Patents
Literature
43 results about "Bio potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biopotentials [-pəten′shəls] a voltage produced by a tissue of the body, particularly muscle tissue during a contraction. Electrocardiography depends on measurement of changing potentials in contracting heart muscle.
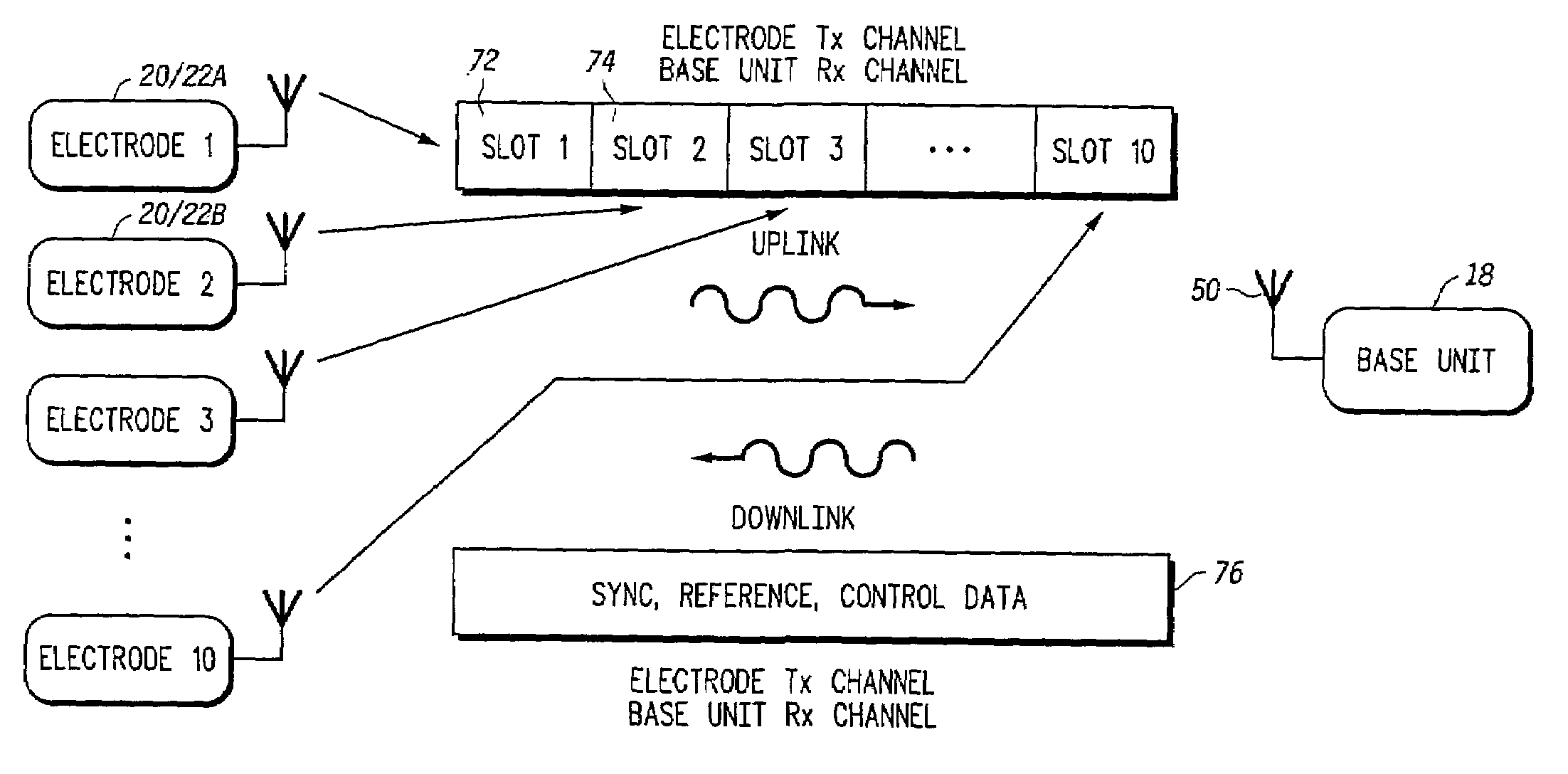
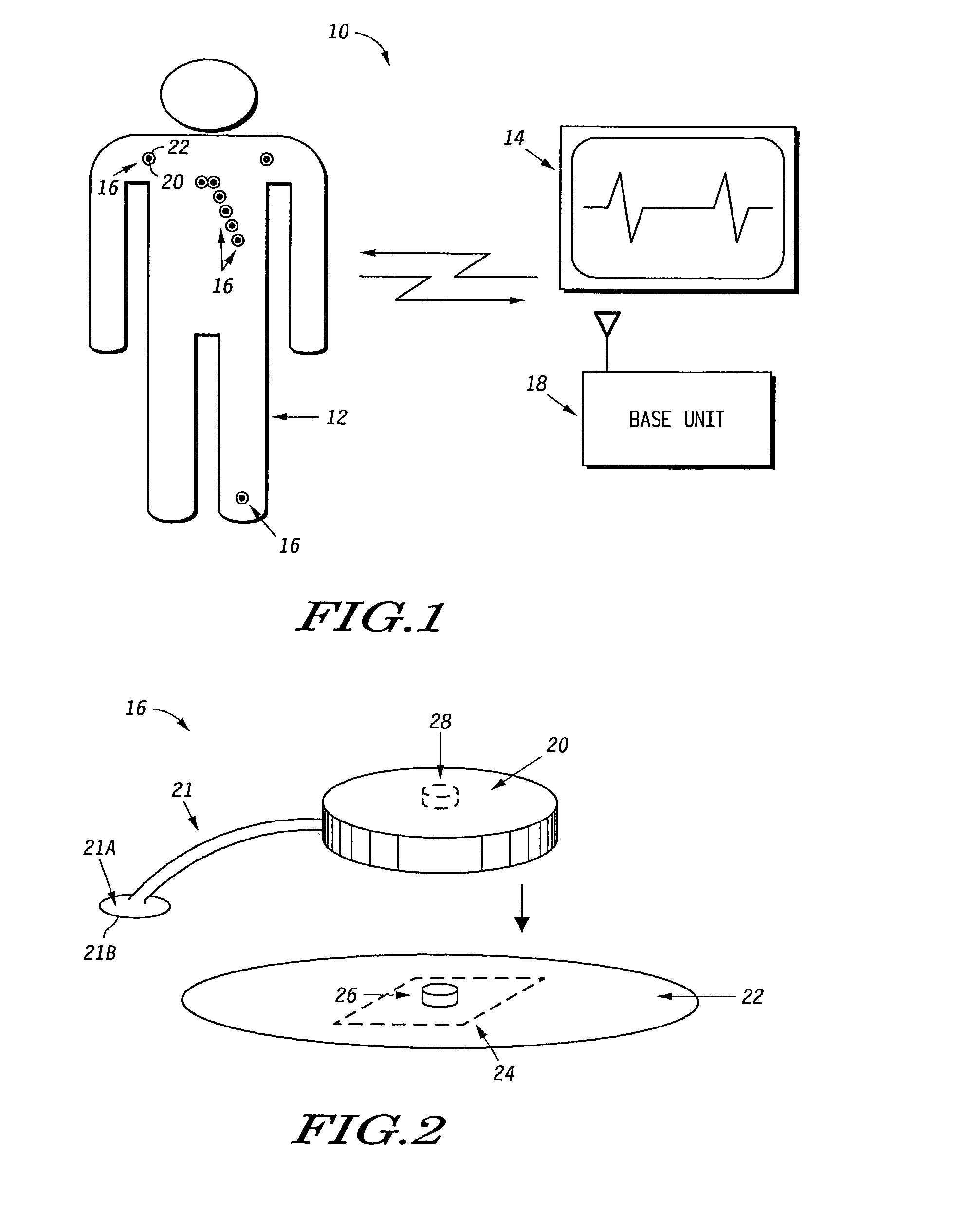
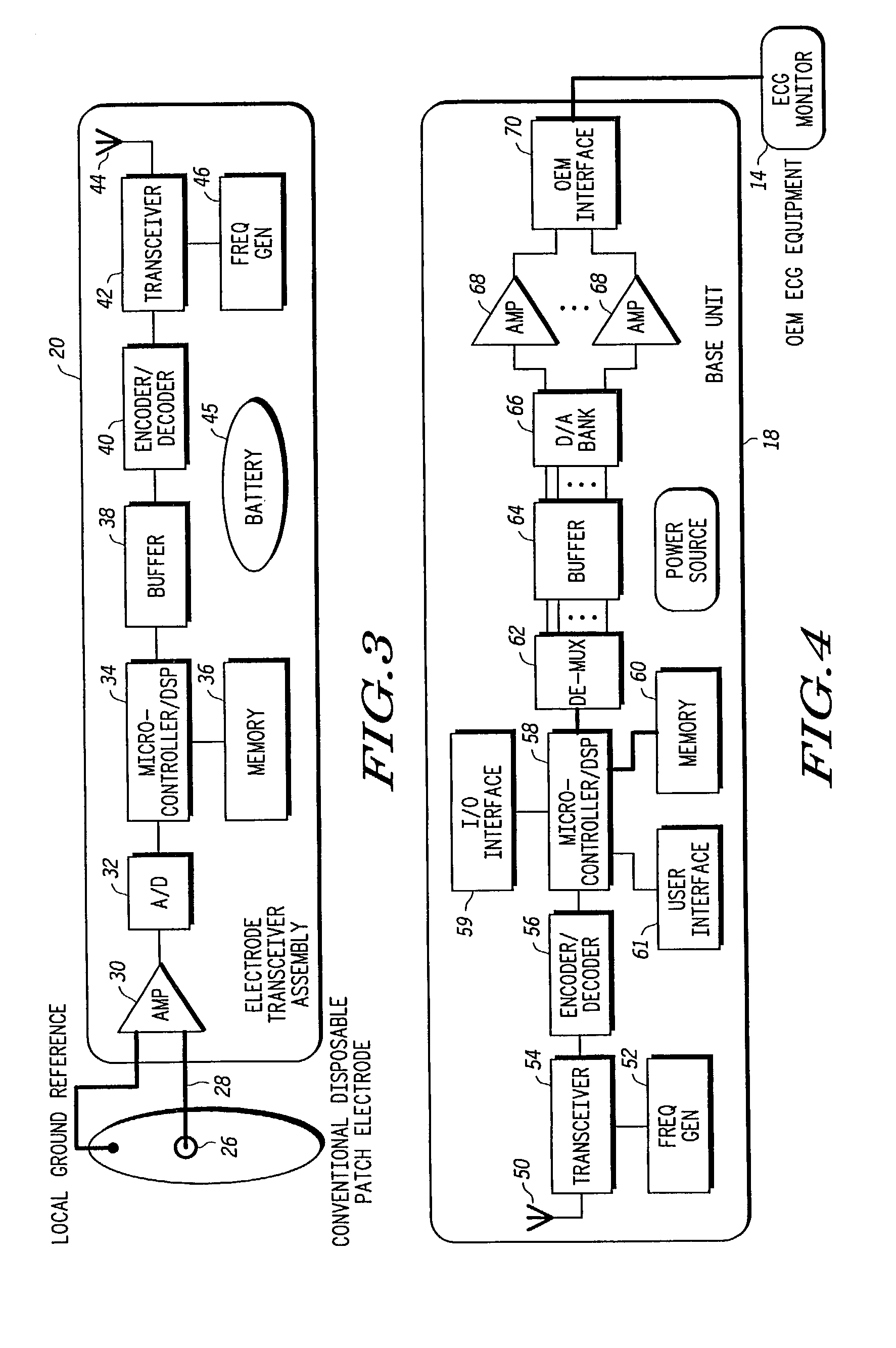
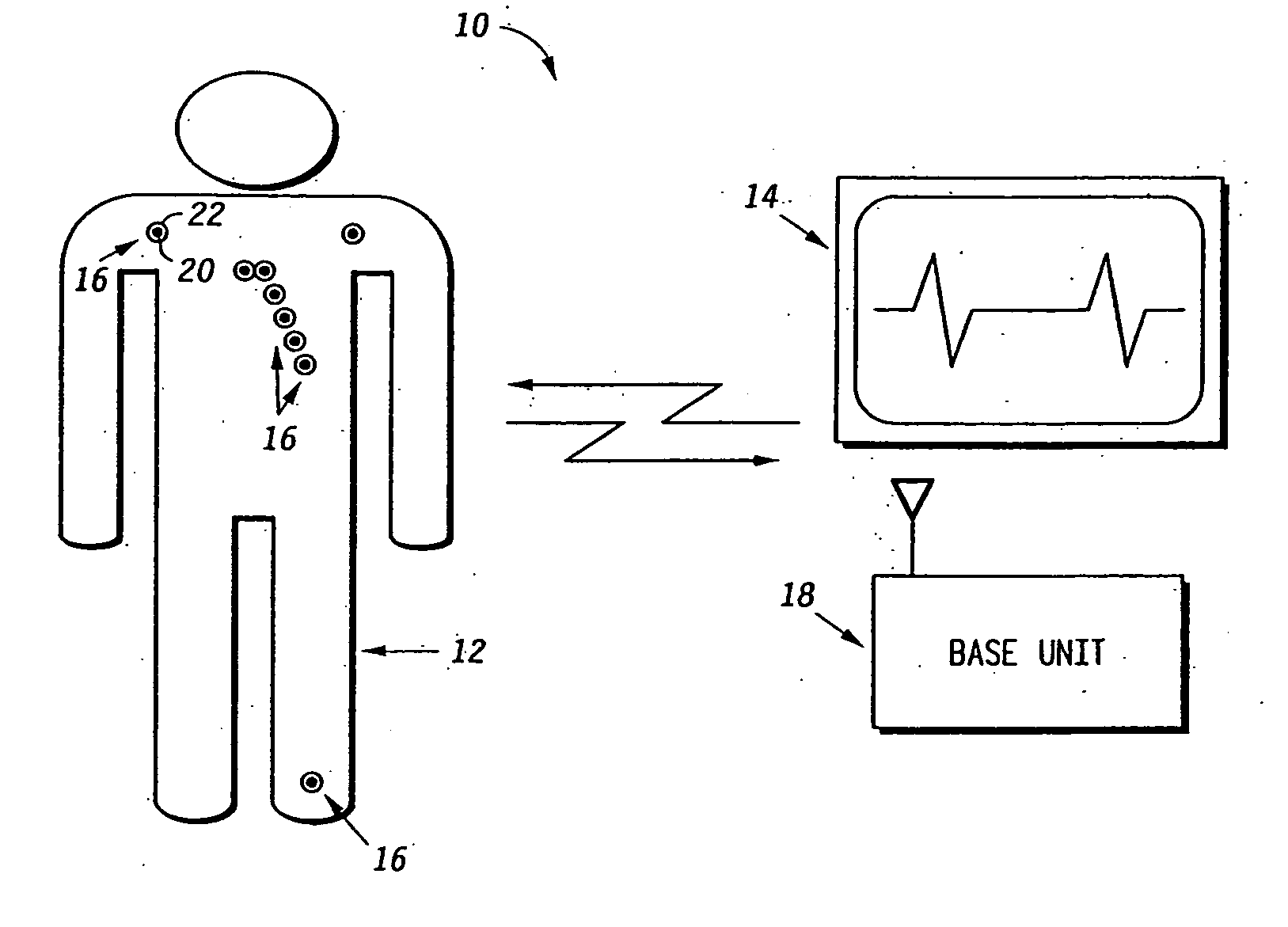
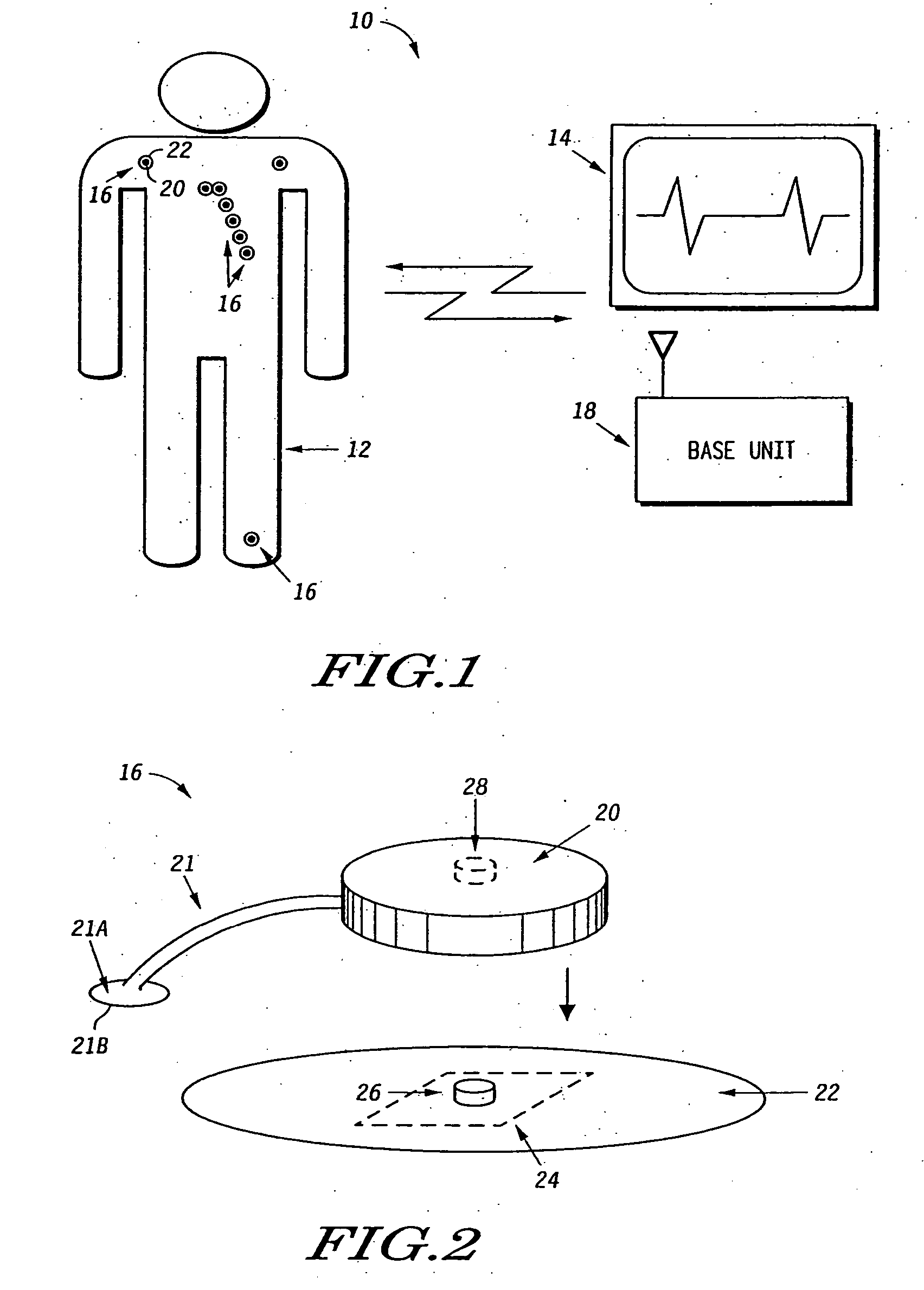
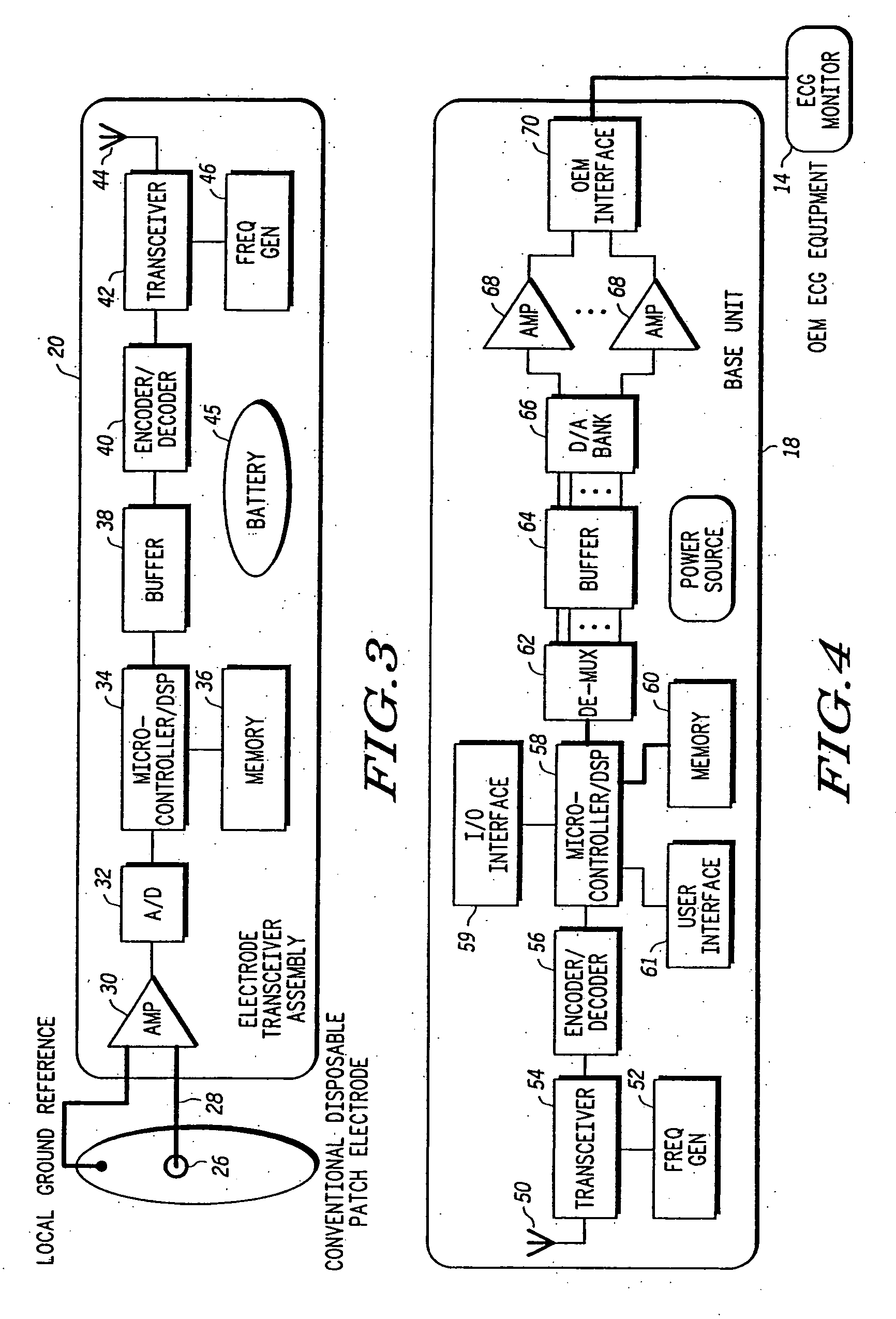
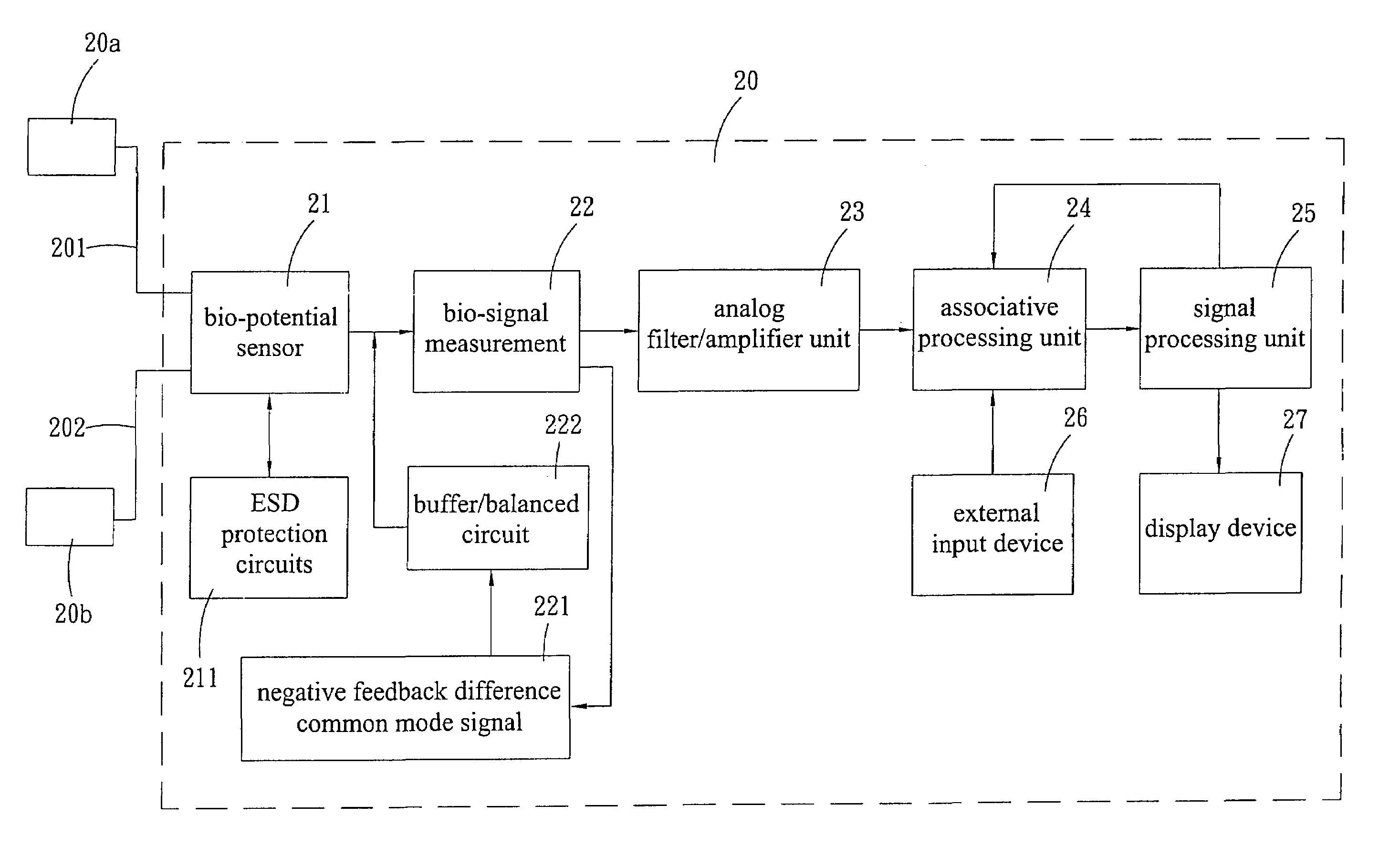
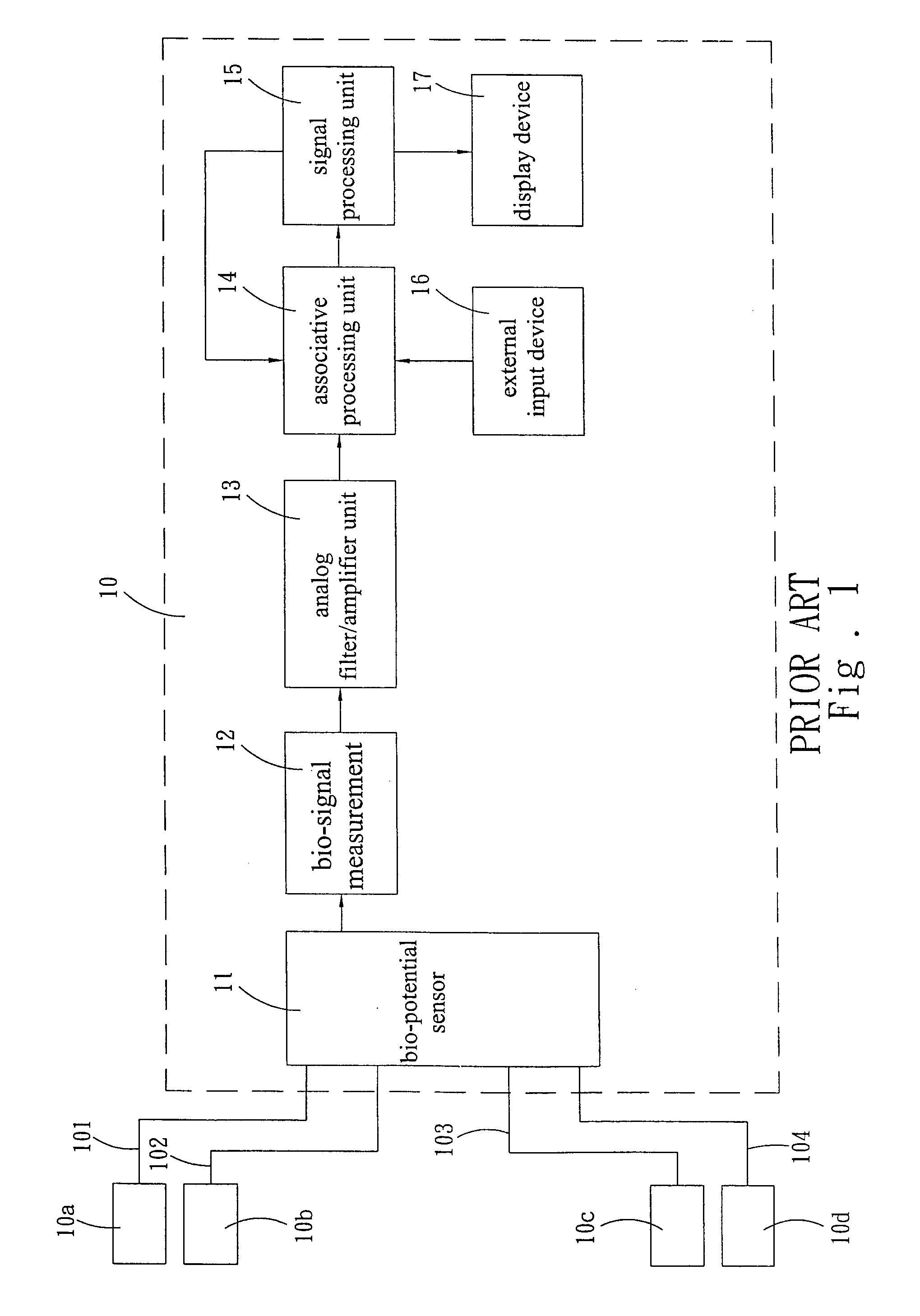
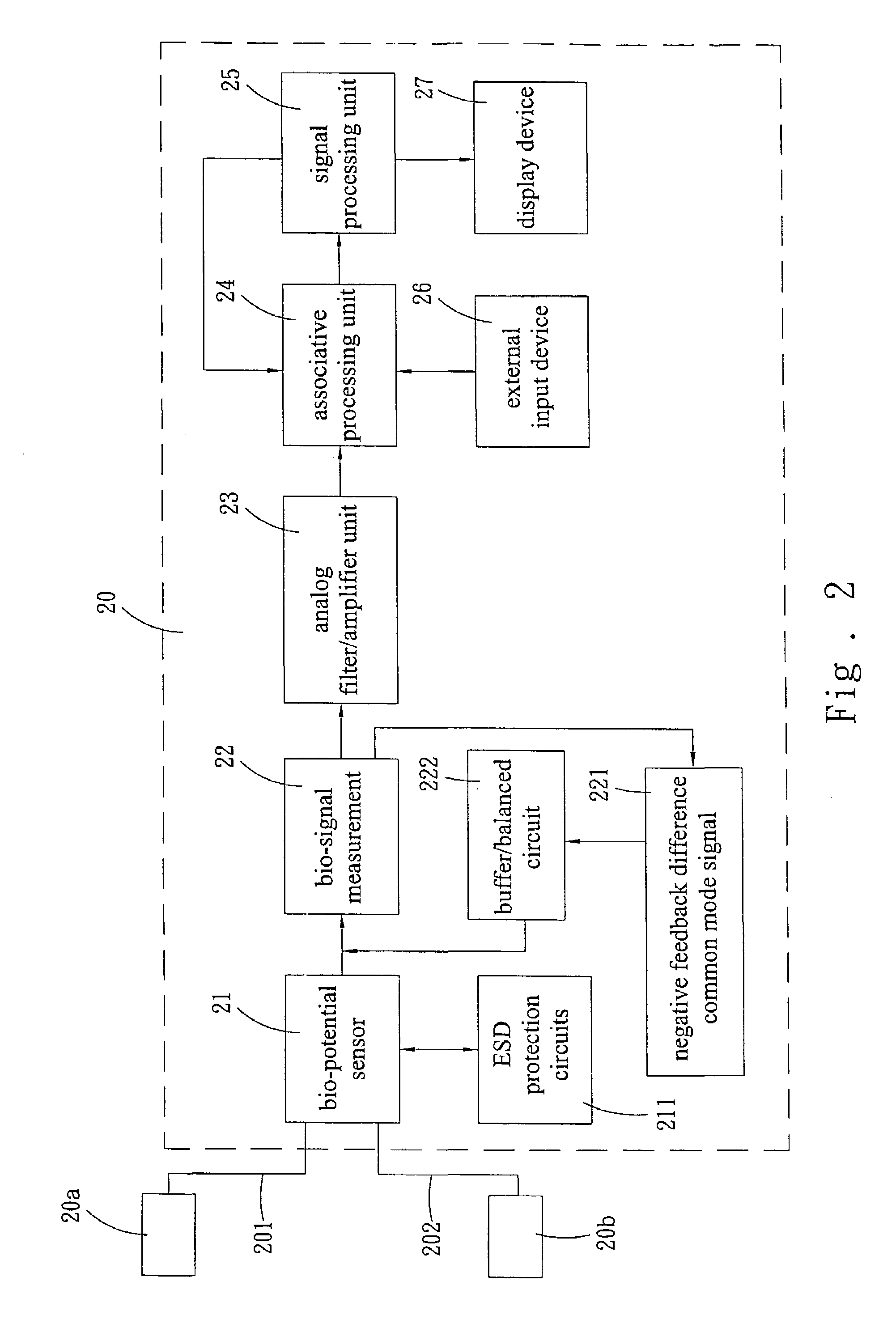
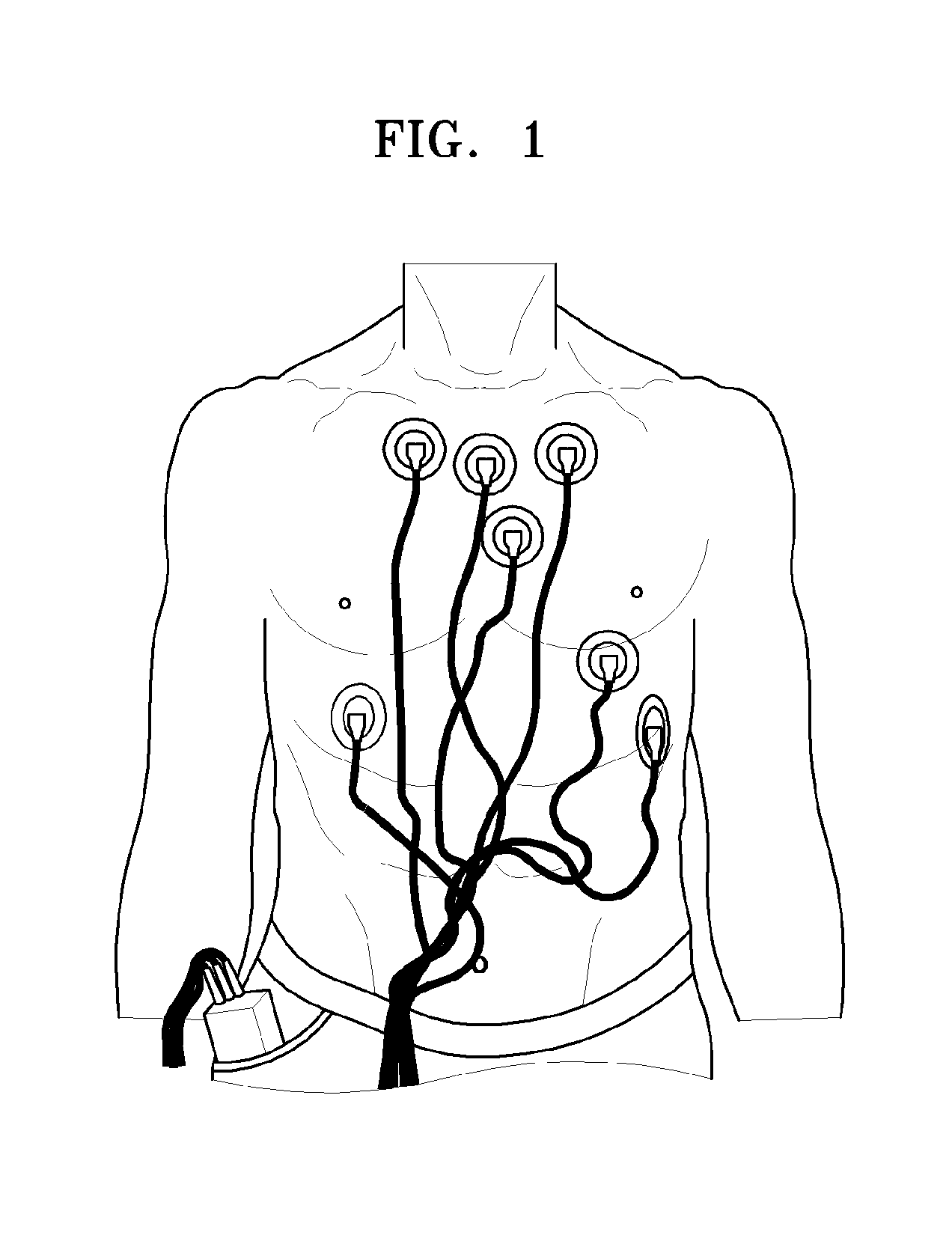
Programmable wireless electrode system for medical monitoring
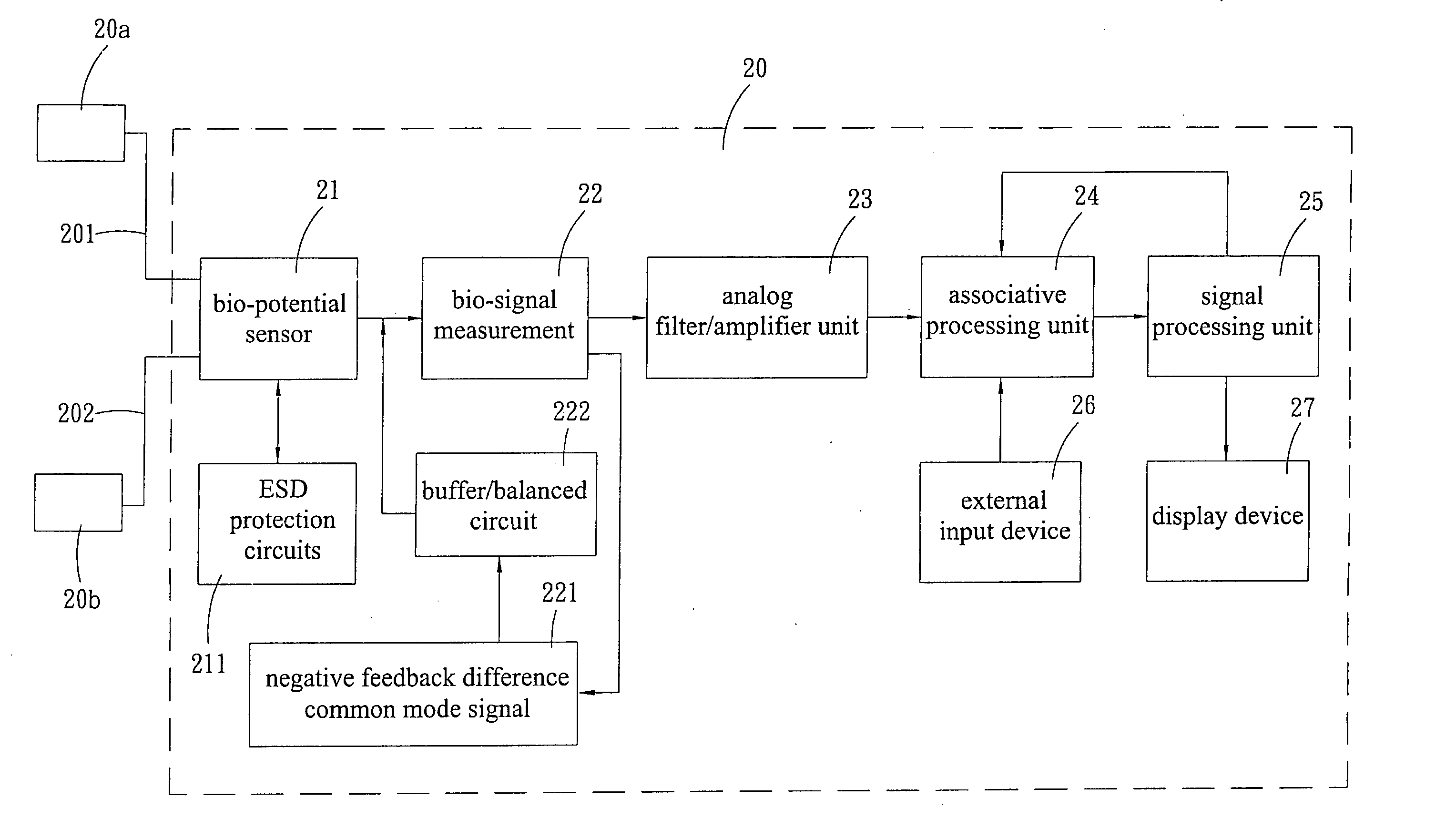
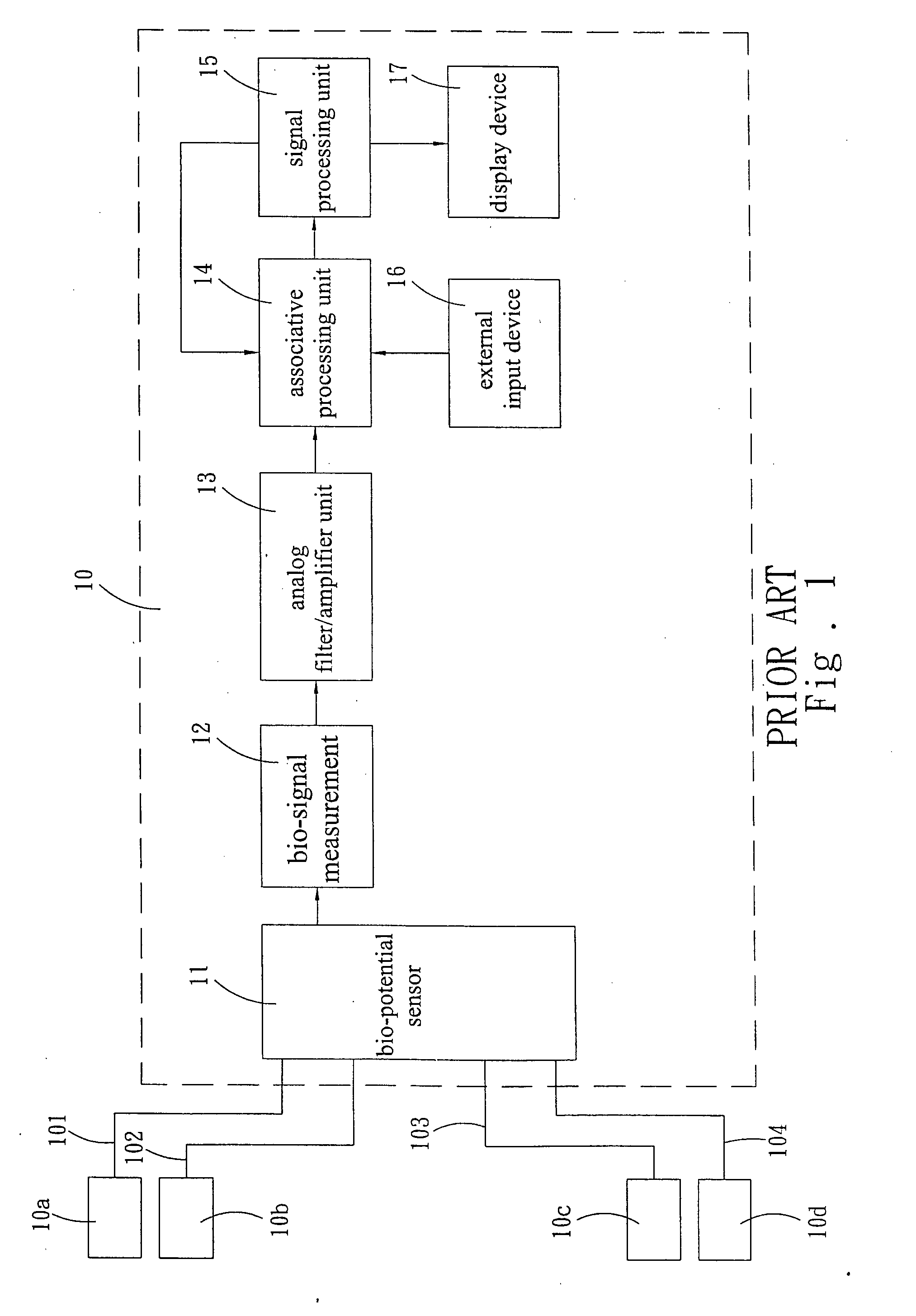
InactiveUS6987965B2Consider flexibilityElectrocardiographyNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless transceiverTransceiver
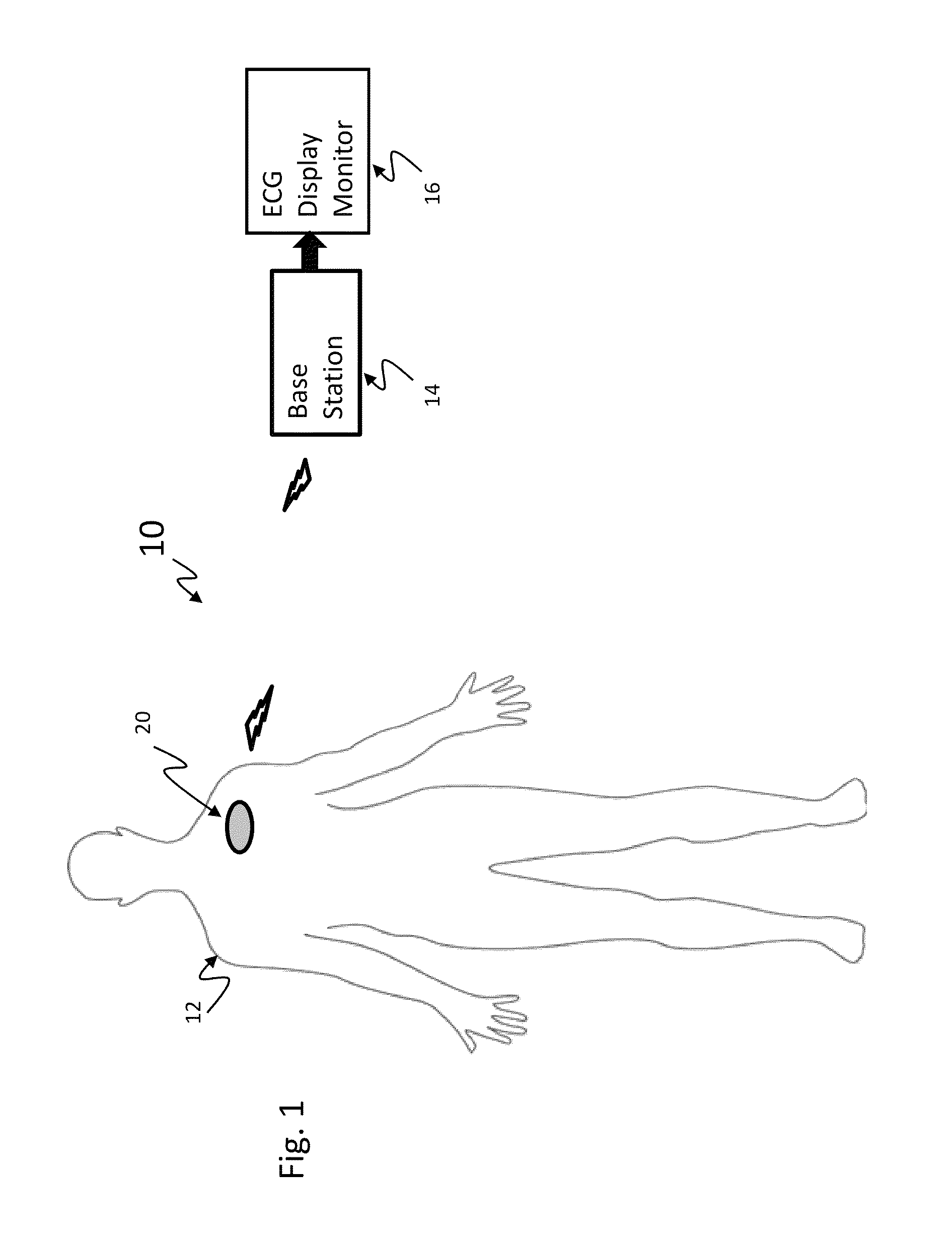
A wireless, programmable system for bio-potential signal acquisition (e.g., electrocardiogram (ECG) data) includes a base unit and a plurality of individual wireless, remotely programmable transceivers that connect to patch electrodes. The base unit manages the transceivers by issuing registration, configuration, data acquisition, and transmission commands using wireless techniques. Bio-potential signals from the wireless transceivers are demultiplexed and supplied via a standard interface to a conventional monitor for display.
Owner:LIFESYNC
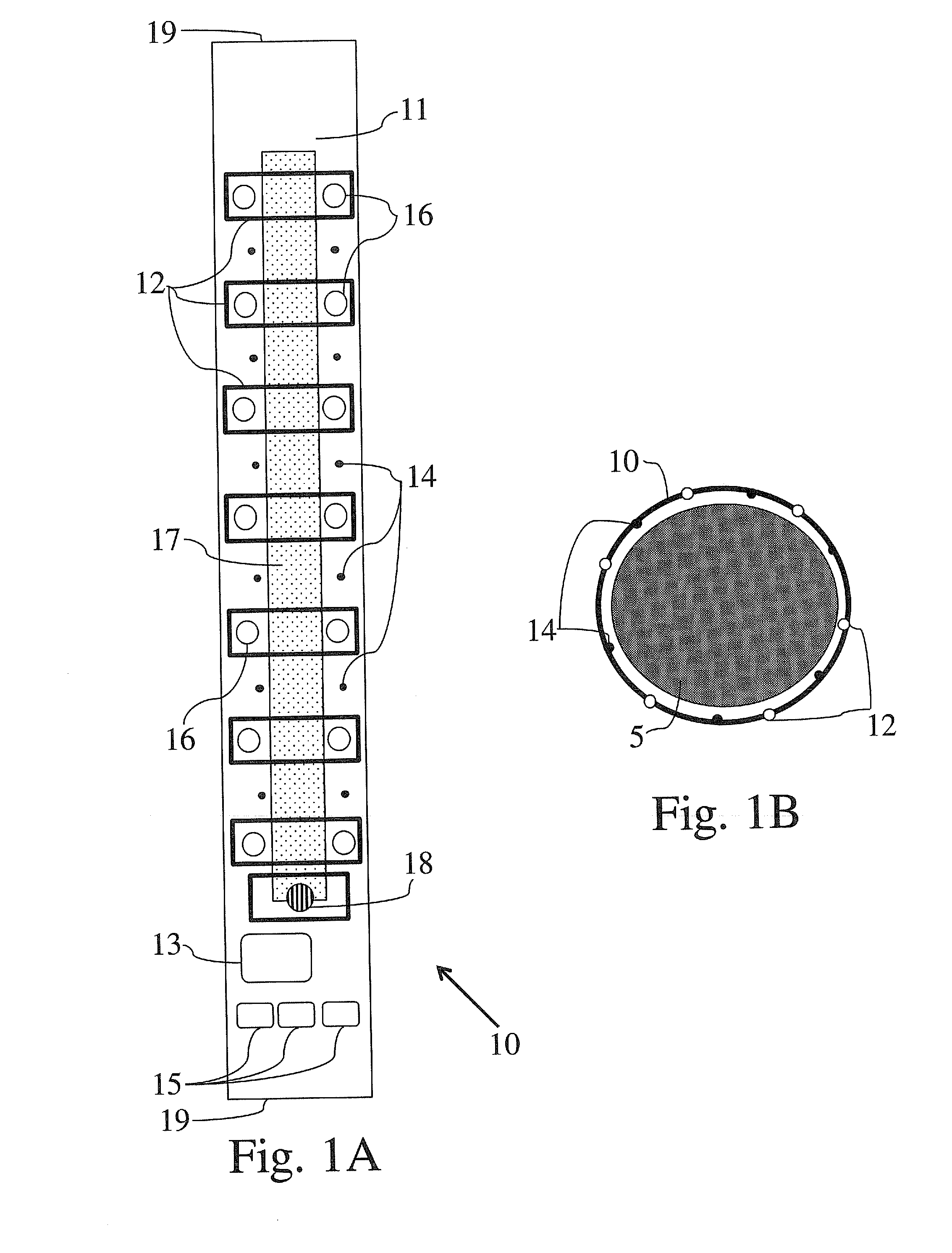
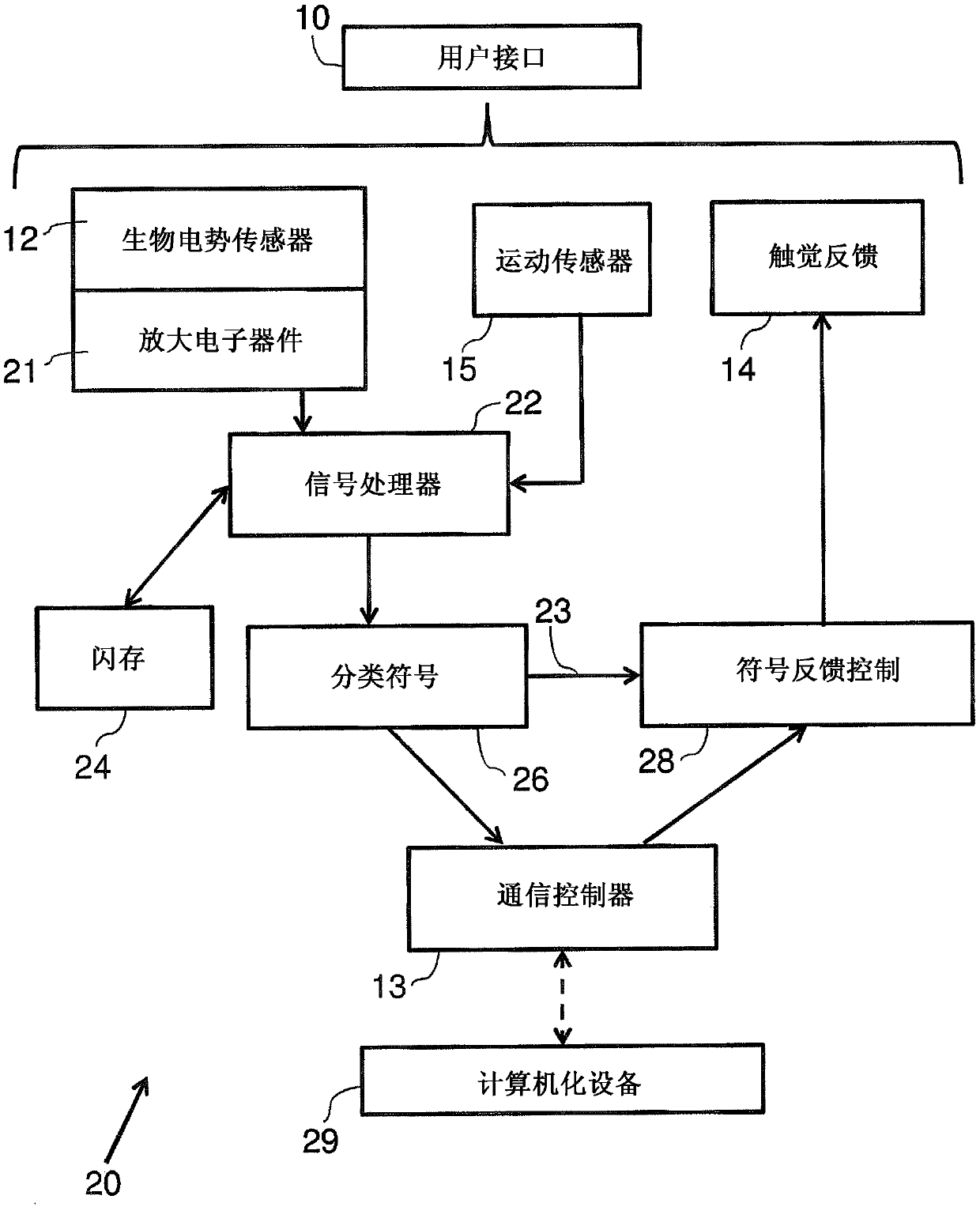
Method and apparatus for a gesture controlled interface for wearable devices
ActiveUS20160313801A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNerve conductionBio potential
A gesture-controlled interface apparatus includes one or a plurality of bio-potential sensors and a processor. The one or a plurality of bio-potential sensors are wearable on a body of a user, for detecting one or a plurality of bio-electrical signals from the body of the user, wherein the one or a plurality of bio-potential sensors include at least one surface nerve conduction (SNC) sensor for detecting at least one surface nerve conduction signal. The processor is configured to compare the detected at least one surface nerve conduction signal with data of a plurality of reference signals corresponding to a plurality of known gestures, each of the reference signals distinctly associated with one of the known gestures, to identify a known gesture from the plurality of known gestures that corresponds to said at least one surface nerve conduction signal, and to communicate the identified known gesture to a computerized device.
Owner:WEARABLE DEVICES LTD
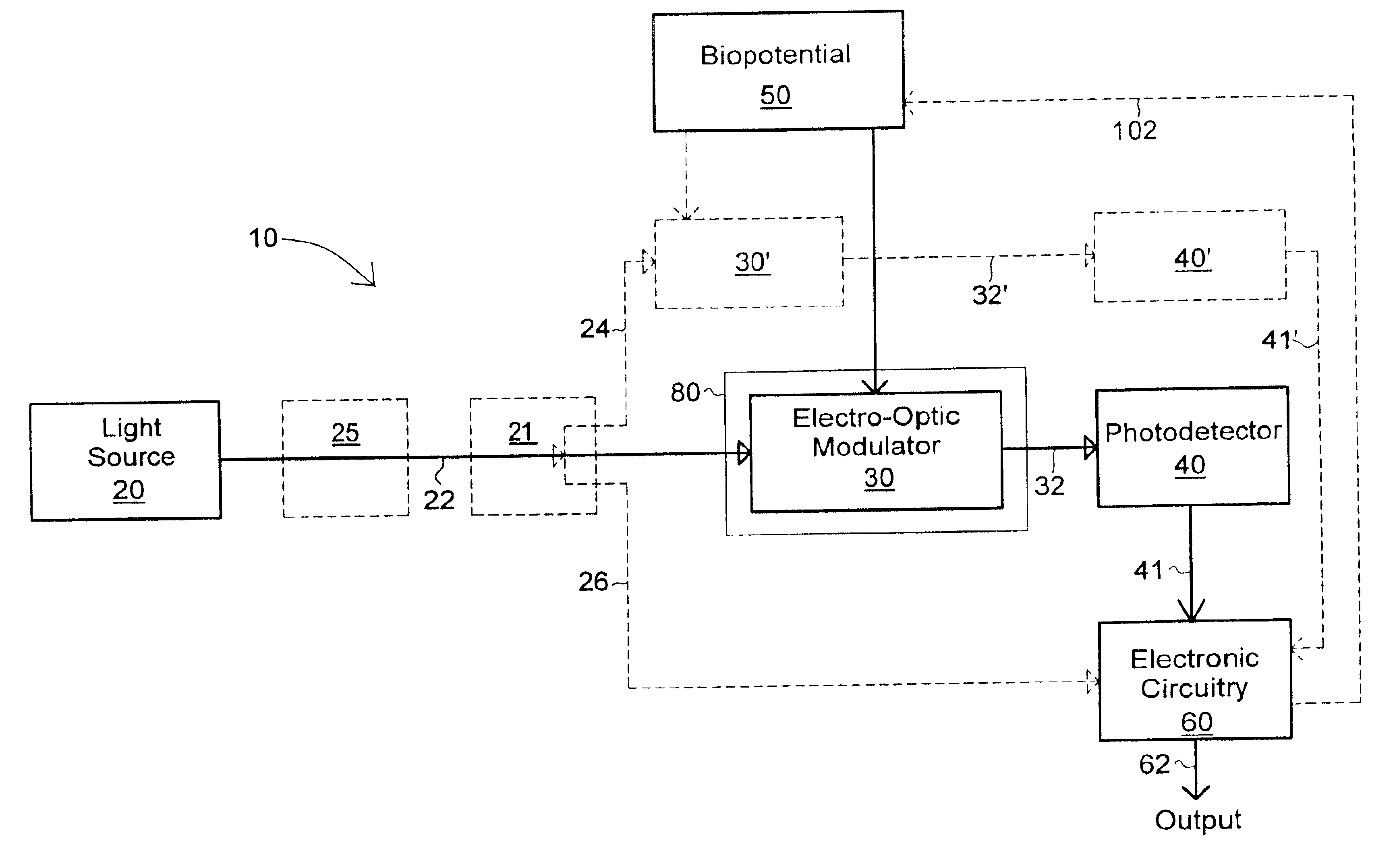
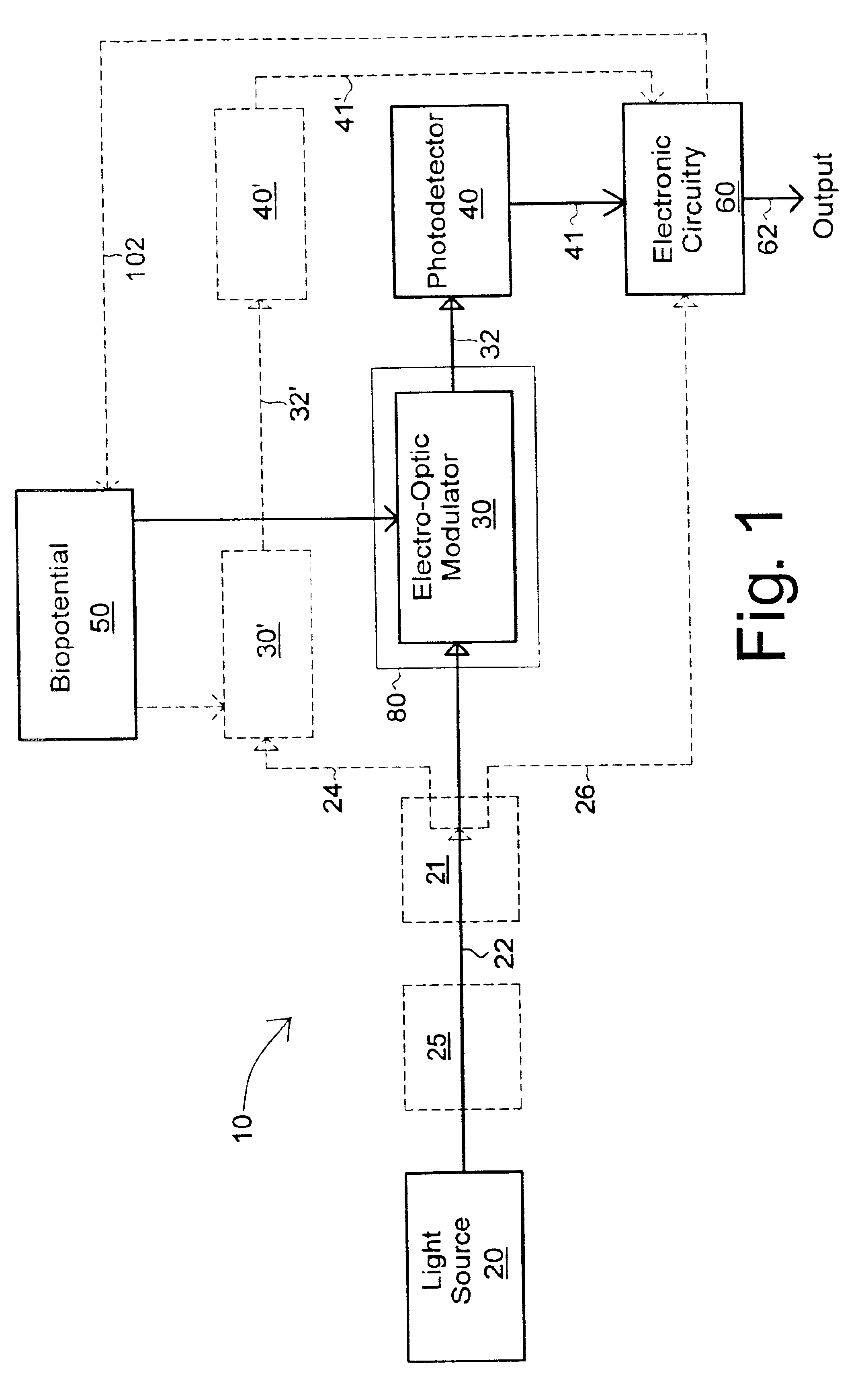
High-impedance optical electrode
InactiveUS6871084B1Prevent removalHigh impedanceElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPhase shiftedOptoelectronics
High-impedance optical electrodes modulate light in response to a life-form bio-potential and then converts the modulated light to an electrical signal that provides traditional EEG and EEC type output. Light splitters are used to provide multiple electrodes and an electronic reference source. A pilot tone is used to achieve high sensitivity and synchronize multiple units while an optical phase-shift modulator is used to reduce optical noise.
Owner:SRICO
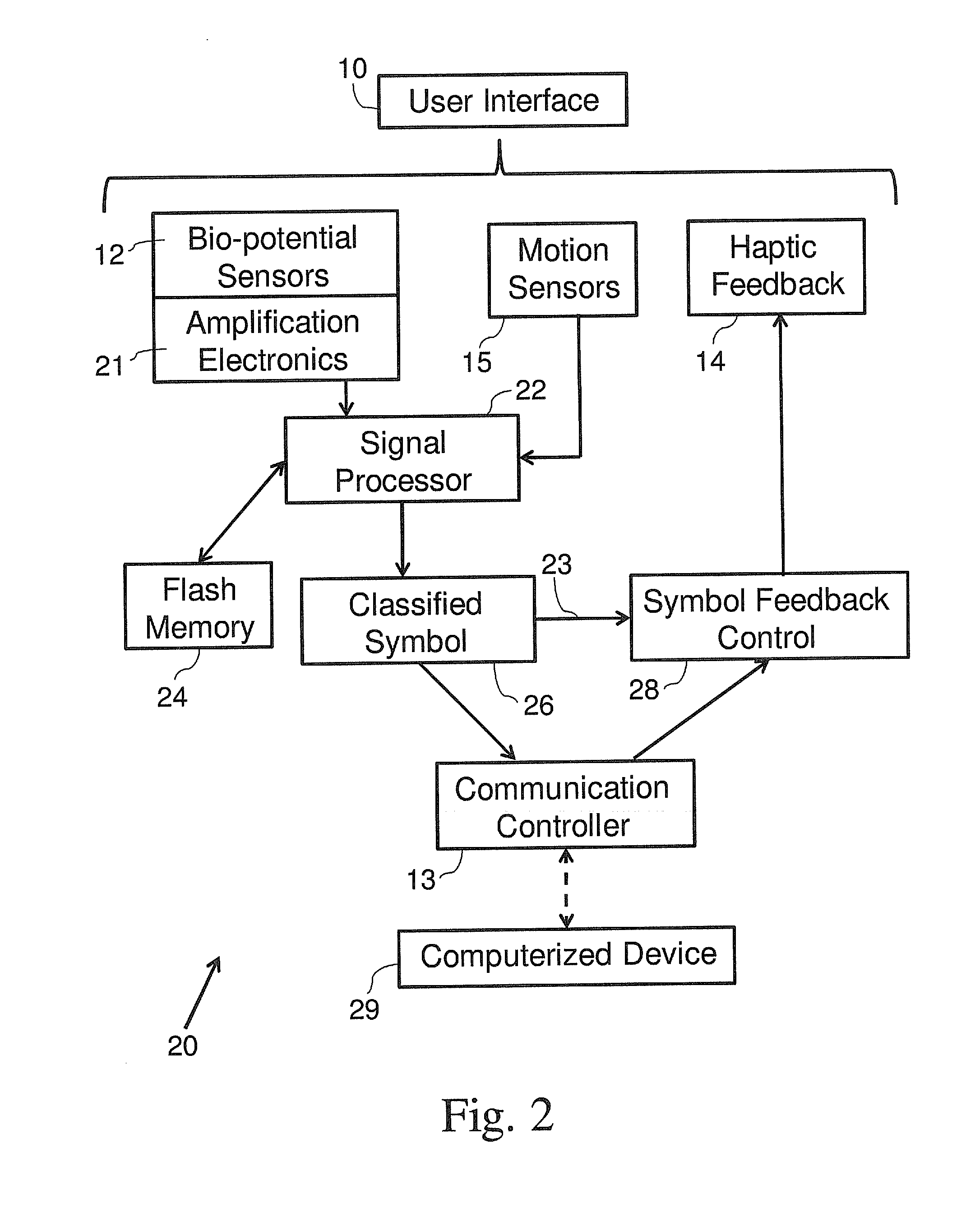
Closed loop feedback interface for wearable devices
ActiveUS20160195928A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsClosed loop feedbackControl system
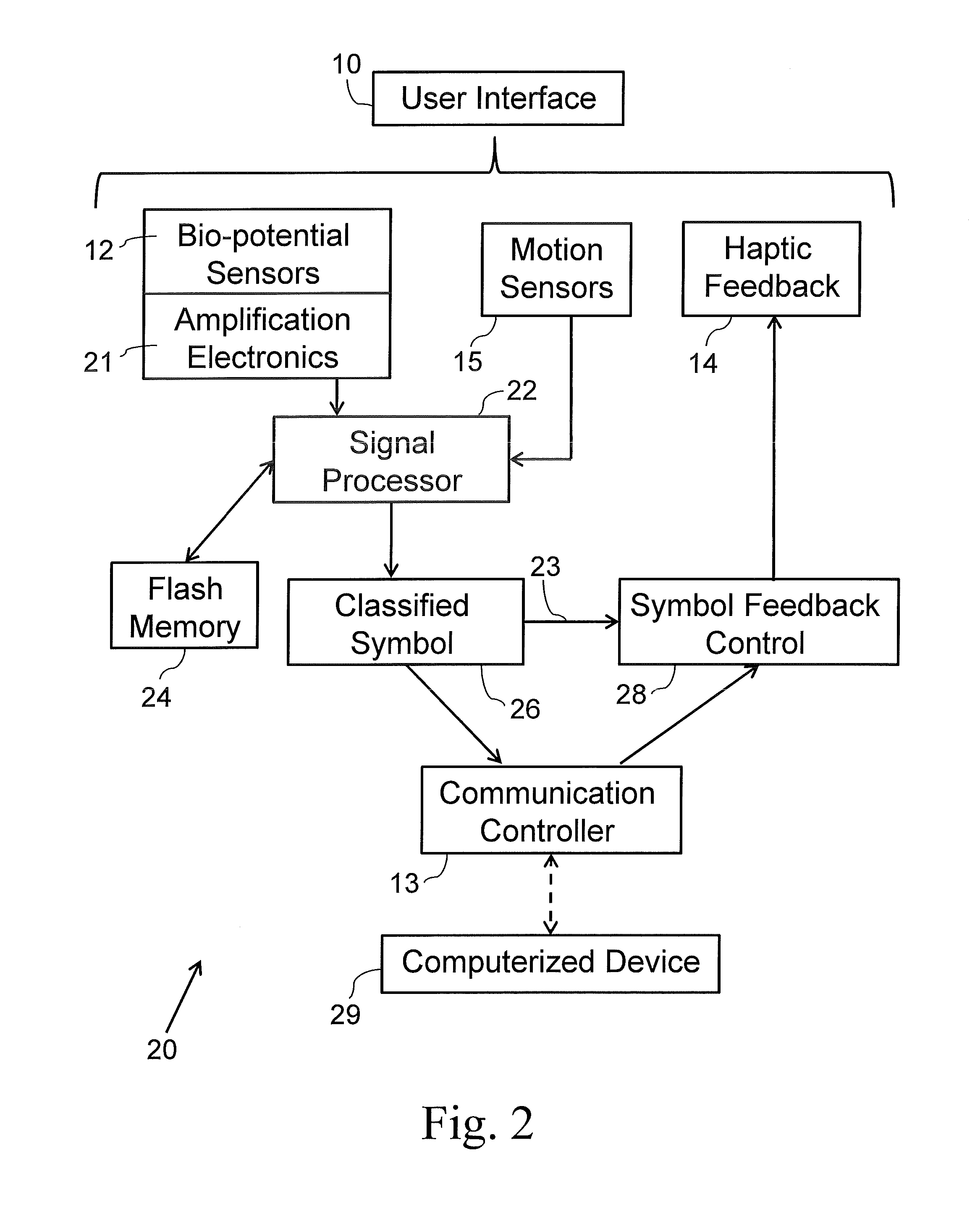
A gesture controlled system wearable by a user and operationally connected to a computerized device, the system comprising: at least one bio-potential sensor; at least one motion sensor; at least one haptic feedback actuator capable of creating haptic feedback corresponding to signals from the computerized device; a memory module, having a database with known records representing different gestures and a gesture prediction model; a signal processor, capable of identifying signal parameters from the sensors as known gestures; and a communication controller capable of transmitting information from the signal processor to the computerized device, wherein the at least one bio-potential sensor and the at least one feedback actuator are in direct contact with the skin of the user, wherein identified signals from the signal processor are transmitted to the computerized device, and wherein the at least one haptic feedback actuator is configured to allow reading text from the computerized device.
Owner:WEARABLE DEVICES LTD
Leadless wireless ECG measurement system for measuring of bio-potential electrical activity of the heart
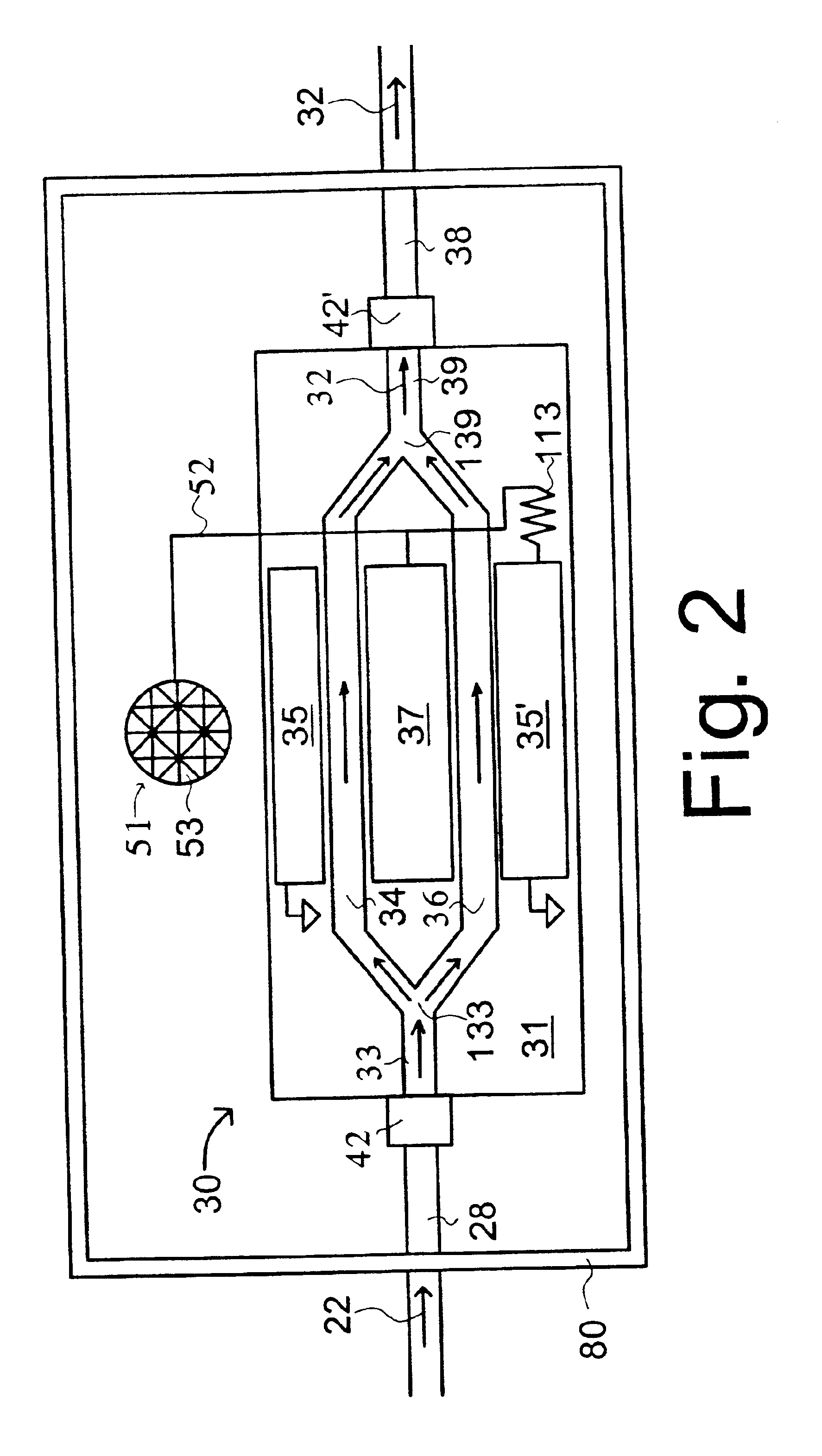
InactiveUS8838218B2Improved design and performanceImprove comfortElectrocardiographySensorsElectricityECG Measurement
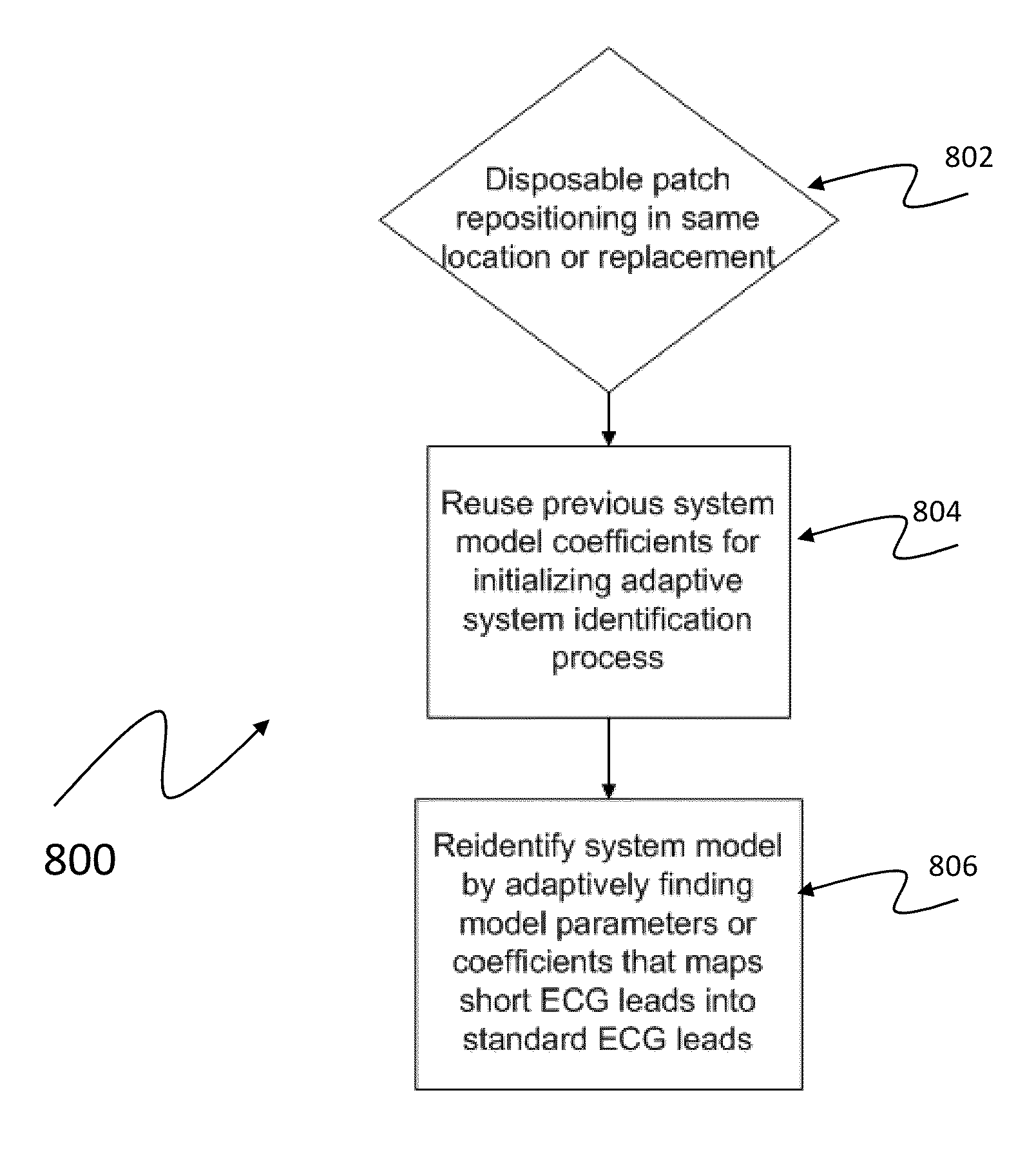
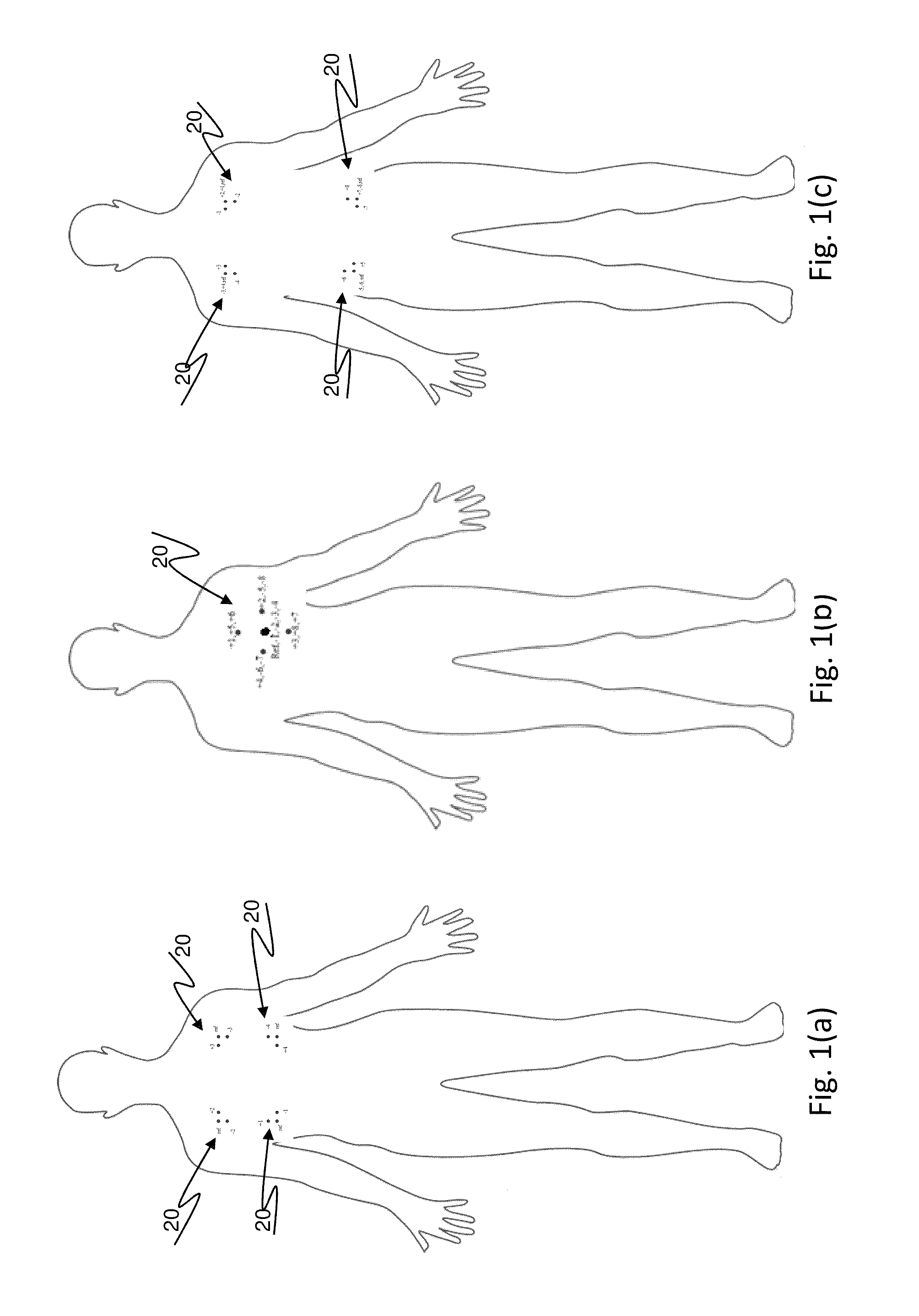
A leadless wireless ECG measurement system for measuring of bio-potential electrical activity of the heart in a patient's body includes at least one multi-contact bio-potential electrode assembly adapted for attachment to the patient's body. The electrode assembly is formed of an electronic patch layer and a disposable electrode layer. The disposable electrode layer has a plurality of contact points for engagement with the surface of the patient's body and is configured to measure short-lead ECG signals in response to electrical activity in the heart. A processing unit is provided and is configured to produce a transfer function which computes estimated long-lead ECG signals based on the measured short-lead ECG signals from the plurality of contact points.
Owner:KHAIR MOHAMMAD
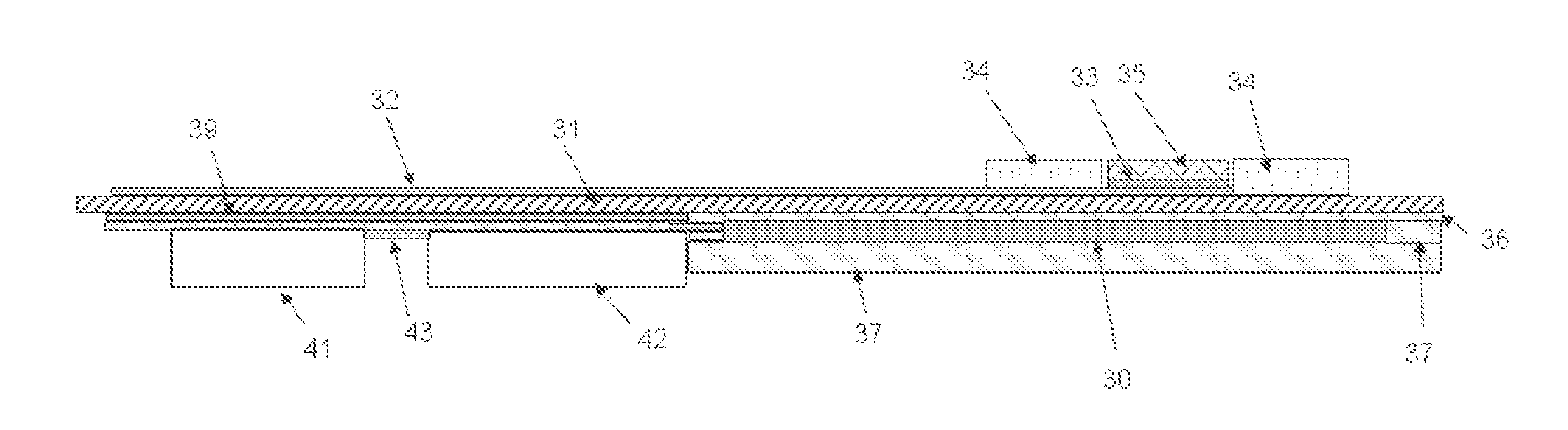
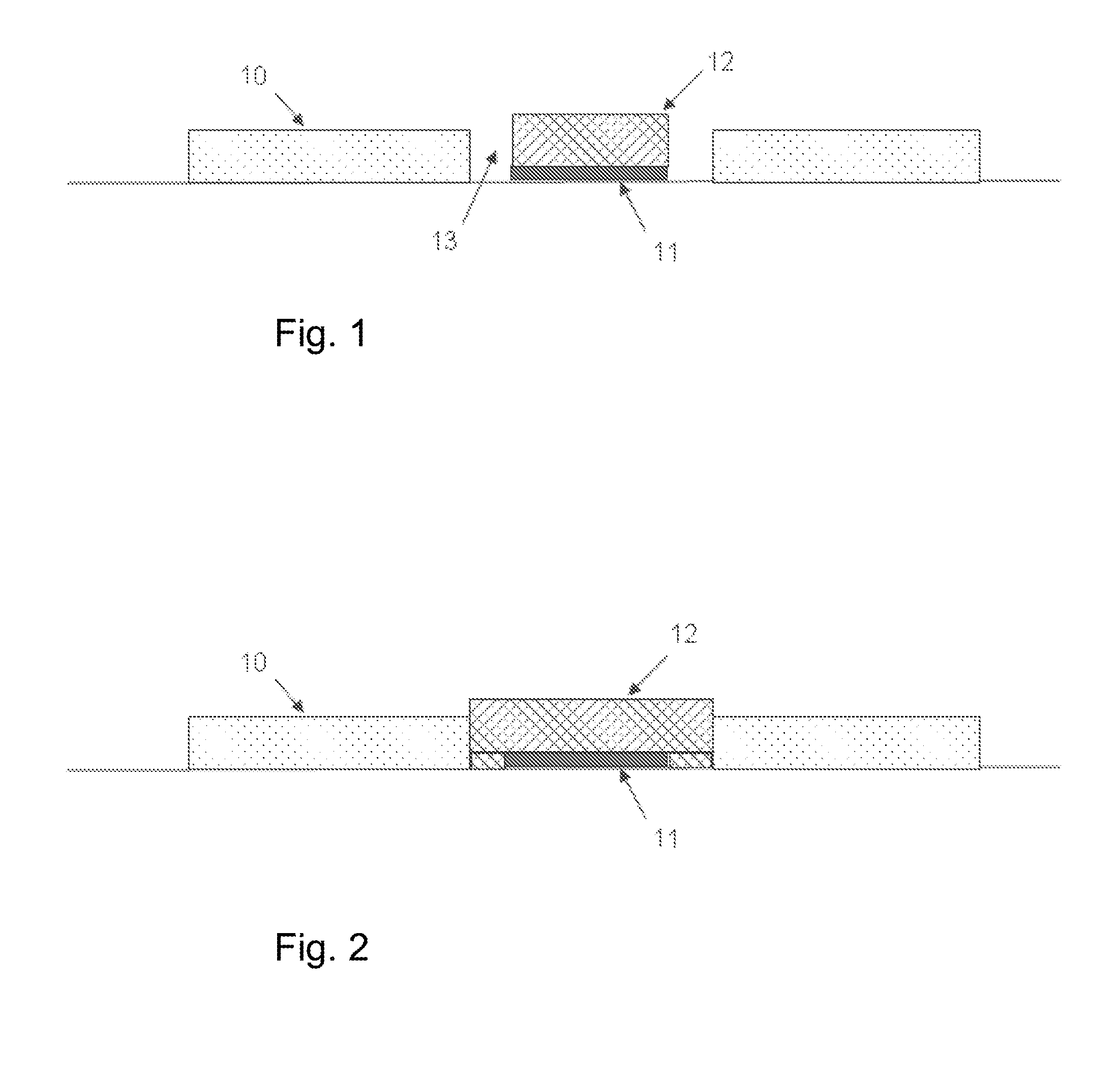
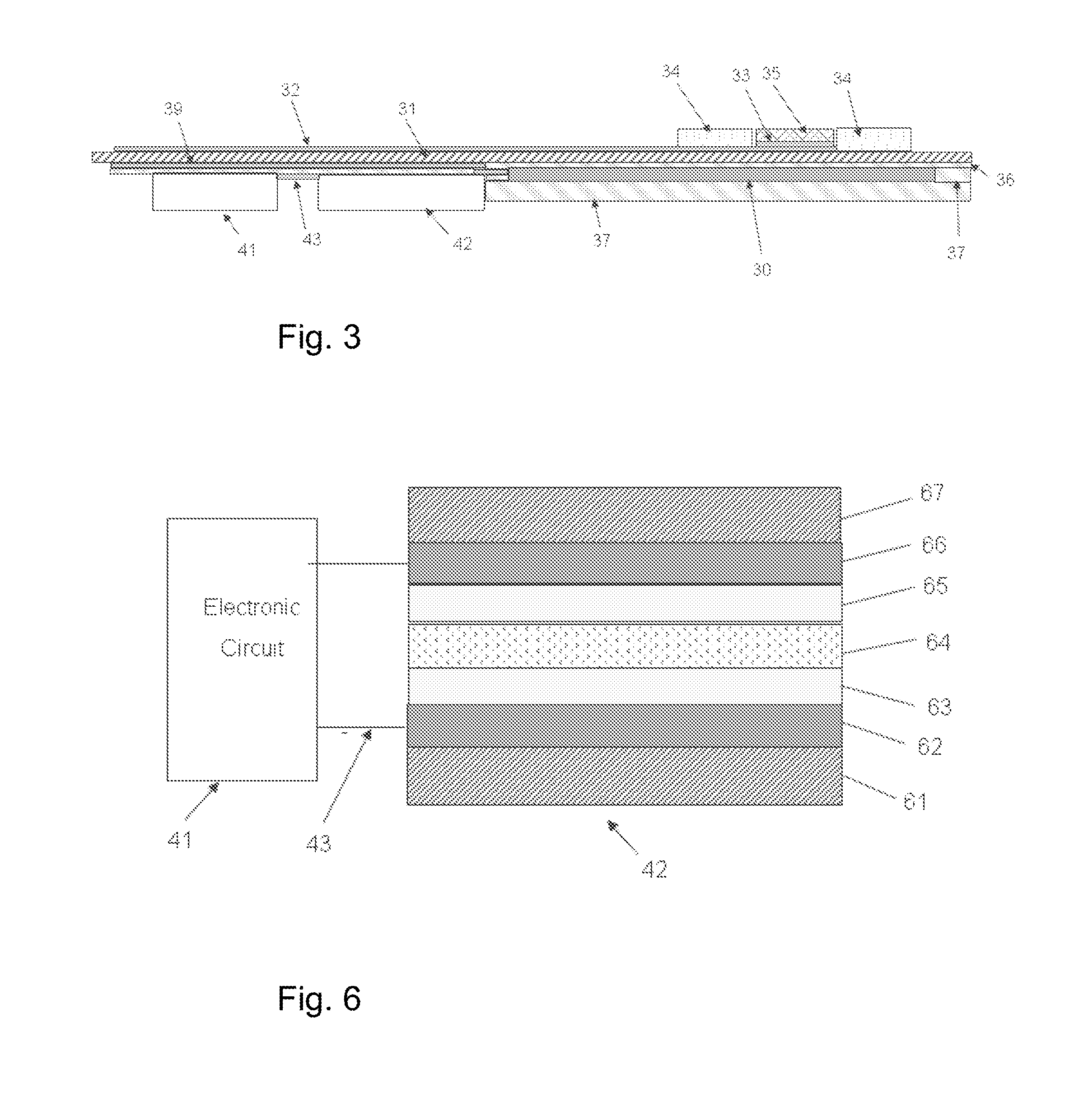
Apparatus for evoking and recording bio potentials
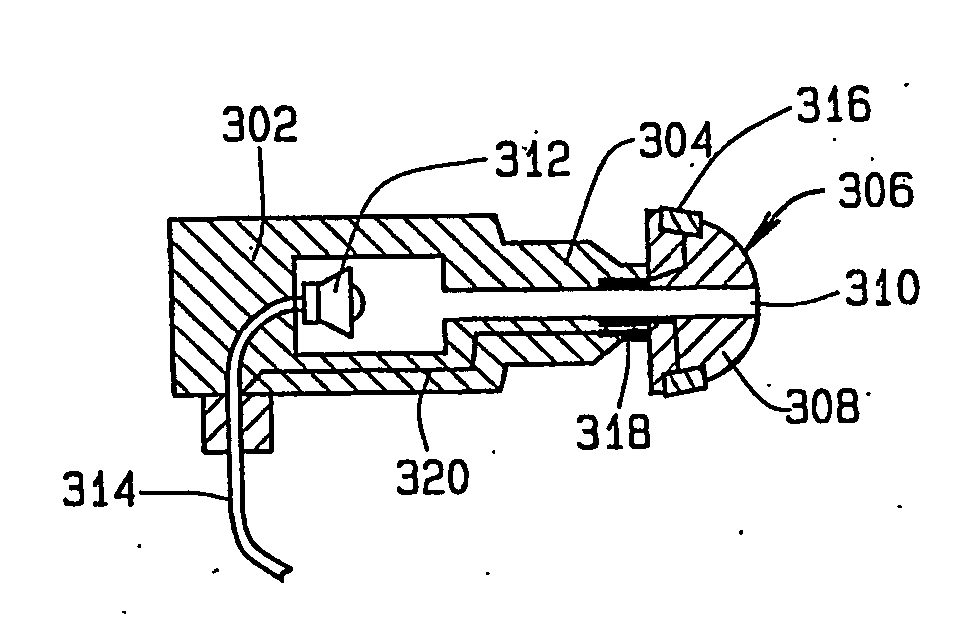
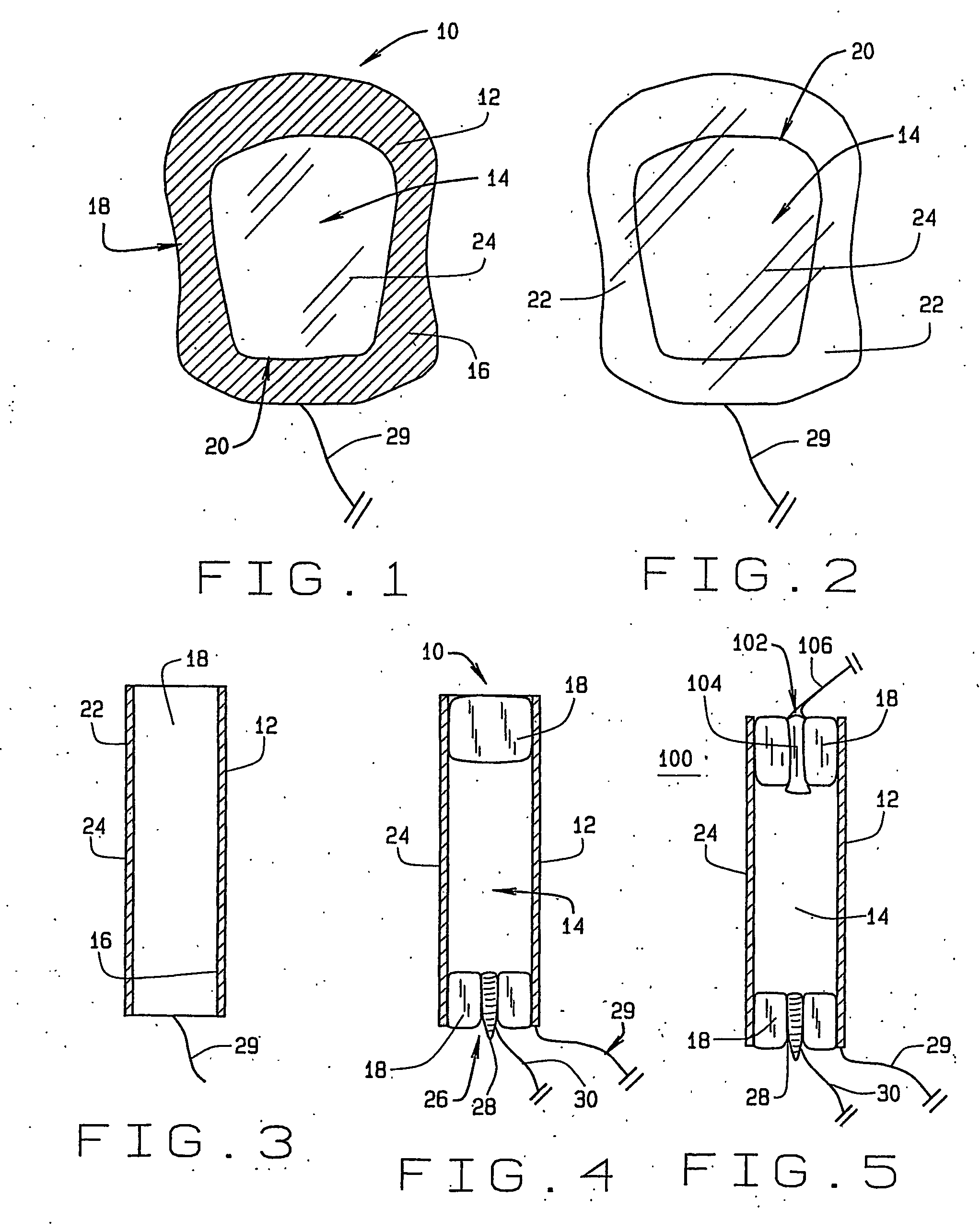
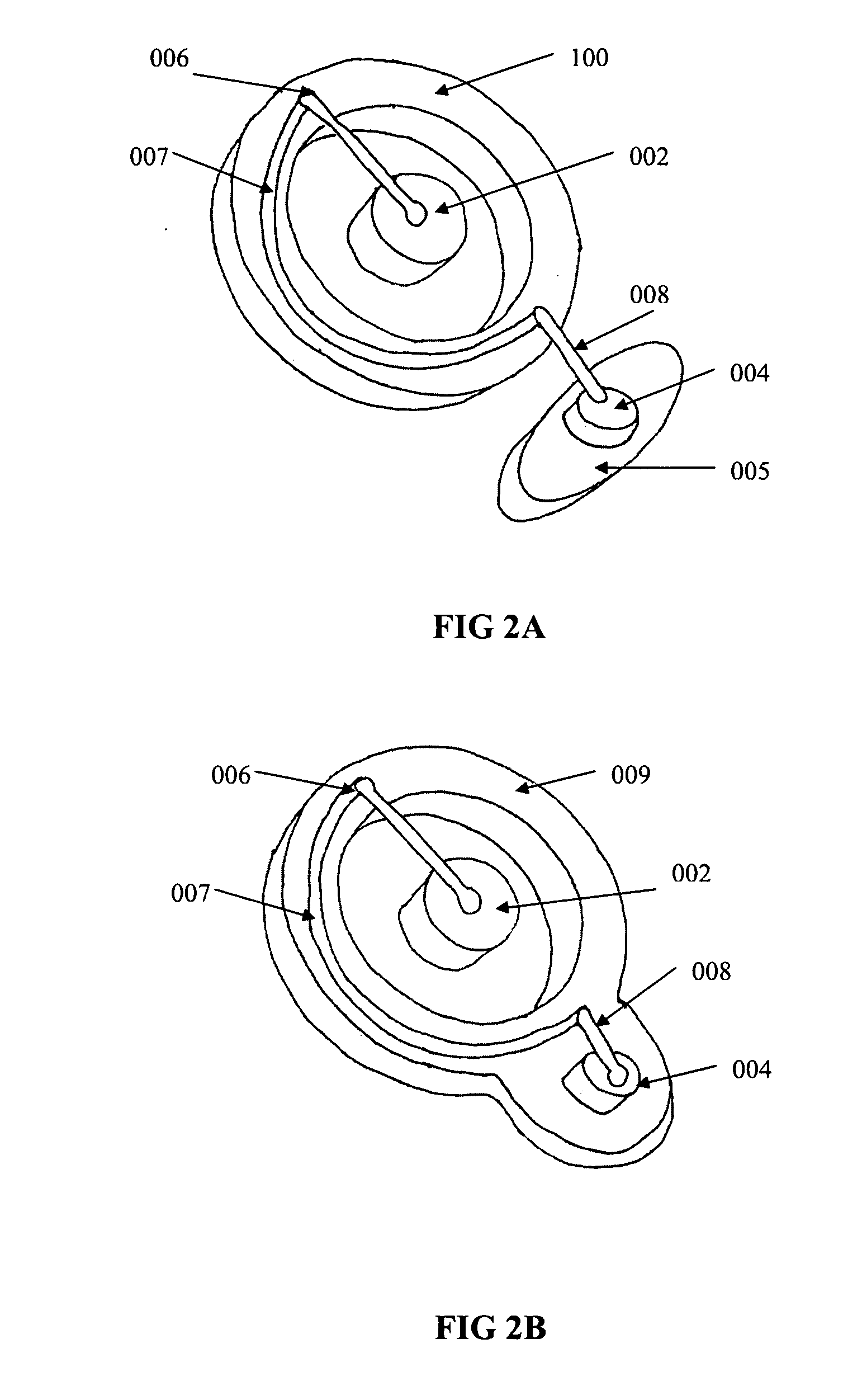
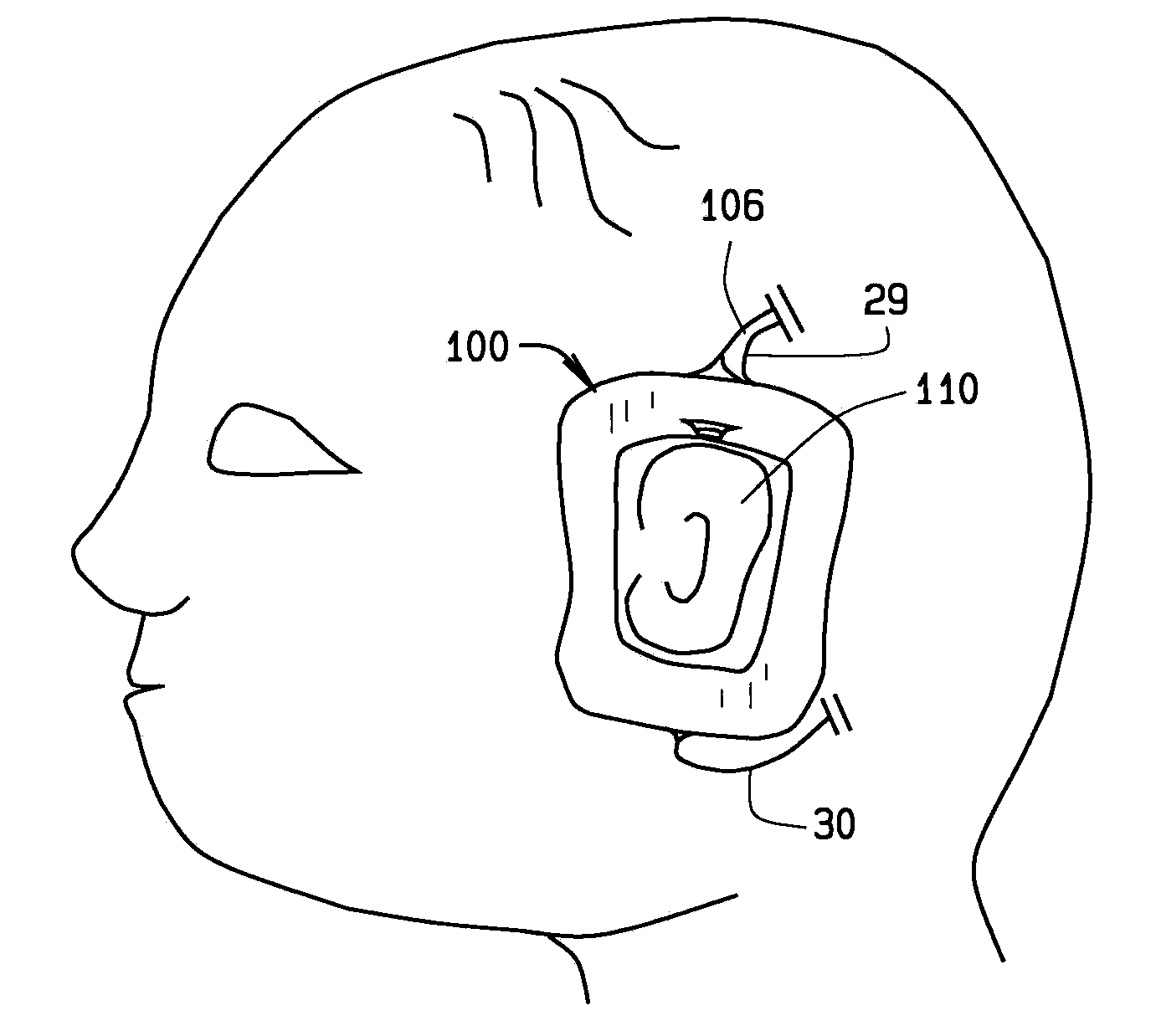
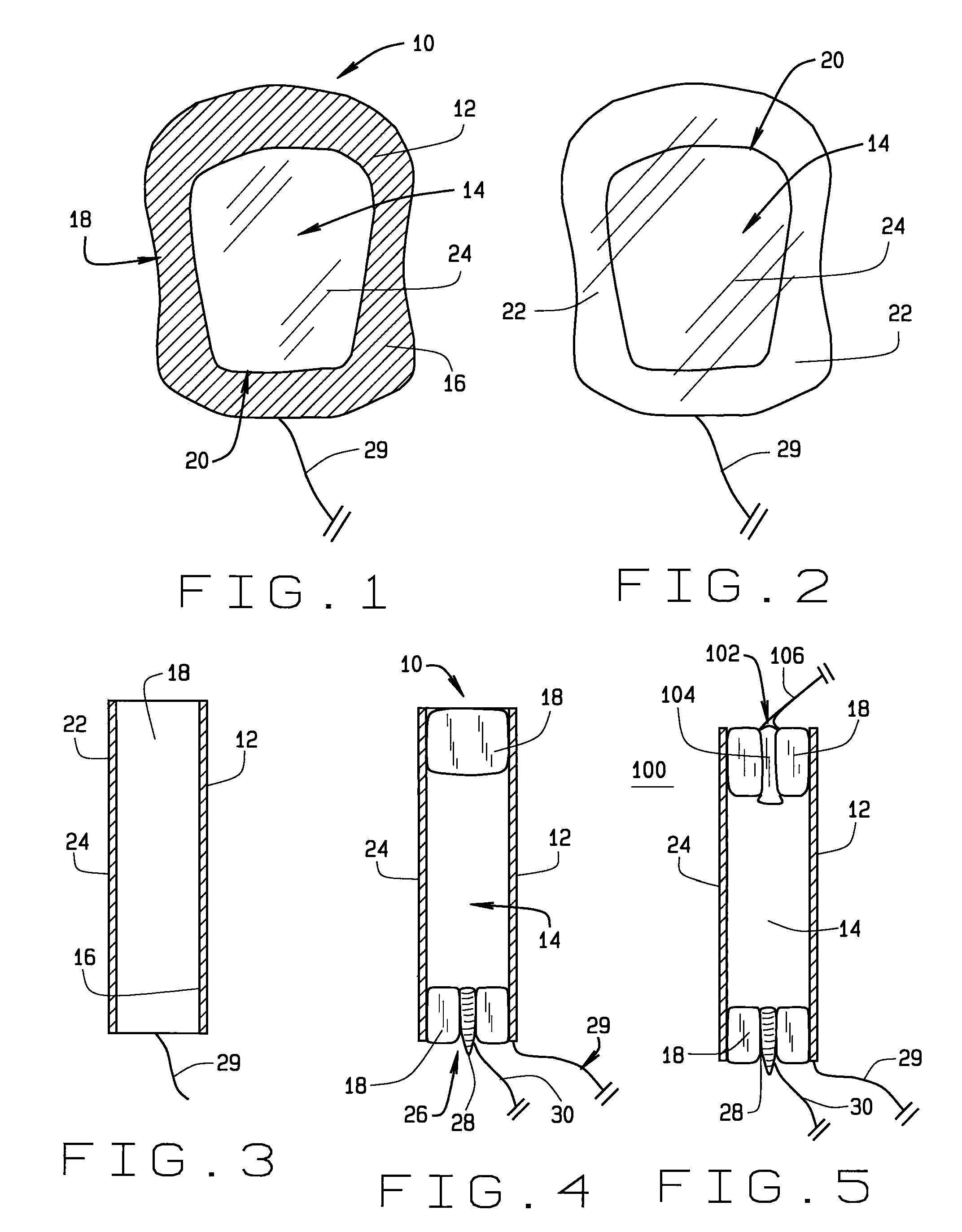
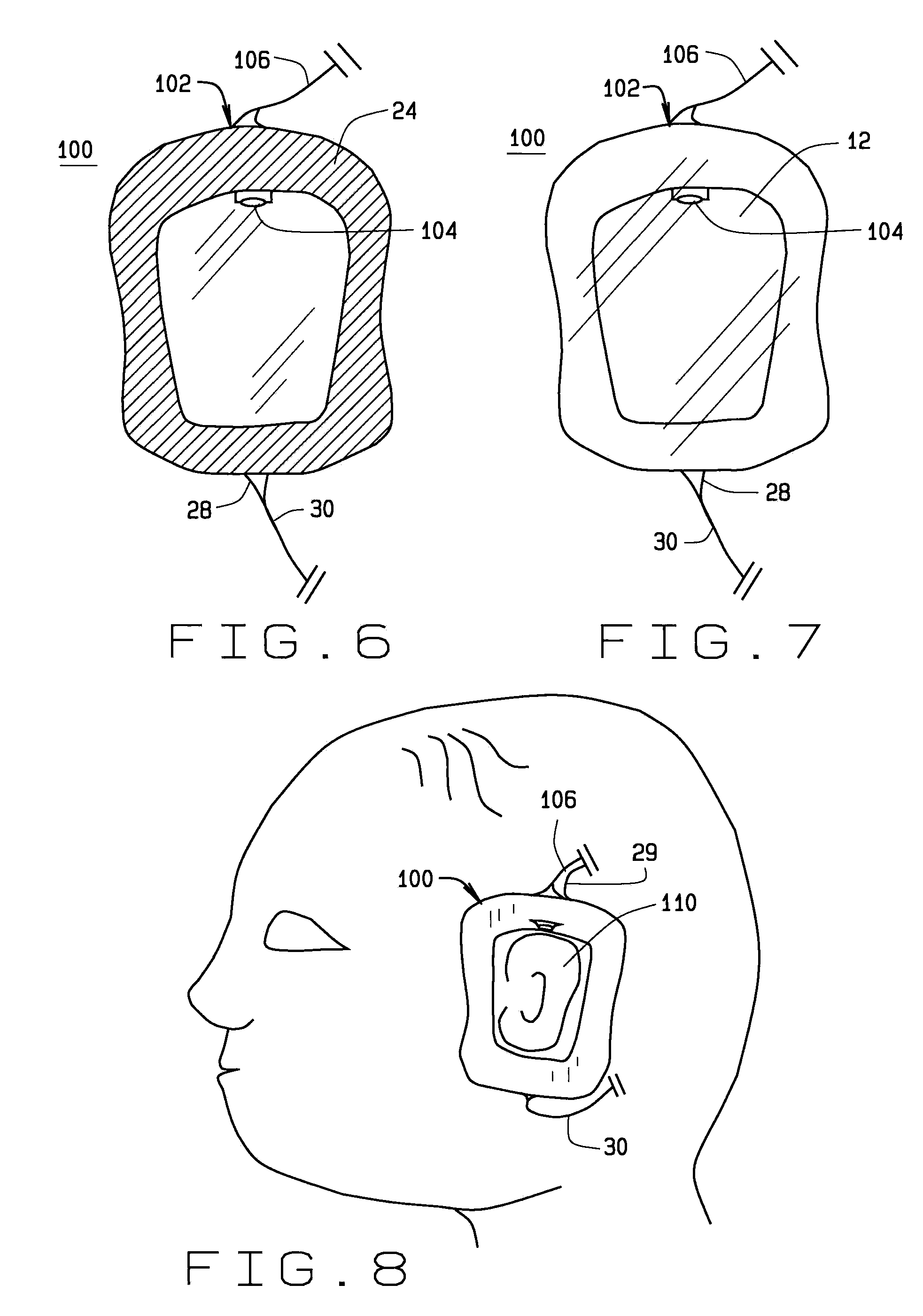
Apparatus (10) for evoking and recording bio-potentials from a human subject and methods of use are described. The apparatus (10) includes a flexible member (18) with a layer of conductive material (12) disposed thereon for contacting a skin surface on the human subject. The dimensions and shape of the flexible member (18) are adapted for conforming contact between the conductive material (12) and the skin surface. A stimulus delivery element (28) is coupled to the flexible member (18) for delivering a sensory stimulus to the subject to evoke bio-potentials, which are detected and received through the layer of conductive material (12).
Owner:EVEREST BIOMEDICAL INSTR +2
Bio-potential sensing materials as dry electrodes and devices
ActiveUS20160089045A1Lower resistanceFacilitate conductionBioelectric signal measurementNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialAnimal bodyBio potential
This invention is directed to materials and devices for sensing bio-potential signals from animals, particularly to sensing bio-potential signals to monitor humans in the medical field. In general, bio-potential sensors may be attached to the body of an animal, such as a human, in order to receive bio-potential signals such that information about the bioelectrical properties of the cells and / or tissues of the animal may be gathered. The bio-potential sensor may generally include a dry electrode that may be placed in contact with the skin of an animal to receive bio-potential signals from the animal. A dry electrode may generally include an electrically conductive solid material which may conduct electrical signals from an animal.
Owner:NEUROREX
Biomedical sensor
A biomedical sensor is provided. The biomedical sensor comprises a printed bio-potential electrode on the biomedical sheet sensor configured to provide an electrical contact with a surface to be measured, and a bi-stable printed electronic ink indicator provided on the biomedical sheet sensor and configured to indicate a loose contact of a bio-potential electrode operation by switching the color of the bi-stable indicator from a first color to a second color when a loose contact is detected.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
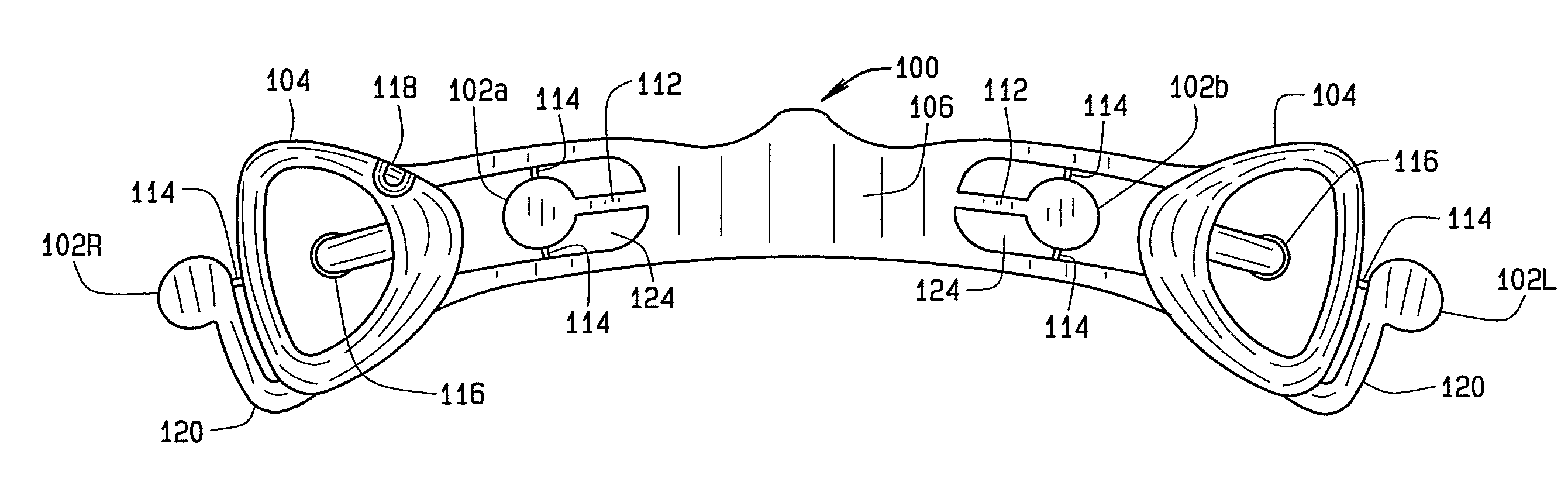
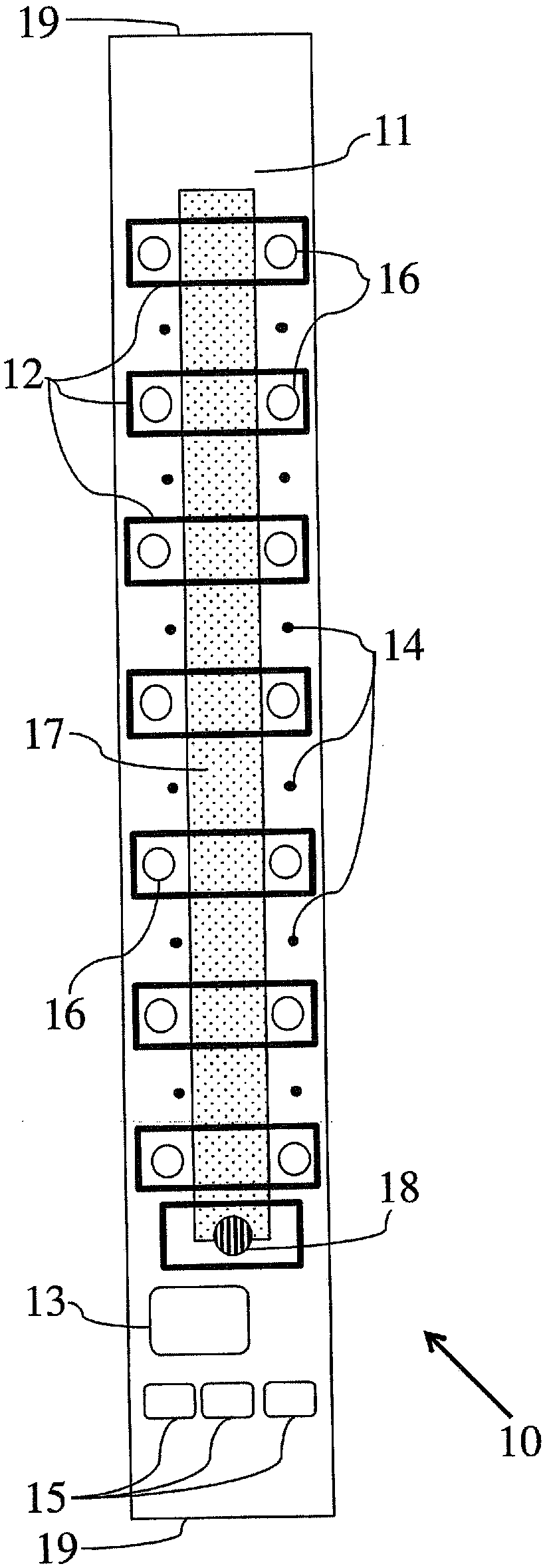
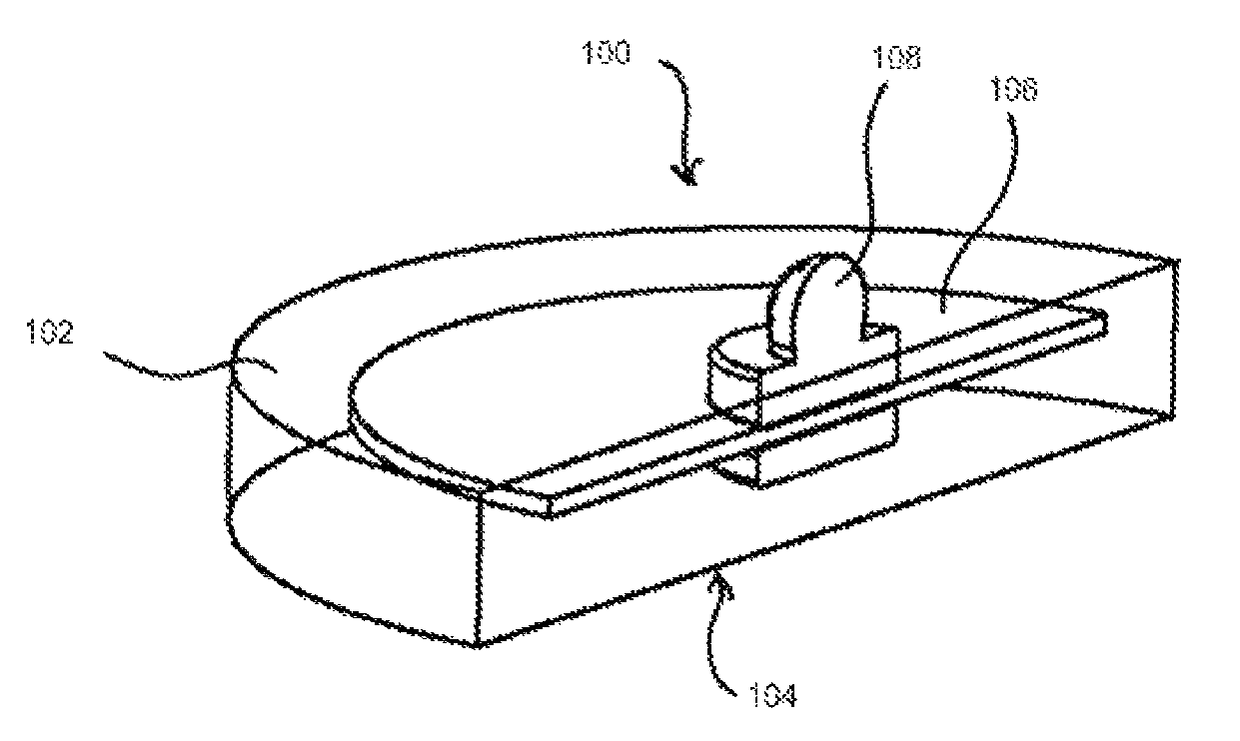
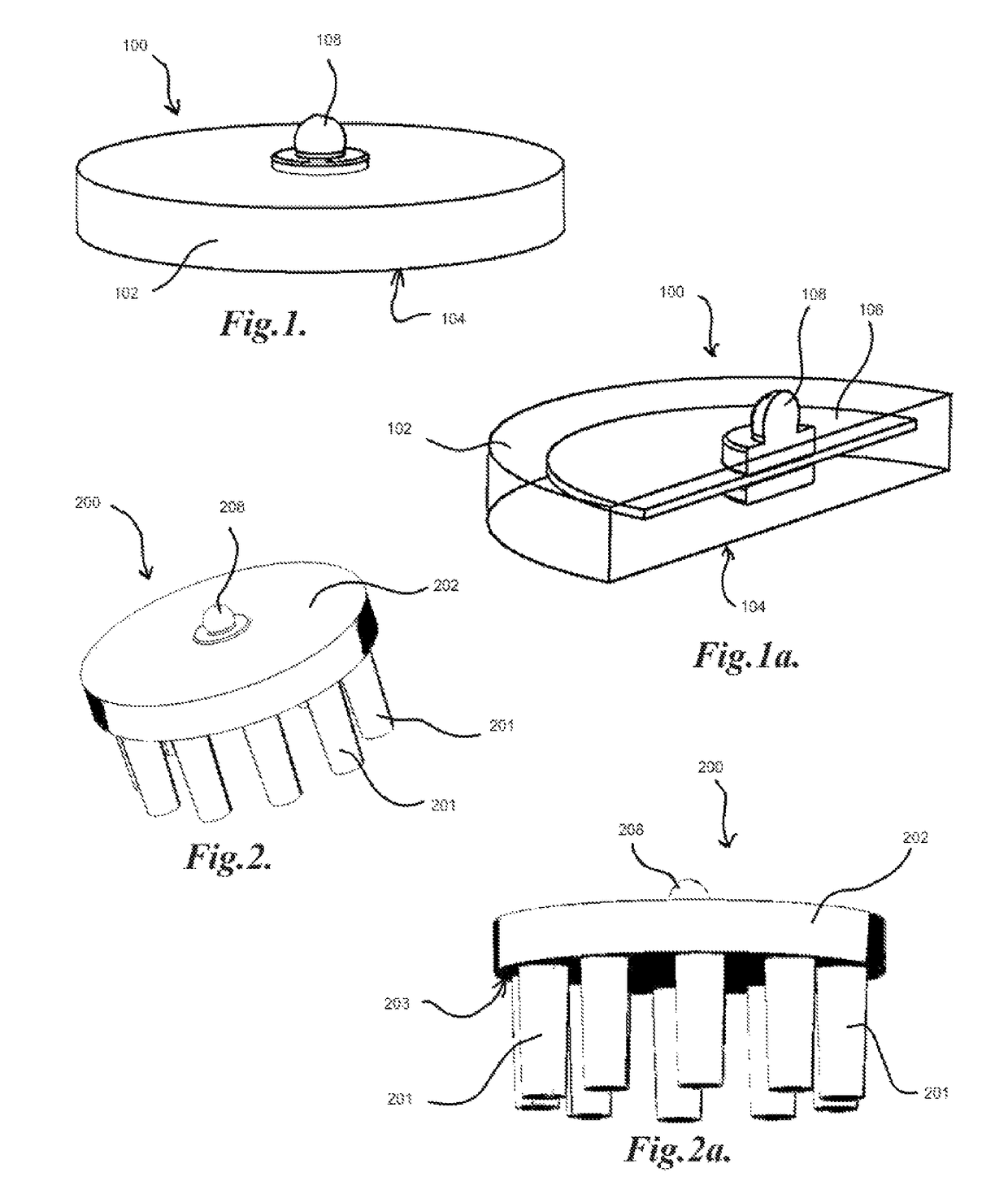
Electrode array
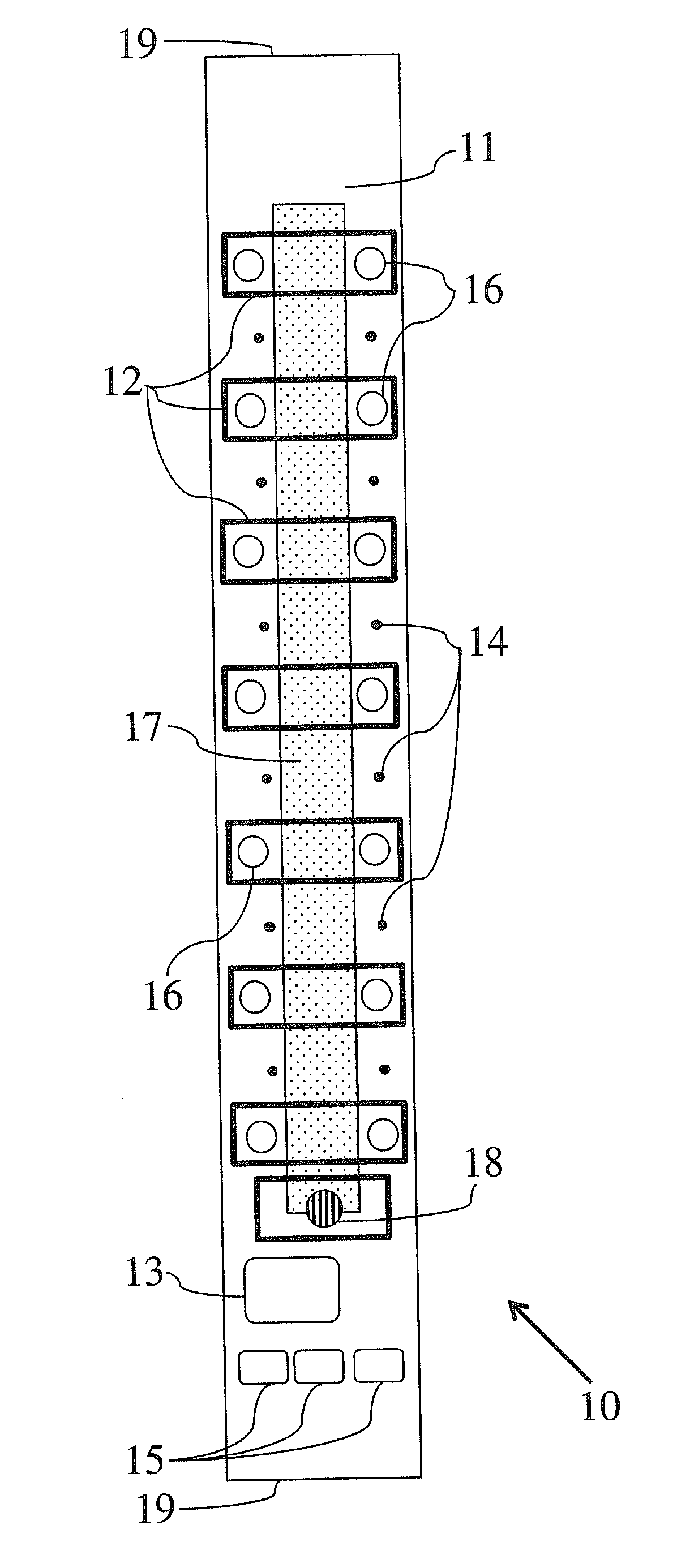
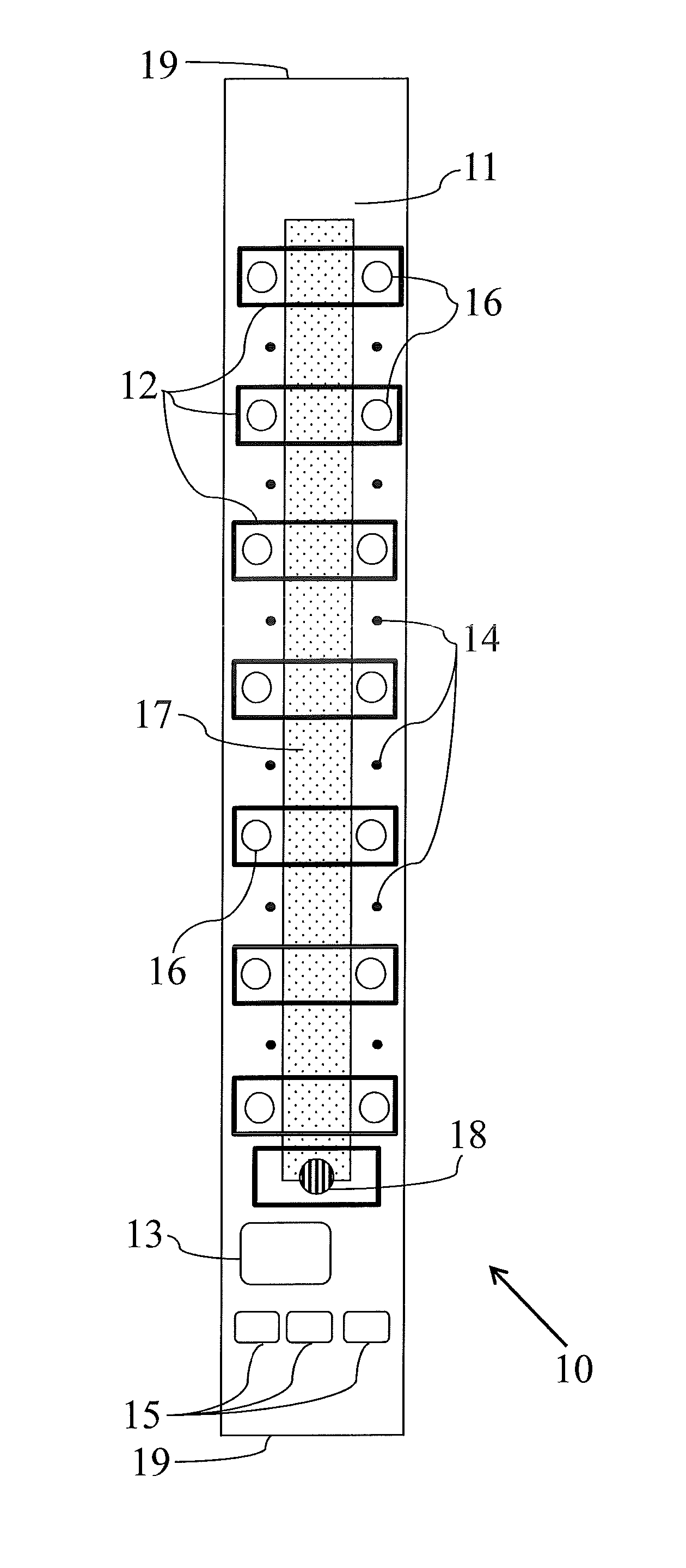
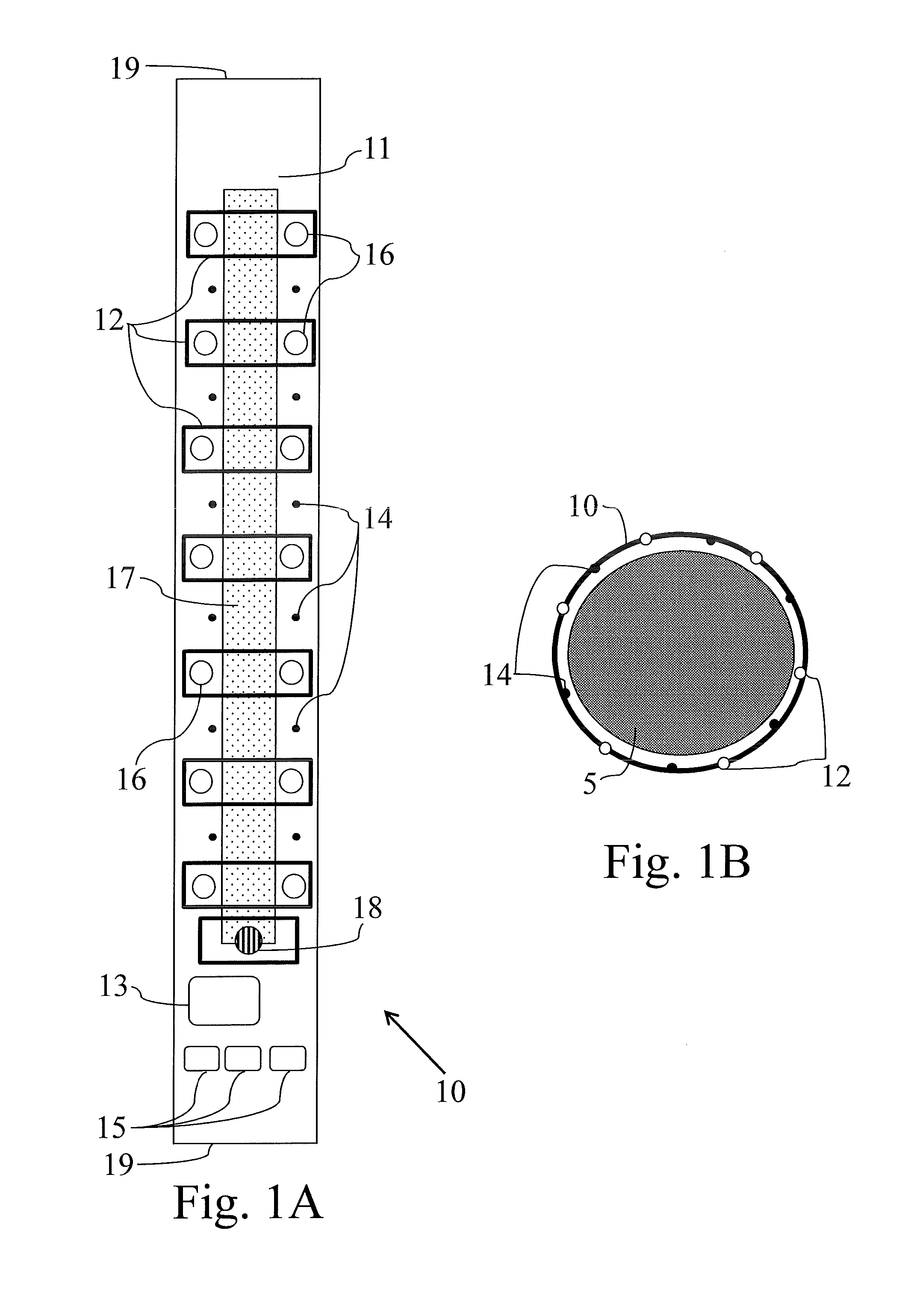
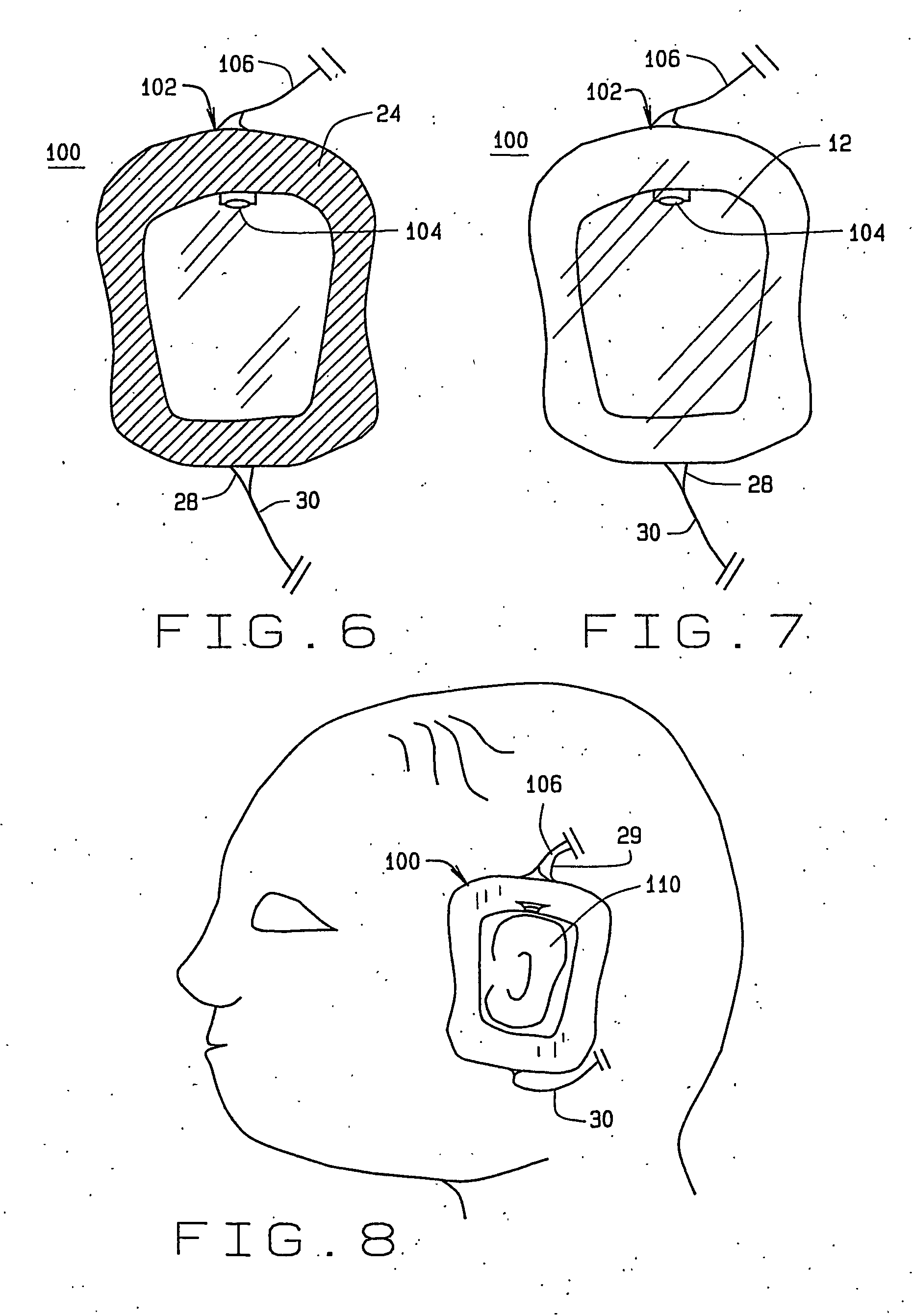
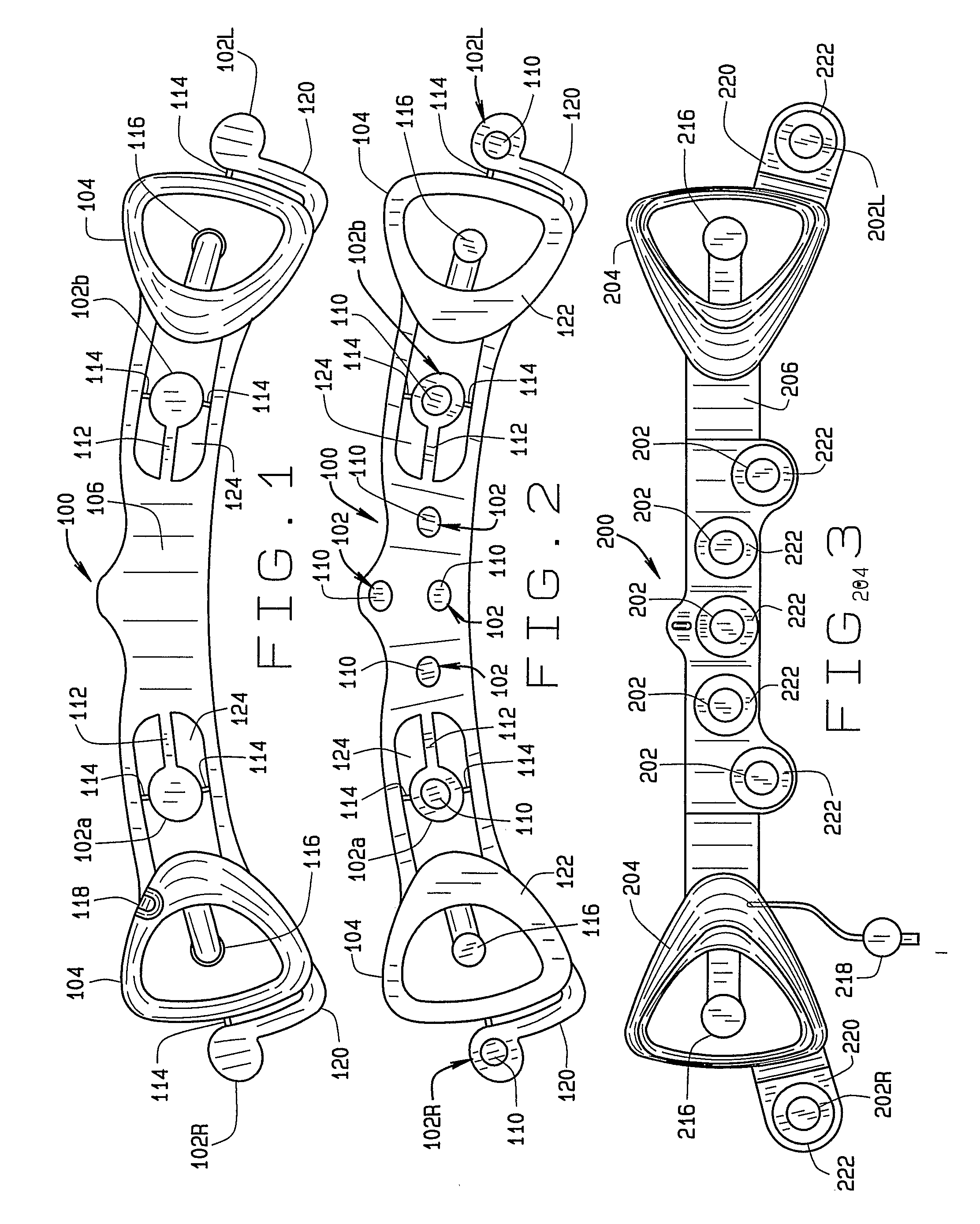
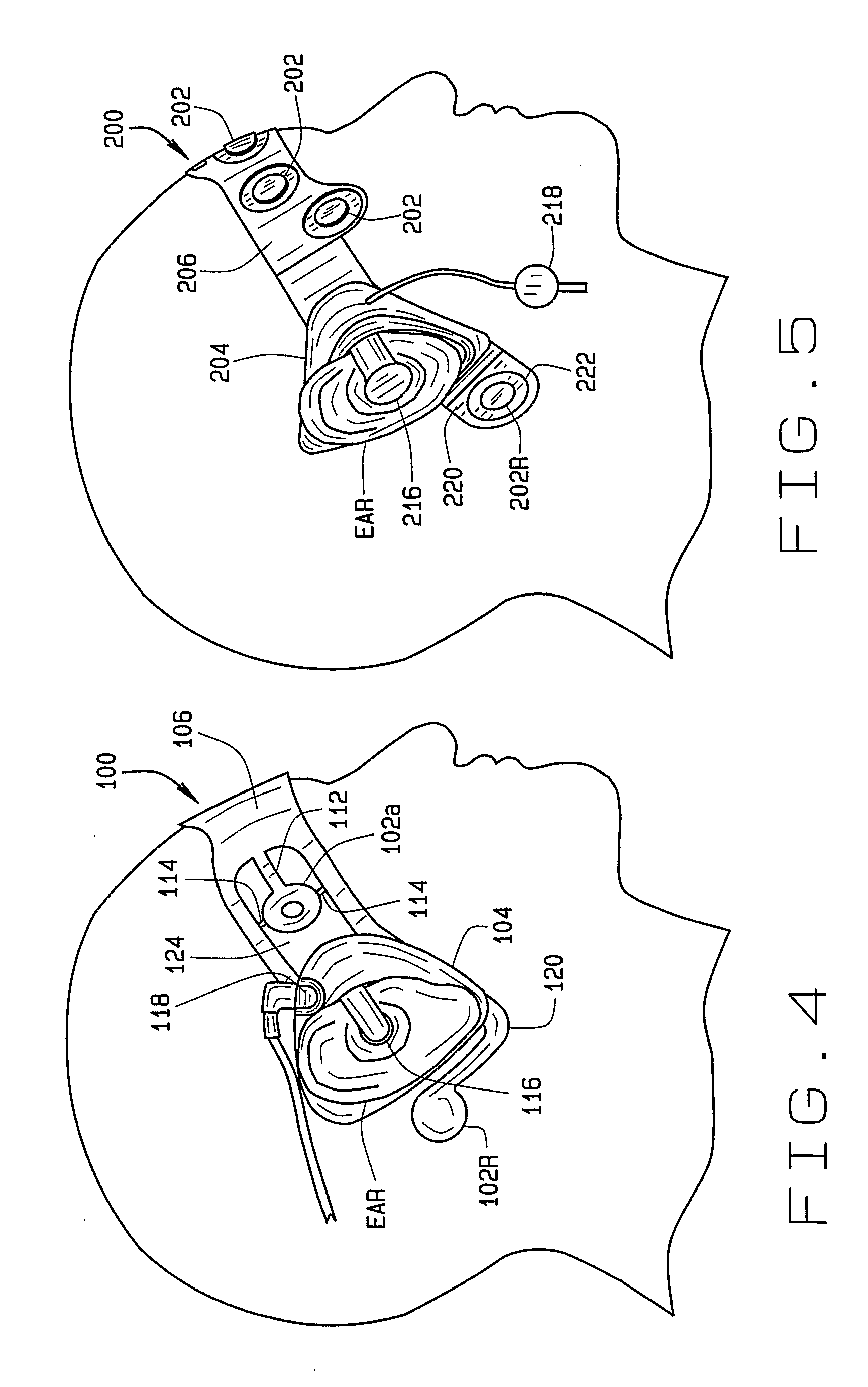
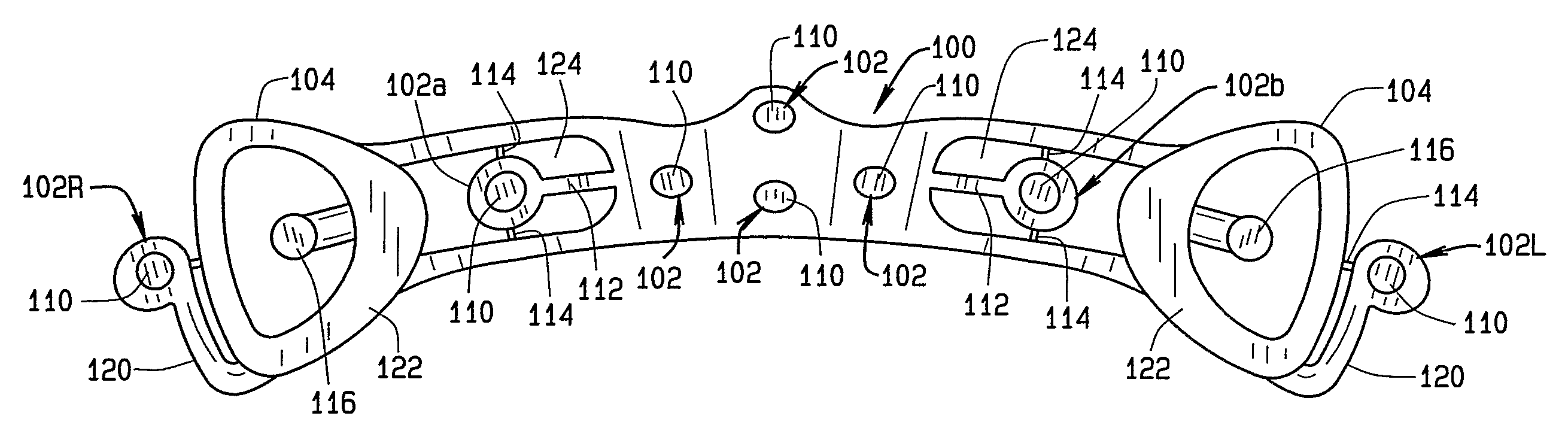
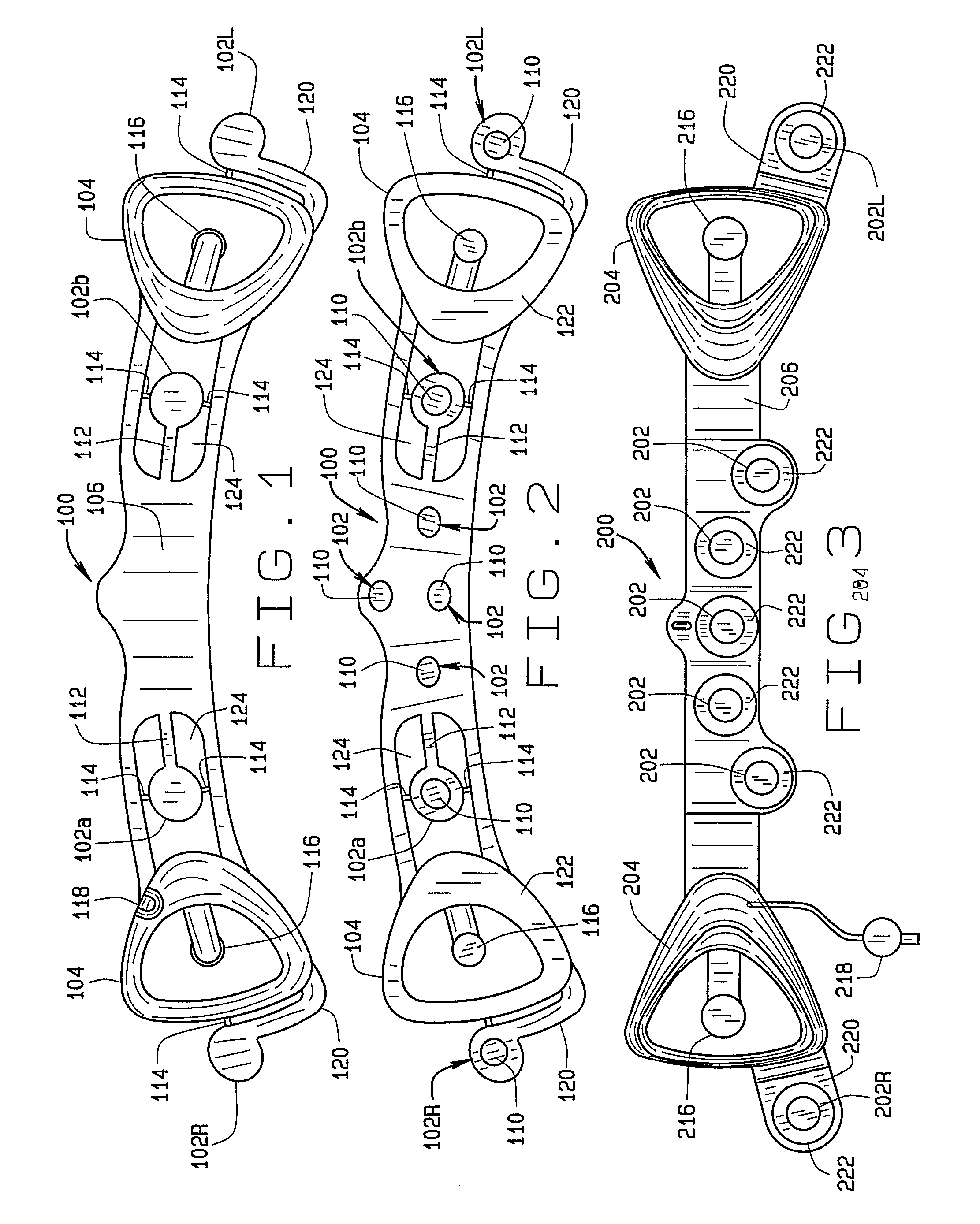
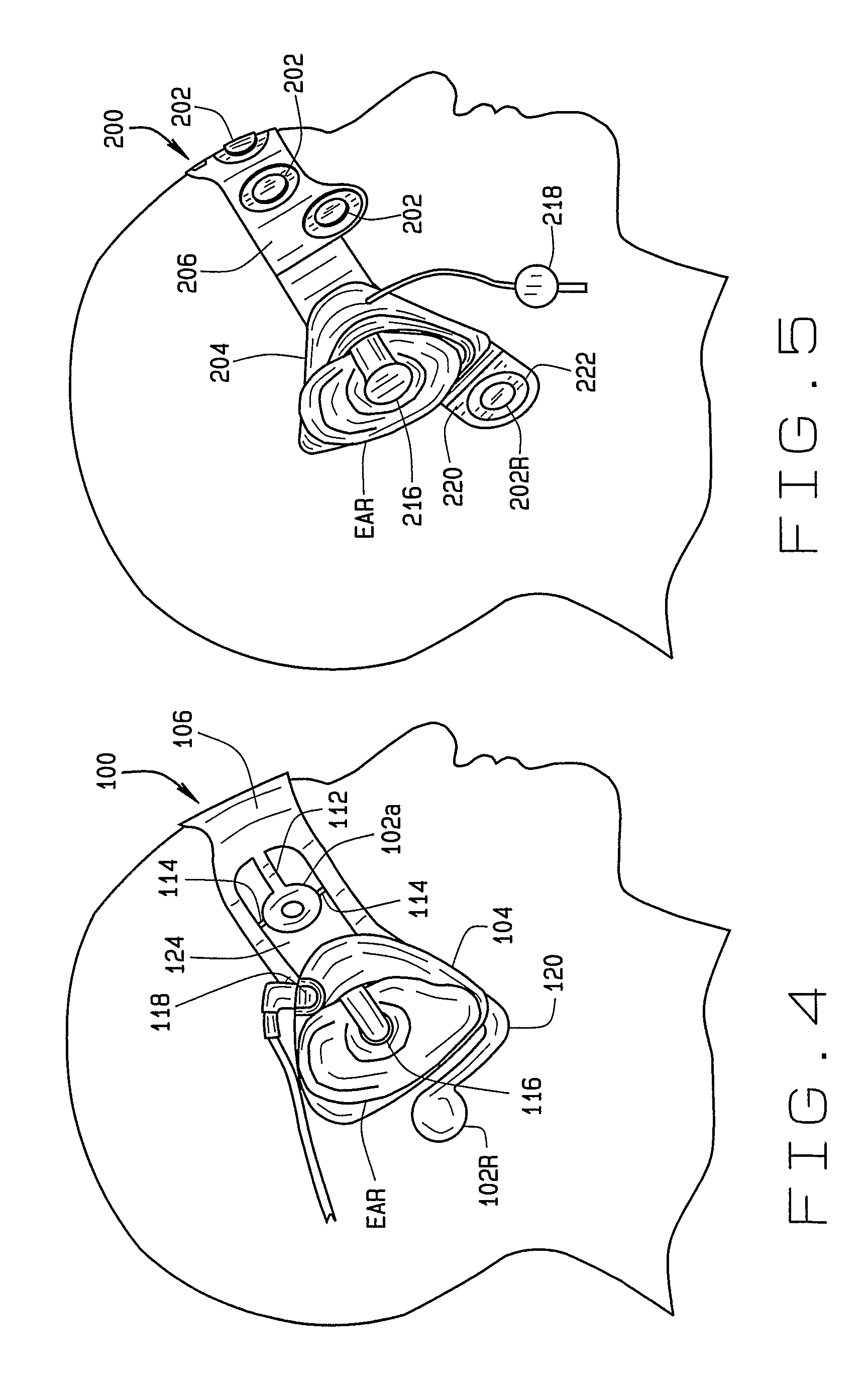
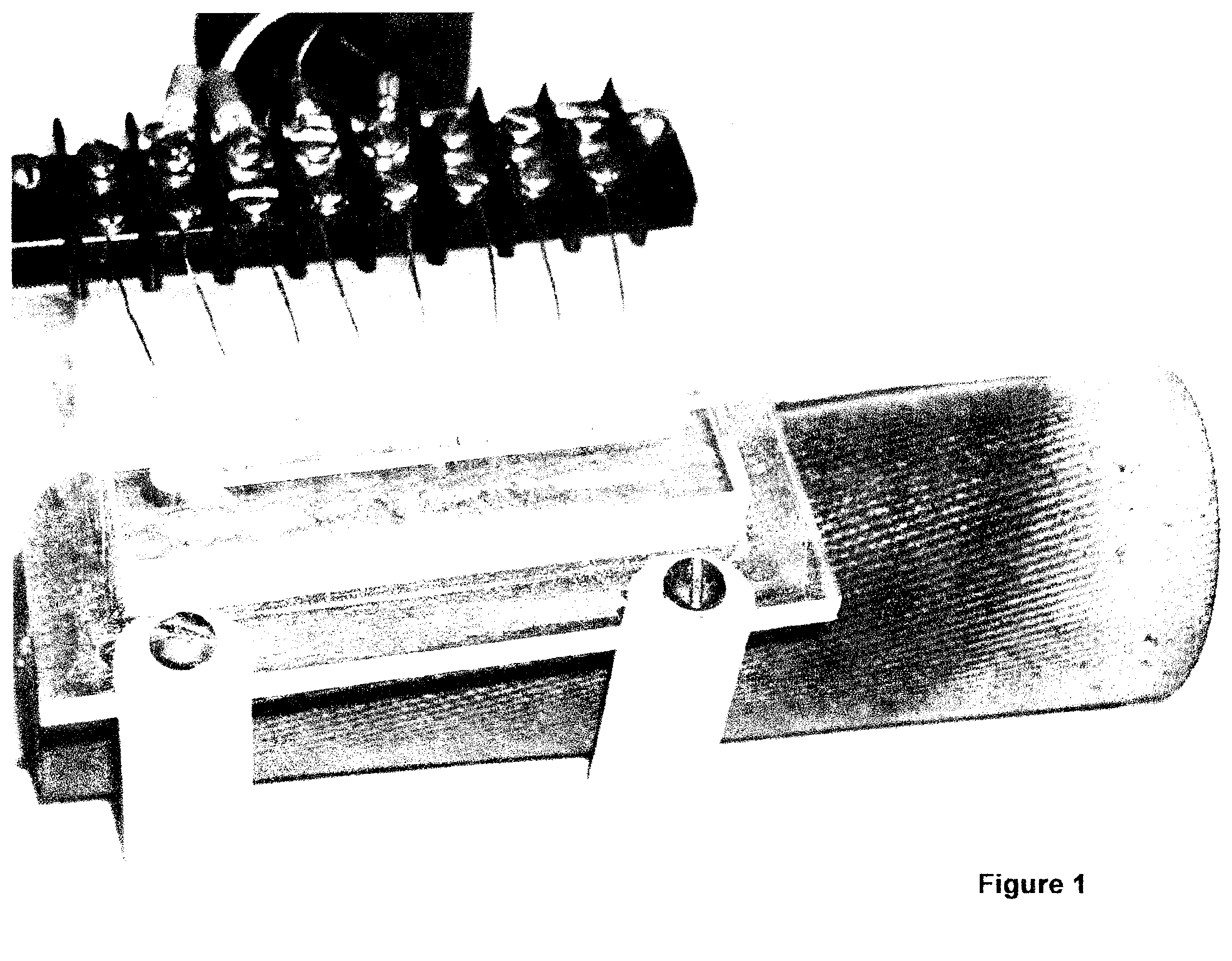
A disposable electrode array 100, 200 including a flexible member 106, 206 in which a plurality of electrodes 102, 202 are disposed, having a shape adapted to contact the forehead skin surface on a human patient. A pair of ear loops 104, 204 coupled to the disposable electrode array 100, 200 secure the disposable electrode array 100, 200 about the patient's ears, with the flexible member 106, 206 disposed across the patient's bow, retaining the electrodes 102, 202 against the skin surface. Additional electrodes 102, 202 are disposed in proximity to the ear loops 104, 204 and are configured to contact the skin surface behind the patient's ears. An auditory stimulus delivery element 116, 216 is coupled with each of the ear loops 104, 204, and positioned to seat in proximity to the patient's ear canal for the delivery of auditory stimulus. Electrical conductors associated with the electrodes 102, 202 and the stimulus delivery elements 116, 216 are routed within the flexible member 106, 206 to a common external connection point 118, 218 for connection to an external system. The disposable electrode array 100, 200 may be configured for both evoking and measuring evoked bio-potentials in the human subject, or for measuring bio-potentials evoked using a separate stimulus delivery system.
Owner:BRAINSCOPE SPV LLC
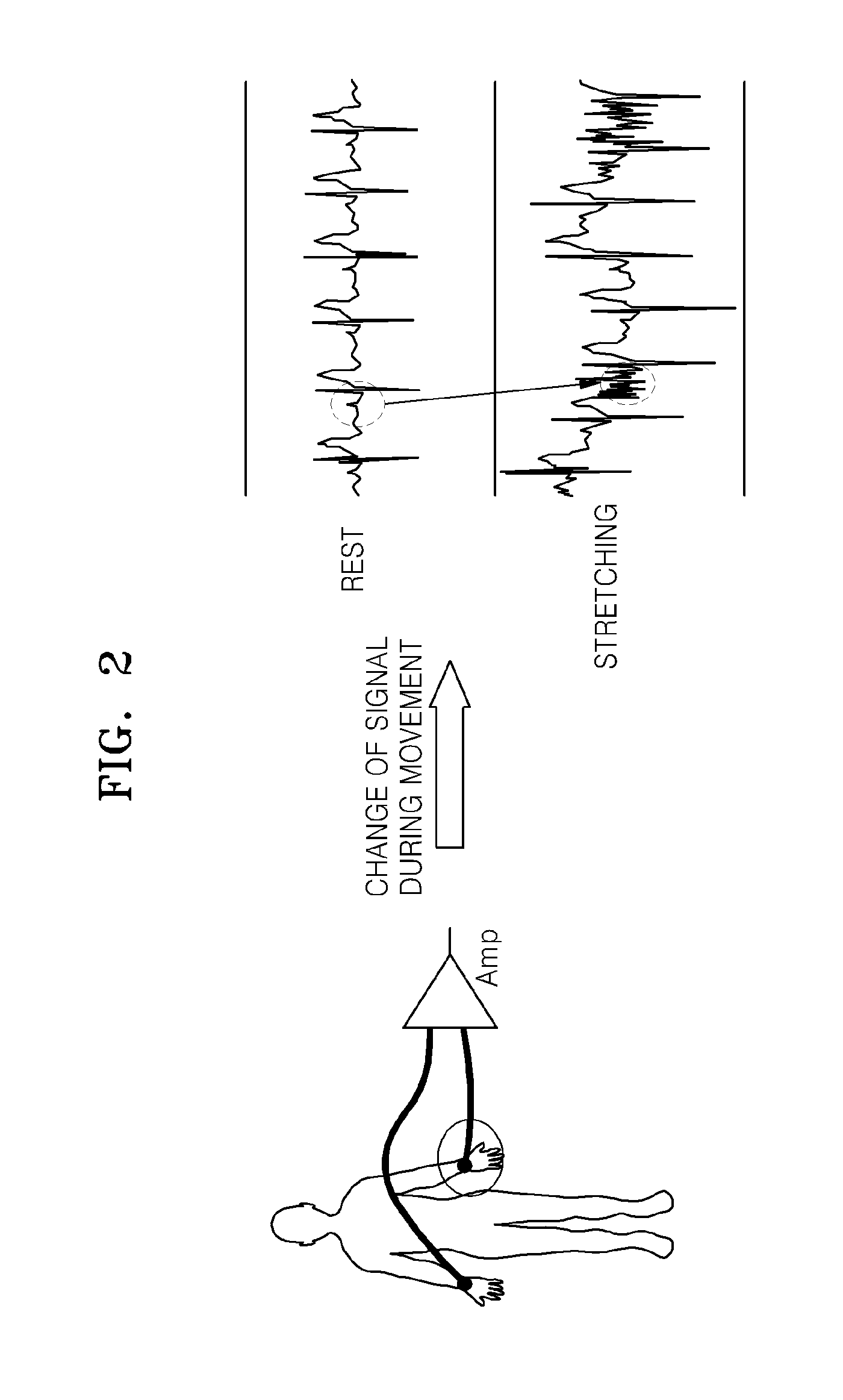
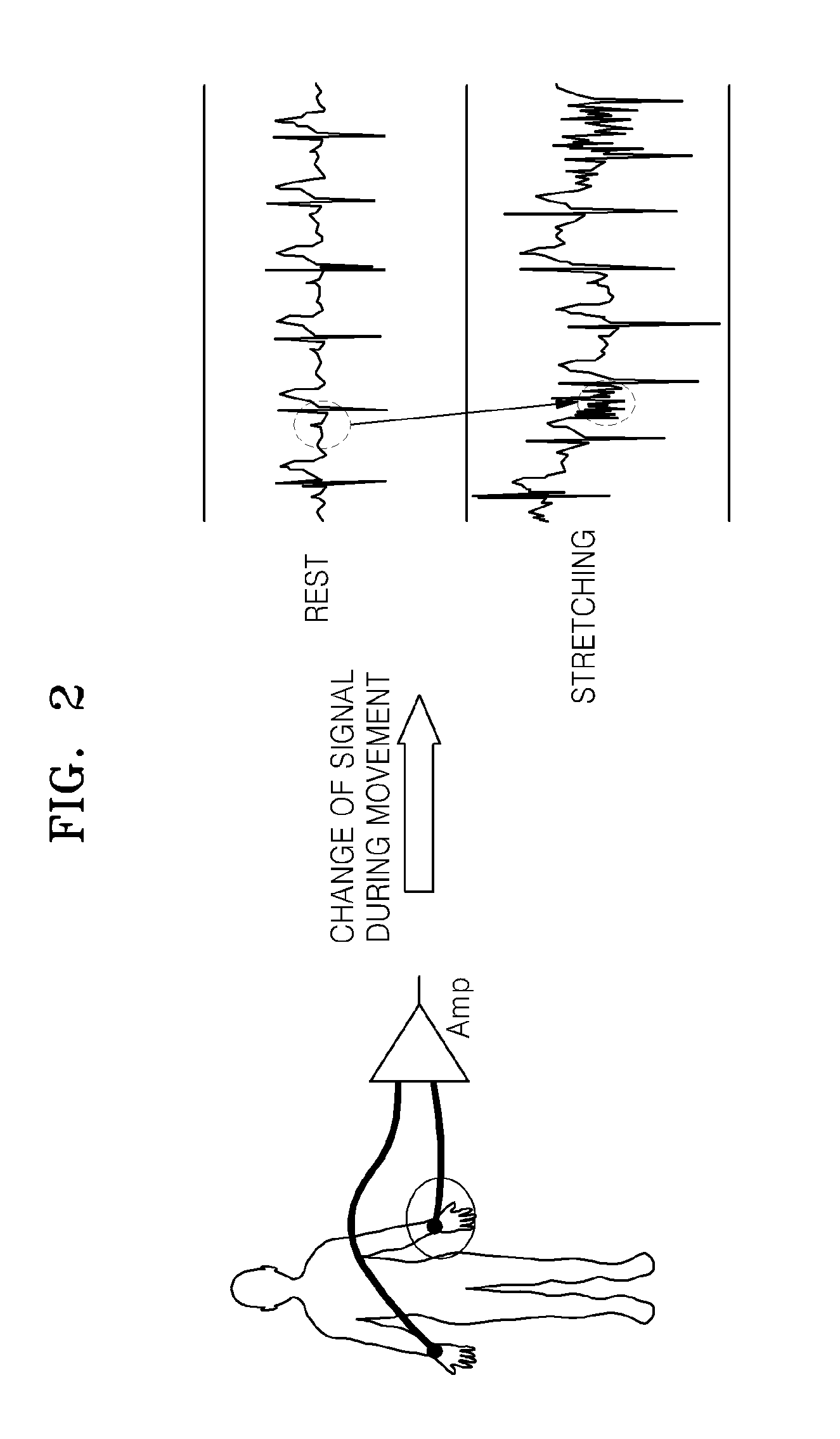
Motion artifacts less electrode for bio-potential measurements and electrical stimulation, and motion artifacts less skin surface attachable sensor nodes and cable system for physiological information measurement and electrical stimulation
InactiveUS20090227965A1Reduce Motion ArtifactsImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectrocardiographyElectromyographyNODALEngineering
Motion artifacts less electrode for bio-potential measurements and electrical stimulation is discussed under the present invention. Three different arrangements of the electrode are introduced. Further the electrode embodiments are generalized for reducing motion artifacts of any skin contact senor or an actuator embodiment. In addition a piggy backed daisy chained sensor nodes or actuator nodes cabling system is introduced to minimize the motion artifacts further. A PPG sensor is constructed according to the generalized sensor embodiment and this PPG sensor is used for constructing an ear wearable heart rate monitoring unit. Moreover an ear wearable EEG monitoring system based on piggy backed daisy chained sensor or actuator nodes and caballing arrangement is illustrated.
Owner:WIJESIRIWARDANA RAVINDRA
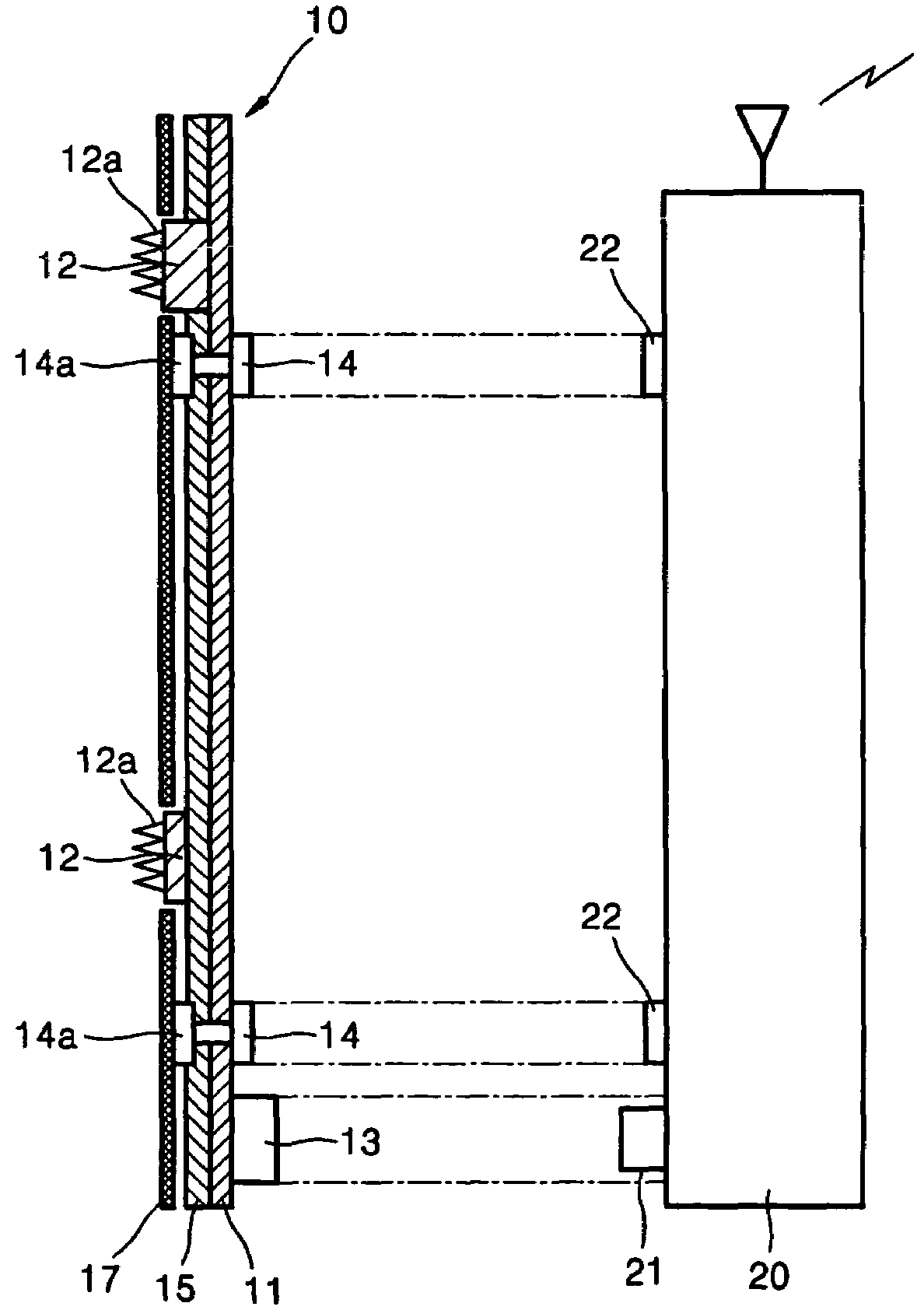
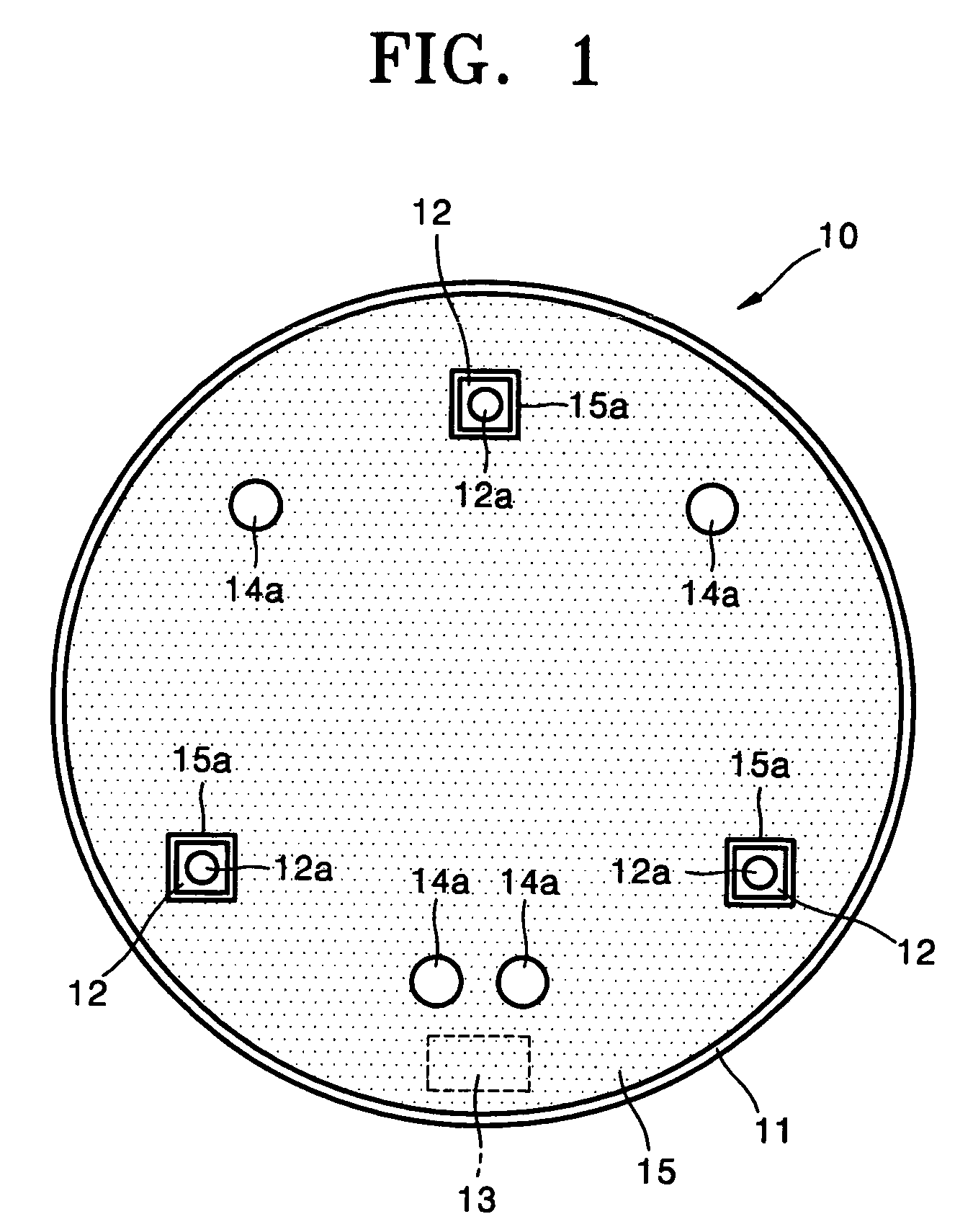
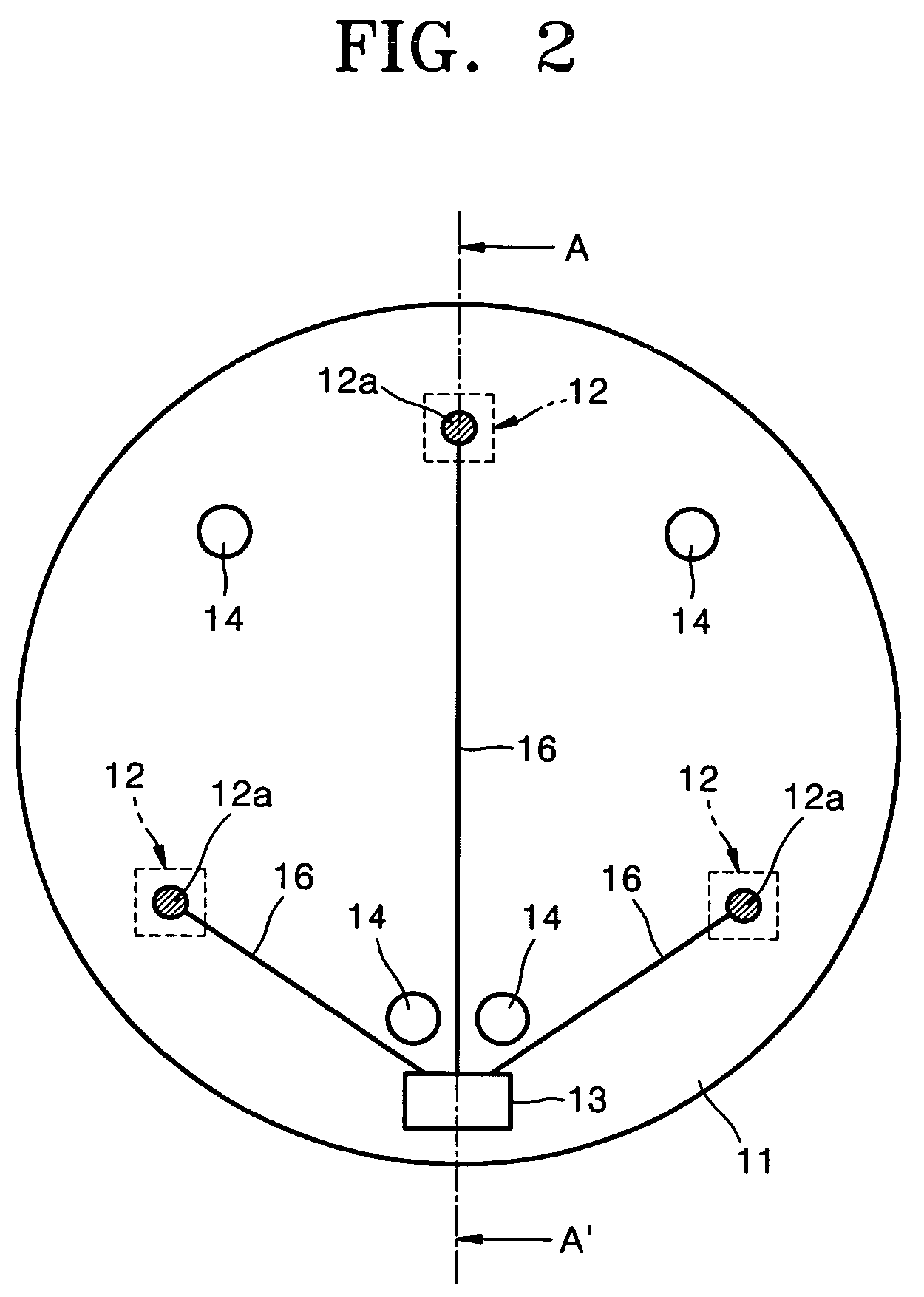
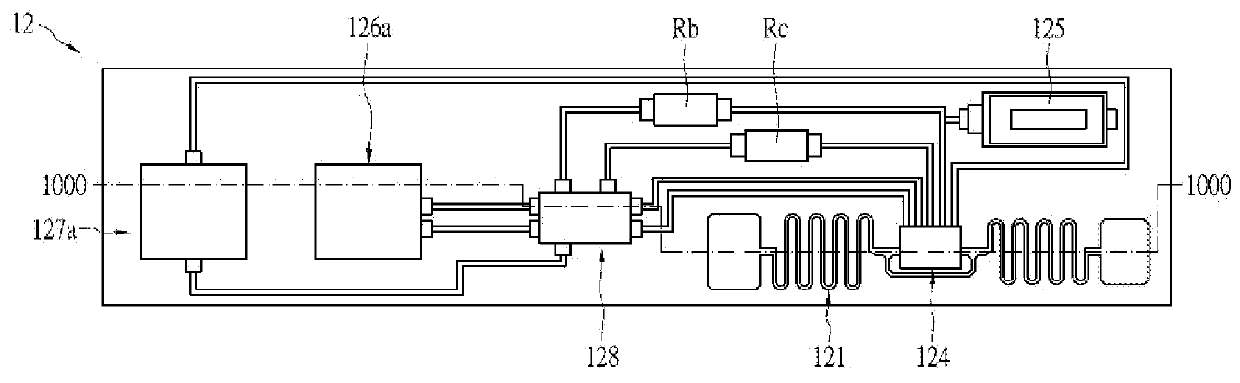
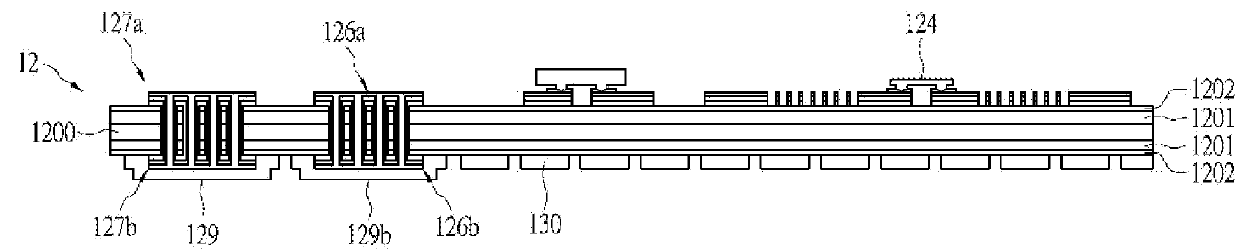
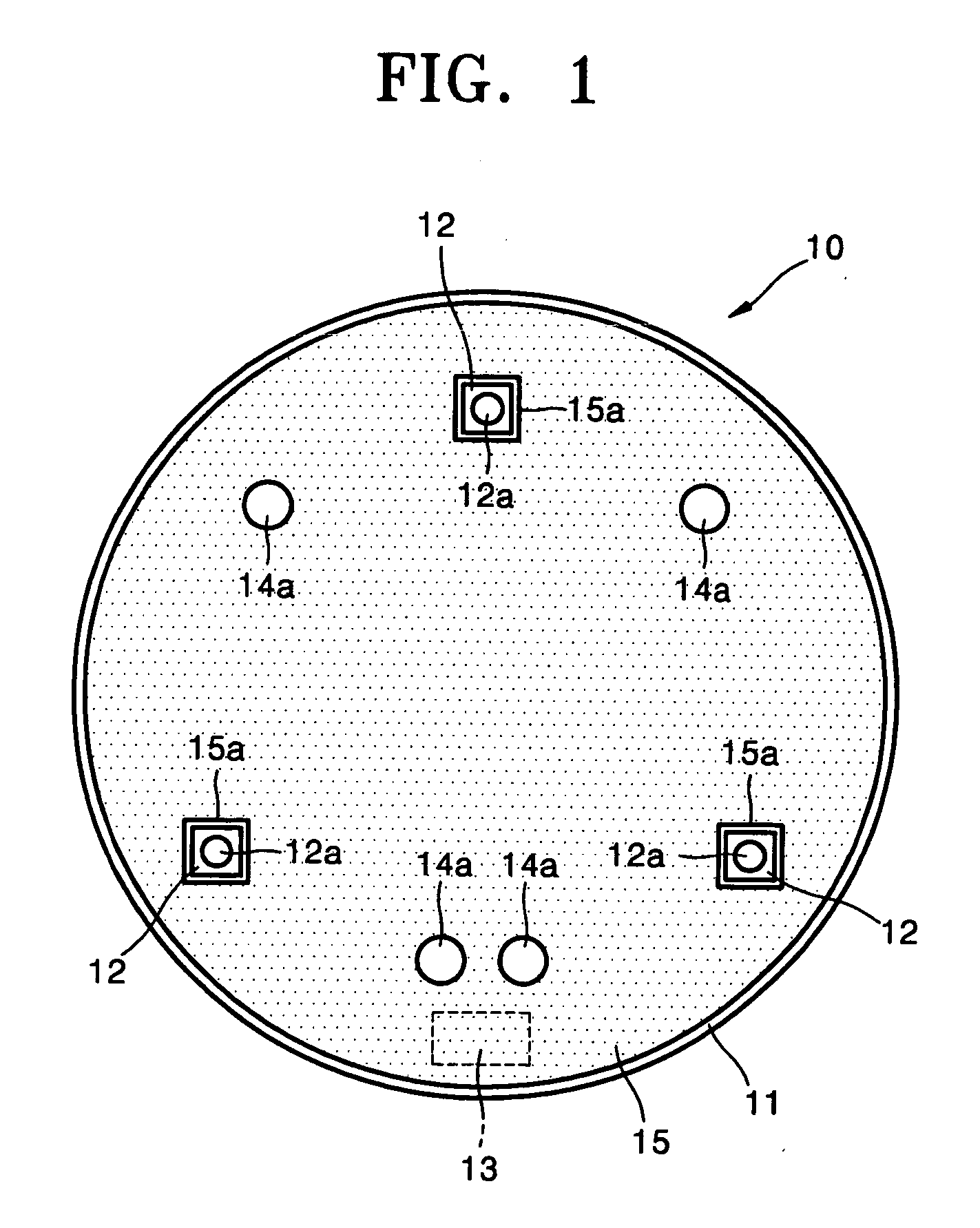
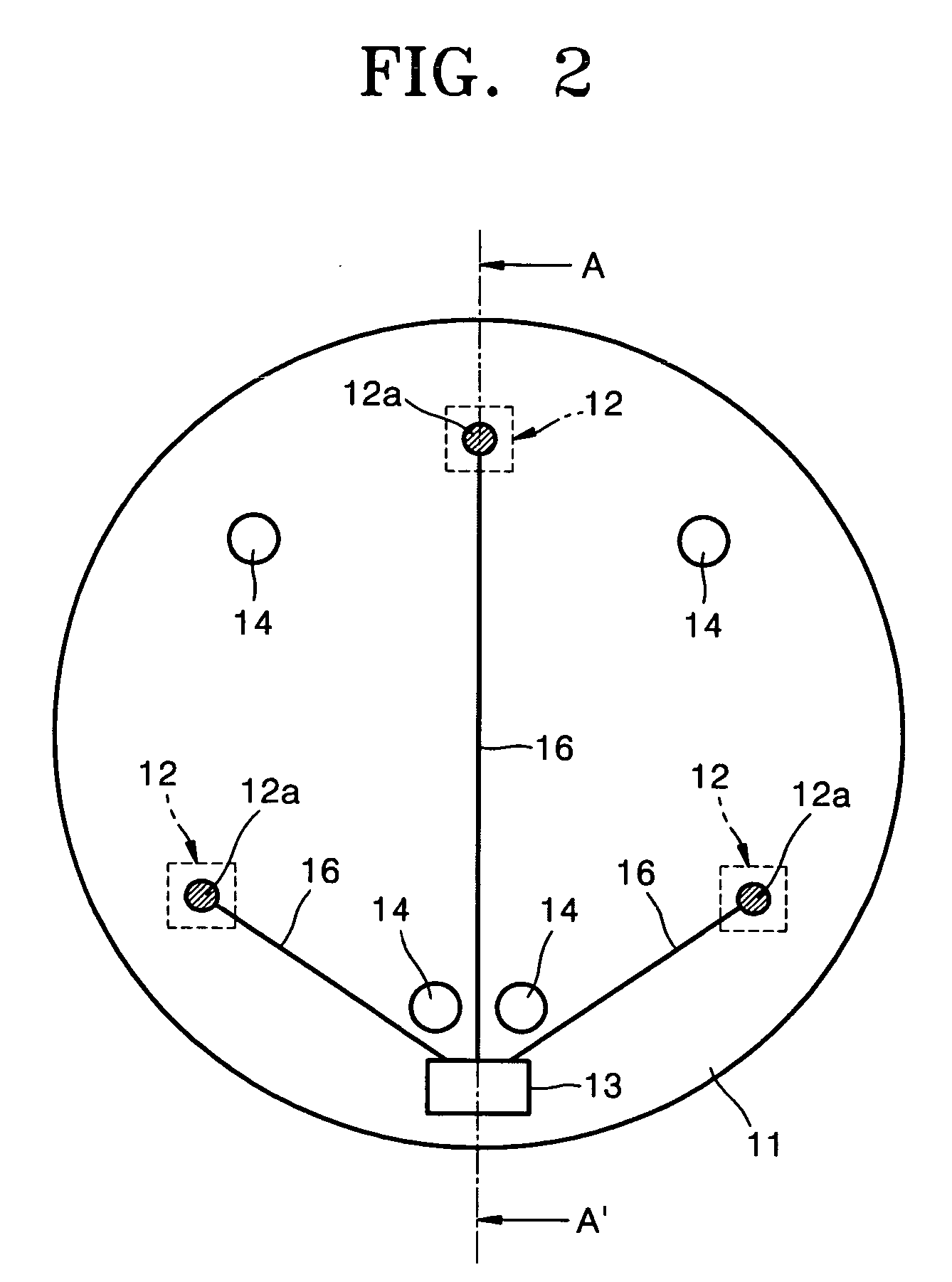
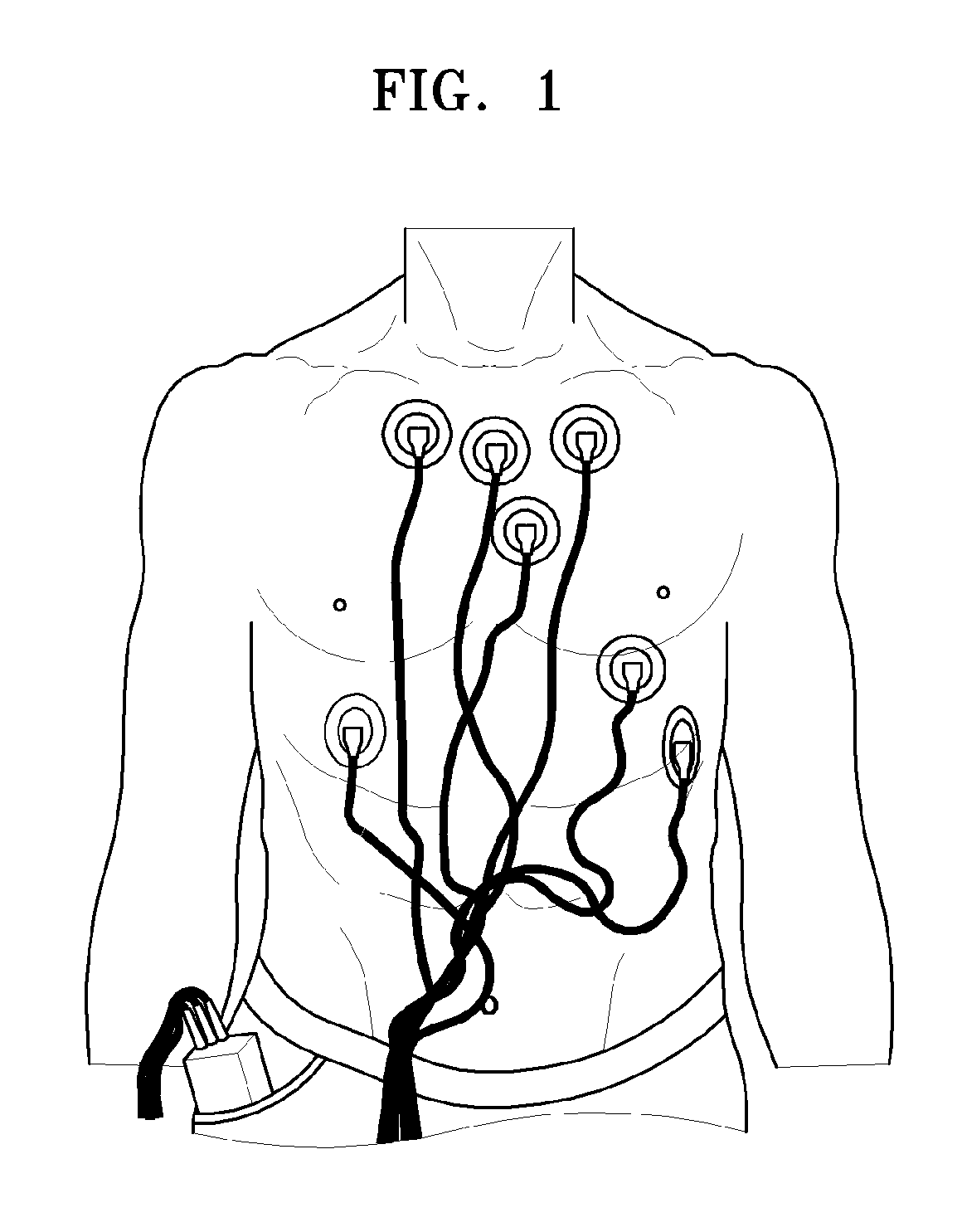
Body surface bio-potential sensor having multiple electrodes and apparatus including the same
In a body surface bio-potential sensor, and an apparatus for detecting biomedical signals having the same, the body surface bio-potential sensor includes a flexible membrane having a wire layer, a plurality of electrodes attached on a first surface of the membrane at predetermined intervals, each of the plurality of electrodes having a plurality of needles on a surface thereof, each of the plurality of needles having a predetermined height, and a cohesive layer covering the first surface of the membrane, the cohesive layer exposing regions of the flexible membrane corresponding to positions of the plurality of electrodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrode array
Owner:BRAINSCOPE SPV LLC
Programmable wireless electrode system for medical monitoring
InactiveUS20060058017A1Consider flexibilityElectrocardiographyNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless transceiverTransceiver
Owner:LIFESYNC
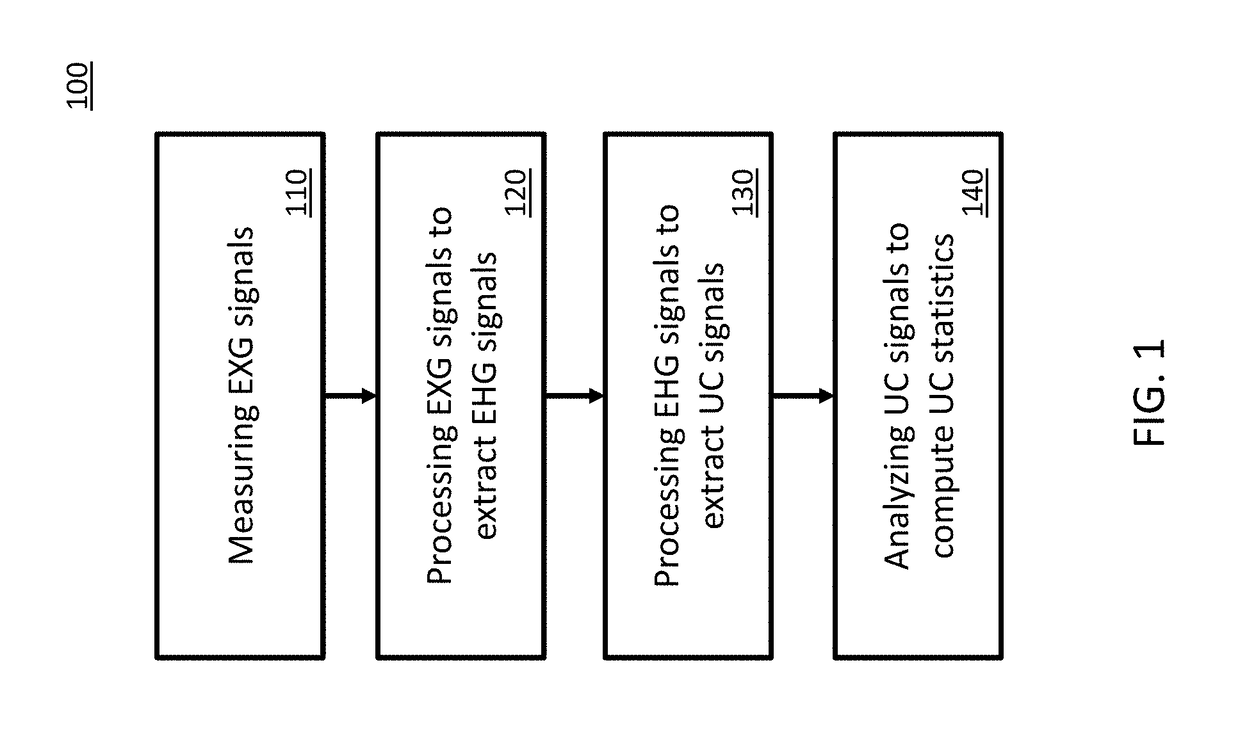
A method and device for contraction monitoring
ActiveUS20180296156A1High sensitivityLower levelElectrocardiographySensorsComputer moduleData transmission
Described herein are systems and methods for contraction monitoring. For example, a system for contraction monitoring includes an electrode patch including at least two electrodes, and a sensor module configured to be connected to the electrode patch. In some embodiments, the sensor module includes a signal acquisition module, a signal processing module, a power management module, a sensor control module, and a memory module and / or a data transmission module. In some embodiments, a method for contraction monitoring includes measuring, using the signal acquisition module, bio-potential signals by providing at least two electrodes on the abdomen of a pregnant woman. In some embodiments, a method for contraction monitoring includes processing, using the signal processing module, the bio-potential signal to extract electrohysterogram signals, maternal electrocardiogram signals and fetus electrocardiogram signals, and processing using the signal processing module, the individual signals to extract uterine contraction.
Owner:BLOOM TECH NV
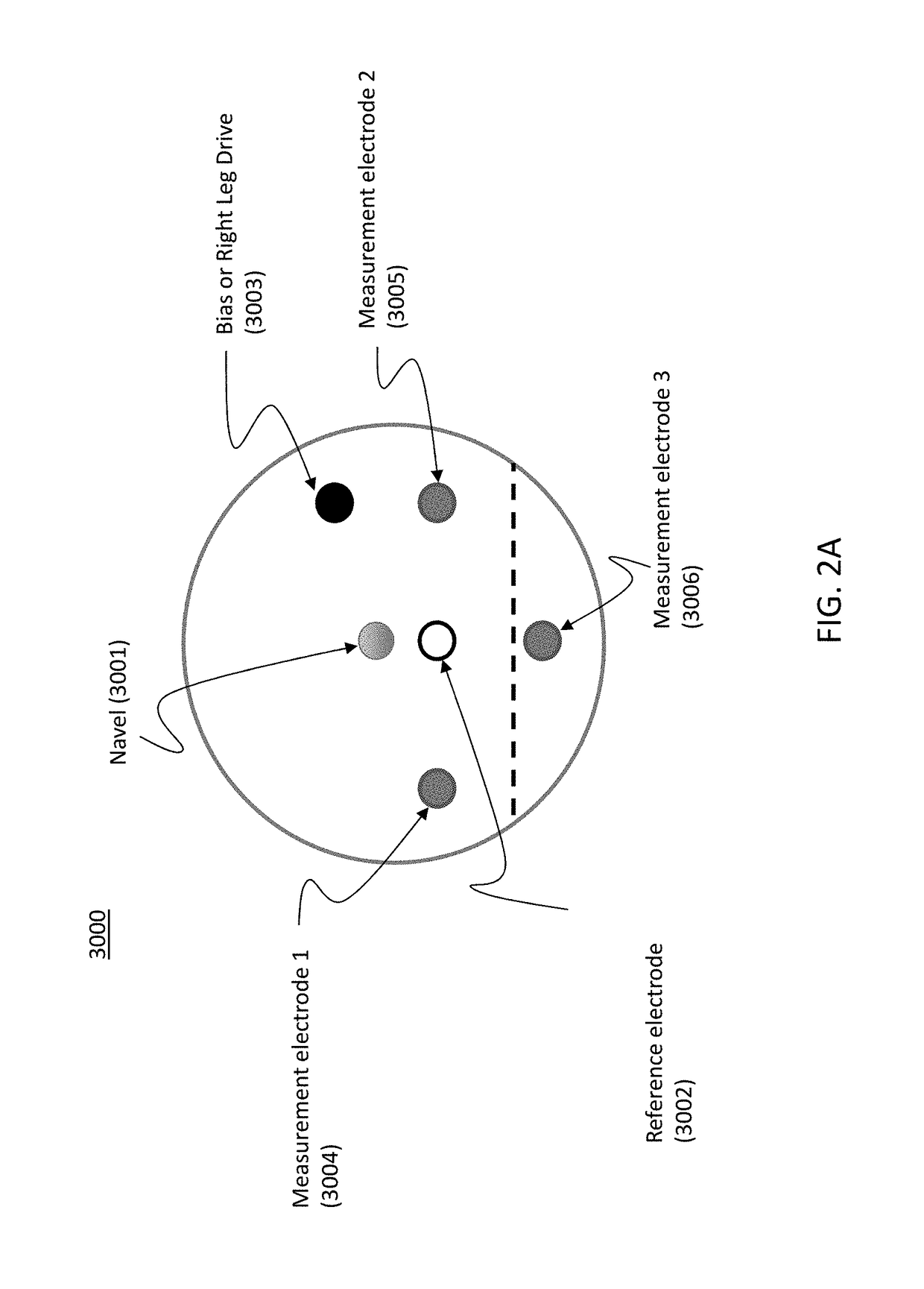
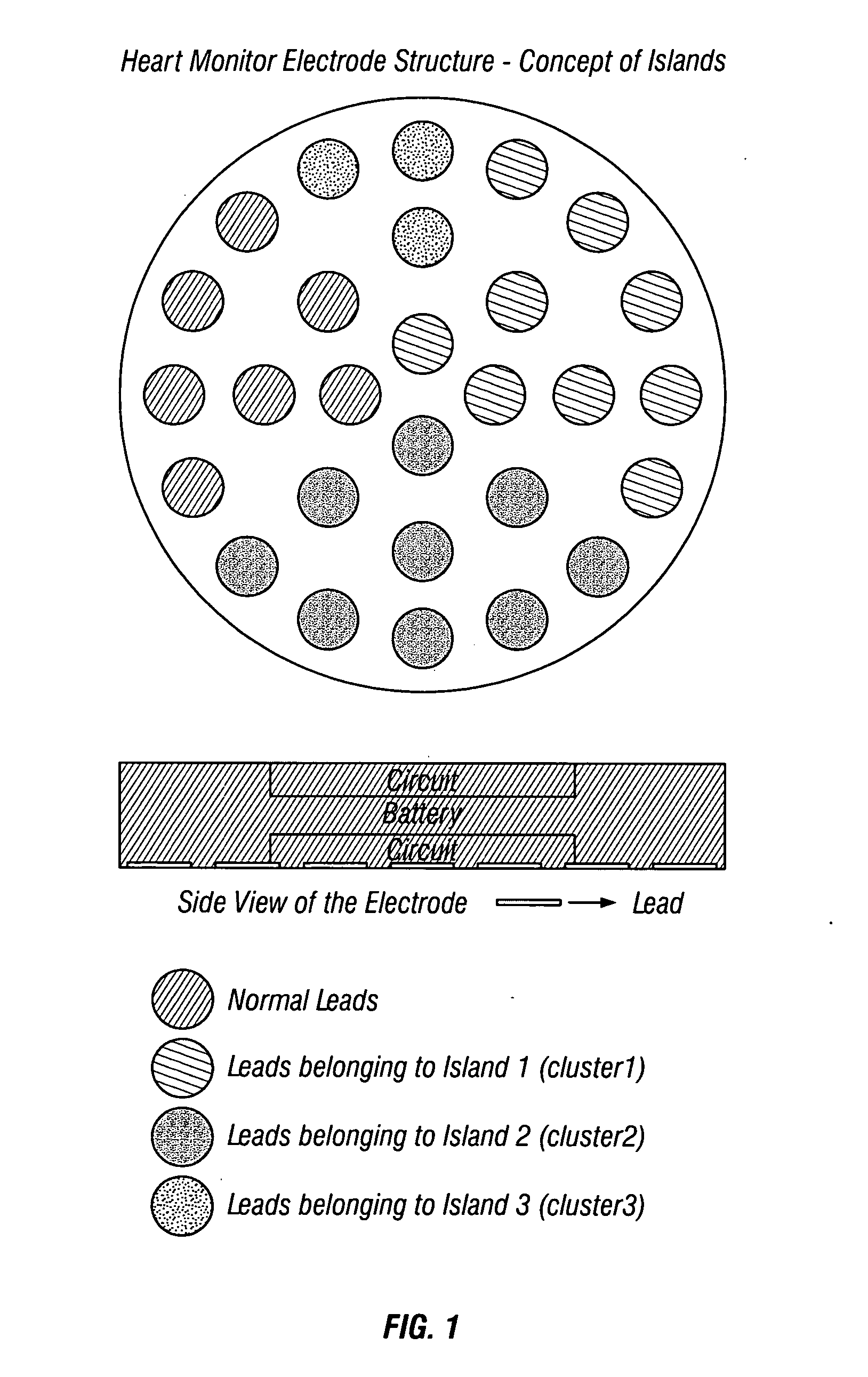
Heart monitor electrode system
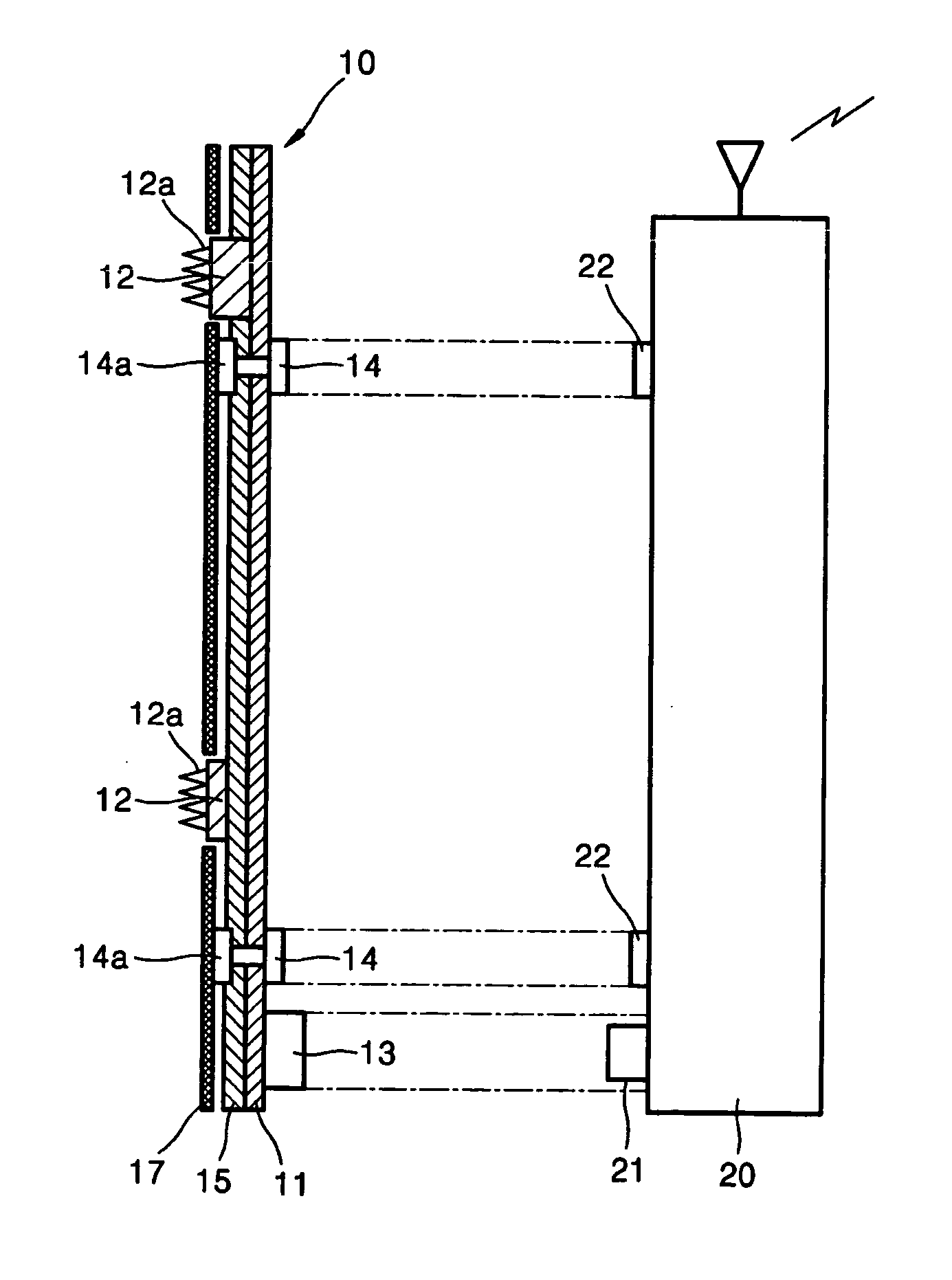
A bioelectric interface for monitoring, detection and transmission of detected ECG data is provided comprising a sensory system for detecting bio-physiological measurements utilizing spatially resolved potential profiles obtained from a localized cluster of sub-electrodes to form constituent sets of miniature sensor arrays. Using only a single macro-electrode, two or more sets of sub-electrode arrays are used to measure bipolar spatial gradients obtained from measured cardiac potentials. The sets of sub-electrodes containing the clusters are optimized to attain measurable gradients of diagnostic value. A minimax procedure allows bio-potential sensory acquisition through a bi-directional digital steering process, which essentially comprises monitoring, detection, selection, grouping, recording and transmission of ECG waveform characteristic data.
Owner:GLOBAL CARDIAC MONITORS
Interface apparatus for manipulating wheelchair and wheelchair using the same
InactiveUS20110168478A1Improve securityWheelchairs/patient conveyanceOptical signallingHand graspWheelchair
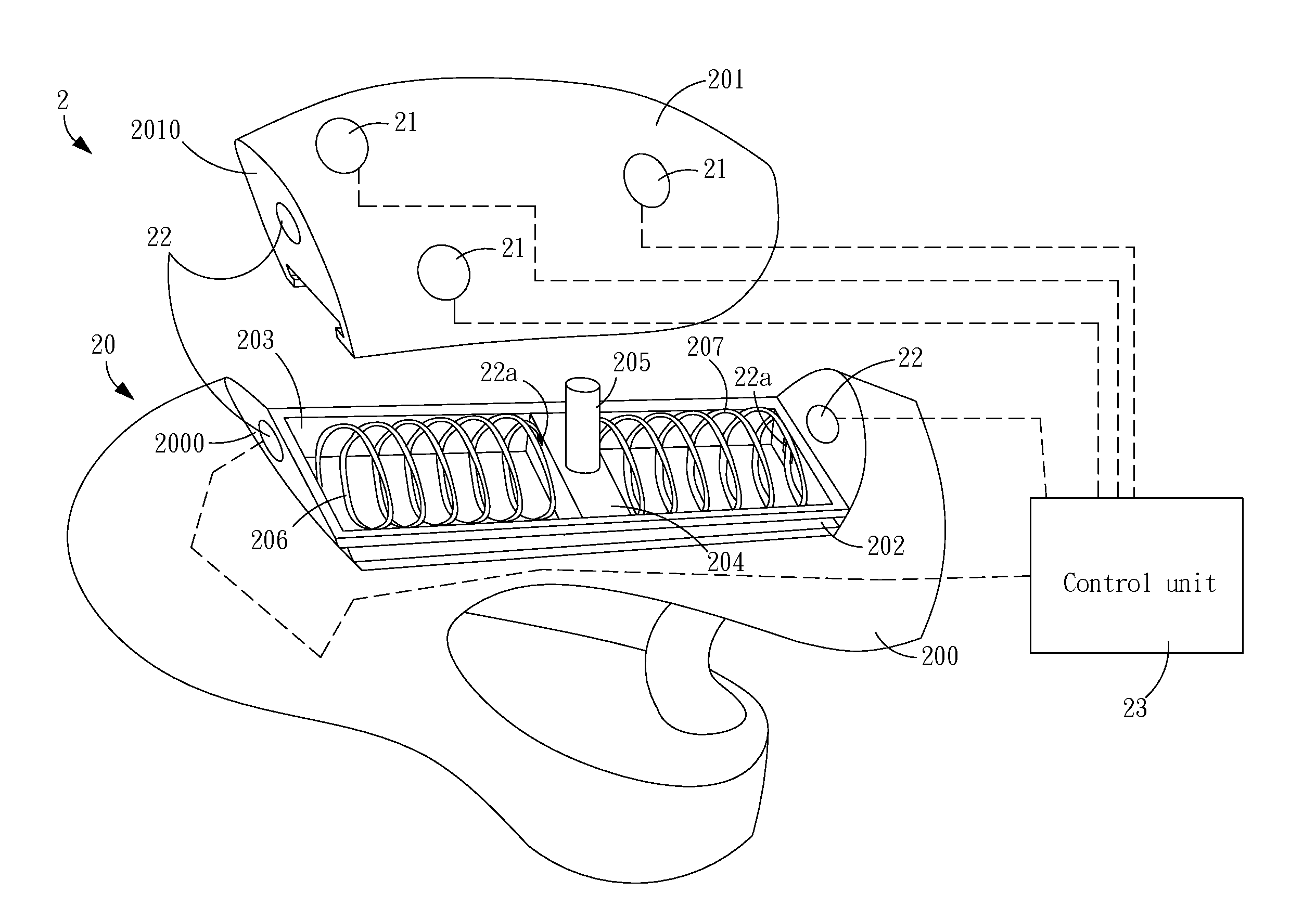
The present invention provides an interface apparatus for manipulating a wheelchair which is capable of controlling the translation / rotation of the wheelchair by means of a pair of sliding mechanisms. In addition, there is at least one physiological sensor being disposed on each sliding mechanism for detecting physiological status of a user sitting on the wheelchair so as to monitor the bio-status of the user via a closed bio-potential circuit. The pair of sliding mechanisms are disposed respectively on their corresponding arm rest of the wheelchair so that the user can manipulating the wheelchair by two hands grasping the corresponding sliding mechanism while the physiological sensor can detect the physiological status of the user. With the aforesaid apparatus and wheelchair, it not only can provide a directly operating way with human-factor concerns but can also monitor the physiological status of the user so as to improve the safety in manipulation.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
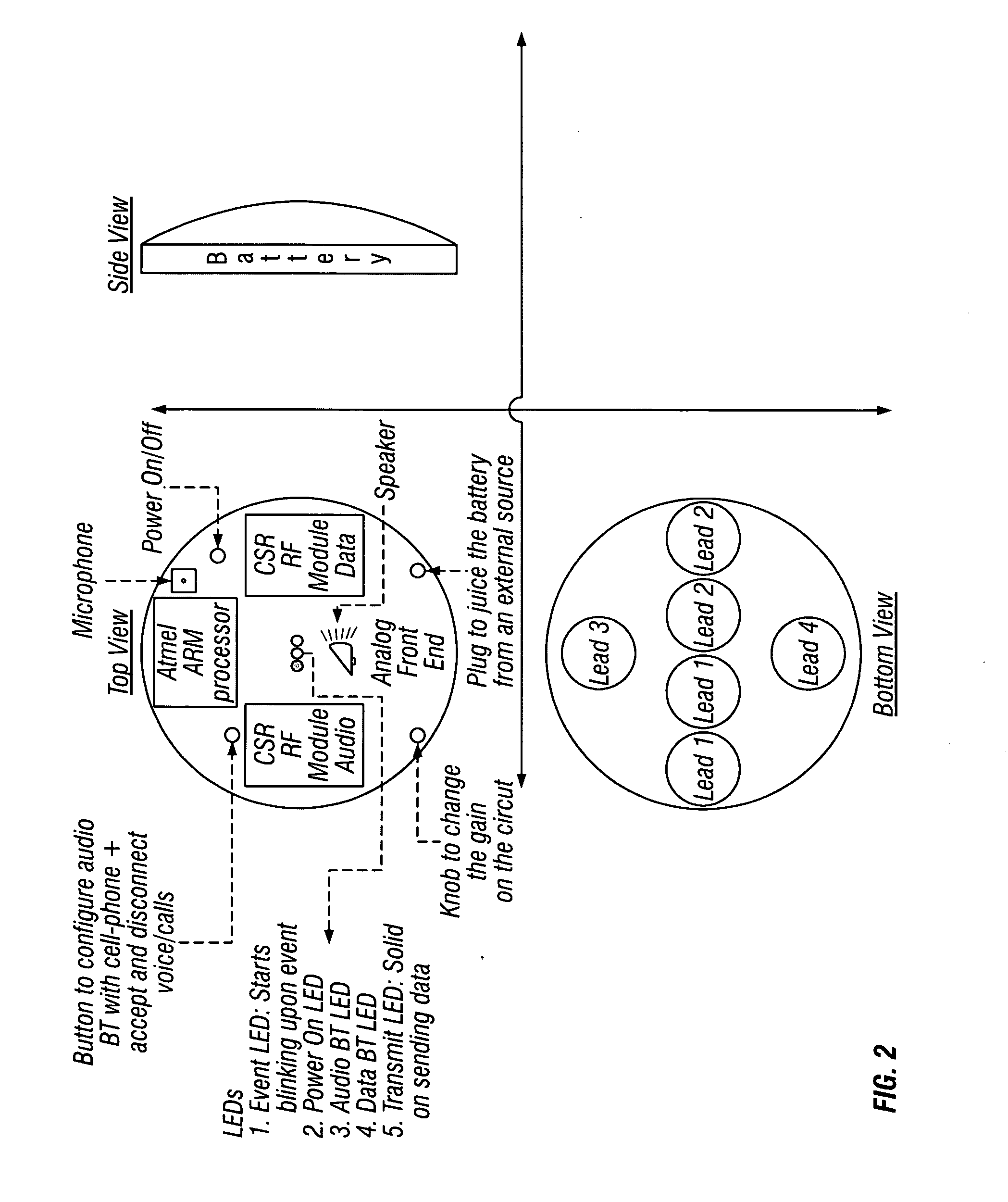
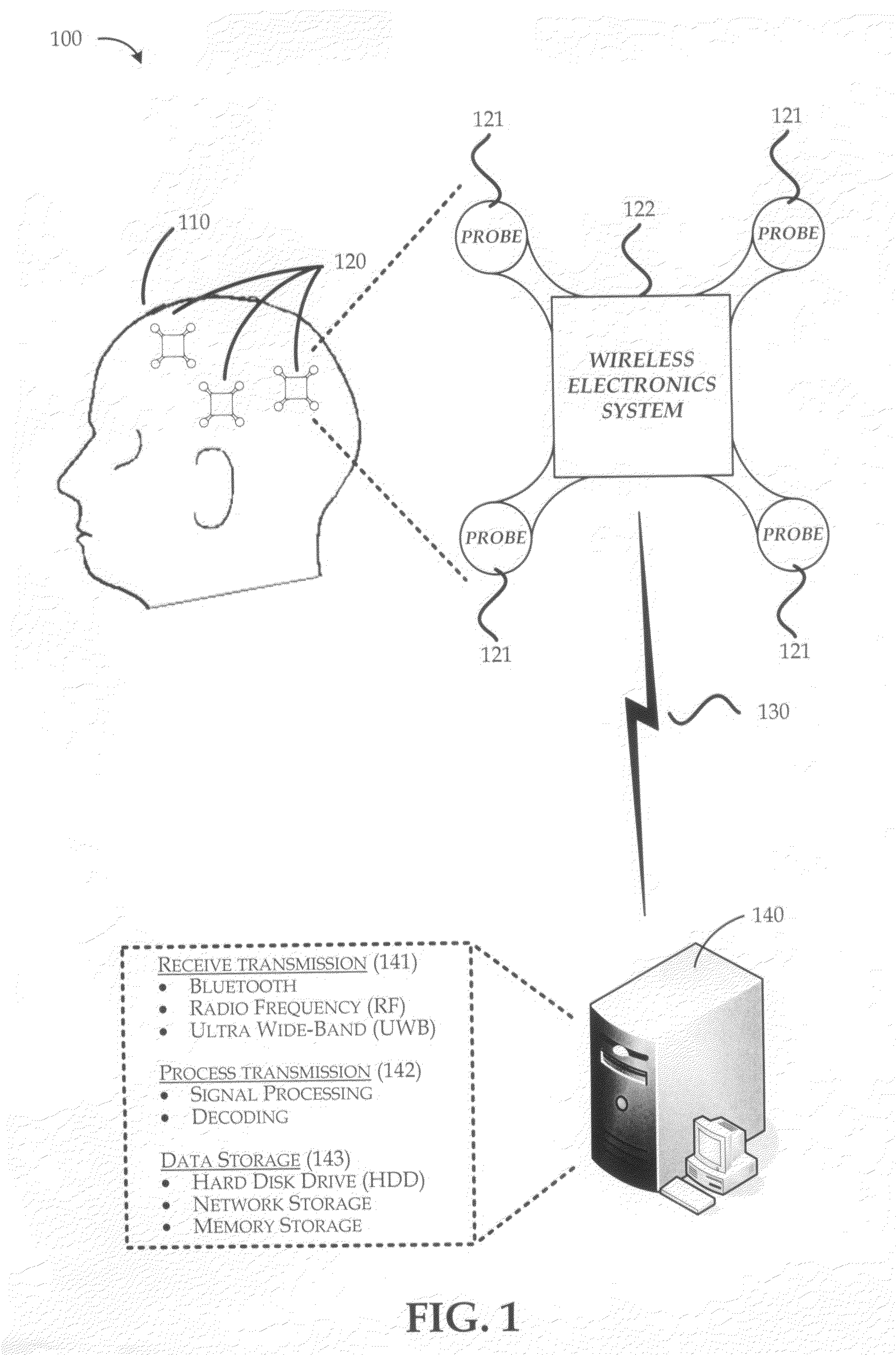
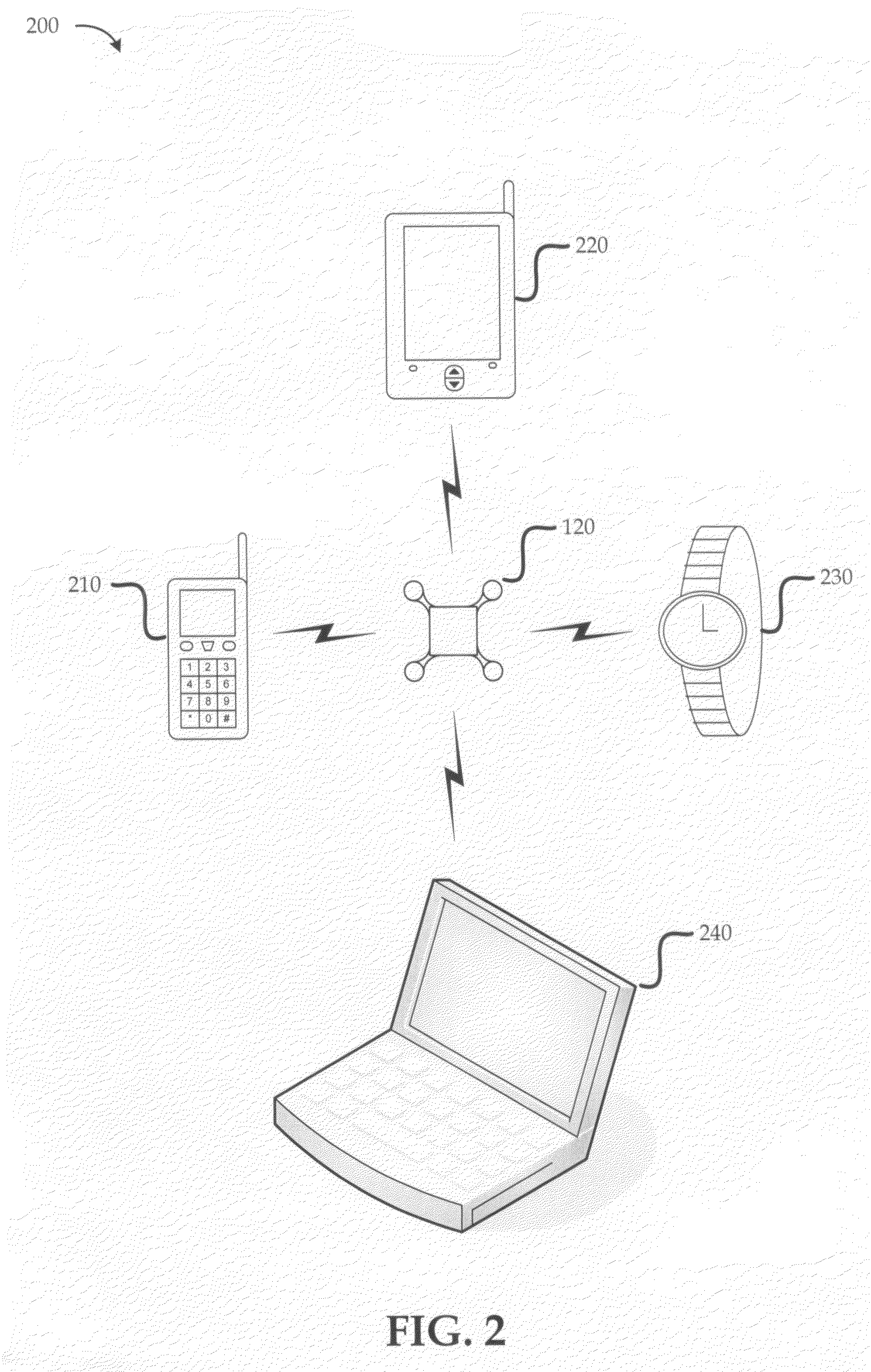
Wireless body sensor with small size background
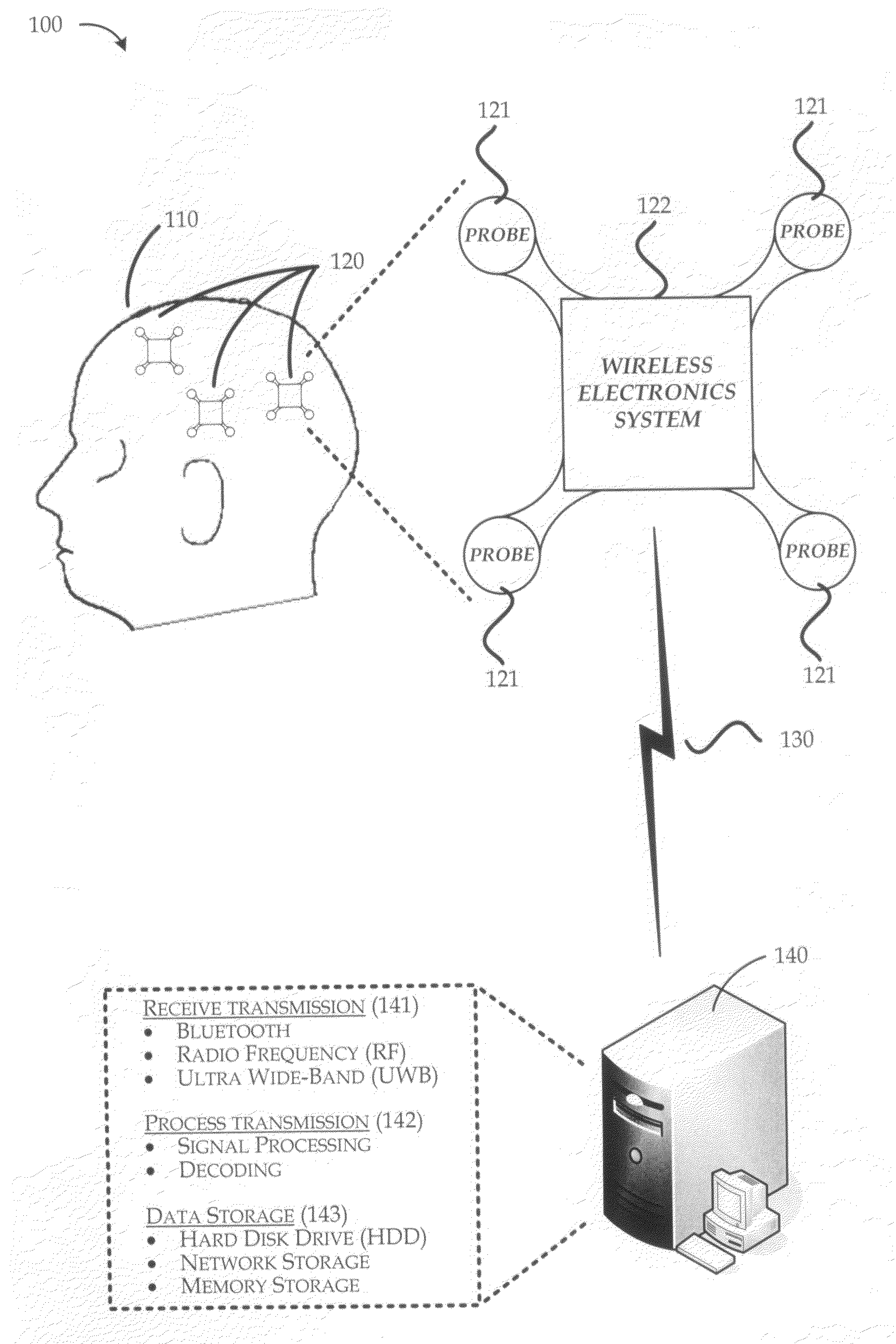
InactiveUS20080208008A1Reduce interferenceReduce noiseElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyDigital signal processingEngineering
A wireless body sensor device includes a number of small probes that are arranged about a wireless electronics system. The wireless electronics system can process bio-potential signals from the probes and communicate bio-potential data to another device such as a wireless telephone, wrist watch, personal data assistant (PDA), laptop computer or any other appropriate device. By forming the probes within a confined short range of the wireless electronics system, interference and noise is greatly reduced. The wireless electronics system includes signal amplifiers that increase the signal levels associated with the bio-potential probes so that the signals can be converted to bio-potential data through an analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) process. Once the bio-potential data is in digital form, the data can be processed by a digital signal processor (DSP), encoded into a signal transmission, and communicated to another device with a radio system and its corresponding antenna.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for a gesture controlled interface for wearable devices
PendingCN107589782AInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPostural controlNerve conduction
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for a gesture controlled interface for wearable devices. The gesture-controlled interface apparatus includes one or a plurality of bio-potential sensorsand a processor. The one or a plurality of bio-potential sensors are wearable on a body of a user, for detecting one or a plurality of bio-electrical signals from the body of the user, wherein the oneor a plurality of bio-potential sensors include at least one surface nerve conduction (SNC) sensor for detecting at least one surface nerve conduction signal. The processor is configured to compare the detected at least one surface nerve conduction signal with data of a plurality of reference signals corresponding to a plurality of known gestures, each of the reference signals distinctly associated with one of the known gestures, to identify a known gesture from the plurality of known gestures that corresponds to said at least one surface nerve conduction signal, and to communicate the identified known gesture to a computerized device.
Owner:可穿戴设备有限公司
Bio-potential sensing materials as dry electrodes and devices
ActiveUS9980659B2Lower resistanceFacilitate conductionBioelectric signal measurementNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialBio potentialPotentiometric sensor
This invention is directed to materials and devices for sensing bio-potential signals from animals, particularly to sensing bio-potential signals to monitor humans in the medical field. In general, bio-potential sensors may be attached to the body of an animal, such as a human, in order to receive bio-potential signals such that information about the bioelectrical properties of the cells and / or tissues of the animal may be gathered. The bio-potential sensor may generally include a dry electrode that may be placed in contact with the skin of an animal to receive bio-potential signals from the animal. A dry electrode may generally include an electrically conductive solid material which may conduct electrical signals from an animal.
Owner:NEUROREX
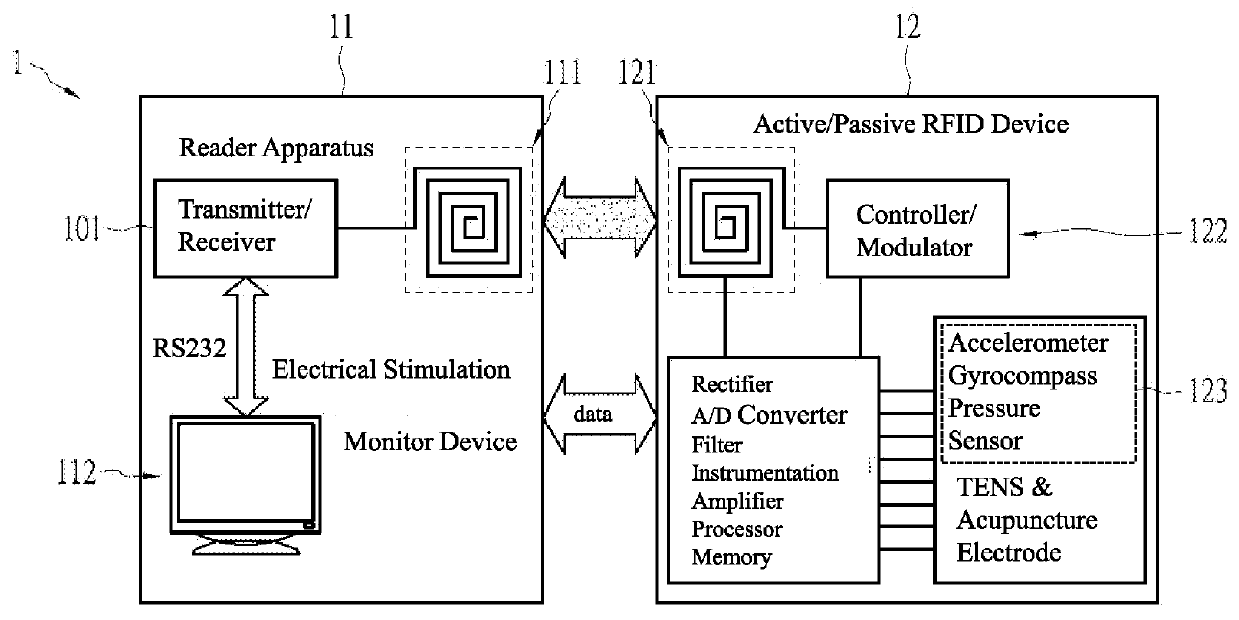
Method for biomedical system
A method used for a biomedical system is disclosed. The biomedical system includes an RFID apparatus and a reader apparatus communicating with the RFID apparatus. The RFID apparatus includes an electrode disposed adjacent to an acupuncture point and a motion monitor device including an accelerometer, a gyrocompass, or a pressure sensor. The method includes sending command information to the RFID apparatus from the reader apparatus; obtaining acupuncture impedance or bio-potential data through an electrode; providing nerve stimulation therapy by the RFID apparatus according to the command information, or using, by the RFID apparatus, the accelerometer, the gyrocompass, or the pressure sensor to obtain measurement data according to the command information; and submitting the acupuncture impedance / bio-potential data or the measurement data to the reader apparatus by the RFID apparatus.
Owner:CHUNG HUA UNIVERSITY
Bio-Potential Activation of Artificial Muscles
The invention relates to the general field of electrical activation of non-biological artificial muscles, such as ionic polymeric synthetic artificial muscles, by means of action potentials produced by a biological nerve, such as mammalian sciatic nerve. This invention demonstrates how to stimulate and activate a non-biological muscle such as an ionic polymeric metal composite (IPMC) electro-active artificial muscle with the biological action potential generated by a mammalian nerve such as a rat sciatic nerve. The said invention further presents settings to generate optimal movement and force in artificial muscle due to the application of a nerve action potential. The invention uses the sciatic nerve to generate an action potential, which is subsequently amplified and applied to a cantilever sample of an electro-active ionic polymeric artificial muscle to cause it to bend, flex, and twitch. The sciatic nerve, in this invention, is stimulated by a separate signal to cause it to generate an action potential in the range of hundreds of μV, which is recorded by the electrodes attached to the nerve. These electrodes carry the action potential to an amplifier to amplify it to between 10's of Volts and subsequently are attached to the ionic polymeric artificial muscle to cause it to flex and twitch. Different frequencies of stimulation are tried to optimize the motion and force generated by the polymeric artificial muscles.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN
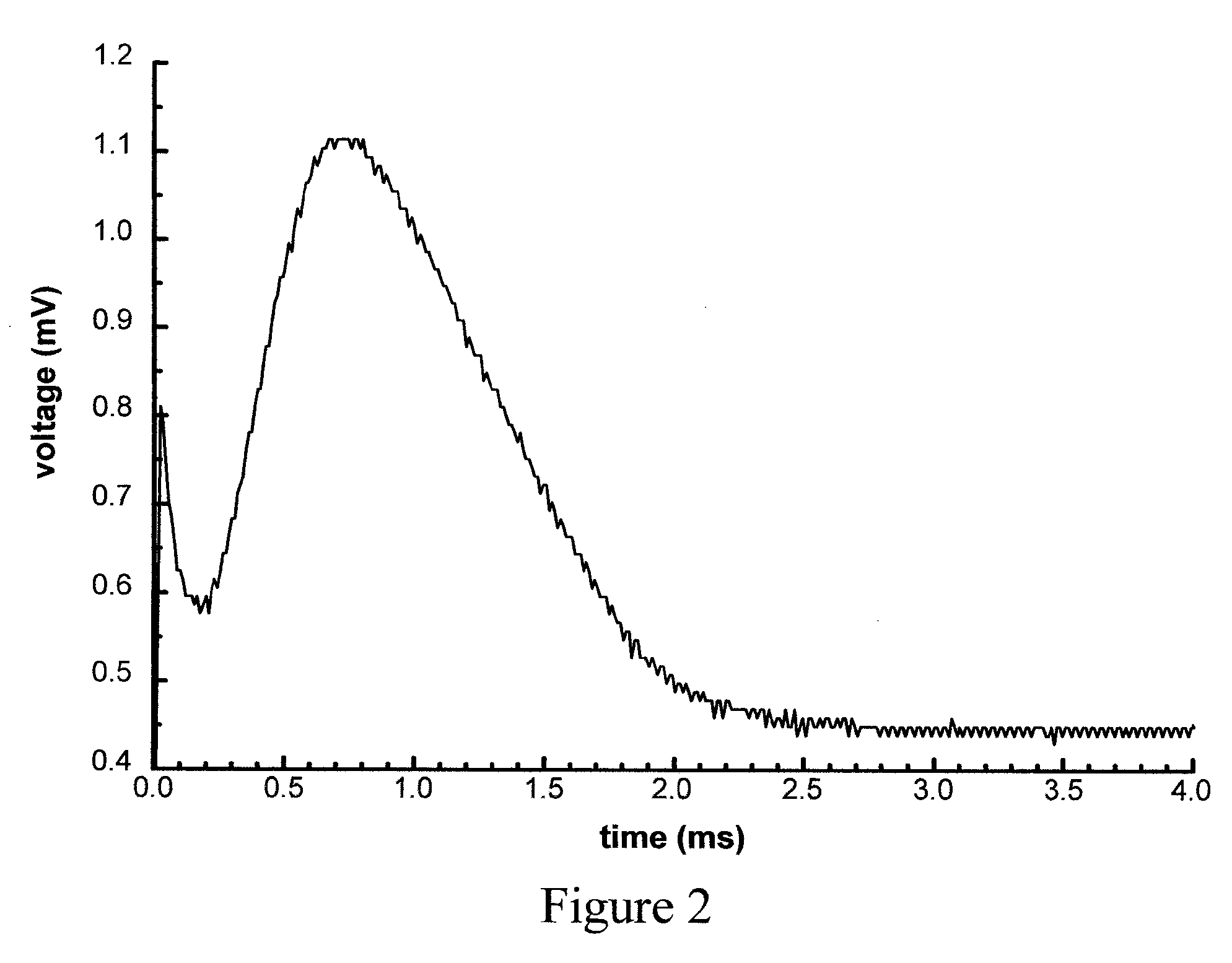
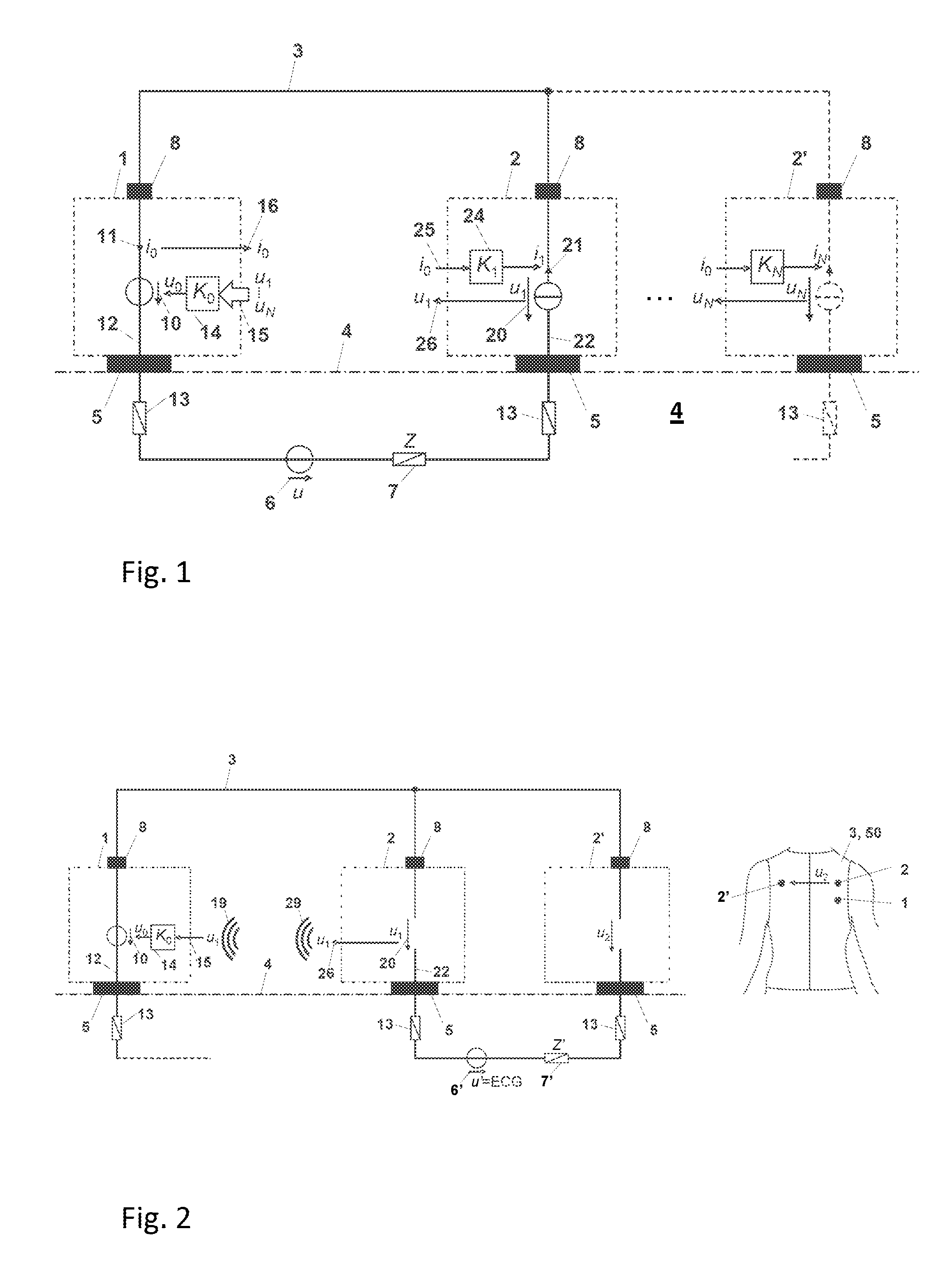
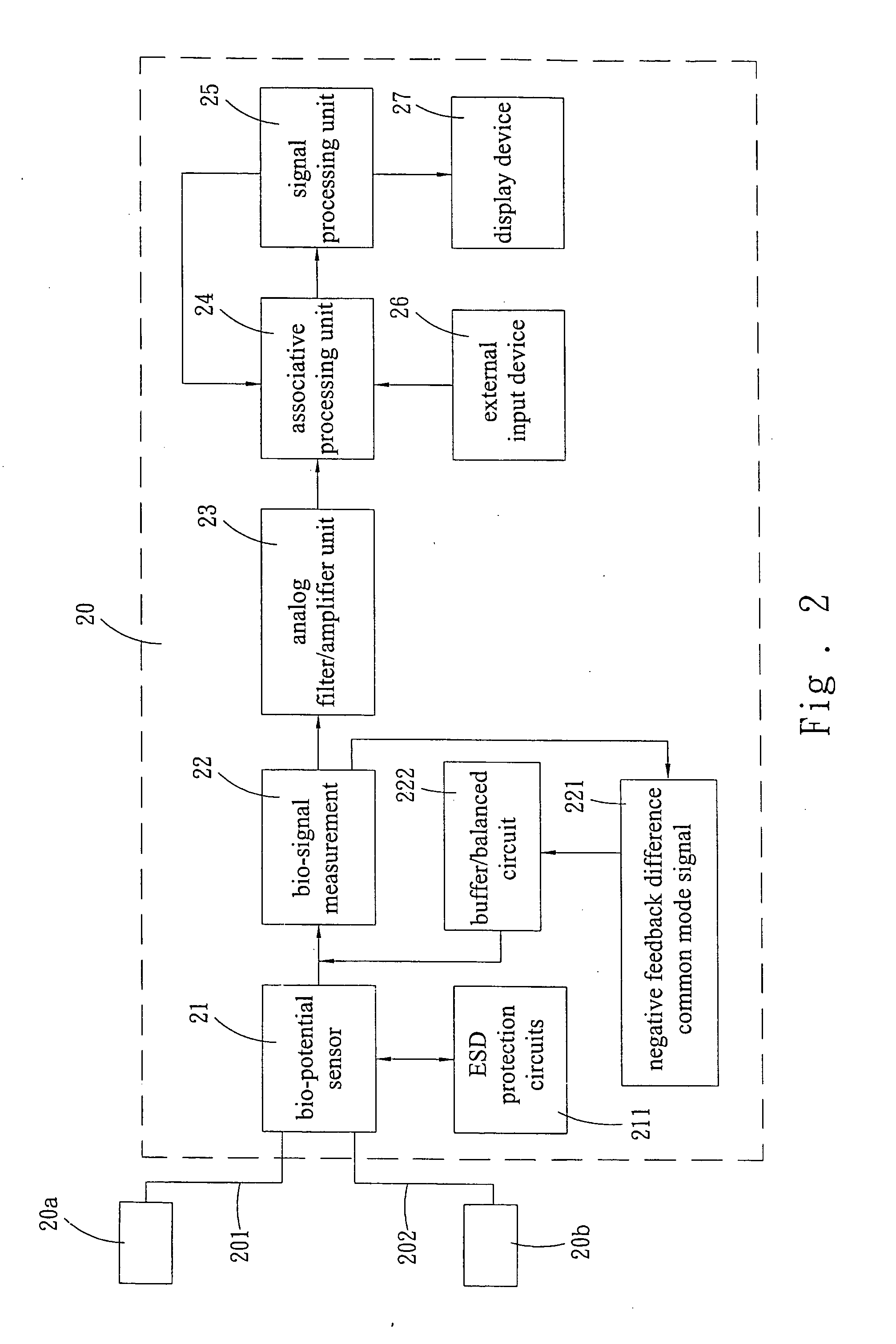
Contact type pulse measurement device
The present invention discloses a contact type of pulse measurement device, which comprises a first active sensor electrode and a second active sensor electrode having corresponding opposite polarities with each other; and the two active sensor electrodes respectively connected to the pulse measurement device by conductive wires and the pulse measurement device comprises a negative feedback difference common mode signal and a buffer / balanced circuit for providing a circuit with a self common point electrode potential. Therefore, the first bio-potential signal can be detected by means of the first active sensor electrode and the common point electrode. Similarly, a second bio-potential signal having the same magnitude but a different phase as the first bio-potential signal can be detected by the second active sensor electrode and the common point electrode.
Owner:BOSON TECH
Apparatus for evoking and recording bio-potentials
Owner:EVEREST BIOMEDICAL INSTR
Body surface bio-potential sensor having multiple electrodes and apparatus including the same
ActiveUS20050154273A1Overcome problemsElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyEngineeringBio potential
In a body surface bio-potential sensor, and an apparatus for detecting biomedical signals having the same, the body surface bio-potential sensor includes a flexible membrane having a wire layer, a plurality of electrodes attached on a first surface of the membrane at predetermined intervals, each of the plurality of electrodes having a plurality of needles on a surface thereof, each of the plurality of needles having a predetermined height, and a cohesive layer covering the first surface of the membrane, the cohesive layer exposing regions of the flexible membrane corresponding to positions of the plurality of electrodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrode for measuring bio potential, method of manufacturing the electrode, and system for measuring physiological signal
ActiveUS20130204110A1Reduce signal to noise ratioReduce skin irritationElectroencephalographyContact member manufacturingBiological bodyAdhesive
An electrode for measuring a bio potential includes a conductive adhesive having one side configured to have at least two metal electrodes attached thereto while the electrode is being used, and another side configured to be attached to a living body while the electrode is being used, the conductive adhesive having a predetermined area and a predetermined thickness; and a supporting element configured to support the conductive adhesive while the conductive adhesive is attached to the living body; wherein an impedance is formed between the at least two metal electrodes while the at least two metal electrodes are attached to the side of the conductive adhesive, the impedance depending on a thickness of the conductive adhesive and having a value that prevents the at least two metal electrodes from being shorted together.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrode for measuring bio potential, method of manufacturing the electrode, and system for measuring physiological signal
ActiveUS9144387B2Reduce signal to noise ratioReduce skin irritationElectroencephalographyContact member manufacturingAdhesiveMetal electrodes
An electrode for measuring a bio potential includes a conductive adhesive having one side configured to have at least two metal electrodes attached thereto while the electrode is being used, and another side configured to be attached to a living body while the electrode is being used, the conductive adhesive having a predetermined area and a predetermined thickness; and a supporting element configured to support the conductive adhesive while the conductive adhesive is attached to the living body; wherein an impedance is formed between the at least two metal electrodes while the at least two metal electrodes are attached to the side of the conductive adhesive, the impedance depending on a thickness of the conductive adhesive and having a value that prevents the at least two metal electrodes from being shorted together.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
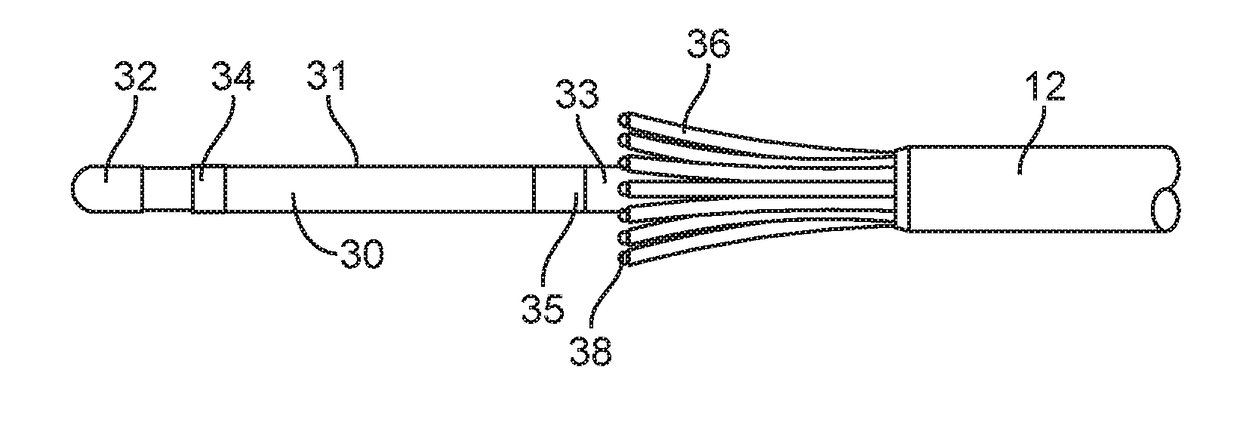
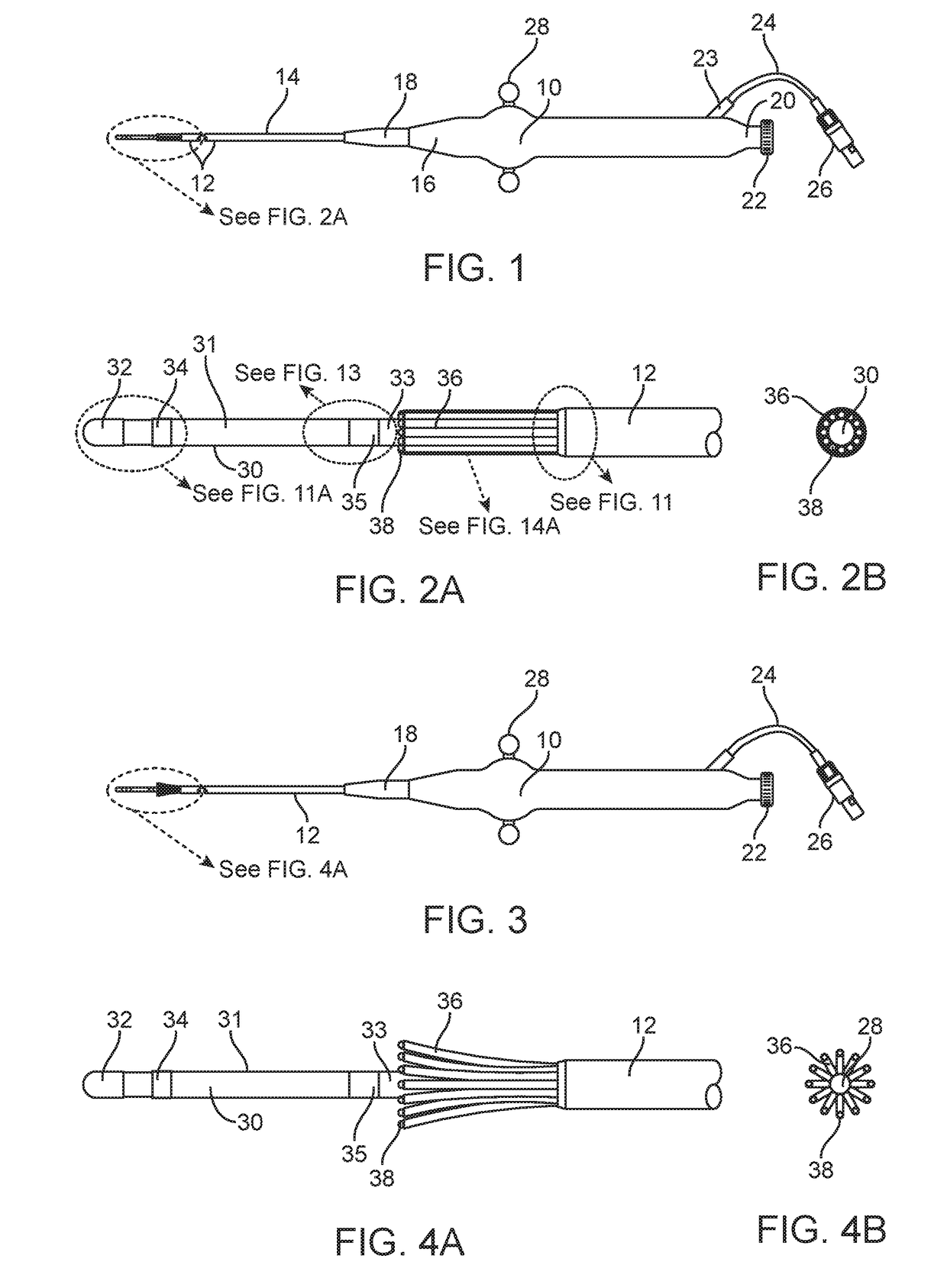
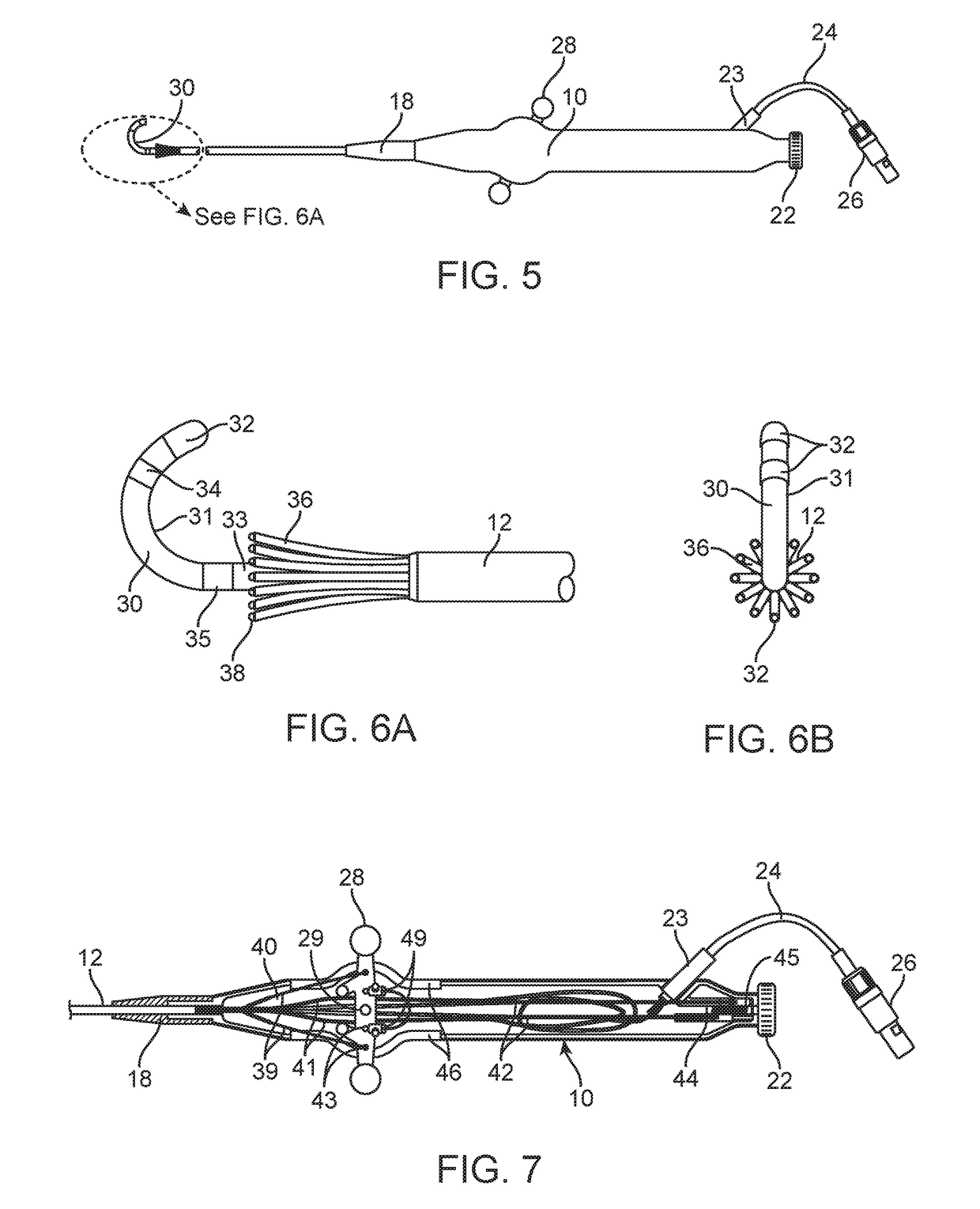
Tentacular Electrode Catheter Apparatus
InactiveUS20180146925A1Assurance of positioning accuracyIncrease contactElectrocardiographyCatheterBio potentialCatheter device
A tentacular electrode catheter having a proximal shaft component and a steerable distal shaft component with a polar array of multiple bi-directionally deflectable tentacles extending longitudinally around the distal shaft component. The distal end of each tentacle has a tip electrode for recording bio-potentials, pacing, and delivering and depositing RF energy. The tentacles are advantageously attached to the proximal shaft component at its junction with the distal shaft component and extend over a portion of the distal shaft component. The portion of the distal shaft component that is axially at the center of the polar array of tentacles thus acts as a centralizer and stabilizer for the tentacles, and is accordingly referred to as a centralizer / stabilizer distal shaft component.
Owner:MOGUL JAMIL
Measurement device for measuring bio-impedance and/or a bio-potential of a human or animal body
ActiveUS20150173677A1High impedanceAvoid excessive impactElectrocardiographySensorsElectricityMeasurement device
Measurement device for measuring a bio-impedance and / or a bio-potential of a human or animal body and adapted to be worn on the body, including: at least two electrode sensors. Each of the at least two electrode sensors includes a first electrical contact configured to be in electrical contact with the skin of the body when the system is worn, and a second electrical contact. A single electrical connector electrically connects the at least two electrode sensors with each other via the second electrical contact. An active device is configured to cooperate with a subset of the at least two electrode sensors such that the potential of the electrical connector is substantially equal to a projected potential determined from the potential of the first electrical contact of each electrode sensor of the subset when the measurement device is worn.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Contact type pulse measurement device
InactiveUS20050203426A1Overcomes shortcomingIncrease contact areaPhysical therapyCatheterNegative feedbackElectrode potential
The present invention discloses a contact type of pulse measurement device, which comprises a first active sensor electrode and a second active sensor electrode having corresponding opposite polarities with each other; and the two active sensor electrodes respectively connected to the pulse measurement device by conductive wires and the pulse measurement device comprises a negative feedback difference common mode signal and a buffer / balanced circuit for providing a circuit with a self common point electrode potential. Therefore, the first bio-potential signal can be detected by means of the first active sensor electrode and the common point electrode. Similarly, a second bio-potential signal having the same magnitude but a different phase as the first bio-potential signal can be detected by the second active sensor electrode and the common point electrode.
Owner:BOSON TECH
Differential voltage sensing method
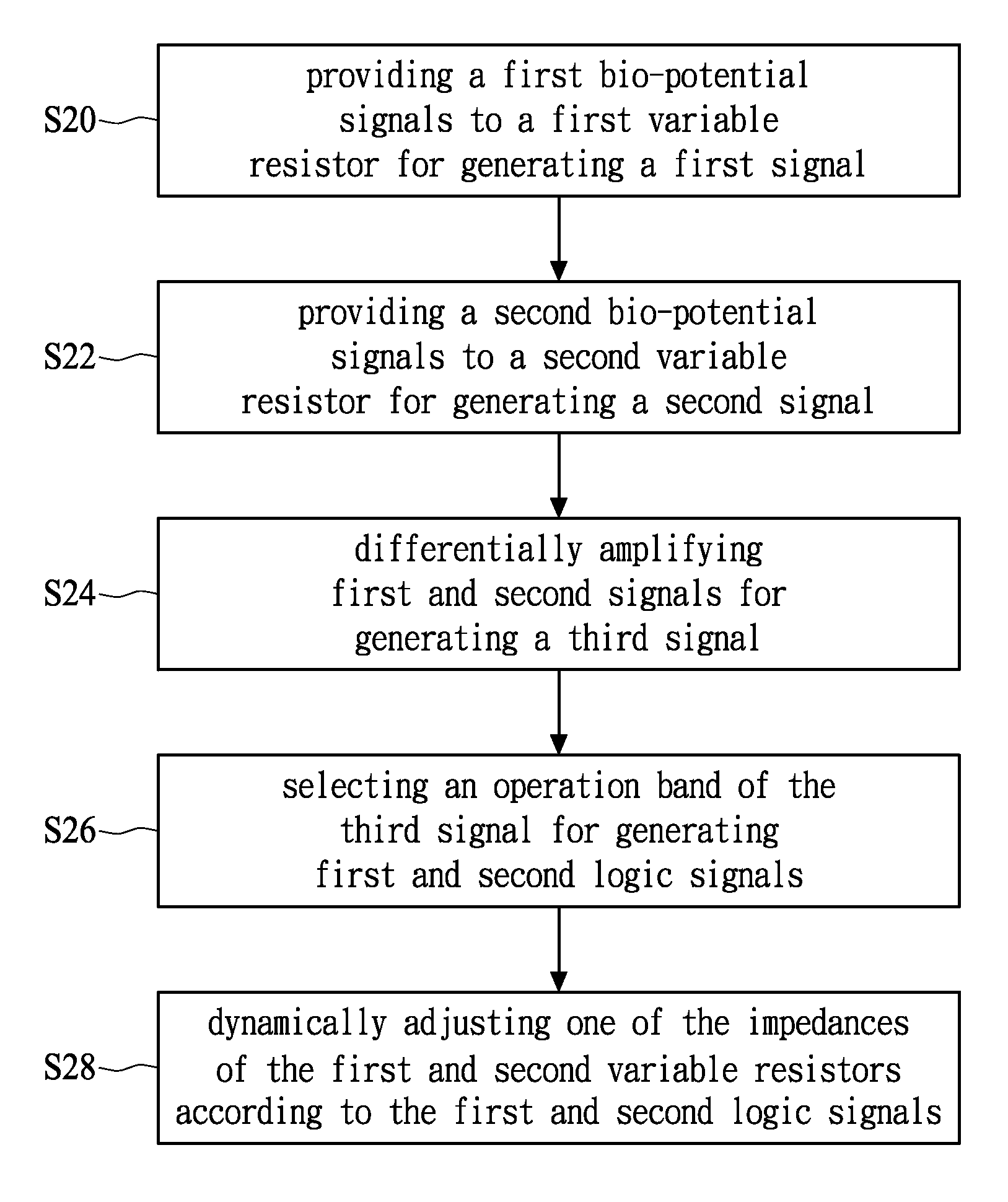
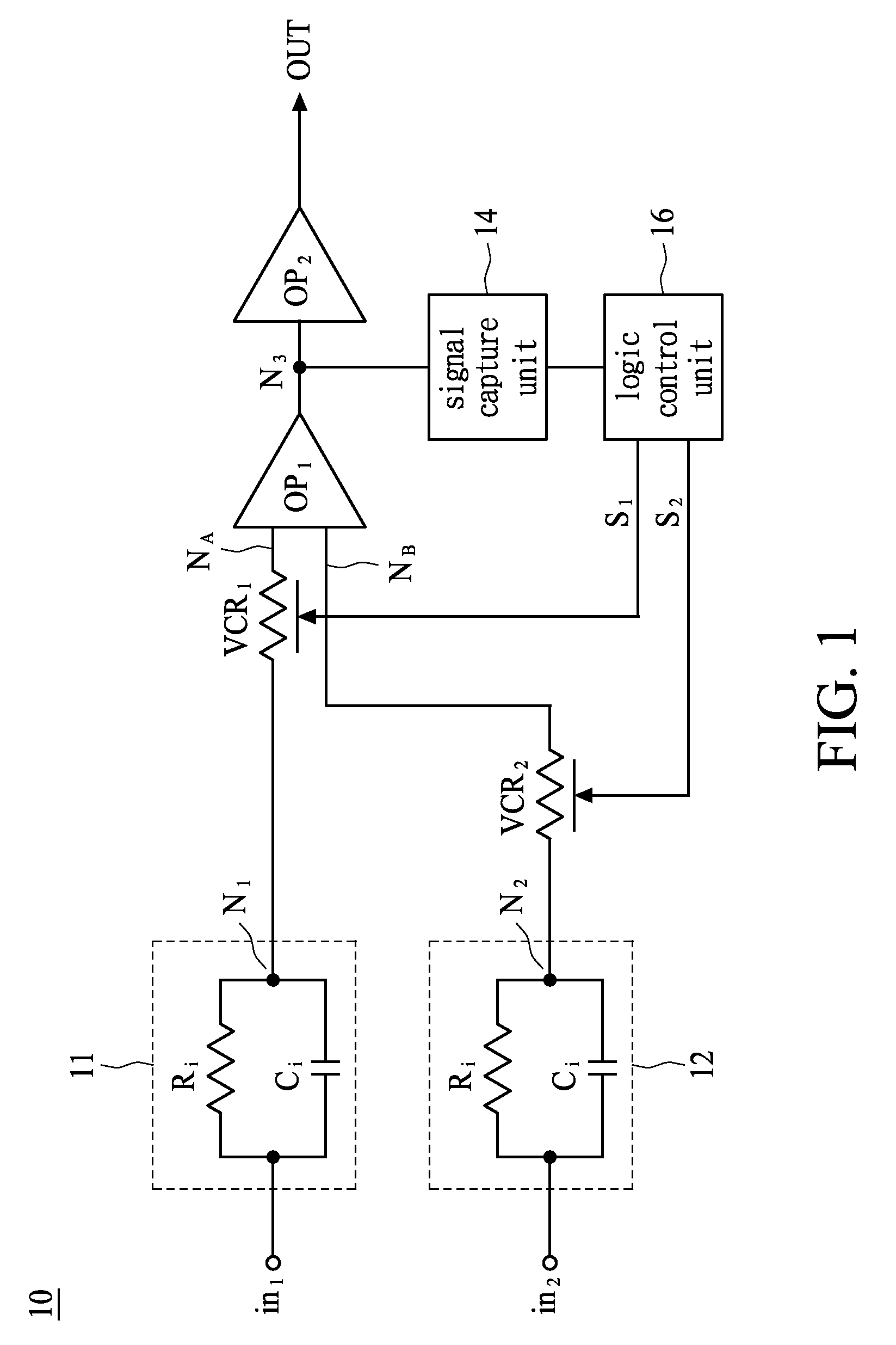
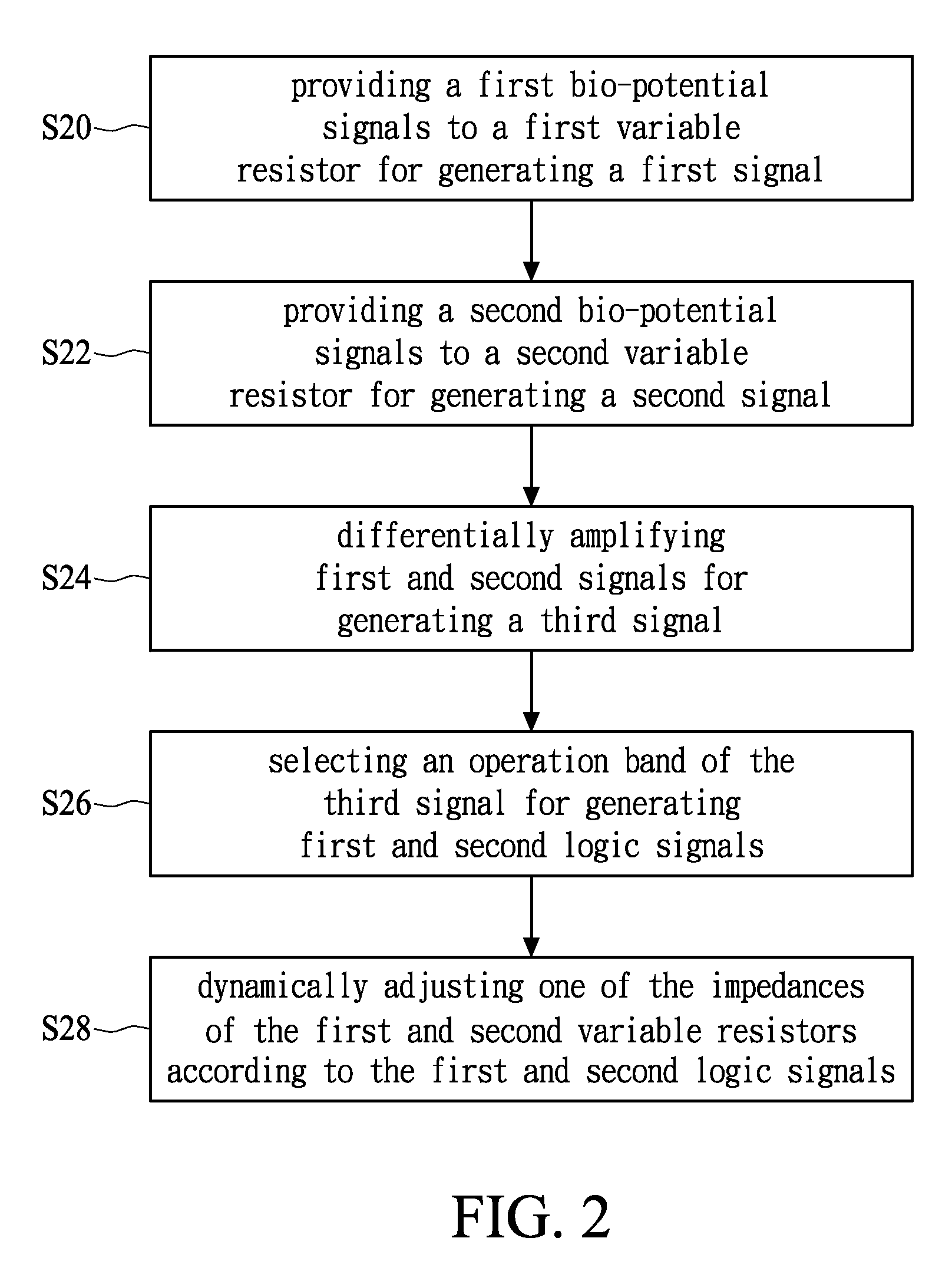
ActiveUS8442628B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringDifferential signalingInput impedance
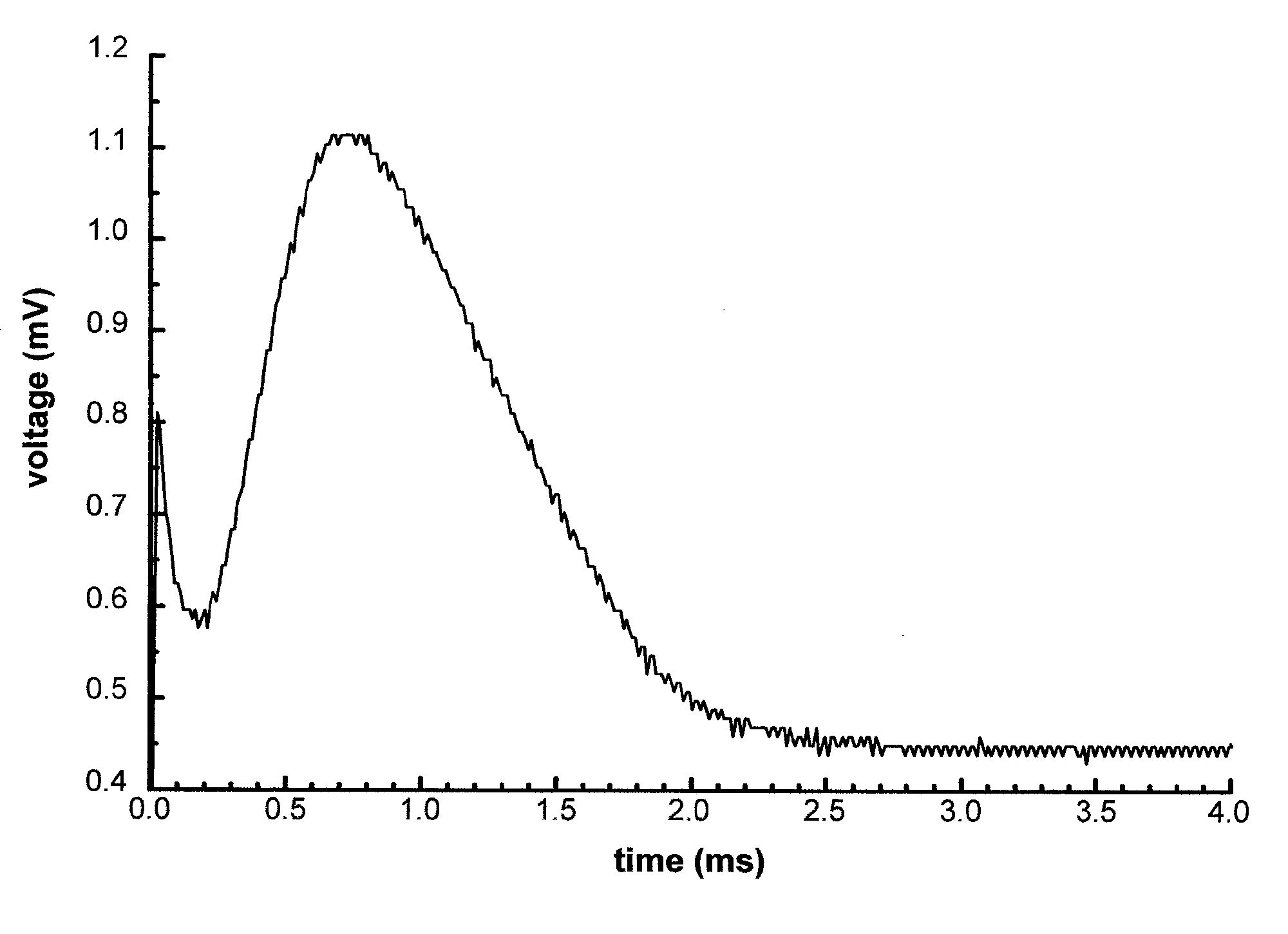
A differential voltage sensing method for achieving input impedance matching comprises the steps of: providing a first bio-potential signal to a first variable resistor for generating a first signal; providing a second bio-potential signal to a second variable resistor for generating a second signal; differentially amplifying first and second signals for generating a third signal; selecting an operation band of the third signal for generating first and second logic signals; and dynamically adjusting one of the impedances of the first and second variable resistors according to the first and second logic signals, wherein each of the first and second bio-potential signals has a common signal voltage level and a differential signal voltage level.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com