Patents
Literature
57results about How to "Fixed spacing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
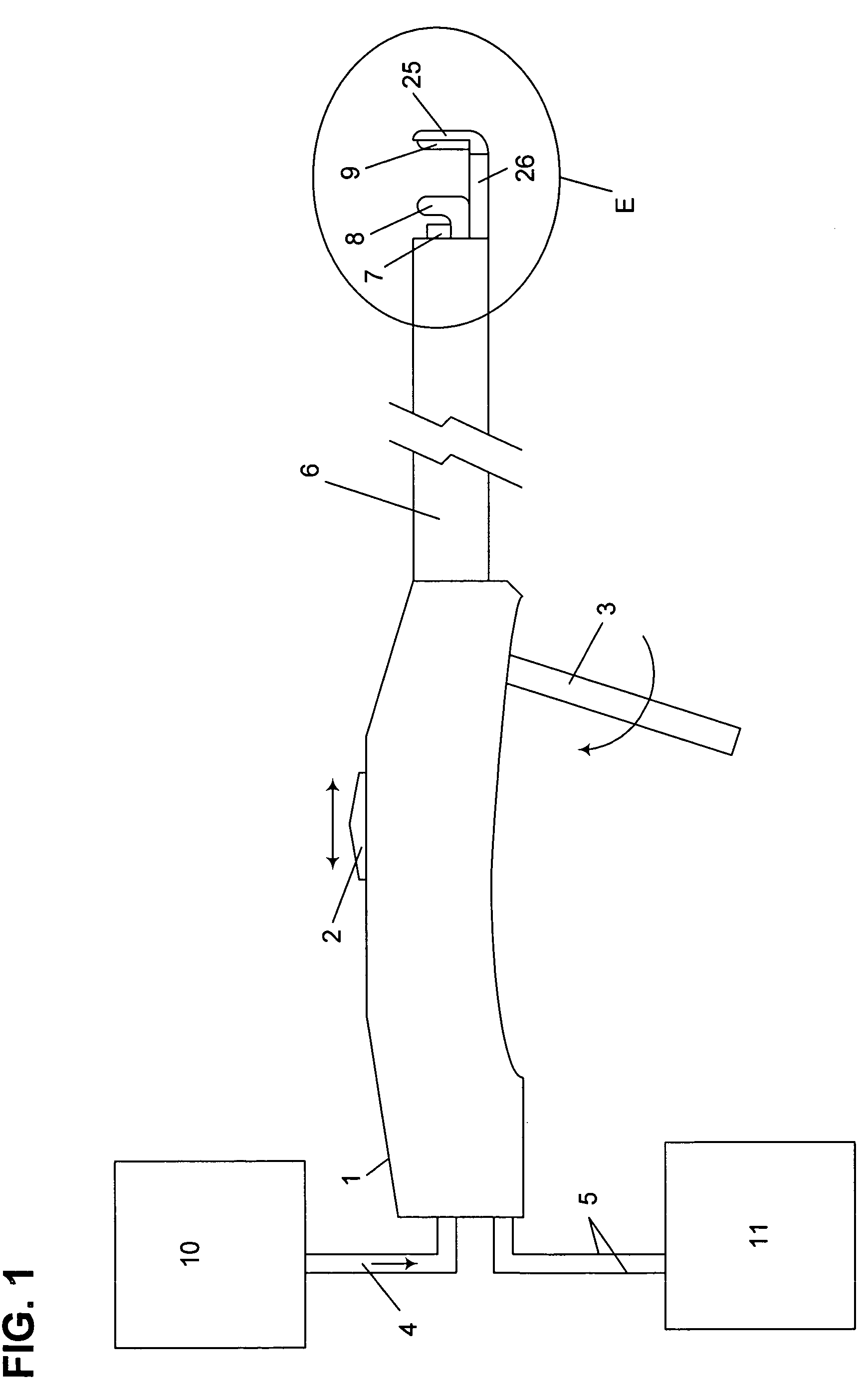
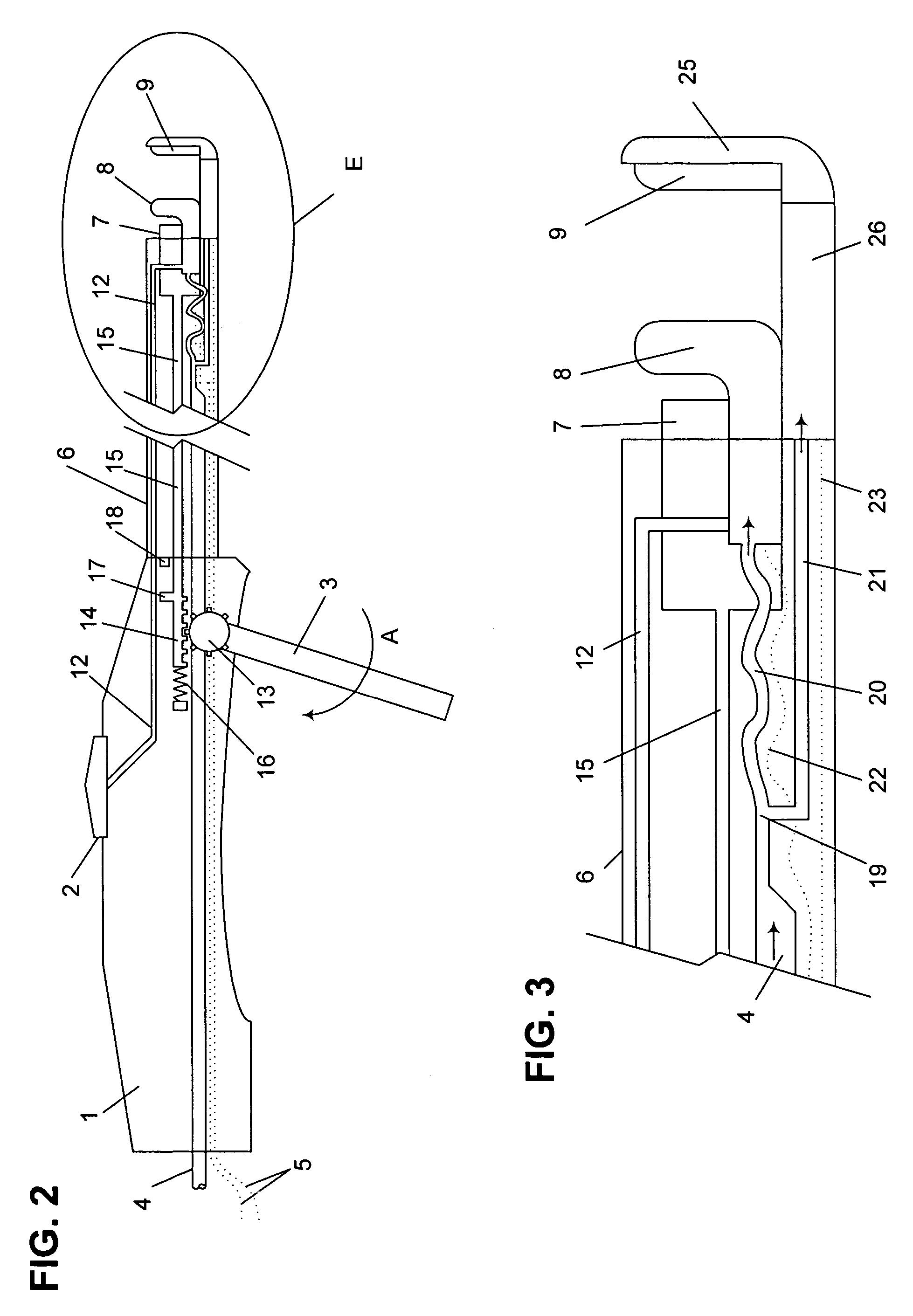
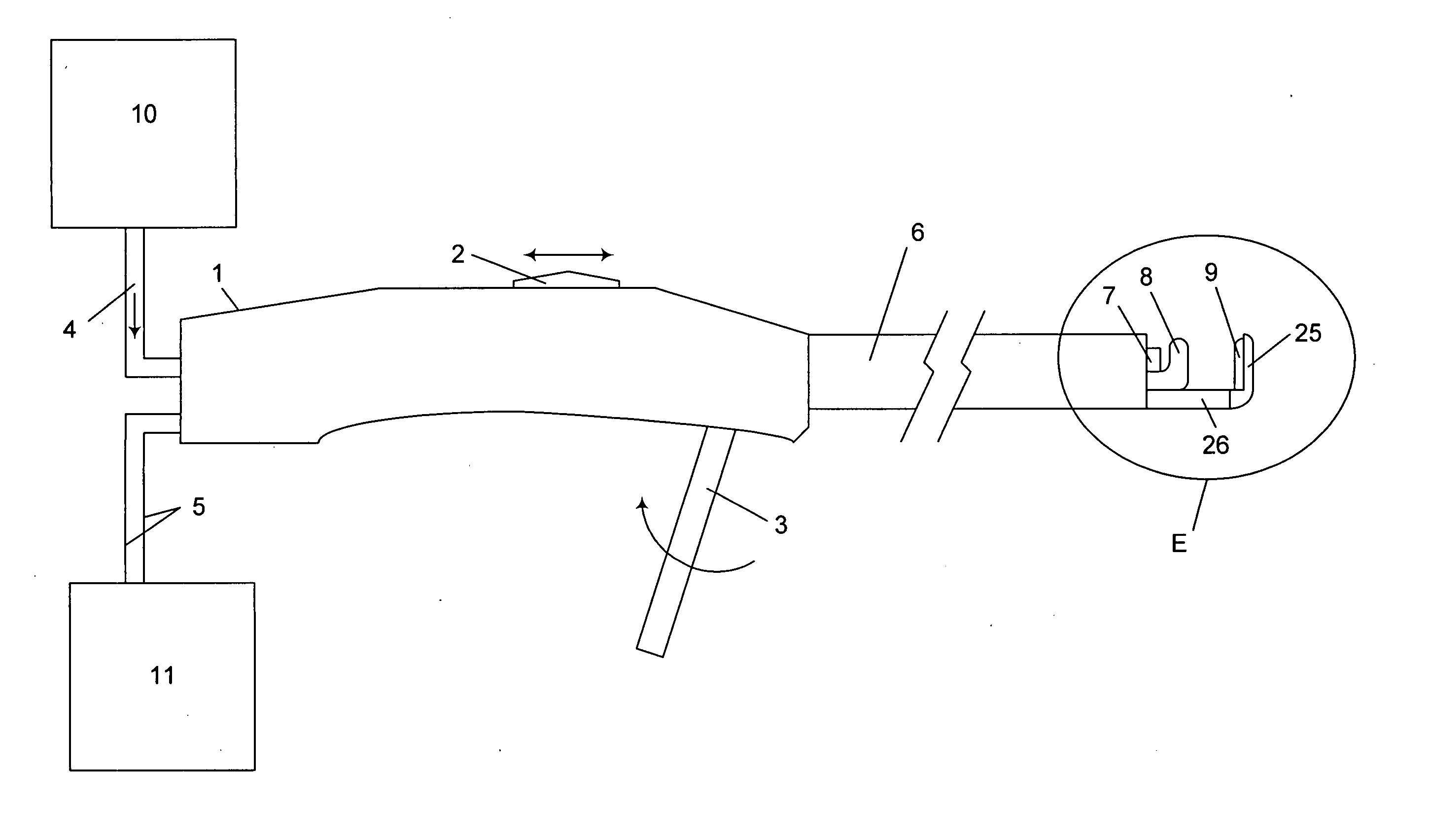
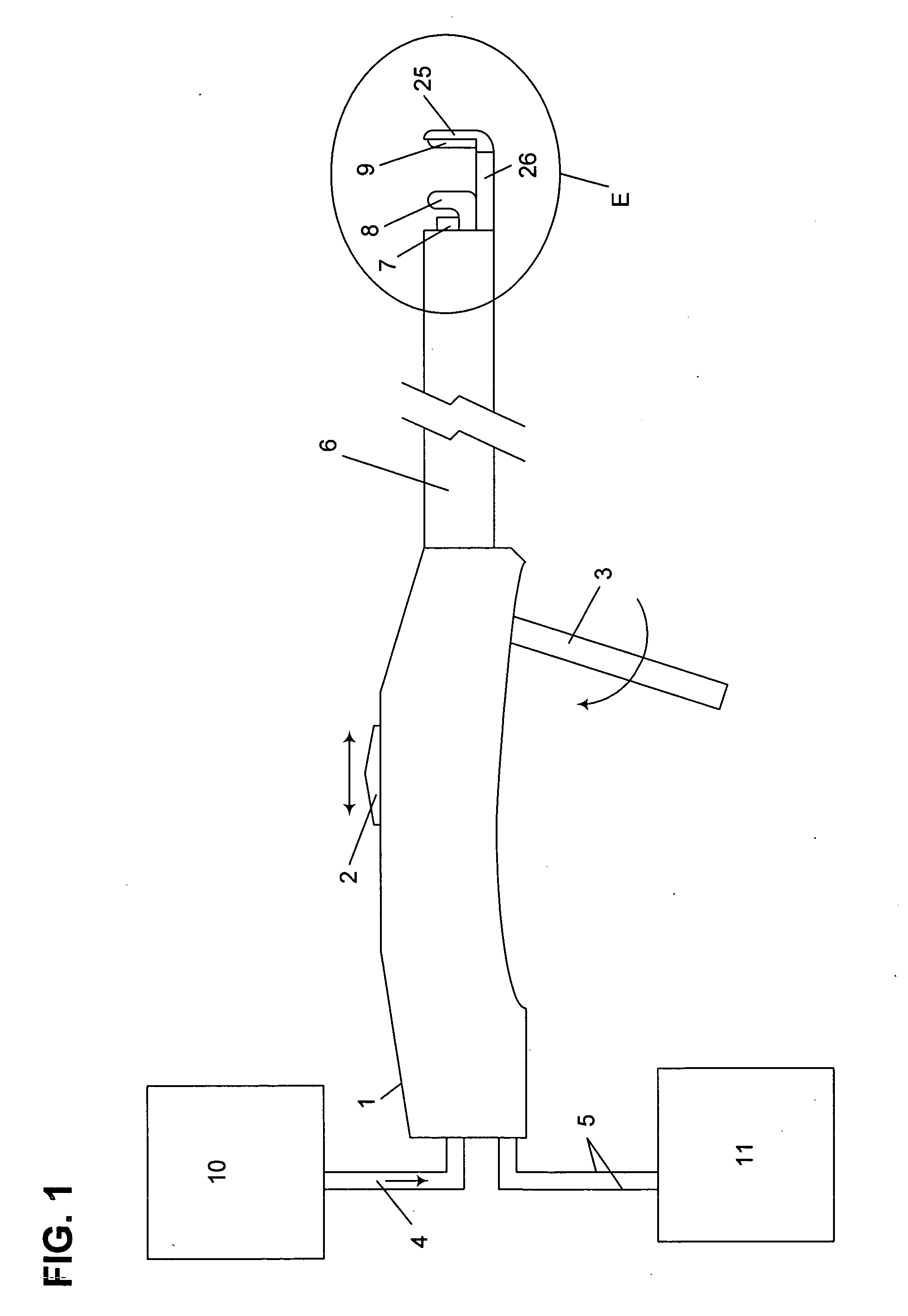
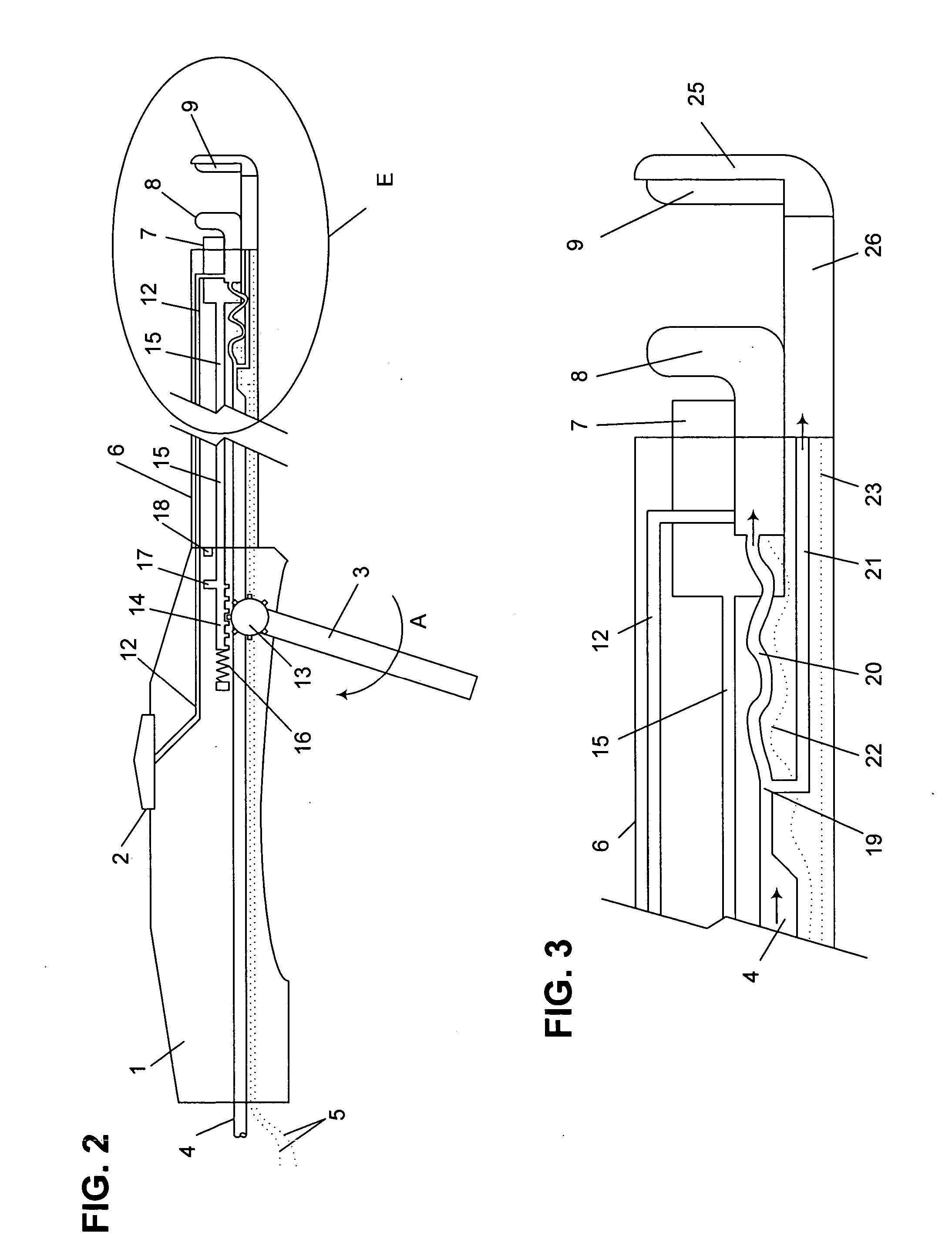
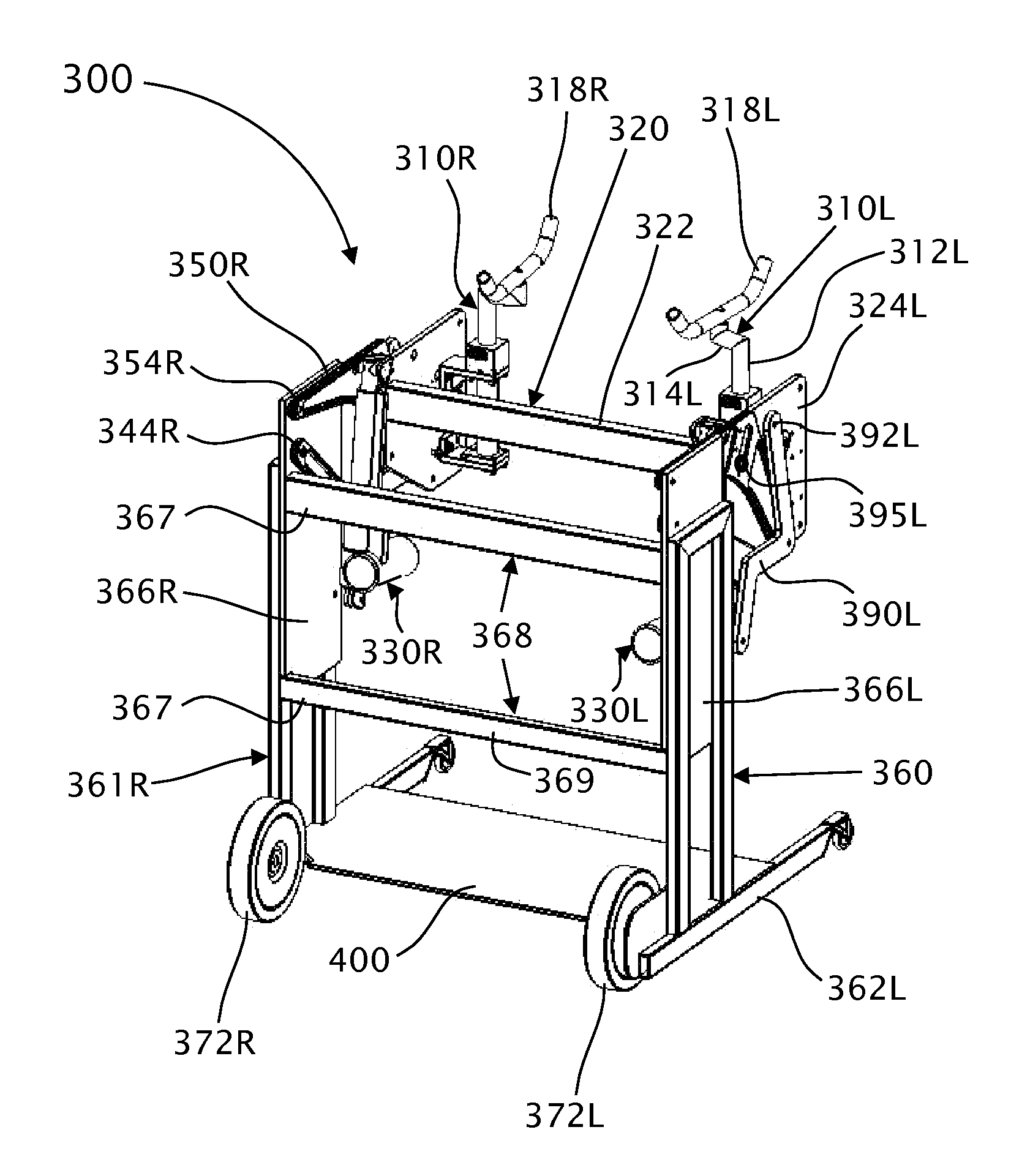
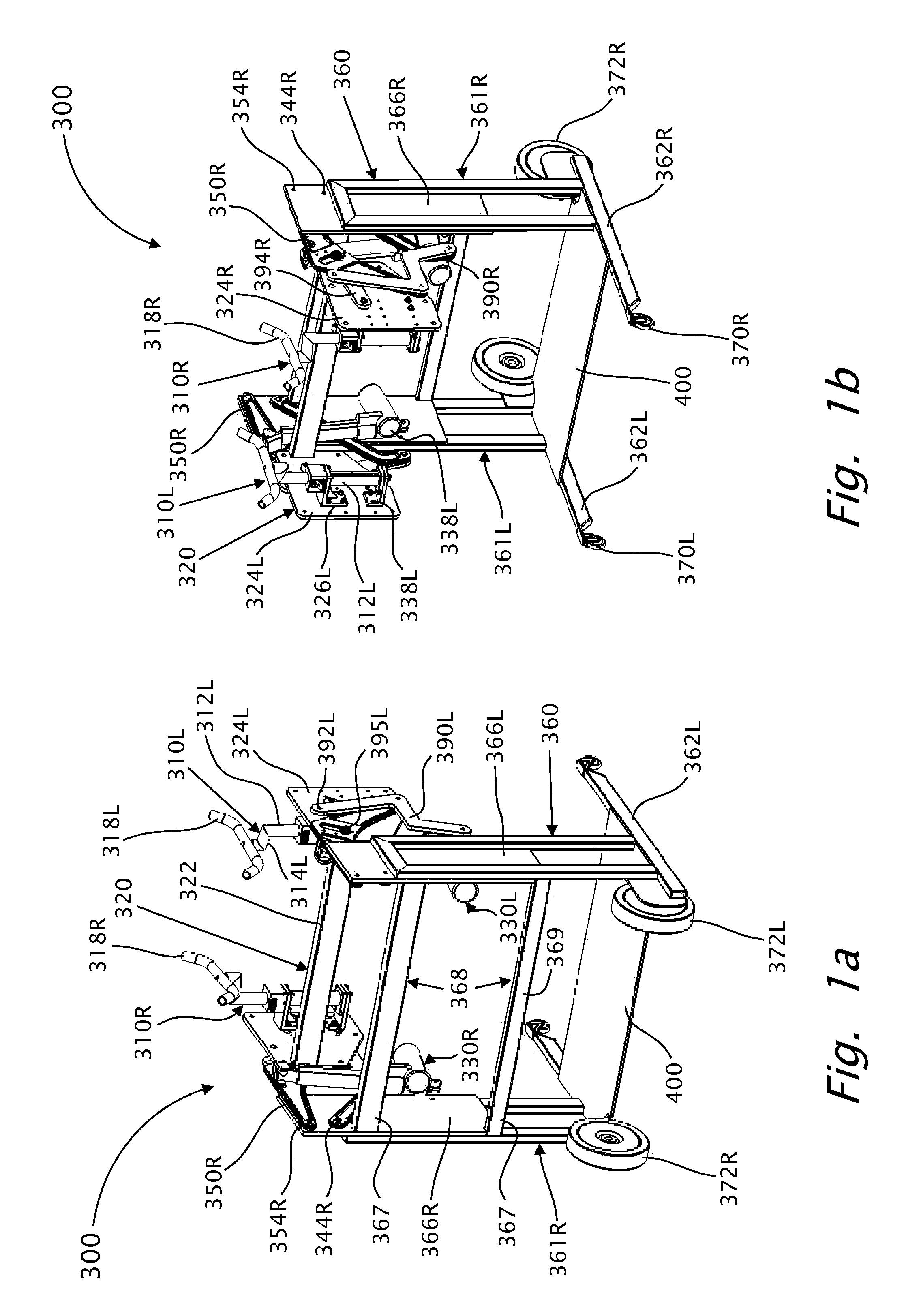
Fluid-assisted medical device
InactiveUS7645277B2Fixed spacingRelieve stressSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsMedical deviceBlood vessel
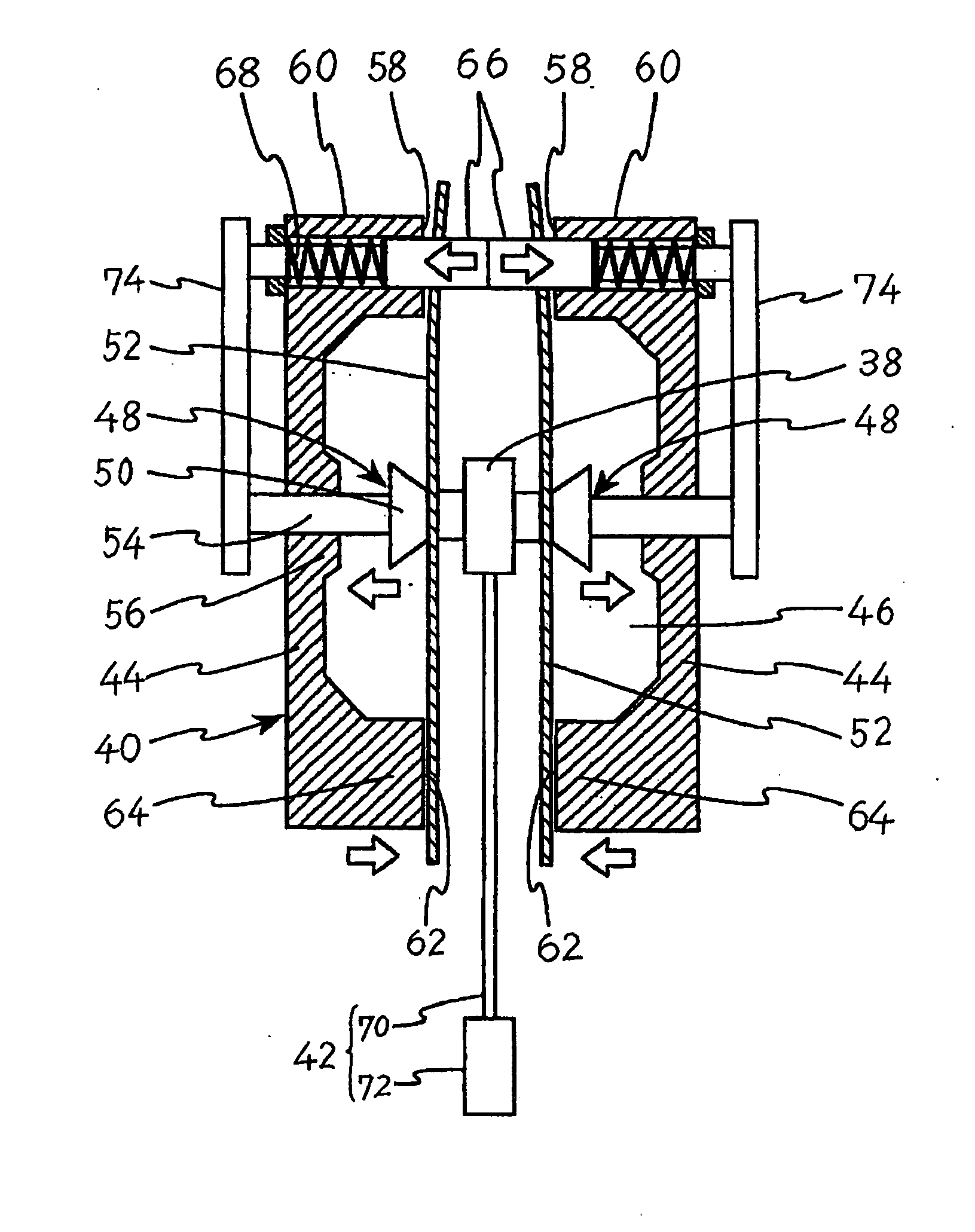
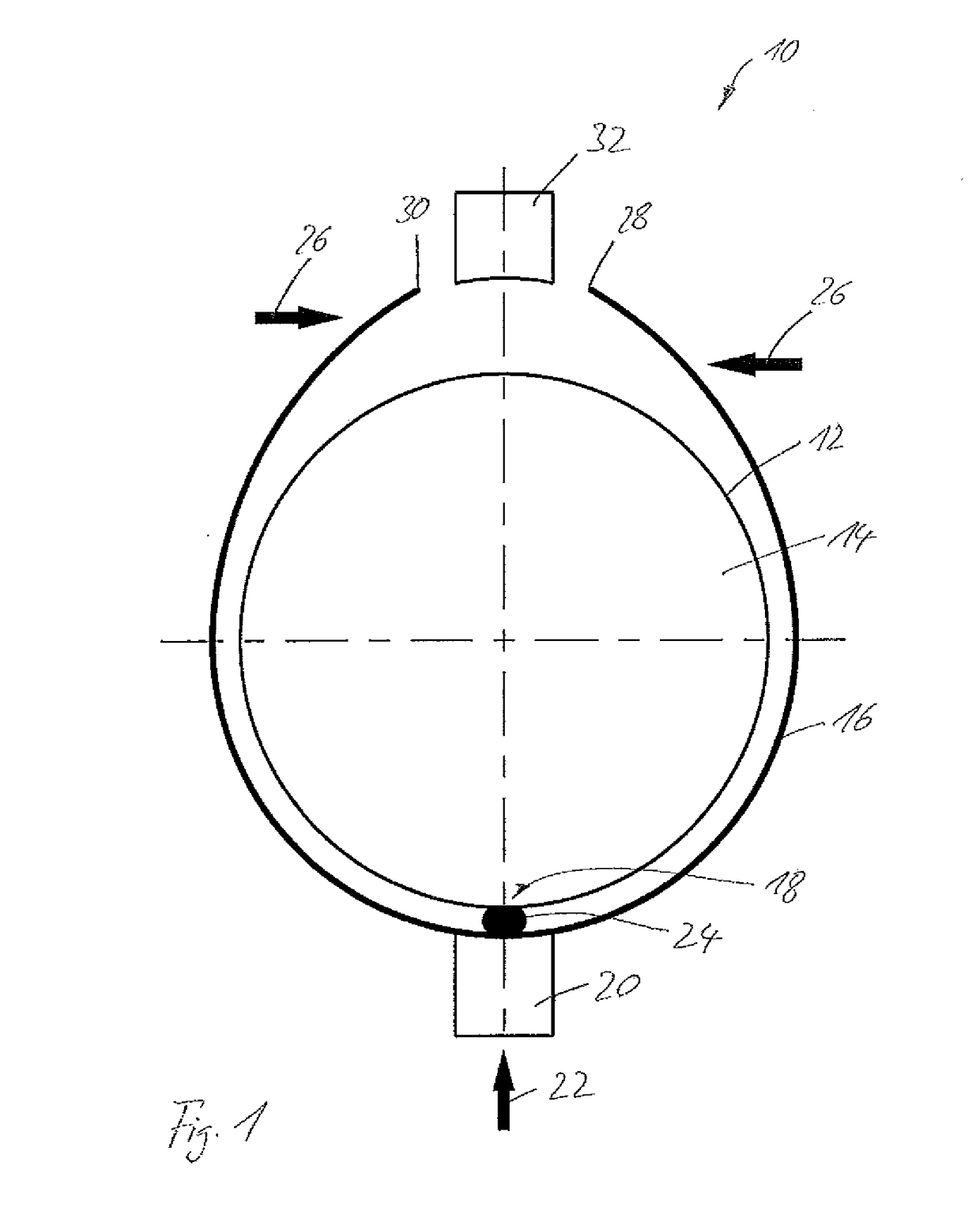
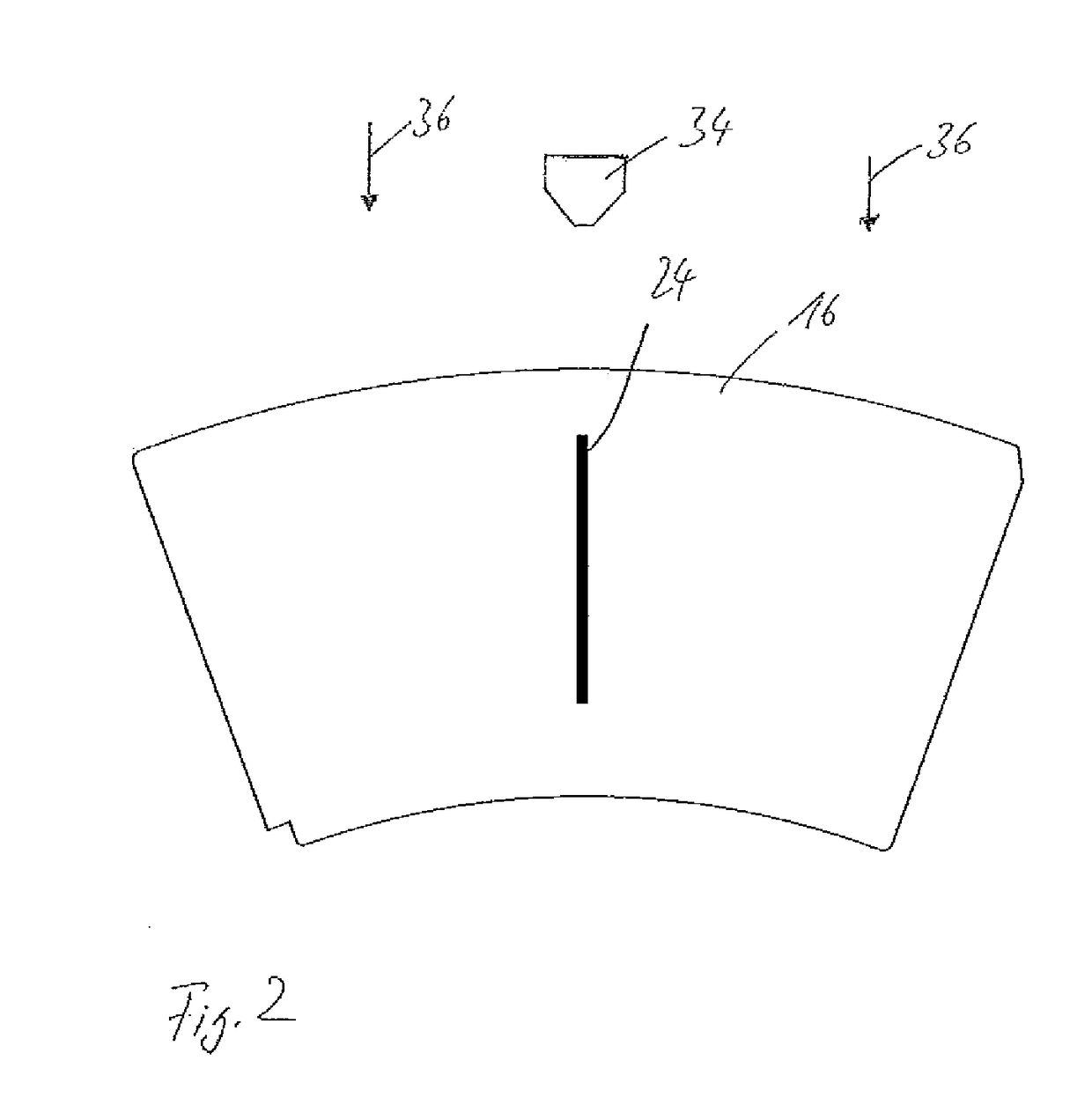
The invention provides a medical device that includes a housing, a tubular member extending from the distal end of the housing, a first arm extending from the distal end of the tubular member, the first arm including a first electrode, a second arm extending from the distal end of the tubular member, the second arm including a second electrode and being disposed coaxially with the first arm, at least one solution infusion opening on each electrode, and a solution delivery channel for delivery of a conductive solution to the solution infusion openings. According to the invention, at least one of the first arm or the second arm is translationally moveable, and at least one of the first arm or the second arm is adapted to be coupled to a source of radiofrequency energy. The invention also provides a corresponding method for treating blood vessels or other tissues of the body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
Fluid-assisted medical device
InactiveUS20060100619A1Fixed spacingRelieve stressSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
The invention provides a medical device that includes a housing, a tubular member extending from the distal end of the housing, a first arm extending from the distal end of the tubular member, the first arm including a first electrode, a second arm extending from the distal end of the tubular member, the second arm including a second electrode and being disposed coaxially with the first arm, at least one solution infusion opening on each electrode, and a solution delivery channel for delivery of a conductive solution to the solution infusion openings. According to the invention, at least one of the first arm or the second arm is translationally moveable, and at least one of the first arm or the second arm is adapted to be coupled to a source of radiofrequency energy. The invention also provides a corresponding method for treating blood vessels or other tissues of the body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
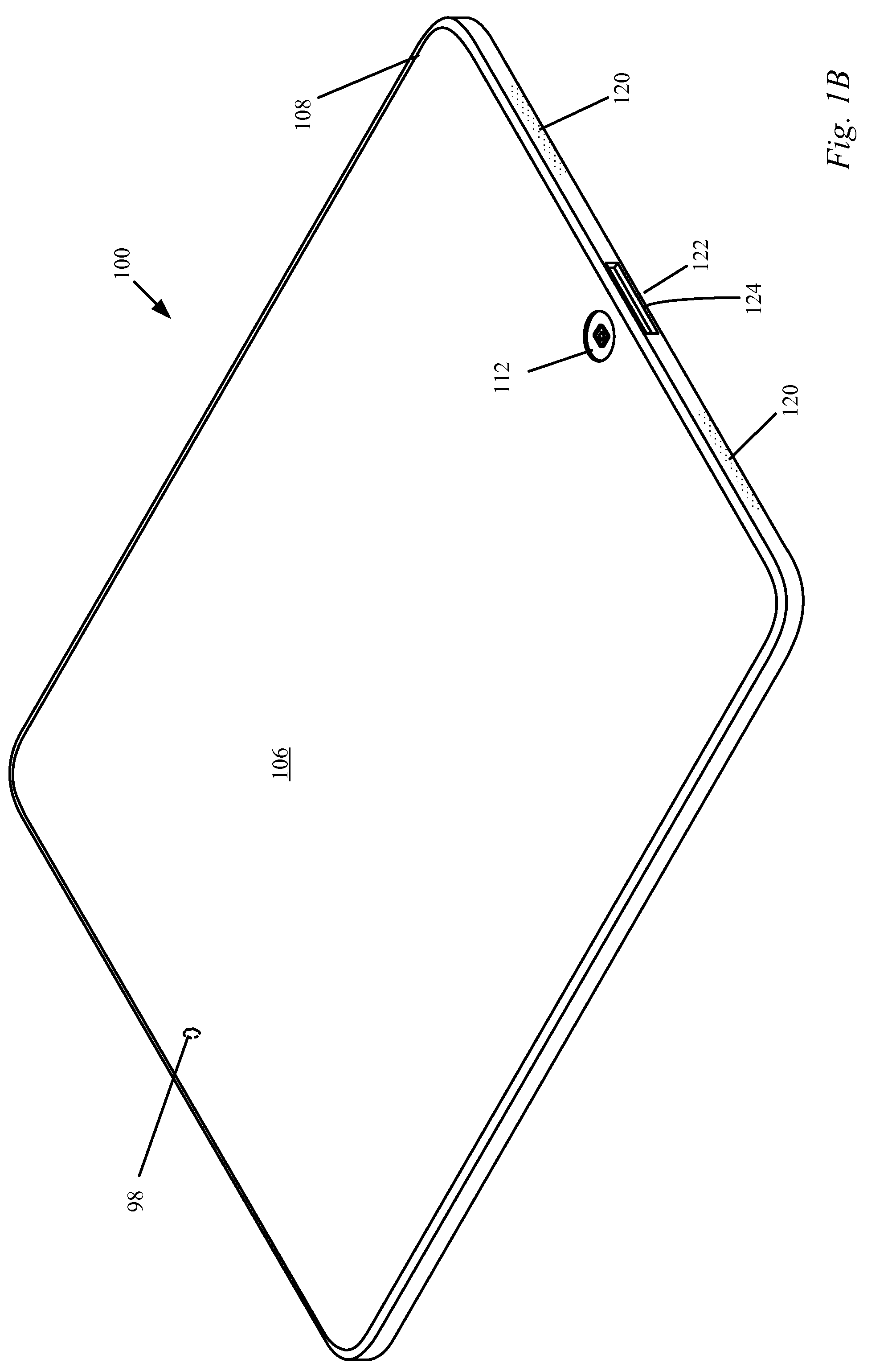
Antenna, shielding and grounding
ActiveUS8665160B2Gap minimizationImprove wireless performanceTransducer detailsAntenna supports/mountingsTablet computerEngineering
Owner:APPLE INC
Keysheet module
ActiveUS6982394B2Reduce in quantityGood clicking feelContact surface shape/structureSnap-action arrangementsFlexible electronicsPrinted circuit board
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
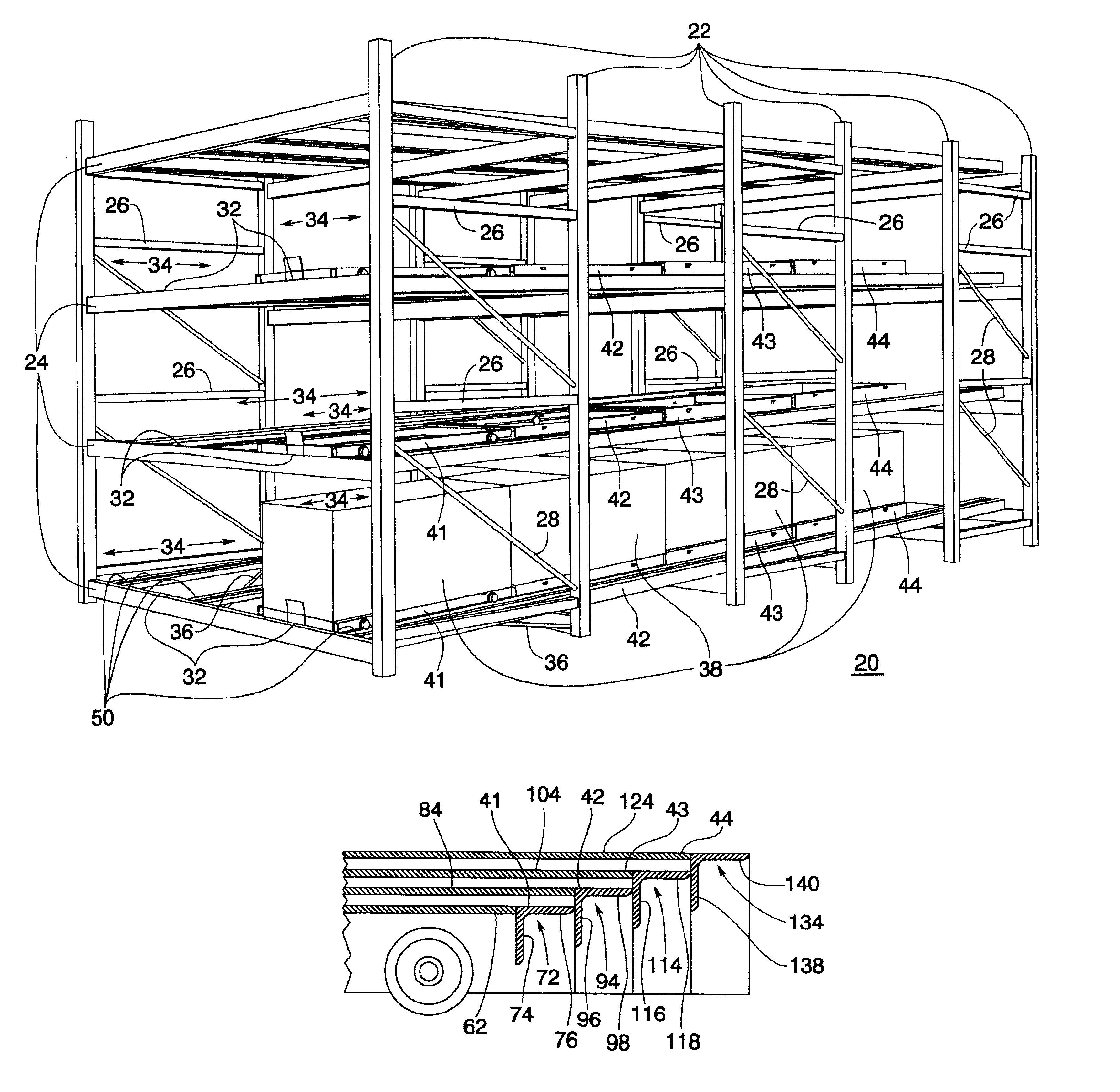
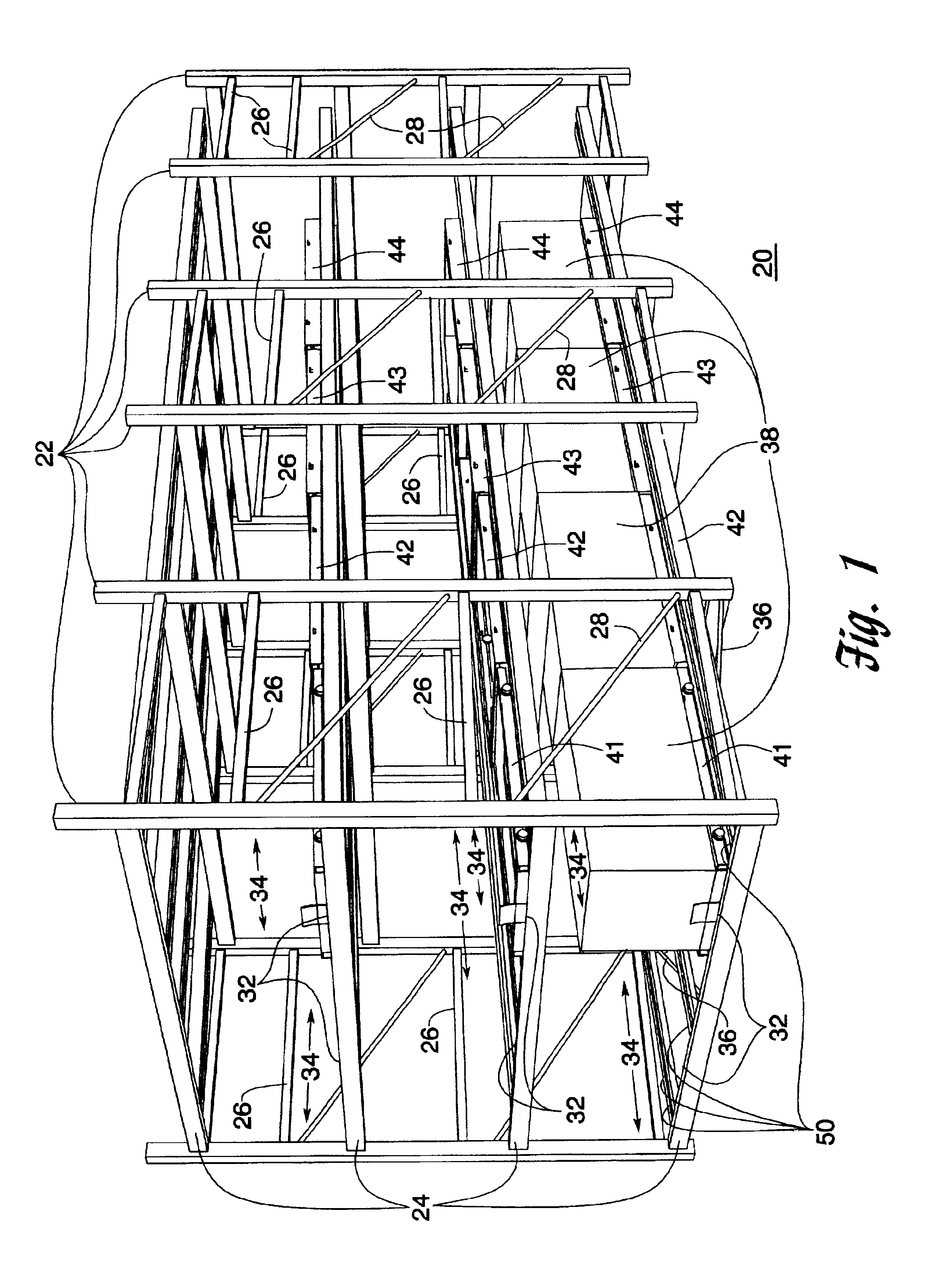
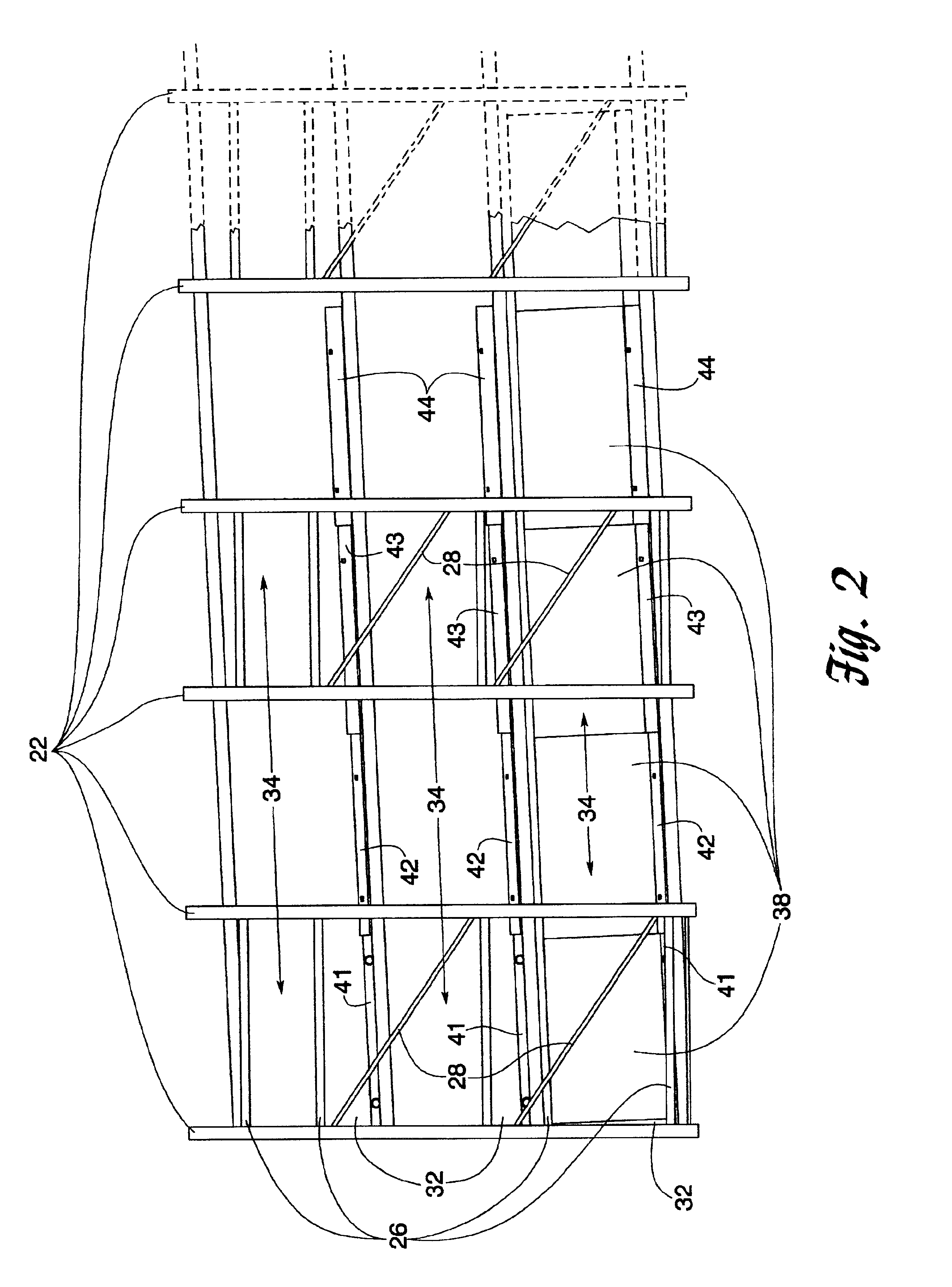
Push back storage rack system
InactiveUS6851562B2Low warpageIncrease vertical heightRacksFolding cabinetsEngineeringSupport surface
A push back storage rack system for storing multiple loads in a single inclined cart lane. Each lane contains at least two wheeled carts, each cart being capable of receiving and storing multiple pallet loads. The carts are vertically spaced so that they can freely slide underneath each other when unloaded. Beginning with the first or lowest level cart in the system, each successively higher cart is also wider and longer than the cart immediately beneath it. The carts are positioned on at least one but potentially two pairs of rectangular tracks or tubes, each tube being capable of supporting two or four individual carts, depending on how the carts are constructed and installed on the tubes. The tubes are mounted on an incline away from a loading end of each lane so that when loads are placed on or are removed from a lane, the carts are biased toward the loading end of the lane by the force of gravity. Each tube has a single, planar upper support surface which has inside and outside edges. The wheels of each cart ride only on either the inside or outside edges of the tubes on which they are mounted, allowing more than one vertically spaced cart to occupy the same tube.
Owner:RIDG U RAK
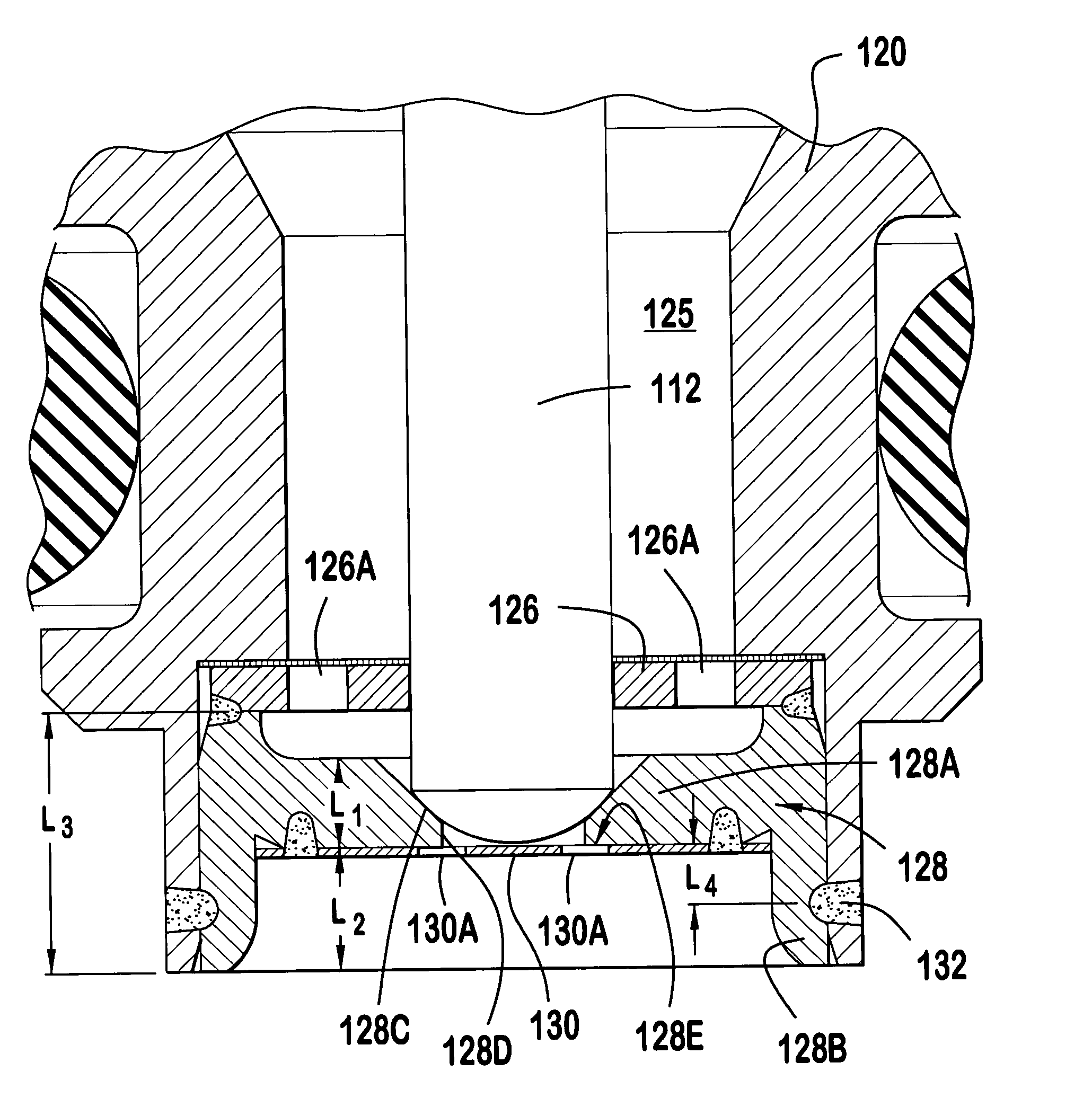
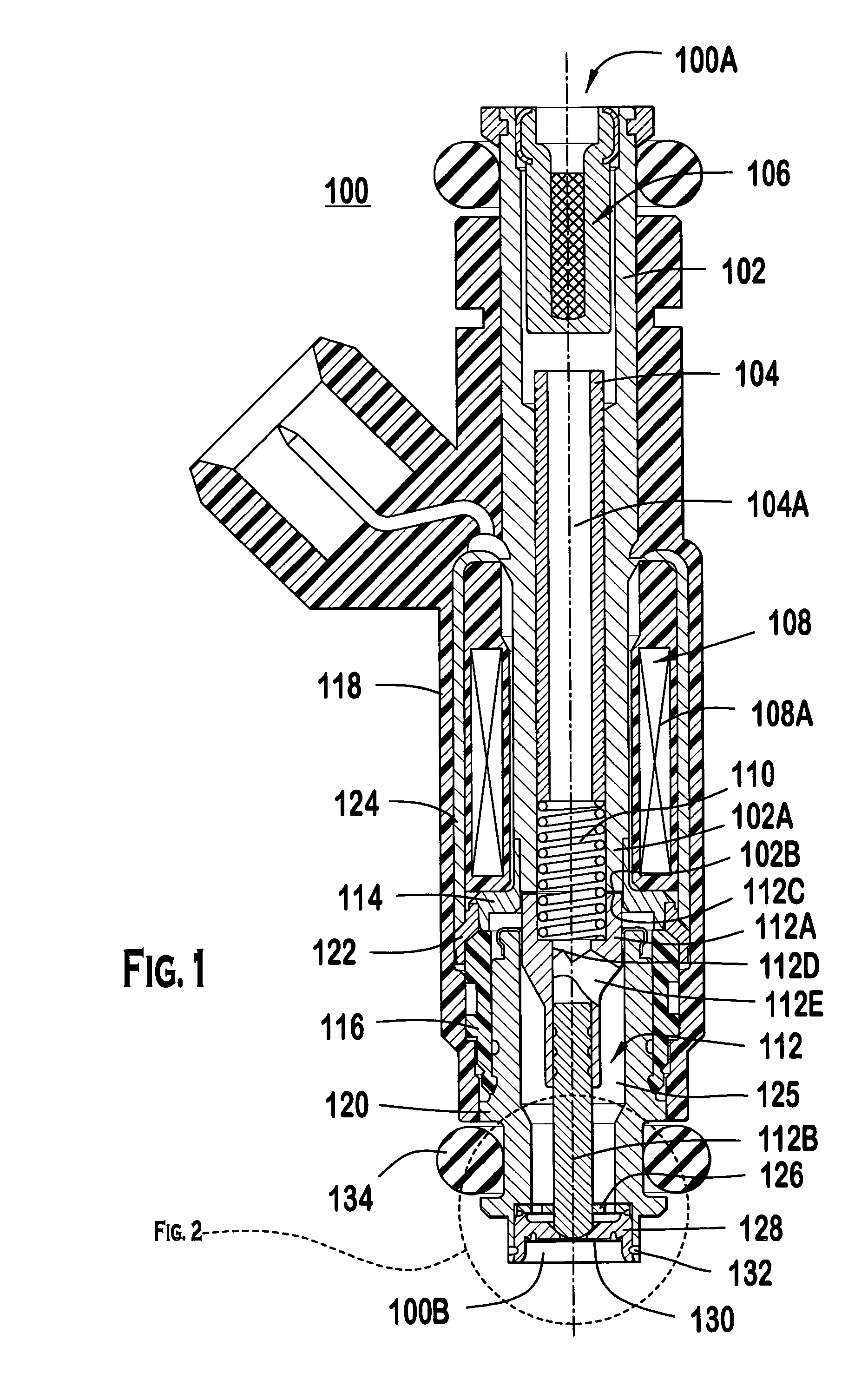
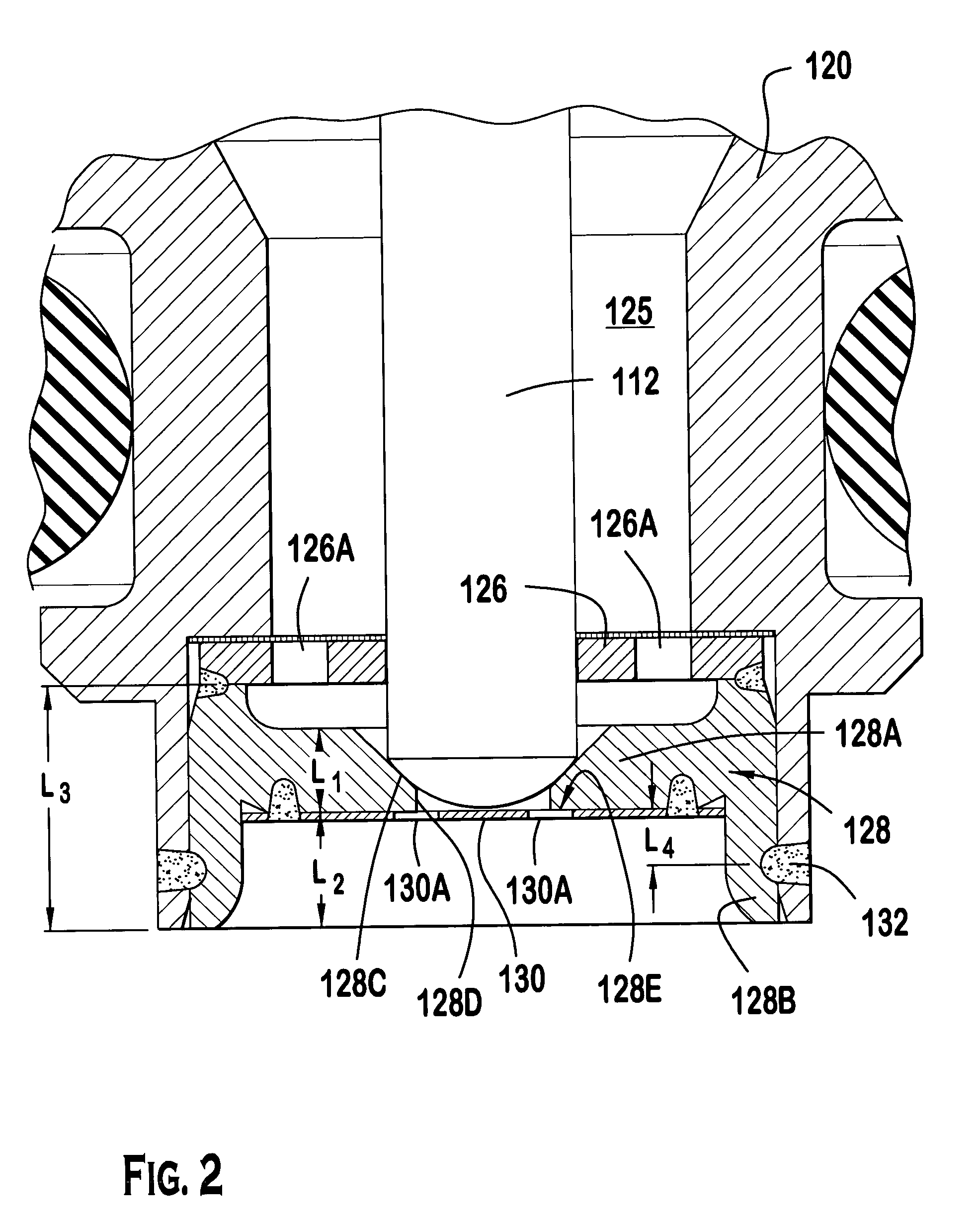
Modular fuel injector with a deep pocket seat and method of maintaining spatial orientation
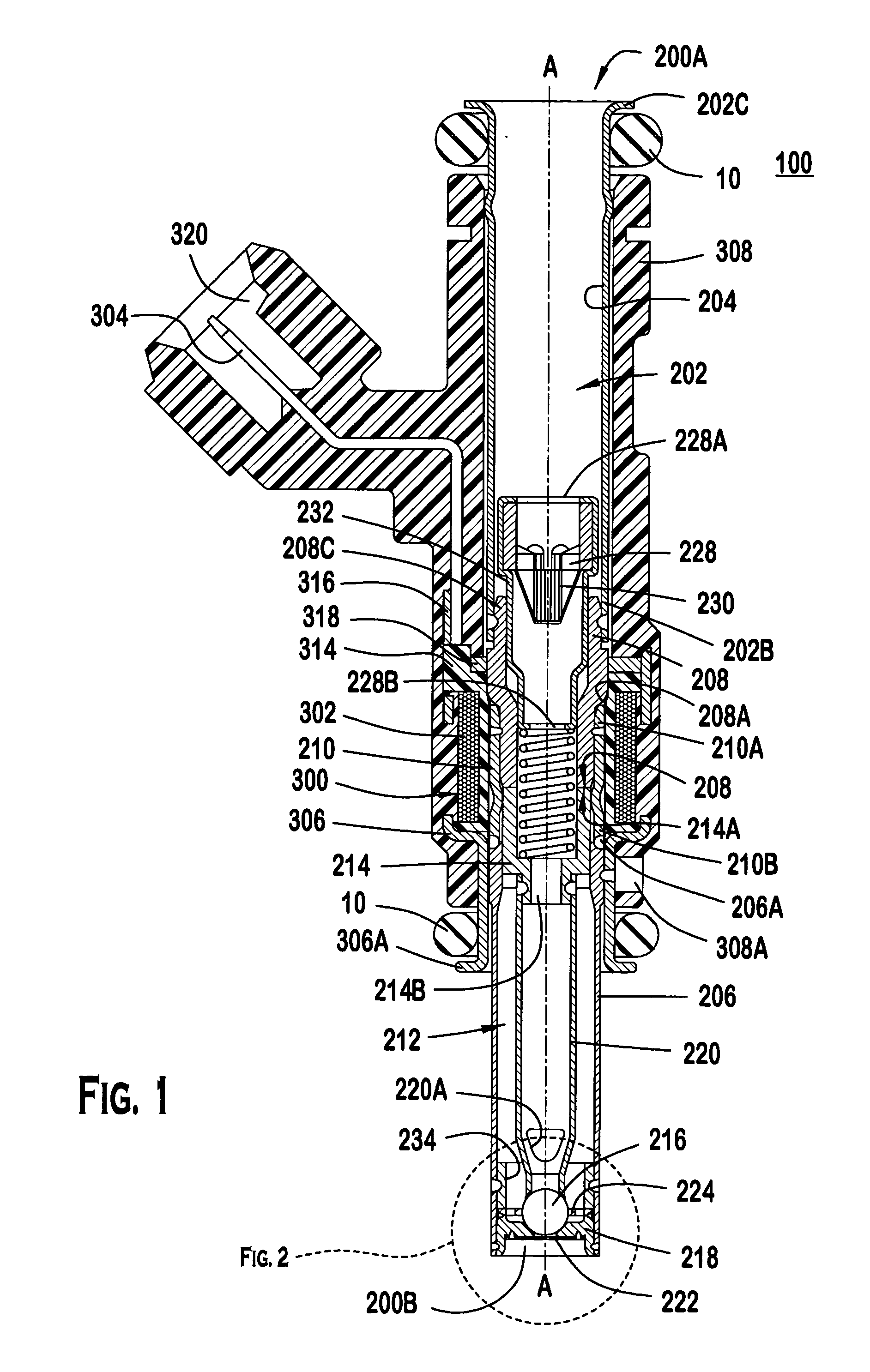
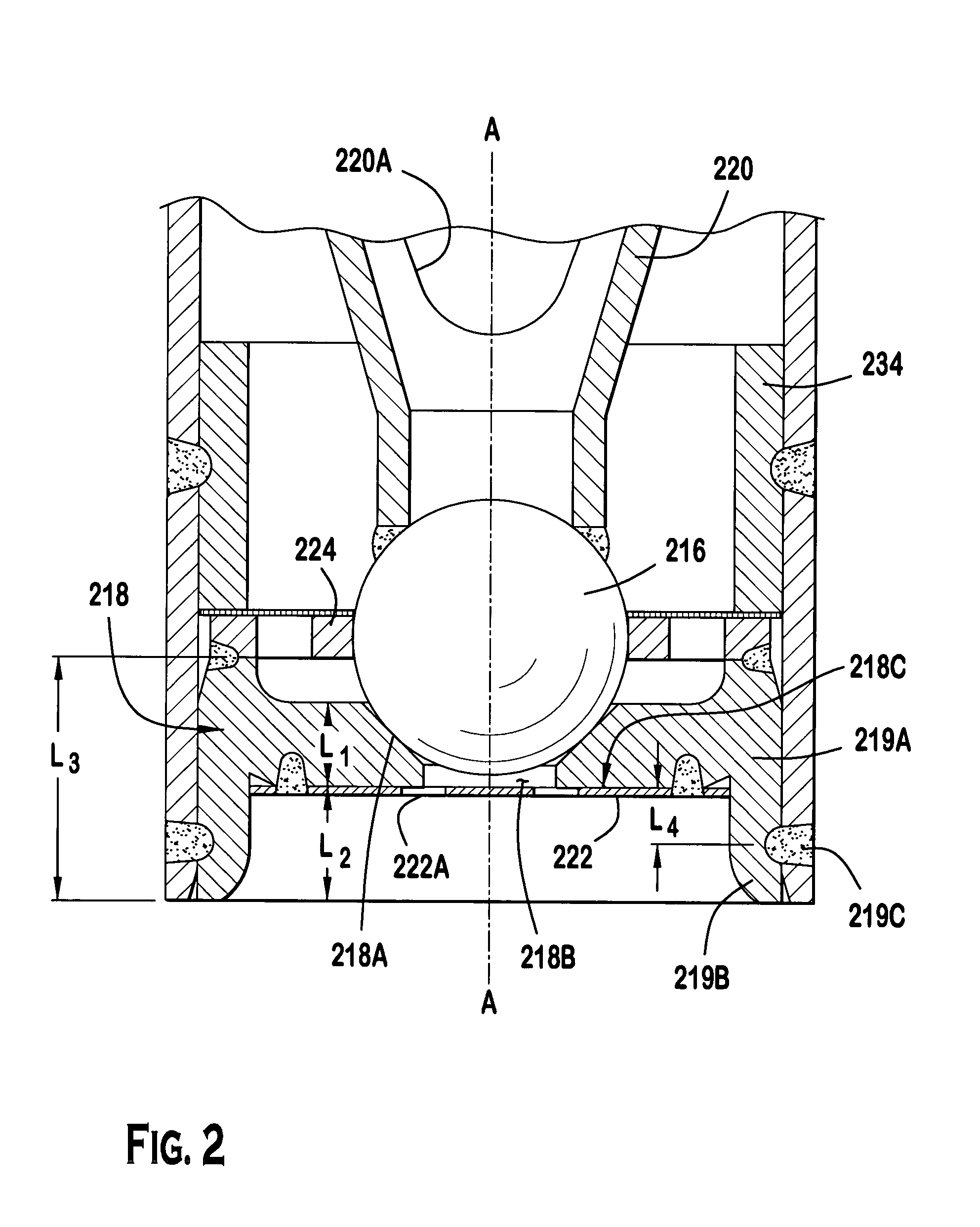
ActiveUS20050040258A1Fixed spacingSpray nozzlesMachines/enginesVena contracta diameterSpatial Orientations
A modular fuel injector that includes a coil group subassembly and a valve group subassembly. The coil group subassembly is independently testable. The valve group subassembly is independently testable and includes a tube assembly having a longitudinal axis extending between a first tube end and a second tube end, and a seat assembly disposed in the tube assembly proximate the second tube end. The seat assembly includes a flow portion and a securement portion. The flow portion extends along the longitudinal axis between a first surface and an orifice disk retention surface at a first length. The flow portion has a seat orifice extending therethrough and an orifice disk coupled to the orifice disk retention surface so that the orifice plate is aligned in a fixed spatial orientation with respect to the flow portion. The securement portion extends along the longitudinal axis away from the orifice disk retention surface at a second length greater than the first length. A method of maintaining a fixed spatial orientation and dimensional symmetry of at least one of the seat and orifice disk in the valve subassembly is disclosed.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
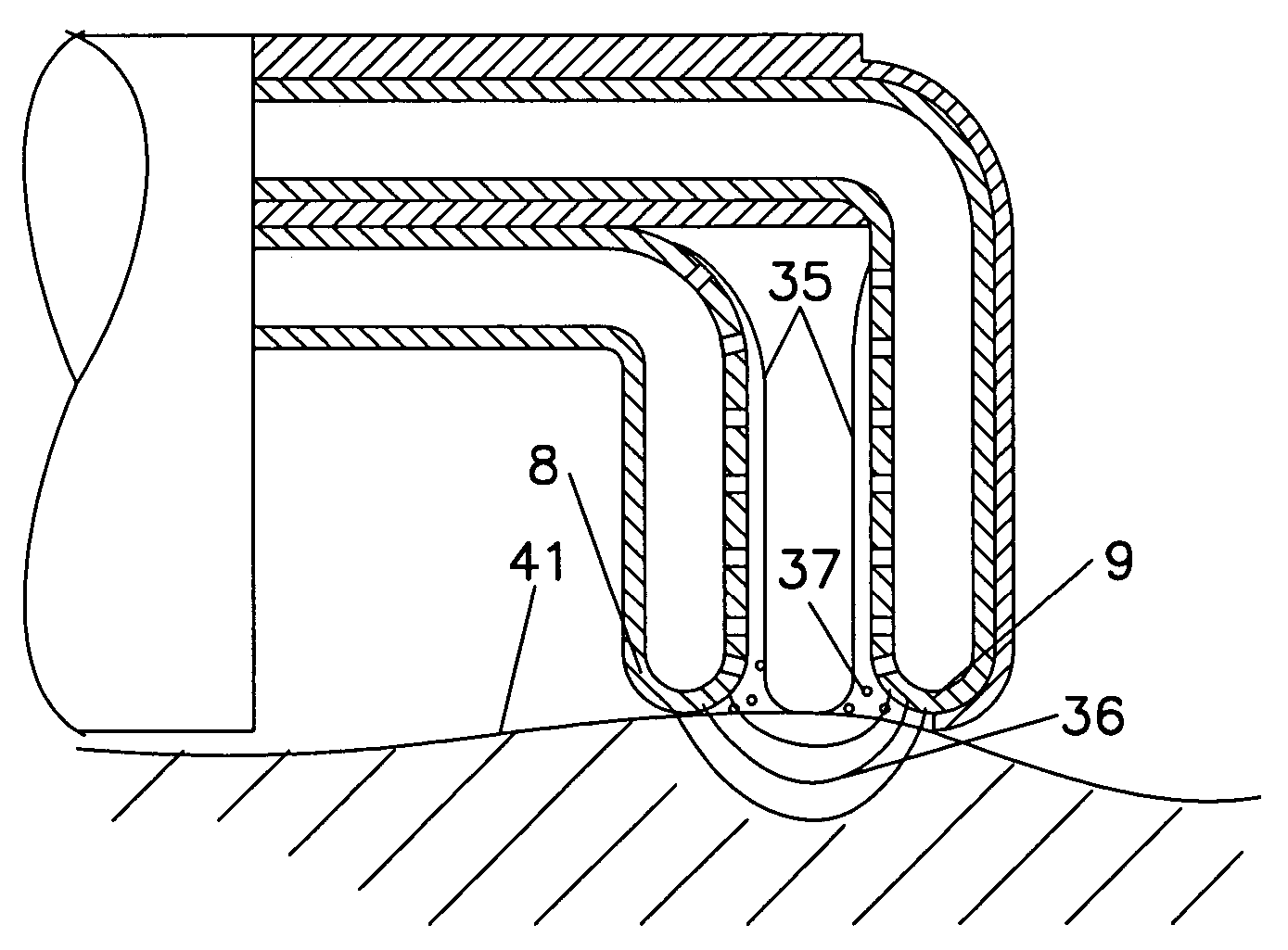
Catheter with concentric balloons for radiogas delivery and booster radiosources for use therewith
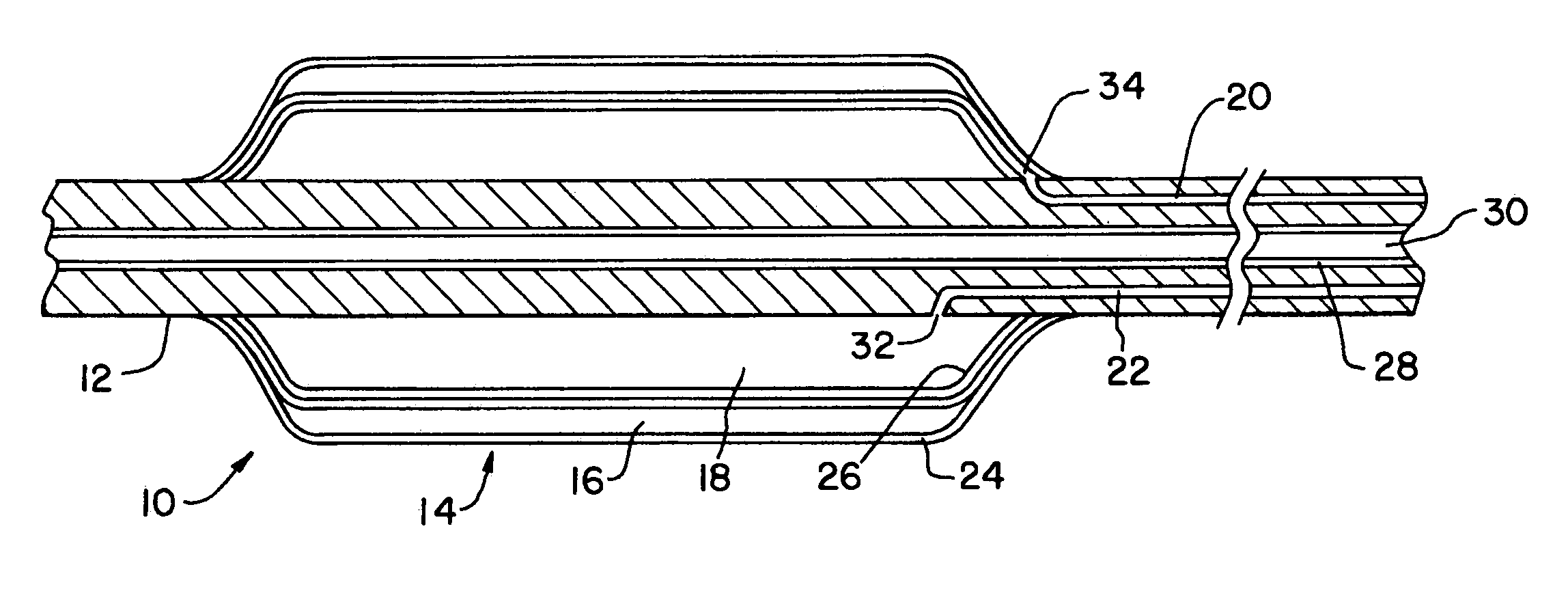
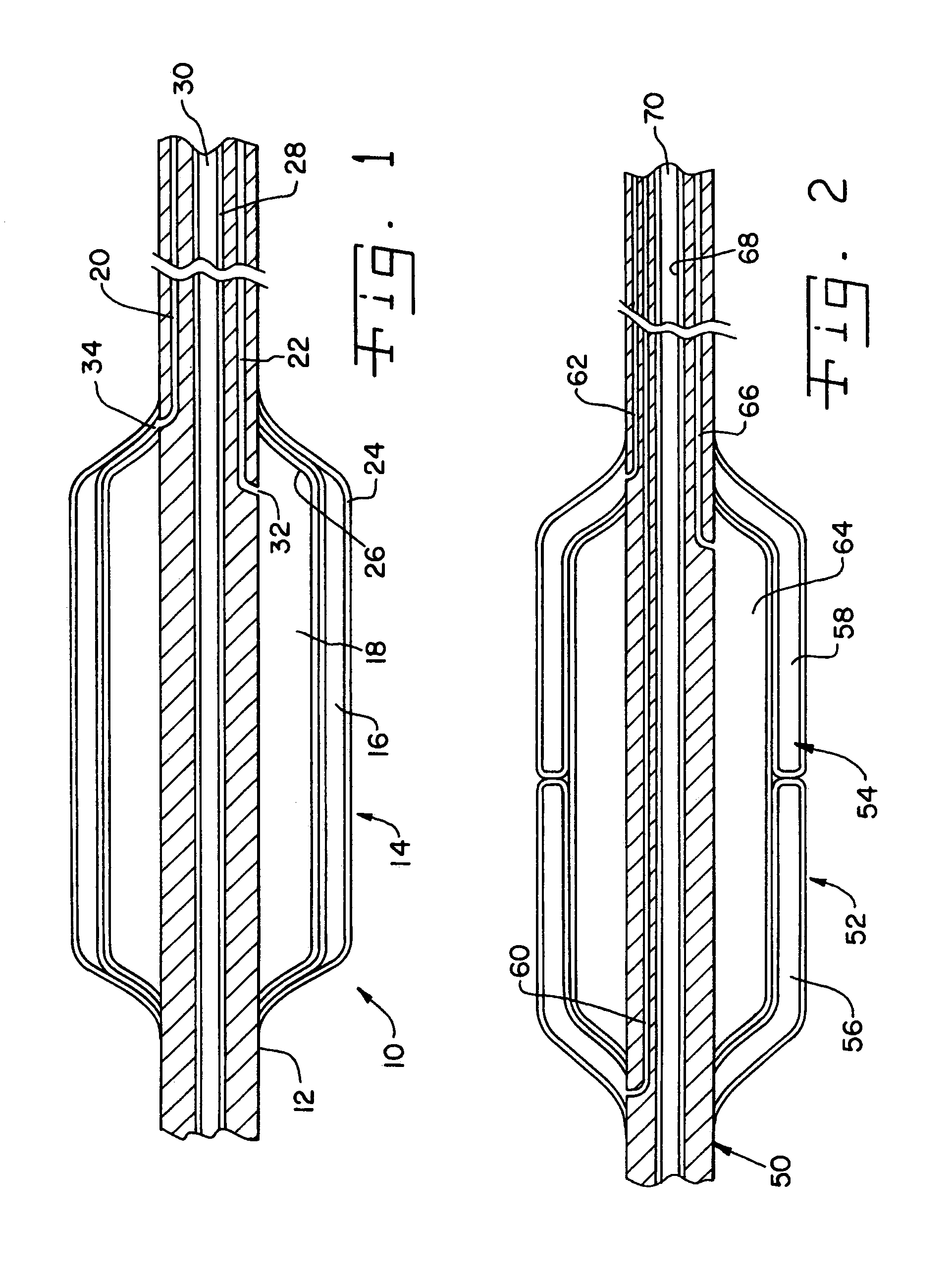
InactiveUS7056274B2Reduce the amount requiredLower the volumeSurgeryDilatorsRadioactive gasExternal catheter
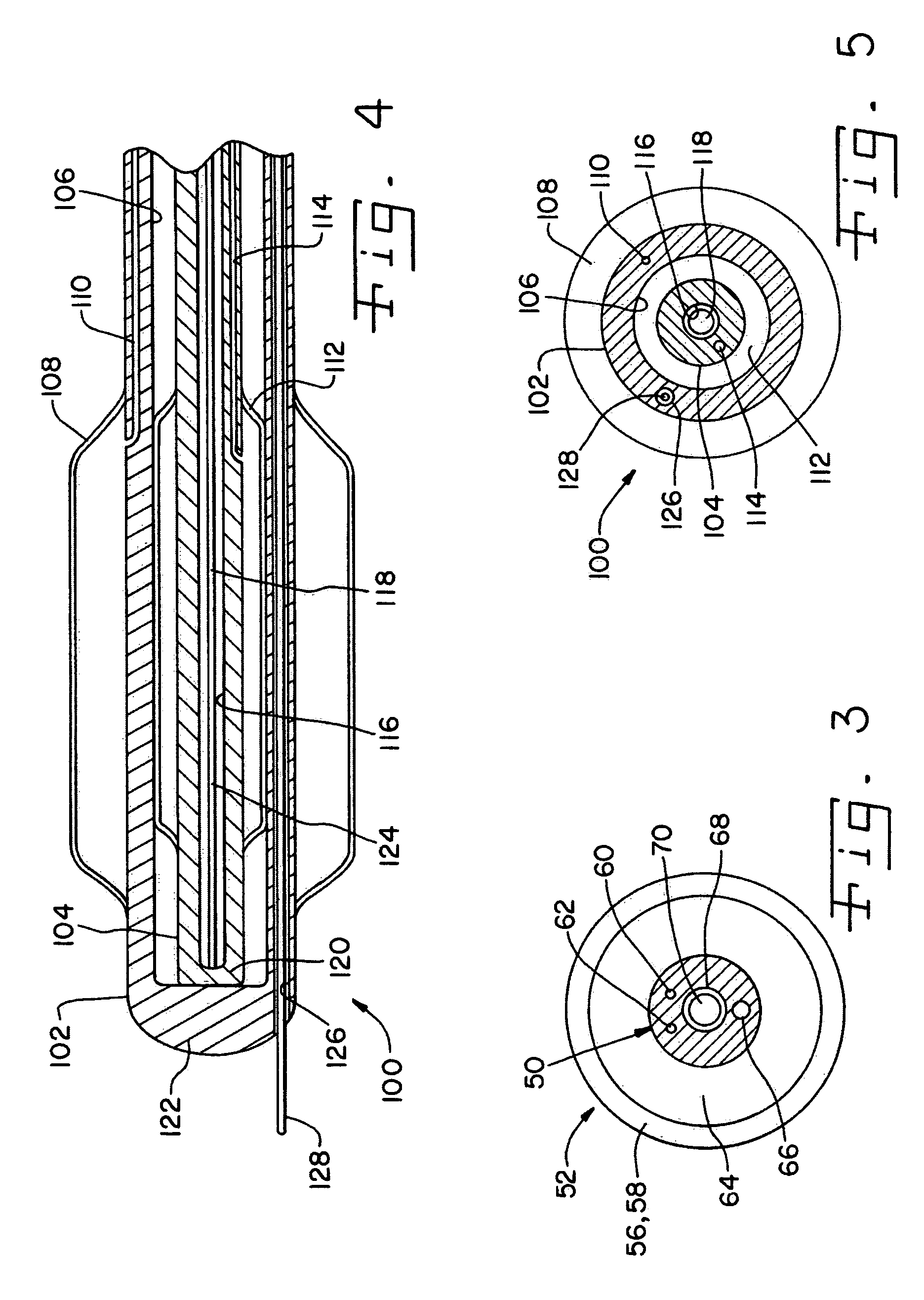
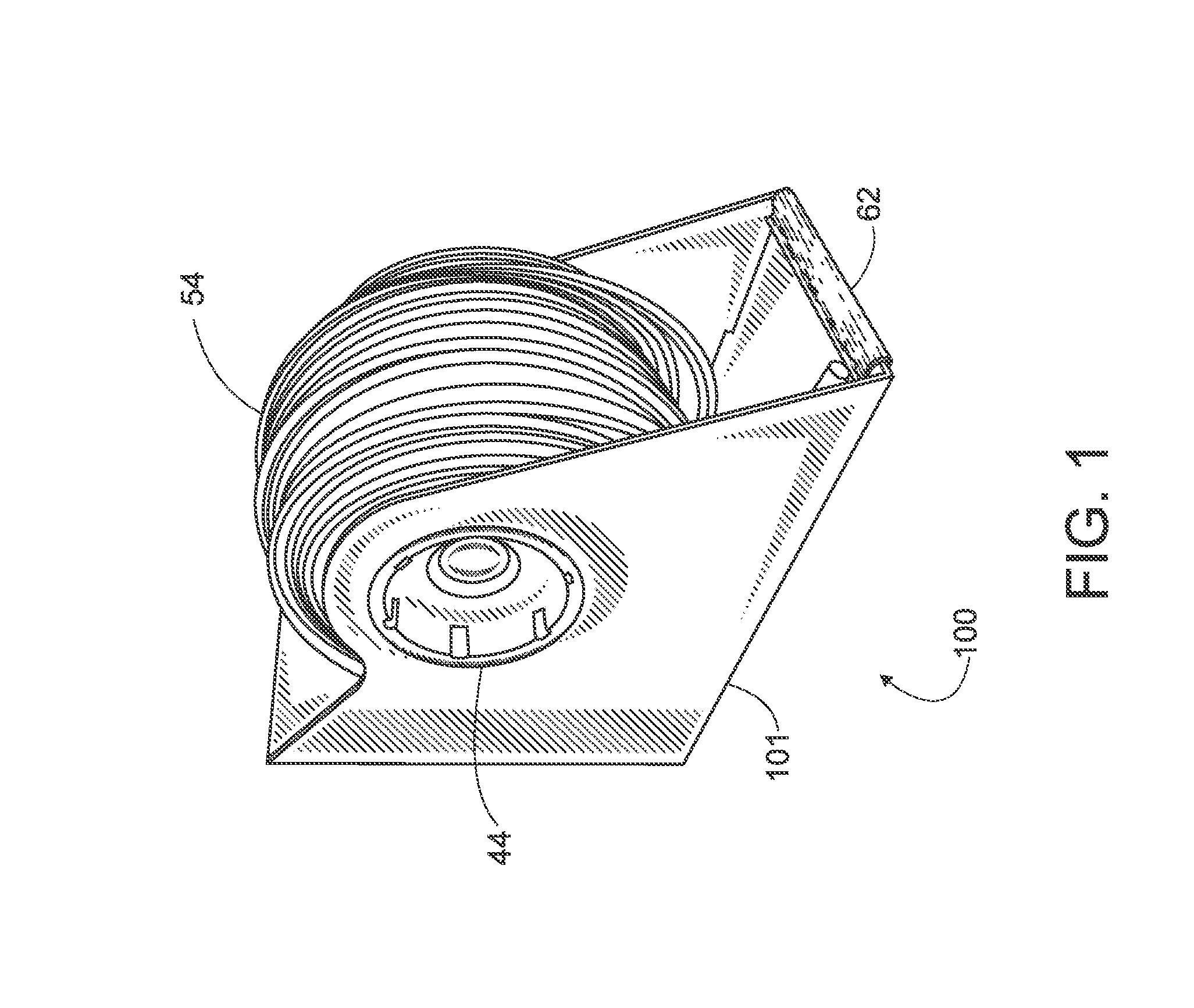
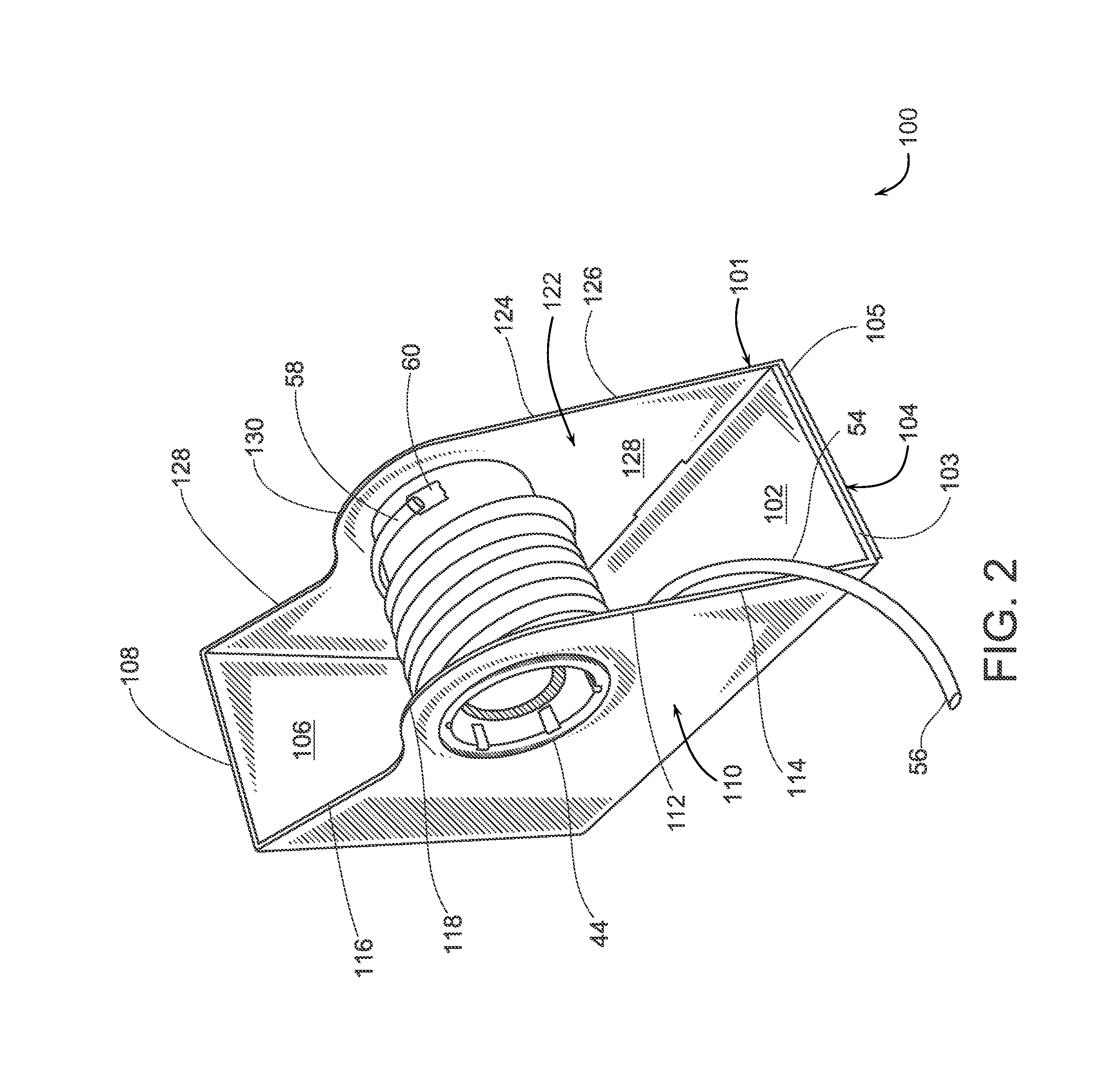
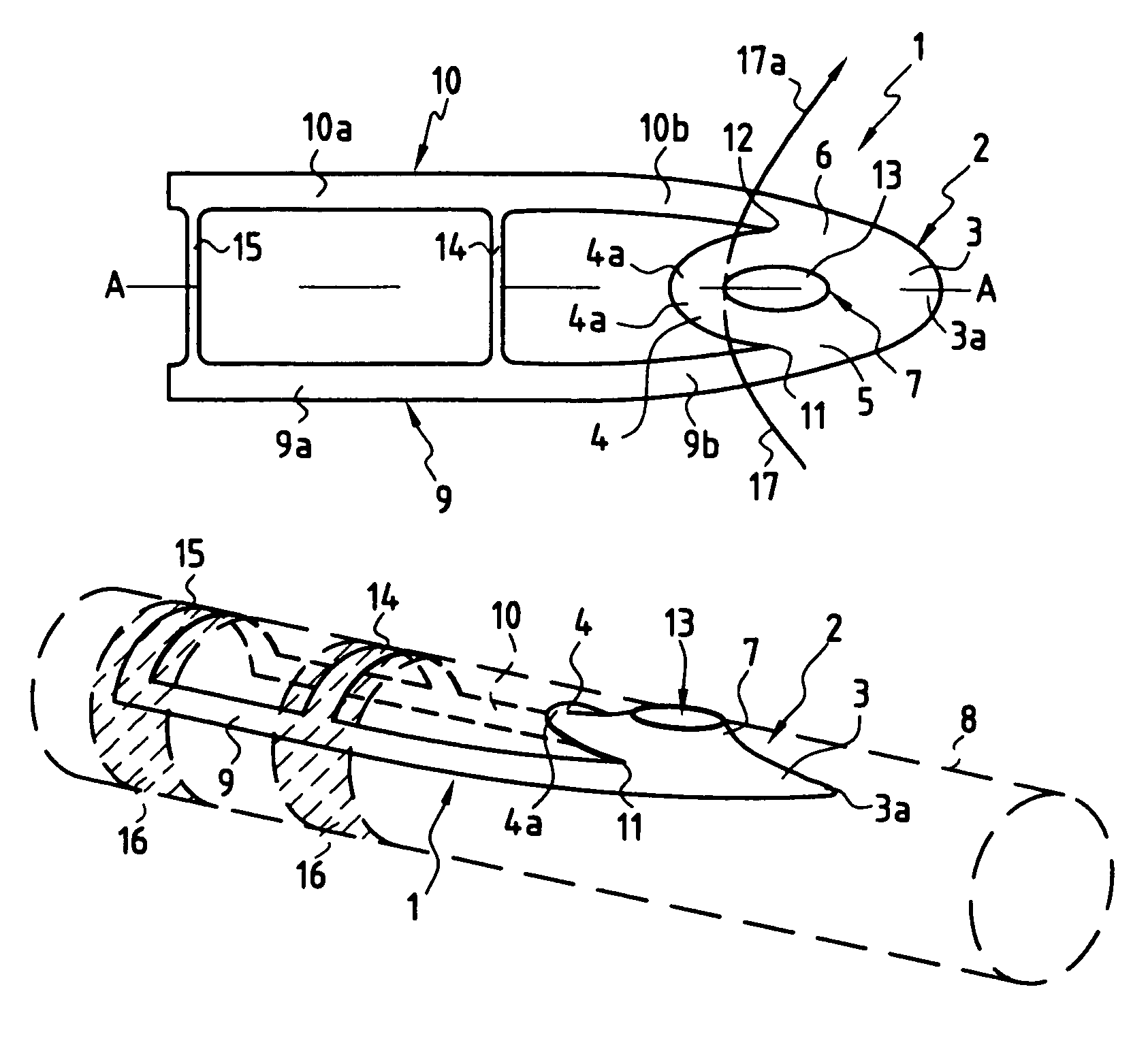
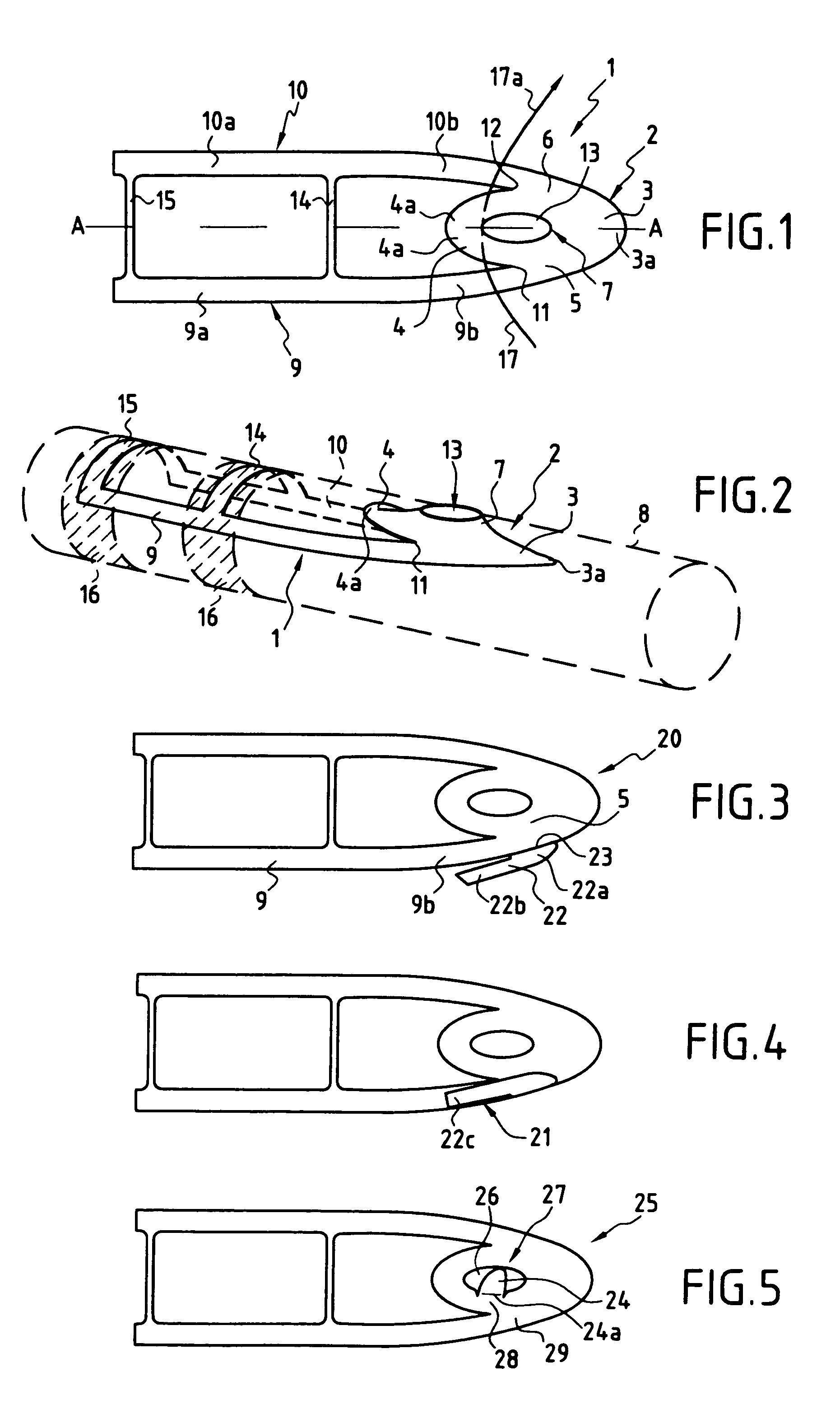
A catheter assembly for use in radiation therapy of a patient by insertion into a vessel, passageway or cavity to deliver radioactive material to a treatment site within the patient. The distal end of the catheter assembly (10) includes a noncompliant inner balloon (18) therearound that is inflatable with a non-radioactive fluid (such as CO2 or saline or contrast medium), and an outer balloon (16) therearound that is inflated with radioactive fluid (such as radiogas like xenon-133 ) and is noncompliant to conform the vessel wall to the balloon's shape at the treatment site for optimal distribution of dose. The inner balloon allows reduction in volume of the amount of radioactive fluid necessary to achieve a desired dose. The inner and outer balloons (112,108) may be affixed to inner and outer catheters (104,102), respectively. Further, a booster radioactive source, preferably removable from the catheter, may also be used to supplement the dose from the outer balloon, such as a radioactive line source (a wire or a seed train (118,234)) within the central catheter lumen (116,230) at the distal end, or a plurality of seeds (320) within flexible cylinders (318) spaced circumferentially around the inner balloon (308) but within the outer balloon (310), or a sleeve (402) around the inner balloon (406) that may be impregnated with iodine-125. A method of providing radiation therapy is disclosed.
Owner:APPLE DR MARC G
Mounting assembly of semiconductor packages prevent soldering defects caused by substrate warpage
InactiveUS20090039490A1Reduce stacking standoffPrevent soldering defectsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor packageEngineering
A mounting assembly of semiconductor packages is revealed, primarily comprising at least a semiconductor package having a plurality of external terminals, a package carrier, and solder paste. The solder paste joints the external terminals to the package carrier. According to the distance to a central line on a substrate of the semiconductor package, the external terminals are divided into at least two different groups. In one of the embodiment, different groups of the external terminals are bumps with non-equal heights to achieve a uniform standoff plane to compensate the warpage of the substrate. The predicted substrate warpage can be compensated without causing any soldering defects. In another embodiment, a plurality of compensating bumps are selectively disposed on one group of the external terminals with larger stacking gaps.
Owner:POWERTECH TECHNOLOGY
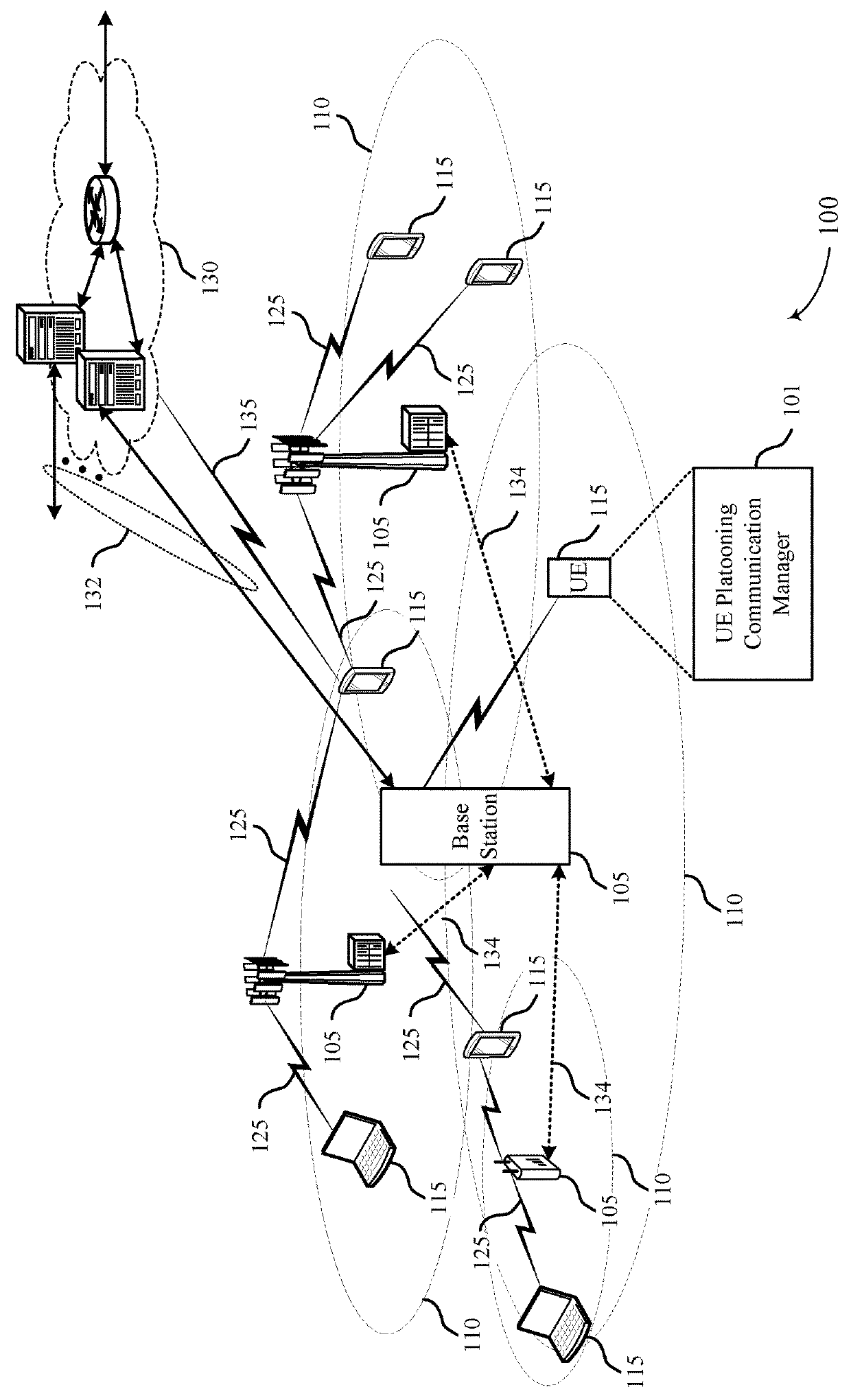
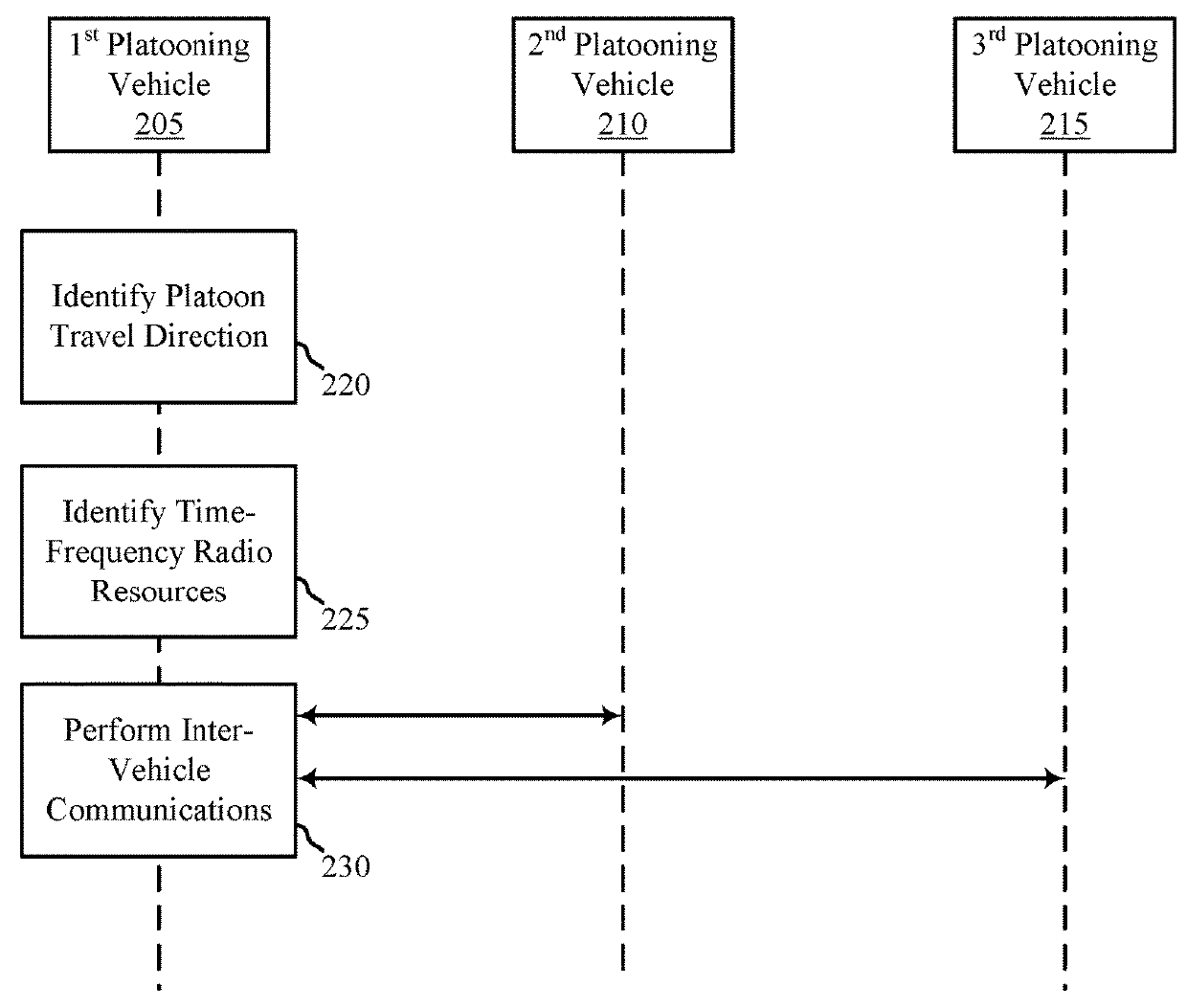
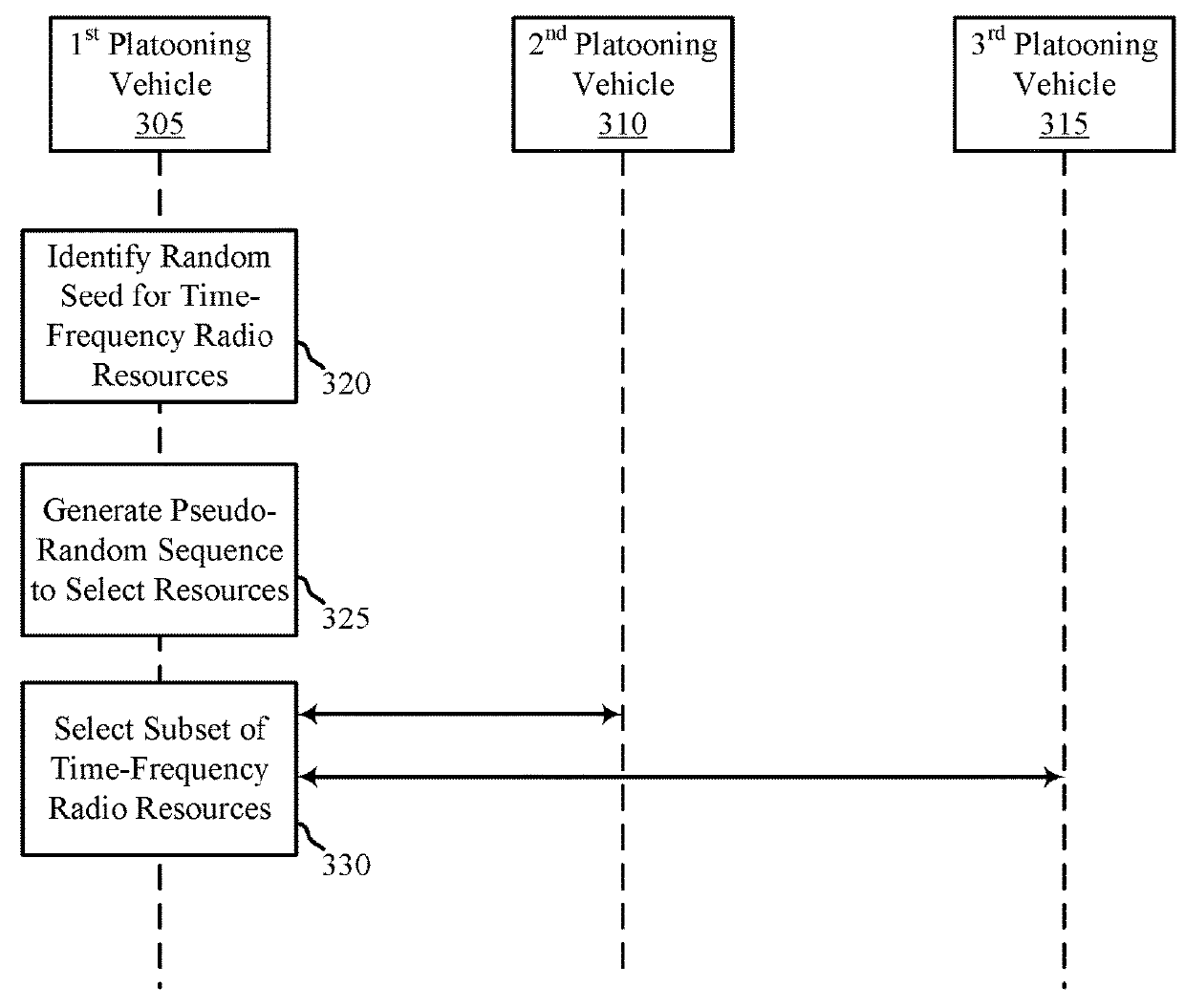
Methods to mitigate inter-platoon interference
ActiveUS20180278385A1Maintain stabilityReduce distanceTransmission path divisionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsInter vehicle communication
Methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described. A user equipment (UE), e.g., a vehicle in a group of platooning vehicles configured for wireless communications, may identify a travel direction of the group of platooning vehicles. The UE may identify a set of time-frequency radio resources allocated to the travel direction. The UE may perform inter-vehicle communications with one or more neighboring vehicles of the group of platooning vehicles using the set of time-frequency radio resources.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
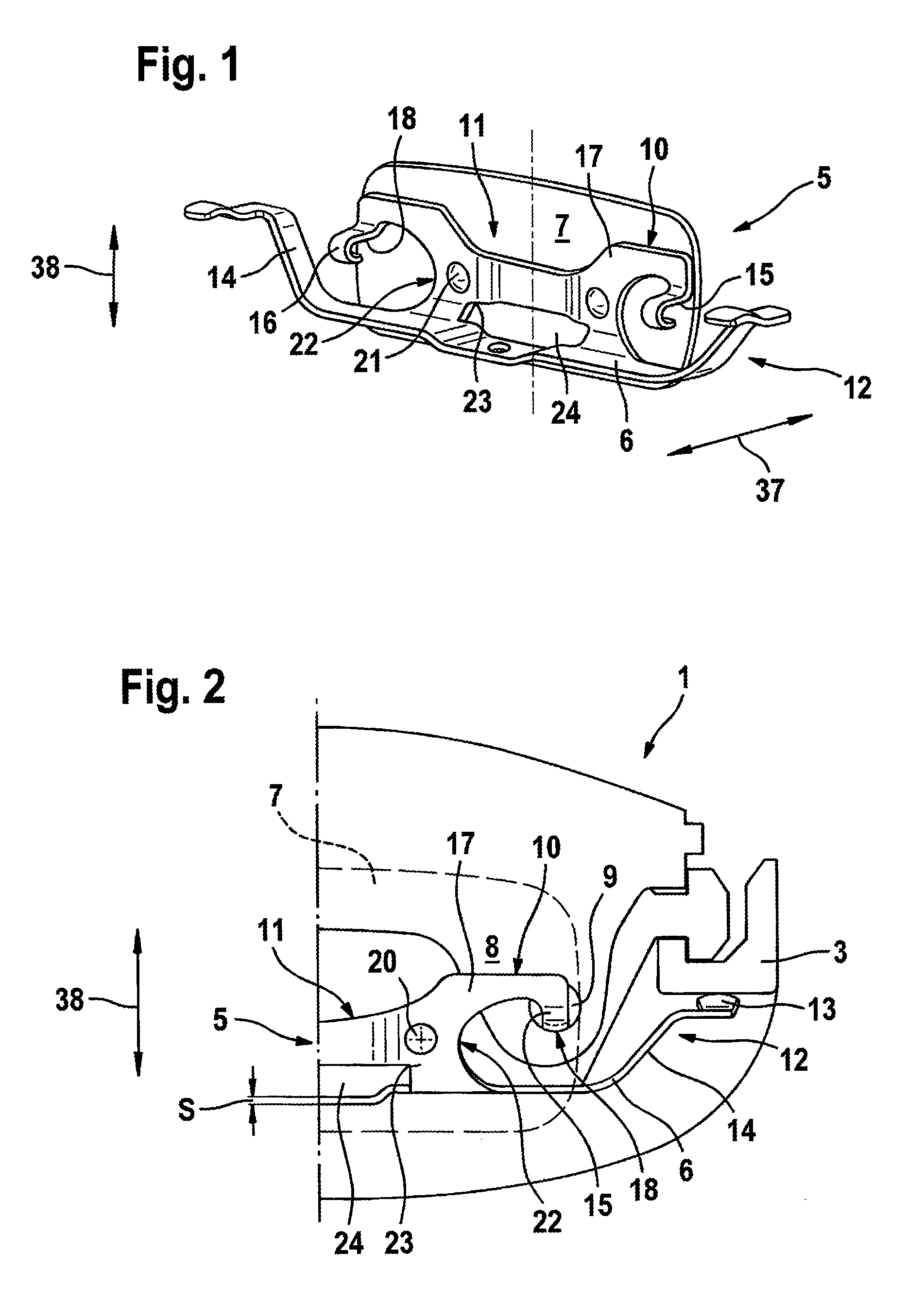
Disk Brake With Guard Screen
ActiveUS20090152056A1Avoid disadvantagesFixed spacingAxially engaging brakesSlack adjustersCalipersBrake lining
A disk brake for a vehicle having a bracket which is fixed with respect to the vehicle and on which brake linings and at least one brake caliper are mounted so as to be movable in an axial direction is disclosed. The bracket and the brake caliper engage around at least one brake disk, and the brake caliper includes a housing limb with at least one actuating device, a further housing limb with at least one housing finger, and a housing bridge. A spring arrangement which generates an elastic preload between the brake caliper and the bracket is provided in such a way that the preload is aligned substantially perpendicular to a movement direction of the brake caliper. The spring arrangement comprises a spring element and a protective panel.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
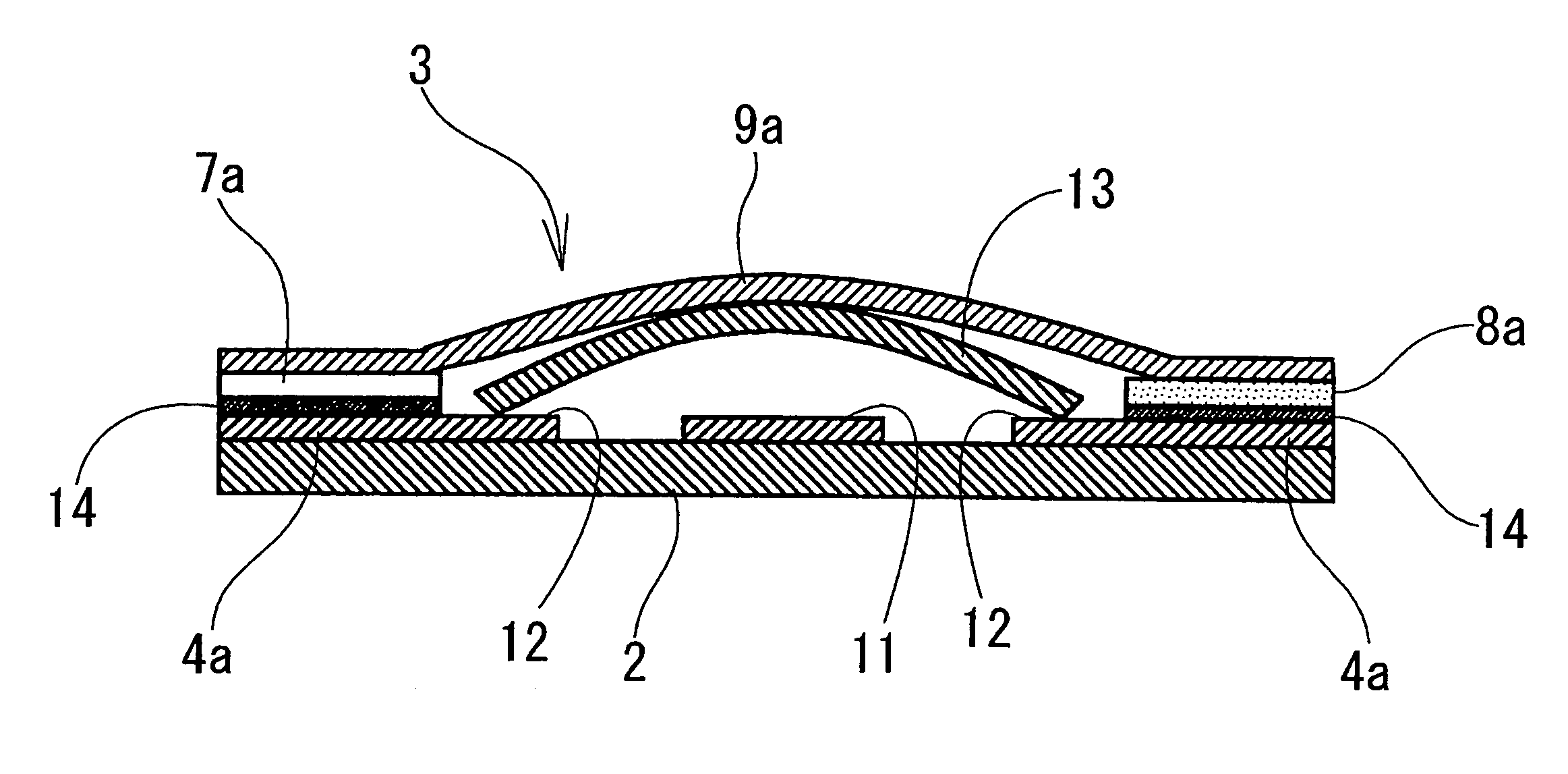
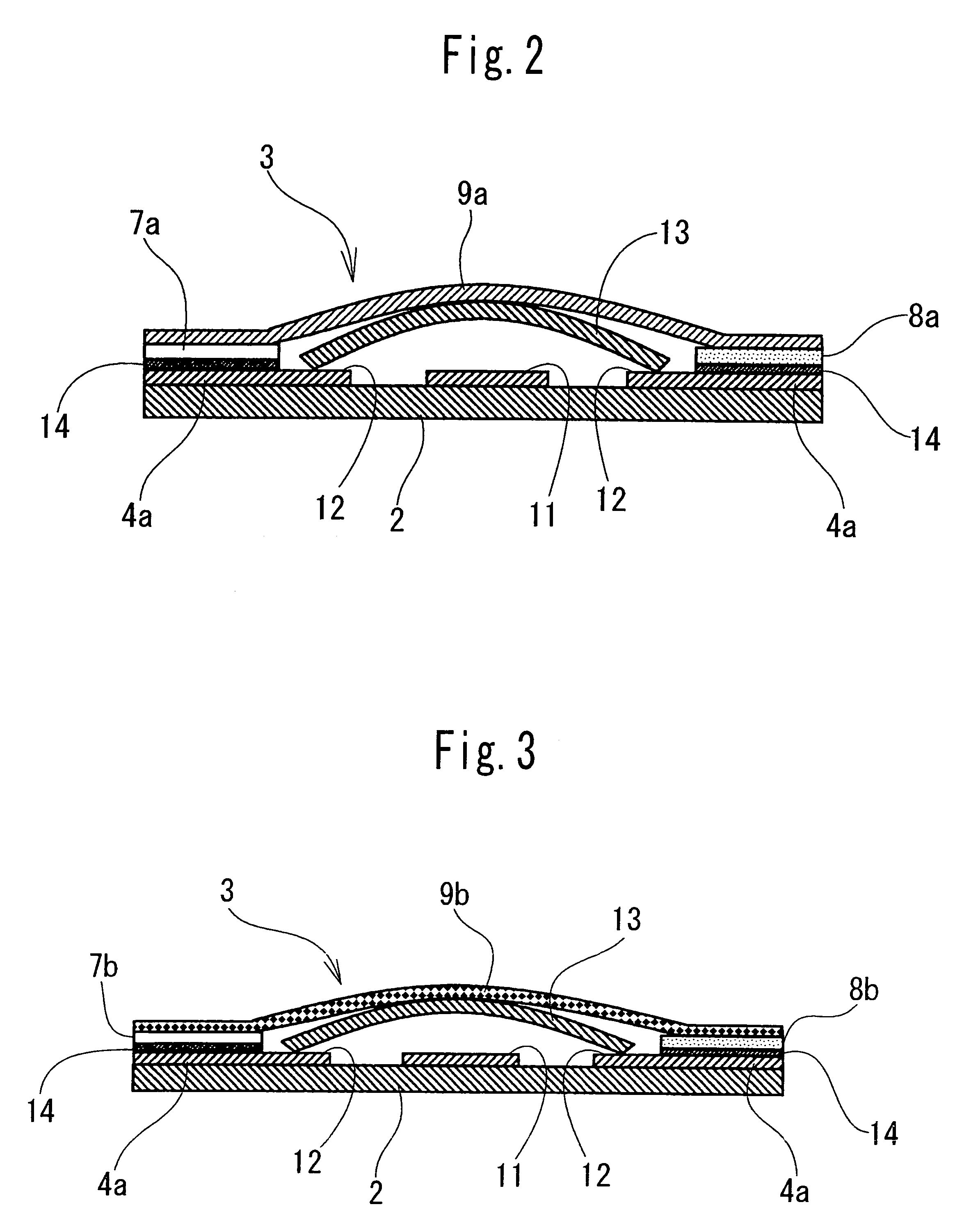
Multiple stacked-chip packaging structure
ActiveUS20050035461A1Facilitate the processFixed spacingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWire bondingElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention provides a multiple stacked-chip packaging structure, including: at least one lower layer chip located on a substrate, wherein a plurality of wires are electrically connected to the bonding pads on the lower layer chip and to the substrate; at least one carrier cap provided on the lower layer chip to provide an accommodating space to the bonding pads and the wires on the lower layer chip; at least one upper layer chip provided on the carrier cap, wherein a plurality of wires are electrically connected to the bonding pads on the upper layer chip and to the substrate; and finally, a Molding Compound used to wrap up the foregoing components. The advantages of the invention are that the invention is not limited by the layout patterns of bonding pads on the chip, that the needed chips can be placed on either the upper layer or the lower layer structure according to the requirement, and that the degree of coplanar can be ensured when performing wire bonding on the upper layer chip so as to facilitate the wire bonding process.
Owner:ASE ASSEMBLY & TEST SHANGHAI +1
Instrument system for the insertion of intervertebral disk implants
InactiveUS20060085011A1Reliable functionHinder surgeonDiagnosticsJoint implantsSpinal Disk ImplantForceps
The invention relates to an instrument system for the insertion of intervertebral disk implants including two implant plates and one implant core comprising at least one trial unit including two trial elements of preferably plate shape for the determination of an implant suitable for the respective patient, at least one machining unit for the preparation of the surfaces of the bodies of the vertebra of the patient which includes operating elements having two sections of preferably forked shape and at least one holding unit which can be coupled to the implant plates for the insertion of the implant, with the trial unit, the machining unit and the holding unit each being able to be coupled to a traction instrument in particular in the manner of forceps for the pressing apart of the trial elements, the operating elements or the implant elements.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Blow molding device
InactiveUS20100092600A1Fixed spacingShorten speedCeramic shaping apparatusDomestic articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A blow molding device capable of securely holding a built-in part in a prescribed position in an interior of a blow molded article with a compact equipment. The blow molding device includes a blow mold and a built-in part holding unit. The built-in part holding unit includes a holding rod adapted to hold the built-in part and arranged to freely advance and retreat to be removed from the blow mold. The blow mold includes a slide core in each of two mold members so as to freely advance and retreat relative to a cavity of the blow mold, and a drive control pin in each of mating faces of split two mold members, and the drive control pin and the slide core are linked with a linking member. The slide core is driven with the drive control pin such that when the blow mold is closed, the slide core retreats from an interior of the cavity to a molding surface defining the same at the same speed as the closing speed of the blow mold.
Owner:FTS
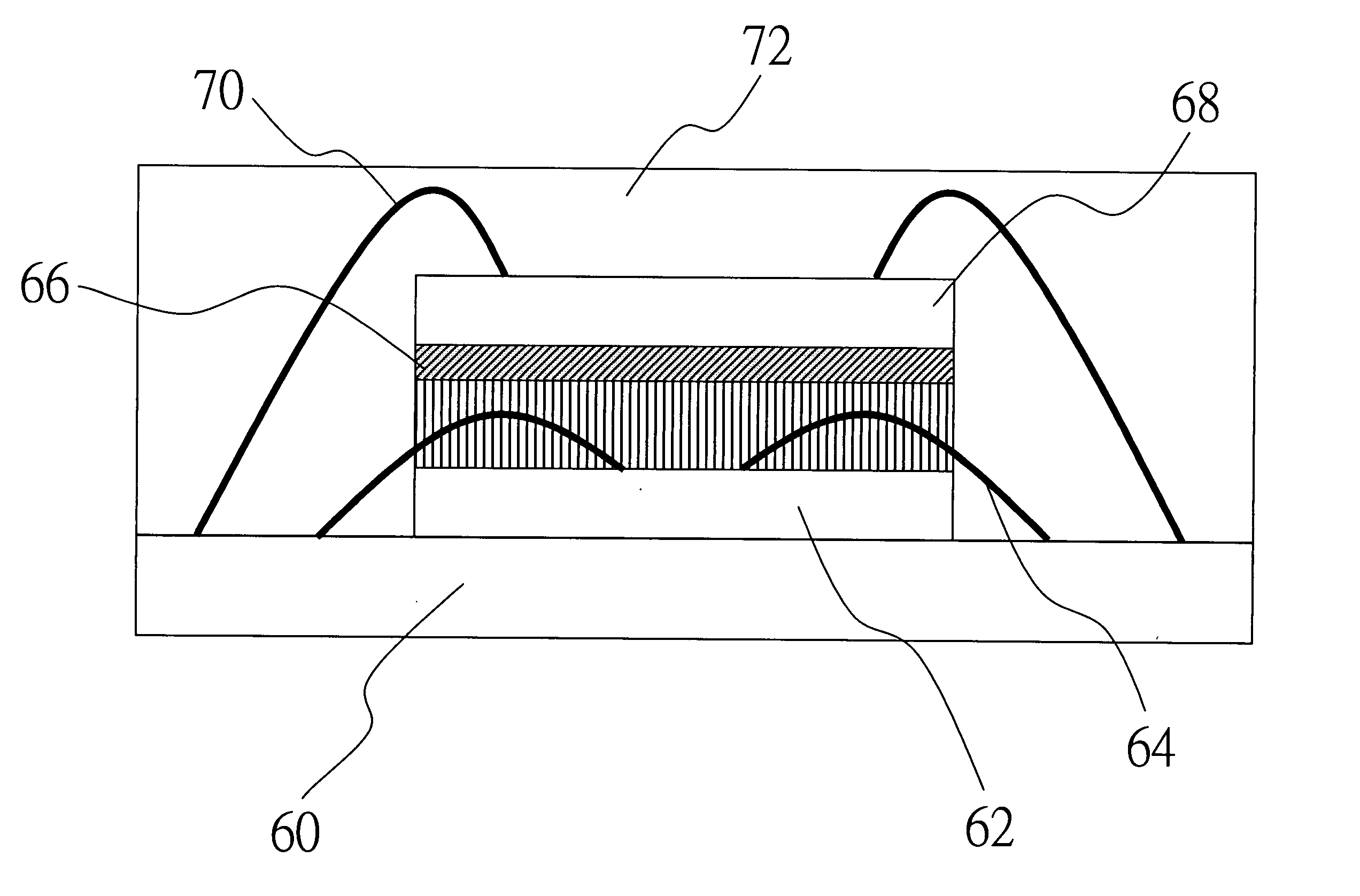
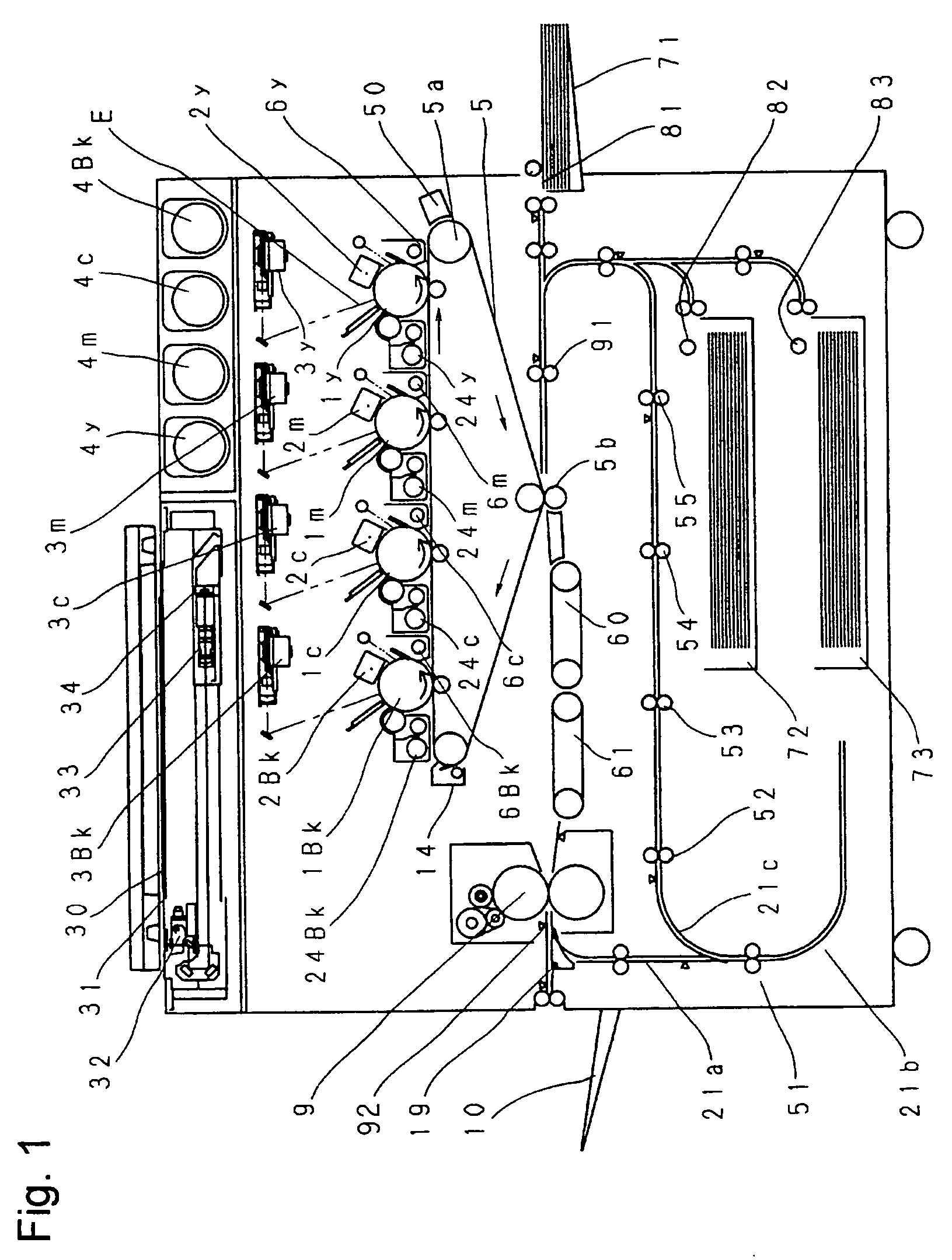
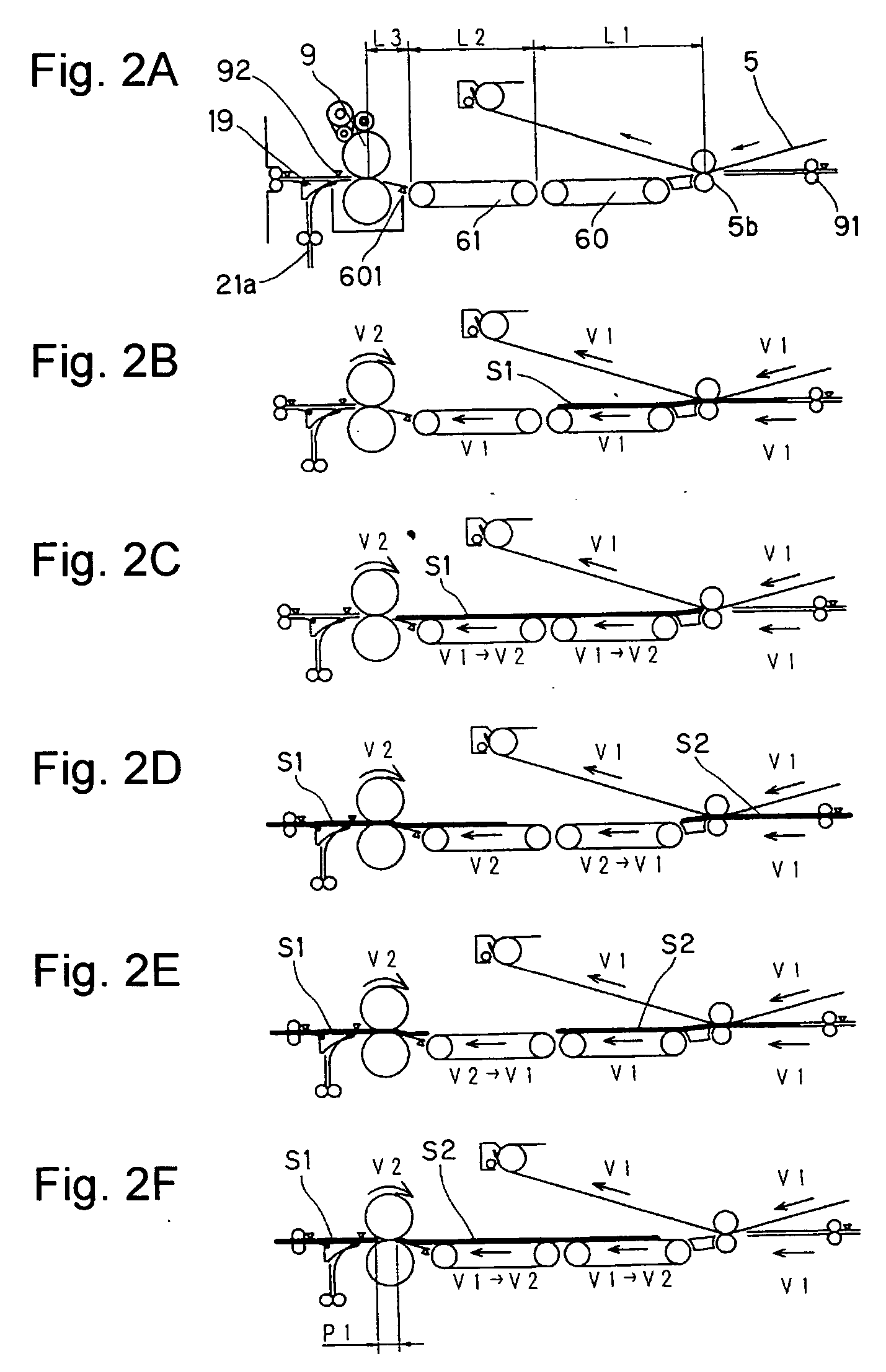
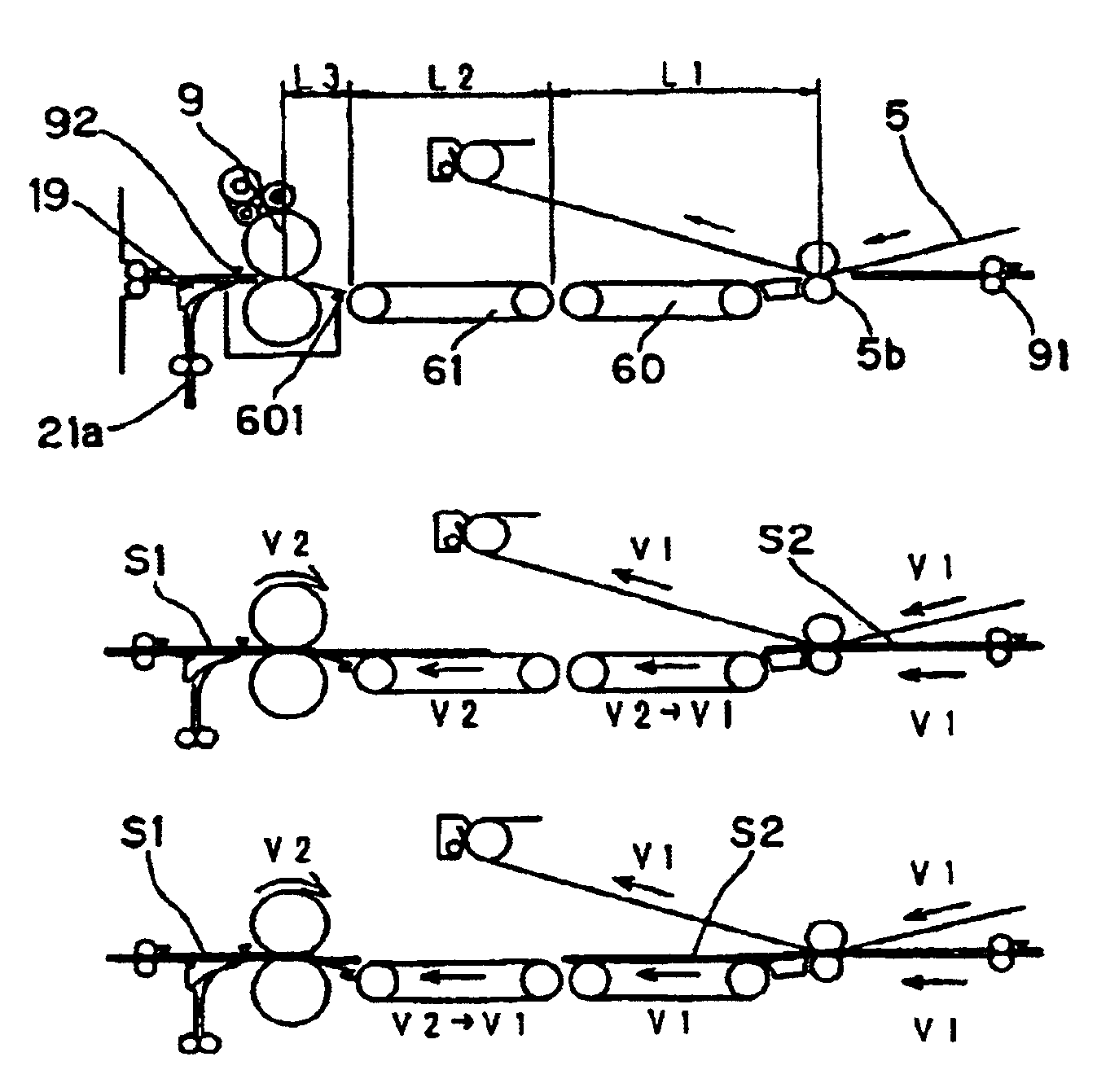
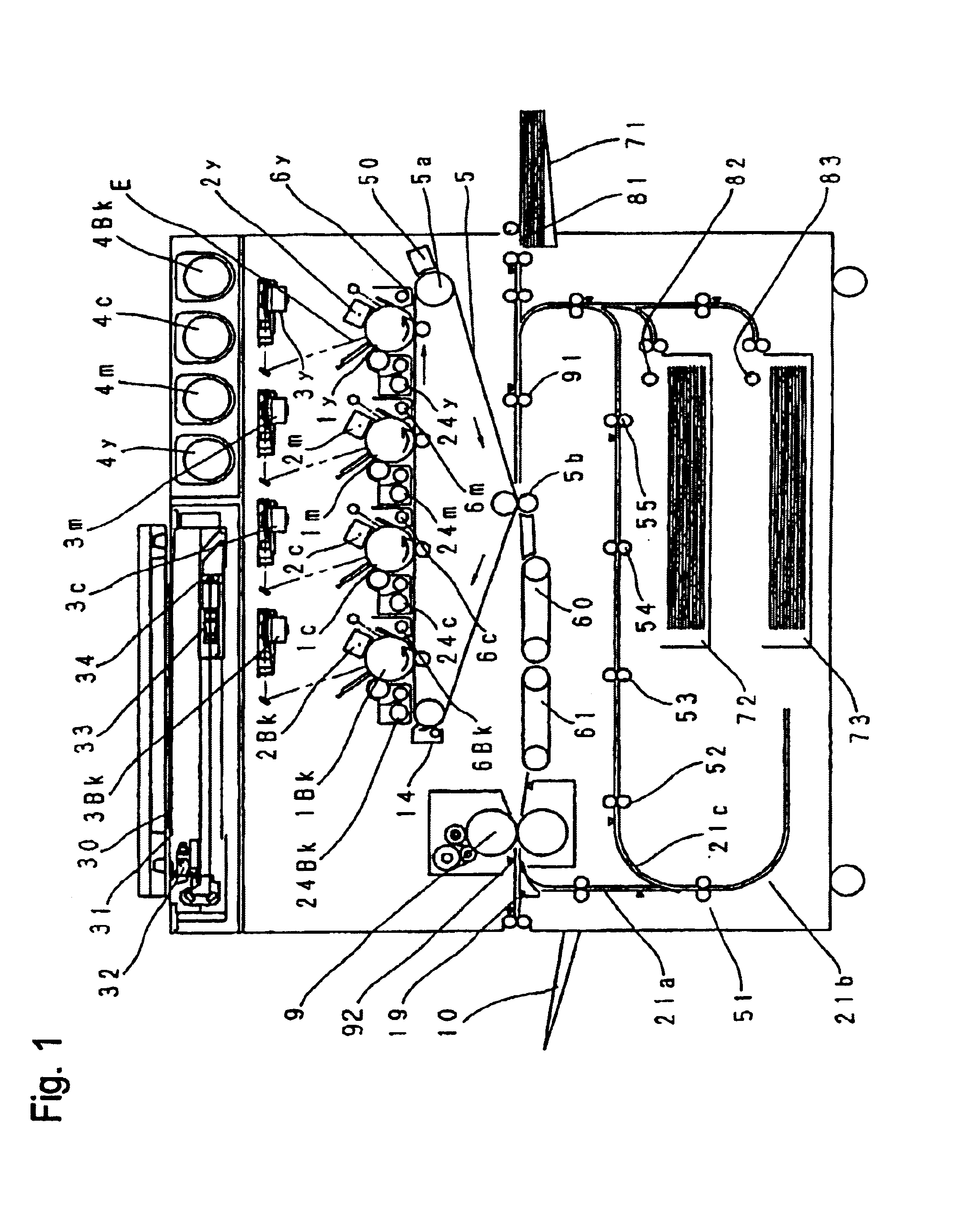
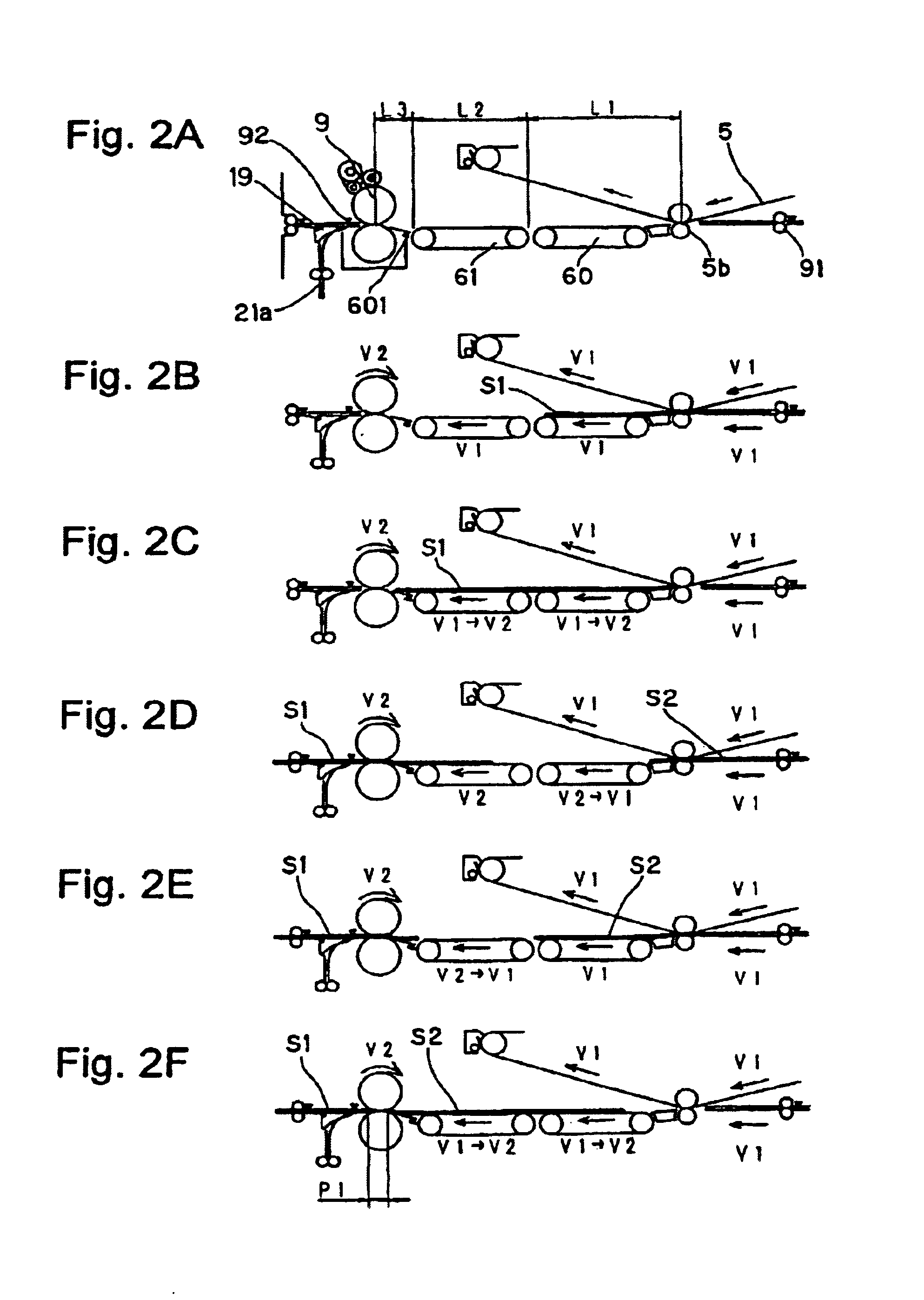
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20050169683A1Shorten the time periodWell formedElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersImaging qualityImage formation
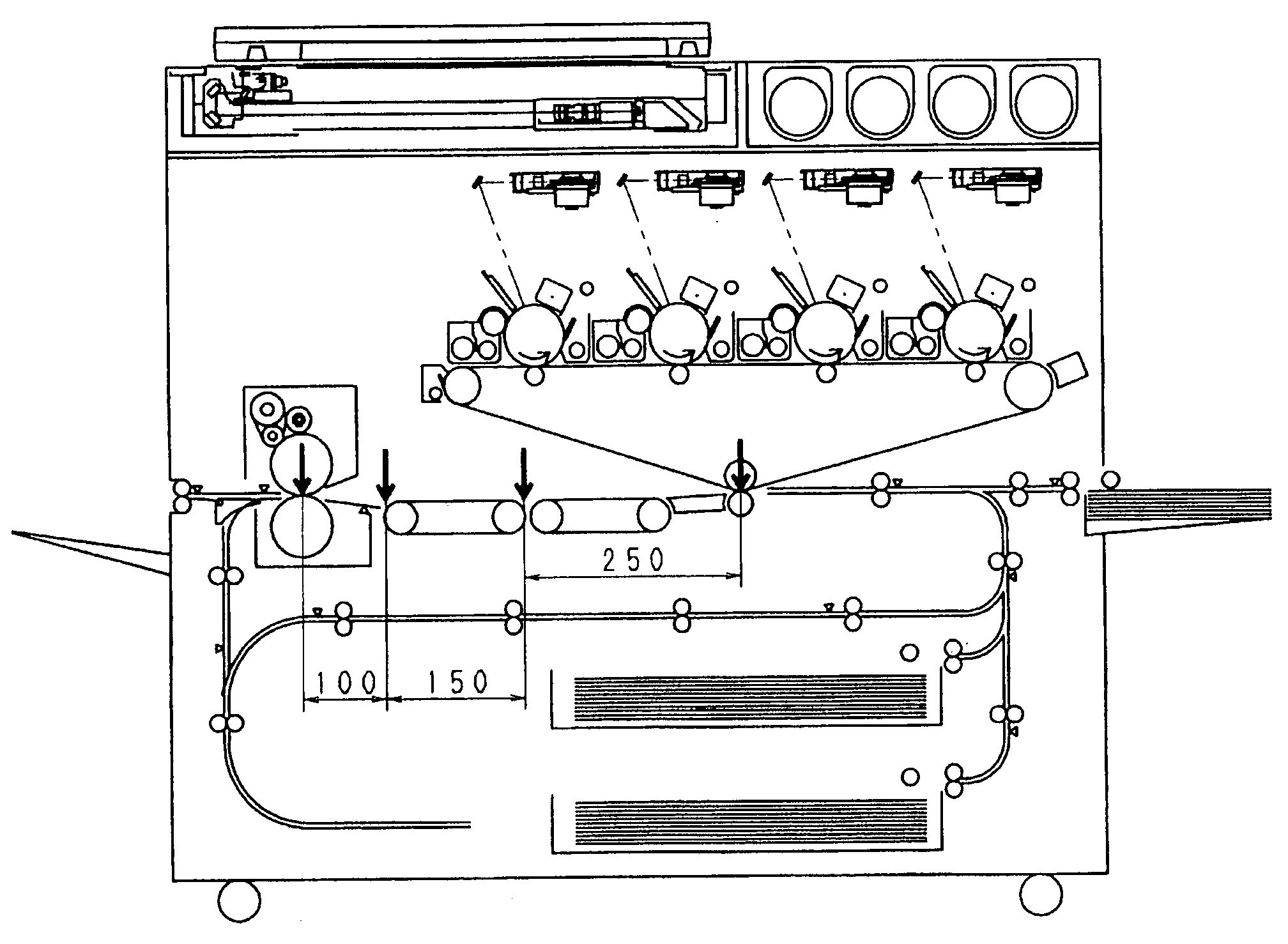
In case a fixing speed is lower than a transferring speed, the individual conveyor units are controlled such that, while a downstream conveyor unit (61) is conveying a sheet (S1) being fixed at the same speed (V2) as the fixing speed, an upstream conveyor unit (60) may convey the succeeding sheet (S2) at the same speed (V1) as the transferring speed. As a result, the spacing of the two sheets in a fixing unit (9) can be sufficiently narrowed to improve the image forming efficiency. Moreover, the transferring speed need not be decelerated according to the fixing speed. It is, therefore, possible to prevent the deterioration in the image quality and to shorten the image forming time period of the first sheet.
Owner:CANON KK
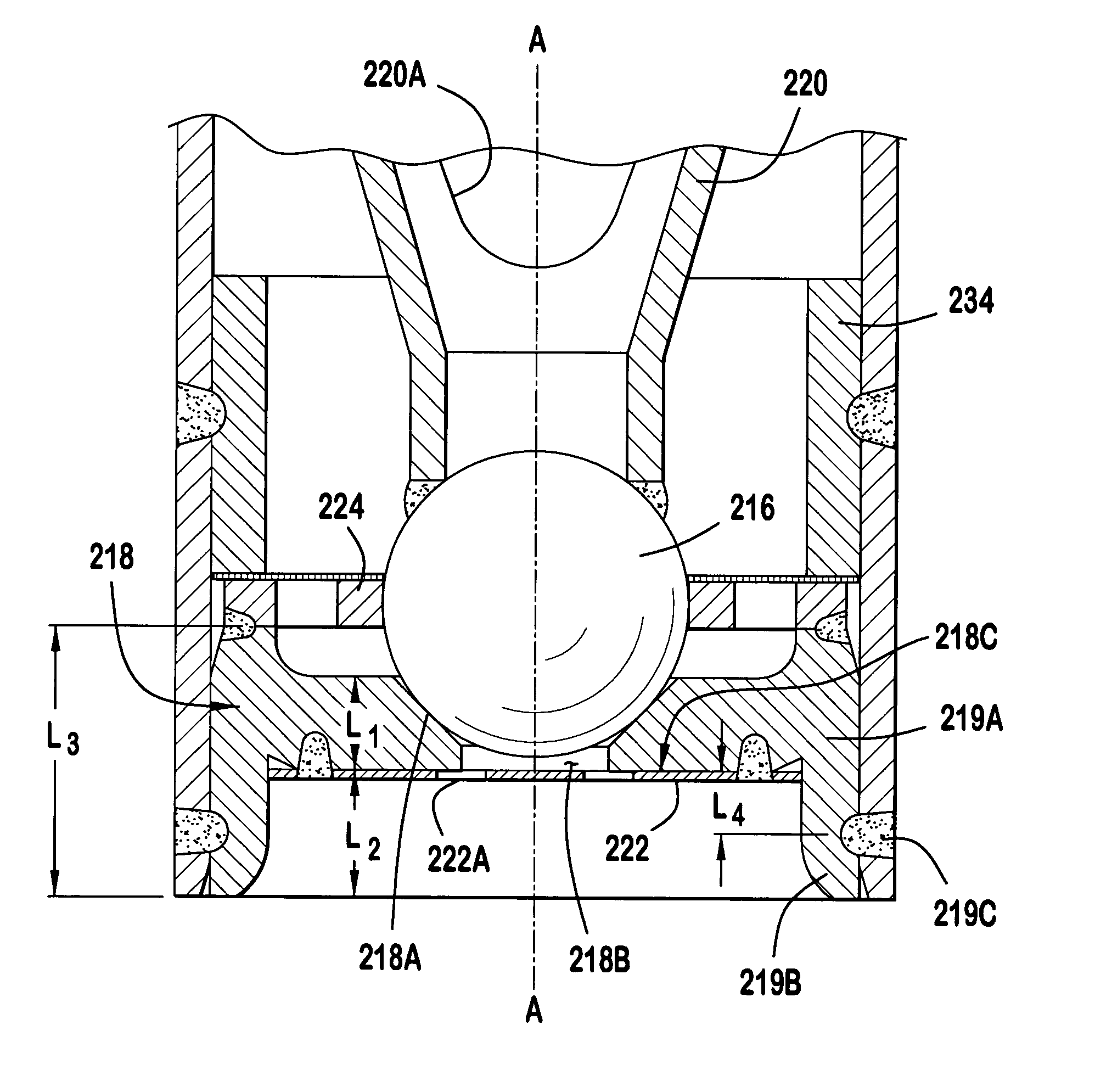
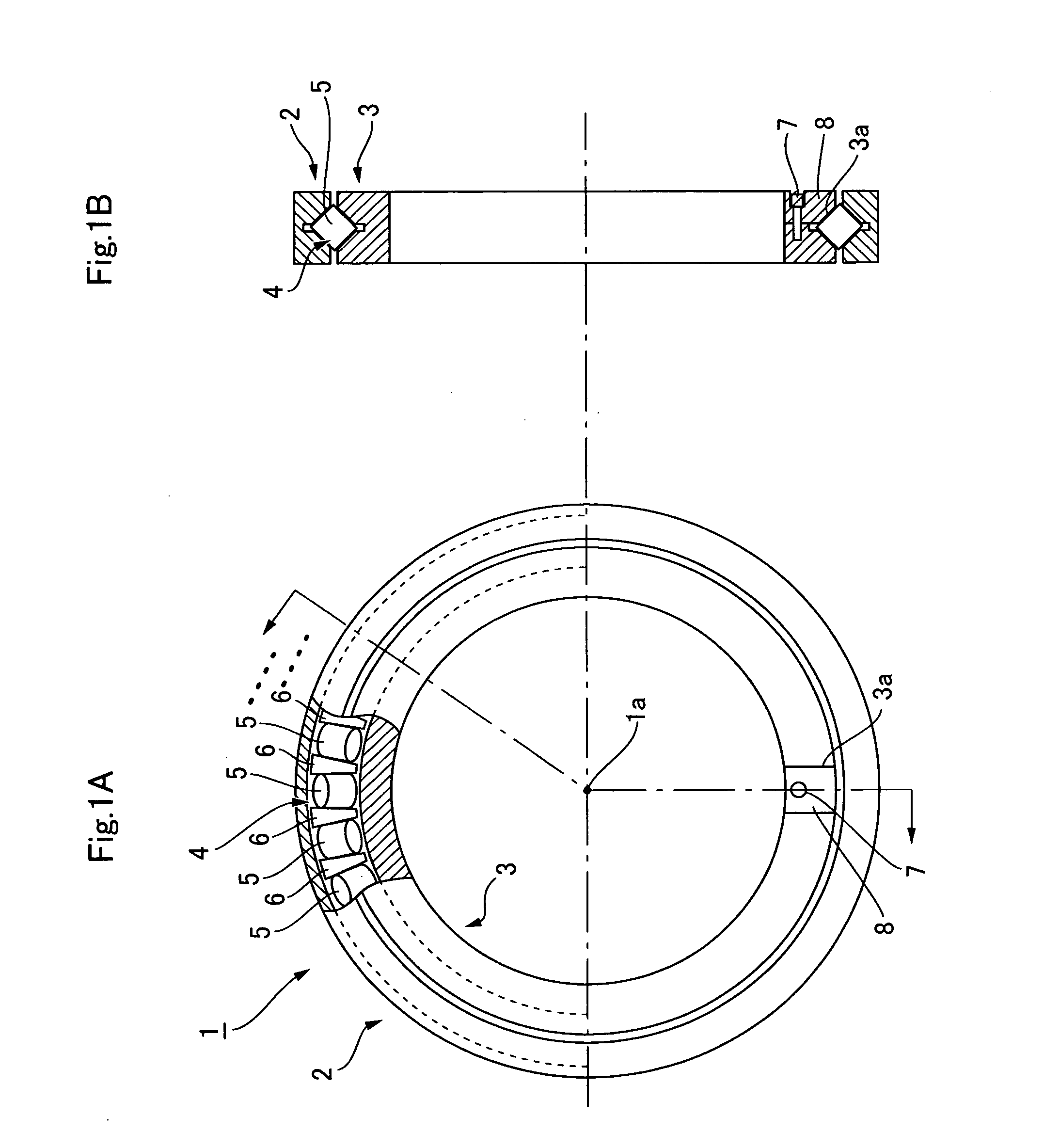
Crossed roller bearing retainer and crossed roller bearing
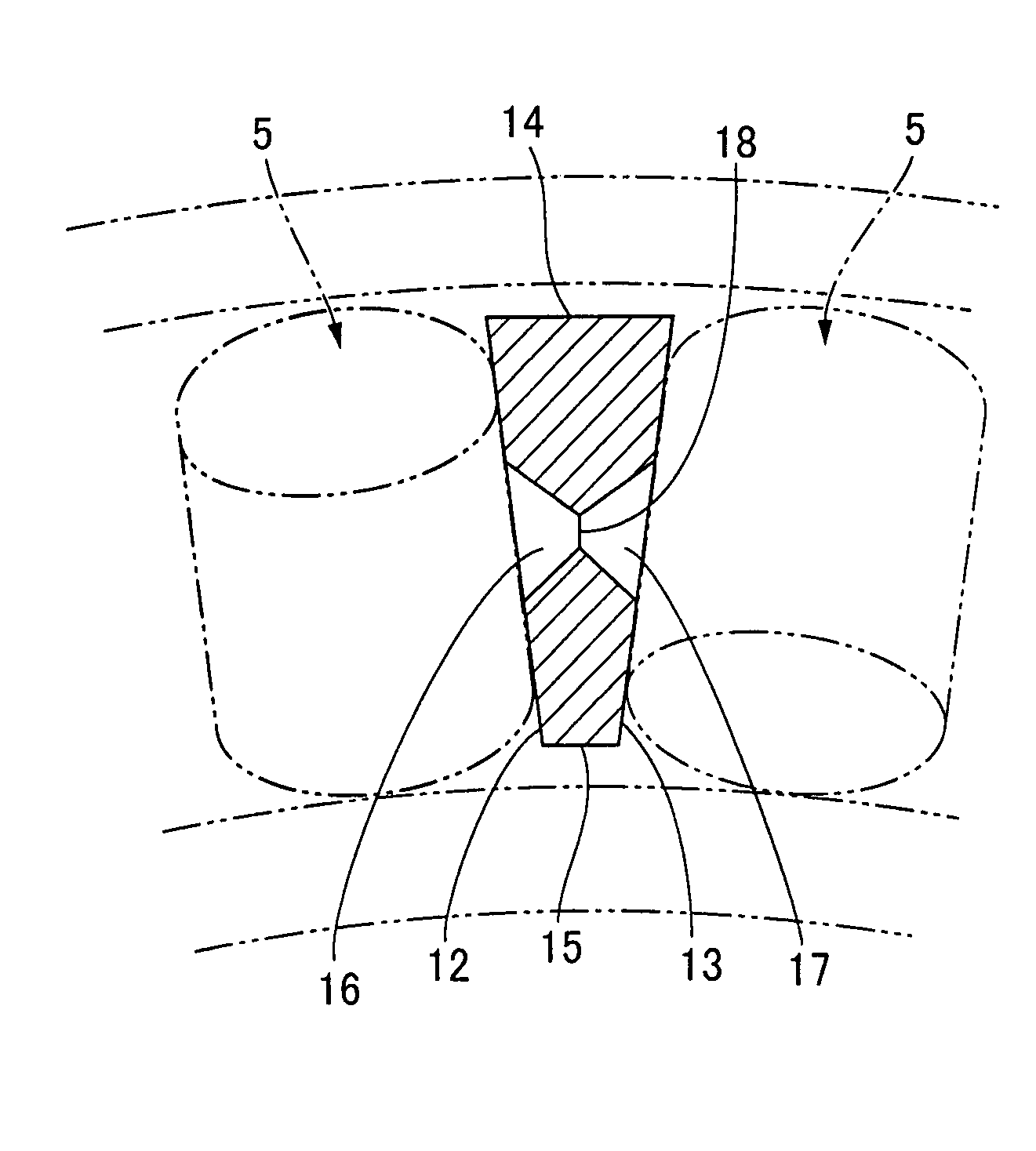
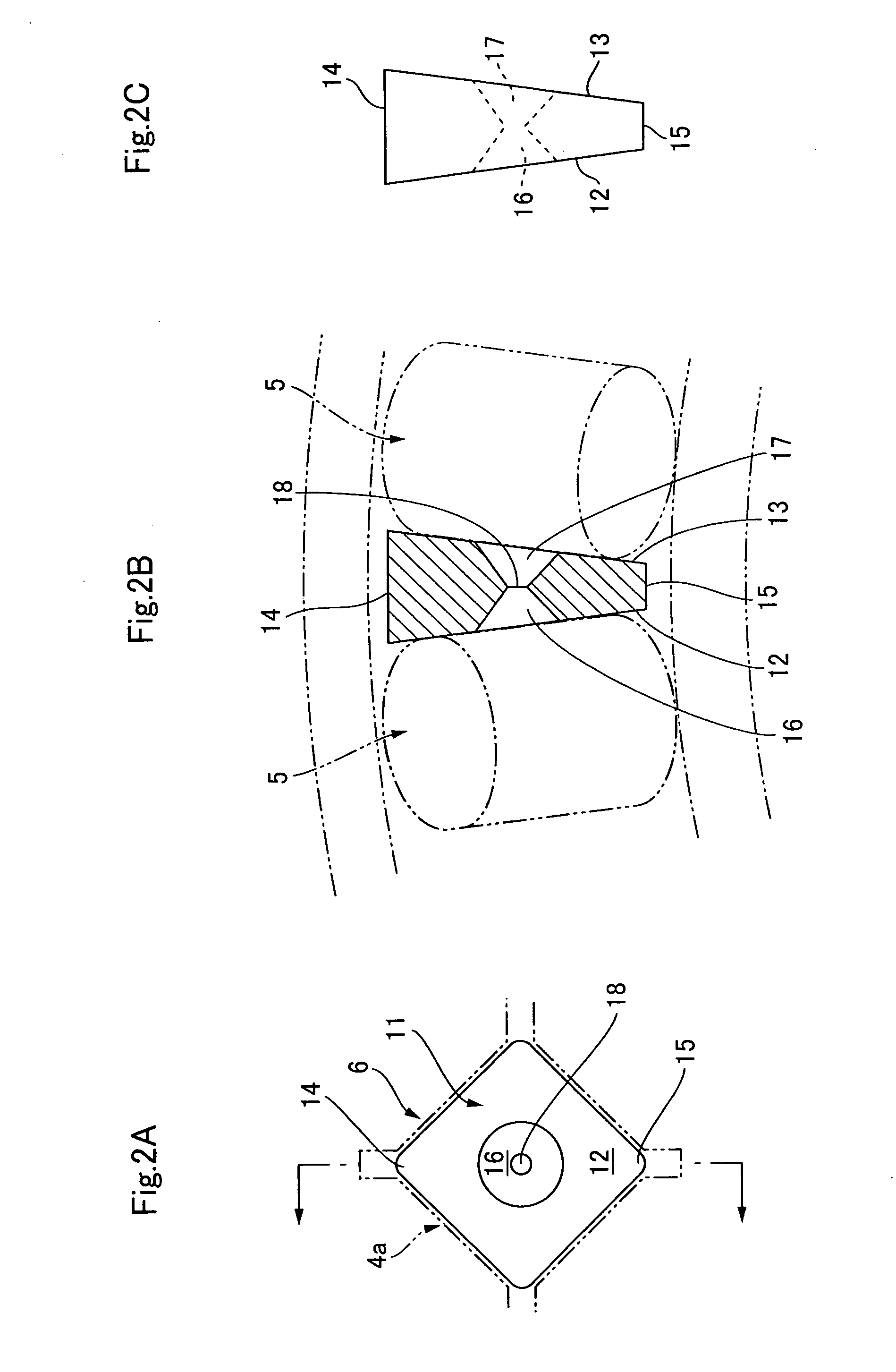
A retainer of a crossed roller bearing has a retainer body plate of rectangular profile corresponding to a rectangular cross-section of a race. Rectangular side surfaces on either side of the retainer body plate are inclined planes that slant in a direction of approaching one another from one corner to another corner along a diagonal line of the surfaces, and extend towards a bearing center in a state of having been installed in the race. Recesses for accumulating grease are formed in center portions of the rectangular side surfaces, the recesses communicating via a through-hole. The rectangular side surfaces are in linear contact with the circular external circumferential surfaces of adjacent rollers and hold the rollers at a fixed spacing. There is obtained a retainer for an uncomplicatedly configured crossed roller bearing that allows adjacent rollers to be held at a fixed spacing and is provided with a grease accumulator.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
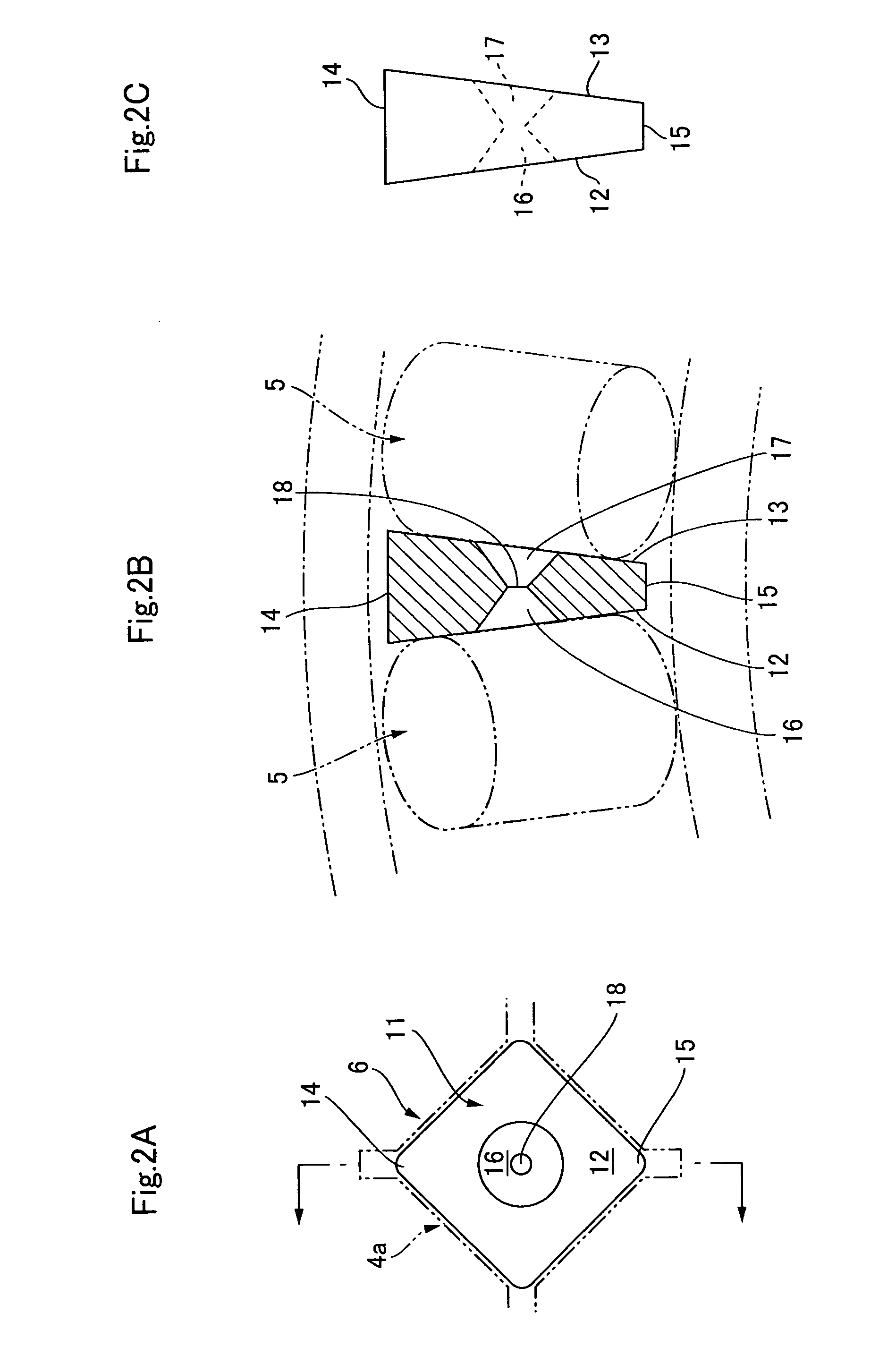
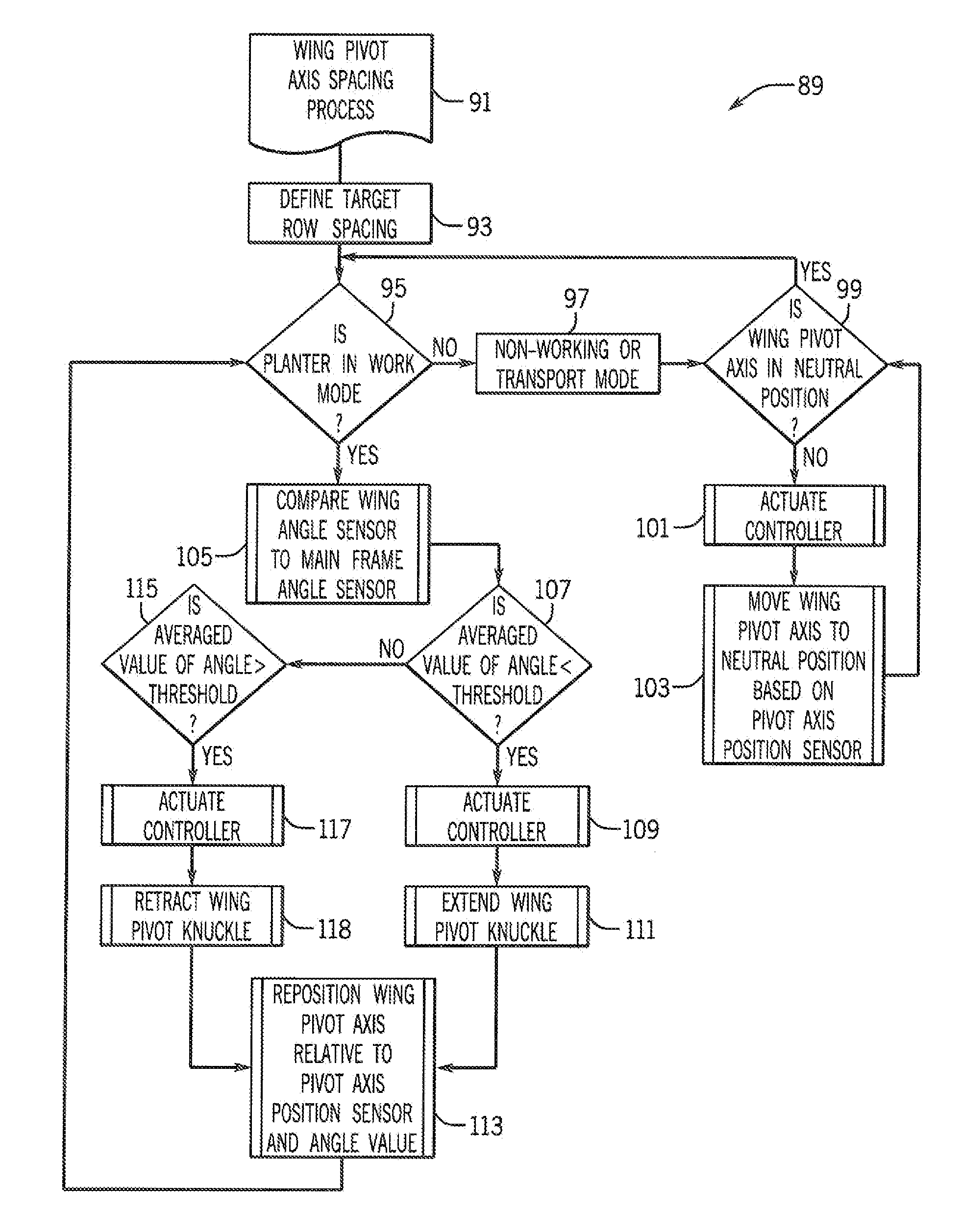
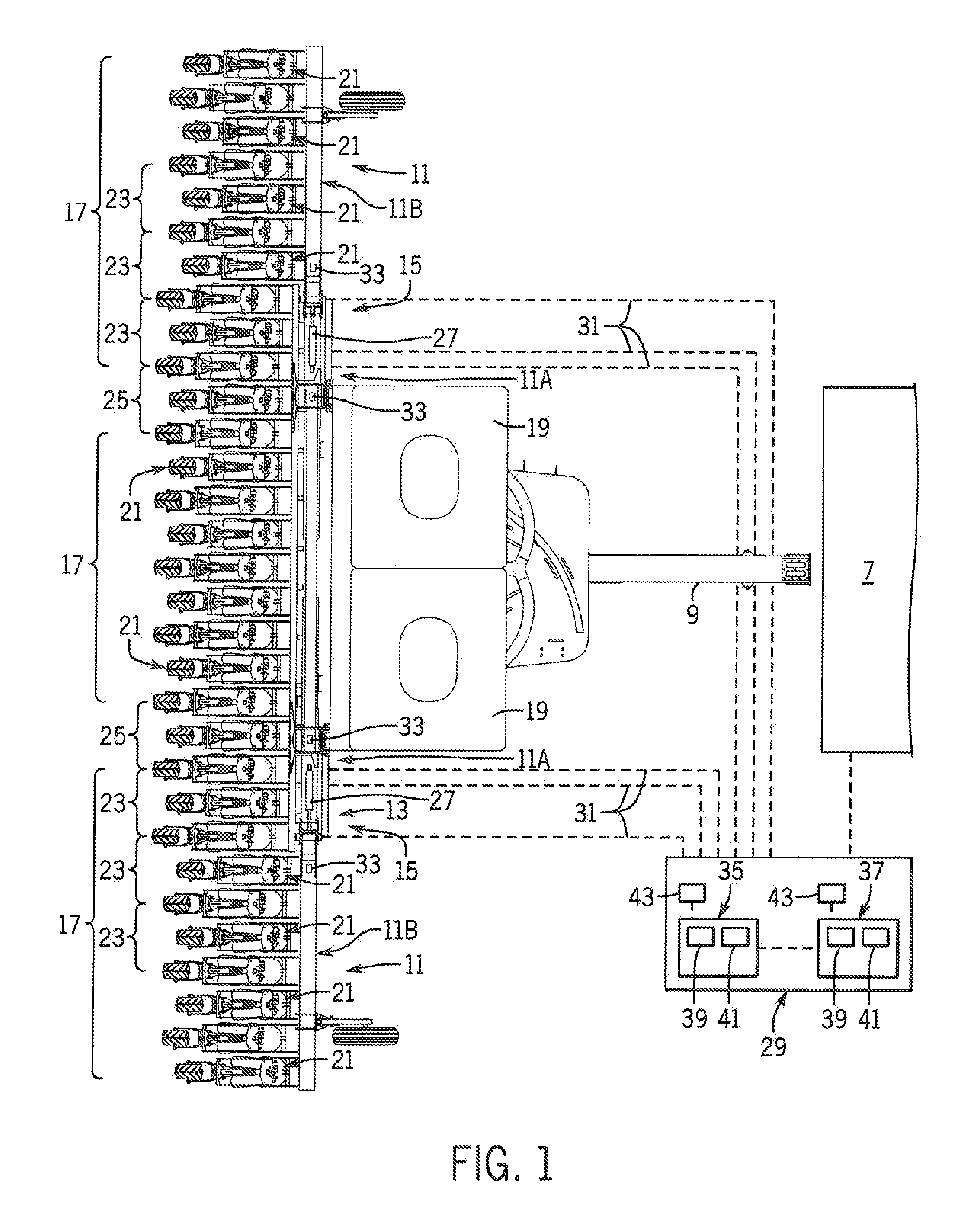
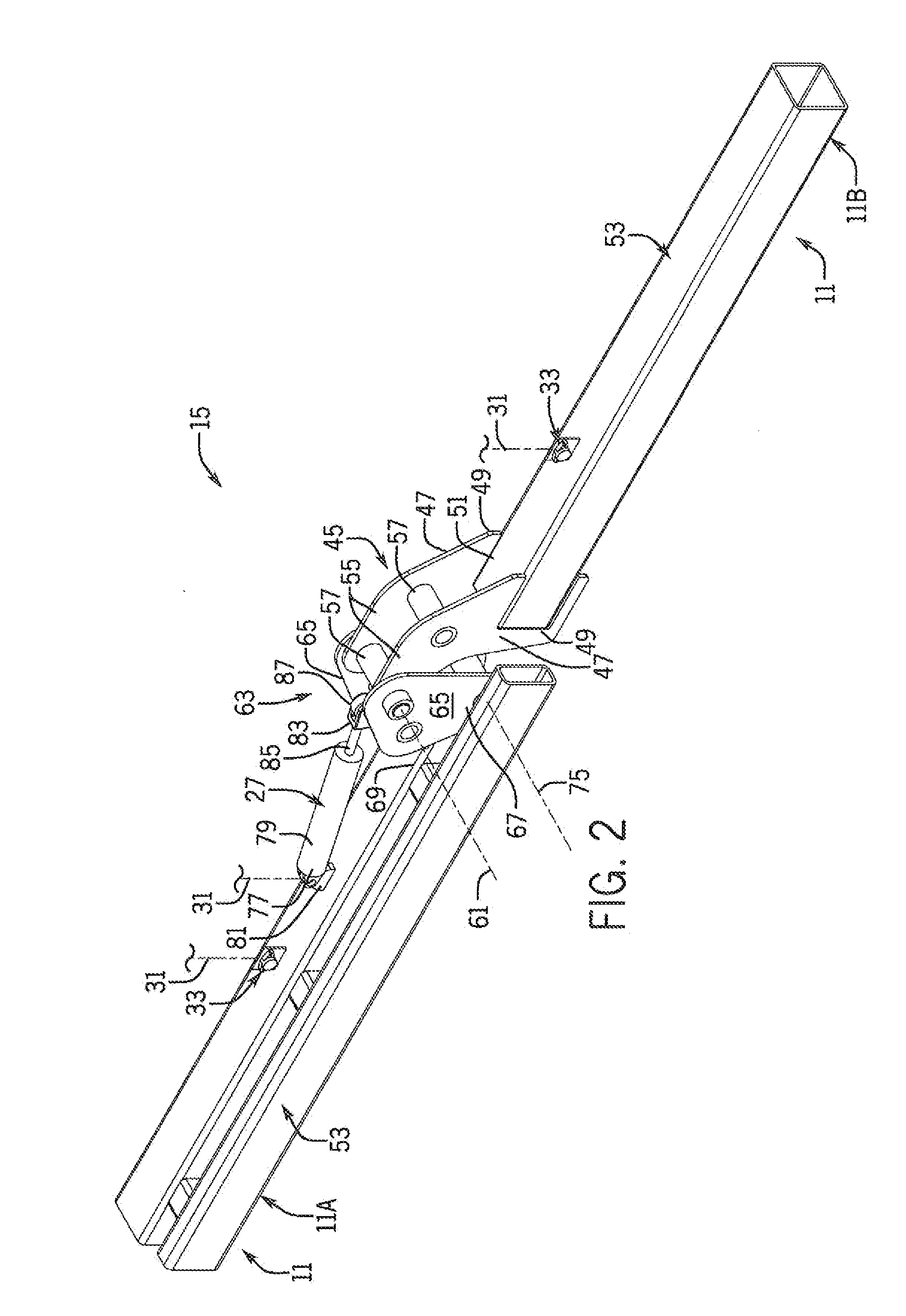
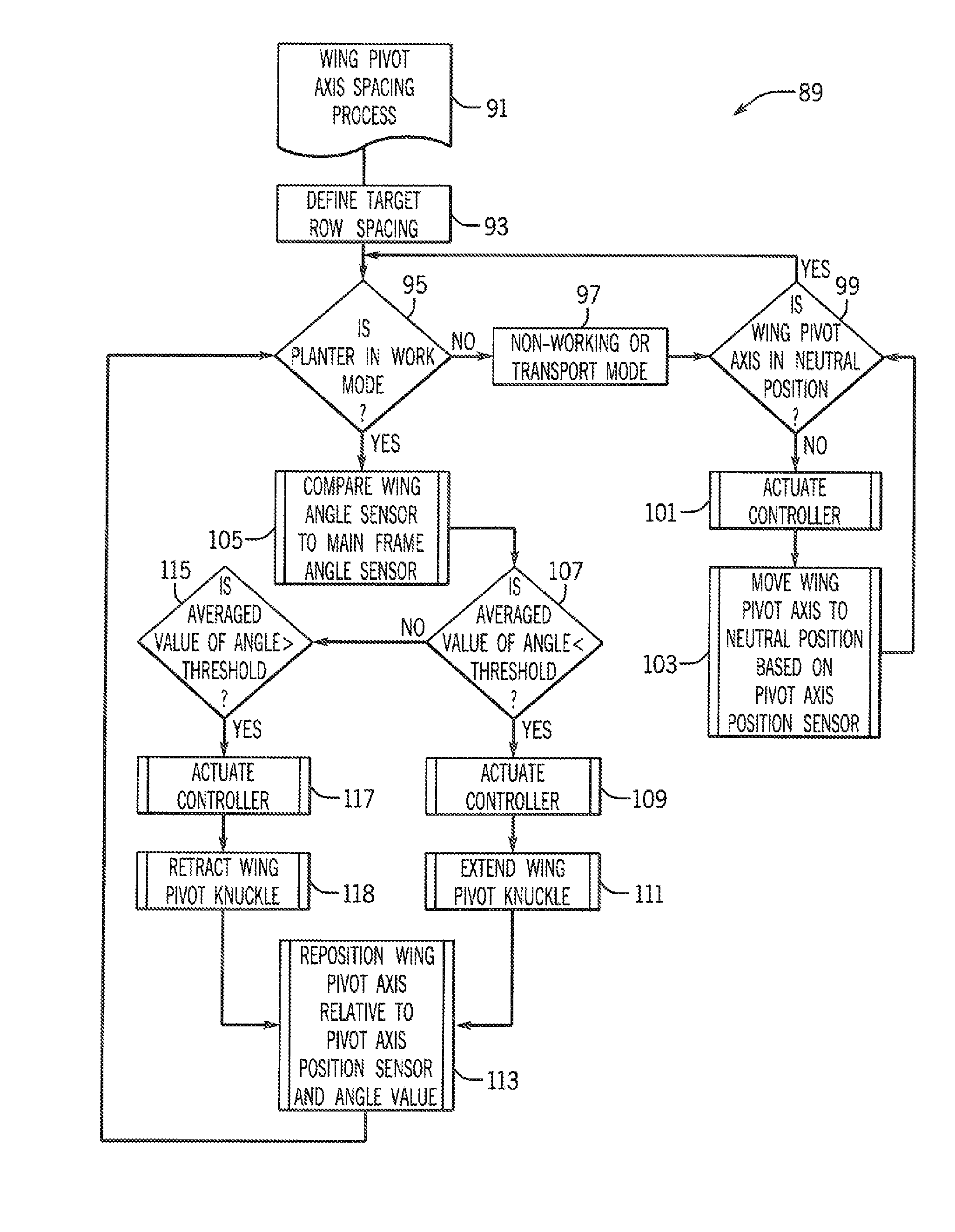
Variable Placement Hinge For Agricultural Implement To Maintain Constant Work Zone Spacing
ActiveUS20150245556A1Correction for variationFixed spacingAgricultural machinesAnalogue computers for trafficWork unitActuator
An agricultural implement is provided that has a variable placement hinge joint that allows adjacent implement sections to flex relative to each other and can be moved by an actuator to control spacing between adjacent work zones defined by the implement sections. This can be done by detecting relative angle changes between adjacent implement sections and moving the hinge joint to maintain a constant distance between the work zones so that row spacing is substantially constant across the entire implement, even between adjacent ground-engaging tools or other working units of different implement sections.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
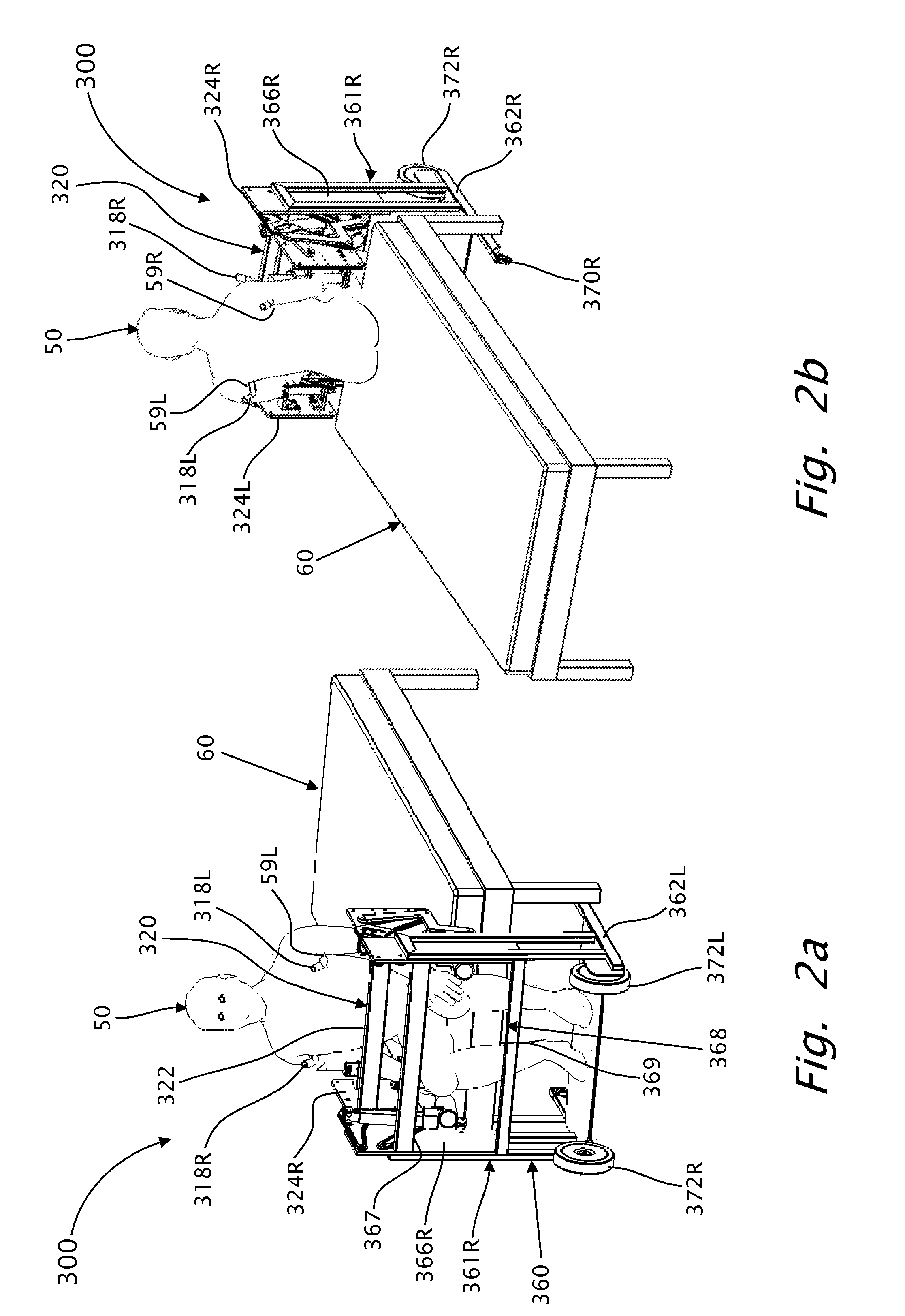
Ergonomic lifting and lowering mechanism for apparatuses for assisting a handicapped person
InactiveUS20160143795A1Facilitate accommodationEasy to changeWheelchairs/patient conveyanceBathroom coversStanding PositionsEngineering
An ergonomic, power-assisted lifting-lowering unit for lifting or lowering a user, such as a disabled person. The lifting-lowering unit includes a body-holder, adapted to firmly hold / support at least at one body member / section of the torso of the user; a lifting-lowering-mechanism; a motion and force transmitting mechanism; and a power activator. The lifting-lowering-mechanism includes a power actuator that is operatively engaged with the body-holder, at preconfigured locations. The power activator activates the power actuator to thereby set in motion the motion transmitting mechanism that causes the body-holder to move in a path closely approximating to the movement of the femur bones, or a in path parallel thereto, when the user is moving between a standing position and a sitting position, the knees being the proximal center of the pivotal motion of the femur bones of the user.
Owner:SCHWARTZ ELI +1
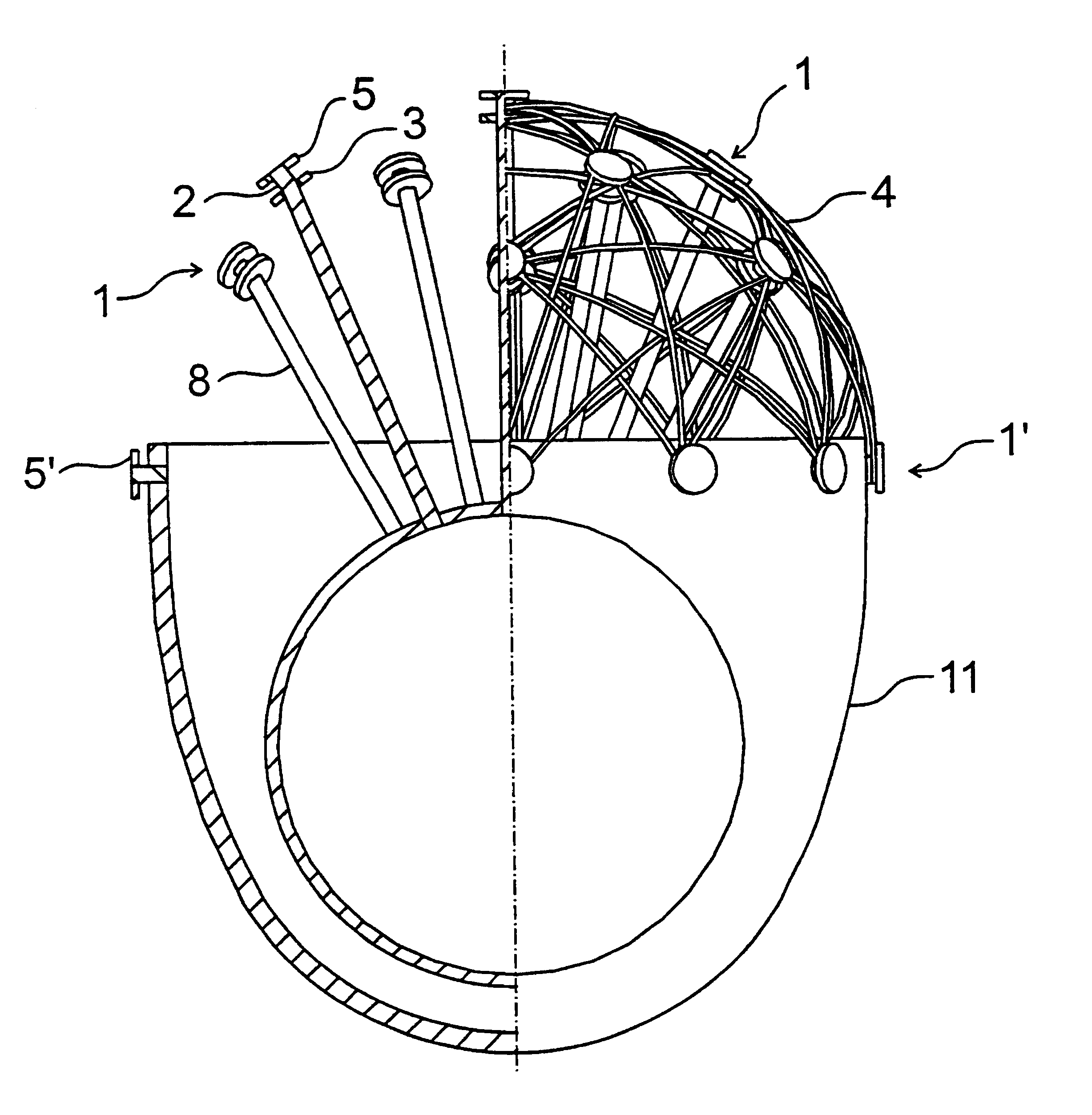
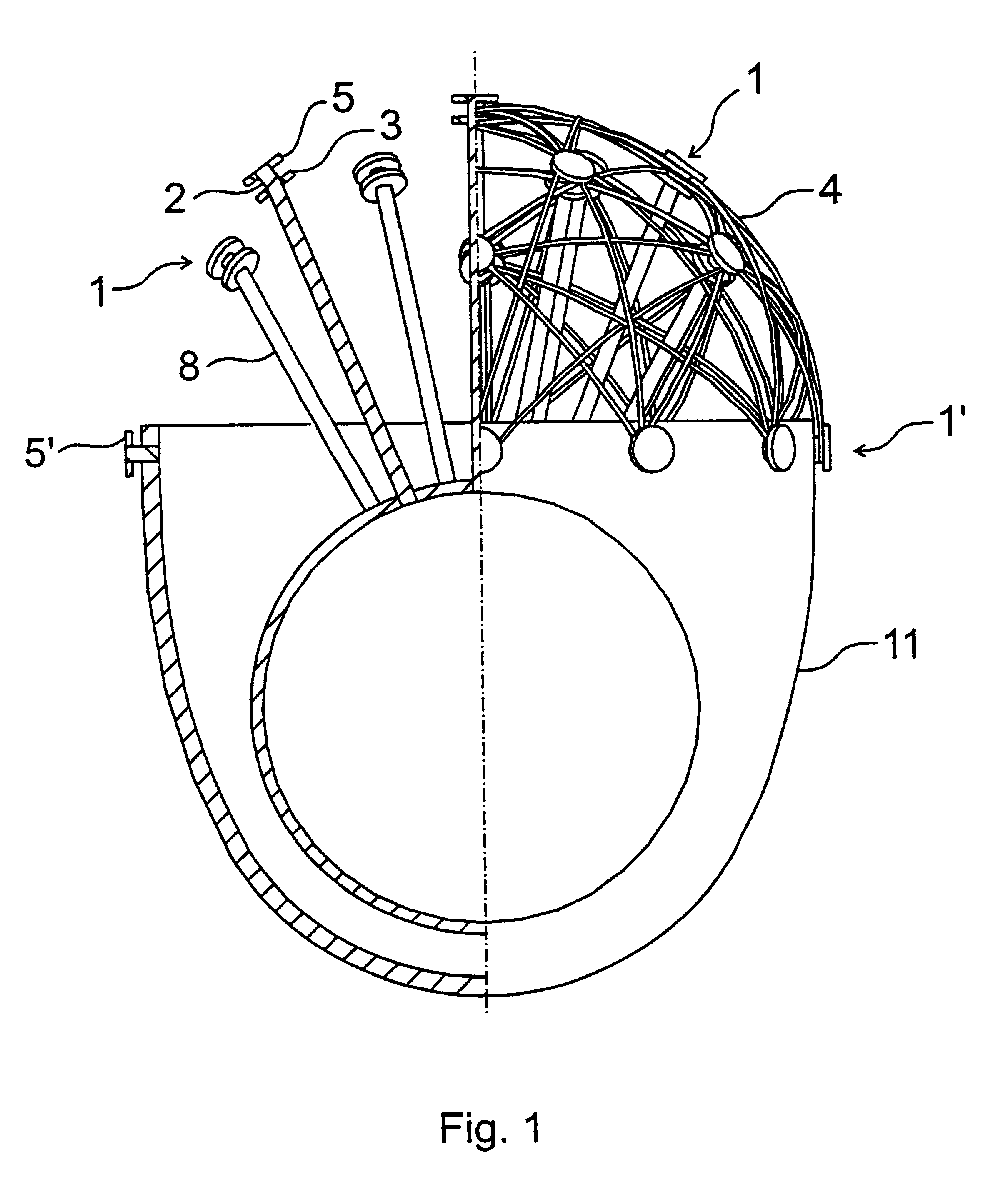
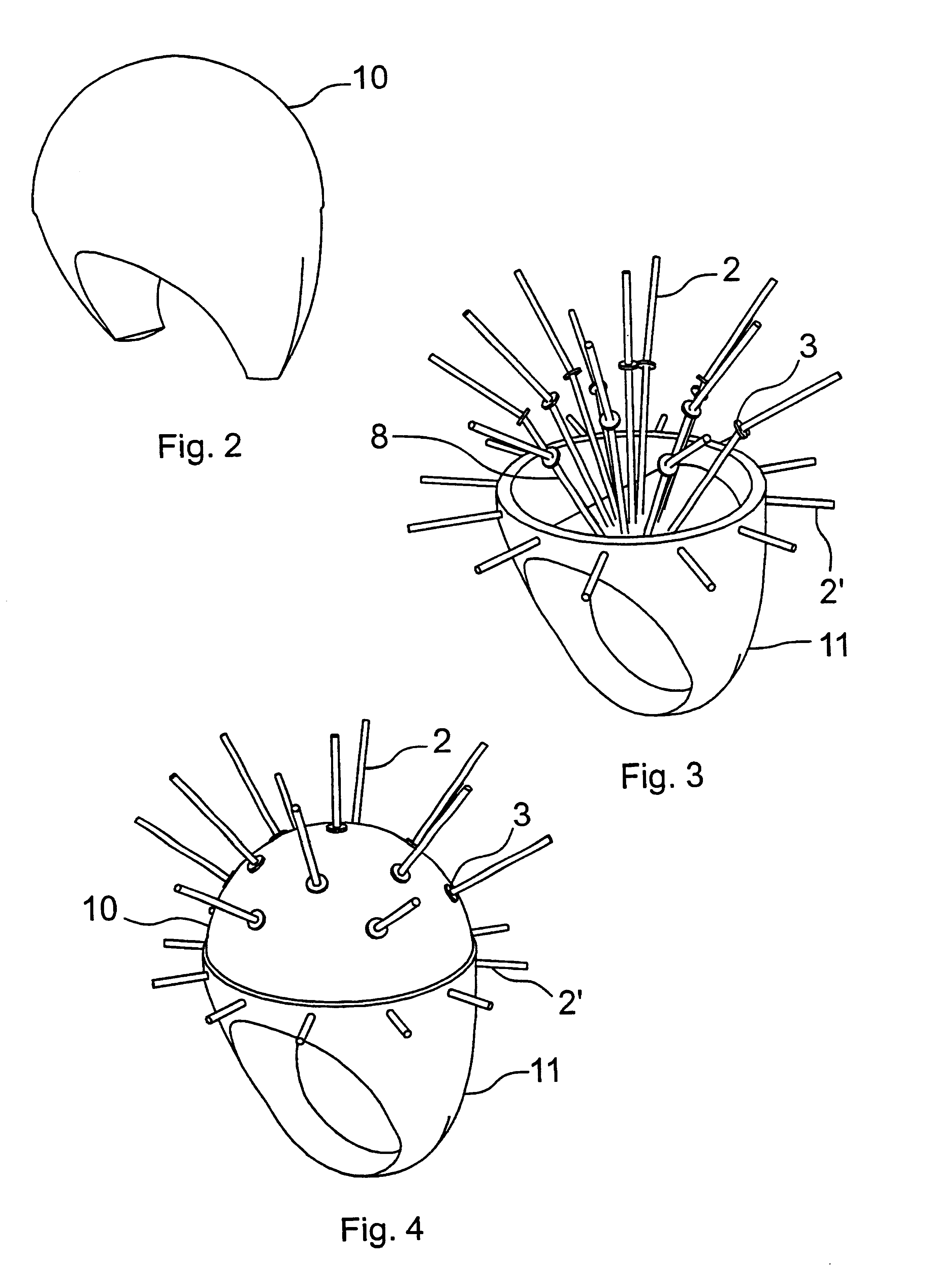
Mesh jewel and method for manufacturing thereof
Owner:VARGA MIKLOS
Variable placement hinge for agricultural implement to maintain constant work zone spacing
ActiveUS9258938B2Correction for variationFixed spacingAgricultural machinesAnalogue computers for trafficWork unitActuator
An agricultural implement is provided that has a variable placement hinge joint that allows adjacent implement sections to flex relative to each other and can be moved by an actuator to control spacing between adjacent work zones defined by the implement sections. This can be done by detecting relative angle changes between adjacent implement sections and moving the hinge joint to maintain a constant distance between the work zones so that row spacing is substantially constant across the entire implement, even between adjacent ground-engaging tools or other working units of different implement sections.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
Corner joint for pultruded window frame
A corner joint between two frame lineals of a pultruded window frame is defined by inserting a leg of a corner member into a hollow interior of each lineal and attaching the legs to the lineals by adhesive. Each leg has a plurality of surfaces thereof each having a first portion at the corner which lies closely adjacent a corresponding surface of the first lineal and a second portion, at the end of the first portion remote from the corner which tapers inwardly away from the corresponding surface of the first lineal such that a spacing therebetween increases in the direction away from the corner. The adhesive is applied to the tapered portion and the taper acts to force the adhesive along the leg to the first portion and to the ends of the lineals where the excess can be wiped away.
Owner:OMNIGLASS
Fuel injector with a deep pocket seat and method of maintaining spatial orientation
A fuel injector has a housing extending along a longitudinal axis between an inlet and an outlet. A seat assembly is disposed in a body proximate the outlet. The seat assembly includes a flow portion and a securement portion. The flow portion extends along the longitudinal axis between a first surface and an orifice disk retention surface at a first length. The flow portion has a seat orifice extending therethrough and an orifice disk coupled to the orifice disk retention surface so that the orifice plate is aligned in a fixed spatial axial orientation with respect to the flow portion. The securement portion extends along the longitudinal axis away from the orifice disk retention surface at a second length greater than the first length. A method of maintaining a fixed spatial axial orientation and dimensional symmetry of at least one of the seat and orifice disk in the body is disclosed.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
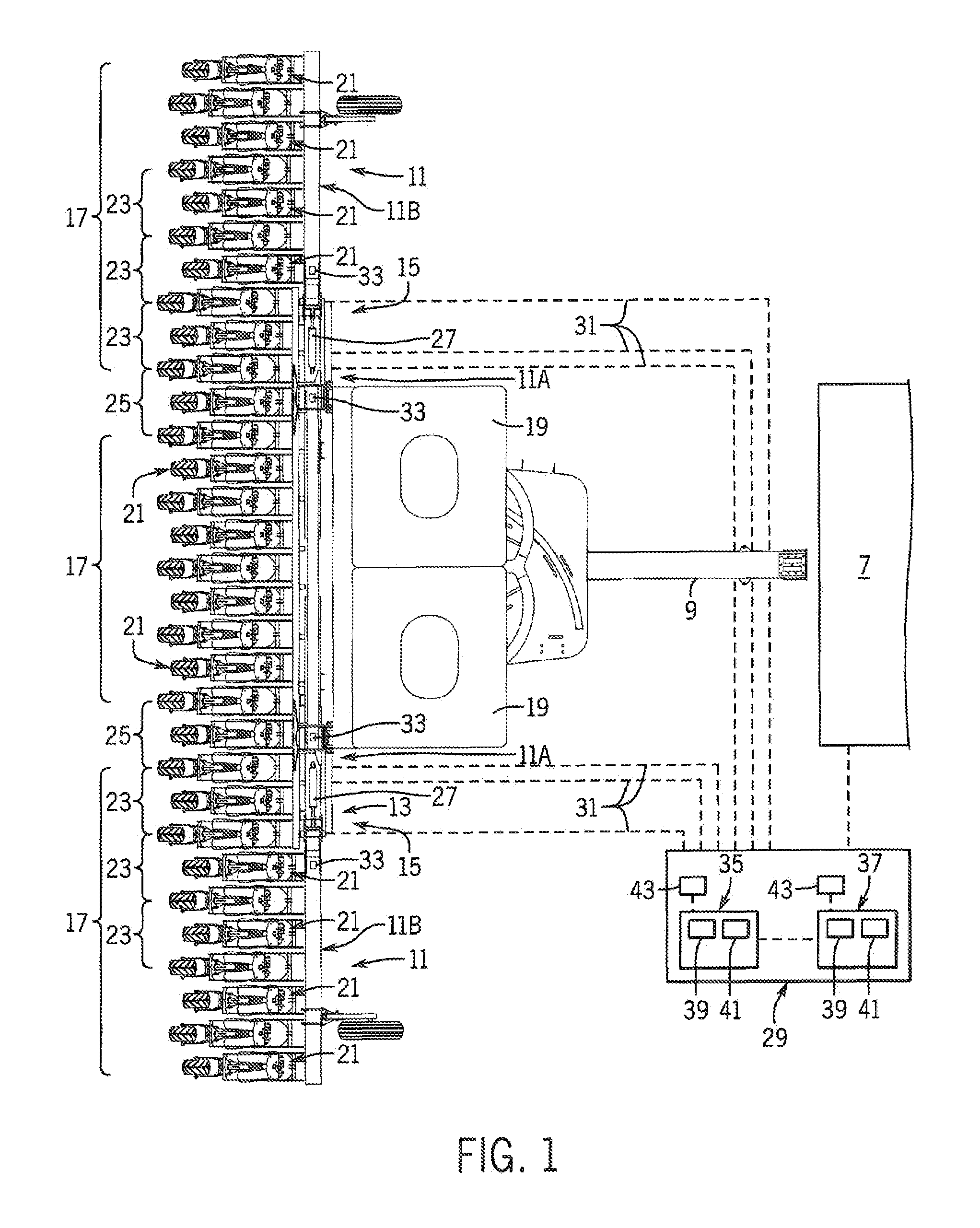
Image forming apparatus including plural conveyor units with conveyance path length/conveyance speed relationships
InactiveUS6909857B2Improved image formingShorten the time periodElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersPath lengthImaging quality
In case a fixing speed is lower than a transferring speed, the individual conveyor units are controlled such that, while a downstream conveyor unit (61) is conveying a sheet (S1) being fixed at the same speed (V2) as the fixing speed, an upstream conveyor unit (60) may convey the succeeding sheet (S2) at the same speed (V1) as the transferring speed. As a result, the spacing of the two sheets in a fixing unit (9) can be sufficiently narrowed to improve the image forming efficiency. Moreover, the transferring speed need not be decelerated according to the fixing speed. It is, therefore, possible to prevent the deterioration in the image quality and to shorten the image forming time period of the first sheet.
Owner:CANON KK
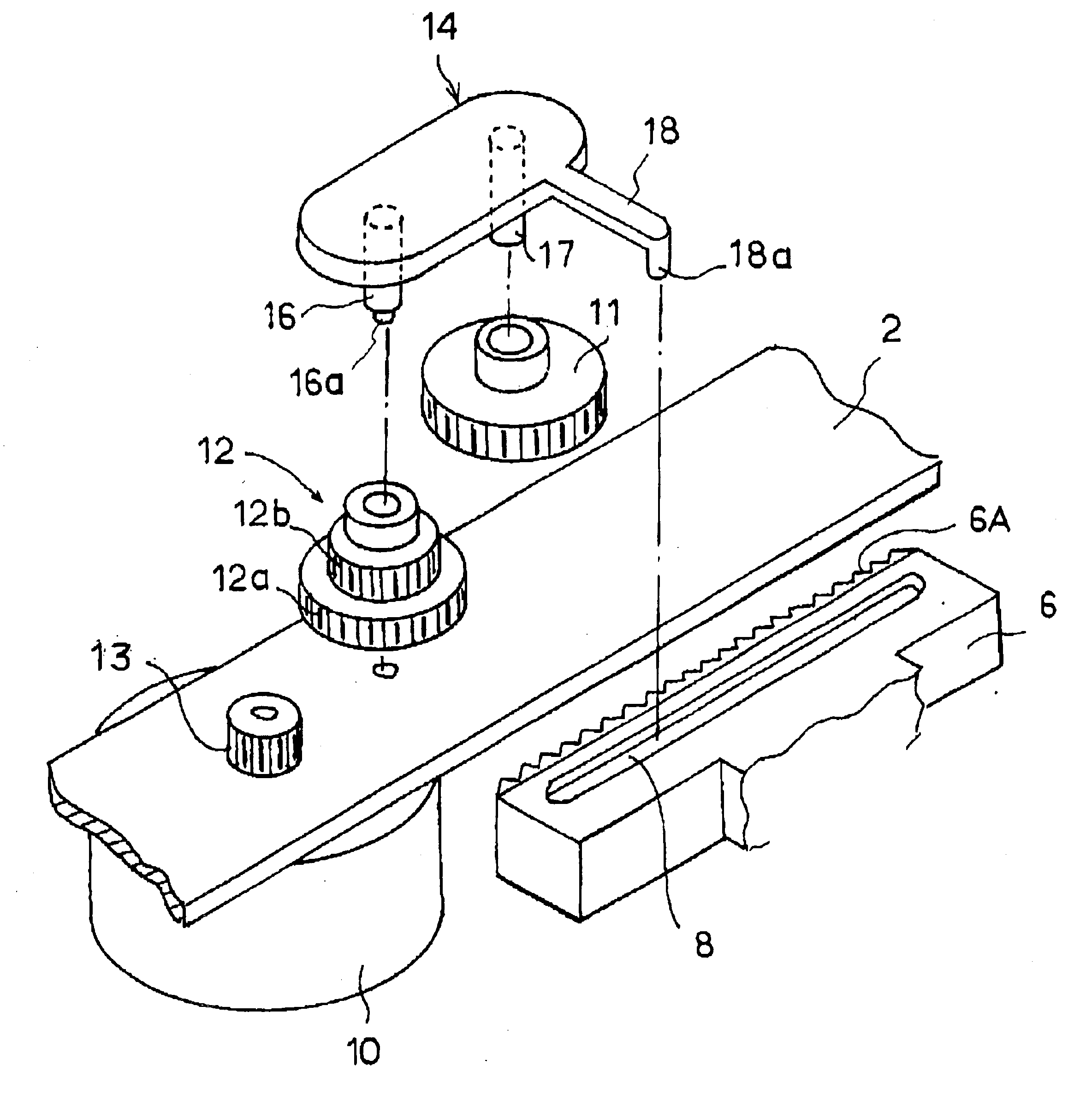
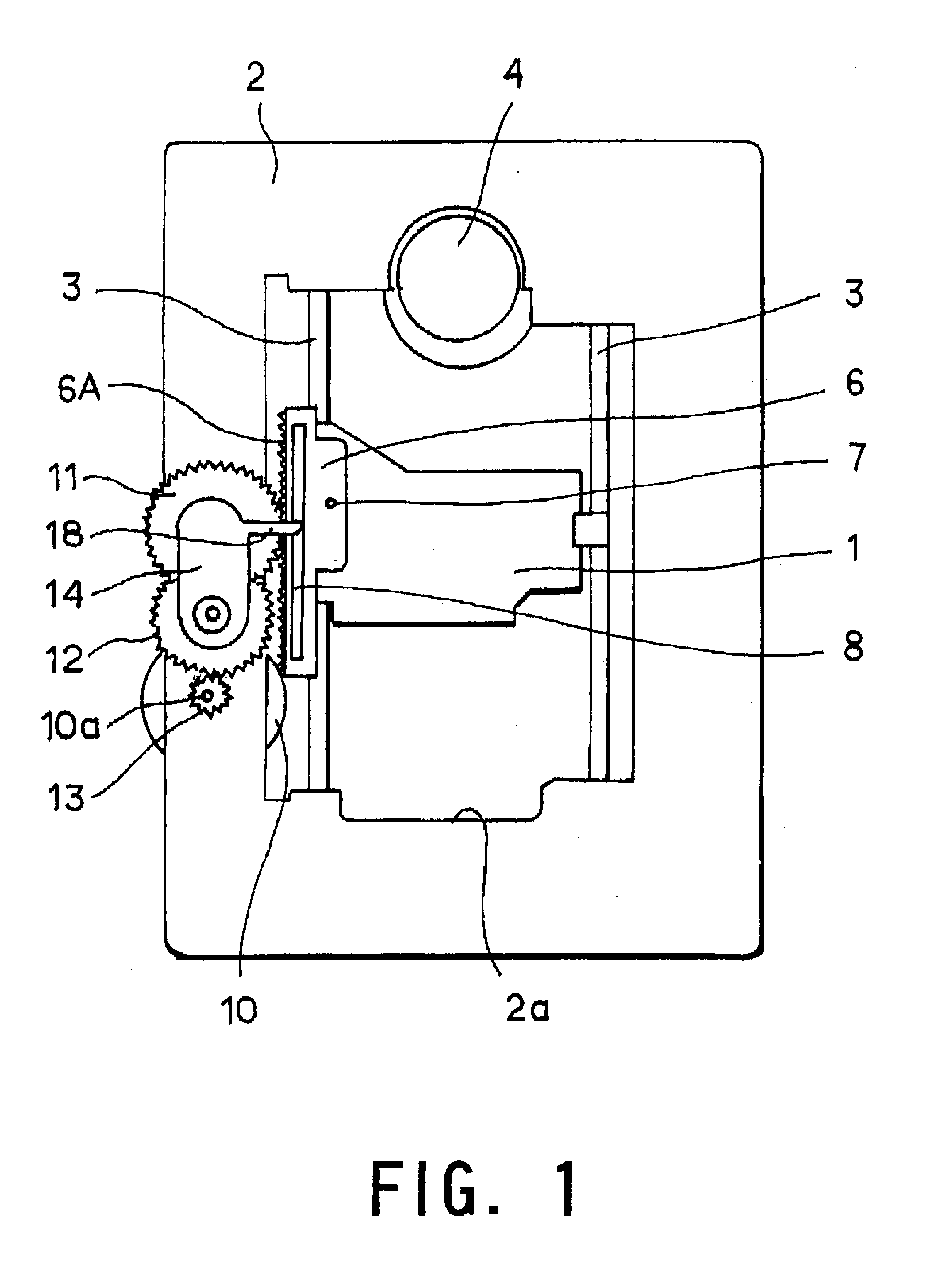
Disc drive head driver
InactiveUS6918129B2SpacingFixed spacingDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageGear wheelDrive motor
The present invention eliminates variations in the engagement between a rack and a pinion, which drive a recording head, to enable the head to move speedily and smoothly. A head driver includes a rack provided on a recording head that slidingly moves over a recording disc and a pinion engaged with the rack and rotated by a drive motor, wherein there are provided a concave groove, provided on the rack and running in parallel with rack tooth, and a swing arm with which a rigid guide, guided by the concave groove, is integrated and on which a rotation axis of the pinion is provided. When the rack is at a slant with the movement direction, the swing arm swings, following the slant of the rack to keep constant the spacing between the rack and the pinion.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
Strip casting apparatus
Owner:NUCOR CORP
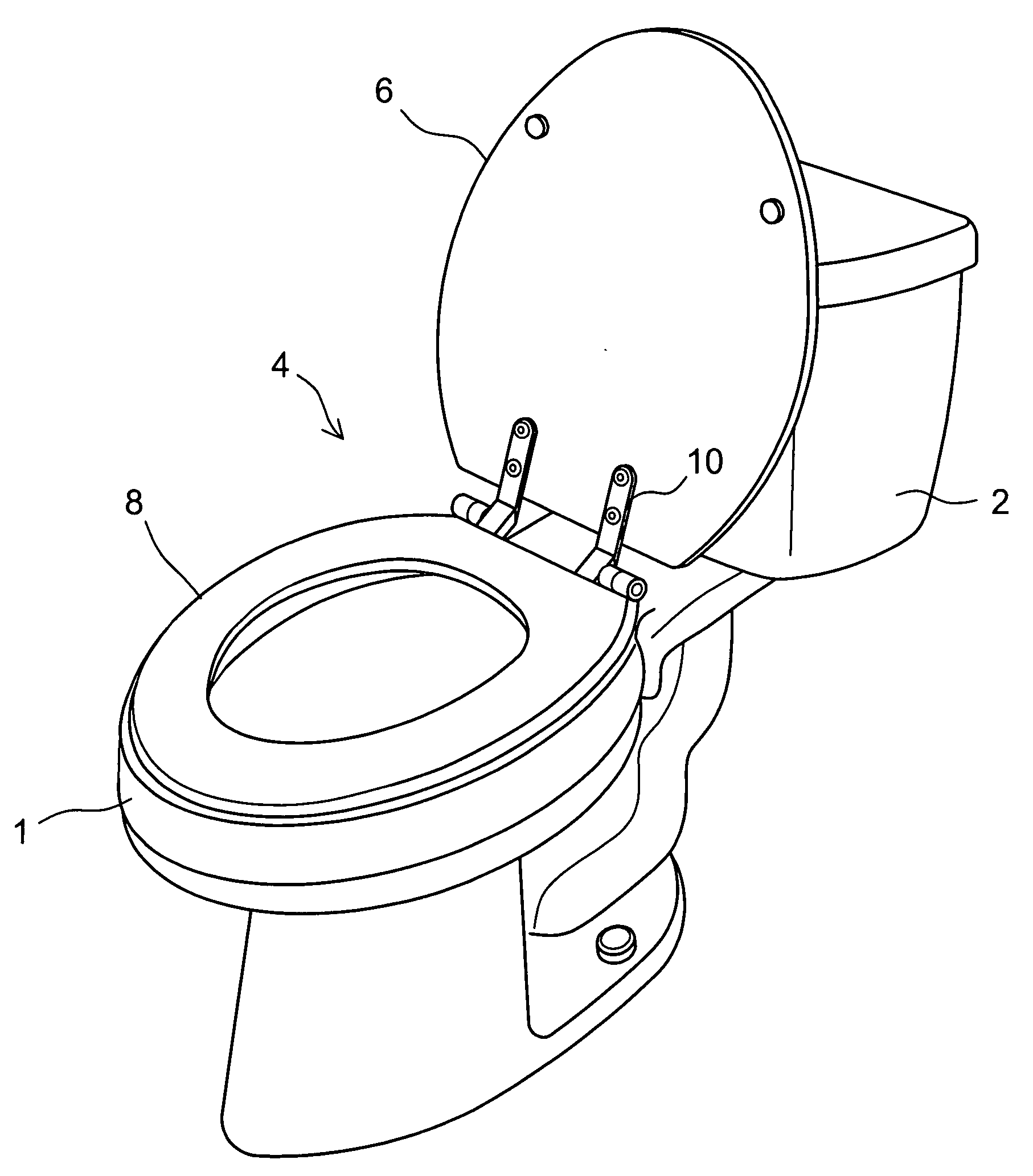
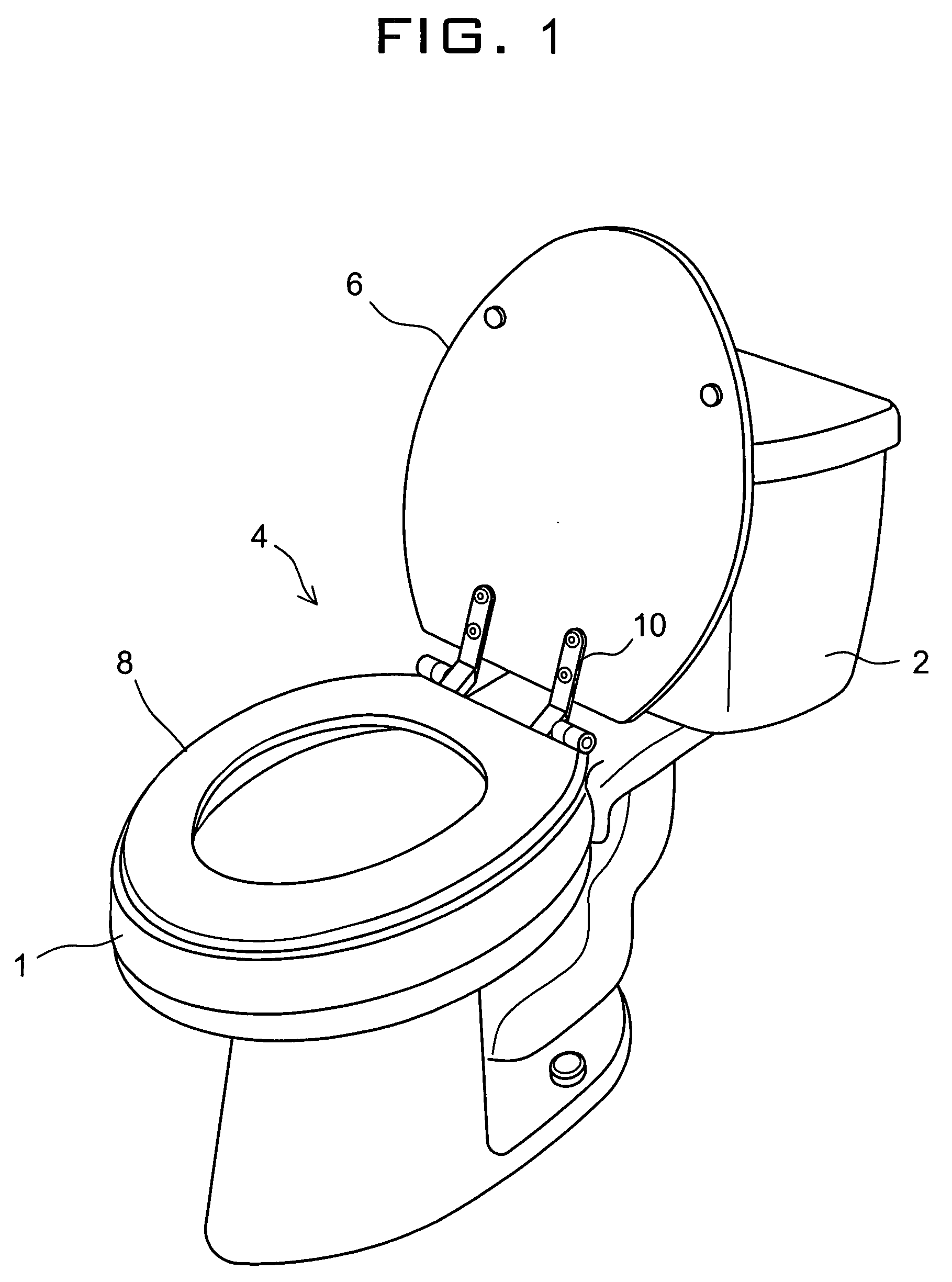
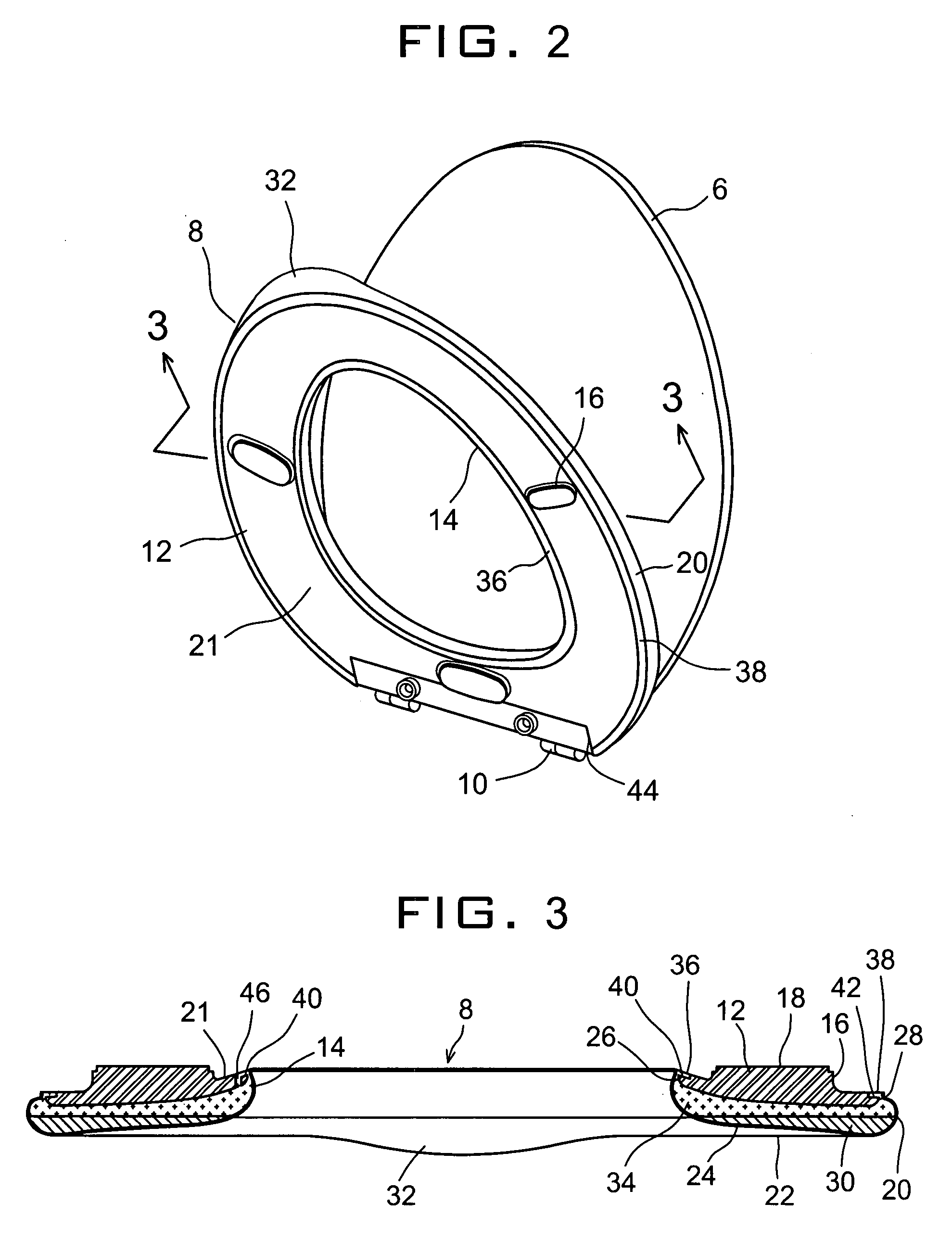
Gel infused toilet seat
A gel-infused seat for a toilet bowl is provided comprising an exposed base section for directly contacting a top rim of the bowl while supporting a user's weight, the base section having a top surface opposite to the bottom surfaces of the seat and at least two edges including an inner circumferential edge and an outer circumferential edge; a foam core layer covering the top surface of the base section and extending to parts of the bottom surfaces of the seat at its inner and outer circumferential edges; a gelatinous overlay for defining a top contour of the seat that yields easily to a pressure applied to give a comfortable softness to the user; and an outer layer for covering the gelatinous overlay and foam core layer leaving the base section exposed with substantially constant space from the base section.
Owner:CHEN LIANG CHOU
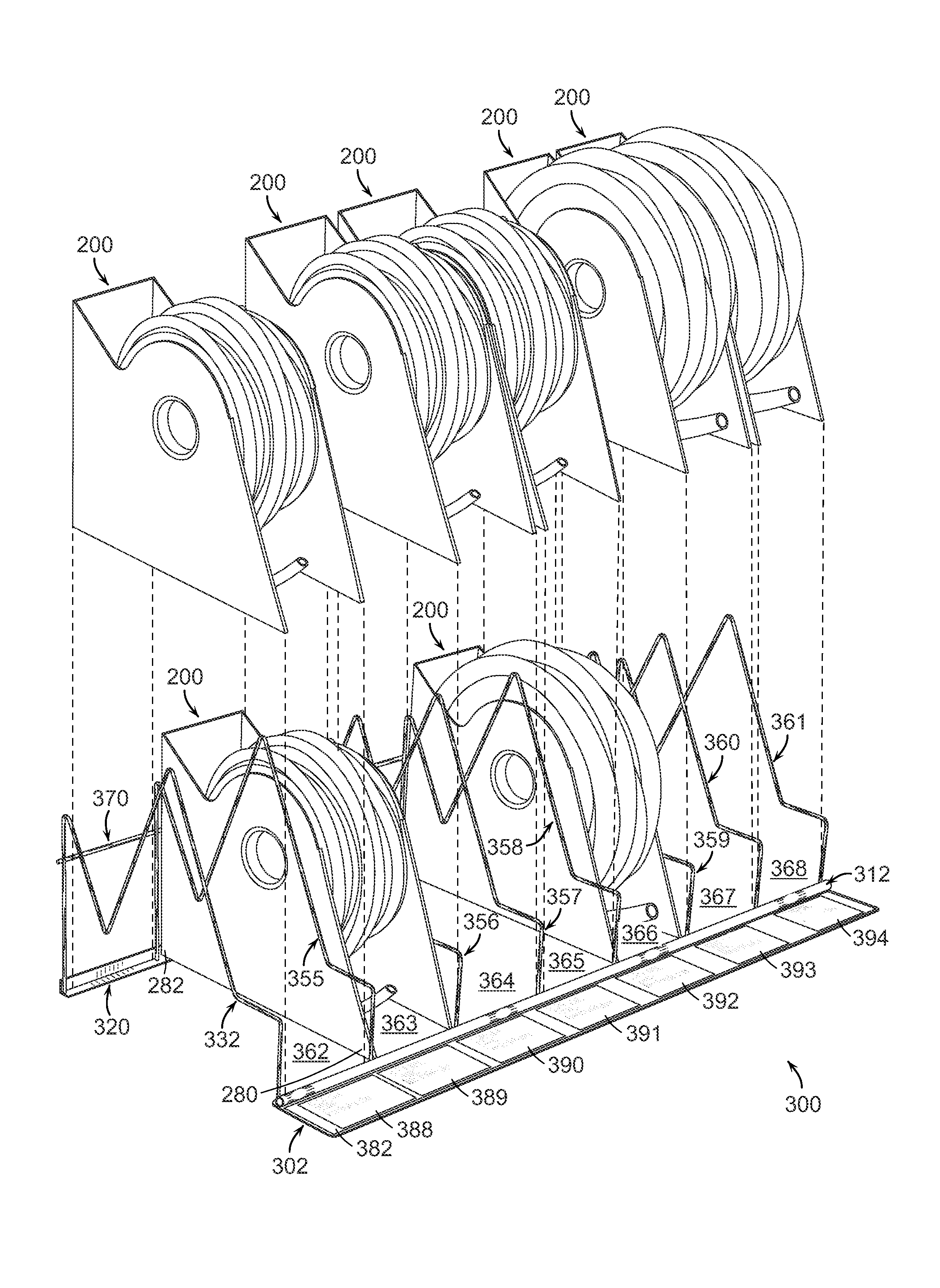
Display rack
InactiveUS8844735B1Reduce movementCost-effectiveRacksContainers for annular articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:3G POLYMERS LLC
Fishing accessory, in particular a line cutter
The line cutter suitable for fitting to the body of a fishing rod is made as a single piece obtained by cutting out and stamping a metal plate. It comprises firstly a main body with a front portion, a rear portion, and two side portions, and secondly two longitudinal prongs extending the side portions of the main body rearwards. The plate is cut out and stamped in such a manner that, when the line cutter is mounted on the body of the fishing rod, the longitudinal prongs and at least the front portion of the main body are in contact with the body of the fishing rod, the rear portion of the main body being raised so as to allow the line to be pass thereunder, and in such a manner that between the rear portion of the main body and the longitudinal prongs, a cutout in the shape of an acute angle on one side defines a cutting zone, while on the other side there is provided a jamming zone for jamming the fishing line. The line cutter is secured to the body of the fishing rod by binding the longitudinal prongs to said body.
Owner:DECATHLON SA
Crossed roller bearing retainer and crossed roller bearing
A retainer of a crossed roller bearing has a retainer body plate of rectangular profile corresponding to a rectangular cross-section of a race. Rectangular side surfaces on either side of the retainer body plate are inclined planes that slant in a direction of approaching one another from one corner to another corner along a diagonal line of the surfaces, and extend towards a bearing center in a state of having been installed in the race. Recesses for accumulating grease are formed in center portions of the rectangular side surfaces, the recesses communicating via a through-hole. The rectangular side surfaces are in linear contact with the circular external circumferential surfaces of adjacent rollers and hold the rollers at a fixed spacing. There is obtained a retainer for an uncomplicatedly configured crossed roller bearing that allows adjacent rollers to be held at a fixed spacing and is provided with a grease accumulator.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Method for producing a twin-wall cup from paper or paper-like material, apparatus for carrying out the method and twin-wall cup
InactiveUS20170113831A1Fixed spacingEasy to useBoxes/cartons making machineryBox making operationsEngineeringPaper sheet
Method and apparatus for producing a twin-wall cup from paper or paper-like material including placing an inner cup with a sleeve and a base onto a mandrel, laying a flat segment onto an outer side of the inner cup, opposite to the mandrel, shaping the flat segment to form an outer jacket, which surrounds the inner cup, and fixing the outer jacket on the inner cup by means of a material engagement connection of outer jacket and inner cup, in particular by means of adhesive bonding, wherein at least one spacer is attached to an inner side of the flat segment and / or to an outer side of the sleeve of the inner cup before the flat segment is laid on the inner cup.
Owner:MICHAEL HORAUF MASCHFAB
Snorkel apparatus with assembly connectors
InactiveUS20170130681A1Rugged in constructionFixed spacingCyclesMachines/enginesMechanical engineeringSnorkel diving
Owner:TALLMAN KYLE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com