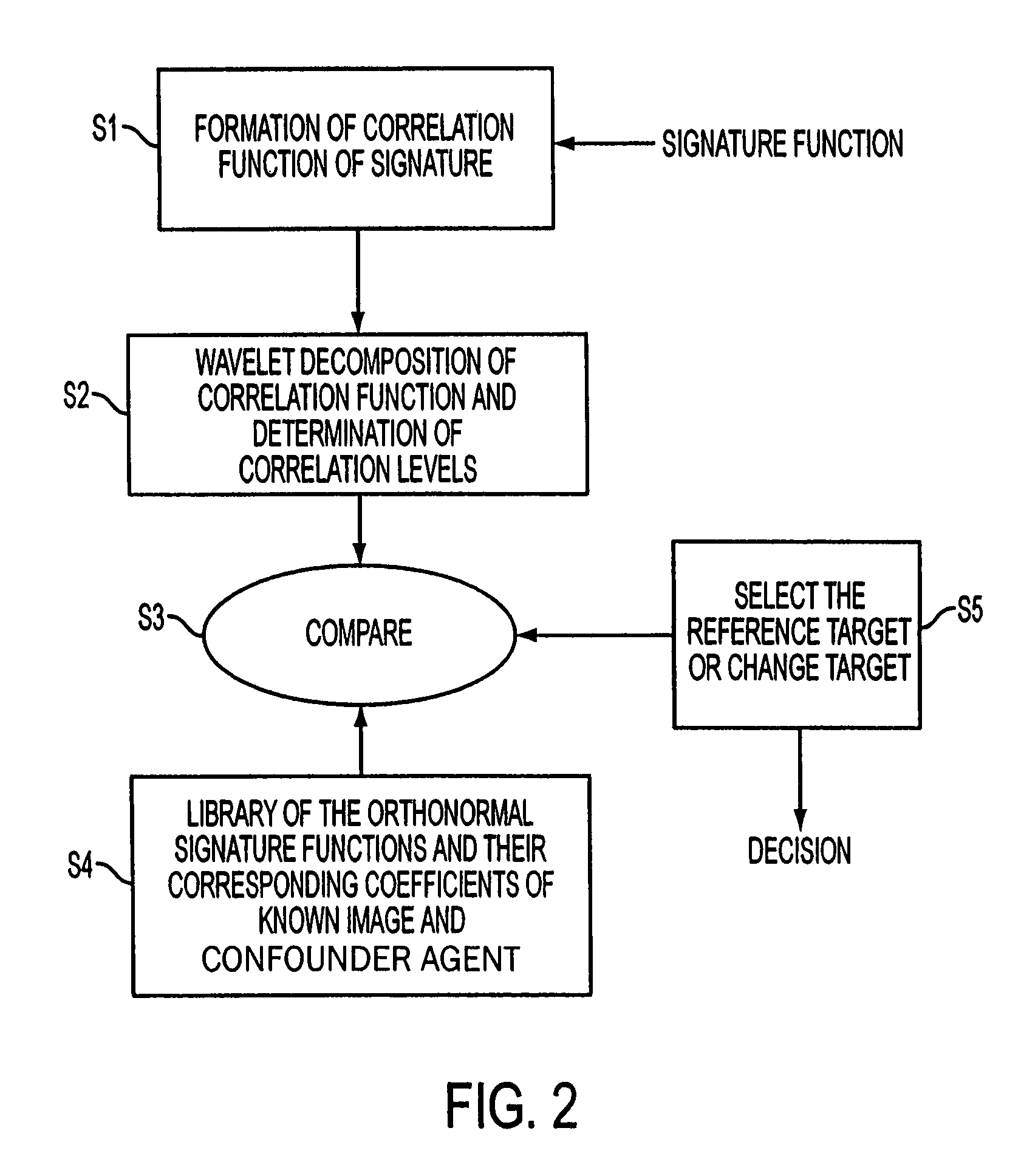
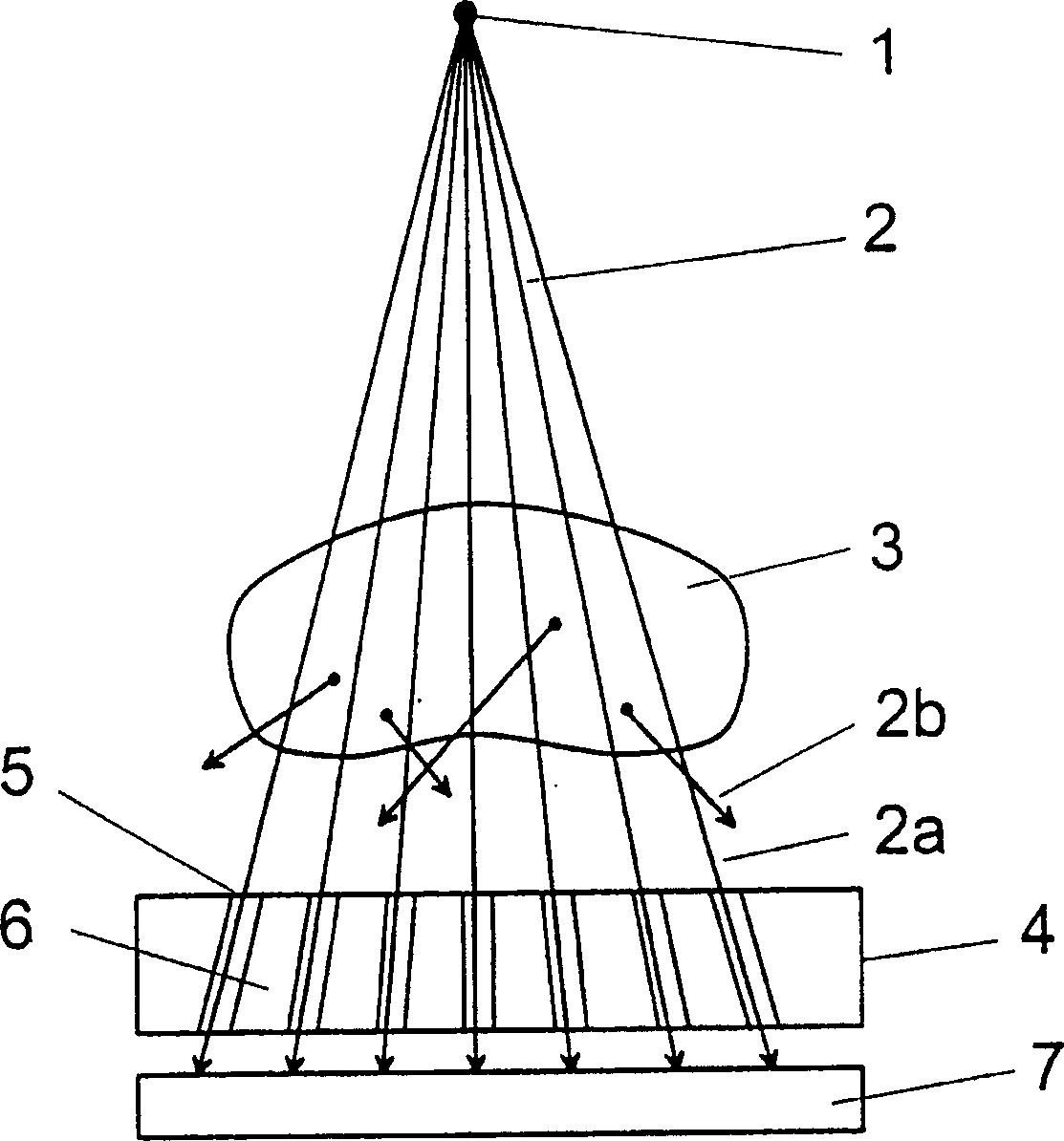
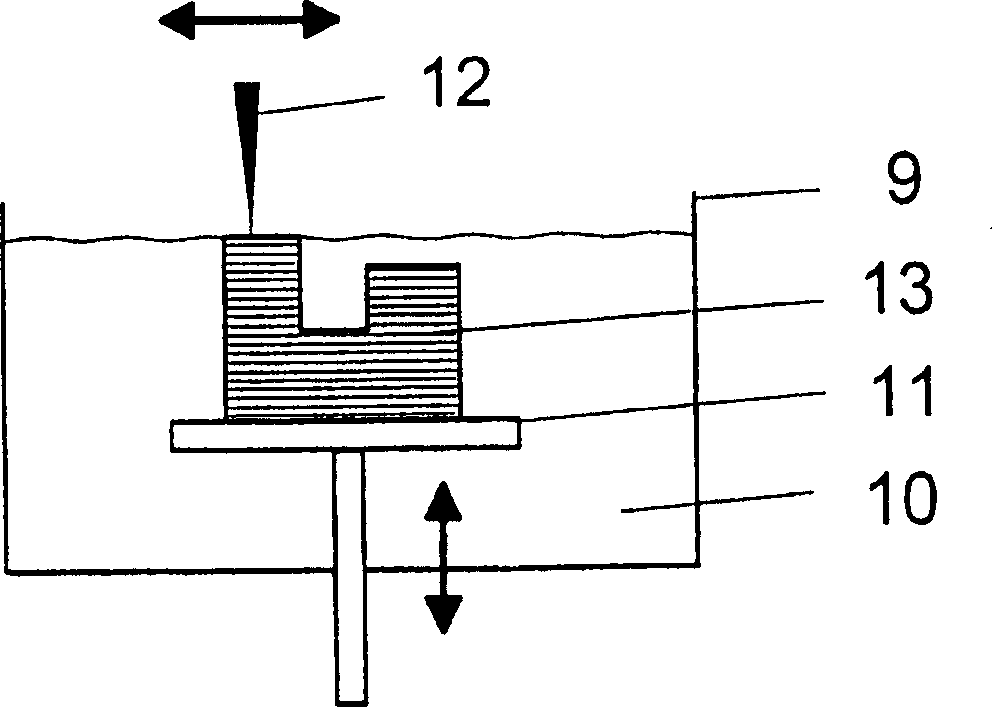
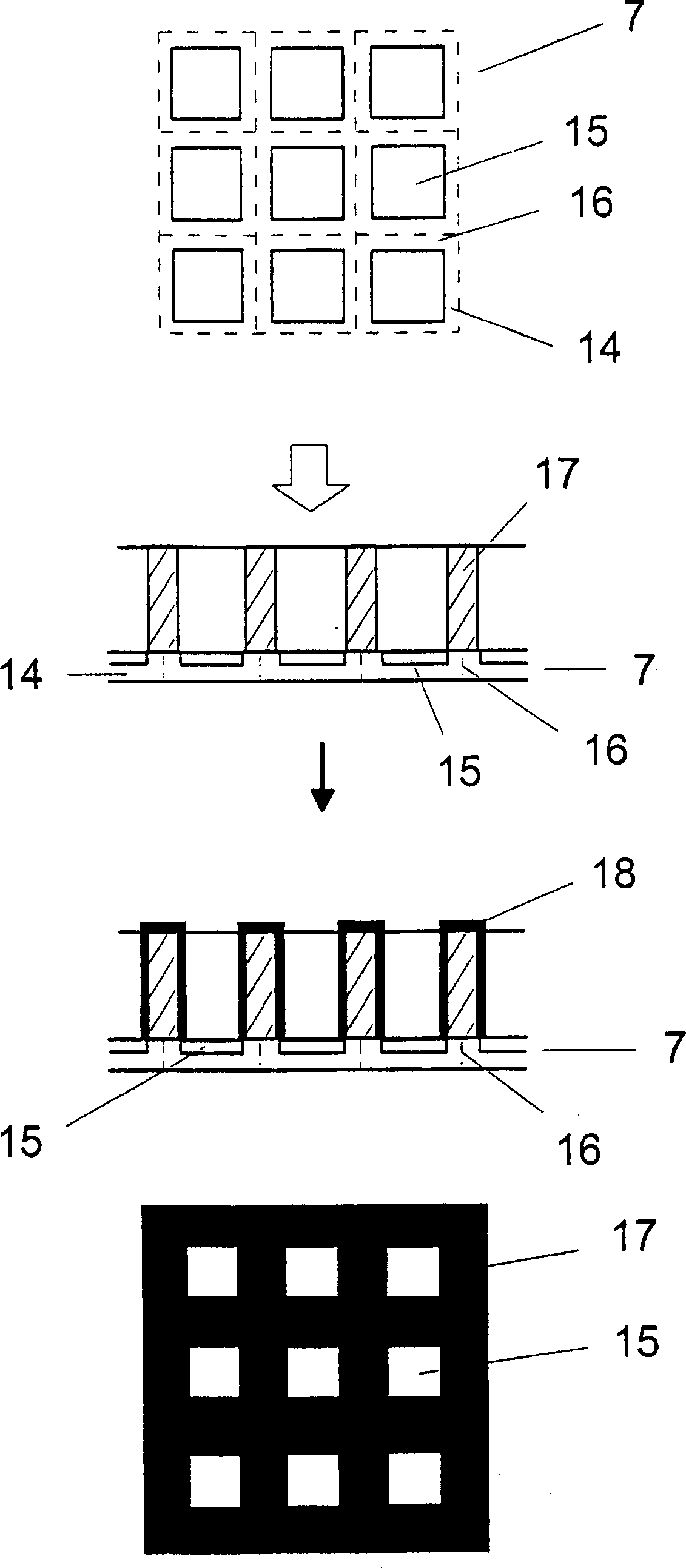
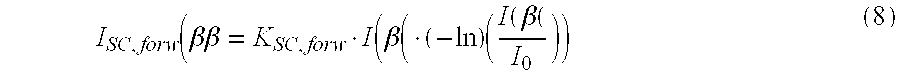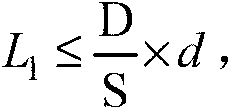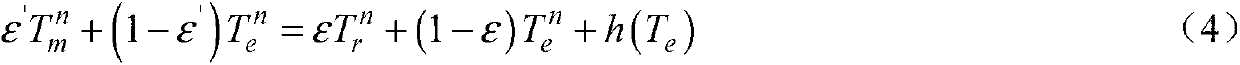Patents
Literature
167 results about "Stray radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
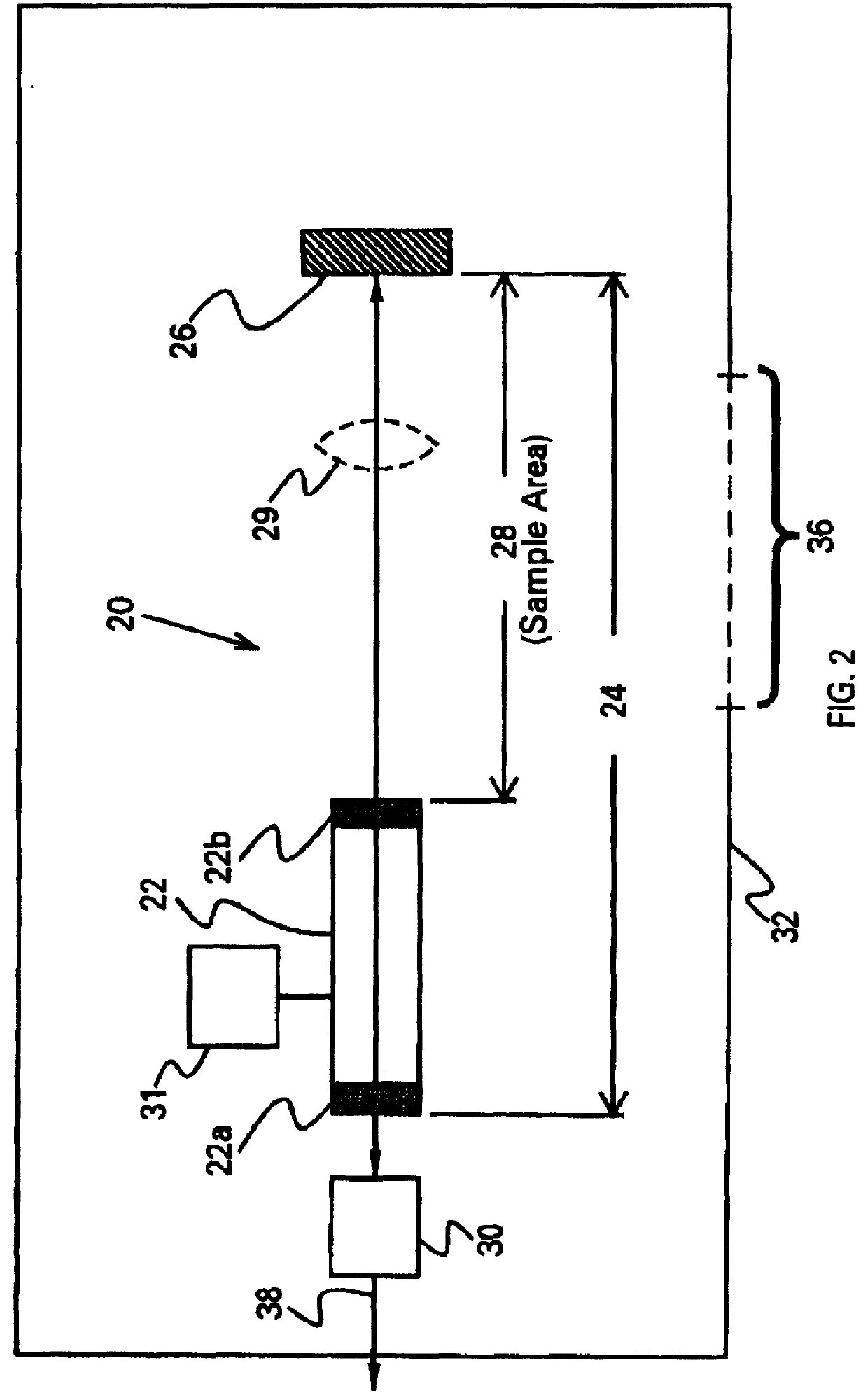
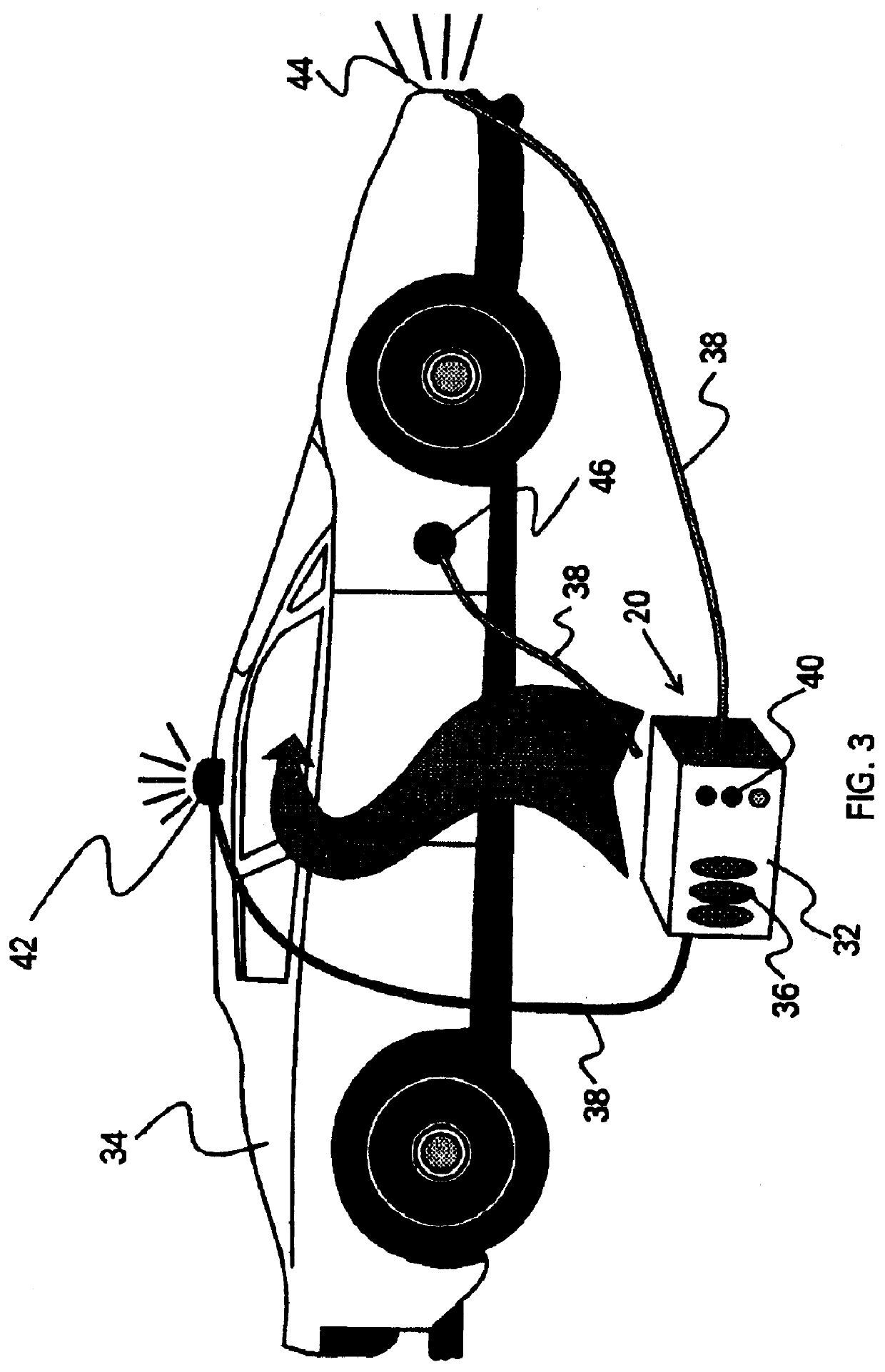
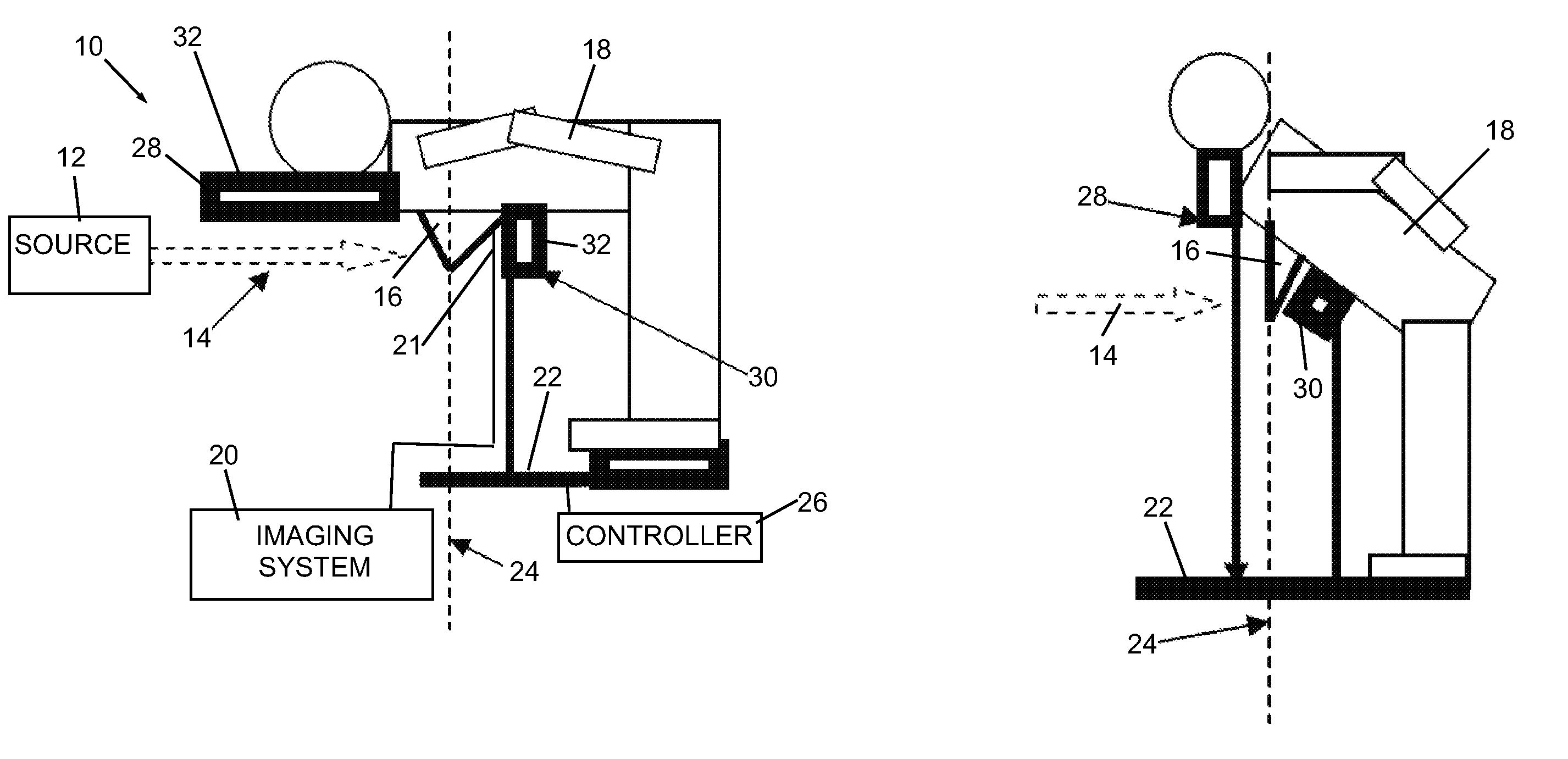
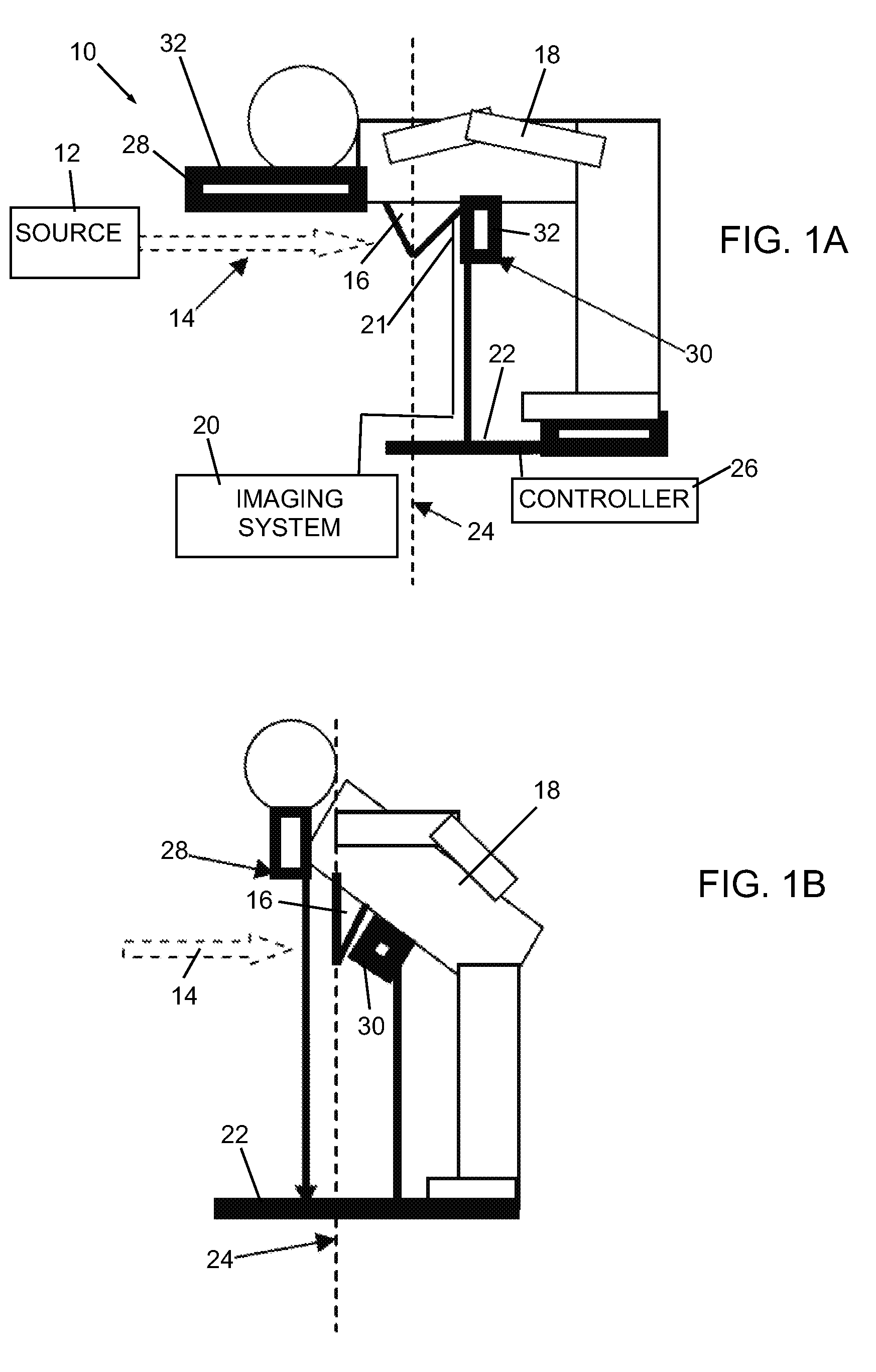
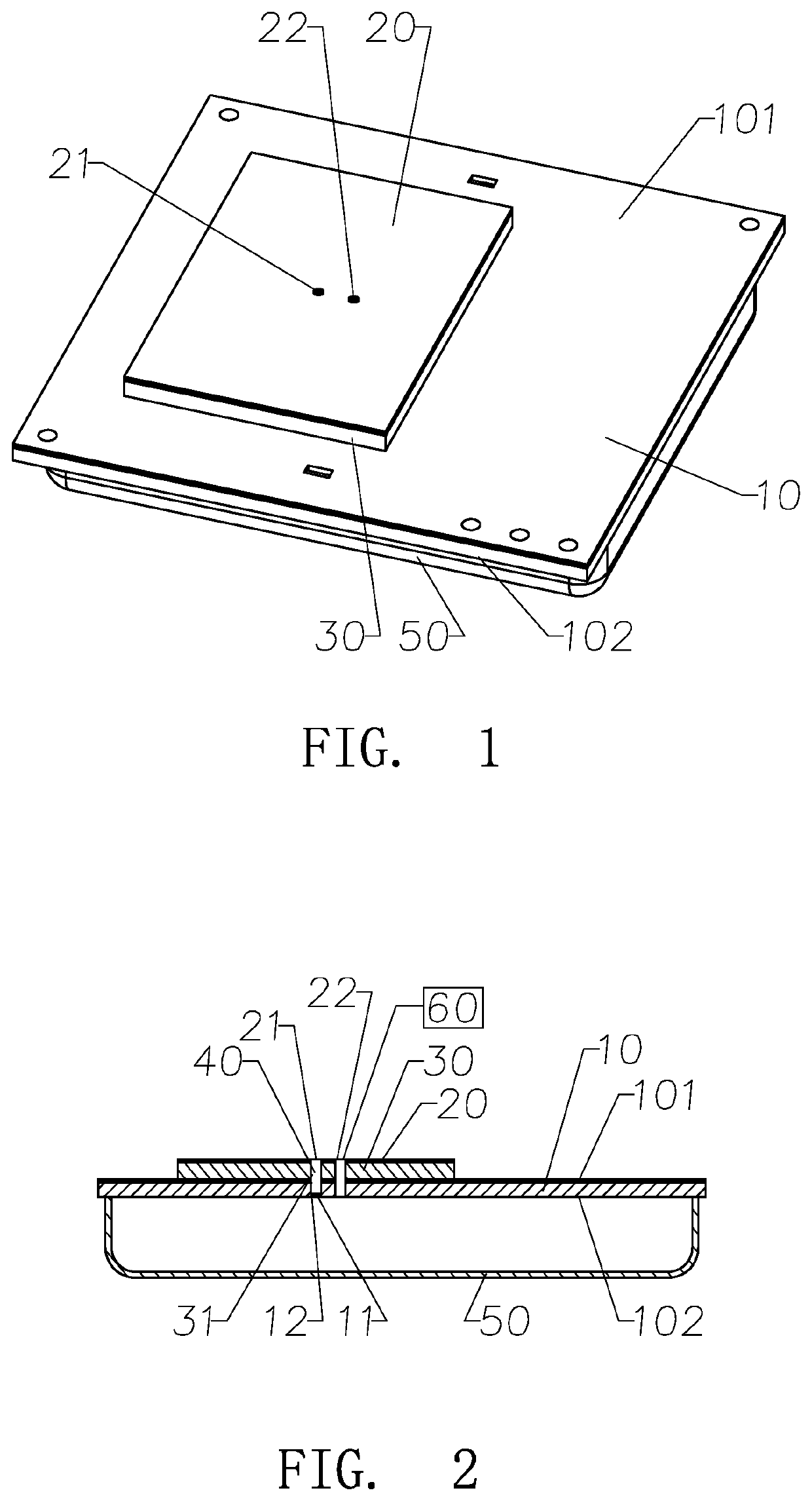
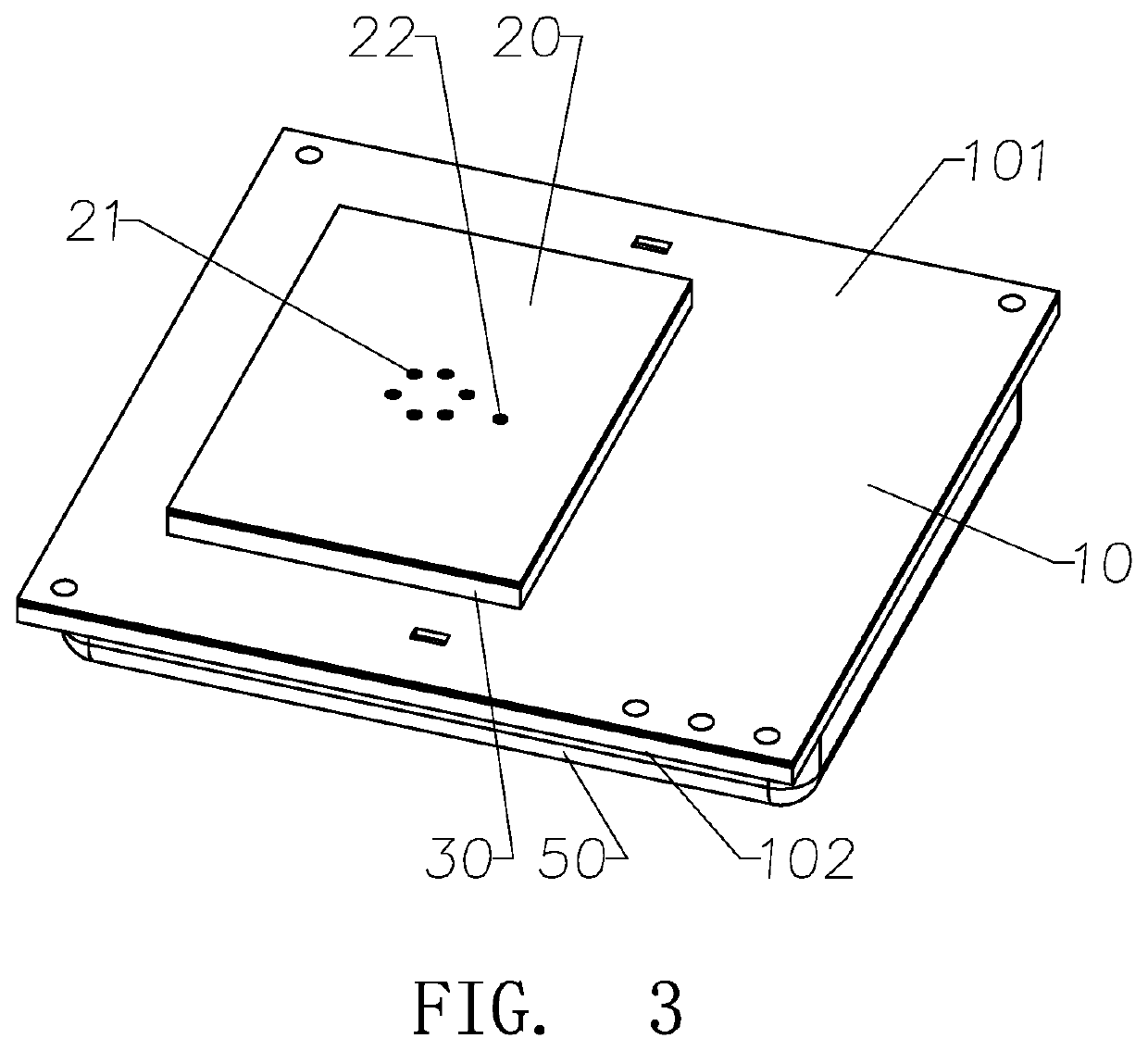
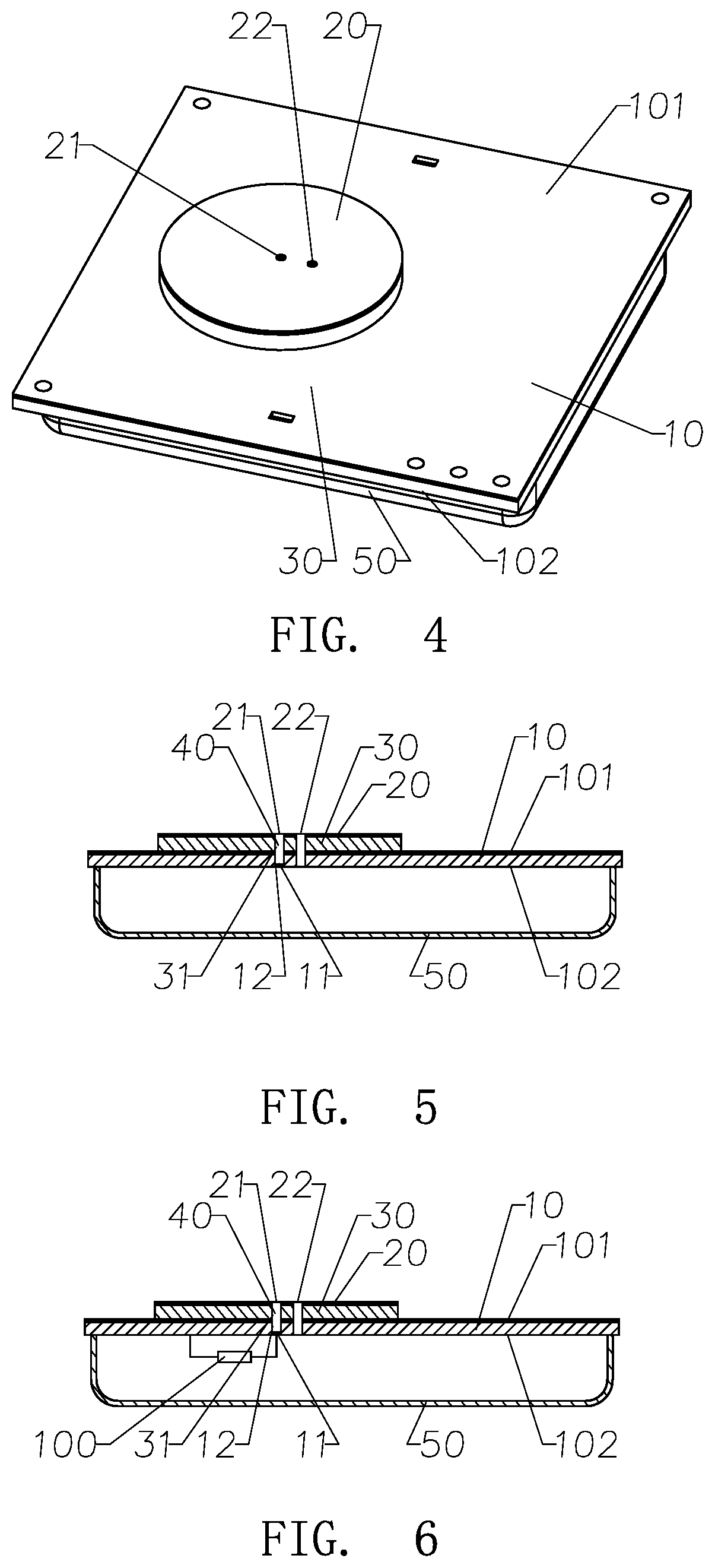
Non-contact medical thermometer with stray radiation shielding
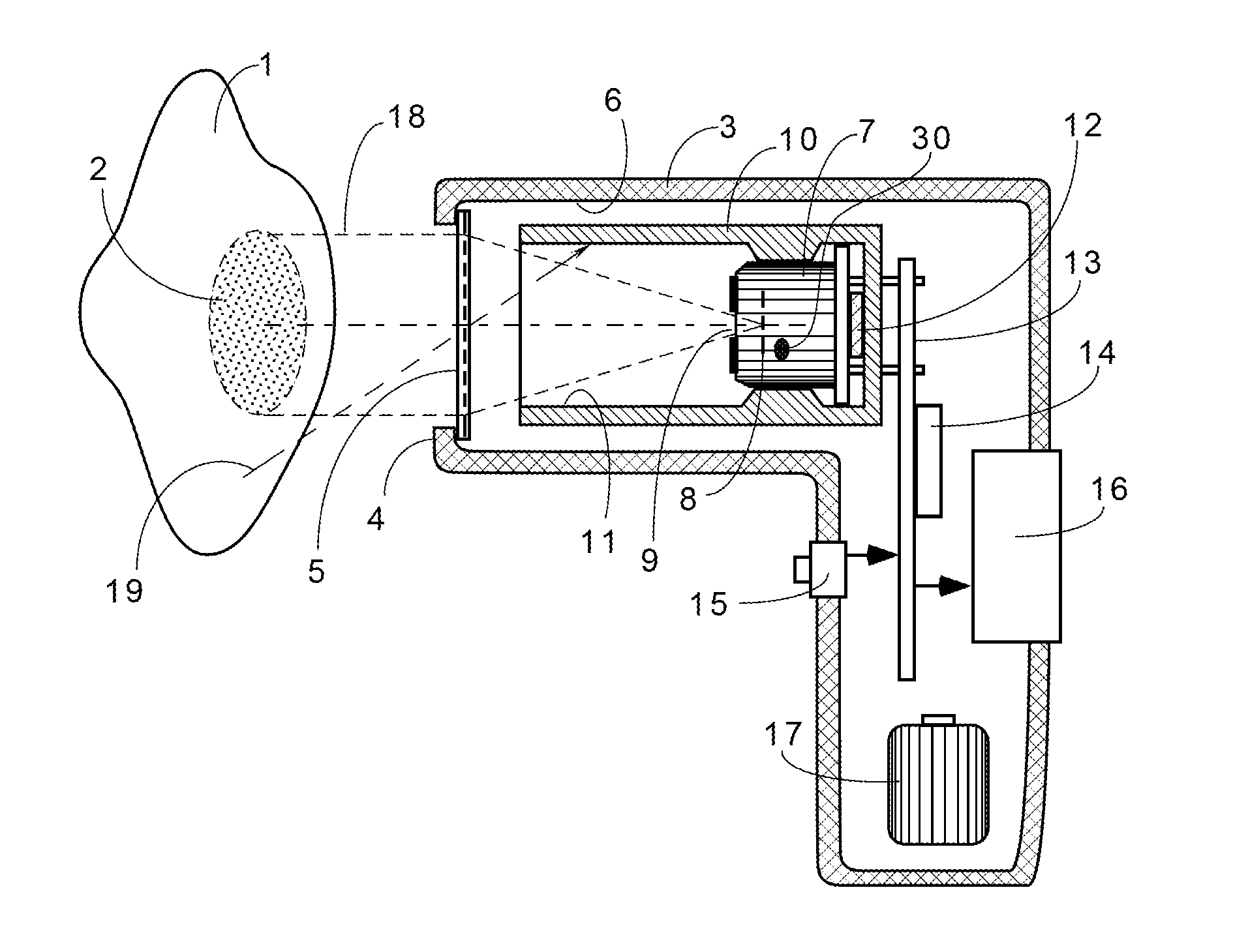
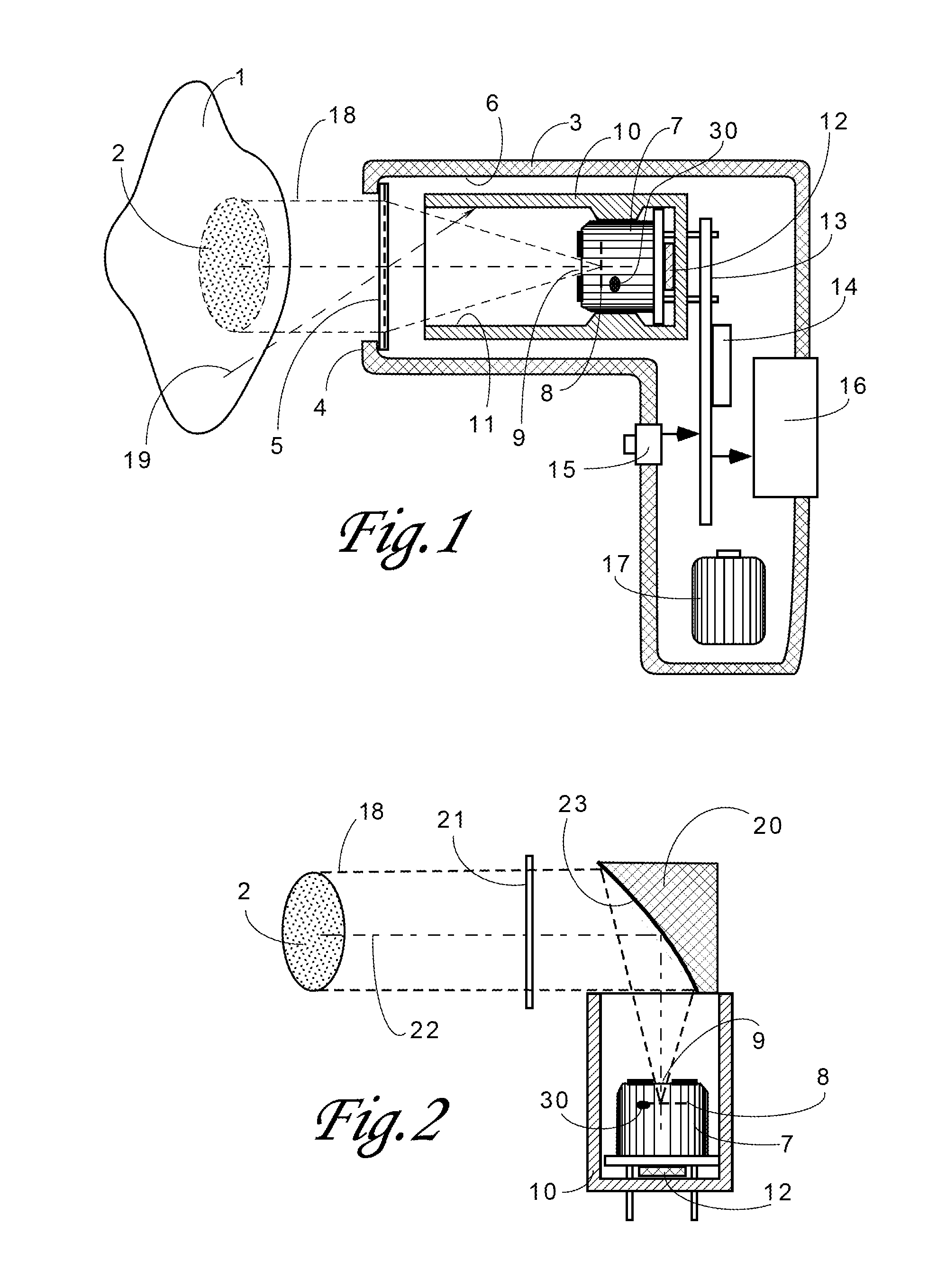
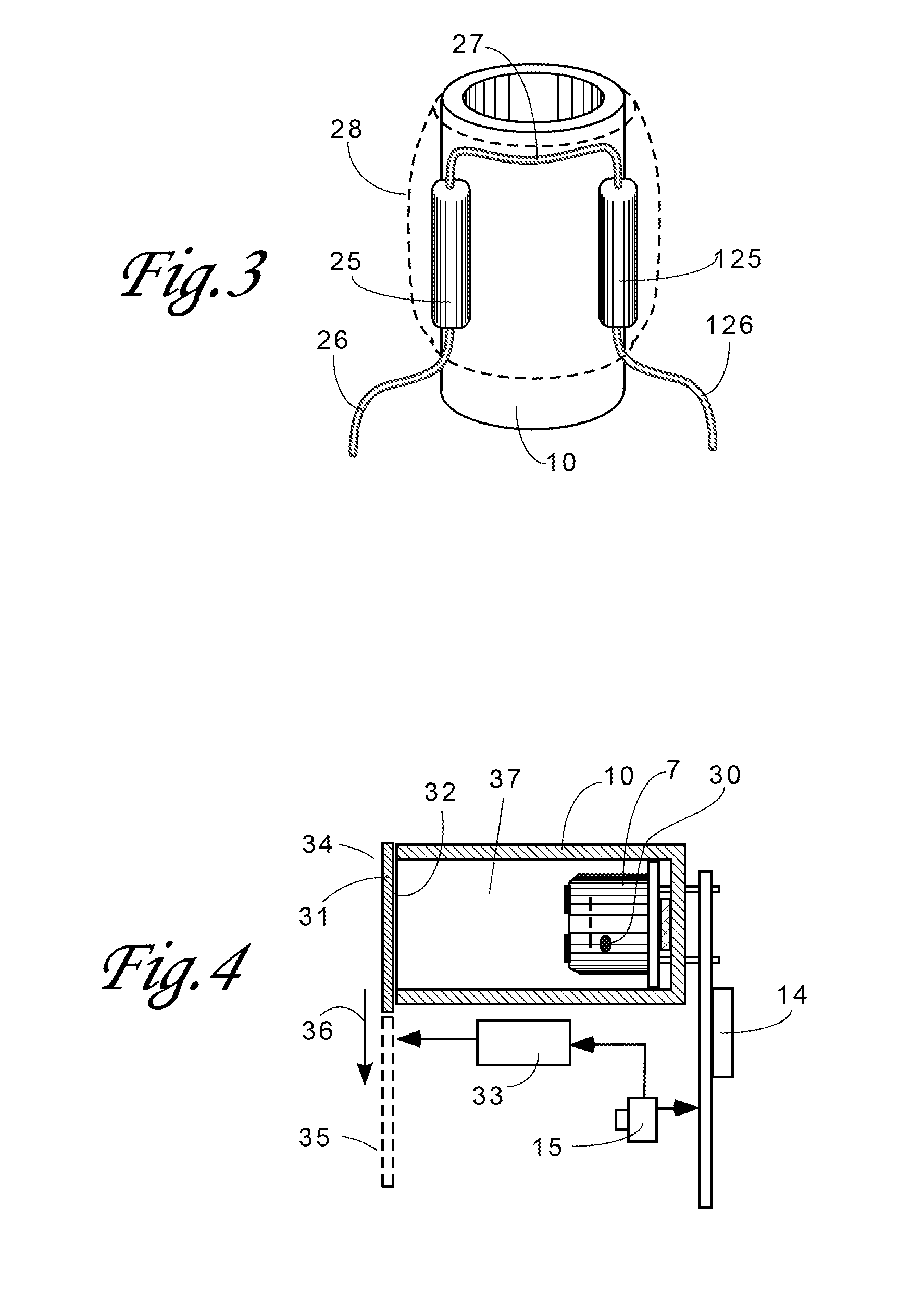
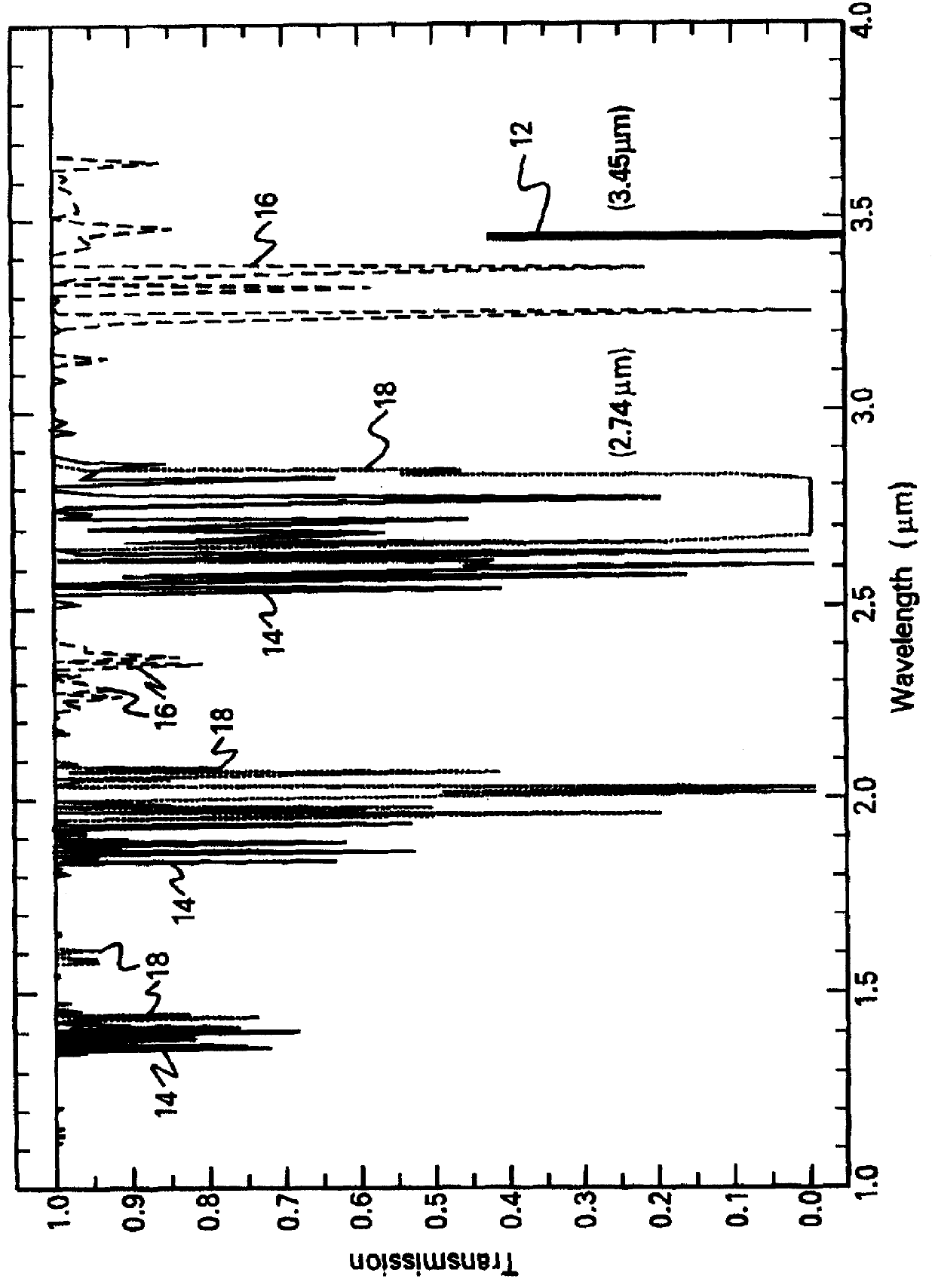
InactiveUS20110228811A1High emissivityLow heat generationRadiation pyrometryDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical thermometerEmissivity
A non-contact infrared (IR) thermometer for measuring temperature from the surface of an object includes an IR radiation sensor attached to a heating element and a thermal shield having an interior surface positioned within the sensor's field of view that has a high emissivity. An electronic circuit controlling the heating element maintains the temperatures of the sensor and shield substantially close to an anticipated surface temperature of the object. The IR radiation sensor is further thermally coupled to a reference temperature sensor. An optical system positioned in front of the shield focuses thermal radiation from the object on the surface of the sensor, while the shield prevents stray radiation from reaching the sensor. Signals from the IR and reference sensors are used to calculate the object's surface temperature.
Owner:HELEN OF TROY LIMITED
ILS sensors for drug detection within vehicles
On-board ILS sensors for detecting illegal drugs and based on intracavity laser spectroscopy (ILS) are provided for detecting the presence of drugs and their metabolized by-product vapors in an enclosed space, such as a vehicle. The sensor comprises: (a) a laser comprising a gain medium having two opposed facets within a laser resonator and functioning as an intracavity spectroscopic device having a first end and a second end, the first end operatively associated with a partially reflecting (i.e., partially transmitting) surface; (b) a reflective or dispersive optical element (e.g., a mirror or a diffraction grating) operatively associated with the second end to define a broadband wavelength laser resonator between the optical element and the first end and to thereby define an external cavity region between at least one facet of the gain medium and either the first end or the second end or both ends; (c) the external cavity region being exposed to air in the enclosed space to enable any drugs or their metabolized by-product molecules to enter thereinto; (d) a detector spaced from the first end; (e) appropriate electronics for measuring and analyzing the detector signal; (f) a housing for containing at least the laser, the partially reflecting surface, and the optical element, the housing being configured to prevent escape of stray radiation into the enclosed space and to permit air from the enclosed space to continuously circulate through the external cavity region for analysis; and (g) means for driving the laser (e.g., electrical or optical). A method is provided for measuring concentration of drug vapors and their metabolized by-product vapors in the vehicle or other enclosed space employing the on-board sensor. The method comprises: (1) sensing any drugs and their metabolized by-product vapors in the enclosed space by the on-board sensor; and (2) providing a signal indicative of presence of any drugs or metabolized vapors.
Owner:INNOVATIVE LASERS
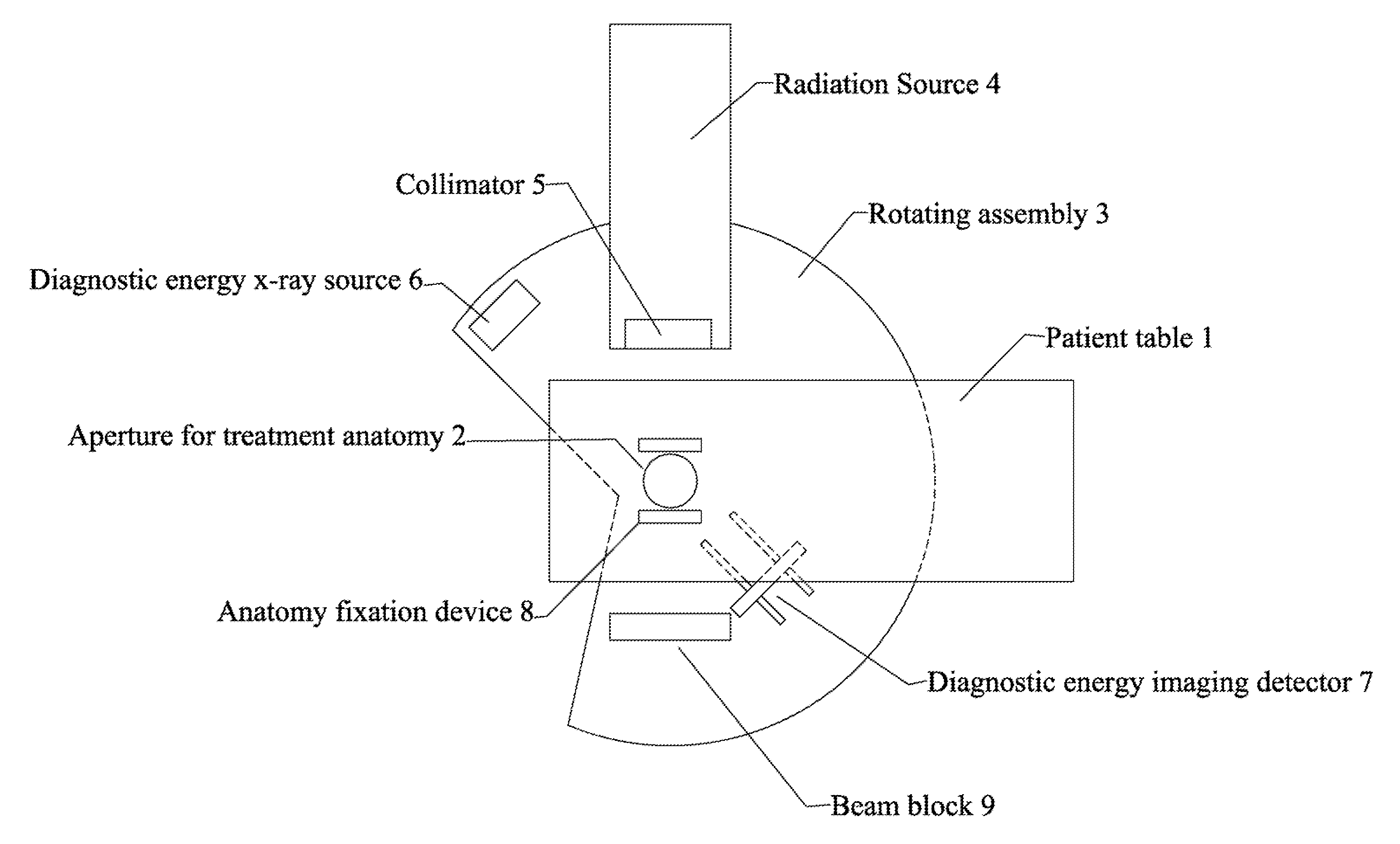
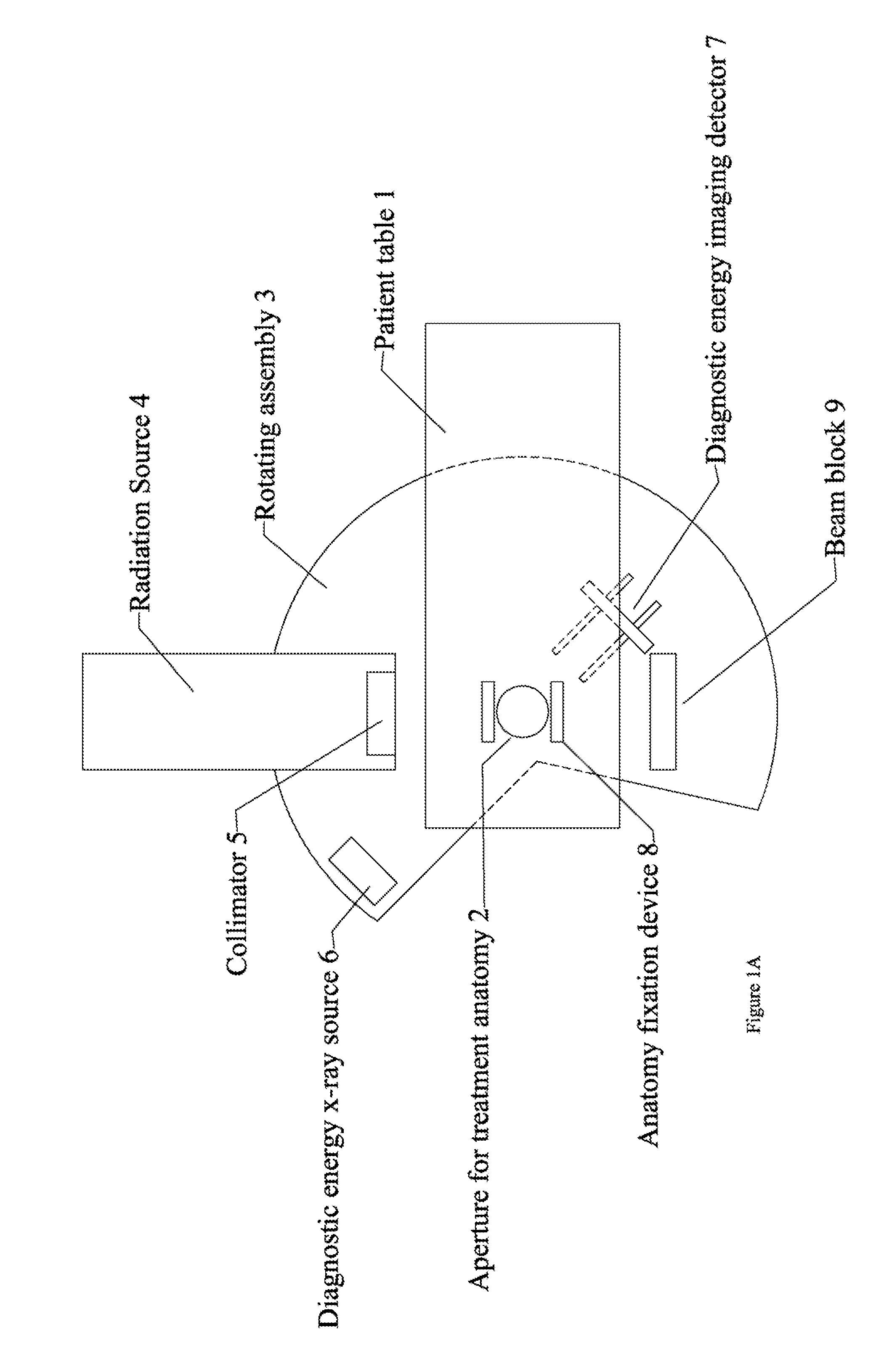
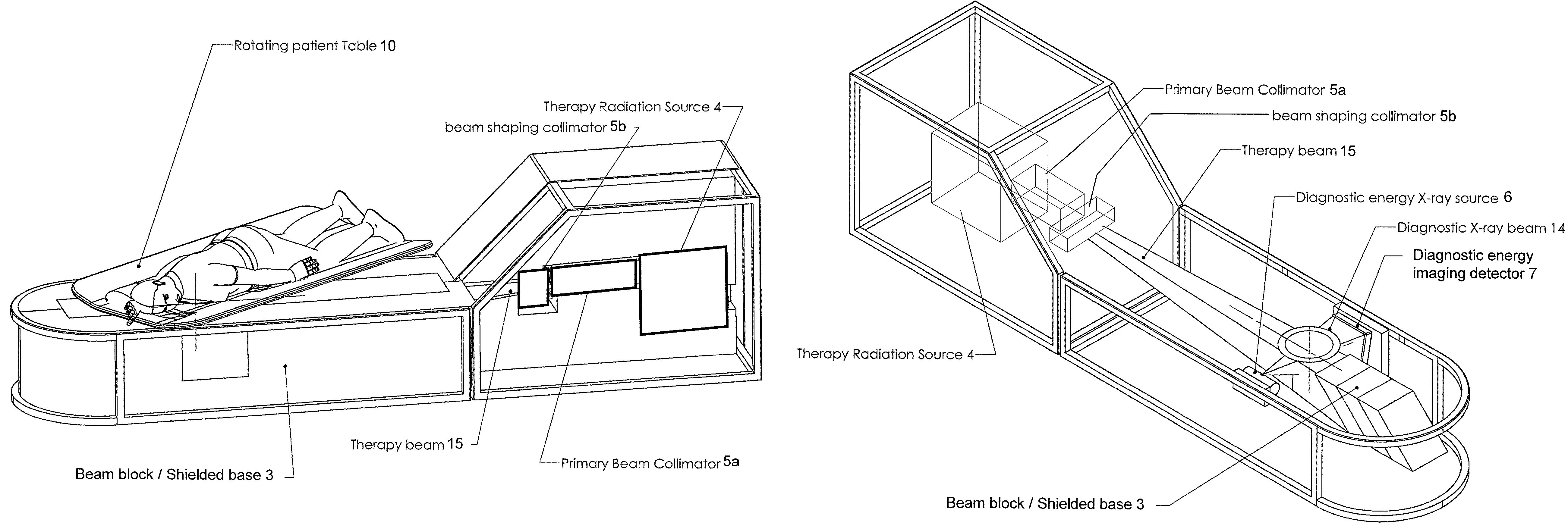
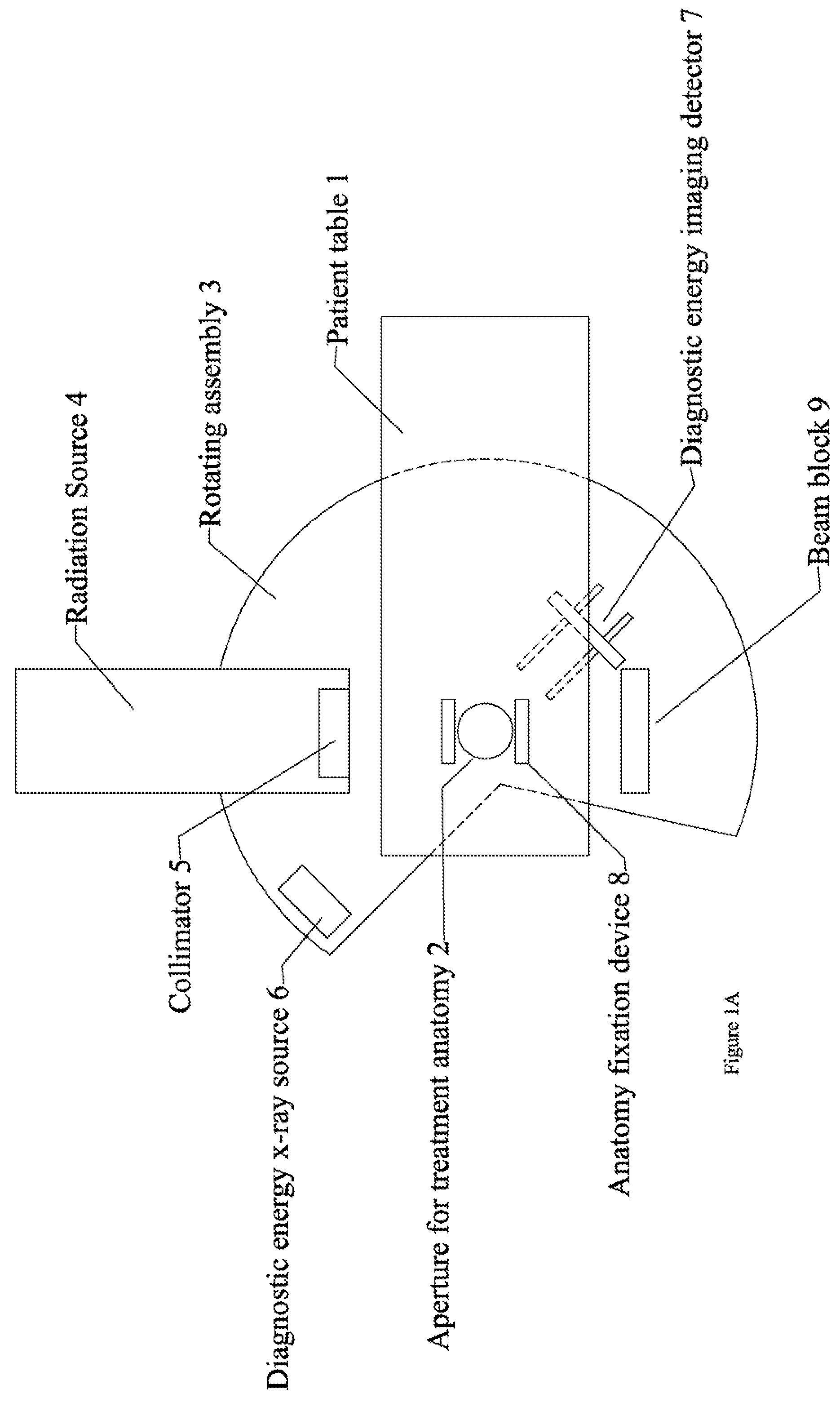
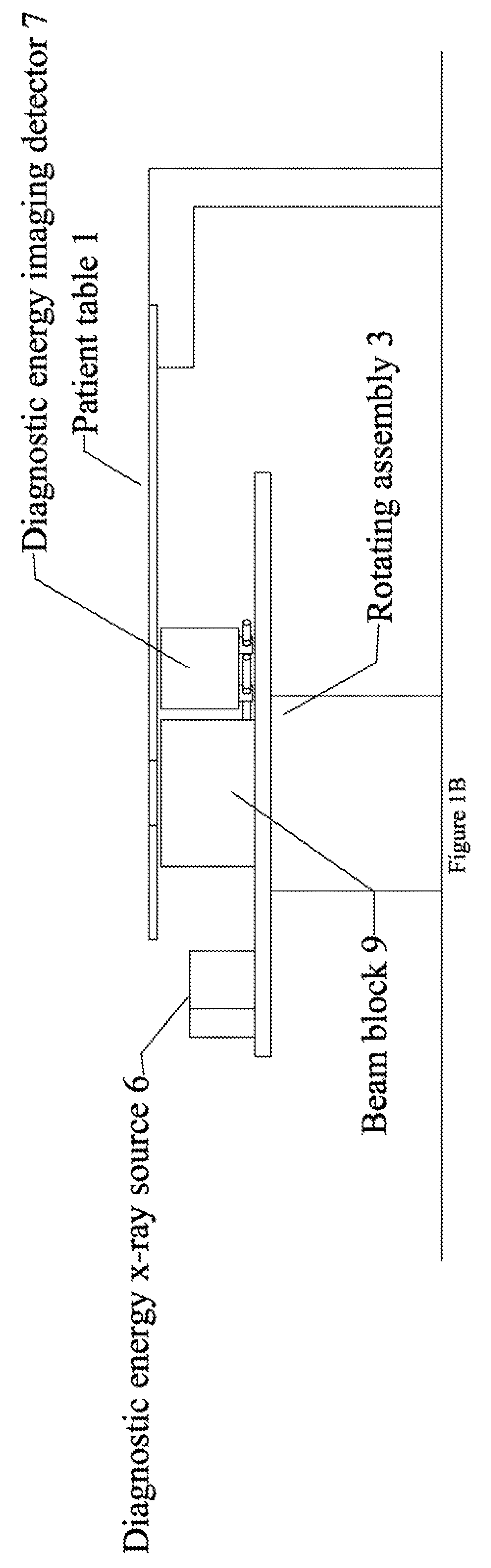
Radiation therapy system for treating breasts and extremities
InactiveUS20070211854A1Maximize separationReduce shielding requirementsPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerCritical structurePrimary disease
A radiation therapy system optimized for treating extremities such as the breast has unique geometrical features that enable the system to deliver an accurately located prescribed dose to a target volume while eliminating or reducing the collateral dose delivered to the rest of the patient. An optional integral imaging system provides accurate target volume localization for each treatment session. Utilizing the effects of gravity on a prone patient maximizes the separation of a target volume within the breast to adjacent critical structures such as the chest wall, heart and lungs, thereby reducing long term complications not associated with the primary disease. A shielded interface surface between the radiation source and the patient reduces patient dose due to scattered or stray radiation. A shielded enclosure for the radiation sources combined with the shielded interface surface eliminates the need for primary shielding in the room and allows the therapy system to be used in a transportable, mobile facility.
Owner:ORBITAL THERAPY
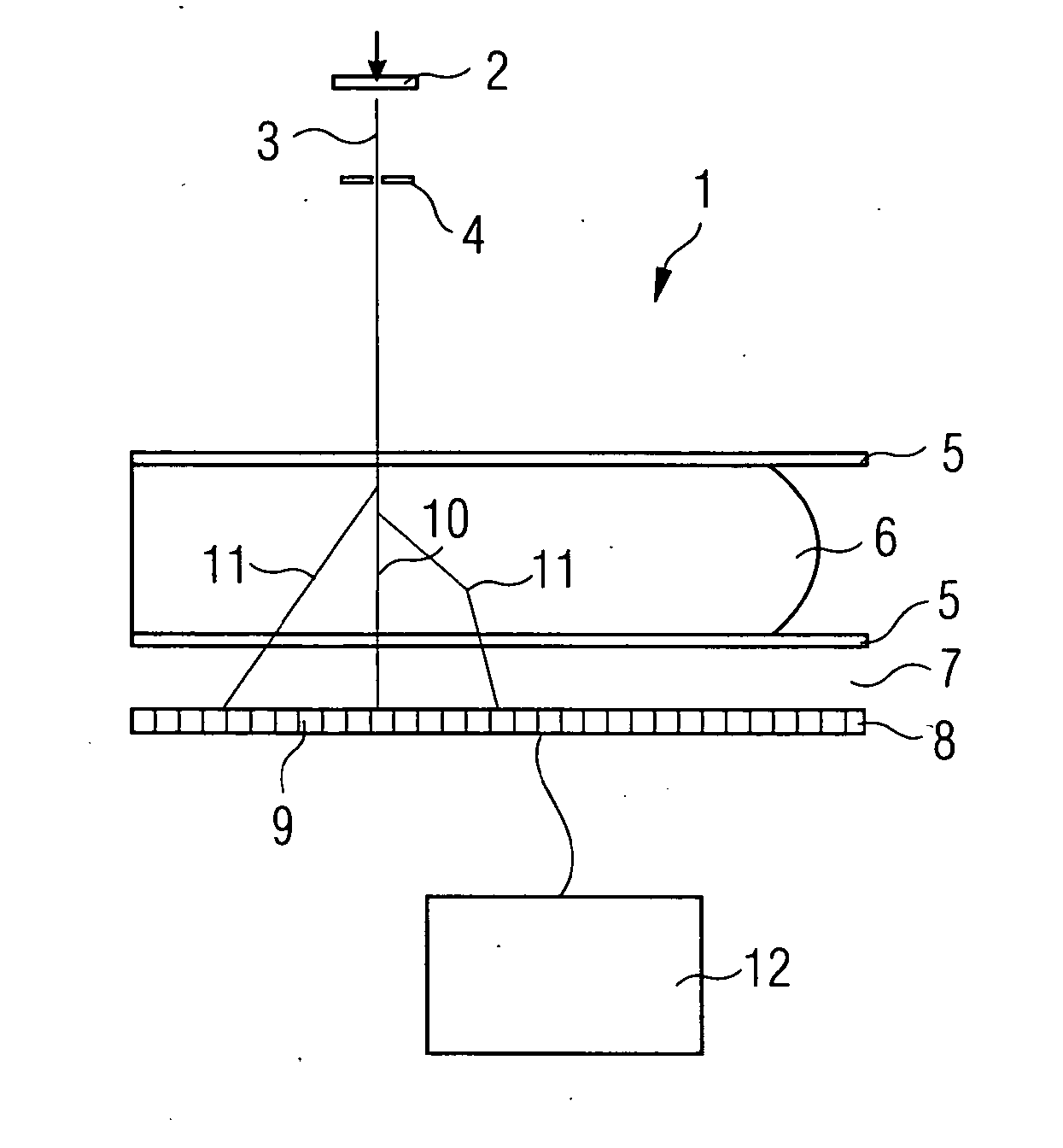
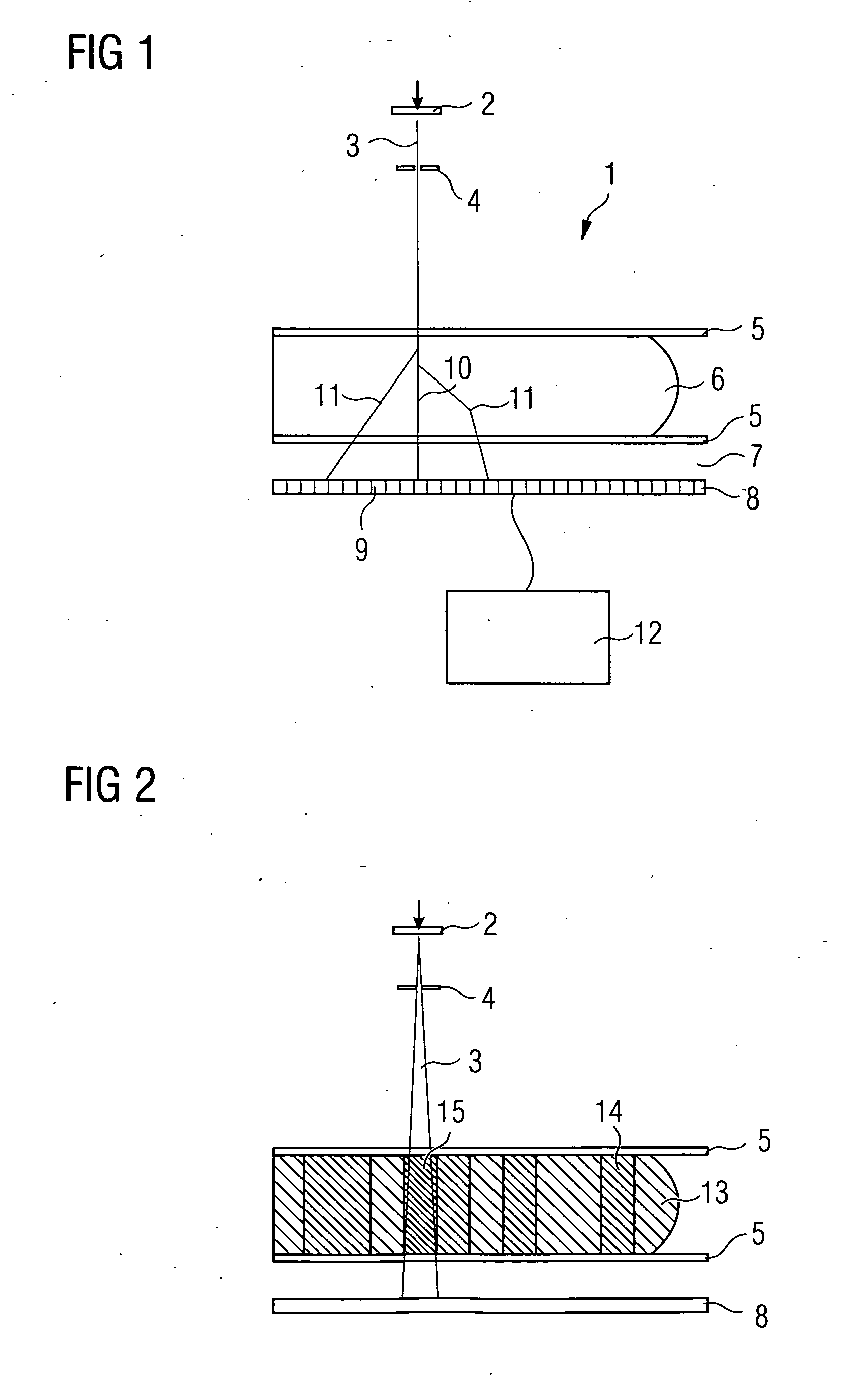
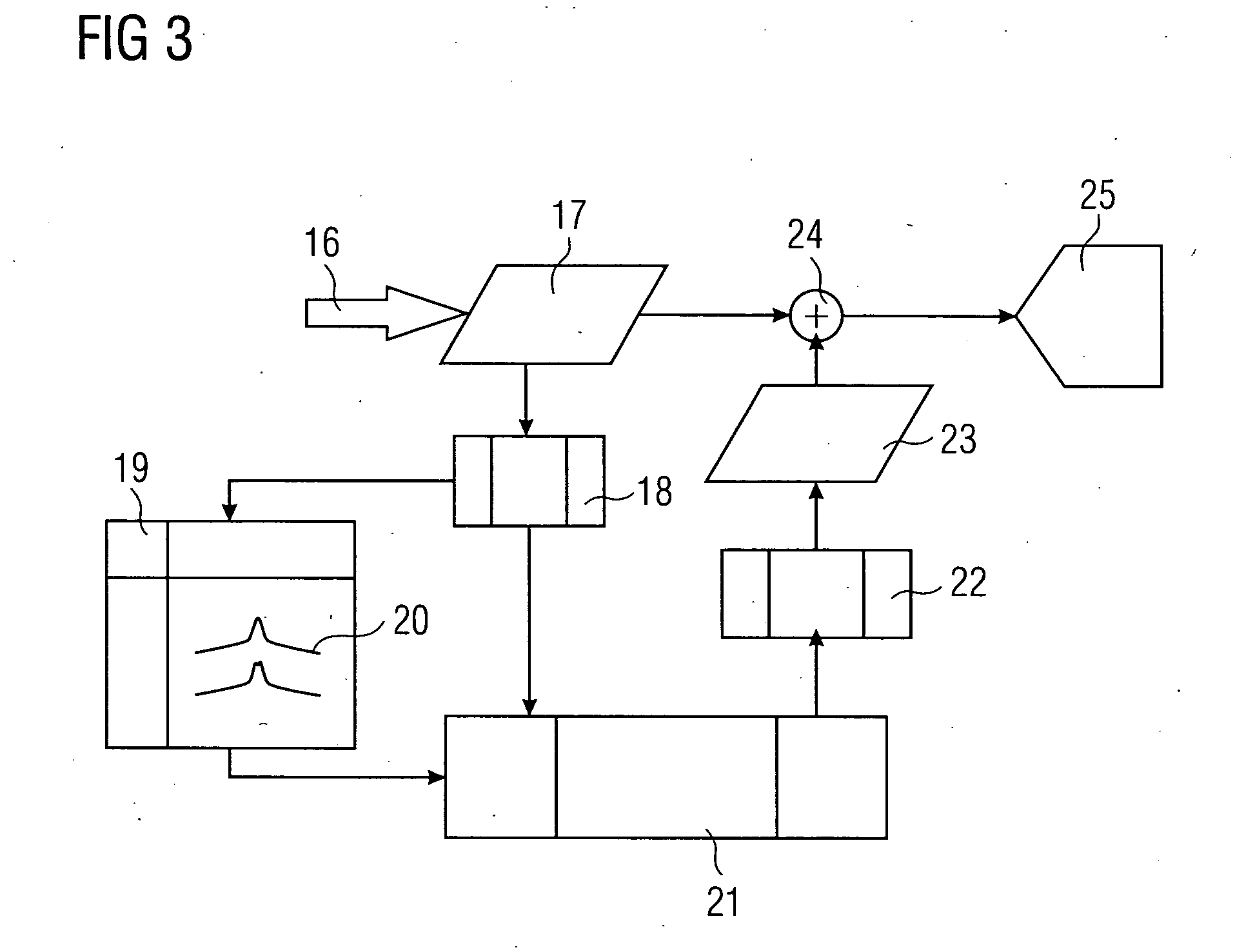
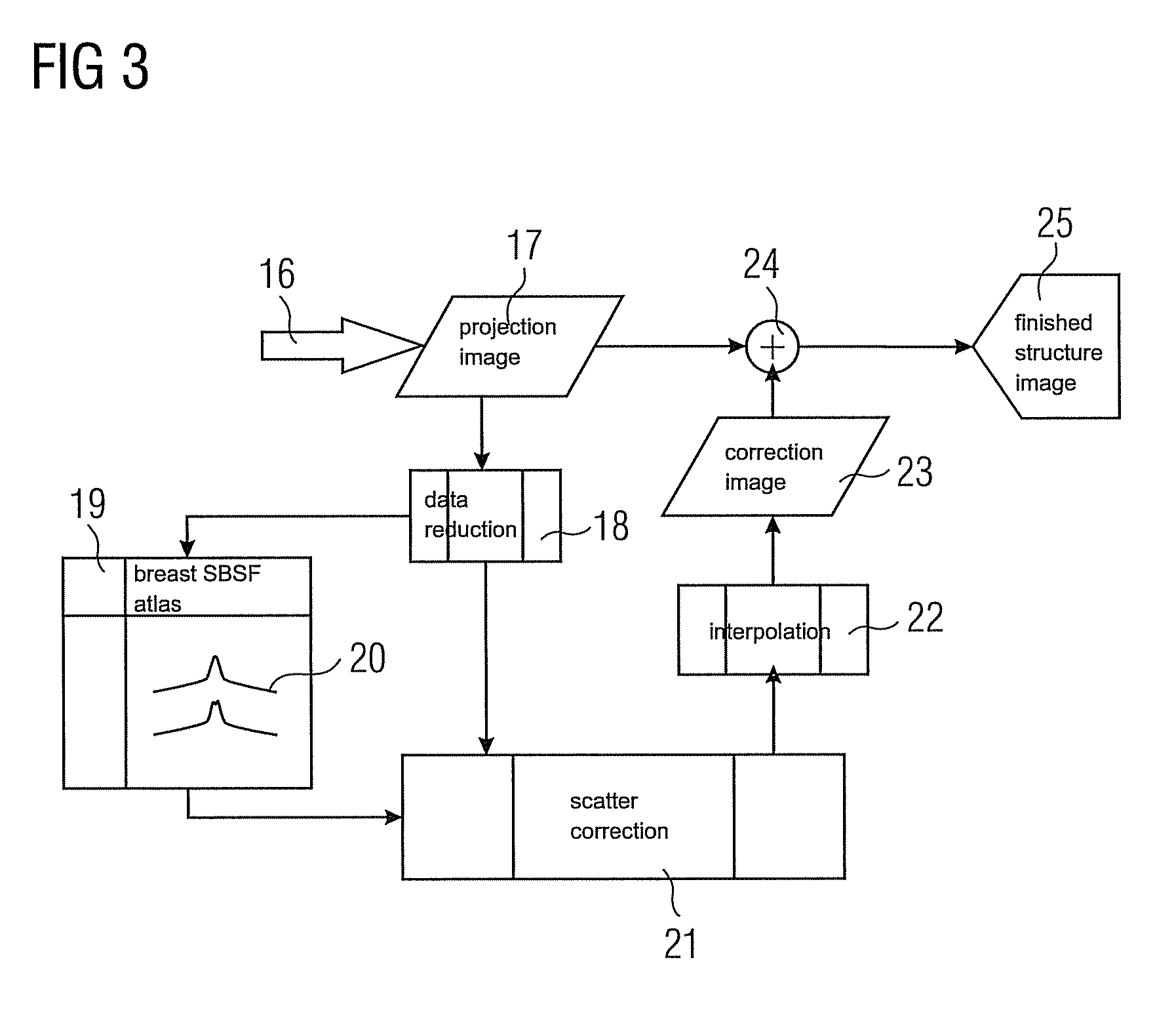
Method for correcting stray radiation in an x-ray computed tomography scanner
InactiveUS6925140B2Sure easyEasy to getImage enhancementImage analysisRecursion methodX ray computed
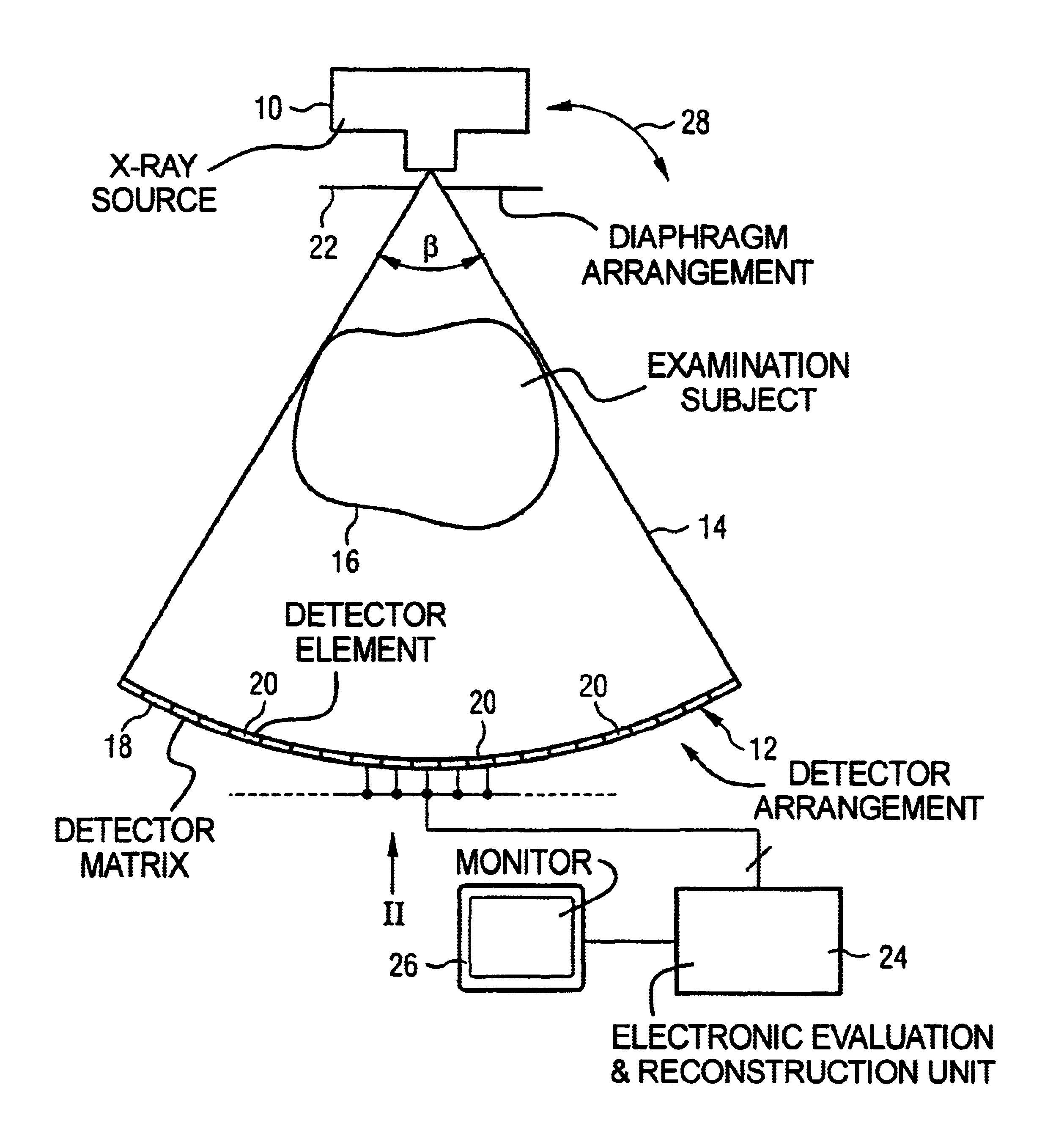
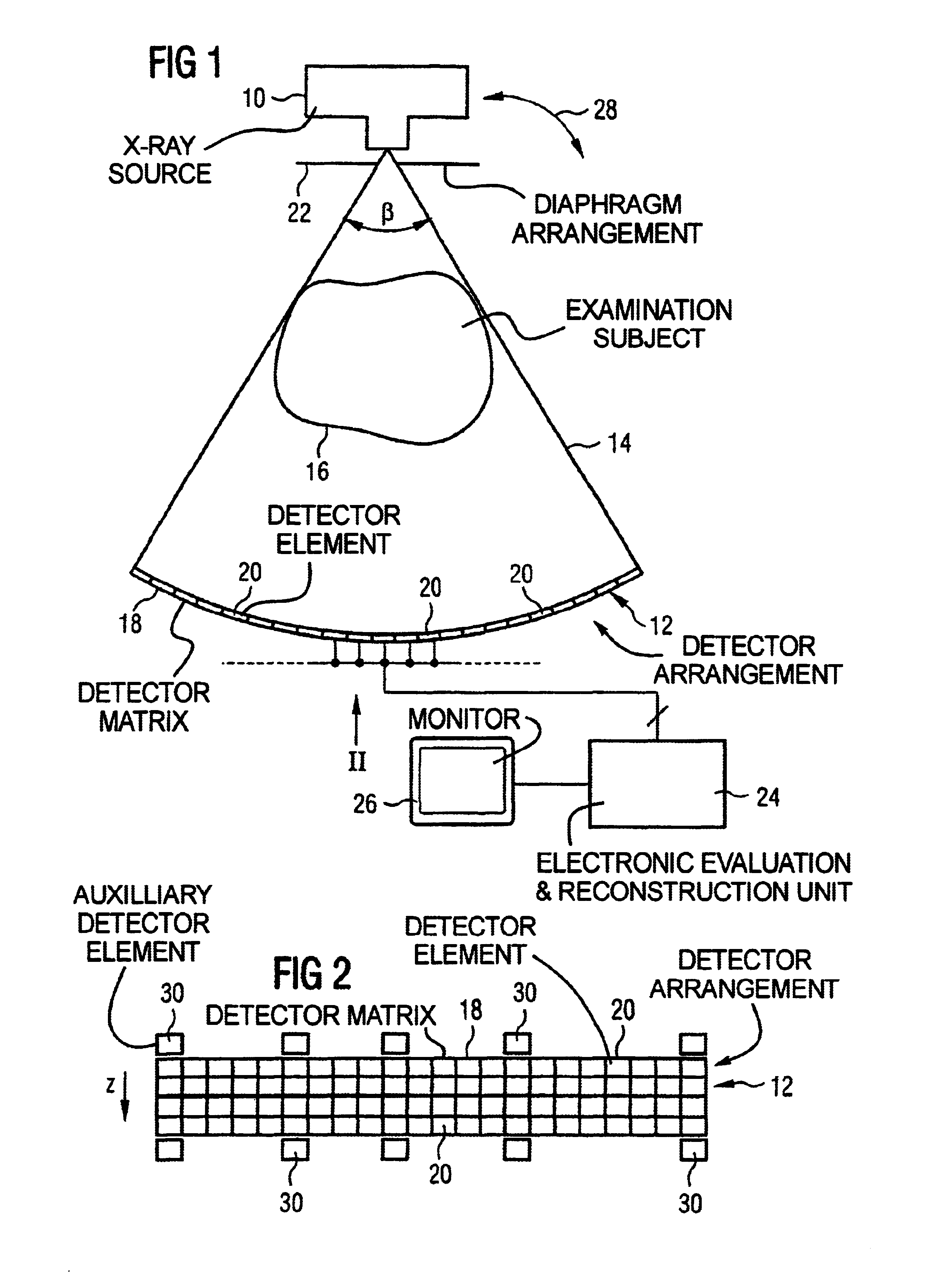
In a method for correcting for stray radiation in measured intensity values, the measured intensity values are obtained in an X-ray computed tomography scanner by means of a detector matrix that is situated in a tomography measuring field of the computer tomography scanner and has a multiplicity of detector elements arranged next to one another in a number of adjacent detector rows. At least one reference distribution of the stray radiation intensity is determined in the row direction of the detector matrix, and a stray radiation component of each measured value of intensity is determined starting from this at least one reference distribution, and the measured intensity values are corrected as a function of their respective stray radiation component. In this case, the stray radiation component of the measured values of intensity of at least a fraction of the detector rows is determined by using a recursion method on the basis of the reference distribution.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
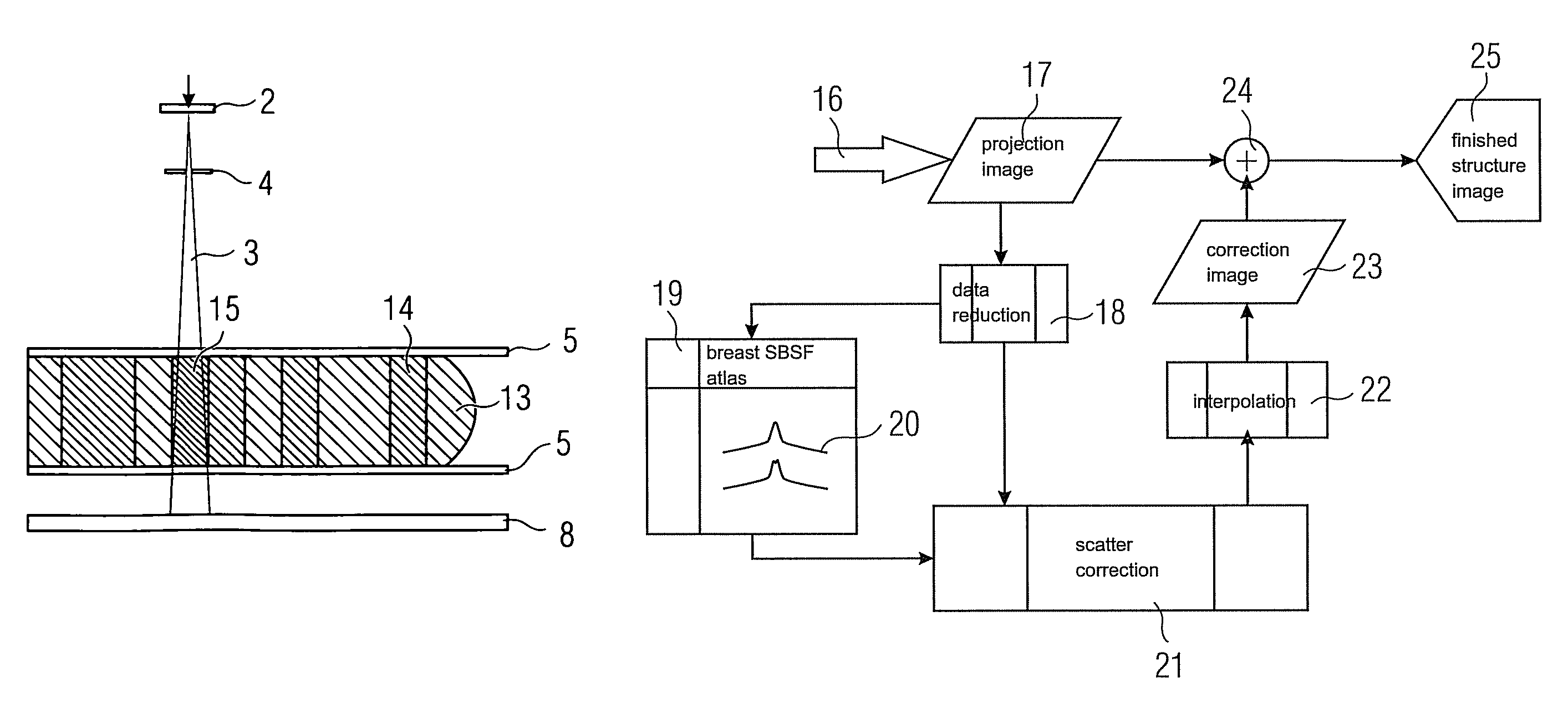
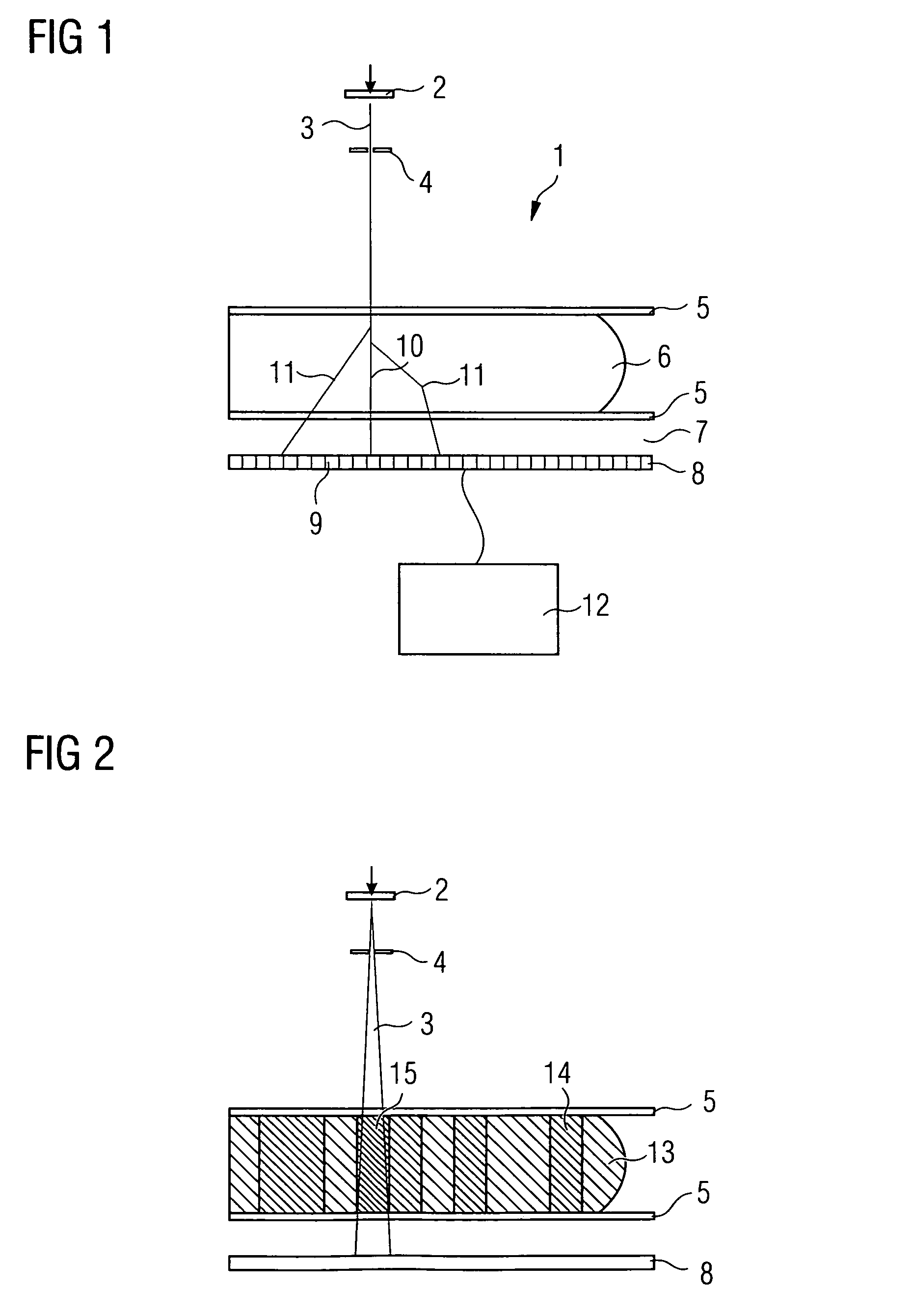
Apparatus and Method for Scatter Correction in Projection Radiography
ActiveUS20080013673A1Reduce computational complexityImprove modeling accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData memoryArtificial intelligence
An apparatus for projection radiography is set up for correcting stray radiation. The apparatus comprises an evaluation unit which evaluates the distribution of stray radiation, which is arranged in a tabular manner in a data memory, for correcting stray radiation, said distribution being initially determined with the aid of Monte-Carlo-Simulation which takes into account multiple interactions of the photons with the object which is to be analyzed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Radiation therapy system for treating breasts and extremities
InactiveUS7526066B2Maximize separationWeaken energyPatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerAnatomical structuresCritical structure
Owner:ORBITAL THERAPY
Apparatus and method for scatter correction in projection radiography
An apparatus for projection radiography is set up for correcting stray radiation. The apparatus comprises an evaluation unit which evaluates the distribution of stray radiation, which is arranged in a tabular manner in a data memory, for correcting stray radiation, said distribution being initially determined with the aid of Monte-Carlo-Simulation which takes into account multiple interactions of the photons with the object which is to be analyzed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Material emissivity measuring method based on infrared thermometer
ActiveCN103091252AHigh precisionEasy to useRadiation pyrometryAnalysis by thermal excitationEmissivityThermodynamics
The invention discloses a material emissivity measuring method based on an infrared thermometer and belongs to the technical field of thermal performance measurement of high-temperature opaque materials. The method disclosed by the invention aims to solve the problems that conventional material emissivity measuring methods are poor in measuring result accuracy, complex in use and low in measuring speed. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of firstly measuring the temperature of a blackbody furnace by using an infrared thermometer, obtaining the stray radiation energy received by the infrared thermometer through calculating, measuring the surface temperature of a test piece made from the to-be-measured material by using a thermocouple thermodetector and obtaining the true surface temperature of the test piece. According to the invention, five measuring temperature values are obtained through measuring the surface temperature of the test piece under the condition of five set emissivities of the infrared thermometer; five material emissivities are obtained through bringing the five set emissivities and the five measuring temperature values into a calculating formula; and the emissivity of the to-be-measured material is obtained through taking the average. The method disclosed by the invention is mainly applied to the technical field of emissivity measurement of the high-temperature opaque materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Far infrared photoconductor array
InactiveUS7180077B1Reduce signalingProvide goodSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityElectrical conductor
Fabrication of far infrared photoconductor arrays, especially for low background astronomy, is particularly challenging due to arrays' relatively large pixel size, susceptibility to stray radiation, and the requirement for low bias levels. A hybrid-far infrared photoconductor array as presented, provides a system and method for the development of large-format far IR arrays. The hybrid-far infrared array is provided with a blocking layer, situated in between a detecting layer and a readout layer, which allows detection of far infrared signals without complications based on readout glow. In particular, the readout glow, detector heating, and thermal mismatch between the readout and the detecting layer are addressed by careful selection of the materials for the blocking layer. The blocking layer is provided with an array of conductive vias passing through the bulk of the blocking layer in order to efficiently transmit electrical signals between the detecting layer and the readout layer.
Owner:TECHNO SCI
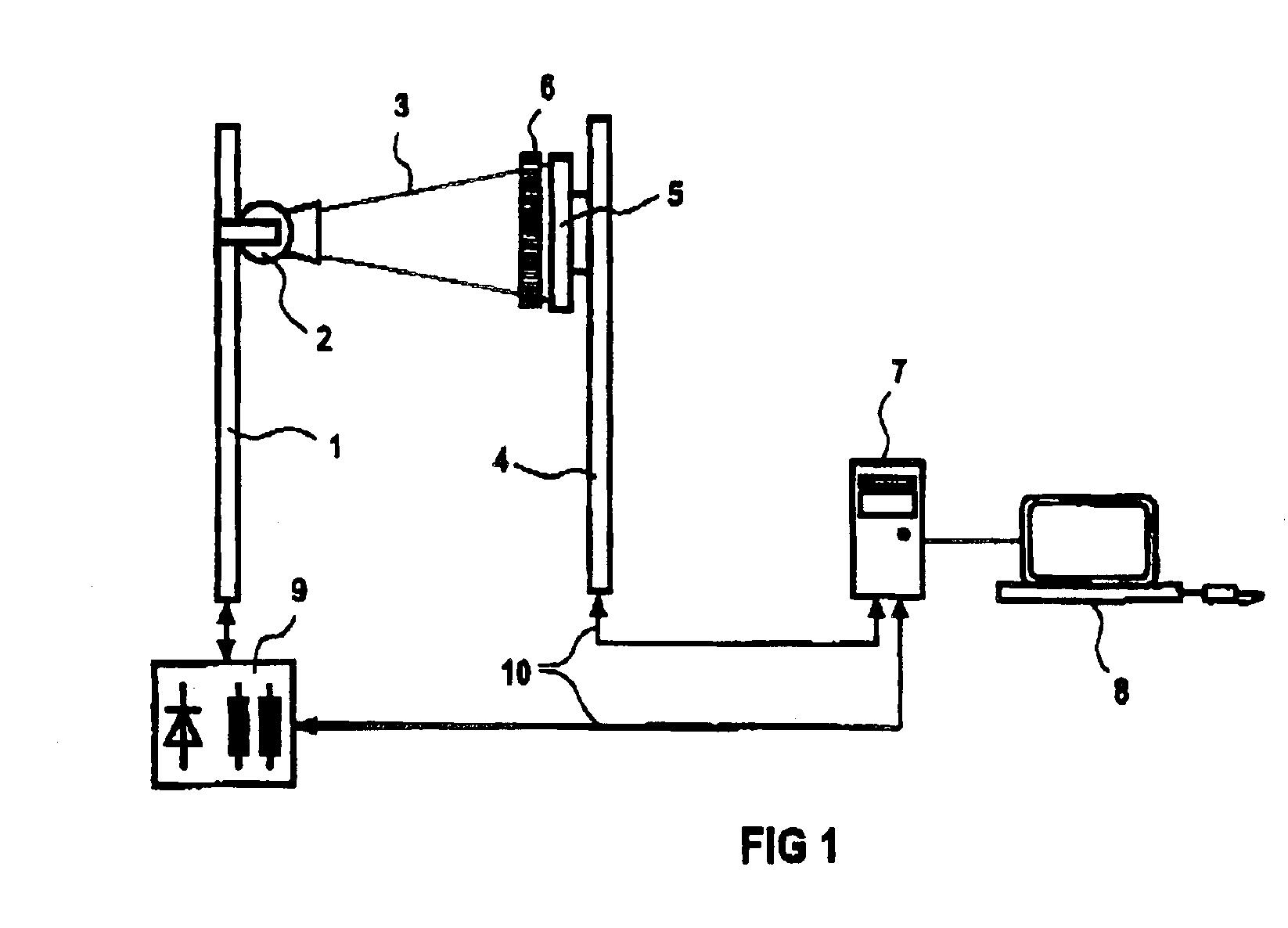
X-ray diagnostic facility having a digital X-ray detector and a stray radiation grid
ActiveUS6912266B2Suppress and reduce aliasing effectTelevision system detailsRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
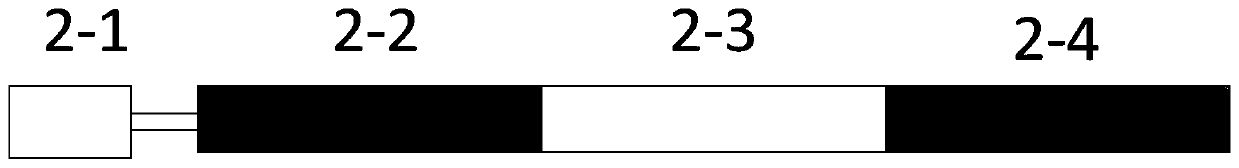
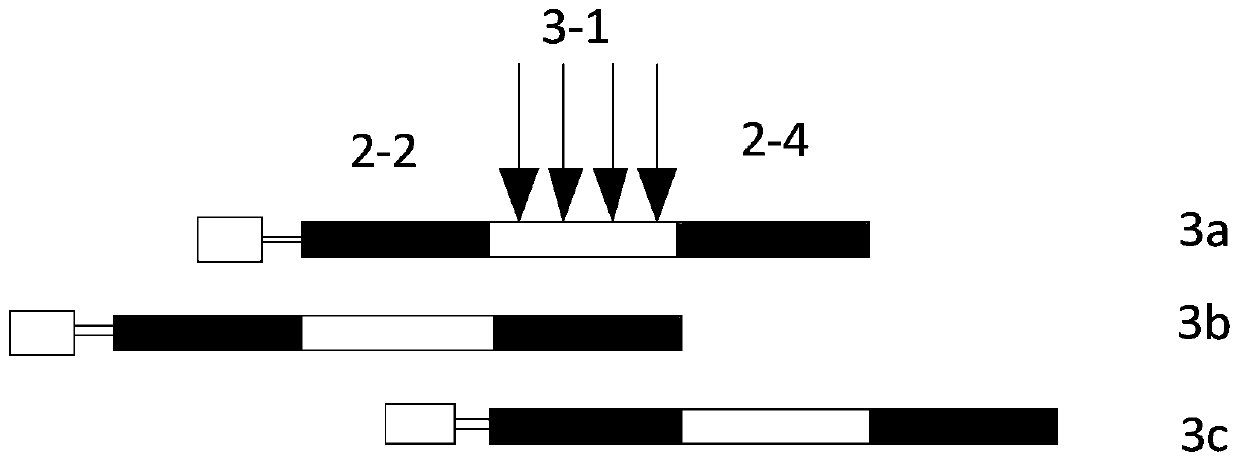
An X-ray diagnostic facility has an X-ray device for generating X-rays, a digital X-ray detector for acquiring the X-rays and for converting them into an electrical signal sequence that has picture elements arranged in a first structure, an image system for processing the electrical signal sequence and a playback device, and a stray radiation grid having a second structure composed of highly absorbent material and highly X-ray transparent material in alternation precedes the X-ray detector. One of the first and second structures is irregularly fashioned.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
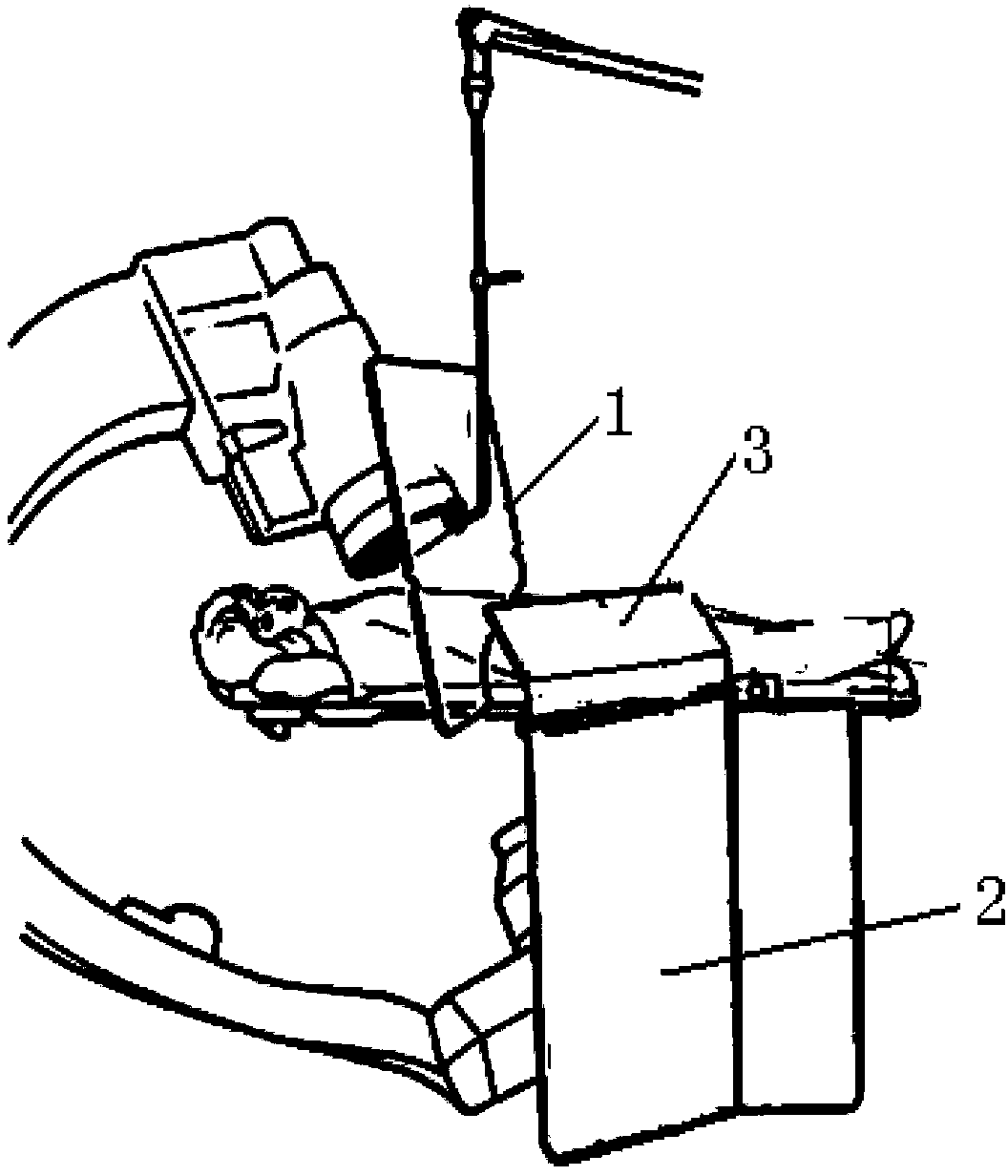
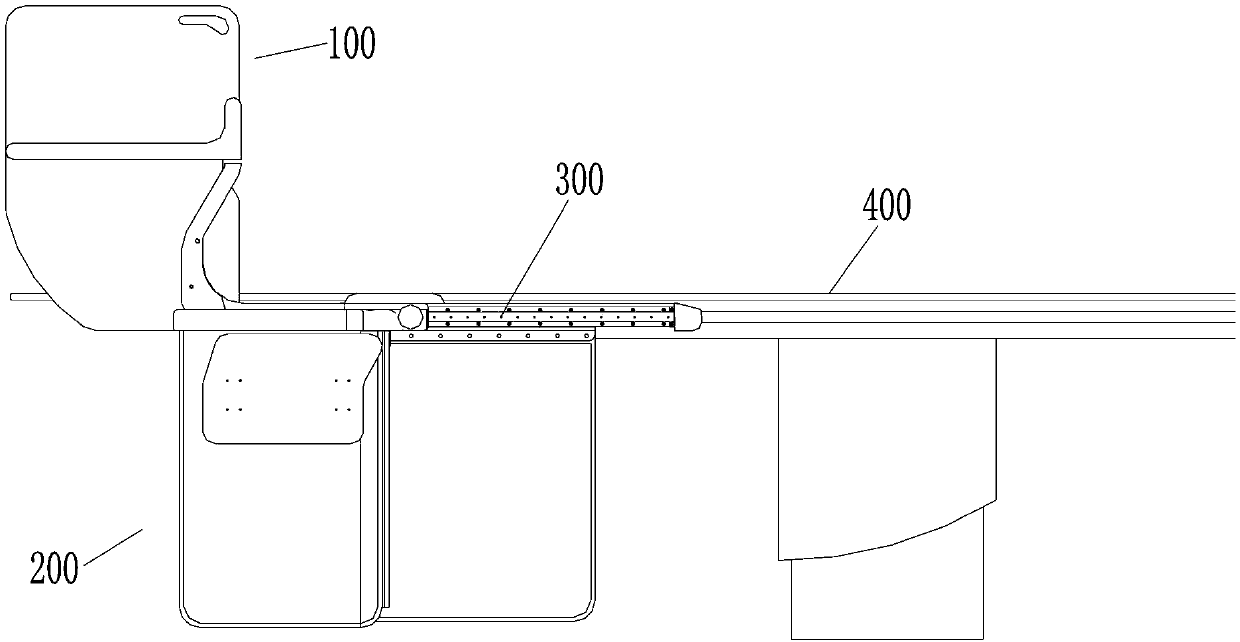
Integrated X-ray protection device on angiography machine
ActiveCN103385733ARealize simultaneous movement with the bedRealize synchronized movementRadiation safety meansAngiographyX-rayEngineering
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to an X-ray protection device with an integrated structure for an angiography machine. The device comprises a protection screen unit, a protection curtain unit and a bedside sliding rail unit, wherein the protection screen unit is arranged on the protection curtain unit, and the protection curtain unit is fixed on the bedside sliding rail unit so as to enable the protection curtain unit and the protection screen unit to synchronously and horizontally move along a bedside. The protection device can synchronously move along with a bed, and in a moving process, the protection device is always in the best protecting state and close to a patient, so that the problem that the radiation, especially the secondary stray radiation caused by the rays reflected by the patient, can not be effectively shielded due to the movement of the bed surface of a conduit bed is effectively solved, and meanwhile, the problems of prolonged surgery time, increased surgery risk and the like that are caused by adjusting the protection screen unit during surgery in the prior art are effectively avoided.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENTAL E T MEDICAL EQUIP
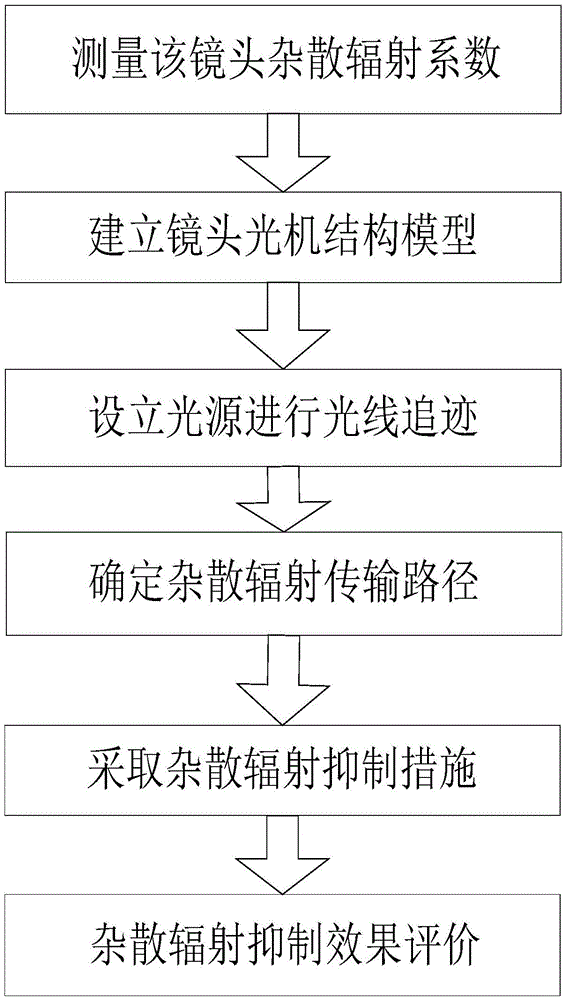
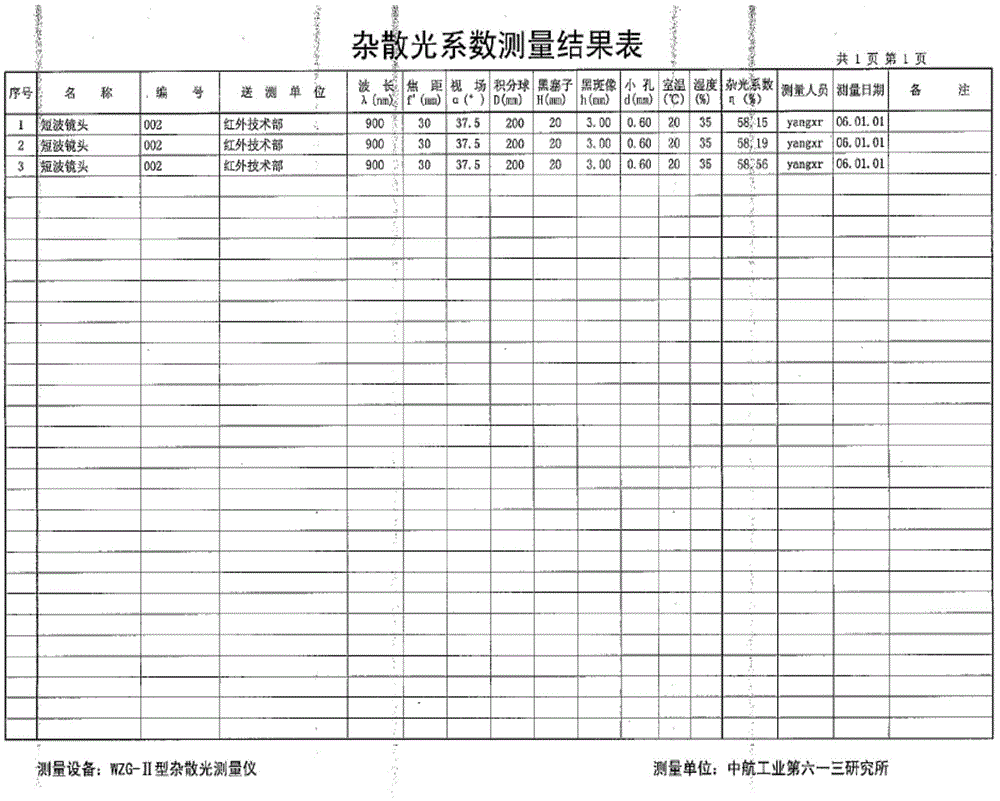
Short-wave infrared lens stray radiation detection method
ActiveCN105547649AEliminate the effects ofAccurate analysisTesting optical propertiesCamera lensEffect light
The invention relates to a short-wave infrared lens stray radiation detection method comprising the following steps: measuring the stray radiation coefficient of an infrared lens, acquiring the optical structure and parameters of the infrared lens, and importing the optical structure of the lens into stray light analysis software to establish a light machine structure model of the lens; searching 'key surfaces' of the surfaces of the lens and 'lighting surfaces' corresponding to different light incidence angles according to the established light machine structure model; and detecting a part with both the 'key surfaces' and the 'lighting surfaces' in the established model, showing that the established model has a stray radiation transmission path at the angle, and taking a corresponding suppression measure according to the detected stray radiation transmission path. By using the method, stray radiation produced by the infrared lens can be analyzed more comprehensively and accurately, a more-targeted accurate suppression measure can be taken in the later period, and the influence of stray radiation on the infrared lens can be eliminated to the greatest degree.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
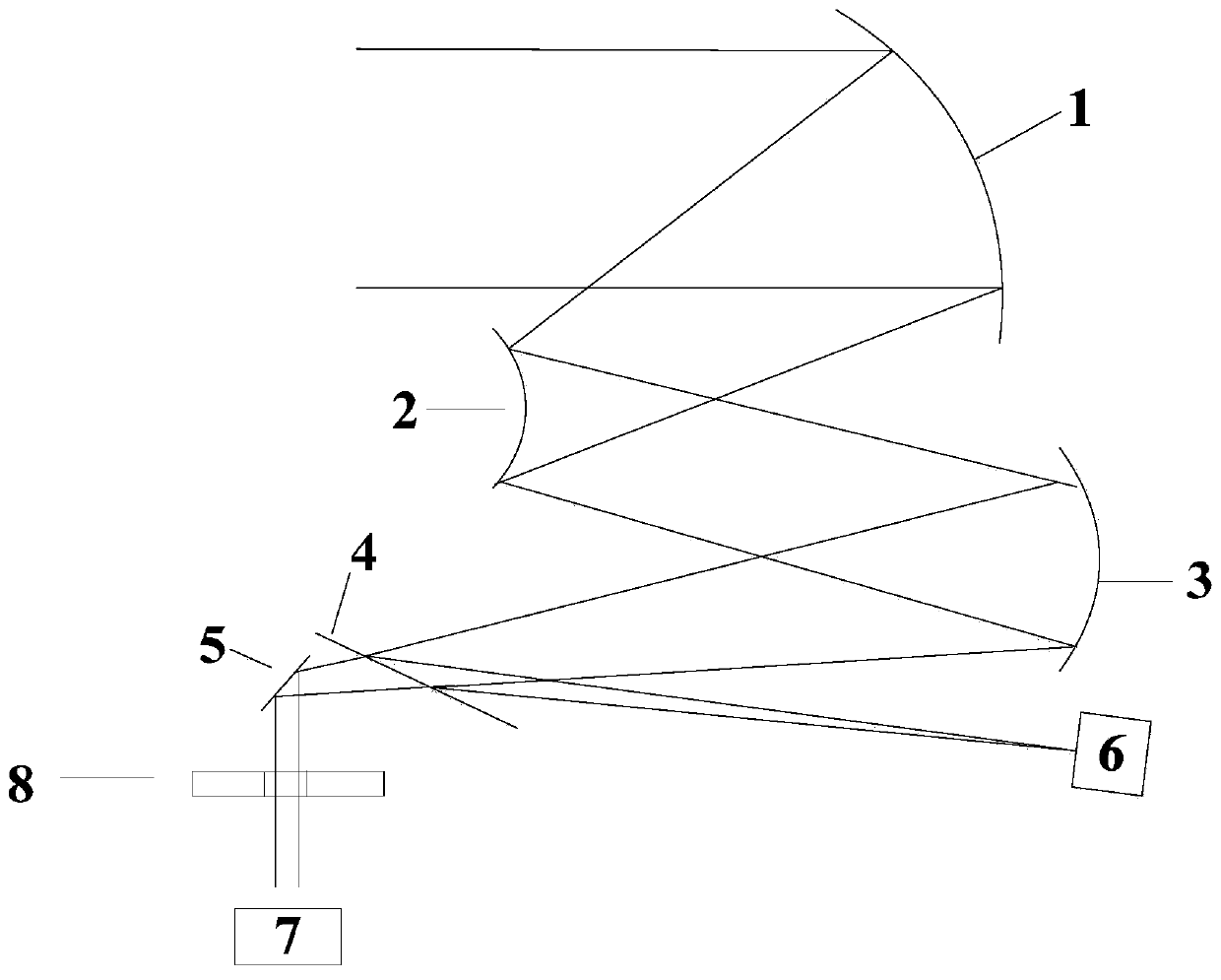
Radiation thermometer using off-focus telecentric optics
ActiveUS20130343425A1Increased rejectUniform magnificationRadiation pyrometryChemical vapor deposition coatingRadiation thermometerOptical axis
A radiation thermometer utilizing an off-focus telecentric lens arrangement in chemical vapor deposition reactors. An object assembly of one or more optical components is positioned at a distance equal to its focal length from an aperture stop. The aperture stop is dimensioned so that the chief rays are substantially parallel with the optical axis of the object assembly, and so that the rays that pass through the aperture stop define a narrow solid angle about the chief rays. The off-focus telecentric arrangement thus configured is focused at infinity, but is utilized to capture radiation from a relatively proximate target (e.g., within a couple meters) that is out of focus. The capture of collimated radiation from the target diminishes the contribution of stray radiation, particularly with targets having a highly specular surface.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
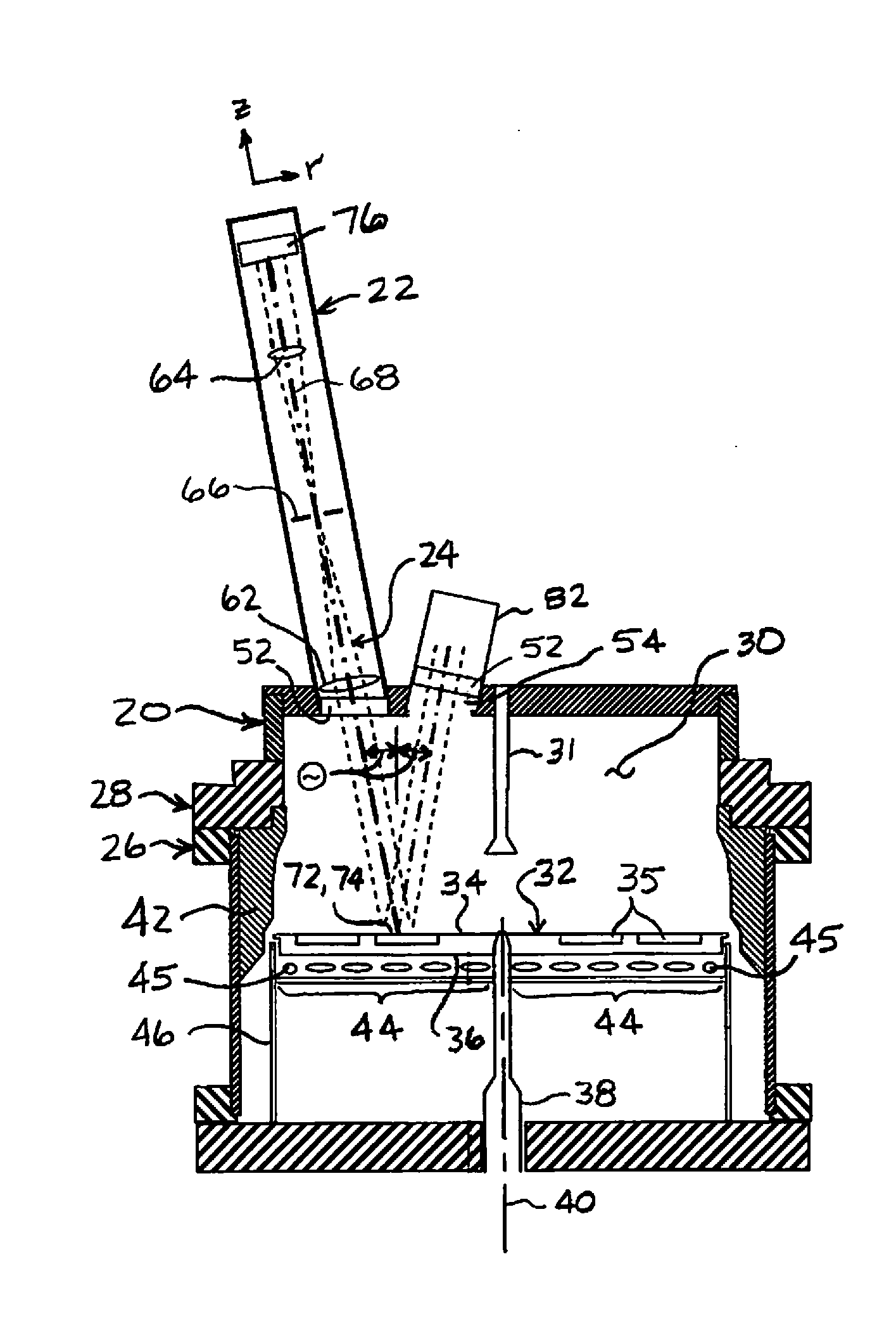
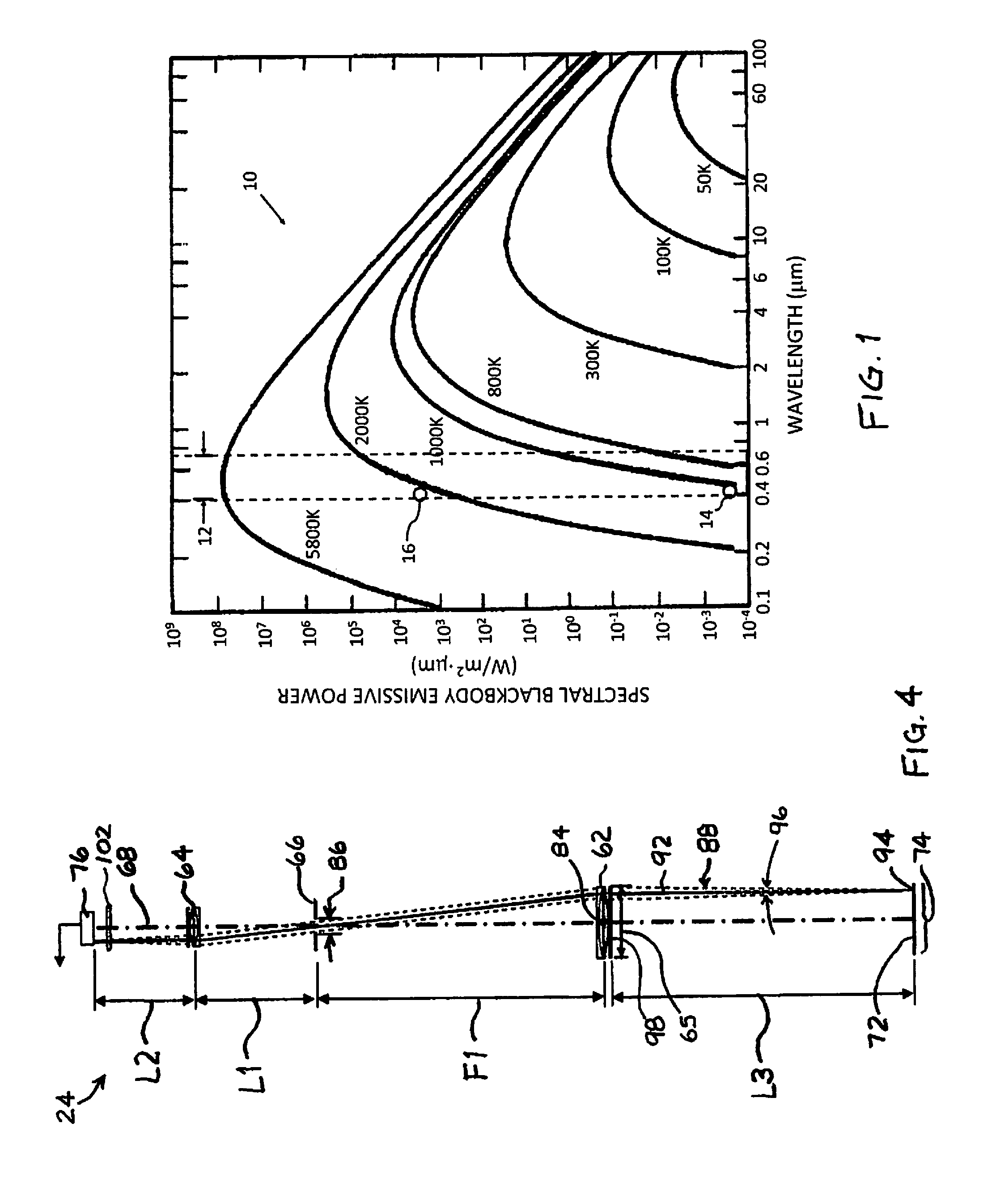
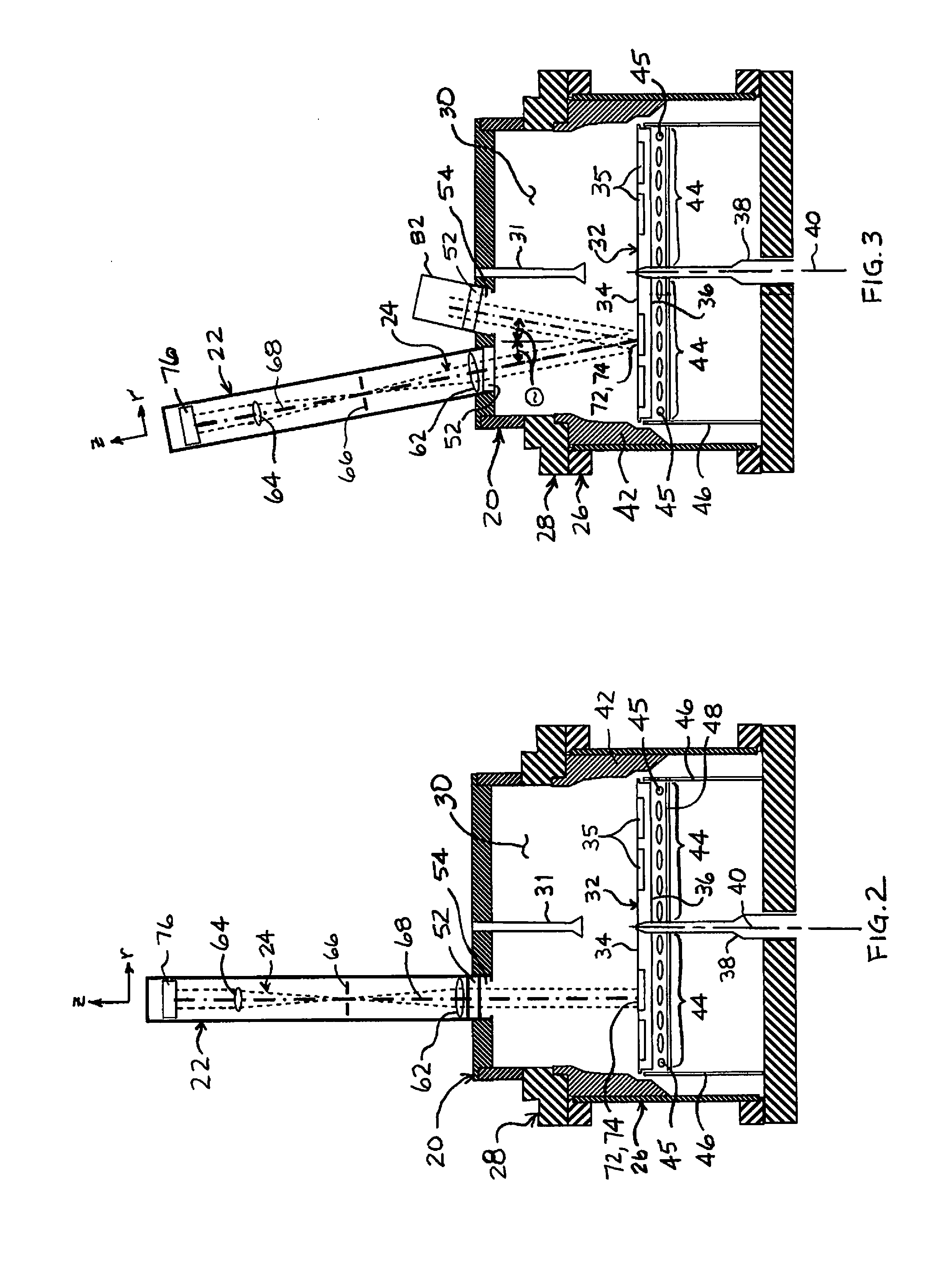
Method of determining stray radiation lithographic projection apparatus
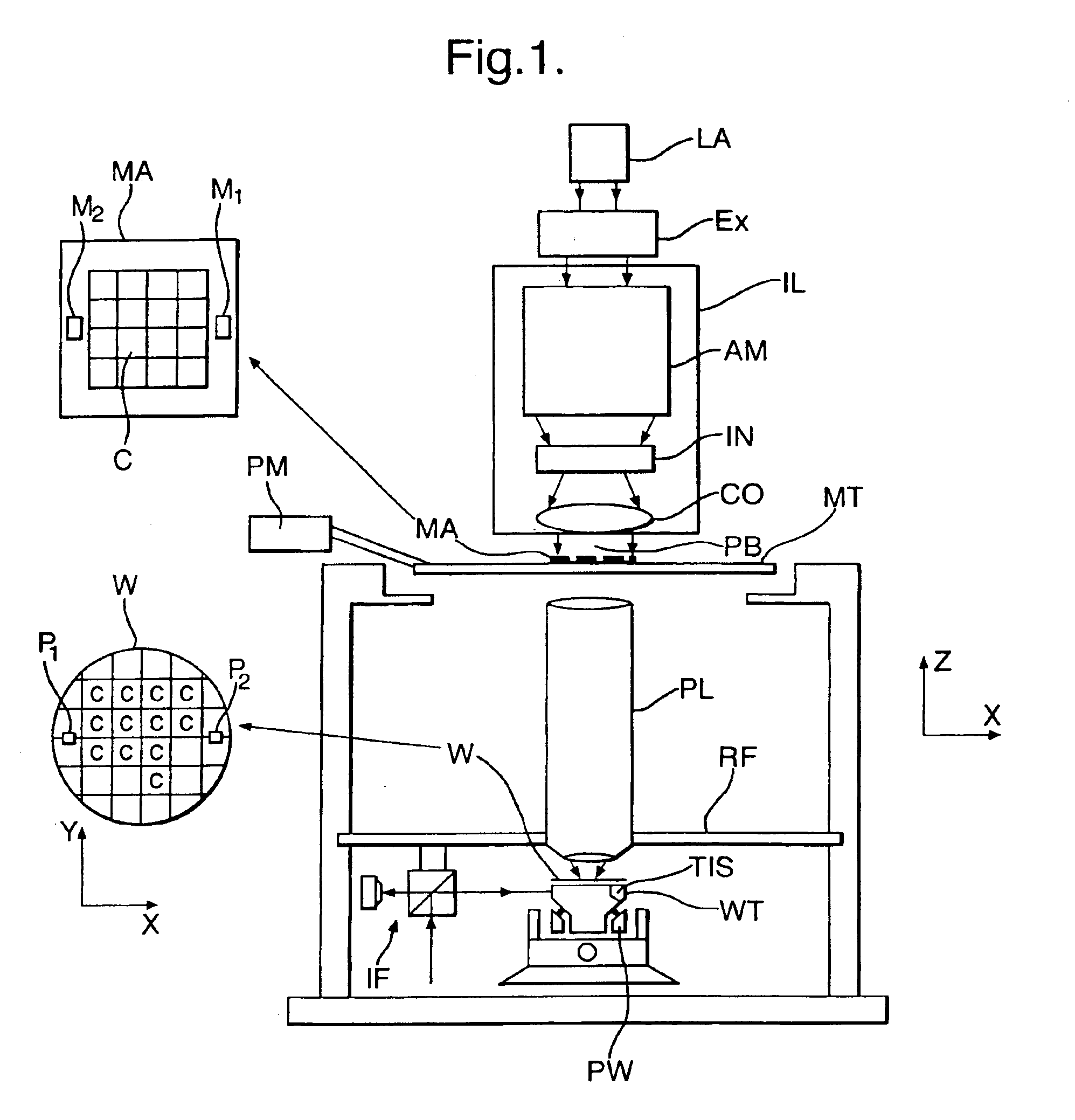
ActiveUS6862076B2Detailed analysisHigh measurement sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight beamScale down
A system and method for determining the stray radiation condition of a projection system, is presented herein. The invention includes providing a detector with a detector aperture coincident with the image plane of the projection system, measuring a reference parameter in accordance with the projection beam intensity, measuring a stray radiation parameter of an image of an isolated feature and calculating a coefficient representative of the stray radiation condition of the projection system based on the measured stray radiation parameter and the reference parameter. The extent of the detector aperture fits within the extent of a notional shape, which is defined by first scaling down the shape of the feature and subsequently displacing each line element constituting the edge of the scaled down shape, parallel to itself, over a distance of at least λ / NA in a direction perpendicular to that line element.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Precision transformer for antenna elements
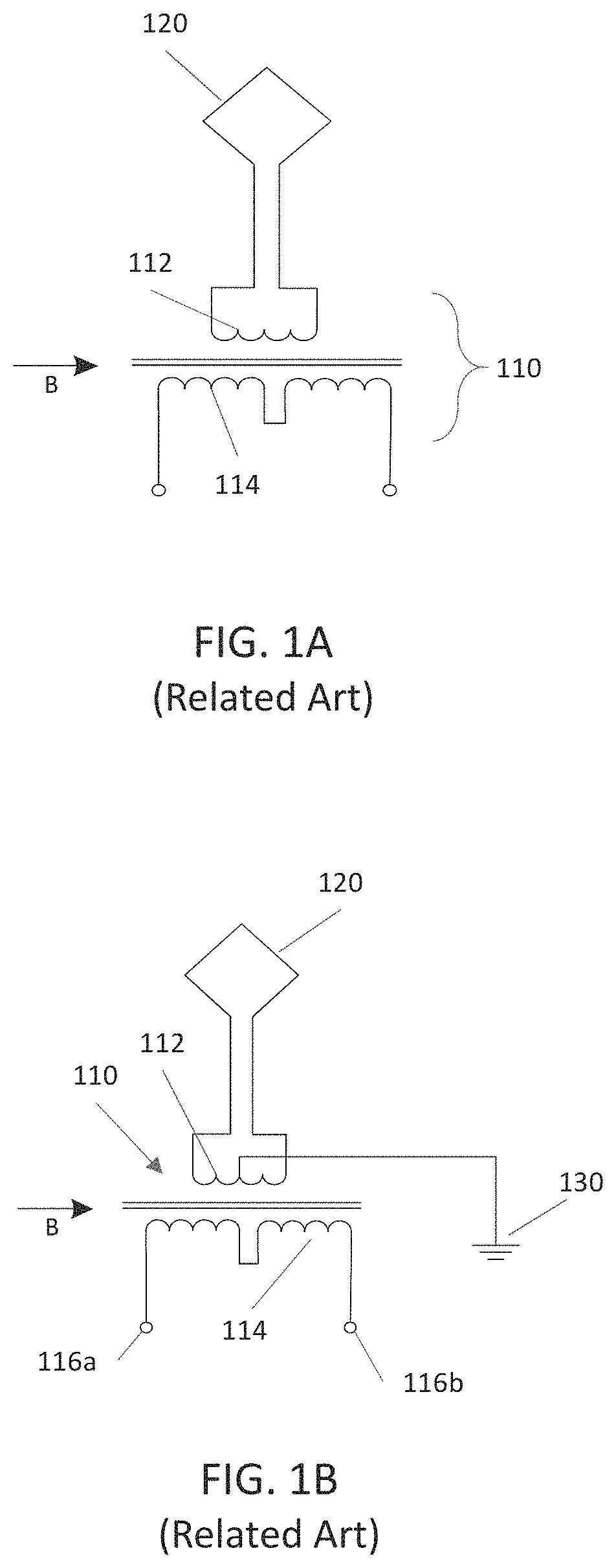
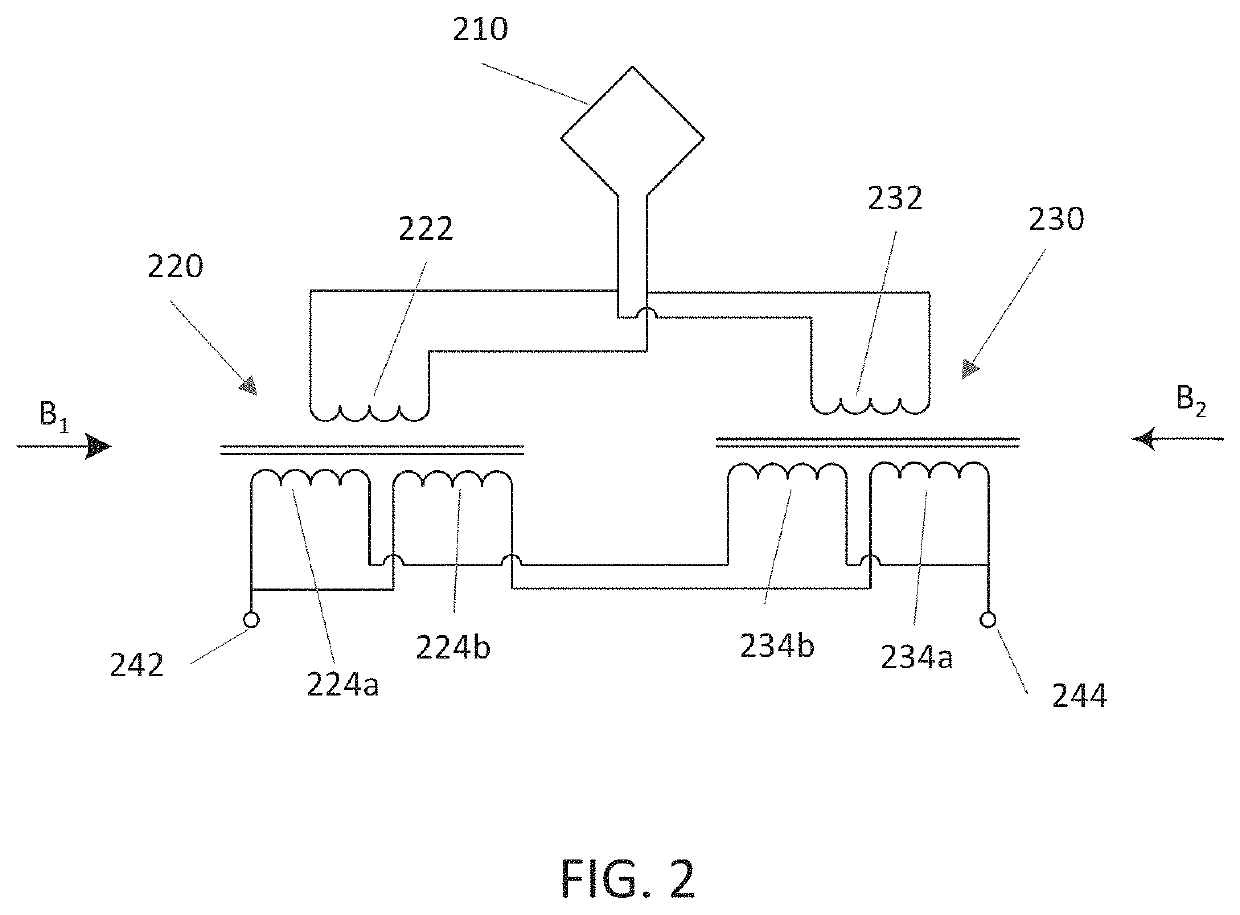
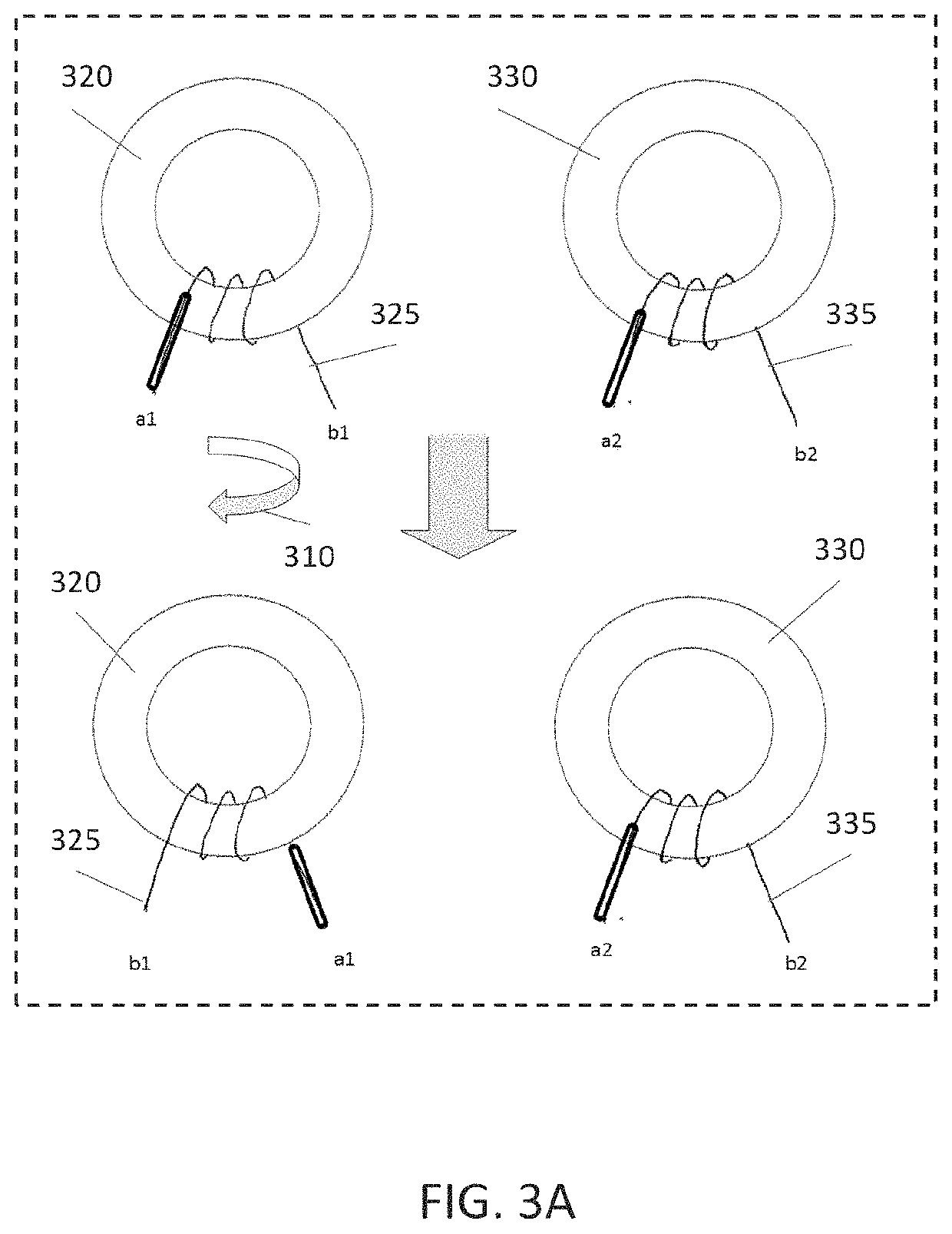
Antenna structures including two anti-symmetrically wound transformers to compensate for stray radiation. In one example an antenna structure includes a transformer assembly connected between an antenna and first and second balanced signal contacts, the transformer assembly including first and second transformer cores independently positionable in space relative to one another, a pair of primary windings connected to the antenna in parallel with one another, and a pair of balanced secondary windings connected in parallel with one another between the first and second balanced signal contacts.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
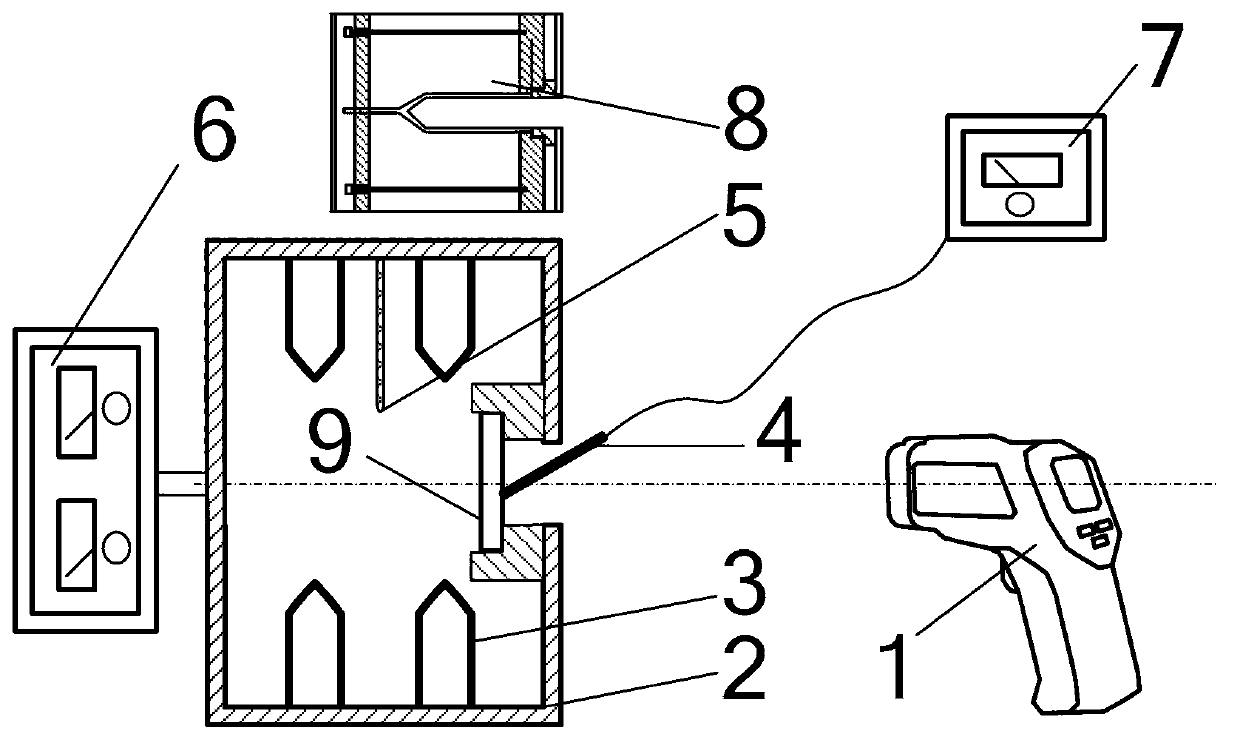
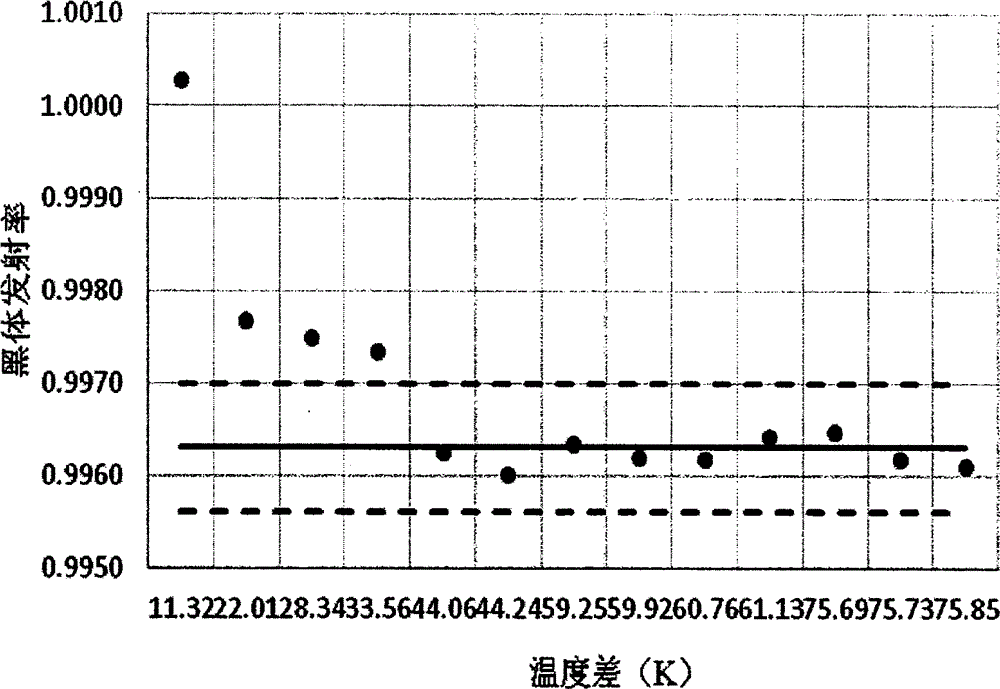
Black body emissivity measuring device based on control background radiation, and black body emissivity measuring method based on control background radiation
The present invention discloses a black body emissivity measuring device based on control background radiation, and a black body emissivity measuring method based on control background radiation. The measuring device comprises a to-be-measured black body; a heat radiation ring located at one side of an opening of the to-be-measured black body; and an infrared radiation thermometer for measuring an acquired radiation signal. A water cooling diaphragm is arranged between the heat radiation ring and the infrared radiation thermometer, and is used to reduce the stray radiation. The black body emissivity measuring device based on the control background radiation analyzes the influence of the temperature change of the heat radiation ring and the black body on a measurement result, and verifies the feasibility of the method applied to the spaceborne calibration black body emissivity on-orbit calibration.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
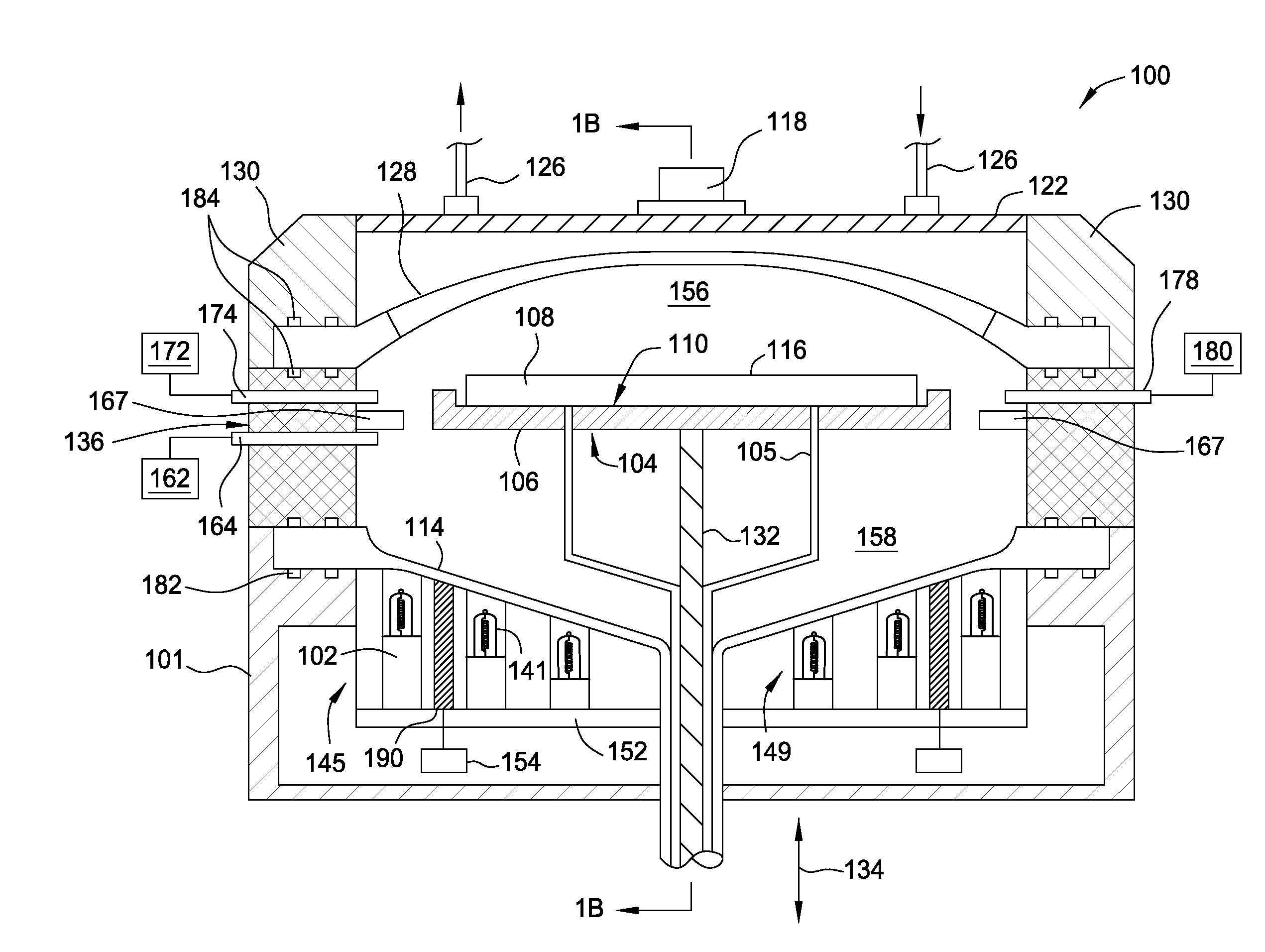
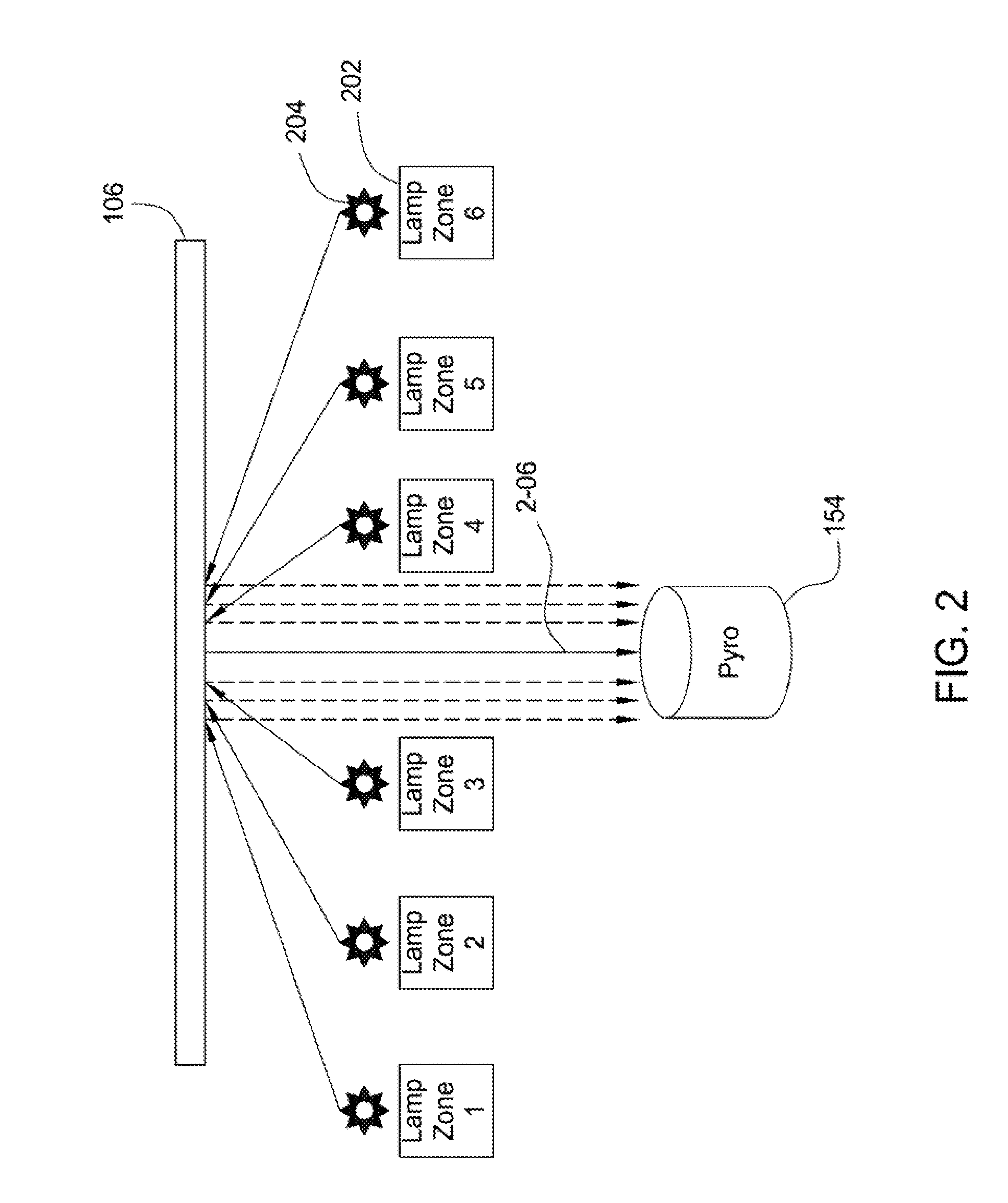
Model based lamp background filtration of stray radiation for pyrometry
InactiveUS20150023385A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermometer testing/calibrationFiltrationEngineering
The embodiments described herein generally relate to methods of noise compensation for proper temperature detection in thermal processing chambers and devices for achieving the same. Methods can include determining noise produced by a lamp zone and extrapolating the noise from the detected photocurrent. Devices can include a processing chamber, a substrate support disposed in the processing chamber, the substrate support having a high thermal mass, a pyrometer below the substrate support and oriented to view radiation emitted by the substrate and a controller configured to subtract a time invariant noise component and a time variant noise component from the pyrometer signal.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
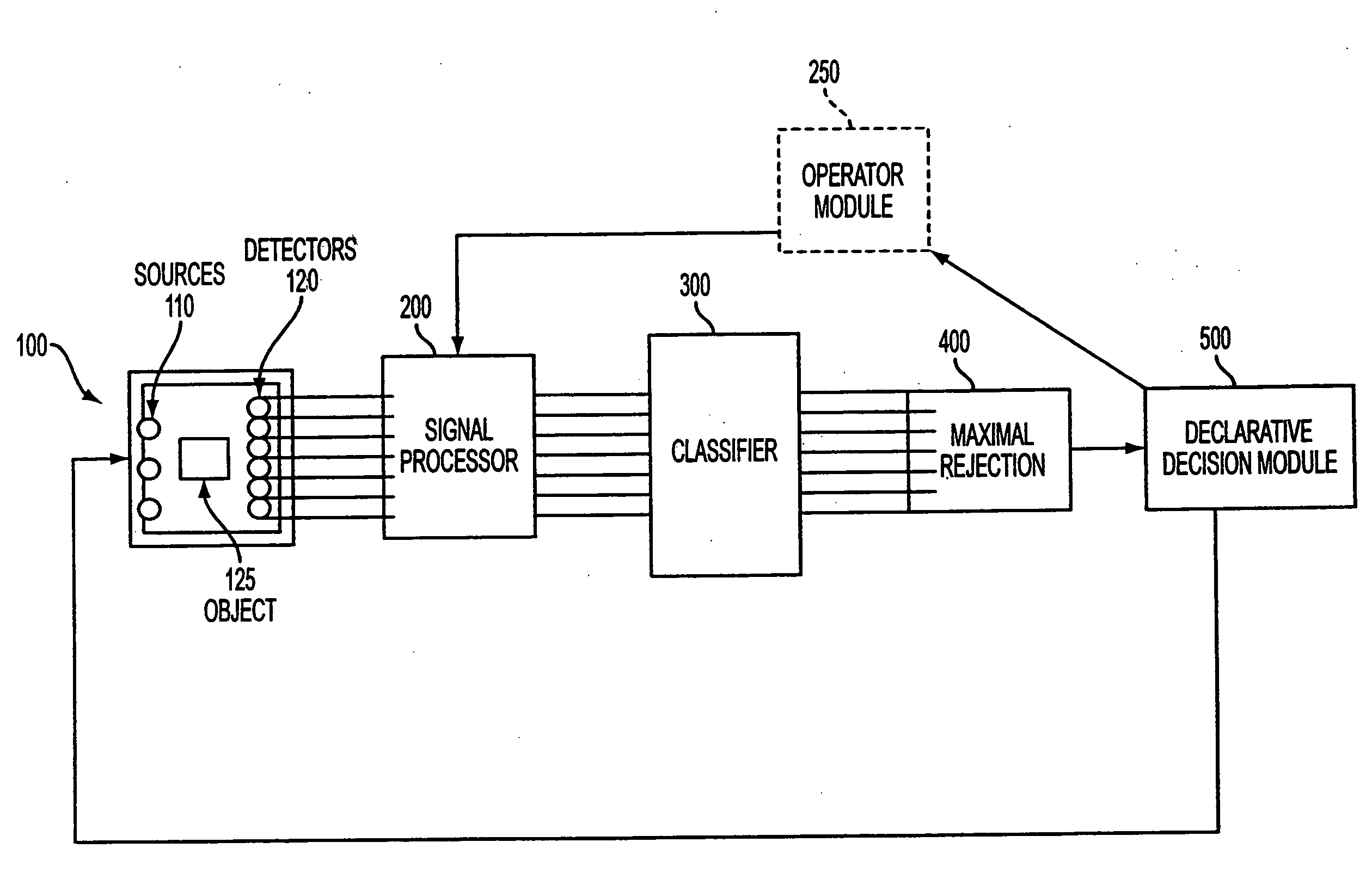
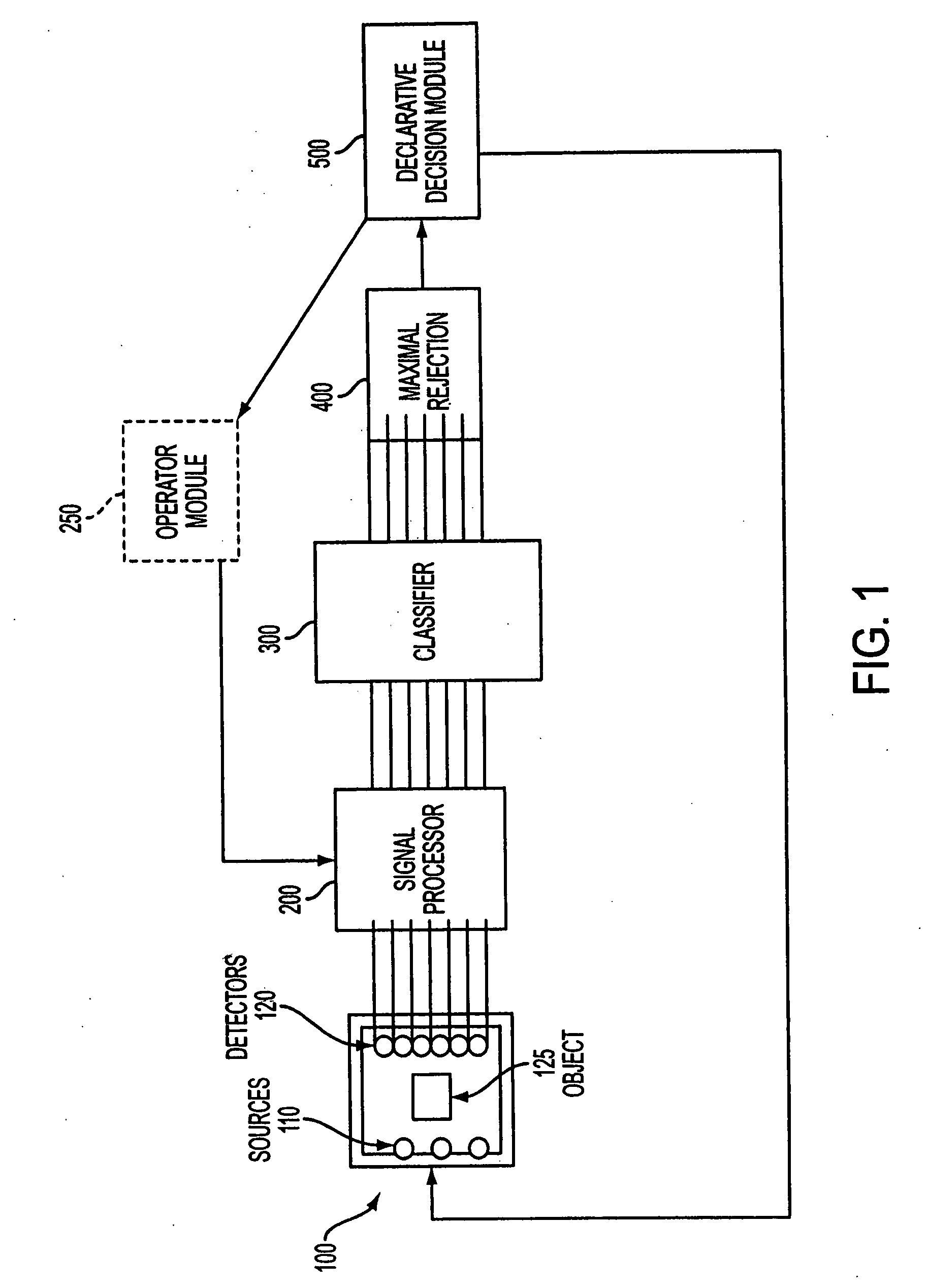
Method and apparatus for detecting and classifying explosives and controlled substances
InactiveUS20090010373A1Overcome limitationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationDetector arrayControl substances
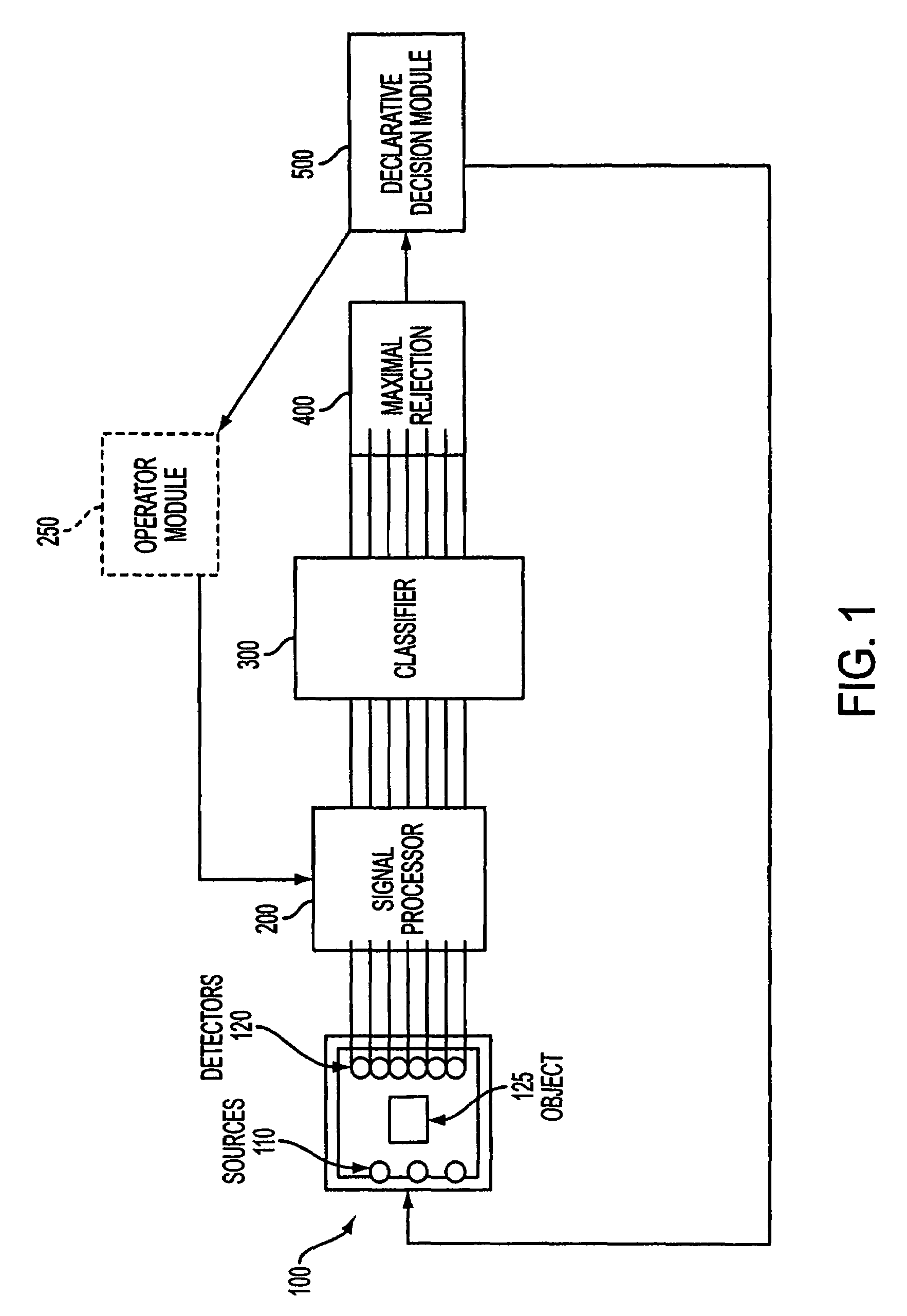
A system for detecting and classifying small amounts of explosives and other controlled substances while rejecting confounders, including a source / detector array formed of a plurality of sources and a plurality of detectors, a signal processor coupled to the source / detector array for processing data received from the detectors, a classifier coupled to the signal processor for classifying data received from the signal processor according to a plurality of algorithms, a maximal rejection classifier coupled to the classifier; and a declarative decision module coupled to the maximal rejection classifier for rendering an accurate decision regarding the contents of the object is provided. The apparatus includes an enclosure, a shield layer disposed within the enclosure, a cavity disposed within the shield layer, a plurality of neutron sources and a detection array disposed within the cavity, and a transport mechanism for moving objects through the cavity past the sources and detection array. The cavity has one or more turns which preclude a straight line trajectory through the cavity. The shield layer is water-filled to prevent stray radiation from exiting the enclosure. The use of multiple lower power neutron sources and the particular geometry of the enclosure provide a compact, relatively lightweight explosive detection system which is practical for use in airports and other public locations.
Owner:FAJ INT HLDG
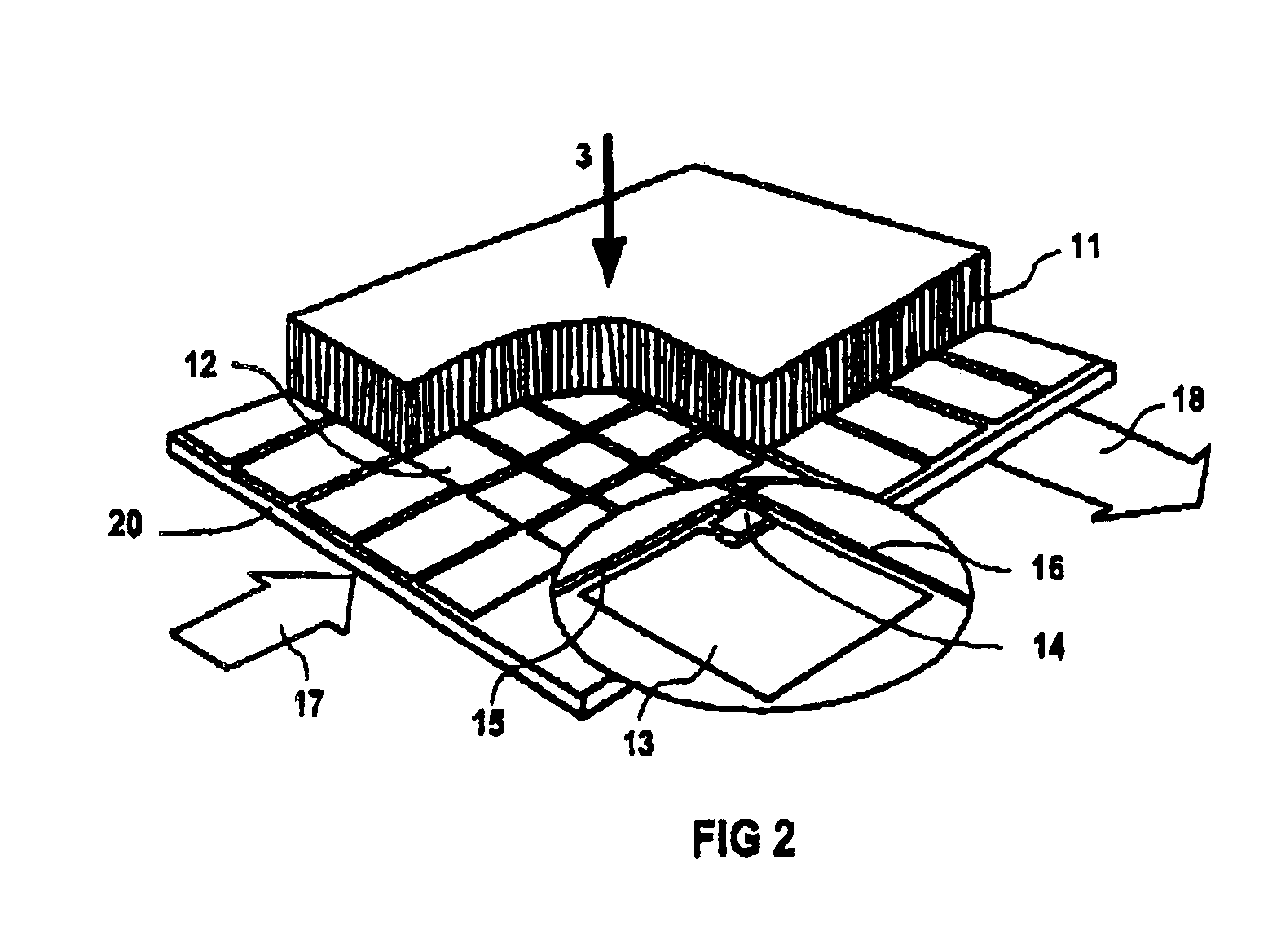
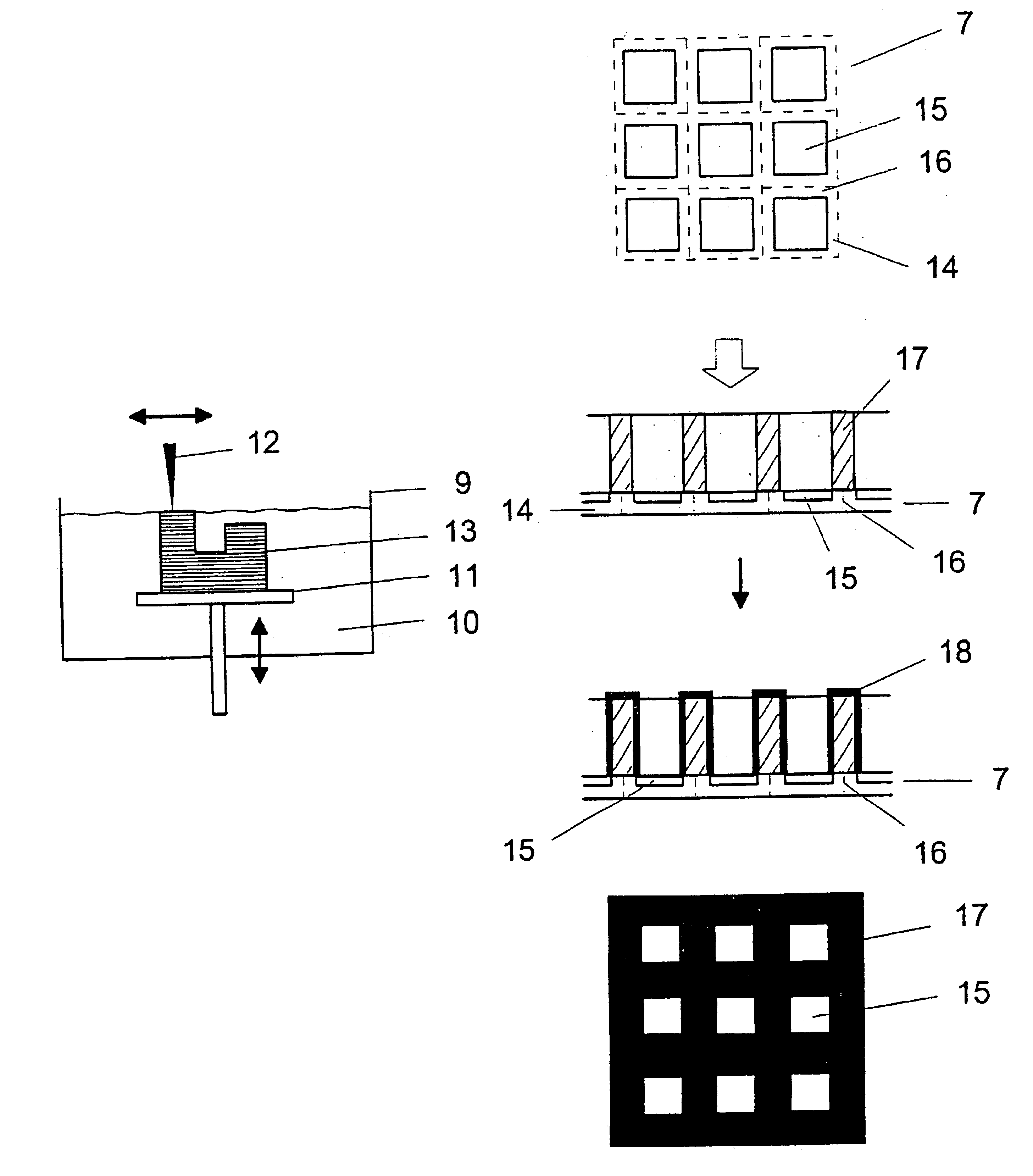
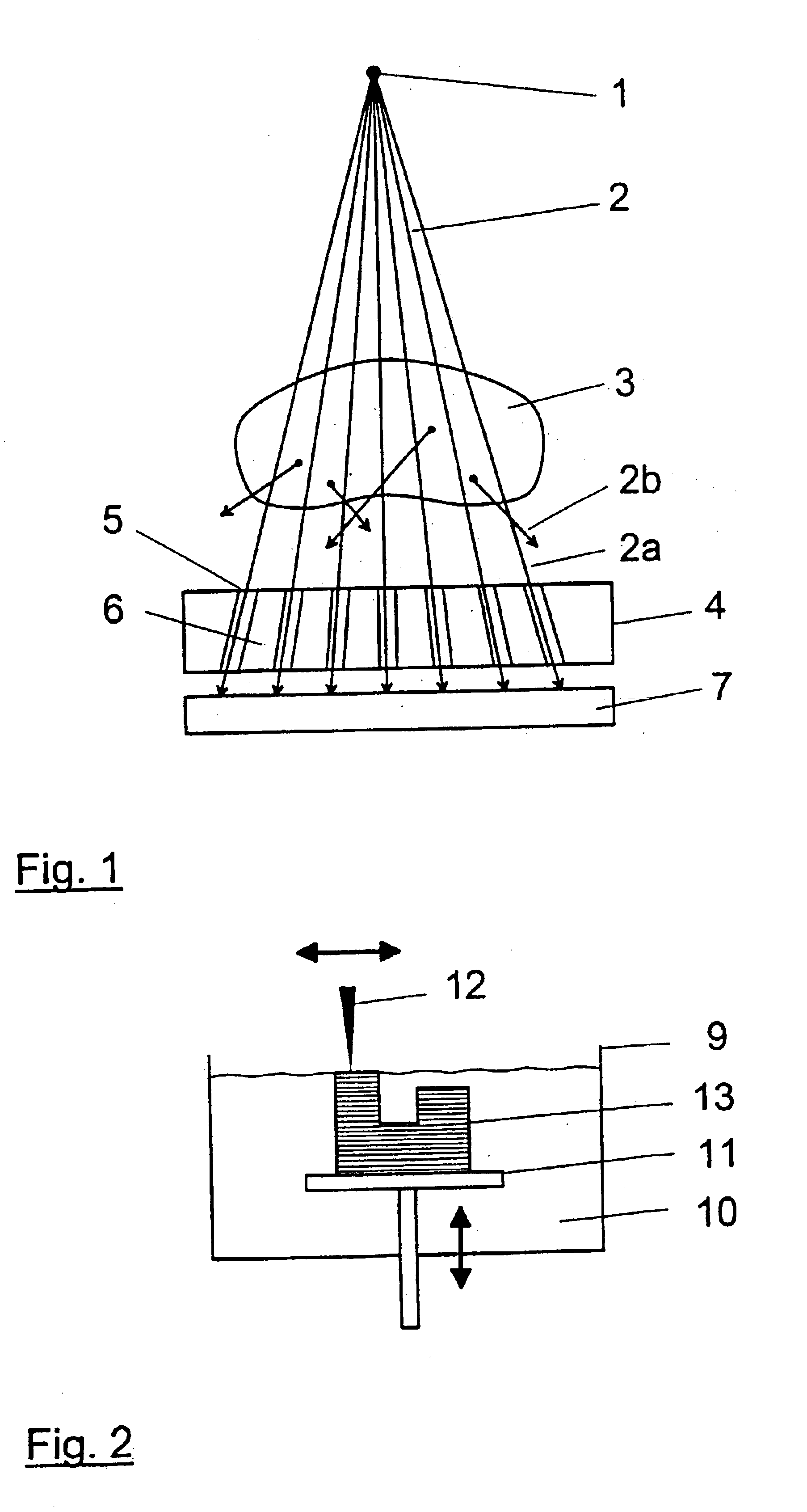
X-ray detector with an applied stray radiation grid, and method for applying a stray radiation grid to an X-ray detector
InactiveUS6847701B2High detective quantum efficiencyImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayDetective quantum efficiency
In an X-ray detector and method for applying a stray radiation grid onto an X-ray detector having detector elements arranged in a matrix that form a detector surface having detection regions sensitive to X-rays and less sensitive intermediate regions, a basic structure for the stray radiation grid is built up over the detector surface directly on the X-ray detector with a rapid prototyping technique and is subsequently coated or filled with a material that is highly absorbent for X-radiation. An absorbent structure thus arises that lies over the less sensitive intermediate regions of the detector surface. Moiré disturbances are avoided in the X-ray image exposure and the detective quantum efficiency (DQE) is increased.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
System and method for testing stray radiation of radio frequency transmitter
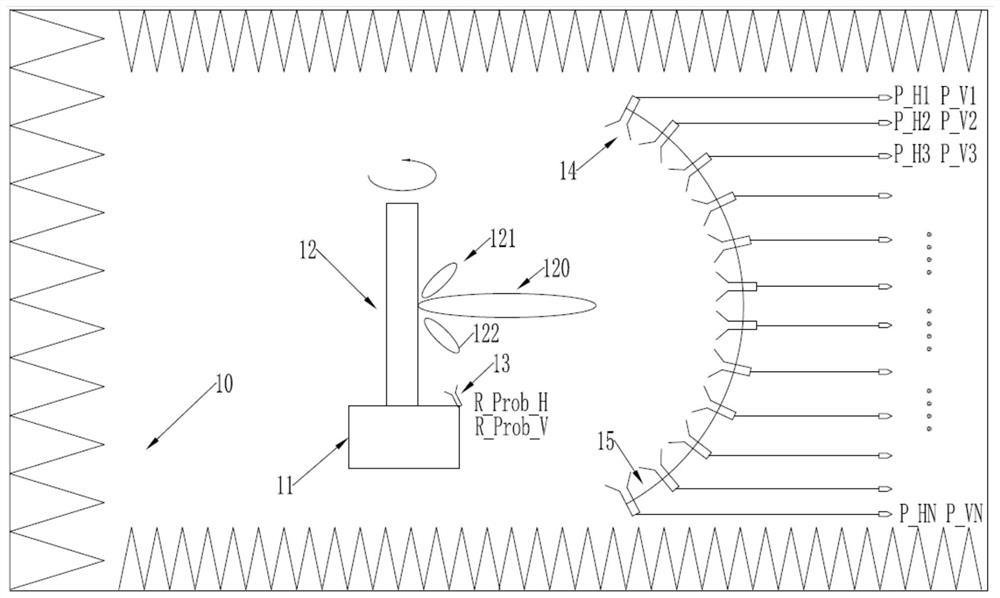
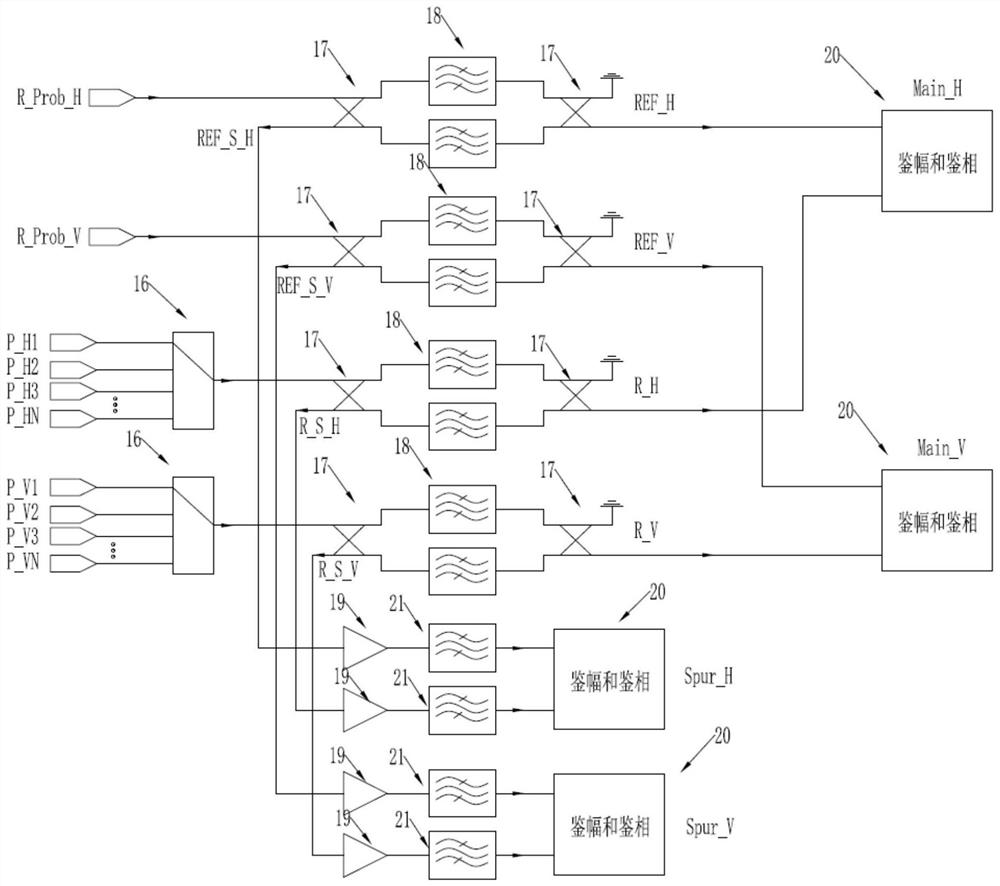
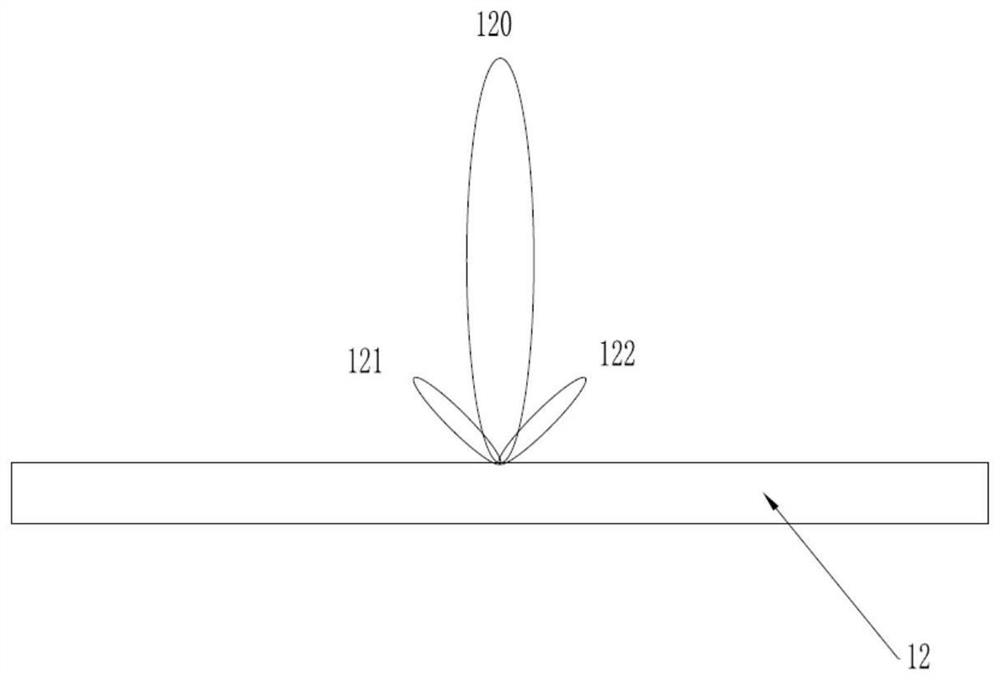
PendingCN111707877AIncrease signal amplitudeHigh purityAntenna radiation diagramsEngineeringField tests
The invention provides a system and a method for testing stray radiation of a radio frequency transmitter. The system is a near-field test system, and a test field is a microwave anechoic chamber; a servo system is a one-axis precision rotary table installed in the microwave anechoic chamber, and an antenna of a radio frequency transmitter to be tested is arranged on the precision rotary table. Aradio frequency subsystem comprises a vector network analyzer. The vector network analyzer receives radiation signals of a radio frequency transmitter antenna to be tested through a test probe to complete amplitude and phase parameter test of the radio frequency transmitter antenna to be tested. The test method adopts a field test method. According to the invention, spherical near-field sampling of an electromagnetic field is realized by using a one-axis rotary table in cooperation with a probe array.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGDA ELECTRONICS
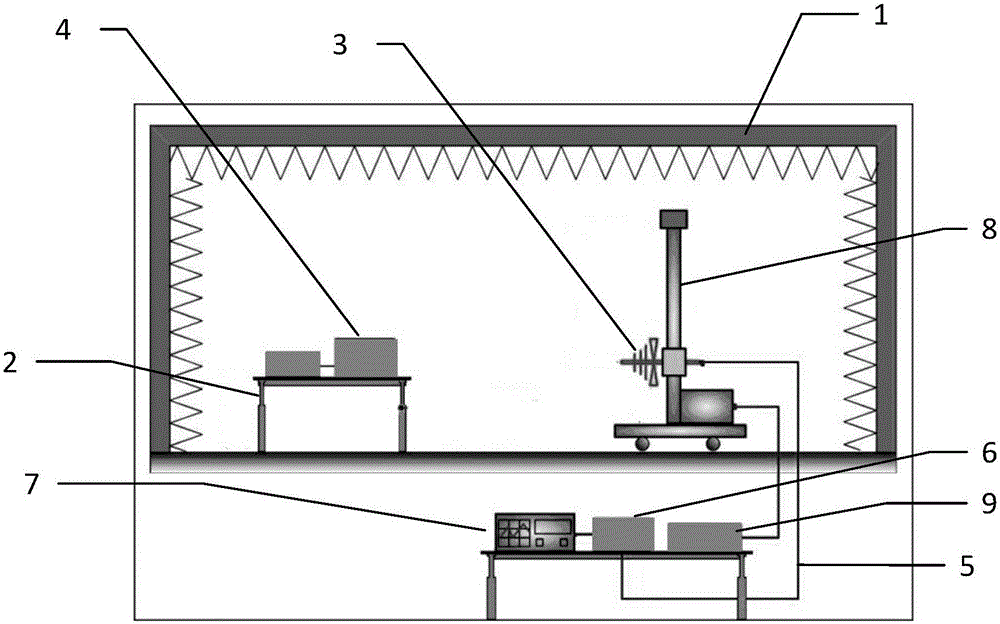
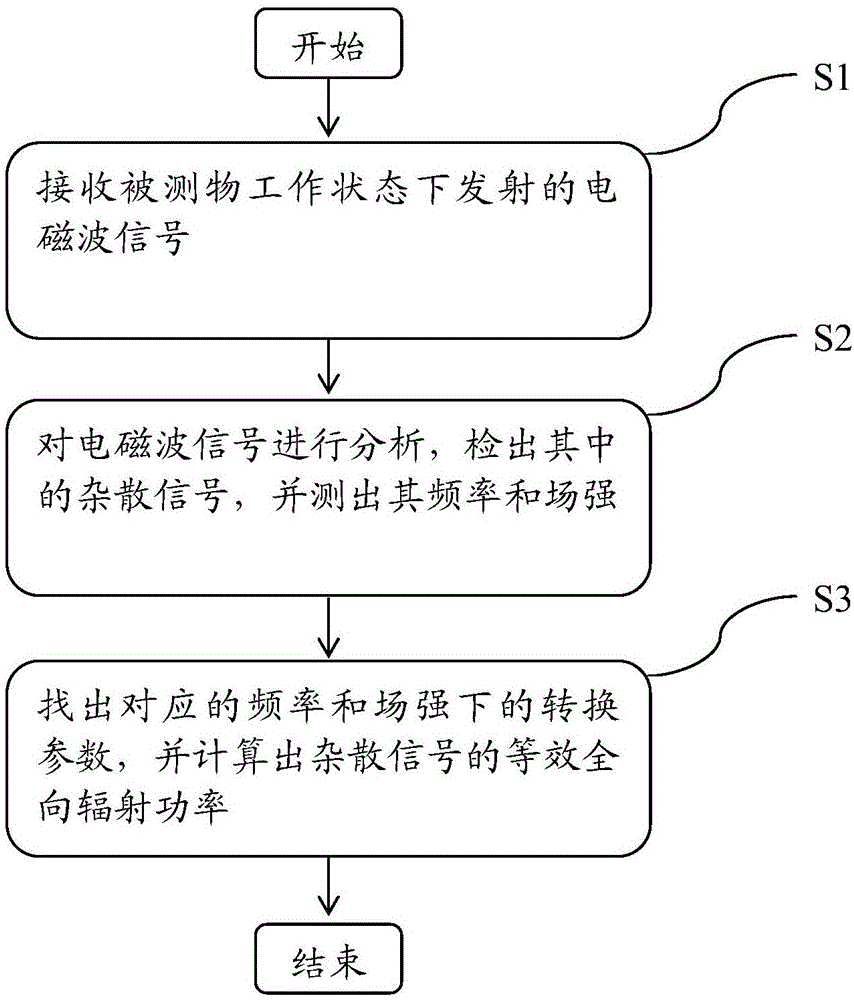
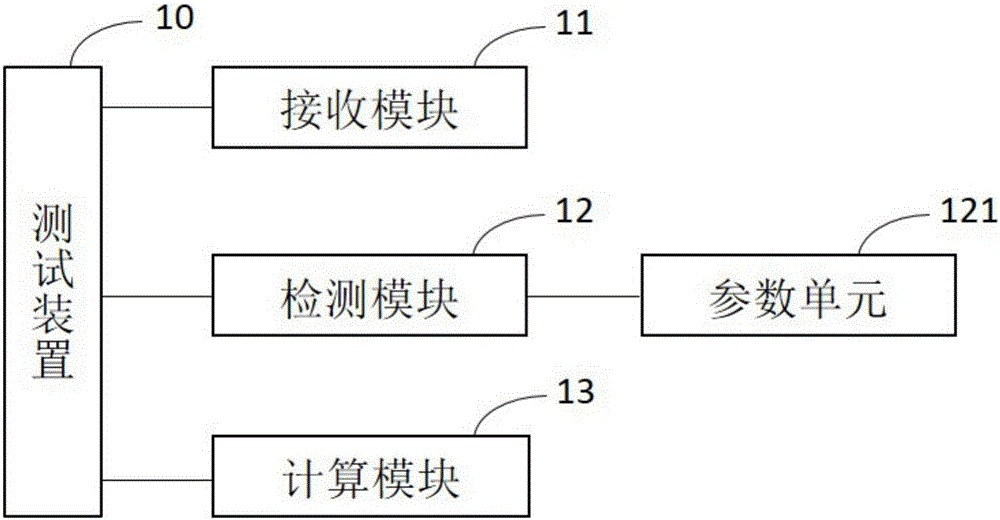
Automatic test method and device for stray radiation
ActiveCN106468741AReduce complexityReduce uncertaintyElectromagentic field characteristicsTest efficiencyProduct testing
The invention relates to the field of wireless product testing, and specifically relates to an automatic test method for stray radiation. The automatic test method comprises the steps of receiving electromagnetic wave signals which are transmitted by a tested object in an operating state; analyzing the electromagnetic wave signals, detecting stray signals in the electromagnetic wave signals, and measuring the frequency and the field intensity of the stray signals; and finding out transformation parameters from a transformation parameter list according to the frequency and the field intensity, and calculating equivalent omnidirectional radiation power of the stray signals according to the transformation parameters. The automatic test method provided by the invention enables a stray radiation test to be more convenient and more efficient, the test efficiency is improved, and the labor input and the field occupation time of a test project are reduced.
Owner:深圳天祥质量技术服务有限公司
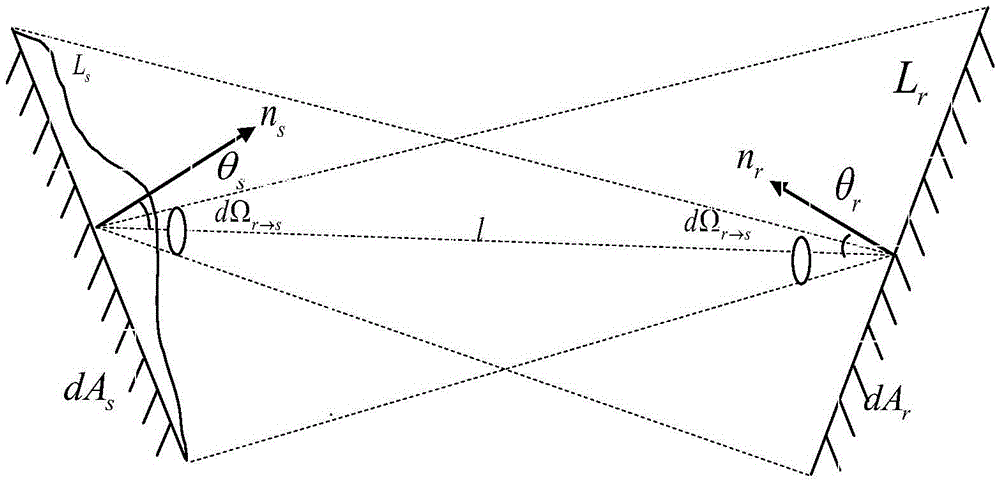
Analysis method for stray radiation of infrared measurement system
ActiveCN106053023ASuppression of stray radiationHigh measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesIlluminanceTransfer procedure
The invention discloses an analysis method for stray radiation of an infrared measurement system. The analysis method comprises the steps of: determining stray radiation sources in the system, wherein the total number of the stray radiation sources is N, and the stray radiation sources comprise thermal radiation of an optical element and thermal radiation of a mechanical structure; for the i-th stray radiation source, calculating radiation power phi which is radiated on a radiation surface and capable of being received by a detector; analyzing the transmission process of the phi, and calculating an irradiance E of the phi on the detector; and calculating the total irradiance E of the N stray radiation sources on the detector, wherein the N is an integer greater than 1, and the i=1,... N. The analysis method can quantitatively analyze the relationship between stray radiation and temperature, so as to provide theoretical guidance for the suppression of stray radiation at different temperatures. Furthermore, the measurement precision of the system can be effectively improved by effectively suppressing stray radiation at different temperatures.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Infrared radiation detector
ActiveUS20120138802A1Reduce in quantityEliminate stray radiationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector circuitsThermodynamics
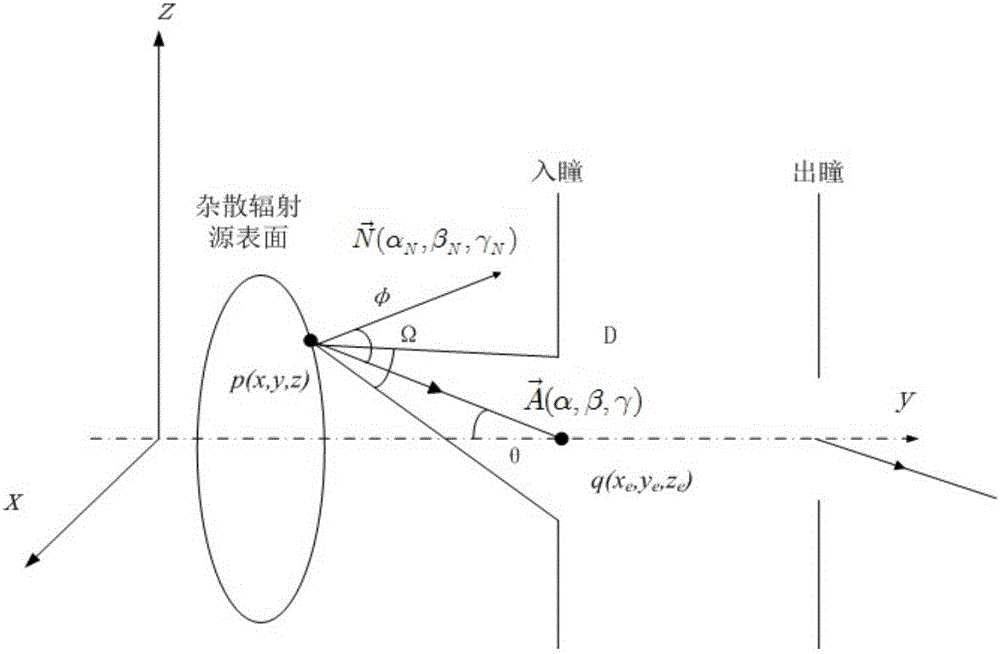
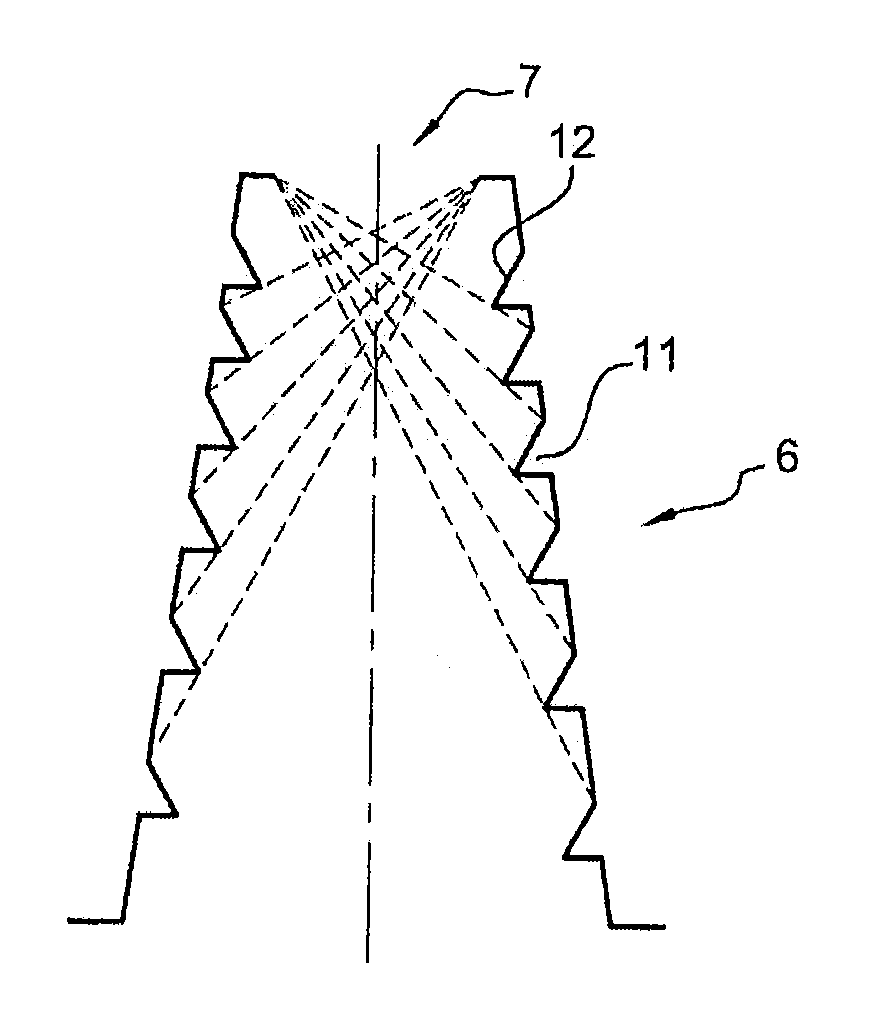
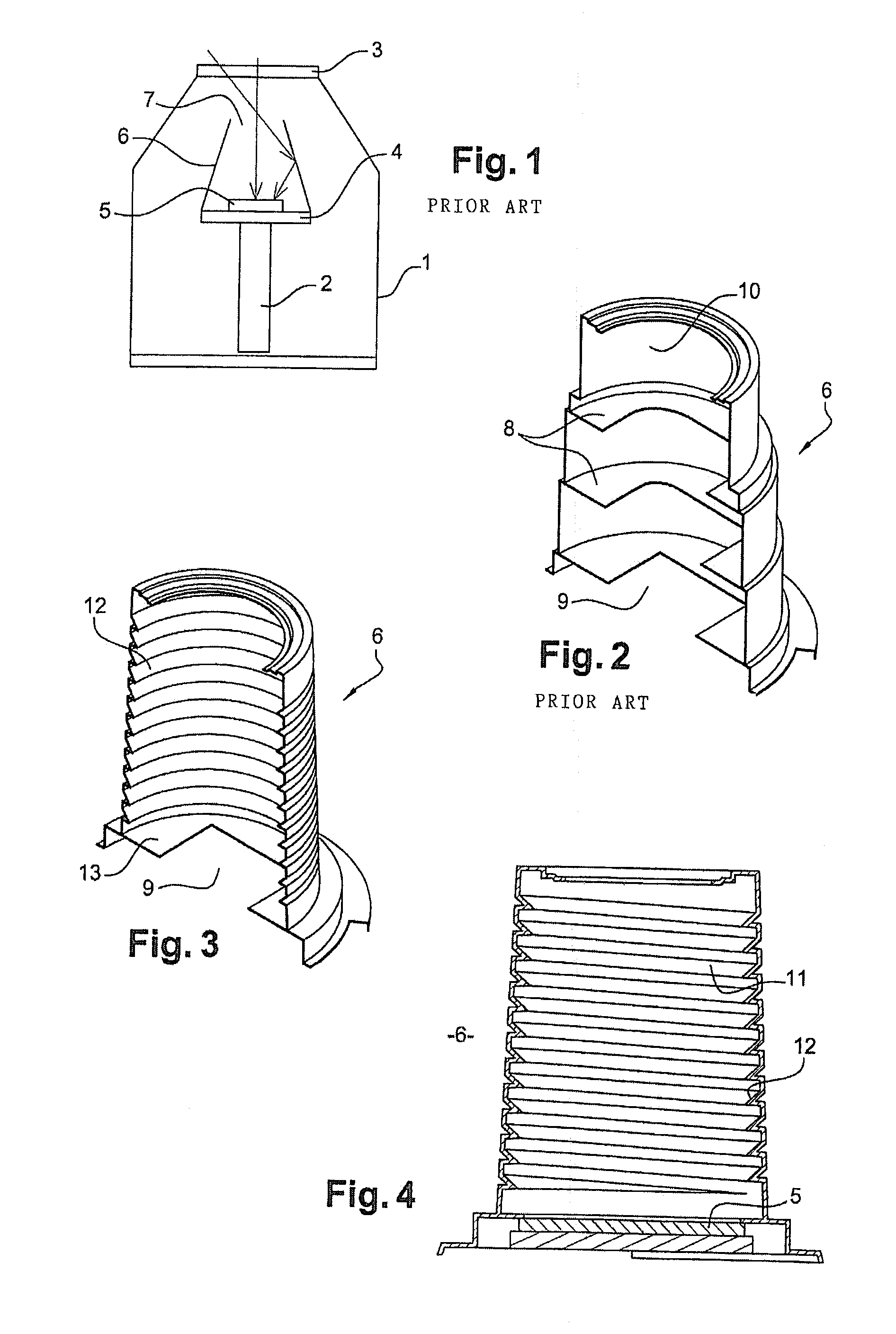
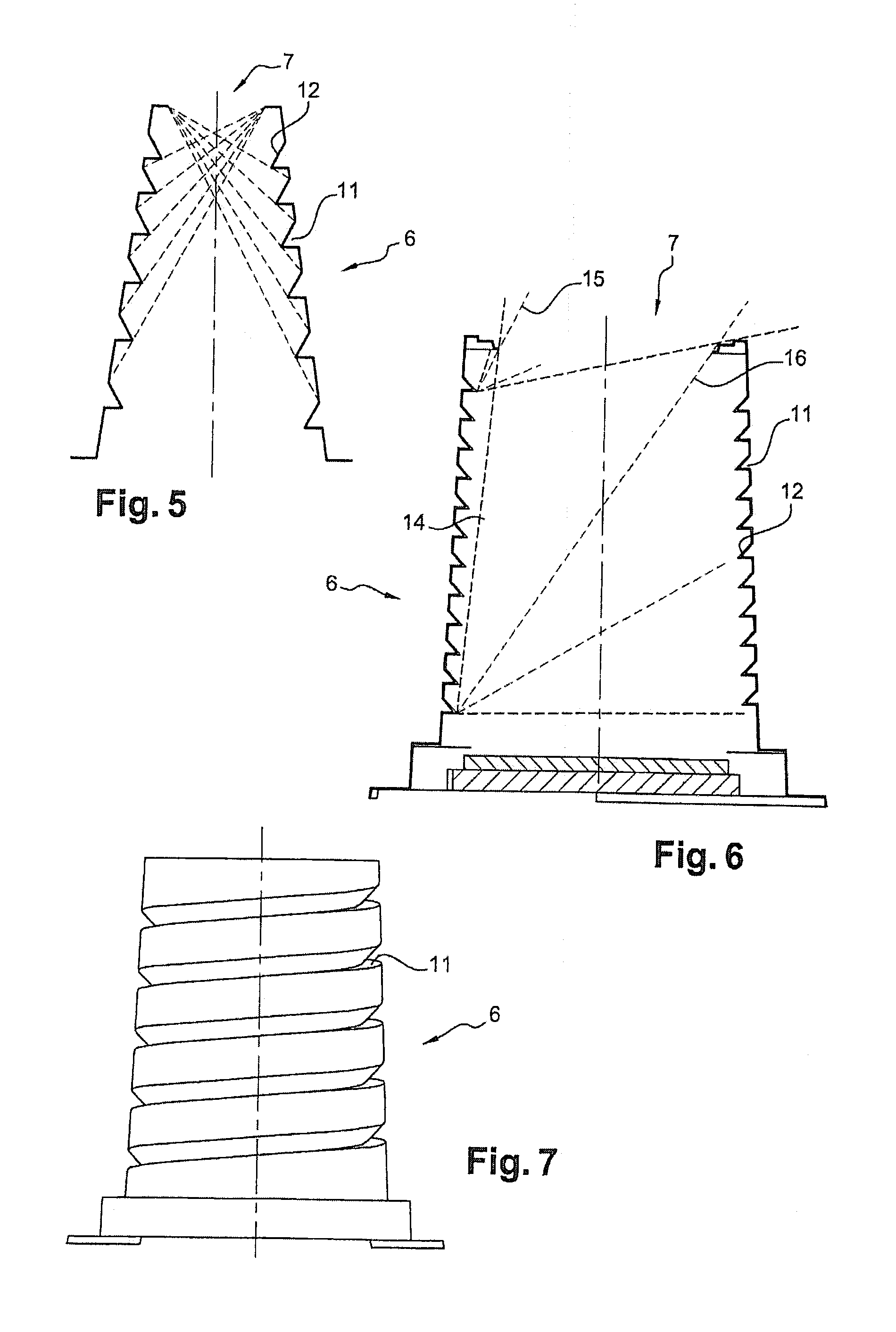
An infrared radiation detector includes: a cryostat having a cold finger ensuring heat exchange with a cold source and a window transparent to infrared radiation to be detected; a mechanically fixed cold plane in heat exchange with the cold finger; a detector unit comprising at least a detector circuit sensitive to the infrared wavelength range to be detected, and in direct or indirect heat exchange with the cold plane; and a mechanically fixed cold shield in heat exchange with the cold plane and limiting stray radiation. The cold shield is rotationally symmetrical. An inside wall of the cold shield has a succession of reliefs distributed in at least one helical pattern. A definition axis of the helical pattern coincides with the axis of revolution of the cold shield.
Owner:DE DETECTEURS INFRAROUGES - SOFRADIR
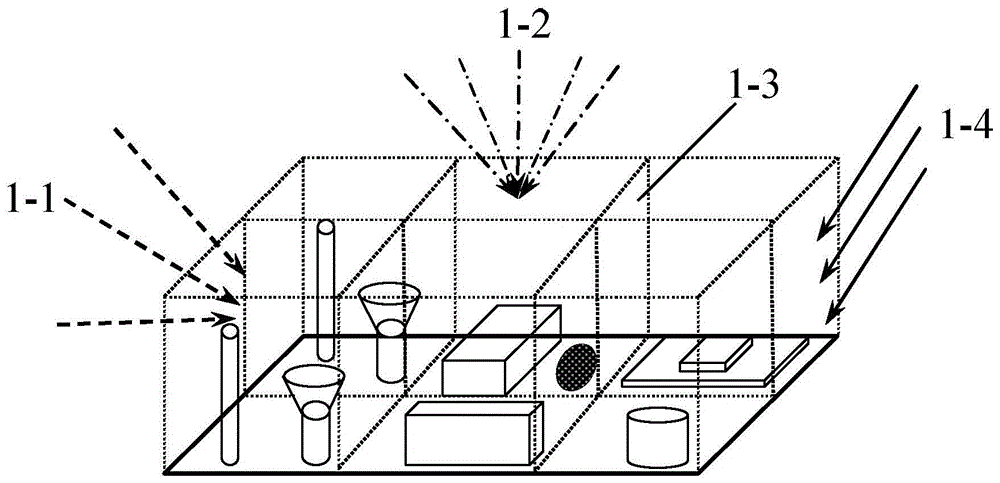
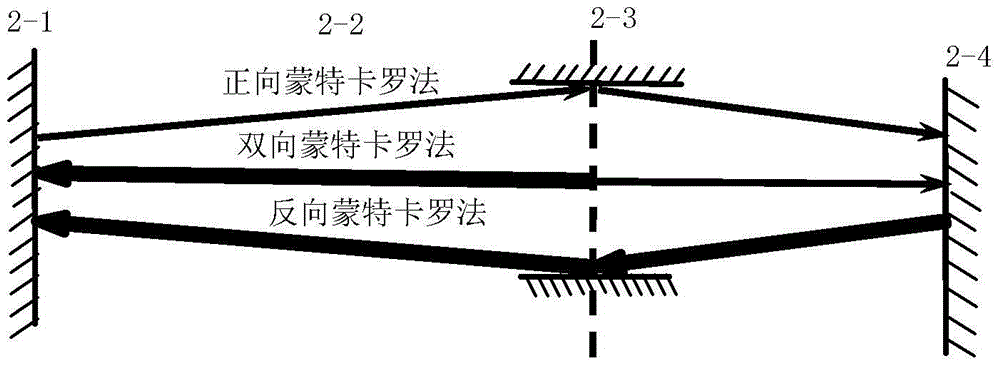
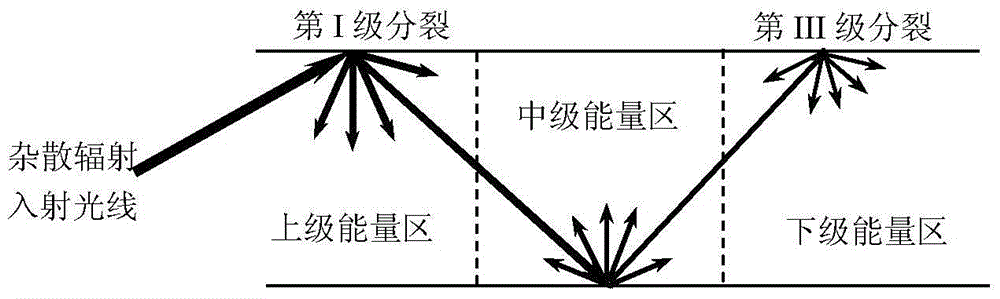
Stray radiation multi-scale simulation method of complex spatial optical detection system
InactiveCN104697751AProbing performance impact reducedRealize quantitative simulation calculationTesting optical propertiesDecompositionComputation process
A stray radiation multi-scale simulation method of a complex spatial optical detection system relates to the field of stray radiation of optical detection systems. The Monte Carlo method of light radiation propagation is used as the basic calculation principle. A modeling is performed under a multi-scale spatial geometric structure and energy levels, so as to perform a simulation calculation to spectral characteristics and energy level information characteristic identifiers. In the calculation process, inter-scale coupling relationships are introduced as bonding points of geometrical characteristics and optical characteristics under different scales. These coupling relationships include regional virtual interface light radiation characteristics, interface energy level division numbers and sampling probability models, and bidirectional reflectance distribution functions of micro-structural stray equivalent surfaces. Then a multilayer domain decomposition technology, a multilevel light division technology, and a reverse / bidirectional Monte Carlo method light tracing technology calculation method are comprehensively utilized for achieving the effective simulation of the multi-scale stray radiation transmission of the spatial optical system. The stray radiation multi-scale simulation method of the complex spatial optical detection system can be applied to the simulation of the multi-scale stray radiation of the optical detection systems.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Support system for breast irradiation
InactiveUS8218723B2Preventing the patient's legs from colliding with adjacentAdd supportPatient positioning for diagnosticsLight therapyRotational axisSupporting system
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
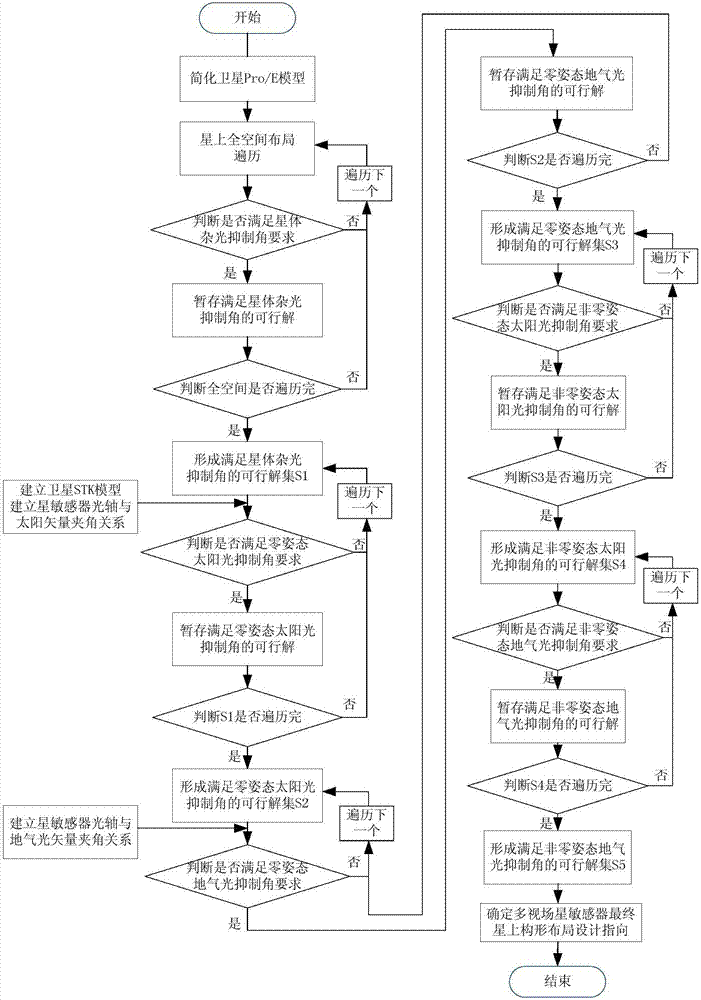
On-satellite configuration layout determining method of multi-field-of-view star sensors
ActiveCN107344630AEngineering practicabilityImprove practicalityCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOptical axisMulti field
Disclosed is an on-satellite configuration layout determining method of multi-field-of-view star sensors. Firstly, all possible optical axis orientations of the three star sensors are traversed according to a satellite Pro / E three-dimensional model, and then feasible solution sets which meet the requirement of a star stray radiation suppression angle of the star sensors are obtained; then feasible solution sets meeting the requirements of a sunlight suppression angle and a geogas light suppression angle at a zero attitude are obtained according to the feasible solution sets meeting the requirement of the star stray radiation suppression angle of the star sensors; and finally feasible solution sets meeting the requirements of the sunlight suppression angle and the geogas light suppression angle at a non-zero attitude are figured out, and therefore ultimate on-satellite configuration layout orientations of the multi-field-of-view star sensors are finished. Compared with the prior art, the method has the engineering practicability, is better than manual experience trial assembly in directivity and effectiveness and is excellent in practical effect.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Antenna with Anti-Interference Arrangement and Its Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20190379124A1Avoid interferenceNarrow bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsResonant antenna detailsElectromagnetic radiationExcitation signal
An antenna includes a reference ground and at least a radiating source spacedly disposed at the reference ground to define a radiating clearance between the radiating source and the reference ground, wherein the radiating source is electrically connected to the reference ground to ground the radiating source so as to narrow a bandwidth of the antenna. When a electromagnetic excitation signal is received at a feed point of the radiating source, the bandwidth of the antenna is narrowed down to prevent any interference of the electromagnetic wave signal received or generated by the antenna in response to nearby electromagnetic radiation frequency or stray radiation frequency of the adjacent frequency bands.
Owner:ZOU GAODI
In-orbit on-satellite Infrared radiation calibration system of multi-light integrated large-aperture space camera
ActiveCN109737987ADeduction of the effects of stray radiationImprove calibration accuracyMeasurement devicesResponsivityRadiance
The invention provides an in-orbit on-satellite Infrared radiation calibration system of a multi-light integrated large-aperture space camera. A low temperature calibration gray body and a high temperature calibration black body are alternately moved into a light path to obtain corresponding images, by obtaining a radiance difference value between the low temperature calibration gray body and thehigh temperature calibration black body and the difference value of picture element gray values of the corresponding images, the influence of internal stray radiation of the camera is effectively removed, and by obtaining the radiation responsivity of the corresponding pixel elements through data processing, the calibration accuracy and the level of quantitative inversion are improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for detecting and classifying explosives and controlled substances
InactiveUS7505544B2Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationControl substancesDetector array
Owner:FAJ INT HLDG
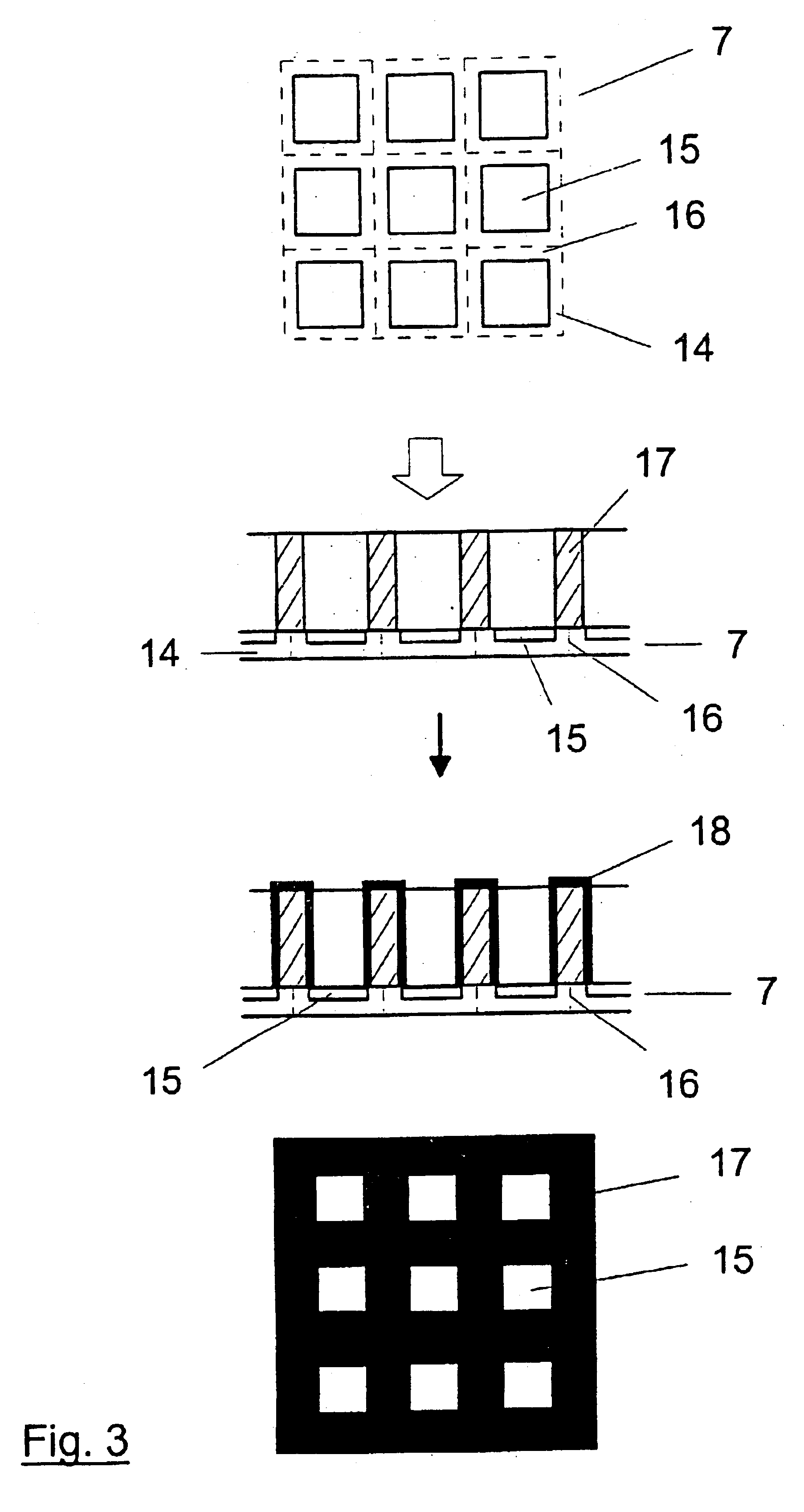
Method for mounting scattered raster on X-ray detector
InactiveCN1414397AAdditive manufacturing apparatusHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayQuantum efficiency
The invention relates to a method for mounting scattered raster on X-ray detector, the detector having a plurality of detector elements (14) arranged in a matrix that form a detector surface having detection regions (15) sensitive to X-rays and less sensitive intermediate regions (16), a basic structure (17) for the stray radiation grid is built up over the detector surface directly on the X-ray detector with a rapid prototyping technique and is subsequently coated or filled with a material that is highly absorbent for X-radiation. An absorbent structure (24) thus arises that lies over the less sensitive intermediate regions (16) of the detector surface. Moire disturbances are avoided in the X-ray image exposure and the detective quantum efficiency (DQE) is increased.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com