Industrial robot base coordinate system calibration method based on laser tracker
A laser tracker, industrial robot technology, applied in manipulators, manufacturing tools, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of complex operation, inability to directly calibrate the robot base coordinates, and the accuracy needs to be investigated, so as to improve the accuracy of measurement and save calibration. Time, the effect of saving the time of repeated calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] In order to illustrate the technical principles of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be described more clearly and completely below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
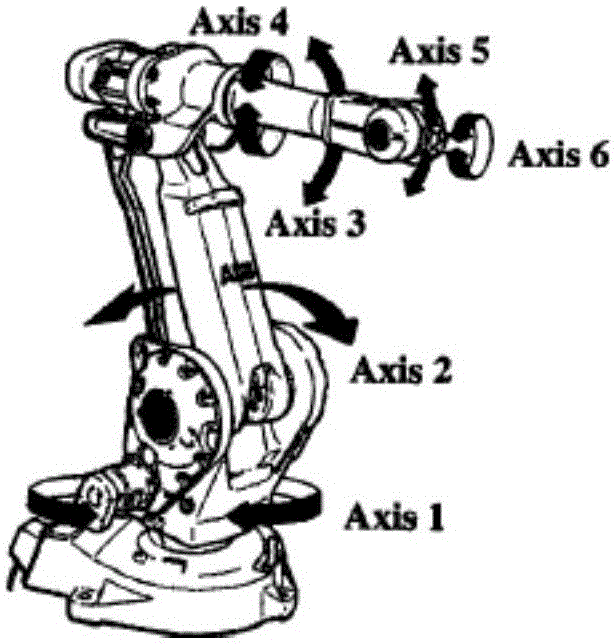
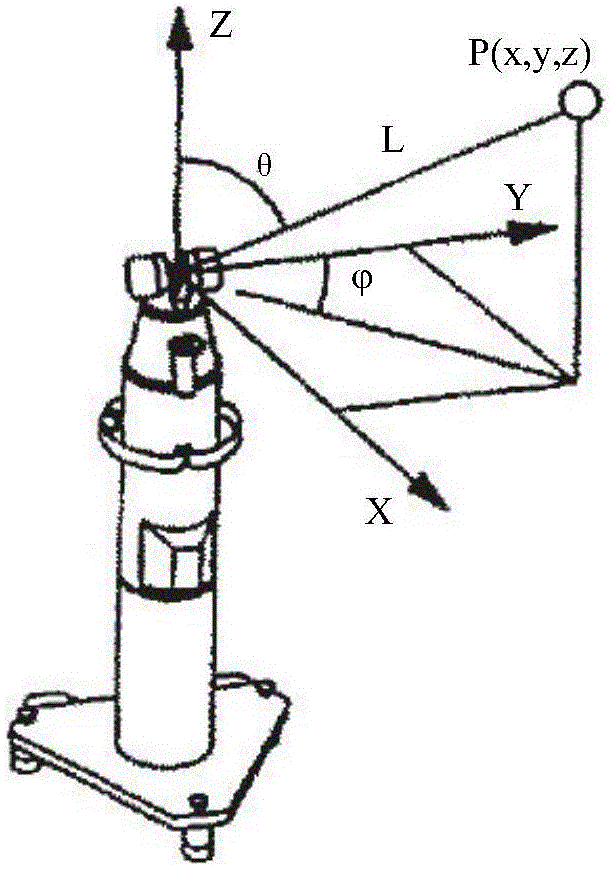
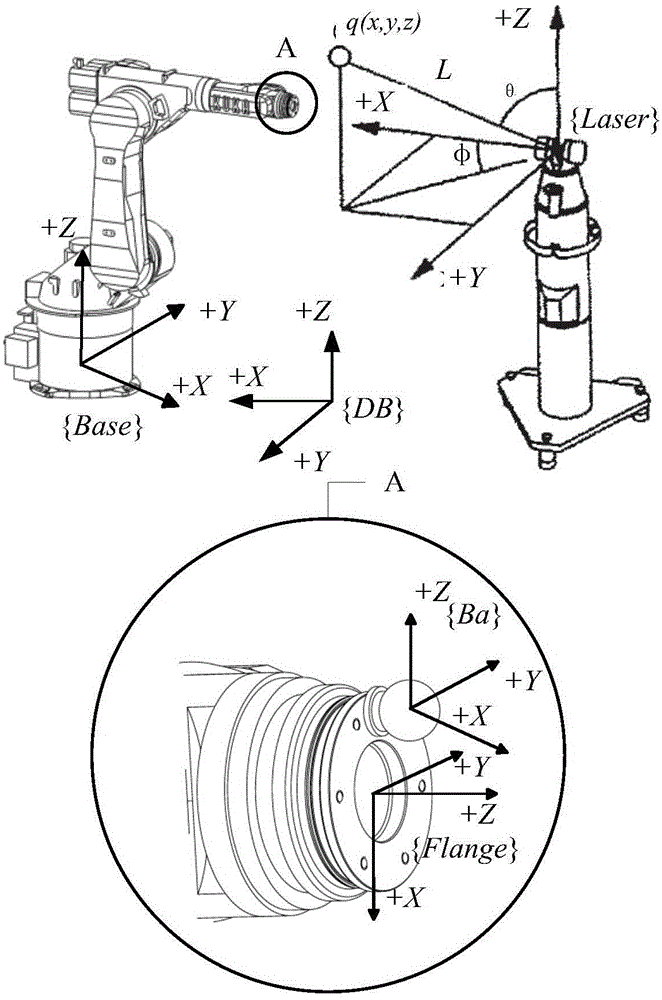
[0026] Typical serial industrial robots such as figure 1 As shown, the robot is installed on the workbench, and the rotation pairs of each joint of the robot are marked in the figure. The required measurement equipment laser tracker uses a spherical coordinate system laser tracker measurement system, the schematic diagram is as follows figure 2 As shown, the measurement tool is a target ball, which can be fixed on the target ball seat to achieve accurate measurement.
[0027] Adjust the robot to an appropriate space position, install three target seats on the robot installation surface, the target seats are at a certain distance apart, and are not located in a straight line; place the laser tracker at a fixed position to ensure that the end position of the robot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com