Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
a medical imaging and patient technology, applied in the field of patient motion compensation, can solve the problems of inability to accurately compensate for motion, complicated image processing methods that require extensive processing power, and difficult to implement in real time, so as to improve image results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
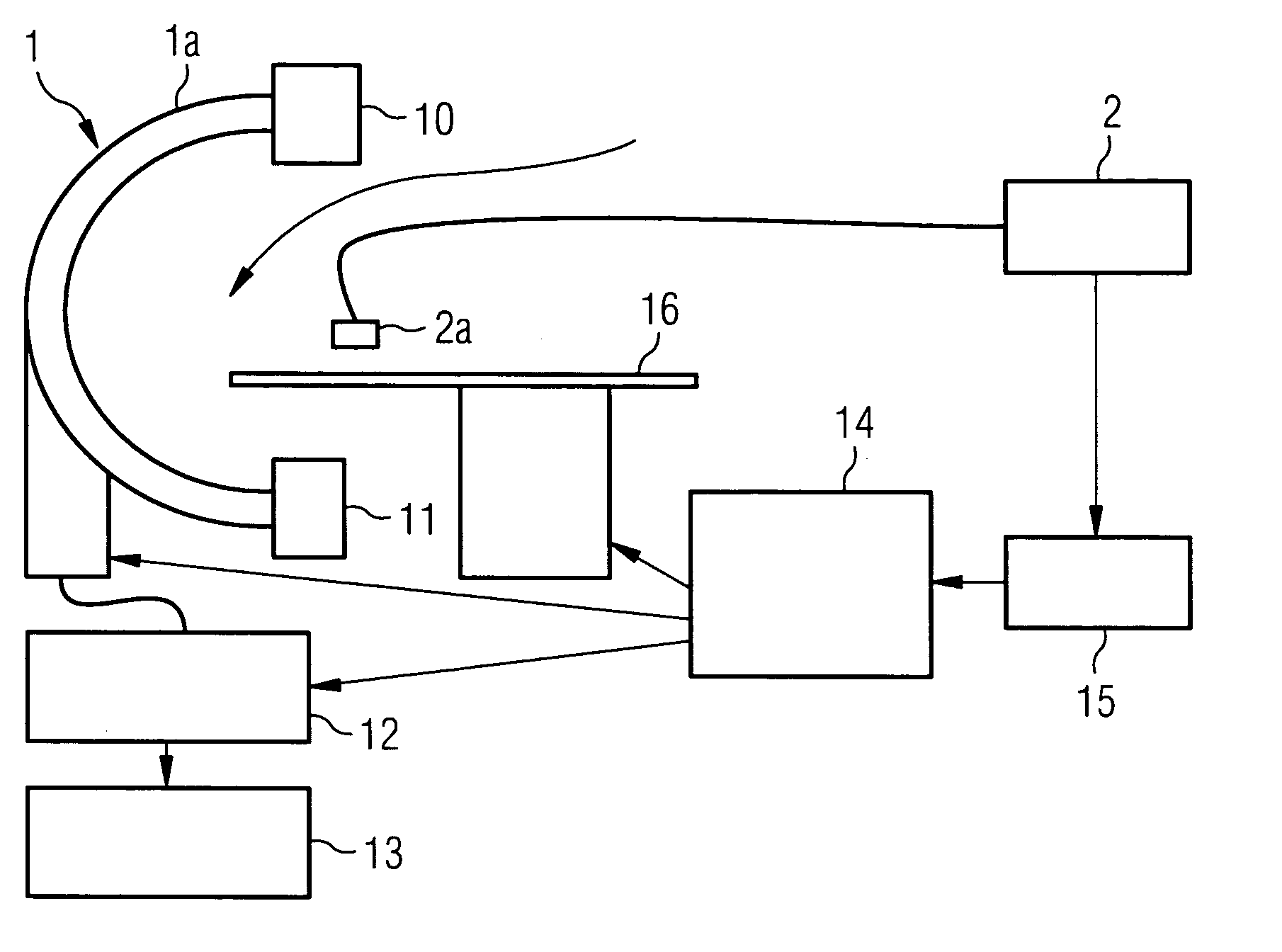
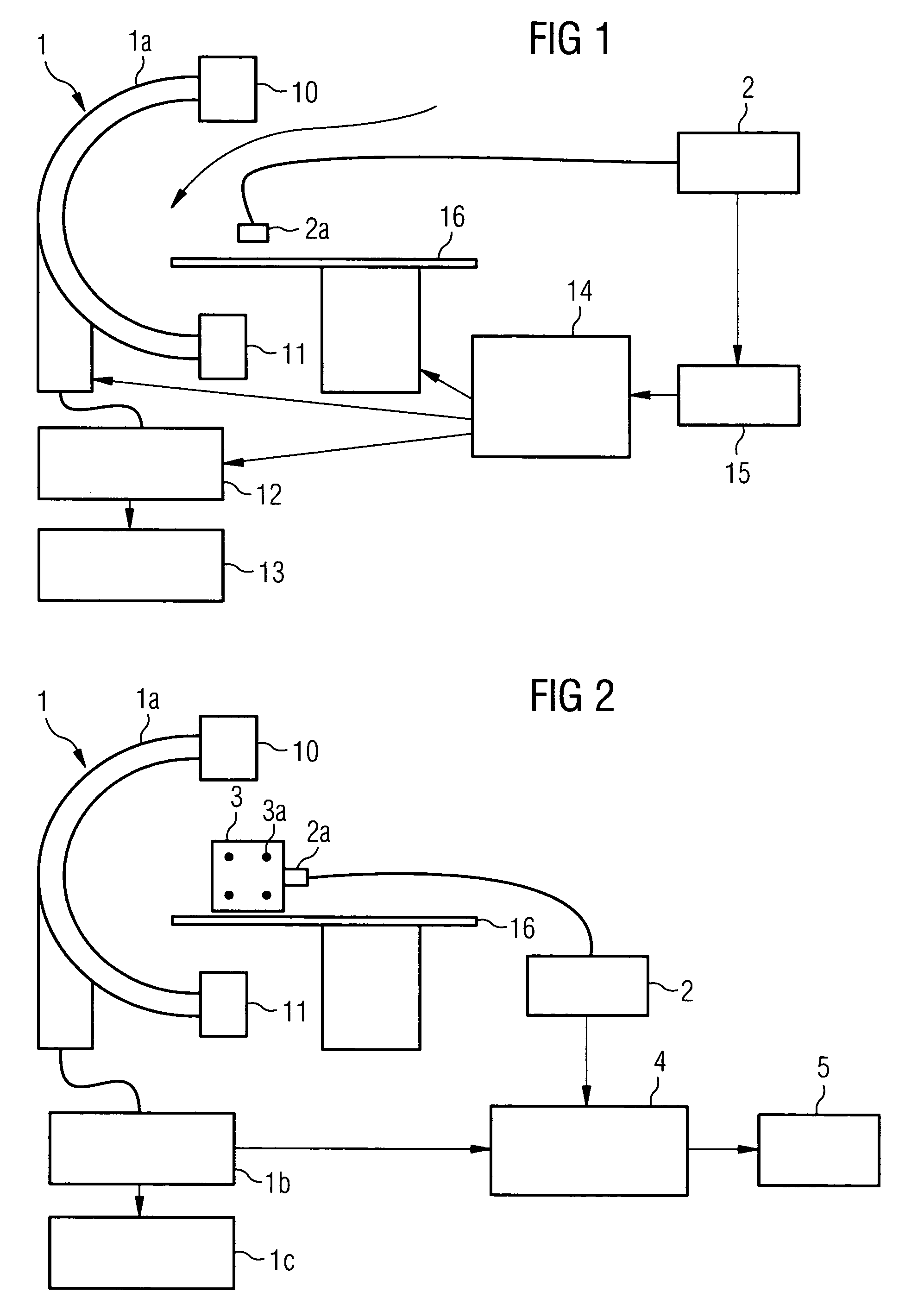
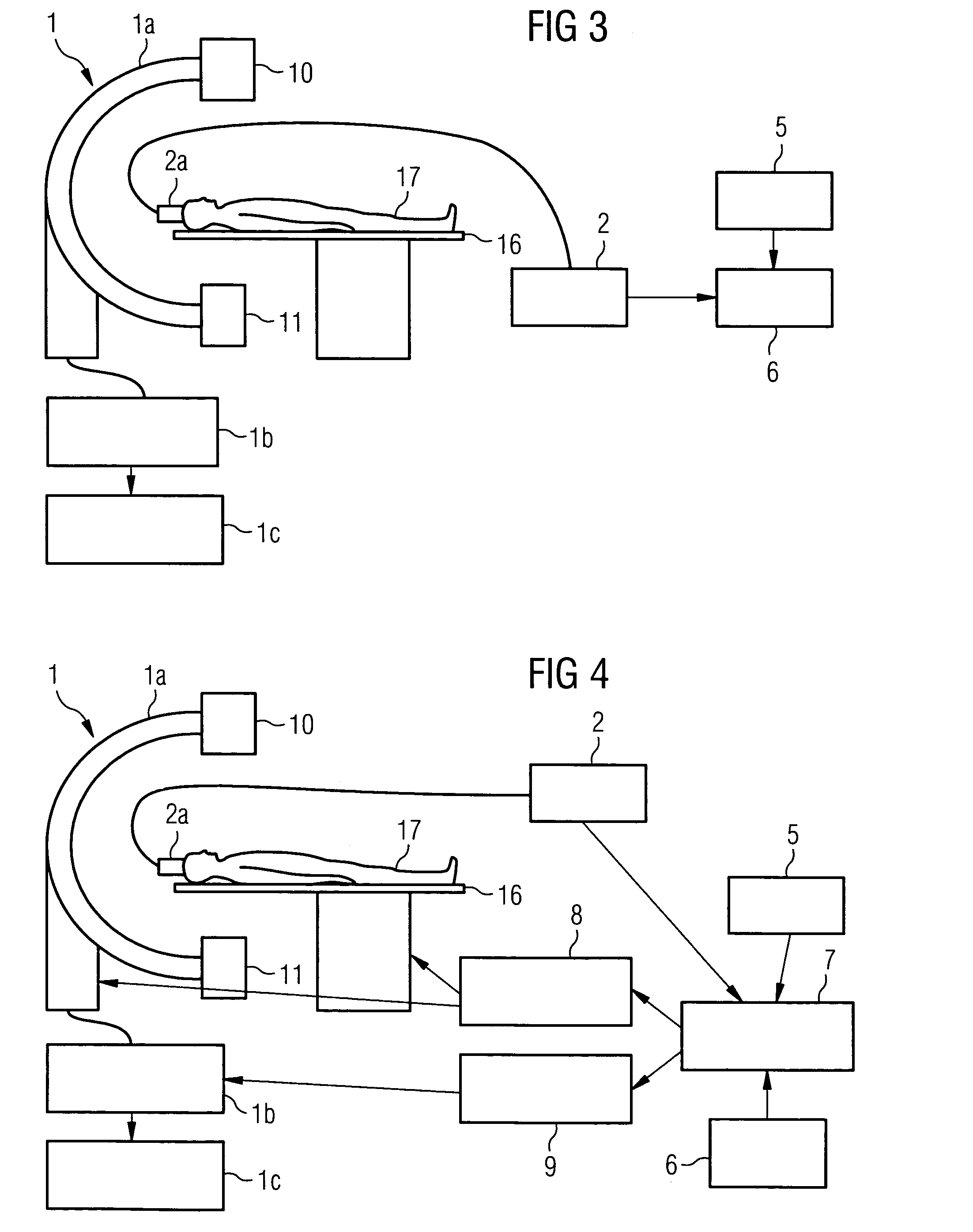
[0028]The present method is described below with reference to an X-ray angiography system for applications in neuroradiology. The method can naturally also be used in other fields in which digital subtraction angiography and / or roadmapping are employed. The present method can also be used with other medical imaging techniques involving having to record a series of images and relate them to one another.
[0029]The embodiments below are typically restricted to the case of correcting the patient's head movements. Since the head can be approximately regarded as a rigid body, the motion can be restricted to the 6 degrees of freedom of the translation and rotation of a rigid body in three-dimensional space.
[0030]An X-ray angiography system 1 for neuro-radiology, which is shown schematically in FIG. 1, is used to record the images. The X-ray angiography system 1 includes a C-arm 1a which can be rotated around two axes, to which an X-ray tube 10 and a detector 11 arranged opposite the X-ray t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com