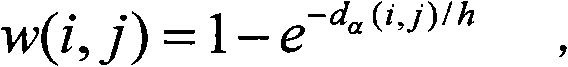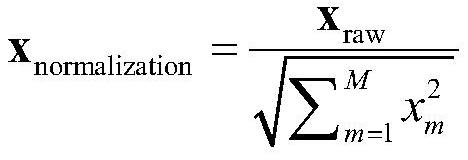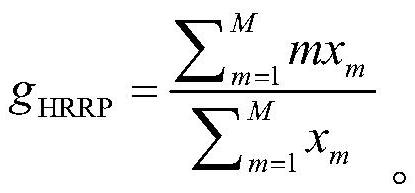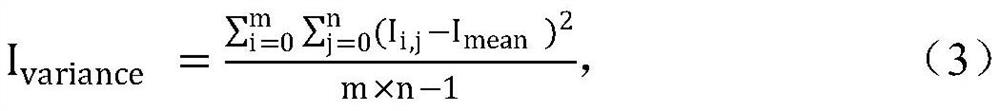Patents
Literature
39 results about "Intensity normalization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In image processing, normalization is a process that changes the range of pixel intensity values. Applications include photographs with poor contrast due to glare, for example. Normalization is sometimes called contrast stretching or histogram stretching.
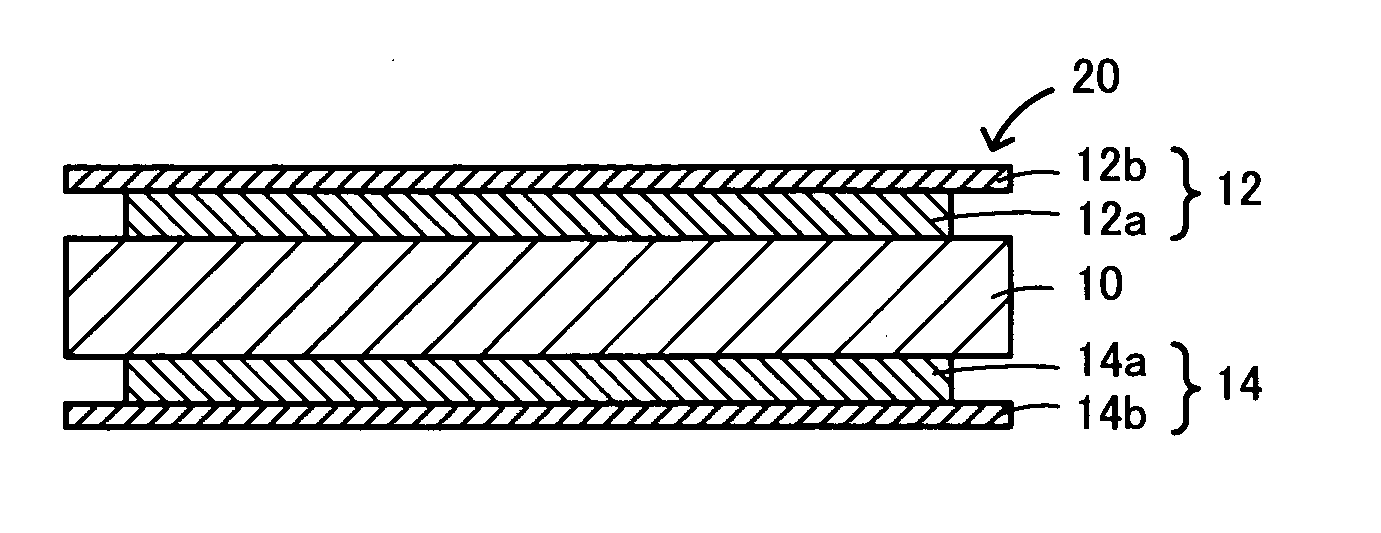
Garnet-type lithium ion-conducting oxide and all-solid-state lithium ion secondary battery containing the same
ActiveUS20110244337A1Improve lithium ion conductivitySmall rate of changeSolid electrolyte cellsElectrolytesAll solid stateIntensity normalization
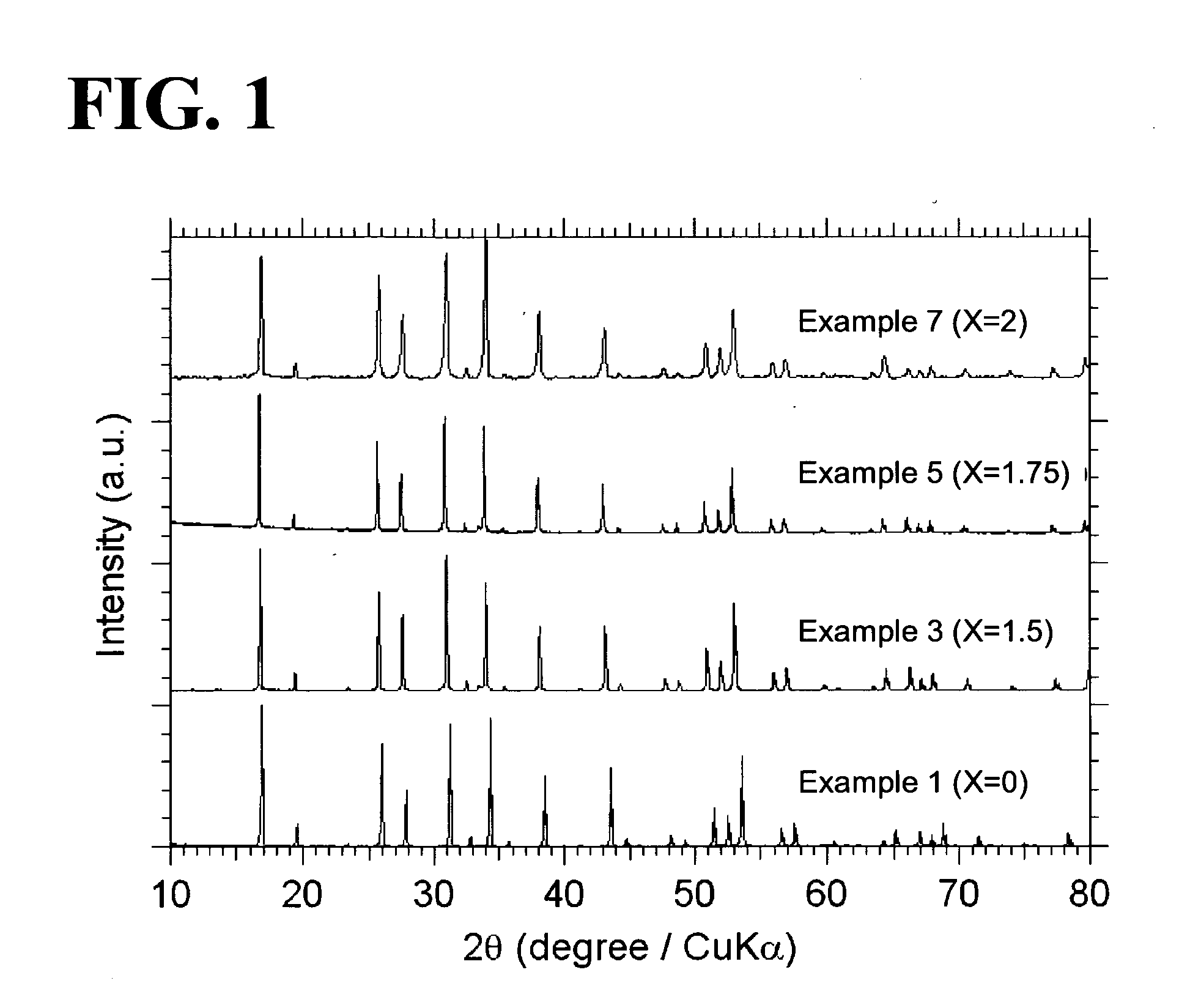
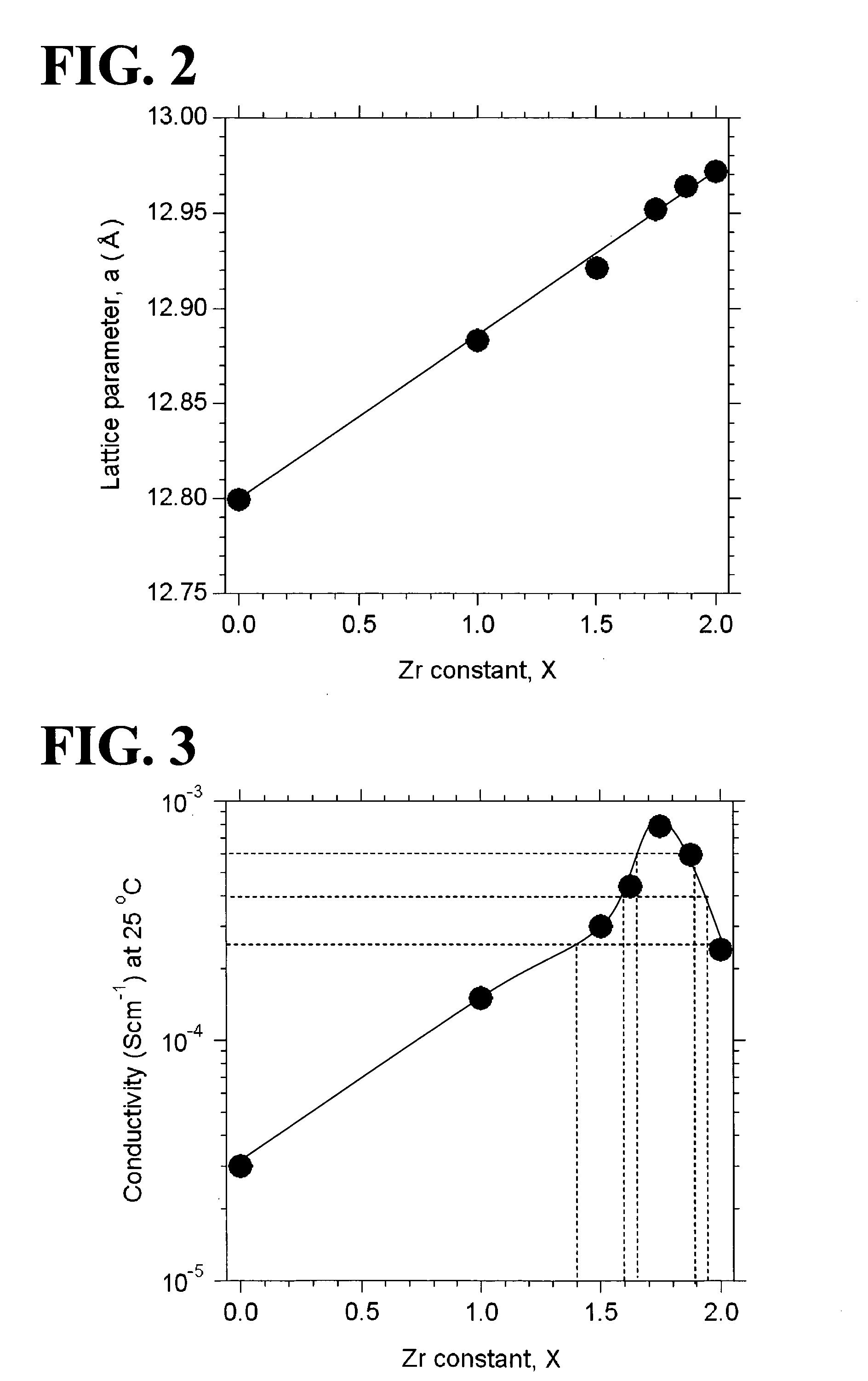
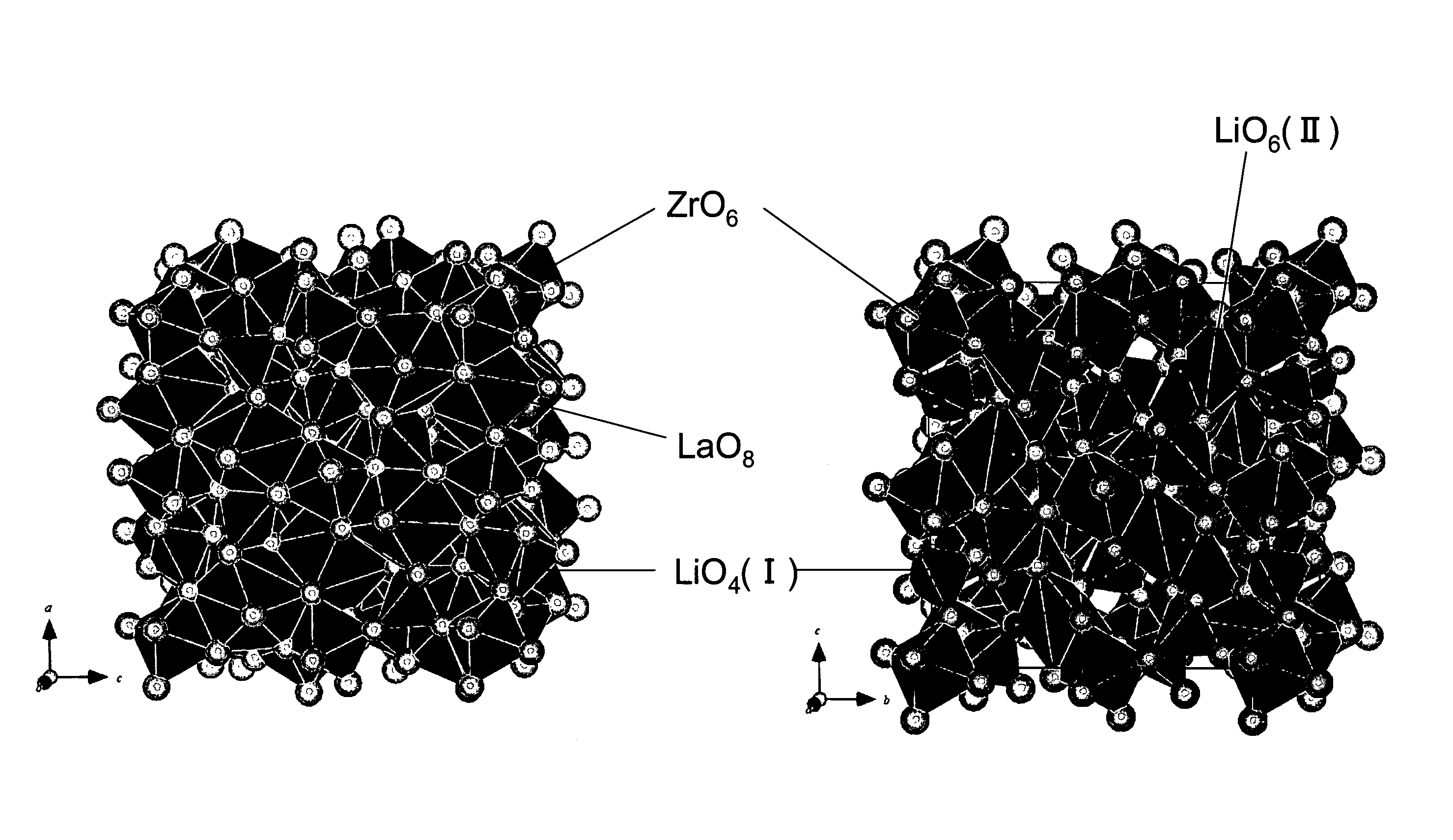
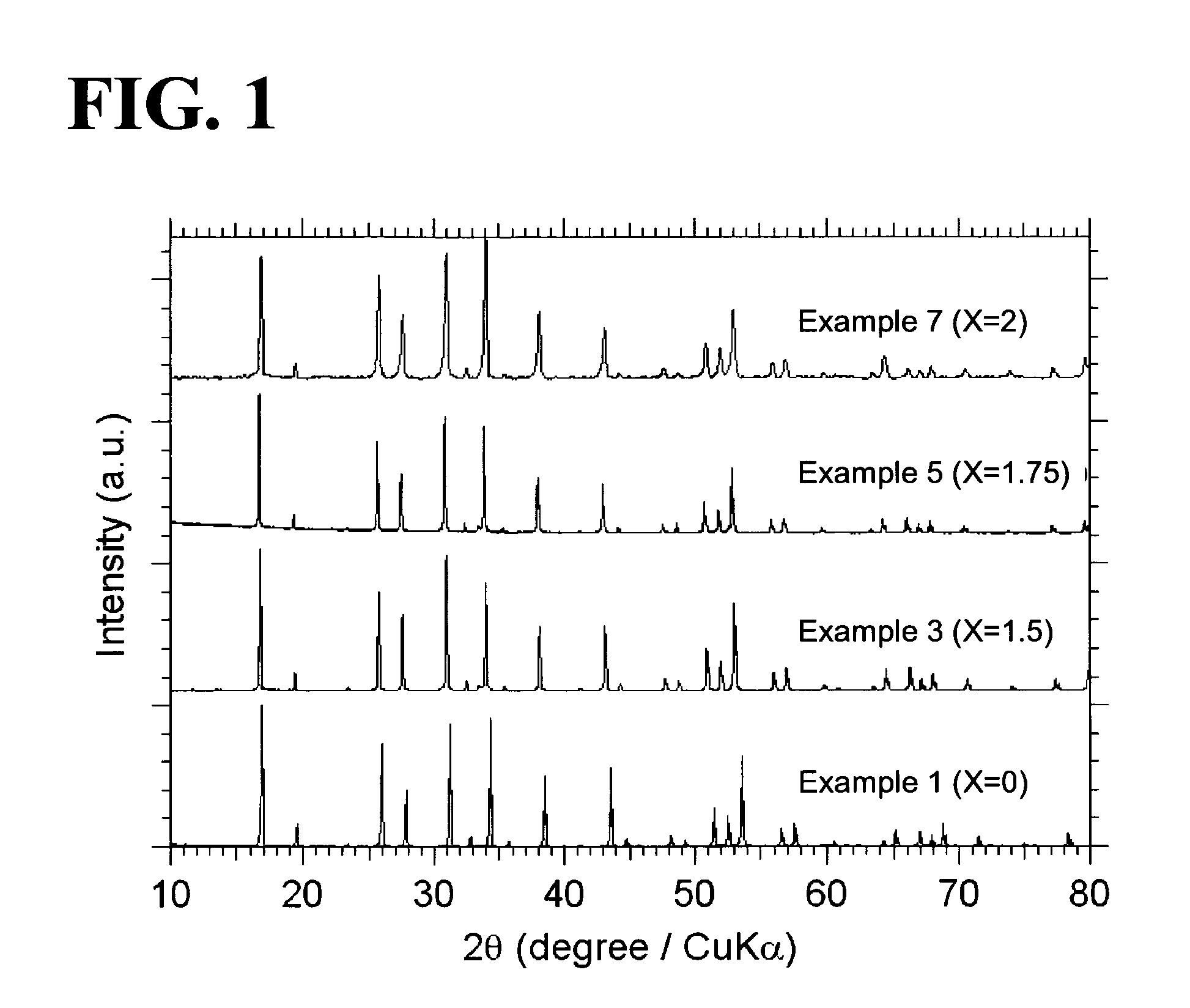
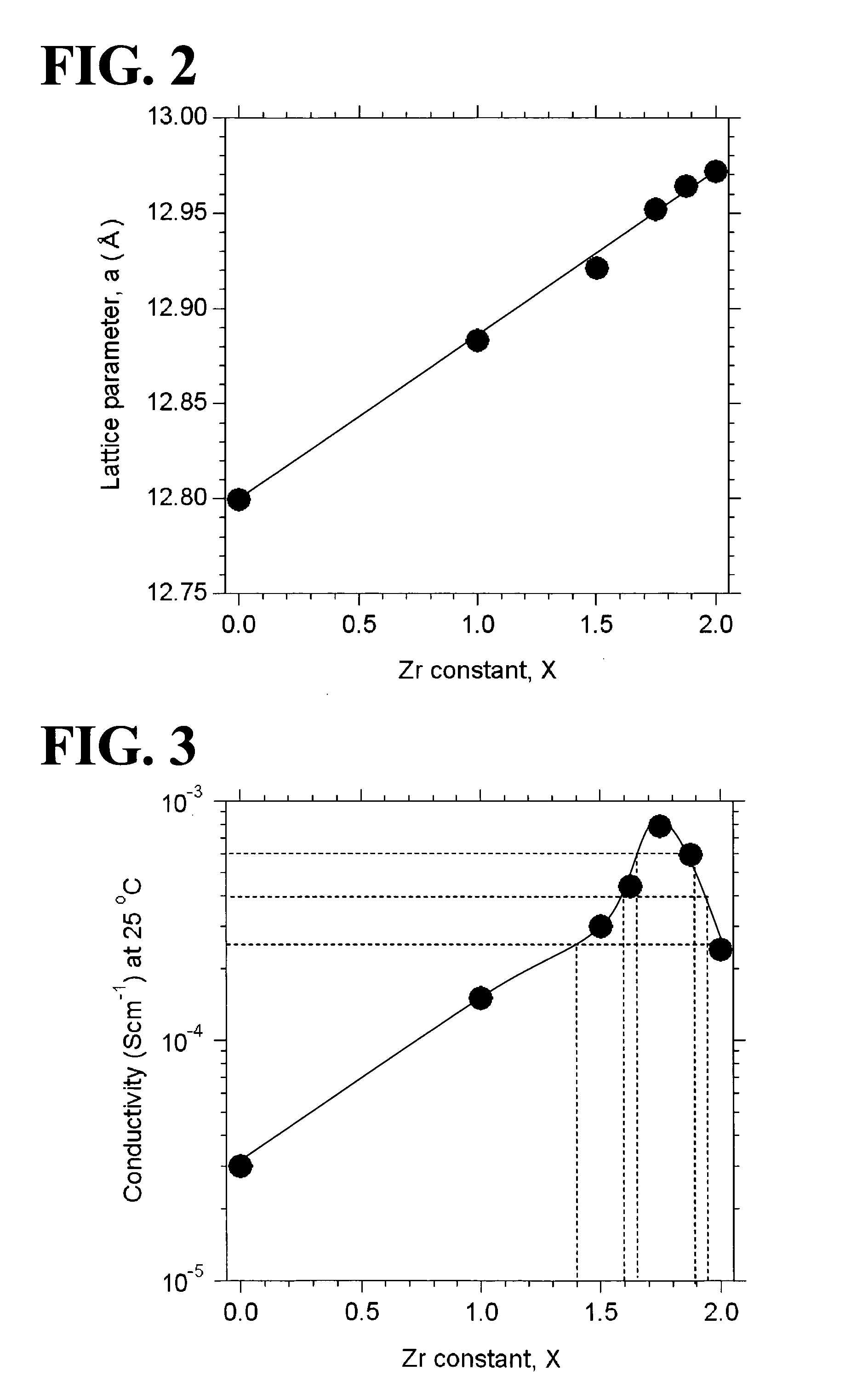
An all-solid-state lithium ion secondary battery containing a novel garnet-type oxide serving as a solid electrolyte. The garnet-type lithium ion-conducting oxide is one represented by the formula Li5+XLa3(ZrX, A2-X)O12, wherein A is at least one selected from the group consisting of Sc, Ti, V, Y, Nb, Hf, Ta, Al, Si, Ga, Ge, and Sn and X satisfies the inequality 1.4≦X<2, or is one obtained by substituting an element having an ionic radius different from that of Zr for Zr sites in an garnet-type lithium ion-conducting oxide represented by the formula Li7La3Zr2O12, wherein the normalized intensity of an X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern with a diffraction peak, as normalized on the basis of the intensity of a diffraction peak, is 9.2 or more.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Remote sensing image change detection method based on neighbourhood similarity and threshold segmentation
InactiveCN101950364AImprove filtering effectEasy to handleImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionIntensity normalizationGray level
The invention discloses a remote sensing image change detection method based on neighbourhood similarity and threshold segmentation and aims to overcome the defect that the traditional method has poor noise immunity and low detection accuracy in terms of the change detection of the target with high noise. The realization process comprises the following steps: (1) using the strength normalization formula to carry out gray level matching on two remote sensing images; (2) using neighbourhood similarity distance measure to construct a similar matrix of the two remote sensing images; (3) combing the similar matrix to construct a difference image of the two remote sensing images; (4) constructing a two-dimension gray level column diagram for the difference image, using the 2D-OTSU method to determine the segmentation threshold value and separating the target area from the background area; and (5) using the fuzzy entropy method to continue classifying the unprocessed edges and noise points. The invention has the advantages of good noise immunity and high detection accuracy for the changing target and can be used for detecting targets with changes of multitemporal remote sensing images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
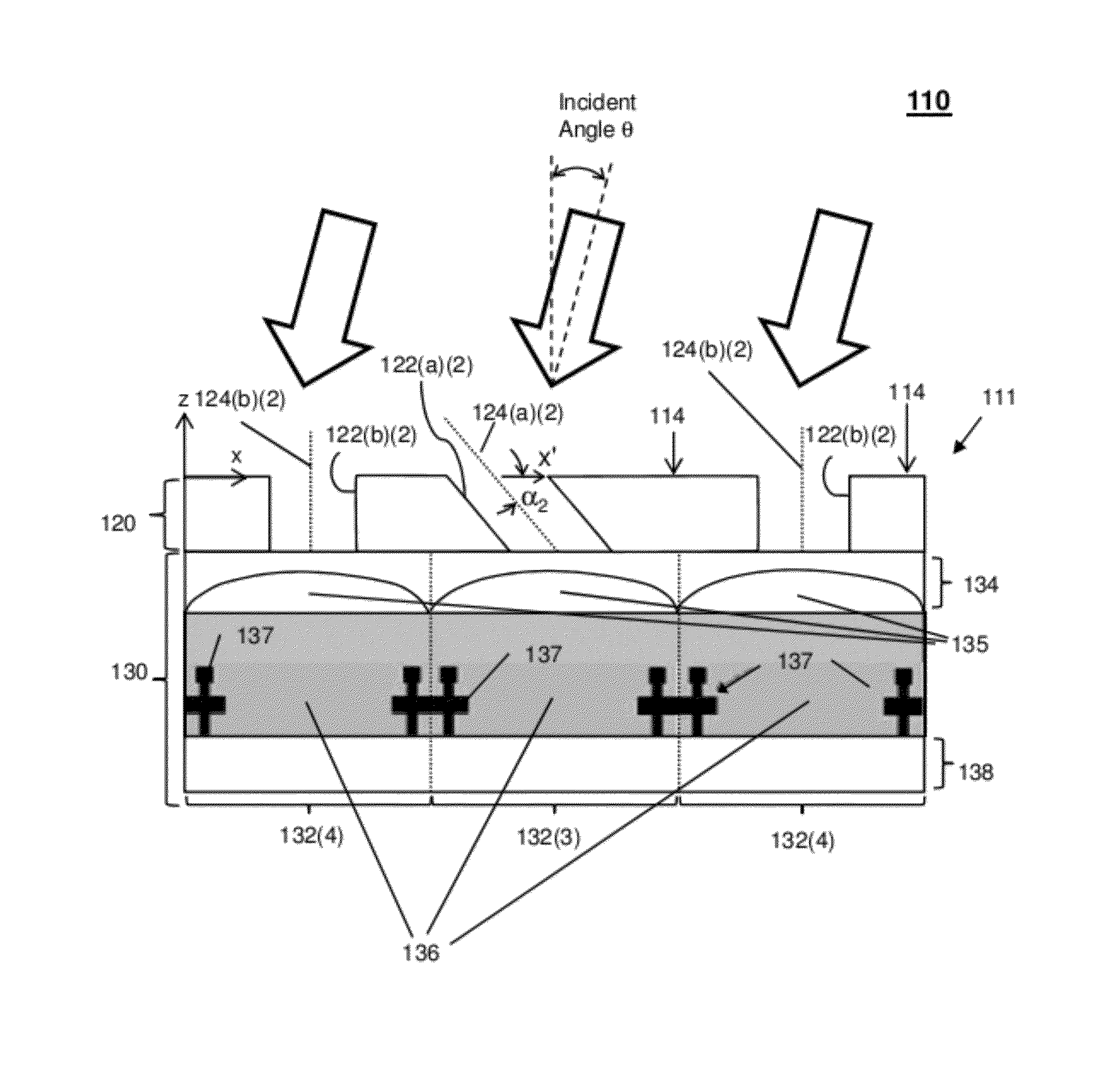
Light-field pixel
ActiveUS20120211644A1Optical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansIntensity normalizationWavefront
A light-field pixel for detecting a wavefront, the light-field pixel comprises an aperture layer, a light detector layer, and a processor. The aperture layer has a non-conventional aperture and a non-conventional aperture. The non-conventional aperture has a higher gradient of transmission at normal incidence than the conventional aperture. The light detector is configured to measure a first intensity of light through the non-conventional aperture and a second intensity of light through the conventional aperture. The processor is configured to detect the wavefront based on the first intensity normalized by the second intensity.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for evaluating influence of speckle coherence on ranging accuracy of single-photon laser radar
ActiveCN109541619AImprove compatibilityImprove the detection rateElectromagnetic wave reradiationIntensity normalizationRadar systems
The invention provides a method for evaluating the influence of speckle coherence on the ranging accuracy of a single-photon laser radar. The method comprises the steps of setting the parameters of the single-photon laser radar system, calculating the autocorrelation function of a receiving aperture of the single-photon laser radar system and the normalized covariance function on the intensity ofthe receiving aperture to calculate the speckle degree of freedom M; calculating the average signal photon number Ns according to the laser radar equation, and calculating the total noise rate Nn of the laser radar system; differentiating time through the detection probability based on the root mean square pulse width [Sigma]s of the laser pulse to obtain the detection probability density functionfs(t) of the echo signal with respect to time t, and obtaining the mean value shown in the description and the variance Var of the time when the detector detects the target point; and obtaining the influence of the speckle coherence on the ranging accuracy of the single-photon laser radar according to the drift error Ra and the random error Rp. The invention has good compatibility, can provide guidance for the system parameter design of the laser radar, improve the detection probability and reduce the ranging error as much as possible under the restraint of satisfying the false alarm probability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
ROI-based assessment of abnormality using transformation invariant features
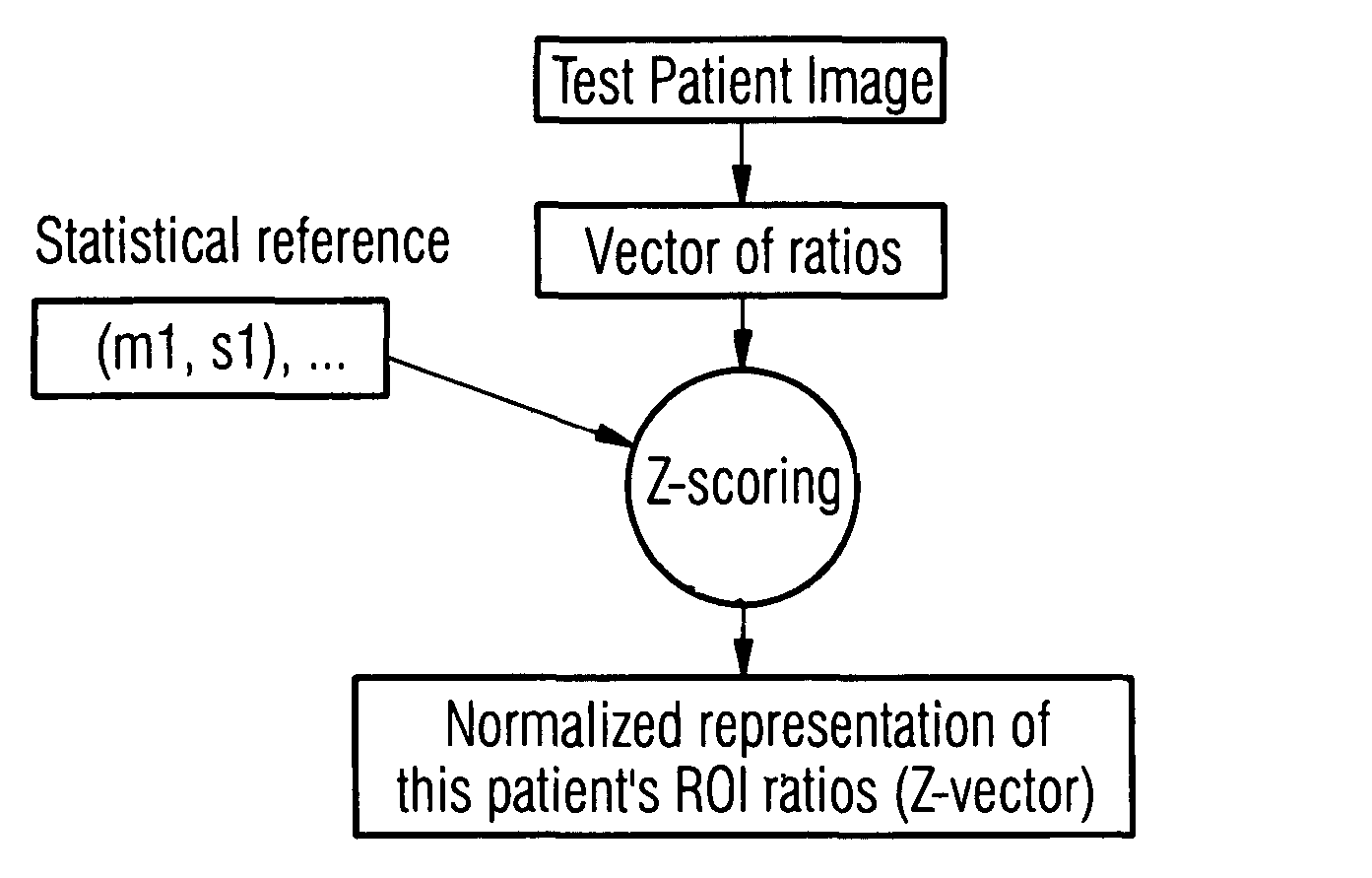
ActiveUS20080069446A1Improve classification performanceImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity normalizationDemographic data
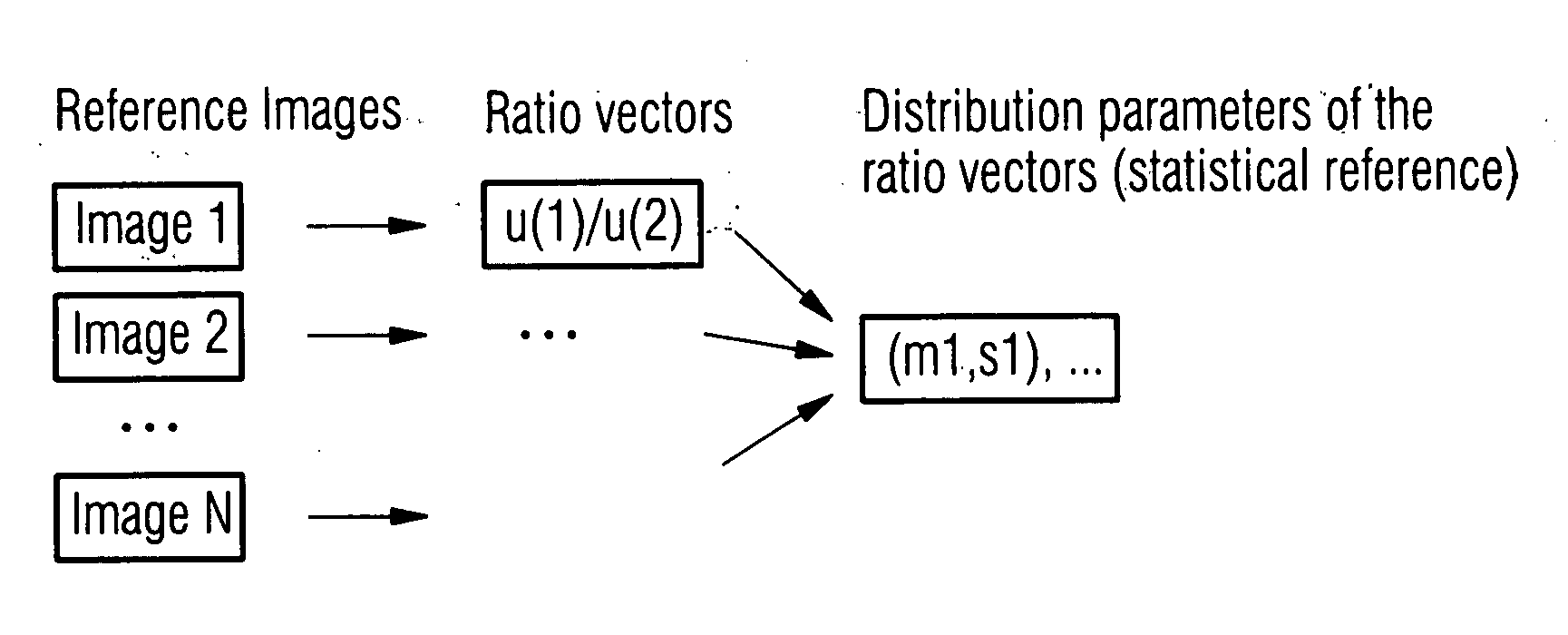
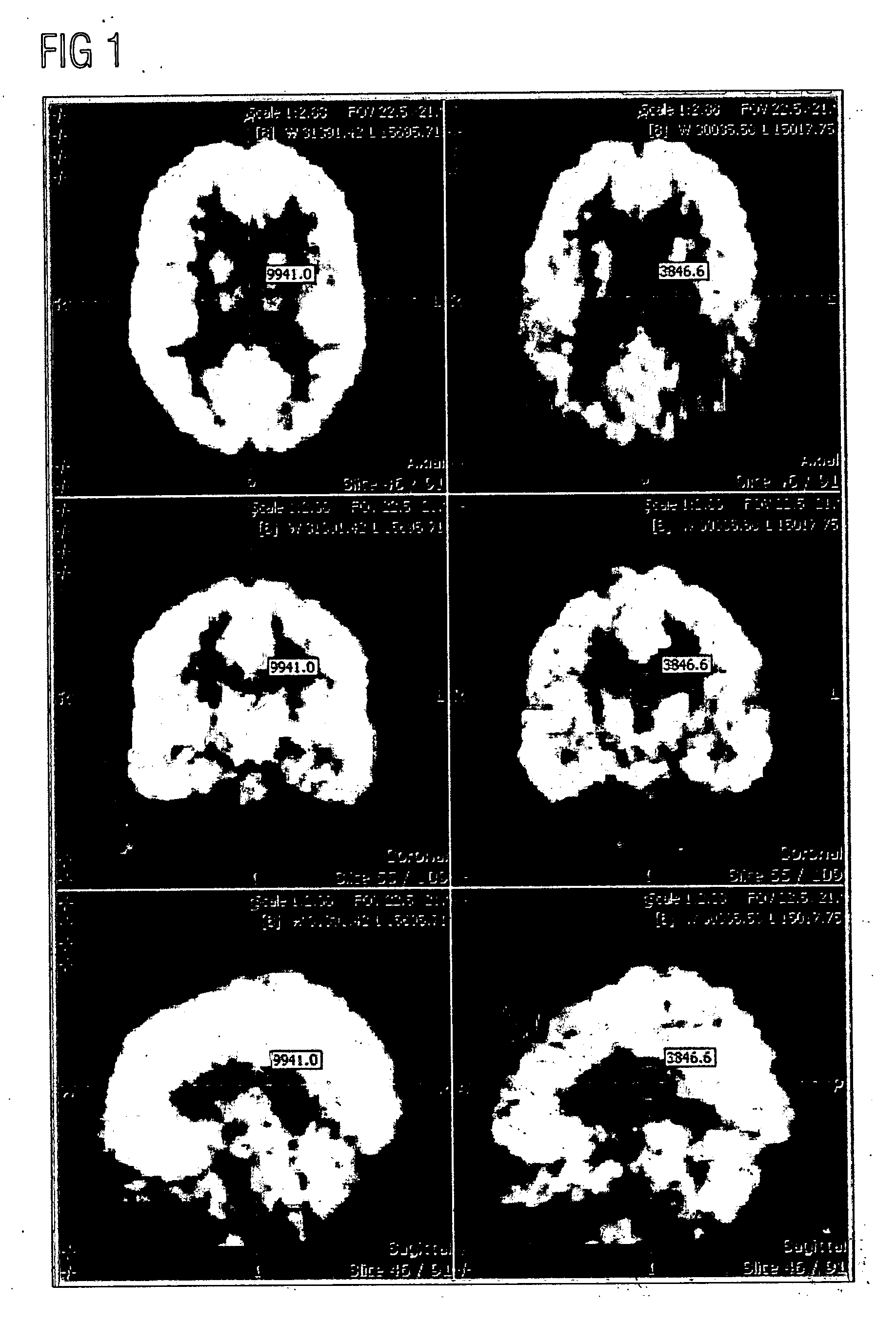
A method of comparing the results of medical imaging by (e.g.) PET scanning is disclosed which dispenses with the need for intensity normalization. The relationships between features extracted from relevant regions of interest in the image are studied. In one example, mean intensities in the principle brain lobes are compared to each other and a short image ID is constructed and used to derive population statistics and diagnosis. The population statistics can be compared with ‘reference’ statistics in order to assess abnormality. Comparison by a number of methods is possible and a further feature of the invention concerns a novel voting mechanism which derives abnormality scores for each region.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Radar high resolution range profile (HRRP) target recognition method based on convolution factor analysis (CFA) model
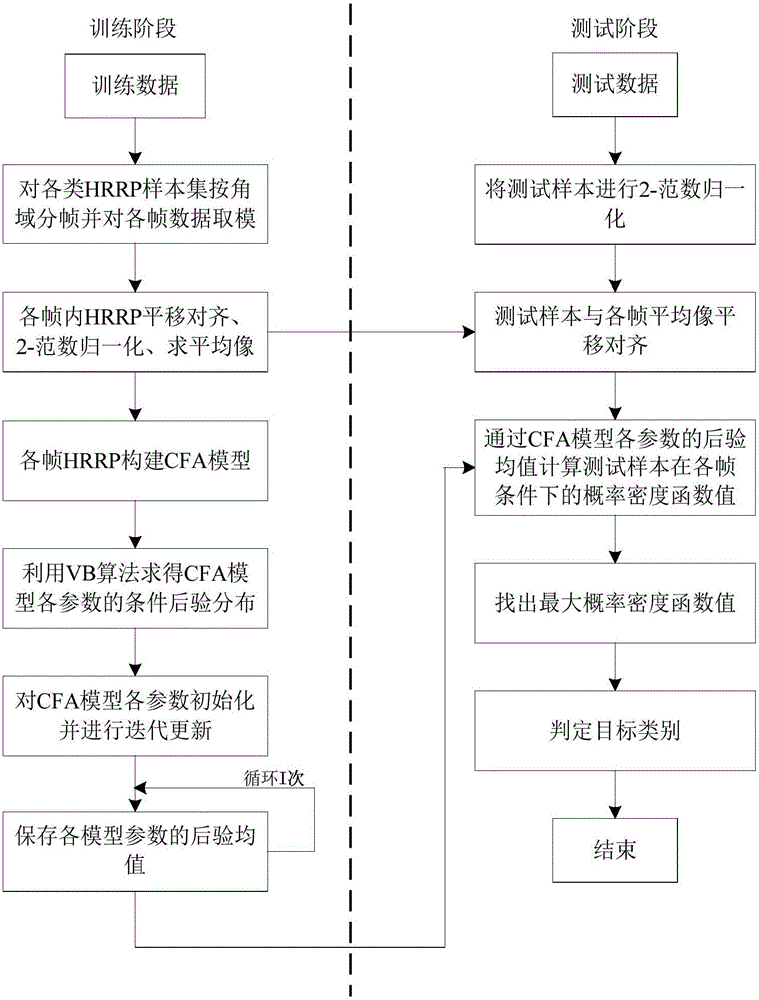
ActiveCN106054155AImplement extractionImplement miningWave based measurement systemsIntensity normalizationPattern recognition
The invention discloses a radar high resolution range profile (HRRP) target recognition method based on a convolution factor analysis (CFA) model. The radar HRRP target recognition method mainly solves the problem of poor target recognition performance under the condition of small samples in the prior art, and is implemented by the steps of: (1) carrying out framing on HRRPs of various kinds of targets according to angular domains, and carrying out modulus operation on each frame of data to obtain time domain features; (2) carrying out per-processing on each frame of data; (3) constructing a CFA model for each frame of HRRP after preprocessing, and calculating condition posterior distribution of each model parameter; (4) initializing each parameter and performing I-th iterative updating; (5) carrying out intensity normalization on a test sample, and translating and aligning frames of average profiles; (6) calculating frame probability density function values of the test sample according to a posterior mean of parameters of the CFA model; (7) and finding out the maximum probability density function value, and determining a type of the test samples. The radar HRRP target recognition method has the advantages of being low in model complexity, and being capable of applied to radar target recognition under the condition of small samples.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
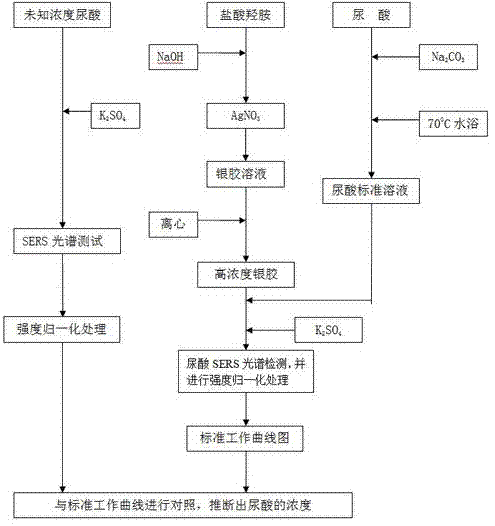
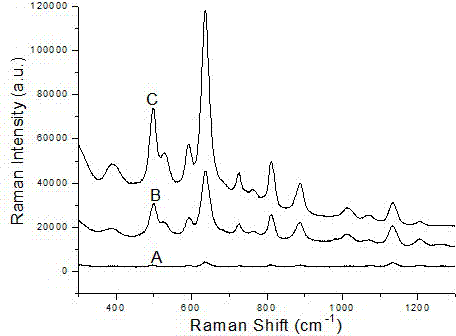
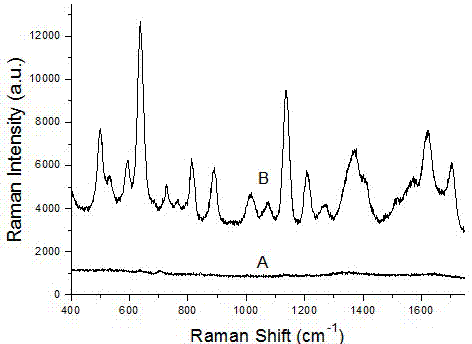
A quantitative detection method for uric acid based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
InactiveCN102288592AReduce dosageRealize quantitative detectionRaman scatteringHigh concentrationIntensity normalization
The invention relates to a method for the quantitative detection of uric acid based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The method comprises the following steps of: adding NaOH and hydroxylamine hydrochloride into an AgNO3 solution to obtain silver colloid; centrifuging the silver colloid to obtain high-concentration silver colloid; mixing uric acid solutions of different concentrations with the high-concentration silver colloid and adding a K2SO4 solution to perform a Raman spectroscopy test to obtain a uric acid SERS spectrum; testing the high-concentration silver colloid to obtain a silver colloid background SERS spectrogram; performing intensity normalization by using a silver colloid background Raman signal as internal standard, establishing a relative intensity-concentration standard working curve diagram of uric acid SERS spectral line; and deducing uric acid concentration by comparing the SERS spectrogram of the uric acid with unknown concentration with the relativeintensity-concentration standard working curve diagram of uric acid SERS spectrum. The method provided by the invention can be used for solving the problems that low-concentration uric acid solution has weak Raman signal and can be interfered with other impurities easily, obtaining high-quality uric acid SERS spectrum and realizing the quantitative detection of uric acid by means of the SERS spectrum.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Light-field pixel for detecting a wavefront based on a first intensity normalized by a second intensity
ActiveUS8822894B2Optical measurementsPhotometry using reference valueIntensity normalizationWavefront
A light-field pixel for detecting a wavefront, the light-field pixel comprises an aperture layer, a light detector layer, and a processor. The aperture layer has a non-conventional aperture and a non-conventional aperture. The non-conventional aperture has a higher gradient of transmission at normal incidence than the conventional aperture. The light detector is configured to measure a first intensity of light through the non-conventional aperture and a second intensity of light through the conventional aperture. The processor is configured to detect the wavefront based on the first intensity normalized by the second intensity.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
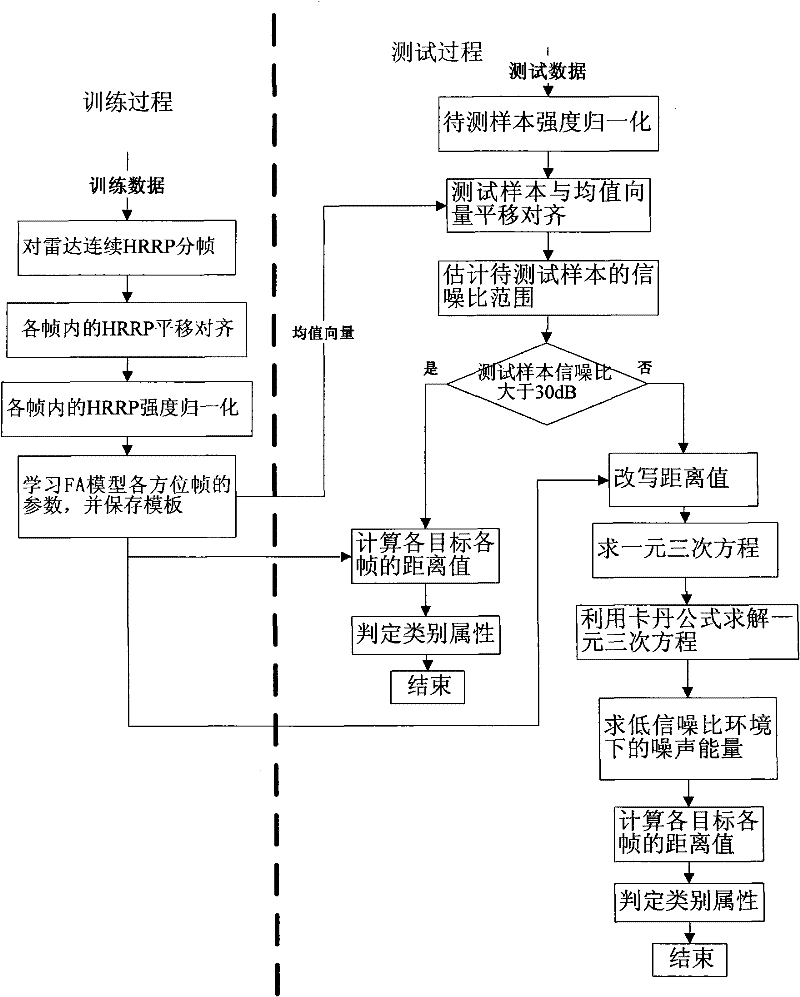
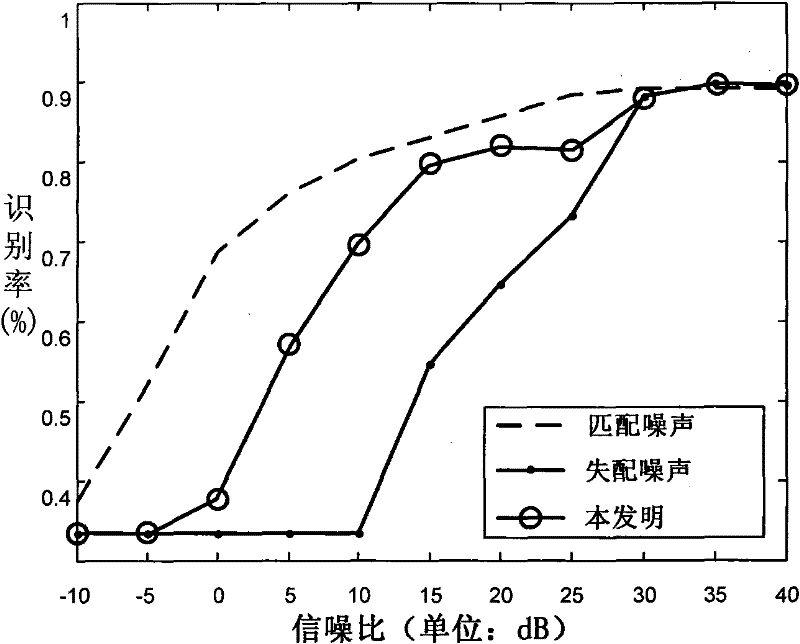
Radar range profile statistics and recognition method based on FA model in strong noise background
ActiveCN101598784AReduce the recognition rateNoise robustWave based measurement systemsIntensity normalizationCategory attribute
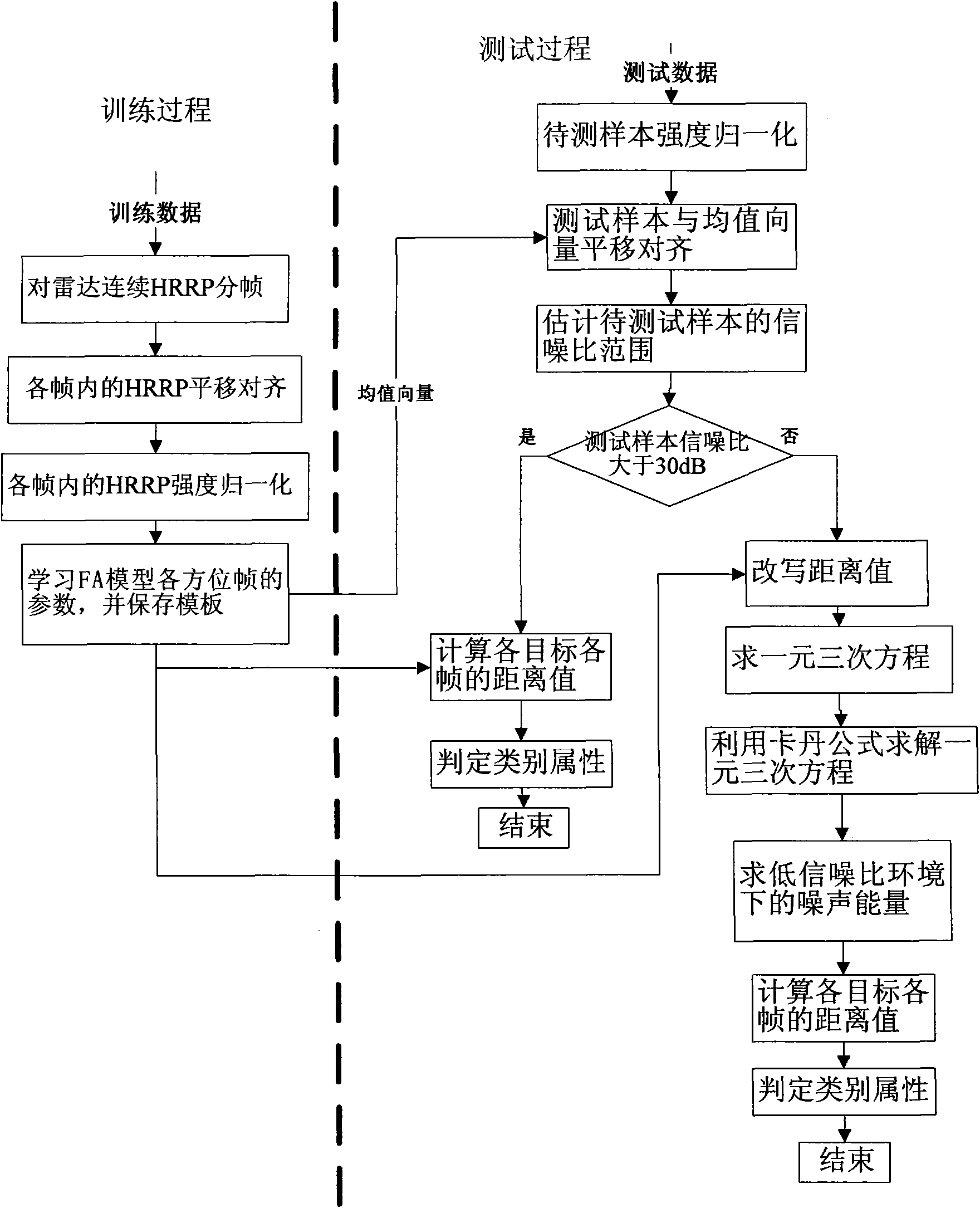
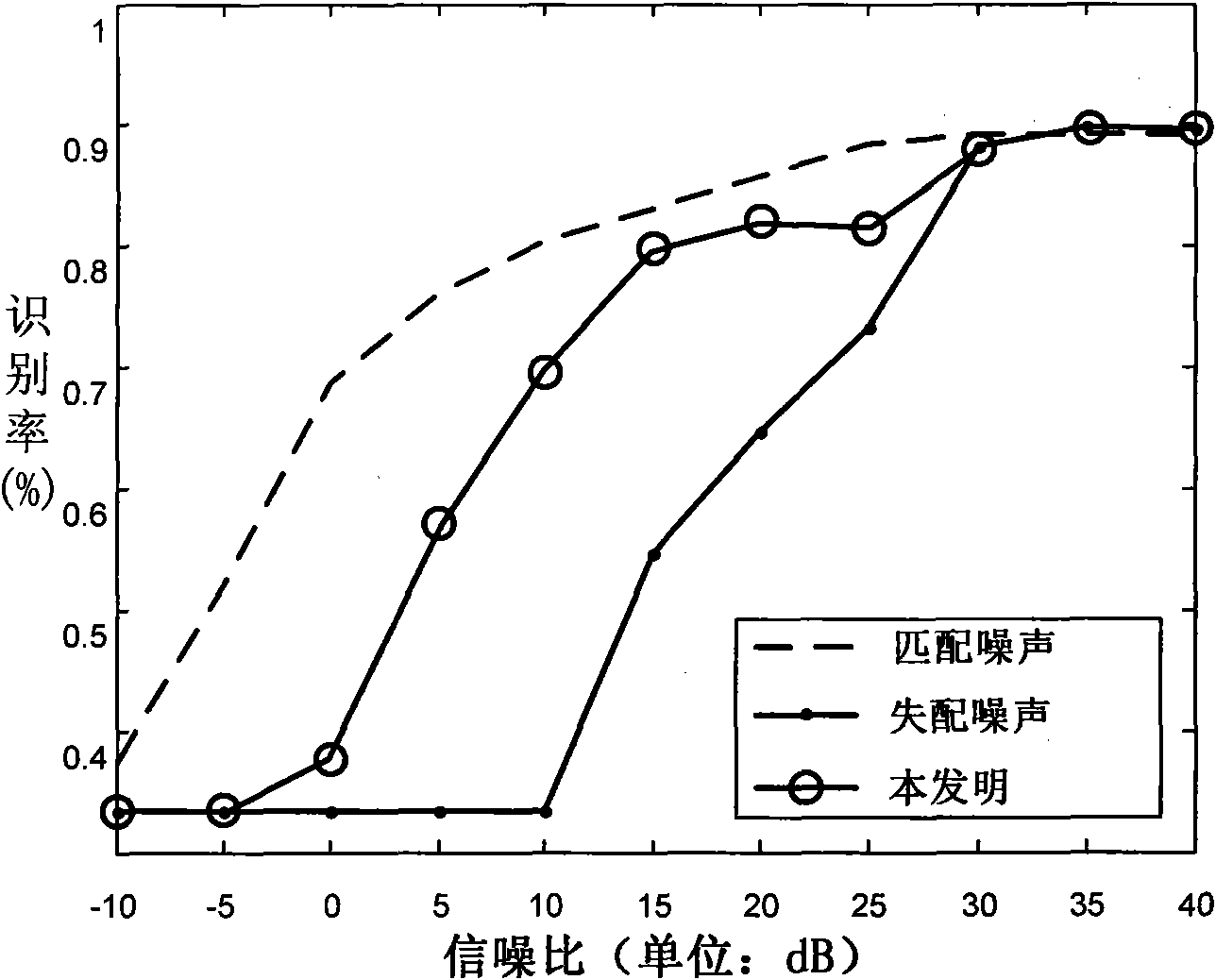
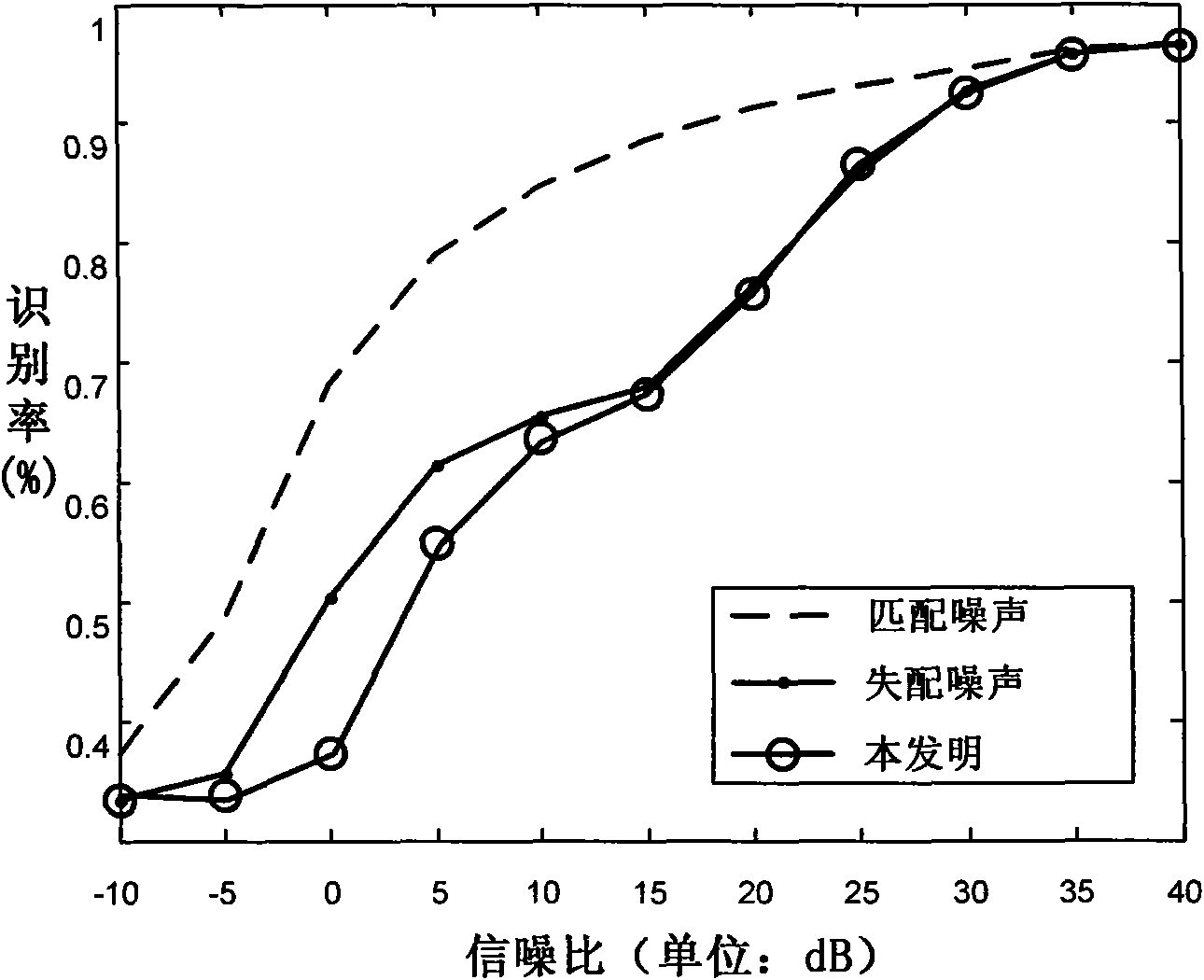
The invention discloses a radar range profile statistics and recognition method based on a FA model in the strong noise background, which relates to the technical field of radar automatic target recognition and mainly solves the problem that the current statistics and recognition methods based on the FA model are not robust to noises. The training phase comprises the following steps: framing, translating, aligning and strength-normalizing radar HPPR continuously, learning the parameters of each azimuth frame of the FA model by adopting the processed HRRP and storing a template. The test phase comprises the following steps: first strength-normalizing, translating and aligning the samples to be tested and then estimating the range of the signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) of the samples; computing the distance value of each frame of each target and deciding the category attribute if the SNR is more than 30dB, and rewriting the distance value, solving the noise energy under SNR condition by minimizing the distance value, finally computing the distance value of each frame of each target and deciding the category attribute if the SNR is less than 30dB. The method has the advantages of robustness to noises and less computation and is applied to identifying radar targets.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
Garnet-type lithium ion-conducting oxide and all-solid-state lithium ion secondary battery containing the same
ActiveUS8986895B2Improve lithium ion conductivityWide potential windowOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideIon-exchanger regenerationCrystallographyAll solid state
An all-solid-state lithium ion secondary battery containing a novel garnet-type oxide serving as a solid electrolyte. The garnet-type lithium ion-conducting oxide is one represented by the formula Li5+XLa3(ZrX, A2-X)O12, wherein A is at least one selected from the group consisting of Sc, Ti, V, Y, Nb, Hf, Ta, Al, Si, Ga, Ge, and Sn and X satisfies the inequality 1.4≦X<2, or is one obtained by substituting an element having an ionic radius different from that of Zr for Zr sites in an garnet-type lithium ion-conducting oxide represented by the formula Li7La3Zr2O12, wherein the normalized intensity of an X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern with a diffraction peak, as normalized on the basis of the intensity of a diffraction peak, is 9.2 or more.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Inspection apparatus, inspection method and device manufacturing method
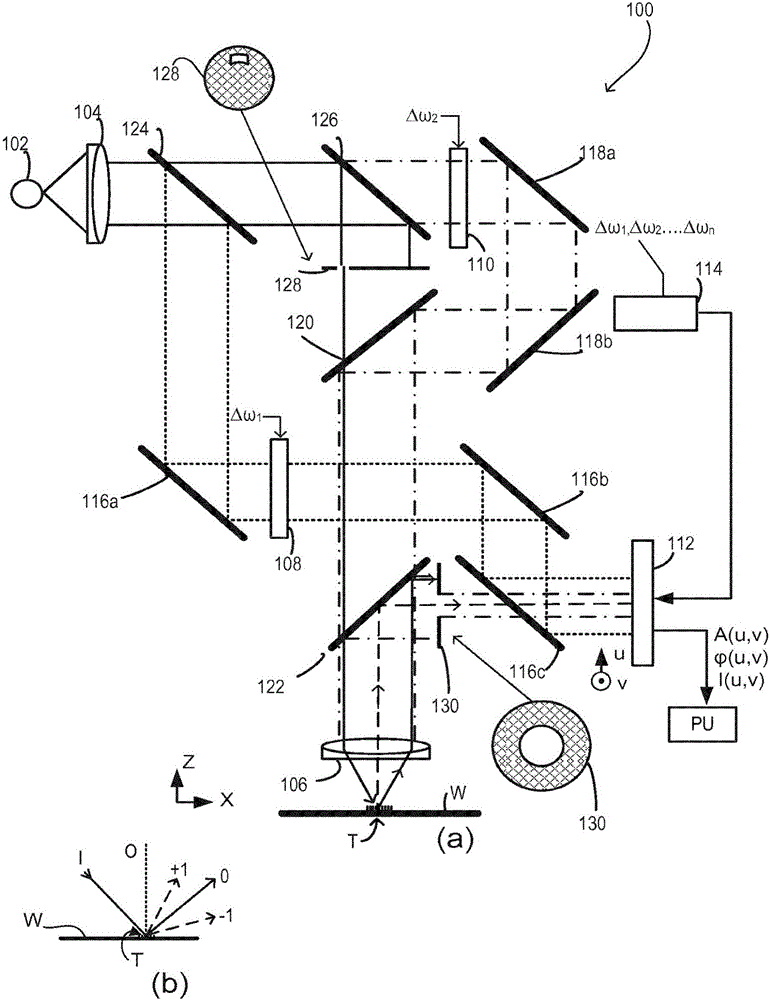
ActiveCN106662824AInterferometric spectrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansIntensity normalizationOptical frequencies
The invention discloses an inspection apparatus, an inspection method and a device manufacturing method. The inspection apparatus (100) is used for measuring parameters of targets on a substrate. Coherent radiation follows an illumination path (solid rays) for illuminating target (T). A collection path (dashed rays) collects diffracted radiation from the target and delivers it to a lock-in image detector (112). A reference beam following a reference path (dotted rays). An acousto-optical modulator (108) shifts the optical frequency of the reference beam so that the intensity of radiation at the lock-in detector includes a time-varying component having a characteristic frequency corresponding to a difference between the frequencies of the diffracted radiation and the reference radiation. The lock-in image detector records two-dimensional image information representing both amplitude and phase of the time-varying component. A second reference beam with a different shift (110) follows a second reference path (dot-dash rays). Interference between the two reference beams can be used for intensity normalization.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
ROI-based assessment of abnormality using transformation invariant features
ActiveUS8170347B2Improve classification performanceImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity normalizationDemographic data
A method and apparatus of comparing the results of medical imaging by, for example, PET scanning dispenses with the need for intensity normalization. The relationships between features extracted from relevant regions of interest in the image are studied. In one example, mean intensities in the principle brain lobes are compared to each other and a short image ID is constructed and used to derive population statistics and diagnosis. The population statistics are compared with ‘reference’ statistics in order to assess abnormality. Comparison by a number of methods is possible, and the invention further provides concerns a novel voting mechanism which derives abnormality scores for each region.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method of constructing SERS spectral probe for detecting breast cancer marker EGFR phosphorylated tyrosine
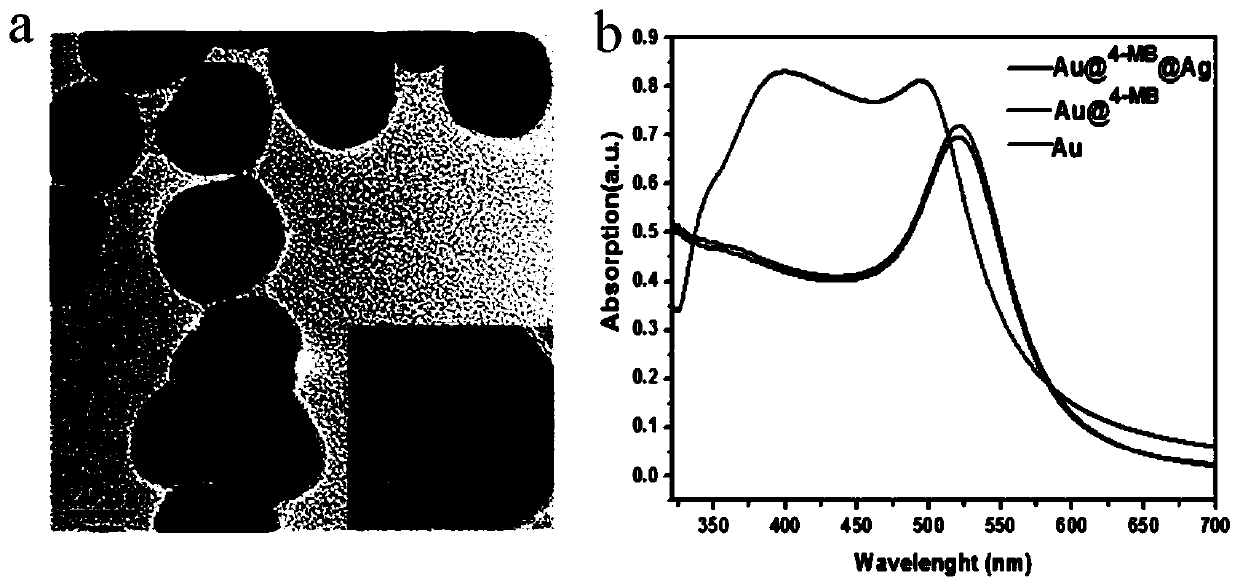
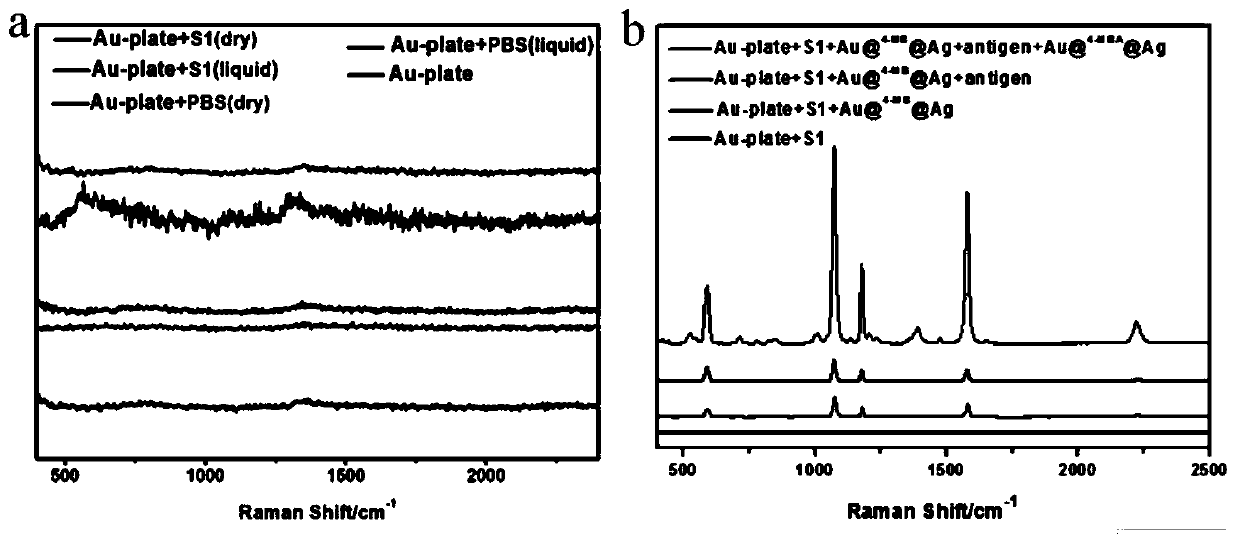
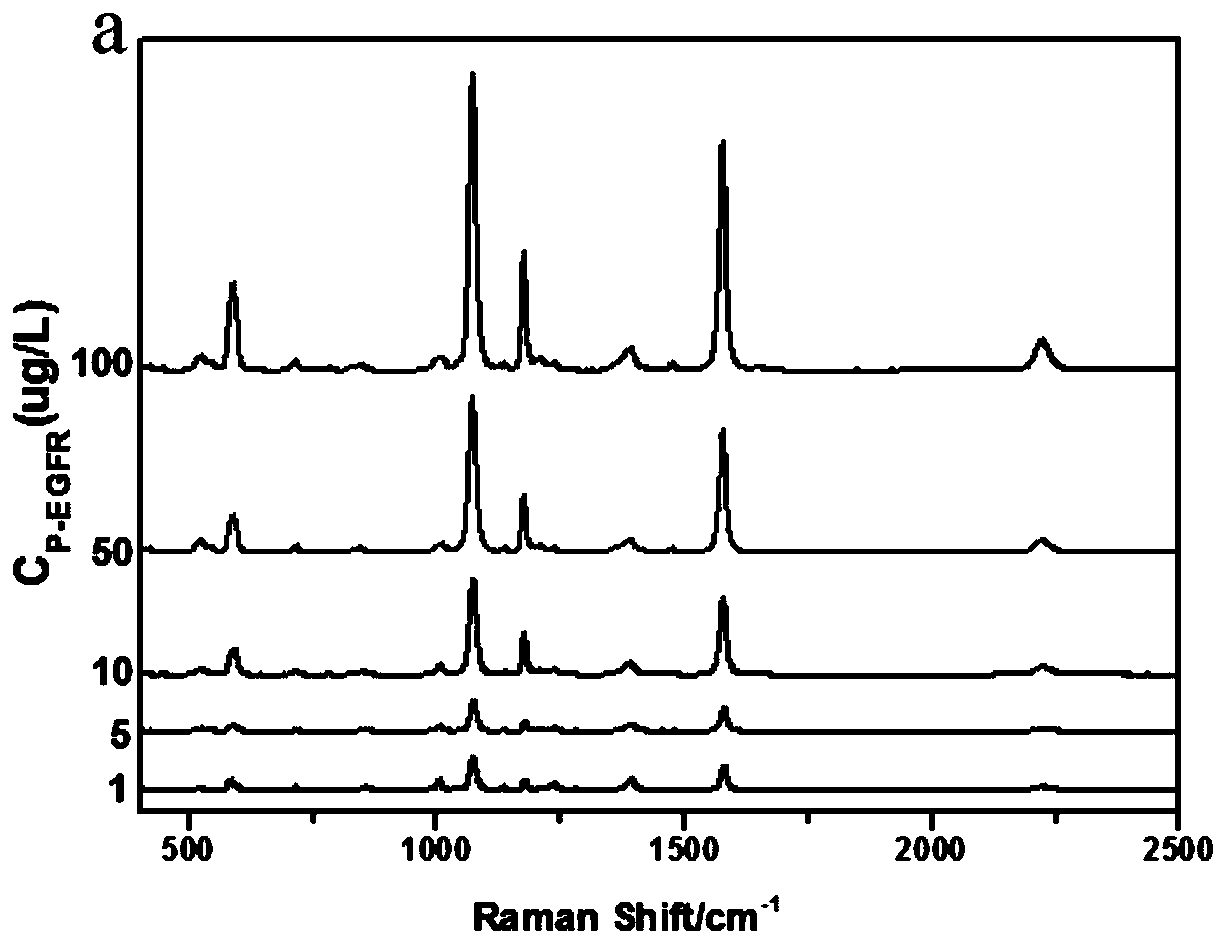
ActiveCN110412291AHigh detection sensitivityGuaranteed reliabilityRaman scatteringBiological testingIntensity normalizationPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a method of constructing an SERS spectral probe for detecting a breast cancer marker EGFR phosphorylated tyrosine. A gold plate is adopted as a base plate, a nanoparticle of acore-shell structure is adopted as a substrate for SERS detection, and a sandwich-configuration probe molecule with high selectivity and sensitivity is developed to detect phosphorylation of the breast cancer marker EGFR tyrosine. The spectral intensity of an SERS at a biomolecule Raman quiet region peak position of 2221cm<-1> in the 4-MB Raman spectrum is adopted as an internal standard, intensity normalization treatment is carried out on a spectral signal of the labeled molecule 4-MBA, and the influence of a Raman signal in a biomolecule fingerprint region on quantitative detection can be avoided, so that a linear relationship between the concentration of an EGFR phosphorylated tyrosine solution and the SERS intensity is greatly improved, and the detection sensitivity of the SERS spectral probe is further improved. The 4-MB and the 4-MBA are located in a middle layer of a gold core and a silver shell, it is ensured that the nature, spatial structure, quantity and the like of the SERSspectral probe are not changed, and thus the reliability of data is ensured. The method has a great potential in the terms of ultrasensitive detection of cancer markers.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Spectral signature extraction for drug verification and identification
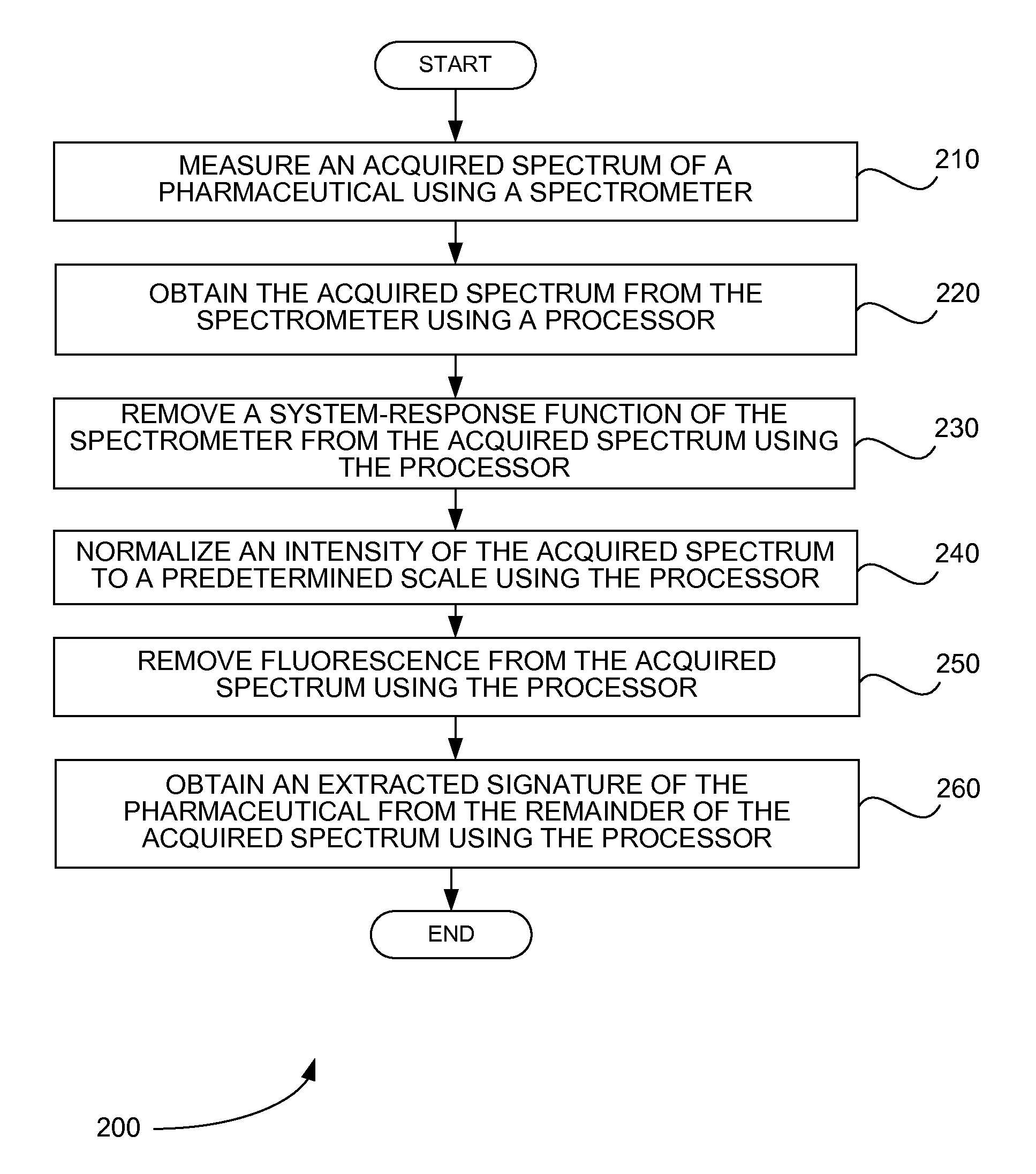
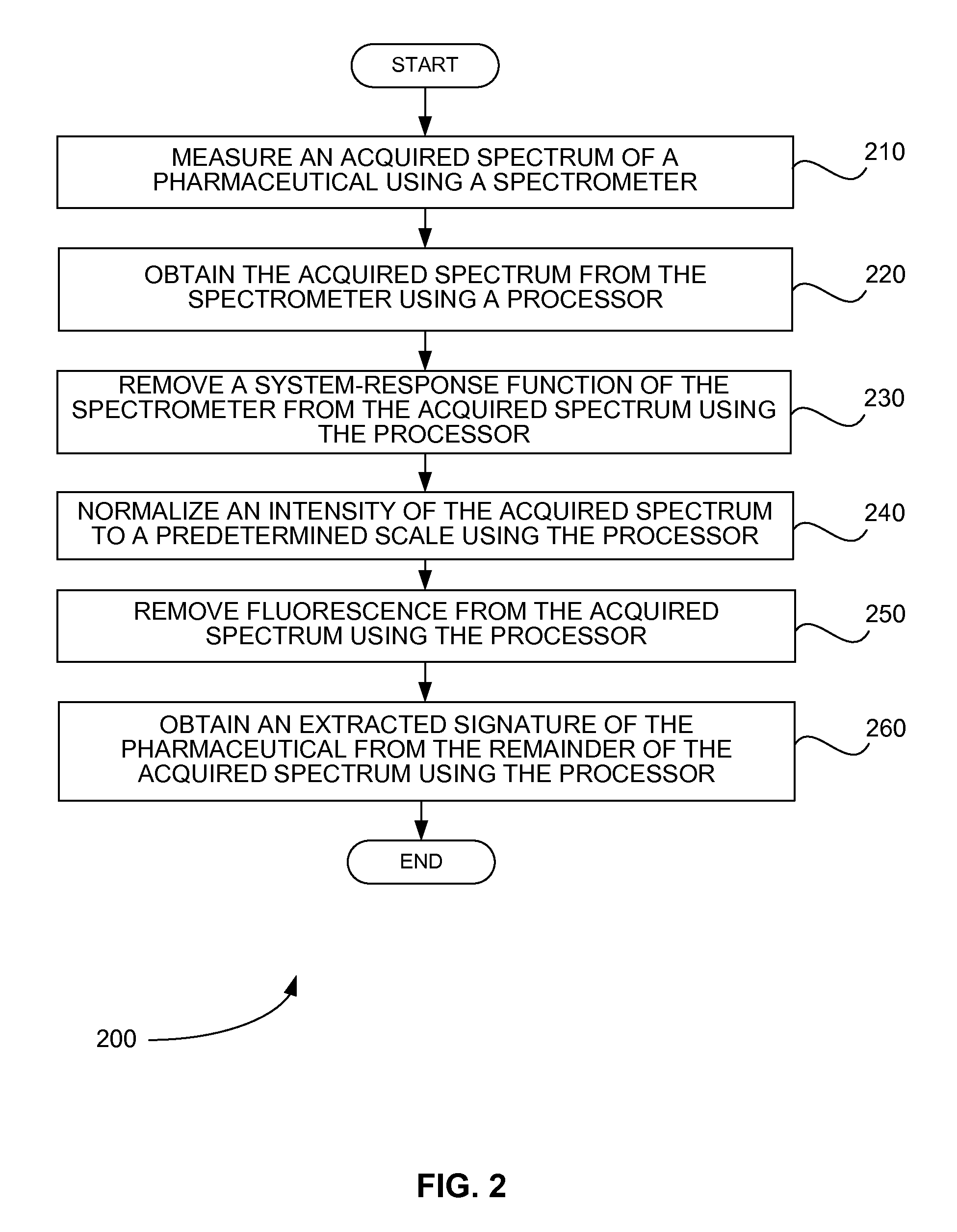
InactiveUS20100045978A1Easy to measureRadiation pyrometryData processing applicationsIntensity normalizationFluorescence
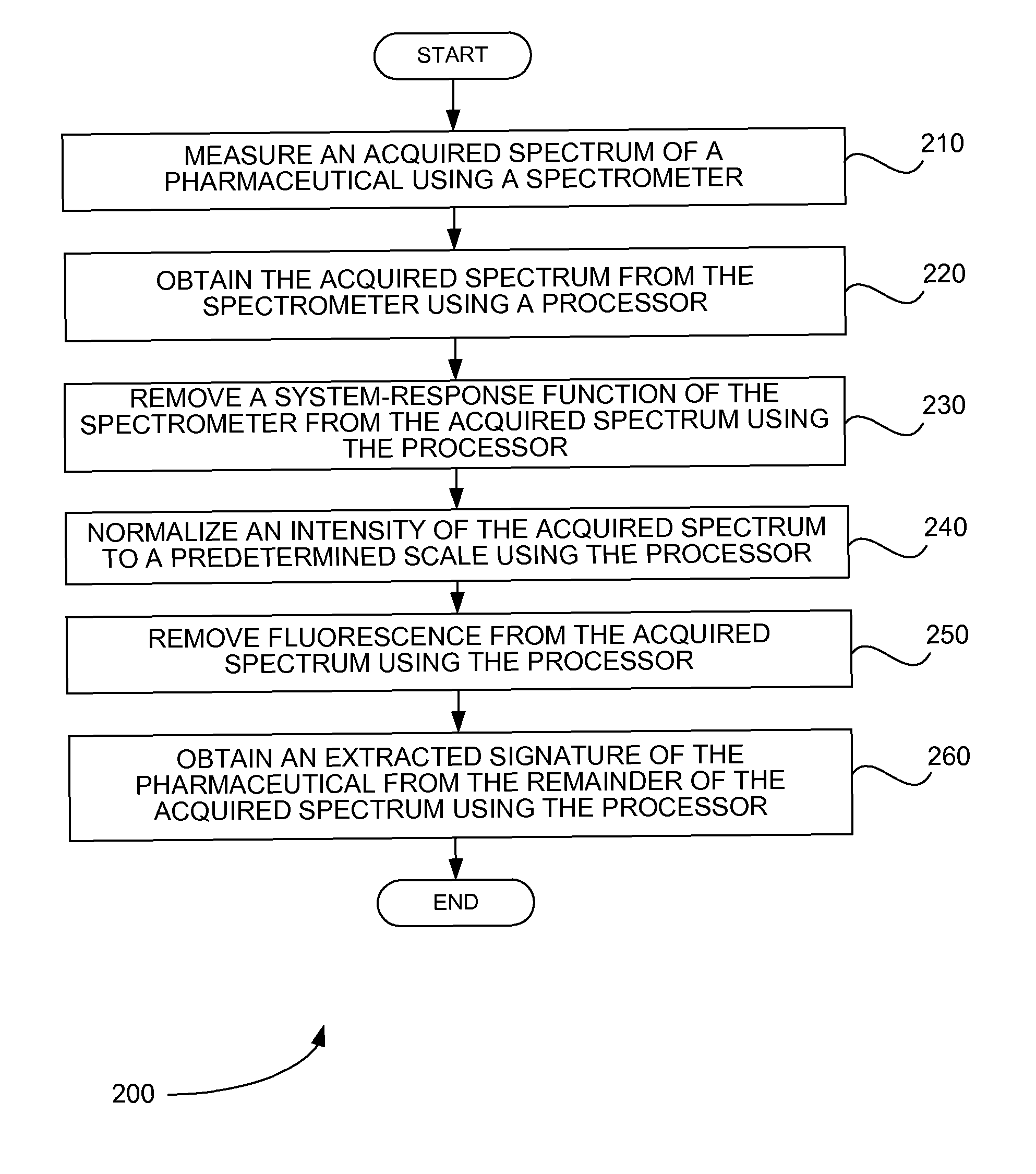
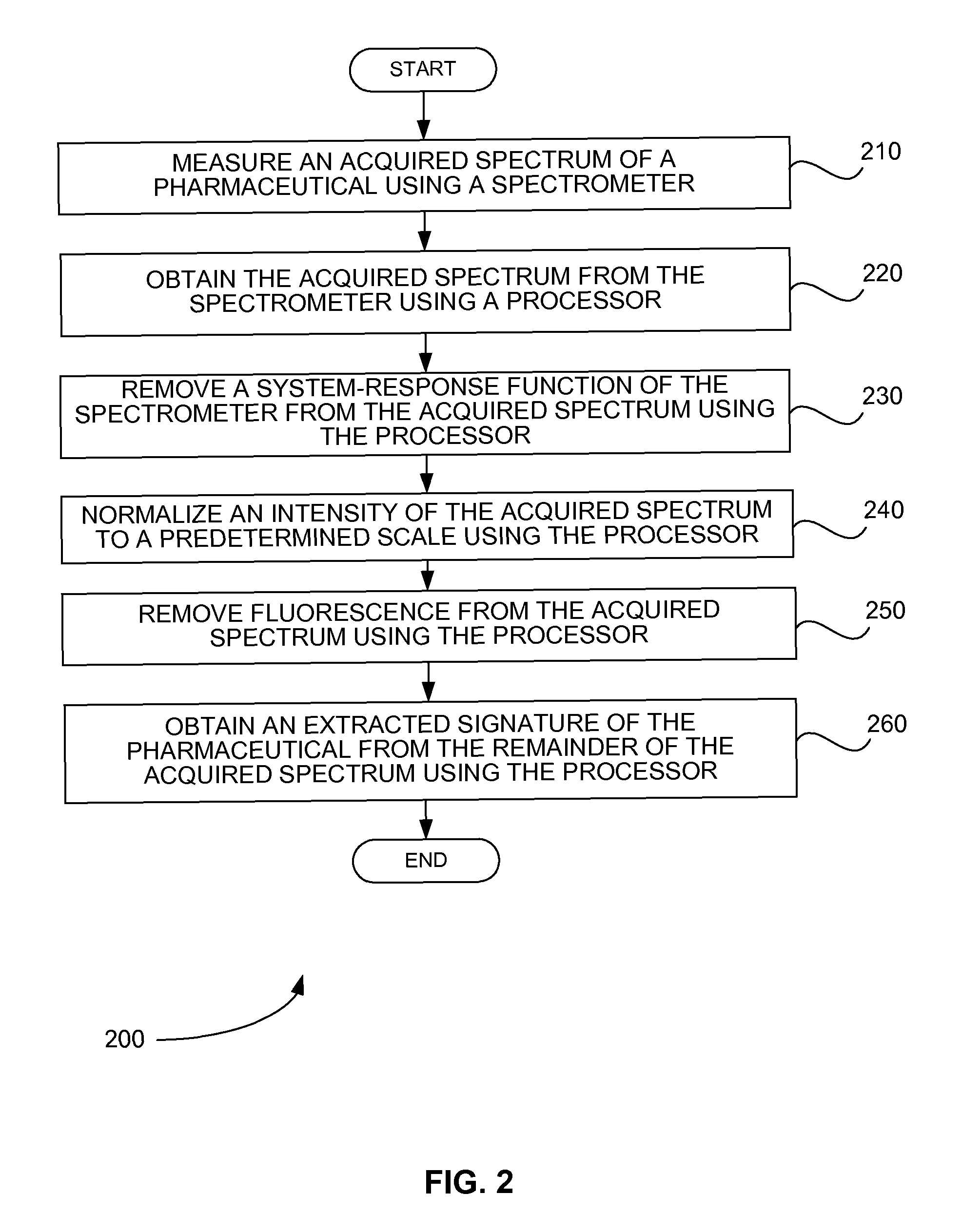
Systems and methods perform signature extraction from an acquired spectrum of a pharmaceutical. An acquired spectrum of the pharmaceutical is measured using a spectrometer. The acquired spectrum is obtained from the spectrometer using a processor. A system-response function of the spectrometer is removed from the acquired spectrum using the processor. An intensity of the acquired spectrum is normalized to a predetermined scale using the processor. Fluorescence is removed from the acquired spectrum using the processor. Finally, an extracted signature of the pharmaceutical is obtained from the remainder of the acquired spectrum using the processor. If the acquired spectrum of the pharmaceutical is measured by the spectrometer through a container holding the pharmaceutical, a spectrum of the container is removed from the remainder of the acquired spectrum to produce the extracted signature of the pharmaceutical using the processor.
Owner:OPTOPO INC D B A CENTICE CORP 215 SOUTHPORT DR +1
Multi-channel spectral measuring device and phase difference analysis method
InactiveCN101435928AImprove measurement efficiencyMeet the needs of the industryUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsIntensity normalizationMeasurement device
The invention discloses a multi-channel Optical Spectrum measurement device, which integrates a multi-channel imaging spectrograph with an optical fiber array type polarized beam steering probe to realize the simultaneous measurement of a plurality of sample spots to be tested. With respect to the design of a polarized beam absorption probe, a polarized beamsplitter is utilized to split received polarized beam into an incident polarized beam and a vertical polarized beam, and the two beams are absorbed by two groups of focusing lenses to the optical fiber array multi-channel imaging spectrograph respectively; thus, when the rotation of the absorption polarized beam probe is not required, a normalized strength spectrum signal of the vertical polarized beam and the incident polarized beam can be rapidly calculated and acquired according to energy loss calibrating parameters and measurement of the polarized components of a p wave and an S wave of the polarized light, and phase separation parameters can be obtained by mathematical manipulation.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for selecting best imaging waveband of molten pool vision based on spectral analysis
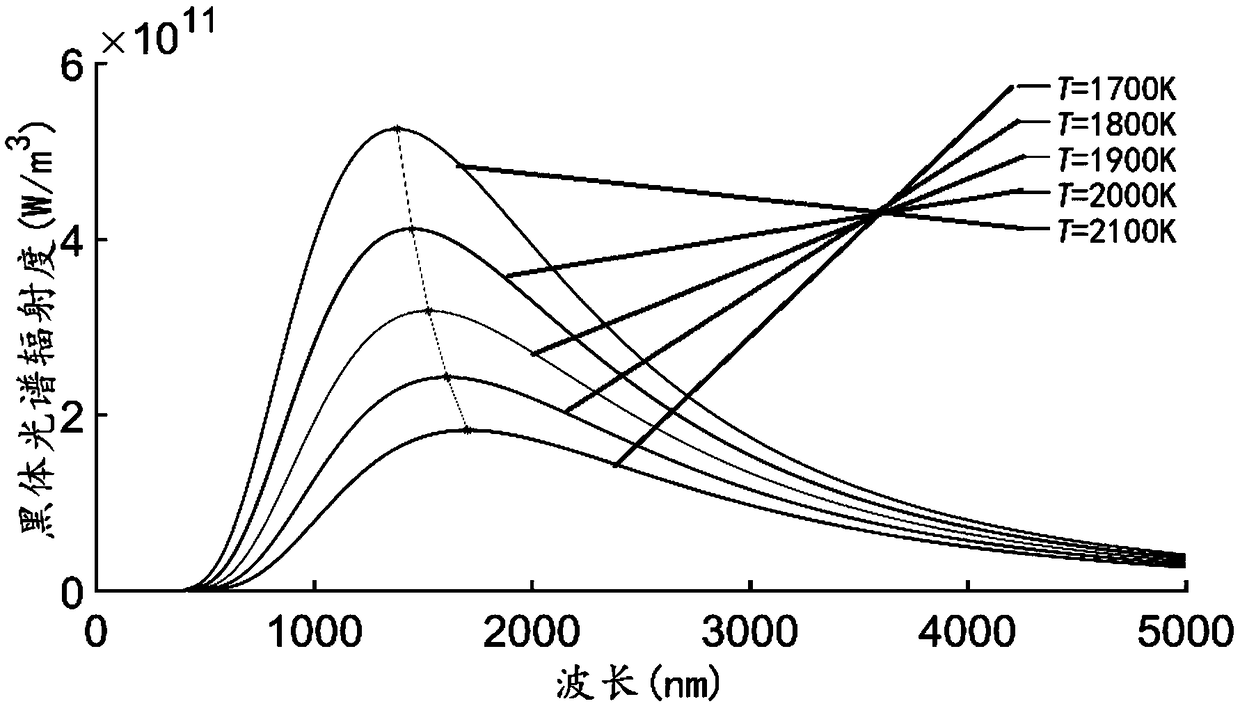
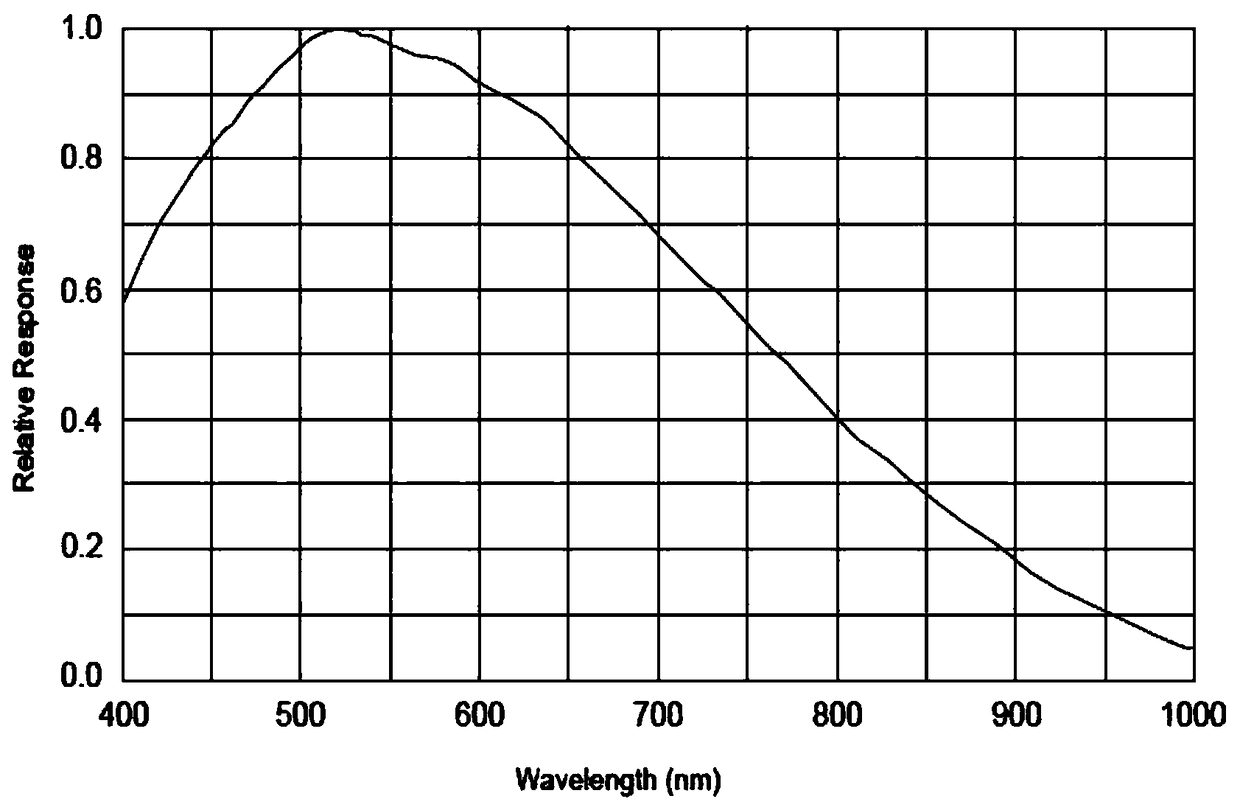
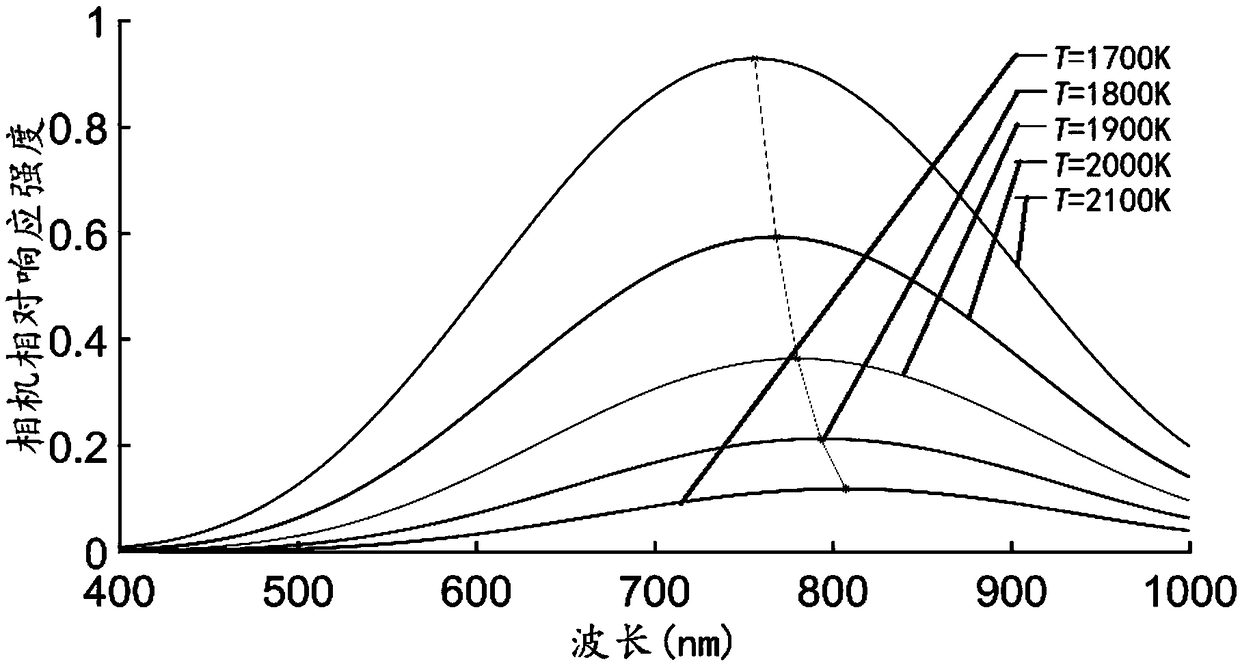
InactiveCN109444134AIncrease radiation doseStrong spectral response of the cameraMaterial analysis by optical meansIntensity normalizationSpectral response
The invention discloses a method for selecting a best imaging waveband of molten pool vision based on spectral analysis. The method includes the following steps: (1) according to the spectral responseof a camera, simulating the response intensity of the camera at different wavelengths under different blackbody temperatures to obtain a camera spectrogram and normalize the camera spectrogram; collecting a molten pool self-radiation spectrogram in the welding process by a spectrometer, and normalizing the corresponding intensity of the collected molten pool self-radiation spectrogram; (2) makinga difference between the relative intensity of the normalized molten pool self-radiation spectrogram at different wavelengths and the relative intensity of the normalized camera spectrogram to obtaina difference value; (3) selecting a waveband with a difference value greater than or equal to 0.4 as the best imaging waveband for molten pool vision. According to the method for selecting the best imaging waveband of the molten pool vision based on spectral analysis, arc light in the bast imaging waveband of the molten pool vision is weaker, the camera spectral response is stronger, and the imaging waveband is wider, so that the radiation amount of the molten pool can be effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
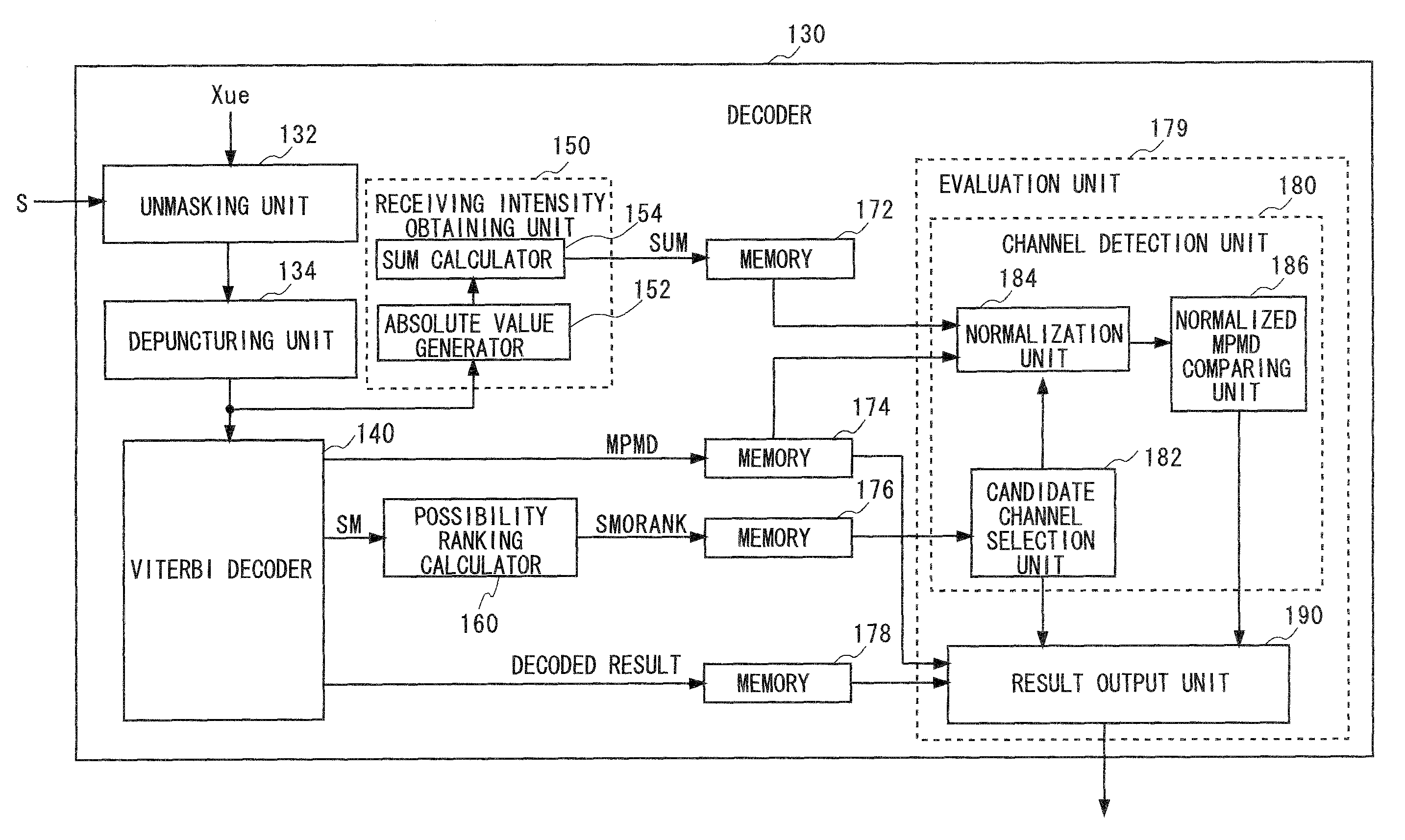
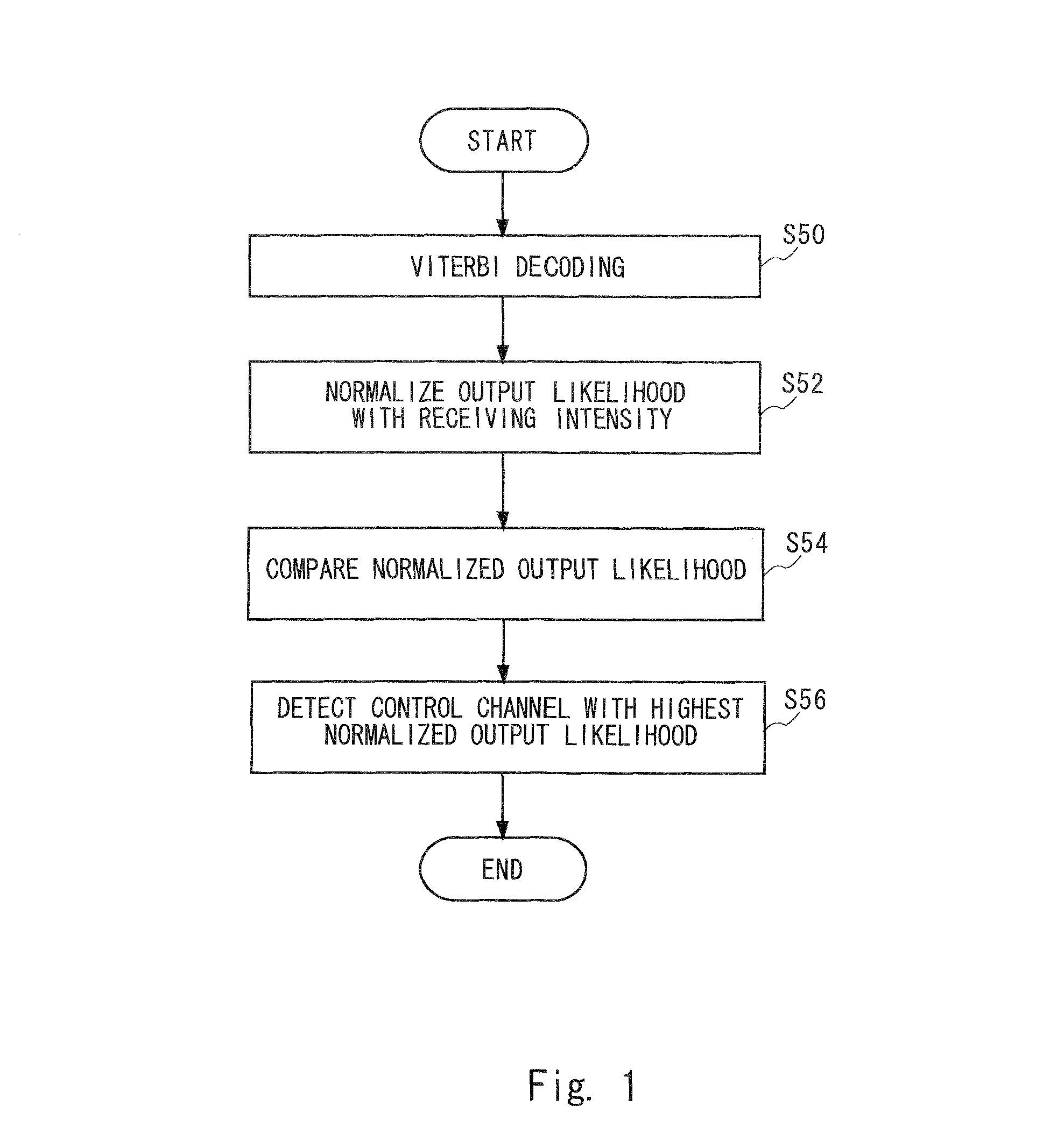
Receiving apparatus
InactiveUS20090207948A1Accurate detectionError preventionOther decoding techniquesIntensity normalizationTelecommunications
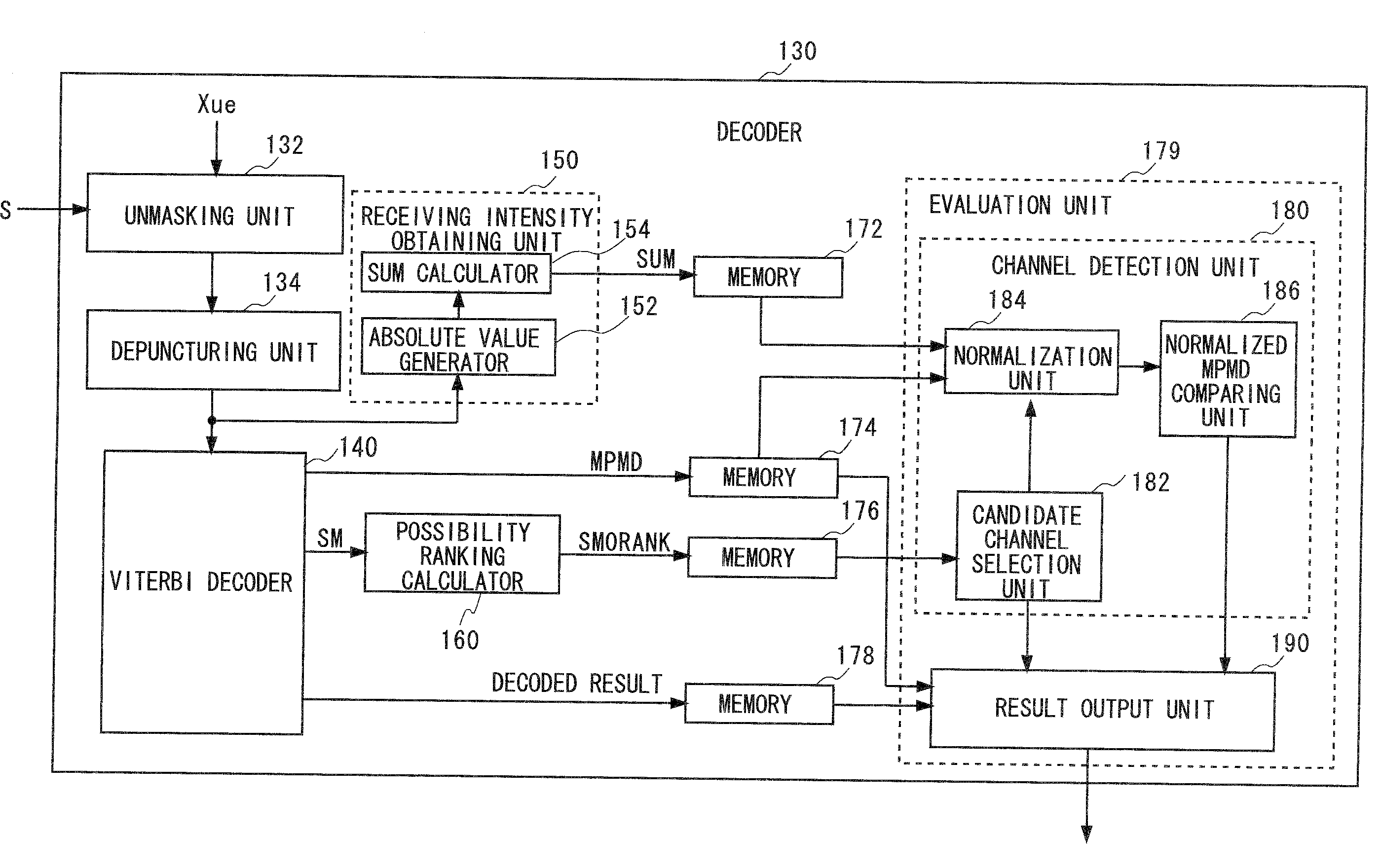
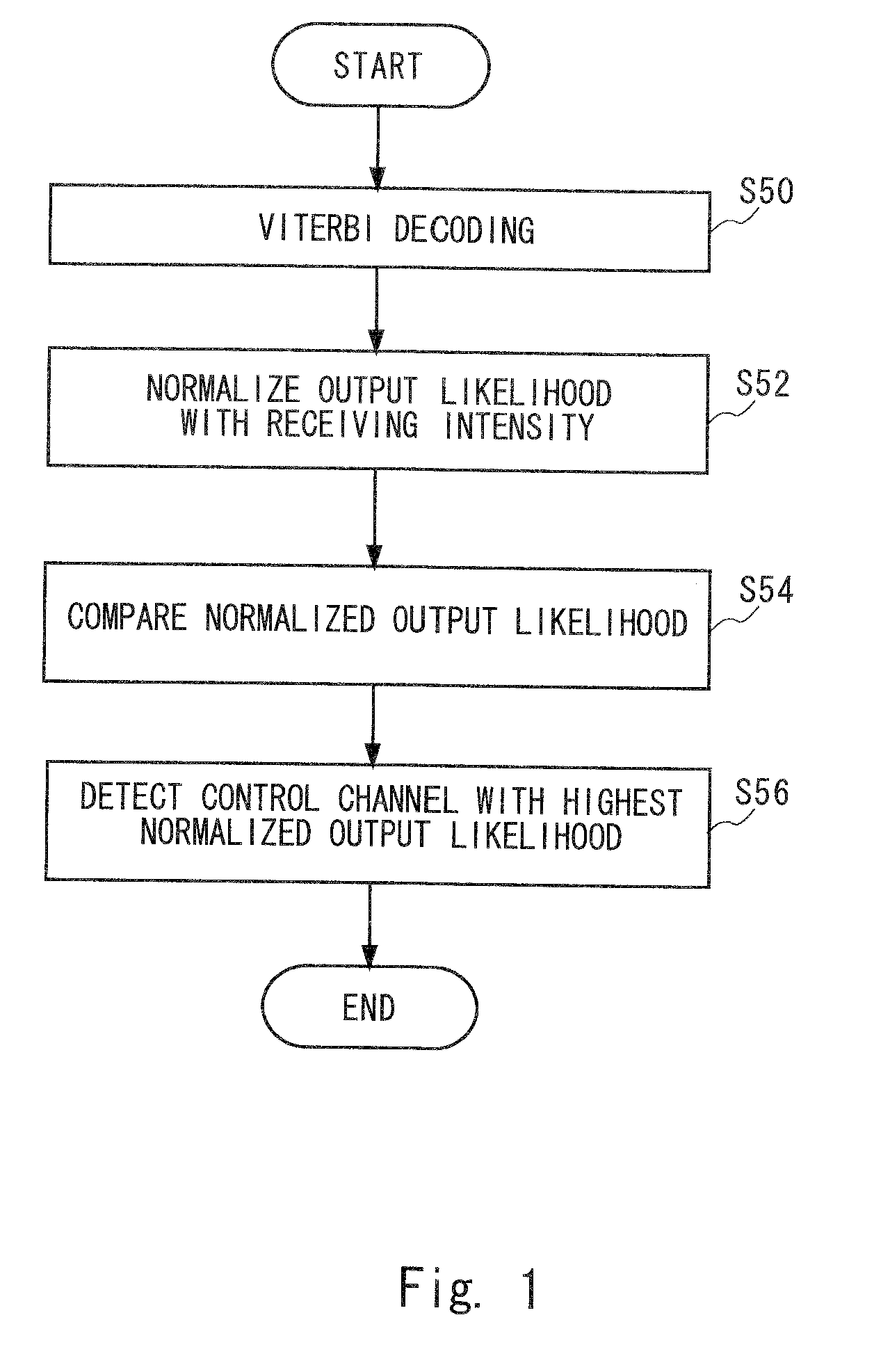
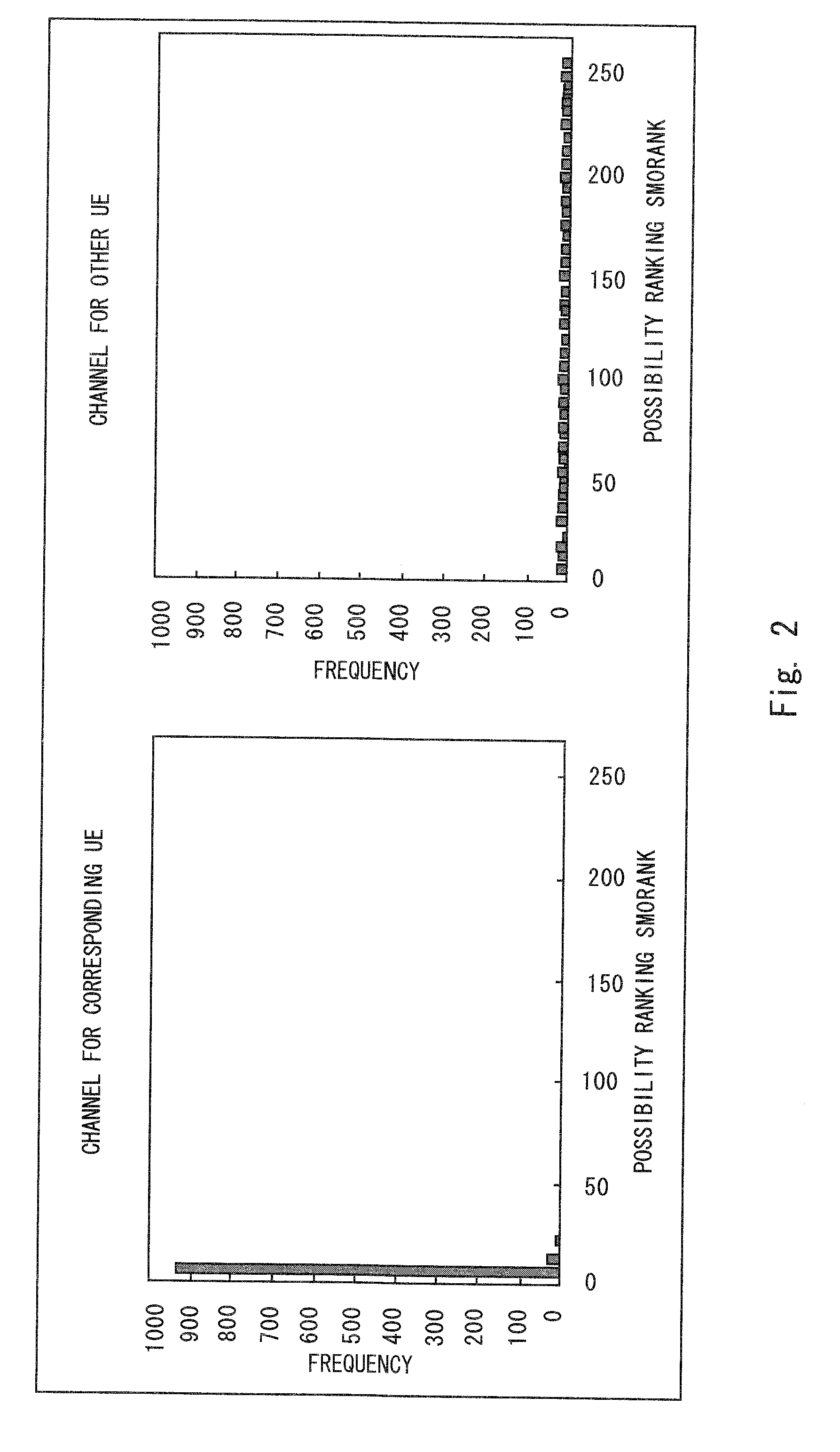
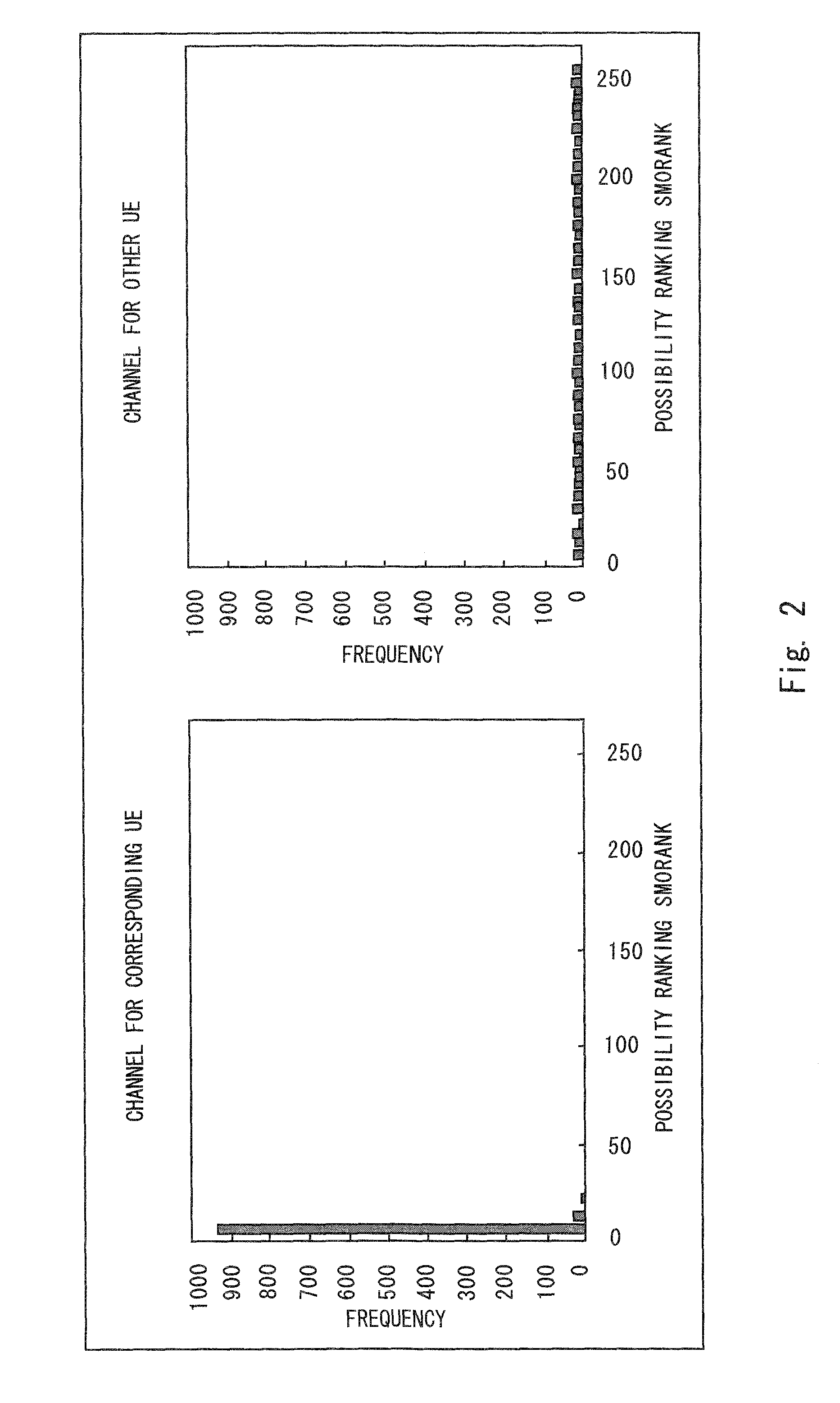
For each of a plurality of control channels, a likelihood indicated by a state metric of each state at the last point which is obtained at the time of Viterbi decoding is obtained. This Viterbi decoding is not cut off and performed to convolutionally coded data of the corresponding control channel. The ranking of the likelihood is obtained as a possibility ranking SM0RANK indicating the possibility of the control channel to be a control channel for a particular receiving apparatus. From the plurality of control channels, the control channels with the possibility ranking SM0RANK more or equal to a predetermined threshold are selected as candidate channels. An output likelihood of each candidate channel which is obtained in the Viterbi decoding is normalized with a receiving intensity of the corresponding candidate channel to detect a candidate channel having the highest normalized output likelihood as the control channel for the receiving apparatus.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for improving measurement accuracy of uneven sample elements based on LIBS
InactiveCN111413325AImprove accuracyEasy to correctAnalysis by thermal excitationIntensity normalizationAlgorithm
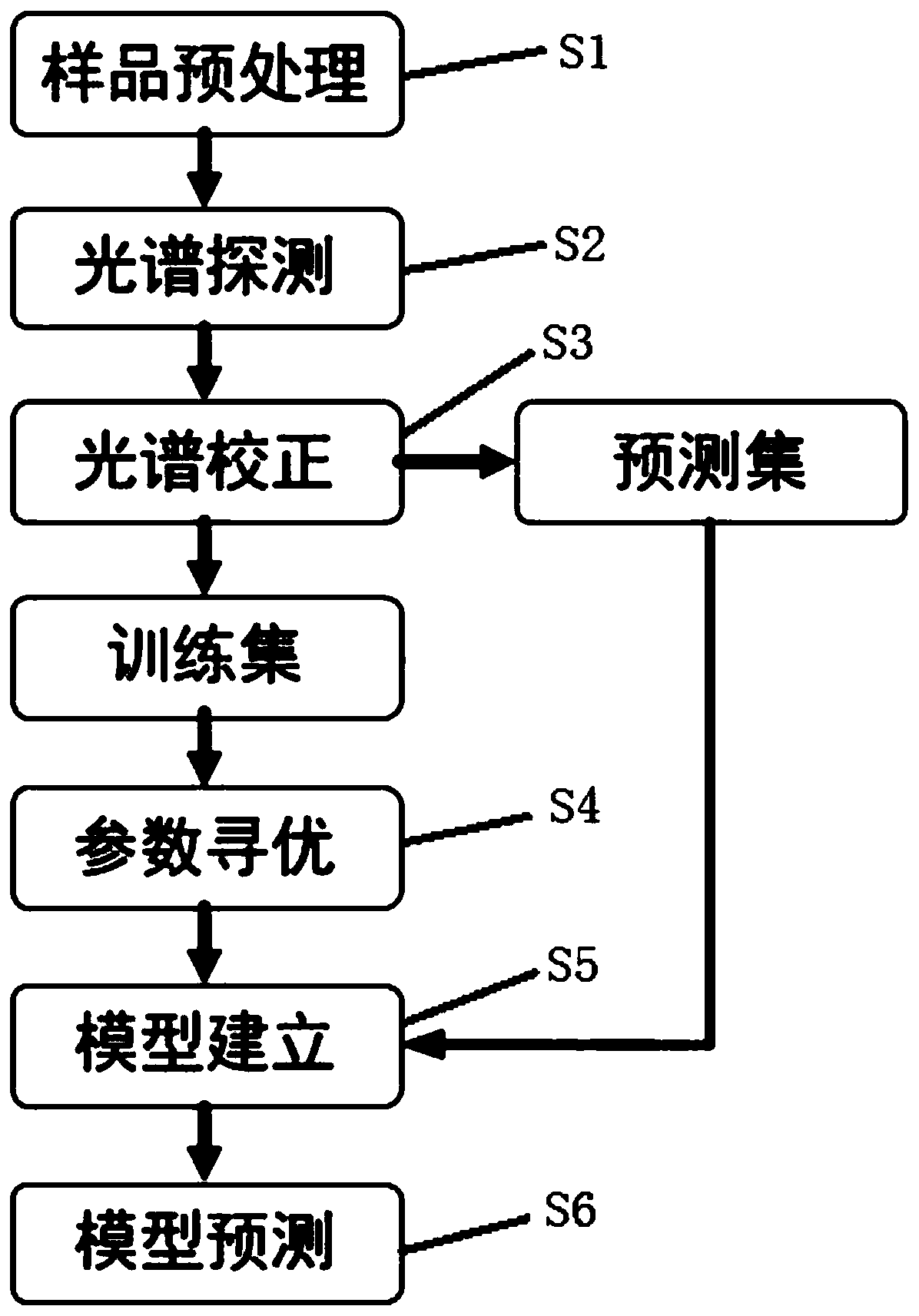
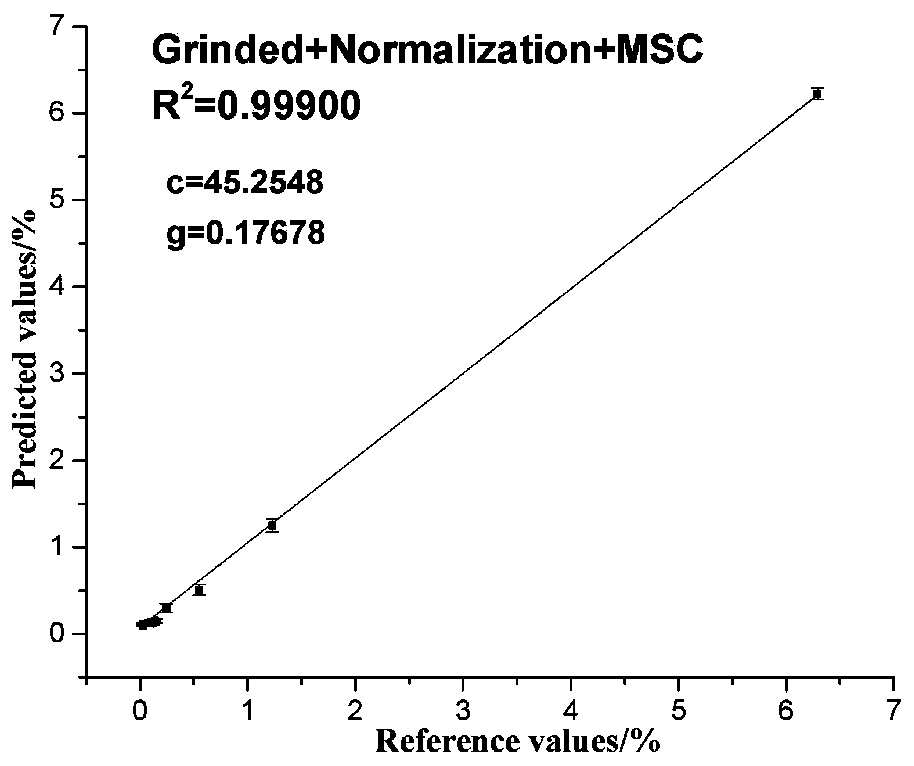
The invention relates to a method for improving measurement accuracy of uneven sample elements based on LIBS. The method comprises the following steps: in a step of sample pretreatment and spectrum detection, carrying out spectral data acquisition on a sample in S1 by utilizing a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technology; in a step of spectral correction: preprocessing the original spectraldata obtained in the S2 by utilizing an intensity normalization and multivariate scattering correction method, extracting characteristic spectral peaks of researched elements in a spectrum, and dividing the characteristic spectral peaks into two groups according to a training set and a prediction set; in a step of parameter optimization: optimizing the parameters of the support vector machine by using the training set data and adopting grid search; carrying out model establishment and model prediction. According to the method, the purposes of simplicity or no need of sample pretreatment, rapidness, high accuracy and the like when the LIBS technology is used for detecting the uneven sample are achieved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Radar target identification method based on convolutional neural network and Bert
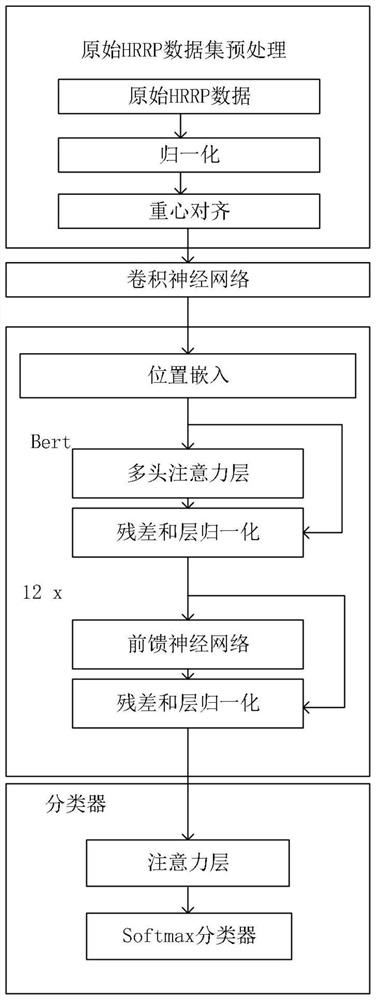
ActiveCN112764024AEasy to useGood abstractionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationIntensity normalizationFeature extraction
The invention discloses a radar target recognition method based on a convolutional neural network and Bert. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting data, dividing the data into a training set and a test set, and carrying out the intensity normalization and gravity center alignment of the data; S2, inputting the processed HRRP sample into a CNN module, and performing feature extraction on the processed sample by using the CNN; S3, using Bert to process the effective features extracted by the CNN, and extracting deeper features; S4, constructing a classifier, classifying an HRRP target, retaining more effective features for the output of Bert by using the attention mechanism again, and finally classifying the output of the network by adopting softmax; and S5, sending the HRRP test set processed in step S1 into the models trained in the steps S2, S3 and S4 for testing.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
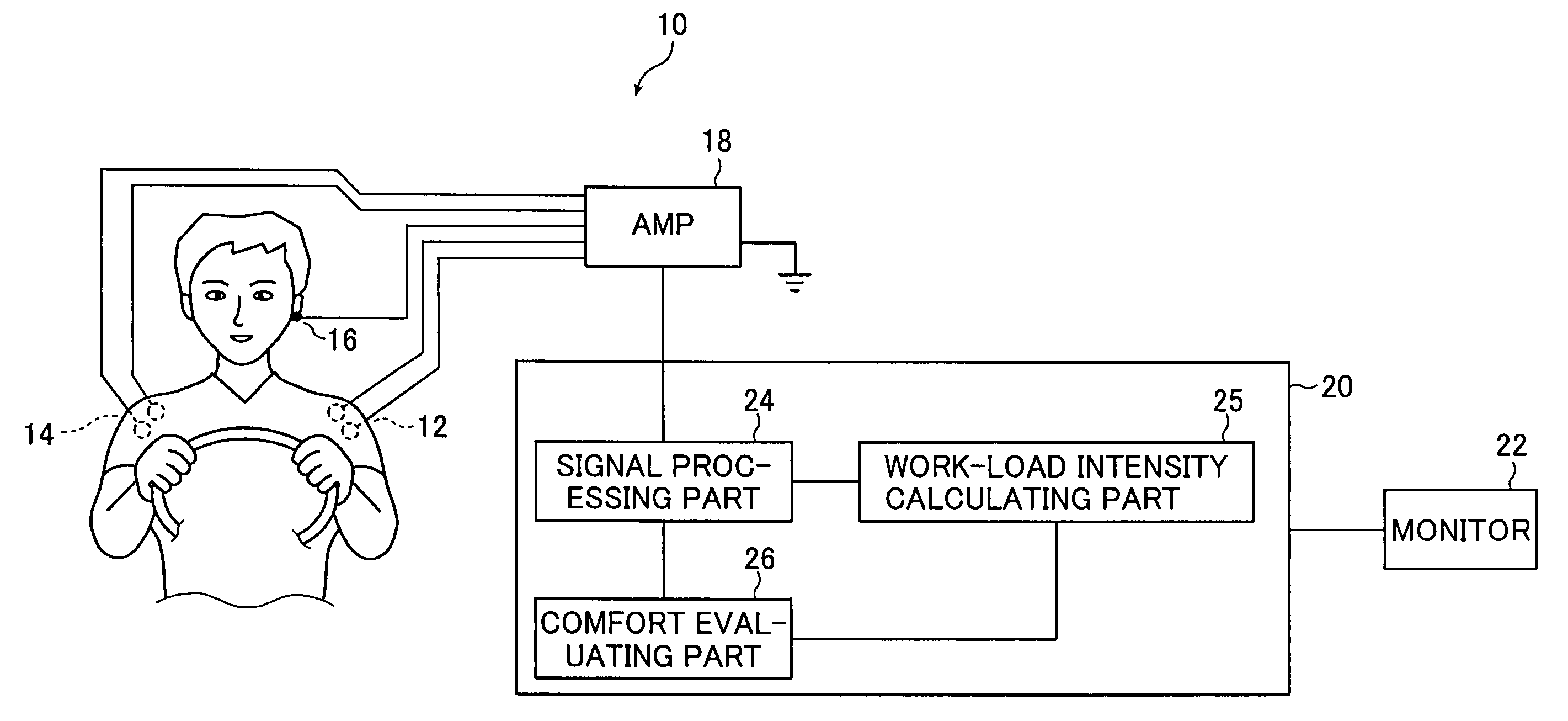
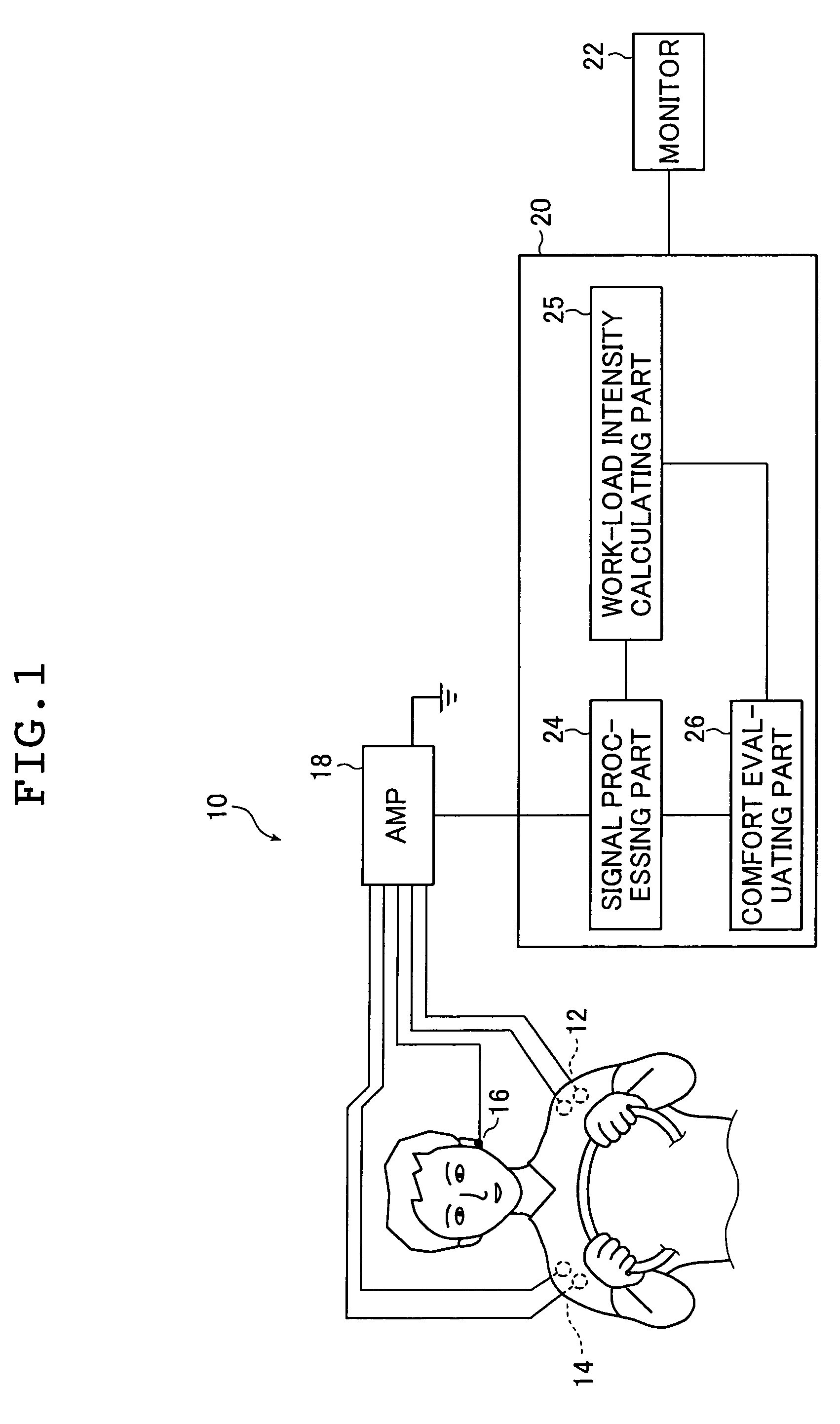
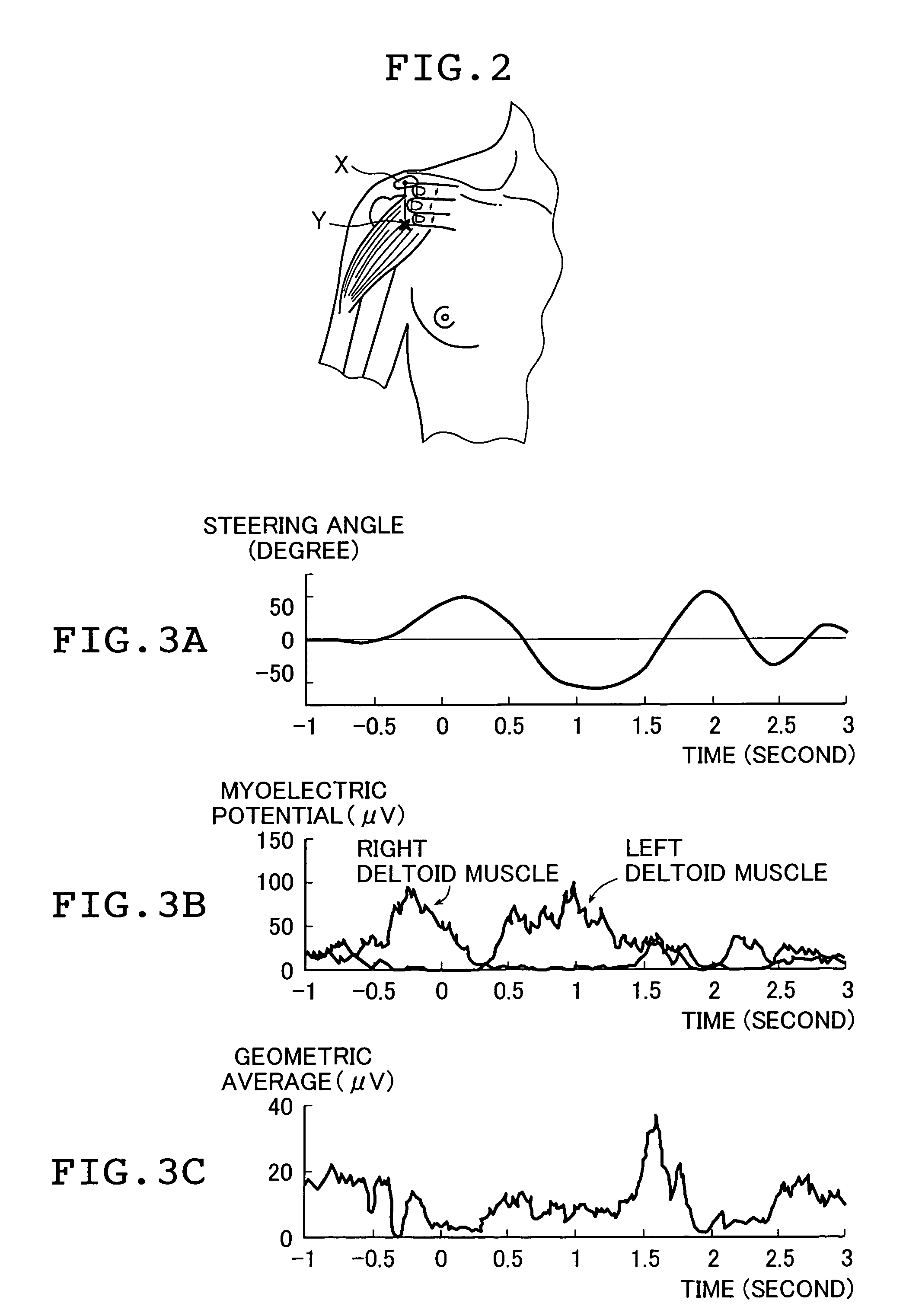
Work comfort evaluating device and work comfort evaluating method
InactiveUS7486987B2Level of comfortElectromyographySensorsIntensity normalizationAudio power amplifier
A work comfort evaluating device is a device for evaluating a level of comfort of work by measuring myoelectric potentials of plural muscles when the work is done by antagonistic activities of the muscles. The device has a pair of detecting sensors, an amplifier, a signal processing part, a work-load intensity calculating part, and an evaluation part. The sensors sense myoelectric potentials of the muscles at a time of the work. The signal processing part calculates a synchronous contraction intensity of the muscles by using myoelectric potential waveforms. The work-load intensity calculating part calculates a level of a work load intensity in the work. The evaluation part evaluates a level of comfort of the work by normalizing the synchronous contraction intensity by the level of the work load intensity calculated.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
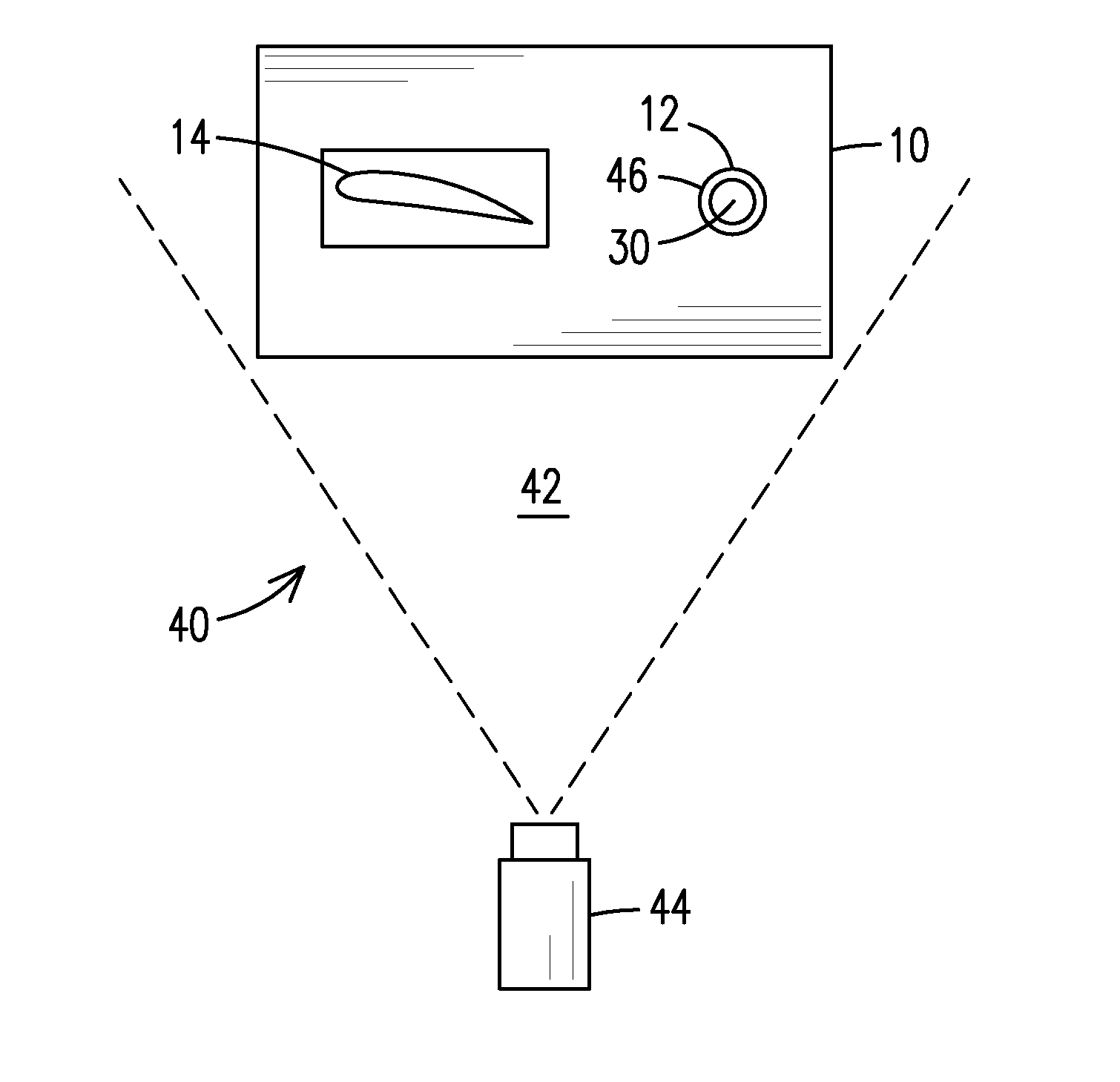
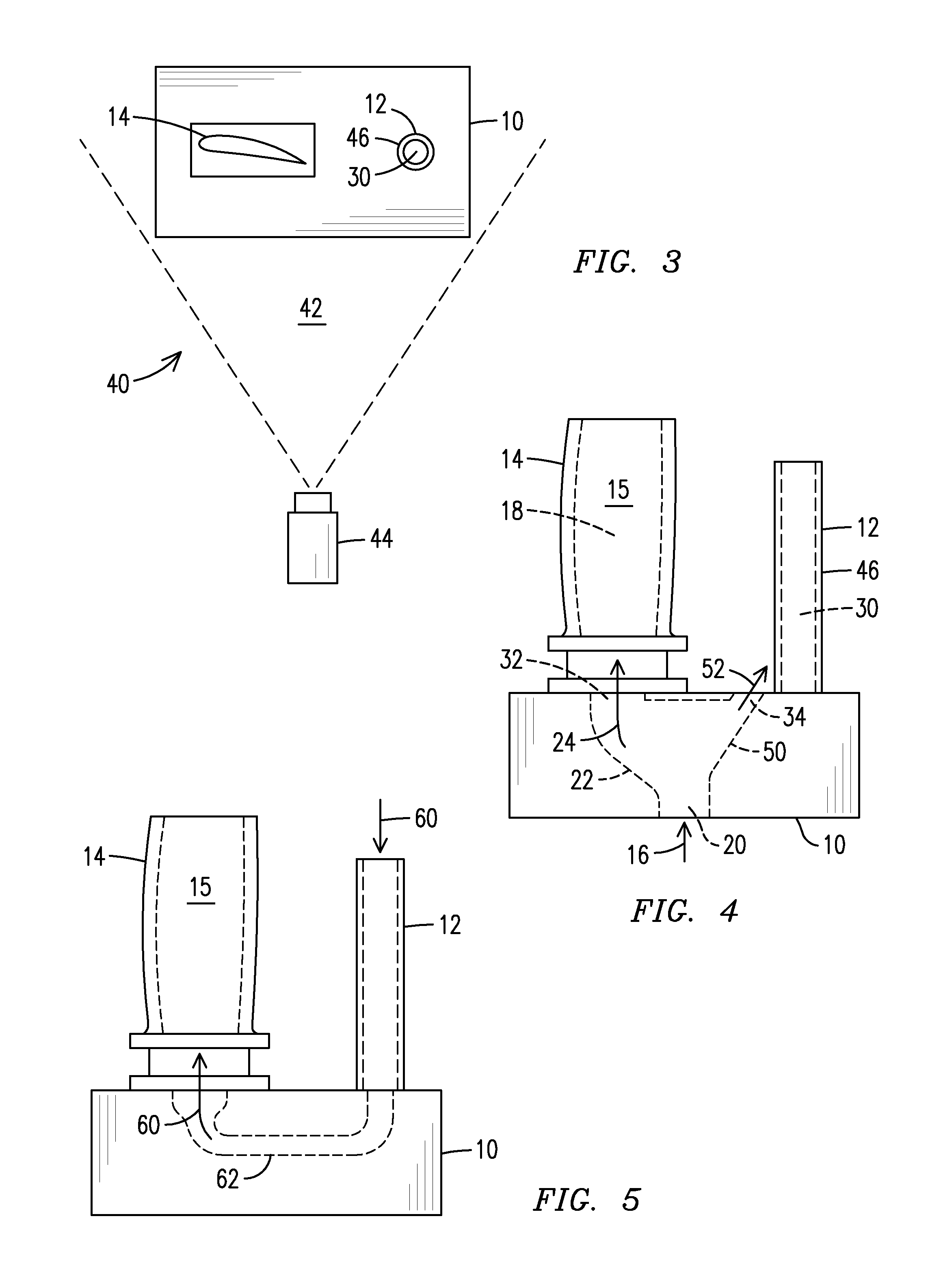
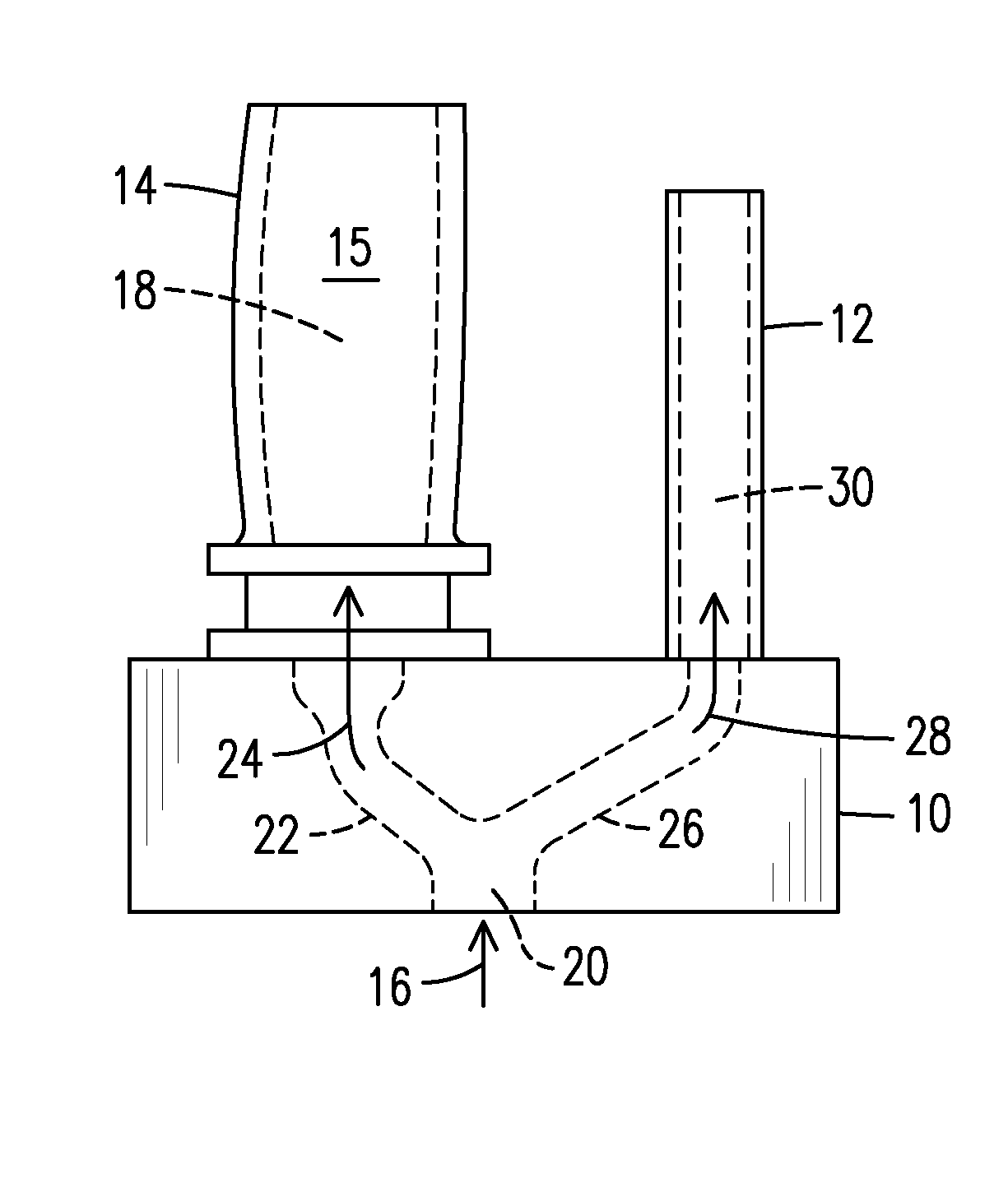
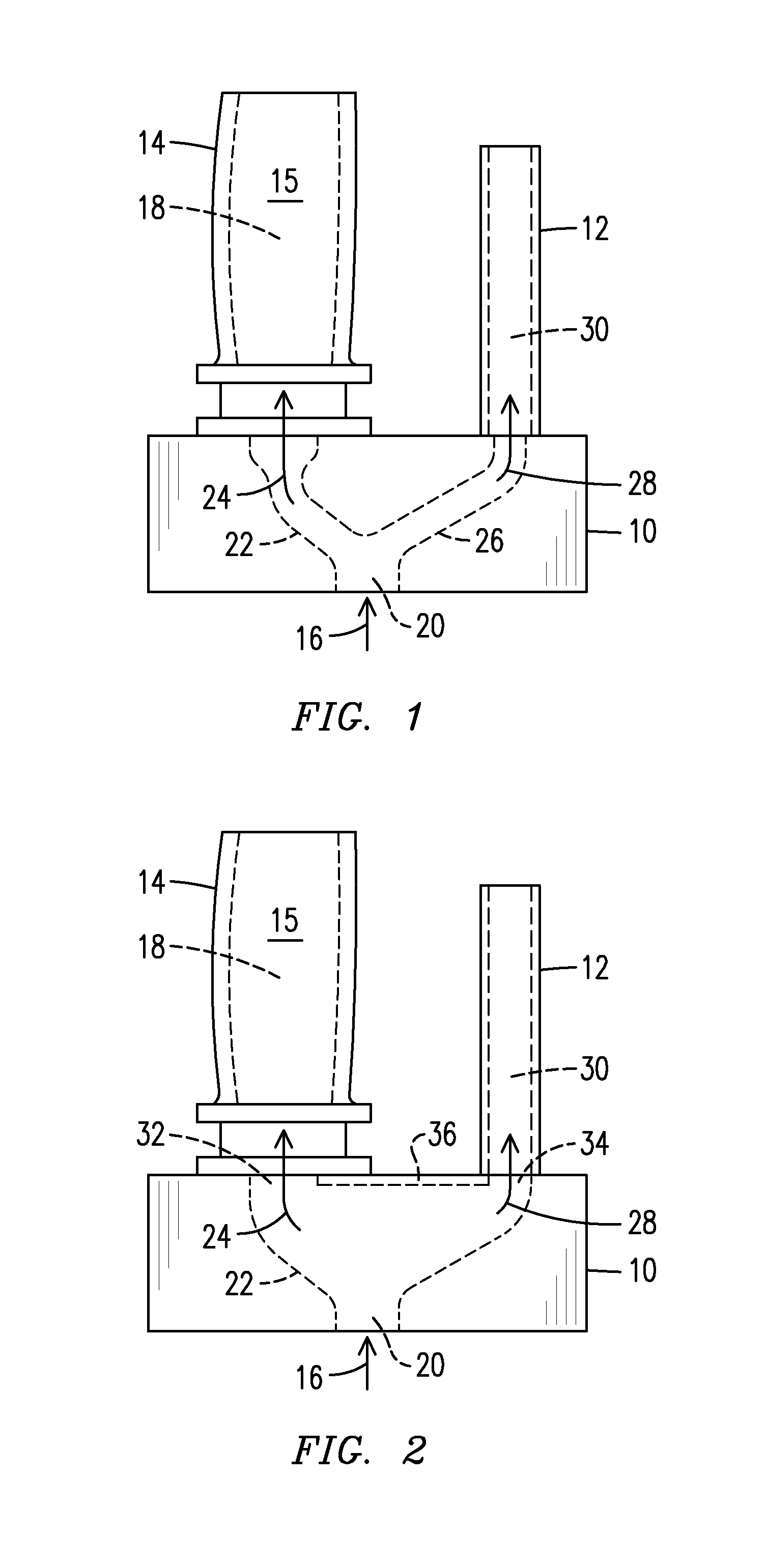
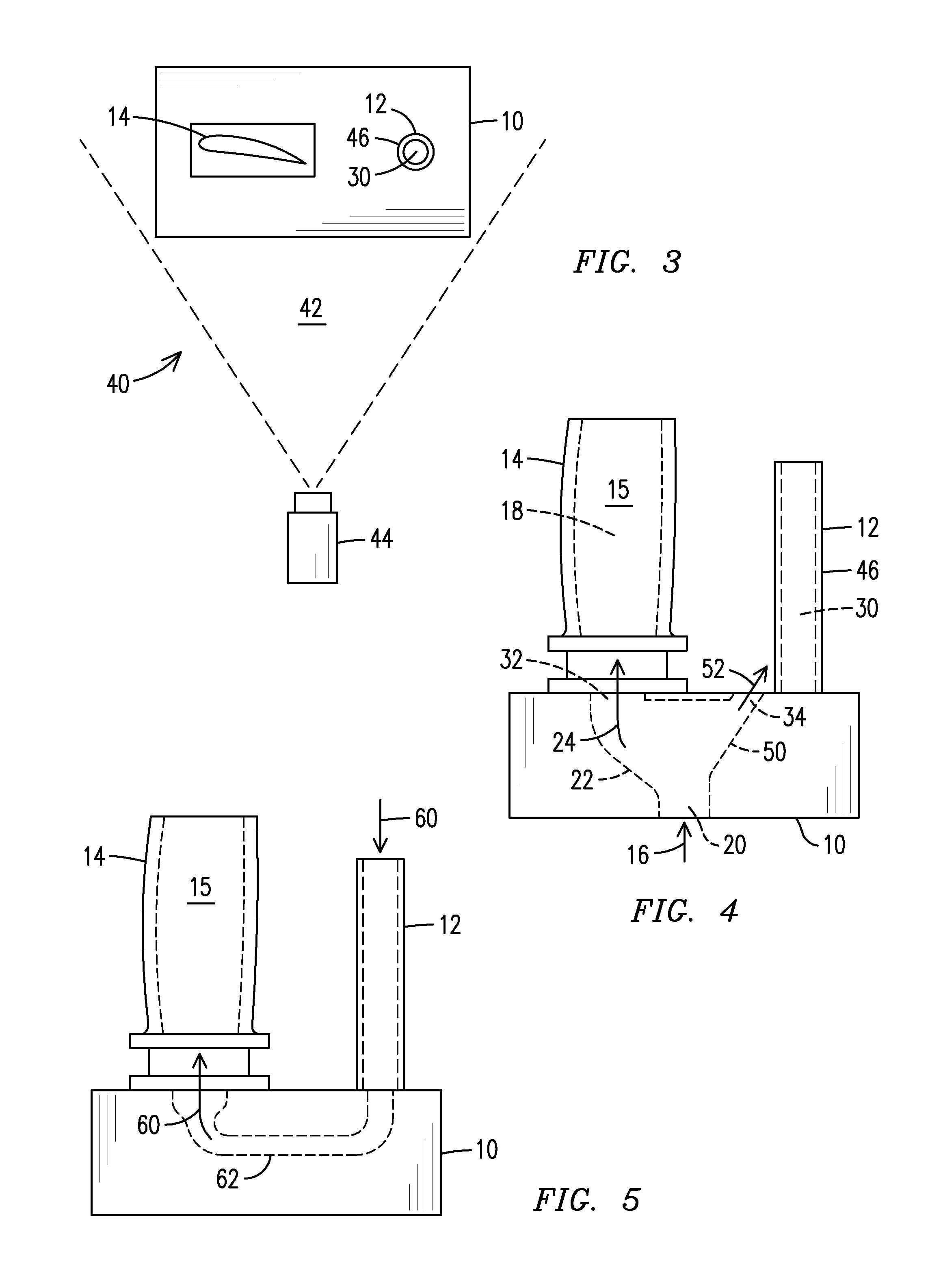
Infrared non-destructive evaluation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20140061476A1Material heat developmentMaterial analysis by optical meansNon destructiveIntensity normalization
A method of nondestructive evaluation and related system. The method includes arranging a test piece (14) having an internal passage (18) and an external surface (15) and a thermal calibrator (12) within a field of view (42) of an infrared sensor (44);generating a flow (16) of fluid characterized by a fluid temperature; exposing the test piece internal passage (18) and the thermal calibrator (12) to fluid from the flow (16); capturing infrared emission information of the test piece external surface (15) and of the thermal calibrator (12) simultaneously using the infrared sensor (44), wherein the test piece infrared emission information includes emission intensity information, and wherein the thermal calibrator infrared emission information includes a reference emission intensity associated with the fluid temperature; and normalizing the test piece emission intensity information against the reference emission intensity.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
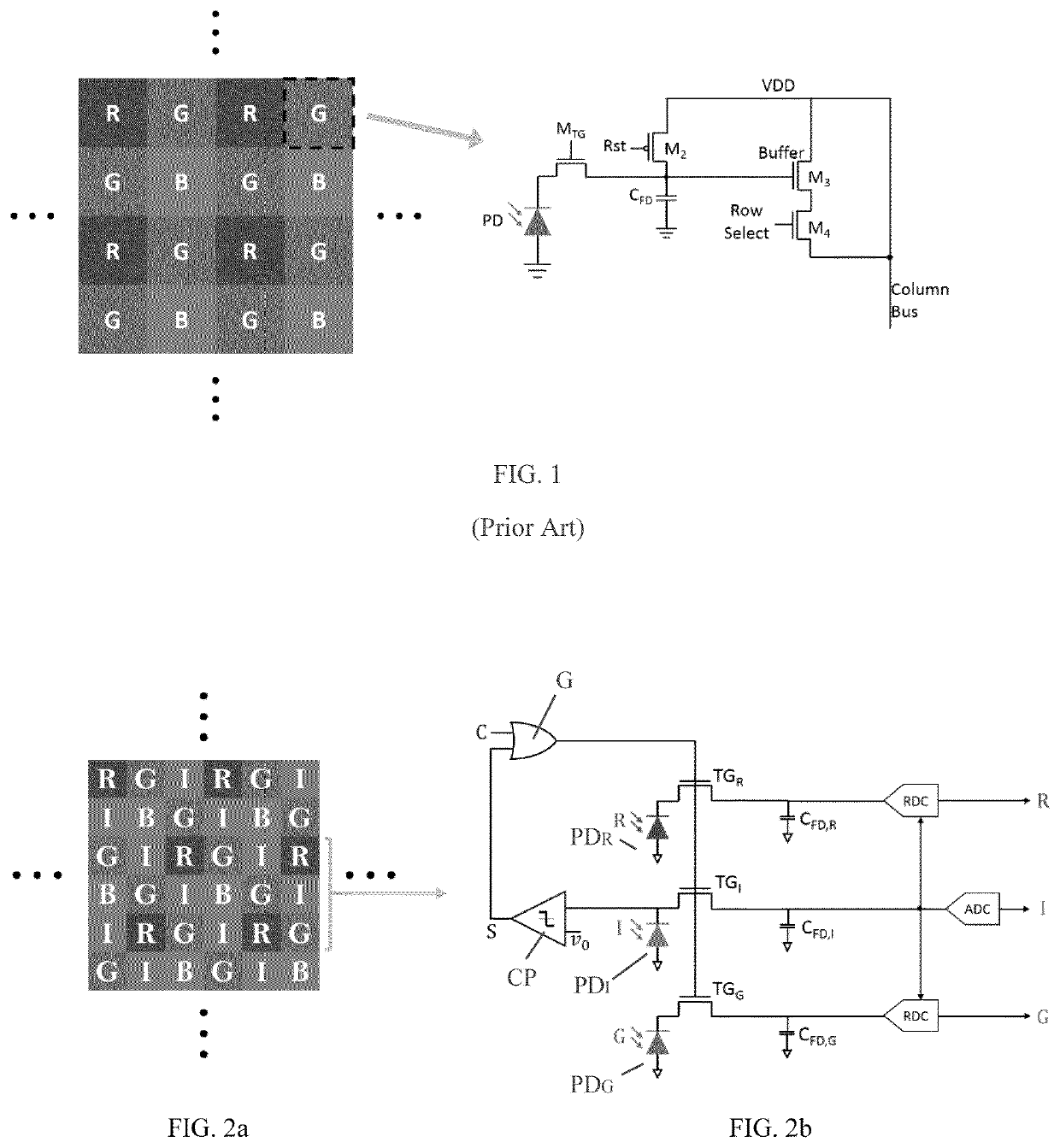
Intensity-Normalized Image Sensor
ActiveUS20210075982A1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesBandpass filteringIntensity normalization
An image sensor has a plurality of rows and columns of pixels, including RGB and bandpass I filters in a predetermined pattern shifted between adjacent columns so that none of the RGBI filters is adjacent the same type of filter. Each pixel includes a photodiode, a transfer gate and a floating diffusion. The transfer gate for all pixels in a pattern is controlled by the same signal, which can be a separate synchronous control signal controlled based on a predefined integration period or an asynchronous signal generated internally by the bandpass filter I and that is compared to a predefined voltage level indicative of a predetermined intensity at filter I. Upon activation of either signal, the integration period for the pixels ends and the charge on the floating diffusion for the R, G and B pixels is digitized in relation to the bandpass pixel I using a ratio-to-digital converter.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Radar range profile statistics and recognition method based on FA model in strong noise background
ActiveCN101598784BReduce the recognition rateNoise robustWave based measurement systemsCategory attributeIntensity normalization
The invention discloses a radar range profile statistics and recognition method based on a FA model in the strong noise background, which relates to the technical field of radar automatic target recognition and mainly solves the problem that the current statistics and recognition methods based on the FA model are not robust to noises. The training phase comprises the following steps: framing, translating, aligning and strength-normalizing radar HPPR continuously, learning the parameters of each azimuth frame of the FA model by adopting the processed HRRP and storing a template. The test phasecomprises the following steps: first strength-normalizing, translating and aligning the samples to be tested and then estimating the range of the signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) of the samples; computing the distance value of each frame of each target and deciding the category attribute if the SNR is more than 30dB, and rewriting the distance value, solving the noise energy under SNR condition by minimizing the distance value, finally computing the distance value of each frame of each target and deciding the category attribute if the SNR is less than 30dB. The method has the advantages of robustness to noises and less computation and is applied to identifying radar targets.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
Infrared non-destructive evaluation method and apparatus
InactiveUS8866084B2Material heat developmentMaterial analysis by optical meansNon destructiveIntensity normalization
A method of nondestructive evaluation and related system. The method includes arranging a test piece (14) having an internal passage (18) and an external surface (15) and a thermal calibrator (12) within a field of view (42) of an infrared sensor (44); generating a flow (16) of fluid characterized by a fluid temperature; exposing the test piece internal passage (18) and the thermal calibrator (12) to fluid from the flow (16); capturing infrared emission information of the test piece external surface (15) and of the thermal calibrator (12) simultaneously using the infrared sensor (44), wherein the test piece infrared emission information includes emission intensity information, and wherein the thermal calibrator infrared emission information includes a reference emission intensity associated with the fluid temperature; and normalizing the test piece emission intensity information against the reference emission intensity.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Polyolefin microporous membrane and production method thereof
ActiveUS20170092920A1Improve breathabilityImprove puncture strengthMembranesSemi-permeable membranesIntensity normalizationPolyolefin
A polyolefin microporous membrane is disclosed. The membrane includes at least one microporous membrane layer, where the microporous membrane layer has an air permeability between about 100 sec / 100 cc and about 220 sec / 100 cc, a pin puncture strength of at least 550 gf, and a crystallization half time t1 / 2 of from 10 to 35 minutes when subjected to isothermal crystallization at 117° C. The air permeability and the pin puncture strength are normalized to a thickness of 16 μm.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
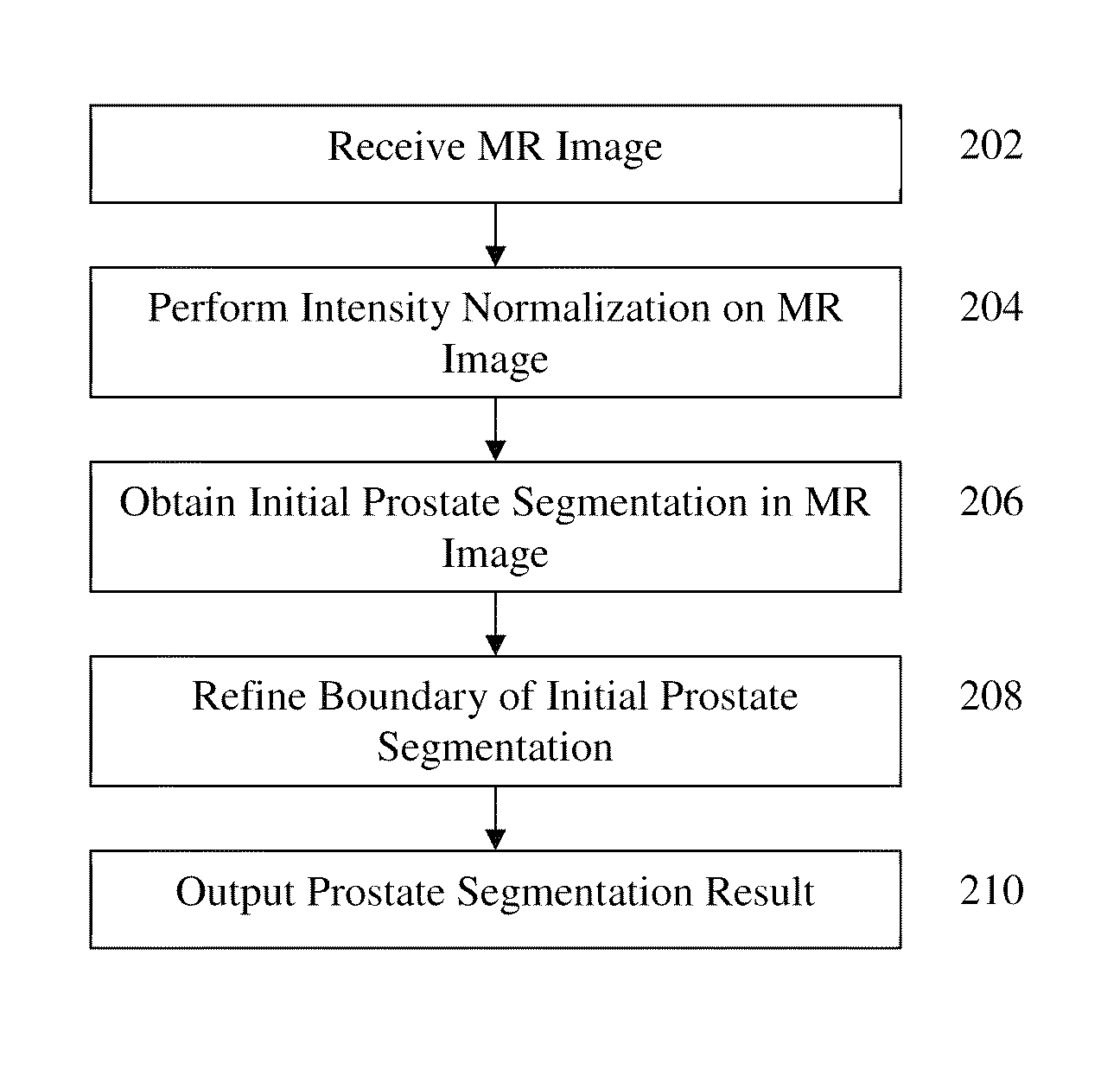
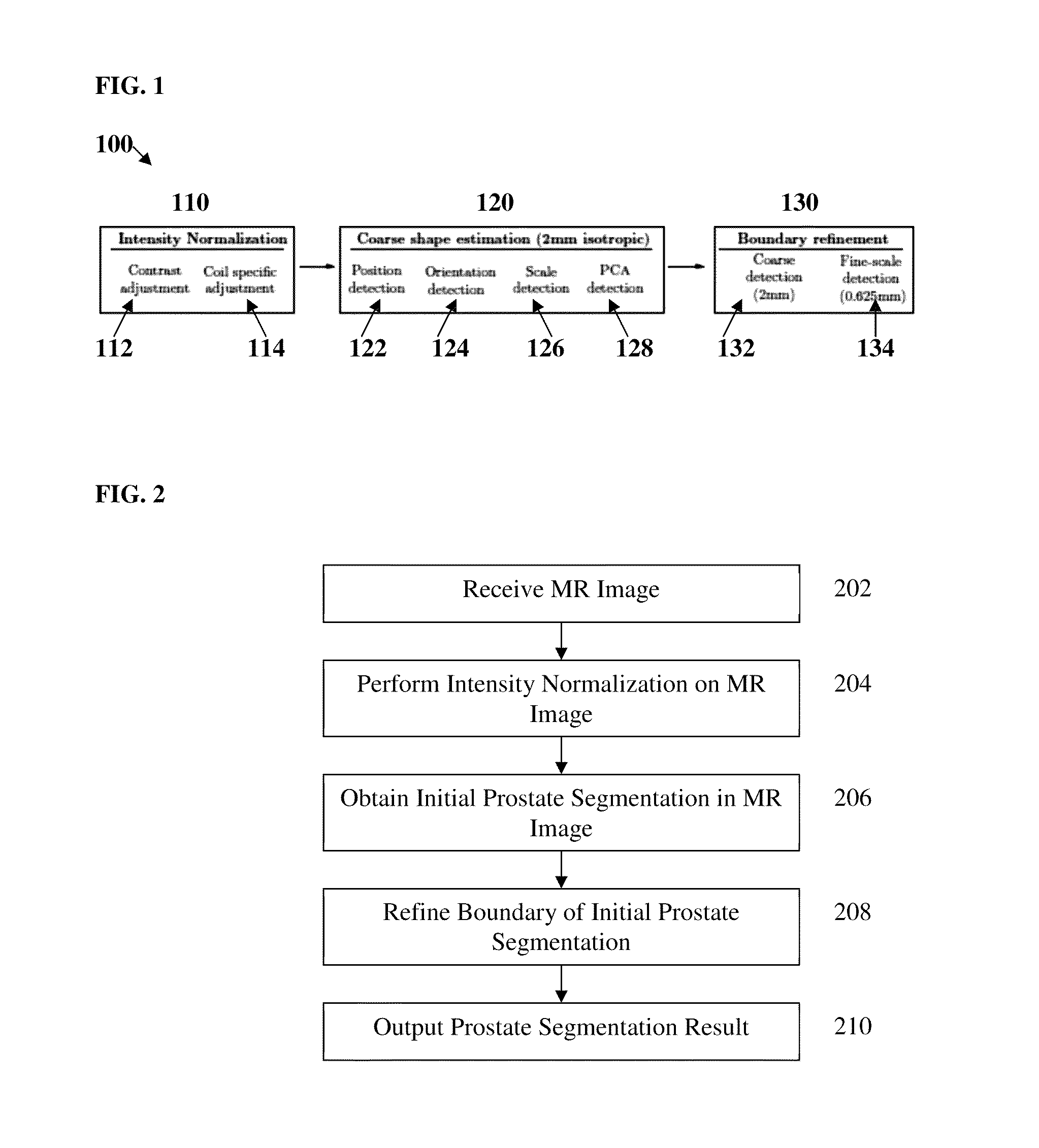
Method and system for automatic prostate segmentation in magnetic resonance images
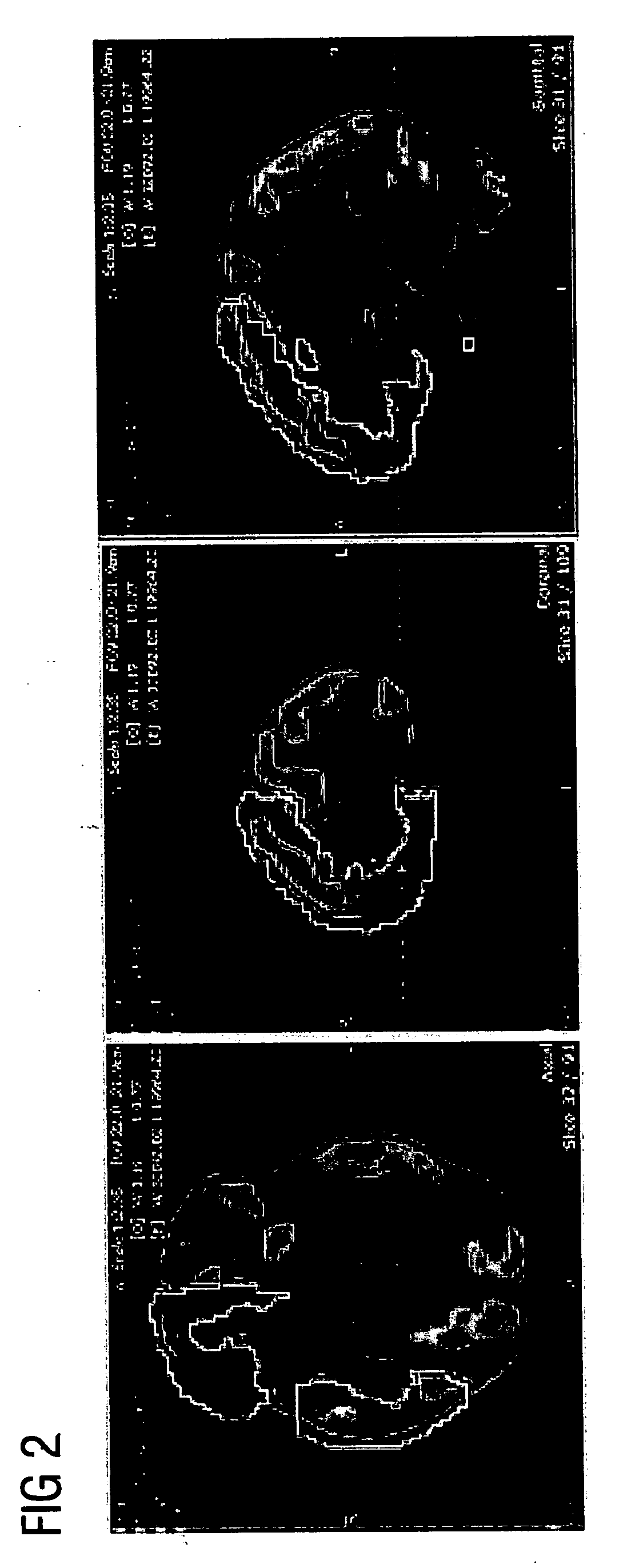
InactiveUS9269156B2Easy to useShort processing timeImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity normalizationMarginal space learning
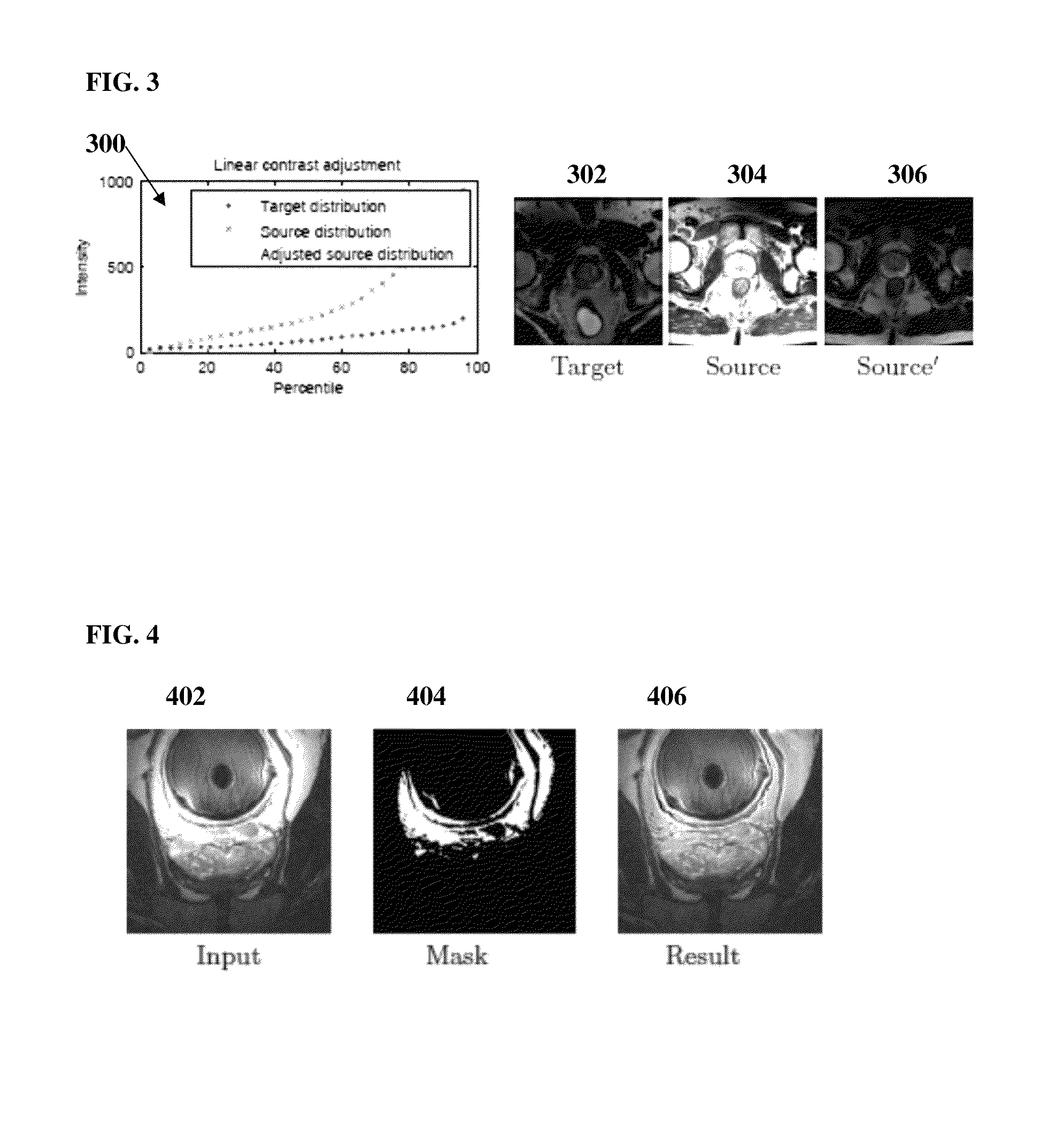
A method and system for fully automatic segmentation the prostate in magnetic resonance (MR) image data is disclosed. Intensity normalization is performed on an MR image of a patient to adjust for global contrast changes between the MR image and other MR scans and to adjust for intensity variation within the MR image due to an endorectal coil used to acquire the MR image. An initial prostate segmentation in the MR image is obtained by aligning a learned statistical shape model of the prostate to the MR image using marginal space learning (MSL). The initial prostate segmentation is refined using one or more trained boundary classifiers.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image processing method based on X-ray energy spectrum micro-area surface scanning
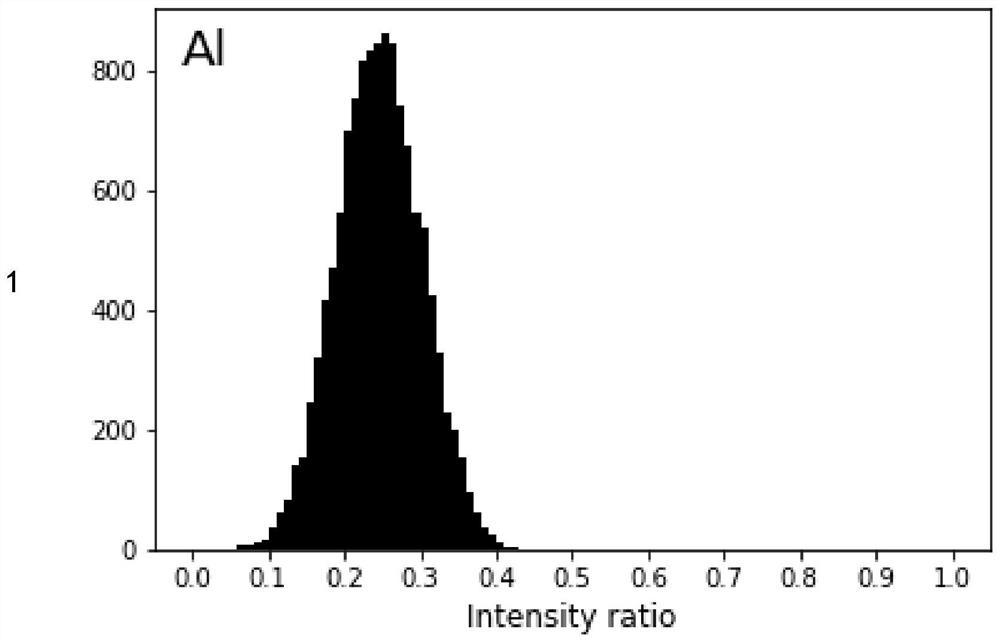
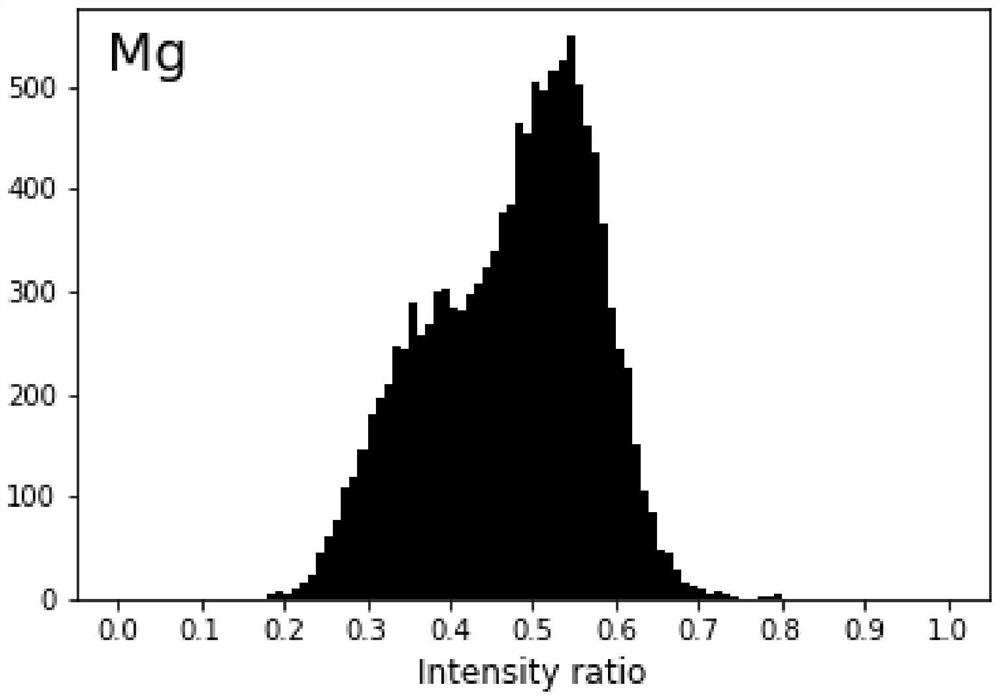
PendingCN114199919AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIntensity normalizationRay
The invention provides an image processing method based on X-ray energy spectrum micro-area surface scanning, and belongs to the field of scanning electron microscope-X-ray energy spectrometer element distribution characterization. According to the method, intensity normalization calculation is carried out on element distribution data of X-ray energy spectrum surface scanning to obtain a distribution intensity ratio frequency distribution histogram of each element, and an imaging threshold value is set, so that the problems of low signal-to-noise ratio, unclear image, high resolution and the like when a scanning electron microscope and an X-ray energy spectrometer are used for micro-area surface scanning analysis in the prior art are solved. Effective information is not prominent, and the analysis efficiency is low.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
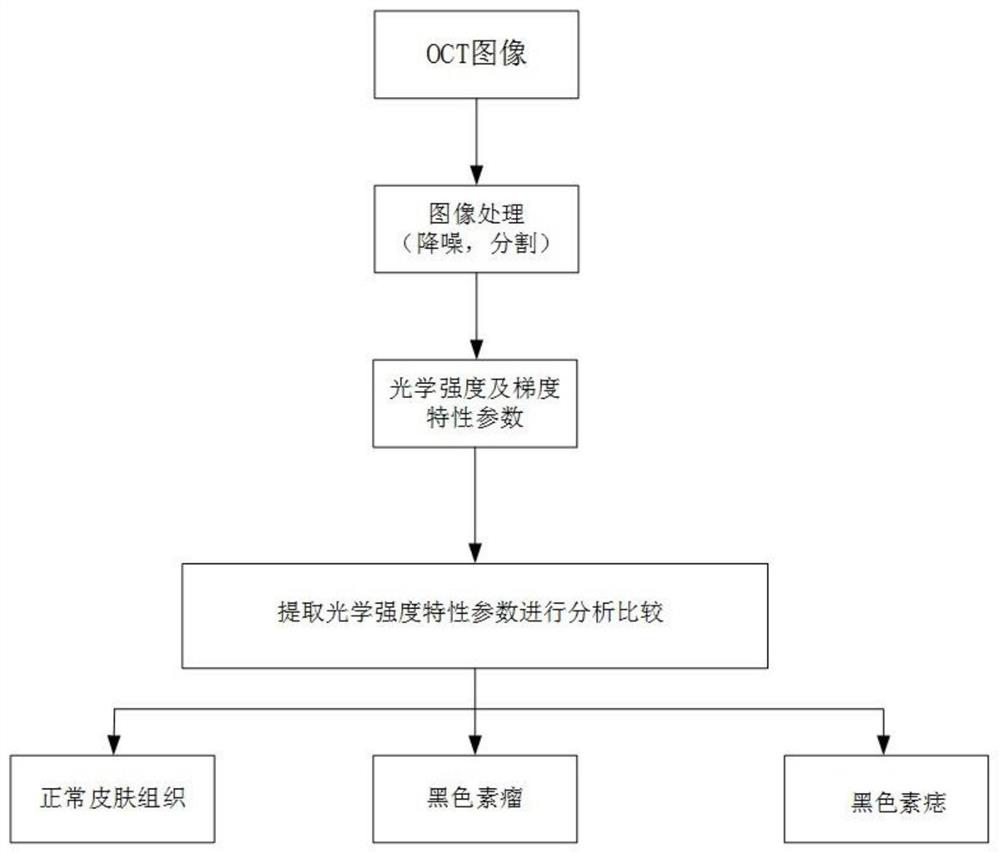
Skin cancer classification method based on optical intensity and gradient of OCT imaging image
PendingCN112116027AAccurate judgmentAvoid discomfortImage enhancementImage analysisIntensity normalizationBoundary values
The invention discloses a skin cancer classification method based on the optical intensity and gradient of an OCT imaging image, and the method comprises the steps: (1) collecting a skin cancer imagethrough an OCT device, and normalizing the intensity in the OCT image into [0, 1]; (2) performing noise reduction on the OCT image through noise reduction processing; (3) extracting optical intensitycharacteristic parameters; (4) calculating to obtain the discrete value of each parameter of the marked sample, and then obtaining the difference and ROC analysis of each characteristic parameter in the marked control group through a mathematical statistics method to obtain a boundary value; and (5) calculating to obtain the discrete value of each parameter of the unknown sample, comparing the discrete value with the boundary value in the step (4), and classifying the unknown sample according to the comparison result. According to the invention, normal skin tissues, melanoma and melanin nevuscan be quickly and accurately judged; discomfort and trauma brought to a patient by an invasive method of skin biopsy are avoided.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Receiving apparatus
InactiveUS8077811B2Accurate detectionError preventionOther decoding techniquesIntensity normalizationTelecommunications
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Spectral signature extraction for drug verification and identification
InactiveUS8417540B2Radiation pyrometryData processing applicationsIntensity normalizationFluorescence
Systems and methods perform signature extraction from an acquired spectrum of a pharmaceutical. An acquired spectrum of the pharmaceutical is measured using a spectrometer. The acquired spectrum is obtained from the spectrometer using a processor. A system-response function of the spectrometer is removed from the acquired spectrum using the processor. An intensity of the acquired spectrum is normalized to a predetermined scale using the processor. Fluorescence is removed from the acquired spectrum using the processor. Finally, an extracted signature of the pharmaceutical is obtained from the remainder of the acquired spectrum using the processor. If the acquired spectrum of the pharmaceutical is measured by the spectrometer through a container holding the pharmaceutical, a spectrum of the container is removed from the remainder of the acquired spectrum to produce the extracted signature of the pharmaceutical using the processor.
Owner:OPTOPO INC D B A CENTICE CORP 215 SOUTHPORT DR +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com