Patents
Literature
81results about How to "Reduce X-ray dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
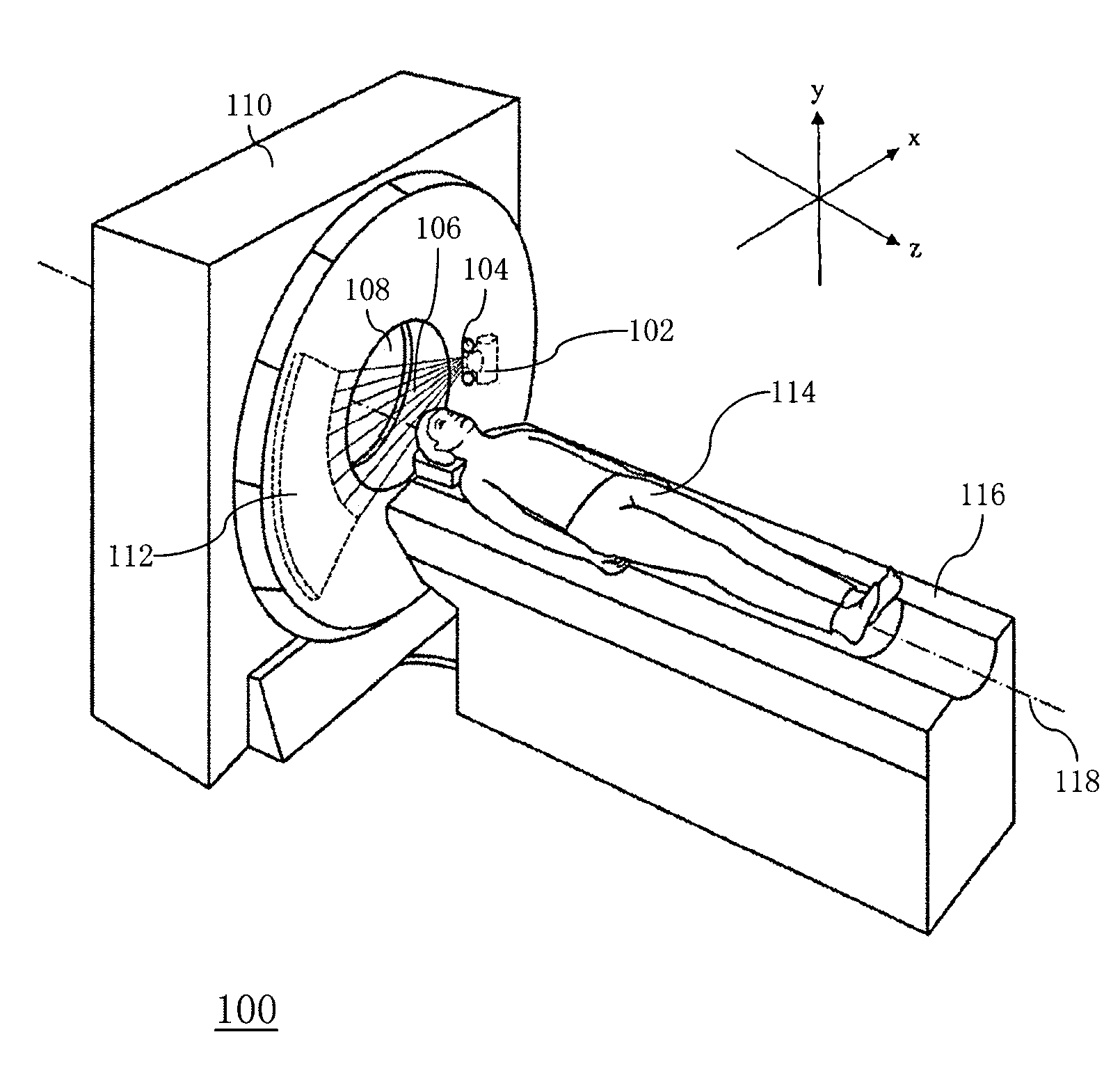
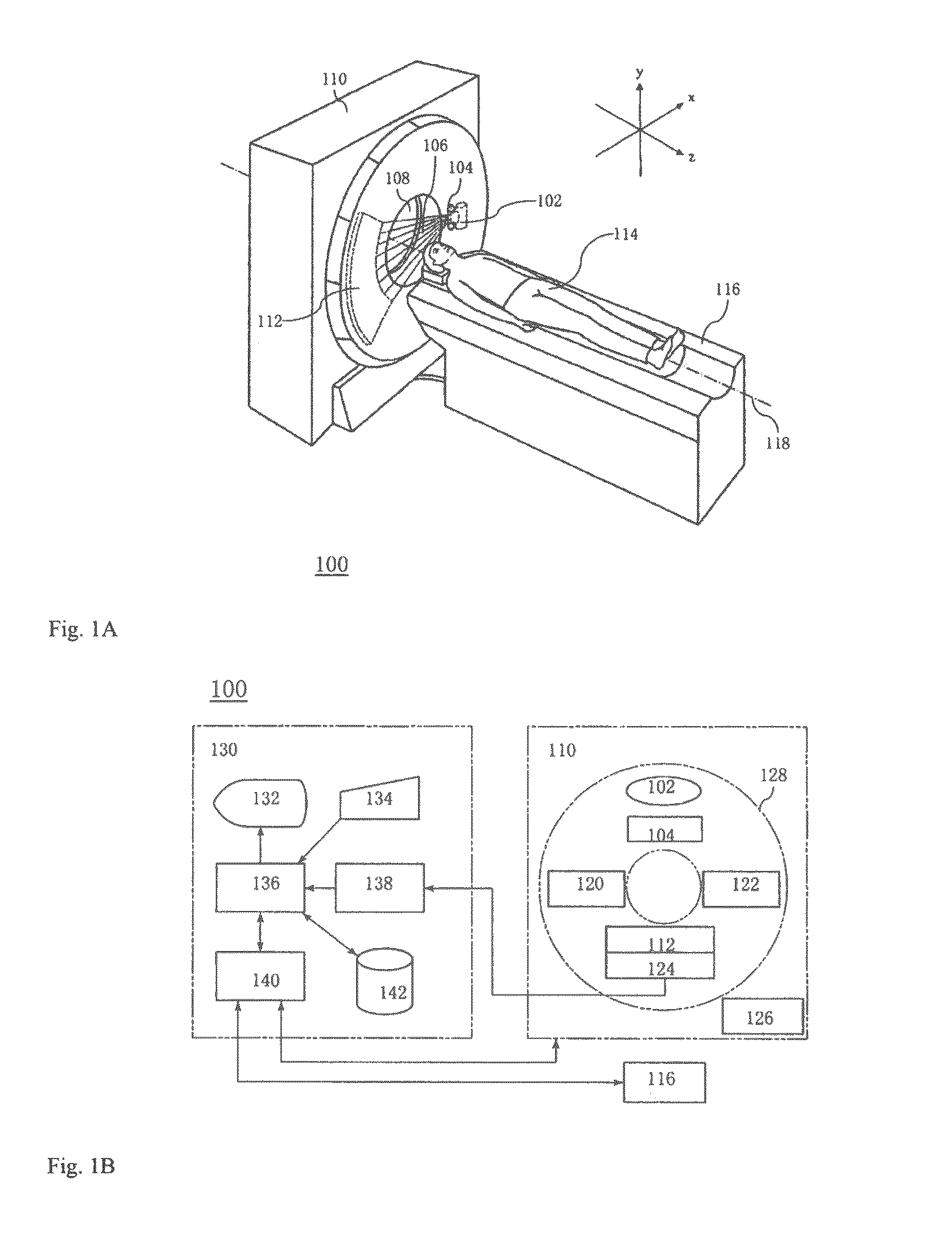
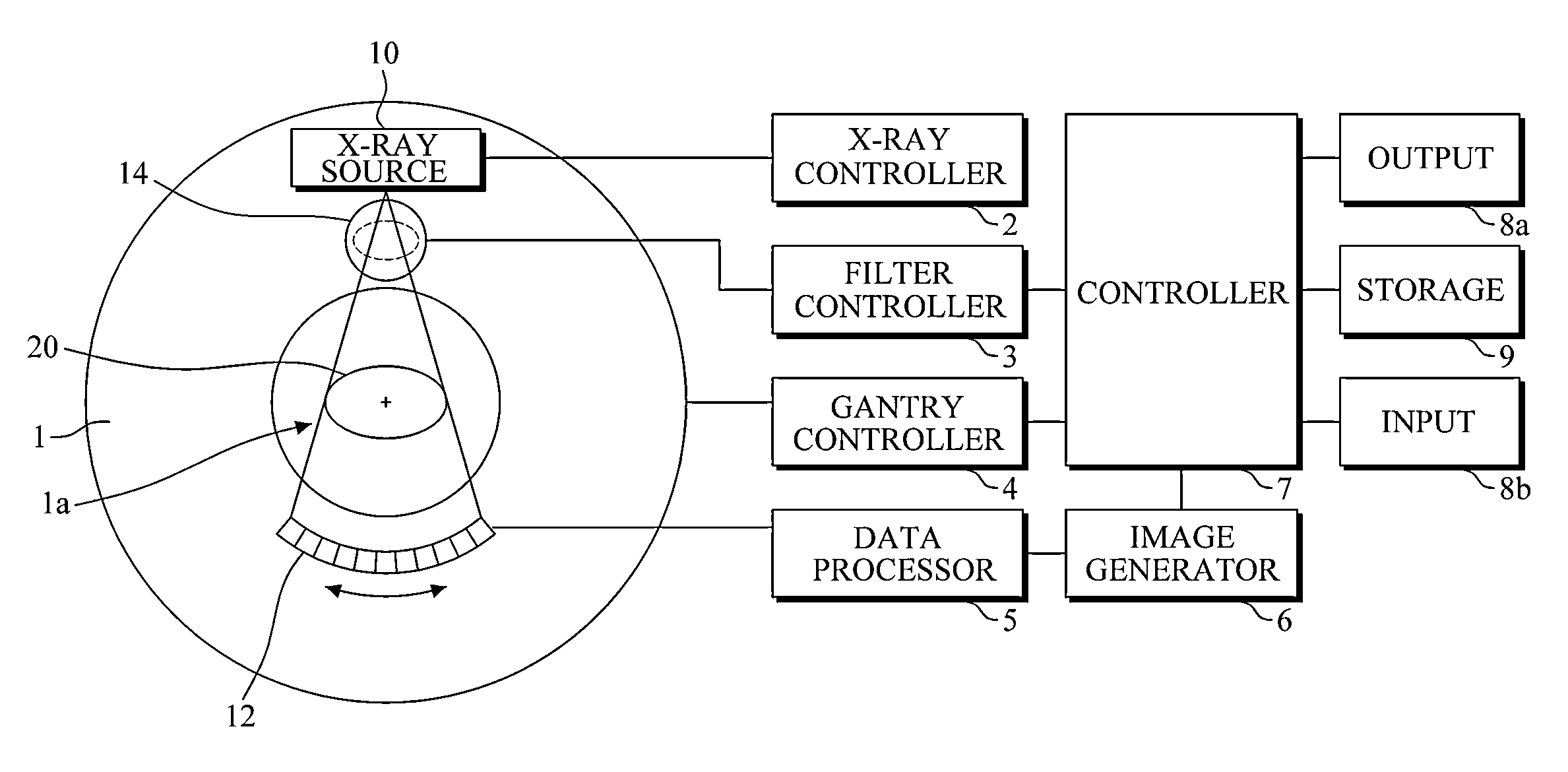
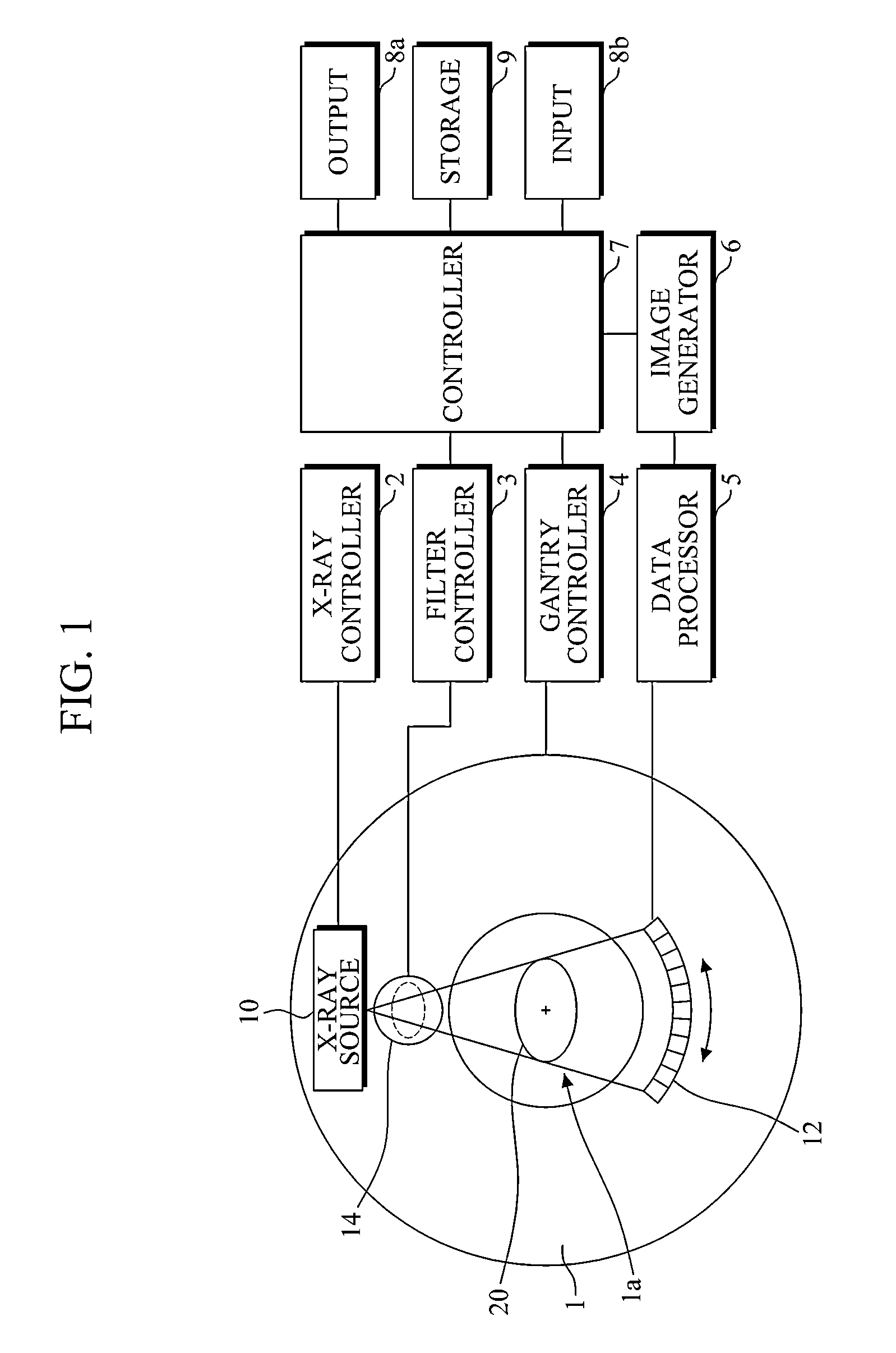
Multi-parameter X-ray computed tomography
ActiveUS8121249B2Eliminate crosstalkIncrease sampling rateRadiation/particle handlingTomographyData setX-ray
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Scanning system for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS9750465B2Reduce contrastReduce X-ray doseComputerised tomographsTomographyX ray imageImaging data
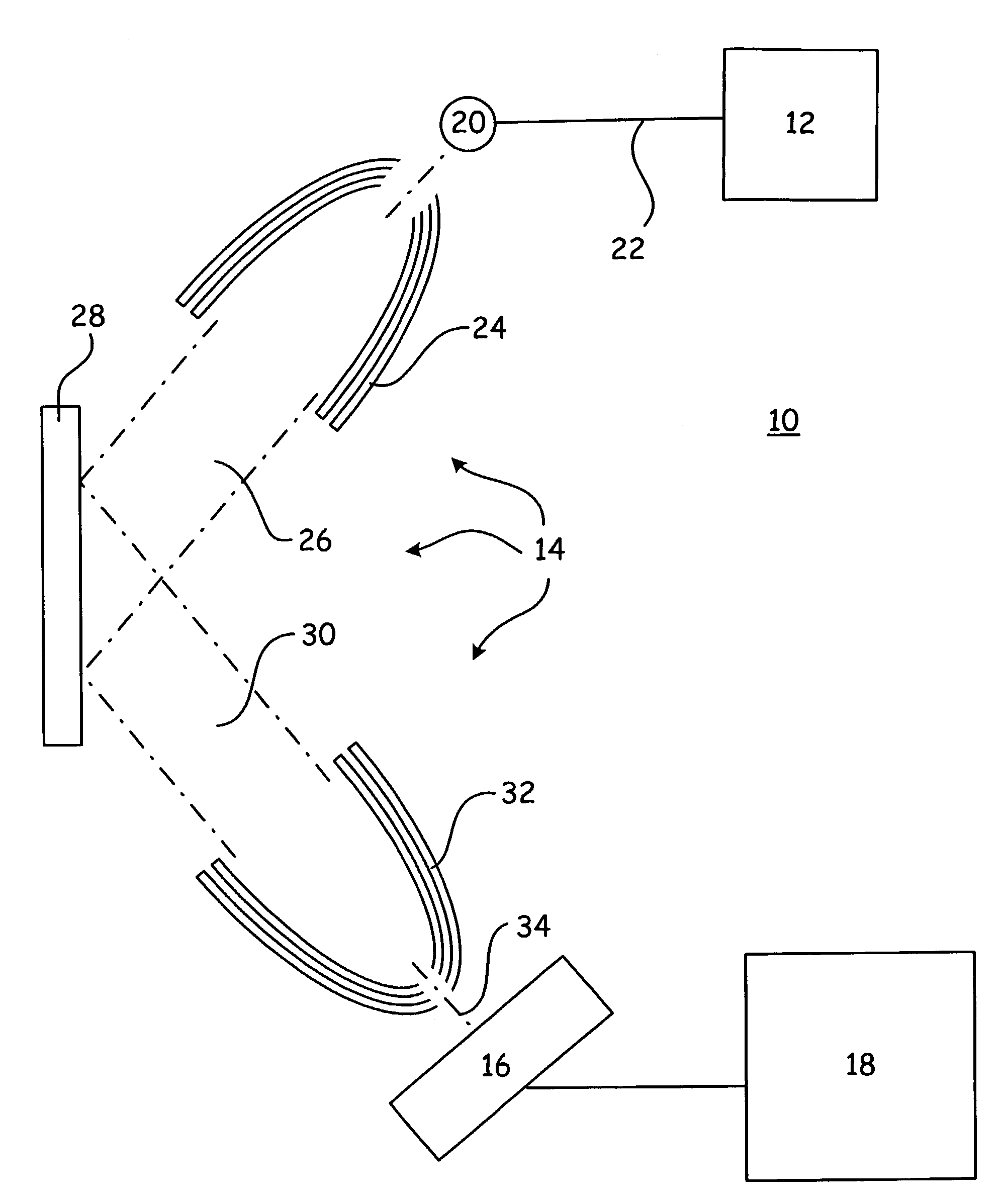
The invention relates to the field of X-ray differential phase contrast imaging. For scanning large objects and for an improved contrast to noise ratio, an X-ray device (10) for imaging an object (18) is provided. The X-ray device (10) comprises an X-ray emitter arrangement (12) and an X-ray detector arrangement (14), wherein the X-ray emitter arrangement (14) is adapted to emit an X-ray beam (16) through the object (18) onto the X-ray detector arrangement (14). The X-ray beam (16) is at least partial spatial coherent and fan-shaped. The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises a phase grating (50) and an absorber grating (52). The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises an area detector (54) for detecting X-rays, wherein the X-ray device is adapted to generate image data from the detected X-rays and to extract phase information from the X-ray image data, the phase information relating to a phase shift of X-rays caused by the object (18). The object (18) has a region of interest (32) which is larger than a detection area of the X-ray detector (18) and the X-ray device (10) is adapted to generate image data of the region of interest (32) by moving the object (18) and the X-ray detector arrangement (14) relative to each other.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Noise suppression for low x-ray dose cone-beam image reconstruction
InactiveUS20130051516A1Reduce noiseMaintain image quality characteristicReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationProjection imageX ray dose
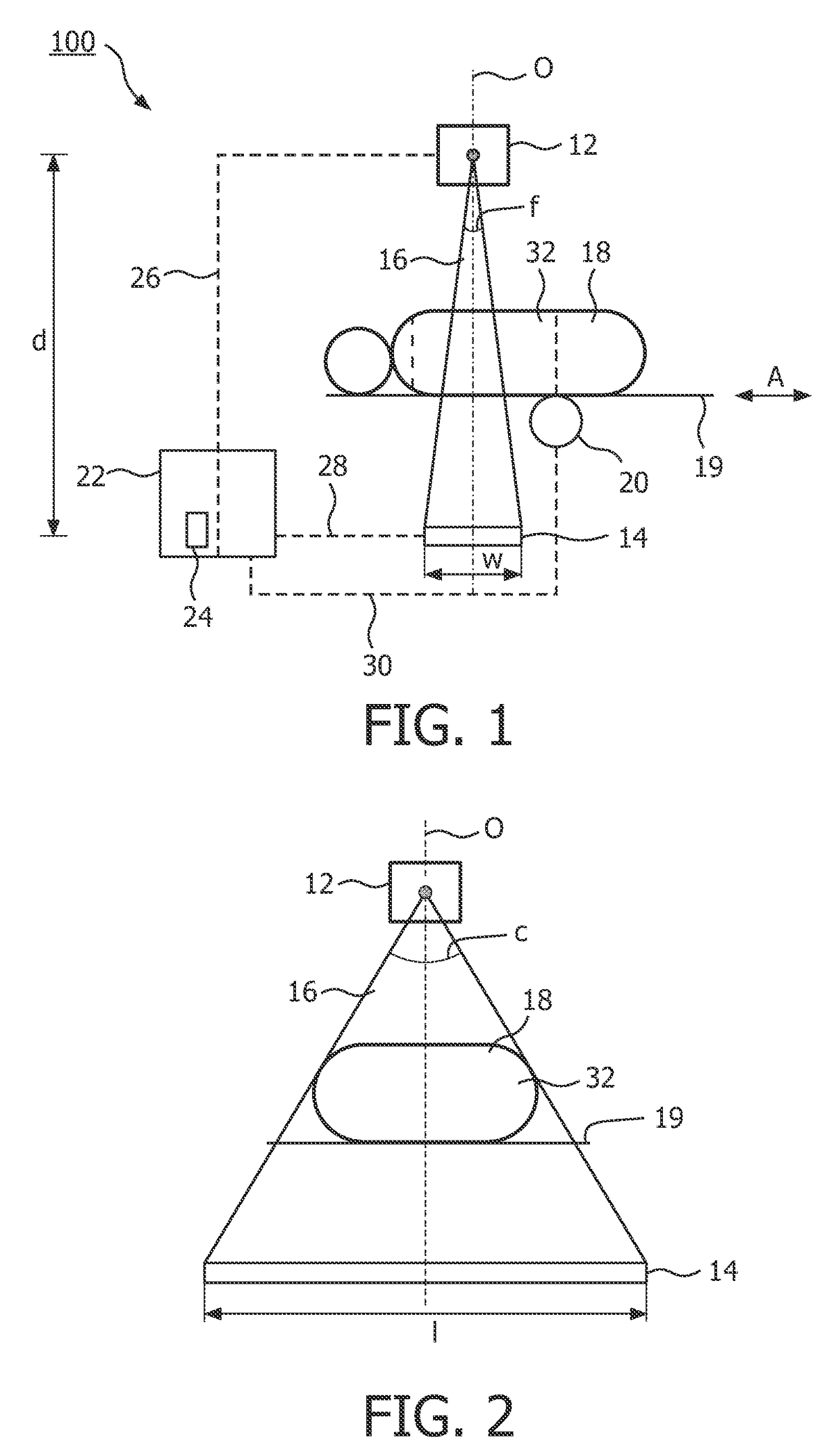
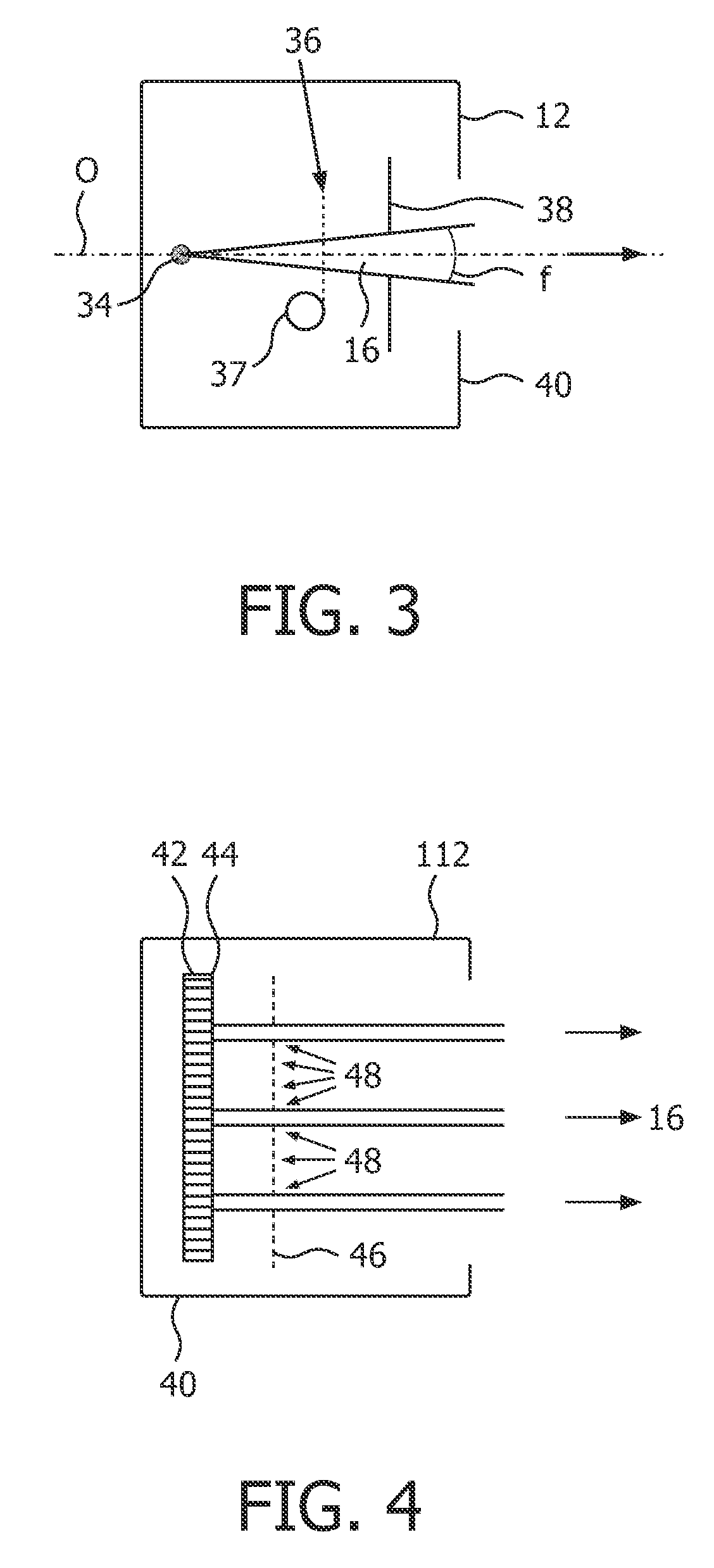
Embodiments of methods and / or apparatus for 3-D volume image reconstruction of a subject, executed at least in part on a computer for use with a digital radiographic apparatus can obtain image data for 2-D projection images over a range of scan angles. For each of the plurality of projection images, an enhanced projection image can be generated. In embodiments of imaging apparatus, CBCT systems, and methods for operating the same can, through a de-noising application based on a different corresponding object, maintain image reconstruction characteristics (e.g., for a prescribed CBCT examination) while reducing exposure dose, reducing noise or increase a SNR while an exposure setting is unchanged.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
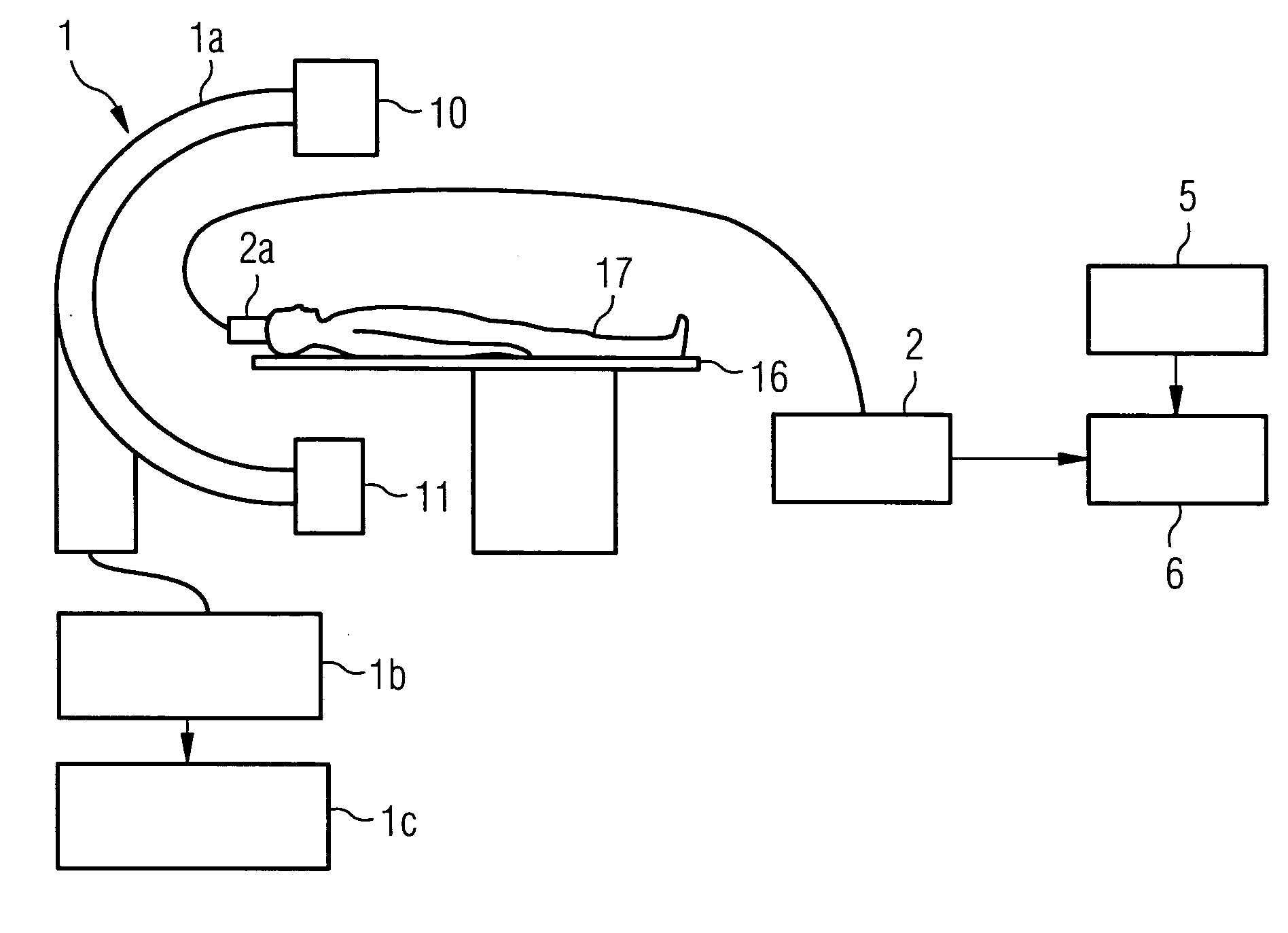
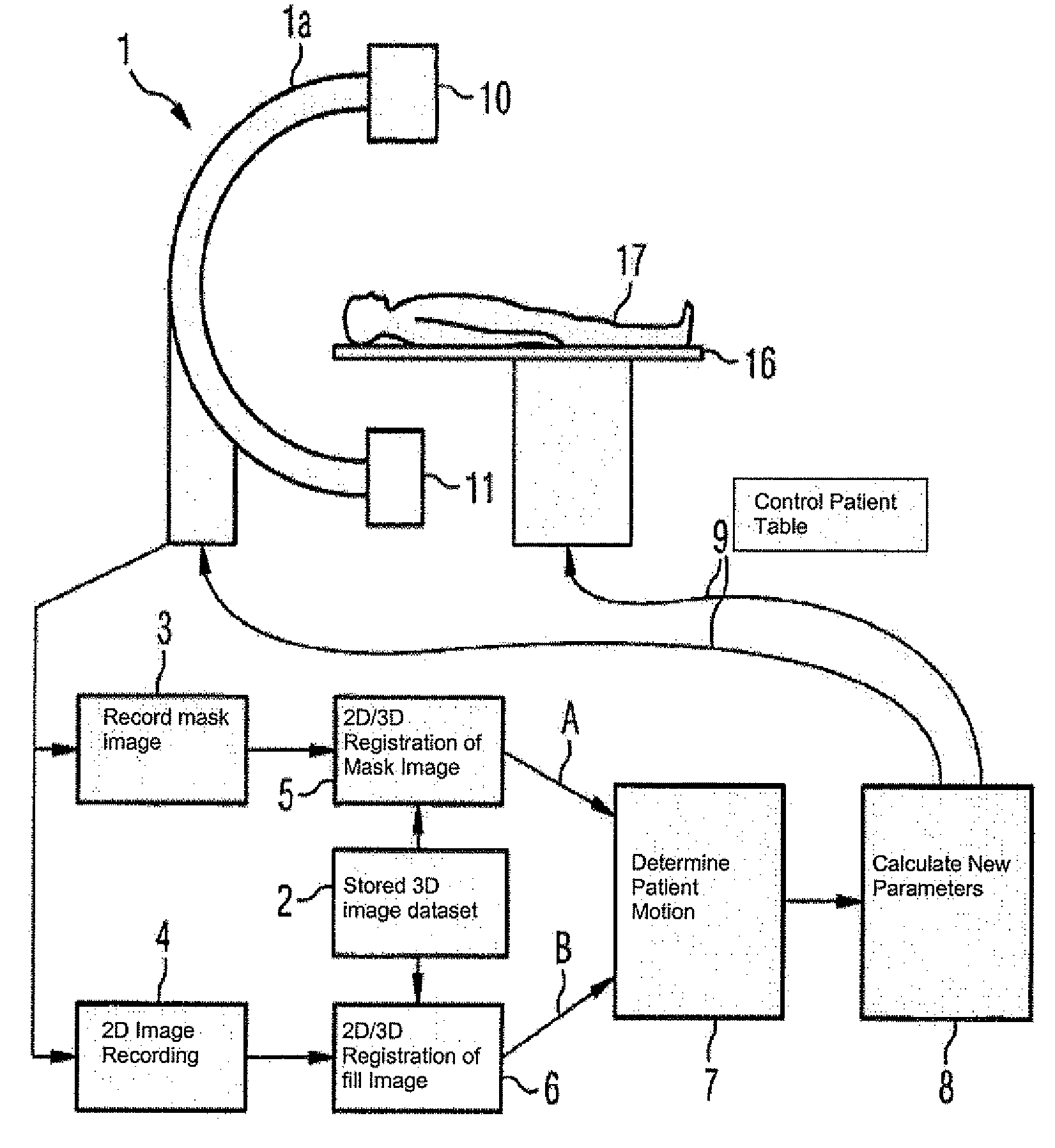
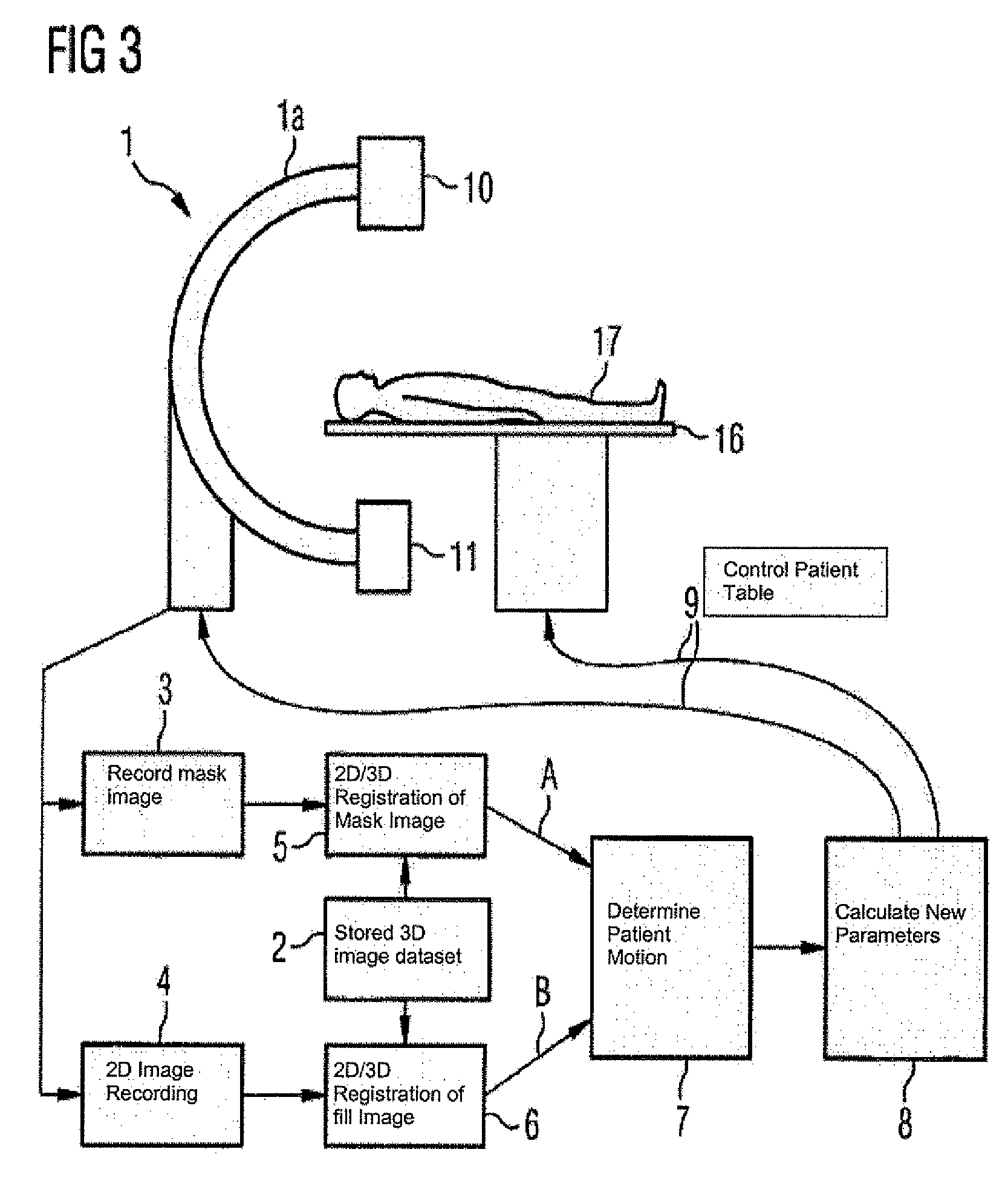
Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
InactiveUS7421061B2Improving Imaging ResultsMotion compensationPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringLocalization systemMedical imaging
The present invention relates to a method and also an imaging system to compensate for patient motion when recording a series of images in medical imaging, in which a number of images of an area under examination of a patient (17) are recorded at intervals with an imaging system (1) and are related to one another. With the method a localization system (2) is used as the series of images are being recorded to permanently or at a time close to the recording of the individual images, record a momentary spatial location of the area under examination in a reference system permanently linked to the imaging system (1), a first spatial location of the area under examination recorded close to the time of recording of a first image is stored, and a deviation of the images recorded momentarily in each case of the first spatial location is determined and by changing the geometrical circumstances of the imaging system (1) at a time to close the recording of the spatial location and / or through geometrical adaptation of an image content of an image just recorded, is at least approximately commentated for, so that the images show the area under examination in the same position and orientation. The method does not require any time-consuming interaction with the operator and is also suitable for compensating for larger movements of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Photostimulable phosphor
InactiveUS6045722AImprove clarityLow noise contentX-ray/infra-red processesRadiation applicationsPhosphorMetal
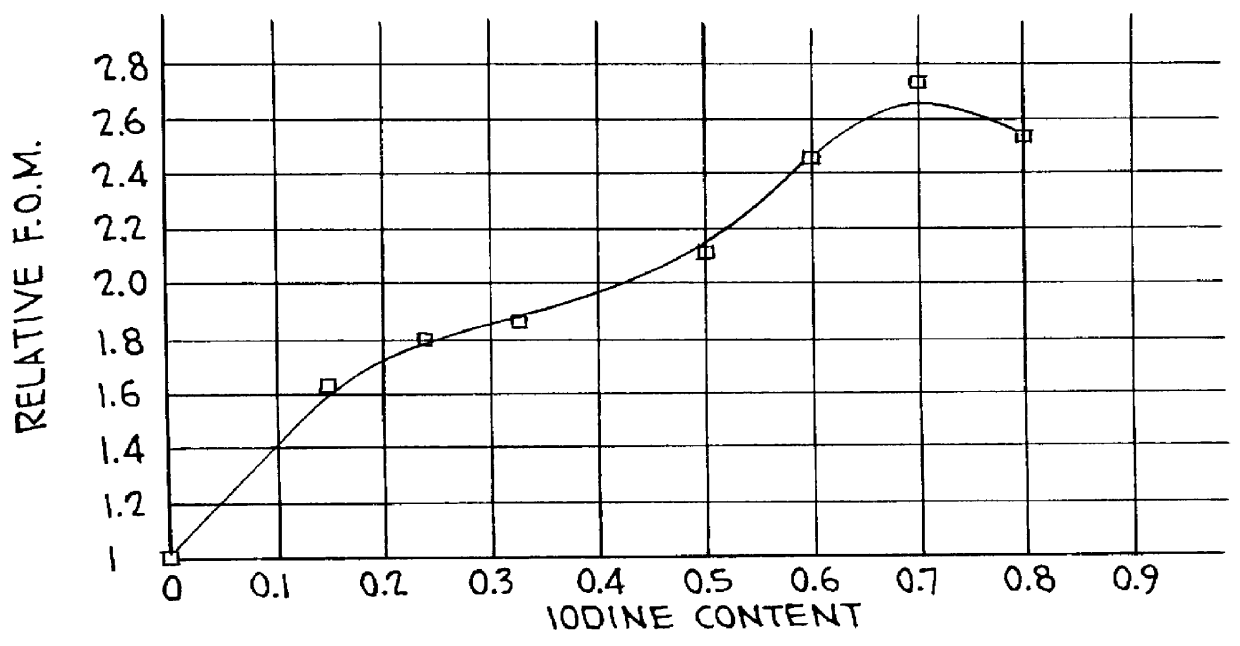
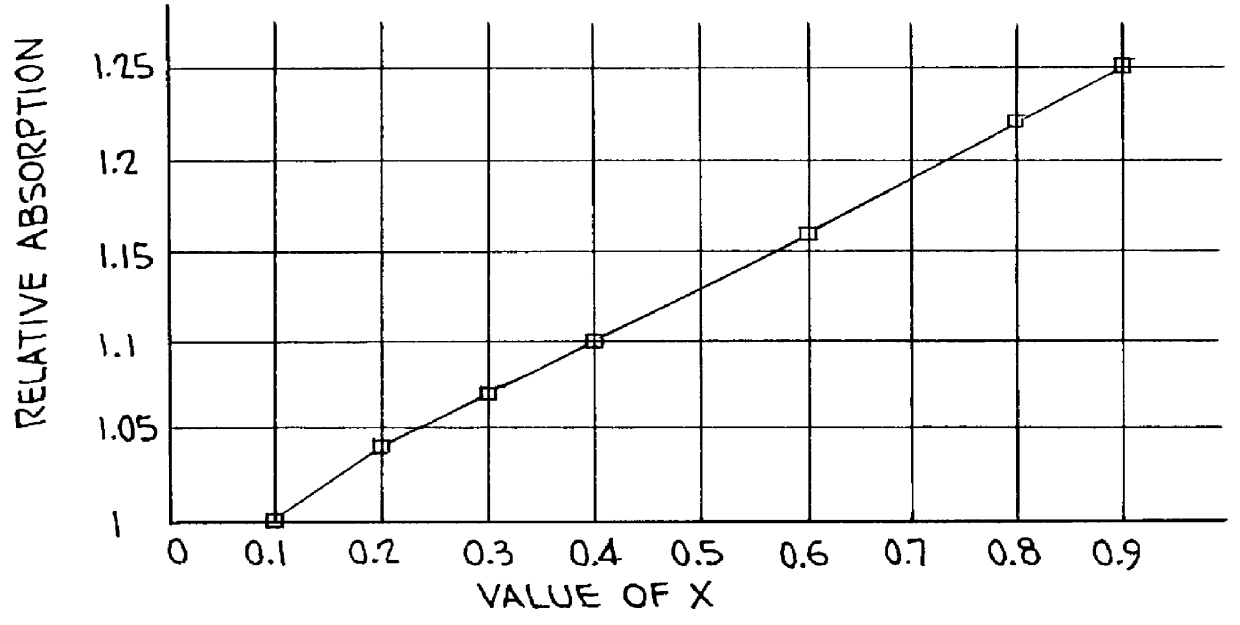
There is provided a photostimulable phosphor according to formula (I)Ba1-x-y-p-3q-zSrxMy2+M2p1+M2q3+F2-a-bBraIb:zEuwherein: M1+ is at least one alkali metal selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs; M2+ is at least one metal selected from the group consisting of Ca Mg and Pb; M3+ is at least one metal selected from the group consisting of Al, Ga, In, Tl, Sb, Bi, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu; 0<x< / =0.30, 0< / =y< / =0.10, 0< / =p< / =0.3, 0< / =q< / =0.1, 0.05< / =a< / =0.76, 0.20< / =b< / =0.90, a+b<1.00 and 10-6< / =z< / =0.2.
Owner:AGFA HEALTHCARE NV
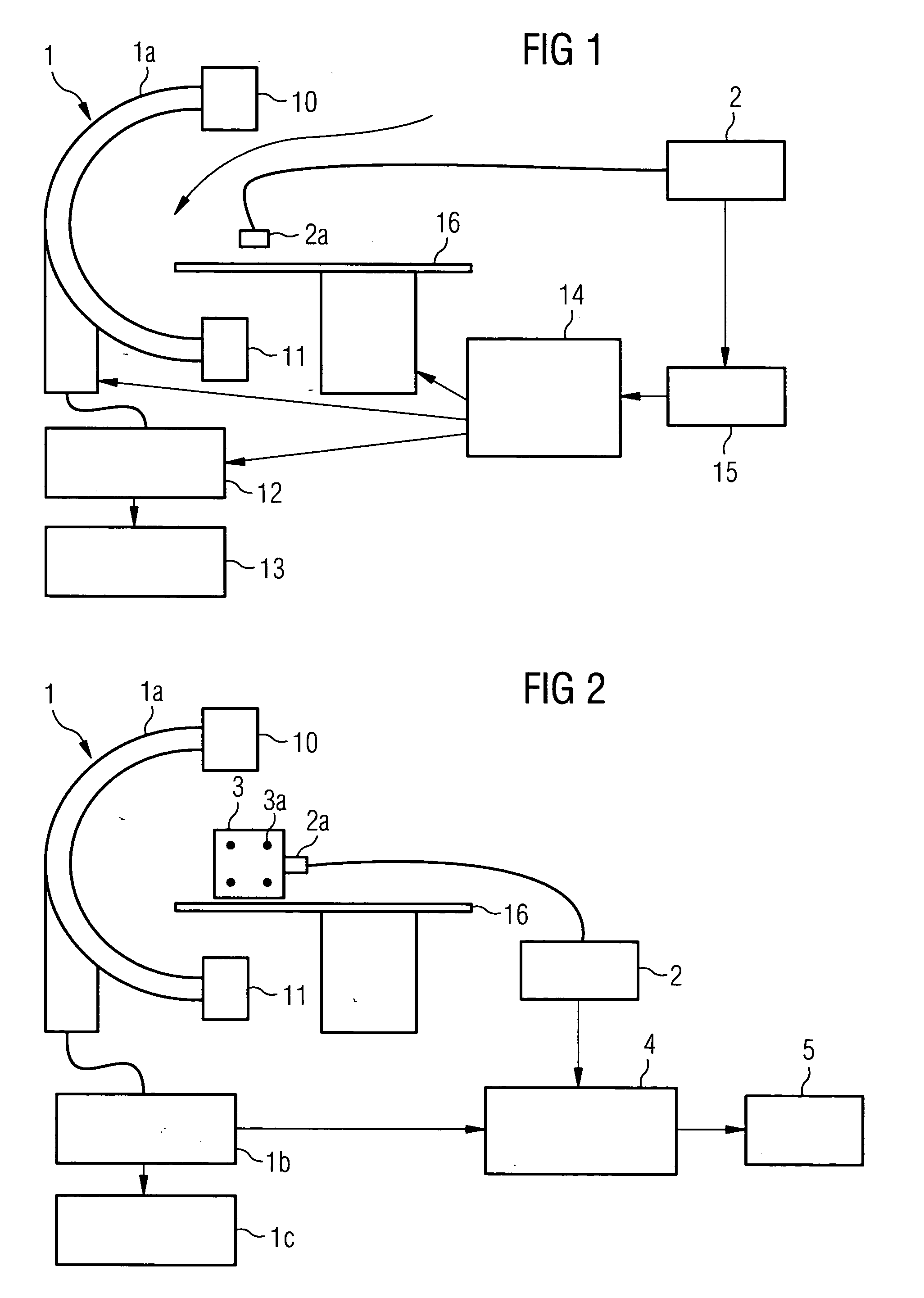
Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
InactiveUS20050203373A1Improving Imaging ResultsSmall possible time outlayImage enhancementImage analysisData set3d image
The present invention relates to a method to compensate for patient motion in series recordings in medical imaging, in which a plurality of images of an examination area of a patient (17) are recorded at time intervals with an imaging system (1) and related to each other. The invention also relates to an imaging system (1) for implementing the method. With the method, before the start of the series recordings a 3D image data set is recorded by a 3D recording of the examination area, which establishes a reference system. A first spatial position of the examination area in the reference system is then either obtained by recording a first image of the series recordings and registering it with the 3D image data set or by calculating it from a known calibration of the imaging system (1). Each further image of the series recordings is registered immediately after recording with the 3D image data set, to obtain the current spatial position of the examination area in the reference system. Finally a difference in respect of the first spatial position is determined and at least some of the difference is compensated for at least approximately by changing geometric relationships of the imaging system (1) in temporal proximity to registration. The method allows patient motion to be compensated for without interaction by the user of the imaging system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus of global de-noising for cone beam and fan beam CT imaging
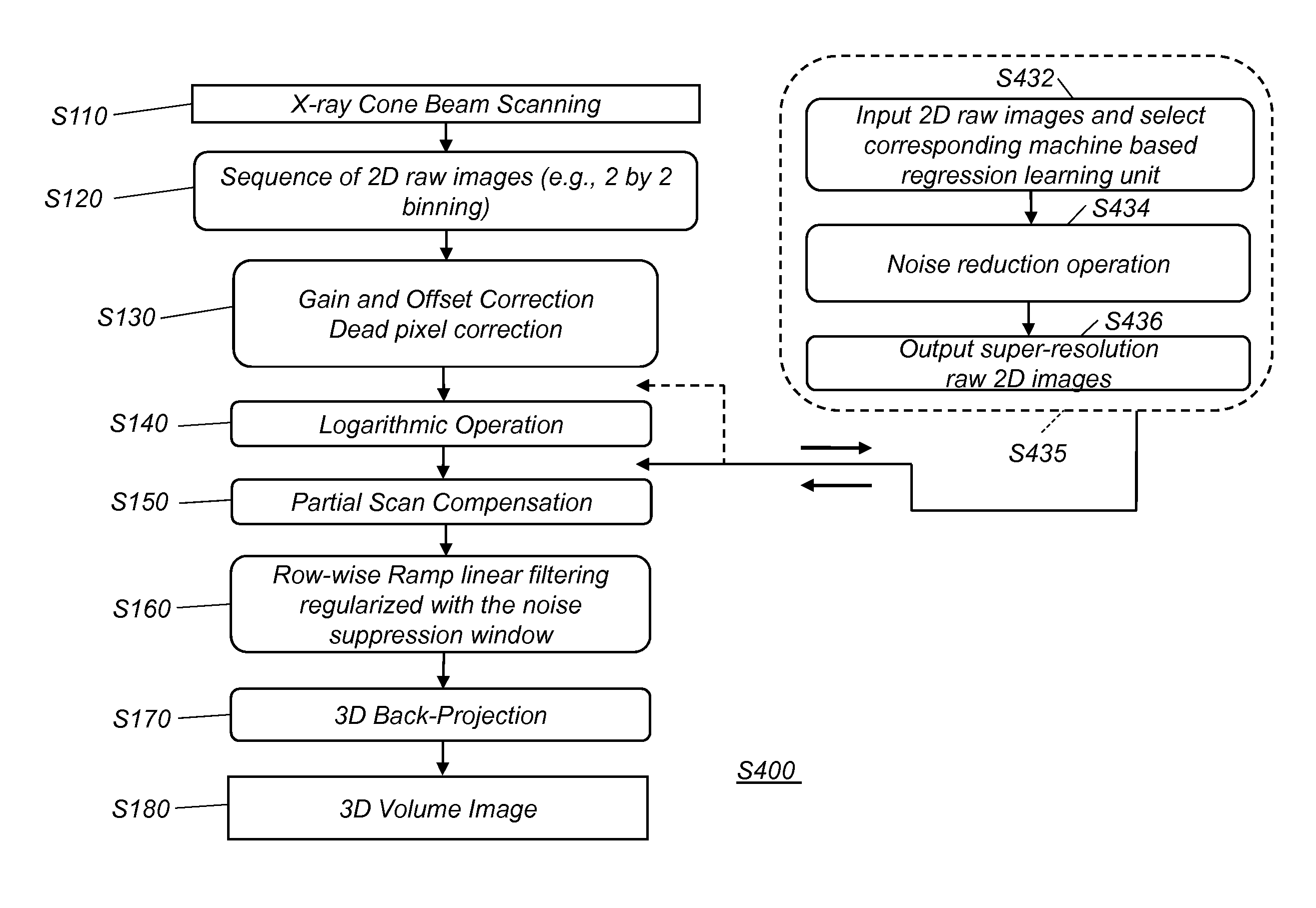
ActiveUS20070053477A1Reduce X-ray doseEfficient and effectiveImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageTomography
Raw cone beam tomography projection image data are taken from an object and are denoised by a wavelet domain denoising technique and at least one other denoising technique such as a digital reconstruction filter. The denoised projection image data are then reconstructed into the final tomography image using a cone beam reconstruction algorithm, such as Feldkamp's algorithm.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method and arrangement for medical X-ray imaging and reconstruction from sparse data
InactiveUS7269241B2Utilize priori informationEfficient use ofReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationSoft x ray
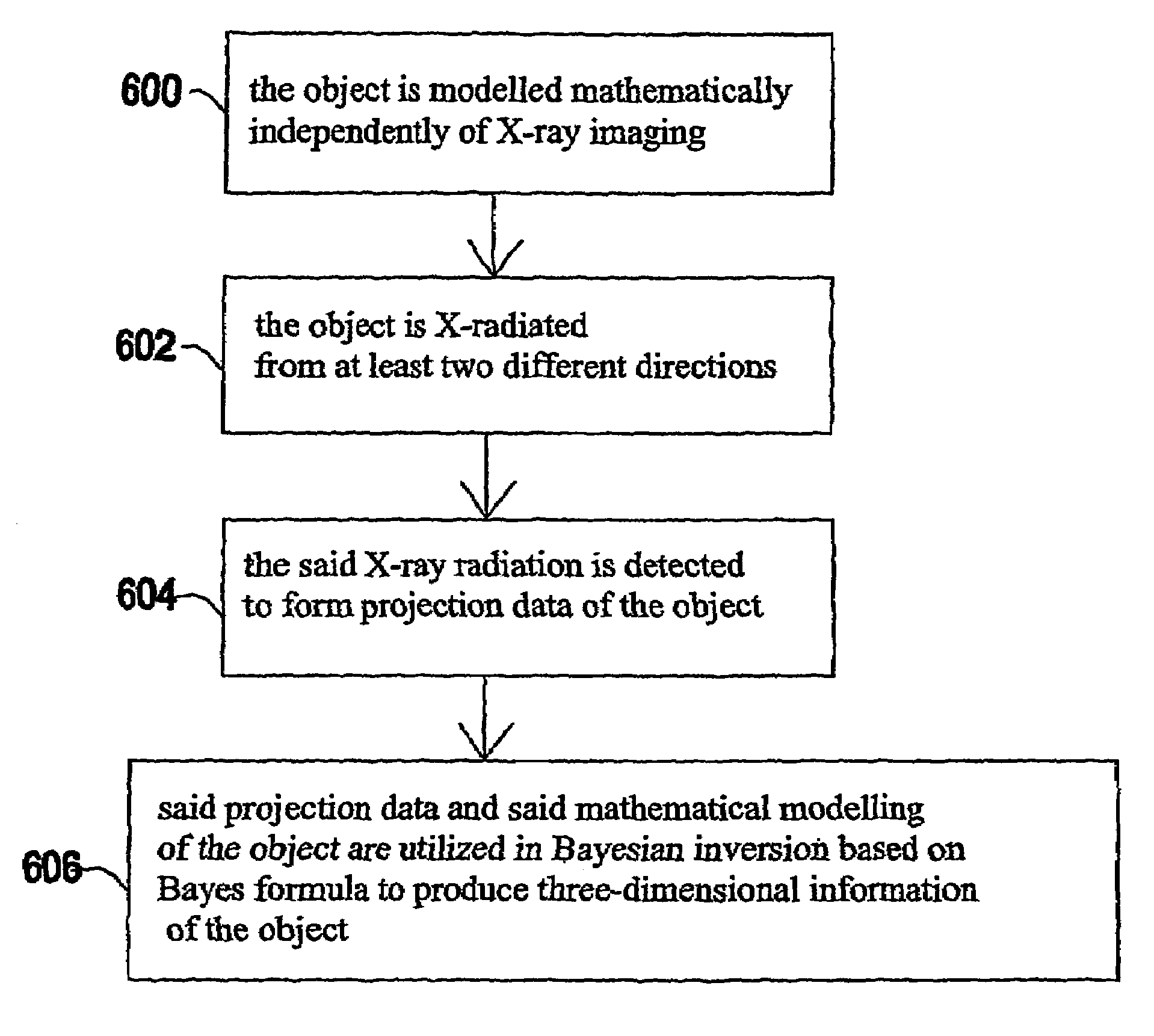
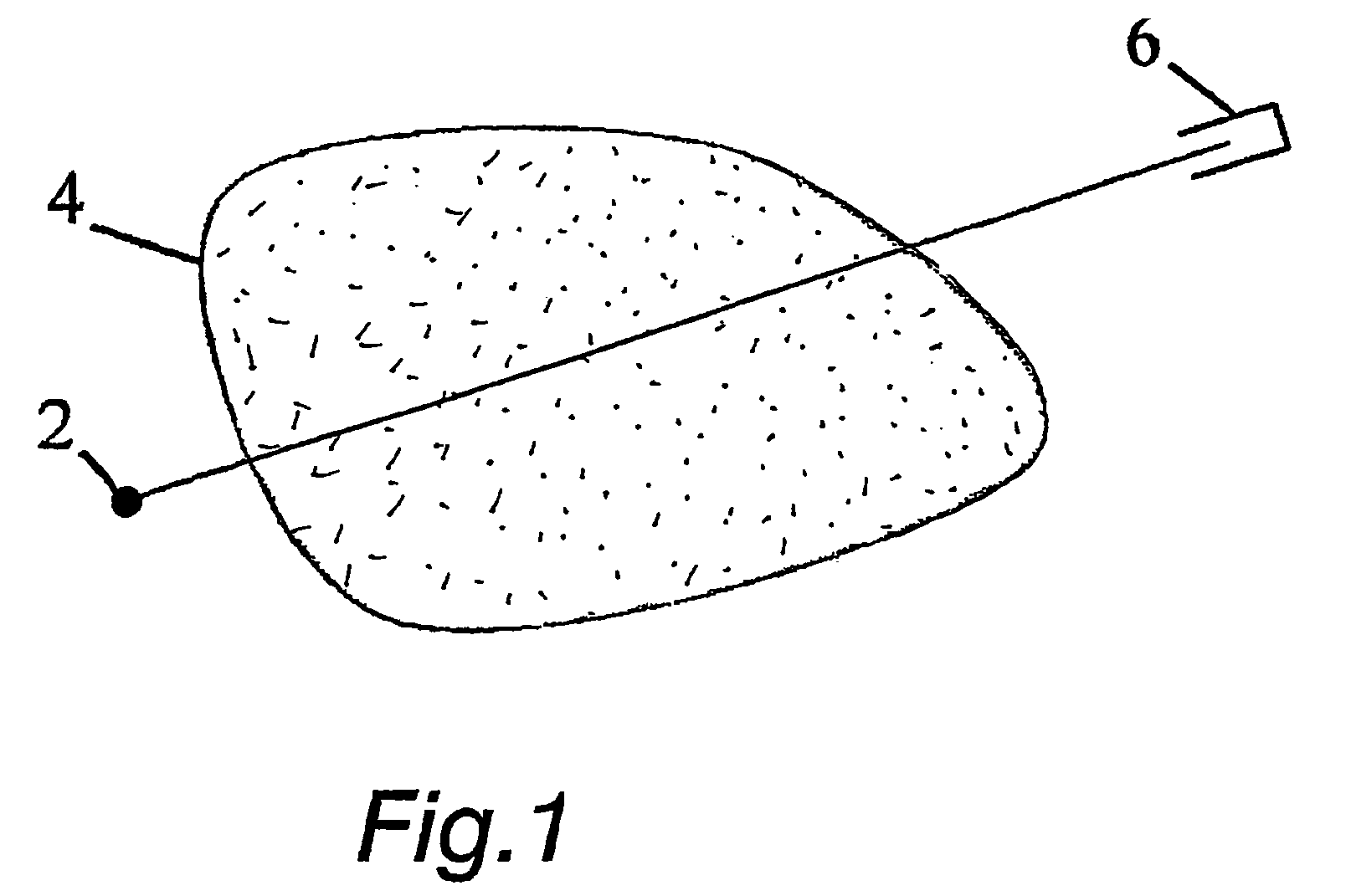
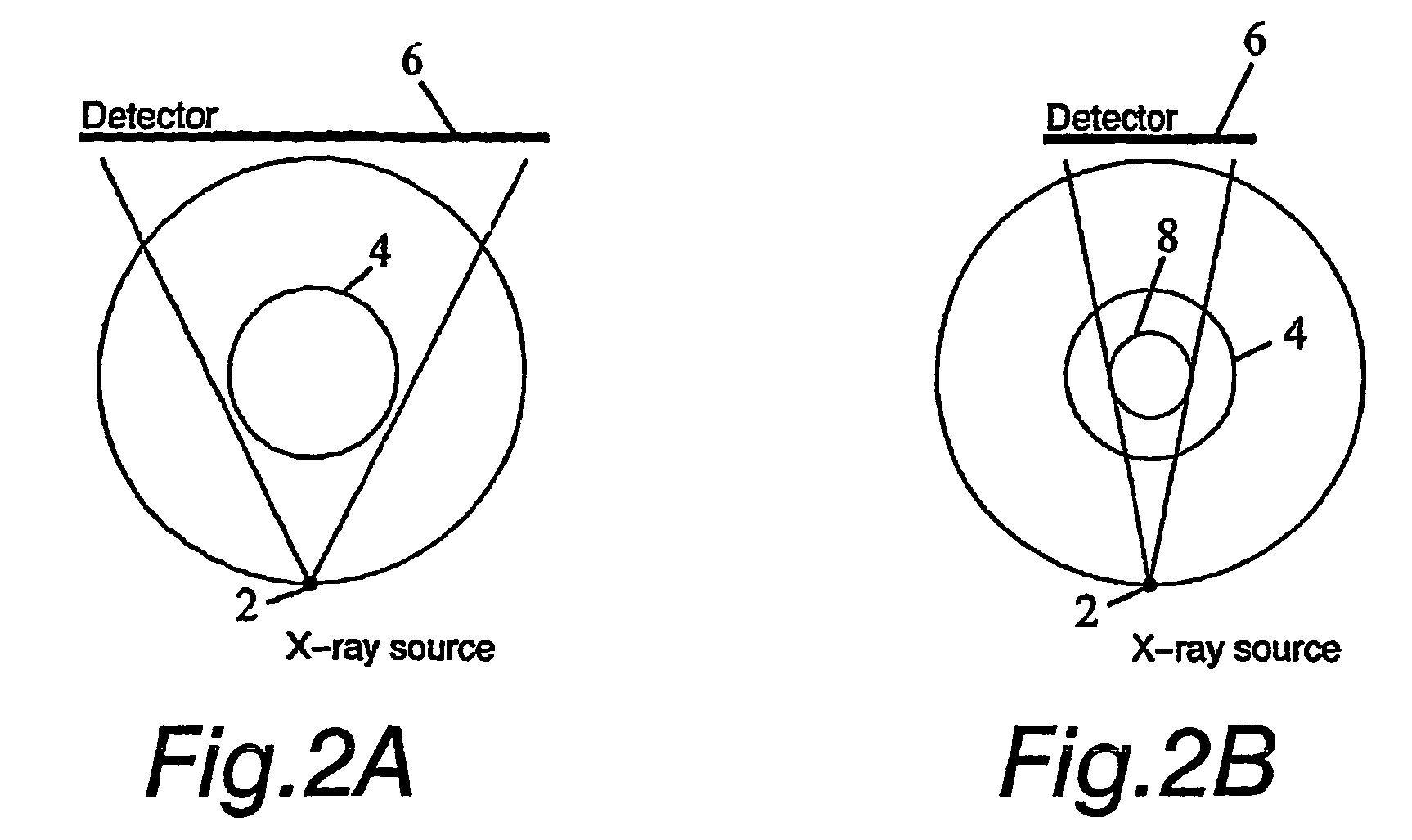
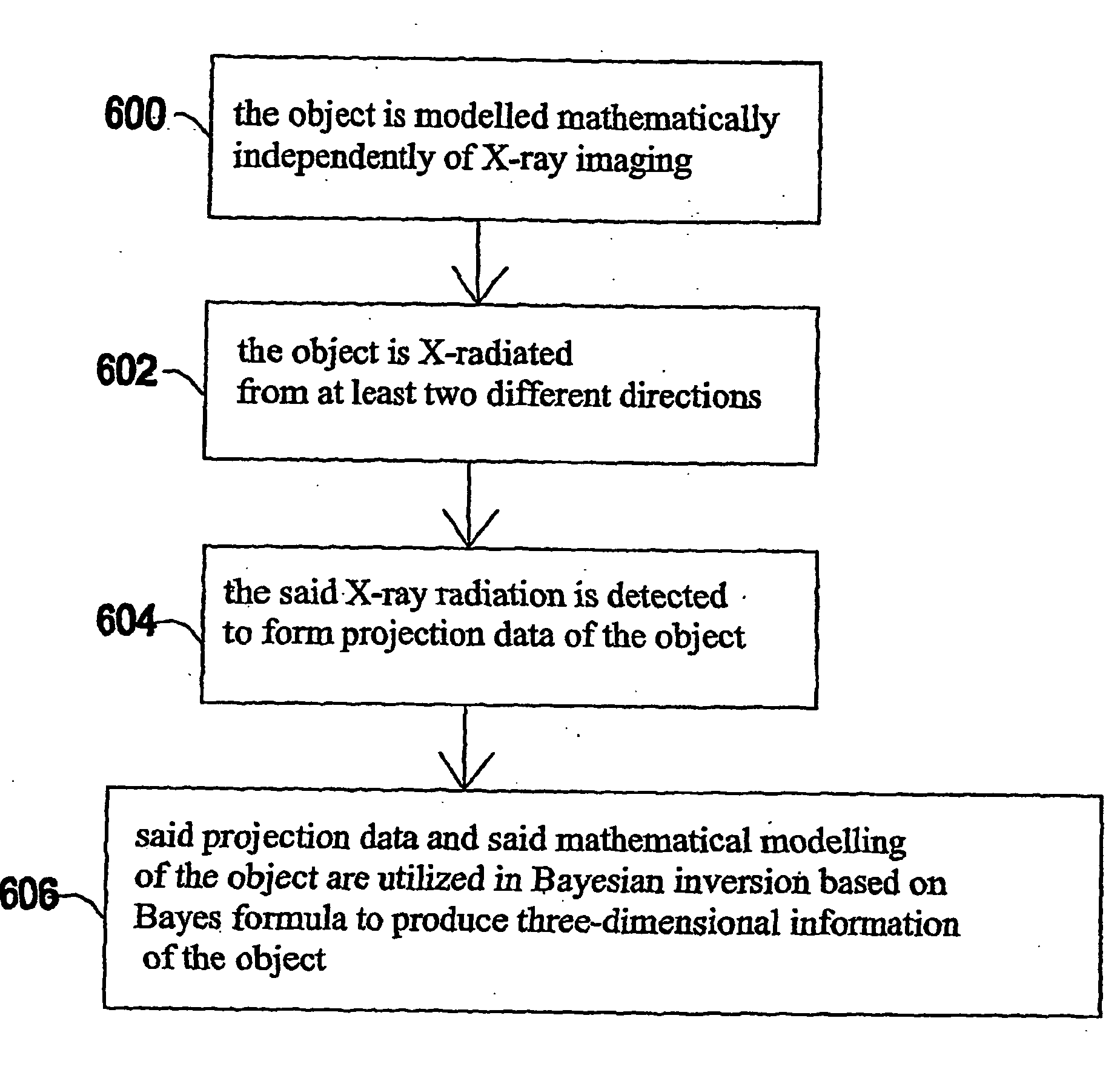
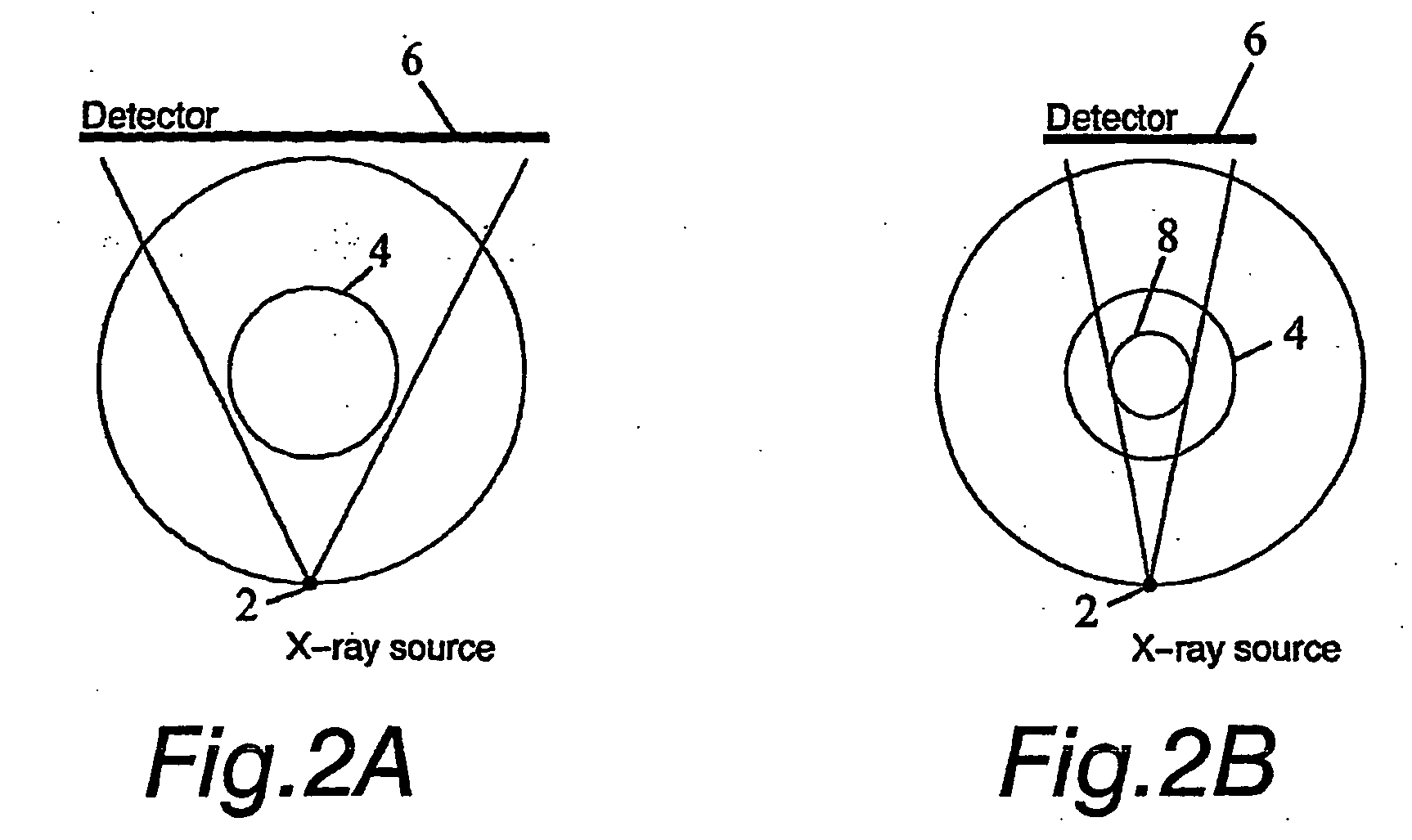
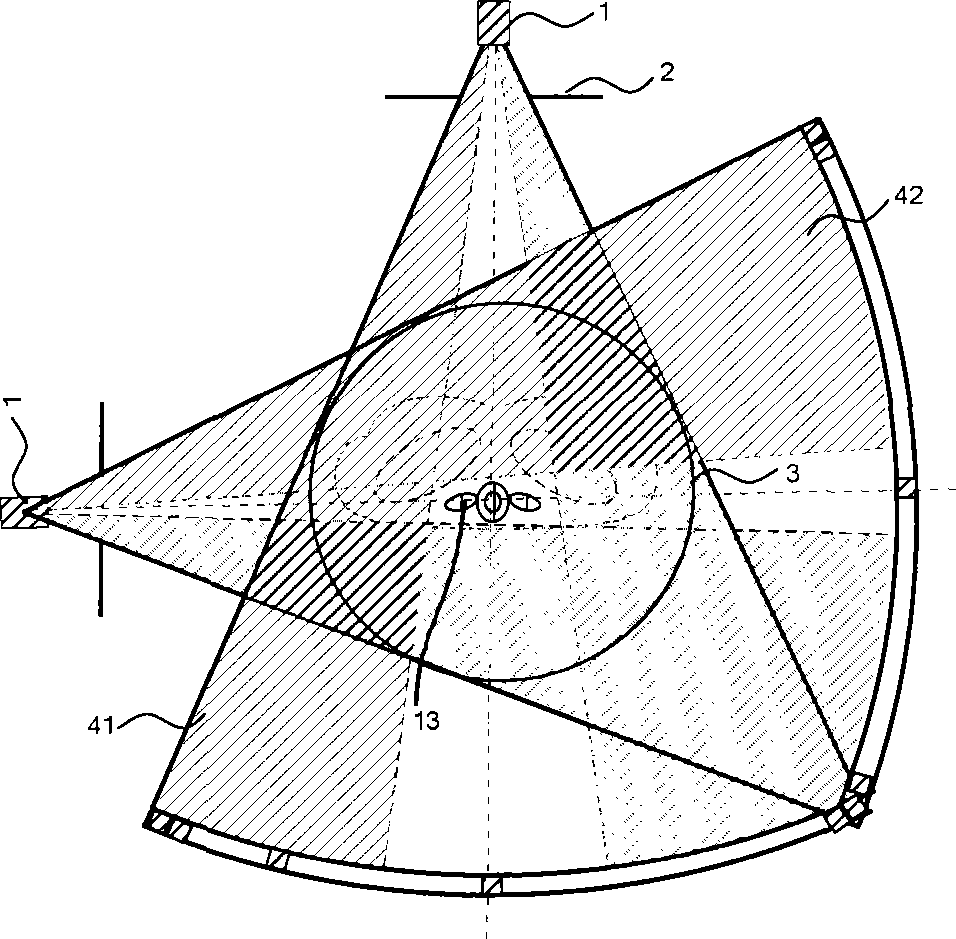
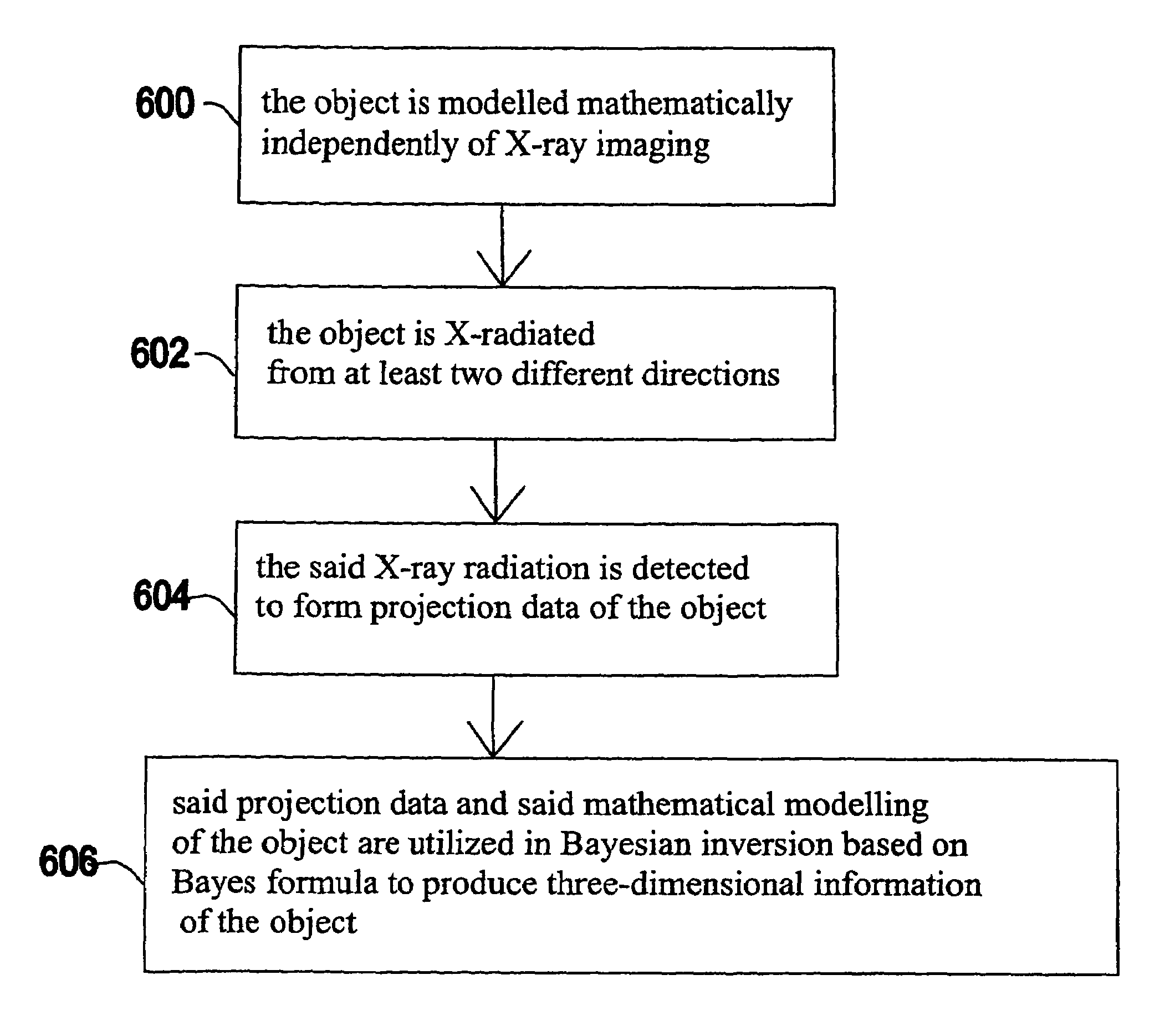
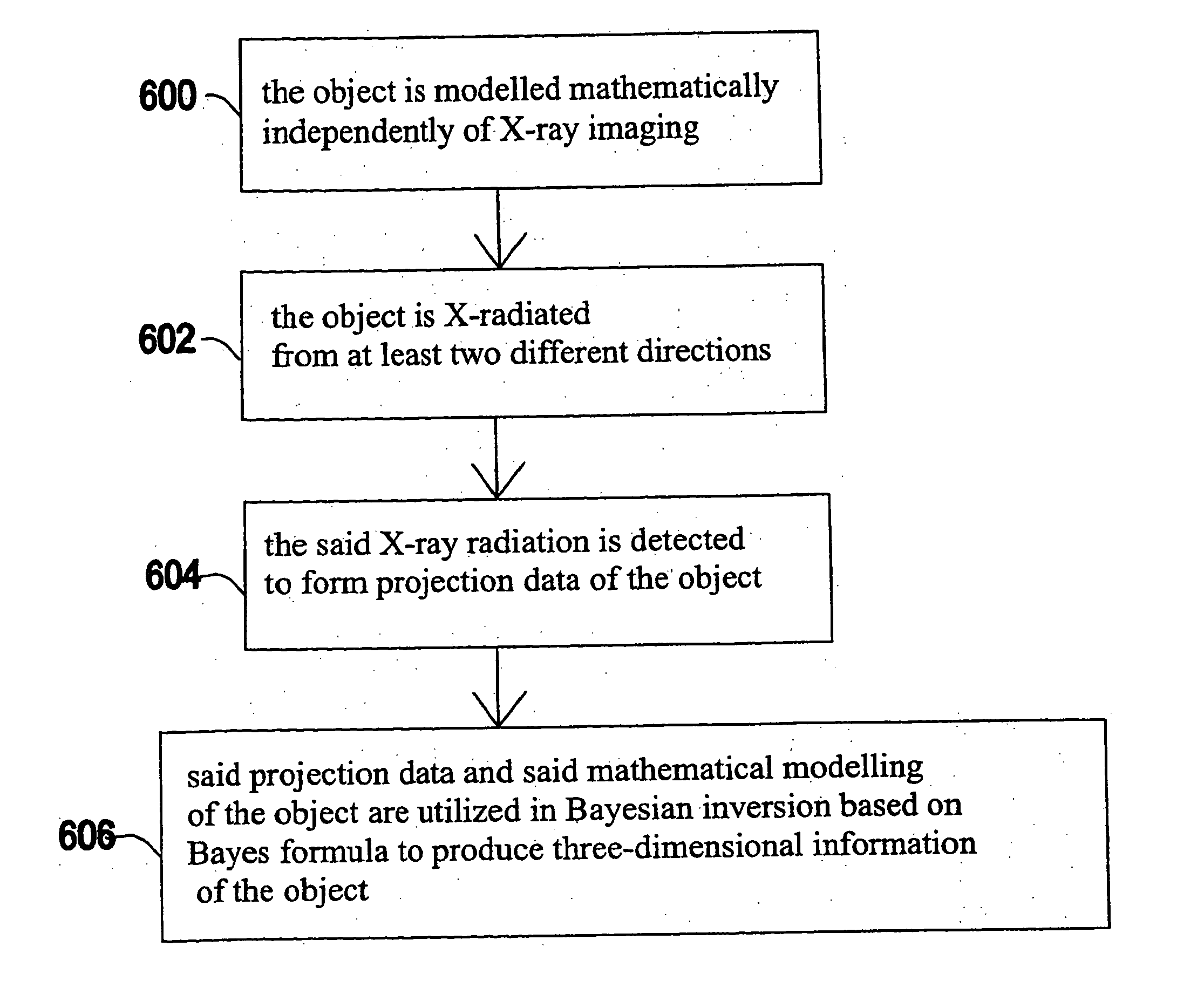
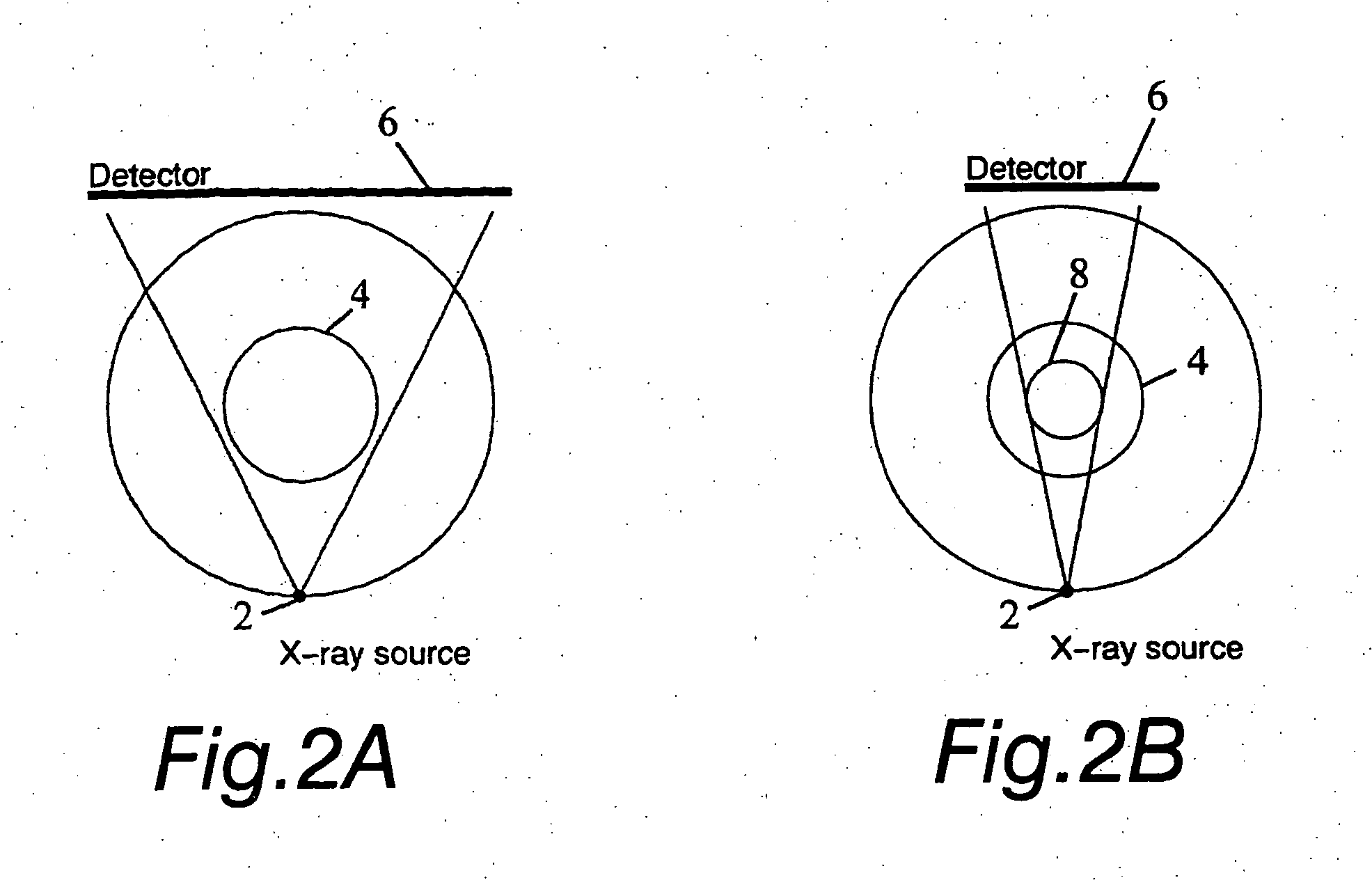
The invention relates to a medical X-ray device 5 arrangement for producing three-dimensional information of an object 4 in a medical X-ray imaging medical X-ray device arrangement comprising an X-ray source 2 for X-radiating the object from different directions and a detector 6 for detecting the X-radiation to form projection data of the object 4. The medical X-ray device 5 arrangement comprises:means 15 for modelling the object 4 mathematically independently of X-ray imagingand means 15 for utilizing said projection data and said mathematical modelling of the object in Bayesian inversion based on Bayes' formulap(xm)=ppr(x)p(mx)p(m)to produce three-dimensional information of the object, the prior distribution ppr(x) representing mathematical modelling of the object, the object image vector x, which comprise values of the X-ray attenuation coefficient inside the object, m representing projection data, the likelihood distribution p(m|x) representing the X-radiation attenuation model between the object image vector x and projection data m, p(m) being a normalization constant and the posteriori distribution p(x|m) representing the three-dimensional information of the object 4.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE FINLAND
Light element measurement
InactiveUS7006596B1Improve efficiencyFaster and accurate measurementX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayX ray dose
A spectrometer for detecting and quantifying elements in a sample. An exciter ionizes atoms in the sample, and the atoms thereby produce characteristic x-rays. A detector receives the x-rays and produces signals based on the x-rays. A filter system selectively blocks the x-rays from attaining the detector. The selective blocking of the x-rays is accomplished based on an energy of the x-rays. An analyzer receives the signals from the detector and detects and quantifies the elements in the sample based at least in part on the signals. In this manner, detector receives the light element x-rays, and the medium and heavy element x-rays are filtered out to avoid overwhelming the detector. This invention combines the large solid angle, high efficiency, and ability to measure the continuous background spectrum of the energy dispersive x-ray detector with the selectivity of the wavelength dispersive x-ray detector. It thus enables faster and more accurate measurement of light elements in thin films. This invention enhances the light element performance of a system by enabling higher throughput, lower e-beam and x-ray dose to the sample, and improved accuracy from the capability to measure the background radiation.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
X-ray ct apparatus
InactiveUS20090122952A1Reduce X-ray doseImprove image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging conditionImaging quality
The present invention provides an X-ray CT apparatus capable of obtaining each tomographic image indicative of X-ray tube voltage dependent information of a subject with the optimum image quality by less reduced exposure. The X-ray CT apparatus includes device for setting a plurality of X-ray tube voltages and sets imaging conditions used in the photography using the respective X-ray tube voltages in such a manner that respective image noise of tomographic images photographed at the X-ray tube voltages become substantially identical to one another. The setting of the imaging conditions is the setting of X-ray tube currents. The X-ray tube currents are set based on geometrical characteristic amounts of the subject determined from each scout image in such a manner that the respective image noise of the tomographic images photographed at the plurality of X-ray tube voltages become substantially identical to one another.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
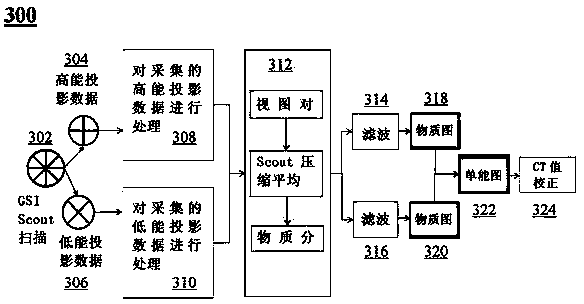
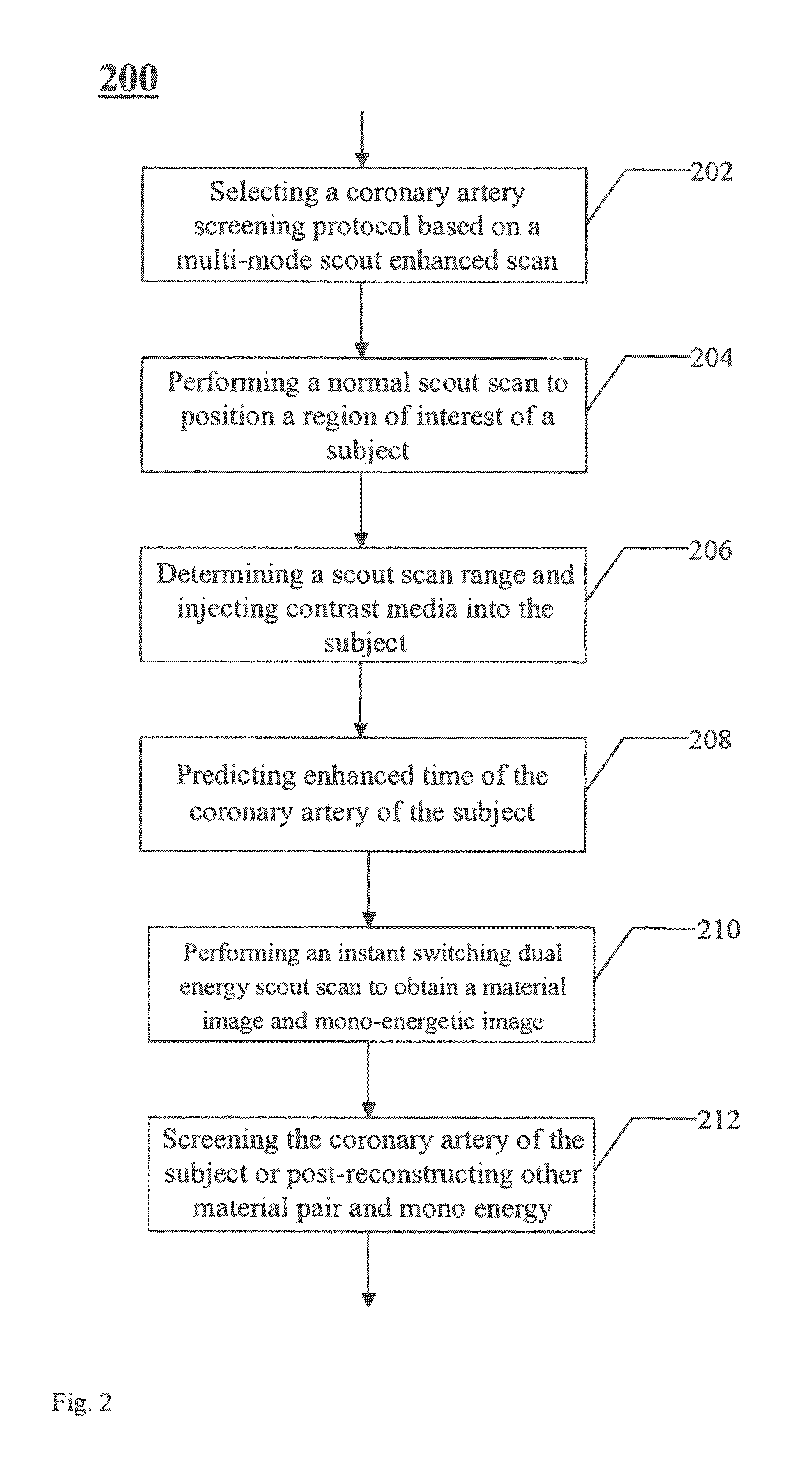
CT (computed tomography) imaging method and CT imaging system based on multi-mode Scout scanning
InactiveCN103892859AReduce X-ray doseReduced imaging timeComputerised tomographsTomographyLow voltageDual energy
A CT imaging method and a CT system based on a multi-mode scout scan. The CT imaging method based on a multi-mode scout scan comprises: performing an instant switching dual energy scout radiation scan on a region of interest of a subject by way of instant switching between high voltage and low voltage to collect dual energy protection data of the region of interest; and reconstructing a material decomposition image and a mono-energetic image based on the collected dual energy projection data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System for navigating a surgical instrument
ActiveUS20170224427A1Reduce X-ray doseReduce acquisition timeSurgical navigation systemsTomography3d imageVirtual position
The invention relates to a system for navigating a surgical instrument (1), comprising a processor configured for:obtaining a first 3D medical image of a first volume (V1) of a patient's body, said first volume (V1) comprising a reference marker (M),registering the first 3D image with said reference marker (M),obtaining a second 3D medical image of a second volume (V2) of the patient's body, said second volume (V2) being different from the first volume (V1) and not containing the reference marker (M) in its entirety, said first and second 3D images being obtained by a single imaging device,registering the second 3D medical image with the first 3D medical image,obtaining a virtual position of the surgical instrument (1) with respect to the reference marker (M) from a tracking system,determining a virtual position of the surgical instrument (1) with respect to the second 3D medical image.
Owner:IMACTIS
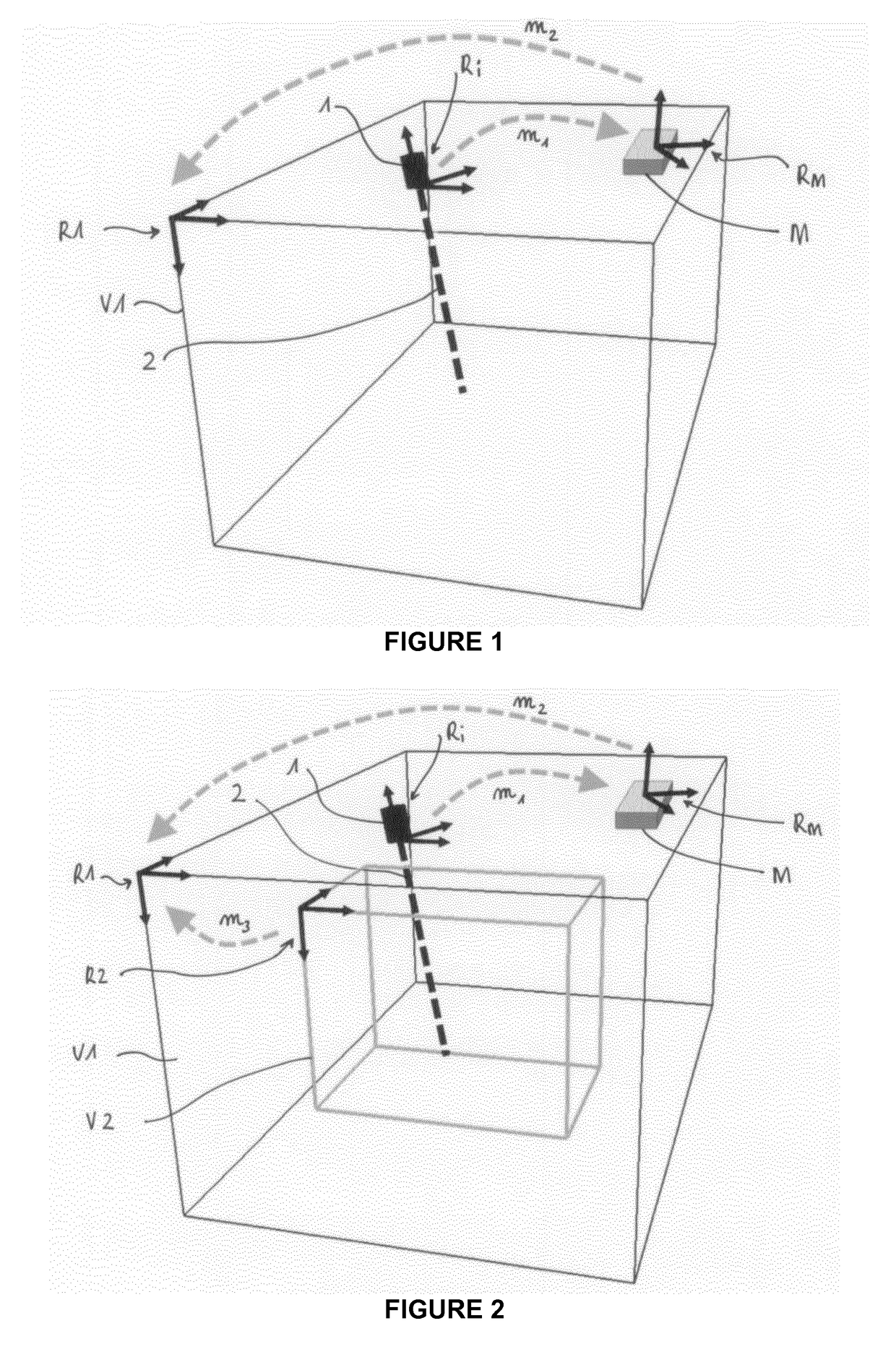
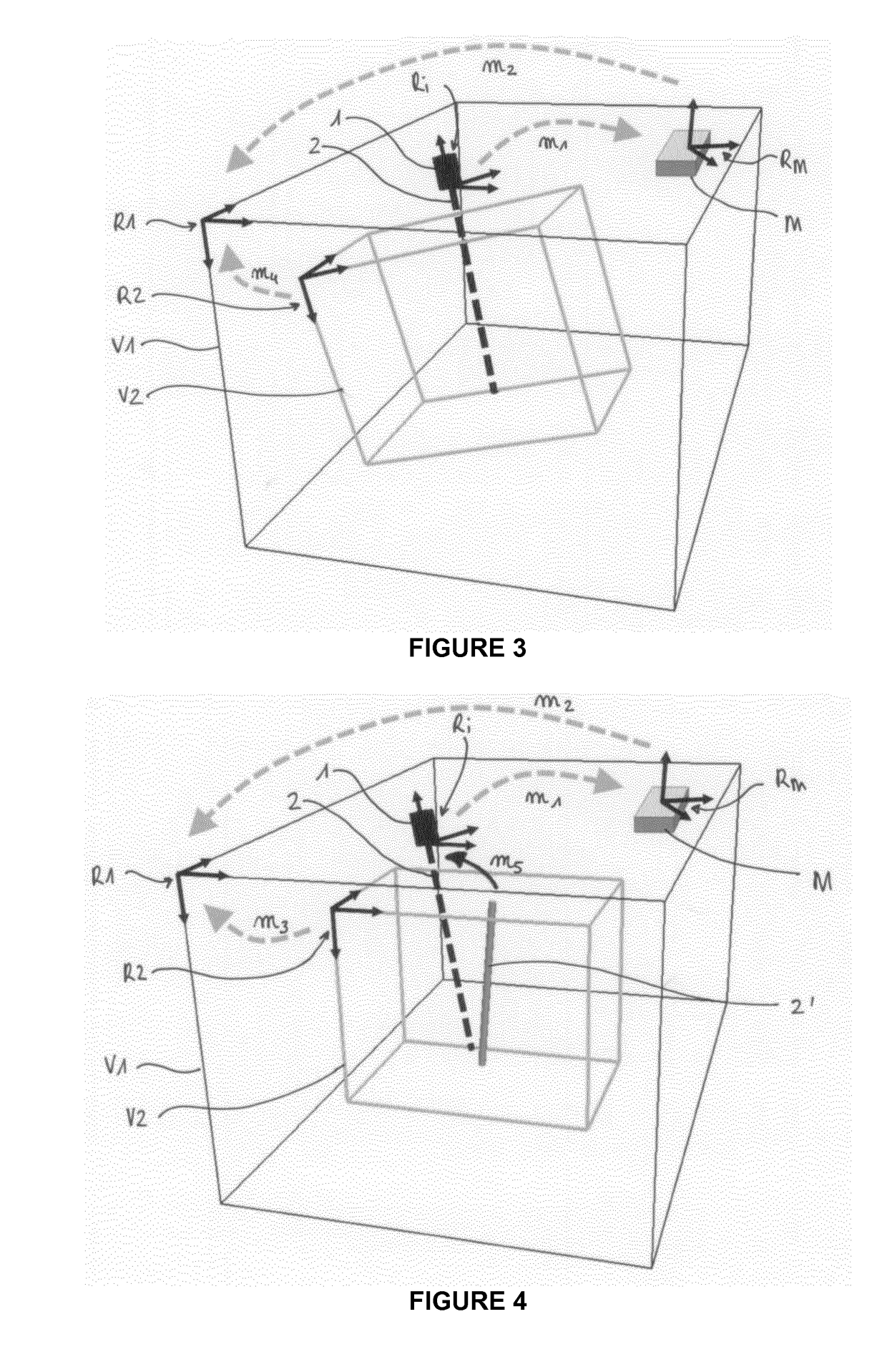
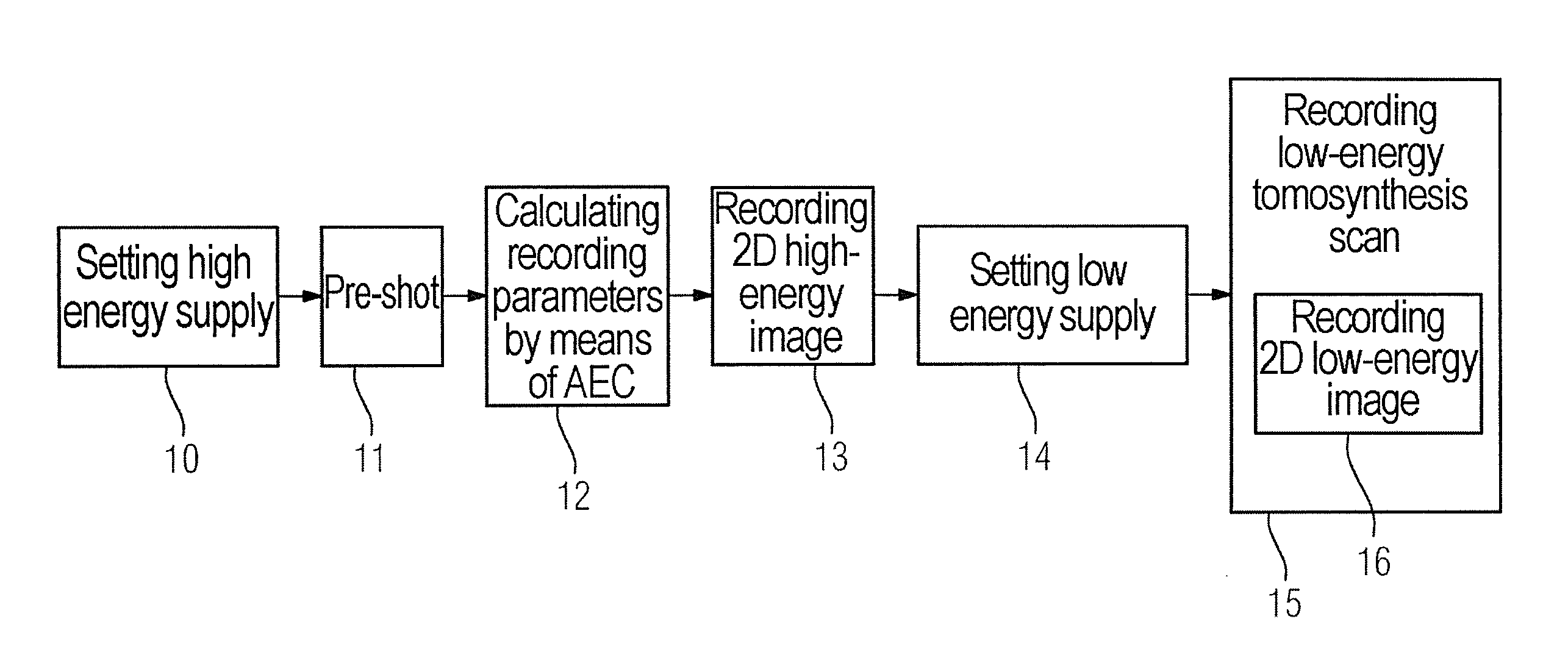
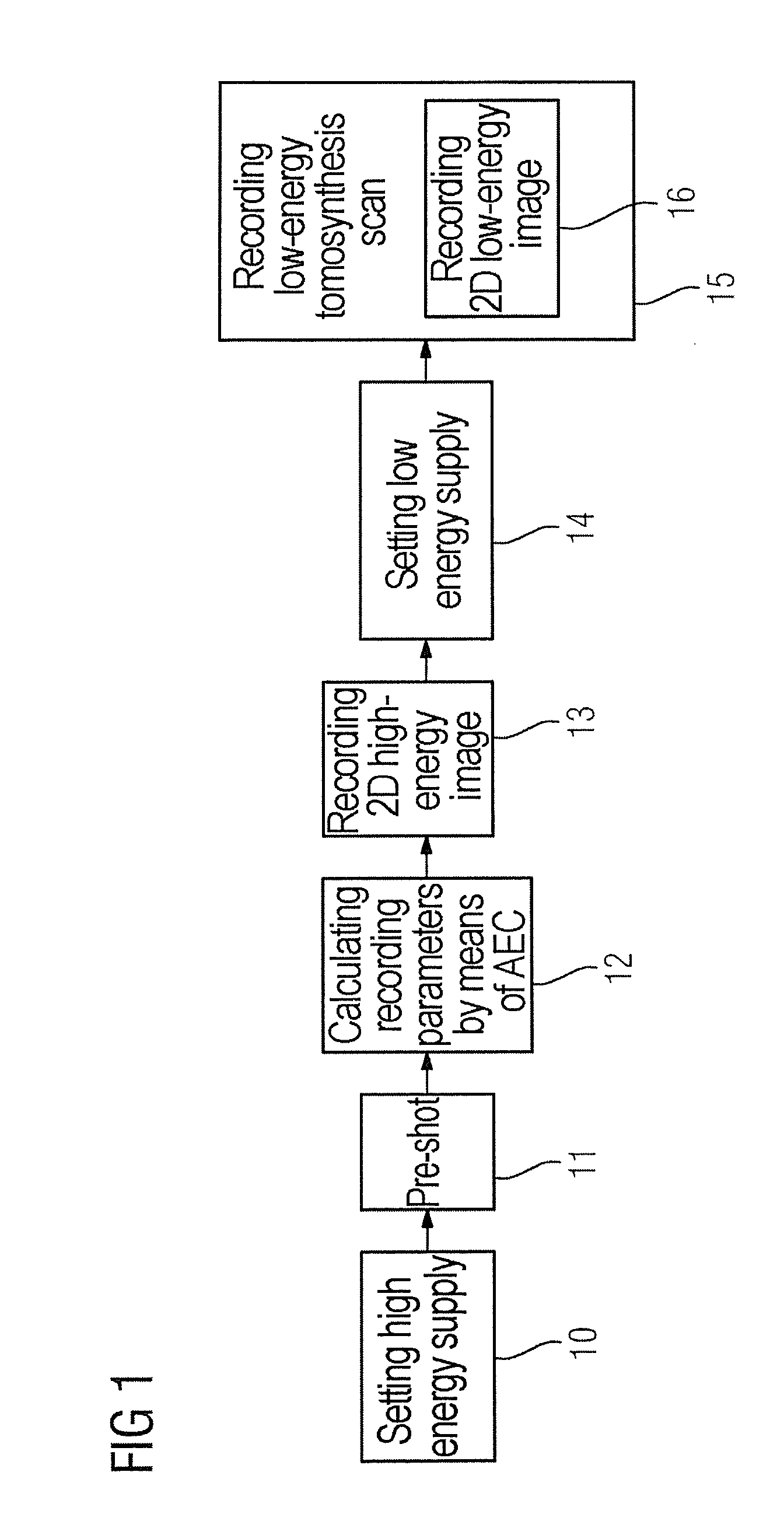
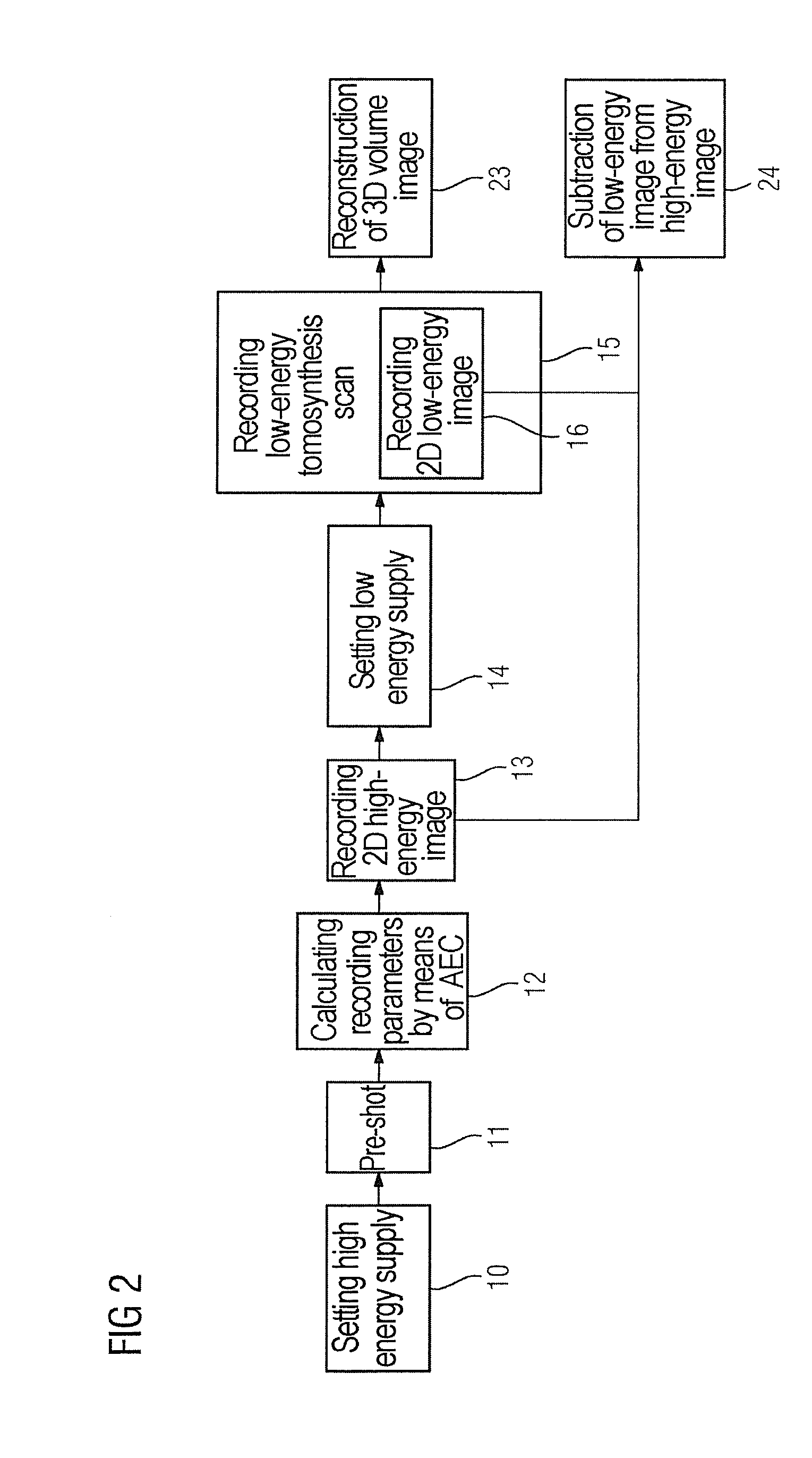
Method and apparatus for combined dual-energy mammography and tomosynthesis imaging
ActiveUS20160007943A1Short timeReduce X-ray doseImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisHigh energy
In a method and tomosynthesis apparatus for combined dual-energy mammography and tomosynthesis imaging of a predetermined volume of an examination subject, while contrast agent is flowing through the volume, an x-ray source is set to radiate x-rays at low and high radiation energy. A pre-shot of the volume is obtained with the high radiation energy, and recording parameters for high-energy images, low-energy images, and low-energy tomosynthesis scans are obtained from the pre-shot. A high-energy image is then obtained, followed by operating the x-ray source at a low energy, and a low-energy tomosynthesis scan of the volume is executed using the recording parameters, and a two-dimensional low-energy image of the volume is generated during the low-energy tomosynthesis scan.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Cast collimators for ct detectors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20070064876A1Reduce X-ray doseLarge atomic numberMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh densityRadiology
Cast collimators for use in CT imaging systems are described, as are methods of making them. Such collimators may comprise pre-patient collimators, pre-patient filter / collimator assemblies, and / or post-patient collimators. The filters and / or collimators may be made of any suitable high-density, high atomic number material such as lead, a lead alloy, tantalum, tungsten, tungsten suspended in an epoxy matrix, tungsten suspended in a slurry, or the like. Embodiments of these collimators comprise specially-designed channels and vanes that allow them to be precision cast to the necessary degree of accuracy. These channels and vanes are preferably tapered. These collimators and filter / collimator assemblies help minimize the x-ray dose to the patient by minimizing the scattered radiation creation mechanism and by collimating out much of the scattered radiation that would otherwise be subjected to the patient. These collimators may be cast as either single piece structures, or multiple pieces that can be operatively connected together.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and arrangement for medical x-ray imaging and reconstruction from sparse data
ActiveUS20060104406A1Utilize priori informationEfficient use ofReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationSoft x ray
The invention relates to a medical X-ray device 5 arrangement for producing three-dimensional information of an object 4 in a medical X-ray imaging medical X-ray device arrangement comprising an X-ray source 2 for X-radiating the object from different directions and a detector 6 for detecting the X-radiation to form projection data of the object 4. The medical X-ray device 5 arrangement comprises: means 15 for modelling the object 4 mathematically independently of X-ray imaging and means 15 for utilizing said projection data and said mathematical modelling of the object in Bayesian inversion based on Bayes' formula p(xm)=ppr(x)p(mx)p(m)to produce three-dimensional information of the object, the prior distribution ppr(x) representing mathematical modelling of the object, the object image vector x, which comprise values of the X-ray attenuation coefficient inside the object, m representing projection data, the likelihood distribution p(m|x) representing the X-radiation attenuation model between the object image vector x and projection data m, p(m) being a normalization constant and the posteriori distribution p(x|m) representing the three-dimensional information of the object 4.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE FINLAND
CT imaging method and CT system based on multi-mode scout scan
InactiveUS20140187932A1Reduce X-ray doseReduced imaging timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDual energyRegion of interest
A CT imaging method and a CT system based on a multi-mode scout scan. The CT imaging method based on a multi-mode scout scan comprises: performing an instant switching dual energy scout radiation scan on a region of interest of a subject by way of instant switching between high voltage and low voltage to collect dual energy protection data of the region of interest; and reconstructing a material decomposition image and a mono-energetic image based on the collected dual energy projection data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
InactiveUS20050171420A1Improving Imaging ResultsRelatively small errorPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringLocalization systemMedical imaging
The present invention relates to a method and also an imaging system to compensate for patient motion when recording a series of images in medical imaging, in which a number of images of an area under examination of a patient (17) are recorded at intervals with an imaging system (1) and are related to one another. With the method a localization system (2) is used as the series of images are being recorded to permanently or at a time close to the recording of the individual images, record a momentary spatial location of the area under examination in a reference system permanently linked to the imaging system (1), a first spatial location of the area under examination recorded close to the time of recording of a first image is stored, and a deviation of the images recorded momentarily in each case of the first spatial location is determined and by changing the geometrical circumstances of the imaging system (1) at a time to close the recording of the spatial location and / or through geometrical adaptation of an image content of an image just recorded, is at least approximately commentated for, so that the images show the area under examination in the same position and orientation. The method does not require any time-consuming interaction with the operator and is also suitable for compensating for larger movements of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
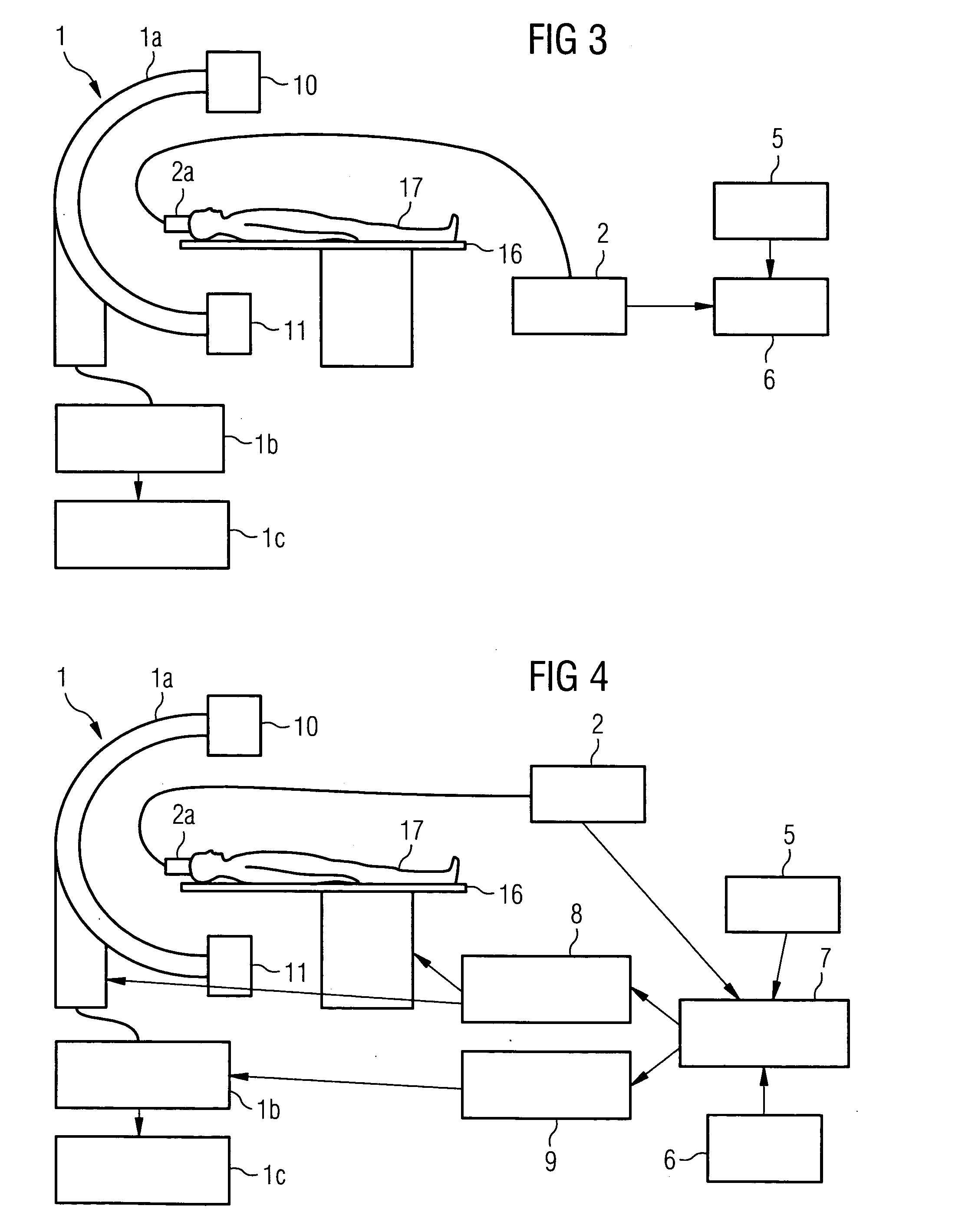
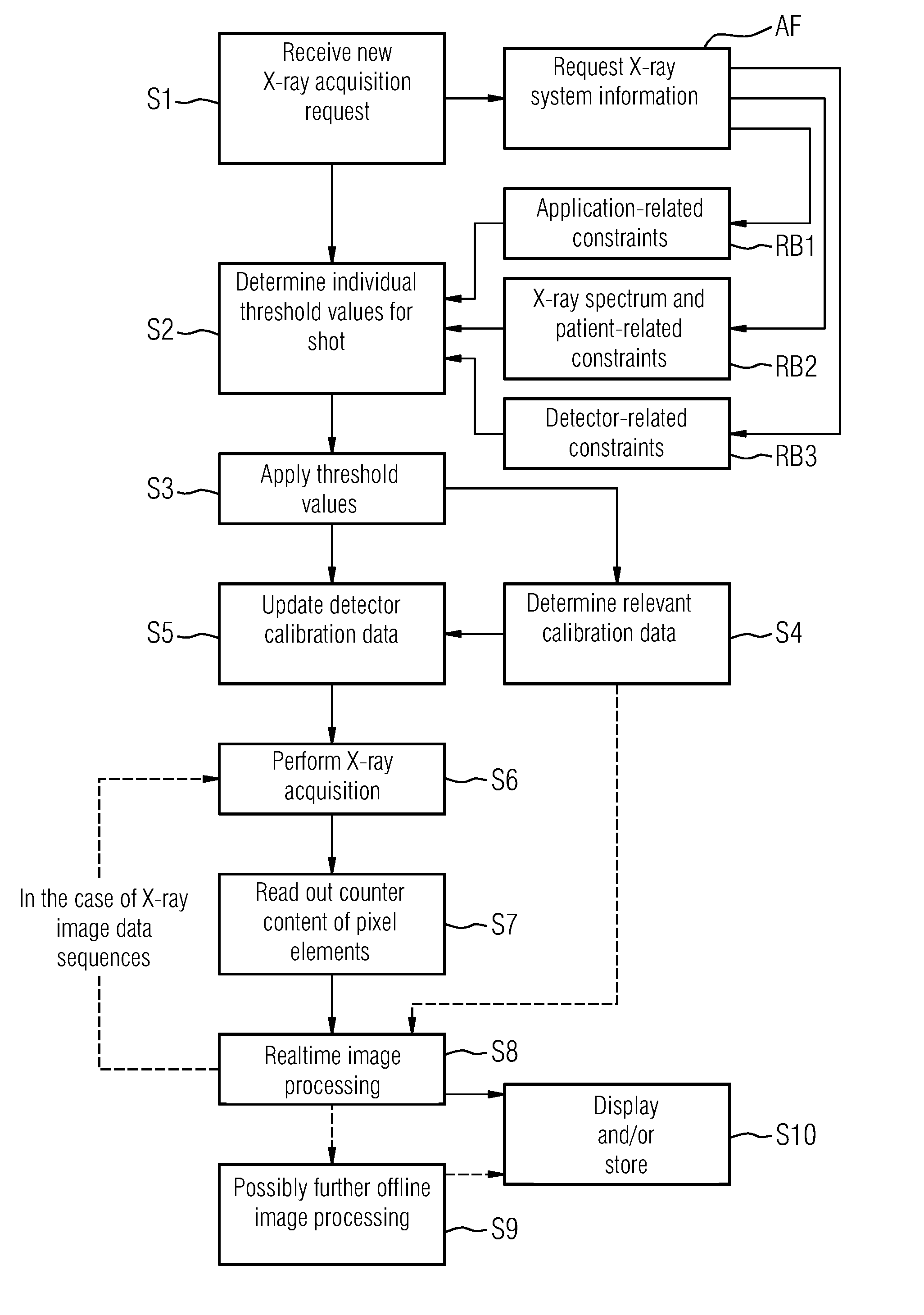
Method and System for Acquiring an X-Ray Image
InactiveUS20140270073A1Improve overall utilizationEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementSoft x rayX-ray
A method acquires an X-ray image via a counting digital X-ray detector of an X-ray system. The X-ray detector has an X-ray converter for converting X-ray radiation into an electrical signal and a matrix having a plurality of counting pixel elements. At least one variable threshold value is applied for each pixel element such that an incoming signal is counted by a memory unit in each instance that the incoming signal exceeds the threshold value. The method includes receiving a request to acquire one or more X-ray images, automatically determining one or more threshold values individually adjusted to the X-ray image(s), setting the threshold values in the X-ray detector, applying X-ray radiation while the threshold values are applied, converting X-ray quanta into count signals, storing the count signals in the X-ray detector, outputting image data representing the X-ray image from the X-ray detector, and displaying or storing the X-image.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
X-ray computer tomography system and method
The invention discloses an X-ray computer tomography system, which comprises an X-ray tube, a collimator and a detector and is used for photographing a plurality of elliptical cross sections of an object to be detected in the scanning direction; the detector comprises a plurality of detector channels; the X-ray tube, the collimator and the detector synchronously rotate around the object to be detected; the collimator is provided with an adjustable opening; the X-ray computer tomography system also comprises a computation assembly and an adjustment assembly, wherein the computation assembly is used for computing opening widths of the collimator, which are required for irradiating each elliptical cross section, under different projection angles, and transmitting the opening widths to the adjustment assembly; and the adjustment assembly is used for adjusting the opening of the collimator according to the opening widths. The invention also discloses an X-ray computer tomography method. Due to adoption of the system and method disclosed by the invention, extra exposure of a surrounding area of the object to be detected can be reduced, and the X-ray dose accepted by a patient can be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Method and arrangement for medical X-ray imaging
InactiveUS7068752B2Utilize priori informationEfficient use ofReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayBayesian inversion
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
Scanning system for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120236992A1Reduce contrastReduce X-ray doseNanotechnologyTomographyX ray imageImaging data
The invention relates to the field of X-ray differential phase contrast imaging. For scanning large objects and for an improved contrast to noise ration, an X-ray device (10) for imaging an object (18) is provided. The X-ray device (10) comprises an X-ray emitter arrangement (12) and an X-ray detector arrangement (14), wherein the X-ray emitter arrangement (14) is adapted to emit an X-ray beam (16) through the object (18) onto the X-ray detector arrangement (14). The X-ray beam (16) is at least partial spatial coherent and fan-shaped. The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises a phase grating (50) and an absorber grating (52). The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises an area detector (54) for detecting X-rays, wherein the X-ray device is adapted to generate image data from the detected X-rays and to extract phase information from the X-ray image data, the phase information relating to a phase shift of X-rays caused by the object (18). The object (18) has a region of interest (32) which is larger than a detection area of the X-ray detector (18) and the X-ray device (10) is adapted to generate image data of the region of interest (32) by moving the object (18) and the X-ray detector arrangement (14) relative to each other.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray CT device
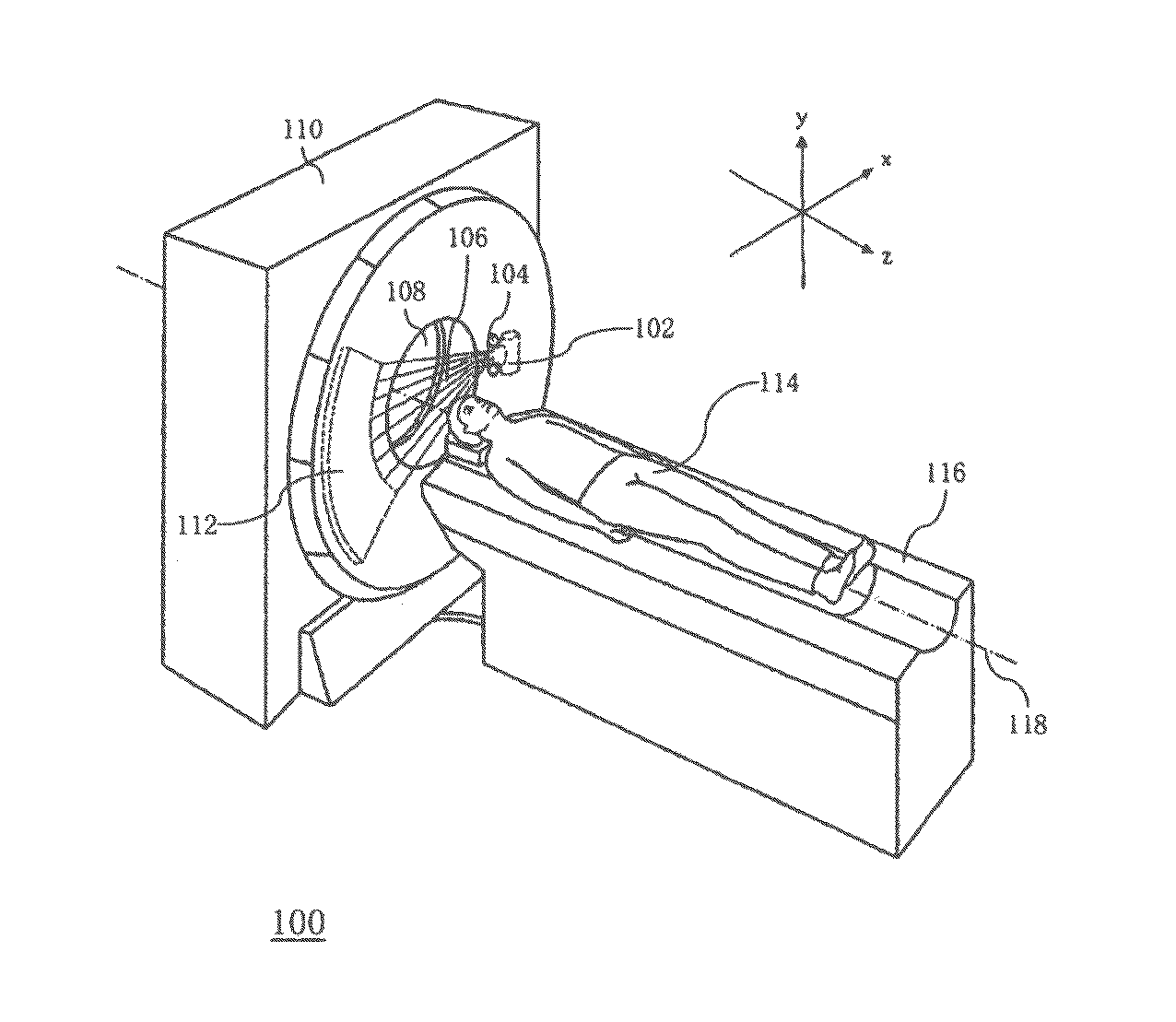
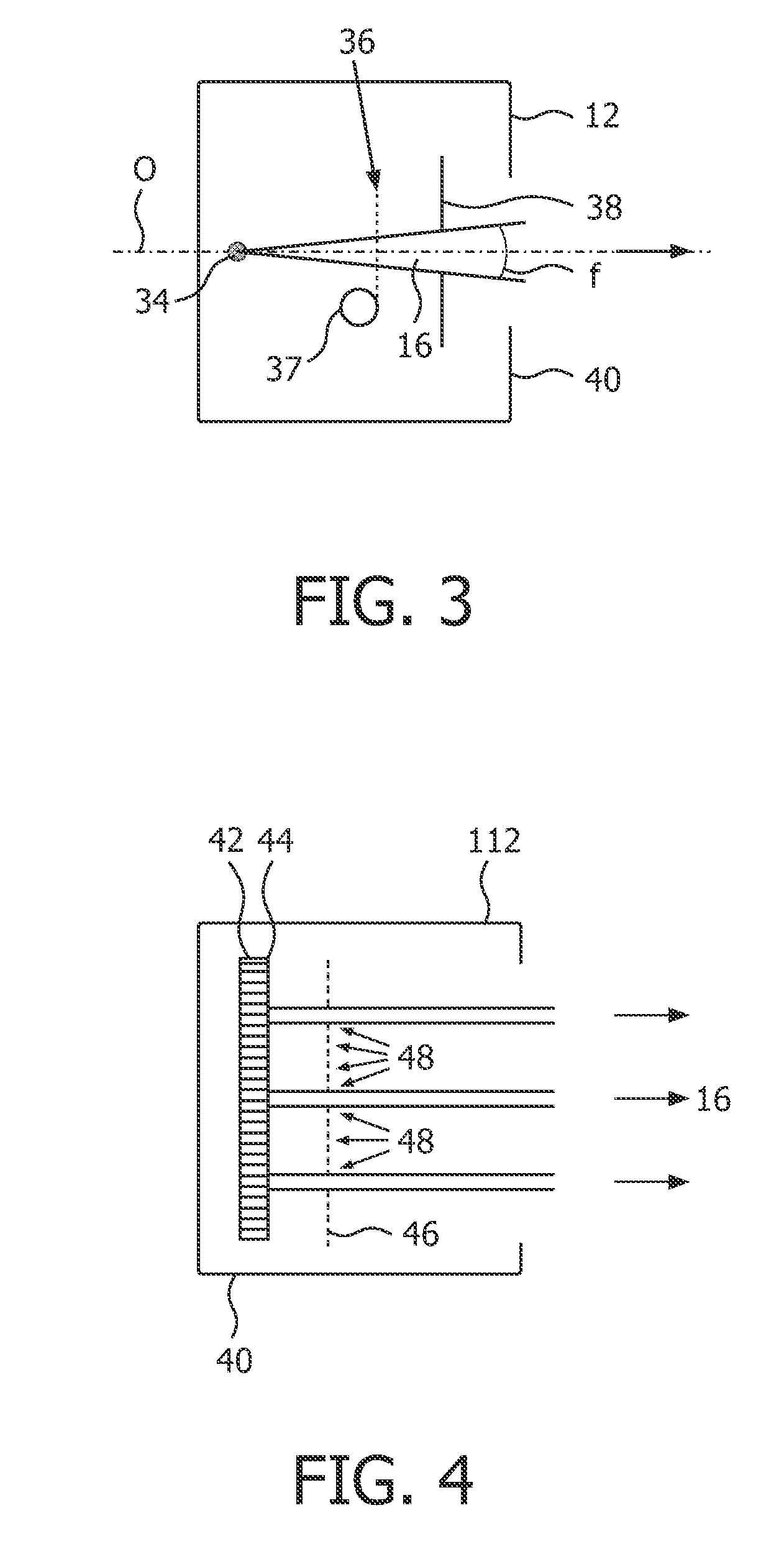
InactiveCN1515228AReduce X-ray doseReduce radiation doseComputerised tomographsTomographySoft x rayImaging processing
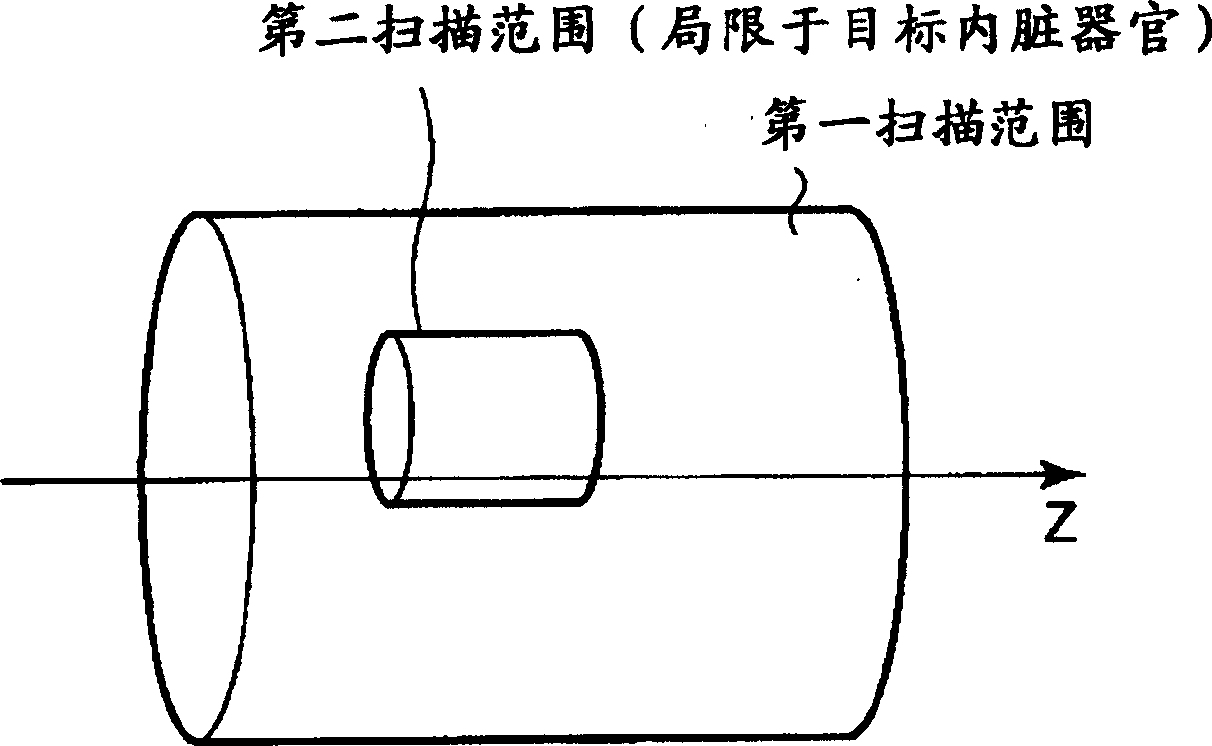
An X-ray CT apparatus, as one example, includes at least one X-ray irradiation source configured to irradiate an X-ray to a volume of interest, at least one X-ray detector including a plurality of detection element segments configured to detect the X-ray penetrated through the volume of interest, at least one collimator configured to create an opening that is movable in at least one of a slice direction and a channel direction, at least one image processing part configured to extract a portion of the volume data, a controller configured to set the opening of the at least one collimator to a second opening size according to a cylinder-like second scanning range that is set to limit the volume of interest and configured to perform a second scan, and at least one reconstruction part configured to reconstruct image data based on data collected by the second scan.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Method and arrangement for medical X-ray imaging
InactiveUS20050105694A1Utilize priori informationEfficient use ofReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingBayesian inversionBayesian formulation
A medical X-ray device 5 arrangement for producing three-dimensional information of an object 4 in a medical X-ray imaging comprises an X-ray source 2 for X-radiating the object from at least two different directions; a detector 6 for detecting the X-radiation to form projection data of the object 4; a computational device 15 for modelling the object 4 mathematically utilizing the projection data to solve the imaging geometry and / or the motion of the object, where the solving concerns either some or all parts of the imaging geometry and / or the motion of the object. The computational device 15 utilizes said projection data and said mathematical modelling of the object in Bayesian inversion based on Bayes' formula p(x,θ❘m)=ppr(θ)ppr(x)p(m❘x,θ)p(m)to produce three-dimensional information of the object.
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
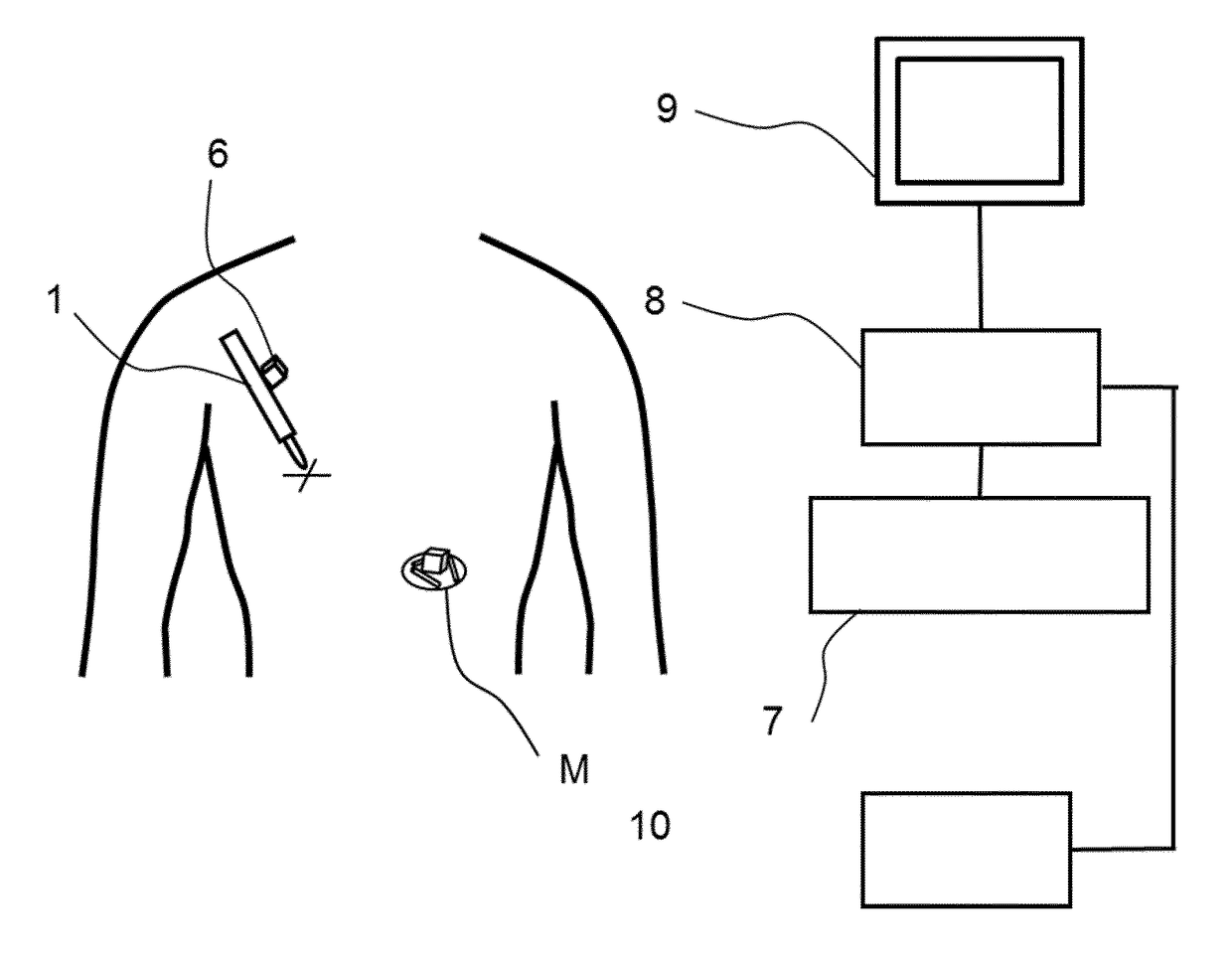
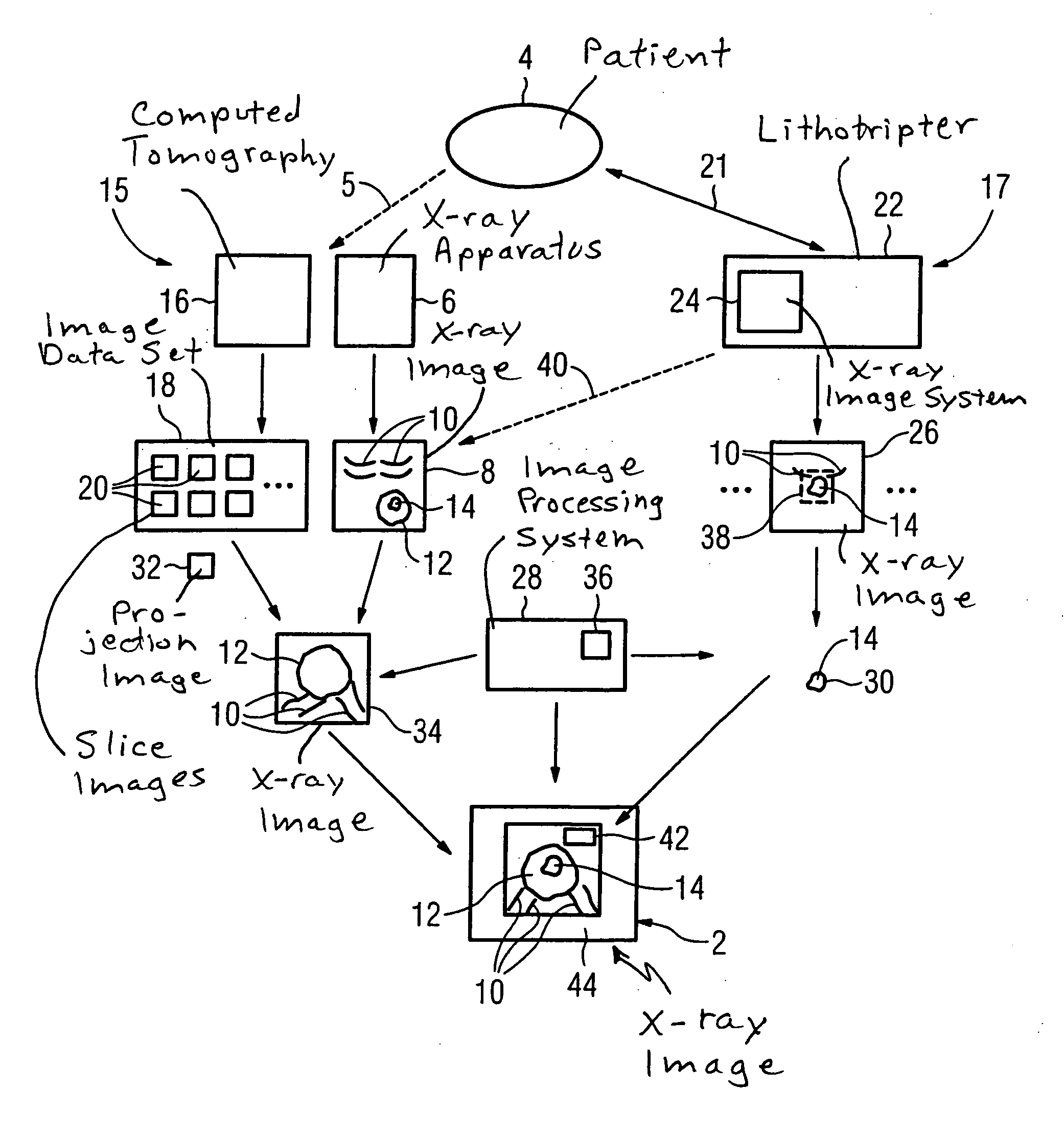
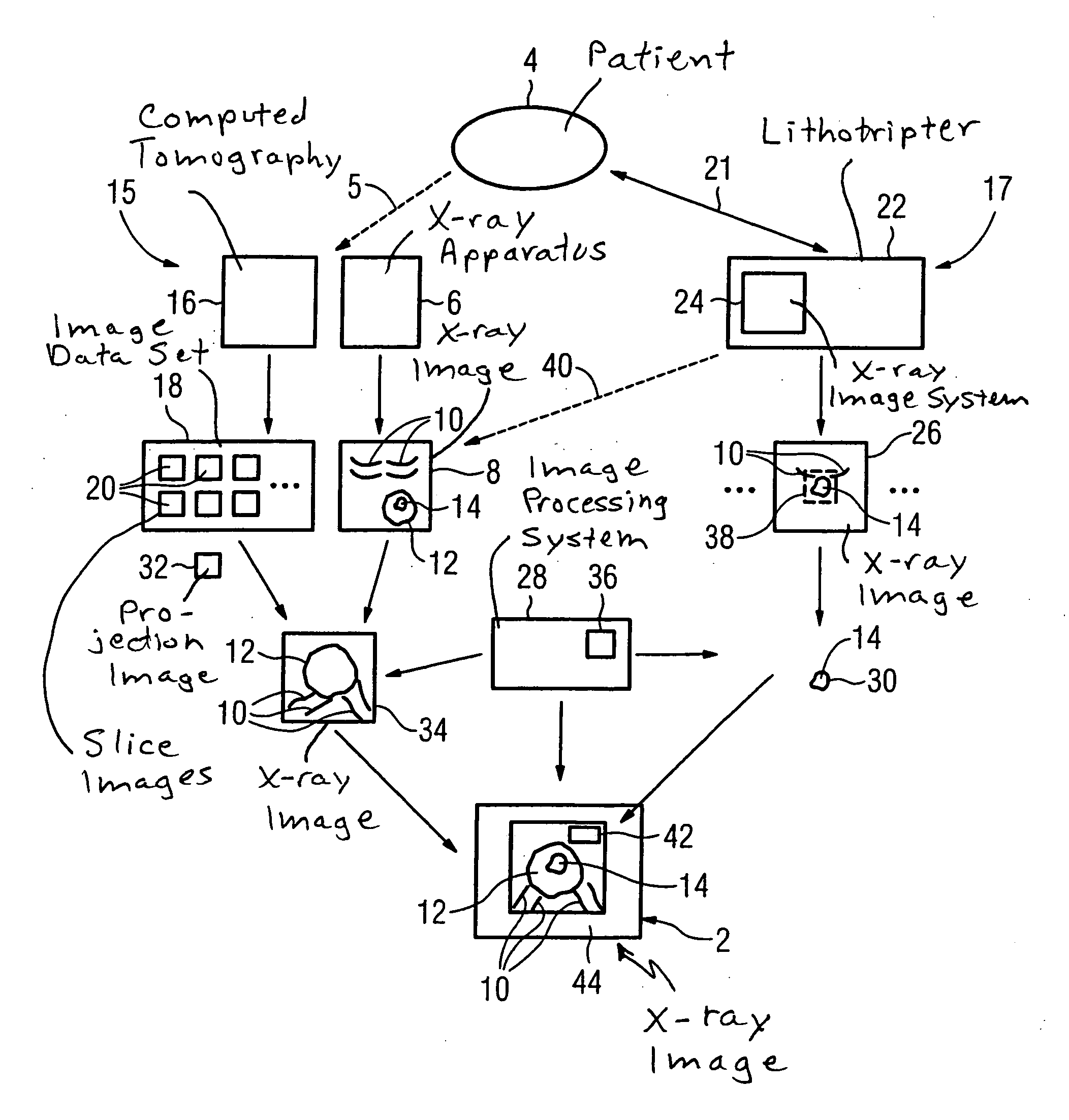
Method and apparatus for x-ray imaging of a patient during a shockwave treatment
In a method for x-ray imaging given a patient containing a subject to be represented during a shockwave treatment, an image data set containing the subject and a marker is generated at a first point in time; an x-ray image showing essentially only the subject (14) and the marker is acquired at a second point in time, the x-ray image is correctly spatially associated with the image data set using the marker, the x-ray image is displayed together with information extracted from the image data set during the shockwave treatment. An apparatus for x-ray imaging a patient containing a subject to be represented during a shockwave treatment has a memory for an image data set generated at a first point in time and containing the subject and a marker, an x-ray system for acquisition of an x-ray image showing essentially only the subject and the marker at a second point in time; an evaluation unit for spatially-accurate association of the x-ray image with the image data set using the marker and for extraction of information from the image data set, and a display unit for display of the x-ray image together with the information during the shockwave treatment.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
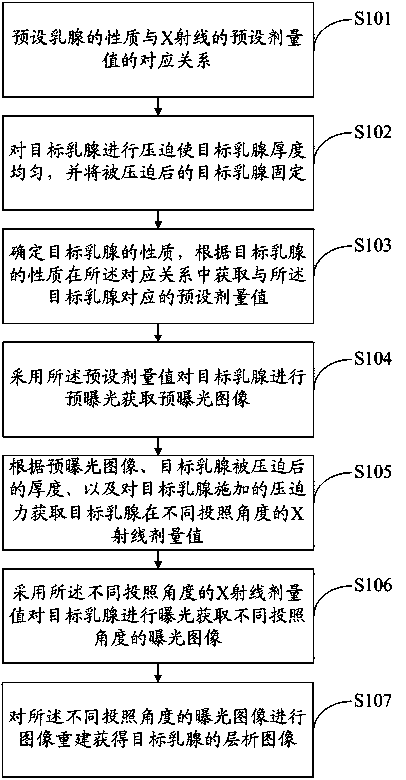
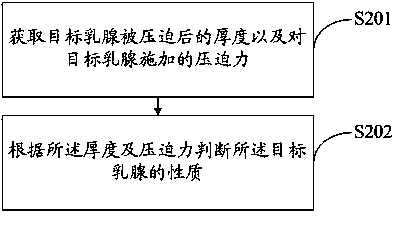
Method and system for controlling X-ray doses of mammary machine
ActiveCN103445795AReduce X-ray doseReduce the effect of X-ray radiationRadiation diagnosticsImaging qualityX-ray
The invention discloses a method and a system for controlling X-ray doses of a mammary machine. The method includes: subjecting targeted mammary glands different in nature to pre-exposure to obtain pre-exposure images and subjecting the pre-exposure images to analytical calculation to obtain the X-ray doses of the targeted mammary glands at different projection angles to ensure acquirement of the best shot images. Due to the fact that an X-ray dose value of each projection angle is best set and the final X-ray dose values are lowered, X-ray radiation effect upon a patient is effectively reduced, image quality is improved, clinical diagnosis is benefited, and doses values of X-ray radiation that the patient received are lowered.
Owner:上海惠影医疗科技有限公司
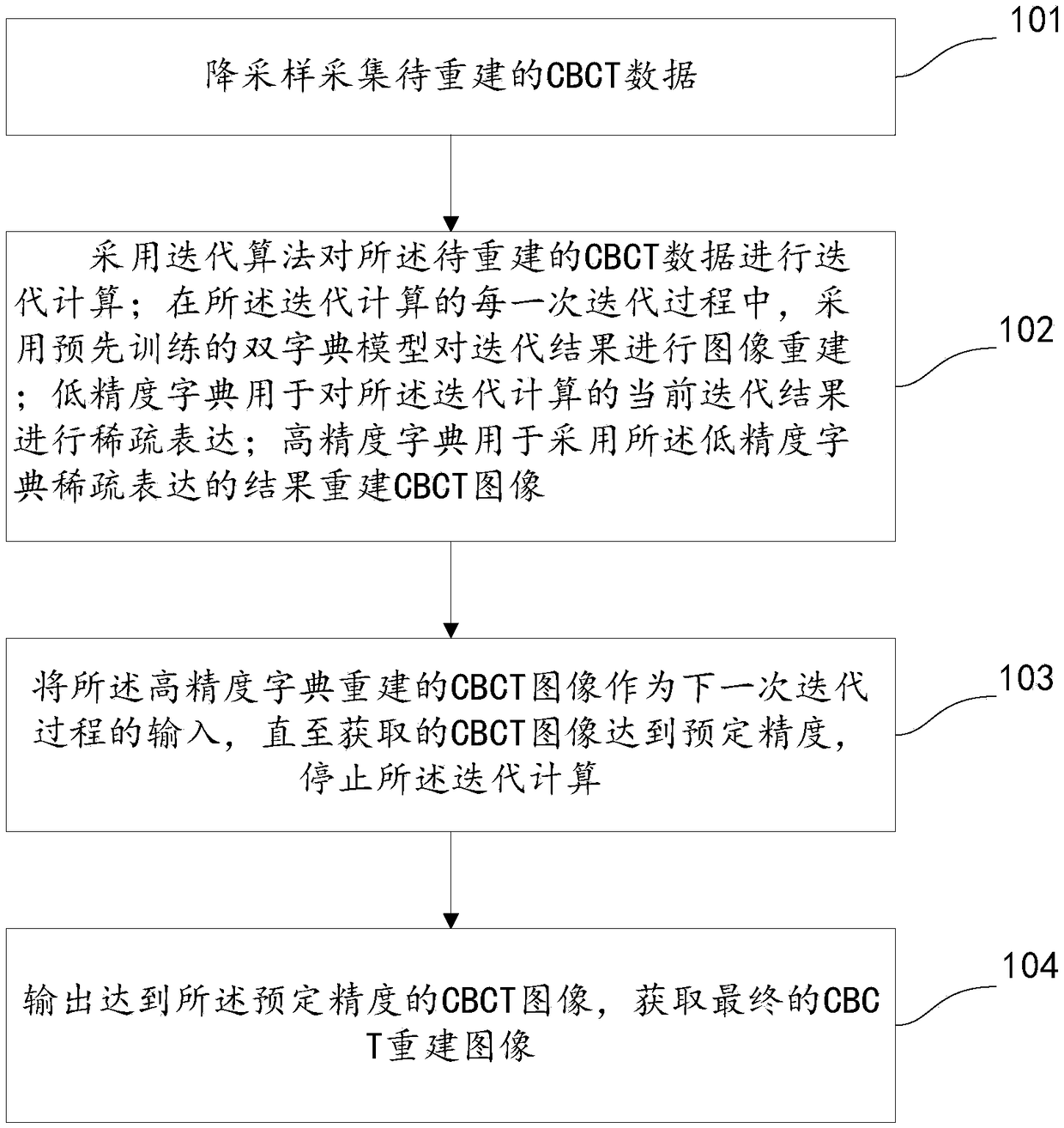
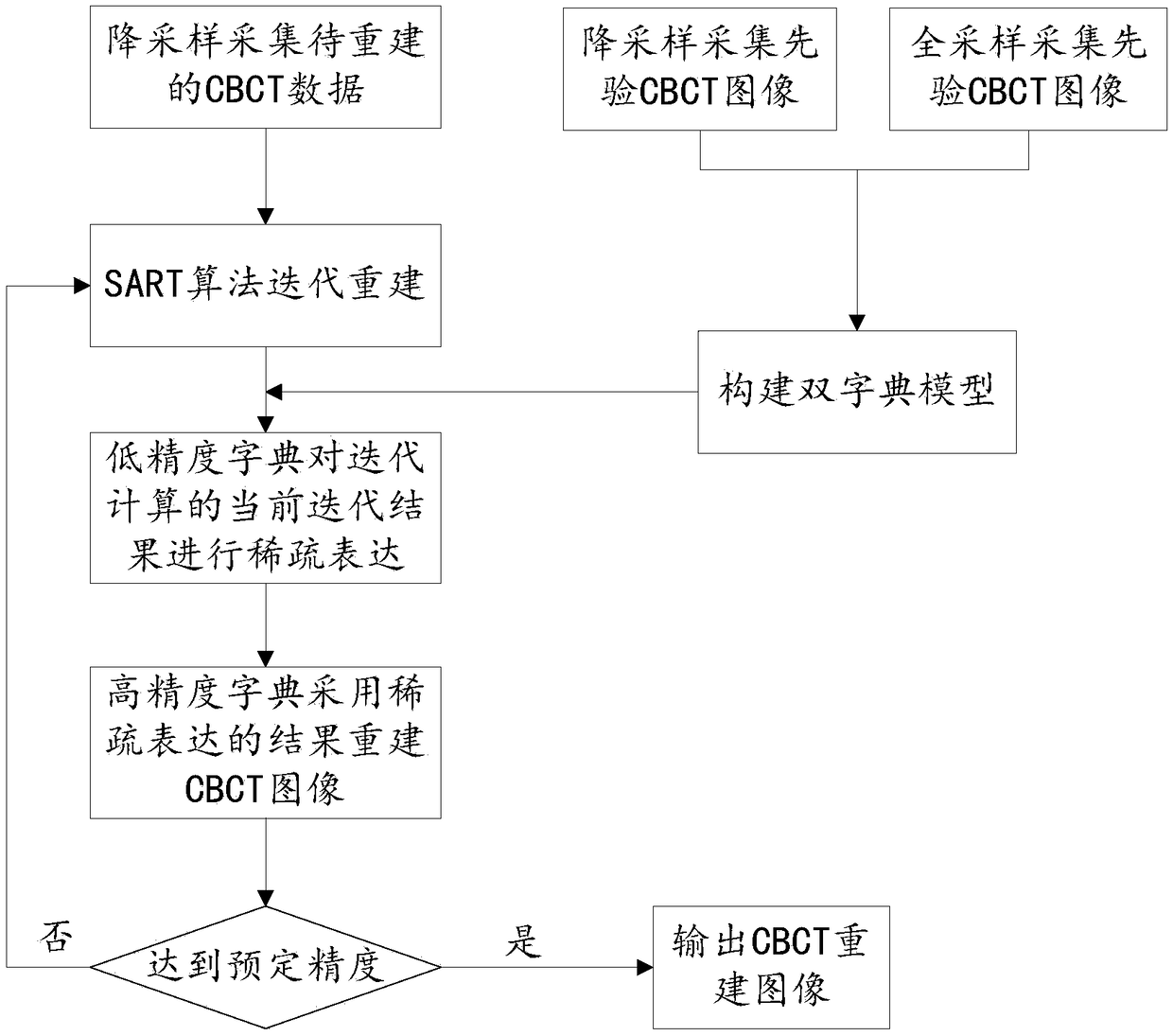
CBCT image reconstruction method based on compressed sensing
PendingCN109035360AReduce scan doseQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAlgorithmX ray dose
The invention discloses a CBCT image reconstruction method based on compression sensing. The CBCT data to be reconstructed are iteratively computed by using iterative algorithm. In each iteration of the iterative computation, the pre-trained dual dictionary model is used to reconstruct the image of the iterative result. The dual dictionary model includes: low-precision dictionary, high-precision dictionary; a low precision dictionary is used to sparsely express the current iterative results of the iterative computation. High-precision dictionary is used to reconstruct CBCT images using the results of low-precision dictionary sparse representation. The CBCT image reconstructed by high-precision dictionary is used as the input of the next iterative process until the acquired CBCT image reaches the predetermined accuracy, and the iterative calculation is stopped to obtain the final CBCT reconstructed image. The technical proposal provided by the invention can remarkably reduce the X-ray dose received by a patient during a single CBCT scan in image-guided radiotherapy on the premise of ensuring the clinical application of the CBCT reconstructed image, and reduce the CBCT scan time.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
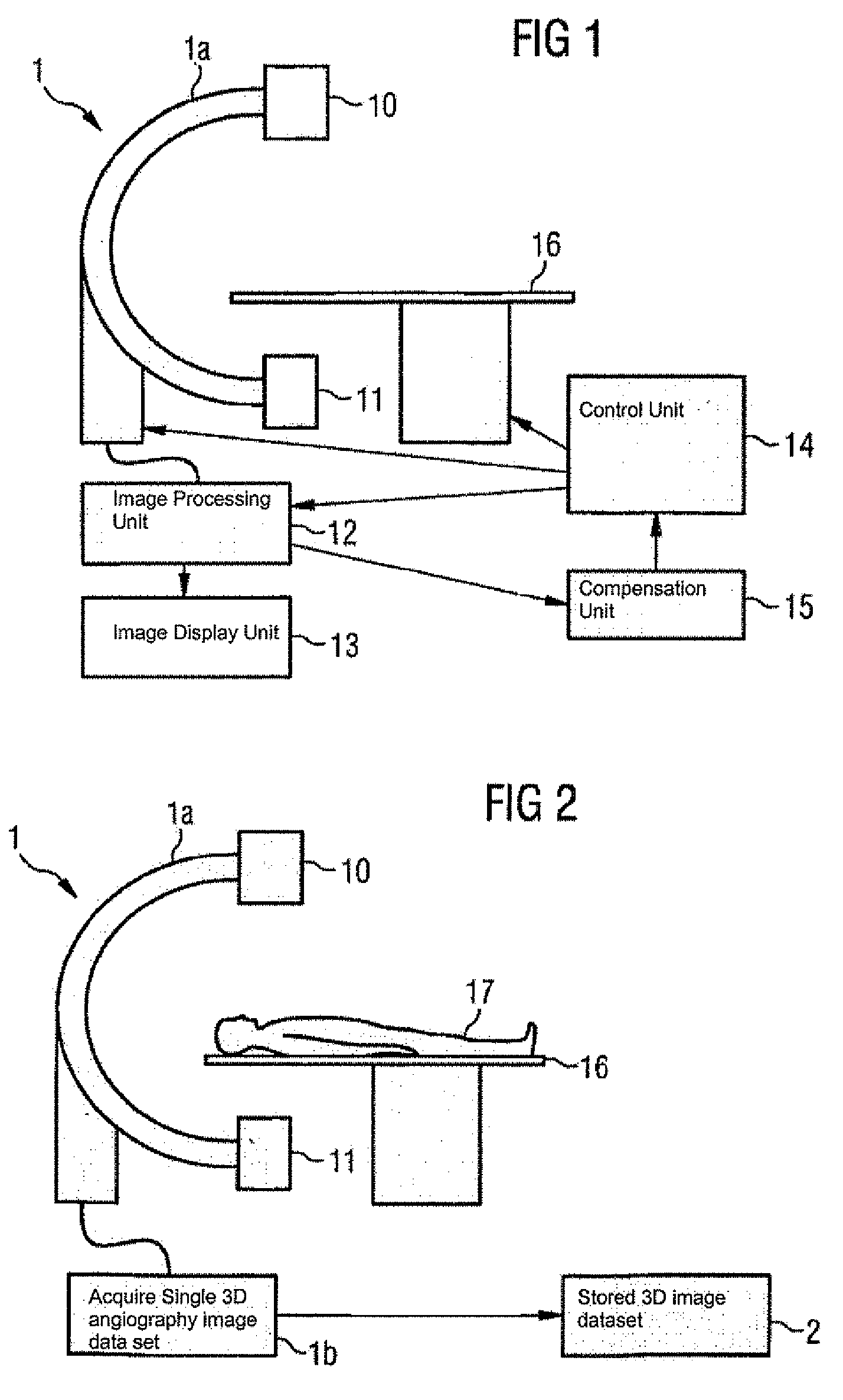
Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
InactiveUS7630751B2Improving Imaging ResultsSmall possible time outlayImage enhancementImage analysisData set3d image
Disclosed herein is a method, and system (1) for implementing same, to compensate for patient motion in series recordings in medical imaging, in which a plurality of images of an examination area of a patient (17) are recorded at time intervals with an imaging system (1) and related to each other. Before the start of the series recordings a 3D image data set is recorded by a 3D recording of the examination area, which establishes a reference system. A first spatial position of the examination area in the reference system is obtained by recording a first image of the series recordings and then registering it or by calculating it. Each further image of the series recordings is registered immediately after recording to obtain the current spatial position of the examination area. Differences in spatial position are compensated for at least approximately by changing geometric relationships of the imaging system (1).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
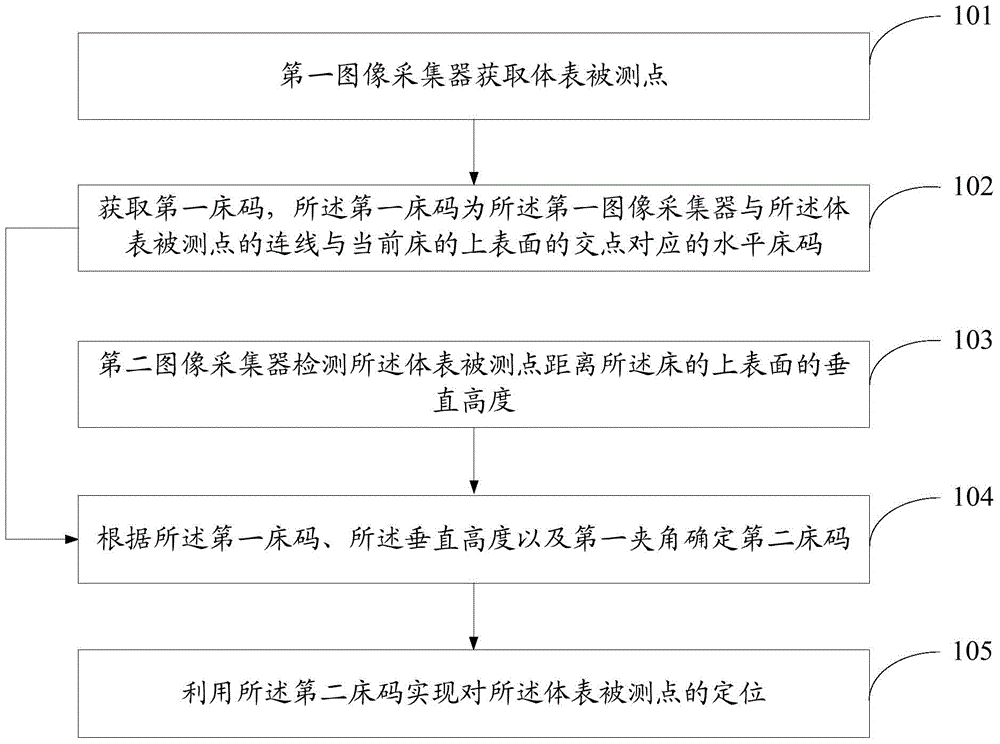
Body surface location method and system
InactiveCN104306012AGood for healthAvoid X-ray RadiationMedical automated diagnosisComputerised tomographsX-rayX ray dose
An embodiment of the invention discloses a body surface location method. The body surface location method includes that a first image collector acquires a test point of the body surface; a first bed size is acquired, to be specific, the first bed size is s horizontal bed size corresponding to an intersection point of the upper surface, of a current bed, and a connecting line, of the first image collector and the test point of the body surface; a second image collector measures the vertical distance from the test point of the body surface to the upper surface of the bed; a second bed size is determined according to the first bed size; the vertical distance and a first inclined angle, to be specific, the second bed size is the horizontal bed size of the test point of the body surface, and the first inclined angle is between the connecting line, of the first image collector and the test point of the body surface, and a straight line, formed by projecting the connecting line to the upper surface of the bed; the test point of the body surface is located by the second bed size. An embodiment of the invention further discloses a body surface location system. By the use of the body surface location method and system, X-ray radiation which is caused by human body surface location and which brings damages to patients is avoided, health of the patients is improved, and X-ray dosage is reduced.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
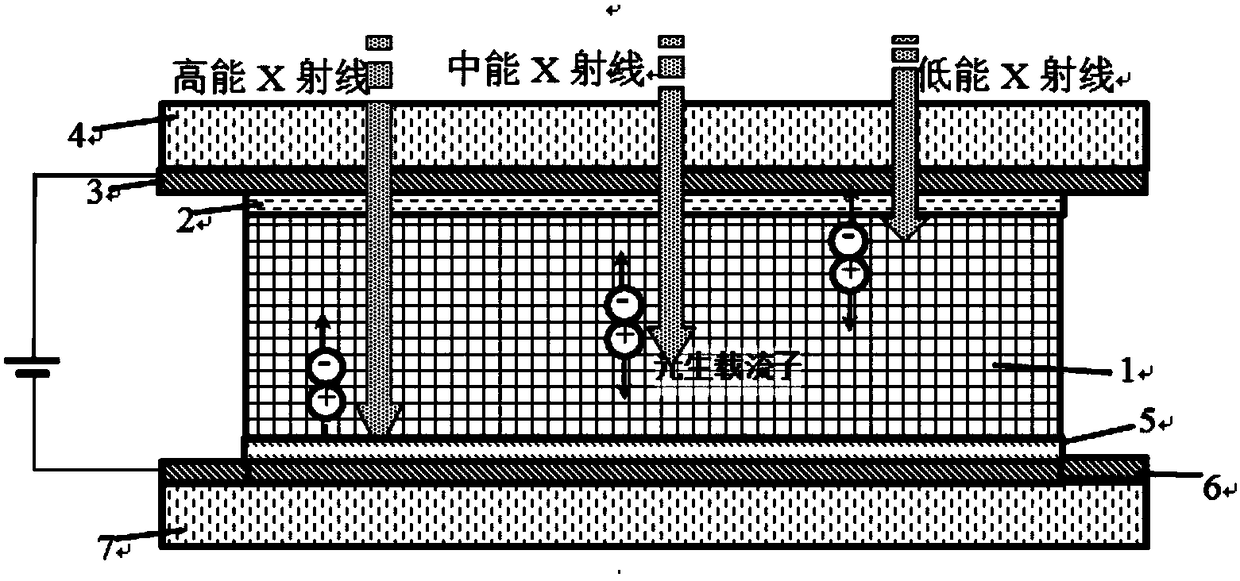
X-ray detector with energy resolution, and detection method of X-ray detector
ActiveCN108183119ARealize image subtractionImprove image qualityX-ray spectral distribution measurementSolid-state devicesSide effectImage subtraction
The invention proposes an X-ray detector with energy resolution, and a detection method of the X-ray detector. The detector sequentially comprises a front collection electrode, an N+ doped layer, an MAPbX3 perovskite monocrystalline active material layer for photoelectric conversion, a P+ doped layer and a rear collection electrode from the top to the bottom. The thickness of the MAPbX3 perovskitemonocrystalline active material layer is not less than 5mm. The front collection electrode is connected with the positive electrode of a detector power supply. The rear collection electrode is connected with the negative electrode of the detector power supply. The detection method comprises the steps: applying different reverse bias voltages to the detector in one X-ray exposure operation, and extracting the detection signal currents of X-ray photons with different energy values based on a corresponding algorithm according to the detection currents under different bias voltages. The detectorand method can achieve the beneficial effects that (1), the detector and method achieve the X-ray detection with the energy resolution capability and the image subtraction of X-ray photon imaging withdifferent energy values; (2), the detector and method just need one X-ray exposure operation, thereby reducing the dosage of X-ray on a patient; (3), the detector and method do not need an additionalcontrast agent, and reduce the toxic and side effect on the patient.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
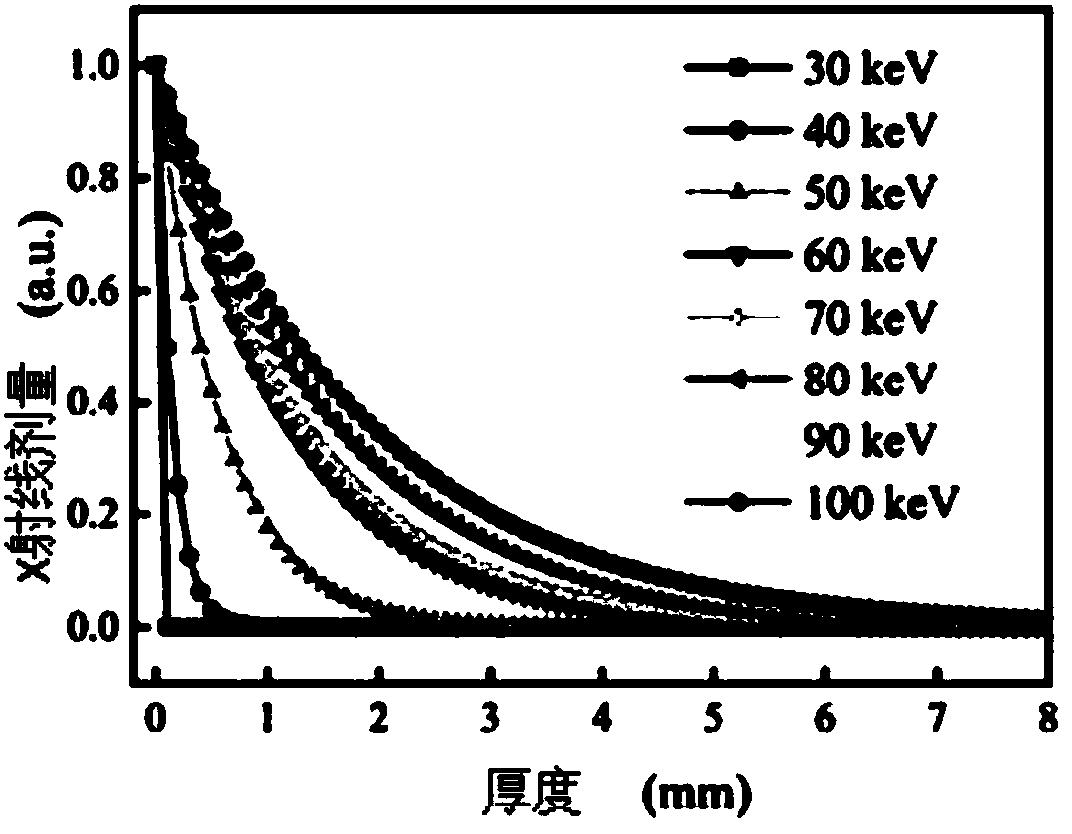
X-ray distribution adjusting filter, CT apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS9390825B2Reduce X-ray doseQuality improvementRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsX-rayUltimate tensile strength
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com