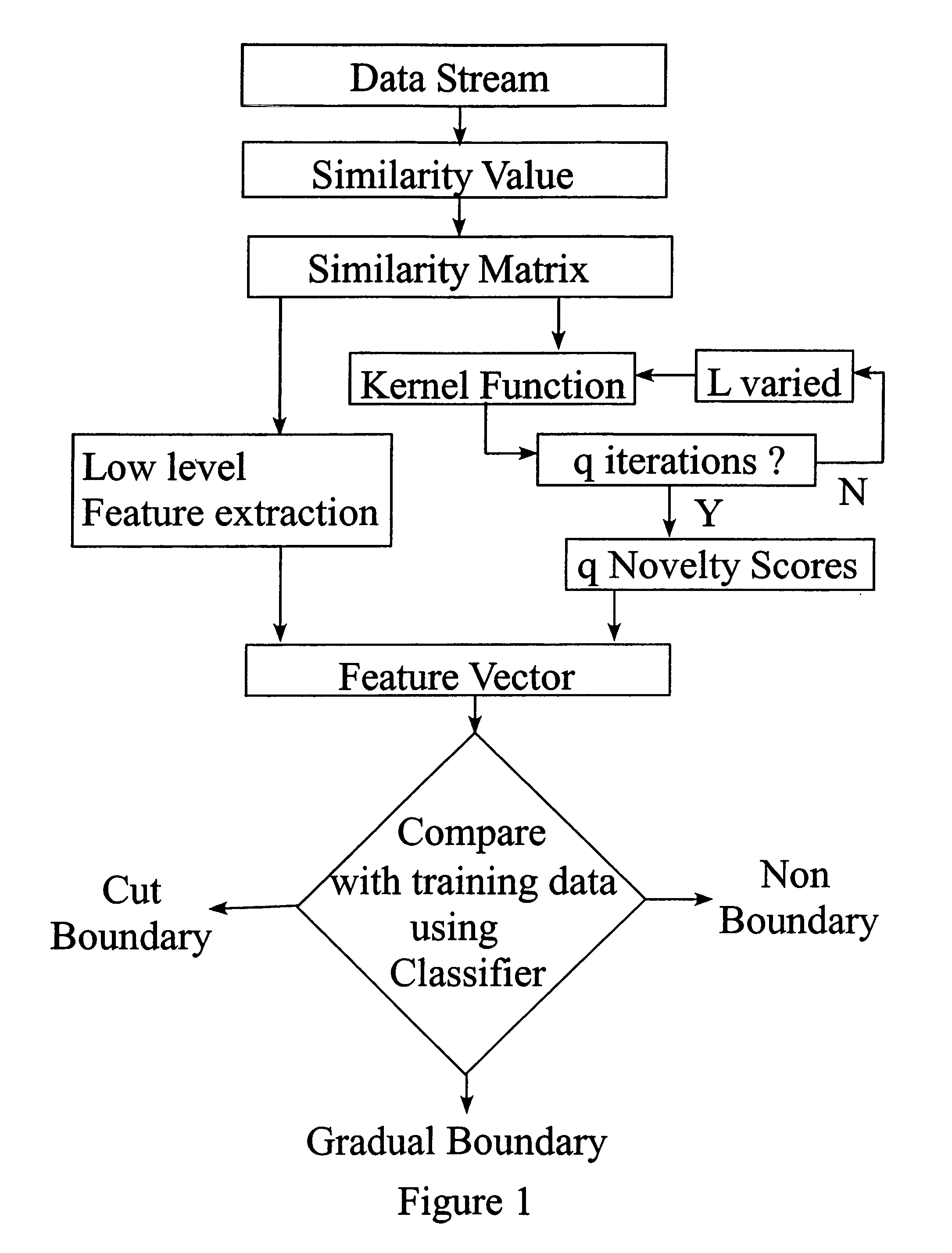
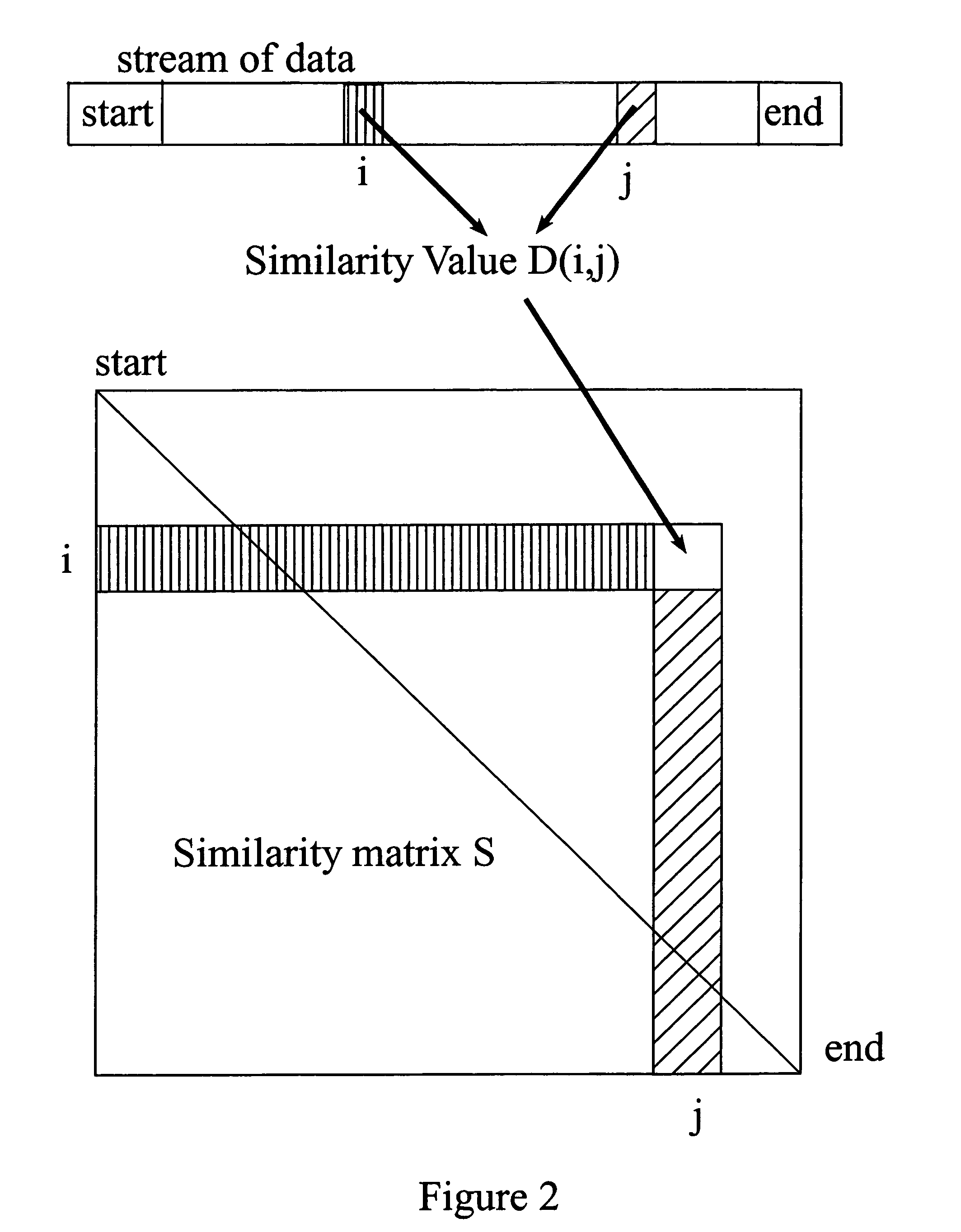
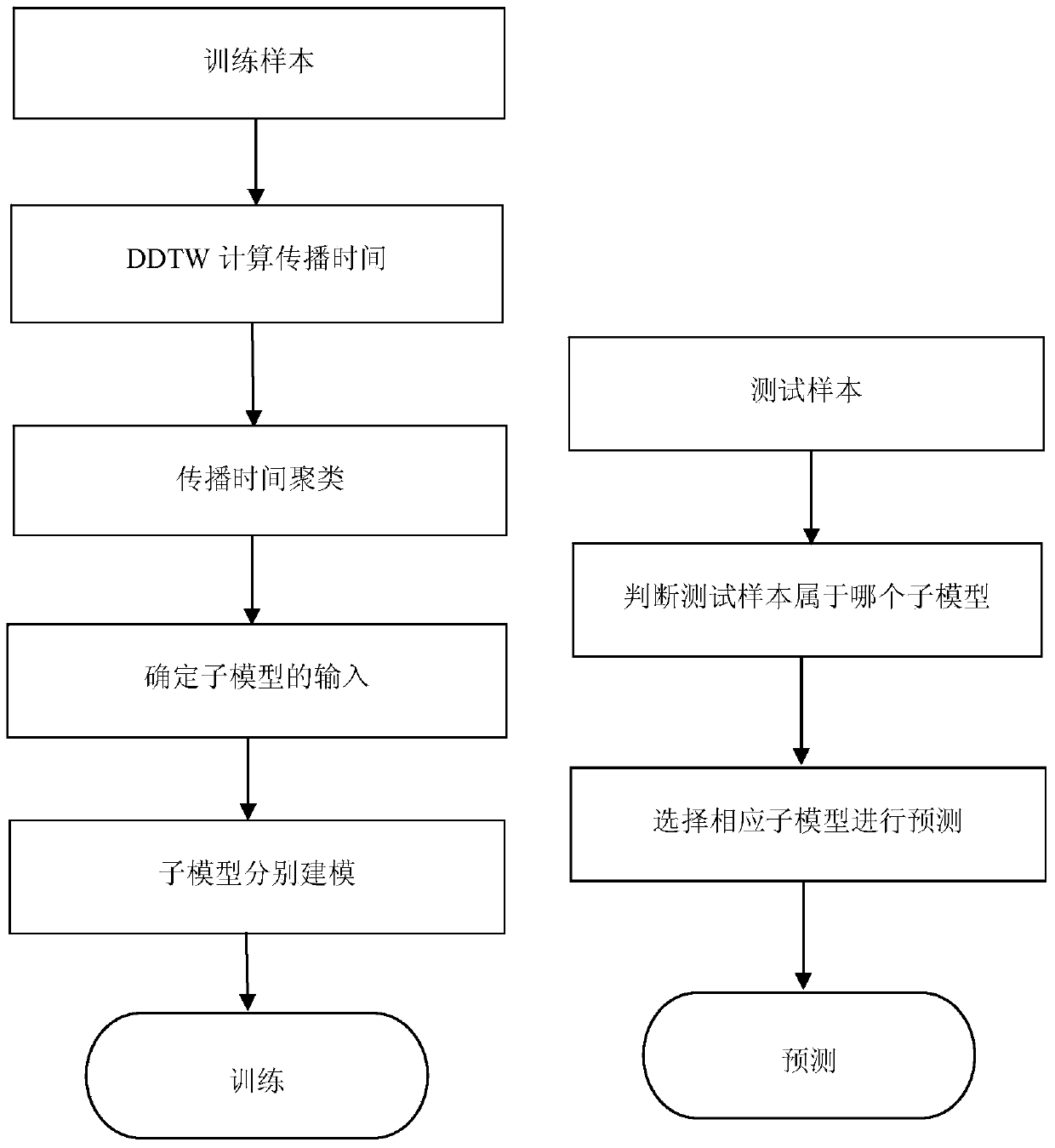
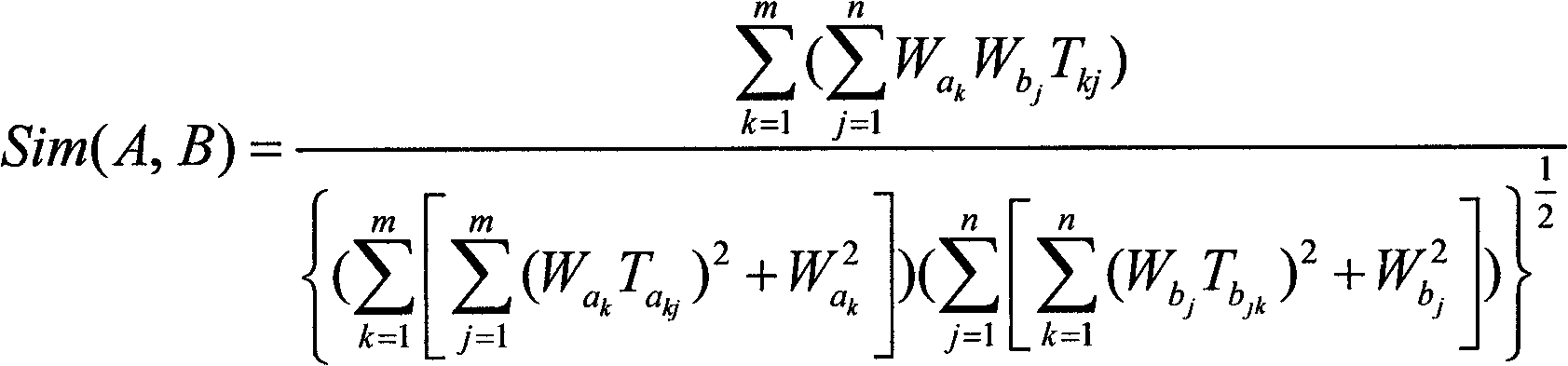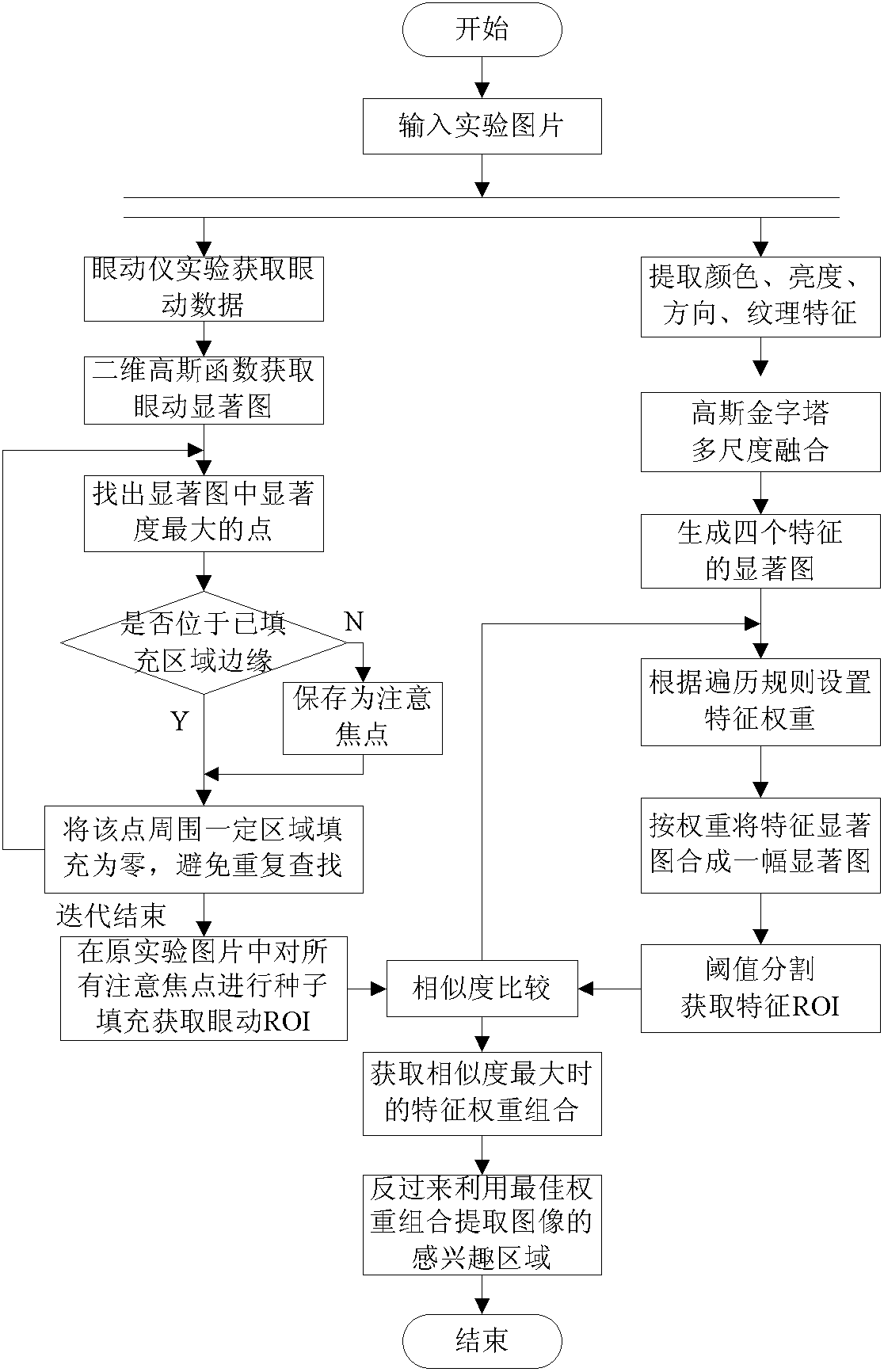Patents
Literature
472 results about "Similarity analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Analysis of similarities. Analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) is a non-parametric statistical test widely used in the field of ecology. The test was first suggested by K. R. Clarke as an ANOVA-like test, where instead of operating on raw data, operates on a ranked dissimilarity matrix.
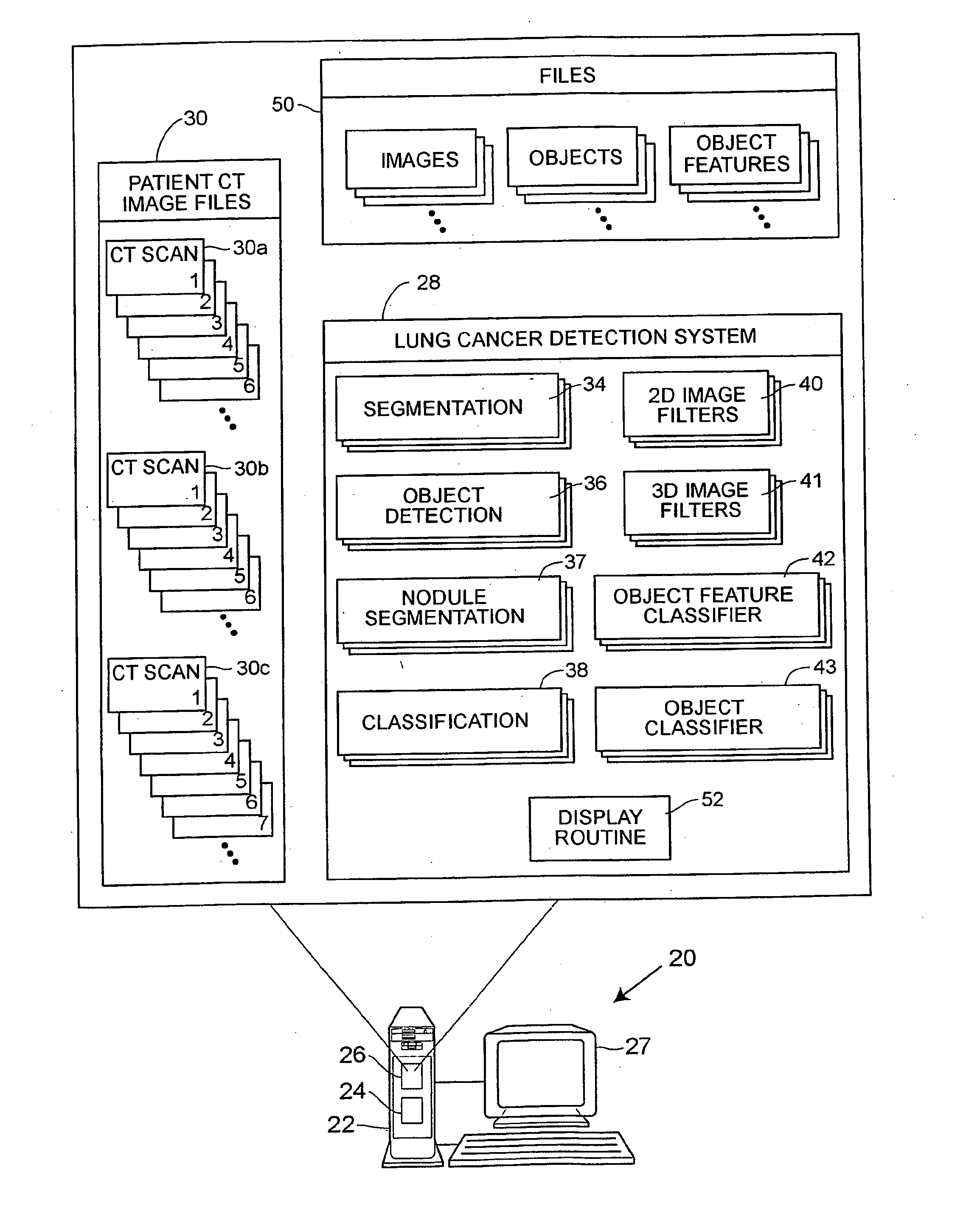
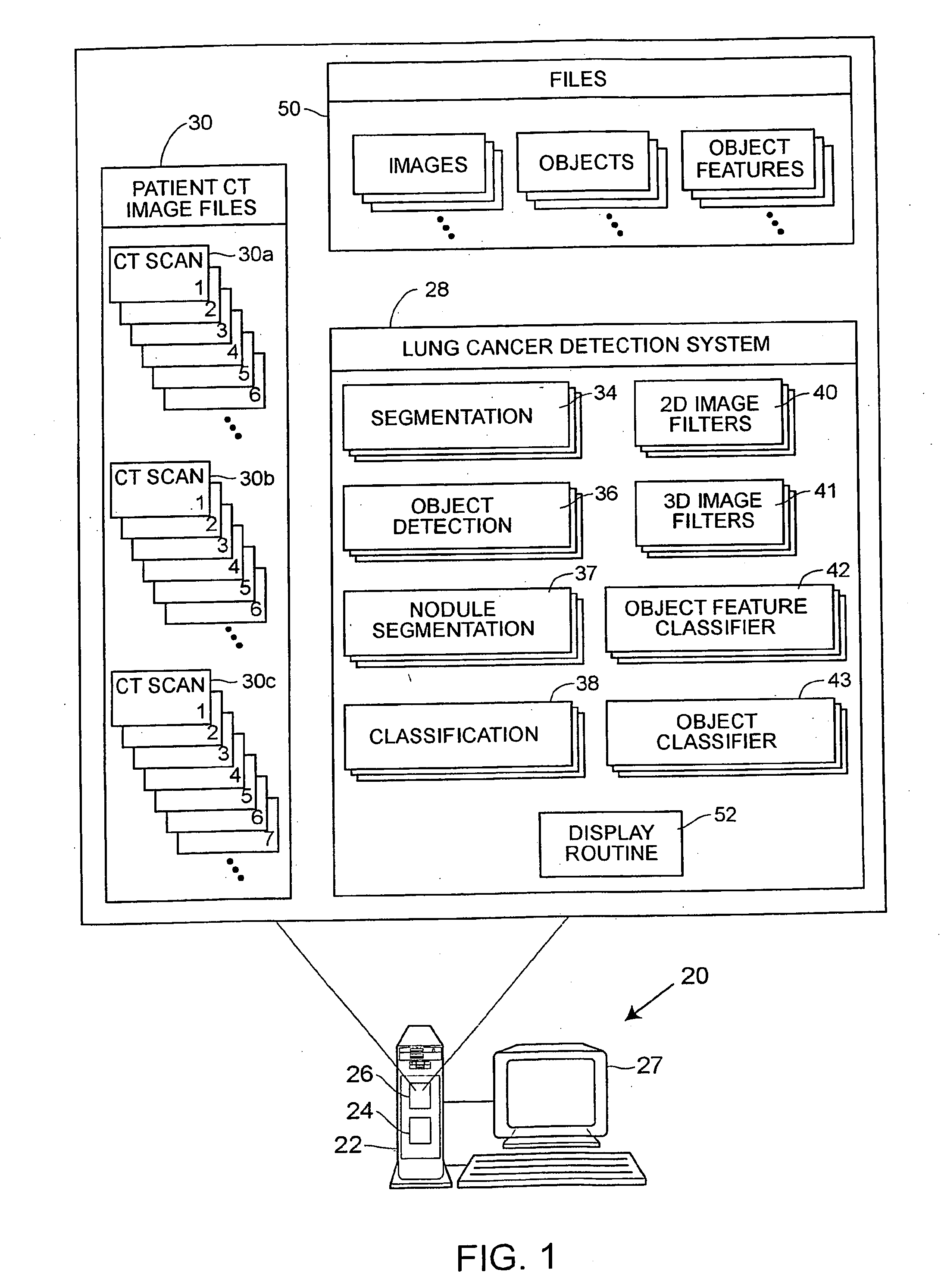
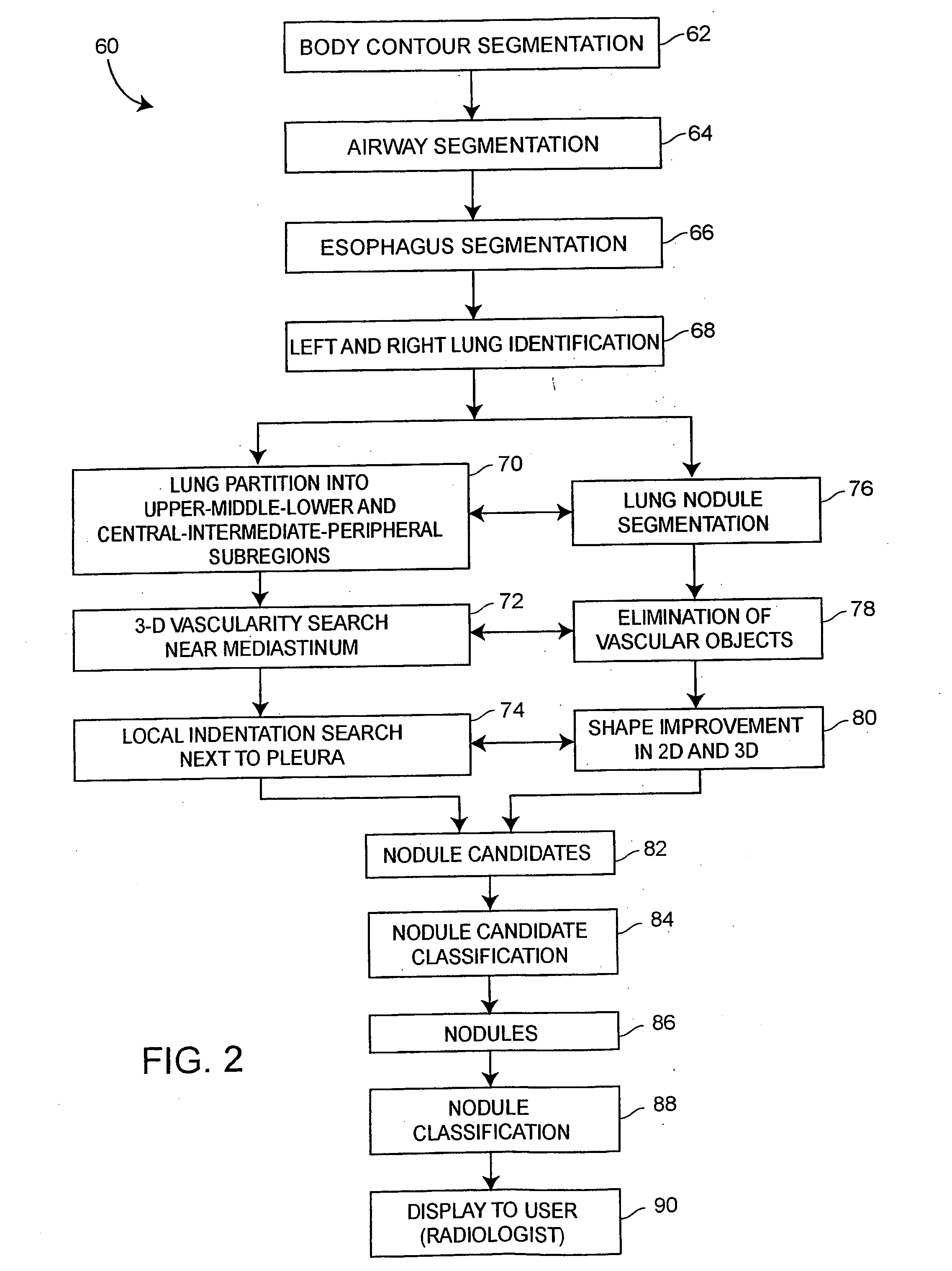
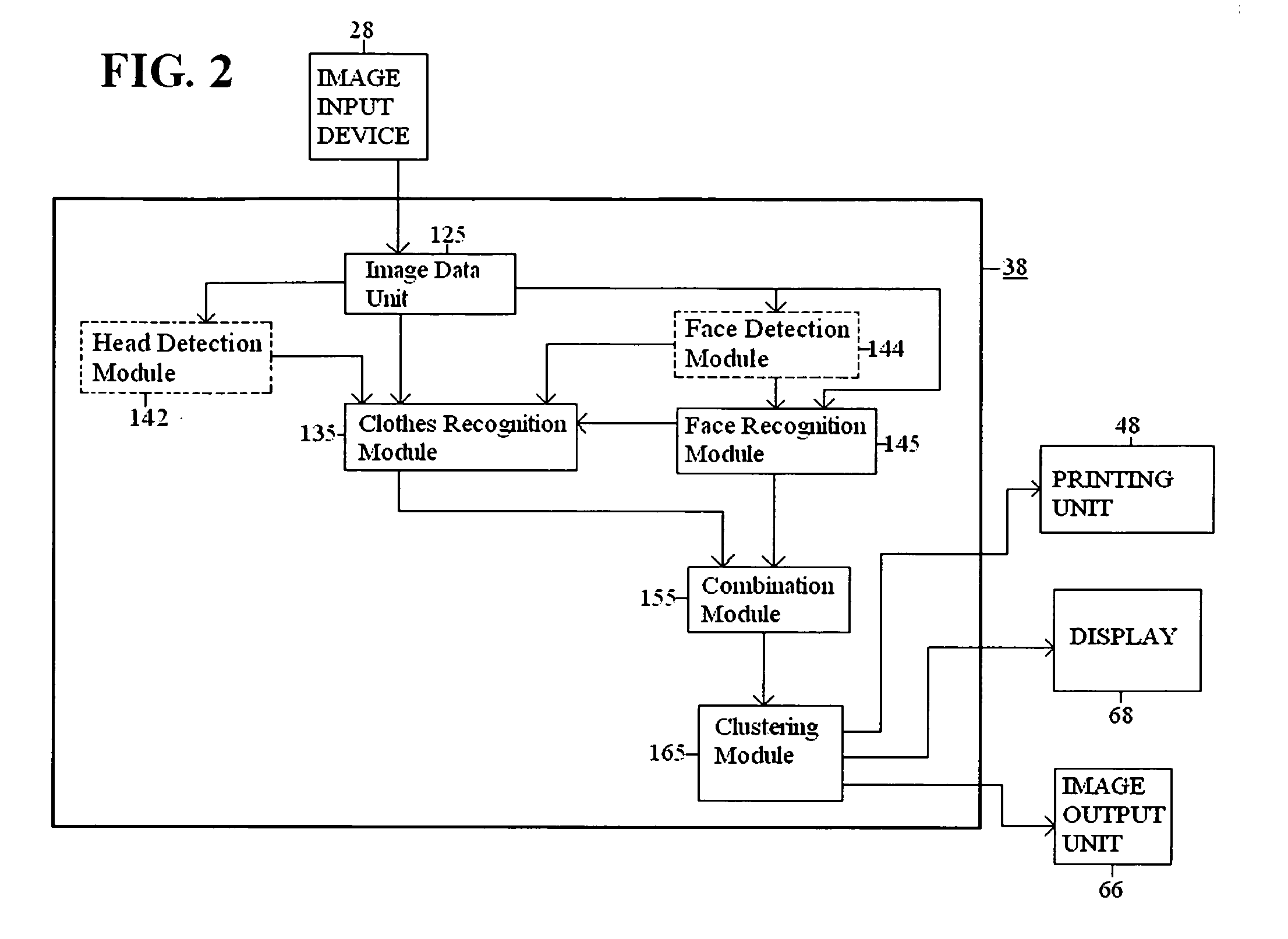
Lung nodule detection and classification
A computer assisted method of detecting and classifying lung nodules within a set of CT images includes performing body contour, airway, lung and esophagus segmentation to identify the regions of the CT images in which to search for potential lung nodules. The lungs are processed to identify the left and right sides of the lungs and each side of the lung is divided into subregions including upper, middle and lower subregions and central, intermediate and peripheral subregions. The computer analyzes each of the lung regions to detect and identify a three-dimensional vessel tree representing the blood vessels at or near the mediastinum. The computer then detects objects that are attached to the lung wall or to the vessel tree to assure that these objects are not eliminated from consideration as potential nodules. Thereafter, the computer performs a pixel similarity analysis on the appropriate regions within the CT images to detect potential nodules and performs one or more expert analysis techniques using the features of the potential nodules to determine whether each of the potential nodules is or is not a lung nodule. Thereafter, the computer uses further features, such as speculation features, growth features, etc. in one or more expert analysis techniques to classify each detected nodule as being either benign or malignant. The computer then displays the detection and classification results to the radiologist to assist the radiologist in interpreting the CT exam for the patient.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
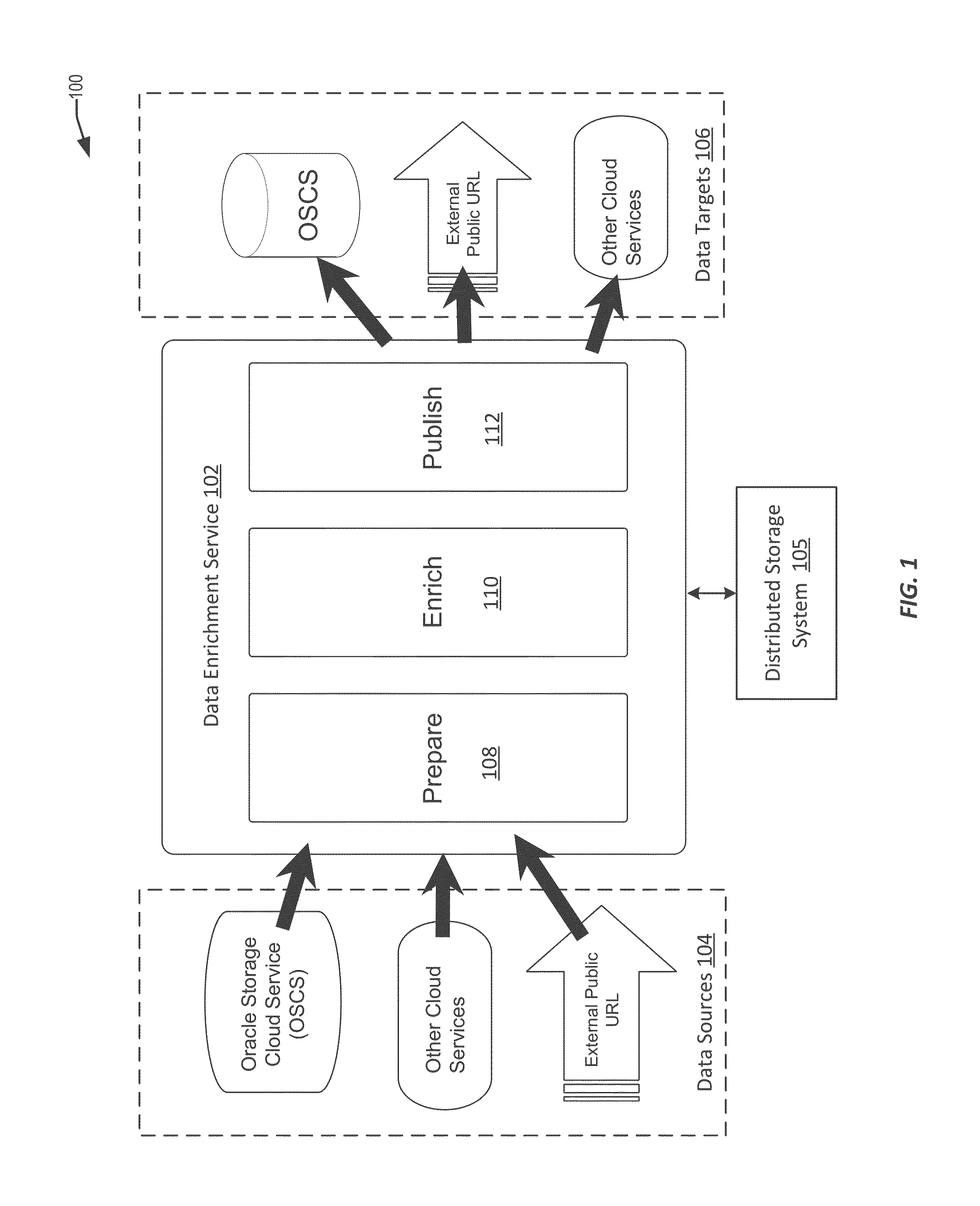
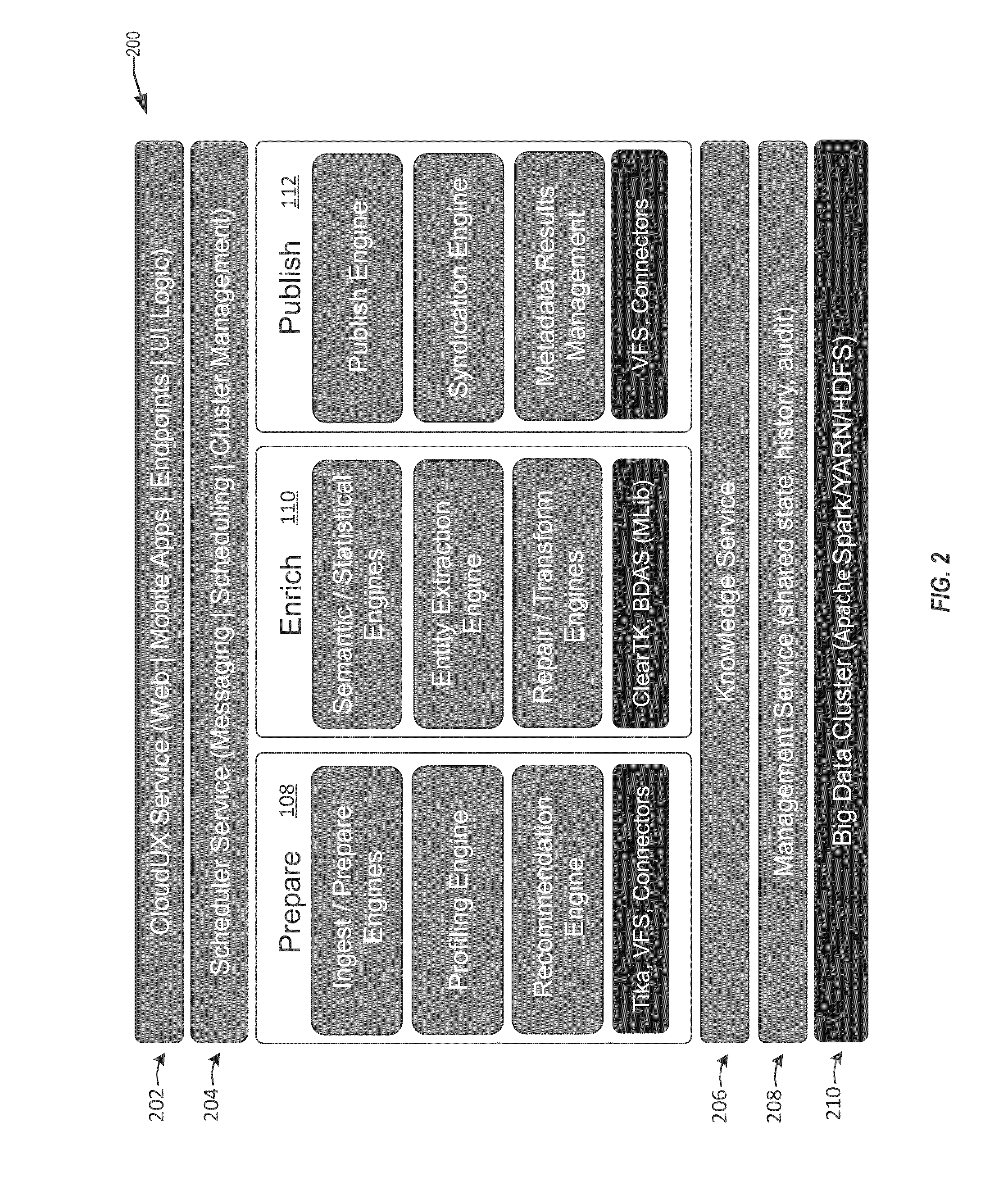
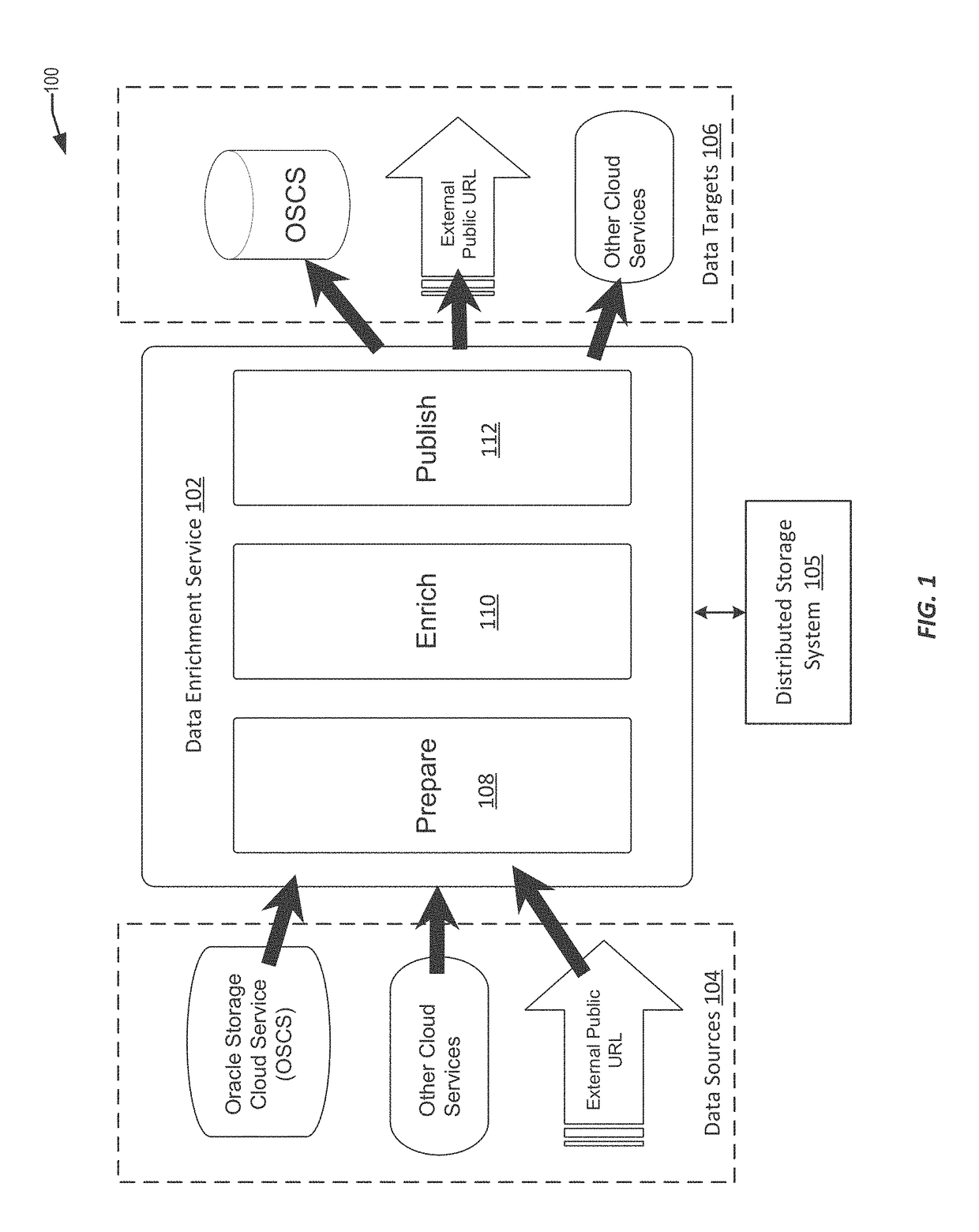
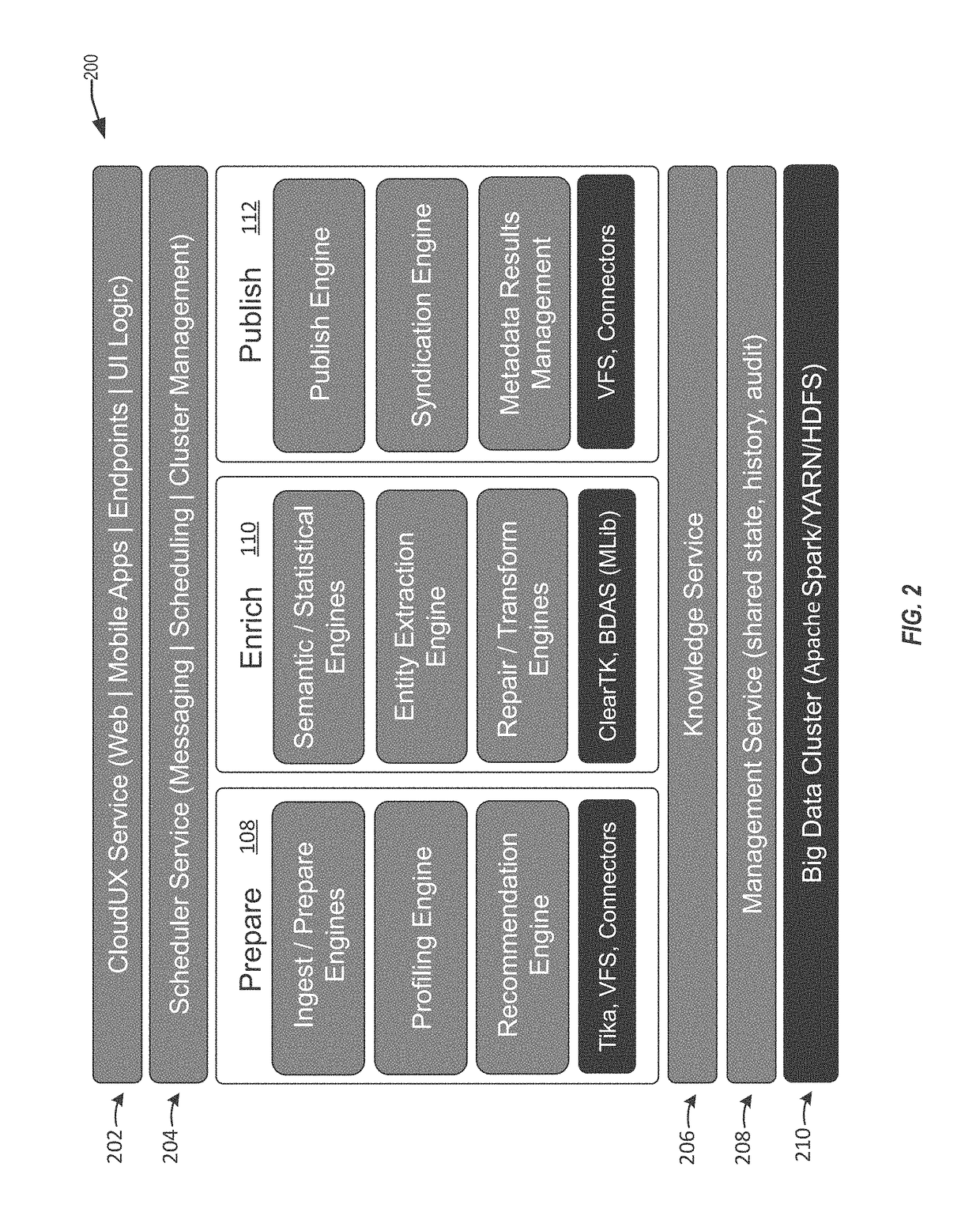
Techniques for similarity analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources
ActiveUS20160092557A1Accurate resolutionAccurate labelingDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesKnowledge sourcesData set
The present disclosure relates to performing similarity metric analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources. A data enrichment service can compare an input data set to reference data sets stored in a knowledge source to identify similarly related data. A similarity metric can be calculated corresponding to the semantic similarity of two or more datasets. The similarity metric can be used to identify datasets based on their metadata attributes and data values enabling easier indexing and high performance retrieval of data values. A input data set can labeled with a category based on the data set having the best match with the input data set. The similarity of an input data set with a data set provided by a knowledge source can be used to query a knowledge source to obtain additional information about the data set. The additional information can be used to provide recommendations to the user.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
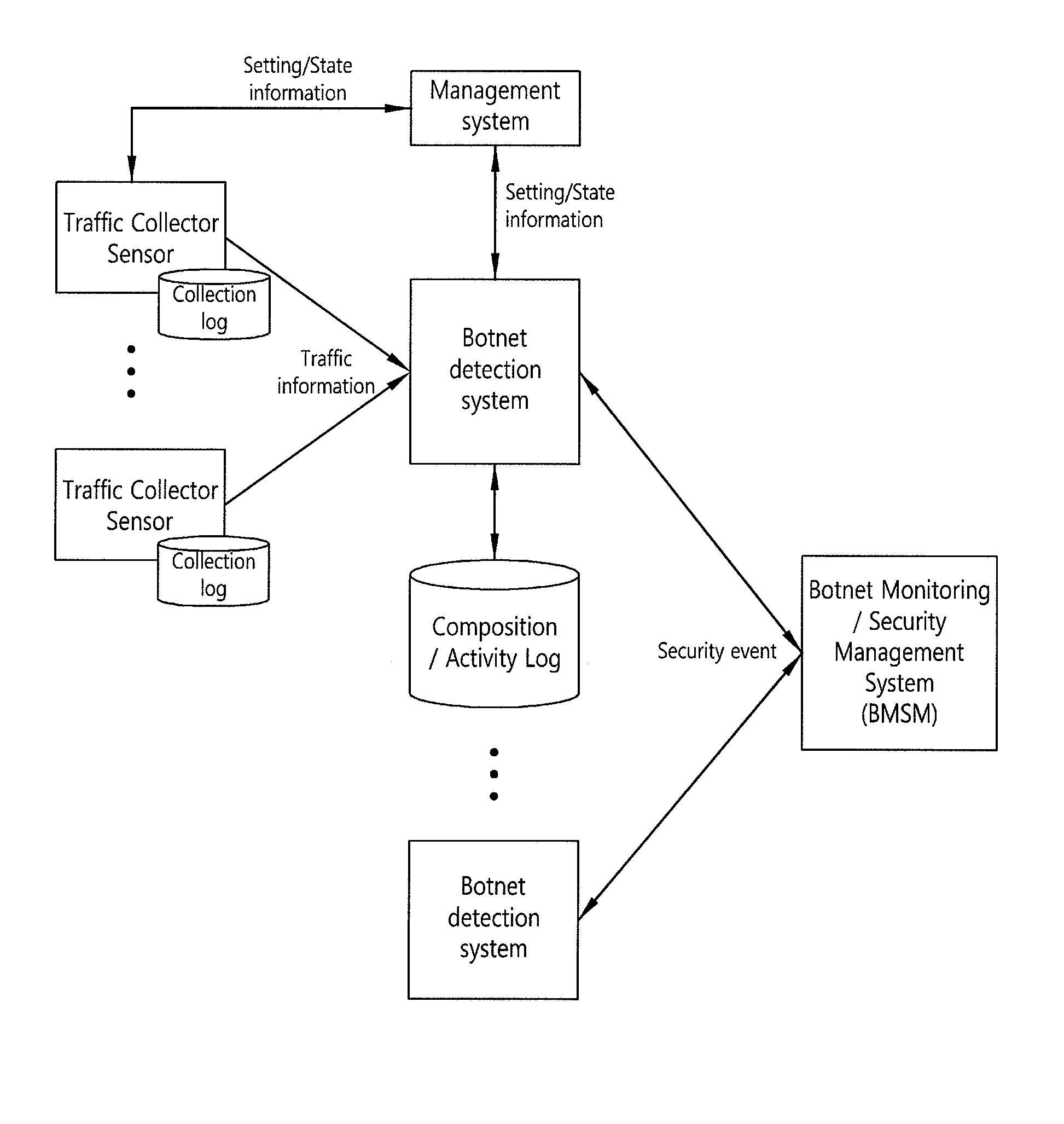
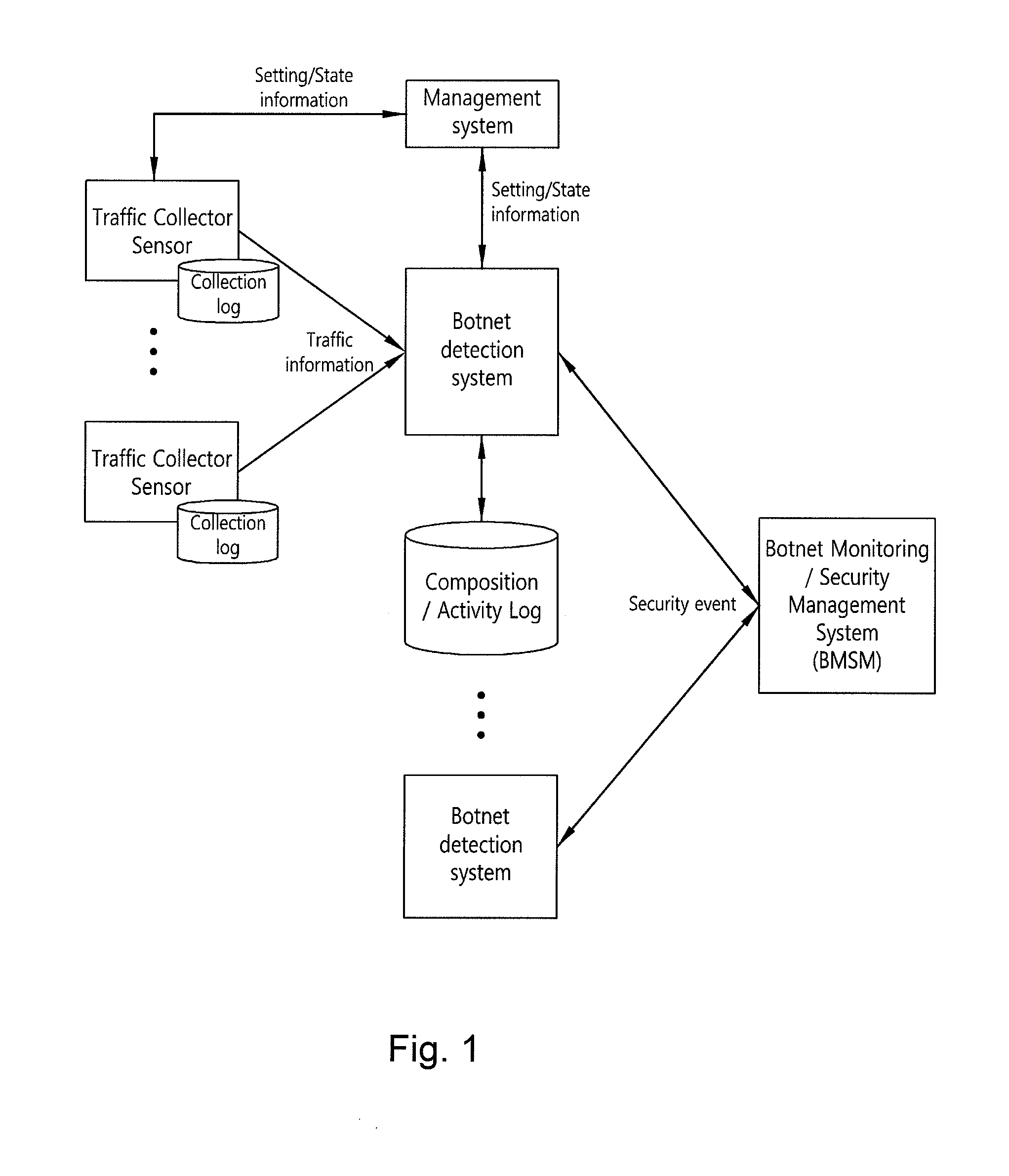
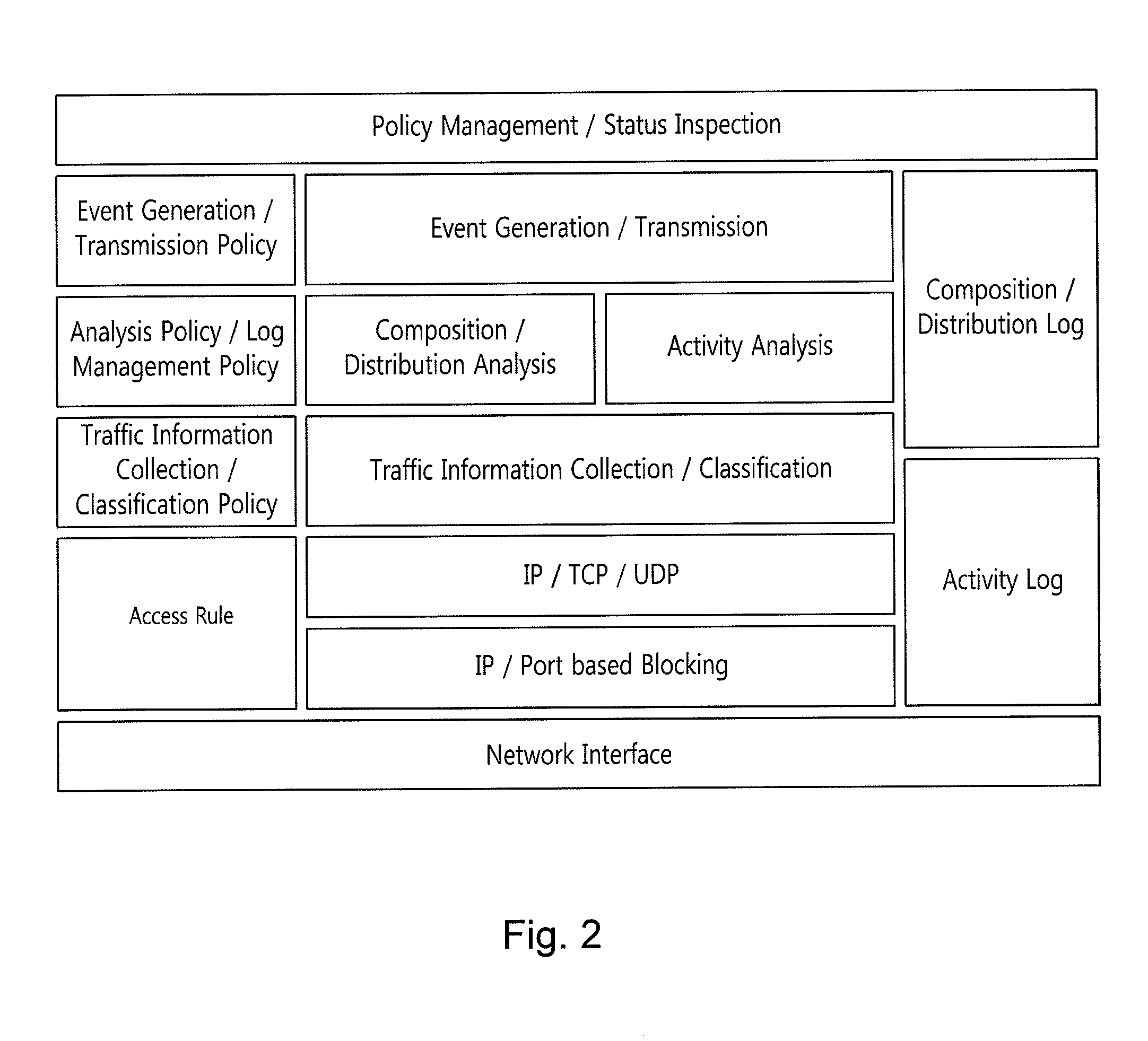
System and method for modeling activity patterns of network traffic to detect botnets
InactiveUS20110153811A1Efficient detectionDigital computer detailsTransmissionNetwork activityActivity classification
The invention relates to a system and method that can detect botnets by classifying the communication activities for each client according to destination or based on similarity between the groups of collected traffic. According to certain aspects of the invention, the communication activities for each client can be classified to model network activity by differentiating the protocols of the collected network traffic based on destination and patterning the subgroups for the respective protocols. Those servers that are estimated to be C&C servers can be classified into download and upload, spam servers and command control servers, within a botnet group detected by modeling network activity, i.e. analyzing network-based activity patterns. Also, botnet groups can be detected by way of a group information management function, for generating an activity pattern-based group matrix based on group data, and a mutual similarity analysis, performed on groups suspected to be botnets from the group information.
Owner:KOREA INTERNET & SECURITY AGENCY
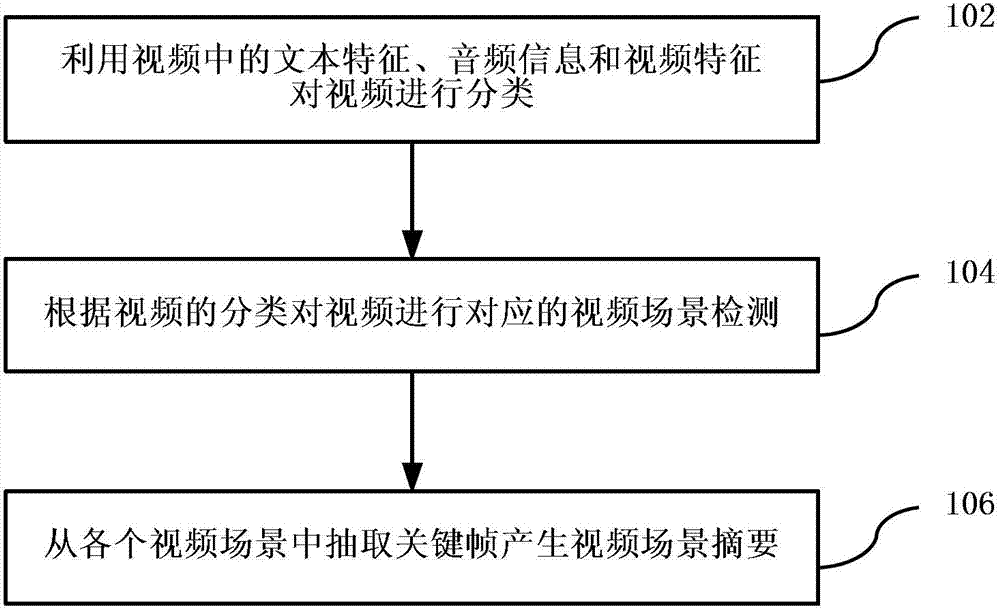
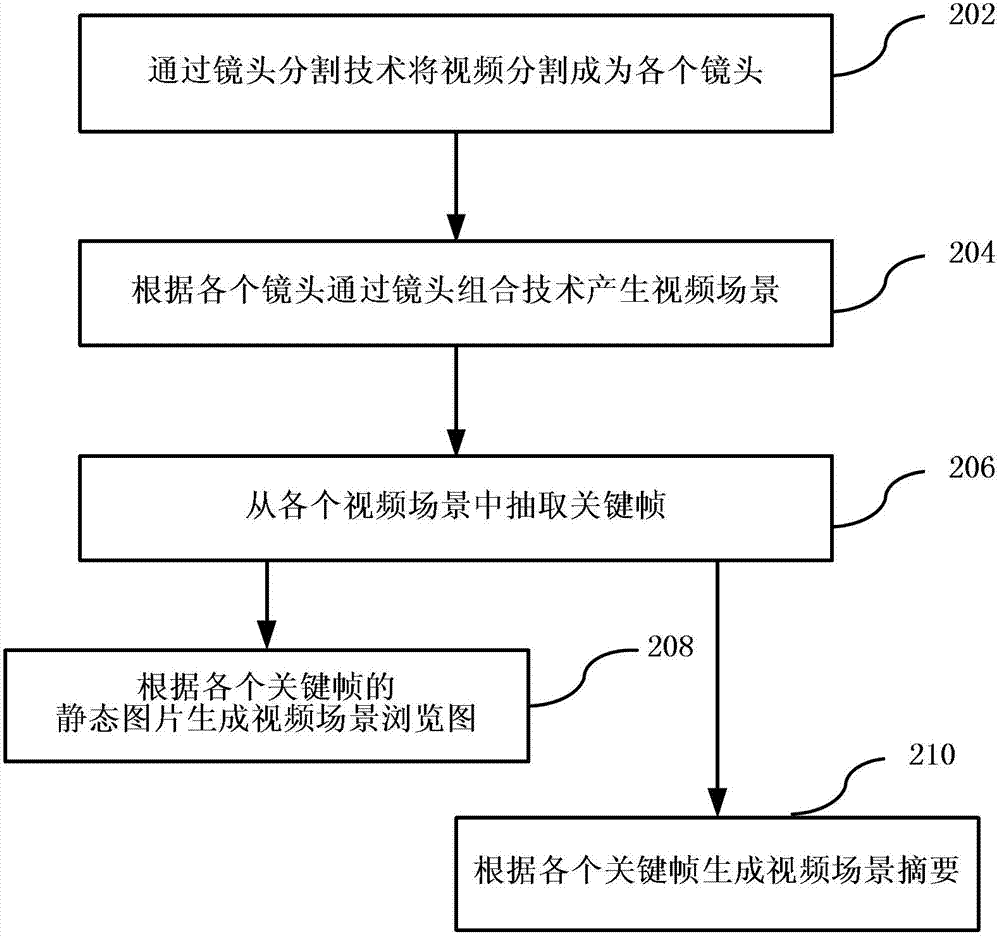
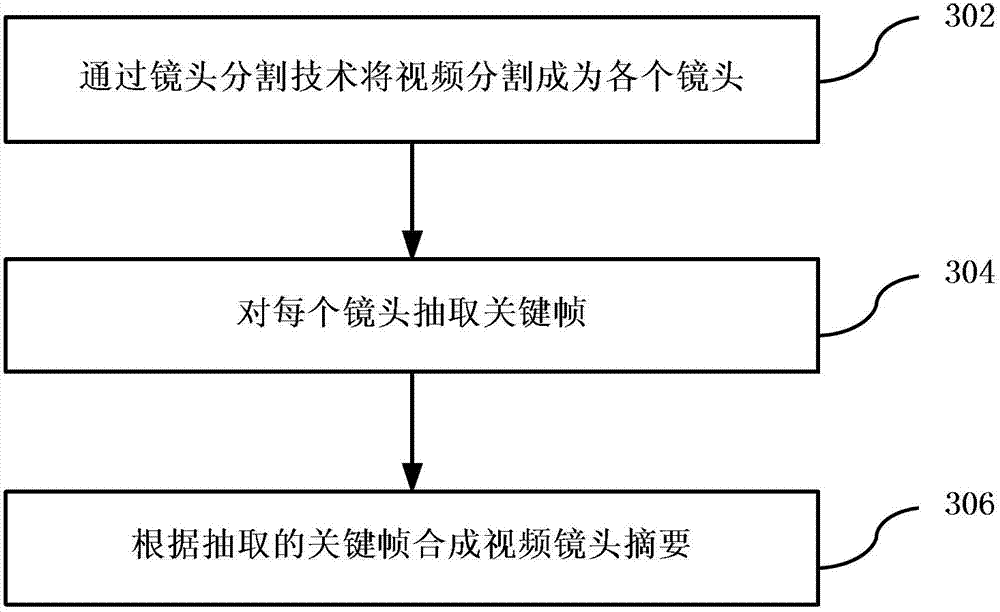
Method and device for generating video summary
InactiveCN103200463AImprove accuracyAccurate summarySelective content distributionSpecial data processing applicationsFace detectionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a method and a device for generating a video summary, and relates to the technical field of video processing. The method comprises the steps of confirming the classification of a video through textual characteristics, audio information and video characteristics in the video, carrying out corresponding video scene detection for the video according to the classification of the video, and extracting key frames in a video scene to generate the video scene summary. The scheme with multi-media content analyses comprises key frame detection, lens boundary detection, image similarity analyses, face detection and identification, text search, news story segmentation, sports key scene analyses and the like. Automatic generation of the functions, such as a video browsing function and a video summarizing and rapid previewing function, of interactive television content is achieved. The functions generated by the interactive television content are automatically achieved based on multi-media content analysis techniques. Time-wasting and expensive labor editing processes can be avoided.
Owner:TVMINING BEIJING MEDIA TECH
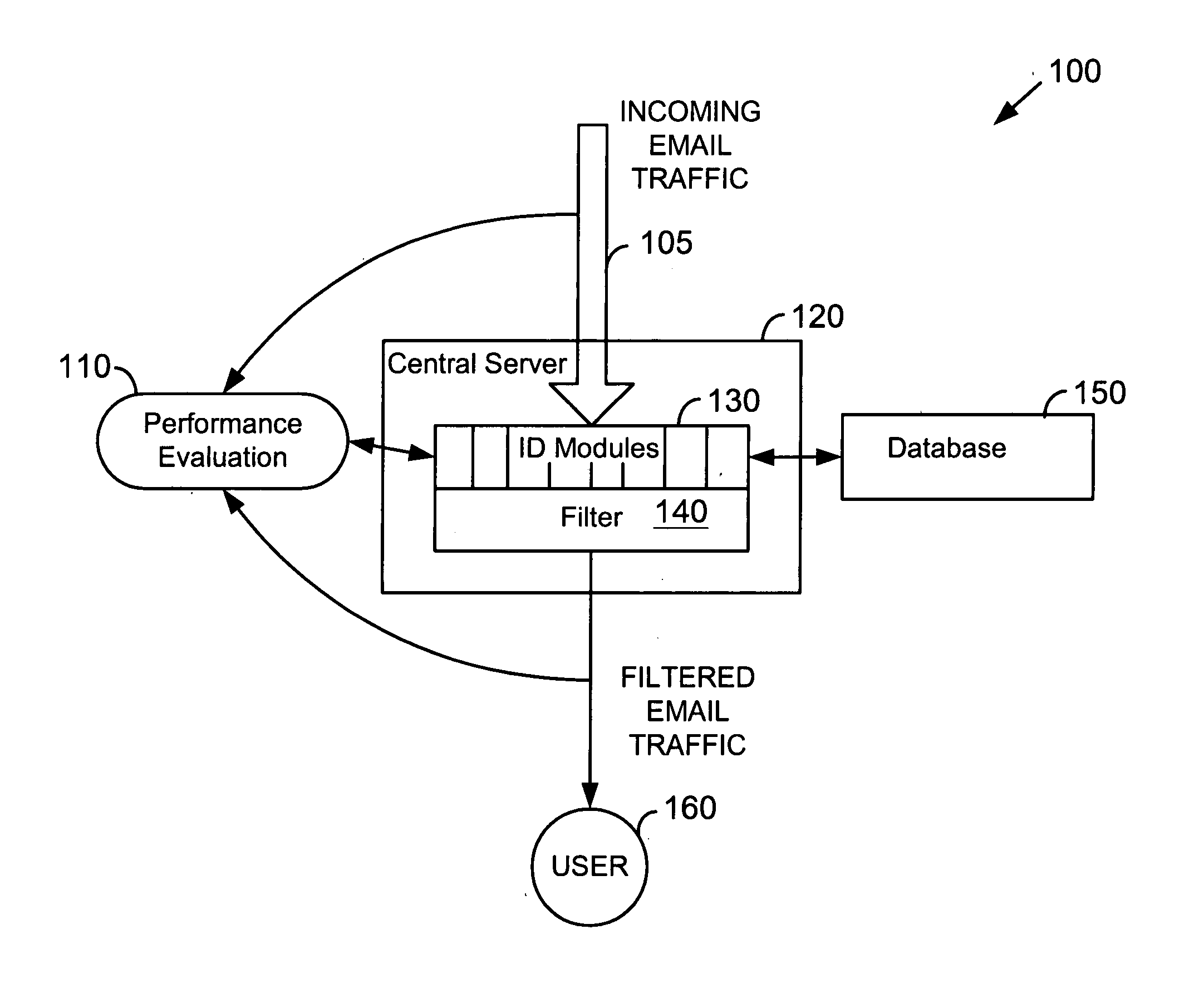
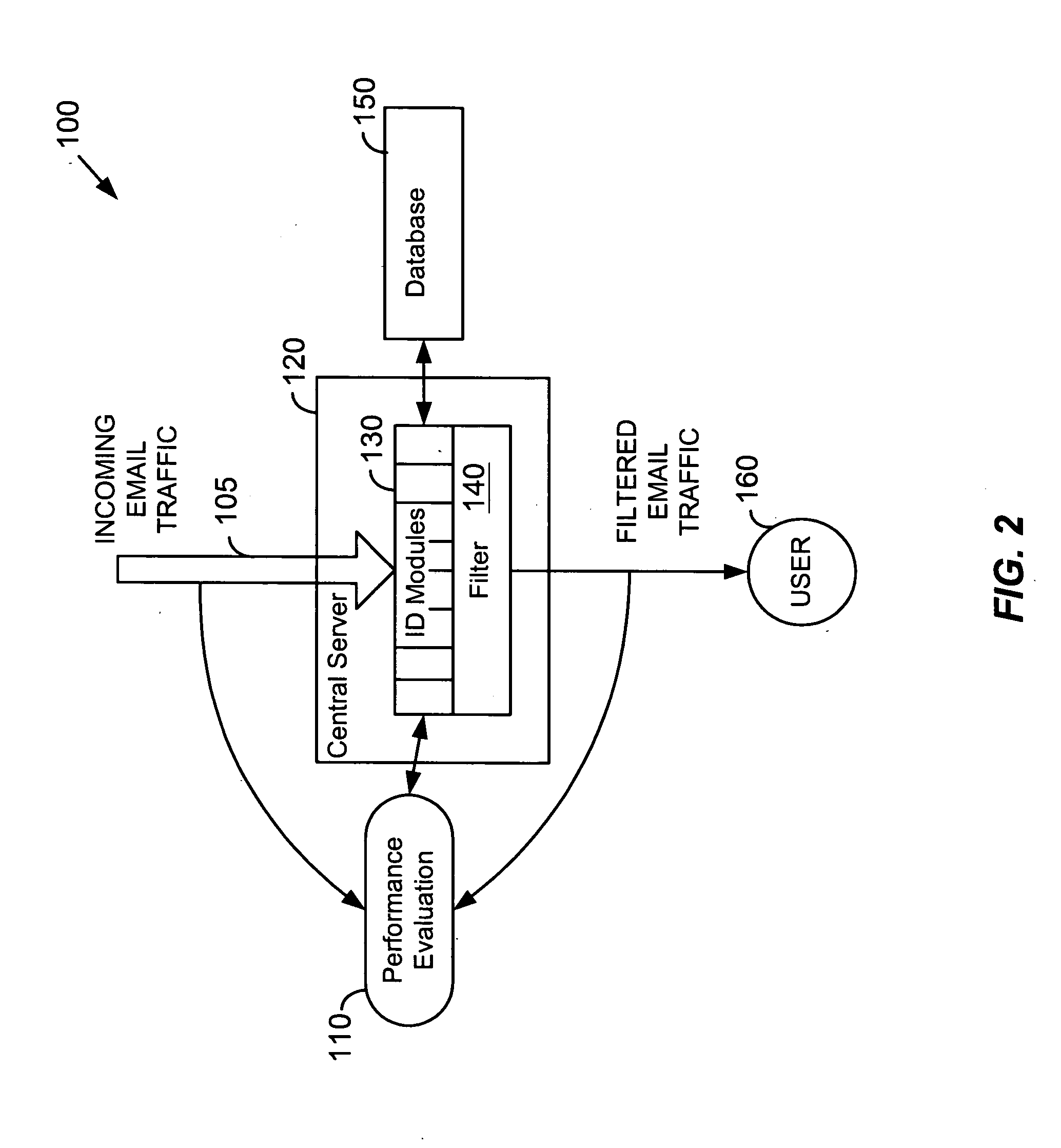
System for determining degrees of similarity in email message information
InactiveUS20050160148A1Improve reliabilityImprove performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksSpammingWord count
Similarity of email message characteristics is used to detect bulk and spam email. A determination of “sameness” for purposes of both bulk and spam classifications can use any number and type of evaluation modules. Each module can include one or more rules, tests, processes, algorithms, or other functionality. For example, one type of module may be a word count of email message text. Another module can use a weighting factor based on groups of multiple words and their perceived meanings. In general, any type of module that performs a similarity analysis can be used. A preferred embodiment of the invention uses statistical analysis, such as Bayesian analysis, to measure the performance of different modules against a known standard, such as human manual matching. Modules that are performing worse than other modules can be valued less than modules having better performance. In this manner, a high degree of reliability can be achieved. To improve performance, if a message is determined to be the same as a previous message, the previous computations and results for that previous message can be re-used. Users can be provided with options to customize or regulate bulk and spam classification and subsequent actions on how to handle the classified email messages.
Owner:GOZOOM COM
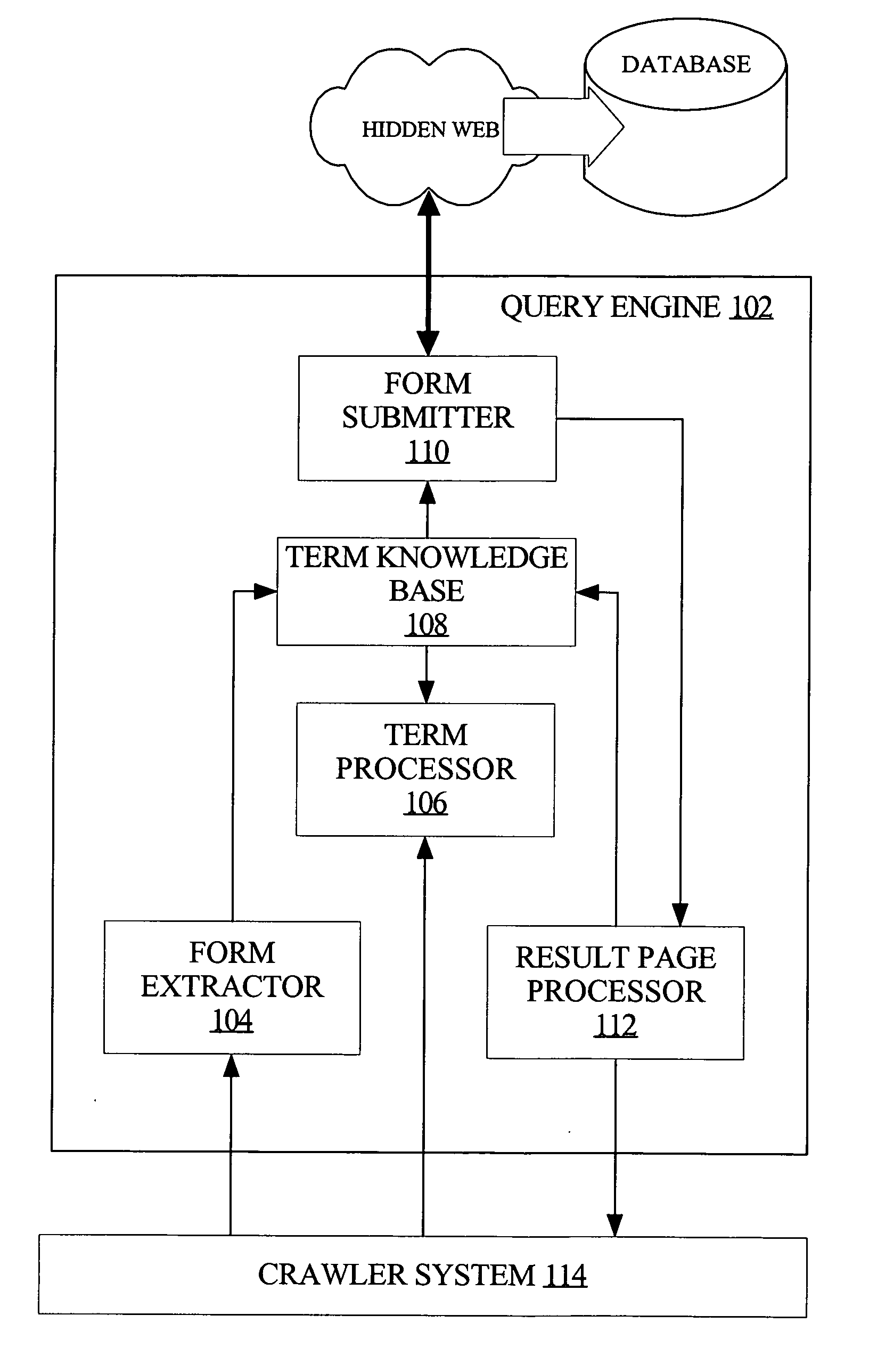
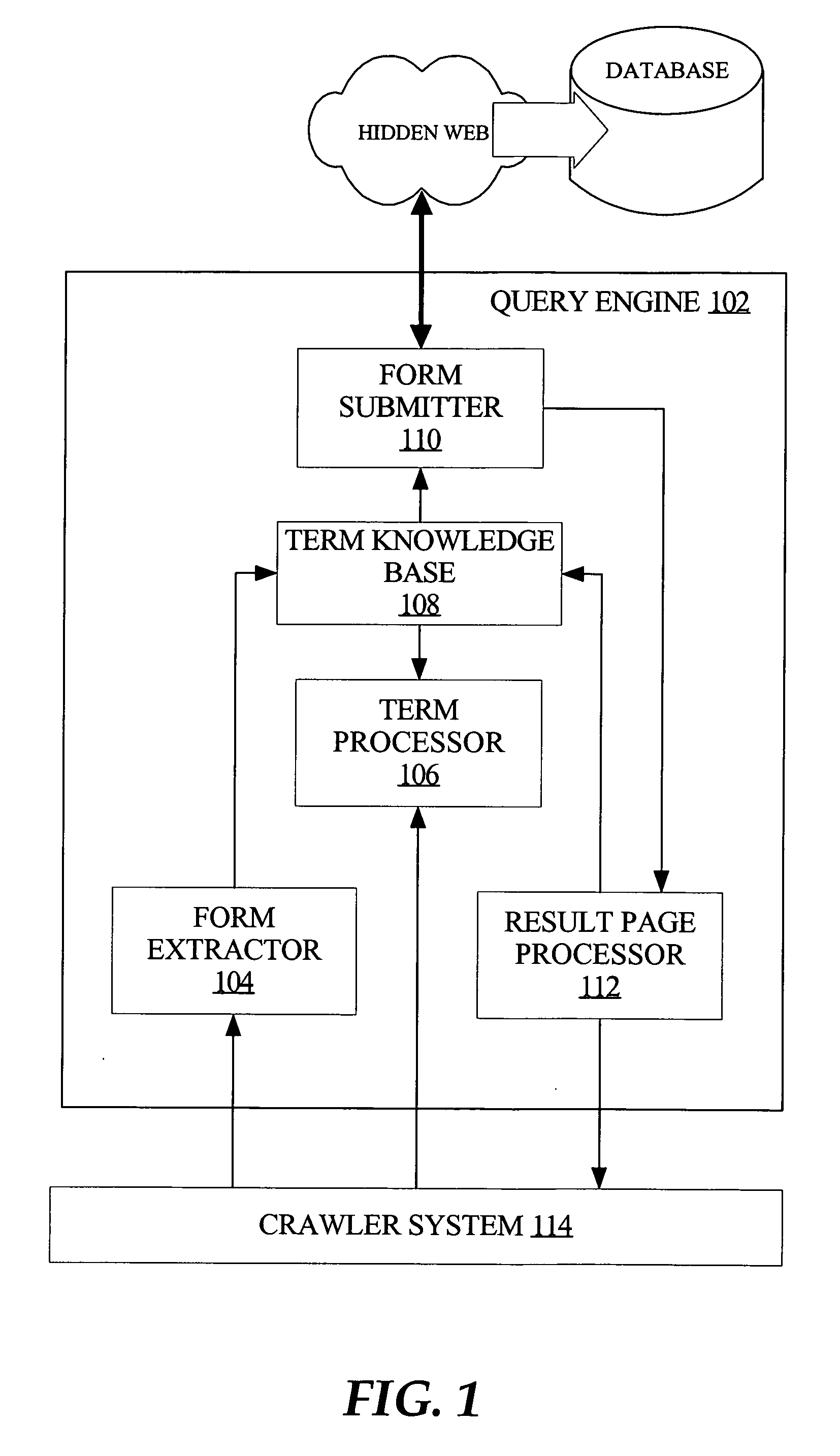
Techniques for unsupervised web content discovery and automated query generation for crawling the hidden web
InactiveUS20070022085A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsWeb siteContent discovery
Unsupervised crawling of the hidden Web utilizes a query engine, coupled to a crawler system, that automatically and intelligently inserts keywords into text input controls in Web page forms so that the filled form can be submitted to a server to retrieve dynamically generated Web content for indexing. The keywords used to fill form controls are based on the content of corresponding Web pages, which is automatically discovered to generate a set of keywords for filling the controls. The set of keywords can be expanded to include related keywords from other Web pages and Web sites and, therefore, to provide more effective coverage for crawling the Web content. The expanded set of keywords can be continuously expanded by recursively performing similarity analyses based on results from crawling the same and other Web sites.
Owner:OATH INC
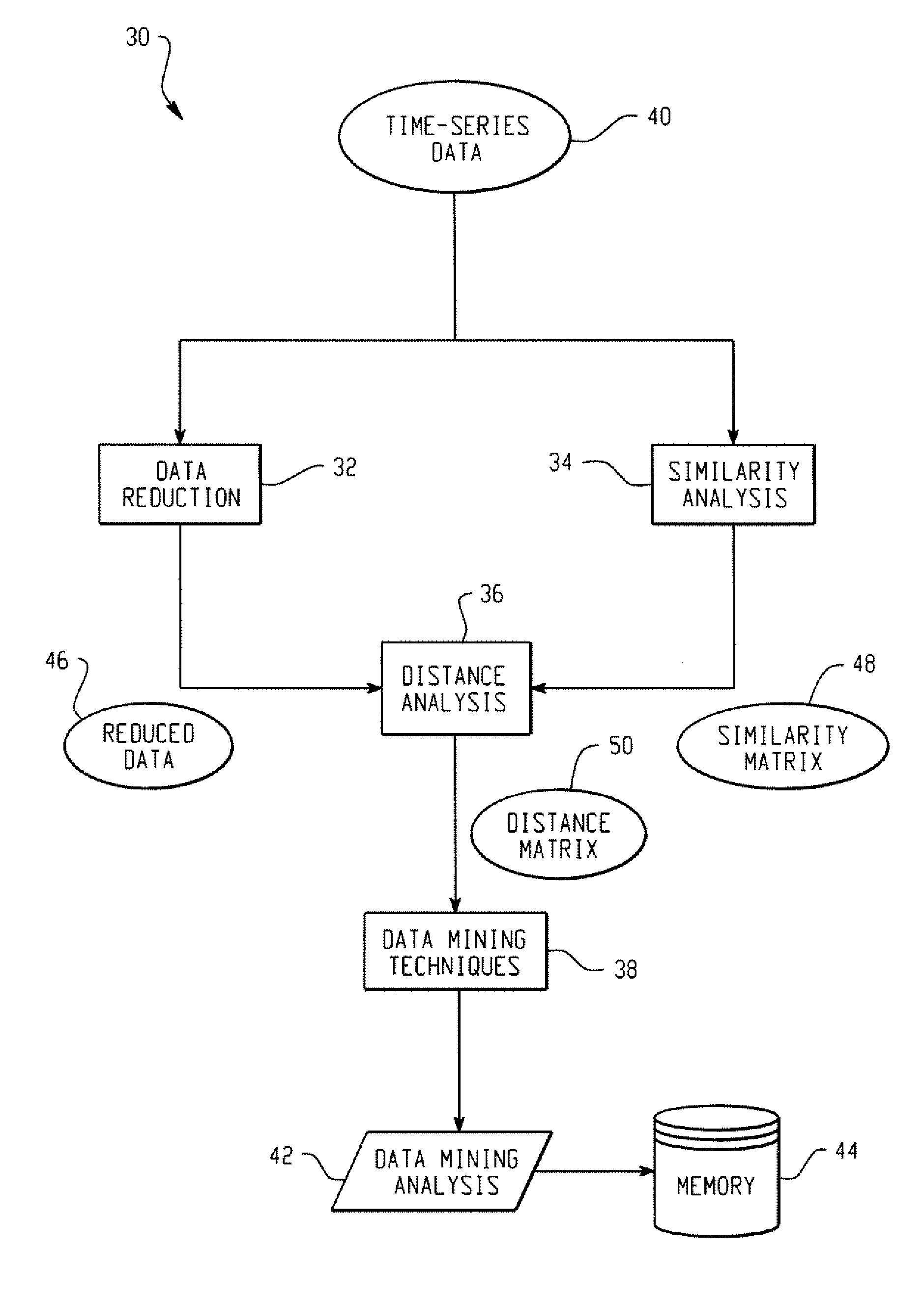
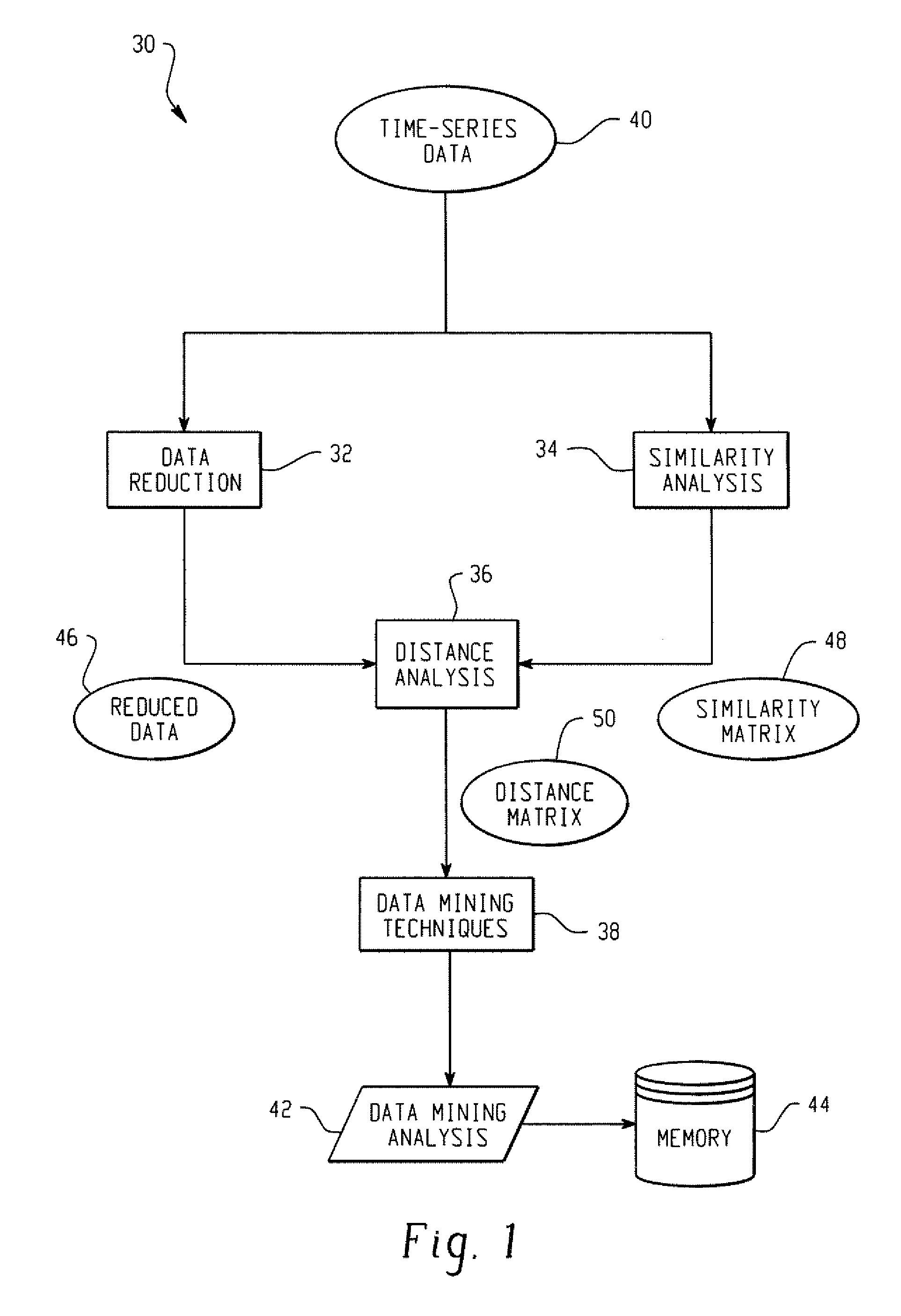
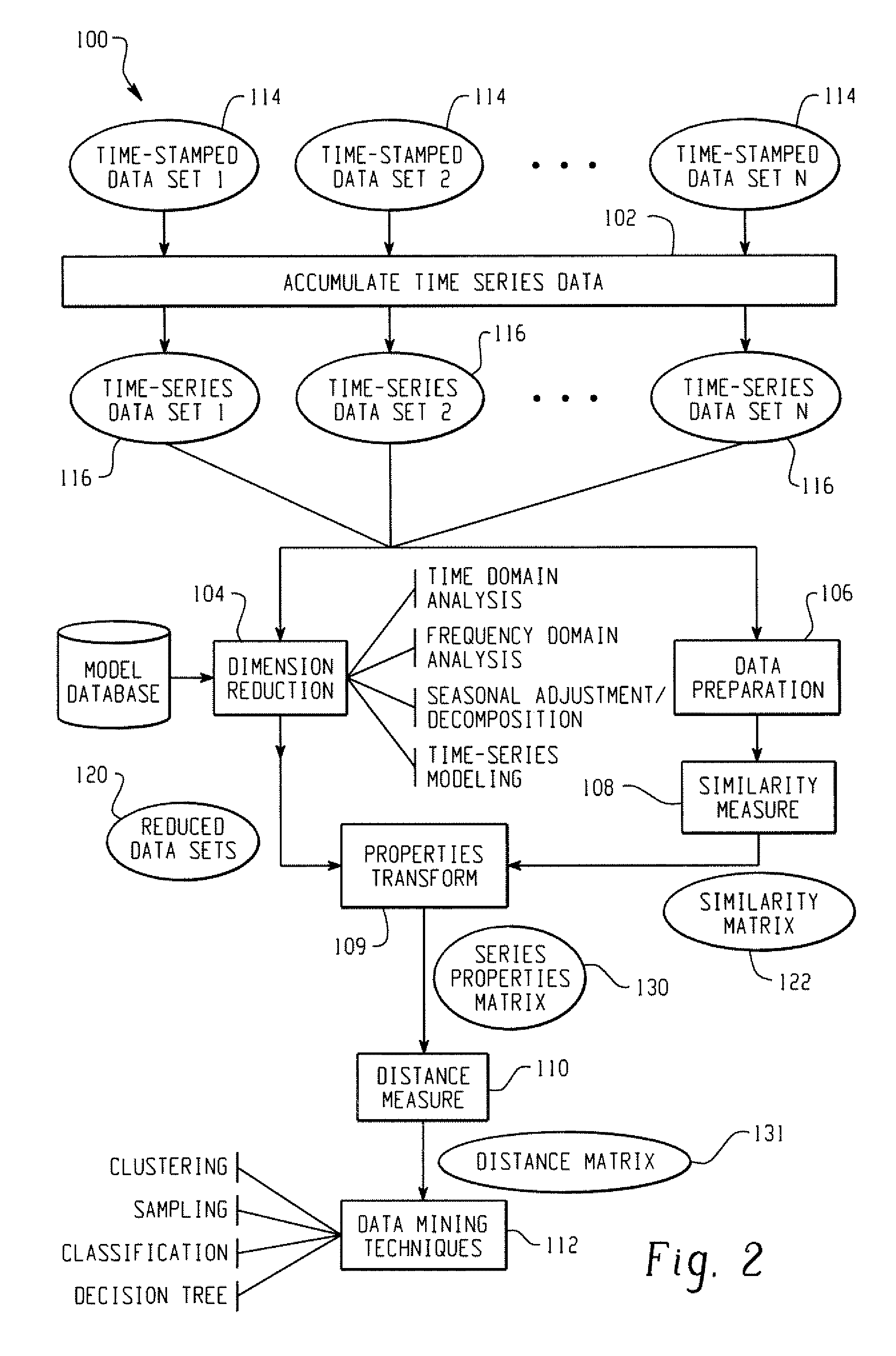
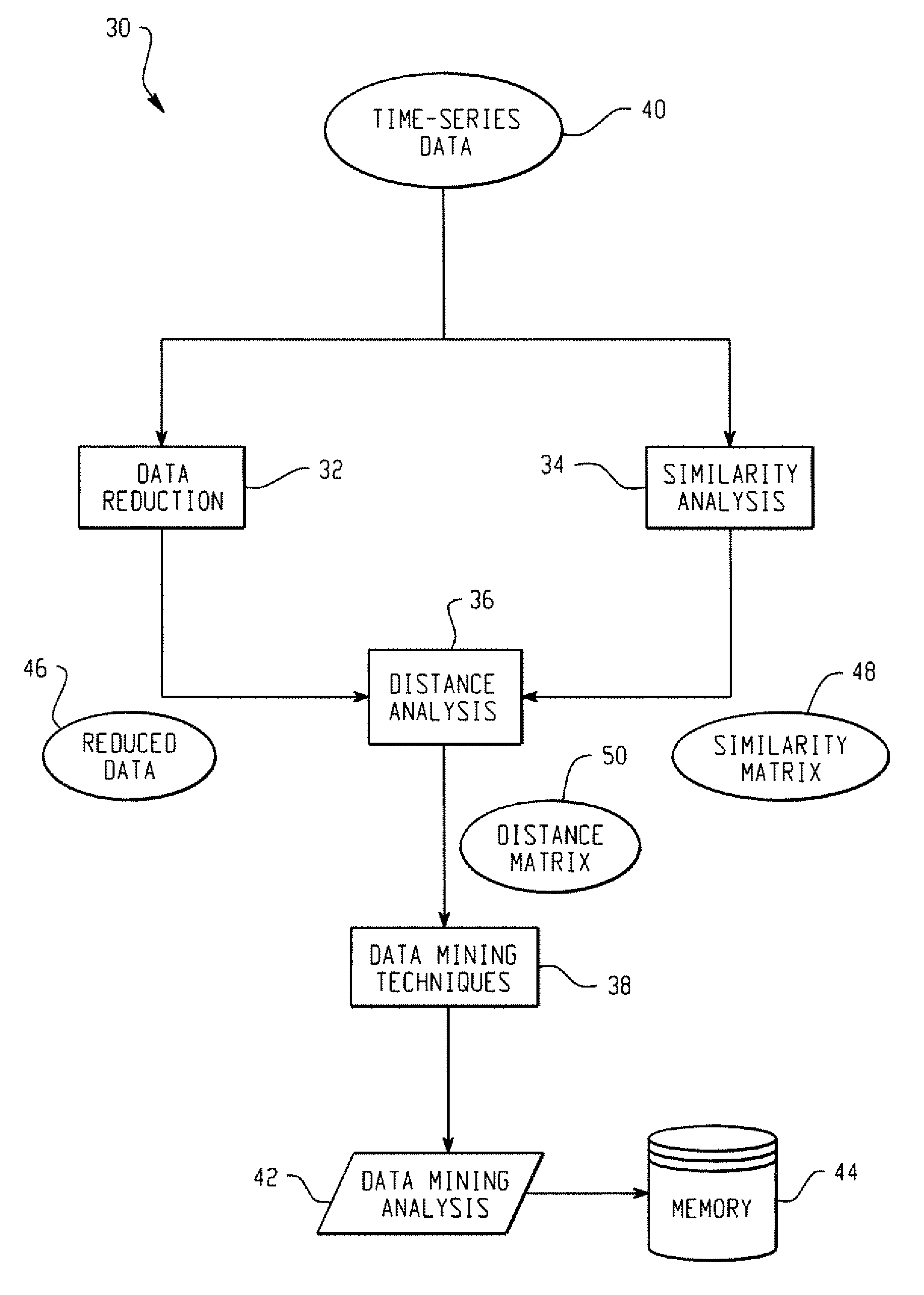
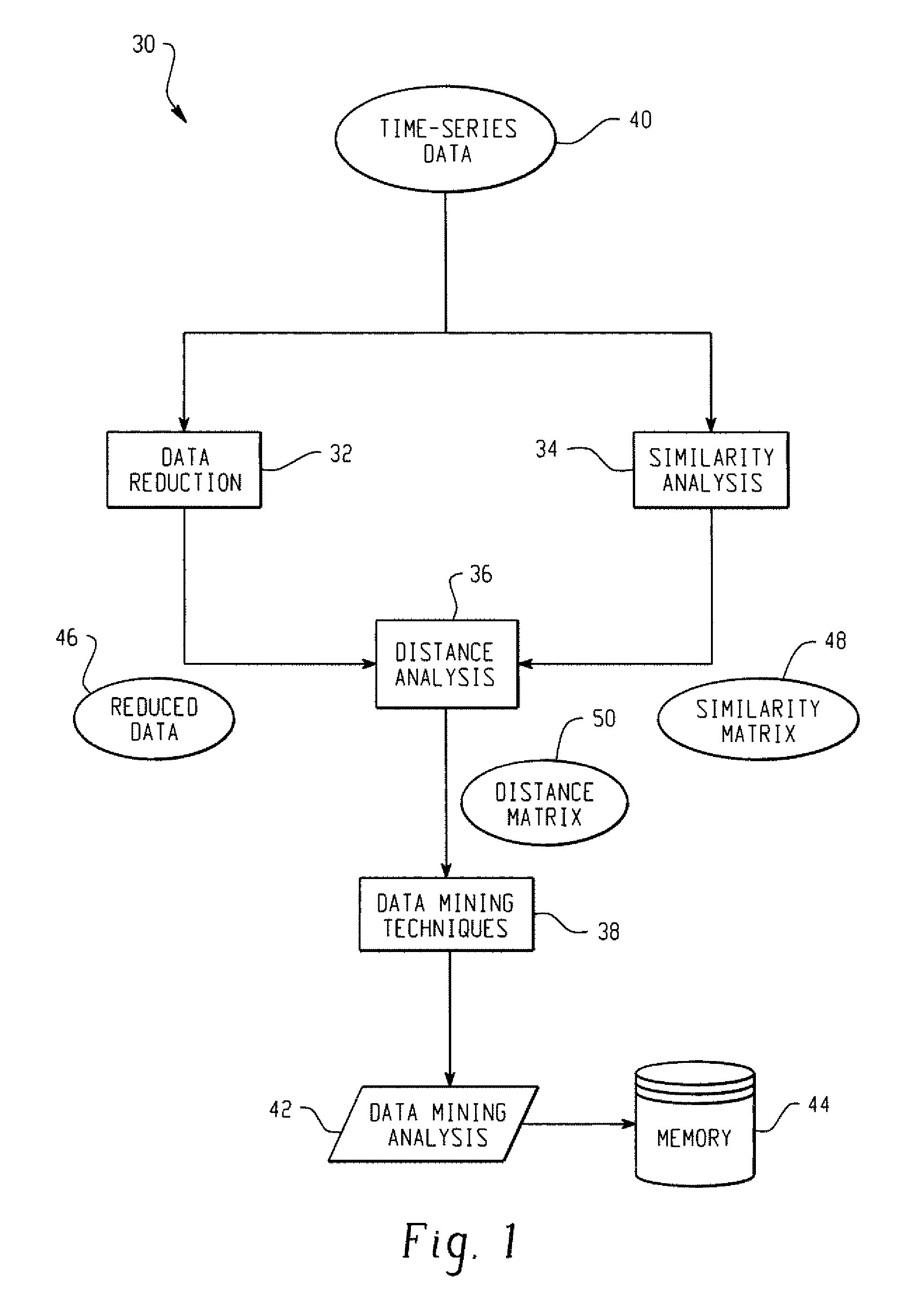
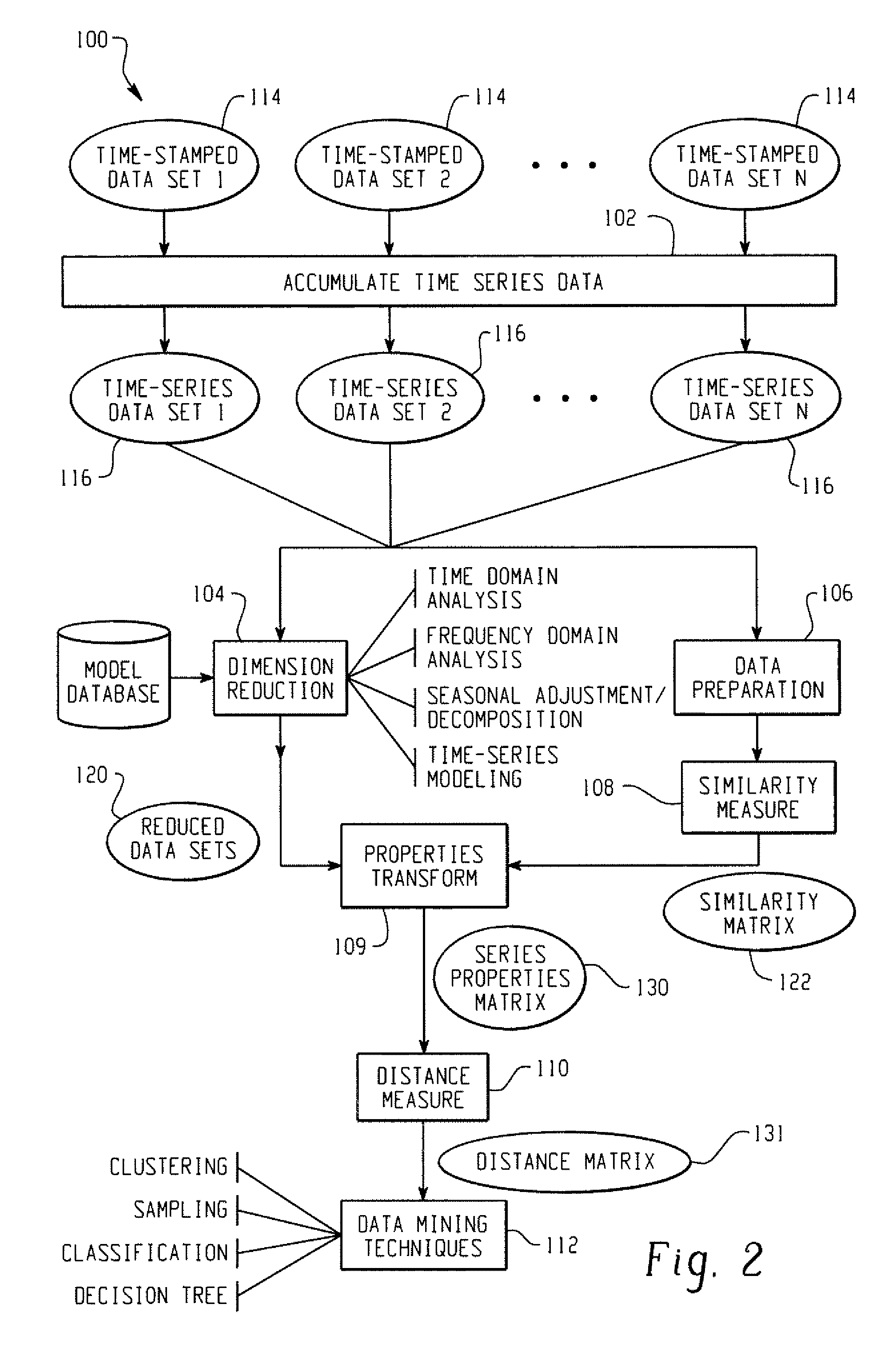
Systems And Methods For Mining Transactional And Time Series Data
ActiveUS20070239753A1Reduce decreaseDigital data processing detailsMarketingDistance matrixSimilarity analysis
In accordance with the teachings described herein, systems and methods are provided for analyzing transactional data. A similarity analysis program may be used that receives time-series data relating to transactions of an organization and performs a similarity analysis of the time-series data to generate a similarity matrix. A data reduction program may be used that receives the time-series data and performs one or more dimension reduction operations on the time-series data to generate reduced time-series data. A distance analysis program may be used that performs a distance analysis using the similarity matrix and the reduced time-series data to generate a distance matrix. A data analysis program may be used that performs a data analysis operation, such as a data mining operation, using the distance matrix to generate a data mining analysis of the transactional data.
Owner:SAS INSTITUTE
Systems and methods for mining transactional and time series data
In accordance with the teachings described herein, systems and methods are provided for analyzing transactional data. A similarity analysis program may be used that receives time-series data relating to transactions of an organization and performs a similarity analysis of the time-series data to generate a similarity matrix. A data reduction program may be used that receives the time-series data and performs one or more dimension reduction operations on the time-series data to generate reduced time-series data. A distance analysis program may be used that performs a distance analysis using the similarity matrix and the reduced time-series data to generate a distance matrix. A data analysis program may be used that performs a data analysis operation, such as a data mining operation, using the distance matrix to generate a data mining analysis of the transactional data.
Owner:SAS INSTITUTE
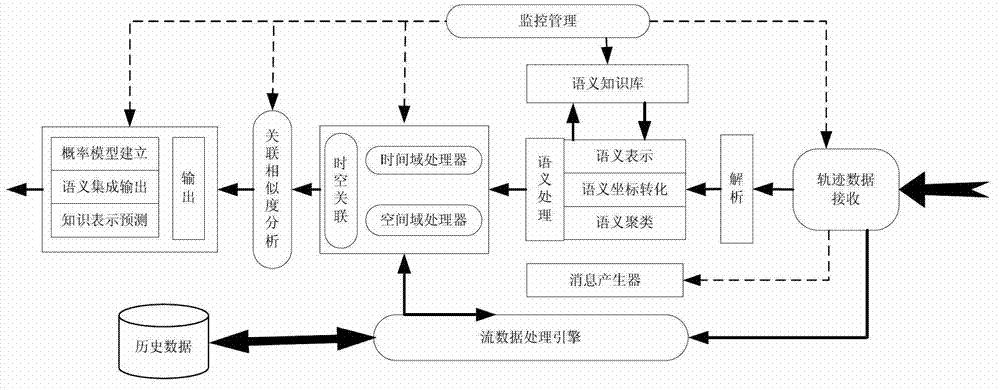
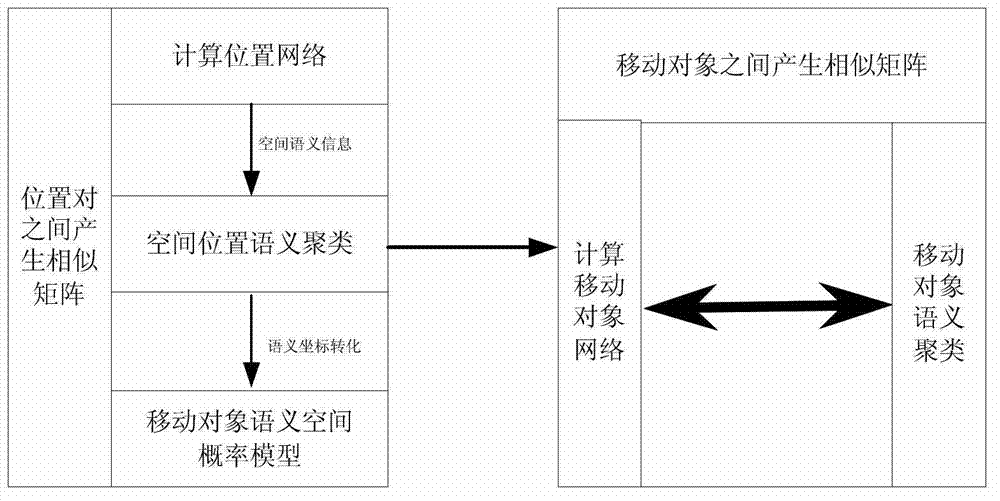
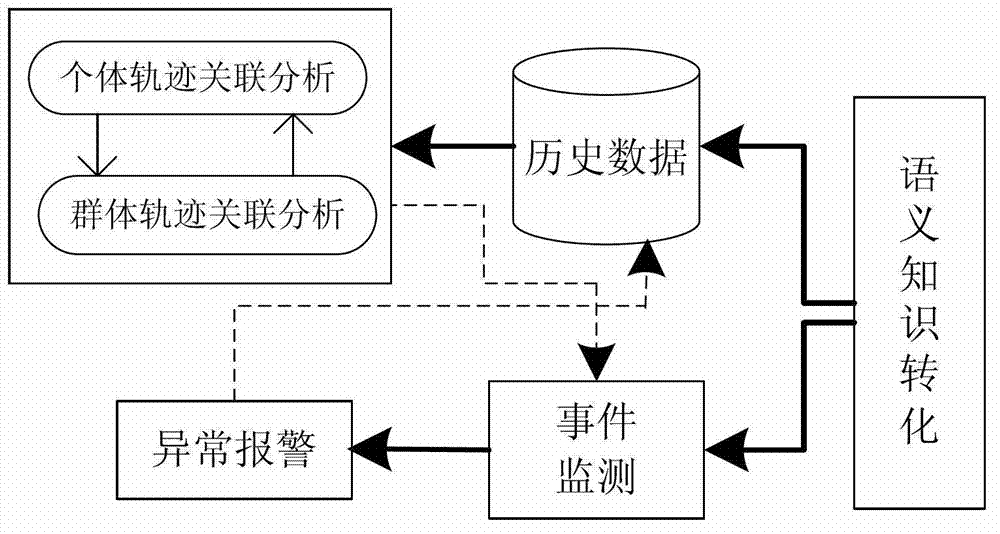
Movement space-time trajectory analysis method in sense network environment
ActiveCN103593361AEasy constructionEasy maintenanceSpecial data processing applicationsReal time analysisCorrelation analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of movement behavioral analysis and prediction in a sense network environment, and specifically to a movement space-time trajectory analysis method in the sense network environment. The movement space-time trajectory analysis method in the sense network environment comprises data reception of receiving trajectory movement position data generated by a positioning device and resolving the data format into a data format applicable to data treatment; semantic treatment of performing clustering operation on the semantic trajectory data; space-time correlation of performing characteristic analysis and statistics on clustered semantic trajectory data in a time domain and a space domain, and performing time-space correlation analysis in combination with the time domain and the space domain; correlation similarity analysis of calculating space-time correlation similarity of the semantic trajectory and performing analysis and calculation on the correlation among different space domains and different movement objects; outputting a result. The movement space-time trajectory analysis method in the sense network environment solves the problem of continuous treatment and mutual correlation of time and space dimensions in a traditional transactional database, and meets the need from a sense network application service to real-time analysis of trajectory movement data.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
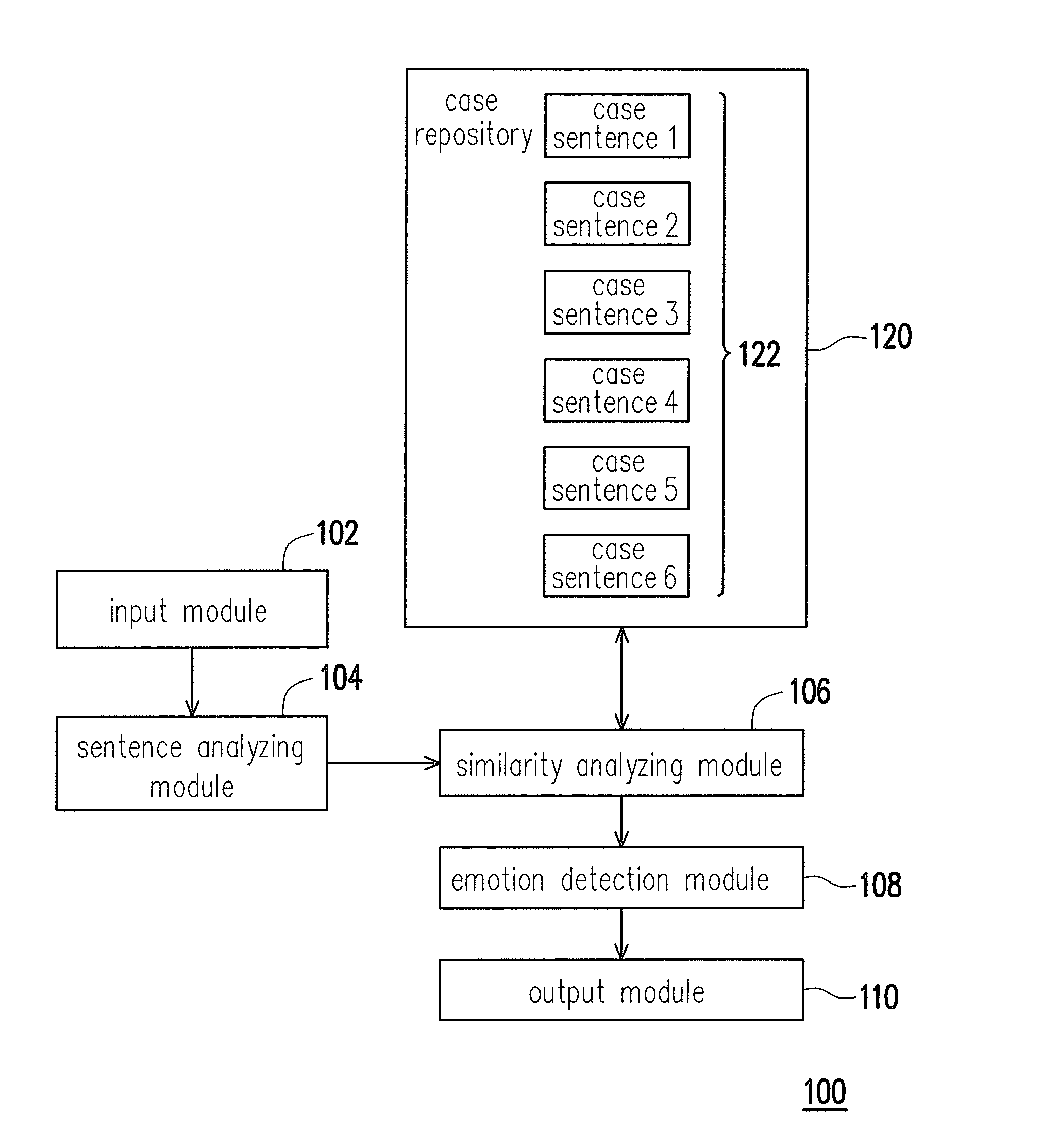
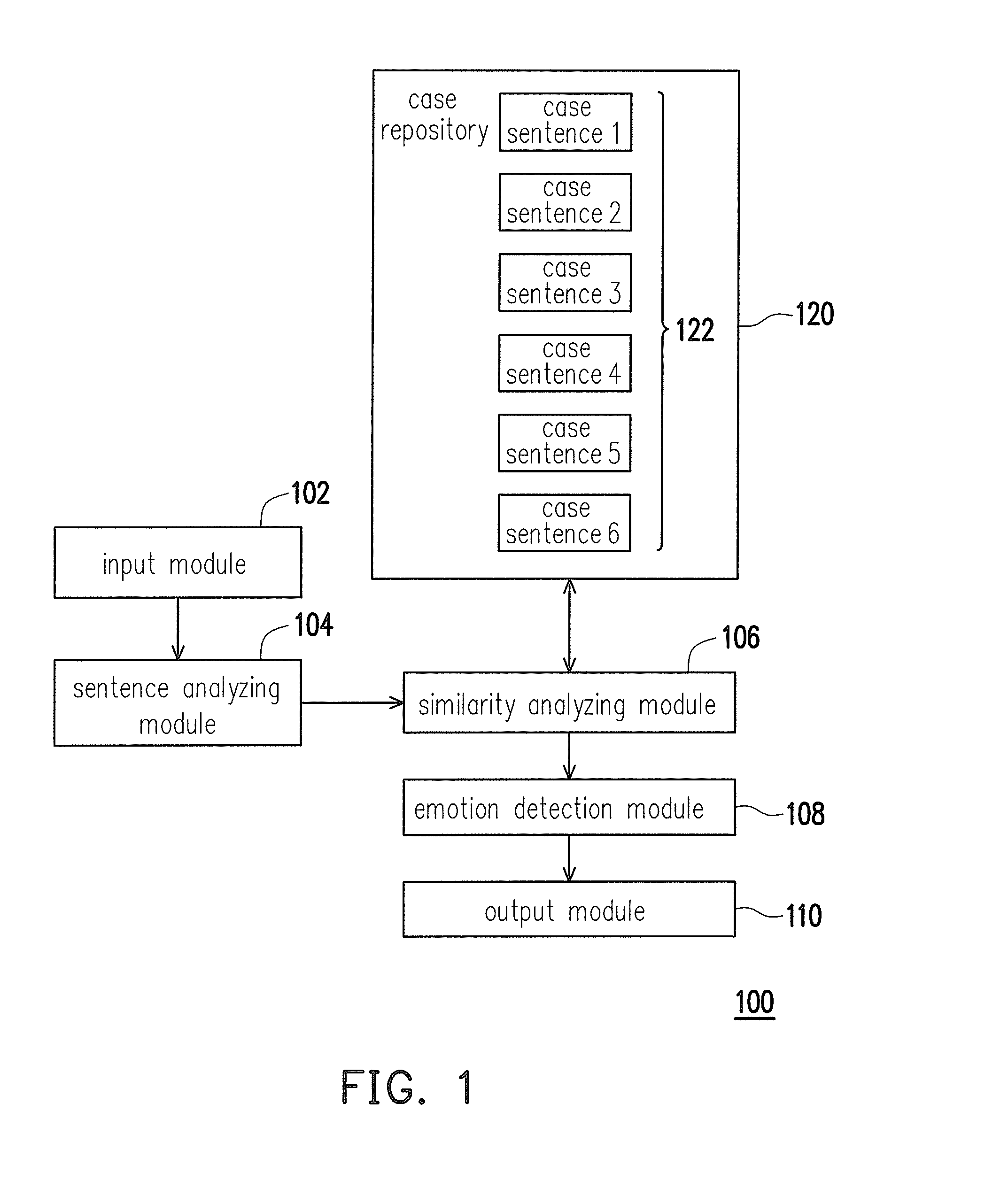
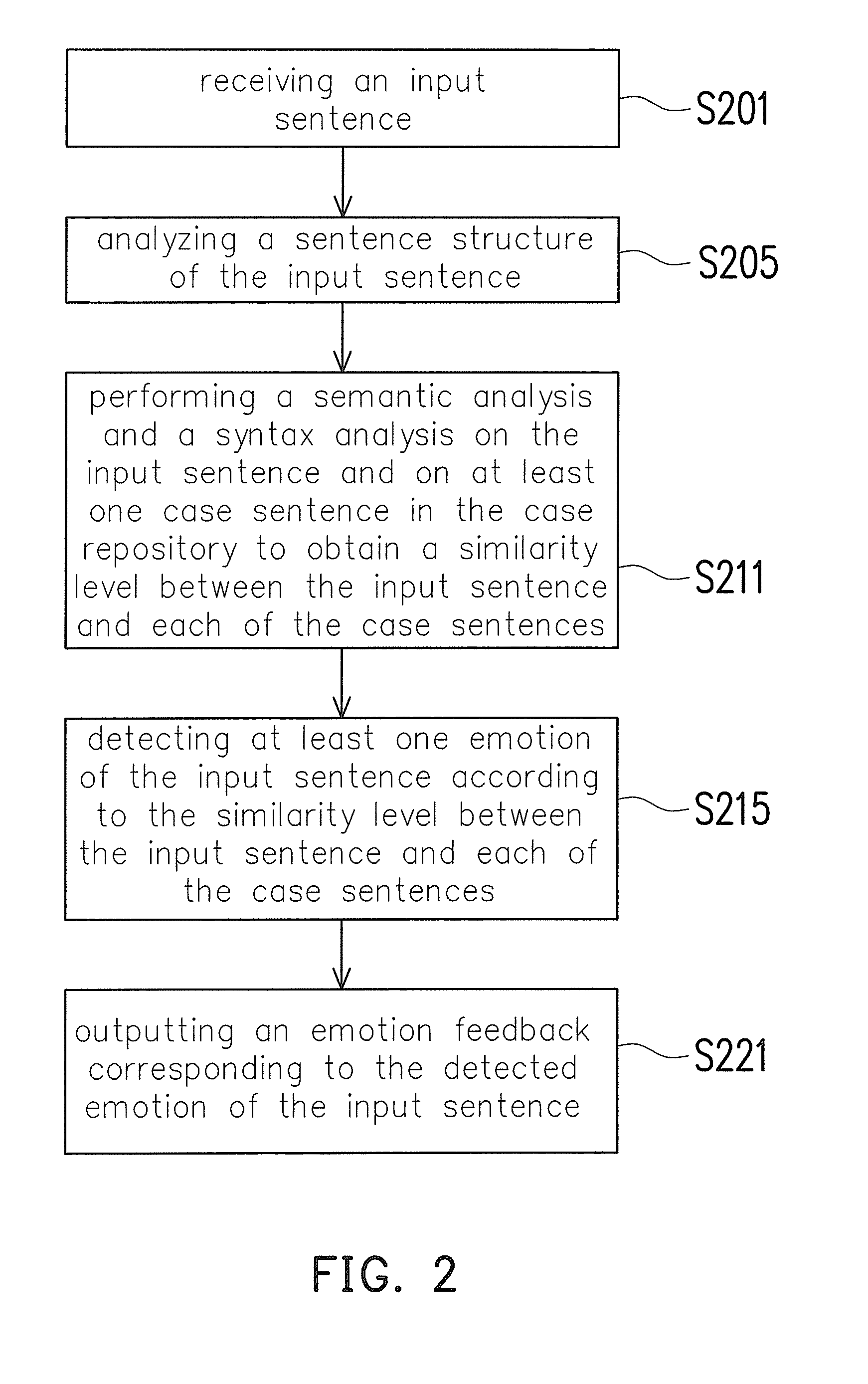
Emotion analyzing method, emotion analyzing system, computer readable and writable recording medium and emotion analyzing device
InactiveUS20110087483A1Accurate detectionImprove accuracyNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionSimilarity analysis
A system for analyzing a sentence emotion is provided. The system comprises a case repository, an input module, a sentence structure analyzing module, a similarity analyzing module and an emotion detection module. The case repository stores several case sentences and each case sentence comprises at least one major term and is corresponding to at least one emotion annotation. The input module receives an input sentence and the sentence structure analyzing module analyzes a sentence structure of the input sentence. The similarity analyzing module performs a semantic analysis and a syntax analysis according to the sentence structure to obtain a similarity level between the input sentence and each of the case sentences. The emotion detection module detects at least one emotion of the input sentence according to the similarity level between the input sentence and each of the case sentences.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
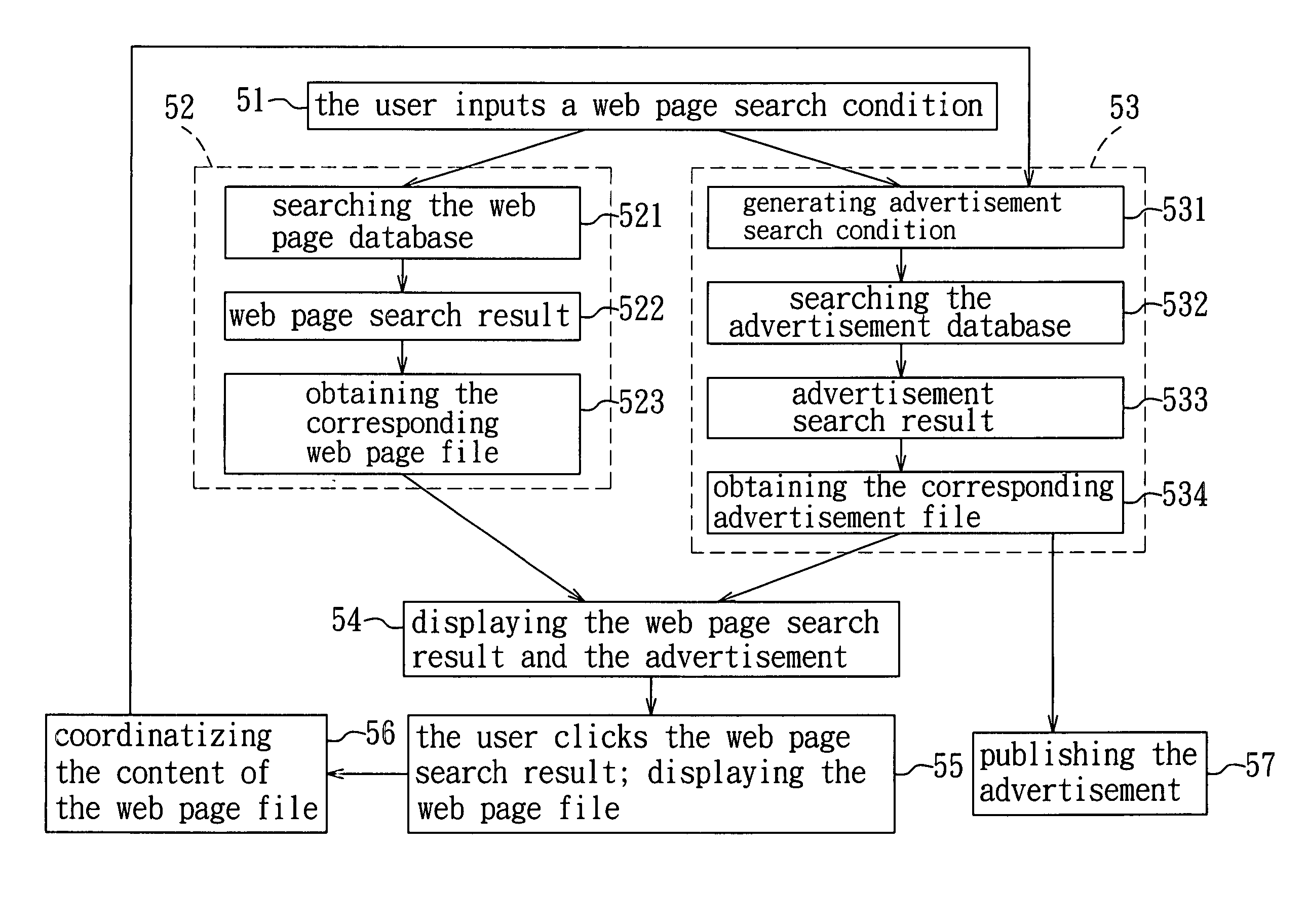
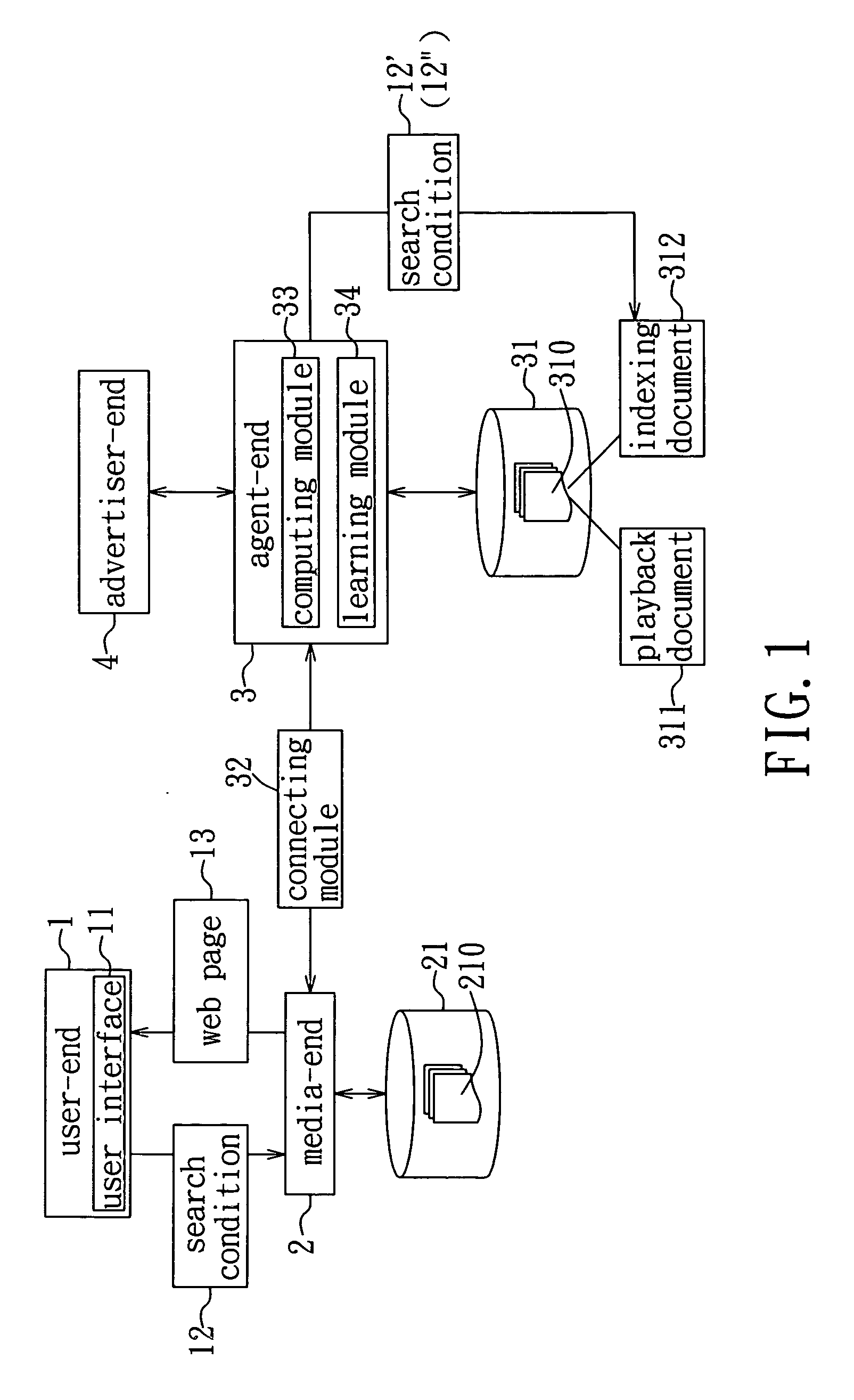
Method and system for web page advertising, and method of running a web page advertising agency
InactiveUS20070027772A1Reduce percentageImprove click-through rateAdvertisementsReal time analysisSimilarity analysis
In a web page advertising method with a learning mechanism, a plurality of advertisement files are transformed to vector equations in advance. Content of a web page file that is being displayed is analyzed and transformed to a vector equation in real time. An advertisement search conditional set is determined according to the analyzed web page file. The advertisement files are subjected to a similarity analysis using vector computations so as to select at least one advertisement file that has a high correlation to the overall concept of the content of the web page. Adjustment and training with the advertisement file are conducted through analyzing actions of a user, thereby increasing considerably the click rate of the advertisement file and achieving full utilization of advertising resources. An advertising agent employing the web page advertising method purchases advertising spaces from a medium and bills advertisers on a pay-per-click basis.
Owner:BRIDGE WILL
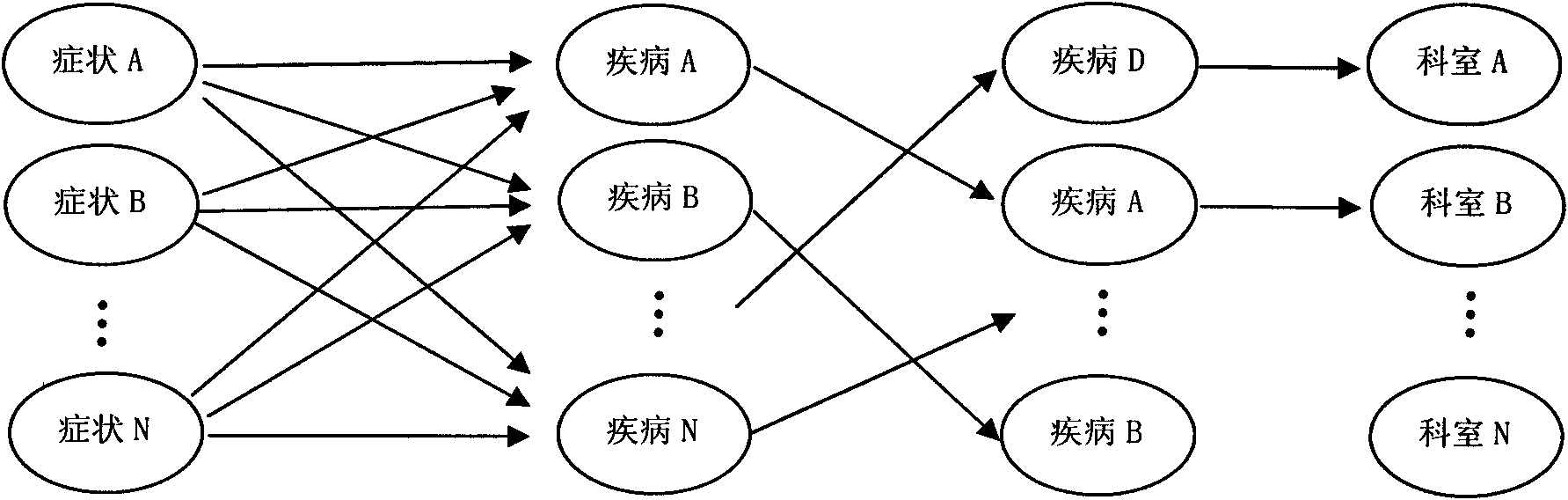
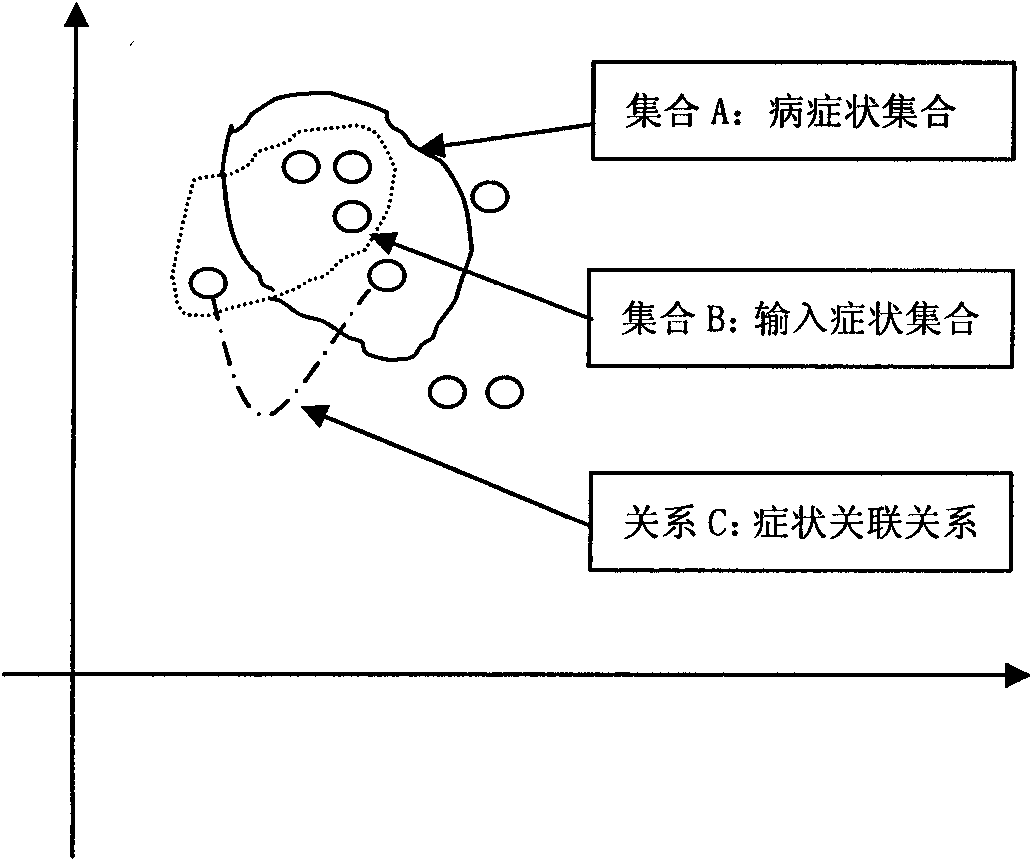
Hospital decision-making aiding method based on symptom similarity analysis
InactiveCN102156812AWeaken errors interfere with resultsAchieve correctnessSpecial data processing applicationsPatient modelInformation analysis
The invention provides a hospital decision-making aiding method based on symptom similarity analysis, belonging to the field of information analysis and decision-making aid. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a disease database, a symptom database, a department database and a correlating relationship; establishing a patient model for symptoms input by users, and calculating the similarity between the patient model and a disease model; and searching one department with corresponding suspected diseases in the department model to serve as hospital reference. The method has the advantages that an error interrupted result is weakened under a condition that a user takes an error symptom as a reasoning condition; a correct symptom participates in the reasoning operation by combining the correlating relationship between the error symptom and the convention symptoms according to the error symptom condition so as to realize the correctness and interruption resistance of reasoning; and a hospital department list is obtained by utilizing the mapping relationship between the disease and the department. The method can be used in electronic reception or health consulting systems, as well as in medical training or clinical reference.
Owner:中国医学科学院医学信息研究所
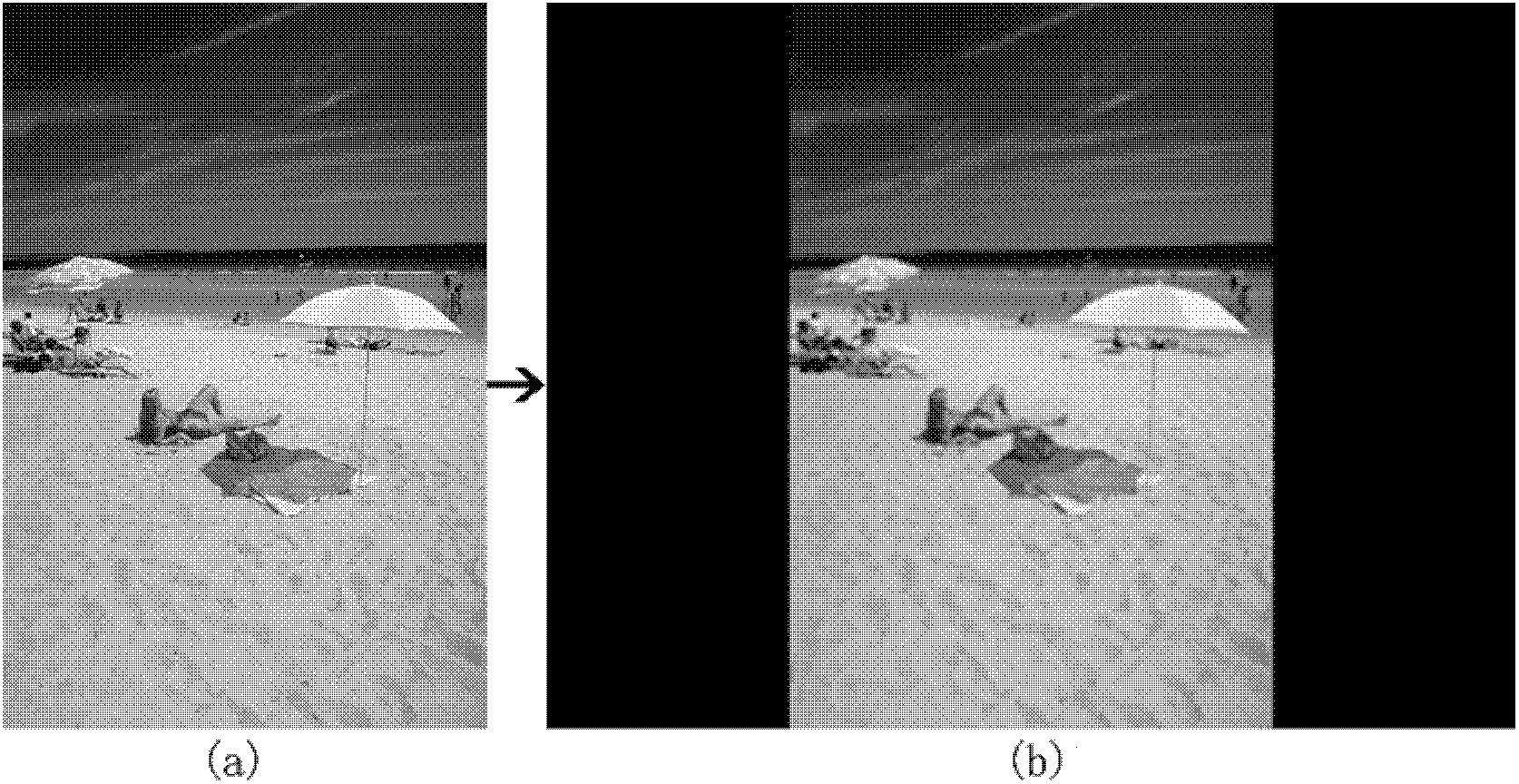
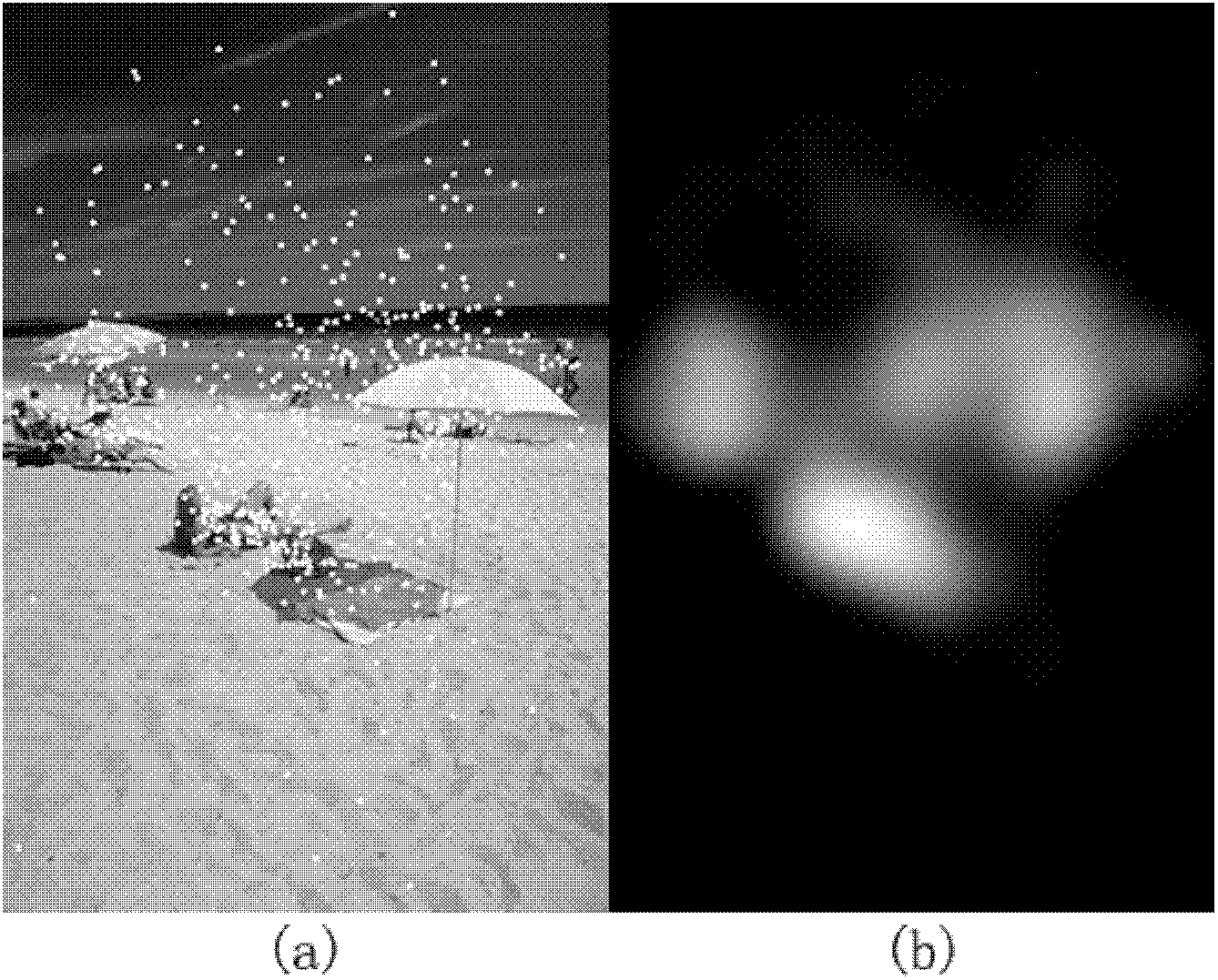
Method for extracting image region of interest based on eye movement data and bottom-layer features
InactiveCN102521595AComplies with semantic understandingBridging the gapImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionOptimal weight
The invention discloses a method for extracting an image region of interest based on eye movement data and bottom-layer features. On one hand, the image region of interest, namely, eye movement ROI (Region Of Interest), for reflecting human real semanteme is extracted by visual point tracking experimental data of an eye movement instrument, and on the other hand, the image region of interest, namely, feature ROI, in a general sense is extracted in a form of bottom-layer feature weighted combination, and weight combination with highest similarity, namely, optimal weight, is found out by similarity analysis of the feature ROI and the eye movement ROI. The region of interest of other image of the same type, extracted by using the weight, can more comply with the semantic demands of users.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
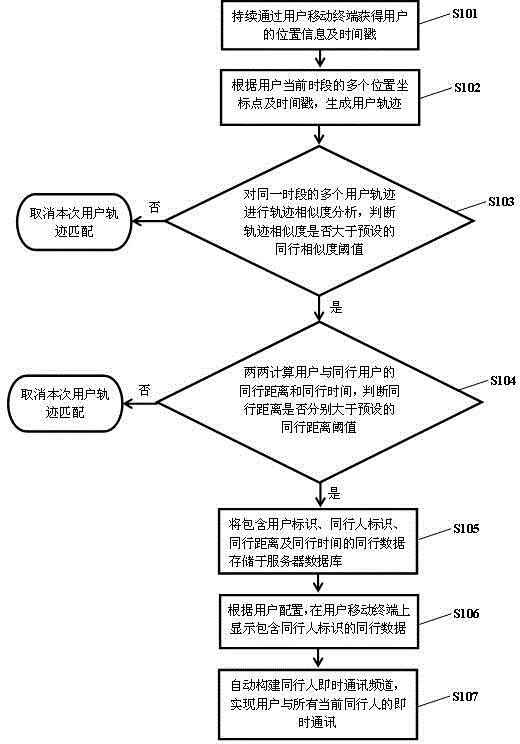
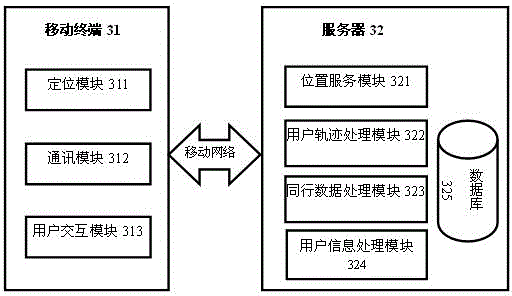
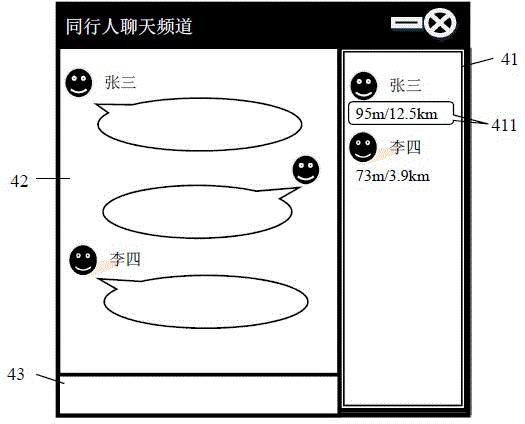
Method and system for realizing instant messaging of people travelling together and travel-together information sharing
InactiveCN104796468AFacilitate communicationData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsInformation sharingSimilarity analysis
The invention relates to a method for realizing instant messaging of people travelling together and travel-together information sharing. The method includes: continuously acquiring the location information and time stamps of a user through a user mobile terminal; generating user trajectories according to the multiple location coordinate points and time stamps of the user at a current time period; performing trajectory time-space similarity analysis on the user trajectories to obtain travel-together trajectories meeting travel-together matching standards in the time-space dimension; performing pairwise calculation according to the travel-together trajectories to obtain the travel-together distance and travel-together time of the user and other users; storing the travel-together data containing user identification, travel-together people identification, travel-together distance and travel-together time in a server database; displaying the travel-together data on the mobile terminal according to user configuration so as to realize travel-together information sharing; automatically building a chatting channel for the people travelling together to realize the instant messaging of all the current people travelling together. The method has the advantages that the people travelling together can be automatically searched and added, the instant messaging channel can be built, and communication of the people travelling together is facilitated greatly; the travel-together information containing the travel-together distance and travel-together time is shared in instant messaging tools and social networks to serve as a dynamic expression of friend degree.
Owner:蔡宏铭
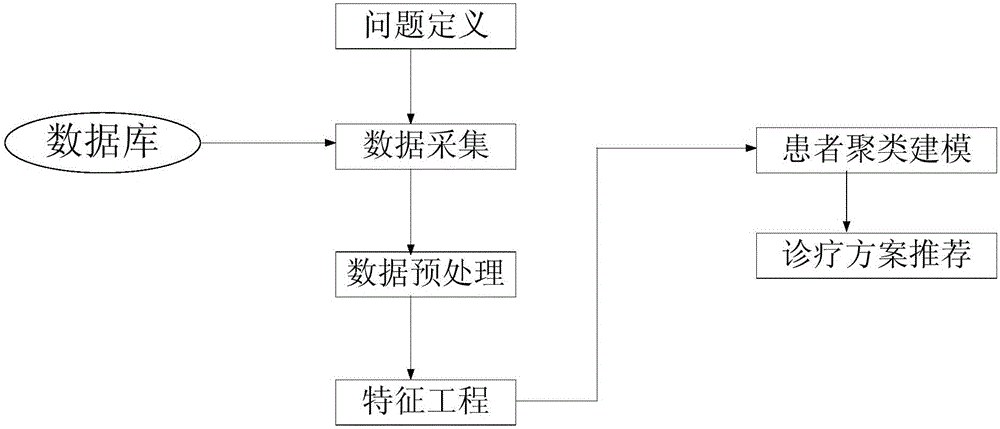
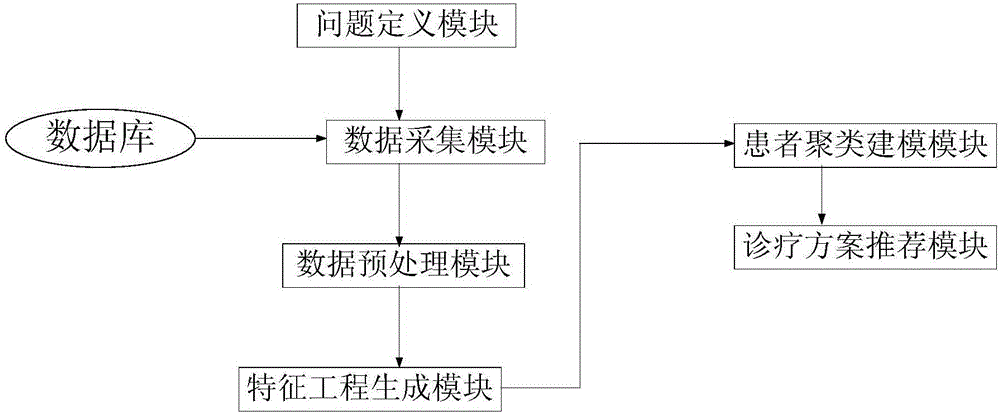
Similarity analysis method and system for patients suffering from cardio-cerebral vascular diseases
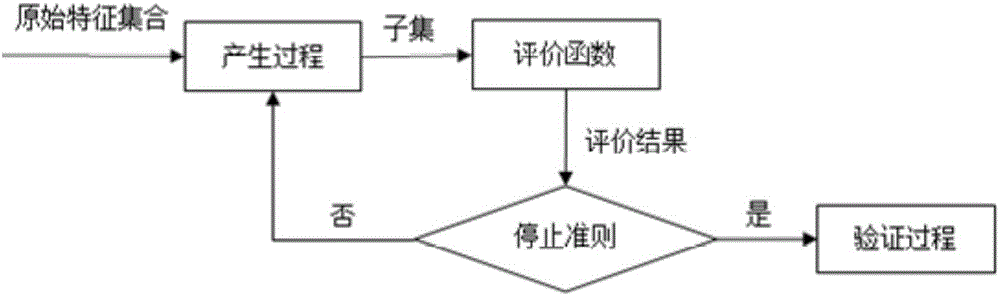
InactiveCN106778042AHuge medicalGreat clinical valueCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisCrowdsCvd risk
The invention provides a similarity analysis method and system for patients suffering from cardio-cerebral vascular diseases. The method comprises the following steps of 1 problem definition, wherein problem definition for the patients suffering from the cardio-cerebral vascular diseases is conduced; 2 data collection, wherein health care data of the patients suffering from the cardio-cerebral vascular diseases is collected; 3 data preprocessing, wherein data integration, data cleaning, missing value processing, feature deleting and abnormal point removing are included; 4 feature engineering, wherein feature construction, feature selection and feature processing are included; 5 patient clustering modeling; 6 diagnosis and treatment scheme recommendation. Accordingly, an effective similarity analysis model for the patients suffering from the cardio-cerebral vascular diseases is built, a clinician can obtain the similar populations of a give patient through the patient features and then recommends a personalized treatment plan to achieve the purpose of accurate medical treatment, population grouping based on similarity analysis can be well conducted on the patients suffering from the cardio-cerebral vascular diseases in the Chinese population, and pointed personalized rehabilitation therapy is conducted on different risk populations as early as possible.
Owner:中电科数字科技(集团)有限公司
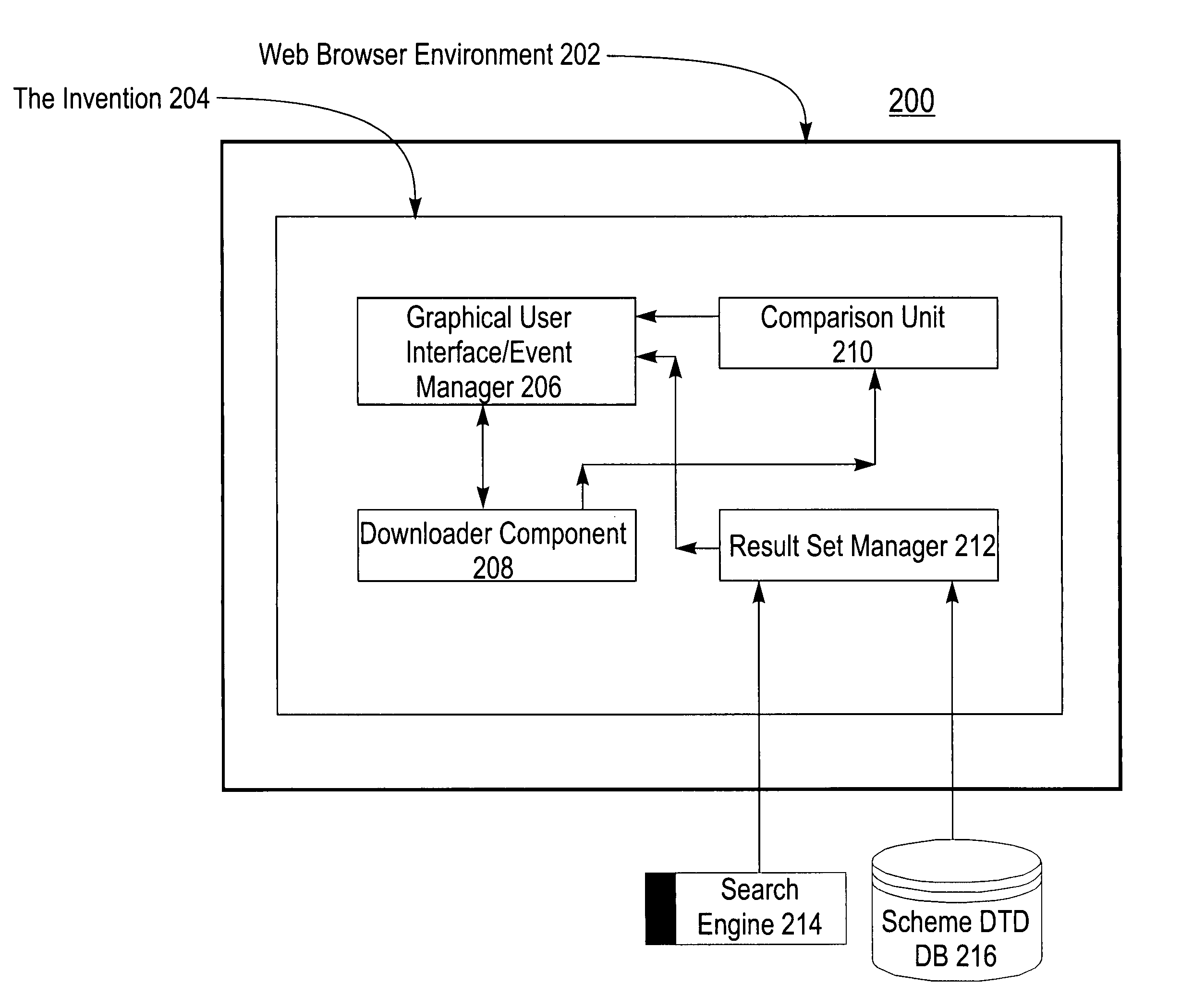
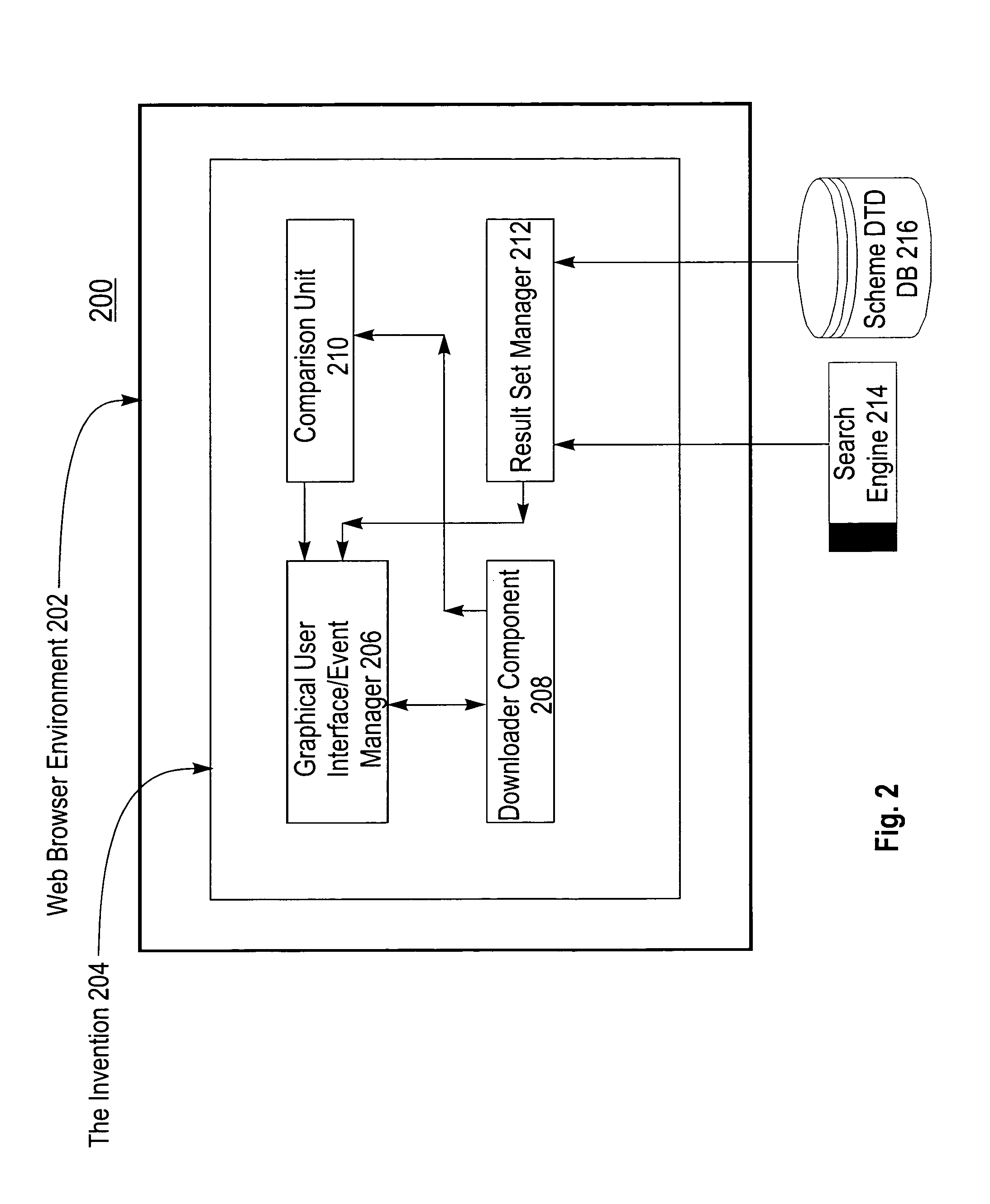
System and method for comparing and representing similarity between documents using a drag and drop GUI within a dynamically generated list of document identifiers
InactiveUS6938034B1Convenient and facile comparisonGood choiceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDrag and dropSoftware system
The present invention relates to the field of data processing, and particularly to a software system and associated method for use with a search engine. The engine searches data maintained in systems that are linked together over an associated network such as the Internet. More specifically, this invention pertains to a computer software product for determining, comparing, and representing the similarity between documents using a drag and drop Graphical User Interface (GUI) within a dynamically generated list of document identifiers. The invention uses this drag and drop GUI interface for convenient selection of document identifiers for further comparison. Then processing of a similarity analysis request using a configurable similarity algorithm is executed; this processing can be done on the client, proxy or server side. When the comparison process is completed, the GUI presents the similarity result of the comparison process as a Venn Diagram to show the level of similarity between the selected documents.
Owner:IBM CORP
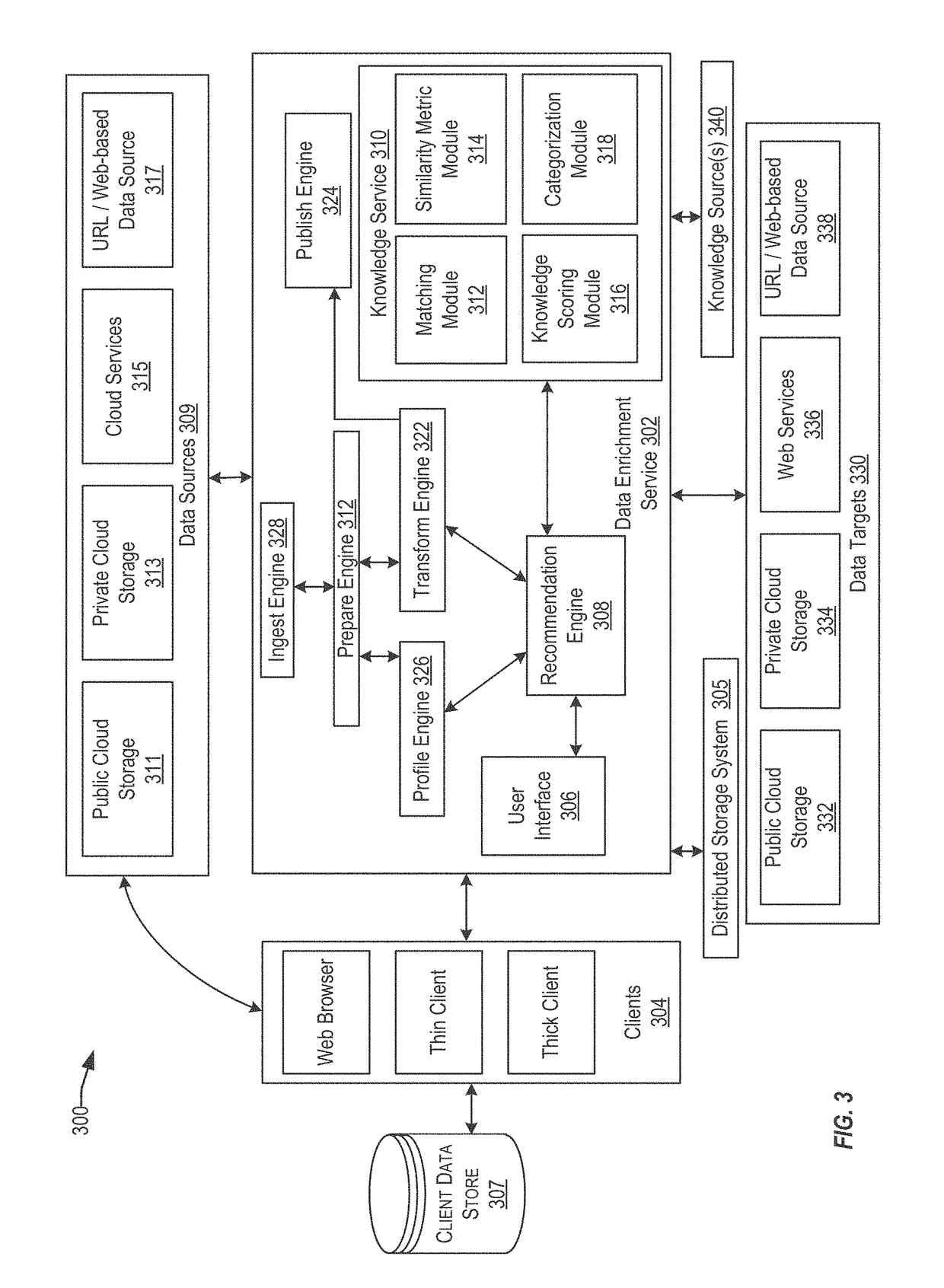
Techniques for similarity analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources
ActiveUS10210246B2Accurate resolutionAccurate labelingRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesData set
The present disclosure relates to performing similarity metric analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources. A data enrichment service can compare an input data set to reference data sets stored in a knowledge source to identify similarly related data. A similarity metric can be calculated corresponding to the semantic similarity of two or more datasets. The similarity metric can be used to identify datasets based on their metadata attributes and data values enabling easier indexing and high performance retrieval of data values. A input data set can labeled with a category based on the data set having the best match with the input data set. The similarity of an input data set with a data set provided by a knowledge source can be used to query a knowledge source to obtain additional information about the data set. The additional information can be used to provide recommendations to the user.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
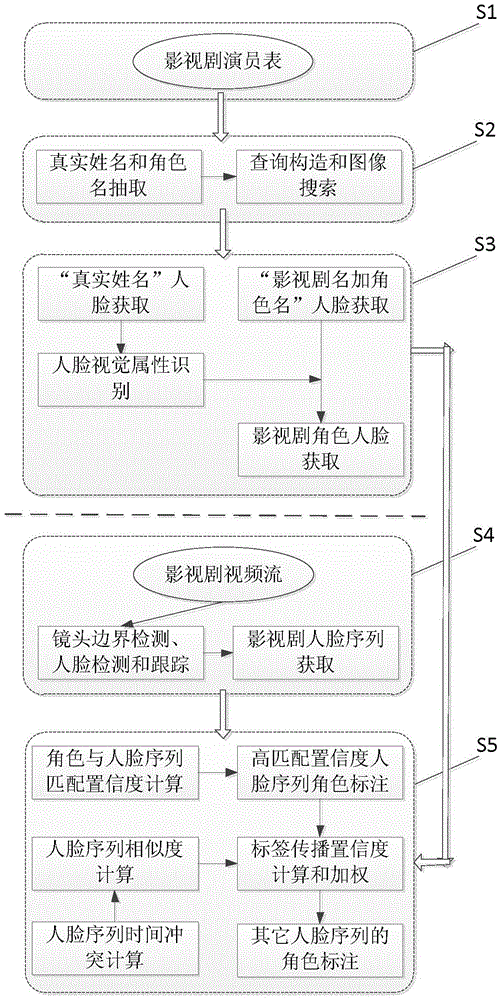
Role labelling method based on search matching
InactiveCN103984738AThe labeling process is fully automaticNo human intervention requiredCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFace detectionExtensibility
The invention discloses a movie and television play role labelling method based on search matching. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining the to-be-labelled object set of a labelling scene and all to-be-labelled object information according to a to-be-labelled object list; constructing a text keyword for each of to-be-labelled objects, and obtaining the corresponding image set by virtue of an image search engine; carrying out face detection and visual attribute analysis on the image of the search result, and removing a noise therein to obtain a role face set which is closely related to the labelling scene, of the to-be-labelled objects; carrying out face detection and tracking on the labelling scene to obtain all face sequences therein; carrying out role labelling on the labelling scene on the basis of a visual similarity among the face sequences, and a visual similarity analysis on the face sequences and the role faces of the to-be-labelled objects. According to the method disclosed by the invention, movie and television play role labelling is carried out by virtue of face images related to movie and television play roles in the Internet; the method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the labelling process is fully-automatic, high in labelling accuracy, and high in method extensibility and universality.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
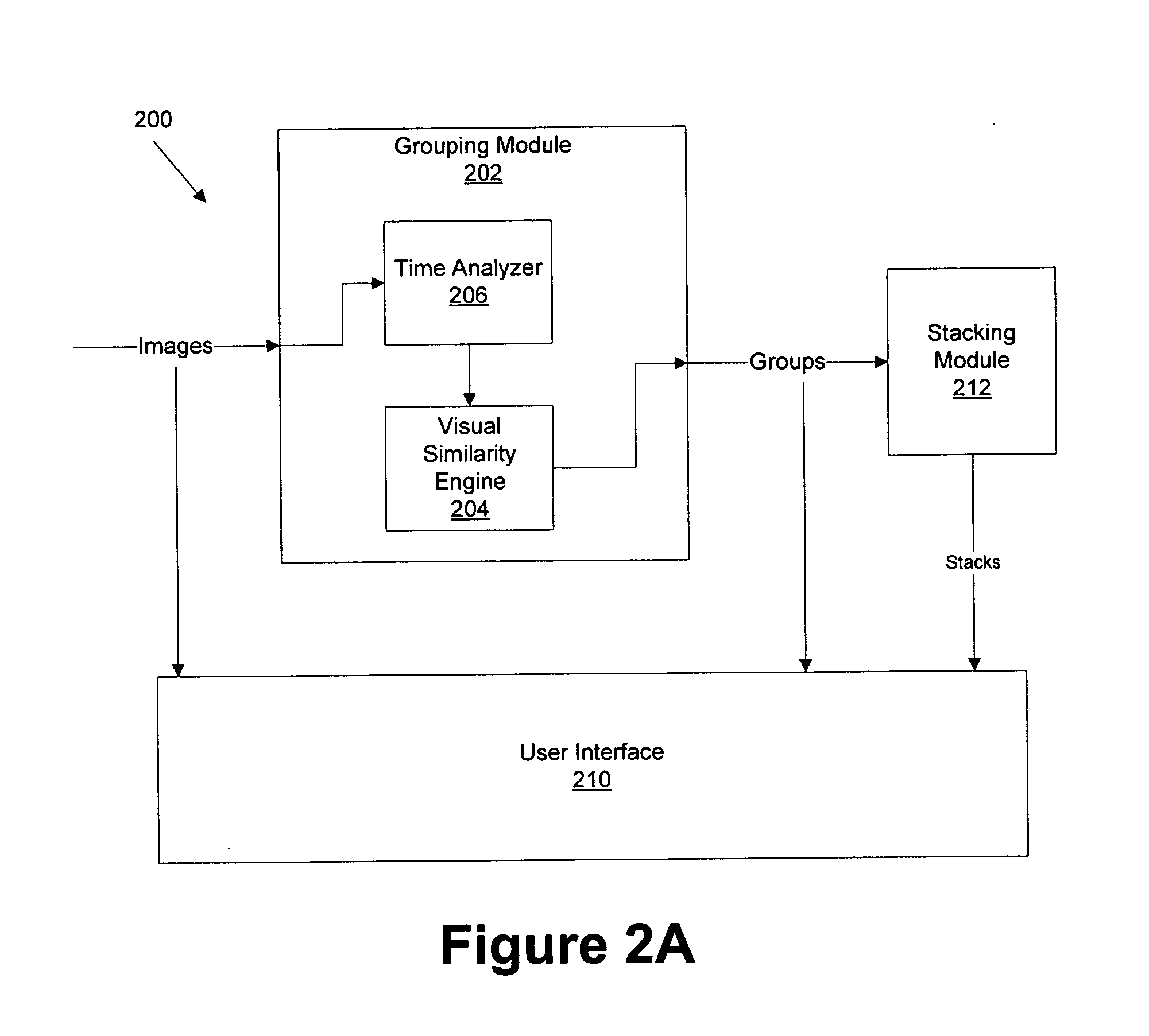
Automatic stacking based on time proximity and visual similarity
ActiveUS20130125002A1Input/output processes for data processingPattern recognitionSimilarity analysis
Automatic stacking based on time proximity and visual similarity is described, including a method, comprising analyzing a time proximity of a plurality of electronic images, performing a visual similarity analysis on the plurality of electronic images, and stacking the plurality of electronic images based on a result of the time proximity analysis and the visual similarity analysis.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
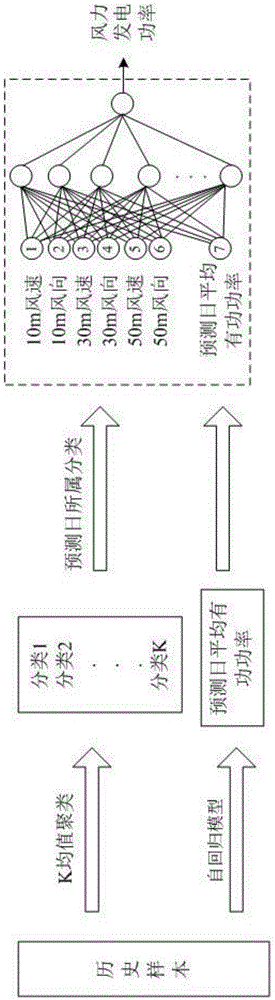
Wind power prediction method based on wind speed information and wind direction information
The invention relates to a wind power prediction method based on the wind speed information and the wind direction information. The method comprises the steps of collecting and arranging the historical wind data of a wind power plant and the actual wind power output data, conducting the normalization pretreatment on the data as a training sample, then conducting the similarity analysis and the clustering analysis, and dividing data objects similar in characteristic attribute as one type, respectively calculating the cluster center for each type of data based on the k-means clustering algorithm, predicting an active power average value on a prediction day based on an auto-regressive model structure, constructing a model to establish different types of wind power prediction models with the combination of the active power average value with the data of wind speed and wind direction of each type jointly as the input and the actually measured active power data on the prediction day as the output, judging the type of normalized daily vectors highest in similarity on the prediction day, and obtaining the predicted wind power on the prediction day based on a wind power prediction model of the same type. The above method is high in prediction accuracy and high in reliability.
Owner:JINZHOU ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +1
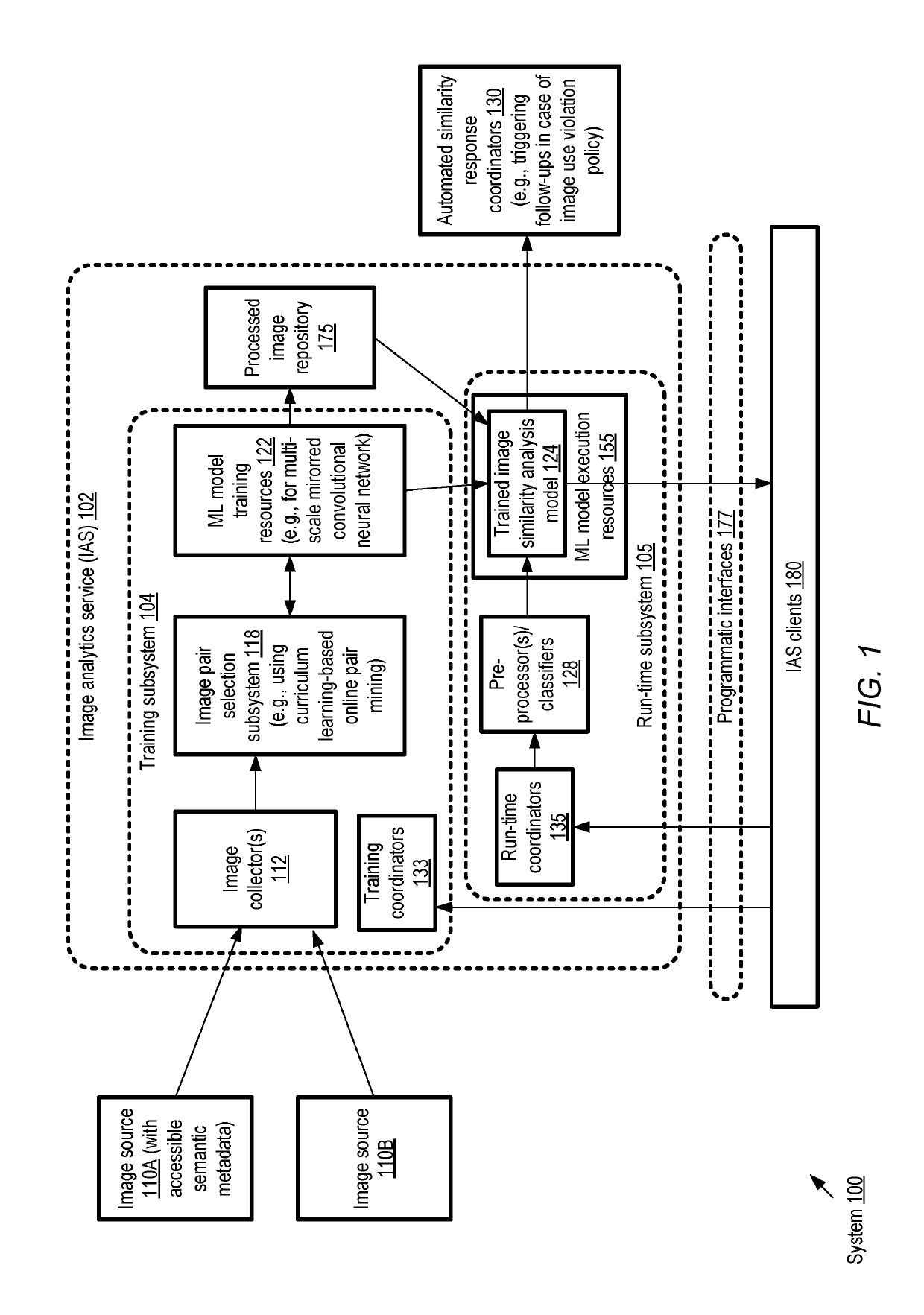
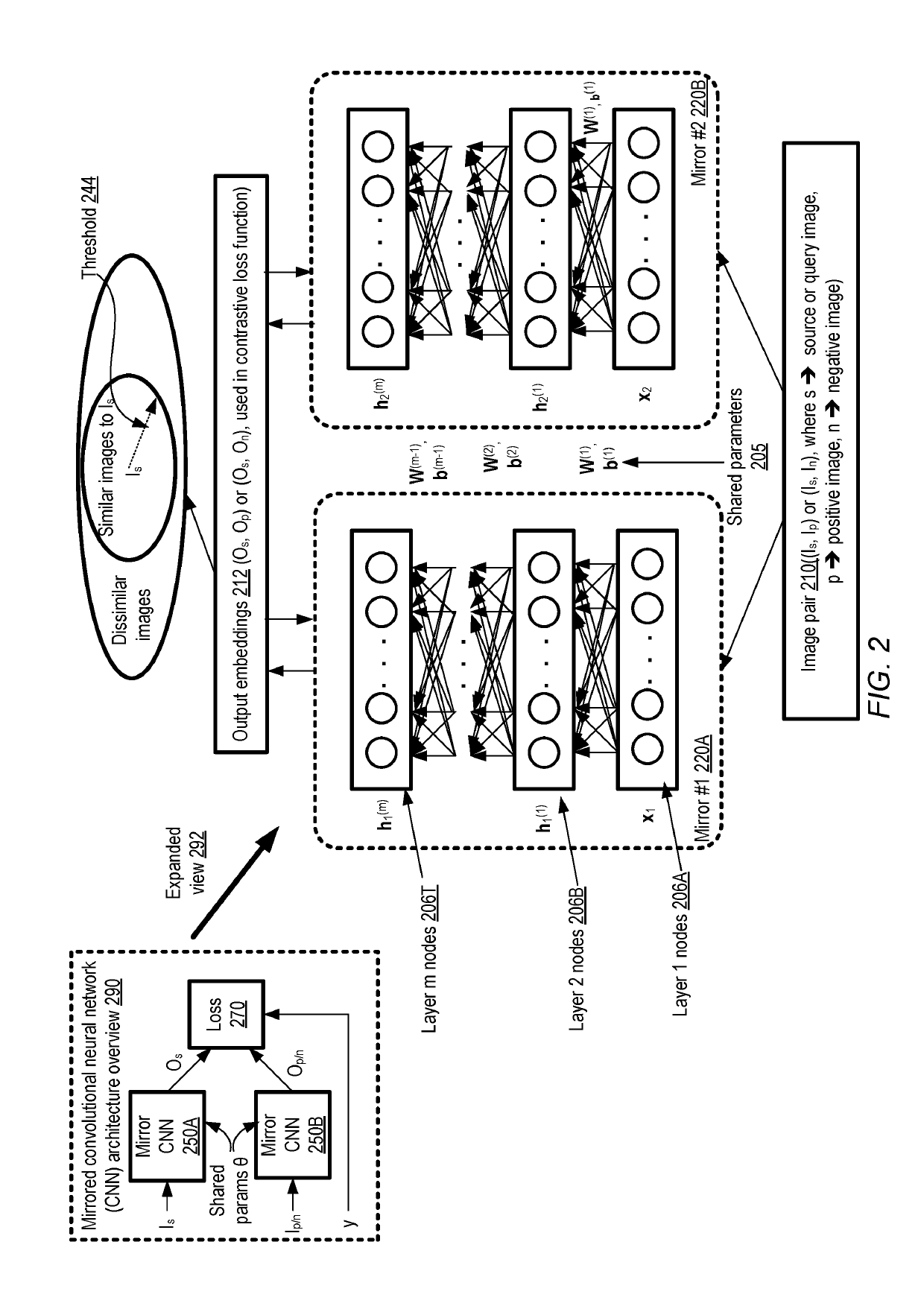
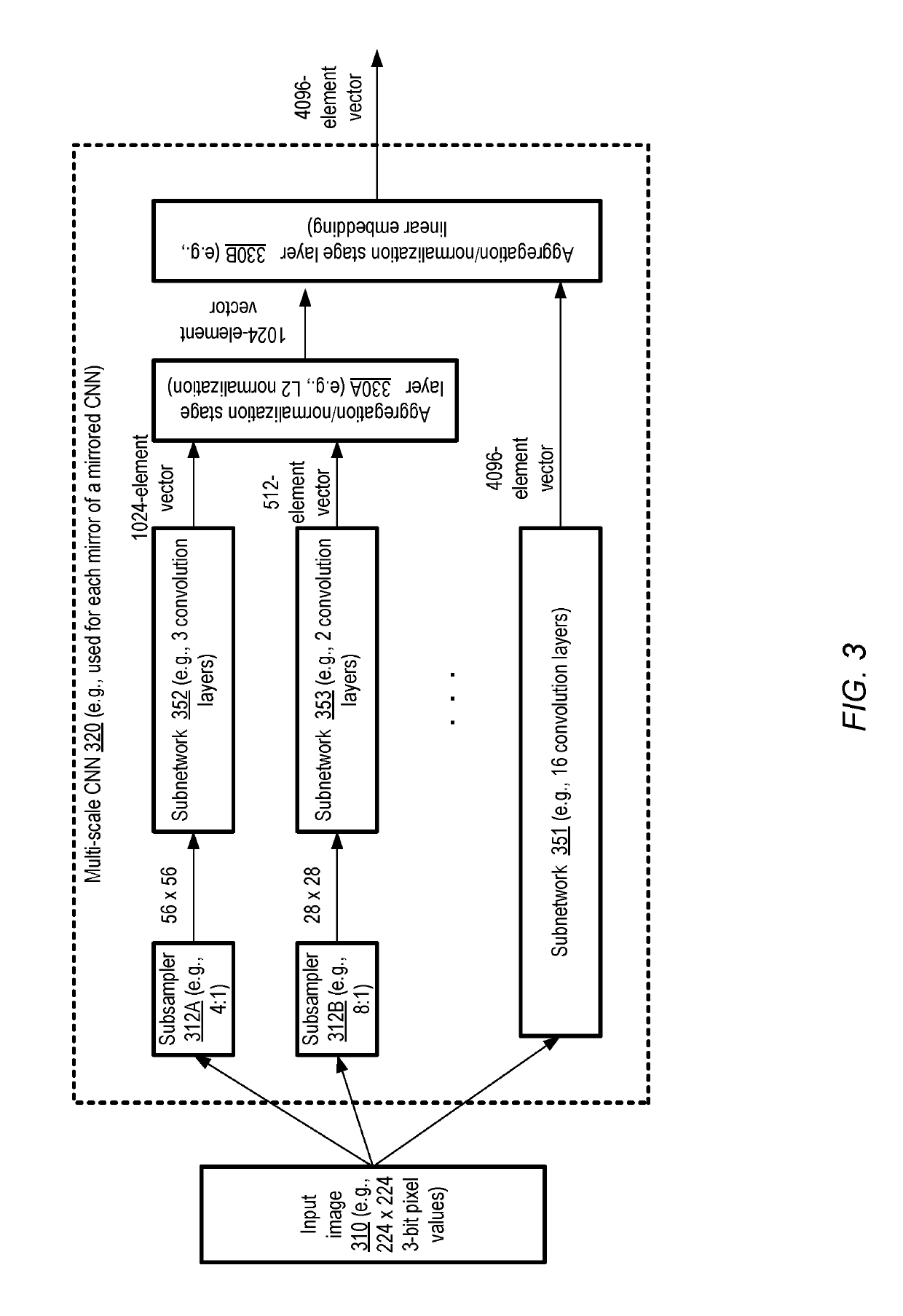
Artificial intelligence system for image similarity analysis using optimized image pair selection and multi-scale convolutional neural networks
ActiveUS10467526B1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionSimilarity analysisNetwork model
At an artificial intelligence system, a neural network model is trained iteratively to generate similarity scores for image pairs. The model includes a first subnetwork with a first number of convolution layers, and a second subnetwork with a different number of convolution layers. A given training iteration includes determining, using a version of the model generated in an earlier iteration, similarity scores for a set of image pairs, and then selecting a subset of the pairs based on the similarity scores. The selected subset is used to train a subsequent version of the model. After the model is trained, it may be used to generate similarity scores for other image pairs, and responsive operations may be initiated if the scores meet a criterion.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
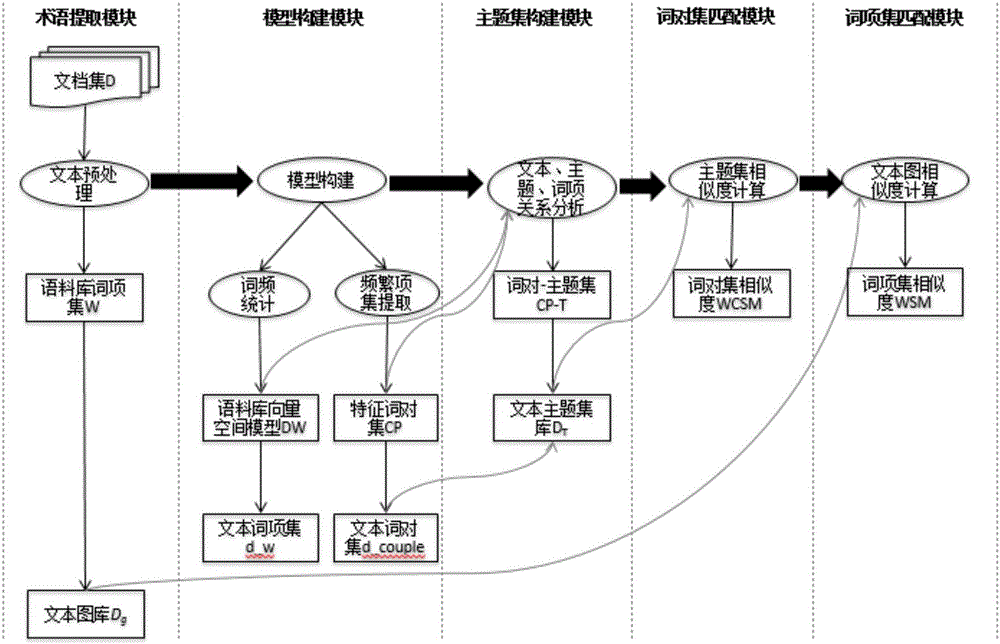
Text semantic similarity analysis method
ActiveCN106547739AAccurate and effective measurementAccurate and effective identificationSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSingular value decompositionLexical item
The invention relates to the text analysis field, particularly to a semantic characteristic-based text semantic similarity analysis method. According to the technical scheme, the similarity degree between texts is analyzed more accurately and effectively by calculation based on semantic relations of internal words of the texts. According to the method, shallow analysis on association relation between texts and between lexical items is performed through singular value decomposition; a lexical item-theme set is constructed by a bayesian network; the semantic similarity between the lexical items is calculated by mutual information and context; and finally, the text similarity is calculated through a graph structure. By adoption of the text semantic similarity analysis method, the semantic relation between texts can be measured and recognized more accurately and effectively.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and apparatus for performing constrained spectral clustering of digital image data
ActiveUS20070239764A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFeature vectorSimilarity analysis
A method and an apparatus process digital images. The method according to one embodiment accesses element data representing a plurality of elements belonging to a plurality of digital images; performs a similarity analysis between the elements from the plurality of elements to obtain inter-relational data results relating to the elements; and performs clustering of the plurality of elements, the step of performing clustering including incorporating in the inter-relational data results at least one hard constraint relating to elements from the plurality of elements, to obtain constrained inter-relational data results, performing a spectral analysis to obtain eigenvector results from the constrained inter-relational data results, and performing discretization of the eigenvector results using constrained clustering with a criterion to enforce the at least one hard constraint to obtain clusters.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
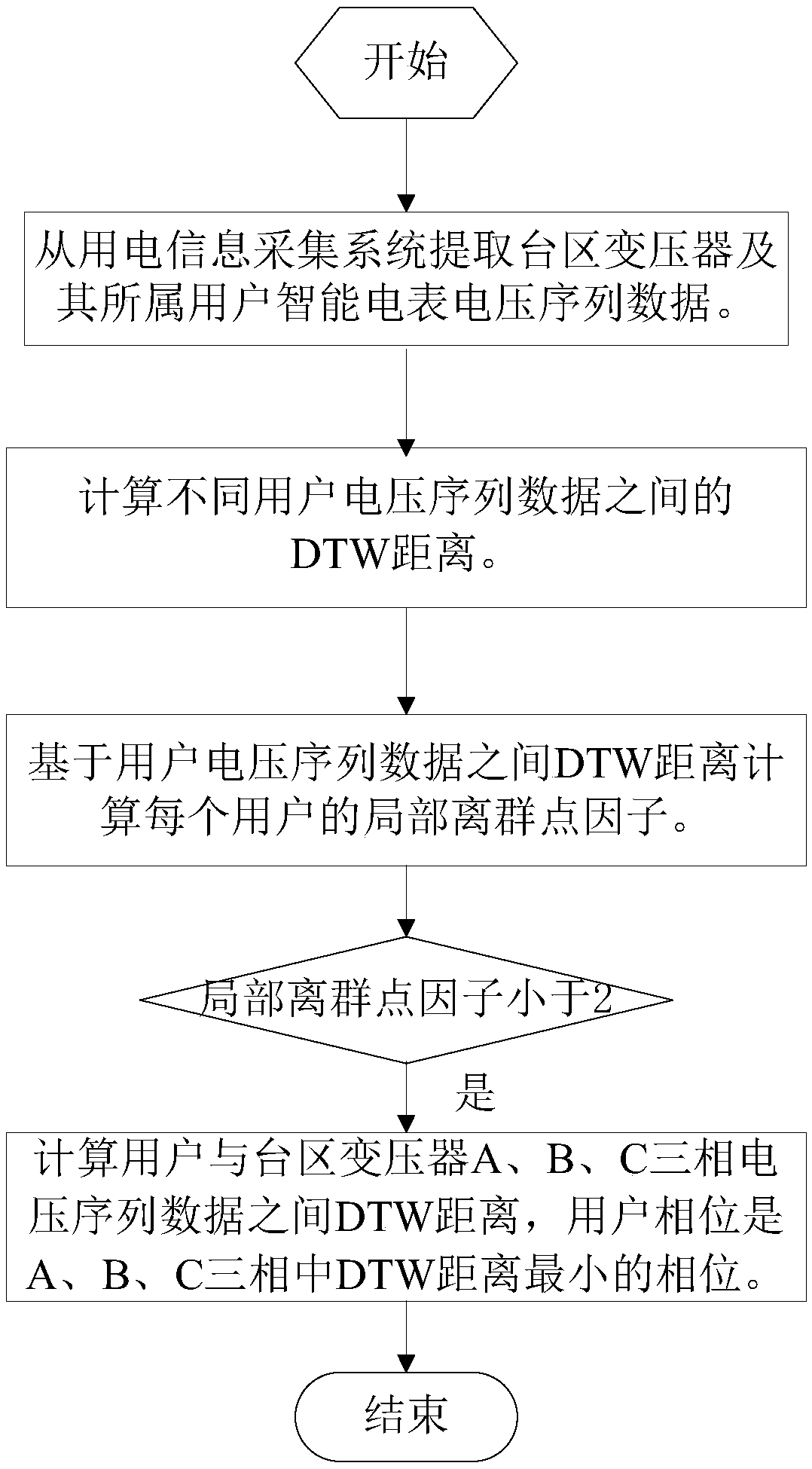
Low-voltage transformer district user phase identification method based on voltage curve similarity analysis
ActiveCN108564485AResolve accuracySolve efficiency problemsData processing applicationsCollection systemTransformer
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +1
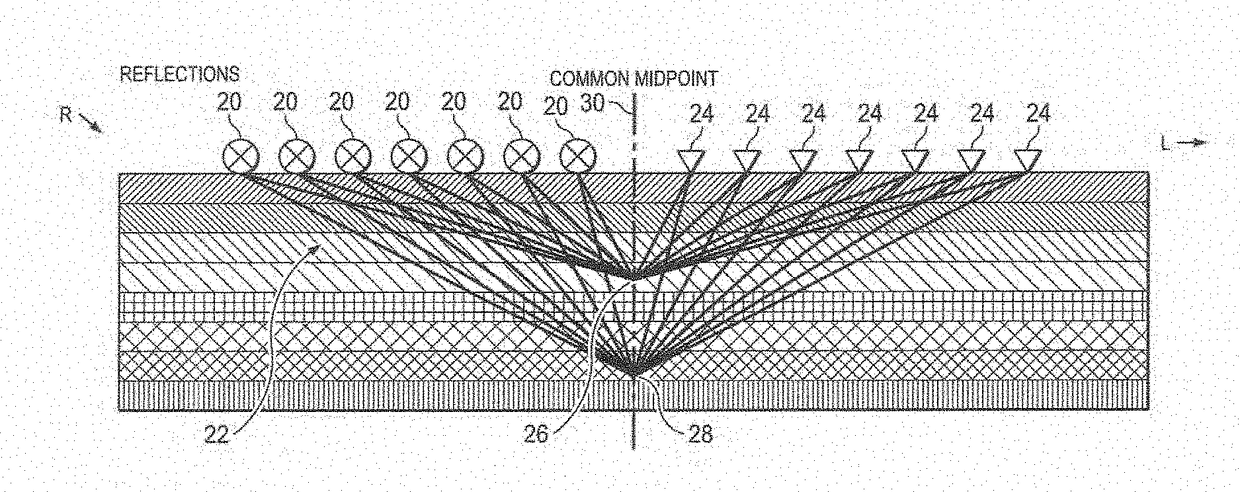
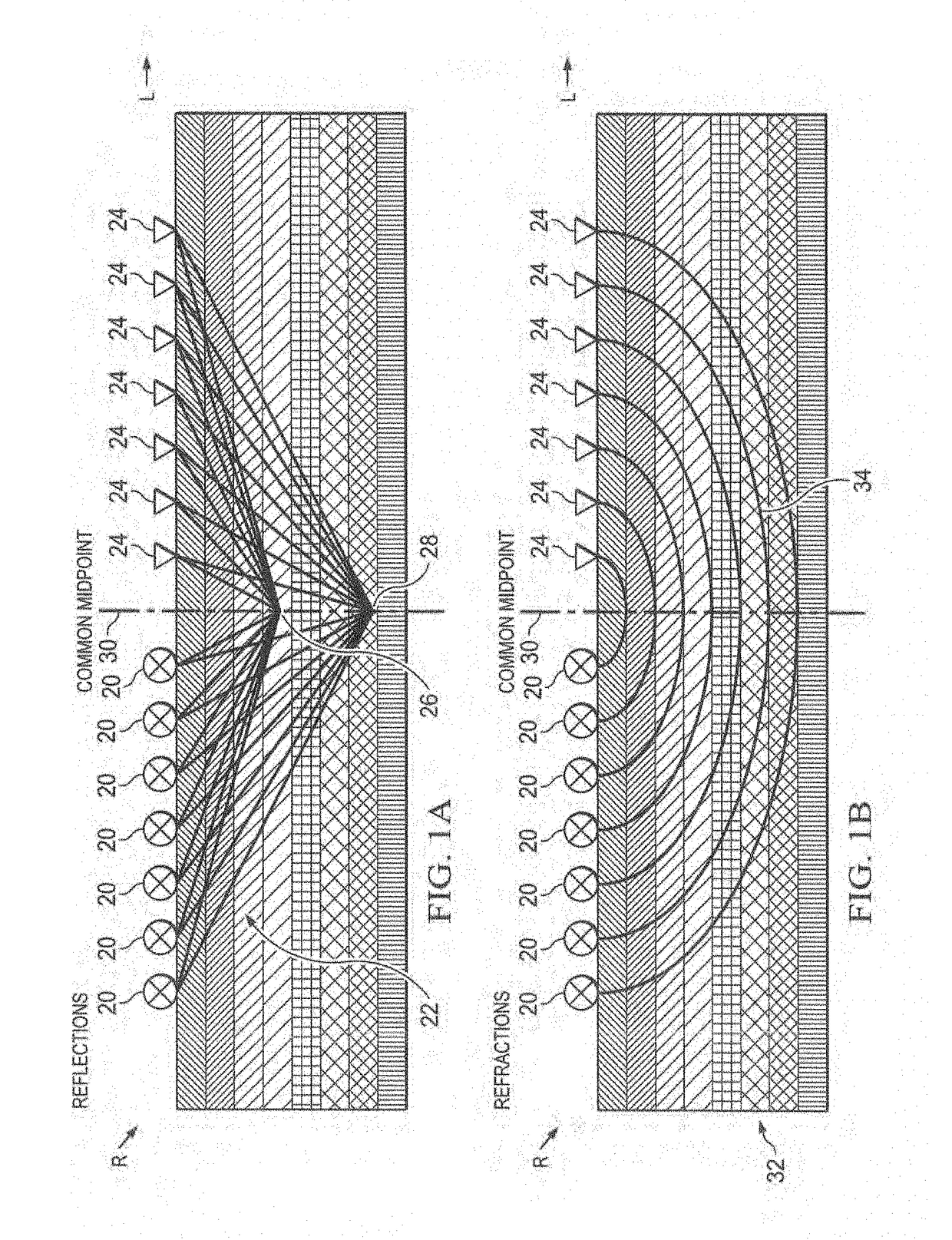
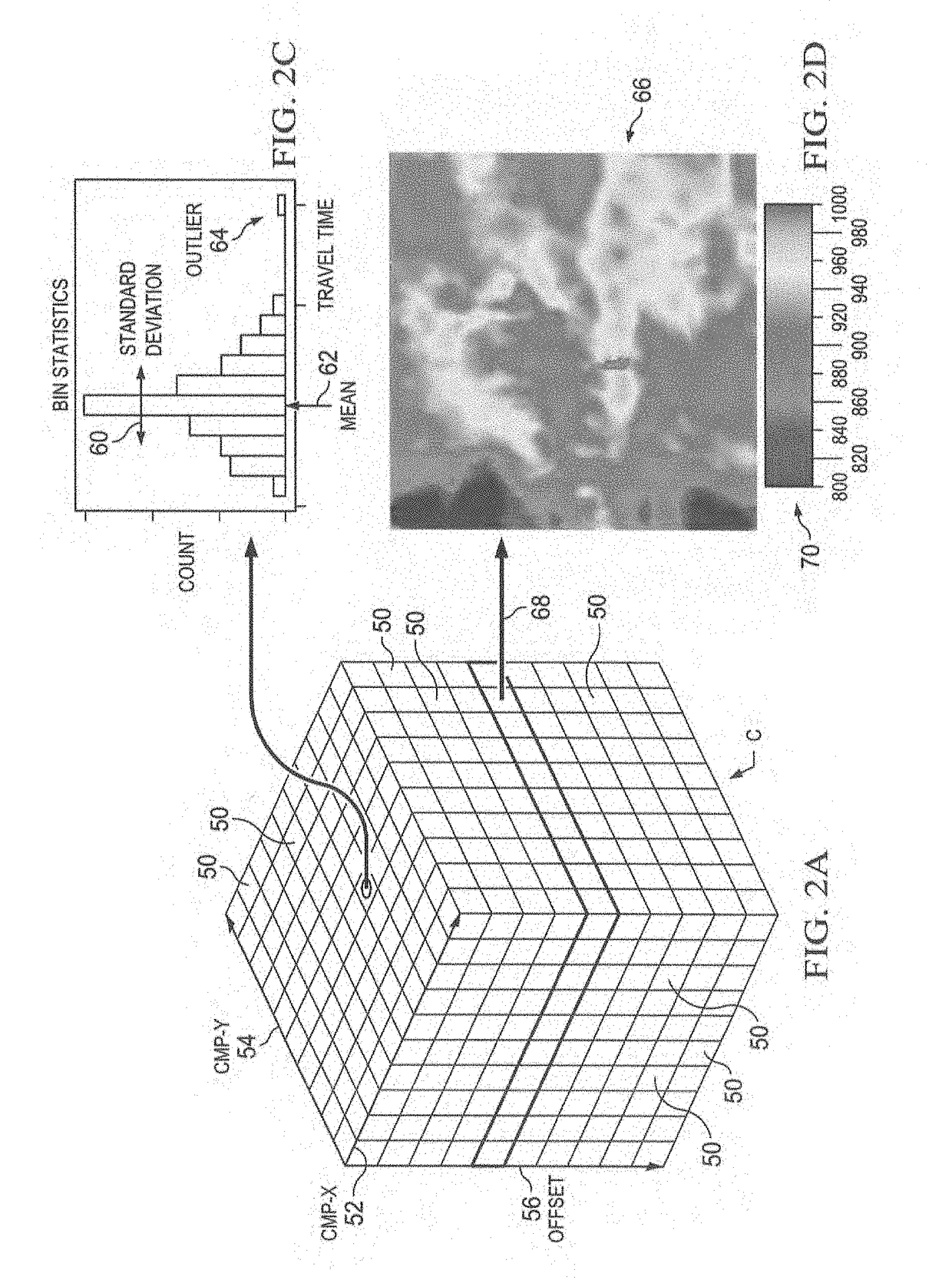
Automated near surface analysis by surface-consistent refraction methods
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
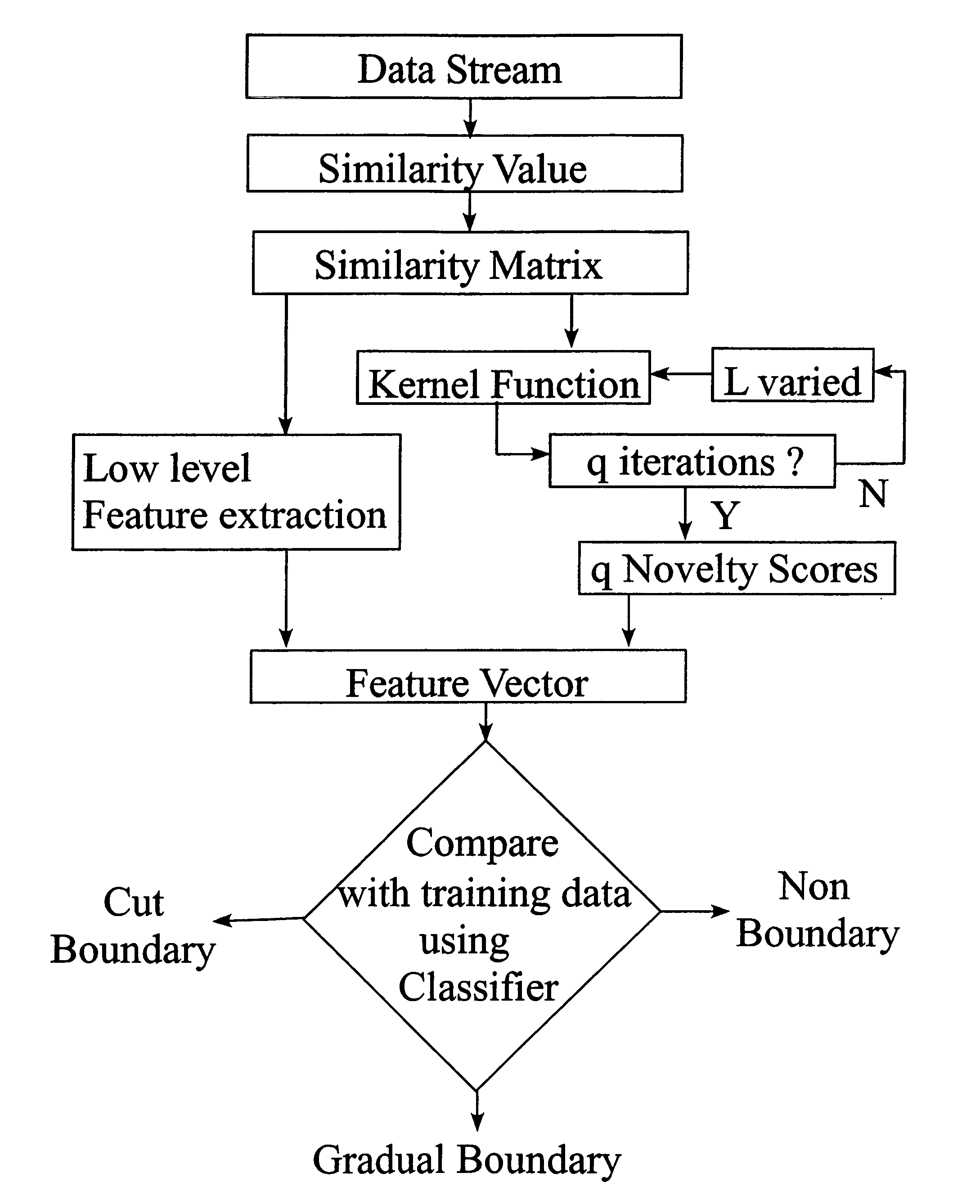
Video segmentation combining similarity analysis and classification
InactiveUS7783106B2Television system detailsDigital data information retrievalFeature vectorSimilarity analysis
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Multi-model integrated flood forecasting method based on propagation time clustering analysis
InactiveCN103729550AAccurate estimation of flood peak propagation timeAccurately determine the inputSpecial data processing applicationsFlow propagationModel synthesis
The invention discloses a multi-model integrated flood forecasting method based on propagation time clustering analysis and belongs to the technical field of hydrologic forecasting. The method includes adopting a derived dynamic time warp matching method for floor process similarity analysis; estimating flow propagation time of each station in the upstream and the downstream; decomposing a sample into a plurality of clusters by performing clustering analysis on the flow propagation time; respectively building an SVM regression model for each sub-flow sequence to simulate the flood forming process; combining the sub-models into a comprehensive model. Comparing a comprehensive forecasting result acquired by the method with a model forecasting result acquired by a single model under conventional conditions and on the basis of flow clustering, the comparison result shows that the comprehensive model is better in comprehensive performance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
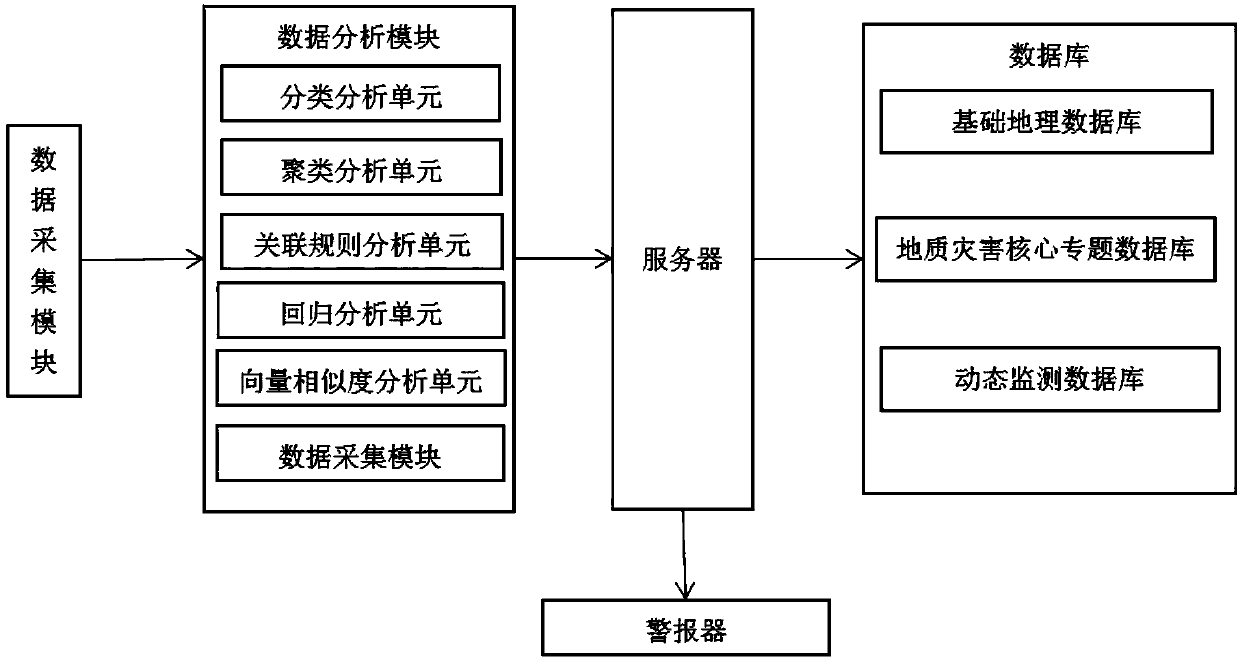
Geology calamity early warning analysis system and method
InactiveCN107610421AEfficient analysisEffective early warningAlarmsRegression analysisData acquisition
The invention discloses a geology calamity early warning analysis system and method; the system comprises a database, a server, a data analysis module, a data acquisition module and an alarm; the dataacquisition module is linked to the data analysis module and the database through the server; the data analysis module comprises a classification analysis unit, a cluster analysis unit, an association rule analysis unit, a regression analysis unit, a vector similarity analysis unit and a time sequence analysis unit; the database comprises a basic geography database, a geology calamity core thematic database and a dynamic monitoring database; the system and method use the data analysis module to effectively analyze the calamity frequently occurring region geology information, thus obtaining the current calamity possible generation probability, and using the alarm to send alarms so as to remind work personnel if the probability reaches certain level. The system is easy to use, simple and fast, and the method can effectively analyze the geology calamities and warn people in advance.
Owner:合肥英泽信息科技有限公司
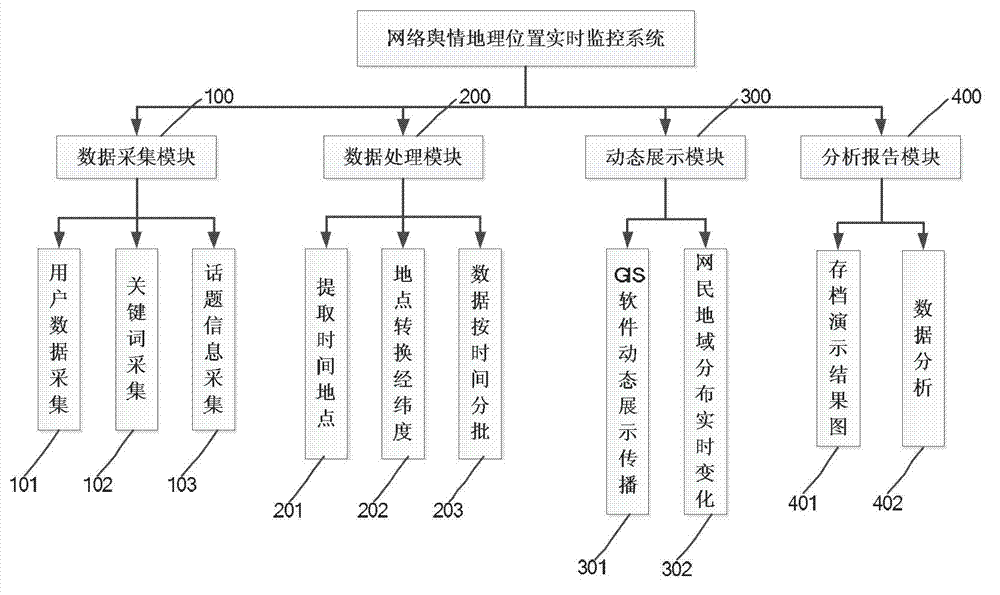
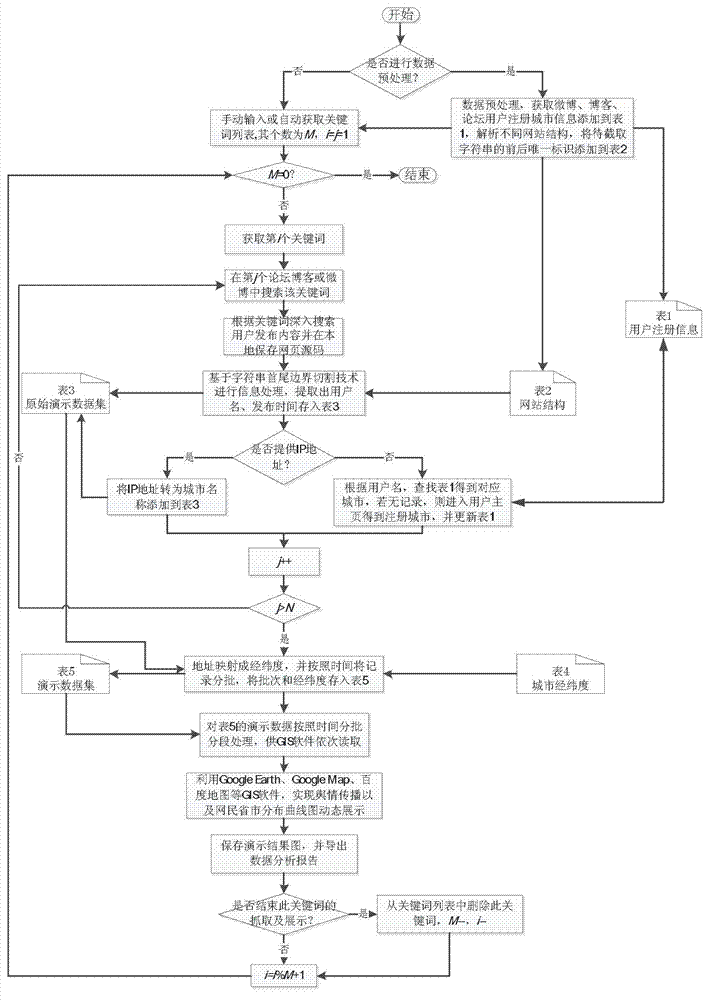
Online public opinion geographical location real time monitoring system and method
ActiveCN103092950ASatisfy the needs of communication trend observationRealize real-time monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsTime informationGeographic site
The invention discloses an online public opinion geographical location real time monitoring system and a method. Topic key word lists are obtained through unifying acquiring methods of microblogs, blogs and forum data and analyzing and removing repeat of similarities; geographical locations and time information are extracted using the technology of front, back and boundary cutting, front, back and boundary are achieved through website structures which are built in advance, and the situation that procedures conduct adjustment according to the website structure is avoided; and data are obtained according to every keyword and the data are processed, spread situations are restored dynamically on a geographic information system (GIS) geographic model, and net citizen number is analyzed. Mapping of network environment and real environment is achieved through transforming network geographic locations into longitude and latitude coordinates, and data are input into GIS software in batches according time to achieve dynamic demonstration spread processes.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and system for monitoring DDOS (distributed denial of service) attacks in small flow
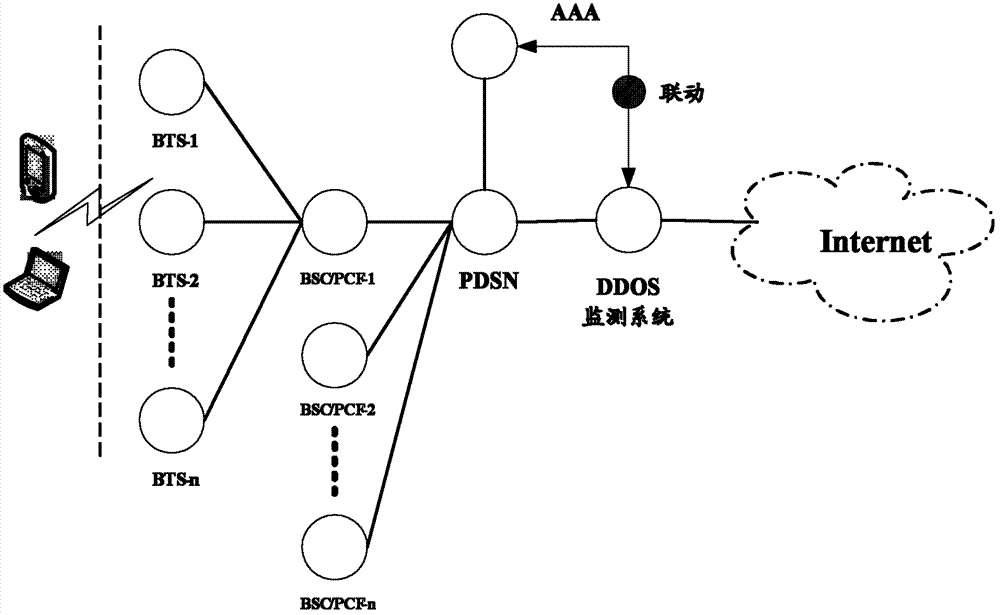
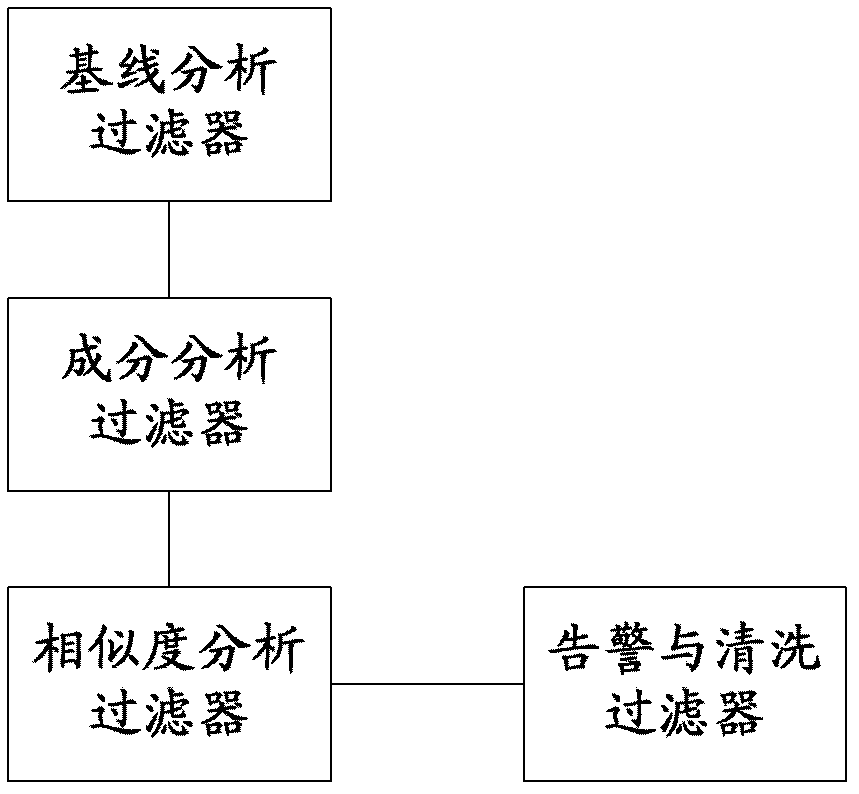
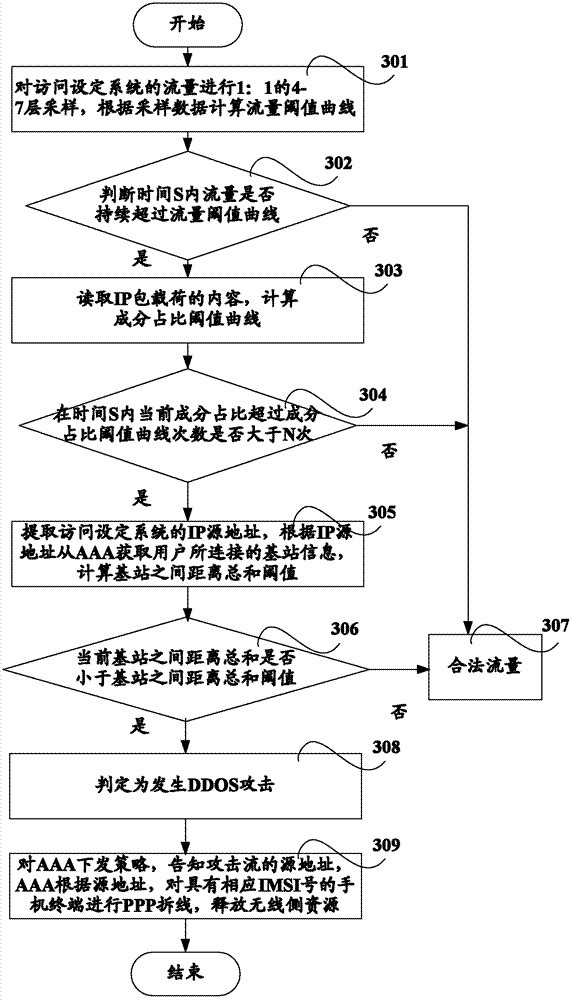
ActiveCN102821081AMake up for the inability to detect low-rate DDoS attacksHigh false positive rateData switching networksSimilarity analysisProtocol Application
The invention discloses a method and a system for monitoring DDOS (distributed denial of service) attacks in small flow, solves the problems that the existing DDOS attack detection technology is high in cost, complex to implement and high in misjudgment rate, cannot respond to DDOS attacks aiming at an application layer and the like, and provides the monitoring scheme of an integrated DPI (dots per inch) technology. A baseline analysis, component analysis and similarity analysis method is used to establish a normal use model, characteristics are accurately matched to detect the attacks in small flow and the application layer attacks, deployment at one point of an operator network and complete coverage of the operator network are achieved, and detection accuracy is increased.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com