High incidence angle retroreflective sheeting
a retroreflective sheeting and high incidence angle technology, applied in the field of retroreflective materials, can solve the problems of limiting use, losing nearly all of the reflectivity, and the apparent brightness of conventional retroreflective materials with the increase of the incidence angle, so as to achieve the effect of maximizing the retroreflectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
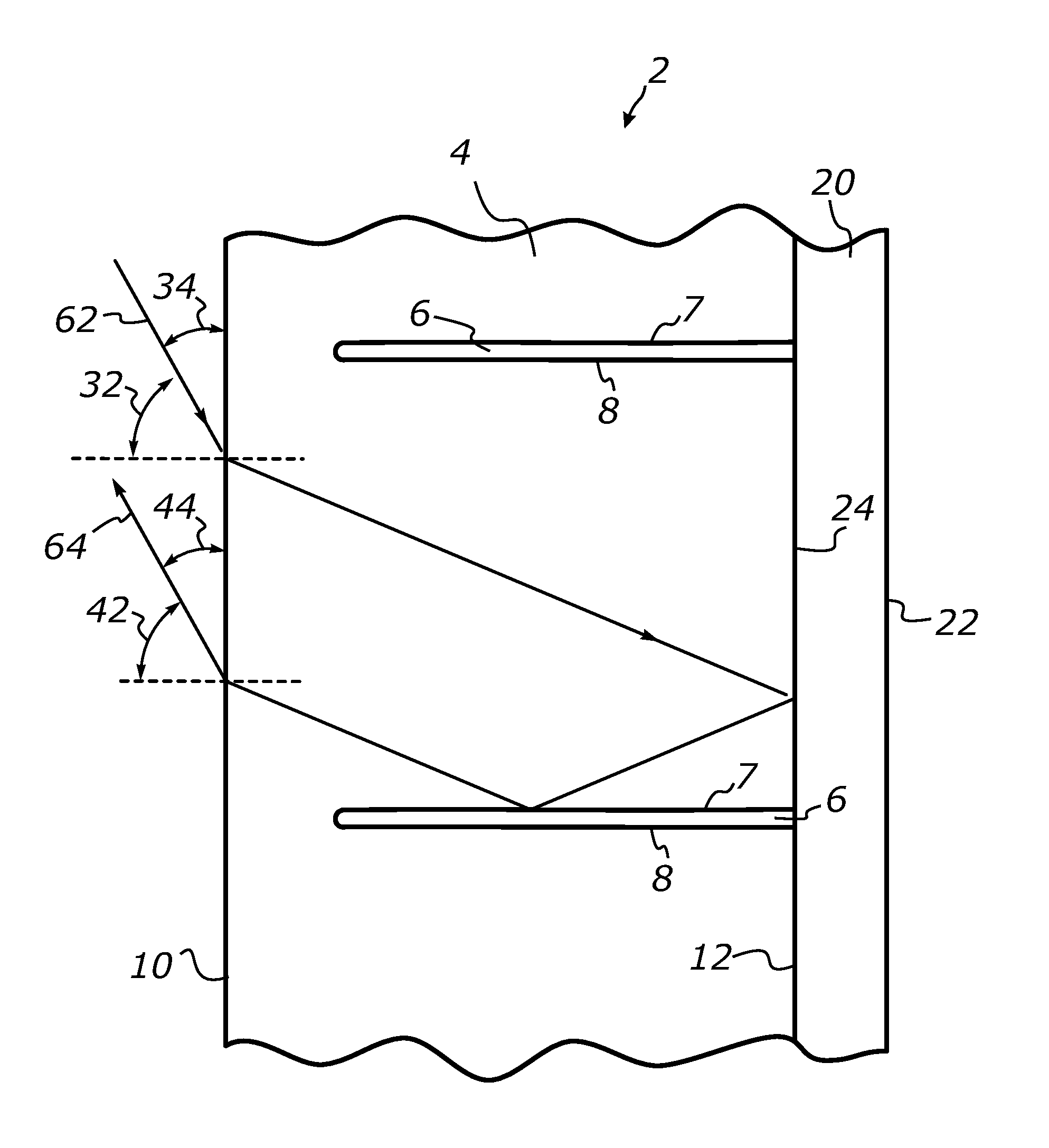
[0165]A retroreflective sheet-form structure as schematically illustrated in FIG. 7 was made by attaching a top optically transmissive layer formed by a 1-millimeter-thick sheet of optically clear thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) to a bottom reflective layer formed by a same-sized sheet of brightness enhancement film BEF II 90 / 24 commercially available from 3M Corporation and having a thickness of about 140 μm (5.5 mils). The BEF II 90 / 24 film product has a microprismatic surface structure formed by an array of right-angle isosceles microprisms having a linear configuration and prism pitch of about 24 μm (0.9 mils).
[0166]An array of parallel TIR micro-channels was formed in the top layer by slitting a surface of the TPU sheet material to a cutting depth of approximately 500 μm using a pack of sharp rotary blades commercially available from KAI Corporation. The micro-channels were formed at a constant spacing of about 600 μm so that the L / D ratio characterizing the channels was about...
example 2
[0170]A retroreflective sheet-form structure as was made as described in EXAMPLE 1 above except that the top layer was made from optically clear plasticized polyvinyl chloride (flexible polyvinyl film). The tests were conducted as described in EXAMPLE 1 above and have shown similar results.
example 3
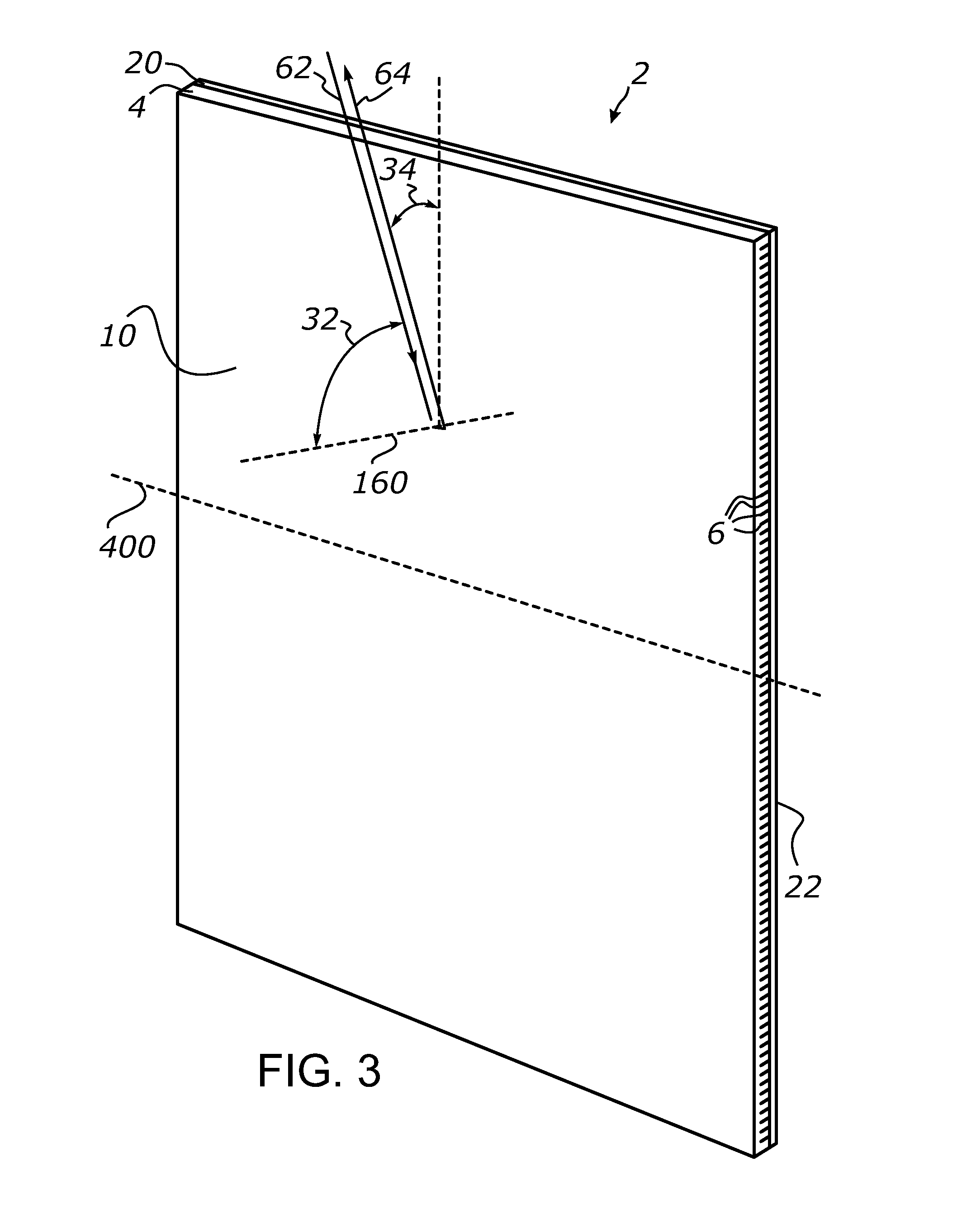
[0171]A retroreflective sheet-form structure as schematically illustrated in FIG. 3 was made by a top optically transmissive layer formed by a 0.5-millimeter-thick sheet of optically clear thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) and attaching it to a bottom reflective layer formed by a metalized polyethylene terephthalate (Mylar®) film. The top layer included an array of parallel TIR micro-channels formed as described in EXAMPLE 1 above and spaced / dimensioned at 1.4 L / D ratio.
[0172]The bottom layer was provided with a high-tack adhesive that was used to attach the retroreflective sheet-form structure to a thin and rigid sheet-form substrate. A strip of approximately 4 centimeters by 50 centimeters of the resulting sheet-form retroreflective structure was cut out such that the longitudinal axis of the strip was parallel to the longitudinal axis of the micro-channels formed in the top layer. The resulting strip was tested by exposing it to a parallel beam of light and measuring its reflectan...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness parameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness parameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com