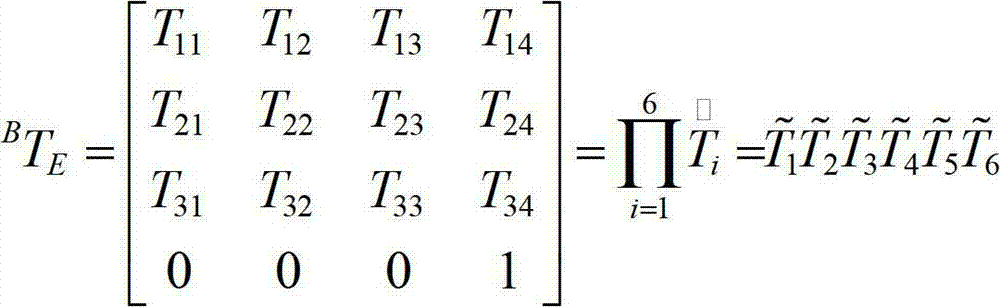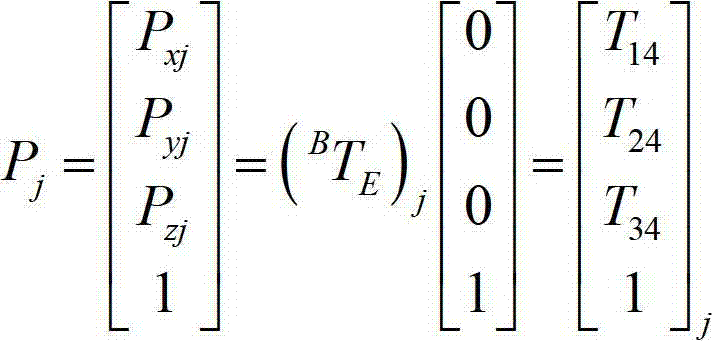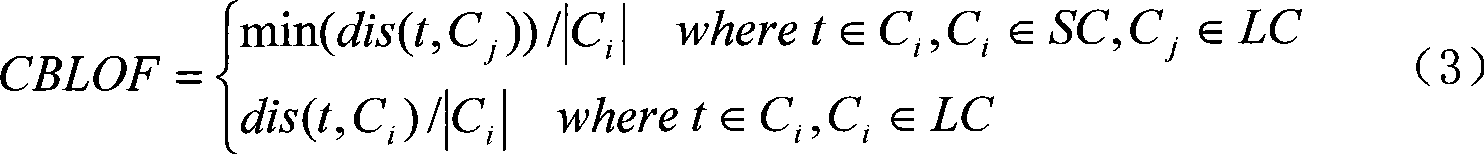Patents
Literature
2515 results about "Industrial robotics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
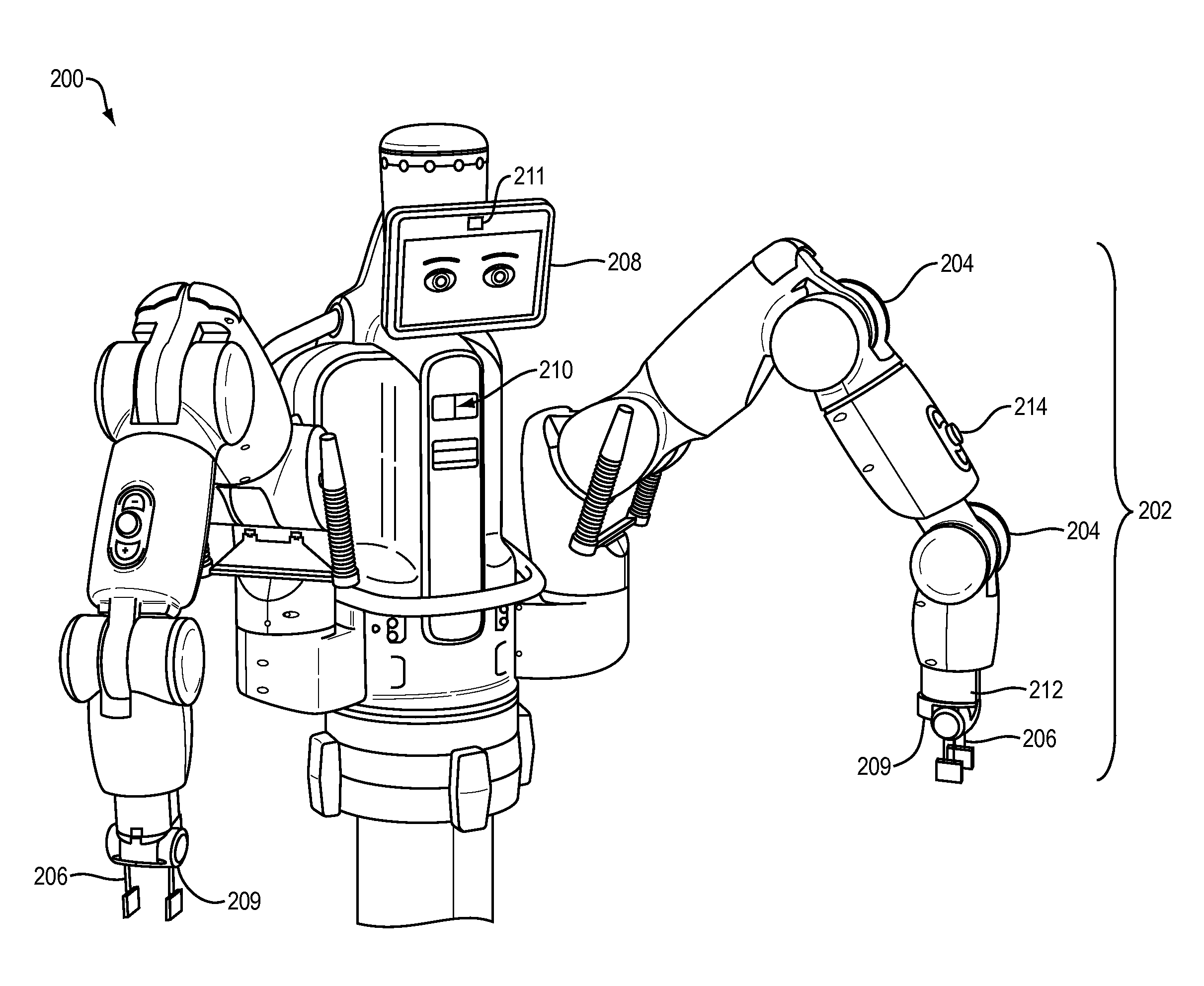
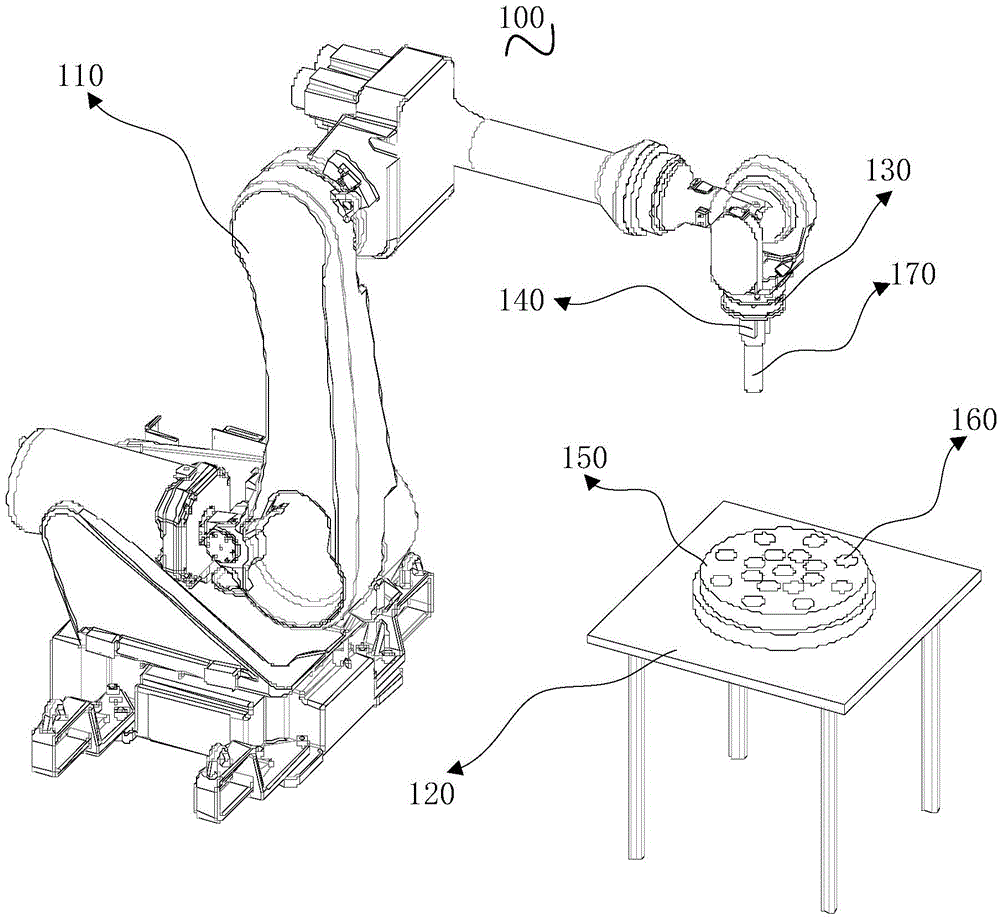
Tool for an Industrial Robot
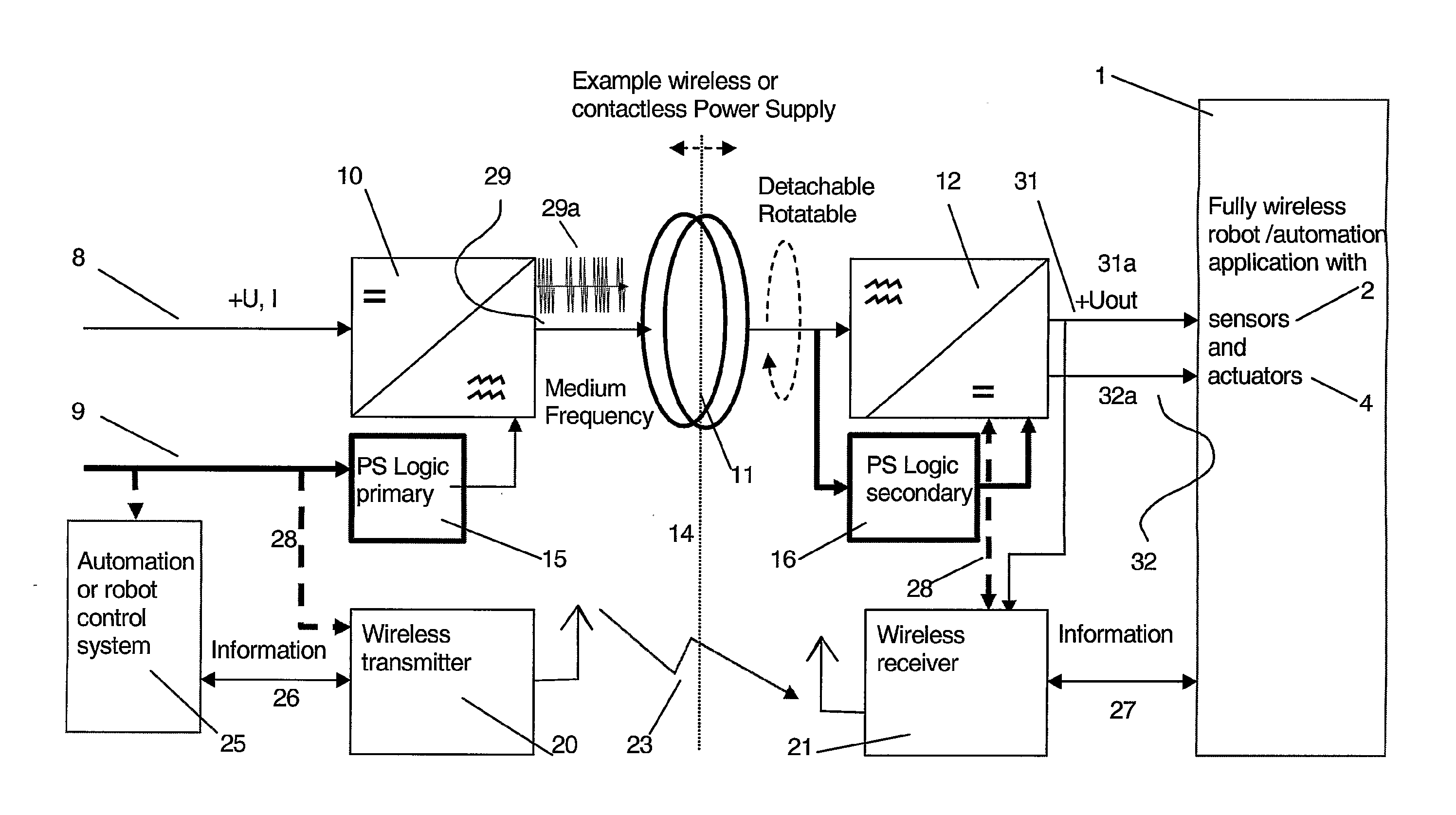
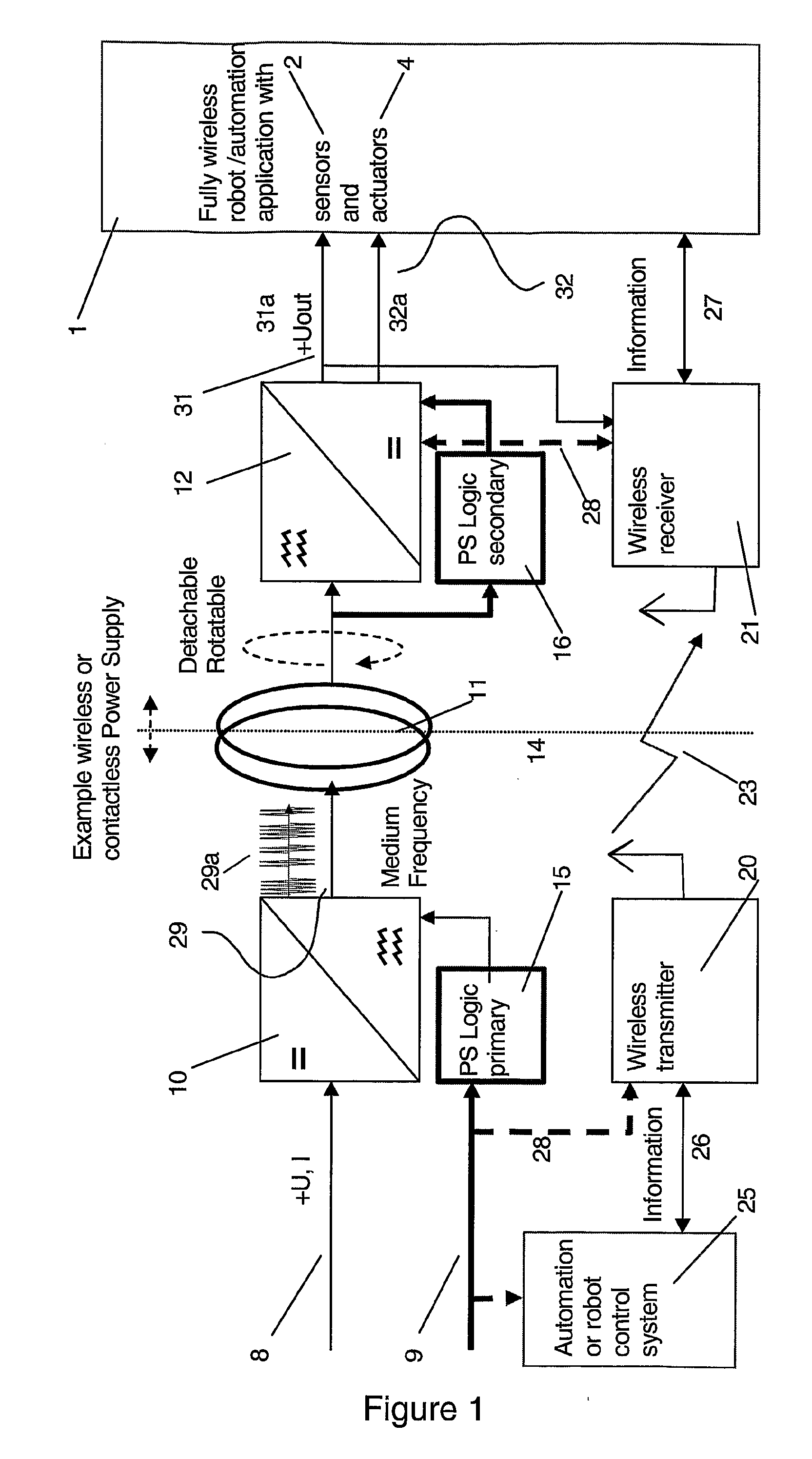
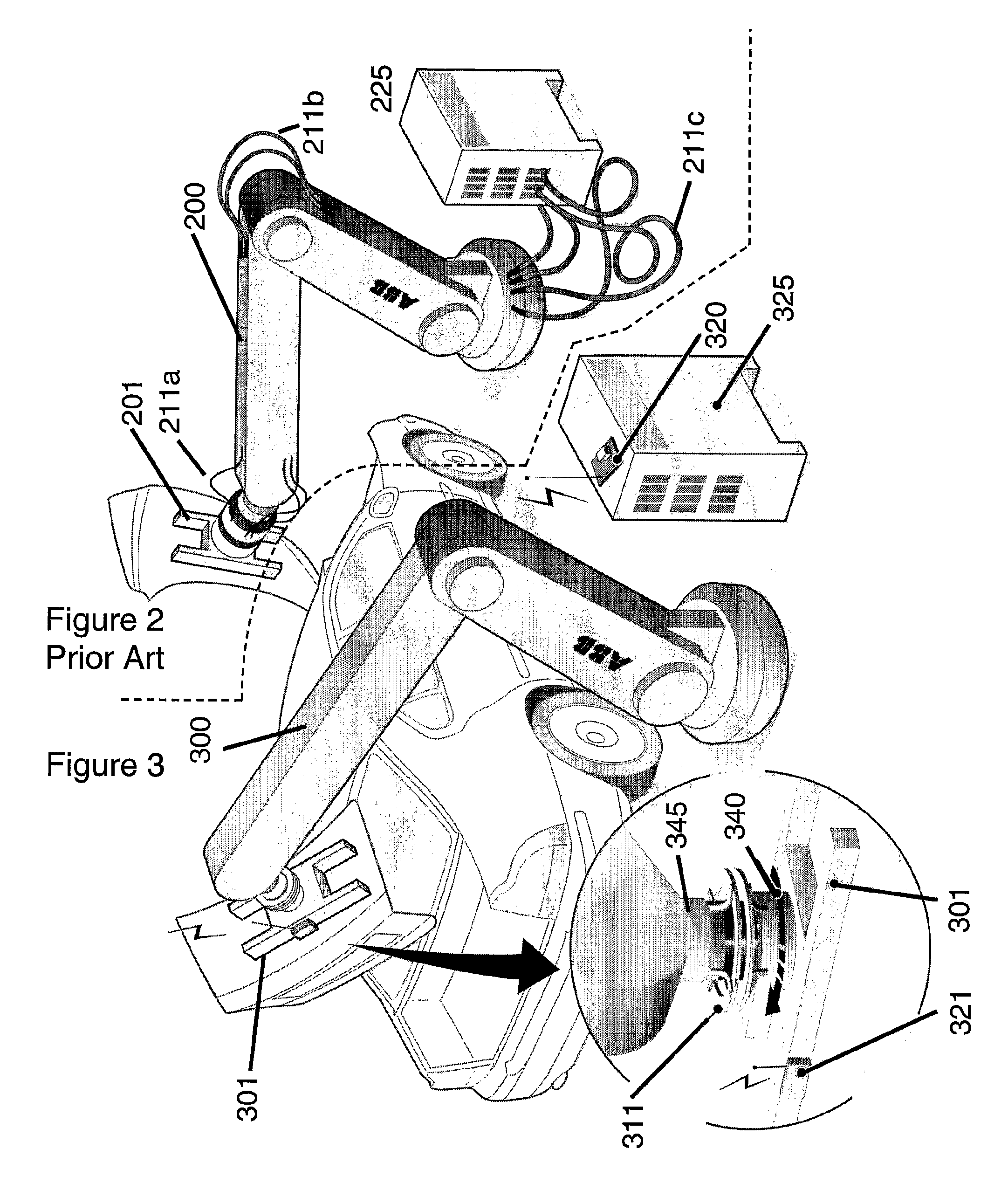
InactiveUS20070276538A1Speeding up changeReduce downtimeSingle-phase induction motor startersProgramme-controlled manipulatorWireless controlIndustrial robotics
A robot or manipulator including a wireless power supply and a wireless communication device. One or more actuators on the robot tool may be wirelessly powered and wirelessly controlled. The robot tool may have one or more wireless communication members for transmission of data from sensors on the tool. The power supply includes a primary power supply member and secondary power supply member. Tool changes may be carried out automatically by the robot. In other aspects of the invention a method, a control system and a computer program for carrying out the method are described.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Industrial robot base coordinate system calibration method based on laser tracker
InactiveCN105058387AReduce calibration timeHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer visionLaser tracker
The invention discloses an industrial robot base coordinate system calibration method based on a laser tracker. The method includes the steps that target bases needed for measurement are installed, a calibration system is preprocessed, coordinate systems needed for calibration are established, the relational expression of posture relation matrixes of the coordinate systems is acquired, data are collected through a control robot and the laser tracker, the corresponding posture matrixes are acquired, and finally the posture relation between a robot base coordinate system and a measurable coordinate system is acquired so as to determine the specific posture of the robot base coordinate system. The robot base coordinate system can be calibrated only through the laser tracker, no repetition is needed after calibration, repeated calibration time is shortened, meanwhile, the accuracy of the laser tracker is high, and the accuracy of acquired data of the base coordinate system is high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
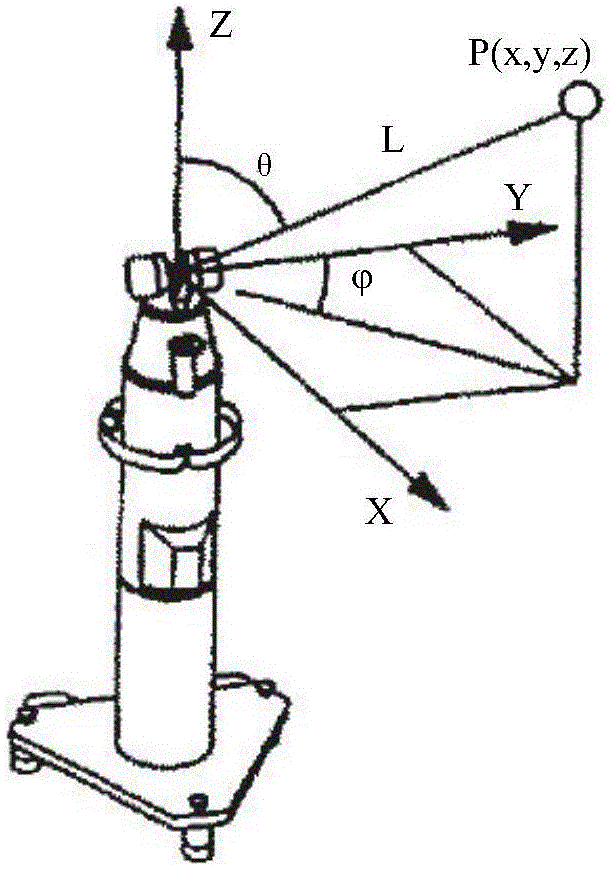
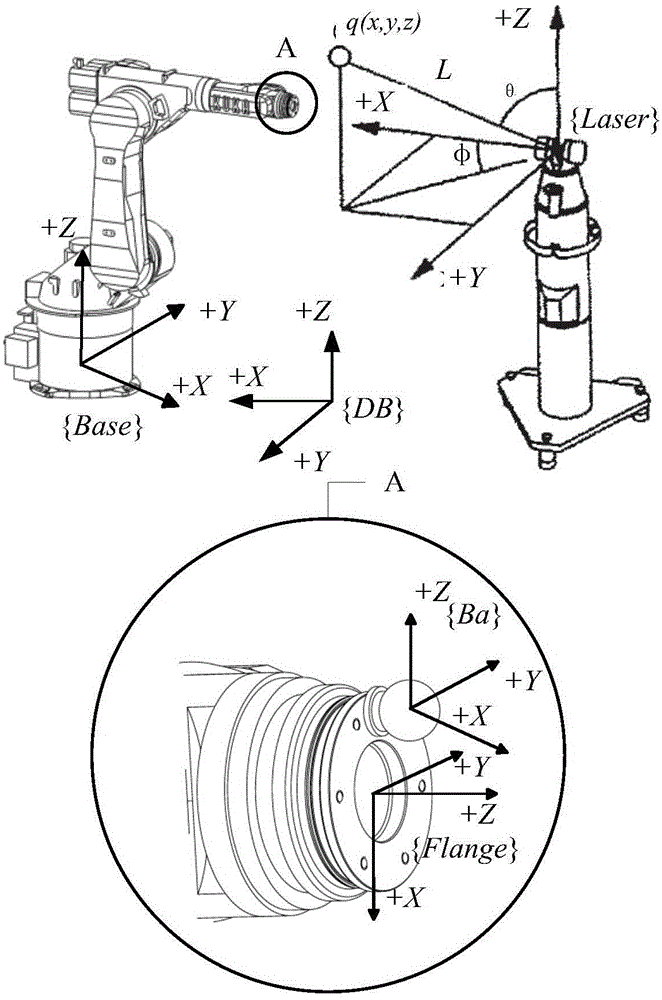
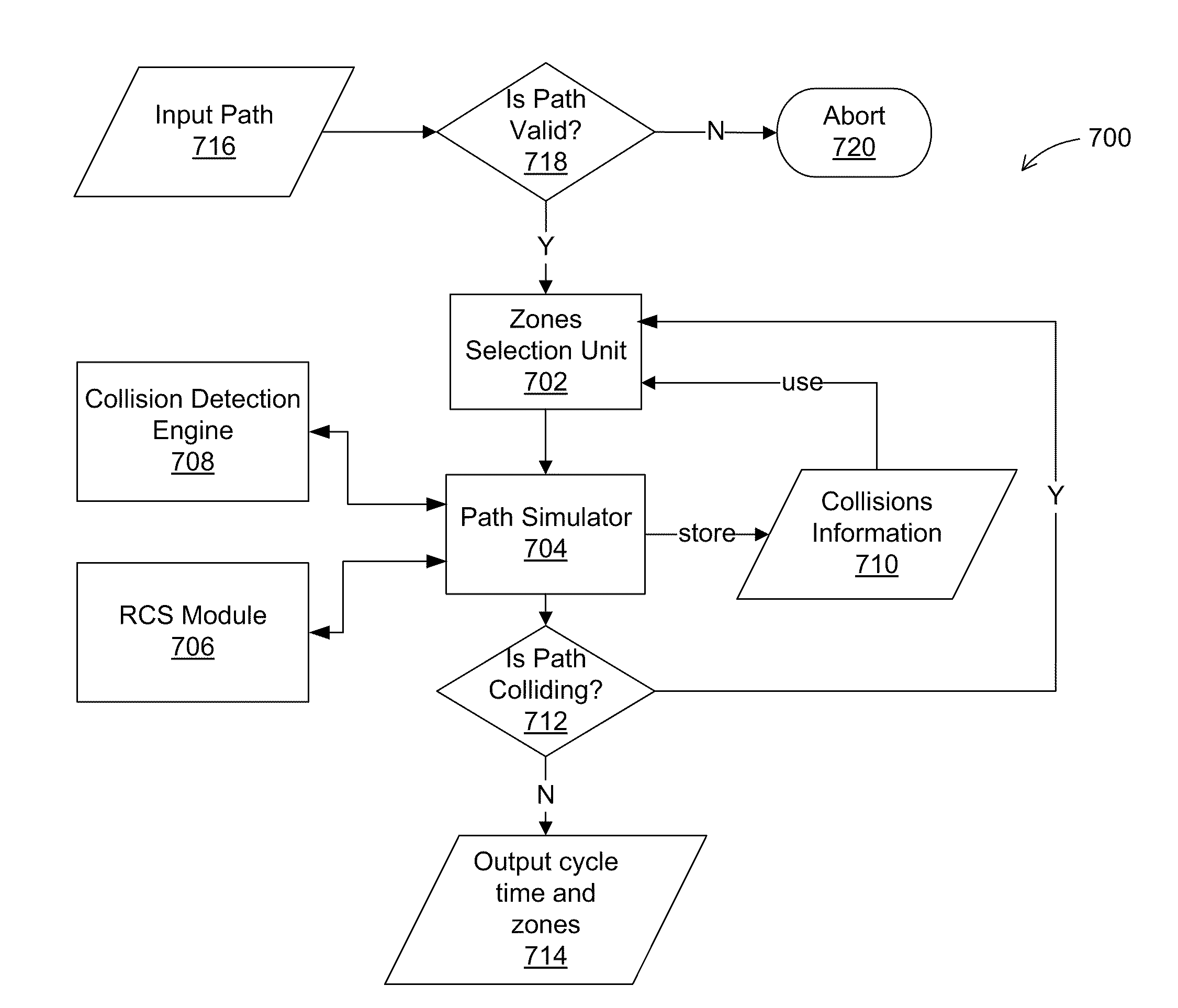
Method and apparatus for industrial robotic pathscycle time optimization using fly by
InactiveUS20110153080A1Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlAnalog robotPosition dependent
A system, method, and computer readable medium. A method for robotic path planning includes receiving a robotic path for a robot and associating a plurality of zones with each location in the robotic path. The method also includes selecting for each location one of the zones associated with the location and simulating motion of the robot over the robotic path using the locations and selected zones. The method further includes determining whether a collision occurred in the simulated motion of the robot. The method still further includes, if there was a collision, identifying a location associated with the collision, selecting a new zone for the identified location other than the currently selected zone, and repeating the steps of simulating motion of the robot and determining whether a collision occurred. The method also includes, if there wasn't a collision, assigning to each location its currently selected zone.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
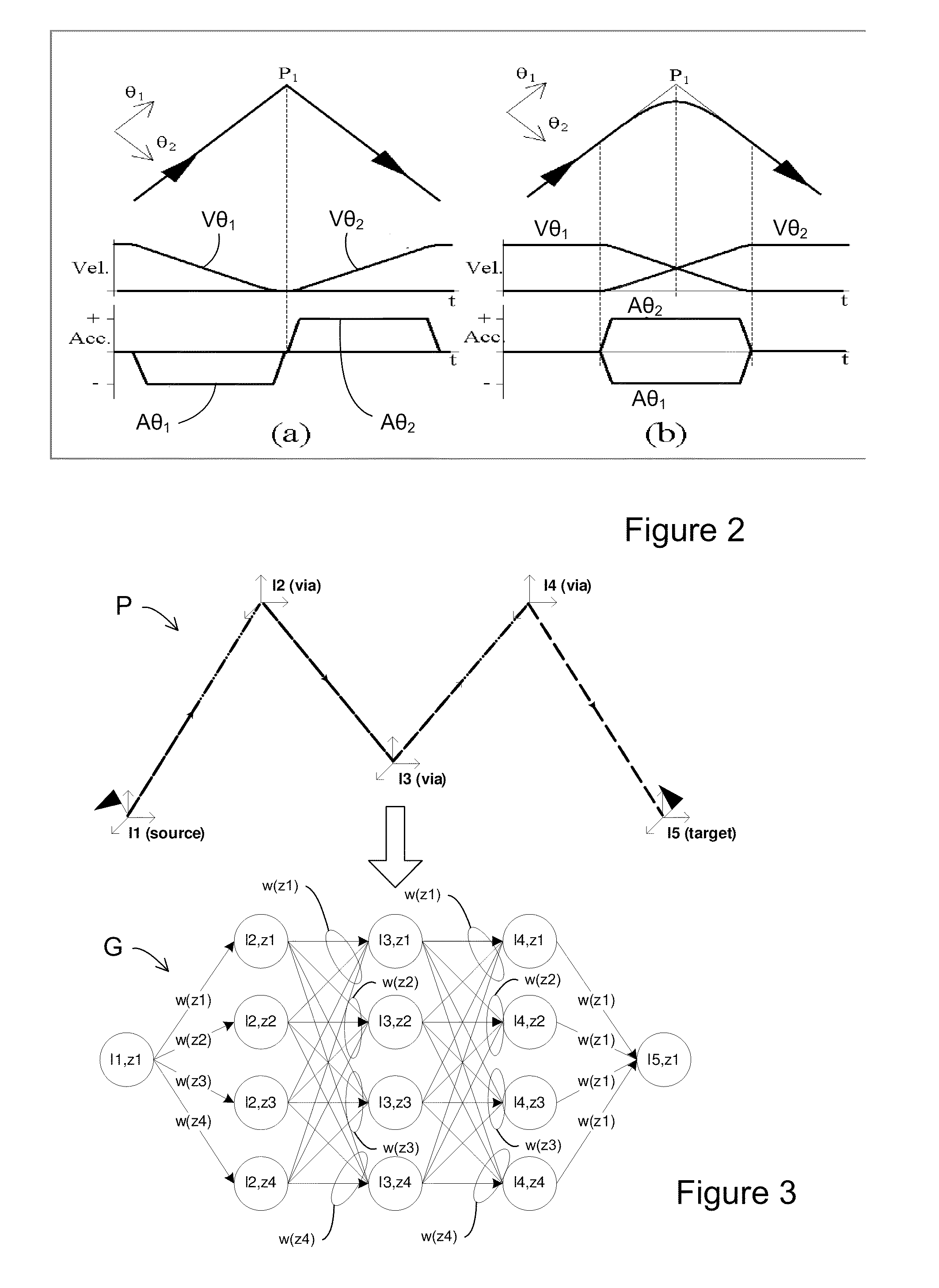
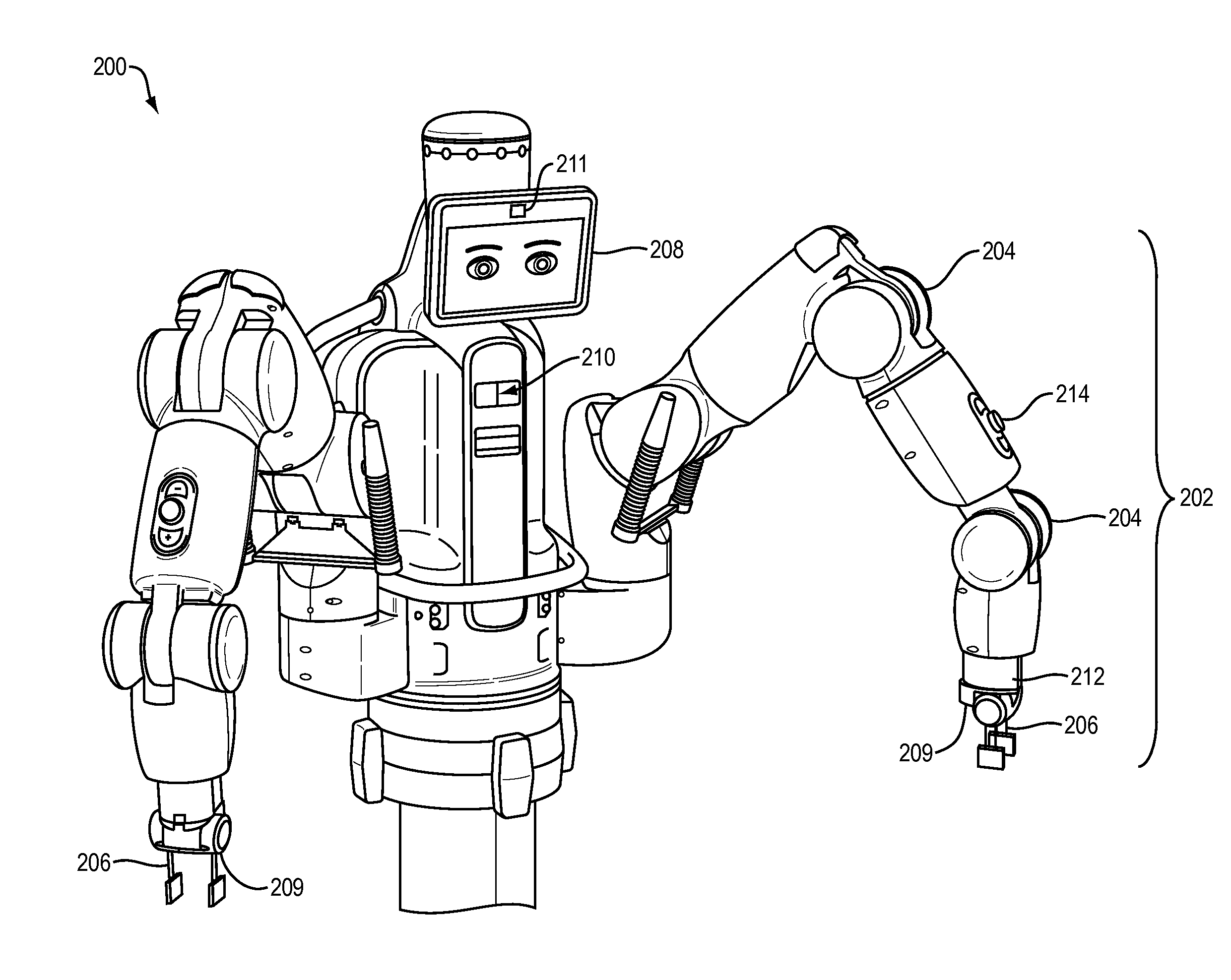
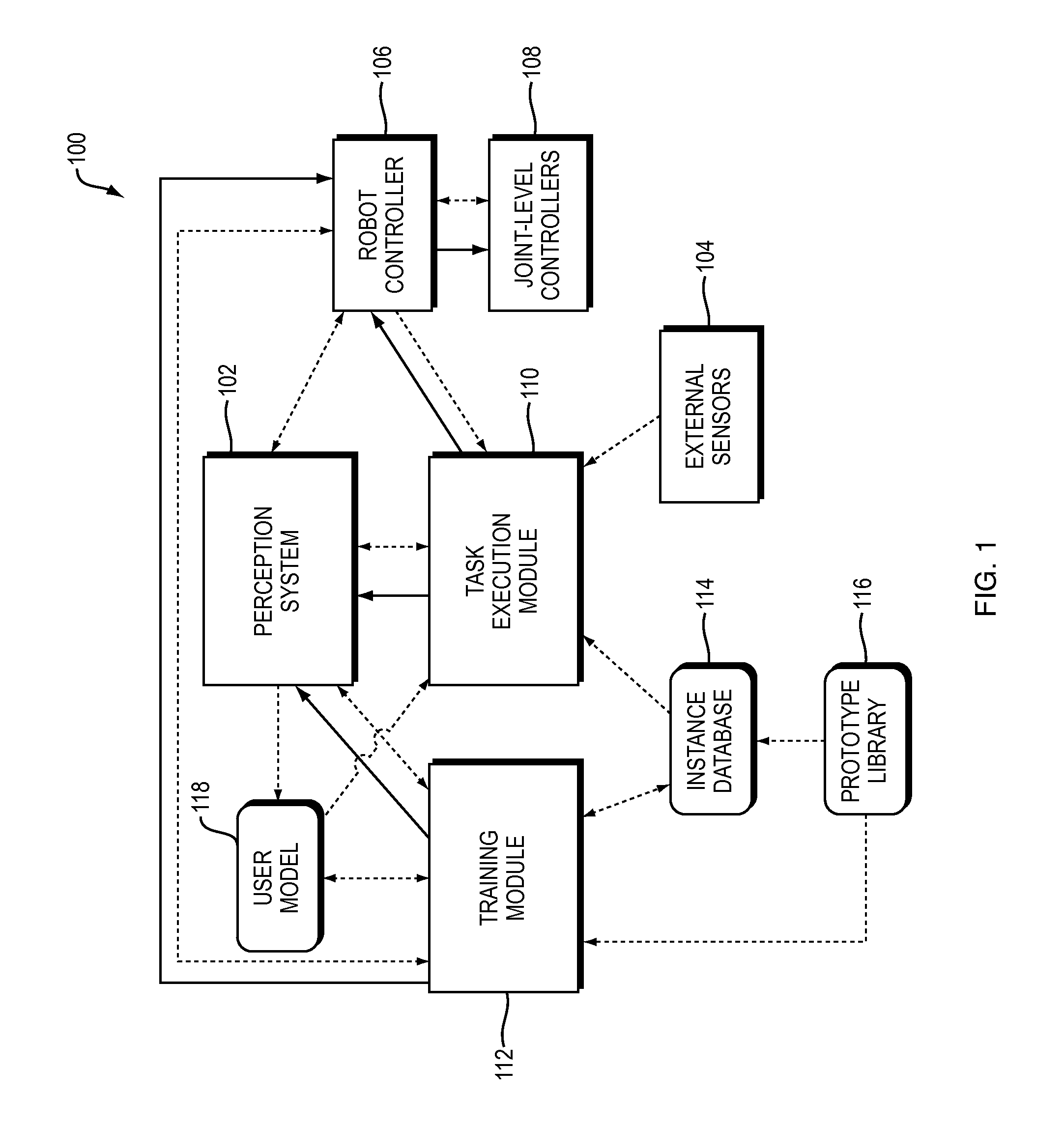
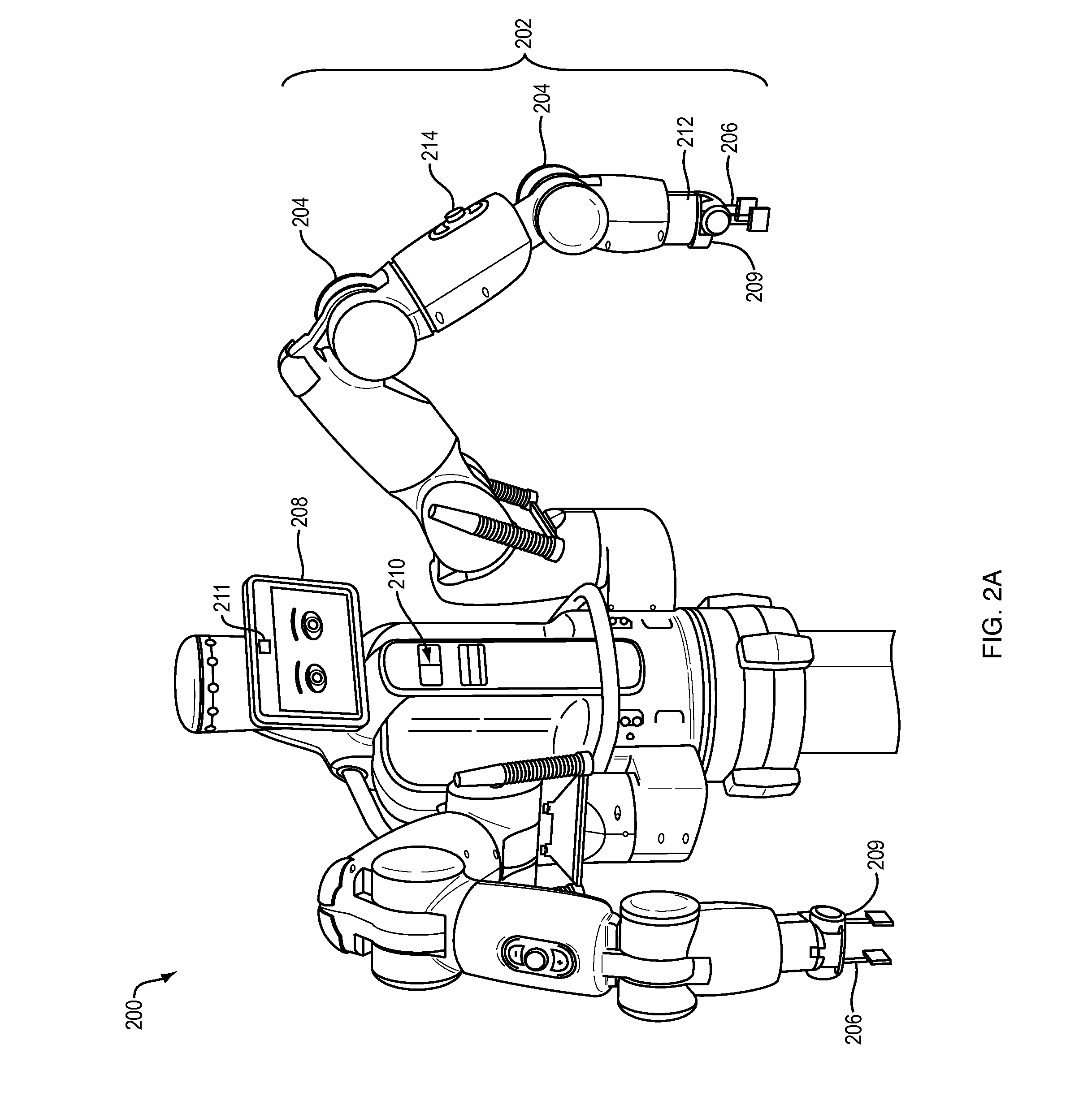
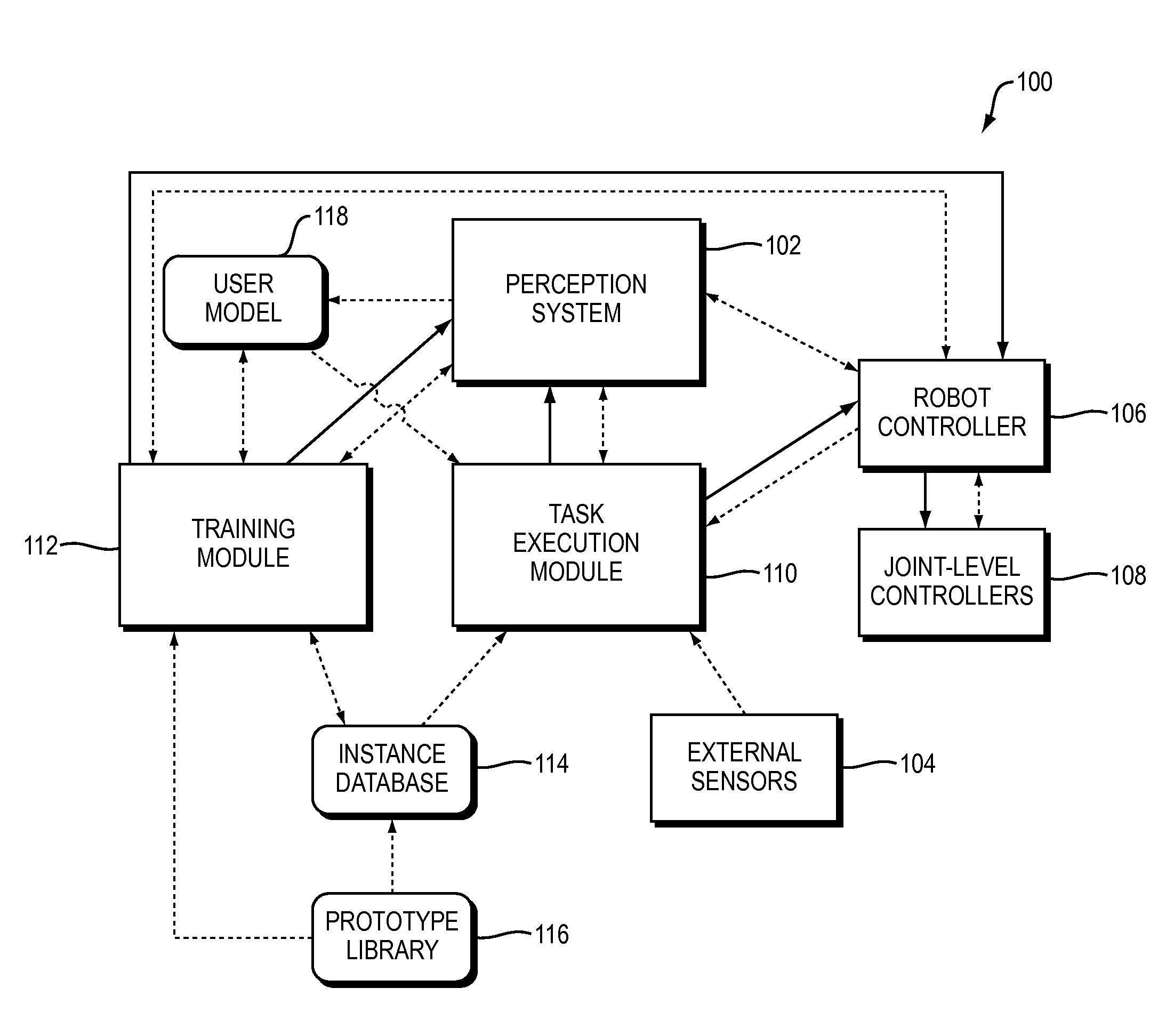
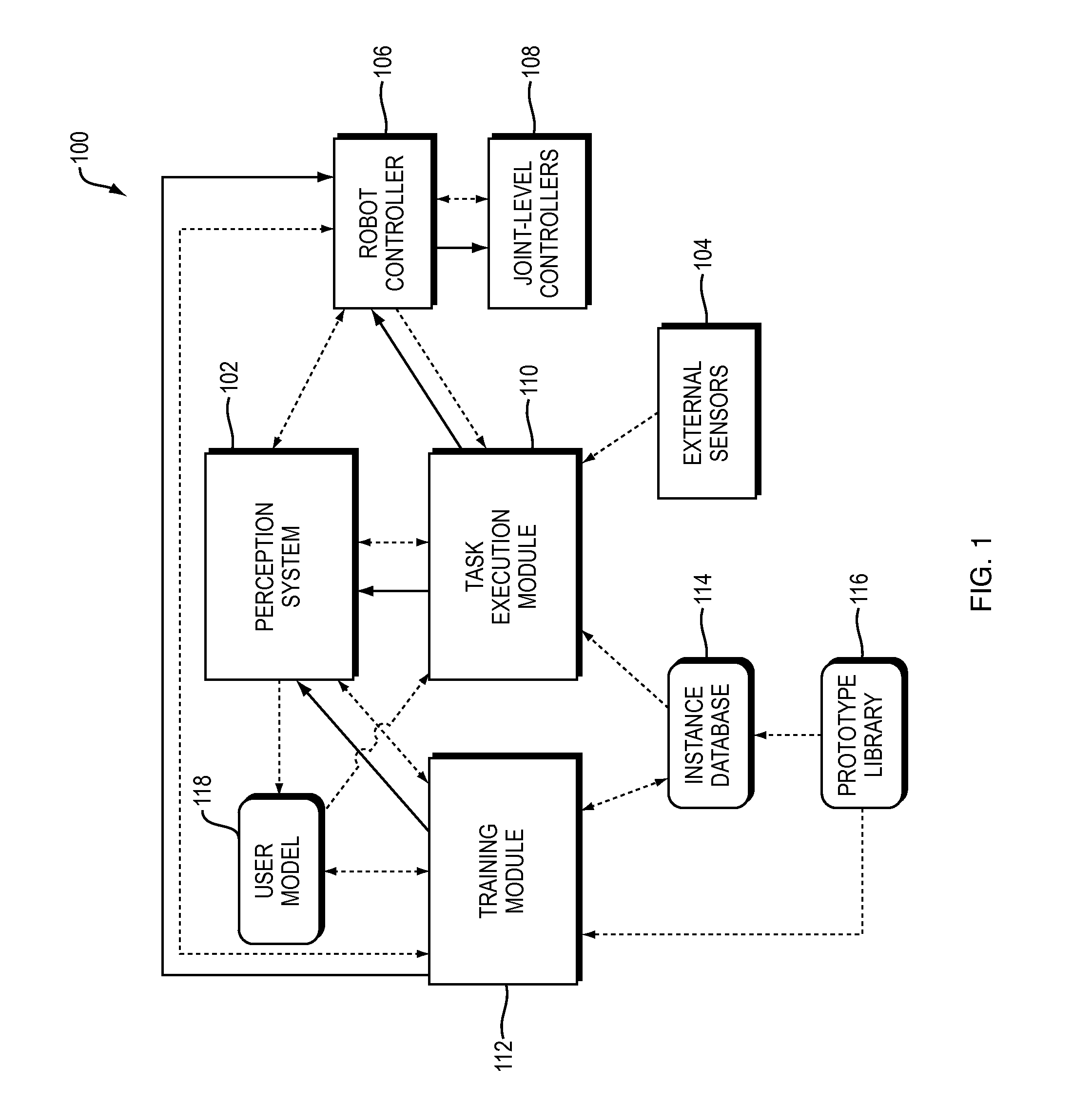
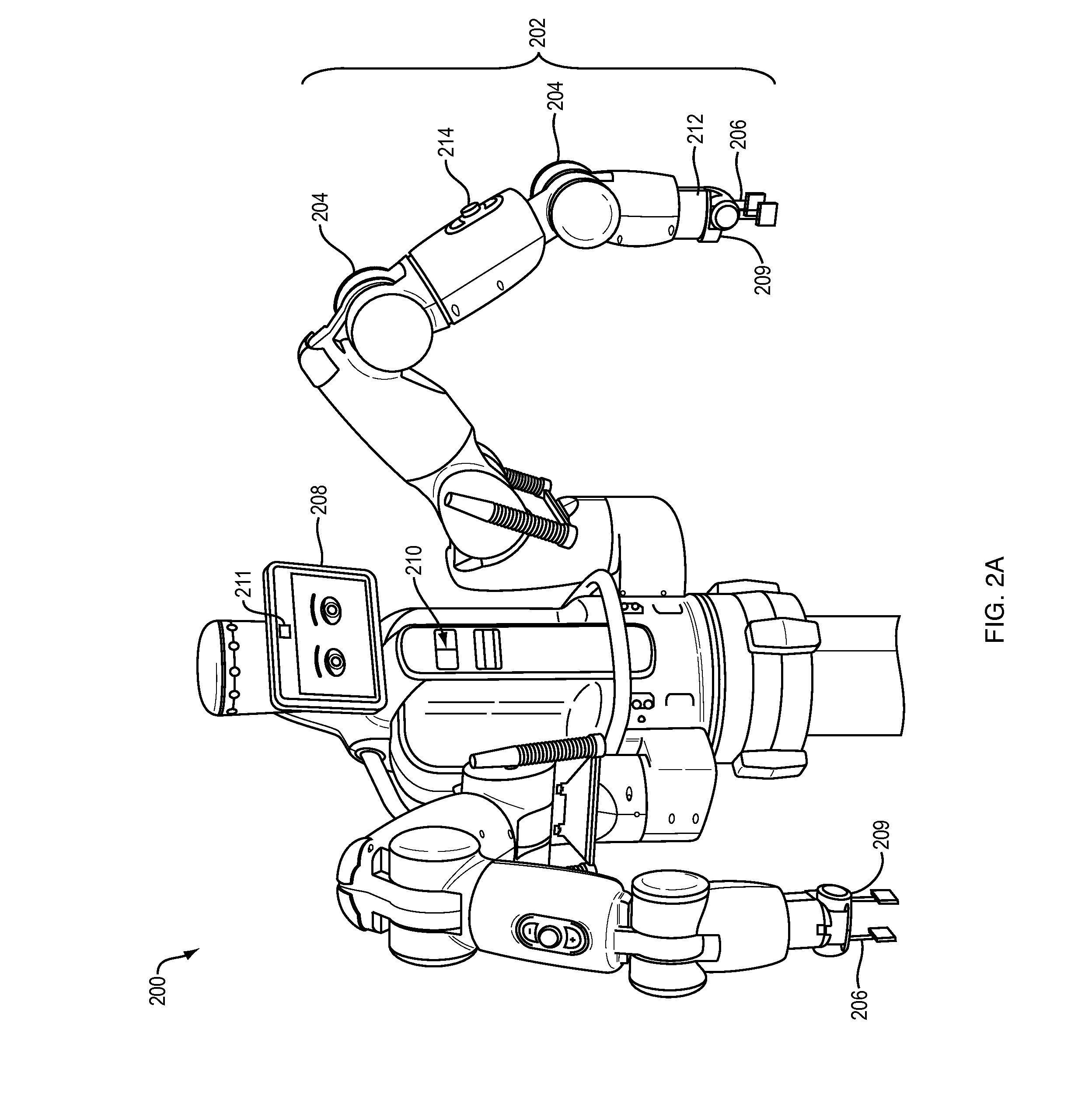
Training and operating industrial robots
ActiveUS20130345875A1Avoid collisionMoreProgramme-controlled manipulatorMathematical modelsObject basedSoftware engineering
Owner:RETHINK ROBOTICS
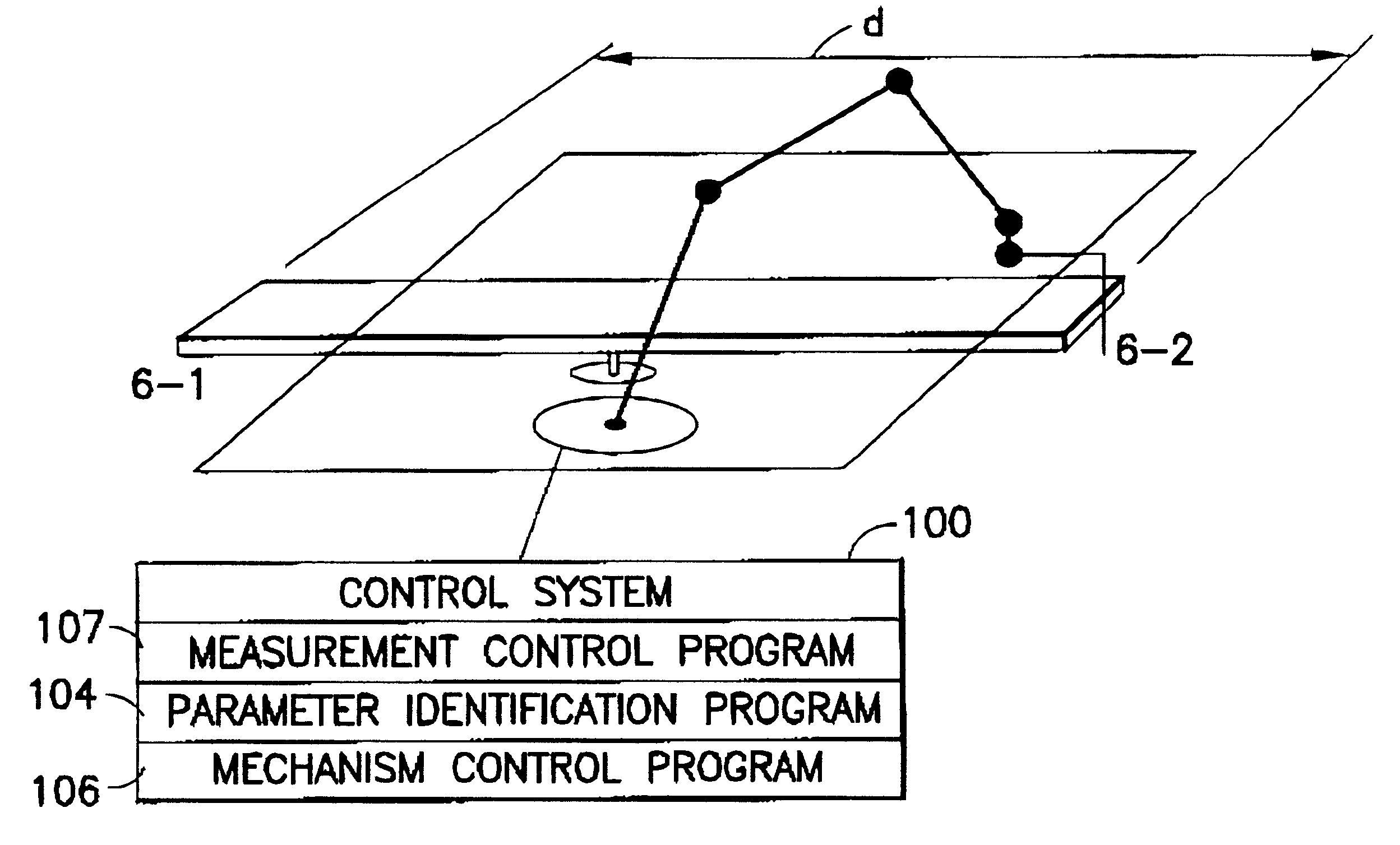
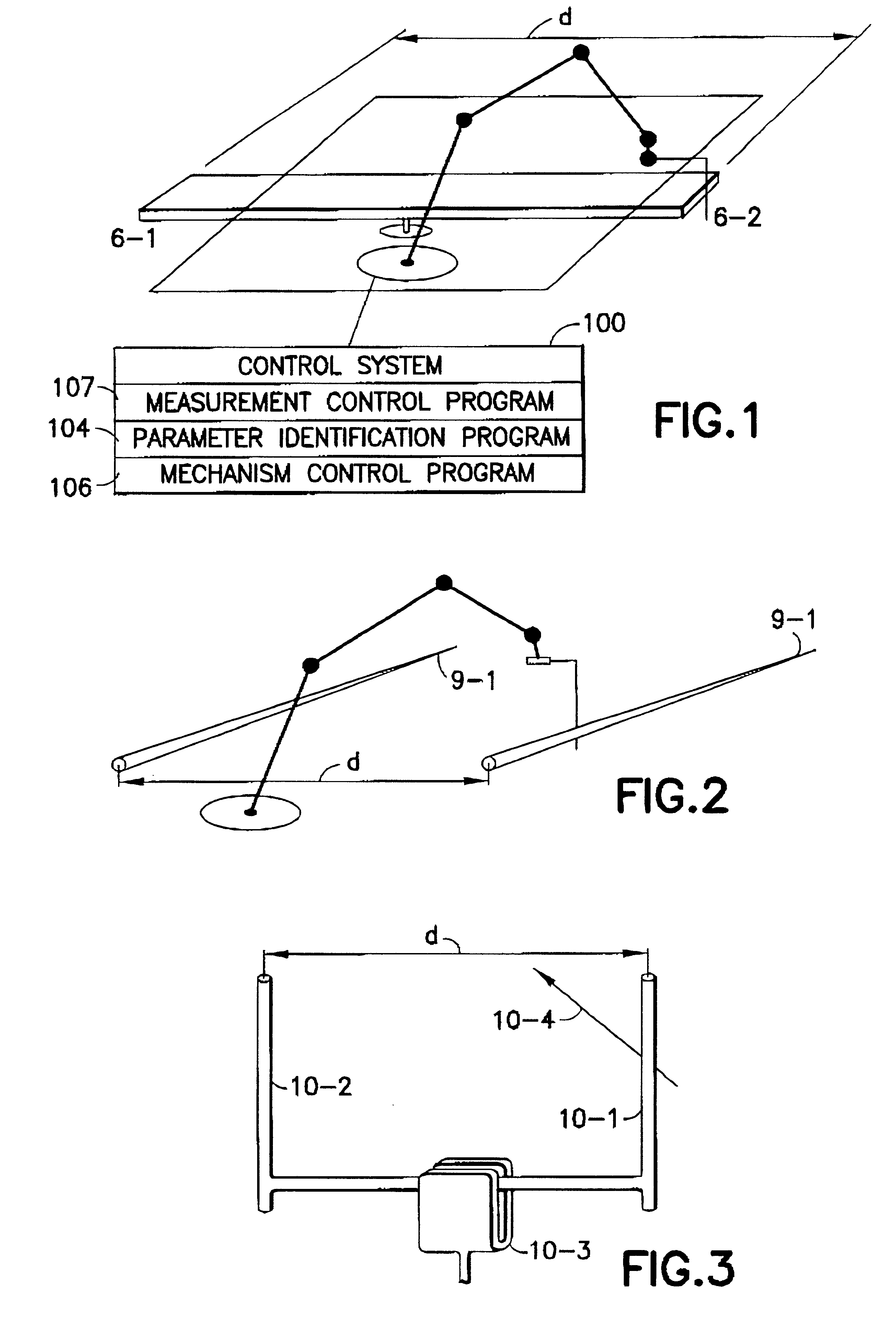
Method and device for the improvement of the pose accuracy of effectors on mechanisms and for the measurement of objects in a workspace
InactiveUS6529852B2Low costHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorMeasurement arrangements for variableInformation processingHyperboloid
A device and a method for measuring the pose of mechanisms includes at least one effector object fixedly joined to a mechanism (e.g., industrial robot, hexapod) in which the at least one effector object moves along one of several axes. The ideal, effective shape of the at least one effector object is a point, a straight line, a plane, an ellipsoid, a cylinder, a hyperboloid or a combination thereof. The movable effector objects interact with reference objects which are arranged in defined positions relative to the mechanism. The interactions are detected by a suitable sensor. The interactions are detected, only the pertaining joint configuration of the mechanism is transmitted to the information processing unit and evaluated and no further continuous values of measuring parameters are required for the evaluation.
Owner:KNOLL ALOIS +1
Training and operating industrial robots
ActiveUS20130345873A1Avoid collisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorMathematical modelsObject basedSoftware engineering
Owner:RETHINK ROBOTICS
Industrial robot
ActiveUS20050129495A1Demand accuracy of controlReduce demandProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusControl theoryControl unit
An industrial robot including a platform arranged for carrying an object. A first arm is arranged for influencing the platform in a first movement and includes a first actuator having a first path and a first carriage linearly movable along the first path. A second arm is arranged for influencing the platform in a second movement, and includes a second actuator having a second path and a second carriage linearly movable along the first path. A third arm is arranged for influencing the platform in a third movement. A control unit controls the movements of the platform. The first and second arms are arranged rotatable in such way that the platform is movable between opposite sides of a second plane passing through and continuously following the first and second carriage. The control unit includes a control adapted to upon command perform a reconfiguration of the platform and the arms of the robot. The reconfiguration includes moving the platform between opposite sides of the second plane.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Unmanned intelligent intensive storage managing method and storage system
Owner:南京萨菲机器人系统有限公司
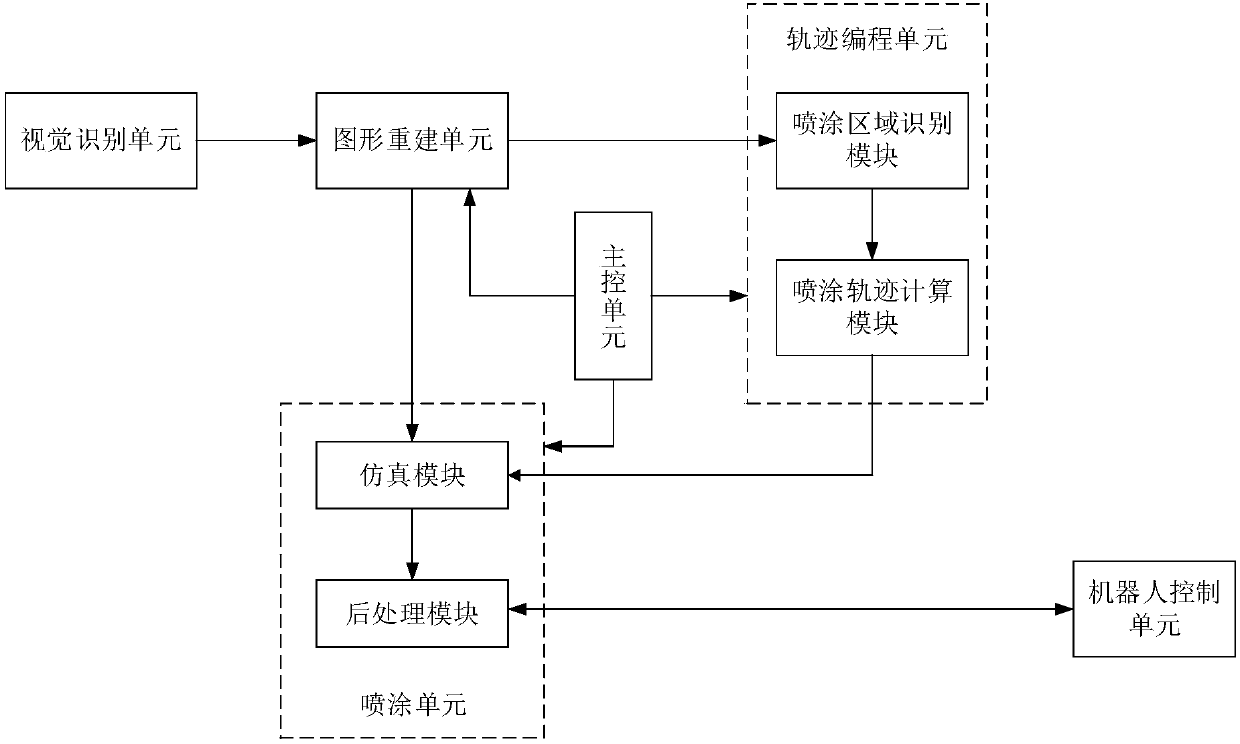
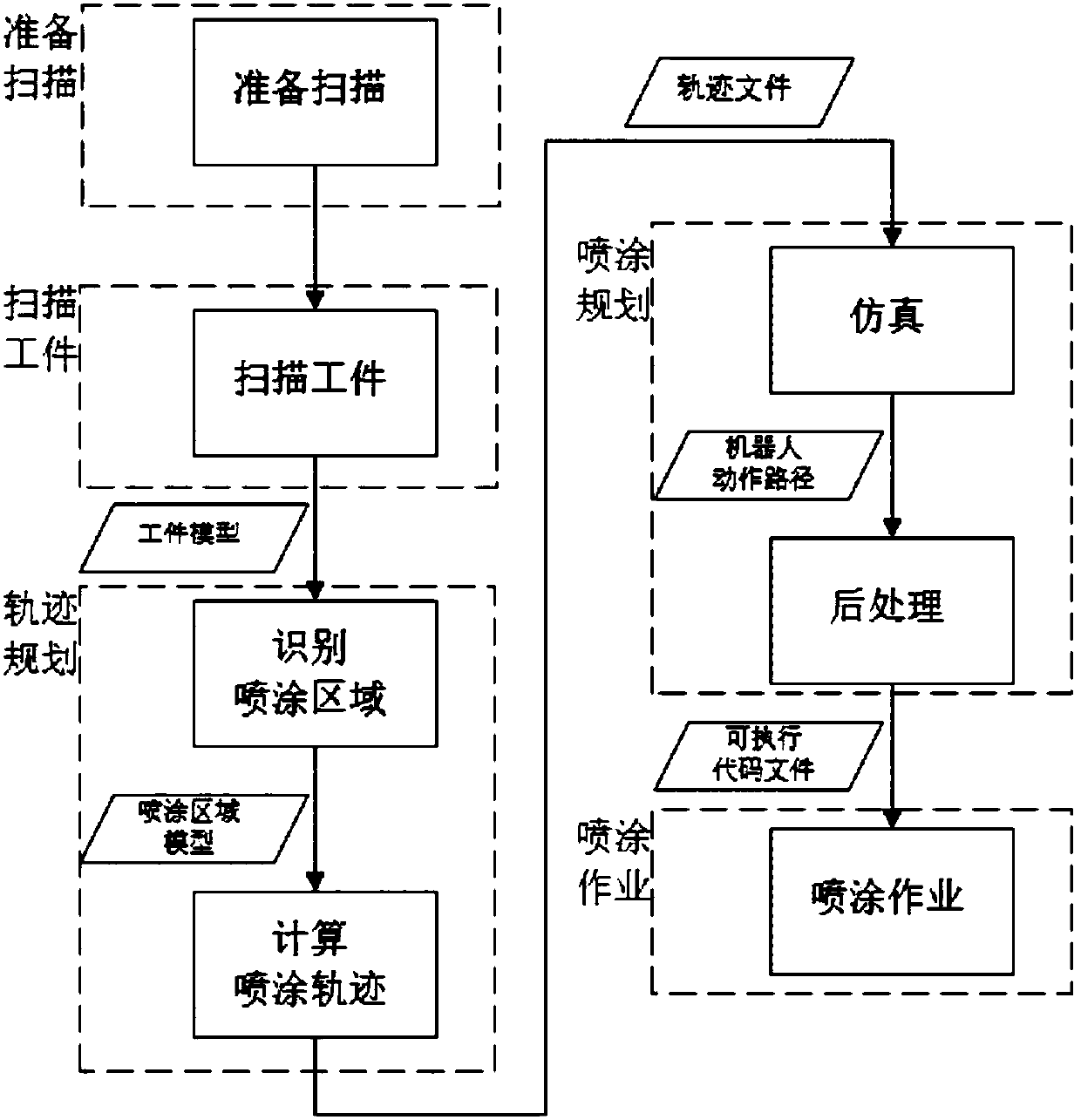
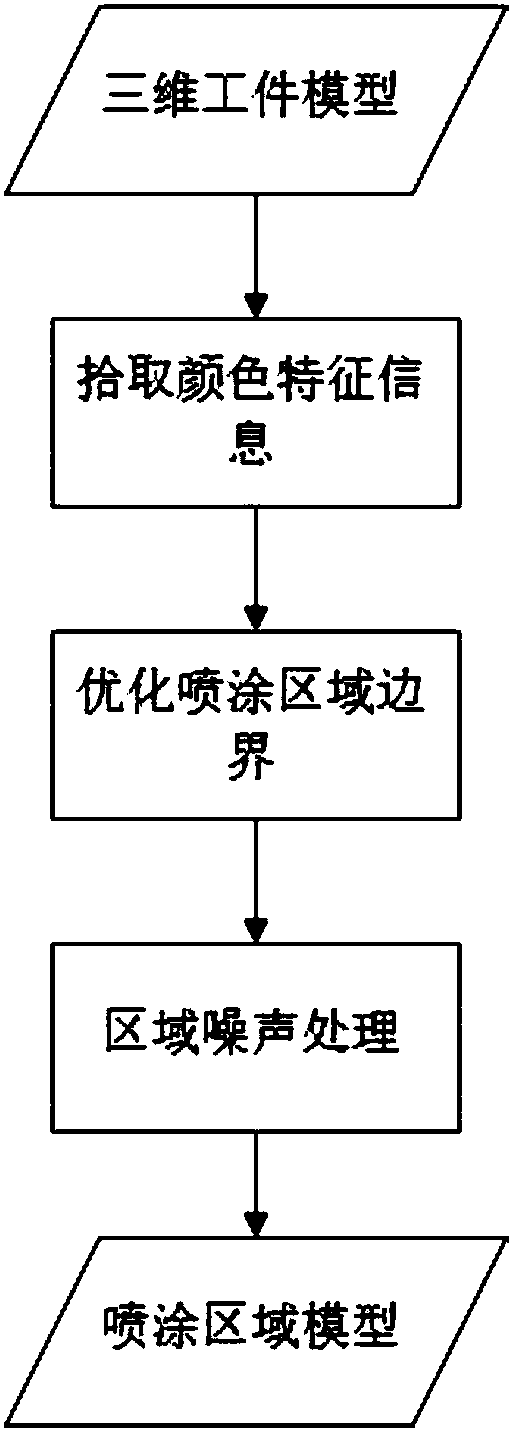
Mobile robot automatic spraying device and mobile robot automatic spraying control system and method
PendingCN107908152AImprove adaptabilityLess programming effortNumerical controlSimulationVisual perception
The invention discloses a mobile robot automatic spraying device and a mobile robot automatic spraying control system and method. The mobile robot automatic spraying control system comprises a visualrecognition unit, a main control unit, a graphic reconstruction unit, a trajectory programming unit, a spraying unit and a robot control unit, wherein the visual recognition unit performs processing on collected image information of a workpiece to obtain geometric information; the graphic reconstruction unit performs optimization processing on the geometric information of the workpiece to obtain agridding three-dimensional model of the workpiece; the trajectory programming unit automatically recognizes a spraying area and calculates a spraying trajectory strategy to obtain a spraying trajectory file; the spraying unit plans a spraying path according to a positional relation between the workpiece of a robot and the spraying trajectory file, and generates codes capable of being executed bythe robot; and the robot control unit controls the industrial robot to execute a spraying action according to the code file. According to the invention, a visual recognition based trajectory planningmethod is adopted, the spraying trajectory is automatically planned in allusion to a workpiece to be sprayed, the robot automatically completes the paint spraying work, the work flexibility is increased, and the programming workload is reduced.
Owner:苏州瀚华智造智能技术有限公司
Industrial robot comprising a portable operating unit which a movable key device for identification of the robot
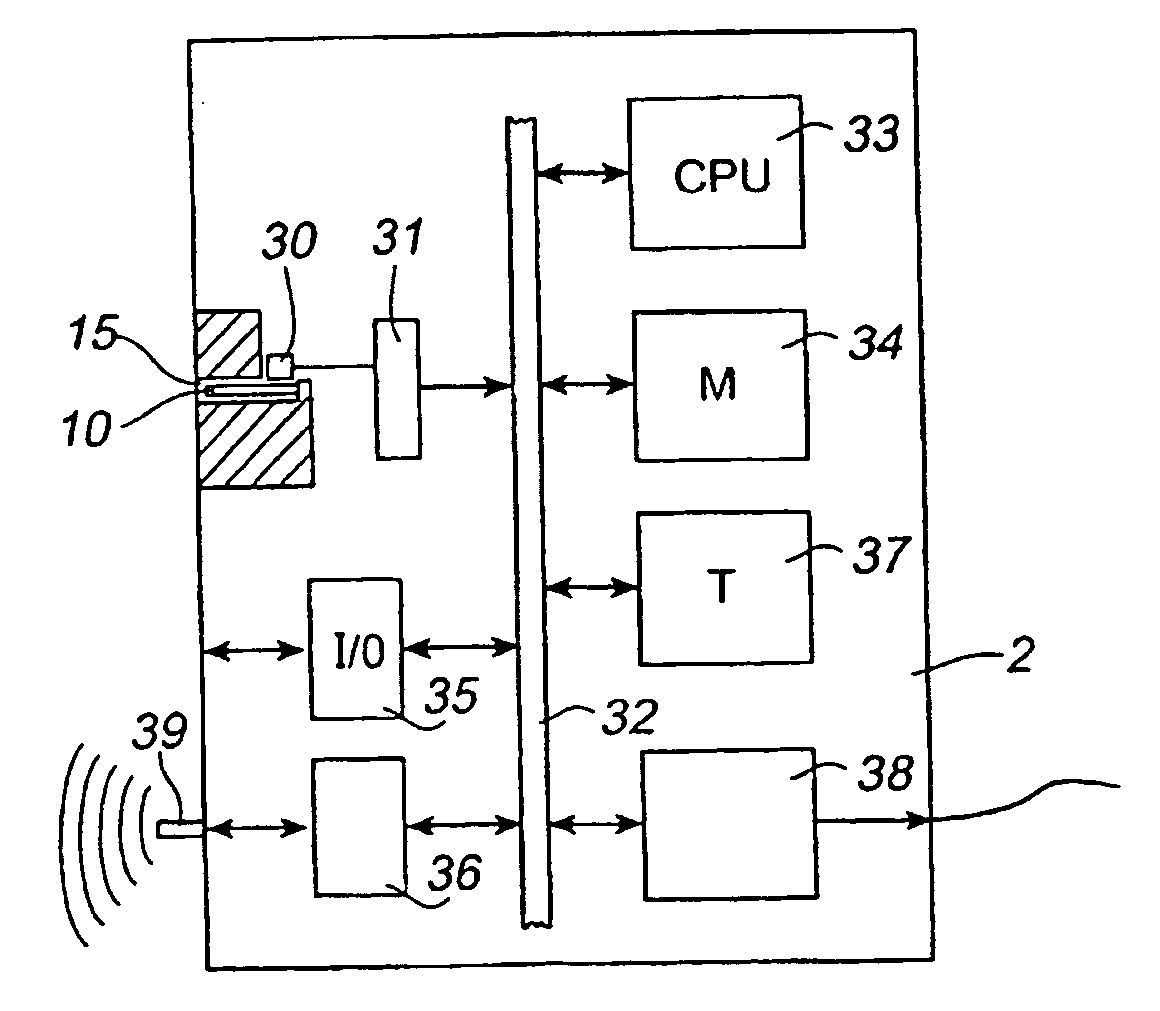
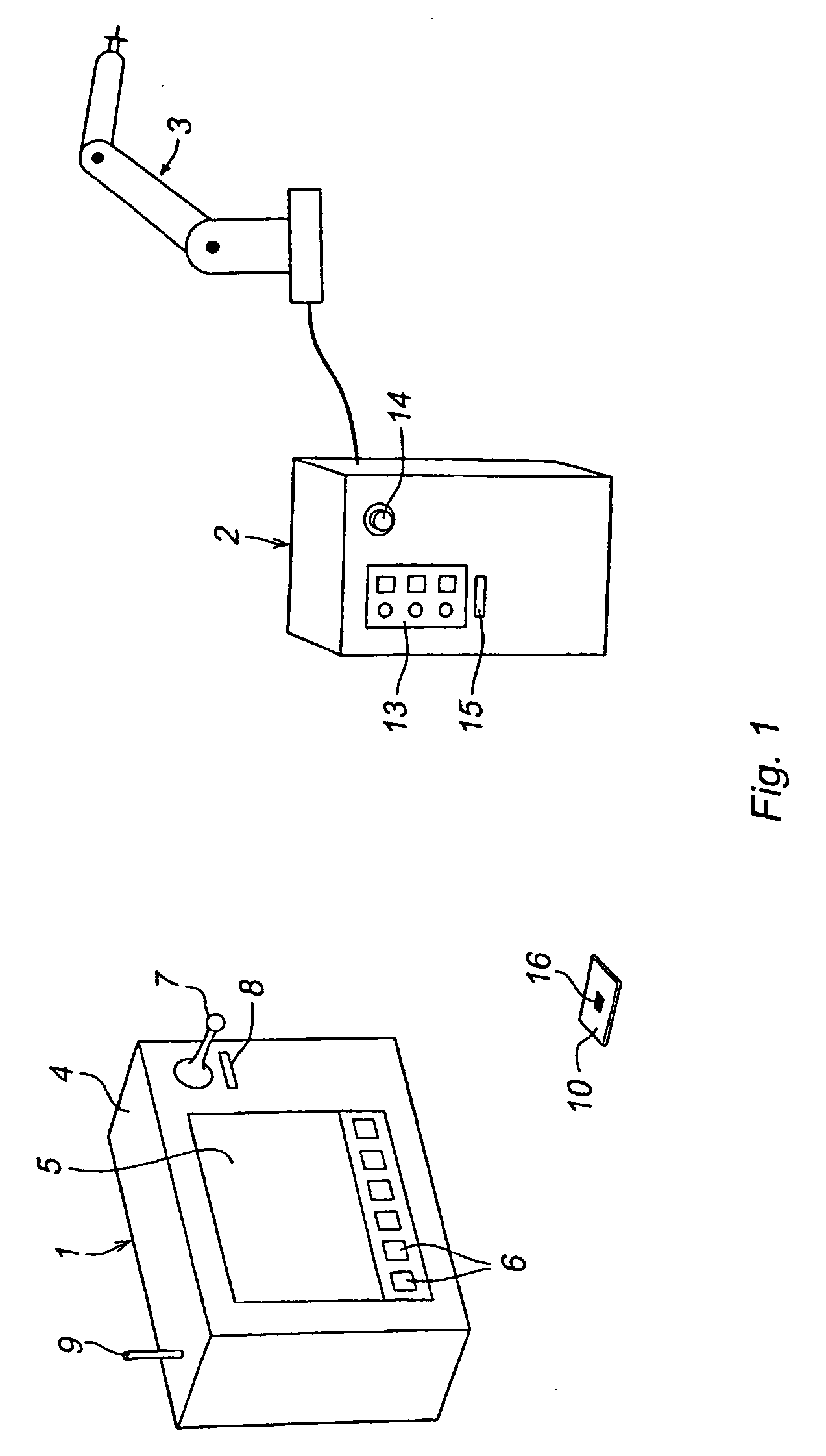
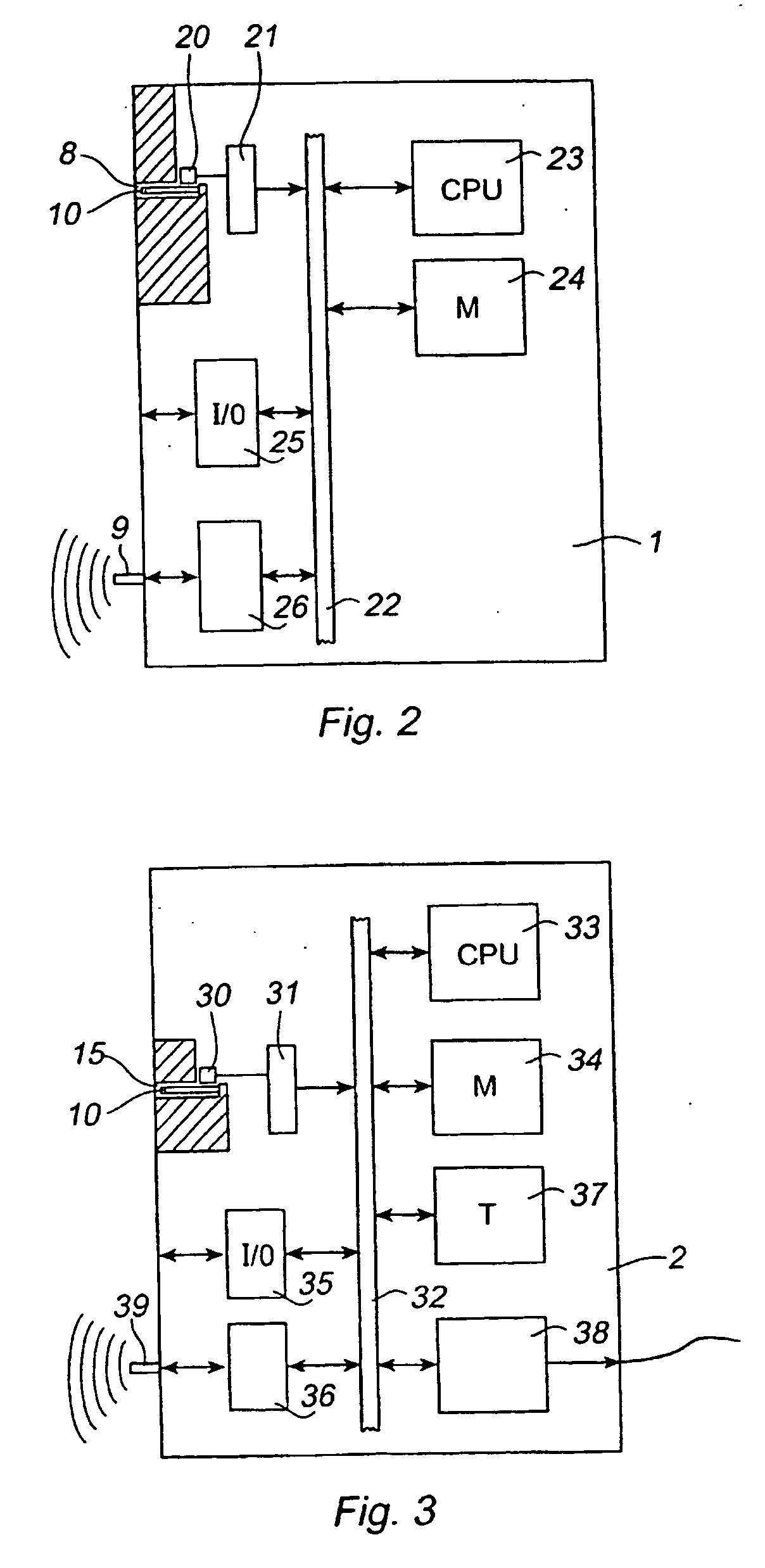
InactiveUS20040148058A1Mistakes due to the operator taking the wrong key device are preventedAvoid mistakesProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEmbedded systemManipulator
An industrial robot comprising a manipulator (3), a control unit (2) having means for automatically operating the manipulator, and a portable operating unit (1) having means for manually operating the manipulator. The robot further comprises a movable key device (10) carrying information about the identity of the robot and said portable operating unit (1) comprising a member (8) for receiving said movable key device and means for reading the robot identity from the key device.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
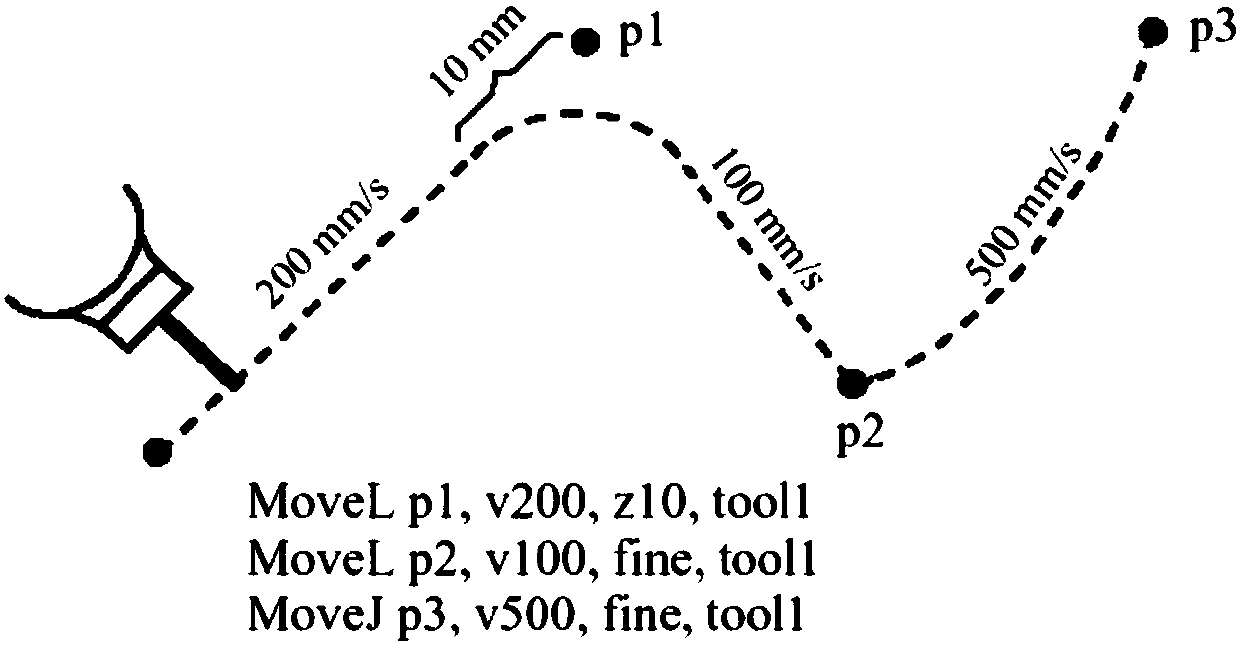
Error-controllable industrial robot fairing movement track generation method
ActiveCN106826829AImprove accuracyFulfil requirementsProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer scienceRobot trajectory
The invention discloses an error-controllable industrial robot fairing movement track generation method which comprises the following steps: S1, generating an MOVEB movement instruction, describing an industrial robot movement track which comprises a track point and posture, a track point error threshold input by a user, and a chord height error threshold; S2, performing interpolation on a robot track point, namely performing interpolation on a high-order B sample curve into the track point according to the track point error and the chord height error threshold by using the high-order B sample interpolation algorithm, and respectively achieving G2 interpolation and G3 interpolation of the robot track point, so as to obtain an interpolation track which has high continuity and meets the track point error and chord height error requirements; S3, performing interpolation on the posture of the robot so as to obtain a robot posture curve with sectional G2 and continuous G3; S4, acquiring a movement track of the robot after interpolation according to the track point interpolation curve and the robot posture curve. By adopting the error-controllable industrial robot fairing movement track generation method, real-time continuous interpolation of the movement track can be achieved, calculation can be simple, efficient and precise, and vibration and abrasion of the robot can be reduced.
Owner:武汉瀚迈科技有限公司
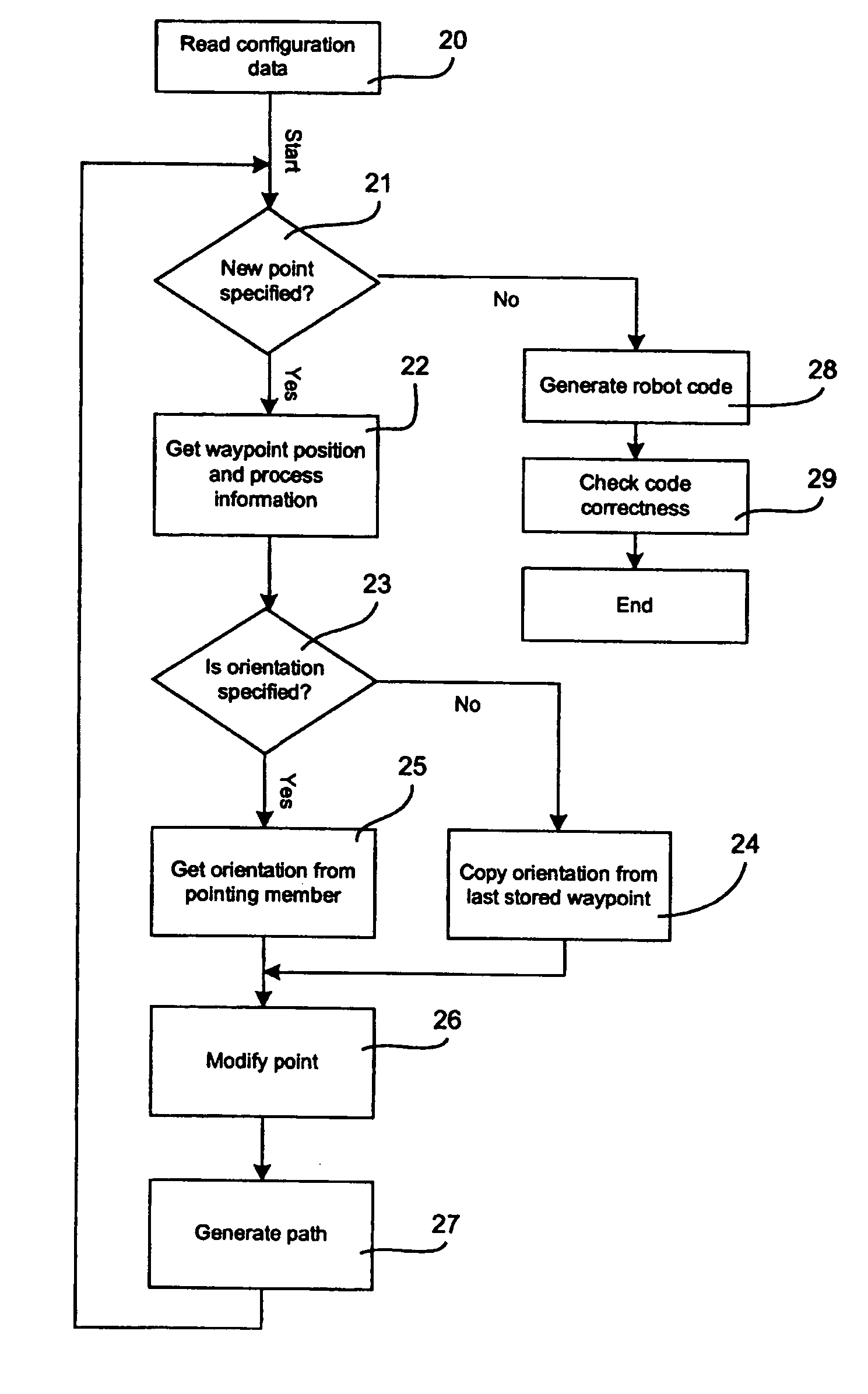
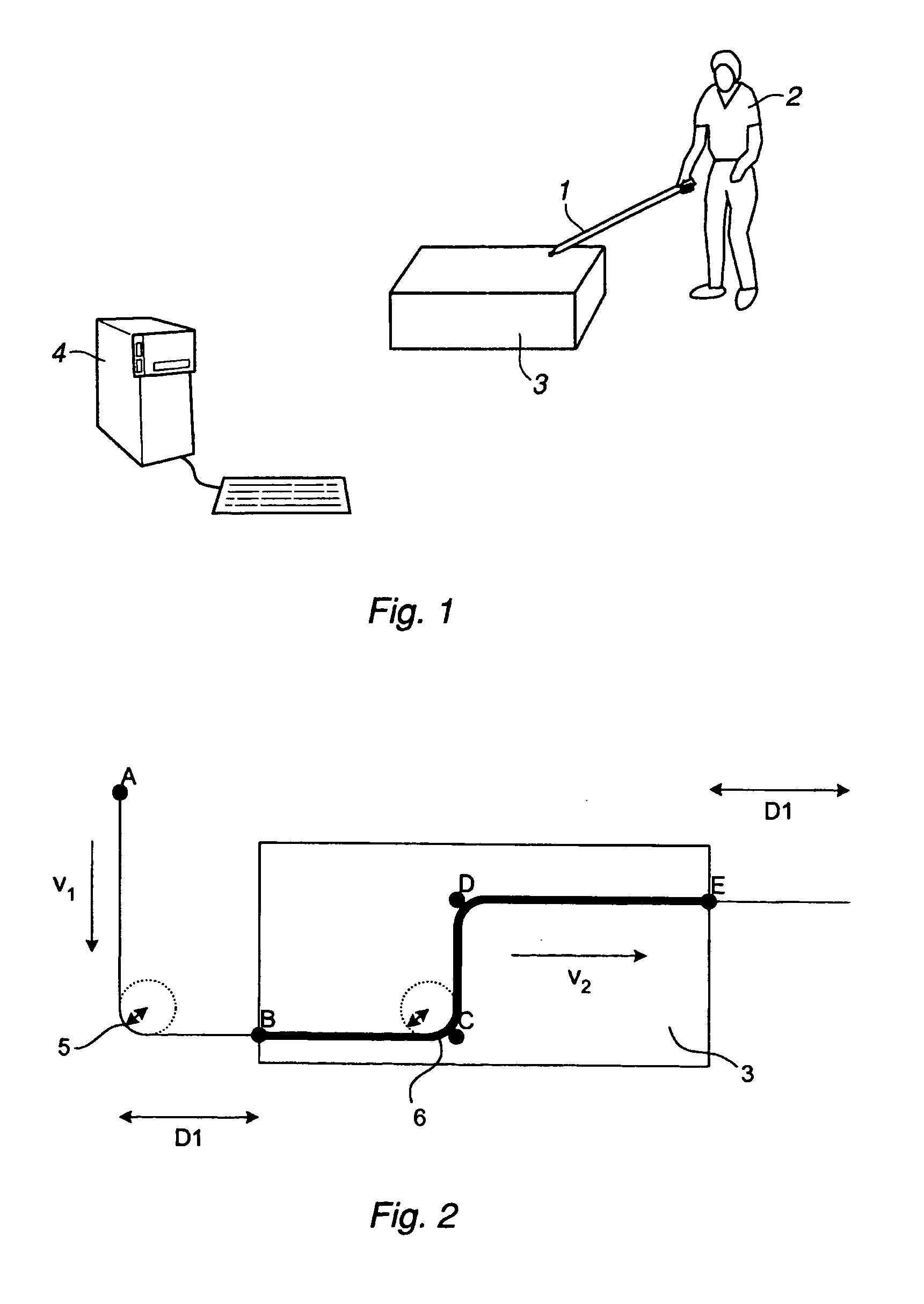
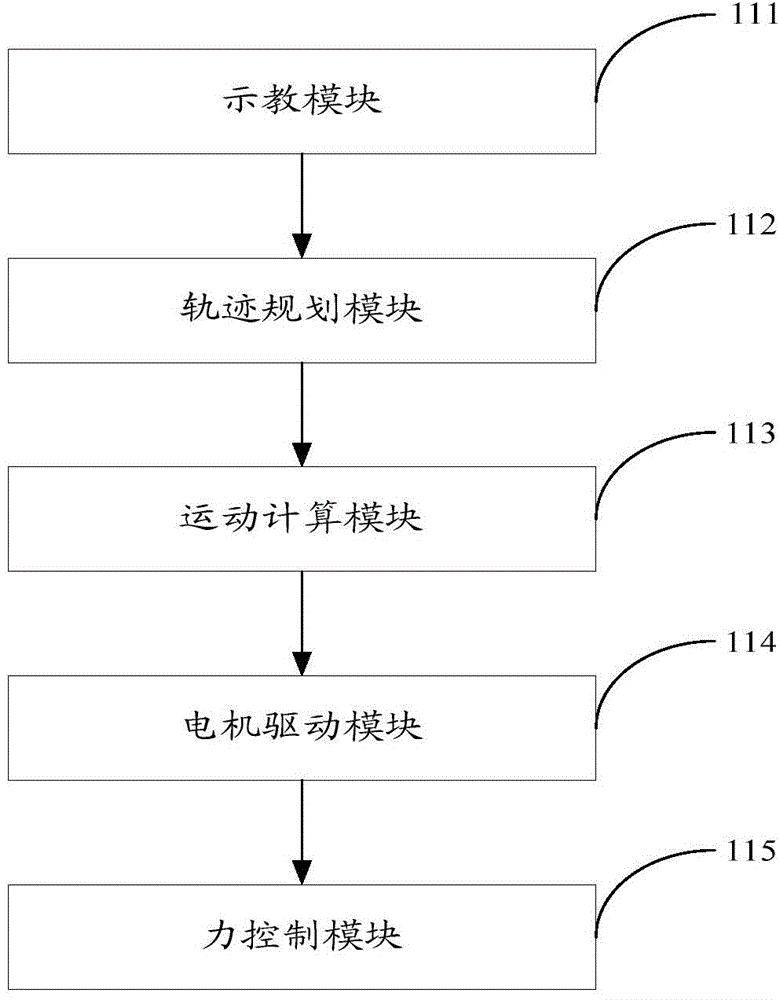
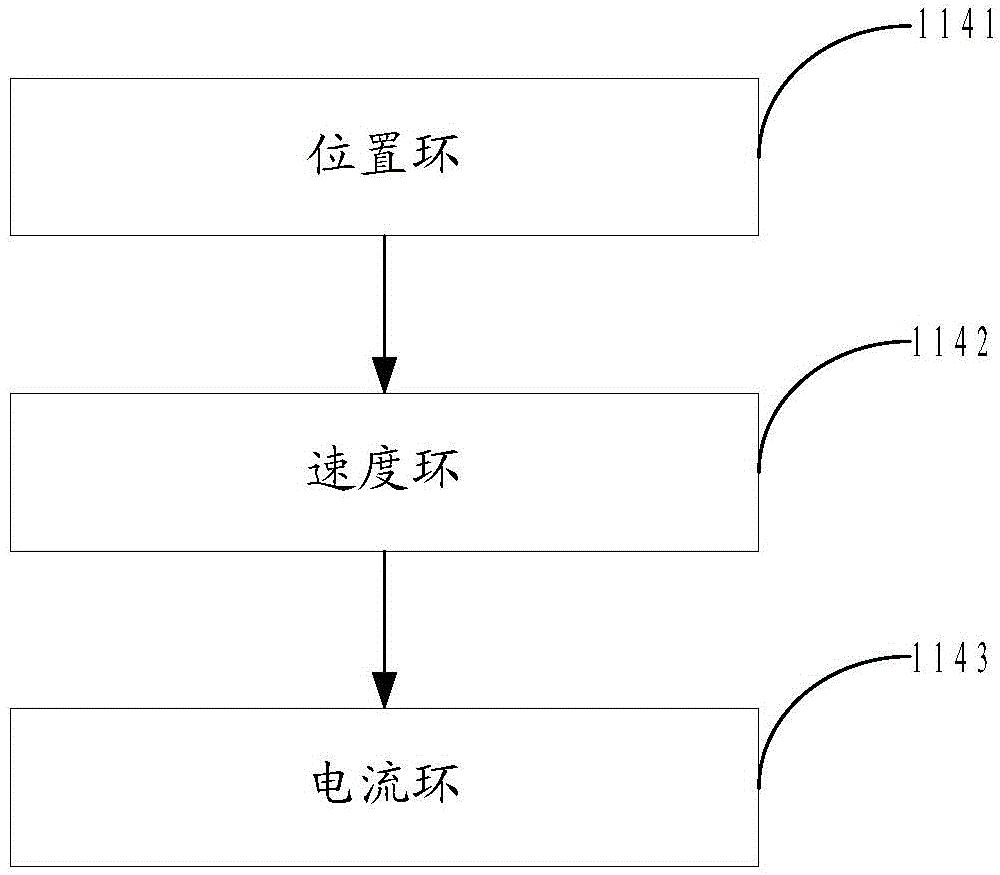
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
ActiveUS20040193321A1Shorten programming timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlComputer visionAlgorithm
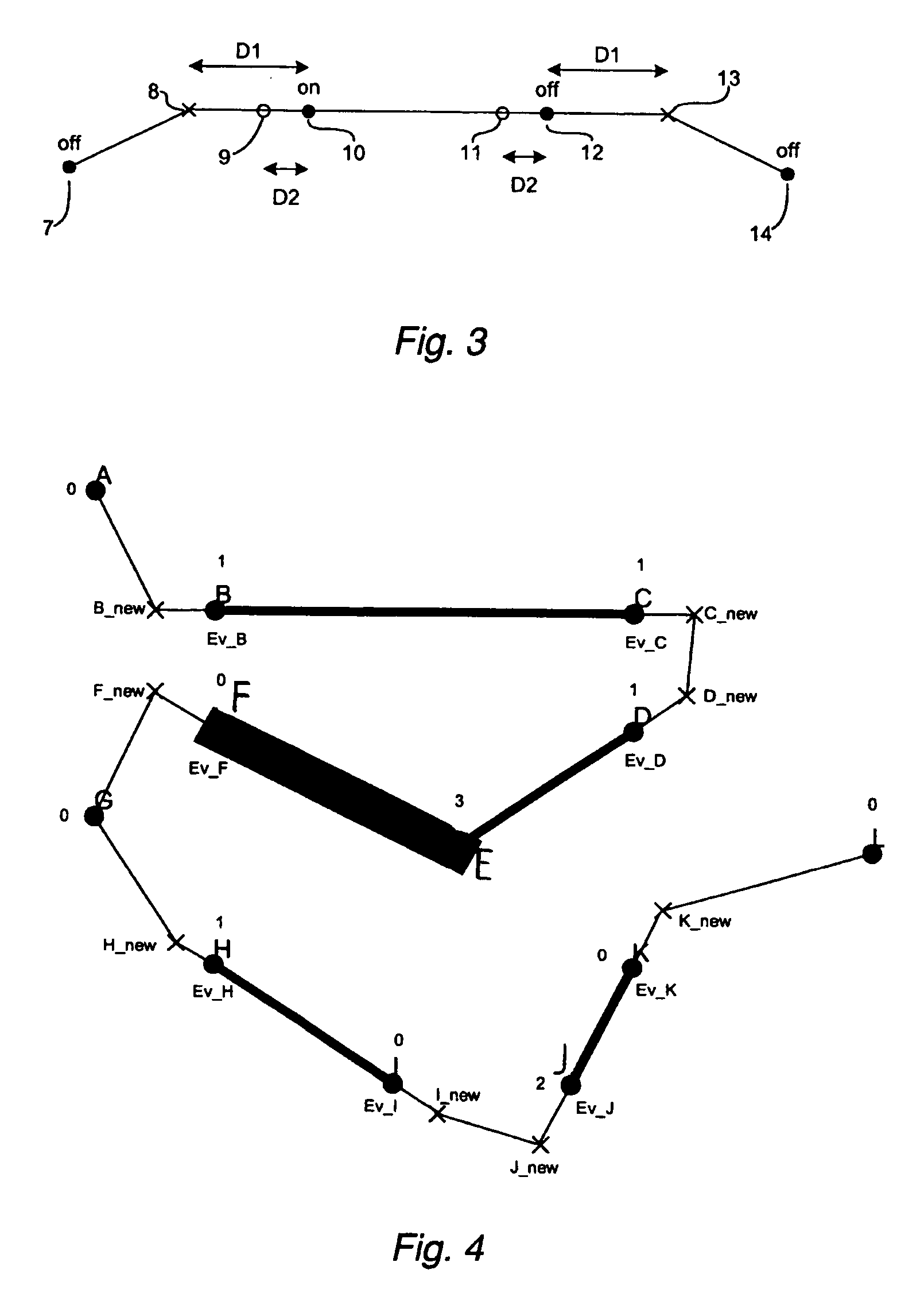
A method for programming an industrial robot having a tool, to perform a process on an object while following a robot path defined by a number of waypoints. The method comprises: obtaining configuration data including configuration data for the tool, configuration data for the robot path and information about the position and orientation of the object in relation to the robot, obtaining a sequence of waypoints, which defines the process in relation to the object, the waypoints comprises information about desired positions of the tool in relation to the object and desired positions of process events in relation to the object, obtaining at least one distance for adjusting the position of a waypoint, deciding whether an obtained waypoint should be modified or not, based on the obtained information about the waypoints, generating a modified sequence of waypoints by modifying the waypoints in the obtained sequence of waypoints, based on said decision, the obtained distance and the obtained information about the waypoints and generating the actual robot path based on the modified sequence of waypoints and the obtained configuration data.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
PSD (Position Sensitive Detector)-based industrial robot self-calibration method and device
InactiveCN102825602ASimple structureLow priceProgramme-controlled manipulatorUsing optical meansLight spotLaser beams
The invention discloses a PSD (Position Sensitive Detector)-based industrial robot self-calibration device, wherein two PSDs are arranged on two plates of a V-shaped clamp respectively; the V-shaped clamp is placed in an achievable range of a robot; when the robot is at different positions, a projection light spot and a reflection light spot of a laser beam emitted by a laser which is fixedly arranged at the tail end of the robot are positioned at positions of central points of the two PSDs respectively; and self-calibration of zero offset of the robot and self-calibration of a spatial posture are performed through two virtual constraint lines. The self-calibration device has a simple structure and is easy to mount and operate and high in positioning accuracy, and the self-calibration of the spatial posture and the zero offset of the robot can be simultaneously realized; and the invention also provides a PSD-based industrial robot self-calibration method.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Shaft hole assembly industrial robot system and working method thereof
ActiveCN104625676ARealize closed-loop controlImprove assembly accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorMetal working apparatusContact forceWorking set
The invention provides a shaft hole assembly industrial robot system which comprises an industrial robot, a shaft hole assembly platform, a force sense sensor, a clamping device, an assembly workpiece, an assembly hole and an assembly shaft. The shaft hole assembly industrial robot system can accurately control contact force and has the obvious advantages for assembly operation with the strict requirements for the small shaft hole interval, high accuracy and shaft hole contact force, the situation that assembly operation fails and even the assembly workpiece is damaged due to the fact that position control accuracy and contact force are not controllable in a position control mode is avoided, the problems of low efficiency and quality and the like caused by manual assembly in certain high-accuracy assembly operation are solved, and the application fields of the shaft hole assembly industrial robot are expanded.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
Industrial robot cutting and processing system applied to auxiliary assembly of airplane as well as method
InactiveCN101372079ARealize cutting functionMeet the machining accuracy requirementsMeasurement/indication equipmentsLarge fixed membersEngineeringLaser tracker
The invention discloses an industrial robot cutting processing system and a method applied to aircraft auxiliary assembly, comprising a six-axis joint typed industrial robot, a robot controller, an operation panel, a high speed electric mainshaft, a tool clamping process device, a tool quick exchanger, a target installation flange and a laser tracker; high speed cutting technique is adopted; process methods and hole preparing process of boring, reaming by milling and final reaming are sequentially carried out so as to improve the diameter precision of the hole; meanwhile, the cutting force can be controlled by finishing the reaming hole; rough milling is carried out firstly, fine milling is subsequently carried out; furthermore, the cutting depth is not more than 0.15mm during the fine milling process, thus ensuring the planeness of the processing surface; the industrial robot cutting processing system can realize various cutting processes of the soft metal (such as aluminium alloy) as follows: boring, hole enlarging, reaming, dimpling, surface milling, cutting, etc. The invention integrates normal robot, high speed electric mainshaft, quick exchanger, etc., and can solve the cutting process problems of operations such as fine processing, skin cutting, and the like of radar cover installation hole in the field of aircraft assembly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Grinding device for machine based grinding of rotor blades for wind energy systems
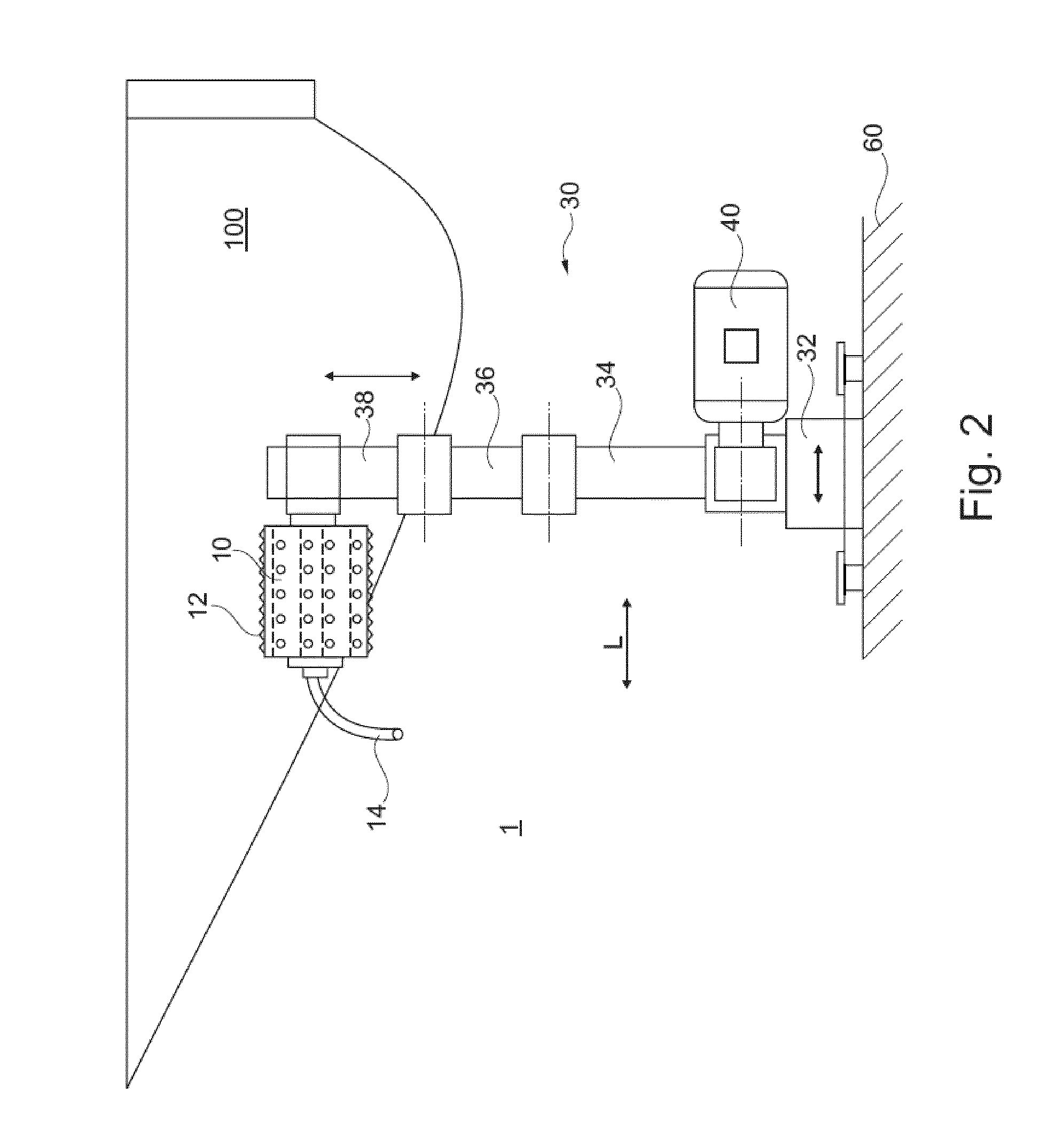
InactiveUS20120322349A1Life time of the grinding means is increasedLow investment costEdge grinding machinesSupport wheelsIndustrial machinePulp and paper industry
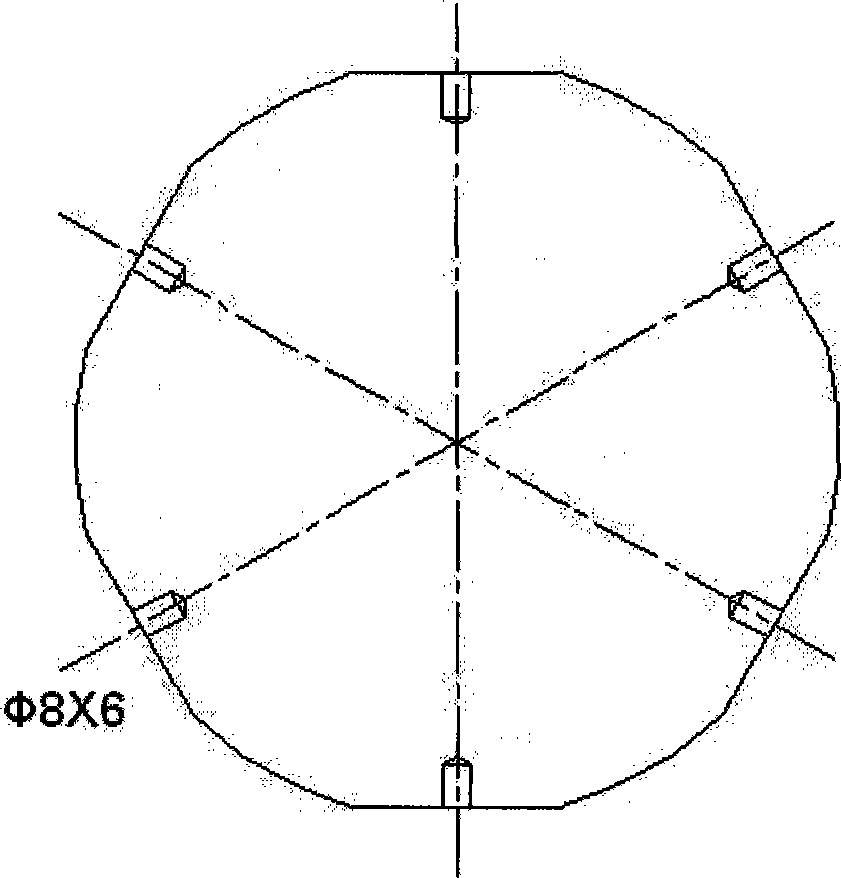
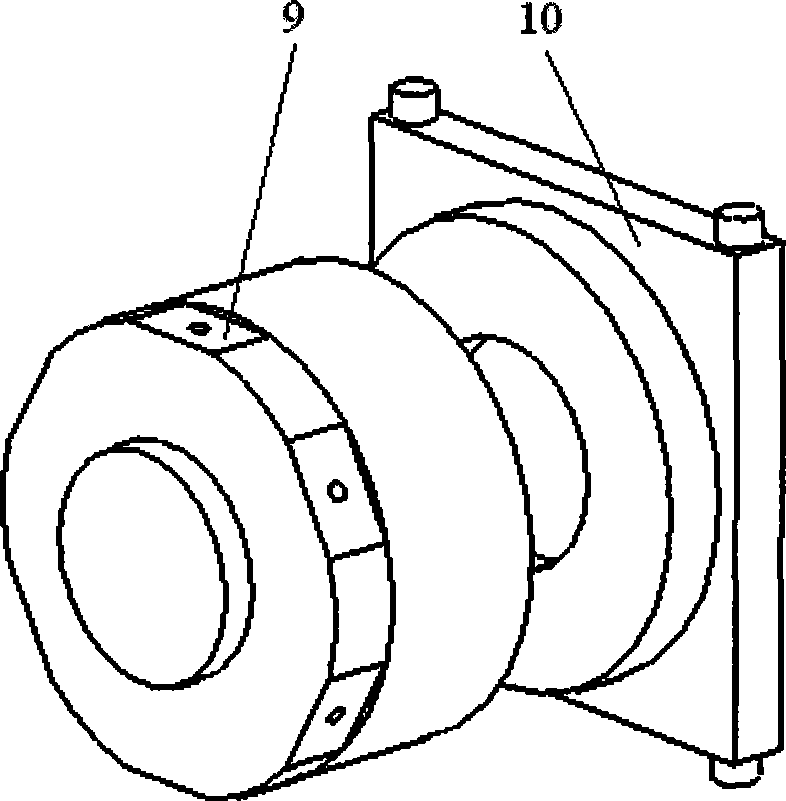
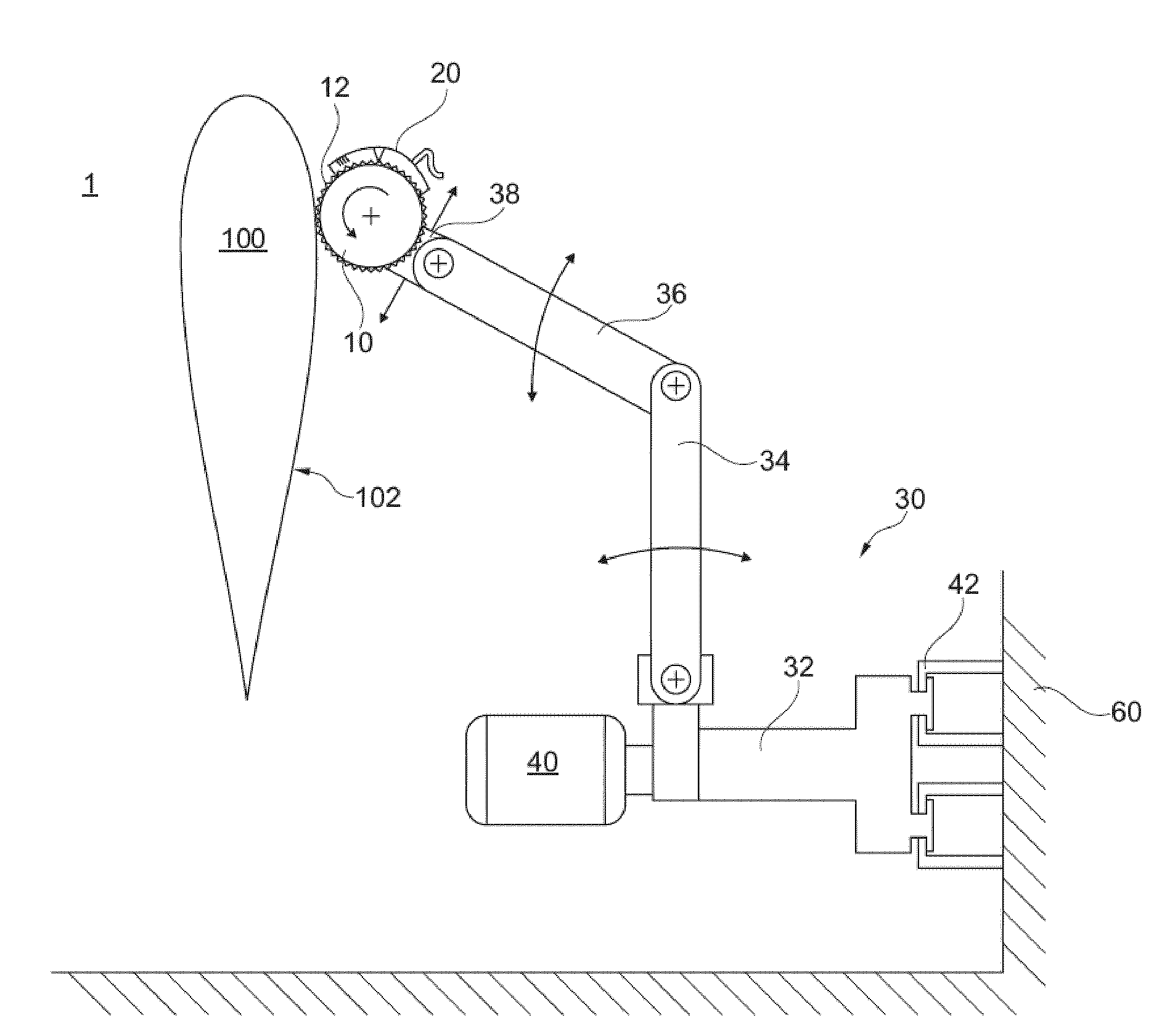
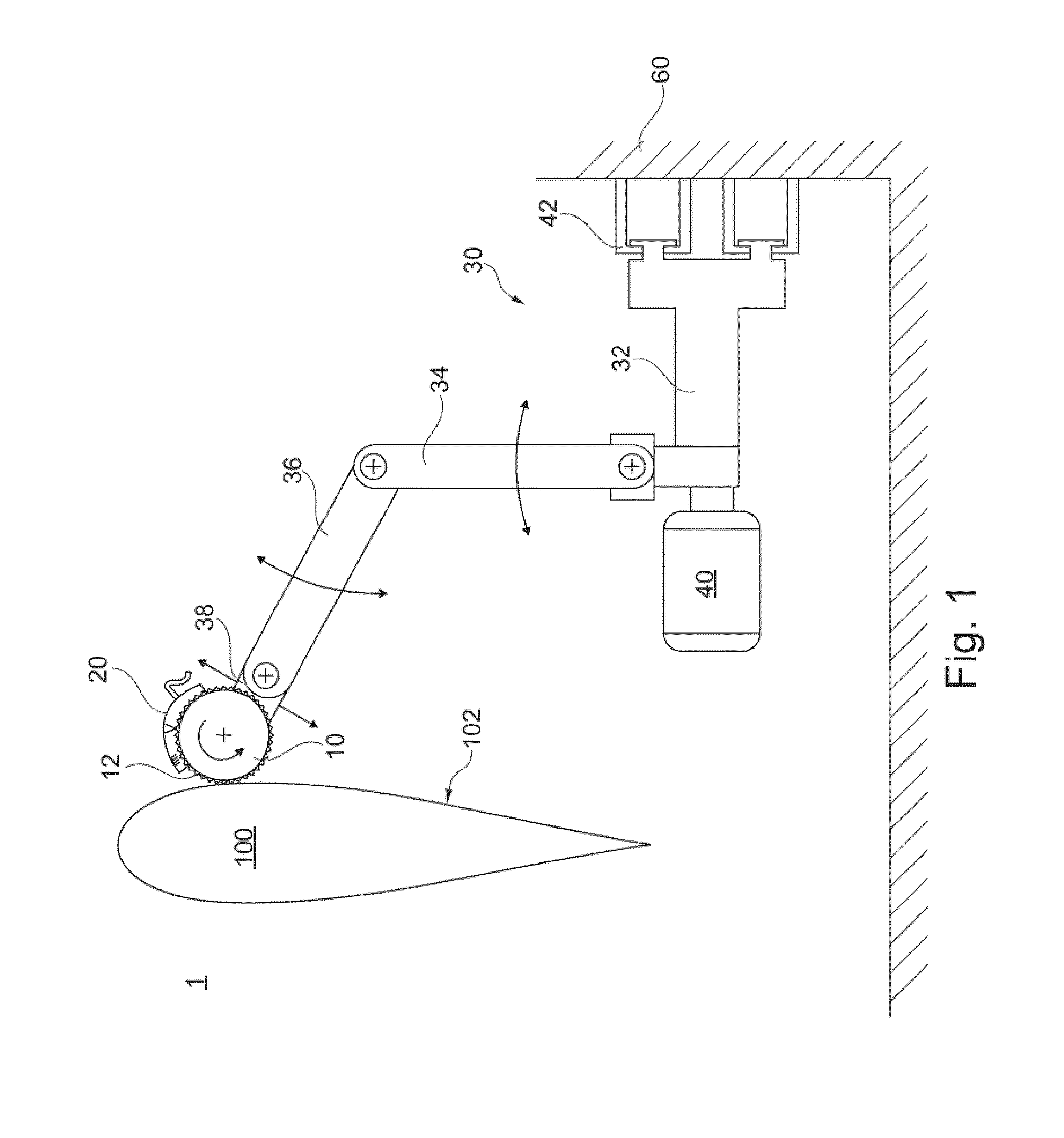
Grinding device 1 for machine-based grinding of rotor blades 100 for wind energy systems, comprising at least one industrial robot 30 and a grinding unit 10, 50, 70 that is guided by the industrial robot 30, wherein the grinding unit 10, 50, 70 comprises a grinding means, 12, 52 and a cleaning device 20, that cleans the grinding means 12, 52 at its grinding surface 64, 53.
Owner:JOST GMBH & CO KG
In-situ consolidation fibre laying method and device for producing resin-based compound material component
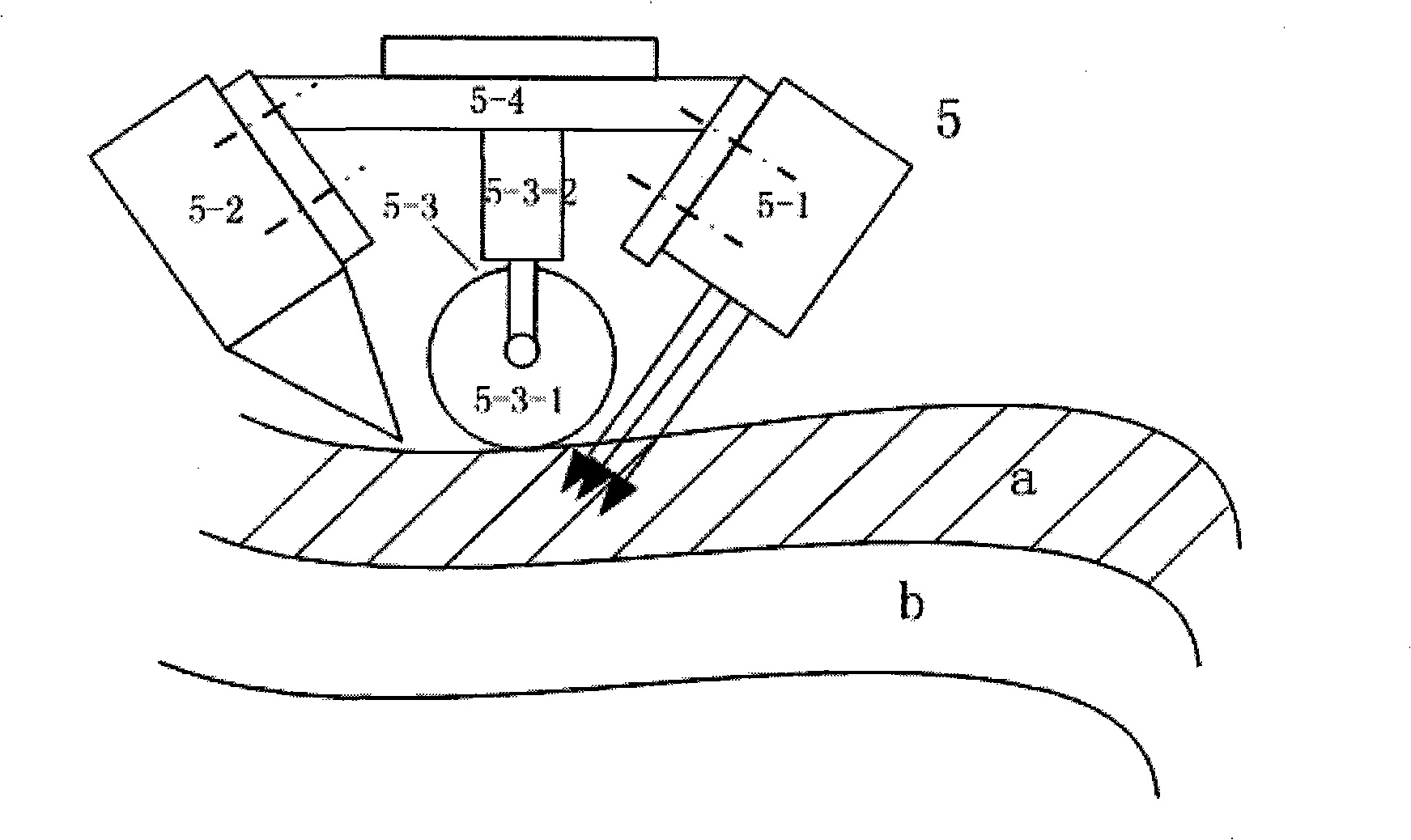
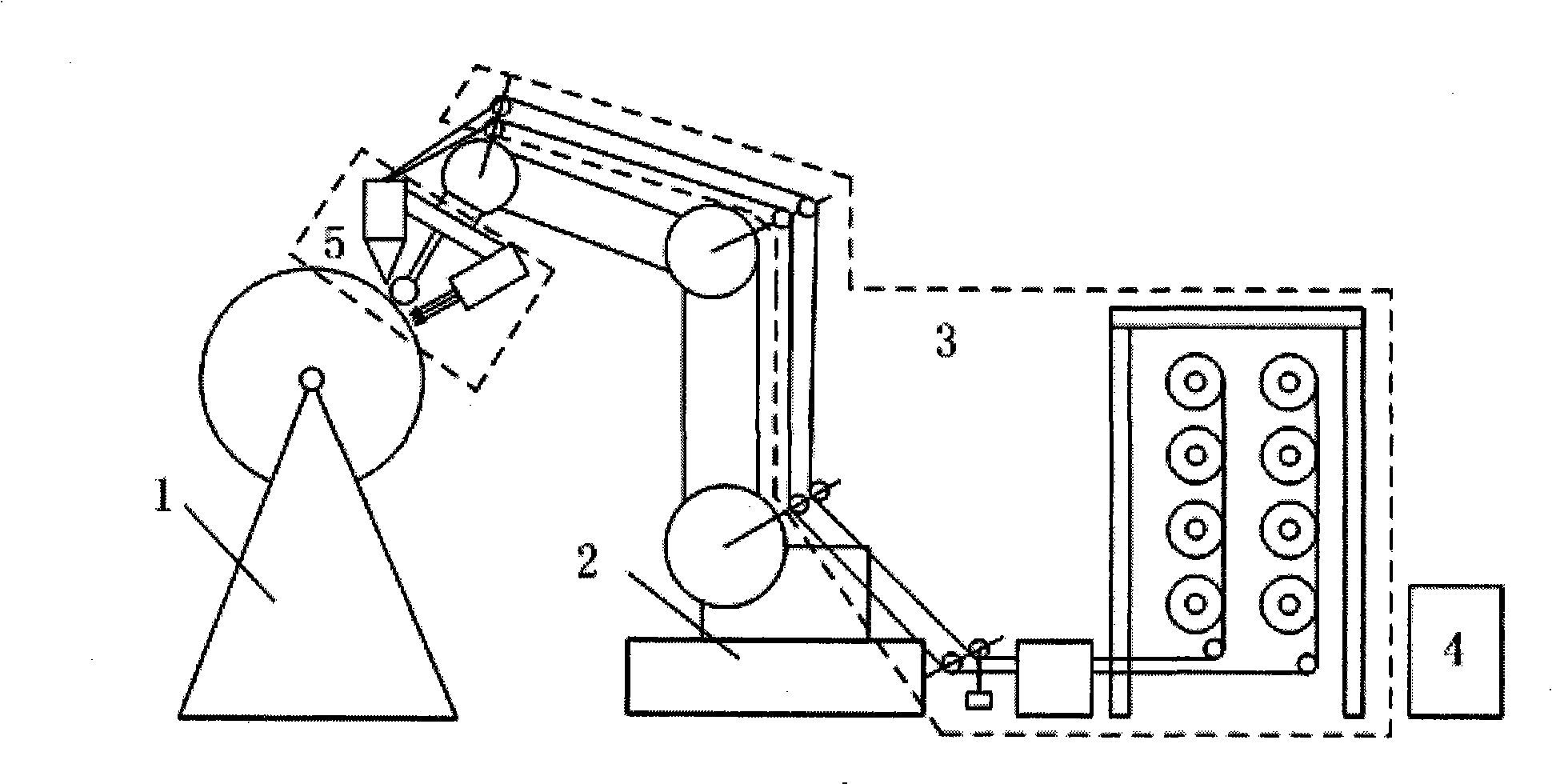
InactiveCN101254652ASimple manufacturing processShorten the manufacturing cycleCrazingThermal deformation
The invention discloses a method and a device for manufacturing resin-based composite material component by using fiber placement technology. By adopting fiber placement technology, the method and the device can place a fiber placement layer on the surface of a core die by a compaction mechanism to solve the problem of conventional winding equipment that is incapable of manufacturing surface component with negative curvature and non-gyrorotor component. Meanwhile, in-situ instantaneous stratified radiation curing is adopted to eliminate the influence of a tensile force in the fiber placement layer on the shape of the product and to solve the problems and disadvantages of large thermal deformation and easy generation of cracks due to autoclave curing treatment, the restriction of the autoclave volume on the component size, high production cost, and long production period. Based on industrial robot as the manufacture body, the device can improve the problems of prior placement equipment such as the deficiency of the flexibility in manufacturing more complex surface and complex structure.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
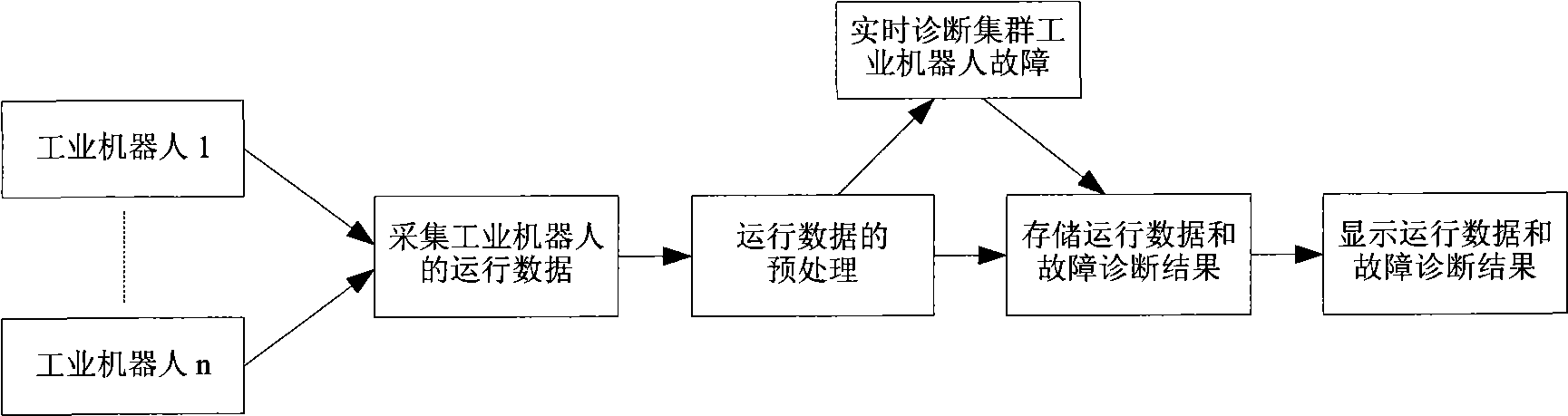
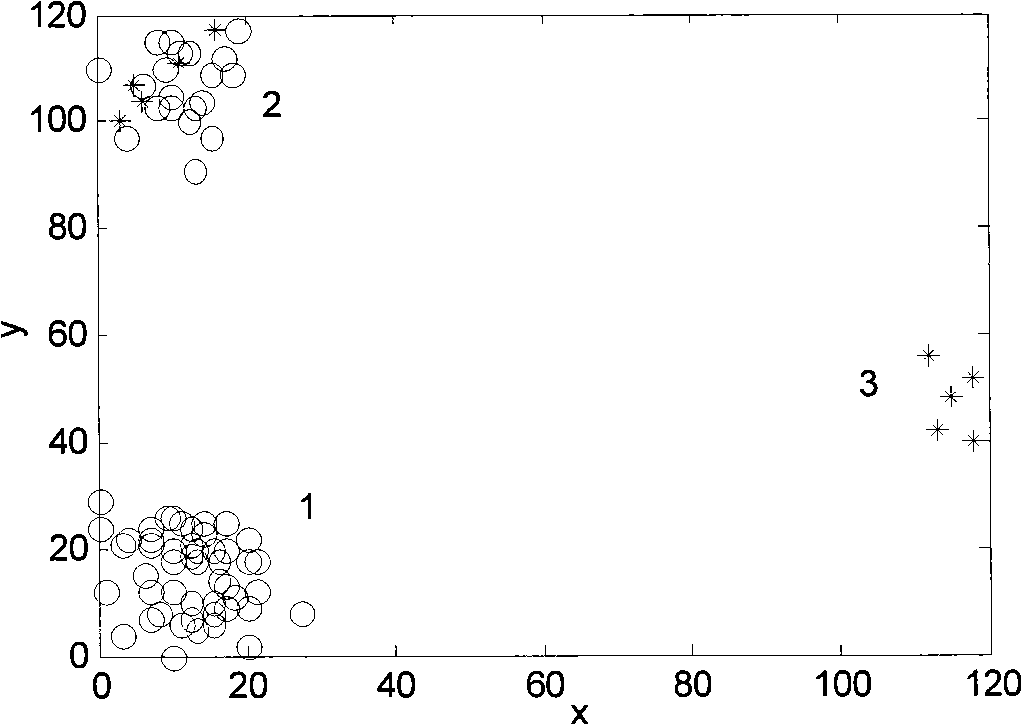
Cluster industrial robot failure diagnosis method based on outlier excavation
InactiveCN101509839AGood fault diagnosisAvoid failureStructural/machines measurementOutlierDependability
The invention relates to a fault diagnosis method for trunked industrial robots based on outliers mining, belonging to the filed of fault diagnosis of electromechanical equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly collecting data of original operating state of the trunked industrial robots and carrying out preprocessing operation of classifying and the like; then using a cluster analysis method to carry out analysis by taking a plurality of robots as a group, so as to lead a plurality of equipment to carry out classification according to operational state; based on clustering, utilizing an outliers mining method to calculate outlier factors of each industrial robot and then obtaining outlier degree thereof; separating outliers according to outlier degree and further determining that whether individual industrial robot represented by the outlier occurs fault or not; and judging the specific parts of faults of the robots according to the types of abnormal operation parameters and obtaining fault diagnosis results. By utilizing the fault diagnosis results, the method can implement targeted and predictive maintenance, thus avoiding the occurrence of faults of equipment, improving the reliability of equipment and guaranteeing reliable operation of trunked operational robots.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
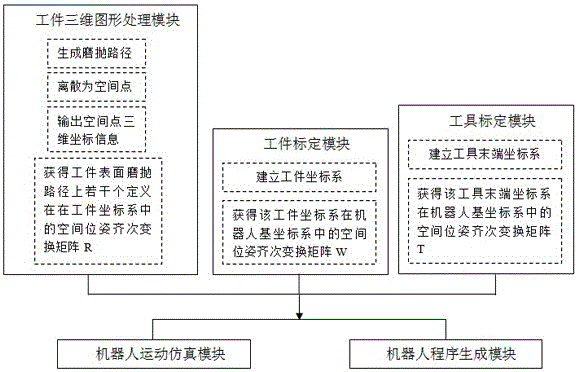
Grinding and polishing industrial robot offline programming method based on workpiece three-dimensional graph
InactiveCN106182018ASimplified offline programming processQuick buildProgramme-controlled manipulatorGraphicsContact position
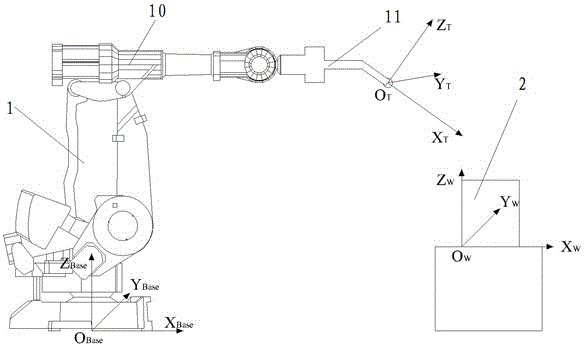
The invention relates to an off-line programming method for grinding and polishing industrial robots based on the three-dimensional graphics of workpieces. Through the workpiece calibration module, the homogeneous transformation matrix W of the spatial position and orientation of the workpiece coordinate system OW in the robot base coordinate system OBase is obtained through calibration; through the three-dimensional workpiece The graphics processing module discretizes the grinding and polishing path into several spatial points, outputs the three-dimensional coordinate information of each spatial point, and calculates several spatial pose homogeneous transformation matrices defined in the workpiece coordinate system OW on the grinding and polishing path of the workpiece surface R; through the tool calibration module, establish the tool end coordinate system OT at the contact position between the robot tool end and the workpiece, and calibrate to obtain the space pose homogeneous transformation matrix T of the tool end coordinate system OT in the robot base coordinate system OBase, to realize The robot is programmed offline. The invention has the beneficial effect of simplifying the off-line programming process of the grinding and polishing industrial robot without relying on off-line programming software of the robot.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Industrial robot remote monitoring and data processing system
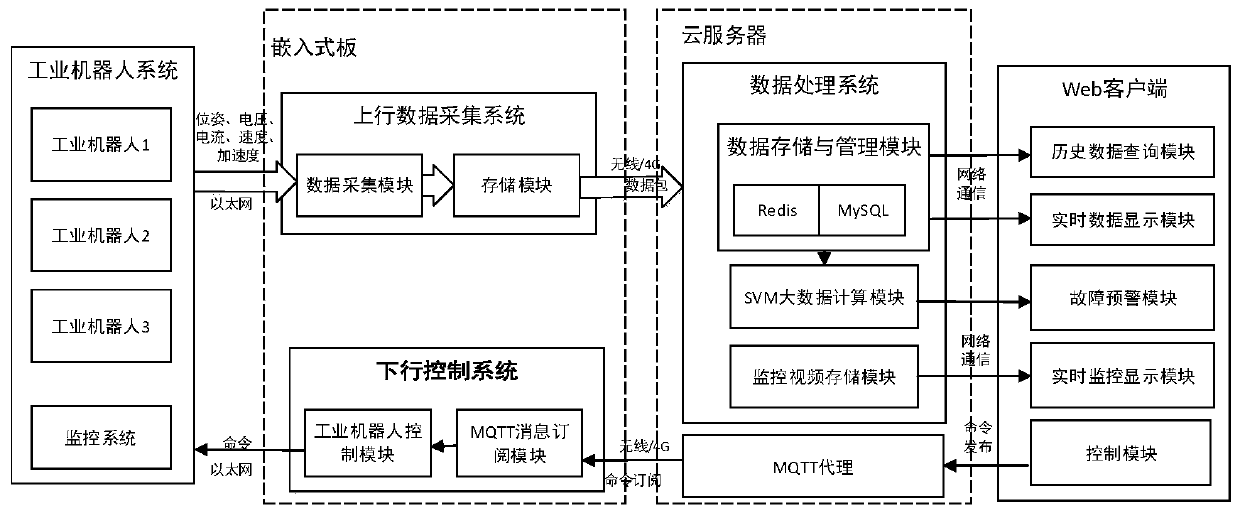
ActiveCN110733038AReduce huge lossesRealize remote controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorData acquisitionIndustrial robotics
The invention discloses an industrial robot remote monitoring and data processing system. The system comprises an industrial robot system located at an industrial site, an uplink data collecting system for collecting robot data to a cloud server, a downlink control system for achieving control over the industrial robot, a data processing system for performing unified management on the collected data and a visualized monitoring interface Web client. The uplink data collecting system and the downlink control system are both integrated into an embedded plate, the embedded plate is connected to acloud server through wireless or 4G, data interaction is achieved between the embedded plate and the cloud server, all obtained data of the industrial robot system is uploaded to the cloud server upwards to be stored, and the pose of the industrial robot is controlled downwards. The loss caused by fault halting can be effectively lowered, most simple fault problems can be solved through data checking and remote debugging, engineers do not need to be arranged to the site specially, and faults can be resolved more flexibly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
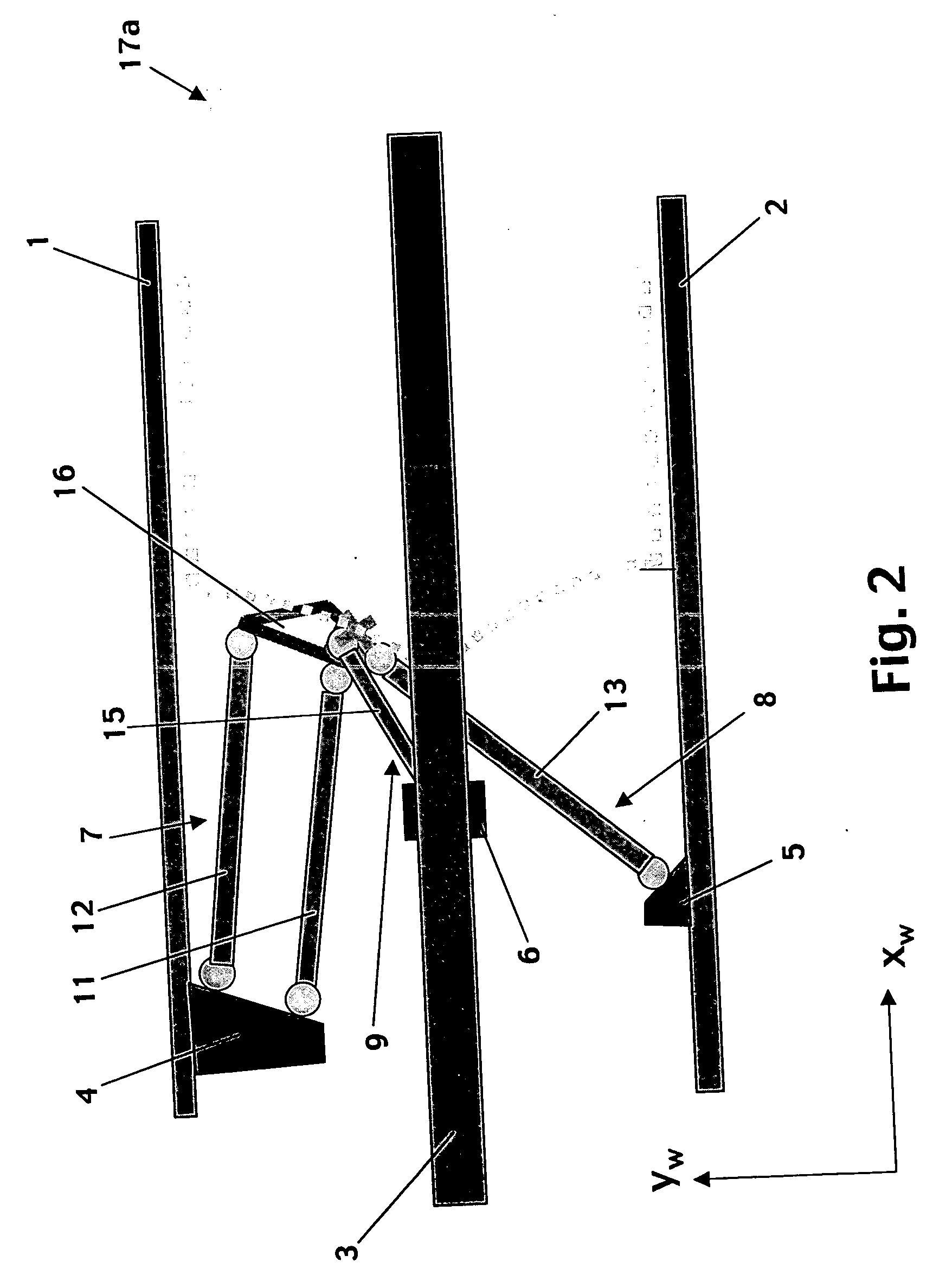
Industrial robot
InactiveUS20050172750A1Improve accuracyHigh stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusParallel kinematicsManipulator
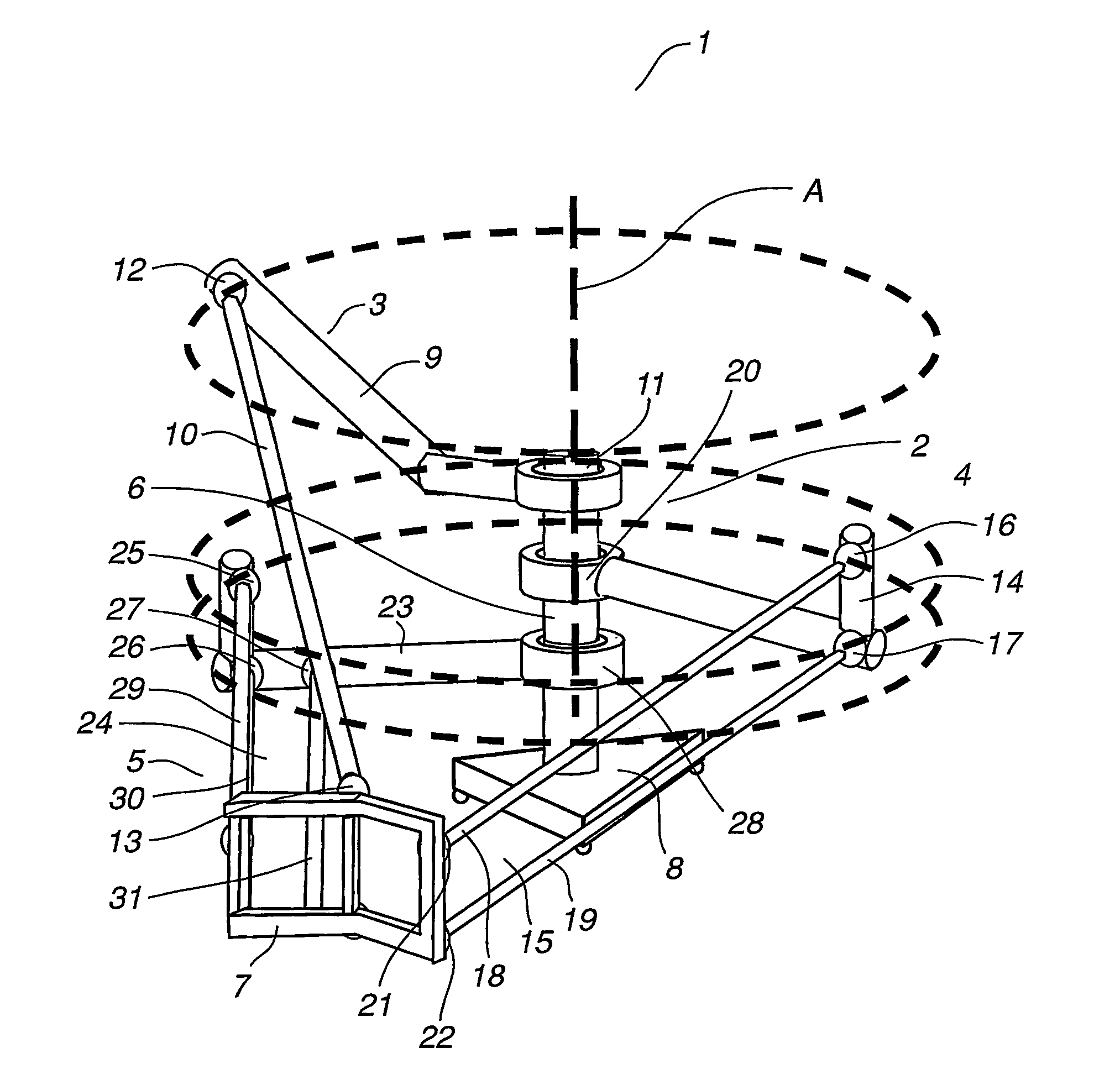
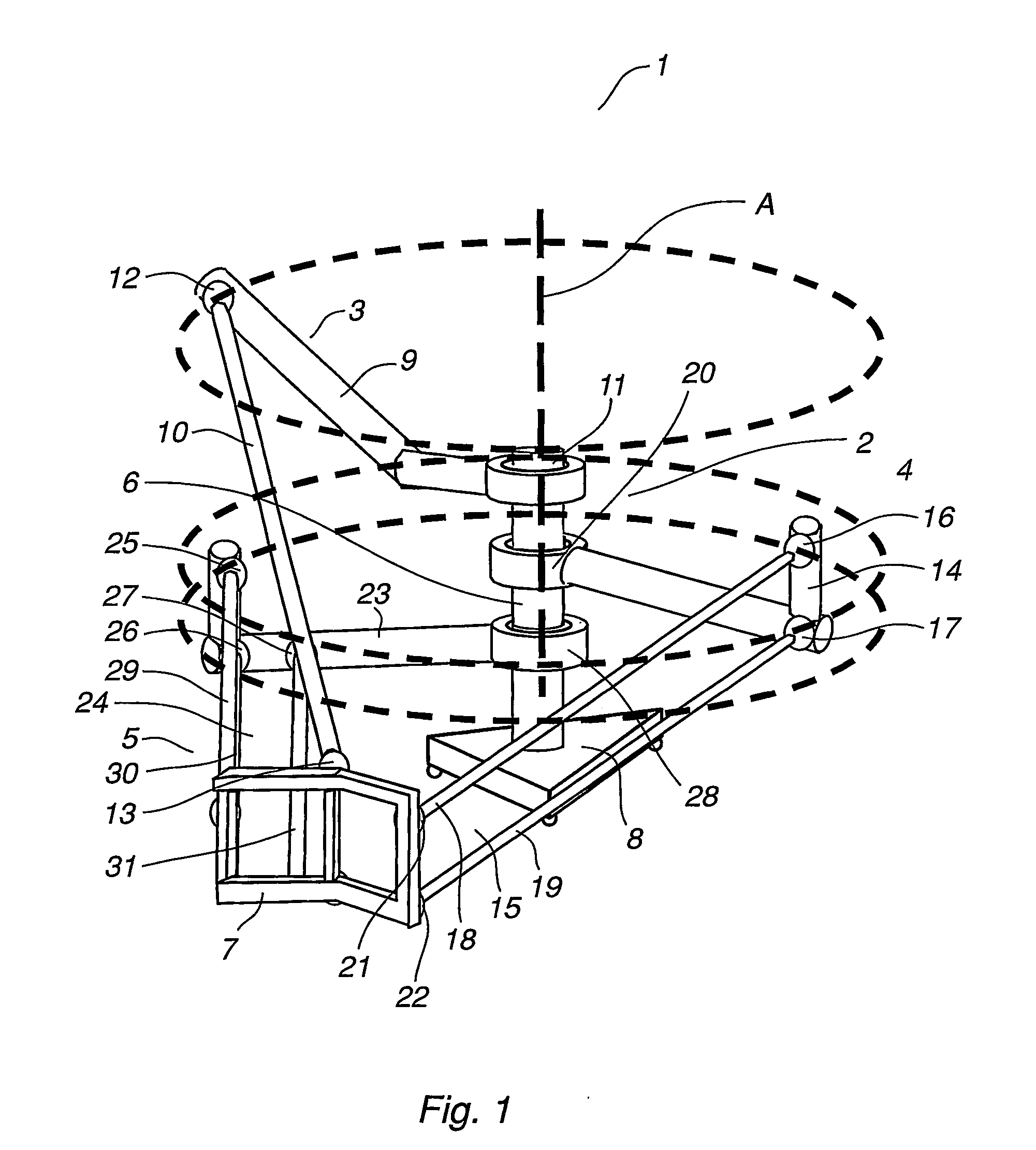
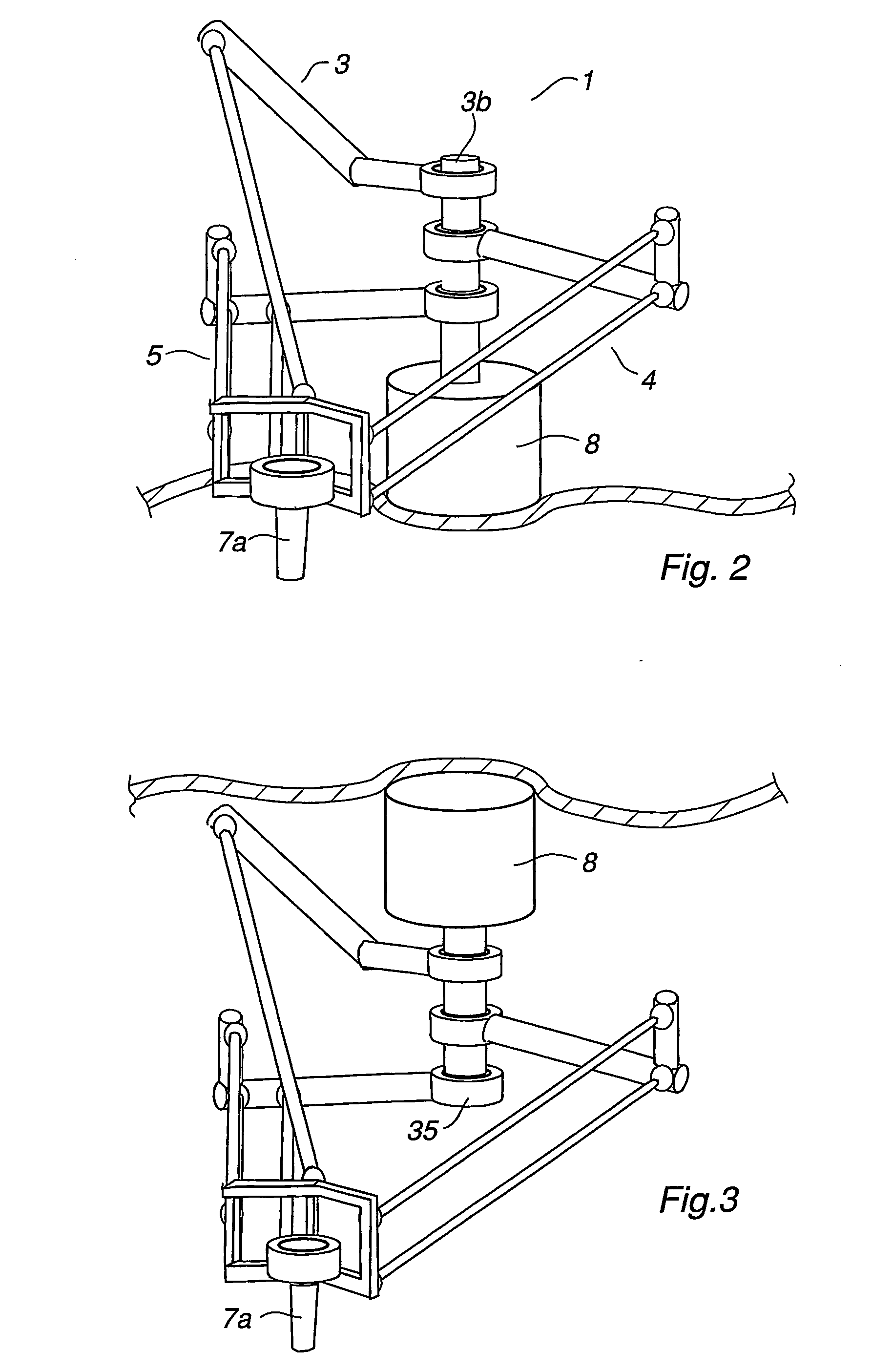
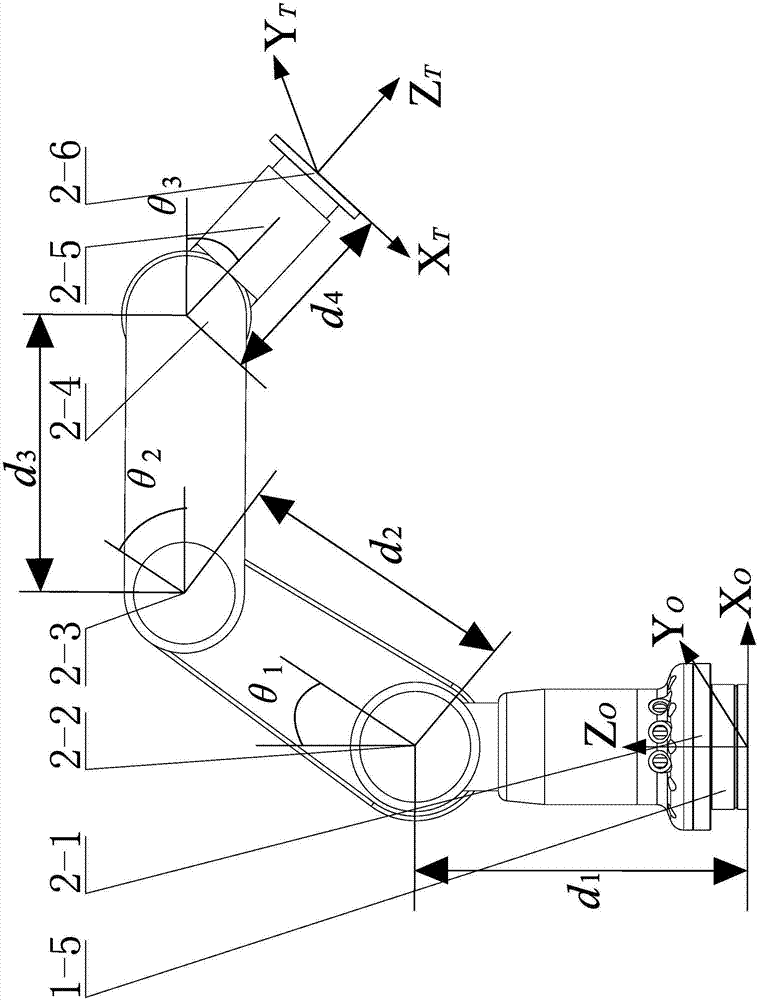
An industrial robot including a parallel kinematic manipulator (2) of an object (7a) in space, where the manipulator (2) includes a stationary platform (6), a movable platform (7) for carrying the object (7a), at least three arms (3, 4, 5) connecting the platforms (6,7). Each arm comprises a first arm part ( ) connected to the stationary platform for manipulating the movable platform (7).
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Industrial robot with pressurized air supply in balancing device
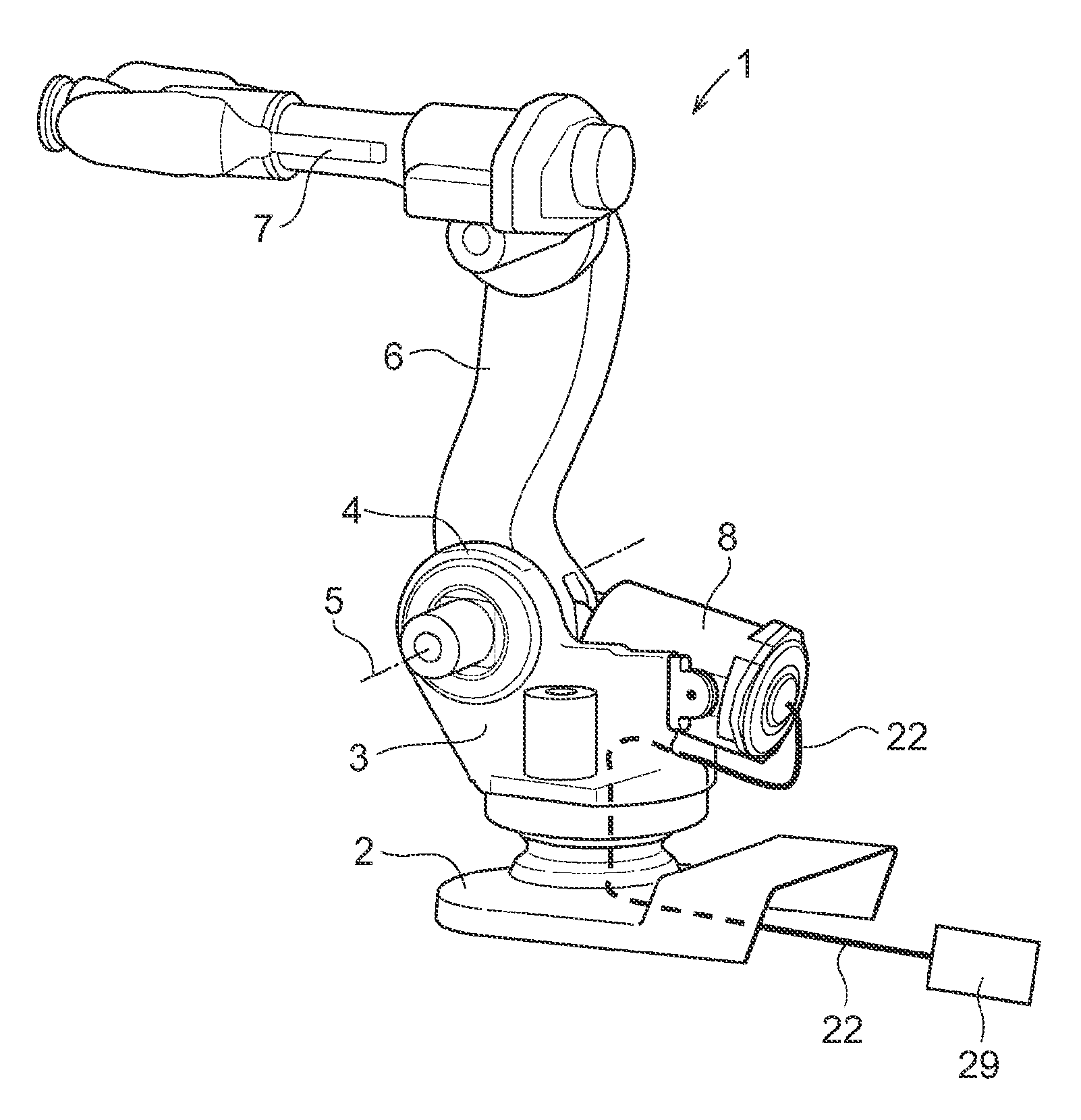
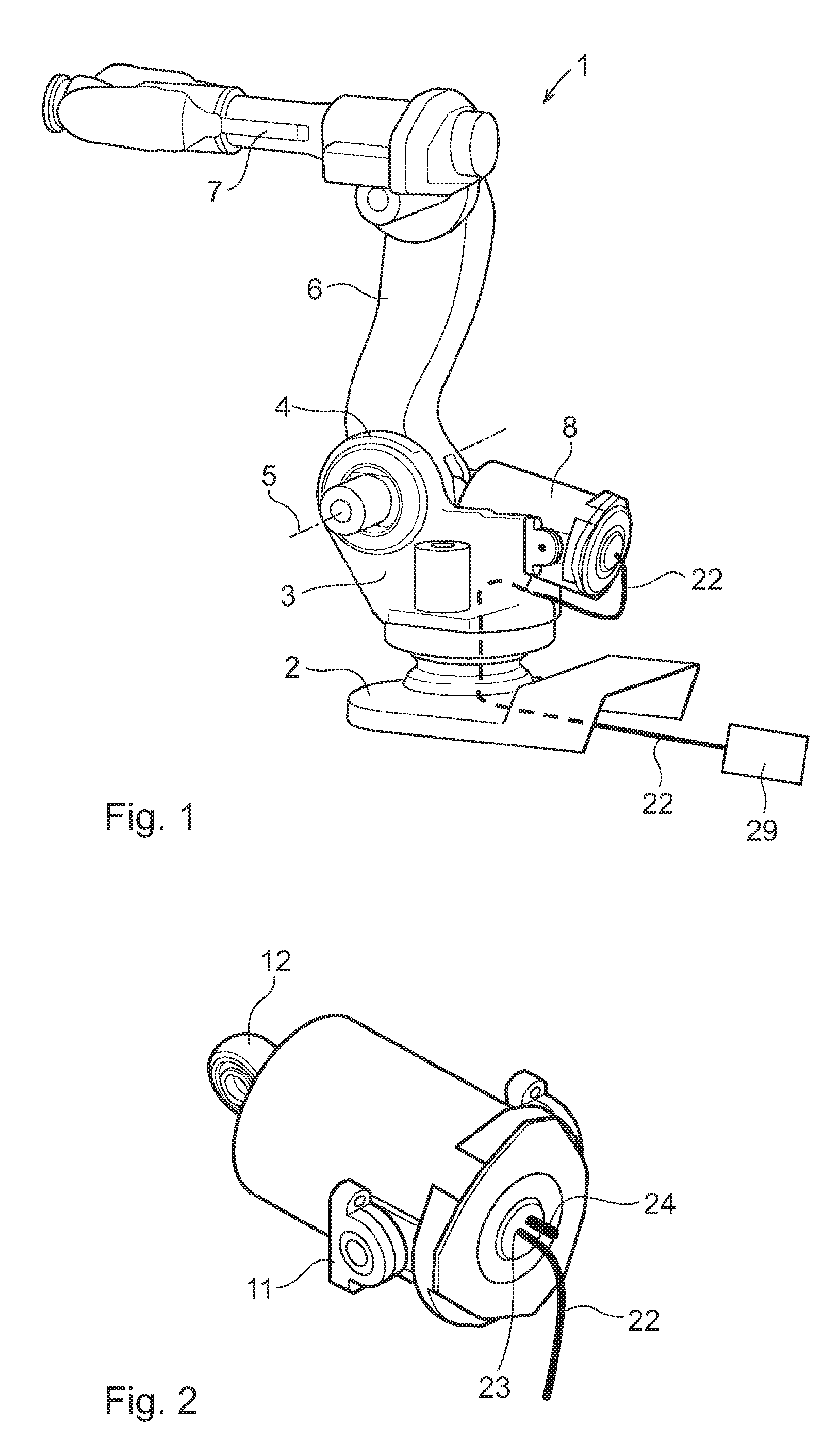
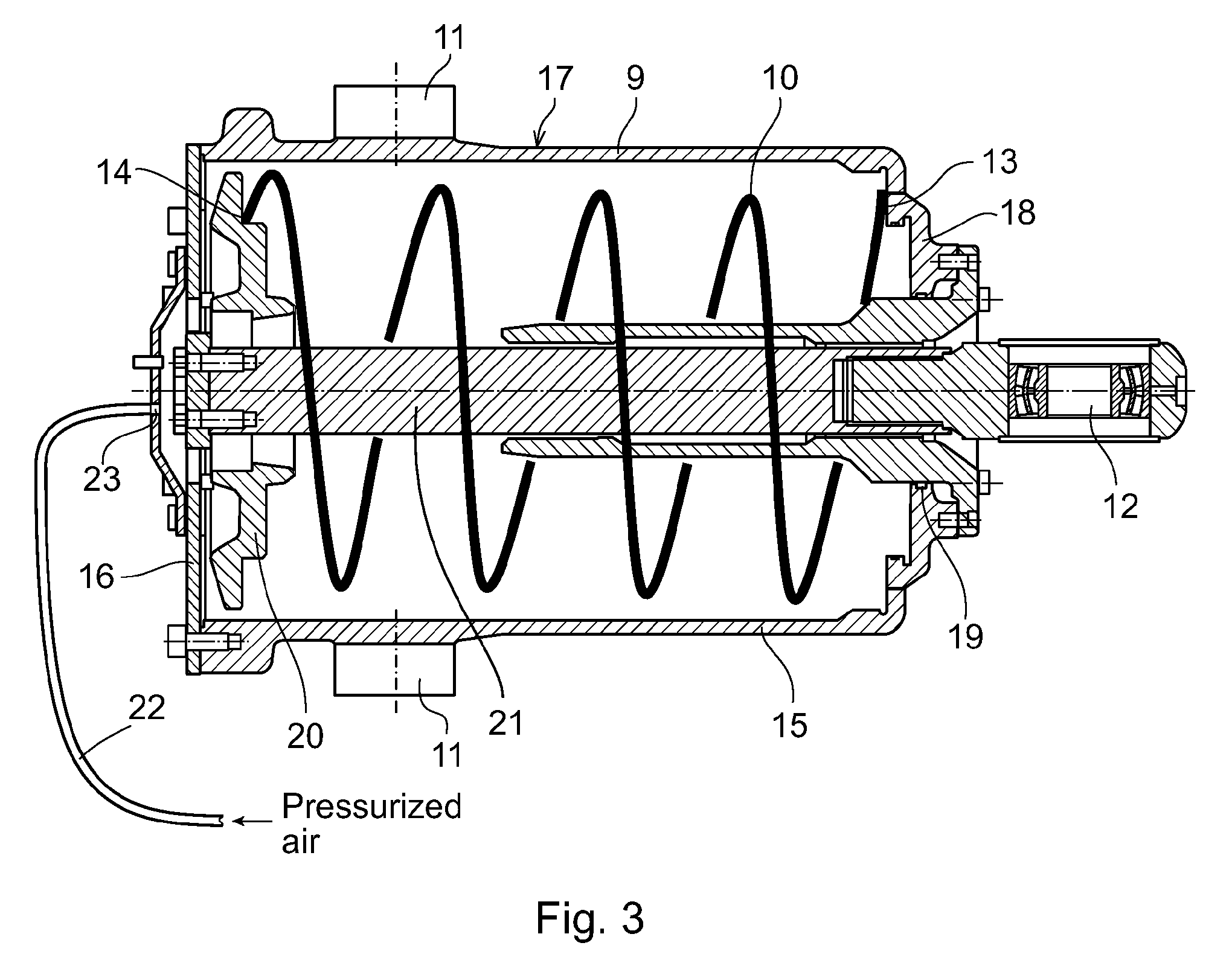
ActiveUS20100043587A1Improve usabilityEliminate riskMechanical apparatusJointsGravitational forceRelative motion
An industrial robot including a first robot part and a second robot part arranged to be moved in relation to each other. A balancing device is arranged between the first robot part and the second robot part. The balancing device is arranged to counteract a gravitational force upon relative movement of the robot parts. The balancing device includes a mechanical spring and a spring housing arranged enclosing the spring. The spring housing includes at least one air inlet adapted for pressurized air supply.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
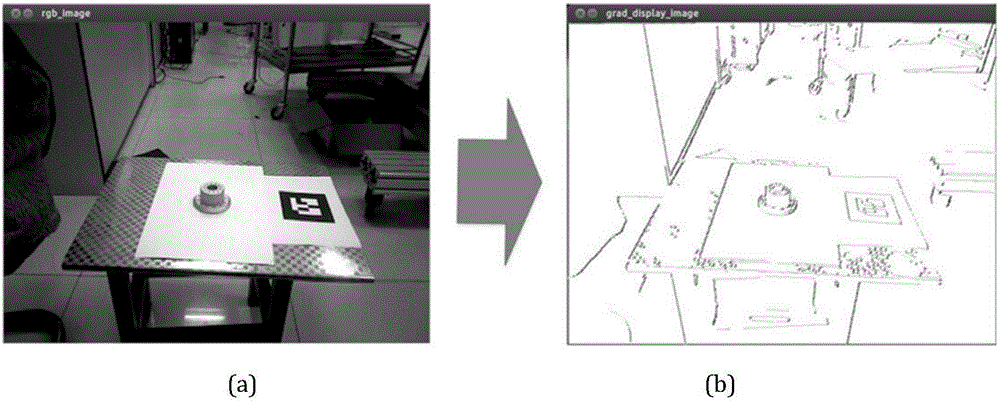
Weak-texture workpiece, and method and system for recognizing and detecting three-dimensional pose
InactiveCN106251353AEasy to operateImproving the accuracy of 3D pose estimationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor image
The invention discloses a weak-texture workpiece, and a method and a system for recognizing and detecting the three-dimensional pose. After a color image of a target workpiece acquired by an RGB-D sensor and a gradient pattern template library are subjected to image pyramid search based on a similarity evaluation function, a three-dimensional point cloud is built on a depth image according to a matching result, and finally, through filtering and iterative closest point computation on the three-dimensional point cloud, the precise three-dimensional pose of the target workpiece is obtained. An industrial robot can accurately and intelligently recognize the weak-texture workpiece and acquire the three-dimensional pose information, and tasks such as grinding and assembling on the workpiece can be completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
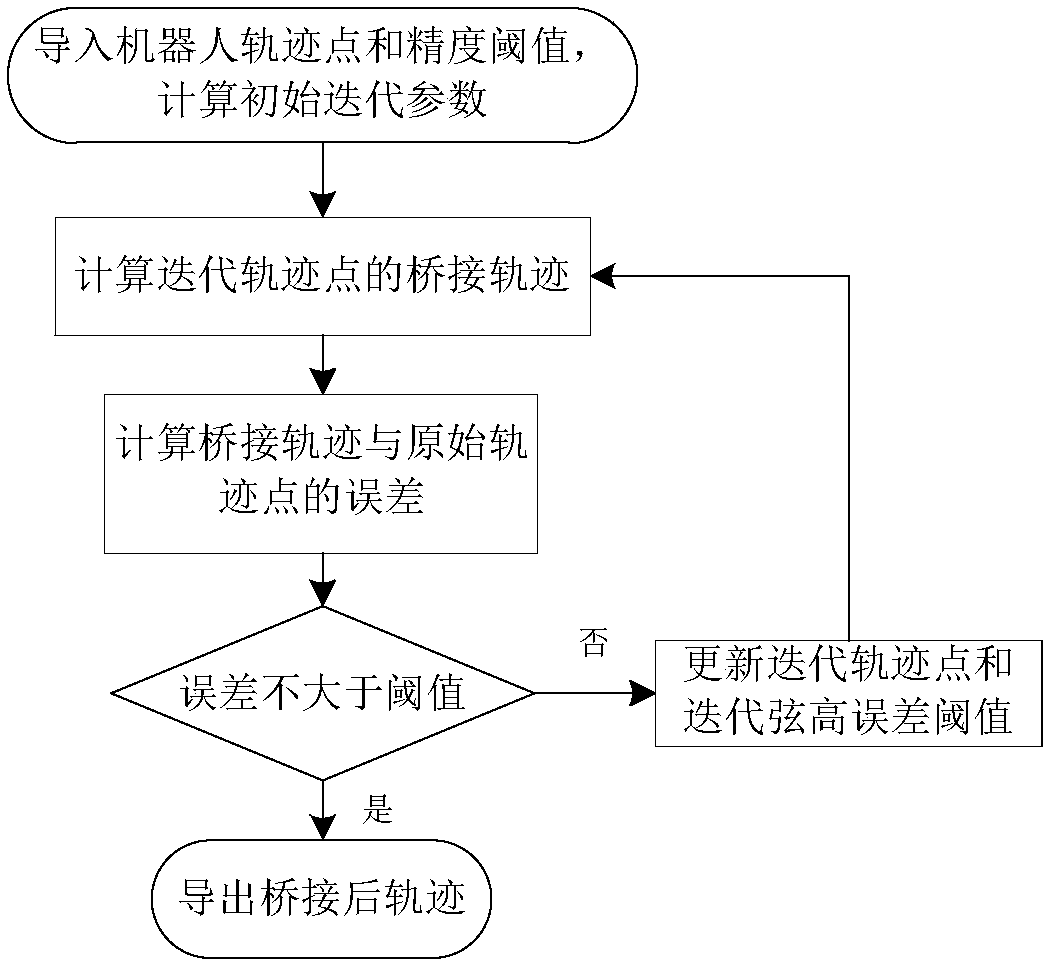
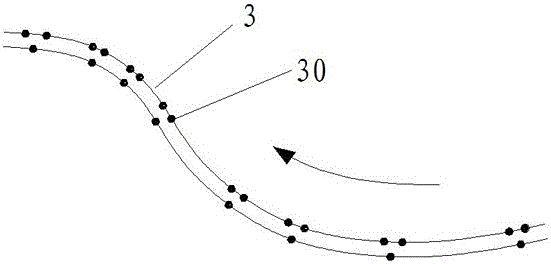
Error-controllable short line segment trajectory smoothing method
ActiveCN109571473AImprove work efficiencyImprove the quality of workProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic control devicesNumerical controlQuality of work
The invention discloses an error-controllable short line segment trajectory smoothing method which comprises the following steps of 1, pretreating robot trajectory points: traversing all trajectory points of a whole trajectory, segmenting according to the distances and the inclined angles between the trajectory points, and dividing the whole trajectory into a plurality of broken line segment sets;and 2, smoothing the trajectory points: traversing the broken line segment sets generated in the step 1, and calculating the smoothing trajectory of each broken line segment according to a trajectorypoint error threshold value, a chord height error threshold value, a continuity requirement and a smoothing requirement. According to the method, the short line segment trajectory is smoothed to generate a smoothed trajectory meeting the continuity requirement, the shape-preserving requirement and the error requirement, so that the working efficiency and the working quality in application of a numerical control machining robot or an industrial robot are improved; a smoothing curve is applied to requirements for different continuity and executing efficiency; and compared with a conventional transition method, the smoothing curve can control the errors of the trajectory points, and achieves the interpolation effect, thereby retaining the characteristics of the trajectory points.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Training and operating industrial robots
ActiveUS20130345874A1Avoid collisionMoreProgramme-controlled manipulatorMathematical modelsObject basedData science
Owner:RETHINK ROBOTICS
Automatic feeding, testing and sorting system and operation method thereof
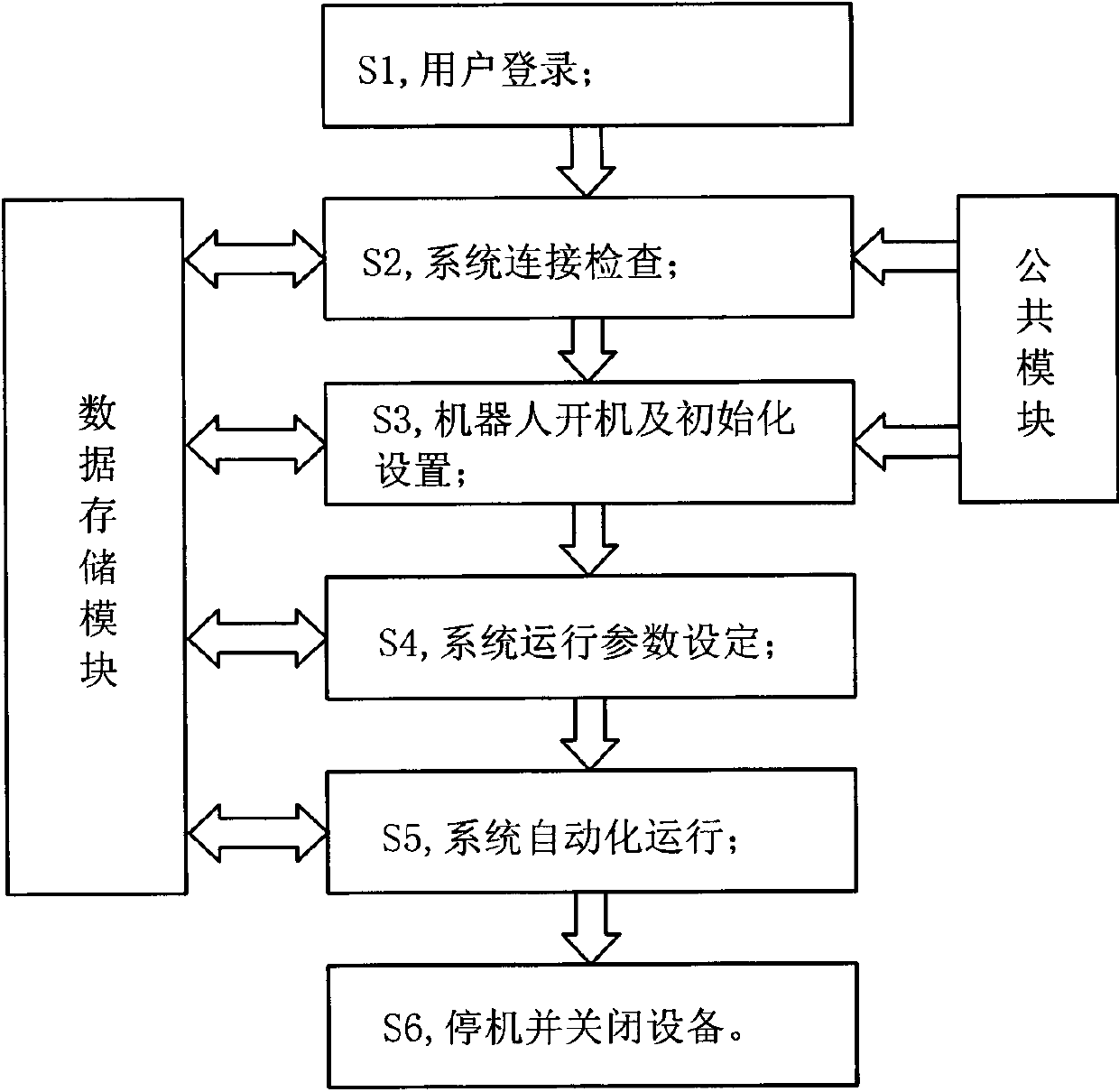
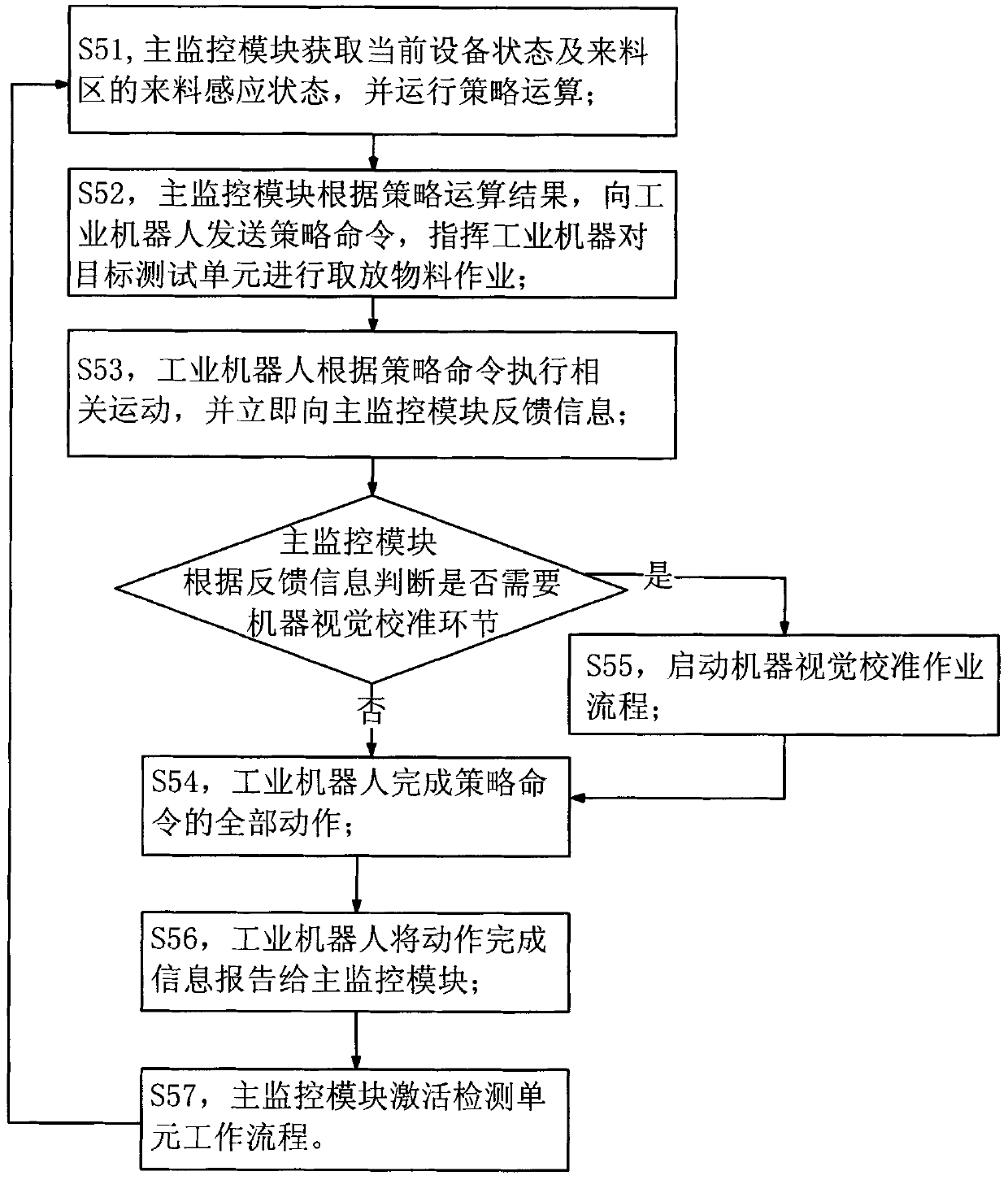
ActiveCN103368795ARealize automatic feedingRealize unmannedData switching networksConveyor partsProgrammable logic controllerControl engineering
The invention discloses an automatic feeding, testing and sorting system and an operation method of the system. The operation method comprises the following steps of: S1, user login; S2, system connection checking; S3, robot starting and initialized setting; S4 system operation parameter setting; S5 system automatic operation; S6 stopping and equipment shutting. The operation method provided by the invention realizes organic combination in controlling test units, an industrial robot, a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) electrical system, an image acquisition module and other peripheral equipment, automation in feeding, starting a test and sorting tested products to corresponding areas, as well as an unmanned testing process. In S2 and S3, required programs can be called from a public module in which global thread programs are stored; in S2, S3, S4 and S5, key variables required during system operation and stored in a data storage document can be called or rewritten so as to greatly improve the calculation efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN JIACHEN TECH
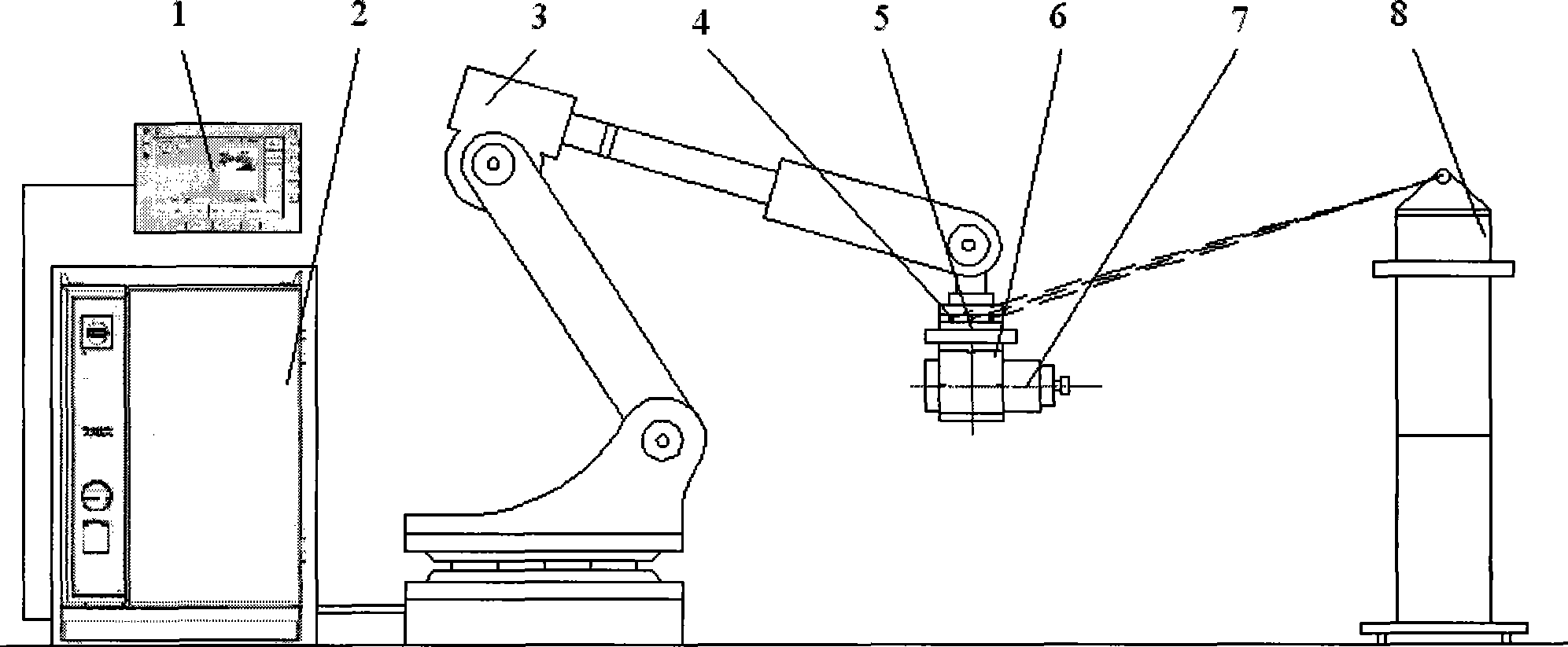
Method for in-line calibration of an industrial robot, calibration system for performing such a method and industrial robot comprising such a calibration system
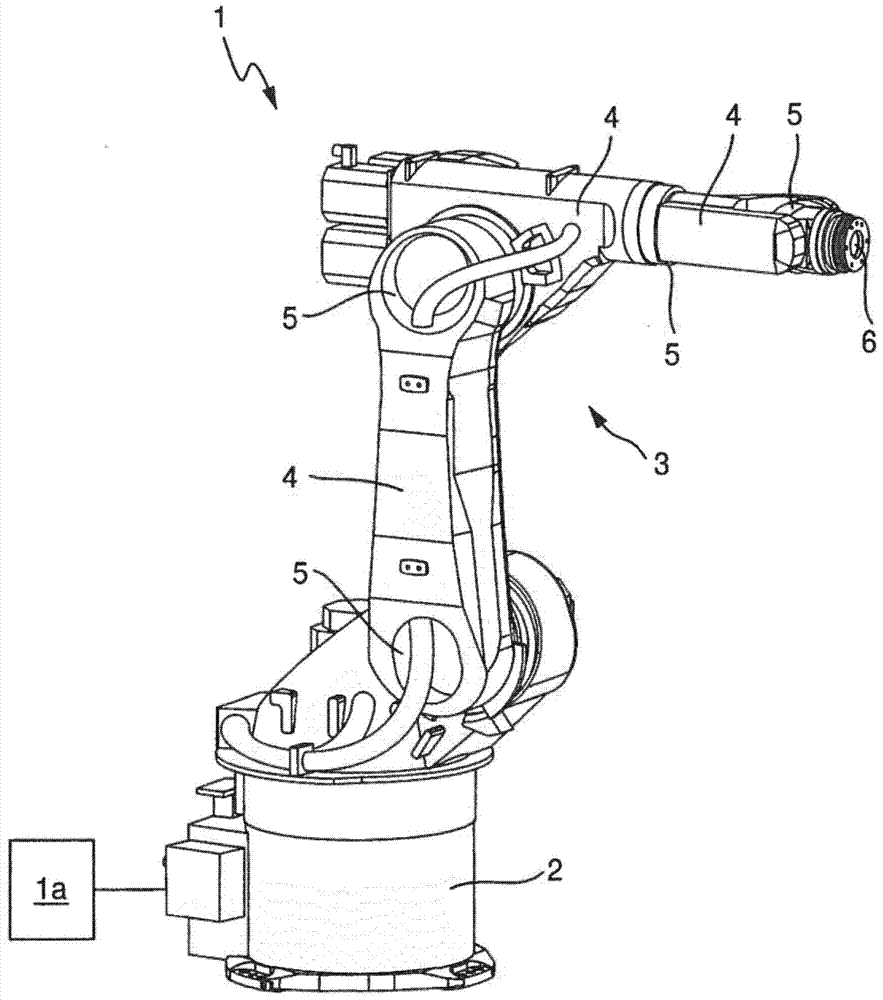
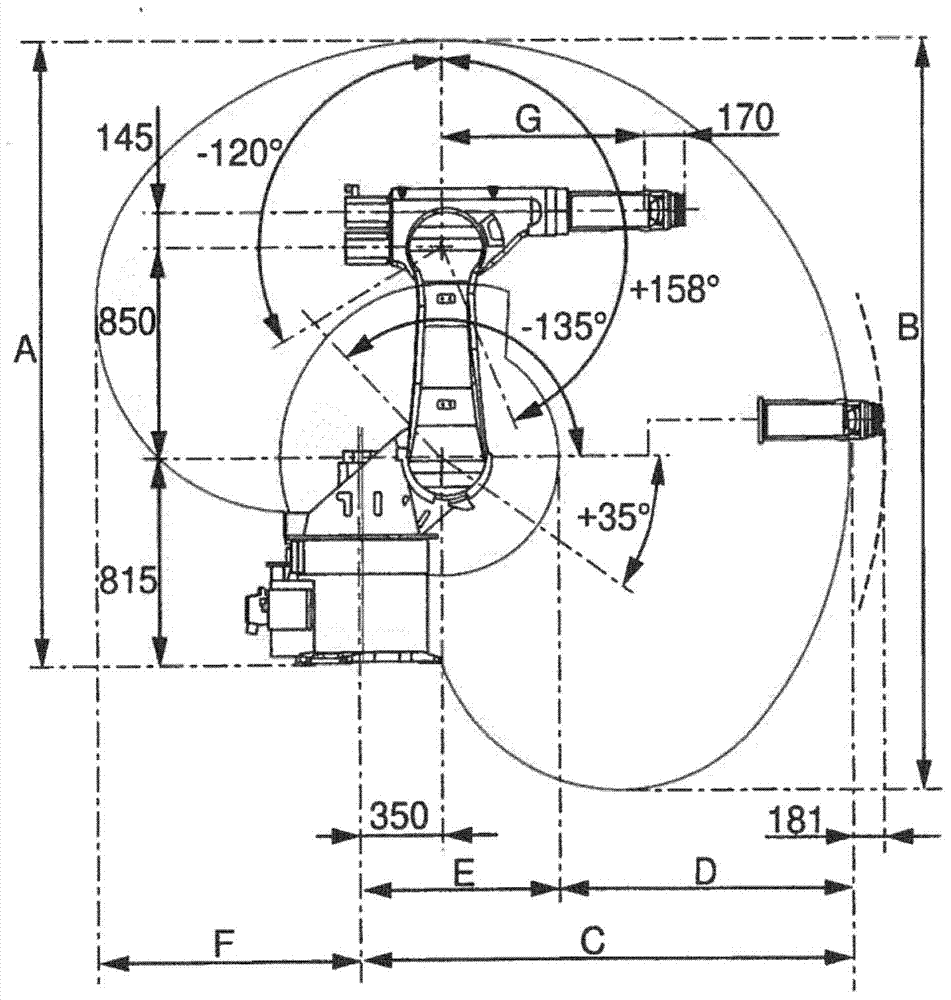
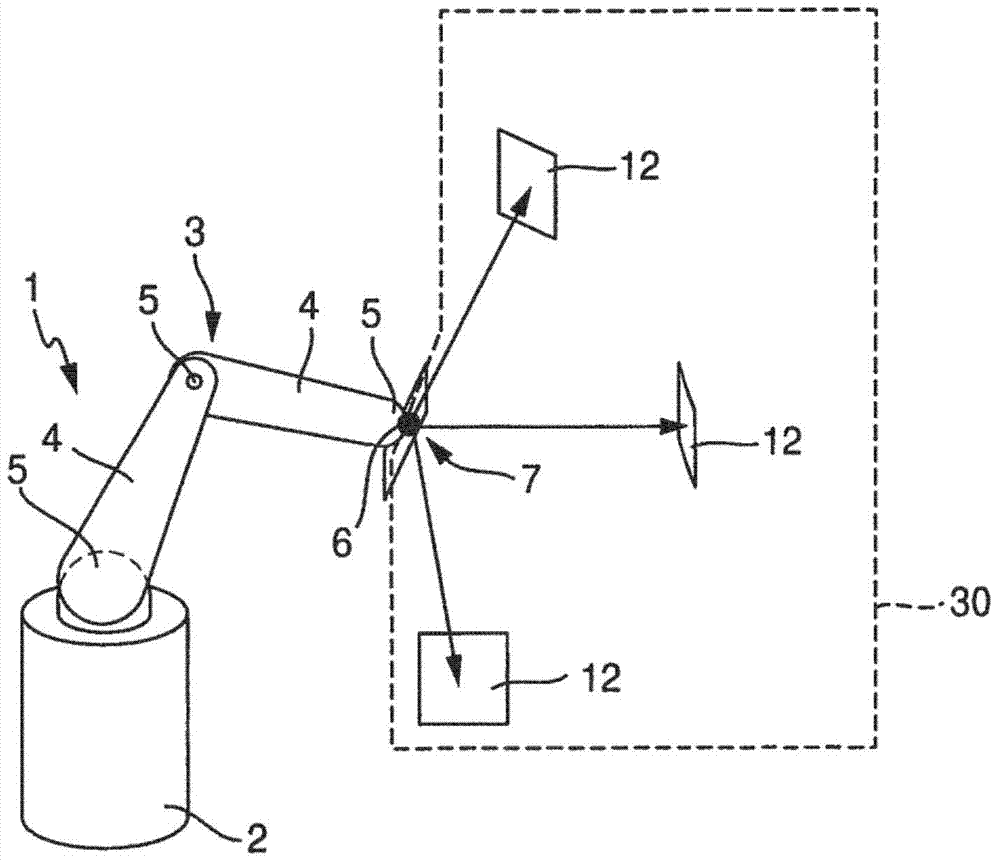
The invention refers to a method for in-line calibration of an industrial robot (1). The robot (1) comprises a fixed base section (2) and a multi chain link robot arm (3). The chain links (4) are interconnected and connected to the base section (2) of the robot (1), respectively, by means of articulated joints (5). An end effector (6) of the robot arm (3) can be moved in respect to the base section (2) within a three-dimensional workspace into any desired location. The idea is to move the end effector (6) into a predefined calibration location and to determine characteristic parameters of the robot (1) for that location. The characteristic parameters are compared to previously acquired values of the corresponding parameters for that calibration location. The differences between the characteristic parameters of the current location and the previously acquired parameters are used for correcting the kinematic model of the robot (1) and during normal operation of the robot (1) to enhance the accuracy of movement of the distal end (6). The end effector (6) is moved exactly into the calibration location by means of an iterative closed loop control process, in which light sources (7) fixedly connected to the end effector (6) emit light rays which impact on at least one optical position sensor (12) fixedly positioned in respect to the robot base (2). The end effector (6) is moved such that the actual ray positions (20) on the sensors (12) are moved to a predefined position (20') corresponding to the predefined calibration location by means of the iterative process.
Owner:INOS AUTOMATIONSSOFTWARE
Full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and valve screwing-twisting method utilizing robot
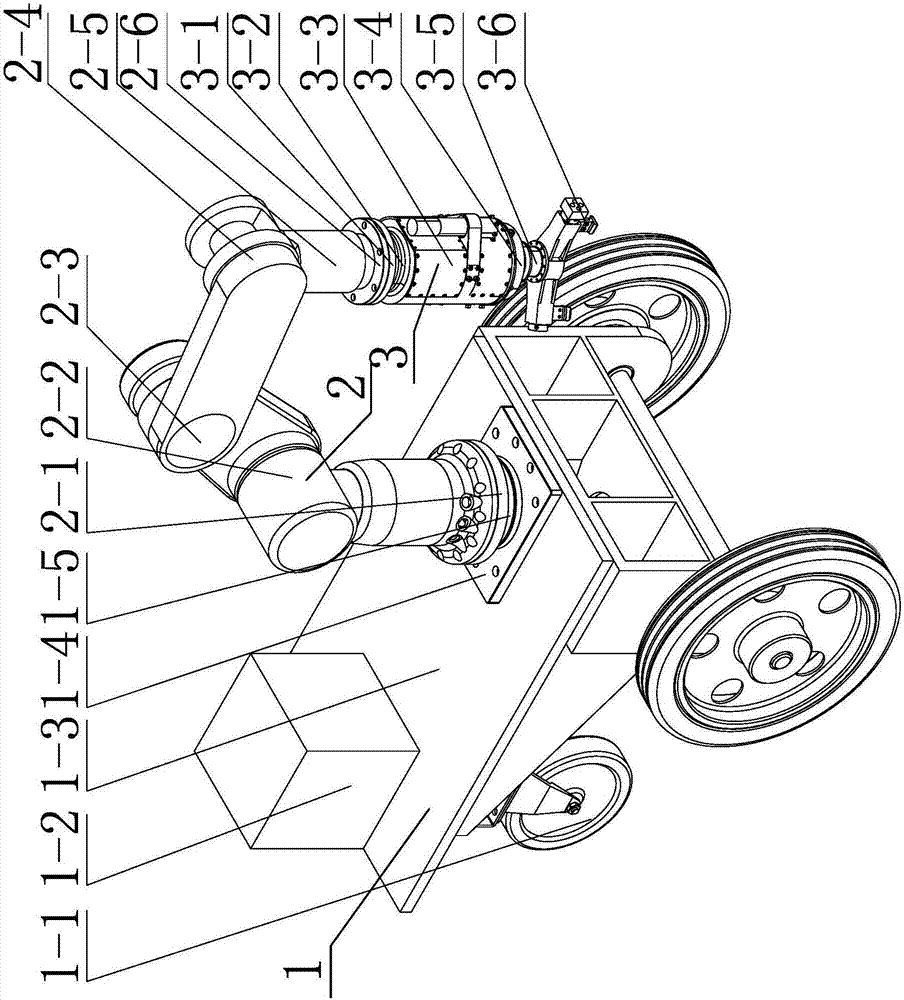
ActiveCN108000477AImprove adaptabilityAvoid Rigid CollisionsGripping headsAxial displacementEngineering
The invention provides a full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and a valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot, and relates to a robot and a valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot. The full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and the valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot aim to solve the problems that an industrial robot cannot conductlarge overall motion, and the operating range is narrow; rigid collision and radial contact force are generated between an end actuator and a valve handwheel; damage of operating devices is possiblycaused due to the fact that screwing-twisting resistance torques of different valves are different; and the valve handwheel can produce axial displacement while rotating, and axial contact force of the tail end is brought. The full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot comprises a wheel type moving platform, a four-degree-of-freedom manipulator and a compliant end actuator, the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator is mounted on the wheel type moving platform, and a six-axis force sensor is mounted between the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator and the wheel type moving platform; the compliant end actuator is mounted at the tail end of the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator, and a six-axis force sensor is mounted between the compliant end actuator and the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator; and through information of the two sensors, impedance control can be conducted on the wheel type moving platform and the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator. The full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and the valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot are suitable for robot remote operation, robot compliant control and valve screwing-twisting operation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
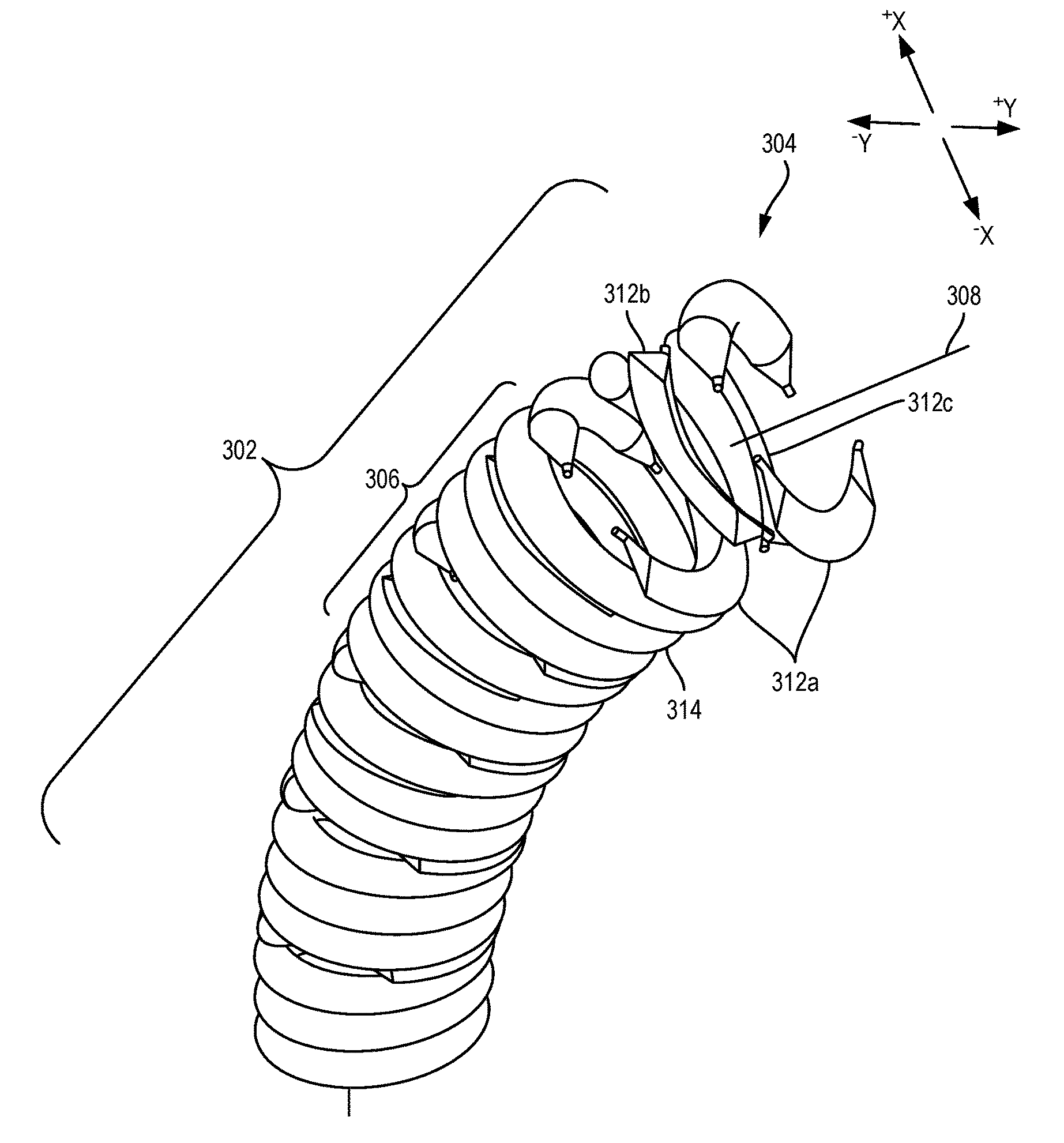
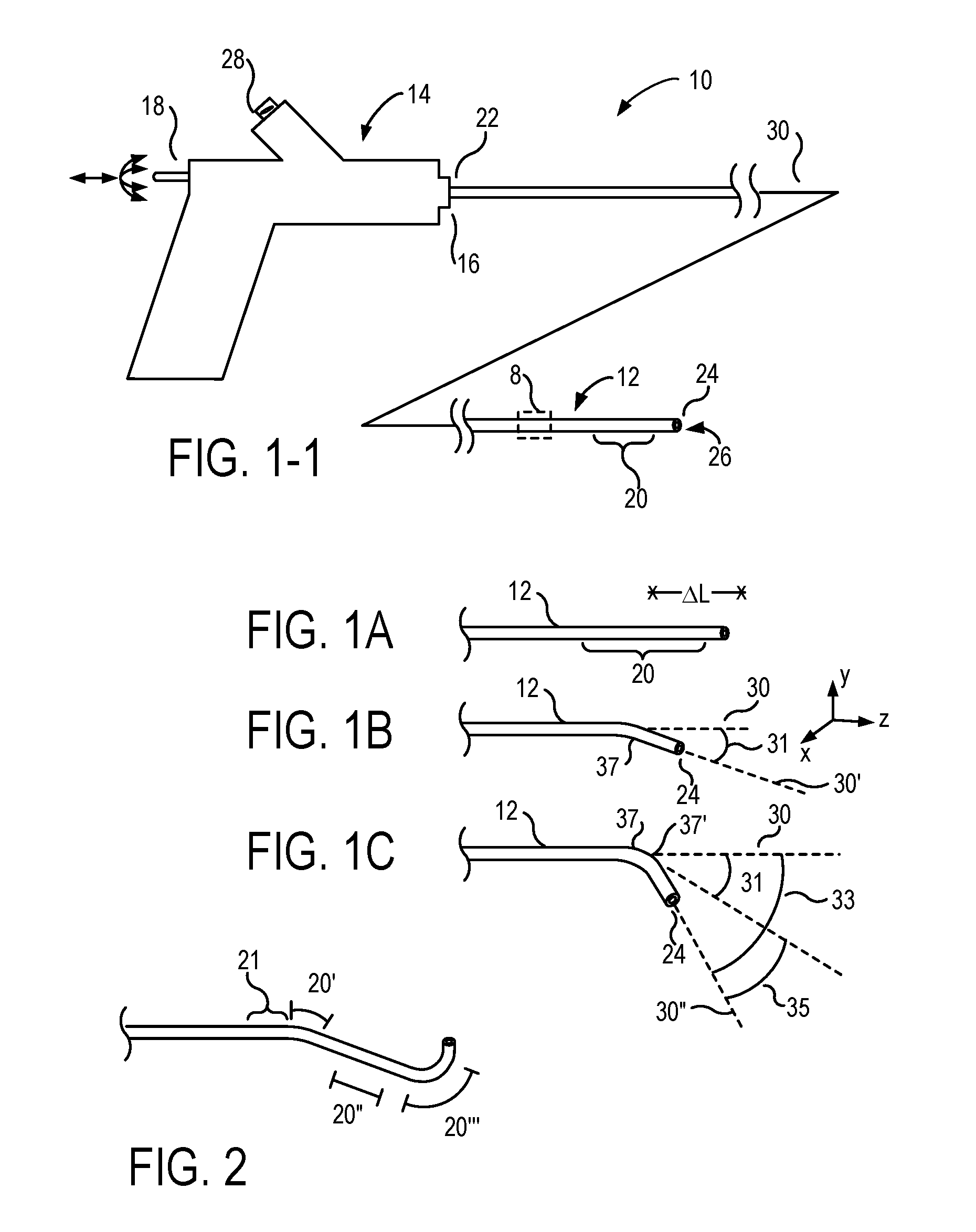
Fluid-Expandable Body Articulation of Catheters and Other Flexible Structures
ActiveUS20170021143A1Improve axial stiffnessEfficient modulationBalloon catheterSurgical navigation systemsHelical coilCatheter
Articulation devices, systems, methods for articulation, and methods for fabricating articulation structures will often include simple balloon arrays, with inflation of the balloons interacting with elongate skeletal support structures so as to locally alter articulation of the skeleton. The balloons can be mounted to a substrate of the array, with the substrate having channels that can direct inflation fluid to a subset of the balloons. The articulation array structure may be formed using simple planar 3-D printing, extrusion, and / or micromachining techniques. The skeleton may comprise a simple helical coil, and the array can be used to locally deflect or elongate an axis of the coil under control of a processor. Inflation fluid may be directed to the balloons from an inflation fluid reservoir of an inflation system, with the inflation system preferably including valves controlled by the processor. The articulation structures can be employed in minimally invasive medical catheter systems, and also for industrial robotics, for supporting imaging systems, for entertainment and consumer products, and the like.
Owner:PROJECT MORAY INC
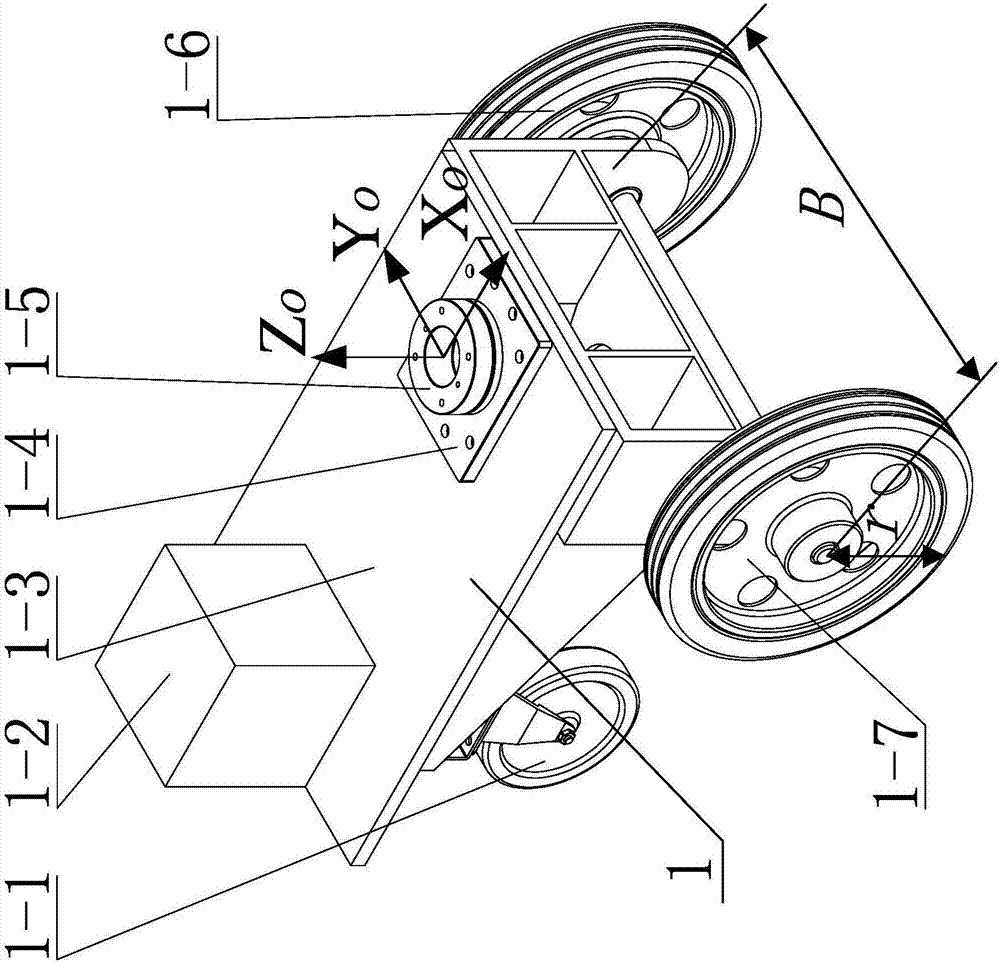
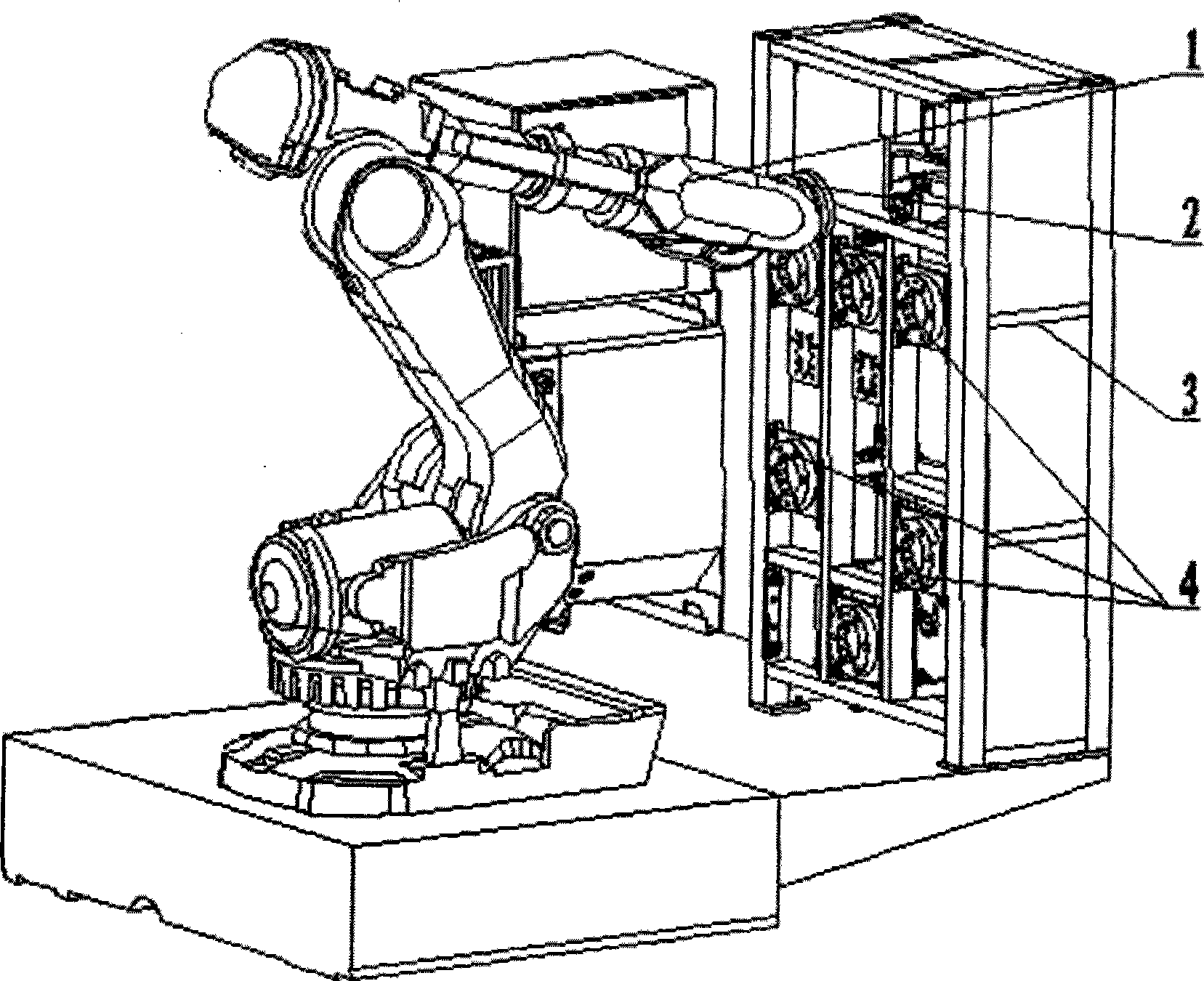
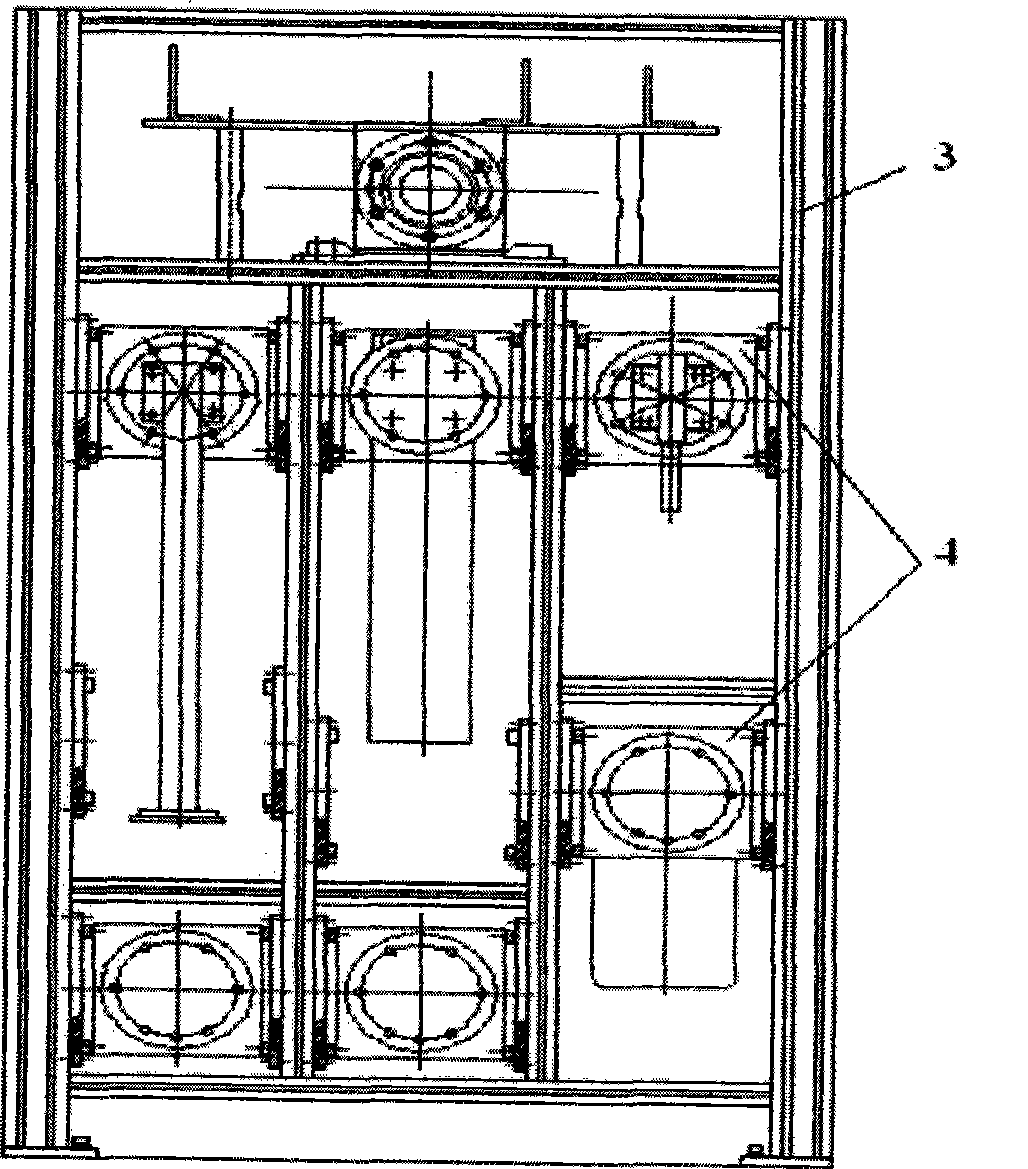
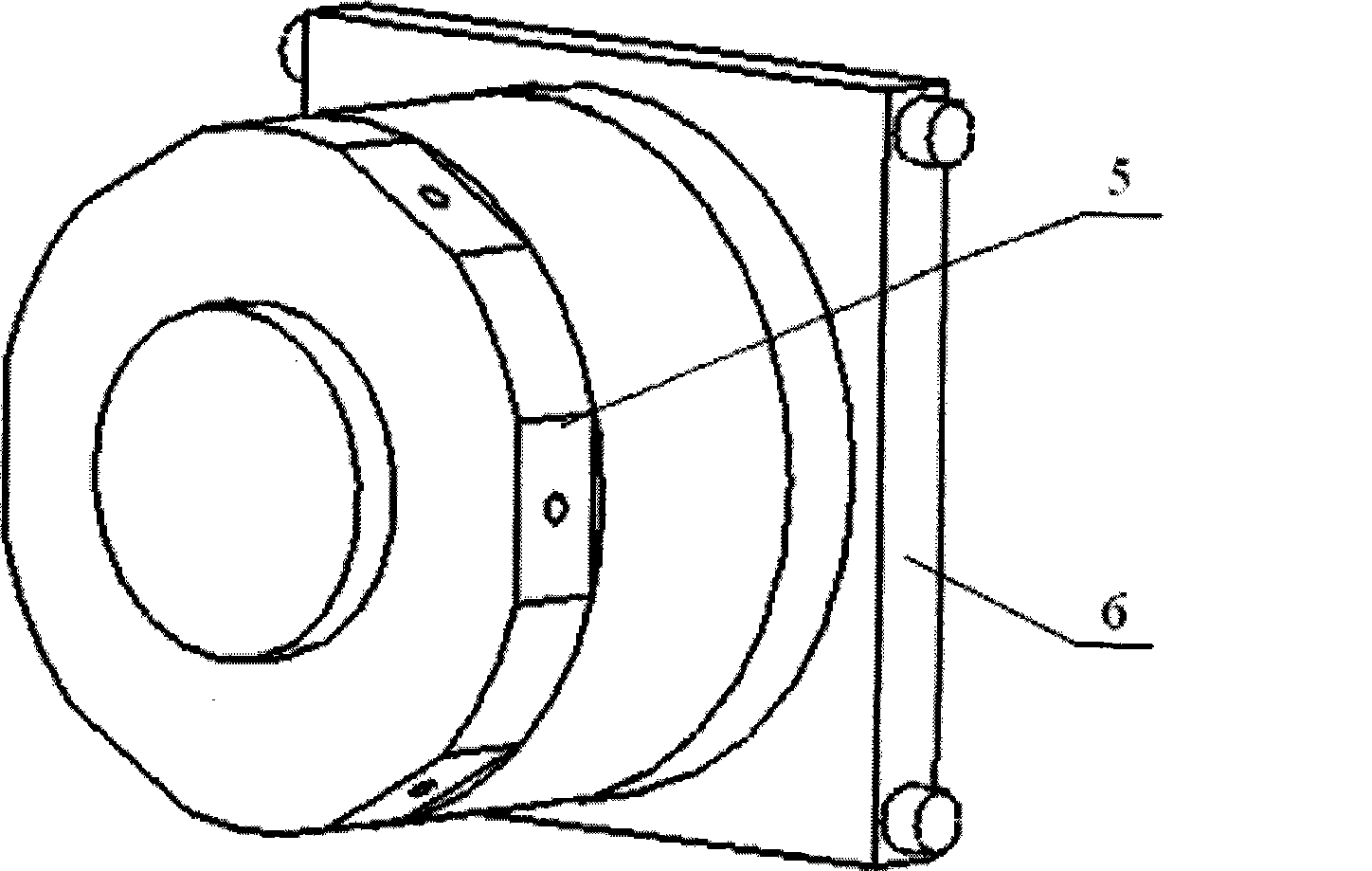
Aircraft system member mounting method and apparatus based on industrial robot
The invention discloses a method and a device for mounting aircraft system components based on an industrial robot. The method uses the industrial robot to automatically grip and replace system component templates through a tool quickly-replacing device, and automatically positions a system component mounting template according to a work path and a target pose calibrated by a laser tracker, so as to achieve auxiliary assembly work task such as gripping and positioning the system components, and the like during aircraft assembly. The device for mounting the aircraft system components comprises the industrial robot, the tool quickly-replacing device, a system component library, and the system component templates. The mobile industrial robot faces to an aircraft body at zero position, and the system component library is positioned at the back of the robot. A plurality of compartments are arranged in the system component library, and the system component templates are hung in the compartments according to codes. The system components are connected with the tool quickly-replacing device through quickly connected interfaces. The tool quickly-replacing device consists of a robot end and a tool end, and finishes automatic gripping of the system component templates through connection and separation of the robot end and the tool end in pneumatic control.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com