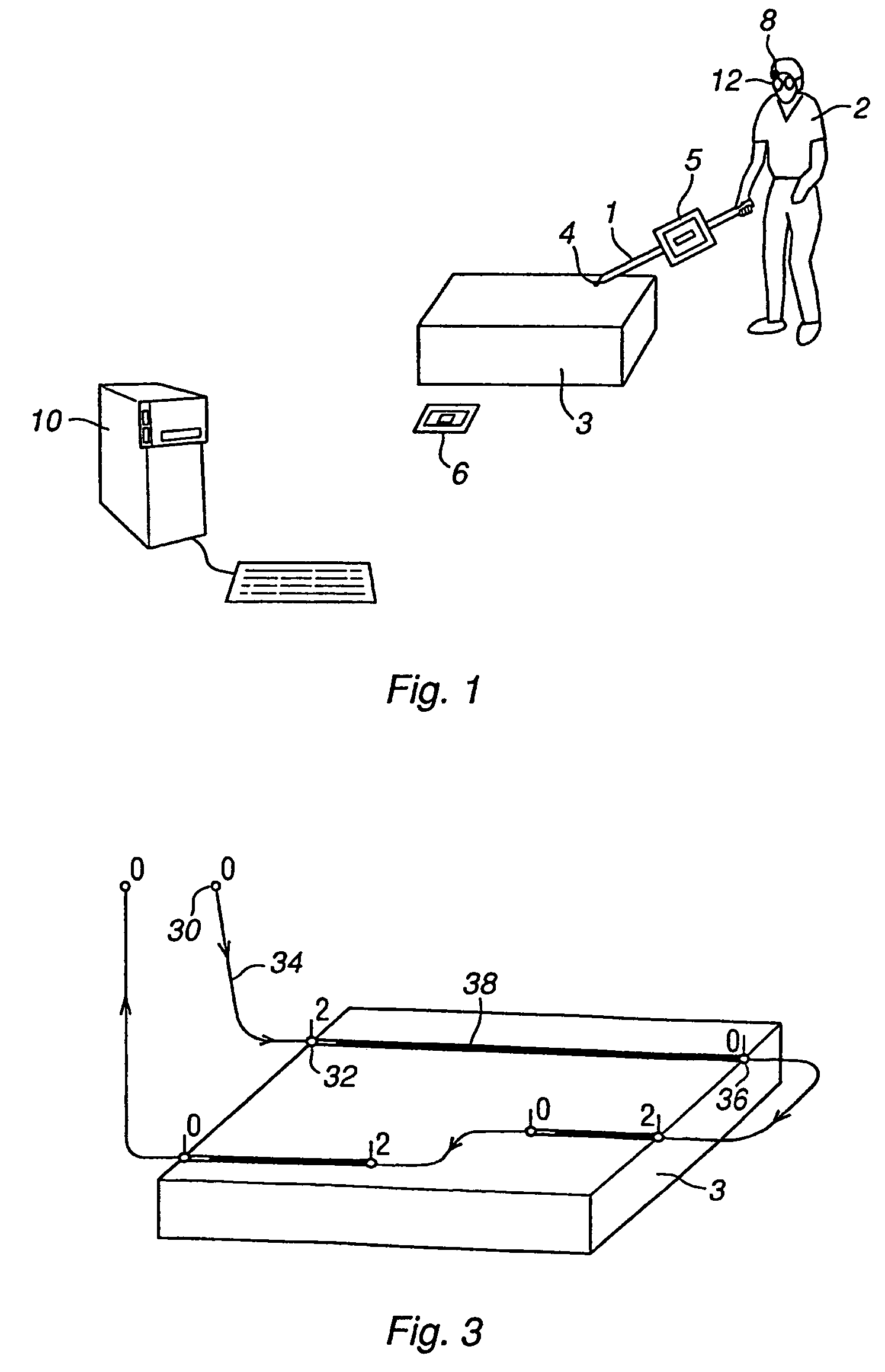
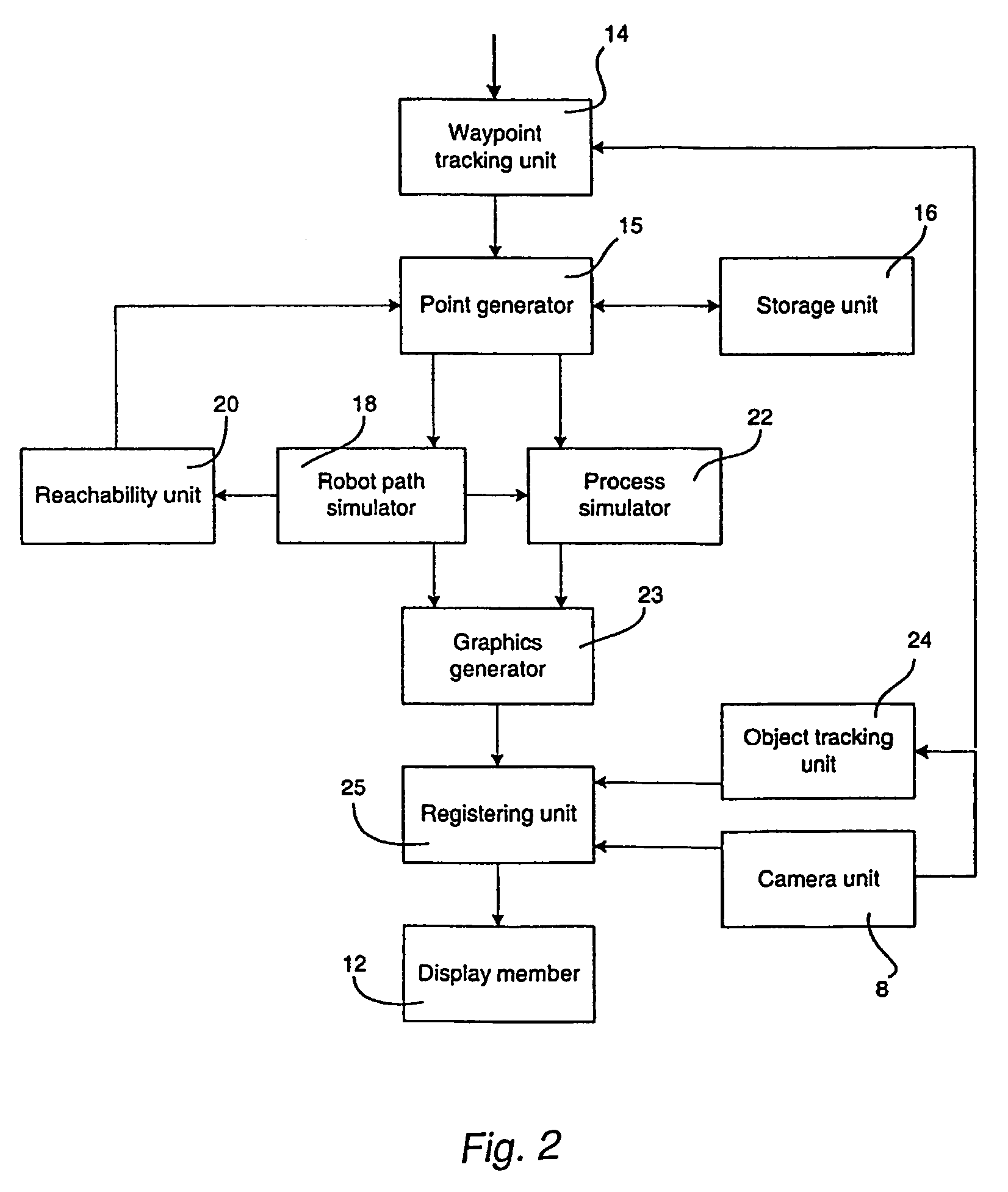
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
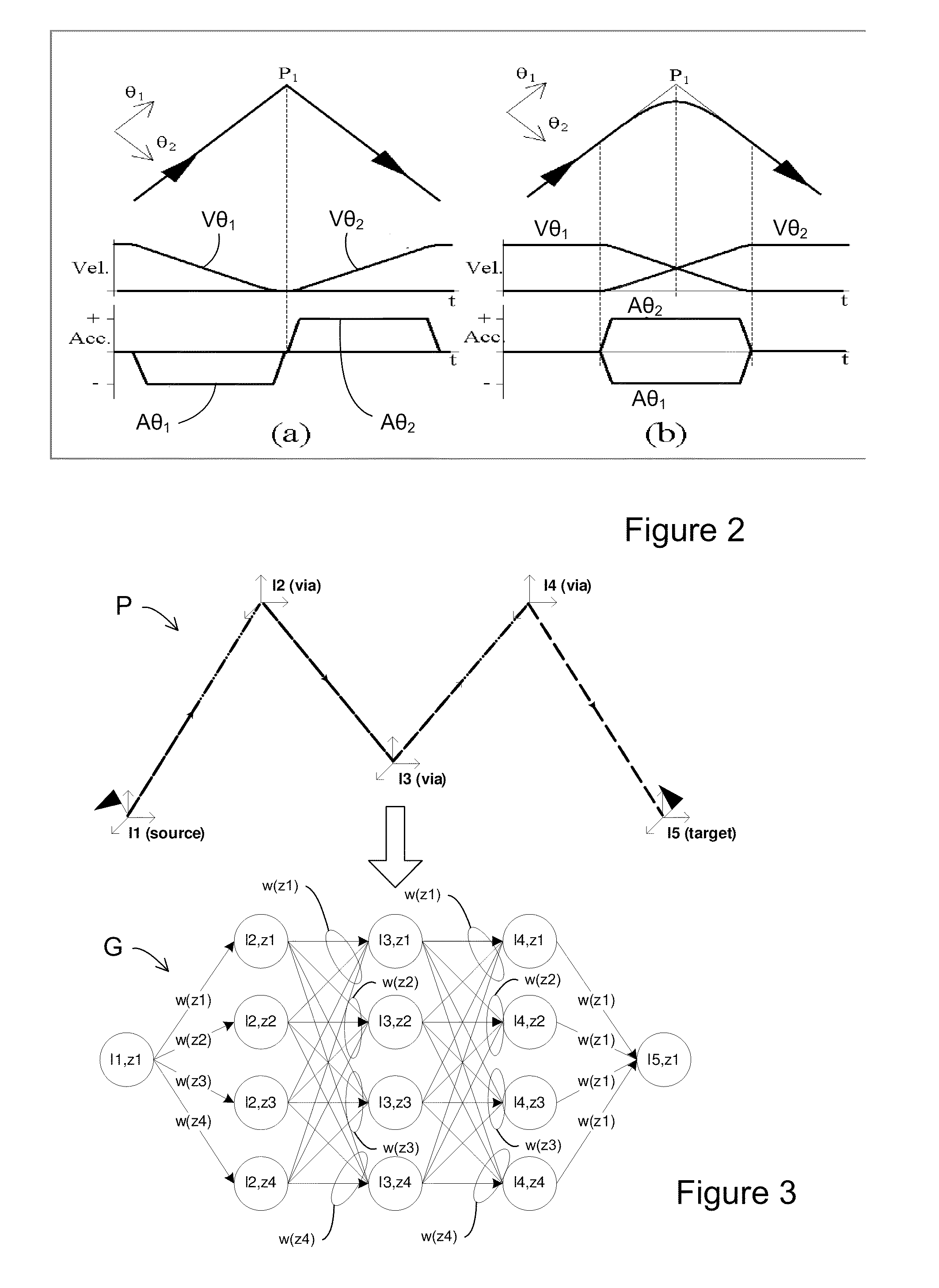
ActiveUS20050149231A1Shorten teaching timeQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsAnalog robot
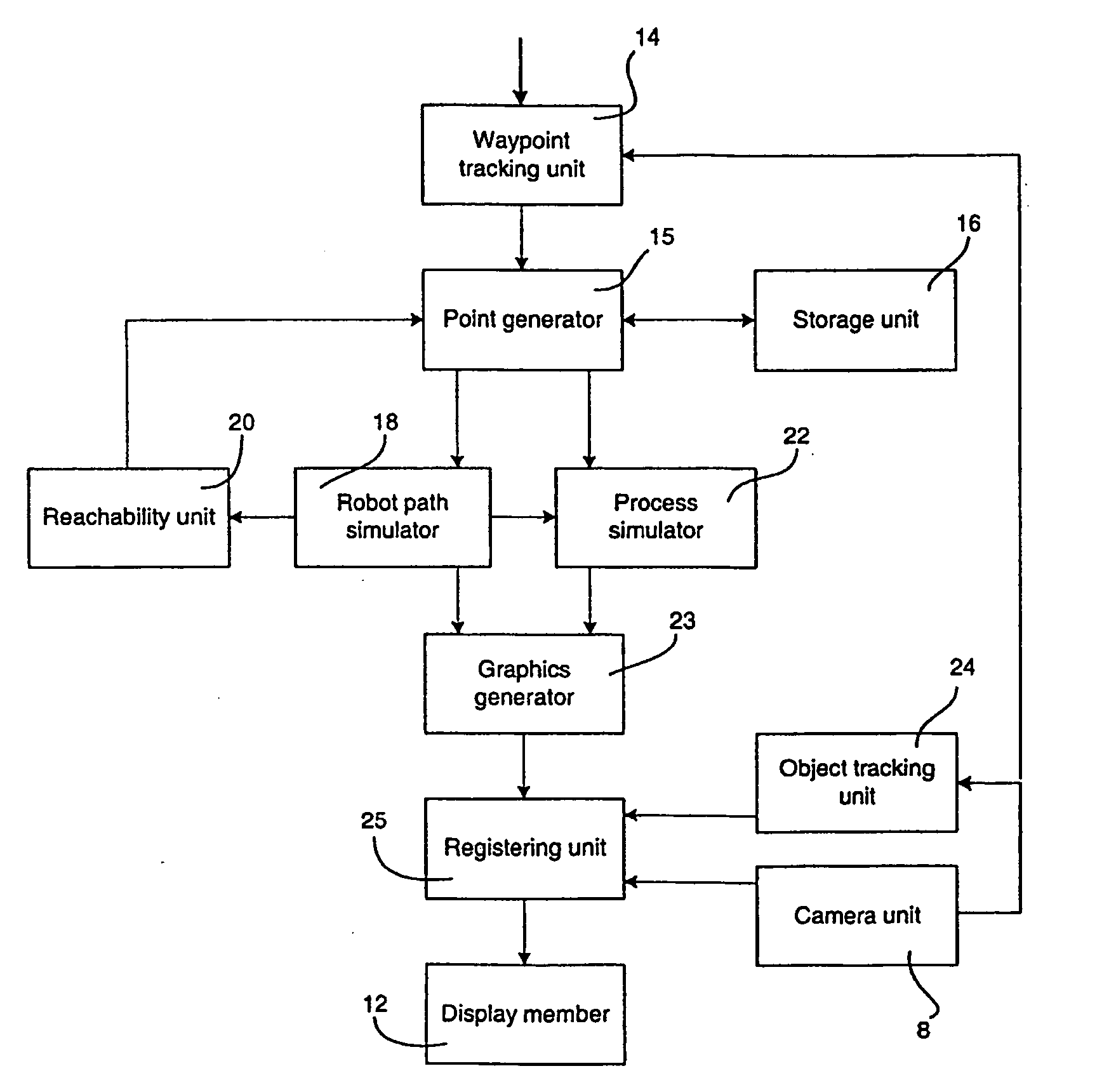
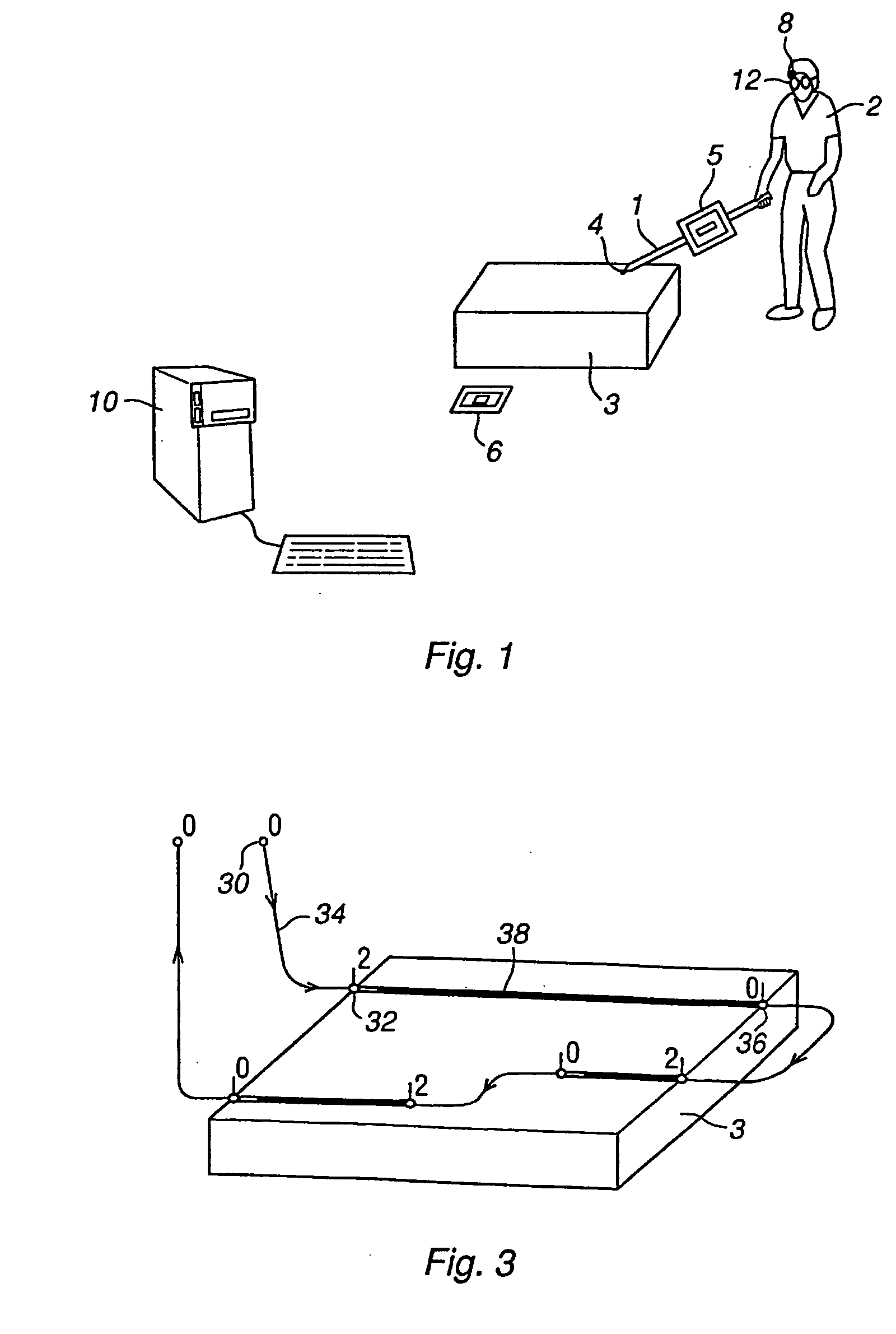
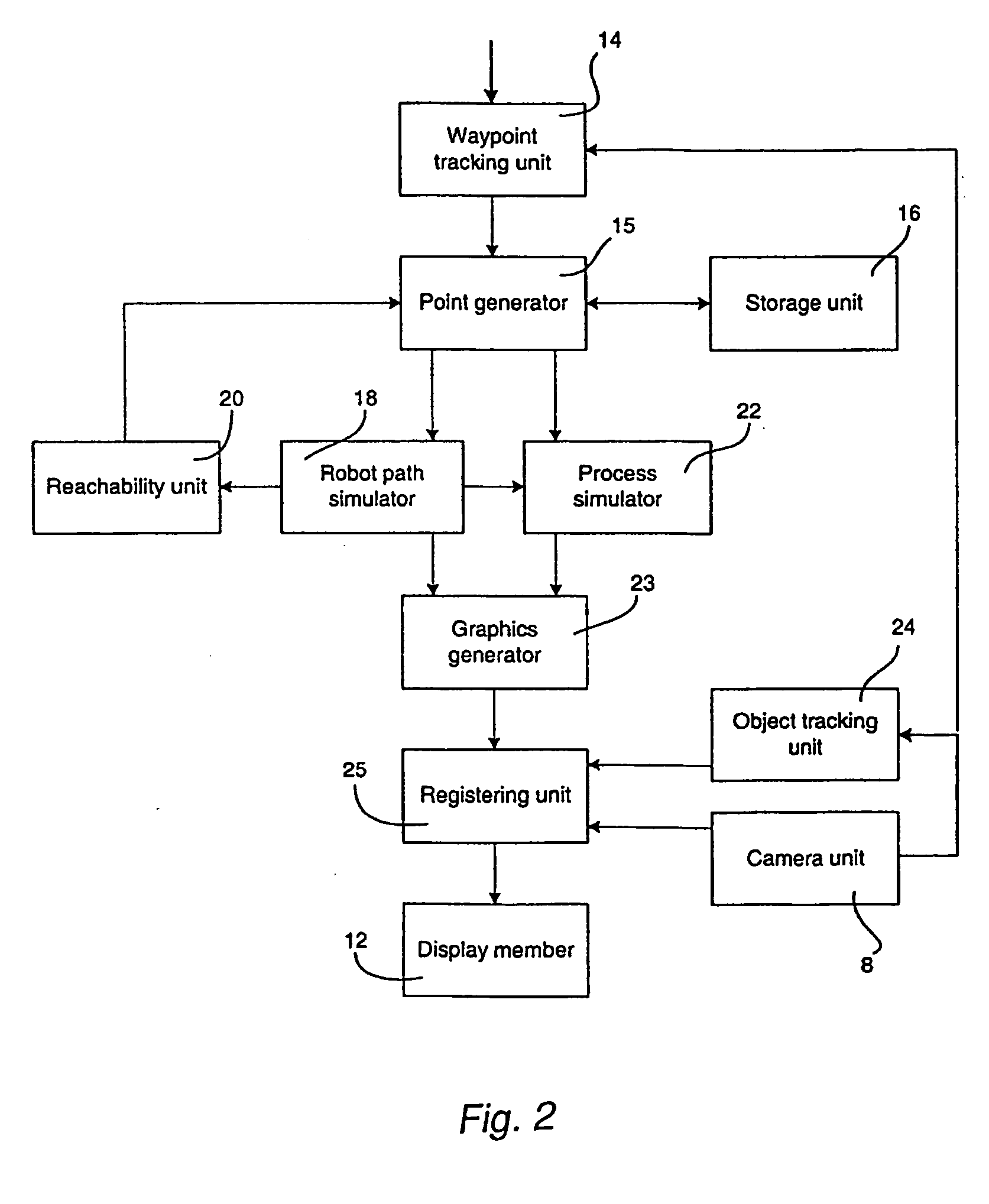
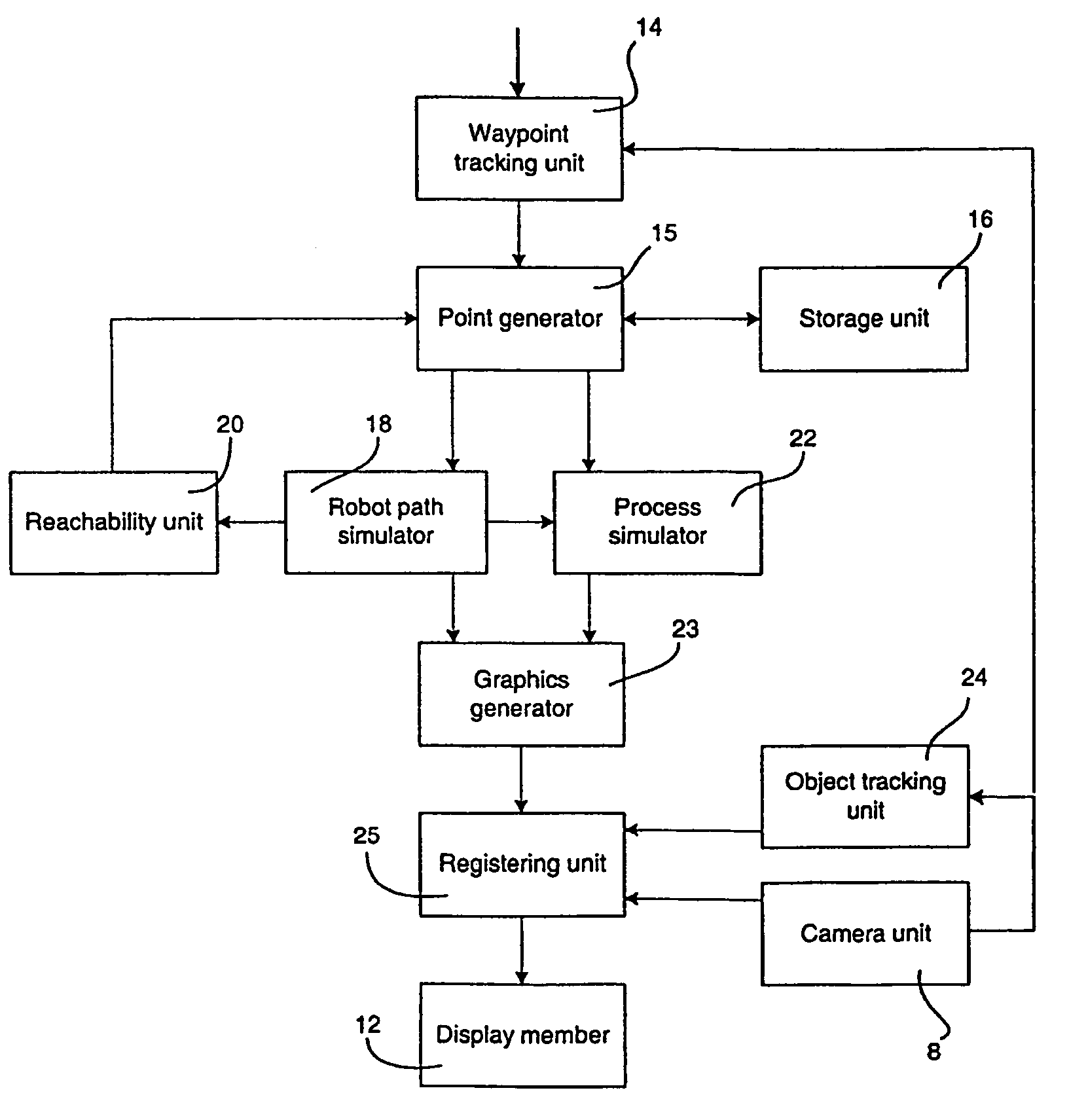
A method and a system for use in connection with programming of an industrial robot, the programming comprises teaching the robot a path having a number of waypoints located on or in the vicinity of an object to be processed by the robot. The system comprises: means for obtaining information about the waypoints of the path in relation to the object, a storage unit (16), for storing the obtained information, a simulation unit (18), simulating the robot path based on the obtained information about the waypoints and a model of the robot, a graphics generator (23), generating a graphical representation of the simulated robot path, and a display member (12) displaying a view comprising the object and said graphical representation of the robot path projected on the object.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method and apparatus for industrial robotic pathscycle time optimization using fly by
InactiveUS20110153080A1Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAnalog robotPosition dependent
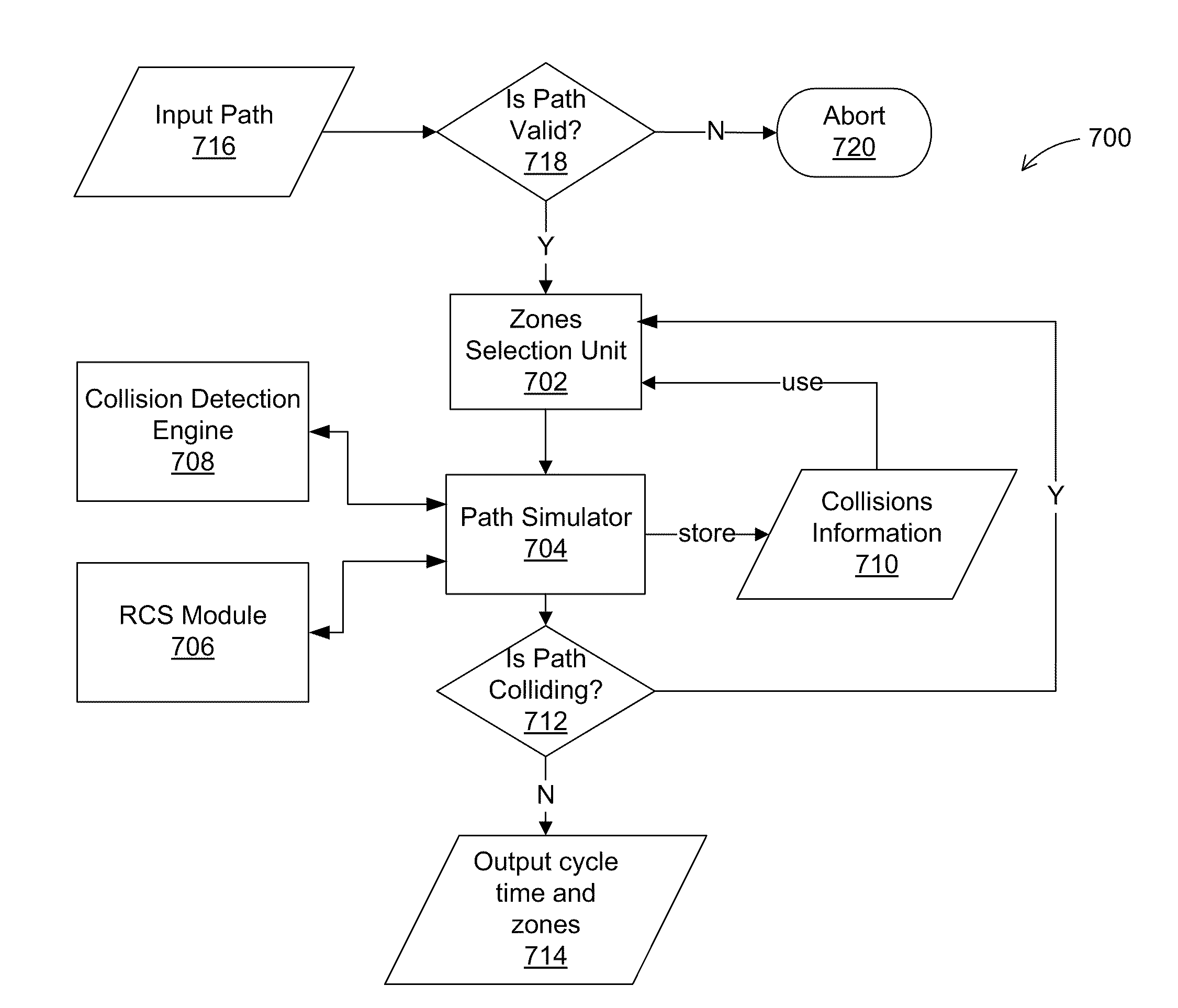
A system, method, and computer readable medium. A method for robotic path planning includes receiving a robotic path for a robot and associating a plurality of zones with each location in the robotic path. The method also includes selecting for each location one of the zones associated with the location and simulating motion of the robot over the robotic path using the locations and selected zones. The method further includes determining whether a collision occurred in the simulated motion of the robot. The method still further includes, if there was a collision, identifying a location associated with the collision, selecting a new zone for the identified location other than the currently selected zone, and repeating the steps of simulating motion of the robot and determining whether a collision occurred. The method also includes, if there wasn't a collision, assigning to each location its currently selected zone.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Robot simulation device, and robot simulation program
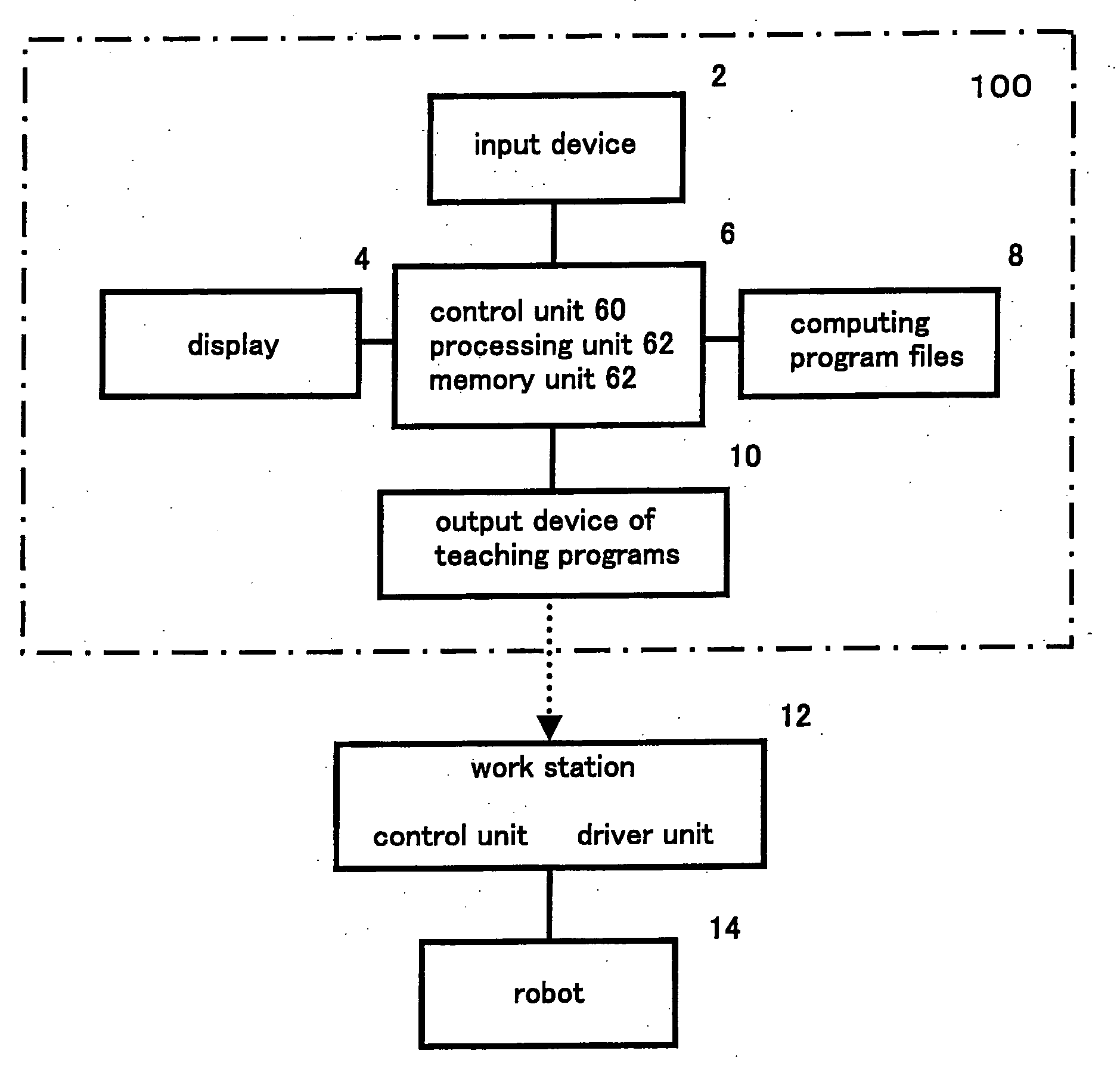
InactiveUS20060184275A1Easy to operateProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsAnalog robotSimulation
A robot simulation device, capable of simulating if a robot can transfer an object without any interference in a working space where obstacles are disposed. The device comprises of an input device, a display, a processing unit, computing programs and an output device of teaching programs. And the device further comprises of: (1) a two-dimensional display part having coordinate axes, (2) a means of displaying the obstacles and working space, a means of displaying a path of the moving robot, and a means of displaying the transferred object by the robot, on the display, (3) a means of interpolating the path by designating moving points of a central point of the moving transferred object, (4) a means of displaying the path of the moving transferred object in the working space, and (5) a means of displaying a region where the path interferes with the obstacles.
Owner:RORZE CORP
Vision-guided alignment system and method
ActiveUS20130147944A1Compensate for such errorProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnalog robotComputer graphics (images)
A vision-guided alignment system to align a plurality of components includes a robotic gripper configured to move one component relative to another component and a camera coupled to a processor that generates an image of the components. A simulated robotic work cell generated by the processor calculates initial calibration positions that define the movement of the robotic gripper such that position errors between the actual position of the robotic gripper and the calibration positions are compensated by a camera space manipulation based control algorithm executed by the processor to control the robotic gripper to move one component into alignment with another component based on the image of the components.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
ActiveUS7236854B2Shorten teaching timeQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsAnalog robot
A method and a system for use in connection with programming of an industrial robot. The programming includes teaching the robot a path having a number of waypoints located on or in the vicinity of an object to be processed by the robot. The system includes elements for obtaining information about the waypoints of the path in relation to the object, a storage unit for storing the obtained information, a simulation unit for simulating the robot path based on the obtained information about the waypoints and a model of the robot, a graphics generator for generating a graphical representation of the simulated robot path, and a display member for displaying a view comprising the object and the graphical representation of the robot path projected on the object.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
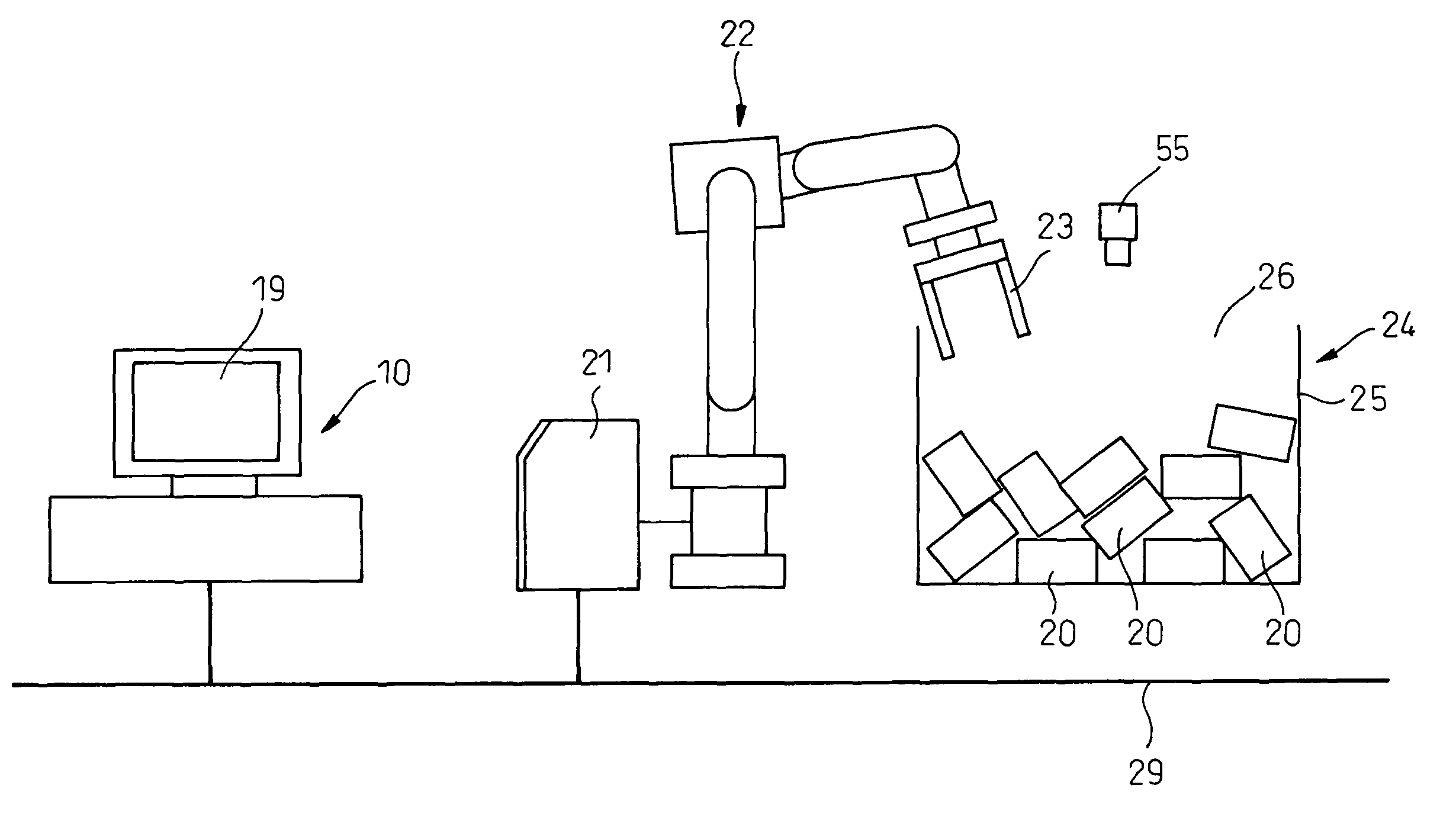
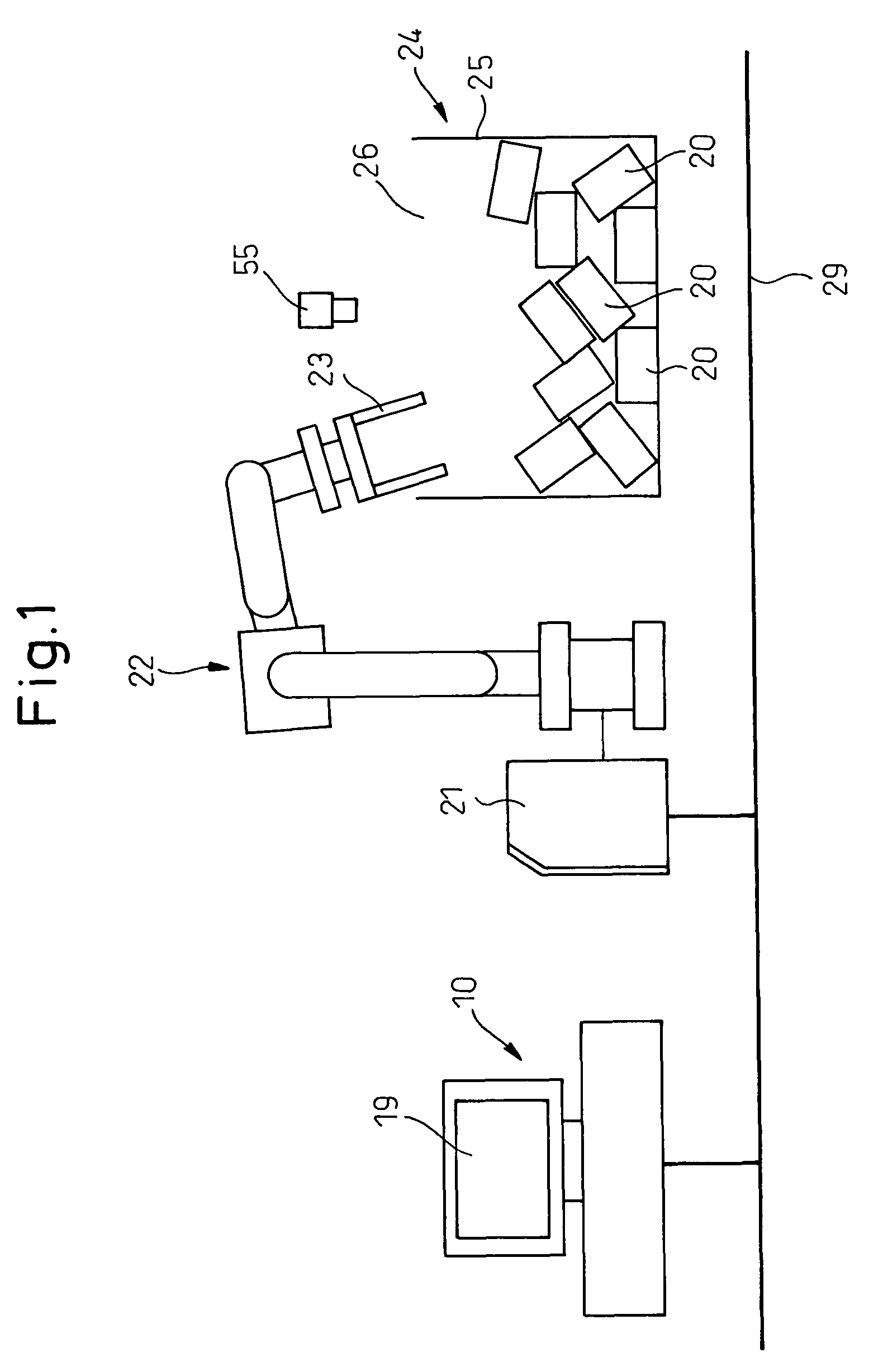
Apparatus simulating operations between a robot and workpiece models
ActiveUS7881917B2Accurately determinedInterference be moreProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual field lossAnalog robot
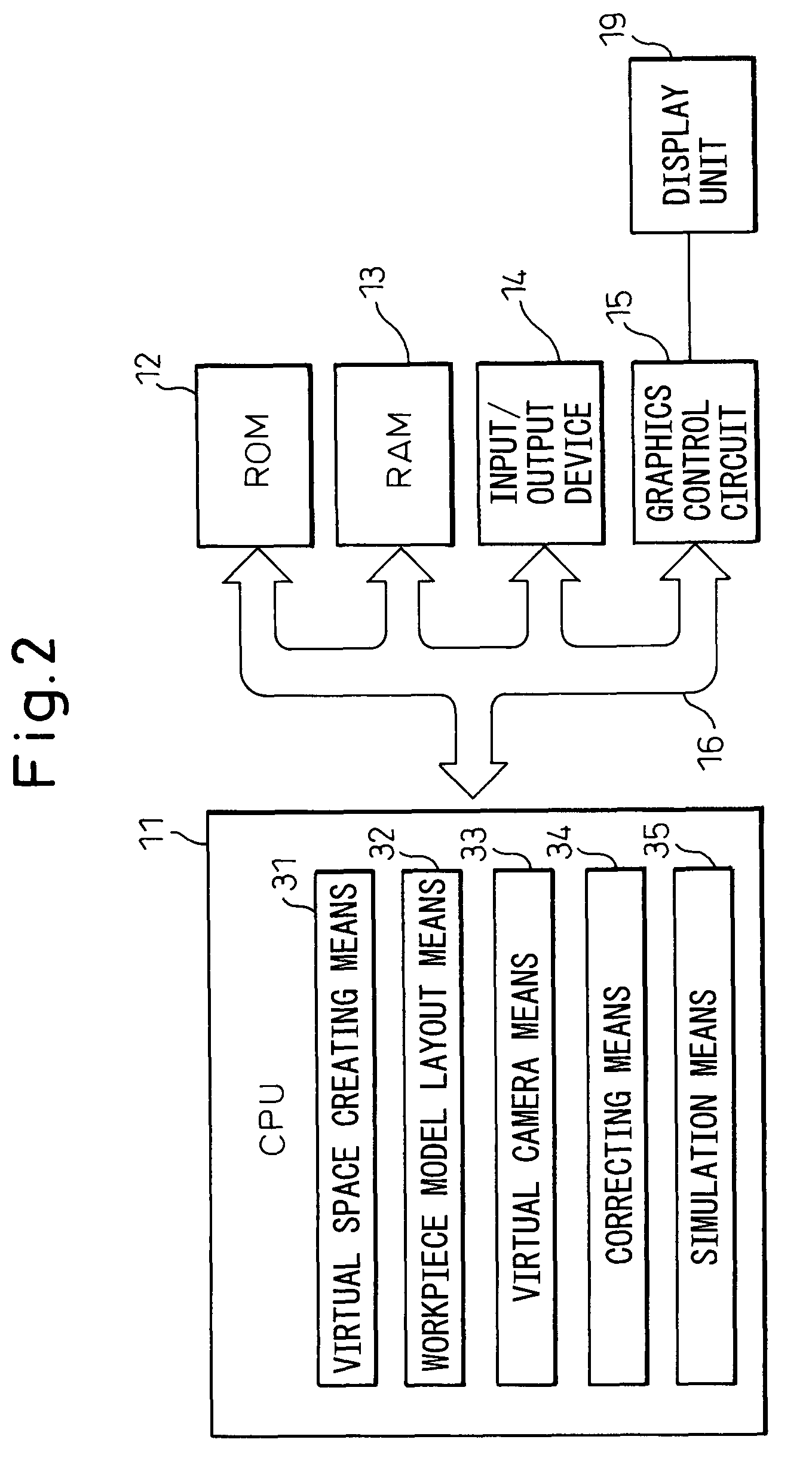
A robot simulation apparatus (10) capable of creating and executing a robot program includes a virtual space creating unit (31) for creating a virtual space (60), a workpiece model layout unit (32) for automatically arranging at least one workpiece model (40) in an appropriate posture at an appropriate position in a workpiece accommodation unit model (24) defined in the virtual space, a virtual camera unit (33) for acquiring a virtual image (52) of workpiece models existing in the range of a designated visual field as viewed from a designated place in the virtual space, a correcting unit (34) for correcting the teaching points in the robot program based on the virtual image, and a simulation unit (35) for simulating the operation of the robot handling the workpieces, and as a result, interference between the robot and the workpieces can be predicted while at the same time accurately determining the required workpiece handling time.
Owner:FANUC LTD
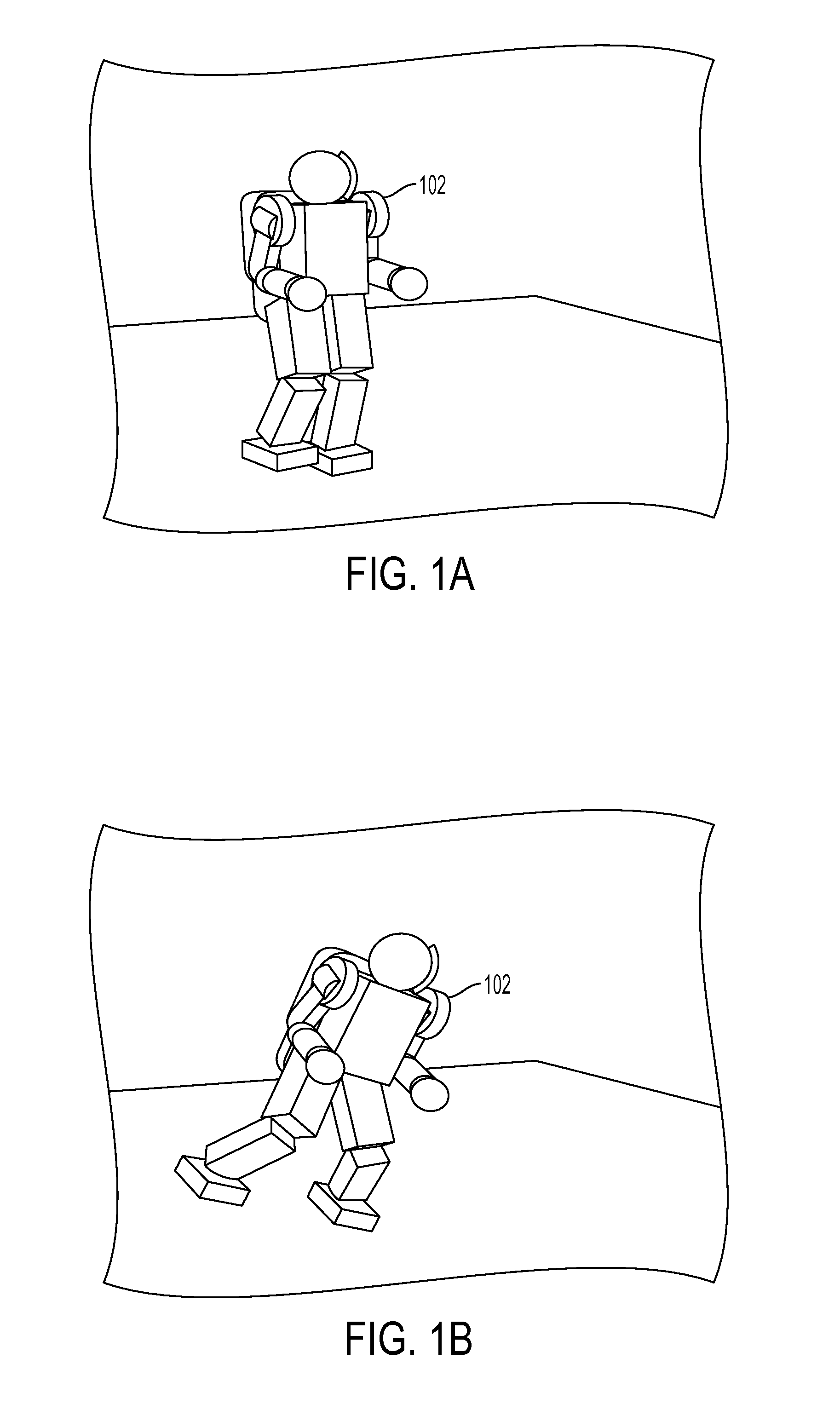
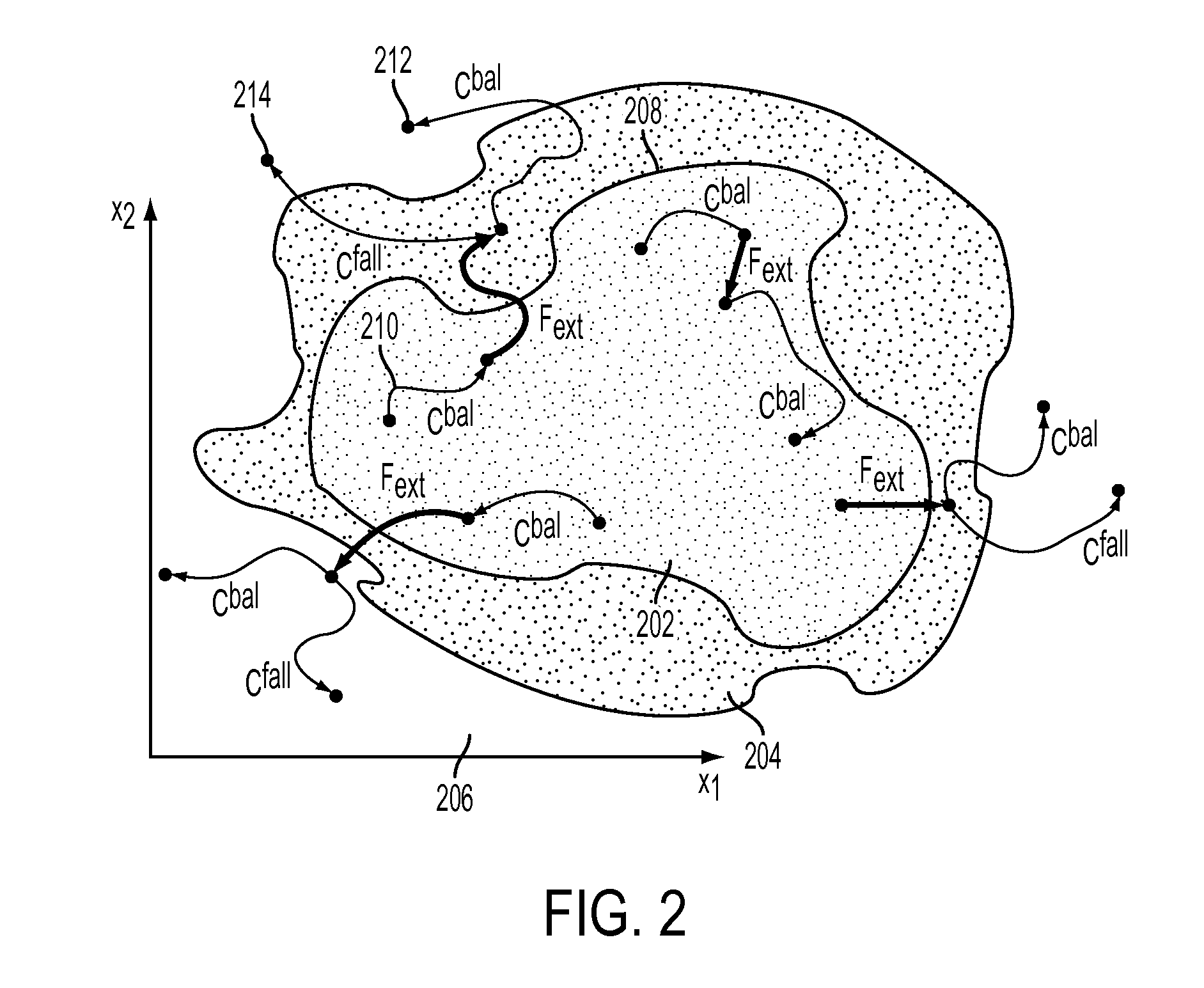
Machine Learning Approach for Predicting Humanoid Robot Fall
ActiveUS20100292838A1Reduce harmProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAnalog robotSimulation
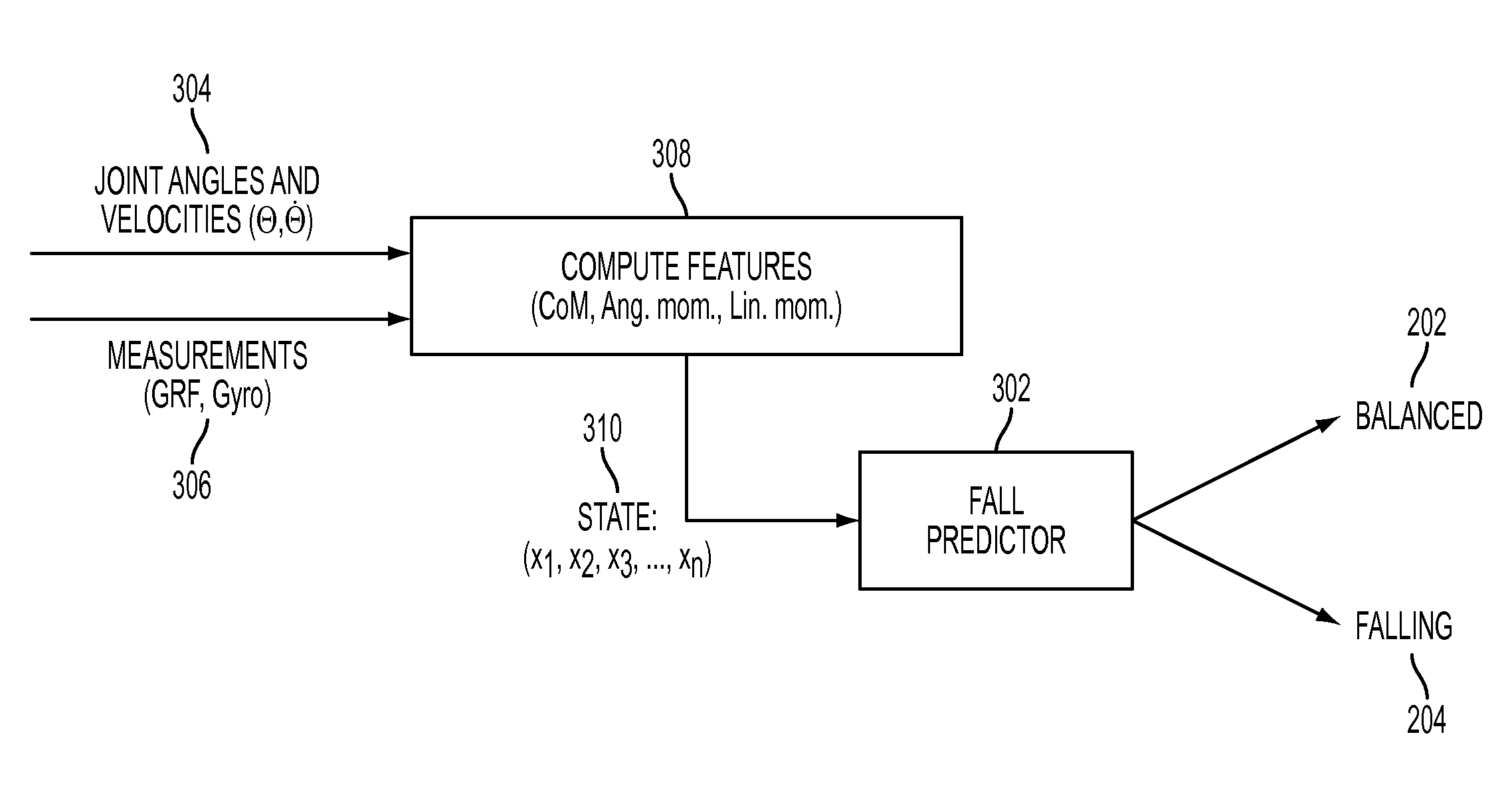
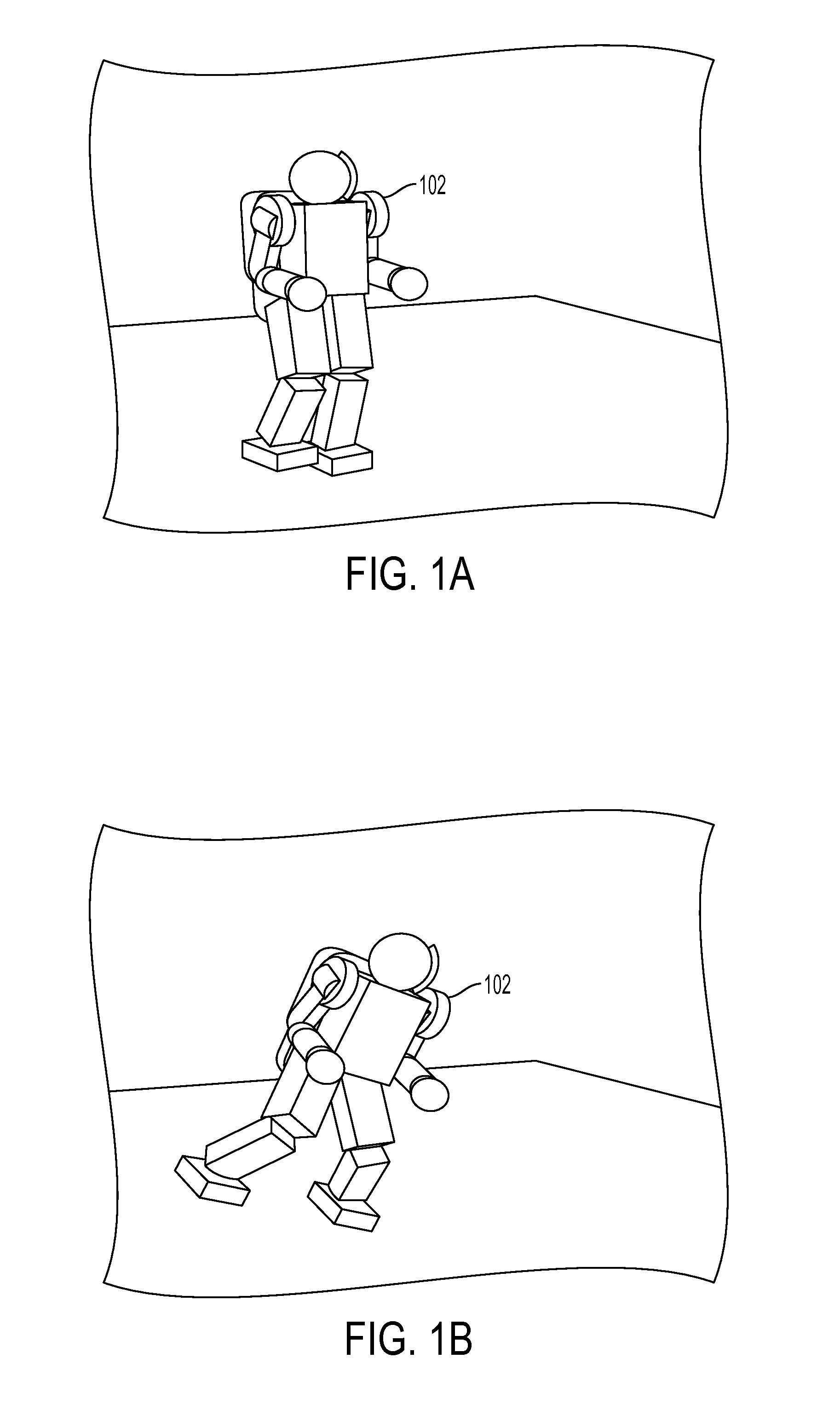
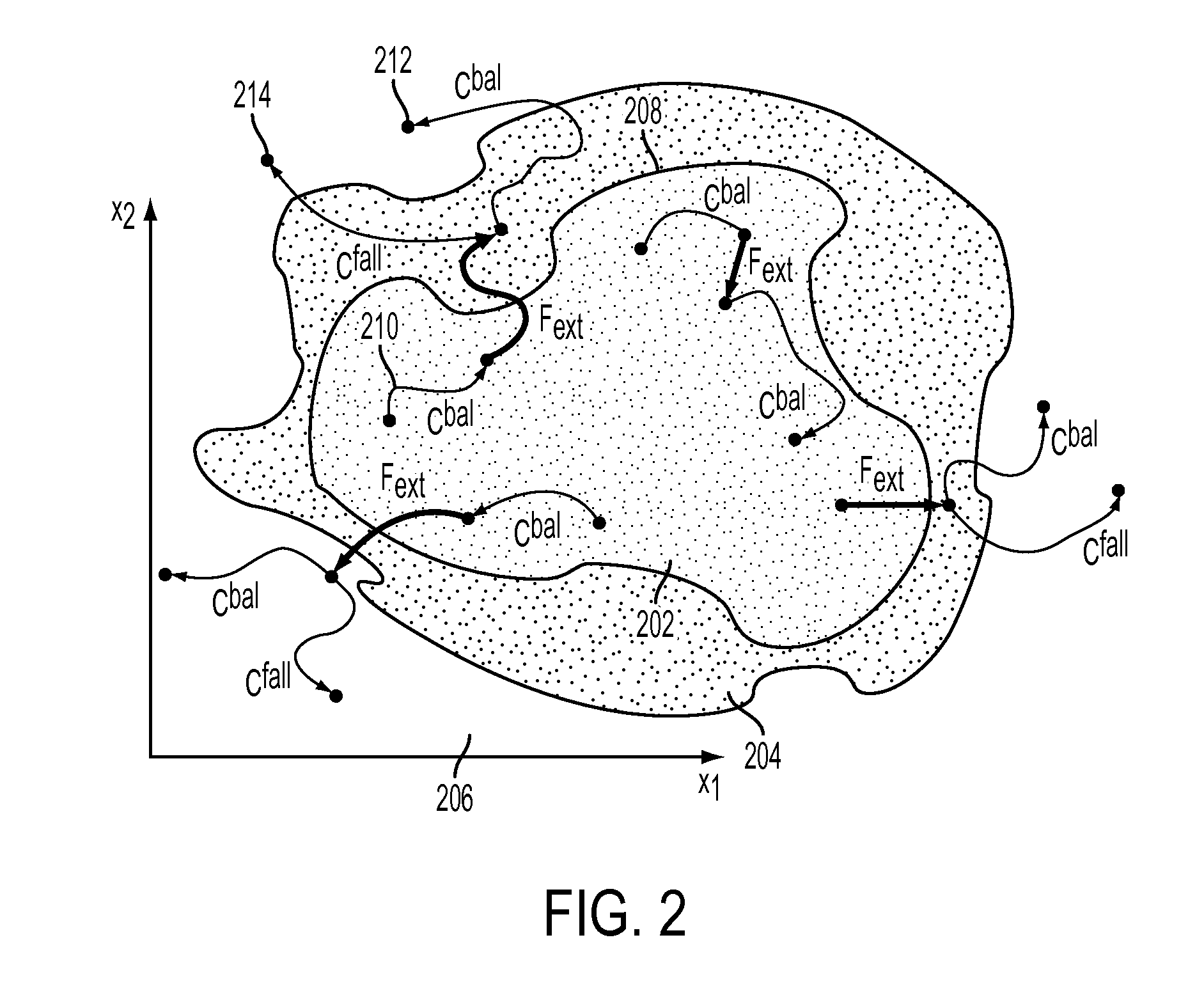
A system and method is disclosed for predicting a fall of a robot having at least two legs. A learned representation, such as a decision list, generated by a supervised learning algorithm is received. This learned representation may have been generated based on trajectories of a simulated robot when various forces are applied to the simulated robot. The learned representation takes as inputs a plurality of features of the robot and outputs a classification indicating whether the current state of the robot is balanced or falling. A plurality of features of the current state of the robot, such as the height of the center of mass of the robot, are determined based on current values of a joint angle or joint velocity of the robot. The current state of the robot is classified as being either balanced or falling by evaluating the learned representation with the plurality of features of the current state of the robot.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Autonomous global relocation method for robots and robot
InactiveCN107908185AQuick calculation of matching degreeAccurate and quick screeningProgramme-controlled manipulatorPosition/course control in two dimensionsAnalog robotRadar
An autonomous global relocation method for robots is provided. The method comprises steps that existing maps are rasterized; the grids with obstacles and without obstacles are assigned to different values; multiple distance data and angle data corresponding to the distance data obtained by a lidar sensor with the same position of a robot scanning external obstacles are marked on the map with the simulation robot position as the origin in the form of laser point location; and the assignment of the grid of the laser point location corresponding to each simulation robot position is integrated, robot positions are screened out, and the correct position of the robot is calculated from the initially selected simulation robot positions by a particle filtering algorithm. Through the differential assignment of grids with obstacles and without obstacles, the position of the laser point location in the map is described, and the matching degree between the lidar sensor information and the electronic map is quickly calculated, the most divergent transfer point is found as the transfer target point, and the self position can be rapidly and accurately found in a known map.
Owner:BENEWAKE BEIJING TECH CO LTD
Simulative mechanical hand with under-driven adaptive mechanism
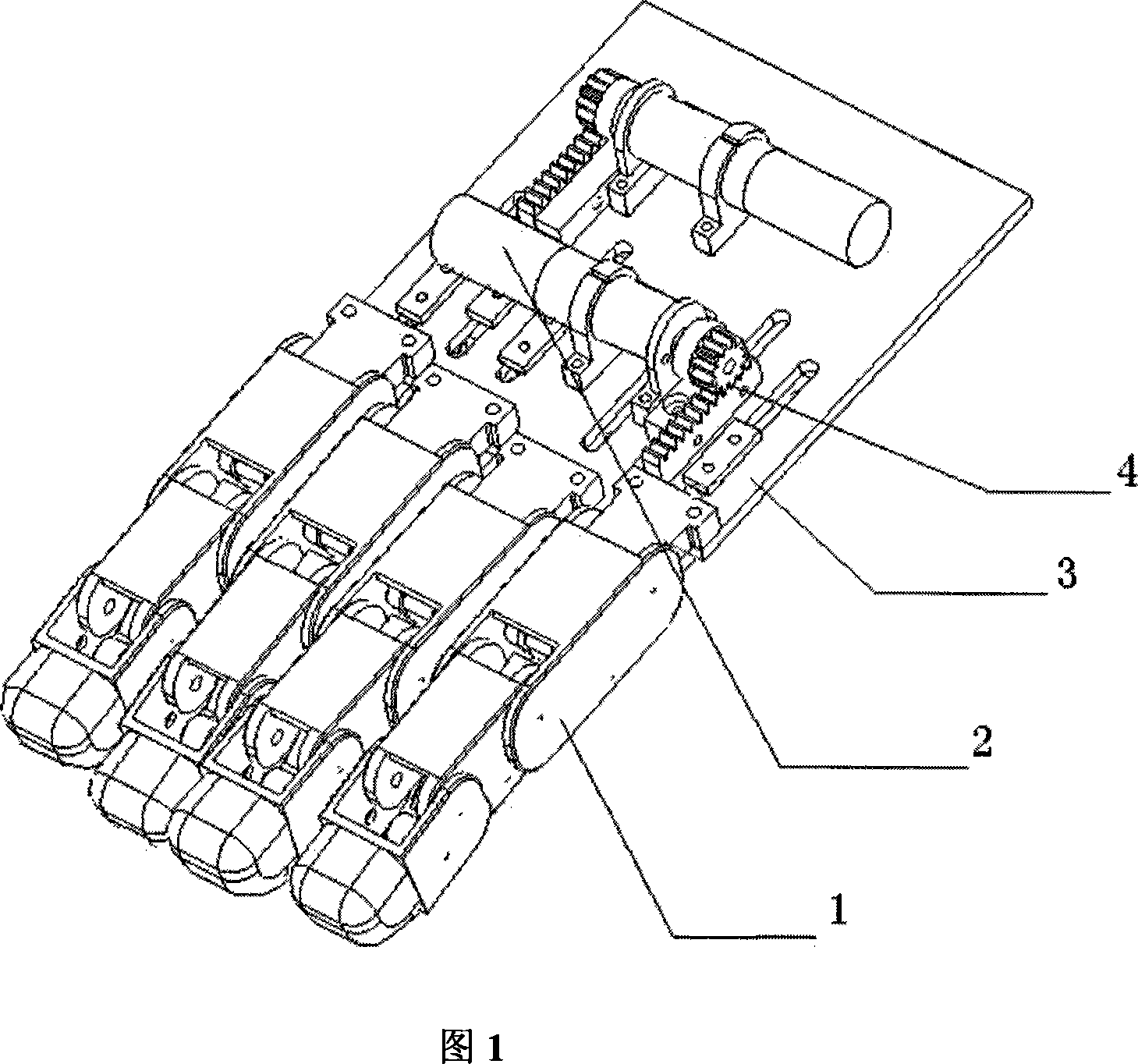
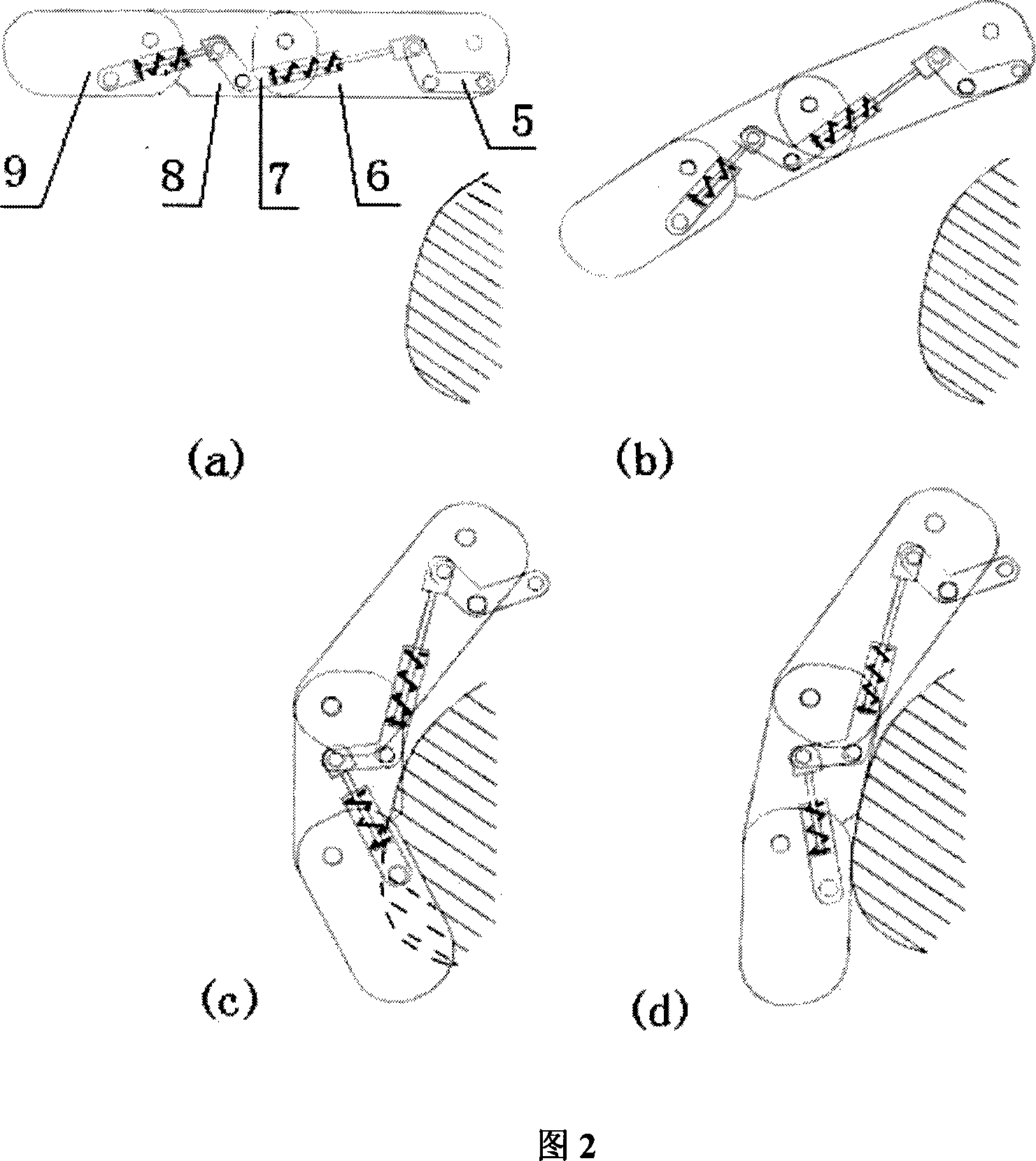
InactiveCN101058184AIncrease flexibilityImprove force distribution problemGripping headsAnalog robotGear wheel
The invention relates to an analog robot, comprising the elastic lever structure and the finger gap difference structure. The finger structure part introduces the length changeable spring lever structure, realizing self adaptation to random article surface, getting rid of the insufficient flexibility of the middle finger, through gear or rack to drive the rotary movement of the motor to linear movement, one end of the active rack connected to a gear, which is teething with two passive racks simultaneously and two passive racks connected to fingers to complete the grasp of the finger through the back and forth movement of the passive racks to as to improve the force distribution between fingers with less power loss and for the benefit of robot miniaturization.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Off-line programming system and method of optical visual sensor with linear structure for welding robot
InactiveCN101973032AIntuitive detection statusIntuitive display of detection statusManipulatorInteractive graphicsSimulation
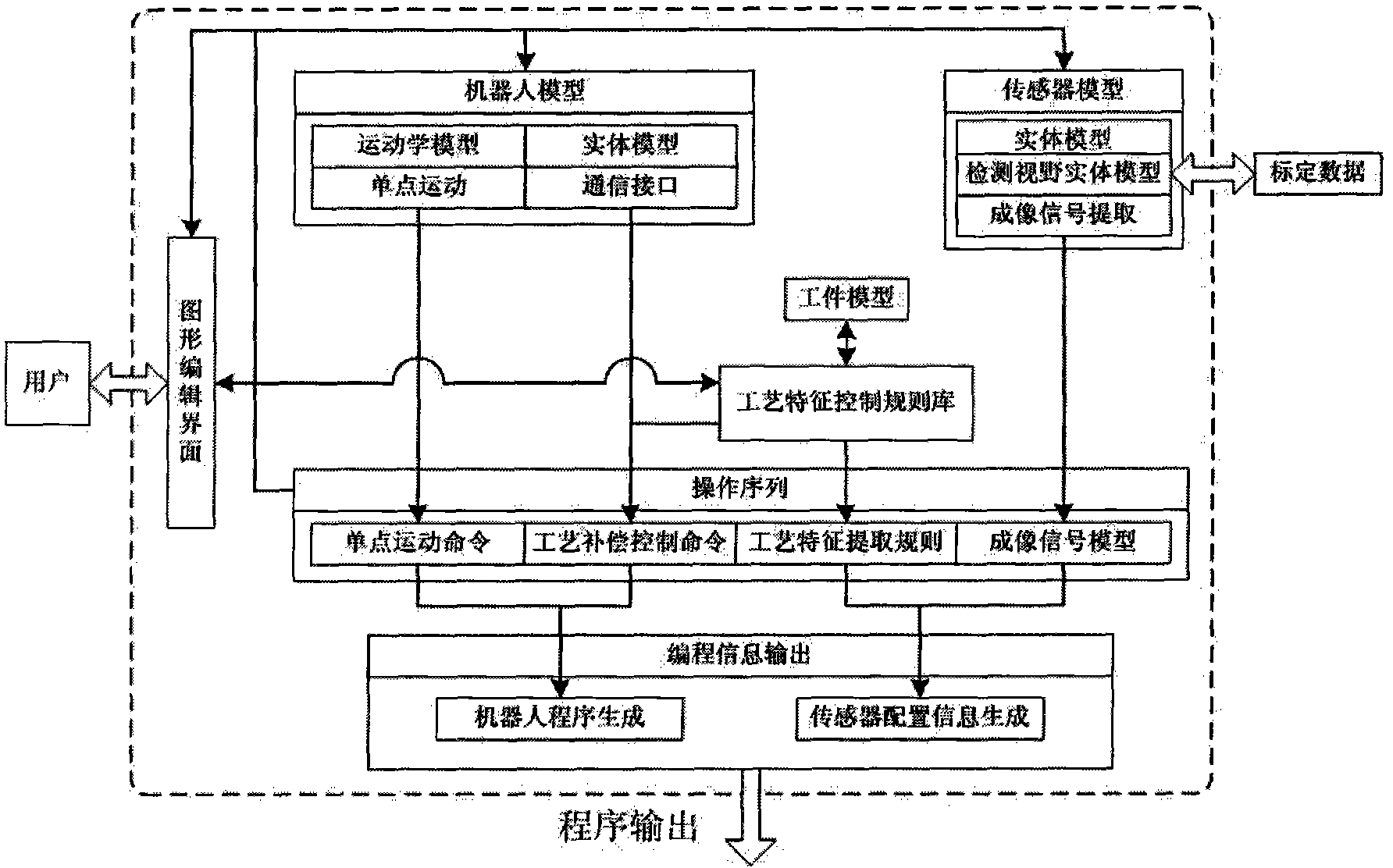
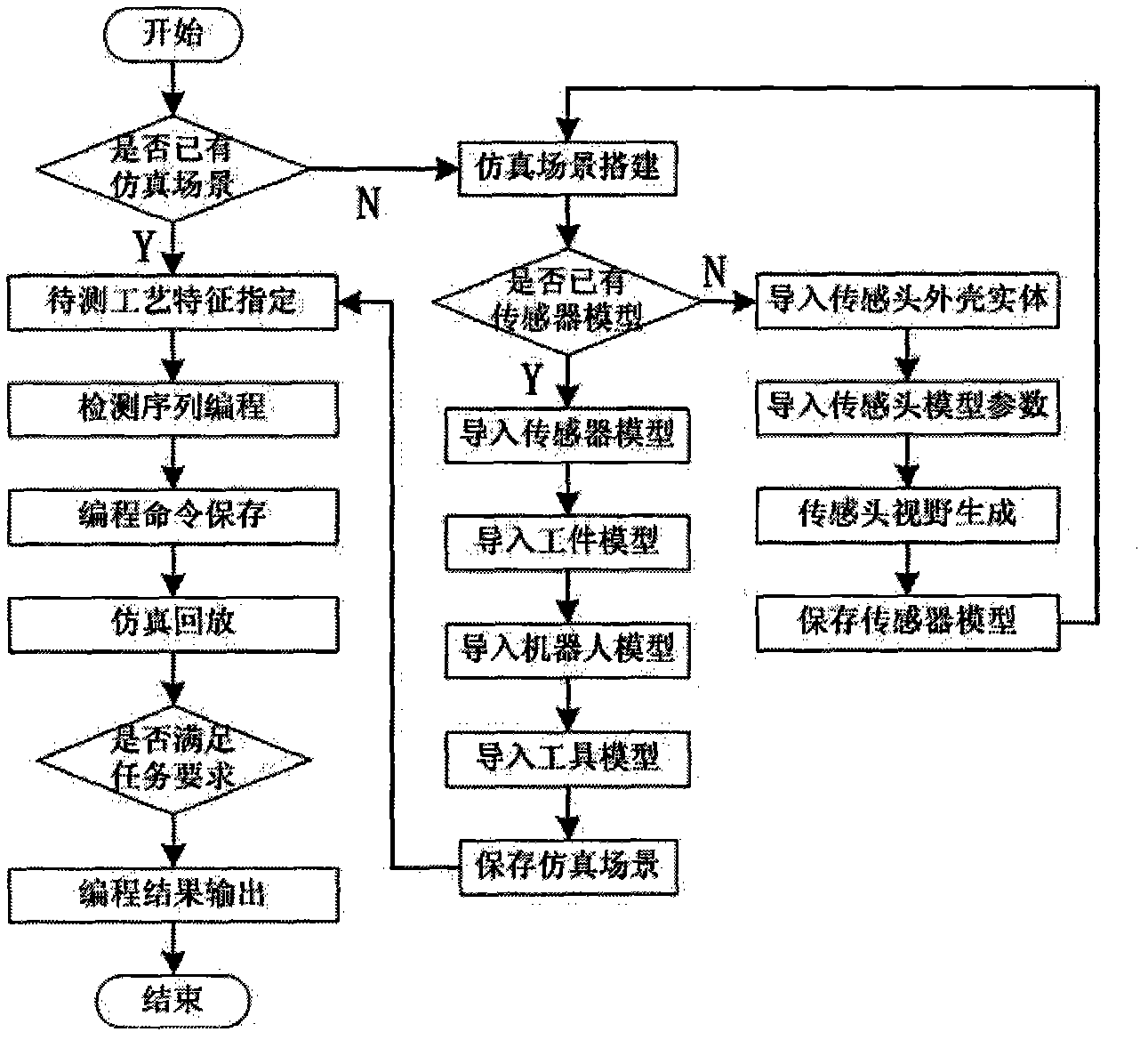
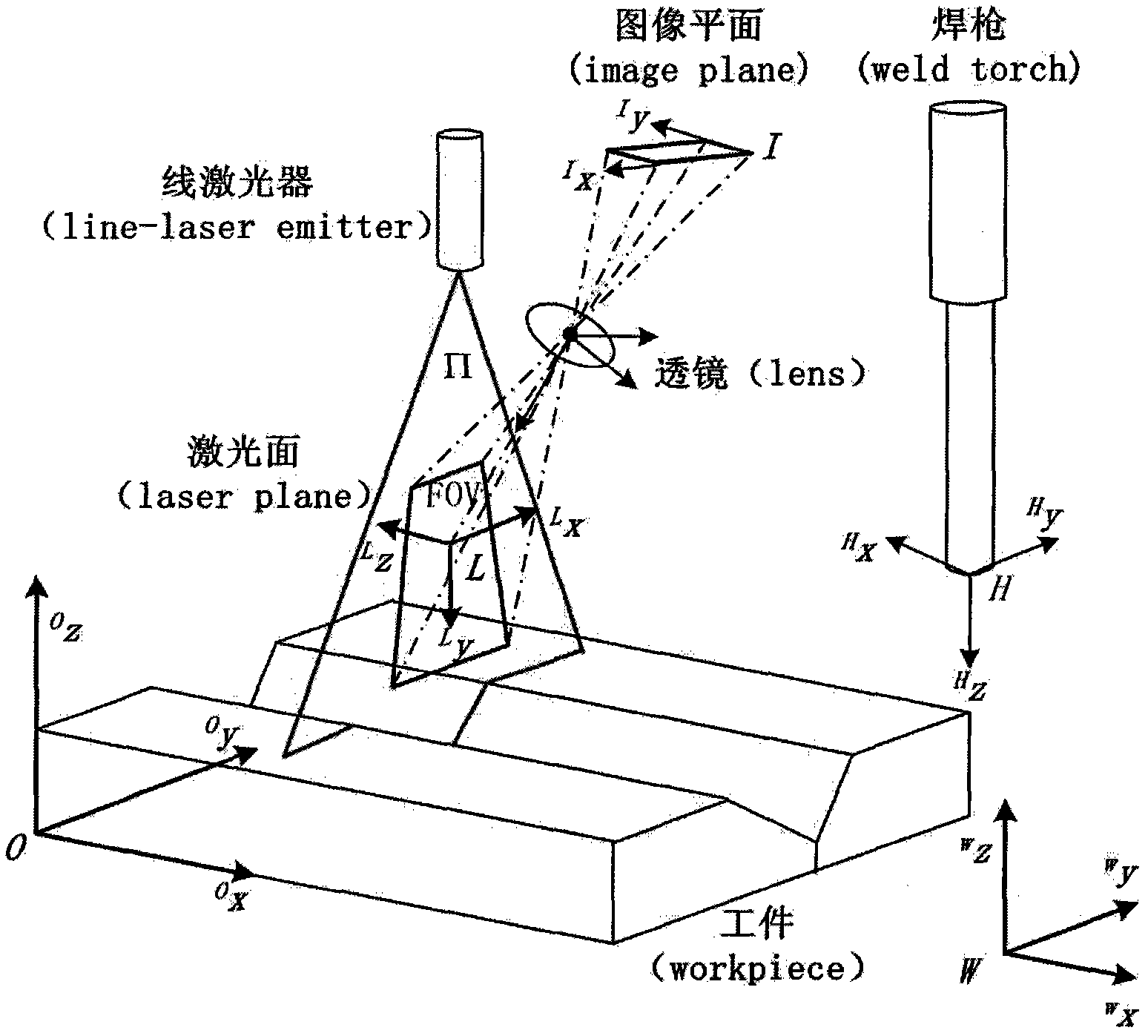
The invention relates to an off-line programming system and method of an optical visual sensor with a linear structure for a welding robot. The system comprises a sensor model, a robot model, a process control rule base, a graphic editing interface, an operation sequence module and a programming information output, wherein the sensor model is used for simulating a sensor imaging process to acquire a view model and simultaneously completing detection view substantiation to be convenient for user graphic programming; the robot model is used for simulating the single-point motion of the robot and providing communication interface information of connecting sensor input signals; the process control rule base is used for providing process feature extraction rules for different welding tasks andcontrol command related information of processes; the graphic editing interface is used for interactive graphic programming between a user and a system; the operation sequence module is used for saving the information of a series of detection points, wherein the information comprises single-point motion commands, process compensation control commands, process feature extraction rules and imaging signal model information; and the programming information output is used for outputting the program text of the robot and the configuration information text of the sensor system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Test platform and test method for movement control of foot type bio-robot and test method
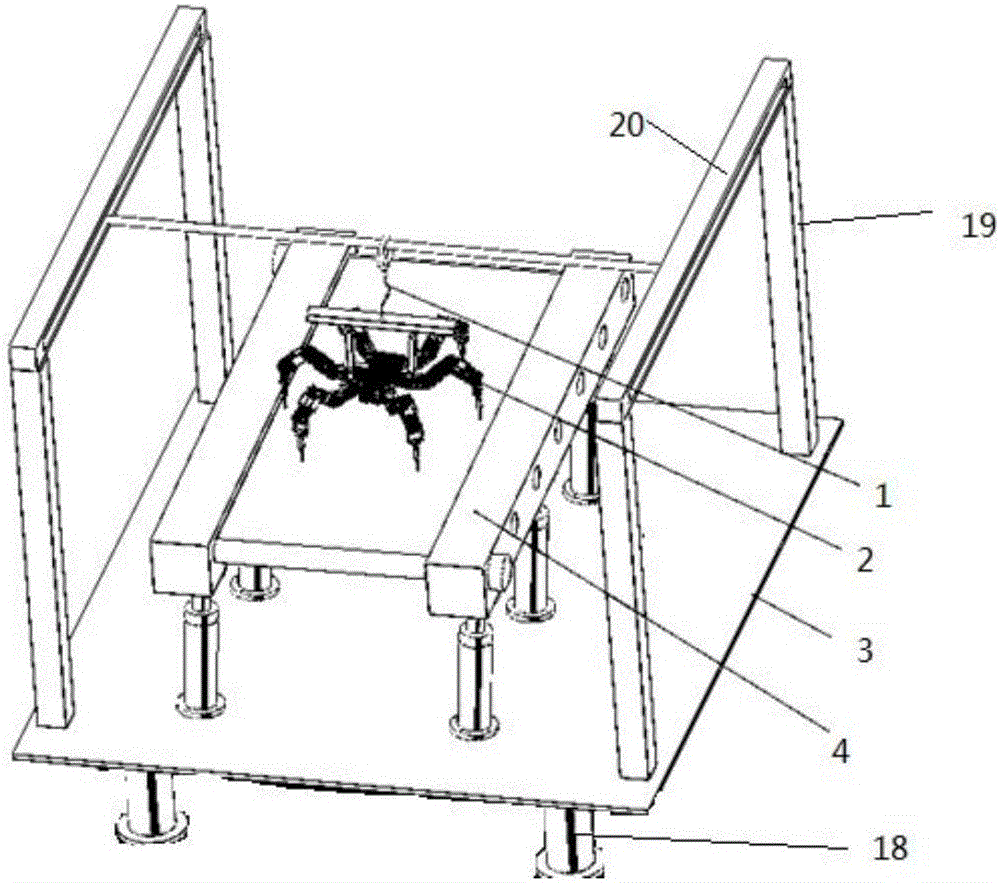
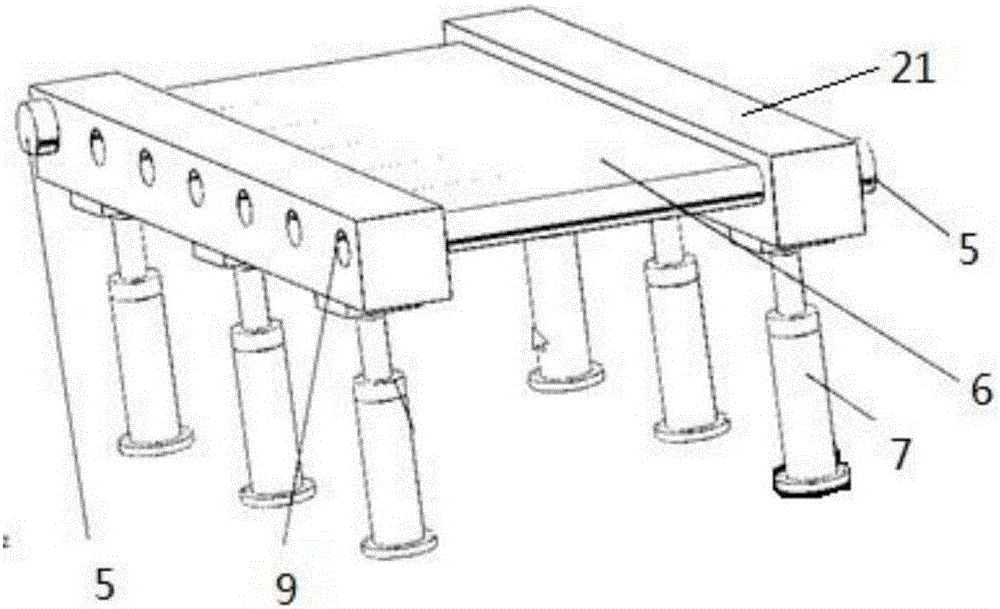
ActiveCN106625778AEnables sports performance testingShorten the timeManipulatorAnalog robotTransmission belt
The invention discloses a test platform and test method for movement control of a foot type bio-robot. The test platform comprises a ramp road surface simulating platform, a supporting and protecting mechanism and a base frame, wherein both the ramp road surface simulating platform and the supporting and protecting mechanism are arranged on the base frame, the ramp road surface simulating platform comprises square columns, air cylinders, motors, transmission belts and idler wheels, several idler wheel columns are vertically arranged between two parallel square columns, the idler columns are parallel to one another, the idler wheel columns on the two end head parts of the square columns are provided with the motors, the motors are arranged on the end heads of the idler columns, several air cylinders are arranged below the two square columns, the outer sides of the several idler wheel columns are wrapped with the transmission belts, and the transmission belts can conduct circulating rotation at the outer sides of the idler wheel columns. According to the test platform and test method for the movement control of the foot type bio-robot, the test platform simulates the outdoor movement test of the robot and simulates the external gradient road surface, the robot can change the movement velocity according to the running of a rotating belt on the ramp road surface simulating platform, a movement performance test is achieved, and the time and the cost are saved.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Machine learning approach for predicting humanoid robot fall
A system and method is disclosed for predicting a fall of a robot having at least two legs. A learned representation, such as a decision list, generated by a supervised learning algorithm is received. This learned representation may have been generated based on trajectories of a simulated robot when various forces are applied to the simulated robot. The learned representation takes as inputs a plurality of features of the robot and outputs a classification indicating whether the current state of the robot is balanced or falling. A plurality of features of the current state of the robot, such as the height of the center of mass of the robot, are determined based on current values of a joint angle or joint velocity of the robot. The current state of the robot is classified as being either balanced or falling by evaluating the learned representation with the plurality of features of the current state of the robot.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fatigue service life testing method of precise speed reducer for robot
PendingCN108287072AImprove accuracyShorten the test cycleMachine gearing/transmission testingSustainable transportationReduction driveEngineering
The invention provides a fatigue service life testing method of a precise speed reducer for a robot, wherein a repeatedly swinging inertia load component is utilized for simulating an actual working condition of a precise speed reducer for the robot and furthermore testing the fatigue service life of the precise speed reducer for the robot. A device according to the method mainly comprises a testing principle, a swinging loading and controlling system and a data processing system. A tested speed reducer is driven from an input end so that an output end performs repeated swinging. The swingingrange is psi; an acceleration / decelerating angle range is alpha; an equal-speed area angle range is psi-2alpha and is not lower than 0. A normal working highest allowable load of the tested speed reducer is used for quickly evaluating the precise speed reducer fatigue service life, and furthermore an equivalent method between the testing fatigue service life and a continuous stable-state torque loading process tested fatigue service life is established. The precise speed reducer fatigue service life testing method can efficiently and accurately test the precise speed reducer fatigue service life for the robot, and furthermore has advantages of high testing precision and low cost.
Owner:中机生产力促进中心有限公司
Simulator for estimating life of robot speed reducer
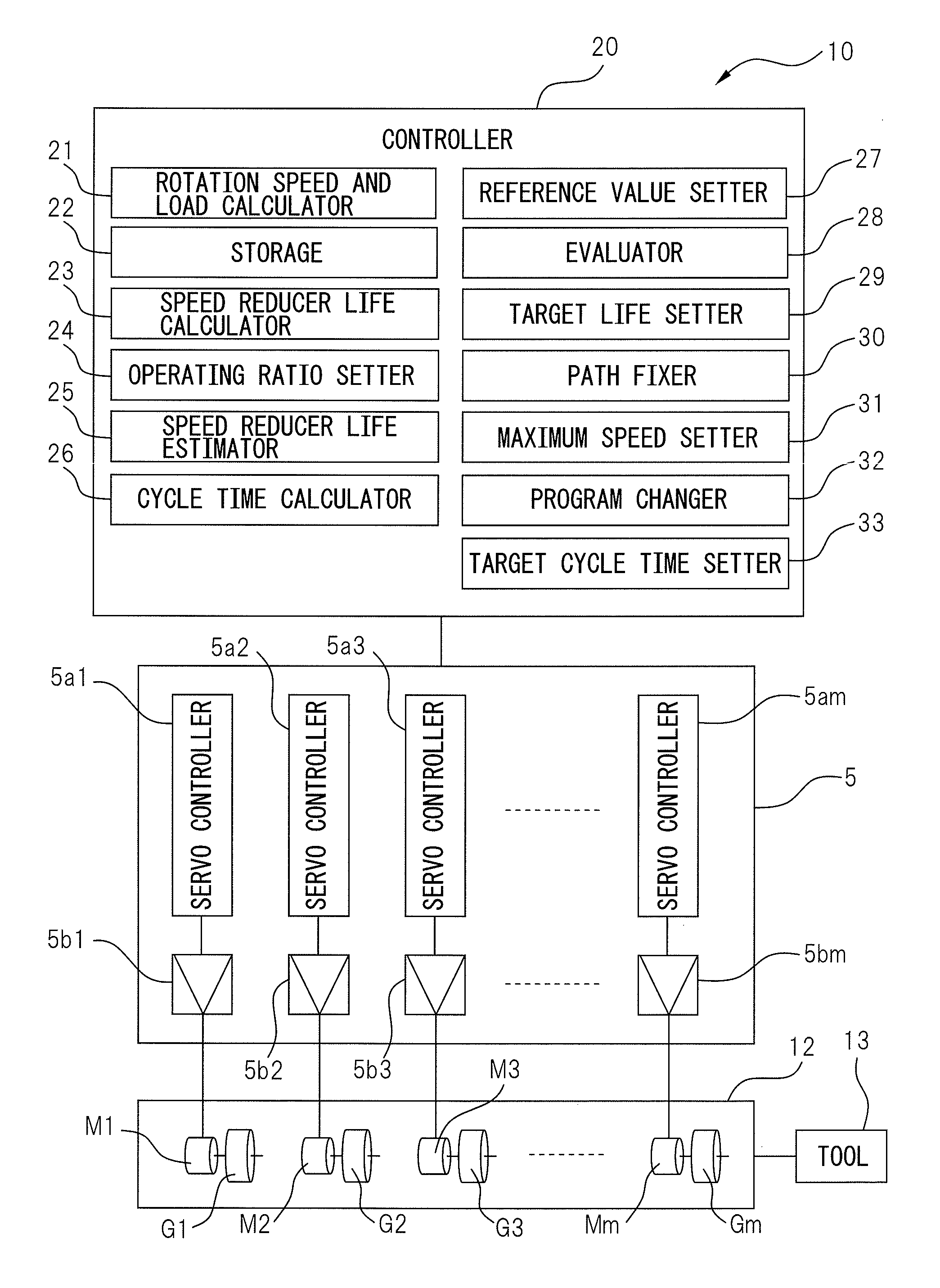
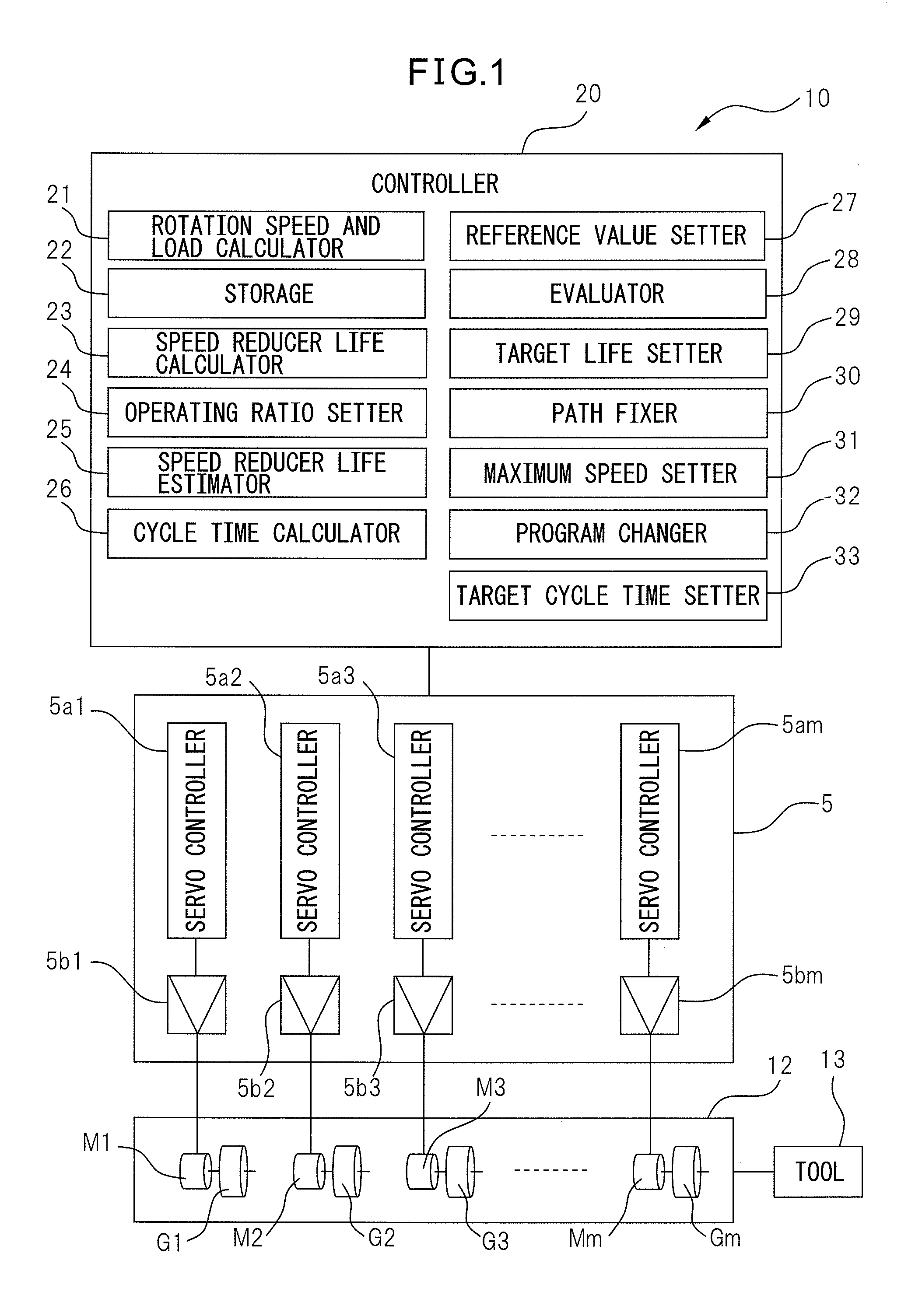
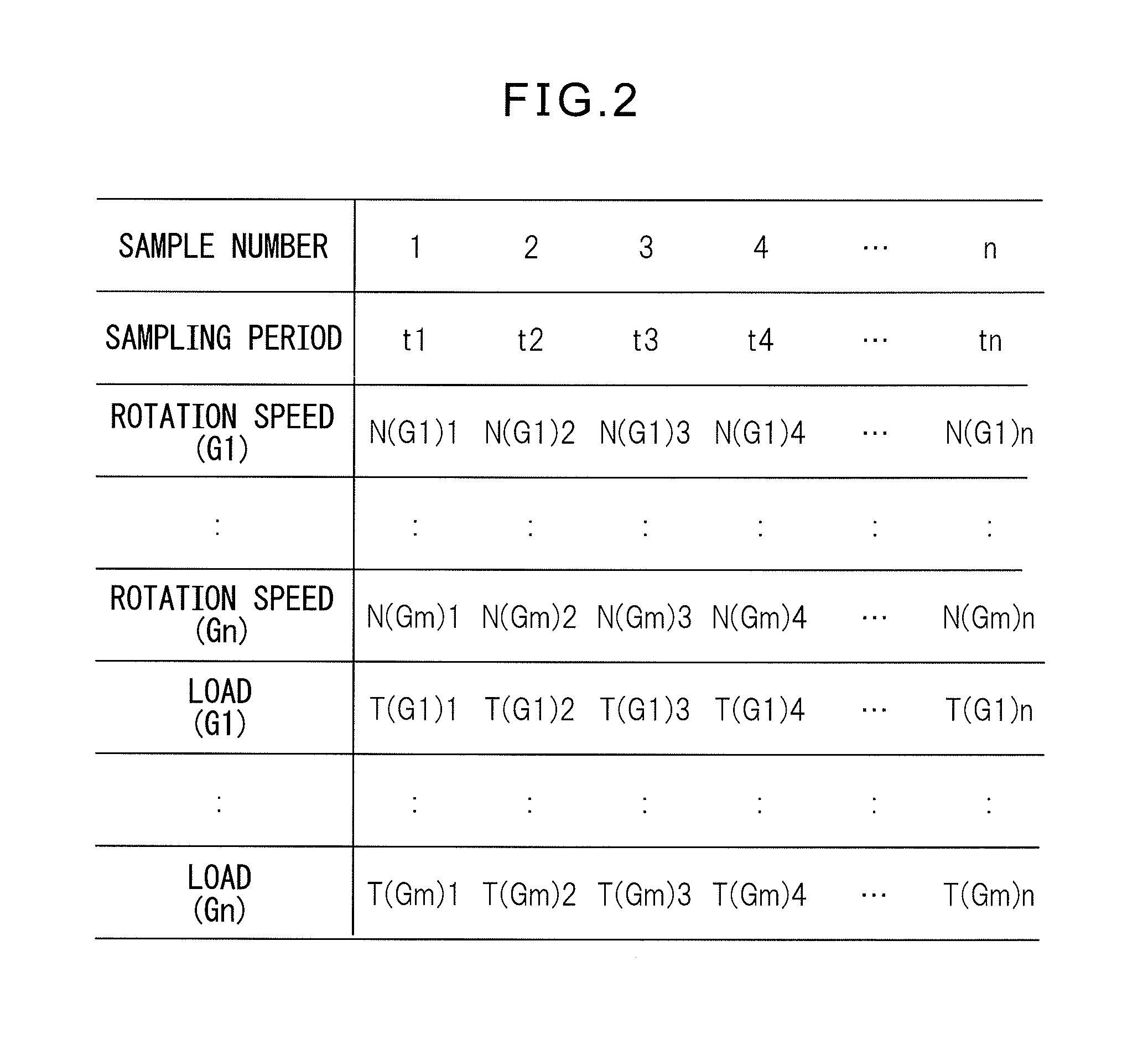
ActiveUS20130151214A1Prolong lifeProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsAnalog robotReduction drive
A simulator (10) for estimating a life of a speed reducer includes a rotation speed and load calculator (21) for simulating the operation program of a robot (12) and calculating the rotation speed of the robot speed reducers (G1-Gm) and the load exerted on the individual speed reducers; a storage (22) for chronologically correlating the rotation speed and the load and storing the rotation speed and the load; a speed reducer life calculator (23) for calculating the life of the individual speed reducers, based on the rotation speed and the load; an operating ratio setter (24) for setting an operating ratio of the robot; and a speed reducer life estimator (25) for estimating the life of the speed reducers, based on the life of the individual speed reducers and the operating ratio.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method and system for increasing new anchor retention
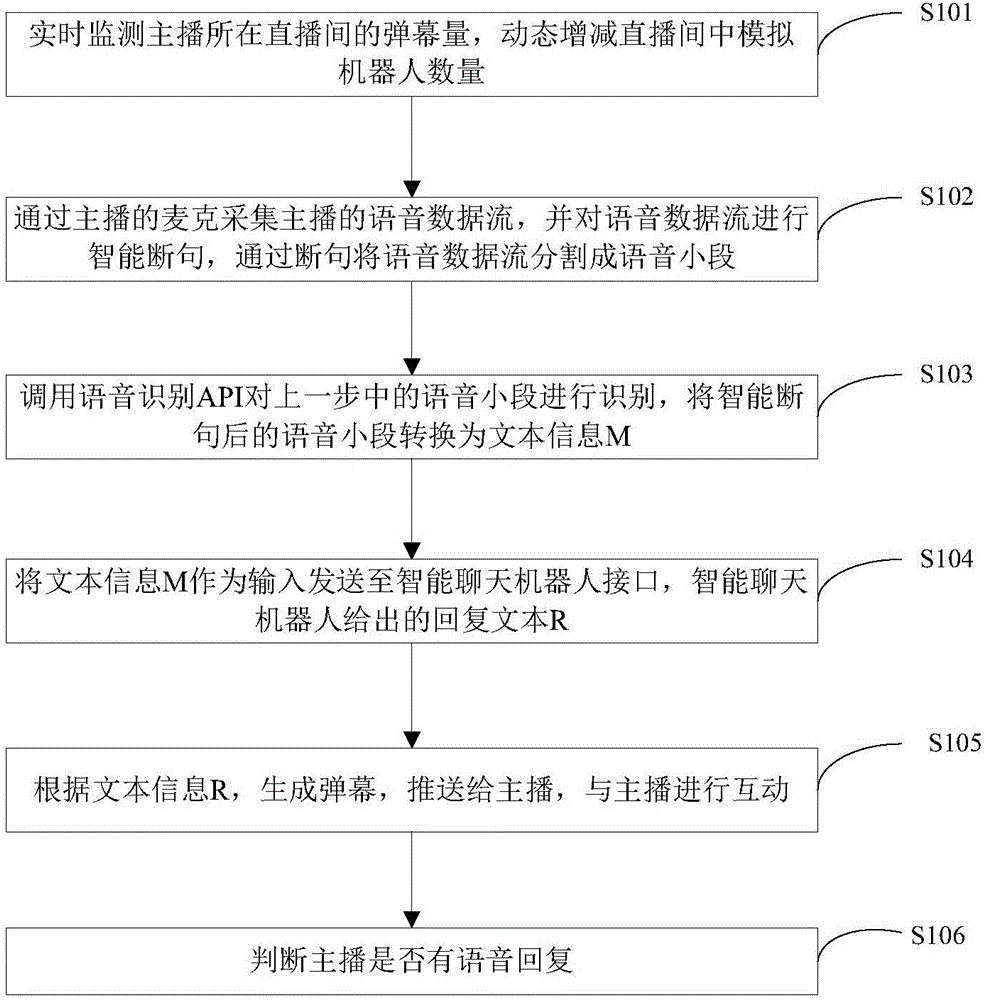
InactiveCN106656767AImpairment of live broadcast enthusiasmIncrease interactive funSpeech recognitionSelective content distributionAnalog robotData stream
The present invention discloses a method and system for increasing new anchor retention. The method includes: 1) monitoring barrage amount of a live room in which an anchor is located in real time, and dynamically increasing or decreasing the number of simulation robots in the live room; 2) collecting a voice data stream of the anchor, and intelligently punctuating the voice data stream, to segment the voice data stream into small voice segments by punctuation; 3) invoking a voice recognition API to recognize the small voice segments in the previous step, and converting the intelligently punctuated small voice segments into text information M; 4) taking the text information M as an input and sending same to an interface of an intelligent chat robot, so that the intelligent chat robot gives response text information R; 5) according to the text information R obtained in step 4), generating a barrage, and pushing same to the anchor; and 6) judging whether the anchor makes a voice response, and performing barrage interaction with the anchor. The method and system can effectively increase the live passion of a new anchor, and enrich the diversity of barrage contents of the live room.
Owner:WUHAN DOUYU NETWORK TECH CO LTD
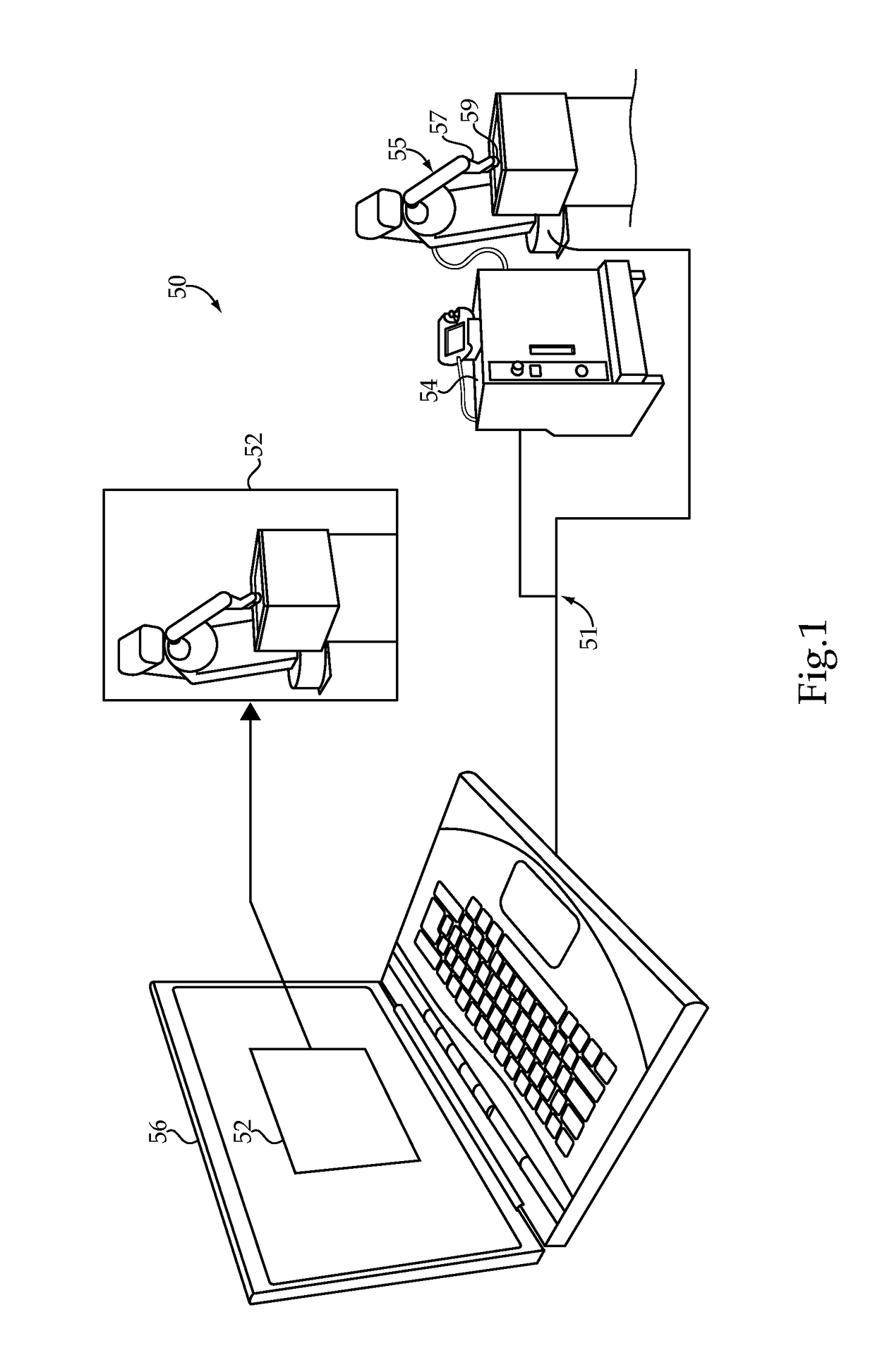
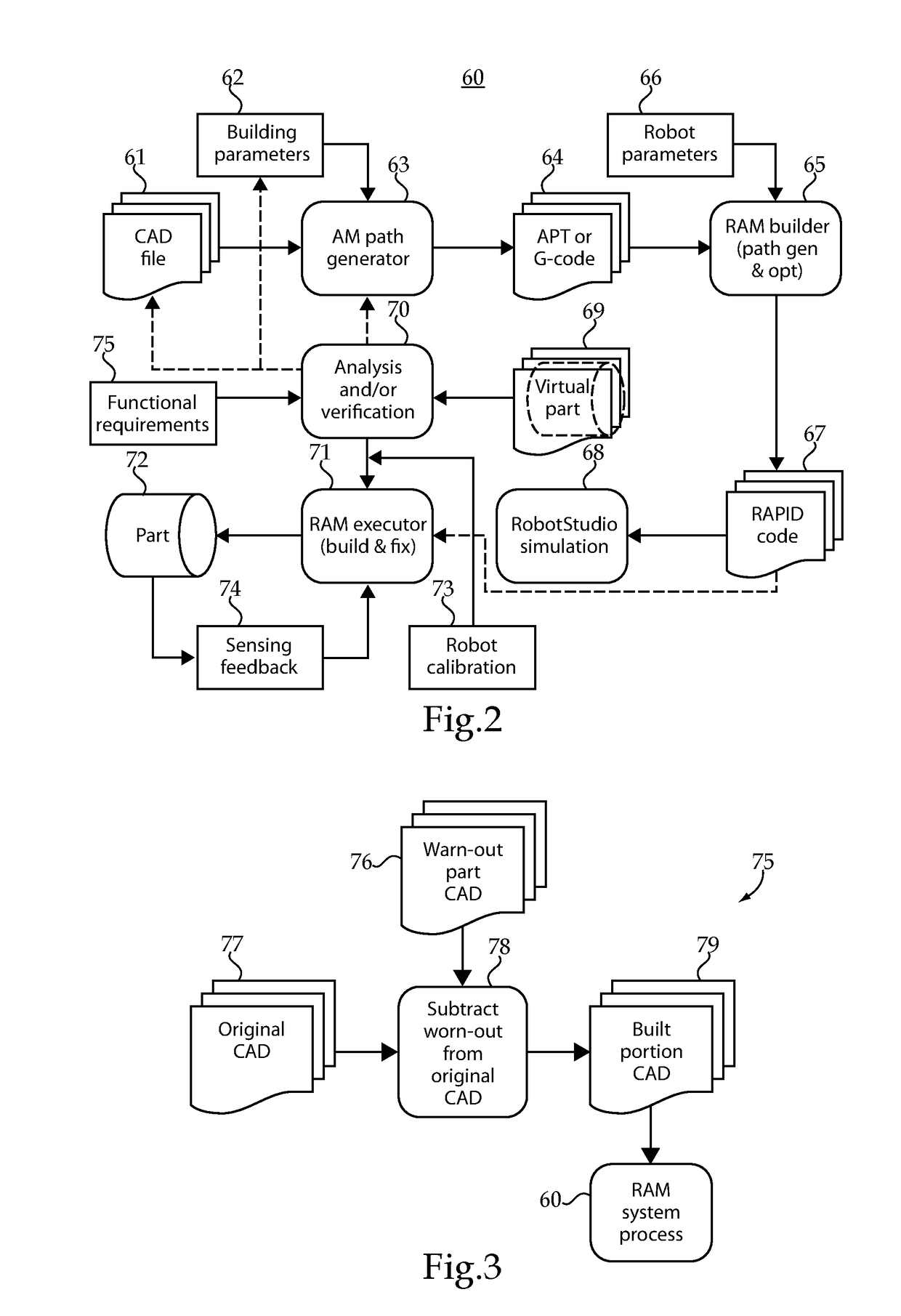
Robotic additive manufacturing apparatuses, systems and methods
One exemplary embodiment is a method comprising generating robot control code from one or more files including part geometry parameters, material addition parameters, and robot system parameters. The robot control code includes instructions to control position and material output of an additive manufacturing tool adjustable over six degrees of freedom. The method includes simulating execution of the robot control code to generate a virtual part file including virtual part geometry parameters and material addition parameters, analyzing the virtual part geometry parameters and material addition parameters relative to the one or more files, and executing the robot control code with the controller to produce the part with robot system if the analyzing indicates that the virtual part satisfies one or more conditions.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
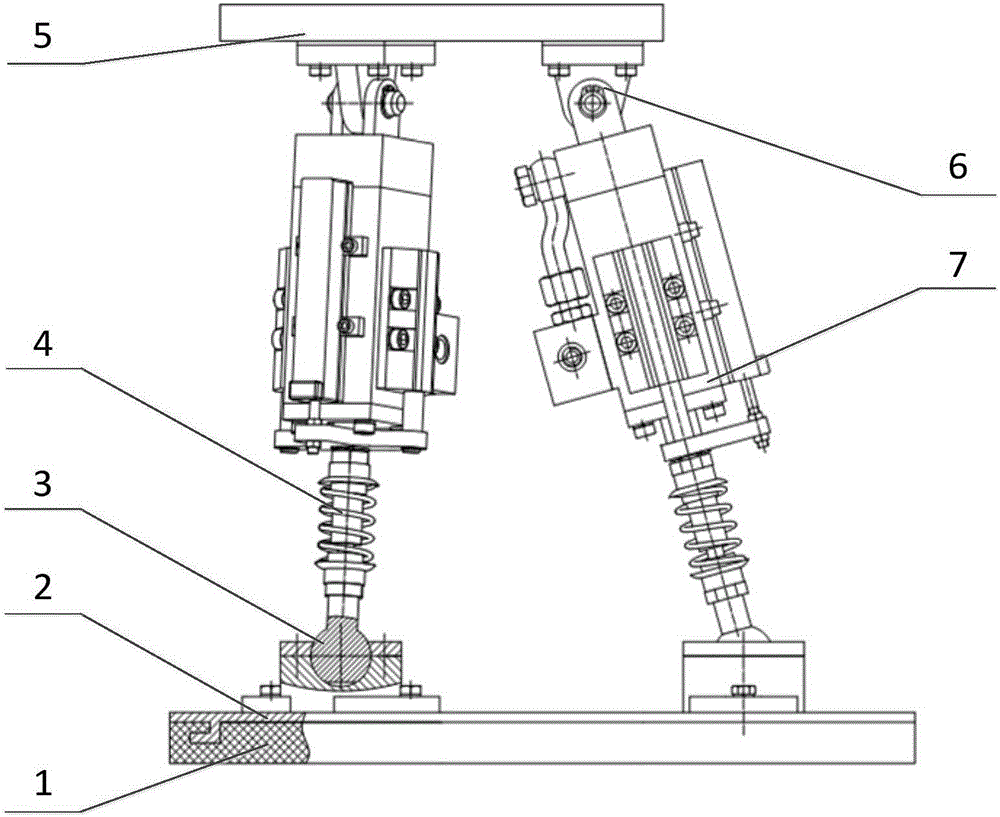
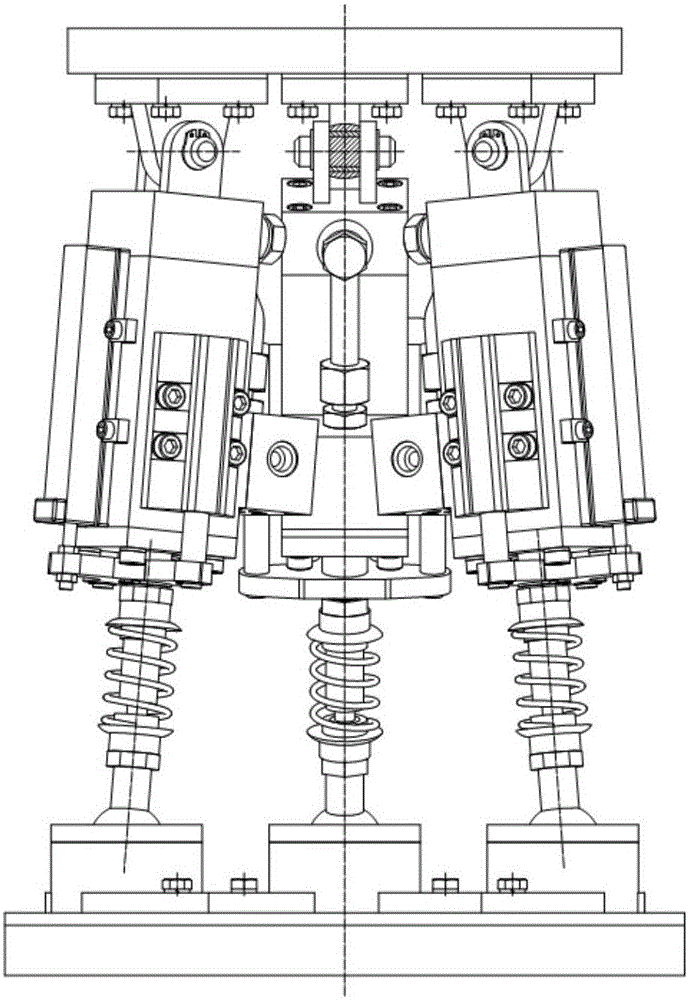
Two-stage vibration reducing ankle-foot integrated parallel low-impact walking foot mechanism and controlling method
InactiveCN106828657AActive and controllable ankle-foot freedomBalance difficultyVehiclesHydraulic cylinderAnalog robot
The invention discloses a two-stage vibration reducing ankle-foot integrated parallel low-impact walking foot mechanism and a controlling method, which can be used for effectively reducing foot-ground impact force and are capable of performing active control. The walking foot mechanism comprises a foot-leg connecting platform, a food end bottom connecting platform, three groups of moving pairs, three groups of revolute pairs and three groups of ball pairs, a lower platform simulates the foot end of a robot, the moving pairs are driving pairs, and are used for simulating legs of the robot, an anti-vibration pad, with frictional force, is inlaid in the lower surface of the food end bottom connecting platform, and is used as first-stage vibration reduction, the three groups of moving pairs are arranged in a mirror symmetry manner, and each group of moving pair comprise a hydraulic cylinder, a spring damper, a servo valve and a controller, wherein the spring damper sleeves a cylinder piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder, and is used as second-stage vibration reduction, so that the whole mechanism forms a lower-mobility parallel mechanism with a three freedom degree structure, and two rotational freedom along the directions of x and y and a translational freedom degree along the direction of z are realized. The mechanism and method provided by the invention have the advantages that the plan and control of the robot are flexible and reliable, and the stability is high.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rope drive flexible robot experimental platform
The invention discloses a rope drive flexible robot experimental platform, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The rope drive flexible robot experimental platform comprises flexible arm modules, a drive module, an angle measuring unit and a tensile force measuring unit, wherein the flexible arm modules comprise first arm sections, second arm sections, third arm sections and drive ropes penetrating through the first arm sections, the second arm sections and the third arm sections, the first arm sections are connected with the second arm sections through joints, and the second arm sections are connected with the third arm sections through joints; the drive module comprises a drive part, a screw rod and a screw nut, the drive part can drive the screw rod to rotate, the screw nut isconnected with the screw rod, the screw nut can be driven by rotation of the screw rod to move in the axial direction of the screw rod, and one end of the drive rope is connected with the screw nut; the angle measuring unit is connected with the joints; and the tensile force measuring unit is connected with the drive rope. Actual working conditions of the robots can be simulated through the rope drive flexible robot experimental platform, and motion parameters of the robots can be measured.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
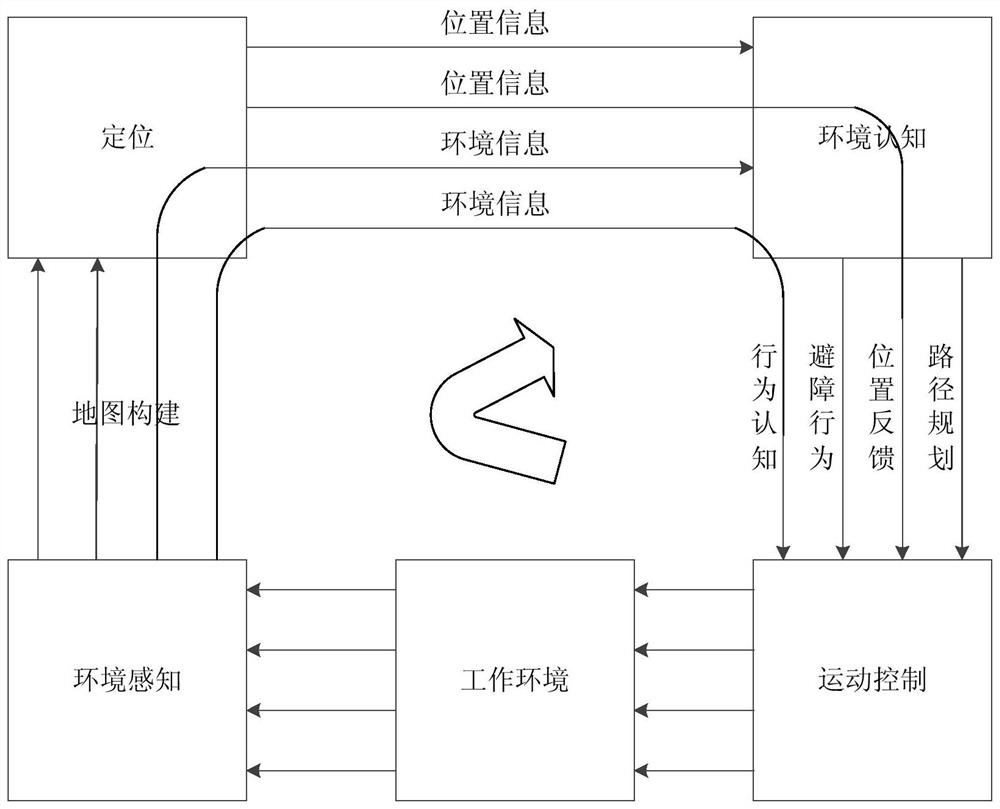
Dynamic environment obstacle avoidance method, controller and robot
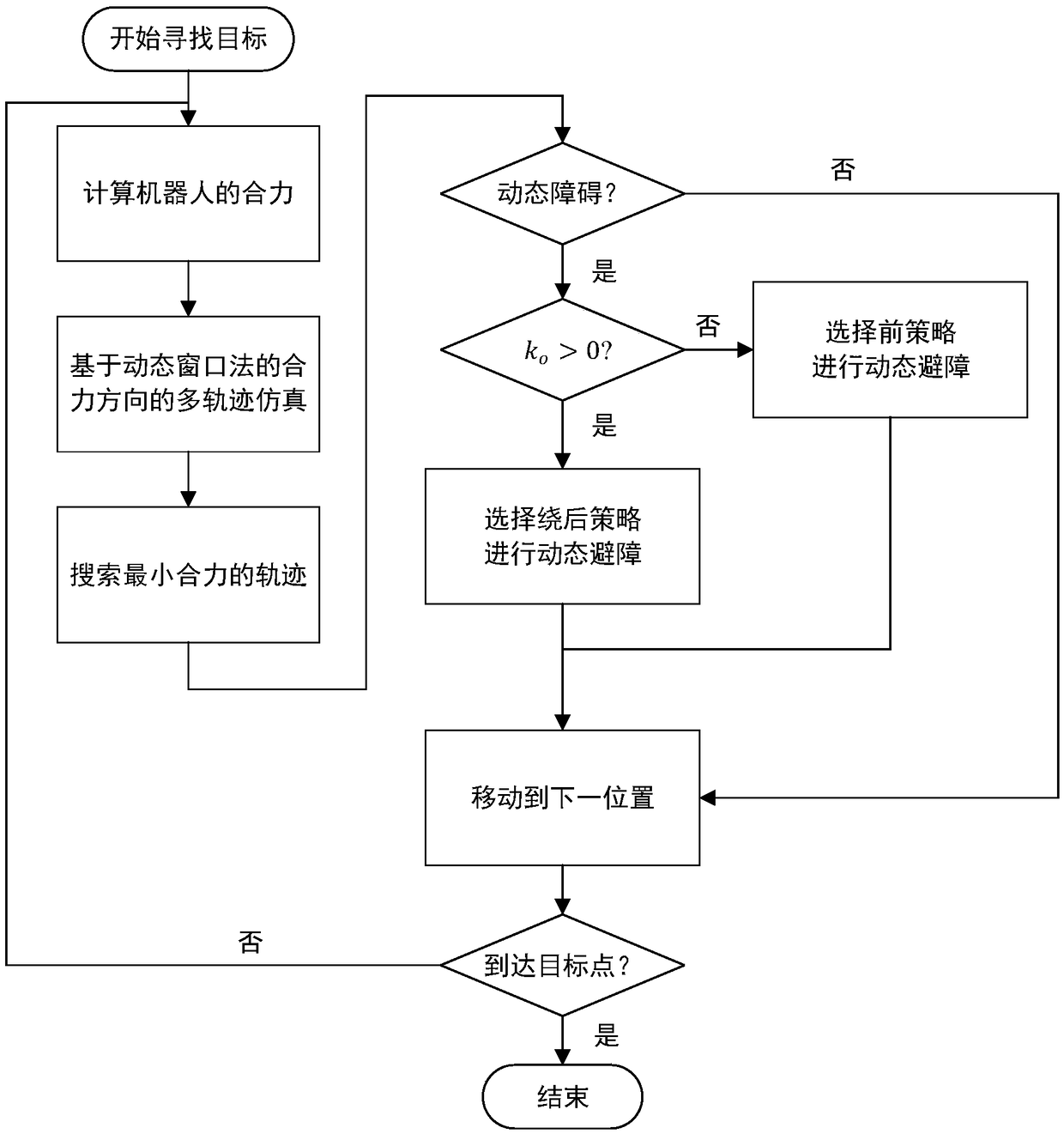
ActiveCN109163728AImprove effectivenessNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsAnalog robotObstacle avoidance
The invention provides a dynamic environment obstacle avoidance method, a controller and a robot. The dynamic environment obstacle avoidance method comprises the steps of calculating a resultant forcesuffered by the robot at the current position, simulating next position points in multiple directions of the resultant force suffered by the robot at the current position based on a dynamic window method, determining the position point with the minimum resultant force from the next position points as a next movement position point of the robot, constructing a local map of the robot, controlling the robot to start dynamic obstacle avoidance if a dynamic obstacle enters the local map of the robot, or else, allowing the robot to move to the next position point till a target point is reached.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Robot simulation apparatus
InactiveUS20070293986A1Shorten the timeSimple designProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsAnalog robotSimulation
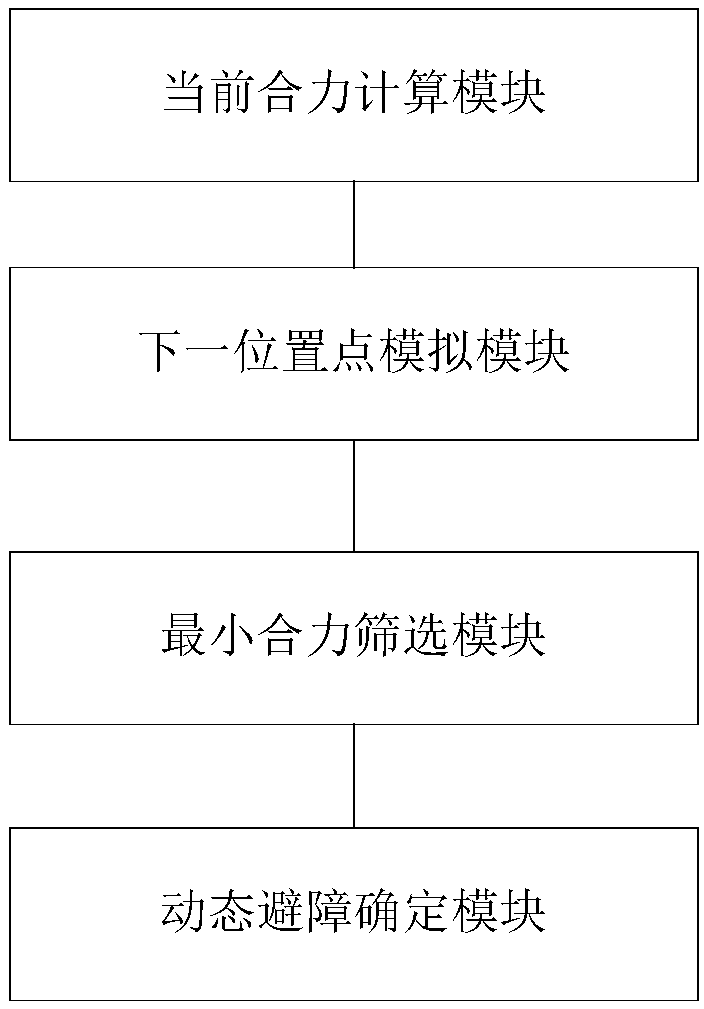
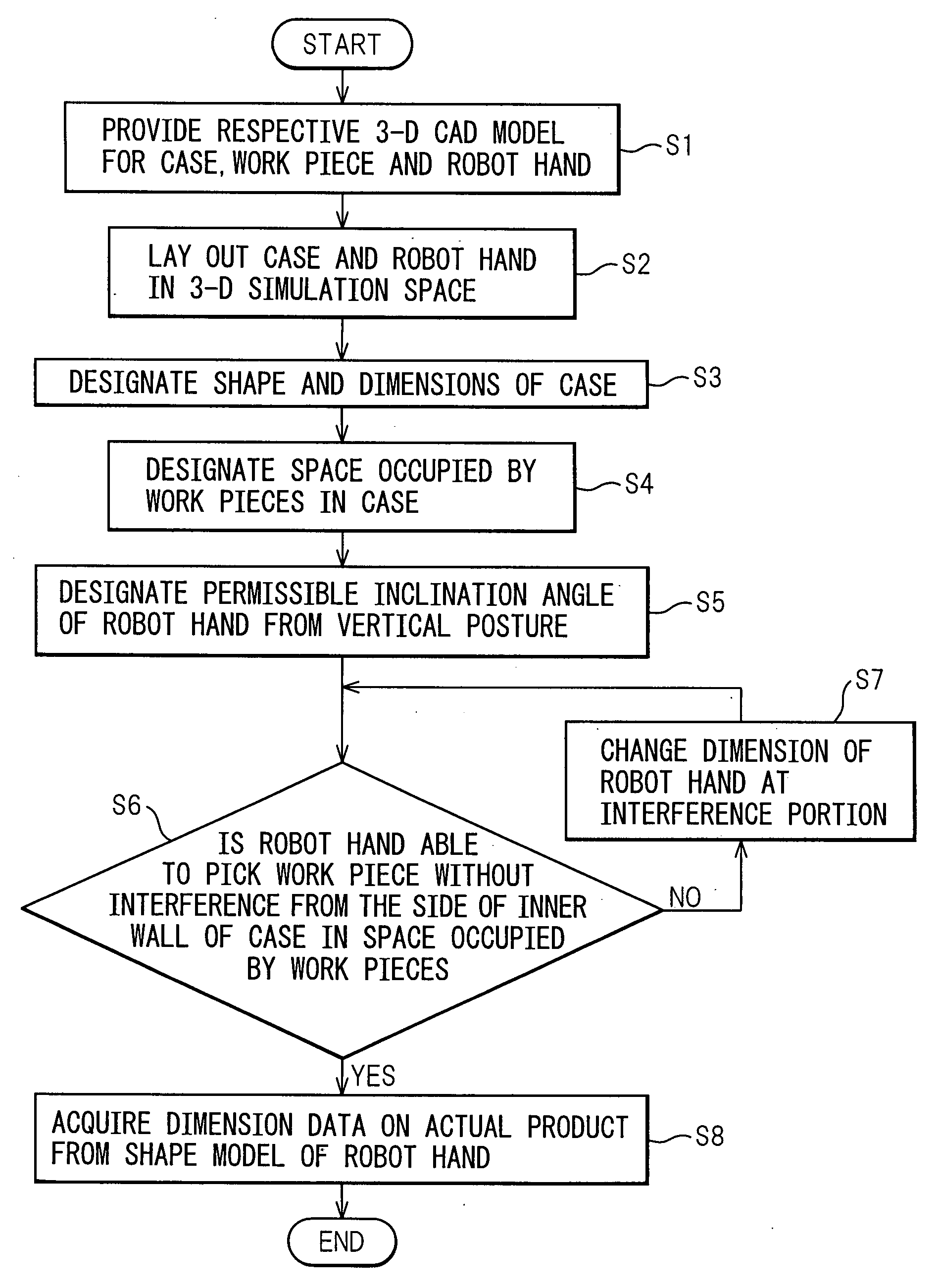
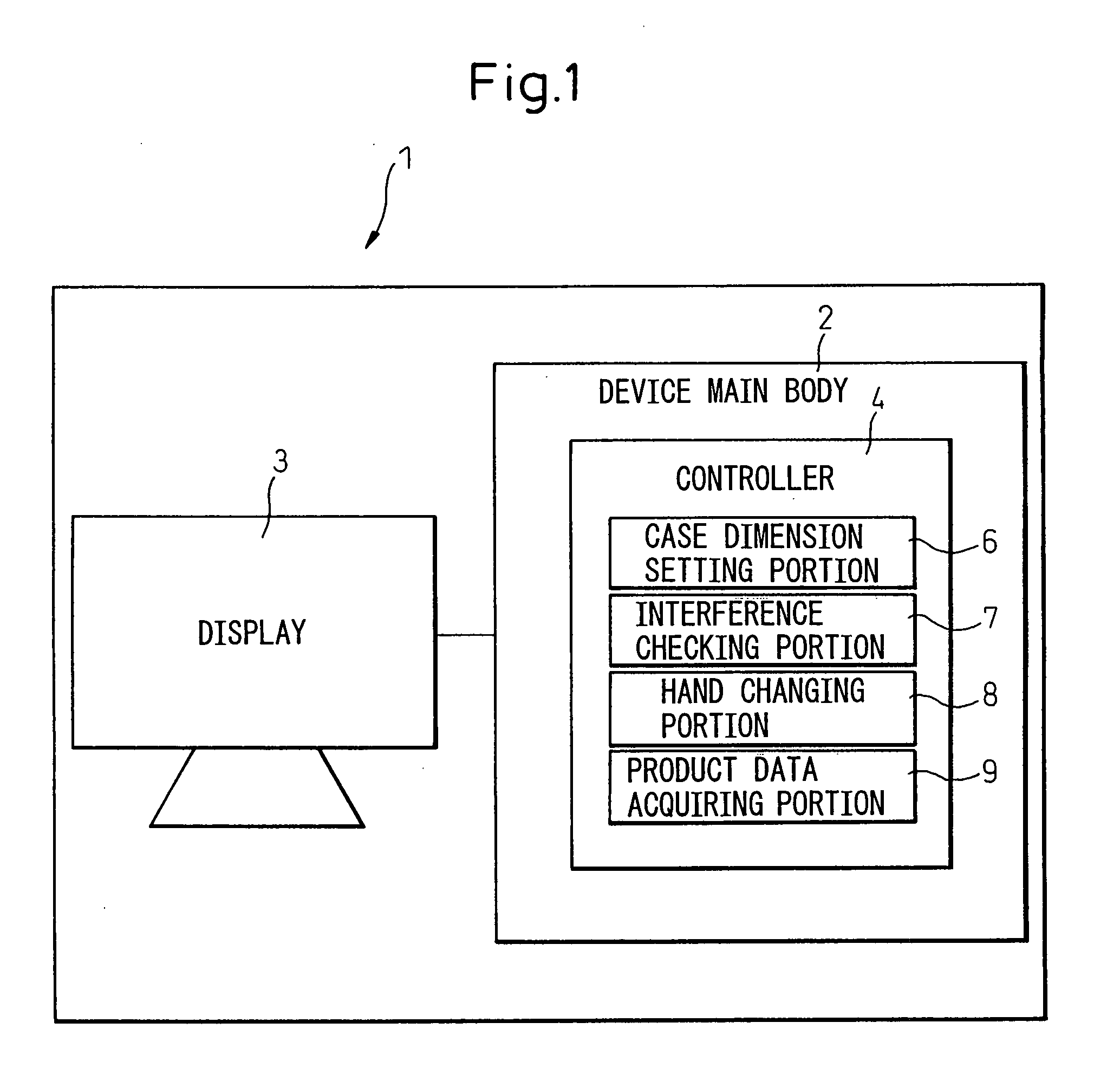
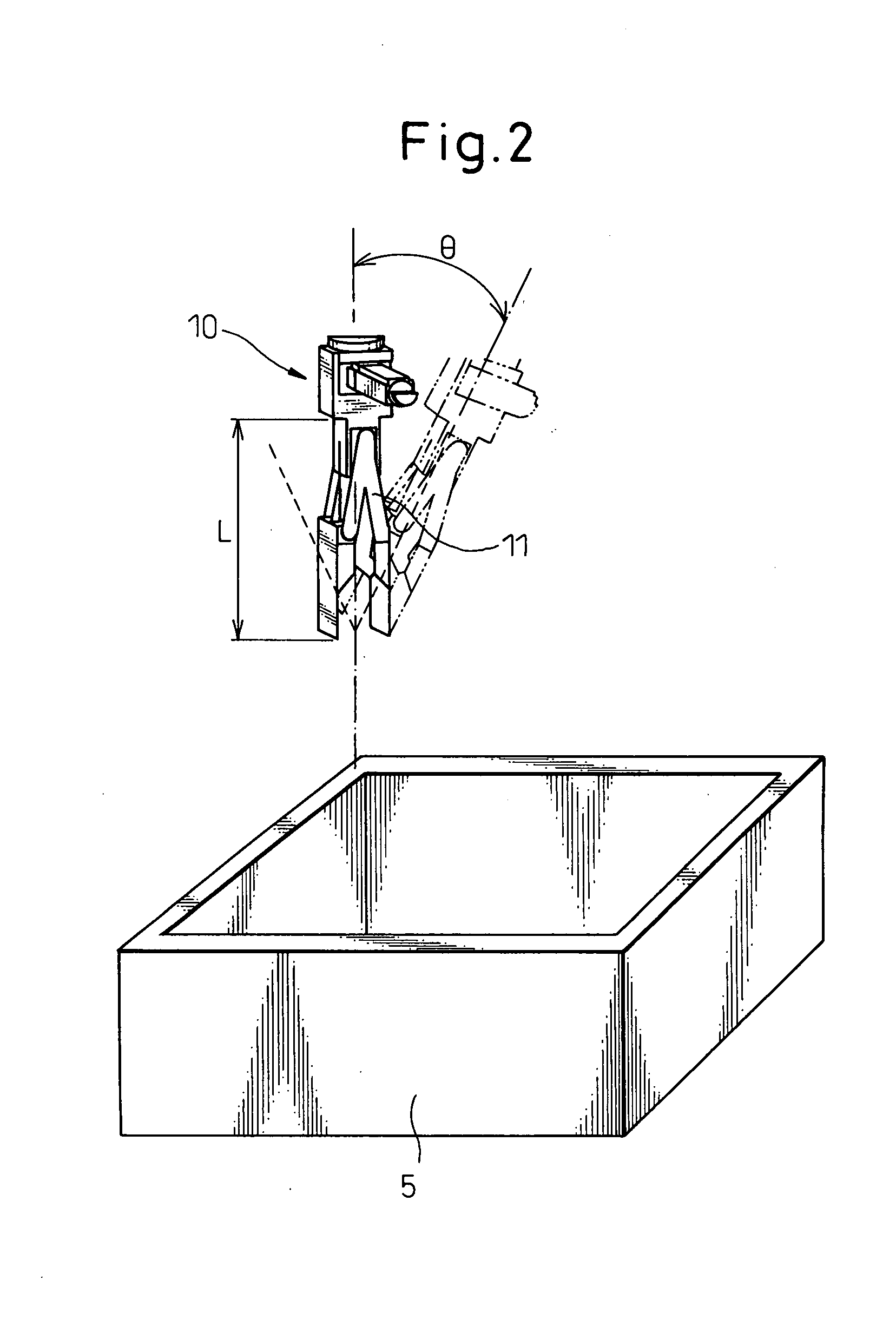
A robot simulation apparatus, which lays out a shape model of a robot equipped with a hand, and shape models of a case and of work pieces contained therein on a display screen in a prescribed positional relationship, and simulates a picking operation of the robot, which picks the work piece with the hand, the apparatus having; a case dimension setting portion for setting the shape model of the case to a prescribed shape and dimensions; an interference checking portion for checking for interference between the hand and the case when the robot is operated to take out a work piece from the side of a inner wall of the case, and if there is interference, identifying the interference; a hand changing portion for changing the shape model of the hand so that there is no longer any interference between the hand and the case when it is determined by the interference checking portion that there is interference between the hand and the case; and a product data acquiring portion for acquiring data on the actual product dimension of the hand from the shape model of the hand changed by the hand changing portion.
Owner:FANUC LTD
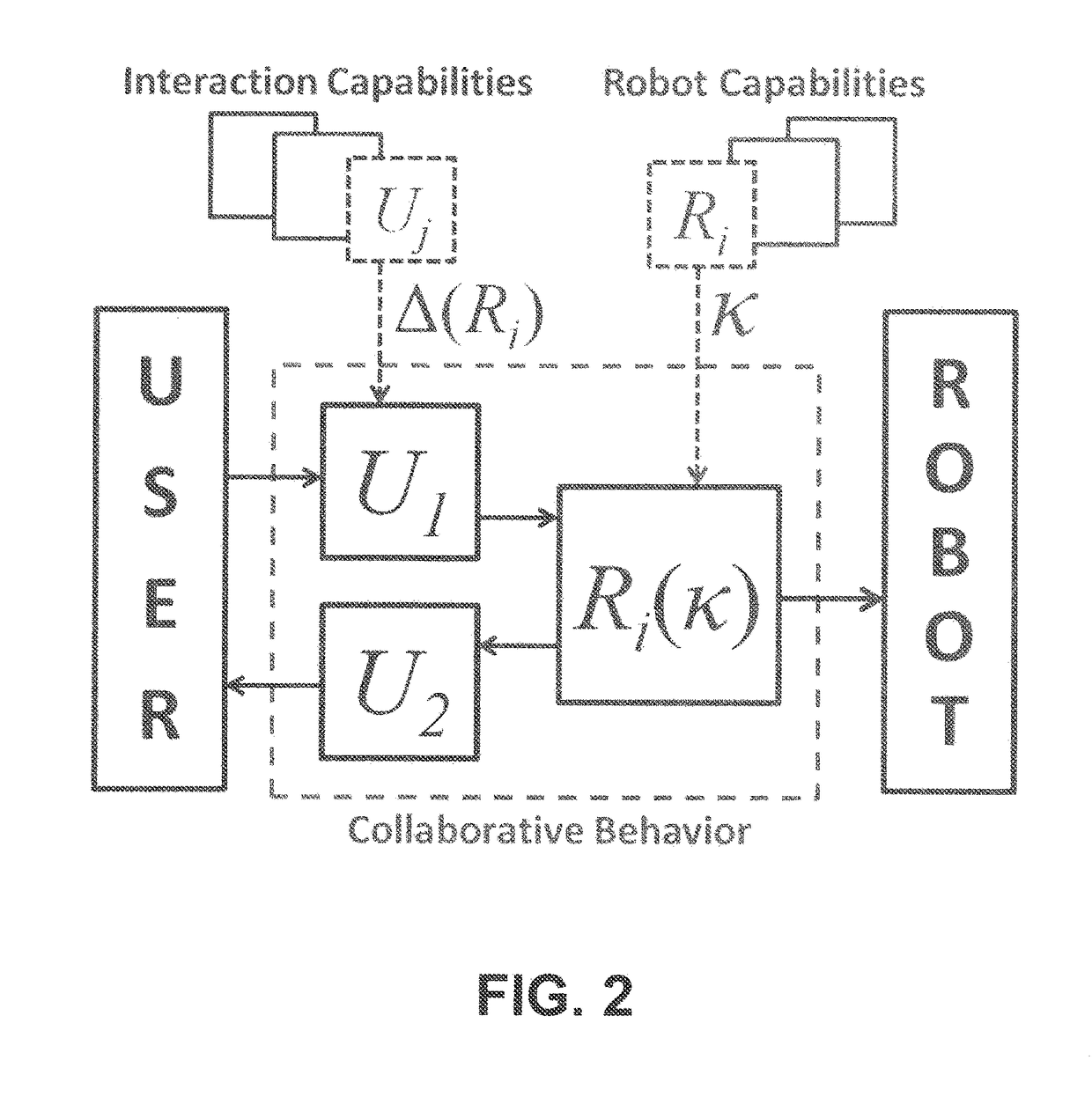
System and method for flexible human-machine collaboration
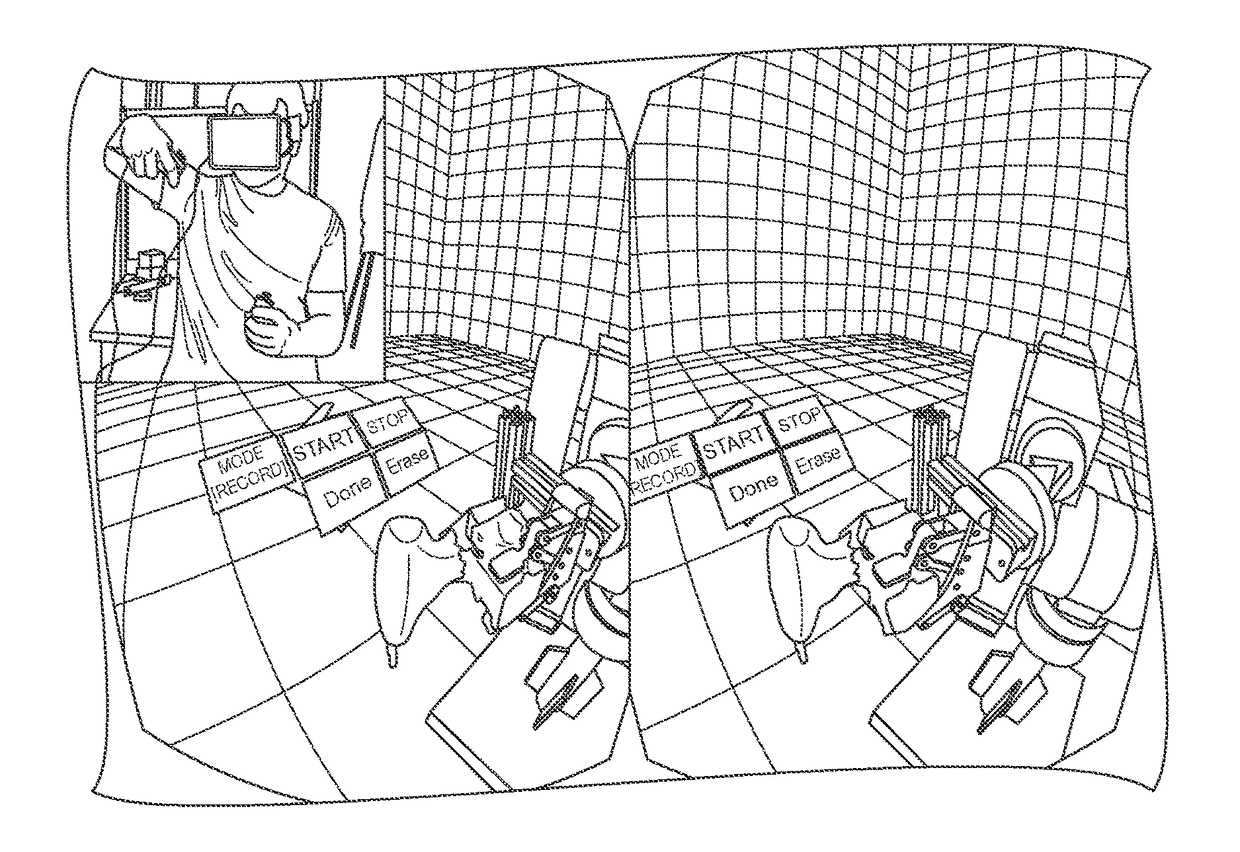
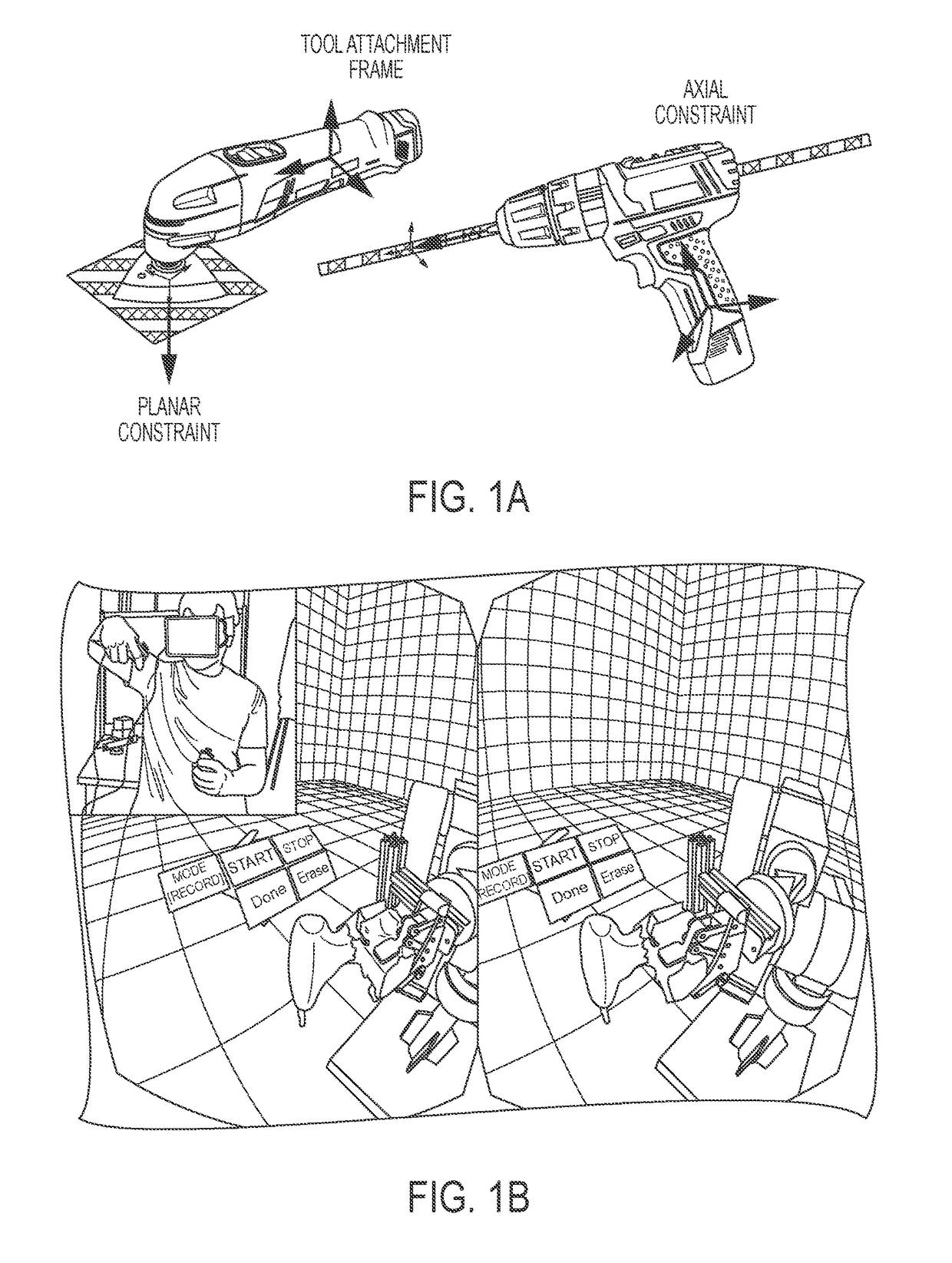
ActiveUS20170144304A1Flexible and efficient user-robotProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnalog robotUser input
Methods and systems for enabling human-machine collaborations include a generalizable framework that supports dynamic adaptation and reuse of robotic capability representations and human-machine collaborative behaviors. Specifically, a method of feedback-enabled user-robot collaboration includes obtaining a robot capability that models a robot's functionality for performing task actions, specializing the robot capability with an information kernel that encapsulates task-related parameters associated with the task actions, and providing an instance of the specialized robot capability as a robot capability element that controls the robot's functionality based on the task-related parameters. The method also includes obtaining, based on the robot capability element's user interaction requirements, user interaction capability elements, via which the robot capability element receives user input and provides user feedback, controlling, based on the task-related parameters, the robot's functionality to perform the task actions in collaboration with the user input; and providing the user feedback including task-related information generated by the robot capability element in association with the task actions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and method for context-driven predictive simulation selection and use
ActiveUS20190219972A1Programme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot environmentSensory Feedbacks
The present approach employs a context-aware simulation platform to facilitate control of a robot remote from an operator. Such a platform may use the prior domain / task knowledge along with the sensory feedback from the remote robot to infer context and may use inferred context to dynamically change one or both of simulation parameters and a robot-environment-task state being simulated. In some implementations, the simulator instances make forward predictions of their state based on task and robot constraints. In accordance with this approach, an operator may therefore issue a general command or instruction to a robot and based on this generalized guidance, the actions taken by the robot may be simulated, and the corresponding results visually presented to the operator prior to evaluate prior to the action being taken.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bending machine numerical control system device with embedded robot for control and method thereof
ActiveCN105911955ASimple structureSolve the defects of complex use processNumerical controlAnalog robotMotion control
The invention discloses a bending machine numerical control system device with embedded robot control and a method thereof. The bending machine numerical control system device comprises a numerical control system, a robot, a rack, a slide block control mechanism, a slide block, an upper mold, a lower mold, a charging frame and a discharging station, wherein the numerical control system is arranged on the rack; the robot is arranged on the rack; the slide block control mechanism is used for pushing the slide block to move up and down; the upper mold is mounted on the slide block; the lower mold is arranged under the upper mold; the lower mold is arranged on the rack; the charging frame is mounted at the left side of the rack; and the discharging station is mounted at the right side of the rack. The robot and bending machining are uniformly programmed and are subjected to synchronous motion control through the numerical control system, so that the robot becomes an embedded part of a numerical control bending machine and a rear bumper structure is cancelled; and the defects in the current market that the common numerical control bending machine and the robot are independently controlled and special software needs to be used for simulating a process of bending the robot so that the use complexity is caused are overcome.
Owner:广州纽蓝客智能科技有限公司
Pneumatic flexible torsion joint
The invention is a pneumatic soft torsion joint. The character is: it is made up of pneumatic soft cylinder, metal plate, and end cover, fixing plate, core and round turntable. Two pneumatic soft cylinders with the same size are arranged on the fixing plate symmetrically, the round turntable can rotate freely around the core relatively to the fixed plate. When inputting compressed air into the two cylinders, the round turntable will rotates for a certain angle by the pushing force of the pneumatic soft cylinder, forms the torsion movement process of robot. The structure is reasonable; the cost is low, reliable, and quick.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
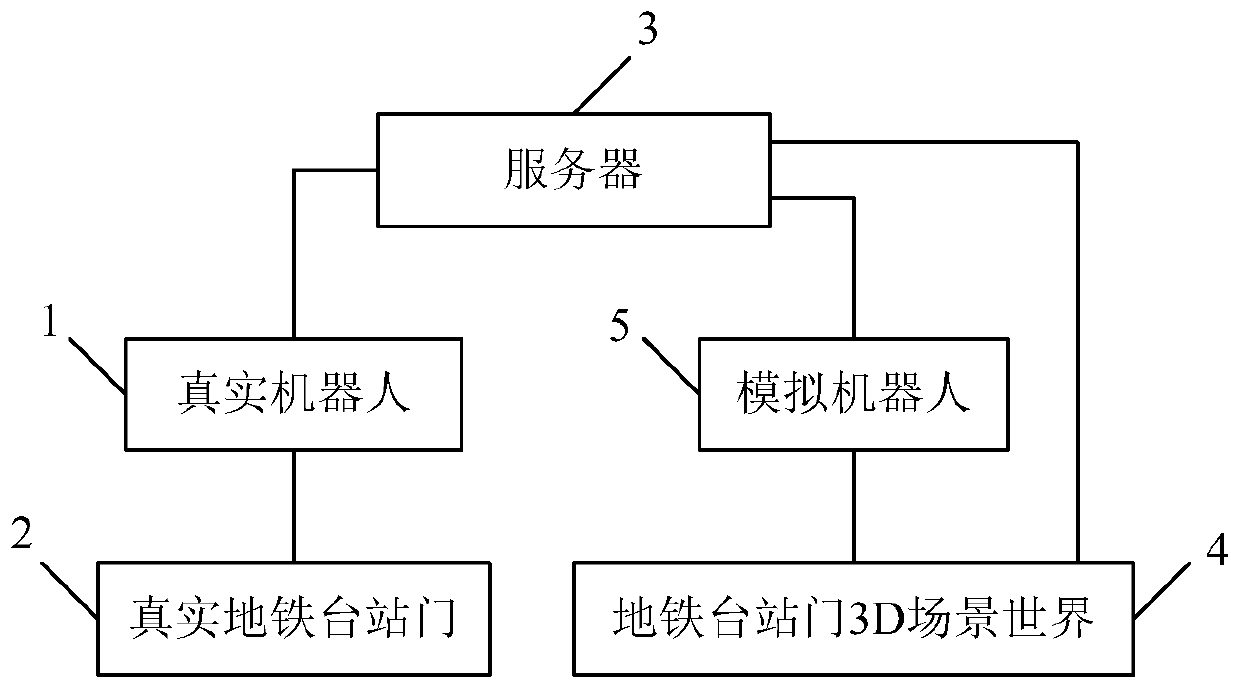
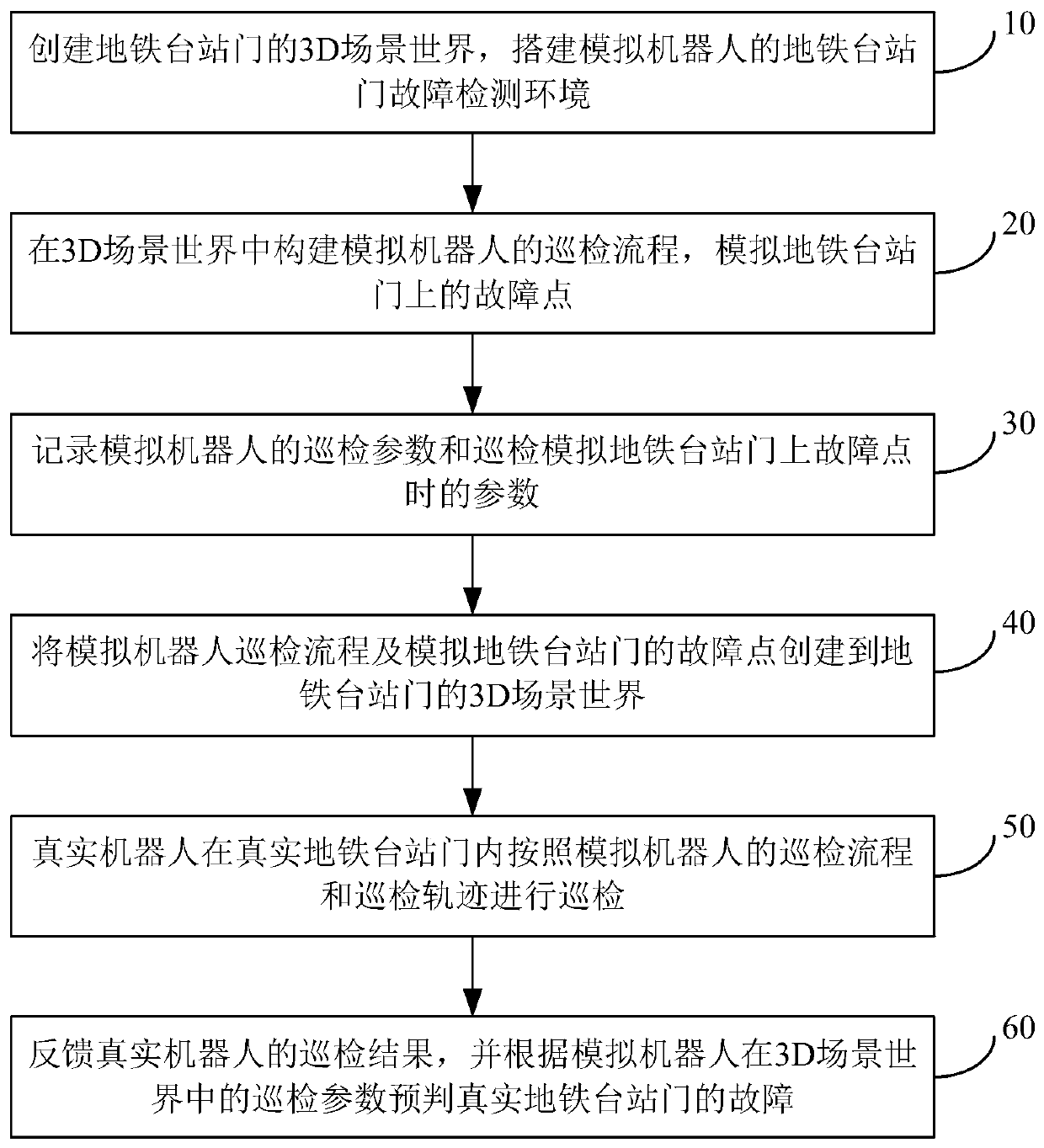
Subway station door fault detection method and system based on digital twin robot
ActiveCN110181519AObservation is intuitive and convenientSave manpower and material costsProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnalog robotSimulation
The embodiment of the invention discloses a subway station door fault detection method and system based on digital twin robots. The method includes the steps that a 3D scene world of a subway stationdoor is established, and a subway station door fault detection environment of the robot is set up; a routing inspection process of a simulation robot is constructed, and a fault point on the subway station door is simulated; routing inspection parameters of the simulation robot and parameters generated during routing inspection of the fault point are recorded, and the 3D scene world of the subwaystation door is established; a true robot conducts routing inspection in a true subway station door according to the routing inspection process and the routing inspection track of the robot; and a routing inspection result of the true robot is fed back, and the fault of the true subway station door is pre-judged according to the routing inspection parameters of the simulation robot in the 3D scenewould. By means of the method, a virtual method is used for observing the routing inspection condition of the robot, the robots do not need to be monitored in real time, big data processing is conducted on the monitoring result of the true robot, the digital twin is matched, and the fault problem happening to an object is predicated in advance, and the cost of manpower and material resources is reduced.
Owner:广东希睿数字科技有限公司
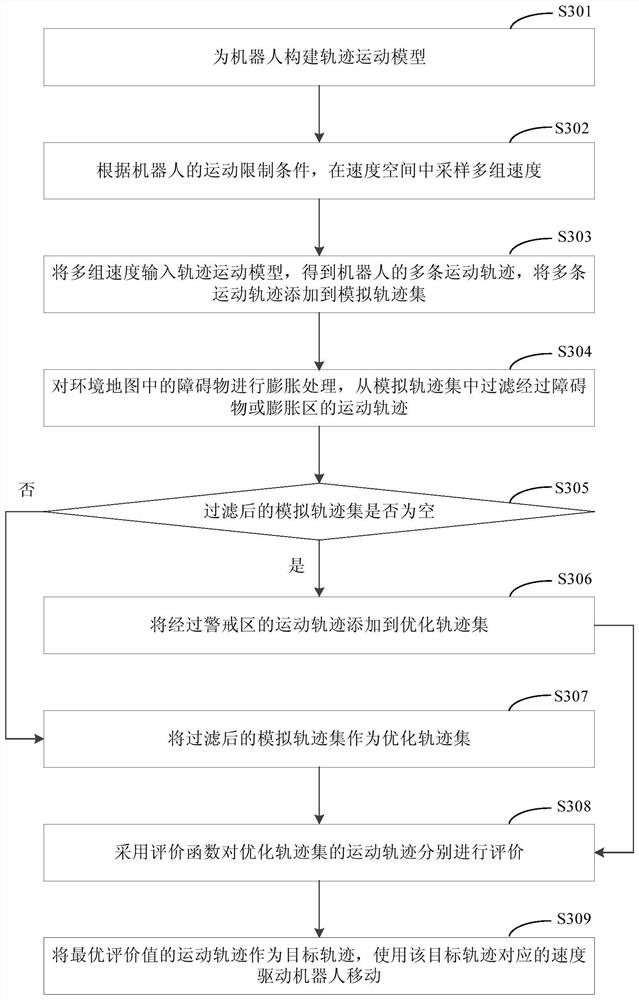
Robot obstacle avoidance method and device
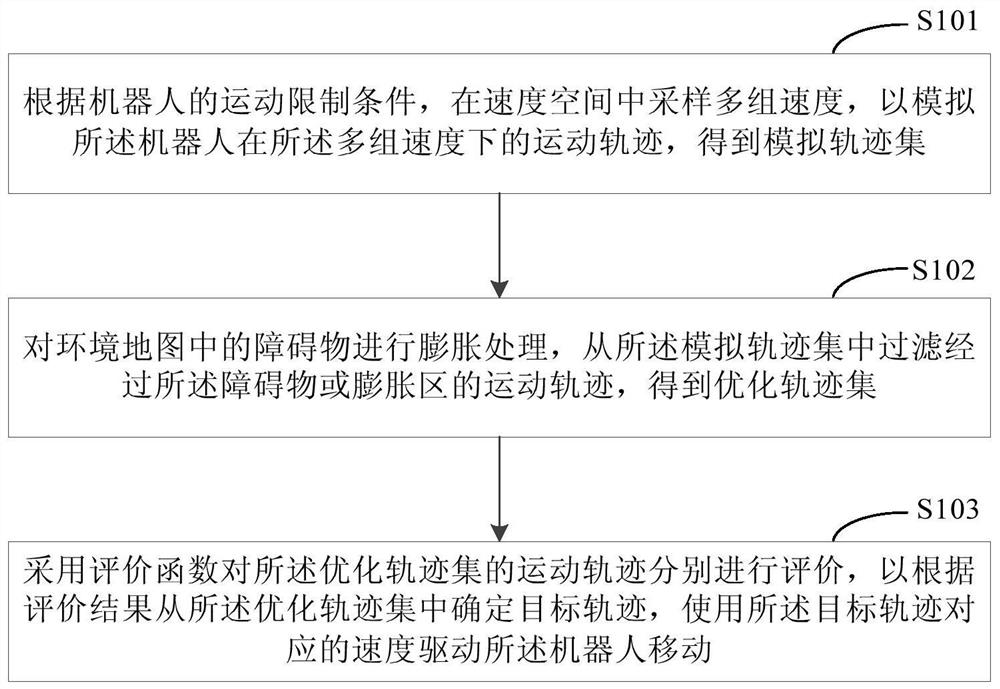
PendingCN112230634AShort timeReduce in quantityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEvaluation resultAnalog robot
The invention discloses a robot obstacle avoidance method and device and relates to the technical field of computers. One specific embodiment of the method comprises steps of sampling multiple groupsof speeds in a speed space according to a motion limiting condition of a robot to simulate a motion track of the robot at the multiple groups of speeds to obtain a simulated track set; wherein the multiple sets of speeds comprise the speeds of the robot at multiple moments; performing expansion processing on obstacles in the environment map, and filtering movement tracks passing through the obstacles or expansion areas from the simulated track set to obtain an optimized track set; and respectively evaluating the motion trails of the optimized trajectory set by adopting an evaluation function so as to determine a target trajectory from the optimized trajectory set according to an evaluation result, and driving the robot to move by using the speed corresponding to the target trajectory. According to the method, after the obstacle is expanded, the motion trail passing through the obstacle or the expansion area in the simulation trail set is filtered, the target trail is determined in combination with the evaluation function, and the robot is prevented from colliding with the obstacle.
Owner:JD DIGITS HAIYI INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
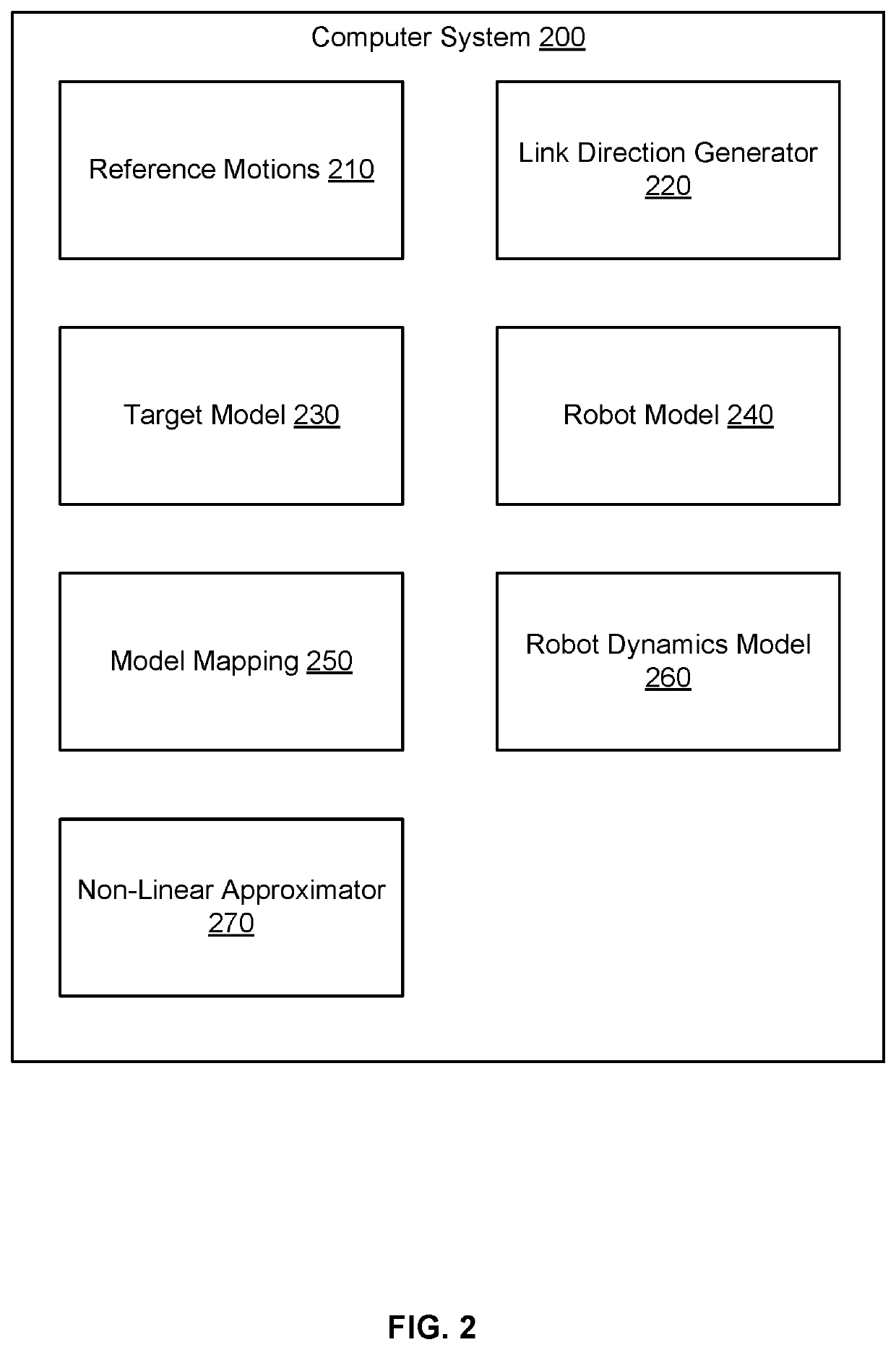
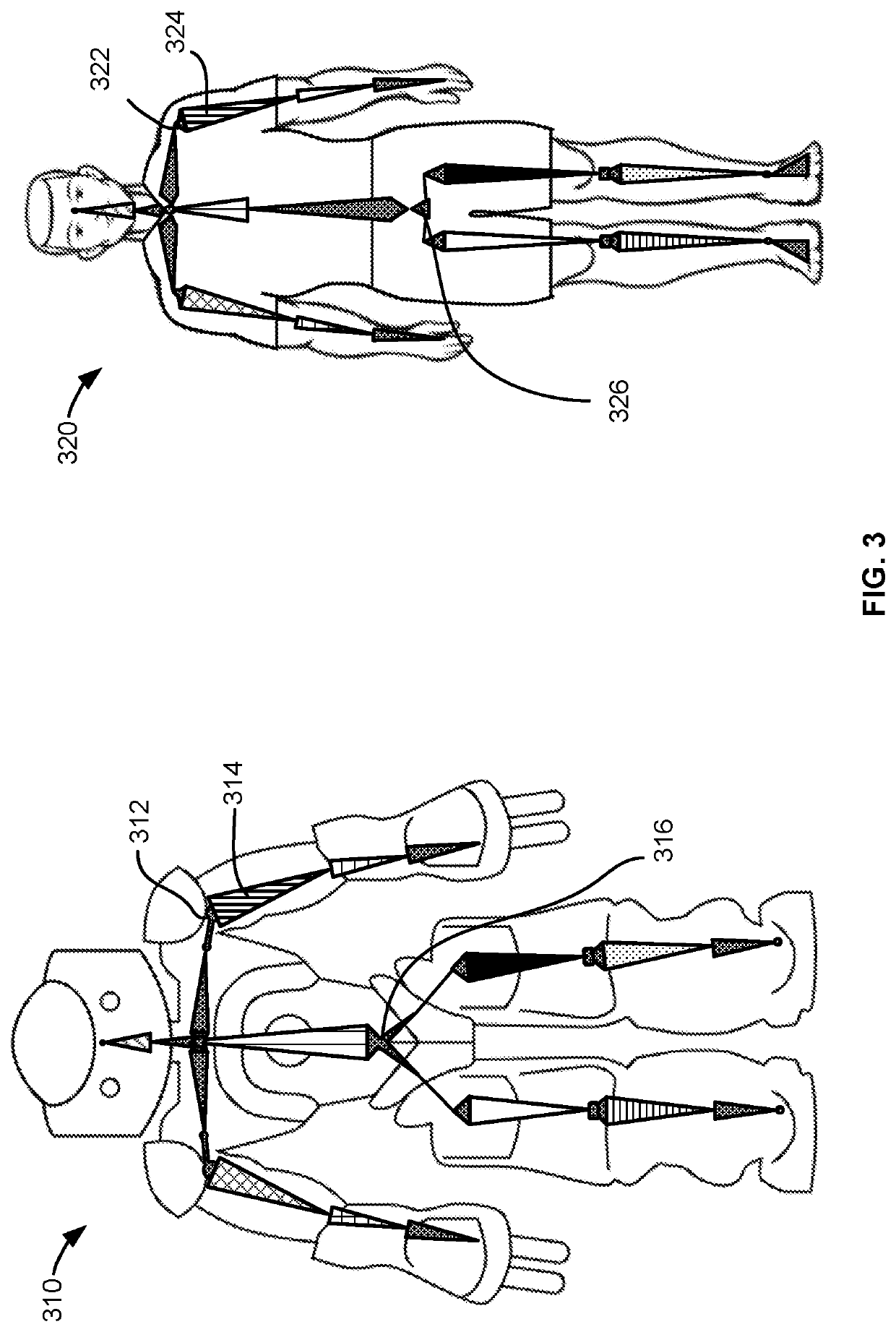
Motion Transfer of Highly Dimensional Movements to Lower Dimensional Robot Movements
Techniques for transferring highly dimensional movements to lower dimensional robot movements are described. In an example, a reference motion of a target is used to train a non-linear approximator of a robot to learn how to perform the motion. The robot and the target are associated with a robot model and a target model, respectively. Features related to the positions of the robot joints are input to the non-linear approximator. During the training, a robot joint is simulated, which results in movement of this joint and different directions of a robot link connected thereto. The robot link is mapped to a link of the target model. The directions of the robot link are compared to the direction of the target link to learn the best movement of the robot joint. The training is repeated for the different links and for different phases of the reference motion.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Intelligent self-balance moving robot target and control method thereof
ActiveCN110440641AAchieve freedom of movementHuman-like exercise effect is goodMovable targetsPosition/course control in two dimensionsAnalog robotSimulation
The invention discloses an intelligent self-balance moving robot target and a control method thereof. The robot target is formed by a two-wheel self-balancing moving platform, a three-dimensional (3D)human-like target, a shooting induction device and a target turnover device, wherein the 3D human-like target is arranged on the top part of the two-wheel self-balancing moving platform through the target turnover device; the shooting induction device is arranged on the two-wheel self-balancing moving platform or the 3D human-like target; the two-wheel self-balancing moving platform is in chargeof the movement speed, the direction and the gesture of the robot target; the 3D human-like target is in charge of simulating a human figure and bearing the shooting damage; the shooting induction device is in charge of receiving and feeding back a shooting signal; and the target turnover device is in charge of simulating 'shot dead' of the robot target through driving the 3D human-like target tofall. The intelligent self-balance moving robot target provided by the invention has a human movement bionic function and a shot simulation function, is high in turning flexibility, is suitable for shooting training of armies, public security and armed police systems, and is capable of effectively improving the skills and tactics level of trainees dealing with emergencies.
Owner:苏州融萃特种机器人有限公司
Robot single joint hydraulic pressure and position control test platform
InactiveCN102830699ASimple structureStable structureElectric testing/monitoringTorque motorClosed loop
The invention discloses a robot single joint hydraulic pressure and position control test platform which comprises a cantilever bracket, a first hydraulic servo drive unit, a torque motor and a matching controller, an angular displacement sensor bracket, an angular displacement sensor, a swing unit and multiple sleeves, wherein a base of the cantilever bracket is fixed on the ground; the angular displacement sensor bracket, the torque motor and the matching controller are fixed at the cantilever end of the cantilever bracket; the angular displacement sensor is fixed on the angular displacement sensor bracket and connected with an output shaft of the torque motor; the swing unit and the sleeves are connected in series on the output shaft of the torque motor; and one end of the first hydraulic servo drive unit is connected with a support lug of the cantilever bracket, and the other end is connected with the swing unit. With a simple, stable and reliable structure, the robot single joint hydraulic pressure and position control test platform disclosed by the invention can simulate the joint rotary inertia of a robot operation arm in different positions and form displacement tracking closed-loop and force control closed-loop motion, simulates the robot joint control function and verifies the control strategy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com