Air conditioner
An air conditioner and internal air technology, which is applied in air conditioning systems, mechanical equipment, machines/engines, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in preventing reverse suction, and achieve the effect of preventing the reduction of fan performance and achieving low power and high air volume.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
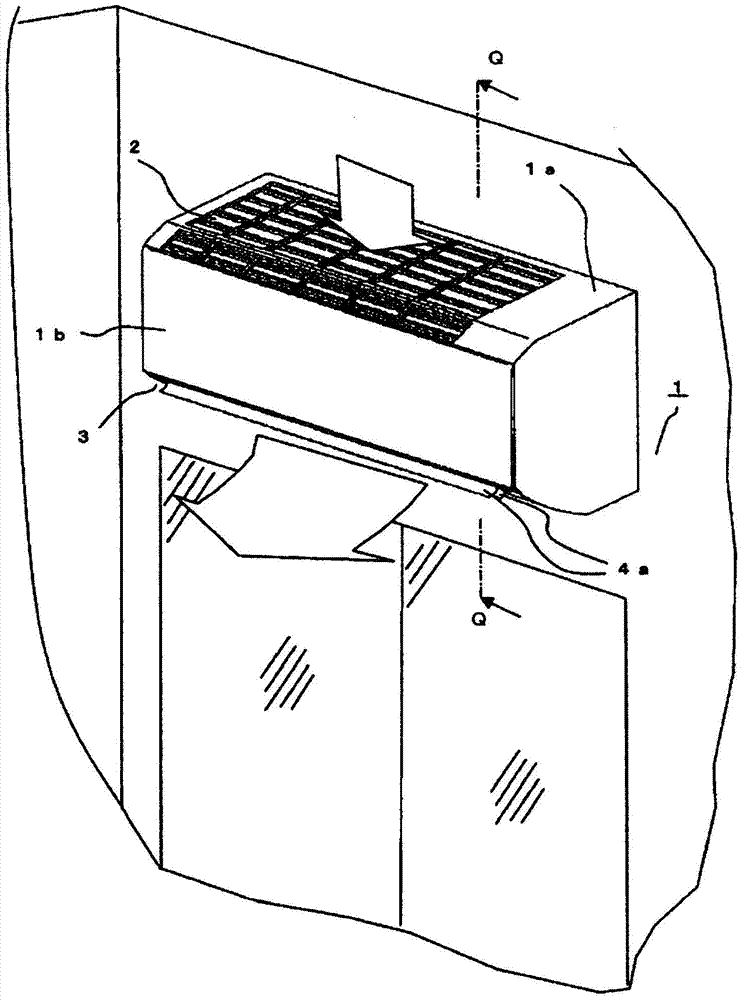
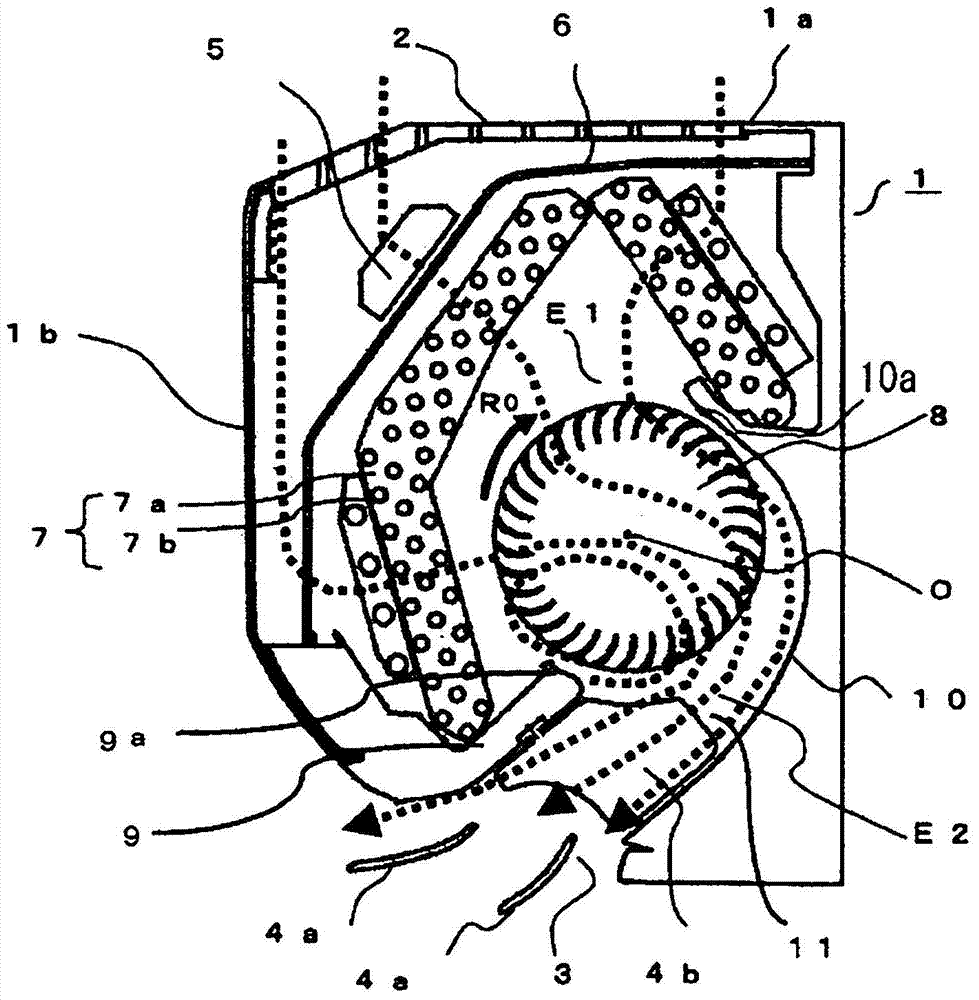
[0049] Hereinafter, Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described based on the drawings. figure 1 is an external perspective view showing an indoor unit 1 of an air conditioner equipped with a cross-flow fan 8 according to this embodiment, figure 2 yes figure 1 A longitudinal sectional view of the Q-Q line. exist figure 1 , the air flow is indicated by a blank arrow, in figure 2 In , the air flow is indicated by dashed arrows. The air conditioner actually consists of an indoor unit and an outdoor unit to form a refrigeration cycle, but here the structure of the indoor unit is involved, and the structure of the outdoor unit is omitted. Such as figure 1 as well as figure 2 As shown, an indoor unit (hereinafter, referred to as an indoor unit) 1 of an air conditioner has an elongated substantially rectangular parallelepiped shape extending in the left-right direction, and is installed on a wall of a room. On the upper part 1a of the main body of the indoor unit...
Embodiment approach 2
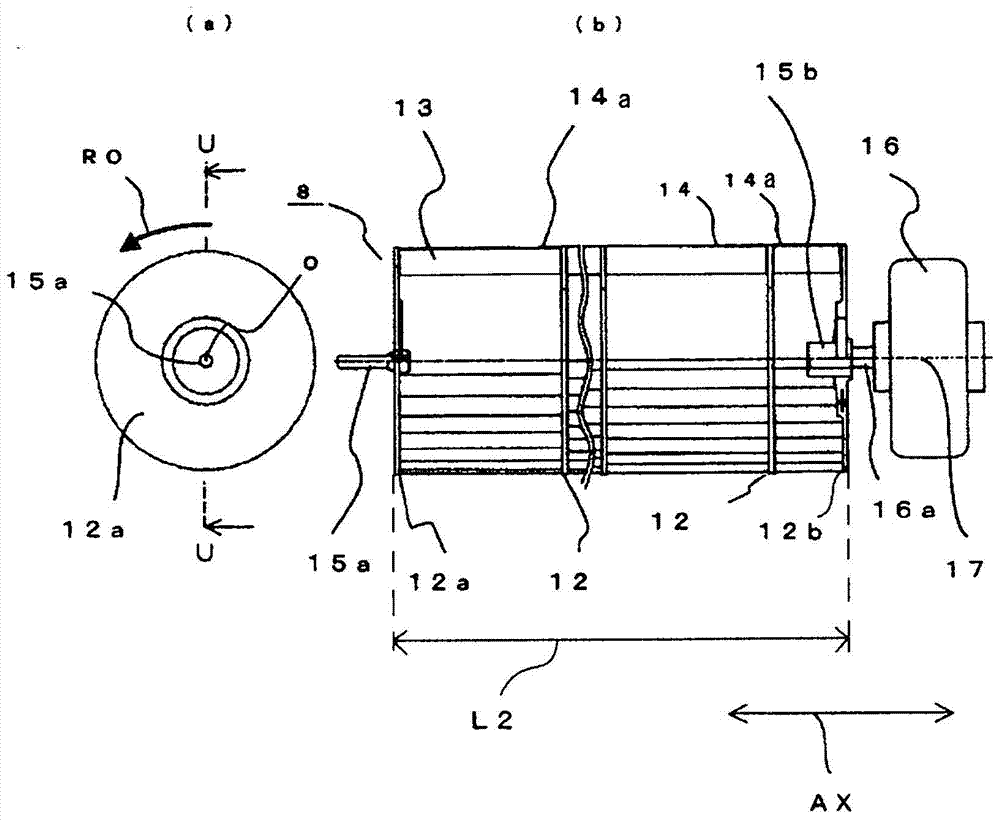
[0081] Figure 17 It is an explanatory diagram showing superimposed wing cross-sections of the air outlet facing wing 13 b and the collision wall facing wing 13 a in the end unit 14 a of the cross-flow fan 8 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and shows a cross section perpendicular to the rotation axis 17 . In the drawings, the same reference numerals as in Embodiment 1 denote the same or corresponding parts. The shape of the indoor unit 1 of the air conditioner near the end unit 14a is the same as that of the first embodiment. Figure 1 to Figure 9 Same shape as shown. Similar to Embodiment 1, in the fan extension portion 8a, the collision wall facing wing 13a facing the collision wall 18 and the blowing outlet facing wing 13b facing the blowing outlet 3 have different wing shapes, especially in this embodiment. In 2, the outlet angle α is configured differently at the blade outer peripheral end portions Ga, Gb.
[0082] Here, the exit angle α will be des...
Embodiment approach 3
[0094] Figure 21 It is Embodiment 3 of the present invention, and is an explanatory diagram showing superimposed wing sections of the air outlet facing wing 13b and the collision wall facing wing 13a in the end unit 14a of the cross-flow fan 8 used in the air conditioner, A section perpendicular to the axis of rotation 17 is shown. In the drawings, the same reference numerals as in Embodiment 1 denote the same or corresponding parts. The shape of the indoor unit 1 near the end unit 14a is the same as that of the first embodiment. Figure 1 to Figure 9 Same shape as shown. Similar to Embodiment 1, the wings of the fan extension 8a facing the collision wall 18, that is, the collision wall facing wing 13a and the blowing outlet facing wing 13b facing the blowing outlet 3 adopt different wing shapes, especially in the Embodiment 3 is characterized in that the warp angle β is configured differently in the blade cross section. In a section perpendicular to the rotation axis 17 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com