Patents
Literature
877results about "Turbine/propulsion fuel valves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
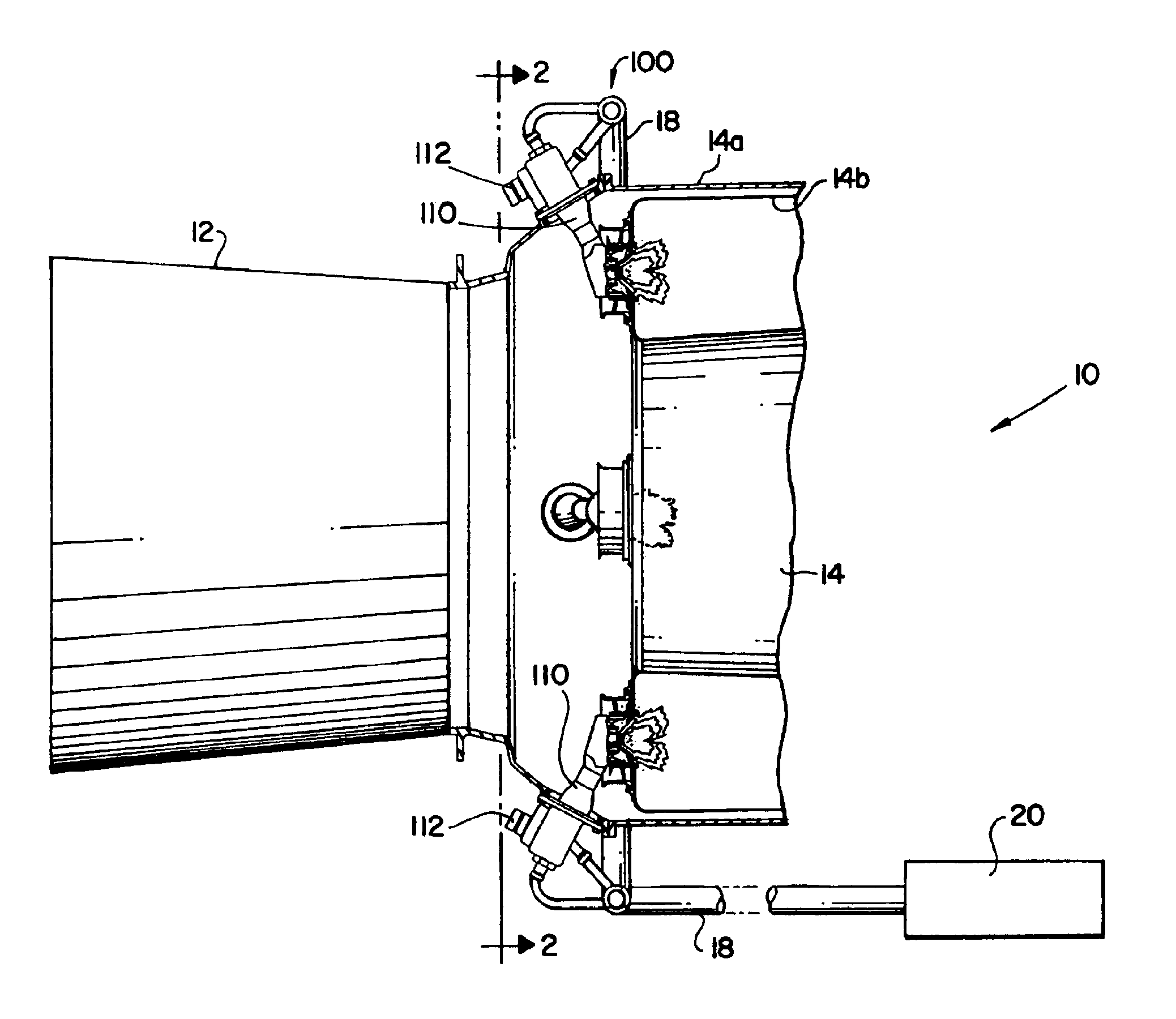
Methods and apparatus for a combustion turbine nitrogen purge system
ActiveUS7730711B2Reduce formationEasy to disassembleLiquid fuel feeder/distributionEngine fuctionsParticulatesCombustion
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Minitype gas turbine generator wellhead shale gas supply device control system
PendingCN111350595AMeet the requirements of water hydrocarbon dew pointGuaranteed uptimeTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesGas turbine plantsMicro gas turbineHydrocarbon dew point
The invention discloses a minitype gas turbine generator wellhead shale gas supply device control system. A control protection system comprises a particle liquid drop control system, a temperature control system, a pressure control system, a liquid level control system, a water hydrocarbon dew point control system, a fine treatment control system and a system safety protection system which are independently arranged side by side, a working condition parameter signal acquisition system transmits acquired signals to a logic judgment command system, the logic judgment command system is correspondingly connected with a parameter setting system, the control protection system and a data storage remote transmission system, and a micro gas turbine power generation system is correspondingly connected with the parameter setting system, the control protection system and the data storage remote transmission system. The control system has the beneficial effects that stable control over the water hydrocarbon dew point is achieved, and normal and stable operation of the micro gas turbine is guaranteed; the pollution discharge is accurately controlled according to the fluctuation condition of theactual working condition, and the overall operation cost is reduced; and automatic liquid drainage under different working condition fluctuations is achieved, and the risks of tripping and blow-by arereduced.
Owner:JEREH OIL & GAS ENG
Fuel/air premixer for gas turbine combustor
InactiveUS20050039456A1Reduce weightReduce overall outer diameterBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustorCombustion chamber
A fuel / air premixer for use in a gas turbine improves the atomization performance and mixing performance of the fuel by guiding an air so as to flow in an outward radial direction. A flow-deflecting tubular body having an annular cross section is disposed on the inside of and coaxially with a liquid film-forming body of an airblast atomizer nozzle disposed at the inlet portion of a premixing tube. The outer peripheral surface of the flow-deflecting tubular body has a wall surface which increases in outer diameter toward the tip end of a first annular passage. The inner peripheral surface of the flow-deflecting tubular body has a form in which the inner diameter has a minimum to form a contracted portion, and then increases dramatically toward the tip end.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Fuel/air premixer for gas turbine combustor
InactiveUS7434401B2Improve performanceAvoid burnsBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustorCombustion chamber
A fuel / air premixer for use in a gas turbine improves the atomization performance and mixing performance of the fuel by guiding an air so as to flow in an outward radial direction. A flow-deflecting tubular body having an annular cross section is disposed on the inside of and coaxially with a liquid film-forming body of an airbiast atomizer nozzle disposed at the inlet portion of a premixing tube. The outer peripheral surface of the flow-deflecting tubular body has a wall surface which increases in outer diameter toward the tip end of a first annular passage. The inner peripheral surface of the flow-deflecting tubular body has a form in which the inner diameter has a minimum to form a contracted portion, and then increases dramatically toward the tip end.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
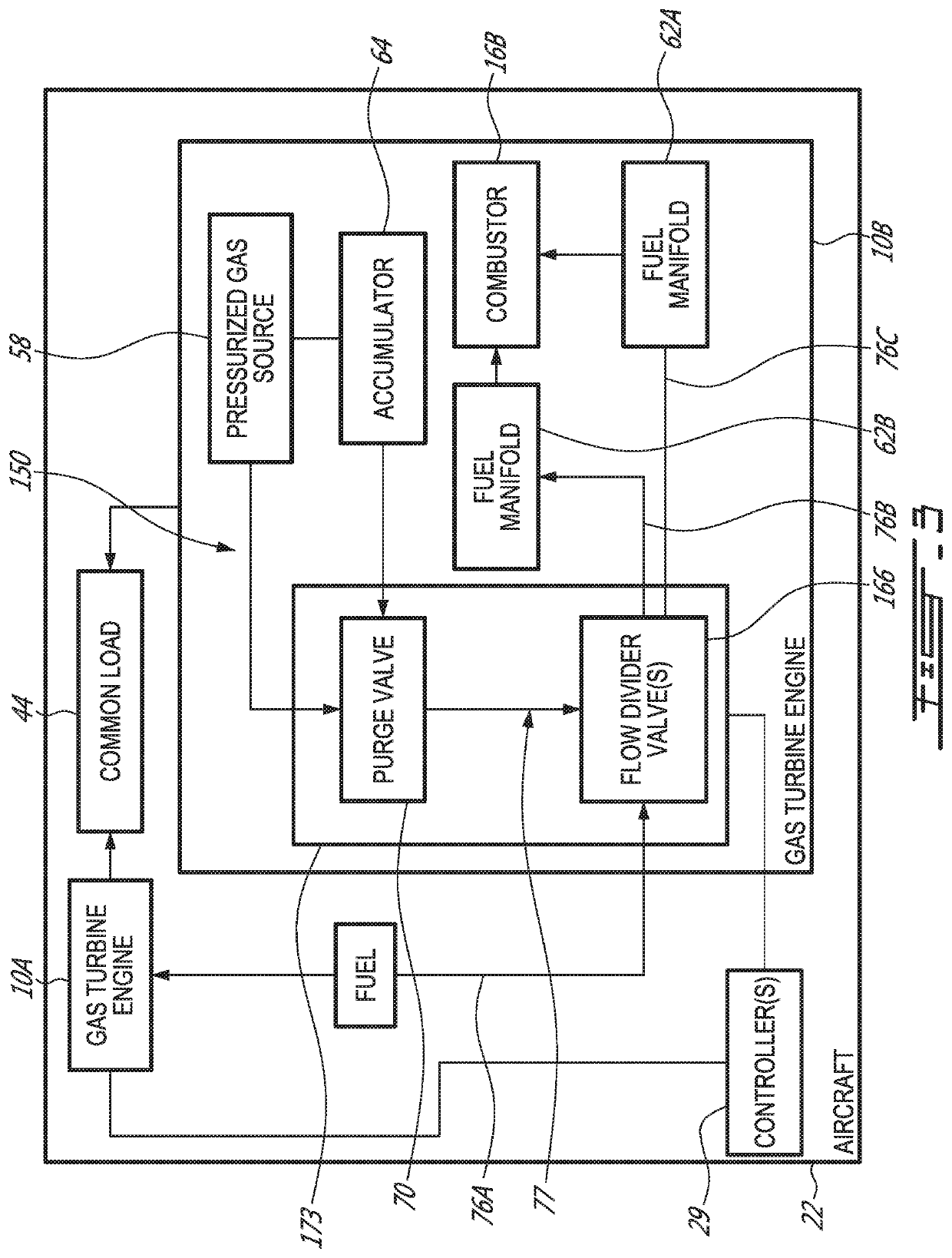
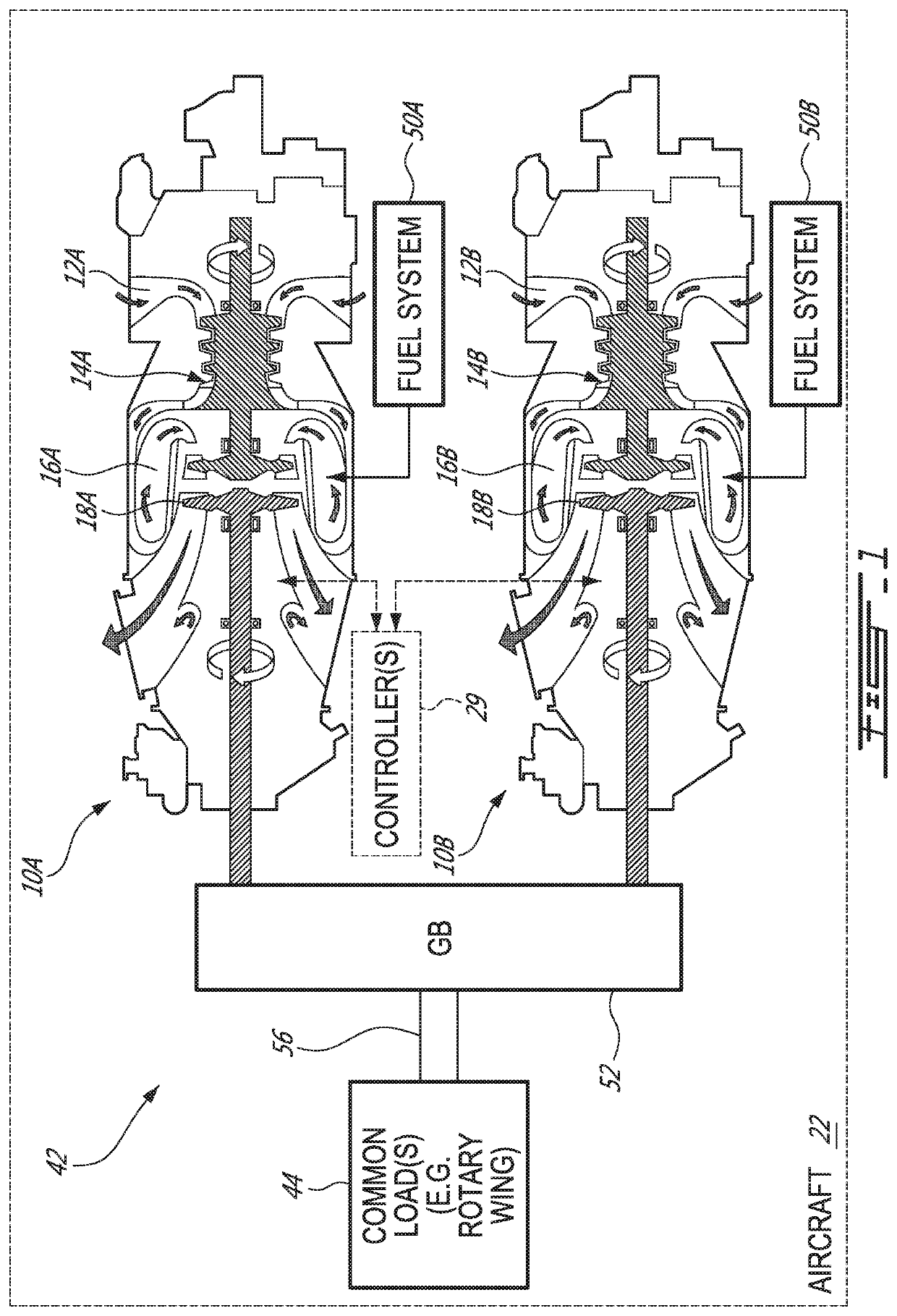
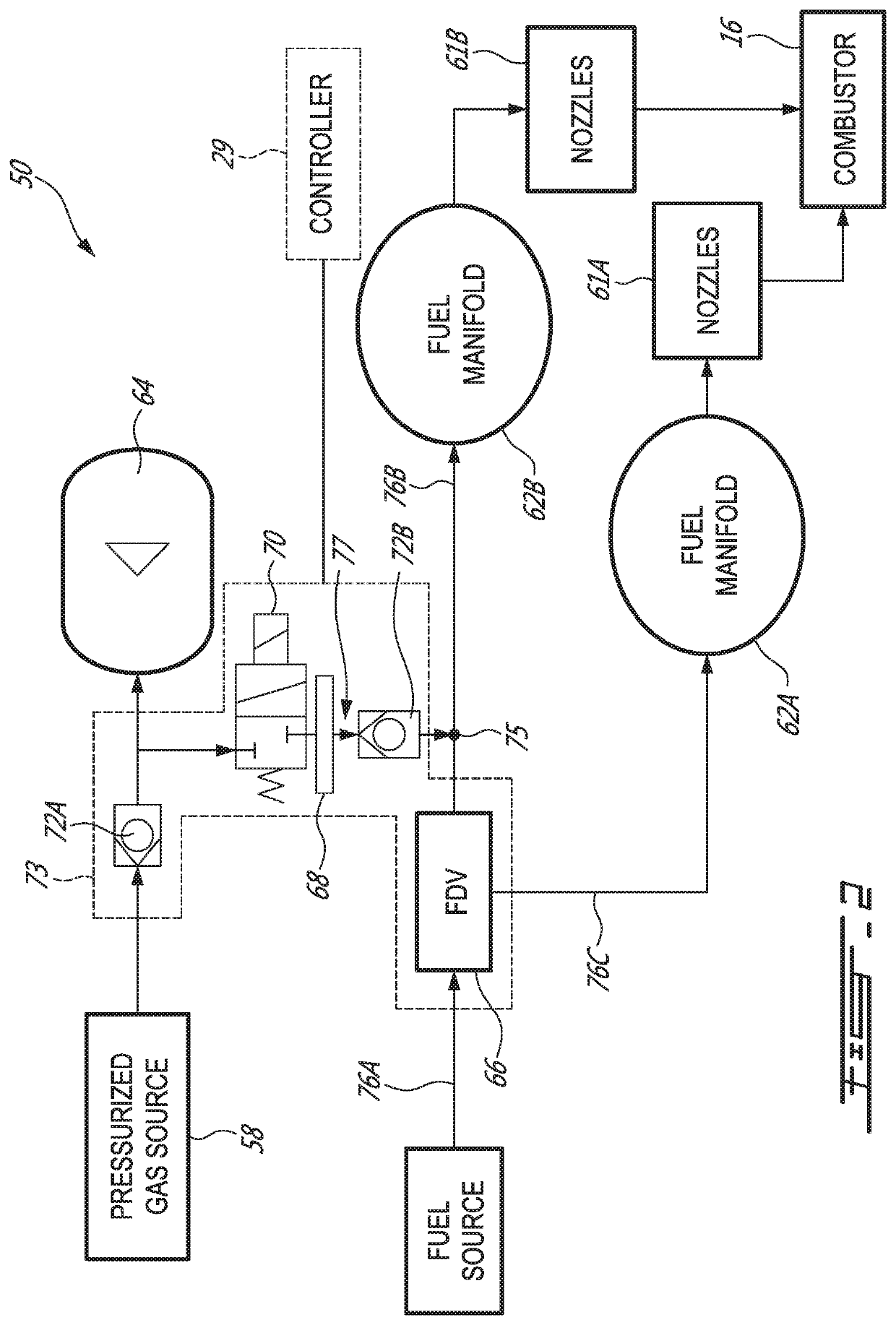
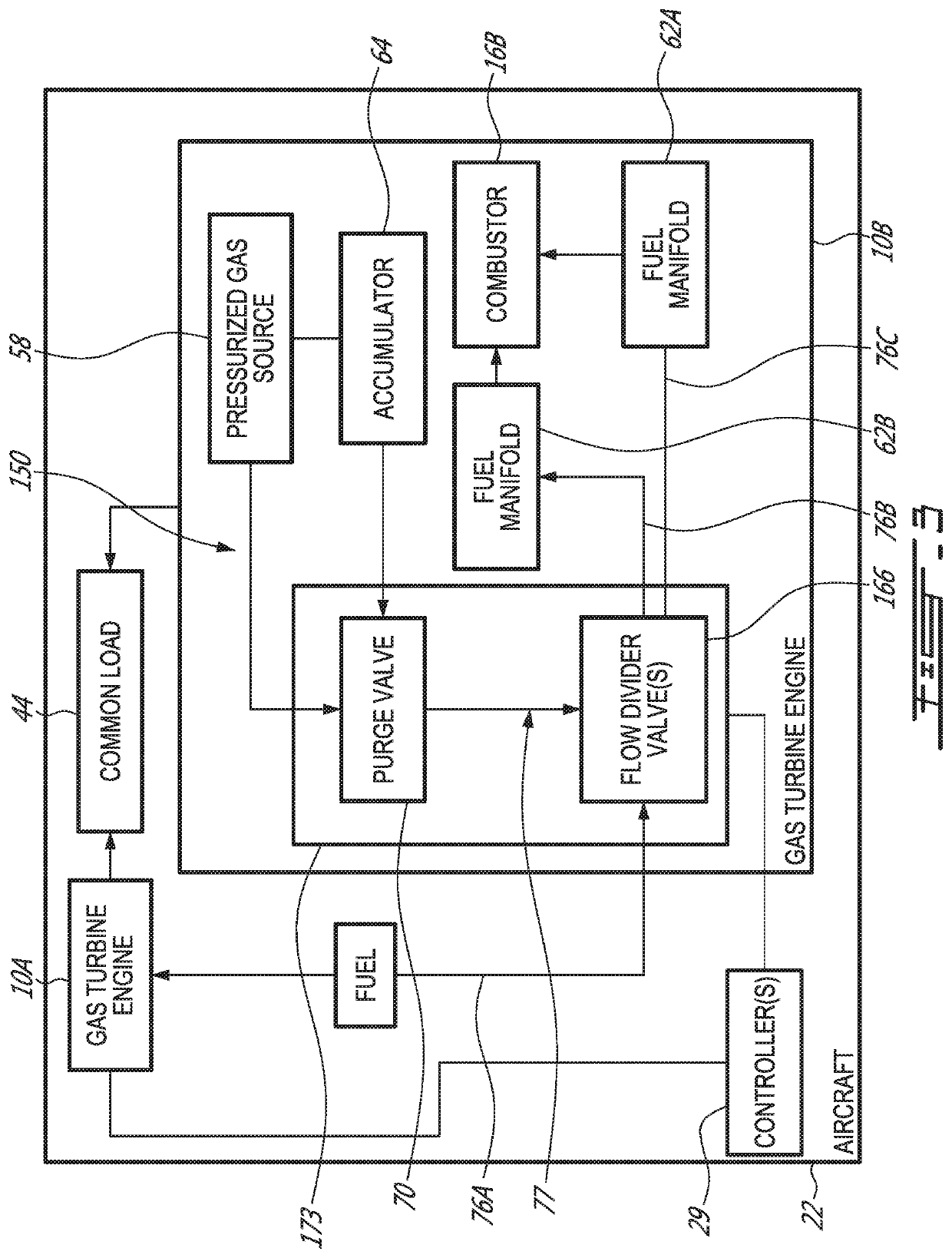
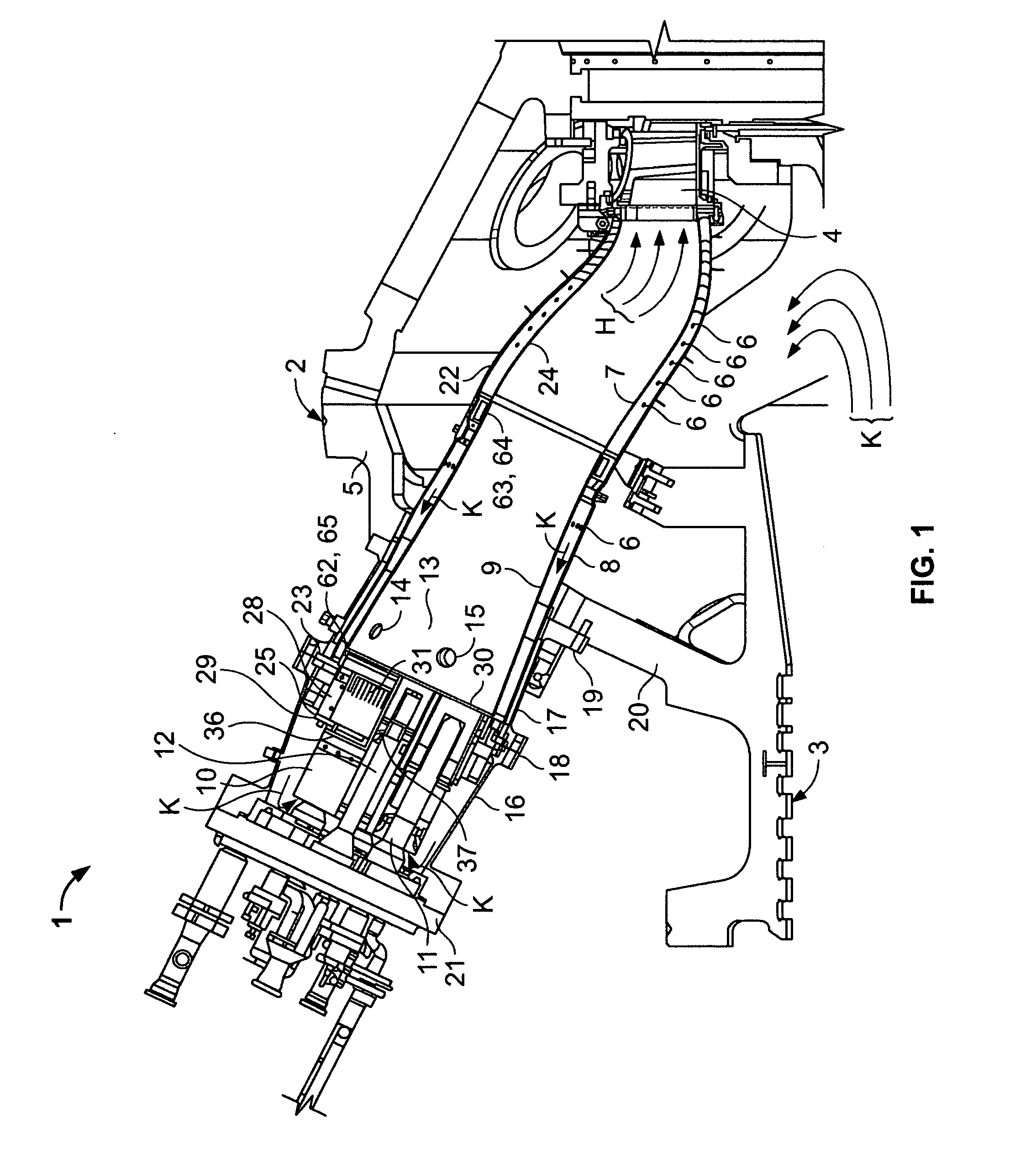
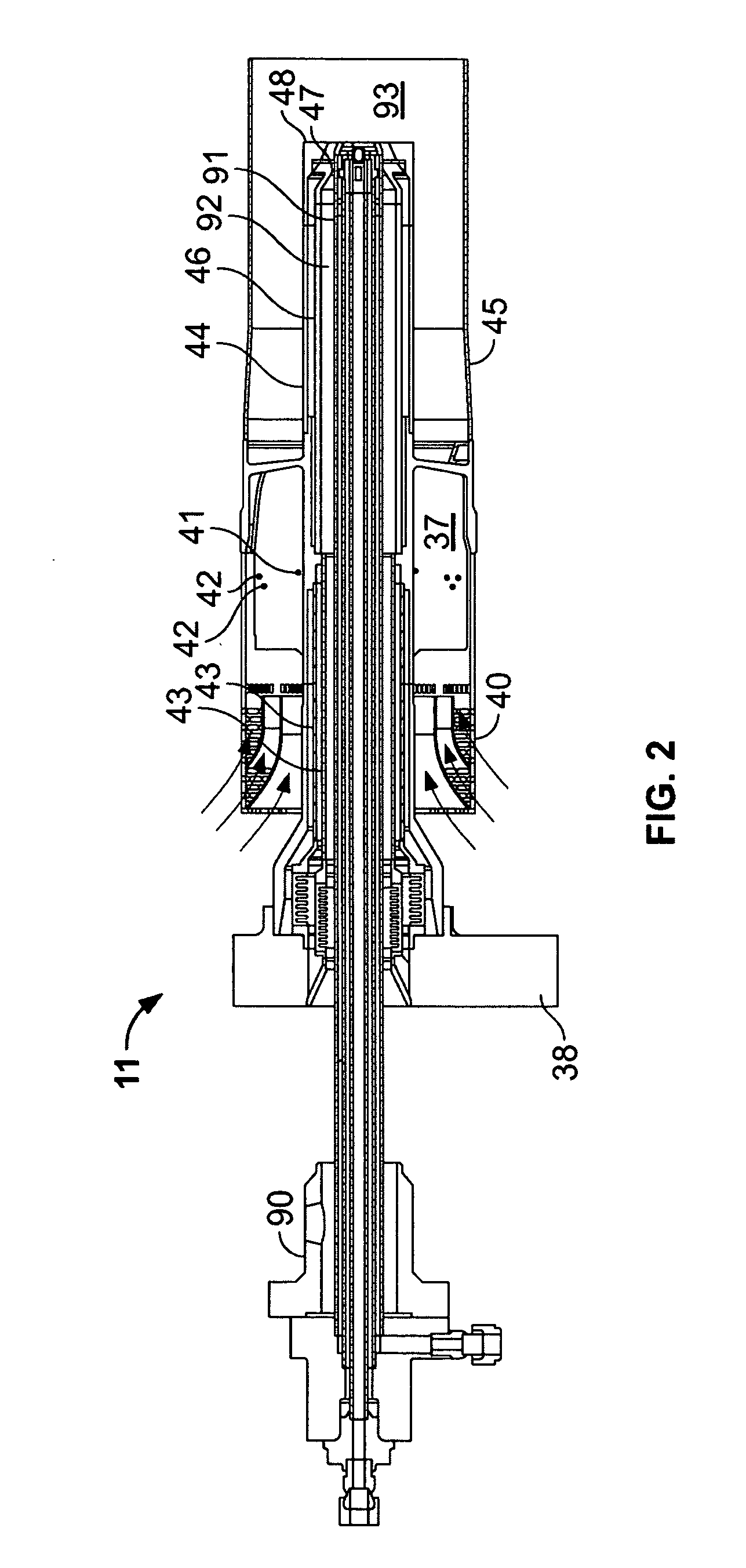
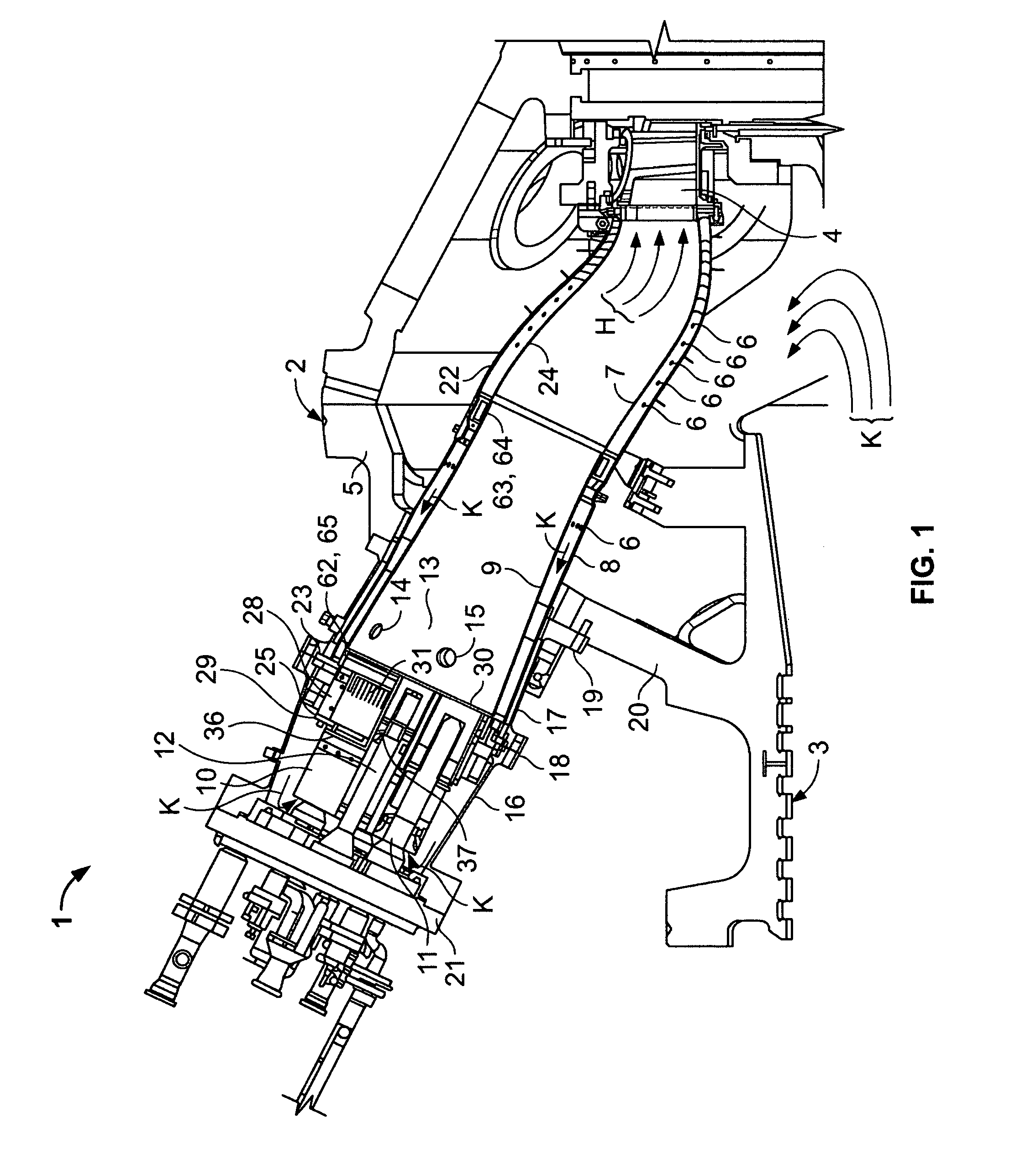
System and method for purging a fuel manifold of a gas turbine engine using a flow divider assembly
Methods and systems of operating a gas turbine engine in a low-power condition are provided. In one embodiment, the method includes supplying fuel to the combustor by supplying fuel to the first fuel manifold via a first flow divider valve and supplying fuel to the second fuel manifold via a second flow divider valve. While supplying fuel to the combustor by supplying fuel to the first fuel manifold, the method includes stopping supplying fuel to the second fuel manifold and supplying pressurized gas to the second fuel manifold via the second flow divider valve to flush fuel in the second fuel manifold into the combustor and hinder coking in the second fuel manifold and associated nozzles.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
System and method for purging a fuel manifold of a gas turbine engine using an accumulator
Methods and systems of operating a gas turbine engine in a low-power condition are provided. In one embodiment, the method includes supplying fuel to a combustor by supplying fuel to a first fuel manifold and a second fuel manifold of the gas turbine engine. The method also includes, while supplying fuel to the combustor by supplying fuel to the first fuel manifold: stopping supplying fuel to the second fuel manifold; and discharging pressurized air from an accumulator into the second fuel manifold to flush fuel in the second fuel manifold into the combustor and hinder coking in the second fuel manifold and associated fuel nozzles.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
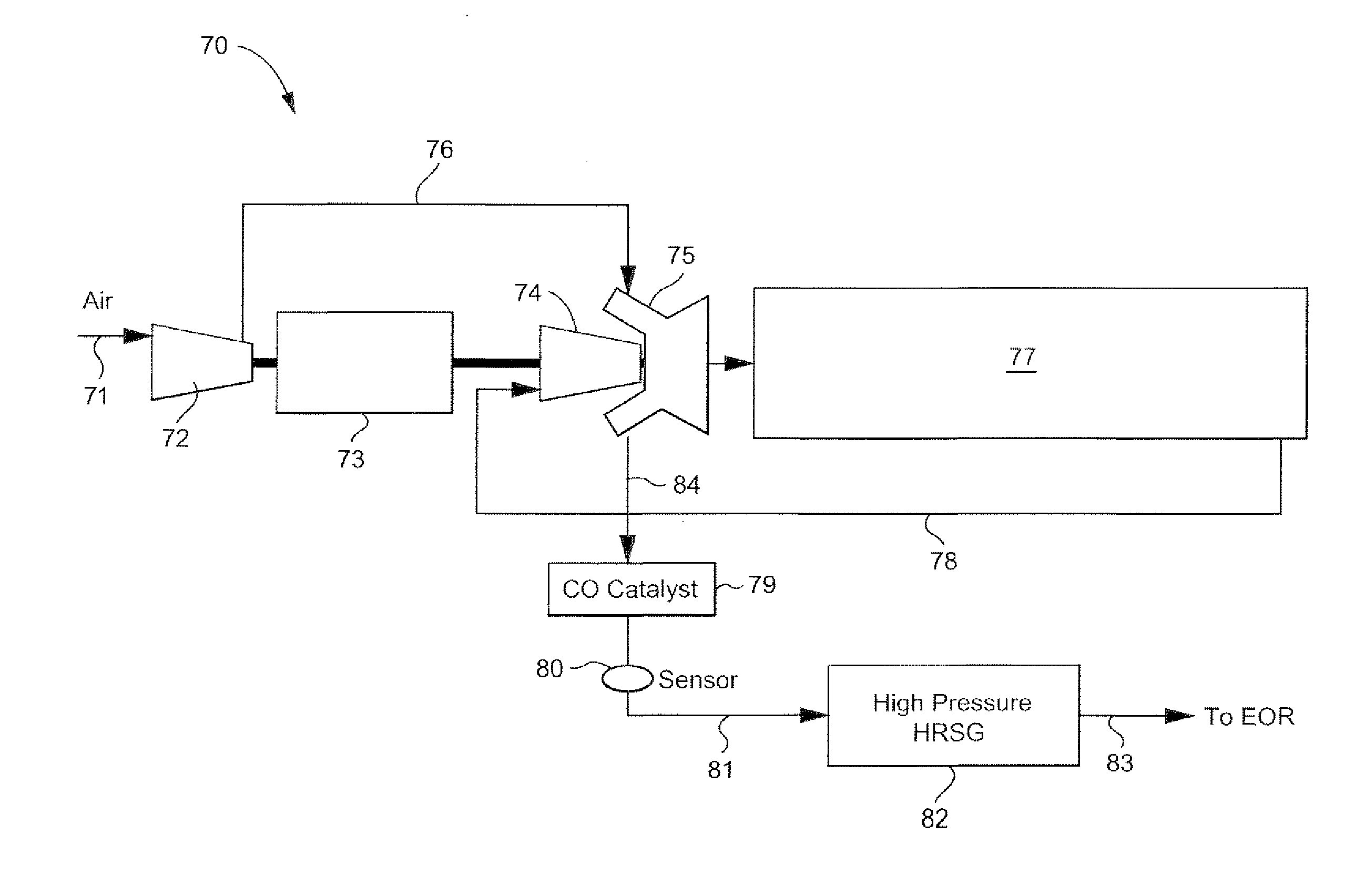
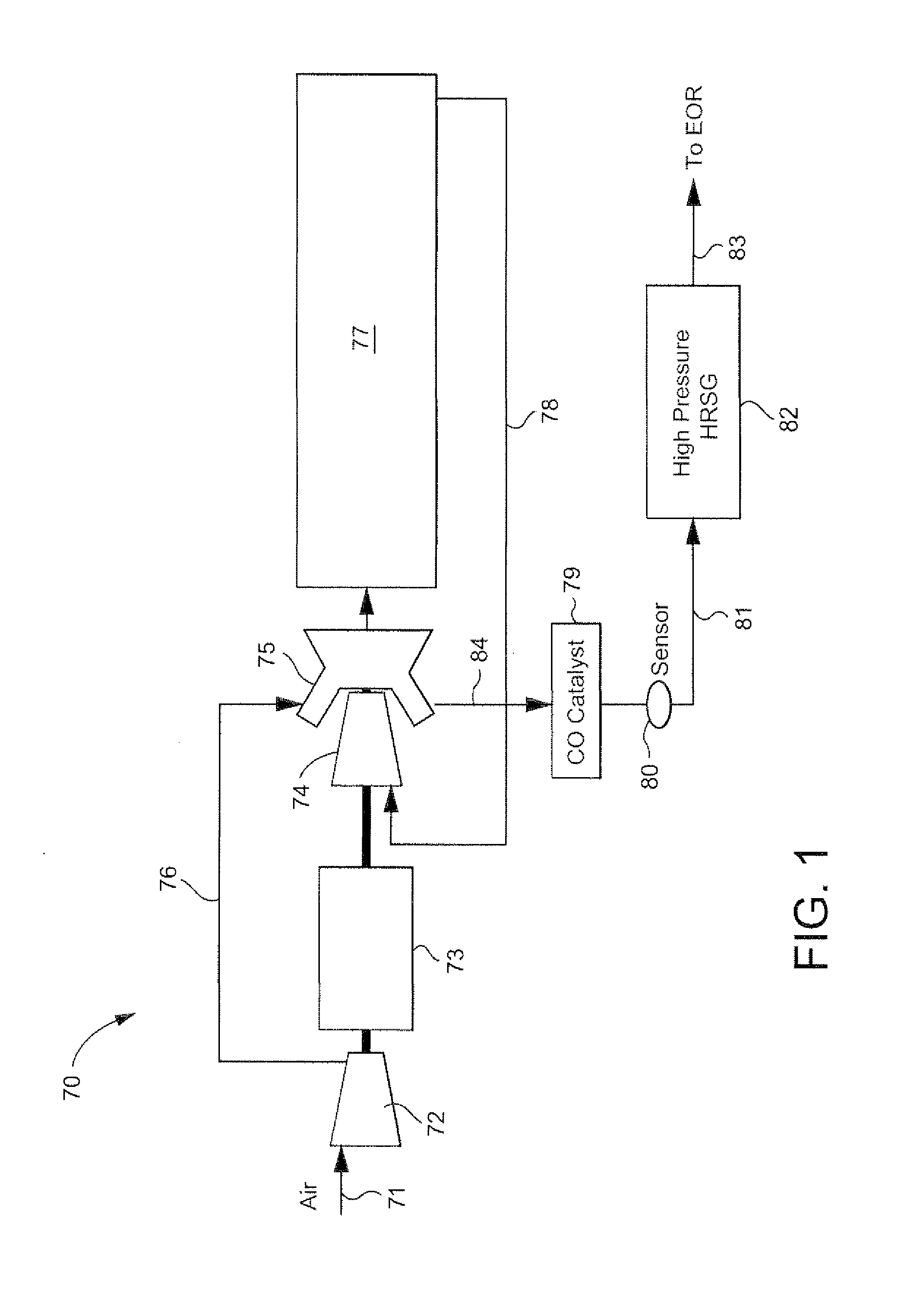
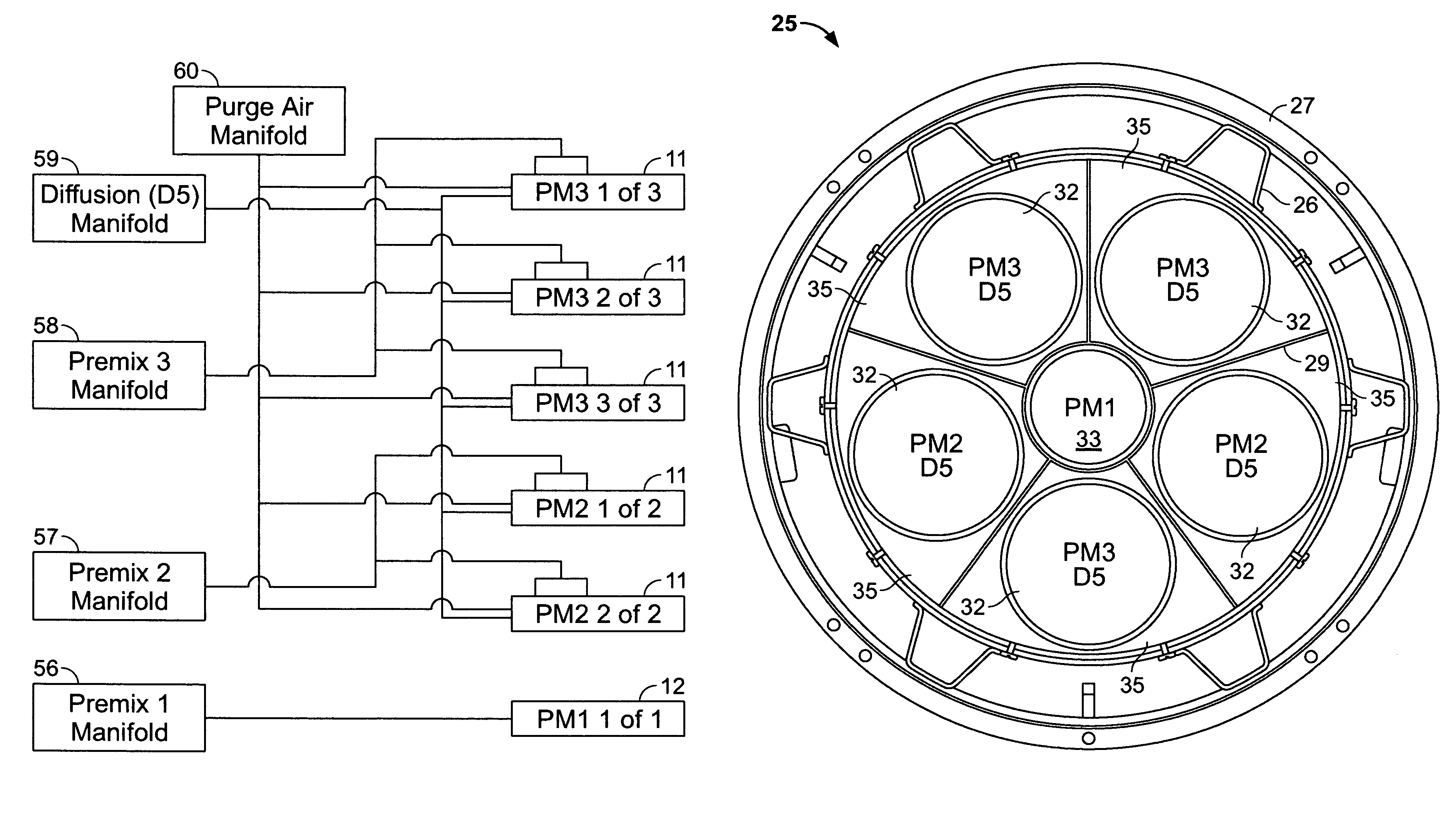
Stoichiometric exhaust gas recirculation and related combustion control
ActiveUS20120185144A1Analogue computers for vehiclesExhaust apparatusOxygenExhaust gas recirculation
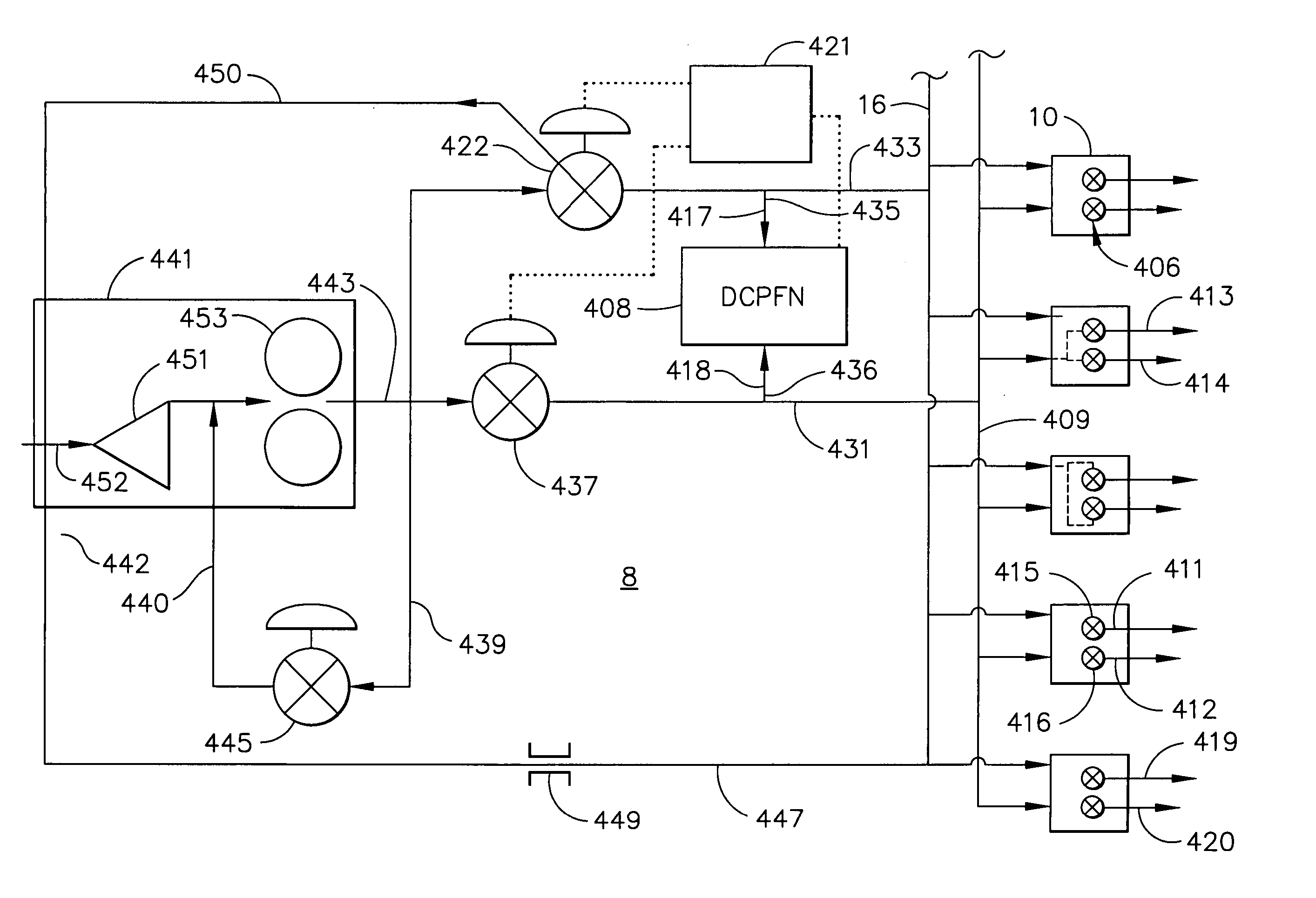
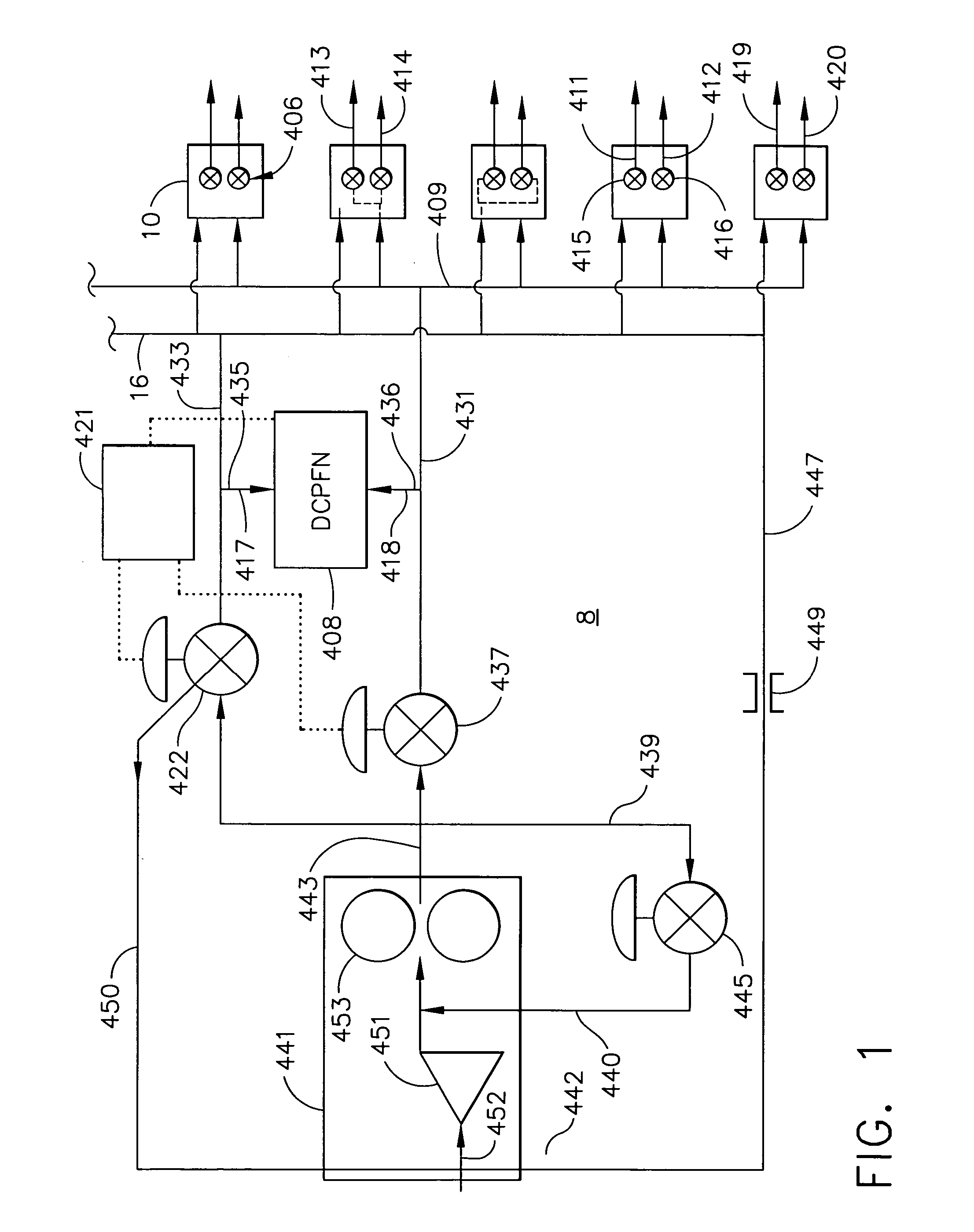
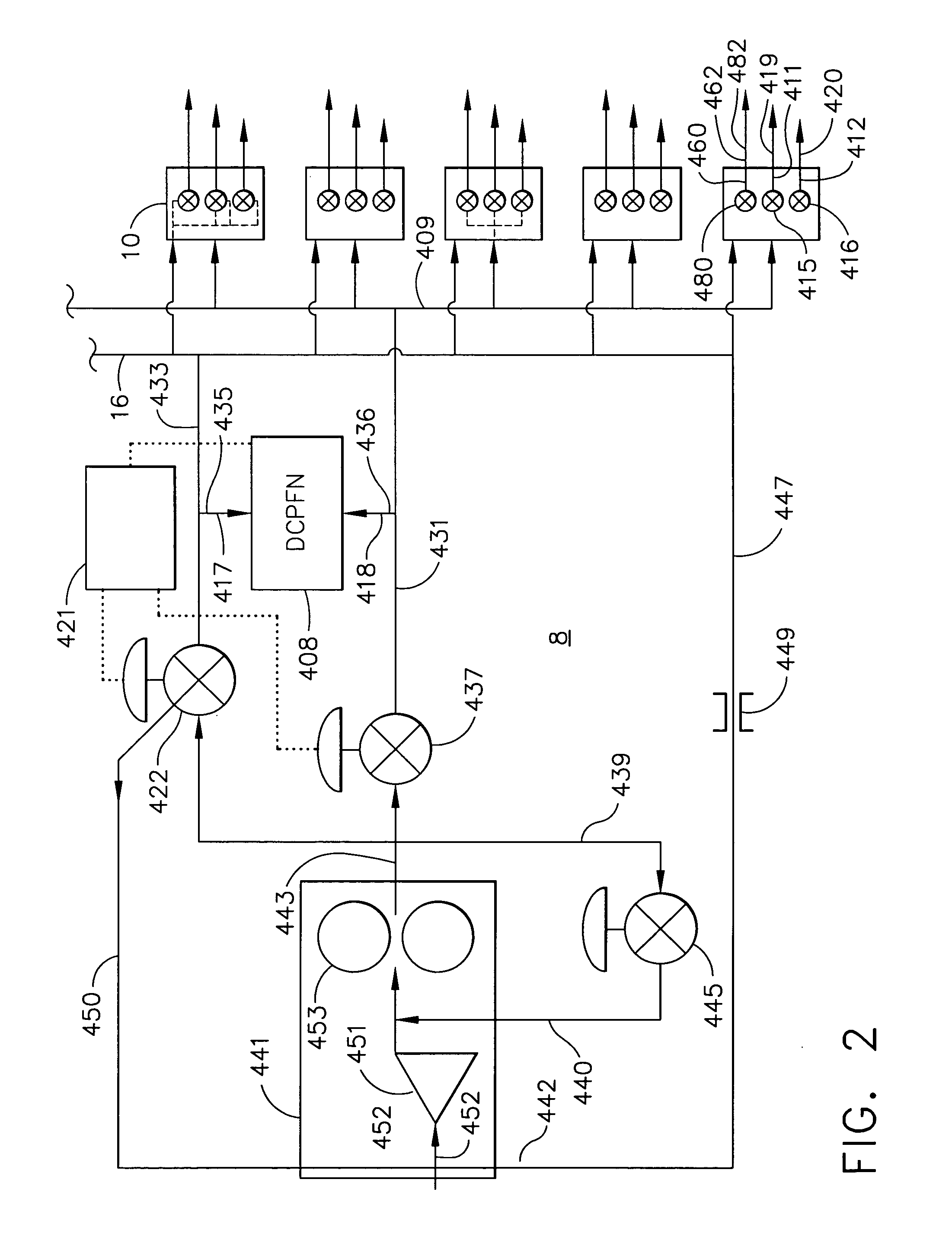
A fuel control system for a gas turbine engine that includes a primary fuel circuit, a fuel tuning circuit, a plurality of combustors connected to the fuel tuning circuit, oxygen and carbon dioxide sensors in the exhaust stream and a feedback control loop operatively connected to the fuel tuning circuit and to the oxygen and carbon monoxide sensors which serve to control the precise amount of fuel and air being fed to each one of the plurality of combustors in the engine. A parallel array of control valves in a tuning fuel circuit connect to corresponding ones of the plurality of combustors in the gas turbine engine. The fuel control system thereby “fine tunes” the amount of fuel and air being fed to each combustor using data regarding the detected oxygen and carbon monoxide concentrations in the exhaust gas as provided through a feedback control loop.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
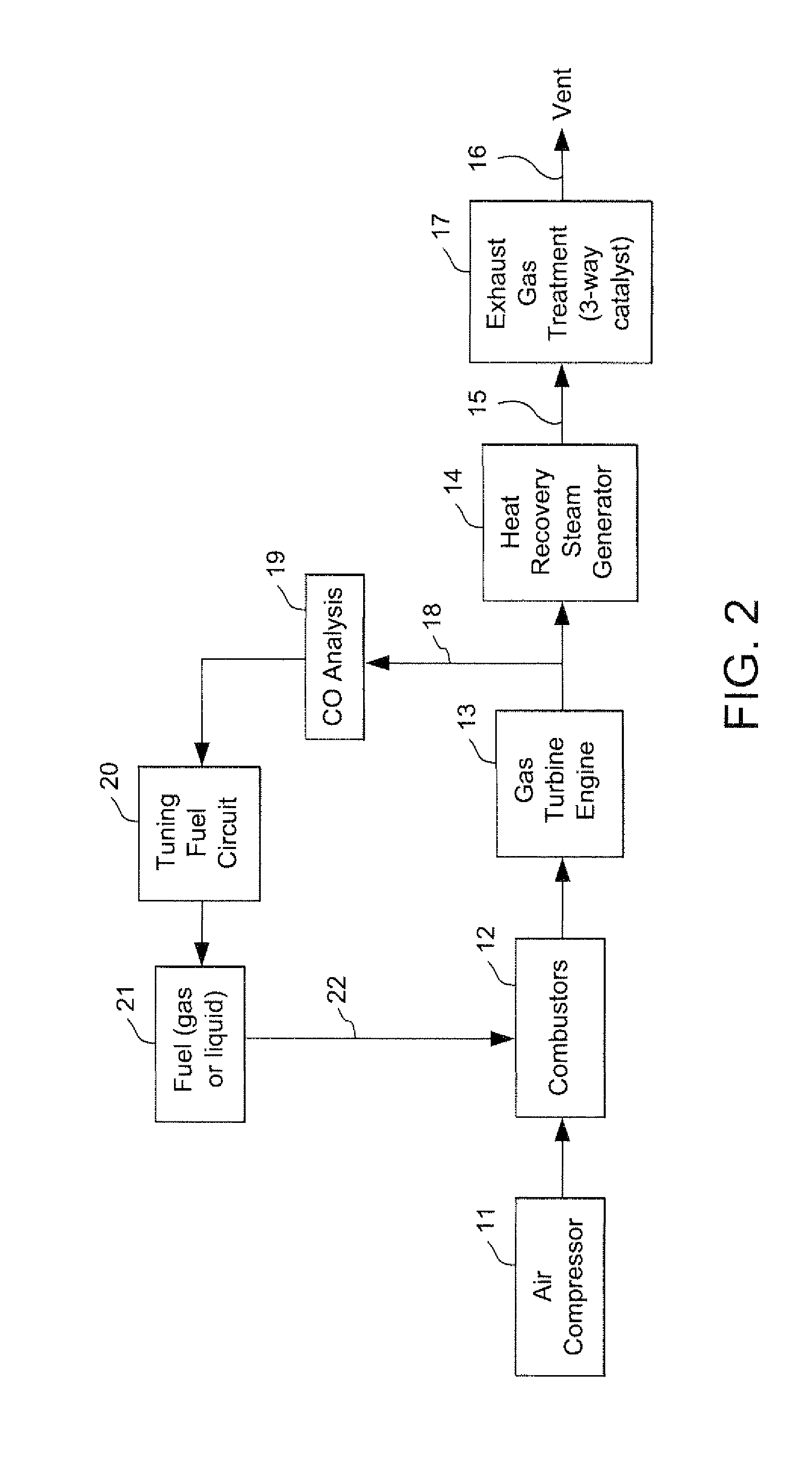
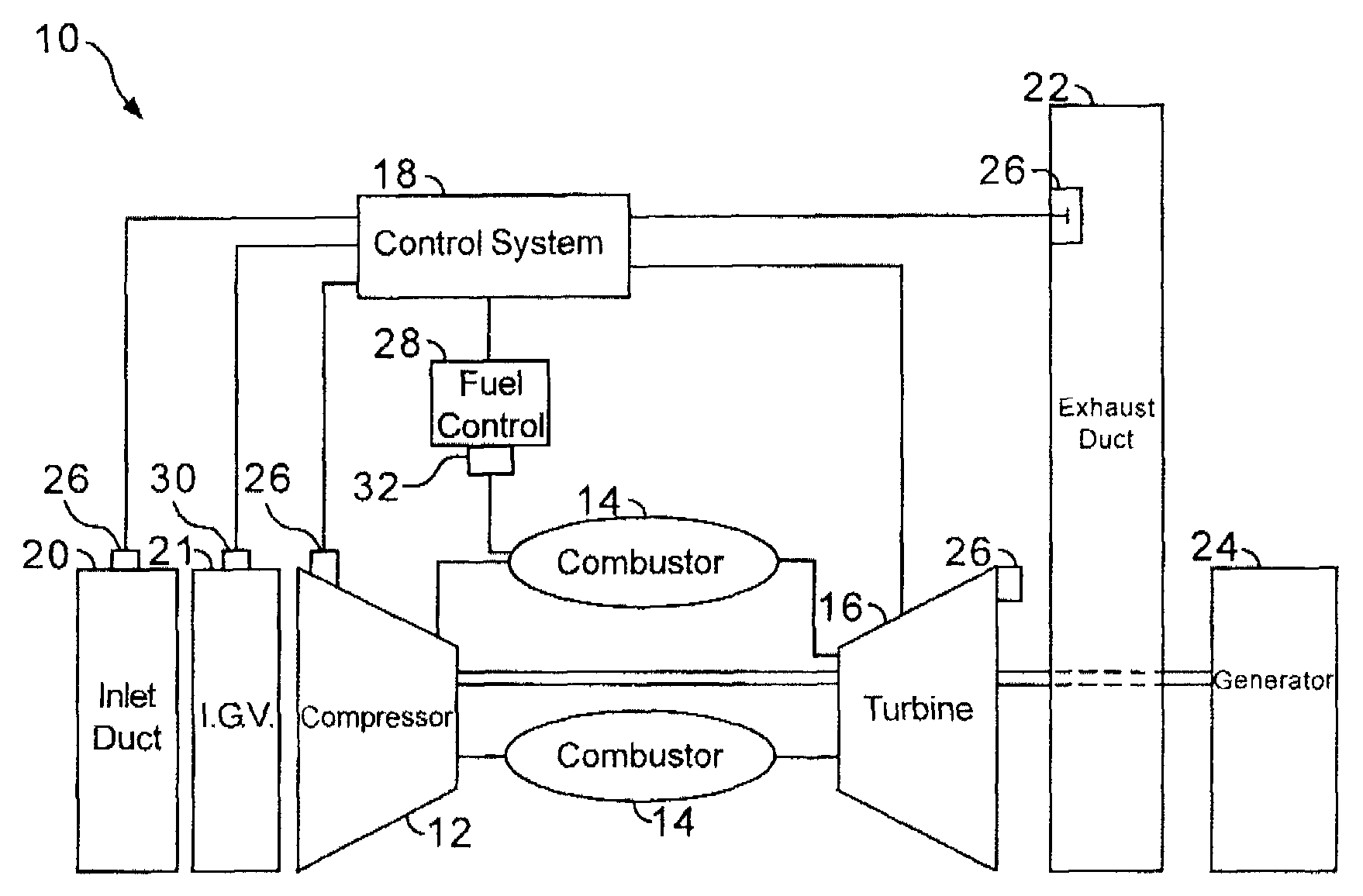
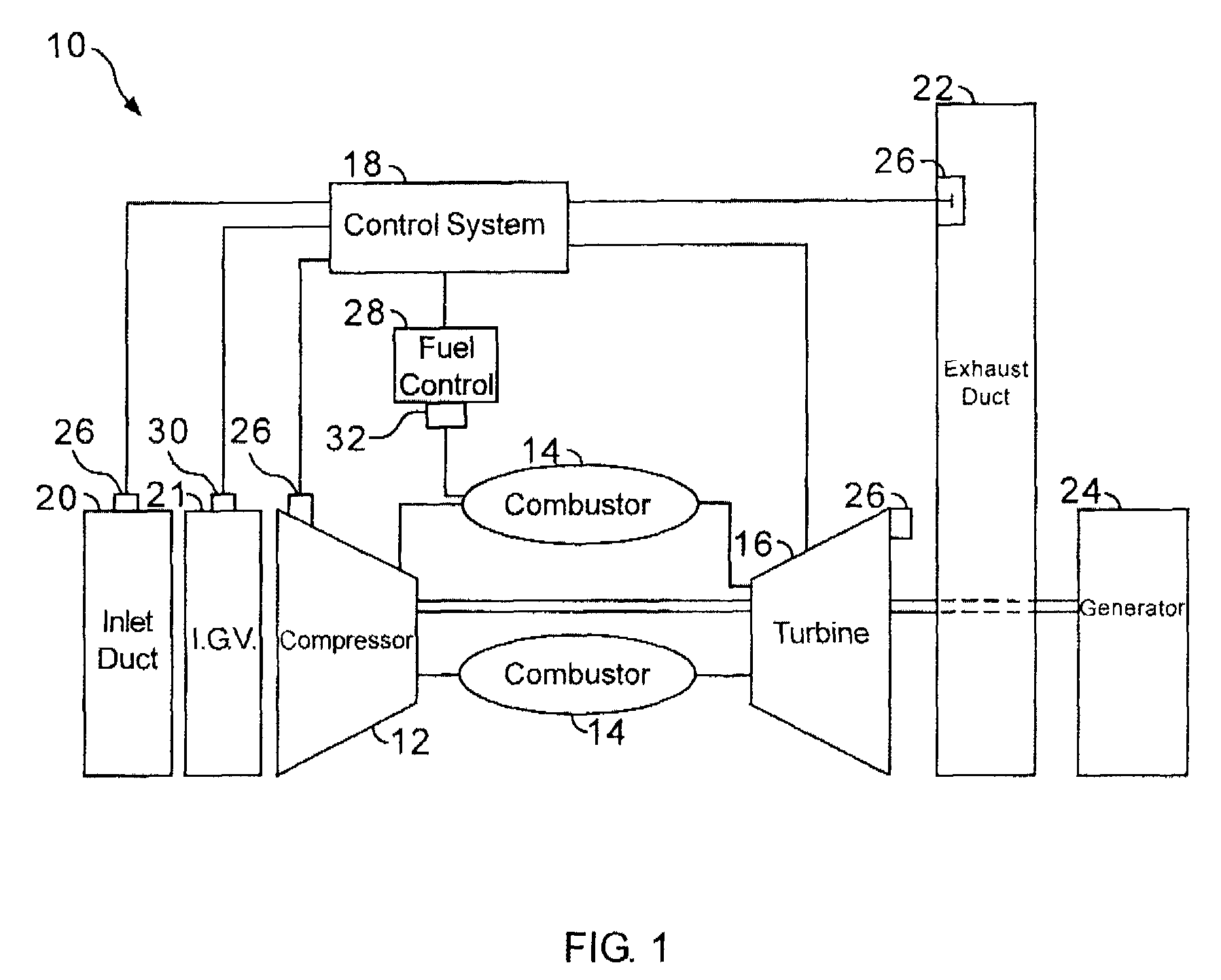
Methods and apparatus for low emission gas turbine energy generation
ActiveUS20050268617A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberEngineeringLow emission
A low-emission method for producing power using a gas turbine includes premixing a plurality of fuel and air mixtures, injecting the fuel and air mixtures into a combustion chamber using a plurality of fuel nozzles, and adjusting a ratio of fuel and air injected by at least one of the nozzles to control a fuel / air concentration distribution within the combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for low emission gas turbine energy generation
ActiveUS7284378B2Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberCombustion chamberLow emission
A low-emission method for producing power using a gas turbine includes premixing a plurality of fuel and air mixtures, injecting the fuel and air mixtures into a combustion chamber using a plurality of fuel nozzles, and adjusting a ratio of fuel and air injected by at least one of the nozzles to control a fuel / air concentration distribution within the combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
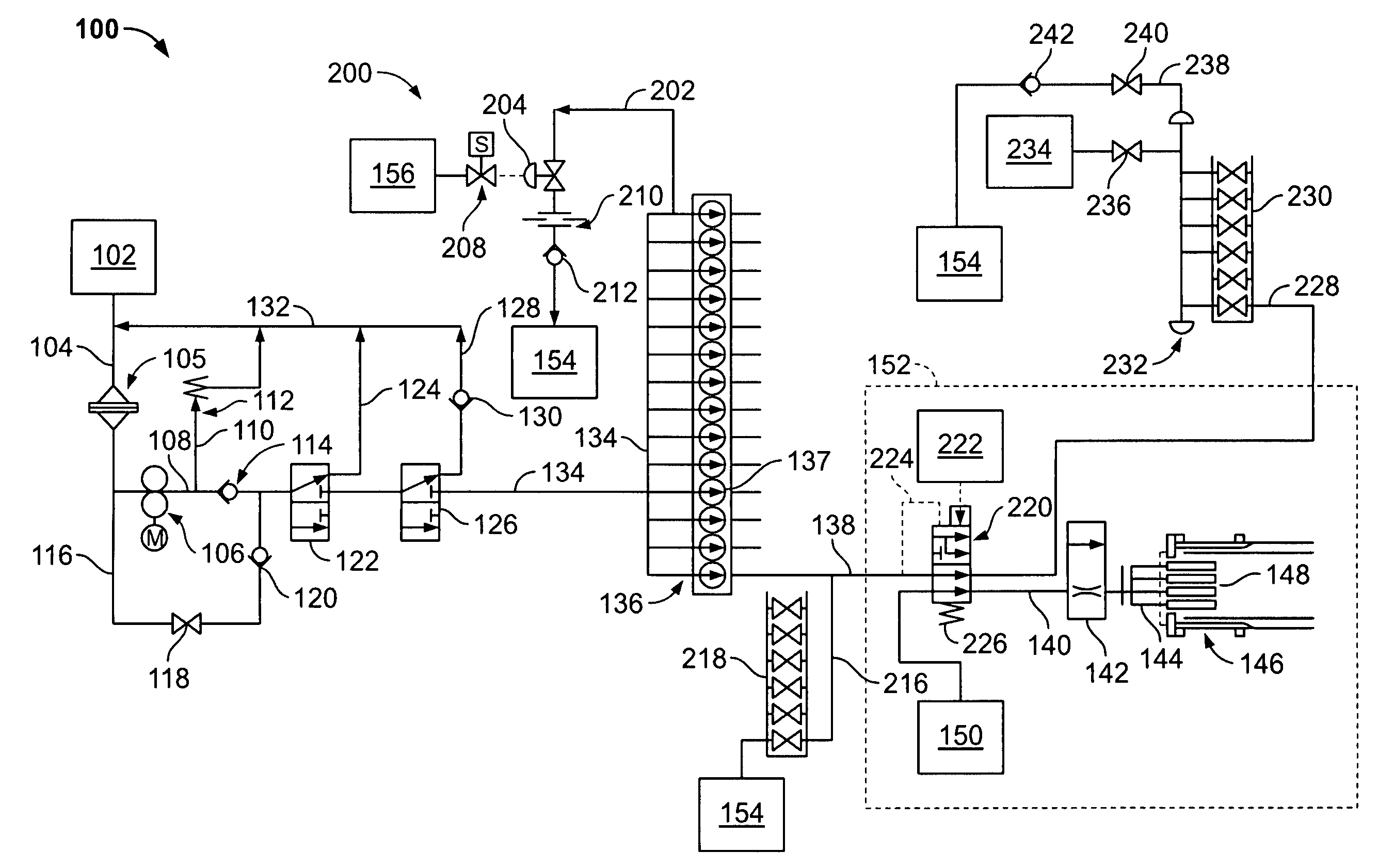
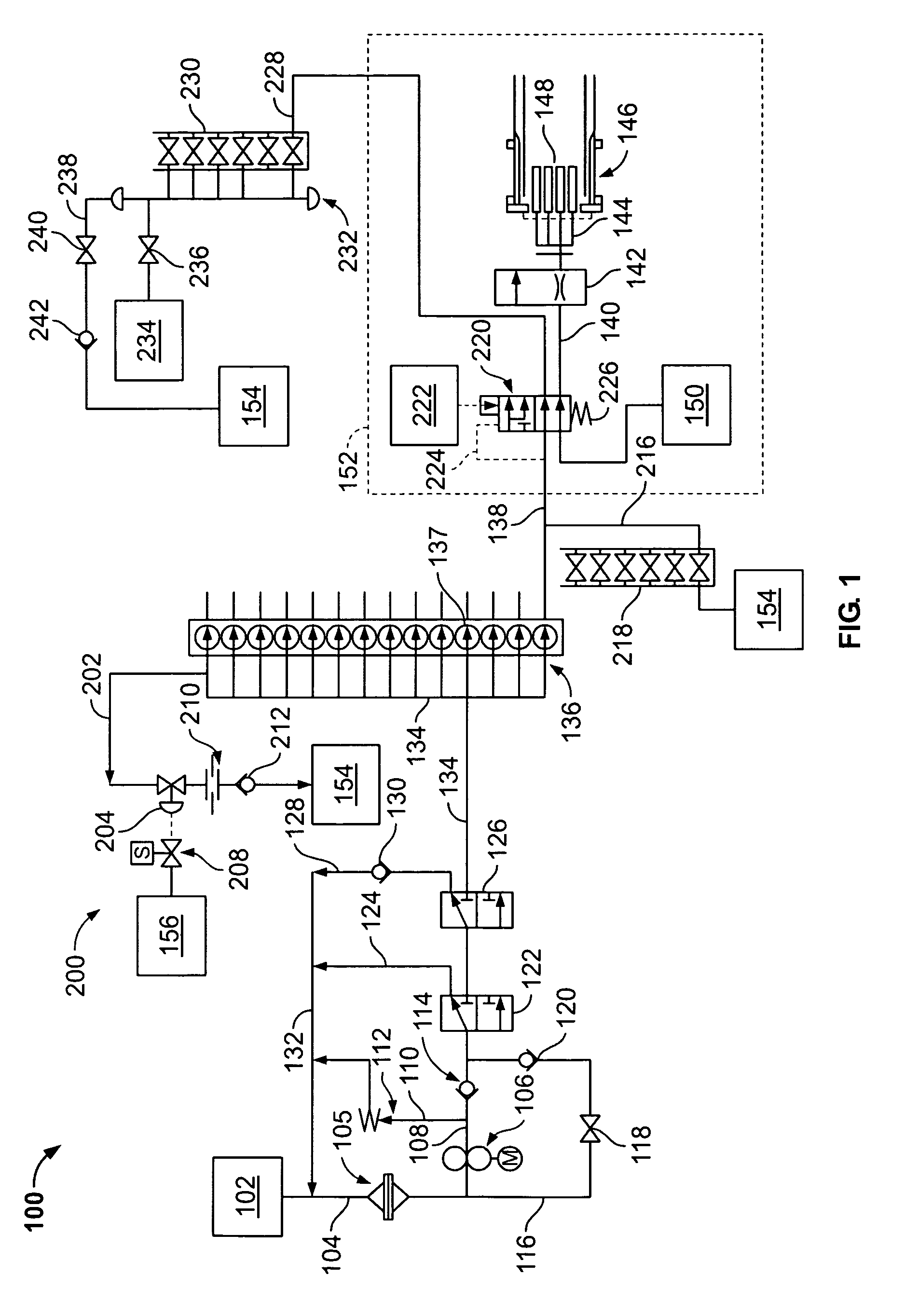
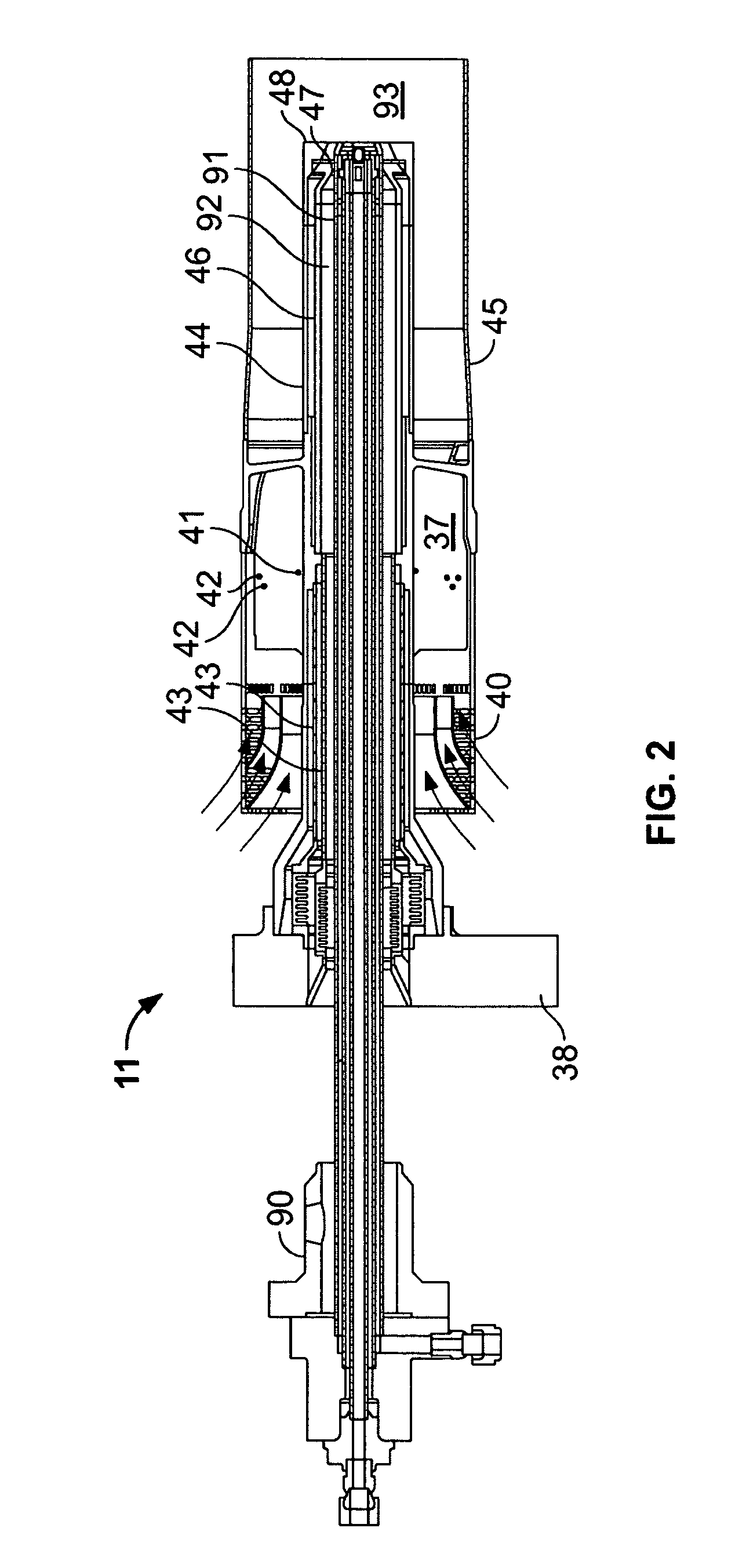
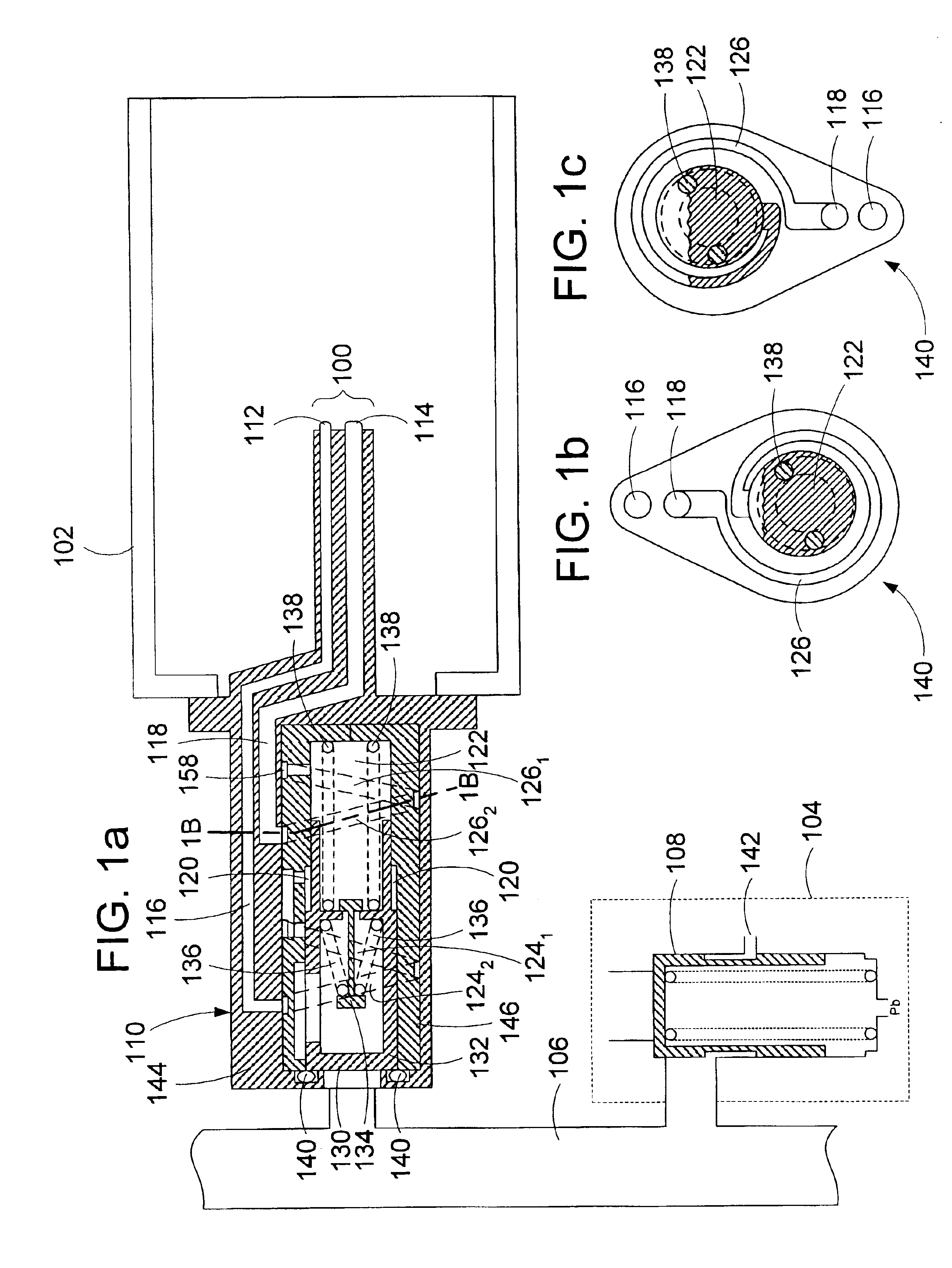
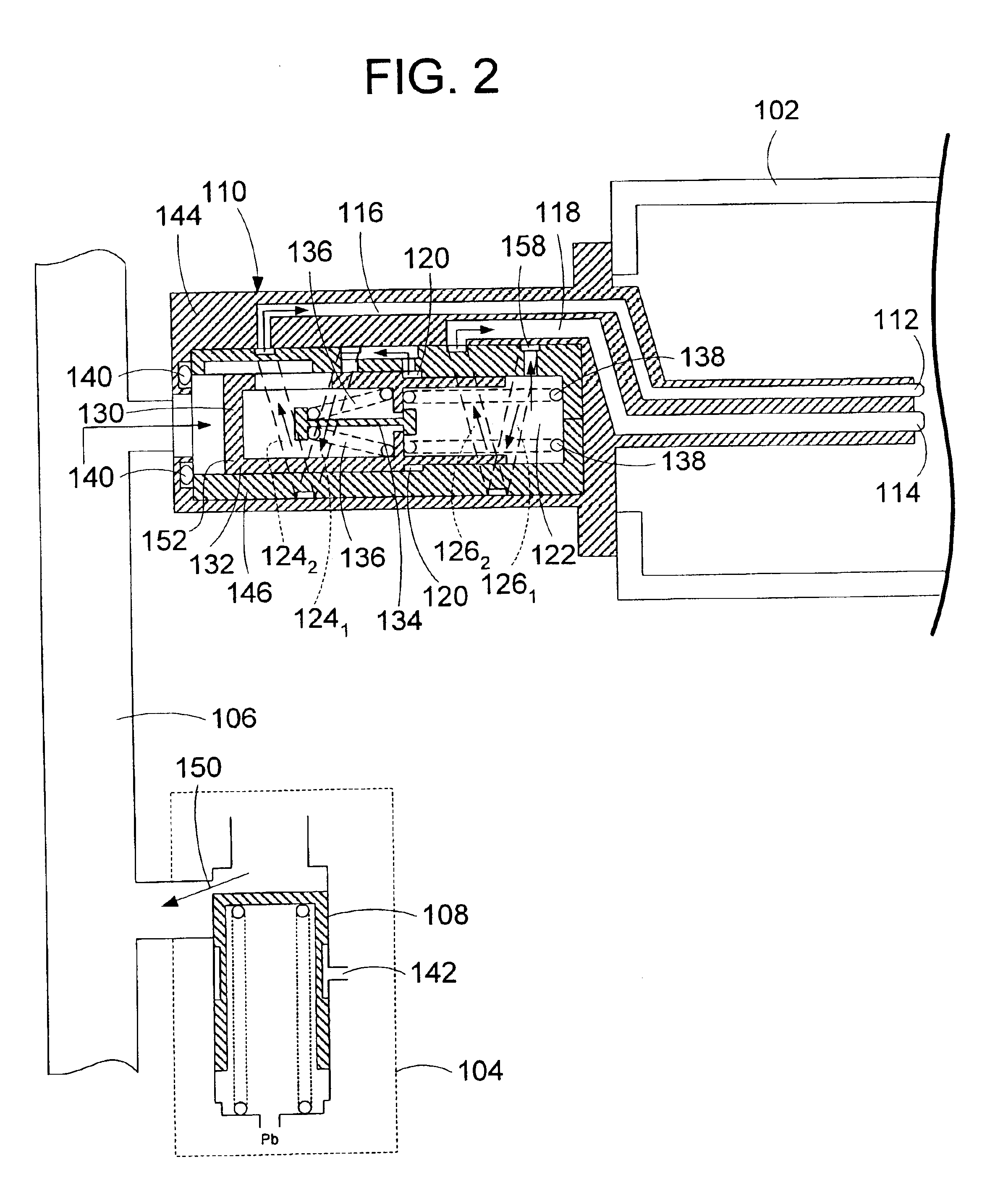
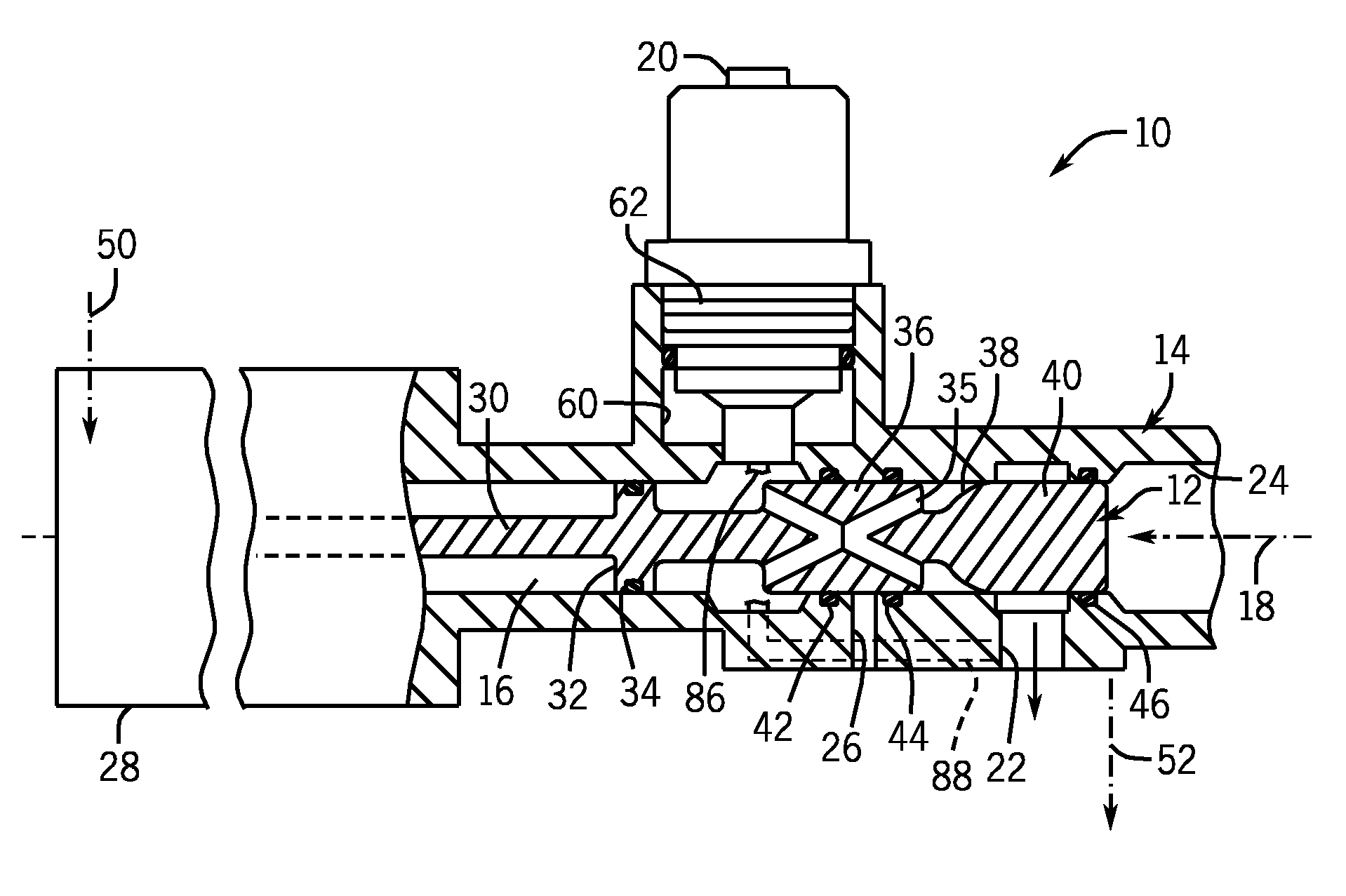
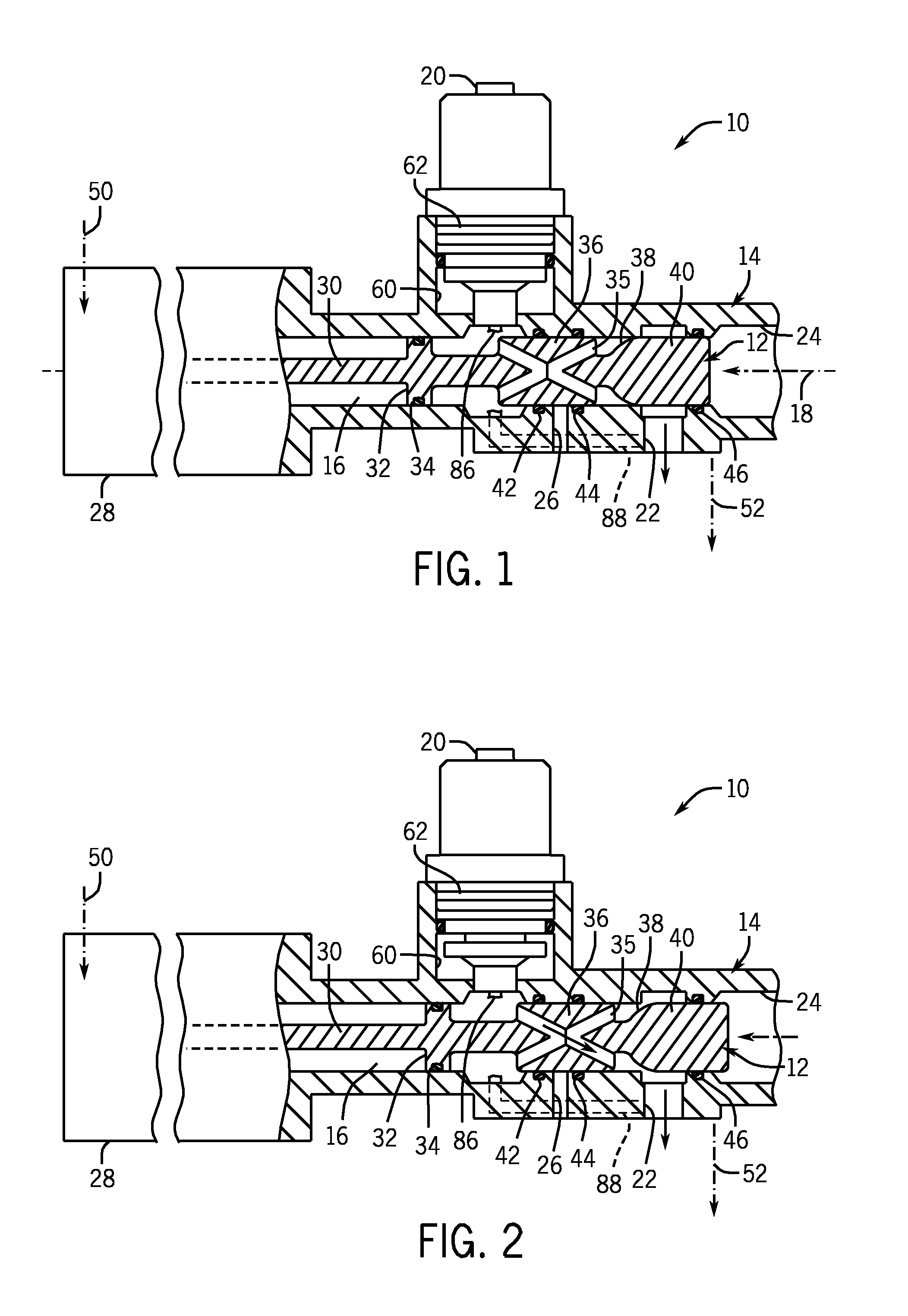
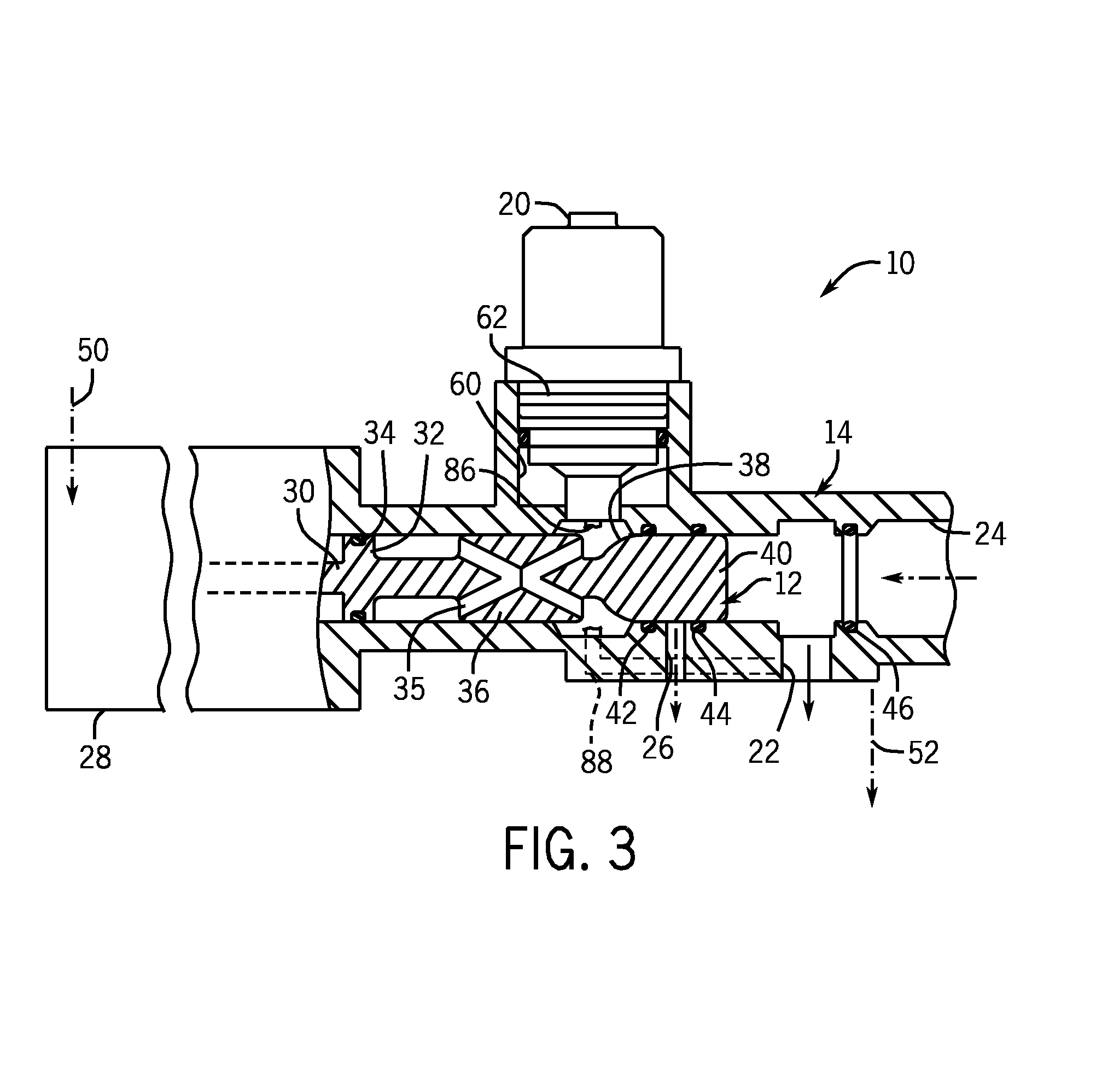
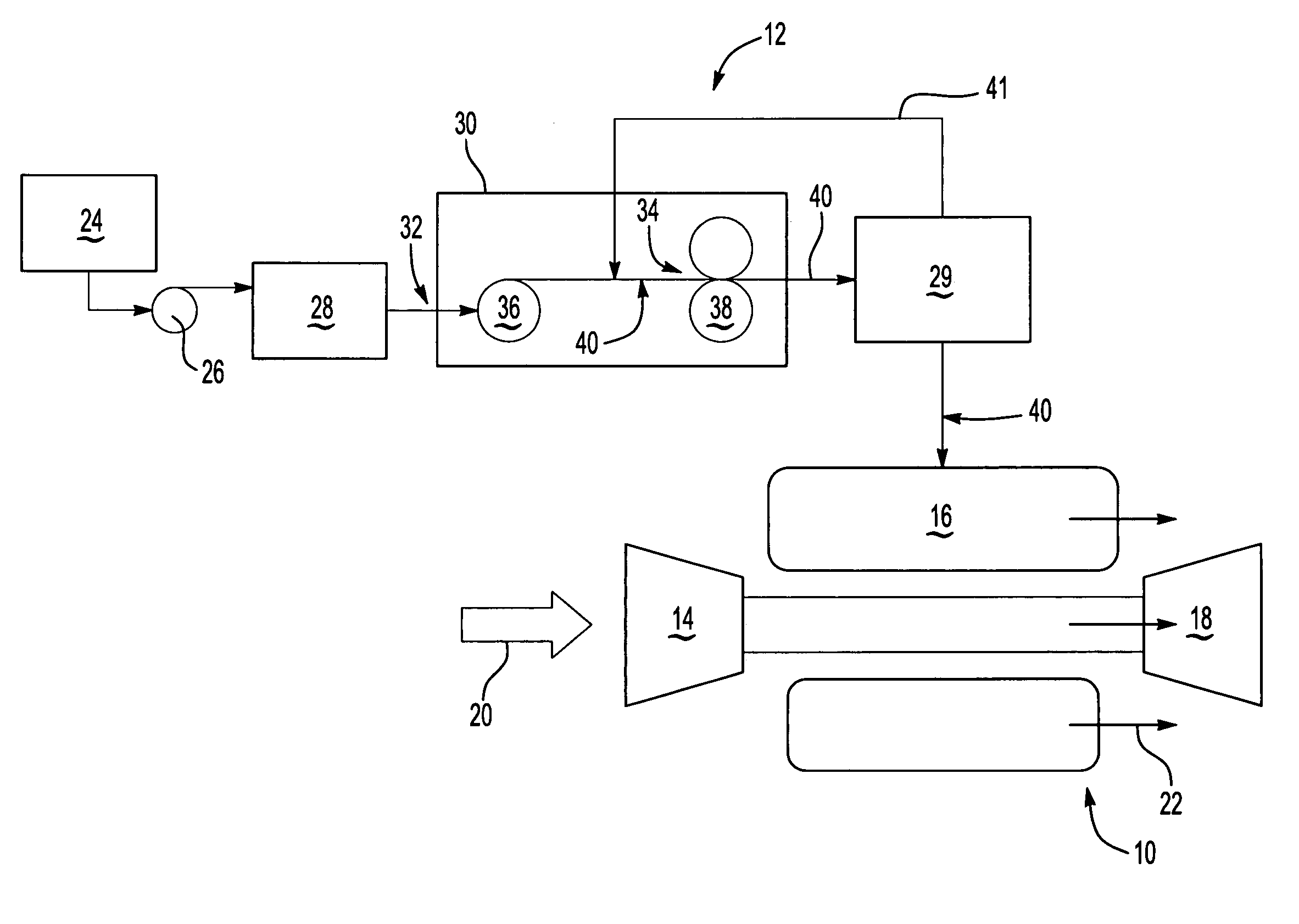
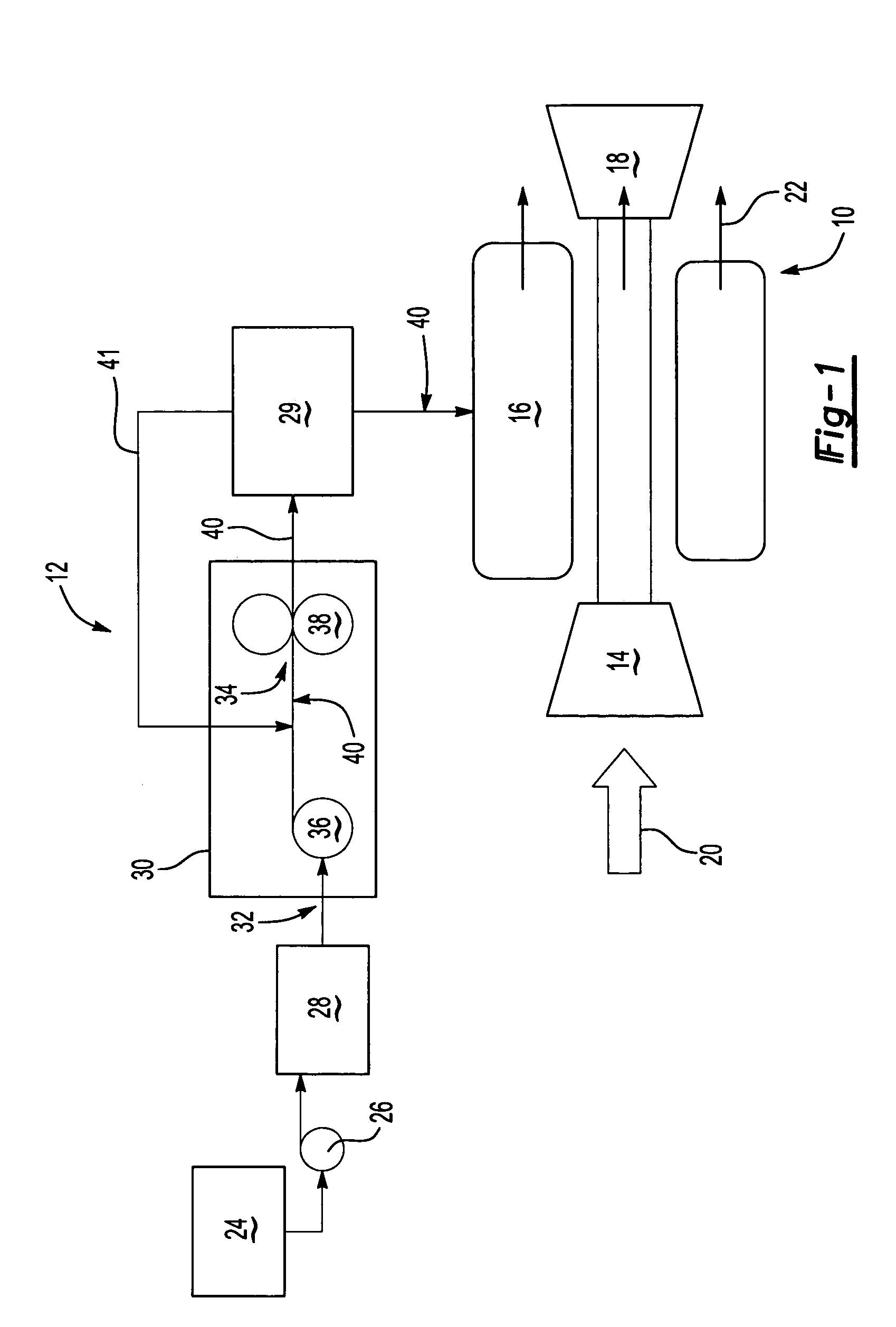
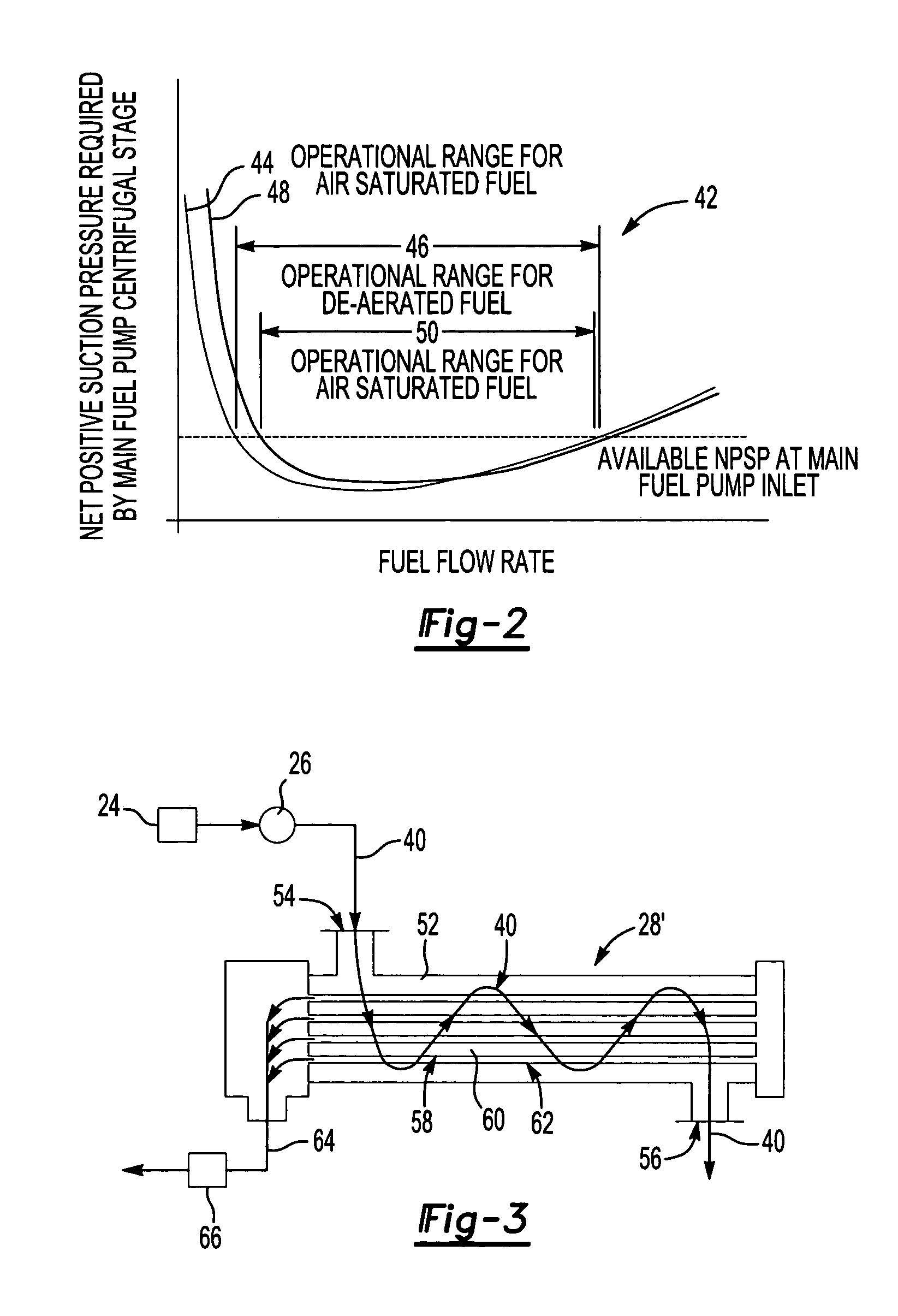
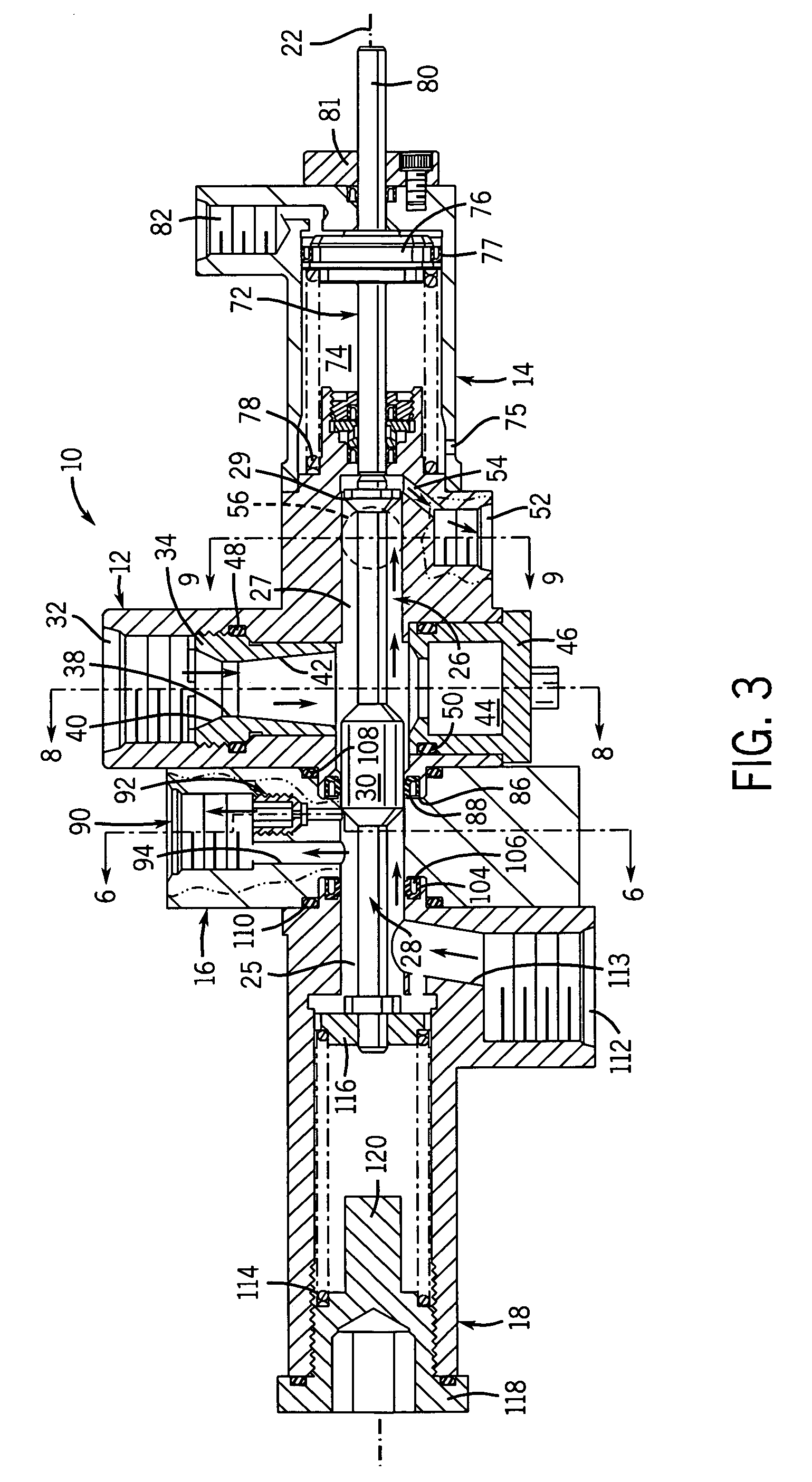
Centrifugal pump fuel system and method for gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20050217236A1Turbine/propulsion fuel deliveryTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesEngineeringAxial force
A fuel system for a gas turbine engine that utilizes a centrifugal pump is presented. The system includes a fuel metering valve that is adapted to set a metered flow of fuel, and a throttle valve that is adapted to accurately control pressure drop across the fuel metering valve. The throttle valve has at least two variable orifices and a compensation chamber between the variable orifices. The throttle valve includes a differential valve piston slidable in a valve body. The differential valve piston comprises working surfaces of at least two different diameters such that changes in chamber pressures effect different axial forces upon the piston.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Method and apparatus for controlling fuel in a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20090313999A1Solution value is not highTurbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesWorking fluidCombustor
A method and system for controlling fuel in a gas turbine engine including a fuel supply system channeling fuel to a combustor are provided. The system includes a first heat exchanger configured to transfer heat between a working fluid and a first cooling medium. The system also includes a second heat exchanger in series flow communication with the first heat exchanger wherein the second heat exchanger is configured to transfer heat between the working fluid and a second cooling medium. The system further includes a modulating valve configured to control the flow of at least one of the first and the second cooling media to maintain a temperature of the first or second cooling medium substantially equal to a predetermined limit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method to transfer fuel in a fuel system for a gas turbine engine
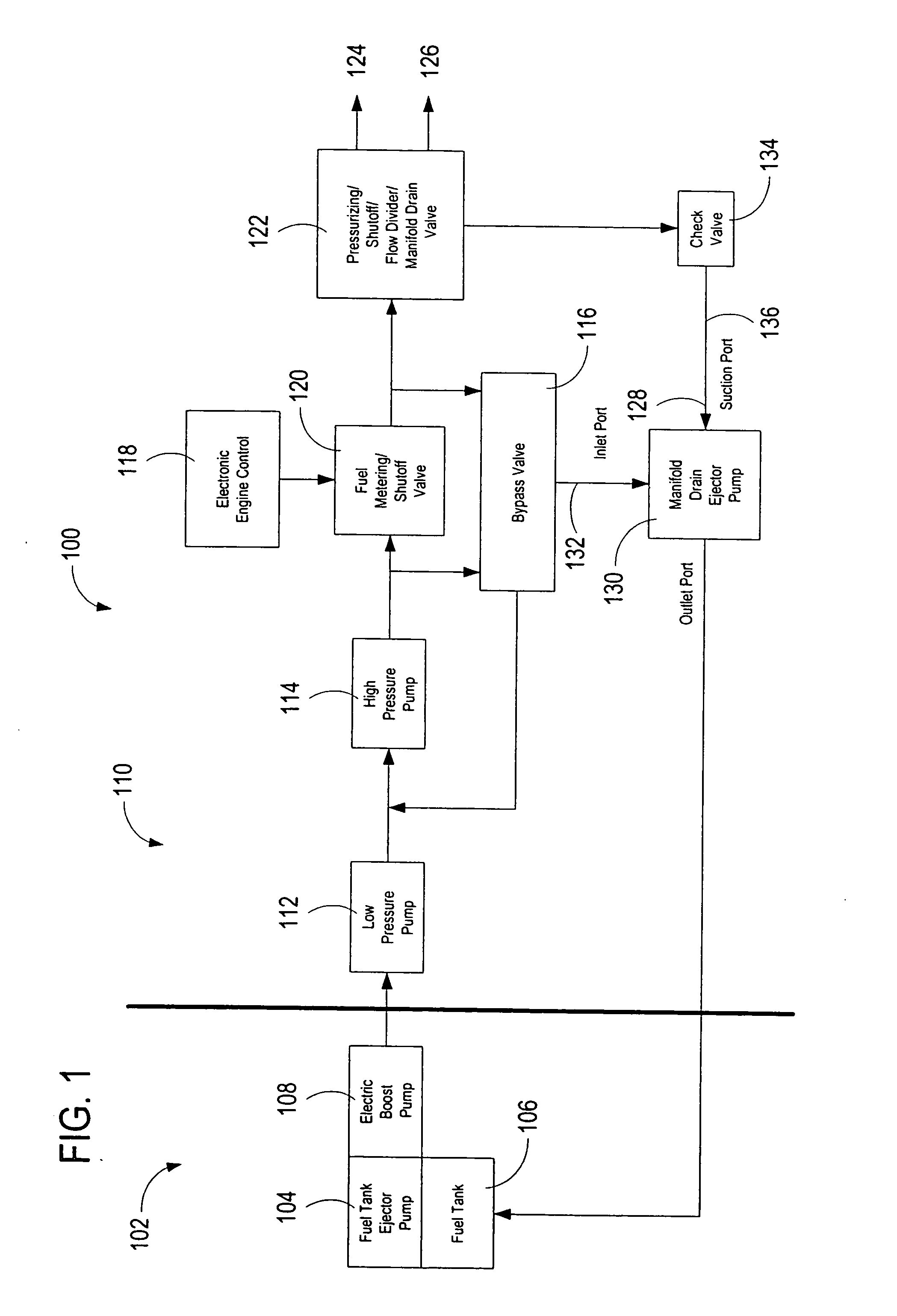
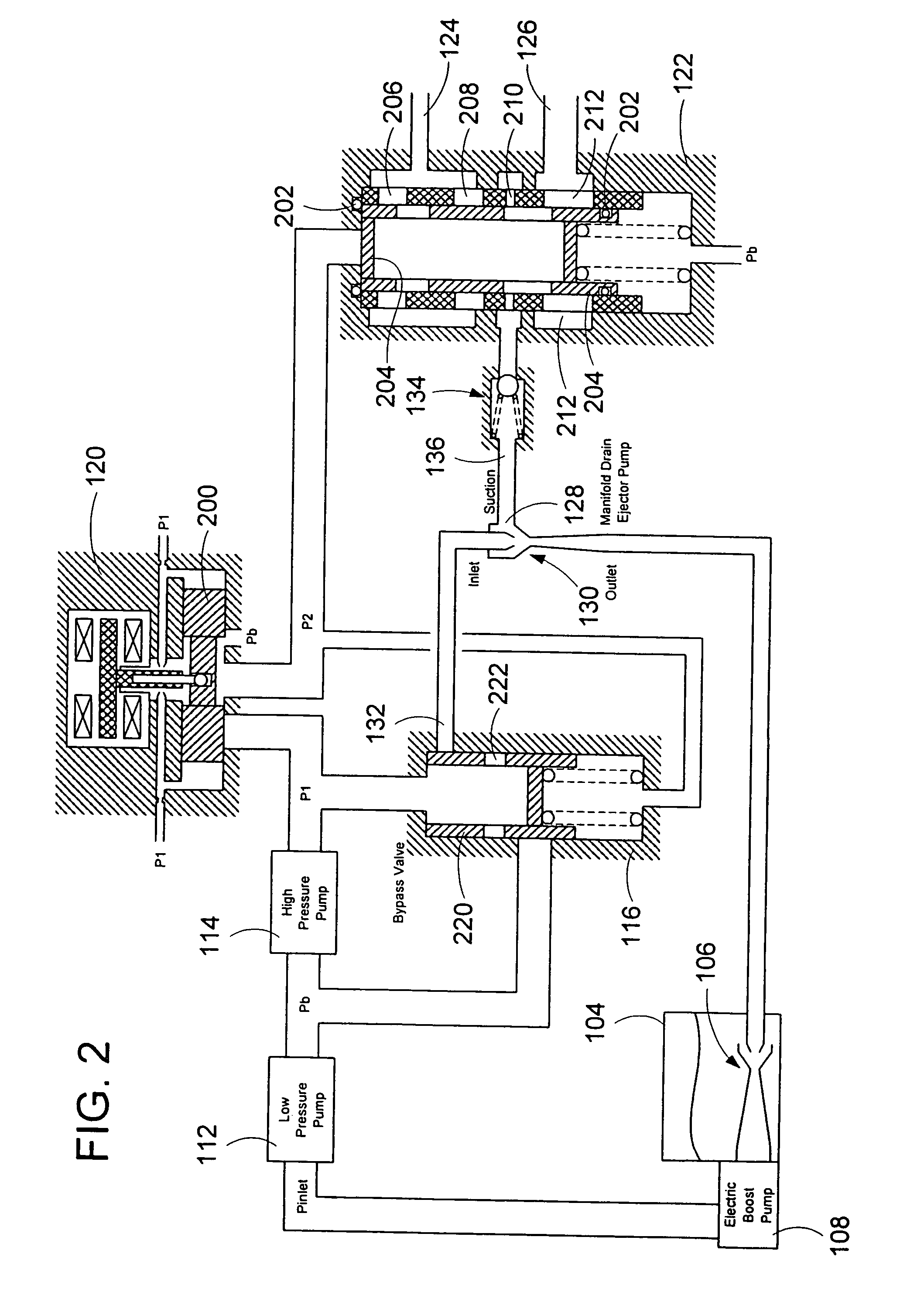
InactiveUS20050279079A1Eliminate needTurbine/propulsion fuel deliveryTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesFuel tankCheck valve
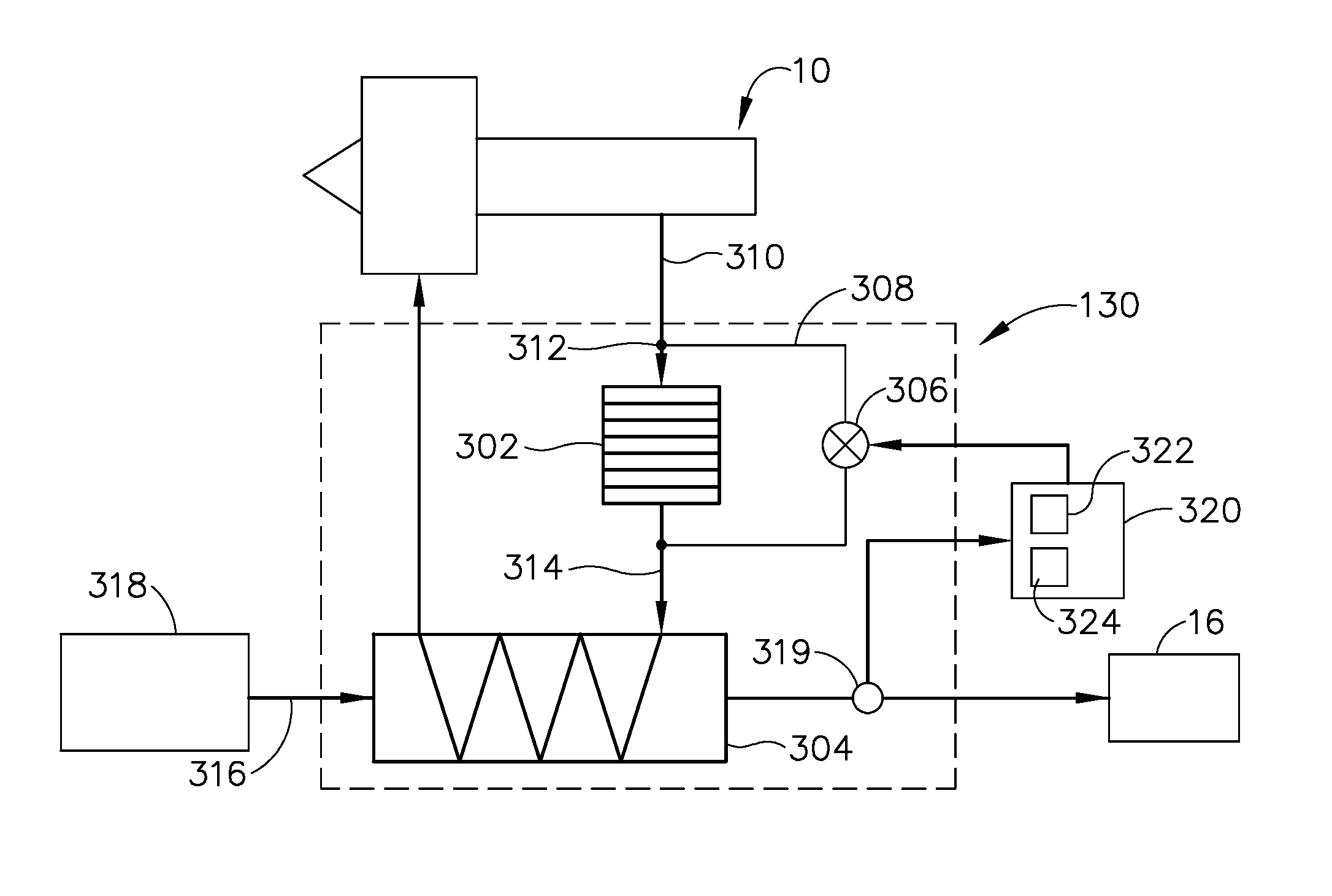
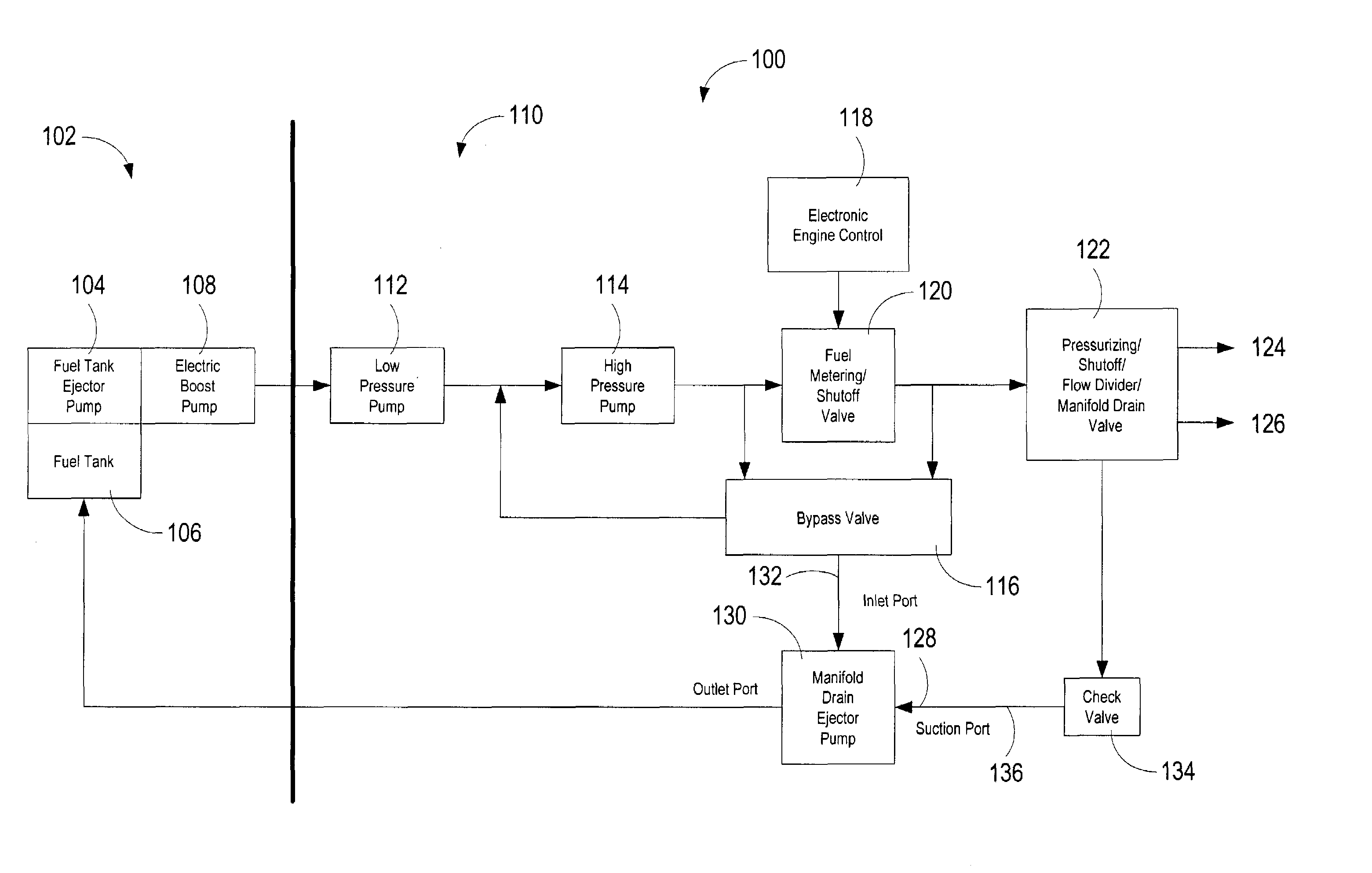
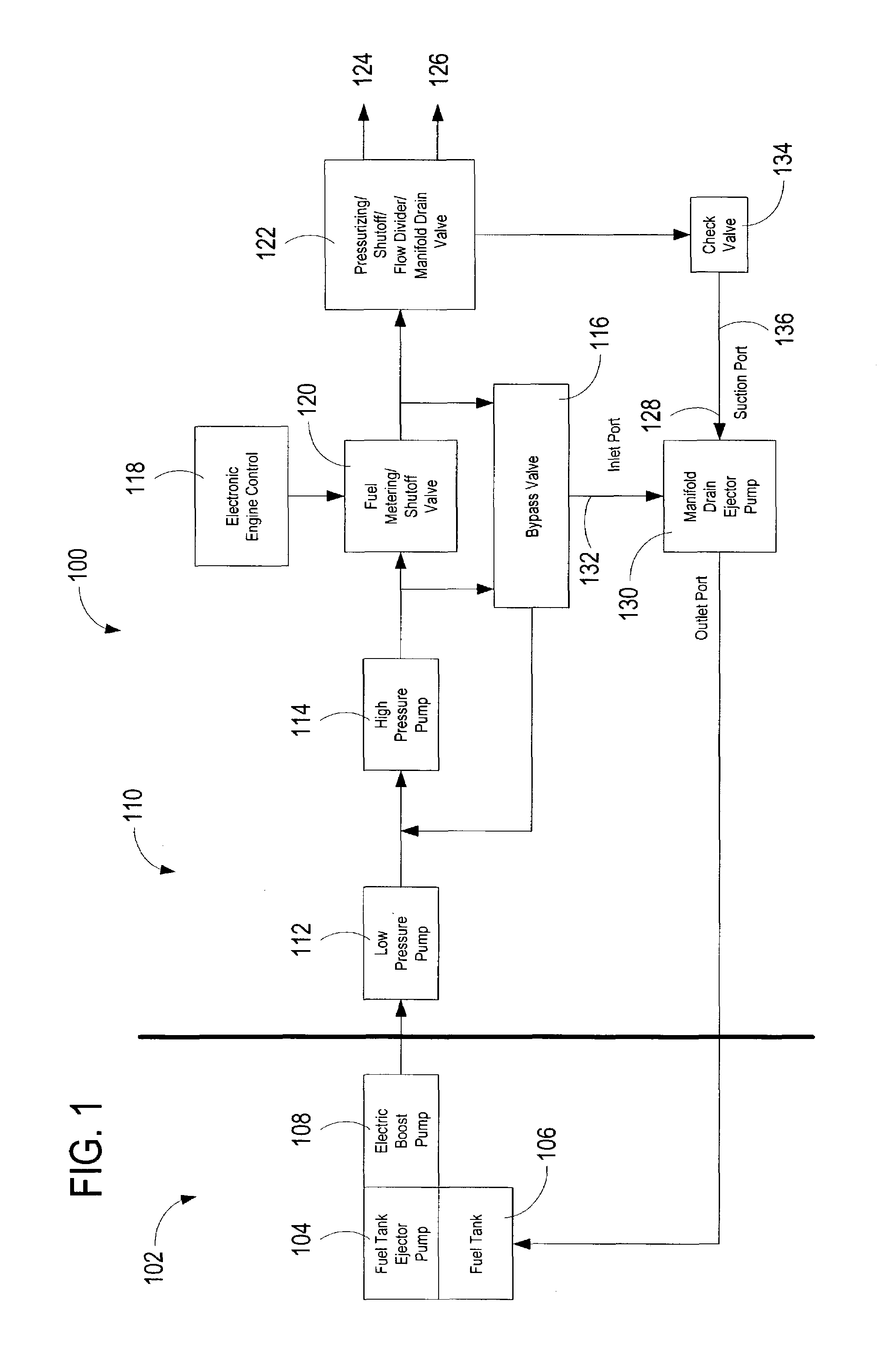
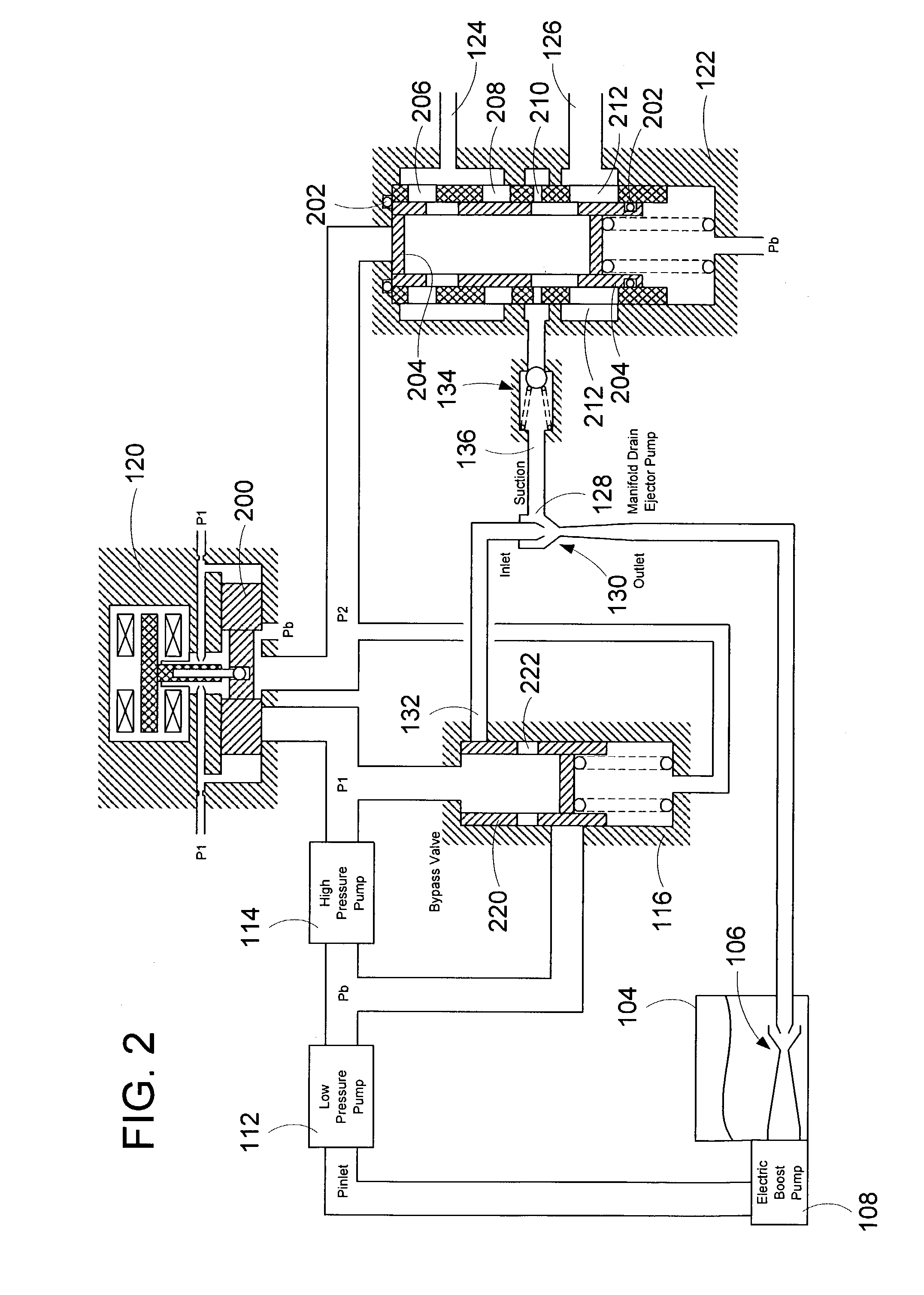
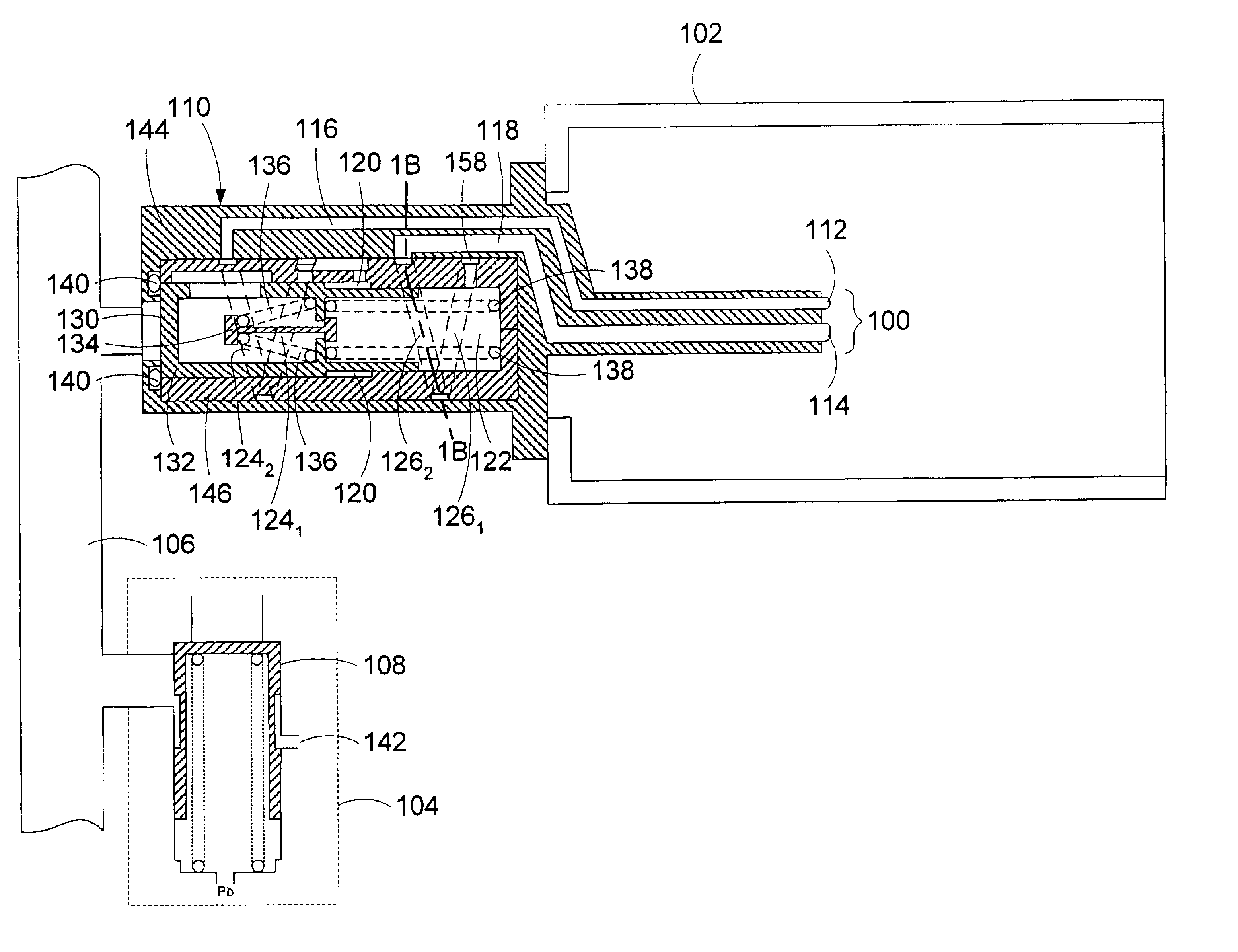
A system for automatically transferring the fuel from one or more engine fuel manifolds directly to the engine fuel tank(s) during engine shutdown using an ejector pump has been presented. A checkvalve, which may be integrated with the ejector pump, is also used. A metering valve initiates fuel flow shutoff and is used in the draining of the fuel manifolds, thereby eliminating the need for an additional solenoid dedicated mainly to the shutoff function. The shutoff and pressurizing valve provides flow division between manifolds and manifold drain for systems having multiple manifolds. The bypass valve is used to turn the motive flow and / or manifold drain functions on and off as a function of engine speed at start and shutdown.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Gas turbine combustor and operating method thereof
InactiveUS6928823B2Low level NOx emissionImprove combustion stabilityContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustion chamberCombustor
A gas turbine combustor has a combustion chamber into which fuel and air are supplied, wherein the fuel and the air are supplied into said combustion chamber as a plurality of coaxial jets.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Fuel supply system
InactiveUS7234293B2Turbine/propulsion fuel deliveryTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesControl systemEngineering
Owner:GOODRICH CONTROL SYST LTD
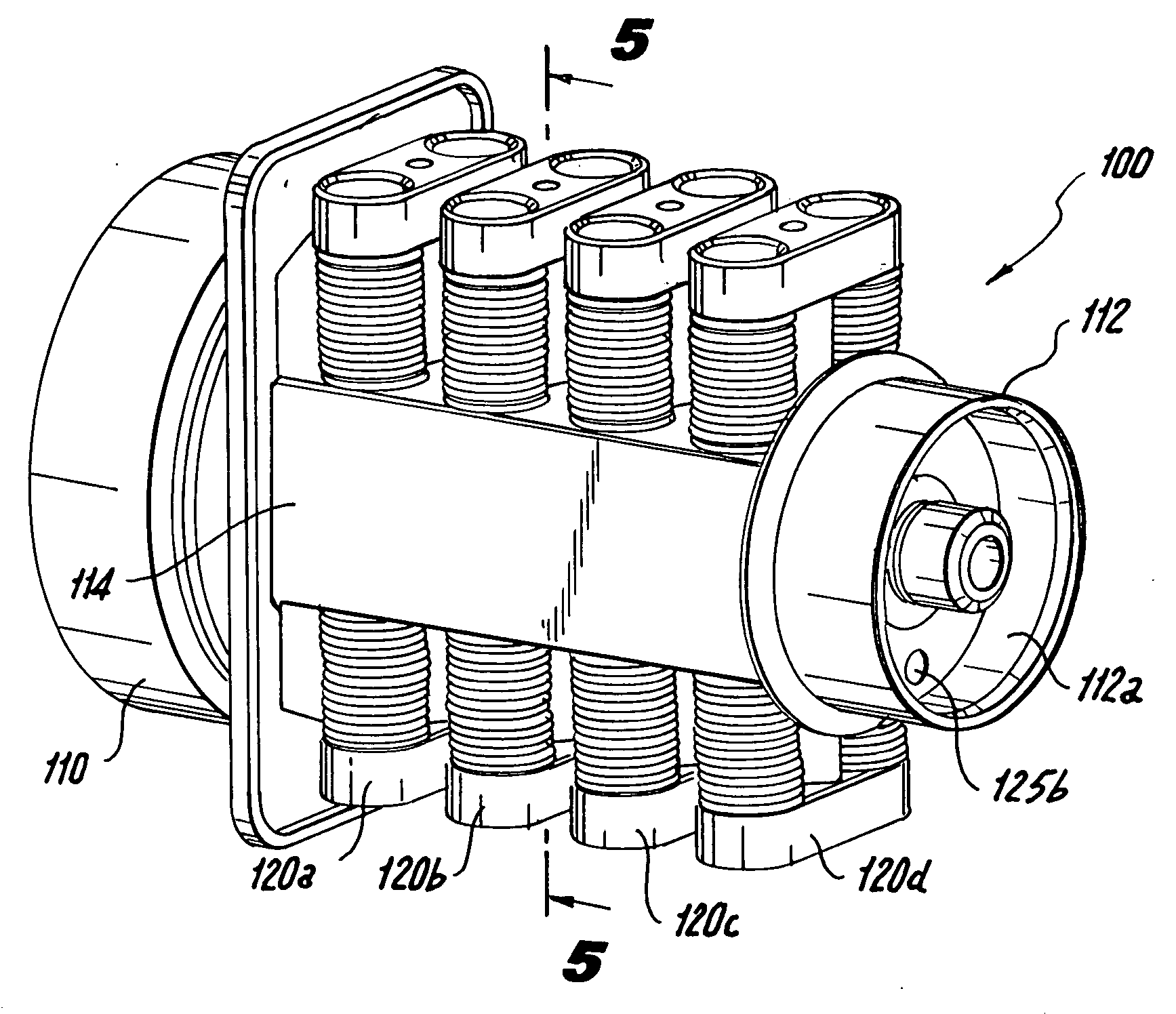
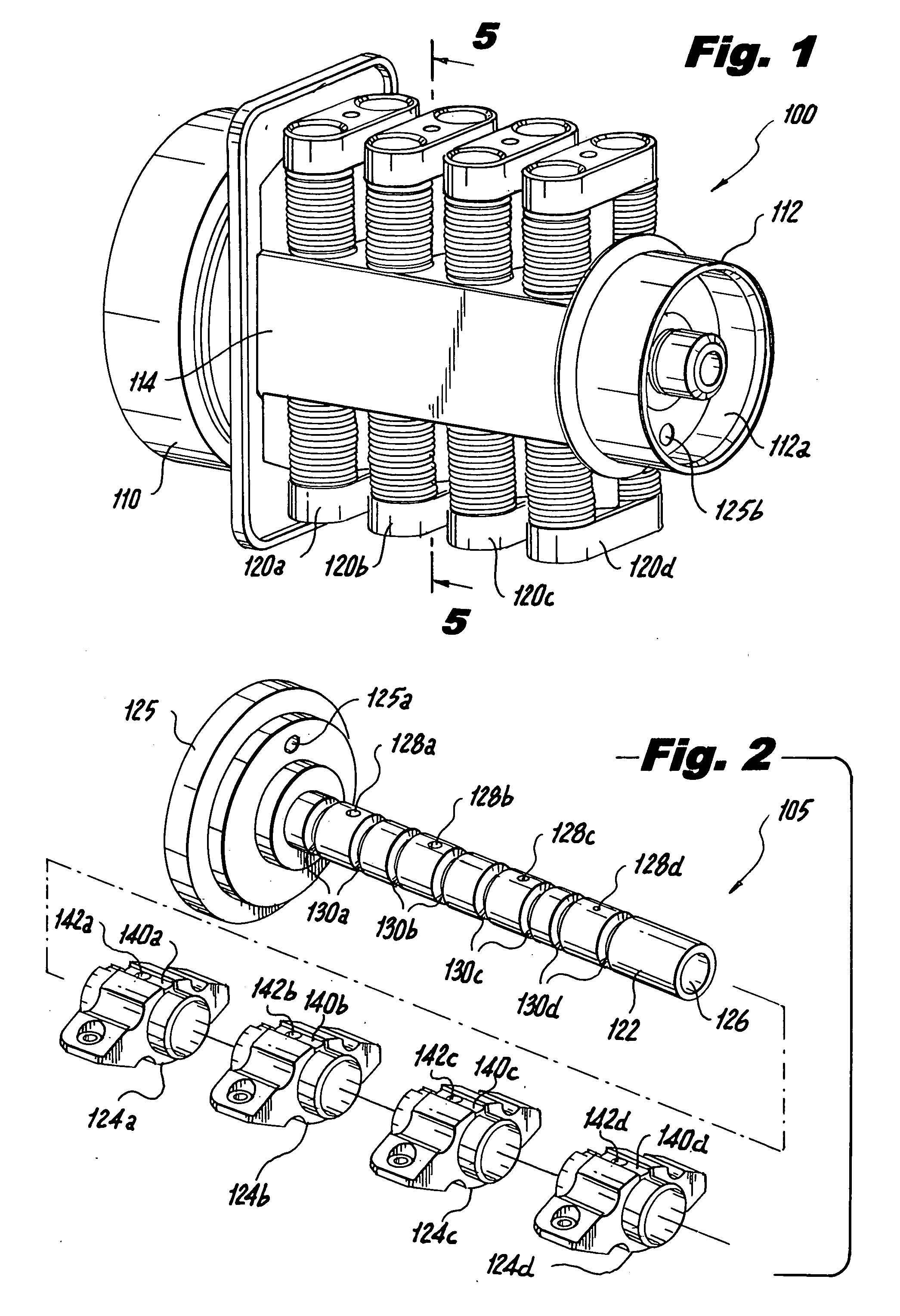
Nested channel ducts for nozzle construction and the like
InactiveUS7028484B2Simpler and economical to manufactureLiquid fuel feeder/distributionContinuous combustion chamberGuide tubeGas turbines
A multiple conduit system for a gas turbine engine, the multiple conduit system extending between a plurality of conduit inlet and outlets. A channel is formed in a surface of a gas turbine engine component, and the channel is adapted for conveying a fluid flow from an inlet to an outlet. At least a first sealing member is disposed within the channel and divides the channel into at least a first discrete conduit and a second discrete conduit. A second sealing member encloses the channel to define the second discrete conduit. The first and second discrete conduits are each adapted to direct an independent fluid flow from respective inlets to respective outlets.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
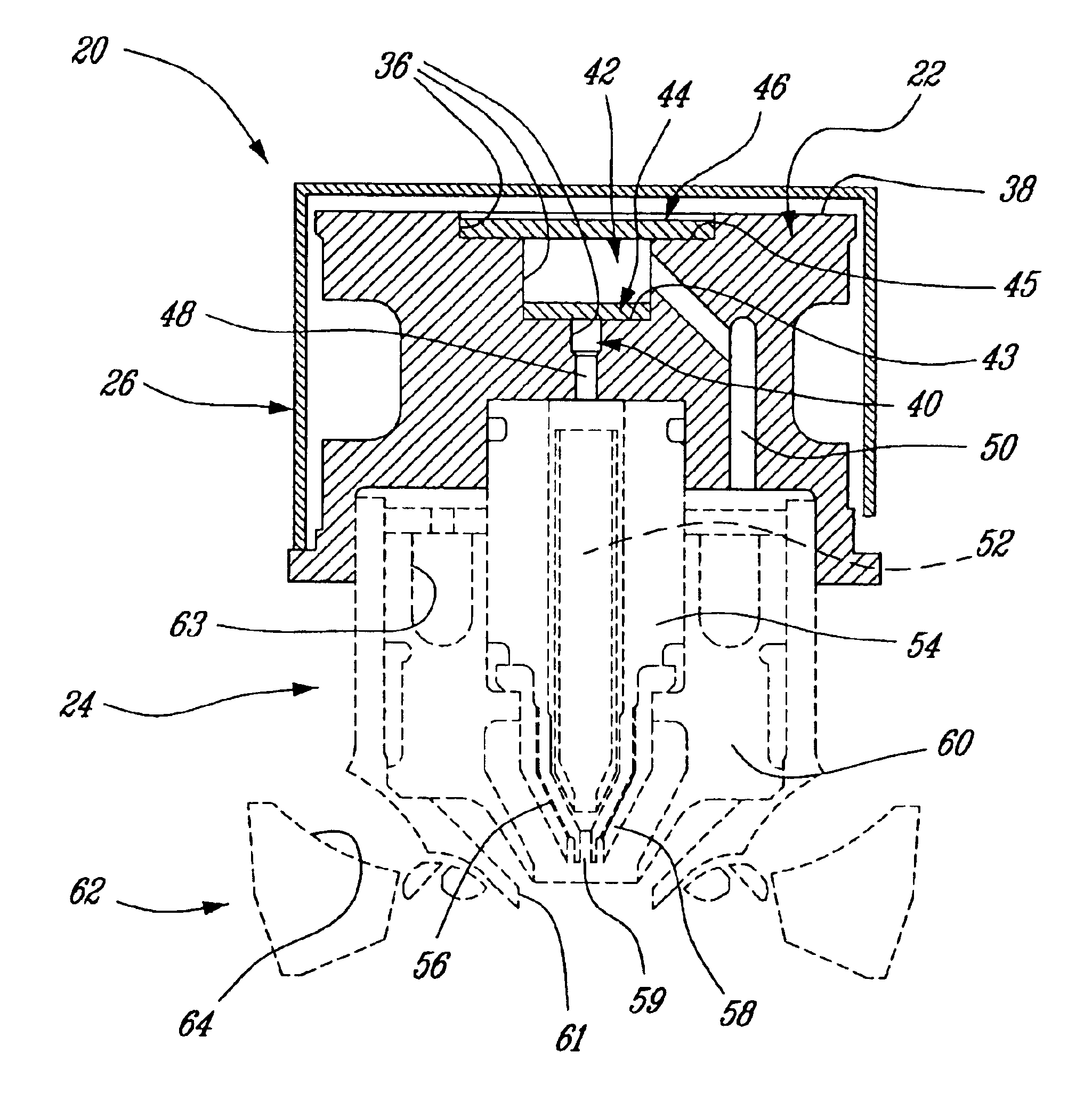
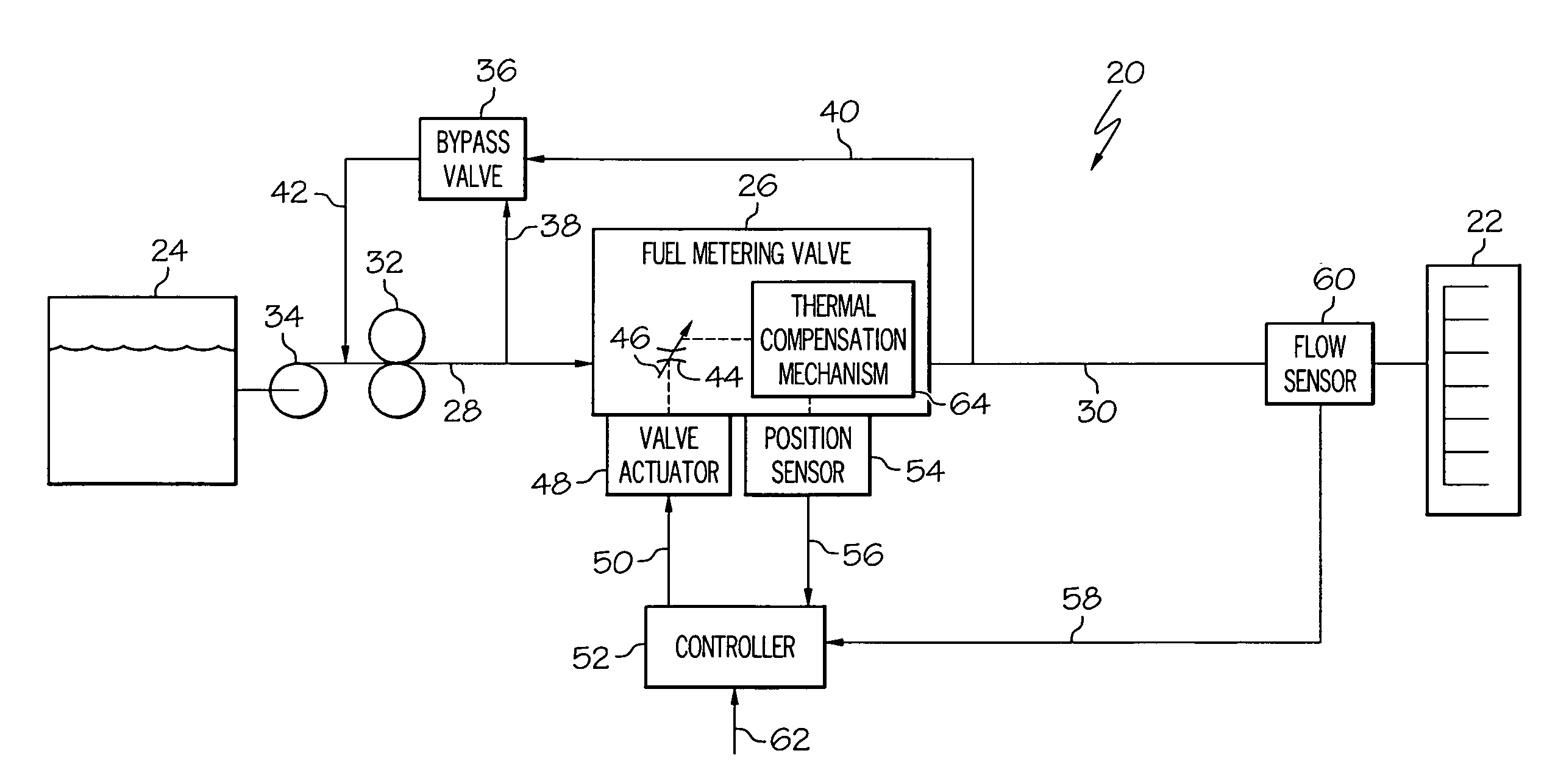
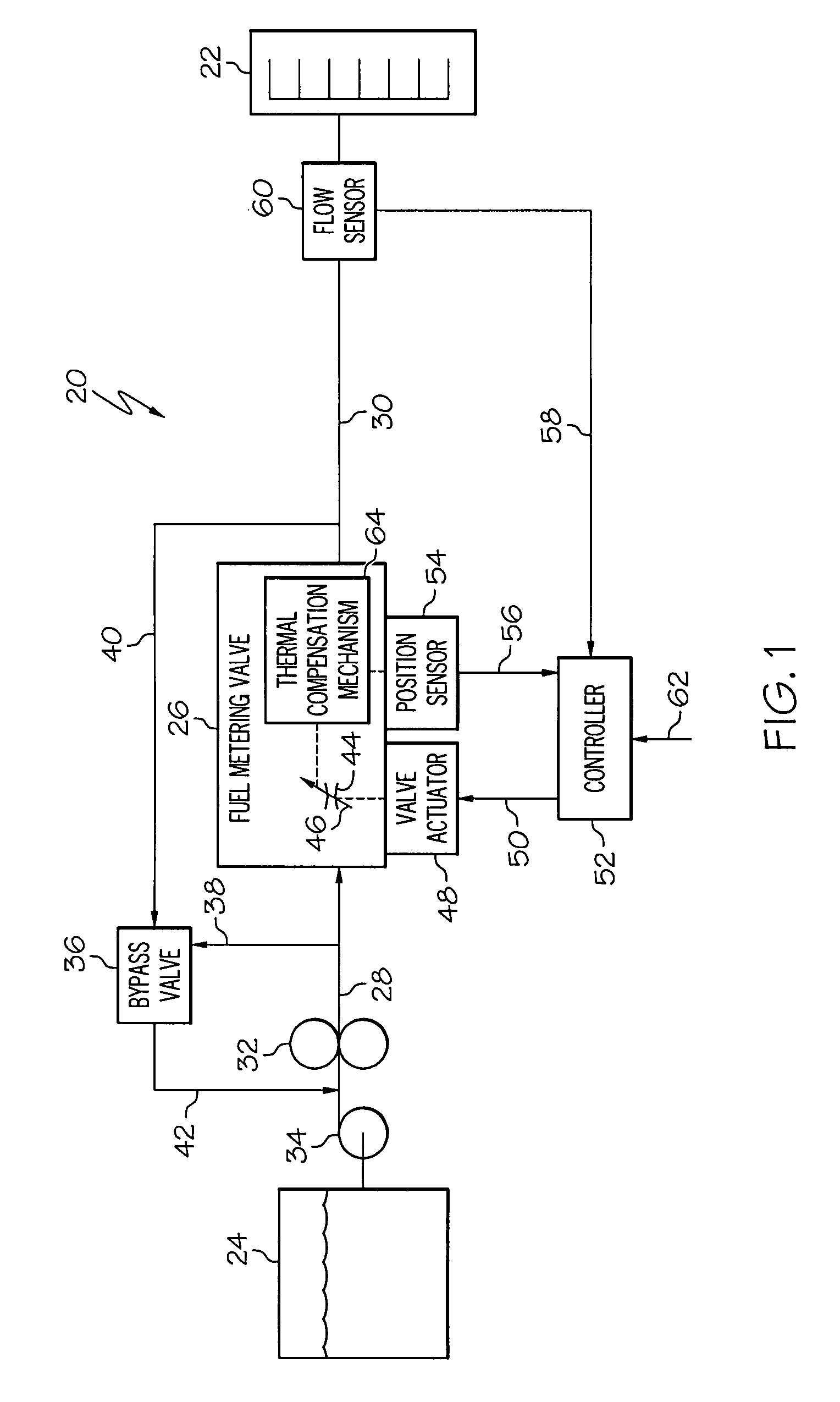
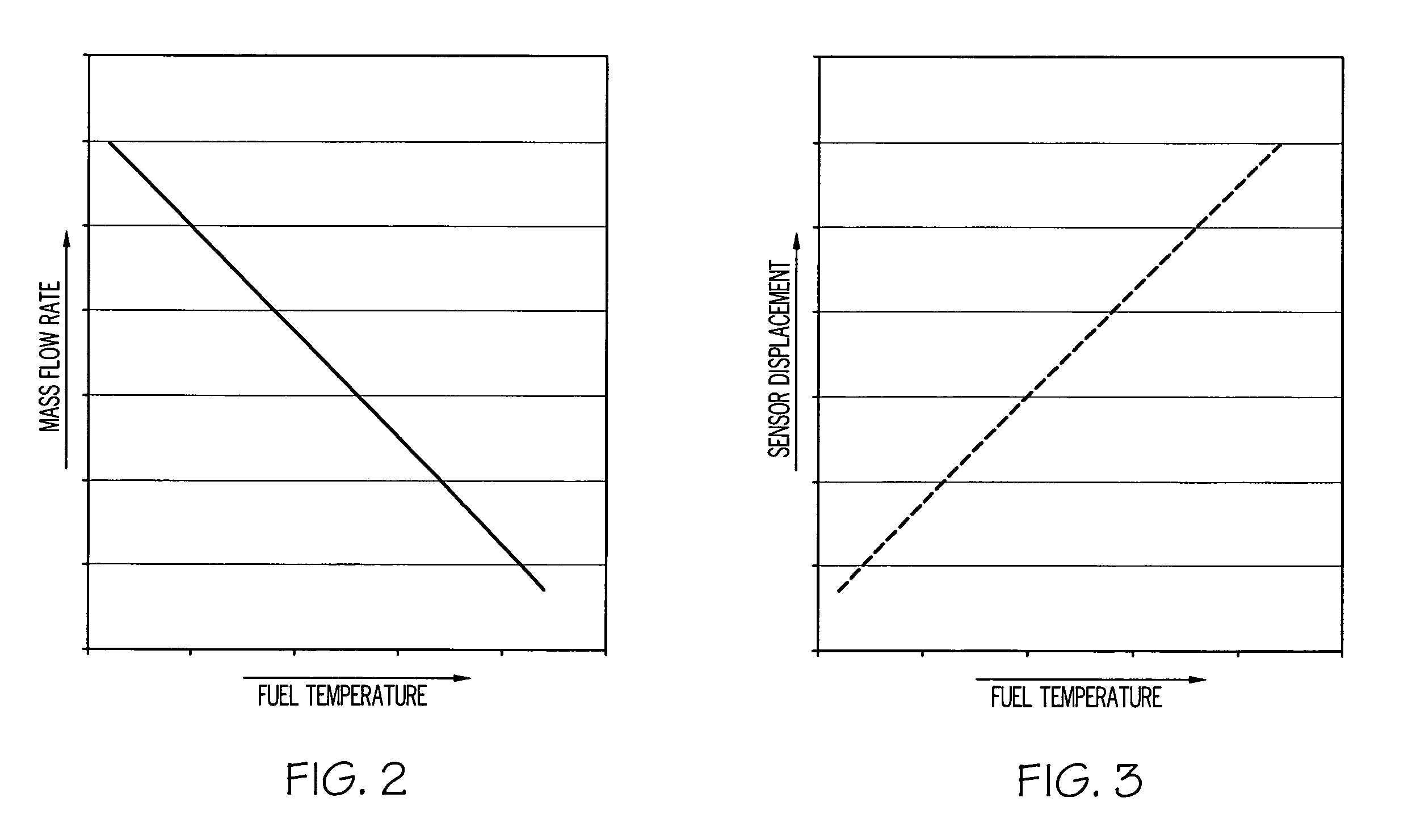
Fuel metering valve assembly including thermal compensation mechanism
InactiveUS20090301575A1Increase widthTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesEfficient propulsion technologiesMechanical engineeringPosition sensor
A metering valve assembly is provided for metering a fluid. The metering valve assembly includes a position sensor, metering valve, and a thermal compensation mechanism. The metering valve includes a valve housing having a flow passage therethrough, and a valve element movably mounted within the valve housing. The thermal compensation mechanism is coupled between the position sensor and the valve element and configured to adjust the displacement of the position sensor relative to the valve element as a function of fluid temperature.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Controlled pressure fuel nozzle system
ActiveUS20050198964A1Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesEngineeringGas turbines
A multi-staged gas turbine engine fuel supply system includes a plurality of fuel injectors and at least first and second staged fuel injection circuits in each of the fuel injectors. Each of the first and second staged fuel injection circuits includes first and second fuel injection points and at least first and second fuel nozzle valves operable to open at different first and second crack open pressures and controllably connected to the first and second staged fuel injection circuits, respectively. A single fuel supply manifold is connected to all of the fuel nozzle valves. A single fuel signal manifold is controllably connected to all of the first and second fuel nozzle valves. The fuel injector may have a valve housing with one of the first fuel nozzle valves and one of the second fuel nozzle valves contained therein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
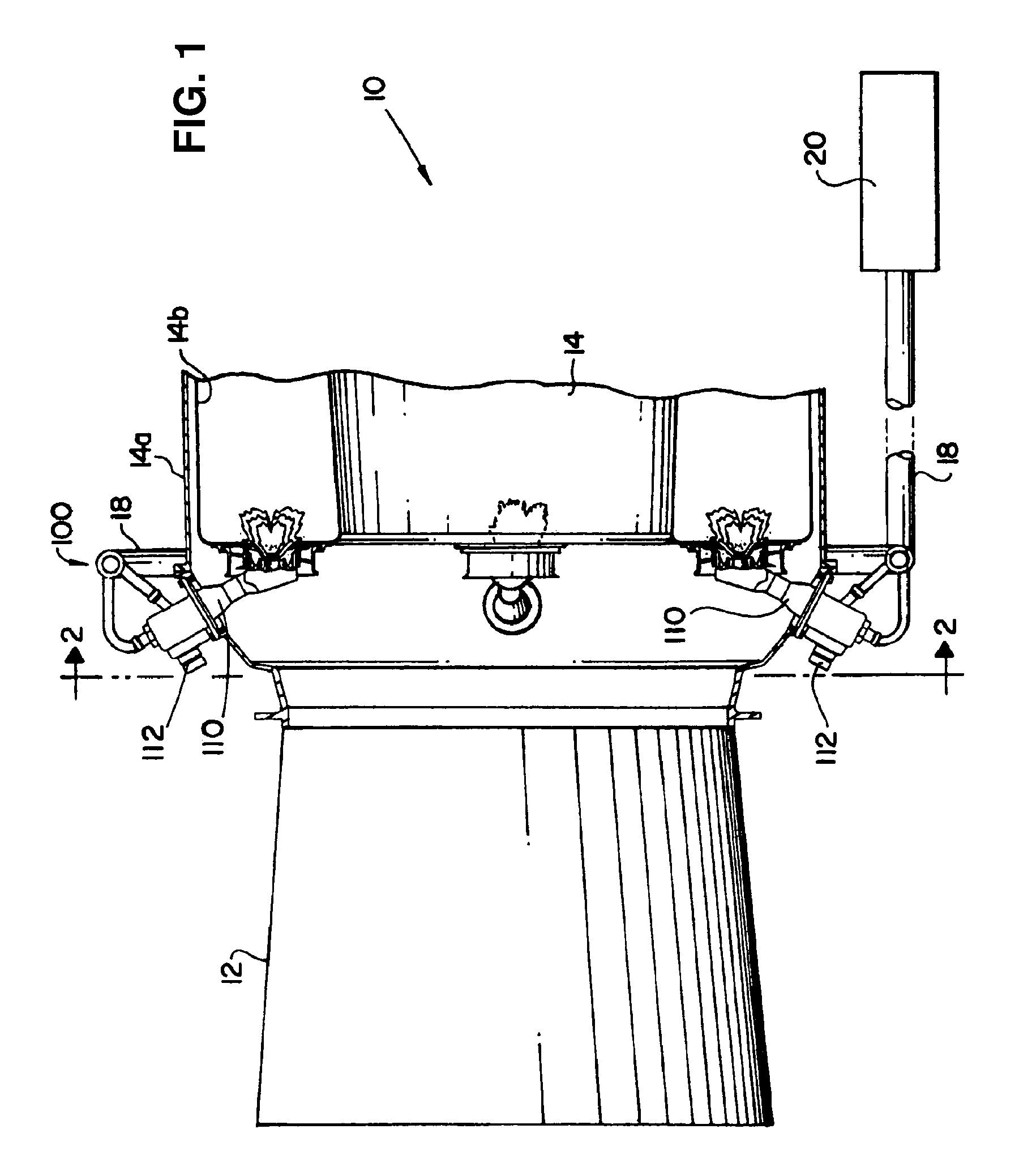
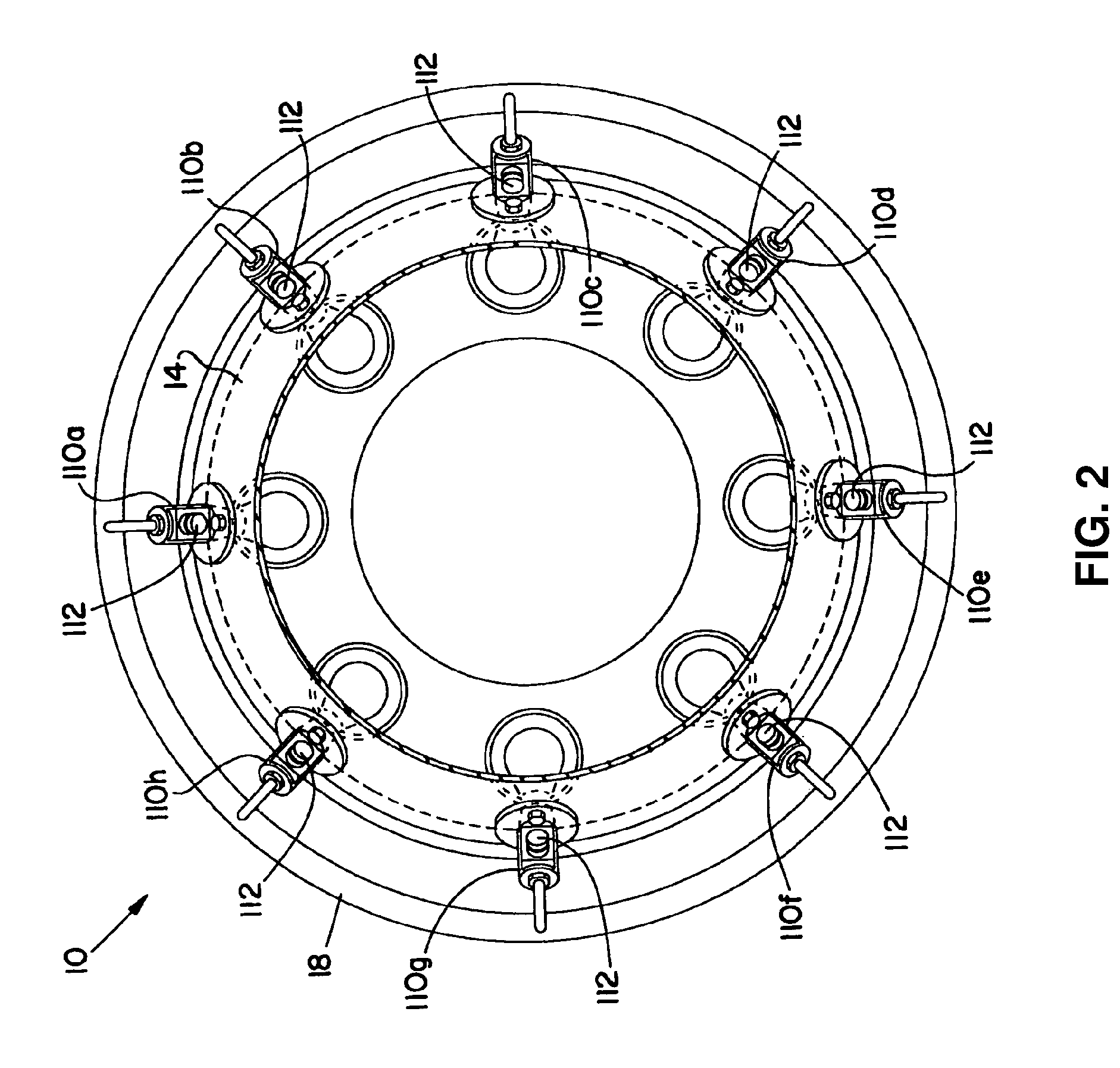
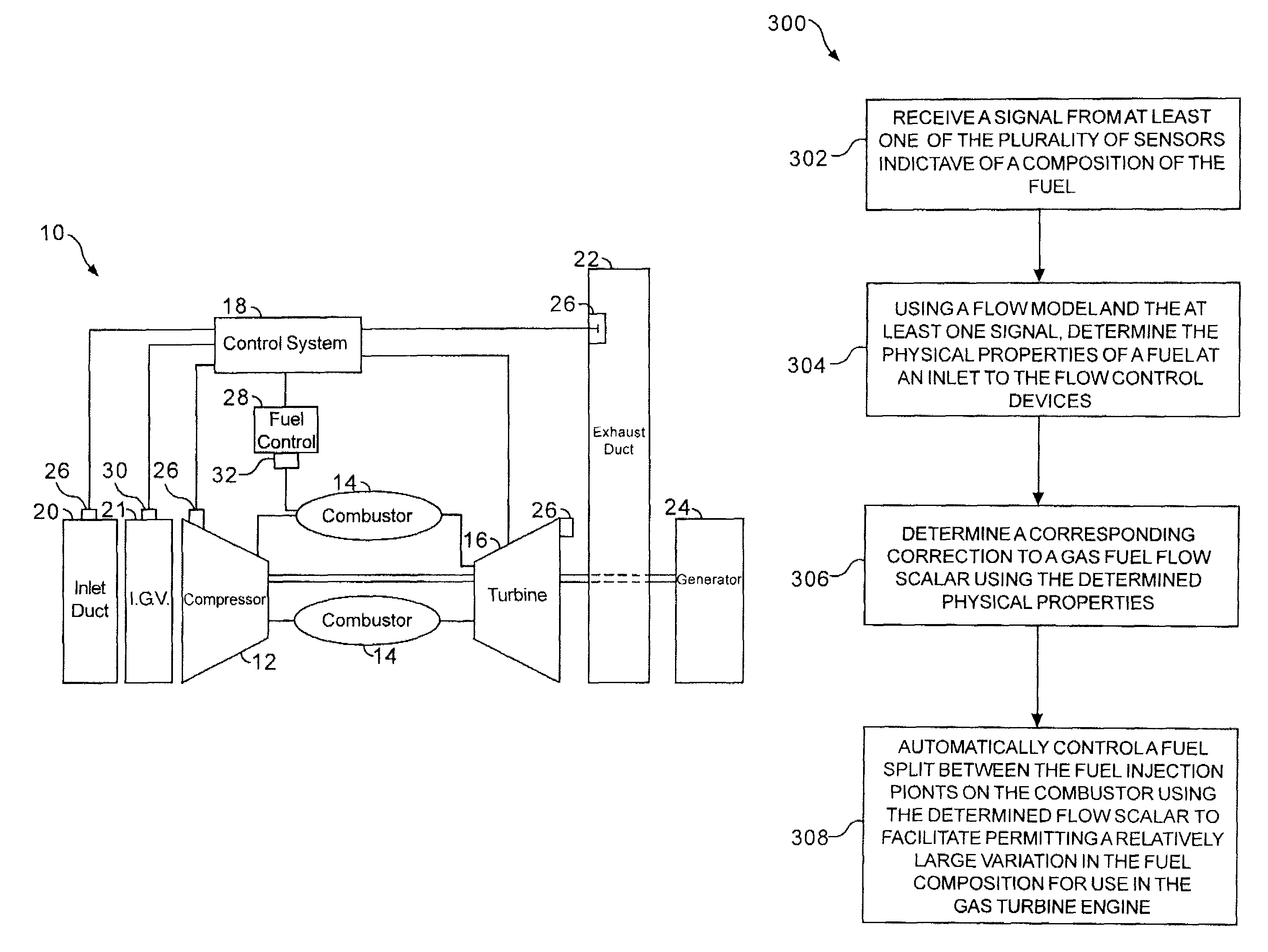
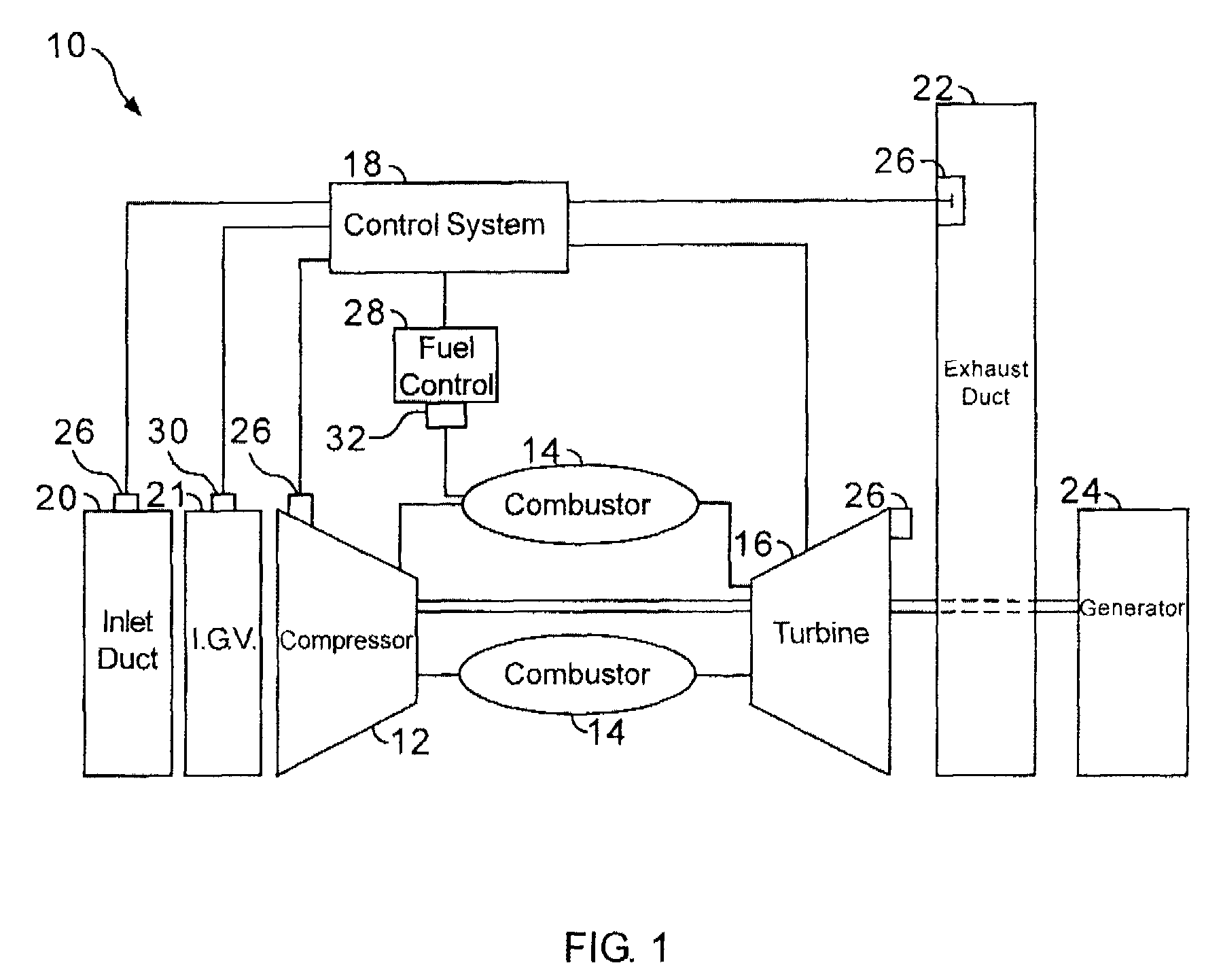
Methods and apparatus for operating gas turbine engine systems
InactiveUS20090193788A1Significant changeTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsEngine fuctionsCombustorControl system
Methods and systems for operating a gas turbine engine system are provided. The system includes a fuel control system. The fuel control system includes a plurality of sensors positioned about the gas turbine engine system and configured to measure at least one parameter associated with the sensor, and a processor programmed to receive a signal from at least one of the plurality of sensors indicative of a composition of the fuel. The processor is further programmed to determine the physical properties of a fuel at an inlet to the flow control devices using a flow model and the at least one signal, determine a corresponding correction to a gas fuel flow gain using the determined physical properties, and automatically control fuel delivery as well as fuel split between the fuel injection points on the combustor using the adjusted flow gain to facilitate permitting a relatively large variation in the fuel composition for use in the gas turbine engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fuel system for a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS7007452B1Eliminate needTurbine/propulsion fuel deliveryTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesFuel tankCheck valve
A system for automatically transferring the fuel from one or more engine fuel manifolds directly to the engine fuel tank(s) during engine shutdown using an ejector pump has been presented. A checkvalve, which may be integrated with the ejector pump, is also used. A metering valve initiates fuel flow shutoff and is used in the draining of the fuel manifolds, thereby eliminating the need for an additional solenoid dedicated mainly to the shutoff function. The shutoff and pressurizing valve provides flow division between manifolds and manifold drain for systems having multiple manifolds. The bypass valve is used to turn the motive flow and / or manifold drain functions on and off as a function of engine speed at start and shutdown.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Nozzle assembly with flow divider and ecology valve
InactiveUS6877306B2Prevent drainageSpraying apparatusTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesEngineeringFlow divider
A fuel system having an ecology valve controlling liquid flow through a retention passage when pressurized liquid is passed through the valve is presented. The retention passage winds between the valve outlet and a cavity such that no matter which way the valve is oriented gravity alone is unable to drain liquid from the cavity to the outlet. The ecology valve serves to suction fuel from fuel nozzle passages upon engine shutdown. Fuel is temporarily stored in the cavity and the retention passage. The ecology valve also provides a fuel splitting function for providing a port geometry determined split between fuel nozzles in the fuel system.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Valve assembly for modulating fuel flow to a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20070151252A1Guaranteed safe operationMove fastFuel supply regulationTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesEngineeringGas turbines
A valve assembly is disclosed for modulating the flow of fuel to a fuel nozzle at a high frequency or in a stepped manner to actively control combustion in a gas turbine engine which includes a valve housing defining an inlet portion for receiving fuel from a fuel source at an initial flow rate and an outlet portion for delivering fuel to a fuel nozzle at the initial flow rate or a modulated flow rate depending upon a detected combustion condition, and a mechanism disposed within the valve housing for modulating the flow rate of fuel to the outlet portion in response to a detected combustion condition.
Owner:DELAVAN
Fluid divider valves
ActiveUS8469059B1Continuous combustion chamberOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:COLLINS ENGINE NOZZLES INC
Fuel control system with metering purge valve for dual fuel turbine
ActiveUS8104258B1Reduce sensitivityPlug valvesLiquid fuel feeder/distributionCrossbar switchSpool valve
The fuel system of a dual fuel turbine includes a flow control valve having a metering purge valve that in one state directly meters fuel to injectors of the turbine, in another state closes of fuel flow and passes purge air to the injectors and in another state positively closes of flow of both fuel and purge air. The metering purge valve is a pressure compensated spool valve that has a unique cross-ported interchange that passes fuel from the inlet through the spool to the metering edge. The direct metering of the valve to the injectors eliminates the need for additional shut off valves, and if used with a combining valve having an integral distributor section metering fuel to multiple injectors, the need for a separate flow divider is also eliminated. The valve can be actively cooled by dedicated coolant lines or lines shared with other flow control components such as additional metering valves for either the primary or secondary fuel.
Owner:JANSENS AIRCRAFT SYST CONTROLS
Extended operability aircraft fuel delivery system
InactiveUS7093437B2Reduce amountExpand the scope of operationEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCavitationOperability
Owner:RTX CORP
Distributor purge valve
A combination distributor purge valve unit for a turbine engine has a pilot air section, a fuel section, a distributor section and a purge air section. A spool moves along a spool axis to control flow through six sets of radially arranged removable fill nozzles and fixed outlet orifices in the distributor section. The spool moves from its initial position in which the distributor outlets are in communication with the inlet to the purge air section and closed off from the inlet to the fuel section so that high temperature purge air can forced passed the downstream side of the spool and into the nozzles in the combustion can of the turbine engine to eliminate coking in these areas. The spool moves against a biasing spring under the force of a pilot air driven actuator piston and the force of the pressurized fuel so that fuel can flow, initially through the fill nozzles and then the outlet orifices, to the combustion can.
Owner:JANSENS AIRCRAFT SYST CONTROLS
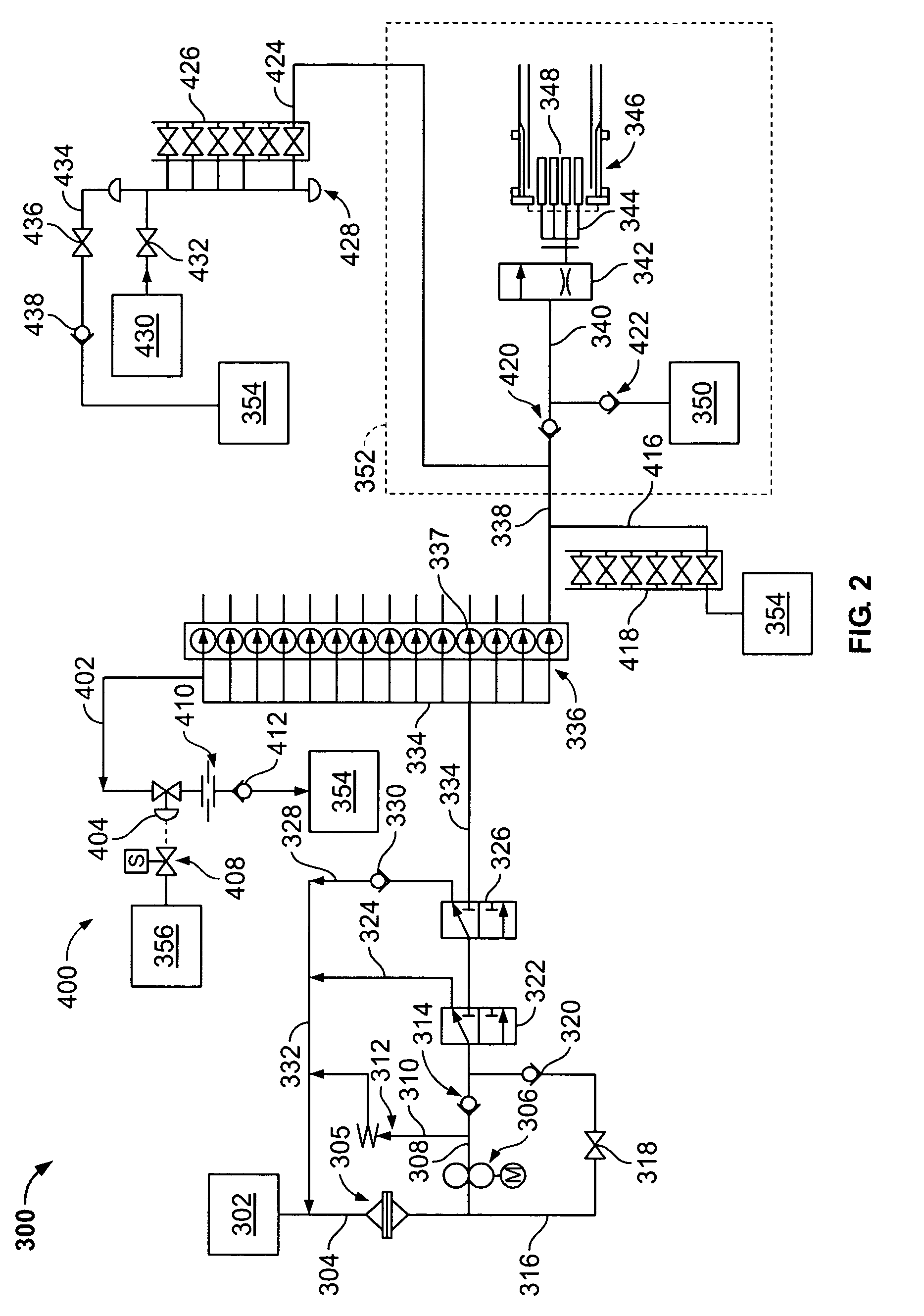
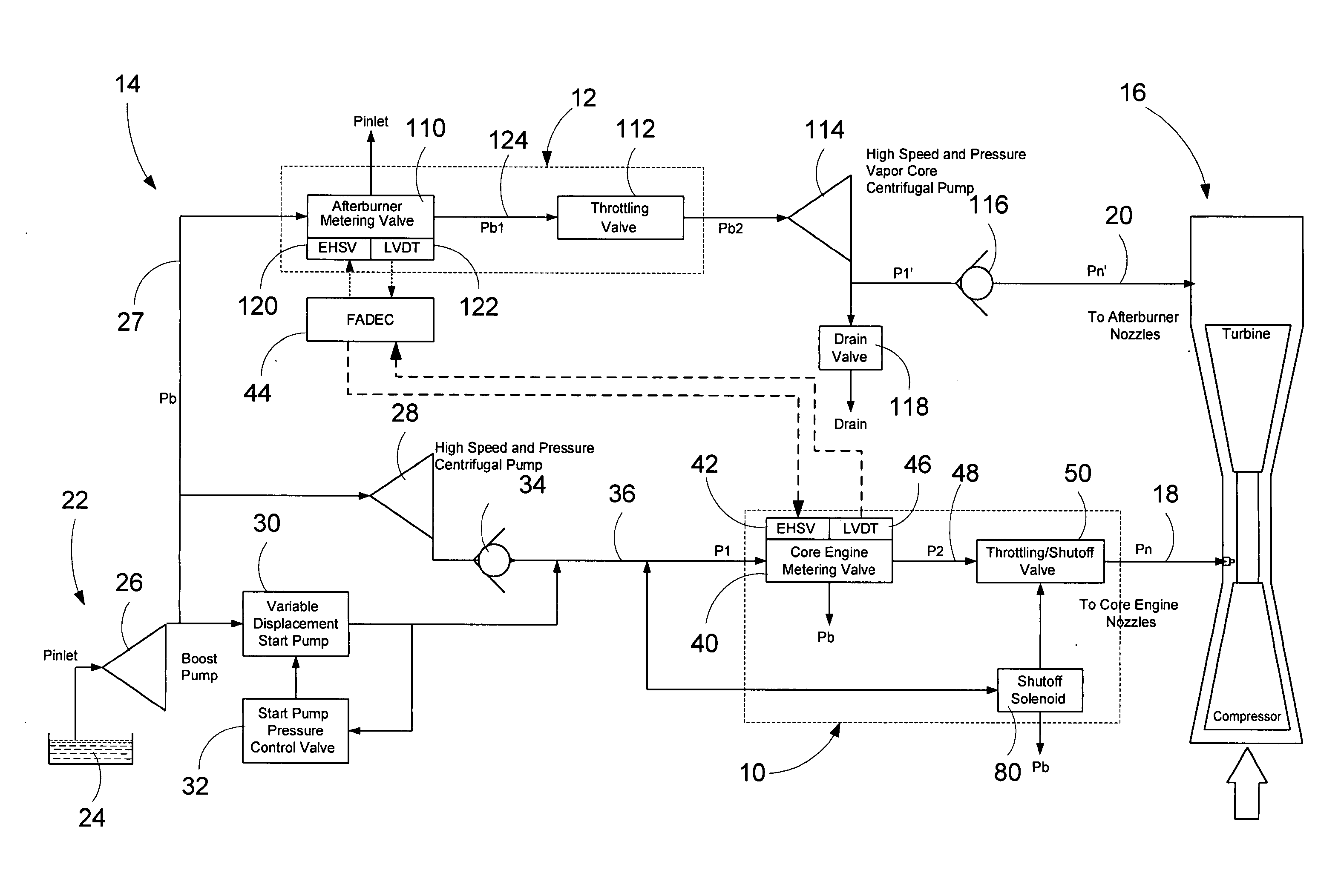
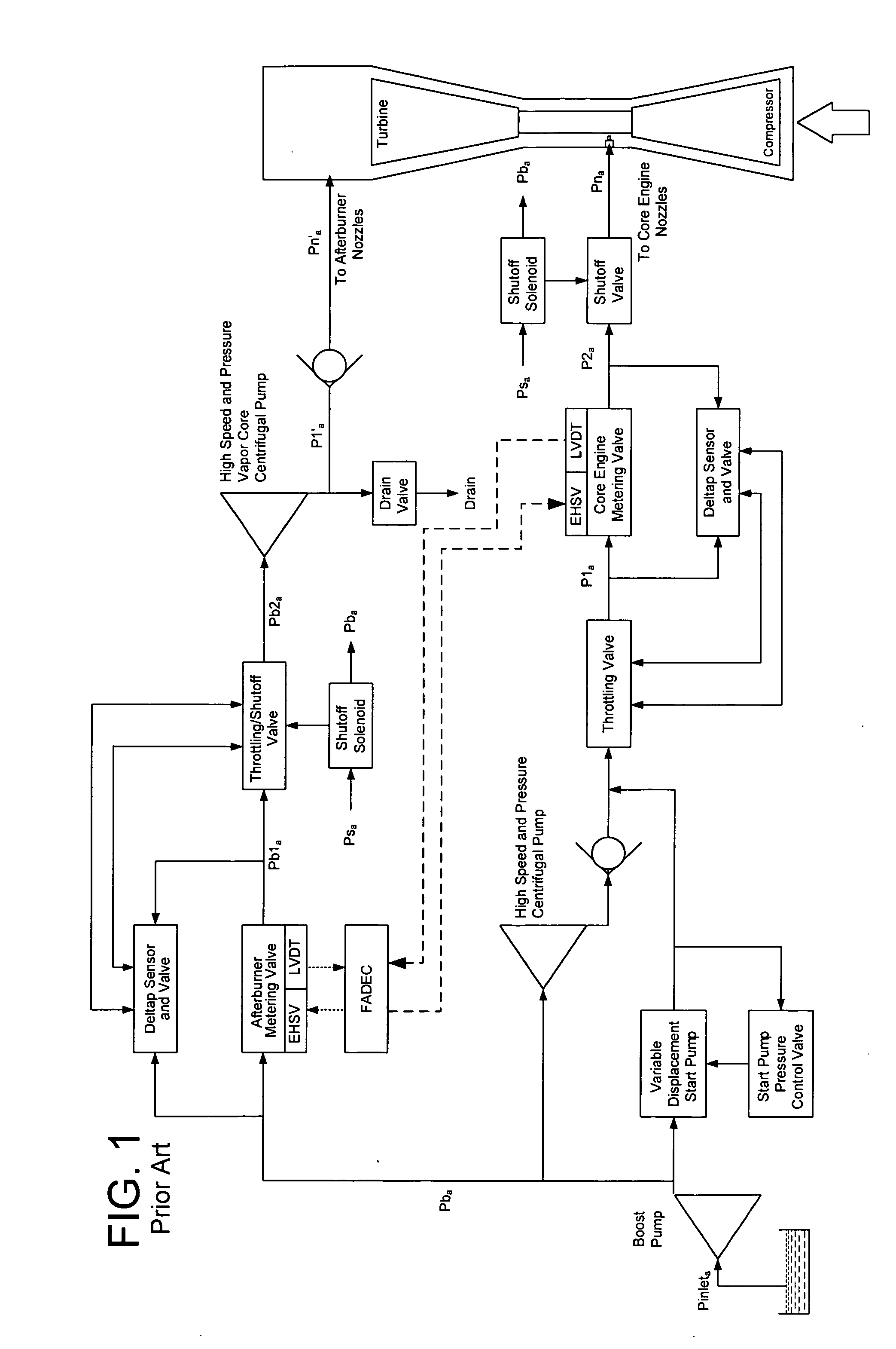
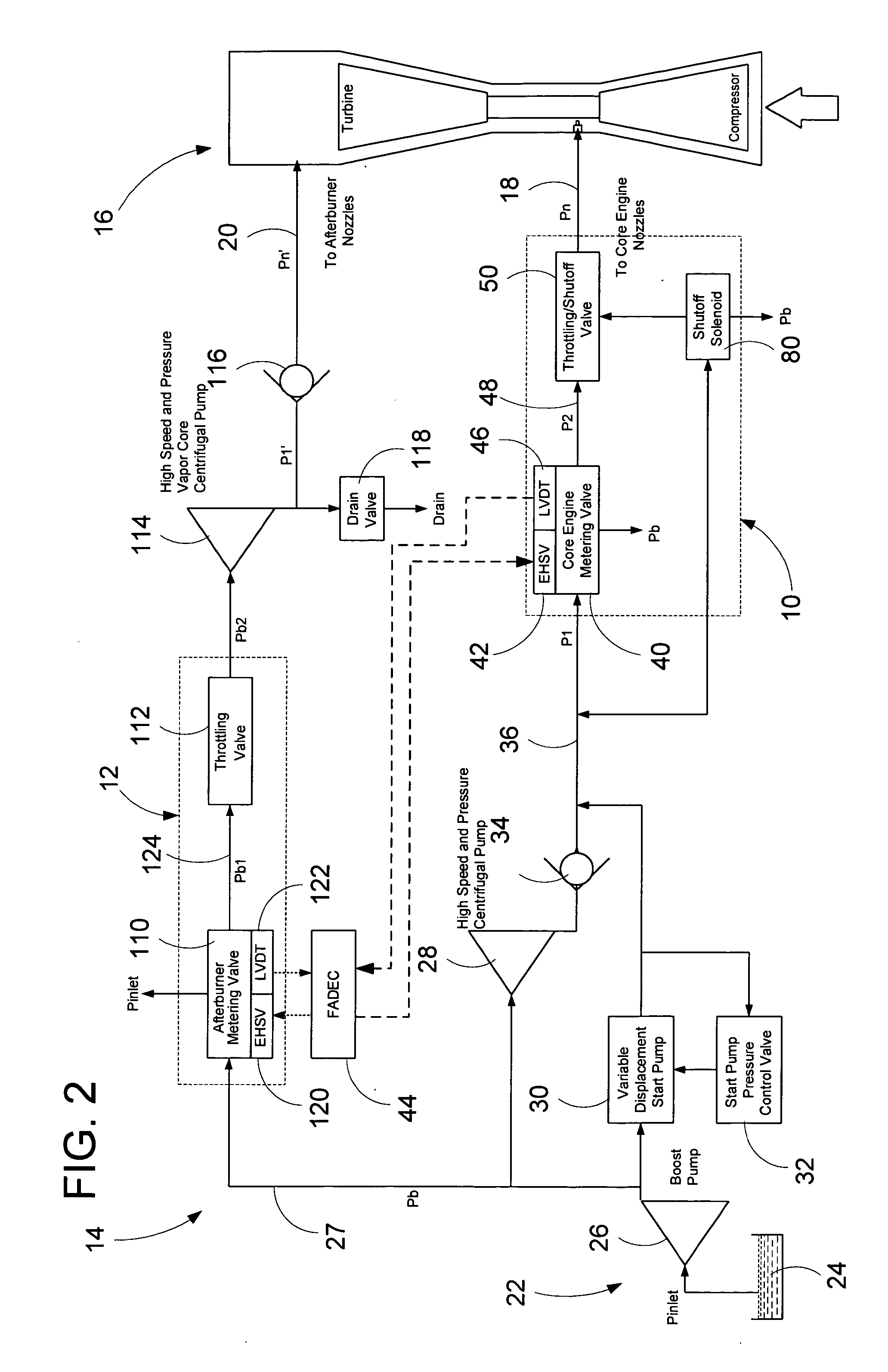
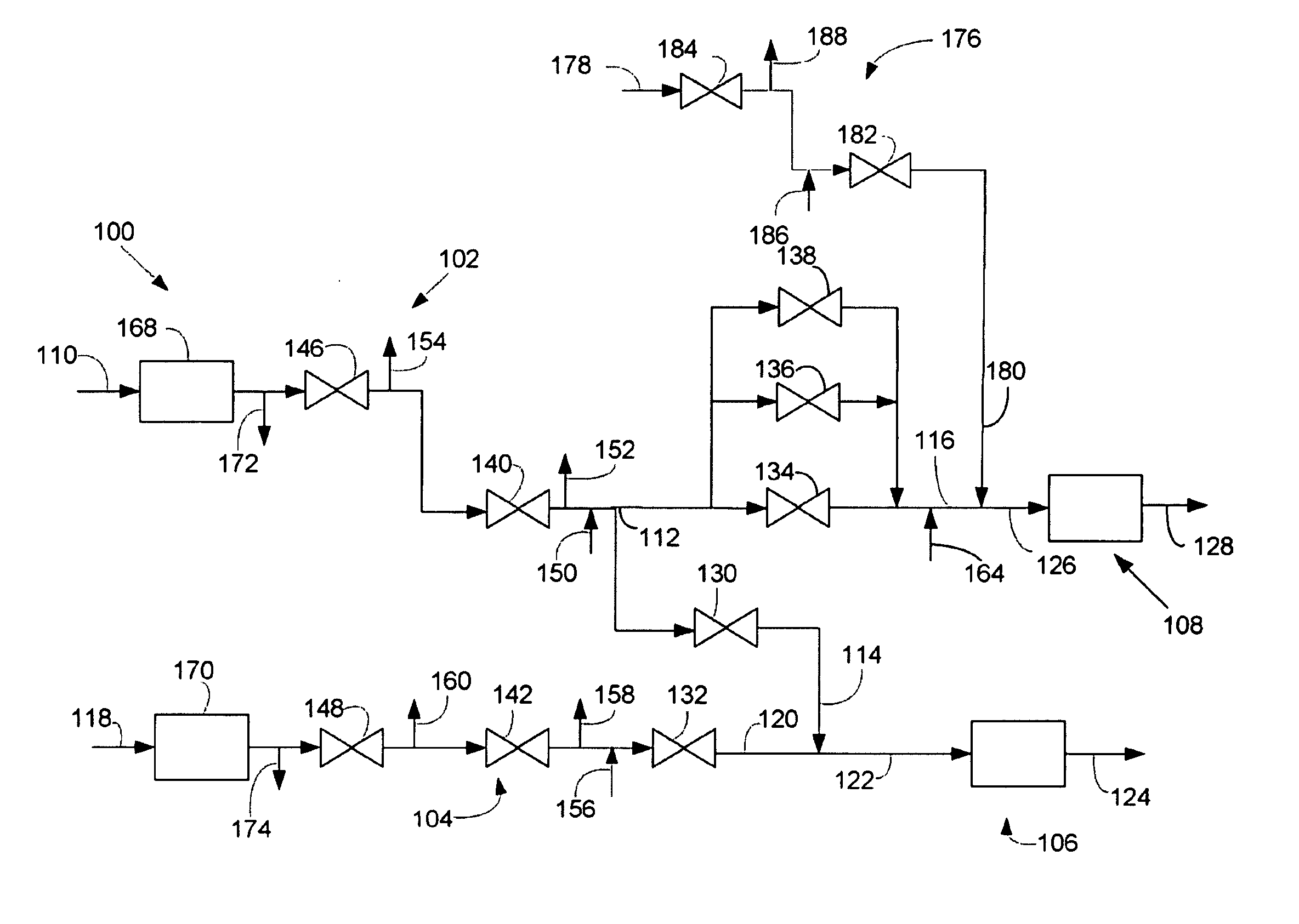
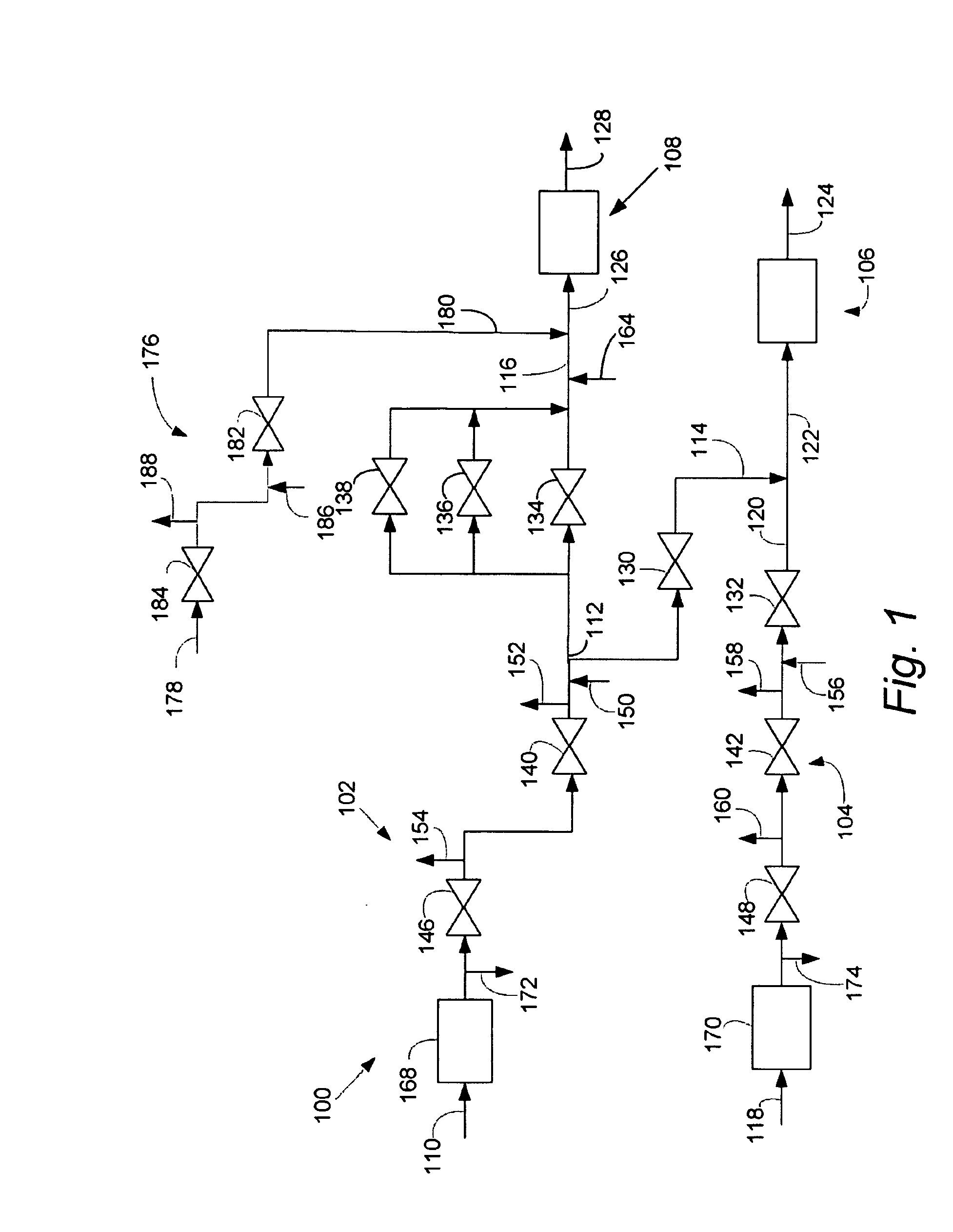
Operation of Dual Gas Turbine Fuel System
ActiveUS20090272118A1Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsEngineeringControl valves
The present application provides a method of operating a dual gas fuel delivery system comprising selecting a manifold and fuel flow split; setting the stroke of a high-energy gas control valve based on the fuel split; measuring the primary manifold nozzle pressure ratio across a primary manifold nozzle outlet; comparing the primary manifold nozzle pressure ratio against a primary manifold specification limit; adjusting the stroke of a primary low energy gas control valve to maintain the pressure ratio across the primary manifold nozzle outlet within the primary manifold specification limit; measuring the secondary manifold nozzle pressure ratio across a secondary manifold nozzle outlet; comparing the secondary manifold nozzle pressure ratio against a secondary manifold specification limit; and adjusting the stroke of a secondary low energy gas control valve to maintain the pressure ratio across the secondary manifold nozzle outlet within the secondary manifold specification limit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable amplitude double binary valve system for active fuel control
InactiveUS20090077945A1Reduce size and weight and complexity and costMinimizing amplitudeContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesCombustion instabilityPhase shifted
A method of controlling combustion stability in a turbine engine having combustion stability control capability includes the steps of providing at least one pair of pulsating valves, mutually arranged in parallel with respect to fuel flow provided to a combustor of the turbine engine, detecting an amplitude and frequency of a pressure wave of at least one periodic combustion instability, selecting an amplitude, frequency and first phase shift, with respect to the pressure wave, of resultant fuel pulsations to reduce the amplitude of the pressure wave, translating the selected amplitude into a second, relative phase shift between each pulsating valve of at least one pair of pulsating valves, and commanding each pulsating valve of at least one pair of pulsating valves to operate at the selected frequency and a relative second phase shift with respect to one another, to yield a resultant fuel pulsation at the selected amplitude, frequency and first phase shift, with respect to the detected pressure wave of combustion instability.
Owner:DELAVAN
Methods and apparatus for operating gas turbine engine systems
InactiveUS7966802B2Significant changeTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsEngine fuctionsControl systemTurbine
Methods and systems for operating a gas turbine engine system are provided. The system includes a fuel control system. The fuel control system includes a plurality of sensors positioned about the gas turbine engine system and configured to measure at least one parameter associated with the sensor, and a processor programmed to receive a signal from at least one of the plurality of sensors indicative of a composition of the fuel. The processor is further programmed to determine the physical properties of a fuel at an inlet to the flow control devices using a flow model and the at least one signal, determine a corresponding correction to a gas fuel flow gain using the determined physical properties, and automatically control fuel delivery as well as fuel split between the fuel injection points on the combustor using the adjusted flow gain to facilitate permitting a relatively large variation in the fuel composition for use in the gas turbine engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Premixing burner with impingement cooled centerbody and method of cooling centerbody
InactiveUS20050268614A1Improving dynamic sensitivityImprove flame stabilityContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesCombustorGas turbines
A gas-air premixing burner for gas turbines includes an air swirler and an annular burner tube surrounding a bluff centerbody. The bluff body serves to stabilize the flame by defining a recirculating vortex. Cooling air is directed to impinge against the bluff face of the centerbody and the spent impingement cooling air flows in a reverse direction towards the air swirler within the centerbody and is discharged through holes at the outer diameter of the centerbody, where it mixes with the fuel / air mixture prior to reaching the flame zone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
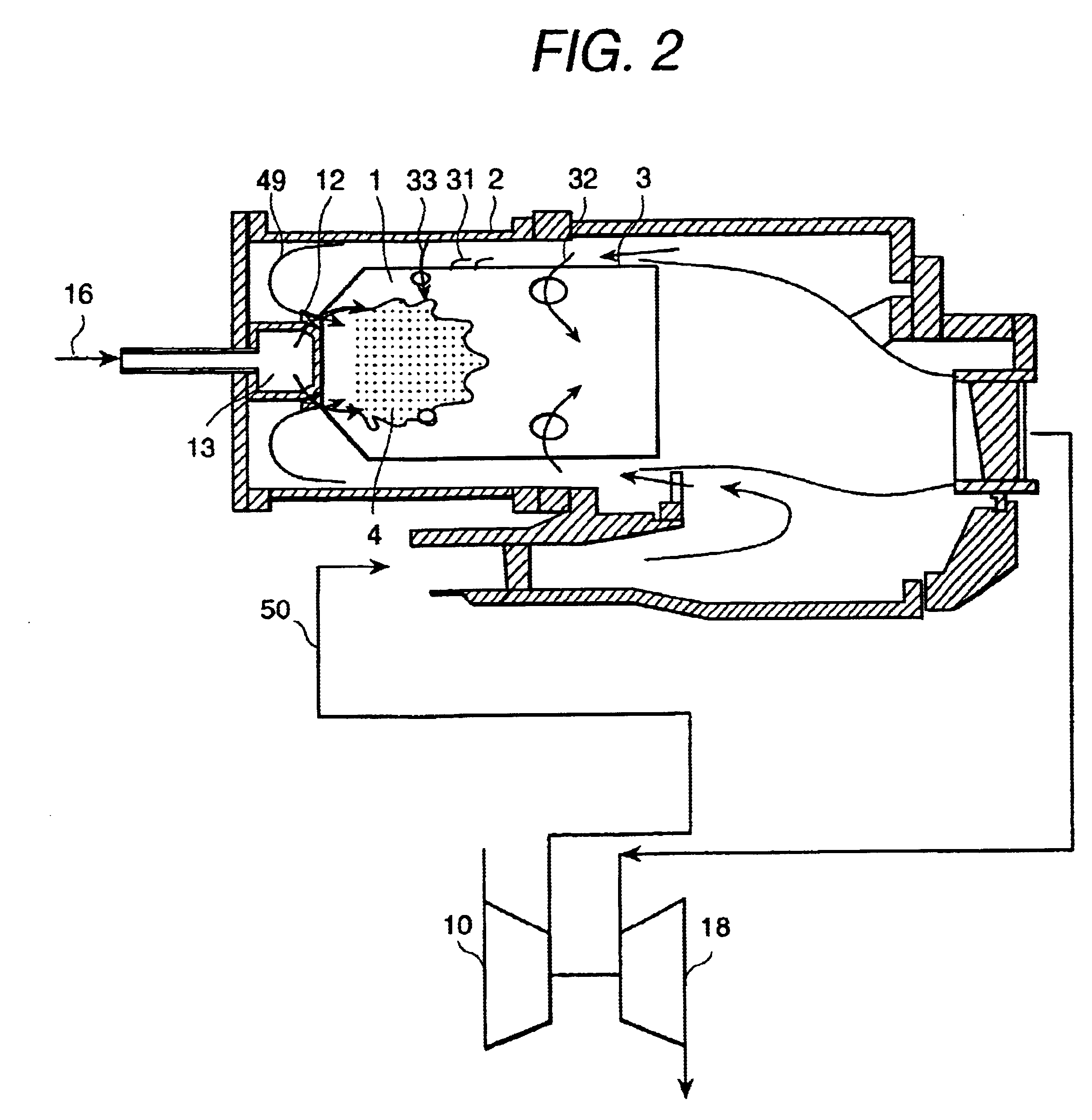
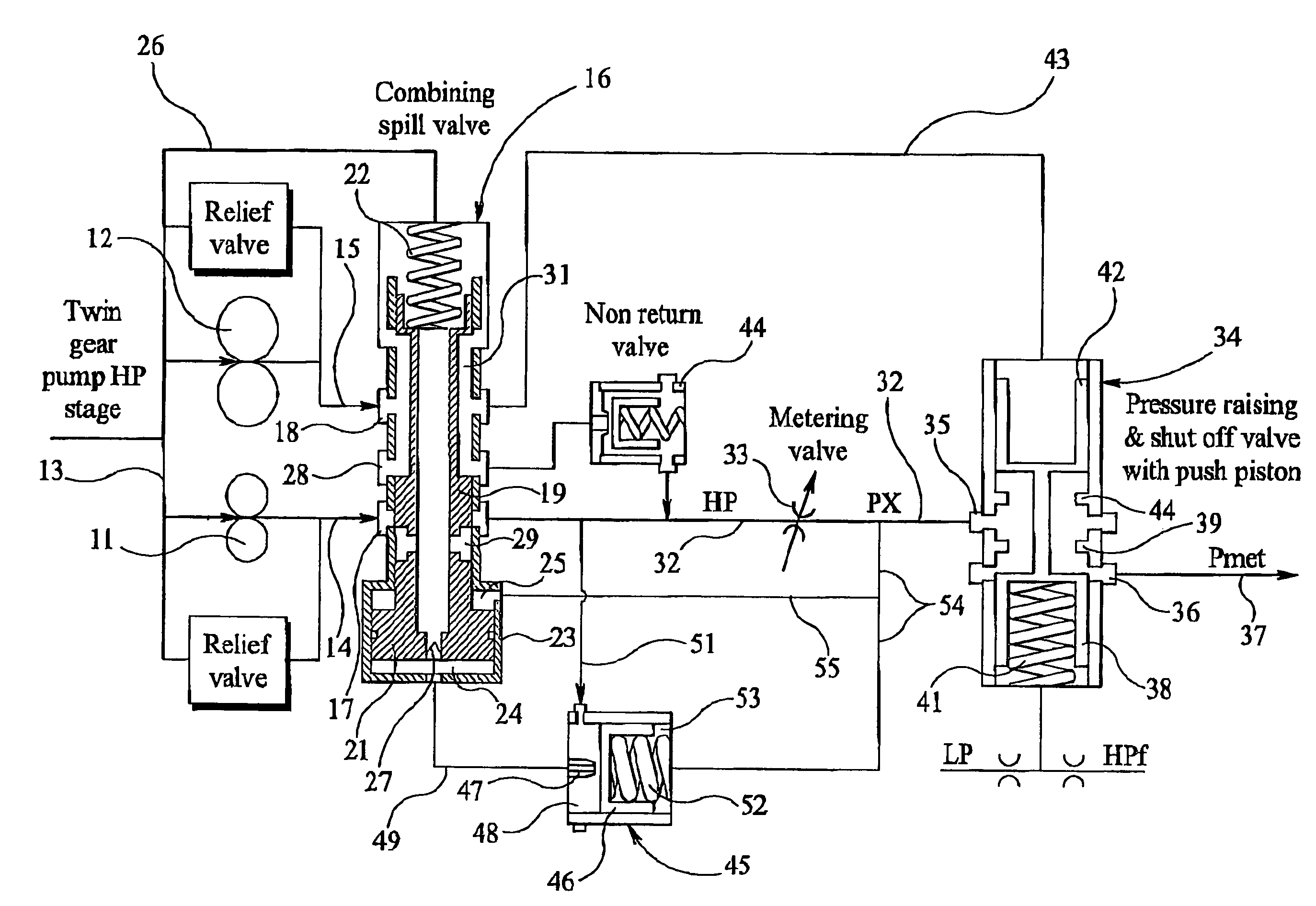
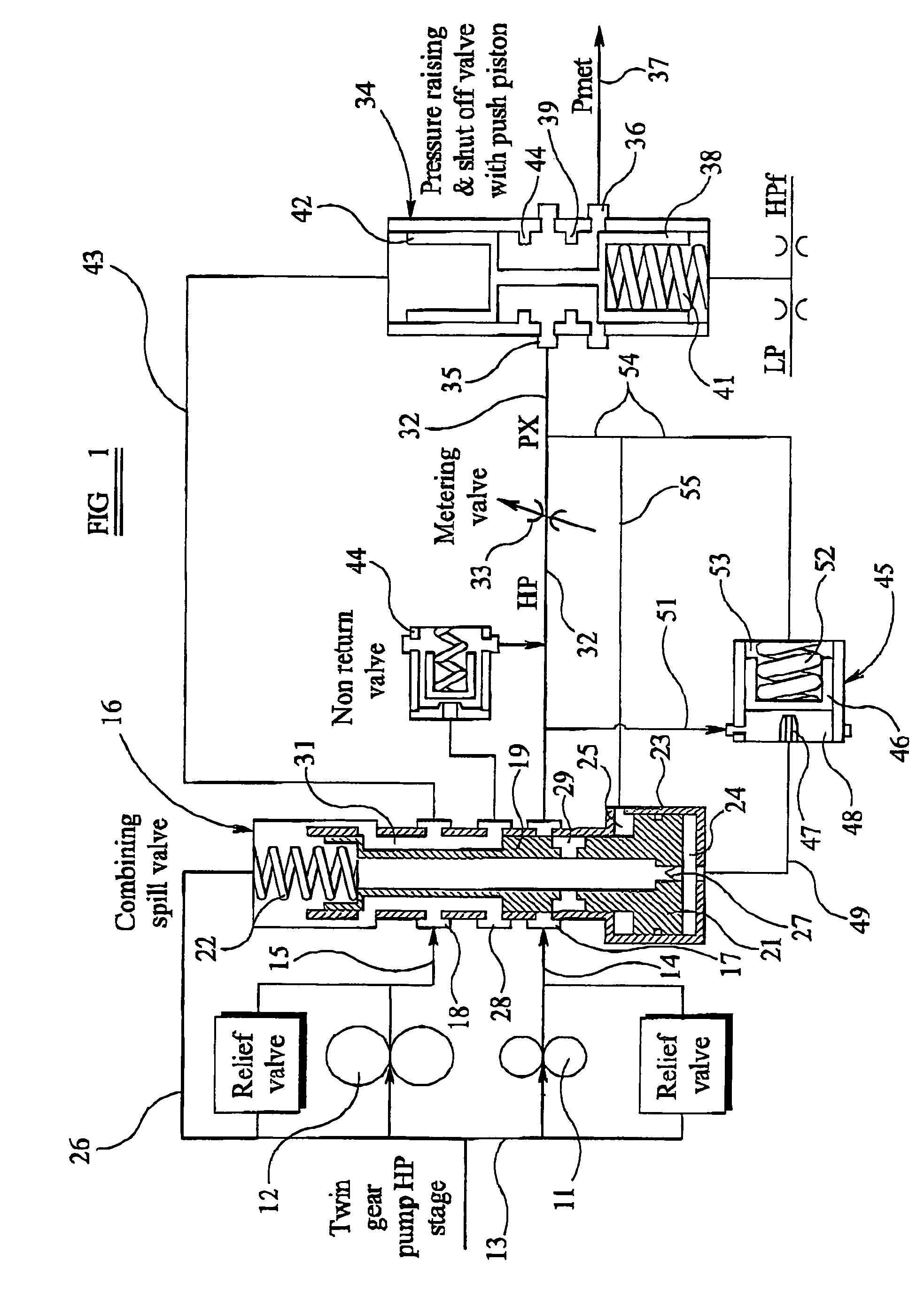
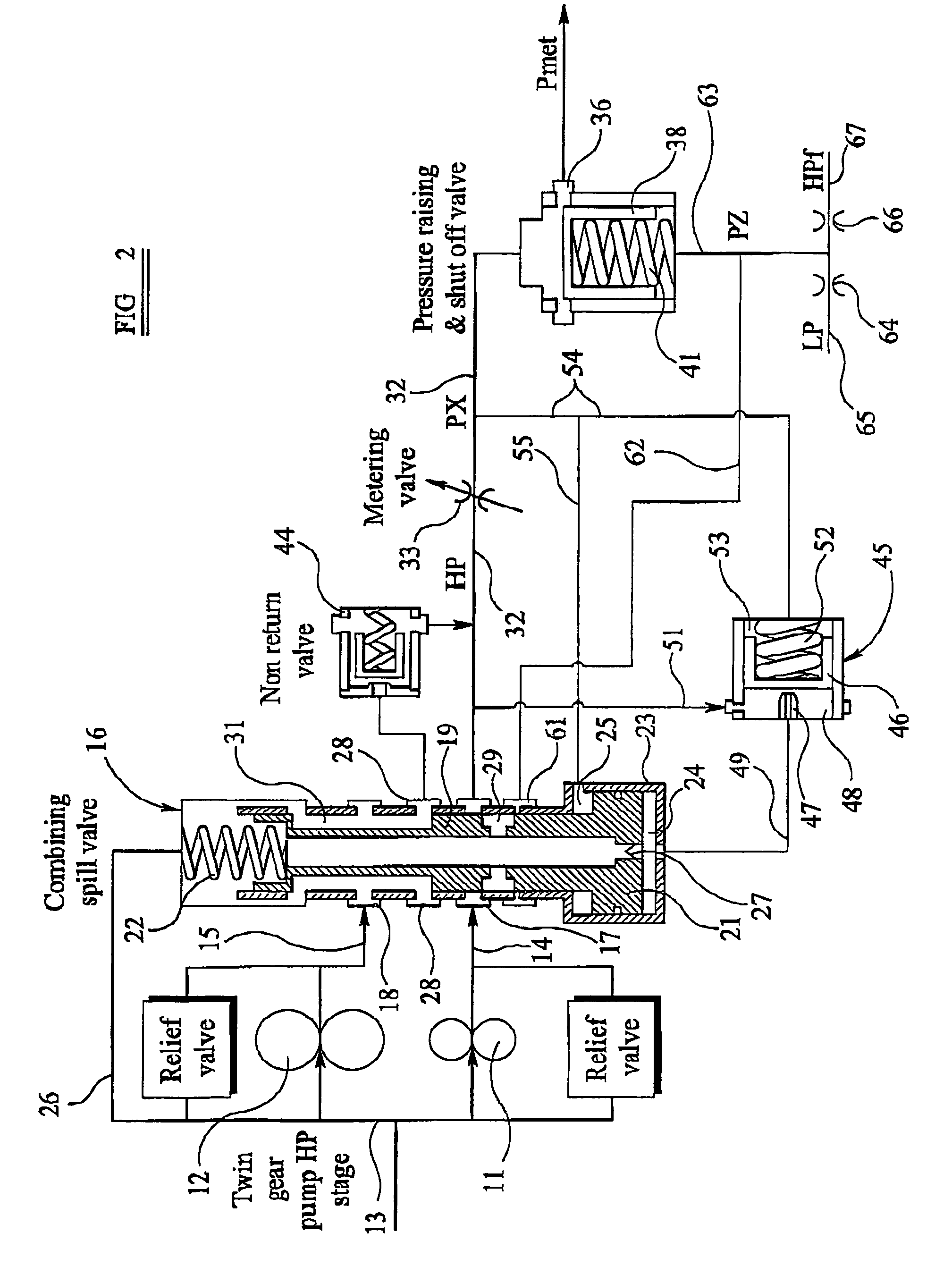
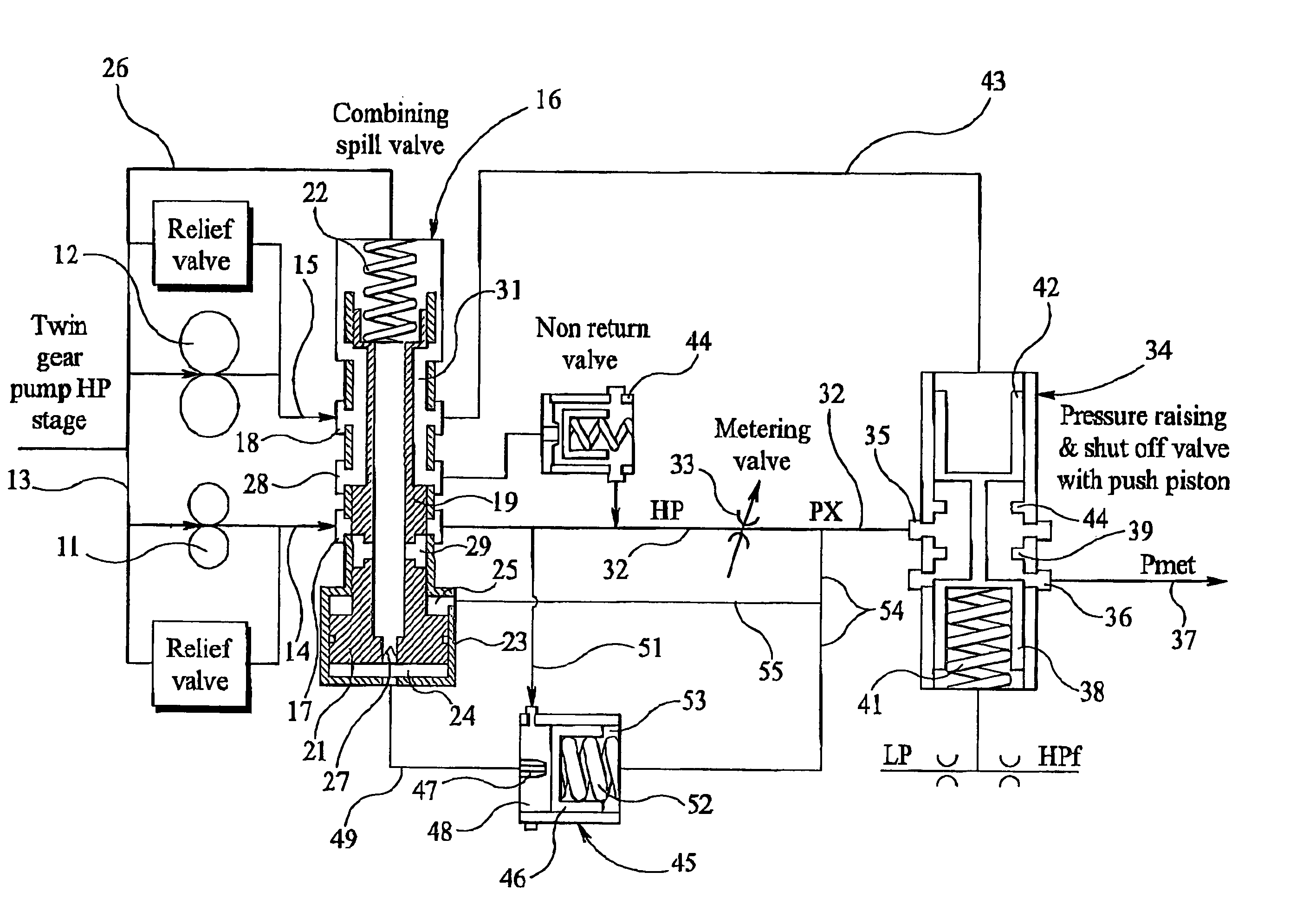
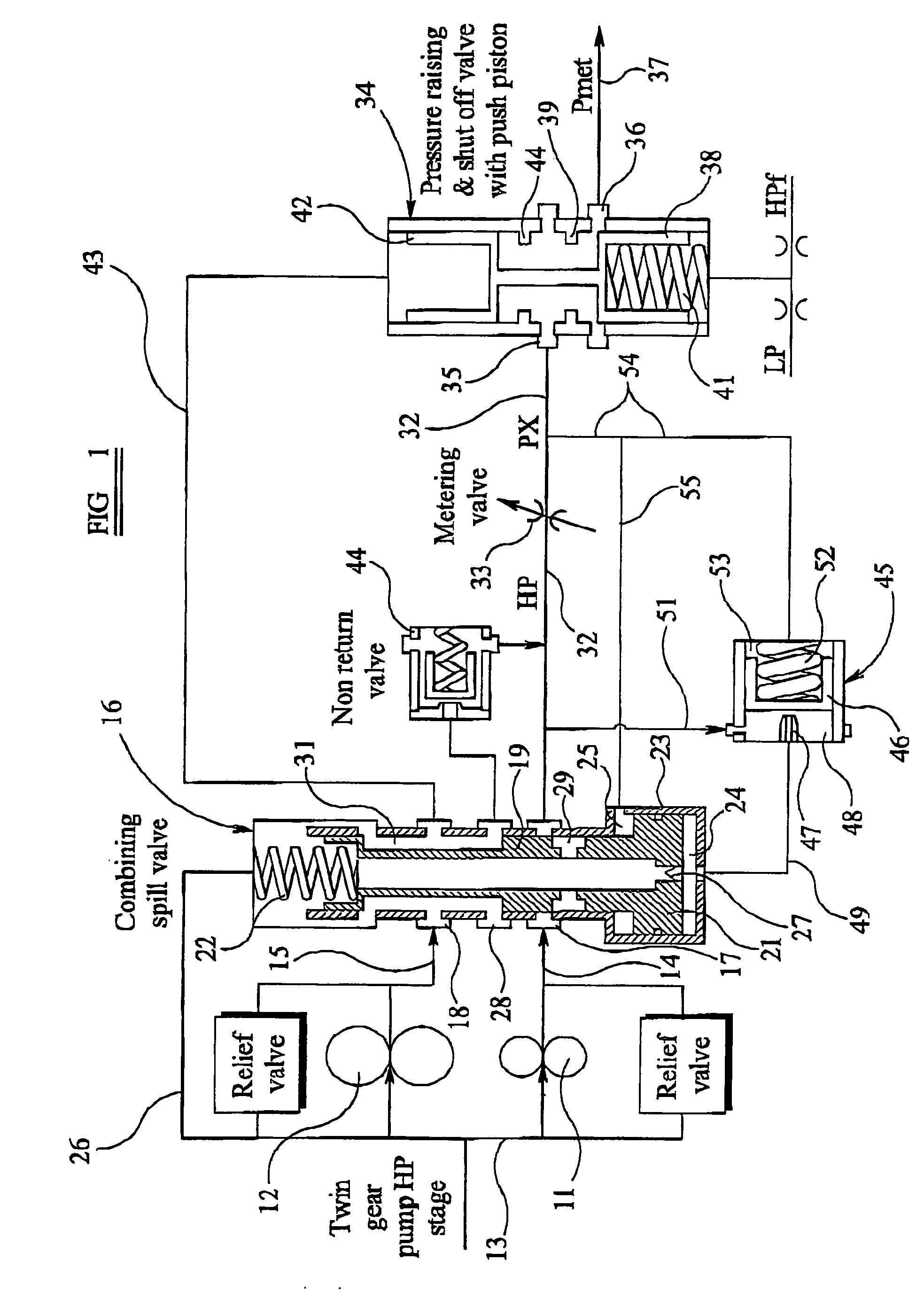
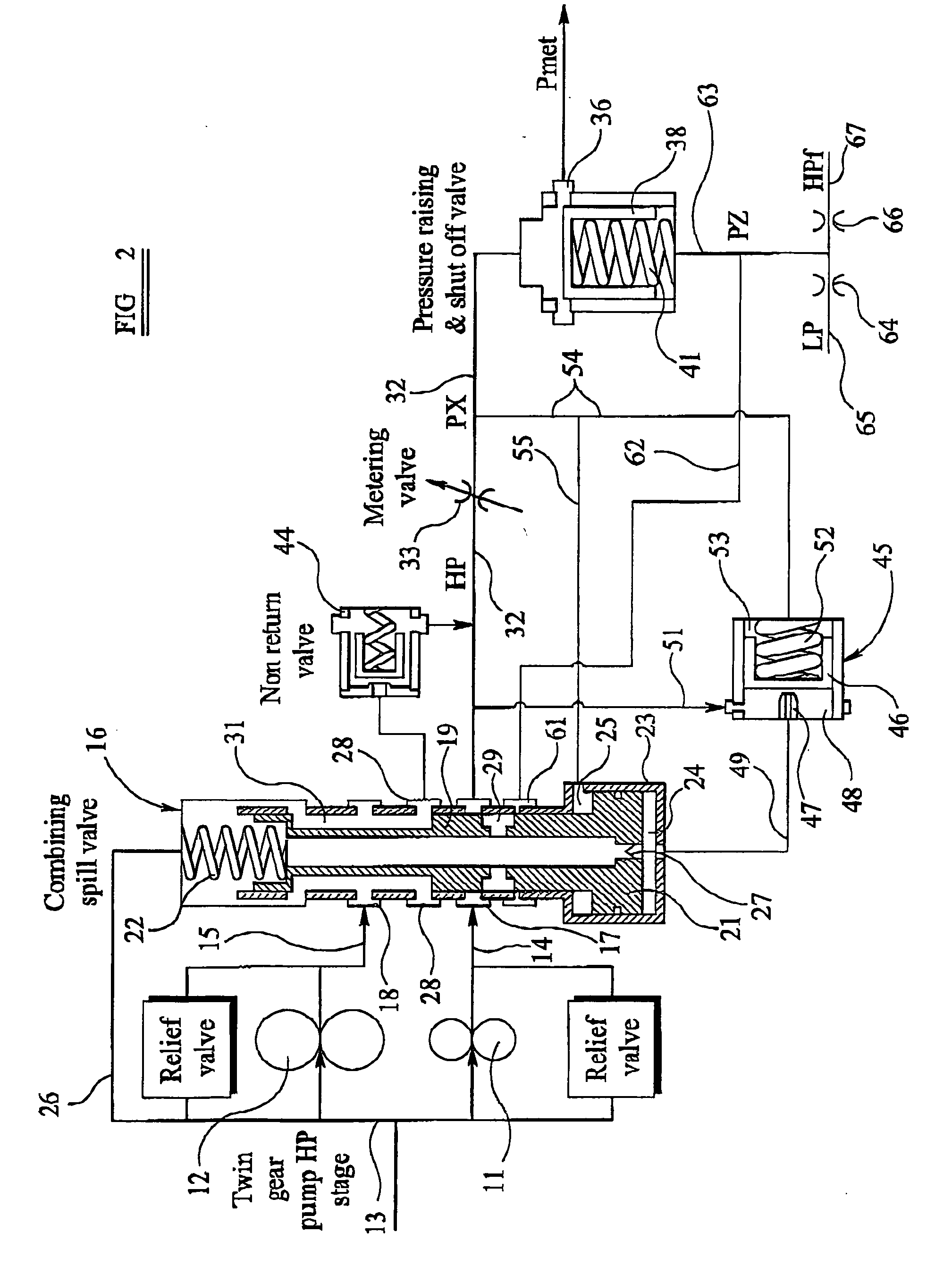
Fuel supply system
InactiveUS20050262824A1Reduce pressureTurbine/propulsion fuel deliveryTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesControl systemEngineering
A fuel supply system for a gas turbine engine including first and second positive displacement pumps operated simultaneously to supply fuel under pressure from a low pressure source, a combining spill valve controlling the output flows from the first and second pumps to combine the outputs of the first and second pumps for supply to a metering valve of the system, or to spill some or all of the output of one or both pumps back to the low pressure supply, a pressure raising and shut off valve arrangement downstream of the metering valve for isolating the fuel system from an associated engine until the fuel pressure upstream of the pressure raising and shut off valve arrangement exceeds a predetermined pressure, and, a control system dependent upon the position of the combining spill valve for reducing said predetermined pressure at which said pressure raising and shut off valve arrangement opens.
Owner:GOODRICH CONTROL SYST LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com