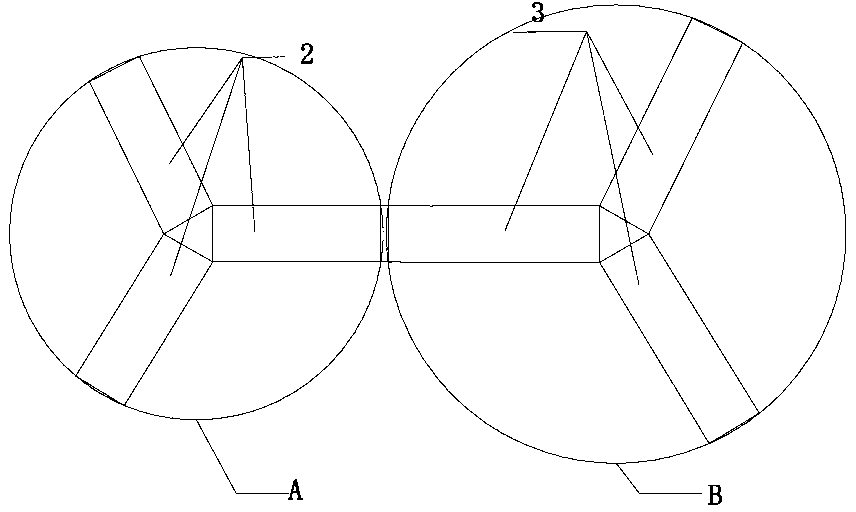Patents
Literature
487 results about "Shock cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
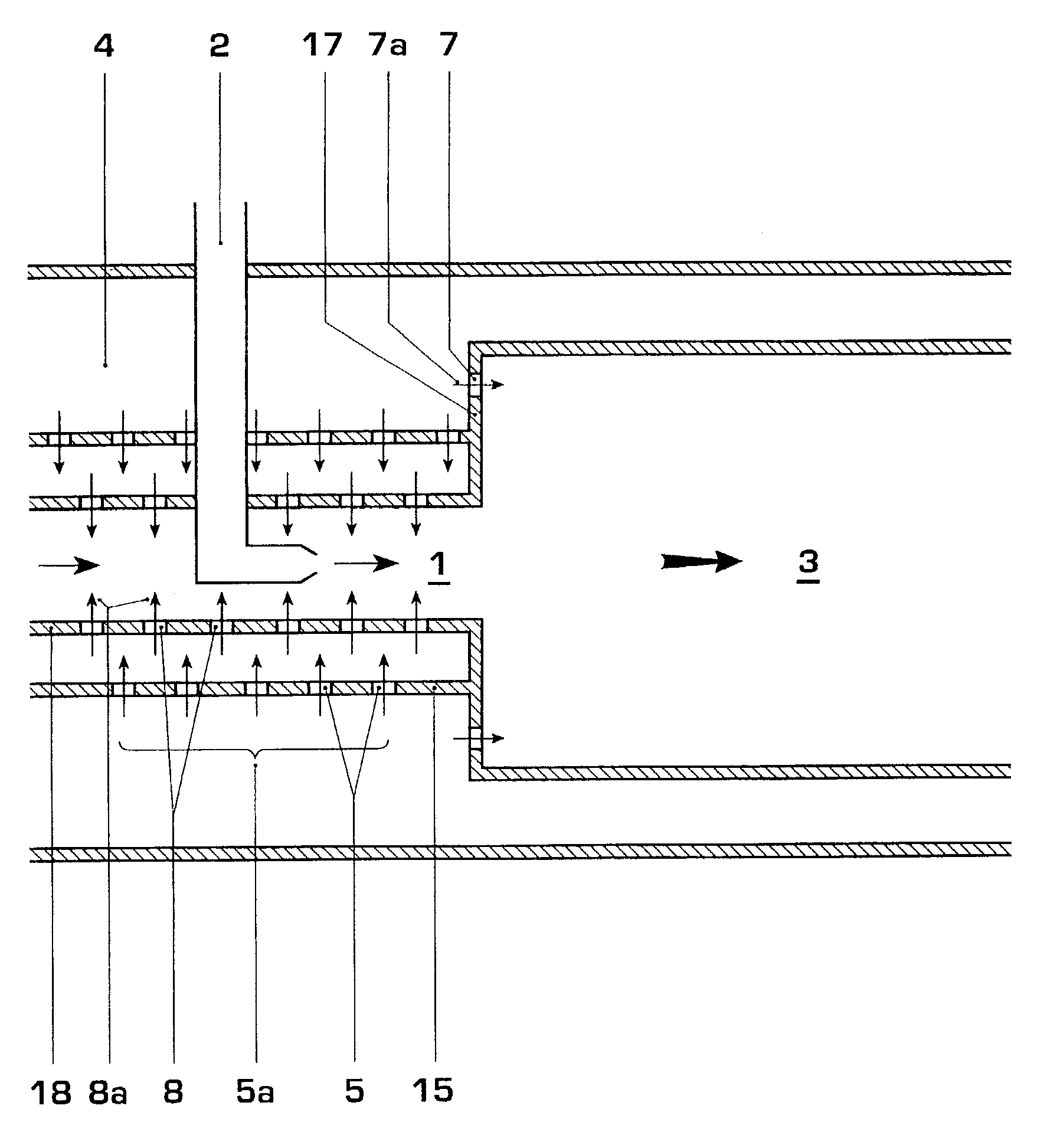
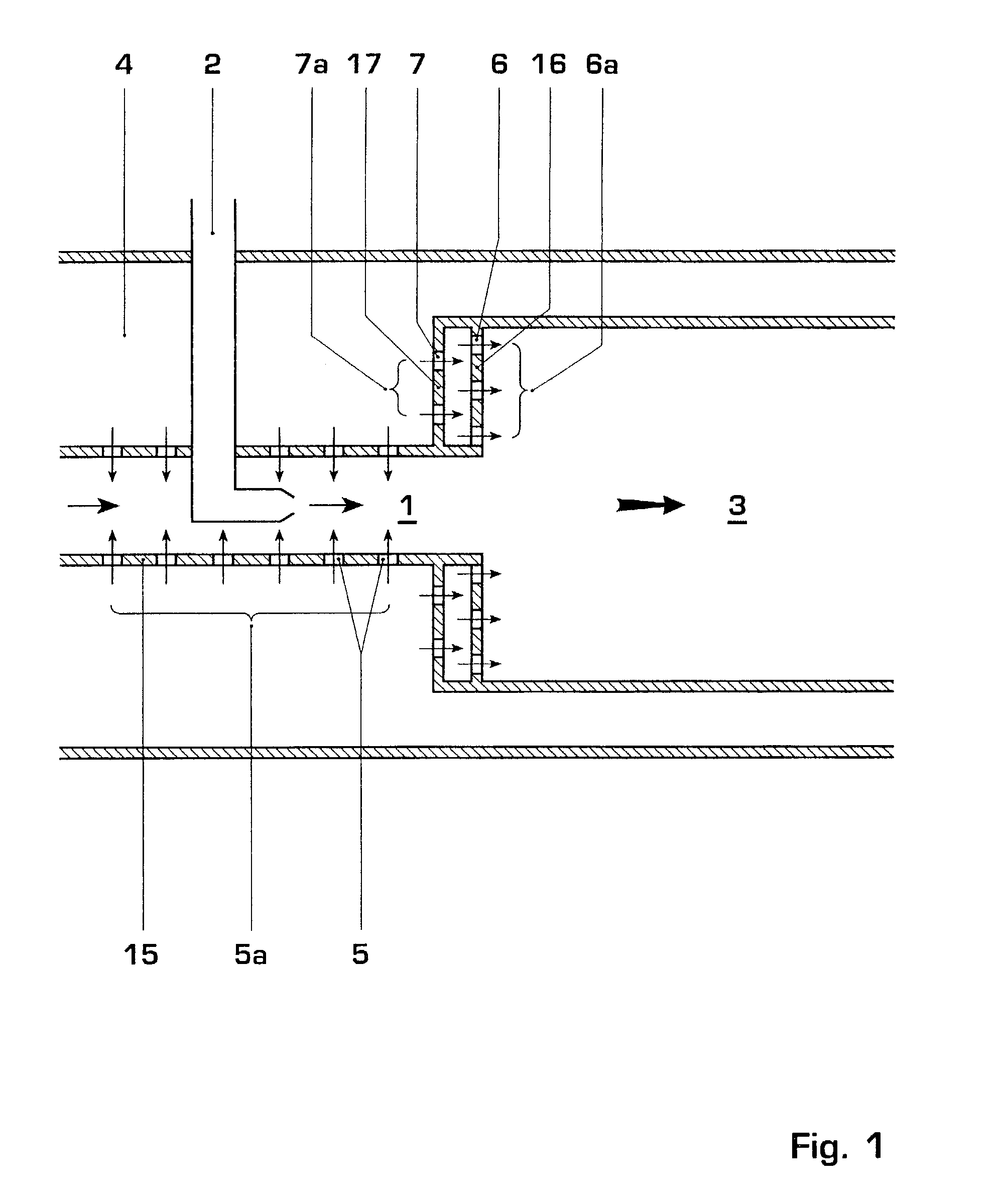
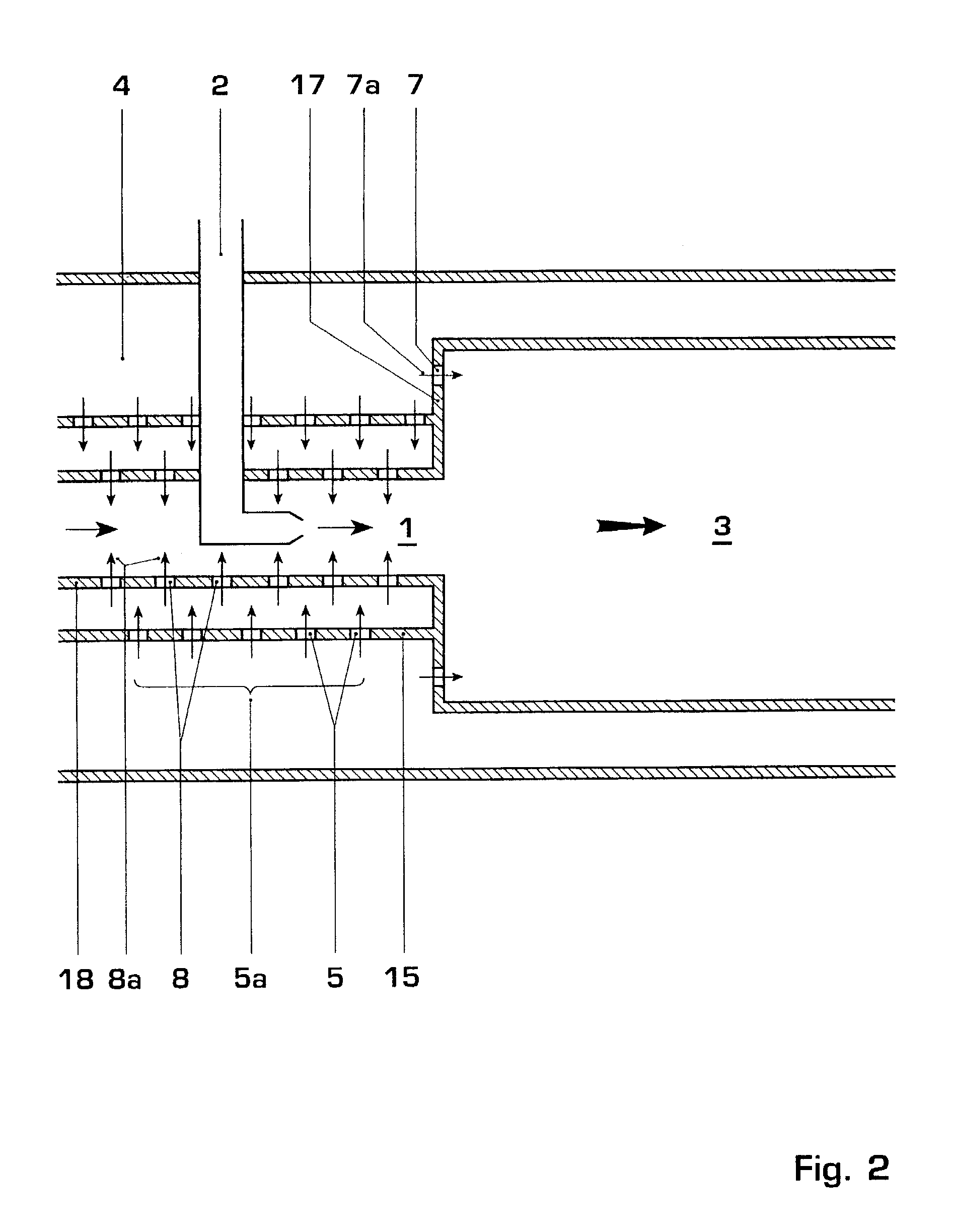
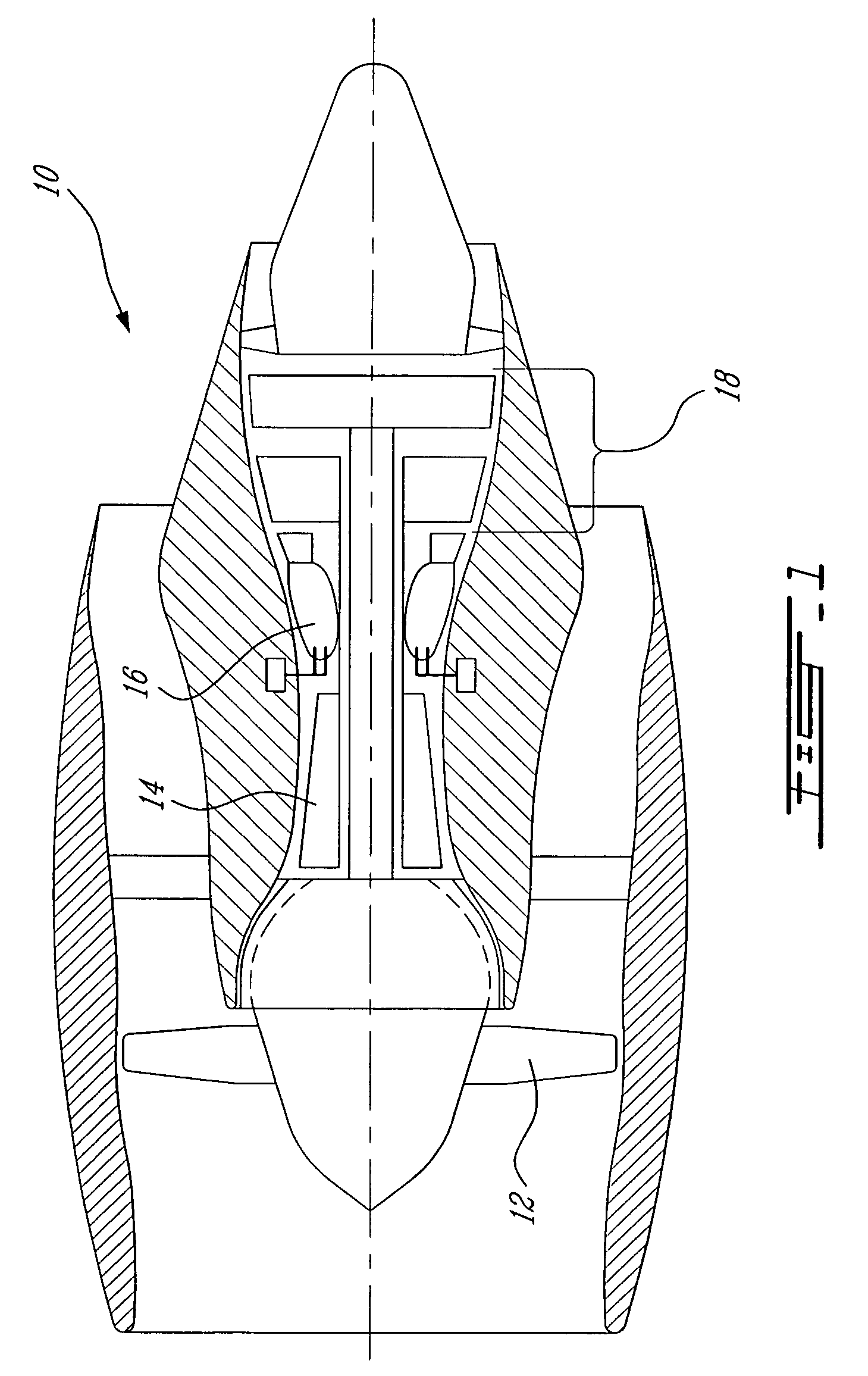
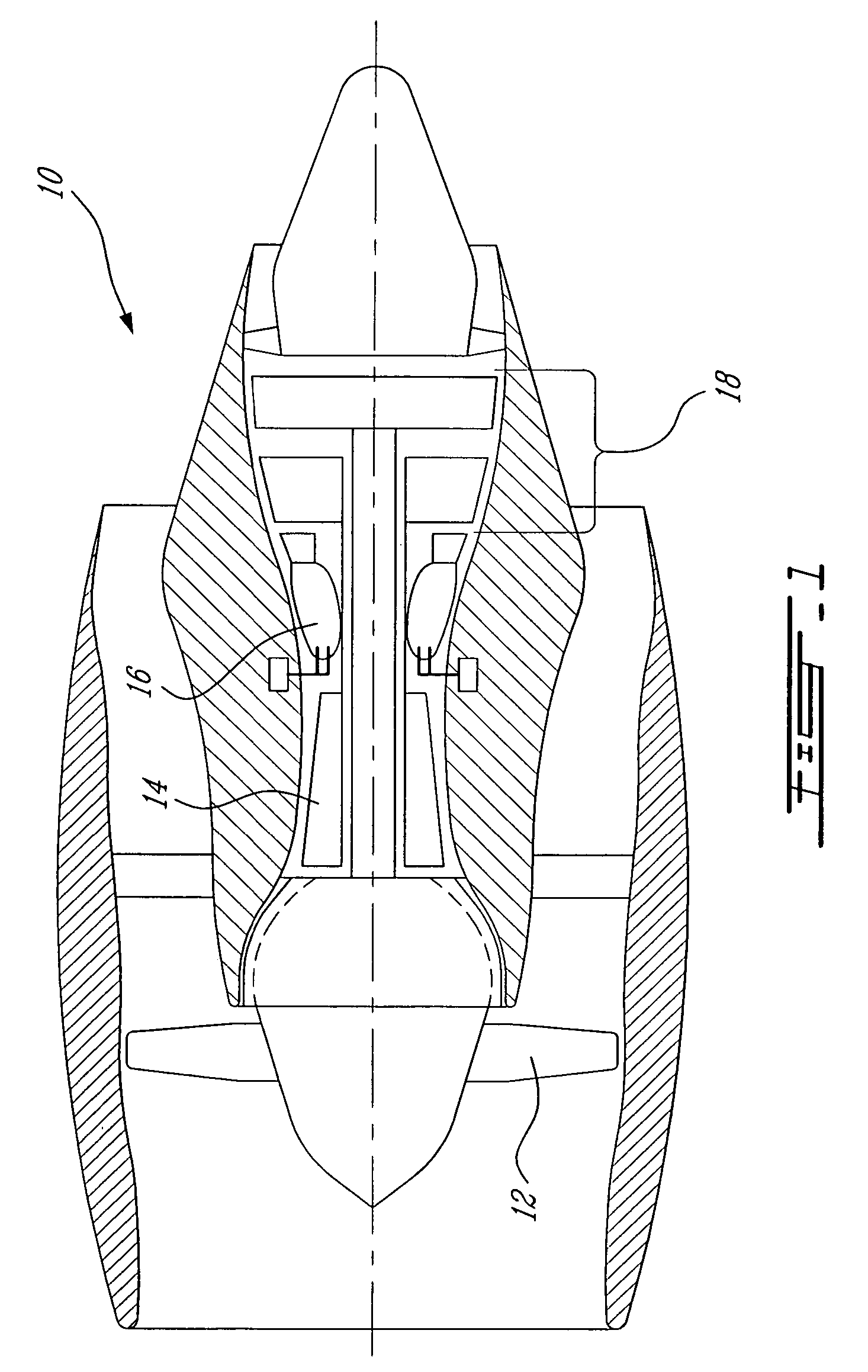
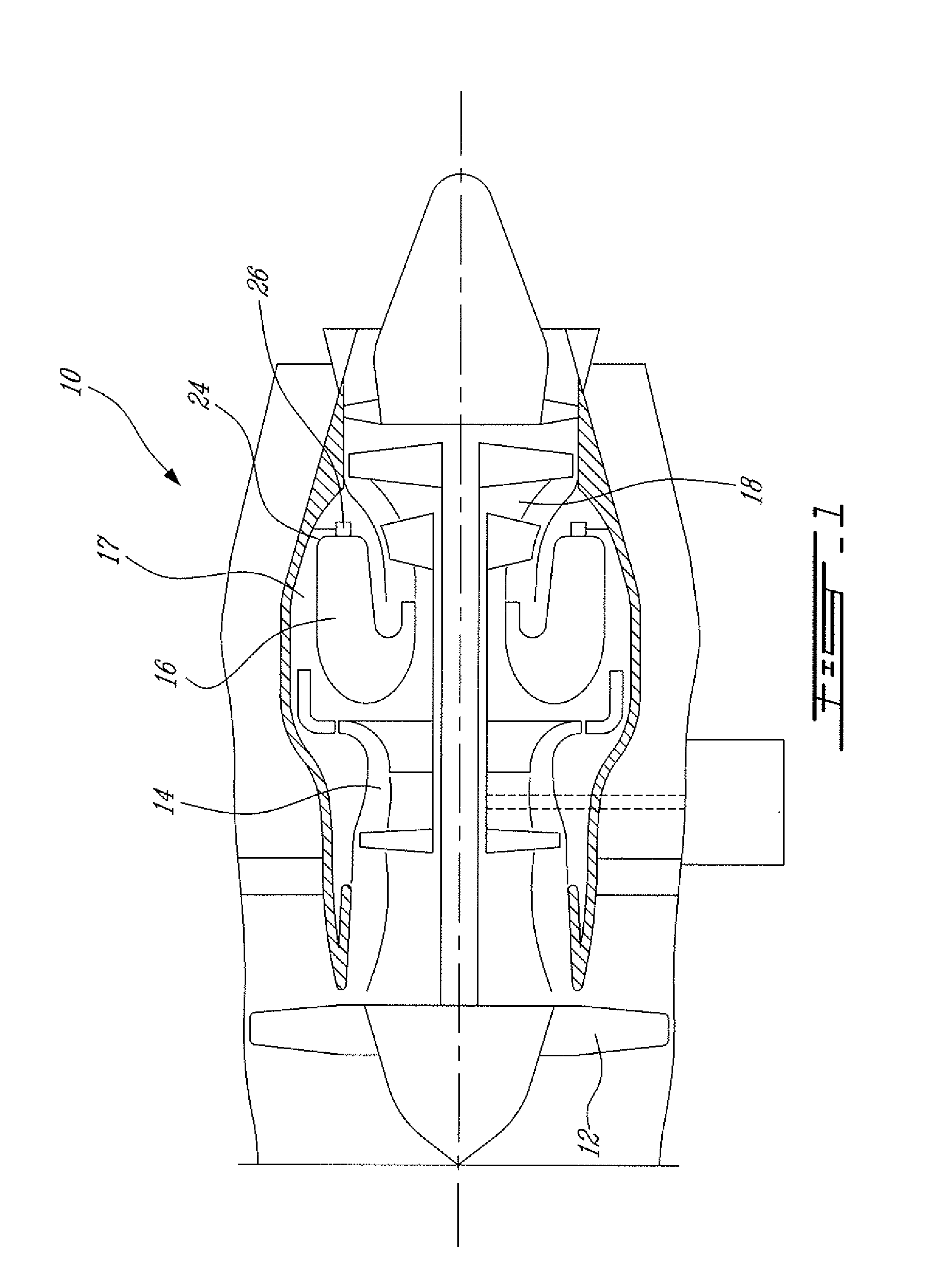
Shock cooling refers to the theory that damage to engines (particularly air-cooled aviation piston engines) may occur because of an excessively rapid decrease in temperature. The situation where rapid cooling arises is on descent from altitude. In this condition, less power is demanded of the engine (it is throttled back) so it is developing much less heat. In a descent, the plane's airspeed increases, simultaneously increasing the cooling rate of the engine. As metals expand and contract under temperature changes, dimensional changes in the engine may exceed tolerance limits.
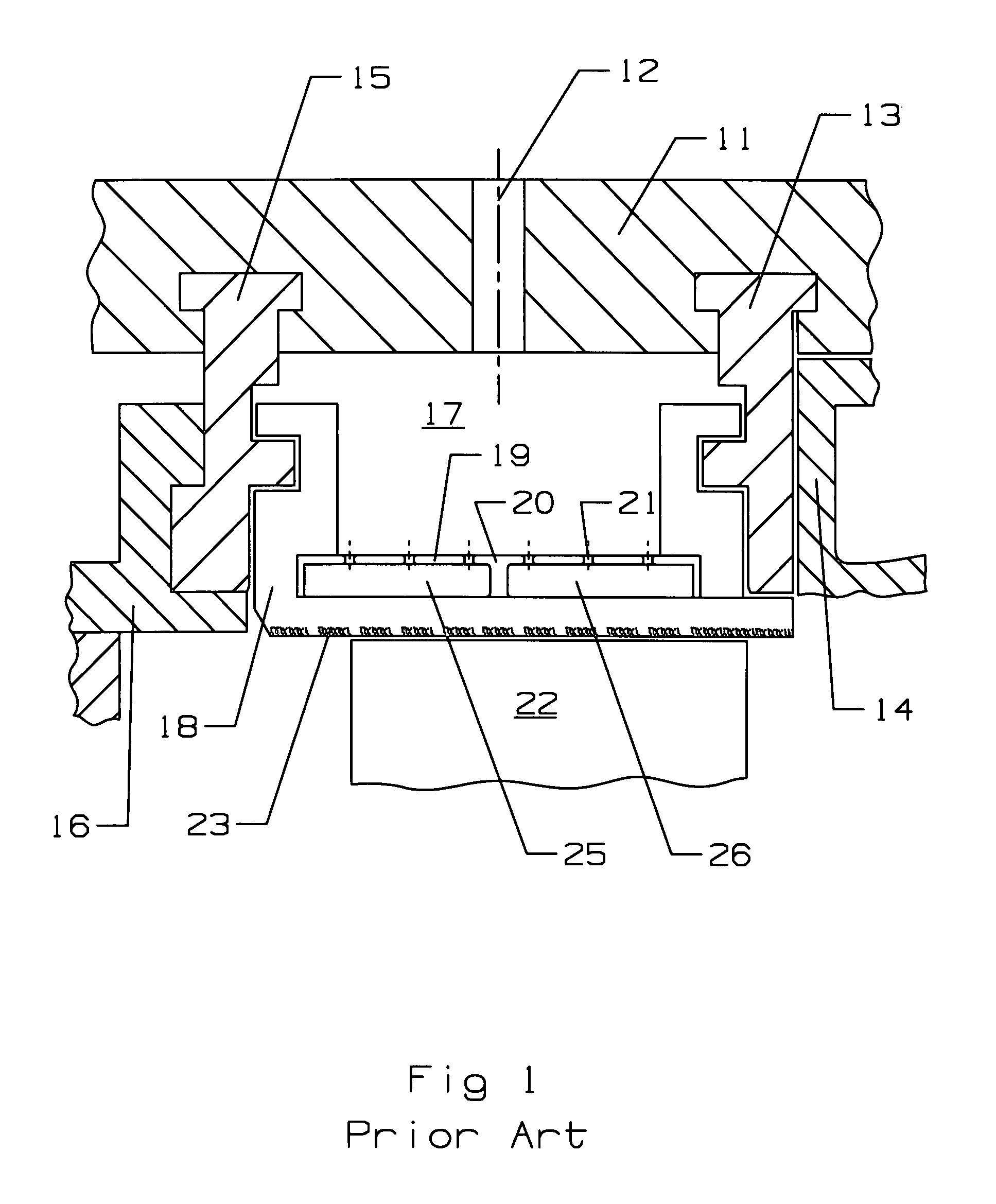
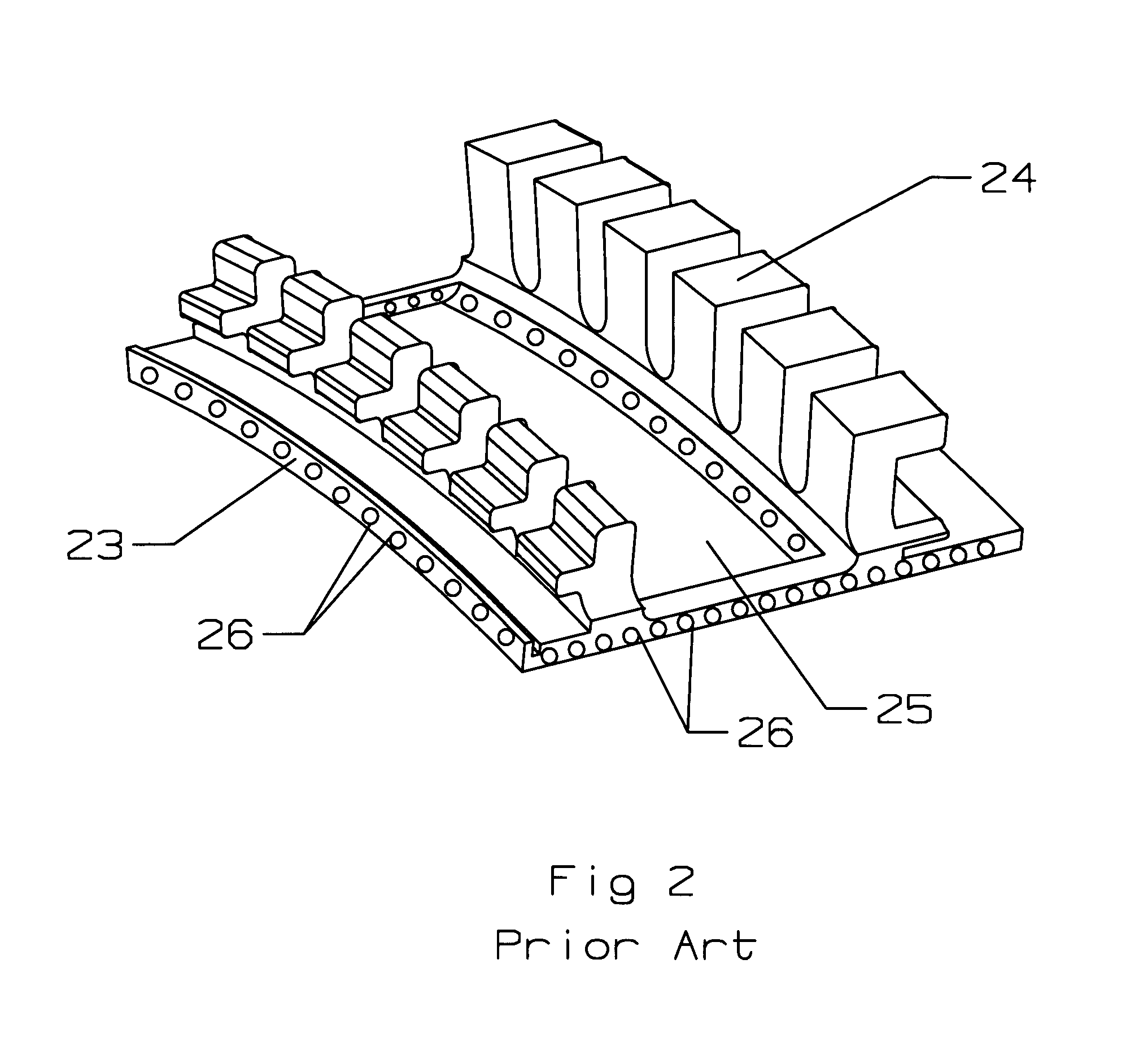
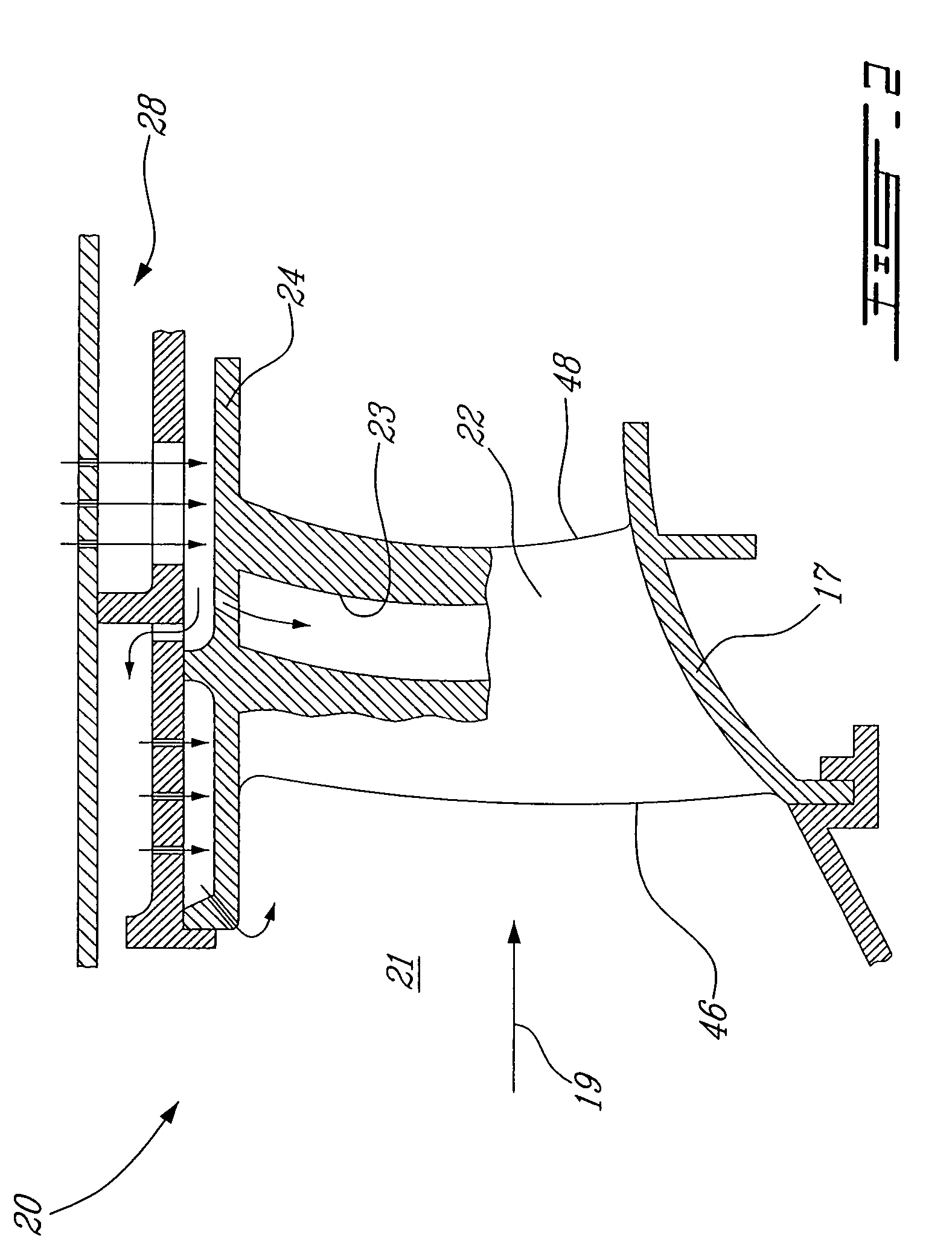
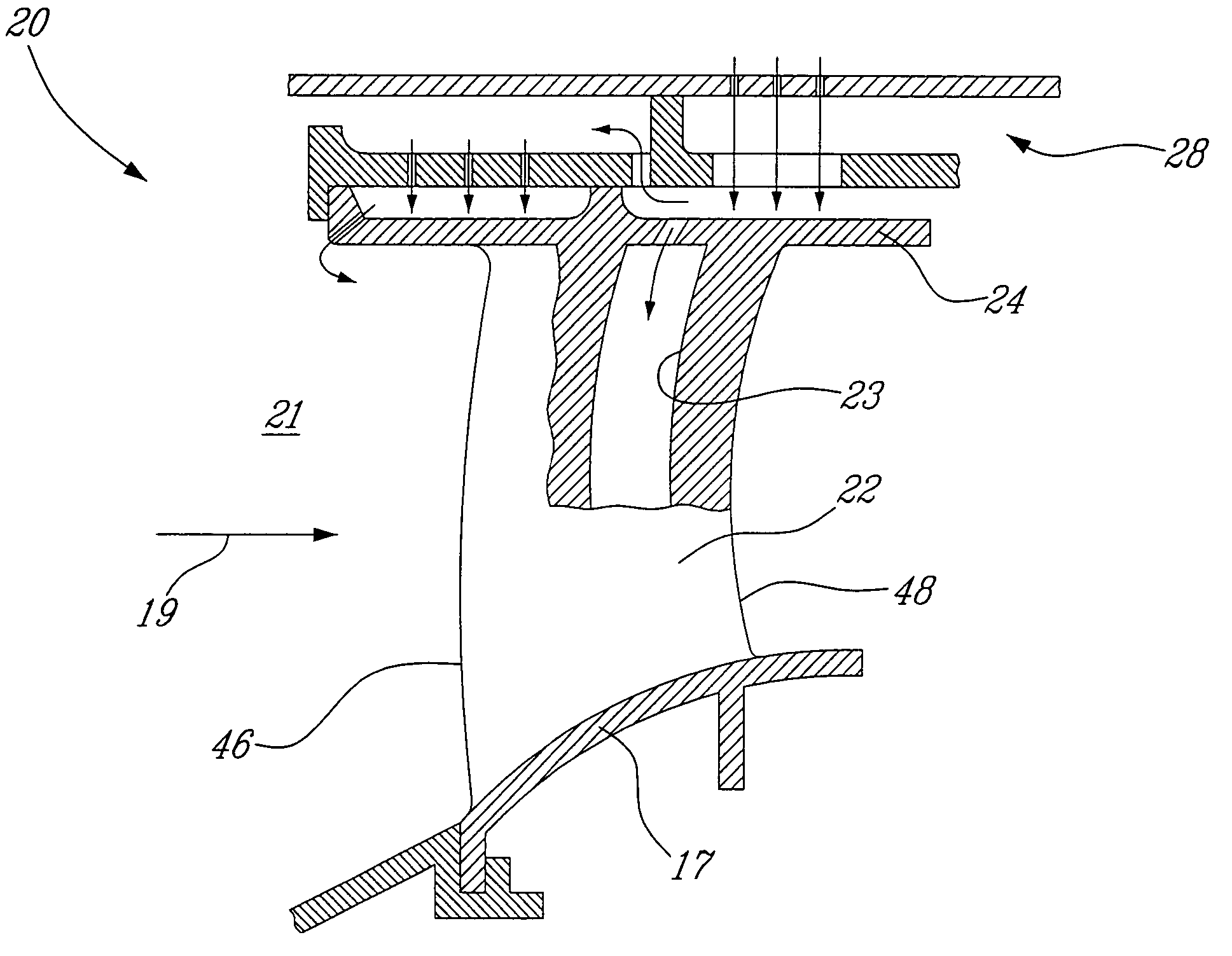
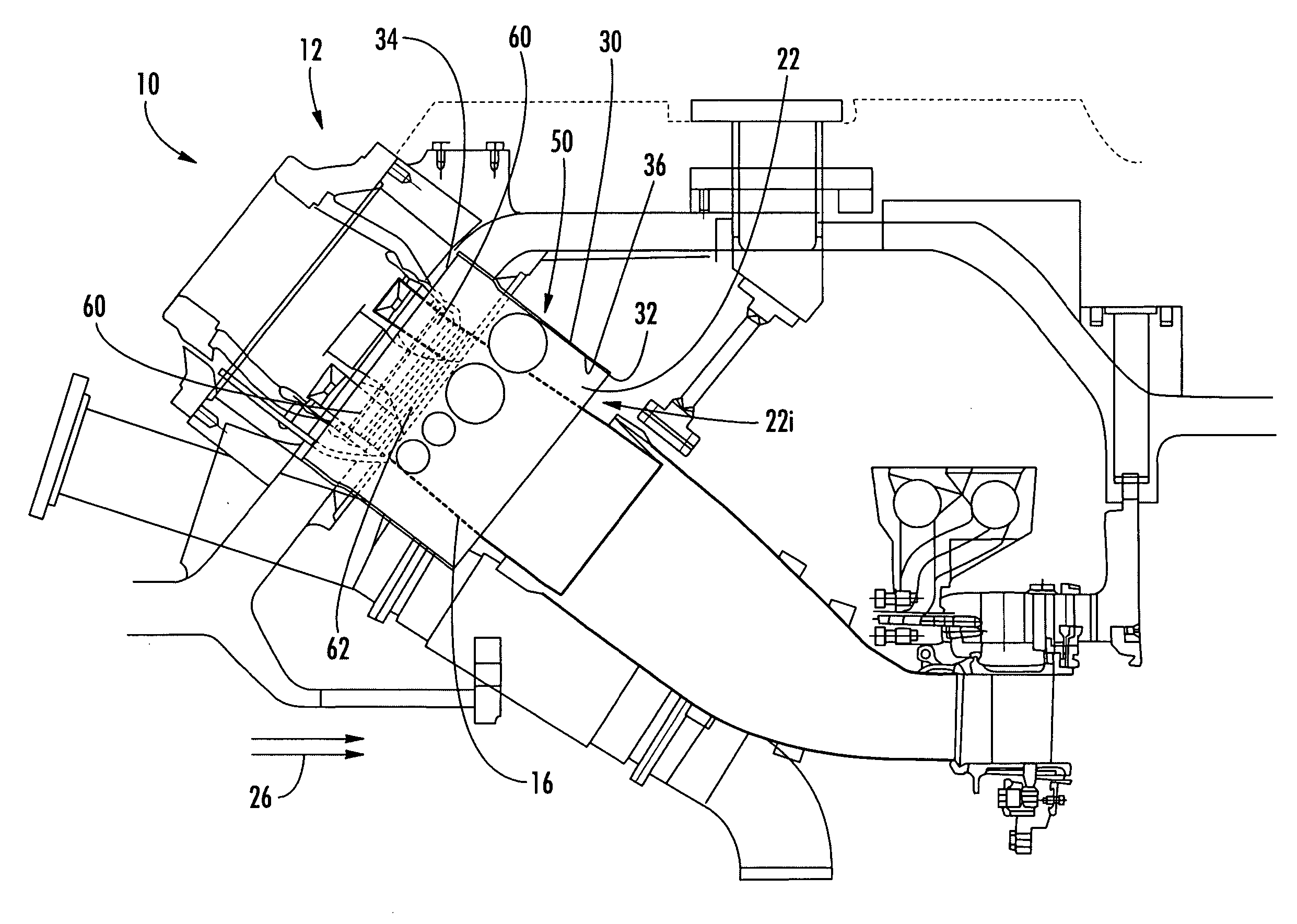
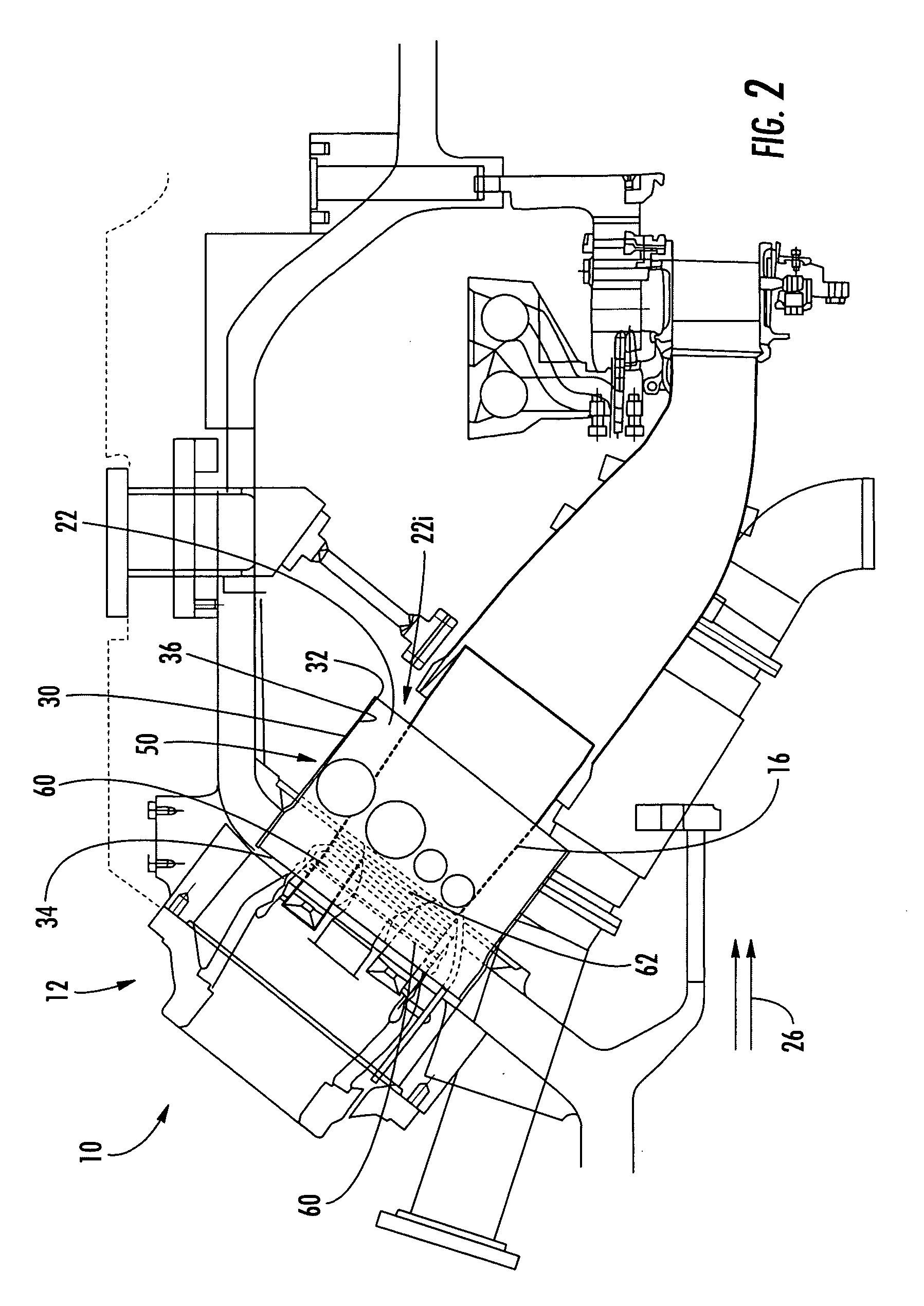
Reheat combustion system for a gas turbine
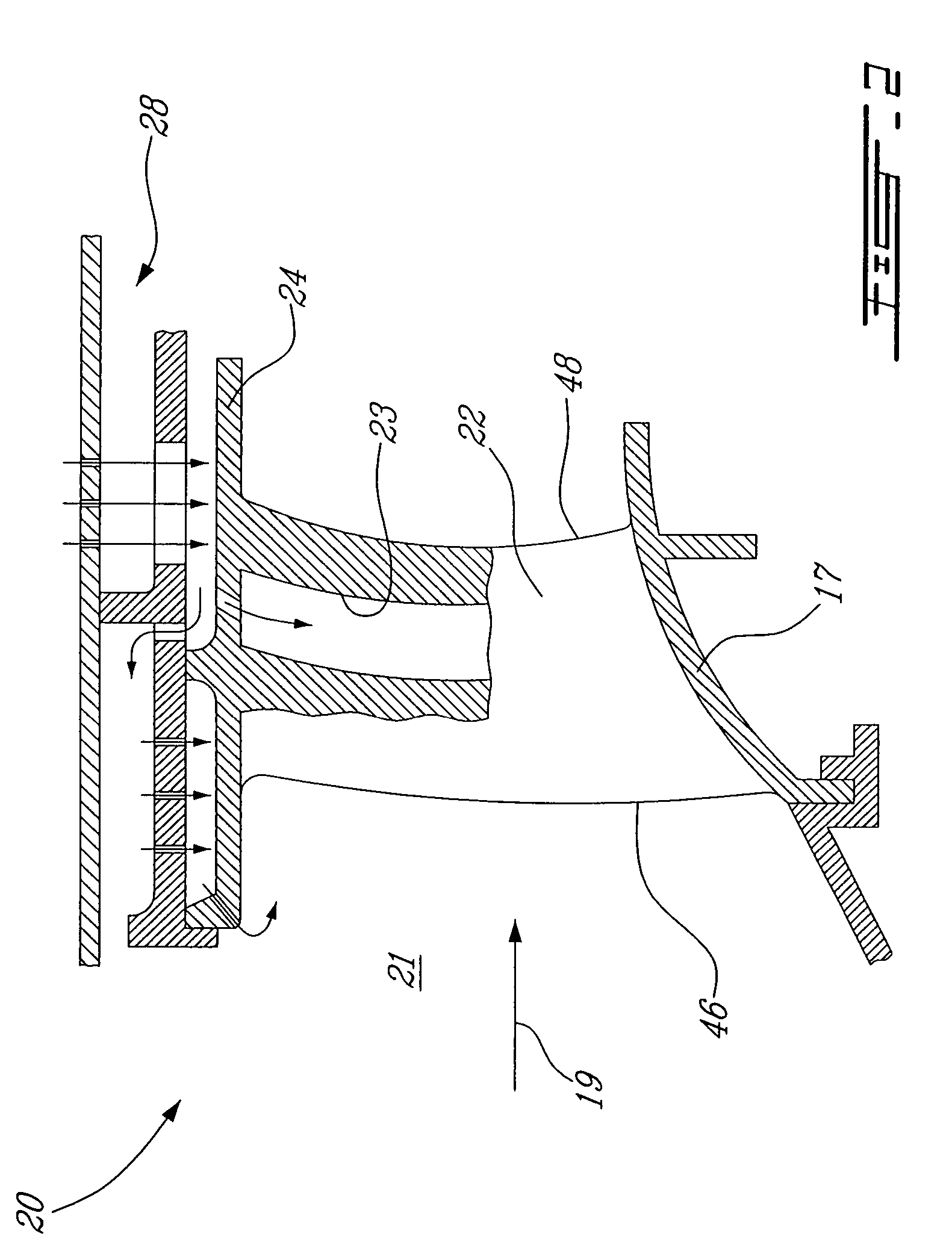
ActiveUS6981358B2Good cooling propertiesDamp pulsationBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustion systemCombustion chamber
A reheat combustion system for a gas turbine comprises a mixing tube adapted to be fed by products of a primary combustion zone of the gas turbine and by fuel injected by a lance; a combustion chamber fed by the said mixing tube; and at least one perforated acoustic screen. The or each said acoustic screen is provided inside the mixing tube or the combustion chamber, at a position where it faces, but is spaced from, a perforated wall thereof. In use, the perforated wall experiences impingement cooling as it admits air into the combustion system for onward passage through the perforations of the said acoustic screen, and the acoustic screen damps acoustic pulsations in the mixing tube and combustion chamber.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
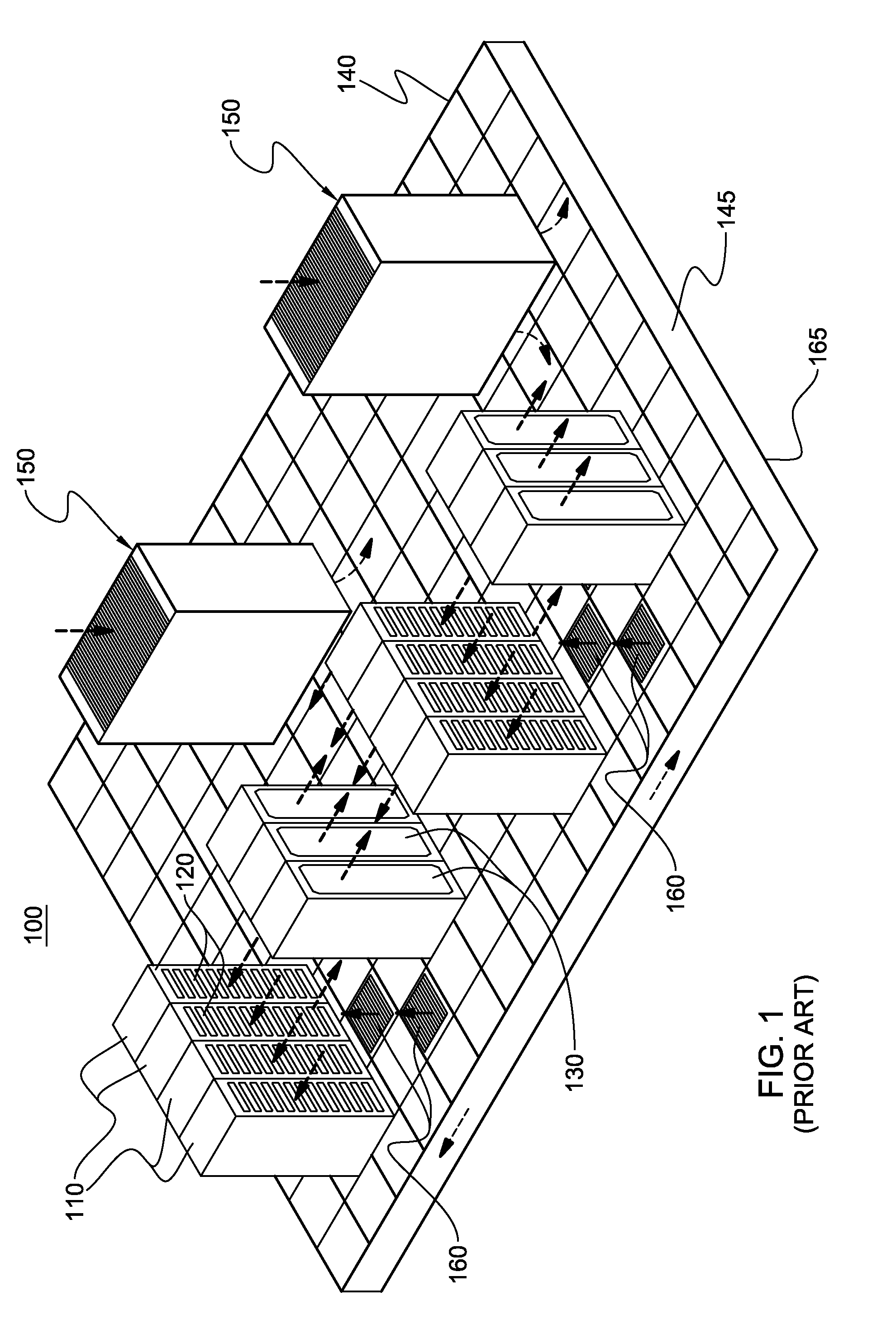
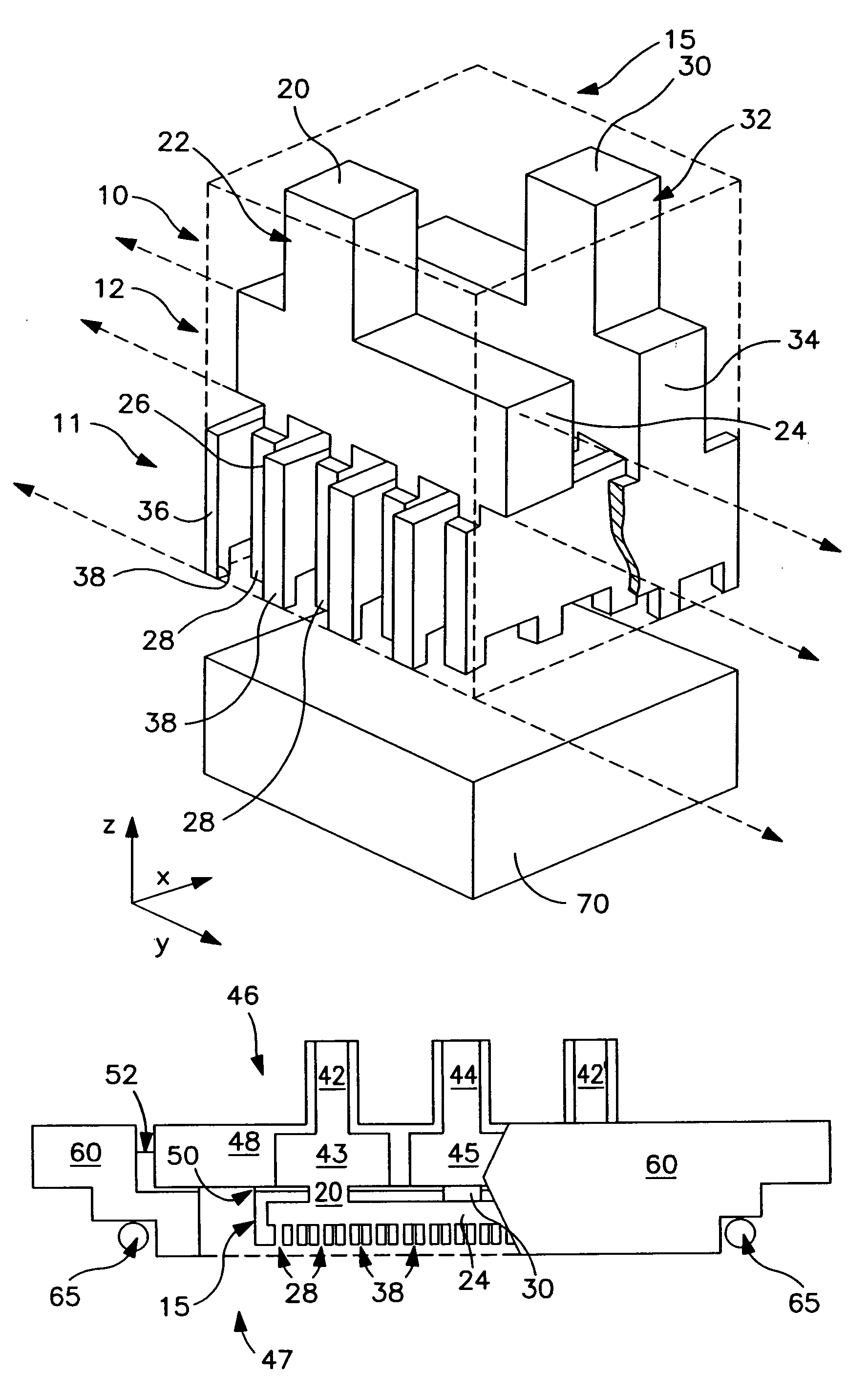
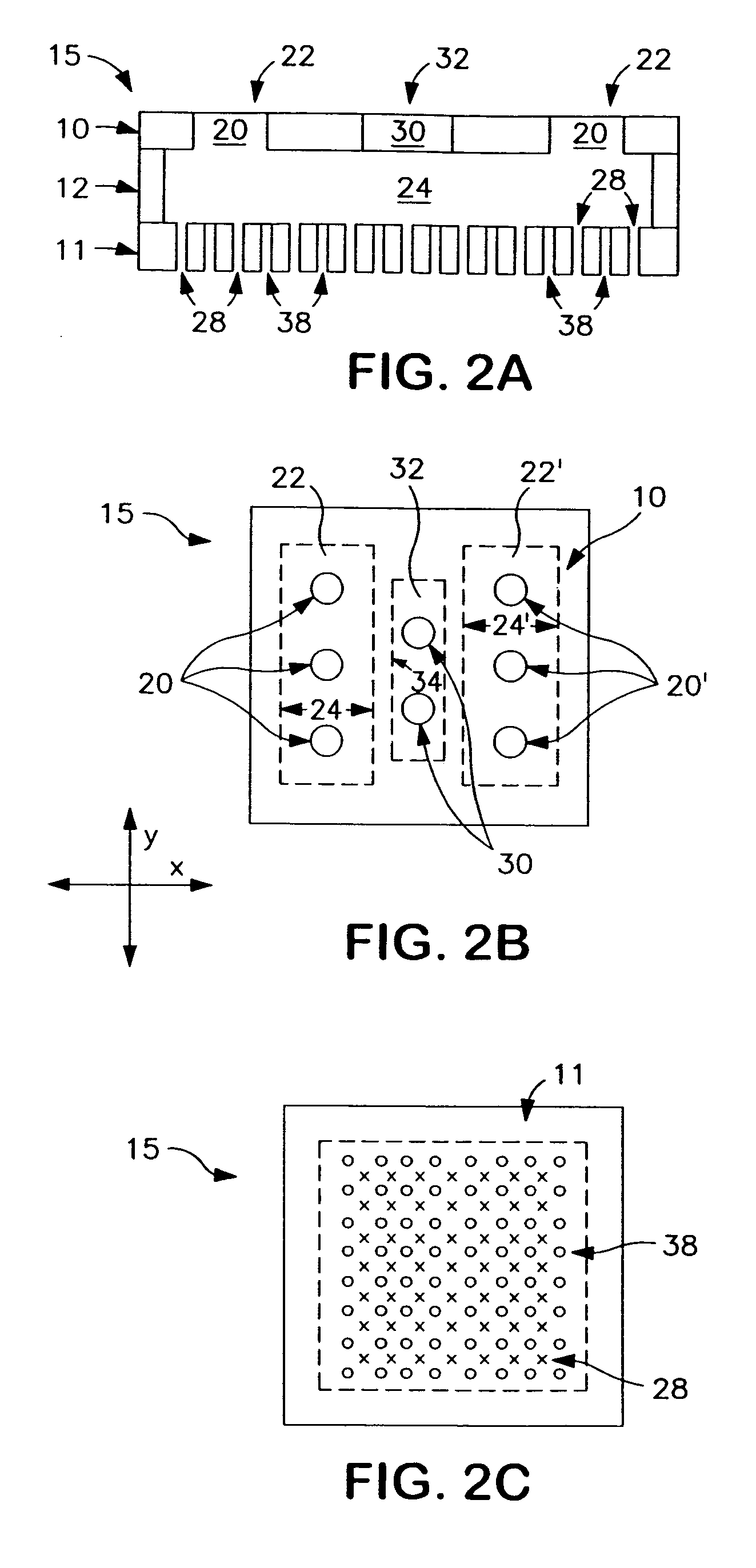
Cooled electronic module with pump-enhanced, dielectric fluid immersion-cooling
ActiveUS8014150B2Facilitating cooling of a heat-generating electronic deviceImprove cooling effectDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricComputer module
Cooled electronic modules and methods of fabrication are provided with pump-enhanced, dielectric fluid immersion-cooling of the electronic device. The cooled electronic module includes a substrate supporting an electronic device to be cooled. A cooling apparatus couples to the substrate, and includes a housing configured to at least partially surround and form a sealed compartment about the electronic device. Additionally, the cooling apparatus includes dielectric fluid and one or more pumps disposed within the sealed compartment. The dielectric fluid is in direct contact with the electronic device, and the pump is an impingement-cooling, immersed pump disposed to actively pump dielectric fluid within the sealed compartment towards the electronic device. Multiple condenser fins extend from the housing into the sealed compartment in an upper portion of the sealed compartment, and a liquid-cooled cold plate or an air-cooled heat sink is coupled to the top of the housing for cooling the condenser fins.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
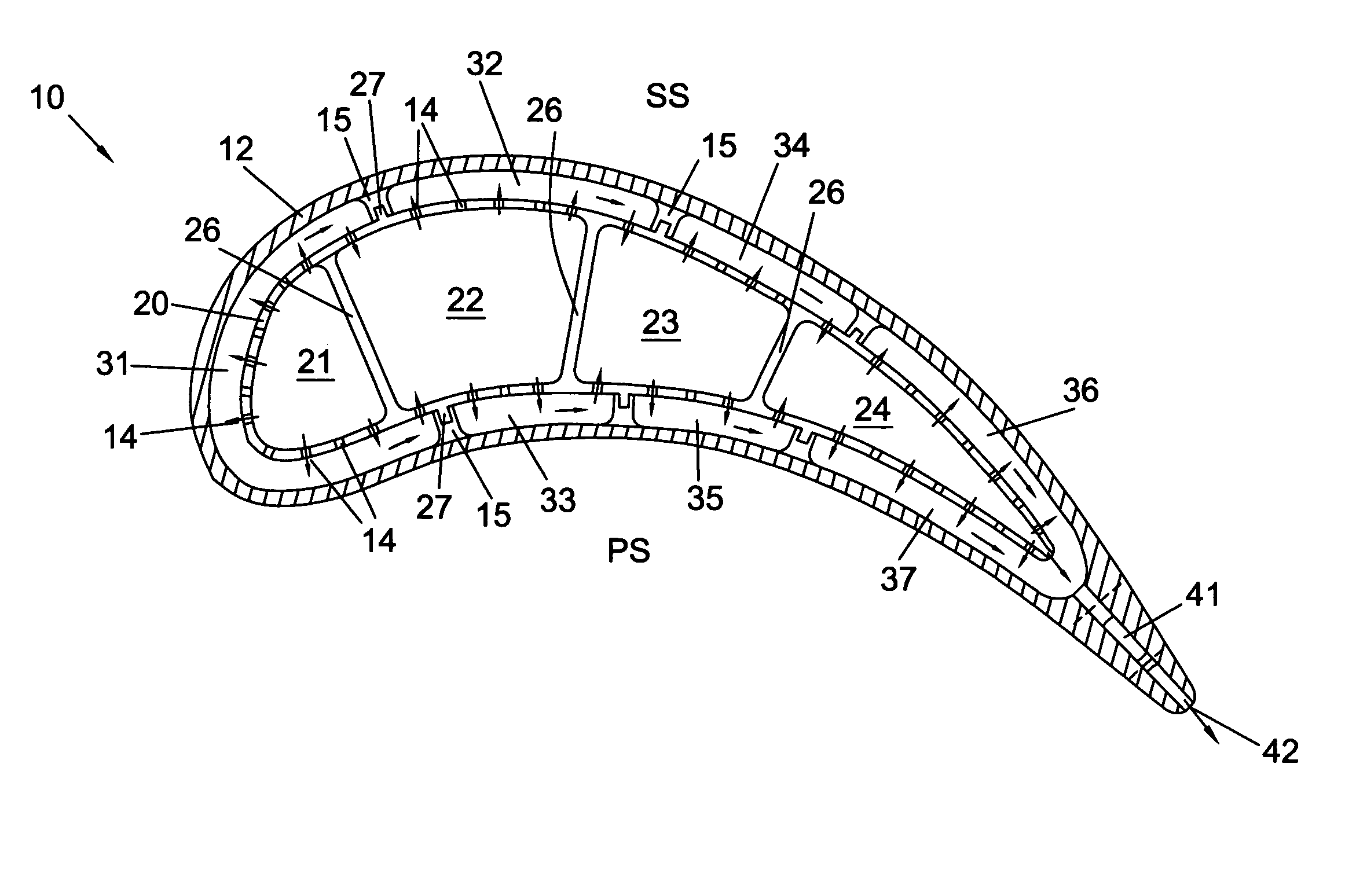
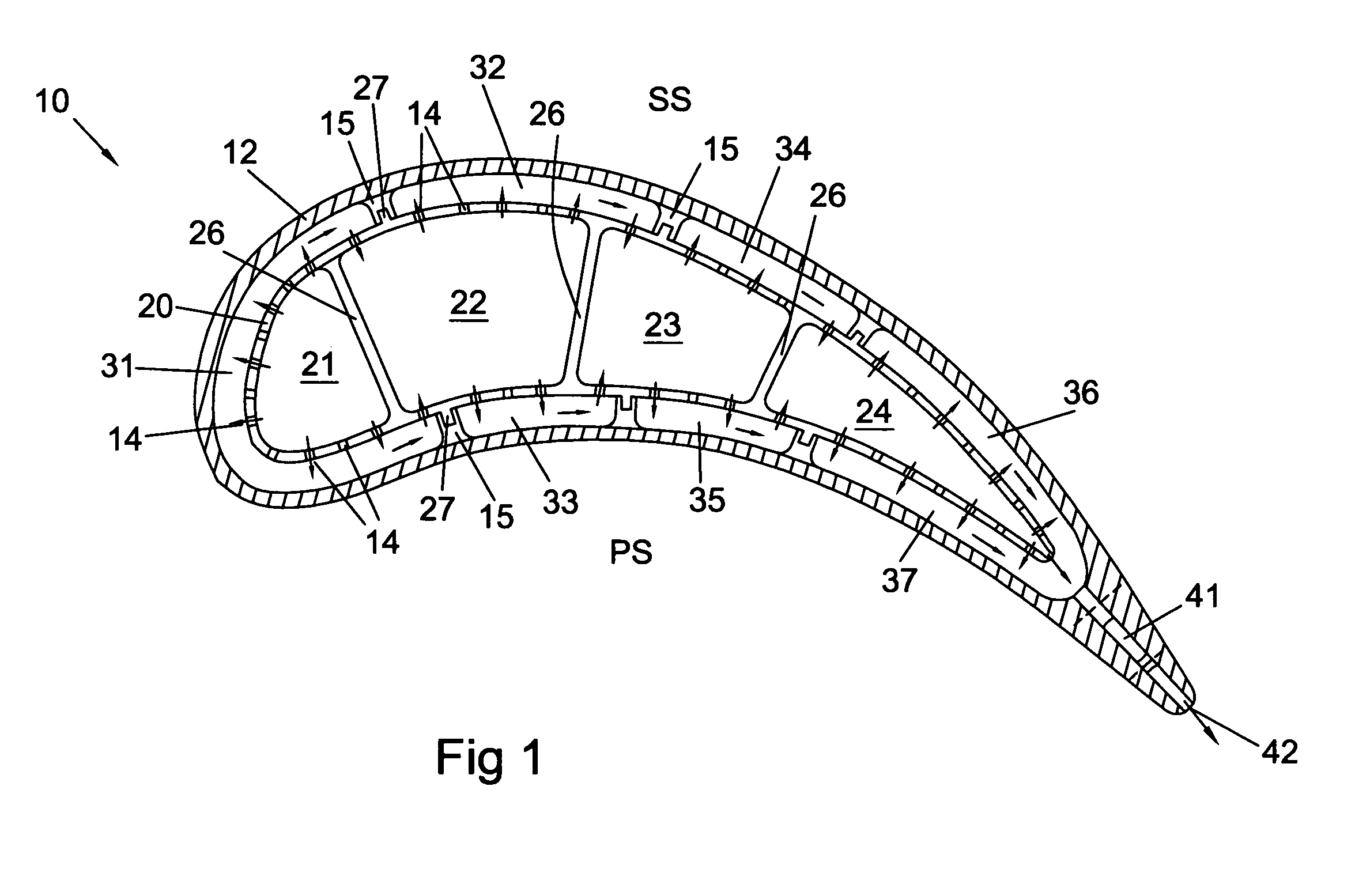
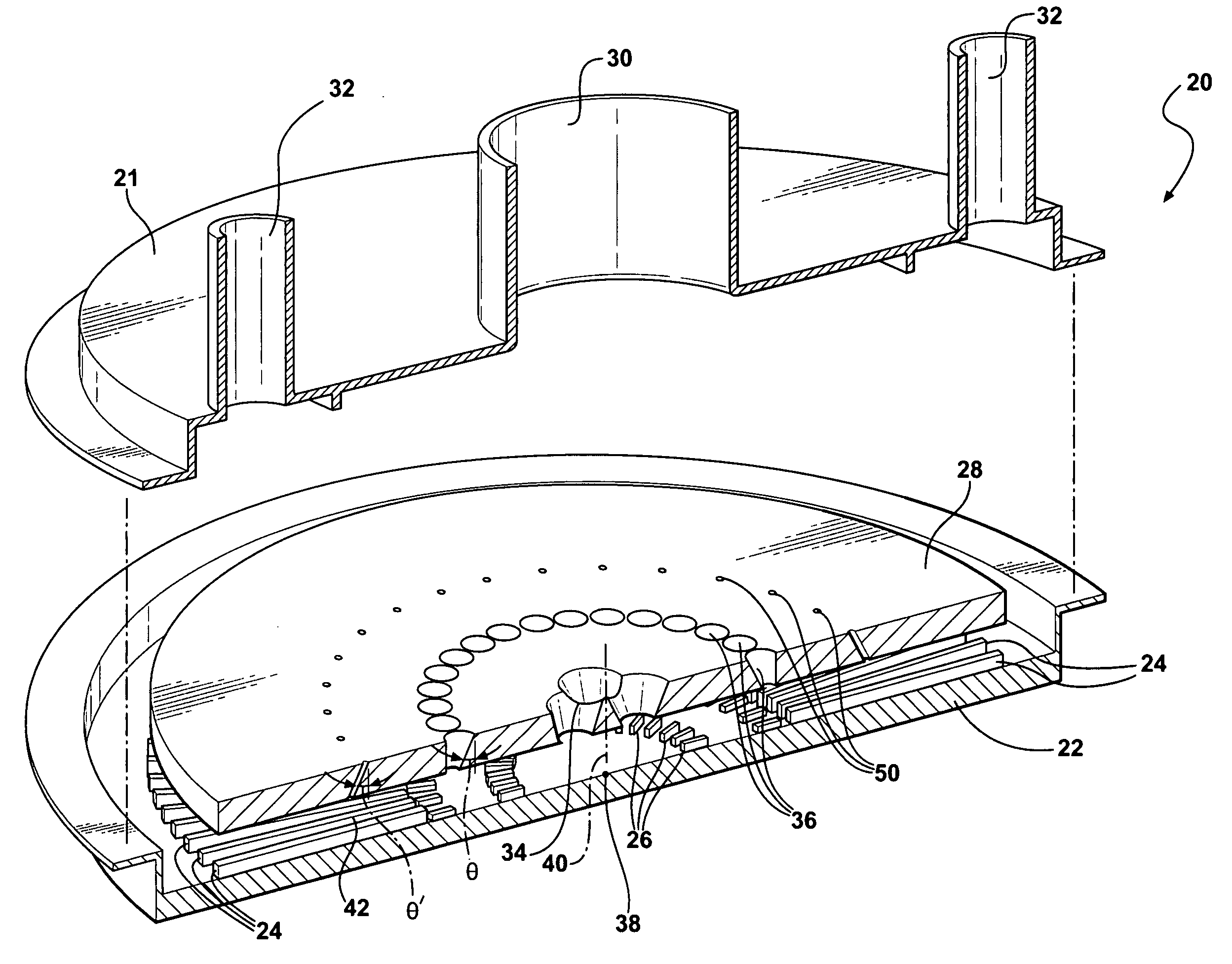
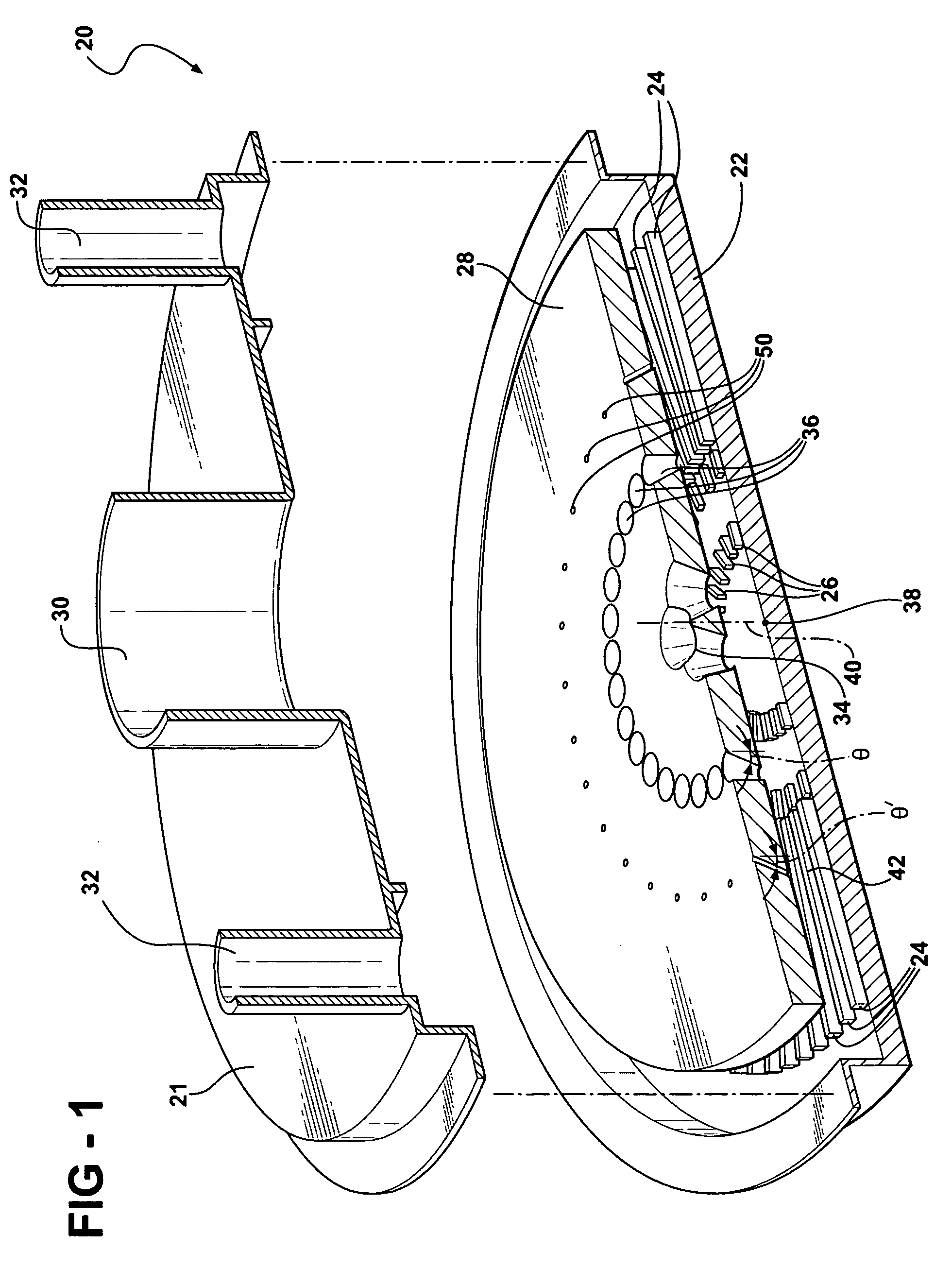
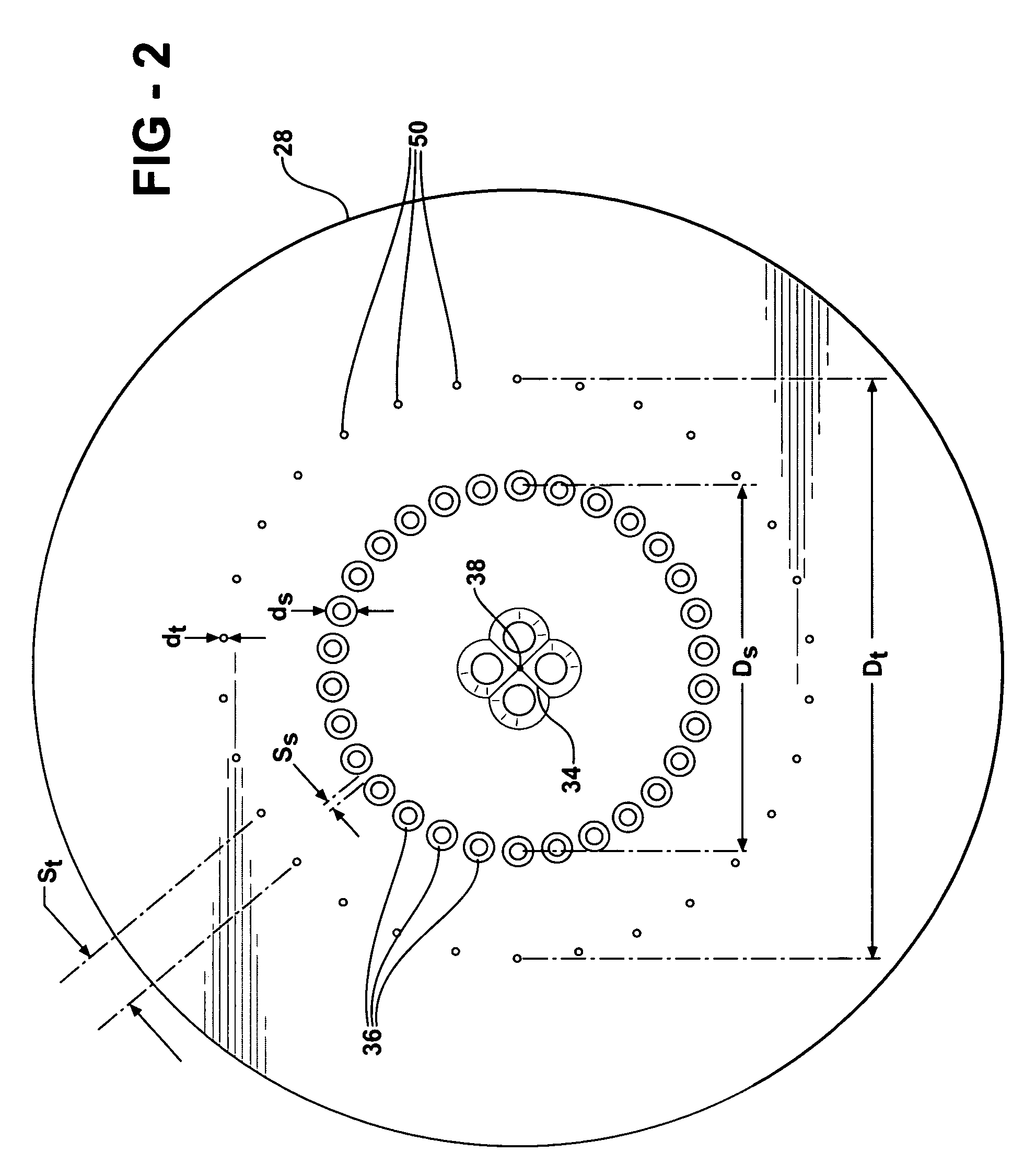
Turbine airfoil with near-wall impingement and vortex cooling
InactiveUS7497655B1Maximize useHigh level of turbulencePropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeTrailing edge
An apparatus and method for impingement cooling of a turbine vane, in which the vane includes an insert having a plurality of impingement cavities formed therein and in series such that cooling air flows from a first impingement cavity onto the wall for impingement cooling, and is then directed into the second impingement cavity and redirected for impingement cooling on another part of the wall. Supports for the insert form seals that direct cooling air from one impingement cavity into the next impingement cavity in the series. A trailing edge impingement cavity directs cooling air through holes to provide impingement cooling to the trailing edge region, the cooling air passing through a trailing edge discharge passage to cool the trailing edge. The insert is formed as a single piece, and has from 3 to 5 impingement cavities separated by ribs.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
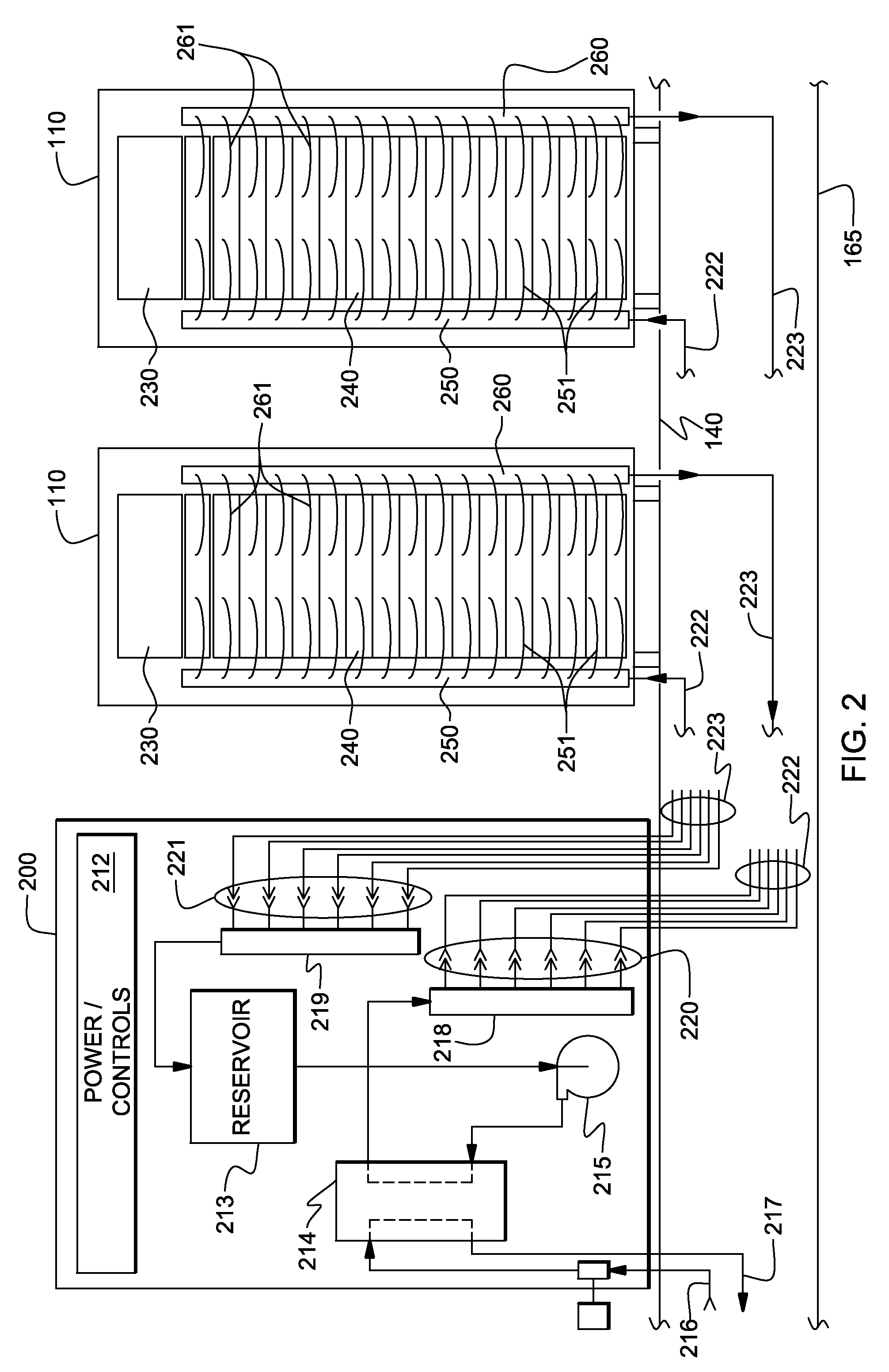
Impingement cooled heat sink with low pressure drop
InactiveUS20070272392A1Reduced life-timeIncrease pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSystem pressureEngineering
Two embodiments of a heat exchanger assembly for cooling an electronic device are shown respectively in FIGS. 1 and 3 and each comprises a housing, a plurality of high fins, a plurality of low fins, a nozzle plate, an inlet, at least one outlet, a primary nozzle, and a plurality of secondary nozzles. In the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1, the housing and the nozzle plate are circular in shape. In the second embodiment shown in FIG. 3, the housing and the nozzle plate are rectangular in shape. Both embodiments include a plurality of secondary nozzles that are aligned outwardly of the primary nozzle and the center axis of the nozzle plate. The secondary nozzles direct the flow of the cooling liquid outwardly of the primary nozzle from the center thus creating an overall system pressure drop lower than that of other assemblies without a plurality of secondary nozzles.
Owner:COOLIT SYSTEMS INC
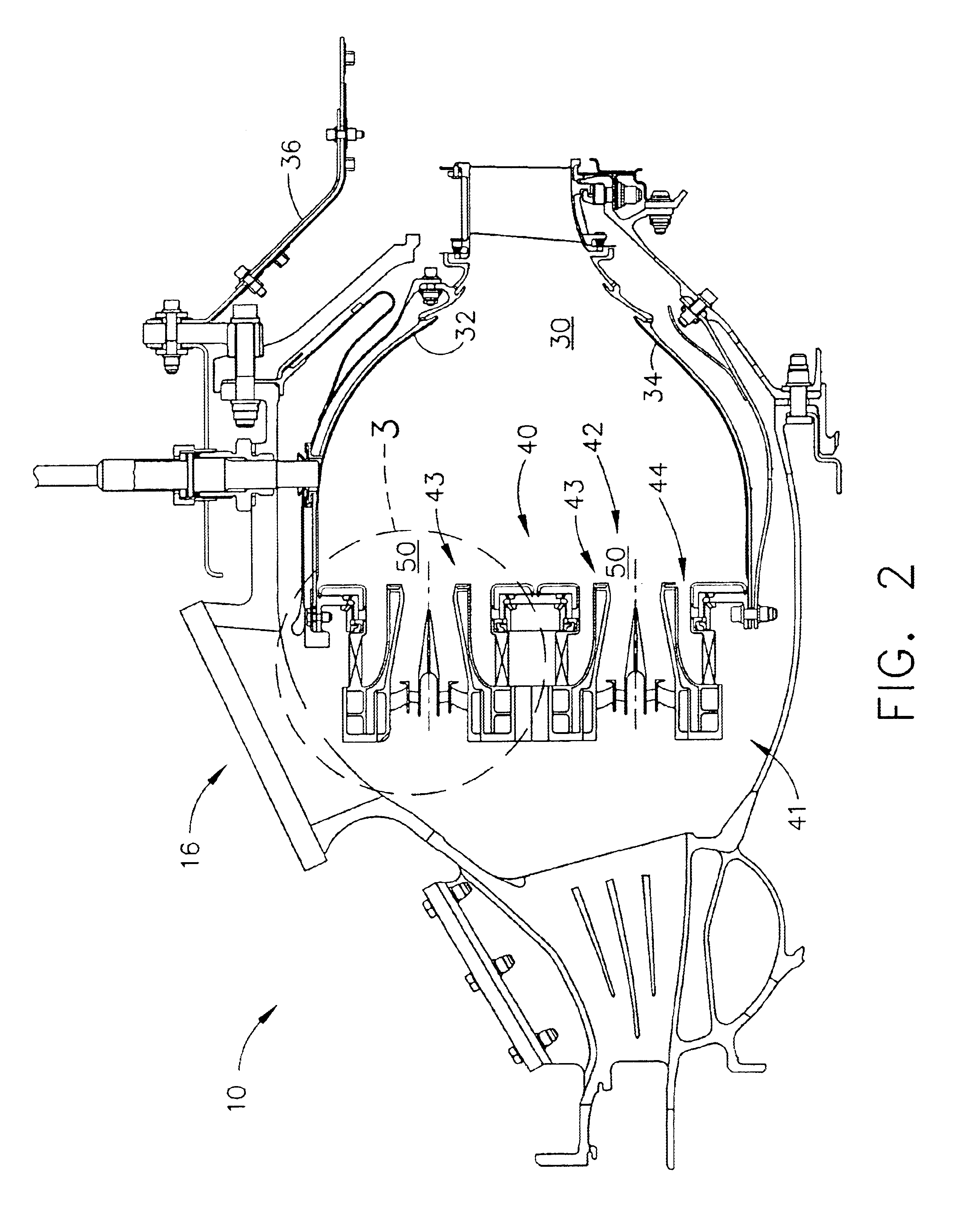
Dual walled combustors with impingement cooled igniters
A combustor for a gas turbine engine includes an inner liner and an outer liner circumscribing the inner liner and forming a combustion chamber with the inner liner. The outer liner is a dual walled liner with a first wall and a second wall. The combustor includes a fuel igniter comprising a tip portion configured to ignite an air and fuel mixture in the combustion chamber and an igniter tube positioning the fuel igniter relative to the combustion chamber. The igniter tube includes a plurality of holes configured to direct cooling air toward the tip portion of the fuel igniter.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus to decrease gas turbine engine combustor emissions
InactiveUS6871501B2Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorTurbine
A method enables a gas turbine engine including a combustor to be operated. The combustor includes a mixer assembly including an air swirler, a premixer, a dome plate, and a heat shield. The method comprises discharging fluids from the air swirler into the premixer, and directing cooling fluids through a cooling opening defined in at least one of the swirler and the dome plate towards an upstream side of the heat shield for impingement cooling of the heat shield.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Jet orifice plate with projecting jet orifice structures for direct impingement cooling apparatus
InactiveUS7362574B2Lower overall pressure dropEasy to disassembleSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVena contracta diameterCoolant flow
A cooling apparatus and a direct cooling impingement module are provided, along with a method of fabrication thereof. The cooling apparatus and direct impingement cooling module include a manifold structure and a jet orifice plate for injecting coolant onto a surface to be cooled. The jet orifice plate, which includes a plurality of jet orifices for directing coolant at the surface to be cooled, is a unitary plate configured with a plurality of jet orifice structures. Each jet orifice structure projects from a lower surface of the jet orifice plate towards the surface to be cooled, and includes a respective jet orifice. The jet orifice structures are spaced to define coolant effluent removal regions therebetween which facilitate removal of coolant effluent from over a center region of the electronic component being cooled to a peripheral region thereof, thereby reducing pressure drop across the jet orifice plate.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Microjet module assembly
InactiveUS7516776B2Maximize heat transfer ratePrevent liquid leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTarget surfacePower flux
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
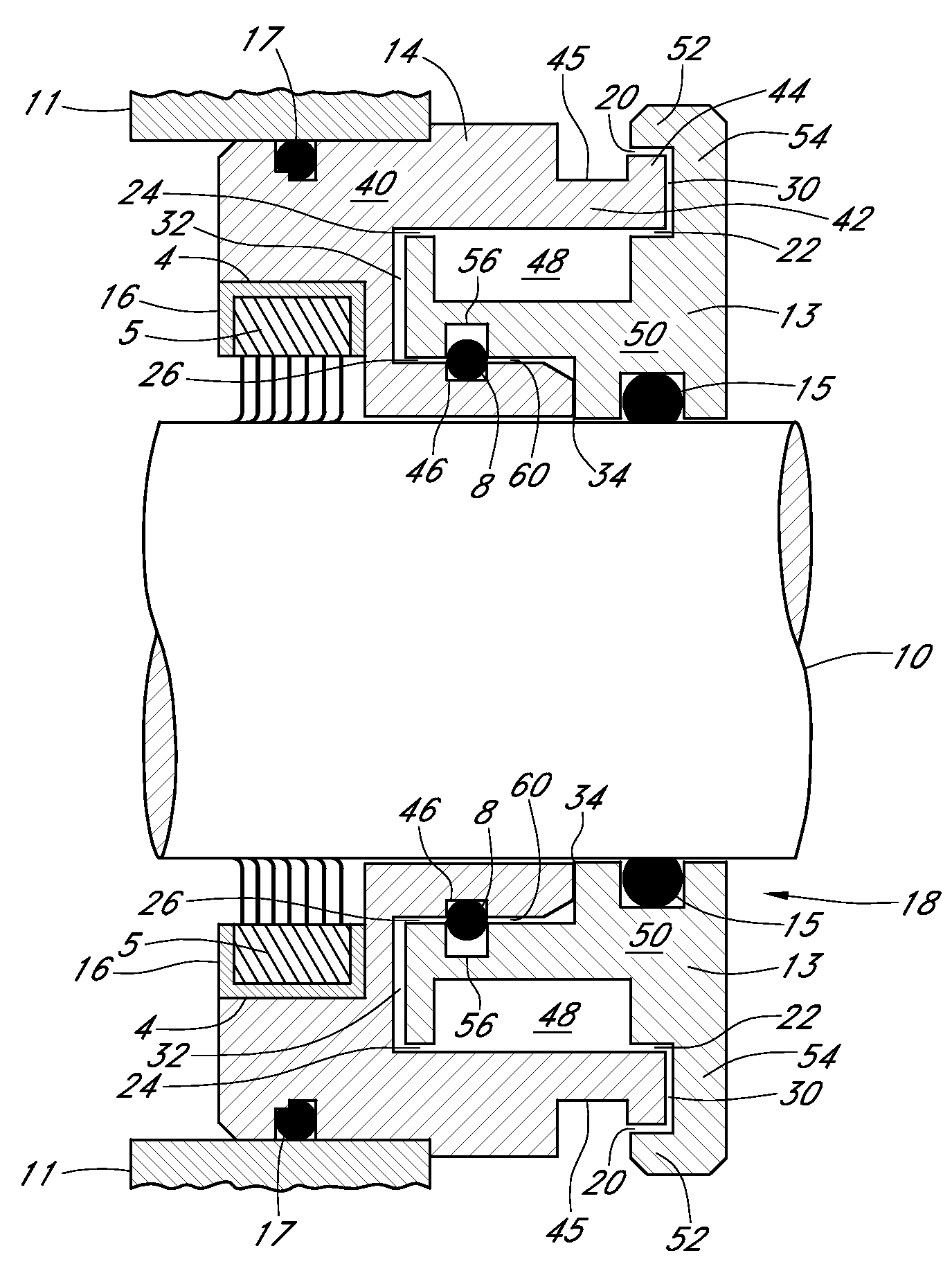
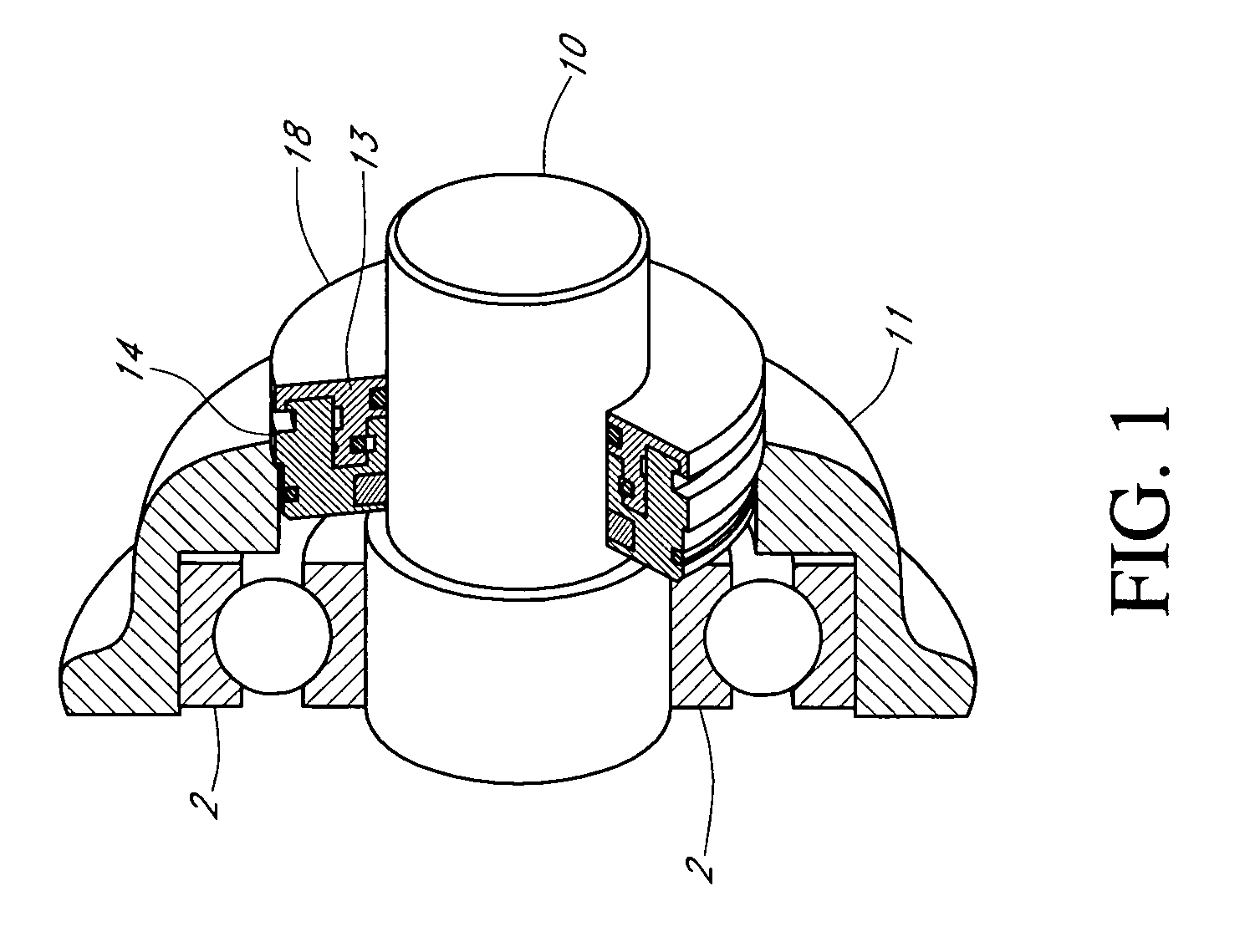
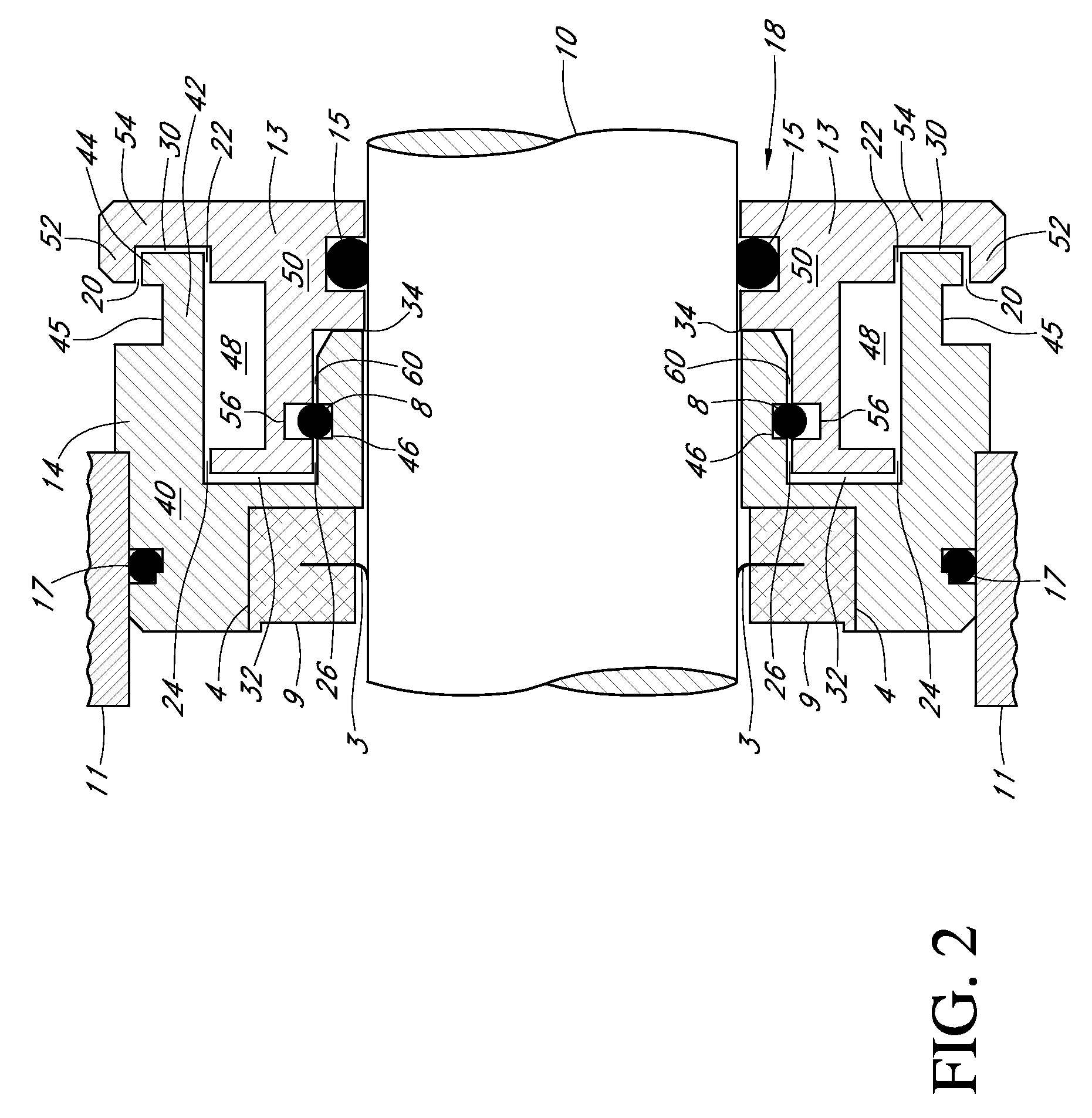
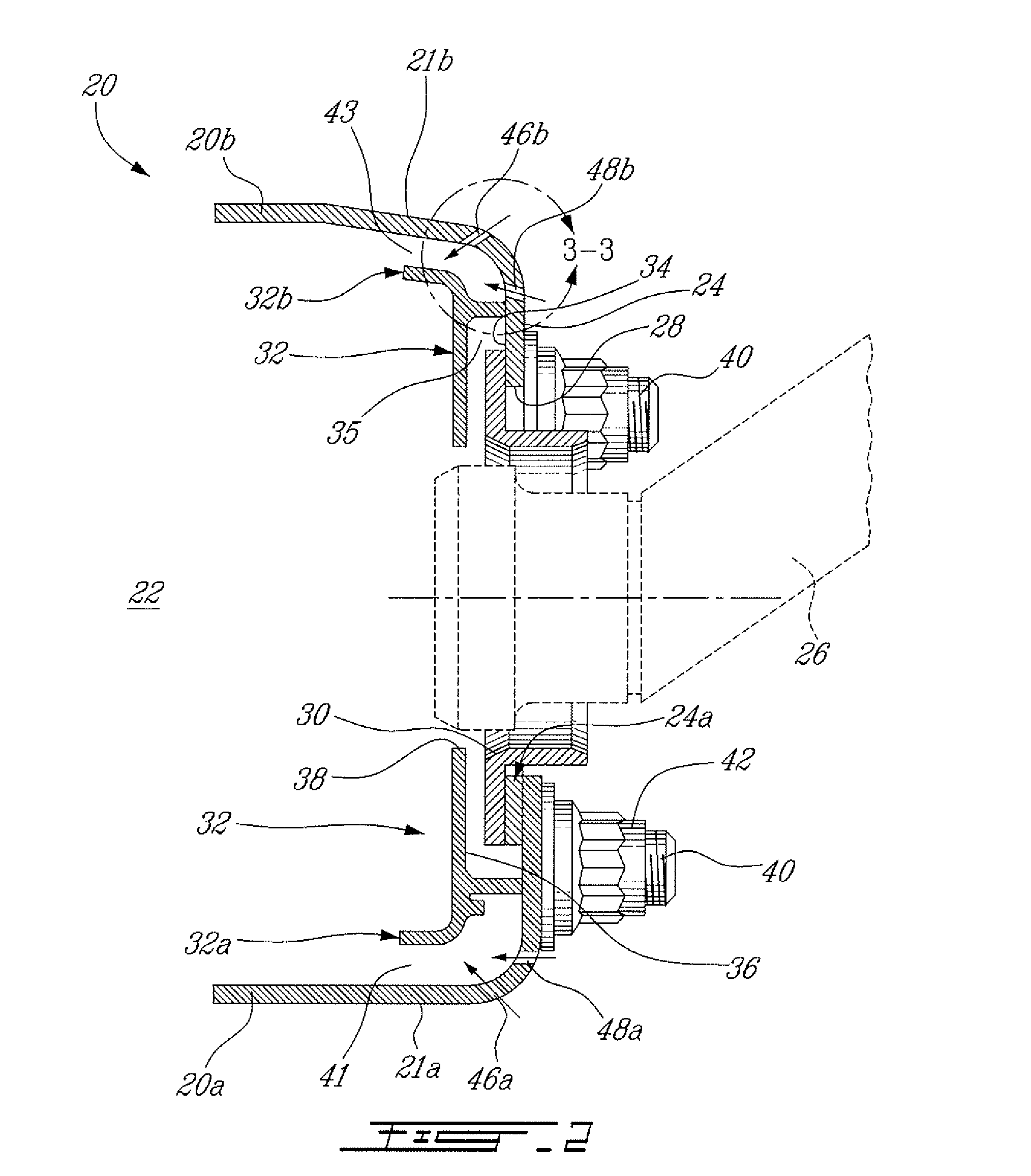
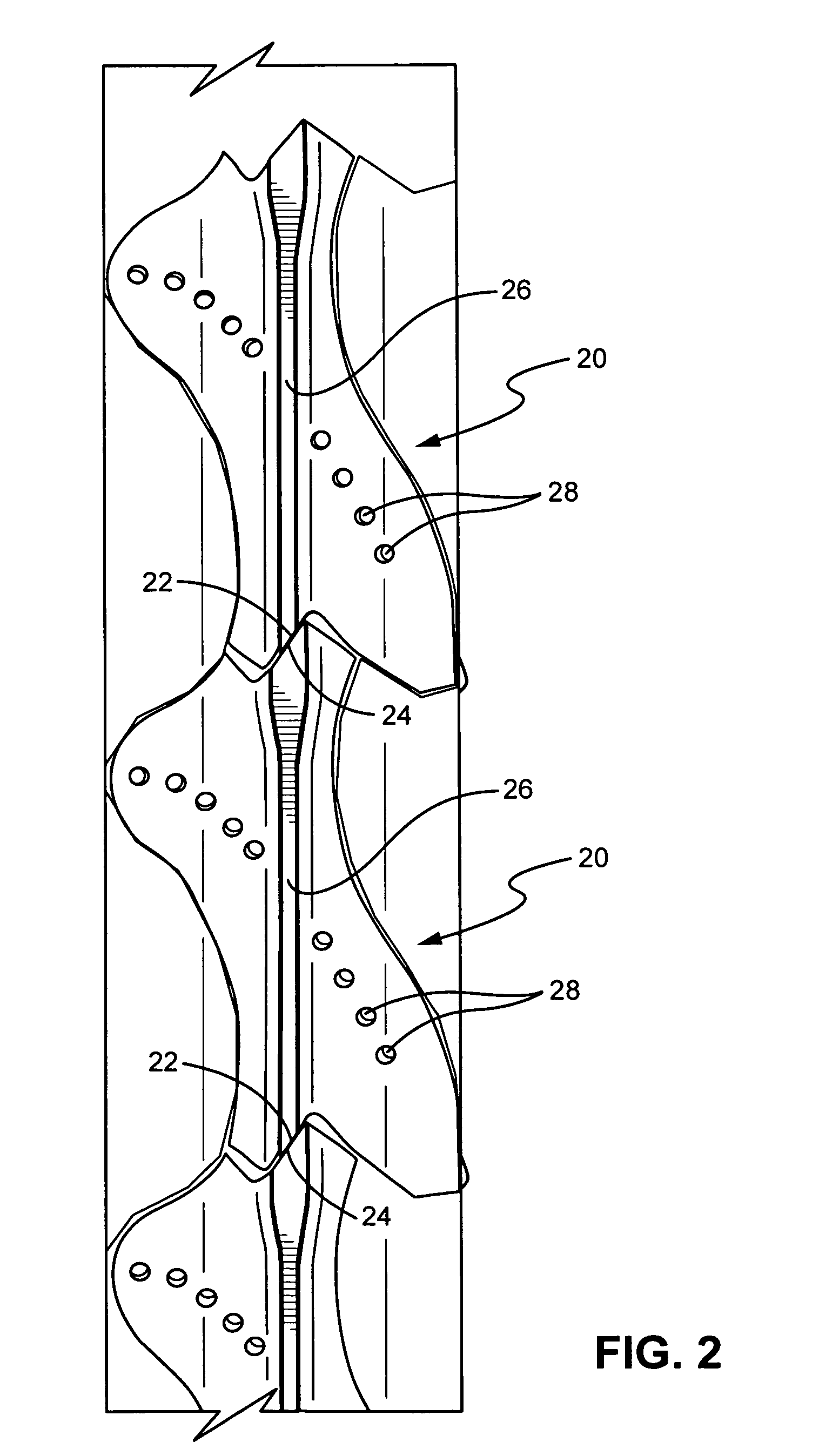
Motor ground seal
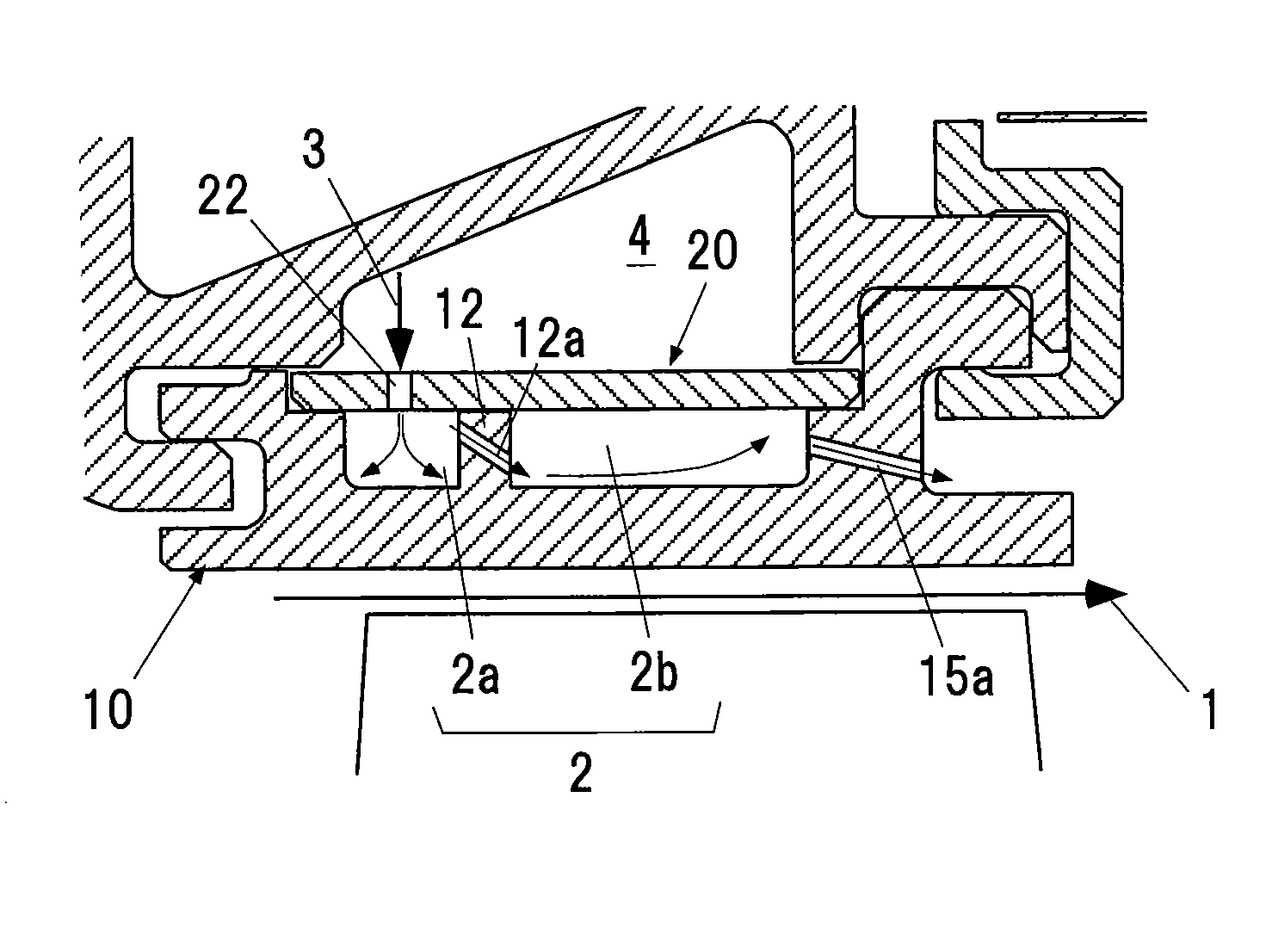
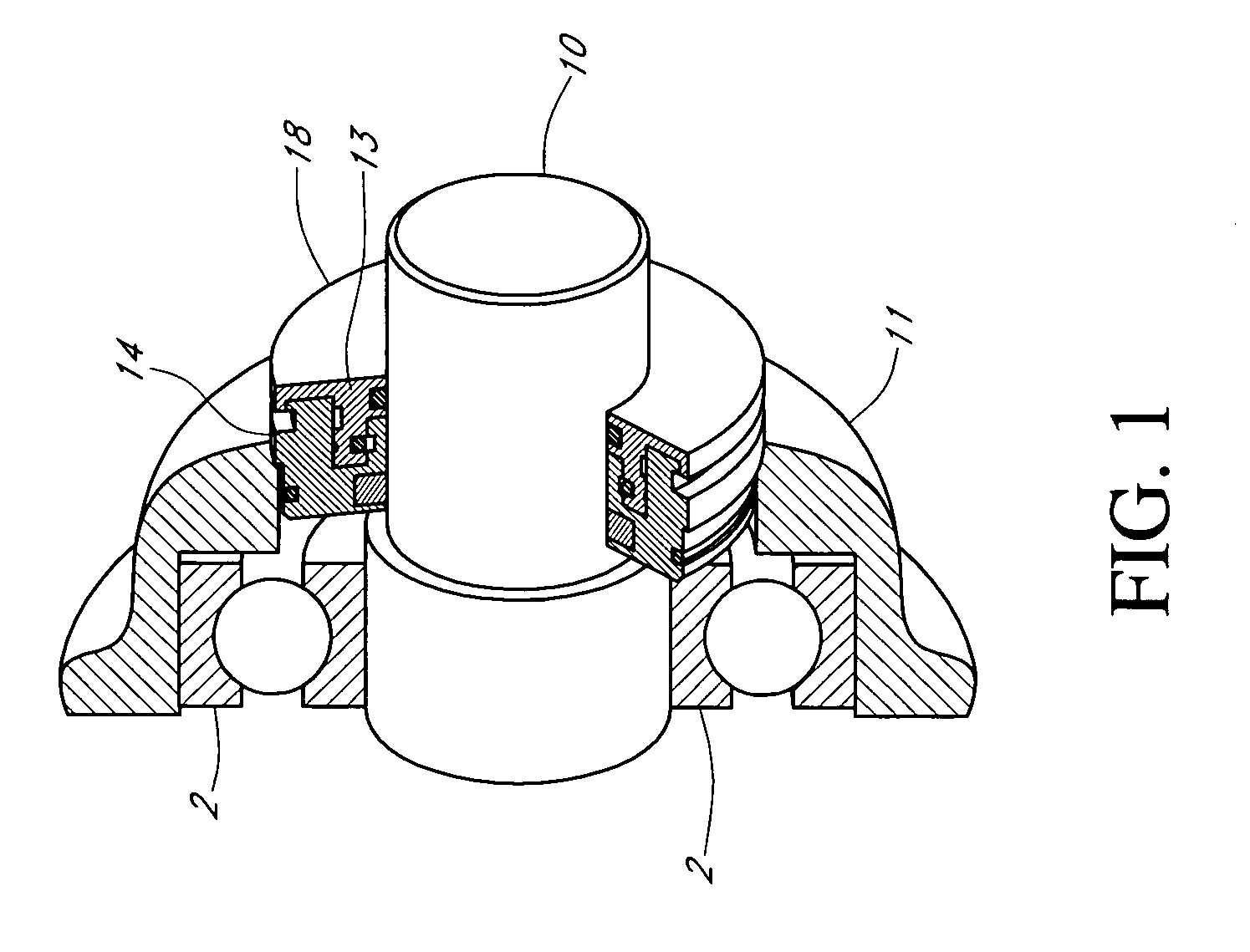
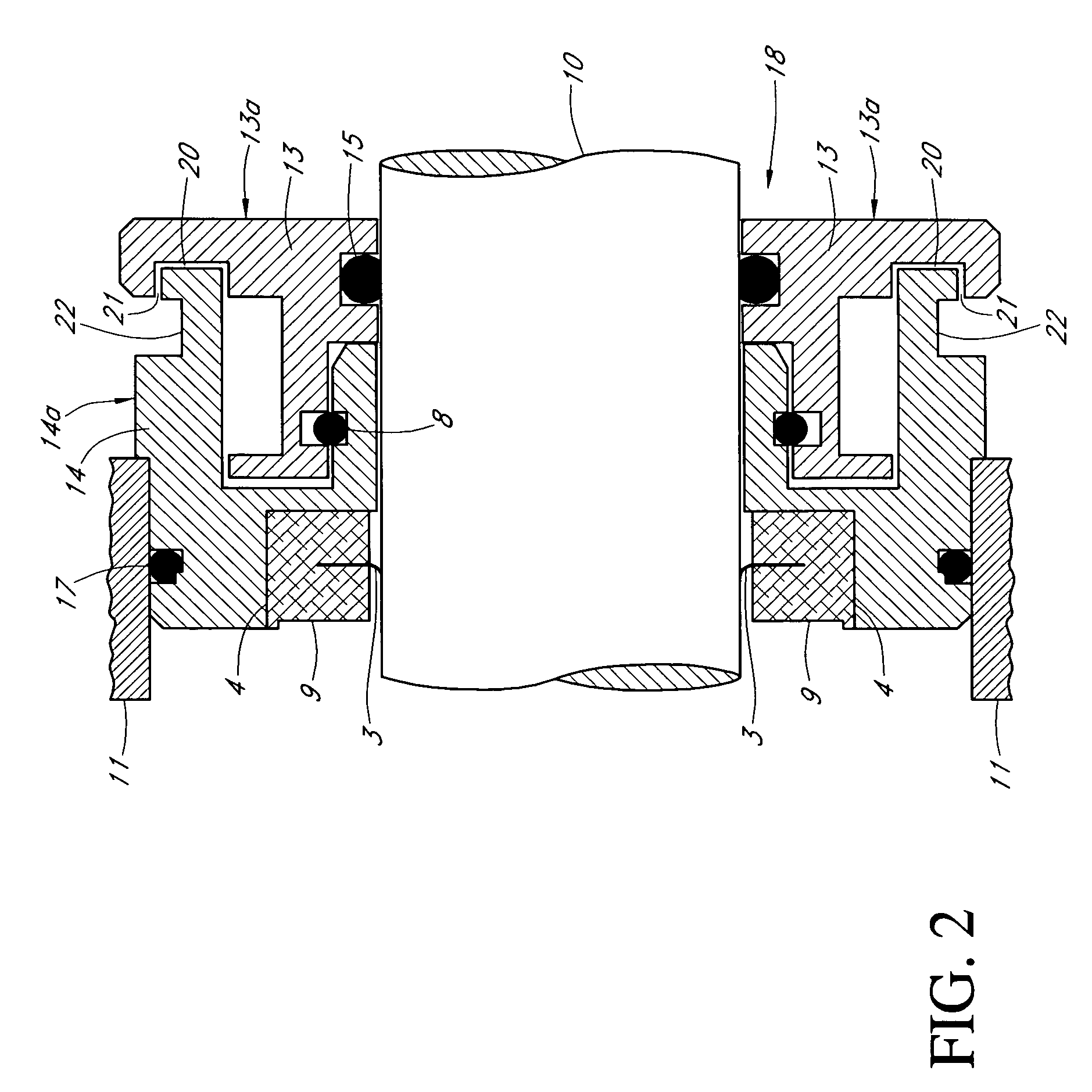
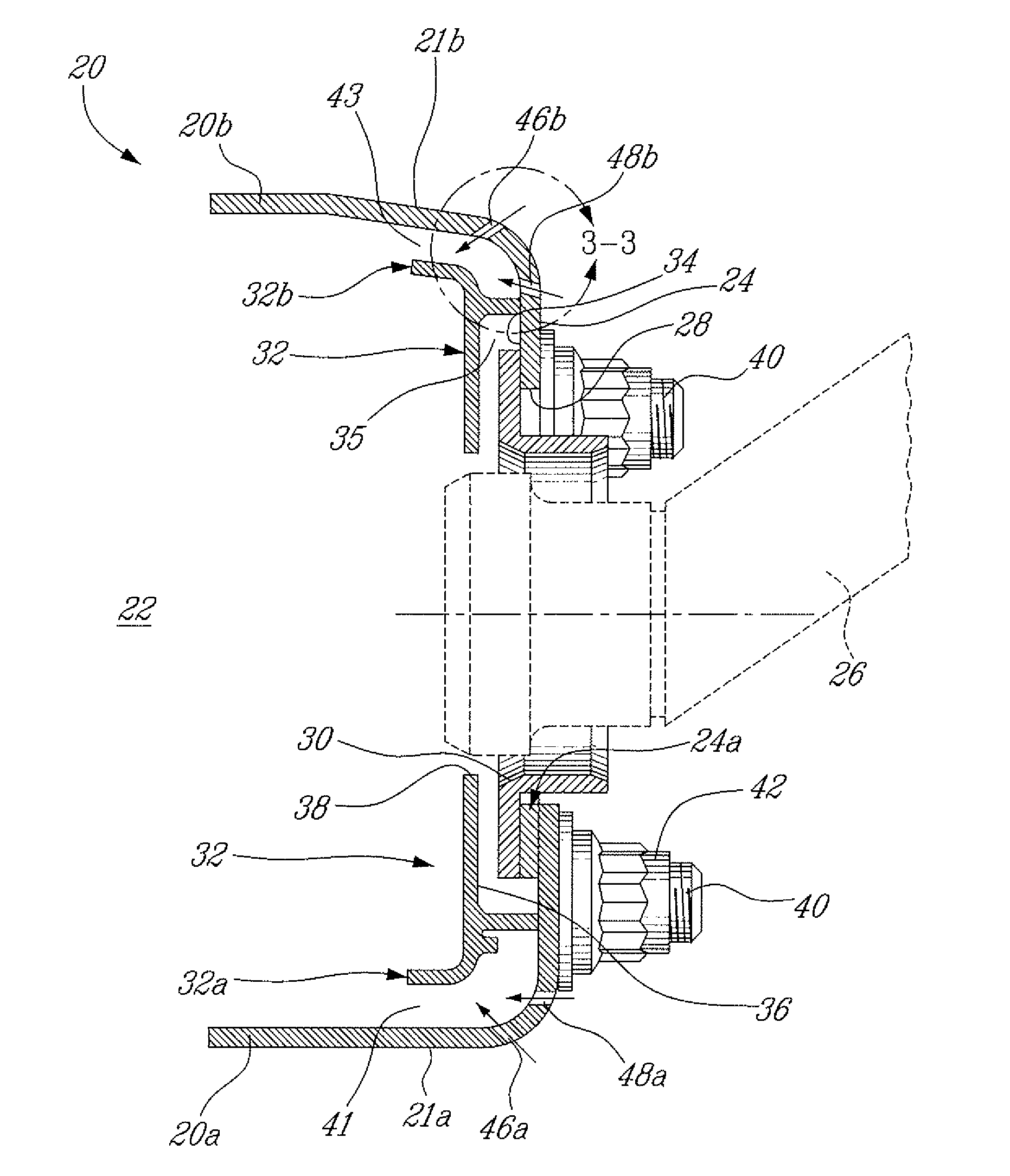
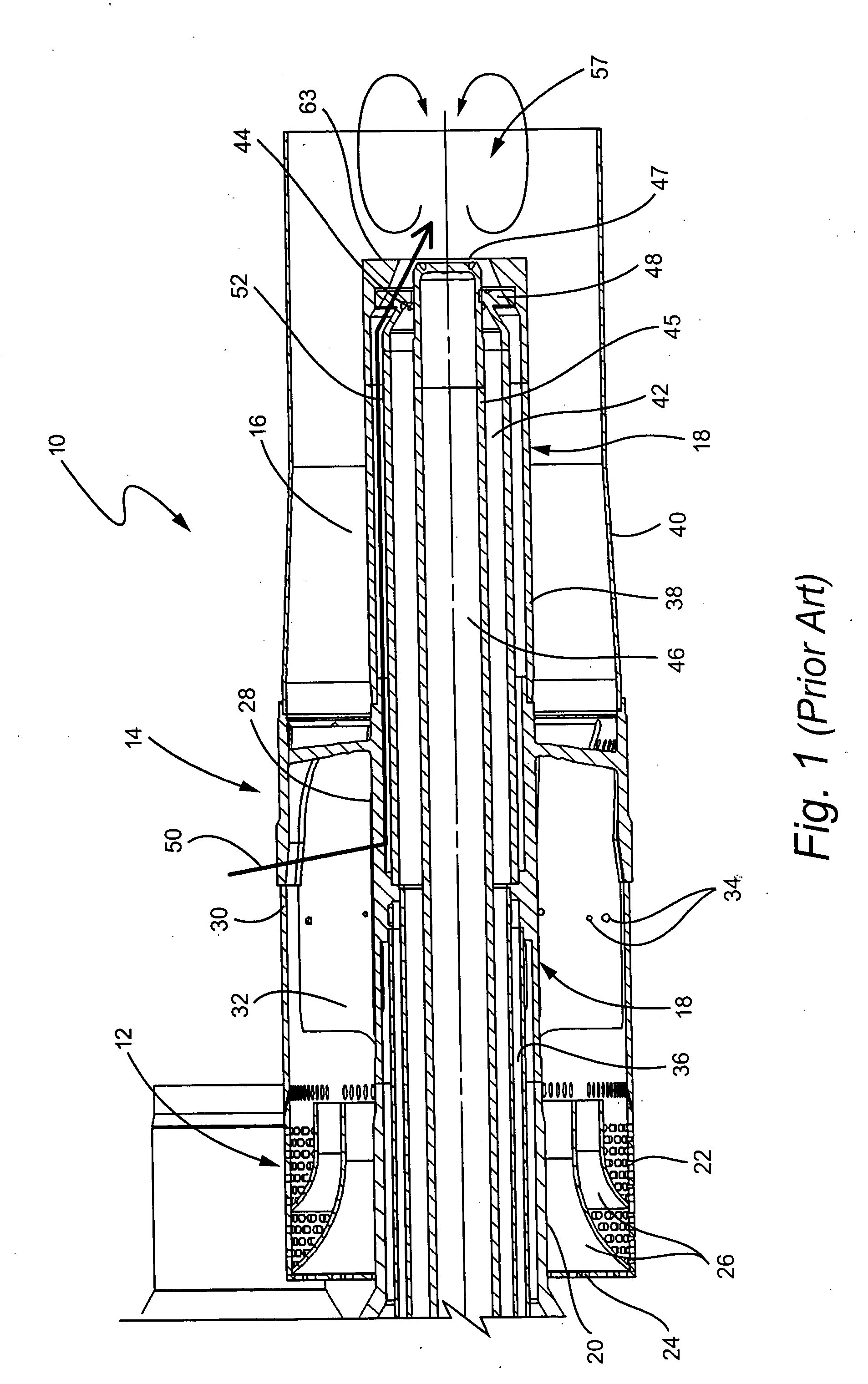
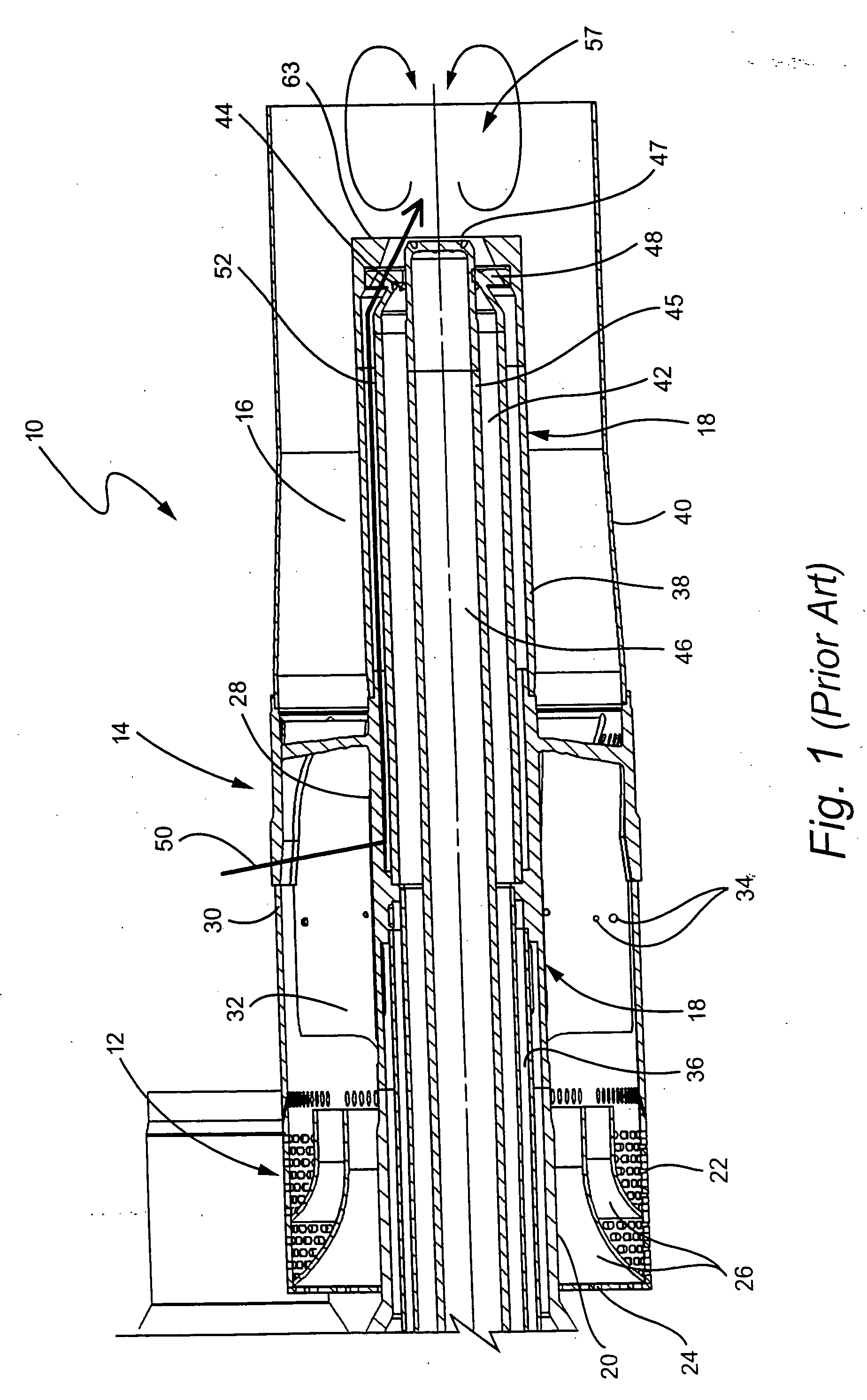
InactiveUS7521827B2Prevent oil leakageImprove sealingEngine sealsAssociation with grounding devicesShock coolingRadial projection
Owner:INPRO INC
Combustor dome panel heat shield cooling
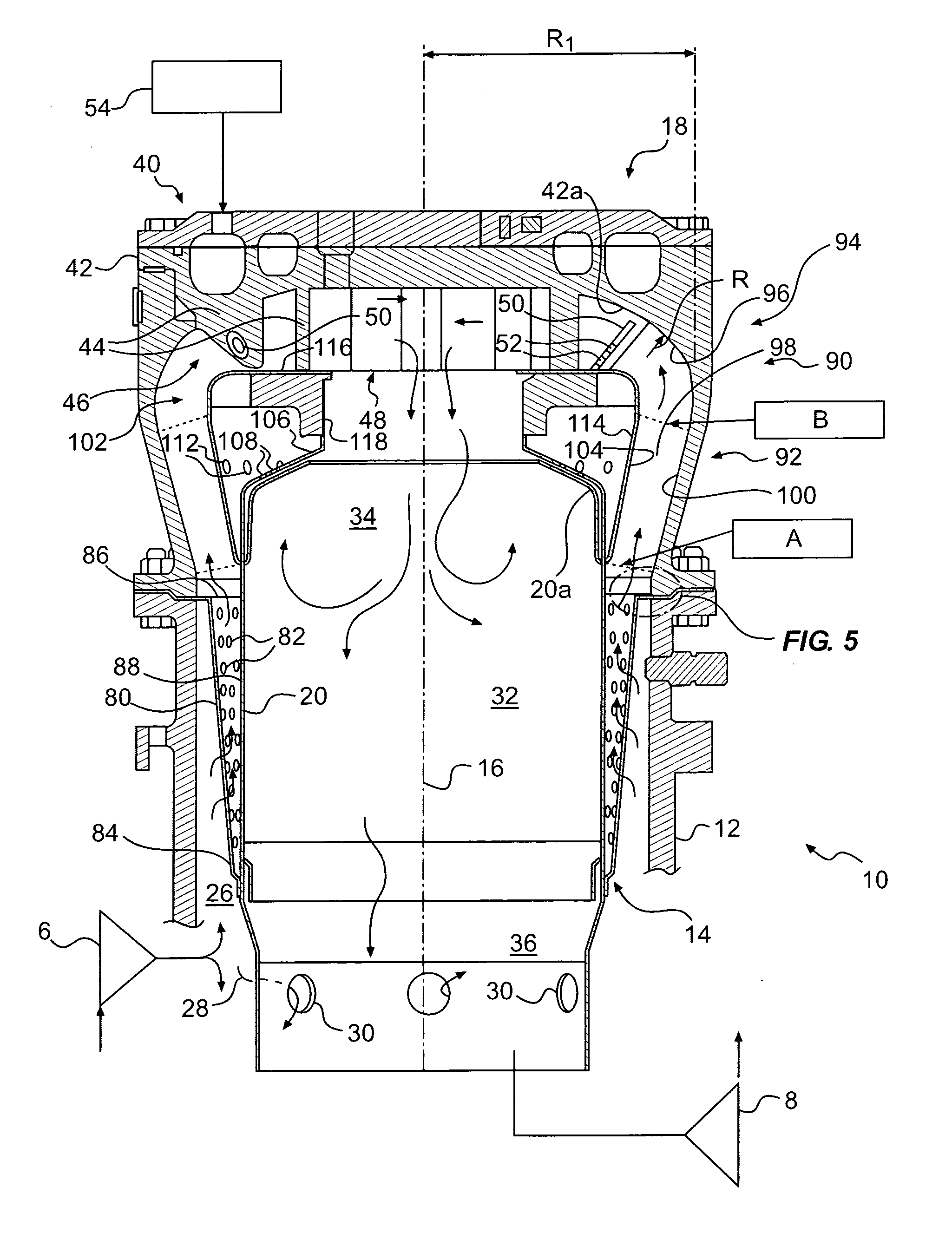
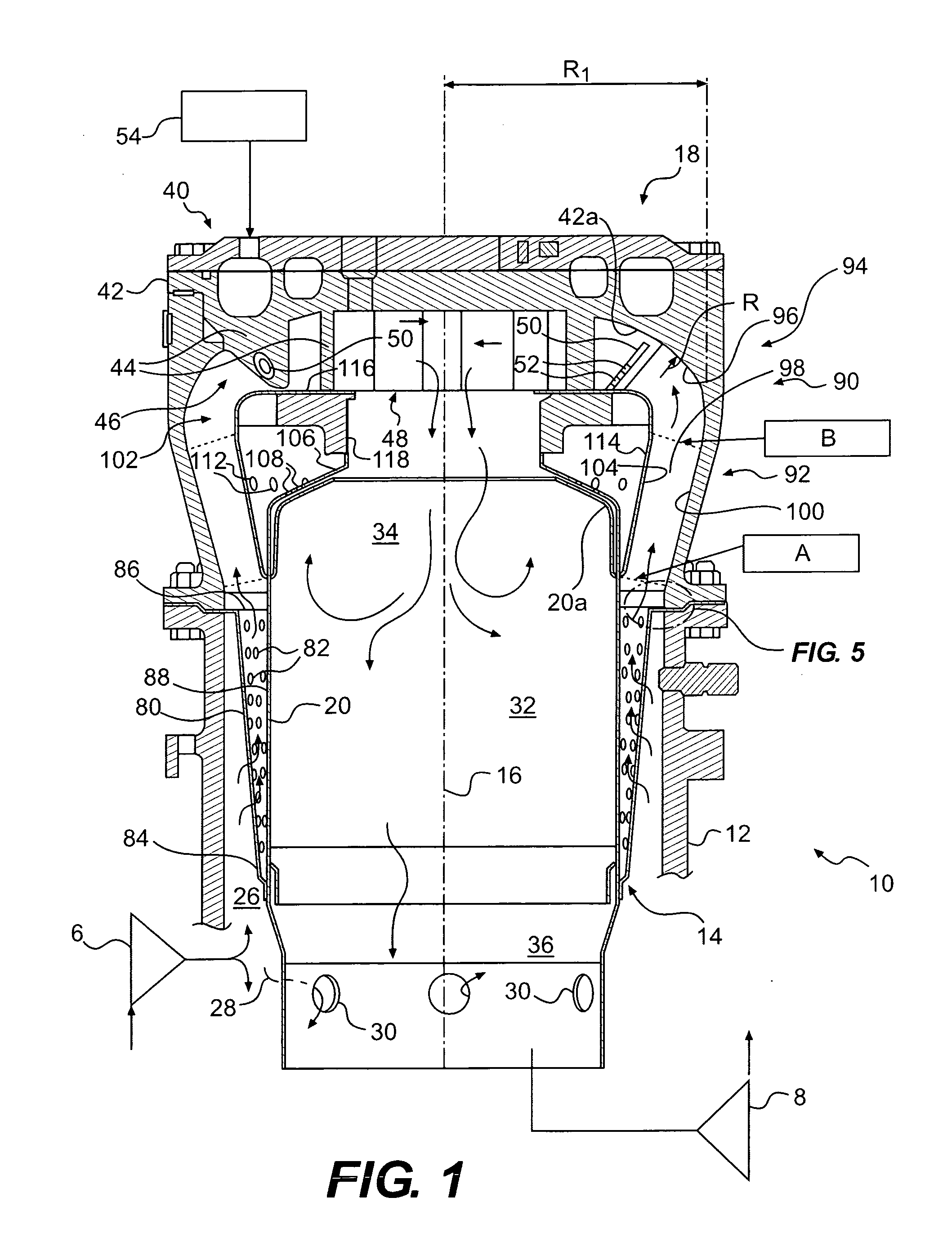
ActiveUS20080104962A1Interference minimizationReduce distractionsContinuous combustion chamberEngine fuctionsCombustion chamberCombustor
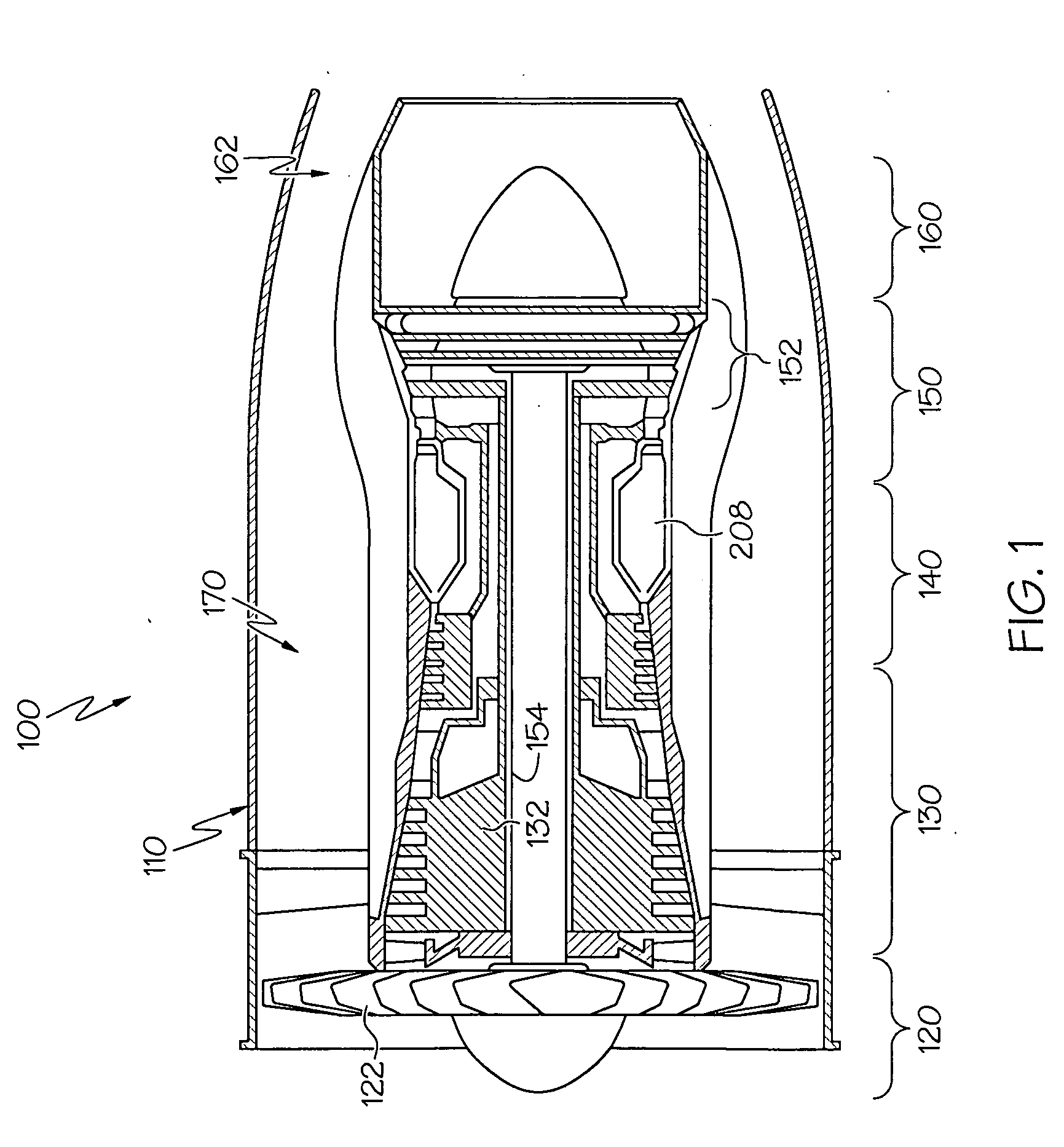
A gas turbine engine combustor having a dome heat shield includes a cooling scheme having a plurality of impingement cooling holes extending through the combustor and a plurality of adjacent ejector holes for directing cooling air past the heat shield lips of the dome heat shields. The impingement and ejector holes are preferably staggered to reduce interaction therebetween.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
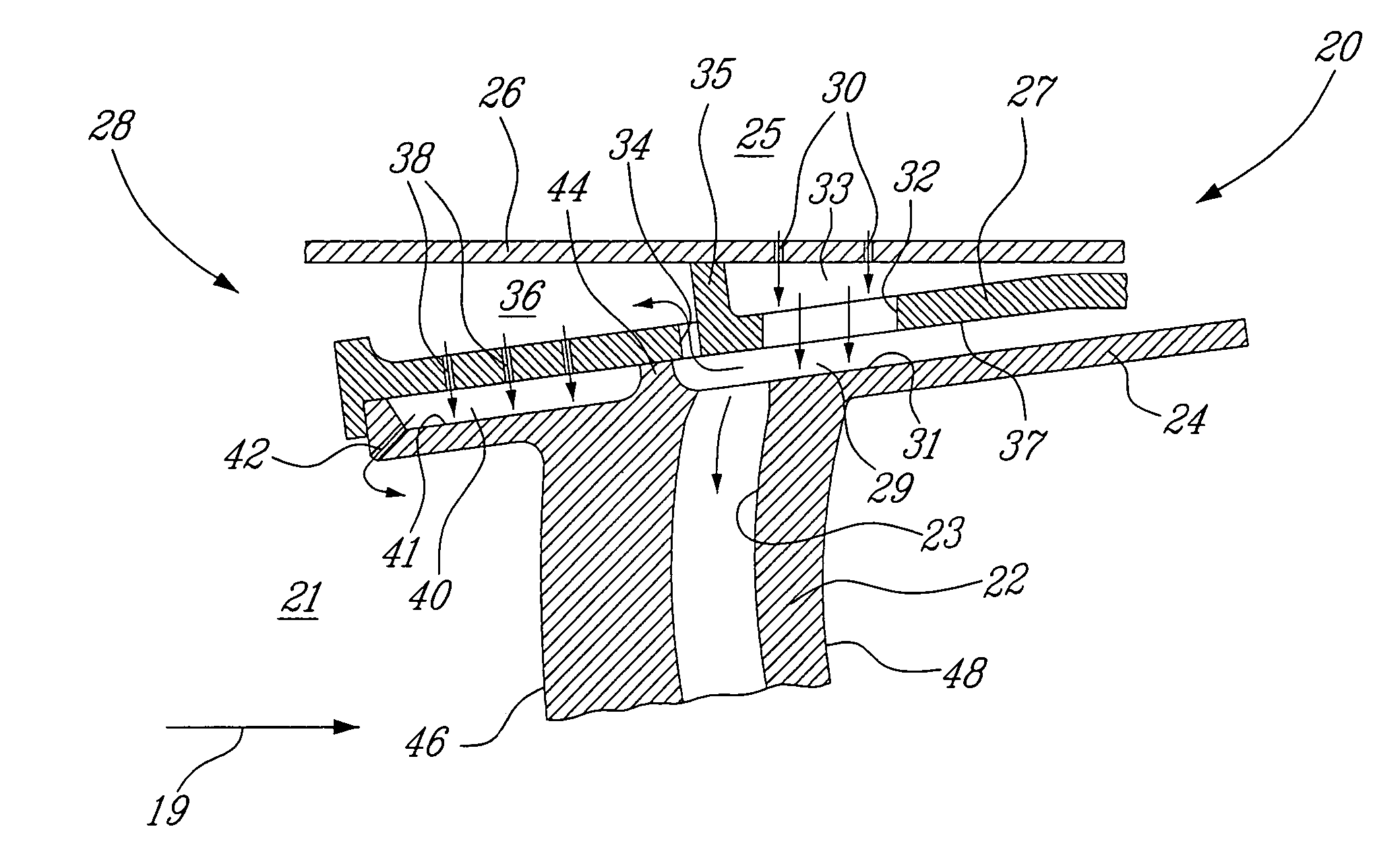
Extended impingement cooling device and method
ActiveUS20050150632A1Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine coolingGas supplyShock cooling
Owner:RTX CORP
Turbine BOAS with edge cooling
A cooling hole having an inlet passage forming an inward spiral flow path and an outlet passage forming an outward spiral flow path in which the two paths are counter flowing in order to improve the heat transfer coefficient. The spiral cooling hole is used in a blade outer air seal (BOAS) for a turbine in which the edges of the shroud segments include a counter flowing micro serpentine flow cooling circuit with thin diffusion discharge cooling slots for the BOAS edges. The total BOAS cooling air is impingement from the BOAS cooling air manifold and metered through the impingement cooling holes to produce impingement cooling onto the backside of the BOAS. The spent cooling air is then channels into the multiple micro serpentine cooling flow circuits located around the four edges of the shroud segments. This cooling air then flows in a serpentine path through the horizontal serpentine flow channels and then discharged through the thin diffusion cooling slots as peripheral purge air for the mate faces as well as the spacing around the BOAS or shroud segments. Trip strips are used in the serpentine flow channels for the augmentation of internal heat transfer cooling capability. The micro serpentine flow cooling air circuits spaced around the four edges of the shroud segments are formed into the shroud segments during the casting process of the shroud segments.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
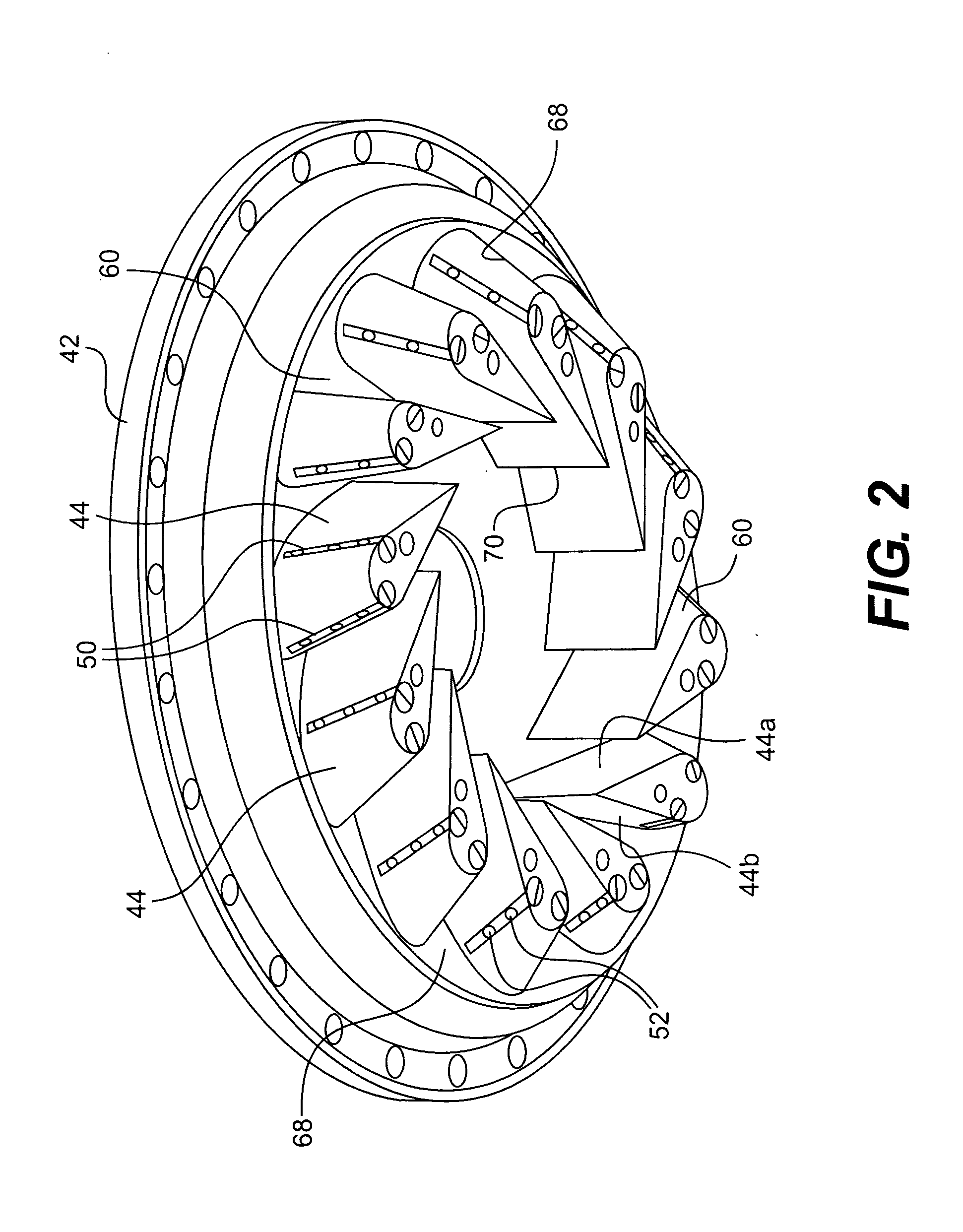
Double impingement vane platform cooling
ActiveUS7097418B2Improved impingement cooling of a turbine vane platformPropellersPump componentsEngineeringGas turbines
A gas turbine engine vane assembly provides double impingement cooling of a vane platform. An impingement structure disposed adjacent the vane platform defines at least first and second plenums in fluid flow communication, respectively defined in part by the vane platform. The vane platform has first and second surfaces defined within the first and second plenums, and which are cooled by successive impingement of secondary cooling air flow through the impingement structure.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Double impingement vane platform cooling
ActiveUS20050281663A1Improved impingement cooling of a turbine vane platformPump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEngineeringGas turbines
A gas turbine engine vane assembly provides double impingement cooling of a vane platform. An impingement structure disposed adjacent the vane platform defines at least first and second plenums in fluid flow communication, respectively defined in part by the vane platform. The vane platform has first and second surfaces defined within the first and second plenums, and which are cooled by successive impingement of secondary cooling air flow through the impingement structure.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Impingement cooled structure
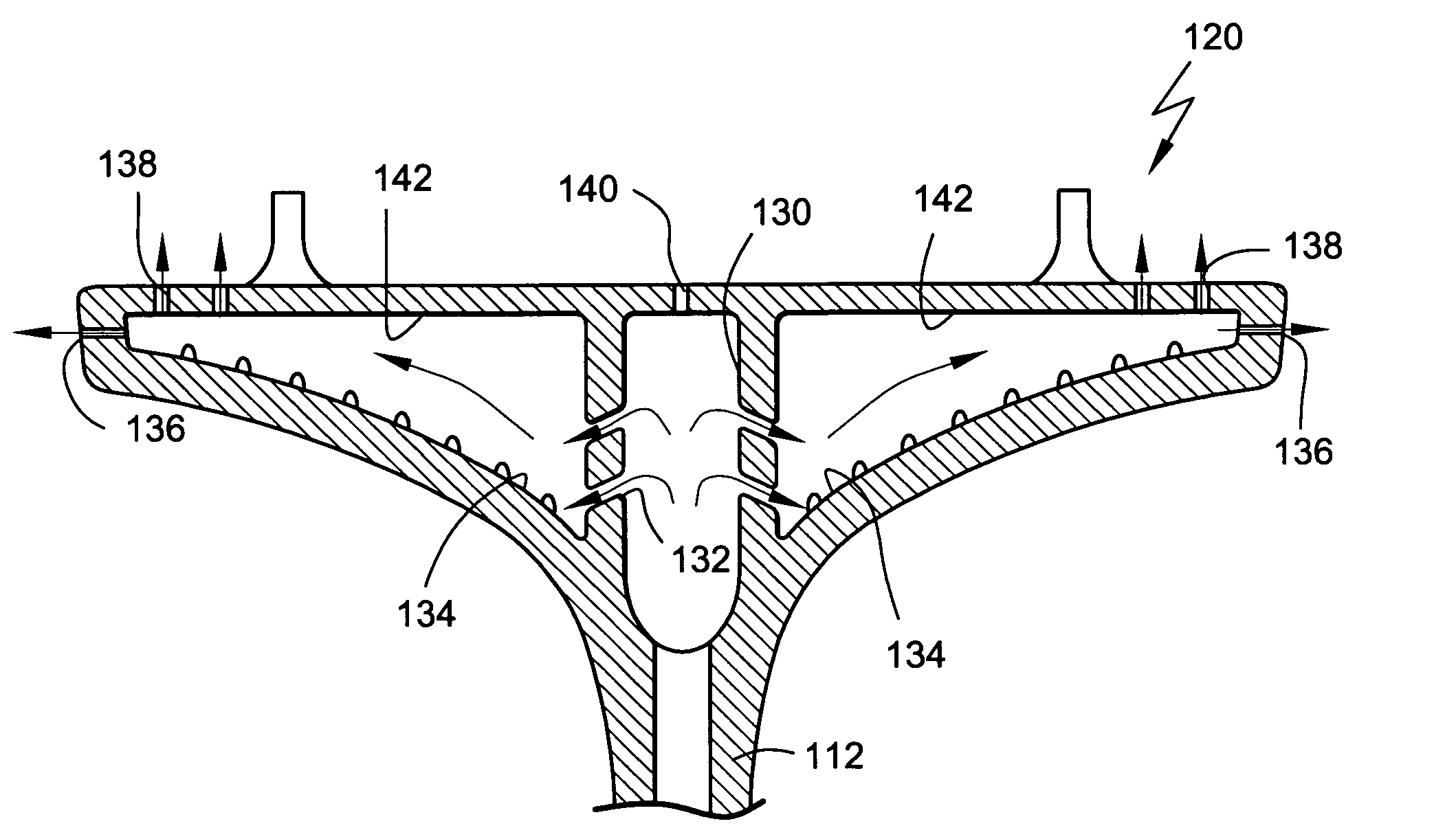
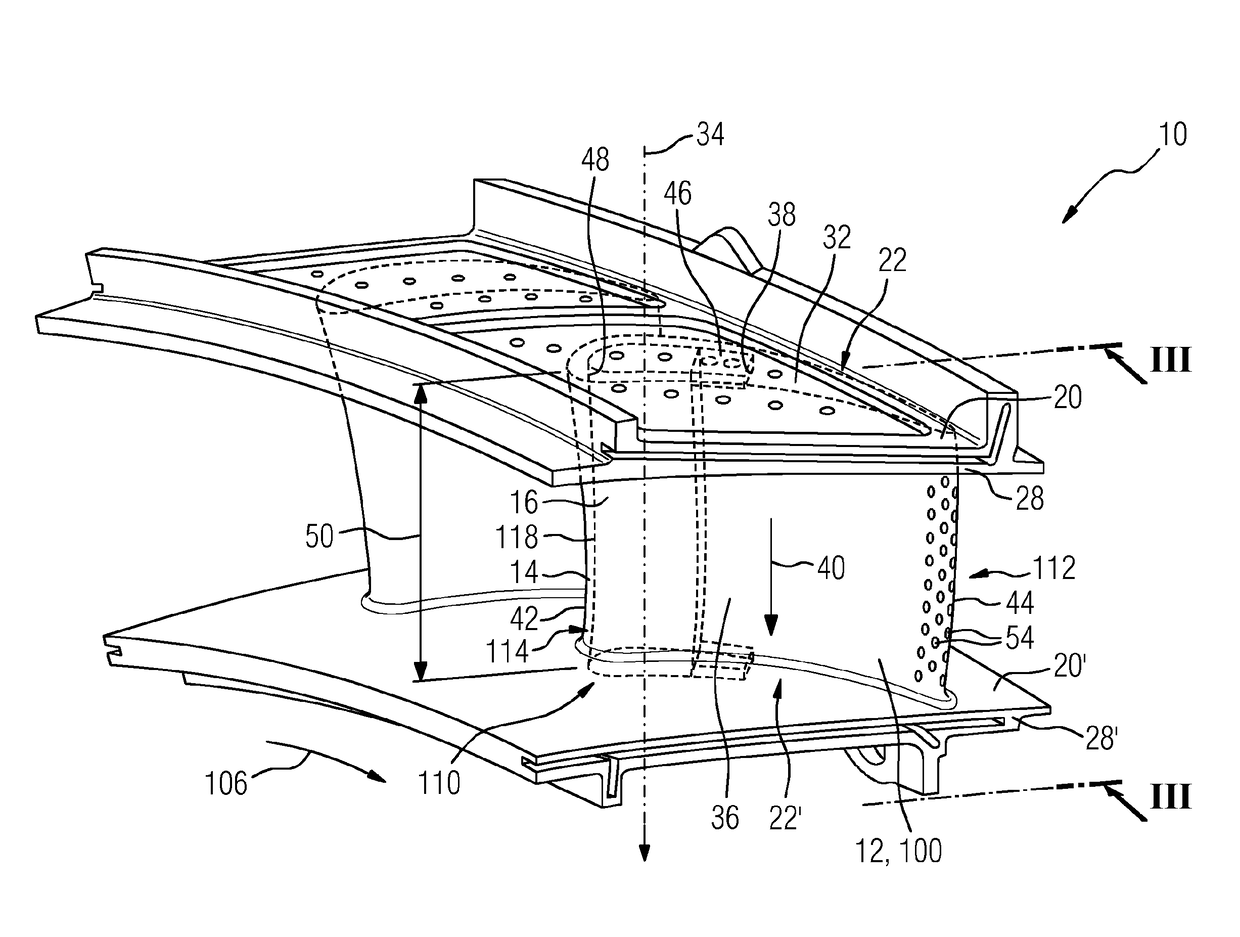
ActiveUS20090035125A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease radial thicknessPump componentsEngine fuctionsShock coolingEngineering
An impingement cooled structure includes a plurality of shroud members disposed in a circumferential direction to constitute a ring-shaped shroud surrounding a hot gas stream, and a shroud cover mounted on radial outside faces of the shroud members to form a cavity therebetween. The shroud cover has a first impingement cooling hole which communicates with the cavity and allows cooling air to be jetted to an inside thereof so as to cool an inner surface of the cavity by impingement. The shroud members each has a hole fin. The hole fin divides the cavity into a plurality of sub-cavities. Further, the hole fin has a second impingement cooling hole which allows the cooling air having flowed through the first impingement cooling hole to be jetted obliquely toward a bottom surface of the sub-cavity adjacent thereto.
Owner:IHI CORP +1
Combustor flow sleeve with optimized cooling and airflow distribution
Embodiments of the invention relate to a combustor flow sleeve for a turbine engine. The flow sleeve can be configured to optimize cooling and airflow distribution. The flow sleeve can include first and second sets of openings. A first set of openings can be provided for impingement cooling the areas of the liner that are subjected to high thermal loads. The second set of openings can be provided to more evenly distribute the airflow into the combustor head-end. By focusing the cooling on the areas of need and by making the airflow more uniform, embodiments of the invention can reduce the system pressure drop and enhance the performance and power of the engine.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
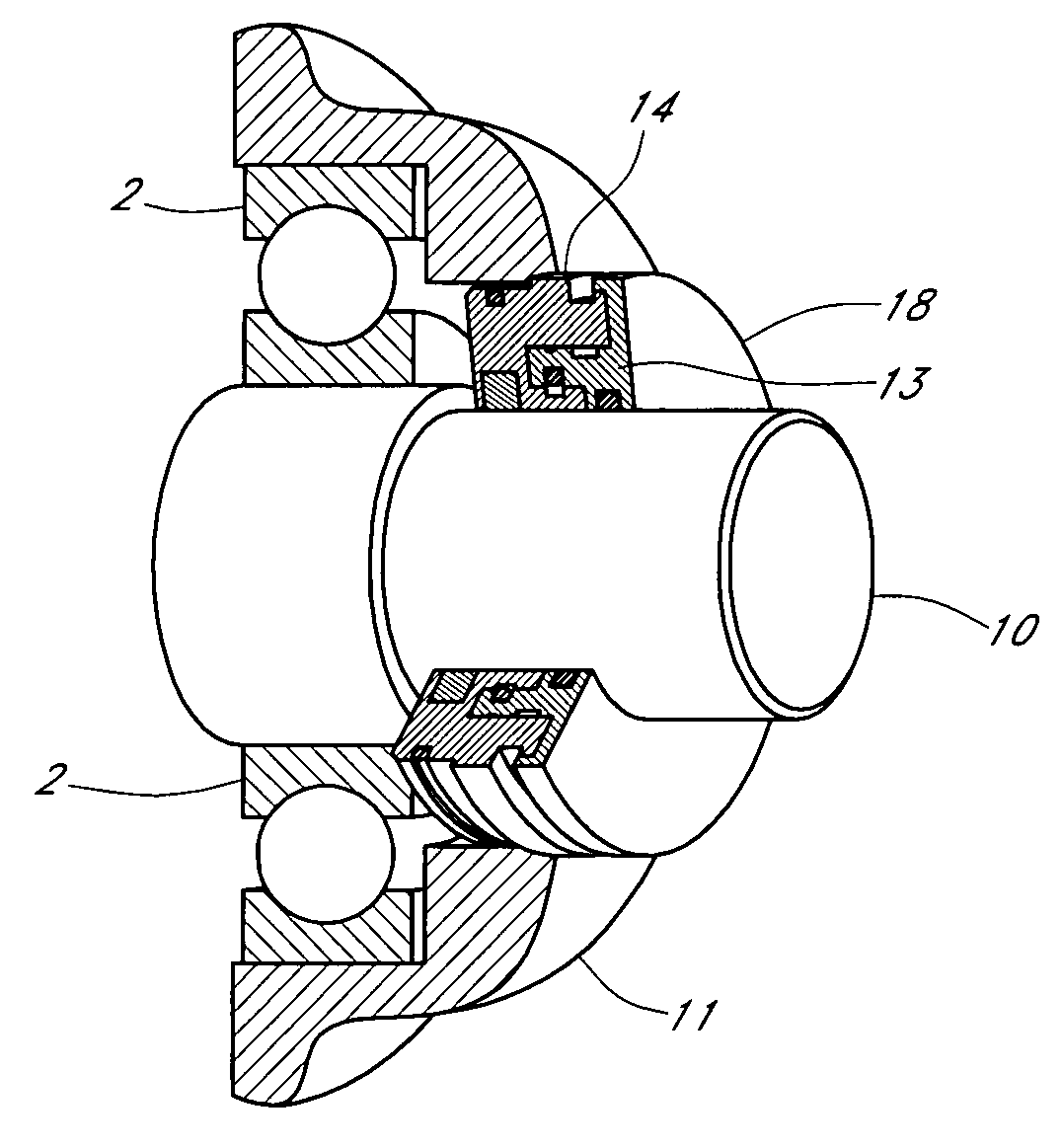
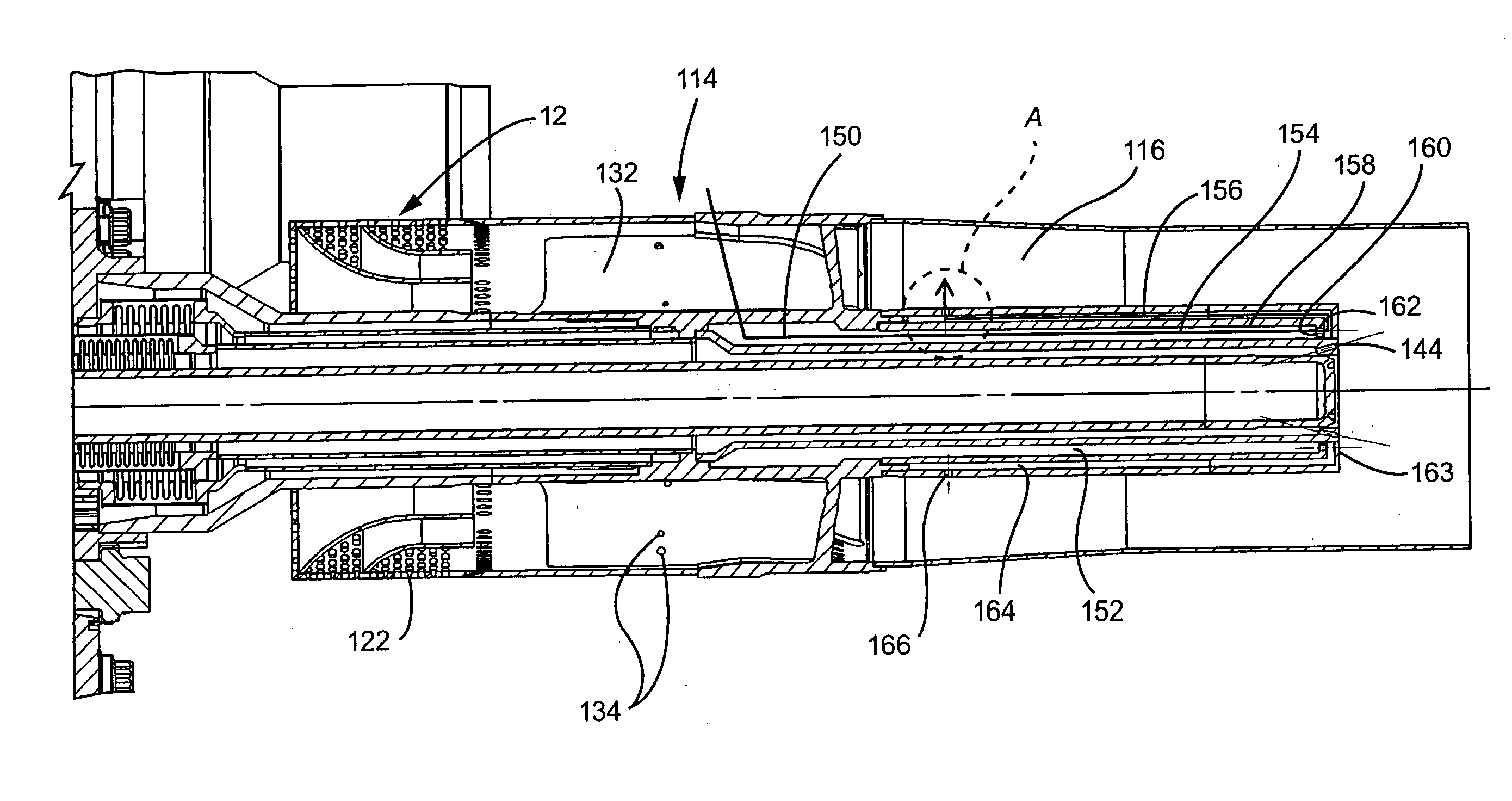
Motor ground seal
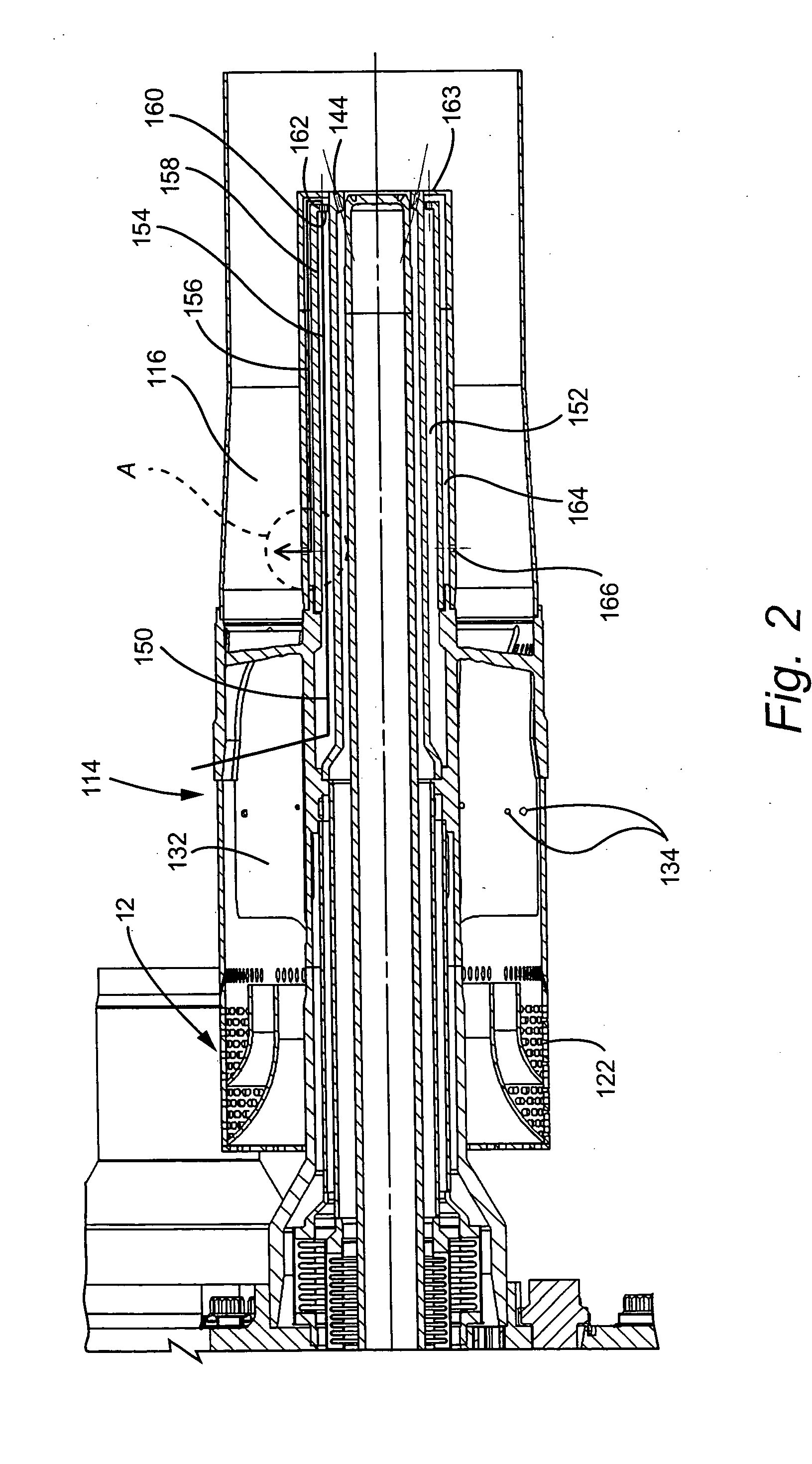
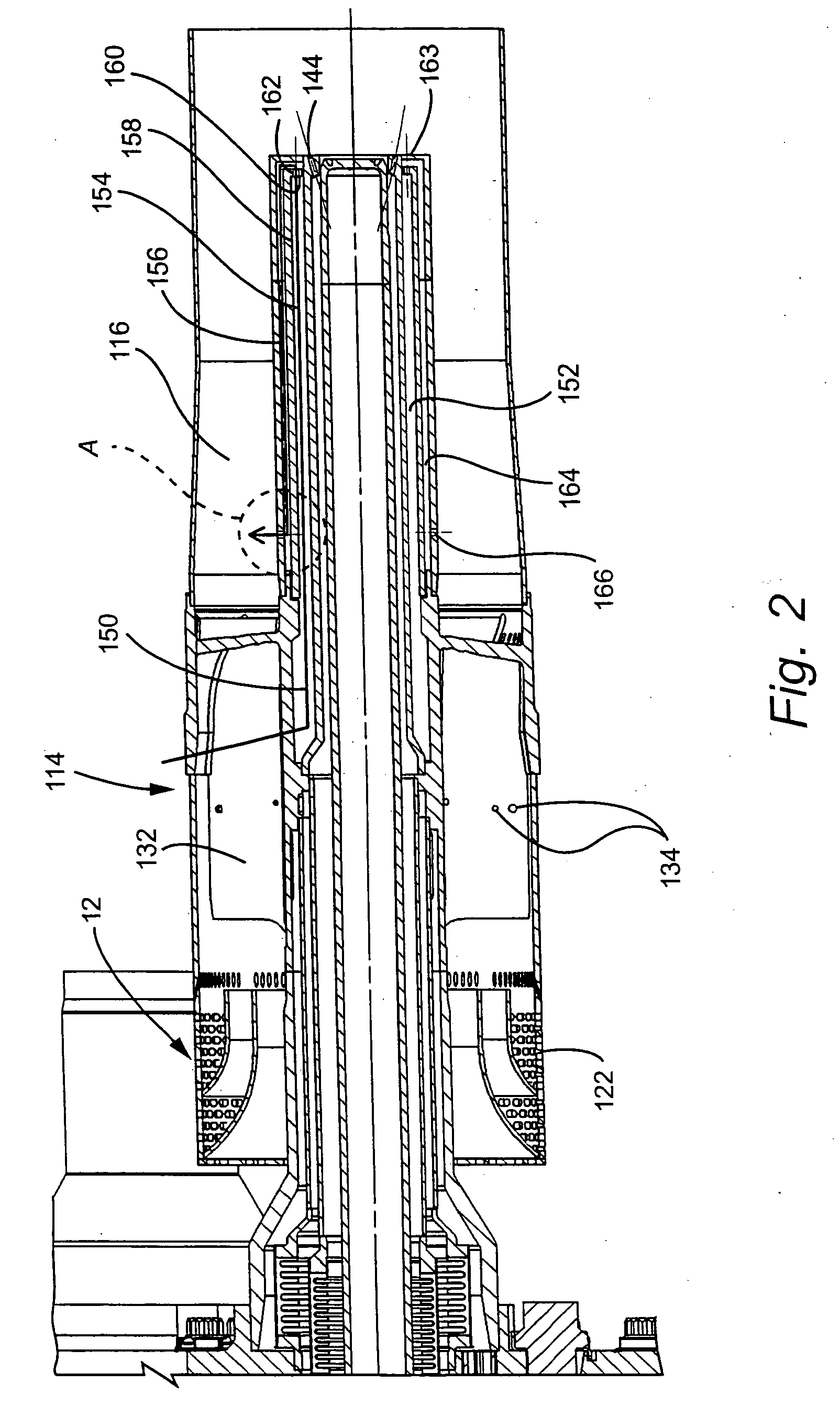
InactiveUS20070138748A1Prevent oil leakageImprove sealingEngine sealsAssociation with grounding devicesEngineeringRelative motion
A shaft seal assembly is disclosed having a stator including a main body and axial and radial projections therefrom. The rotor is radially extended and encompasses the axial and radial projections from said stator. A passageway formed between the radial projection of stator and rotor results in an axial passageway having its opening facing rearwardly from the rotor and away from the source of impinging coolant and / or contaminant. A concentric circumferential receptor groove in the stator facing the housing allows insertion of conductive means for transmission of electrostatic charge away from the shaft through the shaft seal assembly to the housing and ground. The receptor groove is opposite the axial passageway and provides for both a substantially lower contaminant environment and improved engagement with conductive means. The dimension of interface gap between the rotor and the radial projection from the stator, which the access to the shaft of any impinging material is fixed at a predetermined value and does not vary with the relative movement between the rotor and the stator. The shaft seal assembly provides improved rejection or warding off of contaminants from ingress into the labyrinths and ultimately restrains attack of the bearing environment as well as substantial elimination of bearing current and attendant bearing fluting or frosting.
Owner:INPRO INC
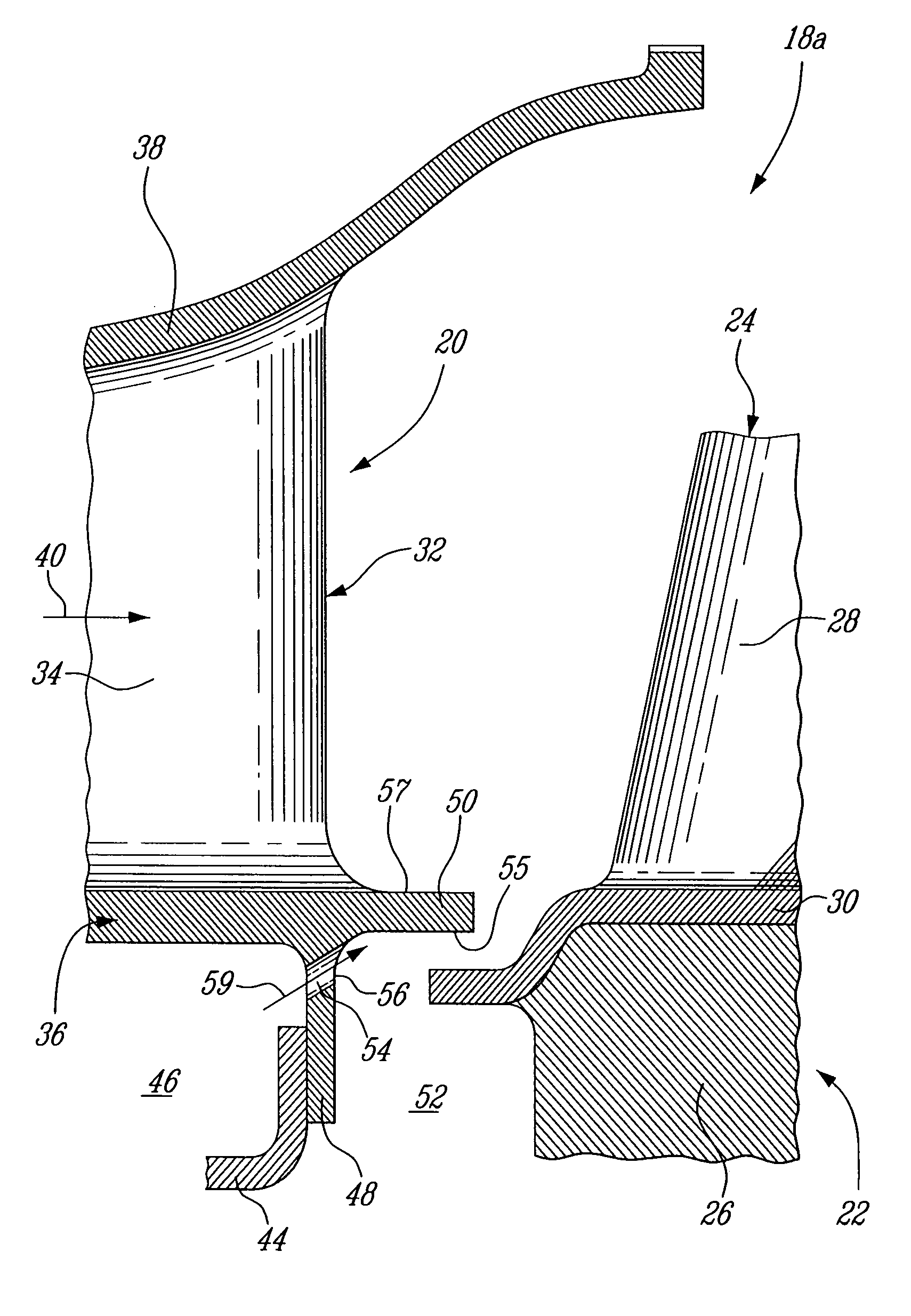
Combustor dome panel heat shield cooling
ActiveUS7770397B2Reduce distractionsMinimize interferenceContinuous combustion chamberEngine fuctionsCombustion chamberCombustor
A gas turbine engine combustor having a dome heat shield includes a cooling scheme having a plurality of impingement cooling holes extending through the combustor and a plurality of adjacent ejector holes for directing cooling air past the heat shield lips of the dome heat shields. The impingement and ejector holes are preferably staggered to reduce interaction therebetween.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Methods and apparatus for cooling gas turbine engine rotor assemblies
A method facilitates fabricating a rotor assembly for a gas turbine engine. The method comprises providing a plurality of rotor blades that each include an airfoil, a dovetail, a shank, and a platform, wherein the platform extends between the shank and the airfoil, and wherein the dovetail extends outwardly from the shank, and forming a cooling circuit within a portion of the shank to supply cooling air to the rotor blade for supplying cooling air to the rotor blade for impingement cooling a portion of the rotor blade and for supplying cooling air to the rotor blade for purging a cavity defined downstream from the rotor blade.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultra low emissions gas turbine combustor
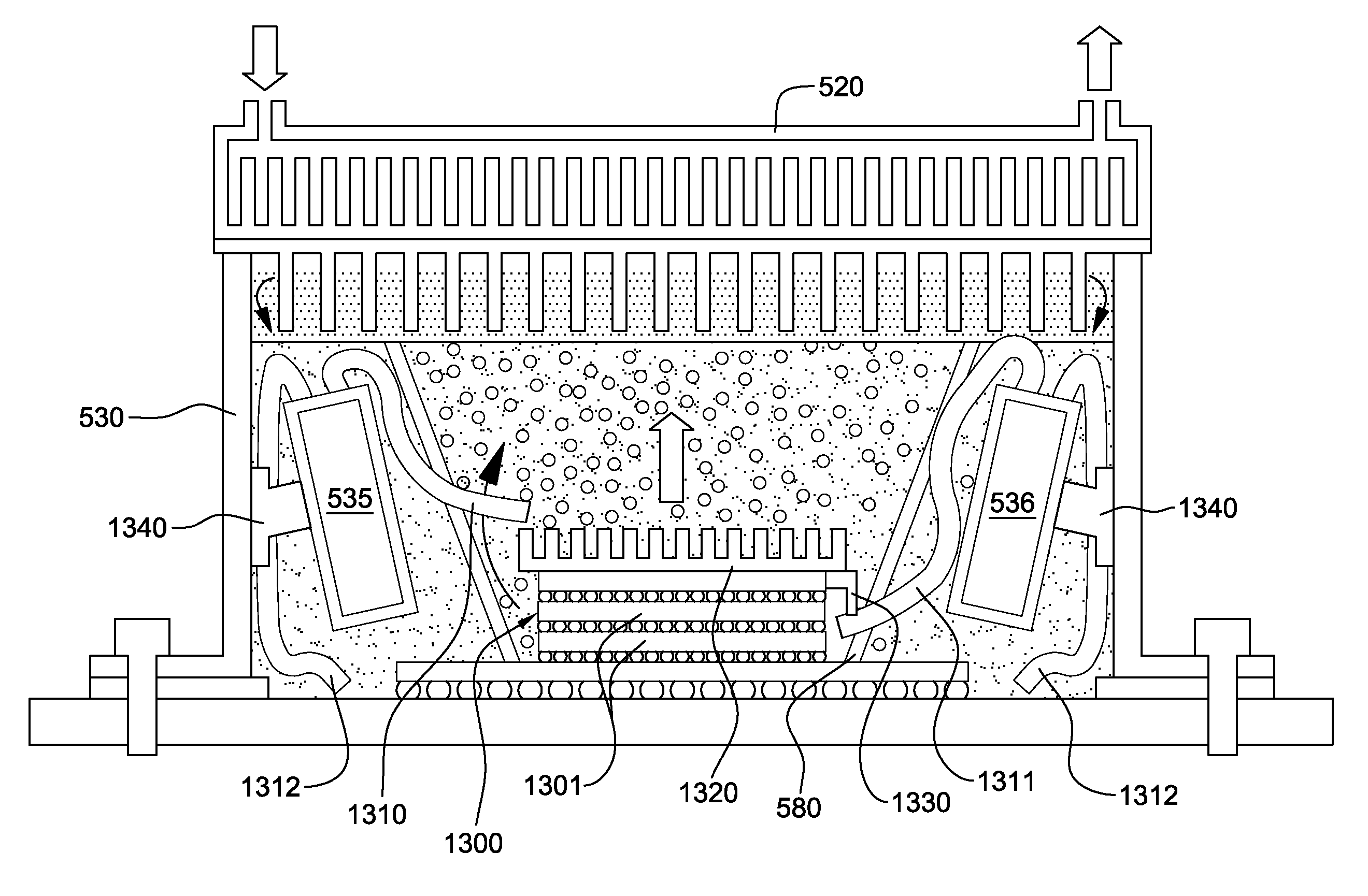
The gaseous fuel-fired can combustor for a gas turbine include a generally cylindrical housing, and a generally cylindrical liner disposed coaxially within the housing to define with the housing a radial outer flow passage for combustion air, the-liner also defining inner combustion and a dilution zone, the dilution zone being axially distant a closed housing end relative to the combustion zone. A fuel / air mixing apparatus disposed at the closed housing end includes a plurality of swirl vanes defining passages each having constant cross-section flow areas along the vanes, and an increasing aspect ratio from the passage inlet to the outlet. An impingement cooling sleeve coaxially disposed in the combustion air passage between the housing and the liner cools the portion of the liner defining the combustion zone. Channeling apparatus is disposed between a downstream end region of the sleeve and the mixing apparatus and includes a diffuser section with a ratio of the outlet flow area to the inlet flow area in a range of 1.3-1.5.
Owner:OPRA TECH
Premixing burner with impingement cooled centerbody and method of cooling centerbody
InactiveUS20050268614A1Improving dynamic sensitivityImprove flame stabilityContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesCombustorGas turbines
A gas-air premixing burner for gas turbines includes an air swirler and an annular burner tube surrounding a bluff centerbody. The bluff body serves to stabilize the flame by defining a recirculating vortex. Cooling air is directed to impinge against the bluff face of the centerbody and the spent impingement cooling air flows in a reverse direction towards the air swirler within the centerbody and is discharged through holes at the outer diameter of the centerbody, where it mixes with the fuel / air mixture prior to reaching the flame zone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Impingement cooled bucket shroud, turbine rotor incorporating the same, and cooling method
ActiveUS7568882B2Effectively cool the blade tip shroudReduce metal temperaturePump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringCooling methods
A localized directional impingement cooling is used to reduce the metal temperatures on highly stressed regions of the tip shroud.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
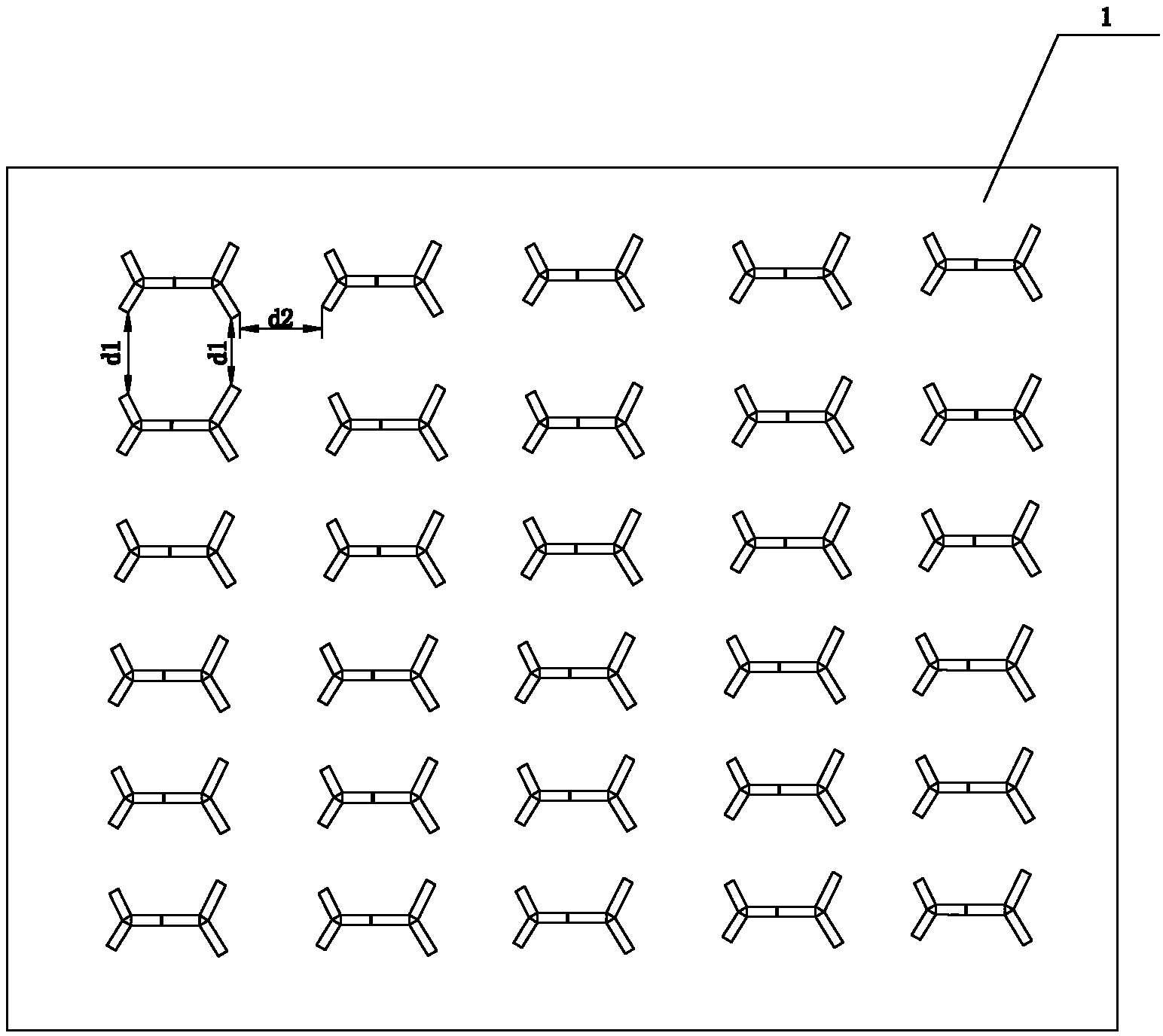
Side by side composite fiber spinneret plate, method of preparing three-dimensional crimp antibacterial fiber with spinneret plate and application of three-dimensional crimp antibacterial fiber
ActiveCN103225118AImprove breathabilityImprove perspirationFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsSOCKSMelt extrusion
The invention relates to a side by side composite fiber spinneret plate, a method of preparing a three-dimensional crimp antibacterial fiber filament, and an application of the three-dimensional crimp antibacterial fiber filament. The method comprises the steps that the side by side composite fiber spinneret plate is used; every two groups of rectangular spinneret orifices in unequal dimensions at 120 degrees form every equilateral three-blade A and B; an ingredient A and an ingredient B with different thermal shrinkage rates are selected; an antimicrobial agent ingredient C is added into the ingredient A; the ingredient A and the ingredient C are subjected to melt extrusion by two twin screws, enter a parallel composite component and the spinneret plate after metered, and are subjected to parallel composite distribution, cross air blow, low-temperature shock cooling, oiling and winding to form a winding yarn; and the winding yarn is subjected to drawing, false twisting and thermoforming to form a DTY (Draw Textured Yarn) or subjected to the drawing and thermoforming to form the DTY. A three-dimensional crimp antibacterial fiber prepared by the method is soft and elastic, has the characteristics of good breathability, wicking, quick drying, antibacterium and the like since various grooves are formed in the cross section, and is applied to the development of shell fabrics of undergarments, sports suits, socks, bedclothes and the like and medical dressings.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Airfoil platform impingement cooling
A gas turbine engine airfoil has a platform cooling scheme including an impingement hole for directing cooling air against an undersurface of the airfoil platform.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Fuel lance cooling for a gas turbine with sequential combustion
ActiveUS20160146468A1Improve mix qualityReduce total pressure lossContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsLeading edgeCombustor
A fuel lance is disclosed for injecting a gaseous and / or liquid fuel mixed with air into an axial hot gas flow flowing through a sequential combustor of a gas turbine, the fuel lance having at least one finger extending in a longitudinal direction into the axial hot gas flow of the gas turbine essentially perpendicular to the hot gas flow. The finger is configured as a streamlined body which has a streamlined cross-sectional profile. The body has two lateral surfaces essentially parallel to the axial hot gas flow. The body includes an enclosing outer wall having a longitudinally extending air plenum for the distributed introduction of air into the at least one finger. The air plenum is provided with a plurality of distributed impingement cooling holes, such that air exiting through the impingement cooling holes impinges on the inner side of the leading edge region of the body.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Turbine airfoil with trailing edge cooling channels
InactiveUS8070441B1Increase flow rateShorten the lengthEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesIndustrial gasTrailing edge
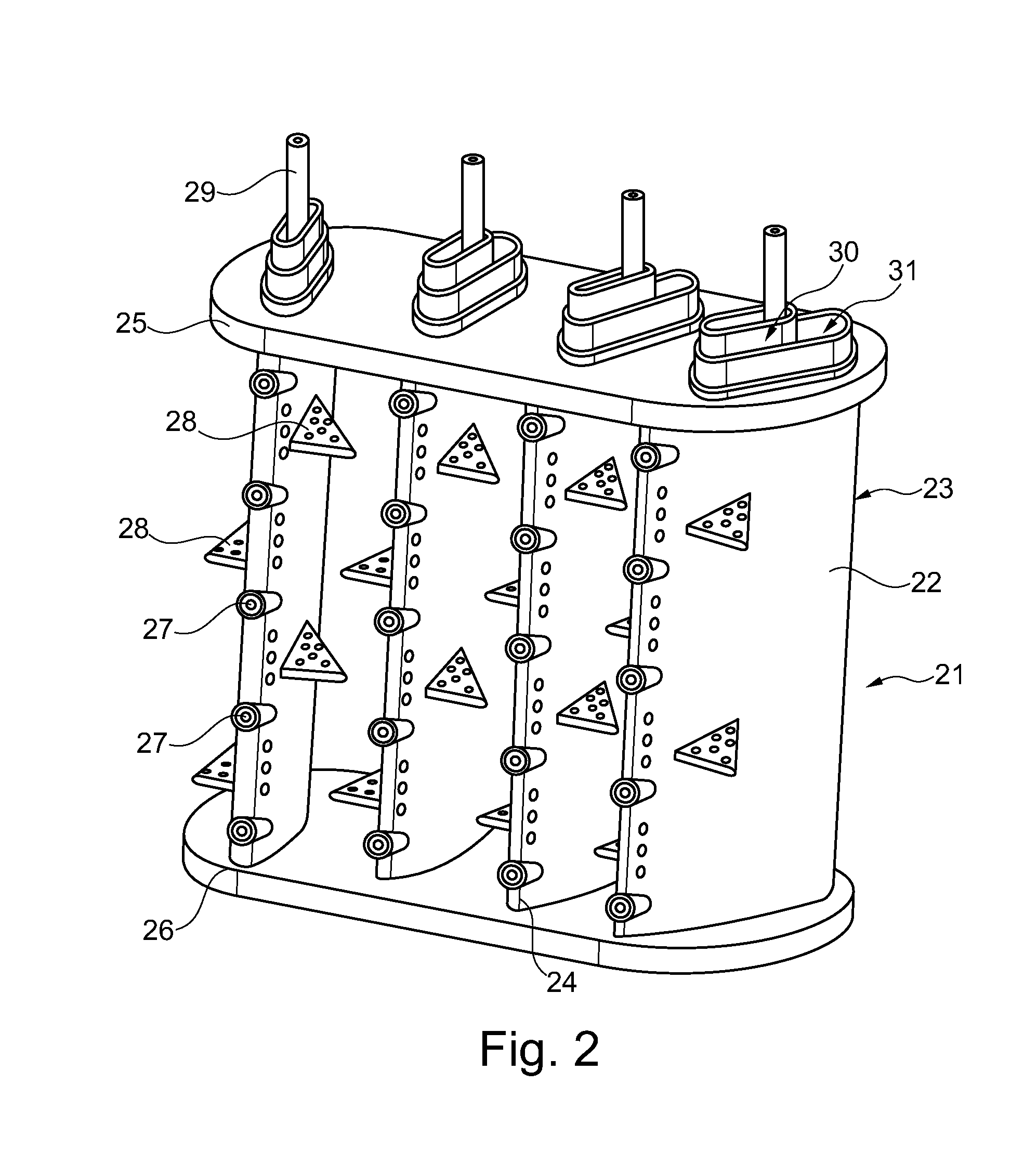
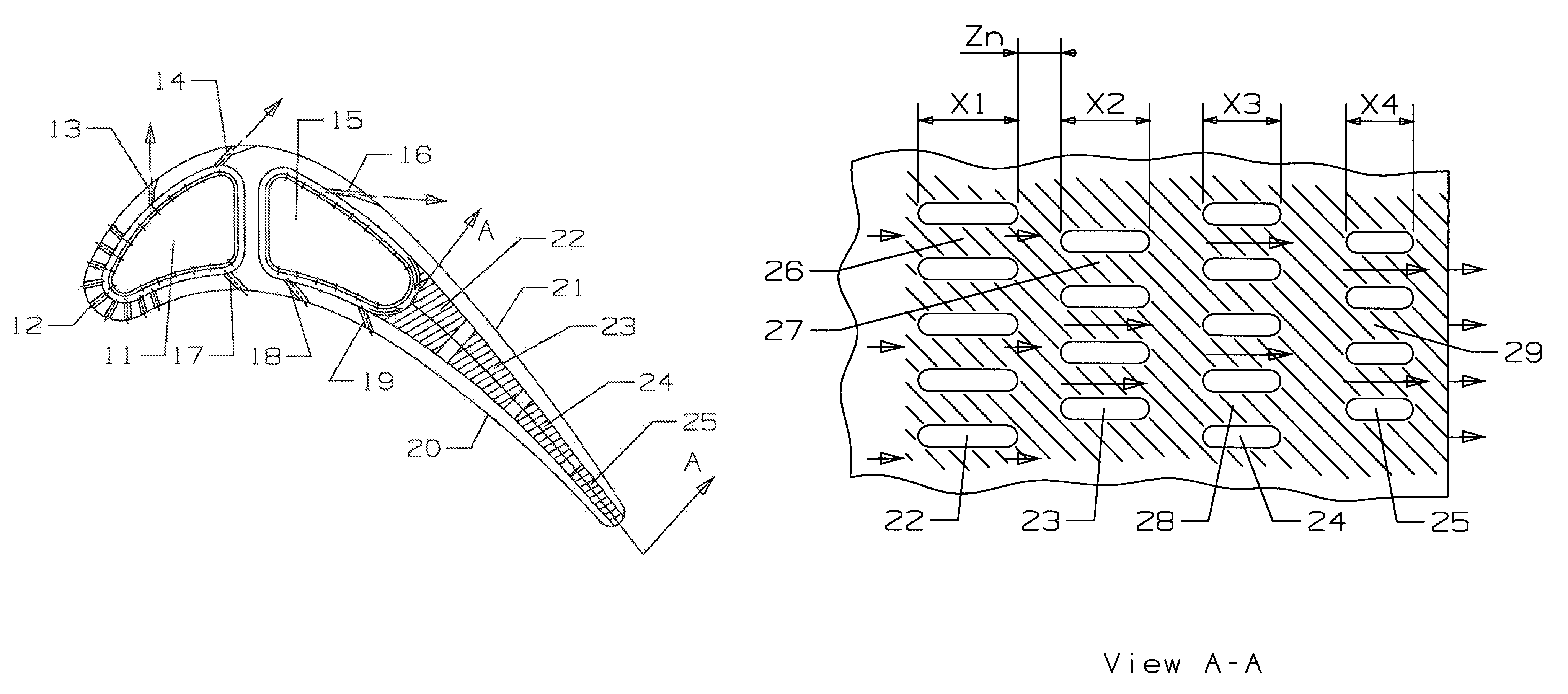
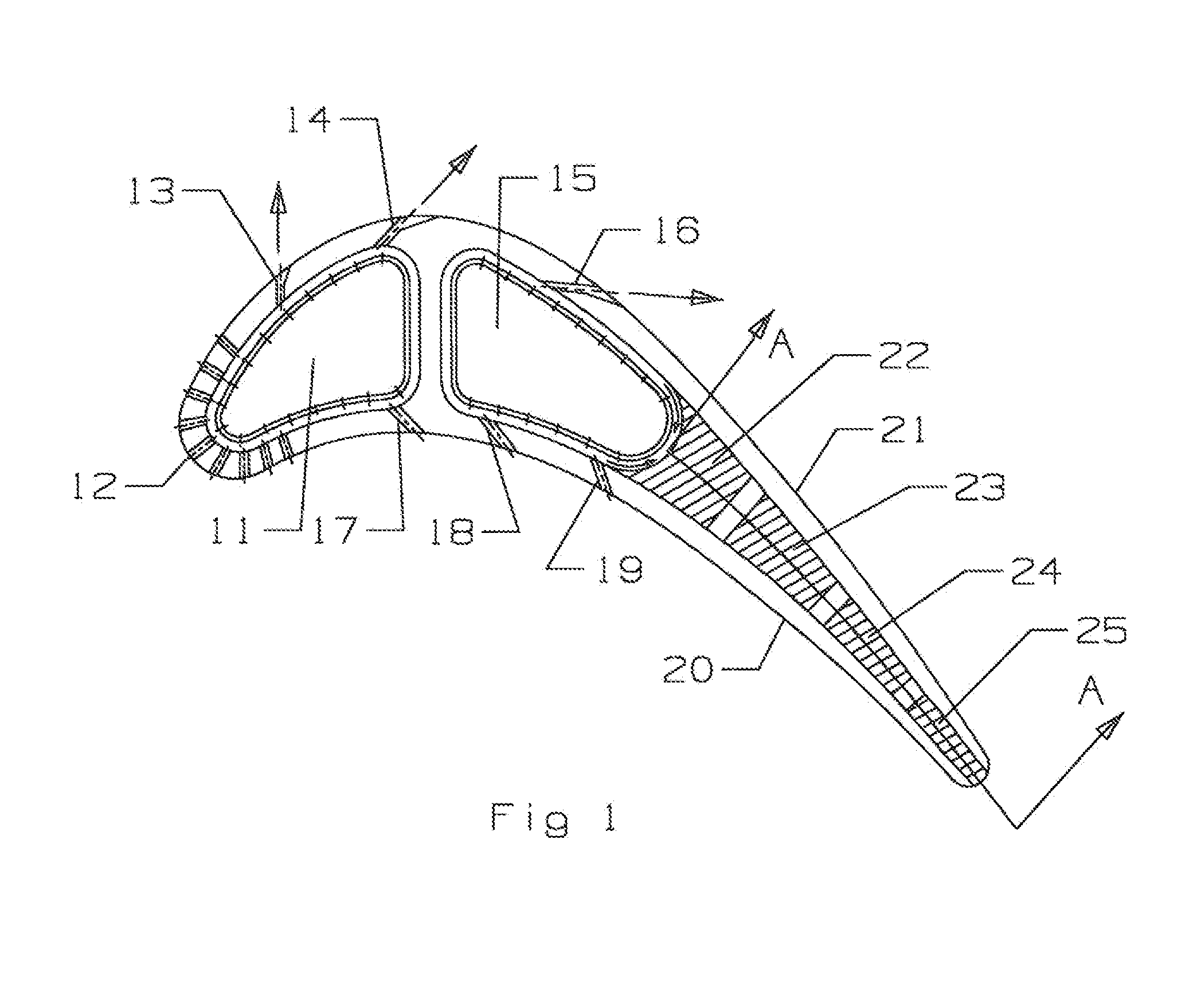
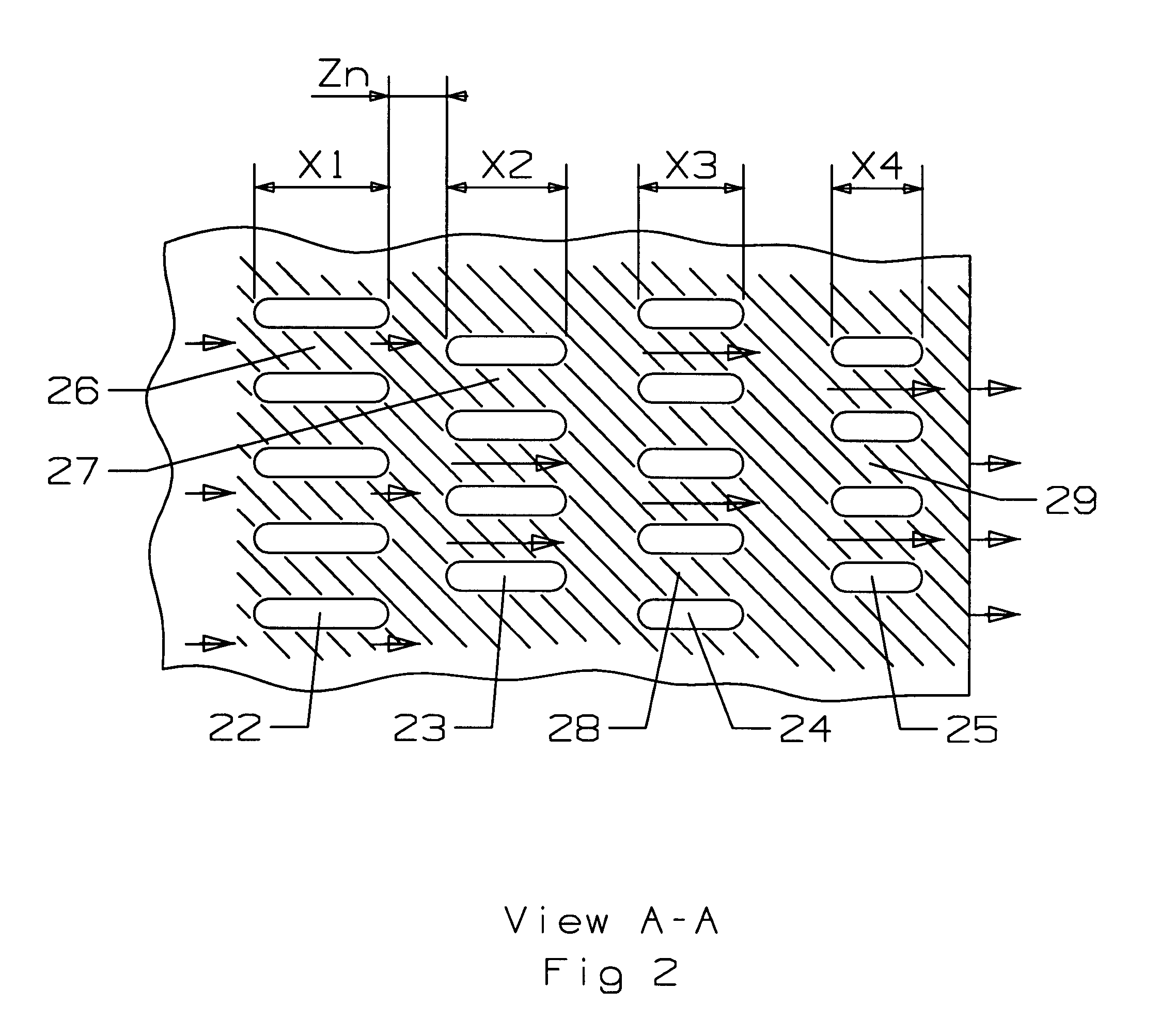
A turbine airfoil such as a turbine stator vane used in an industrial gas turbine engine, the vane including a trailing edge region having a thin wall cooling channel arrangement of mini cooling channels formed by a series of rows of elongated flow blockers that form the mini cooling channels between adjacent flow blockers. The adjacent row of flow blockers are offset from the each other such that the inlet and the outlet flow of cooling air is discharged directly onto the flow blocker in order to produce impingement cooling. The mini cooling channels have a spacing to hydraulic diameter ratio of less than 4.0 and a mini channel length to hydraulic diameter ratio of 5.0 of less in order to maintain a high flow velocity within the mini channels. In one embodiment, the flow blockers have a progressively decreasing length in the flow direction of the cooling air.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
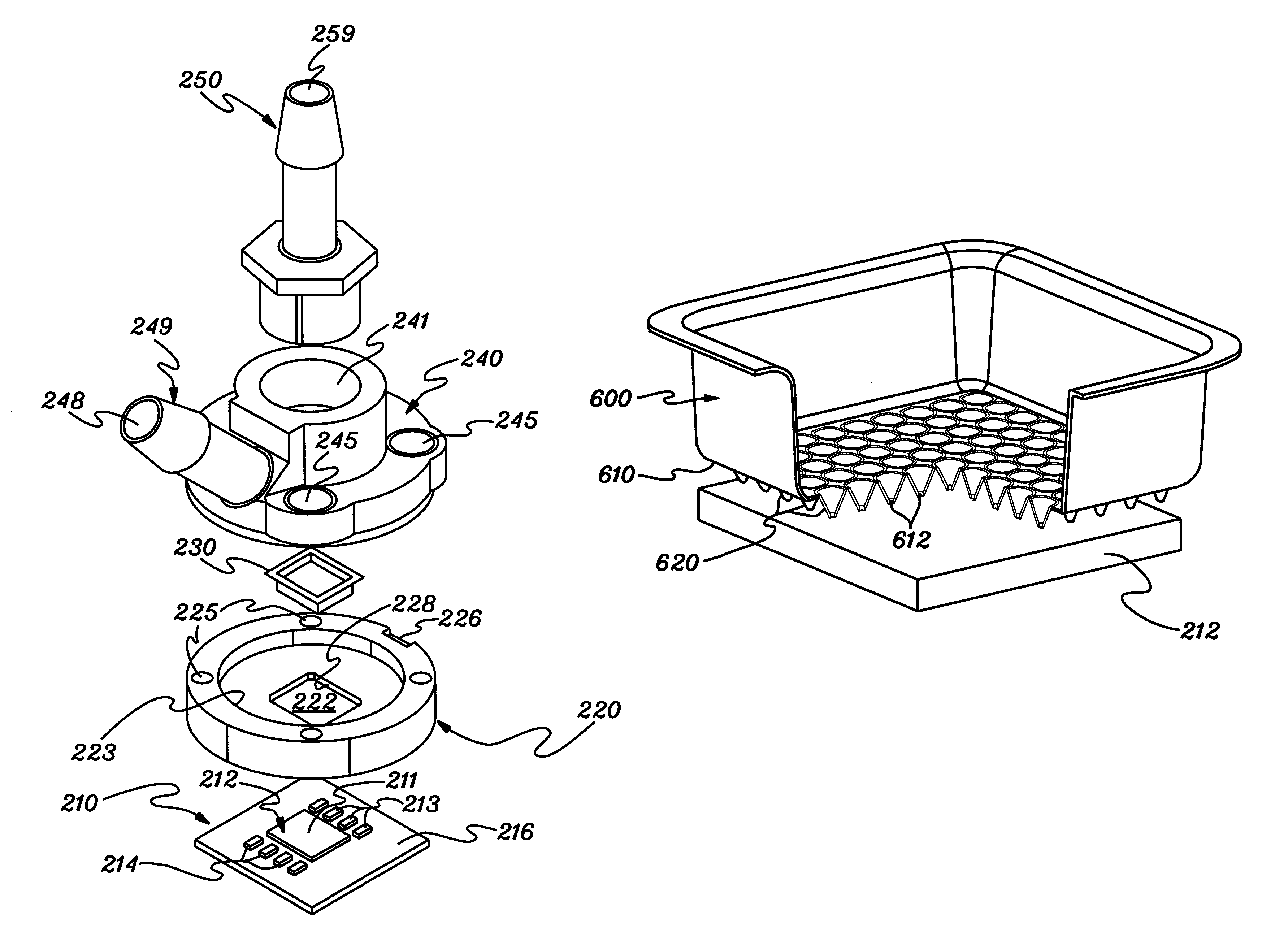
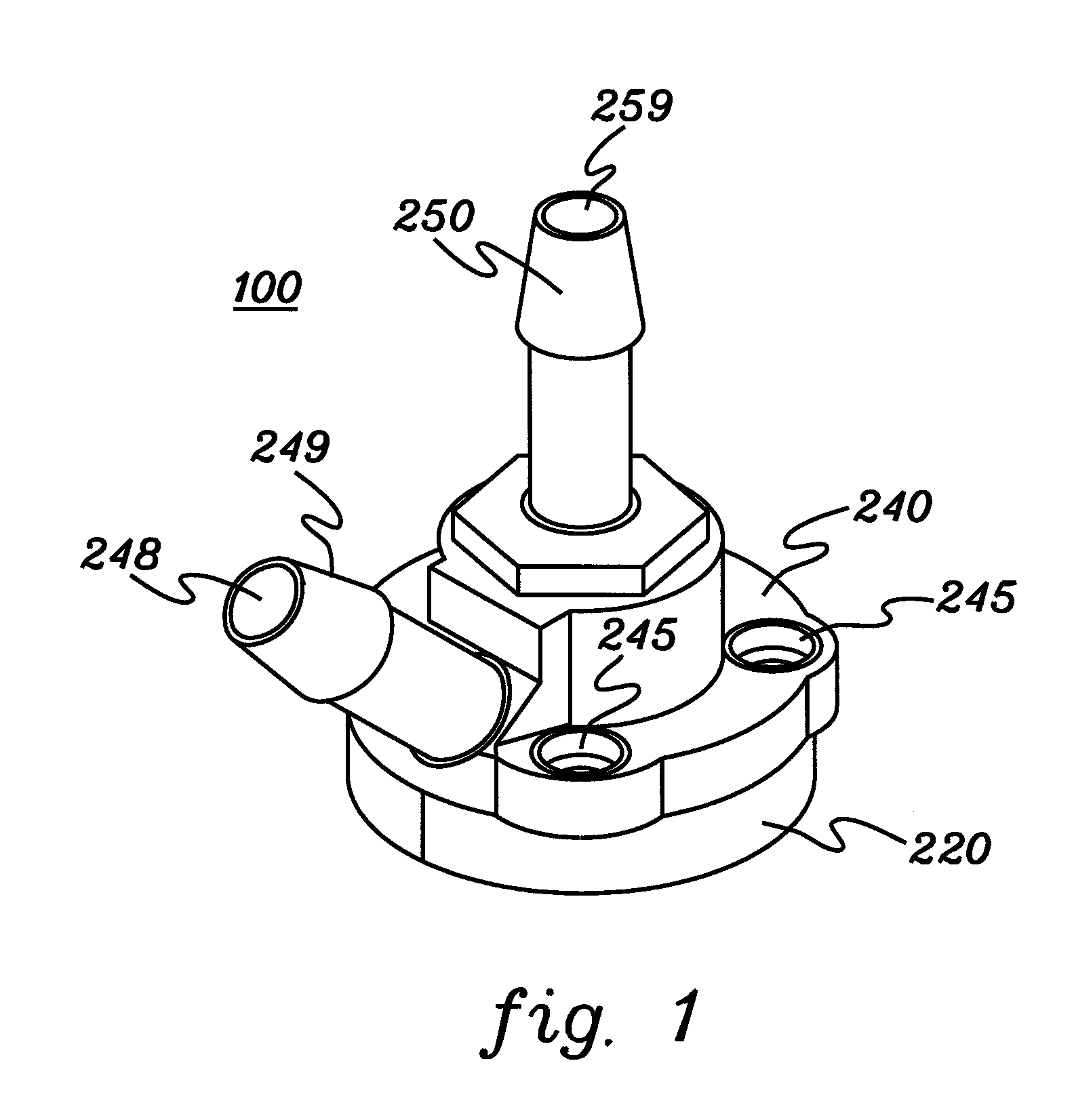
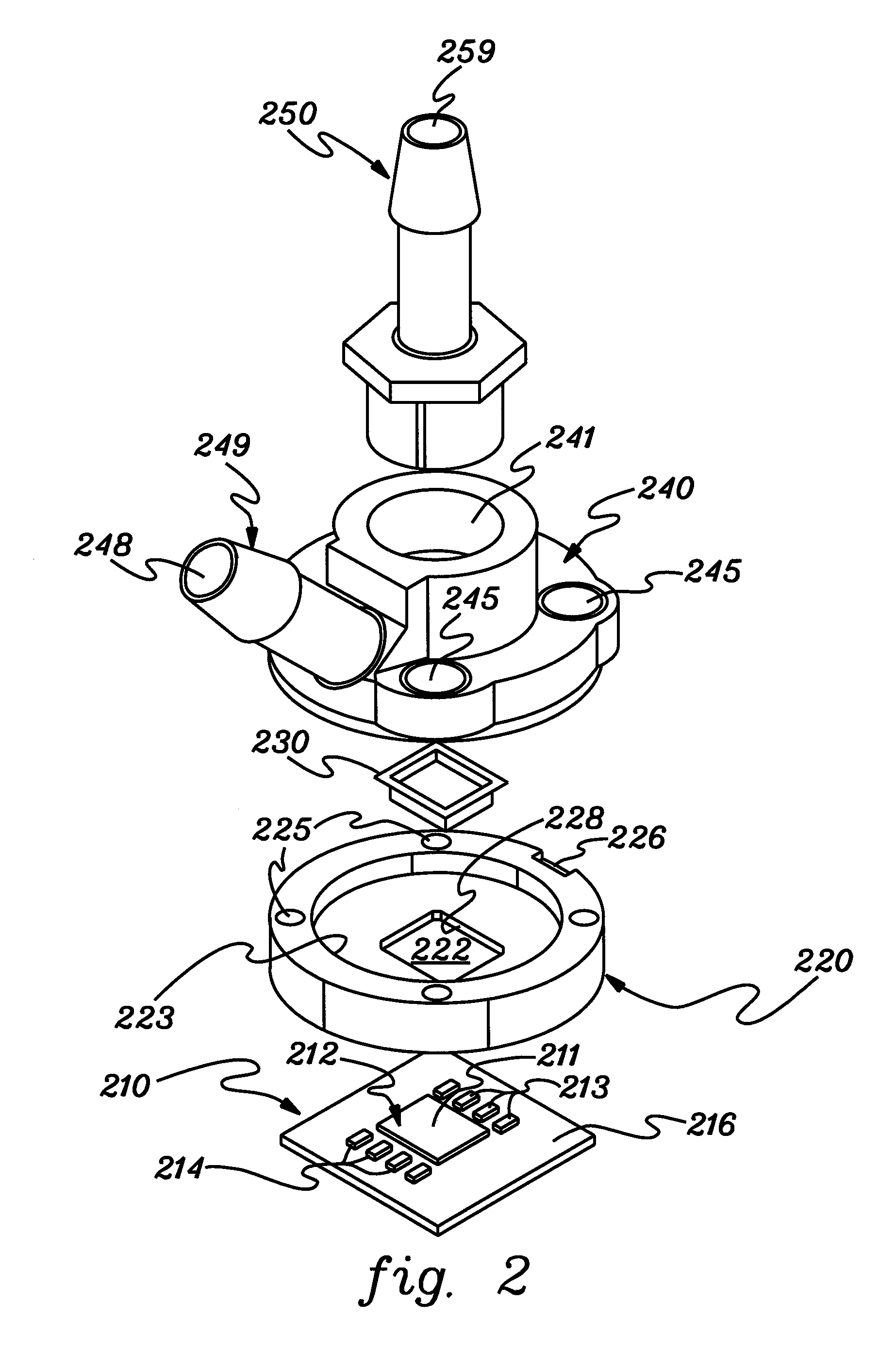
Impingement Cooling
InactiveUS20100097760A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
An apparatus and a method for impingement cooling. The apparatus may include a plenum having a fluid. The plenum may be configured to contact a plate. A duct may be attached to the plate, wherein the duct may include a hole configured to pass the fluid, such as an air or a gas. A heat source, such as an electric or electronic component, may be located proximate to the hole, such as on a printed circuit board. The hole may be configured to make a contact between the fluid and the heat source. Methods to make the foregoing structure are also described.
Owner:ADVANCED THERMAL SOLUTION
Method of cooling centerbody of premixing burner
InactiveUS20060010878A1Improving to fluctuationsImprove stabilityContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustorGas turbines
A gas-air premixing burner for gas turbines includes an air swirler and an annular burner tube surrounding a bluff centerbody. The bluff body serves to stabilize the flame by defining a recirculating vortex. Cooling air is directed to impinge against the bluff face of the centerbody and the spent impingement cooling air flows in a reverse direction towards the air swirler within the centerbody and is discharged through holes at the outer diameter of the centerbody, where it mixes with the fuel / air mixture prior to reaching the flame zone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cooling concept for turbine blades or vanes
ActiveUS20170234144A1Easy and cheap to implementEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesTurbine bladeWall segment
A turbine assembly with a hollow aerofoil having a main cavity with an impingement tube, insertable inside the main cavity for impingement cooling of an inner surface of the main cavity, and a platform at a radial end of the hollow aerofoil, and a cooling chamber for cooling the platform arranged relative to the hollow aerofoil on an opposed site of the platform. The cooling chamber is limited at a first radial end by a wall segment of the platform and at an opposed radial second end from a cover plate. The impingement tube extends in span wise direction through the cooling chamber from the platform to the cover plate and restricts a sub-cavity of the main cavity. The wall segment includes an entry aperture for a cooling medium to enter from the cooling chamber of the platform into the sub-cavity of the hollow aerofoil.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
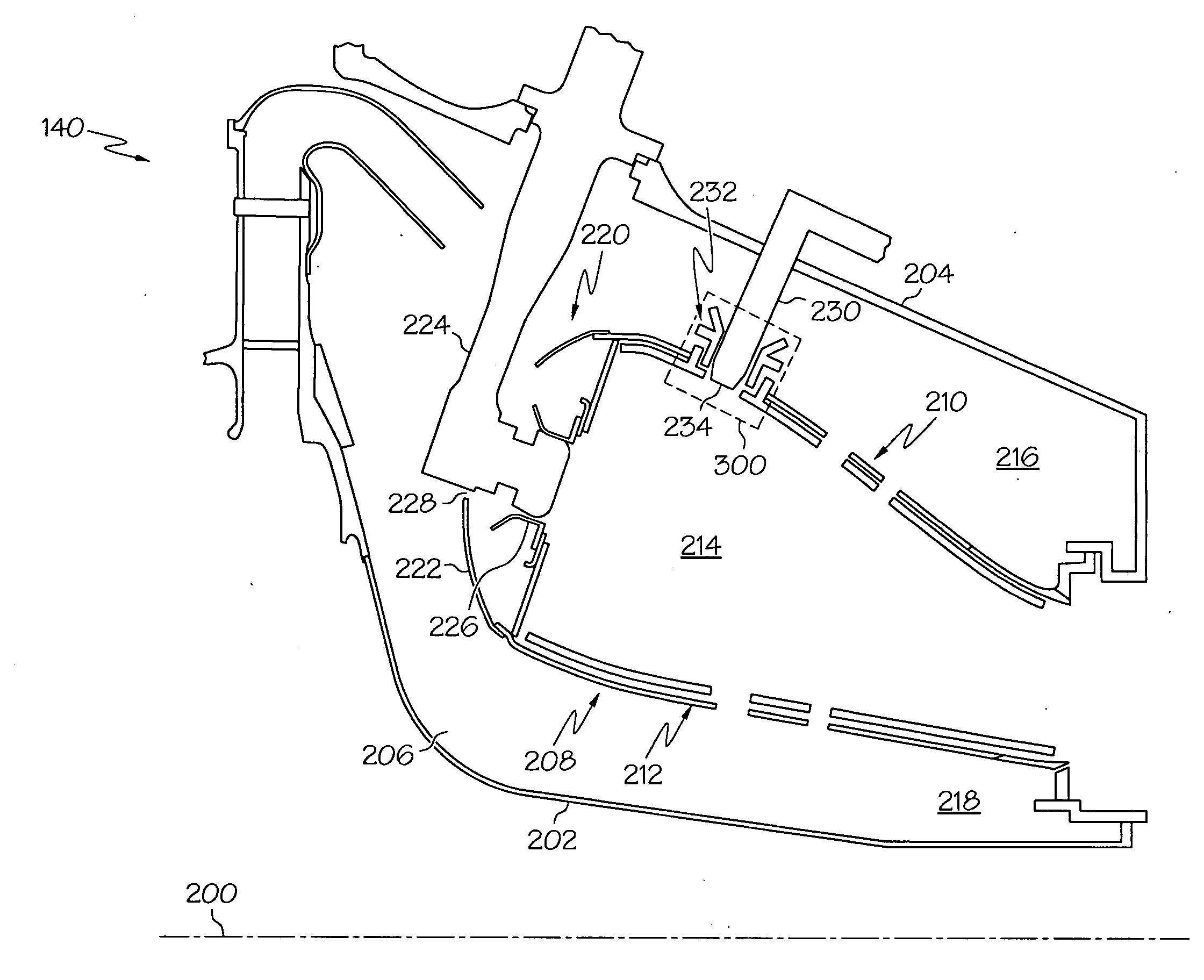
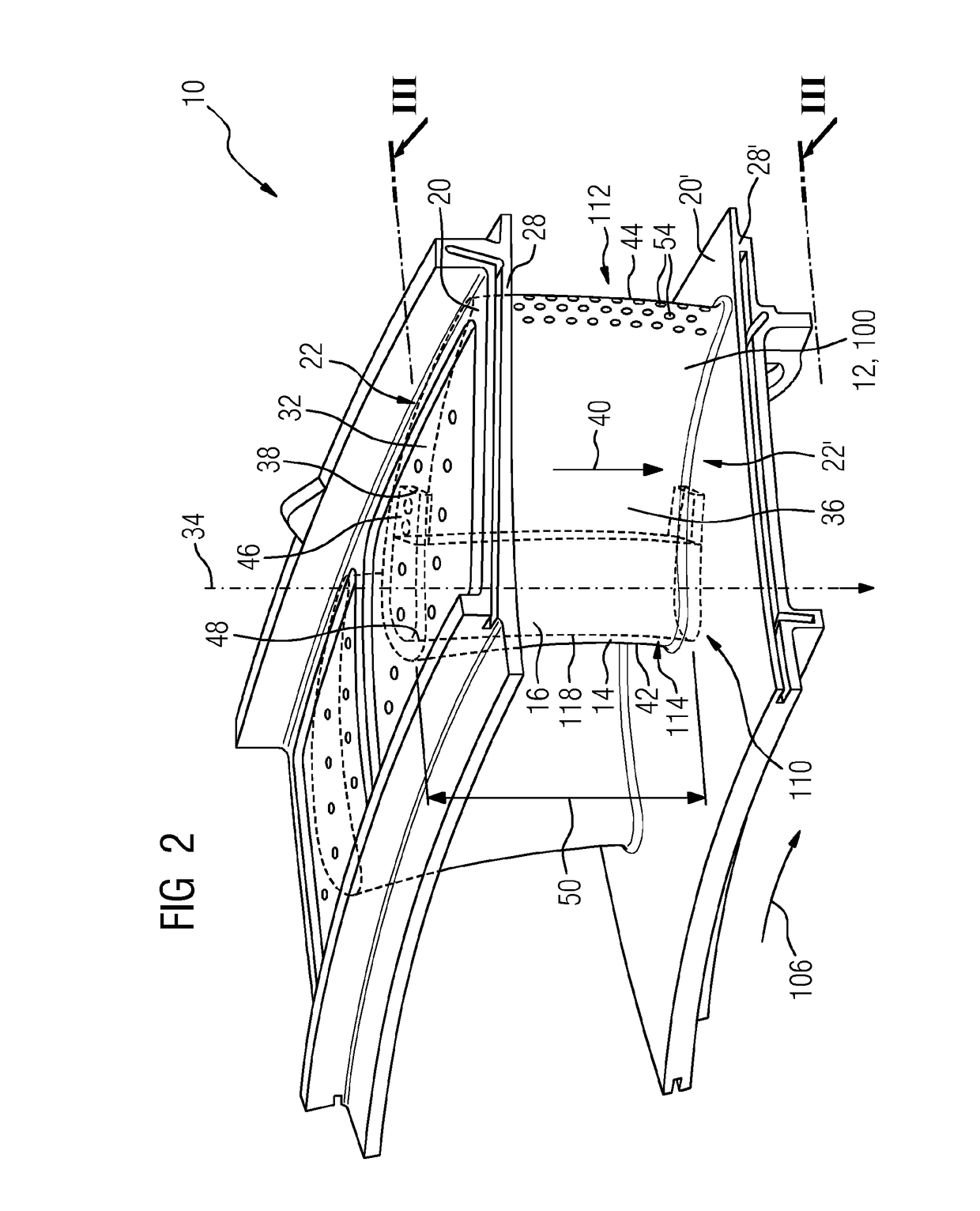
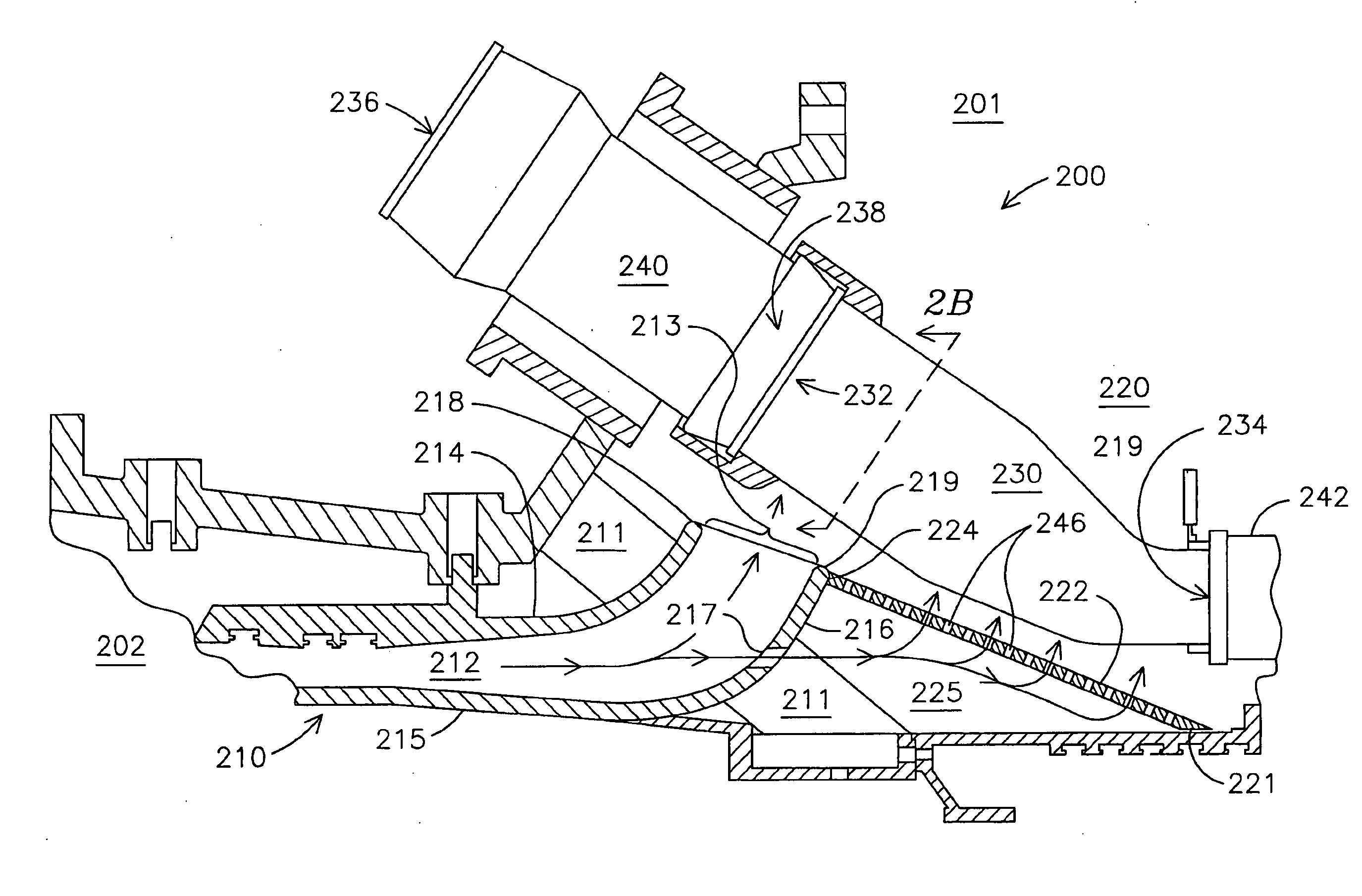
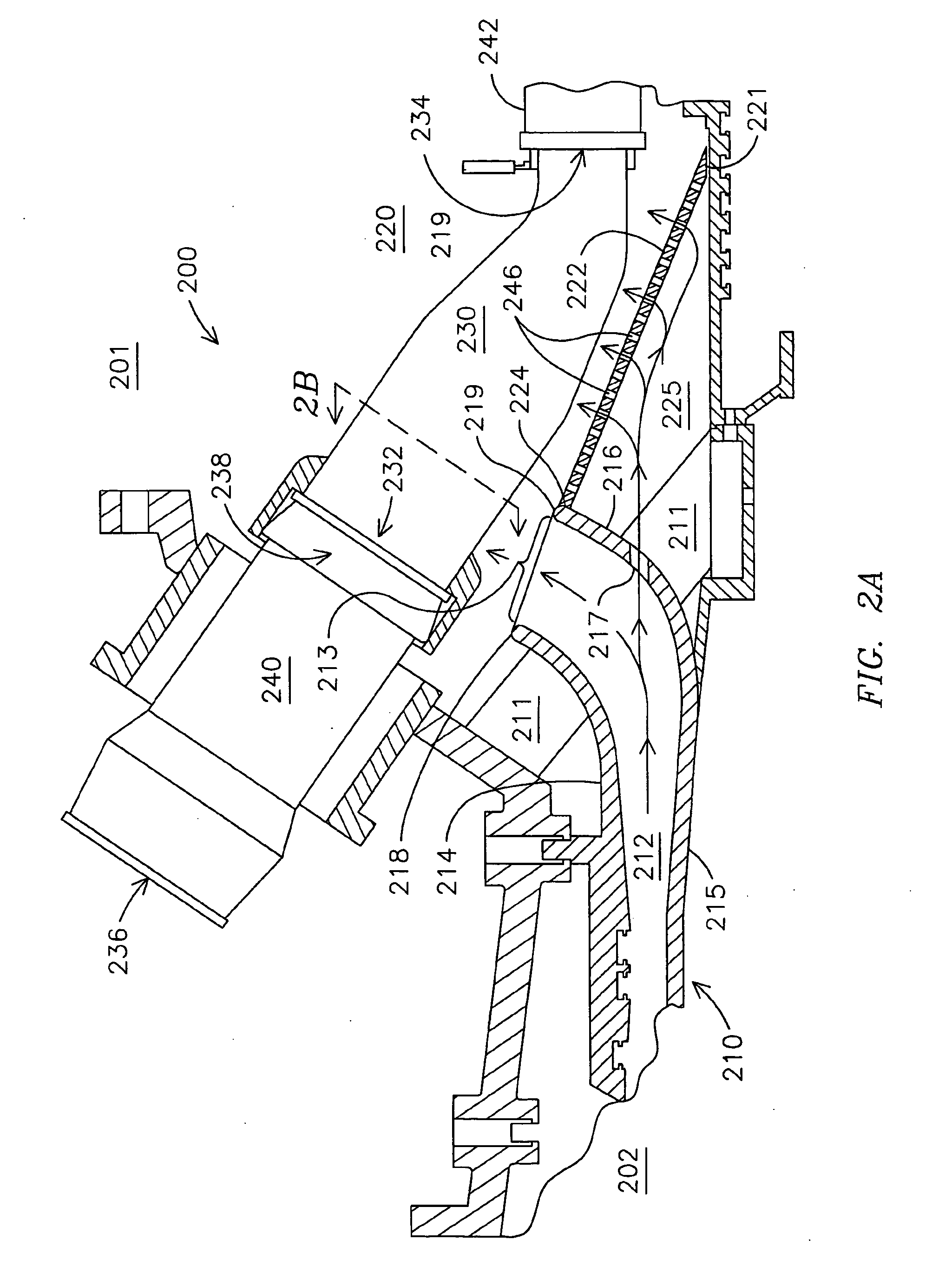
Gas turbine engine curved diffuser with partial impingement cooling apparatus for transitions
A curved diffuser (210) in a gas turbine engine (201) directs a primary portion of air flow from a compressor (202) through a curved discharge opening (213) into a plenum (220). The curved diffuser (210) also comprises ports (217) through which a secondary portion of air passes into confined space (225) that is defined in part by a pressure boundary element that may be comprised of at least one plate (222) or at least one conduit (306). The at least one plate (222) and the at least one conduit (306) respectively comprise apertures (246, 312) through which pass the secondary portion of air to provide impingement-type cooling to transitions (230, 320). In various embodiments the velocity of the air between adjacent transitions (230, 320) may flow at relatively uniform velocity along the longitudinal distance of the respective transitions (230, 320).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com