Patents
Literature
263 results about "Transmission order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reception & Transmission of orders refers to the reception of a purchase or sale order from the client and the immediate transmission of the instructions to the counterparty for execution.
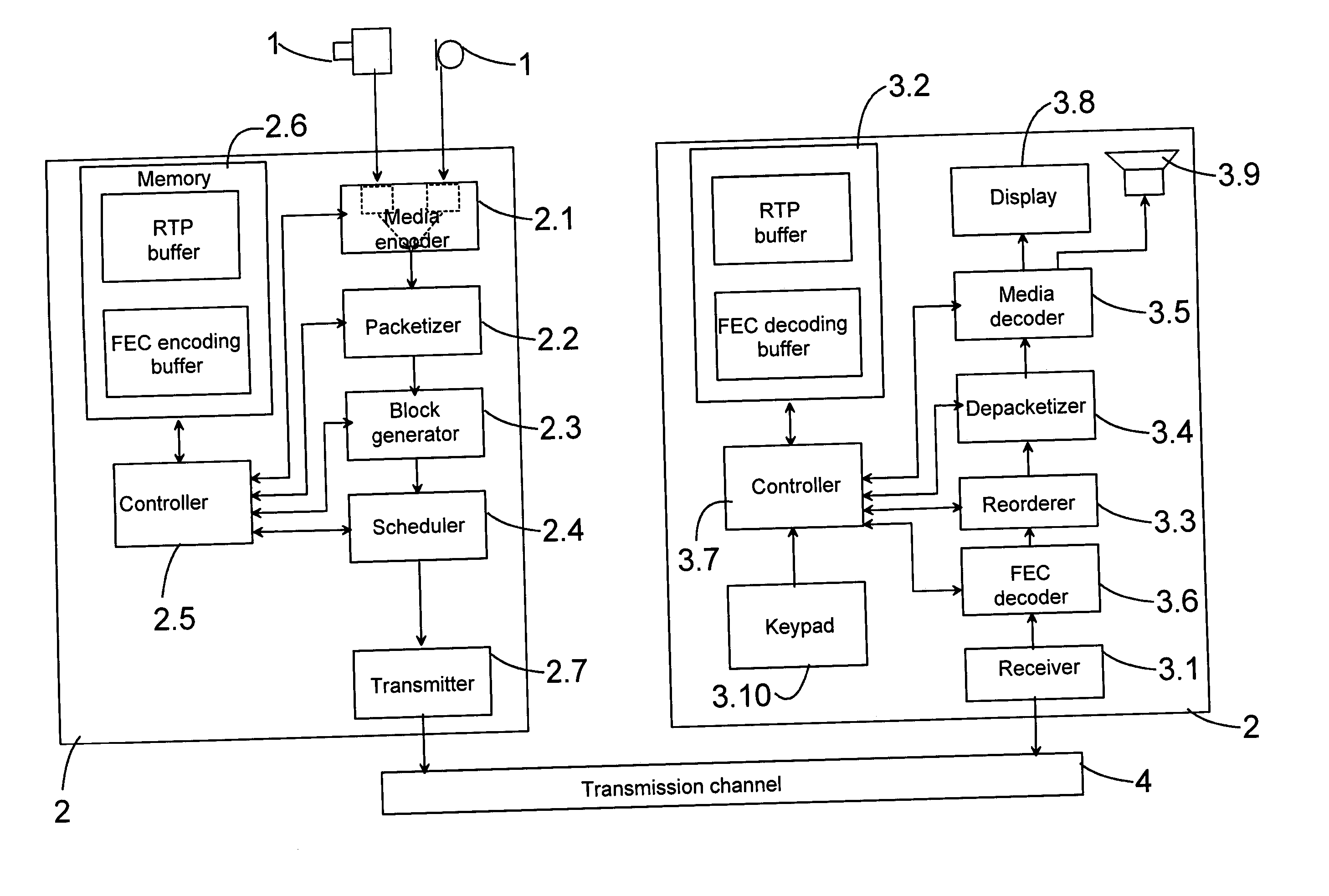
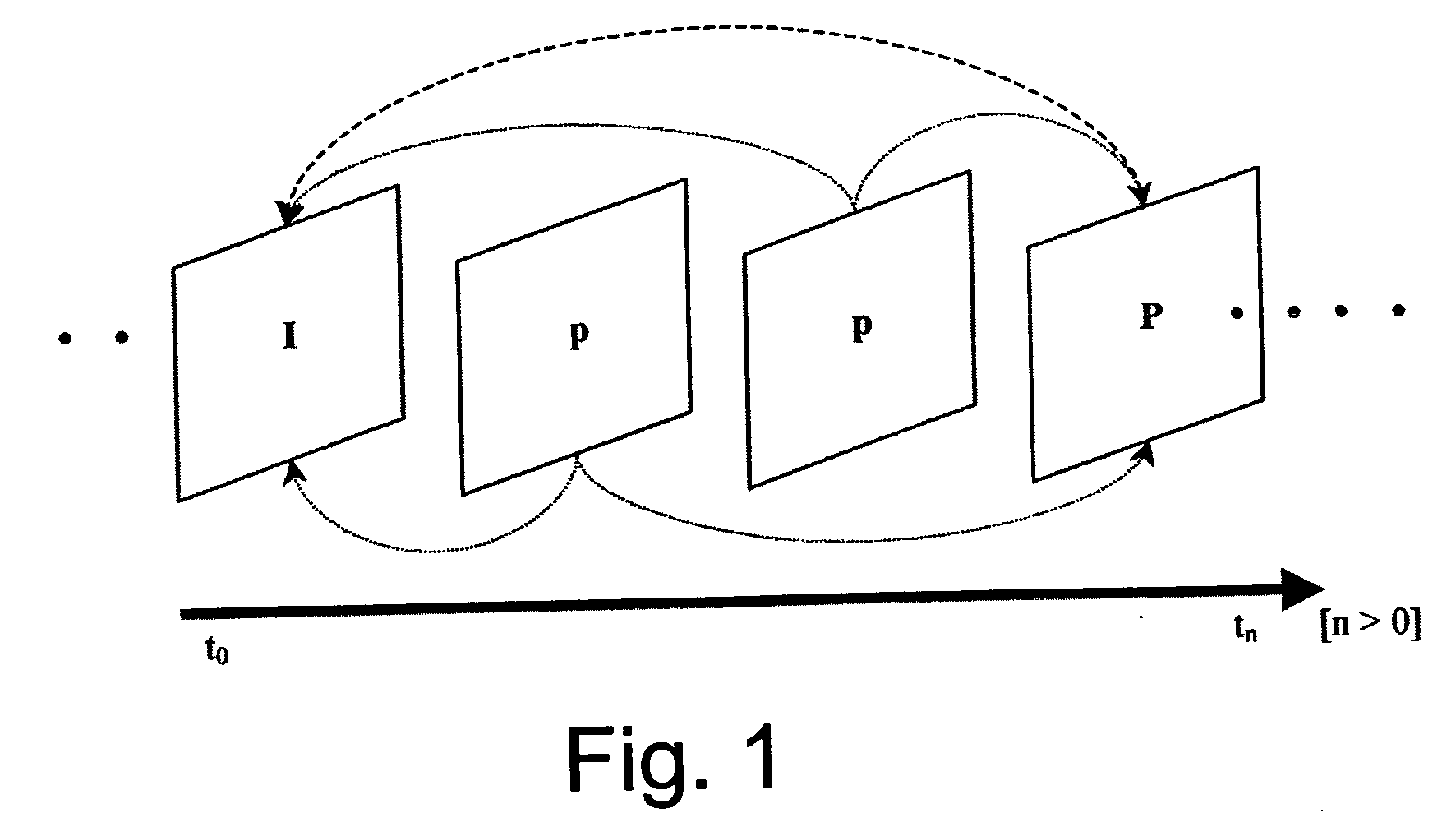
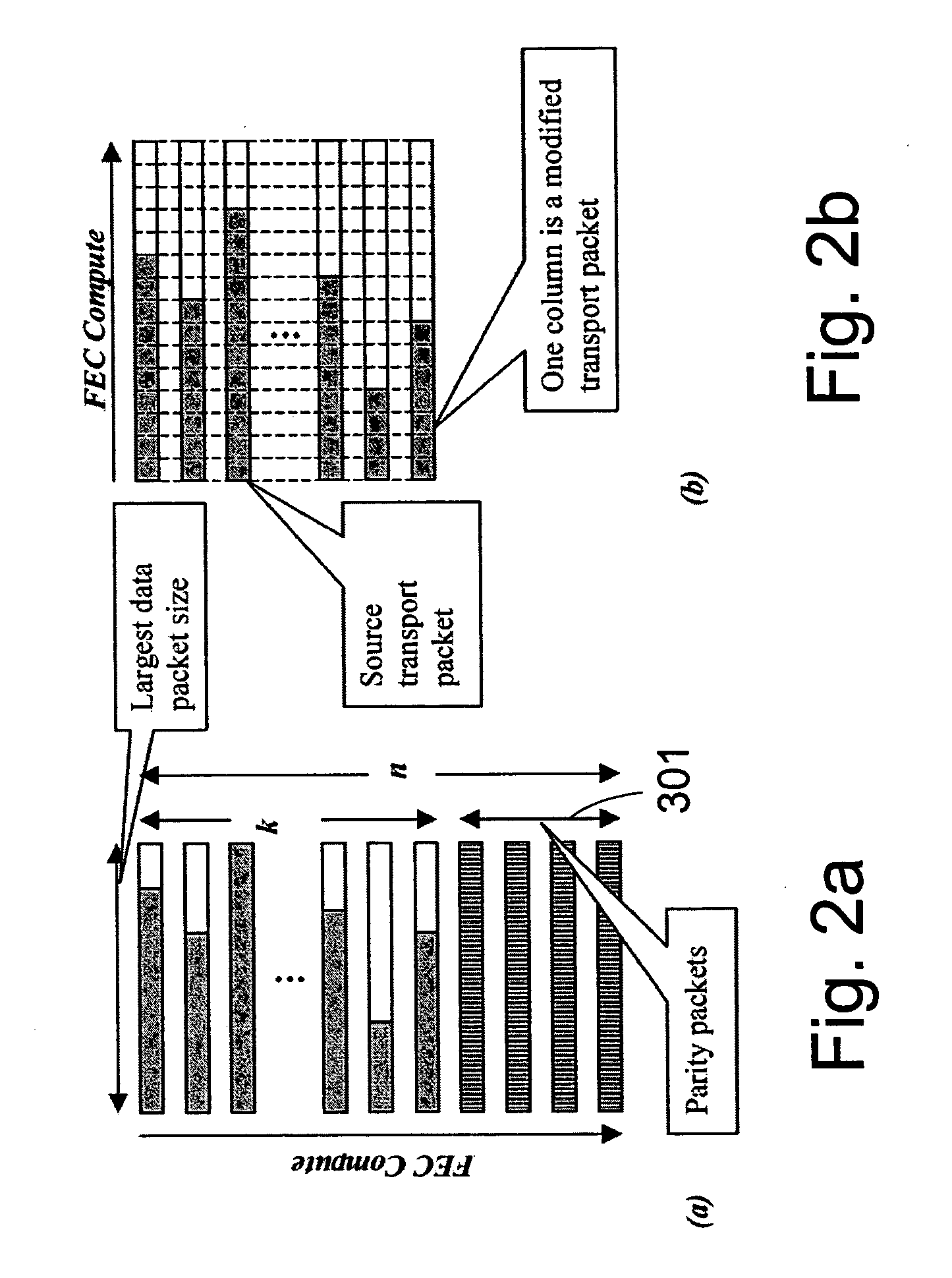
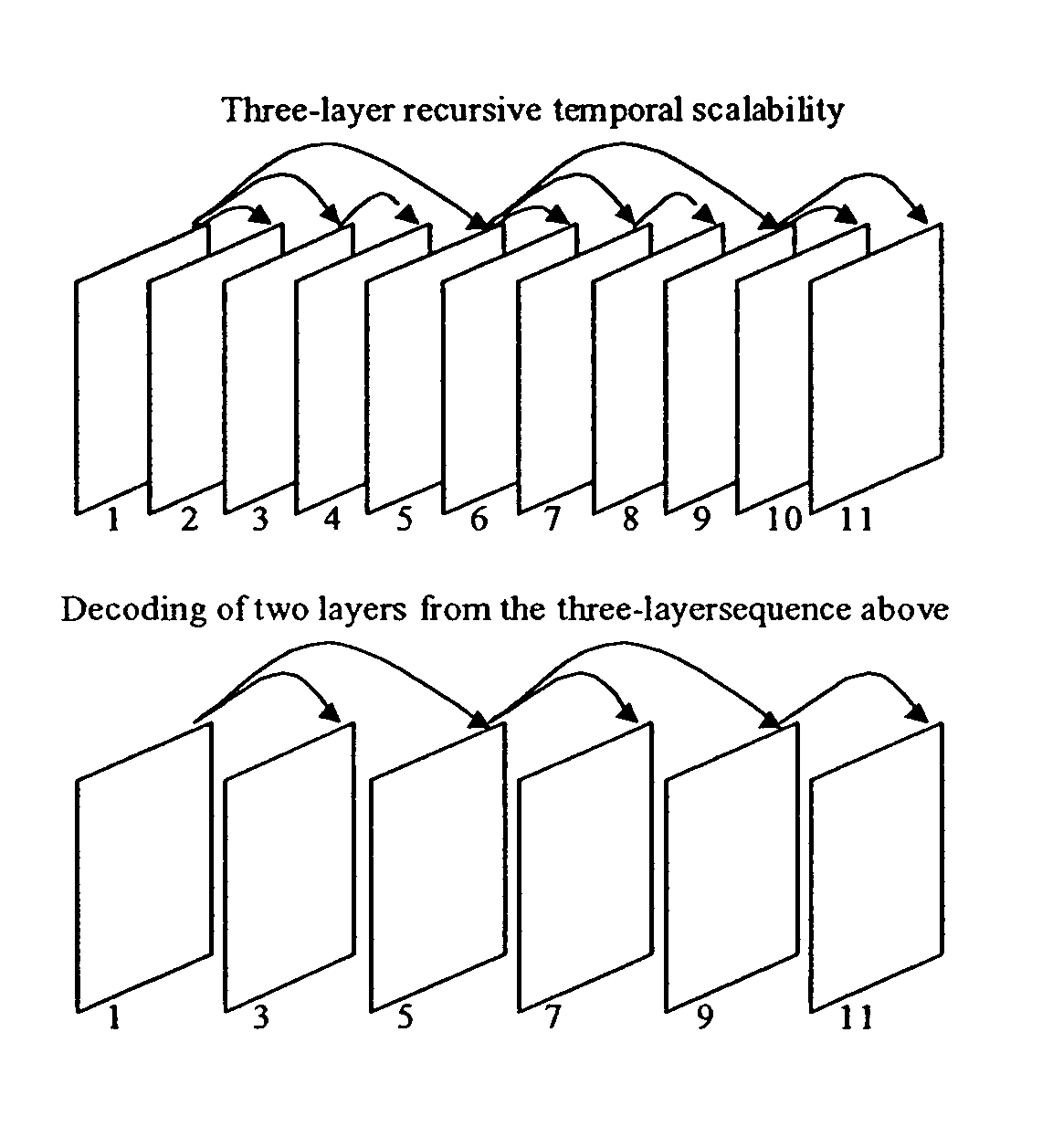
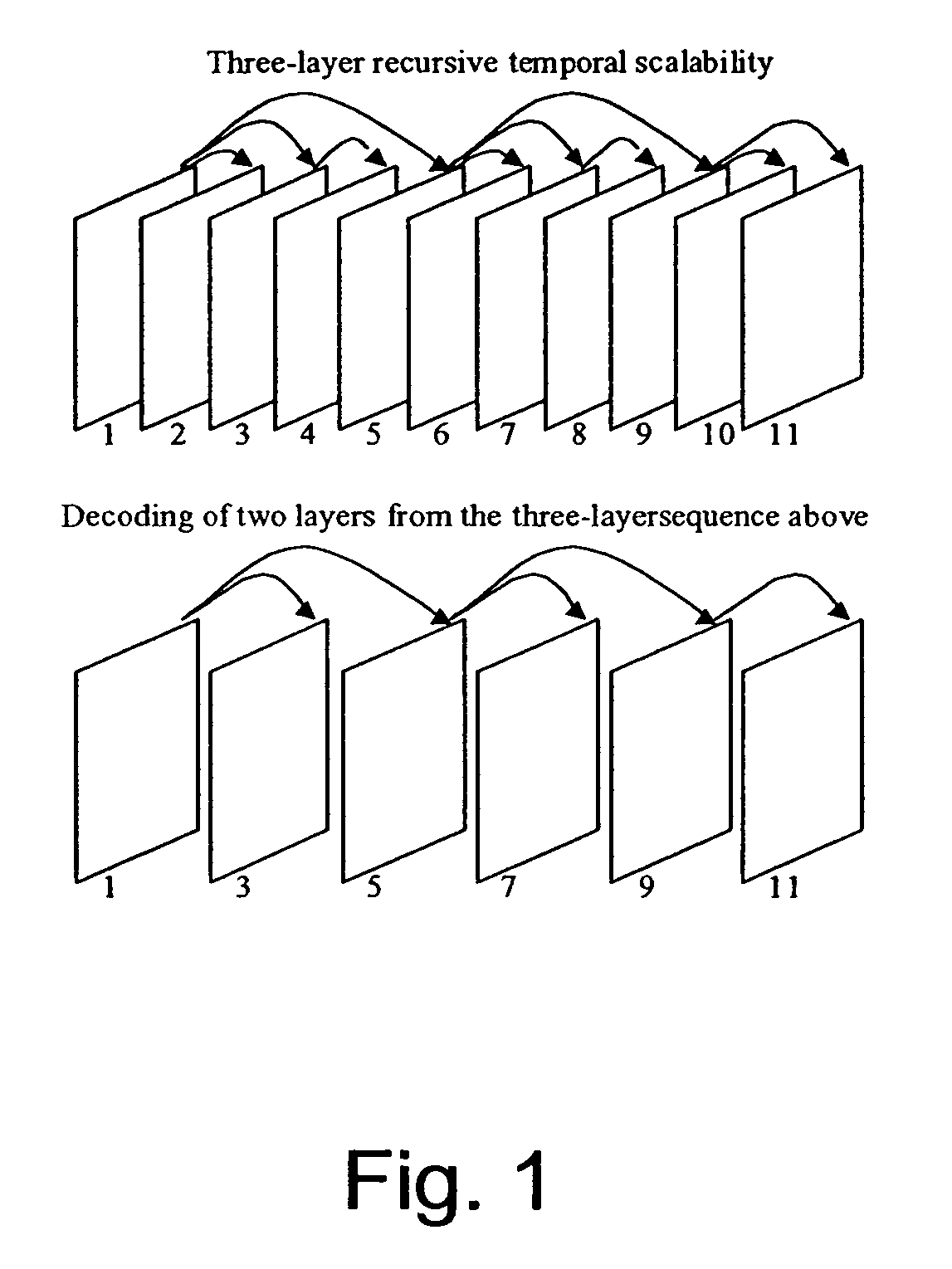
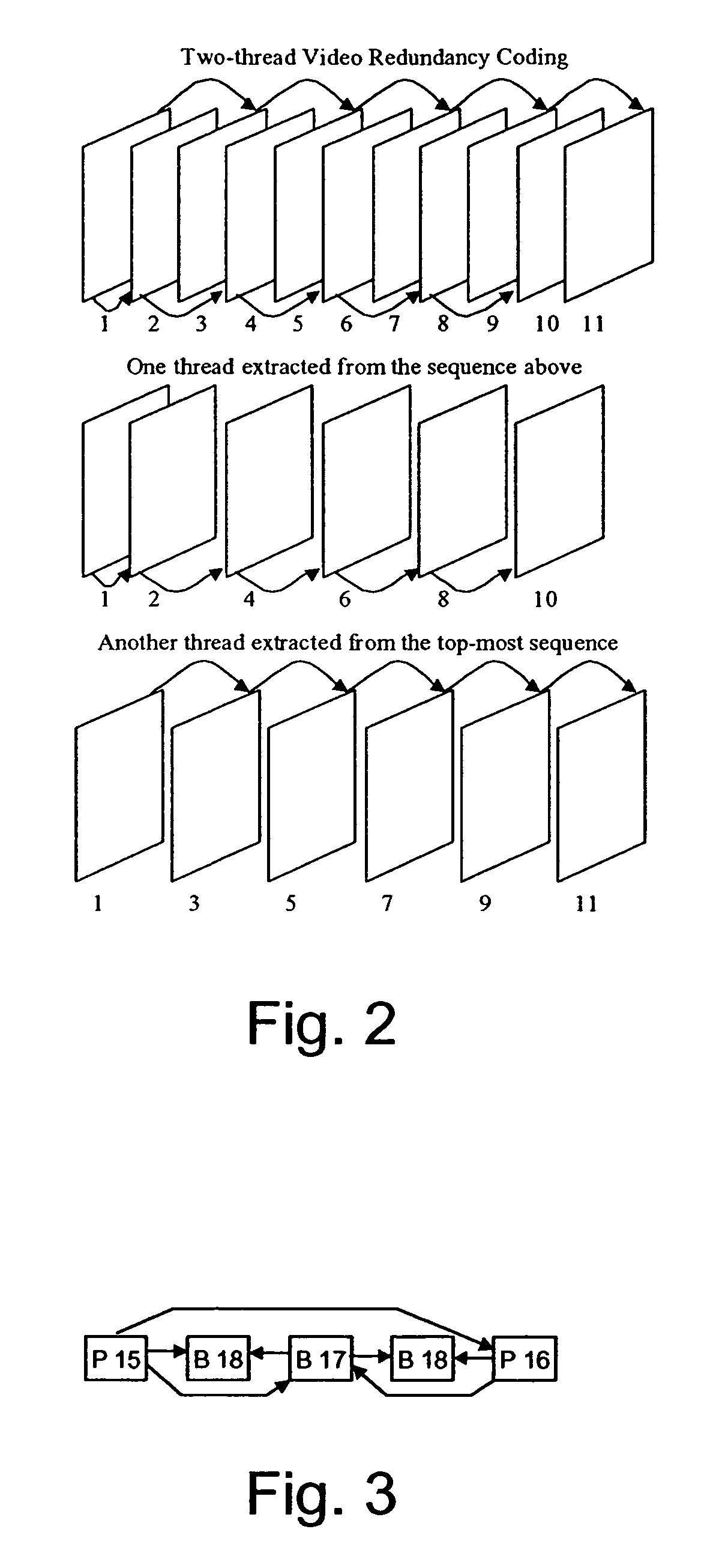
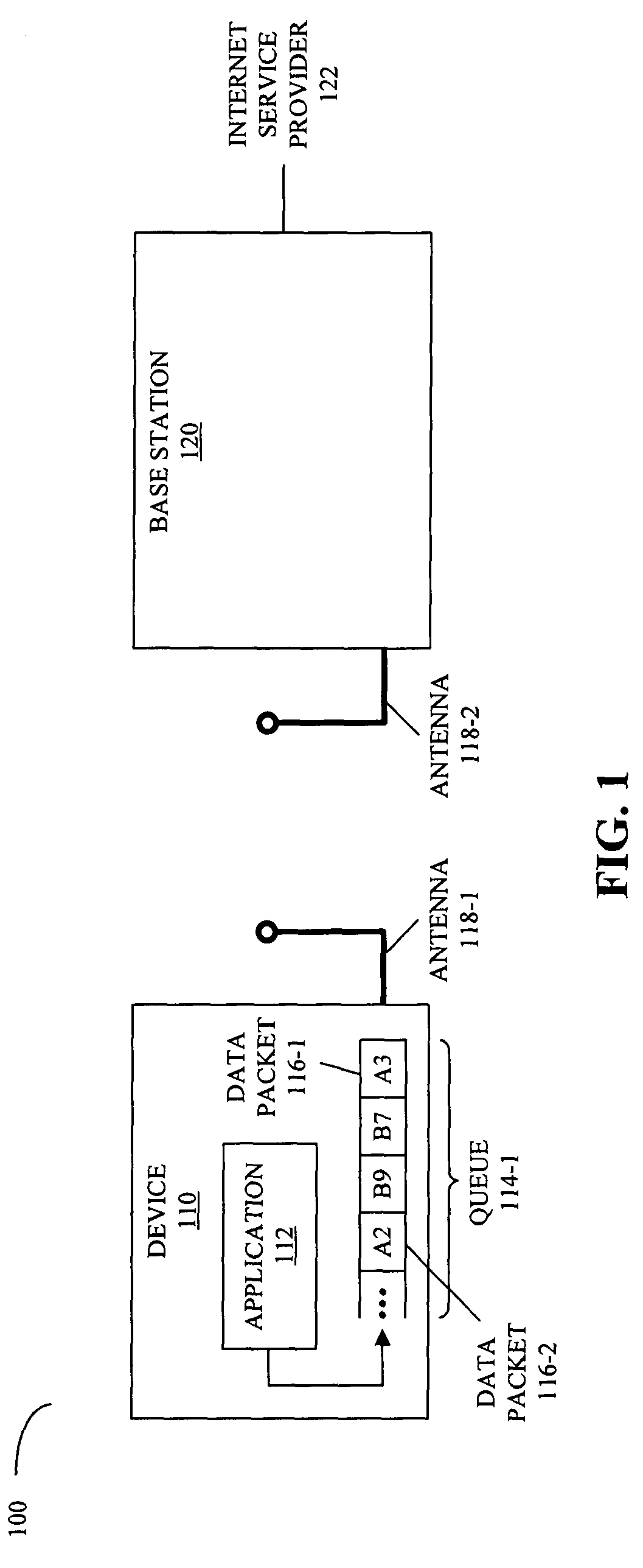
Packet stream arrangement in multimedia transmission
InactiveUS20060109805A1Reduce delaysUnequal error protectionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission orderMultimedia transmission
Transmitting media information from a transmitting device to a receiving device. To perform the transmission a media stream is encoded and packets are formed from the encoded media stream, the packets containing application data units, the application data units having a decoding order. At least two blocks are generated from the packets. The packets of the at least two blocks are organized into a first group and a second group, the first group being decodable without reception of said second group. The transmission order of the packets of said first group is arranged succeeding packets of said second group such that the application data units in the transmission order are at least partly in a different order than the decoding order.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
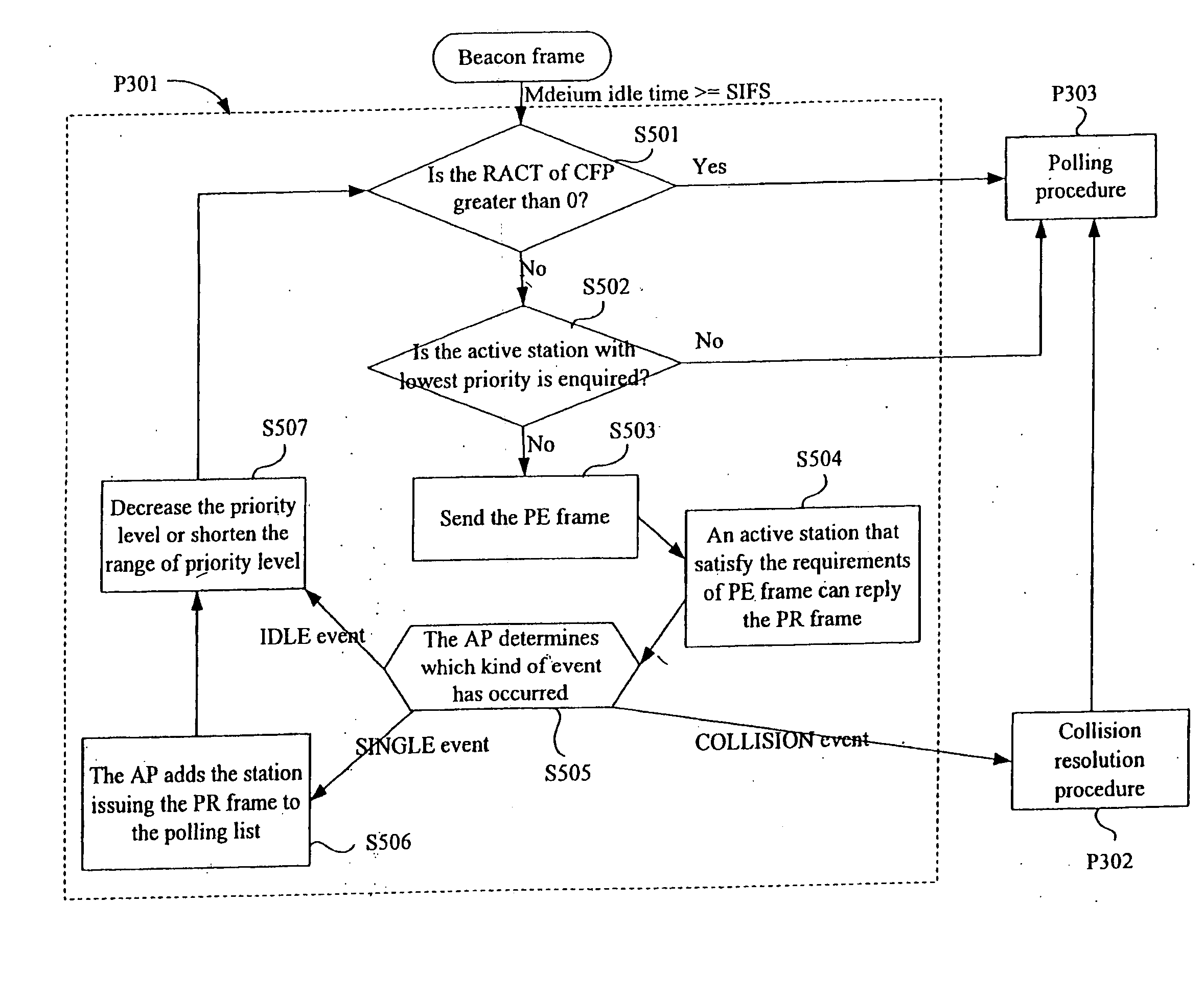
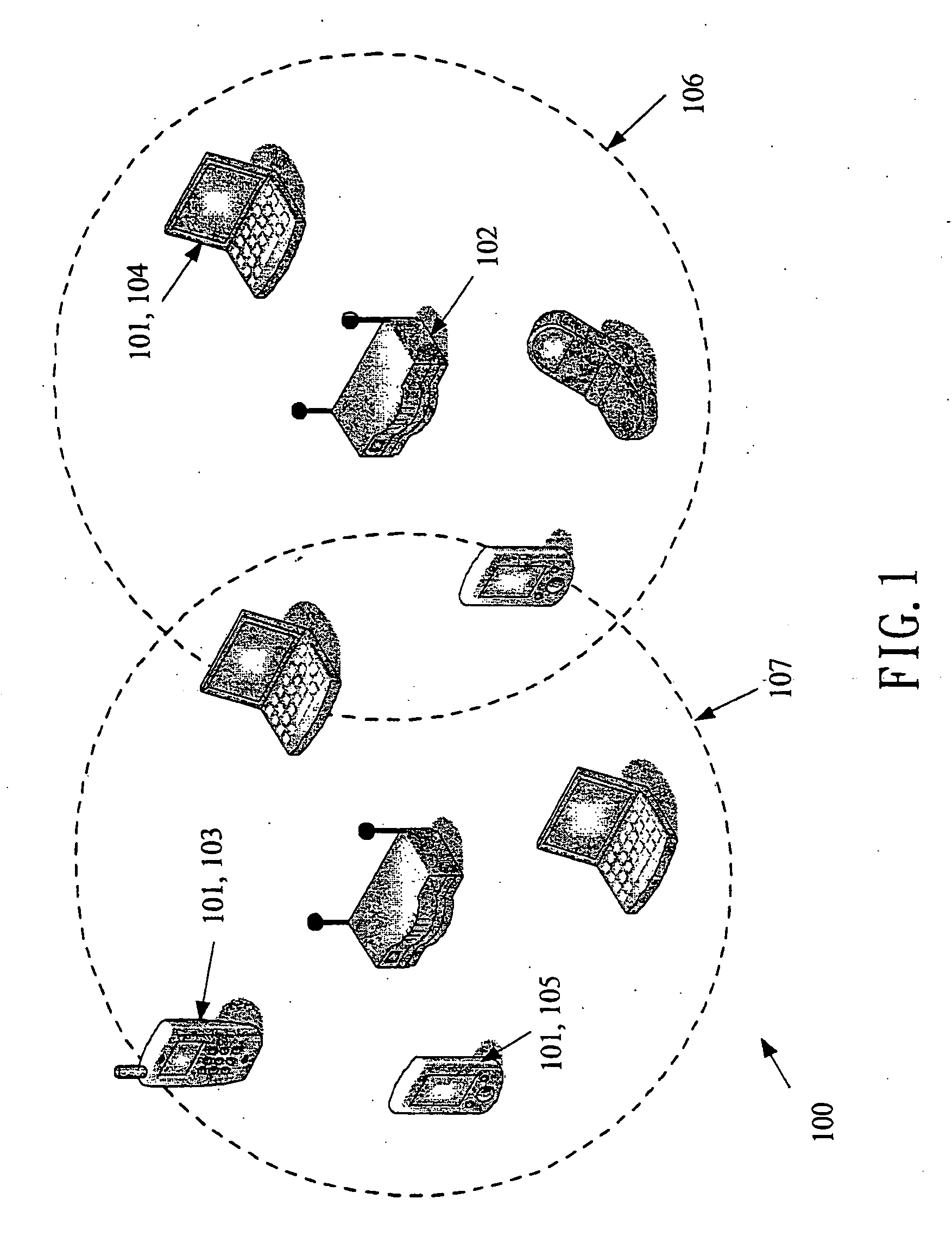
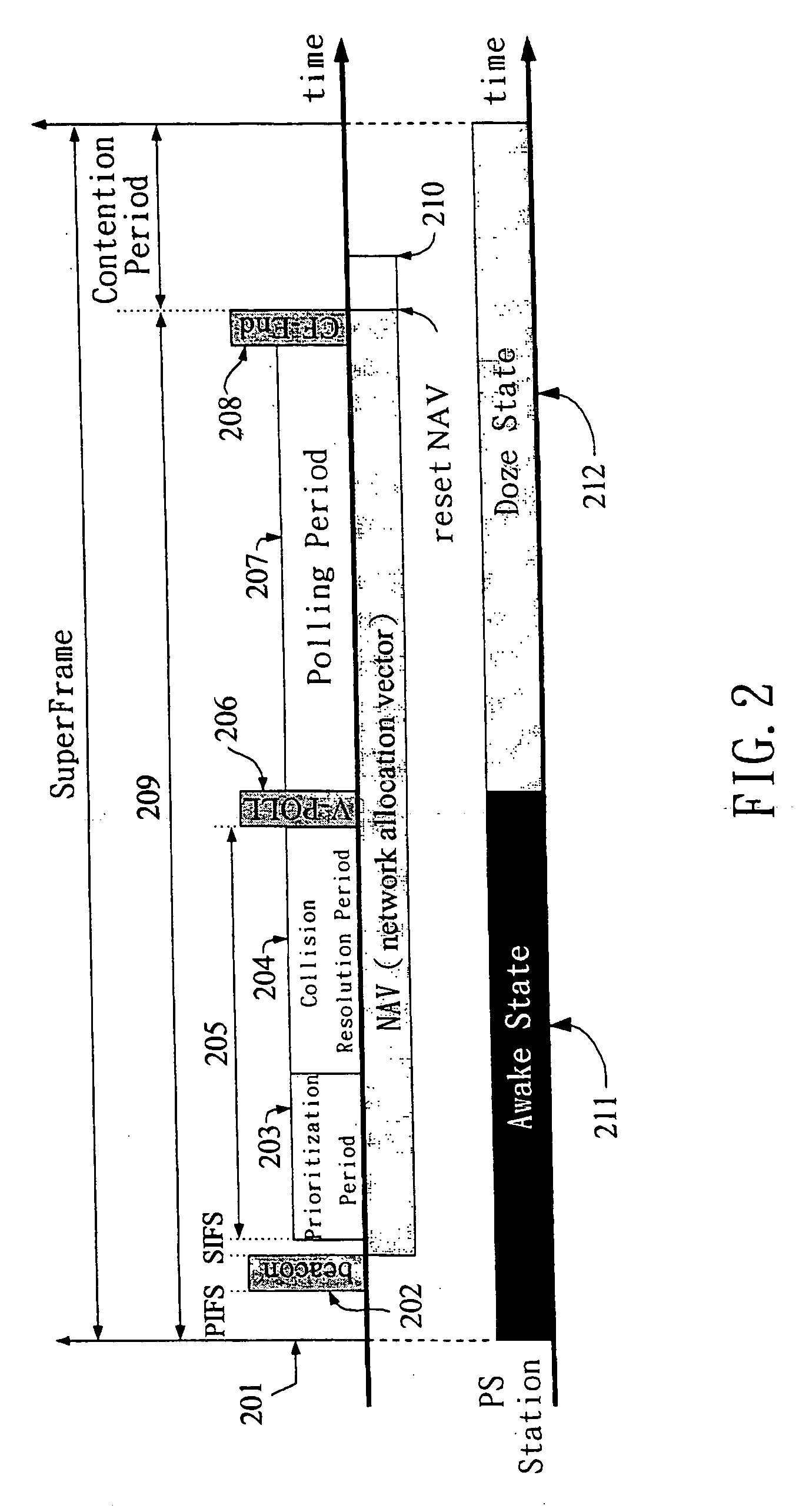
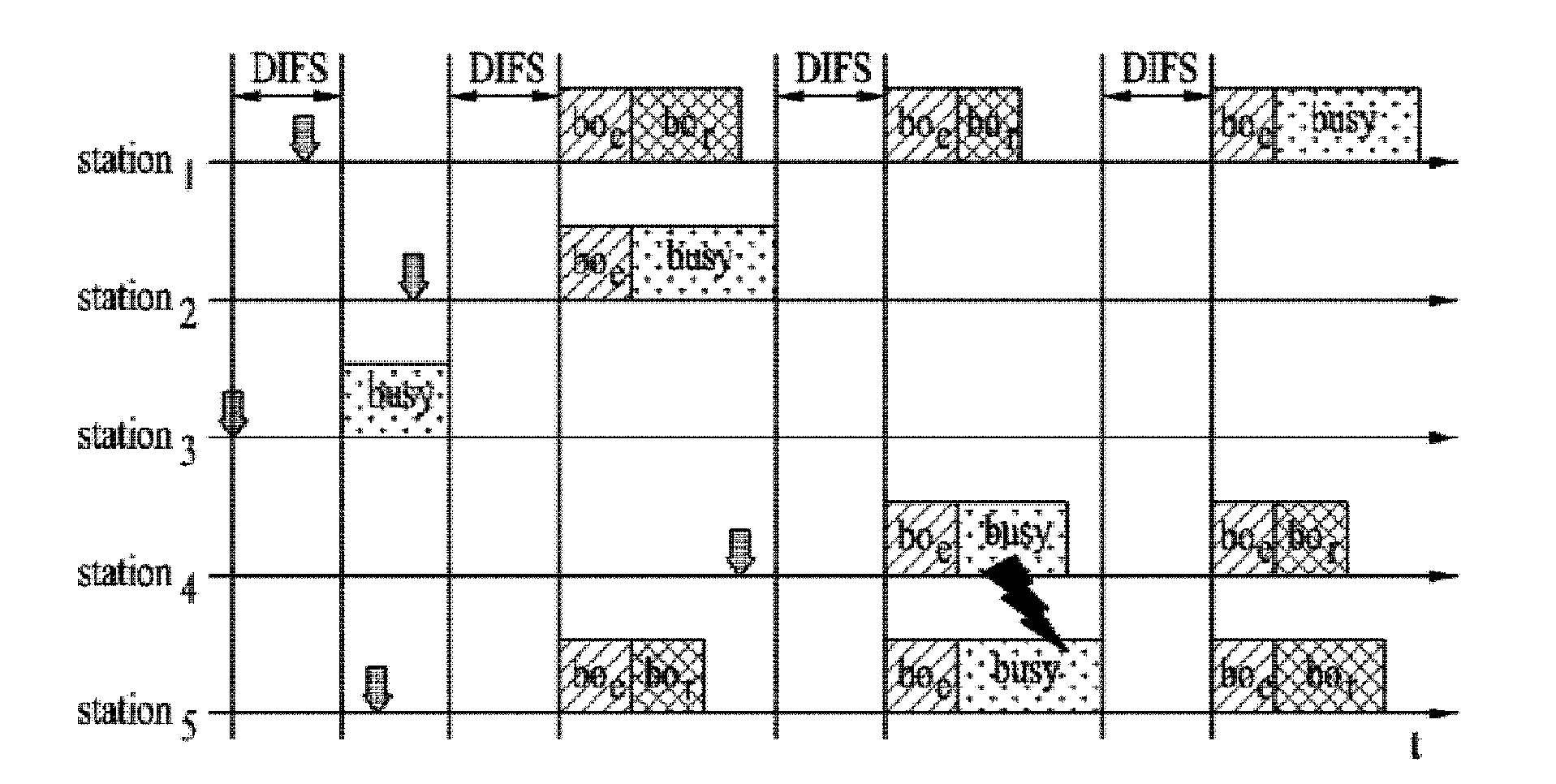
Medium access control methods with quality of service and power management for wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20060062181A1Reduce unnecessary collisionReduce retransmissionEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsQuality of serviceWireless lan
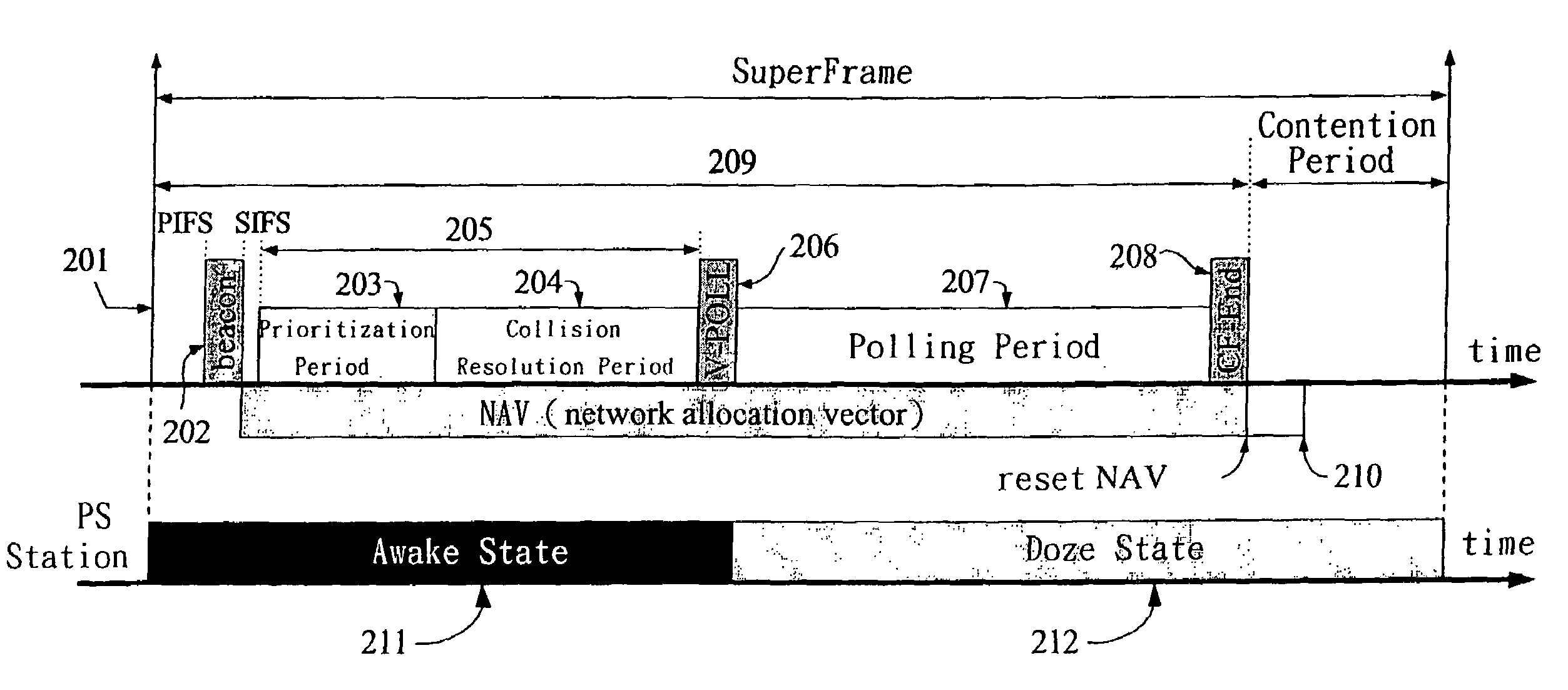
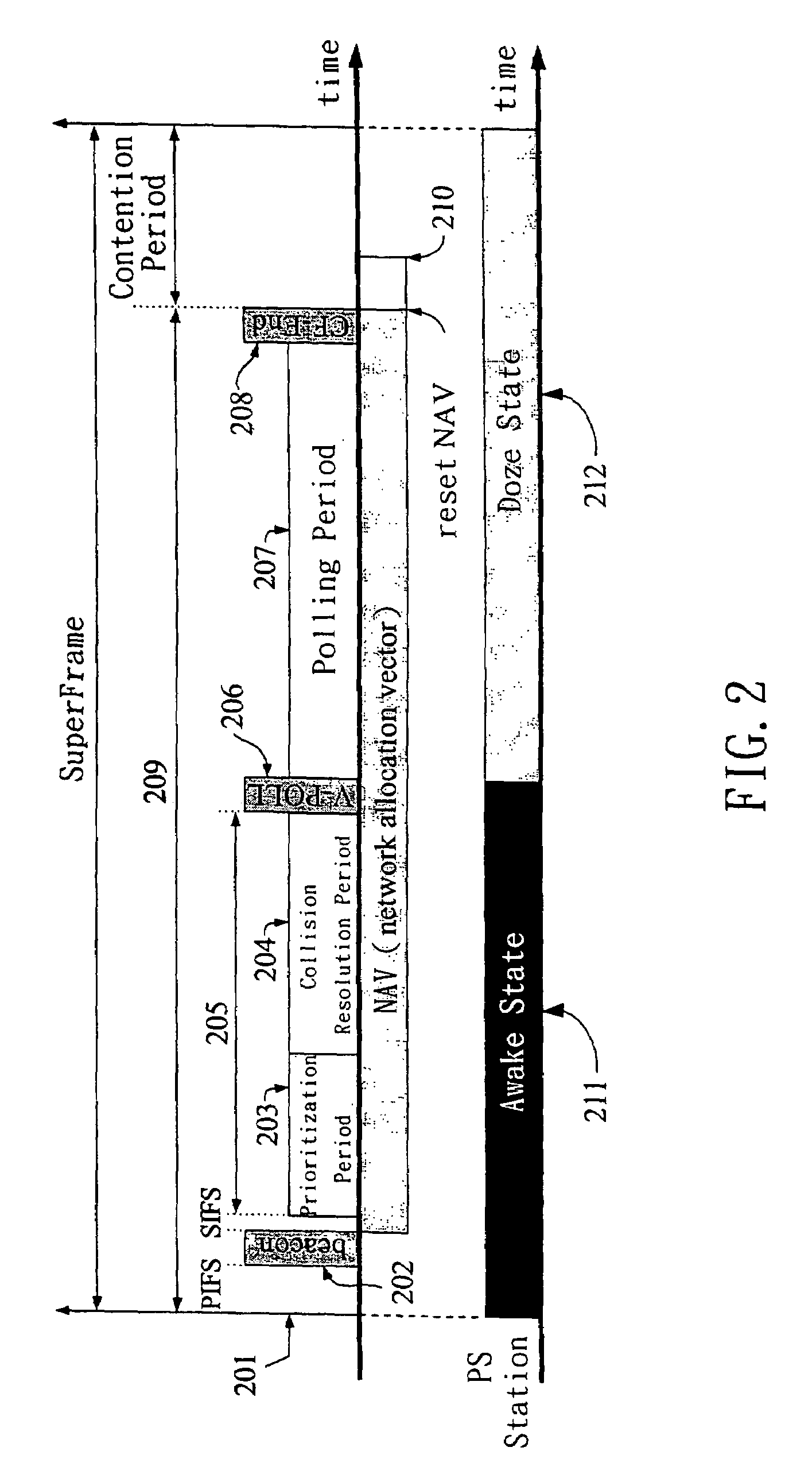
A MAC method has three procedures: a prioritization procedure, a collision resolution procedure, and a polling procedure. The prioritization procedure employs the handshaking method to ensure that a high priority station can join the polling list earlier than a low priority station. The collision resolution procedure employs a tree-splitting algorithm to ensure all active stations that underwent the prioritization period can join the polling list in a bounded time. In the polling procedure, the AP allocates the TXOP for each admitted station and schedules the transmission order of all admitted stations. In addition, the AP broadcasts the schedule information in the V-POLL frame. A power-saving station can wake up at the start of the contention-free period. To conserve power, on inspecting the V-POLL frame, if a PS station finds that it cannot transmit nor receive data frames during the polling period, then that station may return to the doze state.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
System and method for scheduling timeslots for transmission by optical nodes in an optical network
ActiveUS20110255866A1Time-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer networkOptical network unit
A signal strength corresponding to an incoming optical burst from each of a plurality of optical nodes is measured. The measurements can be performed at system start-up, configuration / installation of the optical nodes and / or at certain intervals of operation of the optical nodes. Signal strength information for the optical nodes based on the measurements is stored in memory. When scheduling the optical nodes for transmission, a preferred transmission order is determined in response to the stored signal strength information. In an embodiment, the preferred order is determined to reduce differences in signal strength levels between consecutive optical bursts.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Parameter for receiving and buffering pictures
ActiveUS8670486B2Improve compression efficiencyImprove error resiliencePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer networkTransmission order
The invention relates to a method for buffering multimedia information, wherein a parameter is defined indicative of the maximum amount of transmission units comprising multimedia data that precede any transmission unit comprising multimedia data in the packet stream in transmission unit transmission order and follow the transmission unit comprising multimedia data in decoding order. The invention also relates to a system, a transmitting device, a receiving device, a computer program product, a signal and a module.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Data transfer mechanism for handheld devices over a wireless communication link
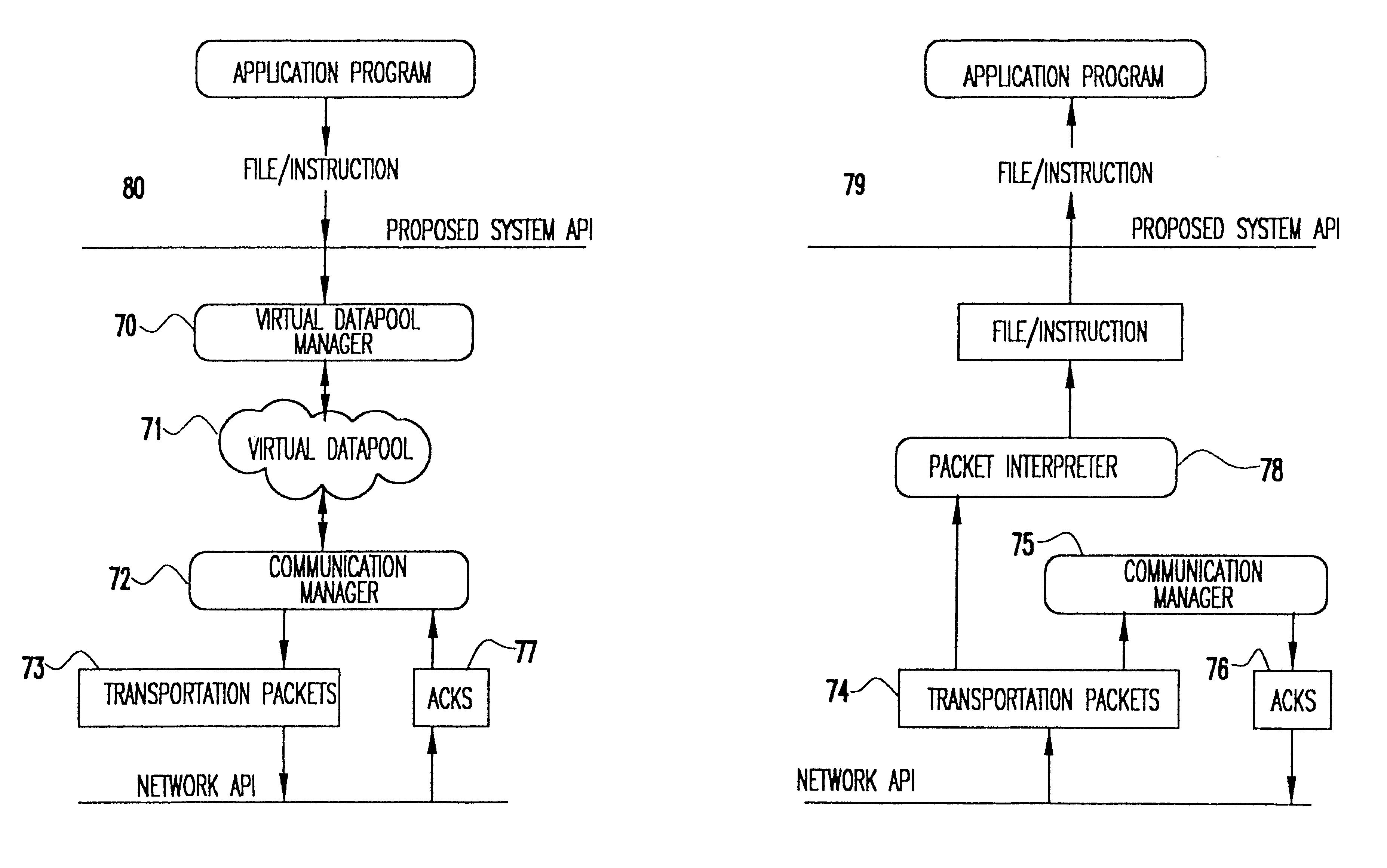
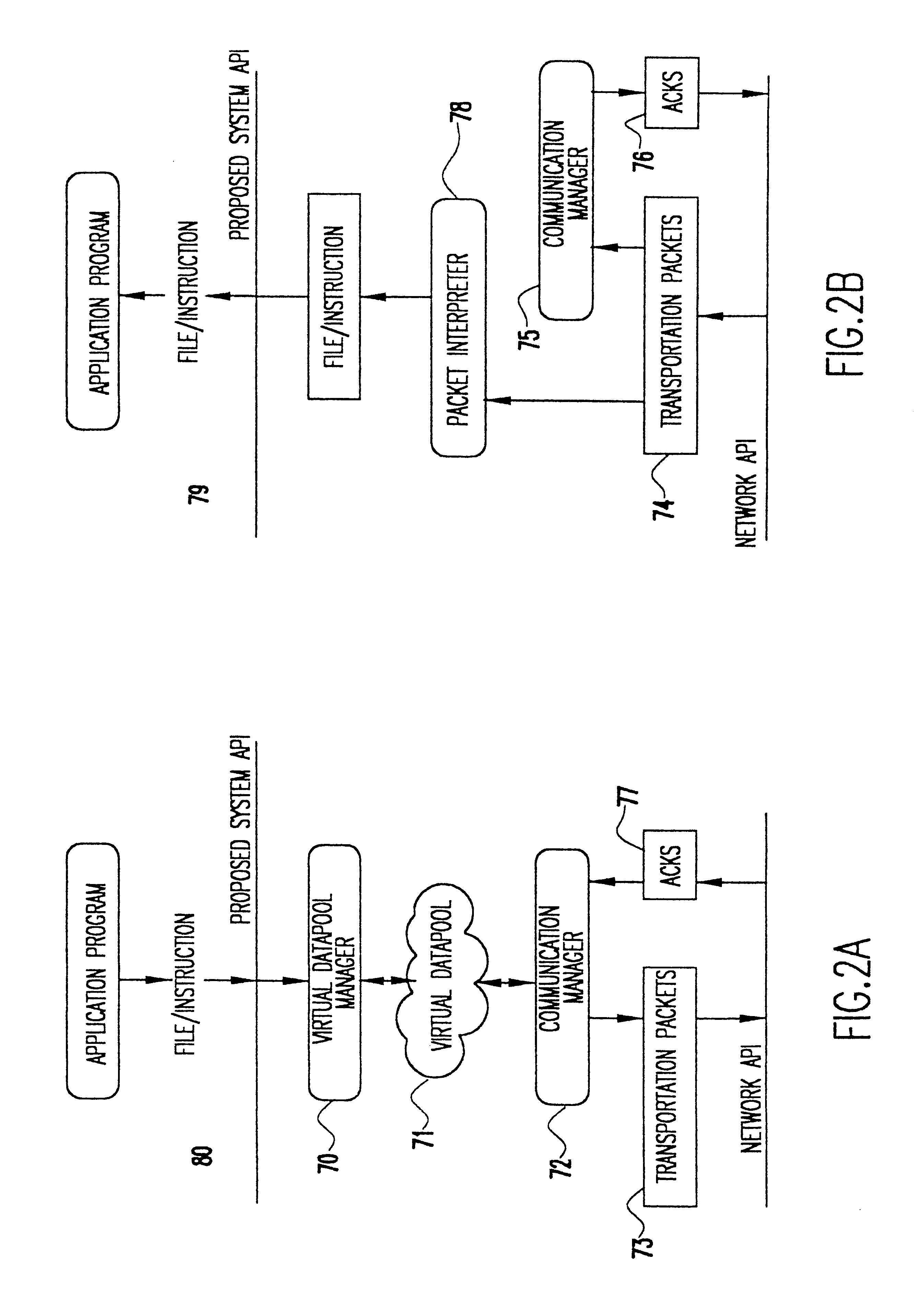
InactiveUS6775298B1Bandwidth is not as inexpensiveReduce battery power consumptionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications linkNetwork packet
A method and apparatus for transferring data between a handheld device and a network over a wireless communications link. A datapool manager breaks files into virtual blocks and adds the virtual blocks to a datapool. A communications manager converts the virtual blocks into transportation packets and controls the transfer of the transportation packets between the handheld device and the network. After a transportation packet is transferred, an acknowledgment is returned indicating that the transfer was successful. If the transfer of a file is interrupted, then, upon reestablishing the wireless link, only those transportation packets for which an acknowledgment has not been returned are transferred. To properly reconstruct the file, a pointer indicates the location of each transportation packet in the file. Furthermore, to enable the use of a partially transferred file, a table of information is maintained indicating the validity of the partially transferred file. Transportation packets are identified as instruction packets or data packets. When determining the order of transfer, priority is placed on the transfer of instruction packets.
Owner:IBM CORP
Picture buffering method
ActiveUS20060072597A1Improve compression efficiencyImprove error resilienceData switching by path configurationDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareData transmission
A method for buffering media data in a buffer where the media data is included in data transmission units which have been ordered in a transmission order which is at least partly different from a decoding order of the media data in the data transmission units. The decoding order is indicated with a quantitative indicator for at least part of the transmission units. In the method a parameter is defined for a relation of the quantitative indicators of transmission units. The relation of transmission units in the buffer is checked against the parameter. The result of the checking is indicative of at least one transmission unit in the buffer preceding, in decoding order, any transmission unit in a sequence of transmission units not having been buffered in the buffer before the checking.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
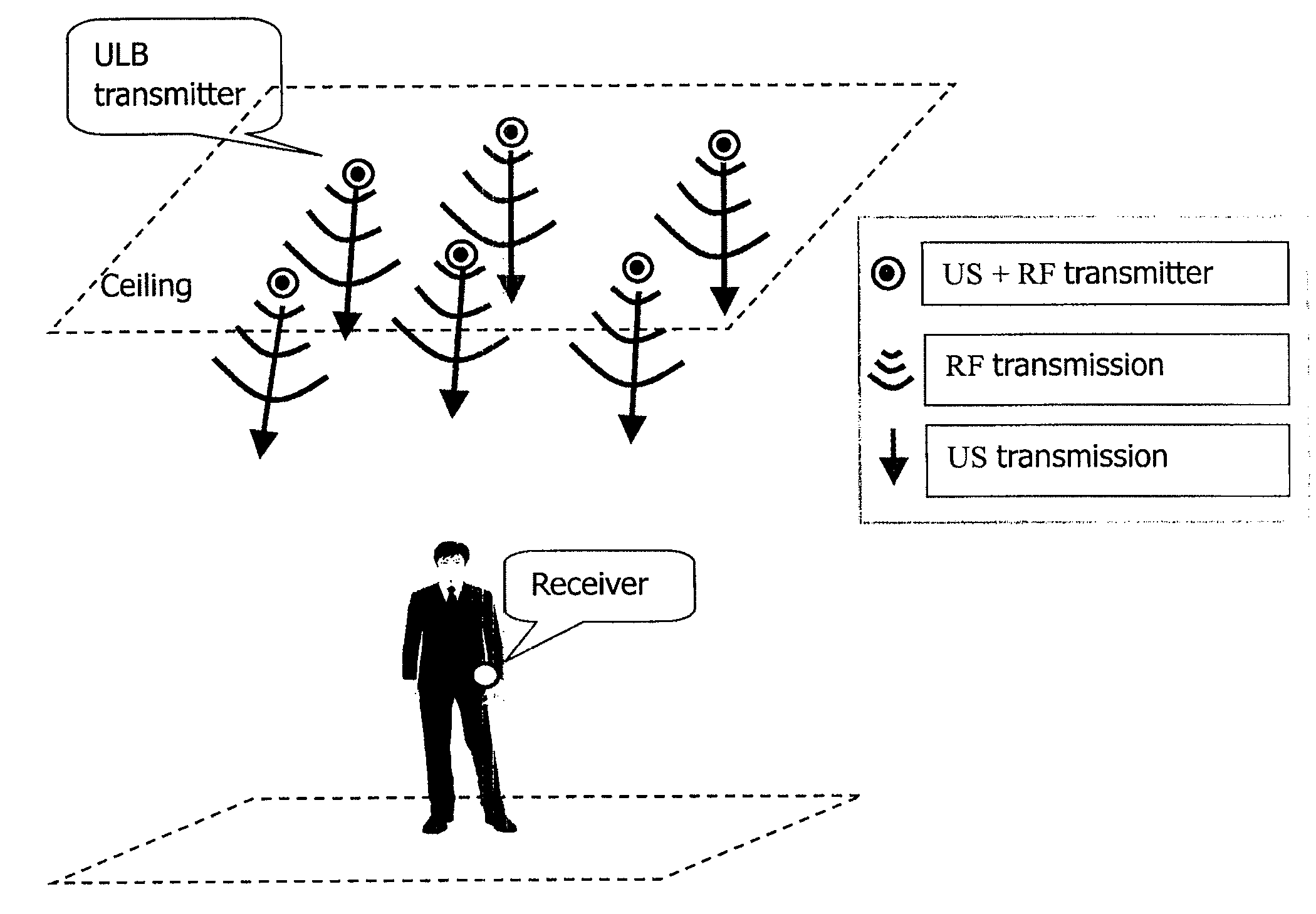
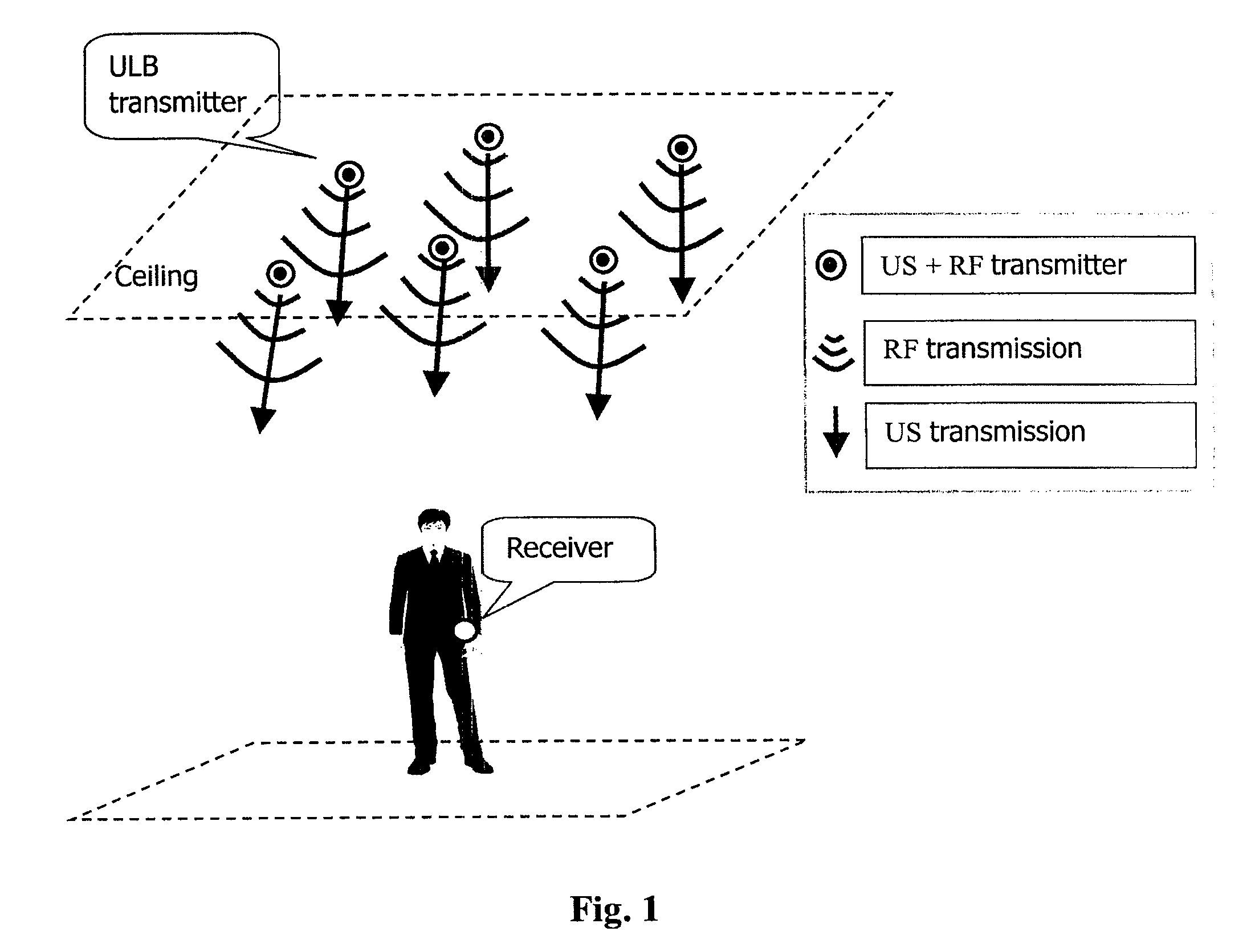
Autonomous ultrasonic indoor location system, apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090295639A1Improve accuracyReduce complexityDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSonificationEngineering
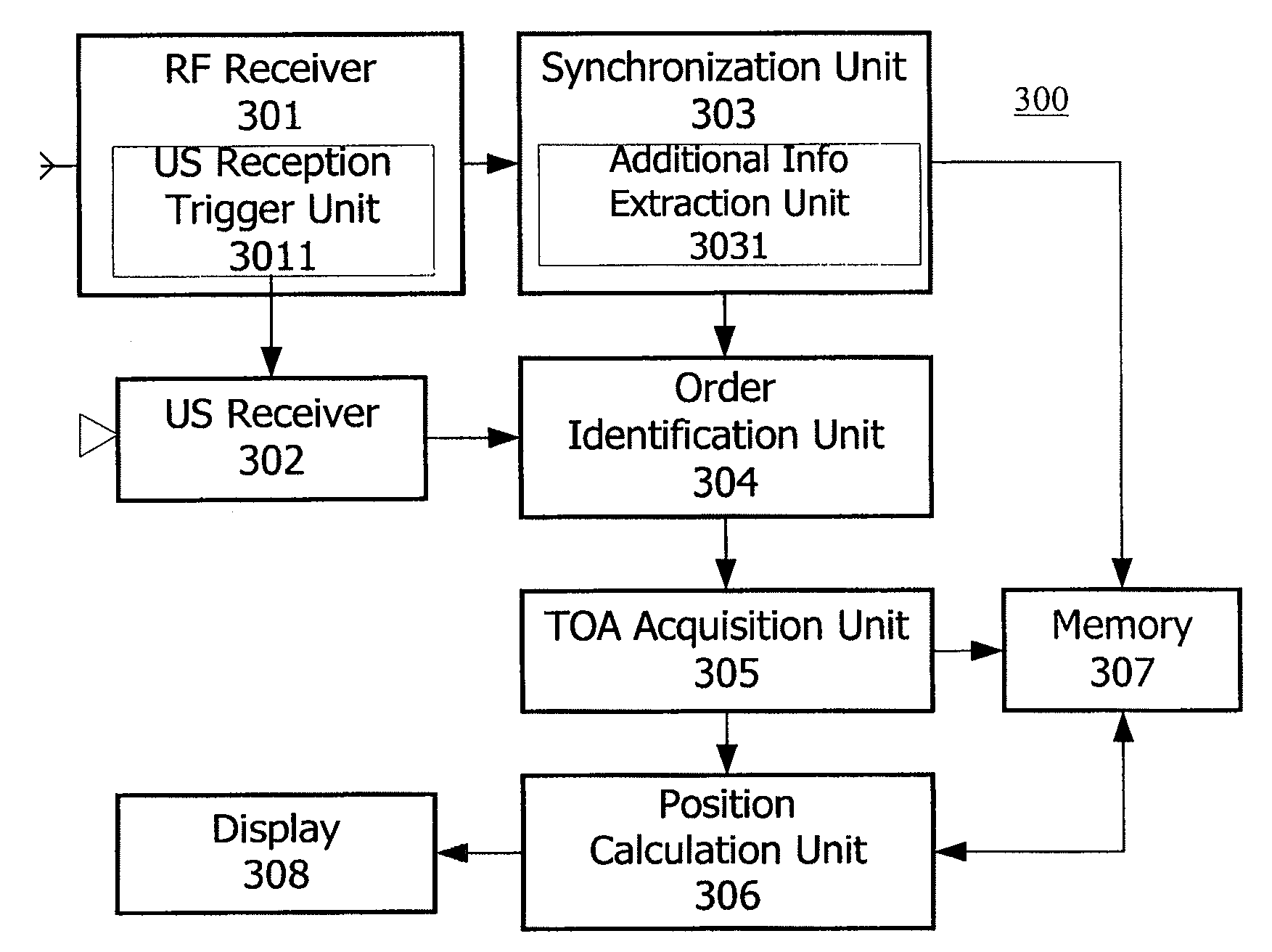
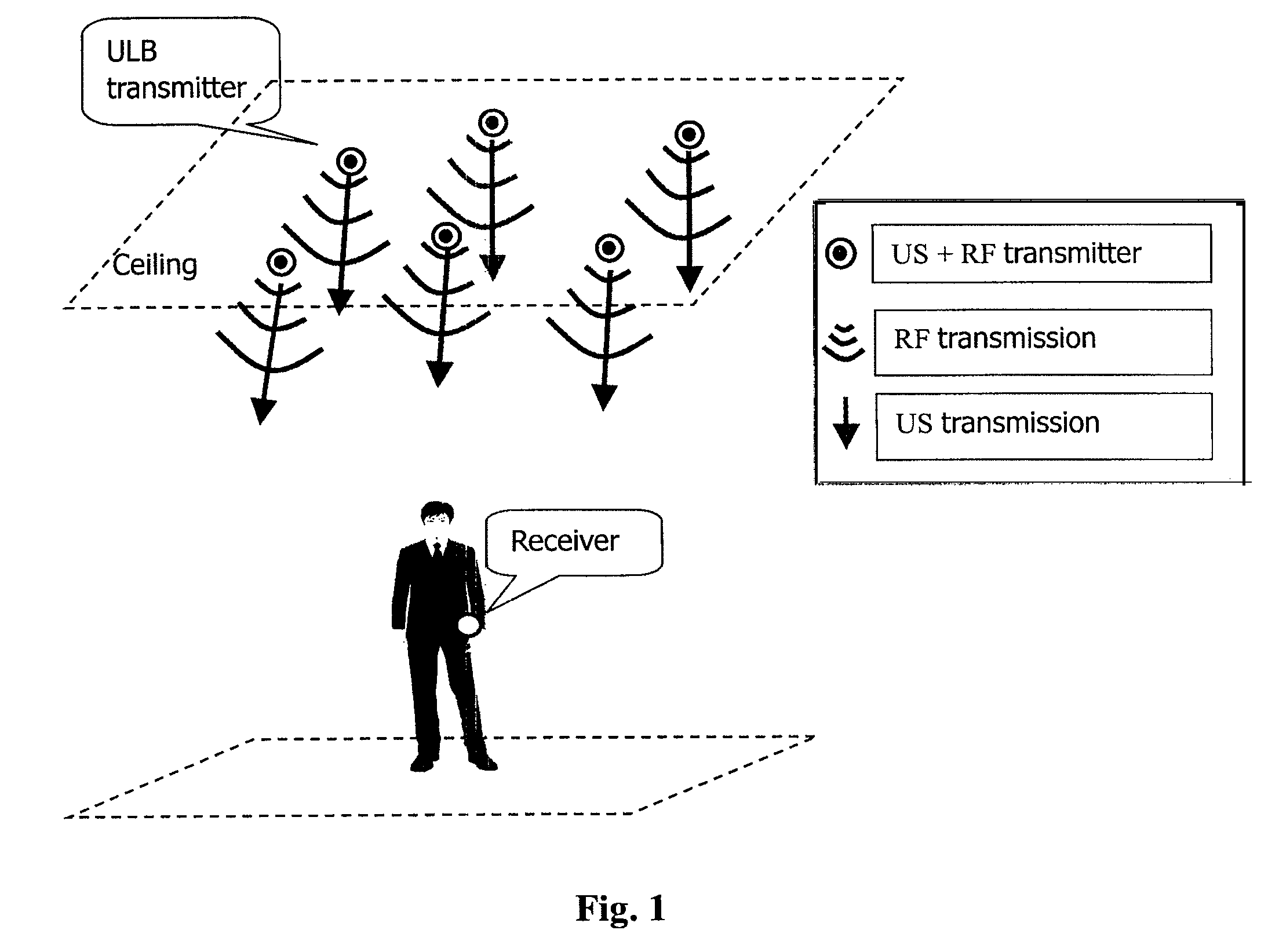
An autonomous ultrasonic indoor location system includes a location beacon transmitting apparatus and a location beacon receiving apparatus. The location beacon transmitting apparatus is configured to sequentially transmit US signals at a predetermined time interval upon transmission of a signal containing synchronization information. The location beacon receiving apparatus is configured to synchronize with the location transmitting apparatus when synchronization information is detected, determine transmission order of the received US signals based on the obtained synchronization timing, infer transmission timings of the respective US signals based on the determined transmission order, calculate TOA information corresponding to each of the received US signal from the transmission timings and reception timings of the respective US signals, and determine location of the location beacon receiving apparatus on basis of the positions of the US transmitters in the transmitting apparatus and the calculated TOA information sequence.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Data transmission method and data transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20050053093A1Simple procedureReduce in quantityError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsManagement unitTransmission quality
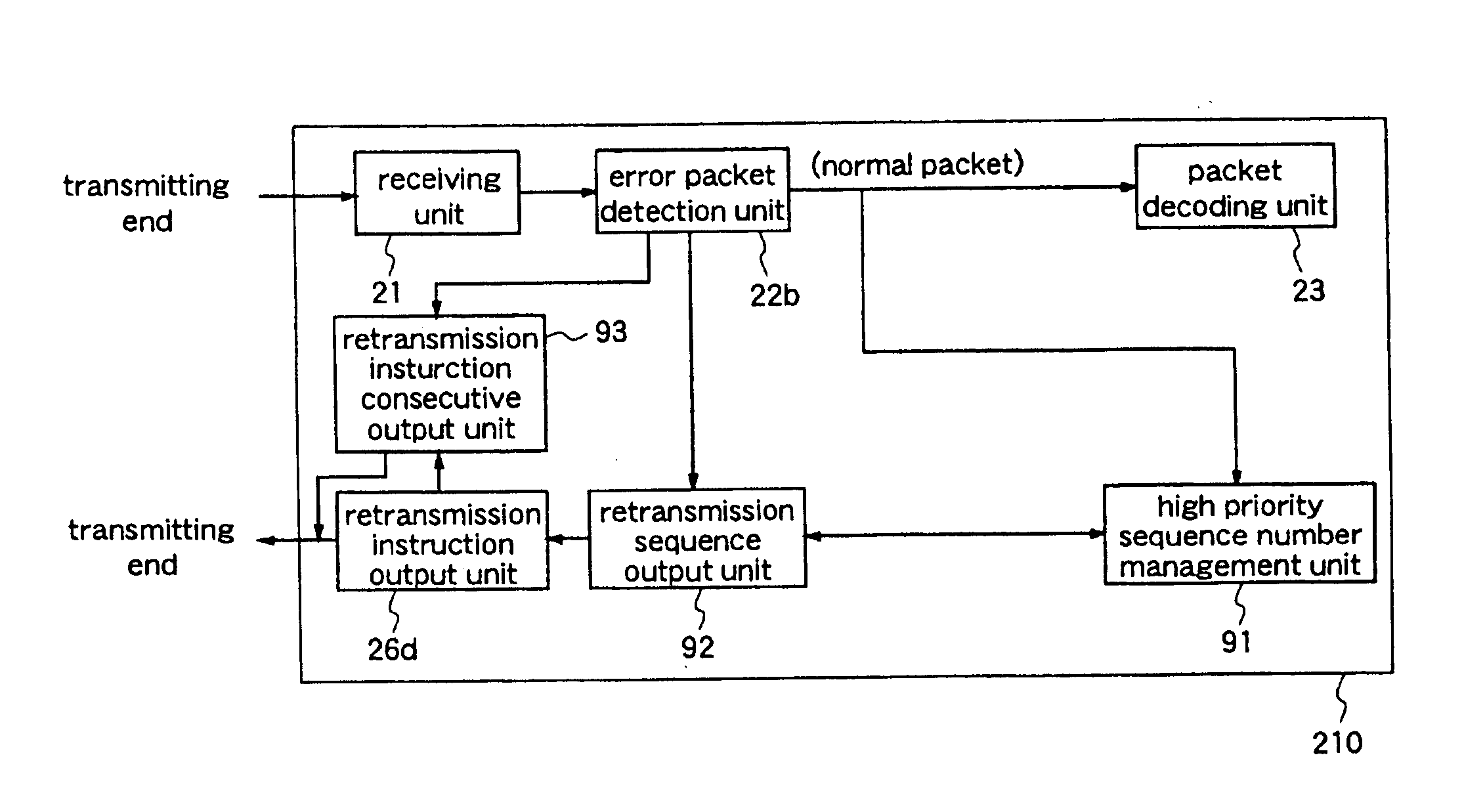
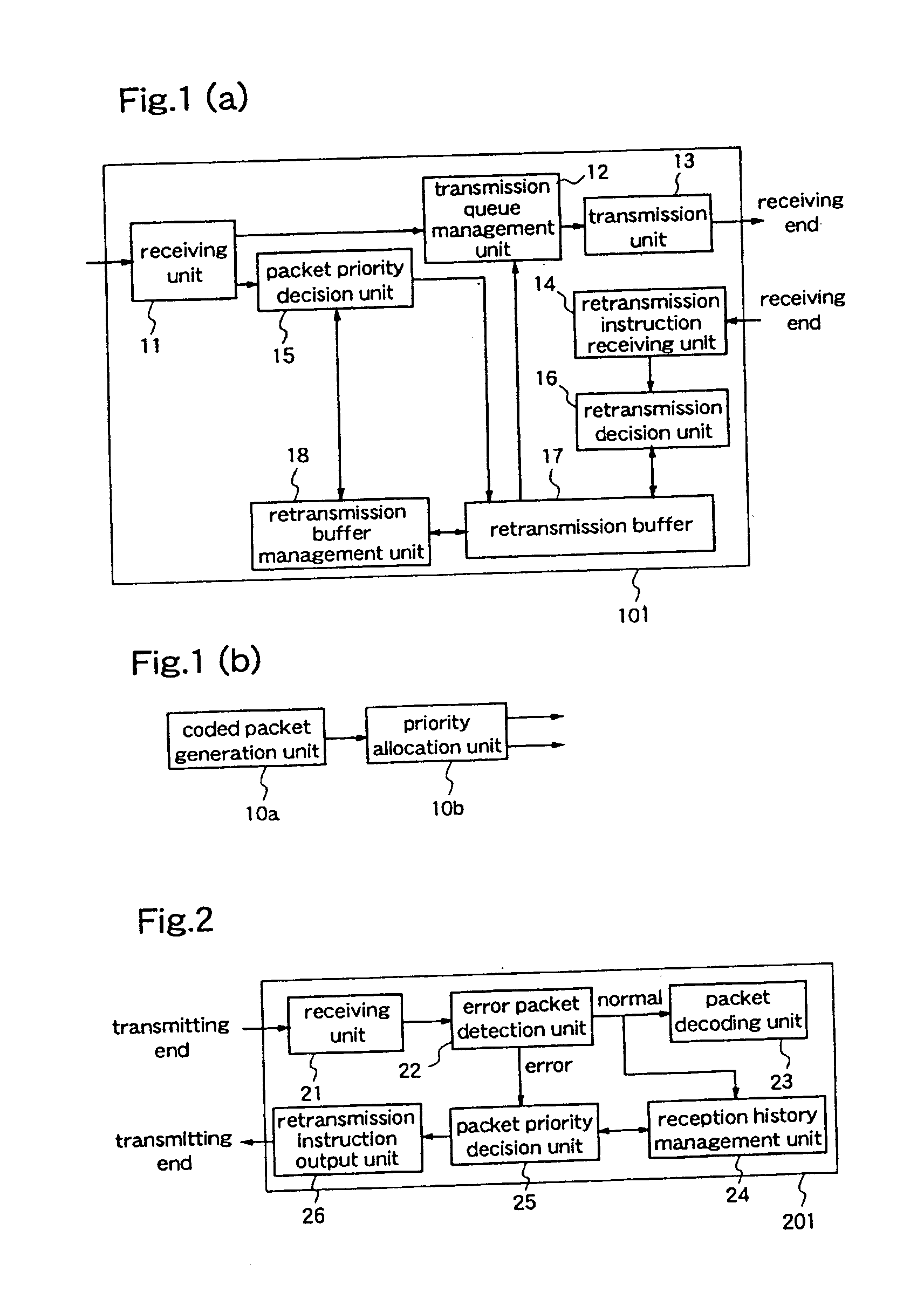
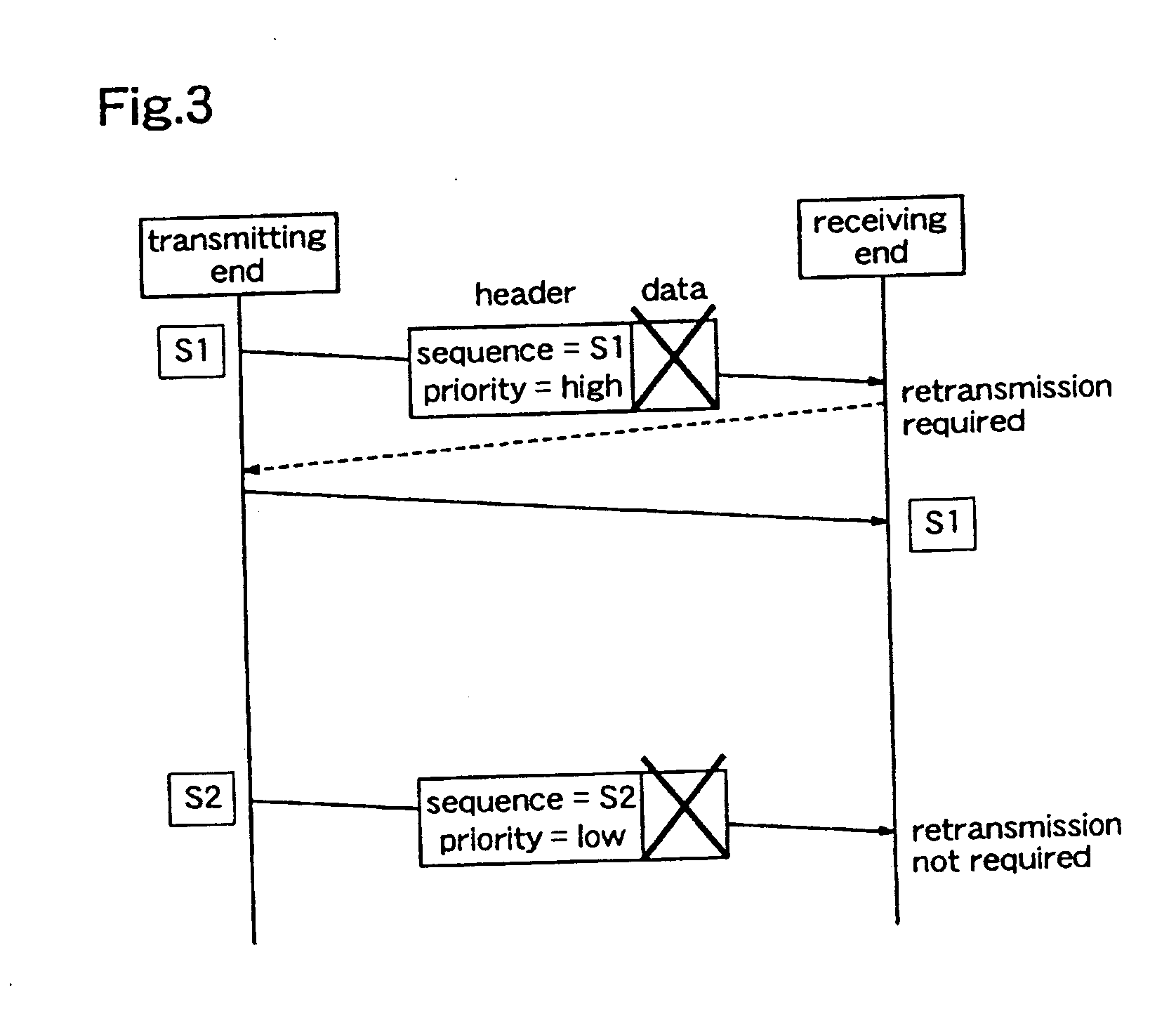
A data transmission apparatus for relaying data transmitted from the transmitting end in units of packets, each packet having additional information relating to its sequence number, priority and data reproduction time, comprises: a receiving unit for receiving packets transmitted from the transmitting end; a priority decision unit for deciding the priority of each of the received packets; a retransmission packet storage unit for storing packets the priorities of which are equal to or higher than a predetermined value, as retransmission packets, on the basis of the priority of each packet decided by the priority decision unit; a retransmission instruction receiving unit for receiving a retransmission request from a terminal at the receiving end; a retransmission decision unit for deciding whether retransmission of the packet for which the retransmission request has been made should be performed or not, on the basis of the retransmission request and the storage status of the retransmission packets in the retransmission packet storage unit a transmission queue management unit for setting the transmission order of the received packets and the packets which have been decided as packets to be retransmitted, on the basis of additional information which is given to each packet; and a transmission unit for transmitting the data of these packets in the transmission order set by the management unit. Therefore, the transmission quality in a radio section in real-time transmission is improved and, further, the number of retransmission times is reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Transmission control protocol queue sorting
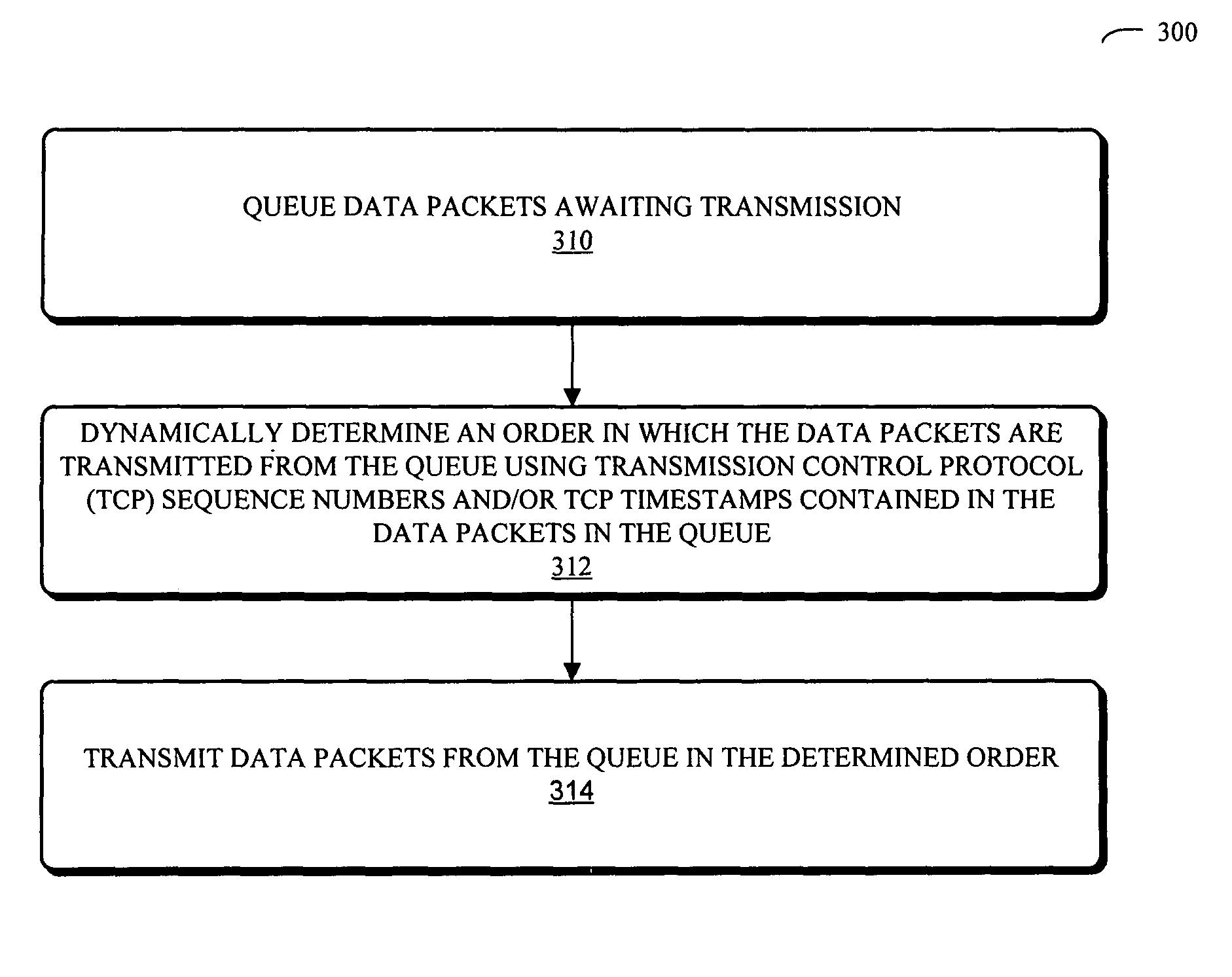
A device that queues and transmits data packets is described. This device includes: a queue configured to store data packets awaiting transmission; a controller configured to dynamically determine an order in which the data packets are transmitted from the queue; and a transmission mechanism configured to transmit the data packets from the queue in the determined order. The transmission order is determined using Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) sequence numbers and / or TCP timestamps contained in the data packets in the queue in order to provide increased utility without reducing existing fairness between independent data streams.
Owner:APPLE INC
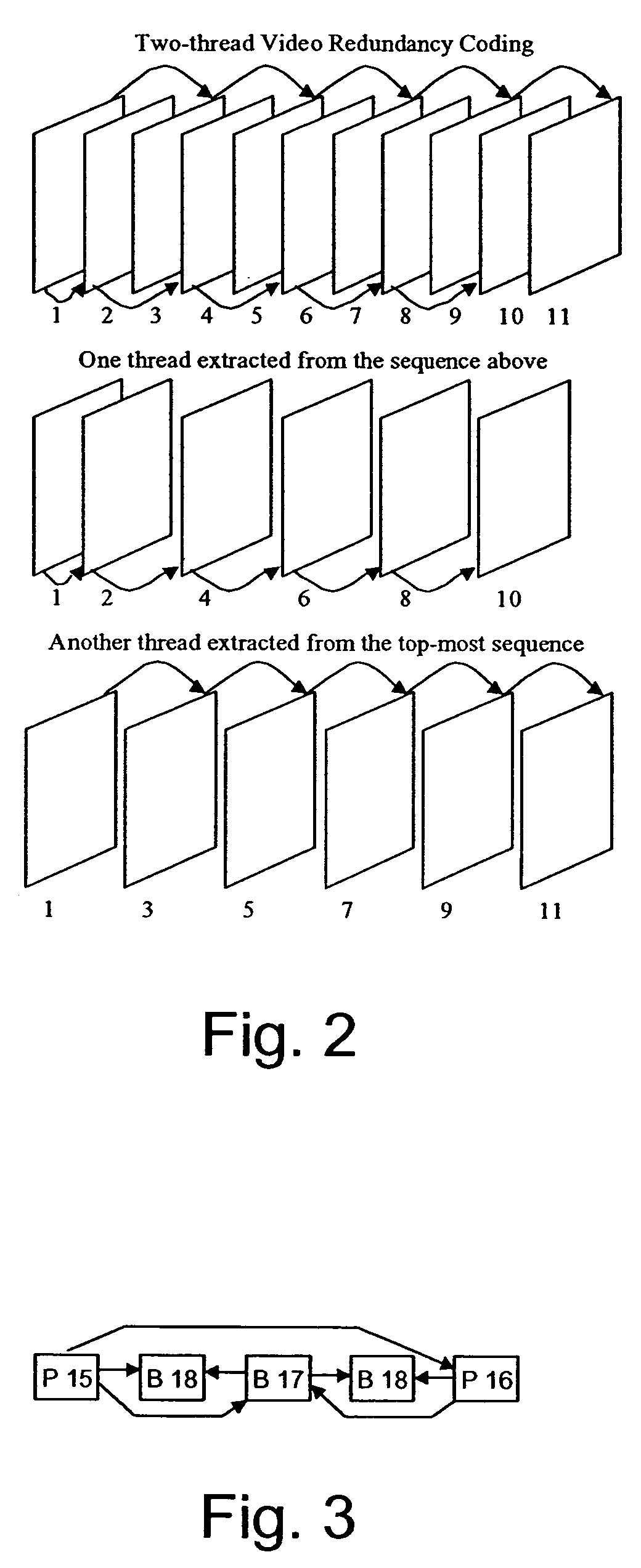
Video compression and encoding method
ActiveUS7606310B1Efficient codingPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionMotion vector
A method of compressing video data having at least one frame having at least one block and each block having an array of pixels is provided. The method transforms the pixels of each block into coefficients and creates an optimal transmission order of the coefficients. The method also optimizes the speed of processing compressed video data by partitioning the data bitstream and coding each partition independently. The method also predicts fractional pixel motion by selecting an interpolation method for each given plurality or block of pixels depending upon at least one metric related to each given block and varies the method from block to block. The method also enhances error recovery for a current frame using a frame prior to the frame immediately before the current frame as the only reference frame for lessening quality loss during data transmission. Enhanced motion vector coding is also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Packet stream arrangement in multimedia transmission
InactiveUS7751324B2Reduce delaysUnequal error protectionError preventionTransmission systemsTransmission orderMultimedia transmission
Transmitting media information from a transmitting device to a receiving device. To perform the transmission a media stream is encoded and packets are formed from the encoded media stream, the packets containing application data units, the application data units having a decoding order. At least two blocks are generated from the packets. The packets of the at least two blocks are organized into a first group and a second group, the first group being decodable without reception of said second group. The transmission order of the packets of said first group is arranged succeeding packets of said second group such that the application data units in the transmission order are at least partly in a different order than the decoding order.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Packet transmission scheduling technique
ActiveUS7515616B2Improve service qualityError preventionTransmission systemsReal time servicesPhysical layer
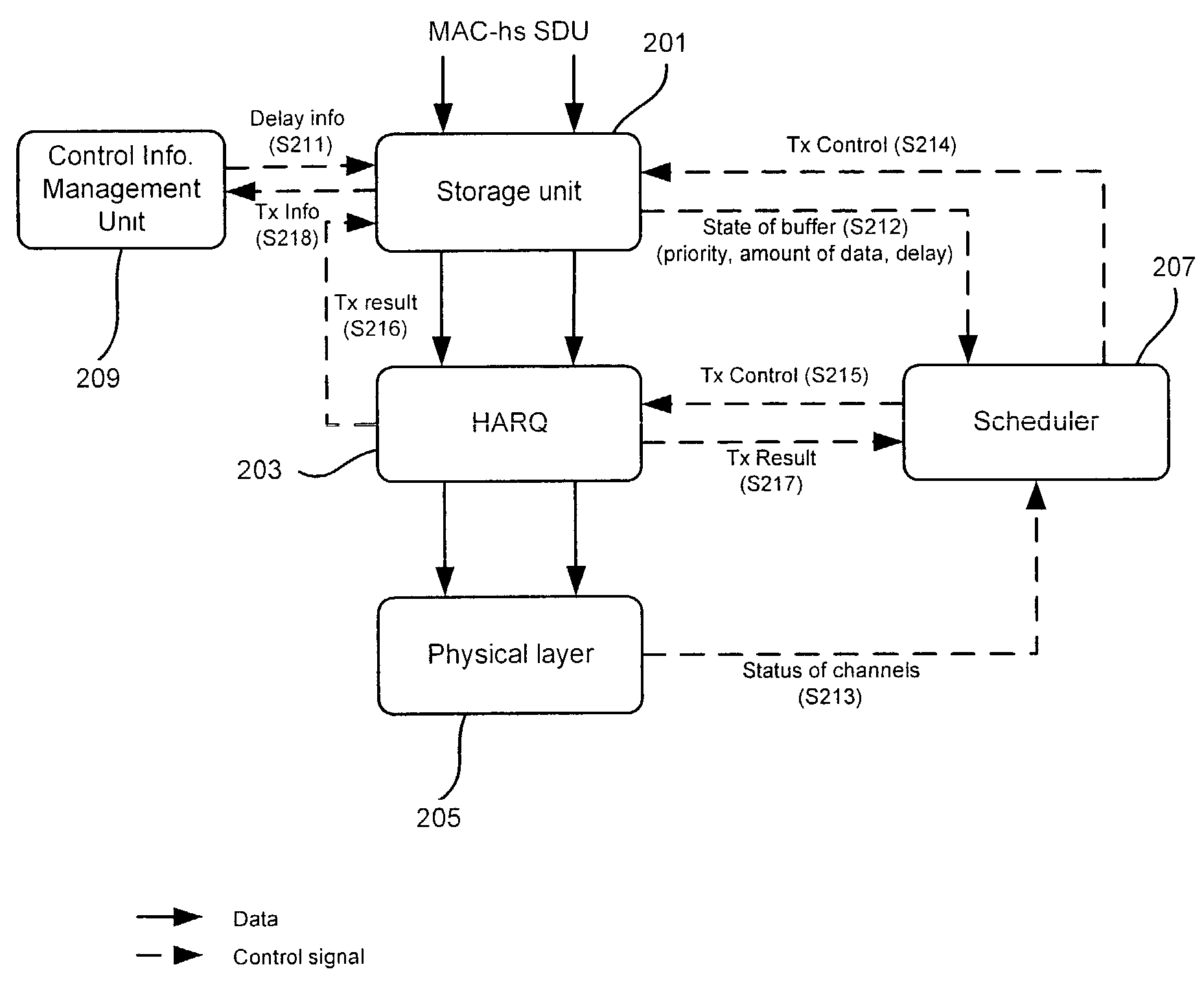
A packet data transmission method of the HSDPA system includes collecting information on the quality of physical channels, a status of the MAC buffer, the priority level of data, the delay of data, and the like, determining the transmission order of data and the size of a data block to be transmitted based on the collected information, and transmitting the data block through the physical layer according to the order of transmissions. Since the HSDPA scheduler takes into account the delay of data, the quality of real-time services can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Transmission scheduling for TDMA networks
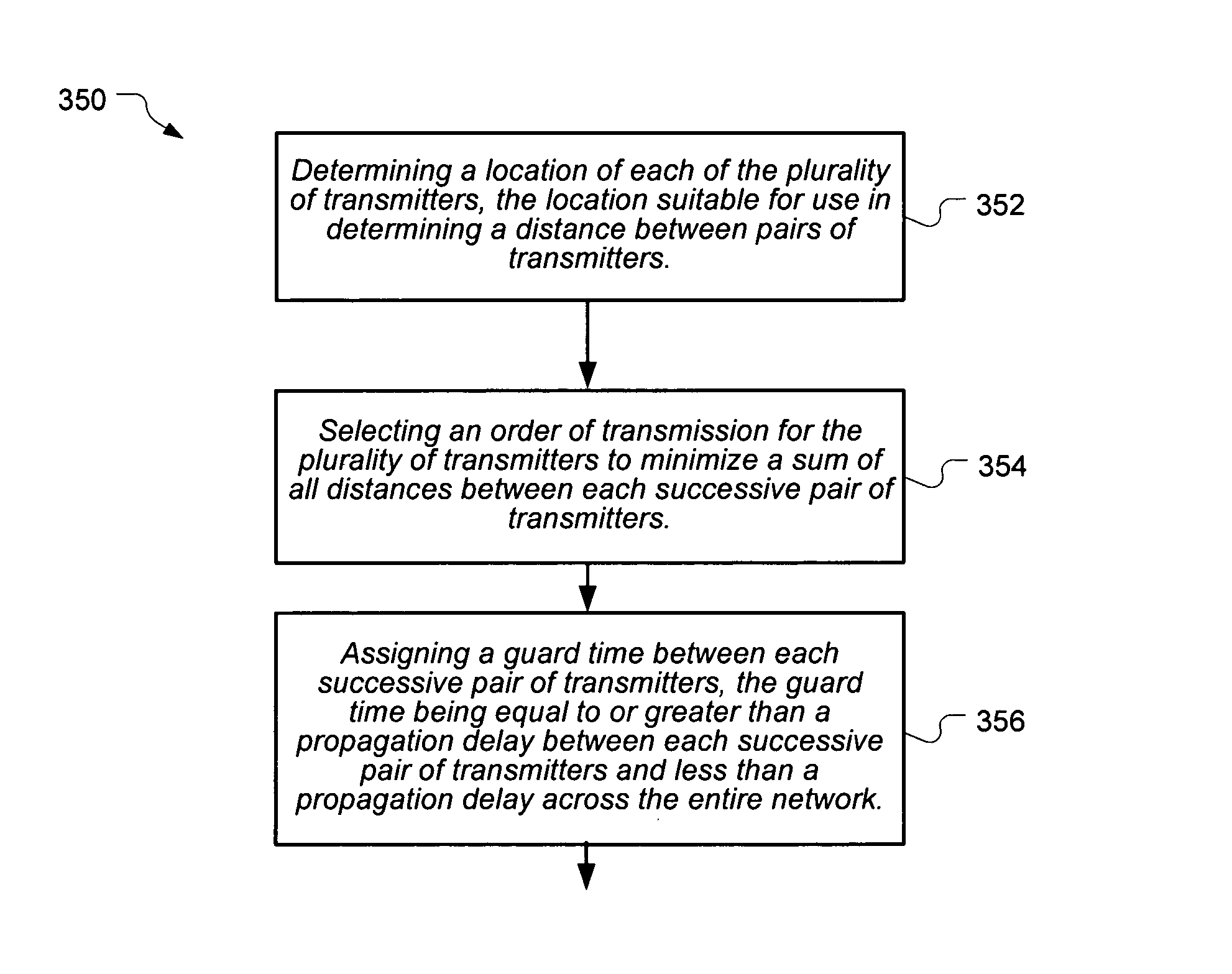
ActiveUS7596113B1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexPropagation delayTransmission order
A technique for scheduling transmissions for a plurality of transmitters in a TDMA network is described. The technique includes assigning guard time between each pair of successive transmitters, where the guard time is related to the propagation delay between the pair of successive transmitters. Total guard time is minimized by selecting an order of transmission for the plurality of transmitters to minimize the total guard time.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
System and method for streaming sequential data through an automotive switch fabric
A system and method for streaming sequential data through a vehicle switch fabric network. This is particular useful in areas such as reprogramming nodes in the automotive switch fabric network where relatively large records or messages need to be transmitted through the switch fabric, although the invention may be used in other areas. In sum, the system and method described herein takes large data records and breaks them down into smaller units (data packets) that fit within the constraints of the physical layer on which communication links in the switch fabric network is built. The smaller data packets are assigned with a message identification and a sequence number. Data packets associated with the same data record or message are assigned with the same message identification but may differ in their sequence number. Each data packet is transmitted over the vehicle switch fabric network to a destination node. At the destination node, the data packets may be reassembled to its original data format based on the message identification and sequence numbers. The reassembled message may then be presented to an application in the node for processing.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Quantum state classical sequence rearrangement encrypition method in quantum key distribution
InactiveCN1477809ASecret communicationSecuring communicationGeneration processData processing system
The quantum state classical sequence rearrangement encryption method in quantum key distribution belongs to the field of quantum secret communication. It mainly utilizes the characteristics of quantum to encipher the production process of quantum key, under the condition of ensuring safety, at the same time, and transfer all the particles of tangled system so as to raise transmission distance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for preventing relay cellular system from uplink and downlink interference
ActiveCN101262691AMeet the transmissionAvoid uplink and downlink interferenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationPropagation delayIdle time
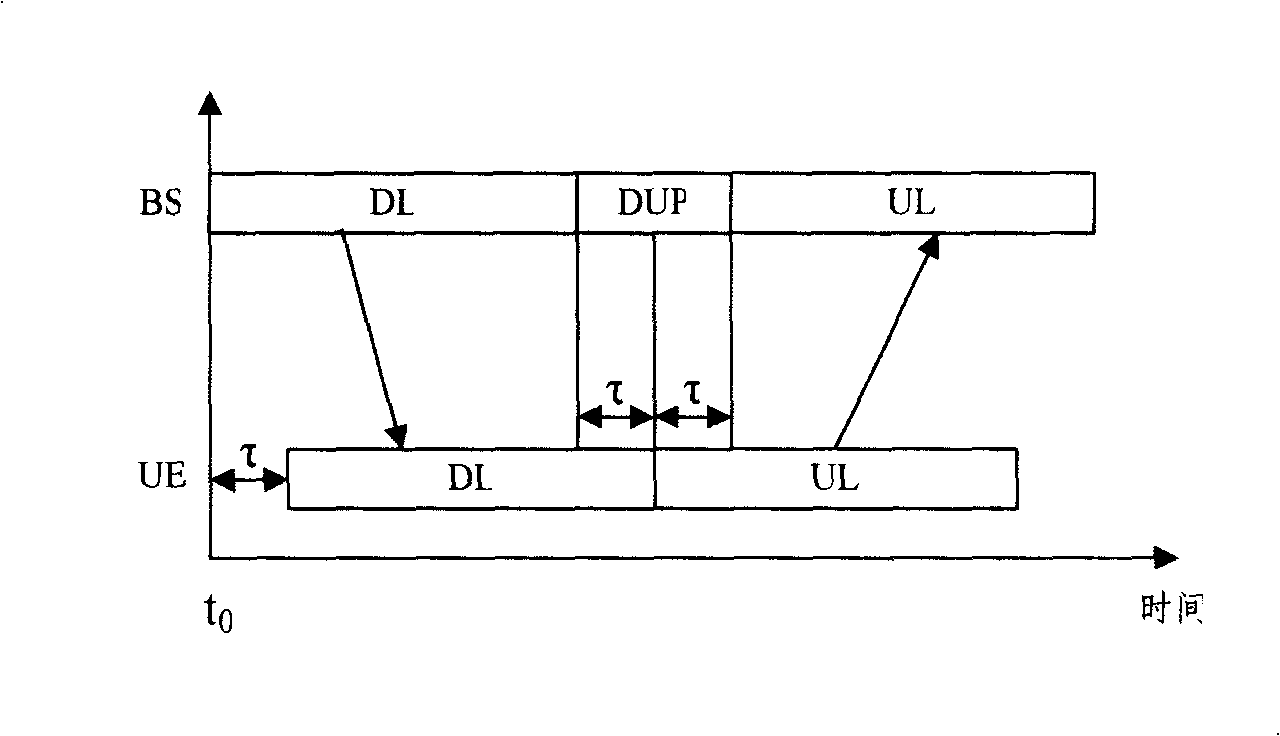
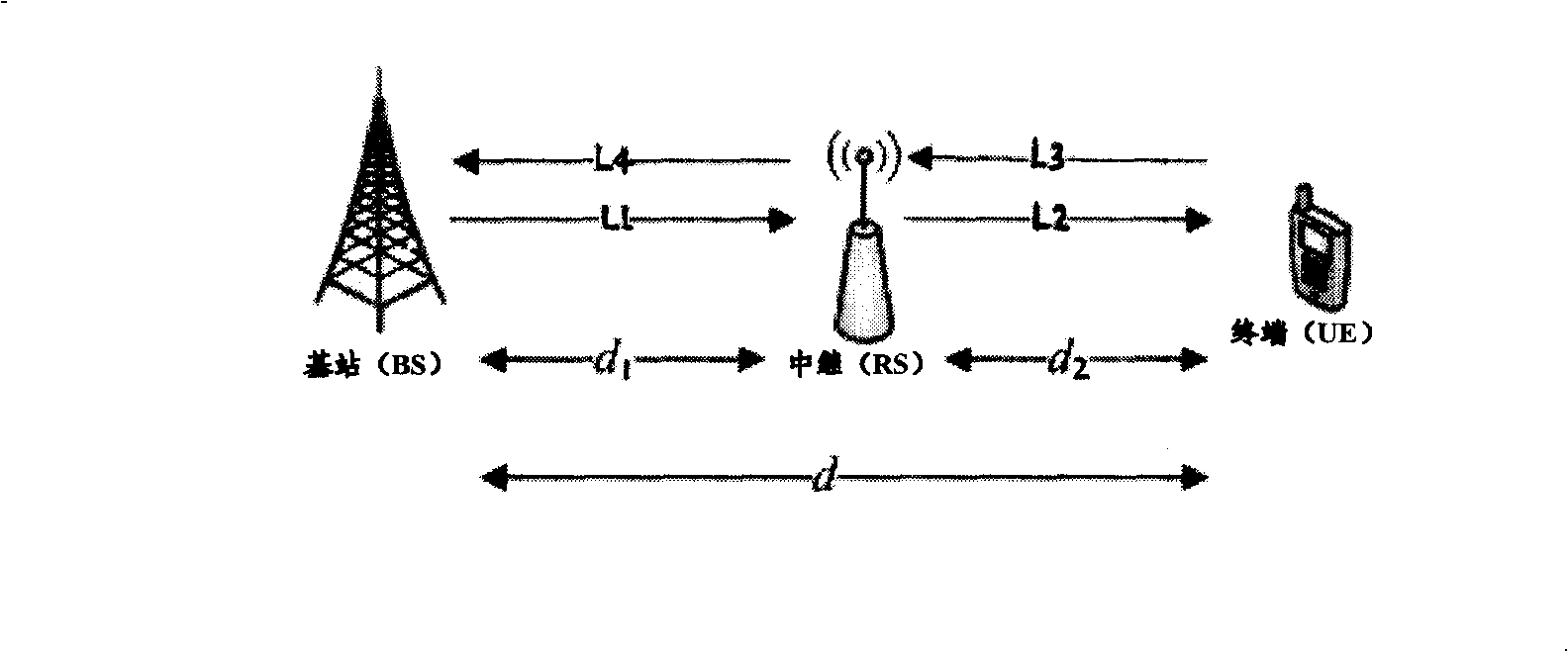
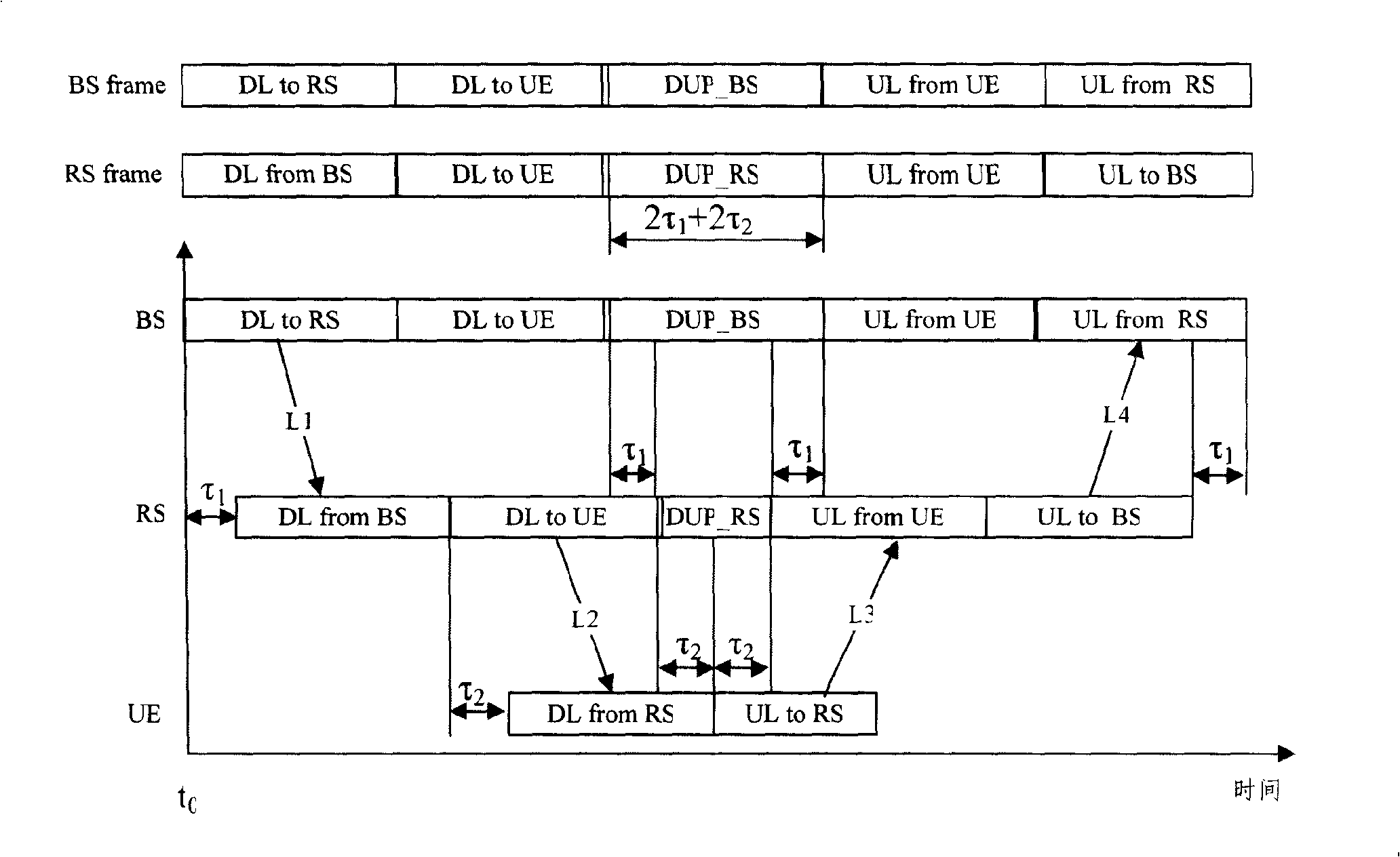
The invention relates to a realization method in which a Relay support cellular system can effectively avoid the interference of uplink and downlink, and a device thereof as well as a solution which allows the interference of the uplink and the downlink to be introduced by the system due to coverage expansion. The invention is realized by a special design of a frame structure and the special design comprises a transmission order of four system links in the frame structure which are a downlink relay link L1, a downlink access link L2, an uplink access link L3 and an uplink relay link L4, and a guard space of a transfer point of the uplink and the downlink. When the transmission order of the four links of the frame structure is L1, L2, L3 and L4, a multiplying adjustment is processed on the required guard space of the transfer of the uplink and the downlink simultaneously allowing for path propagation delays between BS and RS as well as between RS and UE, namely offsetting the propagation delay between RS and UE; when the transmission order of the four links of the frame structure is L1, L2, L4 and L3, the guard space of the transfer of the uplink and the downlink only allows for the propagation delay between BS and RS while the propagation delay between RS and UE can be guarded by idle time which is caused by a sending to BS in advance from RS.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Medium access control methods with quality of service and power management for wireless local area networks
InactiveUS7418004B2Quick and efficientLow powerEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsQuality of serviceMedia access control
A MAC method has three procedures: a prioritization procedure, a collision resolution procedure, and a polling procedure. The prioritization procedure employs the handshaking method to ensure that a high priority station can join the polling list earlier than a low priority station. The collision resolution procedure employs a tree-splitting algorithm to ensure all active stations that underwent the prioritization period can join the polling list in a bounded time. In the polling procedure, the AP allocates the TXOP for each admitted station and schedules the transmission order of all admitted stations. In addition, the AP broadcasts the schedule information in the V-POLL frame. A power-saving station can wake up at the start of the contention-free period. To conserve power, on inspecting the V-POLL frame, if a PS station finds that it cannot transmit nor receive data frames during the polling period, then that station may return to the doze state.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Network-based and host-based mobility management in packet-based communication networks
InactiveUS20100046434A1Wireless network protocolsWireless commuication servicesMobility managementTransmission order
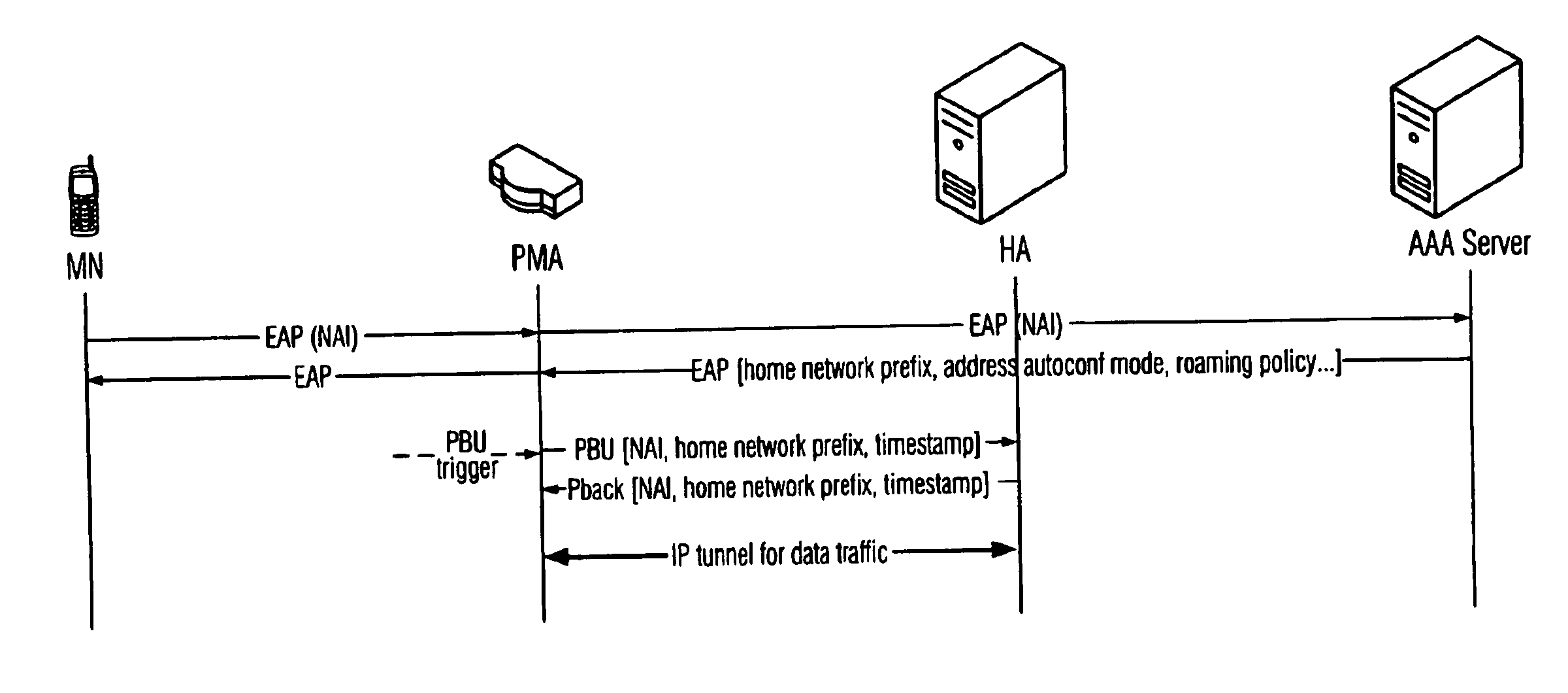
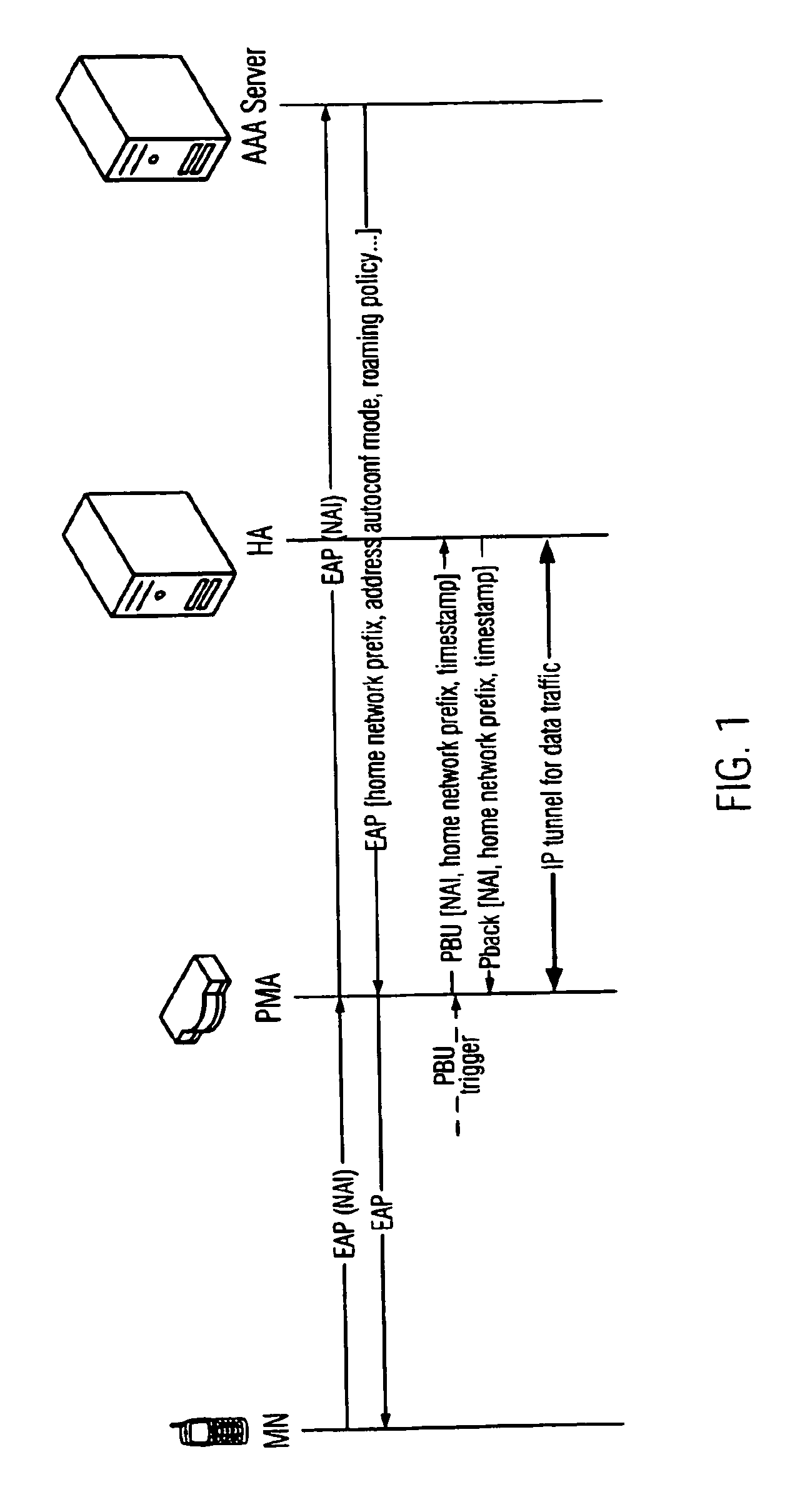
The present invention describes a method for signalling to a mobility anchor point a position of a mobile node in a network using a network-based mobility management scheme for managing the mobility of the mobile node, said method comprising receiving, by a network element, from the mobile node, during or after network authentication of the mobile node, a sequence number used by a process implementing a mobile node-based mobility management scheme for managing the mobility of the mobile node, and transmitting, by the network element, to the mobility anchor point a message on a position of the mobile node in the network, wherein said message comprises the received sequence number. A common sequence number variable for BU and PBU messages is used, so that the HA is able to determine a correct transmission order of PBU / BU messages based on the sequence number in the message.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Communications apparatus and frame control method
InactiveUS20080186973A1Improve data transfer efficiencyEasy to useData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareCommunications system
In a frame control method in a communications system providing a multipath function for controlling a frame having a header area and a data area, attaching, in a transmission apparatus, order information indicating a transmission order to the data area of the frame; outputting, from the transmission apparatus to a network, the frame with the attached order information, through a path selected from a plurality of paths; reading out, in a receiving apparatus, the order information from the data area of the frame received through the network; and determining, in the receiving apparatus, whether or not to transfer the received frame to a processing unit in an upper layer to process control information stored in the header area of the frame, in accordance with the read-out order information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
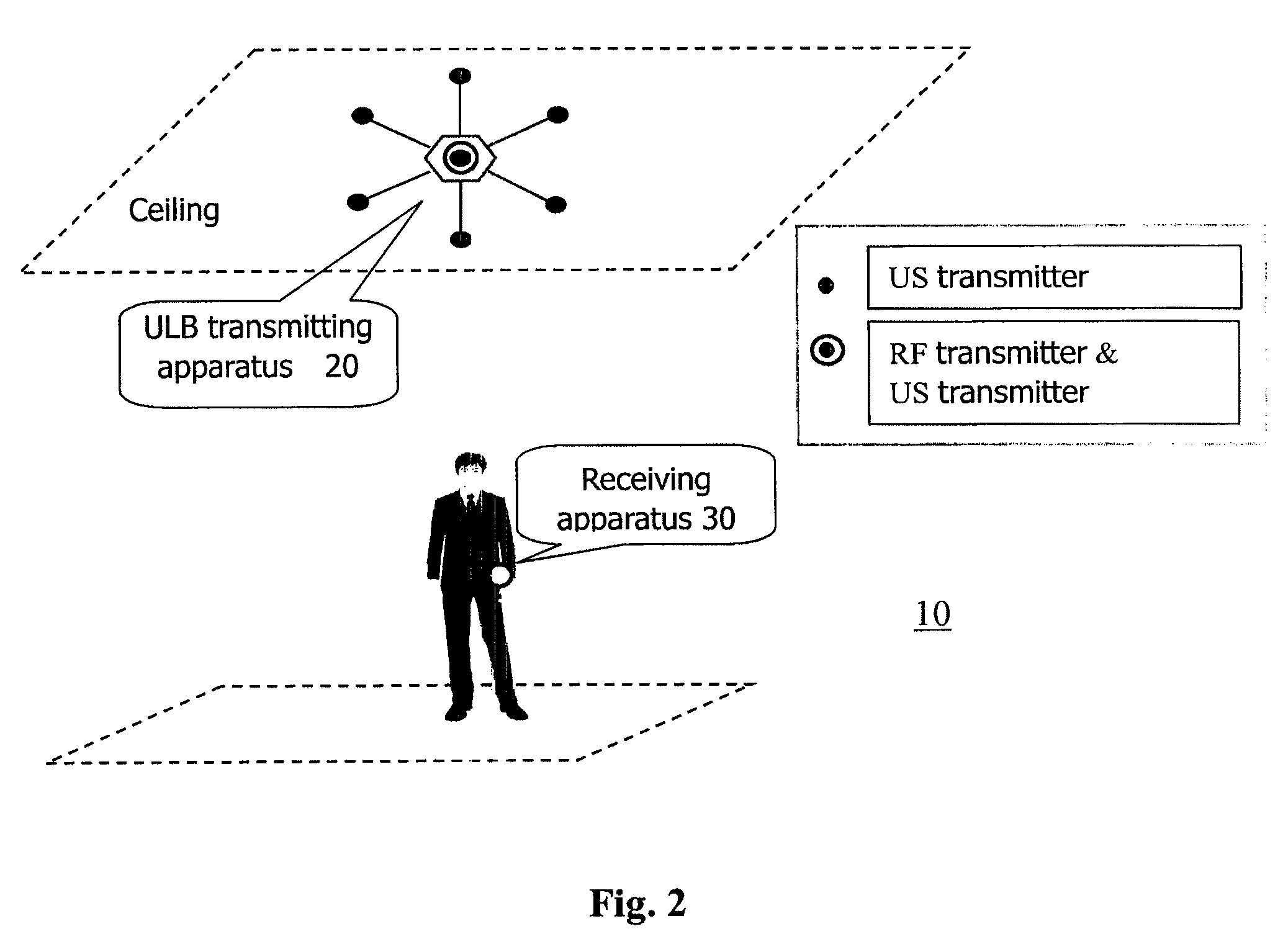
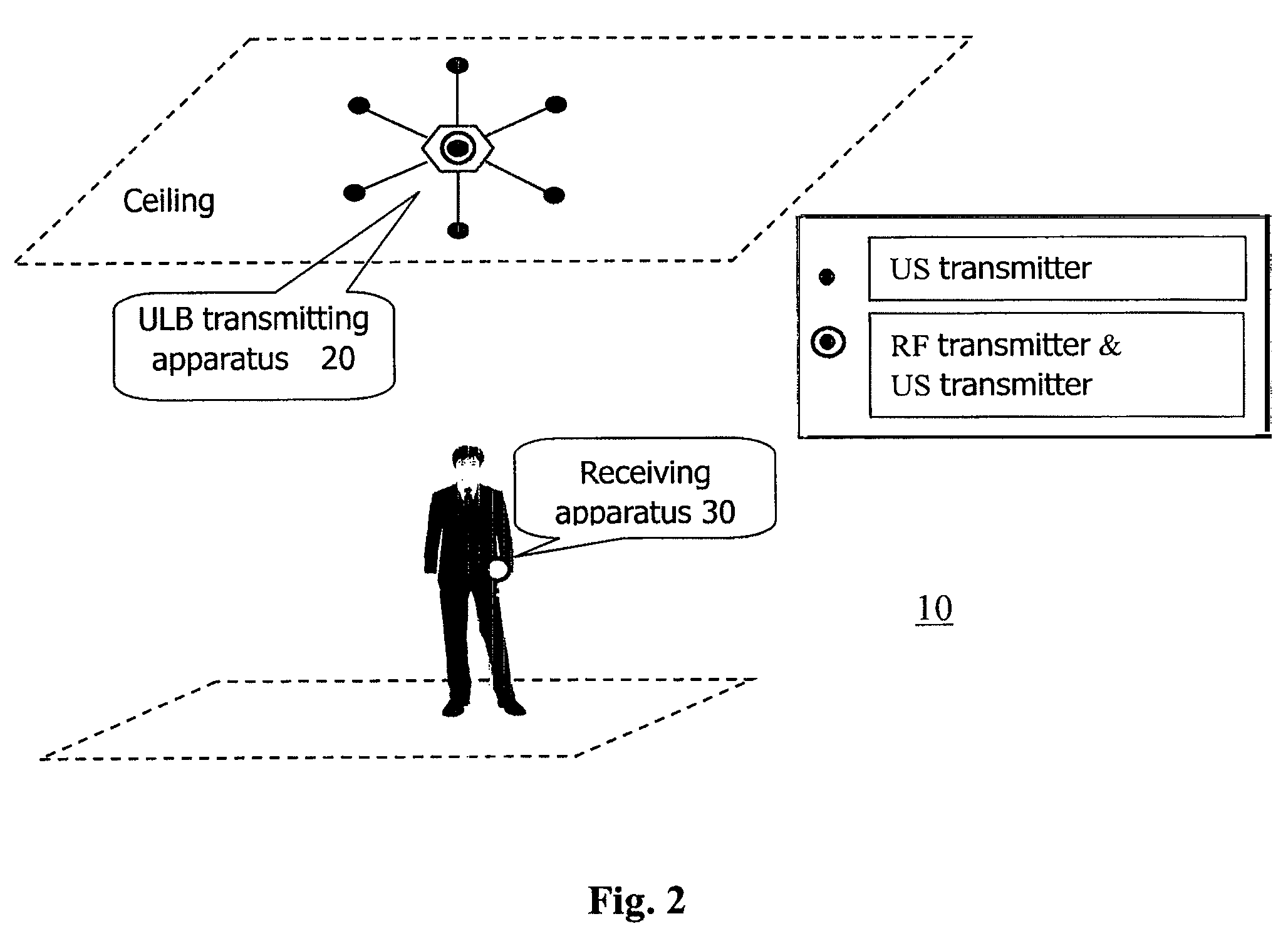
Autonomous ultrasonic indoor location system, apparatus and method
ActiveUS8203910B2Improve accuracyReduce complexityDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSonificationEngineering
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Transmitting station, receiving station, communications method, communications program, computer-readable storage medium containing the program
ActiveUS20070162813A1Effective bandwidthEfficiently usError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsTransmission order
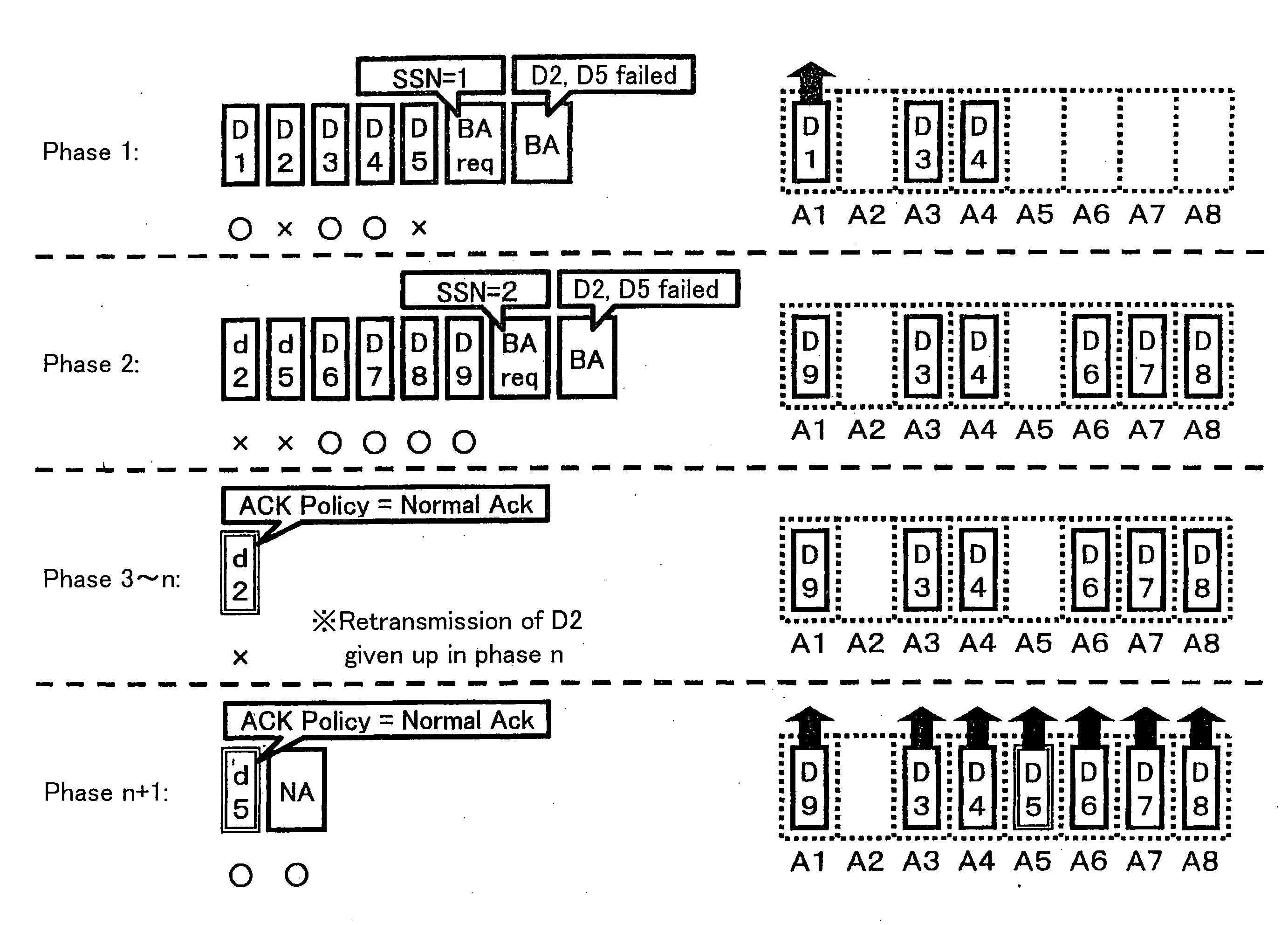
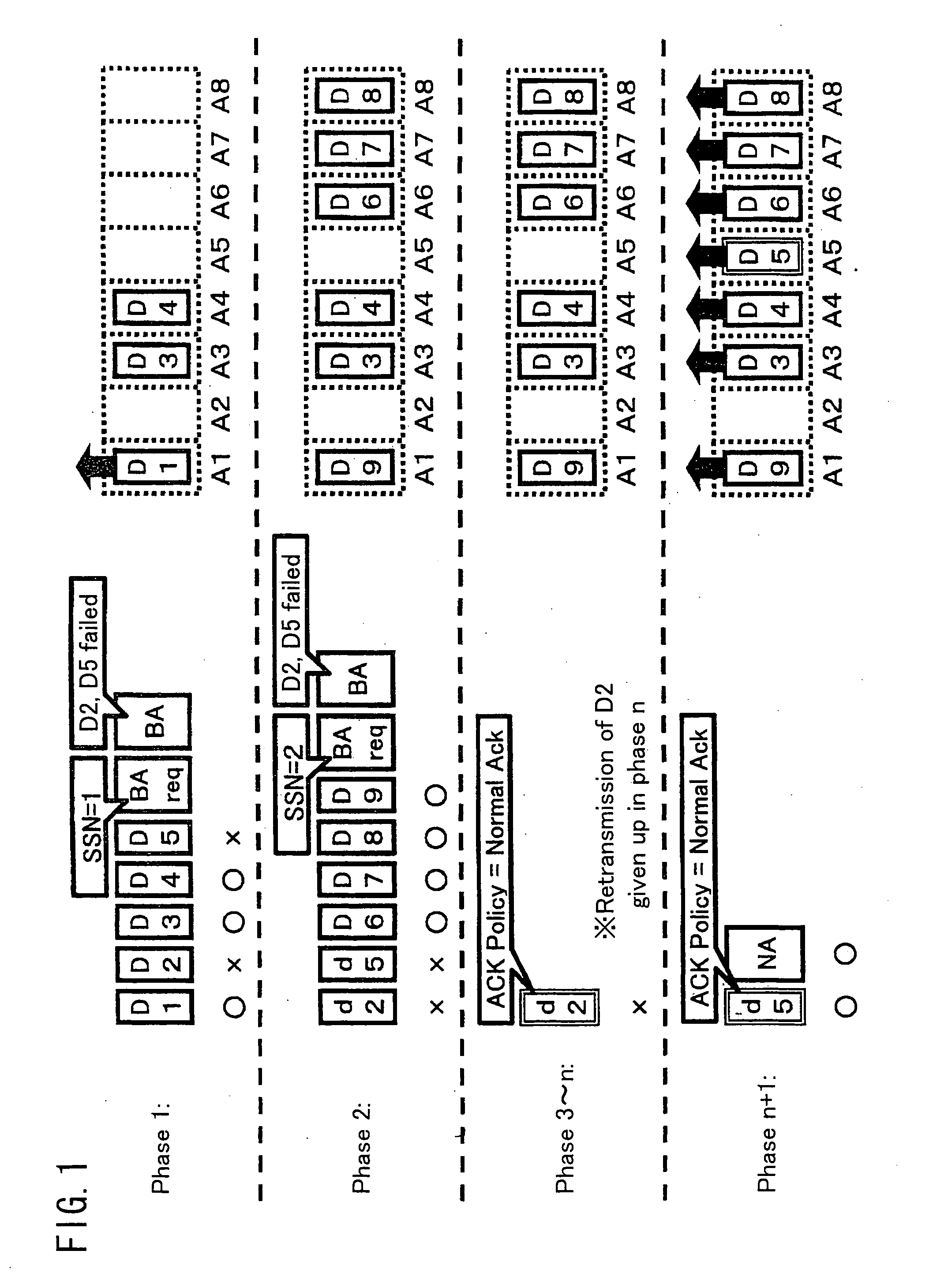
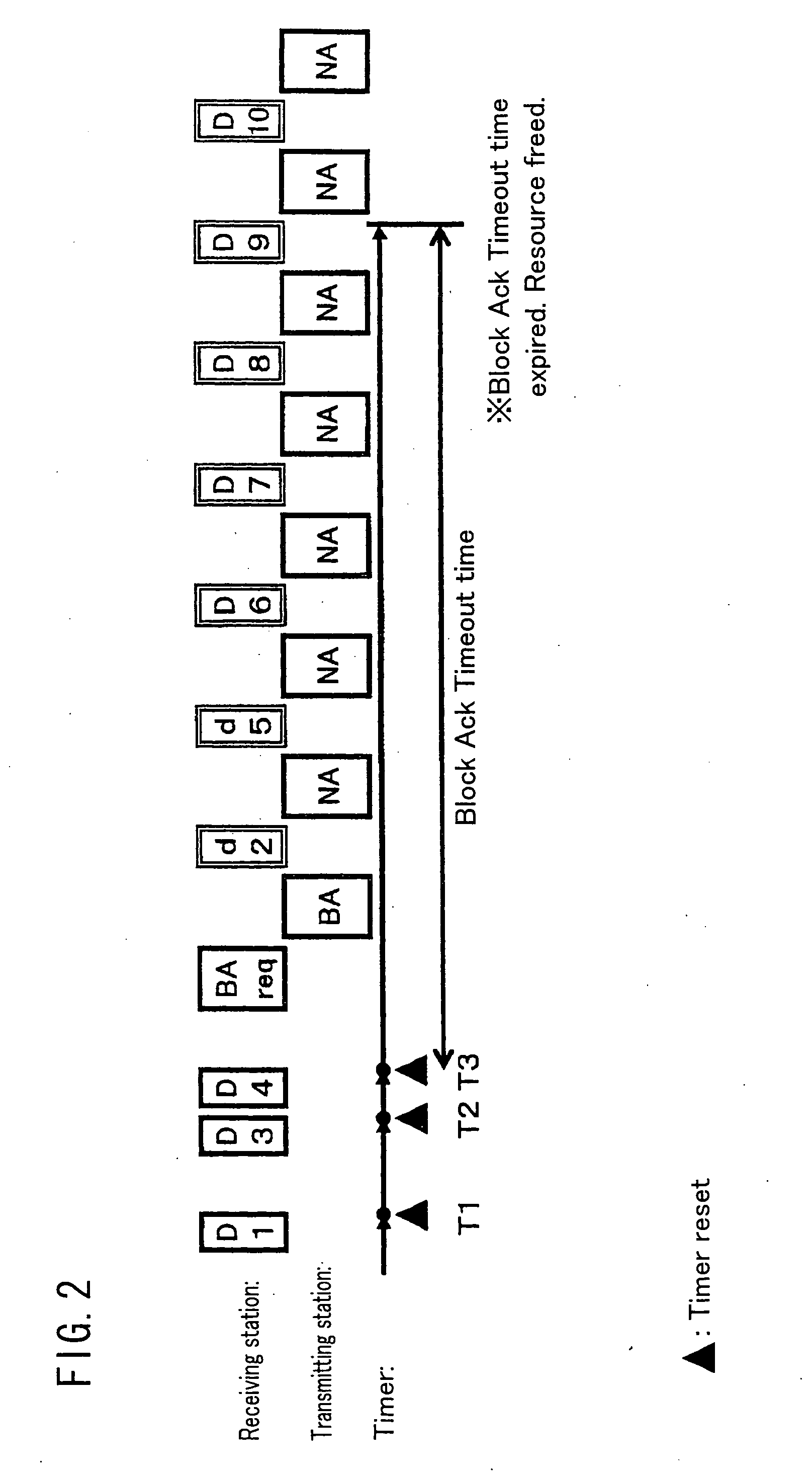
The current Draft IEEE 802.11e standard specifies two types of schemes for obtaining an acknowledgement from a receiving station: BlockAck and NormalAck. The current specifications allow temporary use of NormalAck while transmitting data frames in a BlockAck scheme. The specifications however does not explicitly describe the data frames that are allowed to be transmitted using NormalAck. Should these data frames follow the same rules as in BlockAck schemes, and if the transmitting station has dynamically switched between these two types of schemes, the receiving station can know only with extended delays that unreceived data frames are no longer valid. Therefore, the passing of subsequent, successfully received data frames from the receiving station to an upper layer may be significantly delayed, which is a problem. Another problem occurs if a BlockAck scheme timeout is determined in accordance with the rules in the current draft: the resource being used for BlockAck, which should be released, may not be released forever. The present invention addresses these problems by making suitable changes to the transmission sequence of data that is allowed to be transmitted by NormalAck while transmitting data by BlockAck and the determination process for a BlockAck scheme timeout.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical device with diffractive grating
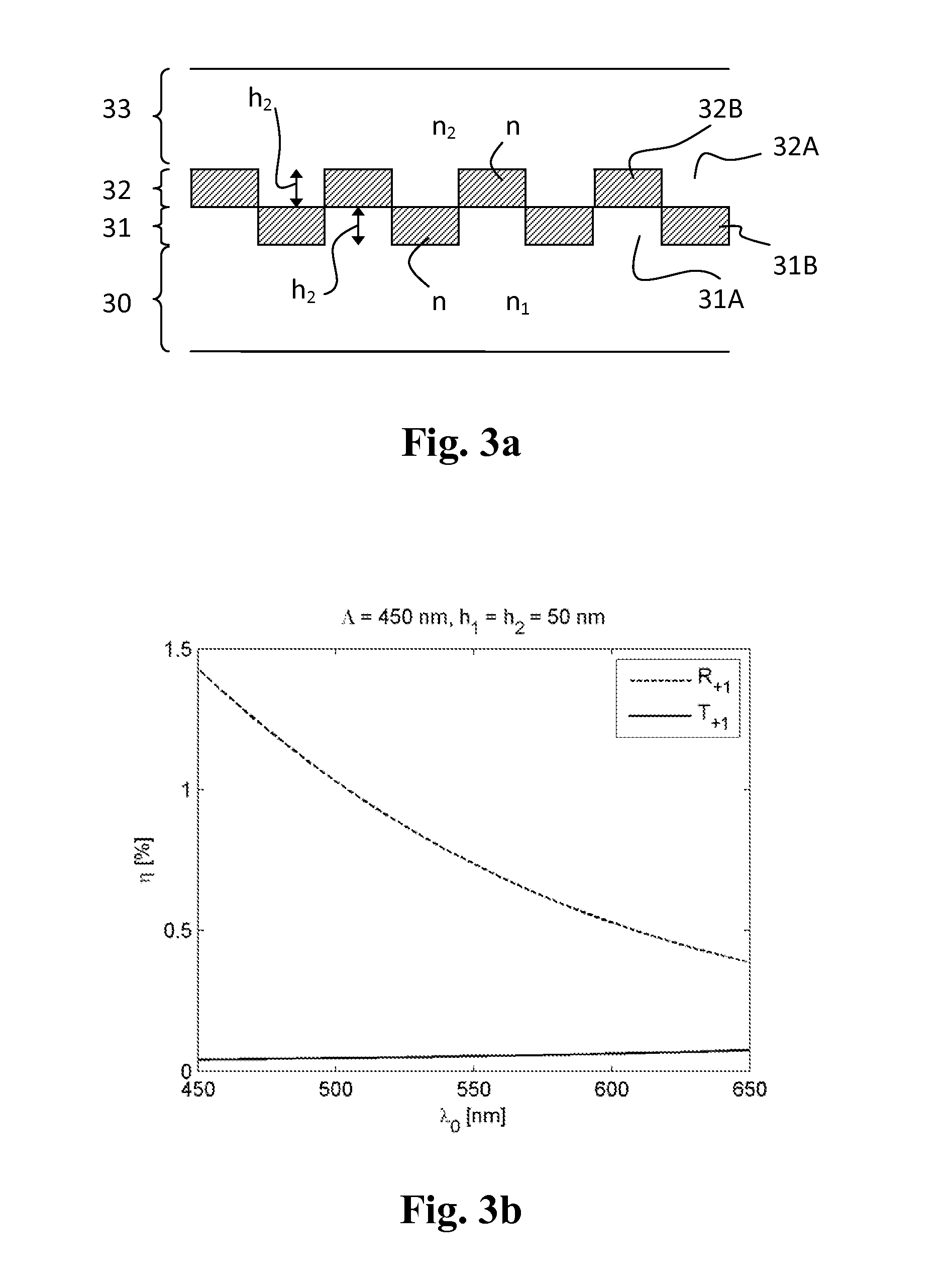
ActiveUS20150253570A1Enhanced inhibitory effectSelection is limitedPicture reproducers using projection devicesAdvertisingPeriodic alternatingHead-up display
The invention relates to optical devices comprising a transparent substrate and a first transparent grating layer on the substrate, the grating layer comprising periodically alternating zones having different refractive indices. According to the invention, the device comprises a second transparent grating layer located on top of the first grating layer and also comprising periodically alternating zones having different refractive indices so that the zones of the first grating layer having higher refractive index are at least partly aligned with the zones of the second grating layer having lower refractive index and vice versa, the second grating layer reducing the amount of light diffracted to non-zero transmission orders. The invention allows for reducing the so-called rainbow effect for example in head-up displays (HUDs).
Owner:DISPELIX OY
Media streaming method and device using the same
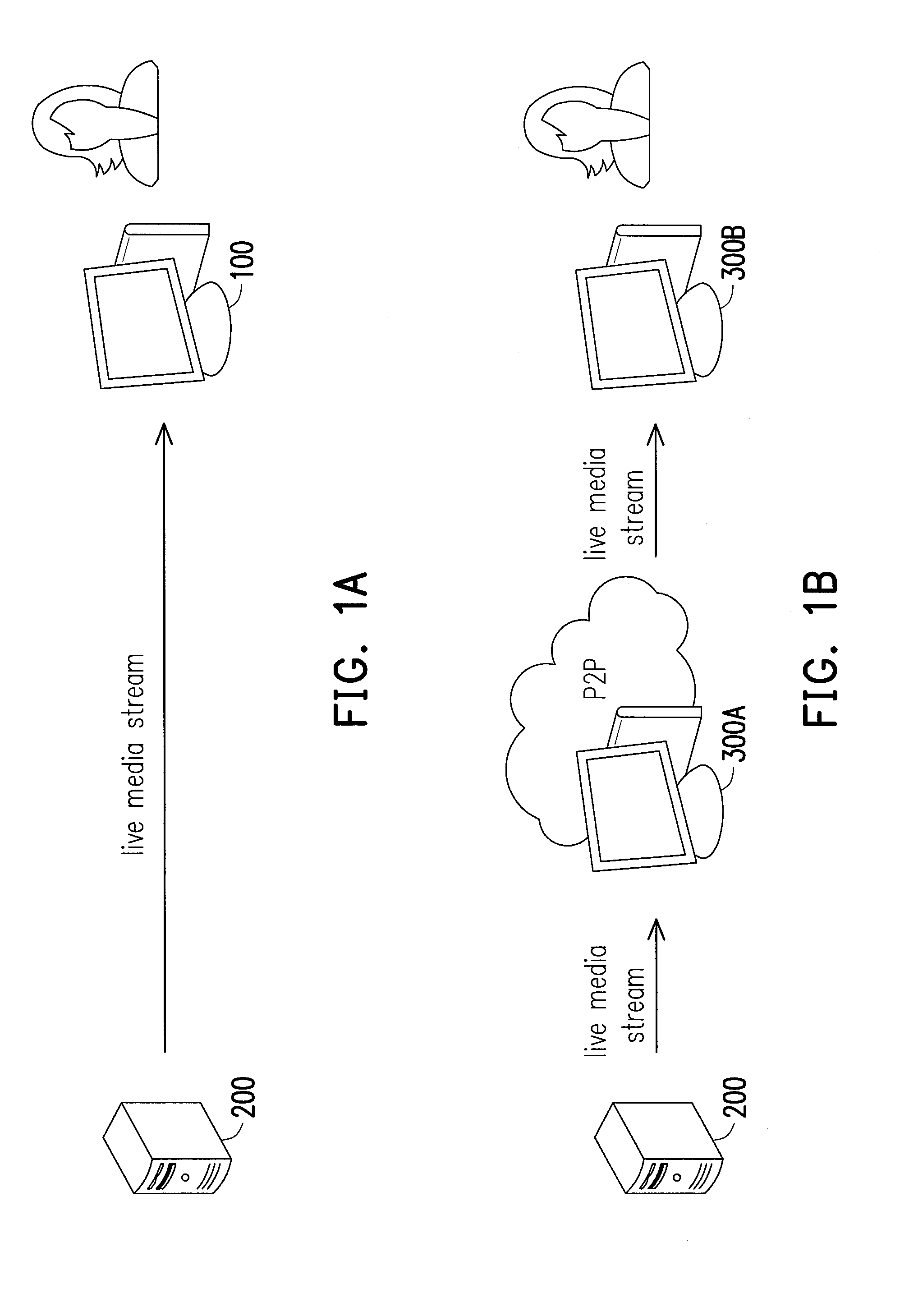
ActiveUS20140173055A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer networkTransmission order
A media streaming method and a device using the same are introduced herein. The disclosure introduces a method for smooth and flawless playback of live media streaming in dynamic network environment. When network congestion occurs for a period, a media receiver may play media data as more as possible by adjusting the transmission order of media data meaningful to the receiver or a provider for providing the media data. In one embodiment, the disclosure introduces a method for smooth and flawless playback of live media streaming by caching a certain amount of media data and then playing them at an appropriate speed to catch up to the progress of the live media streaming, or by dynamically changing bit rates of the live media streaming in time by the provider to meet the most acceptable bit rate according to the network environment between the provider and the receiver.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Communication device and communication control method using lower layer data transmission order control at upper layer
InactiveUS6937600B2Suppressing wasteful executionError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsOrder controlCommunication control
In a communication device using a communication protocol with data loss compensation functions provided at both an upper layer and a lower layer, a transmission order among packets to be transmitted is controlled at the lower layer, according to the transmission states of upper layer connections to which the packets belong, such that when there is at least one non-transmitted packet for each one of at least two different upper layer connections, at least two packets to be transmitted consecutively are belonging to different upper layer connections.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
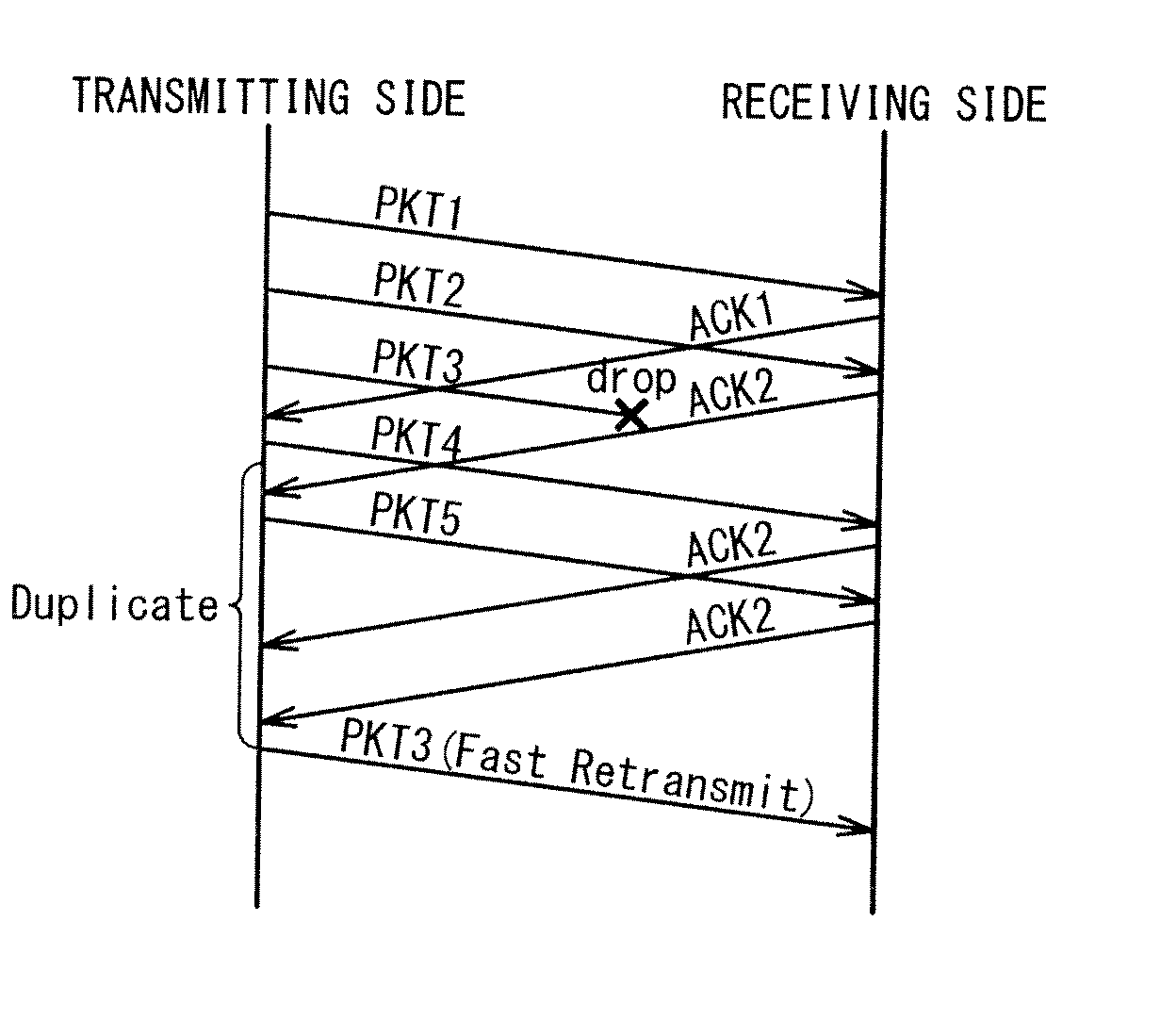
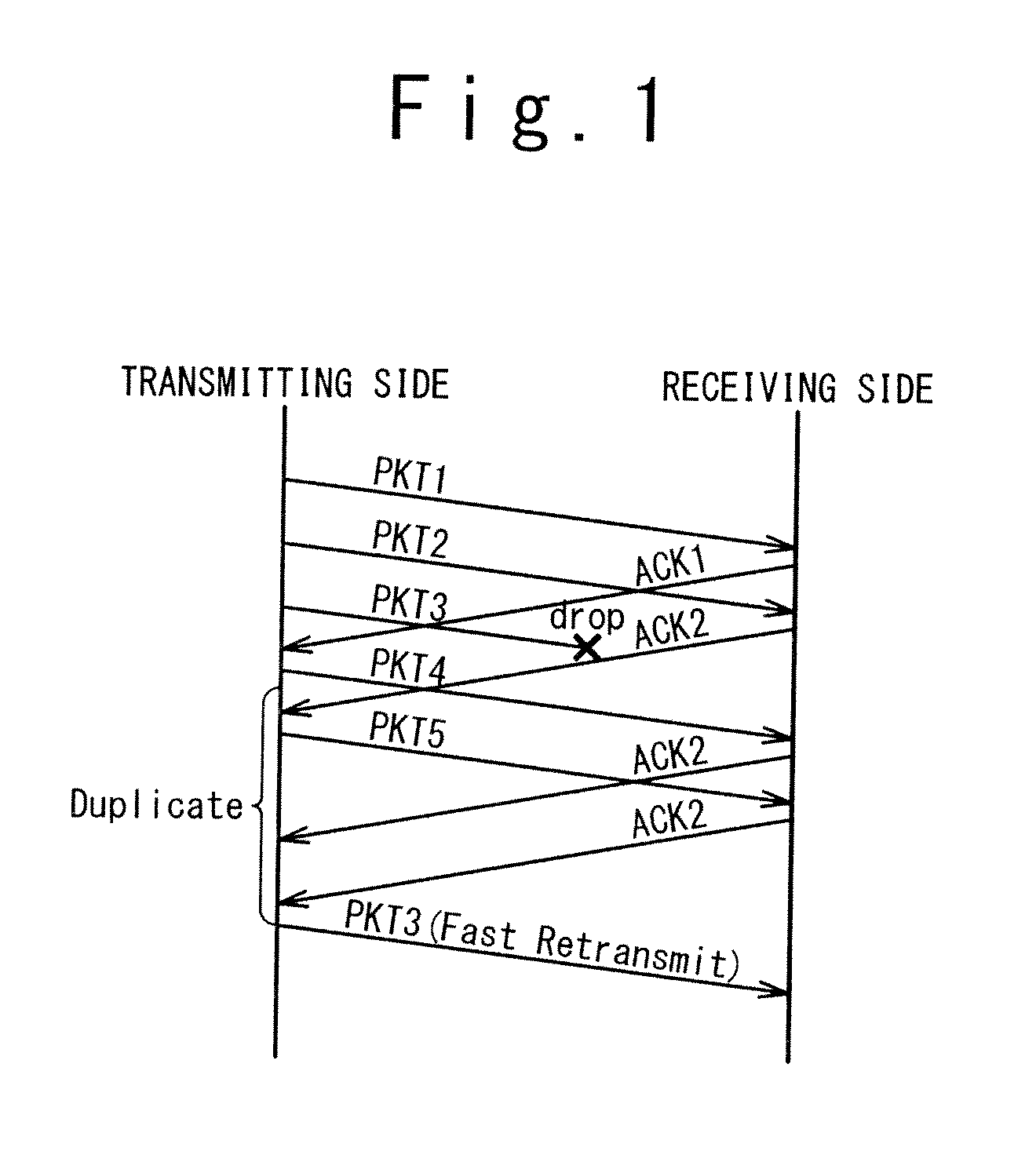
Packet retransmission control system, method and program
InactiveUS20110286469A1Quick controlError preventionData switching by path configurationControl systemComputer science
A lower layer retransmission control unit performs the following processing. When transmitting a transmission packet, giving a sequence number indicating a transmission order to the transmission packet. Receiving, from a receiving device that receives the transmission packet as a reception packet, an ACK packet indicating the sequence number of the reception packet. Referring to the sequence number of the received ACK packet to determine whether or not the ACK packet is received in an order of the sequence number. Transmitting first to third transmission packets and, if receiving a first ACK packet and receiving a third ACK packet following the first ACK packet without receiving a second ACK packet, performing fast retransmission control processing. Specifically, determining whether or not to receive the second ACK packet before a fast retransmission determination period passes after a reception time of the third ACK packet. If failing to receive the second ACK packet within the fast retransmission determination period, retransmitting the second transmission packet.
Owner:NEC CORP
Communications system, communications device, and data retransmission control method
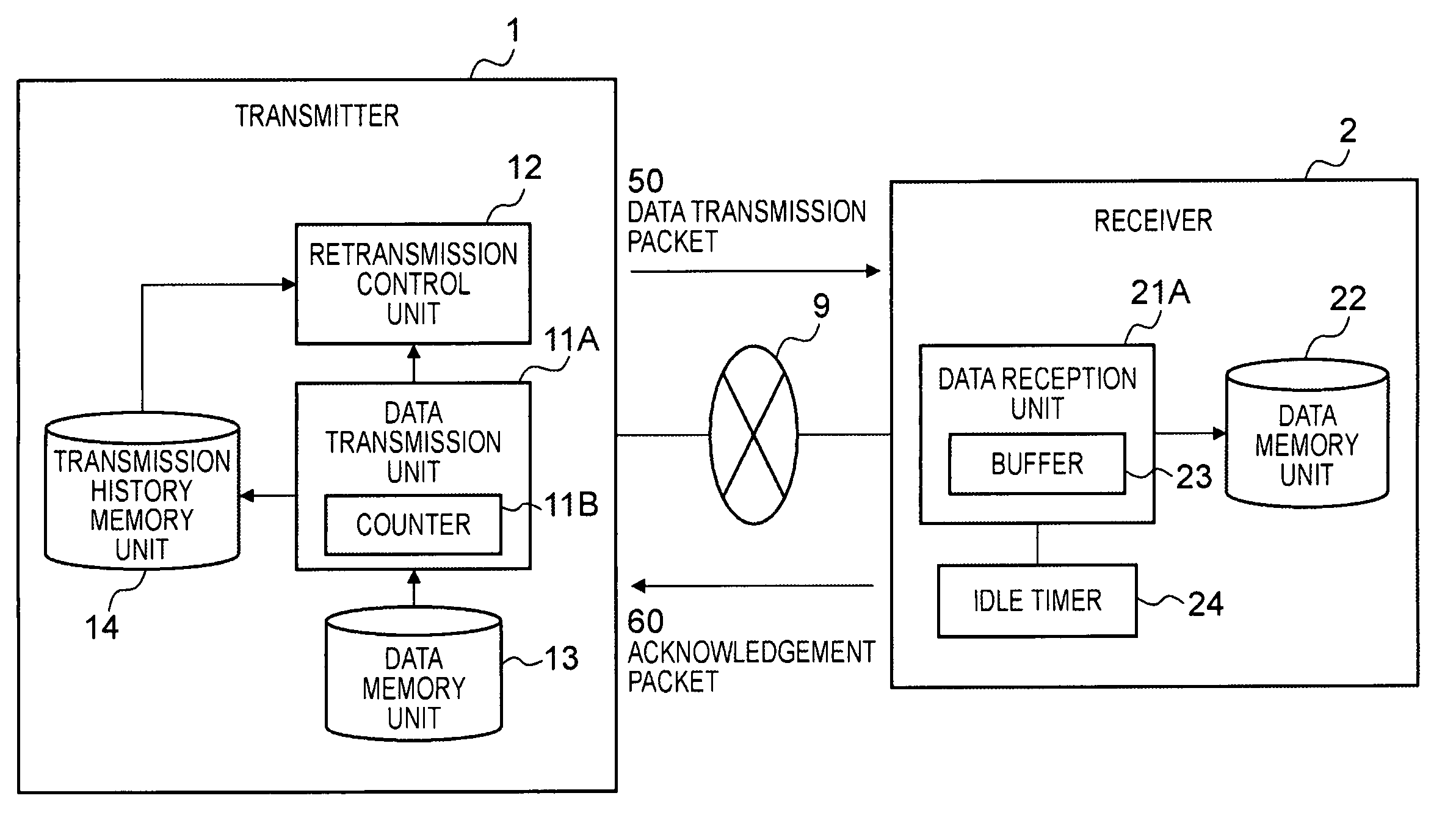
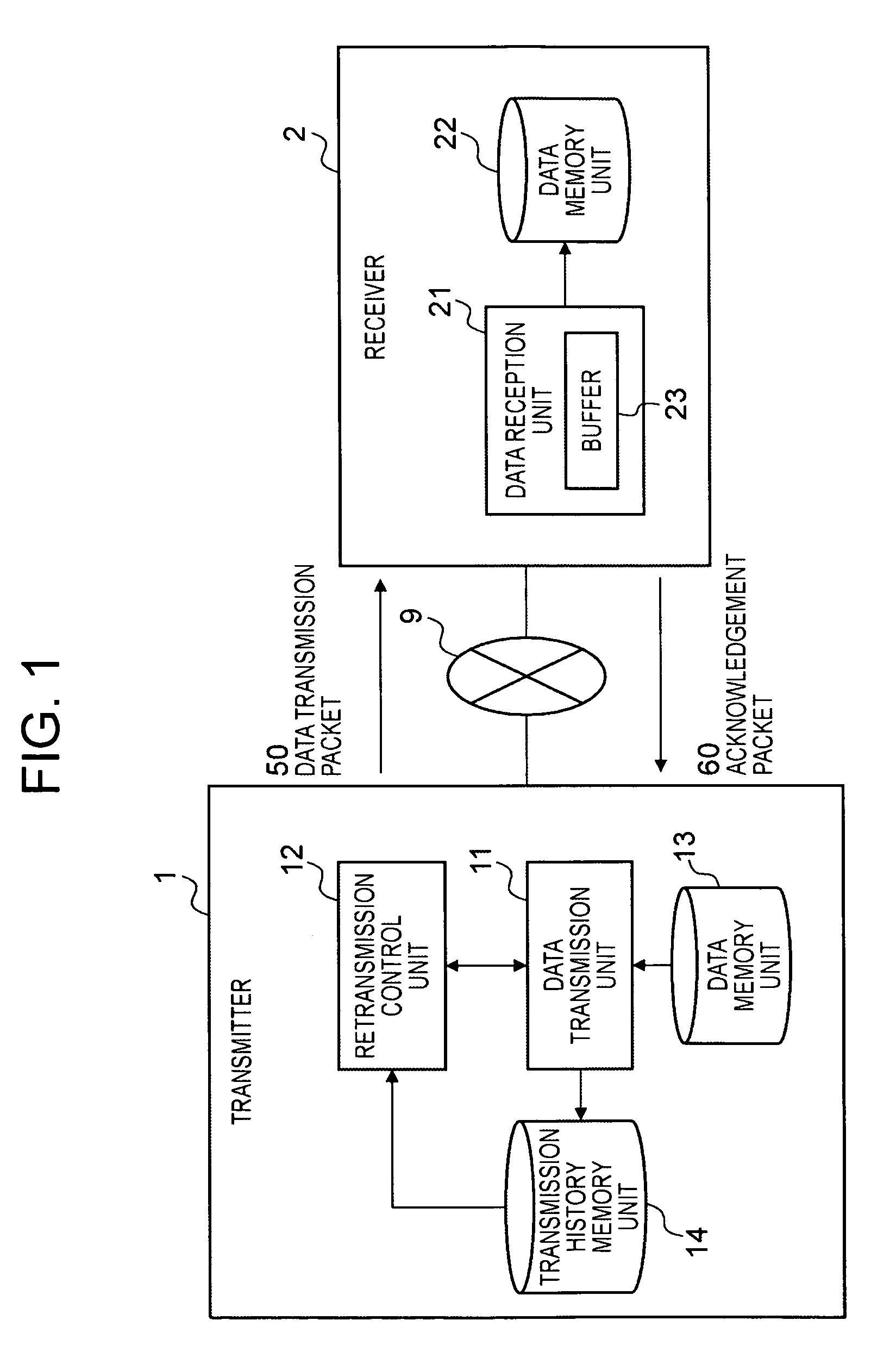
InactiveUS20070064705A1Avoid congestionIncrease speedError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemPacket loss
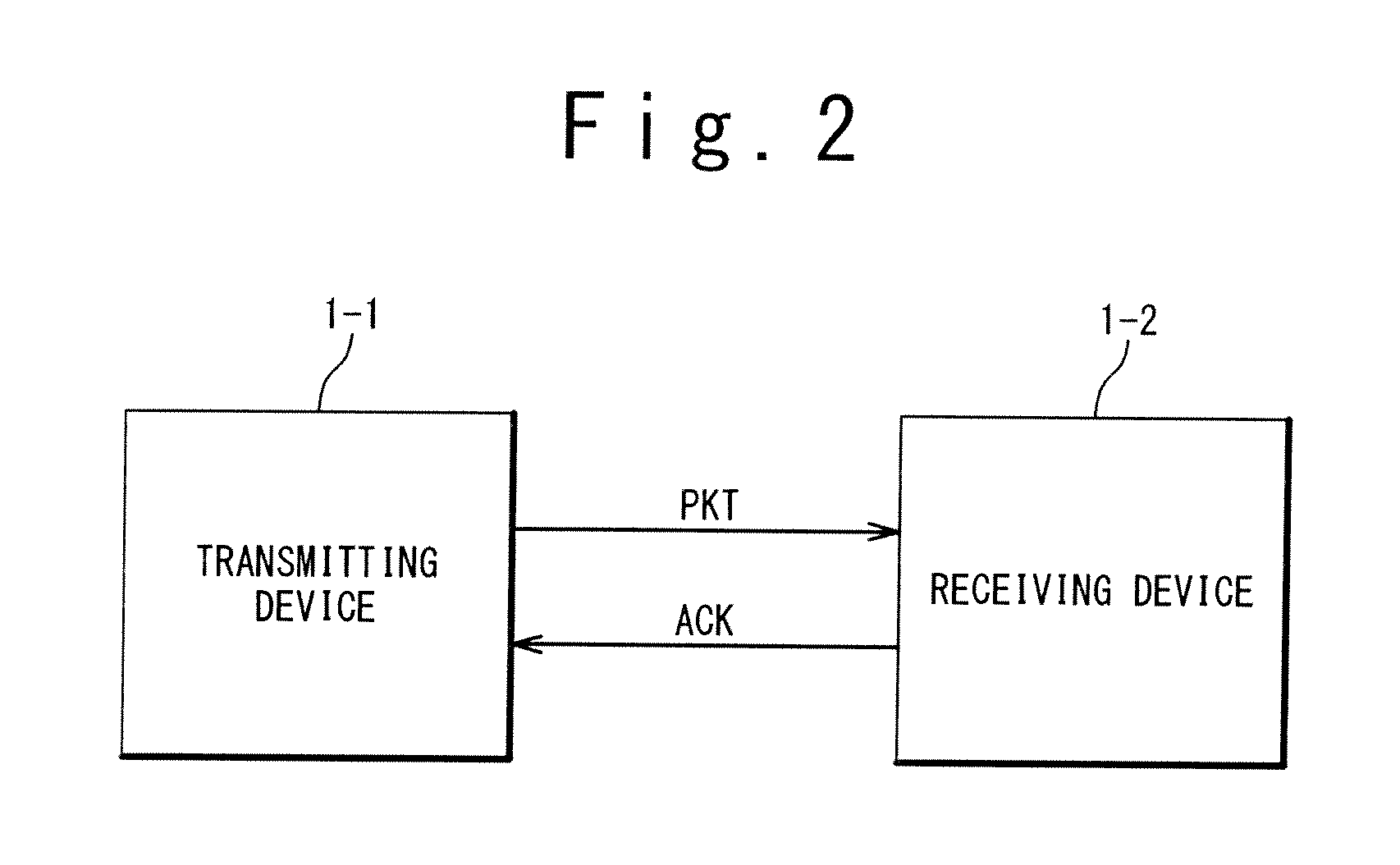
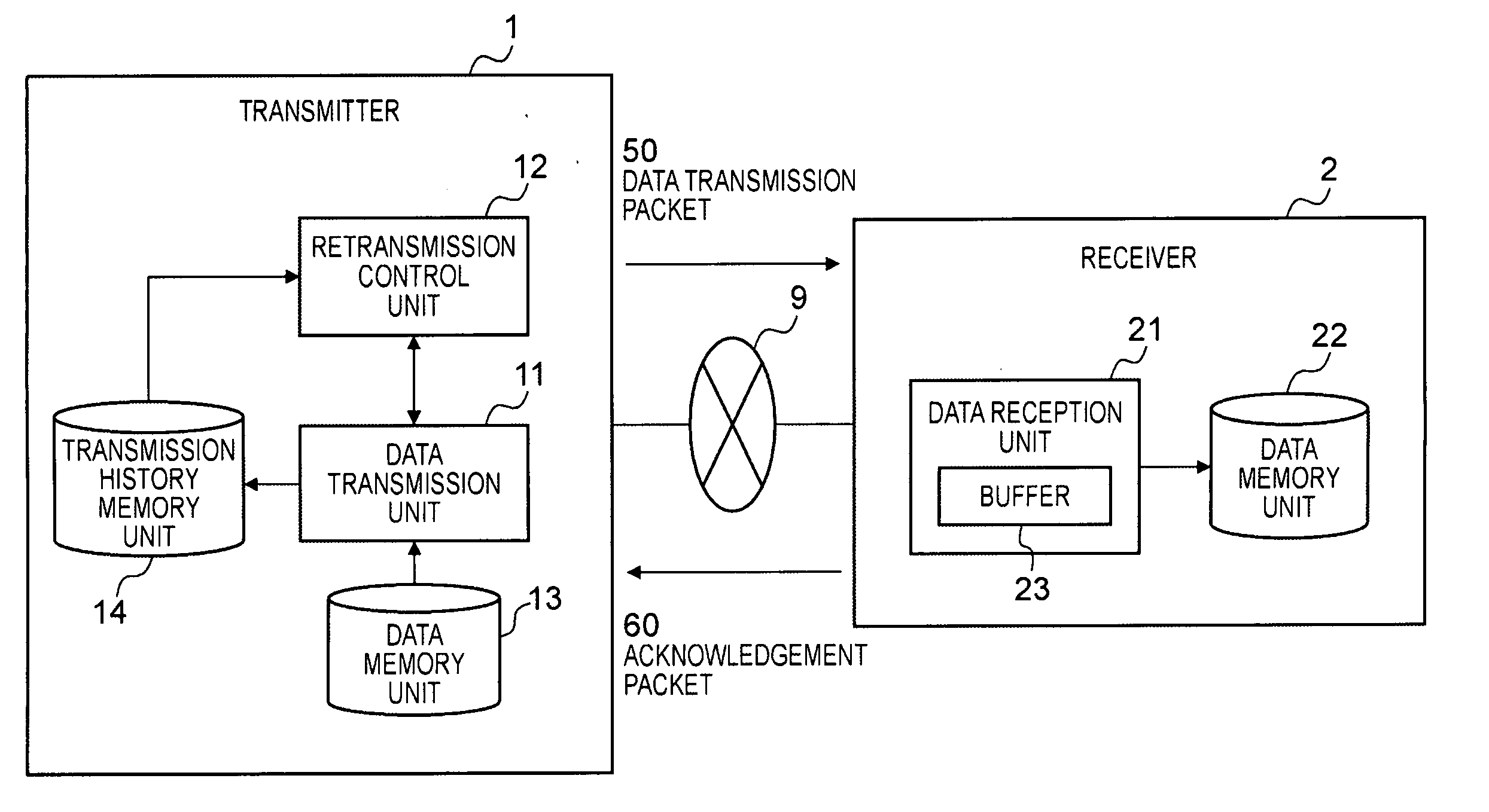
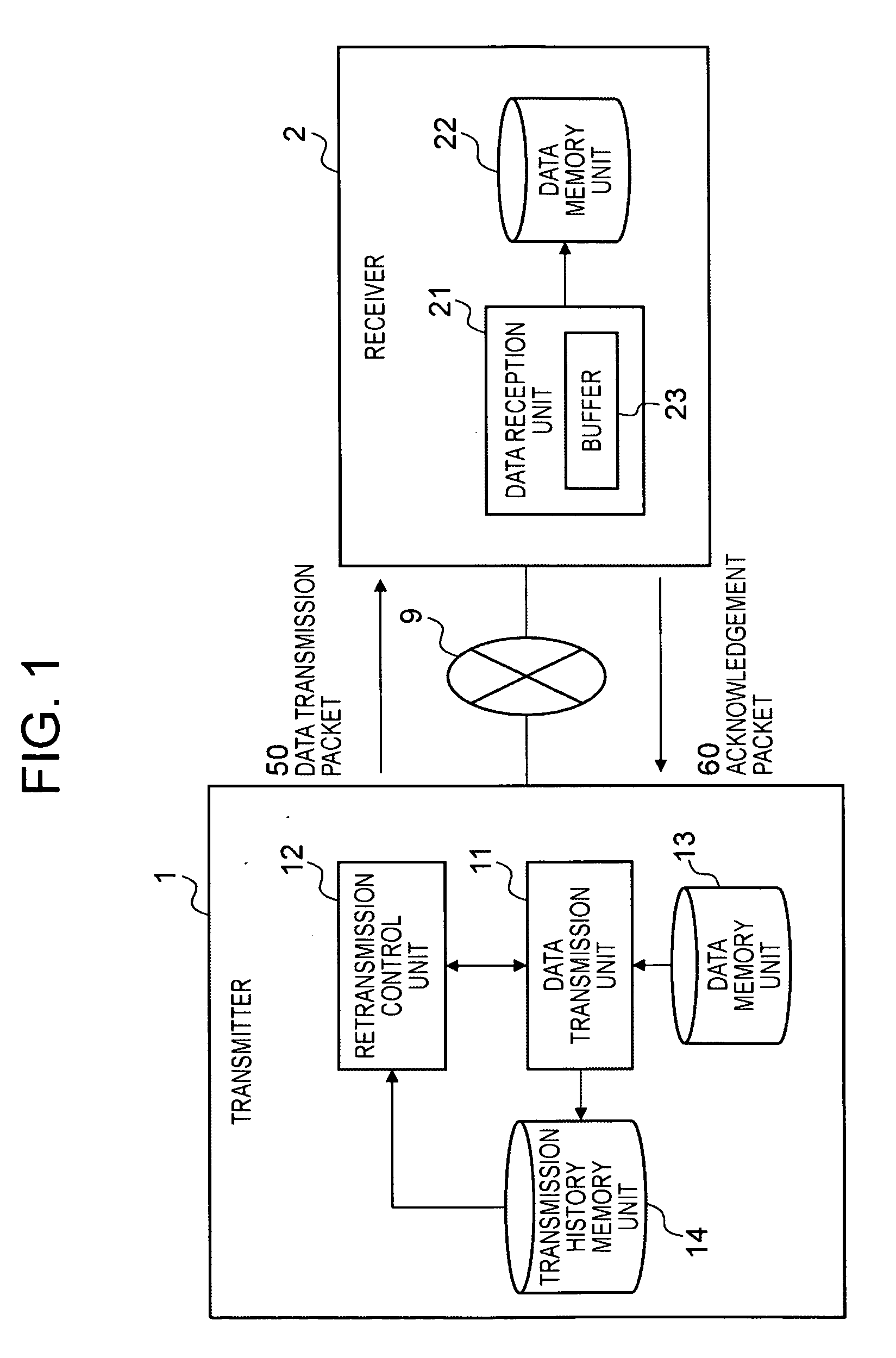
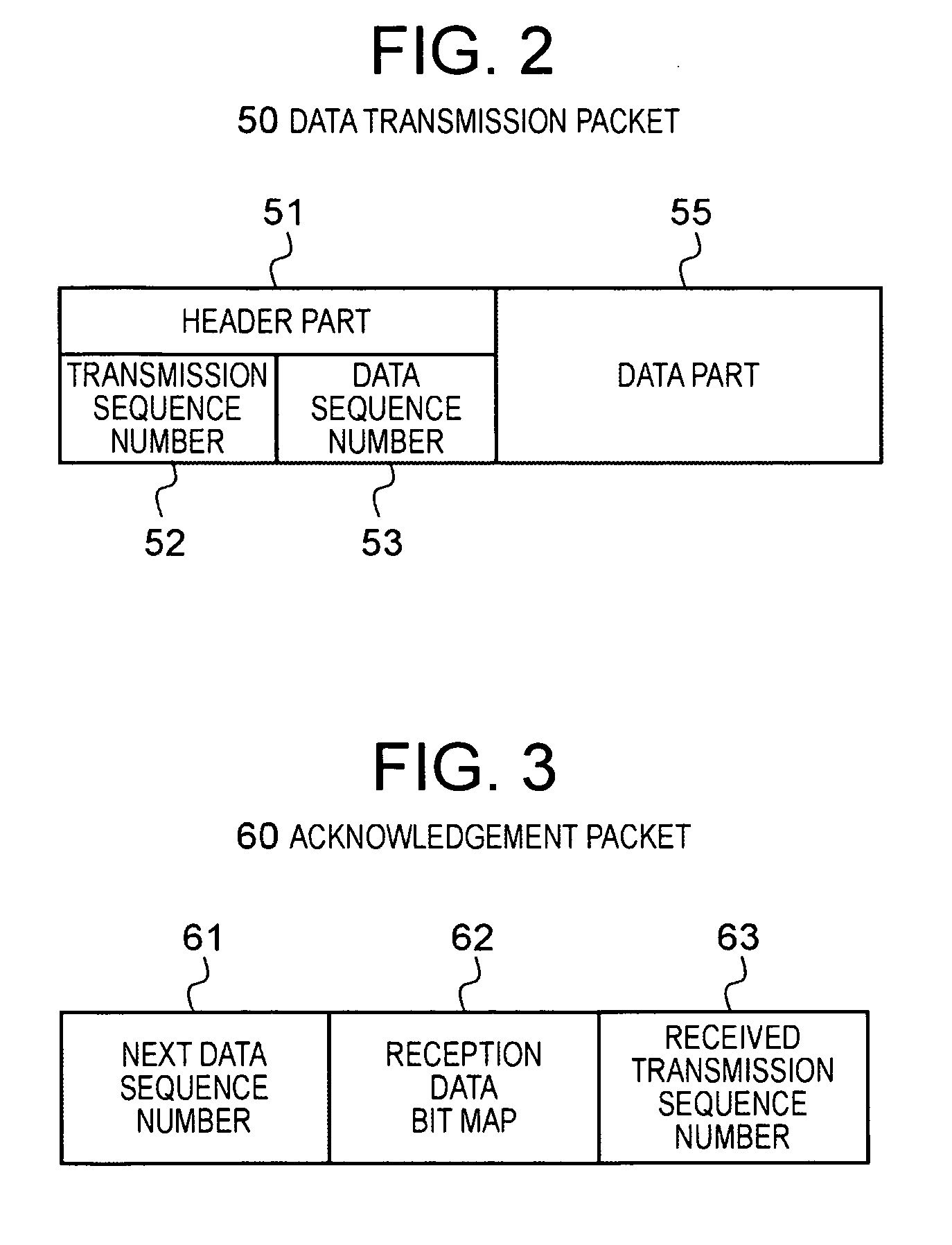
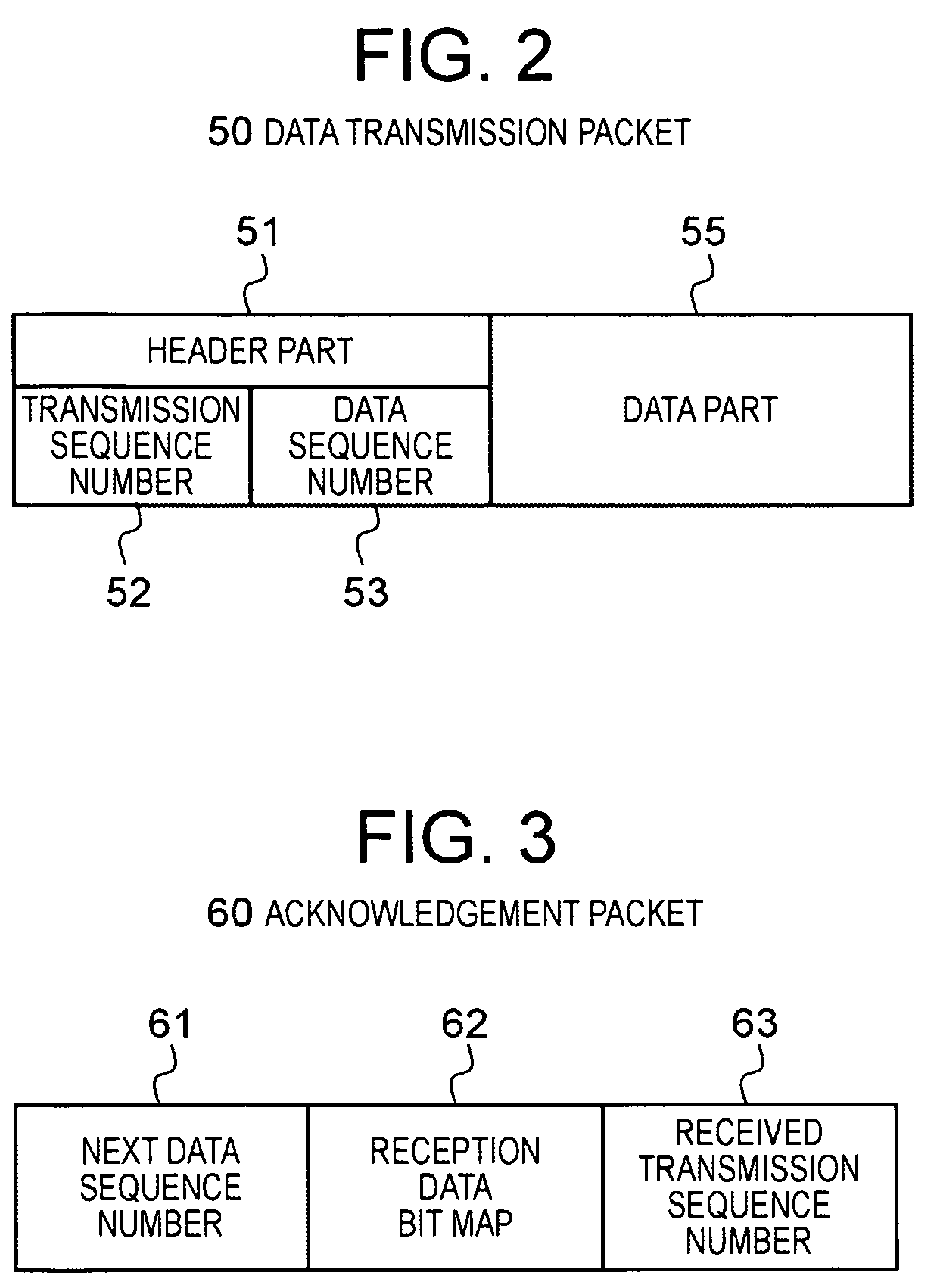
An object is to transmit data such that the transmission speed is not reduced even in a transmission route with a comparatively high percentage of packet loss. The transmitter 1 comprises: a data transmission unit 11 which transmits data packets 50 comprising data, a data sequence number indicating the order of the data, and a transmission sequence number indicating the transmission order, and which receives acknowledgement packets 60 comprising the next data sequence number, a bit string indicating the reception status, and a received transmission sequence number; a transmission history memory unit 14 which memorizes the transmission history of the data packets transmitted by the data transmission unit 11; and a retransmission control unit 12 which refers to the transmission history memory unit 14 and specifies the data sequence numbers requiring retransmission based on the received acknowledgement packets 60, and which directs the data transmission unit 11 to retransmit. The receiver 2 comprises a data reception unit 21 which receives data packets 50 transmitted from the transmitter 1, and which produces and transmits to the transmitter 1 acknowledgement packets 60 corresponding to these packets.
Owner:NOMURA RESEARCH INSTITUTE
Method for transmitting sounding signal in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20120327914A1Guaranteed normal transmissionSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionCommunications systemTransmission order
Disclosed is a method for allowing a station to transmit a sounding signal in a multiple-antenna wireless communication system, the method including receiving a group defining information about a group to which the station belongs from an access point (AP); determining a transmission time taken in transmitting a sounding signal by the respective stations, which belong to the group, on the basis of the group defining information; and transmitting a sounding signal to the AP in accordance with the transmission time and preset transmission order when receiving a sounding request signal from the AP.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Communication system, apparatus and methods for providing and acquiring a system information message
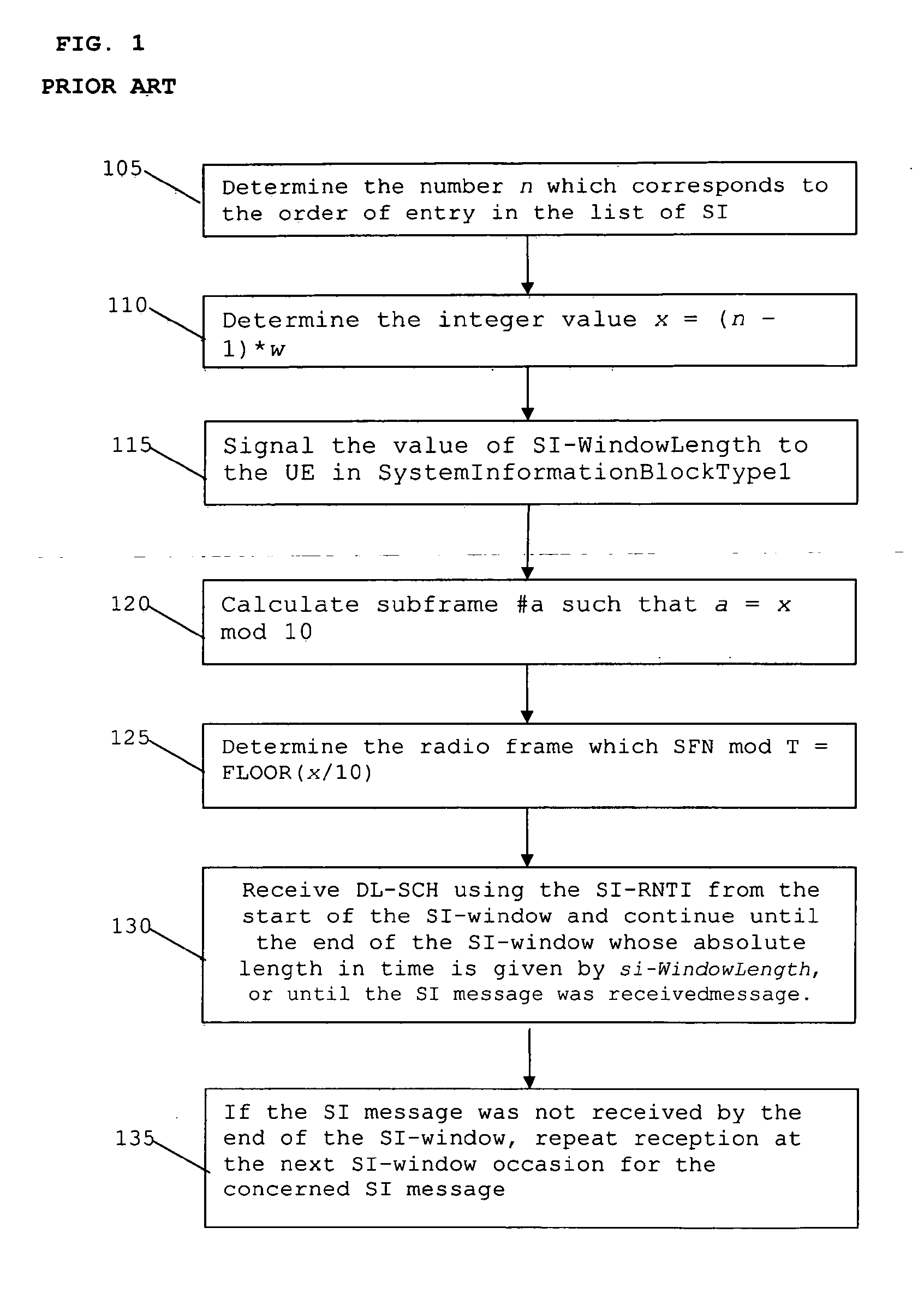
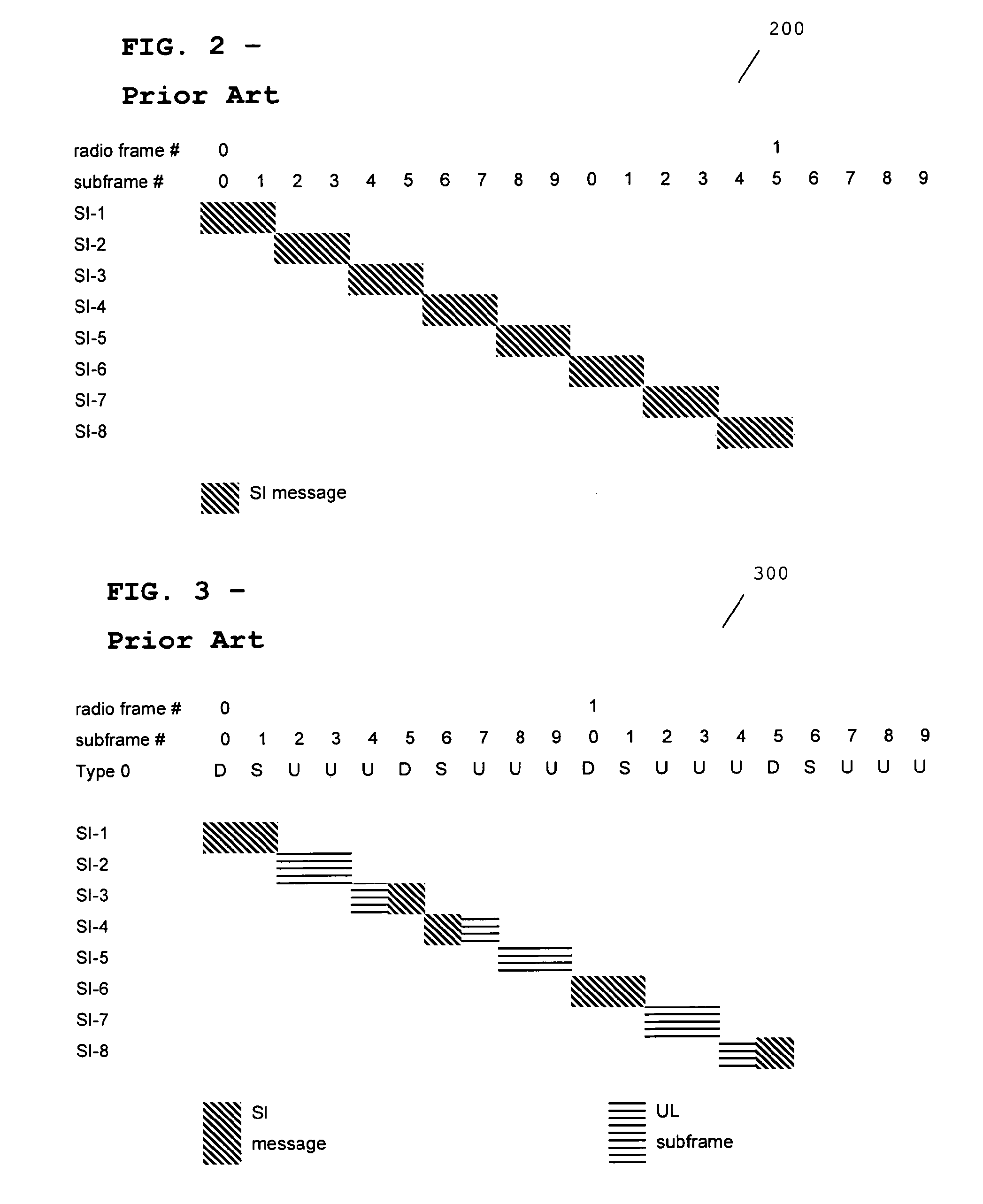
ActiveUS20120063370A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orImprove performanceAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexStart timeTransceiver
A network element for a cellular communication system comprises a signal processing logic module arranged to: generate a single system information message; generate a variable si-Windowlength parameter for transmission to the at least one wireless communication unit; and determine availability for downlink transmissions to the at least one wireless communication unit. The network element further comprises a transceiver arranged to transmit the si-Windowlength parameter and the single system information (S1) message to the at least one wireless communication unit in a variable length transmission time window (S1 window) a number of times, wherein the number of transmissions is based on the si-Windowlength parameter; wherein at least one of: a start time of a transmission of the single SI message, or a duration of the variable length transmission time window (SI window), is determined based on: (i) the si-Windowlength parameter; (ii) a transmission order; and (iii) on the availability for downlink transmissions.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Communications system, communications device, and data retransmission control method
InactiveUS7885264B2Increase speedAvoid congestionError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemPacket loss
An object is to transmit data such that the transmission speed is not reduced even in a transmission route with a comparatively high percentage of packet loss.The transmitter 1 comprises: a data transmission unit 11 which transmits data packets 50 comprising data, a data sequence number indicating the order of the data, and a transmission sequence number indicating the transmission order, and which receives acknowledgement packets 60 comprising the next data sequence number, a bit string indicating the reception status, and a received transmission sequence number; a transmission history memory unit 14 which memorizes the transmission history of the data packets transmitted by the data transmission unit 11; and a retransmission control unit 12 which refers to the transmission history memory unit 14 and specifies the data sequence numbers requiring retransmission based on the received acknowledgement packets 60, and which directs the data transmission unit 11 to retransmit. The receiver 2 comprises a data reception unit 21 which receives data packets 50 transmitted from the transmitter 1, and which produces and transmits to the transmitter 1 acknowledgement packets 60 corresponding to these packets.
Owner:NOMURA RESEARCH INSTITUTE
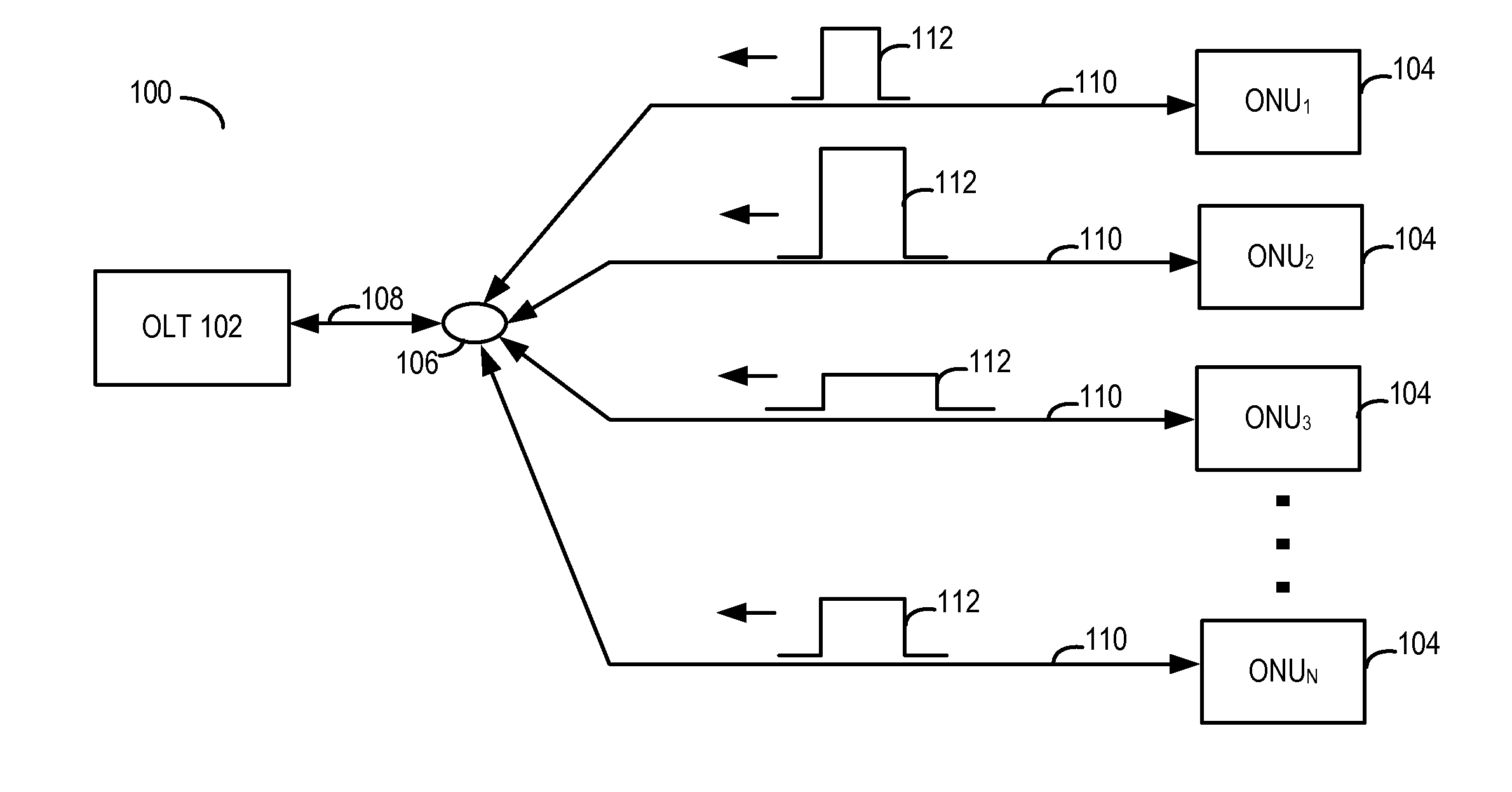
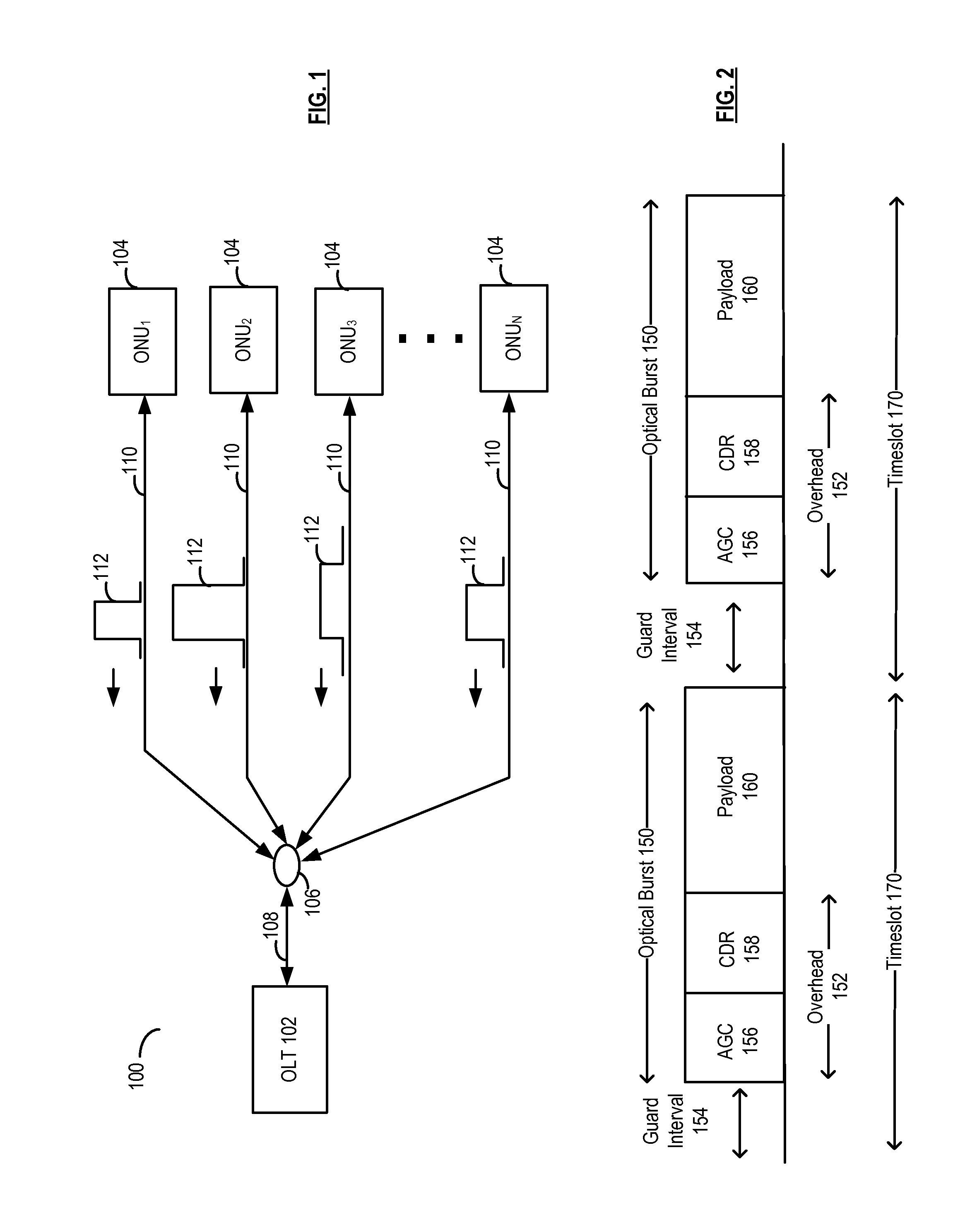
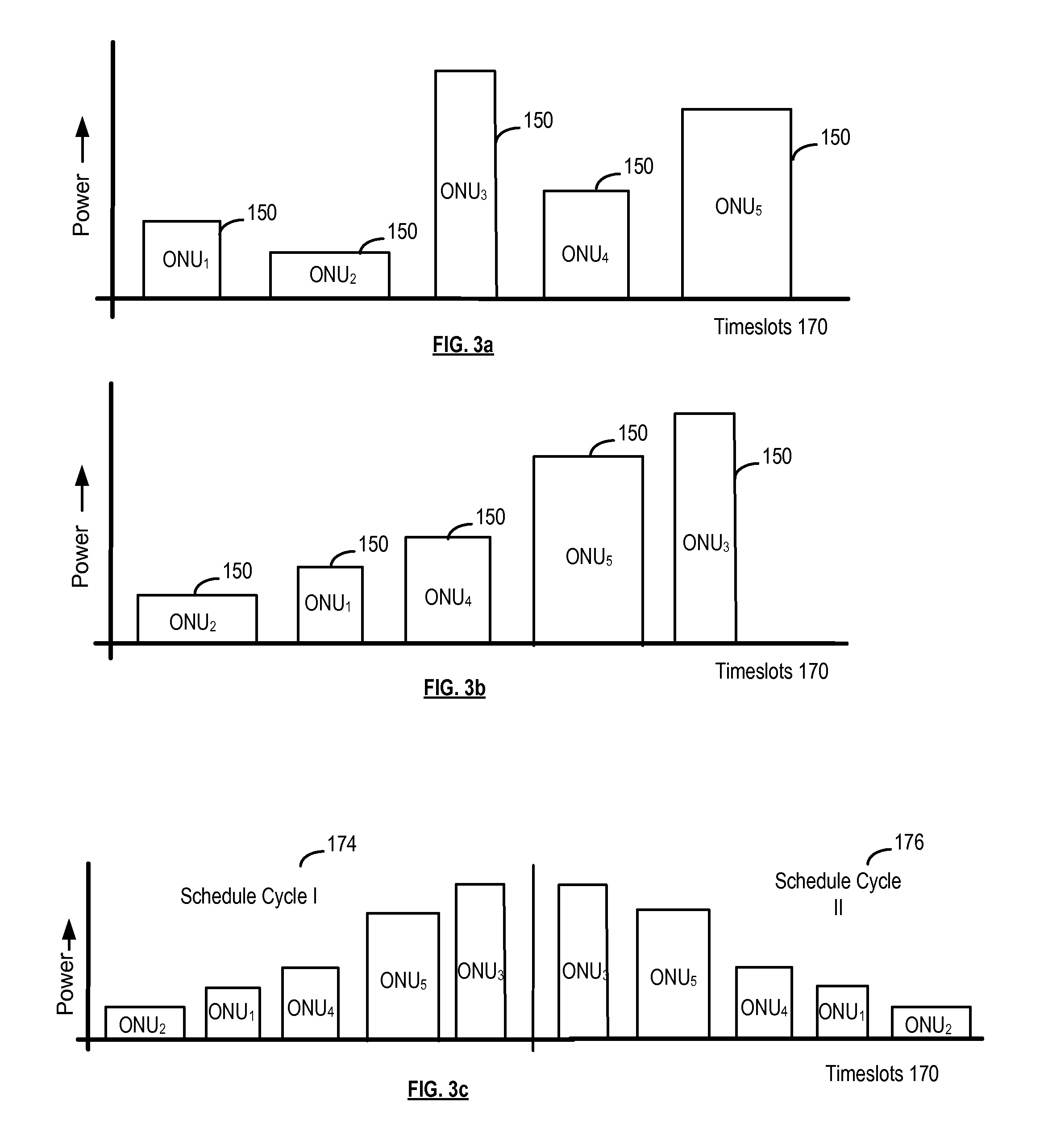
Dynamic bandwidth allocation in a passive optical network in which different optical network units transmit at different rates
ActiveUS20100183304A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDynamic bandwidth allocationOptical network unit
An OLT allocates a bandwidth budget and assigns upstream transmission order by receiving upstream transmission requests from a plurality of ONUs. Each ONU's request includes a requested guaranteed bandwidth and a requested best effort bandwidth. Each ONU has respective first and second attribute values. One attribute is given allocation priority over the other attribute. One attribute is given scheduling priority over the other attribute. Within each attribute, an allocation rank and a transmission rank is assigned to the possible attribute values. The bandwidth budget is allocated in accordance with the allocation priority and ranks. The upstream transmissions are scheduled in accordance with the scheduling priority and ranks.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com