Patents
Literature
130 results about "Specular surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
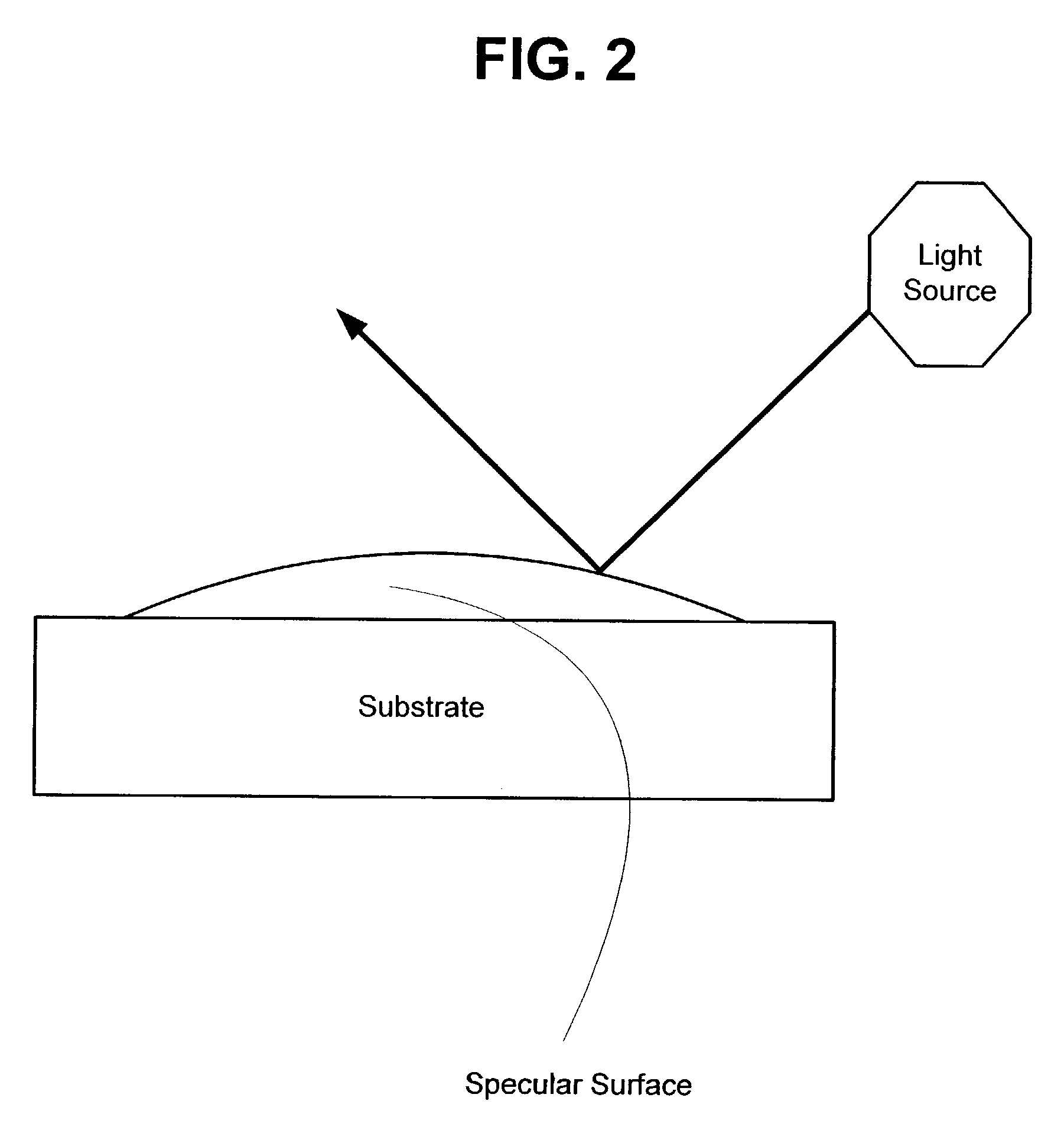
Specular surface. A mirror-like surface which reflects light at an angle equal to that of the incident light.
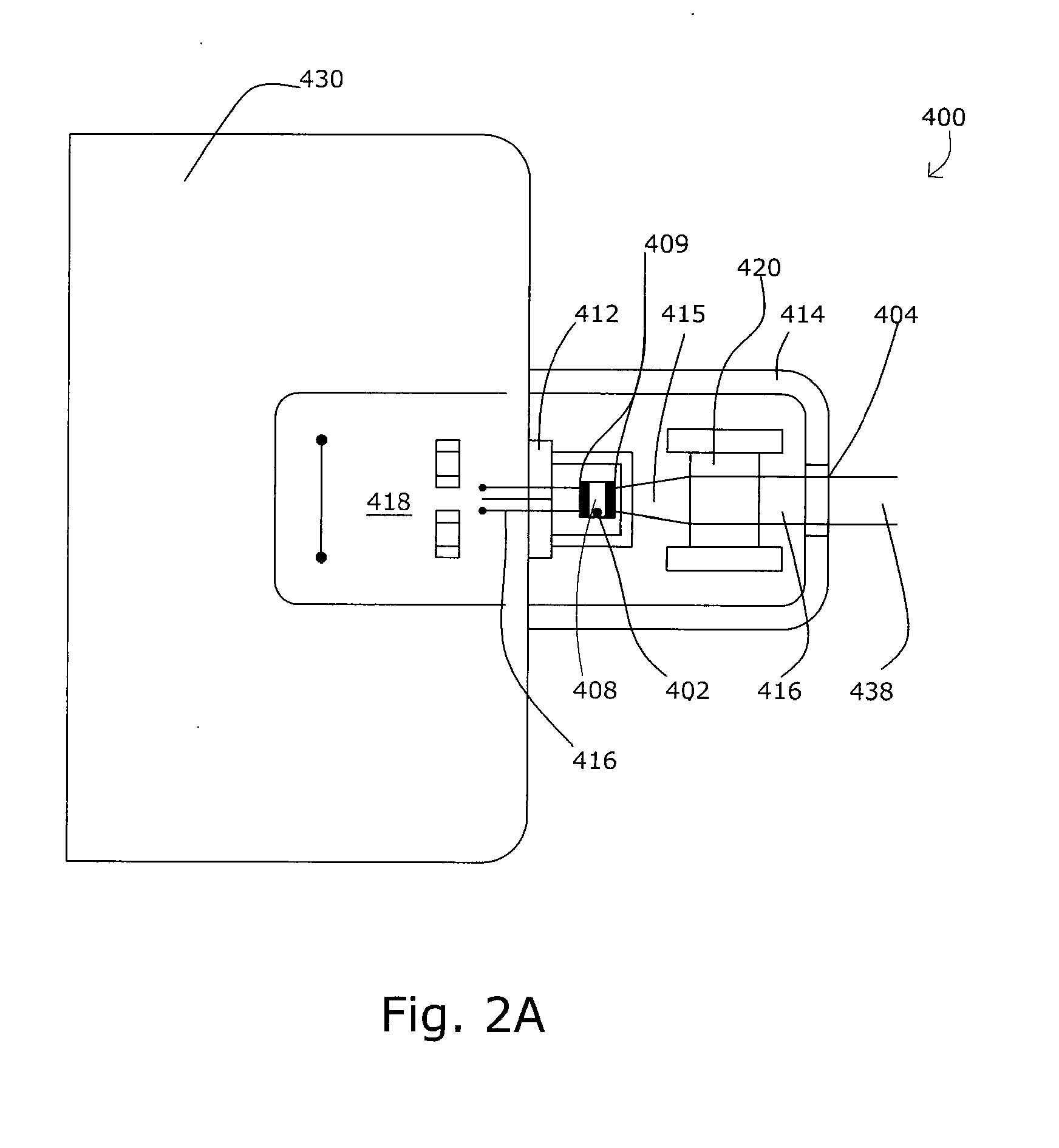
Pointing device with an integrated optical structure
InactiveUS20070146318A1Reduce spendingImprove mobilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPrismImaging lens
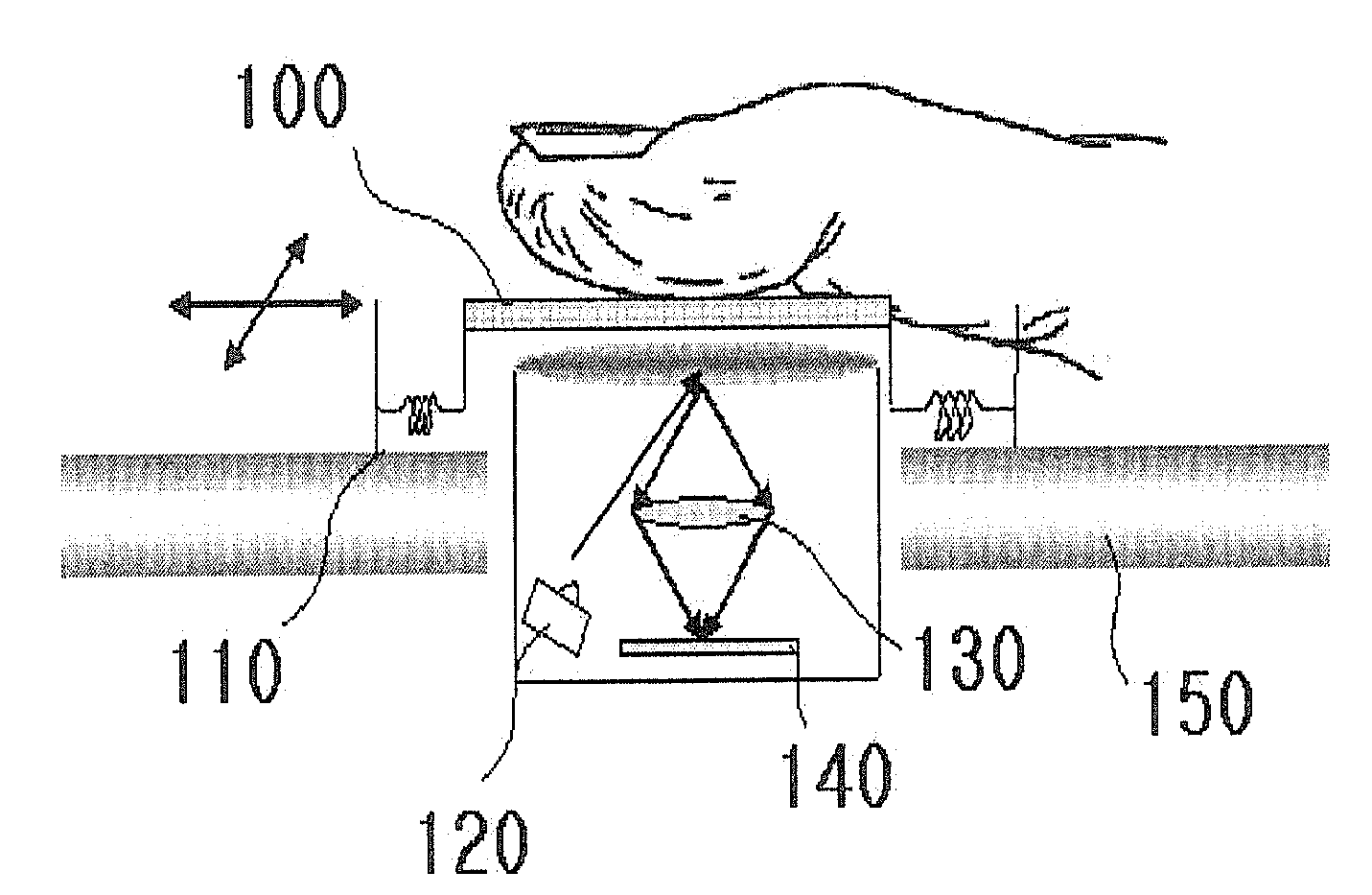
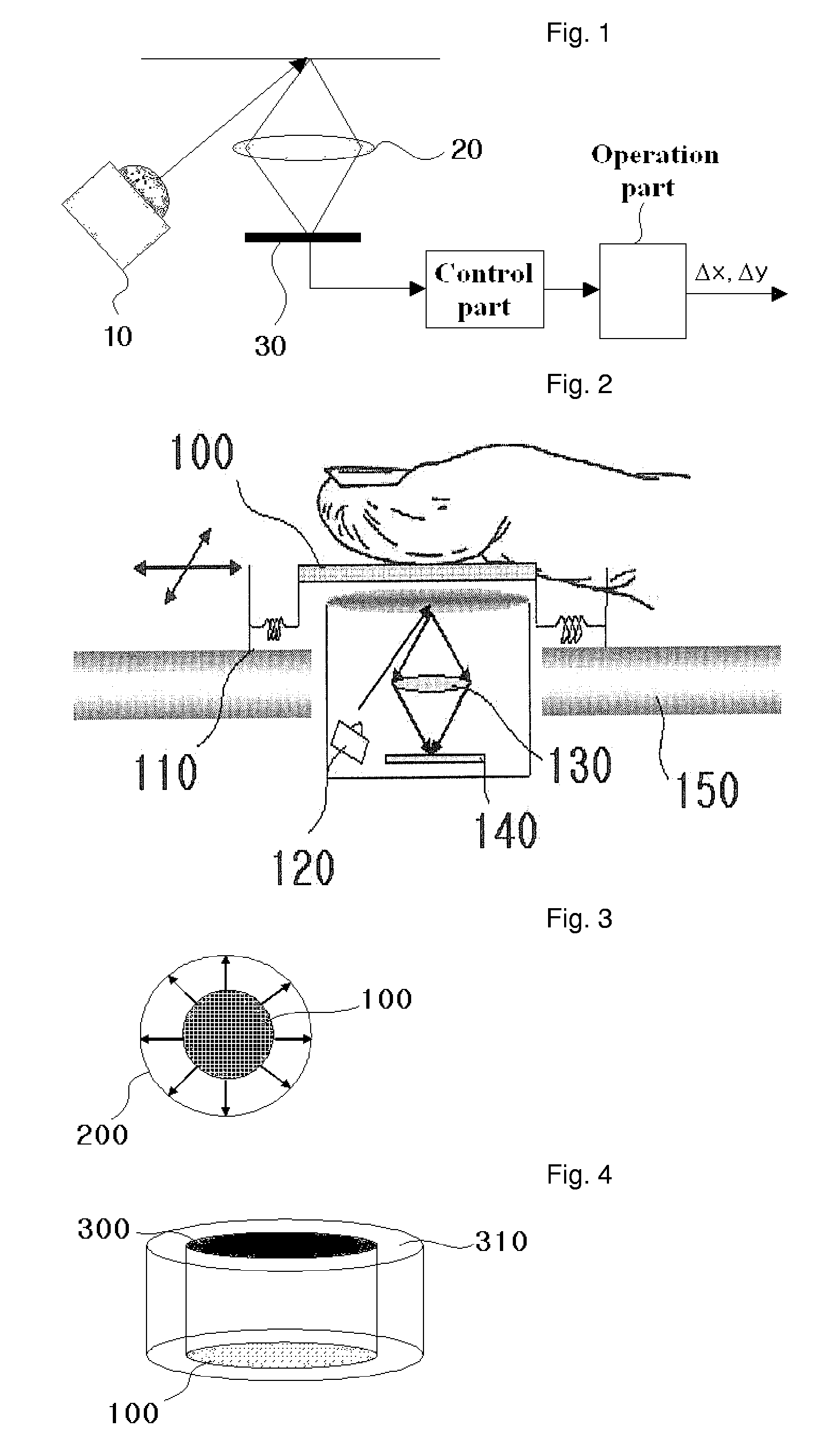
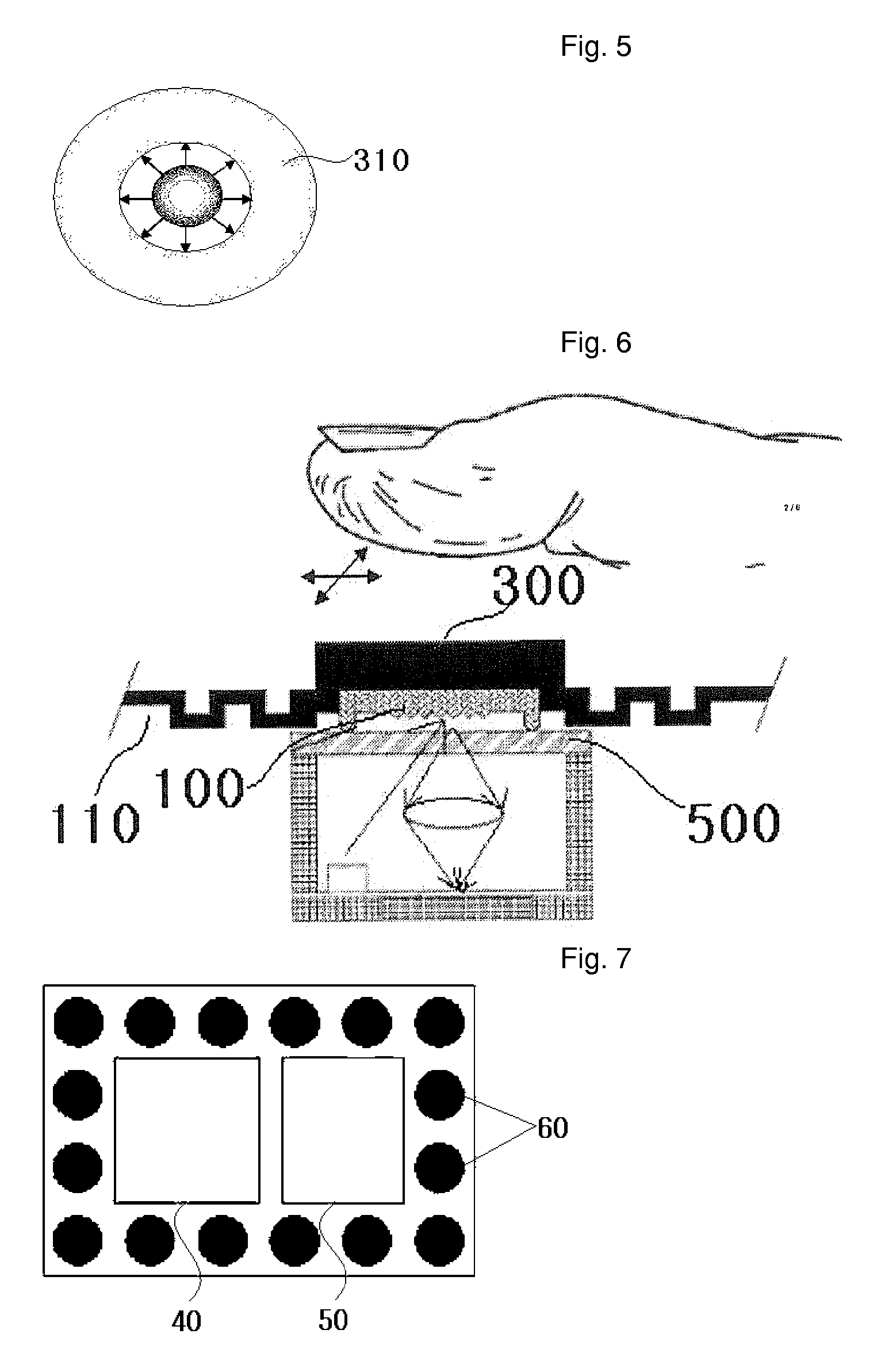
The present invention relates to a micro-optical pointing device suitable for mobile terminals such as a cellular phone and PDA. A disclosed pointing device includes a light source emitting light rays to a subject; a contact member comprising a lattice type or perceivable pattern, which reflects an image of the moving subject; and an automatic transfer device restoring the contact member moved by a finger. The pointing device may further include a flip chip containing an image sensor, which converts the acquired image into an electronic signal, and a circuit for signal processing. The pointing device may include an integrated optical structure comprising a condensing lens, a specular surface, a light output part, and an image-formation lens. The pointing device may include a light guide structure that a parallel light prism lens, an image-formation lens, and a mask for blocking disturbance ray are formed into a single part.
Owner:MOBISOL +1
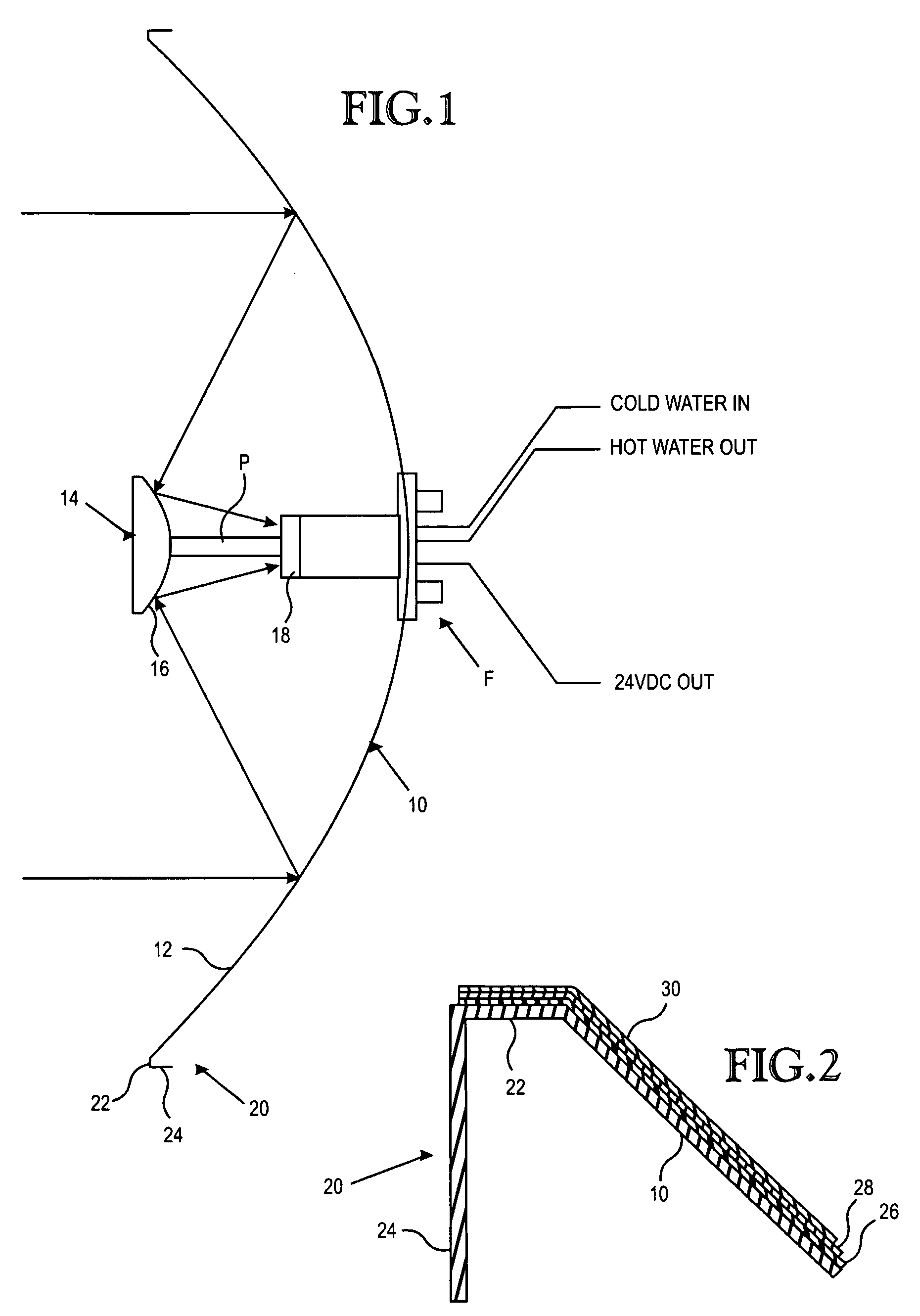
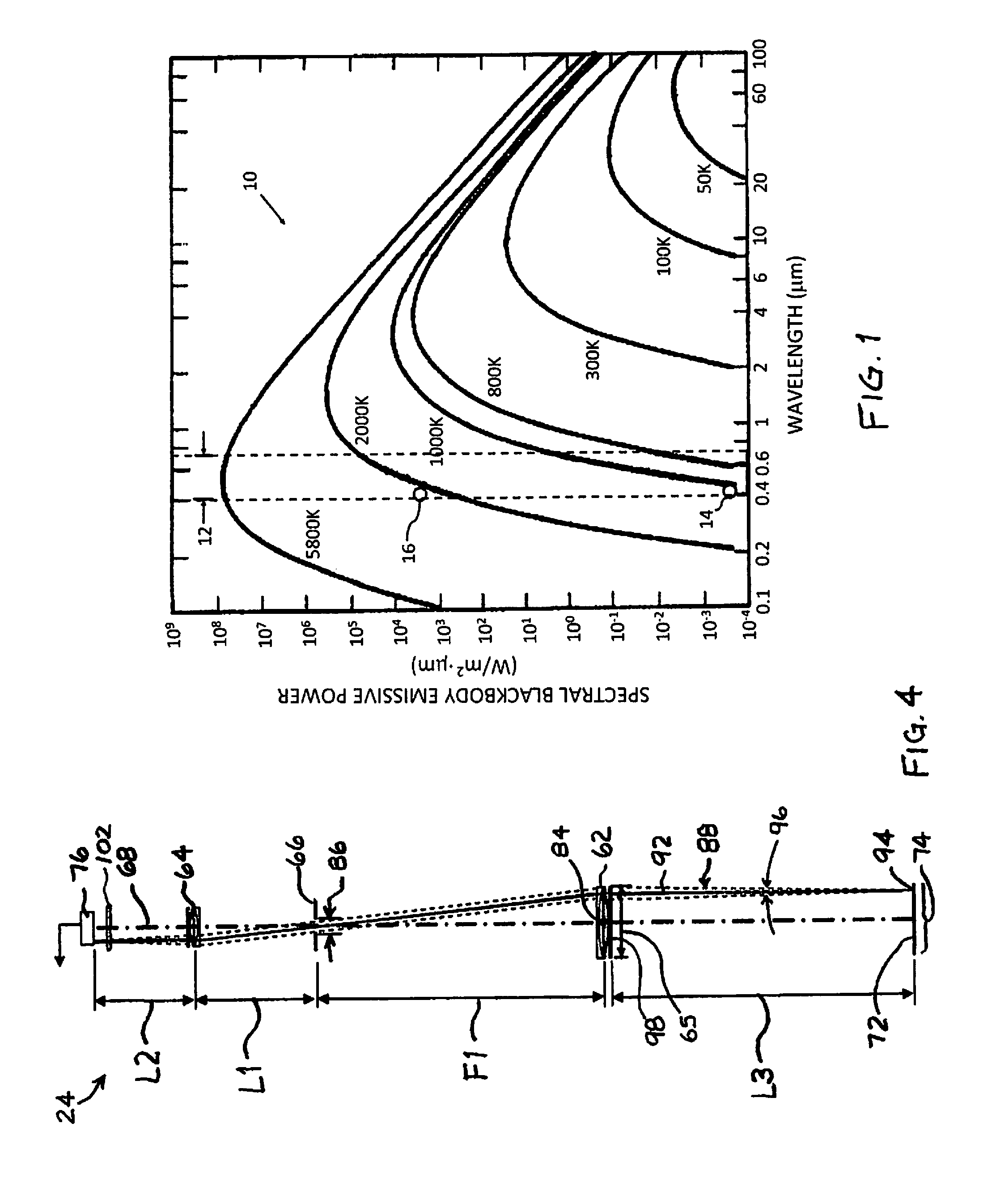
Conversion of solar energy to electrical and/or heat energy
InactiveUS20080163922A1Improve efficiencyIncrease light intensitySolar heating energyMirrorsEngineeringSpecular surface
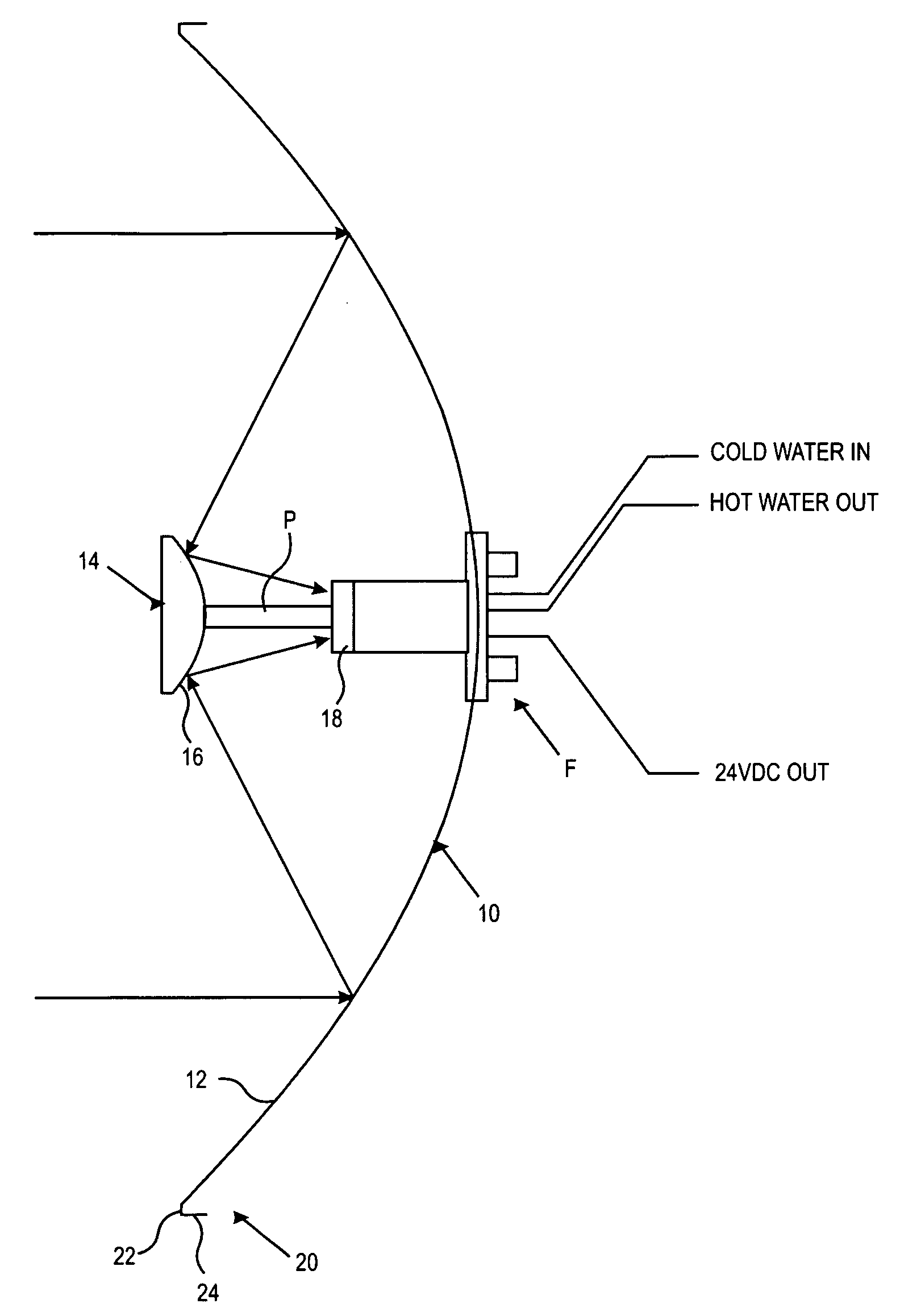
A parabolic primary mirror (10) has a concave specular surface (12) that is constructed and positioned to receive solar energy and focus it towards a focal point. A secondary mirror (14) having a convex specular surface (16) is constructed and positioned to receive focused solar energy from the primary mirror and focus it onto an annular receiver (18). The annular receiver (18) may include an annular array of optical elements (100) constructed to receive solar energy from the secondary specular surface (14) and focus it onto a ring of discreet areas. A ring of solar-to-electrical conversion units are positioned on the ring of discreet areas. A sun sensor that allows accurate solar tracking to keep mirror system aligned with the sun.
Owner:EDTEK INC
Projection-type display devices with reduced speckle
InactiveUS20070195276A1Reduce disagreementExtend your lifeTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceLight beam
Described herein are display devices that provide projection-type video output and use lasers to generate light. To reduce any speckle effects for a projected image cast by a projector onto of a non-specular surface, the present invention decreases coherence of the laser-generated light. Coherence reduction is accomplished by introducing a coherence diffuser in a light path of the laser light. Arranging the coherence diffuser in an unfocused light beam reduces both temporal and spatial coherence in the light. Arranging the rotating diffuser at the focus of a beam reduces only the temporal coherence while maintaining the spatial coherence.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IMAGE
Optical waveguide having specular surface formed by laser beam machining
InactiveUS7324723B2Good effectObtain goodCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesLaser beam machiningIrradiation
An optical waveguide having means for performing optical coupling with high efficiency at a predetermined position in an optical circuit substrate and which optionally includes an optical-electrical circuit board. Also provided are an optical waveguide, an optical path thereof being changed in an optical circuit at a steep angle and the optical waveguide for performing coupling and splitting of light being decreased in size in the optical circuit. The optical waveguide has a core and a cladding layer, and a wall surface, which is formed by cutting out at least a part of the core in a thickness direction of the core through irradiation of a laser beam and crosses at least a part of the core, which is a specular surface.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Microlithography reduction objective and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6902283B2Efficiently maskedThe implementation process is simpleMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage planePhysics
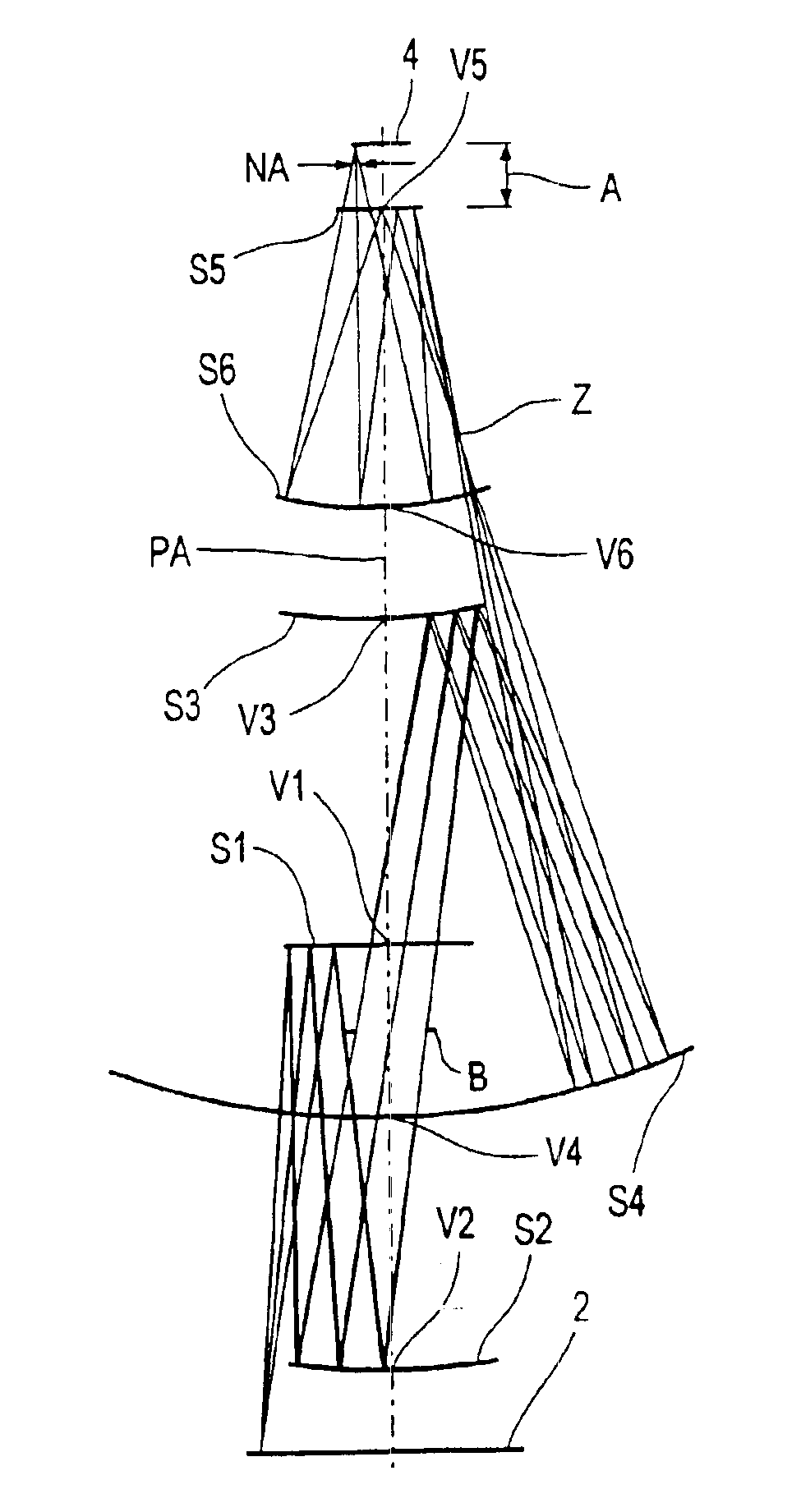
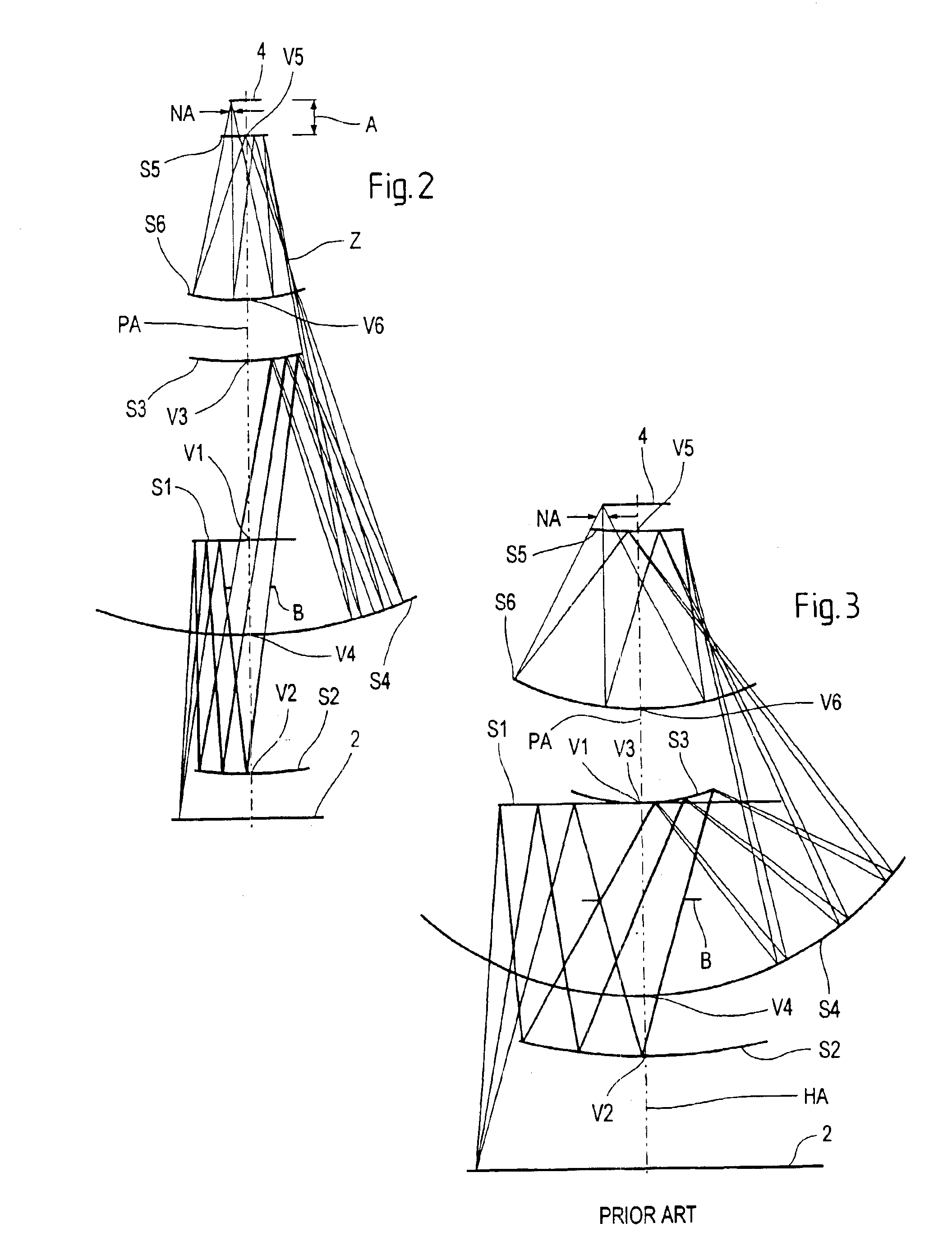
A projection objective formed from six mirrors arranged in a light path between an object plane and an image plane is provided. The projection objective, in some examples, is characterized by having a physical distance between the vertexes of adjacent mirrors that is large enough to allow for the six mirrors to have sufficient thickness and stability properties to prevent surface deformations due to high layer tensions. In some embodiments, mirror thickness are such that surface deformations are prevented with mirrors having layer tensions lower than 350 MPa. Mirror surfaces may comprise multilayer systems of Mo / Be or Mo / Si layer pairs. In some examples, the physical distance between a vertex of the third mirror and a vertex of the sixth mirror (S3S6) satisfies the following relationship: 0.3×(a used diameter of the third mirror S3+a used diameter of the sixth mirror S6)<S3S6. In some examples, a ratio of a physical distance between a vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the third mirror (S1S3) to a physical distance between the vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the second mirror (S1S2) is within the range of: 0.5<S1S3 / S1S2<2. In some examples, the physical mirror surfaces of the mirrors have a rotational symmetry with respect to a principal axis (PA). In some examples, all physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. In some examples, at most five physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. Other examples are provided, along with microlithography projection exposure apparatuses and processes for producing a microelectronic device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS STIFTUNG
Optical waveguide having specular surface formed by laser beam machining
InactiveUS20050074207A1Small sizeCoupling efficiency is highCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesLaser beam machiningOpto electronic
An optical waveguide having means for performing optical coupling with high efficiency at a predetermined position in an optical circuit substrate and which optionally includes an optical-electrical circuit board. Also provided are an optical waveguide, an optical path thereof being changed in an optical circuit at a steep angle and the optical waveguide for performing coupling and splitting of light being decreased in size in the optical circuit. The optical waveguide has a core and a cladding layer, and a wall surface, which is formed by cutting out at least a part of the core in a thickness direction of the core through irradiation of a laser beam and crosses at least a part of the core, which is a specular surface.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
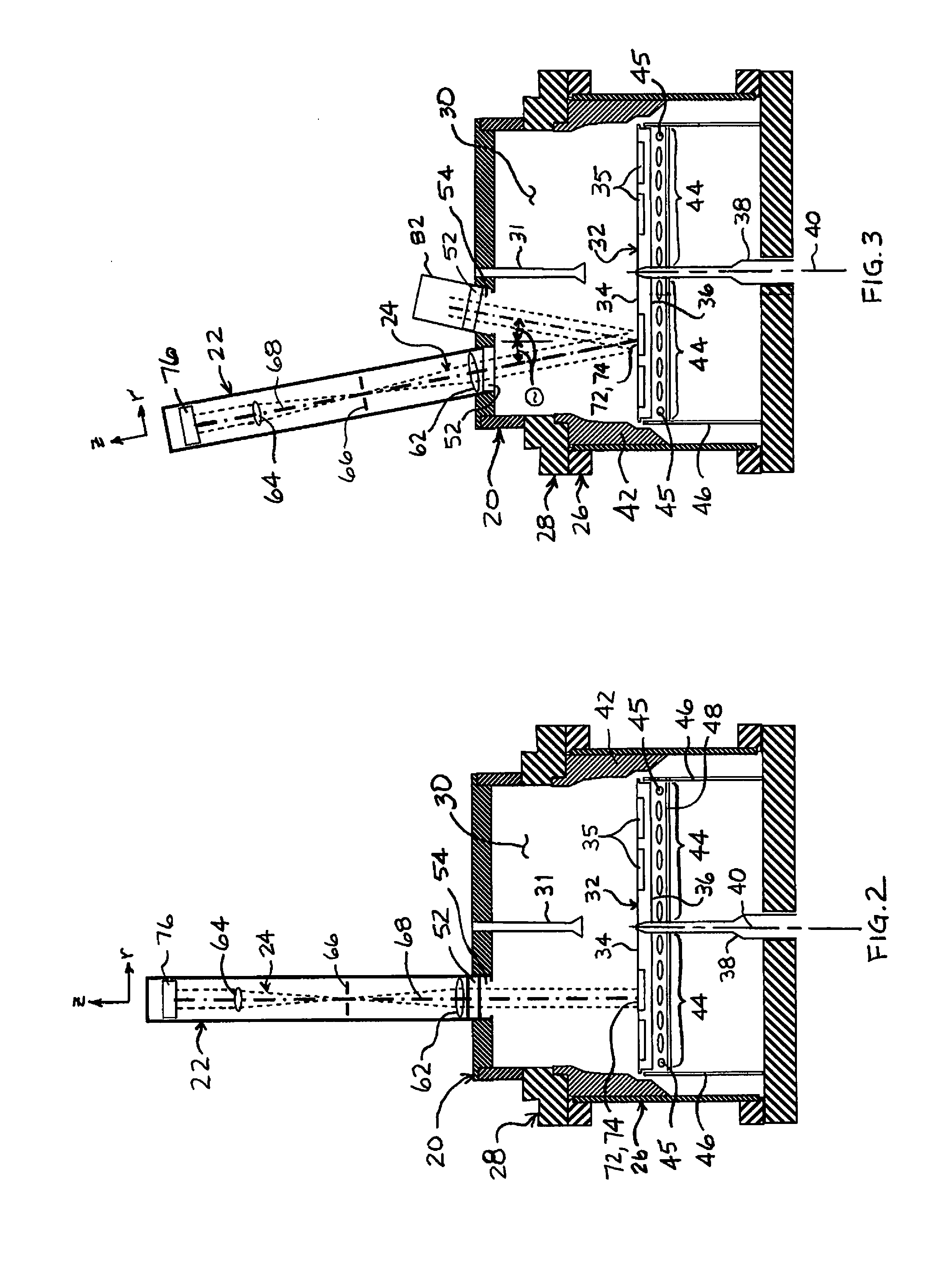
Illuminator
InactiveUS20050052873A1Reduce manufacturing costSimplify the assembly processTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusSpecular surfaceRetroreflector
An illuminator in which etendue of collected light emitted from a light source can be dynamically controlled. The illuminator includes a light source generating and emitting light, a concave reflector reflecting the light in a predetermined direction, and a retro-reflector placed in the path of the light reflected by the concave reflector. The retro-reflector has an aperture transmitting some of the light and a specular surface reflecting the rest of the light toward the concave reflector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for sensing at least one partially specular surface
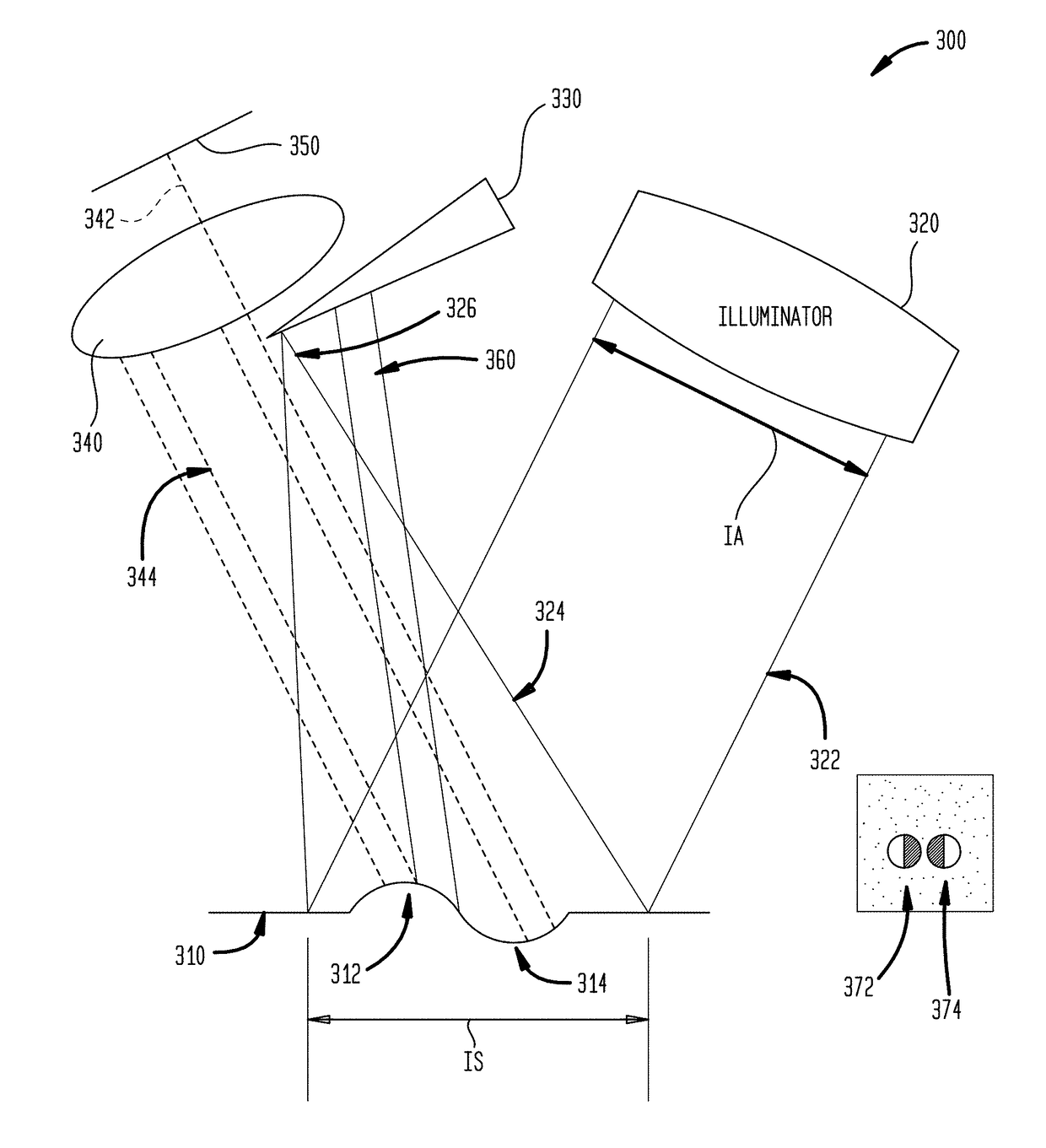
ActiveUS20160169798A1High resolutionScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansSpecular surfaceBiomedical engineering
Among a device and a method for sensing at least partially specular surfaces, the device includes a detection face and an illuminator configured to project a pattern onto the detection face by reflection via the at least partially specular surface.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
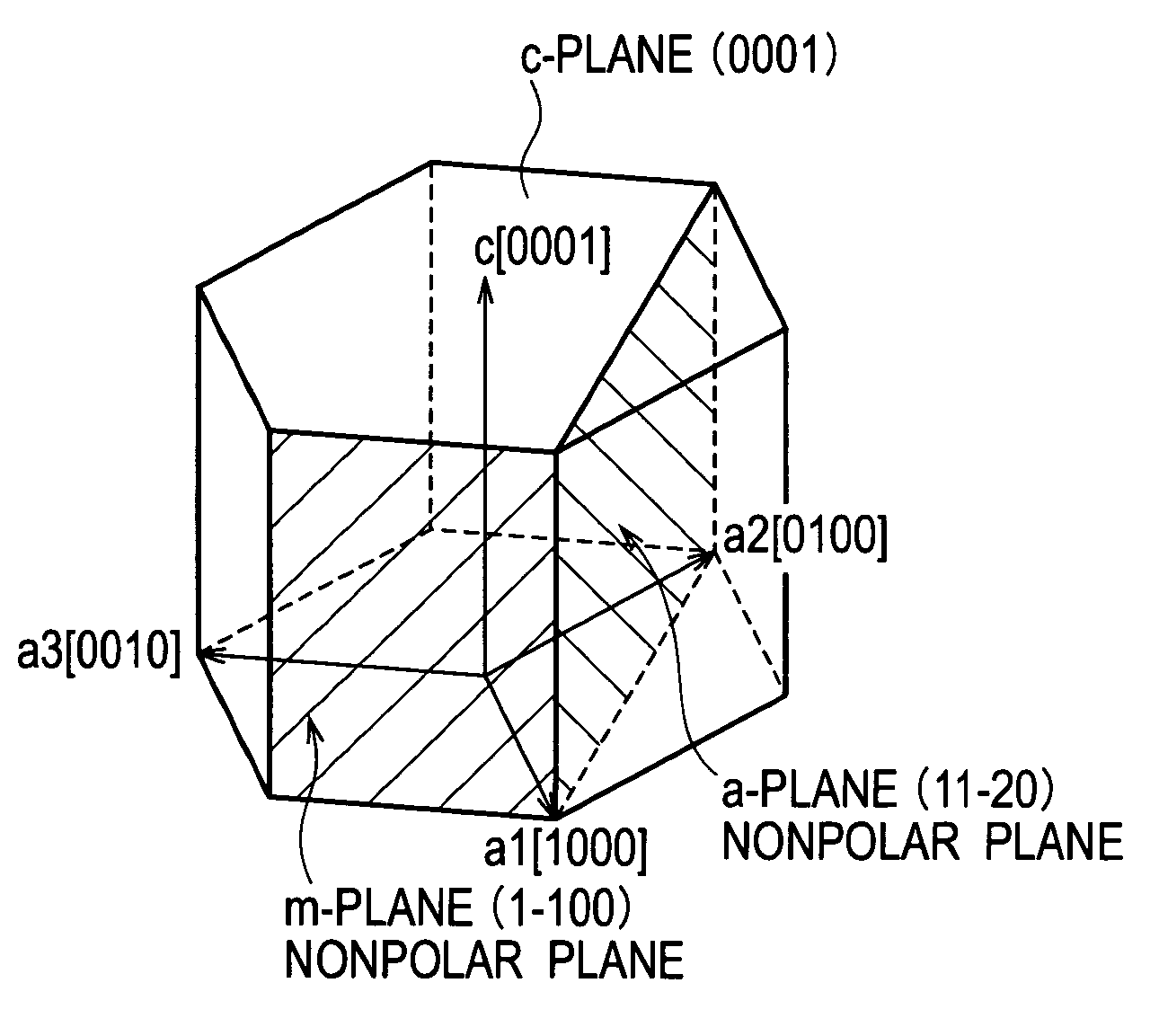
Semiconductor light emitting device
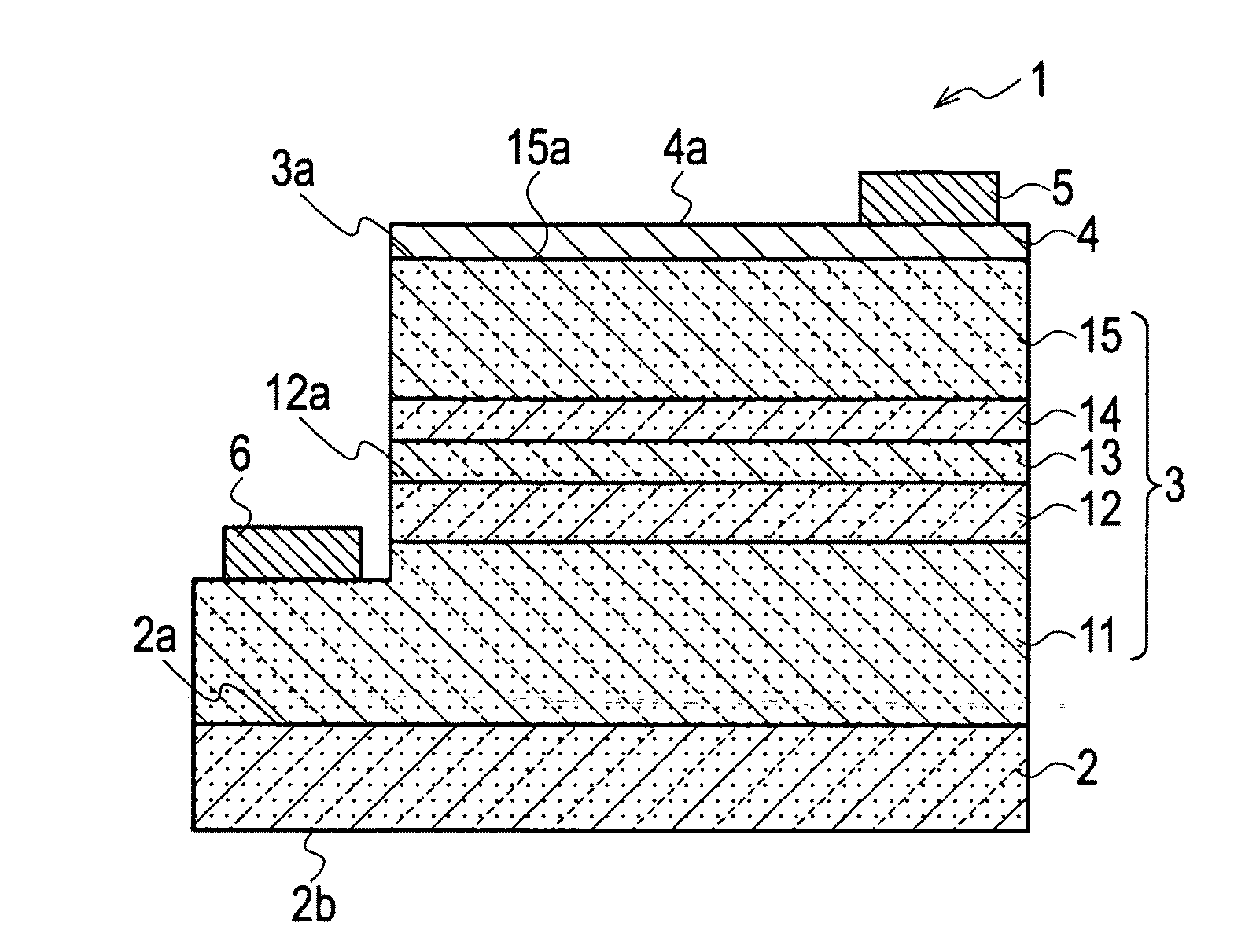
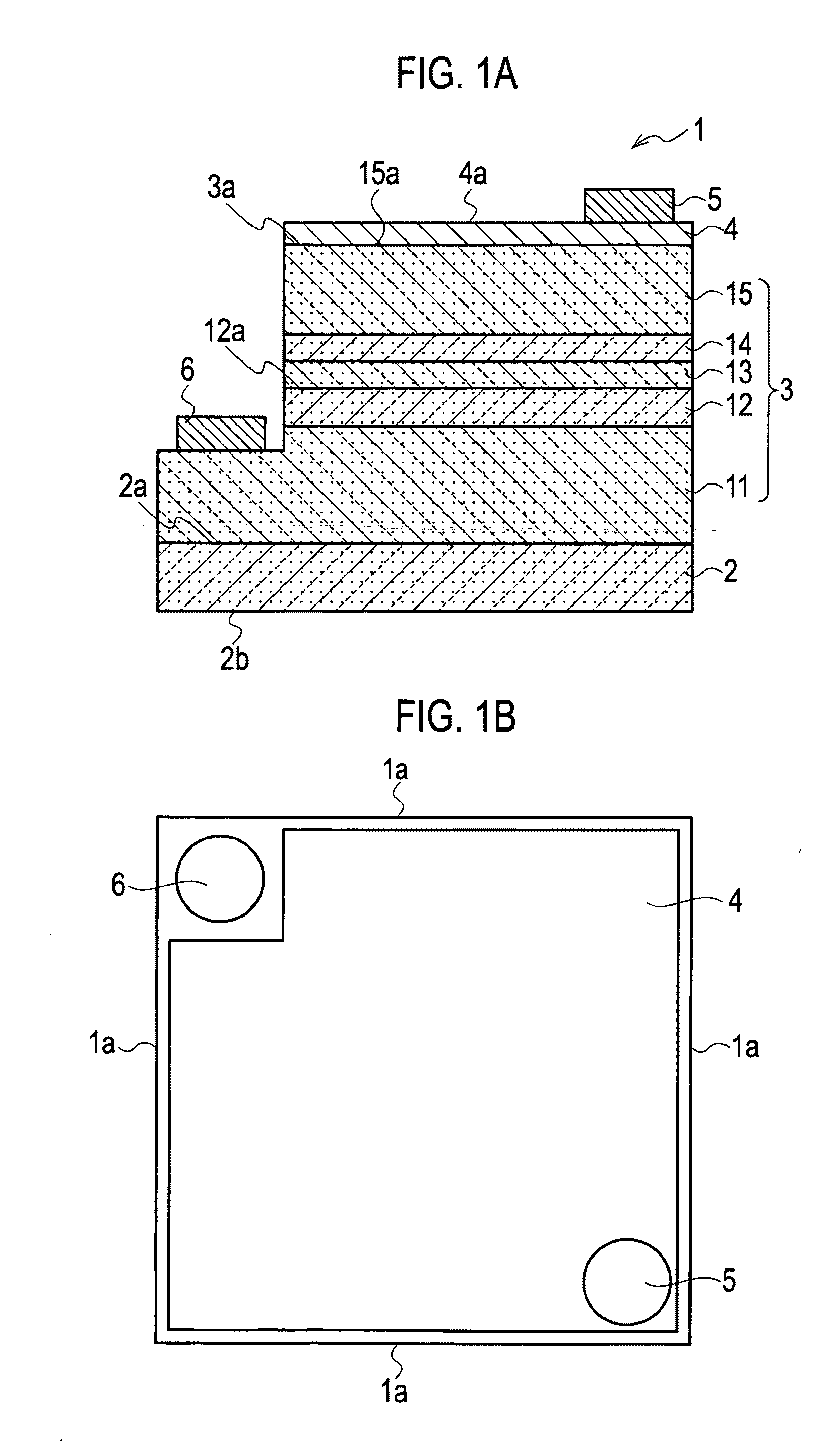
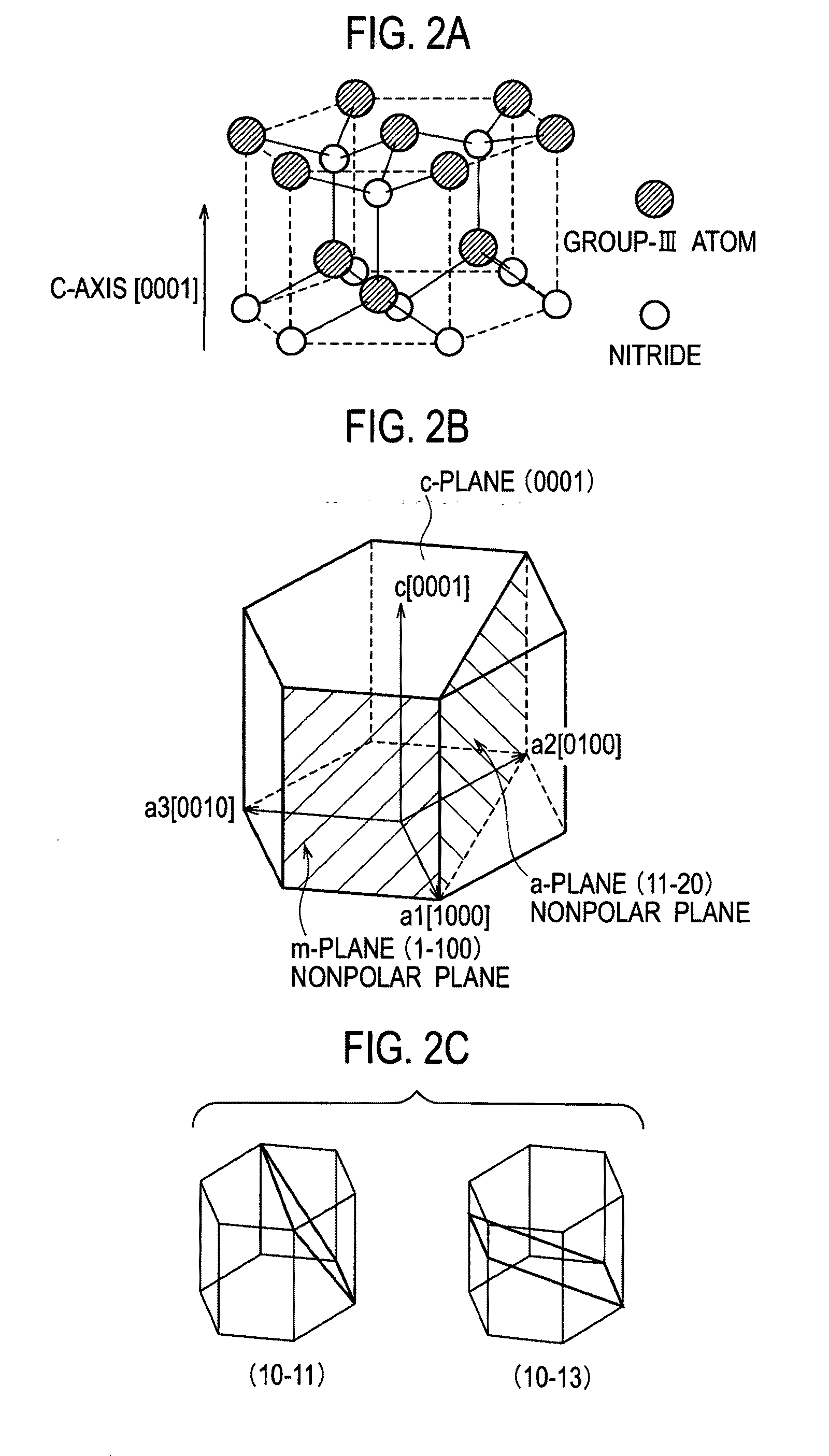
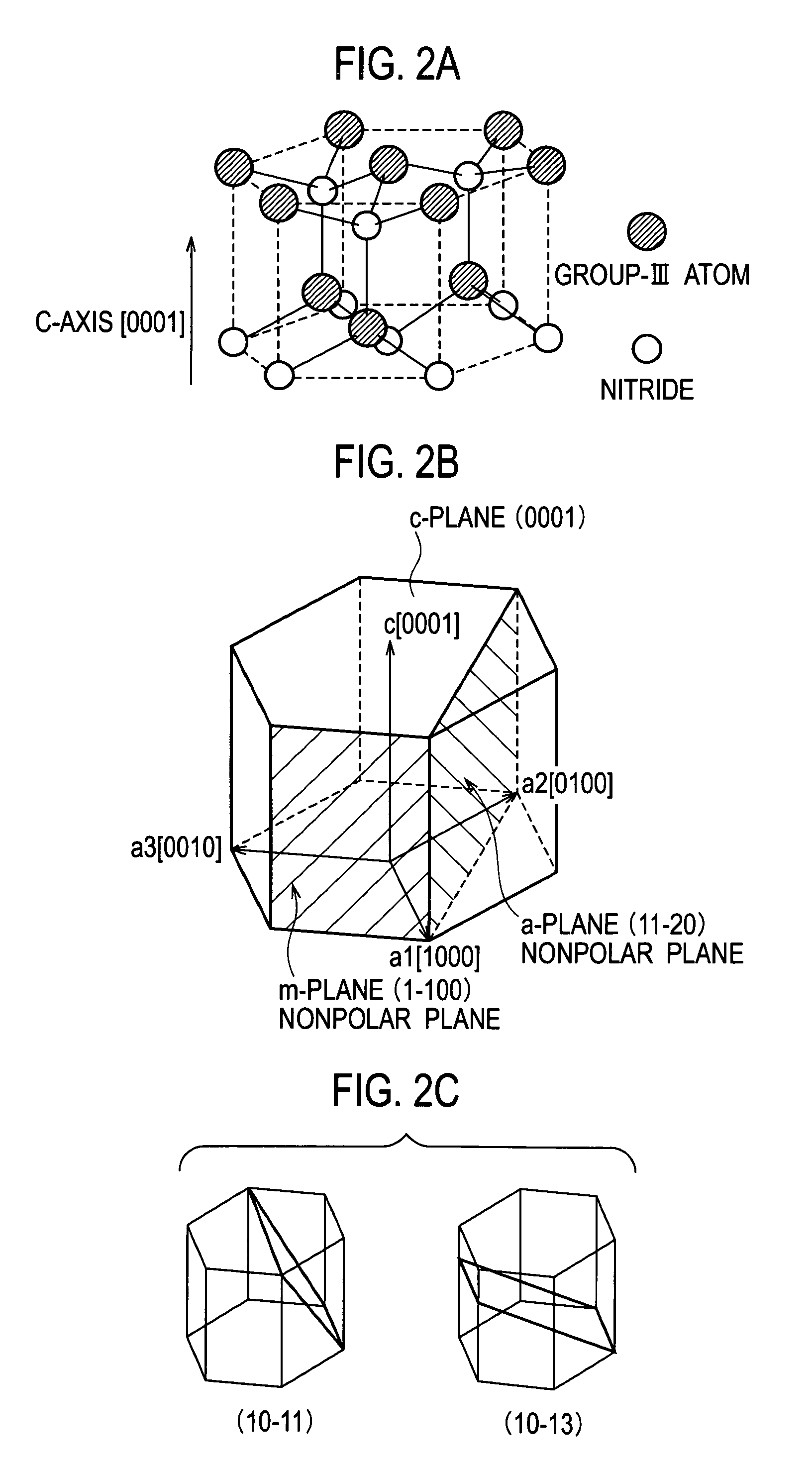
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a substrate, and a light emitting portion that is disposed on the substrate, and includes an active layer formed of a group III nitride semiconductor using a nonpolar plane or a semipolar plane as a growth principal surface, in which side end surfaces of the active layer are specular surfaces.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Steganographically encoding specular surfaces
InactiveUS7162052B2Prevent and detect counterfeitingOther printing matterPaper-money testing devicesDiffuse reflectionSpecular surface
The present invention provides techniques to steganographically mark specular surfaces. In one implementation, we steganographically mark a specular surface by providing a steganographic signal including at least plural-bit data, and arranging ink in a pattern on the specular surface to represent the steganographic signal. The ink preferably provides a diffuse reflection property.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Astigmatism-eliminating three-reflector optical system
InactiveCN1350190AEasy to processEasy to manufactureMirrorsTelescopesOptical axisOptical communication
The anastigmatic three-reflector optical system includes main reflector, second reflector and third reflector. The second reflector is a phserical one, its optical axis is the optical axis of said optical system, and the optical axises of main reflector and third reflector and optical axis of said system are in same plane, and deviated from optical axis of the system, and have no any angular inclination with optical axis of system. The specular surfaces of the main reflector and third reflector are secondary ellipsoial surface respectively. Said invented system mainly is used as space telescopic optical system, also can be used in optical communication field.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
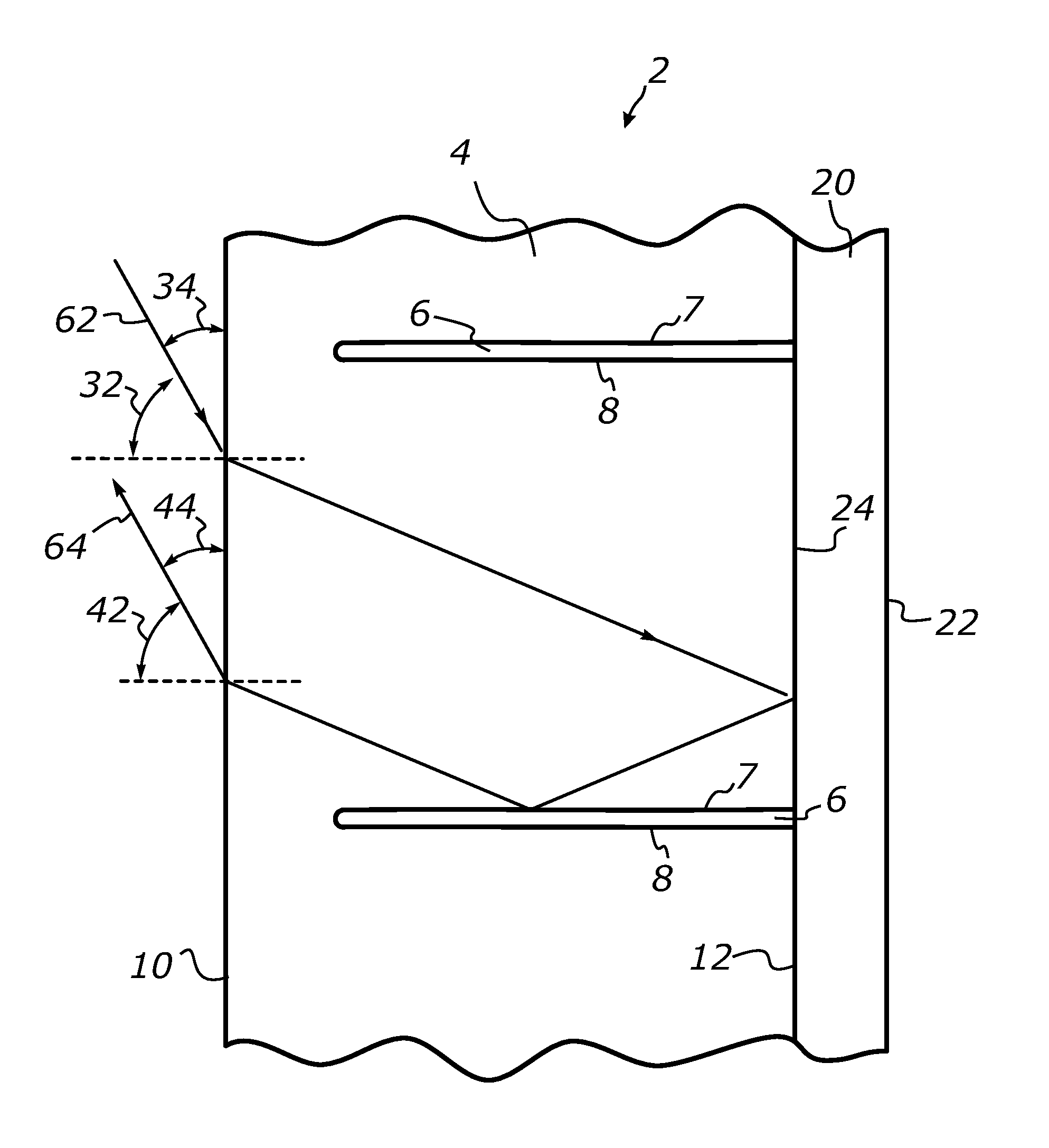
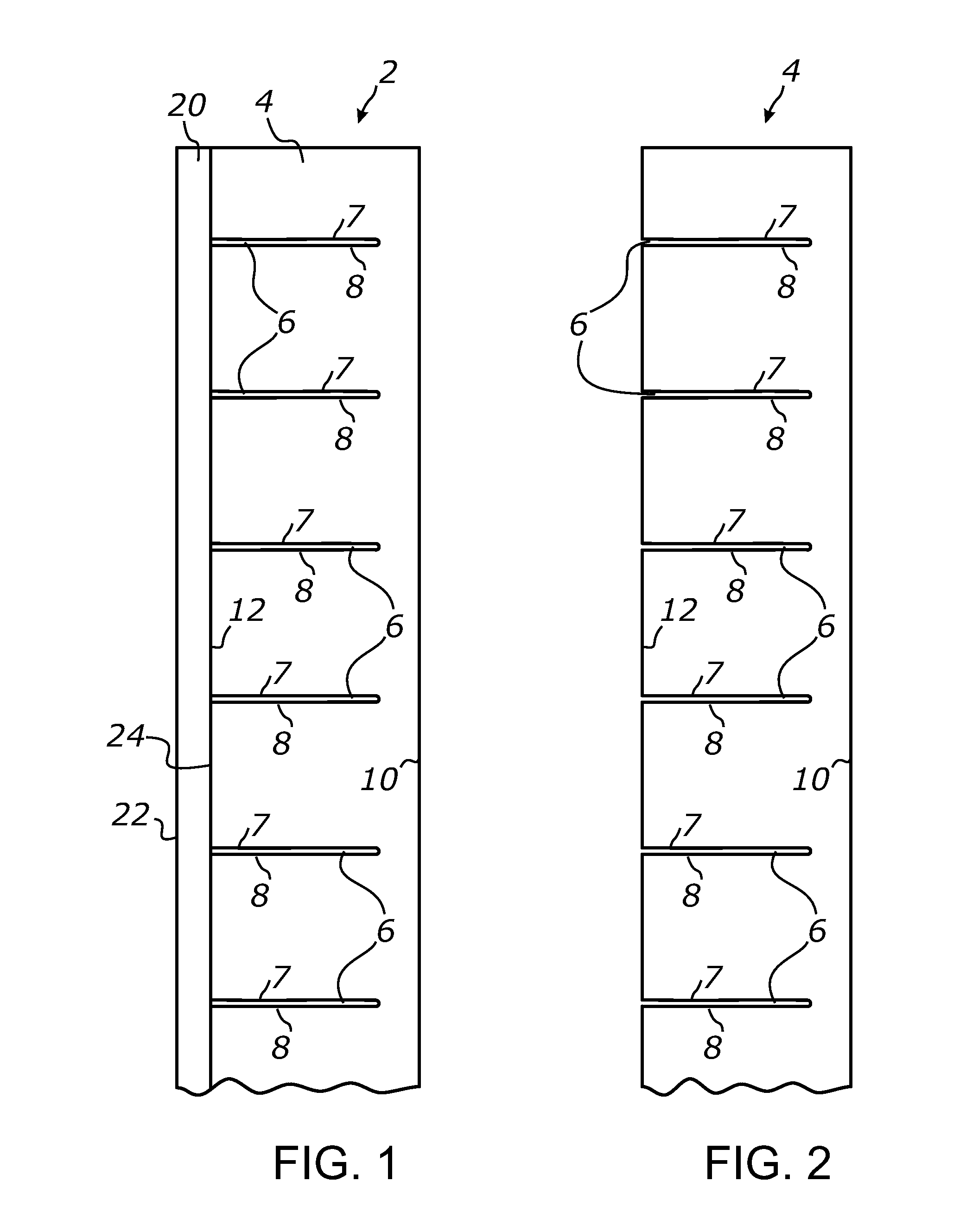
Apparatus and method for measuring decay in intensity of electromagnetic radiation in multipass spectrometry
InactiveUS6940600B1Transmissivity measurementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyMass spectrometryElectromagnetic radiation
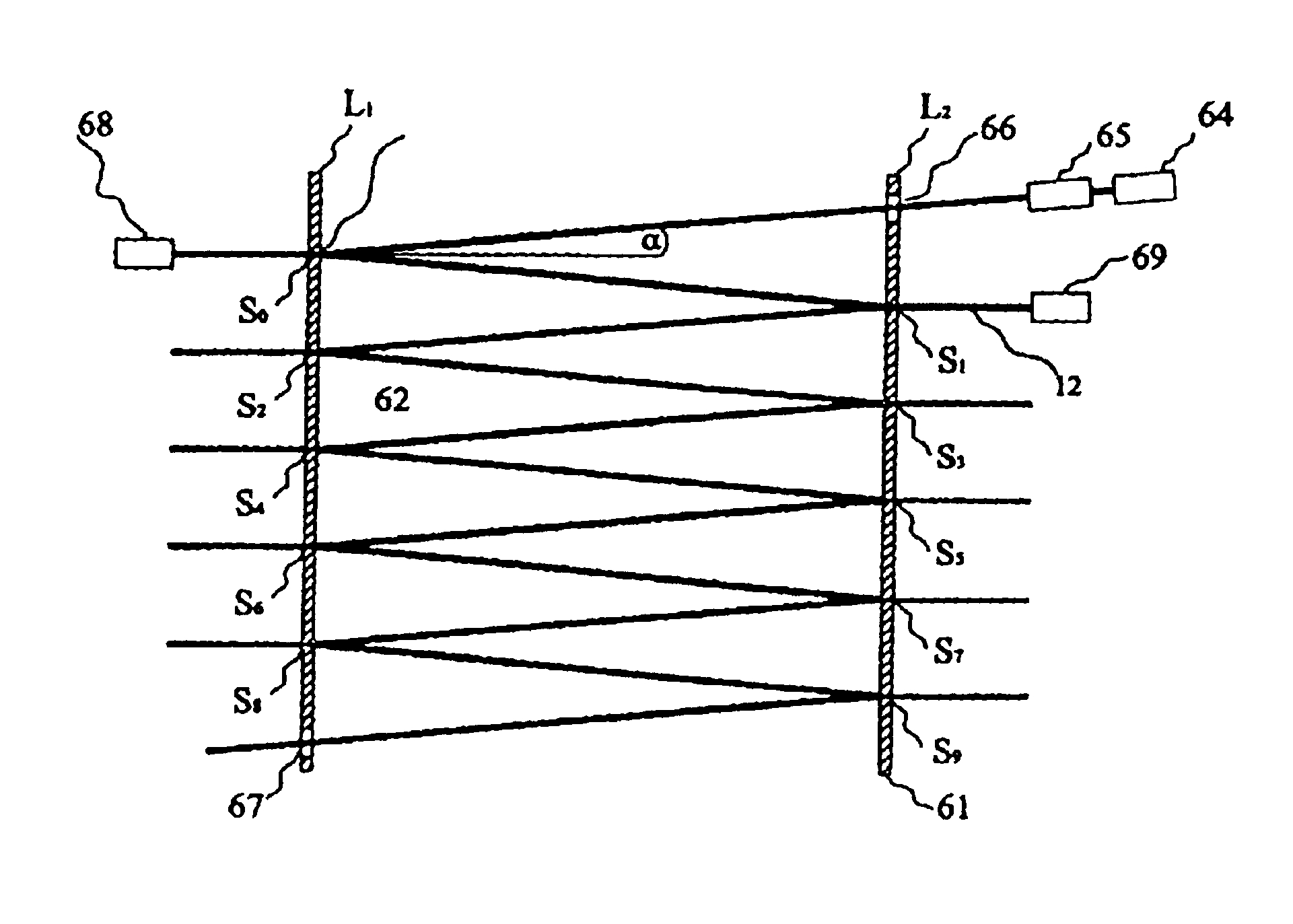
An apparatus for measuring decay in intensity of electromagnetic radiation passing through a radiation-absorbent sample due to absorption of radiation by the sample is disclosed which includes a source of electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength within an absorption band of the sample and a plurality of partially-reflective specular surfaces which are spaced apart from each other along a predetermined path through the sample, each specular surface separating the incident radiation into a reflected part which follows the predetermined path and an unreflected path, the value of the decay being derived from intensity measurements of the unreflected parts made at different positions along the predetermined path.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
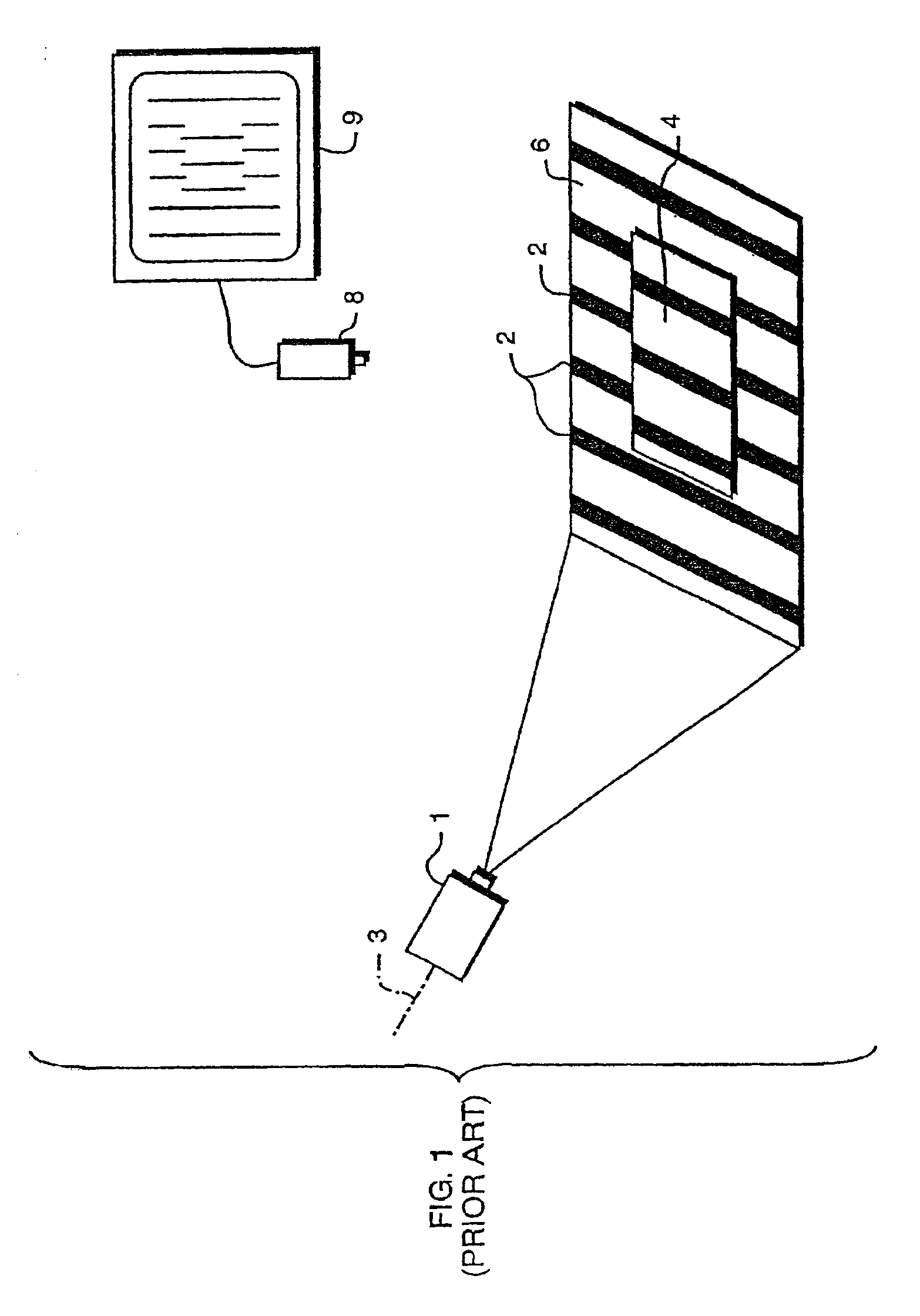
Method for three-dimensional inspection using patterned light projection
InactiveUS7075662B2Decreased F-numberOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansOptical axisTriangulation
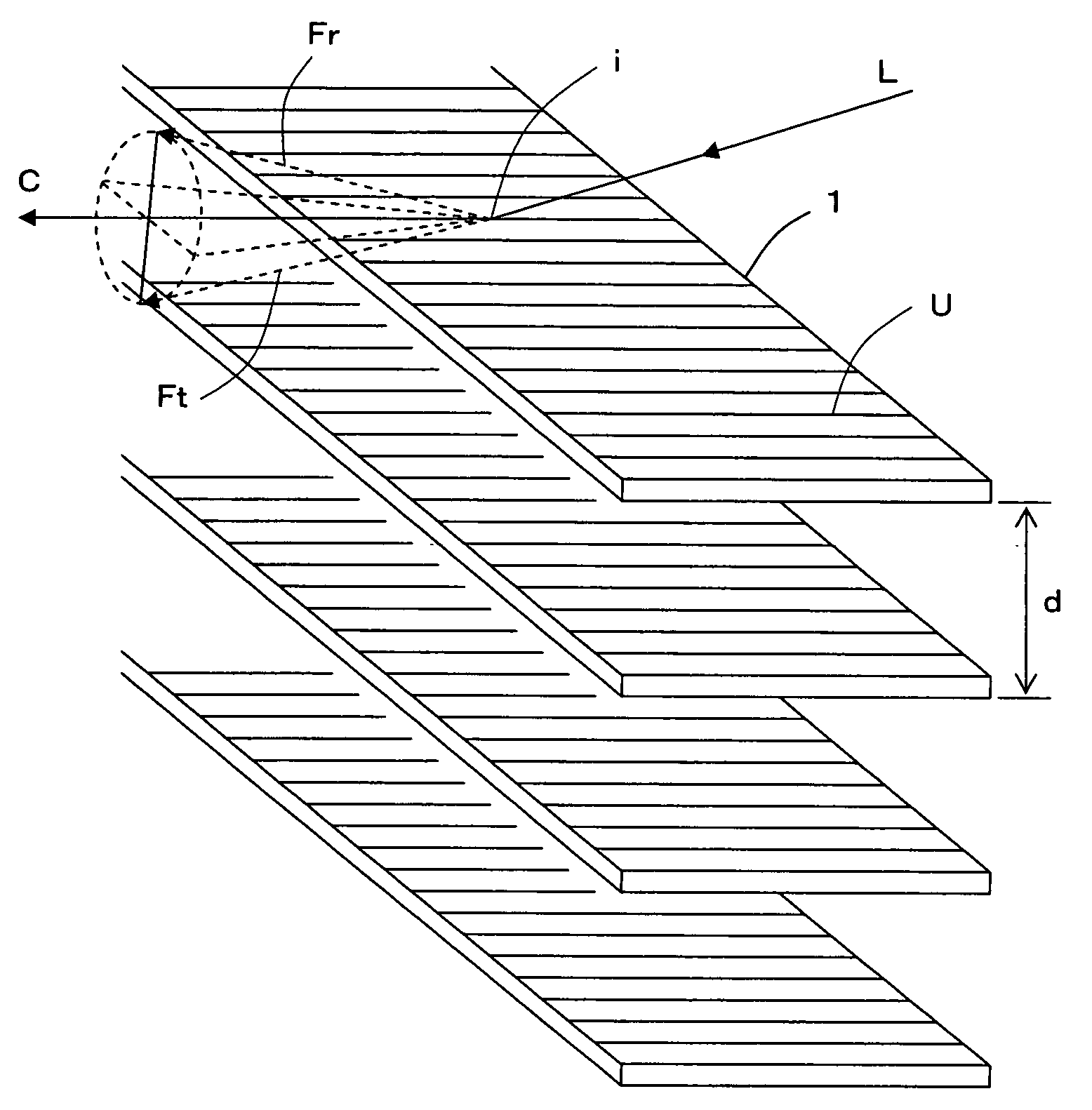
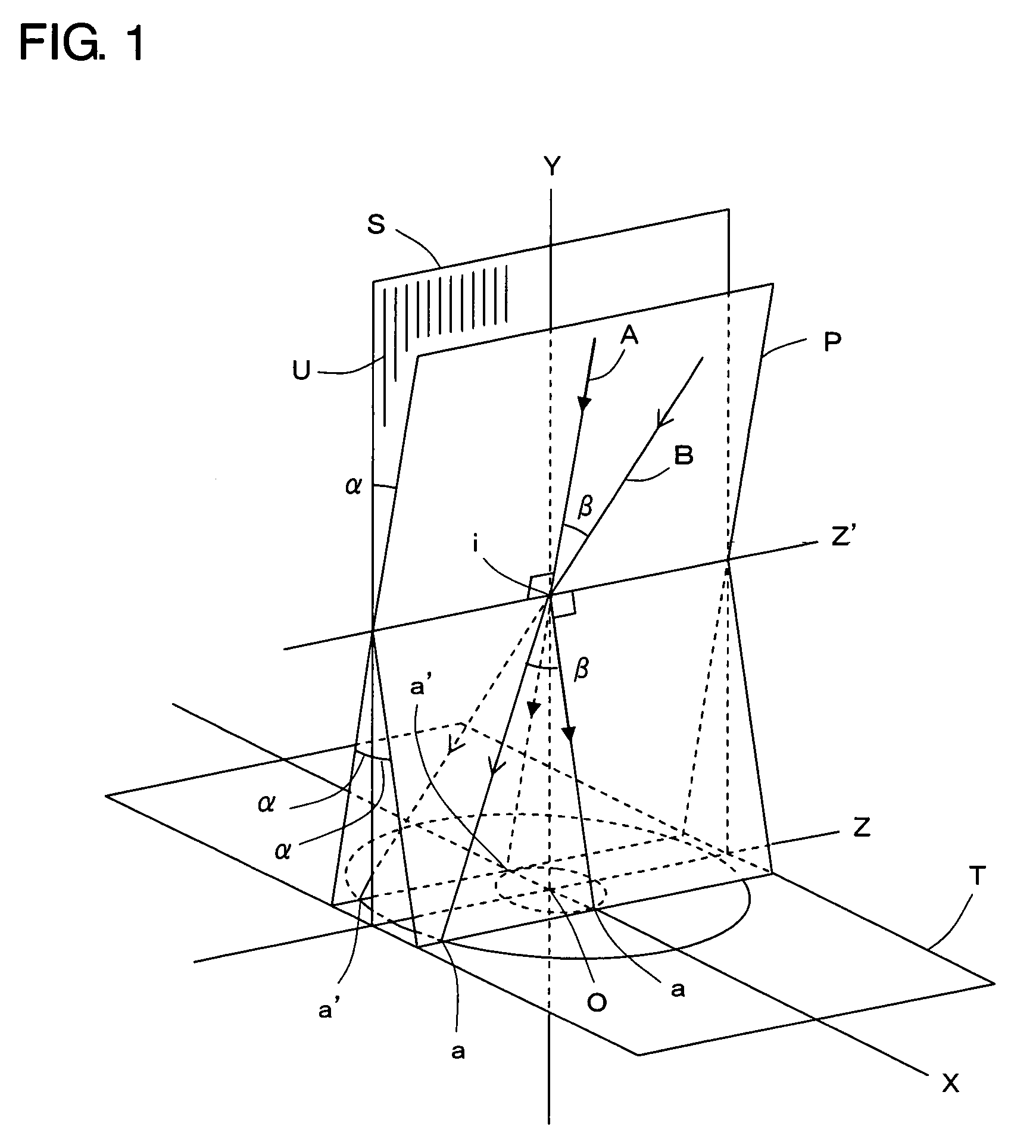
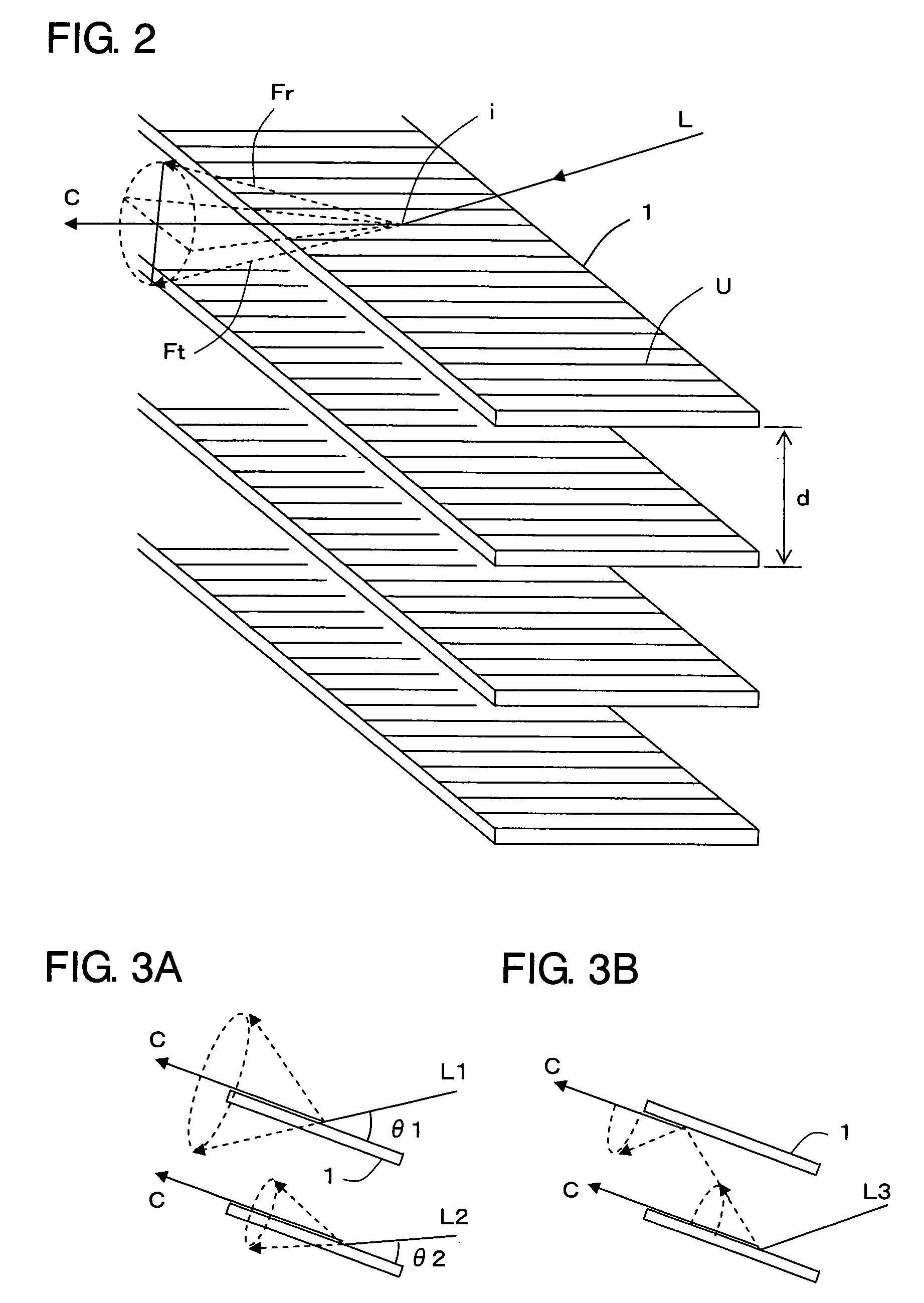
A three-dimensional inspection system and method is used to obtain information about three-dimensional articles with specular surfaces having a shape and positive or negative height by projecting a pattern of light onto the articles at an oblique angle. The system includes a patterned light projector with optical axis disposed at an oblique angle with respect to the plane of the article being inspected, an extended light source, and an image detector disposed above the article to detect the image of the pattern on the article. The light pattern includes lines with a substantially equal thickness and spacing. The spacing of the lines is greater than a spacing or pitch of the specular elements. An image processor, coupled to the image detector, receives the image, locates the lines, and measures the lateral shift of the lines. Height information is determined from the lateral shift and projection angle using triangulation.
Owner:MICROSCAN SYSTEMS
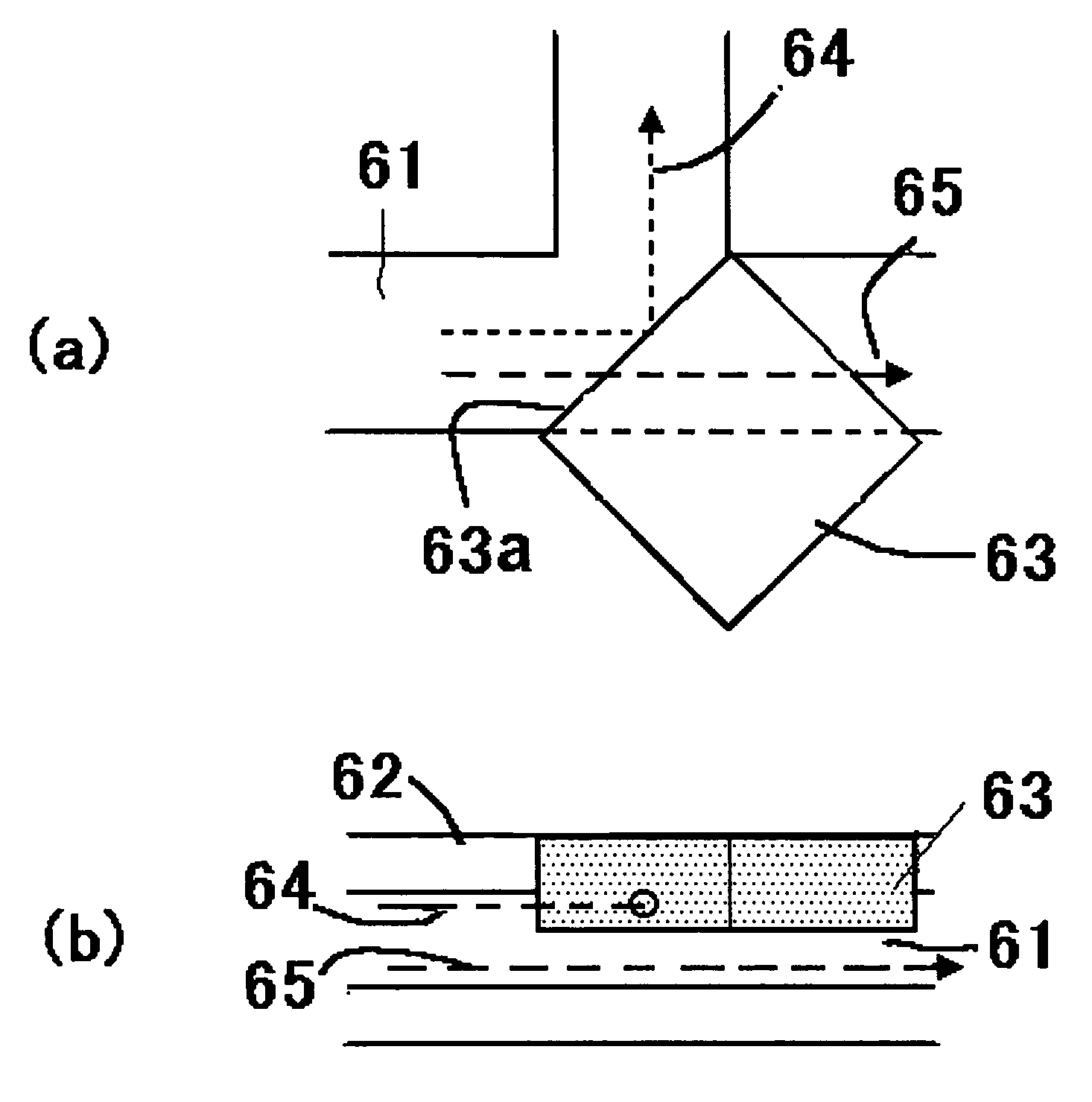
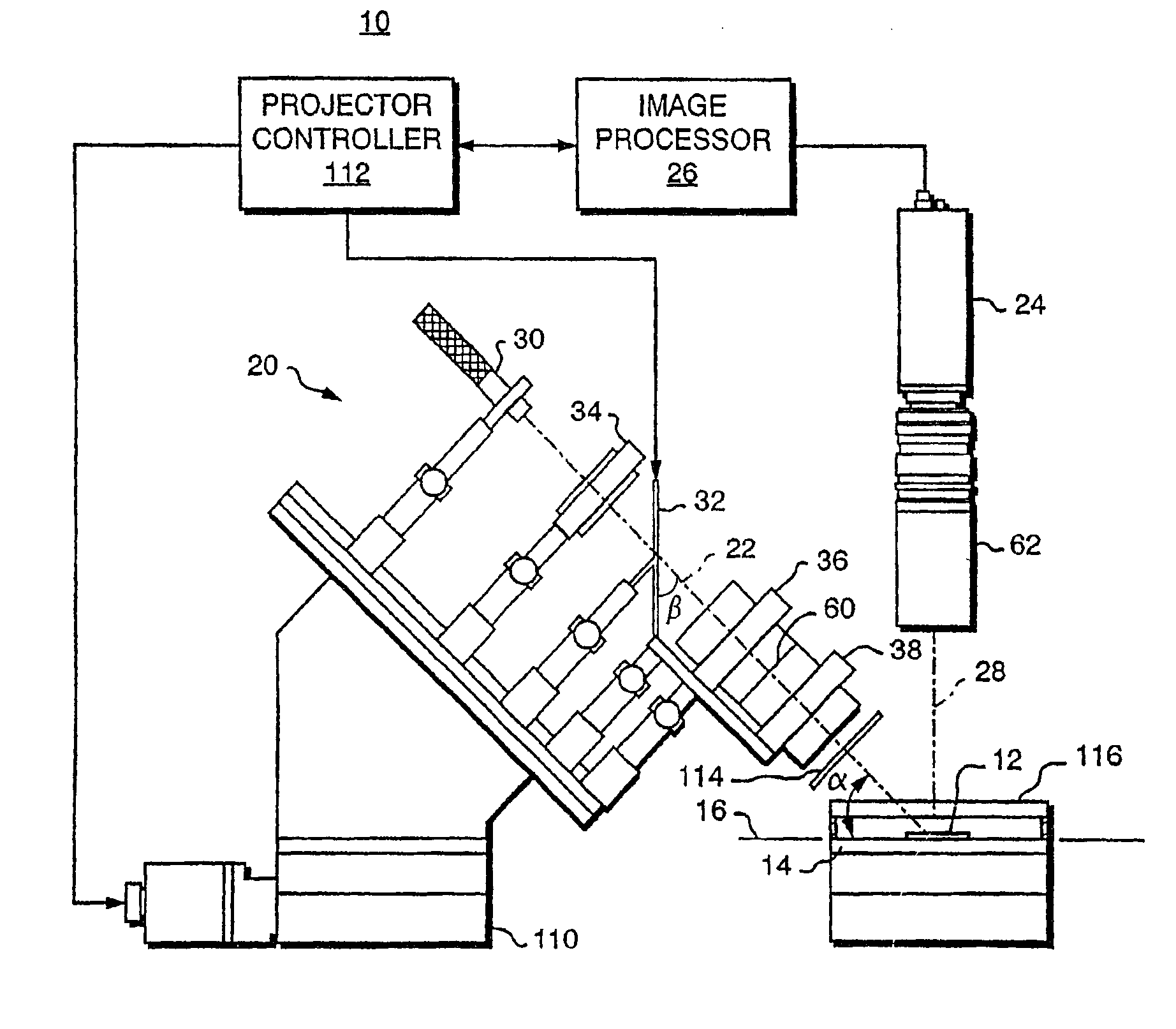
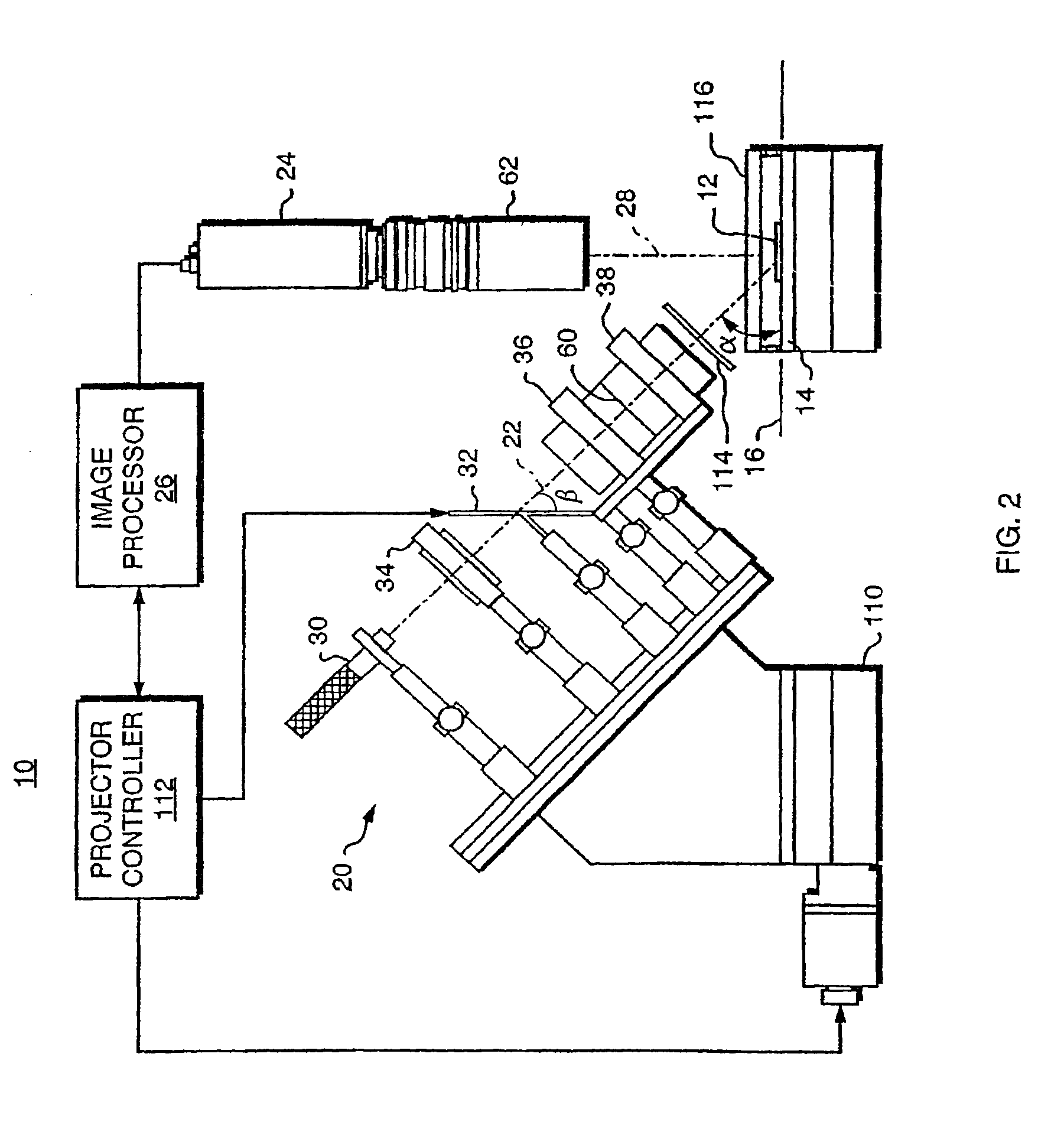
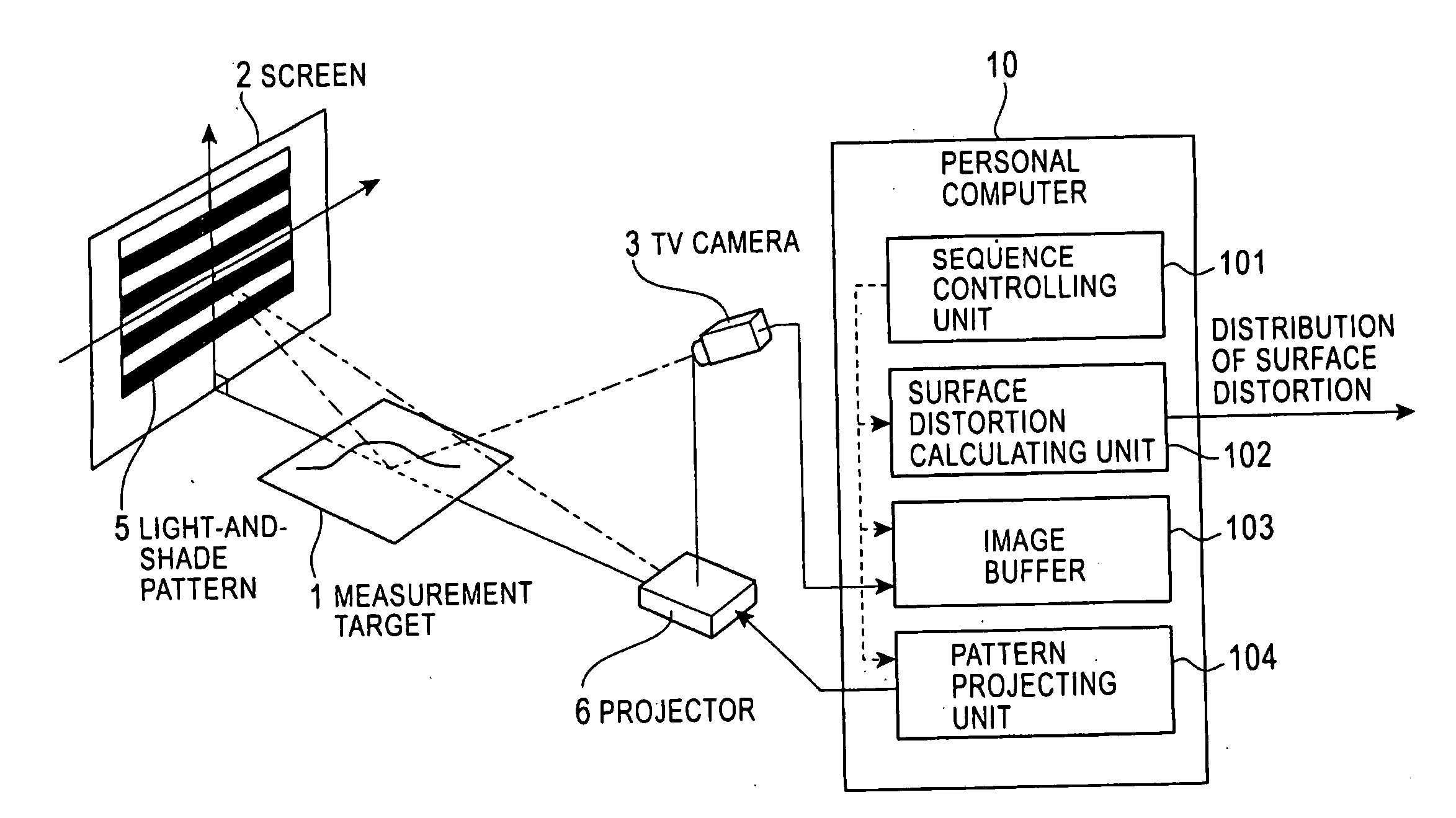
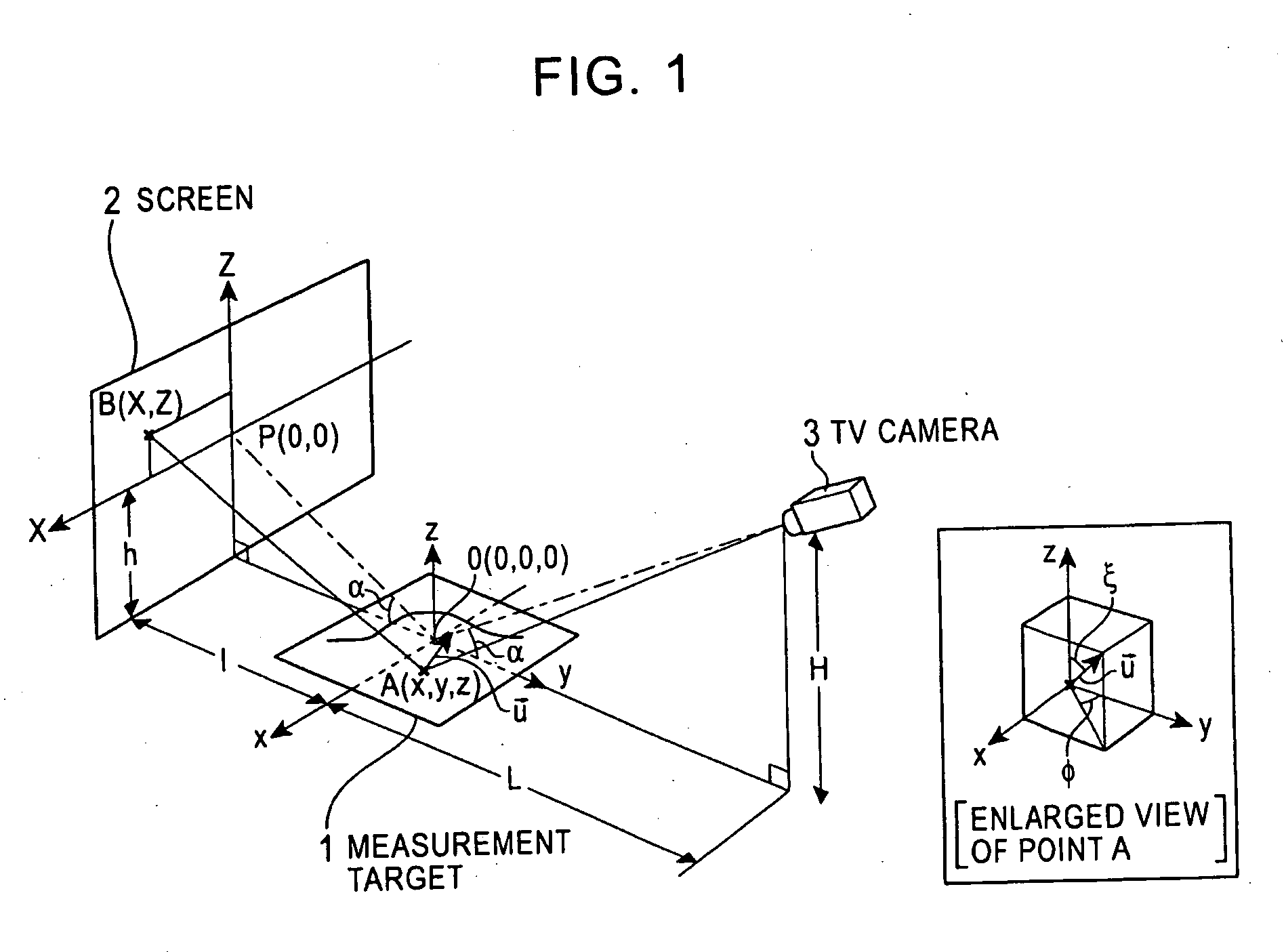
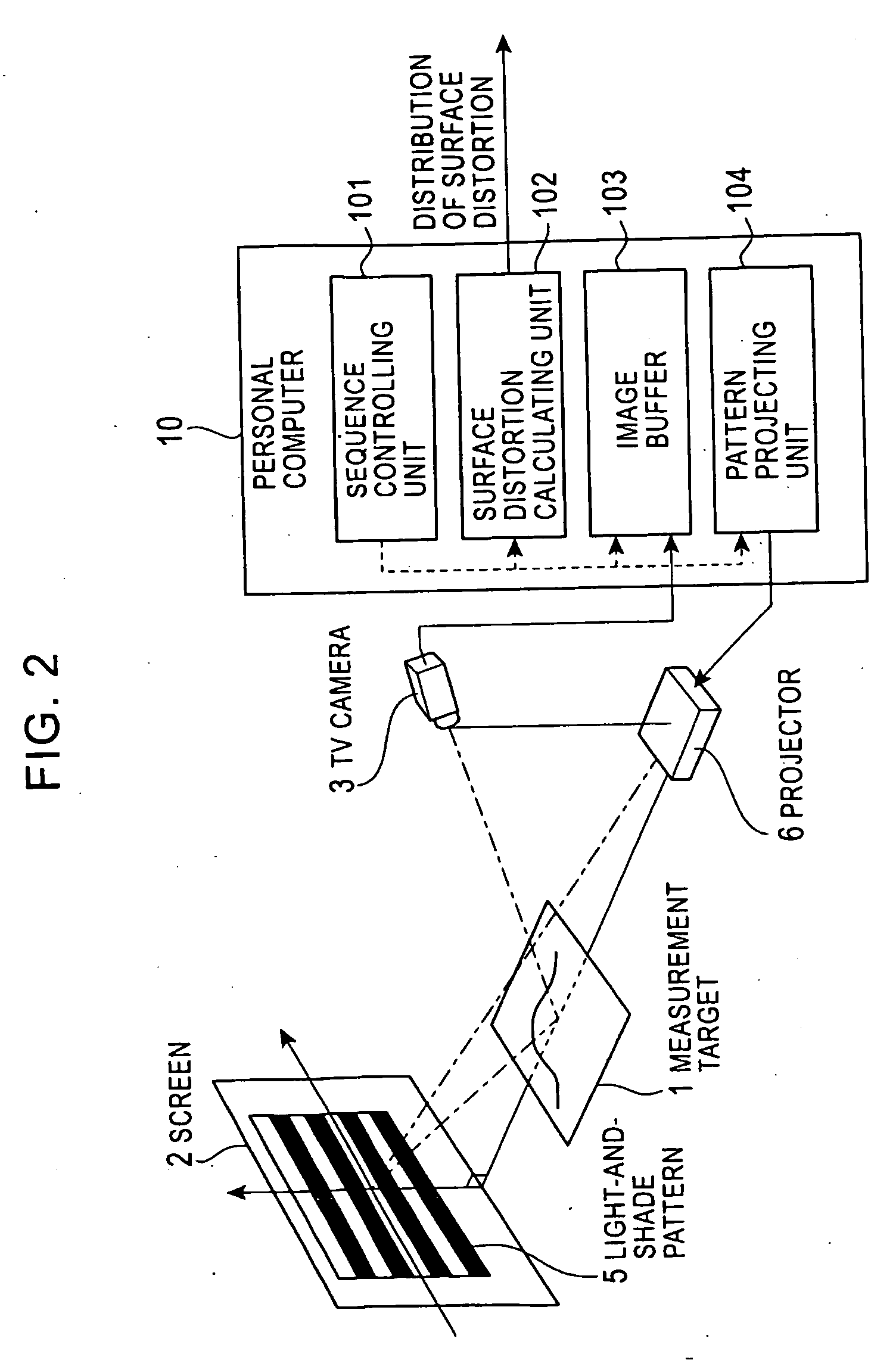
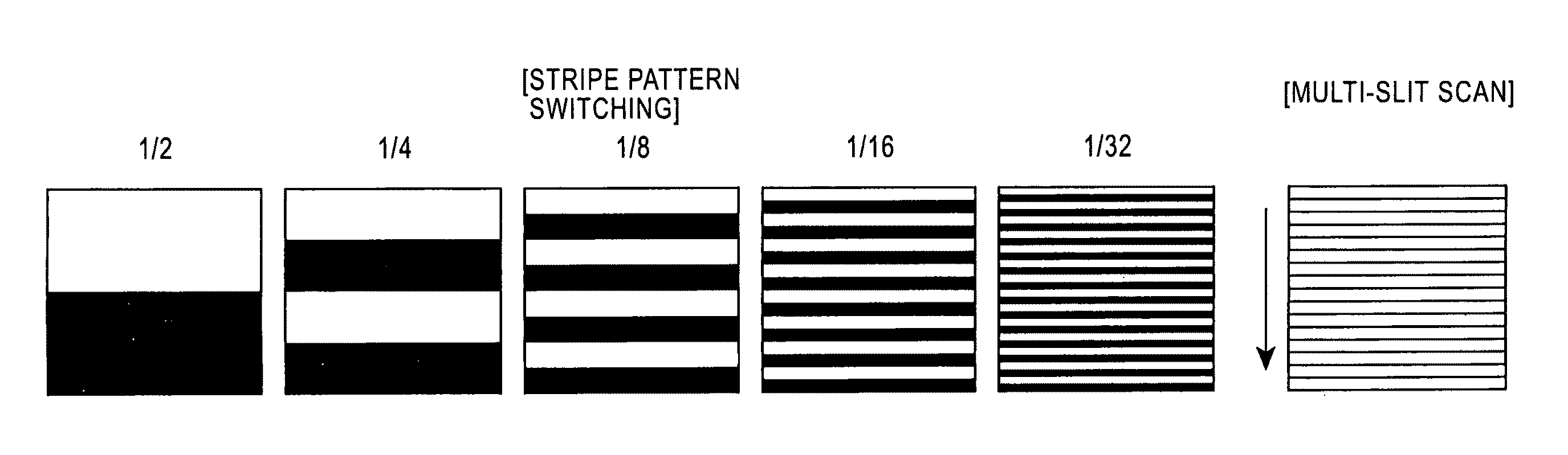
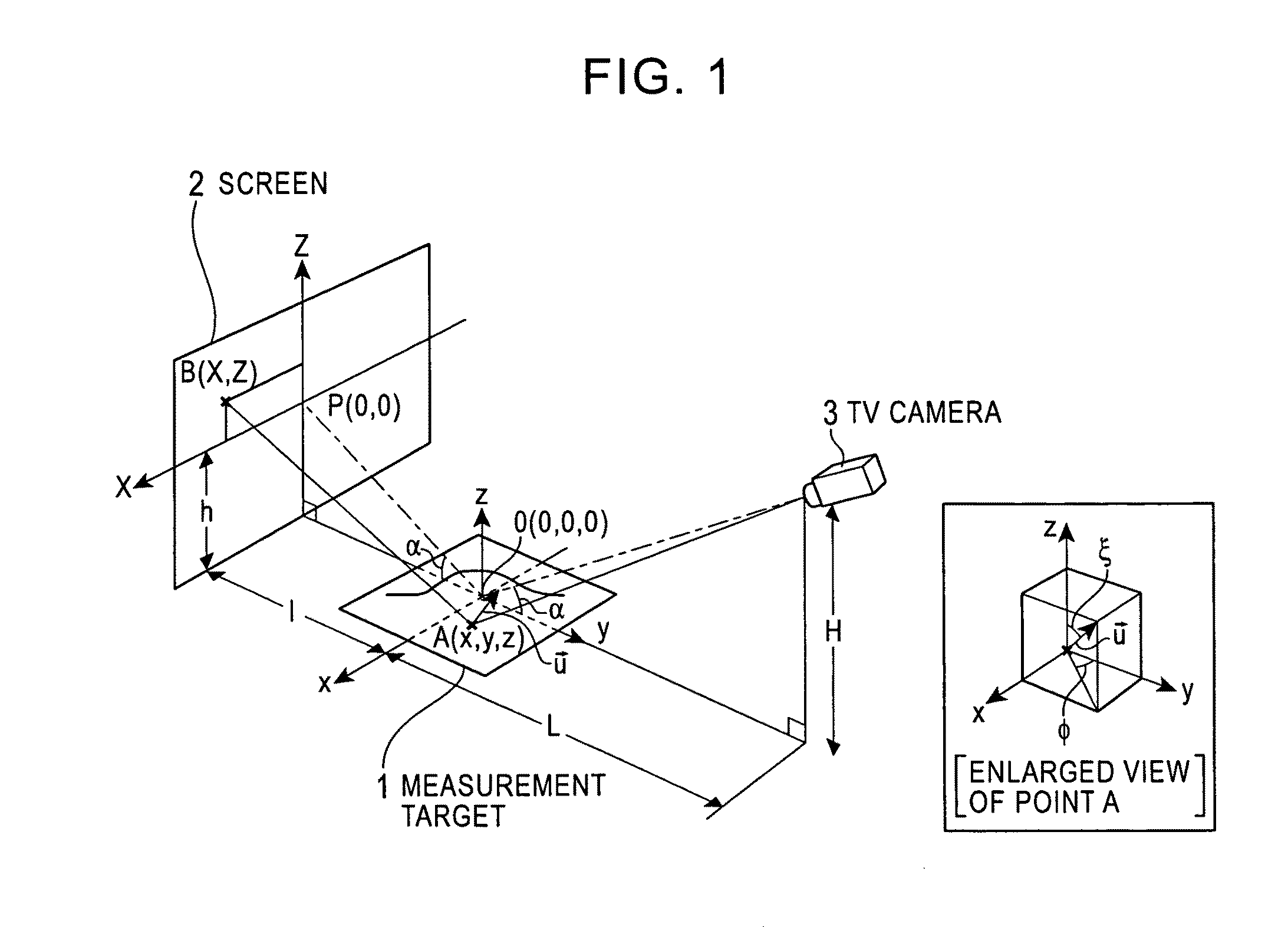
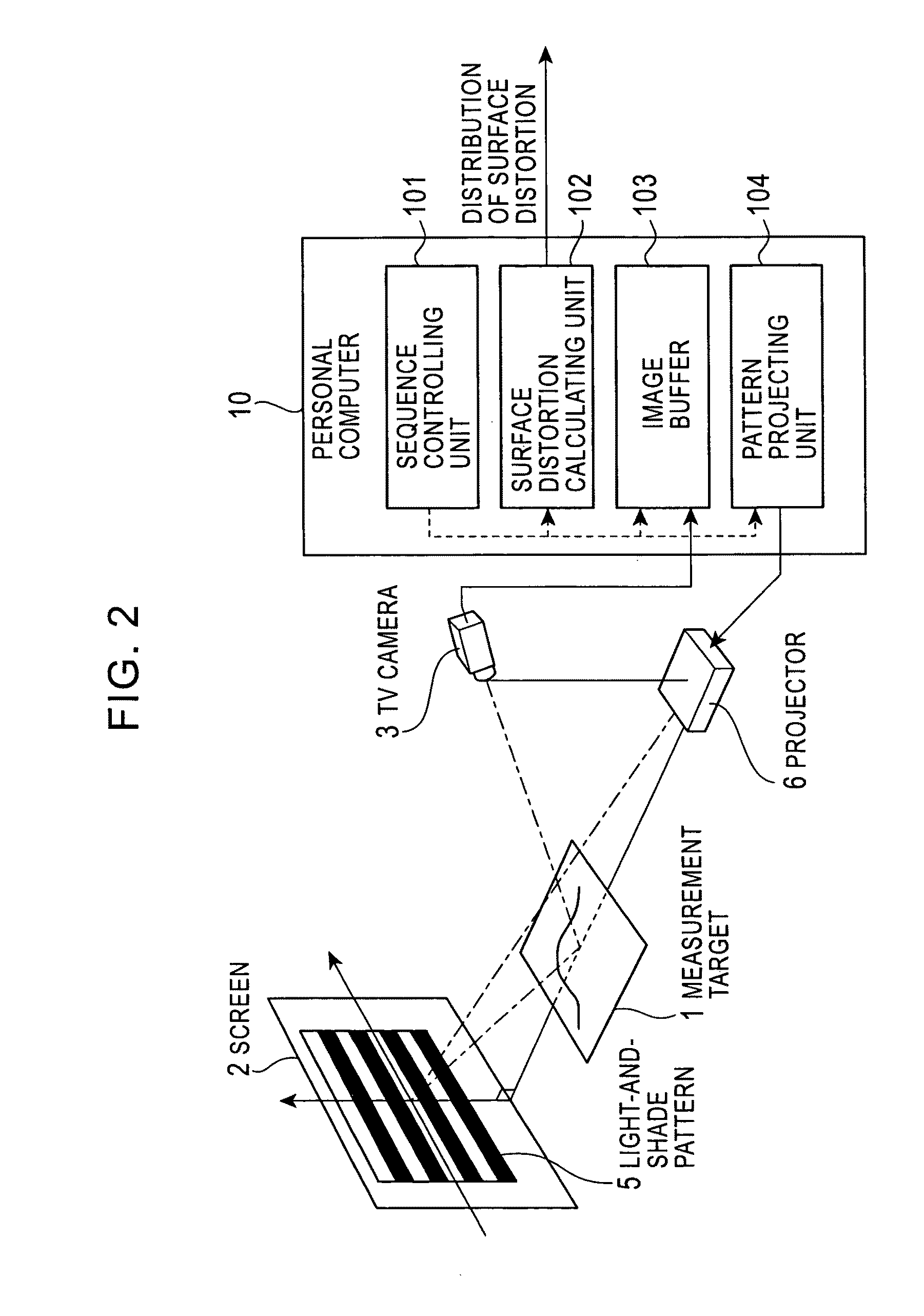
Surface-distortion Measuring Device and Method
ActiveUS20090141287A1Image analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansTarget surfaceMeasurement device
A surface-distortion measuring device and a surface-distortion measuring method can quantitatively, rapidly, and highly accurately measure and evaluate surface-distortion distribution at all of observable points on a specular or semi-specular surface of a measurement target. The device includes pattern displaying means 2 capable of switching and displaying a plurality of kinds of light-and-shade patterns 5, capturing means 3 for capturing mirror images, reflected in the specular or semi-specular surface of a measurement target 1, of the plurality of light-and-shade patterns displayed on the pattern displaying means, and surface-distortion distribution calculating means 10 for performing image processing on the captured mirror images of the plurality of light-and-shade patterns to calculate surface-distortion distribution of the measurement-target surface.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP +1
Surface-distortion measuring device and method
A surface-distortion measuring device and a surface-distortion measuring method can quantitatively, rapidly, and highly accurately measure and evaluate surface-distortion distribution at all of observable points on a specular or semi-specular surface of a measurement target. The device includes pattern displaying means 2 capable of switching and displaying a plurality of kinds of light-and-shade patterns 5, capturing means 3 for capturing mirror images, reflected in the specular or semi-specular surface of a measurement target 1, of the plurality of light-and-shade patterns displayed on the pattern displaying means, and surface-distortion distribution calculating means 10 for performing image processing on the captured mirror images of the plurality of light-and-shade patterns to calculate surface-distortion distribution of the measurement-target surface.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP +1
Light distribution control method, light distribution control device, and greenhouse using the same
InactiveUS20080219010A1Efficient use ofClimate change adaptationRenewable energy machinesDiffraction effectDistribution control
Provided is a plurality of structures each having a number of ridges and formed in a long and thin plate shape or a long and thin film shape. The cross section of each of the ridges forms a portion of a substantial circle and a surface thereof is a practically specular surface. The structures are arrayed such that the ridges of each thereof become parallel to each other and respective adjacent surfaces thereof are corresponding to each other in parallel and apart from each other at a predetermined distance. When light is incident on a point of a surface of one of the structures at an incident angle, in either its reflection or transmittance, the light is diffused in circular conical plane whose vertex is the incident point and center axis is a line parallel to the ridges, by a diffraction effect caused by the arrayed ridges. The flux of reflected diffused light is spread in one lengthwise half of the circular conical plane and the flux of transmitted diffused light is spread in the other lengthwise half of the circular conical plane.
Owner:S T I JAPAN
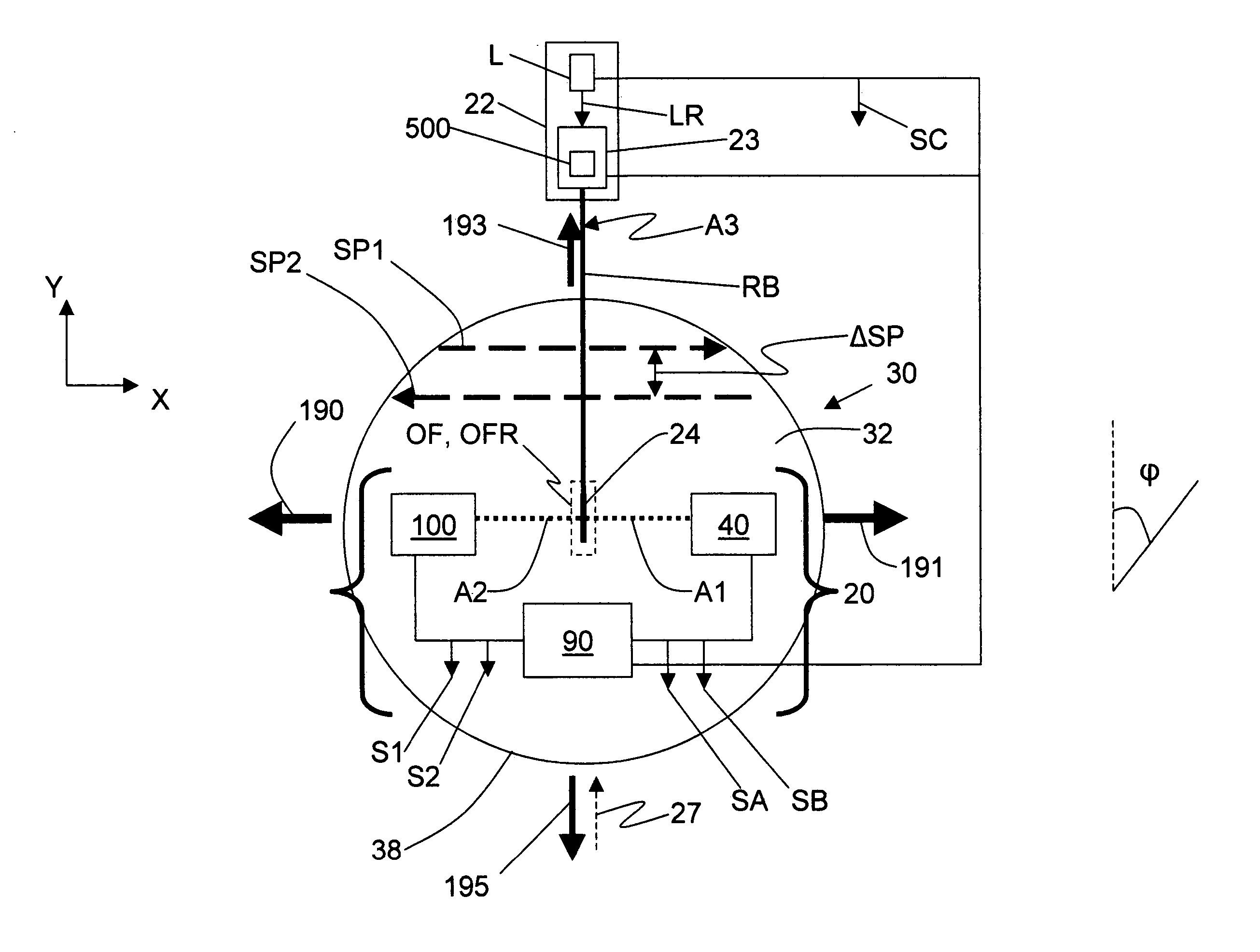
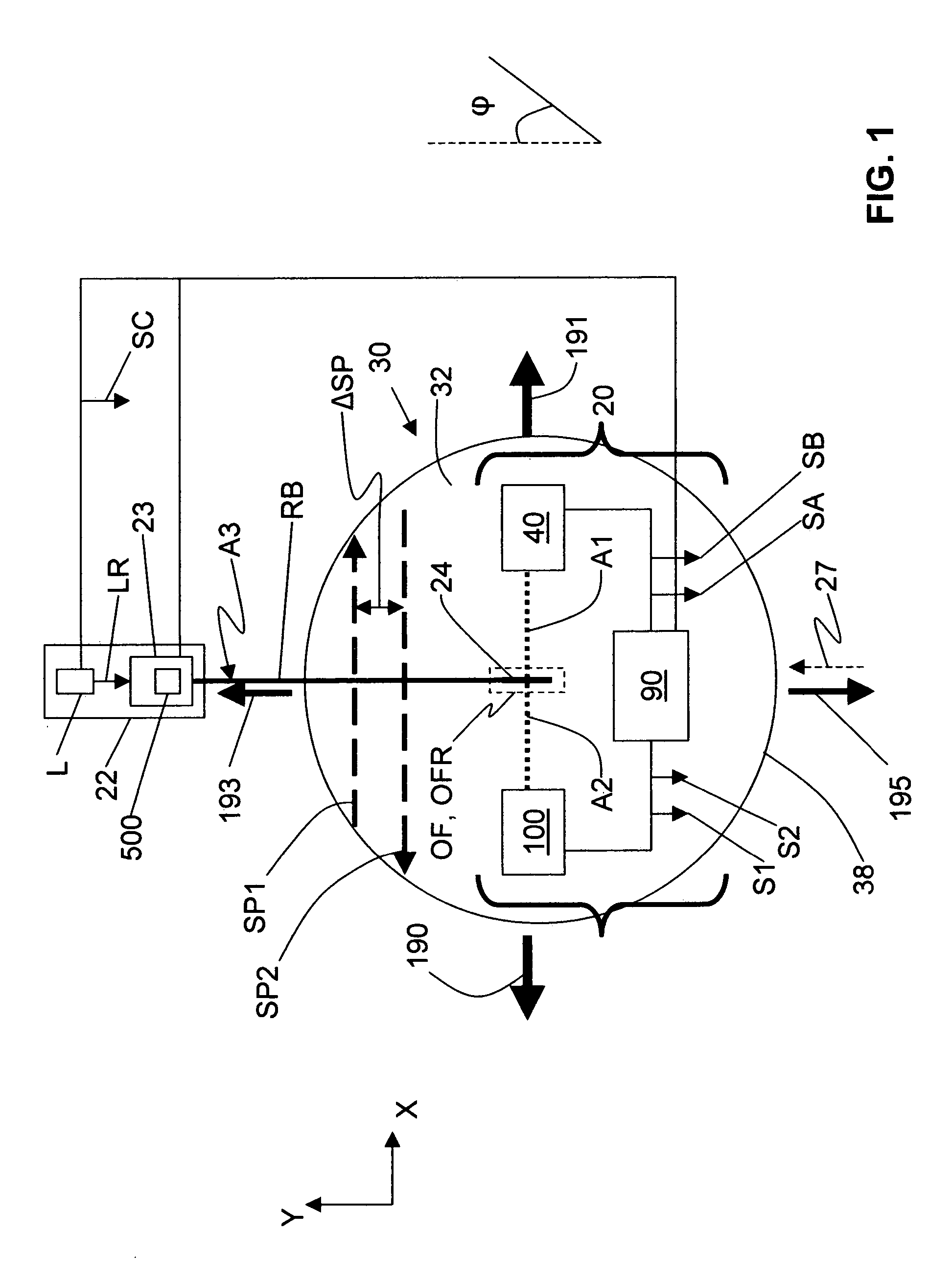
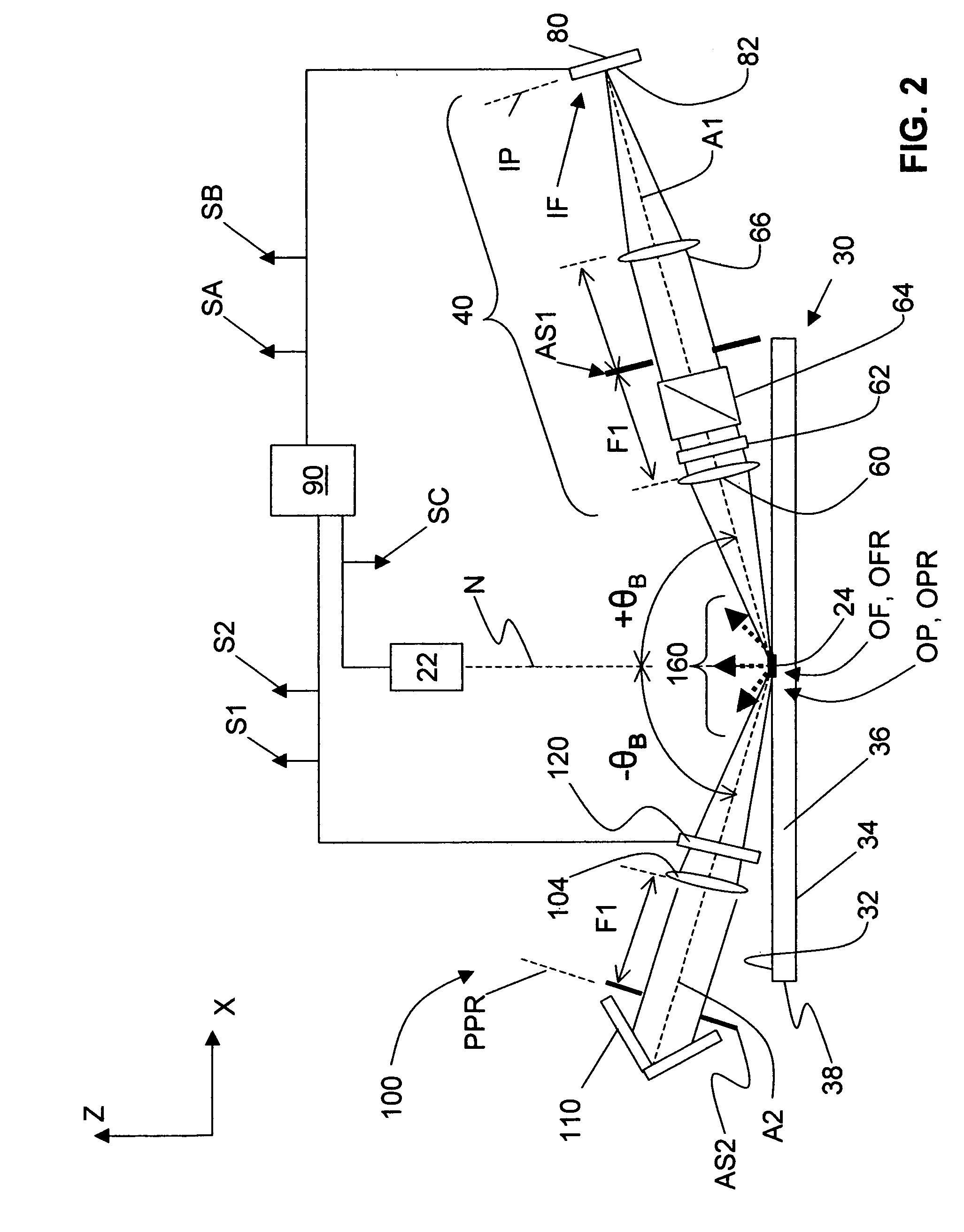
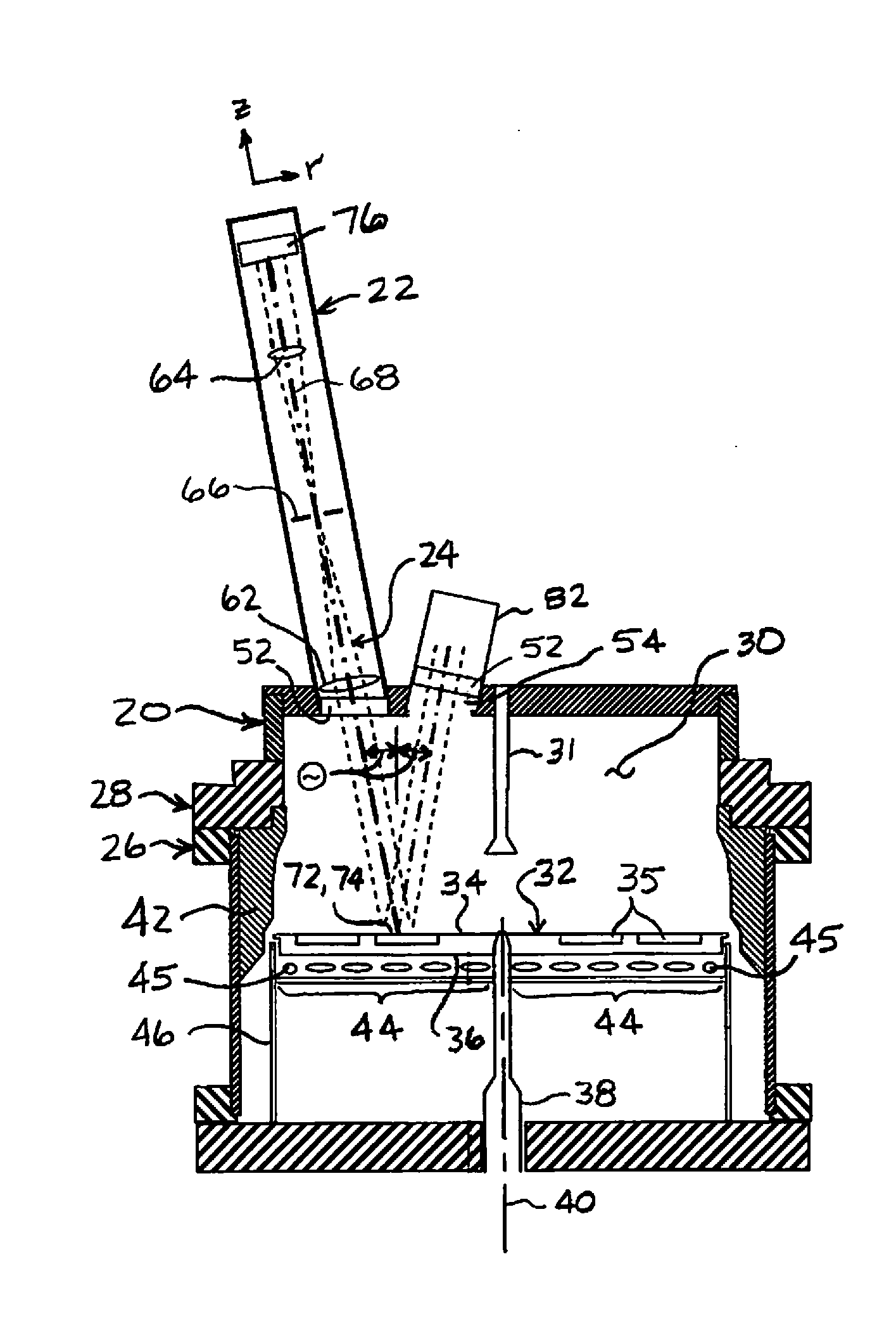
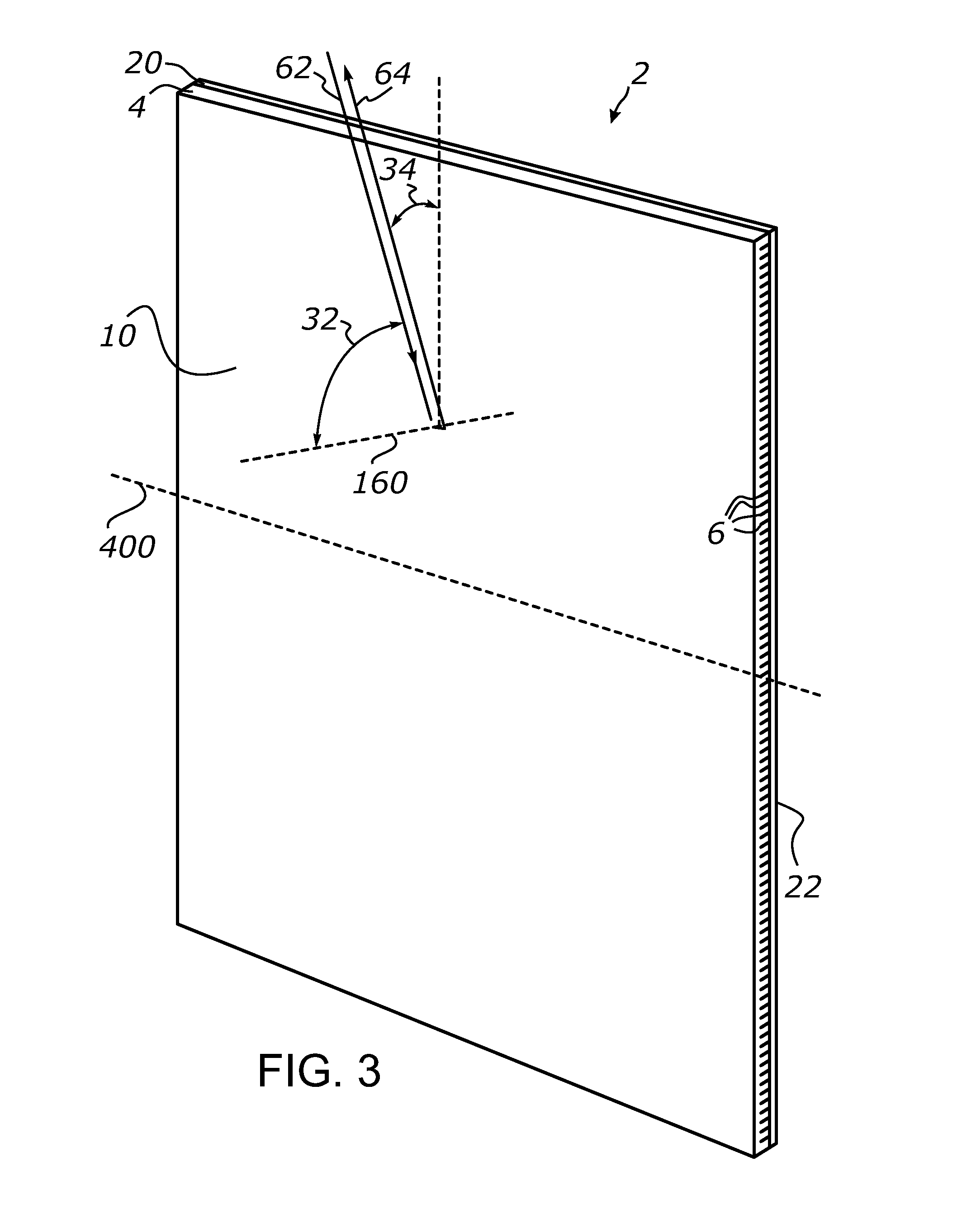
Methods and apparatus for remote temperature measurement of a specular surface
Methods and apparatus for remotely measuring the temperature of a specular surface are disclosed. The method includes taking two different measurements of P-polarized radiation emitted from the surface at or near the Brewster angle associated with the surface. The first measurement (SA) collects and detects a first amount of radiation emitted directly from a surface portion using a collection optical system. The second measurement (SB) includes the first amount of radiation and adds a quantity of radiation collected at or near the Brewster angle and reflected from the surface. This is accomplished with a retro optical system with a round-trip transmission t2 that retro-reflects a quantity of radiation received from the surface portion back to the same surface portion where it is reflected and combined with the first amount of radiation collected by the collection optical system. Measurements SA and SB and the transmission, t2, are used to determine the surface emissivity (ξ). A calibration curve is then used that relates the ratio of the first measurement SA to the surface emissivity ξ, (SA / ξ), to surface temperature. The calibration curve is then used to determine the surface temperature from the SA / ξ value.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Radiation thermometer using off-focus telecentric optics
ActiveUS20130343425A1Increased rejectUniform magnificationRadiation pyrometryChemical vapor deposition coatingRadiation thermometerOptical axis
A radiation thermometer utilizing an off-focus telecentric lens arrangement in chemical vapor deposition reactors. An object assembly of one or more optical components is positioned at a distance equal to its focal length from an aperture stop. The aperture stop is dimensioned so that the chief rays are substantially parallel with the optical axis of the object assembly, and so that the rays that pass through the aperture stop define a narrow solid angle about the chief rays. The off-focus telecentric arrangement thus configured is focused at infinity, but is utilized to capture radiation from a relatively proximate target (e.g., within a couple meters) that is out of focus. The capture of collimated radiation from the target diminishes the contribution of stray radiation, particularly with targets having a highly specular surface.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
High incidence angle retroreflective sheeting
A retroreflective sheeting is disclosed which comprises a top transmissive layer including a plurality of parallel channel formed perpendicular to a surface of the layer, and a reflective bottom layer including a specular surface or a corrugated transmitting surface. The corrugated surface includes a plurality of linear prismatic elements extending perpendicular to the channels of the top layer. The top and bottom layers reflect light in orthogonal directions and act cooperatively to retroreflect incident light back toward the source, particularly at high incidence angles. Various light management devices employing the retroreflective sheeting are also disclosed.
Owner:VASYLYEV SERGIY
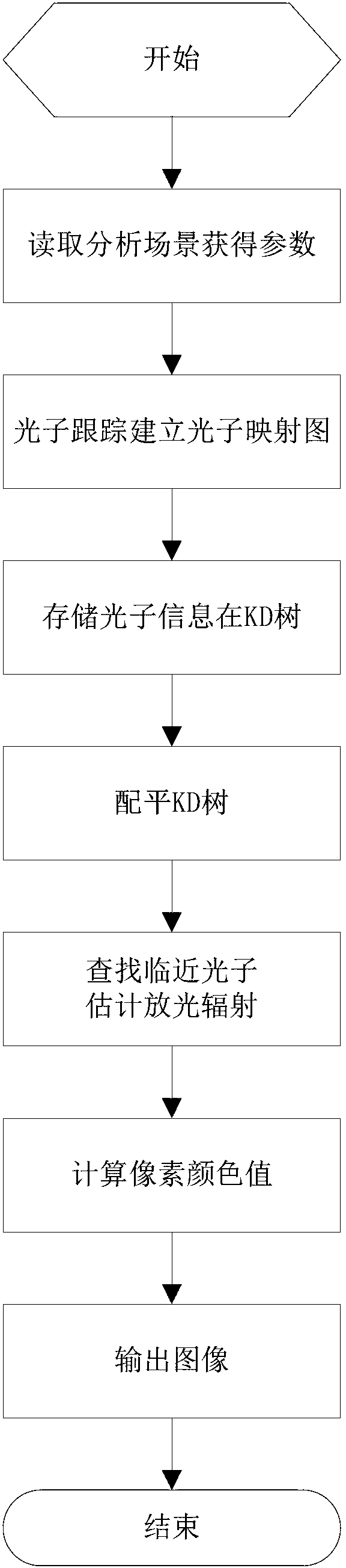
Overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on photon mapping image
InactiveCN102981840ARealistic renderingHigh speedSpecific program execution arrangementsLight treatmentLuminous flux
The invention discloses an overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on a photon mapping image. The method is characterized by comprising that a photon is emitted from a light source to a computer virtualized scene and is tracked, and when the photon strikes the surface of a scene content non-specular surface object, the photon is stored in the photon mapping image; incidence luminous flux of any point in the computer virtualized scene and reflected luminescence radiancy information are extracted by means of statistic technique according to the photon mapping image, calculating the pixel color value, and carrying out image drawing and rendering in the scene. The overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on the photon mapping image is based on the principle of photon mapping, effect of a processed image is life-like, calculating and processing speed is high, and meshing is not needed. The overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on the photon mapping image is especially suitable for light treatment in complex scenes.
Owner:SUZHOU LIANGJIANG TECH
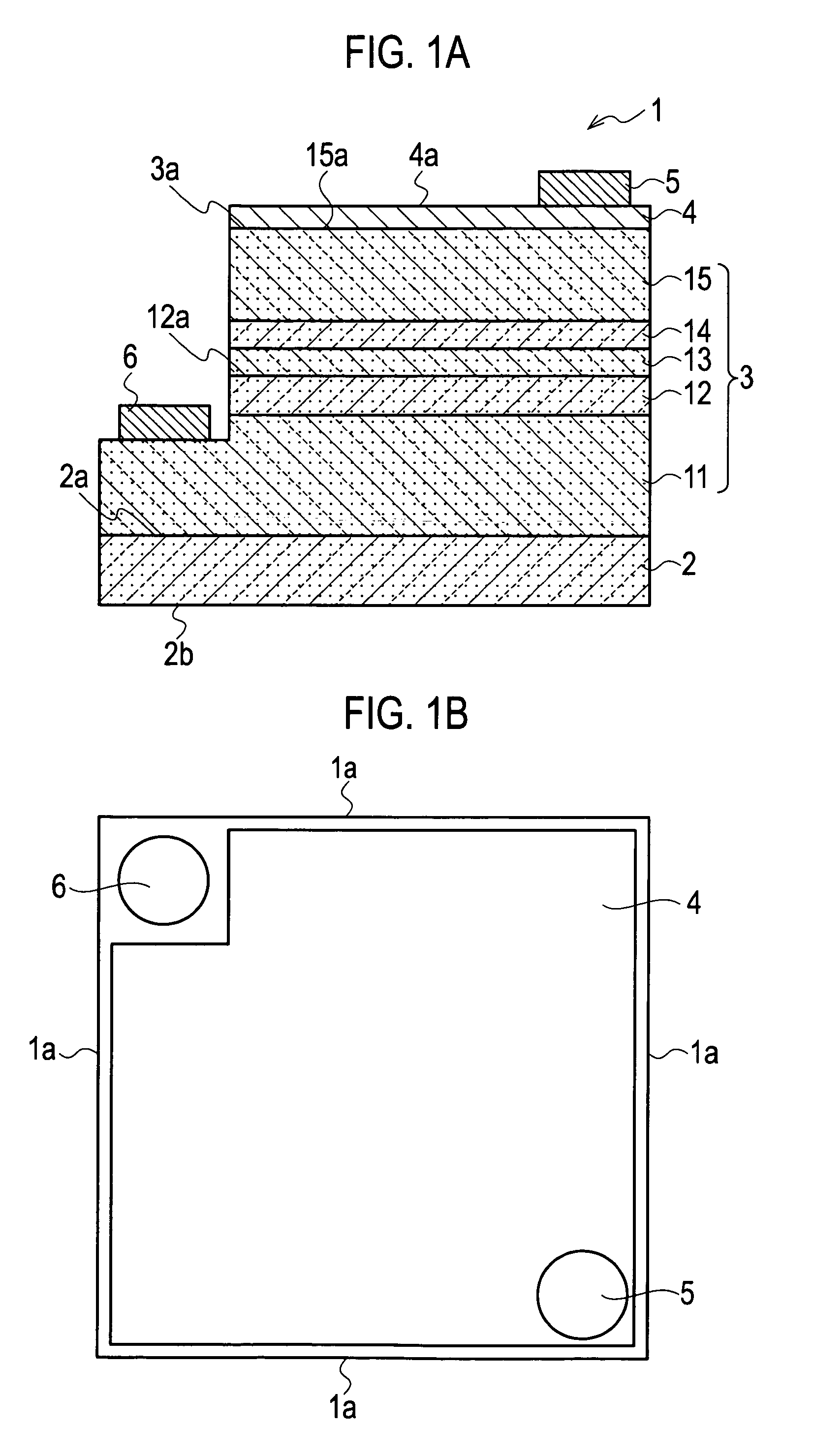
Semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS7858995B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive layerSpecular surface
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Method for Producing Ink Jet Recording Sheet and Ink Jet Recording Sheet
InactiveUS20080038491A1High glossExcellent high image densityDuplicating/marking methodsPretreated surfacesColloidal particleSpecular surface
The present invention relates to a method for producing an ink jet recording sheet characterized by including: applying a coating liquid containing at least both a temperature-sensitive polymeric compound and a pigment the temperature-sensitive polymeric compound having a temperature region where hydrophobicity is exhibited and a temperature region where hydrophilicity is exhibited, the coating liquid becoming more viscous or gelating in the temperature region where hydrophilicity is exhibited, onto either an air-permeable support or at least one undercoating layer provided on an air-permeable support in the temperature region where hydrophobicity is exhibited, to form a coating layer of the coating liquid, bringing the temperature thereof to the temperature region where the temperature-sensitive polymeric compound exhibits hydrophilicity to increase the viscosity of the coating layer or gelate the coating layer, then applying a wetting liquid containing an ink fixing agent (and colloidal particles) onto the viscosity-increased or gelated coating layer, followed by bringing the assembly into contact and press to a heated specular surface and drying to form an ink-receptive layer.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
System and method for imaging through an irregular water surface
InactiveUS7630077B2Assists in determining the polarization state of lightLight polarisation measurementPolarimeterFour component
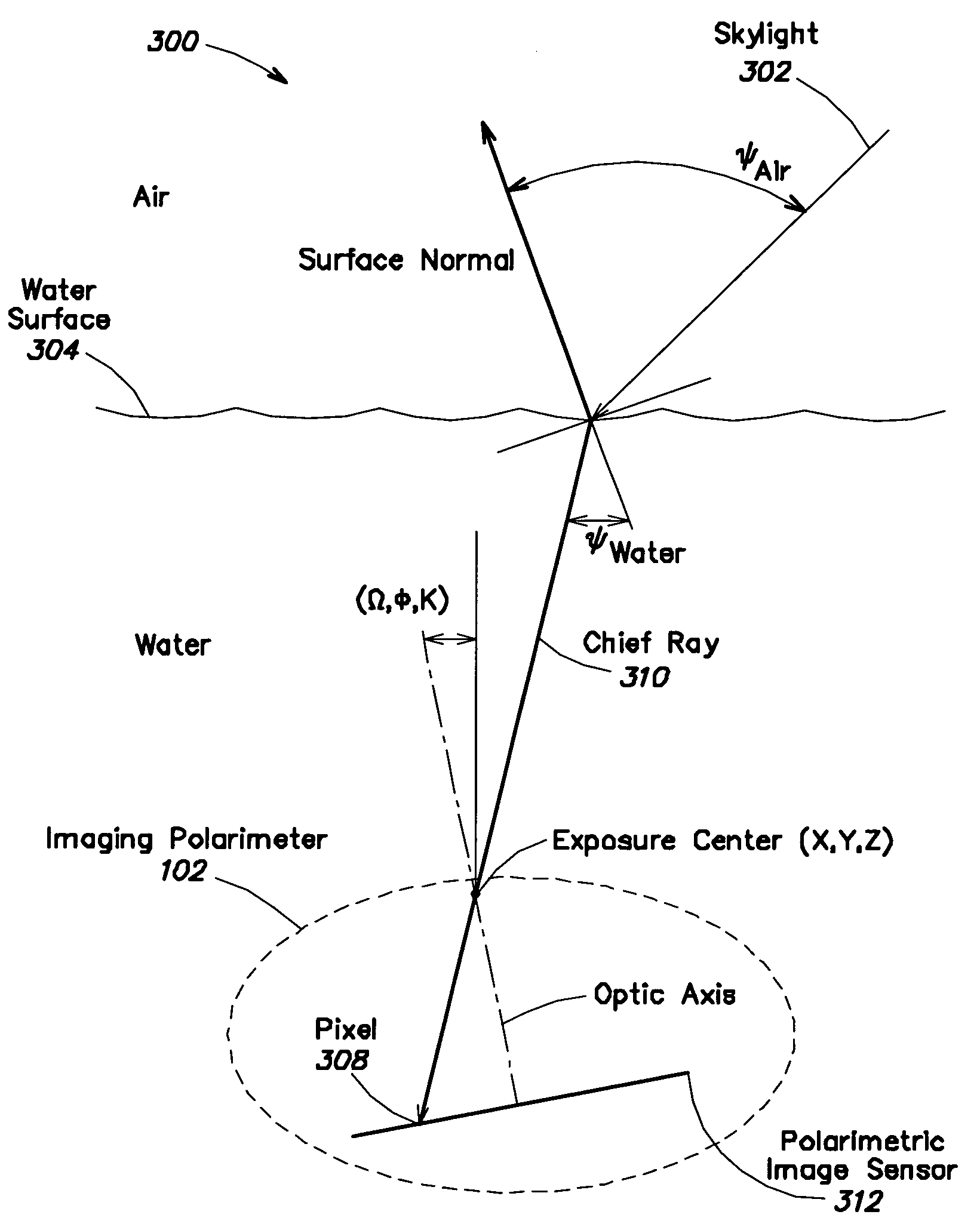
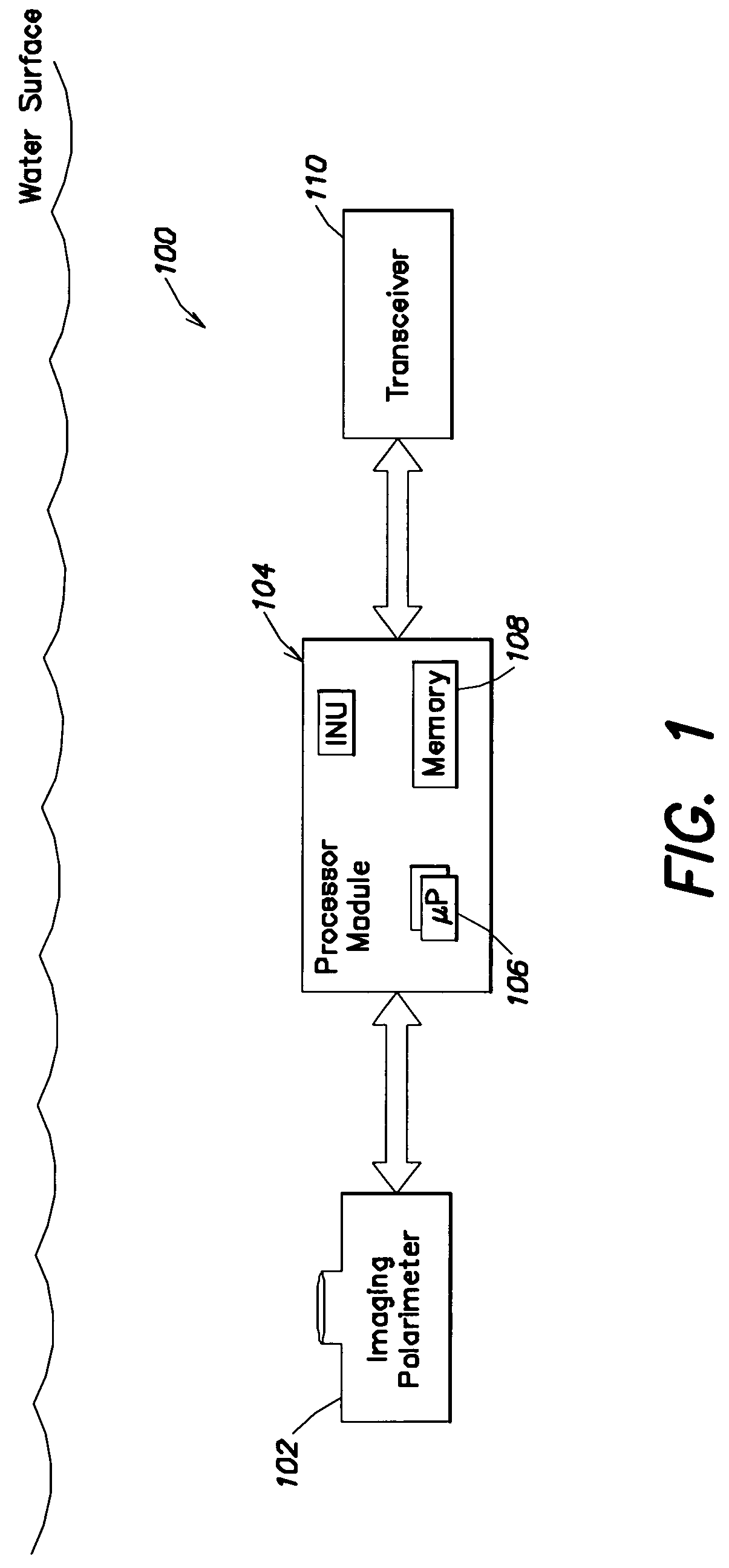
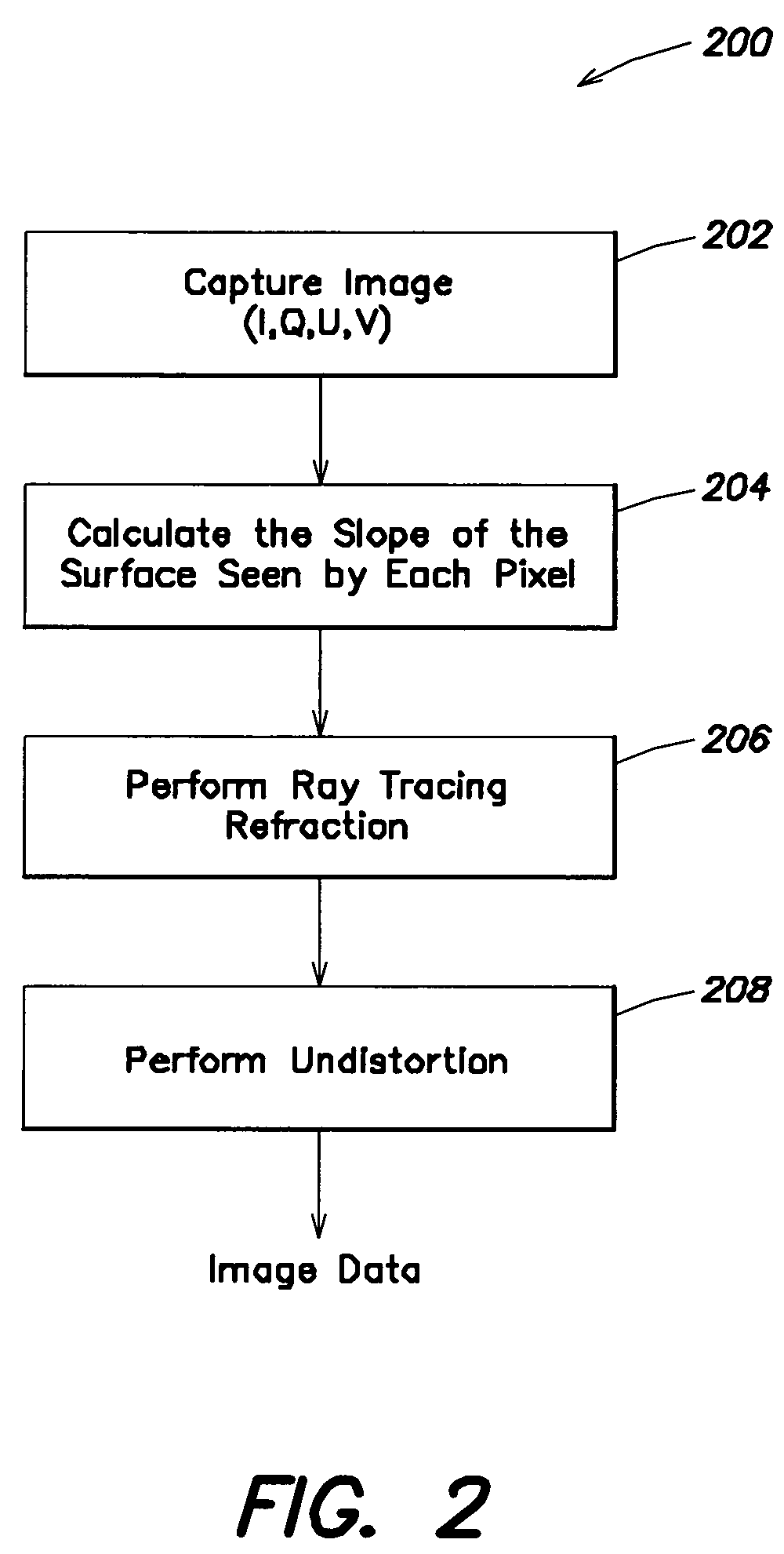
An underwater imaging system includes an underwater imaging polarimeter that captures images of the water surface. The captured images are indicative of the captured light, and are equivalent to four-component Stokes vector S=(I,Q,U,V) data. Advantageously, the passive imaging technique of the present invention utilizes polarmetric data. In contrast, conventional optical remote sensing techniques rely on light amplitude and frequency to carry information about the scattering surface. The imaging technique of the present invention exploits these properties, as well as the polarization properties of light to sense information about the scattering media. The two-dimensional slope field of surface wave can be recovered from a distance without interfering with the fluid dynamics of the air or water. By employing the physics of light scattering by a specular surface, the geometry of the surface can be found by measuring the polarimetric properties of the reflected and / or refracted light. The derived two-dimensional slope field in then used to remove the image distortion caused by light passing through the wavy surface. The undistorted images have the appearance of images taken through a flat water surface.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Variable shape mirror and optical pickup device having the same
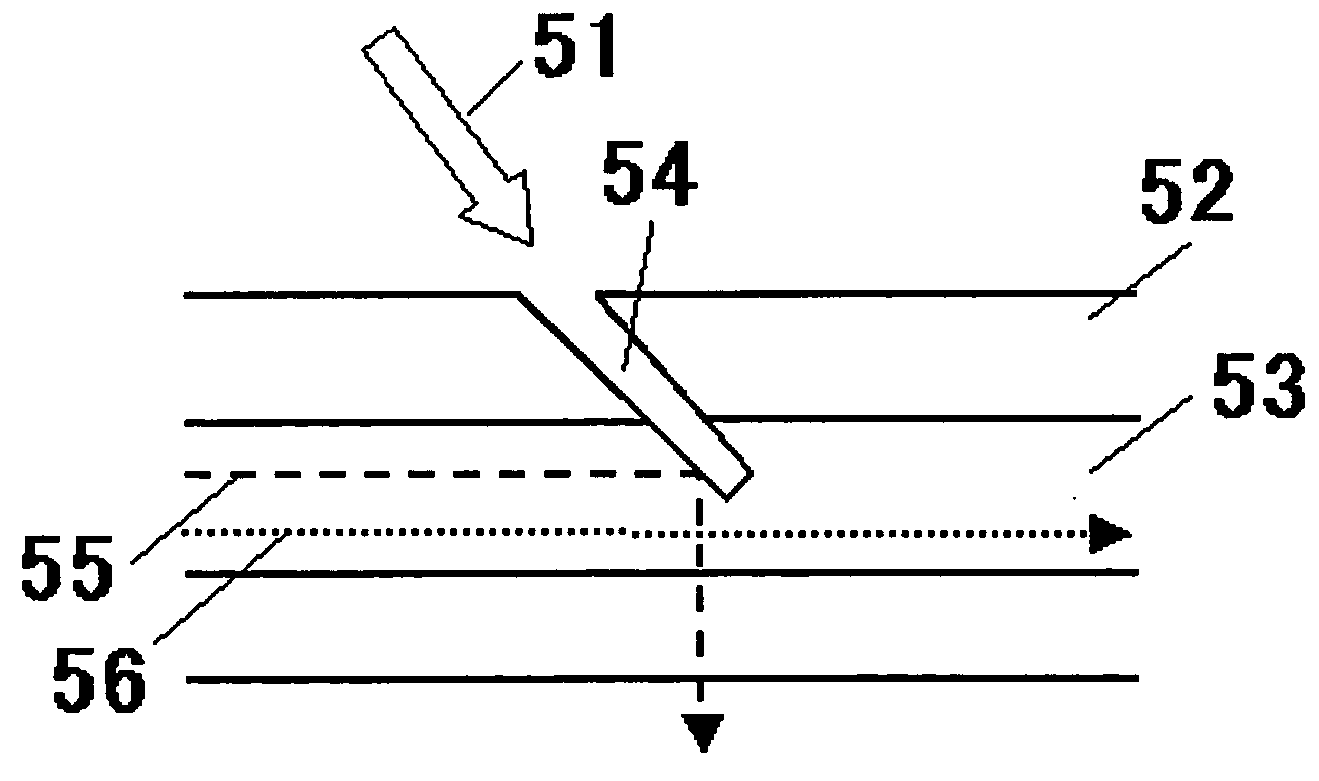
InactiveUS20070206300A1Low costSurface deformationMirrorsRecord information storageOptical pickupEngineering
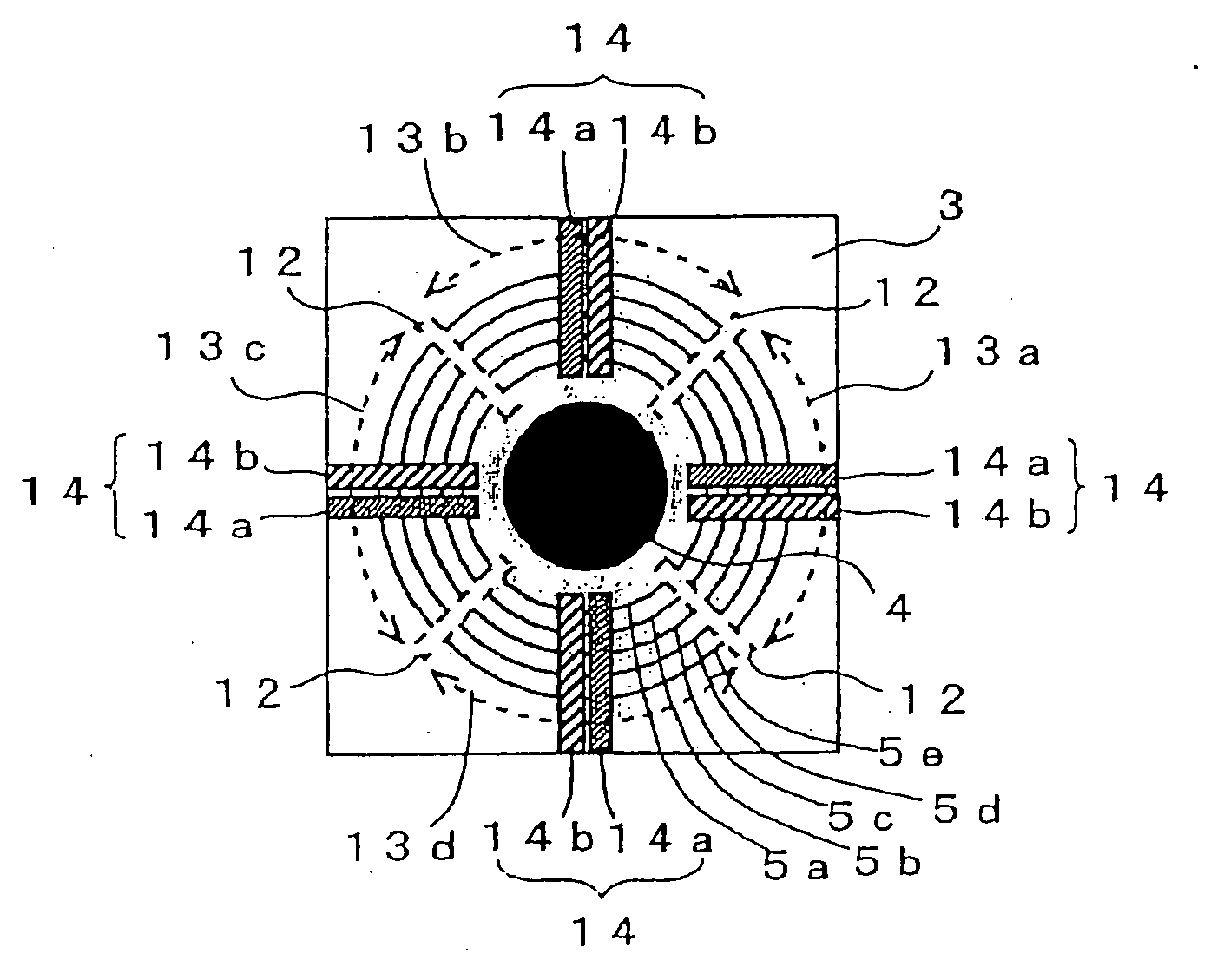
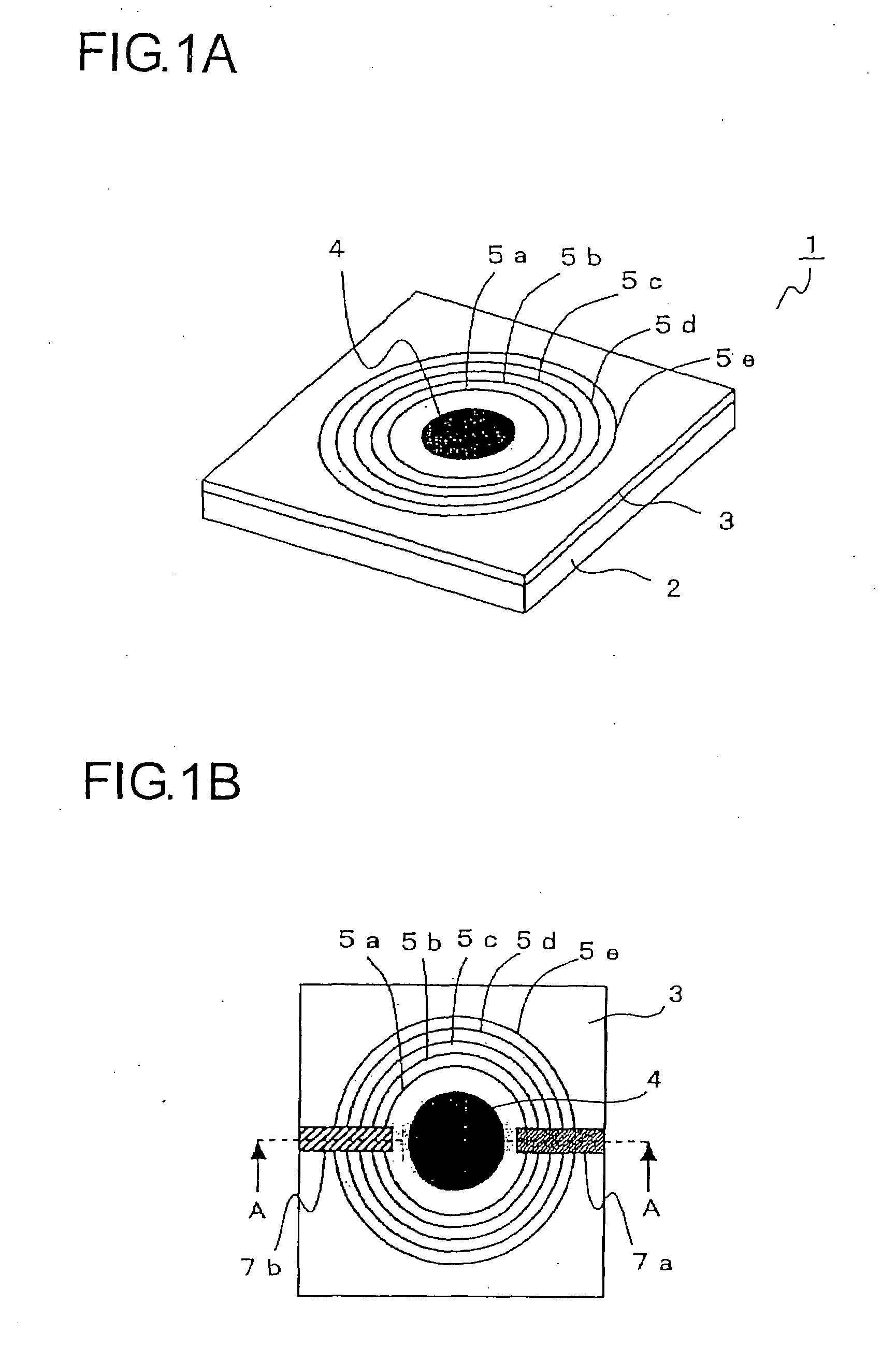
The variable shape mirror (1) includes a substrate (2) and a bulk piezoelectric body (3). On the piezoelectric body (3), a specular surface (4) is formed, and further a plurality of grooves (5a-5e) are formed at a predetermined interval. The grooves (5a-5e) are arranged so as to surround the specular surface (4) and filled with the conductive members. The conductive members embedded in the grooves (5a-5e) are connected electrically to one of a pair of common electrodes (7a and 7b) that is disposed to cross the grooves (5a-5e) and are formed to be electrodes having different polarities in alternating manner in the direction from the inner side to the outer side of the grooves (5a-5e).
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Specular edge extraction using multi-flash imaging
InactiveUS8913825B2Hamper reconstructionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsLight flashesEdge extraction
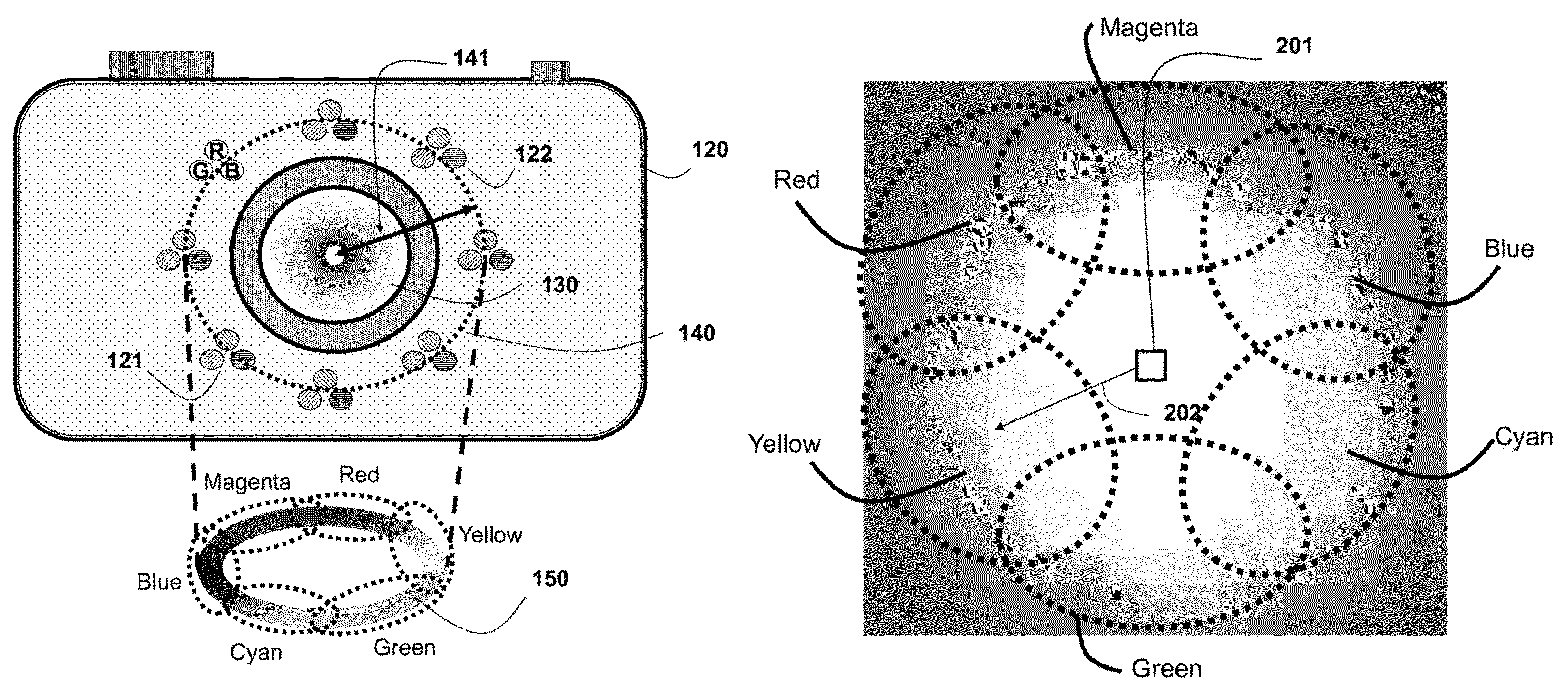
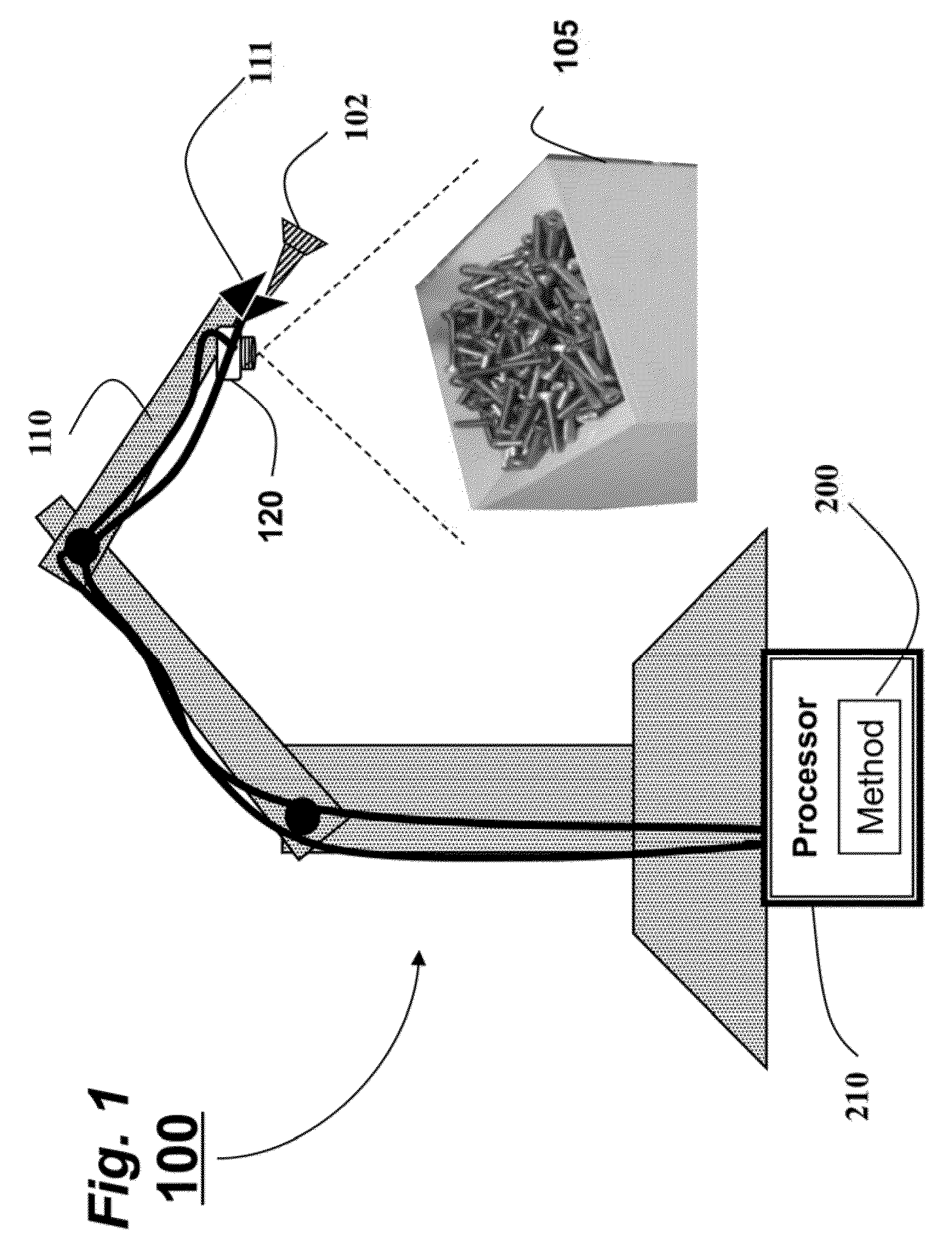
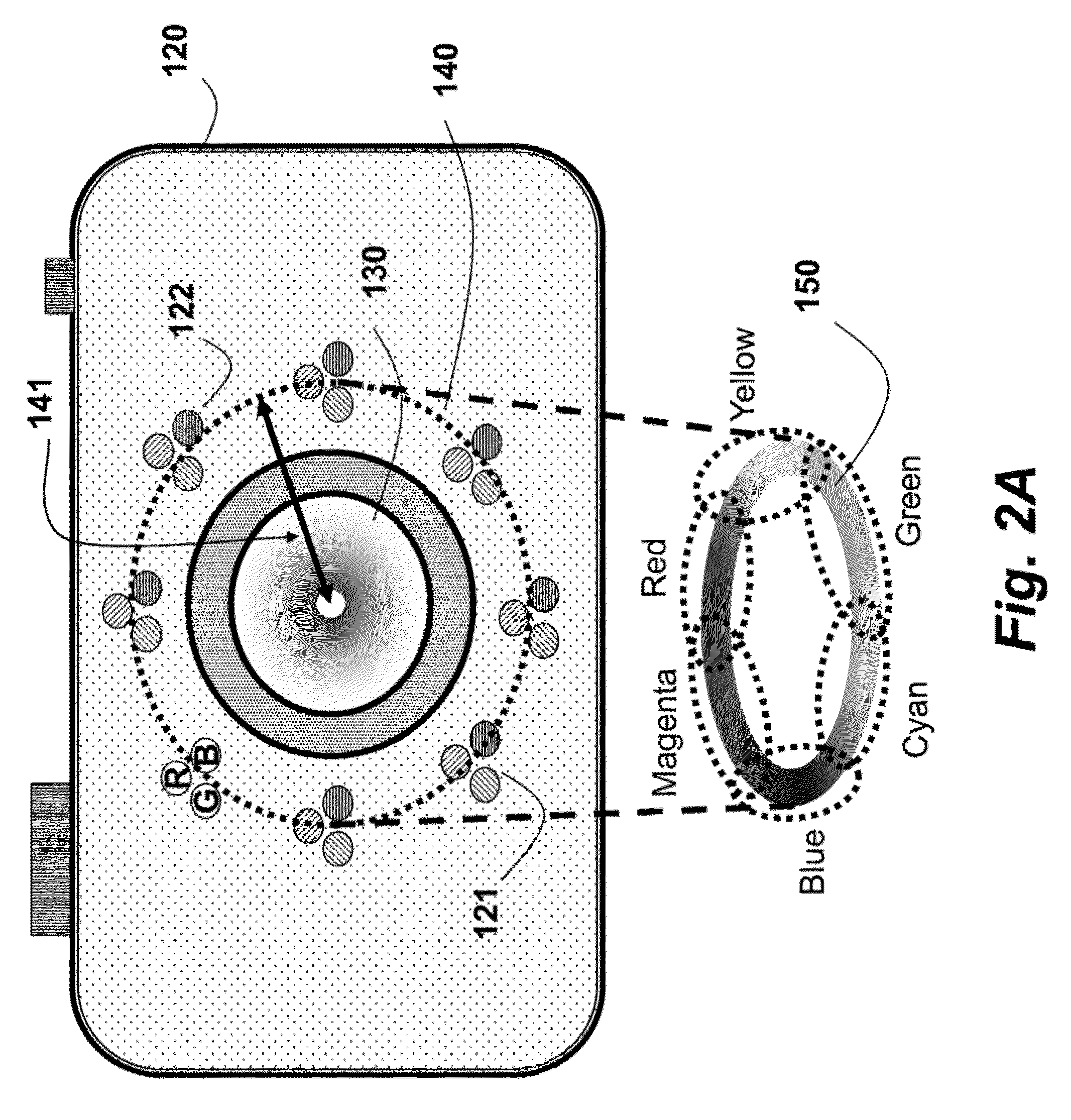
A method and system extract features from an image acquired of an object with a specular surface by first acquiring an image while illuminating the object with a hue circle generated by a set of lights flashed simultaneously. The lights have different colors and are arranged circularly around a lens of a camera. Then, the features correspond to locations of pixels in the image within a neighborhood of pixels that includes a subset of the colors of the lights.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Device for analysing the surface of a substrate
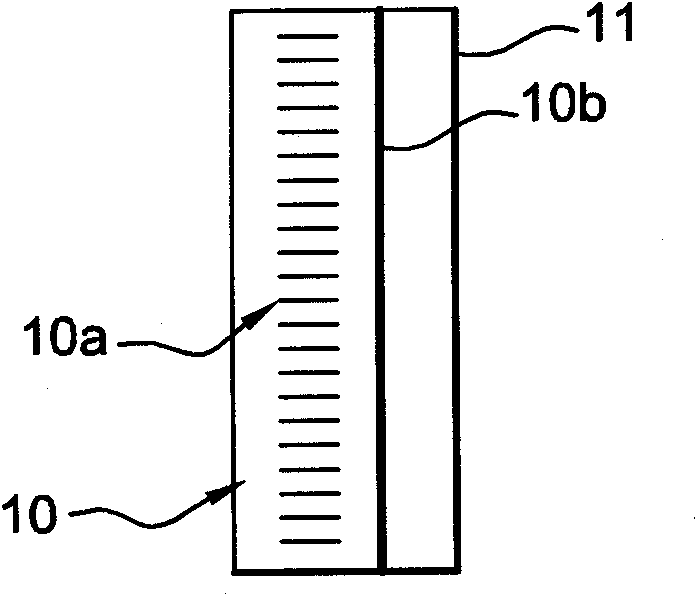
ActiveCN102171554AReduce the occupied areaSmall sizeMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
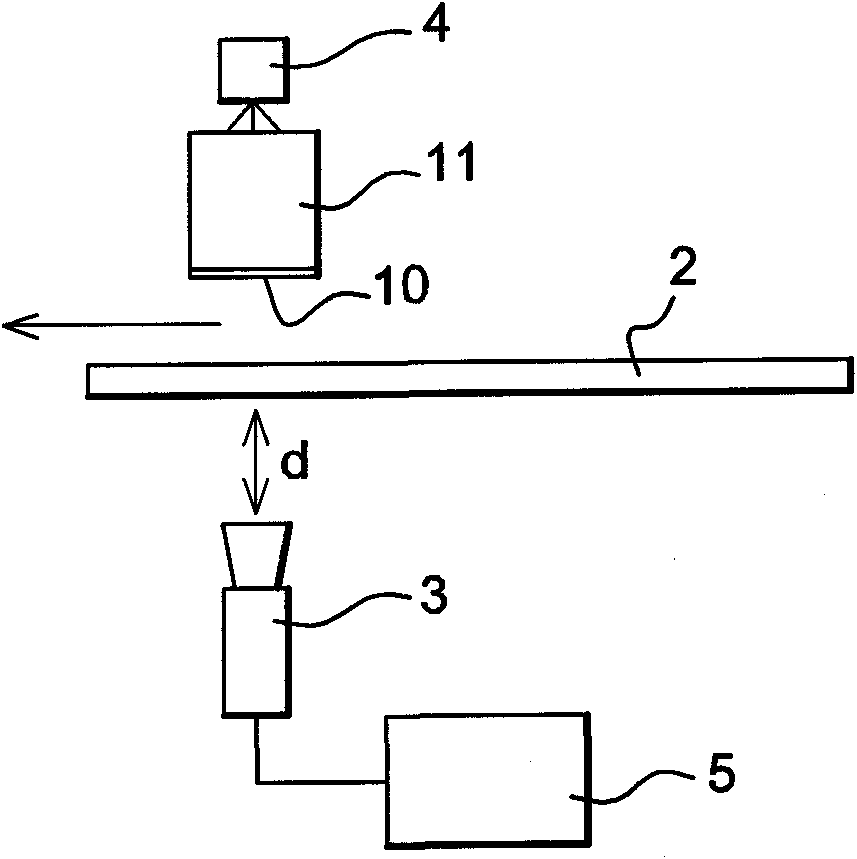
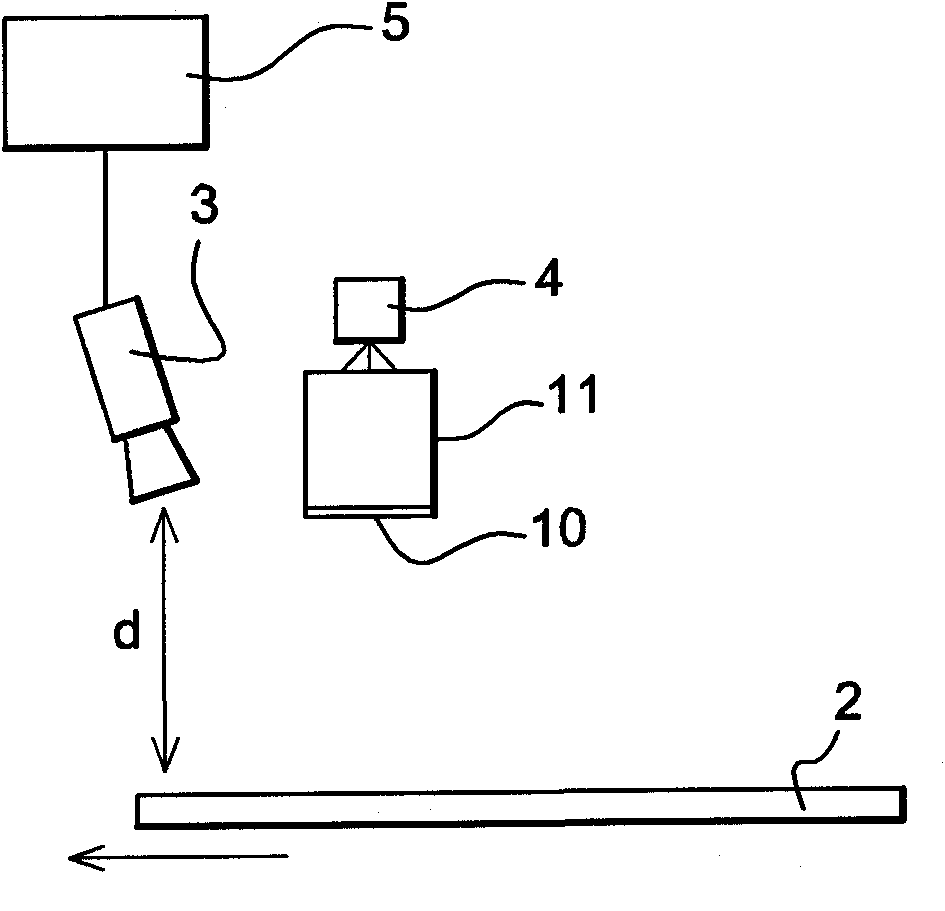
The invention relates to an analysis device (1) for analysing the transparent or specular surface of a substrate (2), said device comprising a raster (10) located opposite the surface of the substrate to be measured, a video camera (3) for capturing at least one image of the raster deformed by the measured substrate, a raster lighting system (4), and an image-processing and digital analysis means (5) connected to the video camera (3). According to the invention, the video camera (3) is a matrix array camera, the raster (10) is provided on a substrate (11) having an oblong shape and is bidirectional in that it comprises a first pattern (10a) extending along a first direction and along the smallest extension of the substrate, the first pattern being transversely periodical to the smallest extension, and a second pattern (10b) extending in a second direction perpendicular to the first pattern and along the largest extension of the substrate.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Large-size MEMS vertical comb micro-mirror and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111552072AThe process is simple and easy to controlImprove alignment accuracyTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLight reflectionEngineering
The invention provides a large-size MEMS vertical comb micro-mirror and a preparation method thereof. The micro-mirror comprises a movable low-light-level reflector structure formed by a movable mirror surface and a fixed supporting structure; a movable platform structure which is positioned below the movable low-light-level reflecting mirror structure and is bonded with the fixed supporting structure; an upper comb tooth structure and a lower comb tooth structure which are arranged on the outer side of the movable platform structure; a substrate which is provided with a motion space and is bonded with the lower comb tooth structure; a metal reflecting layer which is located on the surface of the movable mirror surface, and bonding pads which are located in the upper comb tooth structure lead area and the lower comb tooth structure lead area. According to the structure, the preparation of the large-size MEMS vertical comb micro-mirror is achieved through the MEMS technology, the movable low-light-level reflecting mirror structure is arranged above the micro-actuator, and manufacturing of the large-size large-corner movable low-light-level reflecting mirror structure can be achieved; besides, the manufacturing process is simple and controllable, the structure is suitable for large-scale production, the shape, thickness and the like of the movable low-light-level reflector structure can be flexibly selected according to design requirements, the flexibility is high, and the application range is wider.
Owner:ANHUI CHINA SCI MW ELECTRONIC TECH CO LTD
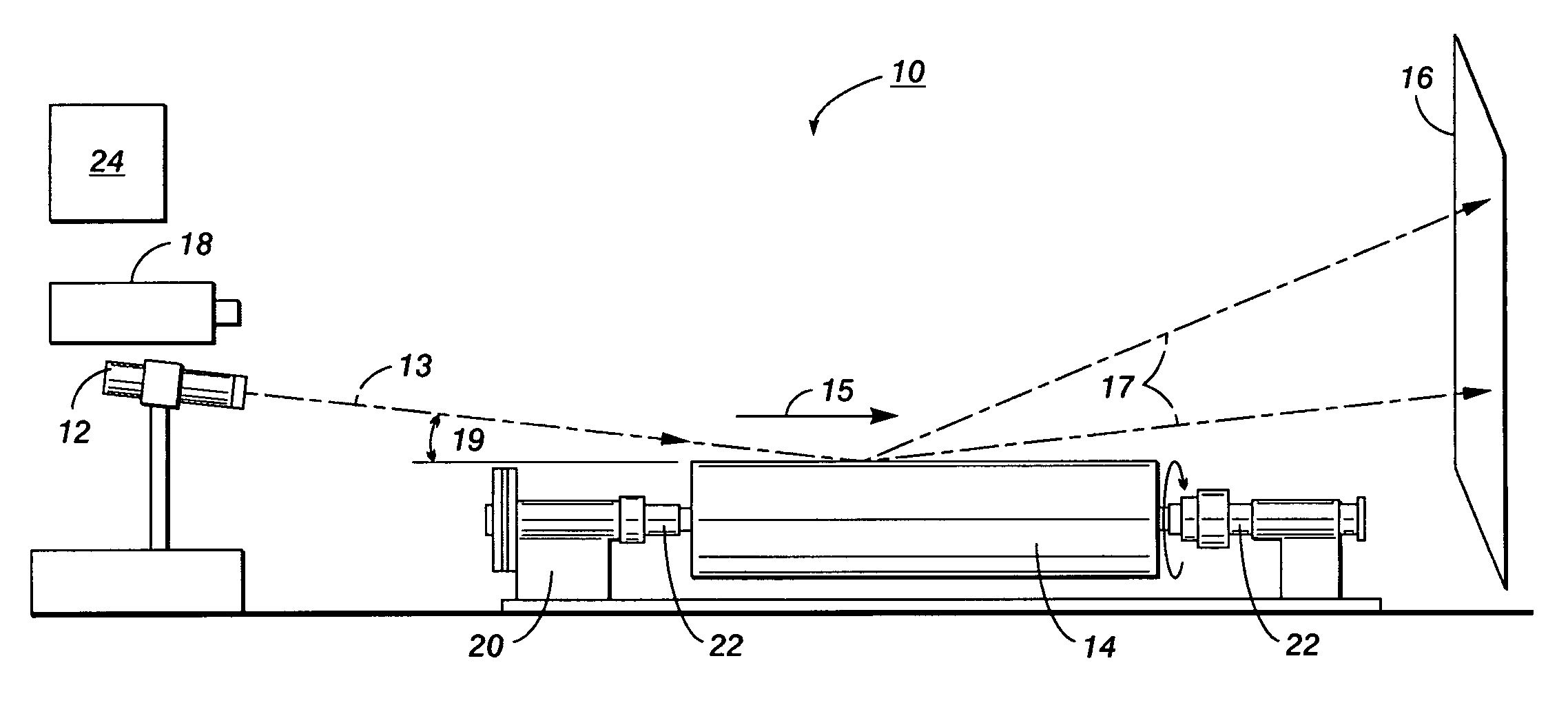
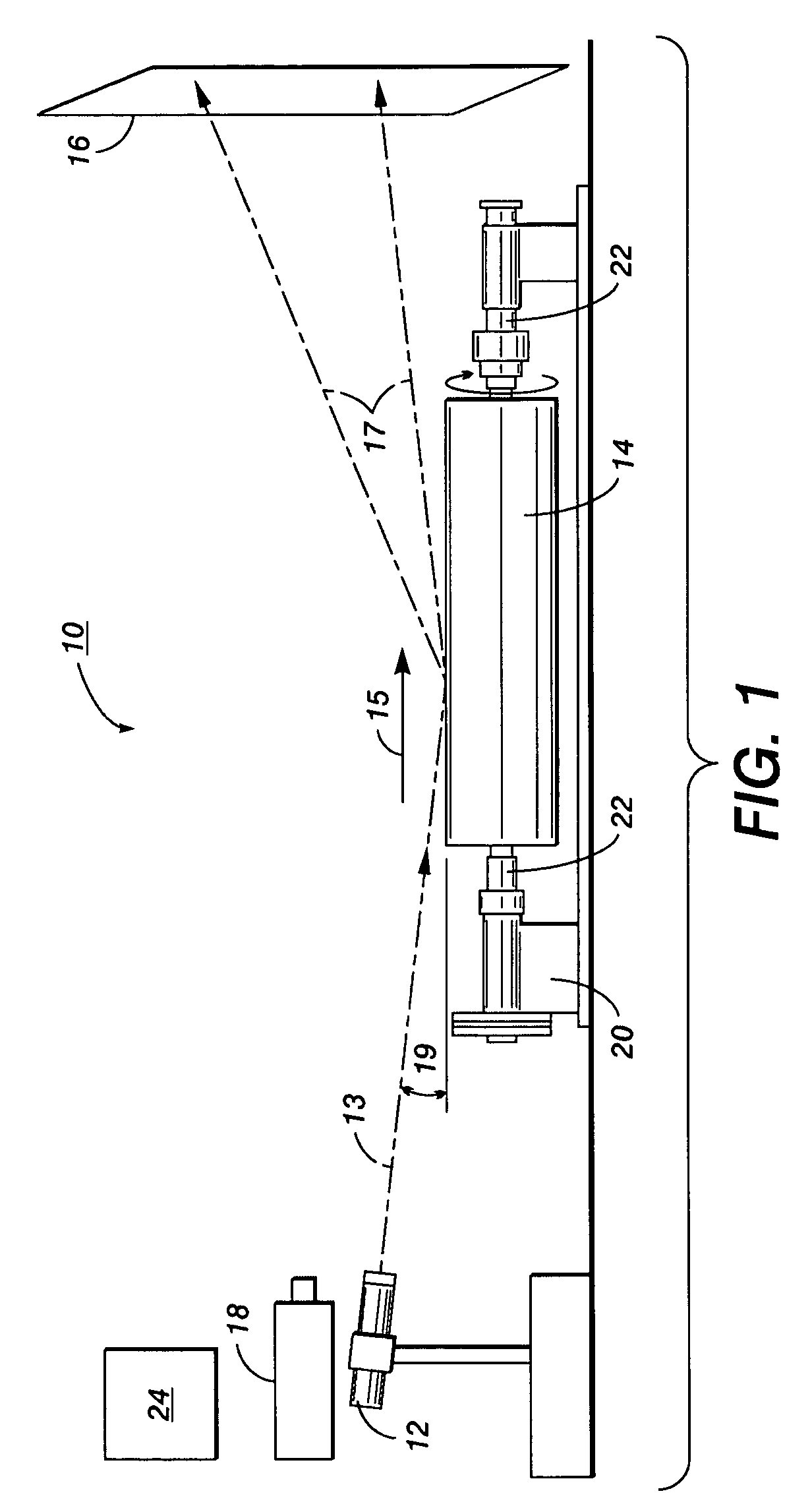
Specular surface flaw detection
InactiveUS7362450B2Equally distributedMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansElectromagnetic radiationOblique angle
An apparatus and a method for detecting low frequency specular surface flaws on coated substrates is disclosed. A method for detecting low frequency specular surface flaws may comprise: impinging visible electromagnetic radiation or light from an electromagnetic radiation source onto the coated substrate at an oblique angle, reflecting the visible electromagnetic radiation off the coated substrate onto a screen material to form a specular surface flaw reflected image, and recording the reflected image off the screen material with a photosensitive device to form a recorded reflected image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
System and method for detecting defects on a specular surface with a vision system
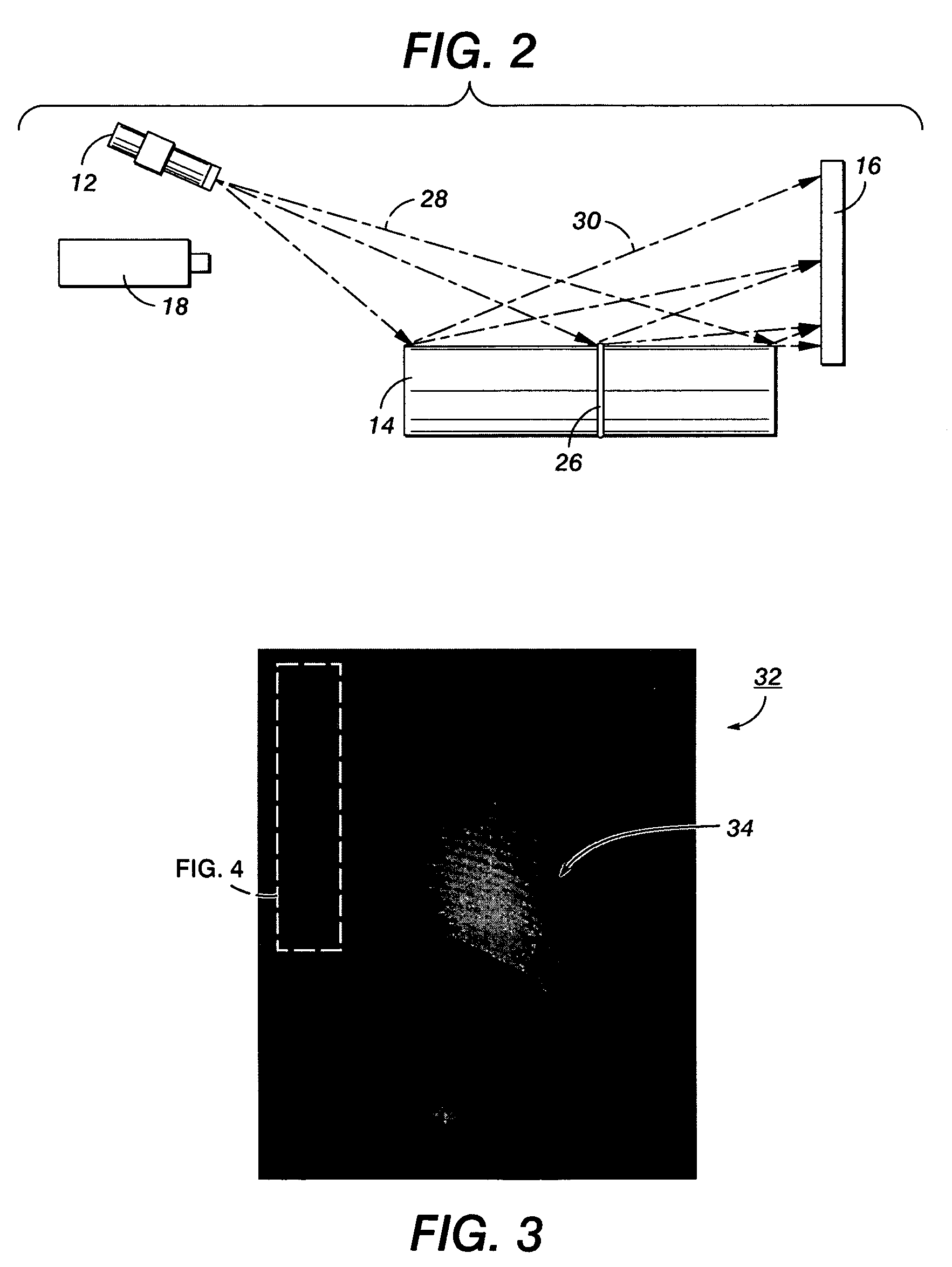
This invention provides a system and method for detecting and imaging specular surface defects on a specular surface that employs a knife-edge technique in which the camera aperture or an external device is set to form a physical knife-edge structure within the optical path that effectively blocks reflected rays from an illuminated specular surface of a predetermined degree of slope values and allows rays deflected at differing slopes to reach the vision system camera sensor. The light reflected from the flat part of the surface is mostly blocked by the knife-edge. Light reflecting from the sloped parts of the defects is mostly reflected into the entrance aperture. The illumination beam is angled with respect to the optical axis of the camera to provide the appropriate degree of incident angle with respect to the surface under inspection. The surface can be stationary or in relative motion with respect to the camera.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Anti-dazzle glass as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an anti-dazzle glass as well as a preparation method an application thereof, and relates to anti-dazzle glass. The anti-dazzle glass is provided with an anti-dazzle layer and a glass substrate; and the anti-dazzle layer is arranged on the glass substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) cleaning the to-be-processed glass substrate to completely eradicate pollutants, such as dust, oil and water stain, on the surface; and 2) conveying the glass substrate, processed in the step 1), into a chemical etching machine, spraying a chemical liquid medicine on the processed face of the glass substrate for chemical etching, thereby etching the glass substrate surface to form even nano particle distribution thereon, wherein the chemical liquid medicine is selected from at least one of hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, ammonium bifluoride, sodium fluoride, nitric acid, concentrated sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, sodium silicate and calcium silicate; and the anti-dazzle glass can be applied to manufacturing of a cell phone panel, a panel display glass faceplate, a projected capacitive touch screen, and so on. A glass specular surface is etched to become a matt diffuse surface, production procedures are simplified, cost is low, and light transmittance is high.
Owner:厦门格林泰新材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com