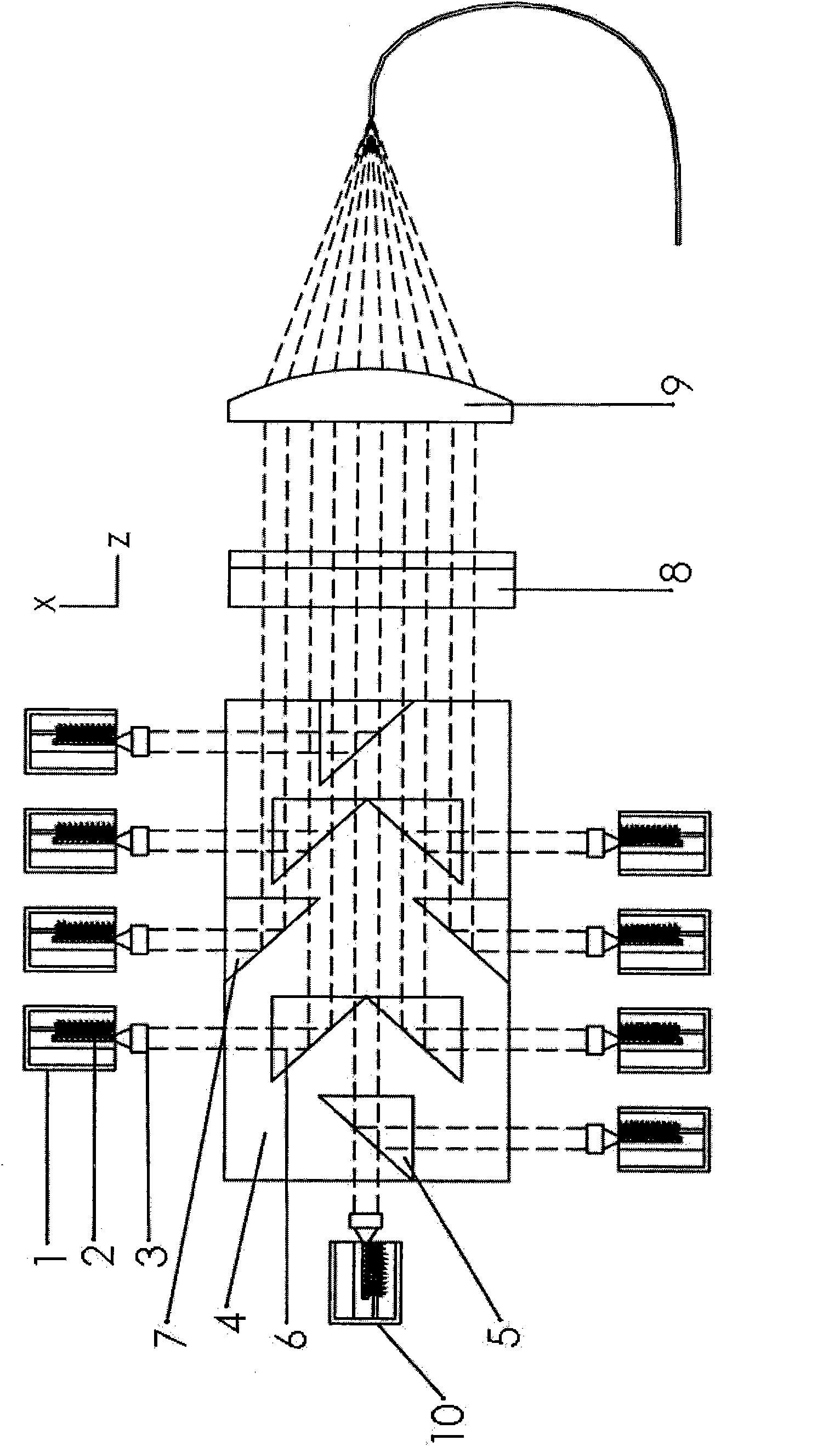
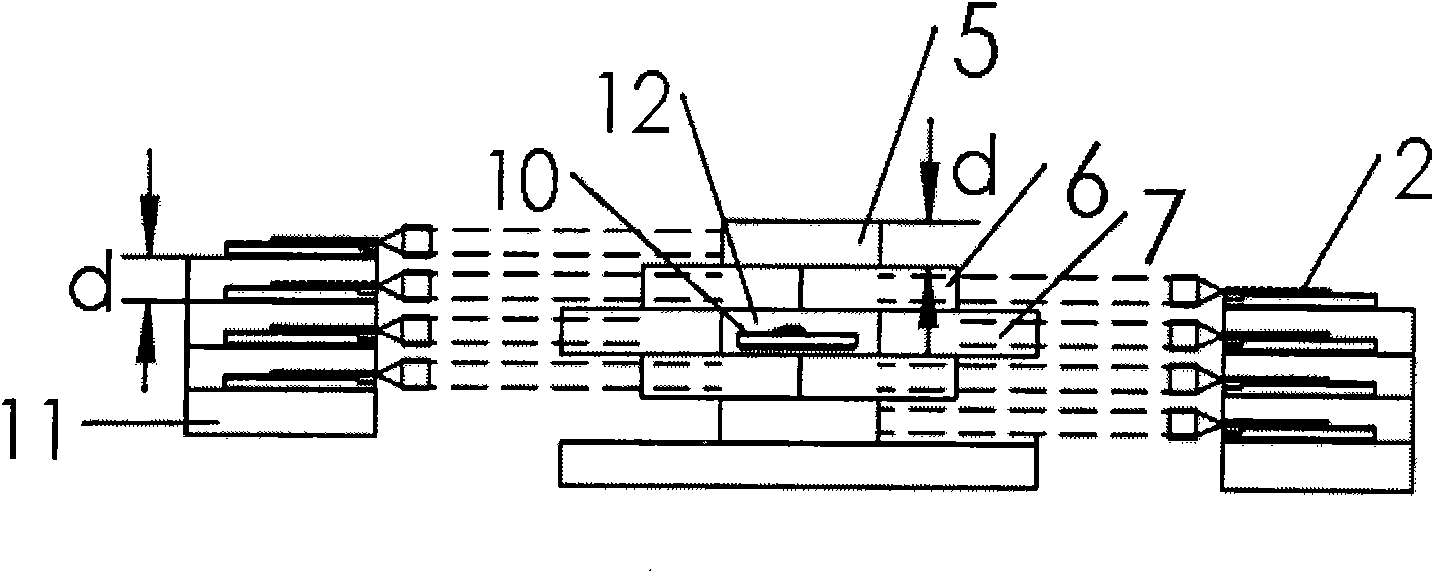
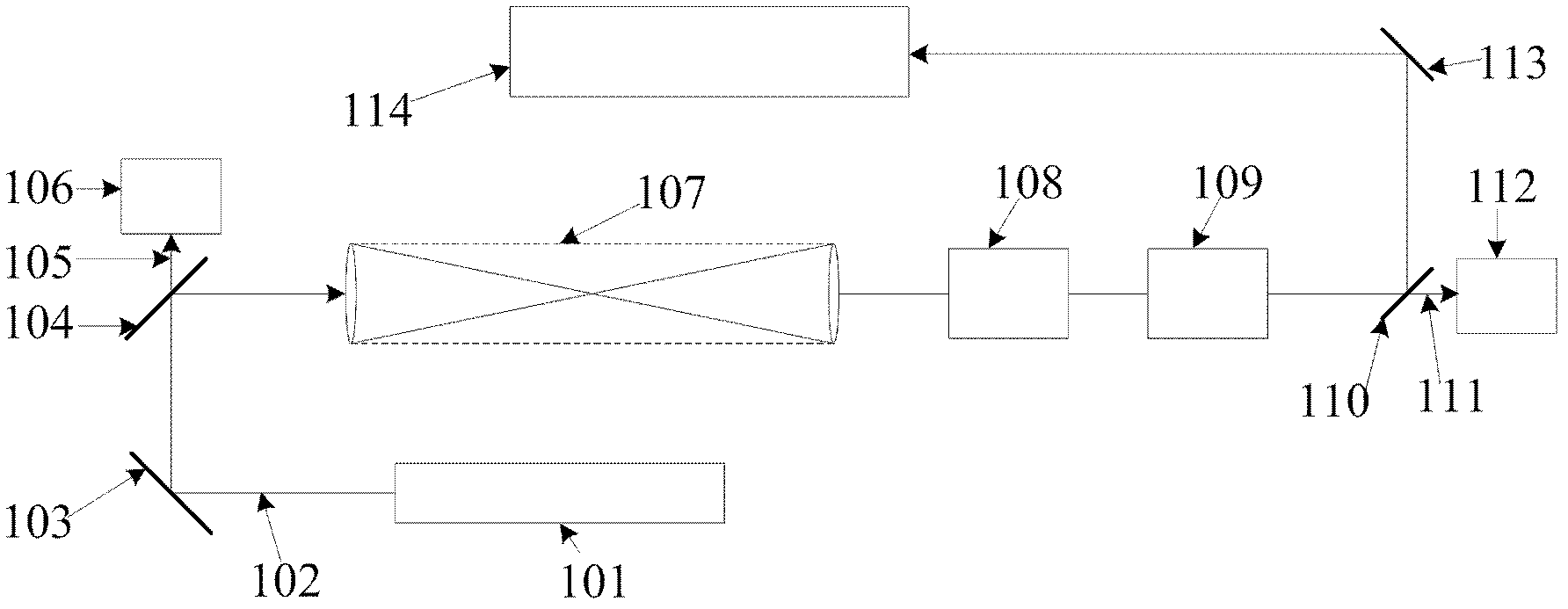
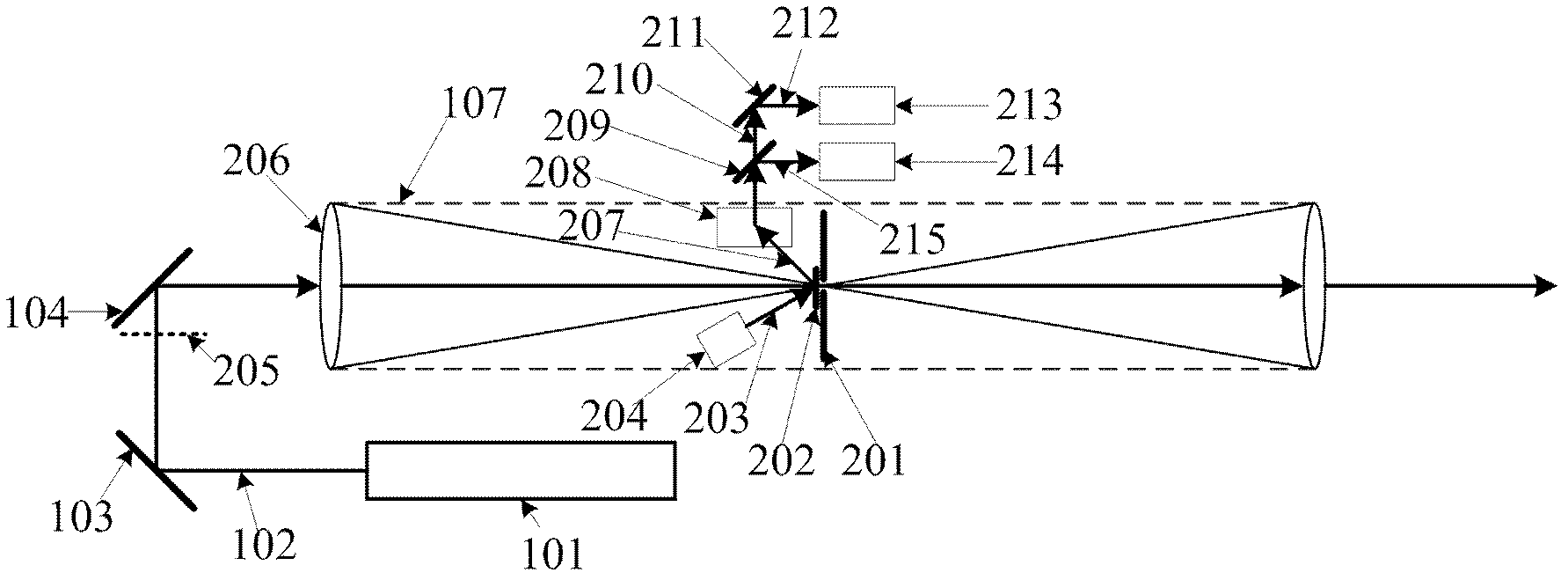
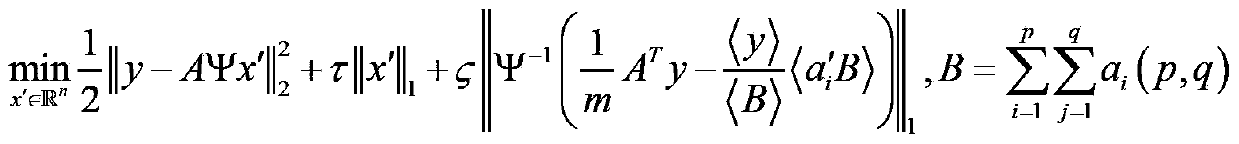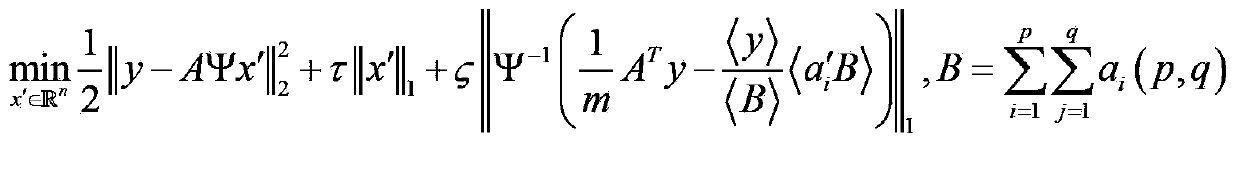Patents
Literature
370 results about "Beam collimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
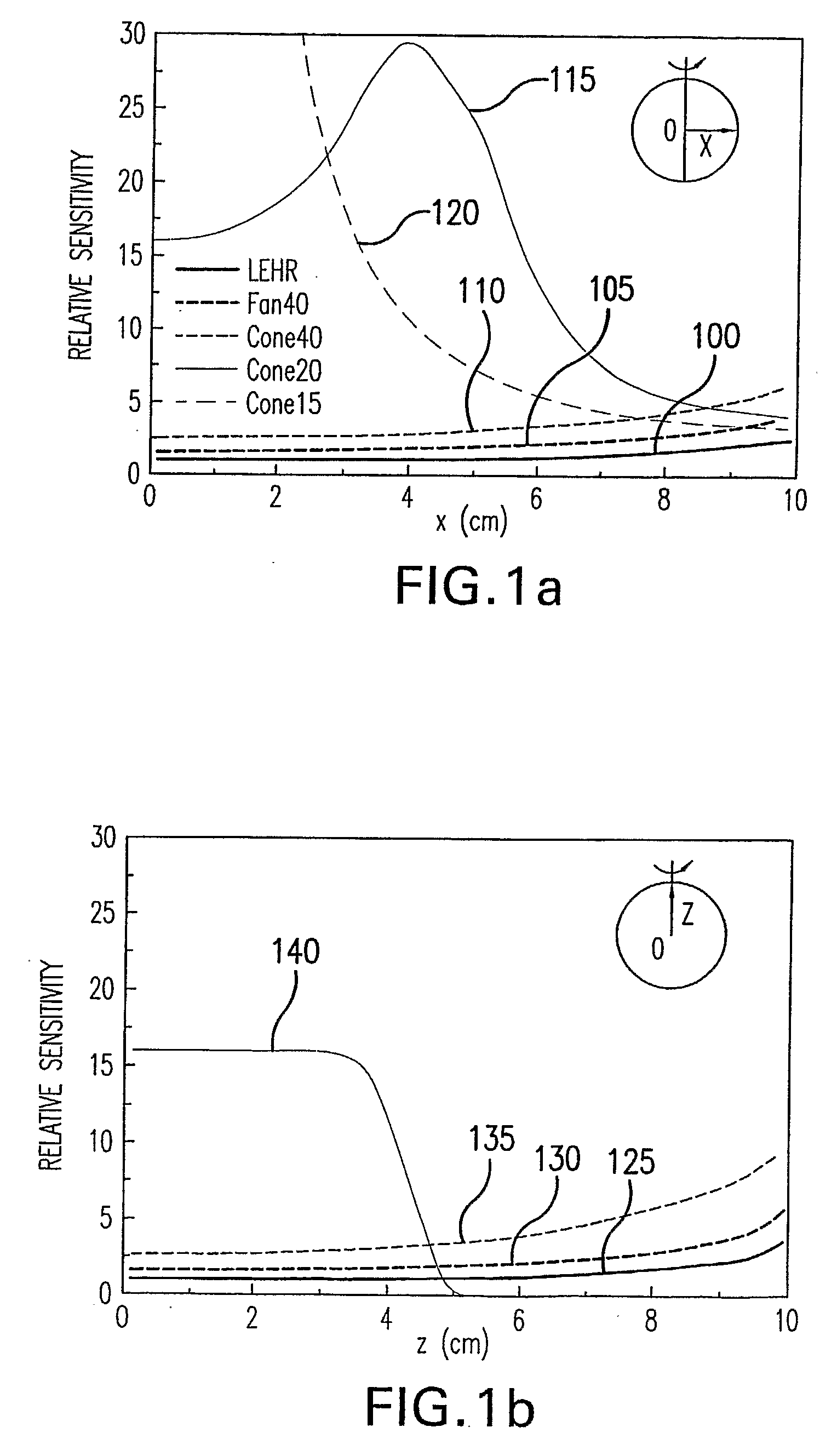
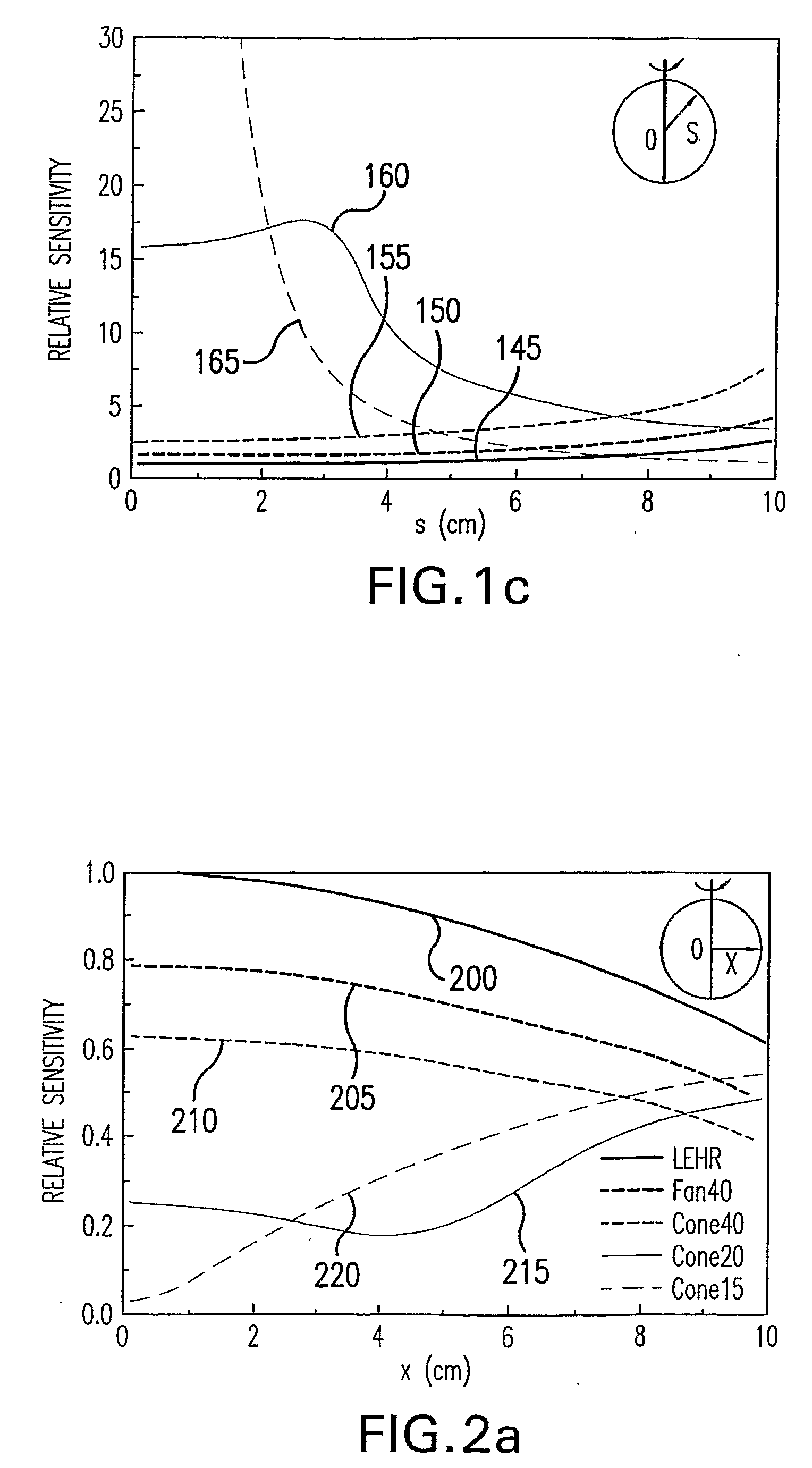
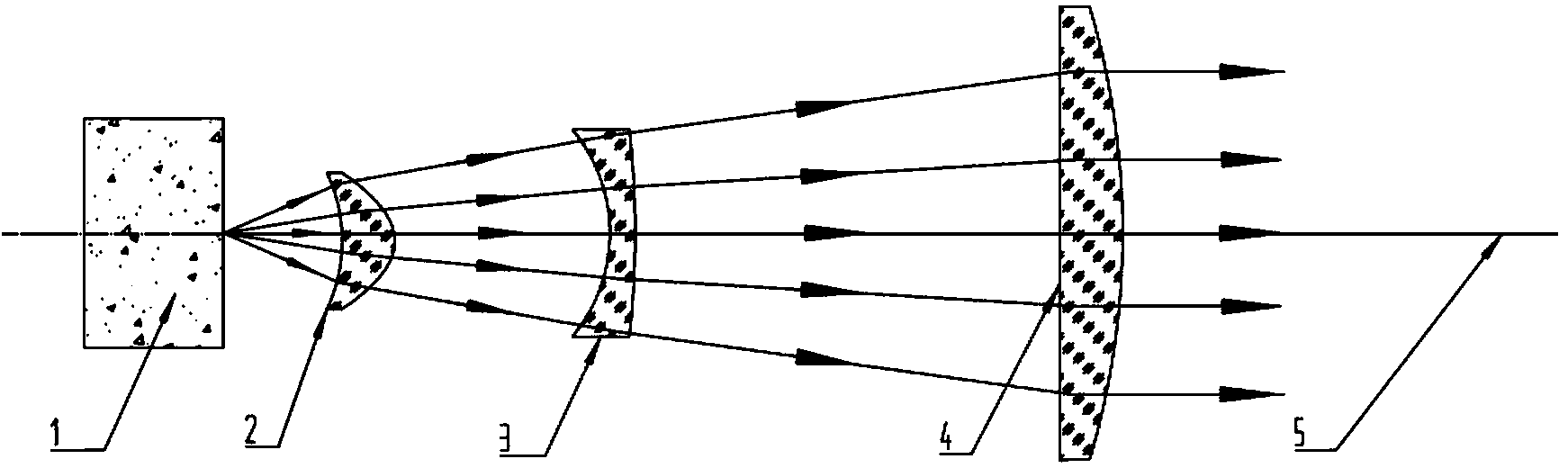
Beam collimation. the restriction of x-radiation to the area being examined or treated by confining the beam with metal diaphragms or shutters with high radiation-absorption power. In addition to protecting the patient and others from scatter radiation, beam collimation reduces radiographic density.
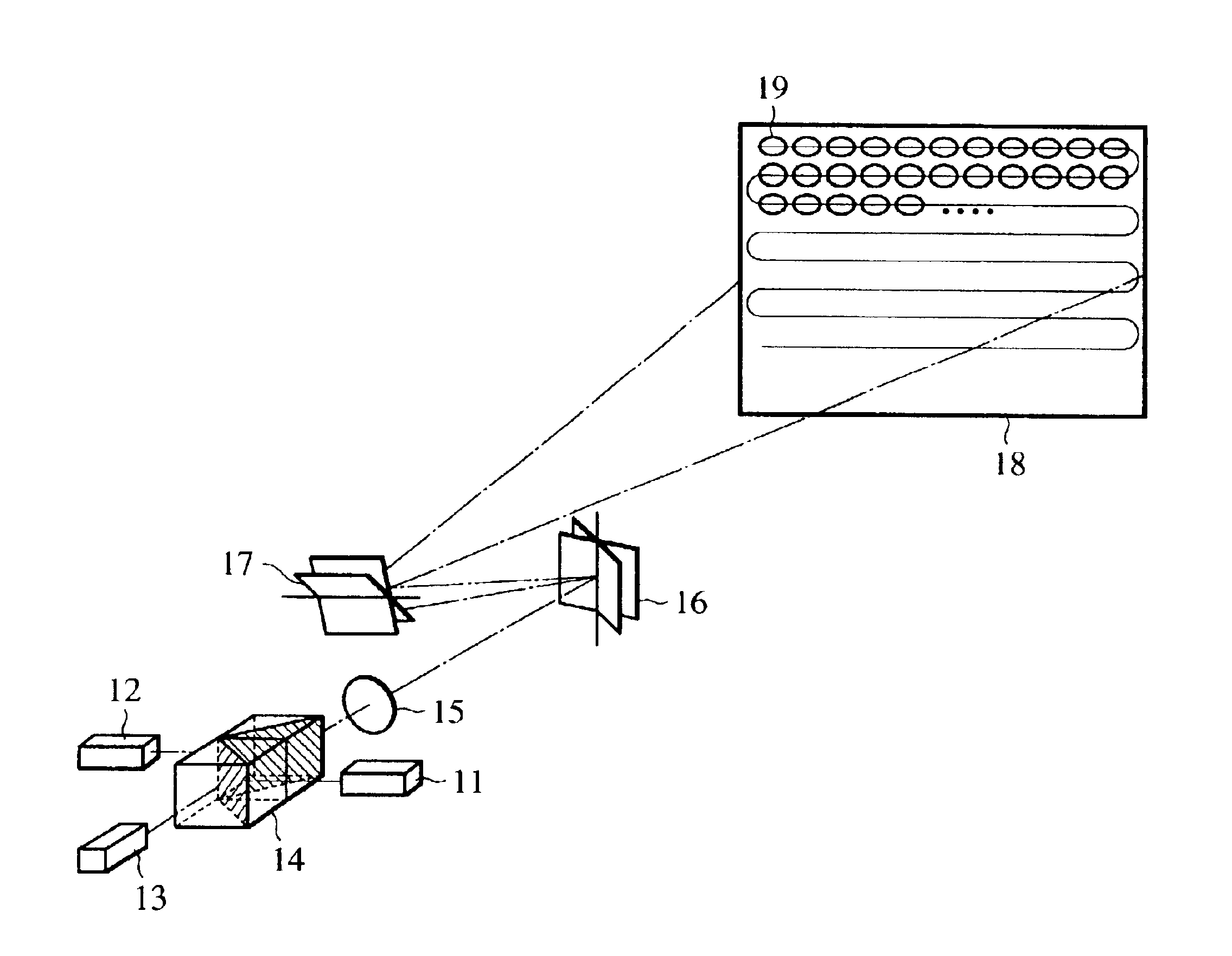
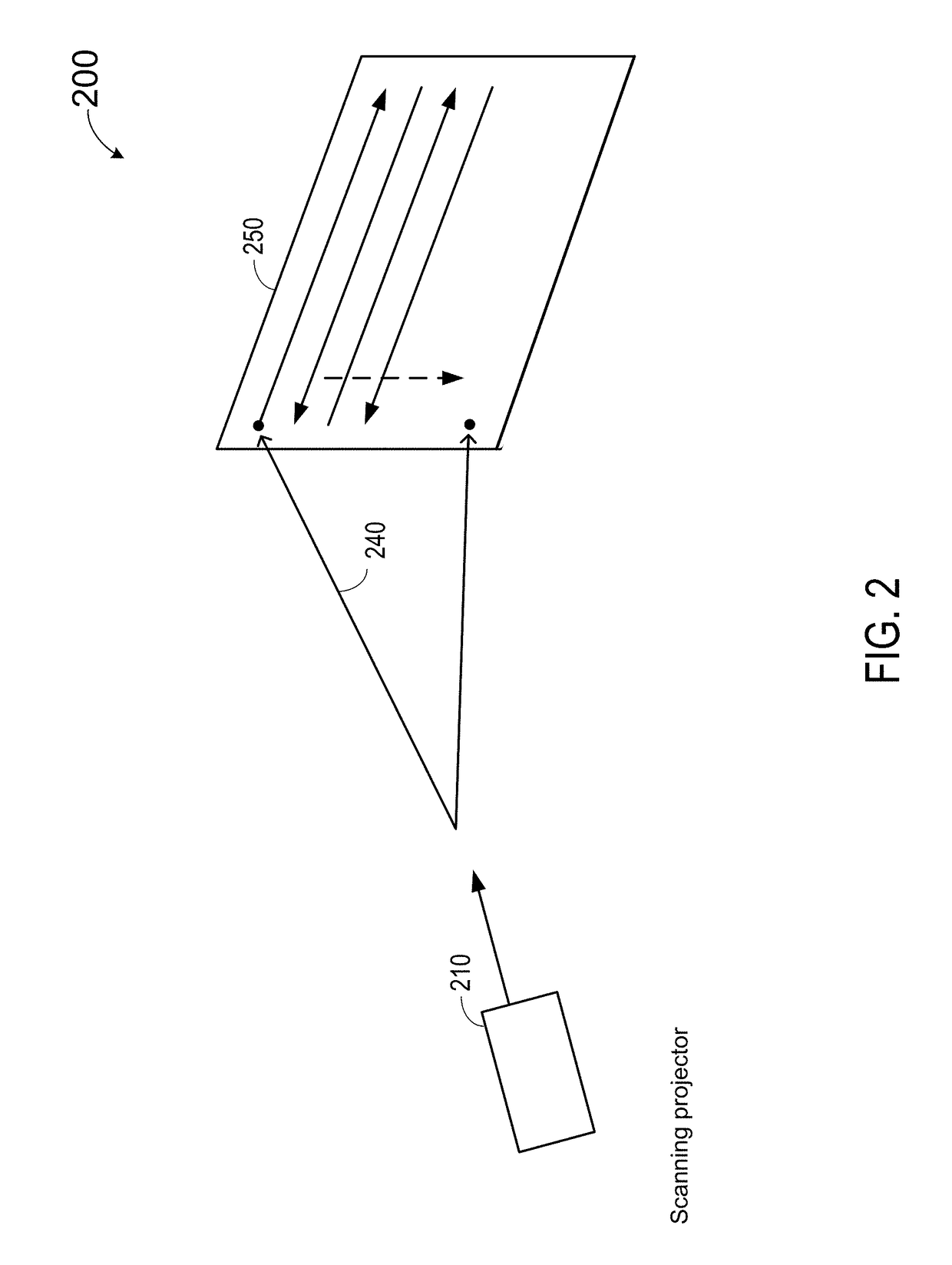
Projection display device
InactiveUS6945652B2Less expensiveAccurate color reproductionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageProjection plane
Light beams having different wavelengths emitted from red and blue semiconductor lasers and a laser diode pumped green solid-state laser are incident on respectively different surfaces of a color combining element and are overlaid on a single light path. Multiple beam interference films of the color combining element allow only the light beams having the oscillating wavelengths corresponding to the respective light sources to pass therethrough or reflect thereon so as to combine the light beams. A collimator collimates the light beams so that the beam waist of the light beams lies around a projection plane. When two-dimensional scanning is performed by radiating the light beams onto a micromechanical mirror and then onto a galvanometer mirror for scanning light in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, a color image is displayed on the projection plane by arranging pixels in array, each pixel consisting of overlapping pulses of light of three colors.
Owner:CANON KK
System and Method for Performing Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (Spect) with a Focal-Length Cone-Beam Collimation
InactiveUS20080302950A1Accurate estimateEasy to detectBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRadiation/particle handlingBeam collimationField of view
A system and method are provided for obtaining data that may be used to generate images of a brain or other bodily organ. The system can include a pair of detecting arrangements and a collimating arrangement associated with each detecting arrangement. A first collimating arrangement can include a cone-beam collimating arrangement having a focal point located within the brain or other organ being imaged. A second collimating arrangement can include a fan-beam collimating arrangement having a focal length selected such that the organ being imaged lies within its field of view to ensure data sufficiency. Cone-beam collimating arrangements having improved hole geometries can also be utilized to provide further increases in imaging sensitivity.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
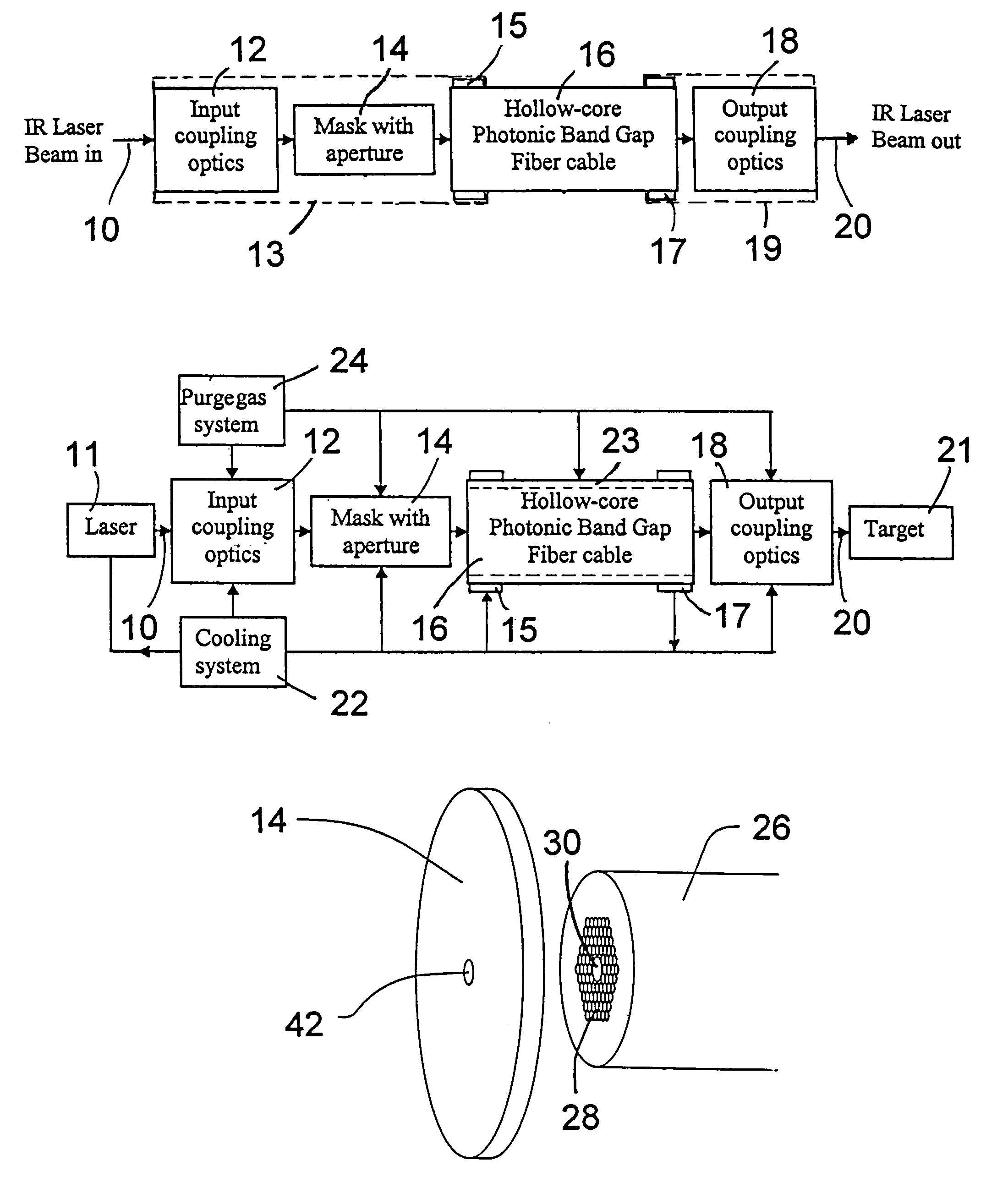
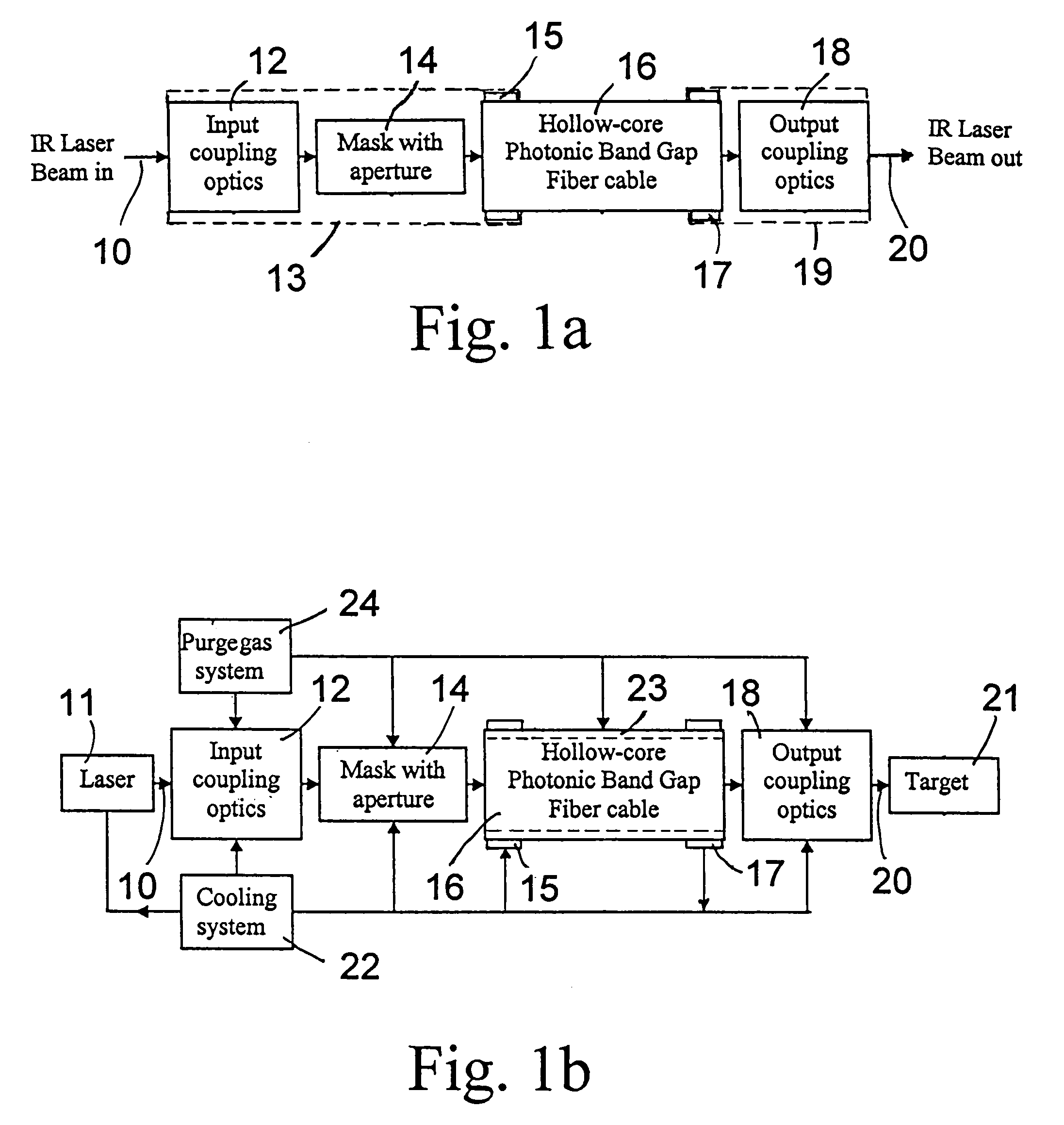
Fiber optic infrared laser beam delivery system
ActiveUS7099533B1Lower Level RequirementsAccurately heldOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesFiberPhotonics
A laser beam delivery system is disclosed, which allows transmission of high-power infrared light through a hollow core photonic band gap (HC-PBG) fiber made of non-silica-based glass. In this system, the infrared beam first passes through input coupling optics which focus the beam onto the hollow core of the HC-PBG fiber. In front of the input end of the HC-PBG fiber, there is provided a mask with a hole aligned with the hollow core, and the infrared beam first passes through this hole before entering the hollow core of the HC-PBG fiber. This protects the photonic band gap structure from being damaged by the beam. After passing through the HC-PBG fiber, which may be from one to several hundred meters in length, the infrared beam exits at the output end of the fiber and passes through output coupling optics which collimate and focus the beam onto a desired target. The various components of the system may be water cooled during the operation or subjected to a gas purge to prevent condensation or gas ionization.
Owner:CHENARD FRANCOIS
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulation radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy
ActiveUS8306184B2X-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationElectron sourceLight beam
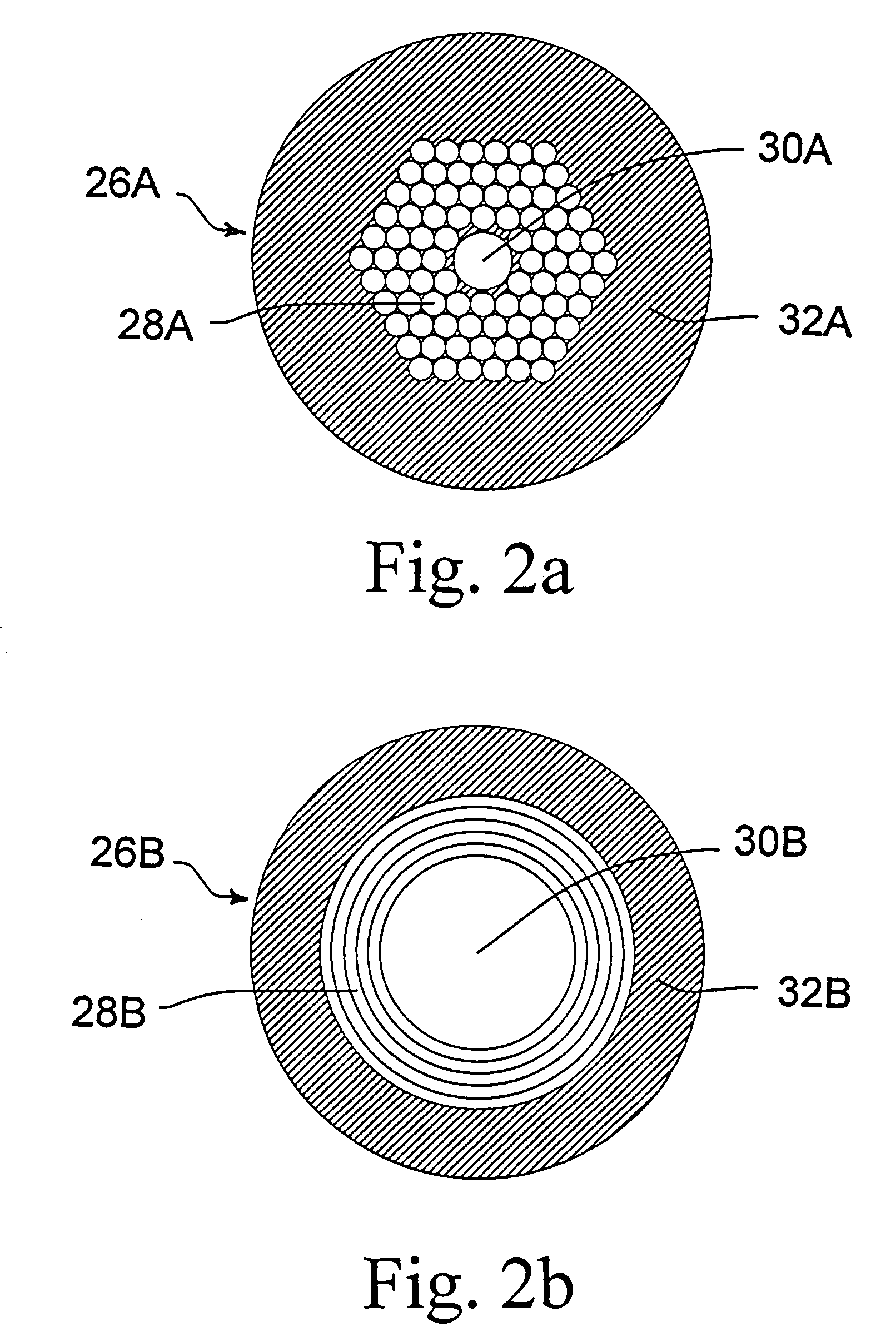
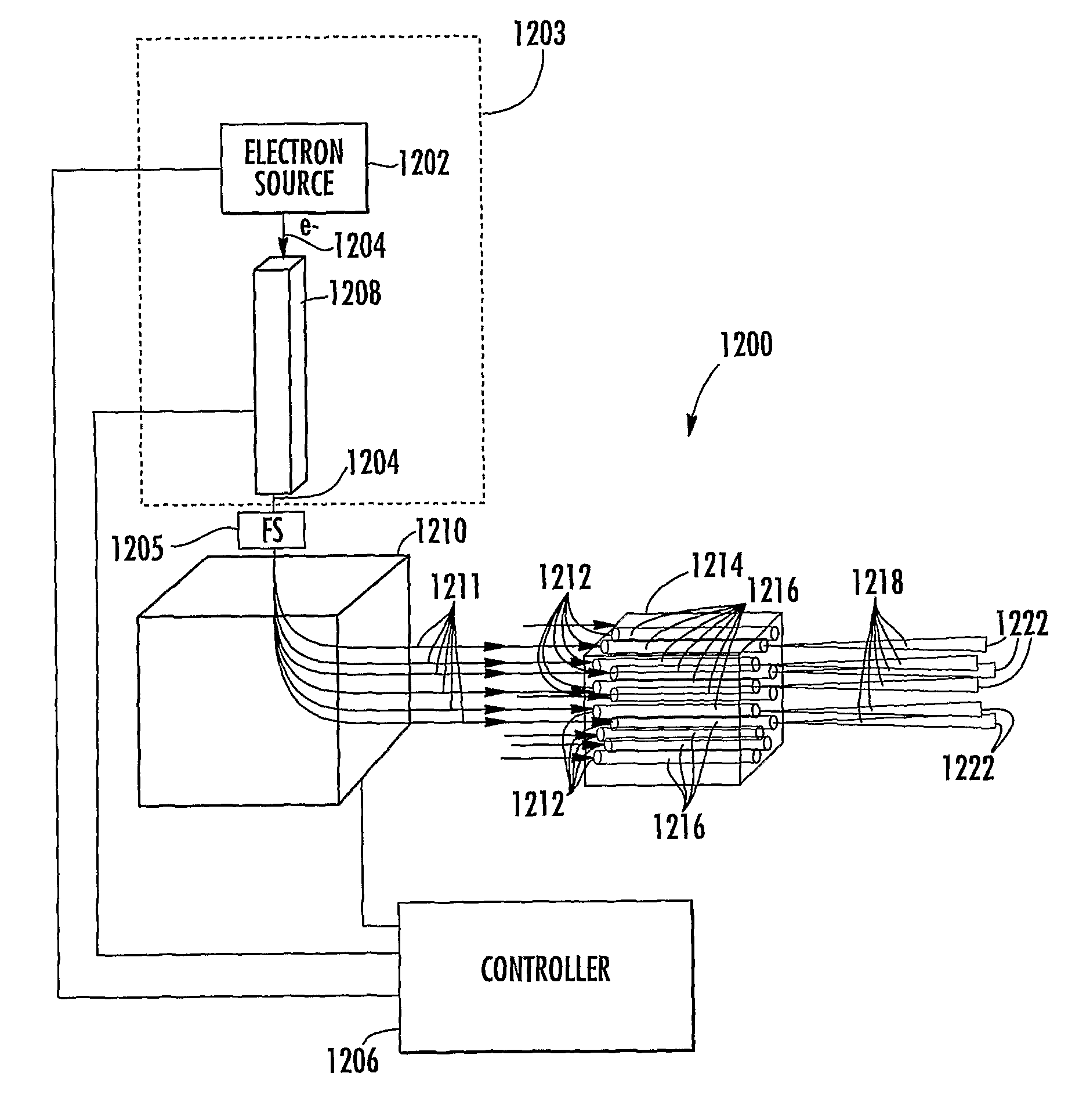
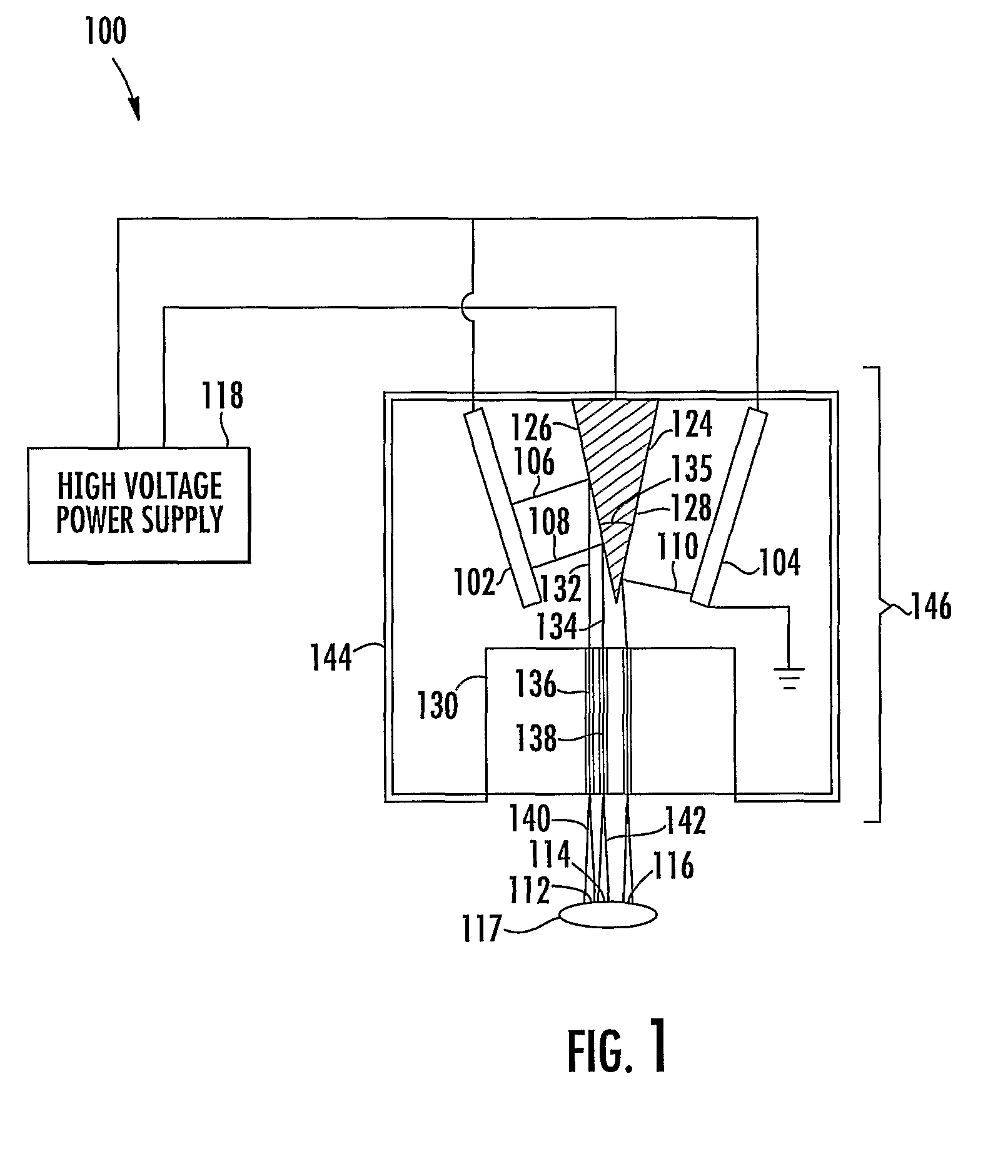
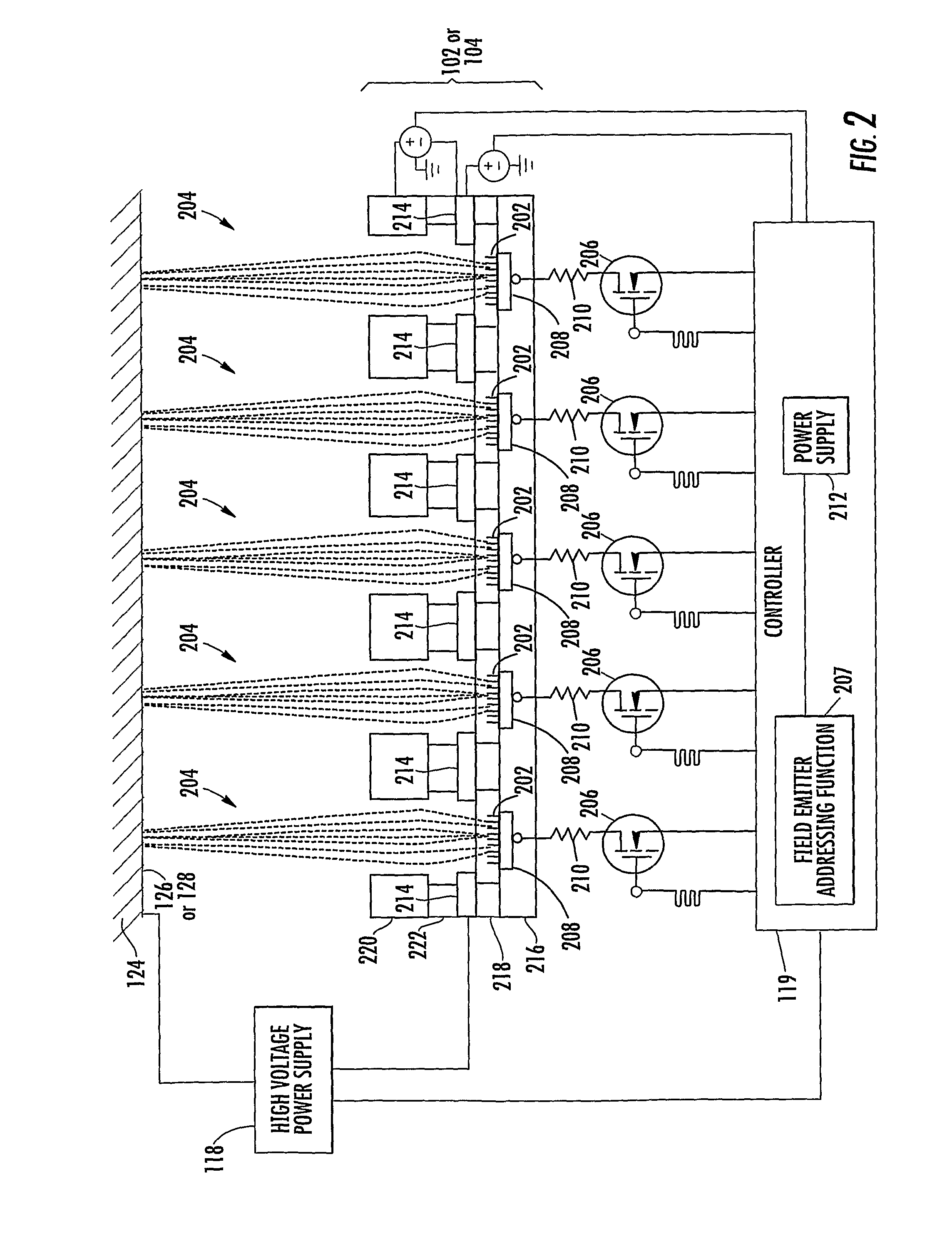
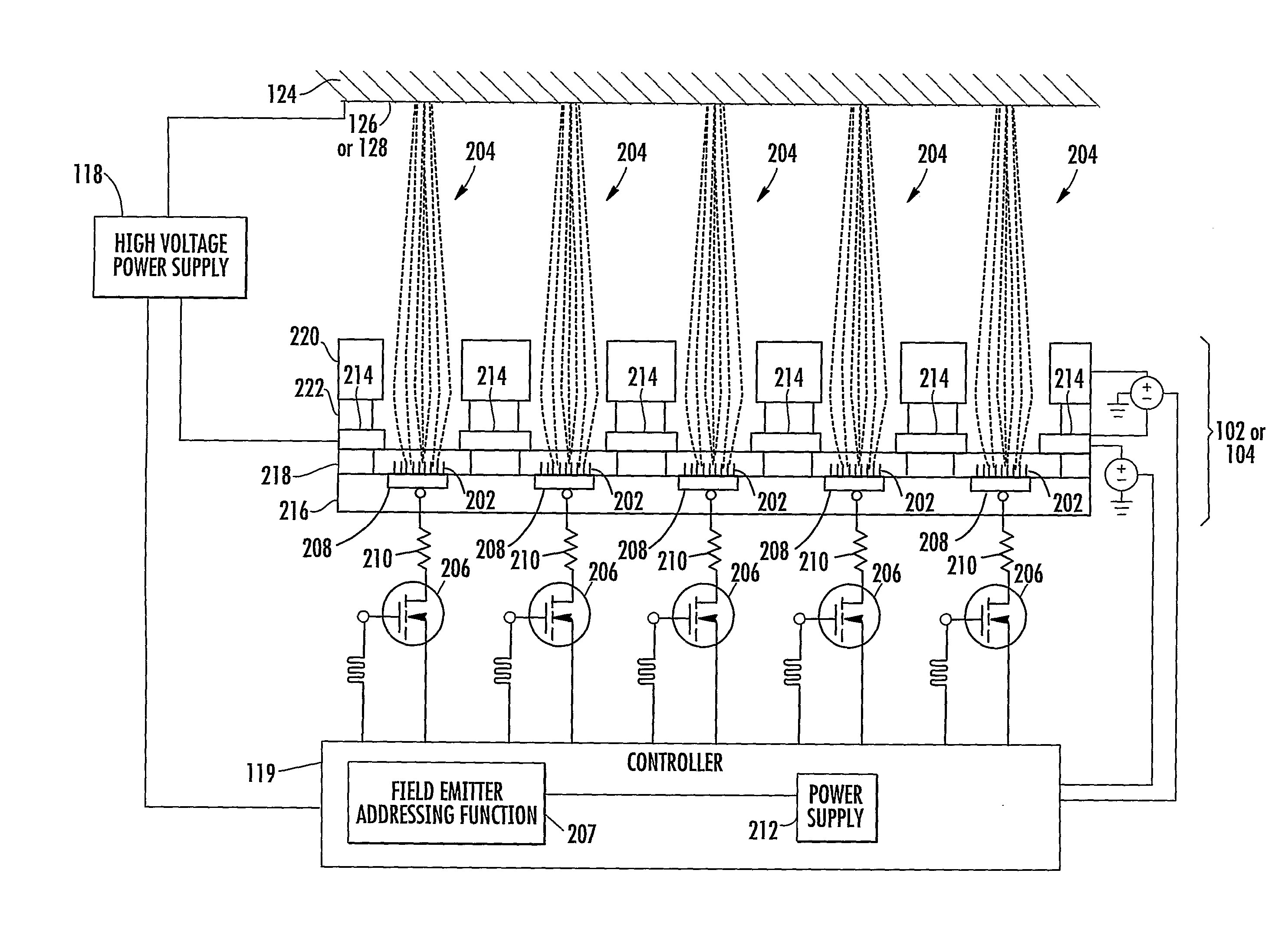
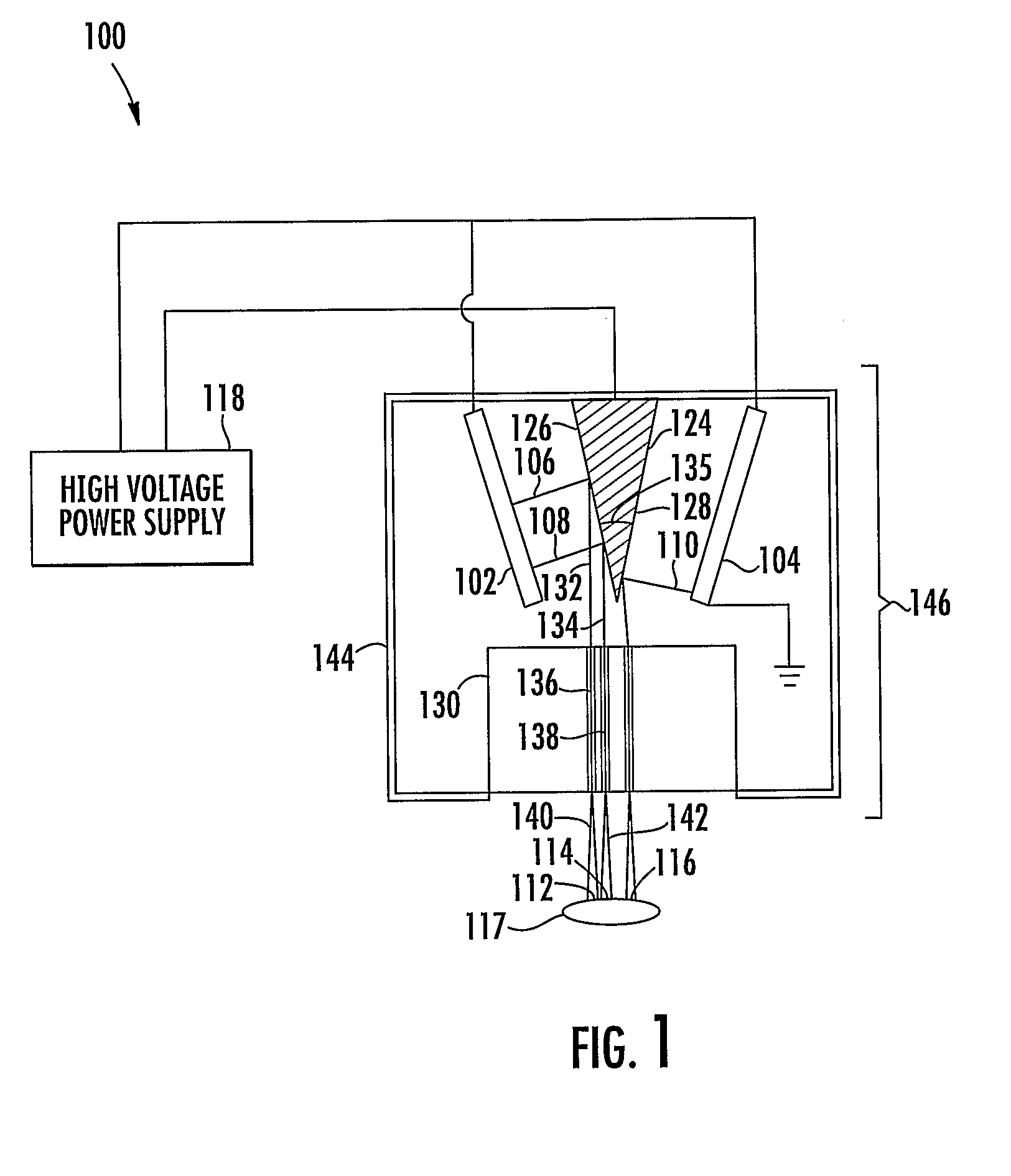
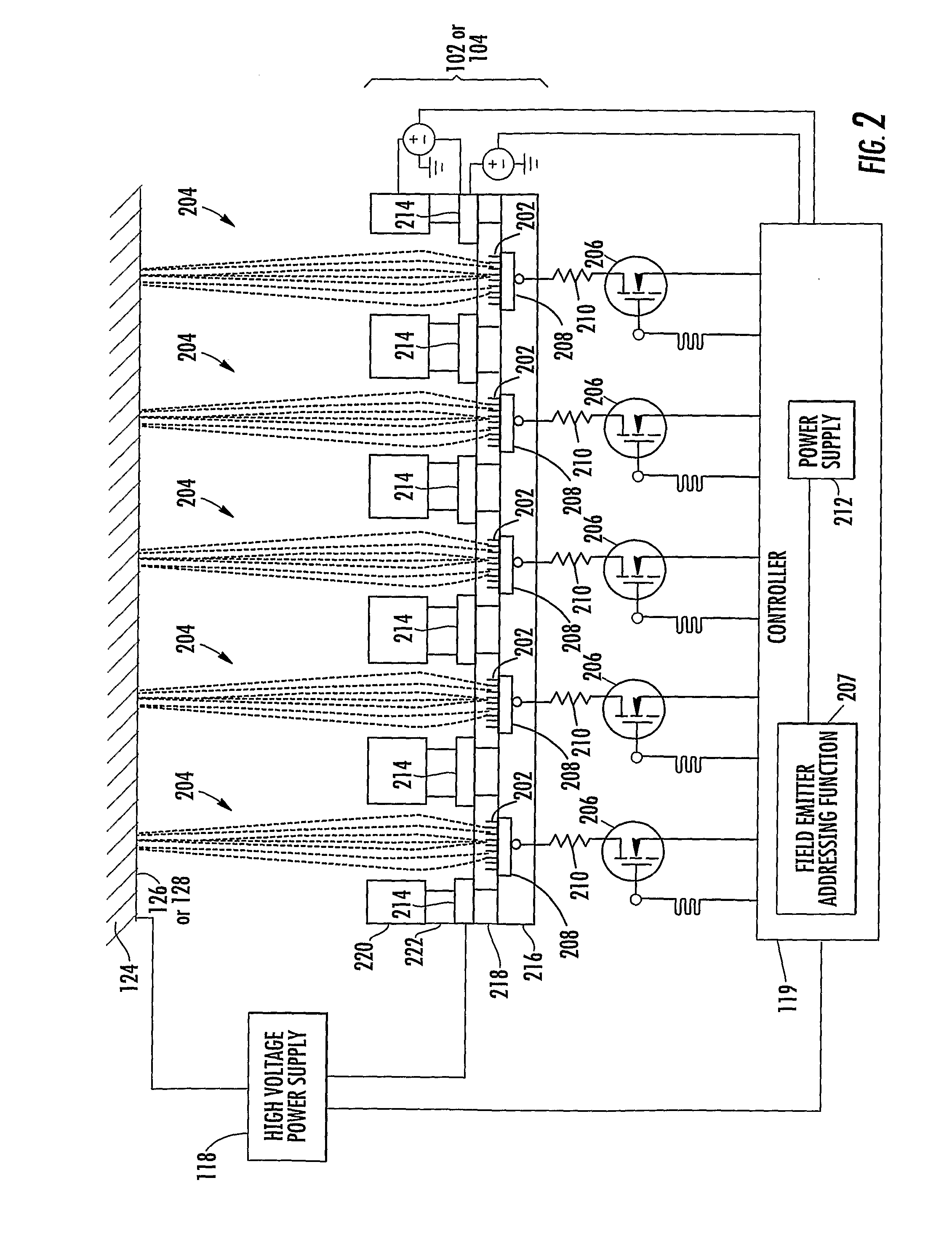
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulating radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy are disclosed. One exemplary pre-clinical system may include addressable electron field emitters (102, 104) that are operable to emit a plurality of electron pixel beams (106, 108, 110). Each electron pixel beam may correspond to an x-ray target (124) and x-ray pixel beam collimation aperture (136, 138) to convert a portion of energy associated with the electron pixel beam to a corresponding x-ray pixel beam (140, 142). Further, the x-ray pixel beam array collimator (130) forms a one-to-one correspondence between individual electron pixel beam and its corresponding x-ray pixel beam. One exemplary clinical system may include a high-energy electron source (1203), an n-stage scanning system (1210), x-ray pixel beam targets (1212), and an x-ray pixel beam array collimator (1214). A controller (1206) may sequentially direct electron beam pulses to predetermined x-ray pixel targets and produce an electronically controlled radiation field direction, pattern; and intensity pattern.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulation radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy
ActiveUS20100260317A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray tube with very high currentSoft x rayElectron source
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulating radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy are disclosed. One exemplary pre-clinical system may include addressable electron field emitters (102, 104) that are operable to emit a plurality of electron pixel beams (106, 108, 110). Each electron pixel beam may correspond to an x-ray target (124) and x-ray pixel beam collimation aperture (136, 138) to convert a portion of energy associated with the electron pixel beam to a corresponding x-ray pixel beam (140, 142). Further, the x-ray pixel beam array collimator (130) forms a one-to-one correspondence between individual electron pixel beam and its corresponding x-ray pixel beam. One exemplary clinical system may include a high-energy electron source (1203), an n-stage scanning system (1210), x-ray pixel beam targets (1212), and an x-ray pixel beam array collimator (1214). A controller (1206) may sequentially direct electron beam pulses to predetermined x-ray pixel targets and produce an electronically controlled radiation field direction, pattern; and intensity pattern.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Fiber coupling module of high-power semiconductor laser
InactiveCN101833150ASolve the lack of spaceAdequate cooling spaceCoupling light guidesLight beamPrism
The invention relates to a fiber coupling module of a high-power semiconductor laser, which comprises a plurality of single-tube semiconductor lasers with the same wavelength in the same polarization state, beam collimation lenses, a glass flat plate, reflecting prisms and a focusing device, wherein expect one path of the single-tube semiconductor lasers, the other single-tube semiconductor lasers are all parallel to an axis x and arrayed in a ladder shape; the beam collimation lenses are arranged in front of each single-tube semiconductor laser, and the light emitted by each single-tube laser passes through a beam collimation lens and then passes through a reflecting prism; each reflecting prism keeps consistent with a single-tube laser corresponding to the reflecting prism on the horizontal height; the light emitted by the plurality of single-tube lasers is transmitted to the focusing device through reflecting; and beams emitted by the single-tube lasers arranged in the direction of an axis z is directly transmitted to the focusing device through gaps among the plurality of the reflecting prisms and then combined with other beams to focus together and then enter a fiber. In the invention, the distances of the welding positions of each single-tube laser become longer, and the high-power semiconductor laser fiber coupling module has easy welding, convenient debugging, good heat radiating effect and high coupling efficiency.
Owner:吉林省长光瑞思激光技术有限公司
Light path collimation integrated device and method for high-power laser device
InactiveCN102354055AAchieving Simultaneous SamplingHigh resolutionOptical elementsGratingHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a light path collimation integrated device and method for a high-power laser device. A transmission grating engraved with references is put near to the small-hole face of a space filter; the transmission grating is irradiated by parallel non-coherent illumination lights produced by a light emitting diode and an illumination collimation lens at a specific angle; a sampling light path is put in a direction of first-stage diffraction light of the transmission grating so as to form a light beam information monitor; the light beam information monitor simultaneously acquiresinformation of a near field and a far field of a light beam; the output of the light beam information monitor is connected to a computer; deviation values of the near field and far field of the lightbeam relative to the respective set positions are determined through an image processing technology; and a corresponding near field adjusting device and a corresponding far field adjusting device areselected according to the respective deviation values so as to adjust light path collimation. The light path collimation integrated device has the characteristics of integration, modularization, simple structure and high precision, and can meet a monitoring requirement of the high-power laser device on large-aperture light beam collimation.
Owner:上海激光等离子体研究所
Super-resolution confocal microimaging method and device based on column polarization vortex beam
The invention provides a super-resolution confocal microimaging device based on a column polarization vortex beam. The super-resolution confocal microimaging device comprises a pinhole filter, a collimating lens, a polarization and phase transformation system, a pupil filter, an optical filter, a detector and a three-dimensional translational platform, wherein a beam emitted from a laser passes the pinhole filter to obtain a Gauss basic mode beam, the collimating lens collimates the Gauss basic mode beam into the parallel beam, the polarization and phase transformation system allows the parallel beam to pass and obtain the column polarization vortex beam with preset polarization and phase distribution, the pupil filter allows the column polarization vortex beam to pass and to be reflected through a beam splitter and focused on a to-be-detected sample through a collecting lens, light signals reflected from the sample pass the collecting lens and the beam splitter to be incident on the optical filter, and the optical filter only allows a fluorescence signal of the light signals to be transmitted, the fluorescence signal is focused on a detecting pinhole through the collecting lens and is detected and converted, through the detector, into an electrical signal to be output, the sample is placed on the three-dimensional translational platform, detection of the sample at different positions can be realized by moving the three-dimensional translational platform, and accordingly three-dimensional scanning imaging of the sample can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Four-dimensional spectral imaging system and method for calculating correlation flight time by means of sparse aperture compression
ActiveCN103472455ALow costReduce system complexityElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpot synthesisIsochronous signal
The invention relates to a four-dimensional spectral imaging system for calculating correlation flight time by means of sparse aperture compression. The four-dimensional spectral imaging system comprises a pulse light source emission unit, an expanded beam lens, a fourth collimating lens, a random optical modulation unit, a total-reflection mirror, a polarized light beam splitter, a first lens, a beam spot synthesis unit, a sparse aperture unit, a free space collimation unit, a beam reflection unit, an expanded beam collimation unit, a spectral beam split unit, a convergence light receiving lens, a linear array detector, a flight time correlation unit and a compression calculation correlation algorithm module. The sparse aperture unit comprises at least three secondary telescope lenses, the free space collimation unit comprises at least three collimating lenses, and the beam reflection unit comprises at least three reflection mirror groups; one secondary telescope lens, one collimation lens and one reflection mirror form a light path; the flight time correlation unit comprises a pulse width regulation unit, an adjustable delay unit and a synchronous signal source.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Double-layer multi-blade collimator
ActiveCN102915784AImprove work efficiencyImproved edge doseHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyHigh frequency modulationMicro motor
The invention belongs to the field of medical equipment, is used for the intensity modulated radiation therapy of tumors and particularly relates to a double-layer multi-blade collimator. The double-layer multi-blade collimator comprises a switching multi-blade collimator on the upper layer and an electric multi-blade collimator on the lower layer; both the switching multi-blade collimator and the electric multi-blade collimator consist of two groups of opposite blades; the front end face of each blade of the switching multi-blade collimator is a straight end face and the rear end of the blade of the switching multi-blade collimator is connected with a micro electromagnetic driving mechanism; each blade of the electric multi-blade collimator is driven by a micro motor; and the blades of the switching multi-blade collimator and the blades of the electric multi-blade collimator move, are laid out in the same direction and have the same numbers. The double-layer multi-blade collimator is applied to a tumor intensity modulated radiation therapy device and has the advantages of simple structure, beam collimation, high working efficiency, high frequency modulation resolution and high safety.
Owner:SHINVA MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
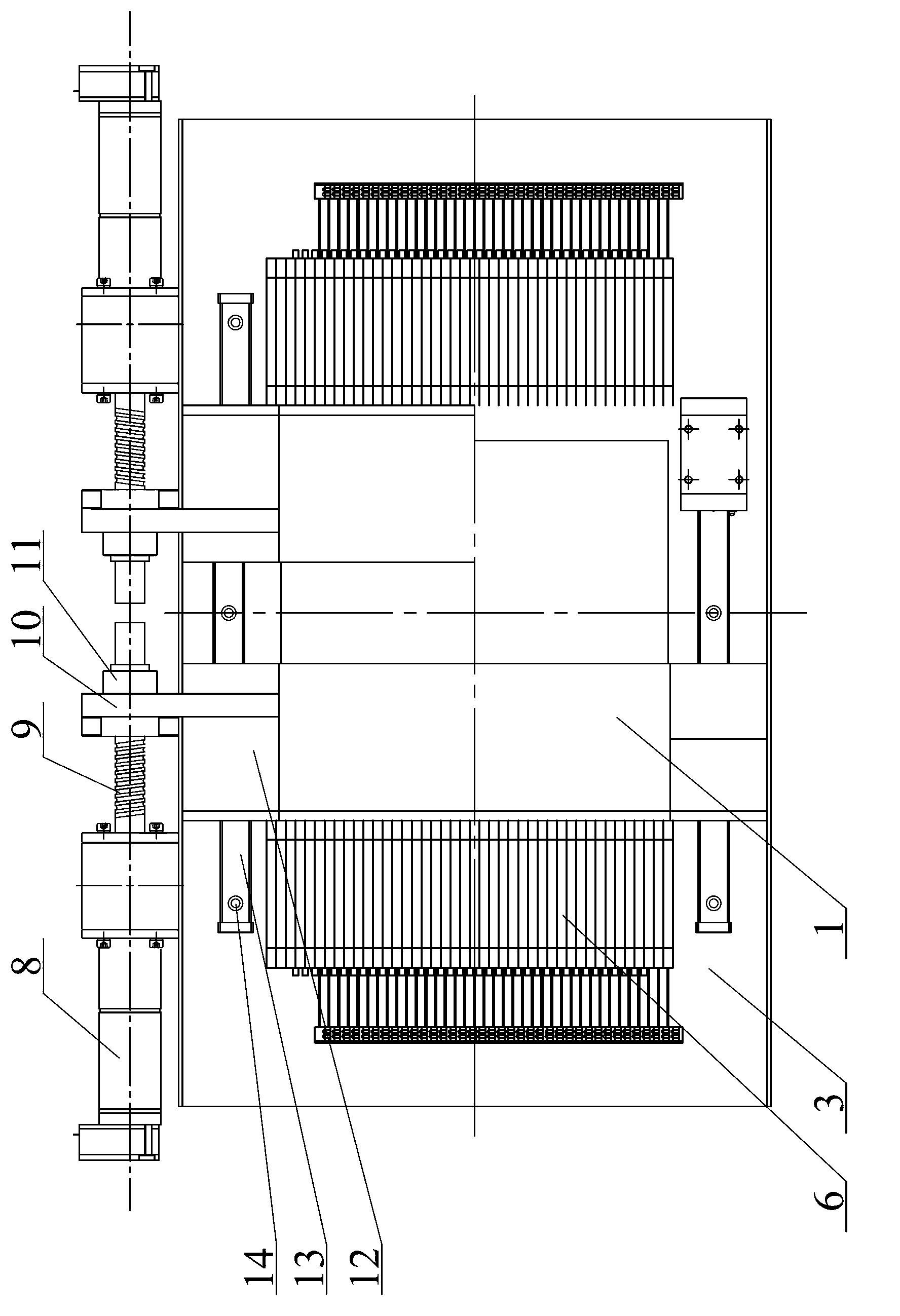
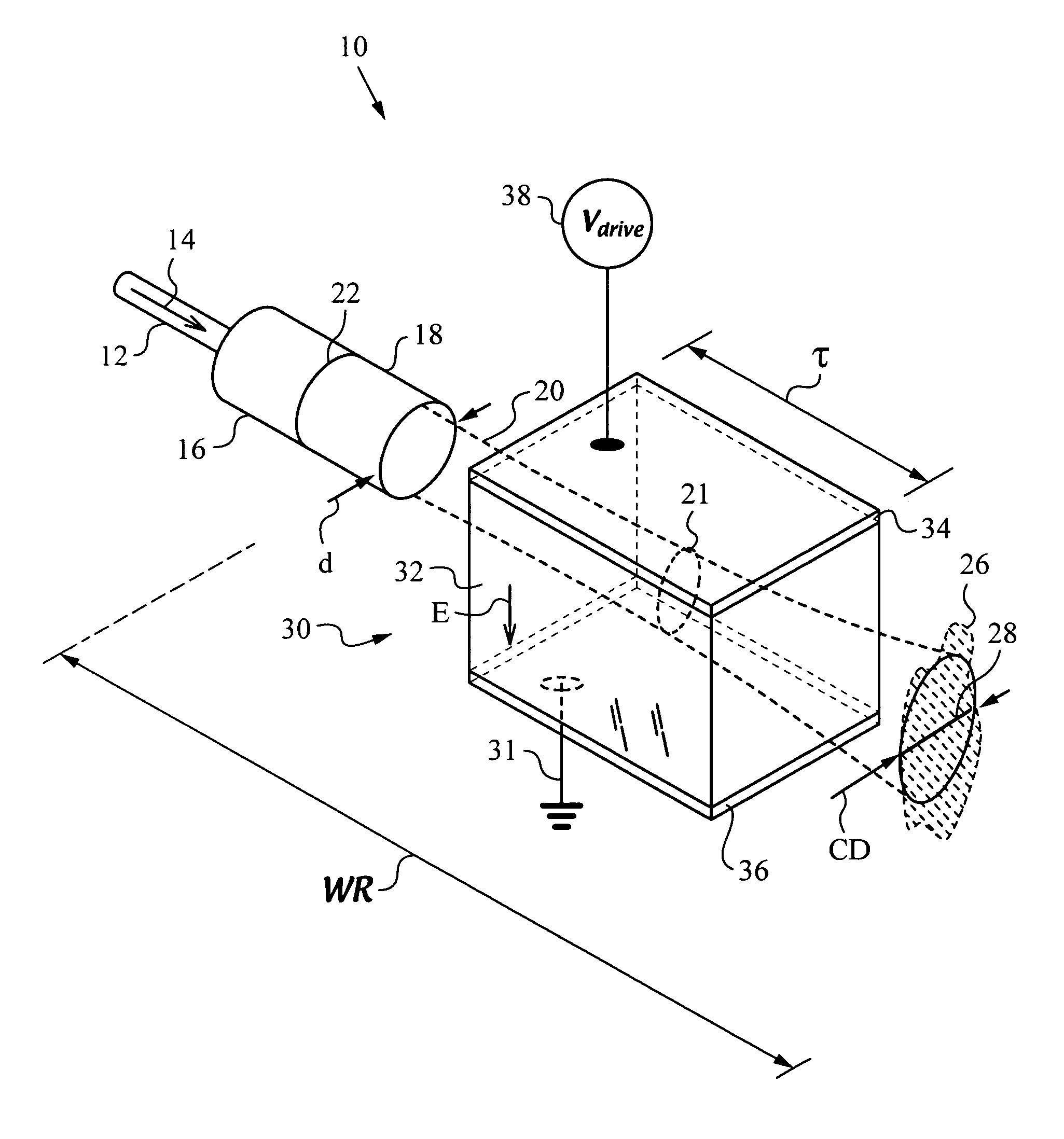
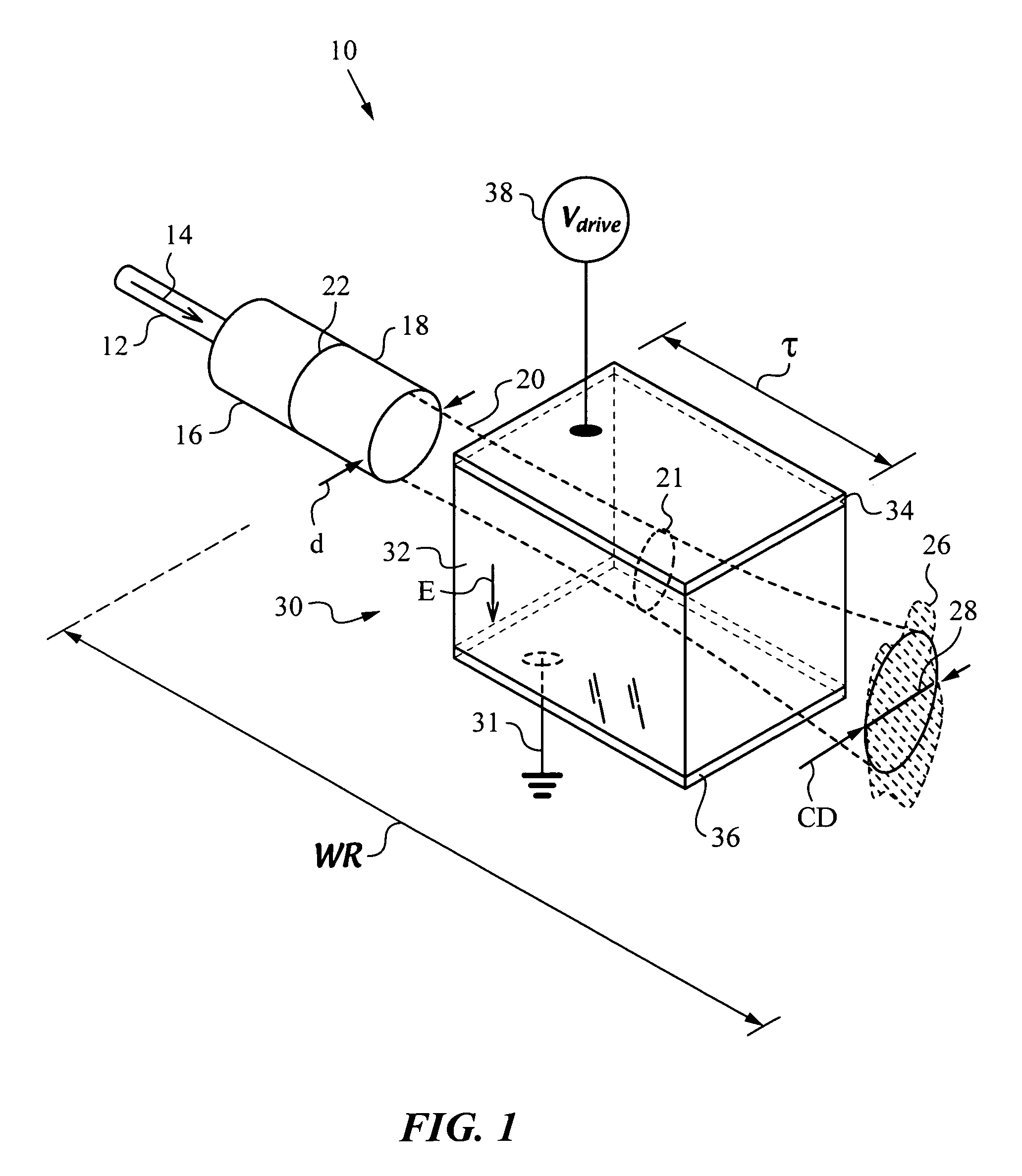
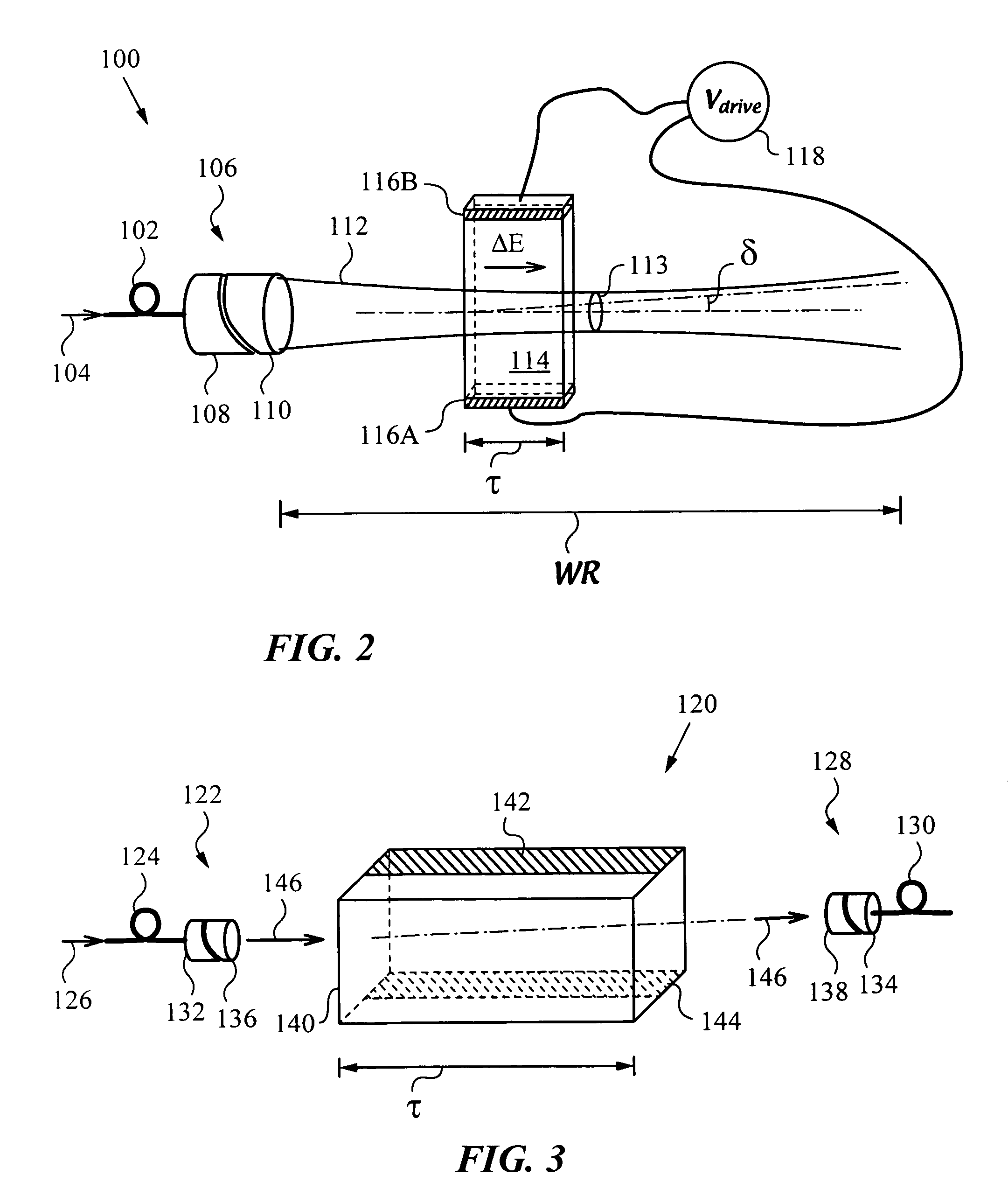
Fiberoptic reconfigurable devices with beam shaping for low-voltage operation
An apparatus and method to operate on a light beam by using a lens that collimates the light beam to a collimated beam with at least one cross-sectional dimension less than a critical dimension of 400 μm or less over a working range WR. The apparatus has a bulk electro-optic material of small thickness τ, e.g., less than 300 μm positioned within working range WR and the collimated beam traverses it along its path. The apparatus has a voltage source for applying a low operating or drive voltage Vdrive, e.g. less than 400 V to the bulk electro-optic material for performing an operation on the collimated beam. The lens for collimating the light beam is a free-space collimator such as a graded index (GRIN) lens or preferably a C-lens. The apparatus is a versatile and scalable platform that can be employed in building various electro-optic devices.
Owner:AGILTRON
Extended cavity laser device with bulk transmission grating
ActiveUS7177340B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingLight beam
A laser apparatus is disclosed utilizing a laser diode having a reflective back facet and a front facet having a reflectance of less than about 1% for emitting an optical beam at a fundamental frequency along an optical path. A collimating lens is provided for collimating the optical beam into a collimated beam. A transmission grating is optically coupled to receive the collimated beam and returns a portion of the collimated beam back into the laser diode by means of diffraction through lens and the laser diode front facet. The laser diode reflective back facet and the transmission grating form an extended laser cavity. In operation, a substantial portion of the collimated beam is transmitted through the transmission grating for producing the laser output beam propagating along the optical path.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Method for implementing beam alignment and uniformization and optical device
The invention discloses a method used for realizing beam collimation and uniformity, and the method comprises the following steps: the first surface of an optical element receives an input and divergent Gaussian beam, and diverges the beam, wherein the first surface has a spherical surface or an aspheric surface; and the second surface of the optical element resets the phase of the beam diverged by the first surface, and obtains a collimated and uniformly distributed flat top beam, wherein the second surface has an aspheric surface. The invention also discloses an optical element which adopts the least optical devices to finish the uniformity and the collimation of the diverged Gaussian beam, thereby avoiding the complex debug of the optical devices, and saving the use cost and the manufacturing cost.
Owner:深圳市高昆通讯设备有限公司
System and method form monitoring side-mode suppression ratio and channel stability of tunable laser
ActiveCN102751656AGuarantee stabilityStable laser characteristicsLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersBeam splitterMonitoring system
The invention discloses a system and a method for monitoring side-mode suppression ratio and channel stability of a tunable laser and relates to the device and the method for monitoring the dominant frequency and side-mode power of the laser through a sampling etalon to judge spectral quality and channel stability of the laser so as to carry out effective control. The monitoring system disclosed by the invention mainly comprises the tunable laser composed of a gain medium, a coupling optical part, a fixed lattice filter, a tunable filter and a reflective optical part, a beam collimation lens, an opto-isolator, a beam splitter component, an F-P (fabry-Perot) etalon, an optical detector, a coupling output lens, a controller, etc. Through a plurality filters outside a laser cavity and a photoelectric detection structure, wavelength lock is carried out; the spectral quality is evaluated; the tunable filter is timely adjusted and controlled; the lasing wavelength is stabilized in the required channel all the time, and good enough spectral quality is achieved. The monitoring system is suitable for online spectral quality monitoring in work of the laser and possible drift correction resulting from switching of the filter inside the cavity.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Trajectory Optimization in Radiotherapy Using Sectioning
ActiveUS20170354832A1Avoids degradation of trajectory optimization qualityOptimal trajectoryX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPatient modelBeam trajectory
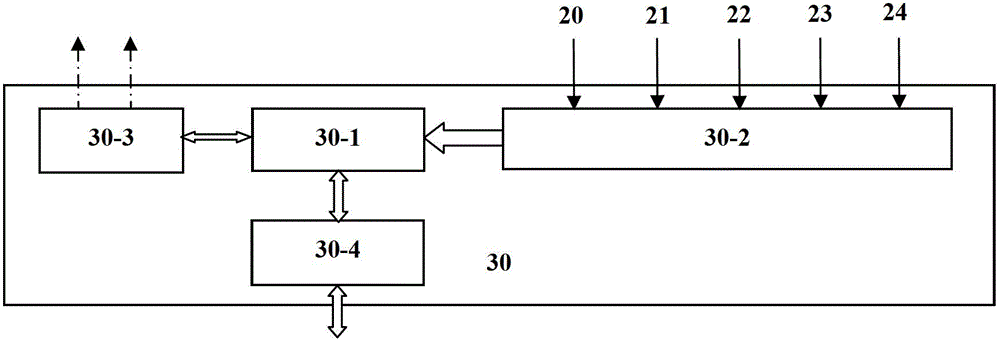
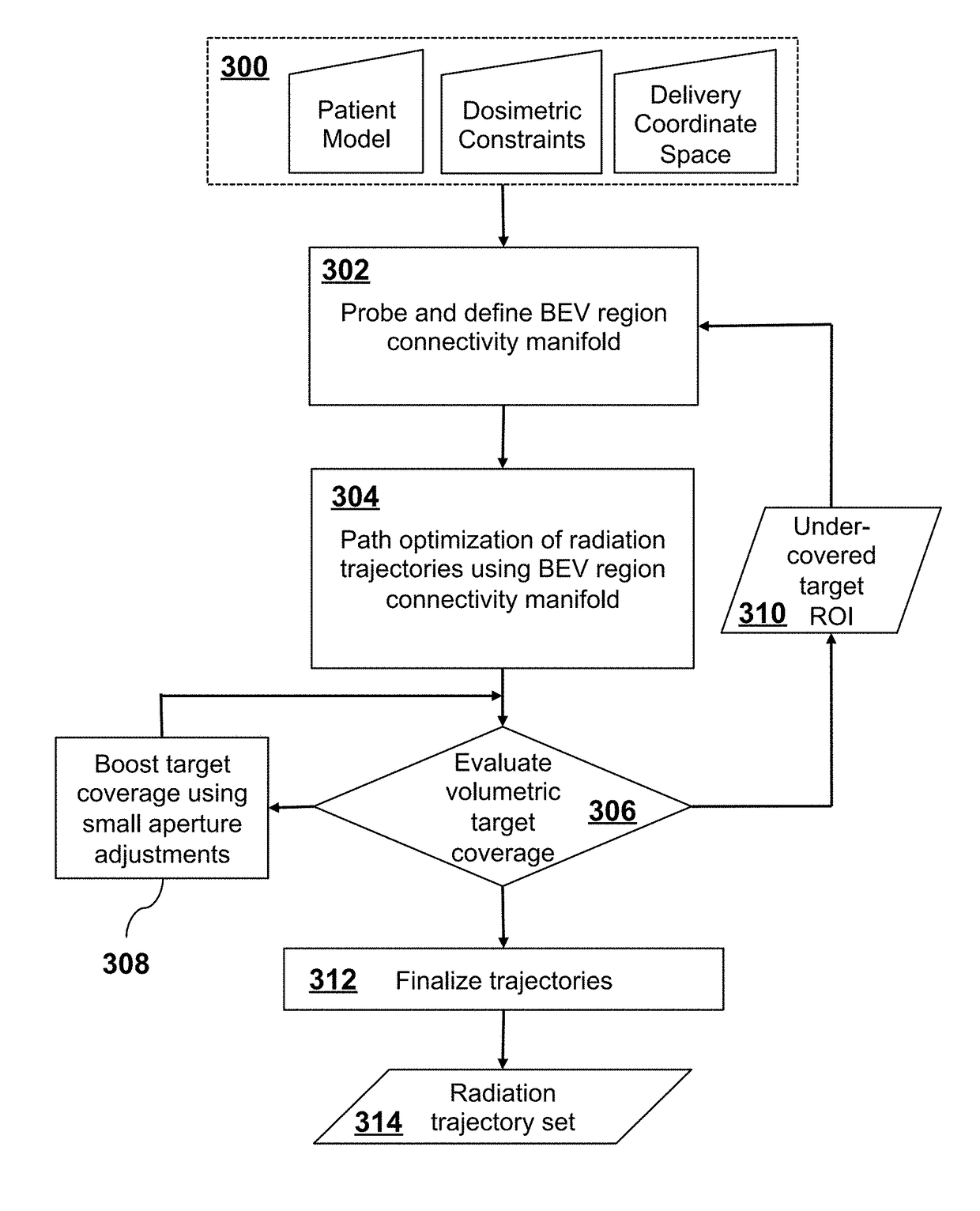
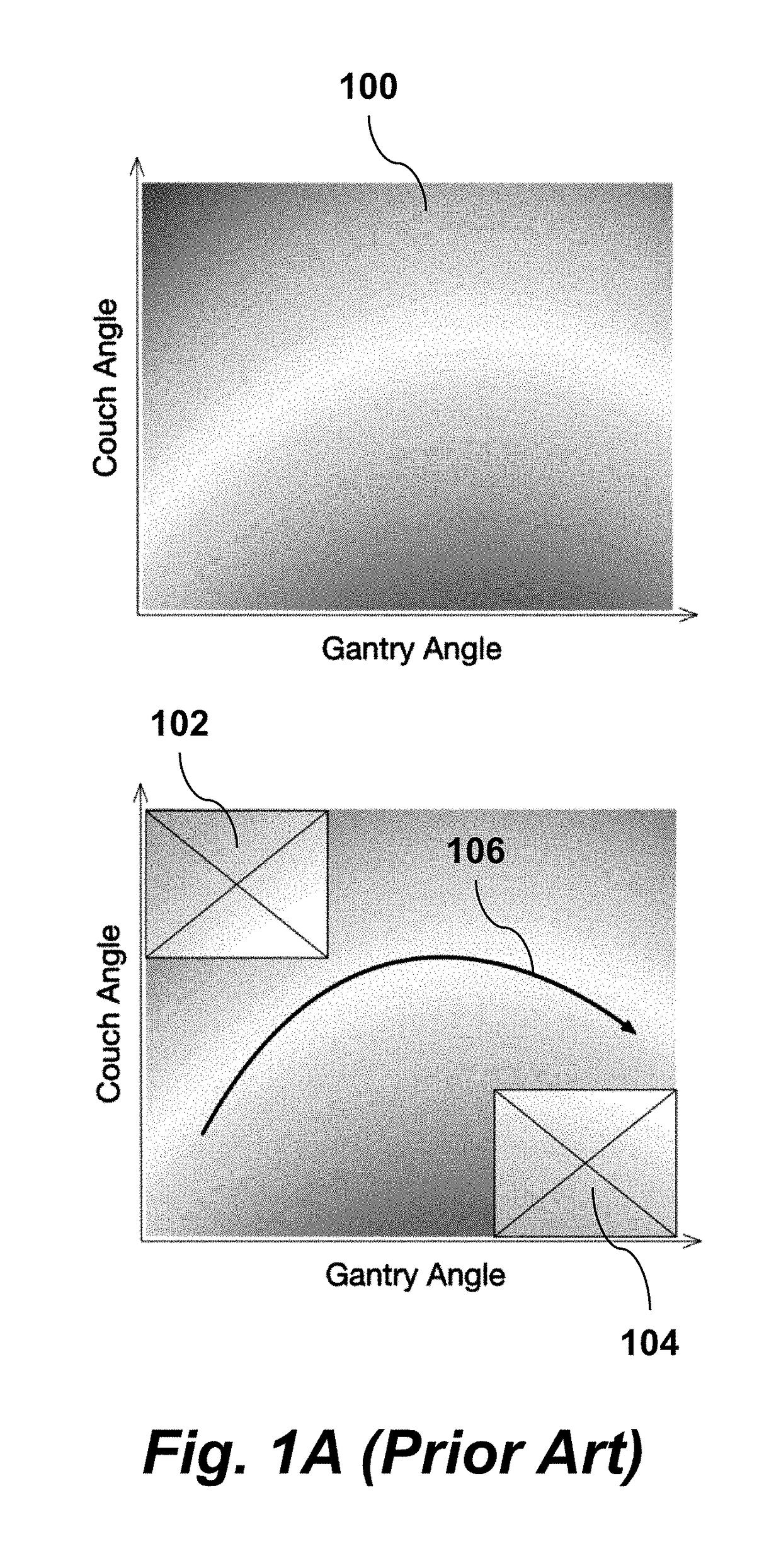
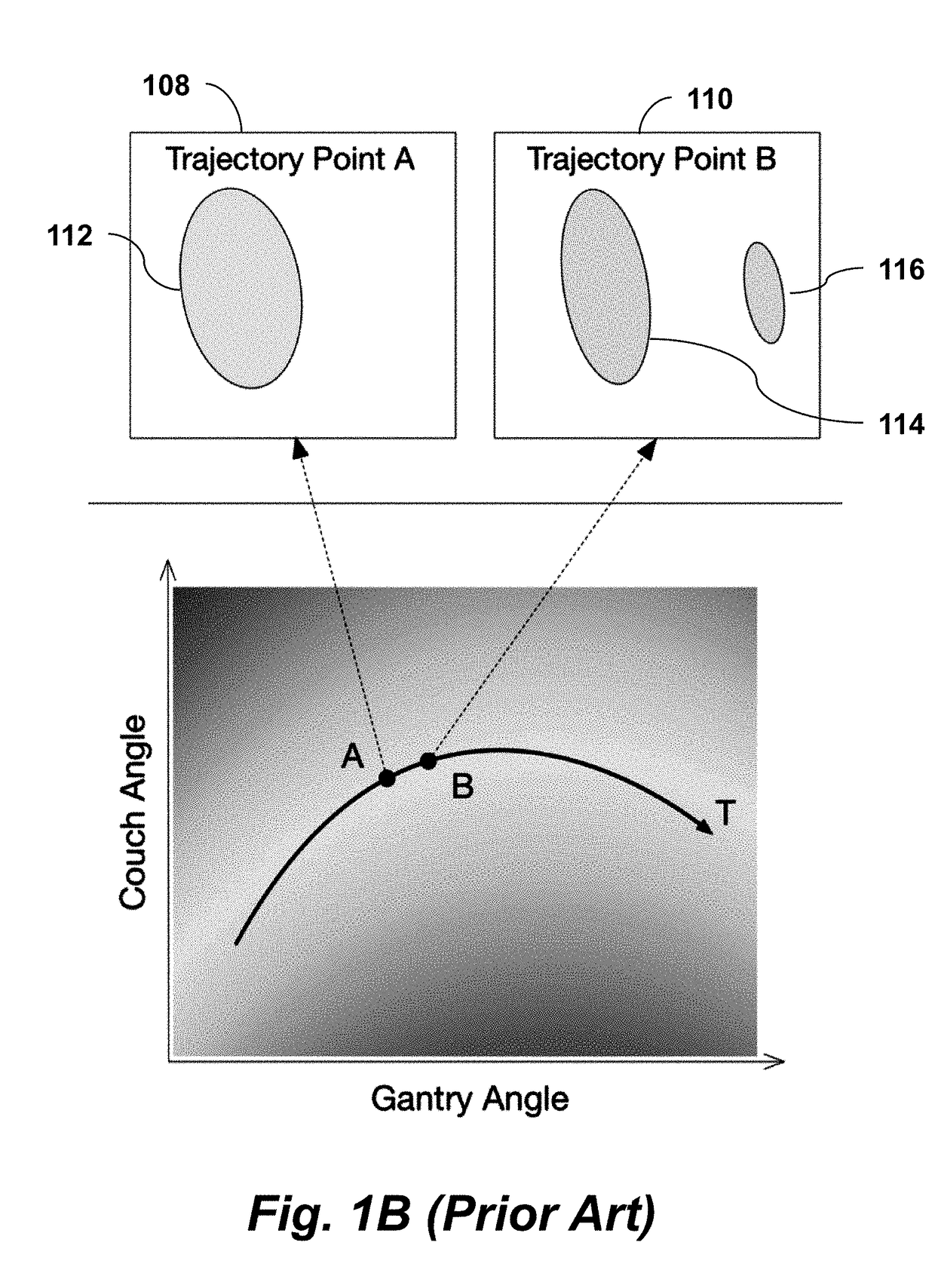
A radiation therapy treatment method includes providing a patient model, dosimetric constraints, delivery motion constraints, and delivery coordinate space of a radiation delivery device, where the delivery coordinate space is represented as a mesh with vertices connected by edges, where the vertices correspond to directions of a beam eye view (BEV) of the radiation delivery device, where each BEV has corresponding area elements resulting from beam collimation. BEV region connectivity manifolds are constructed from the patient model, the dosimetric constraints, the delivery coordinate space, and existing beam trajectories, wherein each of the BEV region connectivity manifolds represents connections between contiguous 2D target regions, where each of the 2D target regions is defined at each of the vertices of the delivery coordinate space. Beam trajectories are selected based on region connectedness information in the BEV region connectivity manifolds, the dosimetric constraints, the delivery motion constraints, and the existing beam trajectories. Radiation is delivered using the radiation delivery device in accordance with the beam trajectories.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Collimating and beam expanding device for semiconductor laser sources of laser radar
ActiveCN103633557AGood collimationGuaranteed divergence angle requirementsLaser output parameters controlOptical elementsDivergence angleRandom vibration
The invention discloses a collimating and beam expanding device for semiconductor laser sources of a laser radar. The collimating and beam expanding device is mainly composed of an aspherical lens, a quartz positive lens, a tunable flange and the like. The collimating and beam expanding device is simple in structure, low in cost and good in beam collimation performance, a divergence angle of a semiconductor laser is compressed from 0.2X0.4rad to below 0.2mrad, and the requirement of the laser radar for probing light sources is met; the device is stable in optical and mechanical properties, can be used under level-18 random vibration at the environment temperature from minus 30 DEG C to minus 50 DEG C, and meets the requirement of the laser radar on stability in bad conditions; the device is provided with the flange, semiconductor laser sources different in divergence angle can be obtained by fine tuning of the flange of the beam expanding device; by tuning of the flange, the device can also be applied to beam collimation of other different-wavelength light sources.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light shaping reflector system and method of manufacture and use
InactiveUS7578605B1Maximize lightFill the subject area with luminanceLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusLight beamEngineering
A reflector system having two-axis control through which beam collimation and wide-angle beam overlapping occur, and a method of manufacturing such a system through cutting flat reflective sheeting and forming the resultant flat parts into the three-dimensional reflectors that collect and shape the light from solid state LEDs, wherein each axis may be customized by changing the cutting and bending of the flat pieces.
Owner:INTENCITY LIGHTING
Beam expander
A laser beam includes a concave or convex mirror which is reflective for wavelength of the high intensity beam. The reflective mirror is located along a preselected path of a high intensity laser beam so that the high intensity laser beam intersects the mirror at a first position. A beam collimator is located in the path of the high intensity beam reflected by the concave or convex mirror. The concave or convex mirror is movably mounted desirably rotatably mounted in the path of the high intensity beam. Desirably the mirror is rotated about a preselected axis. Desirably, the axis is selected so that when the mirror is rotated to a new position, the high intensity beam will be reflected along the same path to the collimator as it was prior to any rotation.
Owner:PHOTONICS IND INTERN
Atom magnetometer without response blind area and method for measuring external magnetic field by employing same
ActiveCN108287322AEfficient detectionSimple stepsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesSpin angular momentum of lightHelmholtz coil
The present invention provides an atom magnetometer without a response blind area. The atom magnetometer comprises a laser, an expanded beam collimation device, a circularly polarized light conversiondevice, an acoustic optical modulator, an Helmholtz coil, an atom air chamber, a reflector set, a photoelectric detector, a lock-in amplifier, a signal processing system and a heating device. The atom magnetometer is simple in structure; and two exciting methods which apply an excitation magnetic field and perform light modulation are combined, and components of the total spin angular momentum ofa sensing atom in two directions are detected to achieve measurement of a blind area without response. The present invention further discloses a method for measuring an external magnetic field by employing an atom magnetometer without response blind area and method. The measurement method is simple, has no response blind area, can rapidly and accurately obtain related data of an external magneticfield, and is high in practicability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Online energy dispersive X-ray diffraction analyser
ActiveUS20100303206A1Reduce background scatterReduce voltageX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayMaterial scattering
An on-line EDXRD analyser including (i) a housing defining an analysis zone and having a passageway through it to allow transport of material in a process stream to pass through the analysis zone, (ii) a collimated source of polychromatic X-rays, (iii) an energy-resolving (ER)X-ray detector, (iv) a primary beam collimator disposed between the source of X-rays and the (ER)X-ray detector comprising an annular slit which defines an incident beam of polychromatic X-rays to irradiate a portion of the analysis zone, (v) a scatter collimator disposed between the primary beam collimator and the ERX-ray detector, the scatter collimator comprising an annular slit which defines a diffracted beam of X-rays scattered by the material to converge towards the ERX-ray detector, and (vi) a detector collimator comprising a conical opening which further defines the diffracted beam of X-rays scattered by the material. The ERX-ray detector measures an energy spectrum of the diffracted X-rays at a predetermined diffraction angle defined by the relative positioning of (ii) to (vi), and where one of (iv) and (v) comprises an aperture arranged to enable a detector to measure the transmission of a direct beam of X-rays through the material.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
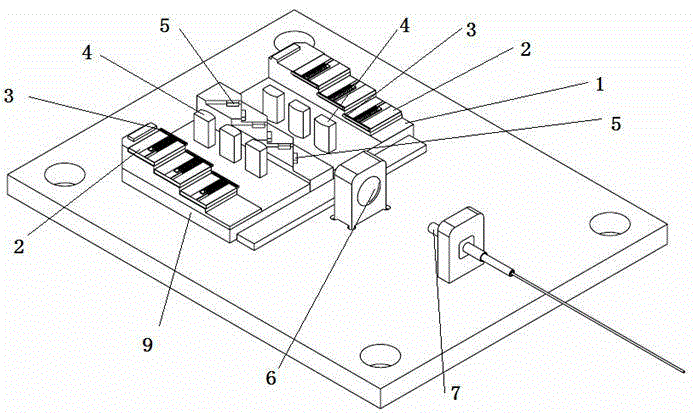
Optical emitter and optical module
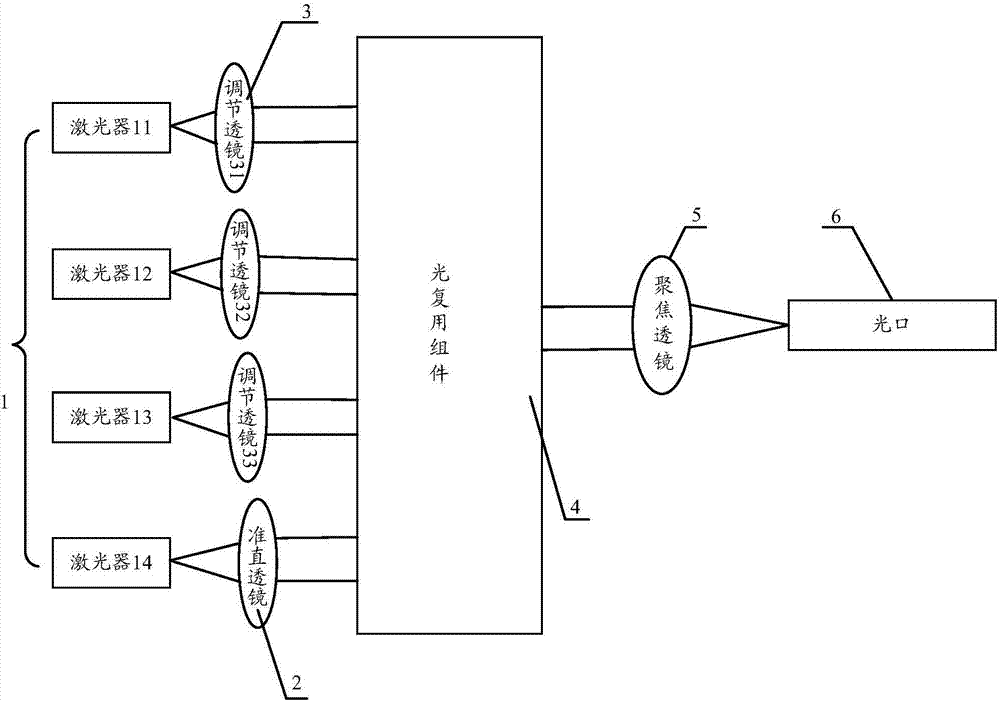
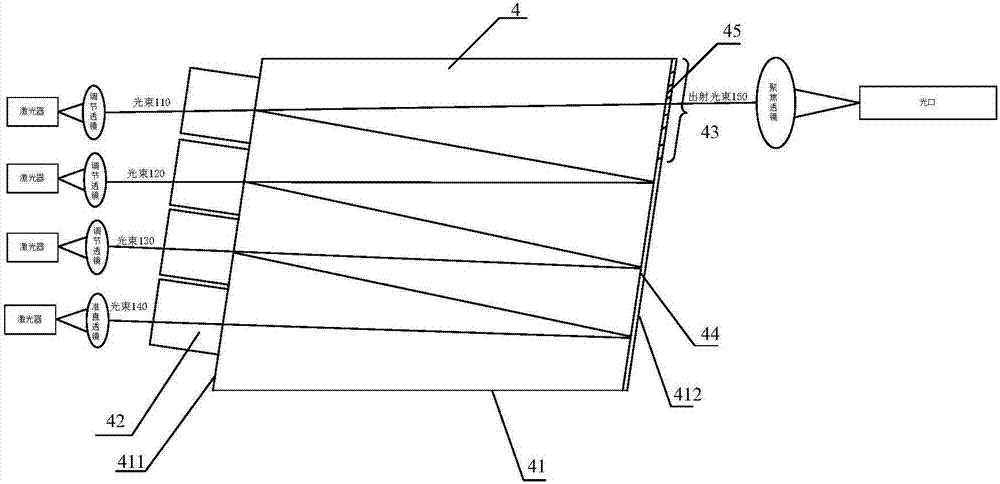
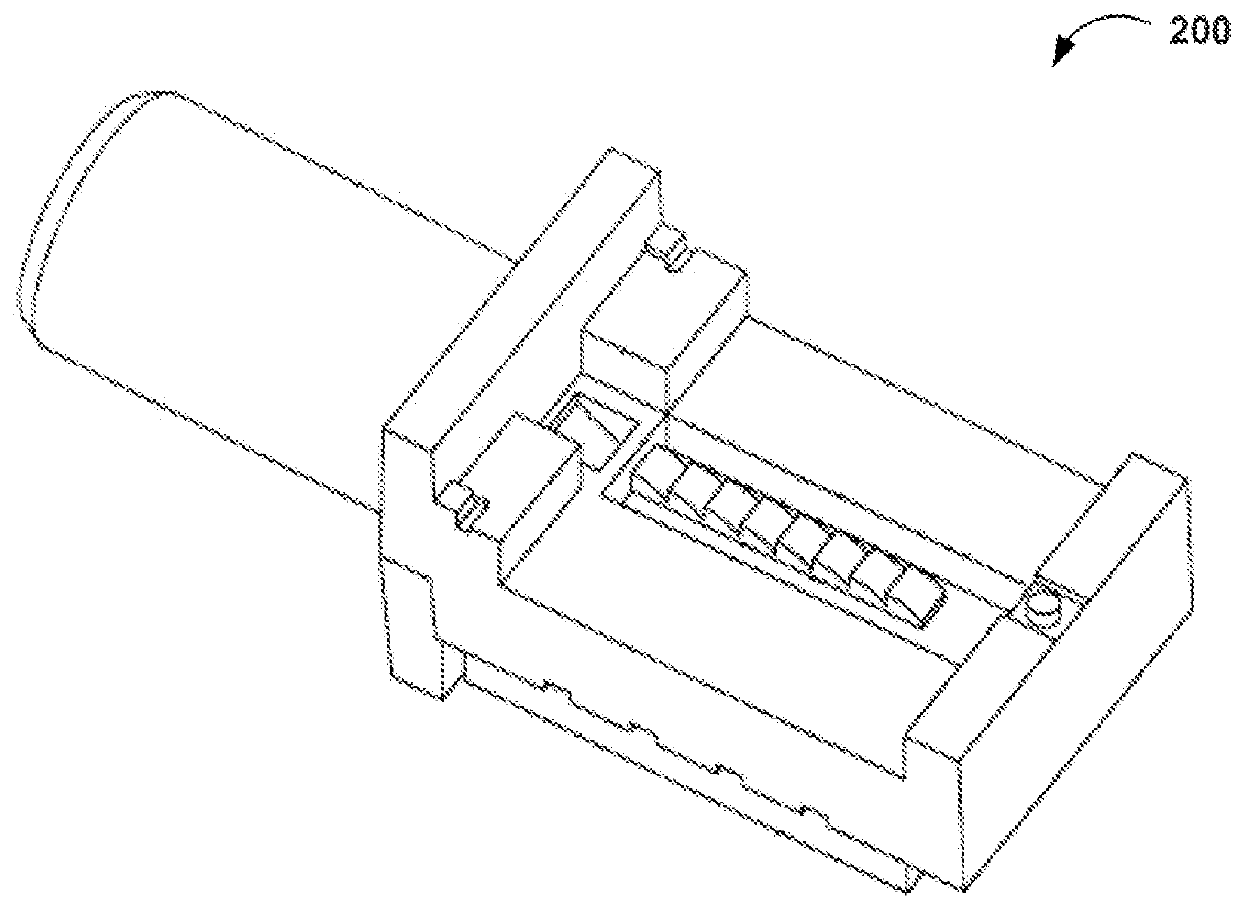
InactiveCN107577015AGuaranteed optical powerShort coupling timeCoupling light guidesOptical ModuleLaser array
The invention provides an optical emitter and an optical module. The optical emitter comprises a laser array, a collimating lens and adjustment lenses; the collimating lens is arranged on the emissionoptical path of one laser, the adjustment lenses are arranged on the emission optical paths of other lasers, and the collimating lens and the adjustment lenses are distributed in a non-linear mode inthe array direction; an optical multiplex component which synthetizes multiple paths of light beams into a path of light beam is arranged on the emergence optical paths of the collimating lens and the adjustment lenses, a focusing lens is arranged on the emergence optical path of the optical multiplex component, and an optical port is formed in the emergence optical path of the focusing lens; thecollimating lens is used for collimating light beams emitted by the lasers and making the collimated light beams irradiate into the optical port through the optical multiplex component and the focusing lens; the adjustment lenses are used for making the light beams emitted by the lasers irradiate into the optical multiplex component in the mode parallel to the collimated light beams. The opticalemitter and the optical module are high in yield and short in coupling time.
Owner:HISENSE BROADBAND MULTIMEDIA TECH
WDM multiplexing/de-multiplexing system and the manufacturing method thereof
A WDM multiplexing / demultiplexing system includes a de-multiplexer configured to separate and guide light beams from an incident ray having a plurality of wavelengths to corresponding lenses on an optical device, a multiplexer configured to guide light beams from optical transmitters having various wavelengths through the corresponding lenses on the optical device and combine the light beams, a lens array including the corresponding lenses to receive and / or transmit the light beams from or to the de-multiplexer and multiplexer, and a light beam collimator configured to function with the multiplexer and de-multiplexer. The light beams received or transmitted by the light beam collimator and the light beams transmitted or received from or to the multiplexer and de-multiplexer are collinear. The light beam collimator and multiplexer / de-multiplexer can be easily positioned to predetermined or designed positions, thereby providing light beams output through the lenses in a plastic optical device. The WDM system advantageously reduces optical signal loss, while increasing the assembly yield.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS
Printing system of holographic stereogram and with abnormal-shaped mask plate
ActiveCN103425035AAvoid cumbersome calculationsImprove print output speedInstrumentsBeam splitterSpatial light modulator
The invention belongs to the technical field of holographic printing and three-dimensional display and particularly relates to a printing system of a holographic stereogram and with an abnormal-shaped mask plate. The printing system is formed by a laser light source, a beam splitter, an expanded beam collimation system, a spatial light modulator, a computer, a total reflection lens, a focusing lens, hologram recording materials, the abnormal-shaped mask plate, a target object and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera. A transformation parallax image of the target object is obtained through the CCD camera and the computer and loaded into the spatial light modulator, a light beam which is emitted from the laser light source is modulated, interference is produced between the modulated light beam and the other laser beam which is reflected by the beam splitter, the two light beams penetrate the abnormal-shaped mask plate to be exposed and recorded on the holographic recording materials, and accordingly printout of the holographic stereogram of the target object is achieved. The printing system of the holographic stereogram and with the abnormal-shaped mask plate has the advantages of being capable of effectively improving the printout speed of the hologram, solving the problem of frequency spectrum leakage of the traditional hard edge aperture printing of the holographic stereogram due to the abnormal-shaped mask plate and improving the representing quality of the holographic stereogram.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
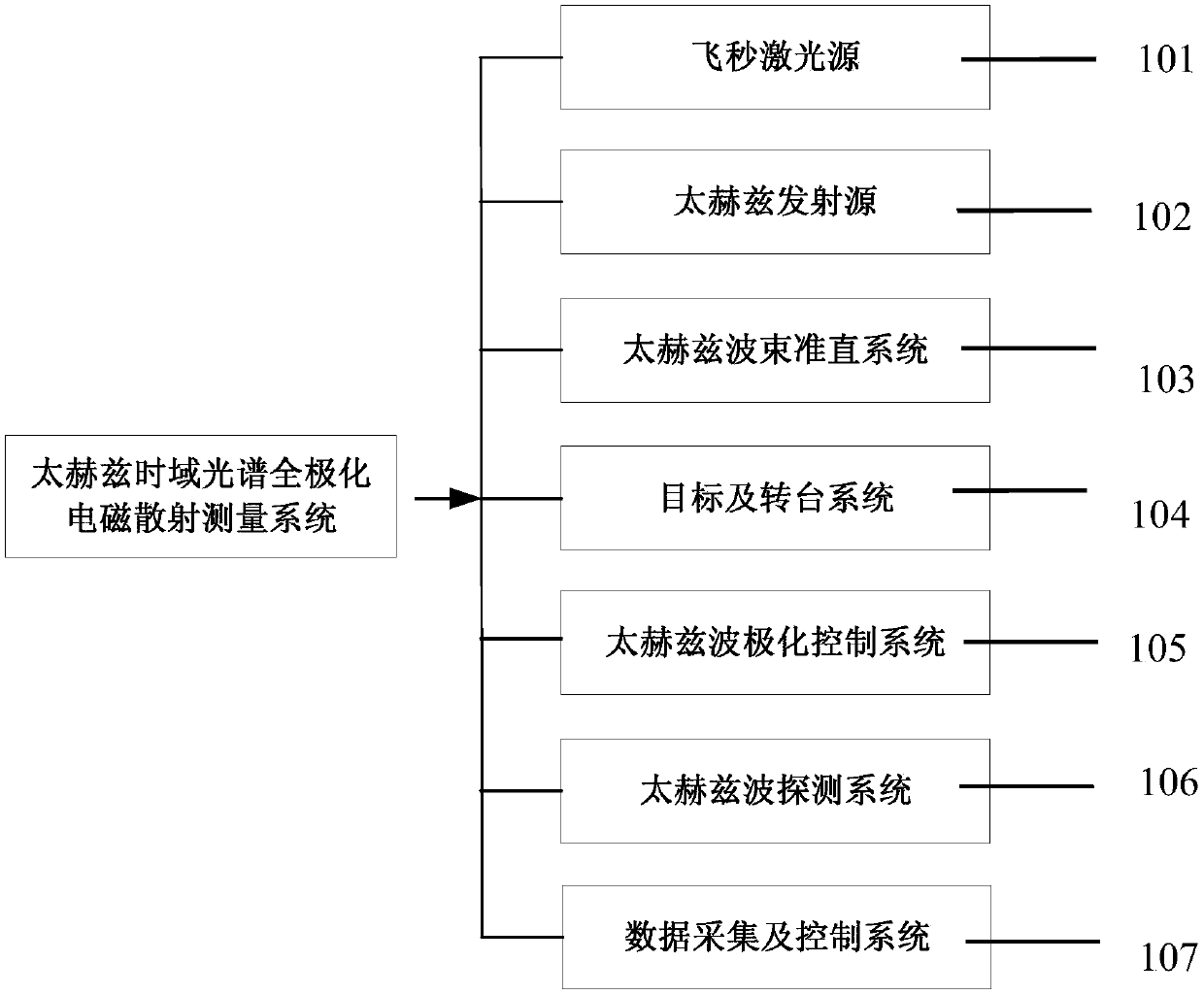
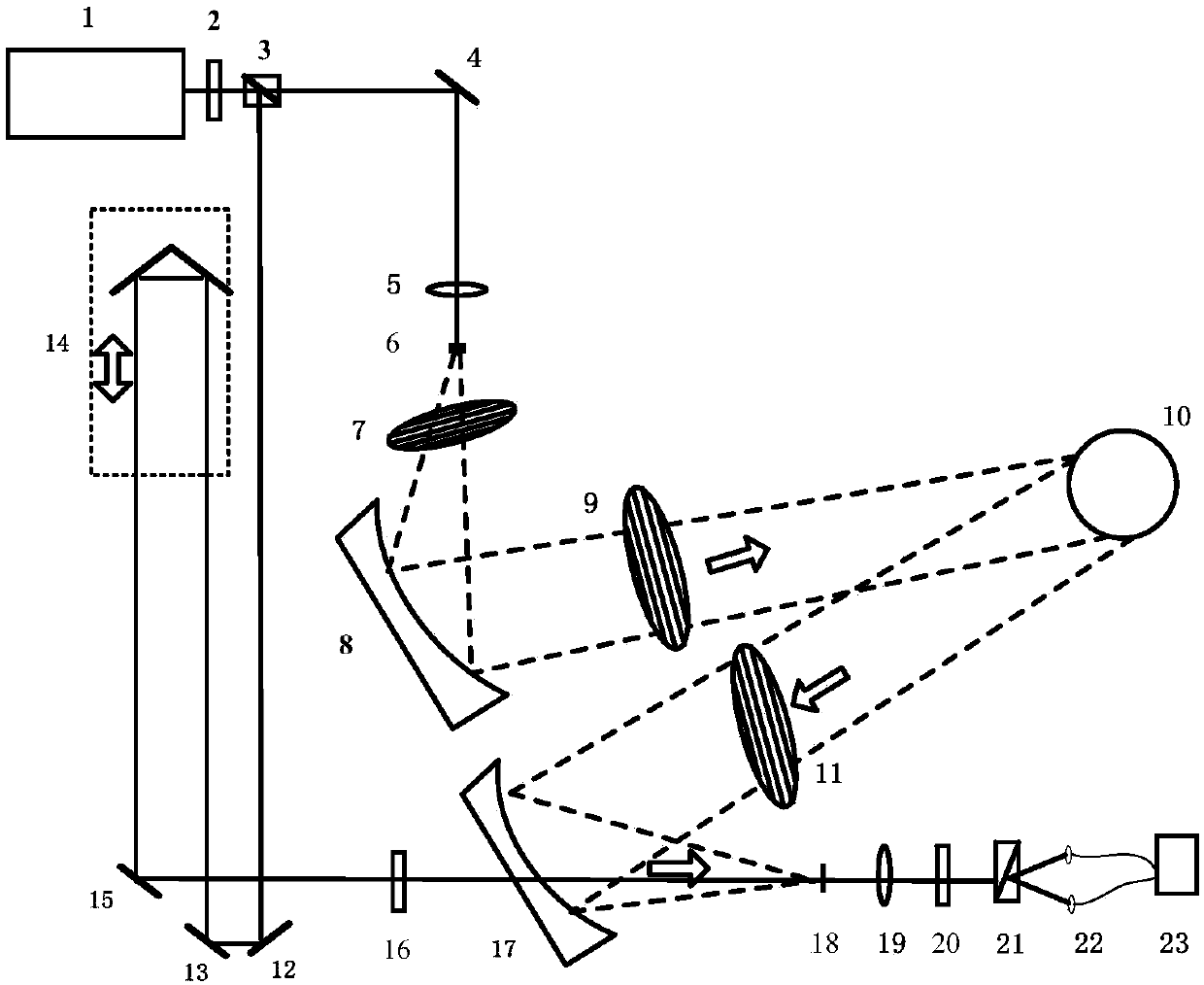
Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy complete polarization electromagnetic scattering measurement system and acquisition method
ActiveCN107782694AGuaranteed mechanical stabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansWave detectionData acquisition
The invention discloses a terahertz time-domain spectroscopy complete polarization electromagnetic scattering measurement system and acquisition method. According to the method, HH transceiving polarization, HV transceiving polarization, VH transceiving polarization and VV transceiving polarization are achieved by the aid of a terahertz time-domain spectroscopy complete polarization target electromagnetic scattering measurement system. The system mainly comprises a femtosecond laser source, a terahertz transmitting source, a terahertz wave beam collimation system, a target turntable system, aterahertz wave polarization control system, a terahertz wave detection system and a data acquisition and control system, a transceiving polarization mode is determined by adjusting rotating directionsof a hertz polarizer and a femtosecond laser half-wave plate, so that a turntable and a time delay line are controlled, and target polarization terahertz time-domain spectroscopy scattering signals under different postures are acquired in a scanned manner. According to the system, scattering characteristic measurement of target complete polarization RCS and 3D (three-dimensional) ISAR and the like within a terahertz high-frequency point and large-spectrum width range can be achieved, and the mechanical stability of the system is further ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
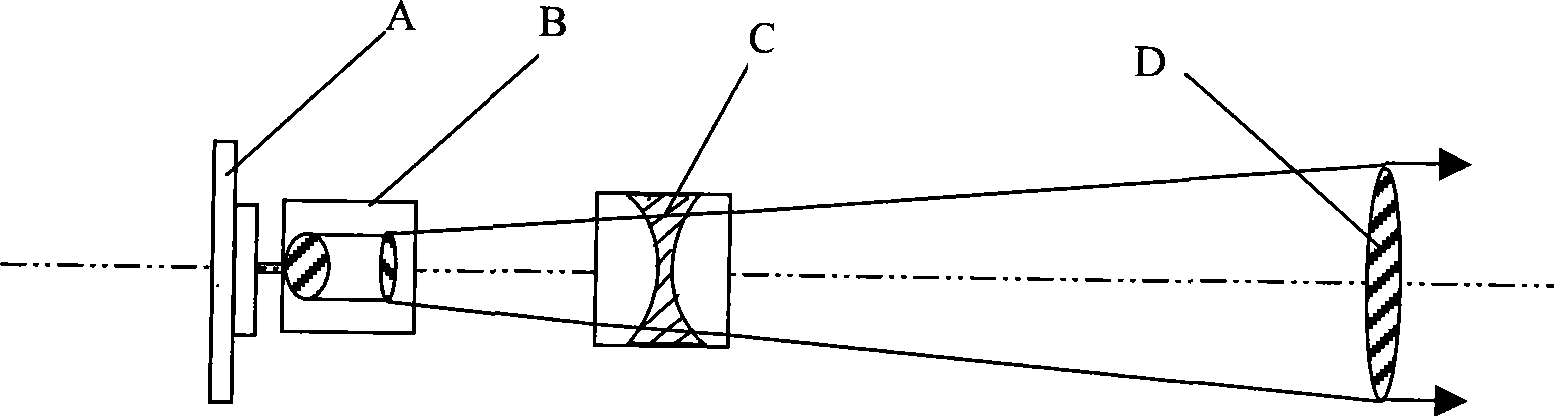
Infrared night vision laser searchlighting machine
InactiveCN101382657AHigh search powerGood beam collimationMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceBeam collimationDust particles
The invention discloses an infrared night-vision laser searchlighting device, which takes an infrared laser diode (LD) as an active infrared night-vision searchlighting device light source and mainly comprises an optical system which takes the LD as the light source and an LD conduction heat abstractor. The optical system comprises a light beam compressing and light beam reshaping unit combined by an optical fiber and a non-spherical lens assembly for correcting the non-axisymmetry of output beams; a light beam expanding unit consisting of a negative lens assembly to prevent a phenomenon of ionization and an ablation phenomenon generating dispersion dust particles caused by laser beam focusing in a transmission process; and a collimation unit consisting of a coated lens assembly for leading the laser beam to form a collimating searchlighting beam. The invention has the advantages of high searchlighting power, good beam collimation property, small volume, light weight and good practicability and is capable of observing a distant target object 2-3km far away at night.
Owner:上海天竹康复科技发展有限公司
Multi-single-tube high-power fiber-coupled semiconductor laser
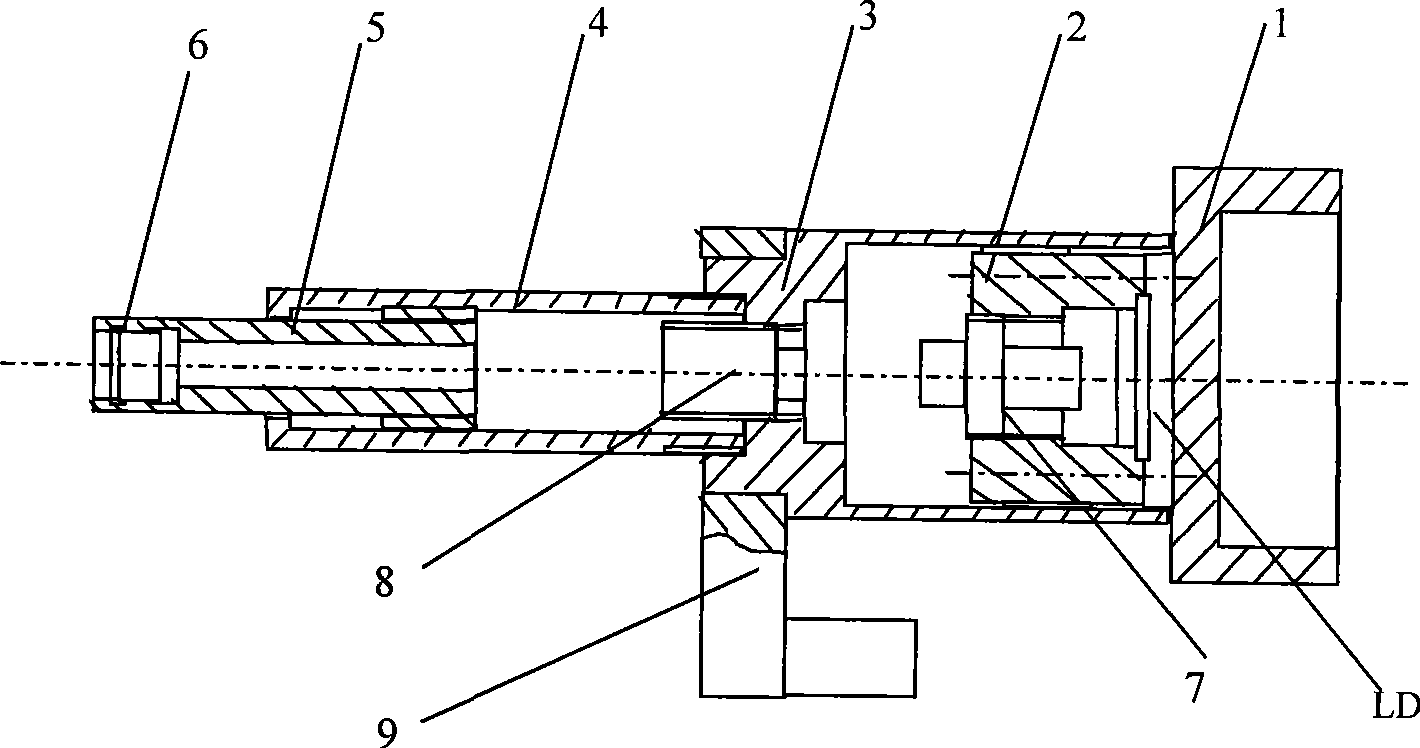
InactiveCN104836113AEasy to correct deviationIncrease powerSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlLight beamSemiconductor package
The present invention discloses a multi-single-tube high-power fiber-coupled diode laser which comprises a shell, two oppositely arranged semiconductor laser groups for generating two groups of N parallel beams, a reflector group which is between the two semiconductor laser groups and is used for combining two groups of N parallel beams to be a nearly square light spot, and a coupling lens for coupling the light spot to an optical fiber. According to the laser, the laser transmission optical path can be reduced, thus a package structure is compact, the adjustment is convenient, the correction of errors caused by laser chip assembly and beam collimation is facilitated, and thus a light beam with high power and good quality is obtained.
Owner:浙江合波光学科技有限公司
Space overlaid and coupled high-power semiconductor laser stack array system
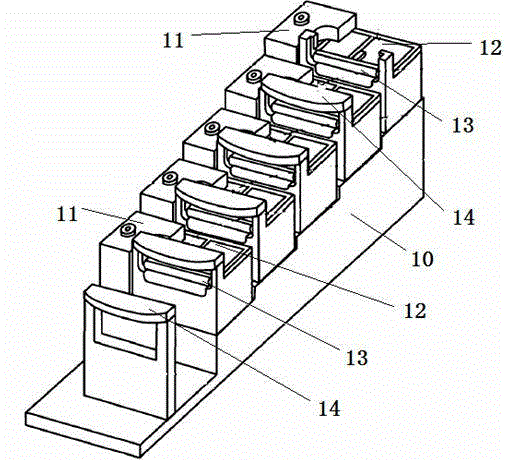
InactiveCN103579905AAvoid damageUniform spot outputSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlElectrical conductorHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a space overlaid and coupled high-power semiconductor laser stack array system. The space overlaid and coupled high-power semiconductor laser stack array system comprises a first semiconductor laser stack array and a second semiconductor laser stack array which are respectively formed by overlaying a plurality of semiconductor labor diode bars in the direction of a fast axis, wherein the number of the diode bars of the first semiconductor laser stack array is equal to the number of the diode bars of the second semiconductor laser stack array. The space overlaid and coupled high-power semiconductor laser stack array system further comprises a first fast axis collimating lens set, a second fast axis collimating lens set, a first slow axis collimating lens array set, a second slow axis collimating lens array set, a periodical space coupling lens, a slow axis beam expanding system and a focus lens. The two laser stack arrays in the system are overlapped in the space through a periodical space coupling lens to output a high-power laser, the beam collimation is achieved through the fast axis collimating lenses and the slow axis collimating lenses, the characteristics of high brightness and linear polarization are kept, and meanwhile internal components are protected through an added feedback optical isolation system. The problem that the existing semiconductor laser technology is complex is effectively solved, and even high-power and strip-shaped light spots are output.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Two-dimensional exit pupil expansion waveguide near-to-eye optical display device
The invention discloses a two-dimensional exit pupil expansion waveguide near-to-eye optical display device. The device comprises a miniature display screen, an ocular lens group, a vertical expansionwaveguide device and a horizontal expansion waveguide device. The miniature display screen and the vertical expansion waveguide device are respectively disposed on the focal plane and the emergent light path of the ocular lens group, and the ocular lens group is used for collimating beams emitted by the miniature display screen into parallel beams. The horizontal waveguide device is disposed on the emergent light path of the vertical waveguide device, and a horizontally coupled incident surface is parallel to the upper and lower surfaces of the vertical waveguide device. The vertical expansion waveguide device is used for increasing the vertical equivalent size of the parallel beams emitted by the ocular lens group, and the horizontal waveguide device is used for increasing the horizontalequivalent size of a vertically expanded beam to obtain a two-dimensional expanded beam and emitting the two-dimensional expanded beam to the pupils of the human eyes. The device can reduce the sizewhile expanding the angle of view, and irons out the defects of vertical axis aberration, curvature of field and distortion.
Owner:SHENZHEN LOCHN OPTICS TECH CO LTD
Method and system for high resolution digitized display
ActiveUS20180149873A1Accentuates focal/accommodation cuesHigh resolutionMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesEyepieceTotal internal reflection
A method and system for increasing dynamic digitized wavefront resolution, i.e., the density of output beamlets, can include receiving a single collimated source light beam and producing multiple output beamlets spatially offset when out-coupled from a waveguide. The multiple output beamlets can be obtained by offsetting and replicating a collimated source light beam. Alternatively, the multiple output beamlets can be obtained by using a collimated incoming source light beam having multiple input beams with different wavelengths in the vicinity of the nominal wavelength of a particular color. The collimated incoming source light beam can be in-coupled into the eyepiece designed for the nominal wavelength. The input beams with multiple wavelengths take different paths when they undergo total internal reflection in the waveguide, which produces multiple output beamlets.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
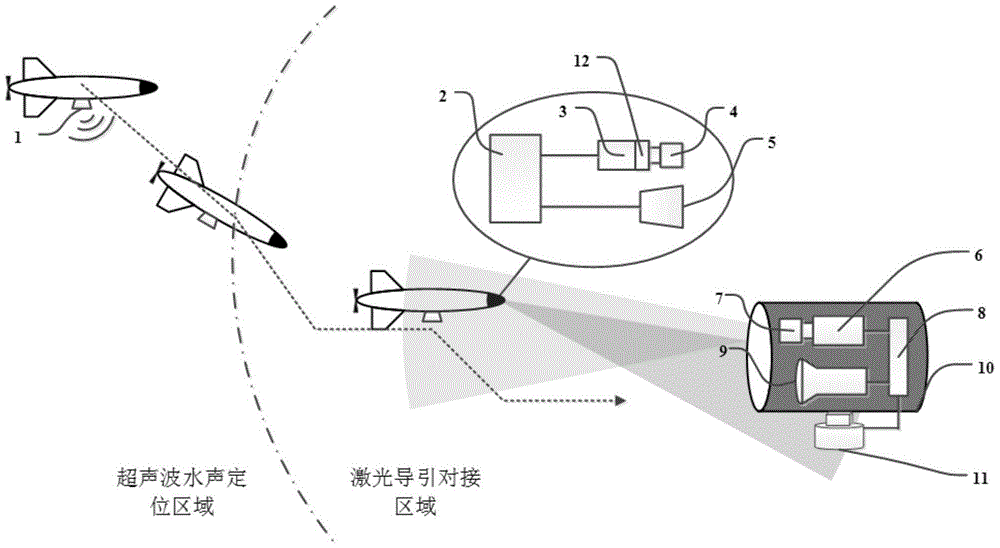
Laser guide and communication device for underwater vehicle docking
ActiveCN105182991AHigh precisionSimple structurePosition/course control in three dimensionsTransceiverBeam collimation
The invention relates to a laser guide and communication device and particularly relates to a laser guide and communication device for underwater vehicle docking. The device comprises a supersonic wave water sound positioning device fixedly mounted on an underwater vehicle, an underwater vehicle end laser transceiver which is fixedly packaged at the front of a cabin body of the underwater vehicle, and a platform end laser transceiver which is used for carrying out communication docking with the underwater vehicle and comprises a holder and the sealed cabin body, wherein the underwater vehicle end laser transceiver comprises a position solution and control unit, a docking laser device, a docking beam collimation lens, an underwater device photoelectric detection device and an electric light modulator. The device employs two laser beams on the underwater device and the docking platform as position indicating means for docking, a four-quadrant photoelectric detector or an image sensor and double silicon band amplification photoelectric detectors are employed for docking and communication, docking precision can be improved, and underwater wireless communication can be realized. The device has advantages of simple structure, flexible operation, technological cost reduction and strong versatility.
Owner:青岛中科芯光集成电路有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com