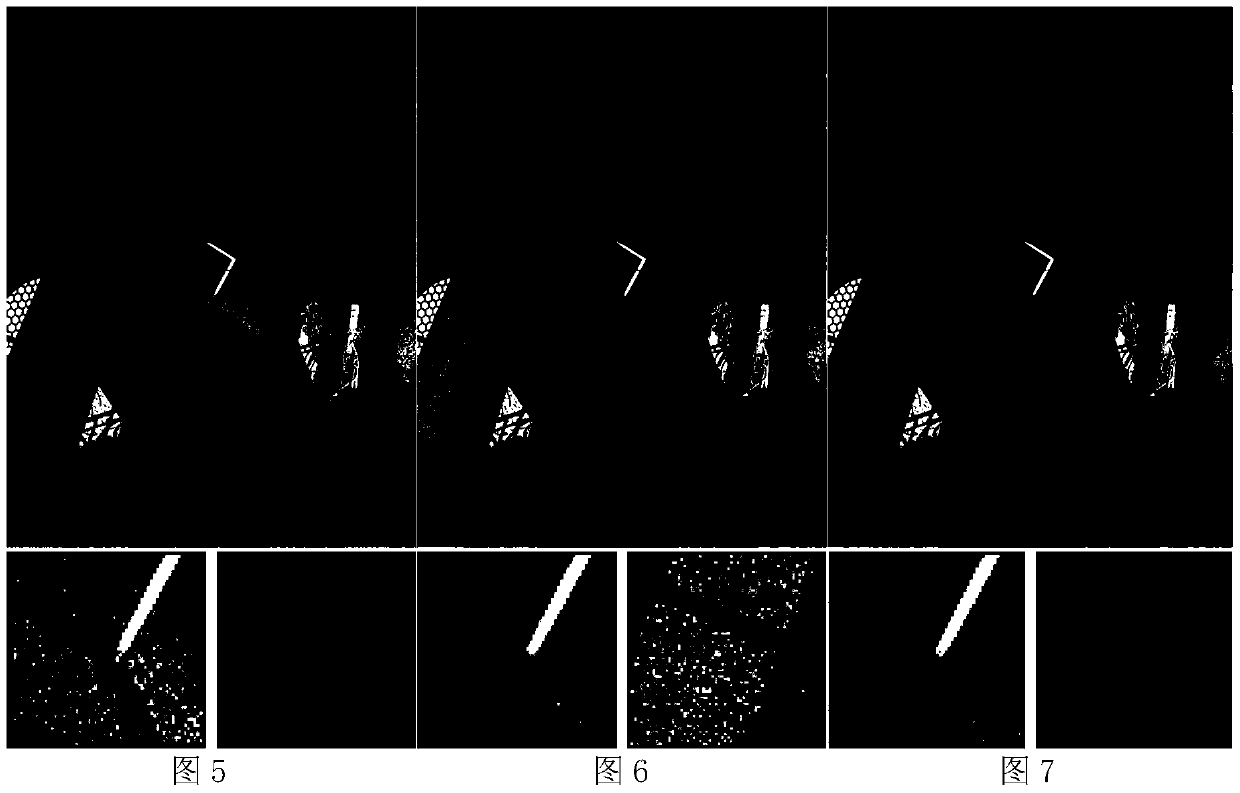
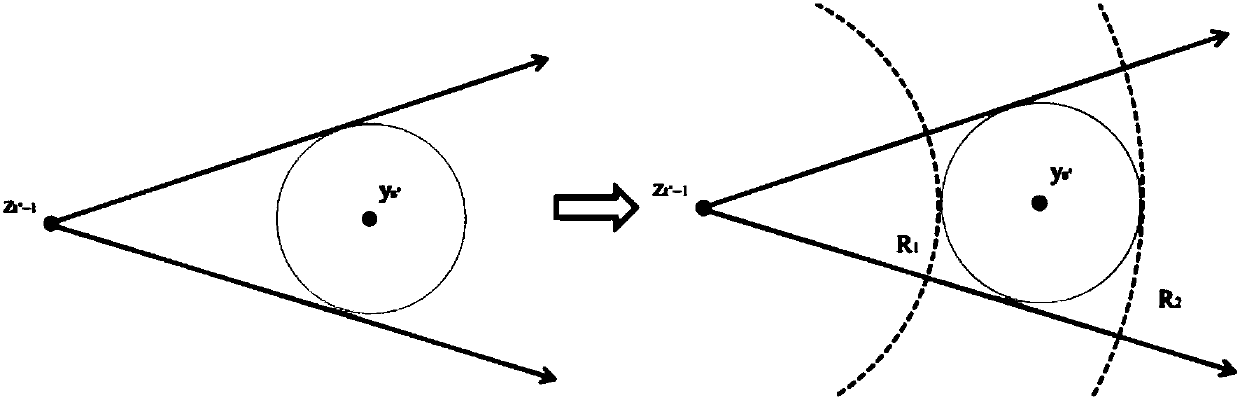
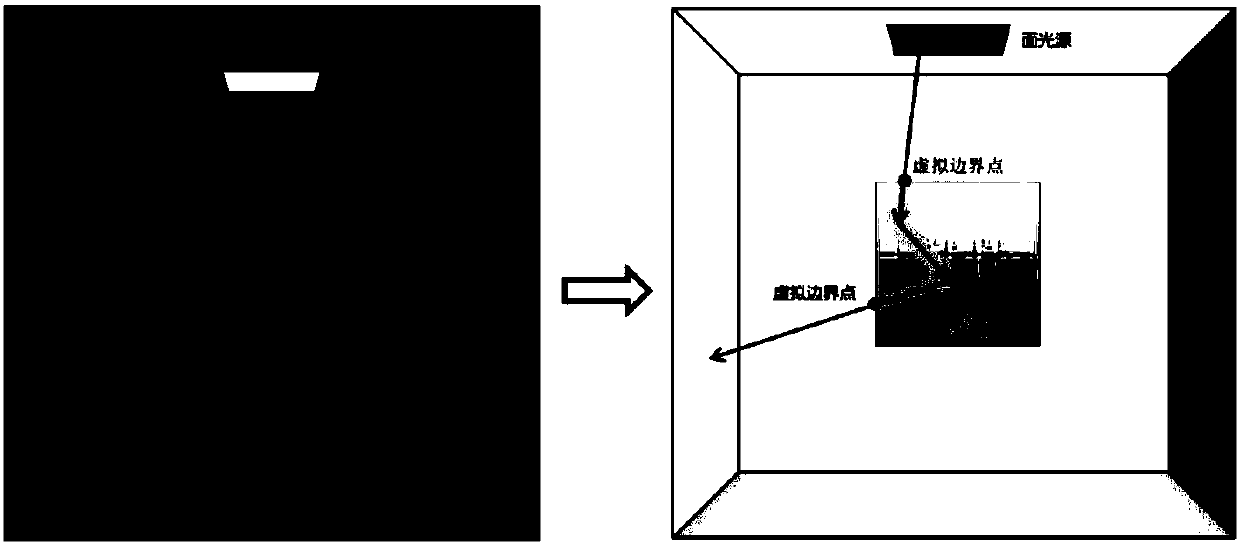
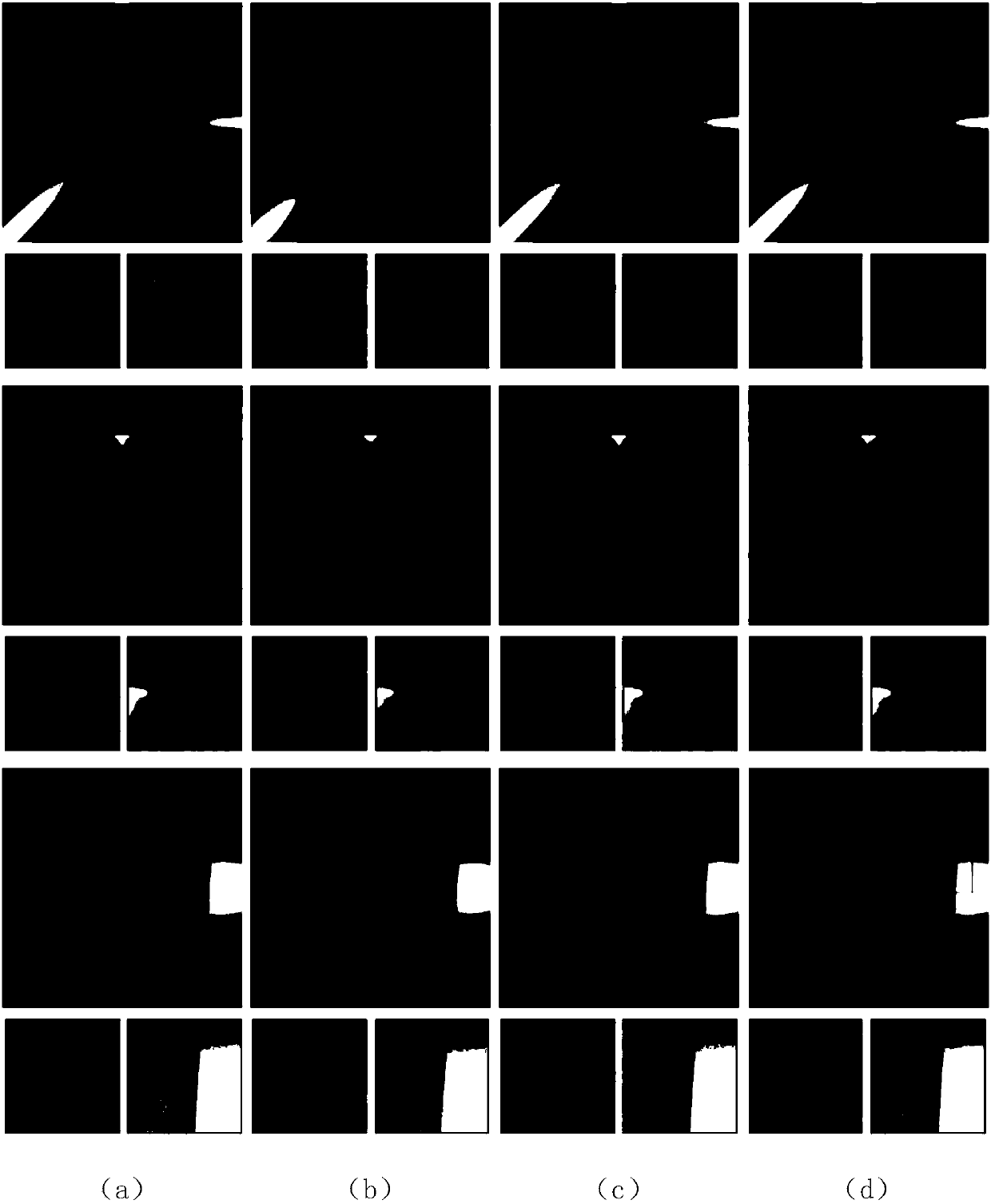
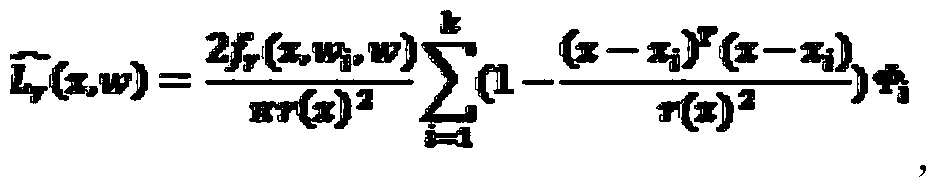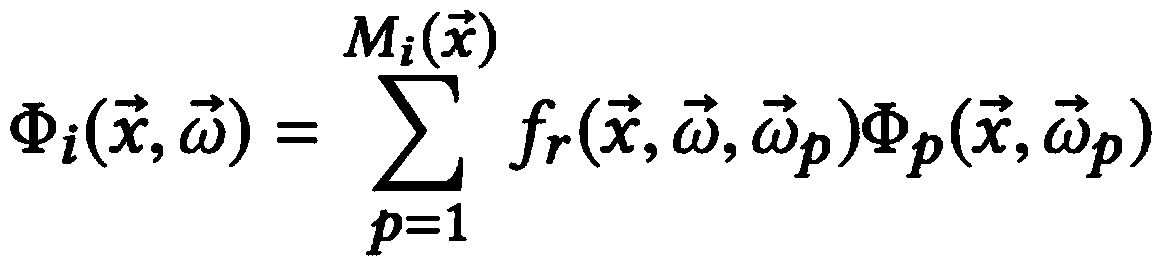Patents
Literature
44 results about "Photon mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
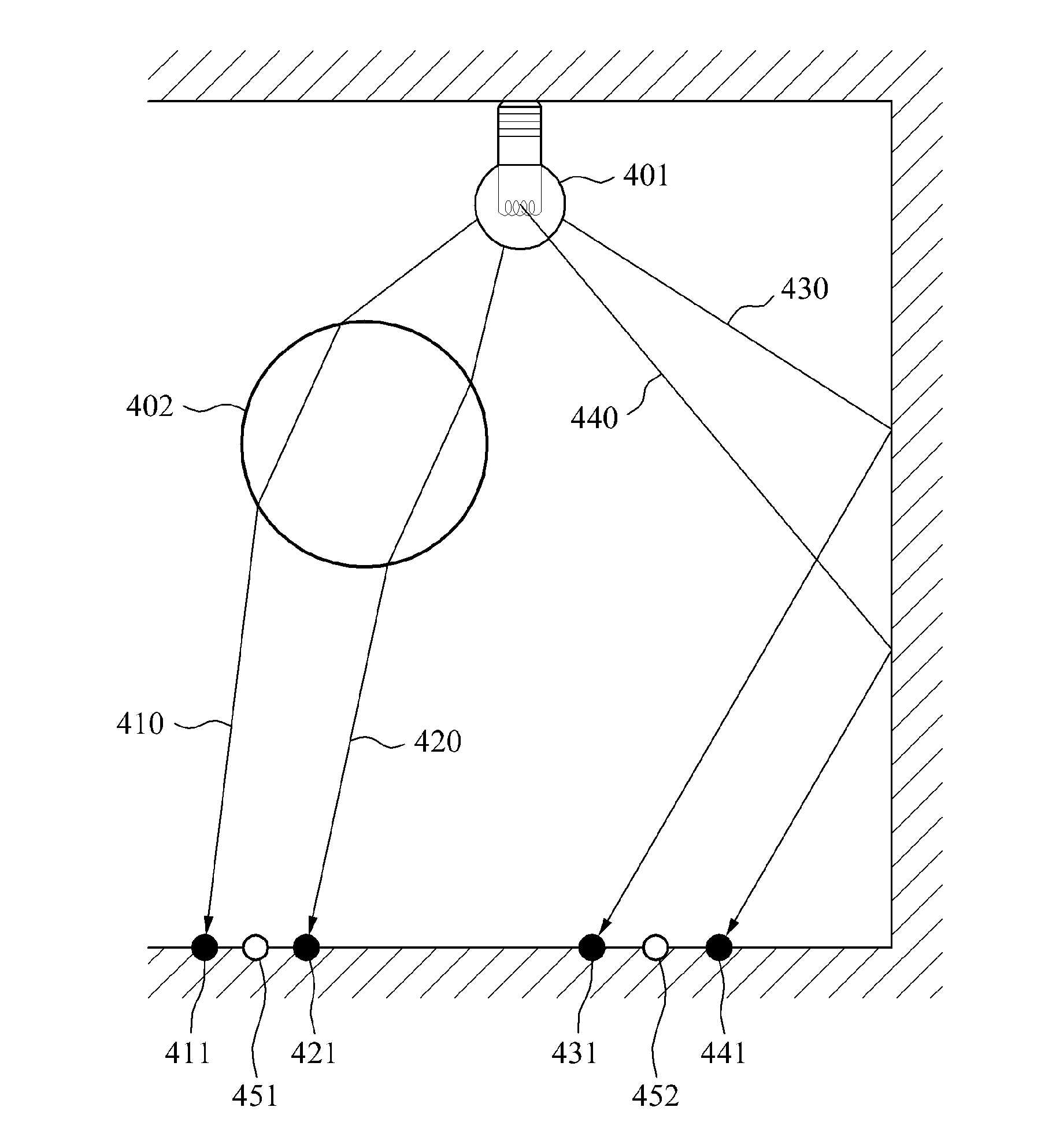
In computer graphics, photon mapping is a two-pass global illumination algorithm developed by Henrik Wann Jensen that approximately solves the rendering equation. Rays from the light source and rays from the camera are traced independently until some termination criterion is met, then they are connected in a second step to produce a radiance value. It is used to realistically simulate the interaction of light with different objects. Specifically, it is capable of simulating the refraction of light through a transparent substance such as glass or water, diffuse interreflection between illuminated objects, the subsurface scattering of light in translucent materials, and some of the effects caused by particulate matter such as smoke or water vapor. It can also be extended to more accurate simulations of light such as spectral rendering.
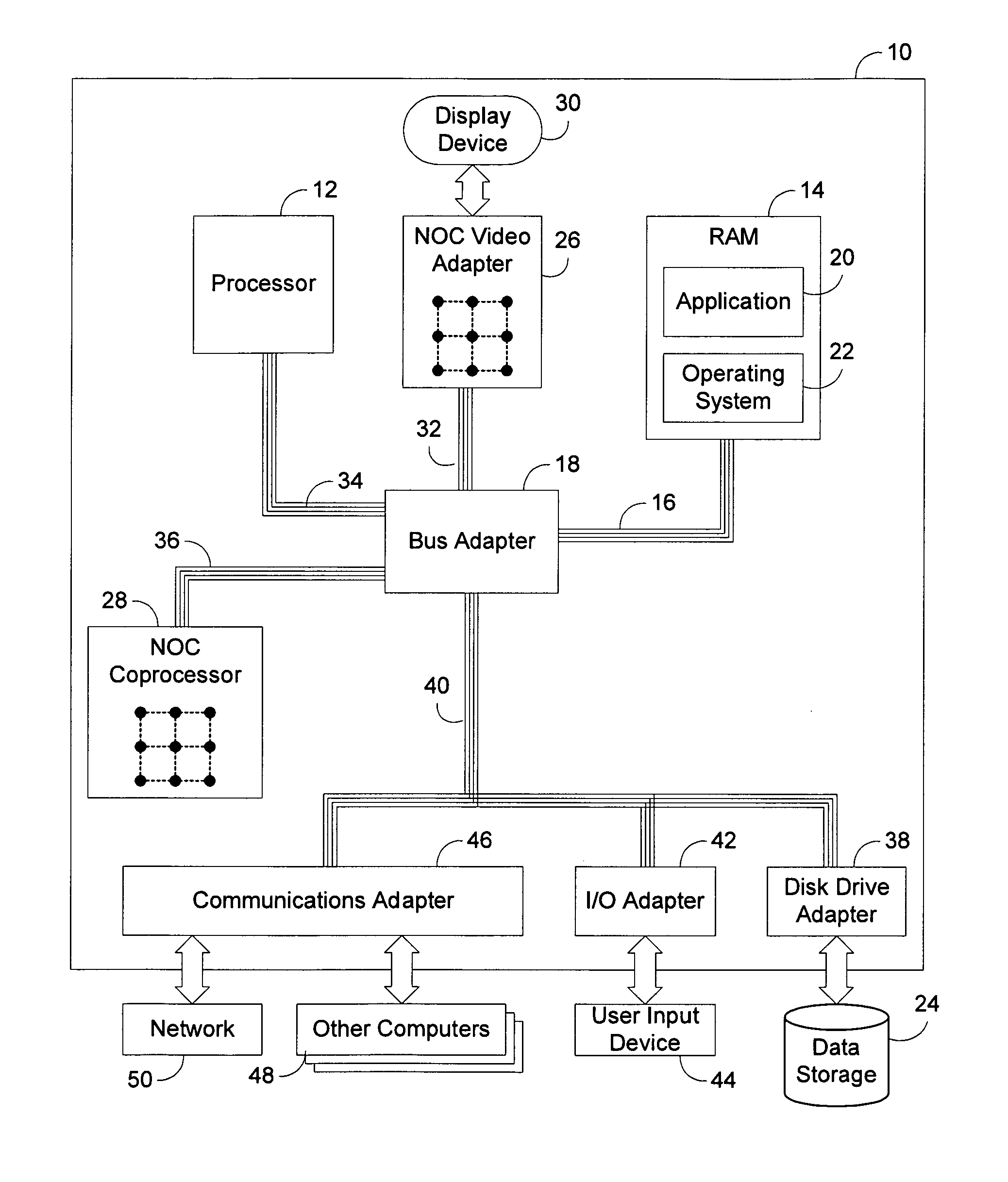
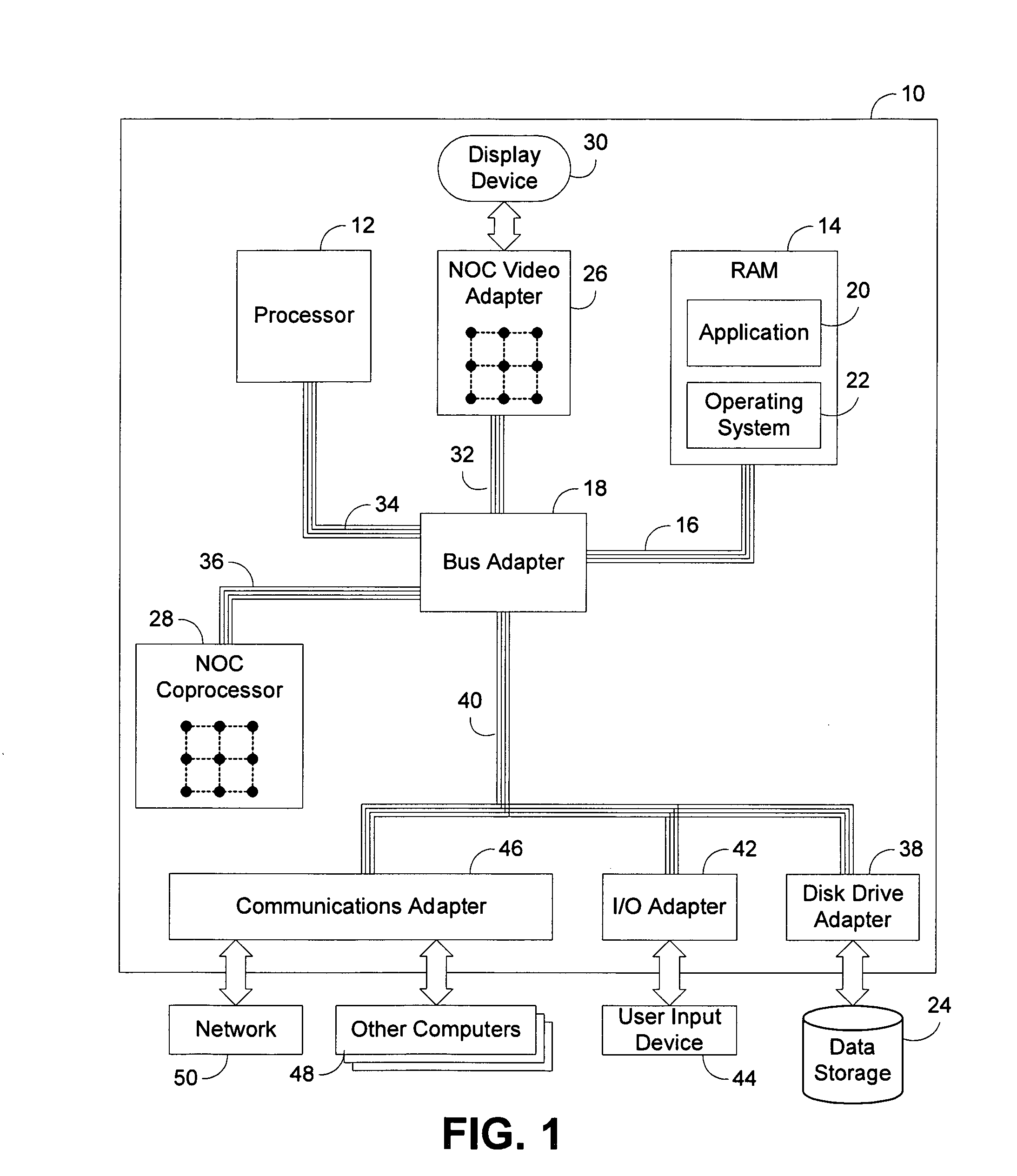
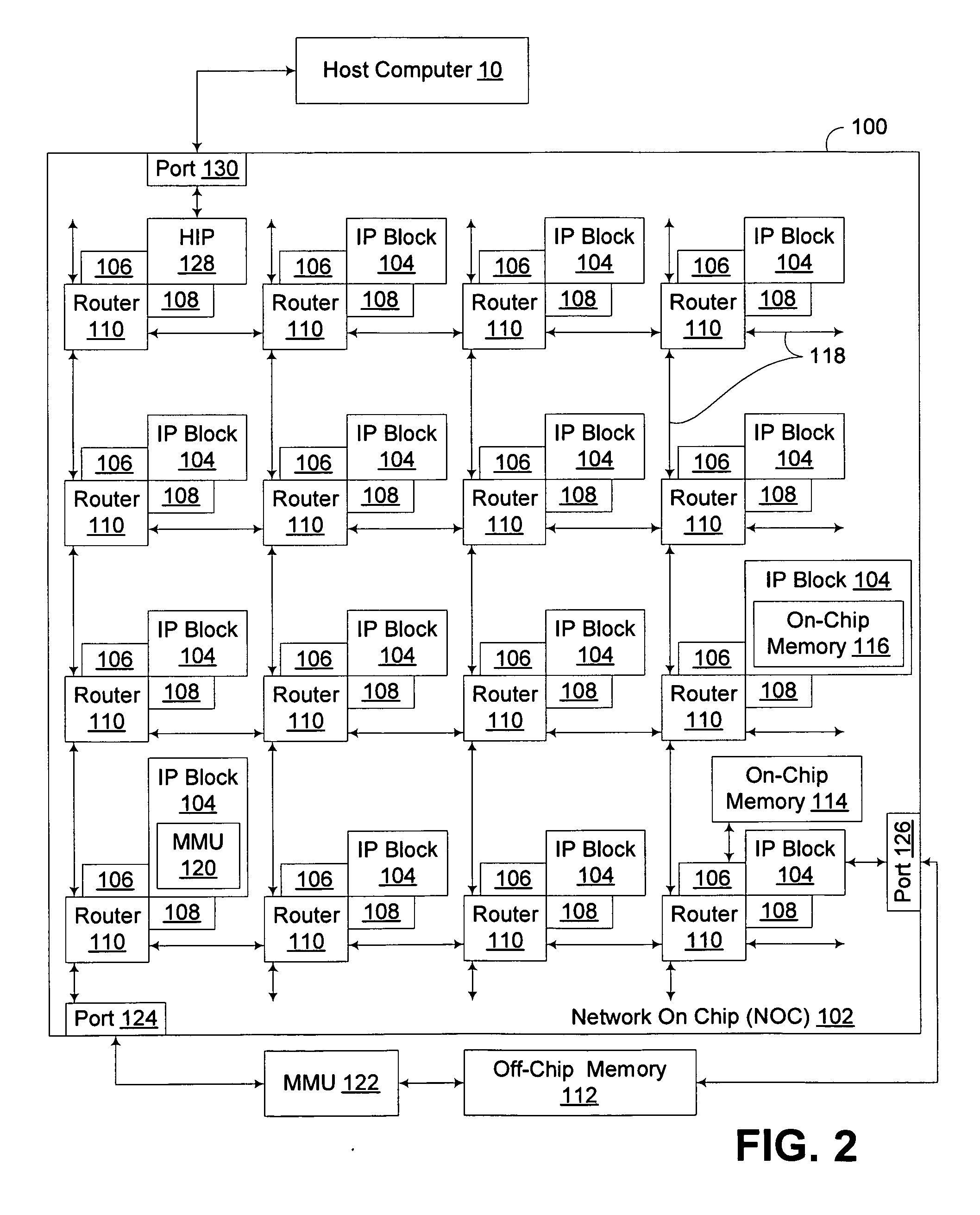
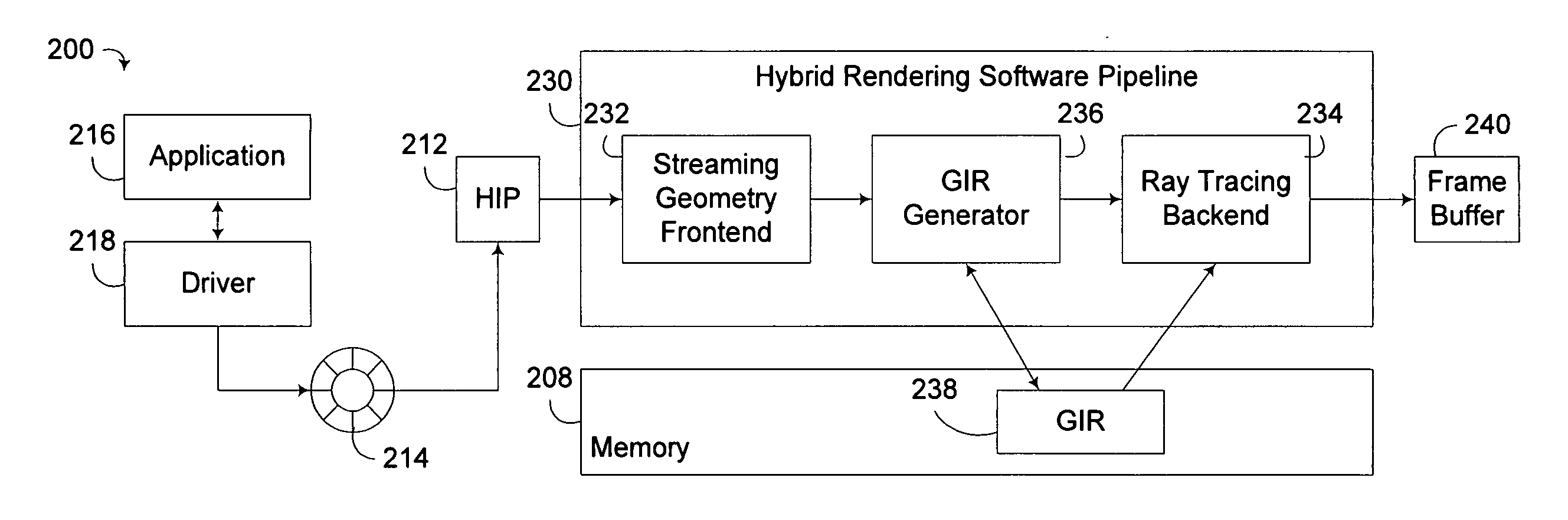
Hybrid rendering of image data utilizing streaming geometry frontend interconnected to physical rendering backend through dynamic accelerated data structure generator
InactiveUS20090256836A1Generate efficientlyEasy to adaptCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails involving image processing hardwareComputer graphics (images)DEVS
A circuit arrangement and method provide a hybrid rendering architecture capable of interfacing a streaming geometry frontend with a physical rendering backend using a dynamic accelerated data structure (ADS) generator. The dynamic ADS generator effectively parallelizes the generation of the ADS, such that an ADS may be built using a plurality of parallel threads of execution. By doing so, both the frontend and backend rendering processes are amendable to parallelization, and enabling if so desired real time rendering using physical rendering techniques such as ray tracing and photon mapping. Furthermore, conventional streaming geometry frontends such as OpenGL and DirectX compatible frontends can readily be adapted for use with physical rendering backends, thereby enabling developers to continue to develop with known API's, yet still obtain the benefits of physical rendering techniques.
Owner:IBM CORP
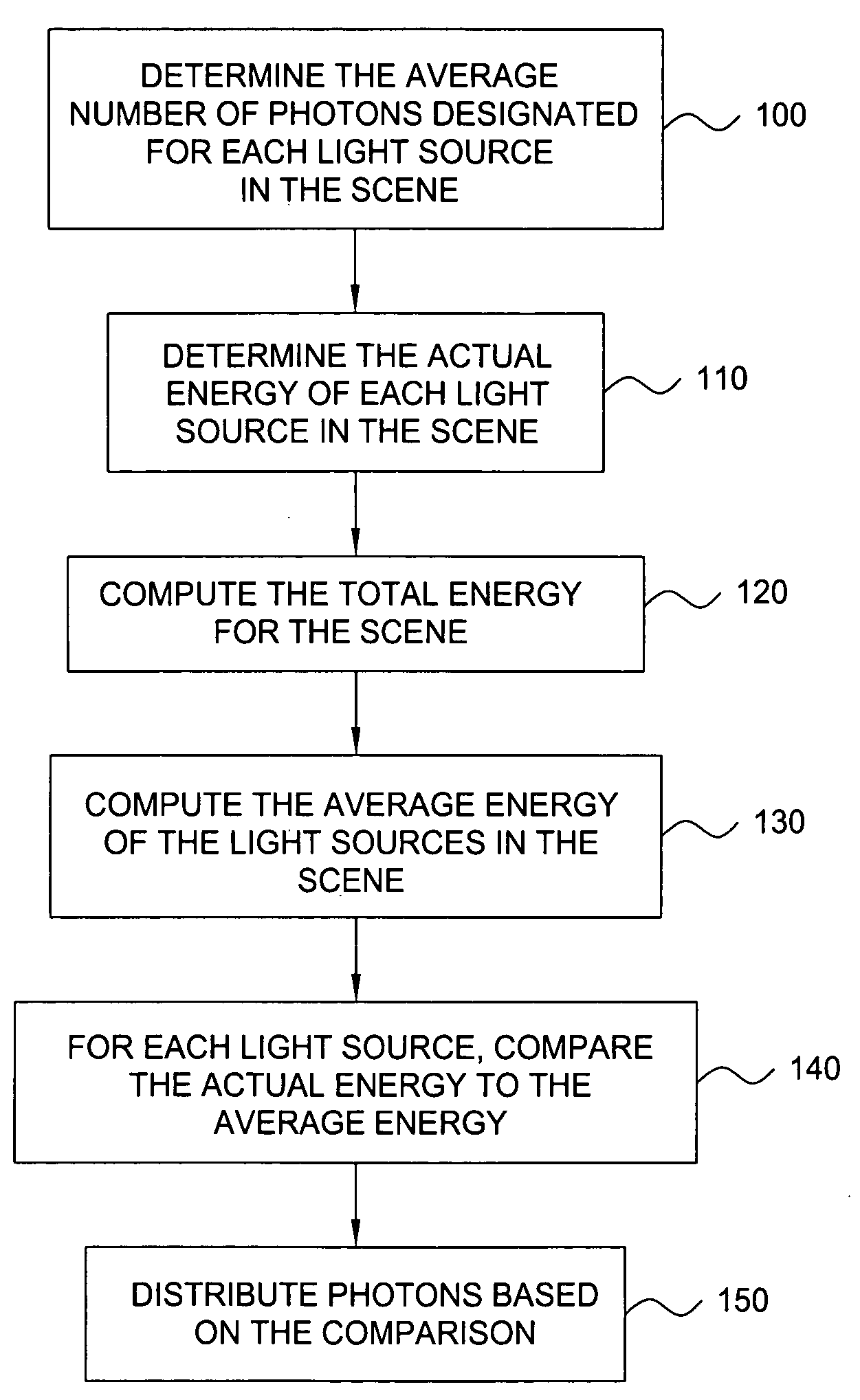
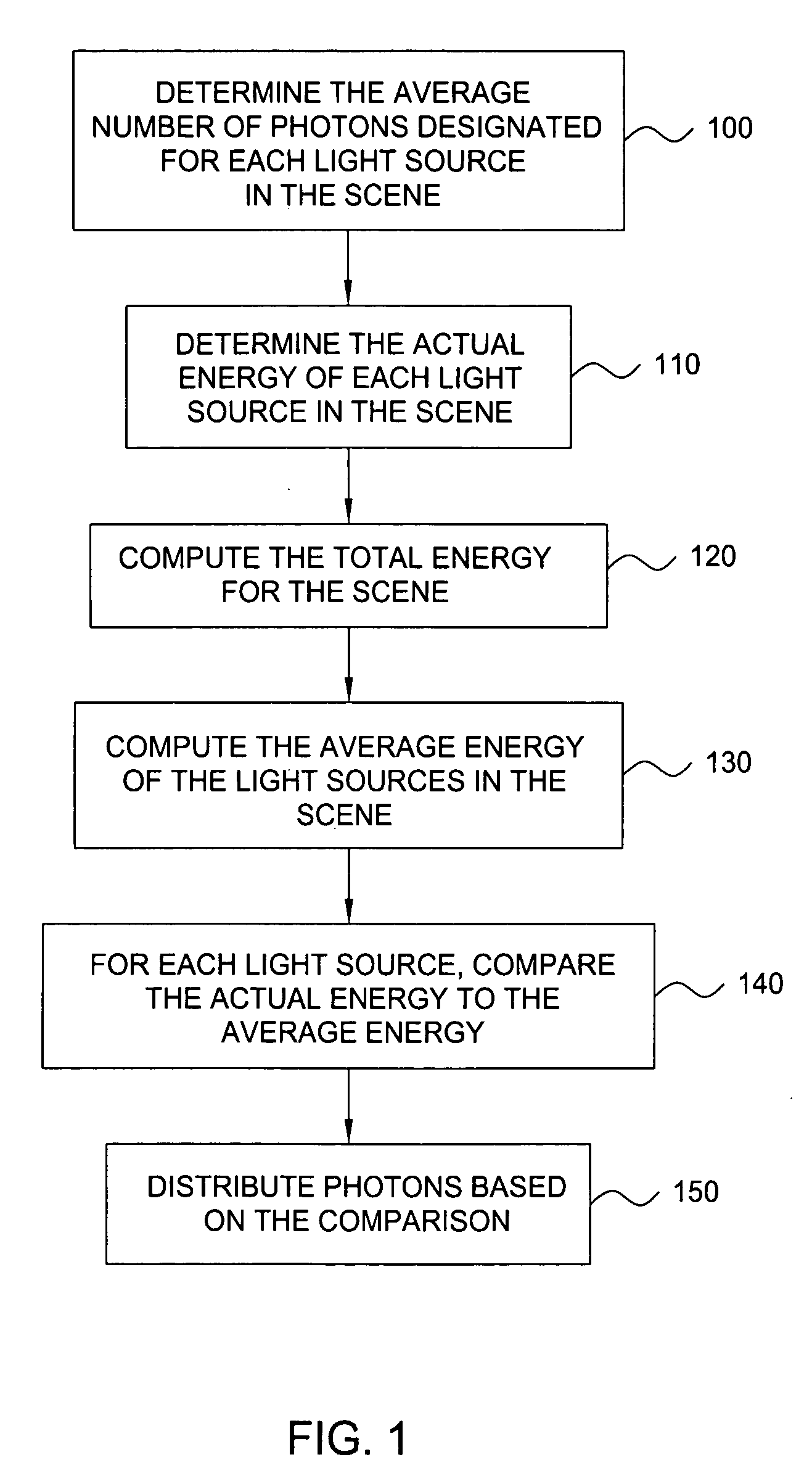
System and method for distributing photons when rendering an image using photon mapping
ActiveUS7221365B1Extended processing timeMore processing time3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Photon mapping
A method for distributing photons among light sources when rendering an image of a scene using photon mapping includes the steps of computing a total energy for the scene, where the scene includes a plurality of light sources, and computing an average energy of the light sources. The method also includes the steps of comparing, for each of the light sources, the actual energy of the light source to an average energy of the light source and distributing photons to each of the light sources based on the comparison.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
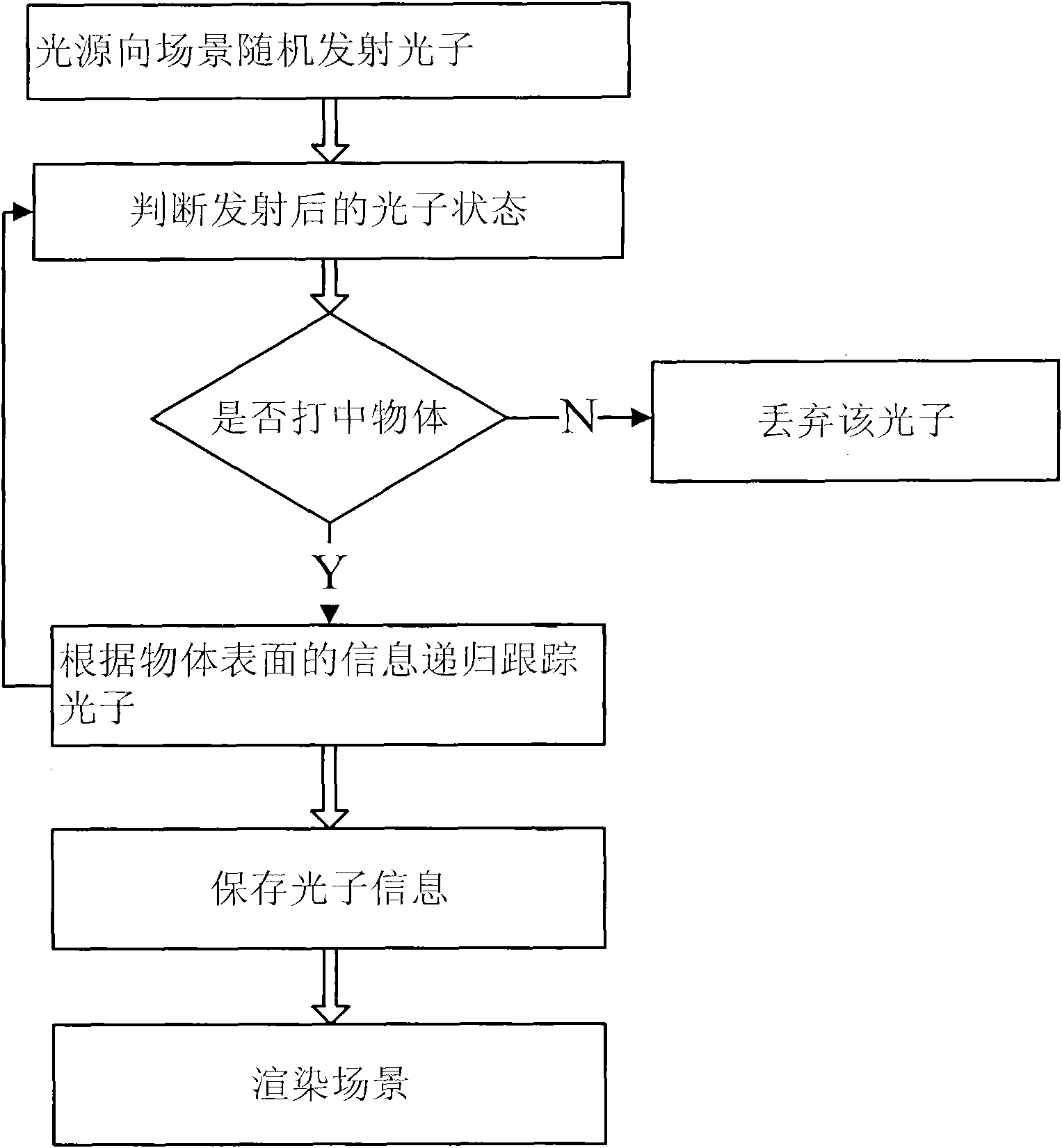
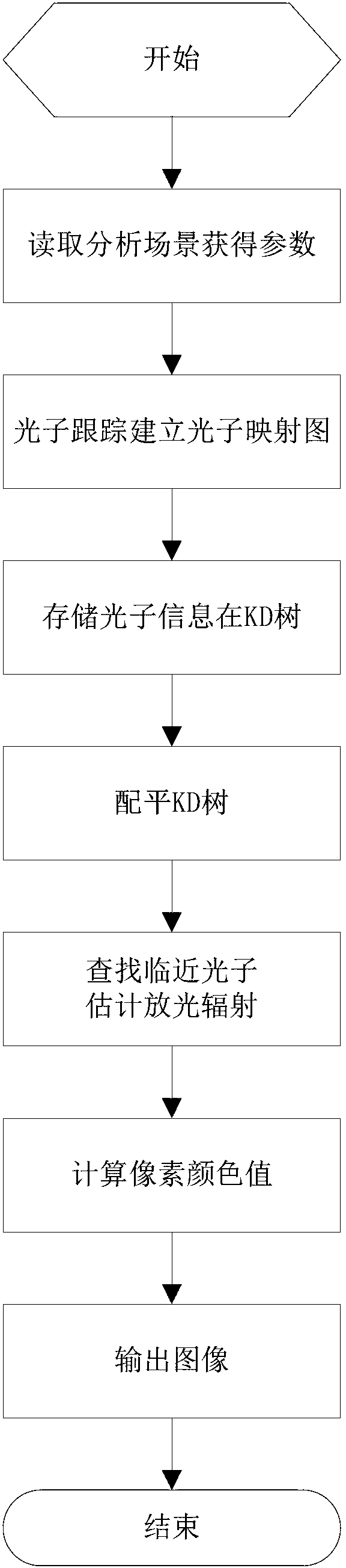
Photon mapping-based global illumination method
InactiveCN101826214AOptimized for speedGood effect3D-image renderingImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
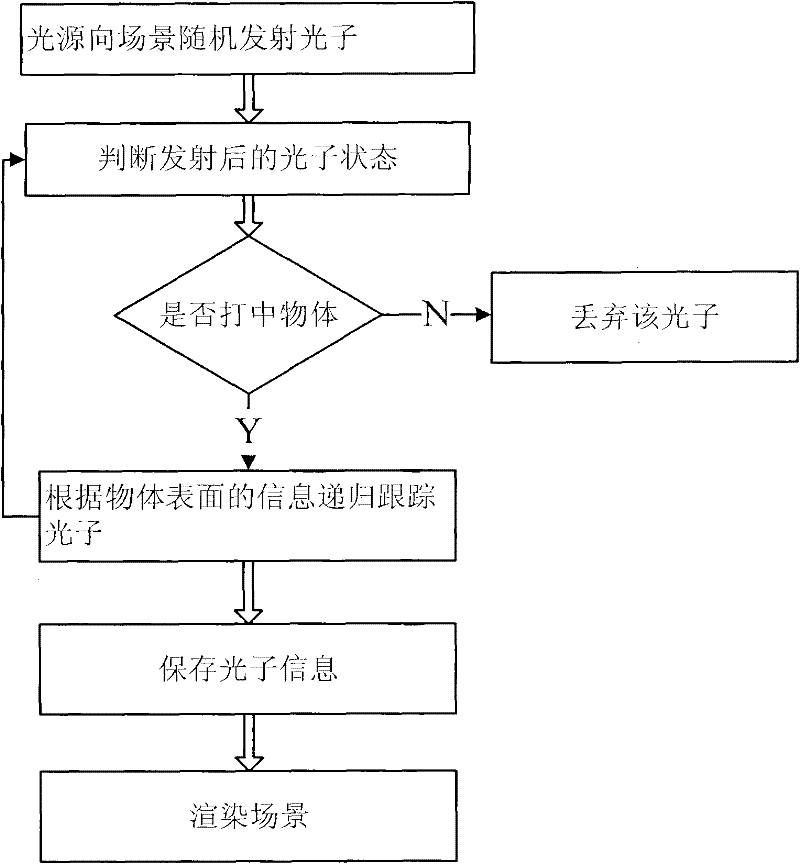
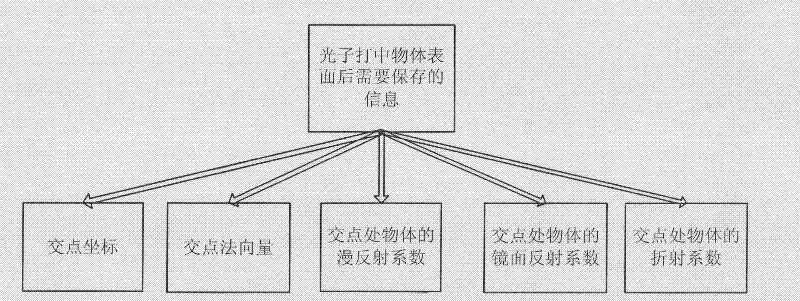
The invention discloses a novel photon mapping-based global illumination method, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method of the invention mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) randomly emitting photons to a scene by a light source; (2) judging the state of the emitted photons; (3) tracing the photons by a recursive method according to the information on the surface of an object; (4) storing the photon information; and (5) rendering the scene, namely rendering the scene by combining the Monte-Carlo backward tracing method and the primary photon mapping method. By using the technical scheme of the invention, the running speed, the rendering effect, the used storage space and the like can be improved to a certain extent.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Photon mapping accelerating method based on point cache
ActiveCN104200509AAvoid multiple queriesImprove efficiency3D-image renderingDirect illuminationIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
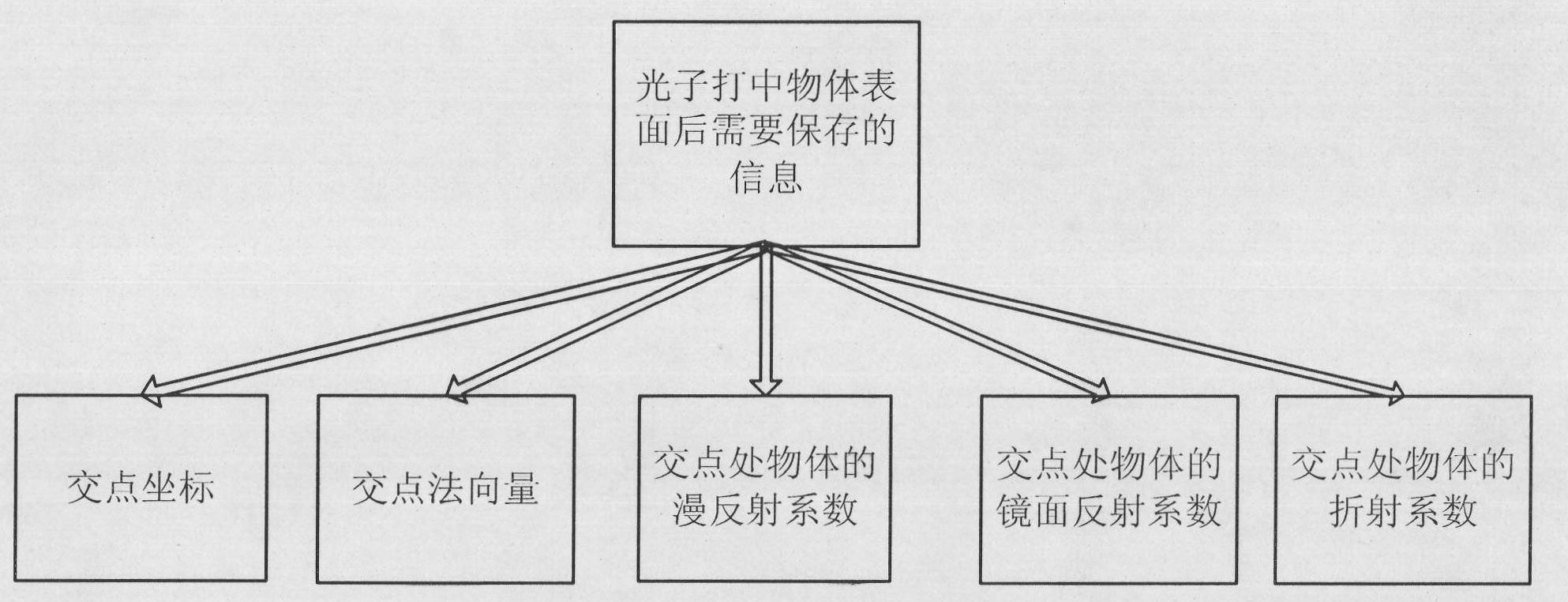
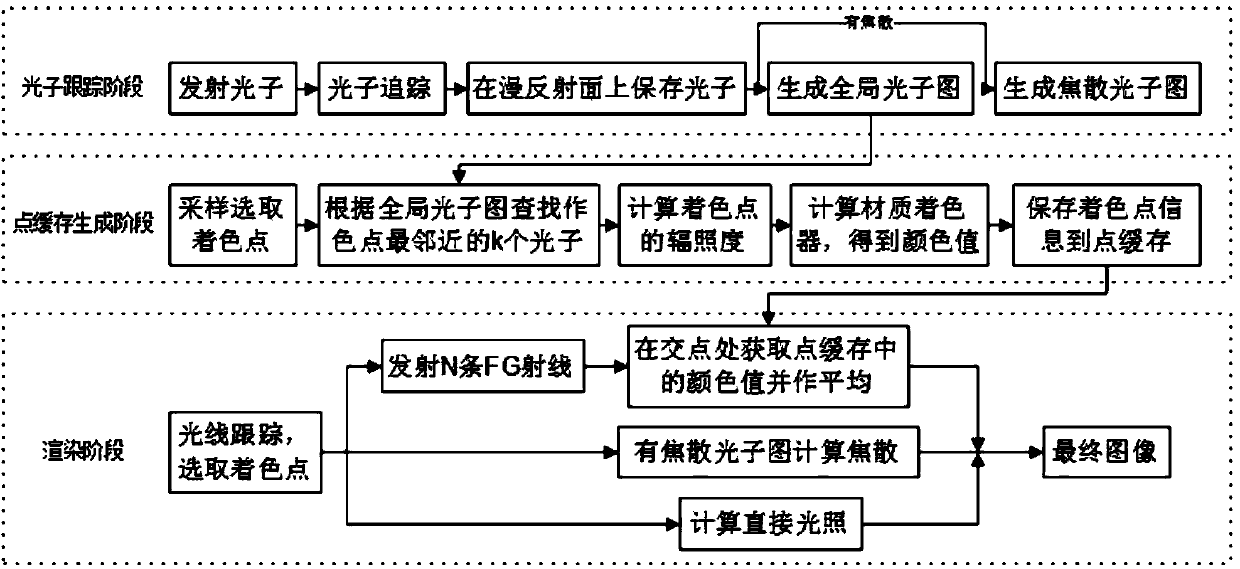
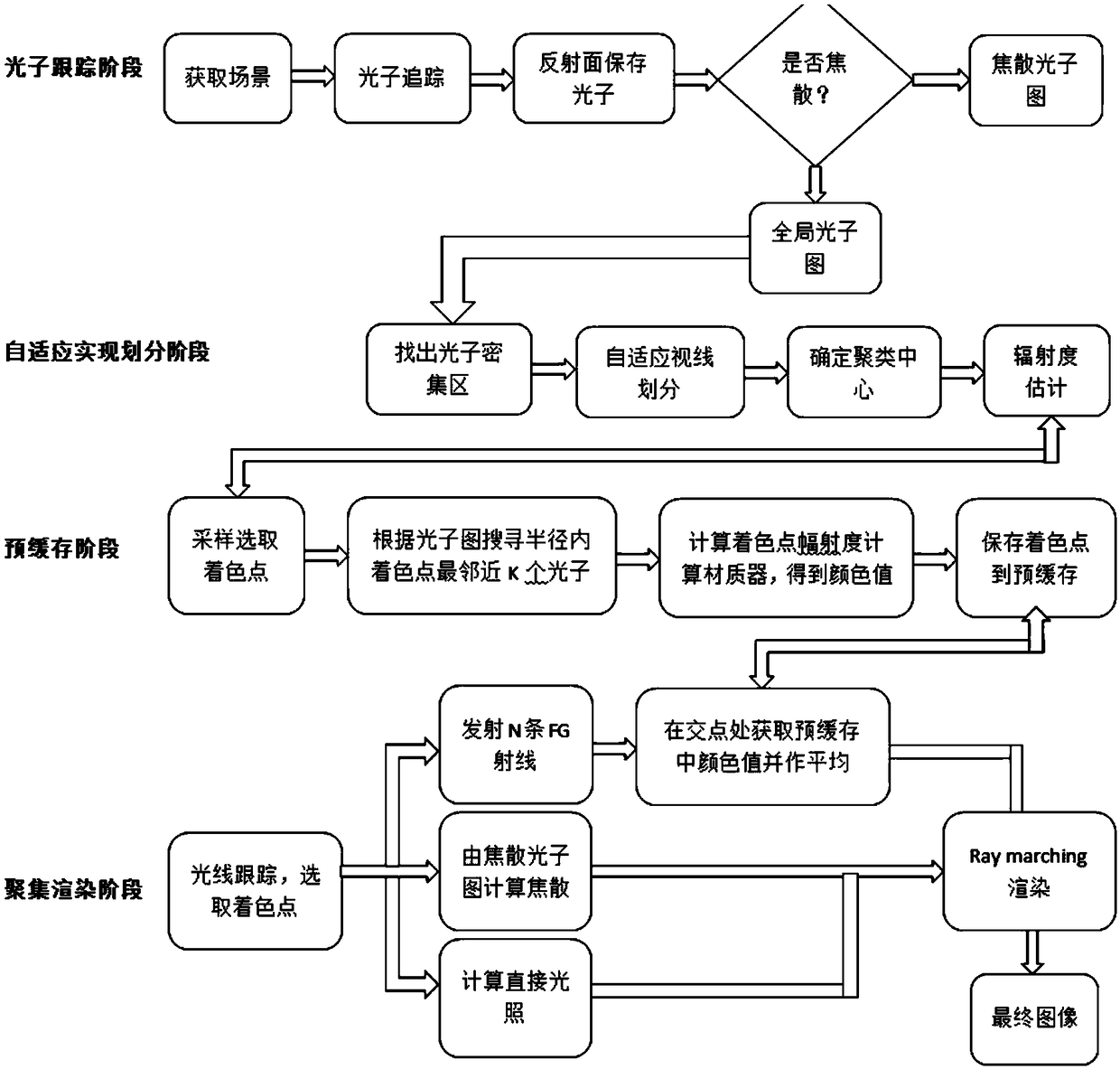
The invention discloses a photon mapping accelerating method based on point cache. The method includes the following steps: 1 photon tracking which includes emitting a certain number of photons to a scene from a light source, then tracking the moving track of the photons, recording the information of the photons in collision with an object and storing the information into a photon picture; 2 preprocessing which includes pre-computing the irradiance, storing the irradiance into the point cache, continuing computing a tinter after the irradiance is computed and storing obtained color values in the point cache mode; 3 rendering which includes conducting rendering according to a light tracking algorithm and emitting tracking reflection, refraction and diffuse reflection light at the intersection point position of light and the surface of the object according to the object surface attribute. A final gathering algorithm emits N diffuse reflection light, the diffuse reflection light intersects with the object on the scene, the color values of N sampling points in the point cache closest to the intersection point are returned, the color values are subjected to mean value computing to serve as the indirect illumination color value, and finally the indirect illumination color value plus the direct illumination color value is the final image.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
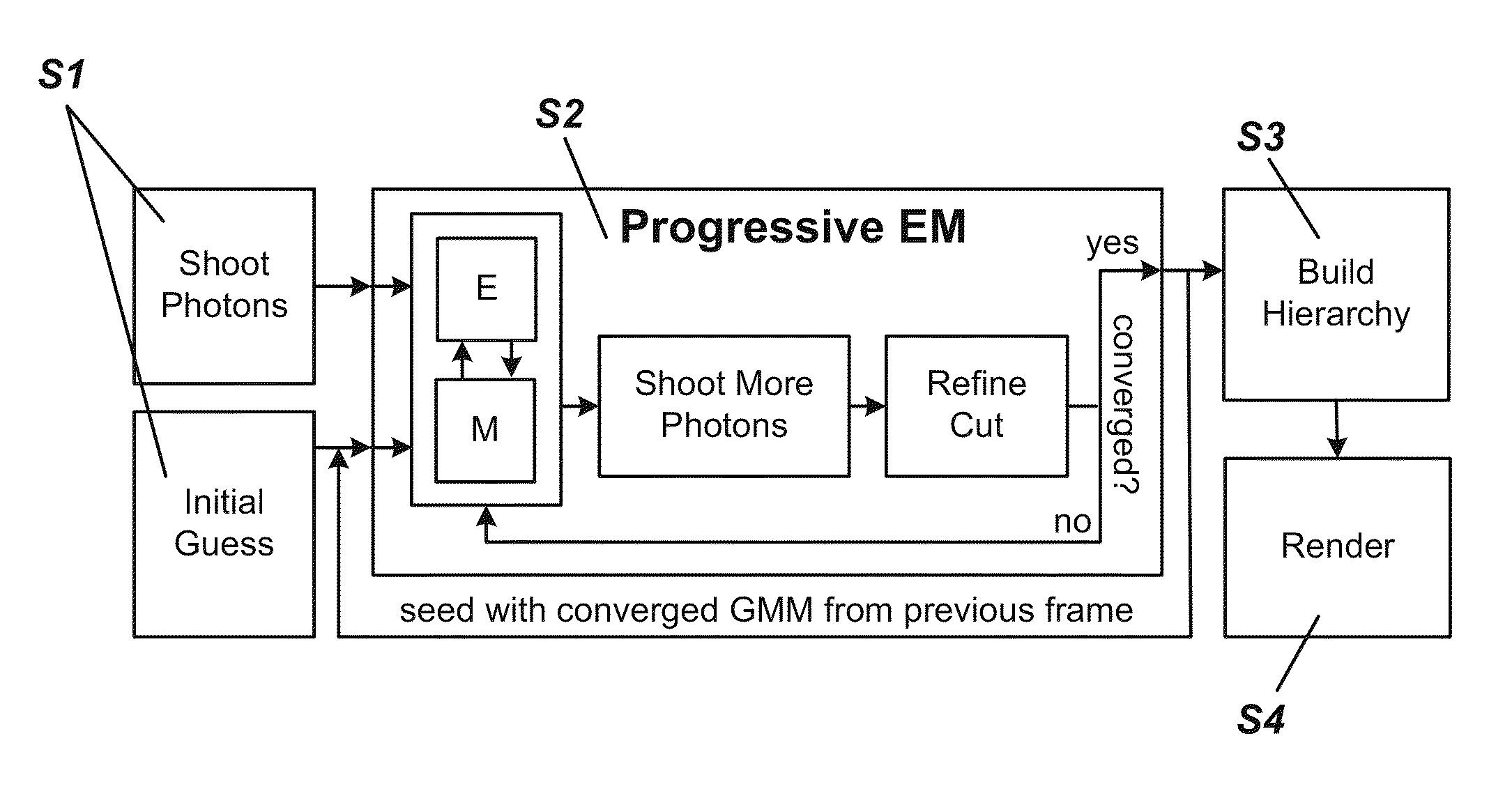
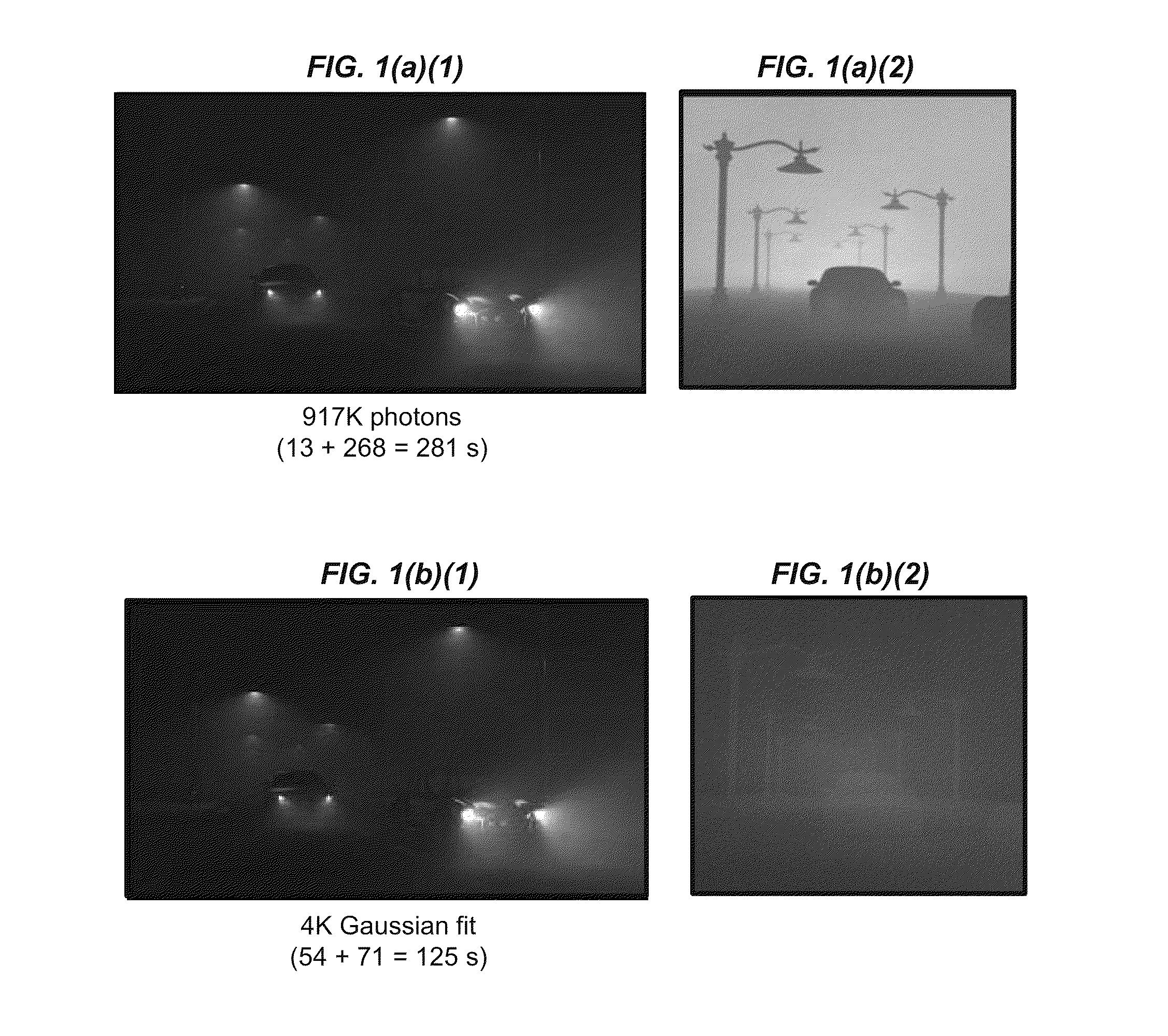
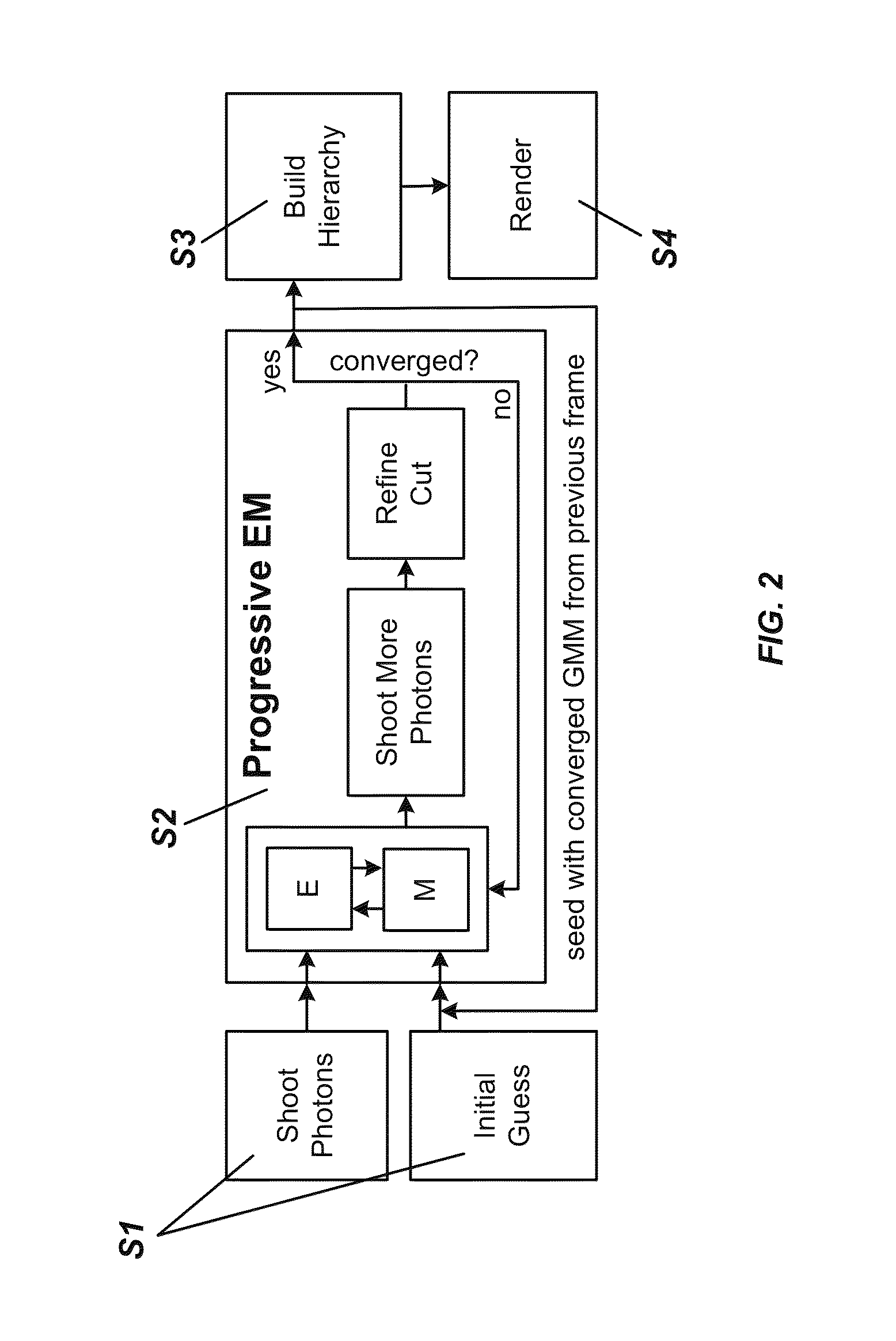
Progressive expectation-maximization for hierarchical volumetric photon mapping
ActiveUS9013484B1EfficientlyAccurate reconstruction3D-image rendering3D modellingExpectation–maximization algorithmRadiance
State-of-the-art density estimation methods for rendering participating media rely on a dense photon representation of the radiance distribution within a scene. A parametric density estimation technique is used to represent radiance using a hierarchical Gaussian mixture. Coefficients of this mixture are efficiently obtained for use in a progressive and accelerated form of the Expectation-Maximization algorithm. Noise-free renderings of high-frequency illumination are created using only a few thousand Gaussian terms, where millions of photons are traditionally required. Temporal coherence is trivially supported within this framework, and the compact footprint is also useful in the context of real-time visualization. A hierarchical ray tracing-based implementation is demonstrated, as well as a fast splatting approach that can interactively render animated volume caustics.
Owner:ETH ZURICH EIDGENOESSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH +1
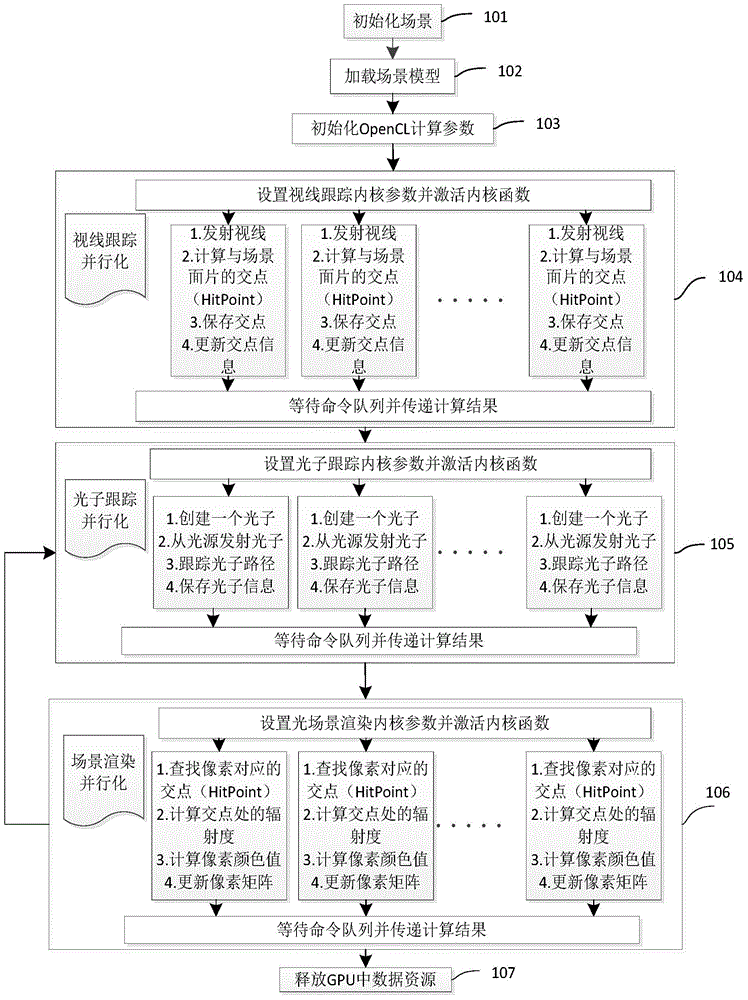
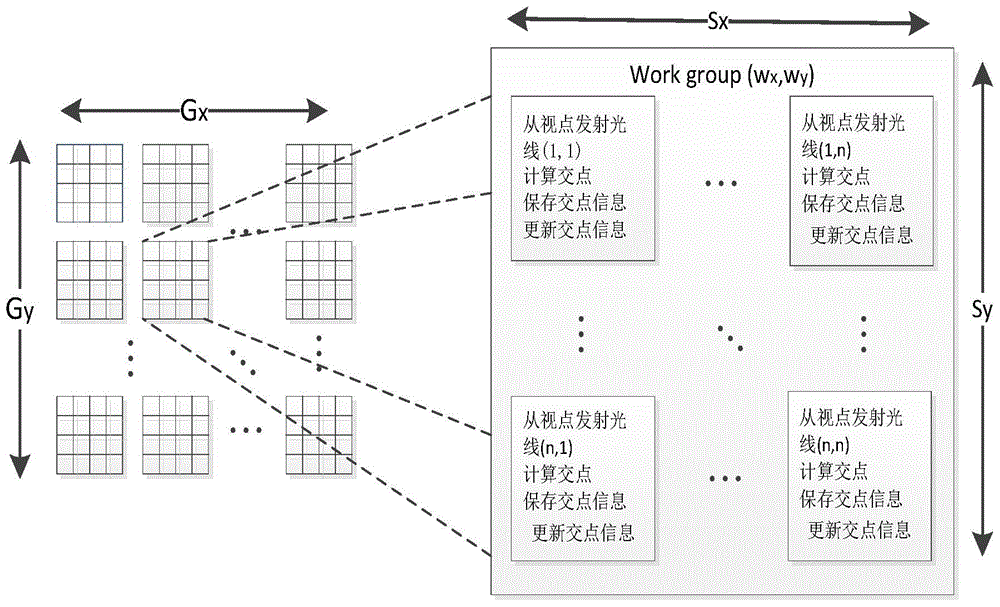
Parallelization type progressive photon mapping method and device based on OpenCL
InactiveCN104090742AImprove execution efficiencyImprove portabilityResource allocationConcurrent instruction executionViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a parallelization type progressive photon mapping method and device based on OpenCL. The parallelization type progressive photon mapping method and device are applied to the overall illumination field in the virtual reality technology. Parallelization type progressive photon mapping is achieved through the OpenCL. The parallelization type progressive photon mapping method comprises the steps that firstly, initialization is conducted, a scene model is loaded, and the OpenCL calculating parameters are initialized; secondly, parallelization is conducted on viewpoint ray tracing, photo tracing and scene rendering based on the OpenCL, working loads are designed on corresponding processors reasonably, and after a command queue is executed, a computation result is read and transmitted to a CPU; finally, data resources stored in the CPU are released through the OpenCL standard library functions. By the adoption of the parallelization type progressive photon mapping method and device based on the OpenCL, the efficiency of the progressive photon mapping algorithm can be improved remarkably, compared with a computation method that design is conducted on the CPU, the efficiency is improved by four to nine times, the transportability is high, and the rendering effect is improved to a certain extent.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
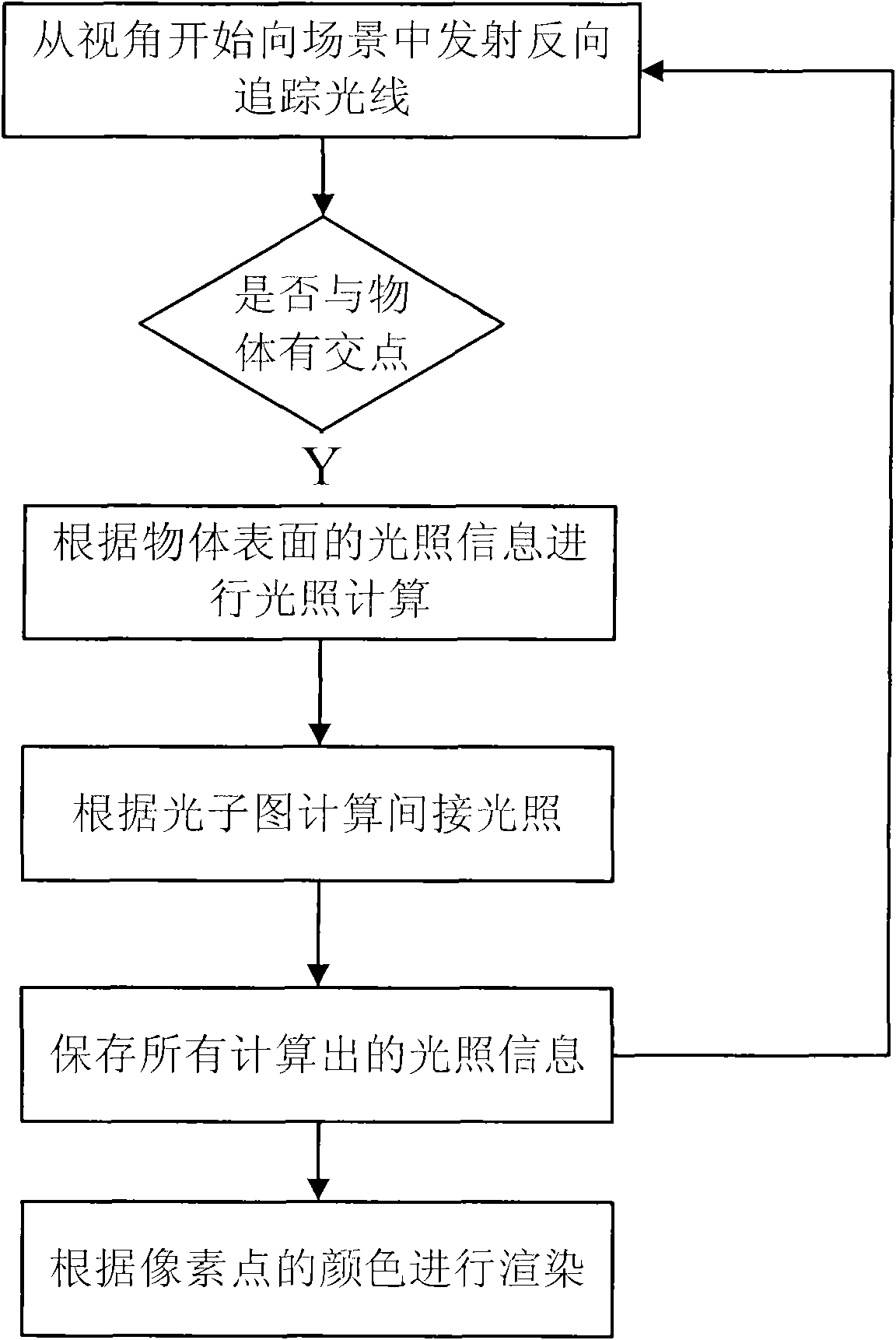
Overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on photon mapping image
InactiveCN102981840ARealistic renderingHigh speedSpecific program execution arrangementsLight treatmentLuminous flux
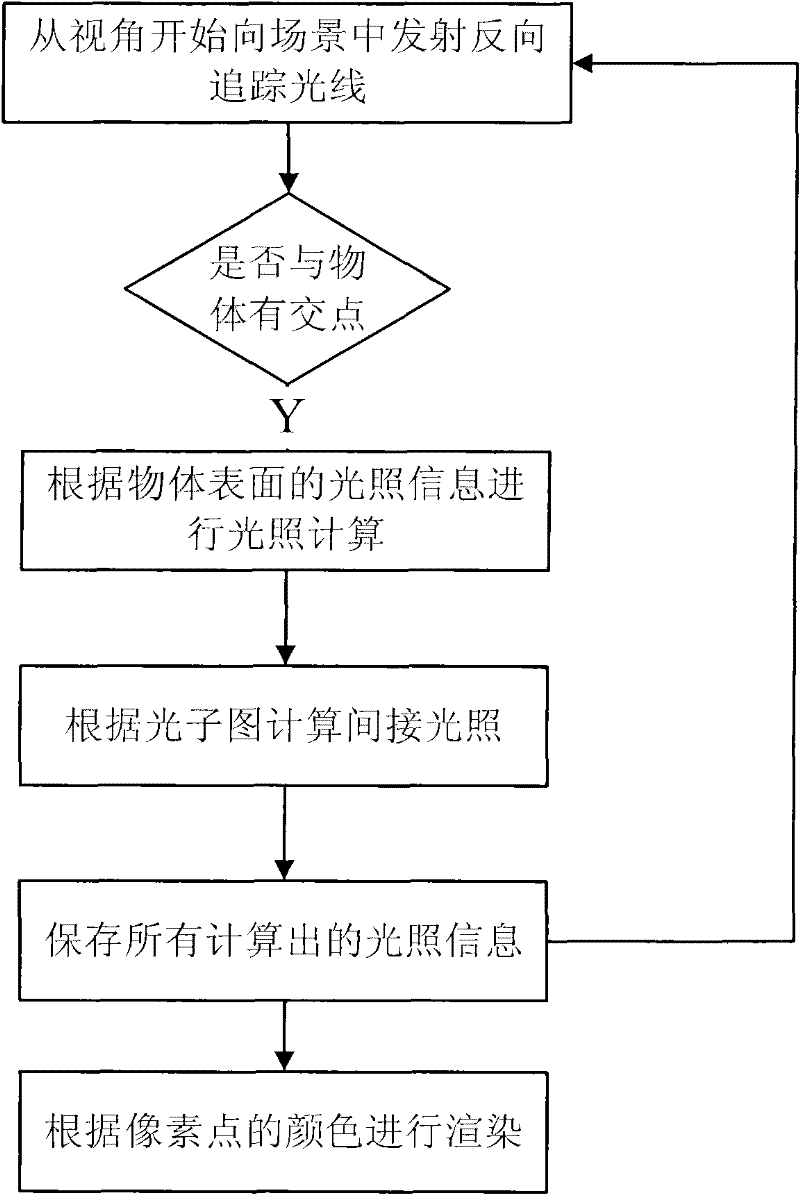
The invention discloses an overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on a photon mapping image. The method is characterized by comprising that a photon is emitted from a light source to a computer virtualized scene and is tracked, and when the photon strikes the surface of a scene content non-specular surface object, the photon is stored in the photon mapping image; incidence luminous flux of any point in the computer virtualized scene and reflected luminescence radiancy information are extracted by means of statistic technique according to the photon mapping image, calculating the pixel color value, and carrying out image drawing and rendering in the scene. The overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on the photon mapping image is based on the principle of photon mapping, effect of a processed image is life-like, calculating and processing speed is high, and meshing is not needed. The overall illumination computer simulation processing method based on the photon mapping image is especially suitable for light treatment in complex scenes.
Owner:SUZHOU LIANGJIANG TECH
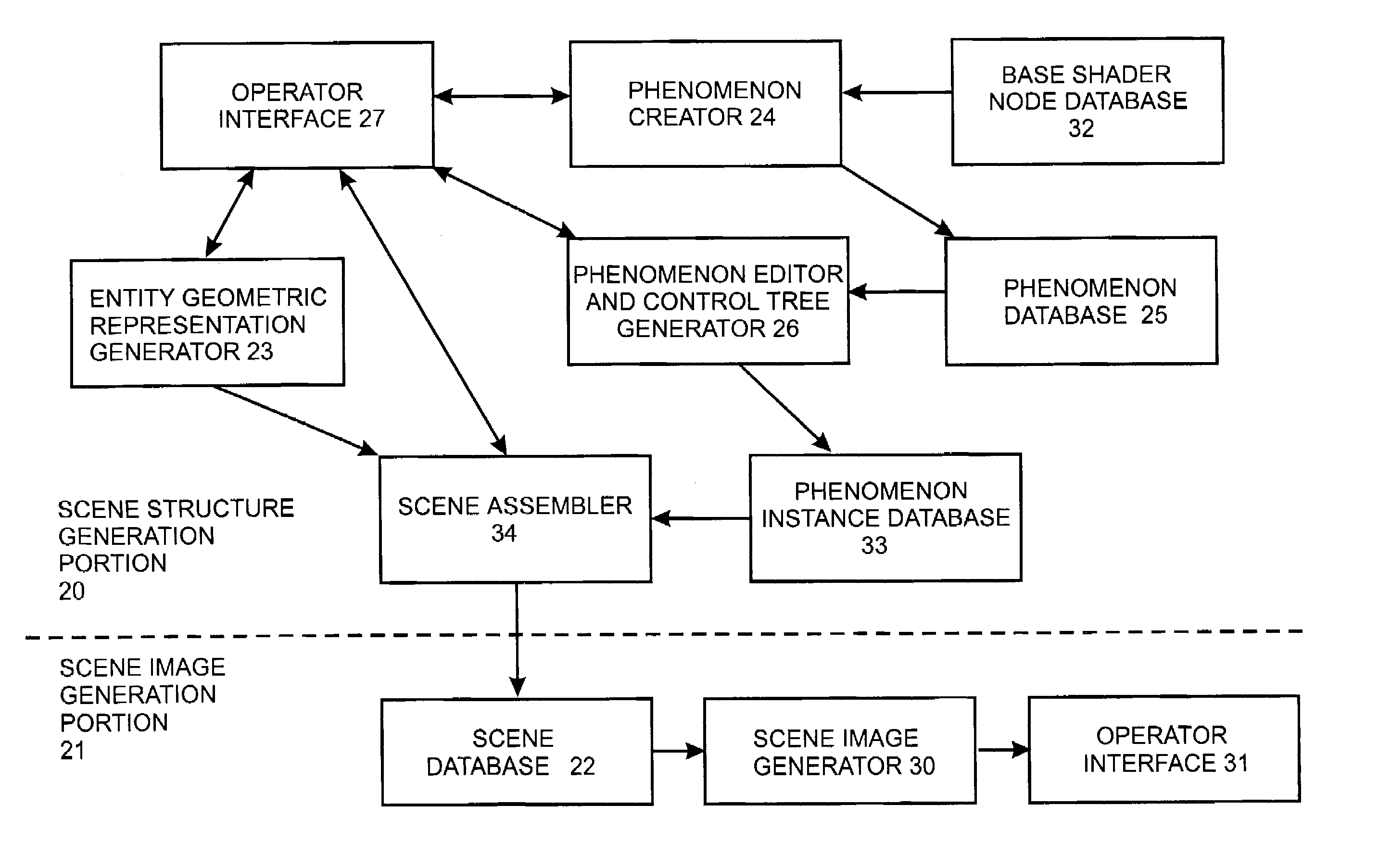
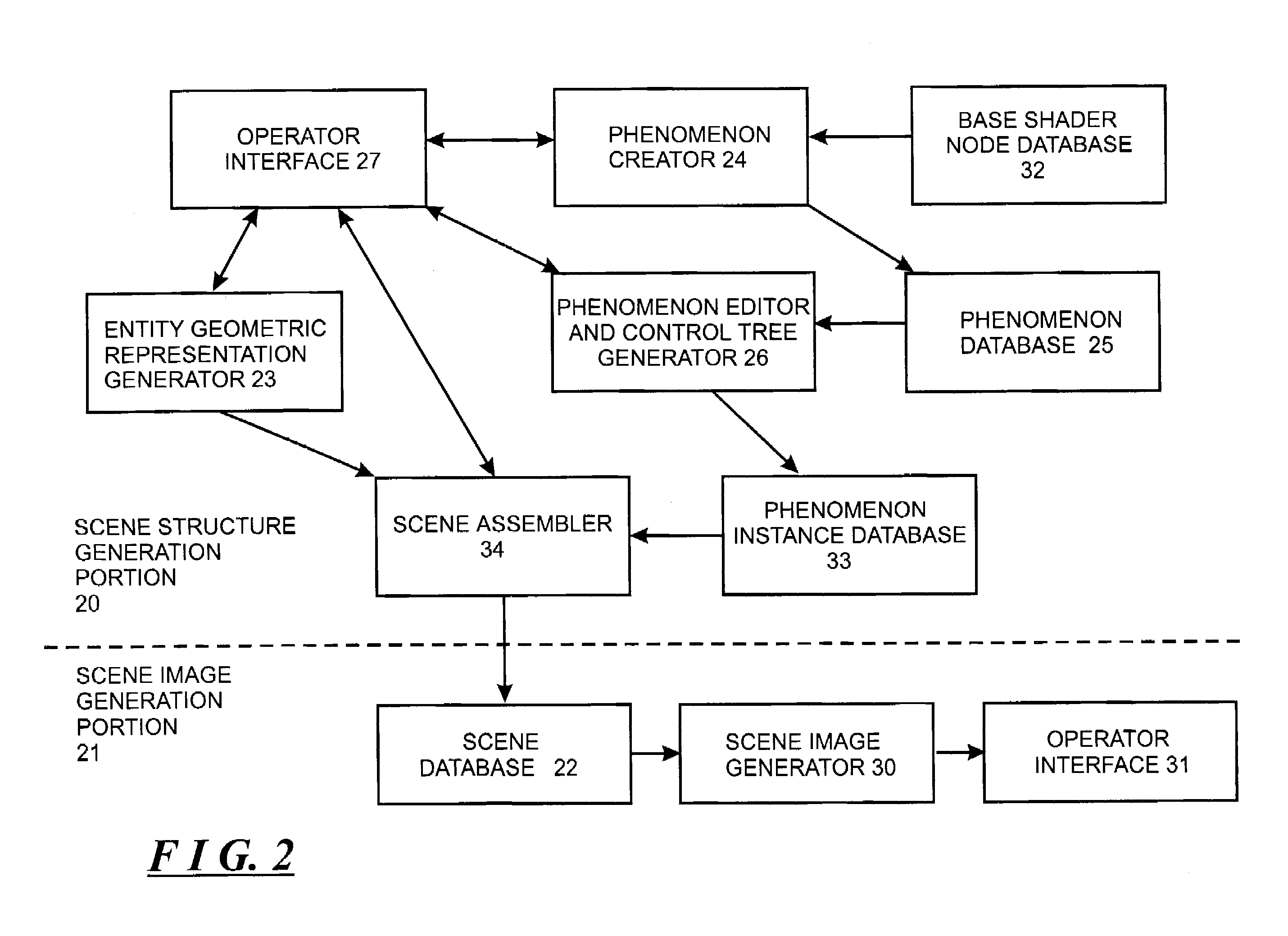
System and method for generating and using systems of cooperating and encapsulated shaders and shader dags for use in a computer graphics system
InactiveUS7173617B2Improve cooperationPromote generationDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage resolutionGraphic system
A computer graphics system is described in which a new type of entity, referred to as a “phenomenon,” can be created, instantiated and used in rendering an image of a scene. A phenomenon is an encapsulated shader DAG comprising one or more nodes each comprising a shader, or an encapsulated set of such DAGs which are interconnected so as to cooperate, which are instantiated and attached to entities in the scene which are created during the scene definition process to define diverse types of features of a scene, including color and textural features of surfaces of objects in the scene, characteristics of volumes and geometries in the scene, features of light sources illuminating the scene, features of simulated cameras will be simulated during rendering, and numerous other features which are useful in rendering. Phenomena selected for use by an operator in connection with a scene may be predefined, or they may be constructed from base shader nodes by an operator using a phenomenon creator. The phenomenon creator ensures that phenomena are constructed so that the shaders in the DAG or cooperating DAGs can correctly cooperate during rendering of an image of the scene. Prior to being attached to a scene, a phenomenon is instantiated by providing values, or functions which are used to define the values, for each of the phenomenon's parameters, using a phenomenon editor. The phenomenon editor allows the operator to view the effects produced by various settings for the parameter values which are selected. During scene image generation, a scene image generator operates in a series of phases, including a including a preprocessing phase, a rendering phase and a post-processing phase. During a pre-processing phase, the scene image generator can perform pre-processing operations, such as shadow and photon mapping, multiple inheritance resolution, and the like. The scene image generator may perform pre-processing operations if, for example, a phenomenon attached to the scene includes a geometry shader to generate geometry defined thereby for the scene. During the rendering phase, the scene image generator renders the image. During the post-processing phase, the scene image generator may perform post-processing operations if, for example, a phenomenon attached to the scene includes a shader that defines post-processing operations.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
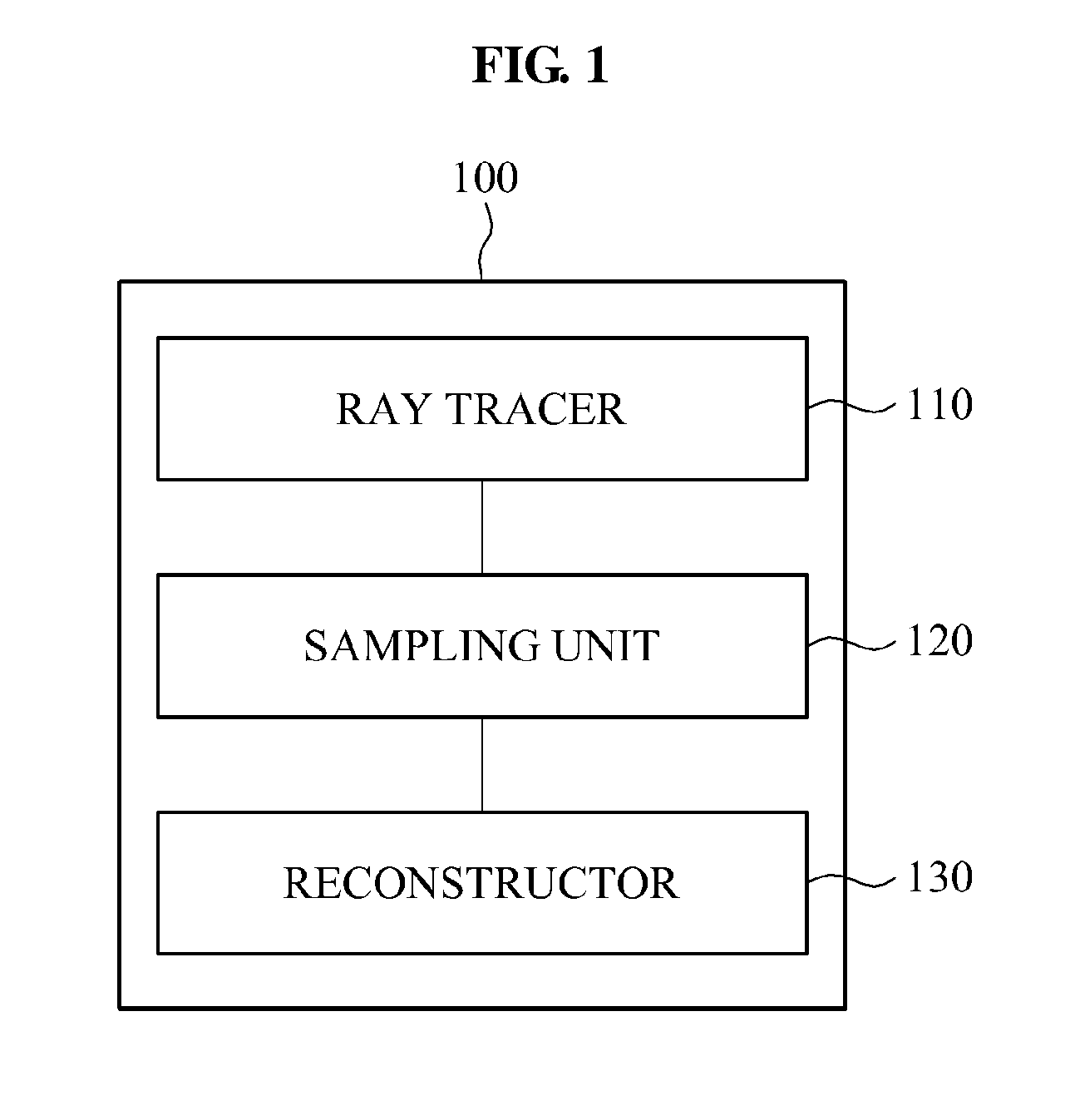
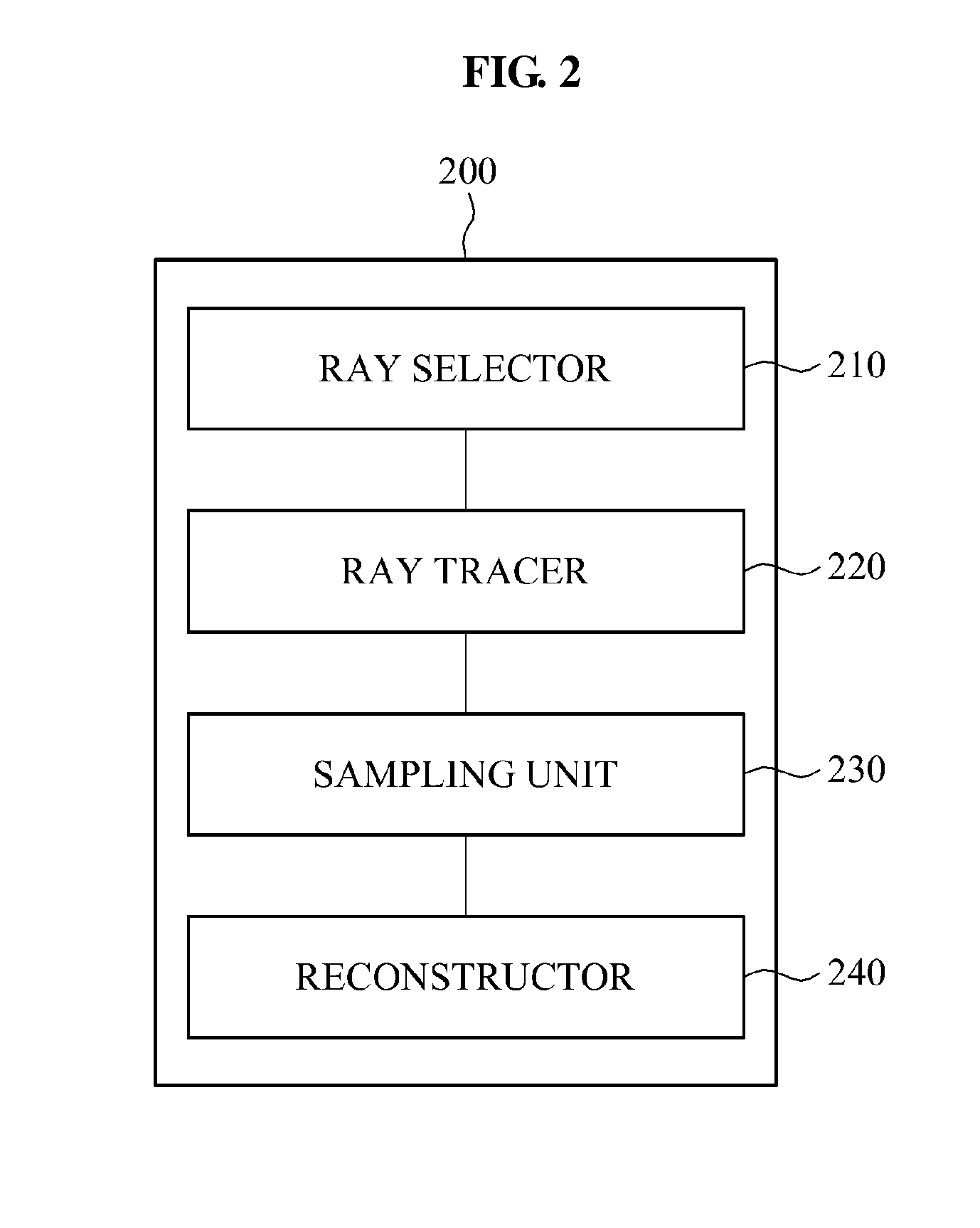
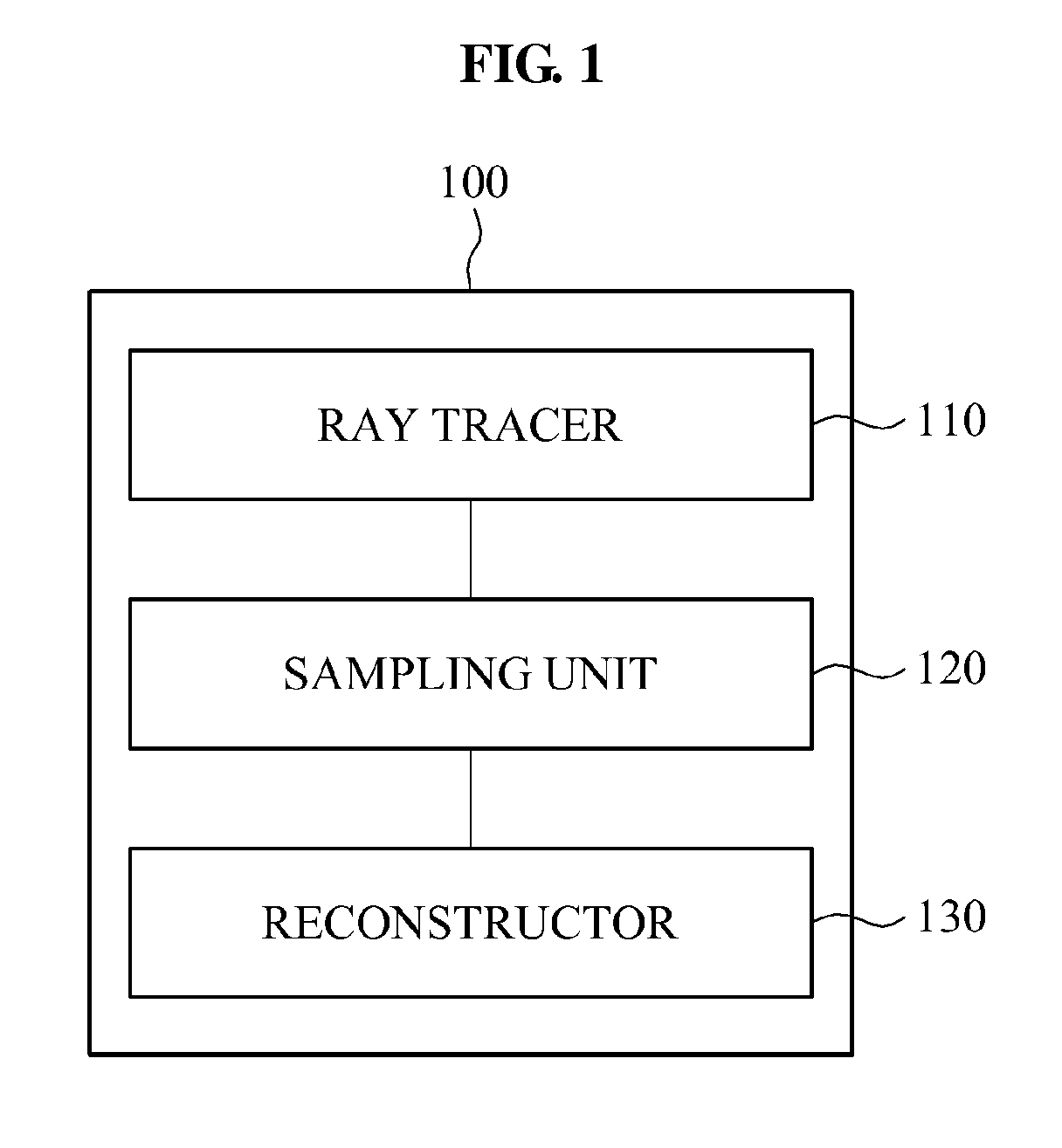
Image processing apparatus and method
Provided is an image processing apparatus for performing photon mapping, and the image processing apparatus may perform ray tracing for photon mapping, sample a ray space based on a result of the ray tracing, and perform pseudo photon mapping using the sampled ray space.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Hybrid rendering of image data utilizing streaming geometry frontend interconnected to physical rendering backend through dynamic accelerated data structure generator
InactiveUS8102391B2Generate efficientlyEasy to adaptCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails involving image processing hardwareComputer graphics (images)DEVS
A circuit arrangement and method provide a hybrid rendering architecture capable of interfacing a streaming geometry frontend with a physical rendering backend using a dynamic accelerated data structure (ADS) generator. The dynamic ADS generator effectively parallelizes the generation of the ADS, such that an ADS may be built using a plurality of parallel threads of execution. By doing so, both the frontend and backend rendering processes are amendable to parallelization, and enabling if so desired real time rendering using physical rendering techniques such as ray tracing and photon mapping. Furthermore, streaming geometry frontends such as OpenGL and DirectX compatible frontends can readily be adapted for use with physical rendering backends, thereby enabling developers to continue to develop with raster-based API's, yet still obtain the benefits of physical rendering techniques.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
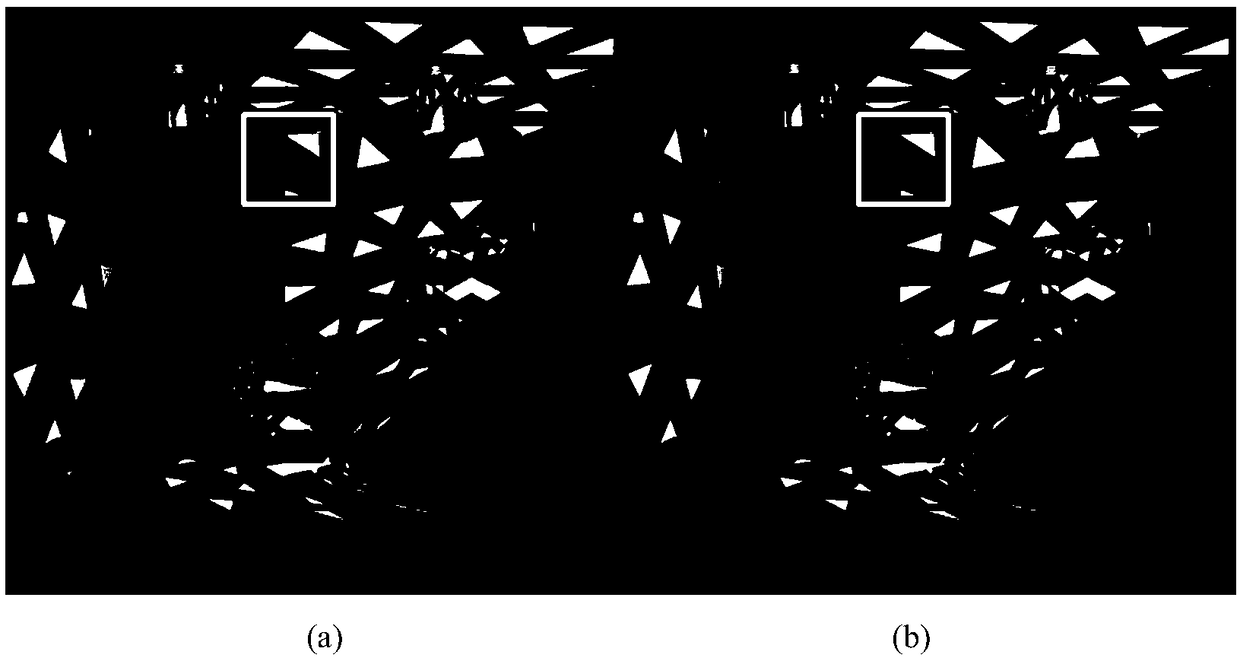
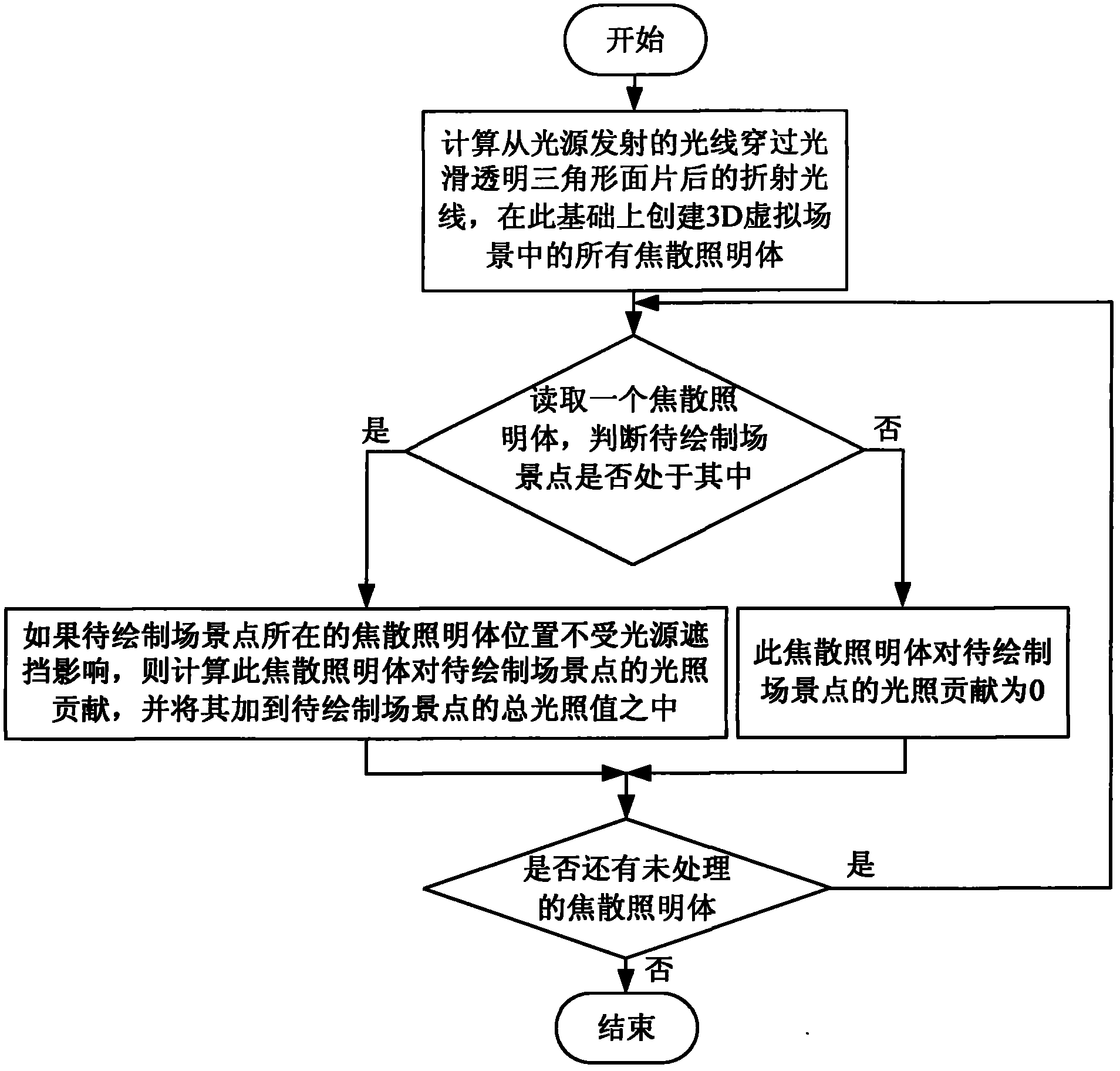
Method for drawing planar caustic effect of 3D virtual scene produced by specular reflection
InactiveCN102074041AImprove drawing efficiencyAvoid tracking operations3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Specular reflection
The invention discloses a method for drawing the planar caustic effect of a 3D virtual scene produced by specular reflection, which belongs to the technical field of the drawing of realistic 3D virtual scenes. At present, a photon mapping algorithm is usually used to draw the planar caustic effect of the 3D virtual scene. The photon mapping algorithm requires to perform tracking calculation on a large amount of photons transmitted by light sources, which can seriously reduce the drawing efficiency of the planar caustic effect of the 3D virtual scene. The method comprises the steps of: calculating reflected light rays at the tops of all triangular patches of the specular reflection first and then determining all caustic illuminants in the 3D virtual scene according to the reflected light rays; and when the 3D virtual scene is drawn, adding the contribution of a caustic illuminant into an illumination value of a scene point if the scene point to be drawn is positioned in the caustic illuminant so as to realize the drawing of the planar caustic effect. The method can be easily integrated into the framework of a ray tracing algorithm, and can remarkably improve the realism of the drawing of the 3D virtual scene.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
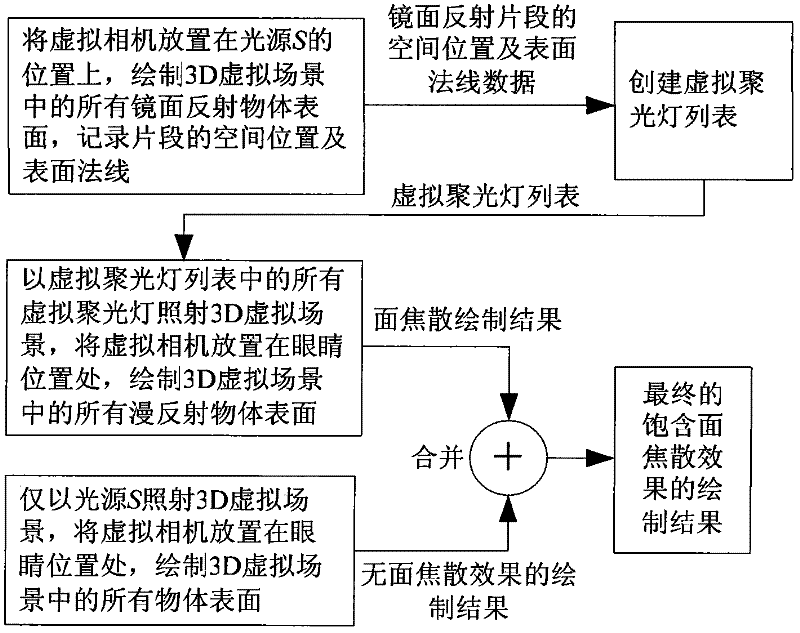
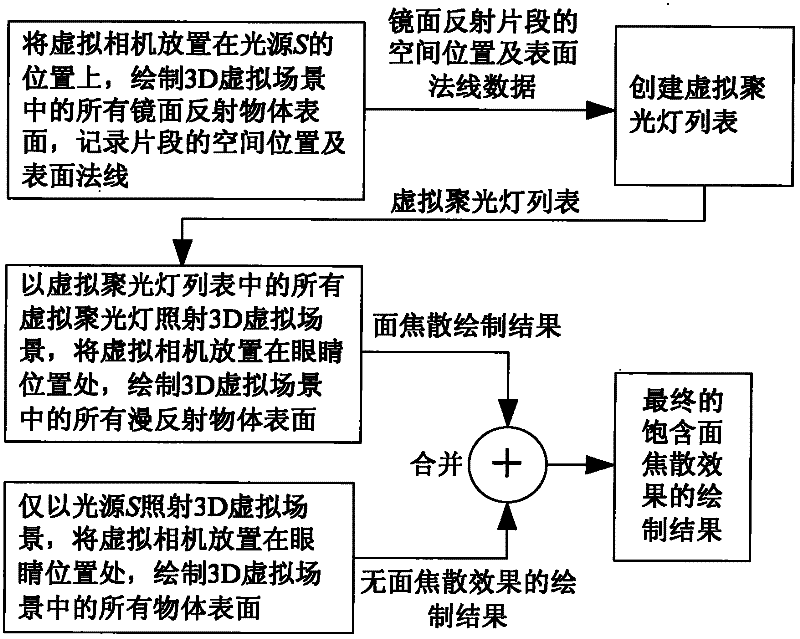
Approximate rendering method of 3D virtual scene including surface caustic effect produced by specular reflection
The invention discloses an approximate drawing method for a 3D (three-dimensional) virtual scene comprising a surface caustic effect generated by mirror reflection, belonging to the technical field of drawing of a real three-dimensional virtual scene. In the method, the 3D virtual scene comprising the surface caustic effect is drawn in three drawing steps. The approximate drawing method comprisesthe following steps of: 1, putting a virtual camera on a point light source, drawing a mirror reflection object surface in the 3D virtual scene, and creating virtual focus lamps to simulate secondaryillumination generated by mirror reflection light rays; 2, putting the virtual camera on eyes, and drawing a diffused reflection object surface of the 3D virtual scene under the irradiation of all virtual focus lamps to obtain a surface caustic drawing effect; and 3, putting the virtual camera on eyes, drawing all object surfaces of the 3D virtual scene under the irradiation of the point light source, and combining drawing results of the second step and the third step to obtain a final drawing result of the 3D virtual scene. The drawing time of the method is only equivalent to 10-15 percent of that of a photon mapping method.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Photon mapping parallel method for MIC (intel many integrated core) framework coprocessor
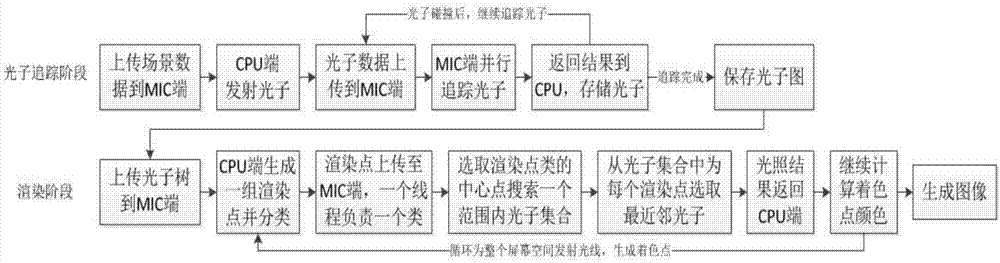
ActiveCN104714784AParallel Acceleration FlexibleReasonable useConcurrent instruction execution3D-image renderingCoprocessorPoint cluster
The invention discloses a photon mapping parallel method for an MIC (intel many integrated core) framework coprocessor. The photon mapping parallel method comprises the following steps: a photon tracking beginning stage, namely uploading scene data to the MIC framework coprocessor end; a photon light ray intersection phase, namely carrying out intersection computation on one ling ray in each thread each time, and feeding back light ray intersection point information; a photon map generating stage, namely executing different photon impact behaviors according to the light ray intersection point information, storing impacted photons into a photon map until all photon ray beams are tracked and generating an intact photon map; a rendering beginning stage, namely uploading the photon map, organizing a plurality of groups of rendering points, and carrying out hierarchical clustering on each group of rendering points; a nearest photon researching stage, namely uploading clustered rendering points, calculating the nearest photon of each rendering point in a rendering point cluster, and determining emergent radiation intensity of each rendering point; and an image generating stage, clustered calculating the colors of the rendering points, and returning the colors of each group of rendering points to a screen space to form a final image.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
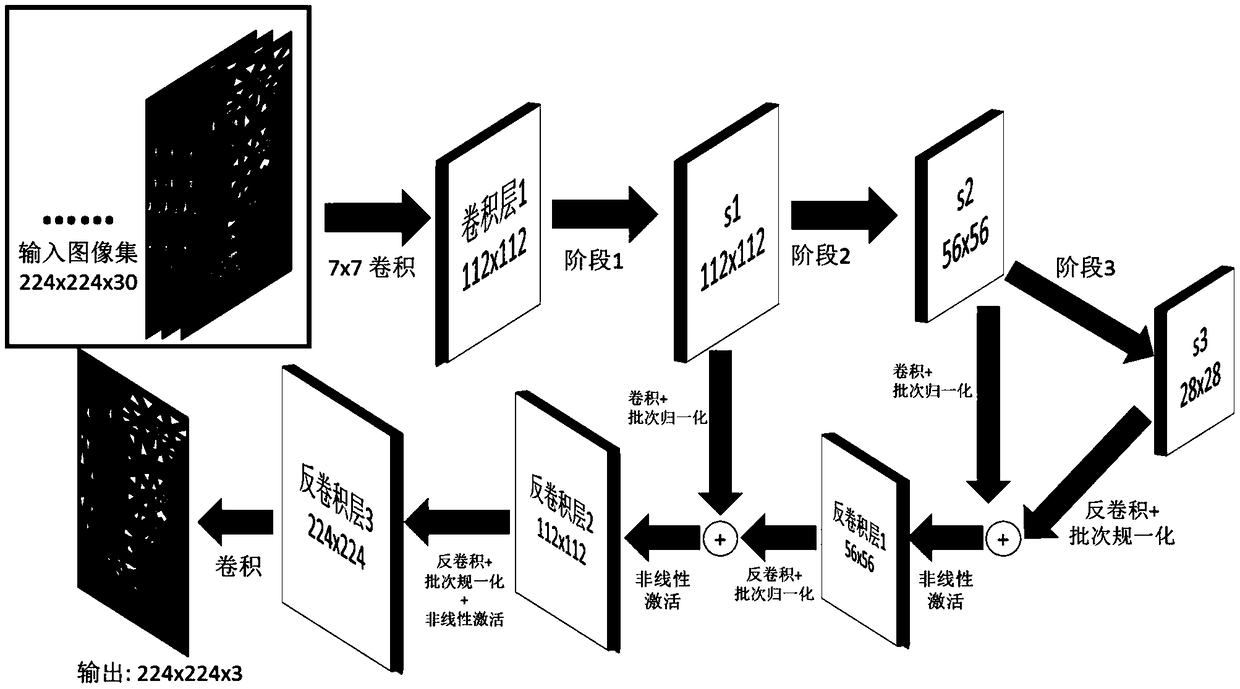
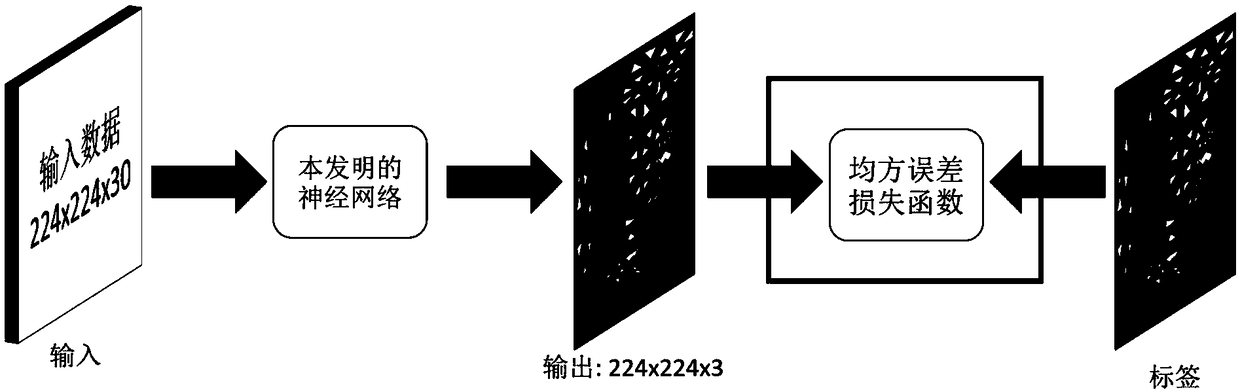
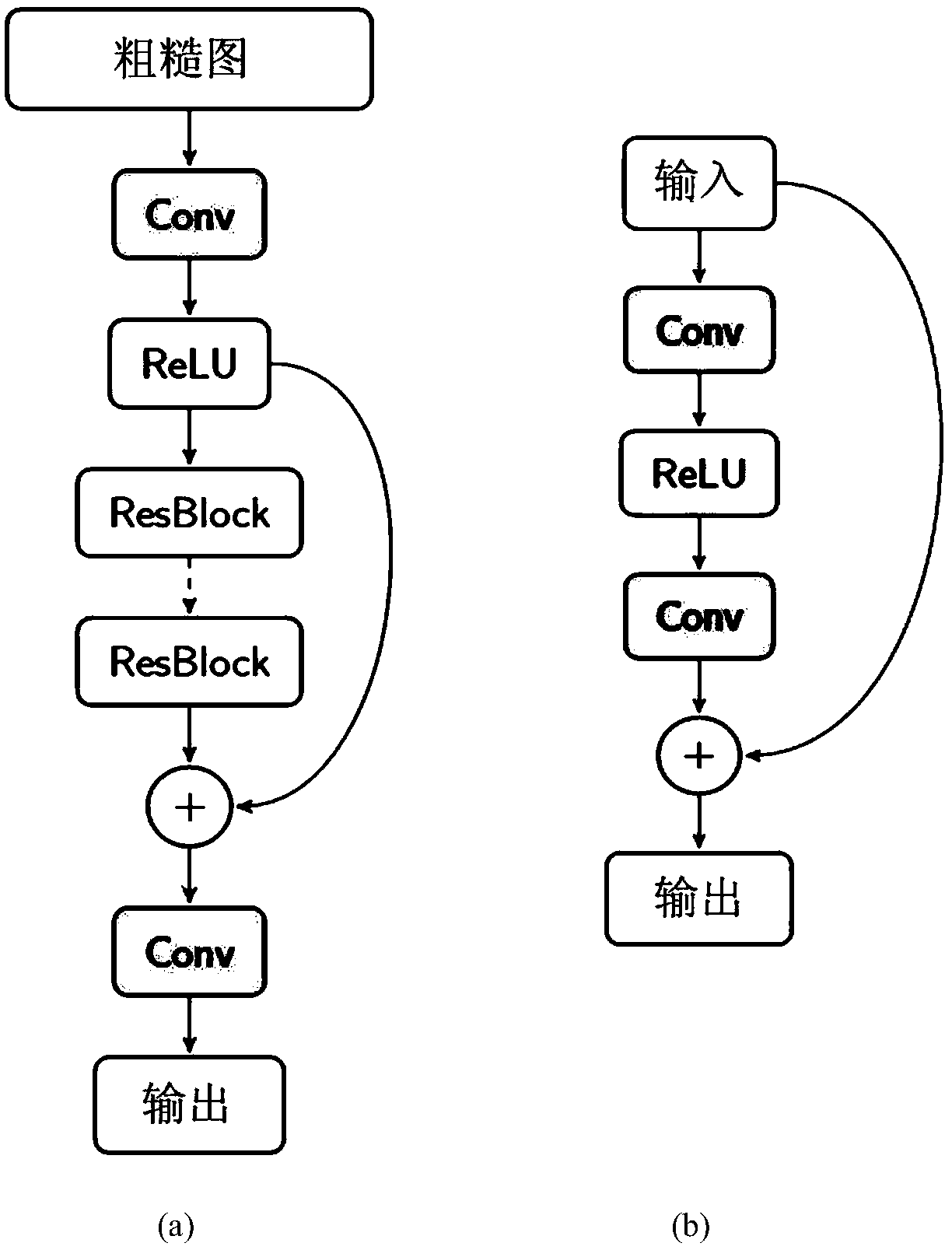
An efficient global illumination rendering method based on depth learning
ActiveCN109389667ADimensions are differentFast renderingNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsColor effectPattern recognition
The invention discloses an efficient global light illumination rendering method based on depth learning, which comprises the following steps: 1) selecting or generating a plurality of groups of images, each group comprising k coarse color effect images which are calculated and rendered by using different photon collection radii for light illumination; For each group of images, k color effect images are stacked on three channels as the input of neural network. 2) training that input data by using the neural network to obtain a neural network model and parameter; 3) executing a photon mapping method according to the viewpoint parameters to be rendered and the three-dimensional scene, generating k color rough effect maps and stacking the k color maps on three channels as input data; Then thecurrent input data is processed by using the neural network model trained in step 2) and various parameters thereof to obtain the final composite rendering image. The invention only needs to illuminate the rough image with little light to synthesize the high-quality realistic rendering effect image.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
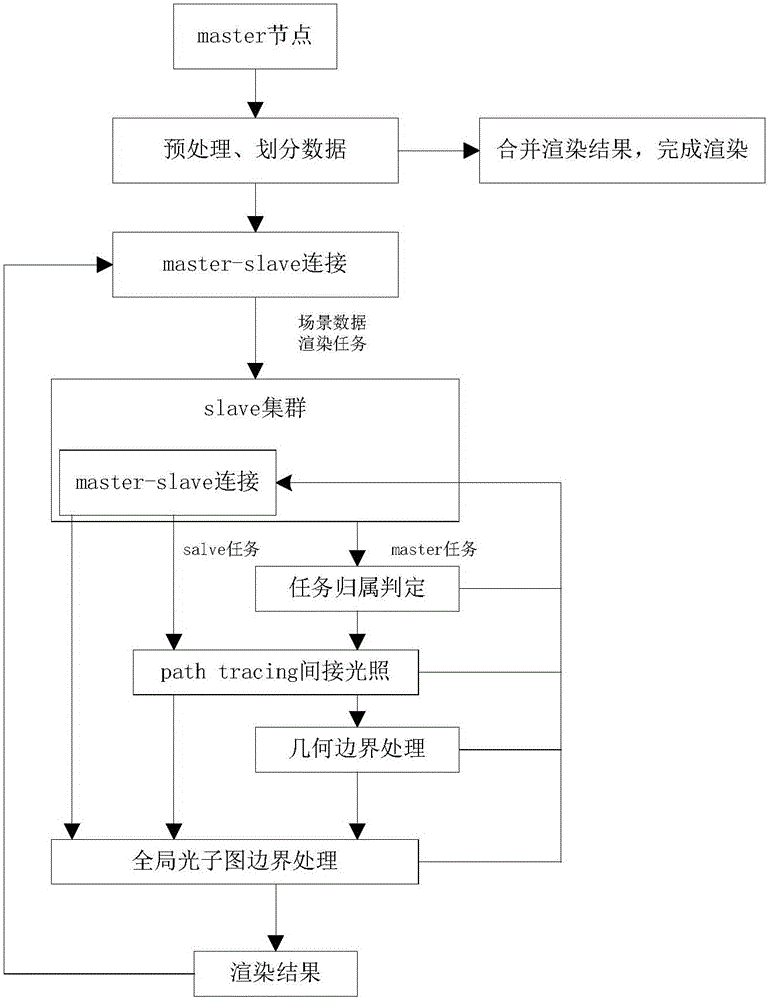
Distributed global illumination calculating method based on photon mapping
ActiveCN106251394AReduce storage loadHigh speed3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Photon mapping
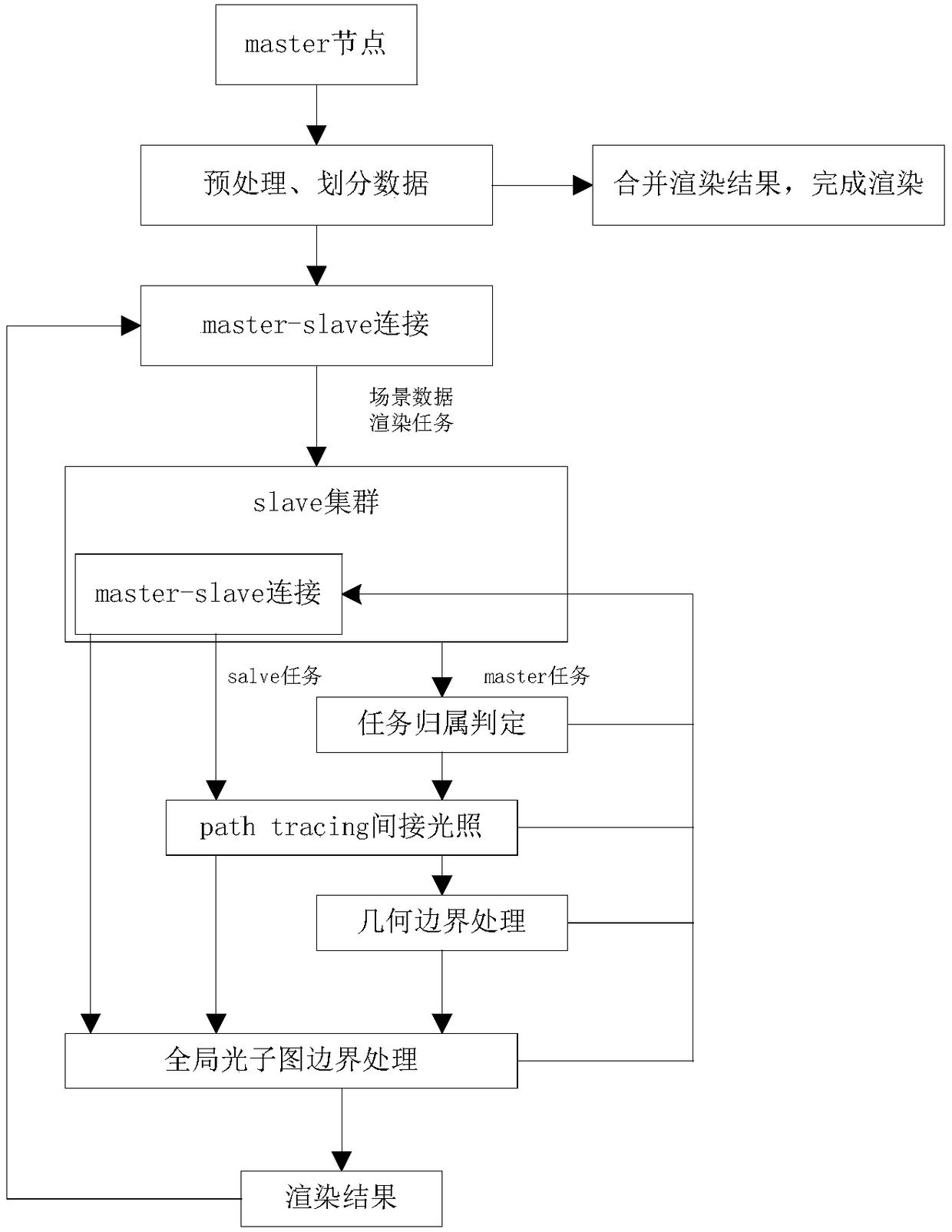
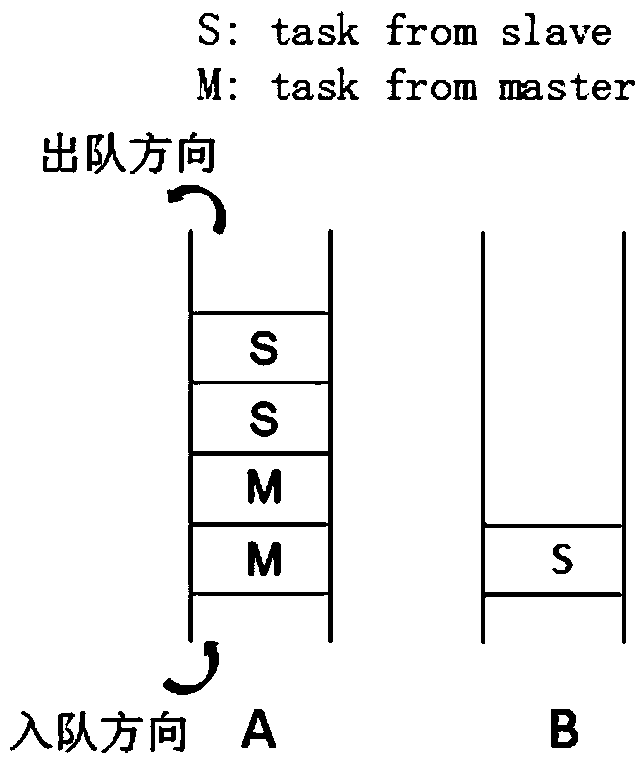
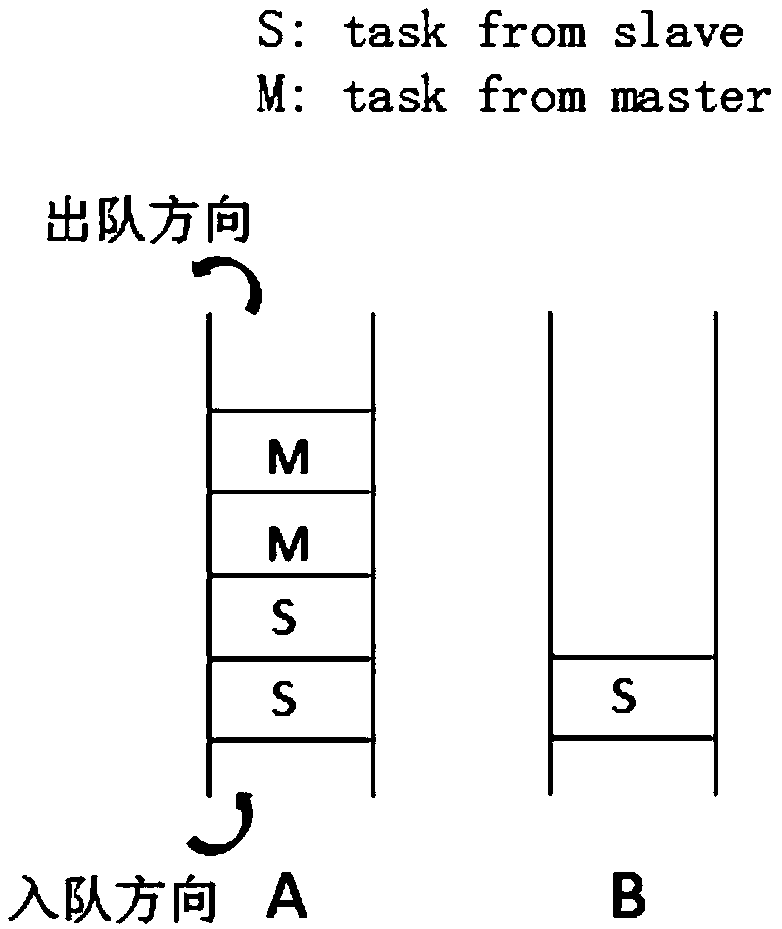
The invention discloses a distributed global illumination calculating method based on photon mapping. The method comprises a master node reads a scene file, scene data is divided and stored in a distributed manner, and according to emitted photons, the master node constructs a global photon graph and sets a photon overlap range; communication between the master node and slave nodes is constructed; the master node divides the whole screen pixel space into multiple blocks, each block serves as a rendering task, rendering tasks are distributed to the slave nodes in the clockwise sequence from inside to outside, and the slave node obtains the tasks distributed by the master node and adds the task into a queue, and determines task ownership of each coloring point in the block; the slave node traverses the global photon graph in the surrounding of each coloring point, and collects an indirect illumination color value obtained by photons, namely a rendering result; and each slave node returns the rendering result to the master node, the master node merges all the obtained rendering results according to the priority, and a rendering picture is generated. According to the invention, the rendering speed and effect are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A photon mapping rendering method and system based on neural network
ActiveCN109509248AGood effectGood global lighting renderingImage enhancementImage analysisColor effectNerve network
The invention relates to a photon mapping rendering method and a system based on a neural network. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adopting a photon mapping method to generate k color effect images with different rendering quality; 2) inputting a plurality of training set composed of k color effect images with different rendering quality into a neural network for training to obtain aneural network model; 3) synthesizing a global lighting render image based on that neural network model. Compared with the existing progressive photon mapping method, the invention requires only the intermediate rough results produced by several iterative photon mappings, The neural network proposed by the invention can be used to infer the rendering result of synthesizing the convergence of the progressive photon mapping, thereby solving the problem that the traditional progressive photon mapping method needs a large number of iterations which are very time-consuming to generate a more idealrendering result.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for drawing surface caustic effect of 3D virtual scene generated by smooth surface refraction
InactiveCN102074038AImprove drawing efficiencyAvoid tracking operations3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Track algorithm
The invention discloses a method for drawing surface caustic effect of a 3-dimesnioanl (3D) virtual scene generated by smooth surface refraction, and belongs to the technical field of real 3D virtual scene drawing. At present, the surface caustic effect of the 3D virtual scene is drawn generally by using a photon mapping algorithm. The photon mapping algorithm requires for tracking and computing a large amount of photons emitted by a light source so as to seriously reduce the drawing efficiency of the surface caustic effect of the 3D virtual scene. The method comprises the following steps of:creating all caustic illuminants in the 3D virtual scene generated by smooth surface refraction, and storing the caustic illuminants into corresponding data structures; and when the 3D virtual scene is drawn, judging whether the contribution of the caustic illuminants needs to be added into the illumination value of a scenic spot to be drawn by calculating the position relationship between the scenic spot to be drawn and the caustic illuminants, and finally implementing drawing of the surface caustic effect. The method can be easily integrated into a ray tracing algorithm framework, and can remarkably improve the third dimension of 3D virtual scene drawing.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Random asymptotic photon mapping image denoising method and system based on neural network
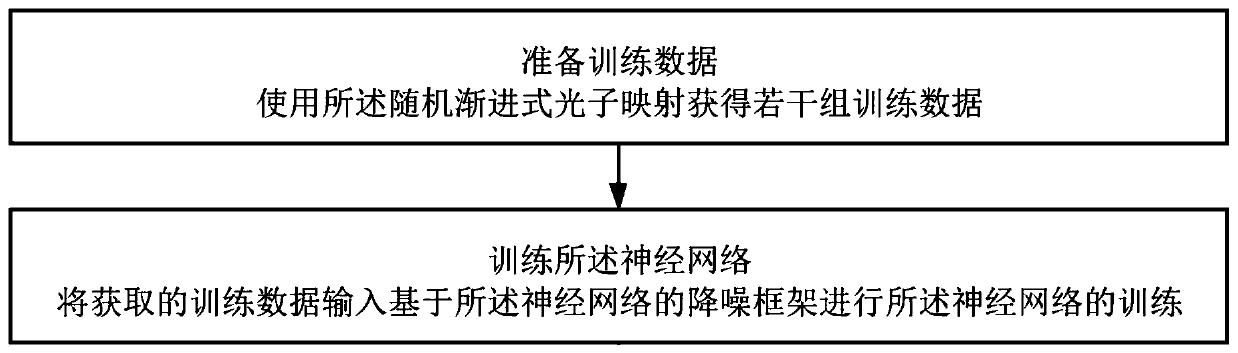
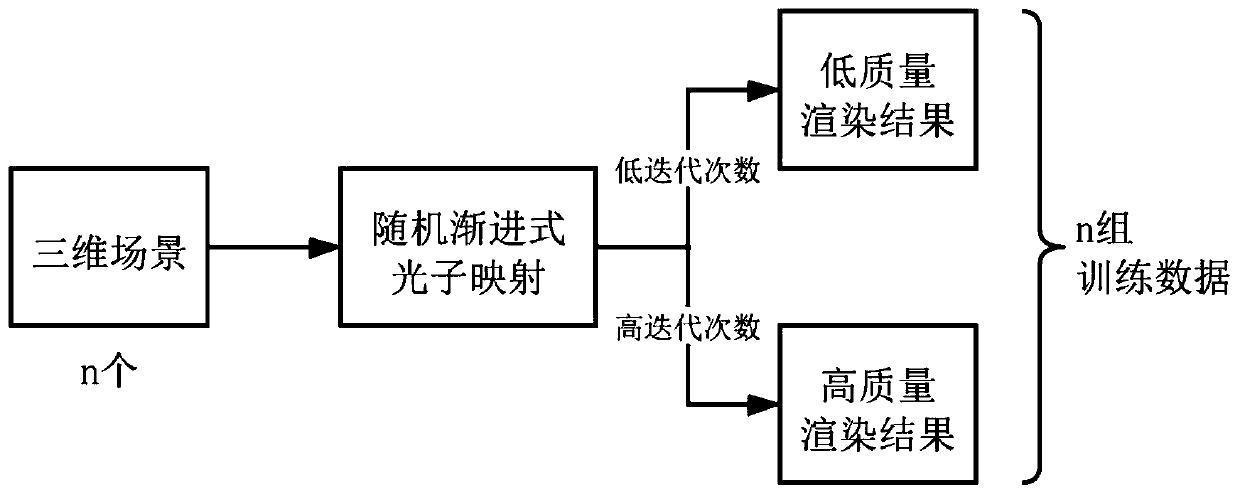
ActiveCN111445422AImprove stabilityEffective multiscale noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage denoising
The invention discloses a random asymptotic photon mapping image denoising method and system based on a neural network, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a three-dimensional scene, and generating a to-be-denoised image based on random asymptotic photon mapping, wherein the to-be-denoised image comprises a rendering image based on global photons and a rendering image based on focal astigmatism; inputting the rendering image based on the global photons into a pre-trained first multiple residual neural network, and outputting a global photon denoising image; inputting the rendered image based on the focal astigmatism photons into a pre-trained second multiple residual neural network, and outputting a focal astigmatism photon denoising image; and synthesizing the global photon denoising image and the focal astigmatism photon denoising image to obtain a final rendering image.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Progressive photon mapping method based on statistical model checking
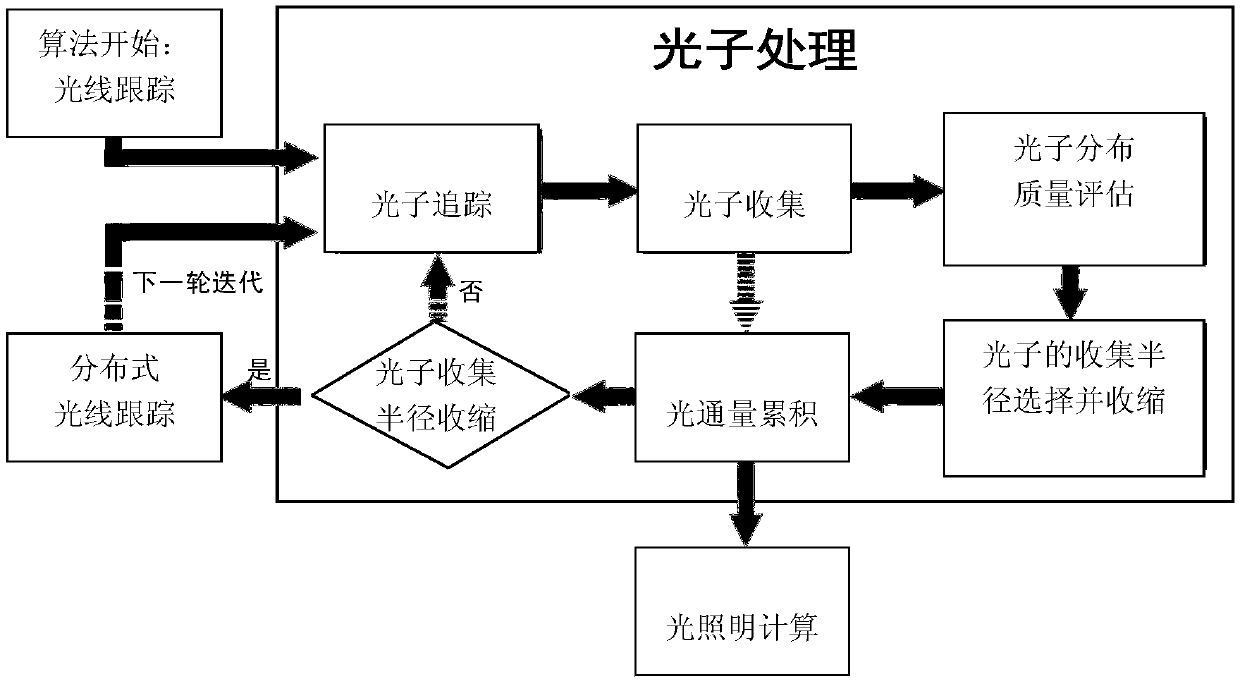
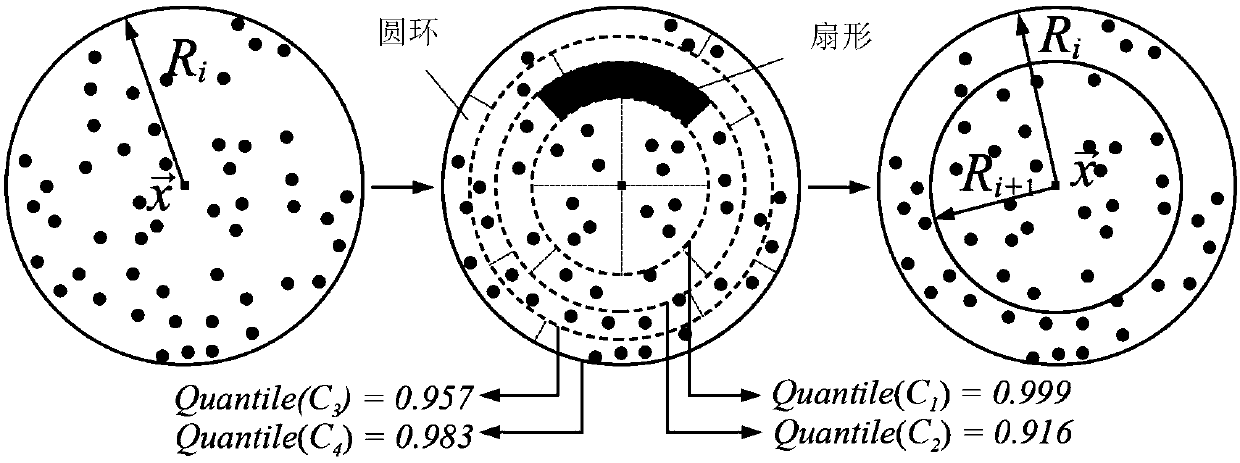
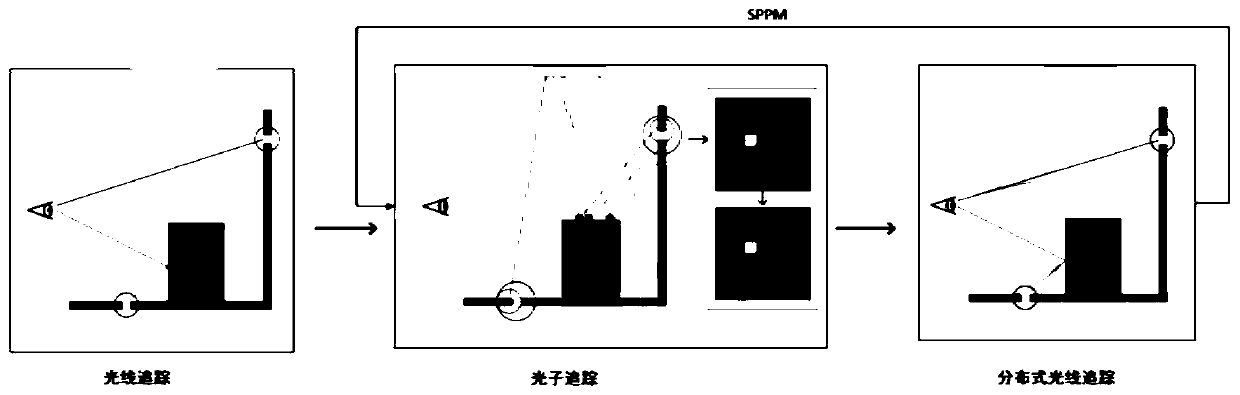
ActiveCN108961372AClear rendering resultsReduce biasImage renderingImage generationStatistical model checkingIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a progressive photon mapping method based on statistical model checking. The method comprises the steps of starting from a viewpoint to emit a ray to a pixel to be calculated on an imaging plane and intersect with a three-dimensional scene to be drawn, and if an intersection point with a diffuse reflection property is found on a tracking path, marking the intersection pointas a hit point; executing a photon step, wherein the photon step further comprises the sub-steps of 31) executing a photon tracking step; 32) for each hit point, executing photon collection processing; 33) if the current round current of the photon step does not need Chi-square detection, carrying out luminous flux accumulation, keeping the collection radius to be unchanged, if the current roundof the photon step needs Chi-square detection, carrying out quality evaluation on the photon distribution, then calculating the photon collection radius in the next round of the photon step accordingto the evaluated attributes of the photon distribution, and performing luminous flux accumulation on the current round of the photon step; and 34) if the photon collection radius is reduced, executingdistributed light tracking, generating a new hit point, then transferring to the step 31), otherwise, directly transferring to the step 31), and starting the new round of photon step iteration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Random asymptotic photon mapping image rendering method and system based on photon resampling
ActiveCN110599579AIncrease coverageReduced execution timeImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsAlgorithm
The invention discloses a random asymptotic photon mapping image rendering method and system based on photon resampling, and the method comprises the steps: transmitting first light from a viewpoint,and recording the position of a collision point between the first light and a scene object; emitting second light from the light source to obtain a photon graph; dividing the photon graph into a plurality of continuous image sub-blocks, and calculating a collision point distance error value and a photon number error value in each image sub-block; in the coloring stage, traversing collision points;during first execution, carrying out photon sampling on each collision point according to a set radius; calculating a plurality of new sampling radiuses of each collision point according to the collision point distance error value and the photon number error value during non-first execution, and resampling photons in the new sampling radiuses of the collision point in the current image sub-blockby utilizing the plurality of new sampling radiuses; and when photon resampling is carried out on all the collision points, obtaining a rendered image, and returning to the coloring stage until the set number of iterations is met, so as to obtain a rendered image.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
A photon graph clustering method based on adaptive line-of-sight partitioning
ActiveCN109509246AEfficient use ofReduce double countingCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingAdaptive learningDirect illumination
A photon map clustering method based on adaptive line-of-sight division combines a photon map ray calculation method of pre-buffering and aggregation replacement with a photon map clustering method ofadaptive line-of-sight division to achieve the purpose of optimizing a photon mapping algorithm, The specific steps are as follows: (1) in the ray tracing stage, acquiring the scene and acquiring thephoton map in the ray tracing stage; (2) Adaptive line-of-sight division stage, which divides the photons into three grades according to the adaptive line-of-sight in the photon-dense region; (3) inthe pre-buffering stage, sampling the photons after clustering to obtain the estimated radiance value and pre-buffering it into a file; (4) In the focusing rendering stage, converging the intersectionvalue, caustic photon value and direct illumination value to optimize the photon mapping and improve the image rendering efficiency and realism.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
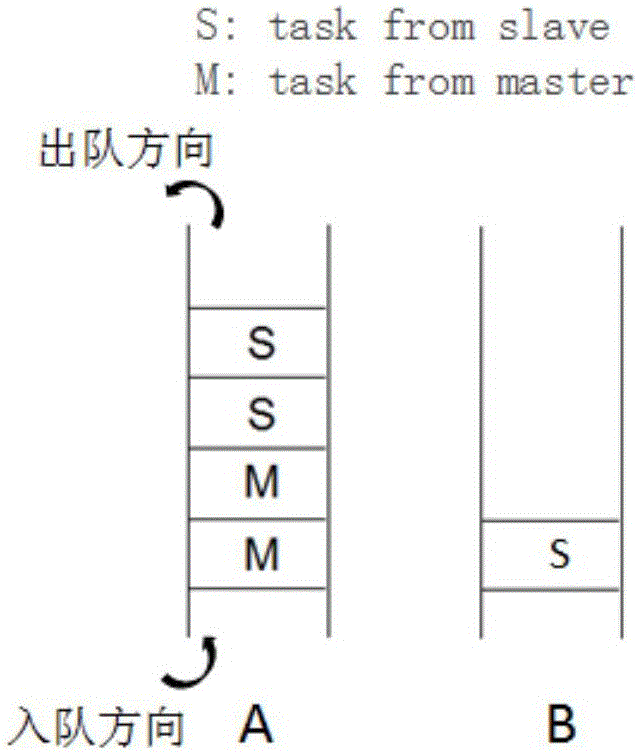
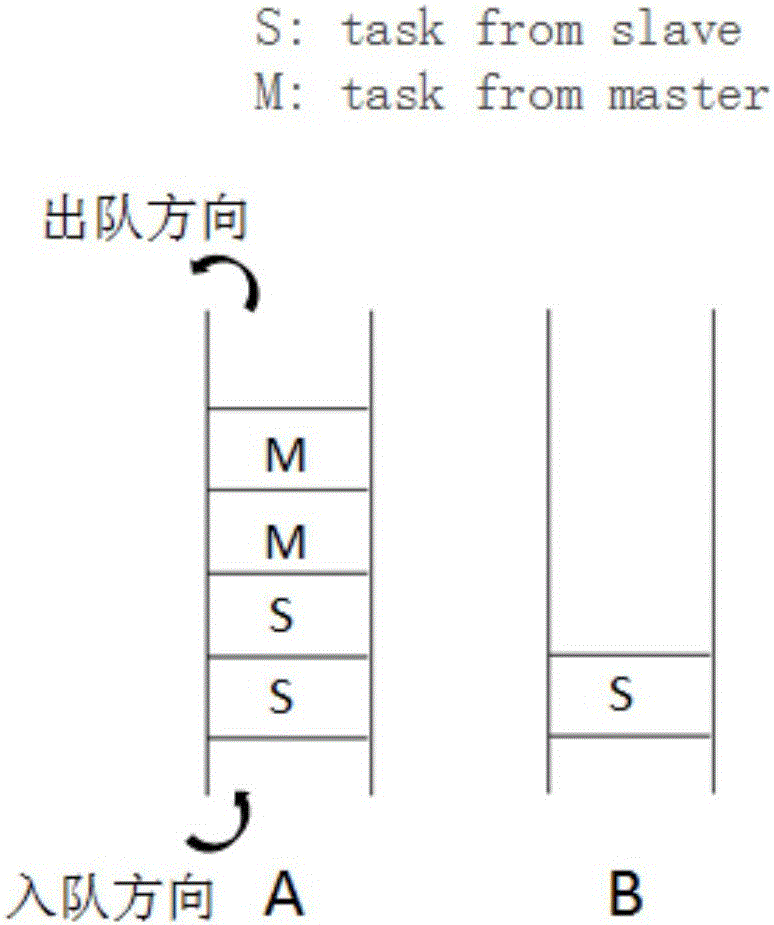
Photon mapping optimization method, device and system based on polygon space division
ActiveCN110211197AImprove scalabilityReduce transmission costsTexturing/coloring3D-image renderingIntersection of a polyhedron with a linePhoton mapping
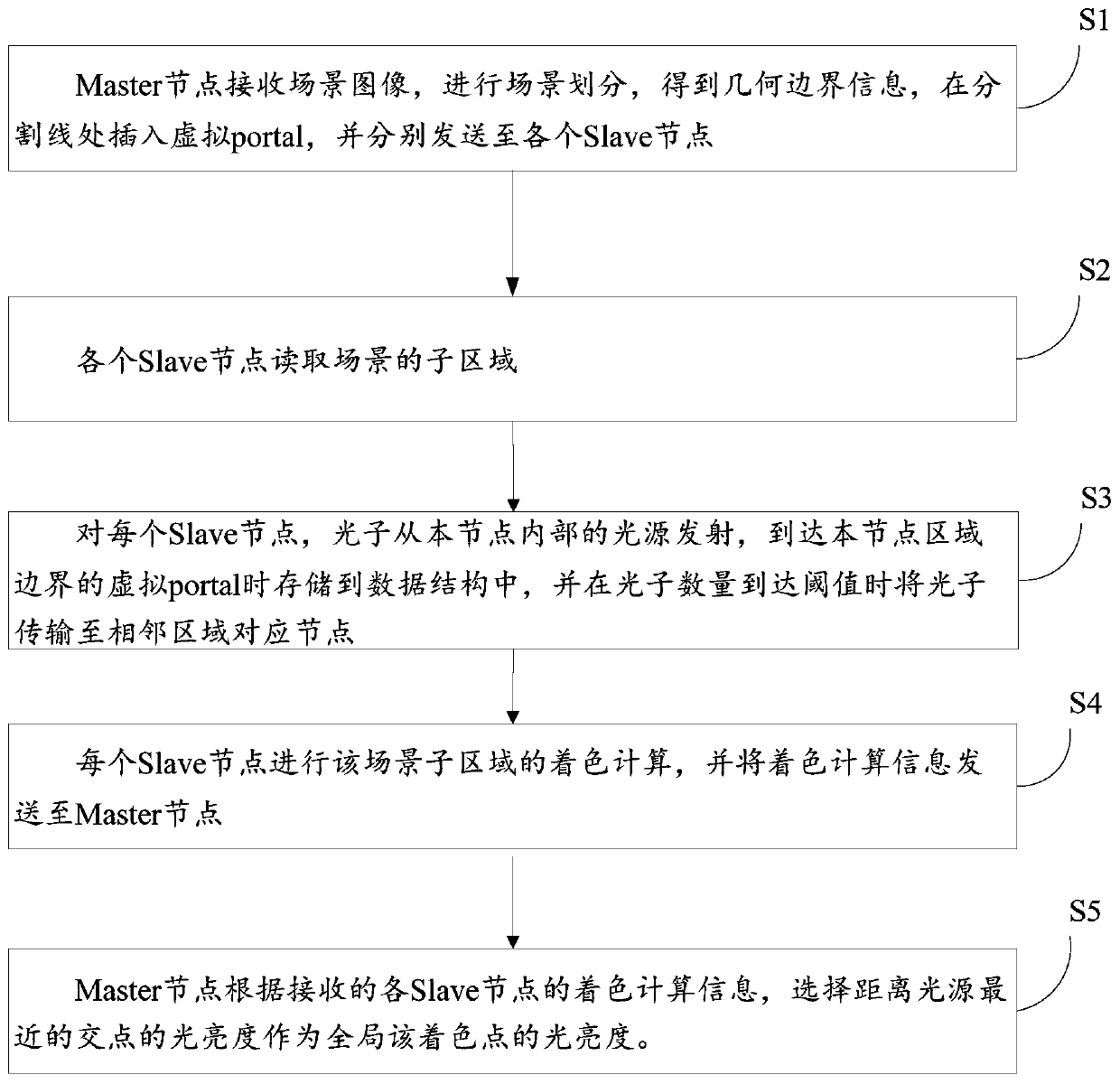
The invention discloses a photon mapping optimization method, device and system based on polygon space division, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a Master node to receive a scene image, carrying out the scene division, obtaining the geometric boundary information, enabling a virtual portal to be inserted at a division line, and enabling the virtual portal to be transmitted to each Slave node; enabling each Slave node to read a sub-region of the scene; for each Slave node, emitting photons from a light source in the node, are storing the photons in the data structure when the photons reaches the virtual port of the boundary of the region of the node, and transmiting the photons to corresponding nodes of an adjacent region when the number of the photons reaches a threshold value;enabling each Slave node to carry out coloring calculation on the scene sub-region and sending coloring calculation information to the Master node; and enabling the Master node to select the brightness of the intersection point closest to the light source as the brightness of the global coloring point according to the received coloring calculation information of each Slave node.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Rendering acceleration method with dynamic blurring for reducing sampling number
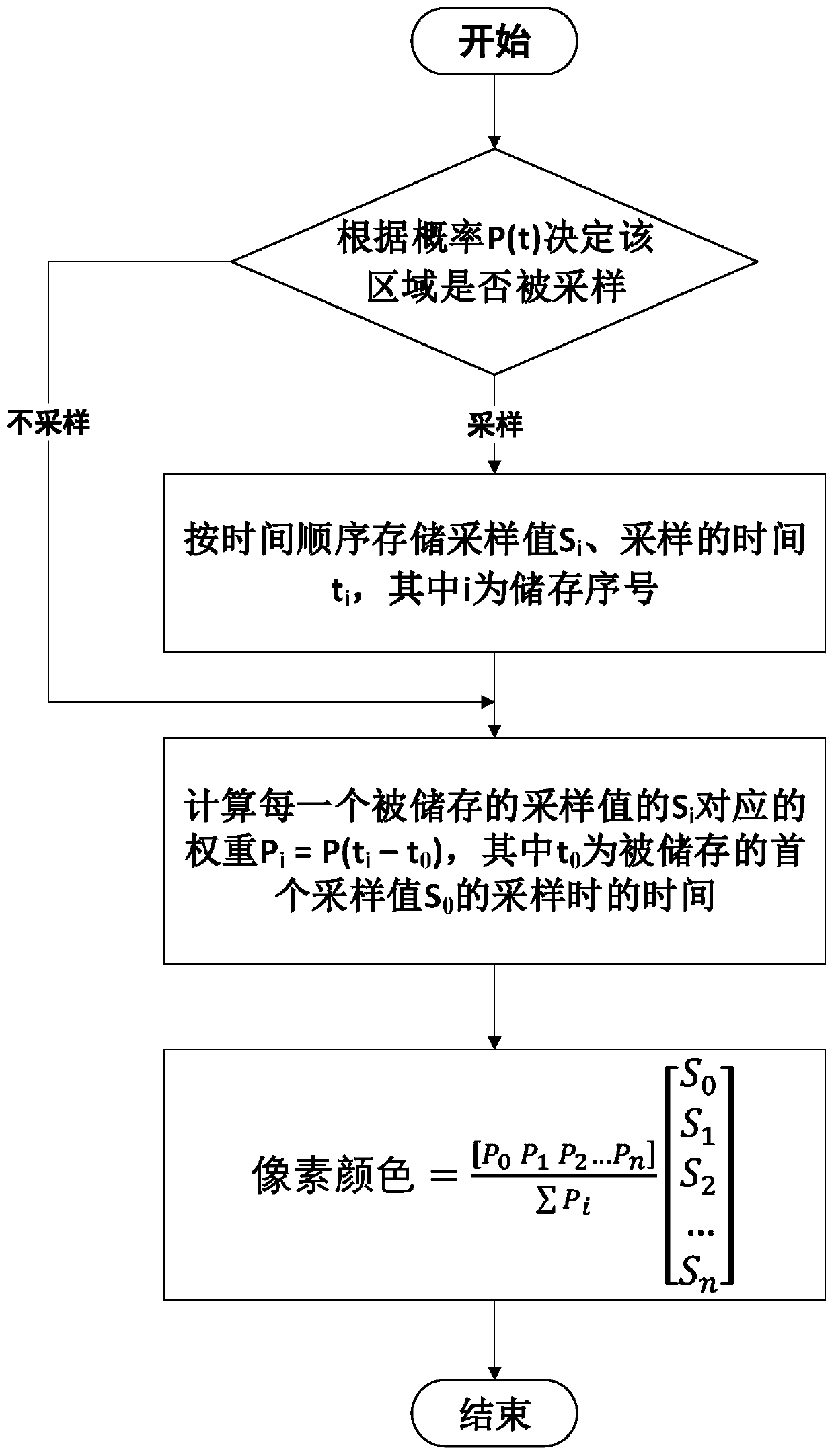
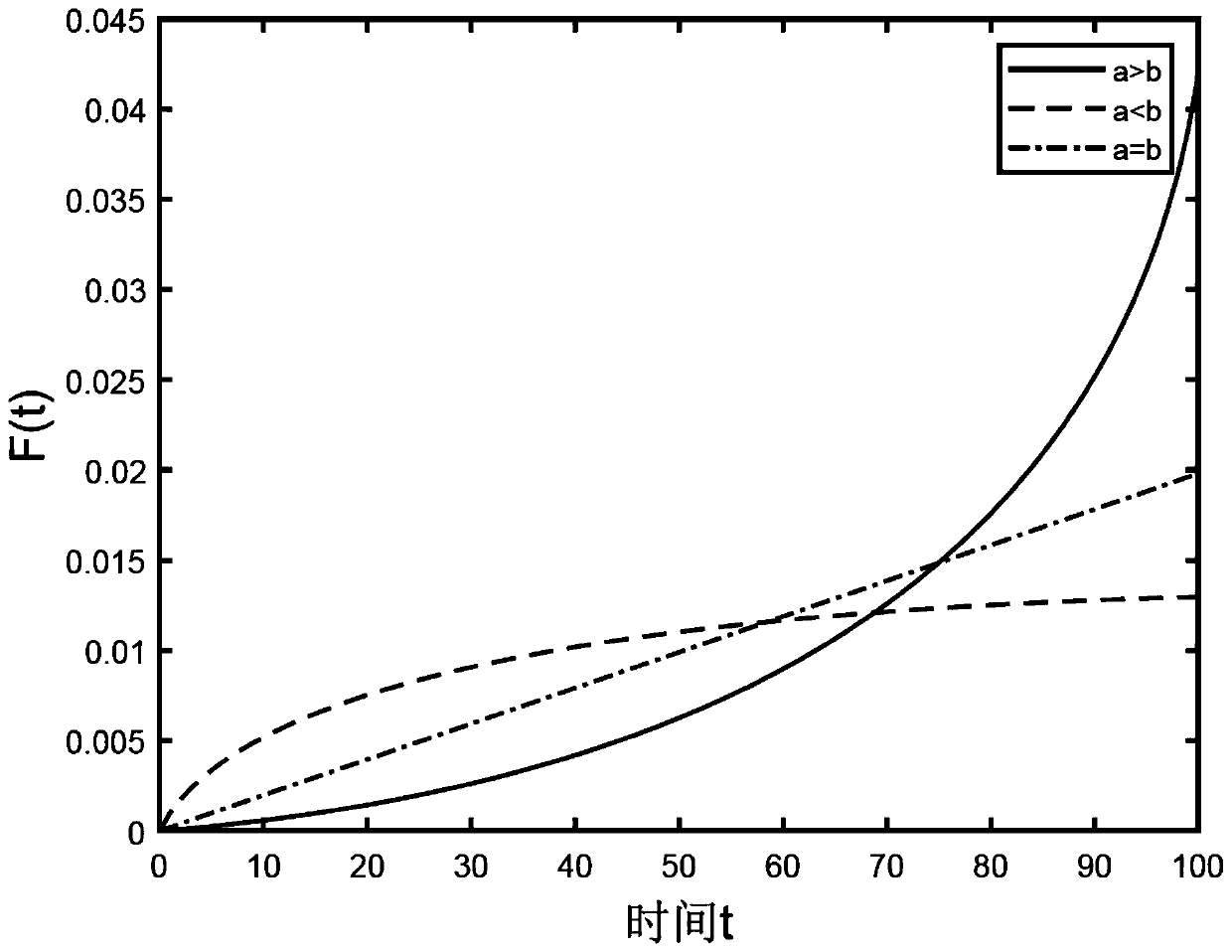
ActiveCN110766617AReduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisNormal densityComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a rendering acceleration method with dynamic blurring for reducing the sampling number, being characterized in that when a new frame of image is generated, only a part of areais sampled, and the color of a final pixel is obtained by weighted averaging of values sampled for continuous times. The probability that the region is sampled and the weight during weighted average are calculated by using the same probability density function, and the image is controlled by a second-order Bezier curve, so that a controllable image-based dynamic blurring effect is obtained. The algorithm can be combined with a geometric dynamic fuzzy algorithm in sampling so as to weaken the influence of the ghosting problem on the visual effect. For algorithms with large sampling expendituresuch as ray tracing and photon mapping in real-time rendering, the calculation time is effectively reduced, and the acceptable rendering quality is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
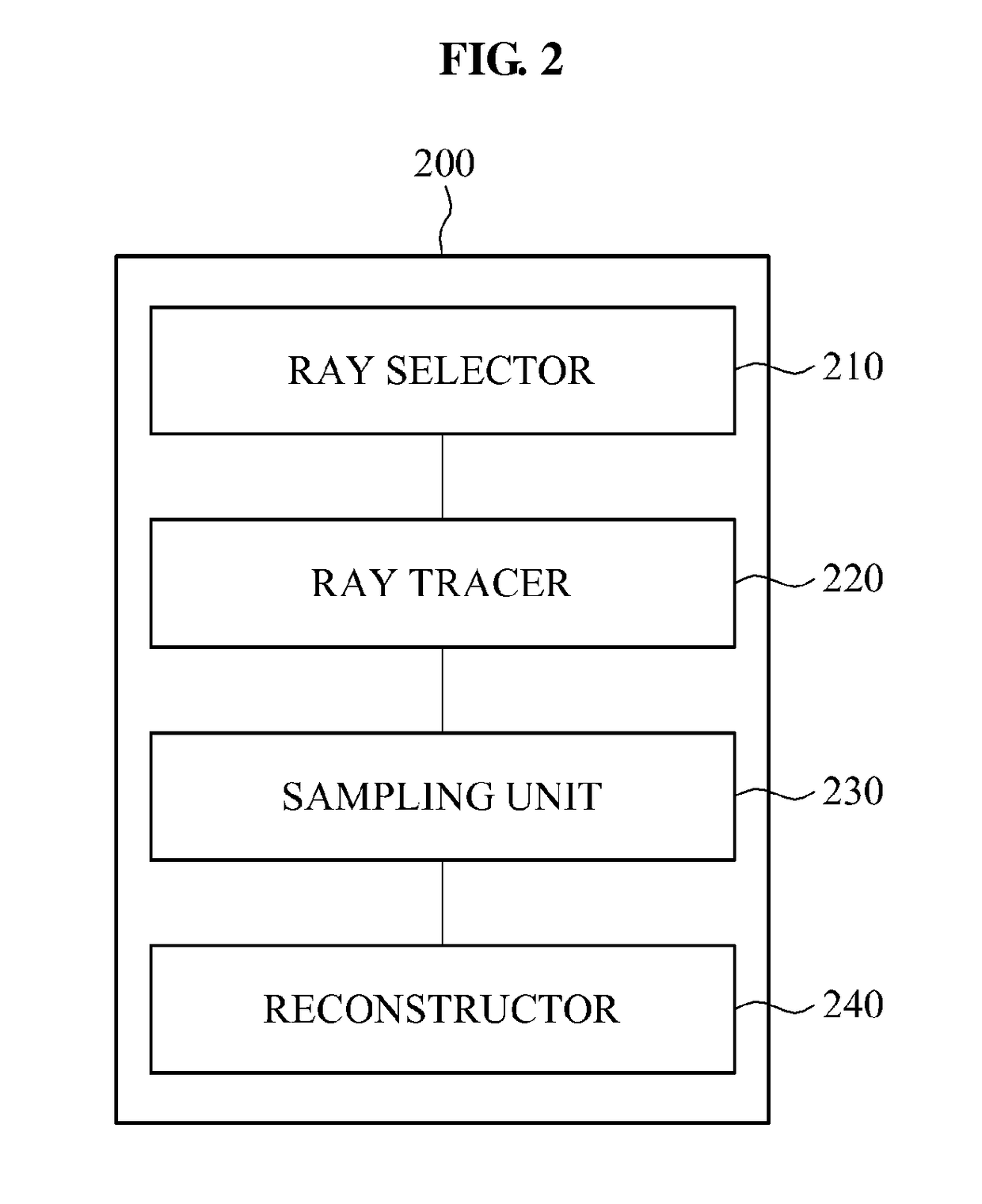
Image processing apparatus and method using photon mapping and ray tracing and increasing a rate of photon mapping
Provided is an image processing apparatus for performing photon mapping, and the image processing apparatus may perform ray tracing for photon mapping, sample a ray space based on a result of the ray tracing, and perform pseudo photon mapping using the sampled ray space.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
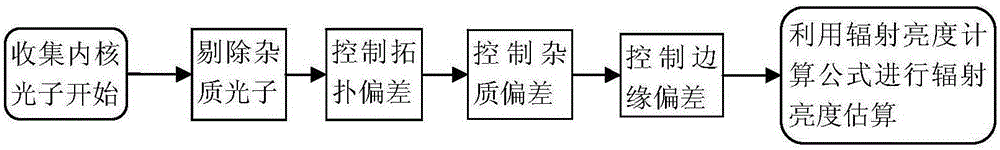
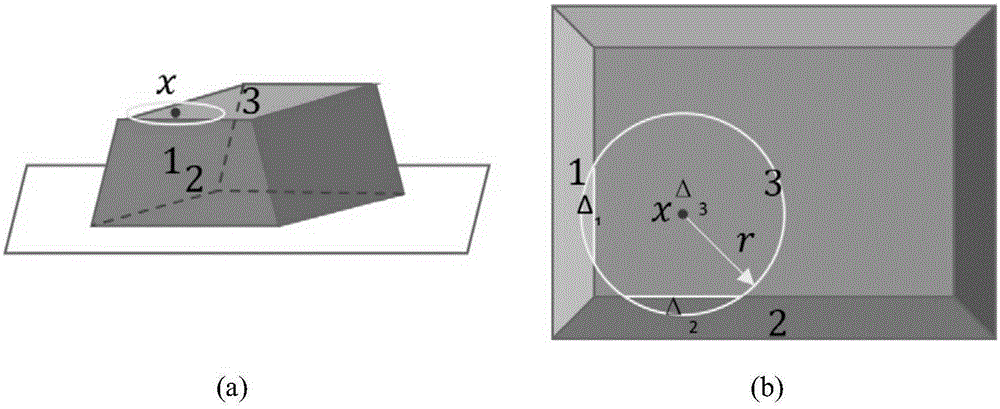
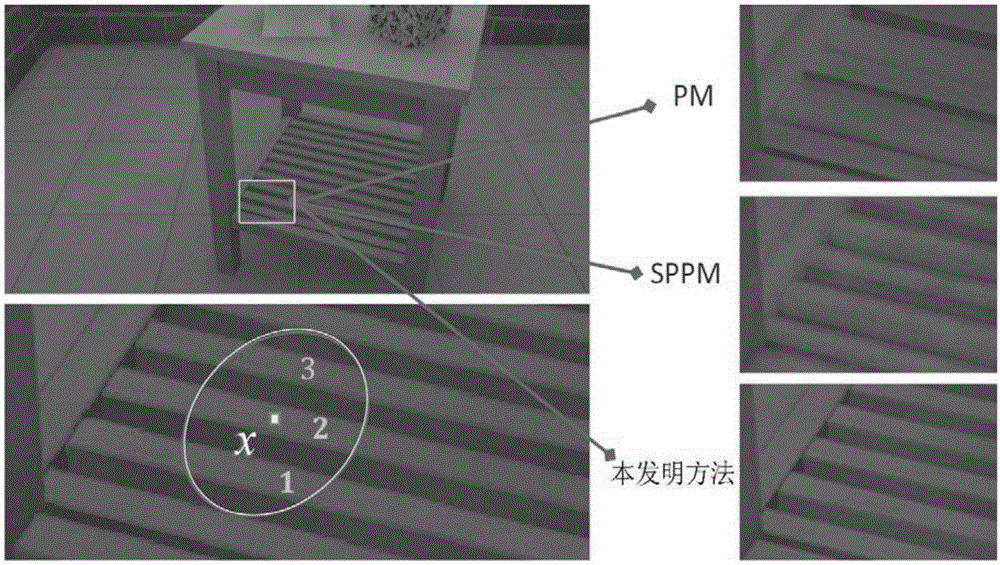
Deviation control method in photon mapping
The invention relates to a deviation control method in photon mapping. The method comprises the following steps: 1, according to an estimated radius of an intersection point generated when light intersects with a scene, and collecting photons nearby the intersection point by use of a KNN method; 2, performing visibility determining on the collected photons so as to reject impure photons; 3, performing topology deviation control on the collected photons through depth continuity detection; 4, according to a normal topology structure of a surface which the collected photons are attached to, performing geometric continuity detection on the surface of the intersection point so as to control impurity deviations; 5, carrying out edge deviation control on the collected photons through convex surface examination; and 6, carrying out radiation brightness estimation by use of a radiation brightness calculation formula by taking residual photons as correct and effective photons. Then an obtained radiation brightness calculation value is converted into a color value, and thus a final highly realistic image is synthesized. The method provided by the invention can effectively eliminate the problem of deviation and noise which are generated by inappropriate collection of the photons.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
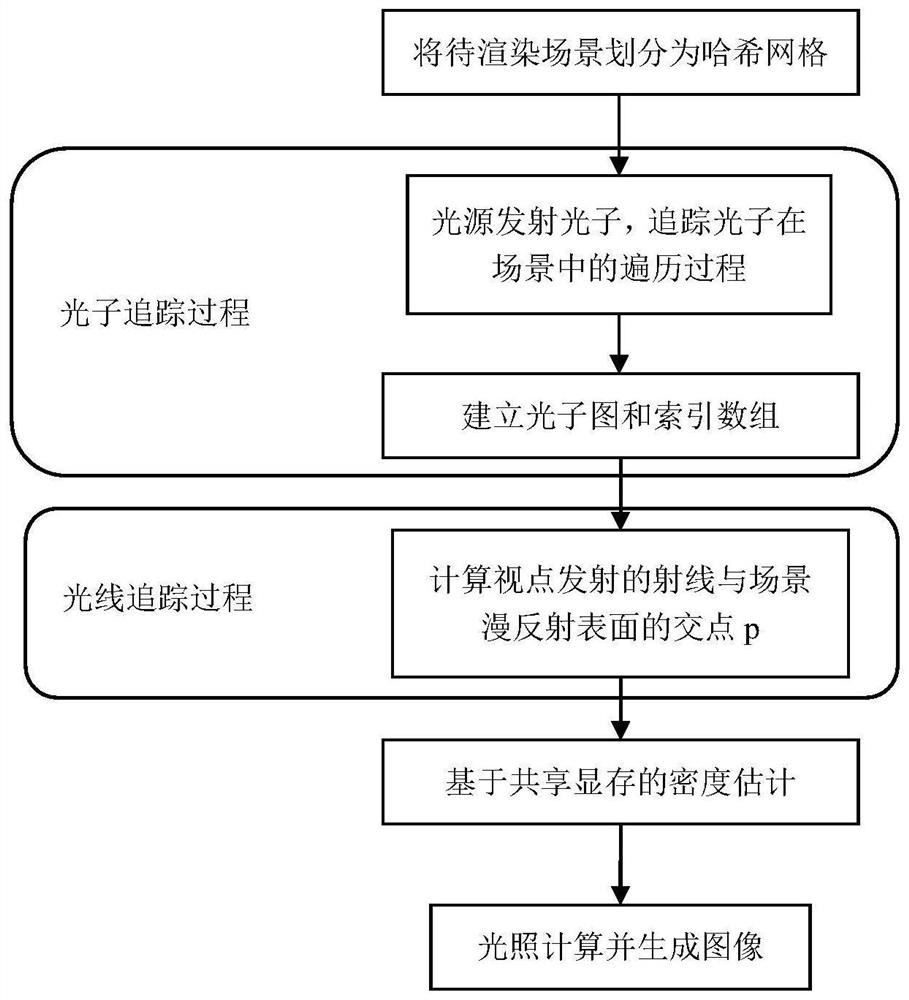
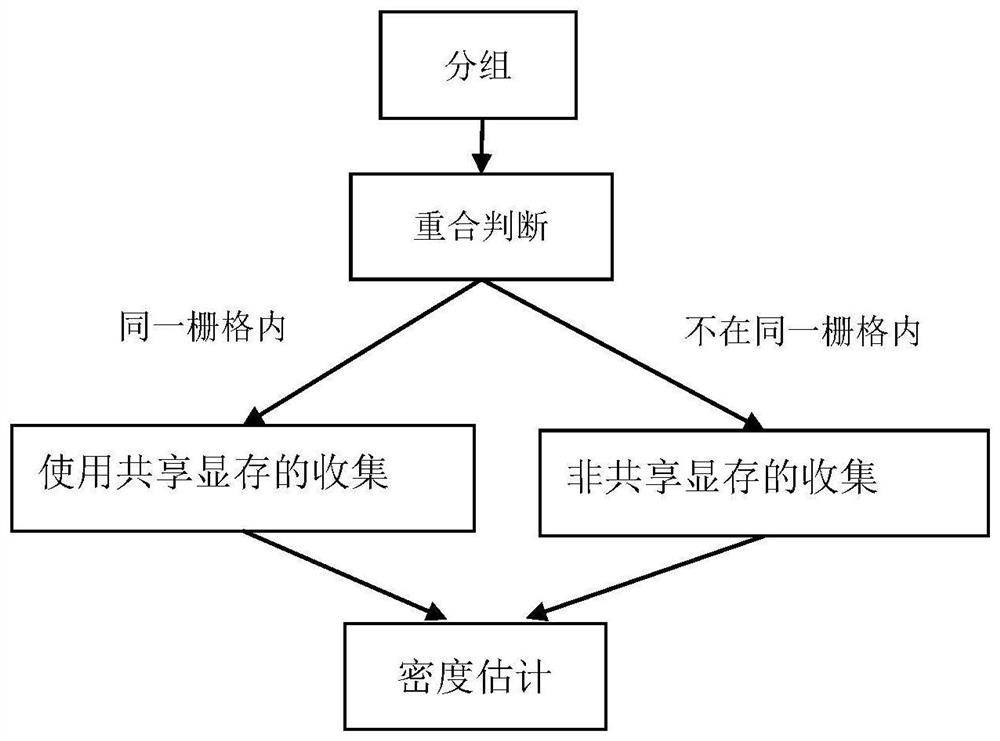
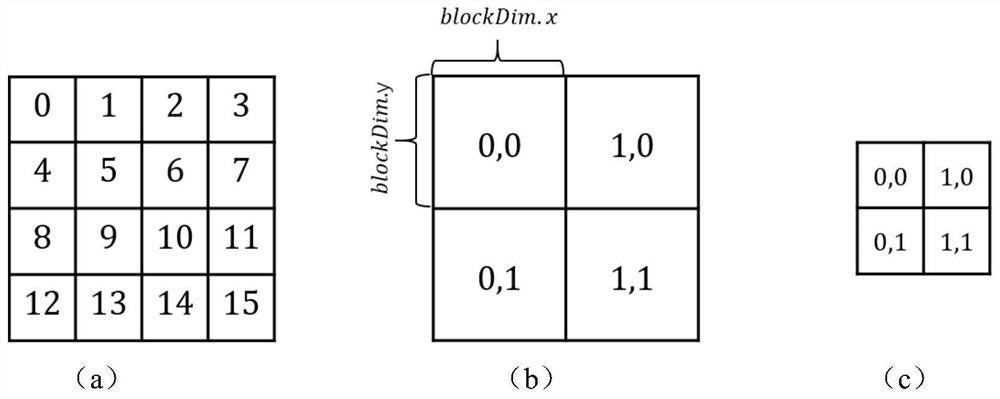
Photon collection method and photon mapping rendering method based on shared video memory optimization
ActiveCN113096248BImprove drawing efficiencyHigh speedImage memory management3D-image renderingVideo memoryComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a photon collection method and a photon mapping rendering method based on shared video memory optimization. The method for collecting photons of the present invention comprises: 1) dividing the entire three-dimensional scene to be rendered into hash grids; 2) the light source emits photons, and when the photons intersect with the diffuse reflection surface in the scene, record the position of the photons, Energy and incident direction information; 3) According to the position of the photon in the record, calculate the corresponding hash value, reorder the photons according to the order of the hash value from small to large and generate an index array; 4) Starting from the viewpoint, to each The pixel emits light, calculates the first intersection point p on the path with the diffuse reflection surface of the scene, and records the position and incident direction of the intersection point p; 5) divides the pixels to be calculated into groups and assigns a thread to each pixel; 6) judges a Whether the hit points of the pixels in the group are located in the same grid, and if they are located in the same grid, shared video memory is used for acceleration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
An Unbiased Photon Mapping Drawing Method
ActiveCN105118083BImprove efficiencyImprove rendering and drawing efficiency3D-image renderingLight energyAnimation
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Method for Unpolarized Photon Mapping in Participating Media
ActiveCN105869204BStability is not affectedMedia drawing is efficient3D-image renderingAlgorithmPhoton mapping
The invention discloses a method for drawing unbiased photon mapping in the presence of a medium. The method improves the unbiased photon gathering method from aspects such as improving subpath sampling technology, reforming theory formula, sampling importance of unbiased item estimation, and discussing medium boundary conditions, etc., which enable continuous obtaining of unbiased drawing results in the scenario of the presence of the medium. According to the invention, improvement is made to the weight of multiple importance sampling so as to combine the method for drawing unbiased photon mapping in the presence of the medium with a bidirectional light ray tracking technology, which enables the two methods to simultaneously exhibit advantages under different contexts.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Photon mapping-based global illumination method
InactiveCN101826214BOptimized for speedGood effect3D-image renderingImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a novel photon mapping-based global illumination method, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method of the invention mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) randomly emitting photons to a scene by a light source; (2) judging the state of the emitted photons; (3) tracing the photons by a recursive method according to the information on the surface of an object; (4) storing the photon information; and (5) rendering the scene, namely rendering the scene by combining the Monte-Carlo backward tracing method and the primary photon mapping method.By using the technical scheme of the invention, the running speed, the rendering effect, the used storage space and the like can be improved to a certain extent.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com