Composite crystal, gamma ray detector and their preparation methods
A composite crystal and gamma ray technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, crystal growth, radiation measurement, etc., can solve the problems of spectroscopic limitation at the bottom of the scintillation crystal and the decrease of detector resolution, etc., and achieve high repeatability, High spatial resolution, easy to produce effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
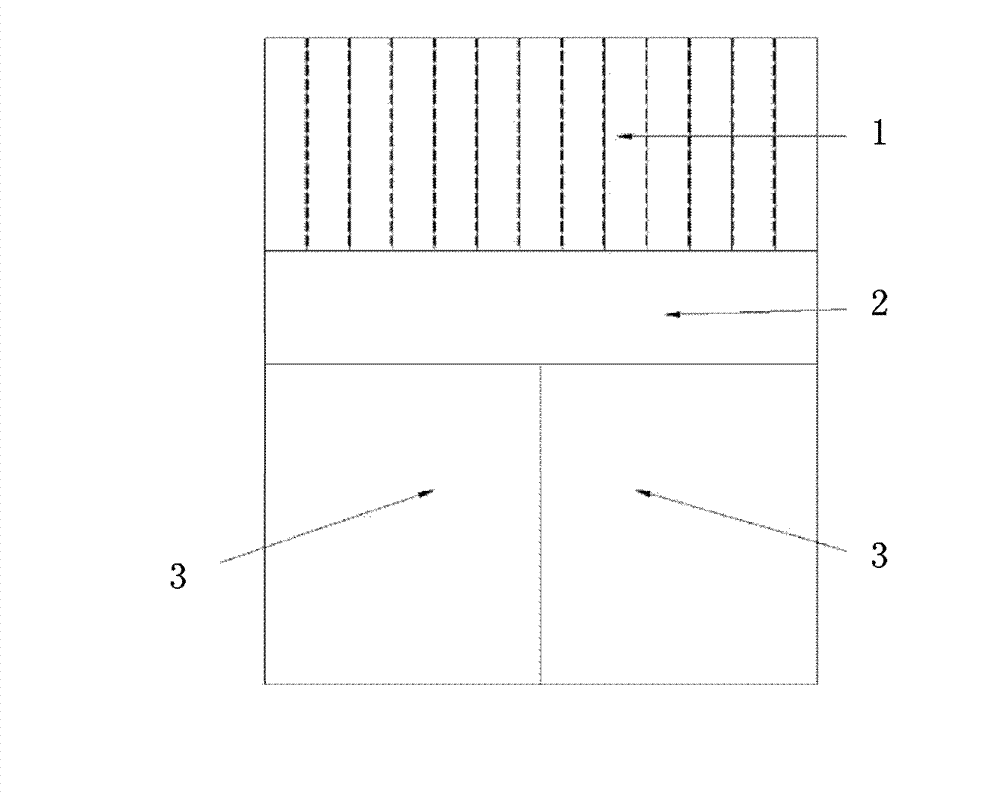
[0046] This embodiment provides a composite crystal for gamma ray detectors, the specific structure of the composite crystal is as follows Figure 2a to Figure 2d shown, where Figure 2a represents a large scintillation crystal, Figure 2b Indicates a bulk light guide, Figure 2c Shown are bulk composite crystals, Figure 2d Shown is a single composite crystal. Figure 2c Among them, the upper half of the large composite crystal is a scintillation crystal, and the lower half is a photoconductive material. The scintillation crystal and the photoconductive material are pasted together by a special adhesive to form a unified large composite crystal. After cutting, grinding and polishing, a single composite crystal for assembling the crystal array is obtained, that is, Figure 2d structure shown.
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment provides a gamma-ray detector made of the composite crystal described in Embodiment 1, such as Figure 3a , Figure 3b and Figure 5bAs shown, the single composite crystals 5 are filled with reflective layers 9 of different lengths to form the composite crystal array 4 . The composite crystal array 4 is coupled together with the photomultiplier tube 3 through an optical coupling agent; the composite crystal array 4 includes a plurality of single composite crystals 5, and the single composite crystals 5 are filled with reflective light of different lengths. layer 9; the composite crystal array 4 is wrapped by a frame bracket 8; the single composite crystal 5 is obtained by cutting, grinding and polishing the composite crystal; the upper part of the single composite crystal 5 is a scintillation crystal 6, and the lower part is a light guide glass 7 (ie light-guiding material). This is similar to Figure 1b The traditional detector using the finger ligh...
Embodiment 3
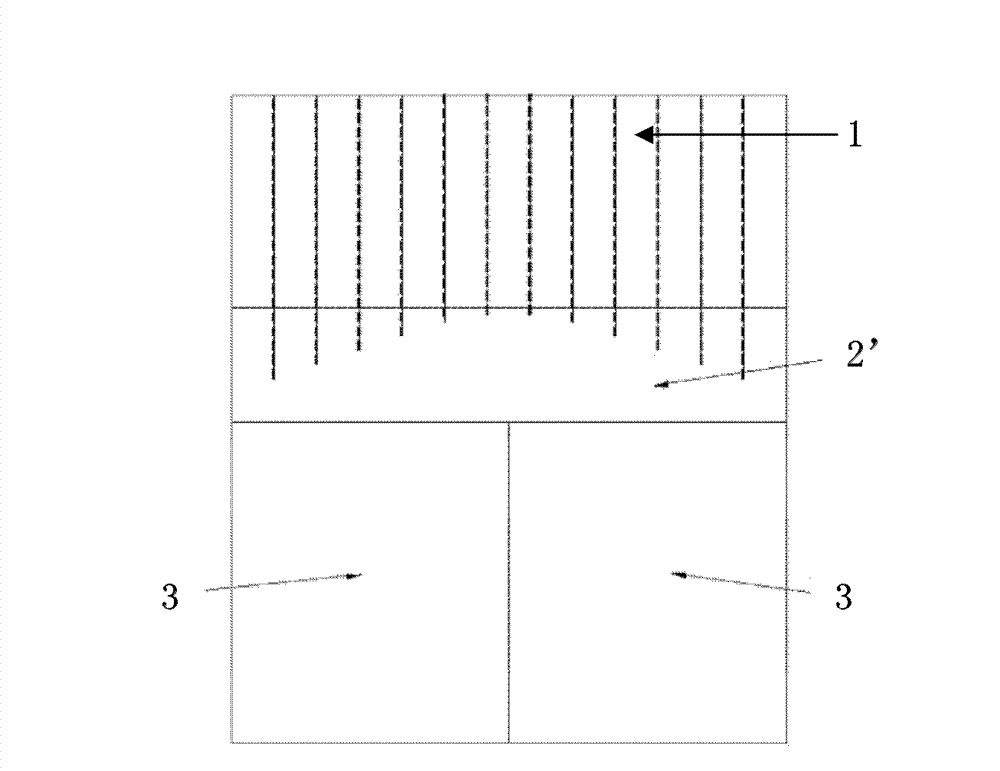
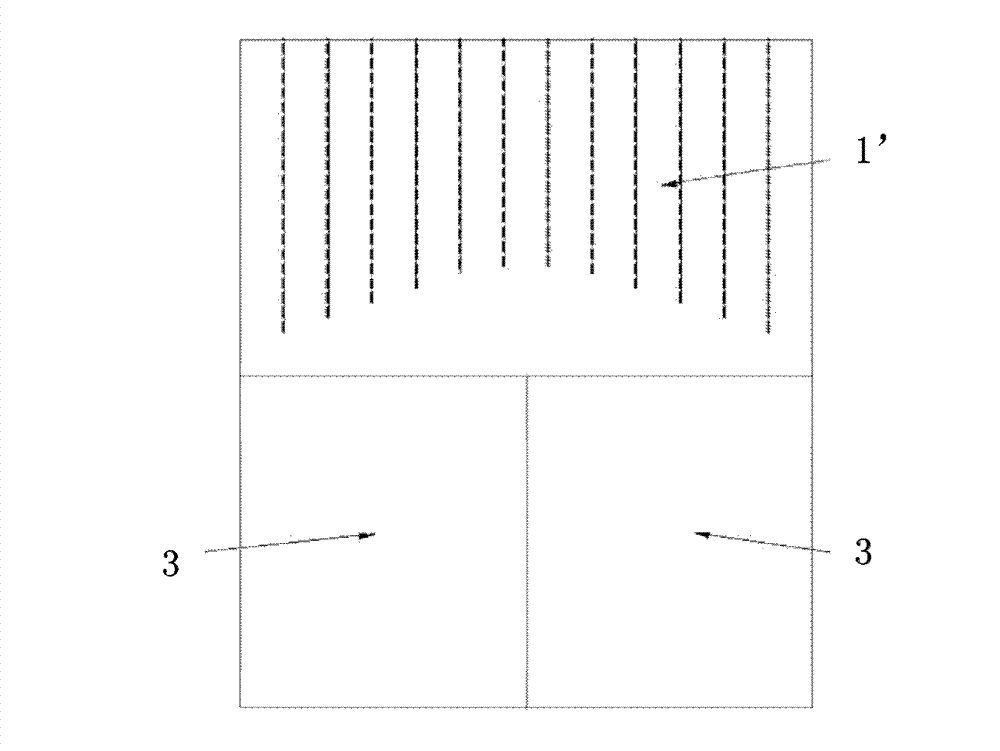
[0052] In this embodiment, the spectroscopic performance of the gamma-ray detector described in Embodiment 2 is compared with that of a traditional gamma-ray detector, as Figure 4b As shown, the gamma ray detector described in the second embodiment can change the propagation direction of the flash by adjusting the length of the middle reflective layer, so as to realize intelligent guidance. Figure 4a The conventional gamma-ray detector shown cannot change the direction of propagation of the scintillation light, while Figure 1b Since the scintillation crystal and the light guide of the detector shown are independent, there are engineering uncertainties in coupling and alignment, resulting in a greatly weakened light-splitting ability.
[0053] Through the above comparison, it can be found that the advantages of the gamma ray detector described in Embodiment 2 are:
[0054] 1. High spatial resolution.
[0055] The spatial resolution of gamma-ray detectors is mainly based on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com