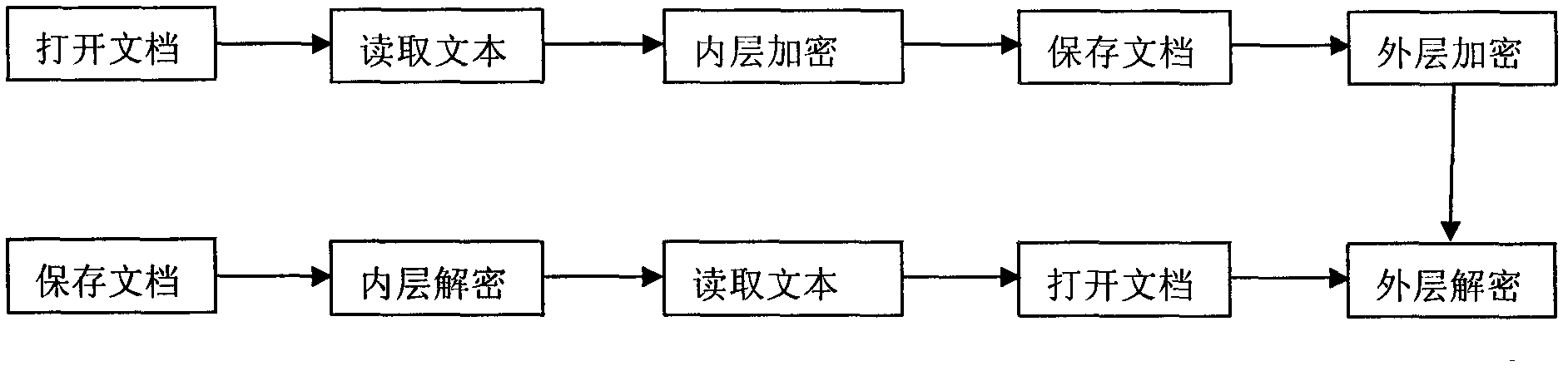
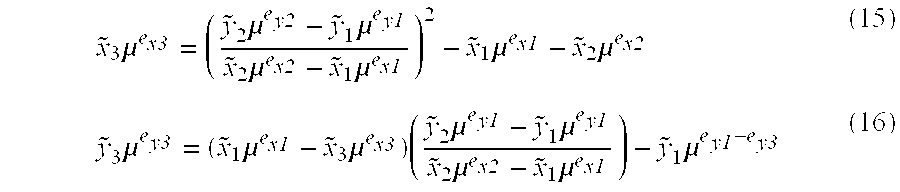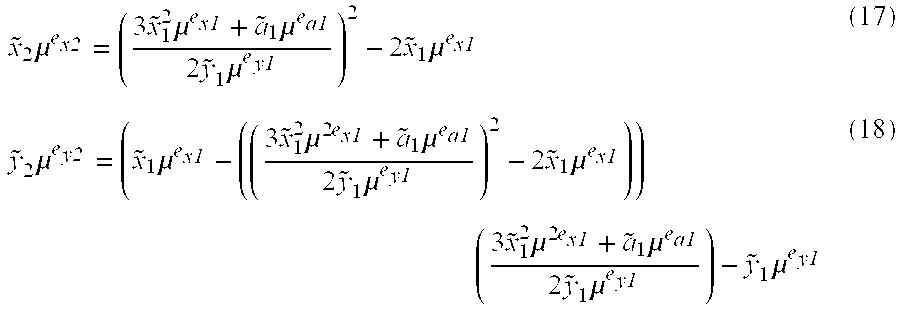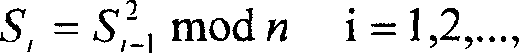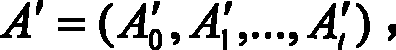Patents
Literature
116 results about "Cryptanalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek kryptós, "hidden", and analýein, "to loosen" or "to untie") is the study of analyzing information systems in order to study the hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic security systems and gain access to the contents of encrypted messages, even if the cryptographic key is unknown.
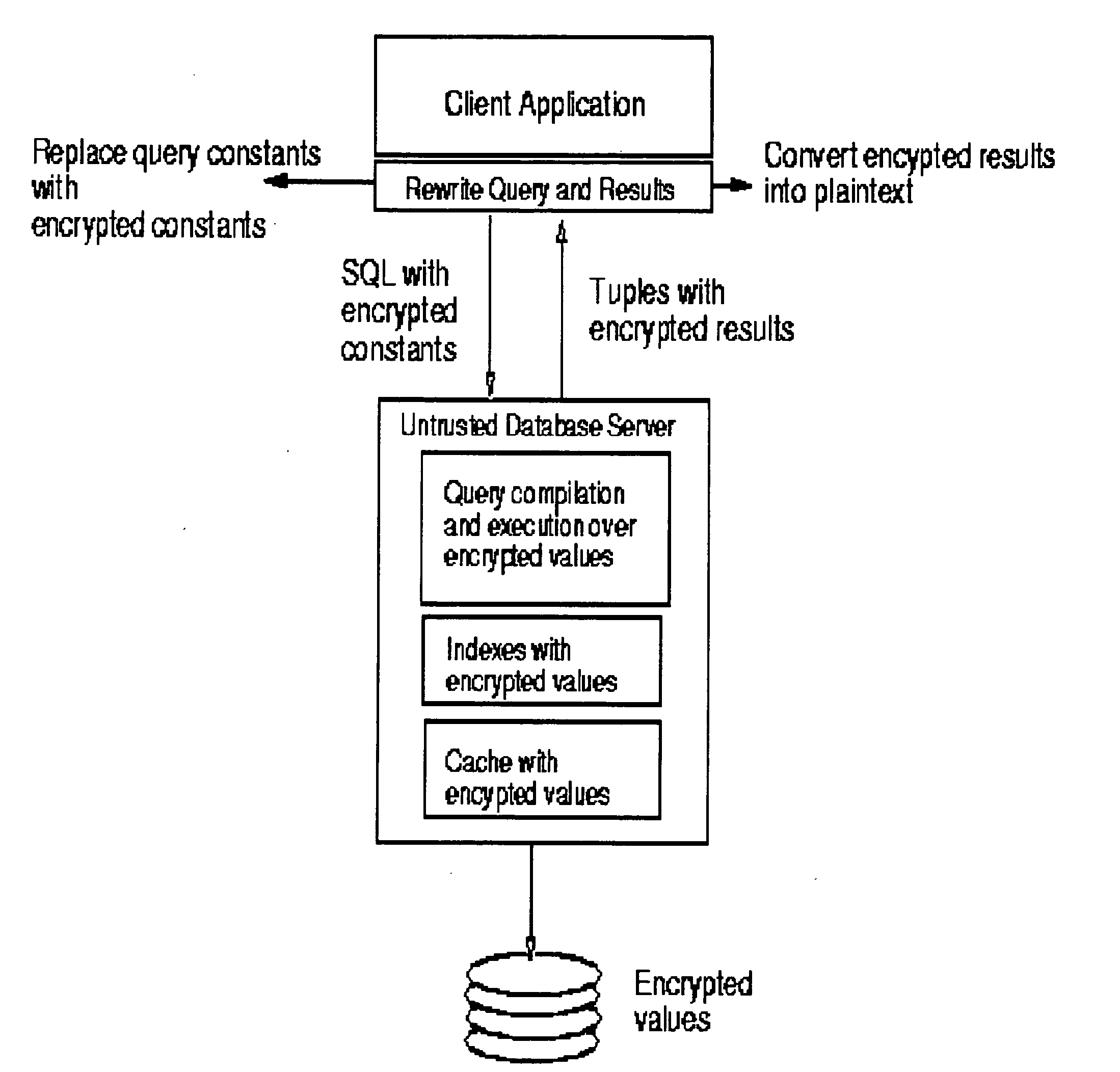
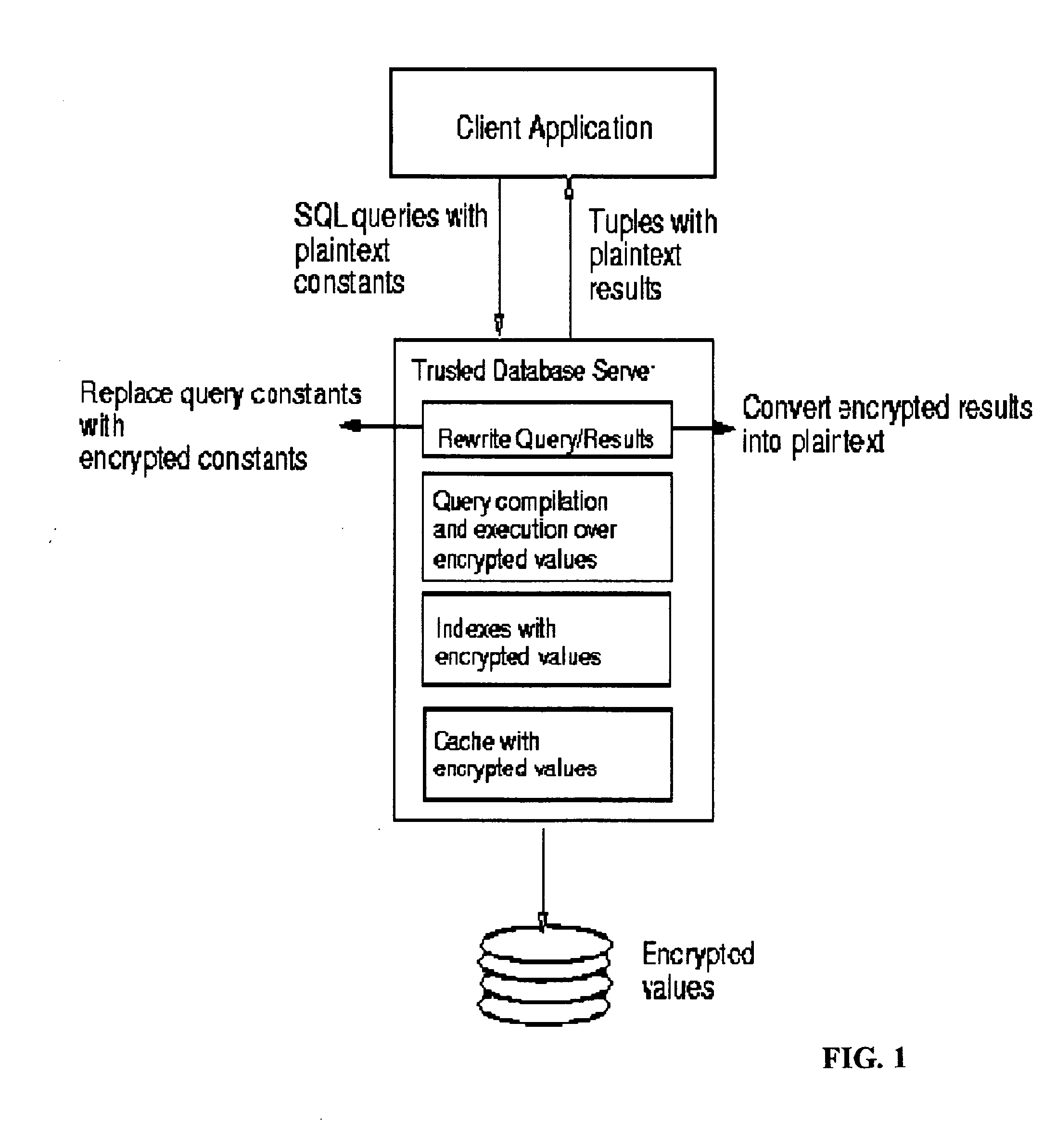
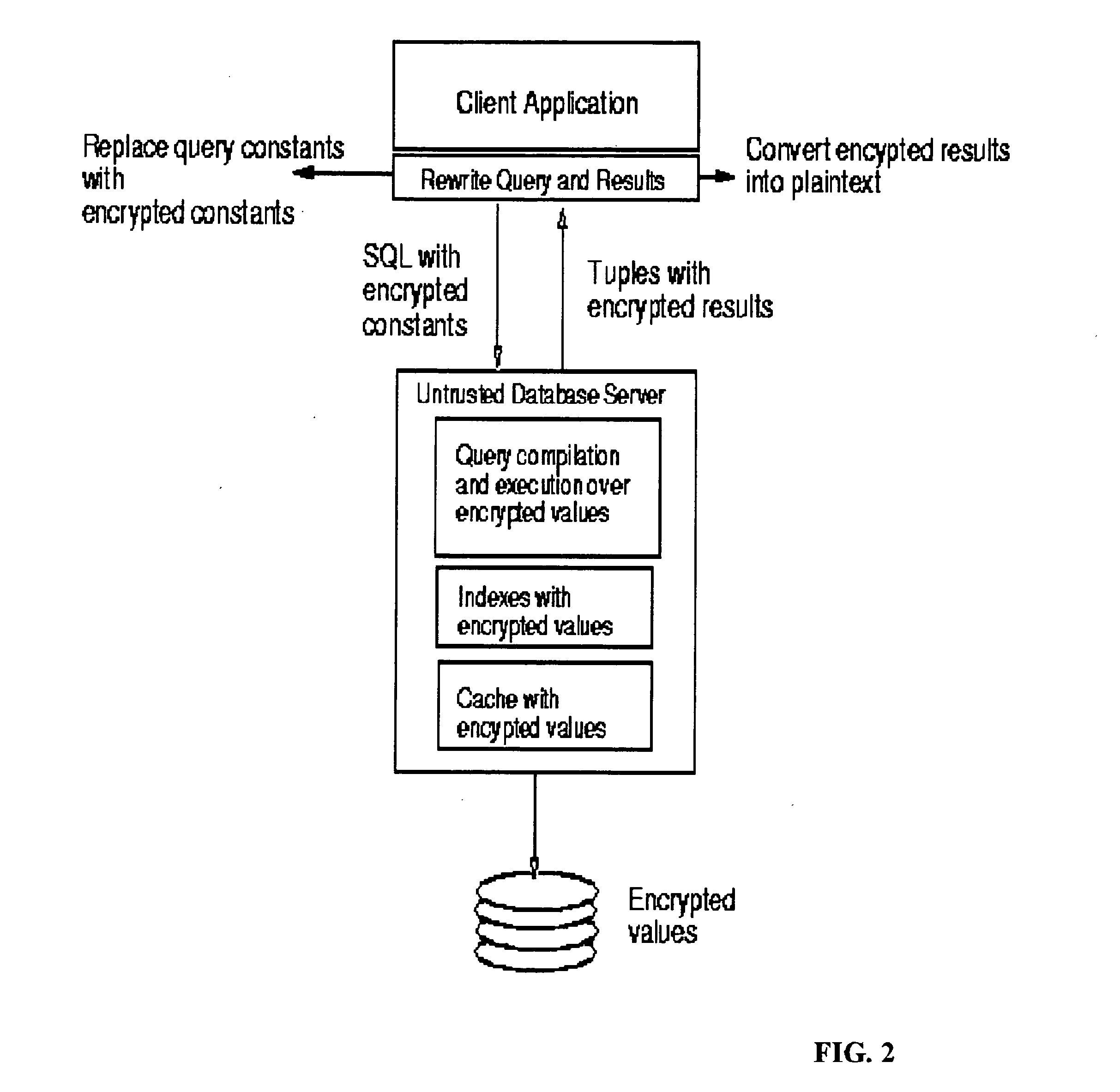
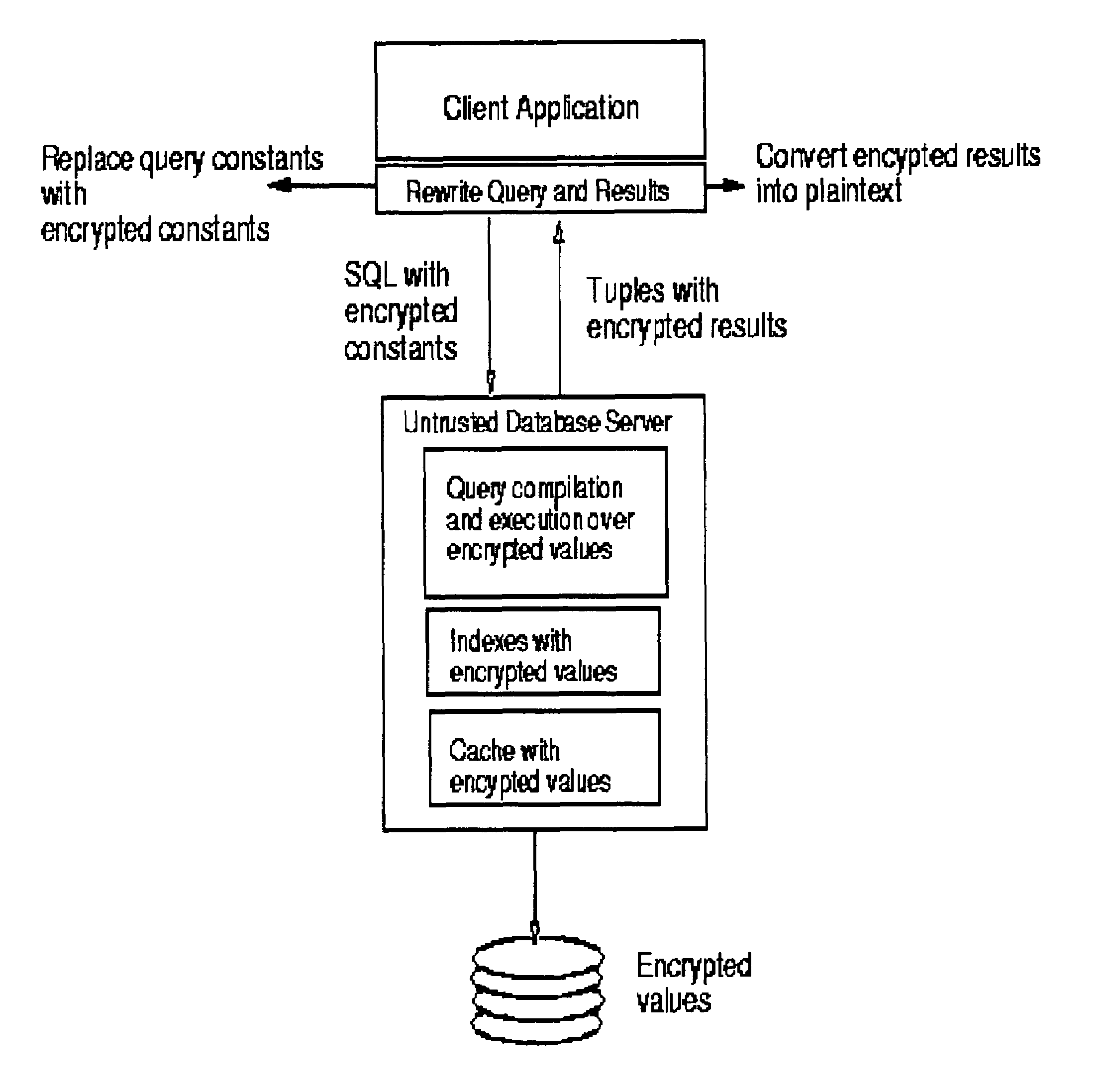
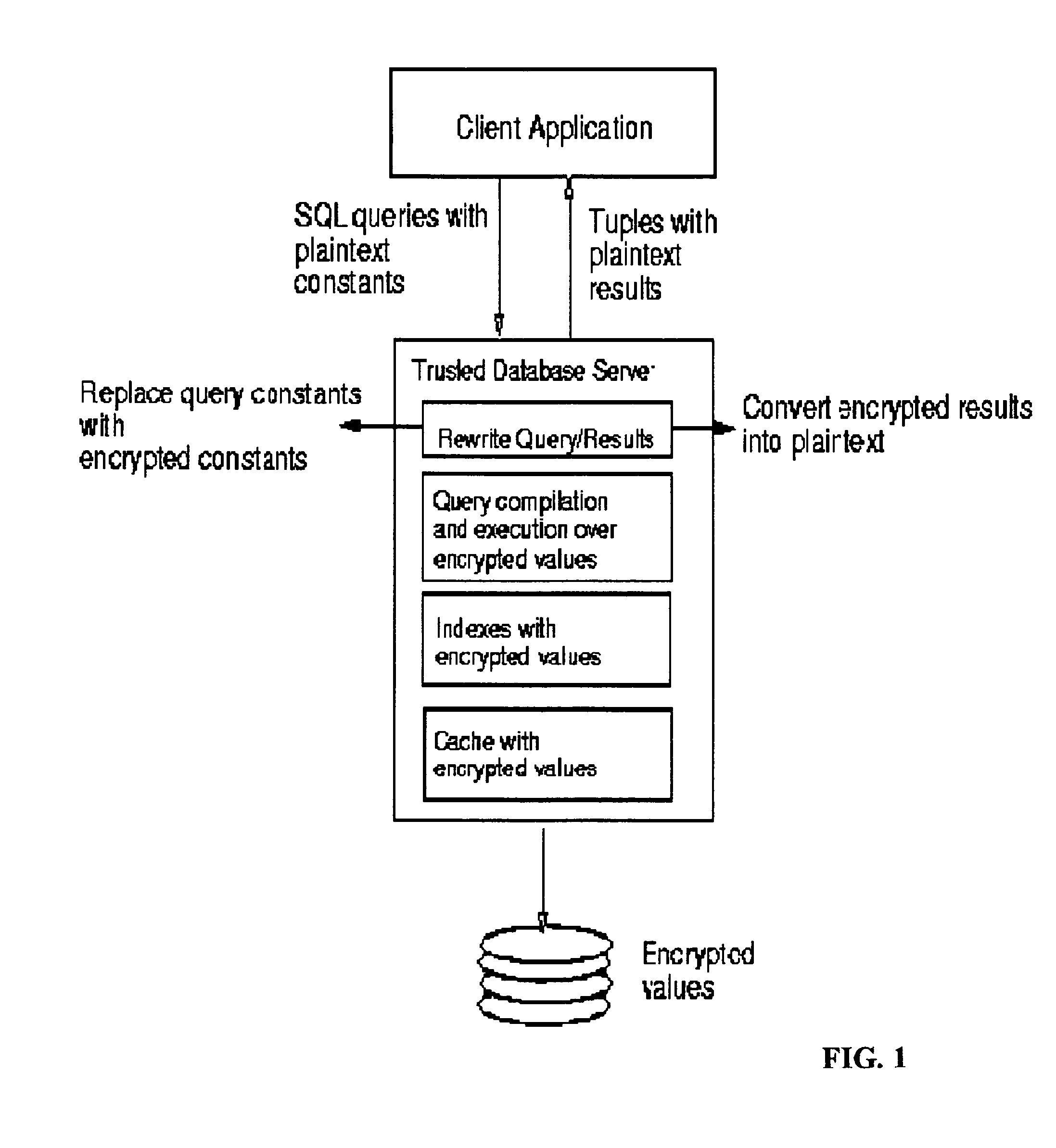
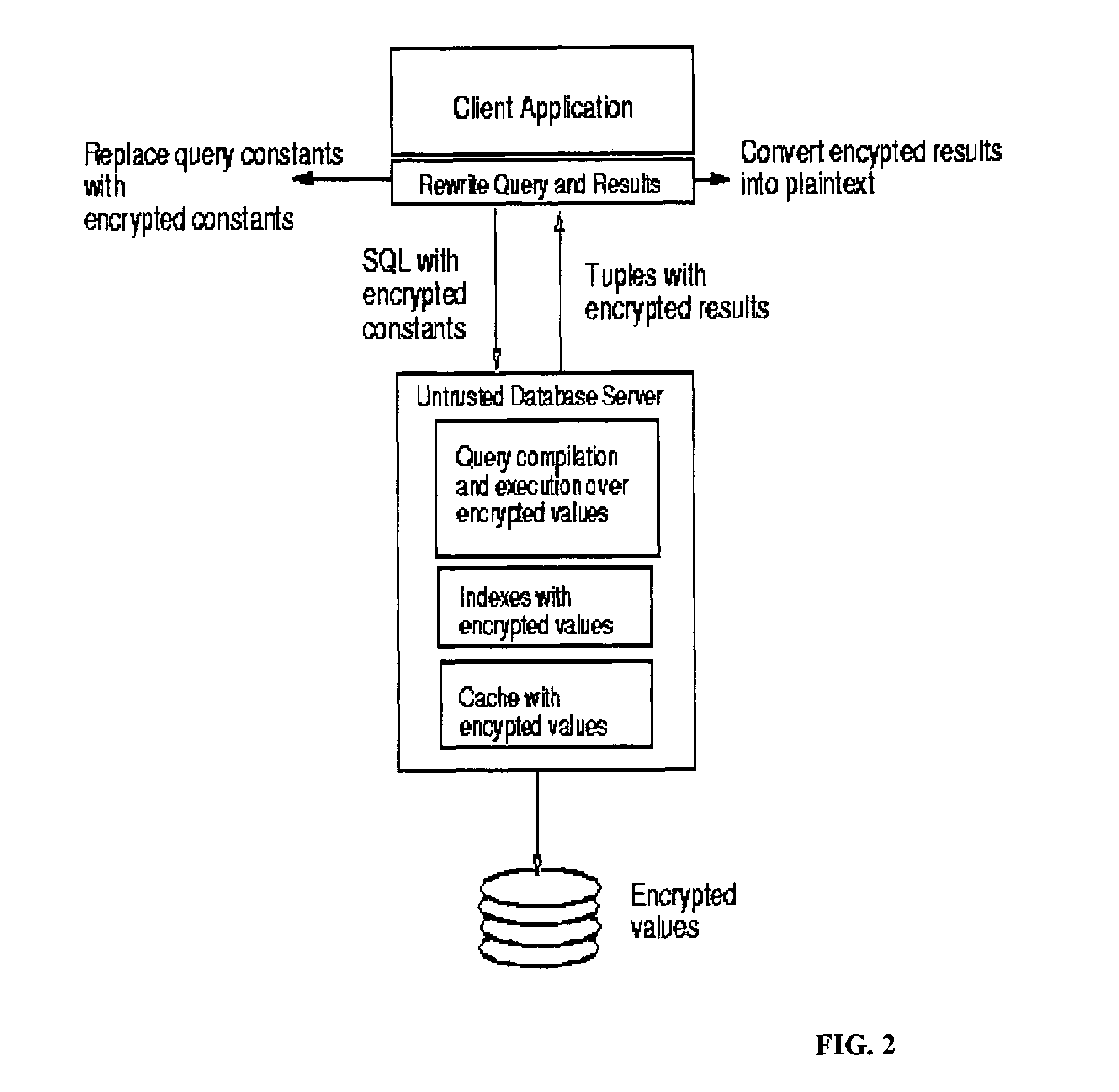
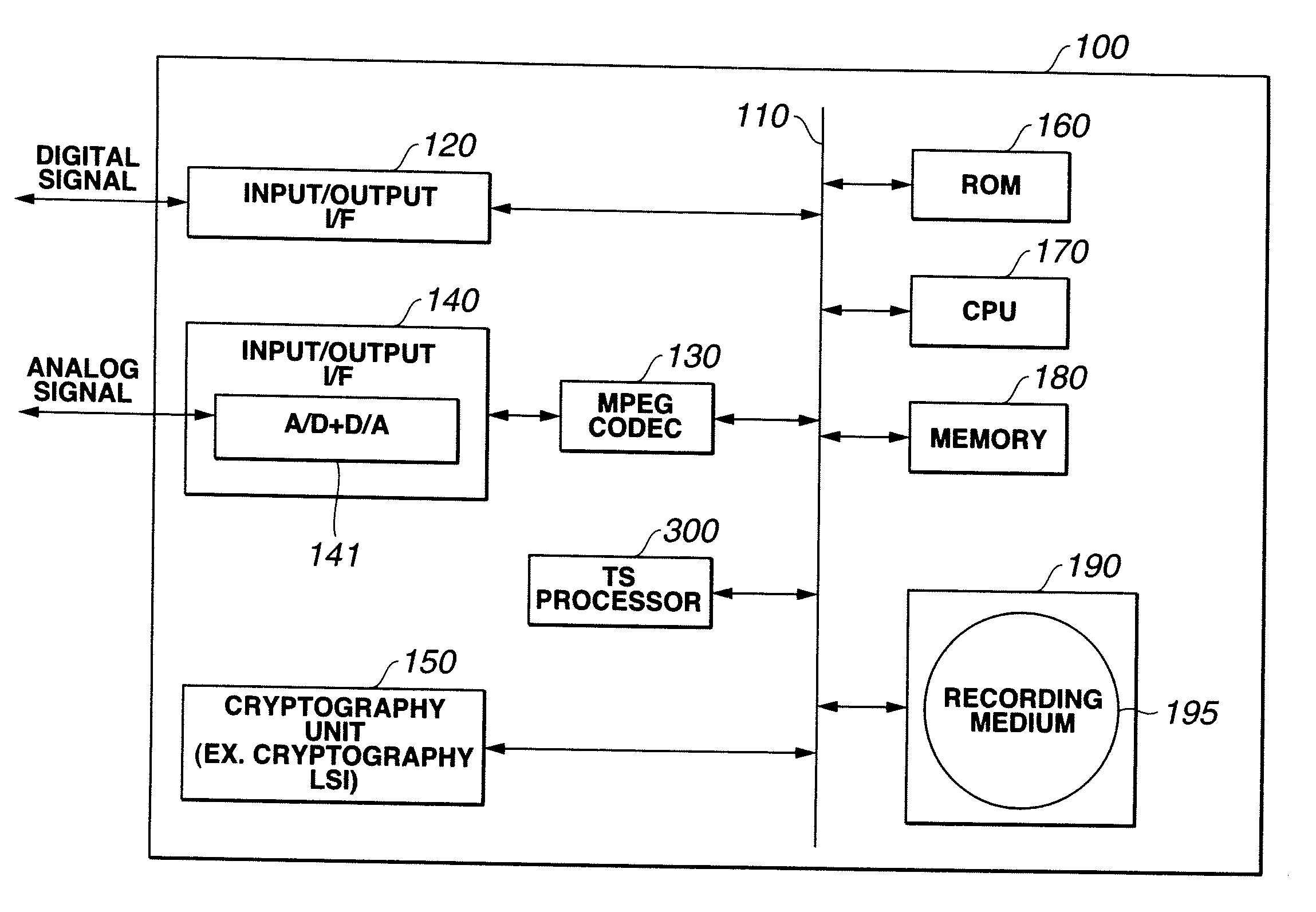
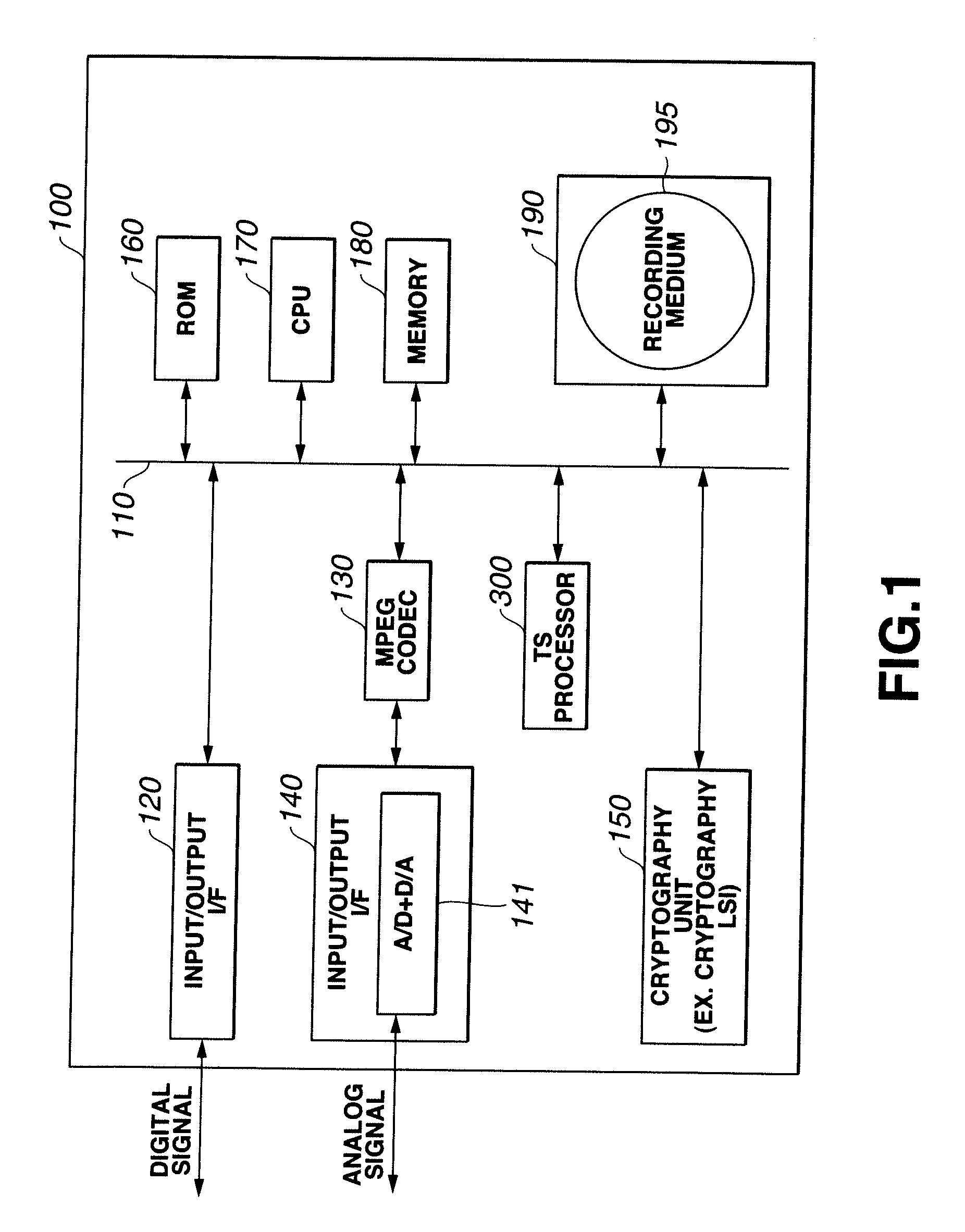
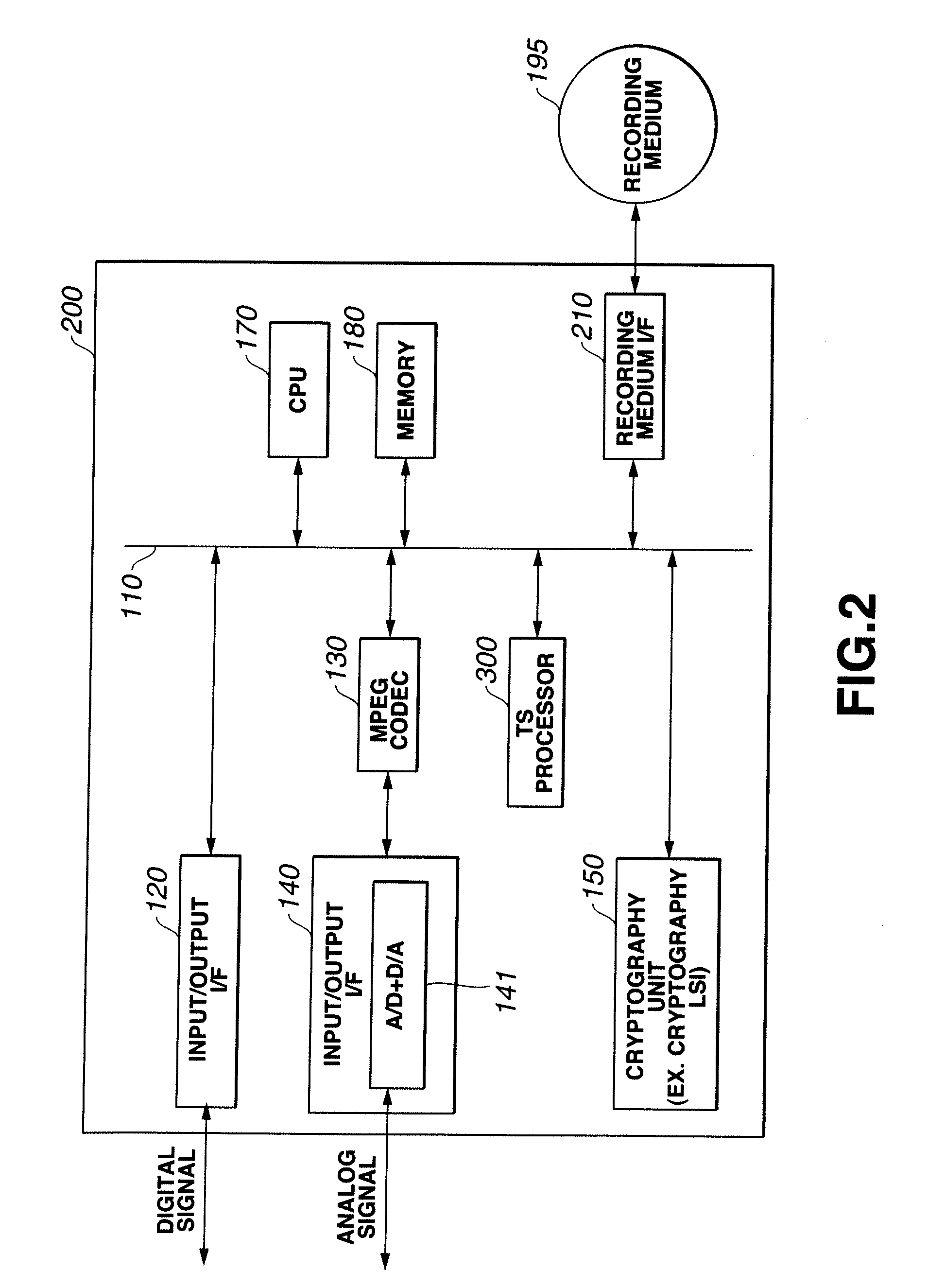
System and method for fast querying of encrypted databases
InactiveUS20050147246A1Improve securityUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringCryptanalysisComputer program
Owner:IBM CORP
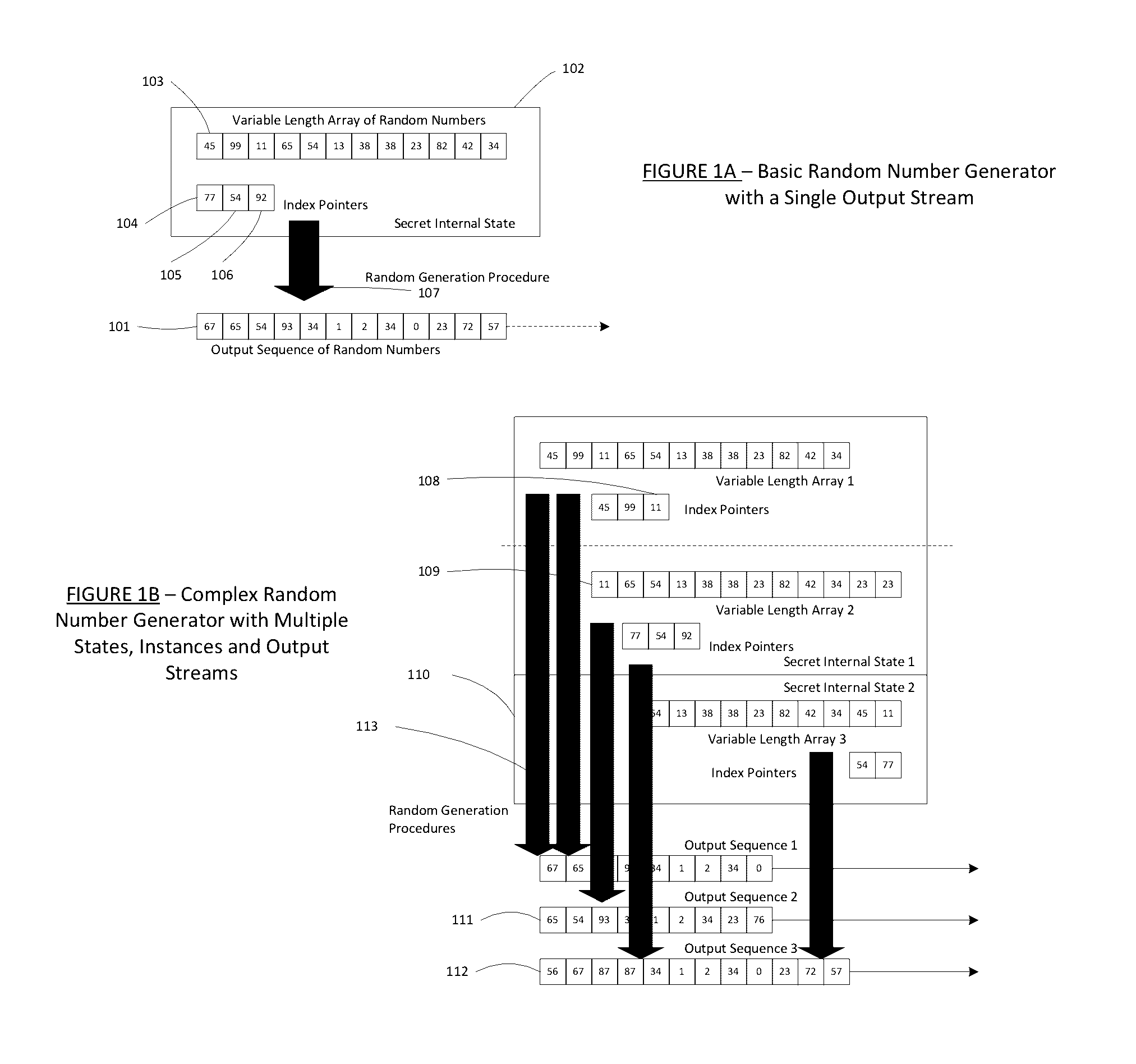
Method for a Dynamic Perpetual Encryption Cryptosystem
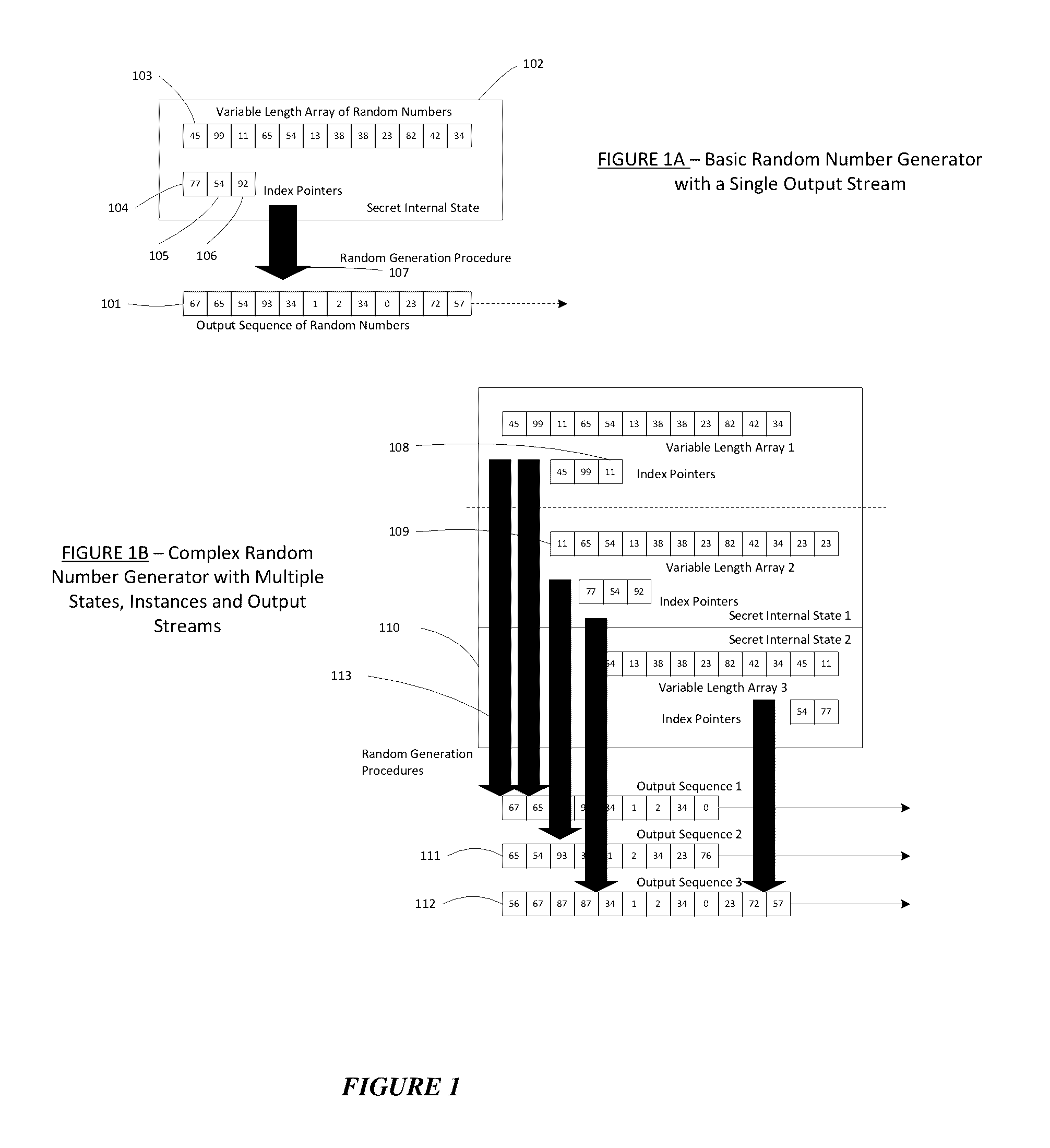
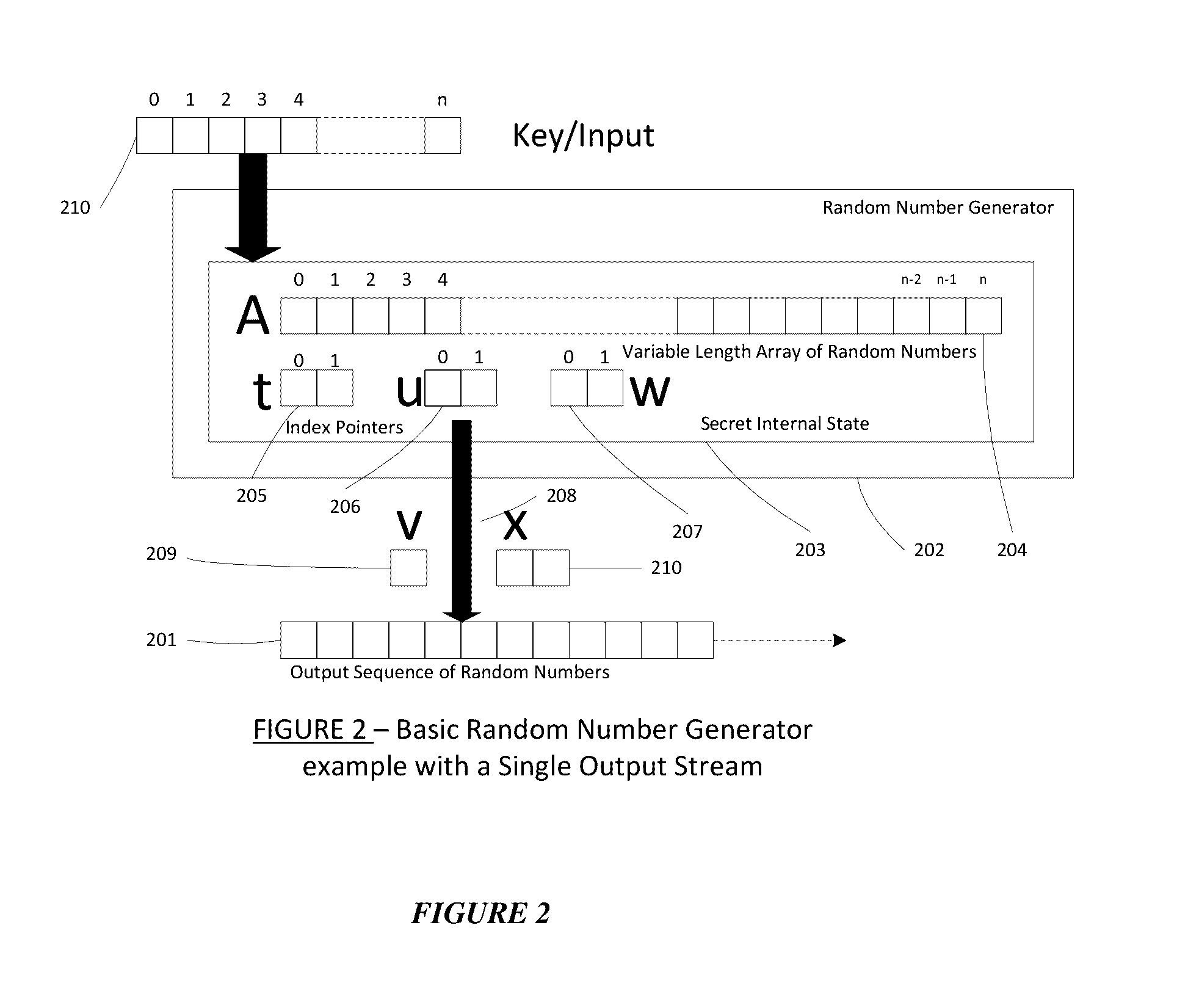
A dynamic computer communication security encryption method or system using an initial seed key and multiple random number generators of a specific design, whereby a sequence of independent random entropy values is produced by one set of random number generators and encrypted along with the message stream using the initial seed key, or the output of a second set of random number generators initialized with the initial seed key, and following the subsequent transmission of the variable encrypted entropy / message block, the entropy values are used to symmetrically or identically augment or increase the current uncertainty or entropy of the cryptosystem at both the sender and the receiver, prior to the next encryption block operation. The encryption process effectively entailing the use of multiple encryption ciphers, and the entropy augmentation process entailing the encryption or application of various logical mathematical operations on the already dynamic but deterministic internal state values of the second set of random number generators, effectively altering their deterministic outputs in a random probabilistic manner.Random length message value sequences from one or more data sources is combined with one or more random length entropy value sequences from an independent source, following which the entropy “updates” may also be used to alter, or change any cryptosystem variable, value or component in a randomly determined manner. In addition, whilst ensuring synchronization, the random entropy sequences also serve to “pollute” the cipher-stream and thereby hinder most current forms of cryptanalysis, whilst simultaneously injecting additional entropy into the cryptographic system and allowing for its propagation to affect any connected system nodes, and thereby introducing unpredictable entropy into the system pseudorandom number generator outputs, and thereby ensuring the perpetual generation of unpredictable random numbers.Super-encryption mechanics are independent of the user data, simple, fast and efficient, and can incorporate compression, error correction and asymmetric encryption authentication routines. But most importantly, super-encryption ensures resistance to brute force attacks (not possible to verify if a message was even sent), an ability to exceed “perfect secrecy” requirements, and an improvement on previous super-encipherment design, since overhead can be dramatically reduced from 100% overhead.Communication links previously established by system nodes with central authorities may be used for secure node authentication and registration, whilst allowing the central authority to broker and synchronize communication channels and providing mutual authentication and other security functions between the system nodes.
Owner:FIGUEIRA HELDER SILVESTRE PAIVA
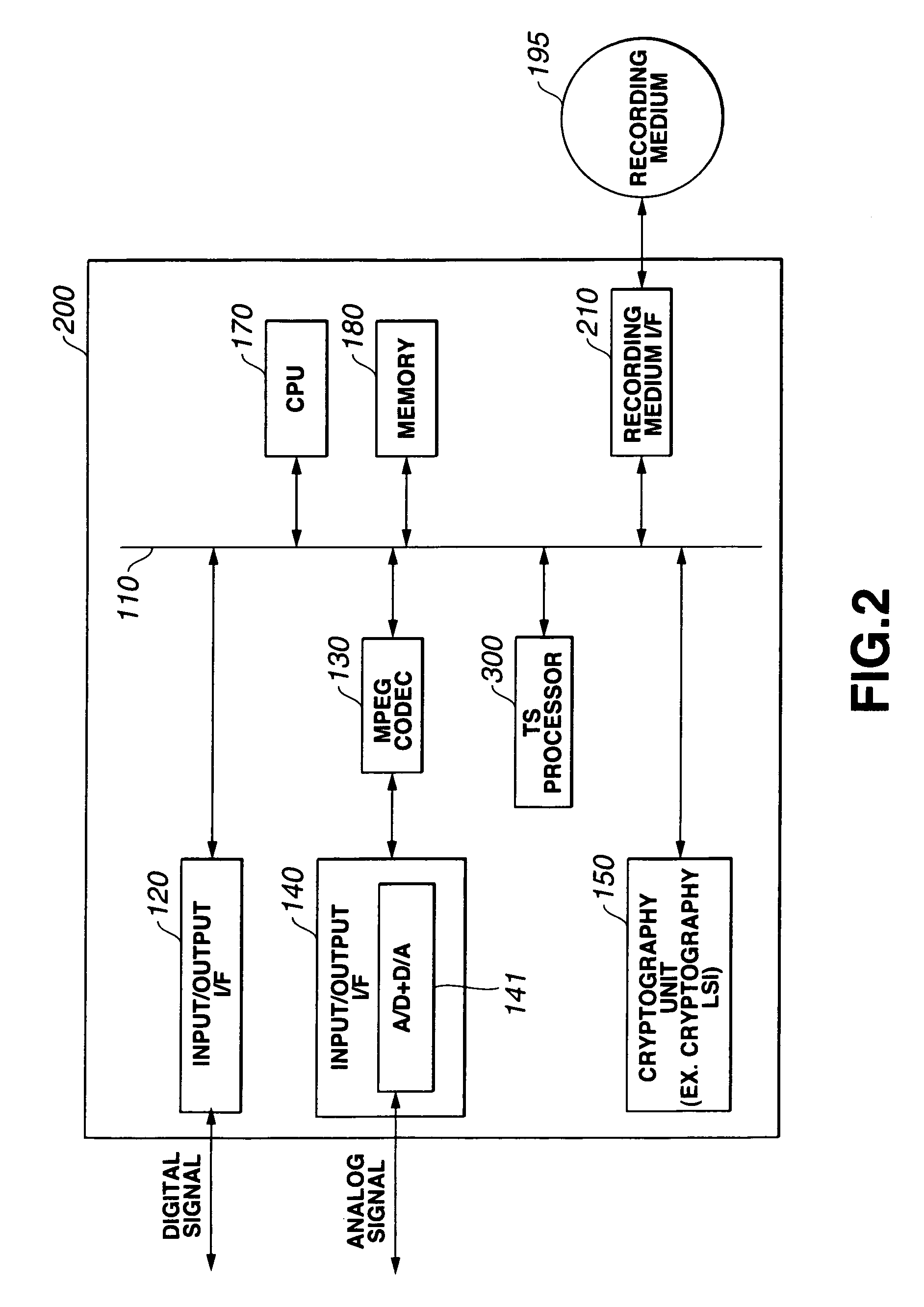
Information recording/playback apparatus and method
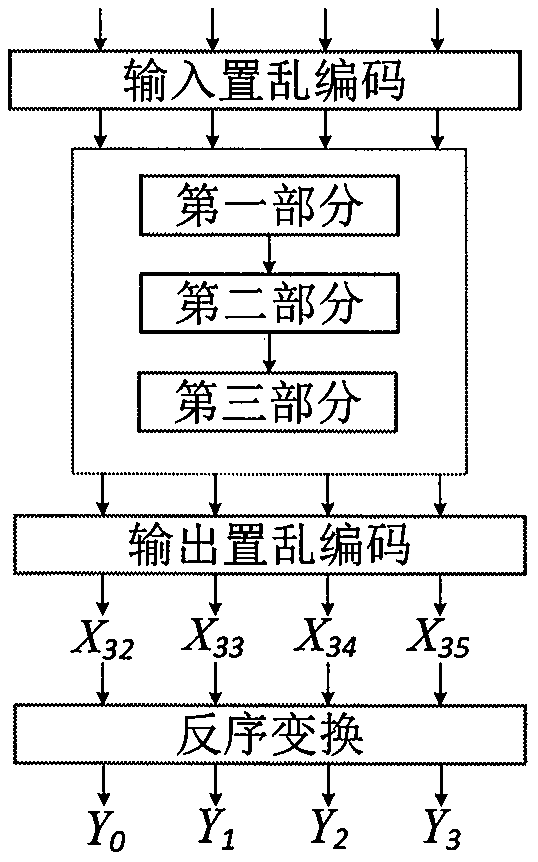
ActiveUS7181624B2Enhance protection against cryptanalysisNarrowing data areaTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareArrival time
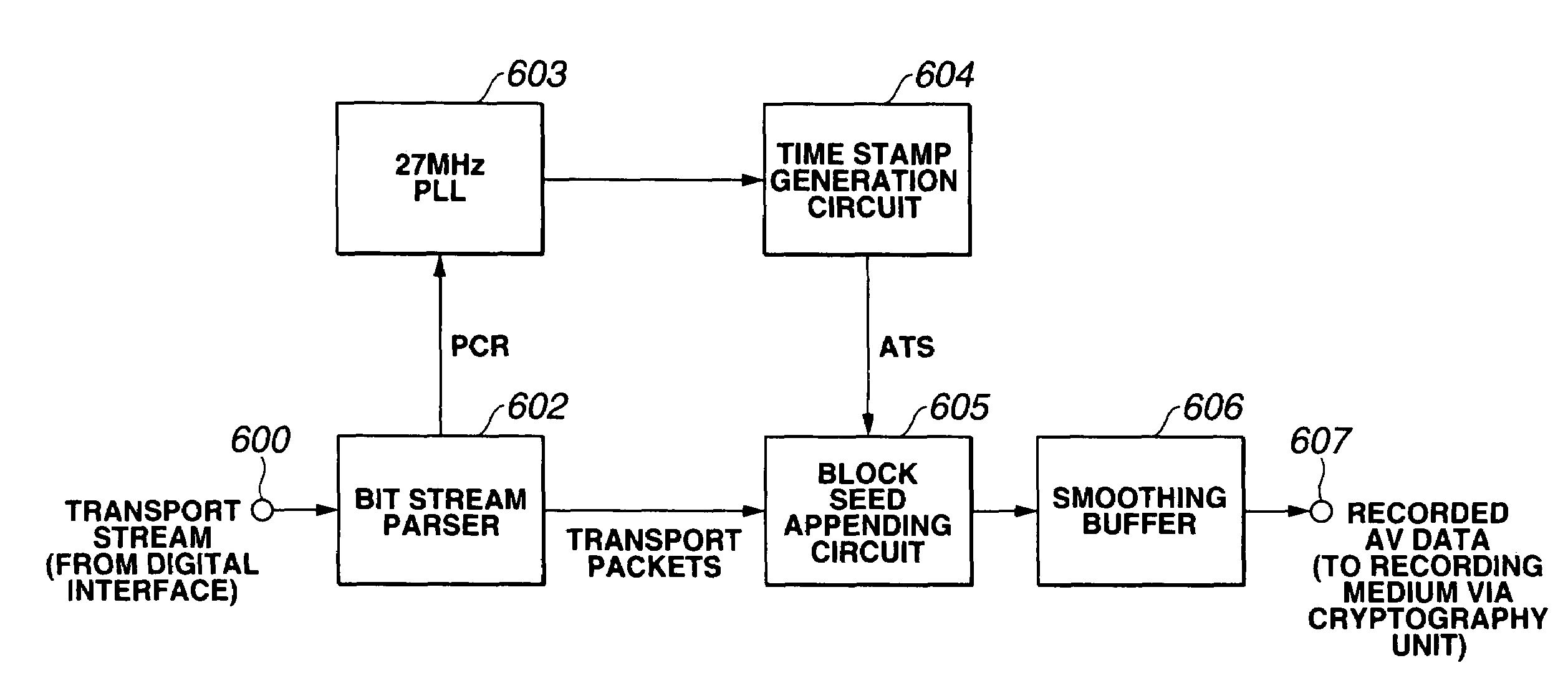
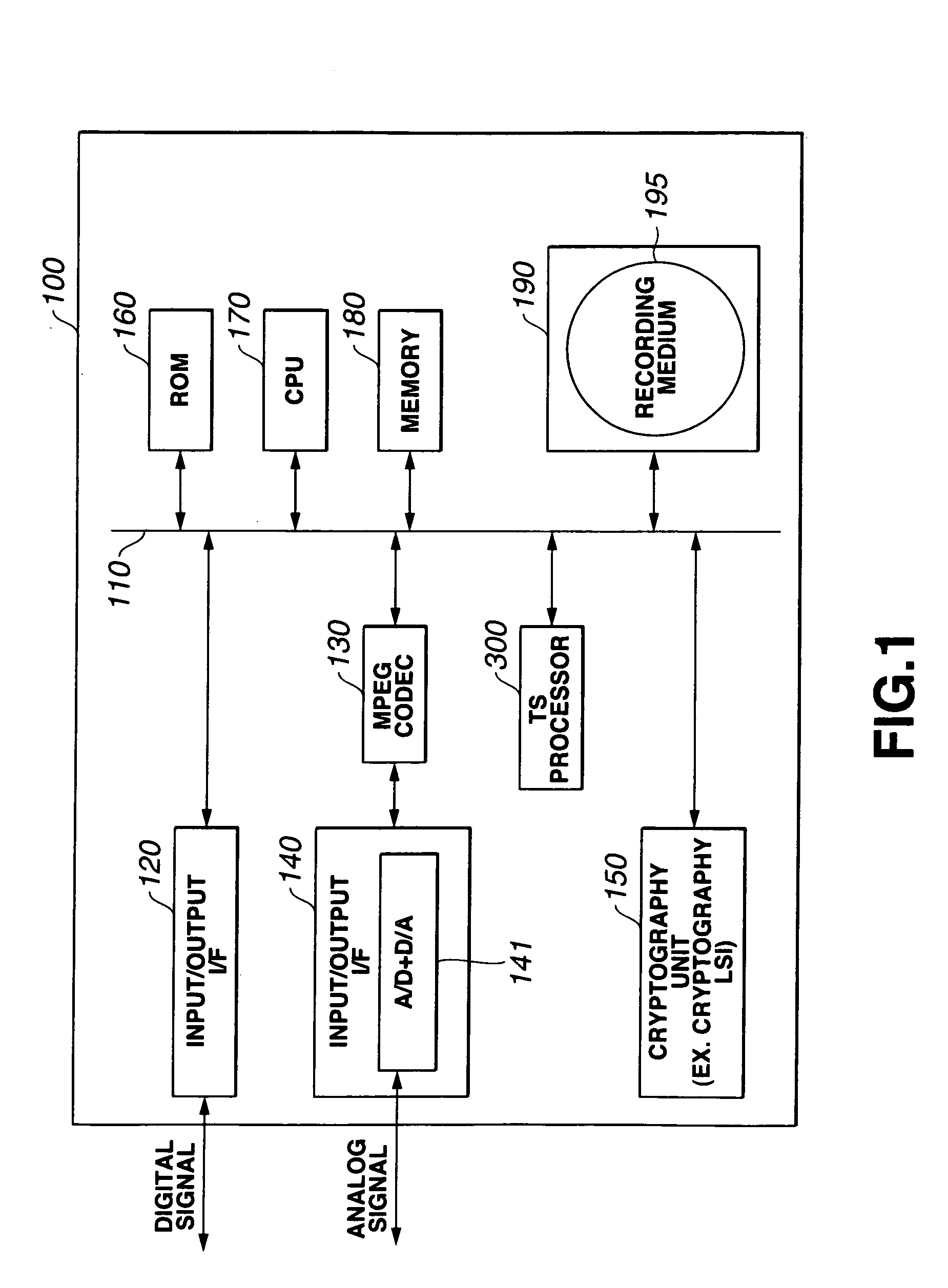
A block key to encrypt block data is generated using an ATS (arrival time stamp) appended to each of TS (transport stream) packets included in a transport stream correspondingly to the arrival time of the TS packet. The ATS is a random data depending upon an arrival time, and so a block-unique key can be generated, which enhances the protection against data cryptanalysis. A block key is generated from a combination of an ATS with a key unique to a device, recording medium or the like such as a master key, disc-unique key, title-unique key or the like. Since an ATS is used to generate a block key, any area for storage of an encryption key for each block may not be provided in a recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
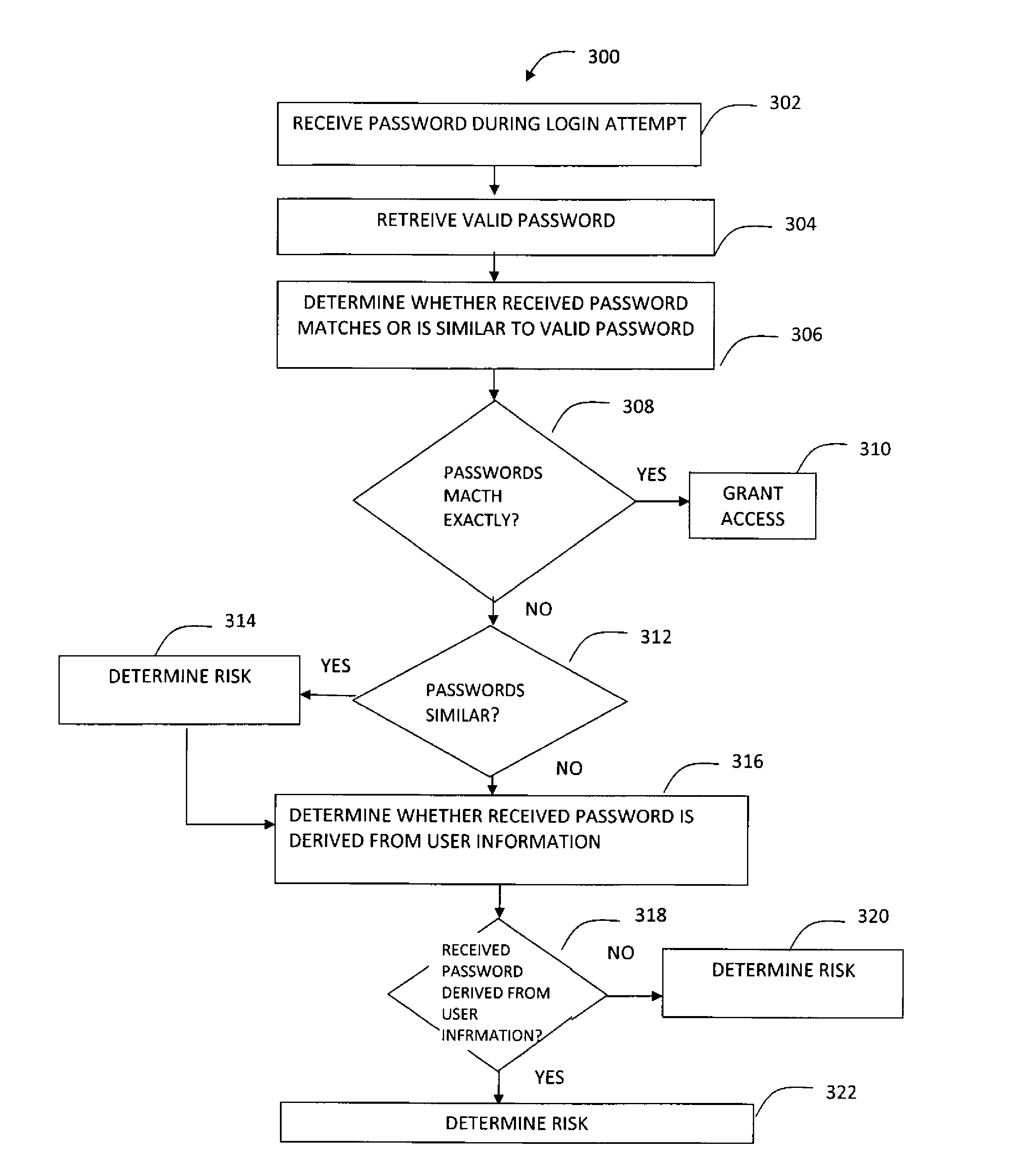
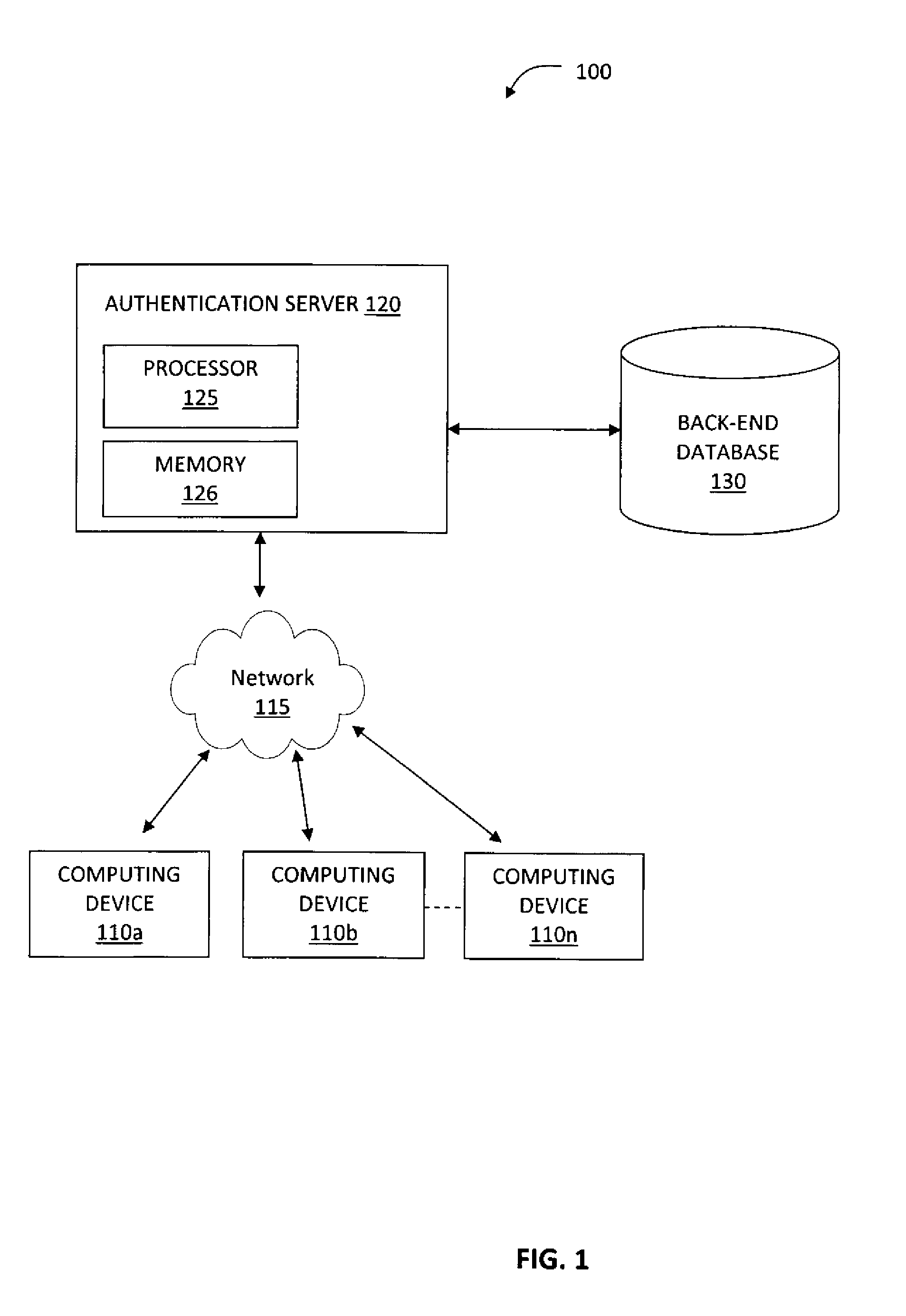
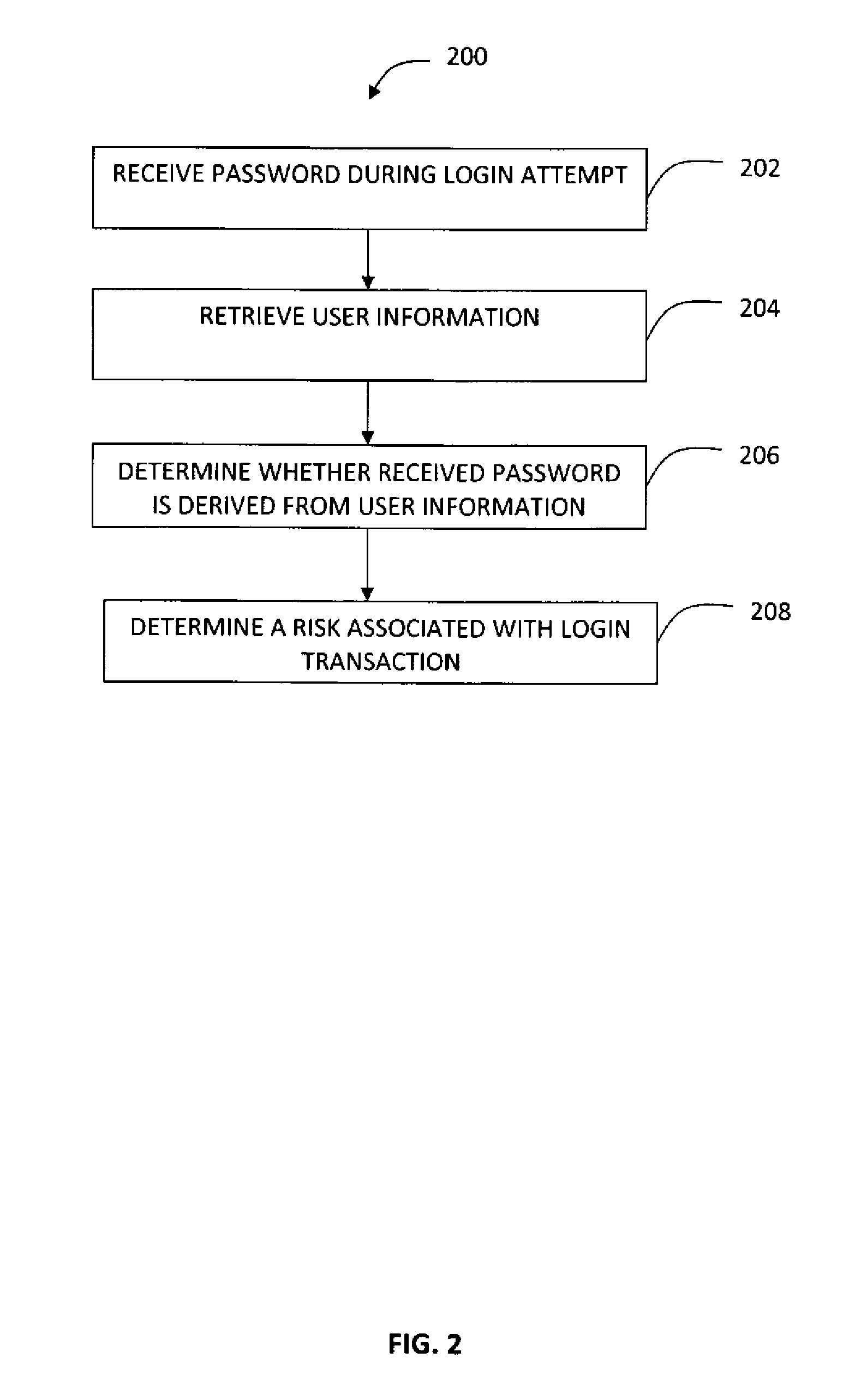
System and Method for Risk Assessment of Login Transactions Through Password Analysis
ActiveUS20130254875A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsPasswordFinancial transaction
A system and method is provided for determining a risk associated with a login transaction. A password received during the login attempt and determination is made regarding whether the received password is derived form user information. A risk is determined based on a determination that the received password is derived from the user information.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Method for communicating securely over an insecure communication channel
InactiveUS20060098814A1Improve securityMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsSecure communicationObject based
A method for enhancing the security of cryptographic systems against side channel attacks and cryptanalysis is based on the concept of object hopping or dynamic transformation of elements between objects that share the same category and / or floating objects which facilitate object hopping. The use of floating objects and floating finite fields to facilitate field hopping is also disclosed. Further, the use of curve hopping and floating elliptic curves to facilitate curve hopping and / or key floating when keys used in cryptosystems are floated through floating fields are also used for enhancing the security of cryptographic systems.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Cryptographic processing apparatus, cryptographic processing method and computer program
InactiveUS20050055596A1Increase the difficultyWithout process algorithmEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsPower analysisInformation analysis
According to the configuration of the present invention, the modulation clock signal is generated in accordance with a signal based on a random number, and a data processing timing is determined in accordance with the modulation clock signal to execute data processing. Accordingly, secret information analysis of an encryption key, a decryption key and the like through measurements of consumption powers in terms of a lapse time of a cryptographic processing apparatus for encrypting and decrypting data, i.e., cryptanalysis based on the power analysis, can be made difficult to thereby realize a cryptographic processing apparatus and method having a high security level.
Owner:SONY CORP
Identity authentication and key agreement method suitable for electricity consumption information collection system
ActiveCN103095696AResist attackImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationElectricityService flow
The invention provides an identity authentication and key agreement method suitable for an electricity consumption information collection system. On the basis of a traditional identity authentication and key agreement method, a digital certificate identity identification mechanism, a signature authentication mechanism using an authoritative institution to inquire the validity of a digital certificate, and a challenge response mechanism based on a symmetric key are introduced to achieve the identity authentication and key agreement of a master station and terminals. The method can effectively resist attacks such as faking of the master station, communication service flow analysis, password analysis and the like, and enhances the safety of the electricity consumption information collection system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Encryption and decryption with endurance to cryptanalysis
InactiveUS6970561B1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationPlaintextCiphertext
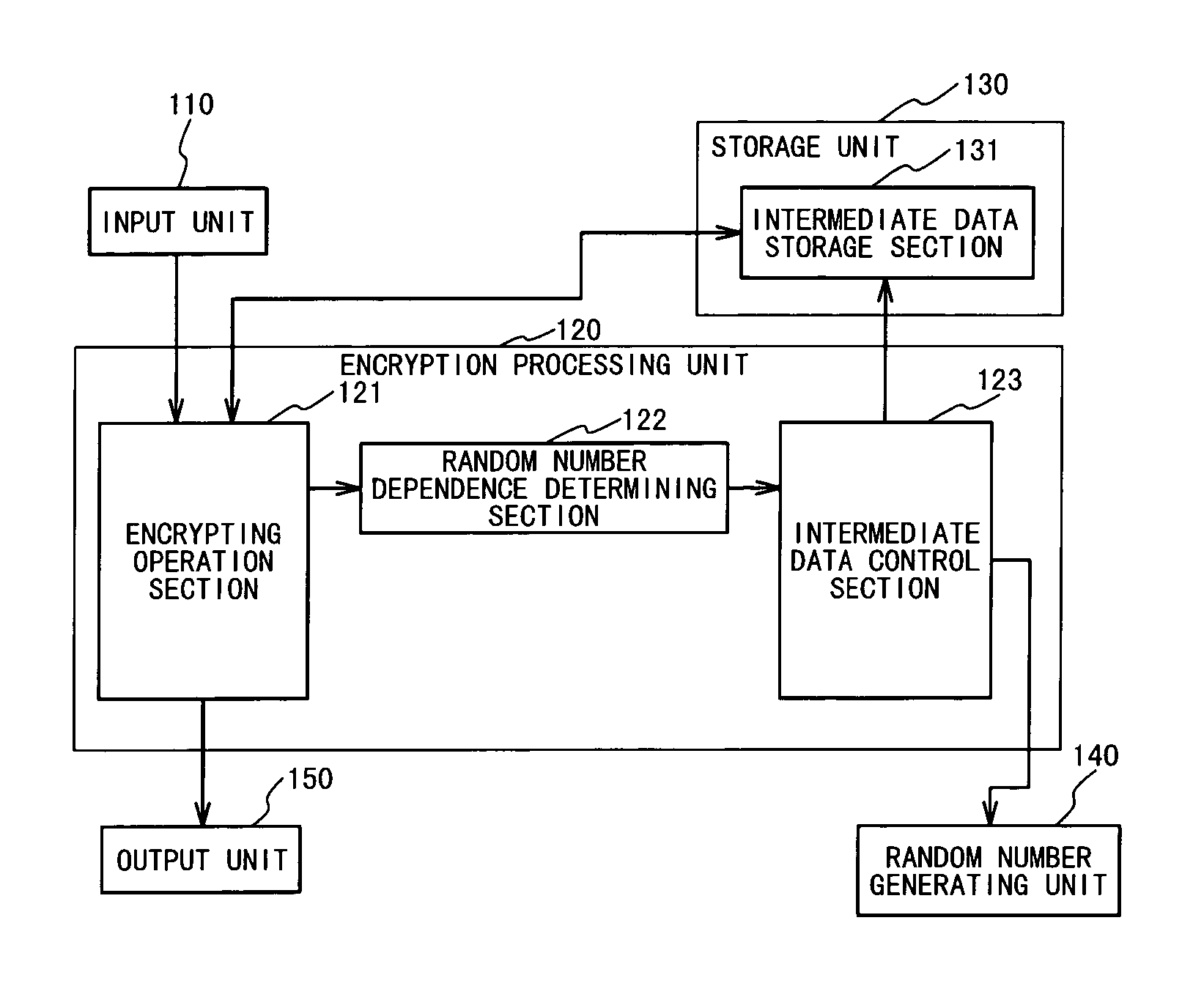
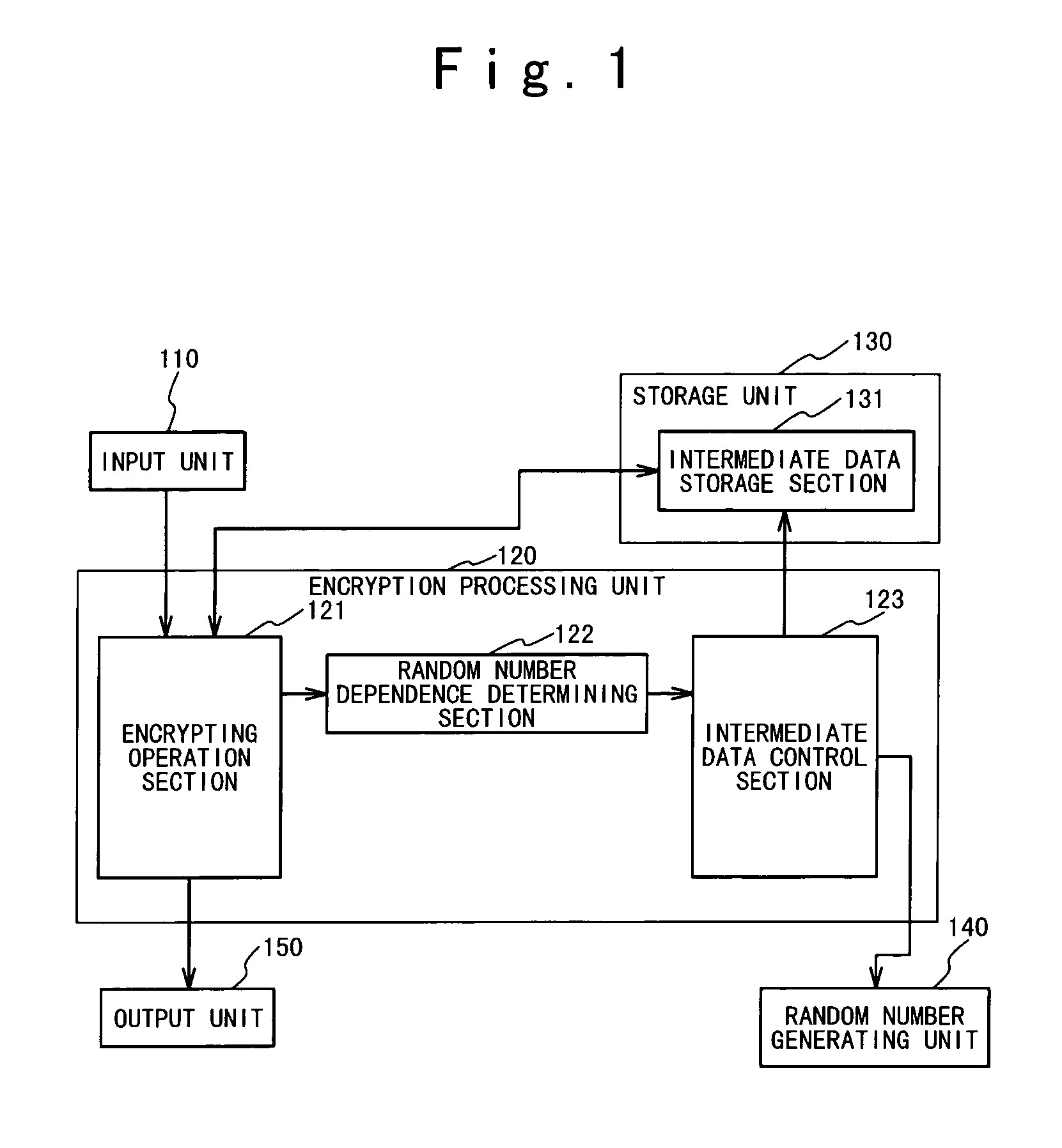
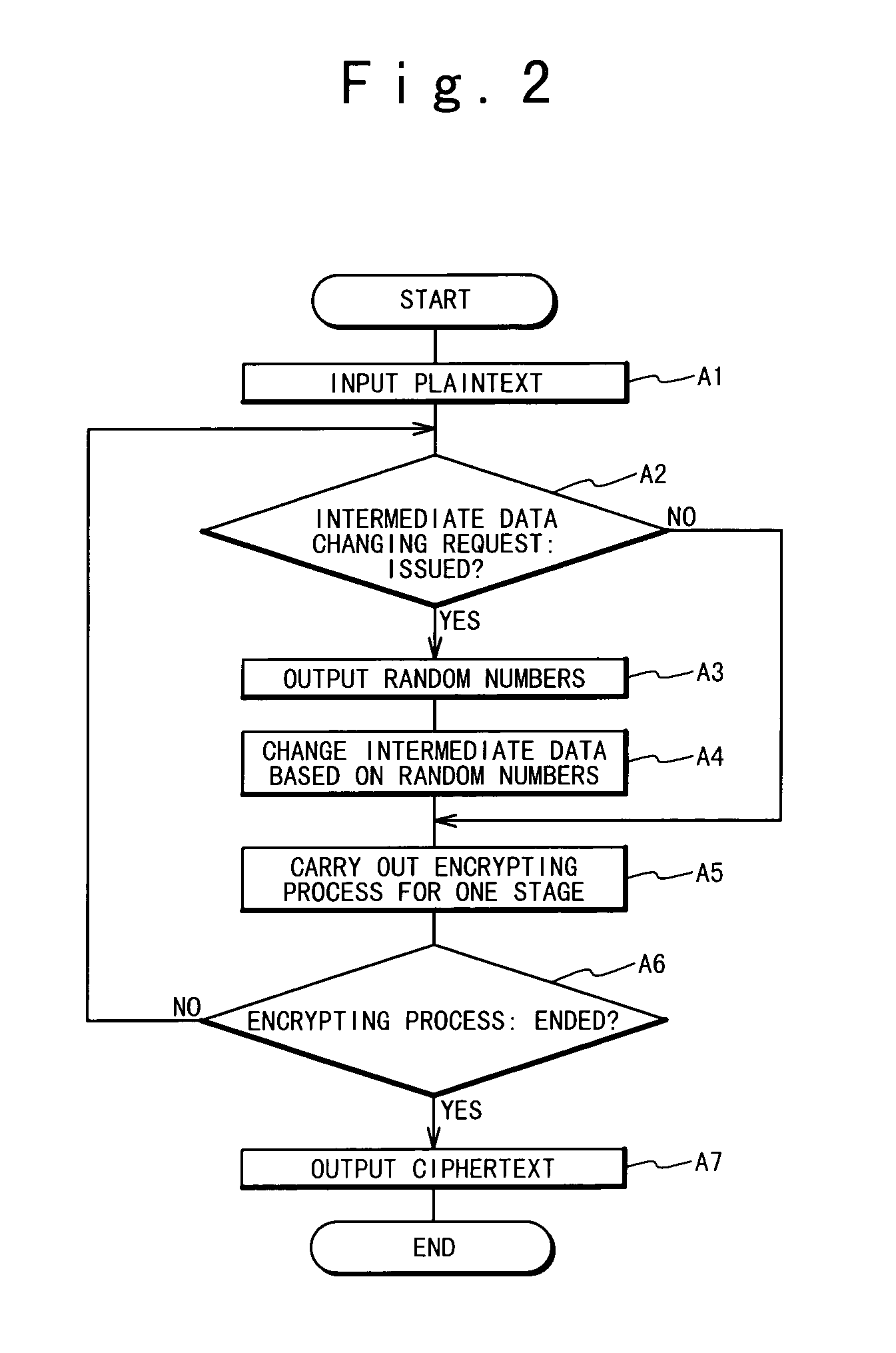
An encrypting apparatus includes an encrypting operation section, a determining section and a control section. The encrypting operation section carries out an encrypting operation to a plaintext using intermediate data at each of a plurality of encrypting stages of the encrypting operation to produce a ciphertext. The encrypting operation section outputs encrypting stage data indicating an encrypting state at each of the plurality of processing stages. The determining section determines whether the encrypting operation at a next encrypting stage should be changed, based on the encrypting stage data at a current encrypting stage from the encrypting operation section. The control section changing the encrypting operation at the next encrypting stage when it is determined that the encrypting operation at the next encrypting stage should be changed.
Owner:NEC CORP
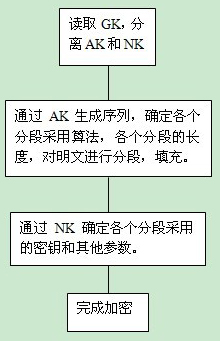
Method for encrypting in sections by using uncertain encryption algorithm
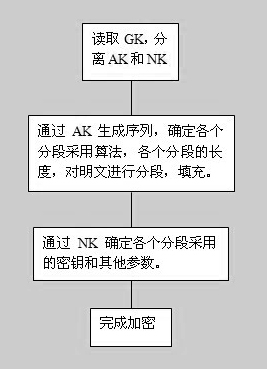
ActiveCN102404111AImprove securityIncrease uncertaintyMultiple keys/algorithms usageAlgorithmPassword
The invention belongs to a novel encrypting method, in particular relates to a method for encrypting in sections by using an uncertain encryption algorithm. The method is used for encrypting the plain text in sections; and the algorithm for encrypting each section is uncertain and secret and determined by generalized keys. The method adopts the generalized keys to determine the length of each section, the encrypting algorithm of each section, various keys and parameters. Because the algorithm is uncertain, password analyzers do not know where to decrypt, though the analyzers get some information, the information means nothing to decrypt other sections.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
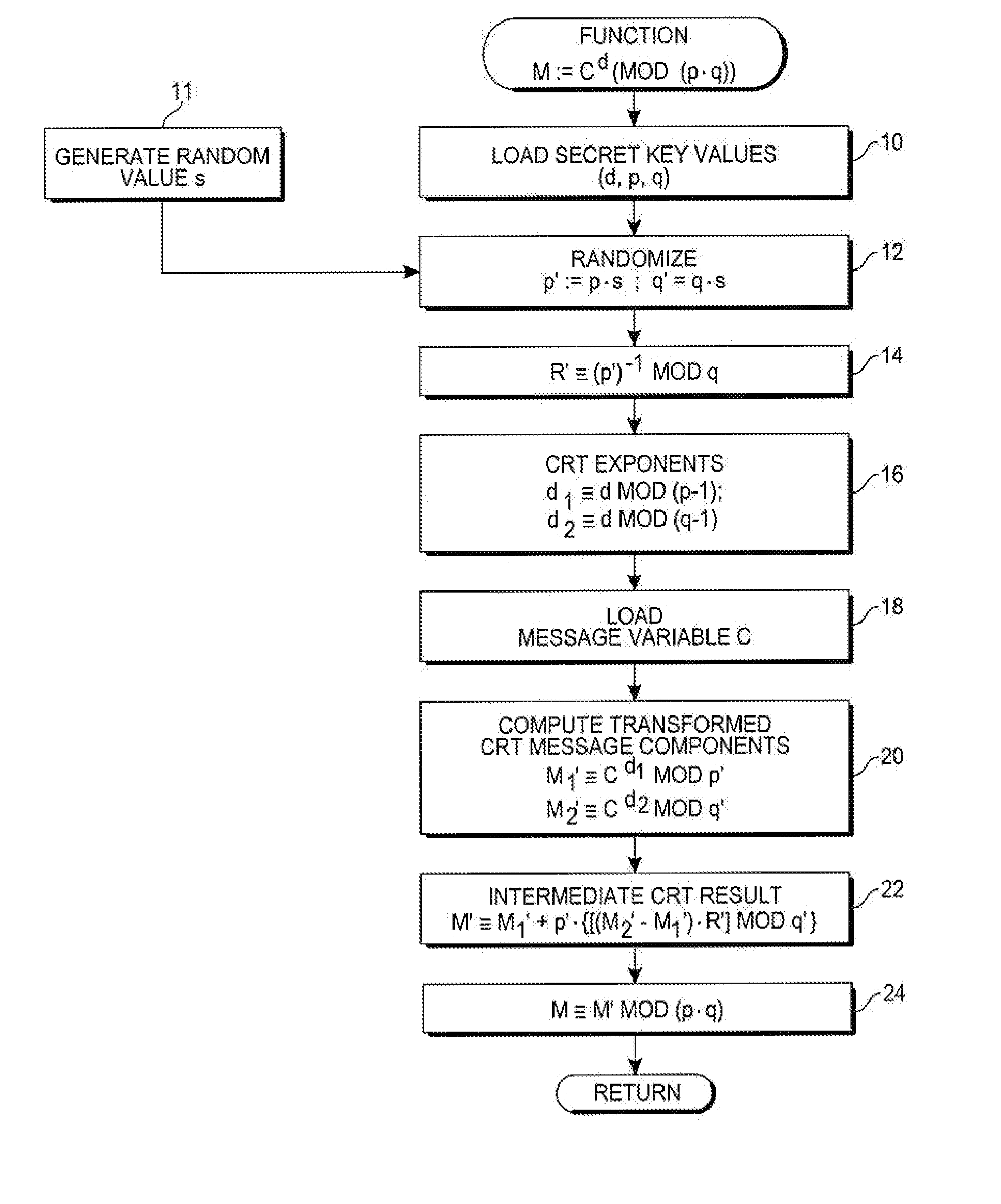
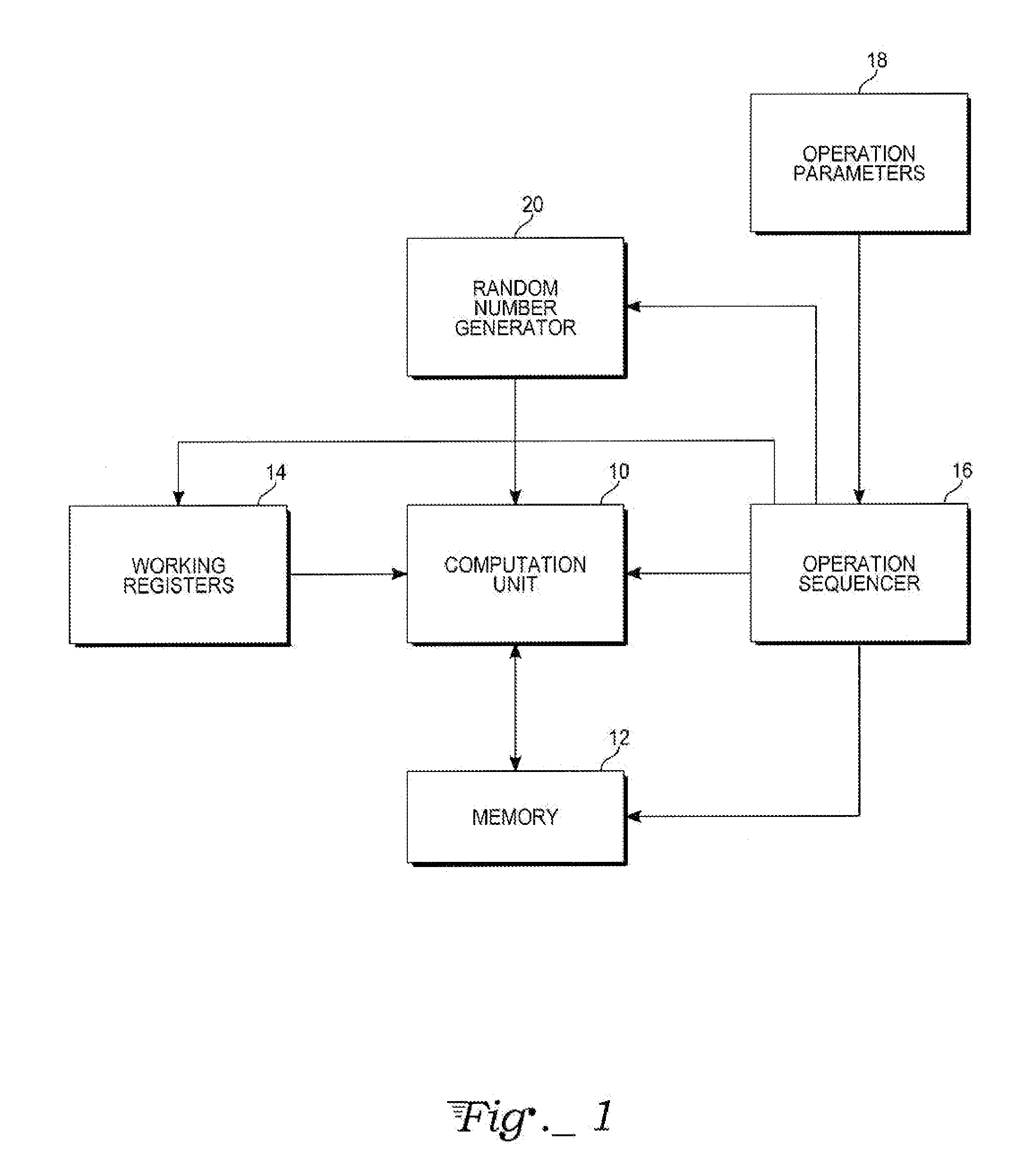
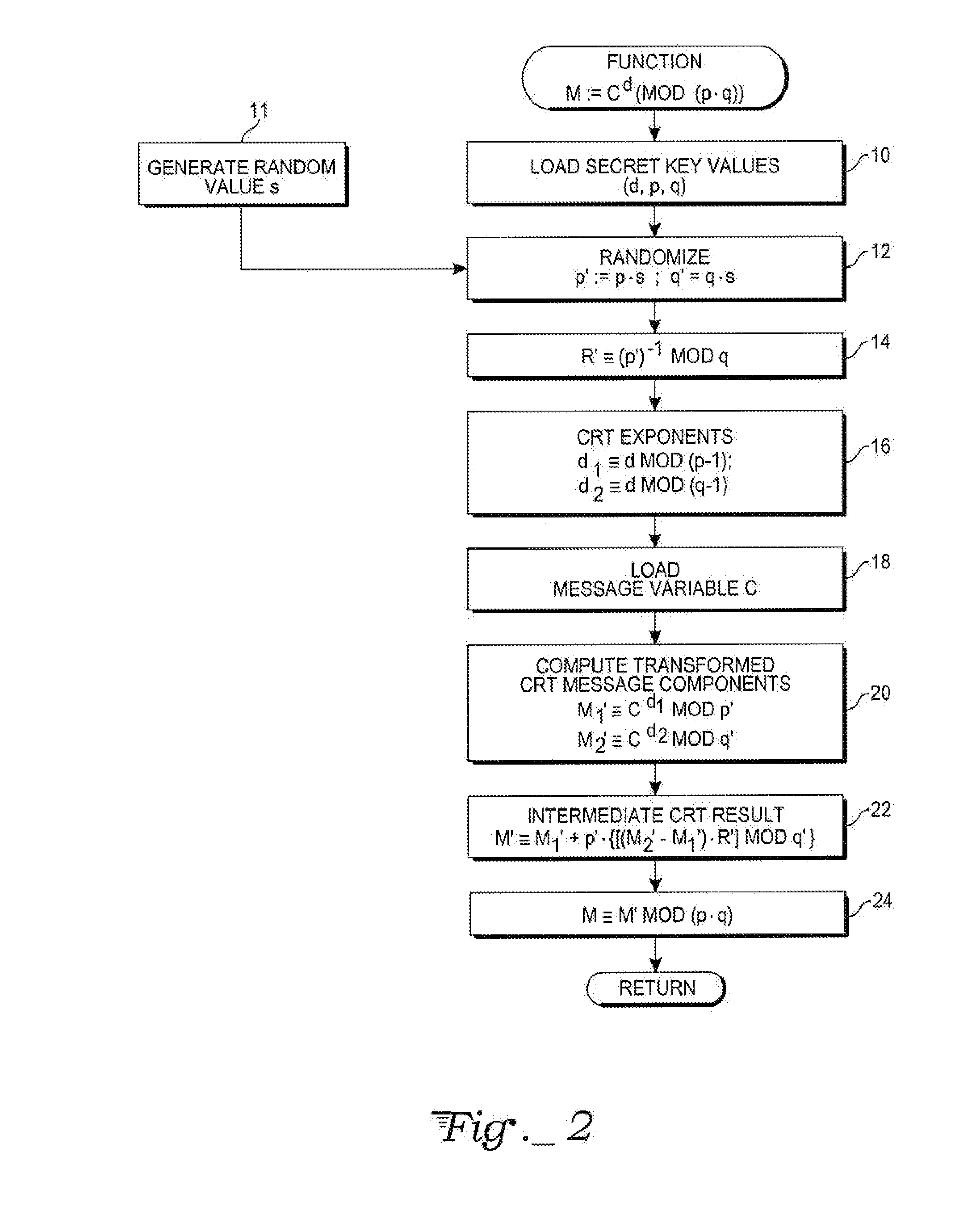
Chinese remainder theorem - based computation method for cryptosystems
ActiveUS20080226064A1Less computational intenseSecure against cryptanalysisRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationChinese remainder theoremCryptosystem
A computer hardware implemented cryptography method computes a modular exponentiation, M:=Cd (mod p·q) upon a message data value C using a Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT) based technique. To secure against cryptanalysis,, the private key moduli p and q are transformed by multiplication with a generated random value s, so that p′:=p·s and q′:=q·s. The CRT steps of the modular exponentiation are applied using the transformed moduli p′ and q′ to obtain a random intermediate message data value M′. A final reduction of M′ modulo p·q yields the final message data value M. Values needed for the computation are loaded into data storage and accessed as needed by electronic processing hardware.
Owner:CRYPTOGRAPHY RESEARCH
Information Processing Apparatus
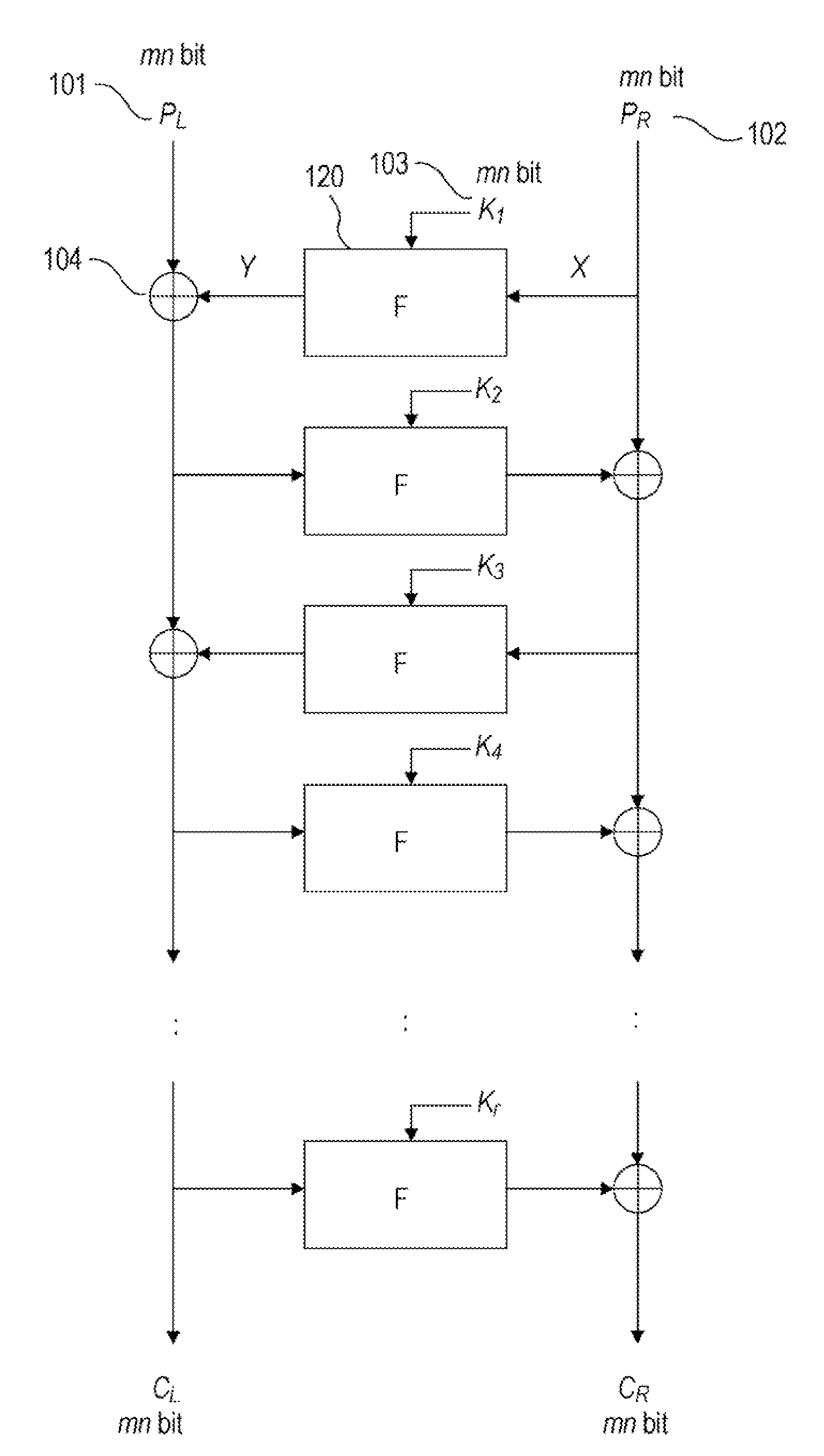
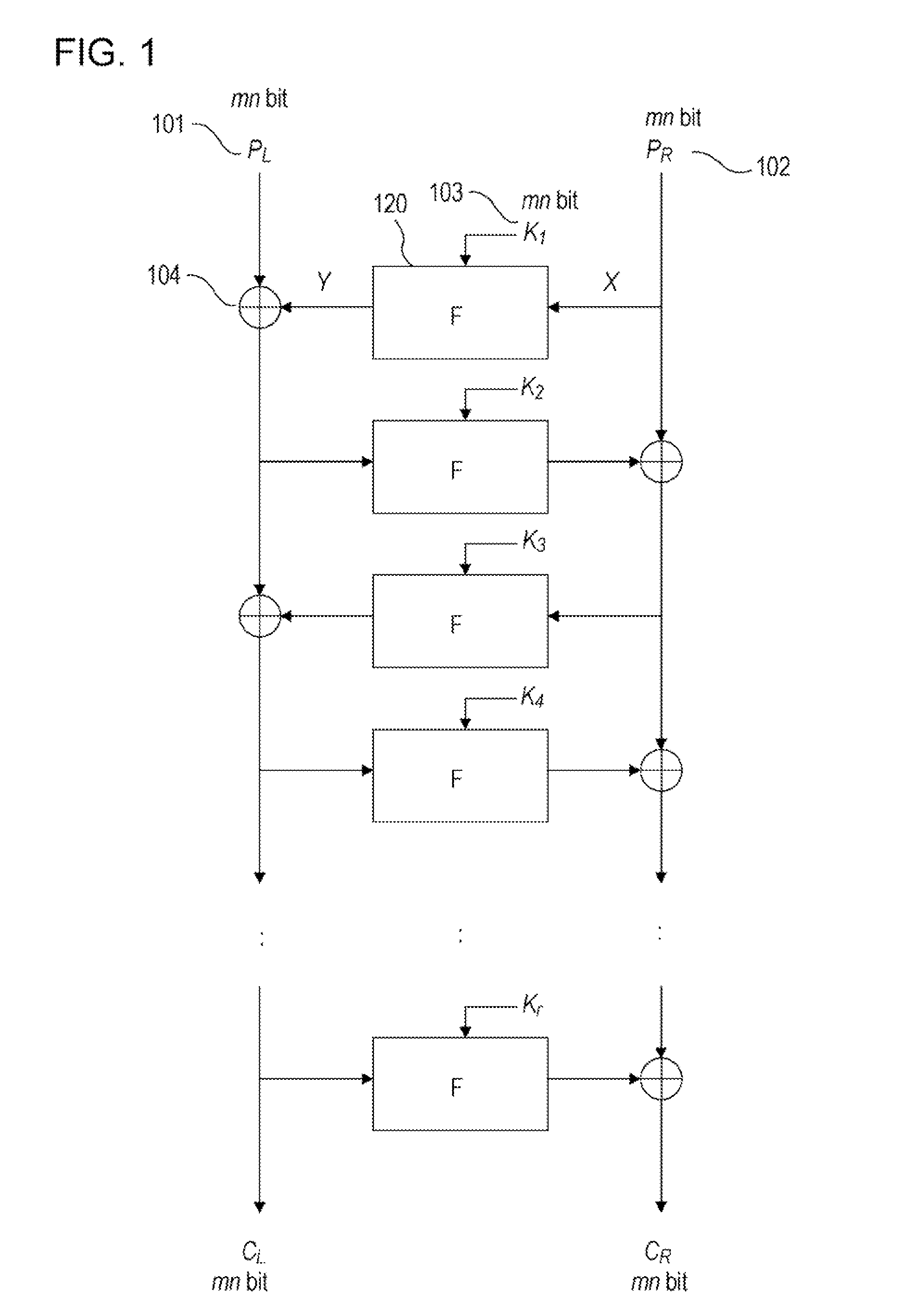
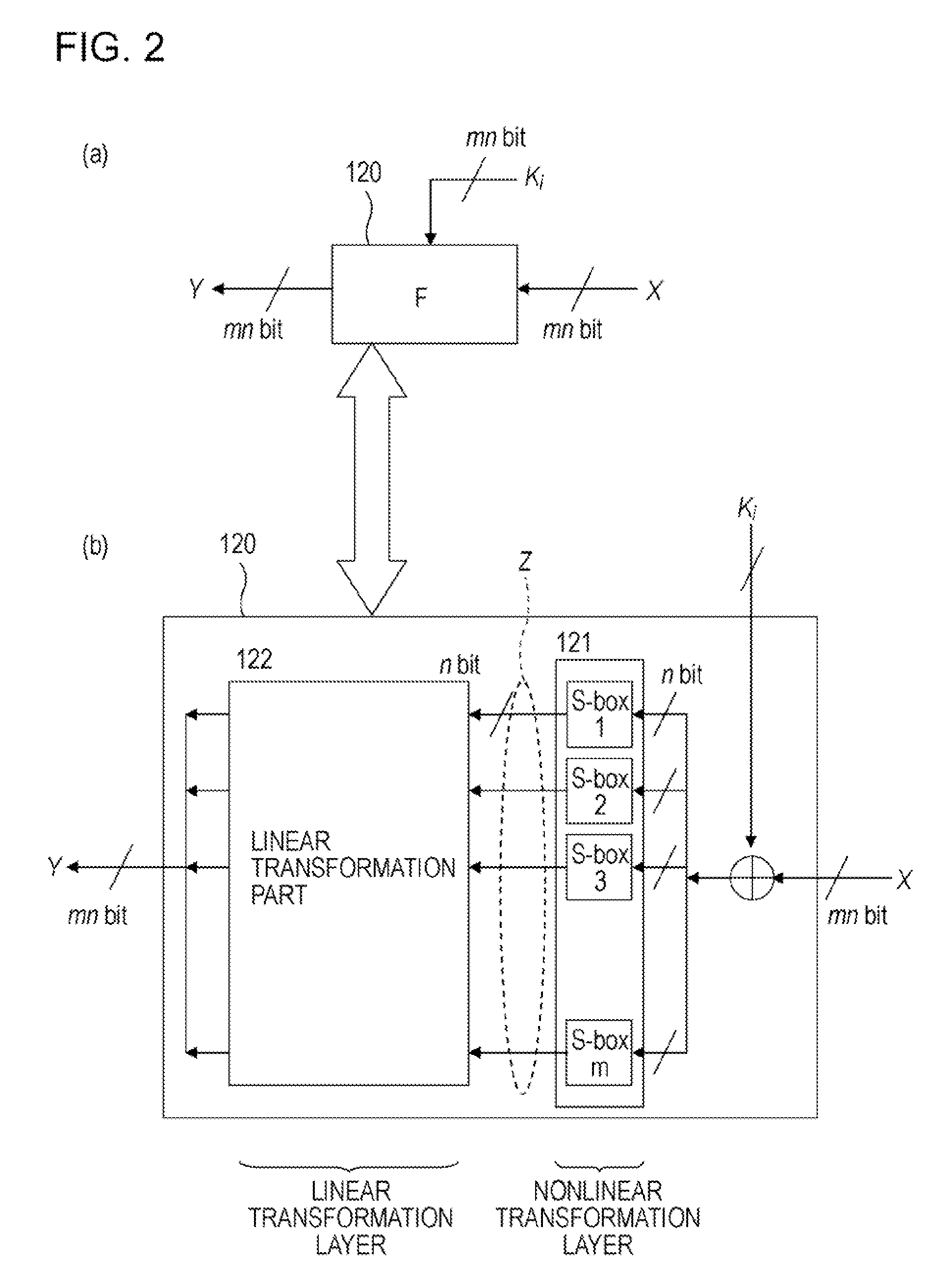
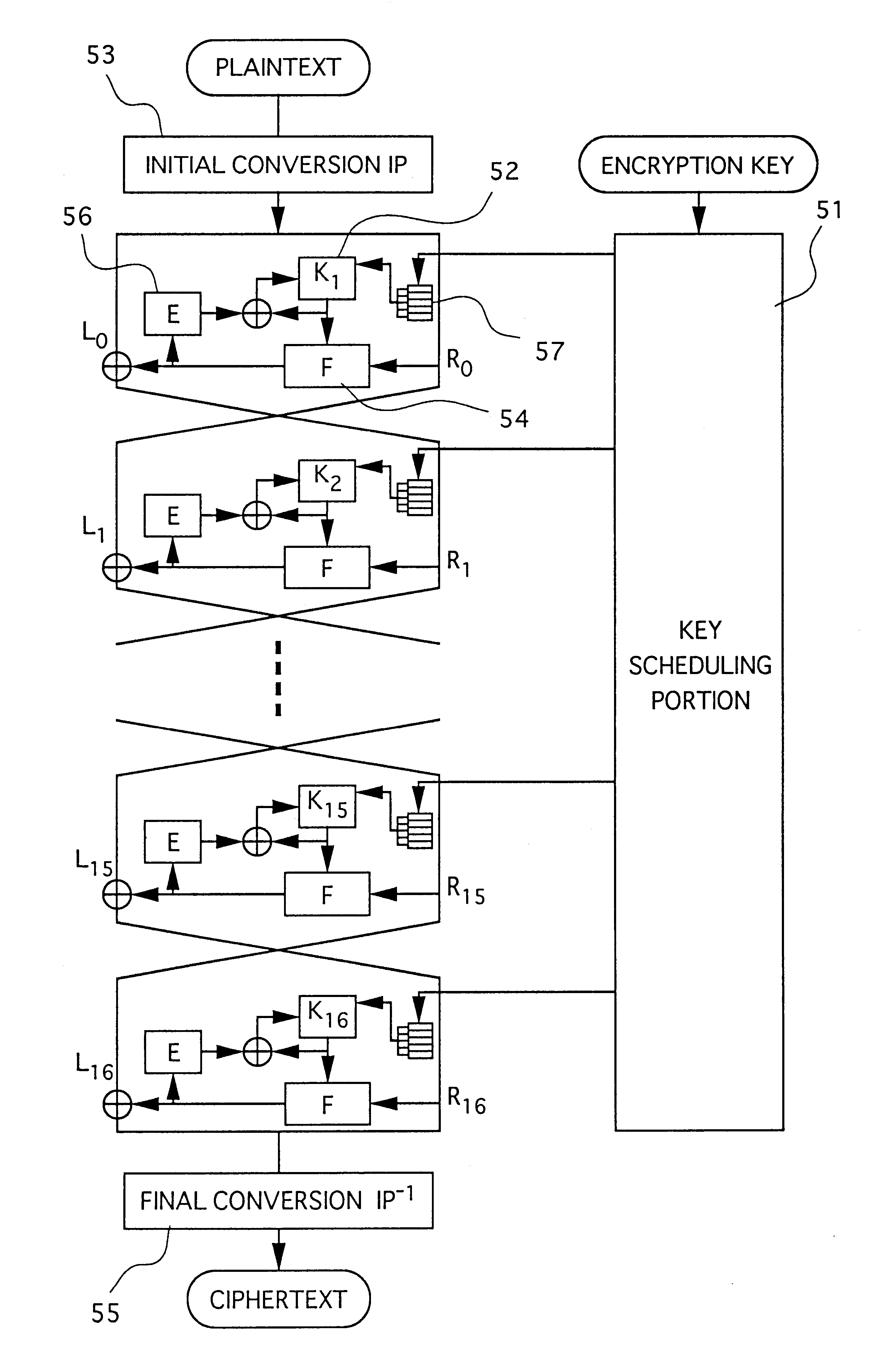
ActiveUS20090103716A1Increase resistanceIncrease the number ofKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHigh resistanceInformation processing
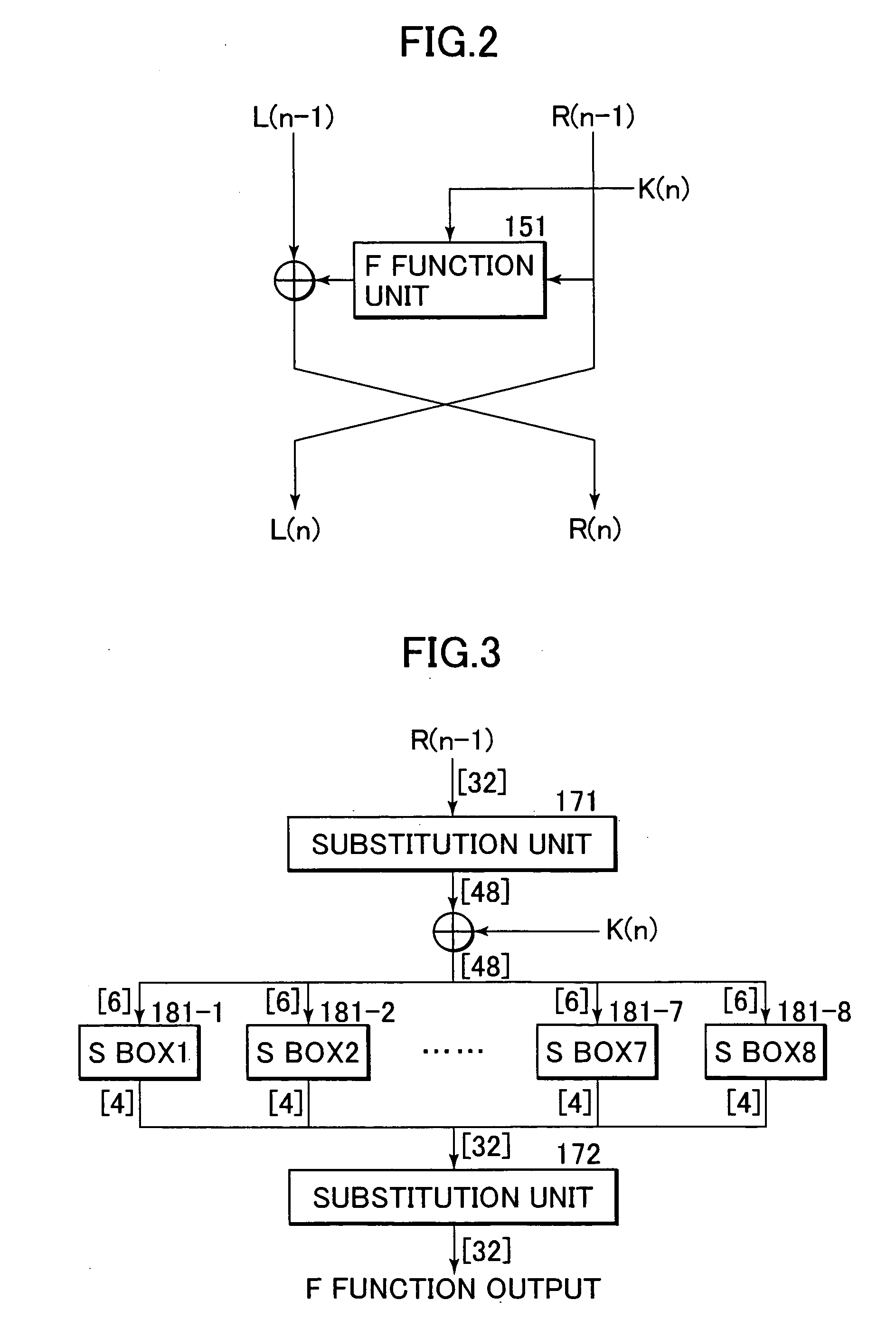
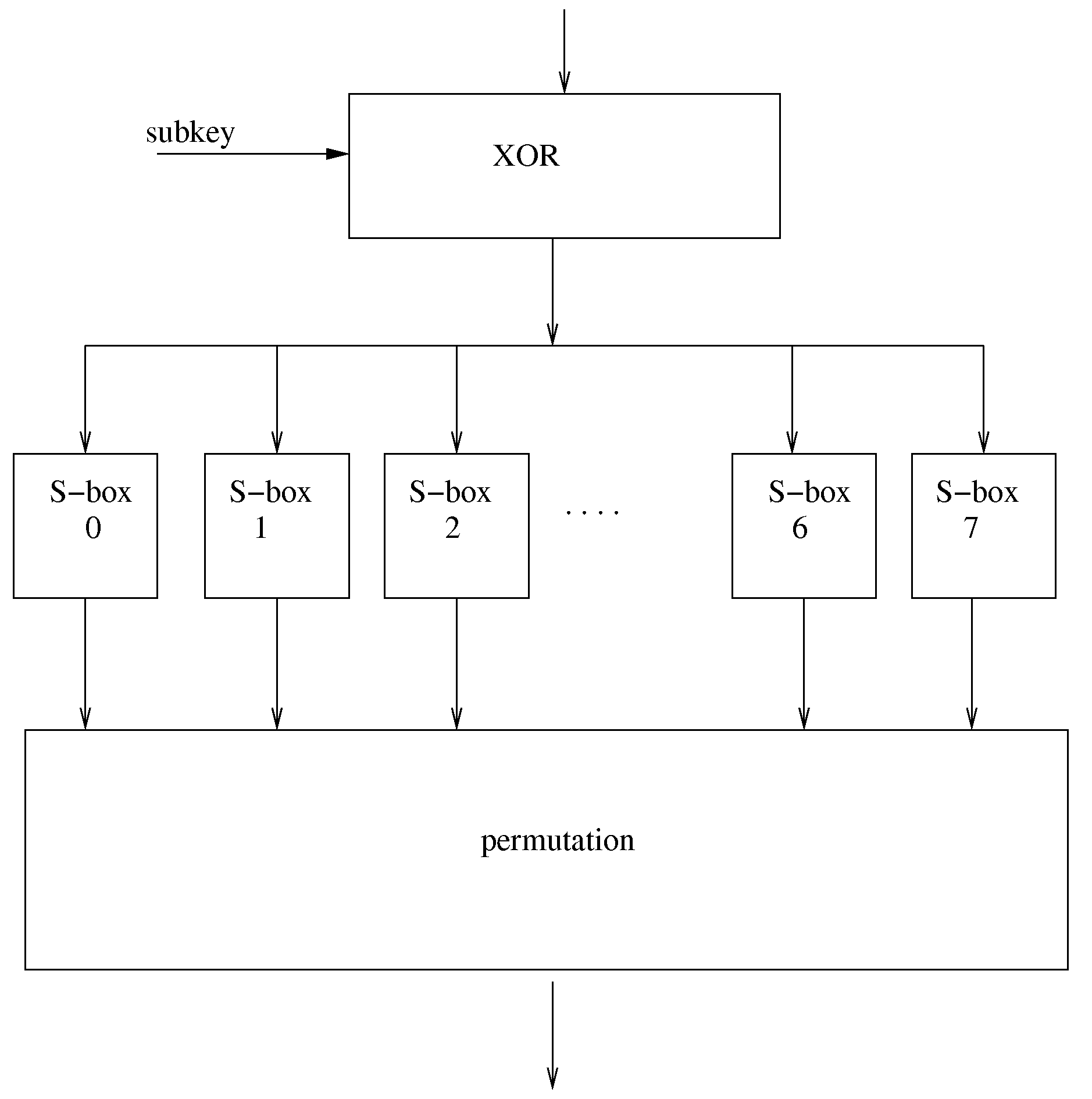
A high-security cryptanalysis-resistant cryptographic processing apparatus and a cryptographic processing method are provided. A Feistel common key block cipher is produced by repeatedly performing an SPN-type F-function including a nonlinear transformation part and a linear transformation part over a plurality of rounds. In each round, a linear transformation process is performed according to an F-function using a matrix determined so as to satisfy a relatively loose constraint whereby high resistance to differential attacks and / or linear attacks is achieved. The relatively loose constraint allows an increase in the number of candidates for usable matrices, and it is possible to maintain the number of active S-boxes to a sufficiently large level. This makes it possible to increase the minimum number of active S-boxes, which is one of measures indicating the degree of robustness of ciphers, and thus it is possible to realize an algorithm of encrypting data in a highly secure manner so that high resistance to attacks is achieved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Encryption apparatus and computor-readable recording medium containing program for realizing the same
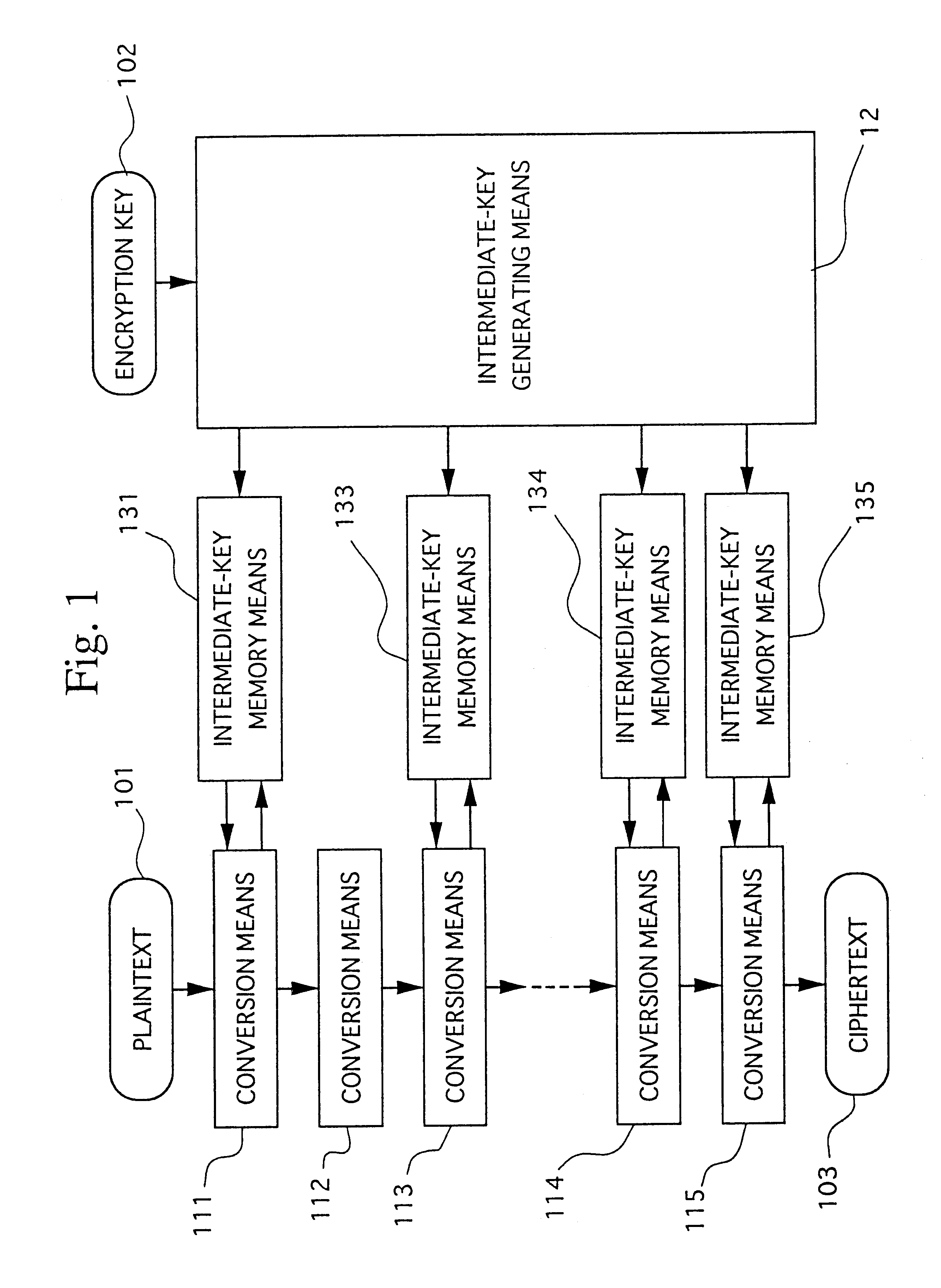
InactiveUS6272221B1Increase typeDecryption is difficultMultiple keys/algorithms usageEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePlaintext
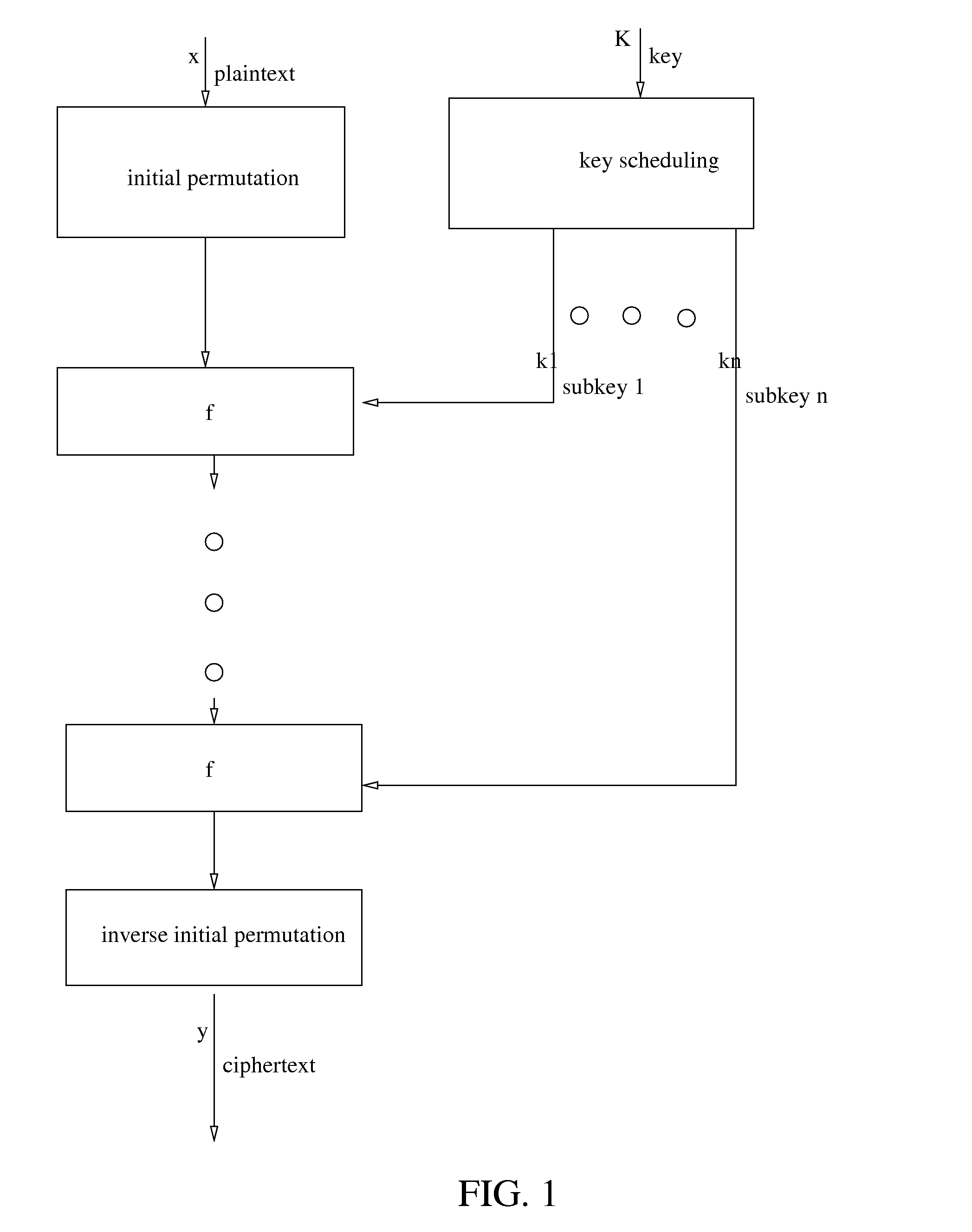
The present encryption apparatus is provided with a plurality of conversion means connected in multiple steps, an intermediate-key generating means for performing linear or non-linear conversion for an intermediate-key and subsequently generating an initial-value of the intermediate-key, and an intermediate-key memory means for updating and storing the intermediate-key update information. The present encryption apparatus provides a ciphertext which is refractory to a chosen plaintext cryptanalysis in the evaluation of the key update information. The present apparatus is capable of high speed operation by parallel processing and is also capable of maintaining high speed operation by higher multiplication of the parallel operation even when the number of repetitive conversion is increased.
Owner:NEC CORP
Data encryption system and method
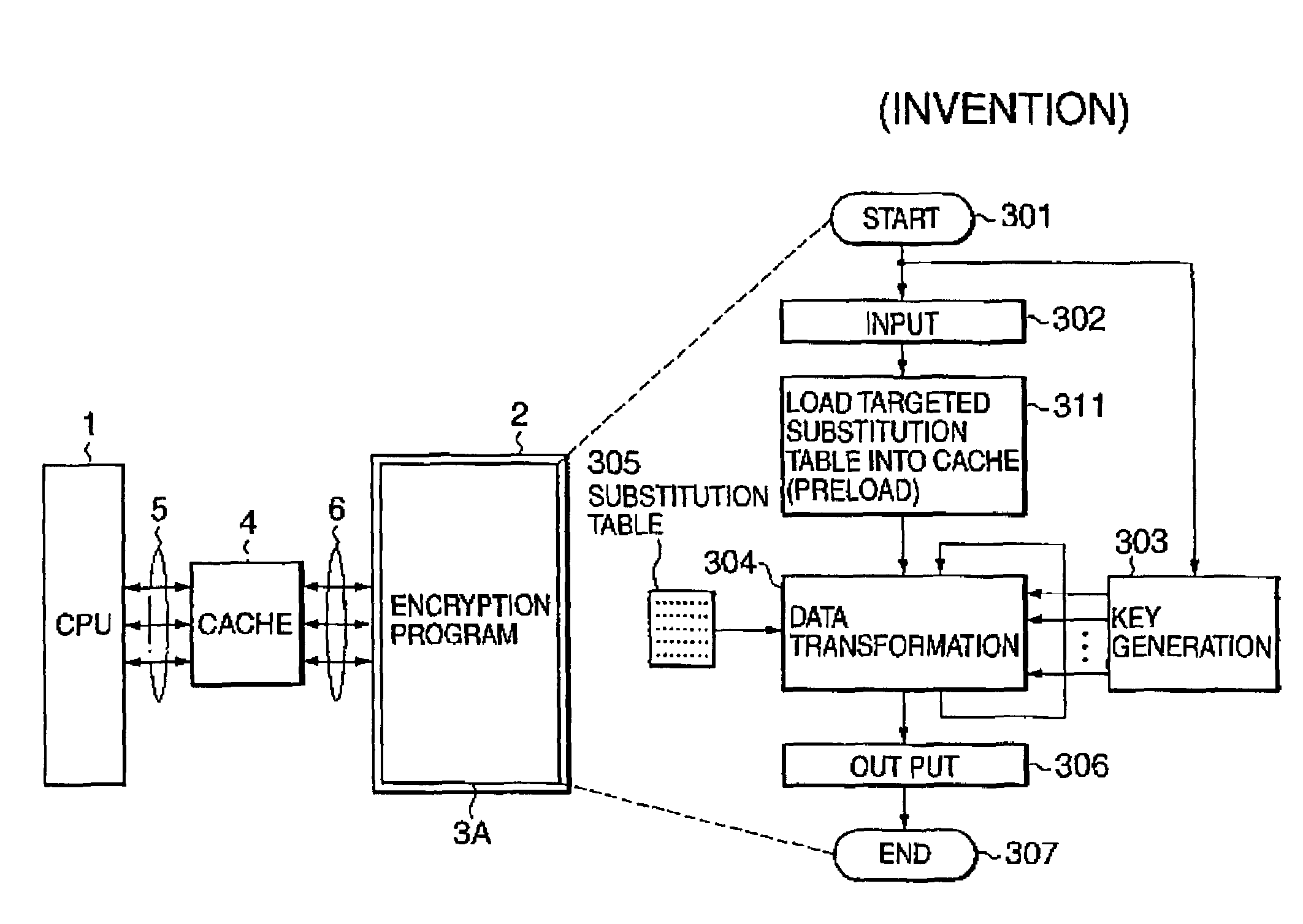
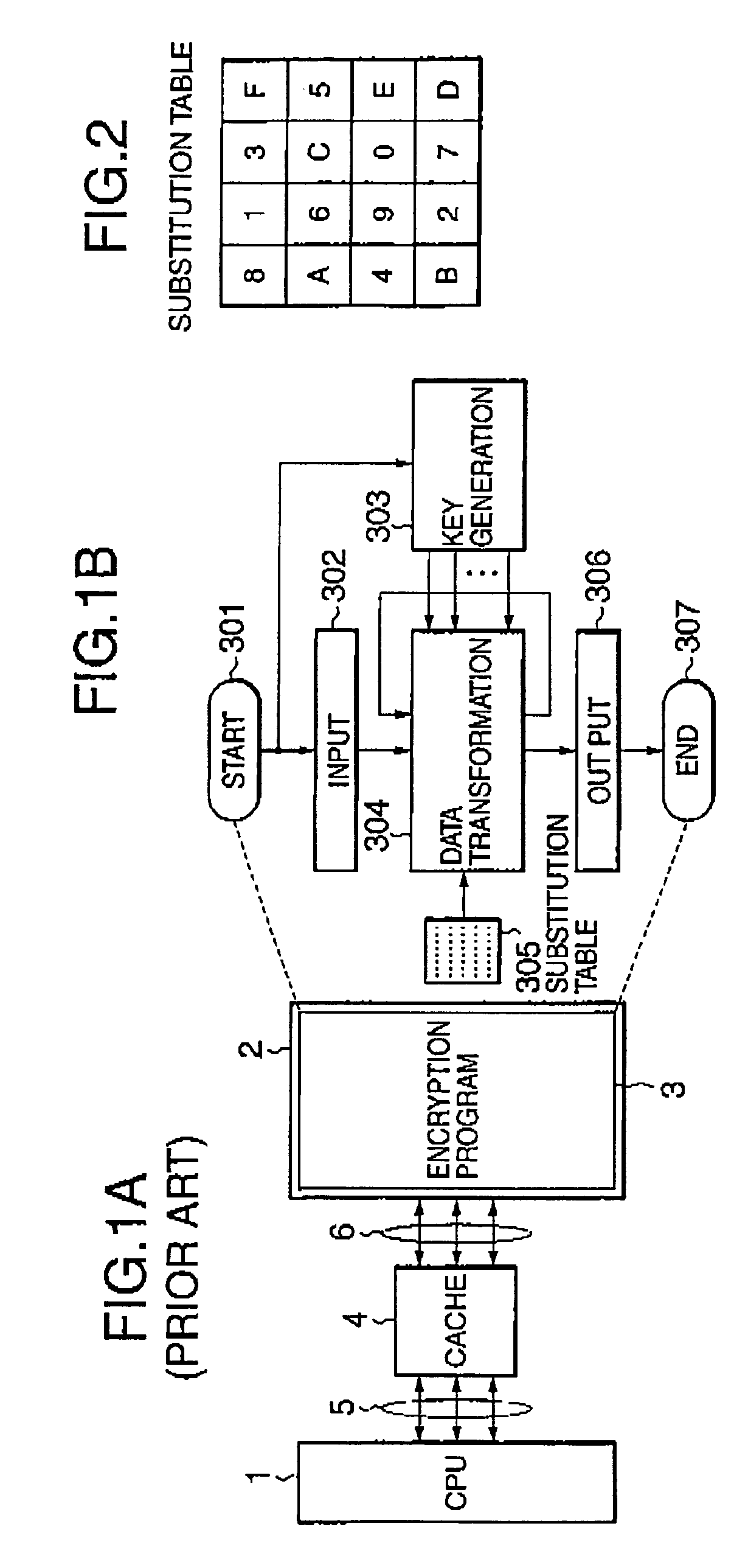
ActiveUS7454016B2Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareCryptanalysis
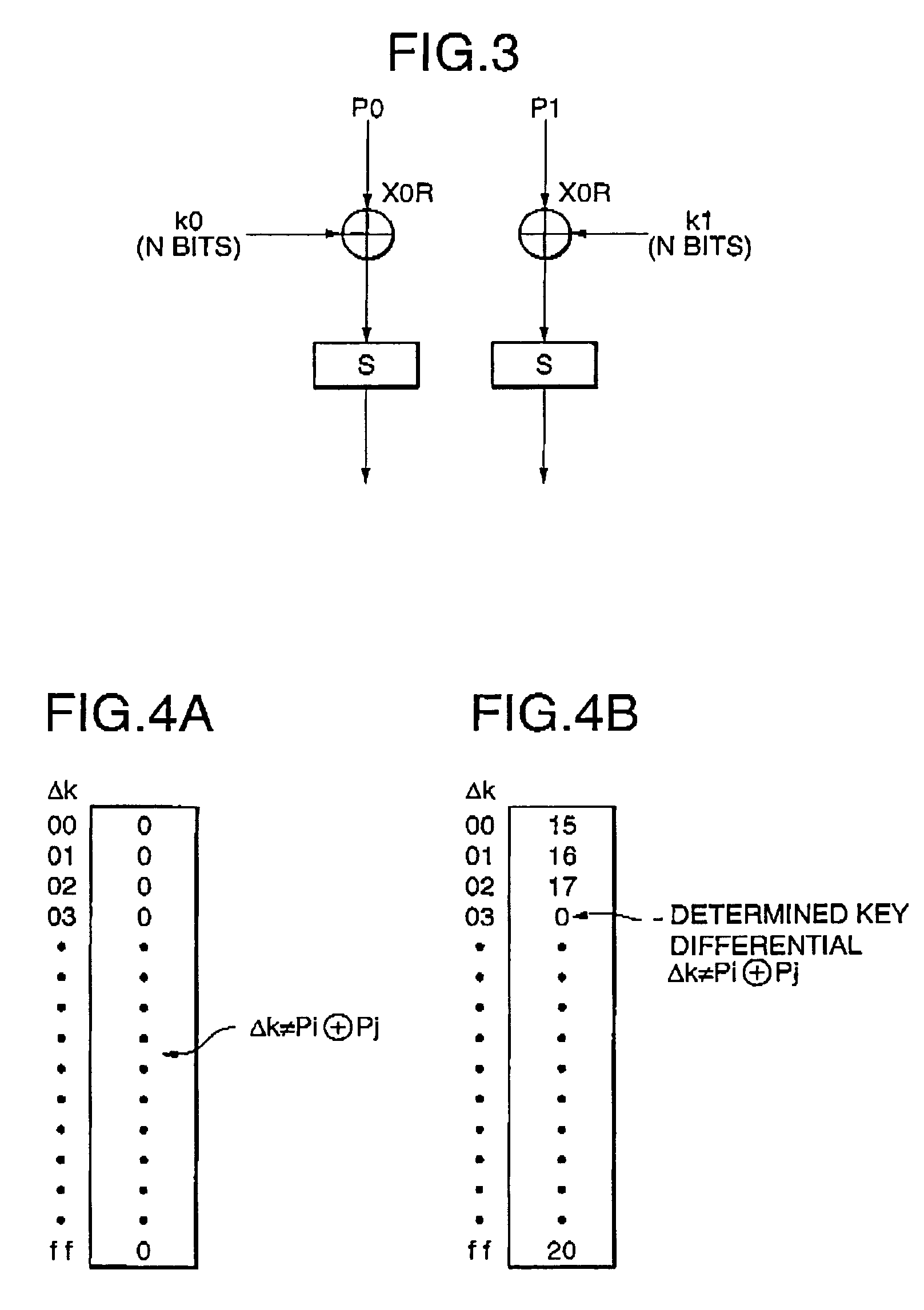
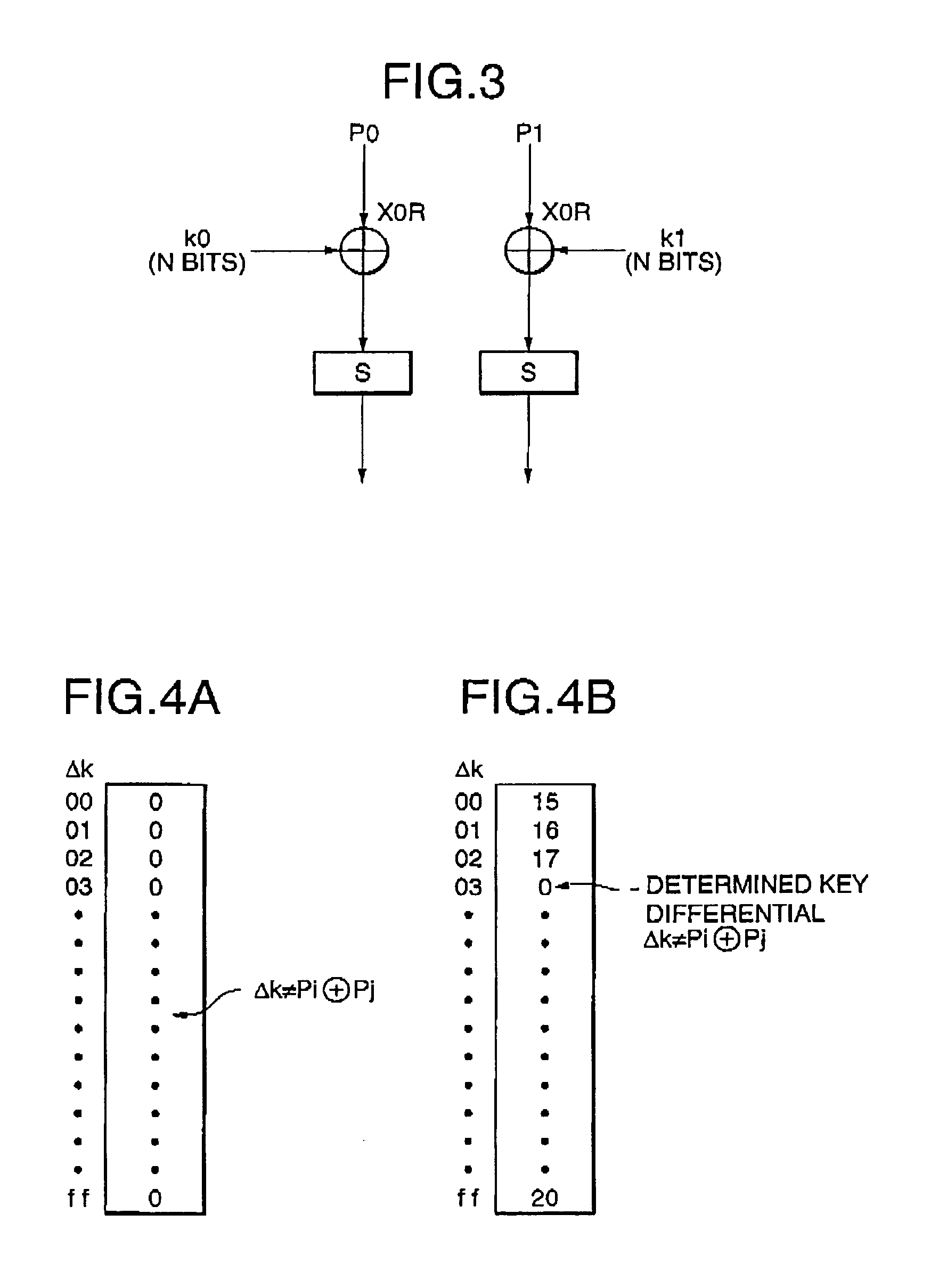
A data encryption system implemented by running on a cache-equipped computer an encryption program including transformation tables each of which contains a predetermined number of entries. All or necessary ones of the transformation tables are loaded into the cache memory before encryption / decryption process. This causes encryption / decryption time to be made substantially equal independently of the number of operation entries for the transformation table. It is very difficult to extract plain texts used to determine a key differential, resulting in difficulties in cryptanalysis.
Owner:NEC CORP
Data encryption system and method
ActiveUS20040062391A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareCryptanalysis
A data encryption system implemented by running on a cache-equipped computer an encryption program including transformation tables each of which contains a predetermined number of entries. All or necessary ones of the transformation tables are loaded into the cache memory before encryption / decryption process. This causes encryption / decryption time to be made substantially equal independently of the number of operation entries for the transformation table. It is very difficult to extract plain texts used to determine a key differential, resulting in difficulties in cryptanalysis.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multiple uncertainty encryption system with misleading function
The invention discloses a multiple uncertainty encryption system with a misleading function, which aims at attacks such as rubber-hose attacks, key stealing, brute force attacks and the like. Multiple encryption is performed, and an algorithm and encryption multiplicity are uncertain, so the system has multiple uncertainty, a password analyzer cannot perform analysis, and even though the brute force attacks are adopted, a plaintext obtained only by incomplete single decryption is meaningless. The encryption multiplicity of the algorithm, encryption algorithms of each layer and keys of each layer are all uncertain, and are all included in a structural master key. The multiple uncertainty makes securer the algorithm. The system is required to comprise an improved one-time pad mechanism, and one-time pad has high reversibility, so the encryption system can obtain pseudo keys in two ways to mislead and confuse the password analyzer, and has high value in military affairs and special occasions.
Owner:桂林轻鸿科技有限公司
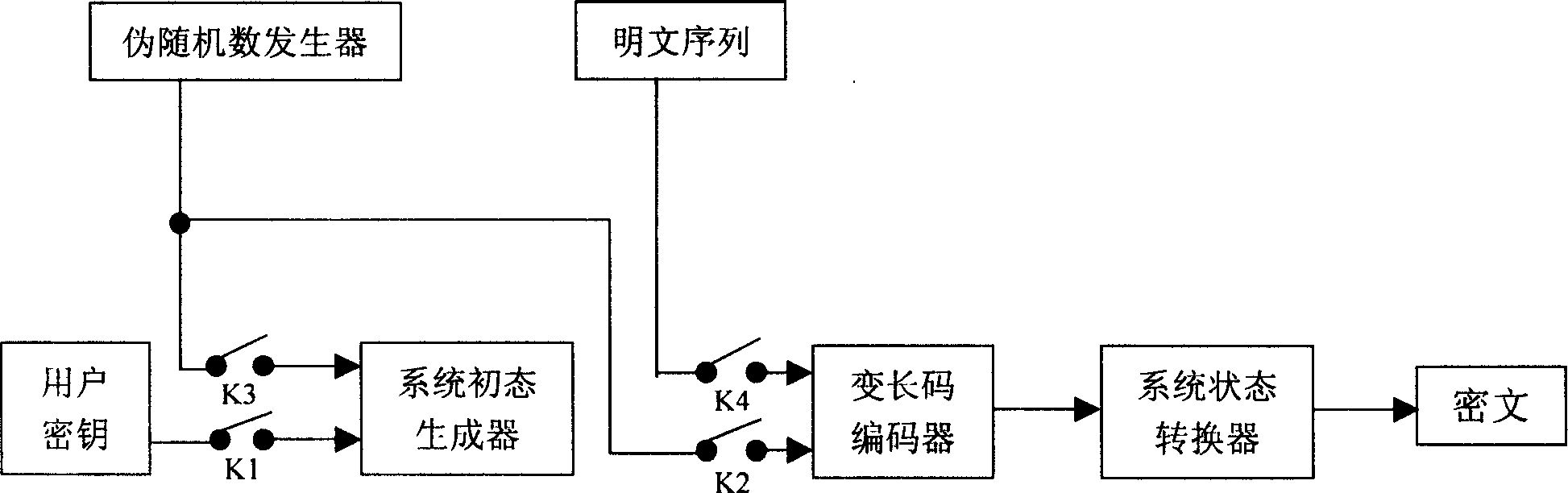
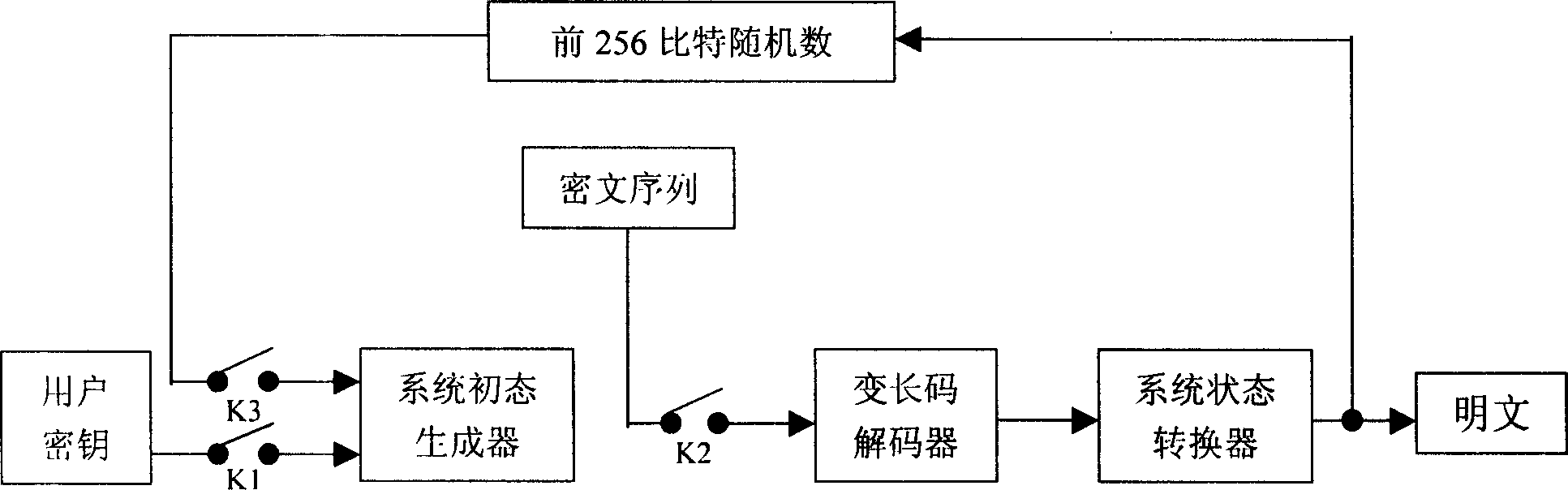
Data encipher and decipher system based on dynamic variable-length code
The invention relates to an information security technology in information technology field, which concretely relates to binary code and decode of data. The invention belongs to sequence coding system; the essence is periodless multi-table code substituting method. It uses dynamic length variable code technology, a group of input data with fixed length (8 bits), the length of the output code is between 1 and 255, the size of the encrypted text is determined according to the state of the coding system. The state of the system will change after coding a group of plain text, and the initial state of the system is determined by the user key, the code analyzer is hard to determine the relation between the encrypted text and the plain text, thus the attacking method to each kind of system can be resisted effectively.
Owner:北京唐桓科技发展有限公司
System and method for fast querying of encrypted databases
InactiveUS7395437B2Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringDatabase indexData management
A system, method, computer program product, and data management service that allows any comparison operation to be applied on encrypted data, without first decrypting the operands. The encryption scheme of the invention allows equality and range queries as well as the aggregation operations of MAX, MIN, and COUNT. The GROUPBY and ORDERBY operations can also be directly applied. Query results produced using the invention are sound and complete, the invention is robust against cryptanalysis, and its security strictly relies on the choice of a private key. Order-preserving encryption allows standard database indexes to be built over encrypted tables. The invention can easily be integrated with existing systems.
Owner:IBM CORP
Iterative symmetric key ciphers with keyed s-boxes using modular exponentiation
InactiveUS20080232597A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareS-box
Disclosed is the design and development of a new cipher called the Dragonfire Cipher. The Dragon cipher includes message authentication code and keyed random number generator. Dragonfire cipher takes this transparent method of generating S-boxes and uses them to create a cipher with keyed S-boxes. This defeats most precomputations for cryptanalysis as the S-boxes are now different between sessions.
Owner:DE MARE MICHAEL
Method for constructing block encryption algorithm based on random function
ActiveCN102571330AImprove securityHeavy calculationKey distribution for secure communicationPlaintextPassword
The invention belongs to the field of information security and relates to construction of encryption algorithm. The password (encryption) algorithm is uncertain and random by using the random function to construct the block encryption method. The uncertainties are determined by partial data in the secret key and some information of plaintext. The encryption method has the advantage that the indeterminacy of the algorithm ensures that the password analysis becomes very difficult as a result of the lack of the information about the algorithm, so that a great amount of known (selected) plaintext ciphertext pair of the same algorithm and the same secret key cannot be acquired, and the condition for password analysis is destroyed to enhance the security. The existing abundant password analysis aims at determined algorithm, and the password analysis is difficult to perform when the algorithm is random. The uncertainty of the password system is increased through multiple ways. The encryption algorithm of the plaintext is uncertain, and the algorithms of different blocks are different, therefore, the secret key space can be increased so as to enhance the safety.
Owner:桂林碧琪信息科技有限公司
Random sequence based encryption method with misleading function
ActiveCN102412963AAvoid synchronizationHeavy calculationDigital data authenticationSecuring communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext-only attack
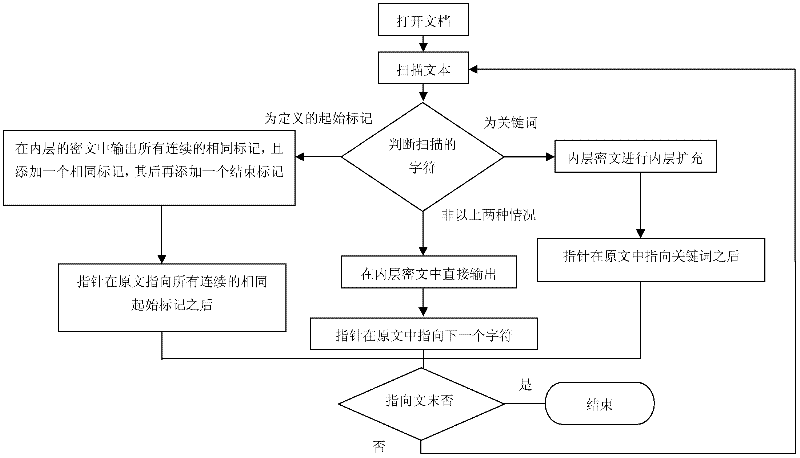
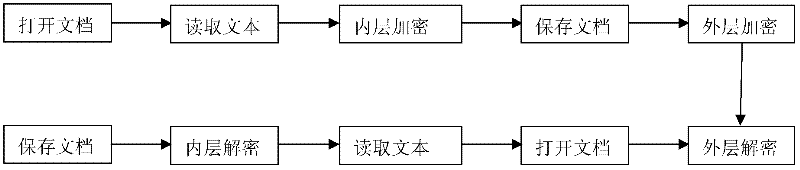
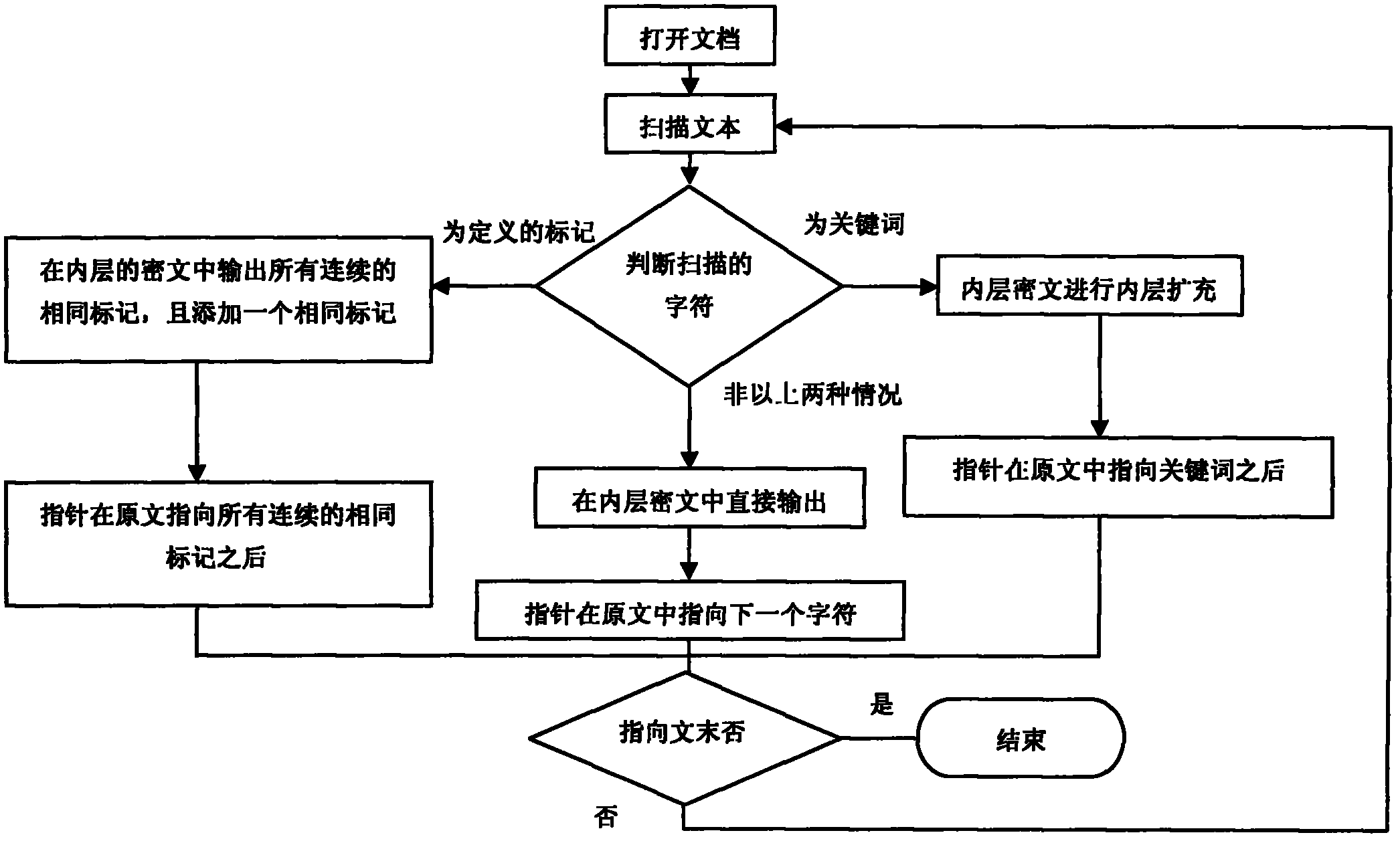
The invention relates to an encryption method with a misleading function, which is used for the stealing of keys, and the seizing, rubber-hose cryptanalysis and ciphertext only attacks to a key holder. When the encryption is performed by using the method disclosed by the invention, a false key can be obtained easily so as to mislead a password analyst, and the misleading is decided by an inner key, for carrying out any misleading, a sub-key is generated by using a long random sequence, and the long random sequence can be generated through quantum key distribution. Tags in a document are processed in a special processing mode, so that even a specified tag appears in a text, a confusion phenomenon does not occur. In the process of encryption, a key word database is required, so that in the process of inner encryption, the expansion on key words is performed by using the database, and the outer encryption is performed by using the conventional encryption method. In the method, in the process of decryption, the support of the database is not required, thereby avoiding the occurrence of a database synchronization problem. The method disclosed by the invention has a certain application value in encryption applications in various occasions, especially in the military field.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Dynamic ciphering system and method based on broad sense information field
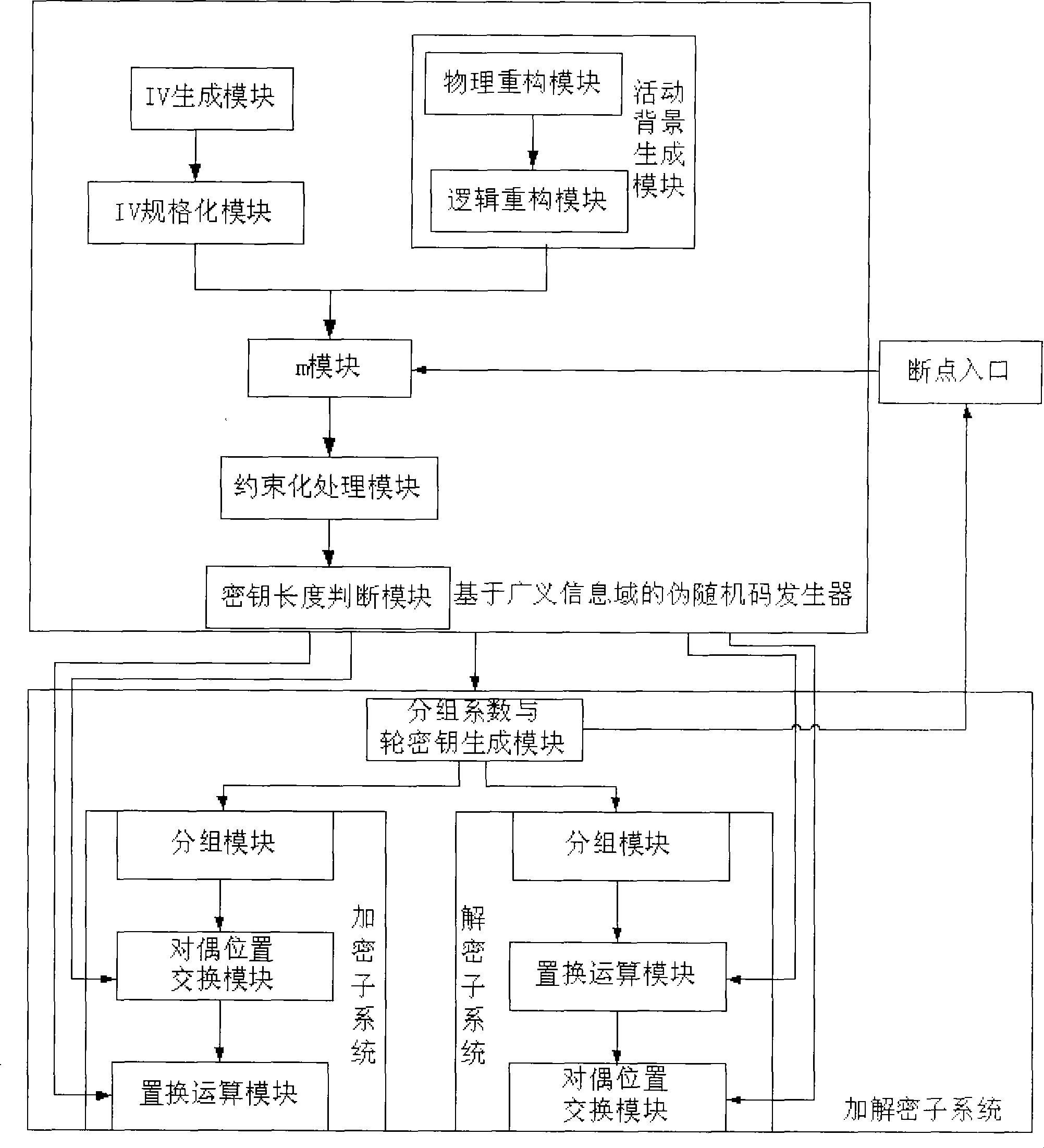
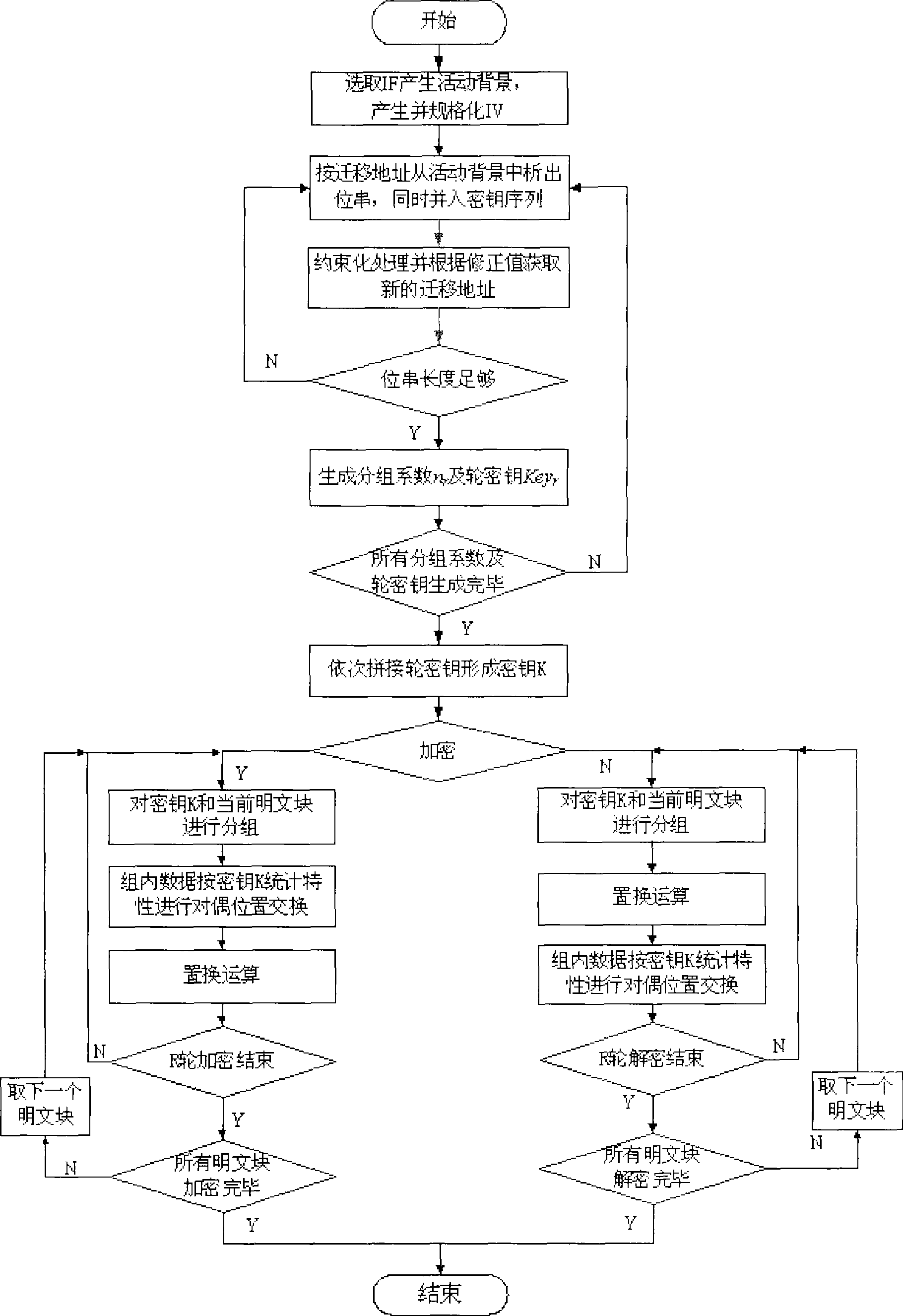
The invention provides a dynamic encrypt system based on a generalized information field, which comprises a pseudo-random code generator based on the generalized information field and an encryption and decryption subsystem, wherein the pseudo-random code generator is connected with the encryption and decryption subsystem, and the encryption and decryption subsystem comprises an encryption subsystem and a decryption subsystem. The pseudo-random code generator based on the generalized information field comprises an initial address message IV generating module, an IV normalized module, an m module, a constrained processing module and a key length judgment module which are connected in sequence, wherein the m module is connected with an activity background generating module, and the activity background generating module comprises a physical reconstruction module and a logical reconstruction module. The encryption subsystem and the decryption subsystem both comprise grouping coefficient and round key generating modules, grouping modules, position interchange modules and substitution operation modules. The invention introduces the generalized information field, and realizes the key safety to transfer towards the generalized information field safety; the cryptanalysis resistance is strong.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Iterative symmetric key ciphers with keyed S-boxes using modular exponentiation
InactiveUS8130946B2Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareS-box
Disclosed is the design and development of a new cipher called the Dragonfire Cipher. The Dragon cipher includes message authentication code and keyed random number generator. Dragonfire cipher takes this transparent method of generating S-boxes and uses them to create a cipher with keyed S-boxes. This defeats most precomputations for cryptanalysis as the S-boxes are now different between sessions.
Owner:DE MARE MICHAEL
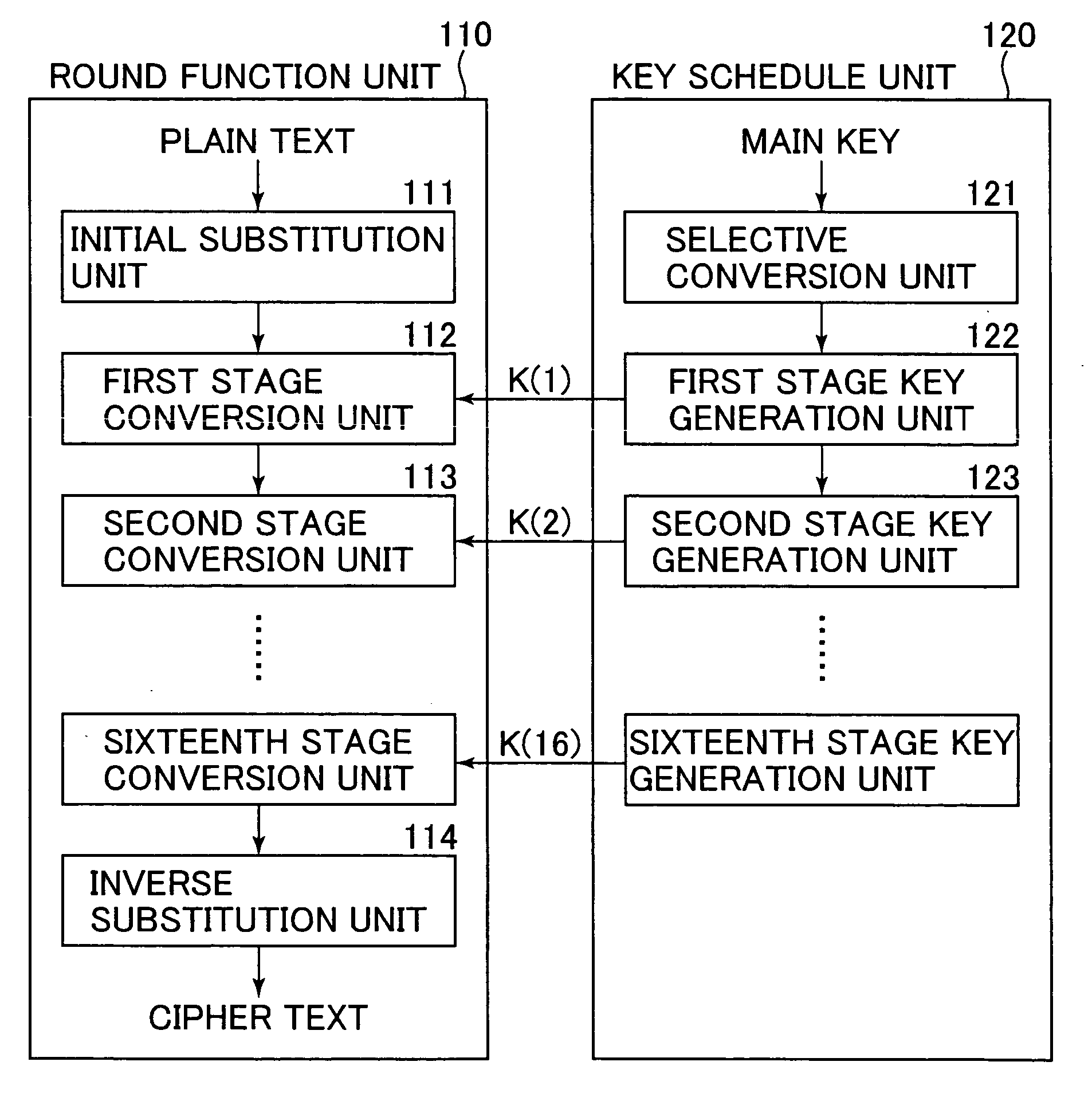
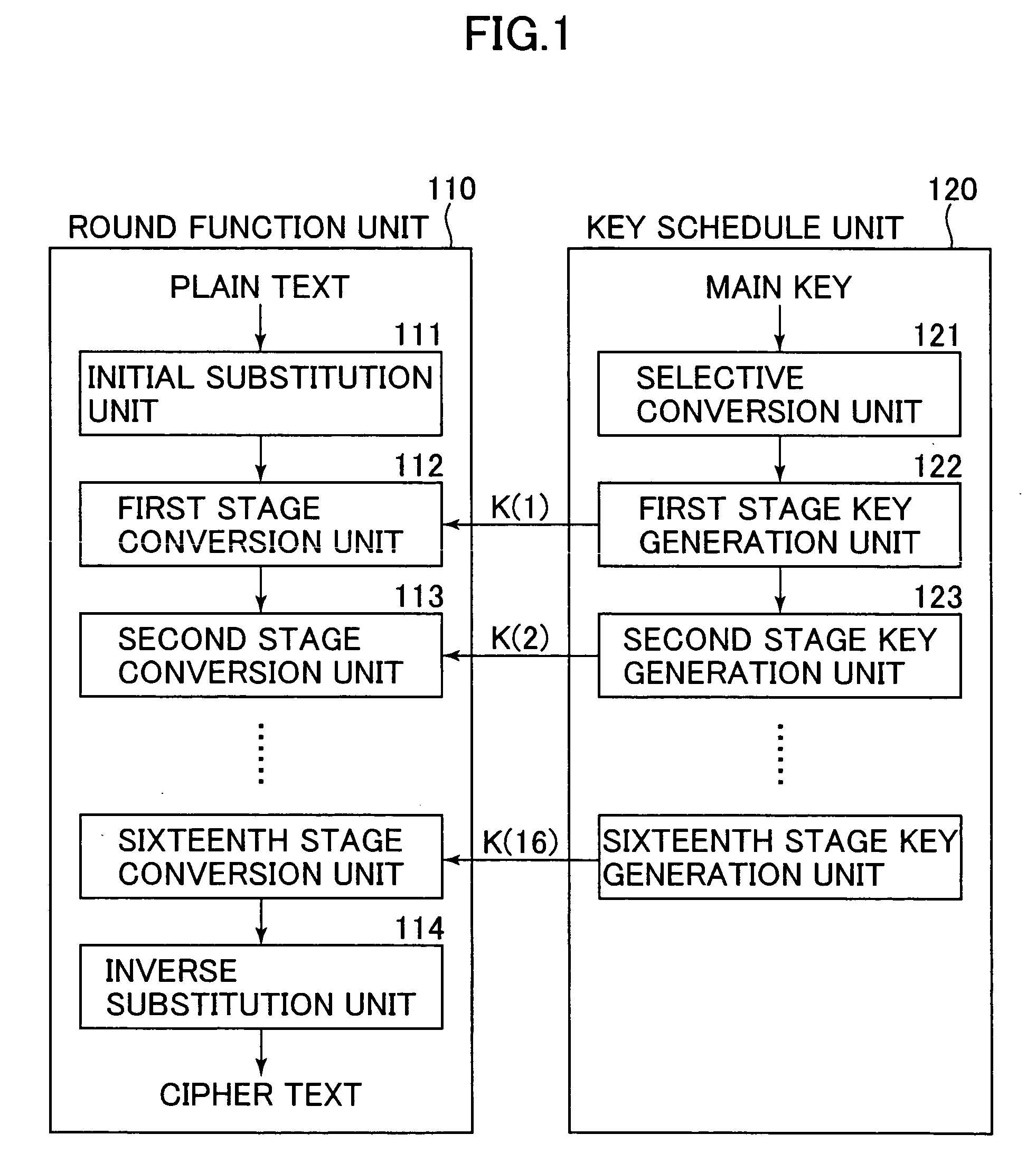
16-wheel SM4-128/128 white box password implementation method
InactiveCN110278072AImprove computing efficiencyIntegrity guaranteedEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePassword
In an unsafe environment, a cryptographic analyzer can implement attacks on an algorithm and a secret key by tracking a binary system operated by a program, reading the secret key in a memory and a program execution intermediate result, carrying out static analysis and the like, and a white-box cryptographic algorithm can protect the secret key in the unsafe environment. The invention discloses a 16-round SM4-128 / 128 white box password implementation method, which describes a new mode of improving an SM4 password algorithm when the encryption round number is 16, and the mode improves the structure of a round function, namely the iterative process of the encryption algorithm. An improved SM4 white-box cryptographic algorithm is provided, and the whole encryption and decryption process can be converted into a form of calculating randomly selected affine transformation and lookup tables. The principle is that the internal state of a coding hiding algorithm is input and output scrambled, the secret key is embedded into a lookup table in a coding mode, and meanwhile, a block matrix is used for reducing the scale of the lookup table.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH INST
Information recording/playback apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070116278A1Improve protectionNarrow areaTelevision system detailsMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareArrival time
A block key to encrypt block data is generated using an ATS (arrival time stamp) appended to each of TS (transport stream) packets included in a transport stream correspondingly to the arrival time of the TS packet. The ATS is a random data depending upon an arrival time, and so a block-unique key can be generated, which enhances the protection against data cryptanalysis. A block key is generated from a combination of an ATS with a key unique to a device, recording medium or the like such as a master key, disc-unique key, title-unique key or the like. Since an ATS is used to generate a block key, any area for storage of an encryption key for each block may not be provided in a recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
Dynamic deficiency encryption system
InactiveCN103684772APrevent complete recoveryUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationComputer hardware
The invention provides a dynamic deficiency encryption system. The system is characterized in that ciphertext data transferred during communication randomly loses part of valid data and is rearranged, so that information is not complete, ciphertext can not be directly conducted to cryptanalysis and cracking, interception is prevented, and secure communication channels are reinforce. The system adopting verification codes can find lost ciphertext through multiple trial operation, further performs decryption recovery to complete ciphertext. The invention also discloses a high-security protection reinforcement system adopting dynamic deficiency, identification certification, environment locking, periodical activation and random scrambling.
Owner:BEIJING HUFU TECH
Circuit arrangement with non-volatile memory module and method for registering attacks on said non-volatile memory module
InactiveCN101243450AImplement and improve teachingInternal/peripheral component protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceElectronic data processingMemory module
In order to further develop a circuit arrangement ( 100 ), in particular an integrated circuit, for electronic data processing as well as a method for detecting and / or for registering and / or for signaling the irradiation of at least one non-volatile memory module ( 10 ) with at least one light source in order to be capable of securely averting an attack, in particular an E[lectro]M[agnetic] radiation attack, for example a side-channel attack, or in particular a crypto-analysis, for example a current trace analysis or a D[ifferential]P[ower]A[nalysis], such attack or such analysis in particular being targeted on finding out a private key, it is proposed that an access timing for at least one read access to the memory module ( 10 ) is generated, in particular that at least one additional read access to the memory module ( 10 ) is added in at least one test mode (T), in particular in at least one D[isable]A[ll]W[ordline] mode, this test mode (T) preferably allowing to detect if the memory module ( 10 ) is currently exposed to any light of a certain energy.
Owner:NXP BV
Encryption method using random sequence on-demand and having misleading function
ActiveCN102447558AAvoid synchronizationHeavy calculationKey distribution for secure communicationKey sizeKey distribution
Aiming at various attacks possibly existing in reality, the invention discloses an encryption method with a misleading function. A pseudo key can be easily obtained after using the encryption method, thus, a cryptanalyst can be misled, the misleading is dependent on an inlayer key, for performing any misleading, a sub-key is generated by long random sequences, and the long random sequences can be generated by quantum key distribution. For saving keys, the shortest key length is intercepted as needed, in decryption, corresponding information is obtained, and the key length intercepted in encryption also can be determined so as to keep synchronous. A keyword database is needed for encryption, keyword expansion for inlayer encryption of the encryption process is executed based on the database, and the outer layer encryption uses a conventional encryption method. The method has certain use value in the encryption in various occasions, particularly in the aspect of military affairs.
Owner:广西创美信息技术有限公司
Misguiding encryption method capable of correcting pseudorandom sequence
ActiveCN102360414AAvoid synchronizationHeavy calculationDigital data protectionComputer hardwareCiphertext-only attack
The invention discloses an encryption method with a misguiding function, aiming at attacks such as secret key stealing, secret key holder seizing, rubber-hose cryptanalysis, ciphertext-only attack and the like. A pseudo secret key can be easily obtained through encryption with the method disclosed by the invention, thus a password analyzer can be misguided, the misguiding is determined by an internal secret key and comprises information for generating a secret key flow and correction information, and the misguiding effectiveness can be enhanced according to actual demands by using the correction information. For a special processing mode adopted by signs in a document, the specified signs can not be confused when possibly occurring in a text. A keyword database is needed during encrypting, internal encryption is subjected to keyword expansion by using the database, and the traditional encryption method is adopted in external encryption. The invention does not need the support of the database during encrypting so as to avoid the problem of synchronization of the database. The invention has a certain use value in the encryption application of various occasions, especially military.
Owner:广西创美信息技术有限公司
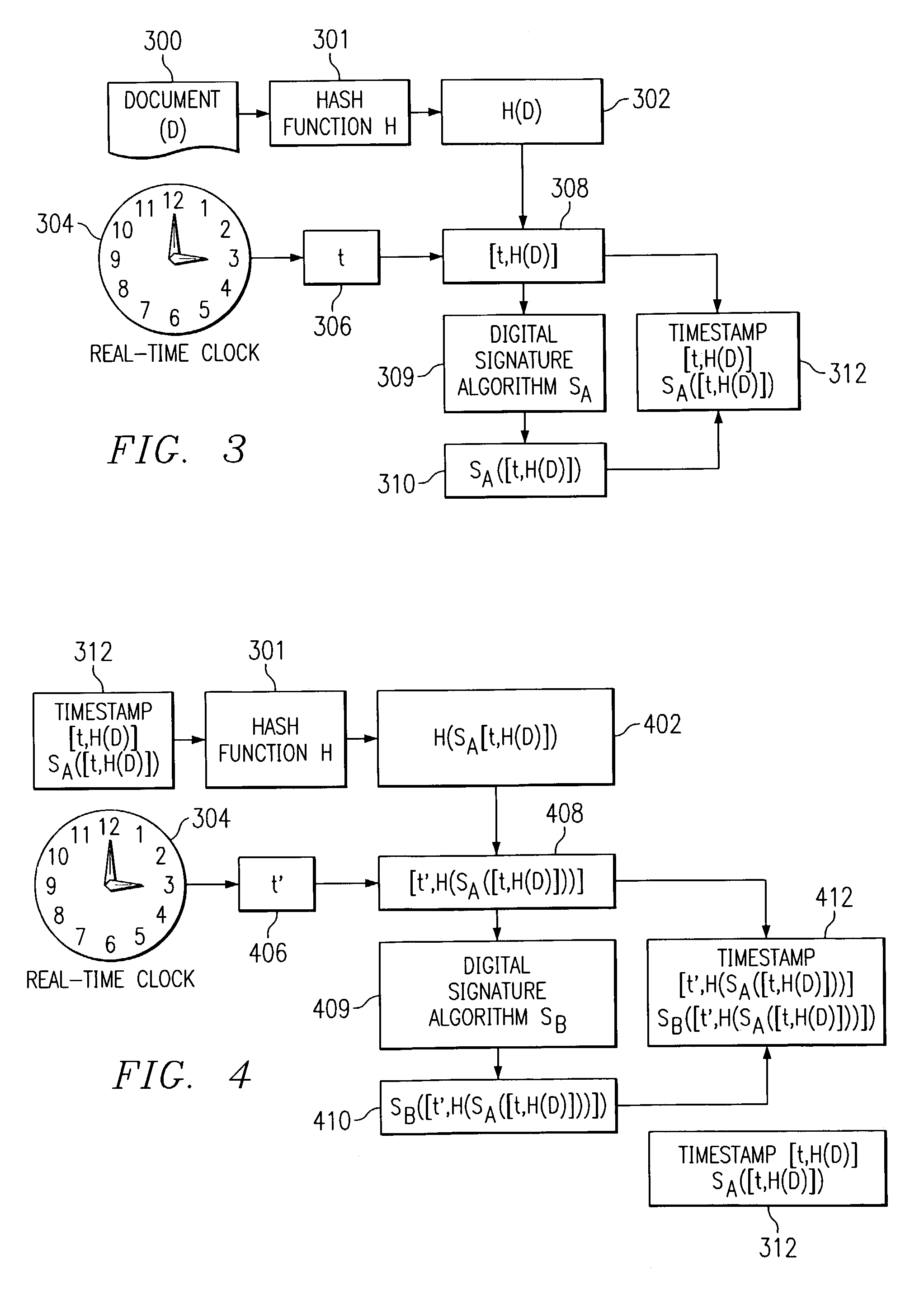
Upgradeable timestamp mechanism
ActiveUS7167986B2Avoid breakingUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionData processing systemTimestamp
A method, computer program product, and data processing system for generating and validating an upgradeable digital timestamp of a document is disclosed. The digital timestamp includes a hash value, a current time, and a digital signature. Over time, as computer and cryptanalytic technology progresses, upgrade timestamps are applied to the document that take advantage of more advanced, more difficult to break hash functions or digital signature schemes. These upgrade timestamps are applied preventatively at a point in time just prior to the timestamp's being able to be compromised.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
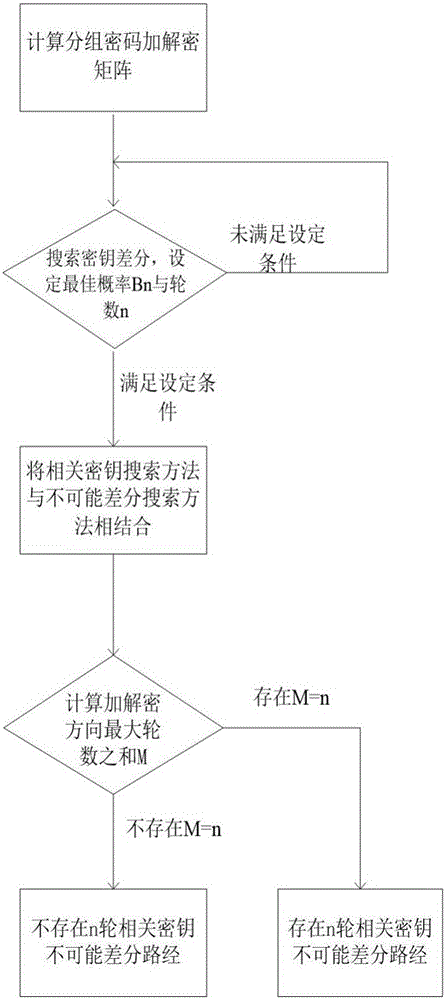
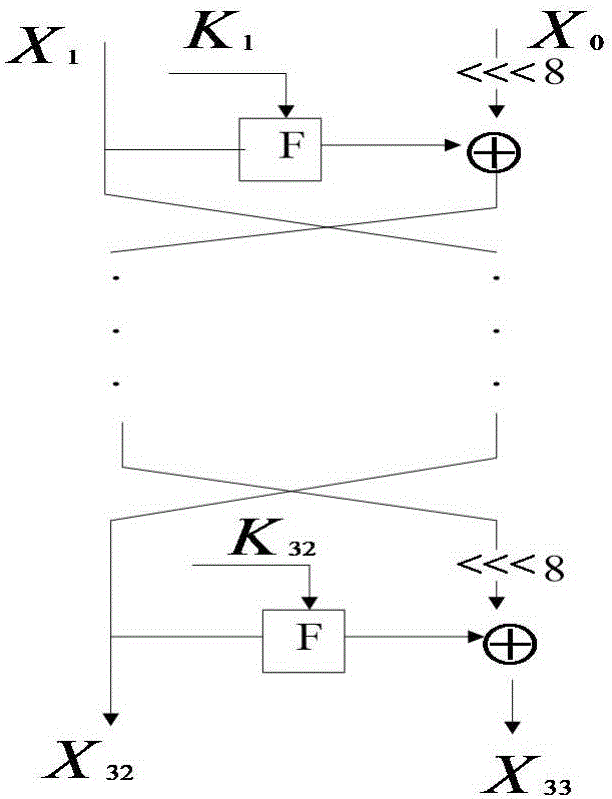
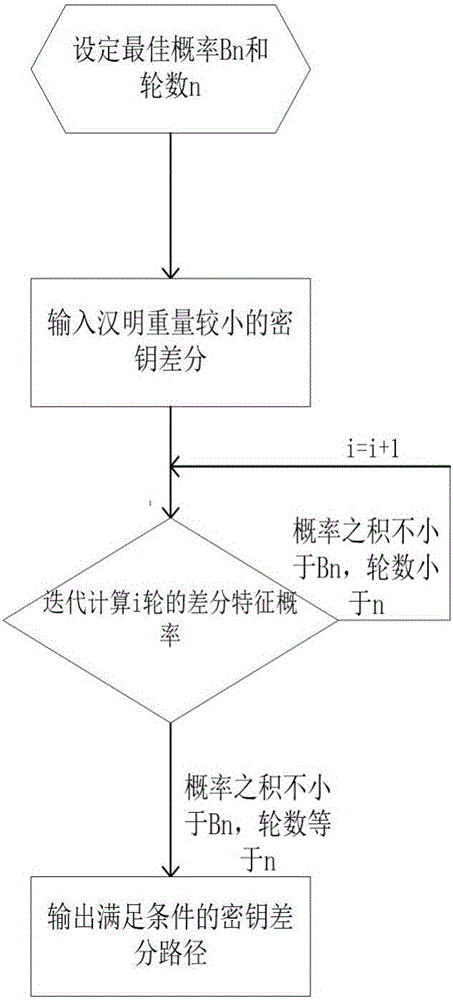
Searching method for impossible differential path of related key of block cipher
ActiveCN106027226ASolve the problem of findingIn-depth analysisEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesRelated-key attackTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a searching method for an impossible differential path of a related key of a block cipher. As an impossible differential attack method and a related key attack method are combined, the problems of automatic searching of the impossible differential path of the related key and searching of a longest analysis path in cryptanalysis are solved, and deeper and more thorough analysis for a cryptographic algorithm can be carried out. According to the searching method for the impossible differential path of the related key of the block cipher, the method for searching the impossible differential path of the related key is upgraded from the traditional manual analysis to computer automatic searching, the disadvantages that an existing manual analysis method is fussy and error-prone when being used for analyzing the cryptographic algorithm are avoided, the maximum length of the impossible differential path of the related key of the block cipher algorithm can be calculated rapidly and accurately, and the cryptanalysis efficiency is improved. The searching method for the impossible differential path of the related key of the block cipher realizes transformation of the cryptographic algorithm from a non-generalized Feistel structure to a generalized Feistel structure, can be widely applied to automatic search of the impossible differential paths of related keys of various cryptographic algorithms in different structures.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com