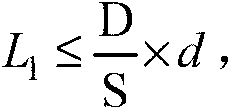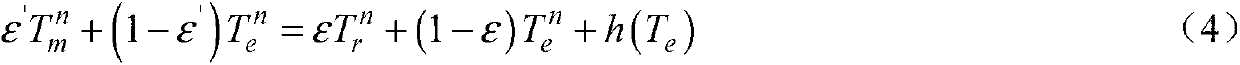Material emissivity measuring method based on infrared thermometer
A technology of infrared thermometer and measurement method, which is used in material excitation analysis, optical radiation measurement, material analysis, etc., and can solve the problems of poor measurement result accuracy, slow measurement speed, and complicated use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
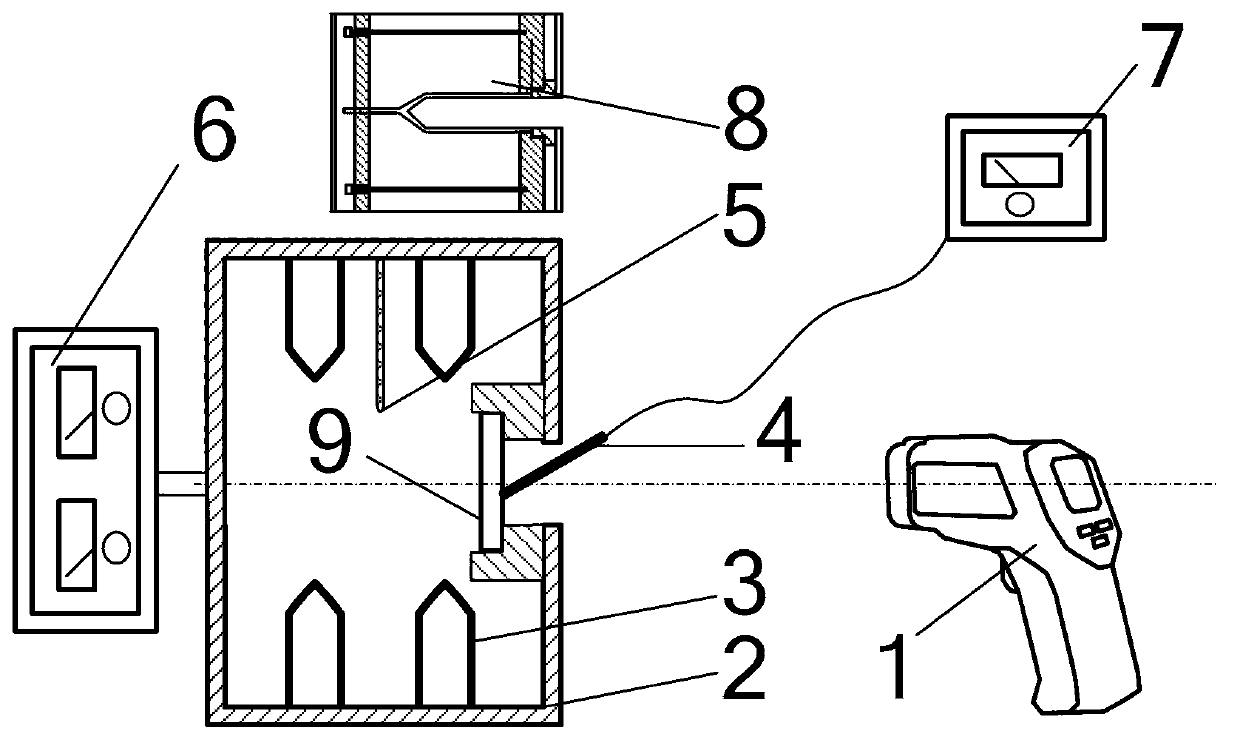
[0059] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the material emissivity measurement method based on an infrared thermometer described in this embodiment is realized by using an infrared thermometer 1, a thermocouple probe 4, a thermocouple thermometer 7, a black body furnace 8 and a temperature control system For the measurement of material emissivity, the temperature control system includes a heating furnace 2, a heater 3, a temperature acquisition device 5 and a temperature inspection controller 6, and the heating furnace 2 is provided with a circular light hole to realize material emission The rate measurement process is:
[0060] Step 1. First, the material to be tested is made into a circular test piece 9, wherein the material to be tested is an opaque material, and then the entrance pupil of the infrared thermometer 1 is aligned with the light transmission hole of the blackbody furnace 8. The blackbody furnace The emissivity of 8 is ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0071] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the stray radiation energy is calculated using the stray radiation subtraction algorithm described in the step 1, and the specific method is as follows:
[0072] The operating band of the infrared thermometer 1 is an atmospheric window, and the temperature measurement formula of the infrared thermometer 1 is expressed as,
[0073] ε′f(T m )+(1-ε′)f(T e ) = εf(T r )+(1-α)f(T e )+g(T e ) (1)
[0074] In the formula, T m is the temperature measured by infrared thermometer 1, unit K;
[0075] T r is the real temperature of the tested circular test piece 9, unit K;
[0076] T e is ambient temperature, unit K;
[0077] ε is the emissivity of the tested circular specimen 9;
[0078] ε' is the emissivity setting for the infrared thermometer 1;
[0079] α is the surface absorptivity of the tested circular test piece 9;
[0080] g(T e ) is stray radiant energy;
[00...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0096] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that in the step 7, the material emissivity ε of the material to be tested is calculated in the temperature range from room temperature to 1500°C. The specific implementation method is as follows:
[0097] The material emissivity ε expression is as follows,
[0098] ϵ = ϵ ′ ( T m n - T e n ) - g ( T e ) C T r ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com