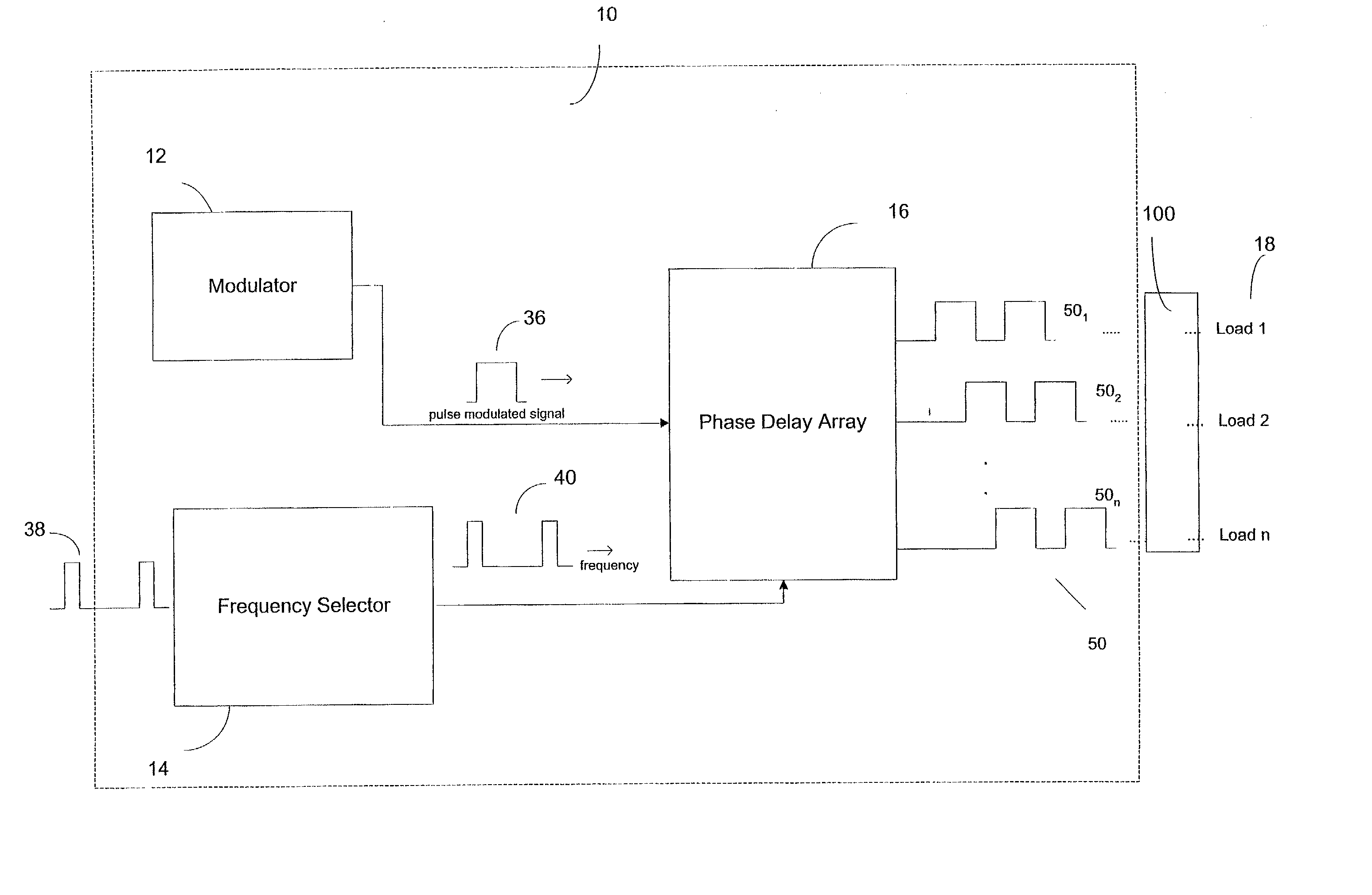Patents
Literature
44results about How to "High noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
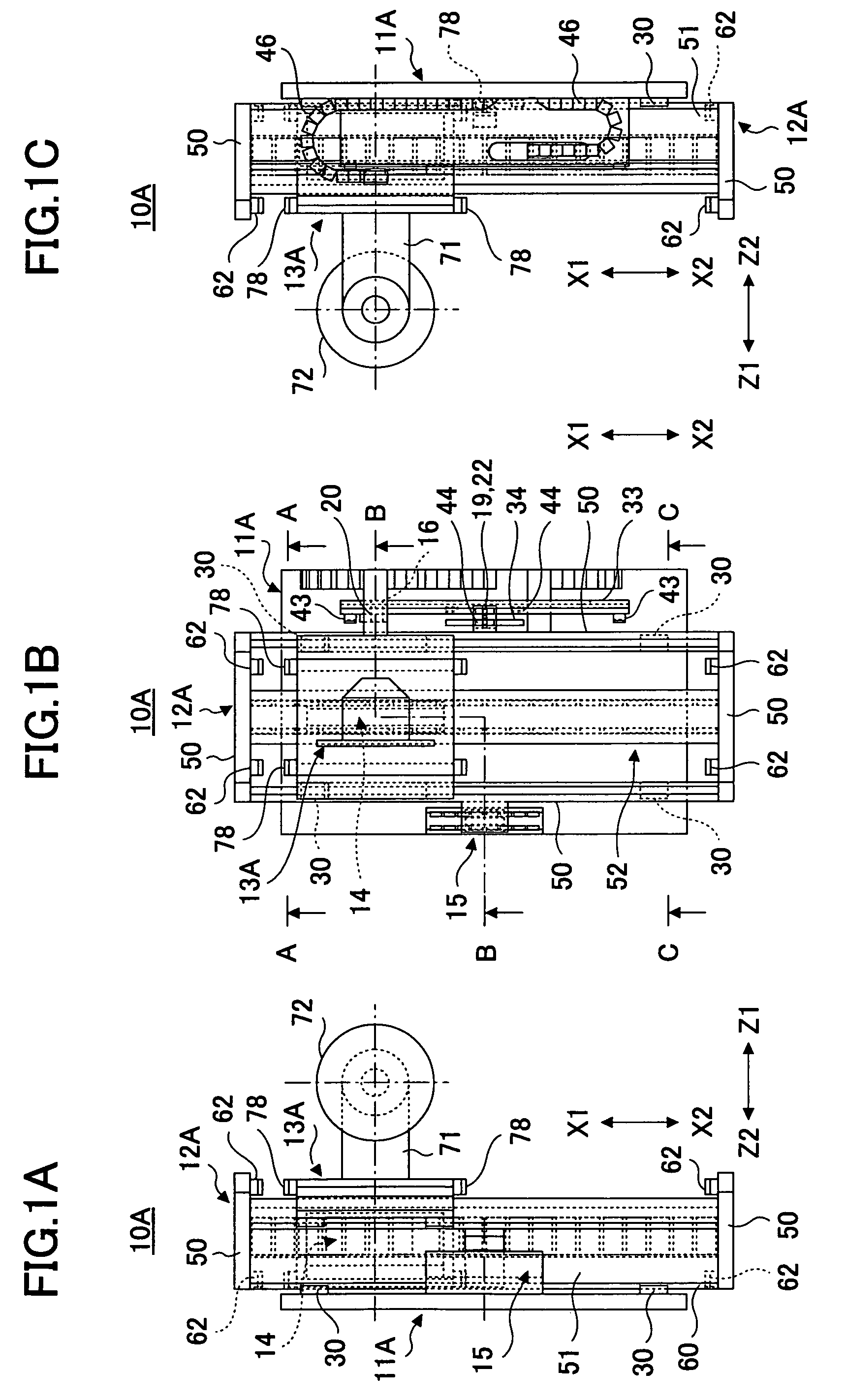
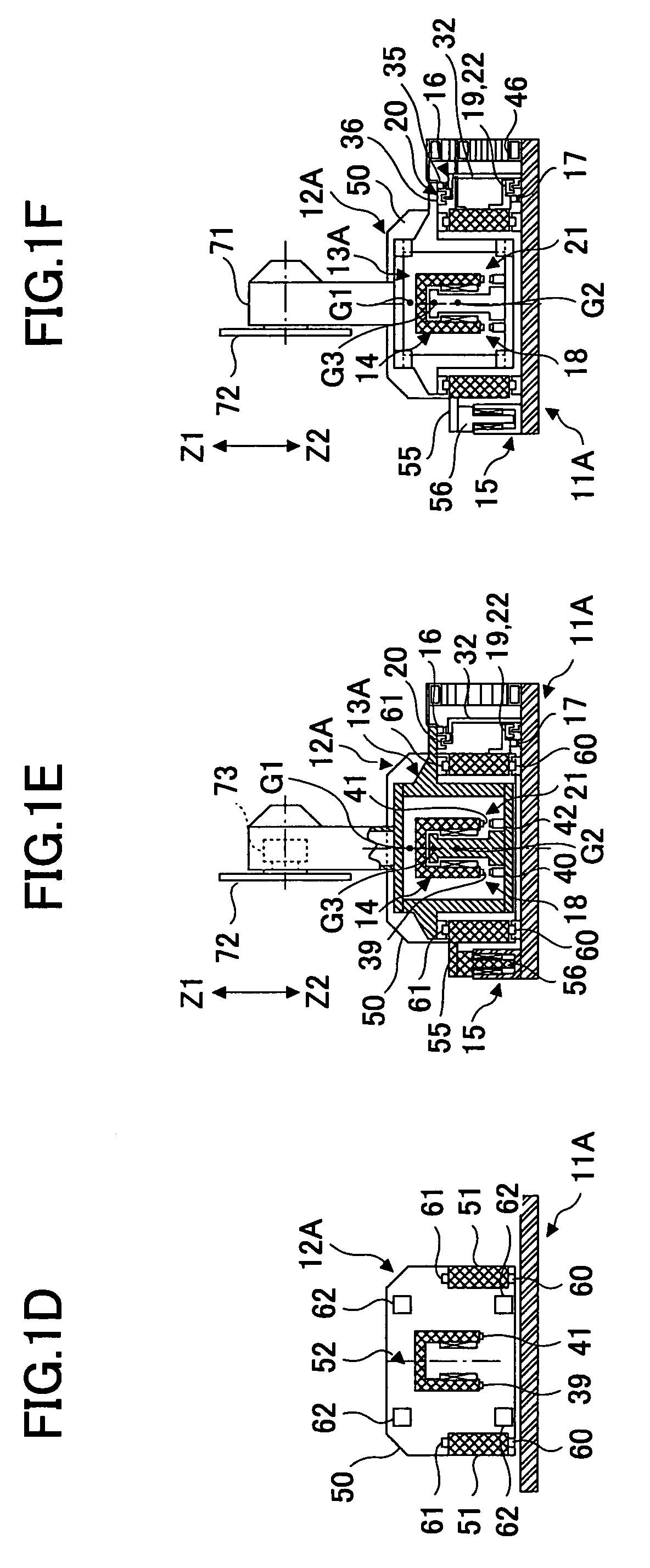
Personnel safety utilizing time variable frequencies
InactiveUS20100289662A1High noiseIncrease resistanceSafety devices for lifting equipmentsEngineering safety devicesOmnidirectional antennaDirectional antenna
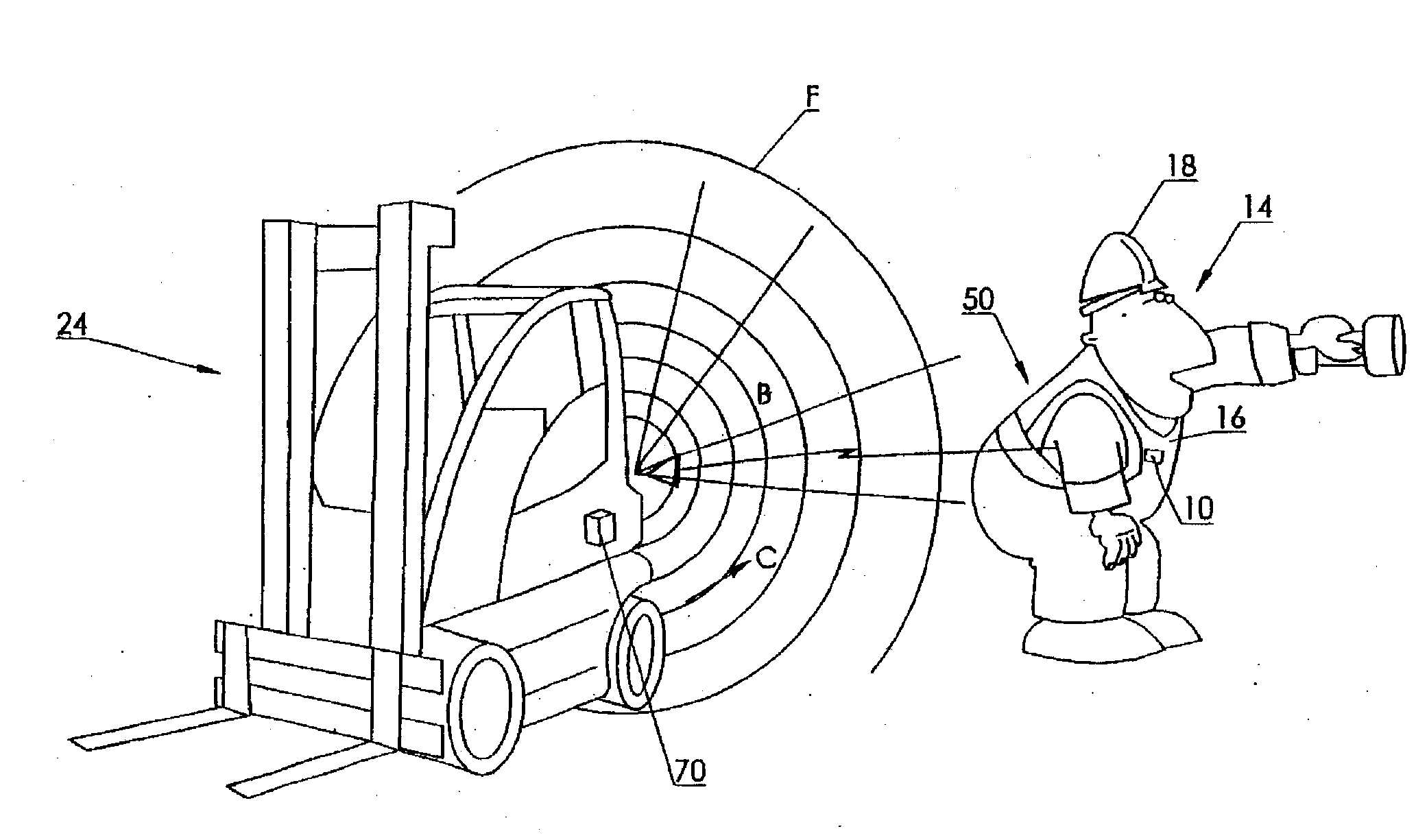
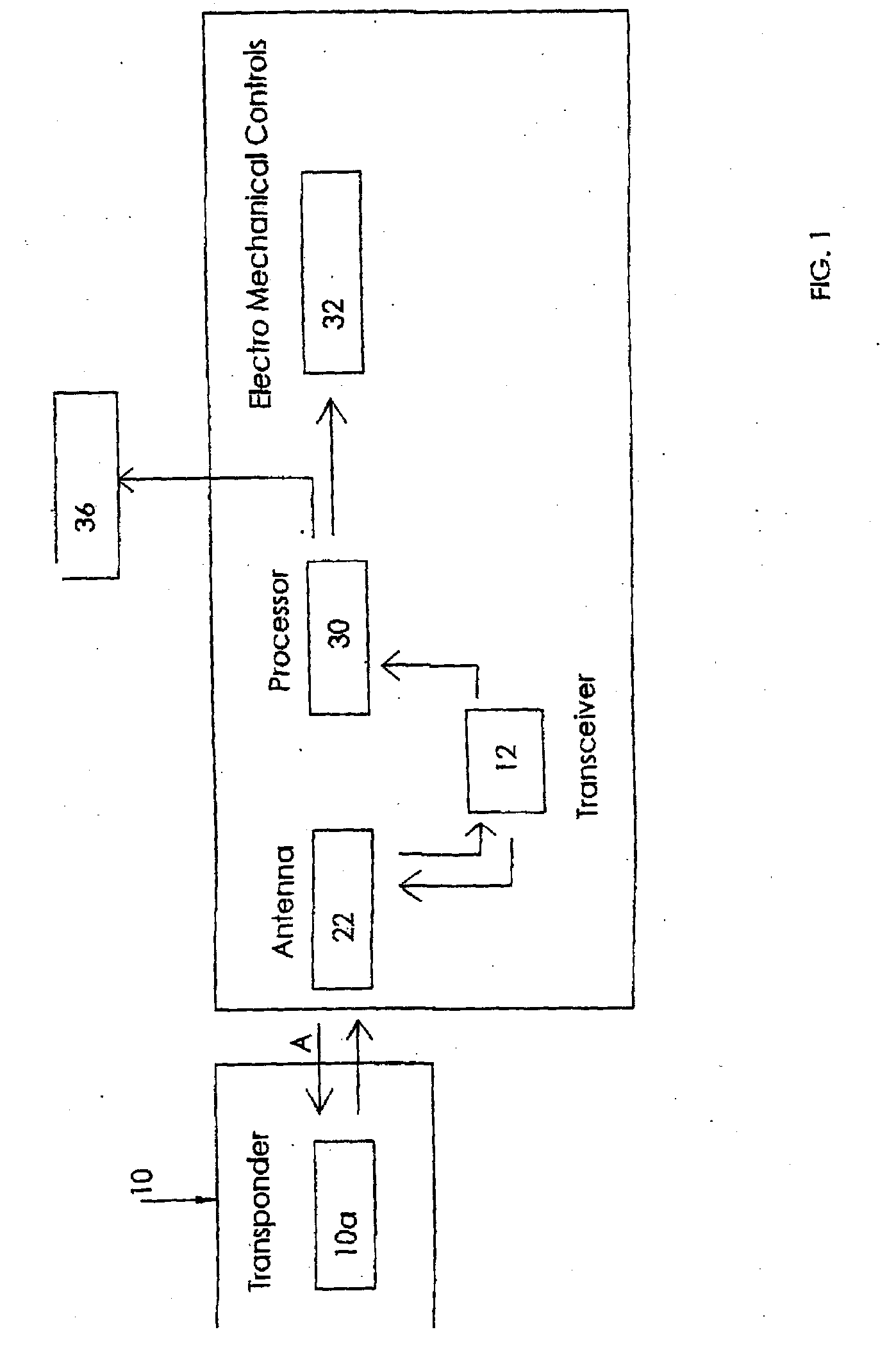
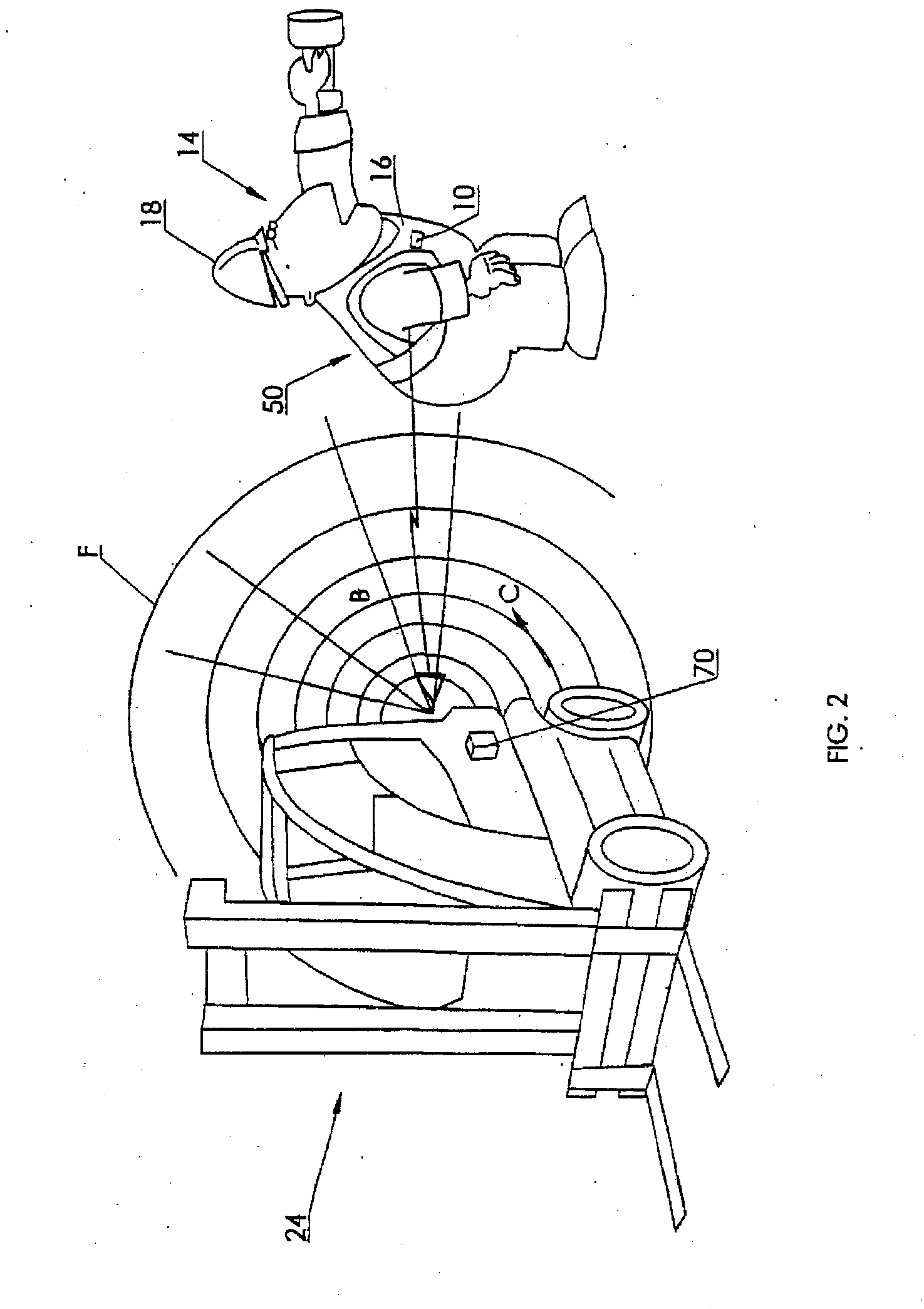
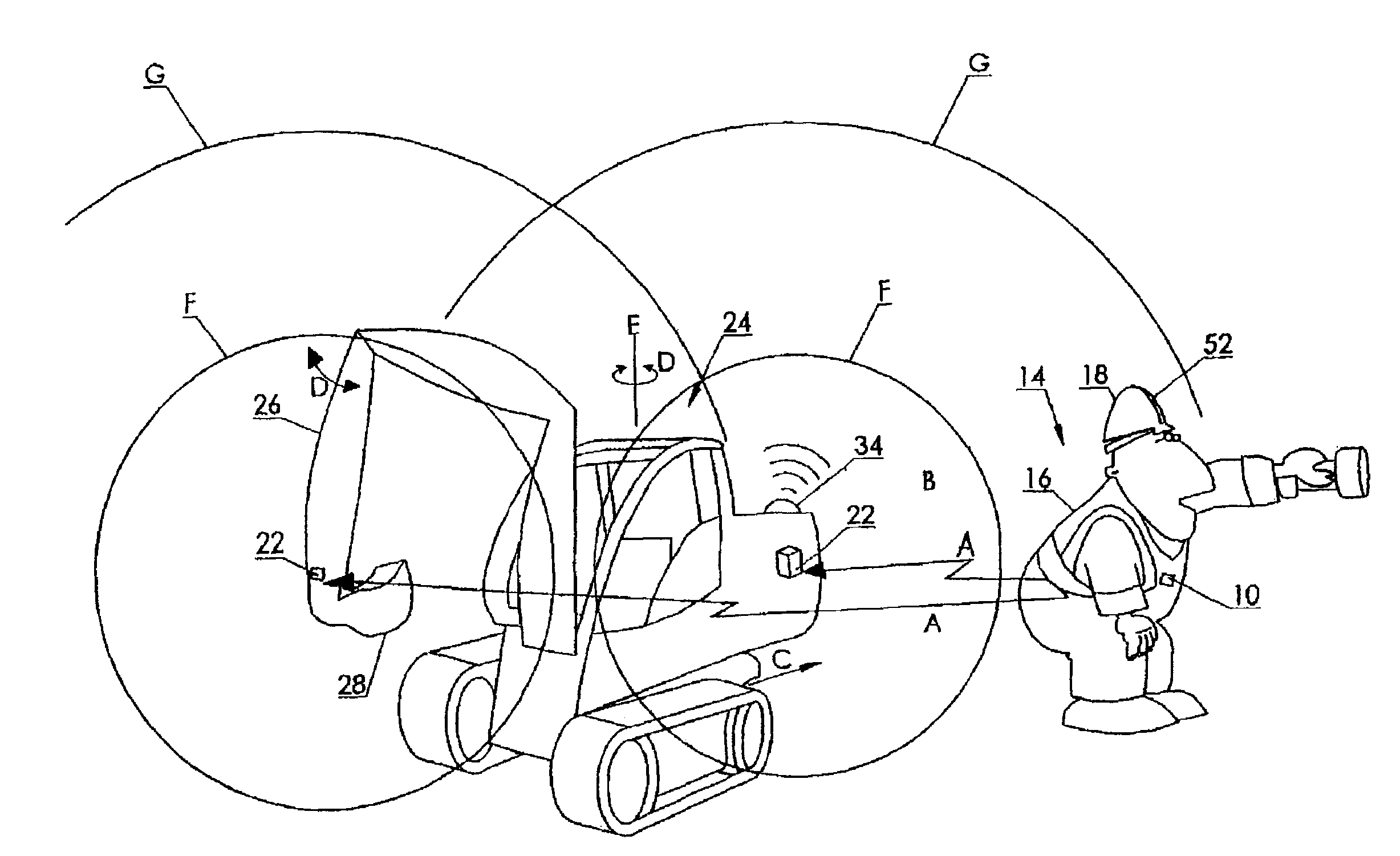
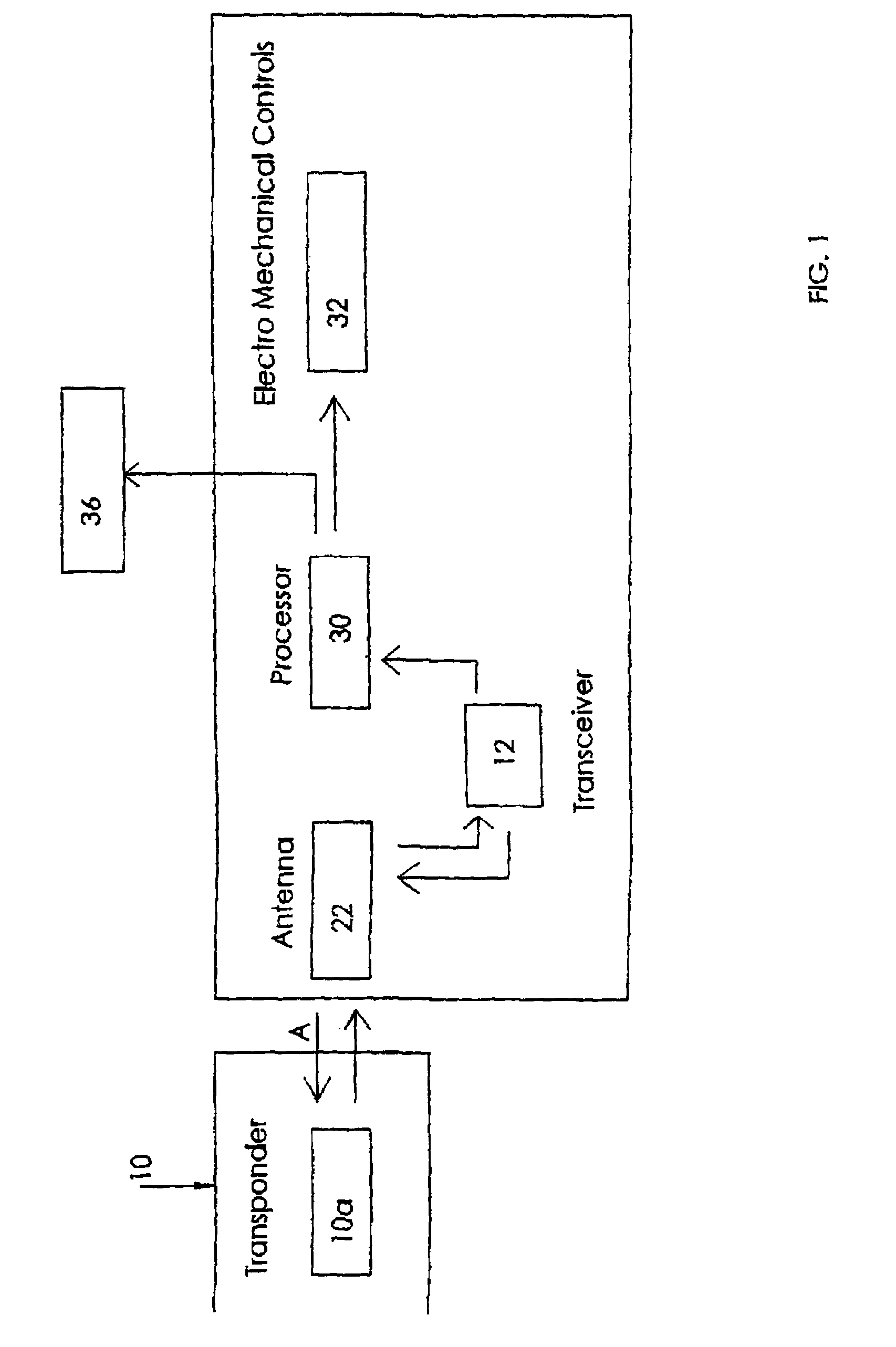
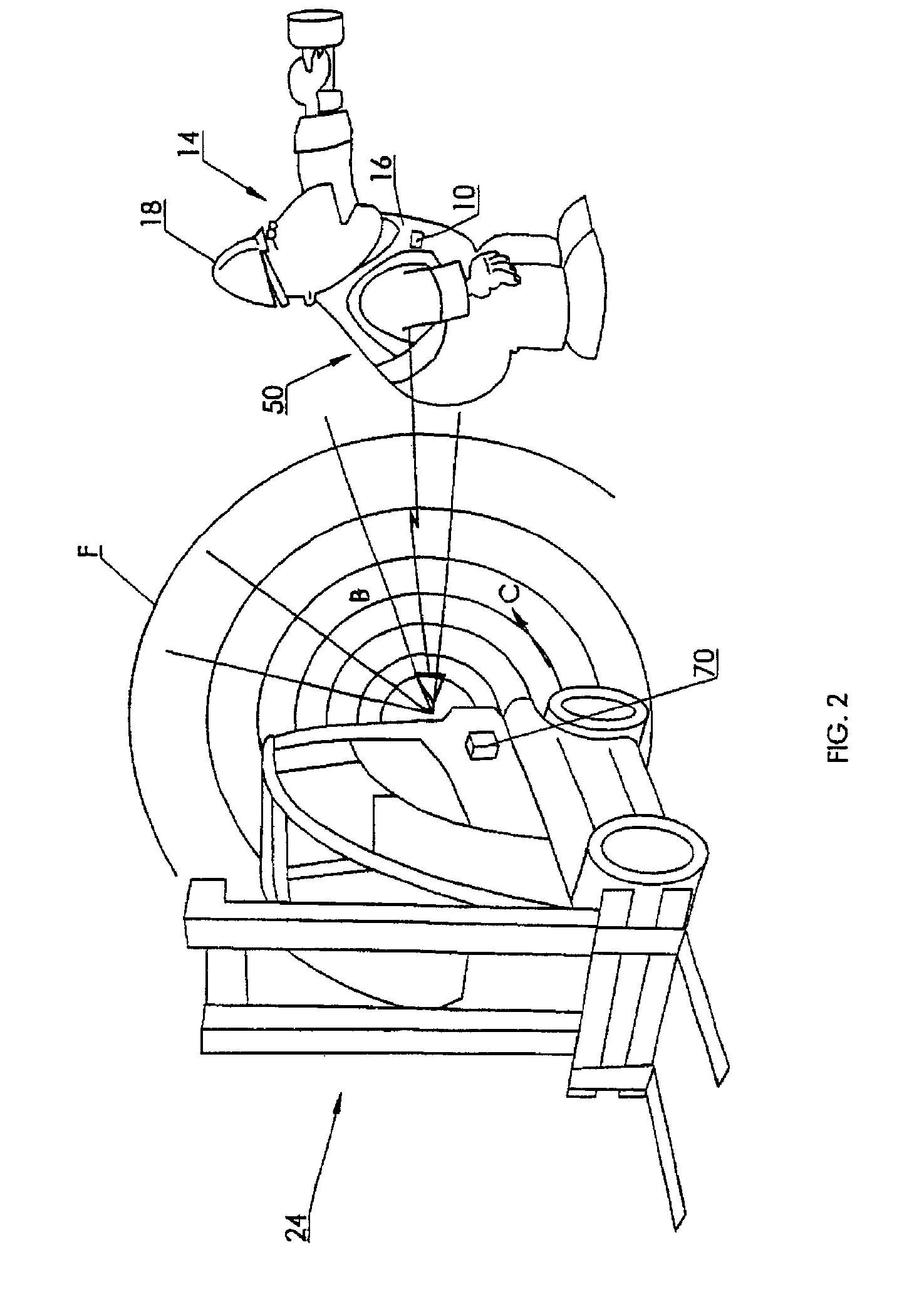
A system to improve safety of workers who are in proximity to mobile machines includes a machine mountable radio-frequency identification reader that wirelessly monitors radio-frequency identification tags worn by workers moving relative to and in proximity to a mobile machine when the reader is mounted on the machine. The reader includes a processor and an antenna front-end which is switchable between an omni-directional antenna or at least one directional antenna. The omni-directional antenna is mountable so as to monitor a machine circumference completely around the mobile machine. Each directional antenna is mountable so as to monitor only either a front or a back of the mobile machine relative to the machines direction of motion.
Owner:PSST MOBILE EQUIP - RICHARD SHERVEY +1
Personnel safety utilizing time variable frequencies
InactiveUS8248263B2High noiseIncrease resistanceSafety devices for lifting equipmentsEngineering safety devicesOmnidirectional antennaDirectional antenna
A system to improve safety of workers who are in proximity to mobile machines includes a machine mountable radio-frequency identification reader that wirelessly monitors radio-frequency identification tags worn by workers moving relative to and in proximity to a mobile machine when the reader is mounted on the machine. The reader includes a processor and an antenna front-end which is switchable between an omni-directional antenna or at least one directional antenna. The omni-directional antenna is mountable so as to monitor a machine circumference completely around the mobile machine. Each directional antenna is mountable so as to monitor only either a front or a back of the mobile machine relative to the machine's direction of motion.
Owner:PSST MOBILE EQUIP - RICHARD SHERVEY +1
Passive physiological monitoring (P2M) system
InactiveUS20060063982A1Easy to deployAccurate measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterInternal bleedingBand-pass filter
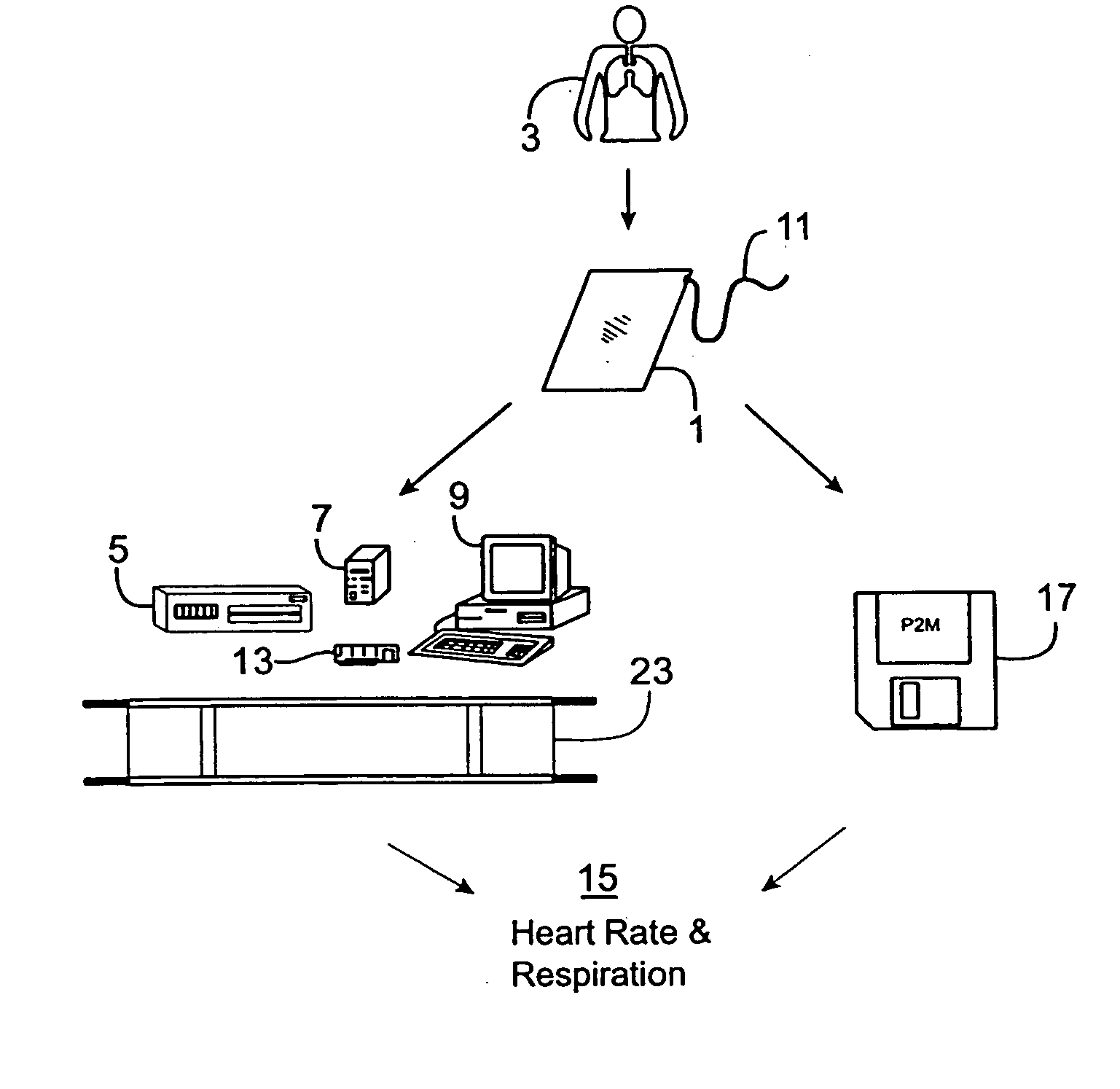
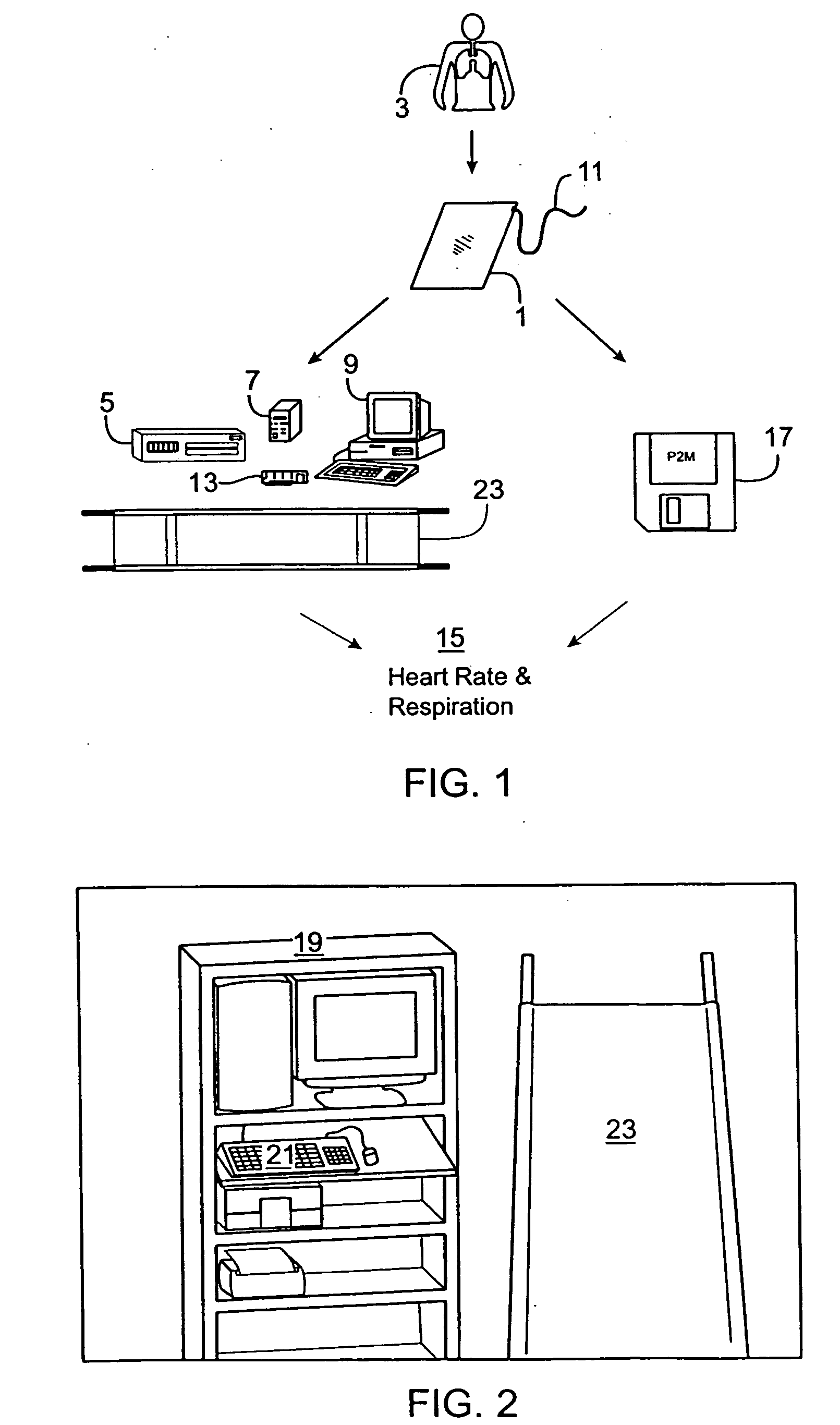
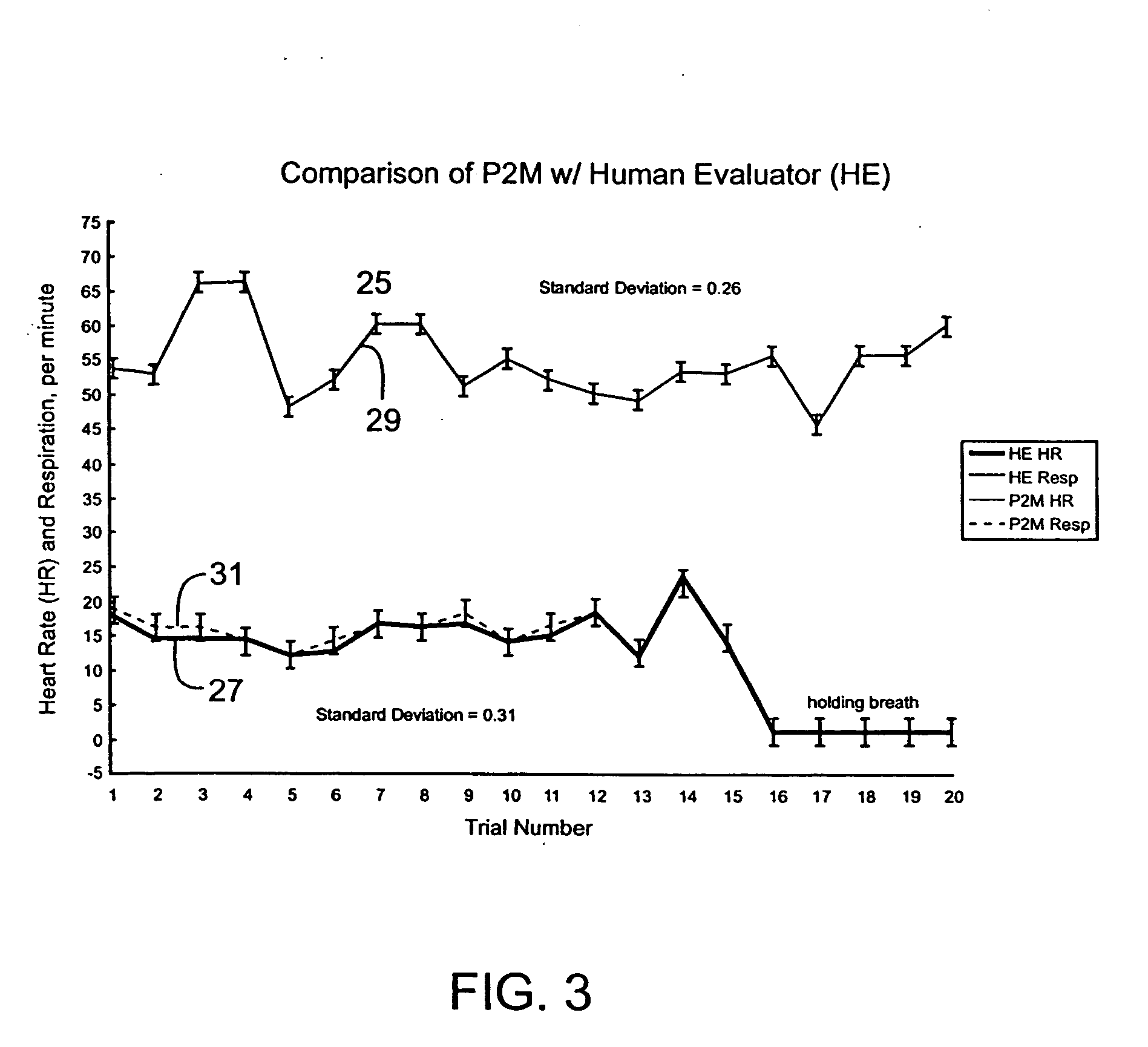
Passive physiological monitoring apparatus and method has a sensor for sensing physiological phenomenon. A converter converts sensed data into electrical signals and a computer receives and computes the signals and outputs computed data for real-time interactive display. The sensor is a piezoelectric film of polyvinylidene fluoride. A band-pass filter filters out noise and isolates the signals to reflect data from the body. A pre-amplifier amplifies signals. Signals detected include mechanical, thermal and acoustic signatures reflecting cardiac output, cardiac function, internal bleeding, respiratory, pulse, apnea, and temperature. A pad may incorporate the PVDF film and may be fluid-filled. The film converts mechanical energy into analog voltage signals. Analog signals are fed through the band-pass filter and the amplifier. A converter converts the analog signals to digital signals. A Fourier transform routine is used to transform into the frequency domain. A microcomputer is used for recording, analyzing and displaying data for on-line assessment and for providing realtime response. A radio-frequency filter may be connected to a cable and the film for transferring signals from the film through the cable. The sensor may be an array provided in a MEDEVAC litter or other device for measuring acoustic and hydraulic signals from the body of a patient for field monitoring, hospital monitoring, transport monitoring, home, remote monitoring.
Owner:HOANA MEDICAL
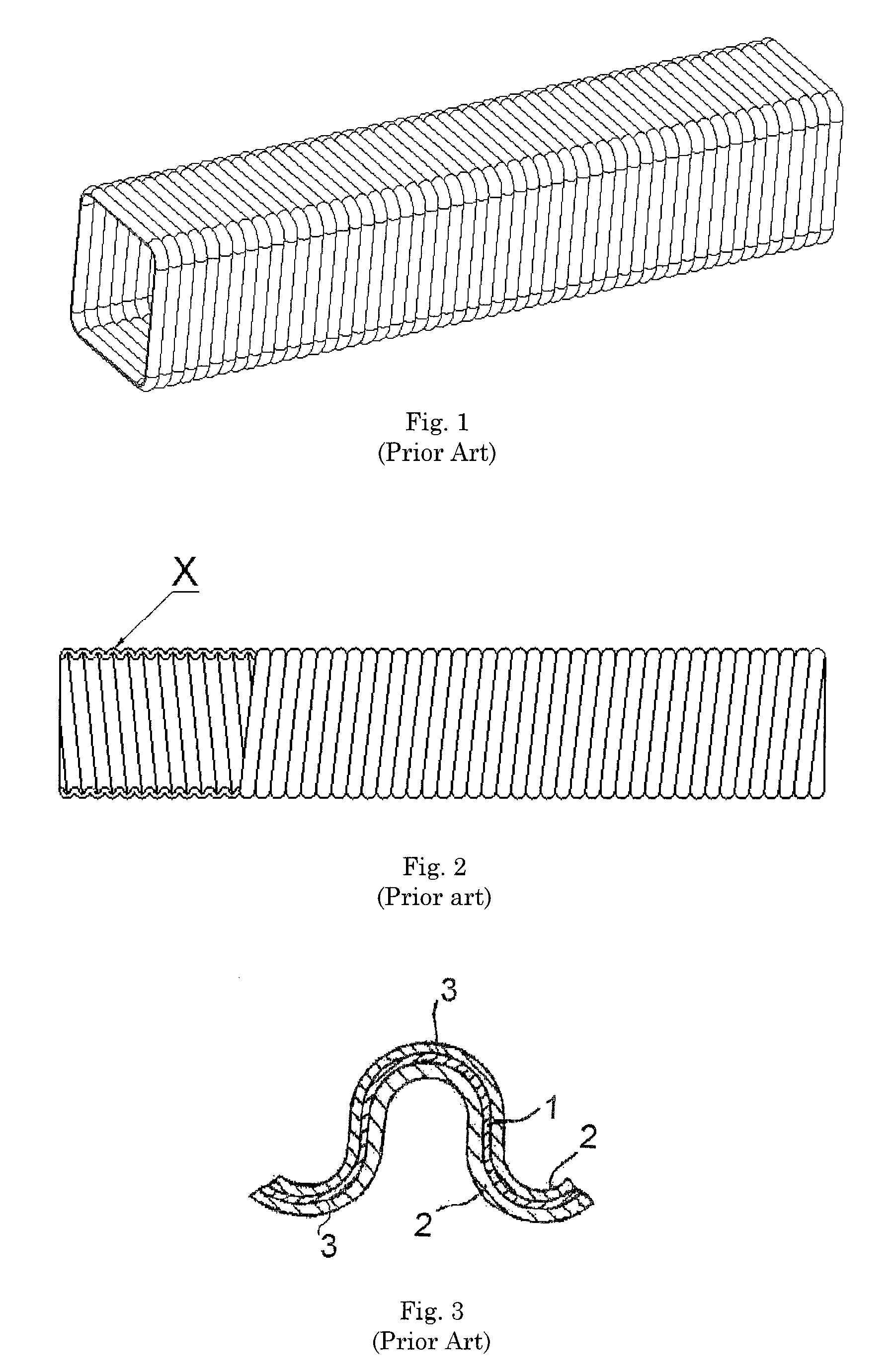
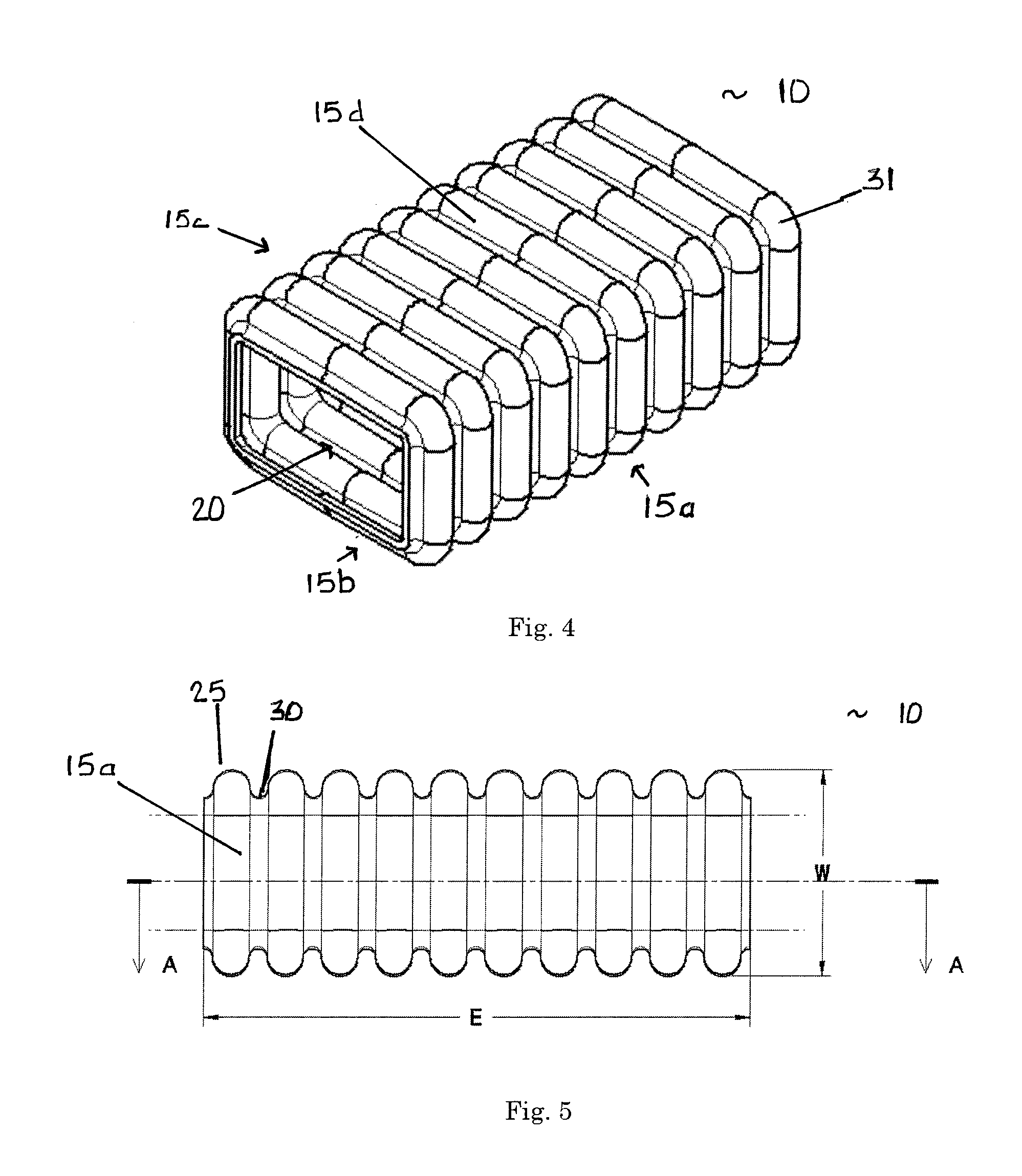
Corrugated tubular energy absorbing structure
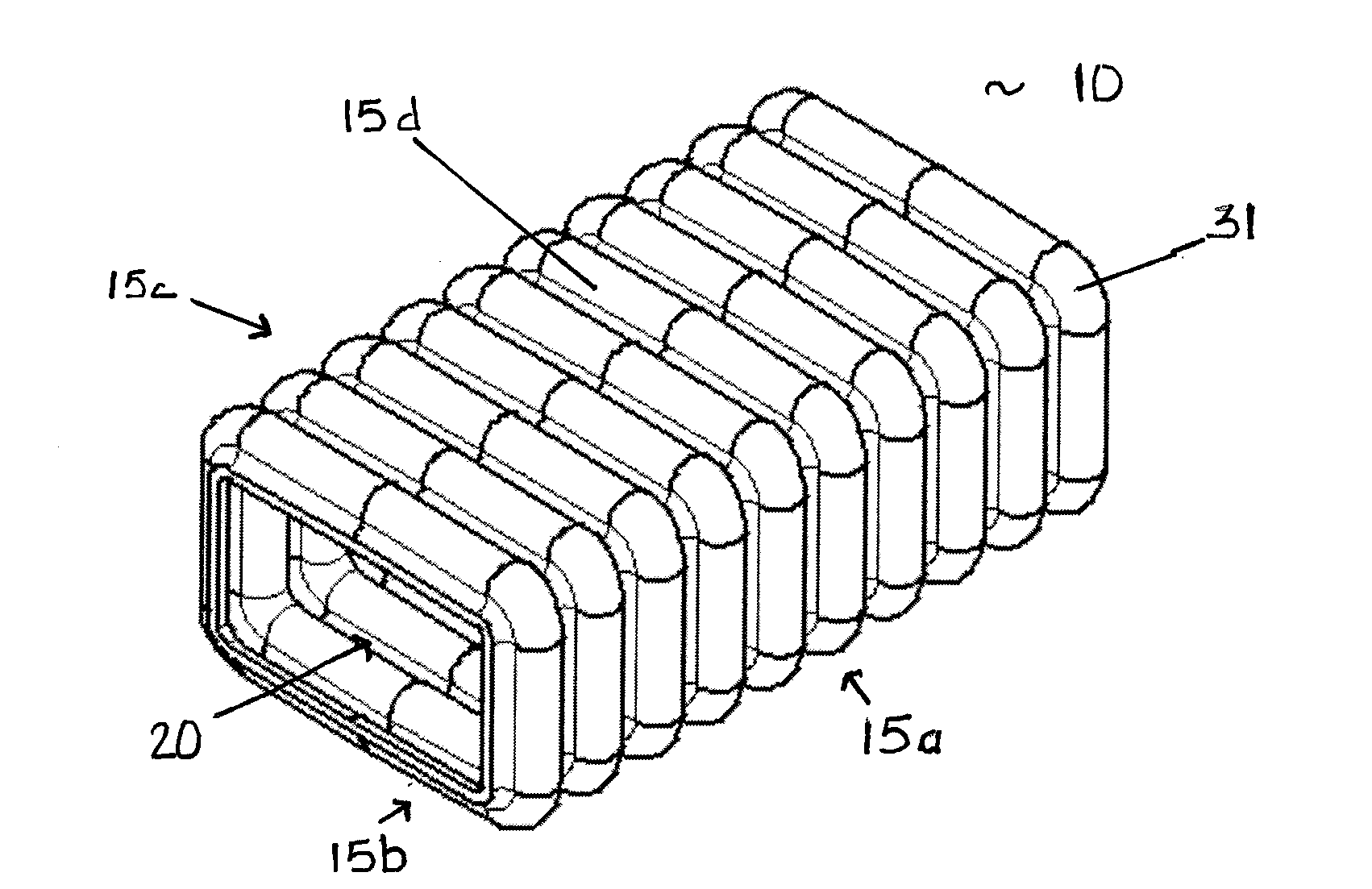
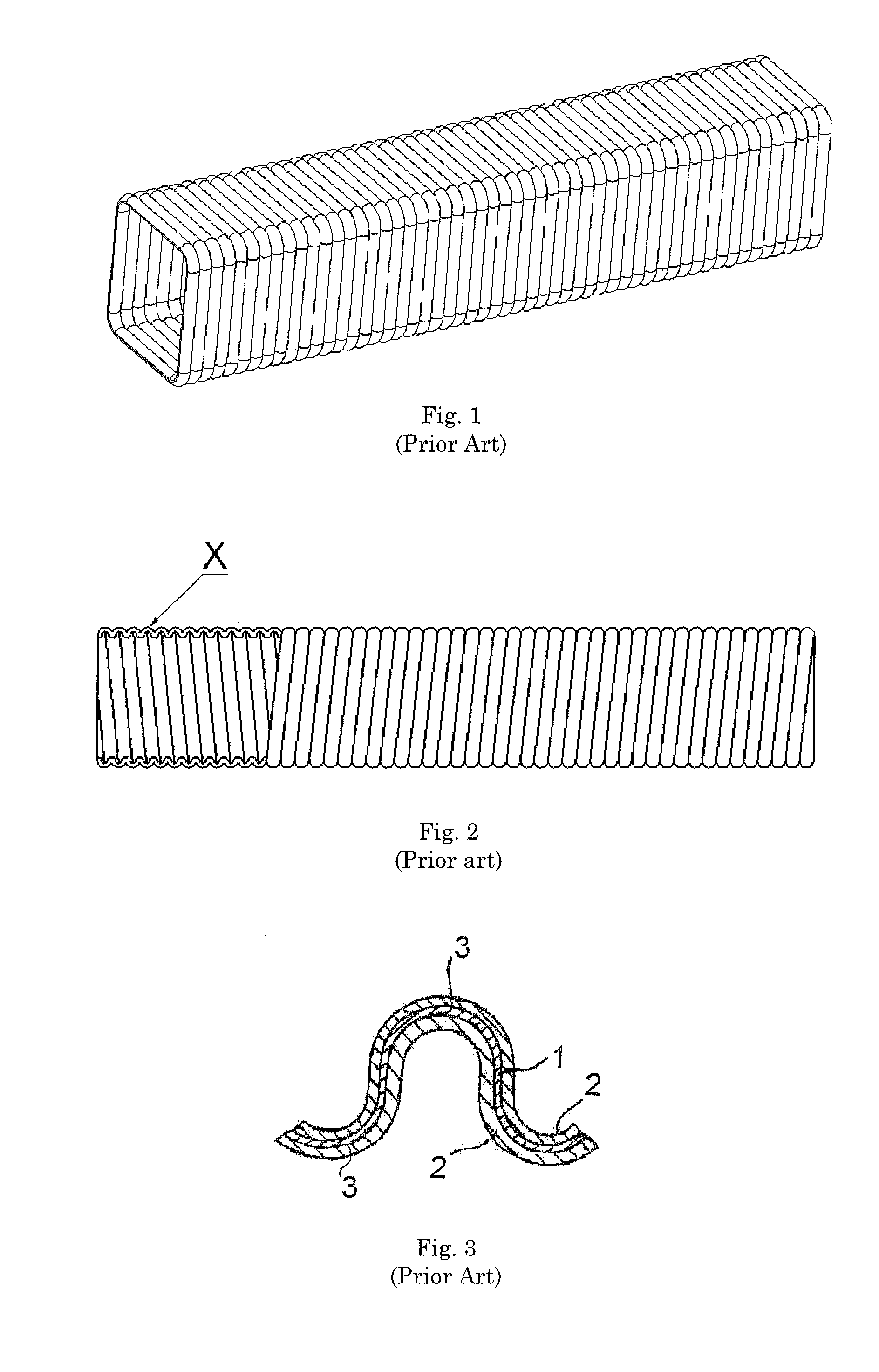
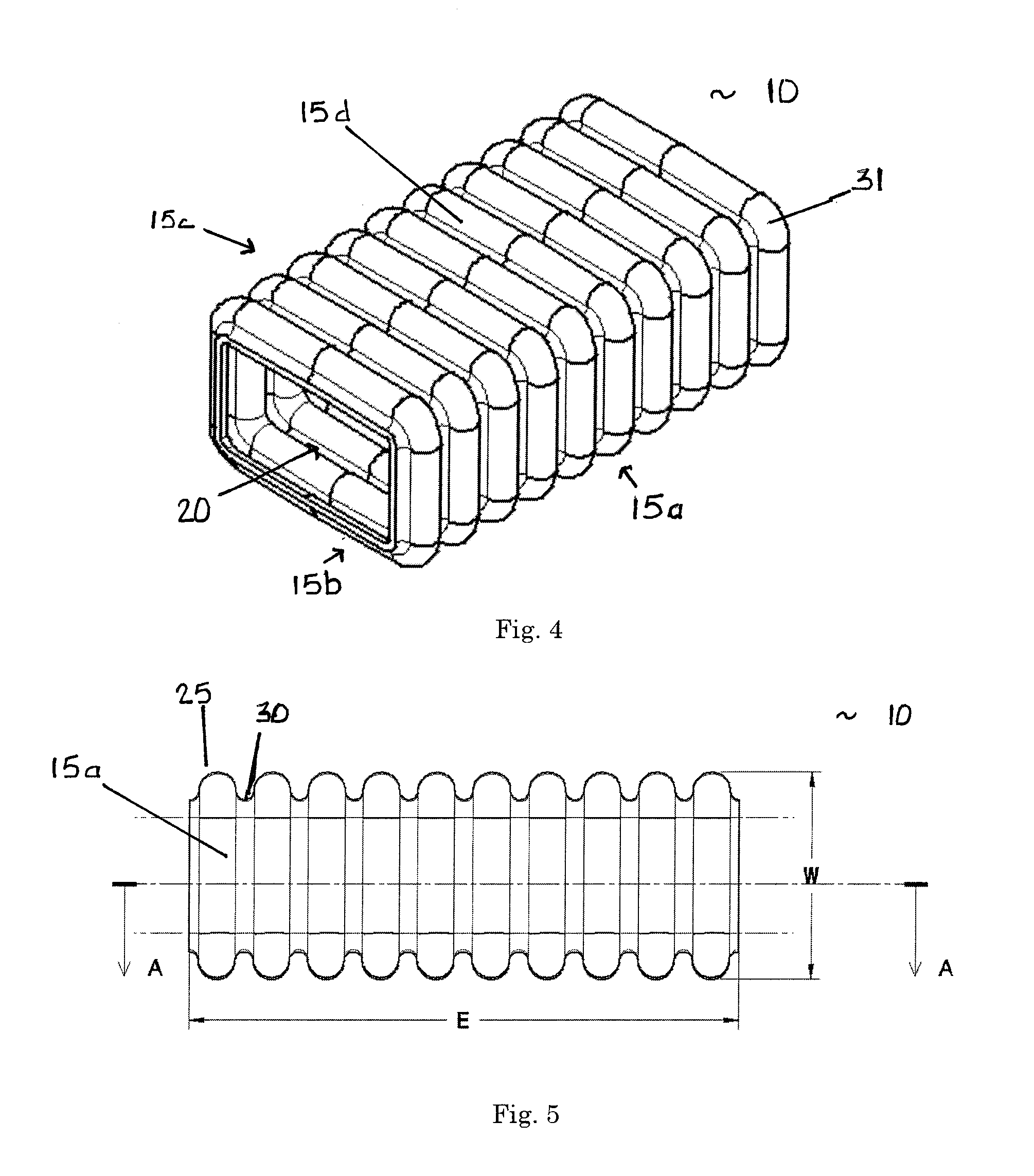
ActiveUS20080036242A1Efficiently absorb impact energyLow costVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEnergy absorbingEngineering
An energy absorbing tubular structure is formed of a molded or extruded polymer. The tube has a quadrangular cross-section with rounded corners. The walls of tube are corrugated with alternating convex and concave corrugations surfaces having a continuous constant radius, preferably with no flat spots. The corrugated walls have a constant thickness. The corrugations progressively deform during impact thereby providing a near perfect square wave force vs. deflection energy absorption curve at any predetermined nearly constant force level. The tube may be filled with polymer foam to vary the impact performance of the structure.
Owner:O FLEX GRP
Treatment device
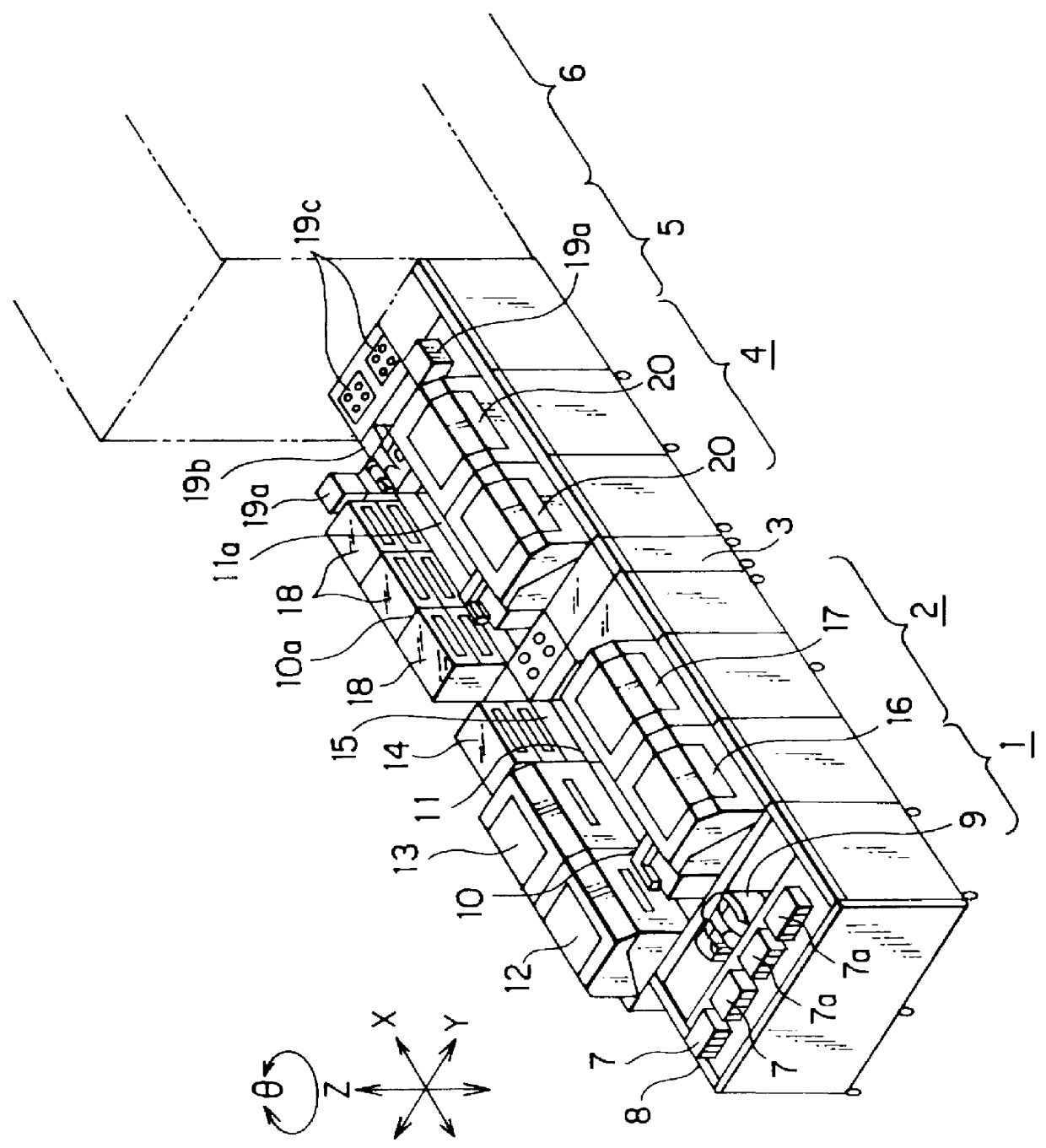
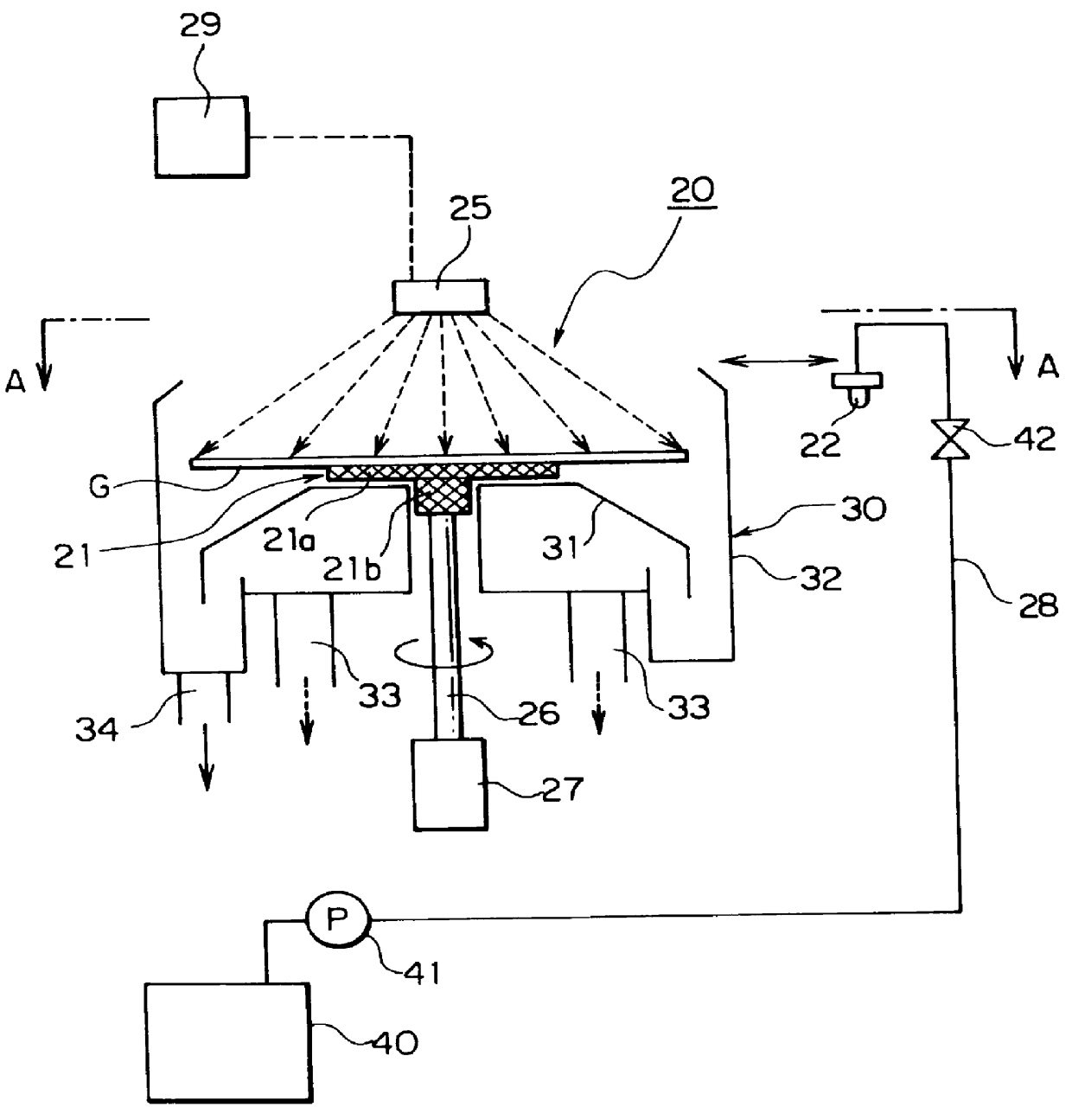
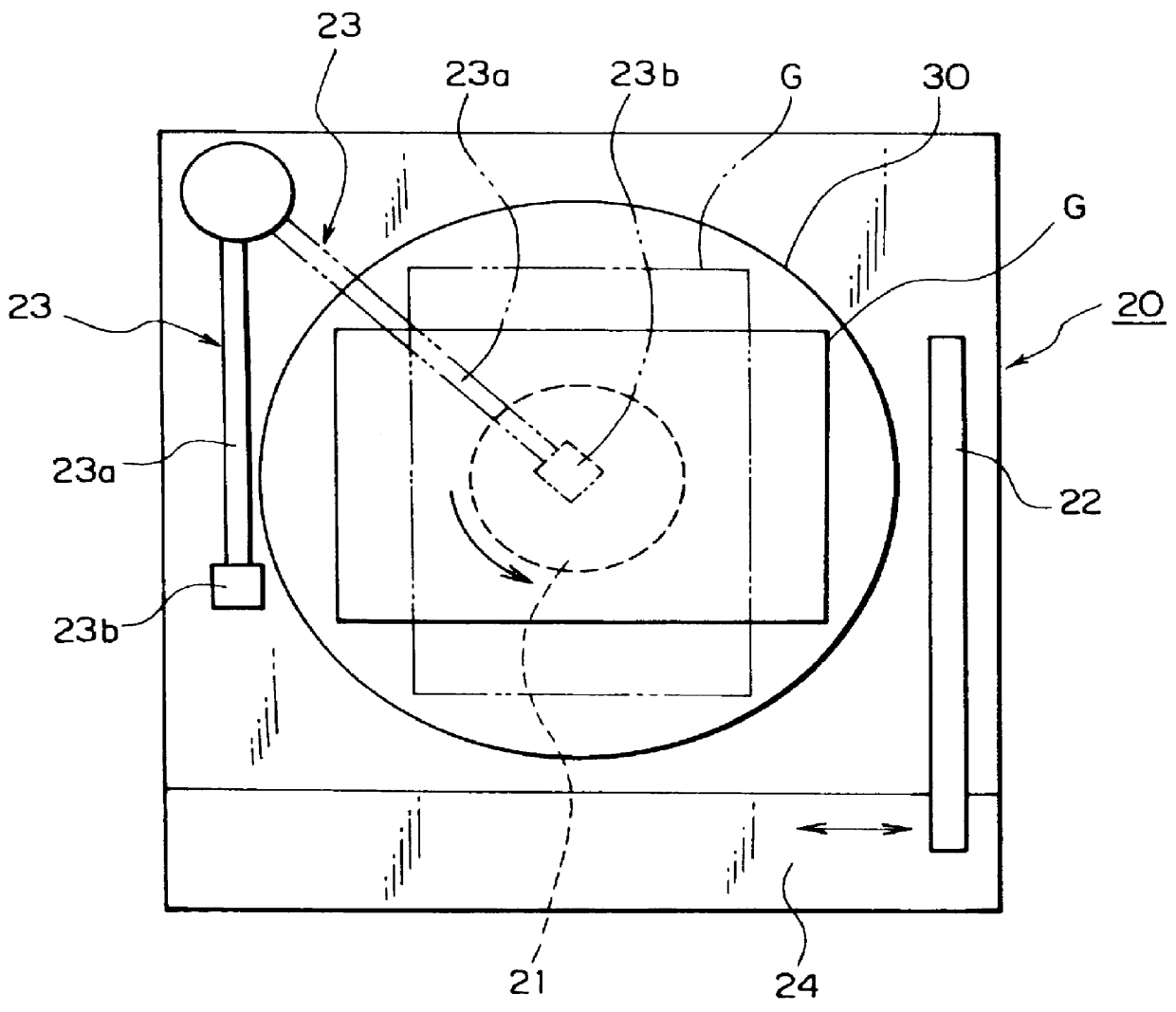
InactiveUS6062240AReduce chargeReduce the amount requiredLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduct gasEngineering
A treatment device comprising a holding method for holding a substrate such as an LCD substrate; and a treatment solution supply method for supplying a treatment solution on a surface of the substrate wherein the holding method has a substrate-placing portion on which the substrate is disposed, the substrate-placing is made of a synthetic resinous material. Since the holding method has a substrate-placing portion which is made of a synthetic resinous material, the electric charge amount of the substrate can be reduced to prevent various static electricity caused troubles such as the electrostatic destruction of the device formed on the substrate. Further, a discharge noise trouble due to discharge phenomenon from the substrate to a transporting method can be prevented. Further, it is possible to reduce the electric charge amount of the holding method and destaticize the holding method by supplying a destaticizing fluid such as ionized pure water or ionized gas towards above or below the holding method. Thus, it is possible to prevent various static-electricity caused troubles such as the electrostatic destruction of the device formed in the device from occurring and further, possible to prevent noise troubles from occurring because the generation degree of the discharge which occurs between the substrate and the transport method can be reduced further. The electric charge amount of the substrate can be reduced by making the thickness (distance) of the substrate-placing portion formed of a dielectric thick (long).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Sequential burst mode activation circuit
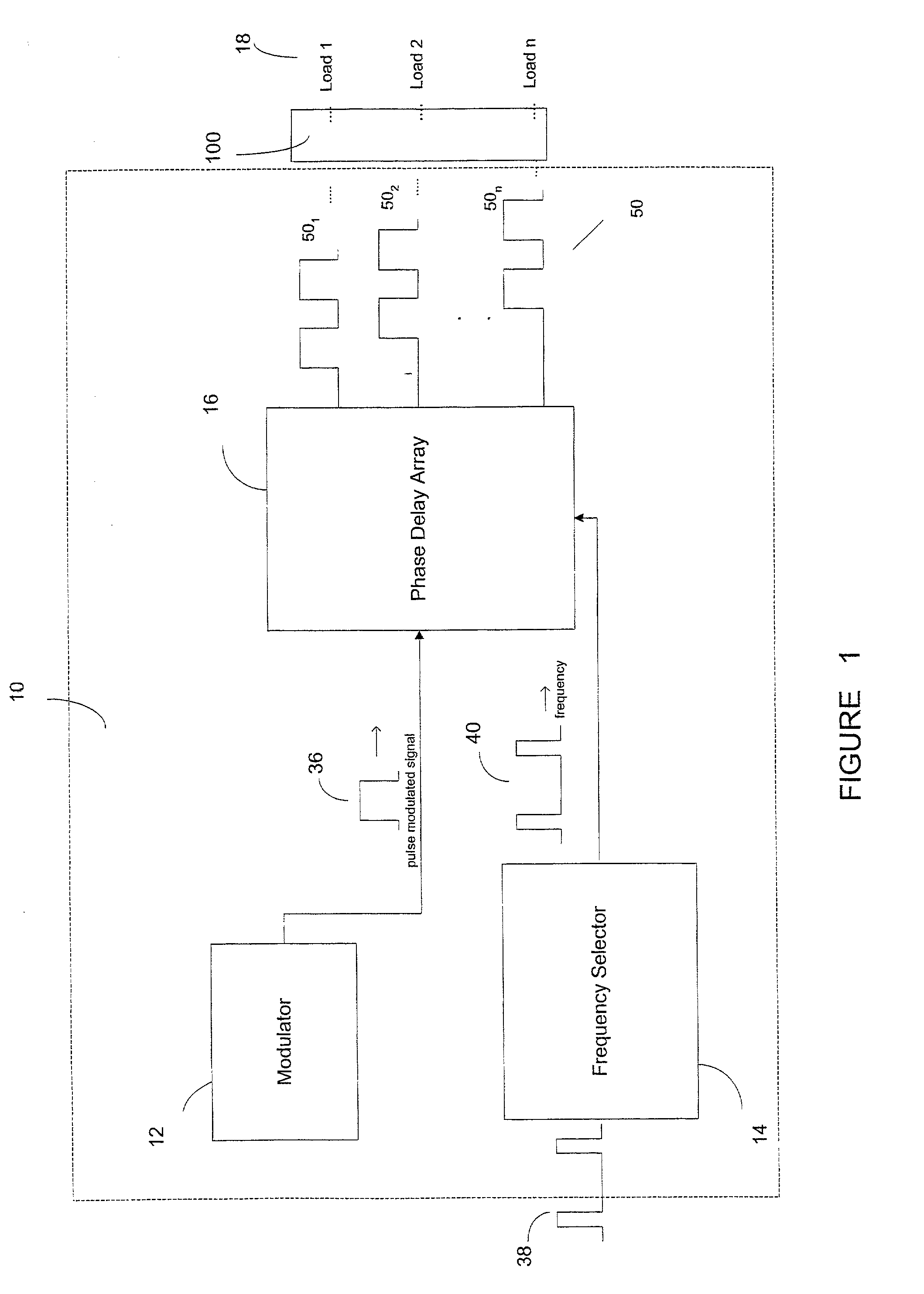
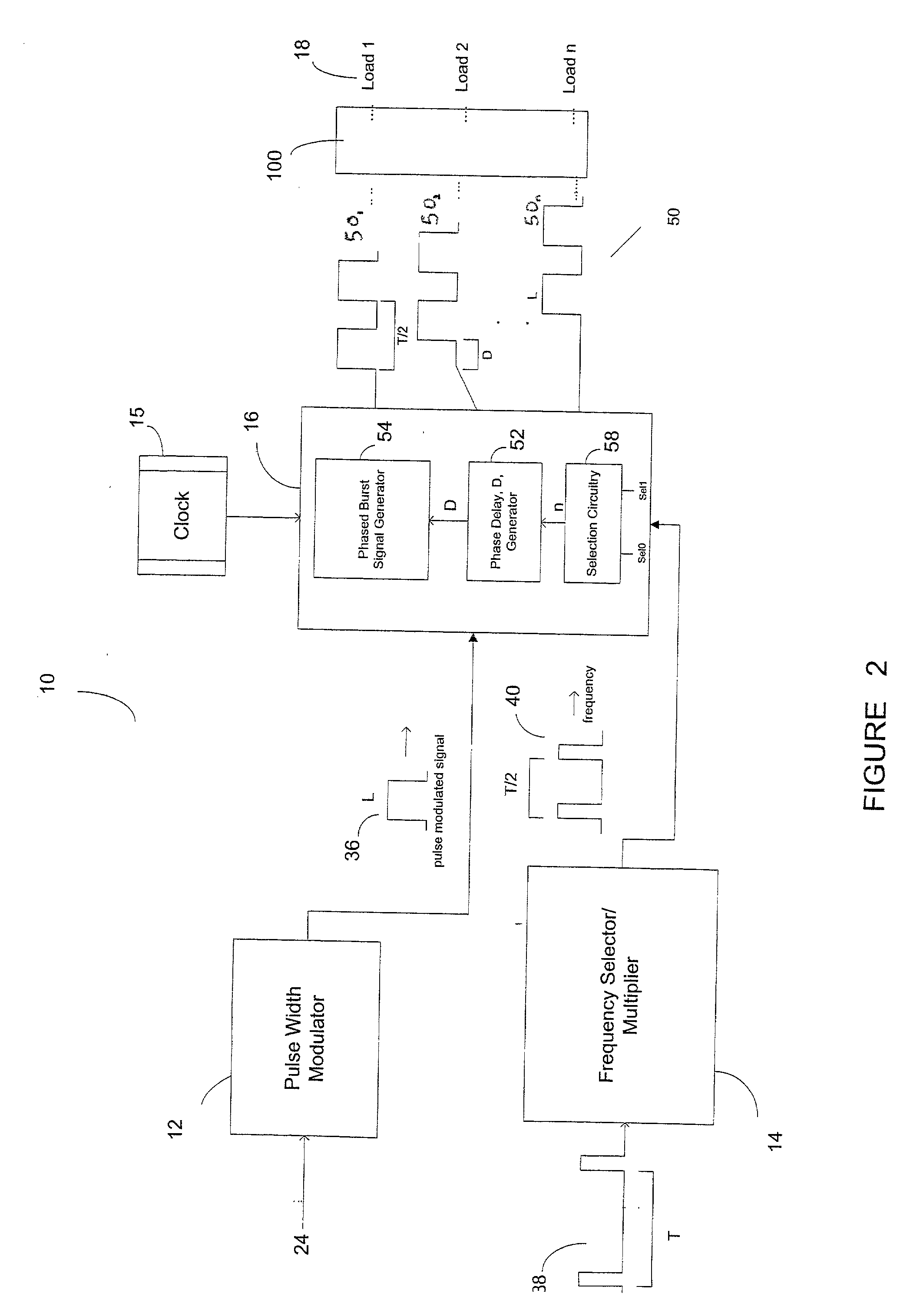
InactiveUS20020125863A1Eliminating instantaneous high current rippleRemove noiseAc-dc conversionLoad balancing in dc networkBiological activationSignal generator
A sequential burst mode regulation system to deliver power to a plurality of loads. In the exemplary embodiments, the system of the present invention generates a plurality of phased pulse width modulated signals from a single pulse width modulated signal, where each of the phased signals regulates power to a respective load. Exemplary circuitry includes a PWM signal generator, and a phase delay array that receives a PWM signal and generates a plurality of phased PWM signals which are used to regulate power to respective loads. A frequency selector circuit can be provided that sets the frequency of the PWM signal using a fixed or variable frequency reference signal.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
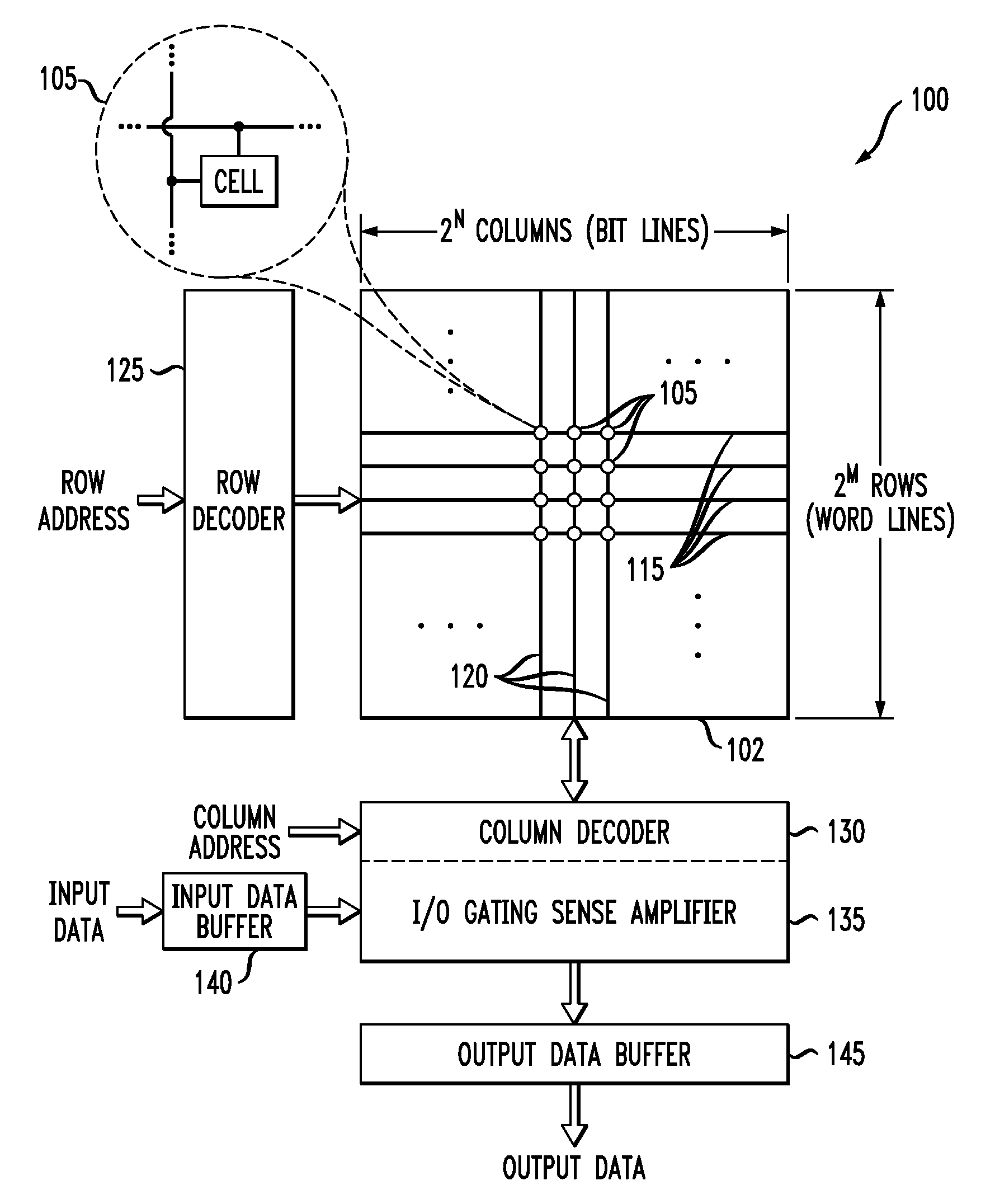
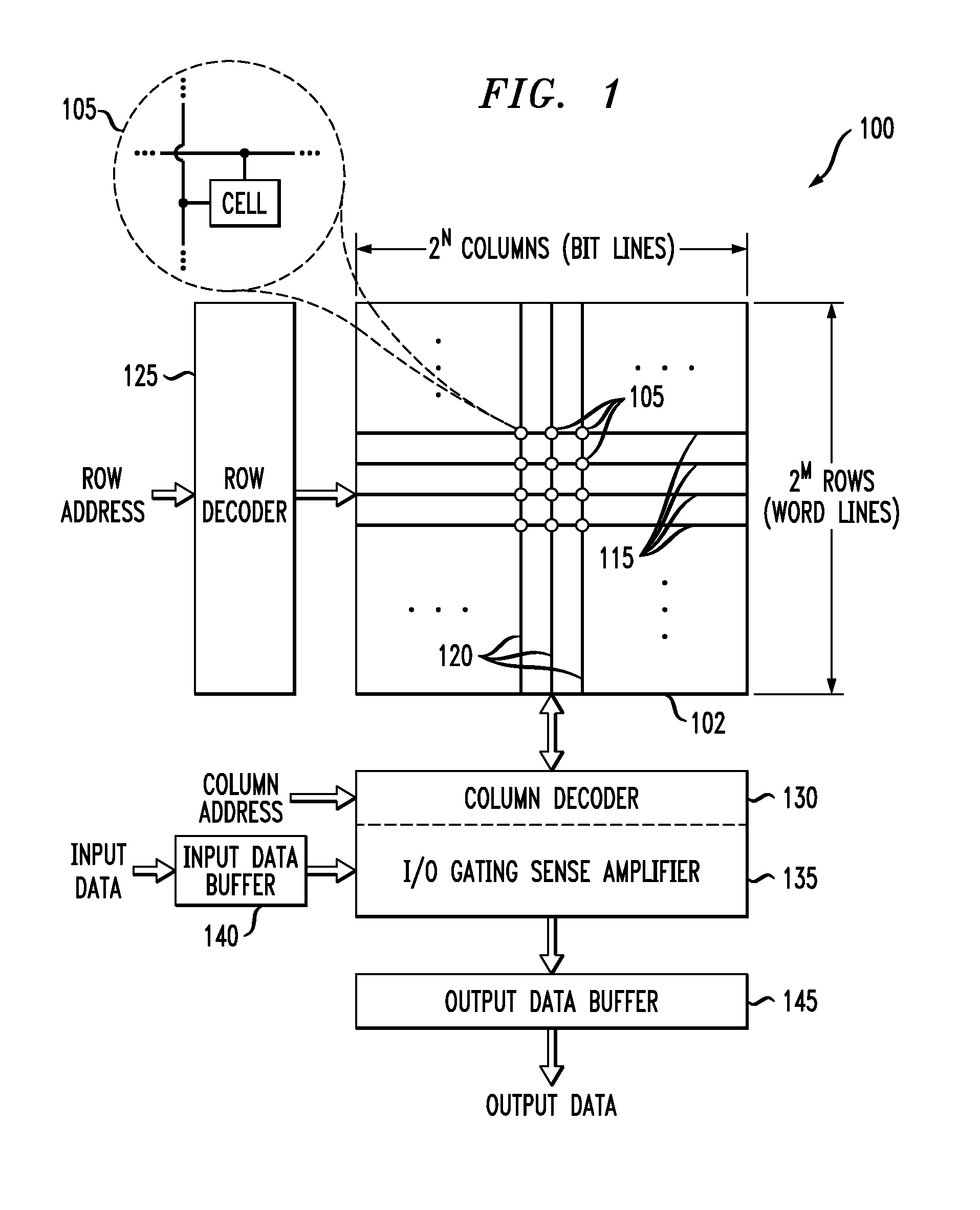
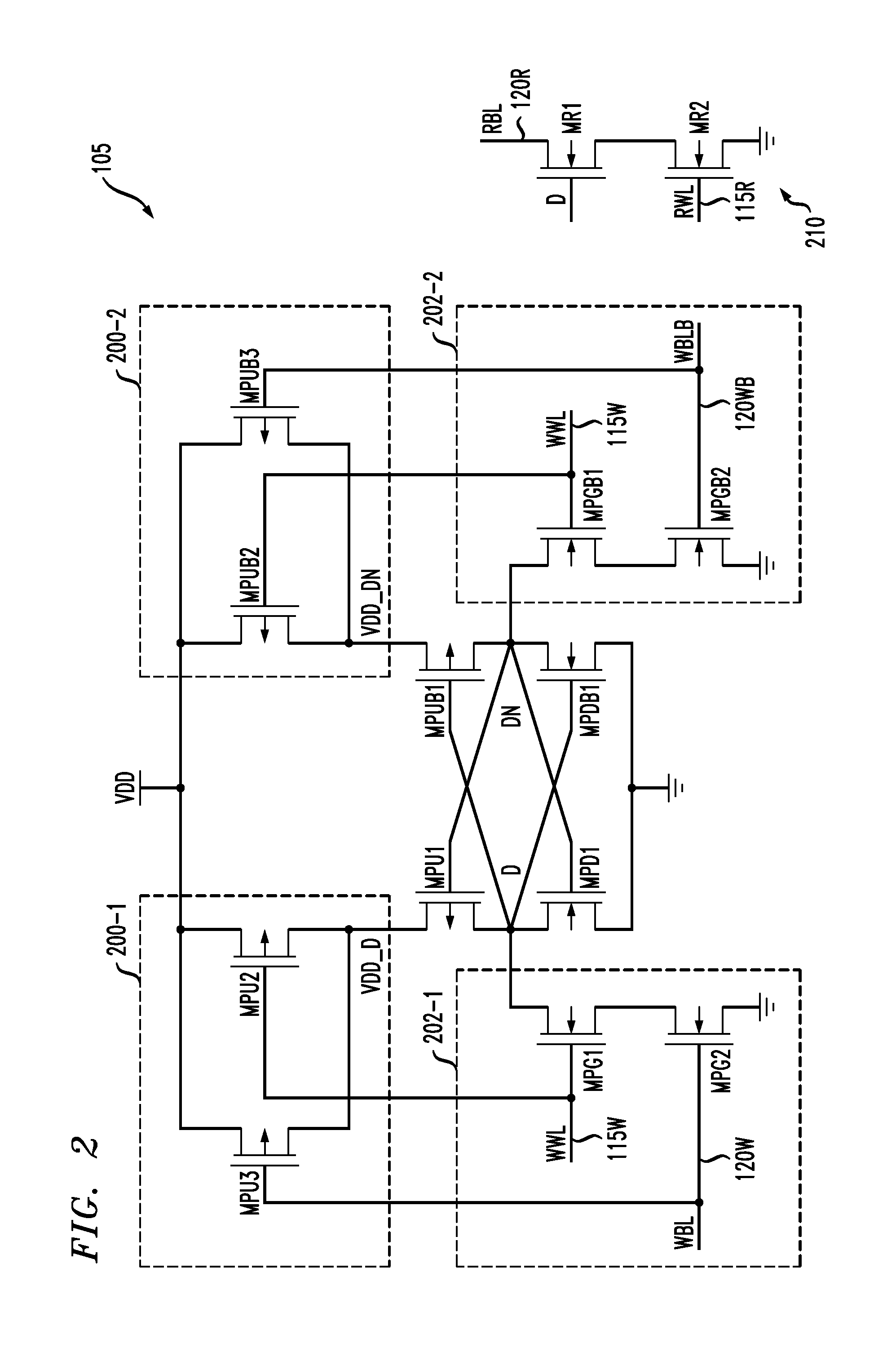
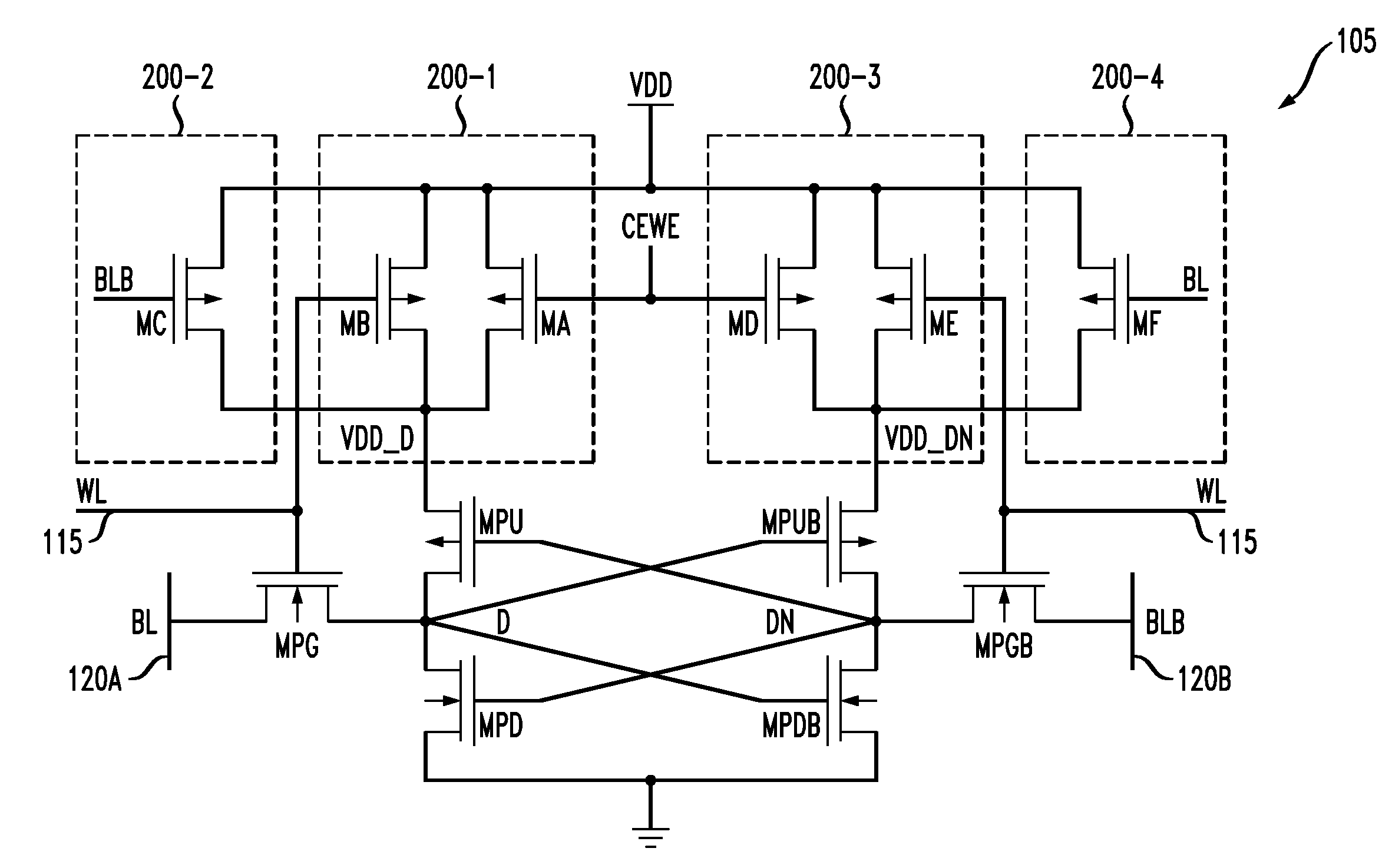
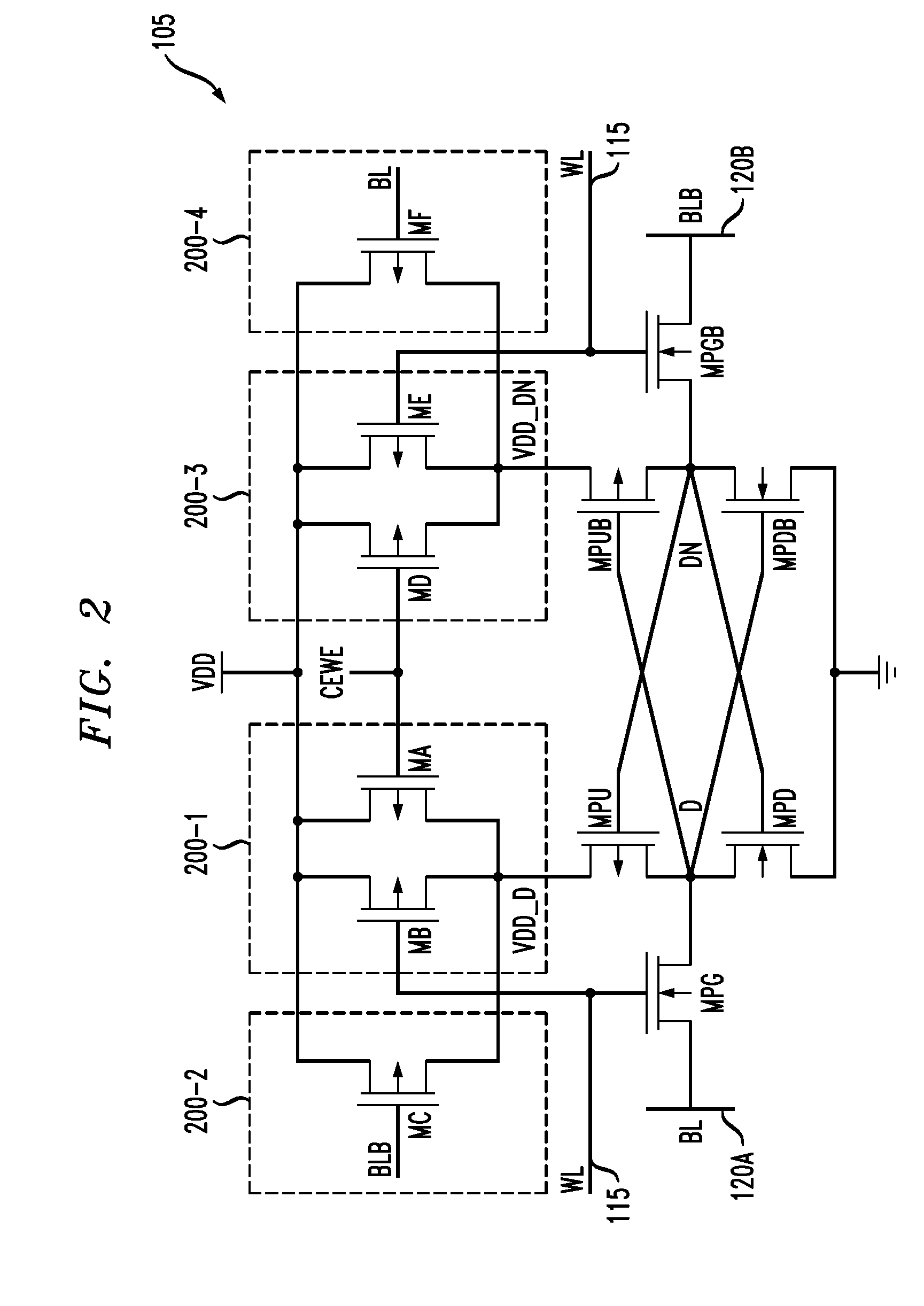
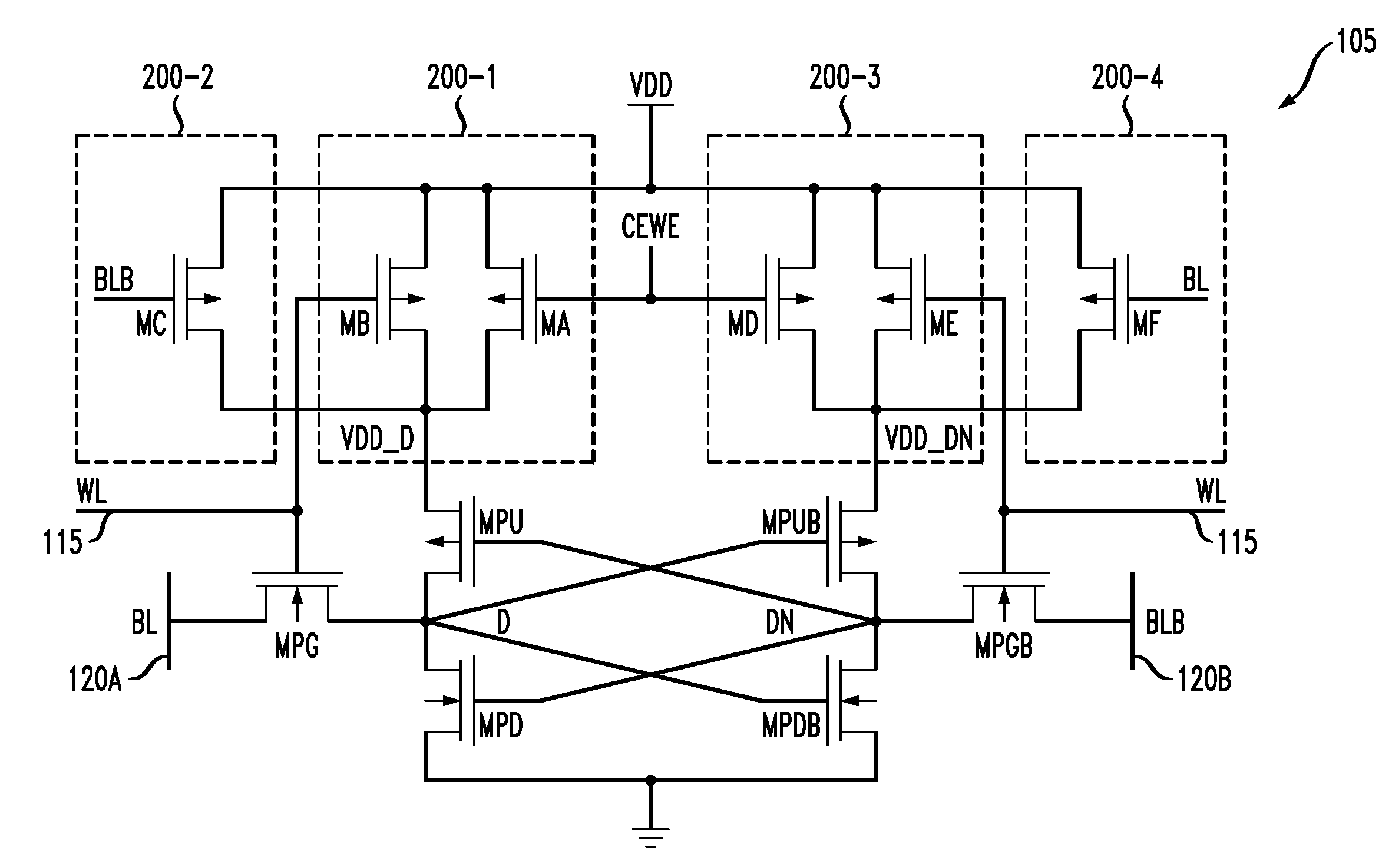
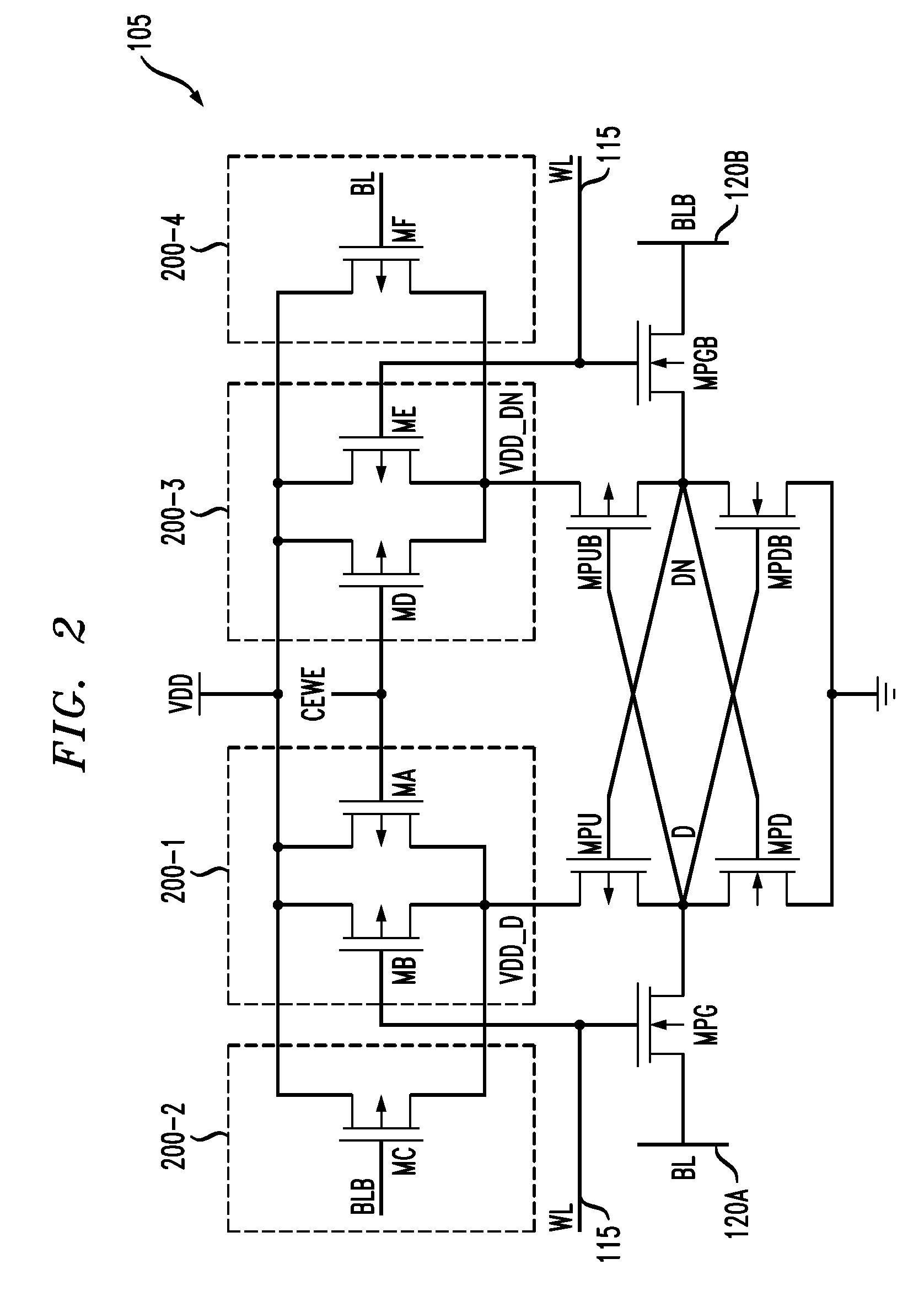
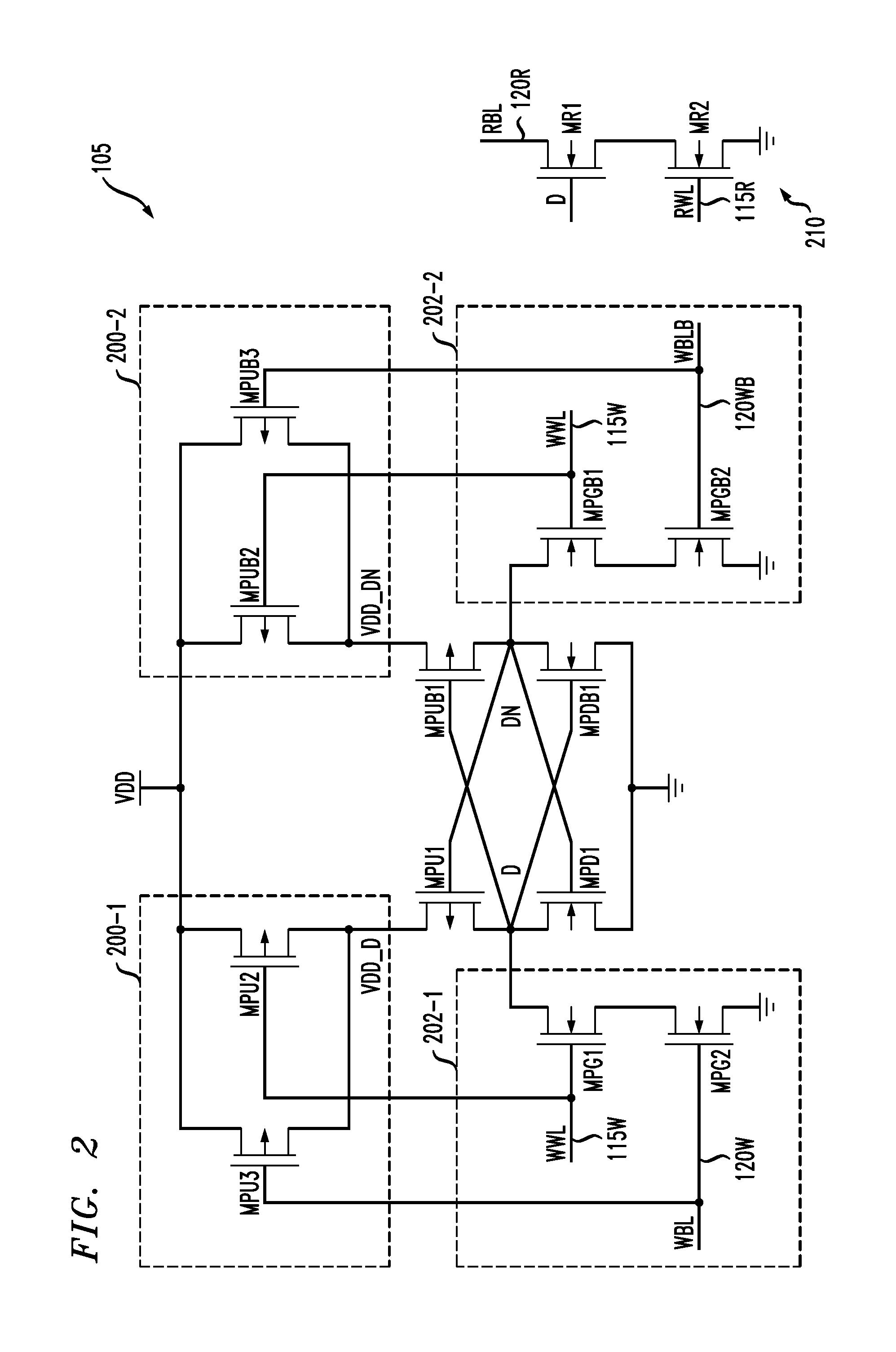
Memory device having memory cells with write assist functionality
ActiveUS20120212996A1Lower performance requirementsImproved pass gate circuitryDigital storageComputer scienceCross coupled
A memory device includes a memory array comprising a plurality of memory cells. At least a given one of the memory cells comprises a pair of cross-coupled inverters and associated write assist circuitry. The write assist circuitry comprises first switching circuitry coupled between a supply node of a device of the first inverter and a supply node of the memory cell, and second switching circuitry coupled between a supply node of a device of the second inverter and the supply node of the memory cell. The first and second switching circuitry are separately controlled, with the first switching circuitry being controlled using a wordline and an uncomplemented bitline of the memory device, and the second switching circuitry being controlled using the wordline and a complemented bitline of the memory device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Memory Device Having Memory Cells with Enhanced Low Voltage Write Capability
ActiveUS20120155151A1Accurate low voltage write performanceLower performance requirementsDigital storageLow voltageComputer science
A memory device includes a memory array comprising a plurality of memory cells. At least a given one of the memory cells comprises a pair of cross-coupled inverters and associated write assist circuitry. The write assist circuitry comprises first switching circuitry coupled between a supply node of a device of the first inverter and a supply node of the memory cell, and second switching circuitry coupled between a supply node of a device of the second inverter and the supply node of the memory cell. The first and second switching circuitry are separately controlled such that during a write operation of the memory cell the supply node of one of the devices is connected to the supply node of the memory cell while the supply node of the other device is not connected to the supply node of the memory cell but is instead permitted to float.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Memory device having memory cells with enhanced low voltage write capability
ActiveUS8441842B2Lower performance requirementsEnhanced write assist capabilityDigital storageLow voltageHemt circuits
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Joint arrangement
InactiveUS20070209160A1Reduce frictionMinimizing actuation forcePin hingesWing openersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A multi-joint hinge for a motor vehicle having a body and a panel, the hinge allowing the panel to be moved between an open position and a closed position relative to the vehicle body. The hinge includes at joint having at least one roller bearing, and is preferably a four bar joint having two bearings mounted on the body and two bearings mounted on the panel.
Owner:STABILUS
Memory device having memory cells with write assist functionality
ActiveUS8625333B2Lower performance requirementsImproved pass gate circuitryDigital storageBit lineHemt circuits
A memory device includes a memory array comprising a plurality of memory cells. At least a given one of the memory cells comprises a pair of cross-coupled inverters and associated write assist circuitry. The write assist circuitry comprises first switching circuitry coupled between a supply node of a device of the first inverter and a supply node of the memory cell, and second switching circuitry coupled between a supply node of a device of the second inverter and the supply node of the memory cell. The first and second switching circuitry are separately controlled, with the first switching circuitry being controlled using a wordline and an uncomplemented bitline of the memory device, and the second switching circuitry being controlled using the wordline and a complemented bitline of the memory device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
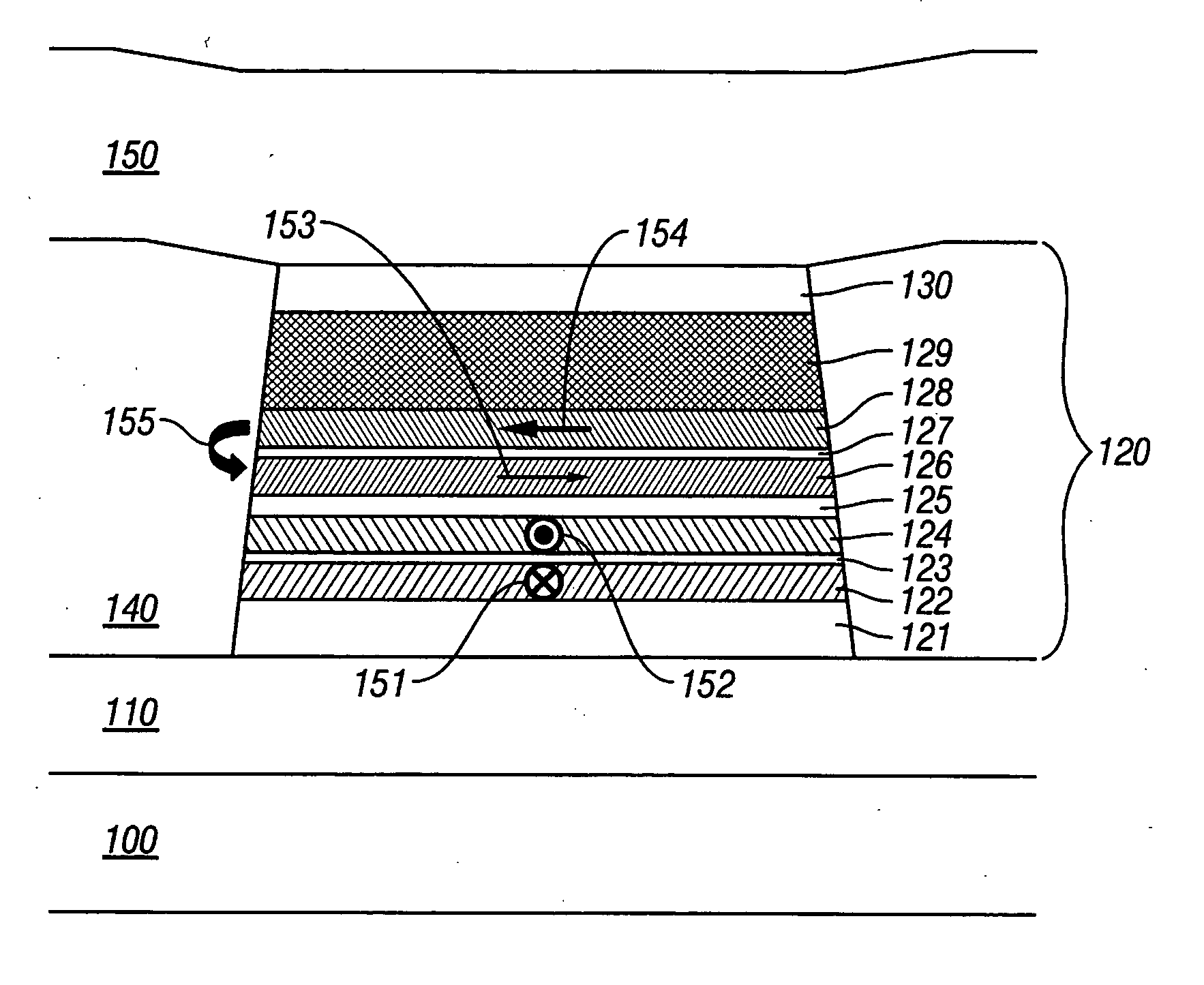
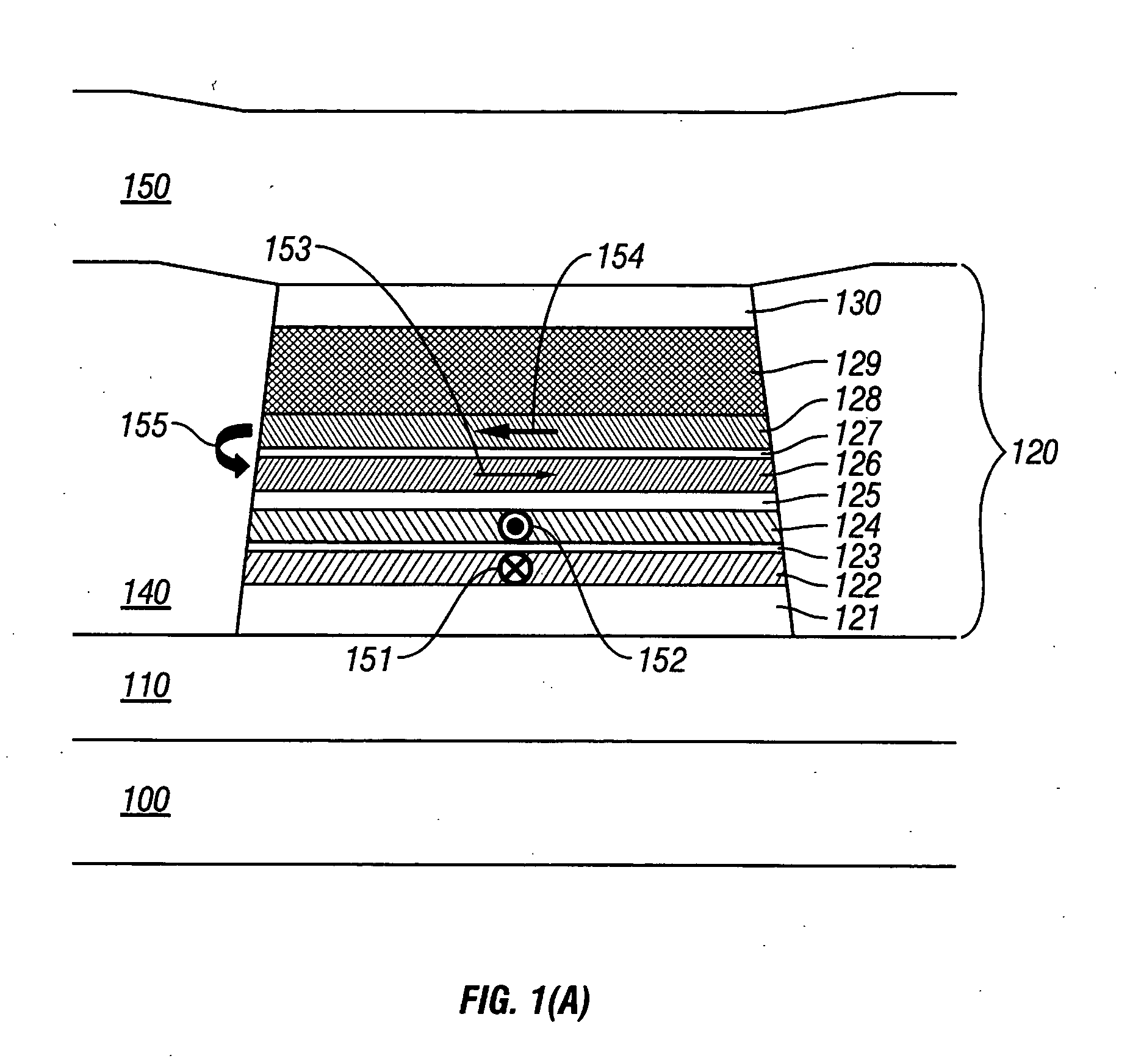
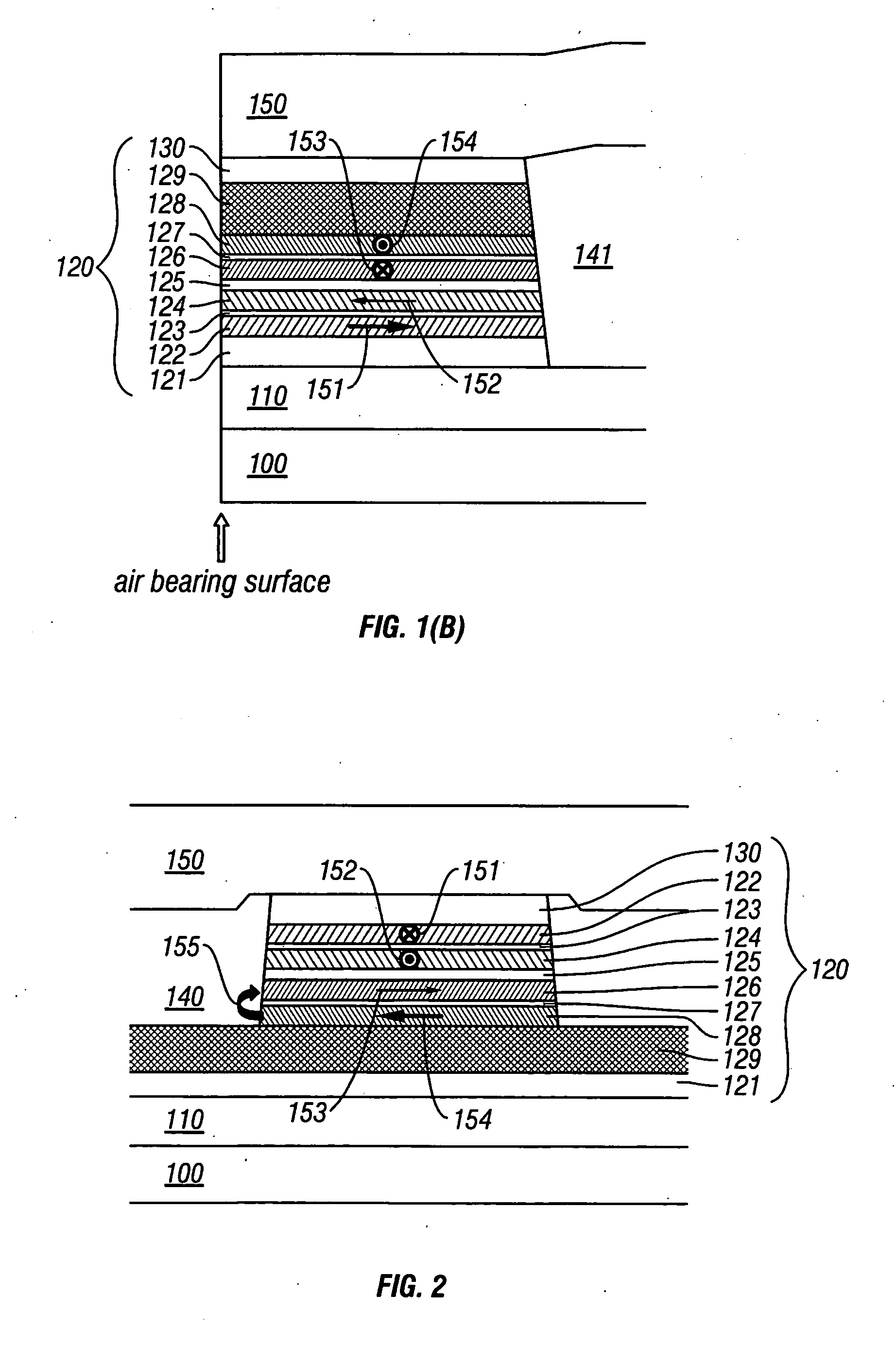
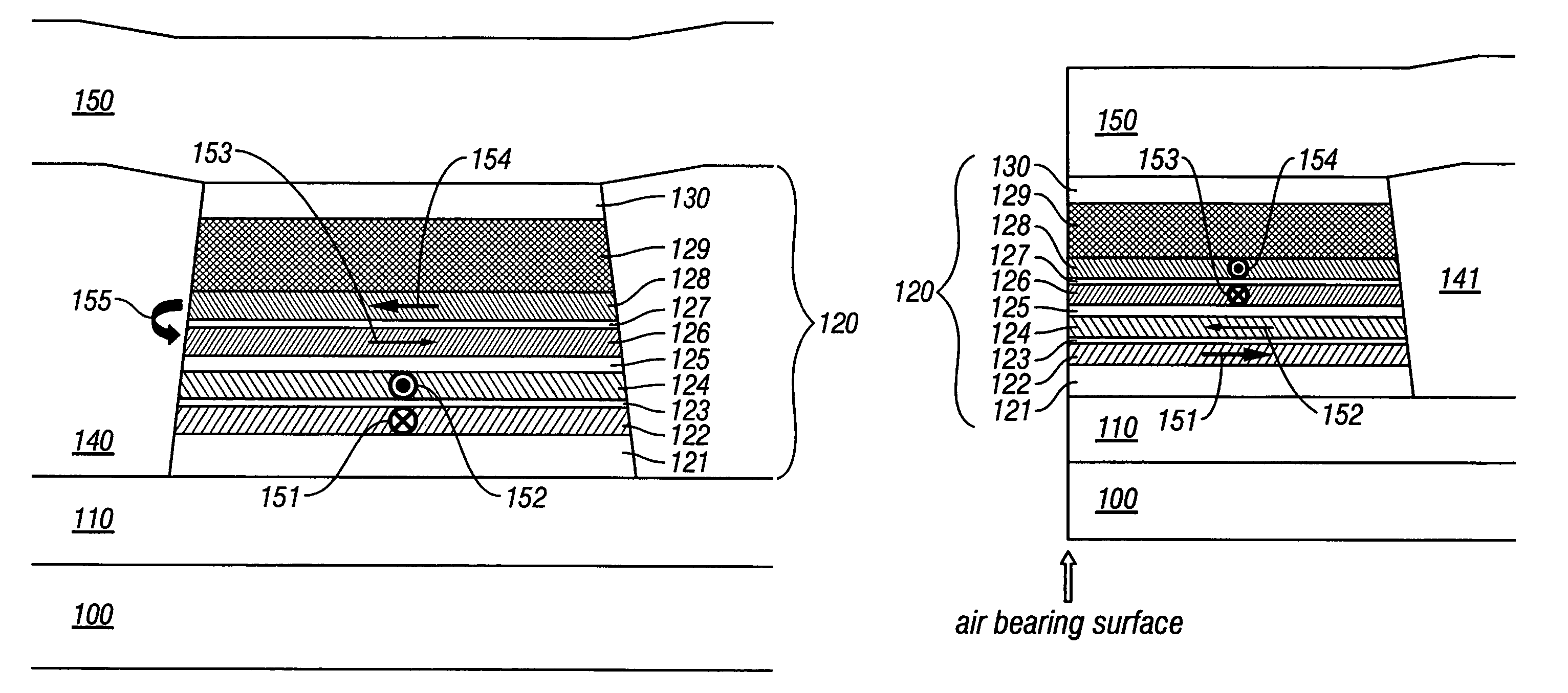
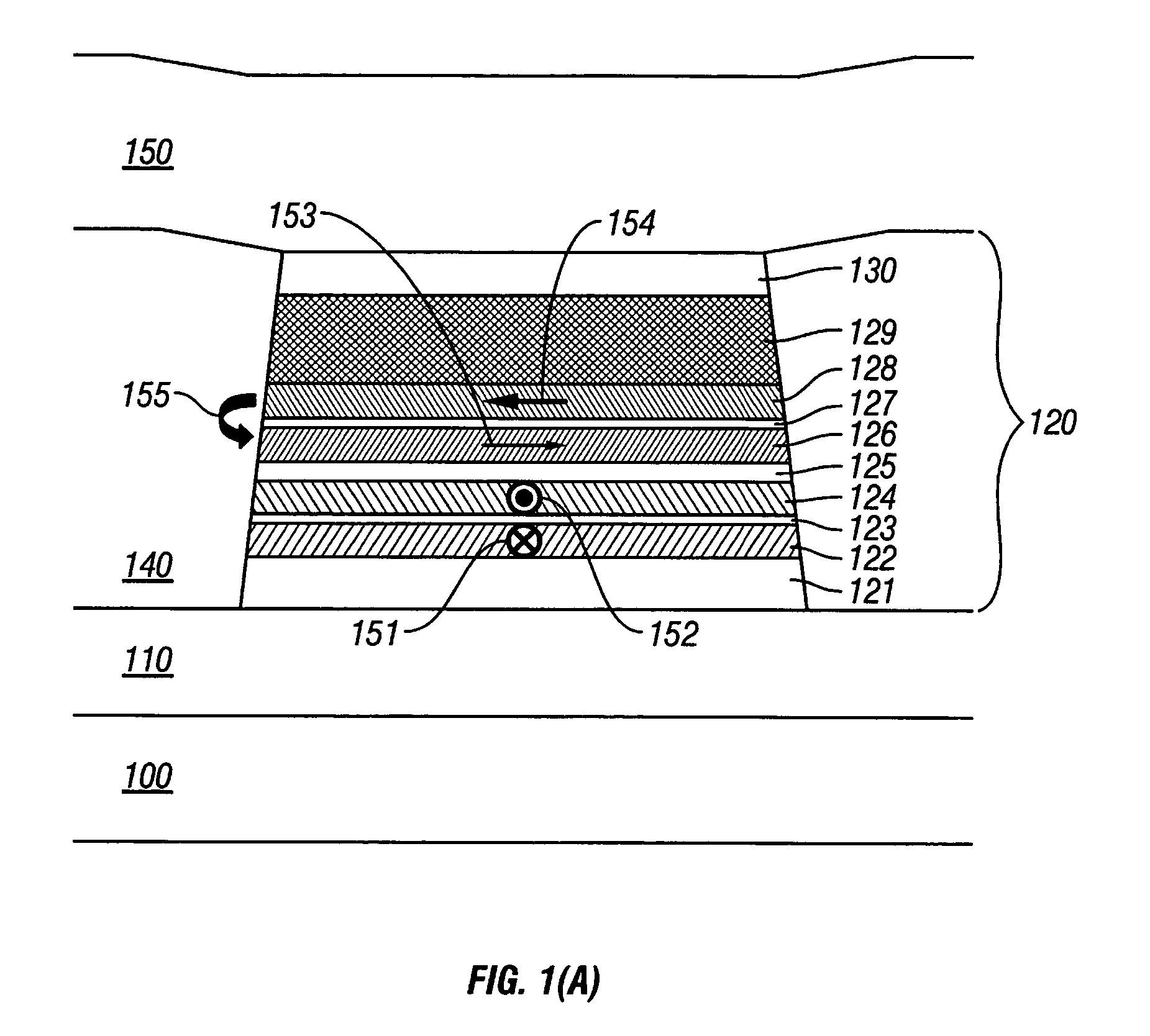
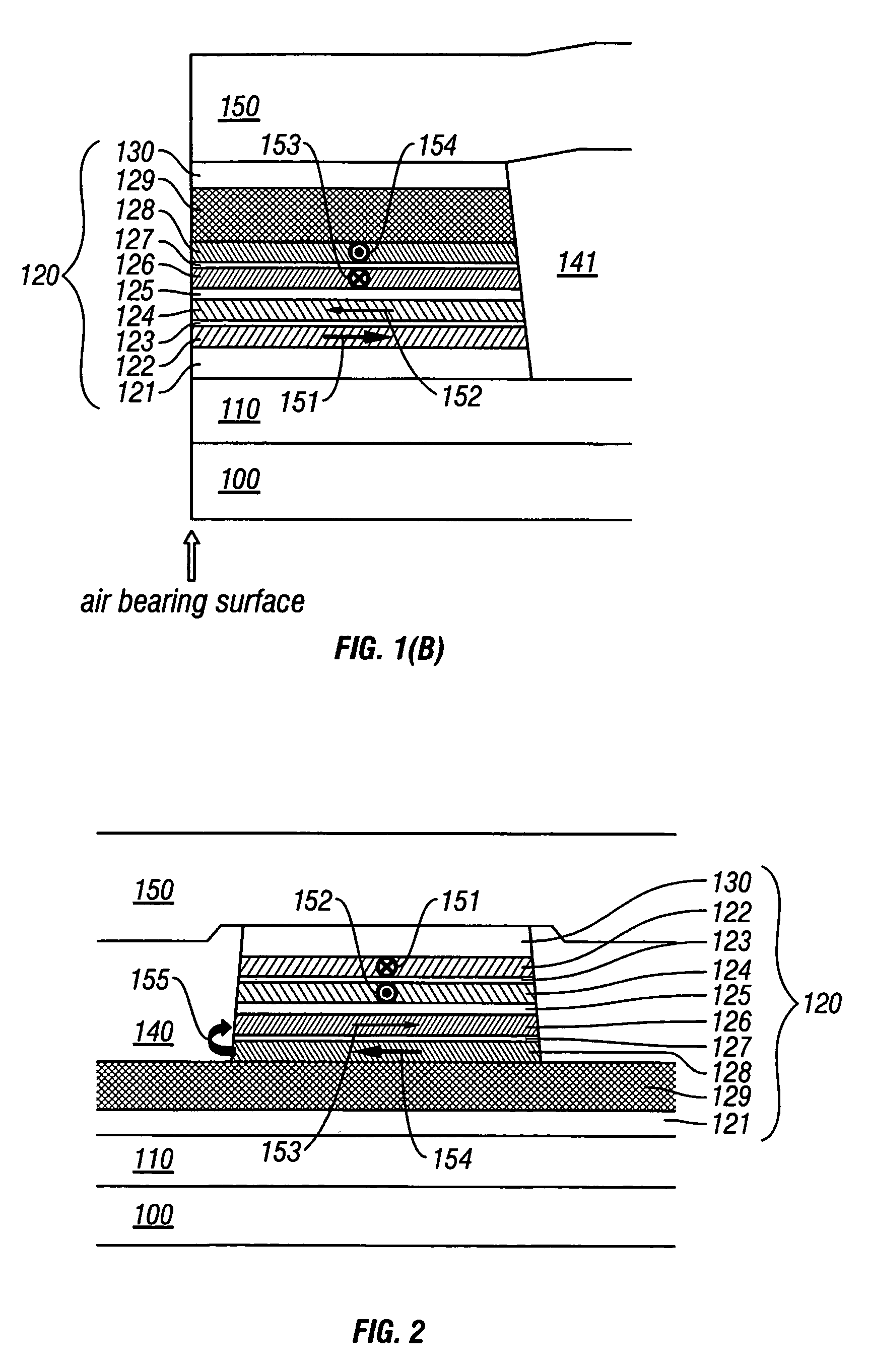
Magnetoresistive head with improved in-stack longitudinal biasing layers and fabricating method
InactiveUS20050162786A1Easily controlling magnetization directionGood effectMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsRecord information storageLow noiseRoom temperature
A magnetoresistive head and a fabricating method thereof accomplishing high sensitivity and low noise are provided even if track width narrowing makes progress. In one embodiment, a pinned layer includes a laminate which includes at least two magnetic layers and where adjacent magnetic layers are coupled antiferromagnetically to each other, and a mechanism to apply a longitudinal biasing field to a free layer is made to function by laminating a nonmagnetic separate layer / longitudinal biasing layer / antiferromagnetic layer connecting the free layer and opposite a nonmagnetic conductive layer (or nonmagnetic tunneling barrier layer). Controlling a magnetization direction of the longitudinal biasing layer which bears application of a longitudinal biasing field to the pinned layer and free layer is achieved by annealing carried out while applying a magnetic field in a track width direction and applying a magnetic field at room temperature.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
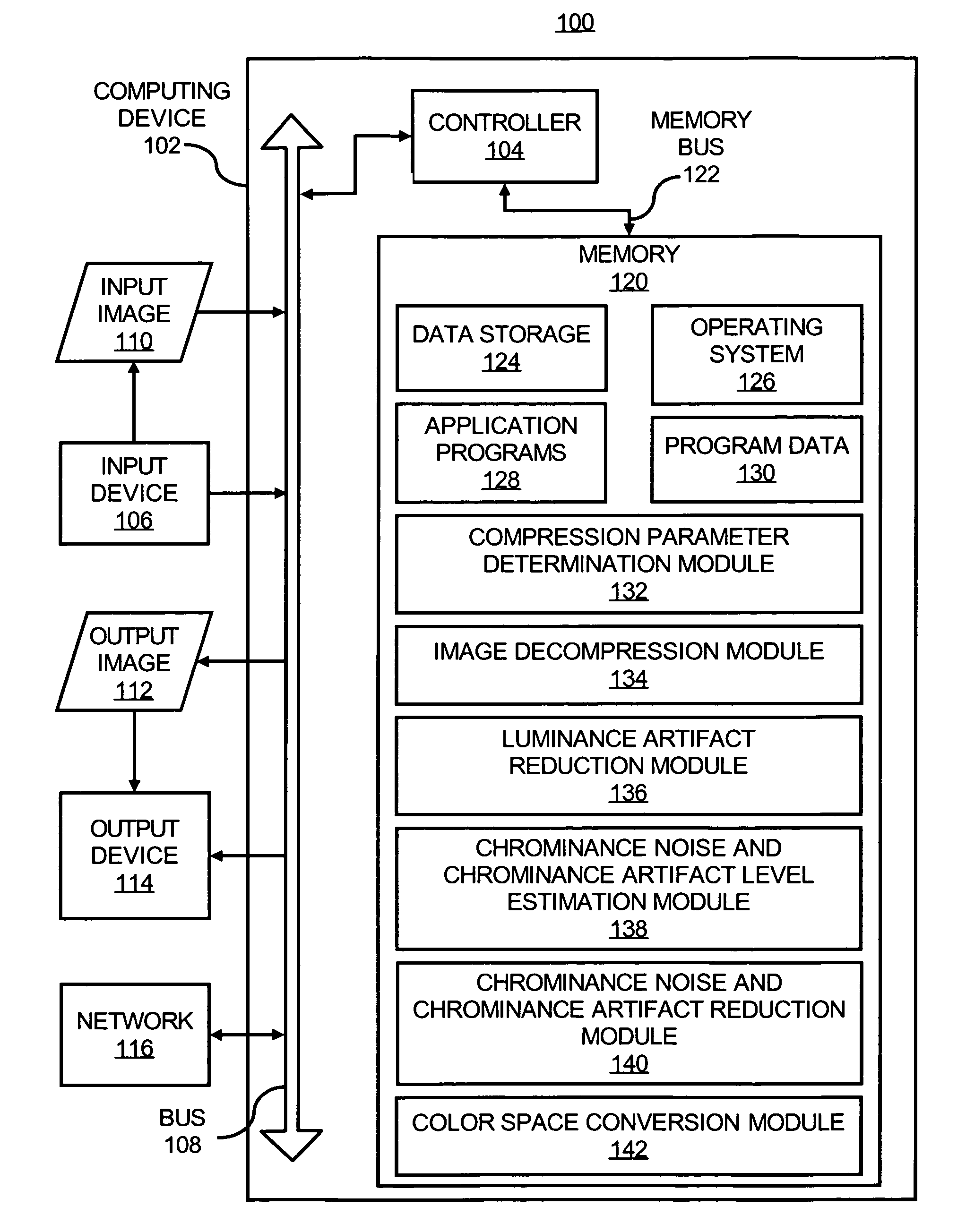
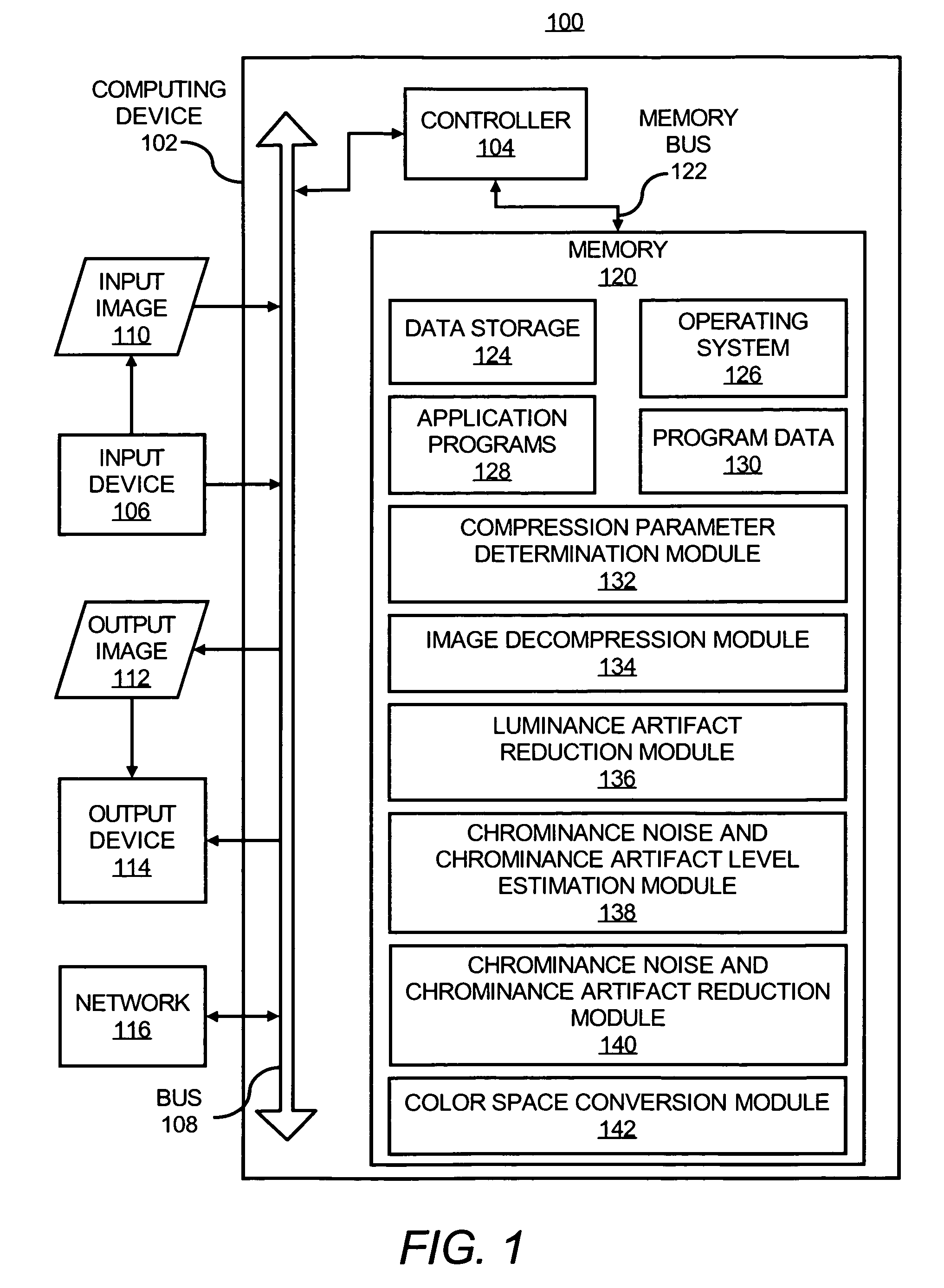
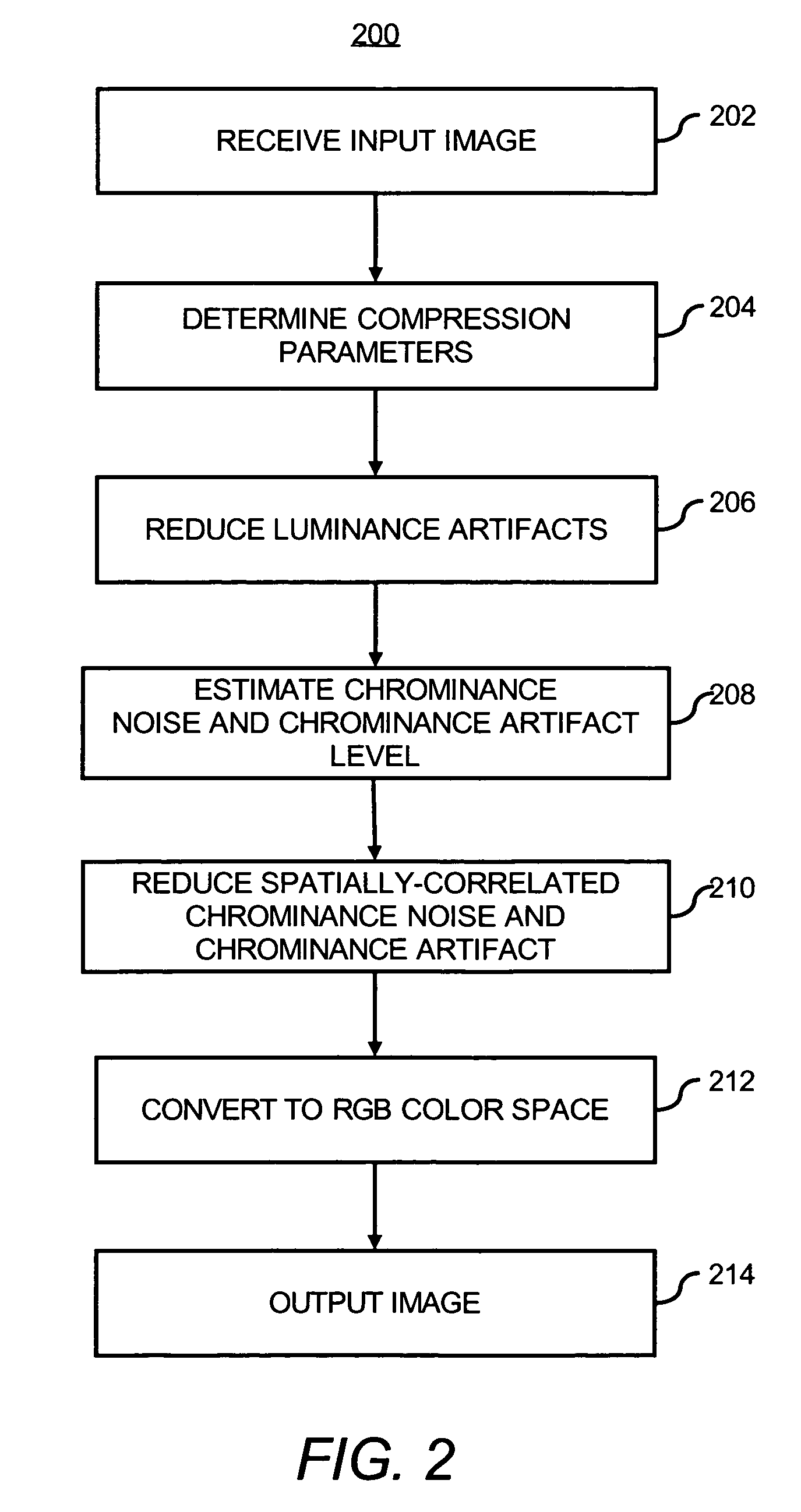
Reducing noise and artifacts in an image
InactiveUS7868950B1Reduce eliminate of compressionReduce eliminate of and noiseTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionLightness
In a method of processing an input image, compression parameters of the input image are determined and luminance artifacts in the input image are reduced to obtain an improved luminance component of the input image, where the determined compression parameters guide the luminance artifact reduction. In addition, a chrominance noise and chrominance artifact level of the input image is estimated and a spatially-correlated chrominance noise and chrominance artifact of the input image is reduced with the improved luminance component, where the estimated chrominance noise and chrominance artifact level guide the spatially-correlated chrominance noise and chrominance artifact reduction to obtain an improved chrominance component of the input image. Moreover, an output image having the improved luminance component and the improved chrominance component is outputted.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Corrugated tubular energy absorbing structure
InactiveUS7963378B2Effectively absorb impact energyLow costPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementUnderstructuresConstant forceEnergy absorption
An energy absorbing tubular structure is formed of a molded or extruded polymer. The tube has a quadrangular cross-section with rounded corners. The walls of tube are corrugated with alternating convex and concave corrugations surfaces having a continuous constant radius, preferably with no flat spots. The corrugated walls have a constant thickness. The corrugations progressively deform during impact thereby providing a near perfect square wave force vs. deflection energy absorption curve at any predetermined nearly constant force level. The tube may be filled with polymer foam to vary the impact performance of the structure.
Owner:O FLEX GRP
Vibration absorbing alloy member, and rubber vibration isolator, floor vibration damping apparatus, tires, steel cord and rubber sesmic isolator using the same
InactiveUS20070085251A1High damping performanceReduce noise and vibrationNon-rotating vibration suppressionMultiple spring combinationsMn alloyMaterials science
A damping alloy member 1 is constructed in such a manner that the improvement consists of a twin crystal type damping alloy made of Cu—Al—Mn alloy, Mg—Zr alloy, Mn—Cu alloy, Mn—Cu—Ni—Fe alloy, Cu—Al—Ni alloy, Ti—Ni alloy, Al—Zn alloy, Cu—Zn—Al alloy, Mg alloy, Cu—Si alloy, Fe—Mn—Si alloy, Fe—Ni—Co—Ti alloy, Fe—Ni—C alloy, Fe—Cr—Ni—Mn—Si—Co alloy and Ni—Al alloy, and has a shape of a flake, a wire or a spring for optimizing a deformation of the alloy. Moreover, a rubber vibration isolator, a floor vibration damping apparatus, a tire, a steel cord and a quake-absorbing rubber are constructed by using the damping apply member.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Radio frequency integrated circuit for enhanced transmit/receive performance in low power applications and method of making the same
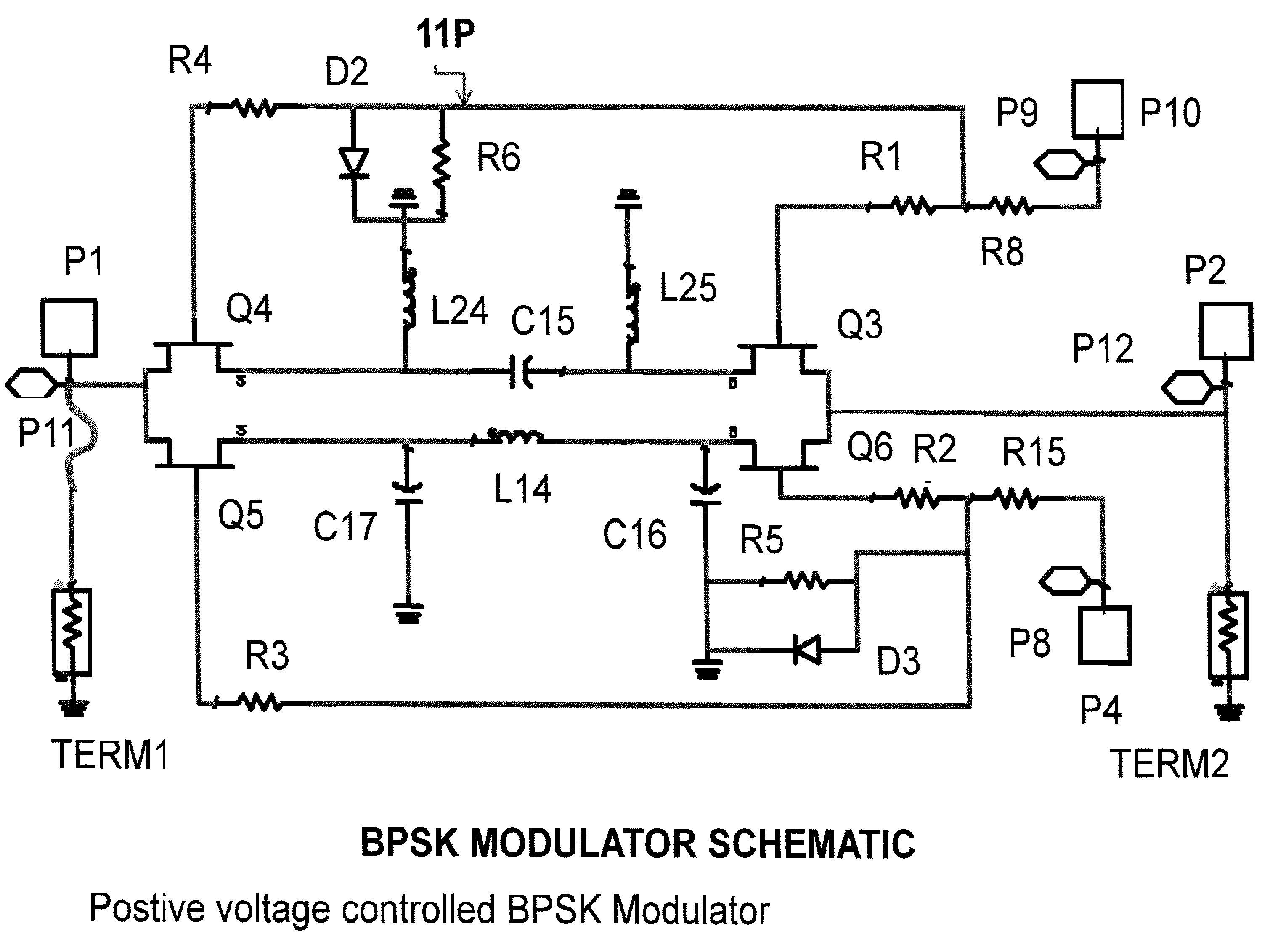
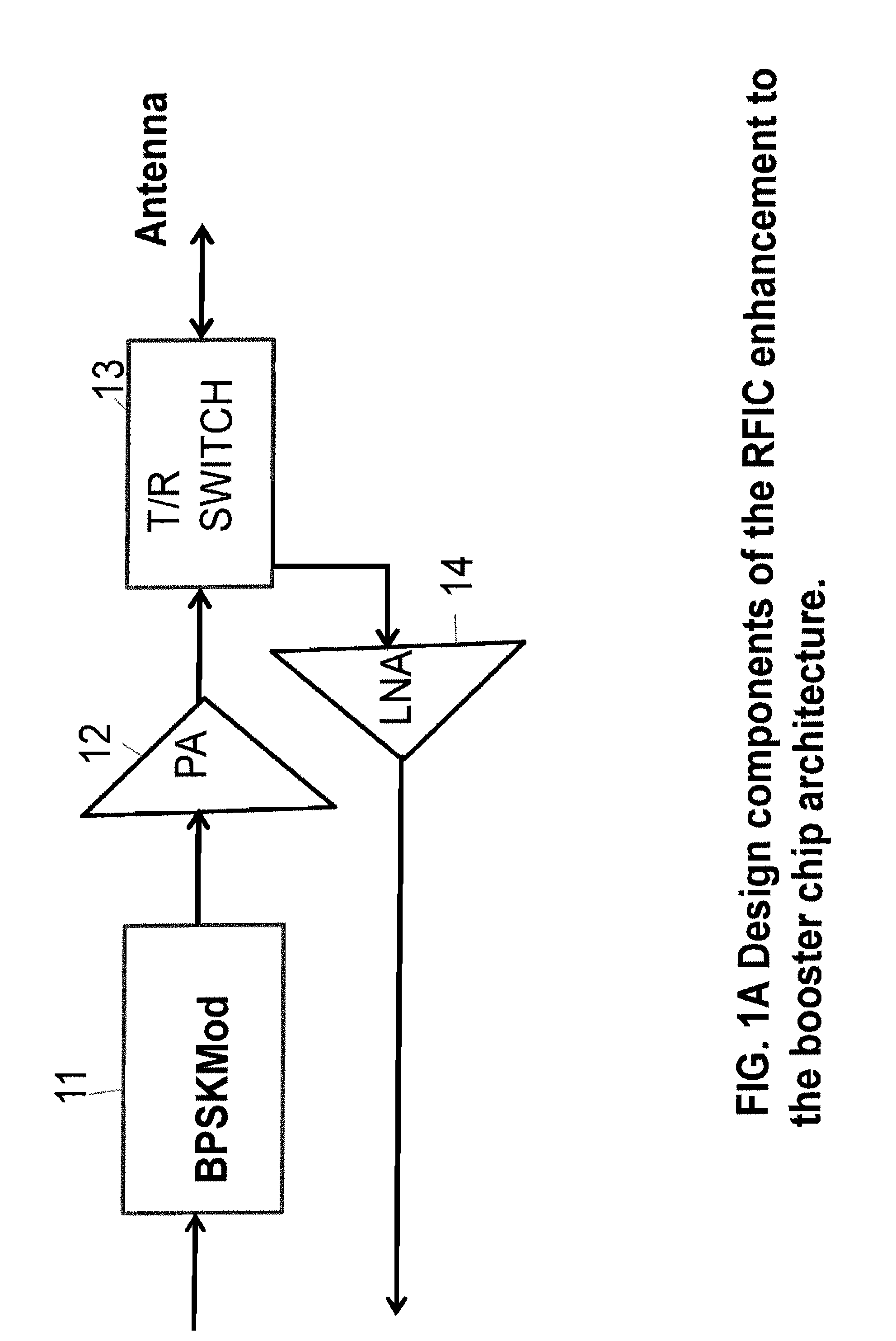
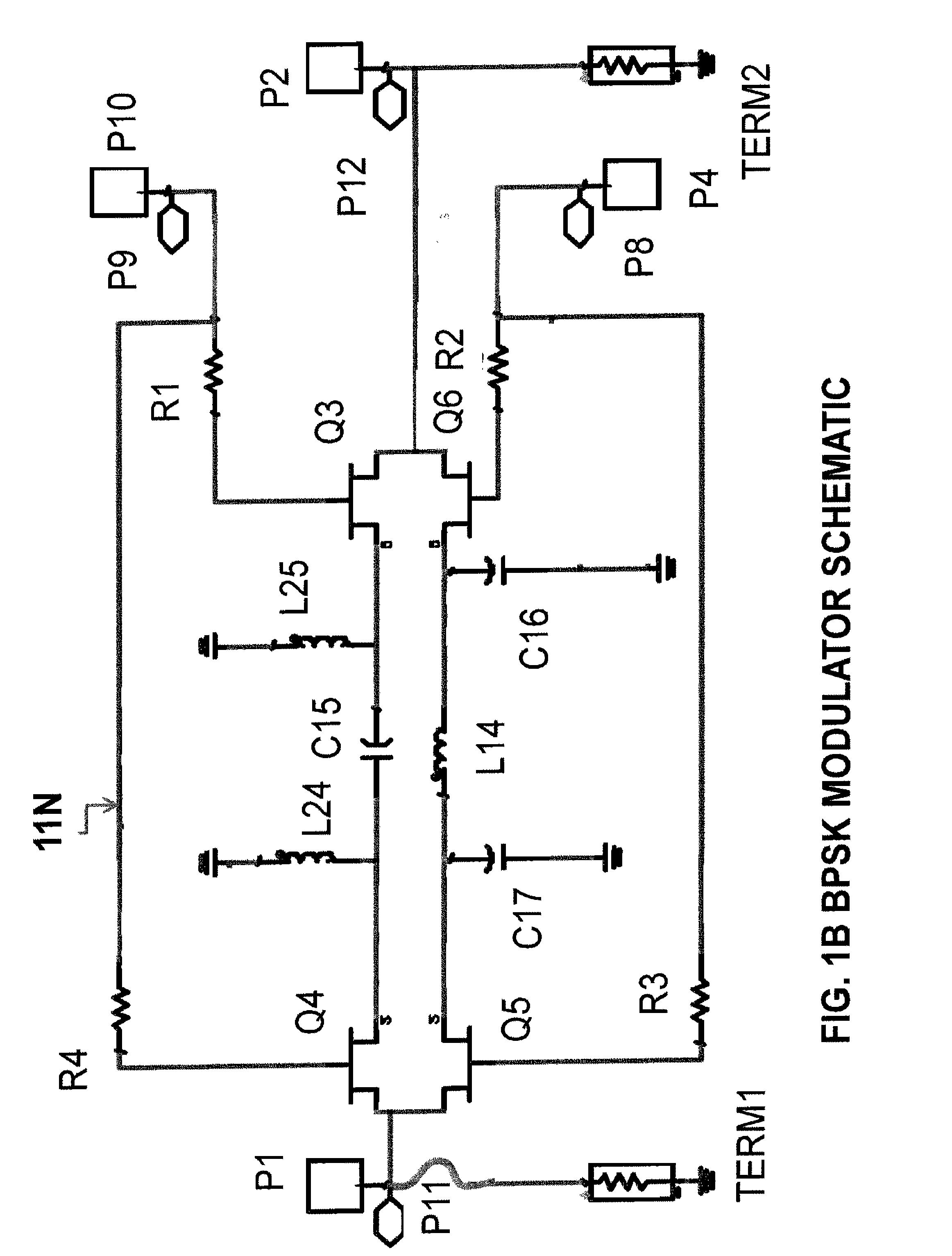
InactiveUS20120062330A1High noiseEnhance performanceAngle modulationPhase-modulated carrier systemsPhase-shift keyingRadio frequency
A radio frequency integrated circuit (and method of making) for enhancing wireless communication and / or sensing systems comprising a base comprising a gallium arsenide (GaAs) substrate; a binary phase shift keying modulator fabricated on the base; a power amplifier fabricated on the base and operatively associated with the binary phase shift keying modulator; the power amplifier having a first shunt operatively associated therewith; a transmit / receive switch fabricated on the base, the transmit / receive switch being operatively associated with the power amplifier and being alternately connectable to an antenna port adapted to be connected to an antenna; a low noise amplifier fabricated on the base; the low noise amplifier being alternately connectable to the antenna port, the low noise amplifier having a second shunt operatively associated therewith; the circuit operating in a transmit stage in which the power amplifier is connected to the antenna port and in a receive stage in which the low noise amplifier is connected to the antenna port; whereby in the receive stage the power amplifier is bypassed by the first shunt to reduce current consumption and substantially isolate the receive stage from the transmit stage; and in the transmit stage the low noise amplifier is bypassed by the second shunt to reduce current consumption and to substantially isolate the transmit stage from the receive stage.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Heat-conducting lubricating grease for high-speed all-steel angular contact bearing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102703179ASimple manufacturing methodReduce manufacturing costLubricant compositionLow noiseElectricity
The invention relates to heat-conducting lubricating grease for a high-speed all-steel angular contact bearing and a preparation method of the lubricating grease; the heat-conducting lubricating grease for the high-speed all-steel angular contact bearing is composed of the following raw materials by weight: 85-95% of barium-base lubricating grease, 3-10% of a heat-conducting agent and 2-5% of antioxidant; according to a technical proposal of the invention, the heat-conducting agents namely nano particles are added based on composite barium-base lubricating grease; so that the heat-conducting lubricating grease has a higher speed coefficient and a preferable heat-conducting performance; the bearing is characterized by low noise, low temperature rising, low vibration and longer service life; in addition, situations that speed coefficient of current domestic lubricating grease is short of an operation demand and the current domestic lubricating grease has poor heat conductivity are solved; an electric main shaft oil supply device is eliminated; noise when the high-speed all-steel angular contact bearing is operated is reduced; and temperature rising and vibration values are reduced.
Owner:国创(洛阳)轴承产业技术研究院有限公司
A detector device with majority current and a circuitry for controlling the current
ActiveUS20190025414A1Adjustable resolutionHigh noiseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesControl circuitCarrier current
The invention relates to a detector device assisted by majority current, comprising a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type, a plurality of control regions of the first conductivity type, at least one detection region of a second conductivity type opposite to the first conductivity type and a first source for generating a majority carrier current associated with an electrical field, characterized in that it further comprises control circuitry arranged for controlling the first source and controlling individually at least one of said first majority carrier currents.
Owner:SONY DEPTHSENSING SOLUTIONS SA NV
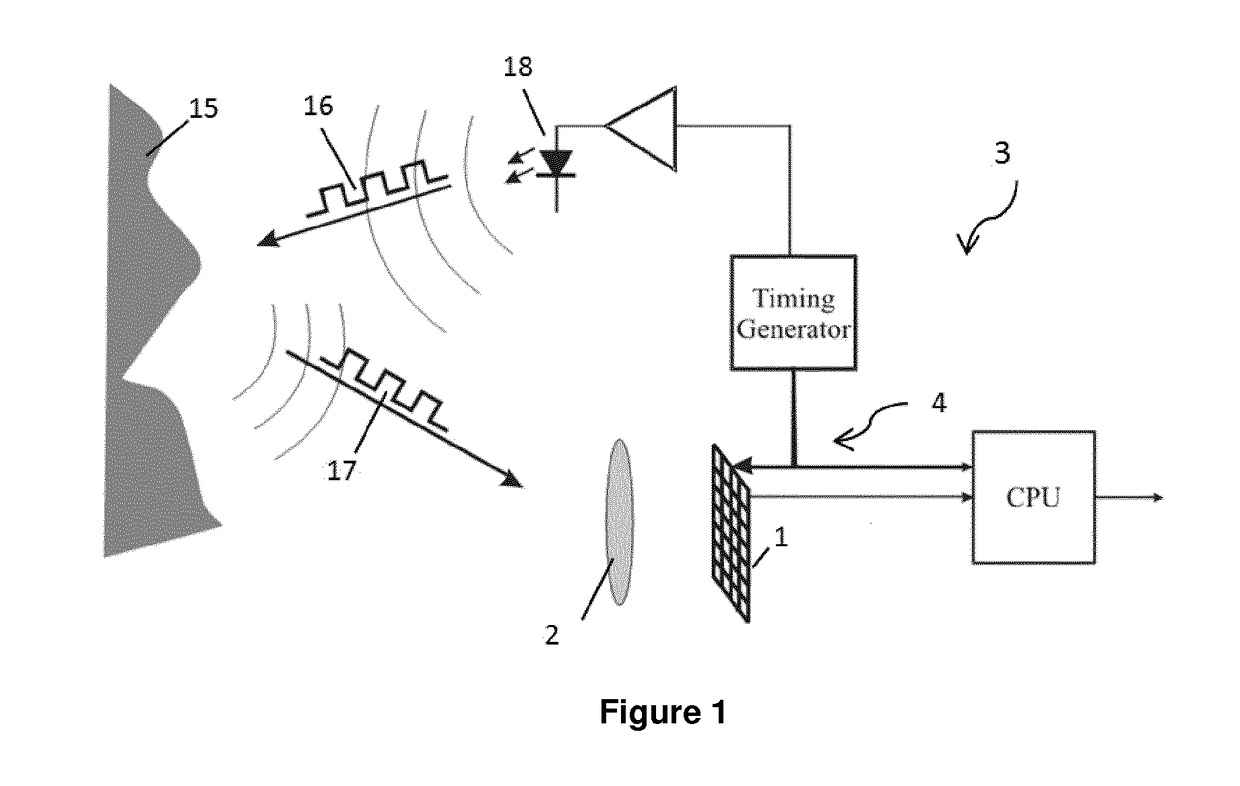
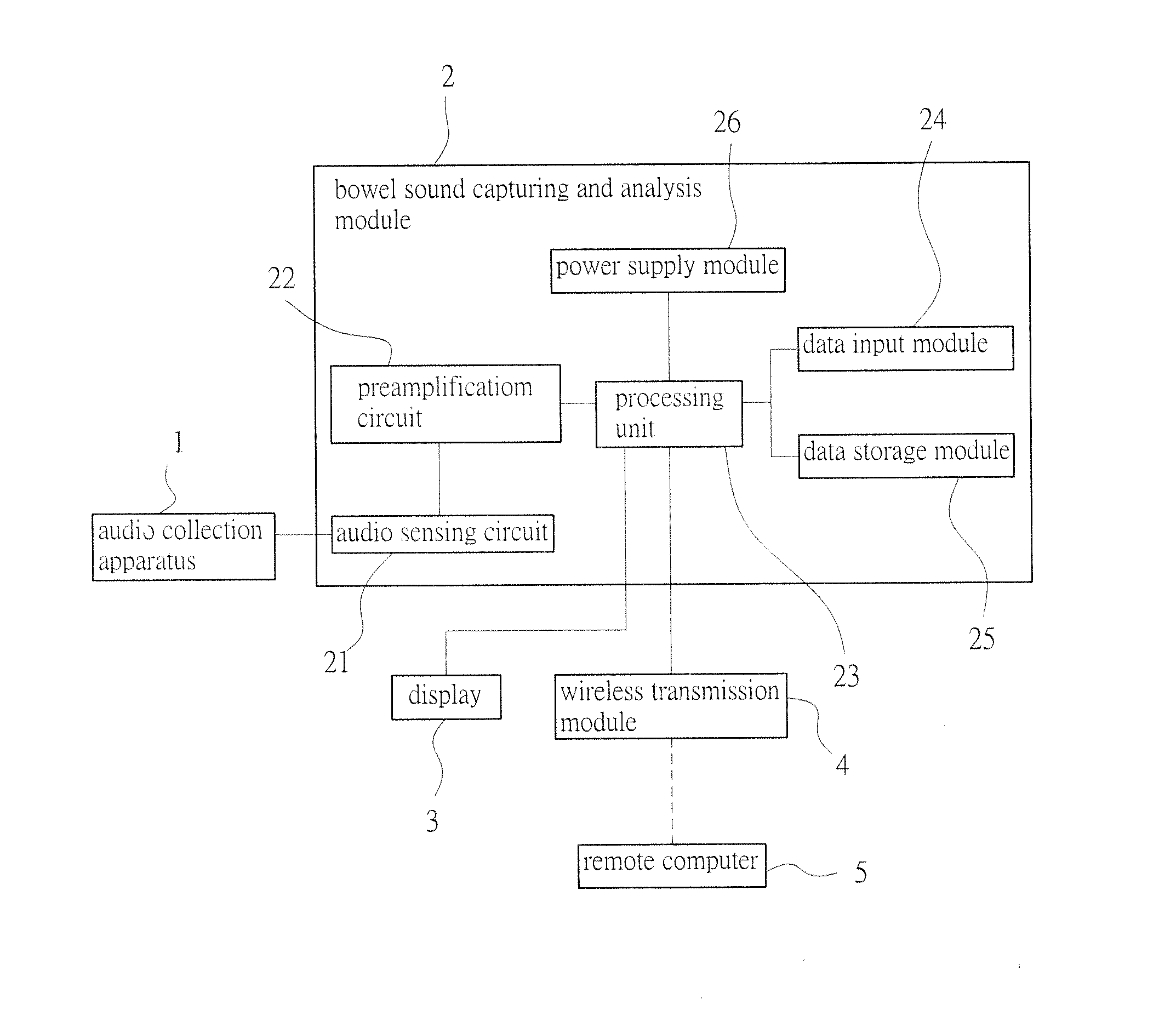
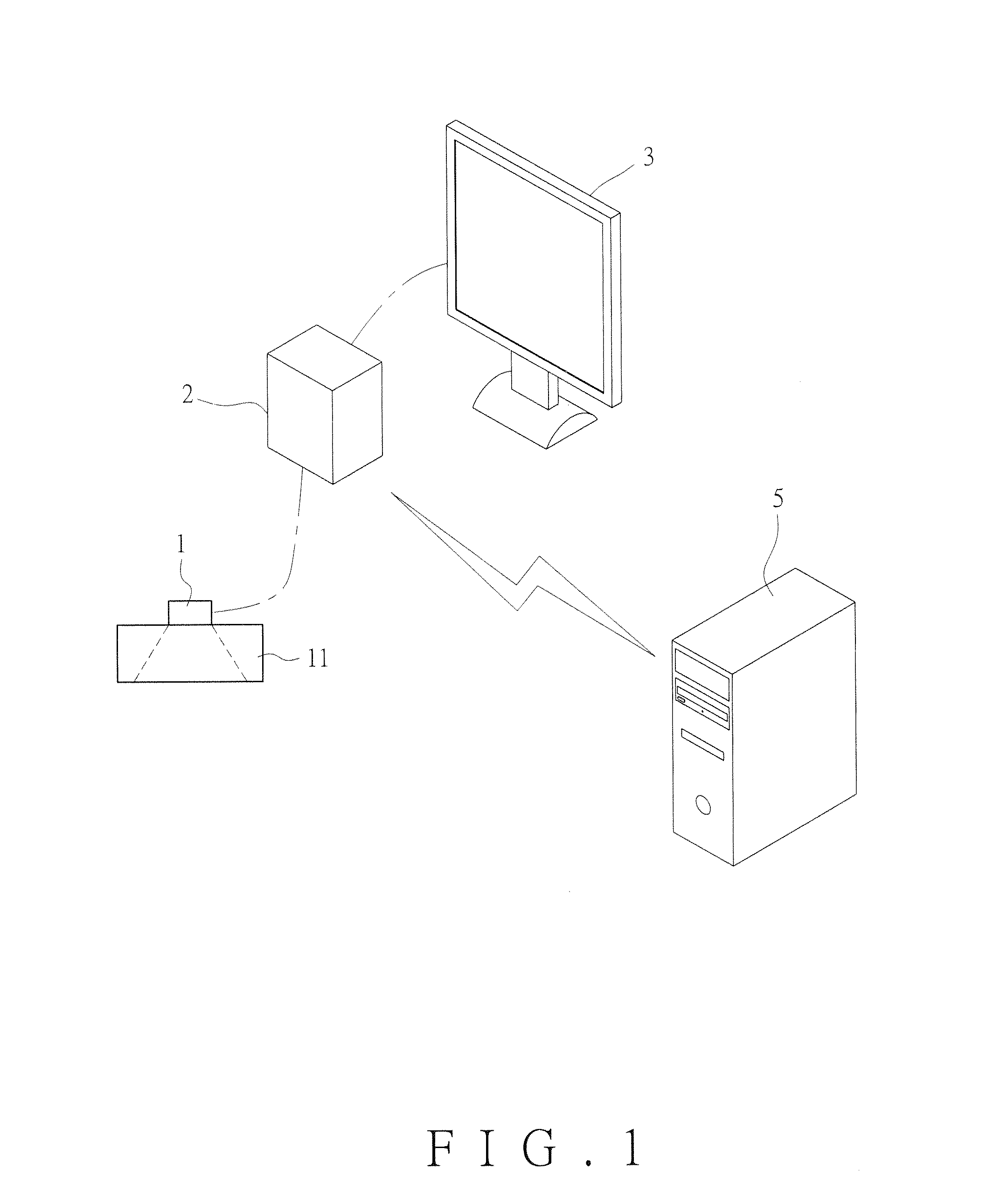
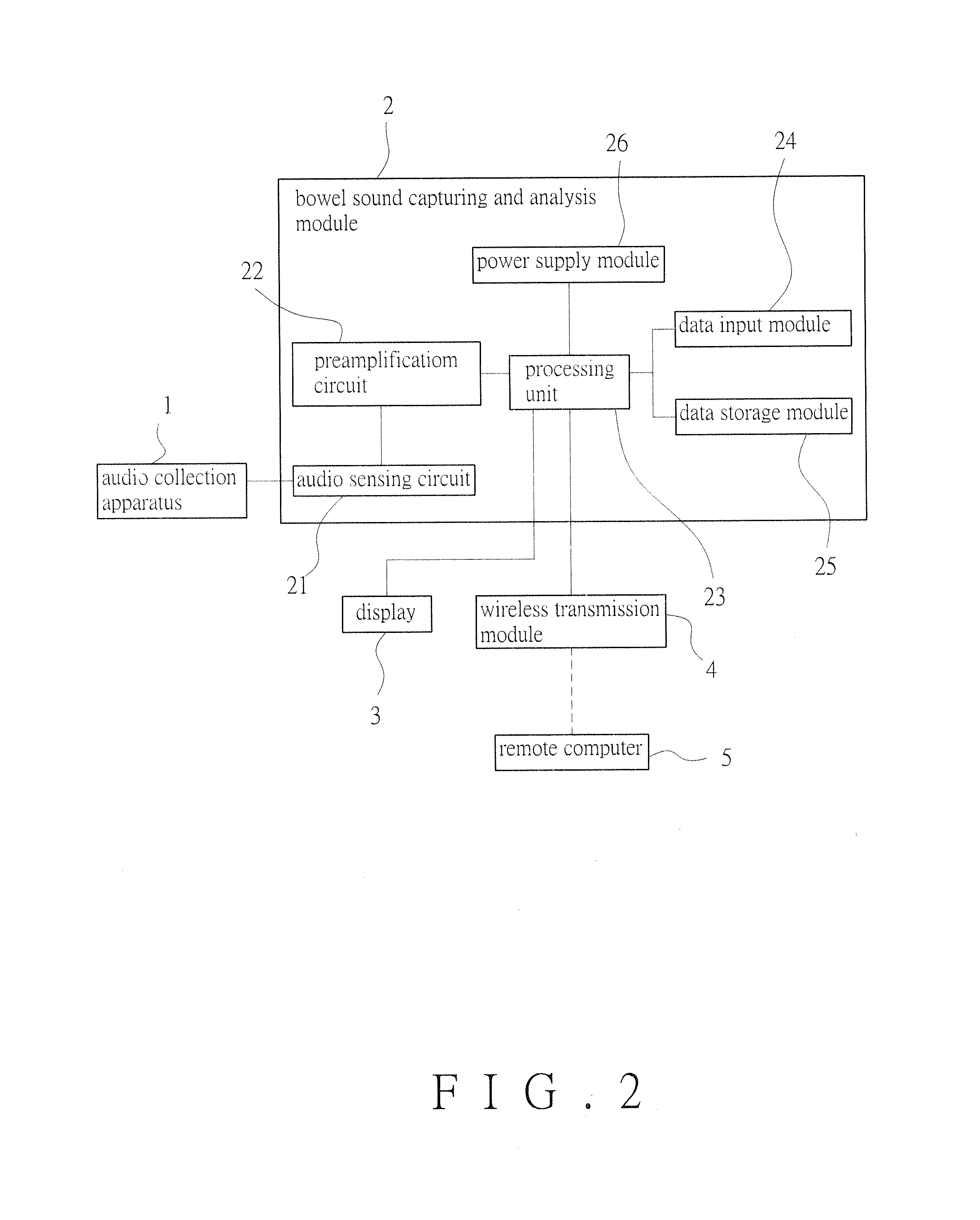
Bowel sound analysis method and system
InactiveUS20160199020A1High noiseReduce medical costStethoscopeSensorsIntestinal motilityHigh complexity
A bowel sound analysis method and system utilizes an audio collection apparatus to continuously monitor an abdominal cavity of an examinee and collect a bowel sound signal of an intestinal tract inside the abdominal cavity, converts the bowel sound signal into a digital signal, then removes noise from the digital signal by using higher-order statistics (HOS) and captures a high-complexity feature from the digital signal by using fractal dimension algorithm, and subsequently defines the high-complexity feature as an intestinal motility signal. The refore, according to the intestinal motility signal, a time point when intestinal motility occurs in the intestinal tract inside the abdominal cavity of the examinee can be learned, and bowel sound features such as the amplitude, frequency, and period of the intestinal motility signal may further be analyzed to determine a health condition of the intestinal tract.
Owner:CHI MEI MEDICAL CENT
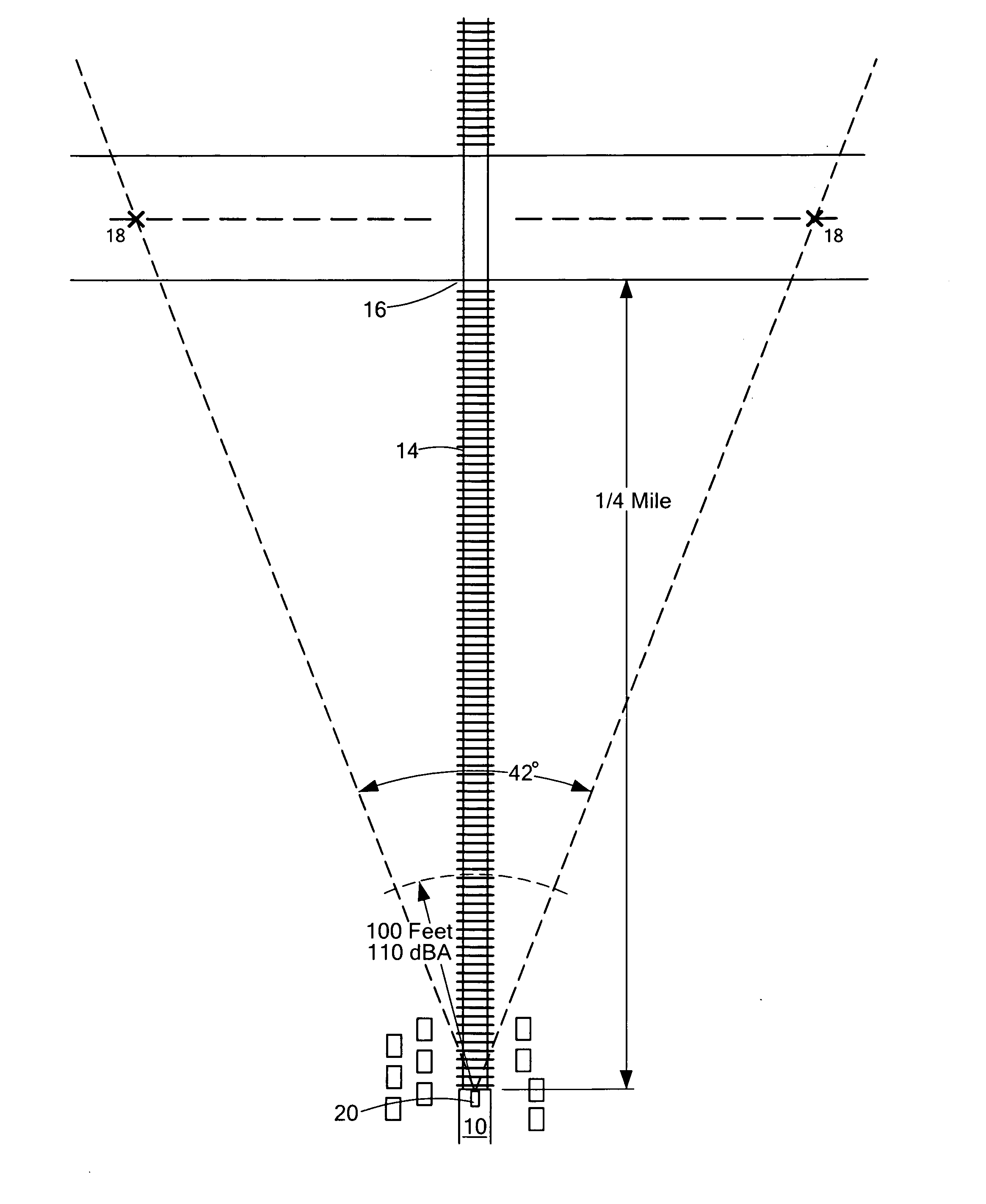
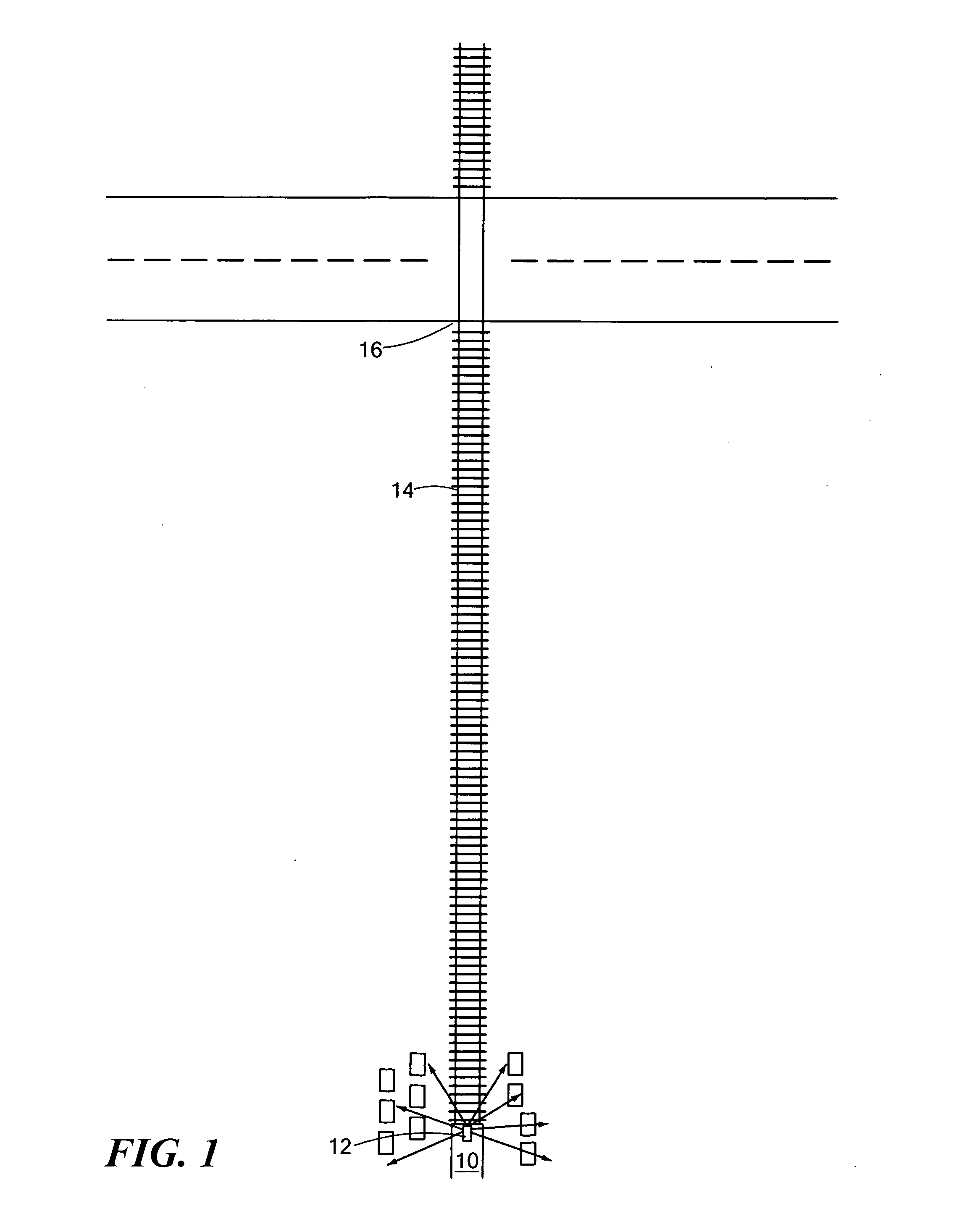
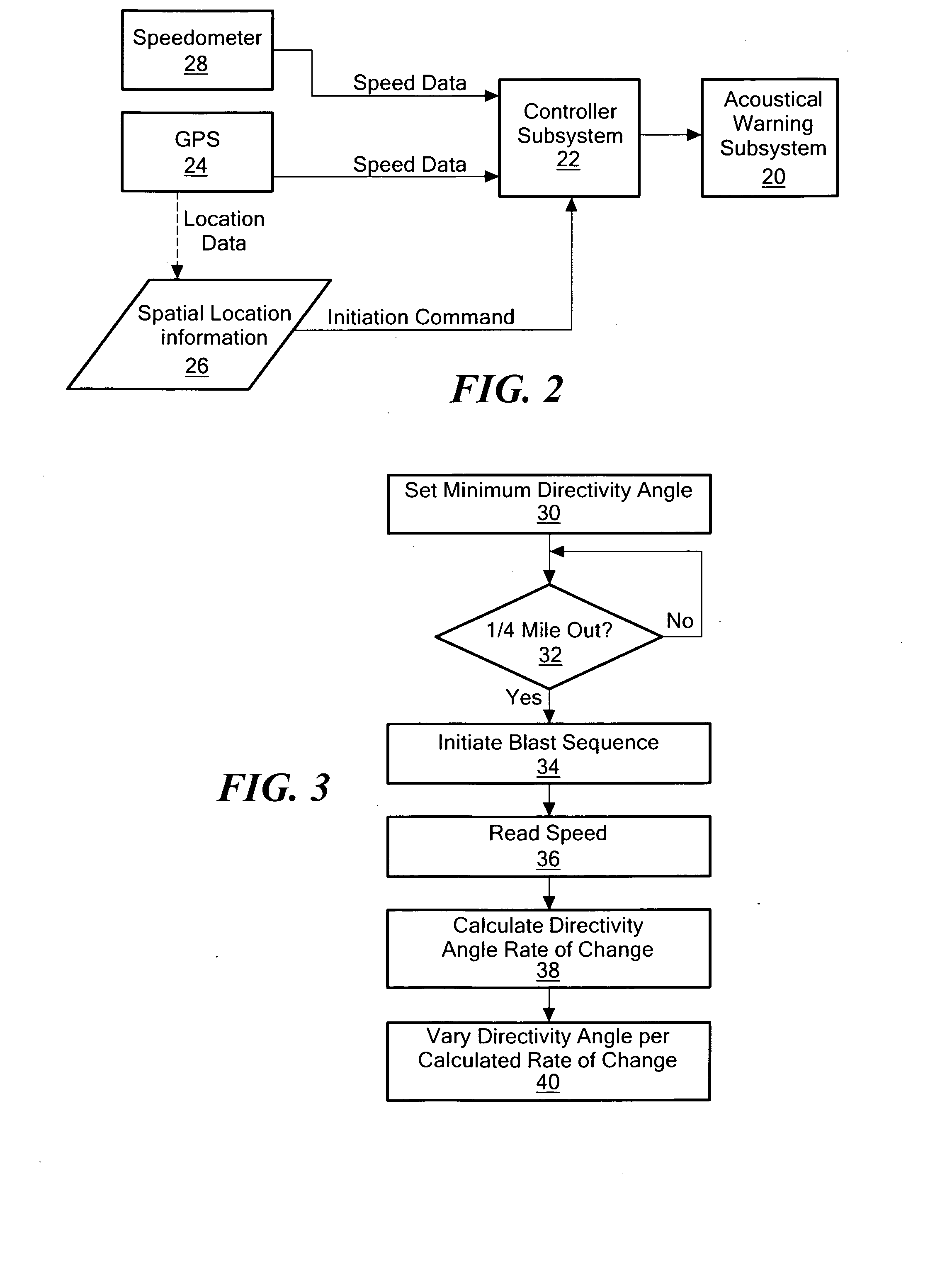
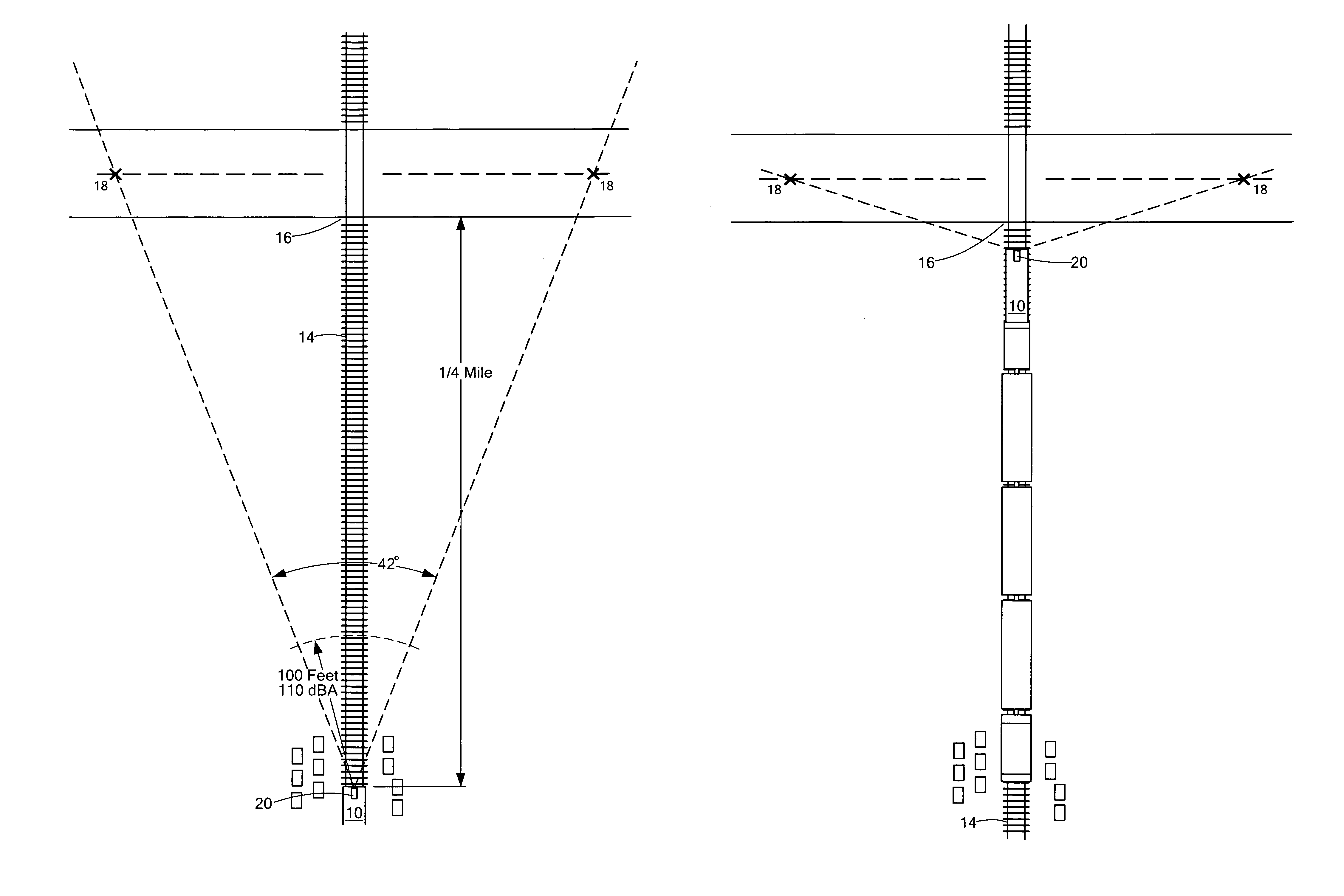
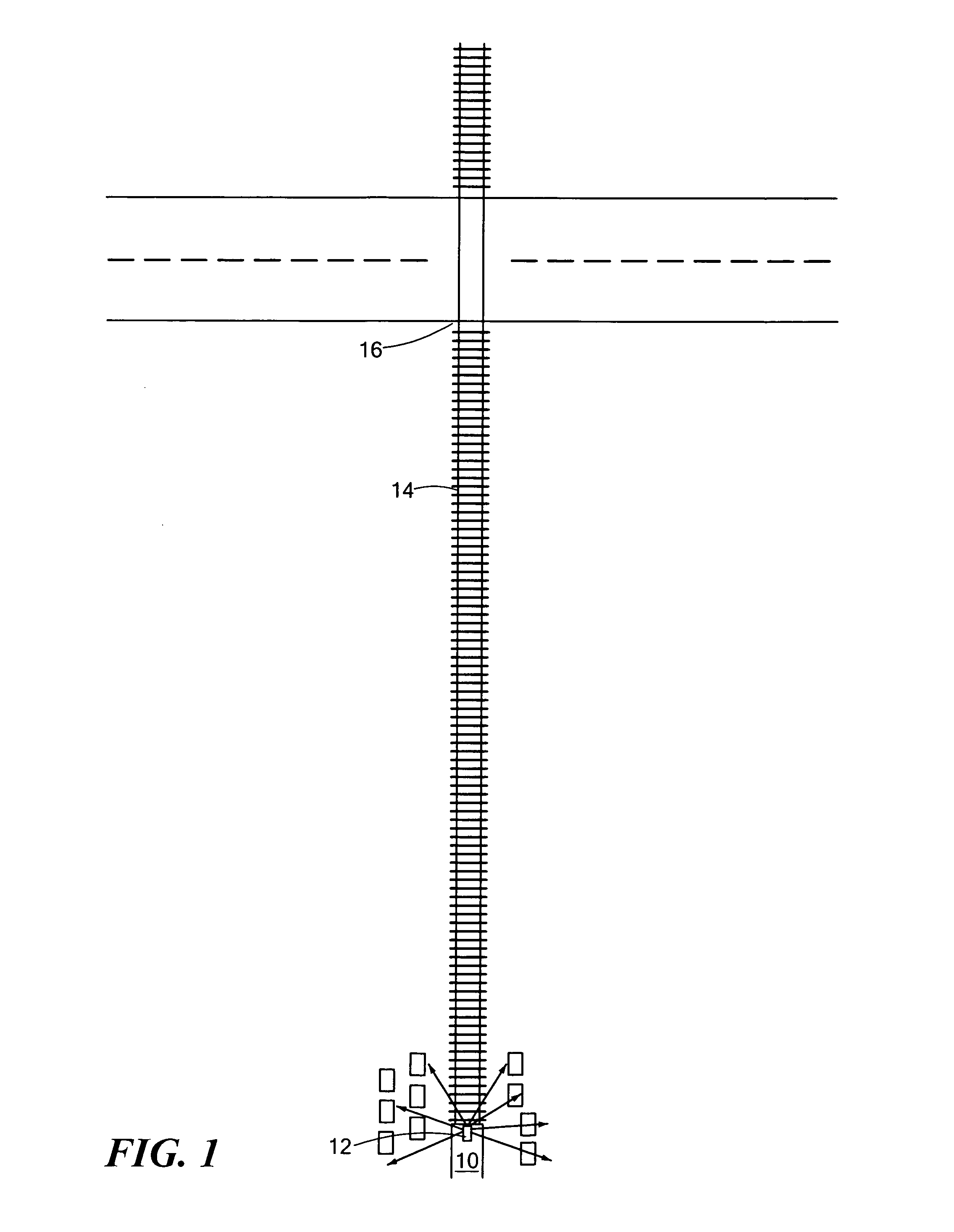
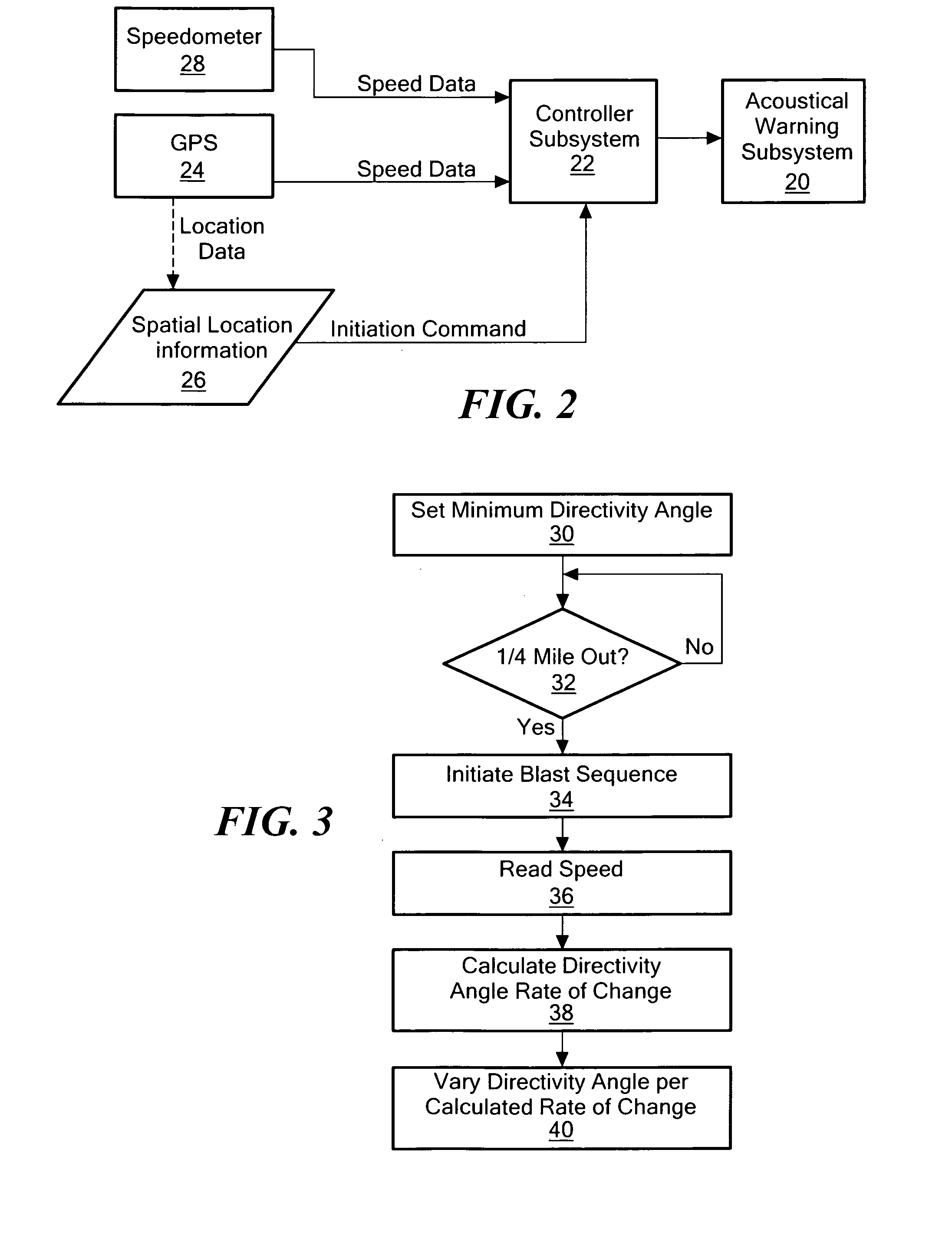
Acoustical warning system
InactiveUS20120318932A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh noiseAudible signalsVisible signalsEngineeringDirectivity
A locomotive warning system includes an acoustical warning subsystem configured to emit variably directed sound. A controller subsystem is responsive to an initiation command and is configured to trigger the acoustical warning subsystem to begin a sounding sequence when the initiation command is received at a first directivity angle and to continue the sound blast sequence at increasing directivity angles for a pre-establish time and / or distance traveled.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
Magnetoresistive head with improved in-stack longitudinal biasing layers and fabricating method
InactiveUS7535683B2Easily controlling magnetization directionGood effectMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsRecord information storageLow noiseRoom temperature
A magnetoresistive head and a fabricating method thereof accomplishing high sensitivity and low noise are provided even if track width narrowing makes progress. In one embodiment, a pinned layer includes a laminate which includes at least two magnetic layers and where adjacent magnetic layers are coupled antiferromagnetically to each other, and a mechanism to apply a longitudinal biasing field to a free layer is made to function by laminating a nonmagnetic separate layer / longitudinal biasing layer / antiferromagnetic layer connecting the free layer and opposite a nonmagnetic conductive layer (or nonmagnetic tunneling barrier layer). Controlling a magnetization direction of the longitudinal biasing layer which bears application of a longitudinal biasing field to the pinned layer and free layer is achieved by annealing carried out while applying a magnetic field in a track width direction and applying a magnetic field at room temperature.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
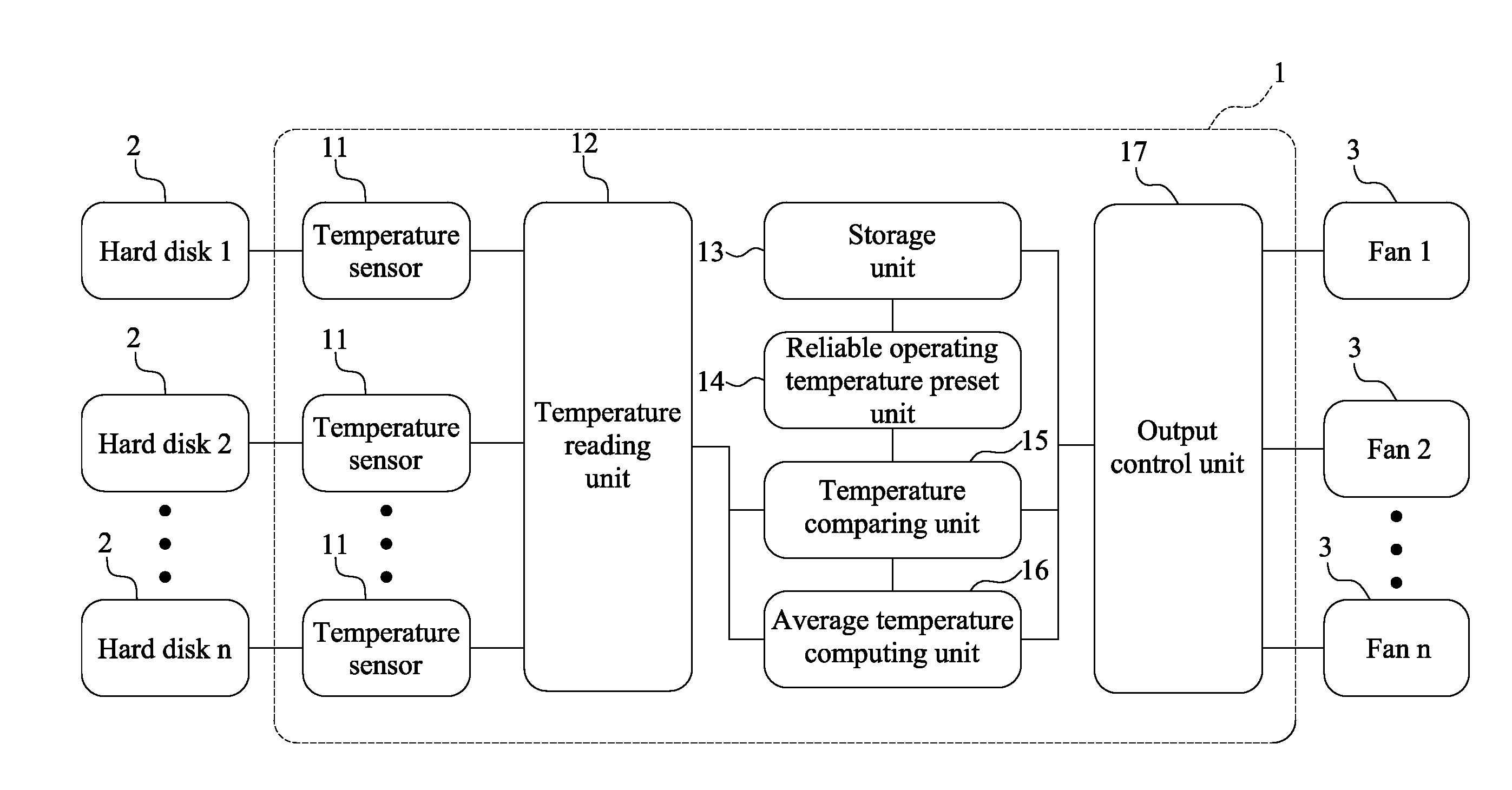
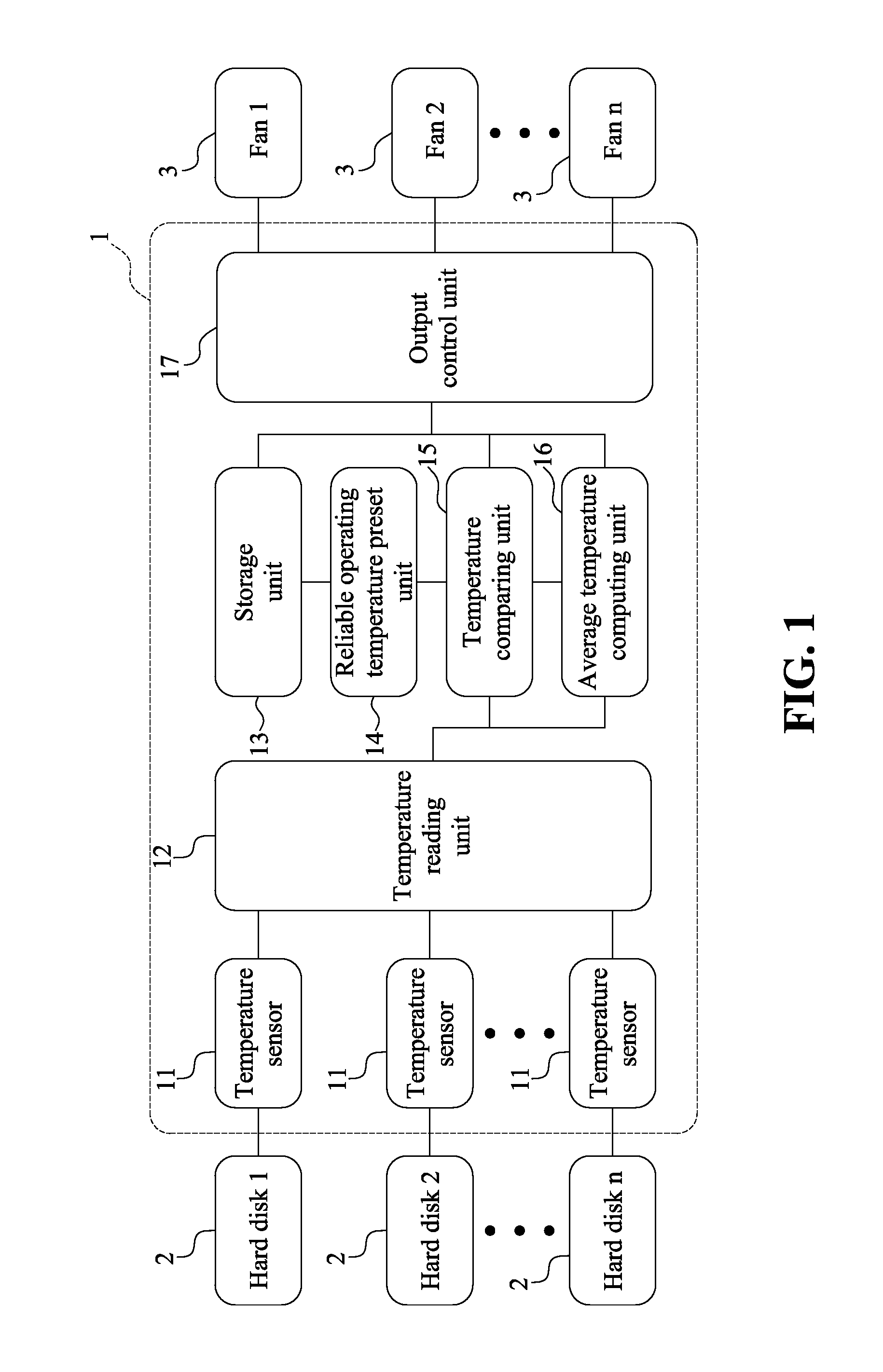
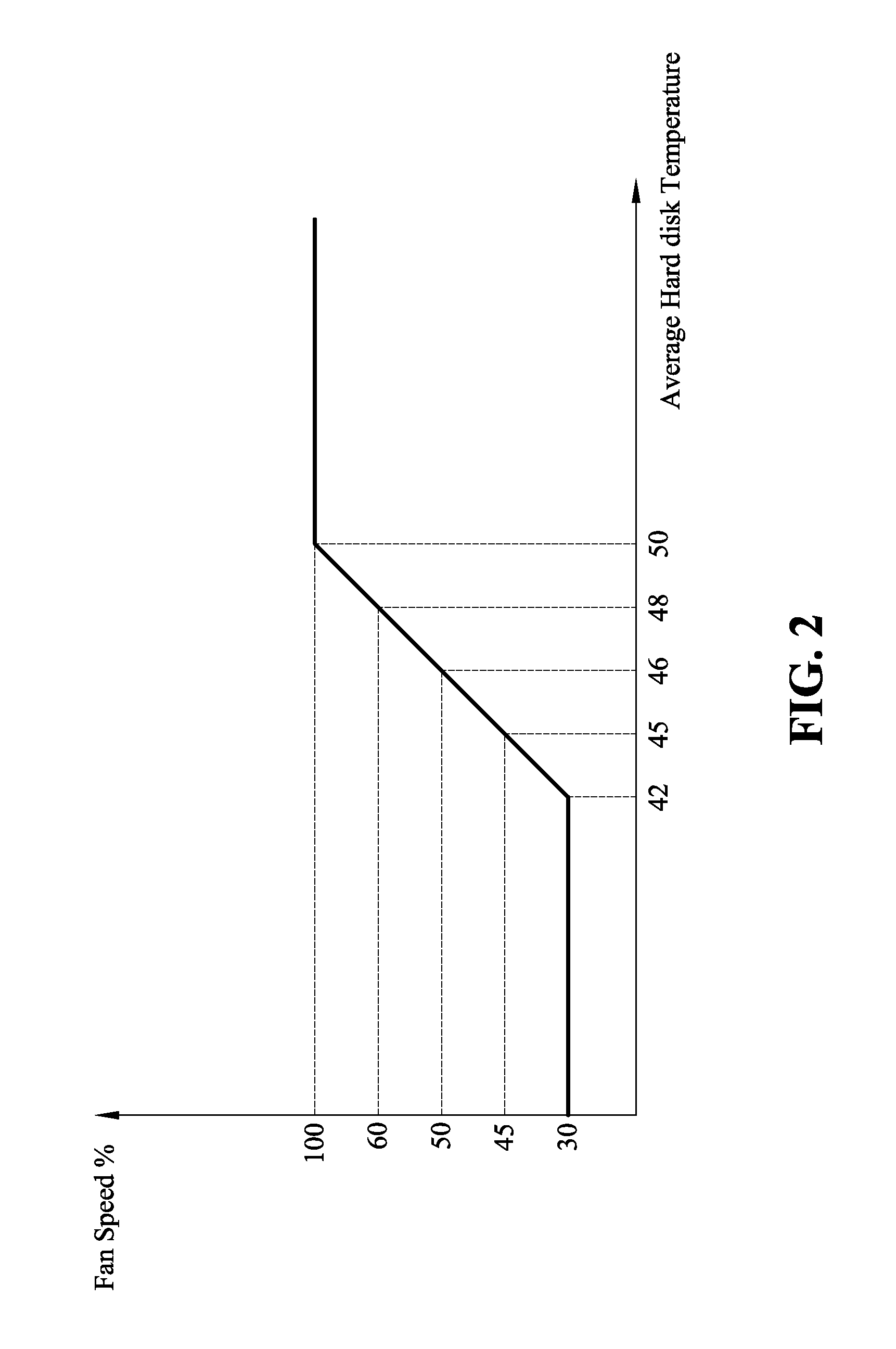
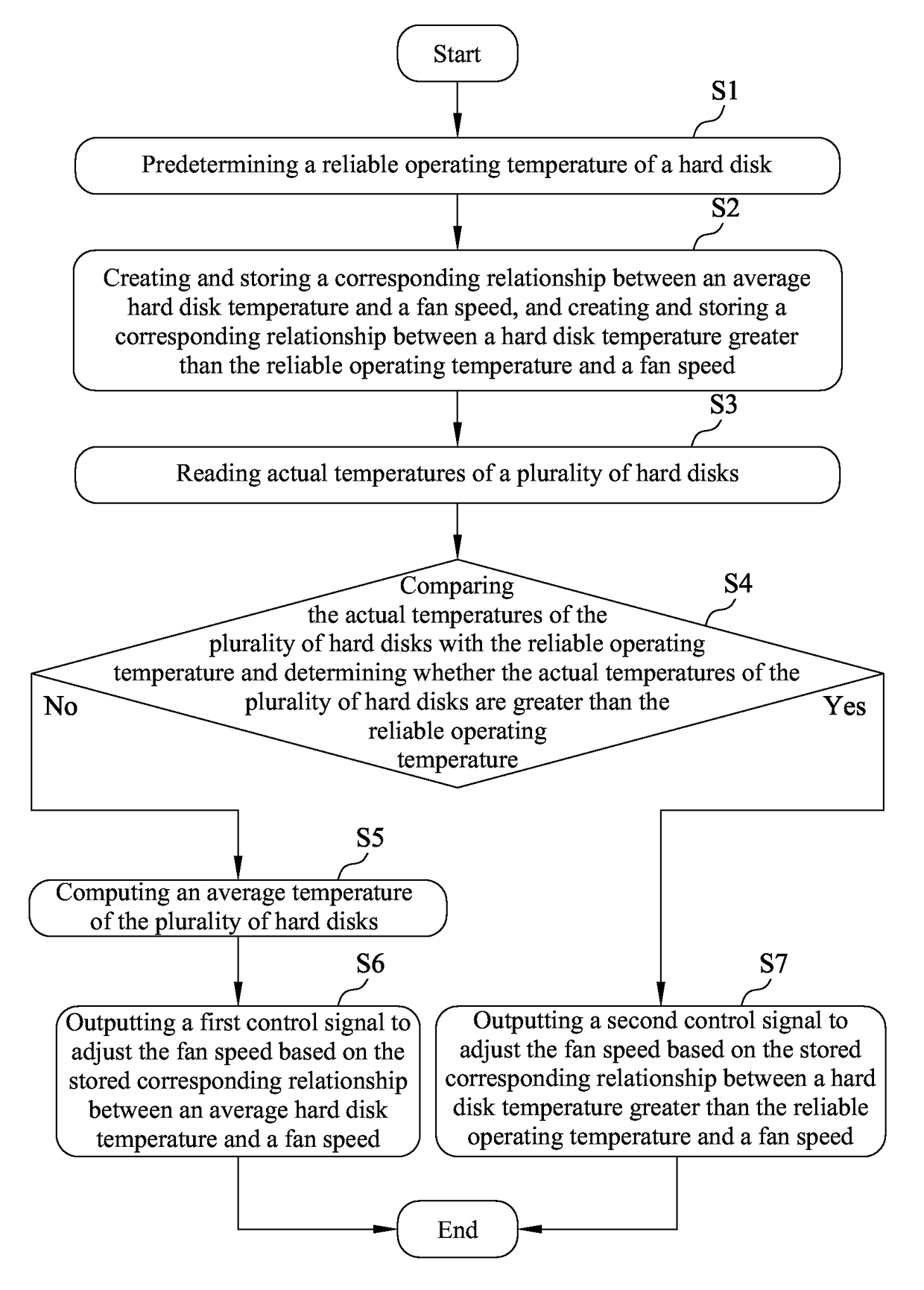
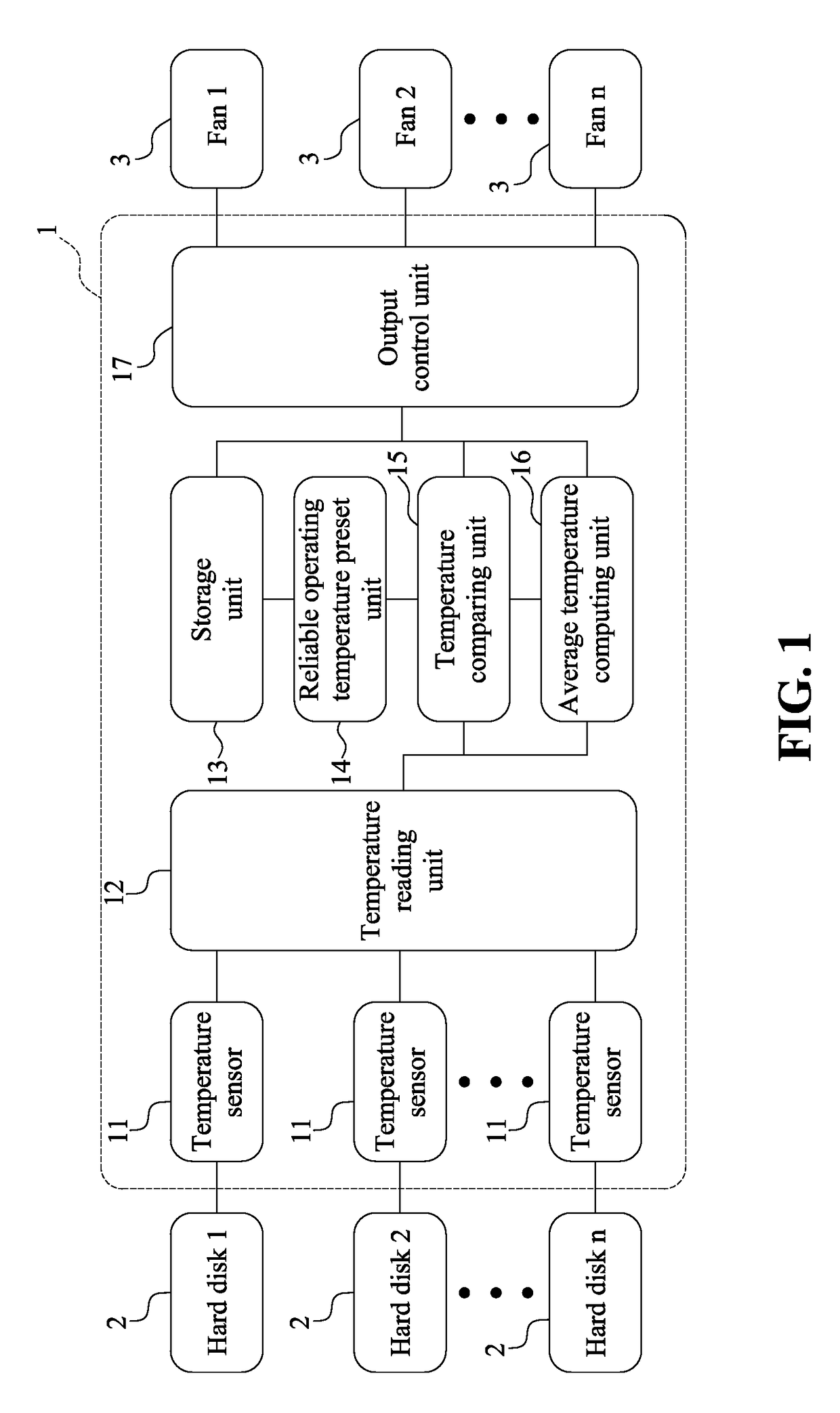
Fan control system and method thereof
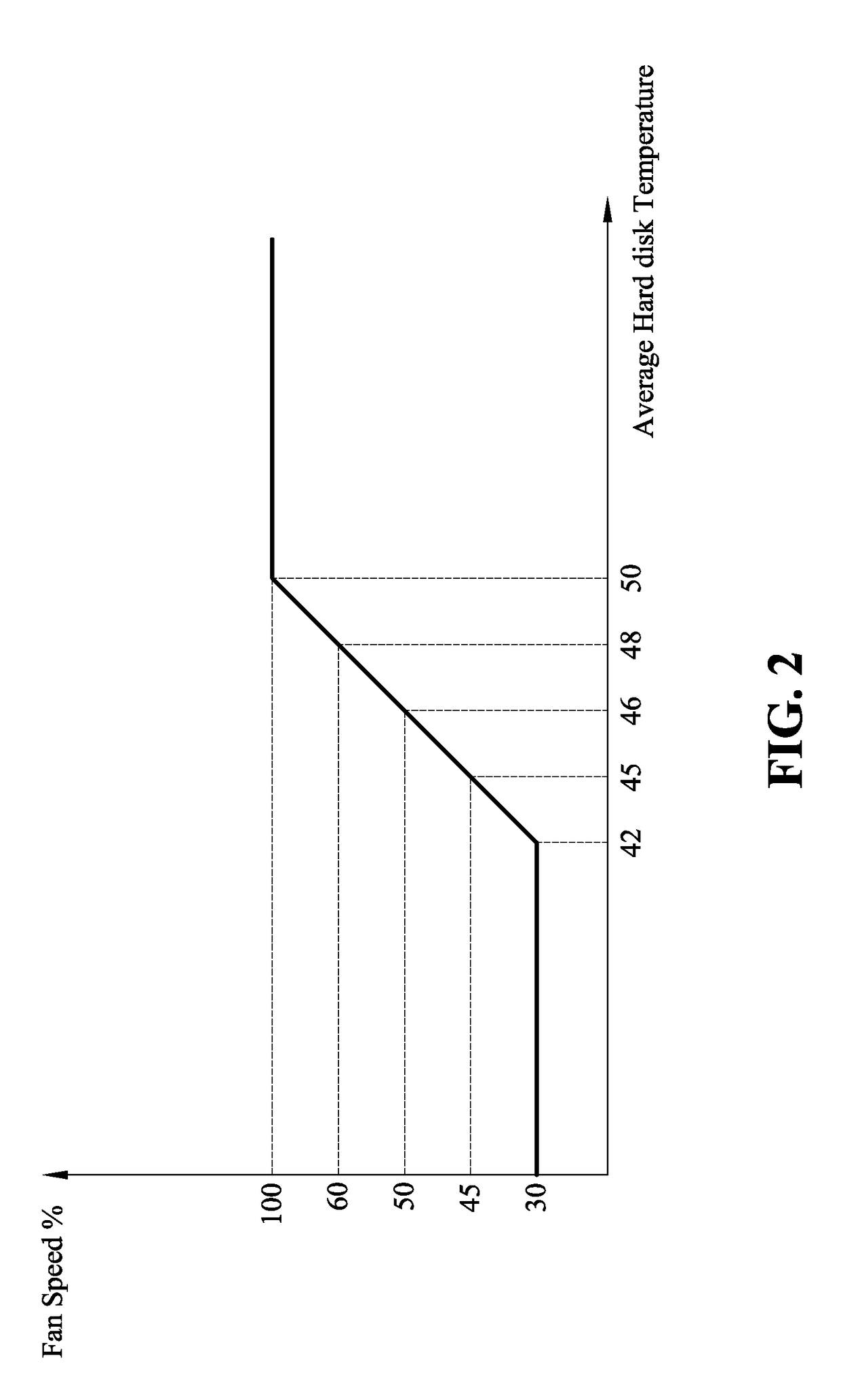
ActiveUS20160076544A1Increase hard disk reliabilityReduce power dissipationSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlControl systemControl signal
Provided are a fan control method and a fan control system. The fan control method of the present invention includes the steps of predetermining a reliable operating temperature of a hard disk; creating a storing a corresponding relationship between an average hard disk temperature and a fan speed, and creating and storing a corresponding relationship between a hard disk temperature greater than the reliable operating temperature and a fan speed; reading actual temperatures of the plurality of hard disks; comparing the actual temperatures of the plurality of hard disks with the reliable operating temperature; computing an average temperature of the plurality of hard disks; and outputting a control signal to adjust the fan speed based on the stored corresponding relationship between an average hard disk temperature and a fan speed. Accordingly, the present invention may increase hard disk reliability and decrease power dissipation of a fan and system noise.
Owner:CELESTICA TECH CONSULTANCY SHANGHAI
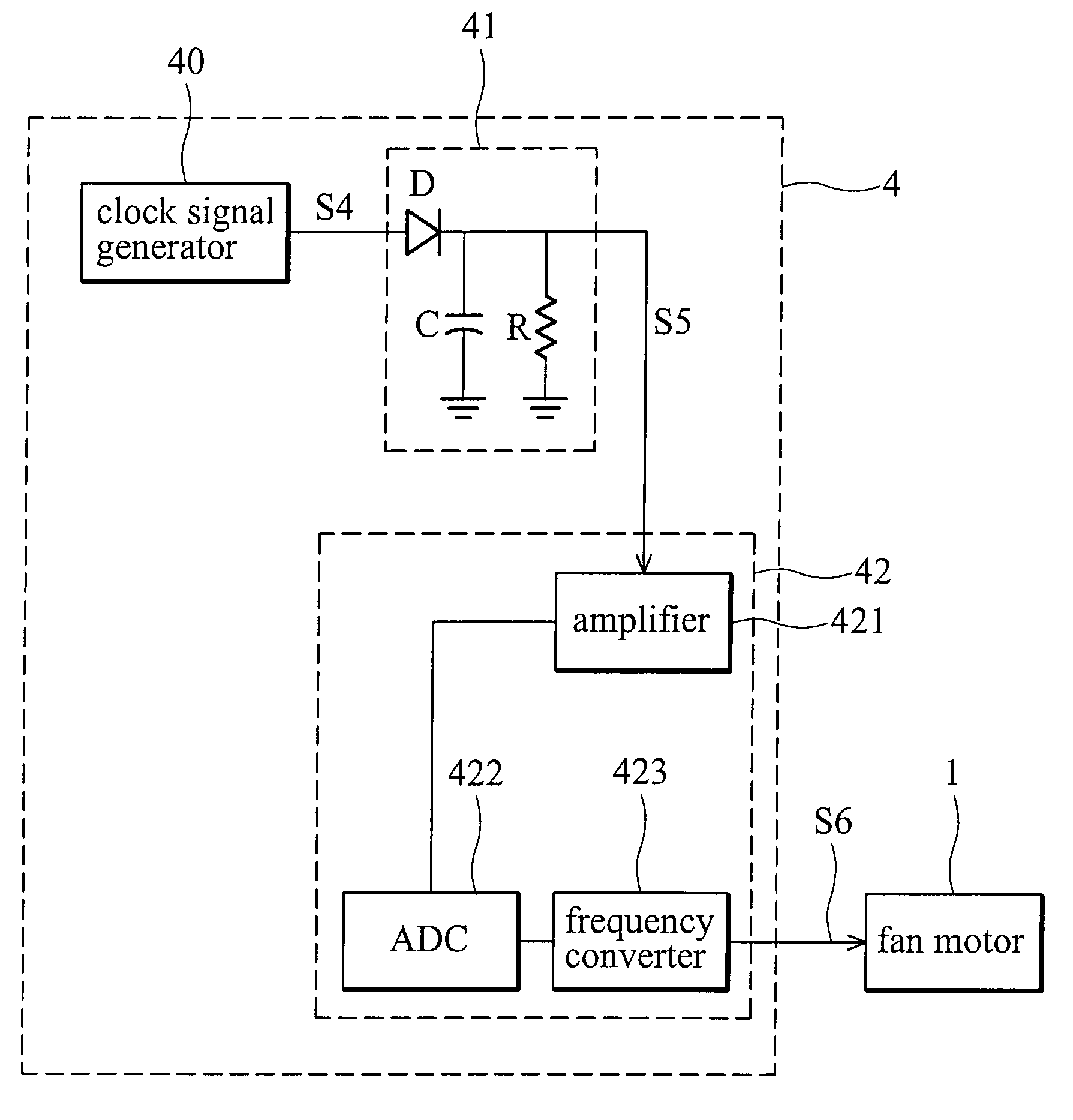
Fan motor control method and device thereof
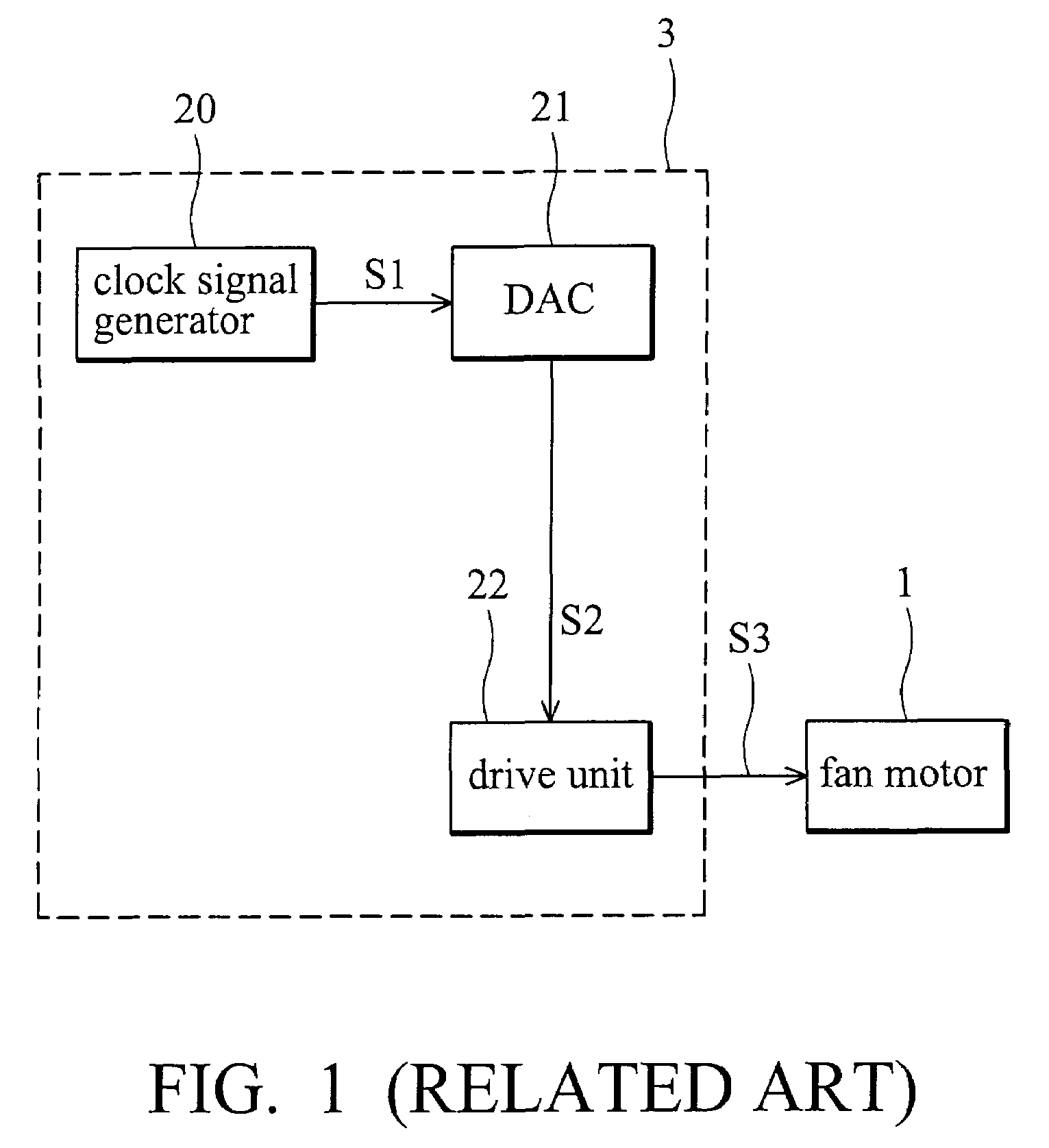
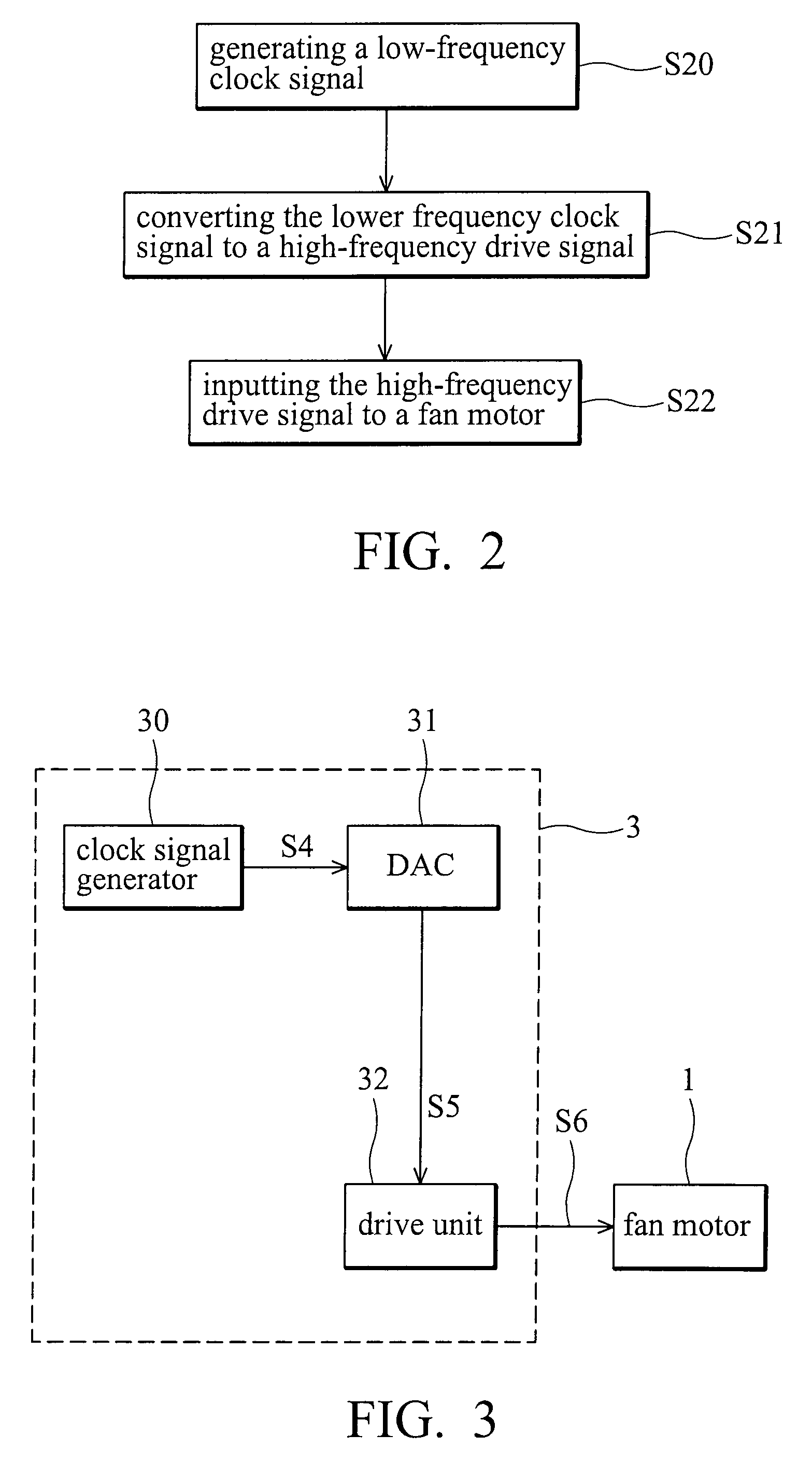
ActiveUS7545112B2Additional drawbackHigh noiseTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor controlEngineering
A fan motor control device comprises a clock signal generator and a drive unit. The clock signal generator generates a low-frequency clock signal. A frequency of low-frequency clock signal is less than 23 KHz. The drive unit converts the low-frequency clock signal to a high-frequency drive signal and outputs the high-frequency drive signal to drive the fan motor. A frequency of the high-frequency drive signal is higher than 23 KHz.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus for measuring air amount of engine oil and method using the same
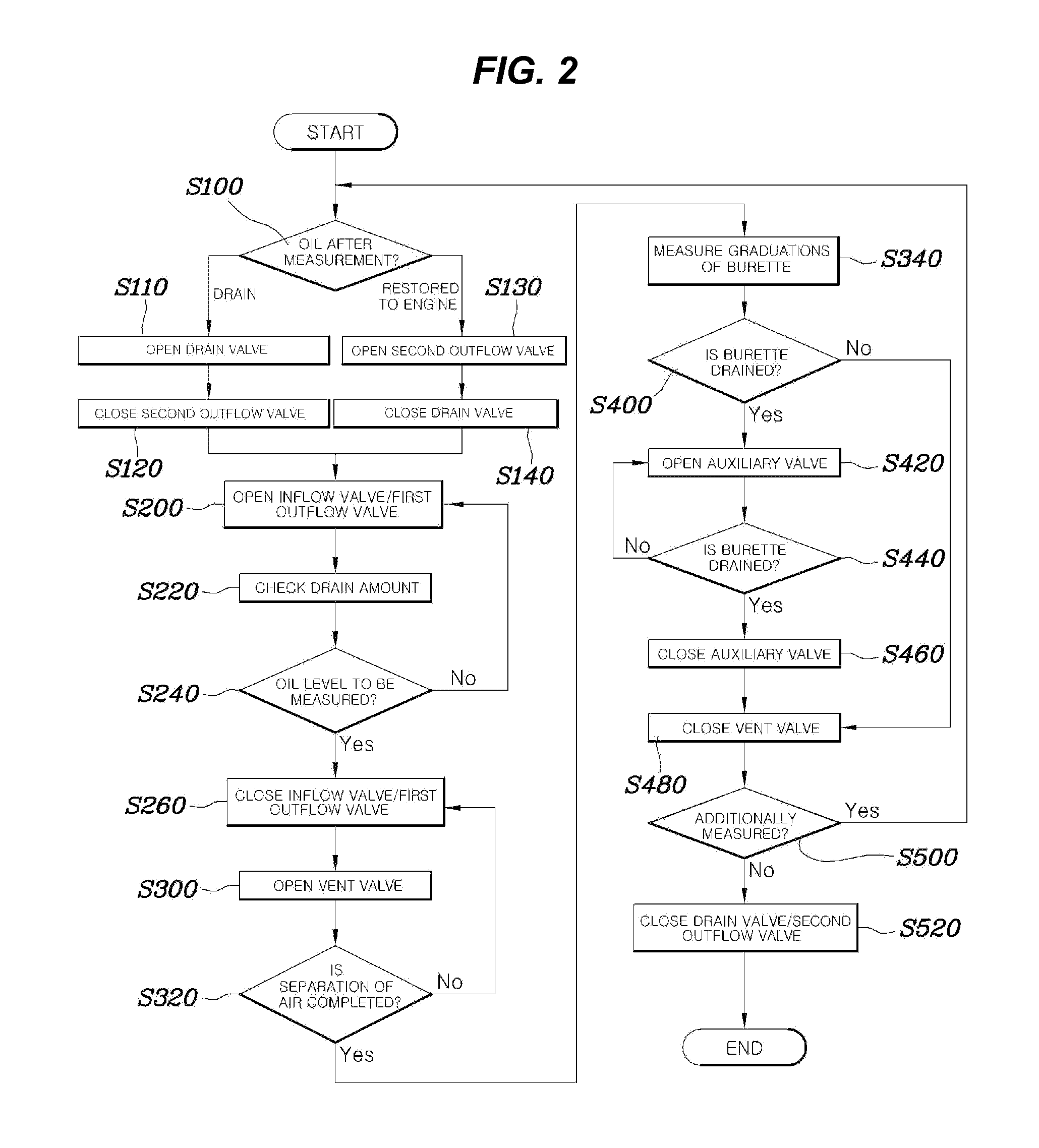
InactiveUS20130118234A1Improve reliabilityImprove test efficiencyVehicle testingVolume measurement apparatus/methodsBuretteDraining tube
An apparatus for measuring air amount of engine oil includes an inflow pipe in which the engine oil flows in connection with an engine and an inflow valve, a measuring burette having an inflow hole connected with the inflow pipe and an outflow hole formed at the other side and a measurement camera provided at the side of the measuring burette to photograph graduations, a vent pipe branched from the outflow hole of the measuring burette and a bent valve provided on the vent pipe, a drain burette having a drain pipe connected with the outflow hole provided at one side thereof and having a drain valve provided on the drain pipe, an auxiliary drain pipe having one side branched from the inflow hole and the other side connected to the drain burette and an auxiliary valve provided on the auxiliary drain pipe, and a control unit.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Air conditioner
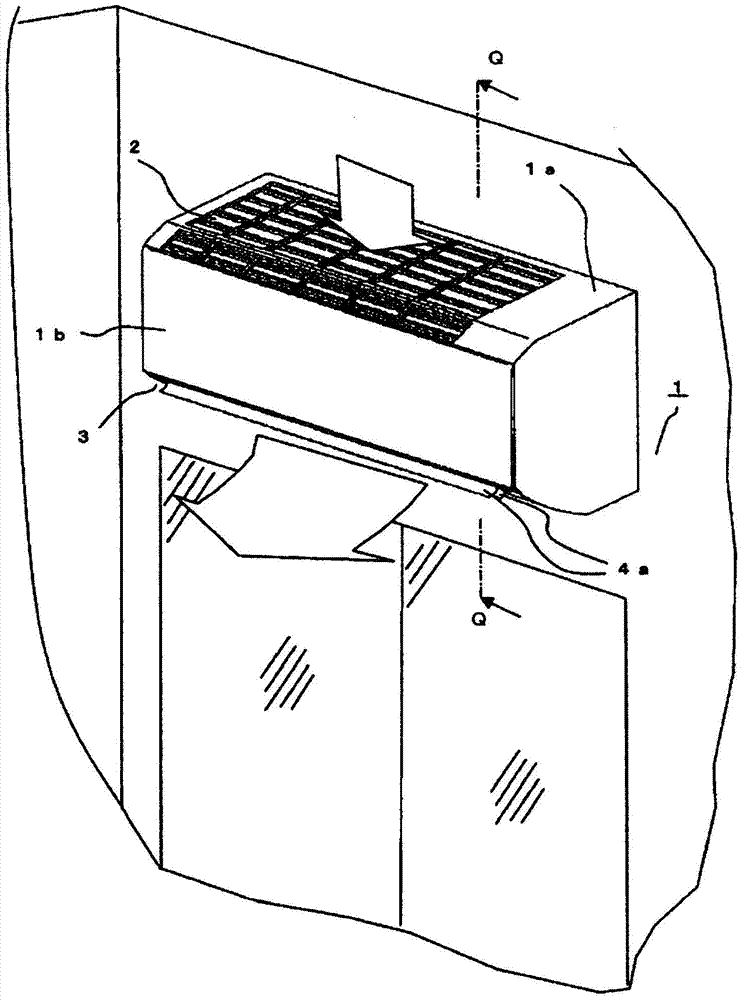
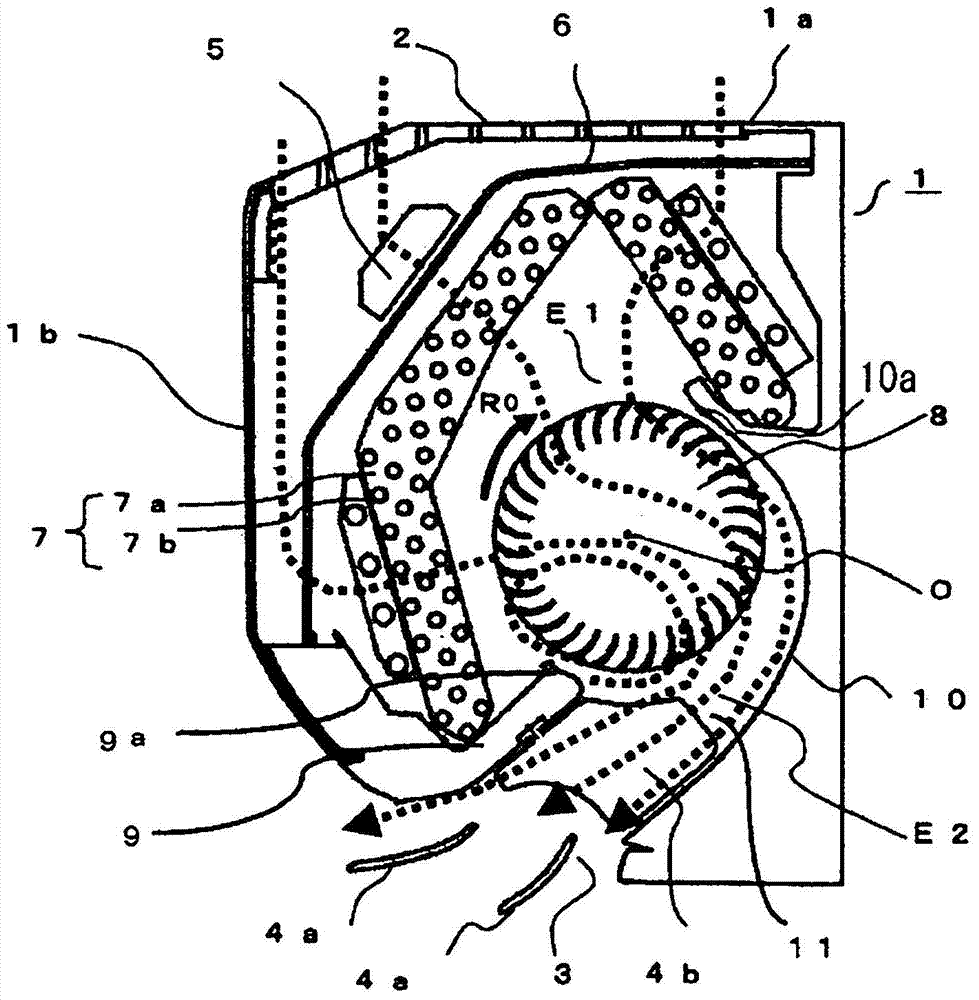
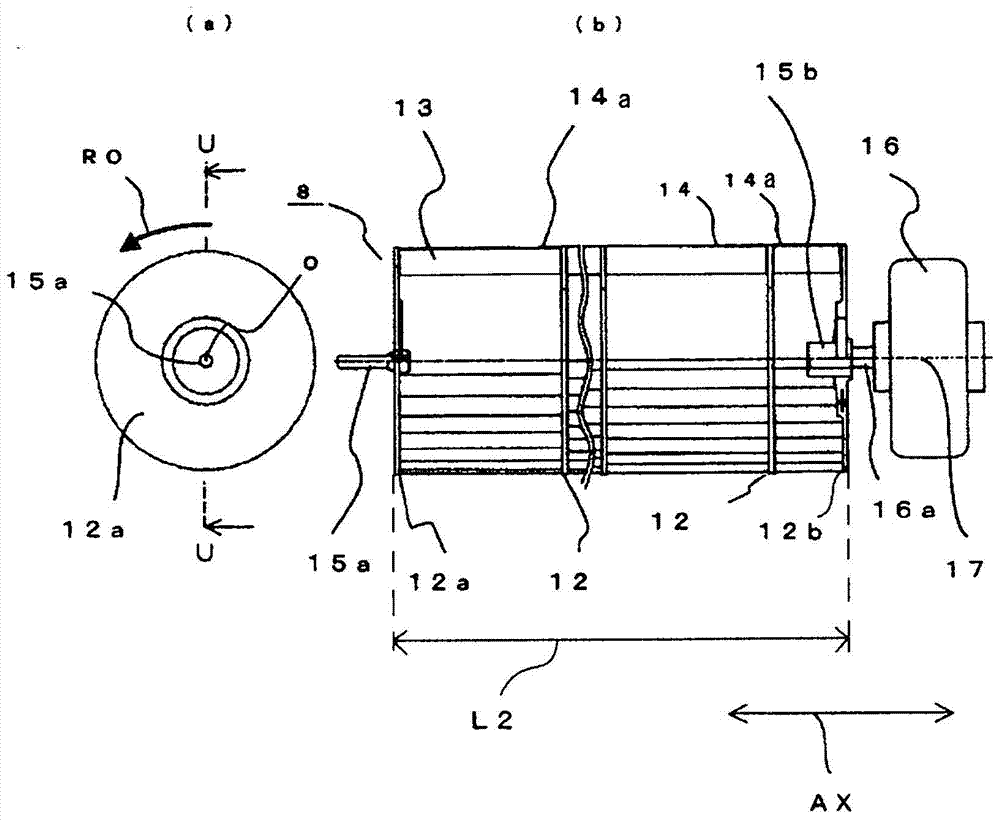
ActiveCN103597288AReduce performanceLoud noisePump componentsLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringAir conditioning
There is obtained an air conditioner capable of minimizing backflow of indoor air from indoors to the interior of an air conditioner at the two longitudinal-direction end parts of an air outlet in an indoor unit of the air conditioner, and capable of maintaining the high flow rate of a blower, thereby reducing noise and power consumption. The length of a cross-flow fan (8) in the axial direction of rotation (AX) is greater than the lengthwise-direction length of the air outlet (3), and the cross-flow fan (8) has an extension (8a) that projects from the two ends of the air outlet (3) in the axial direction of rotation (AX). Also provided is a collision wall (18) with which the airstream discharged from the extension (8a) of the cross-flow fan (8) collides, the collision wall being disposed in the air conditioner body. Vanes (13a) on the extension (8a) of the cross-flow fan (8) and vanes (13b) facing the air outlet (3) have different shapes and are configured so that the flow rate of the airstream discharged from the vanes (13a) is less than the flow rate of the airstream discharged from the vanes (13b).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Acoustical warning system
InactiveUS8998148B2Reduce the amount of solutionHigh noiseTraffic crossing safety meansEngineeringDirectivity
A locomotive warning system includes an acoustical warning subsystem configured to emit variably directed sound. A controller subsystem is responsive to an initiation command and is configured to trigger the acoustical warning subsystem to begin a sounding sequence when the initiation command is received at a first directivity angle and to continue the sound blast sequence at increasing directivity angles for a pre-establish time and / or distance traveled.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
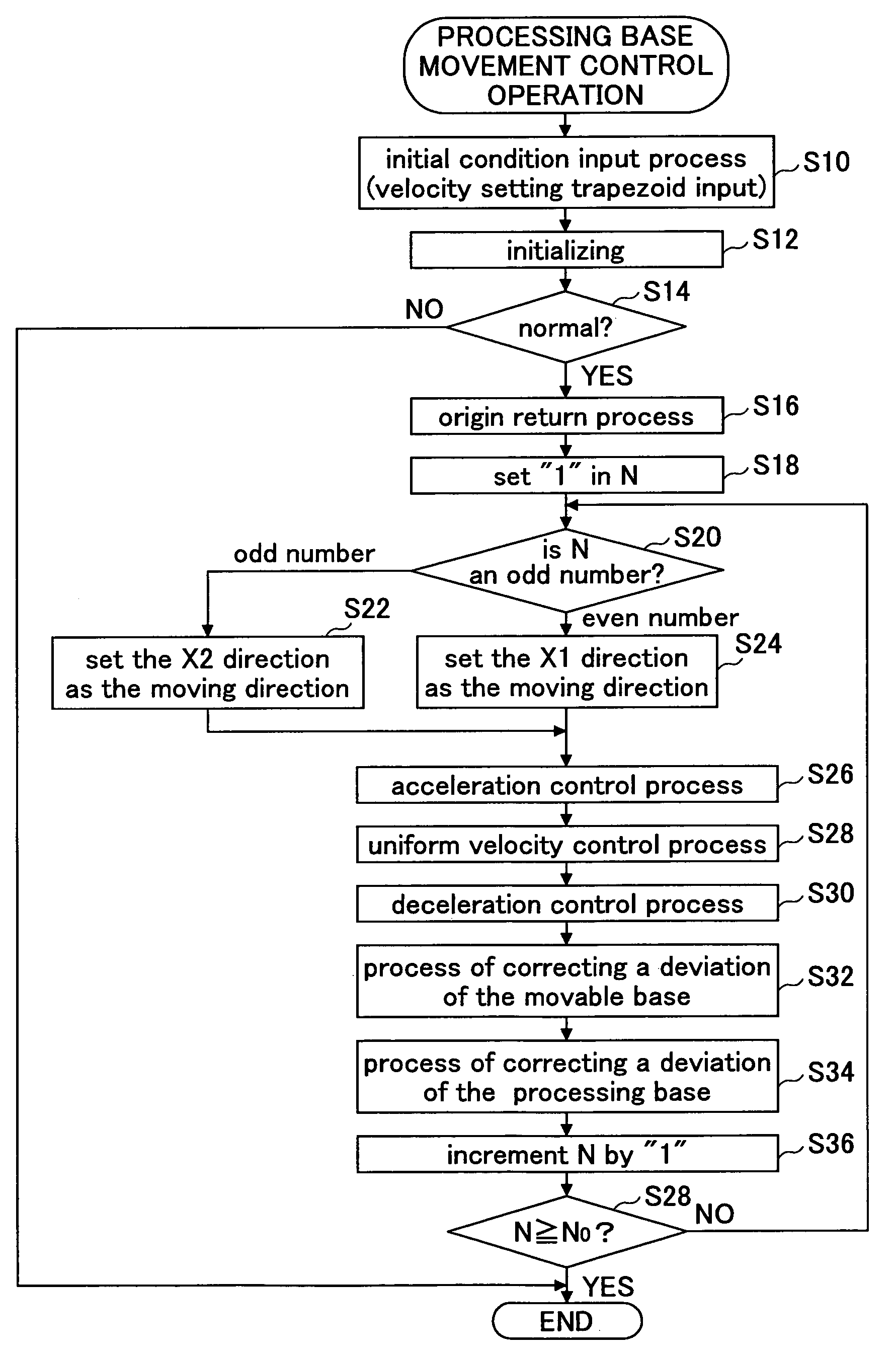
Method of controlling mover device
InactiveUS7597531B2Improve impact performanceHigh noiseDC motor speed/torque controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringGenerating unit
Embodiments of the invention are directed to a method of controlling a mover device The method includes generating a moving force from a moving force generating unit to move a processing base with respect to a movable base, thereby moving the processing base with respect to a fixed base as a result of the movement of the processing base with respect to the movable base; moving the movable base on the fixed base in the opposite direction to the moving direction of the processing base by virtue of a reaction force caused by the moving force generated from the moving force generating unit to move the processing base, so that the movable base moves in the opposite direction to the moving direction of the processing base on the fixed base. The method further includes controlling the moving velocity of the processing base with respect to the fixed base.
Owner:SEN CORP AN SHI & AXCELIS
Fan control system and method thereof
ActiveUS9829867B2High dissipationHigh noiseEfficient regulation technologiesPump controlControl signalControl system
Provided are a fan control method and a fan control system. The fan control method of the present invention includes the steps of predetermining a reliable operating temperature of a hard disk; creating a storing a corresponding relationship between an average hard disk temperature and a fan speed, and creating and storing a corresponding relationship between a hard disk temperature greater than the reliable operating temperature and a fan speed; reading actual temperatures of the plurality of hard disks; comparing the actual temperatures of the plurality of hard disks with the reliable operating temperature; computing an average temperature of the plurality of hard disks; and outputting a control signal to adjust the fan speed based on the stored corresponding relationship between an average hard disk temperature and a fan speed. Accordingly, the present invention may increase hard disk reliability and decrease power dissipation of a fan and system noise.
Owner:CELESTICA TECH CONSULTANCY SHANGHAI
Disk system using memory control signal of processor
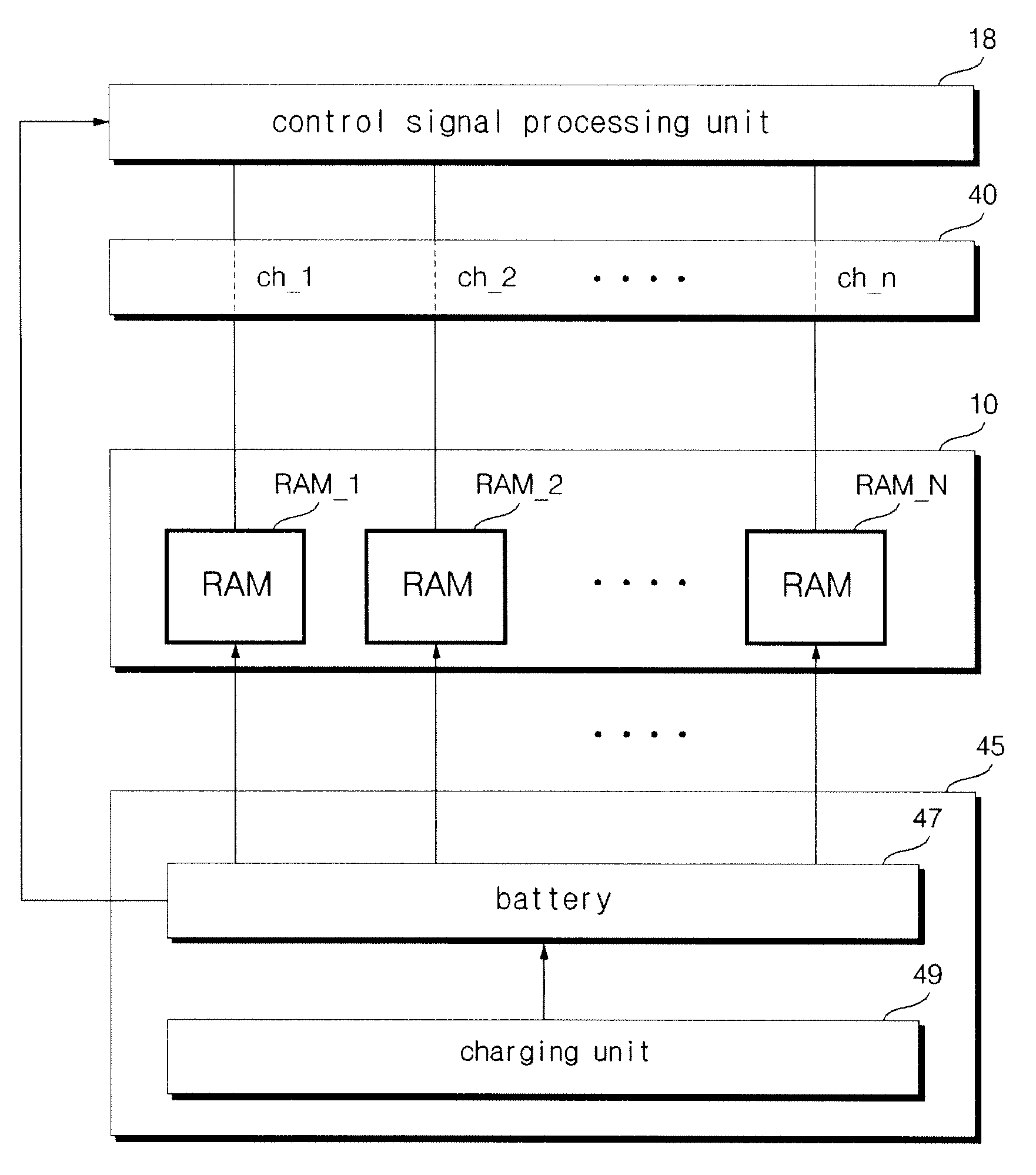
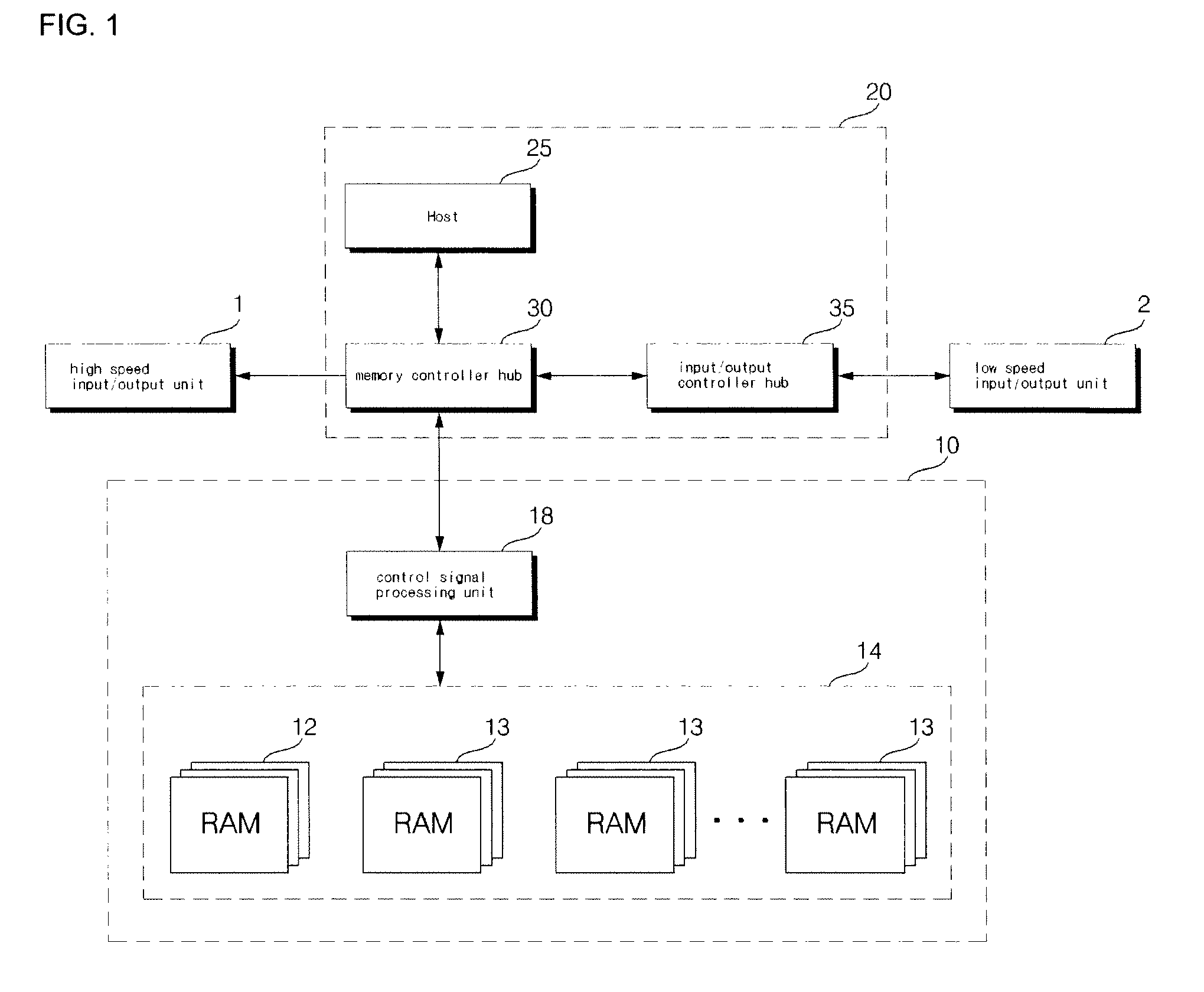
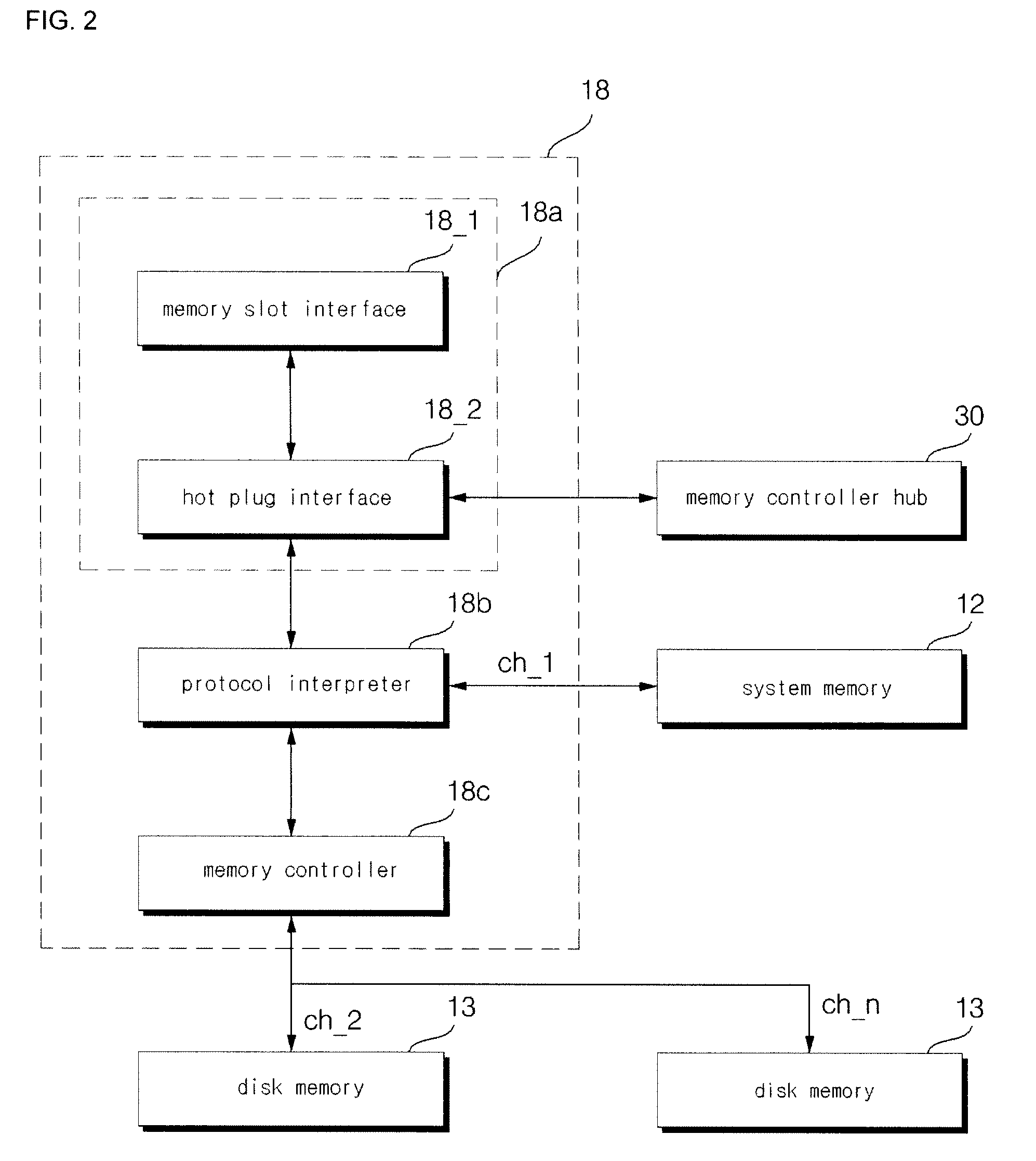
InactiveUS20100161893A1Increase speedLight weightBatteries circuit arrangementsInput/output to record carriersRAM driveControl signal
The disk system of the present invention decreases defects of a volume restriction and a volatile characteristic of a RAM disk using a memory control signal of a host. The preset invention provides a disk system including a central control unit generating a memory control signal corresponding to a RAM memory and an external instruction and controlling the RAM memory, and wherein the RAM memory including a RAM disk constituted by RAMs and storing a system program and data; and a control signal processing unit converting the memory control signal into first and second memory control signals based on access information included in the memory control signal and controlling the RAM disk to access to the system program and the data by the second memory control signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Garbage disposer
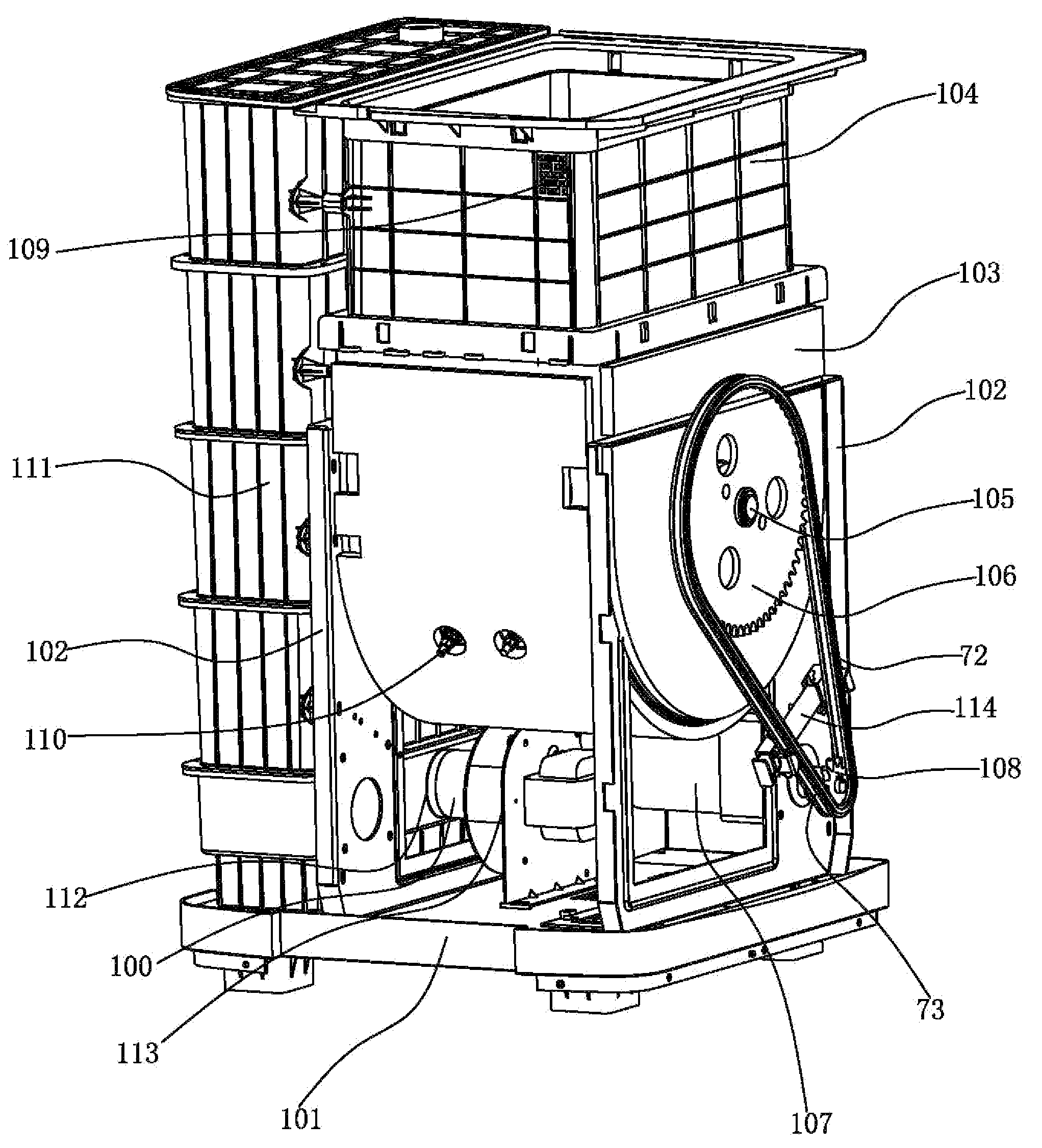
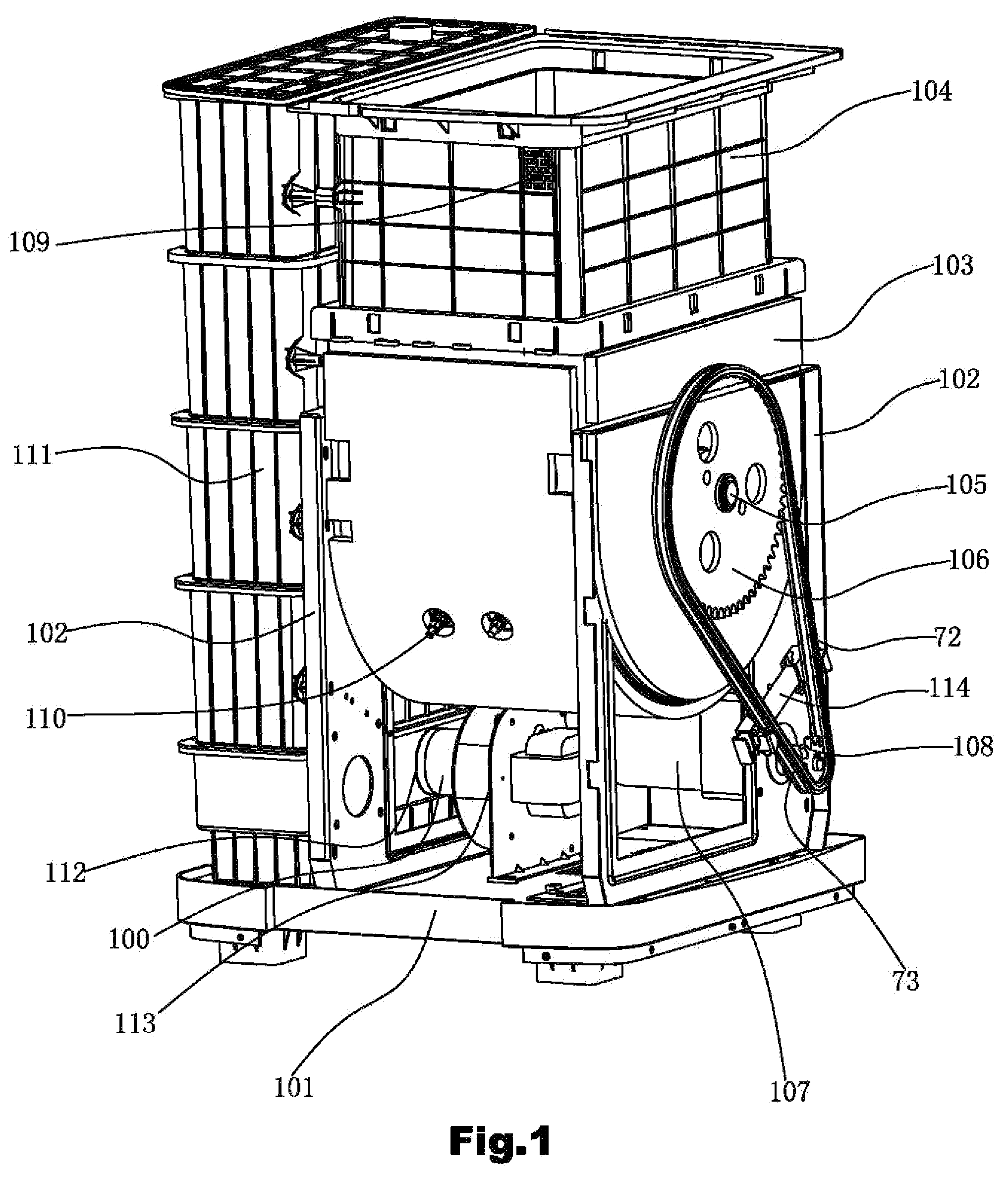
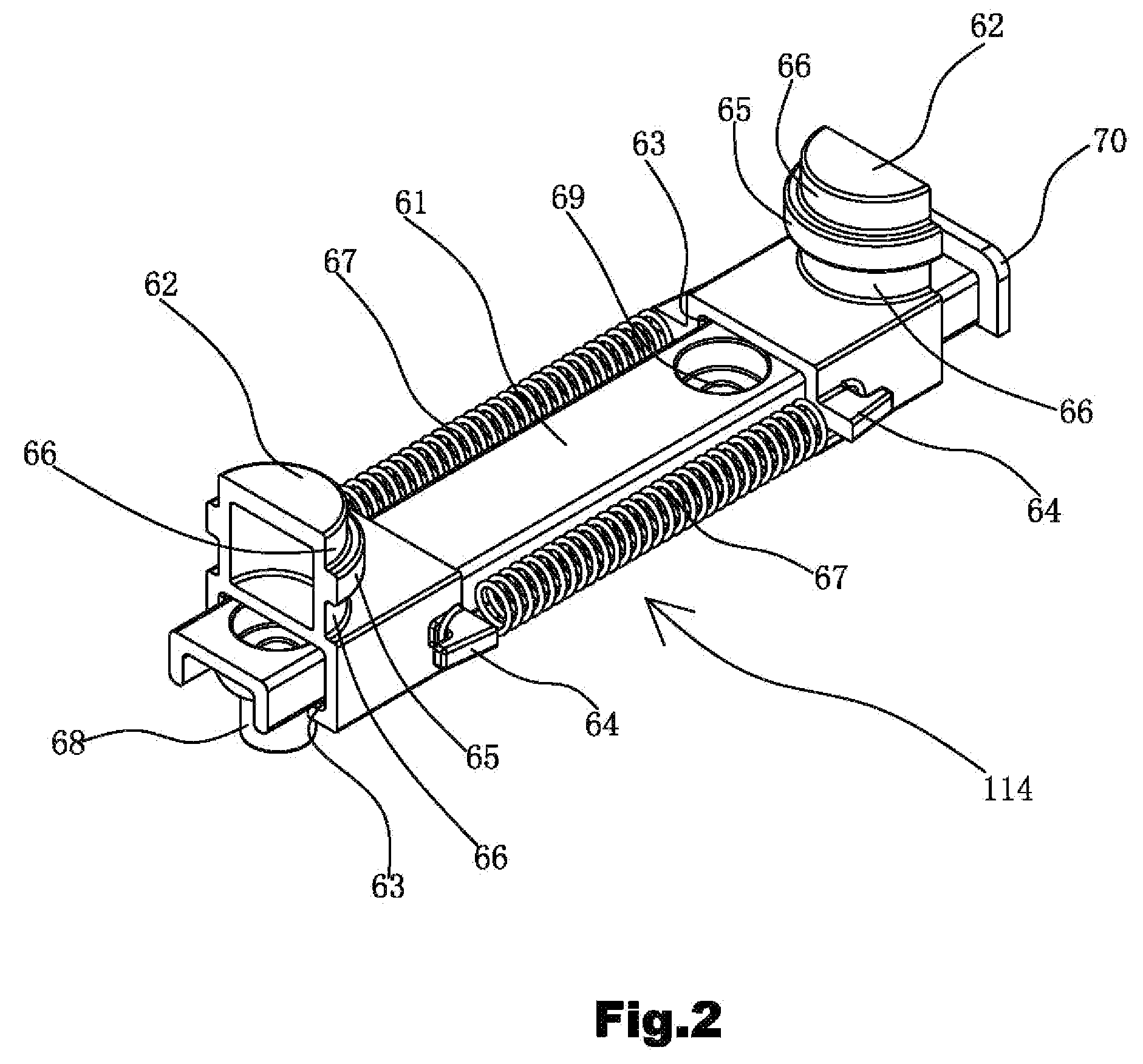
InactiveUS20110147506A1Easy to installSolve excessive vibrationGas current separationPump componentsImpellerEngineering
A garbage disposer includes a casing, a garbage cup (103), a stirrer, an electrical heater (110), a deodorizing box (111) and a blower (113). An impeller (3) is arranged in the chamber surrounded by the mounting board (1) of the blower and the blower casing (2). An electromotor (4) is arranged at the other side of the mounting board. The output shaft of the electromotor drives the impeller (3) through the mounting board (1). The inlet (96) of the blower is provided on the blower casing in the axis direction of the impeller. The outlet (97) of the blower is provided on the circumference of the blower casing. The mounting board (1) includes a board body (81) and a mounding portion (82) formed integrally. The board body (81) and the mounding portion (82) are perpendicular to each other. Several recesses (85) are formed by punch on the outside of the right angle (83) formed by the board body (81) and the mounding portion (82). Then the stability of the blower can be improved and the vibration and the noises can be reduced.
Owner:XU XIAOHUA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com