Patents
Literature
233 results about "Neutron generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
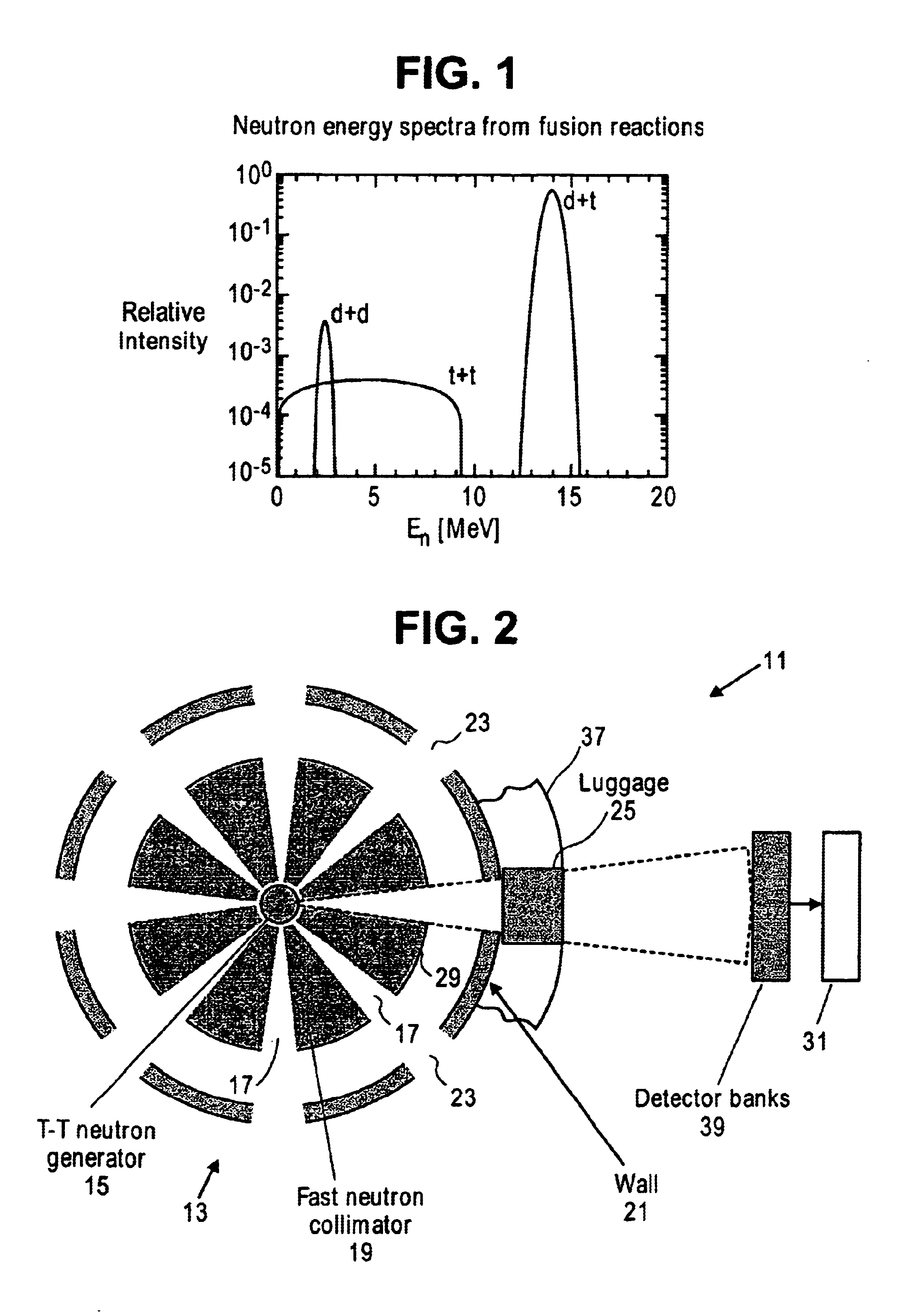
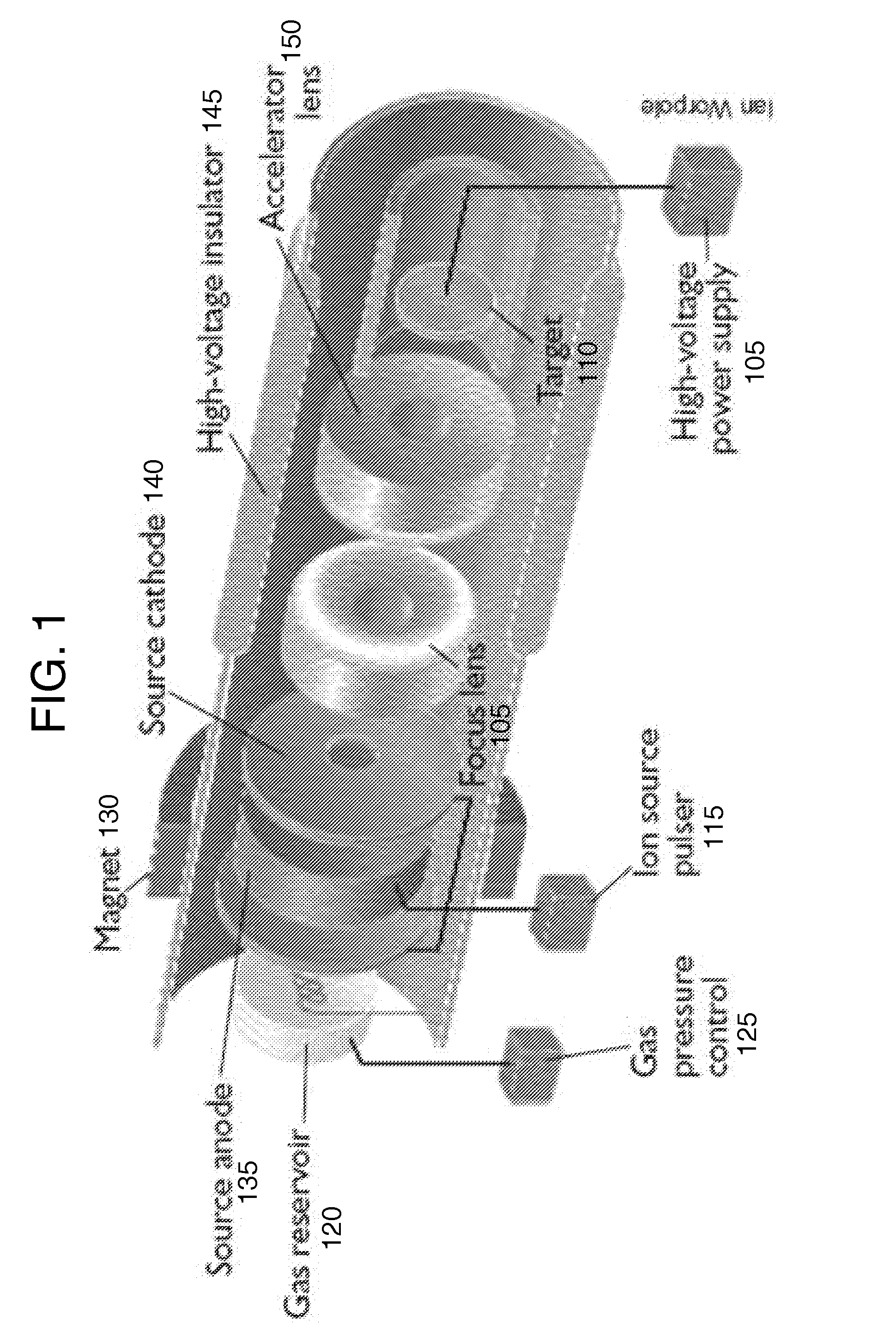
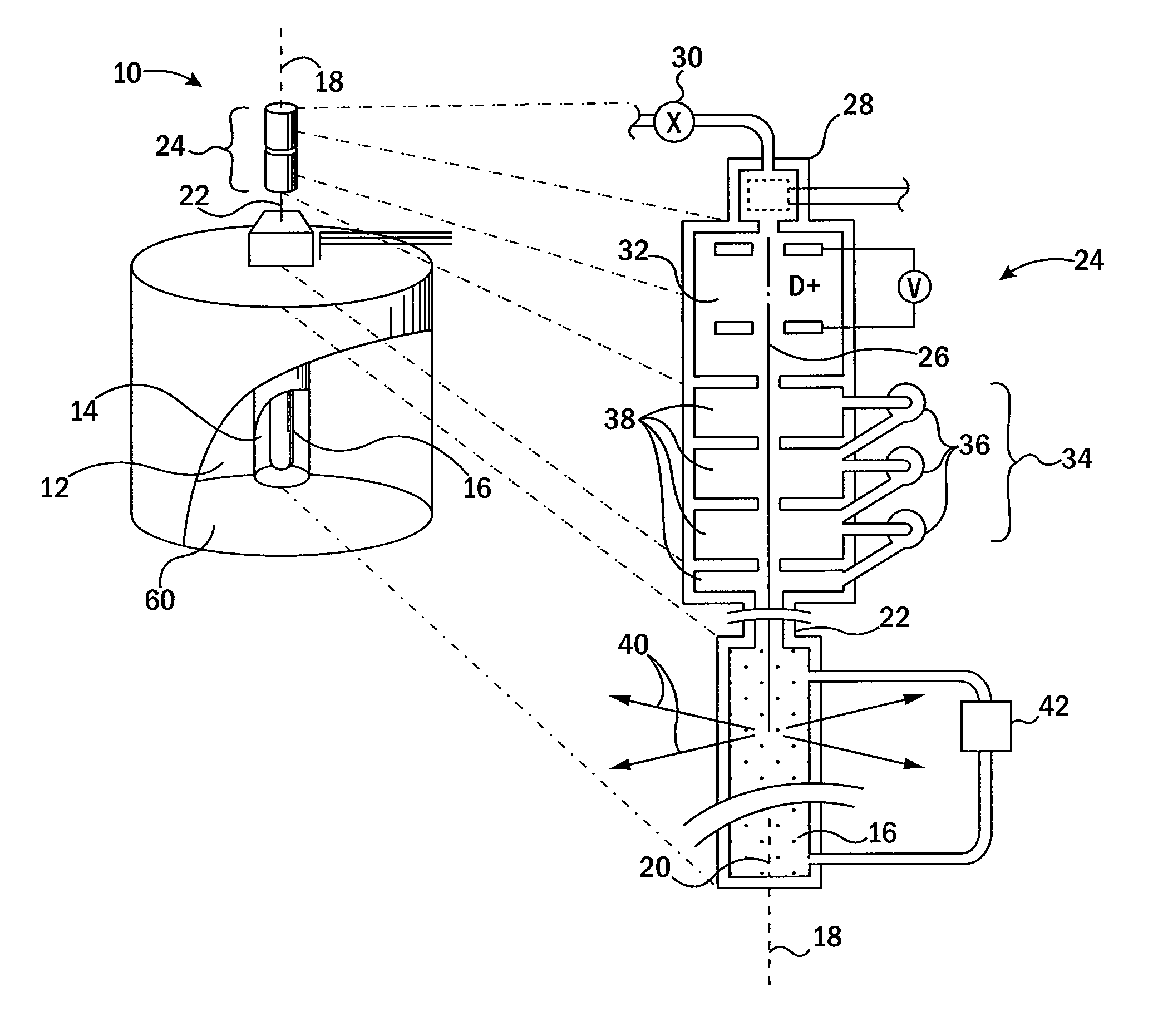
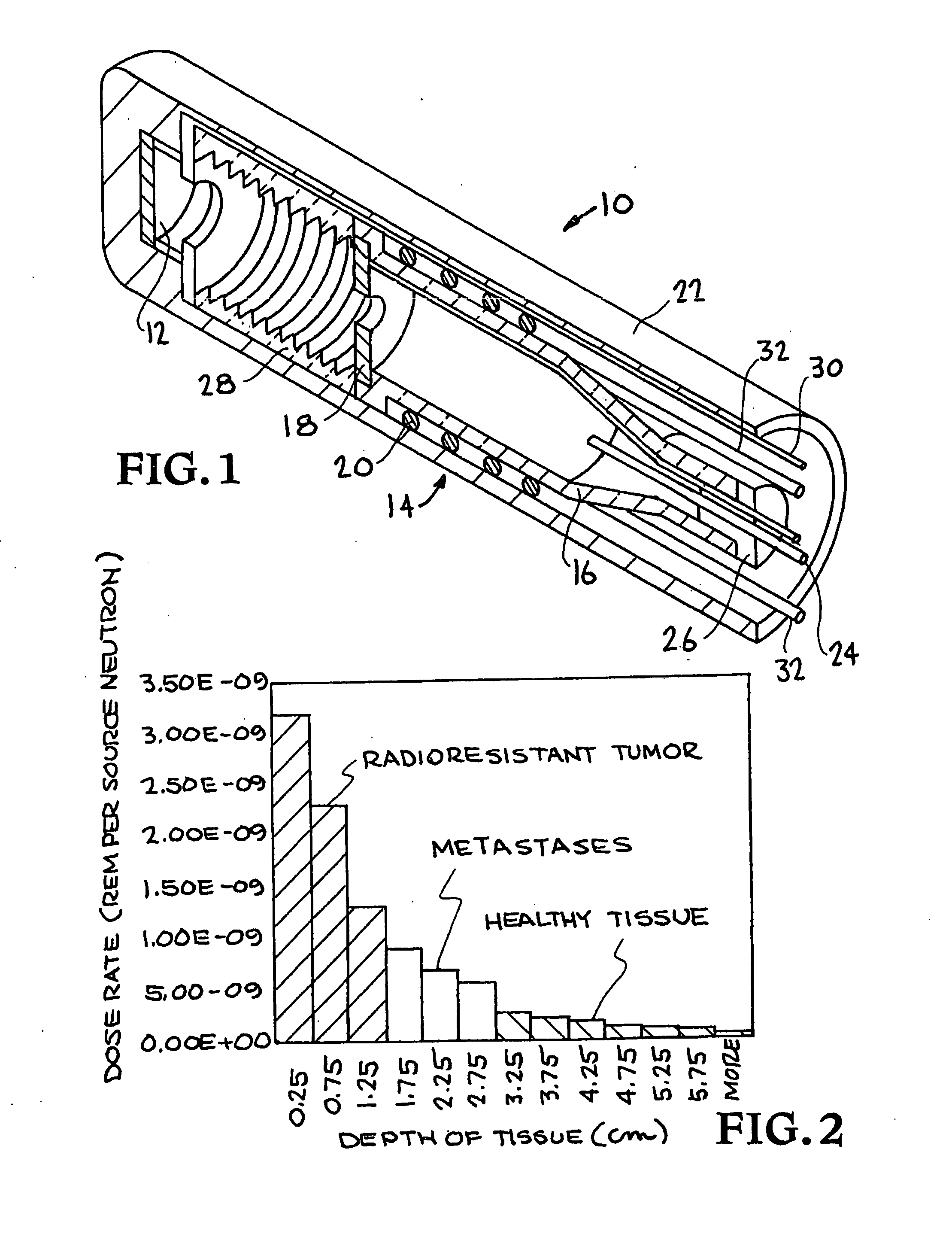
Neutron generators are neutron source devices which contain compact linear particle accelerators and that produce neutrons by fusing isotopes of hydrogen together. The fusion reactions take place in these devices by accelerating either deuterium, tritium, or a mixture of these two isotopes into a metal hydride target which also contains deuterium, tritium or a mixture of these isotopes. Fusion of deuterium atoms (D + D) results in the formation of a He-3 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 2.5 MeV. Fusion of a deuterium and a tritium atom (D + T) results in the formation of a He-4 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 14.1 MeV. Neutron generators have applications in medicine, security, and materials analysis.
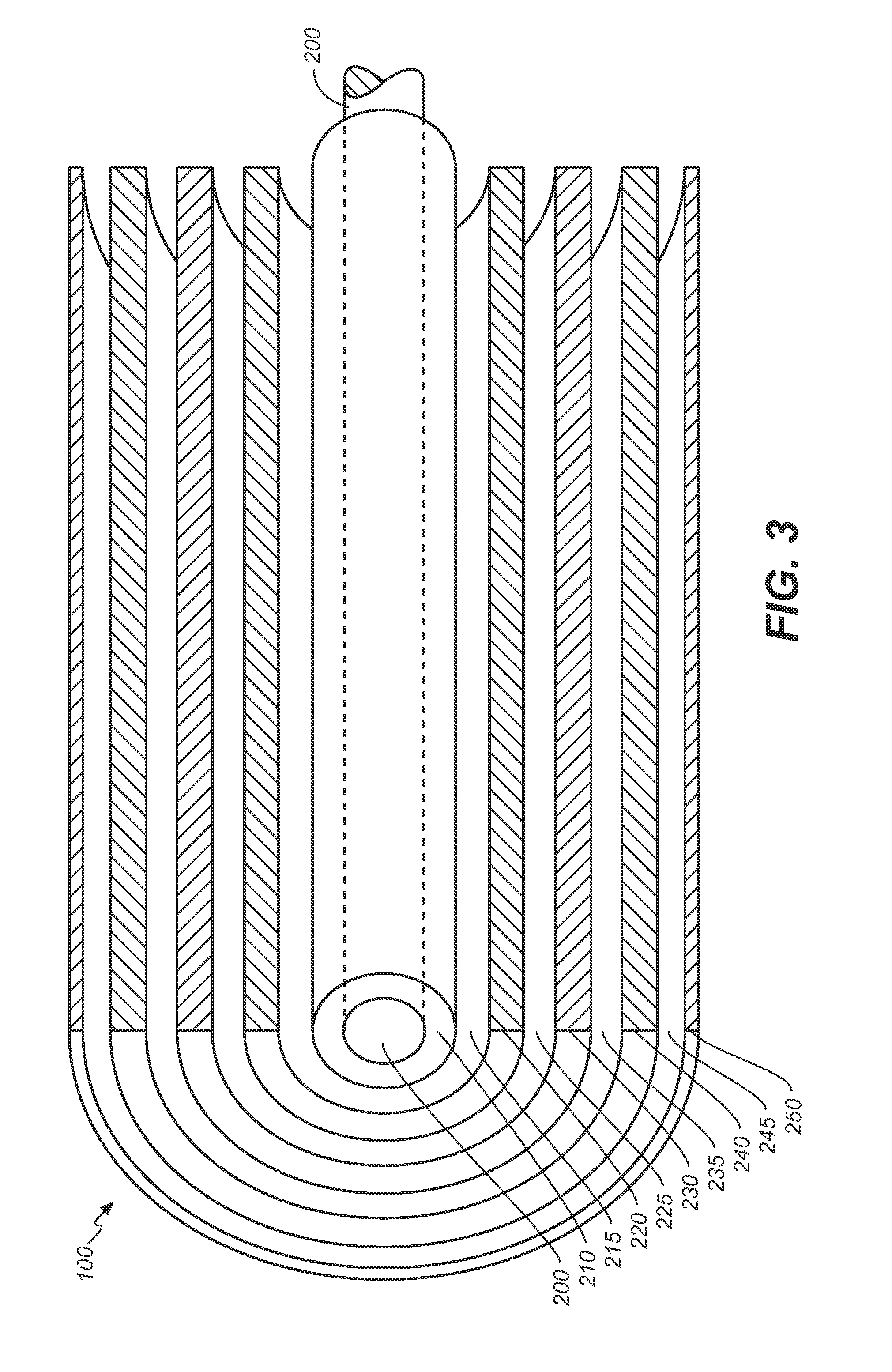
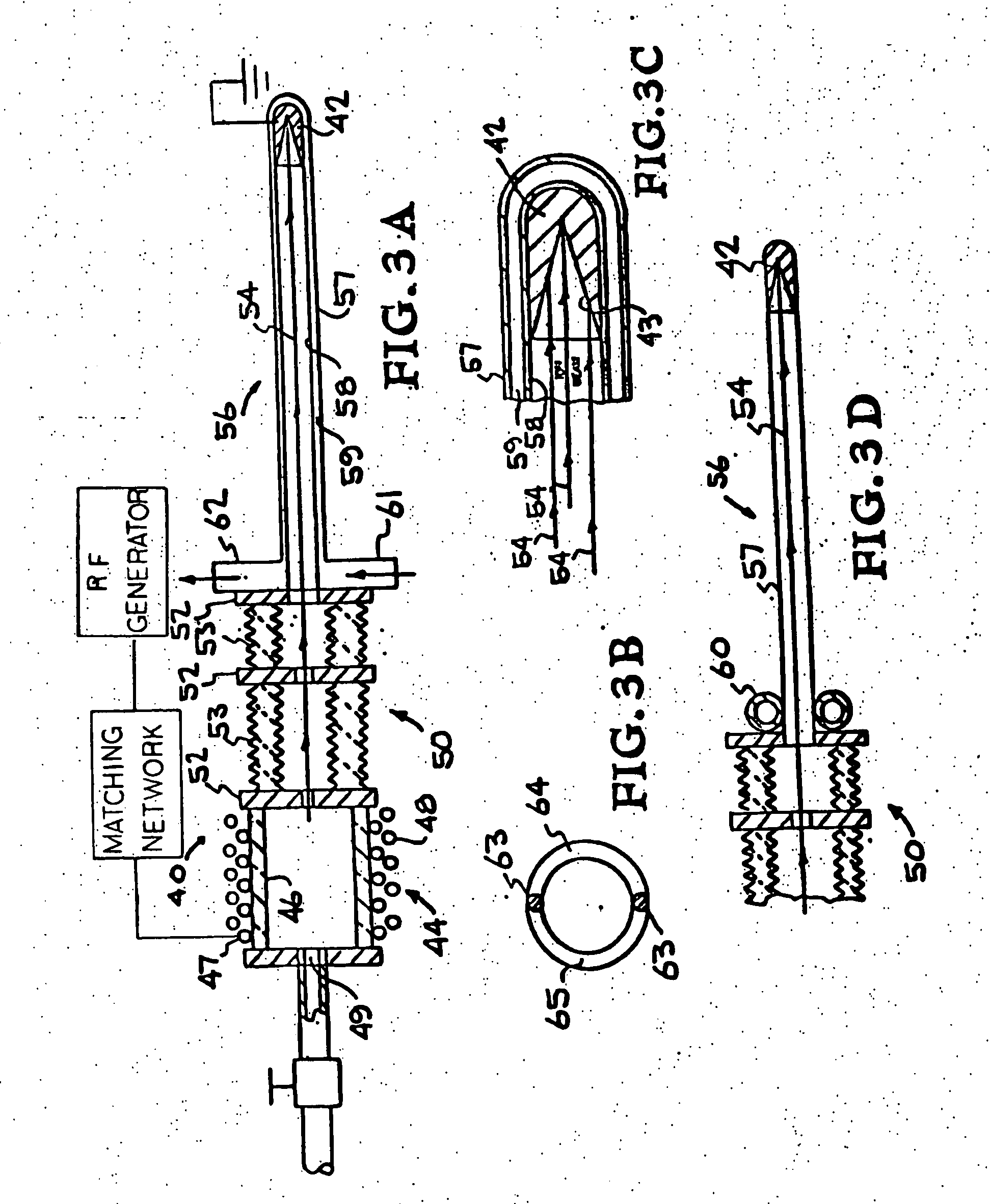
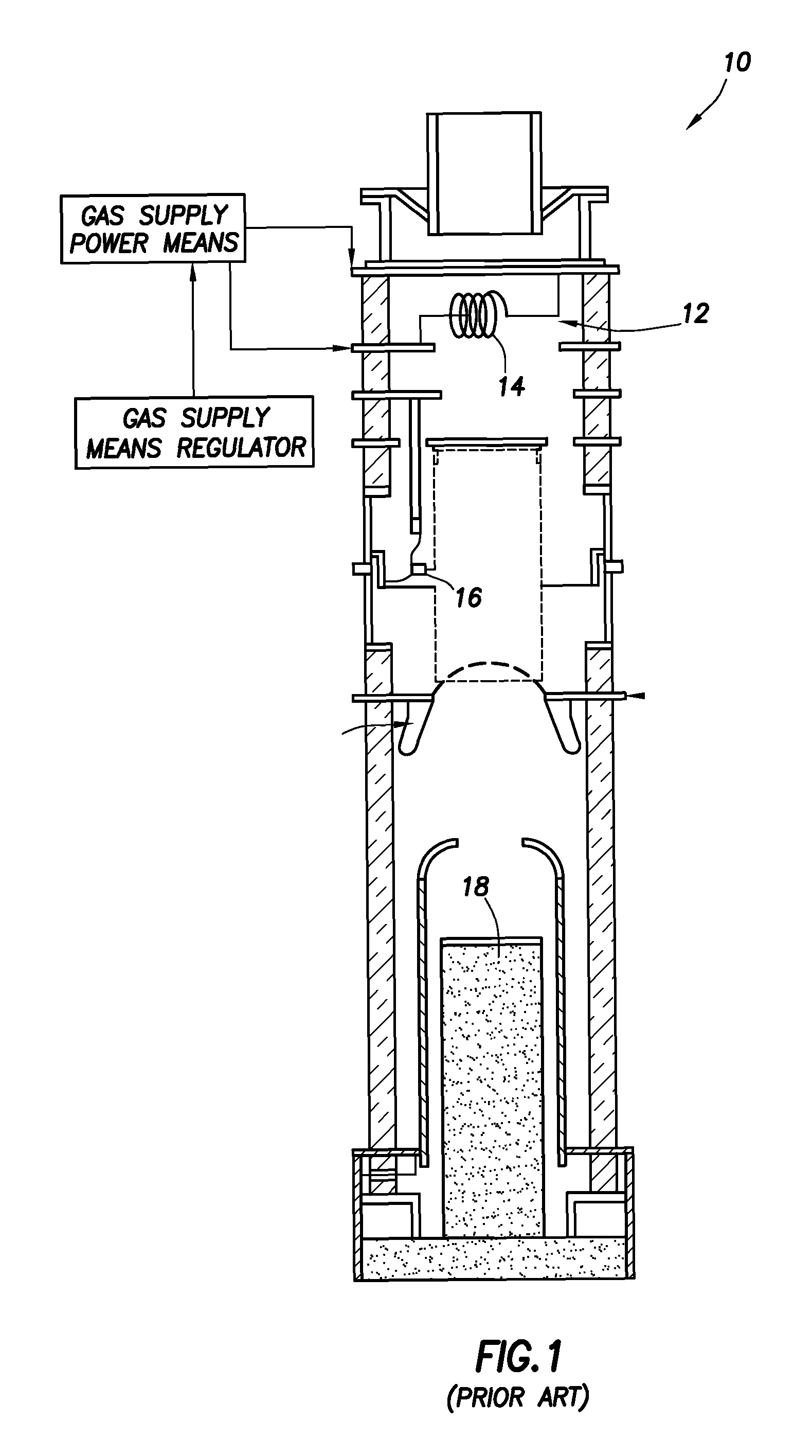
Gas-target neutron generation and applications
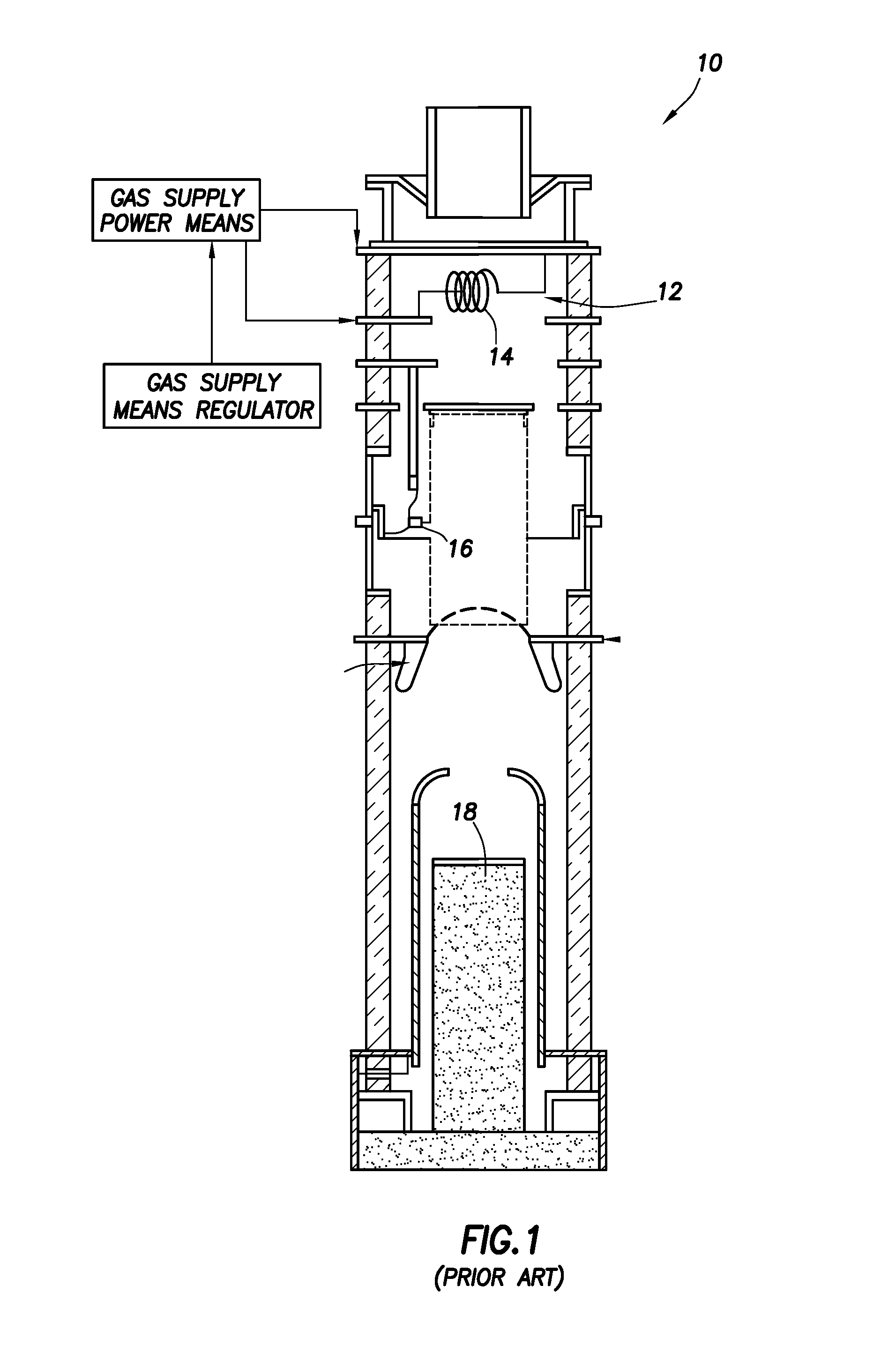
InactiveUS6922455B2Improve performanceMaximize productionNuclear energy generationX-ray tube electrodesHigh resistanceNeutron emission
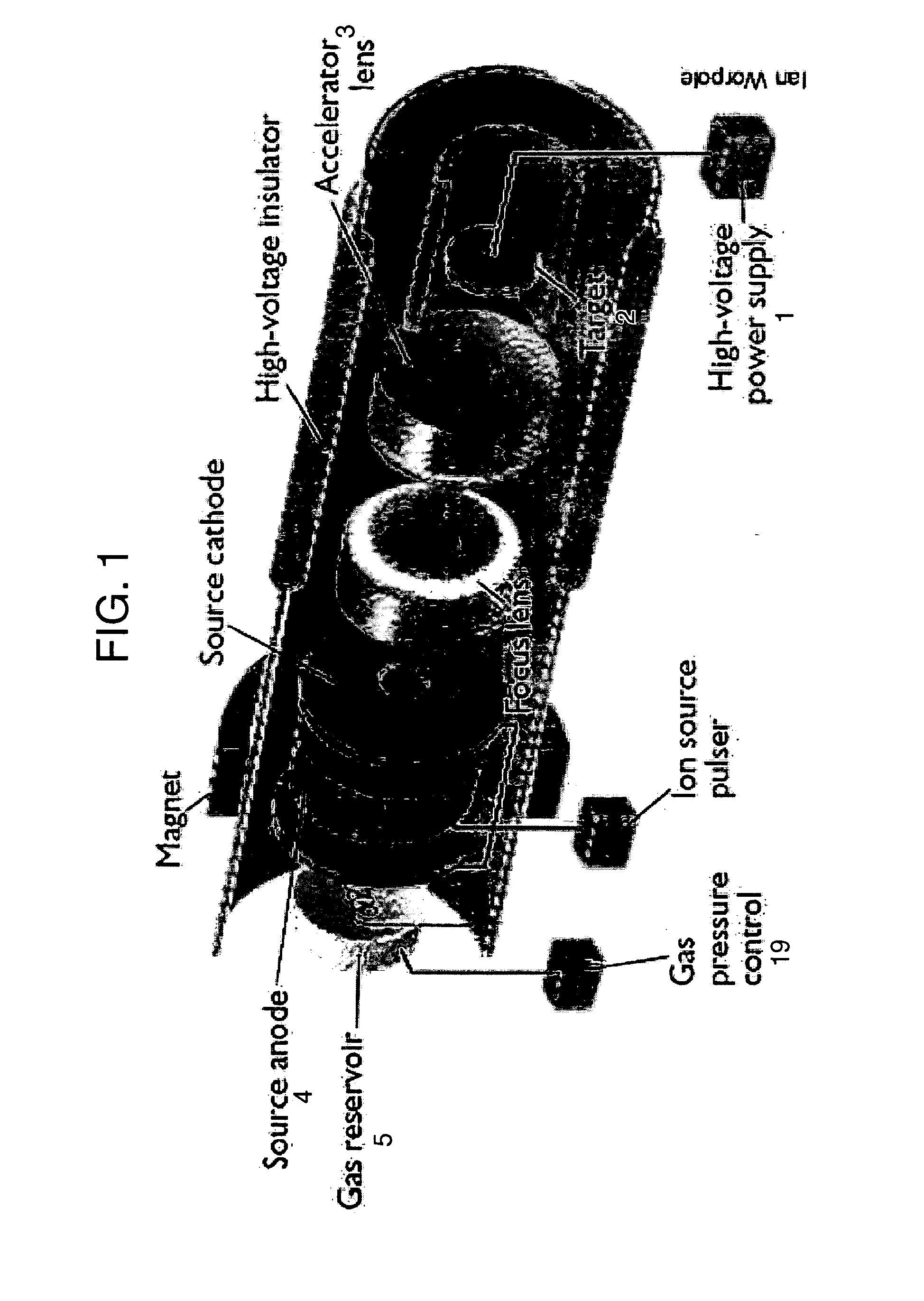
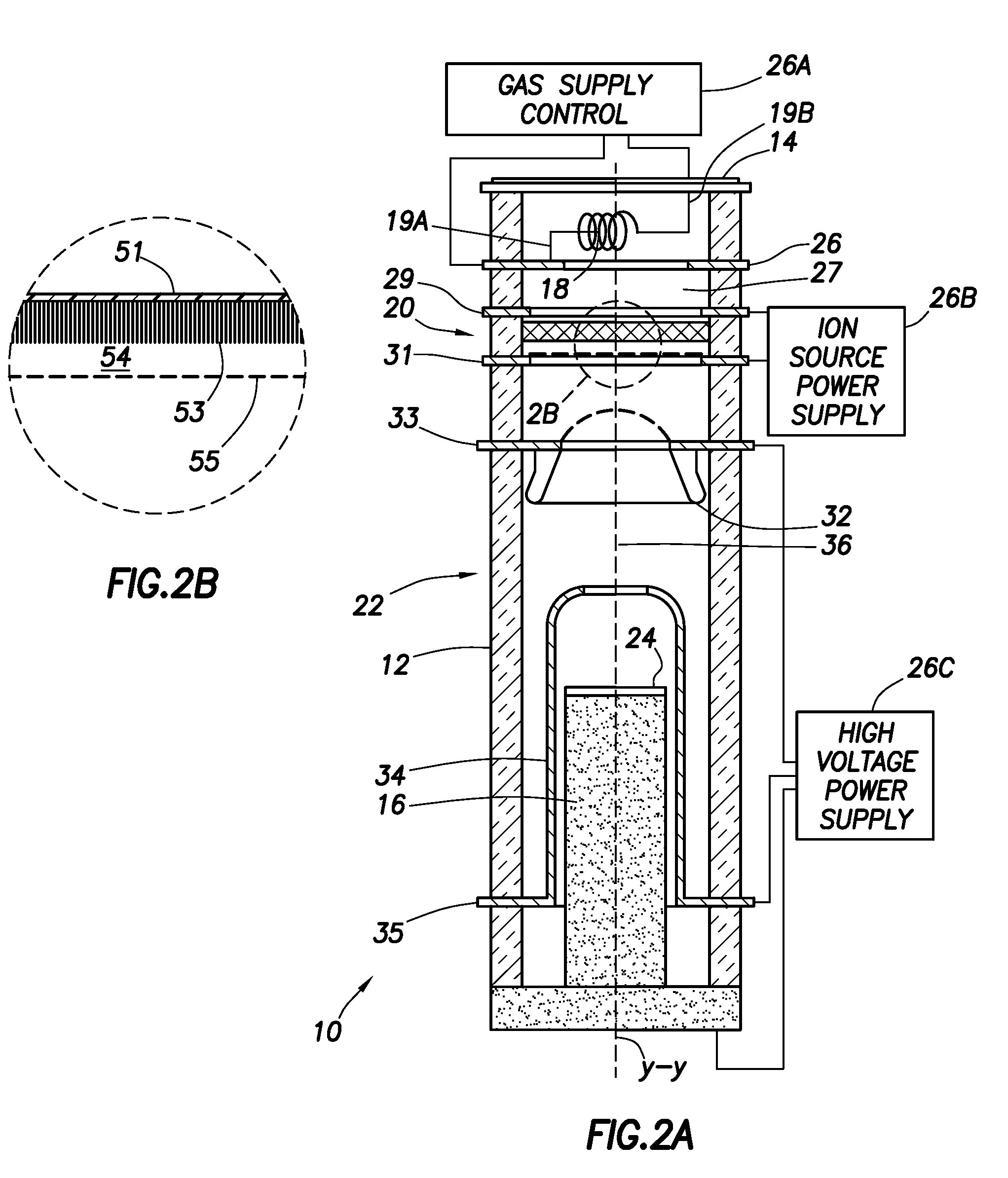
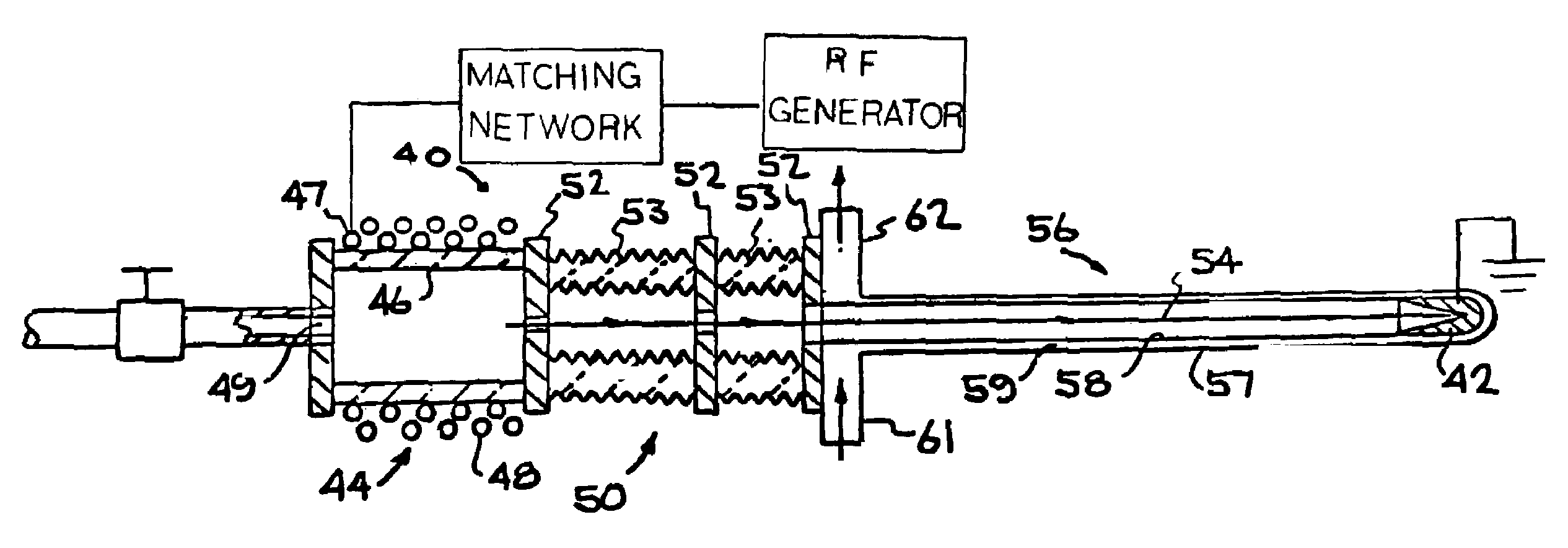
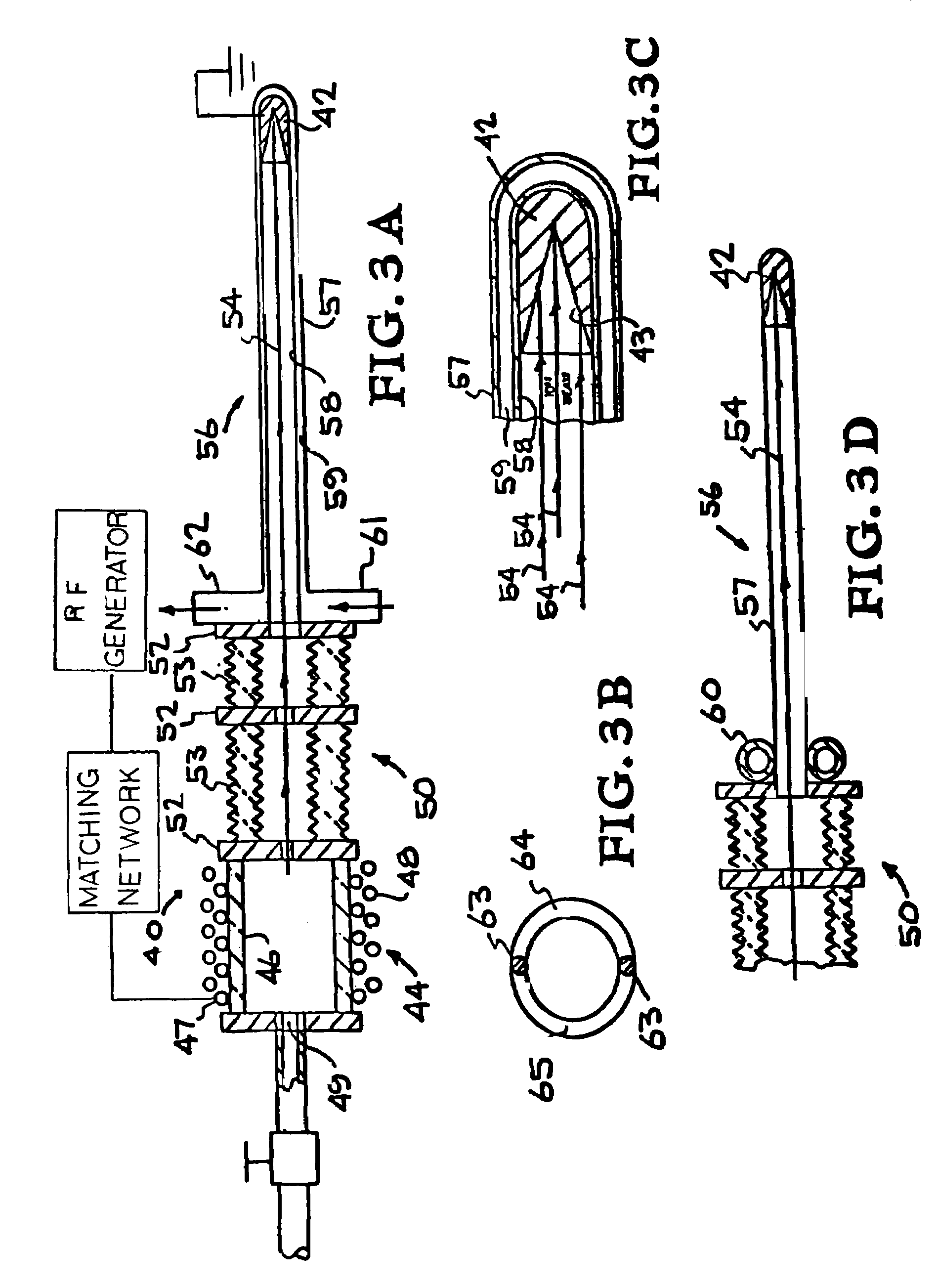
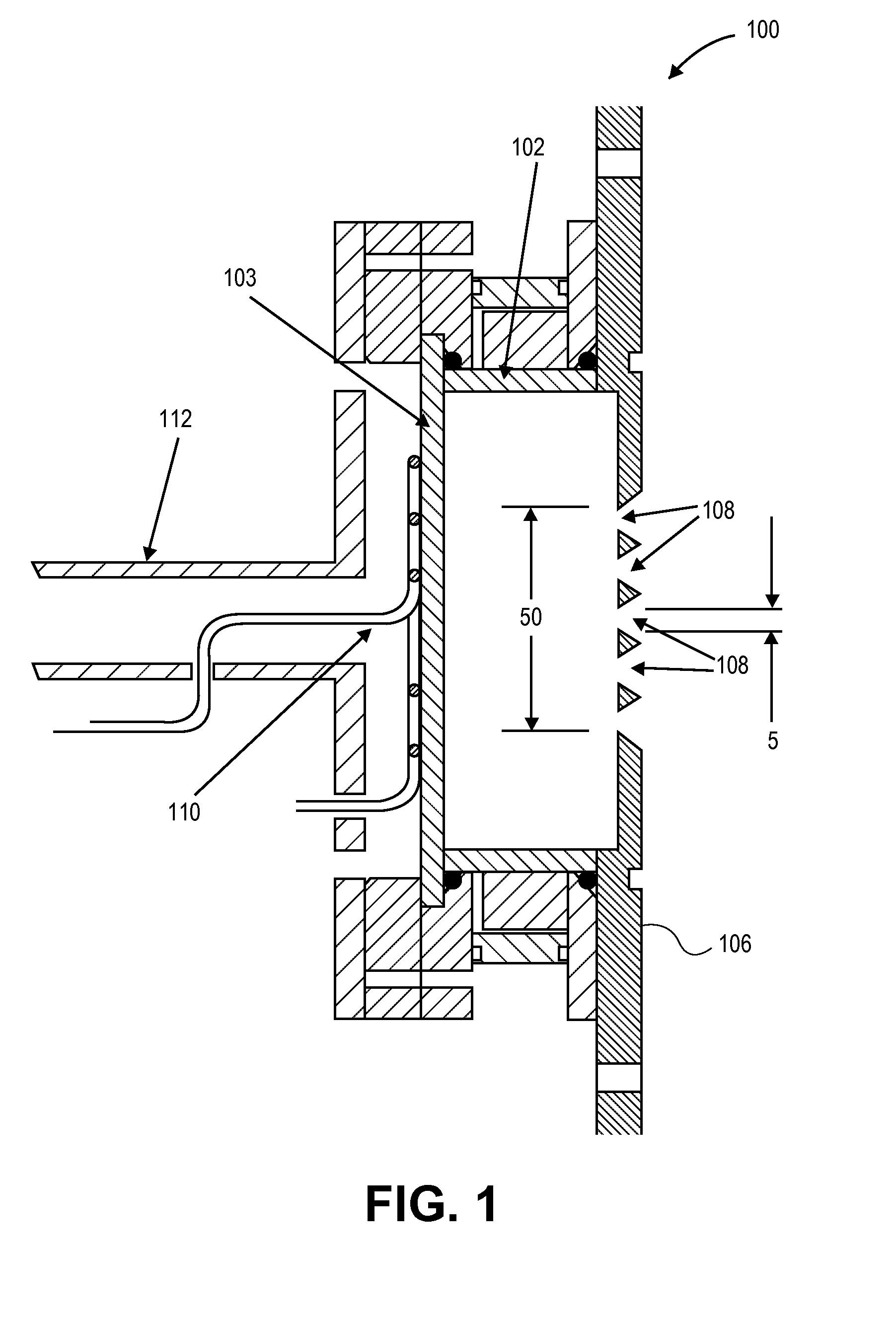
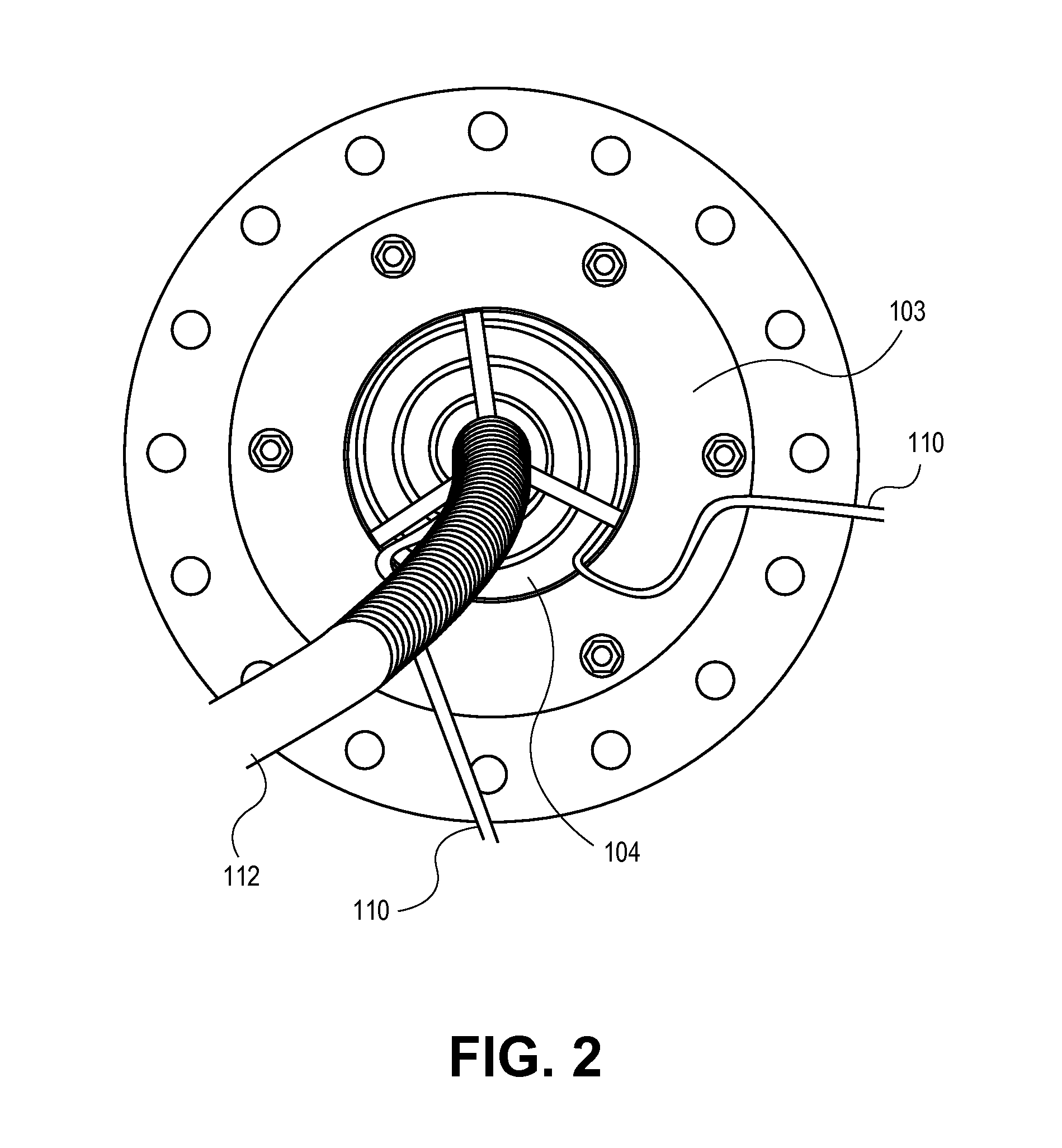
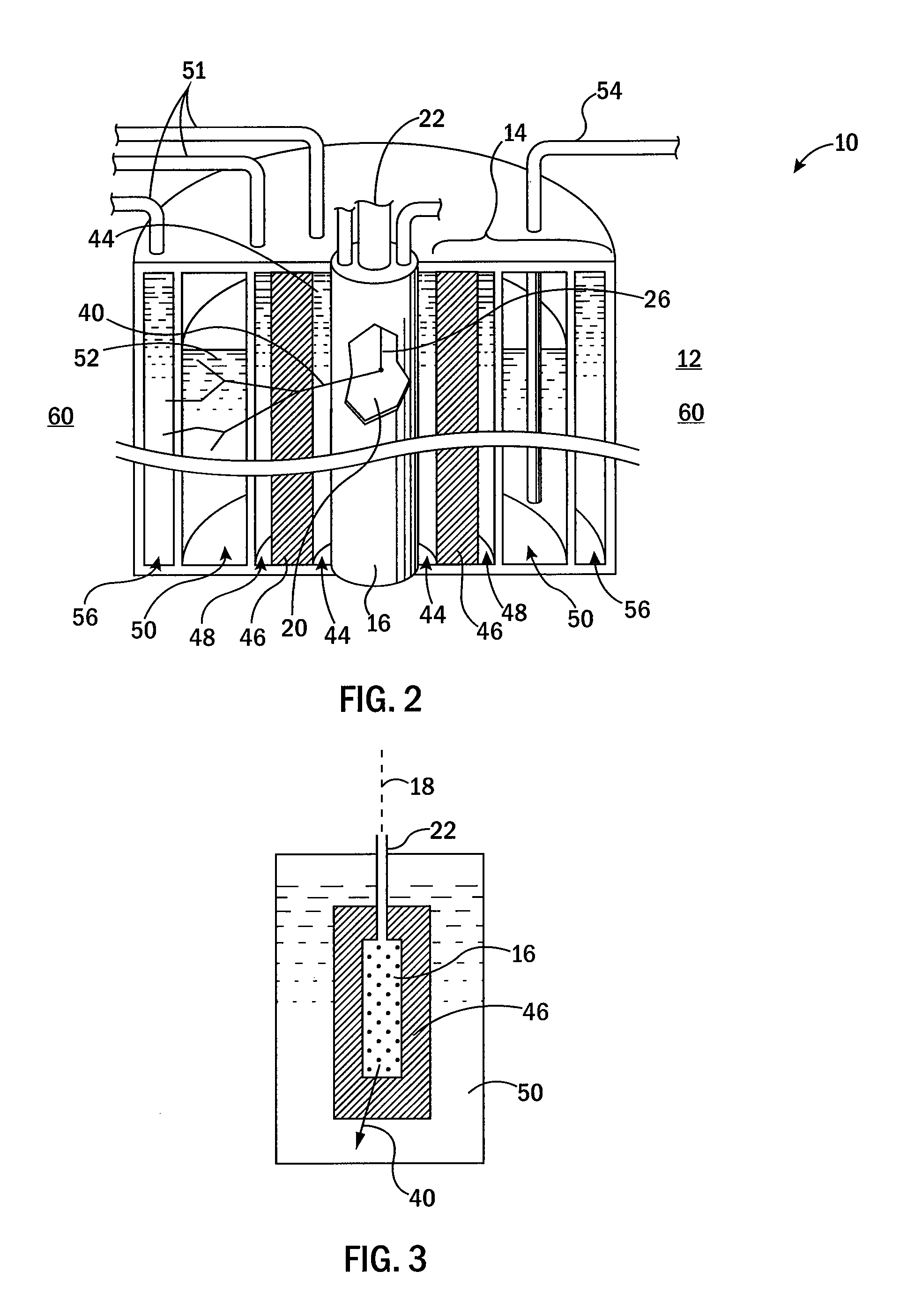
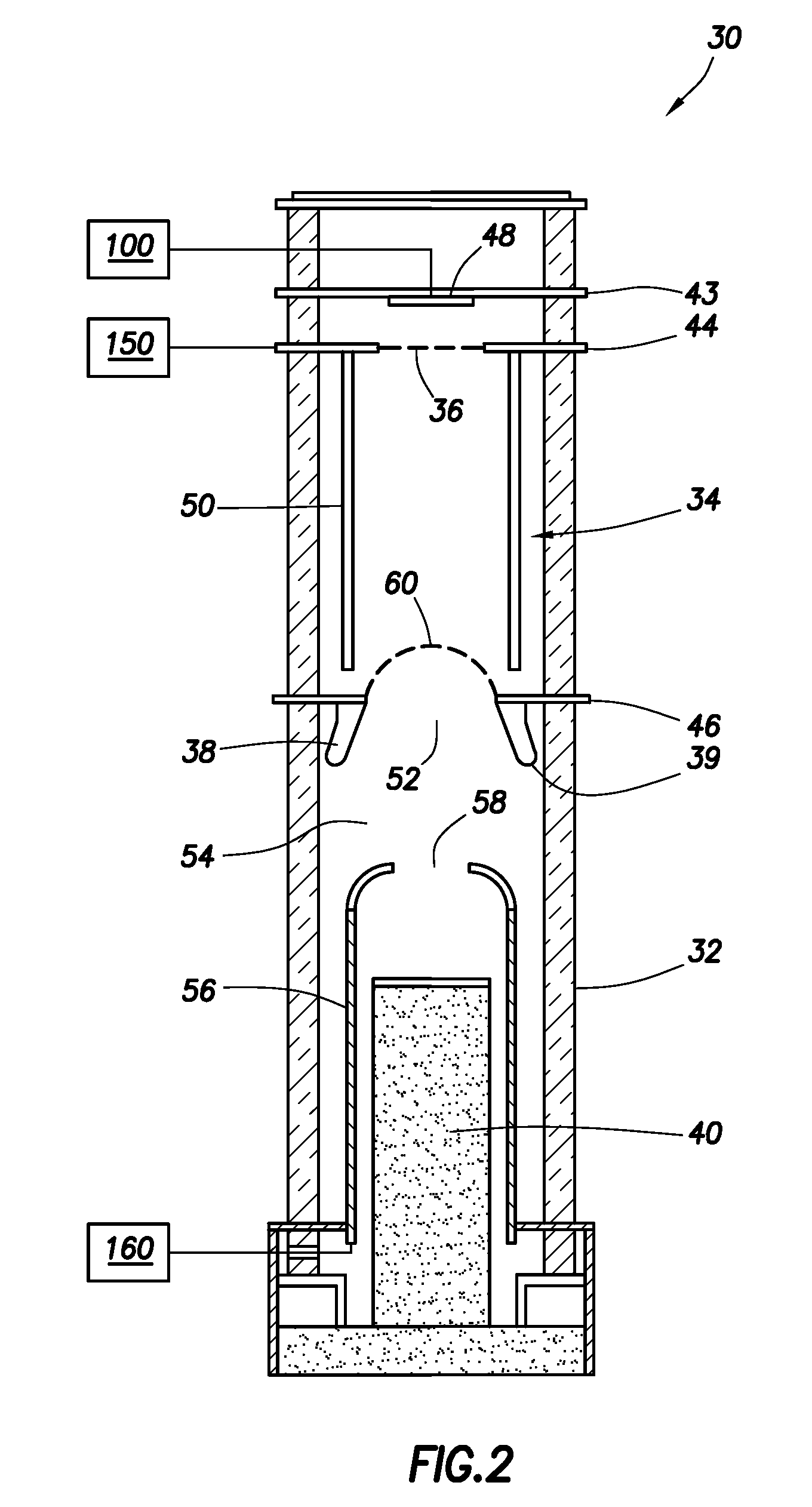
Described herein are integrated systems for generating neutrons to perform a variety of tasks including: on-line analysis of bulk material and industrial process control (as shown in FIG. 1), security interrogation (as shown in FIG. 2), soil and environmental analysis, and medical diagnostic treatment. These systems are based on novel gas-target neutron generation which embodies the beneficial characteristics of replenishable fusible gas targets for very long lifetime, stability and continuous operation, combined with the advantageous features common to conventional accelerator neutron tubes including: on / off operation, hermetically sealed operation, and safe storage and transport. Innovative electron management techniques provide gas-target neutron production efficiencies that are comparable or surpass existing sources. The high-pressure high-resistance gaseous discharge is presented as a favorable gas-target neutron generator embodiment, combining ion source regions, accelerator regions, gas-target regions and electron management components within a single simple cost-effective device that is adaptable to various geometric configurations that provide specific neutron emission profiles for greater analysis capacity.
Owner:STARFIRE INDS MANAGEMENT
Long life high efficiency neutron generator
ActiveUS20110044418A1Small sizeLow efficiencyNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsEngineeringEnergy spectrum
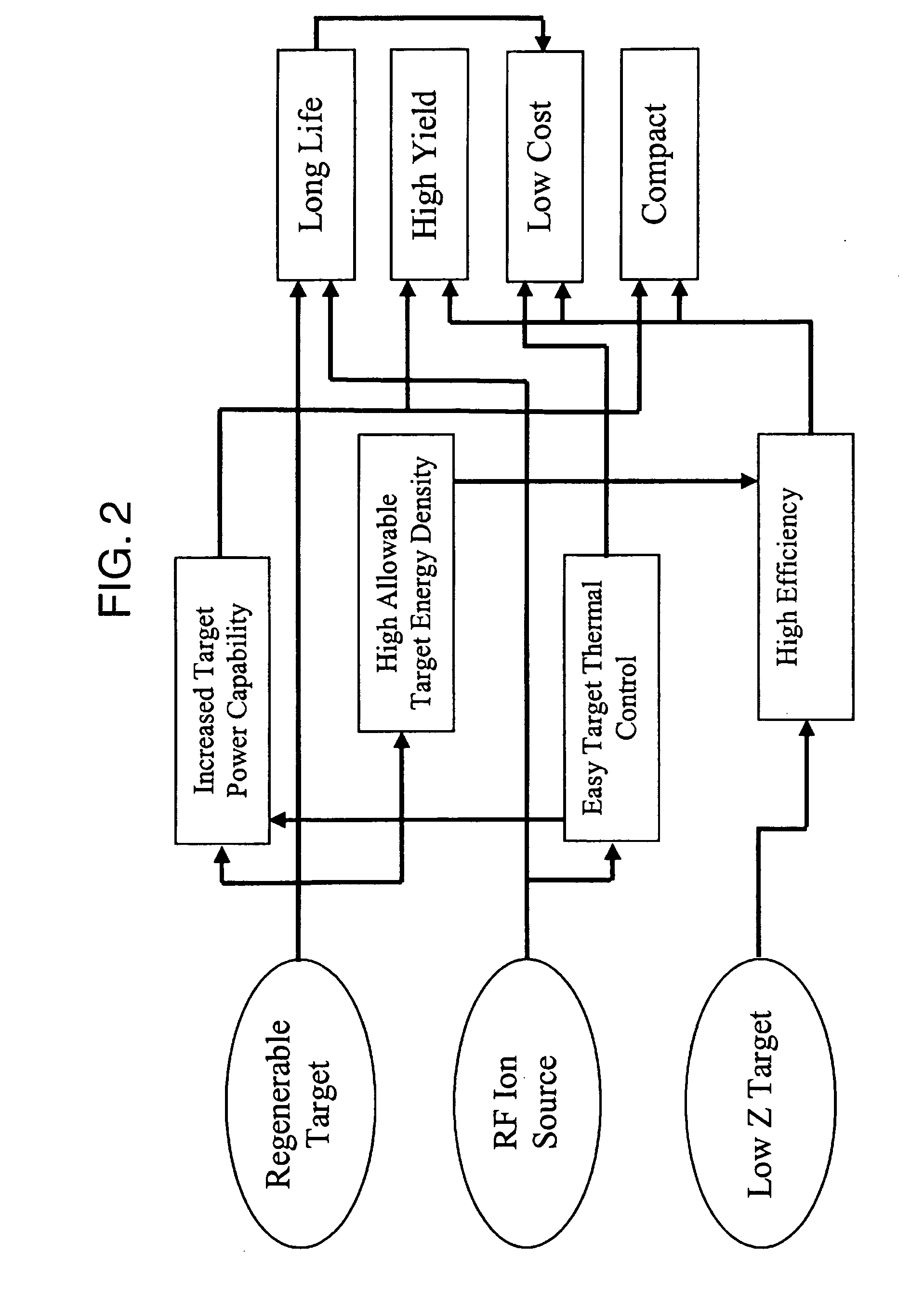
The design of a compact, high-efficiency, high-flux capable compact-accelerator fusion neutron generator (FNG) is discussed. FNG's can be used in a variety of industrial analysis applications to replace the use of radioisotopes which pose higher risks to both the end user and national security. High efficiency, long lifetime, and high power-handling capability are achieved though innovative target materials and ion source technology. The device can be scaled up for neutron radiography applications, or down for borehole analysis or other compact applications. Advanced technologies such as custom neutron output energy spectrum, pulsing, and associated particle imaging can be incorporated.
Owner:STARFIRE IND LLC
Neutron Generator
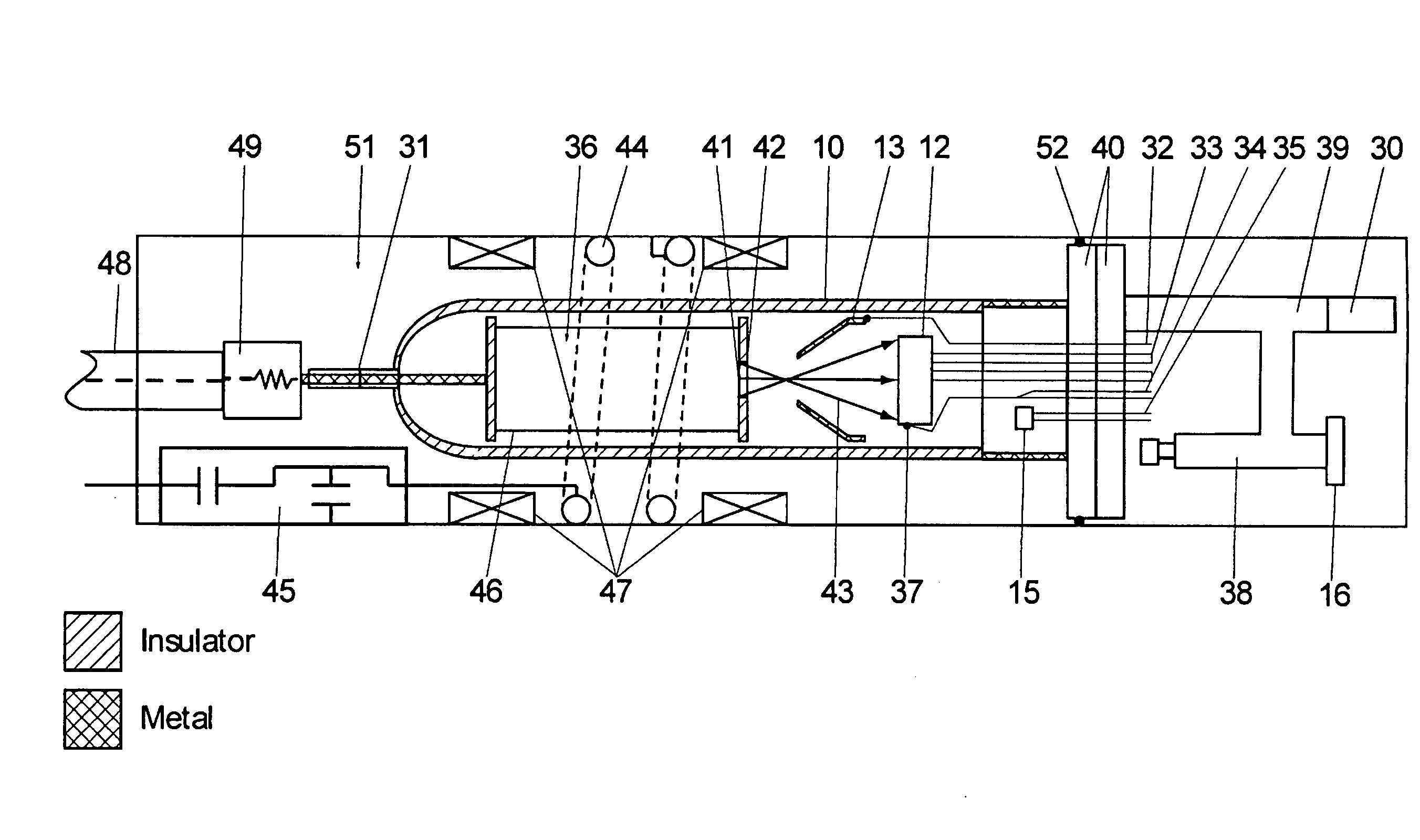
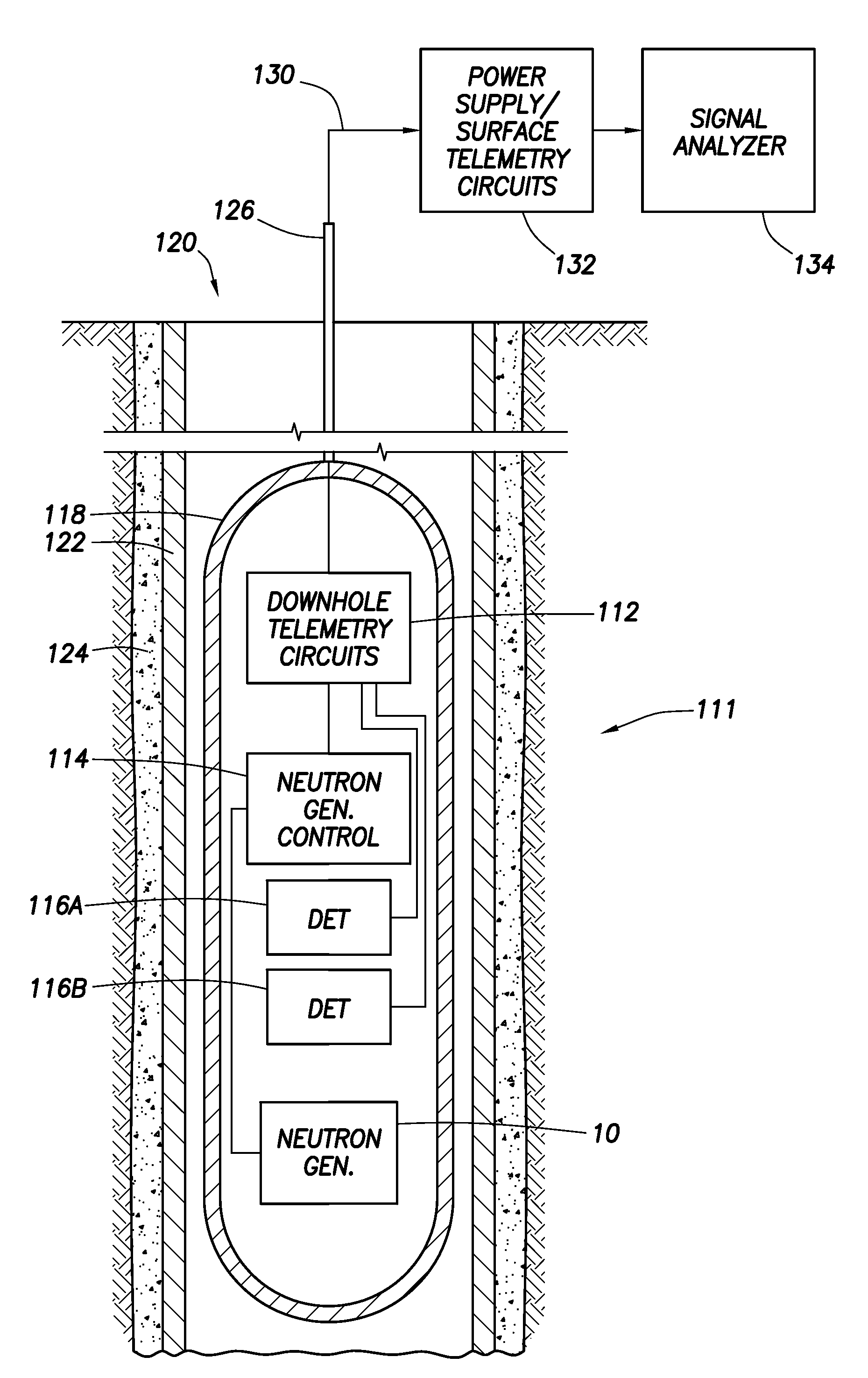
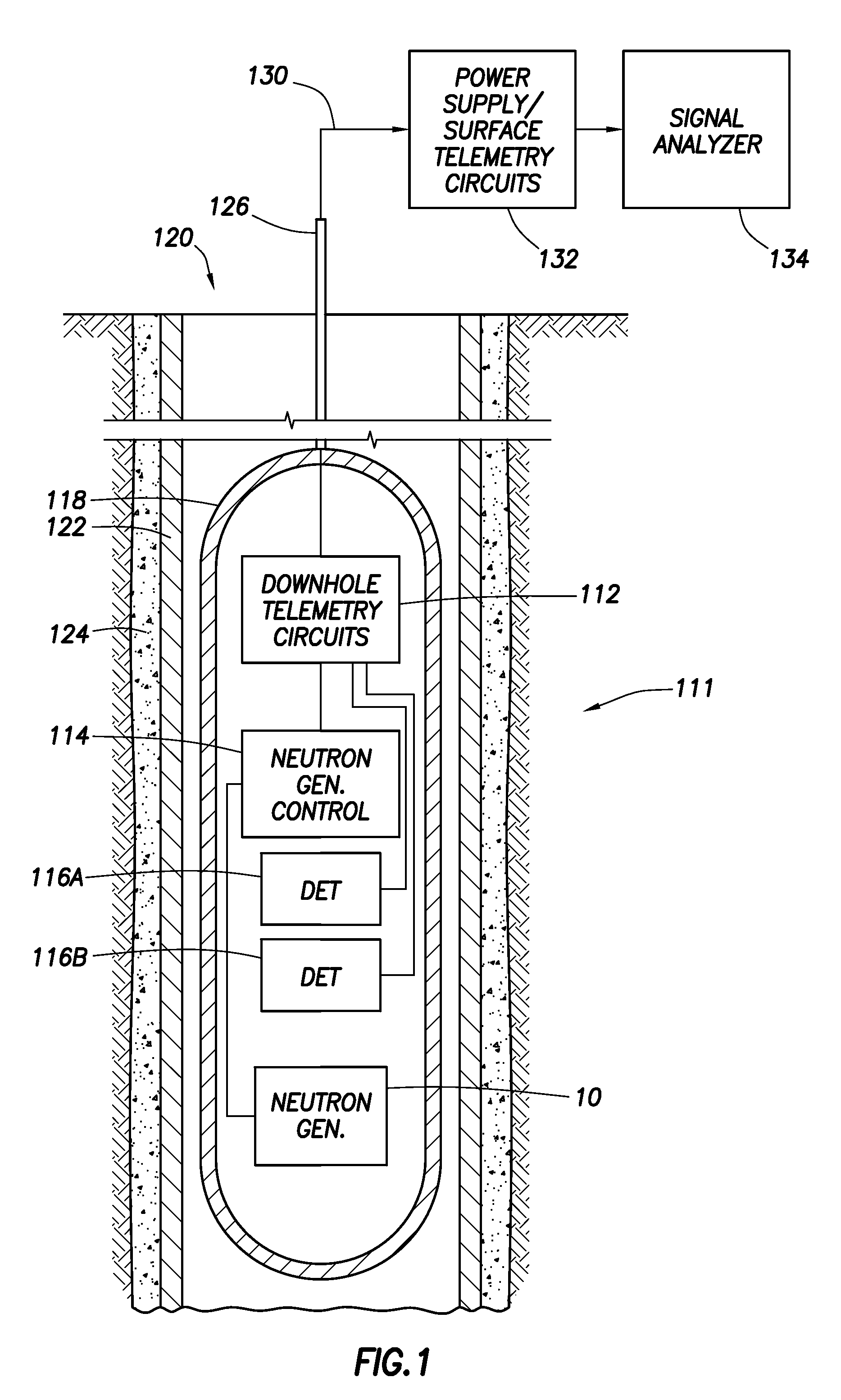
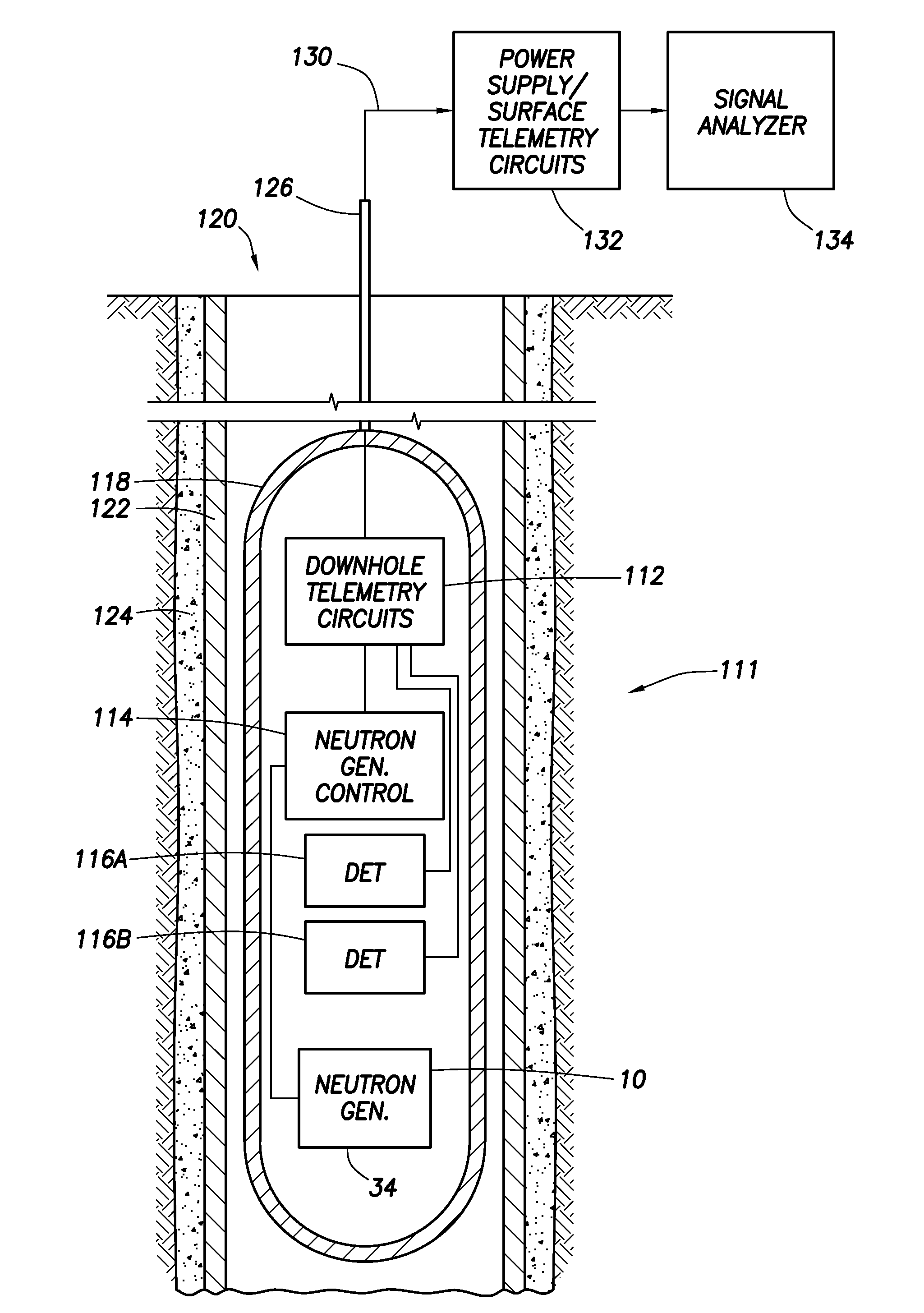
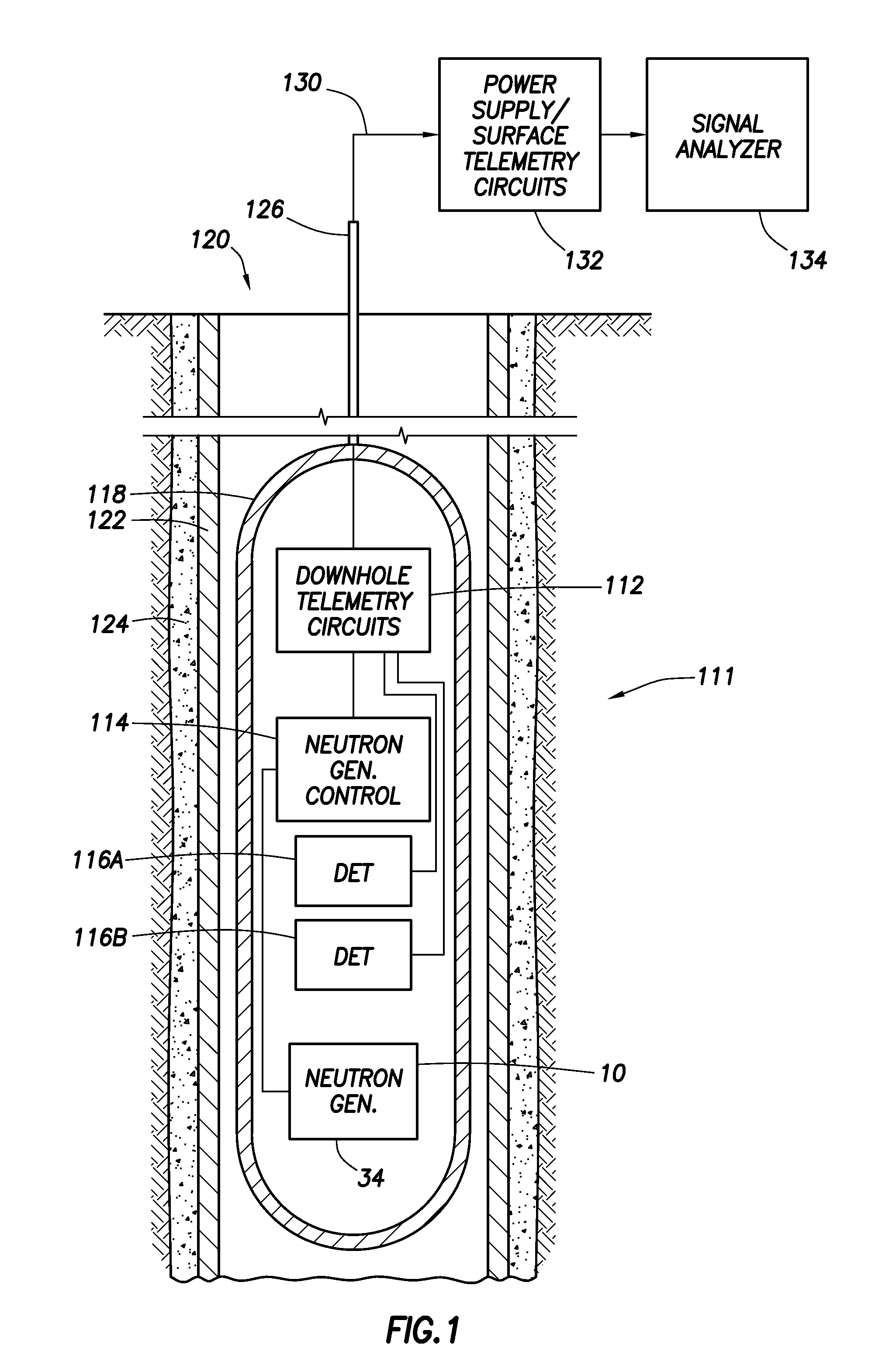
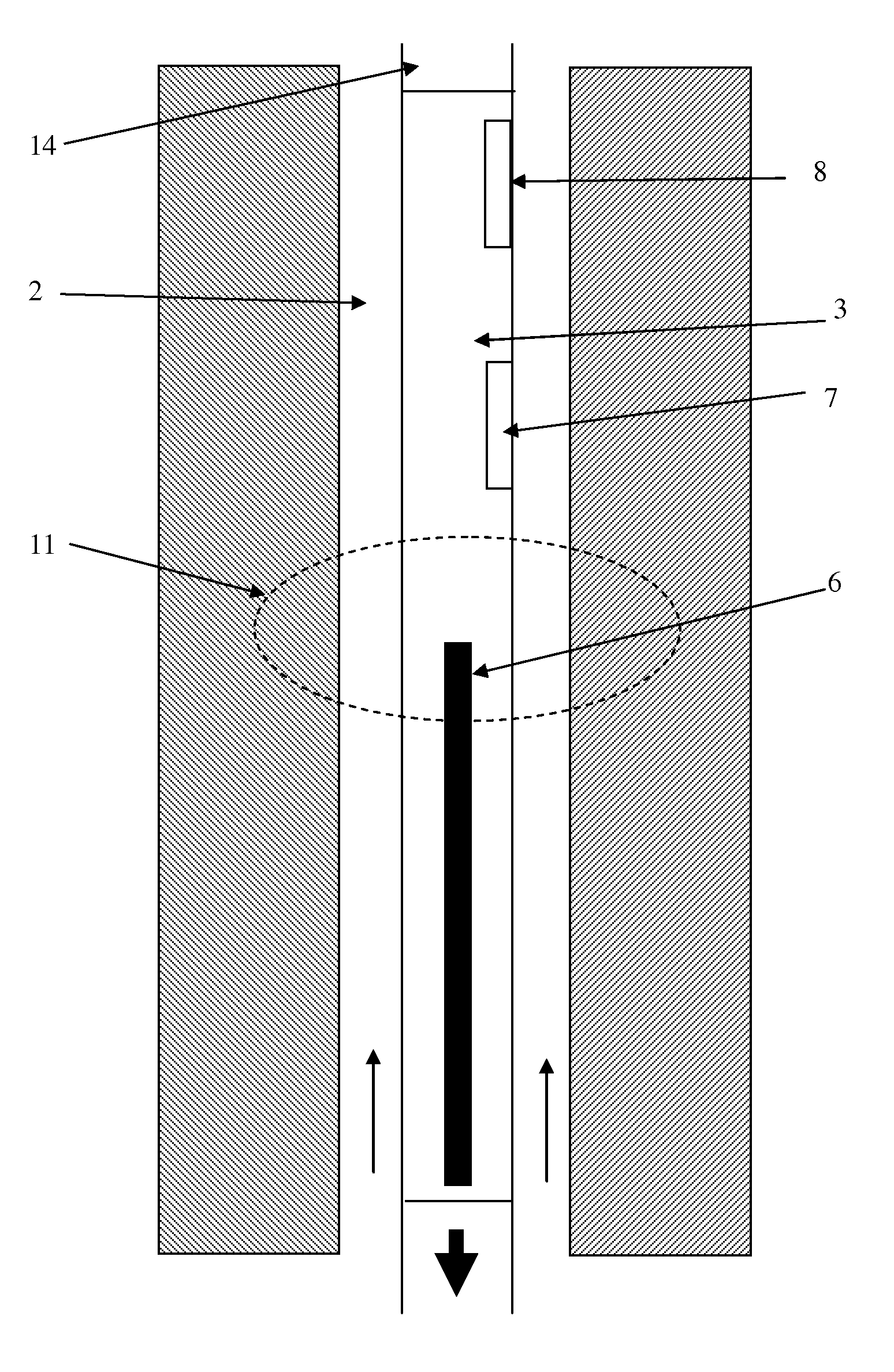
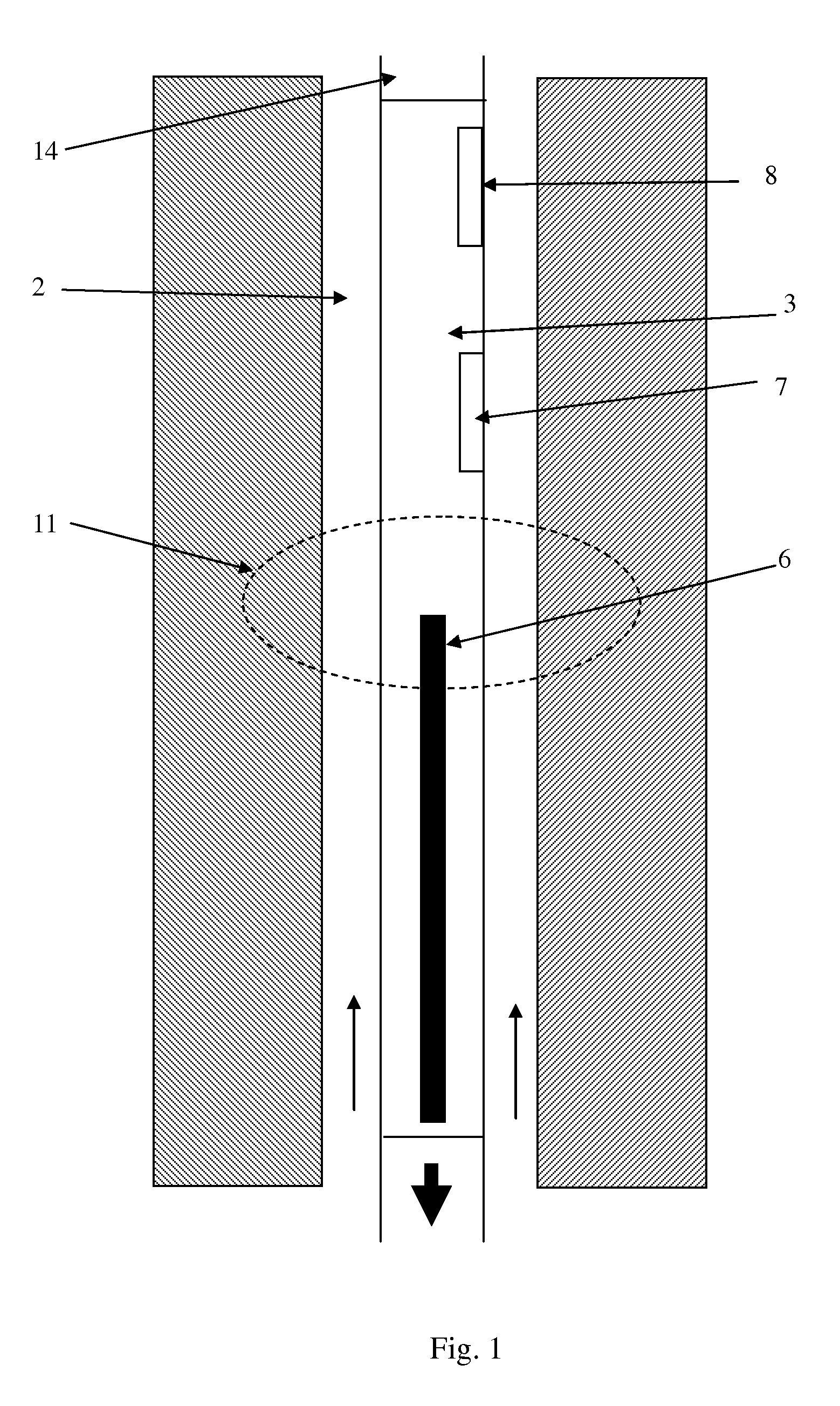
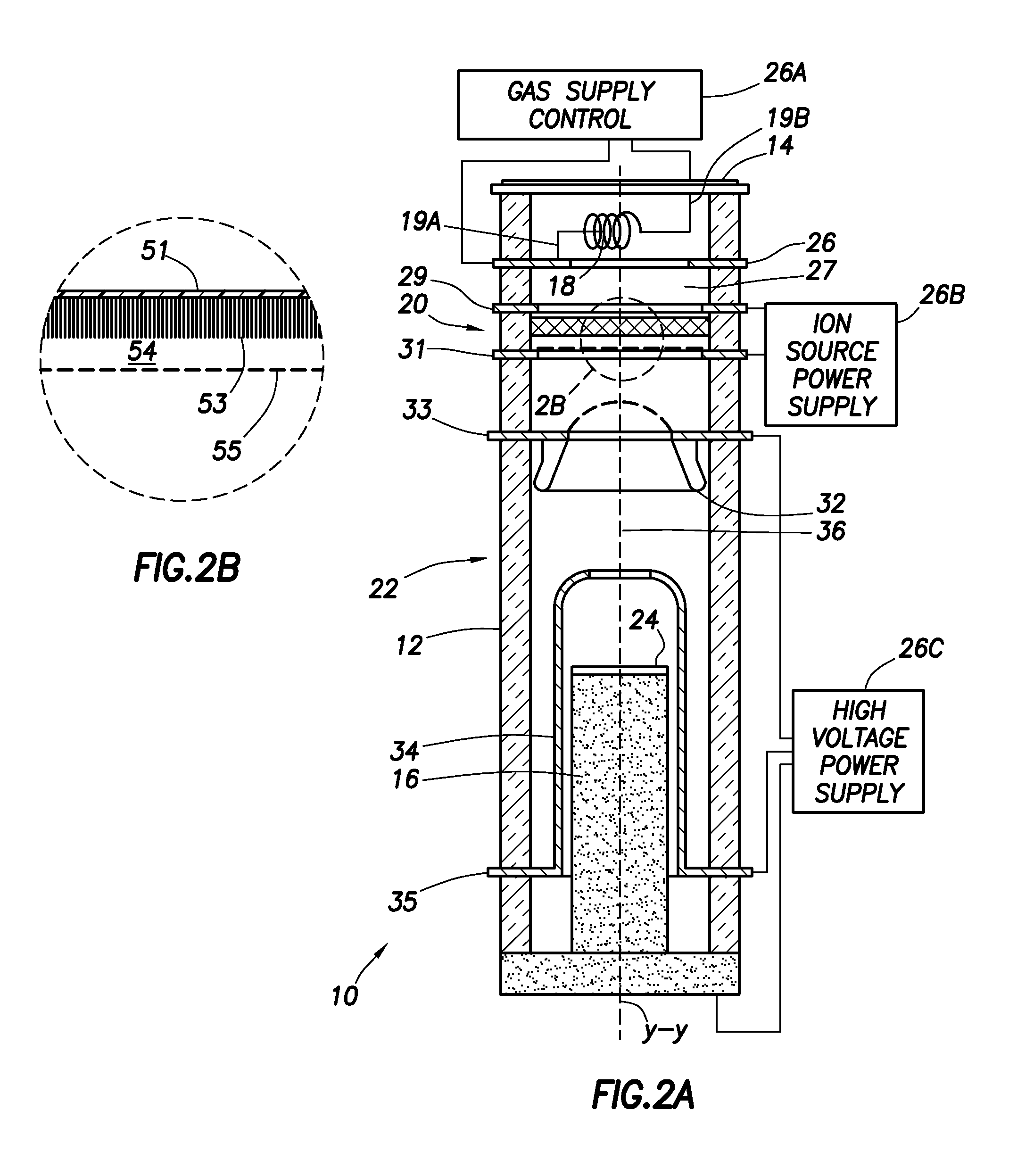
A neutron generator includes an ion source disposed in a pressurized environment containing an ionizable gas. The ion source includes a substrate with a bundle of carbon nanotubes extending therefrom. The ends of the nanotubes are spaced from a grid. Ion source voltage supply circuitry supplies a positive voltage potential between the substrate and the grid of the ion source to cause ionization of the ionizable gas and emission of ions through the grid. An ion accelerator section is disposed between the ion source and a target. The ion accelerator section accelerates ions that pass through the grid towards the target such that collisions of the ions with the target cause the target to generate and emit neutrons therefrom. The ion source, accelerator section and target are housed in a sealed tube and preferably the carbon nanotubes of the bundle are highly ordered with at least 106 carbon nanotubes per cm2 that extend in a direction substantially parallel to the central axis of the tube. The neutron generator provides gas ionization at much higher atomic to molecular ratio that the prior art, which allows for small compact size designs suitable for logging tools that are used in space-constrained downhole environments.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Cylindrical neutron generator
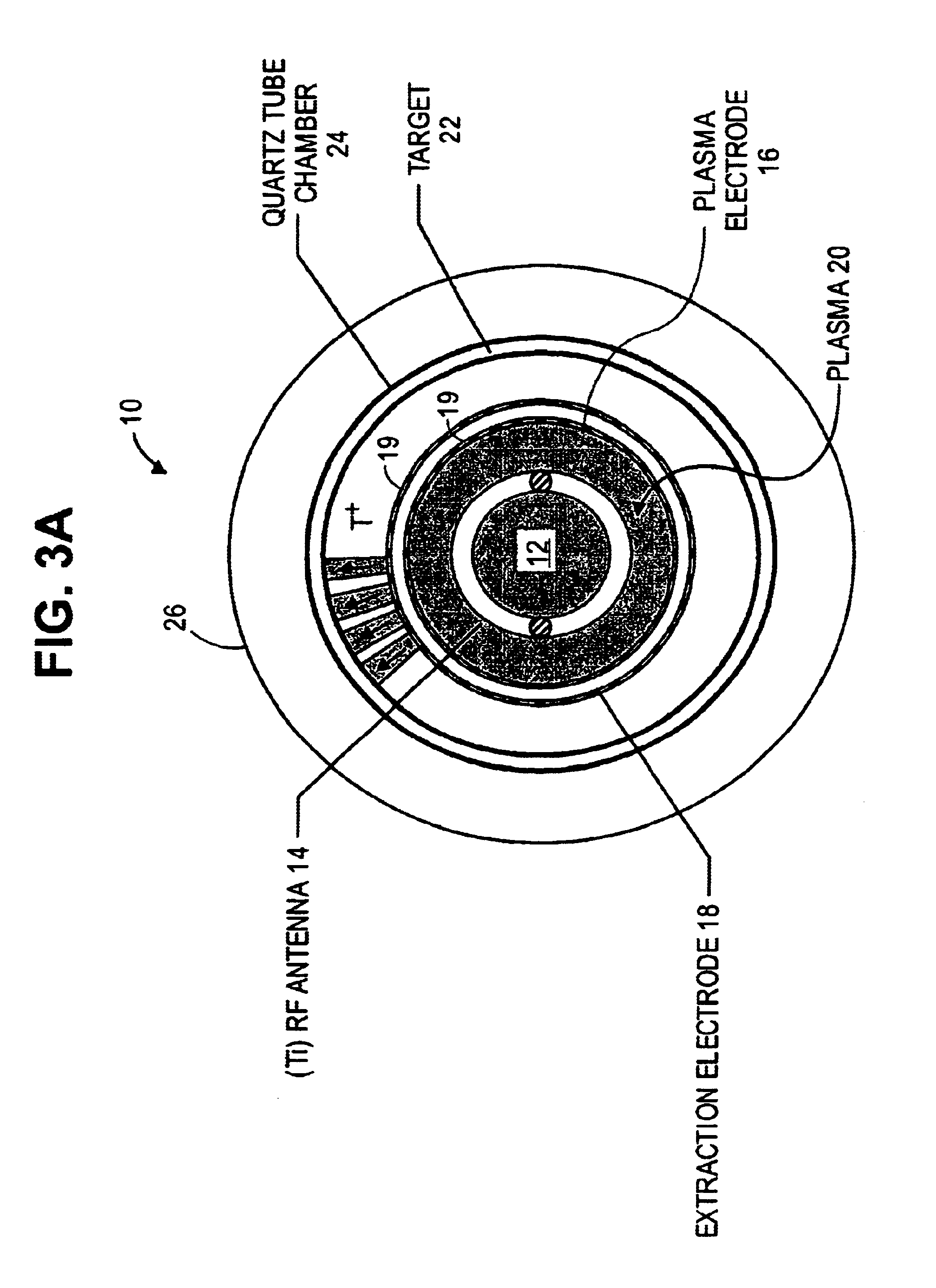
InactiveUS6907097B2Increase neutron fluxHigh densityConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationPlasma generatorNeutron flux
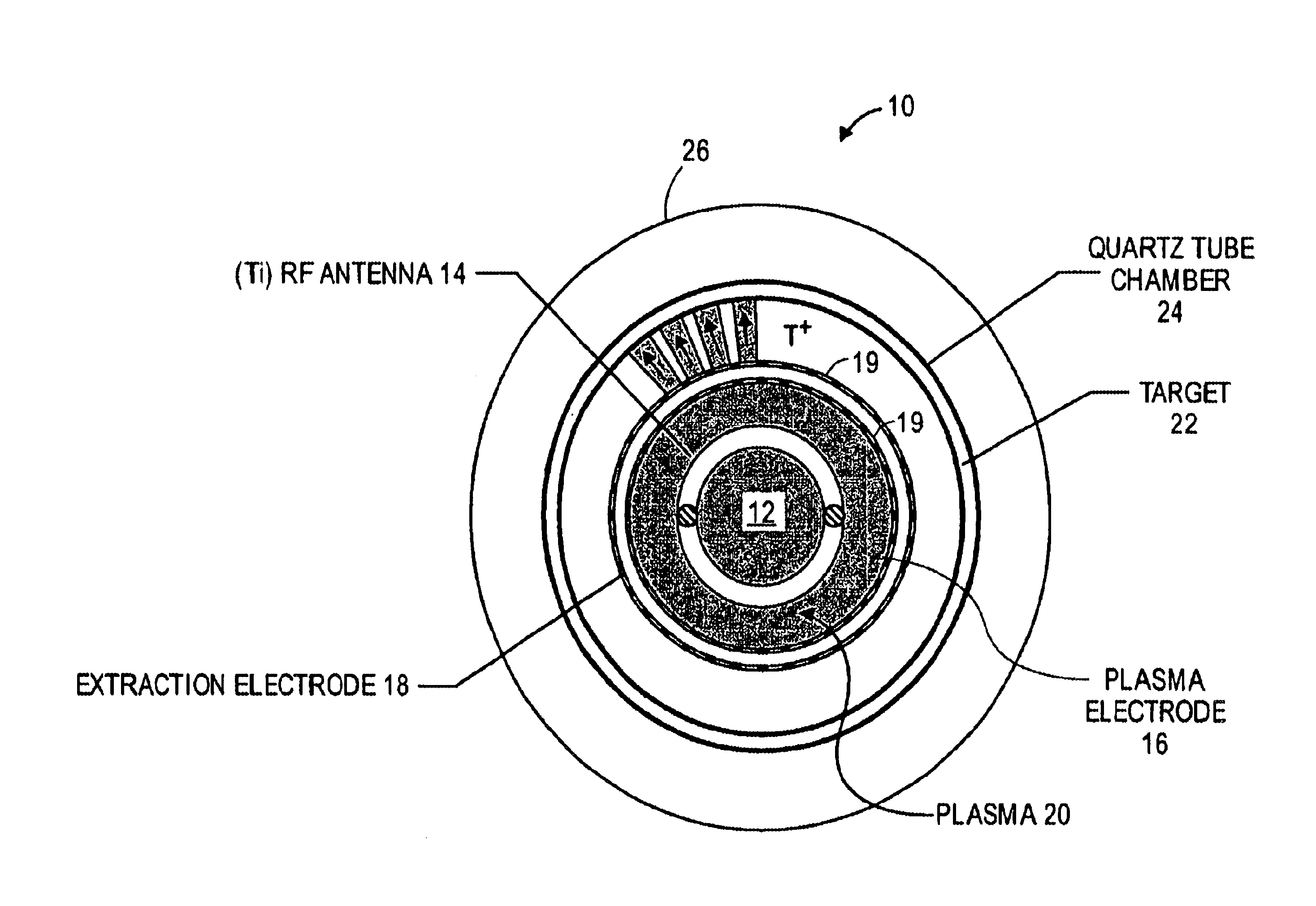
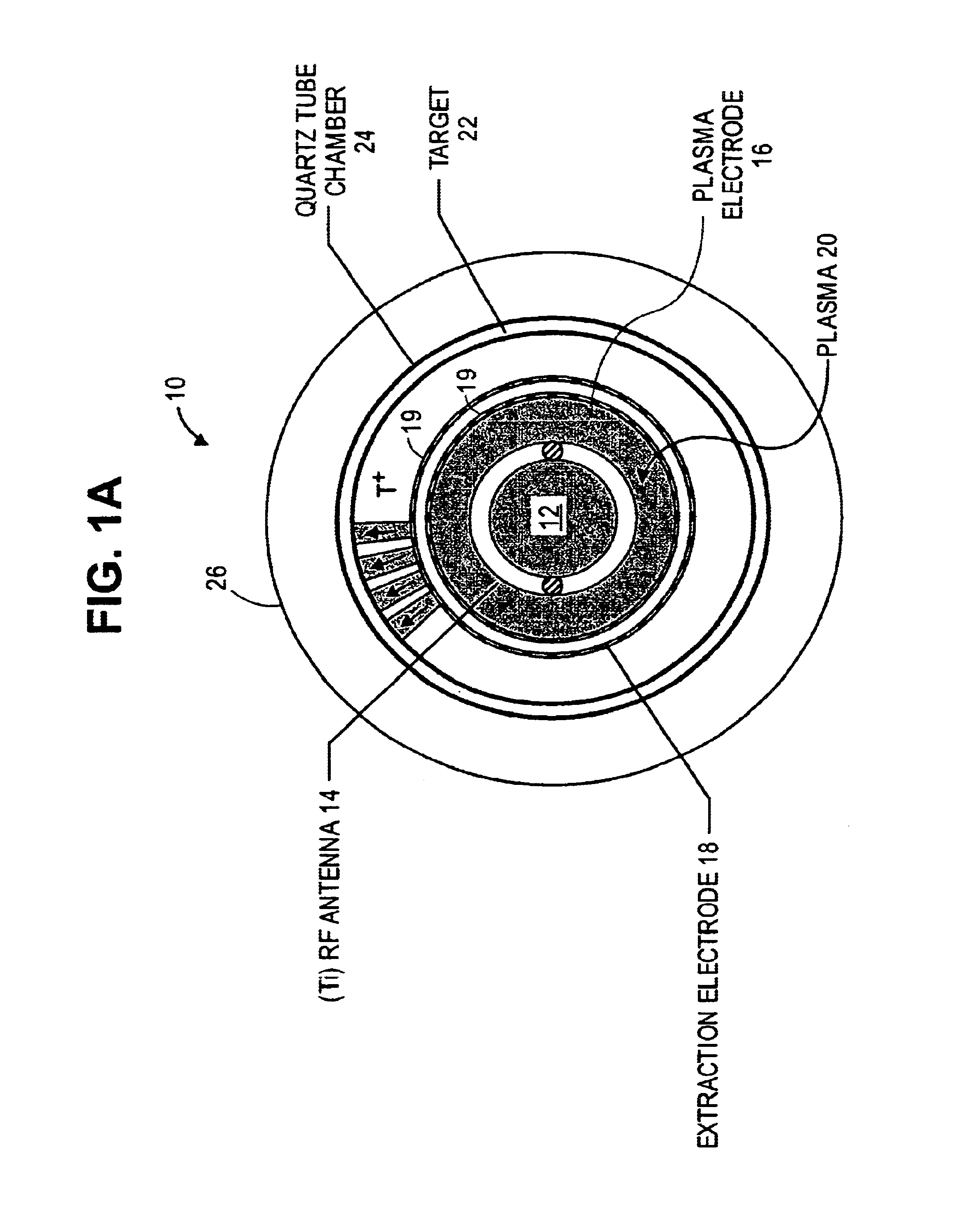
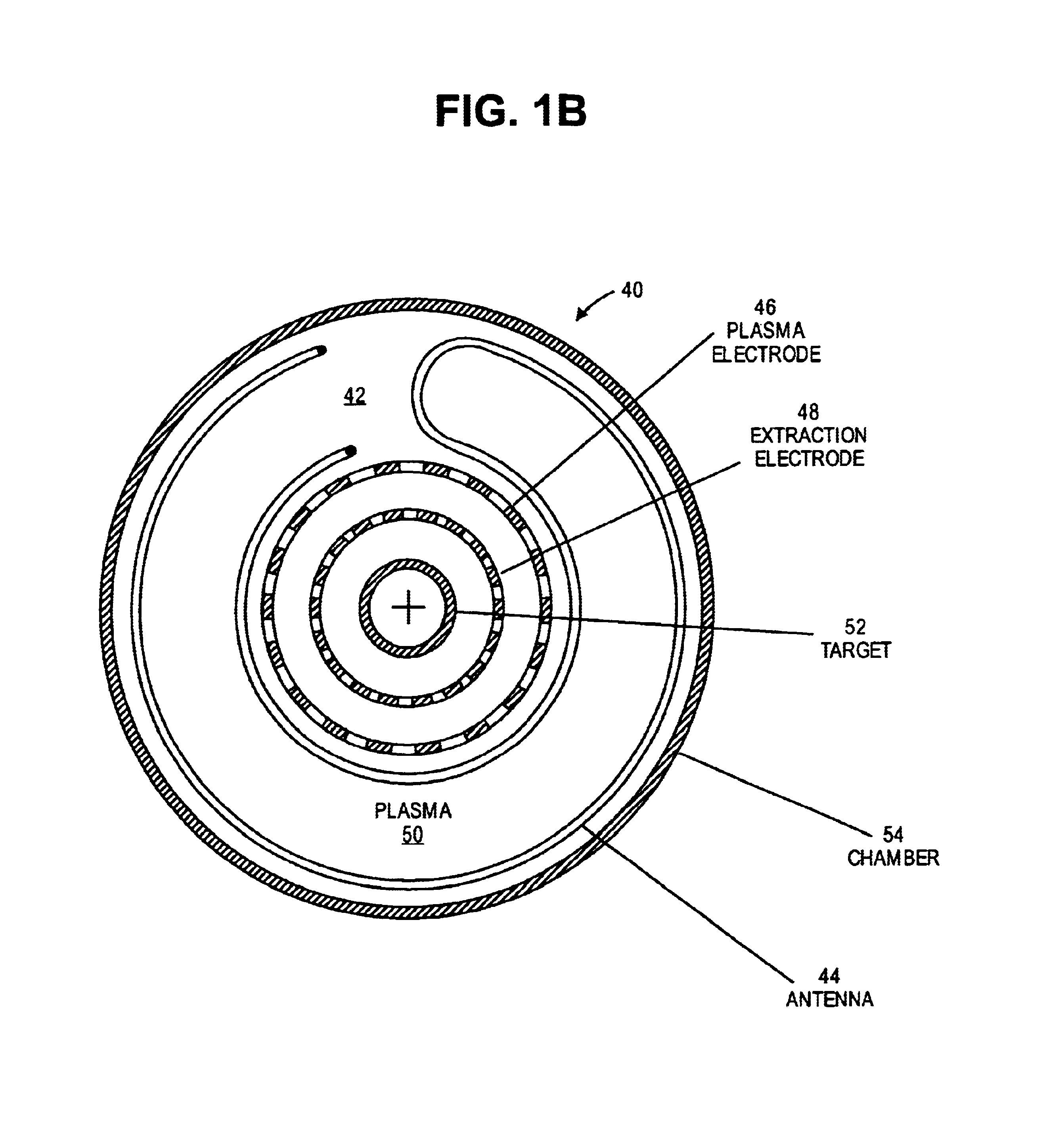
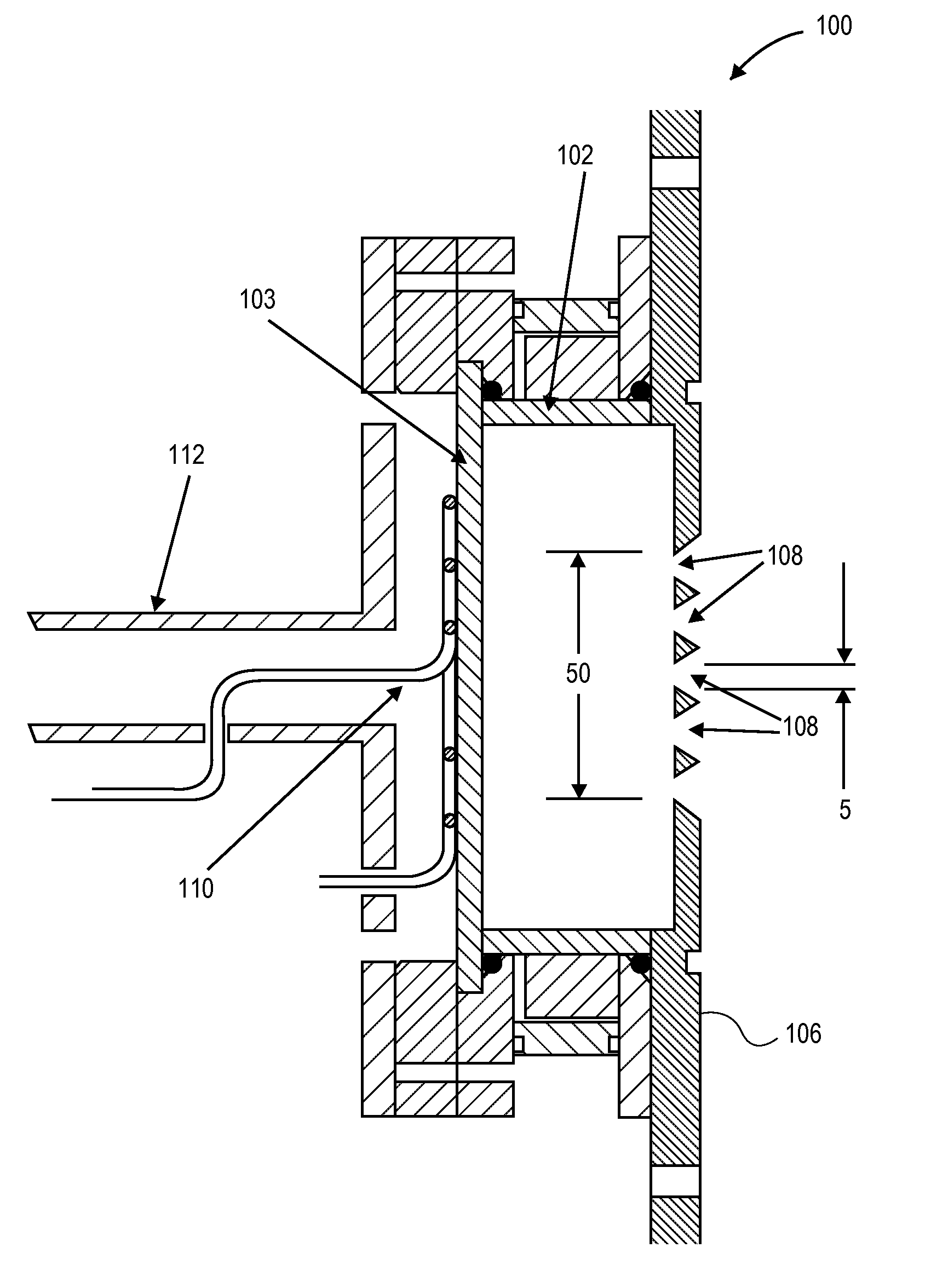
A cylindrical neutron generator is formed with a coaxial RF-driven plasma ion source and target. A deuterium (or deuterium and tritium) plasma is produced by RF excitation in a cylindrical plasma ion generator using an RF antenna. A cylindrical neutron generating target is coaxial with the ion generator, separated by plasma and extraction electrodes which contain many slots. The plasma generator emanates ions radially over 360° and the cylindrical target is thus irradiated by ions over its entire circumference. The plasma generator and target may be as long as desired. The plasma generator may be in the center and the neutron target on the outside, or the plasma generator may be on the outside and the target on the inside. In a nested configuration, several concentric targets and plasma generating regions are nested to increase the neutron flux.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Neutron generator
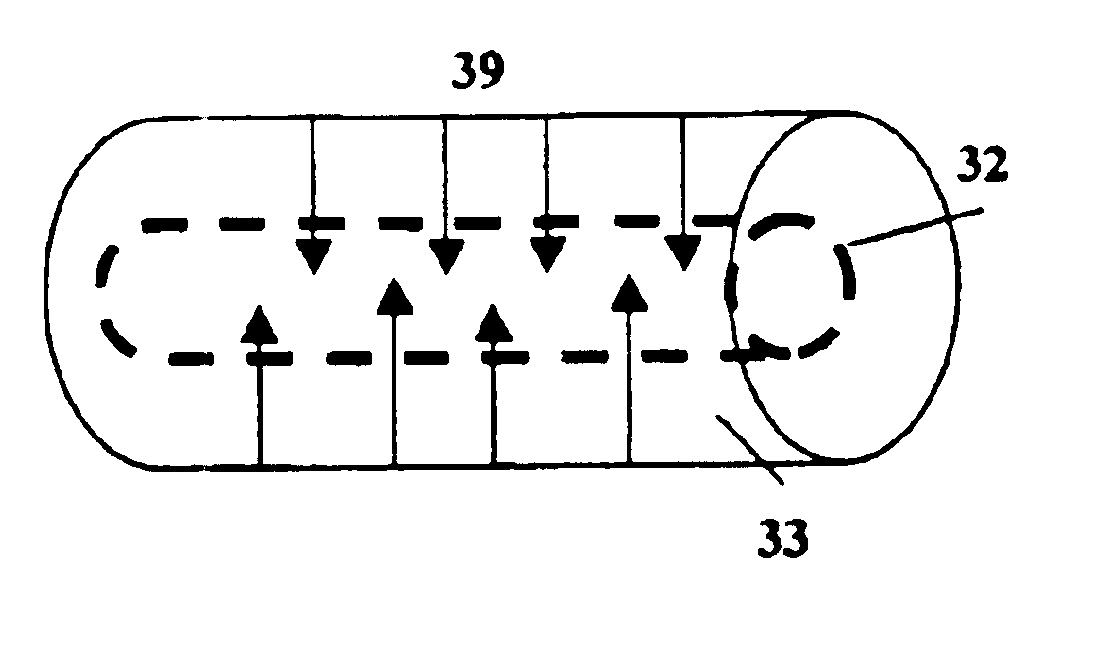
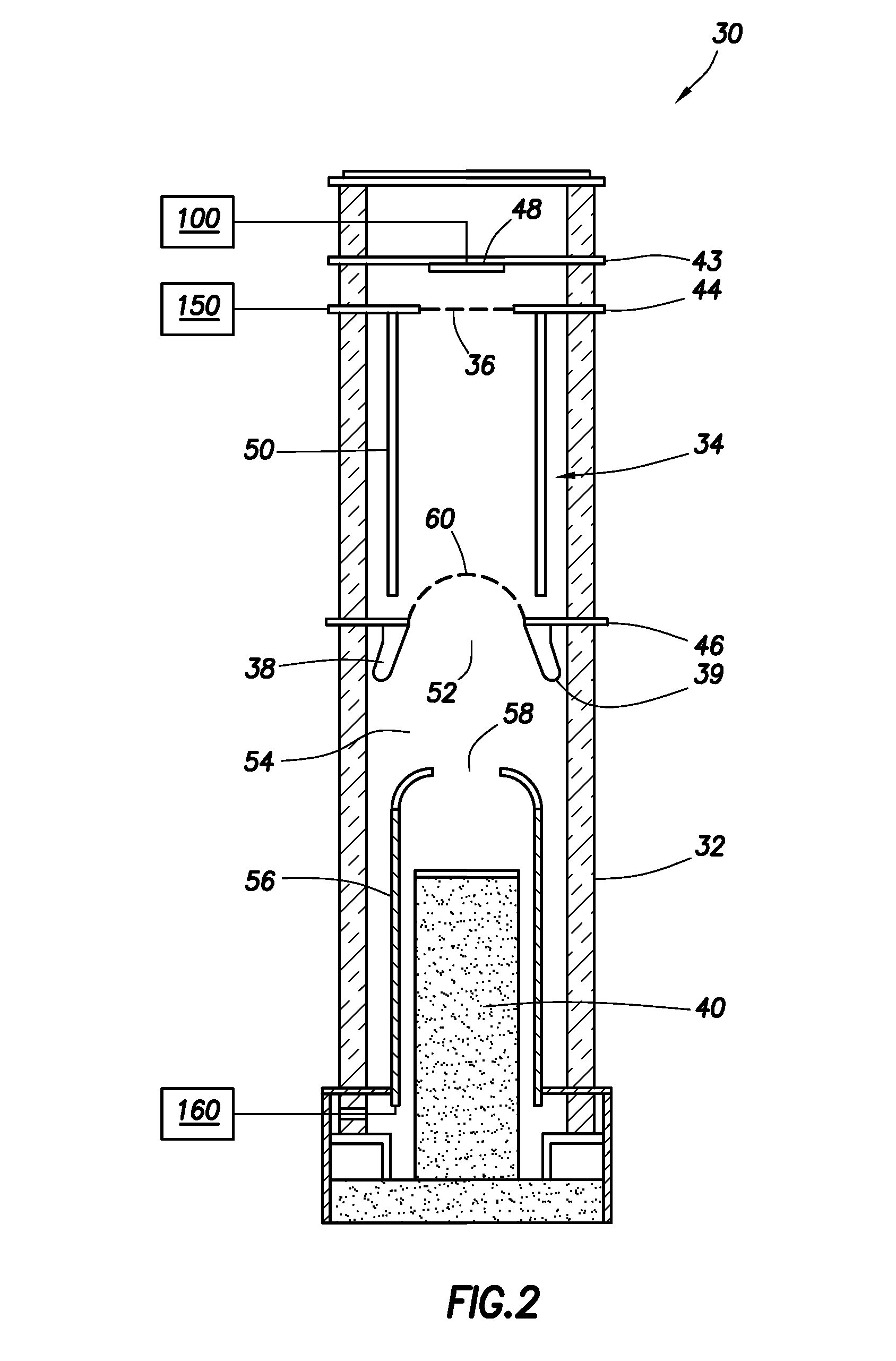
ActiveUS20110180698A1Poor thermal conductionImprove cooling effectNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsLow voltageHigh pressure
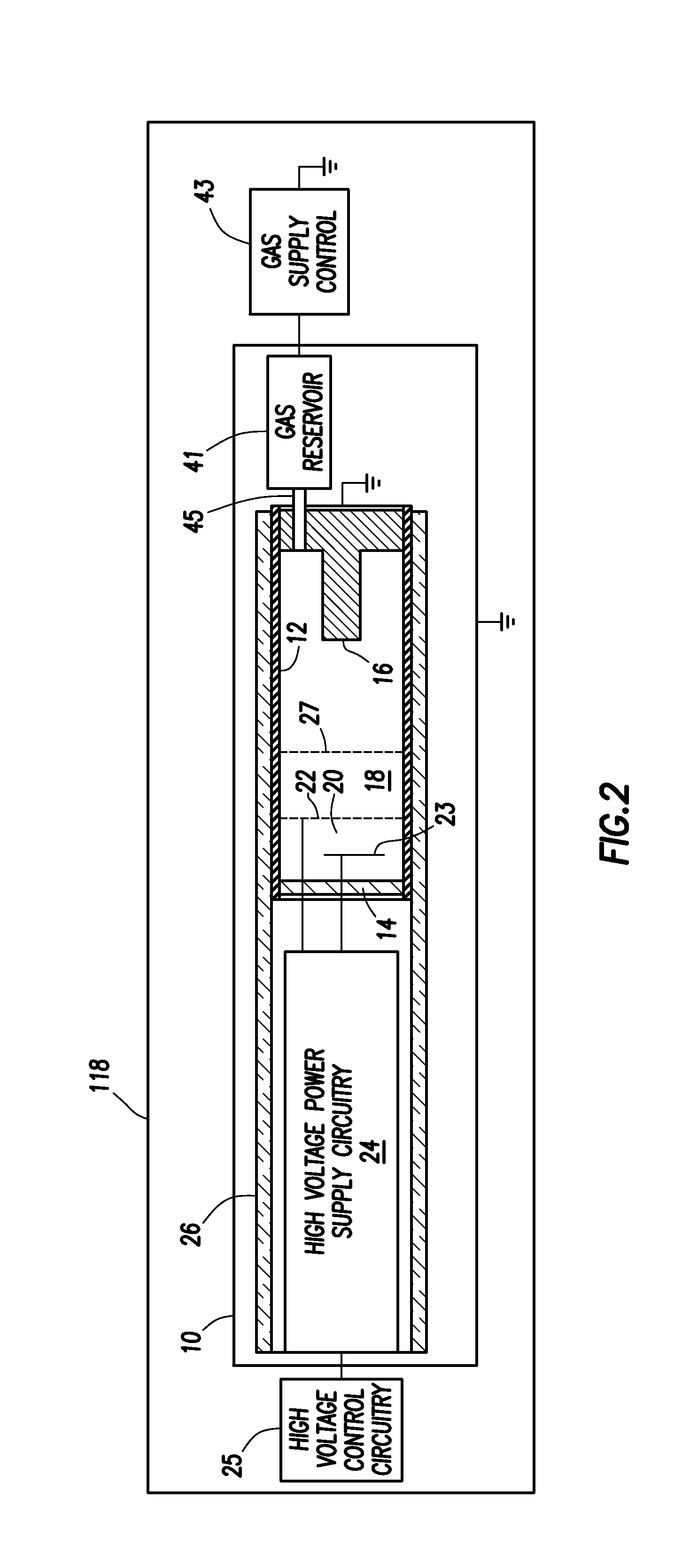
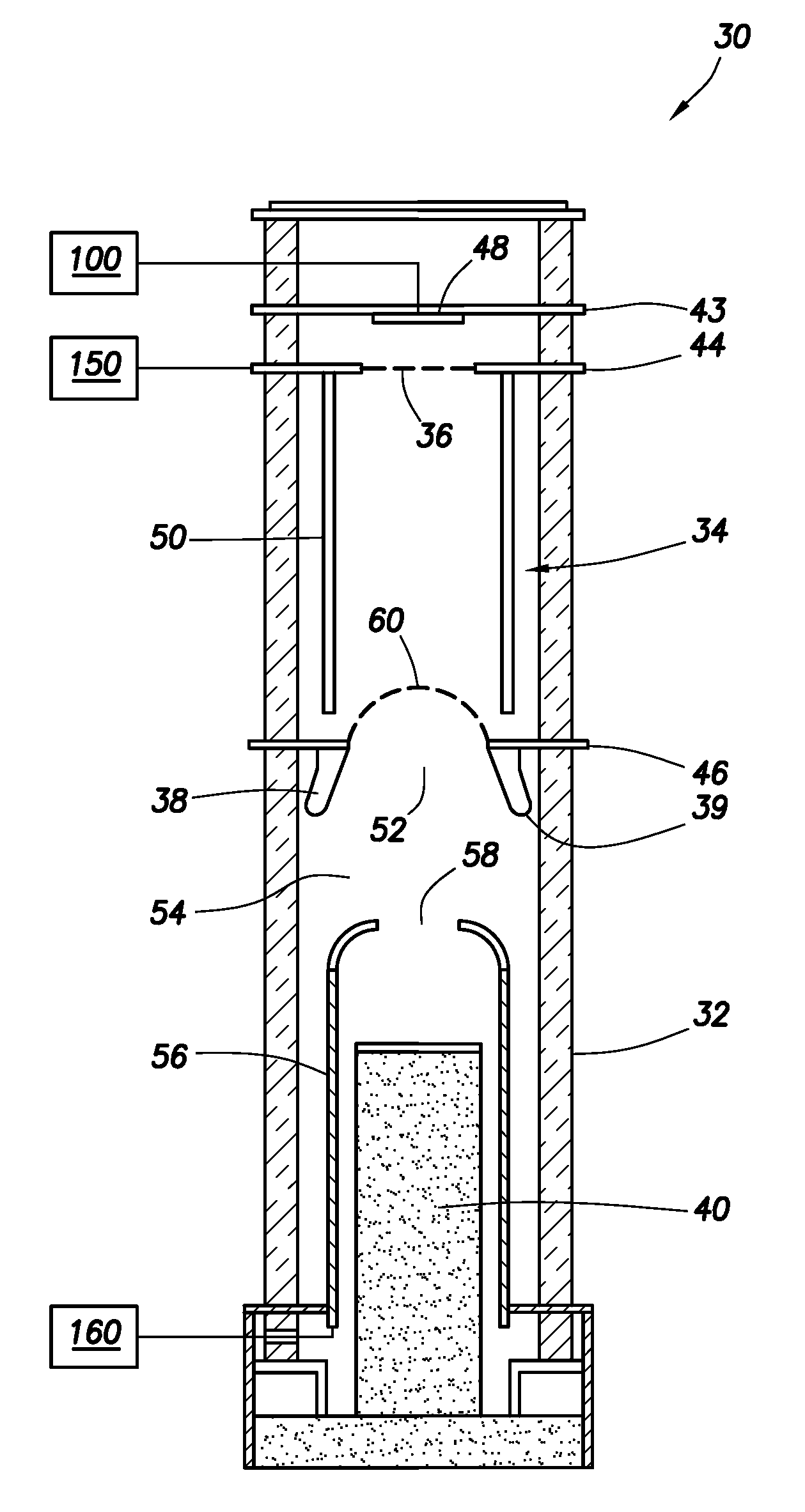
A neutron generator includes a sealed envelope providing a low pressure environment for a gas. One end of the envelope defines an ion source chamber. A target electrode is disposed at the other end of the envelope. An extracting electrode is spaced apart from the target electrode by an accelerating gap. The extracting electrode bounds the ion source chamber. A dispenser cathode electrode and grid electrode are disposed in the ion source chamber for inducing ionization in the ion source chamber. The dispenser cathode electrode, the grid electrode and the extracting electrode operate at a positive high voltage potential and the target electrode operates at or near ground potential. This configuration provides an electric field gradient that accelerates ions towards the target electrode to induce collisions of ions with target material, thereby causing fusion reactions that generate neutrons. High voltage power supply circuit means supplies a positive high voltage signal to the electrodes of the ion source. The positive high voltage signal has a low voltage signal component floating on a positive high voltage signal component. For the dispensing cathode electrode, the low voltage signal component can be a DC or AC signal suitable for emitting electrons from the dispensing cathode electrode. For the grid electrode, the low voltage signal component can be a positive pulsed-mode signal (preferably with magnitude in the range between 100 to 300 volts). High voltage insulation surrounds and electrically insulates the high voltage power supply circuit means. Other ion source electrode configurations, such as cold cathode (Penning) ion source and RF-driven ion source, can also be used.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Low Power Neutron Generators
A neutron generator and method of constructing the same. The generator includes a grid configured to produce an ionizable gas when heated by electrons impinging thereon. A cathode emits electrons to heat the grid and to collide with produced ionizable gas atoms to generate ions. Neutrons are generated from a collision of ions impinging on a target in the generator. A tool for subsurface use incorporating the neutron generator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Compact neutron generator
InactiveUS6870894B2Reasonable levelMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsTarget surfaceTitanium
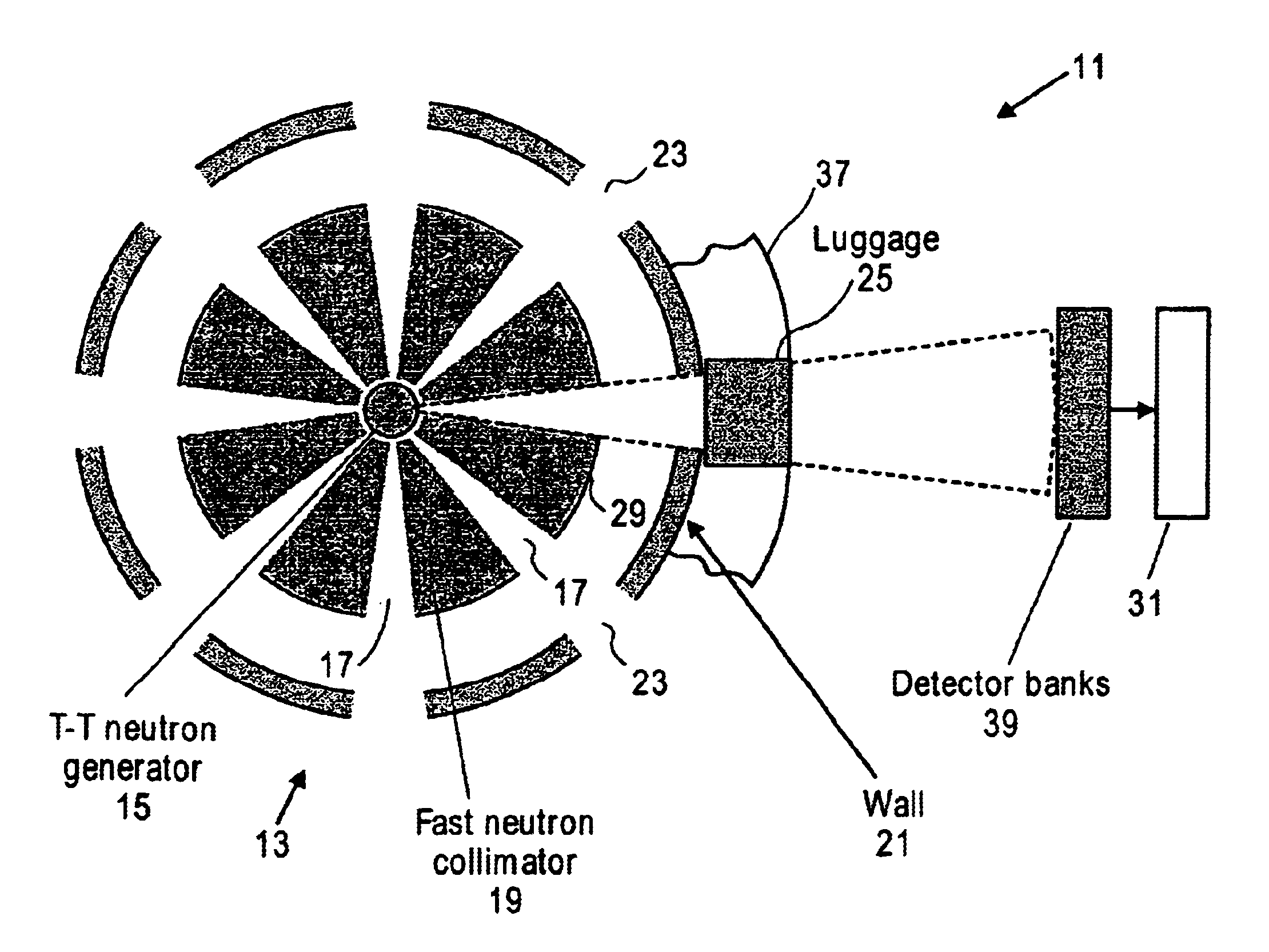
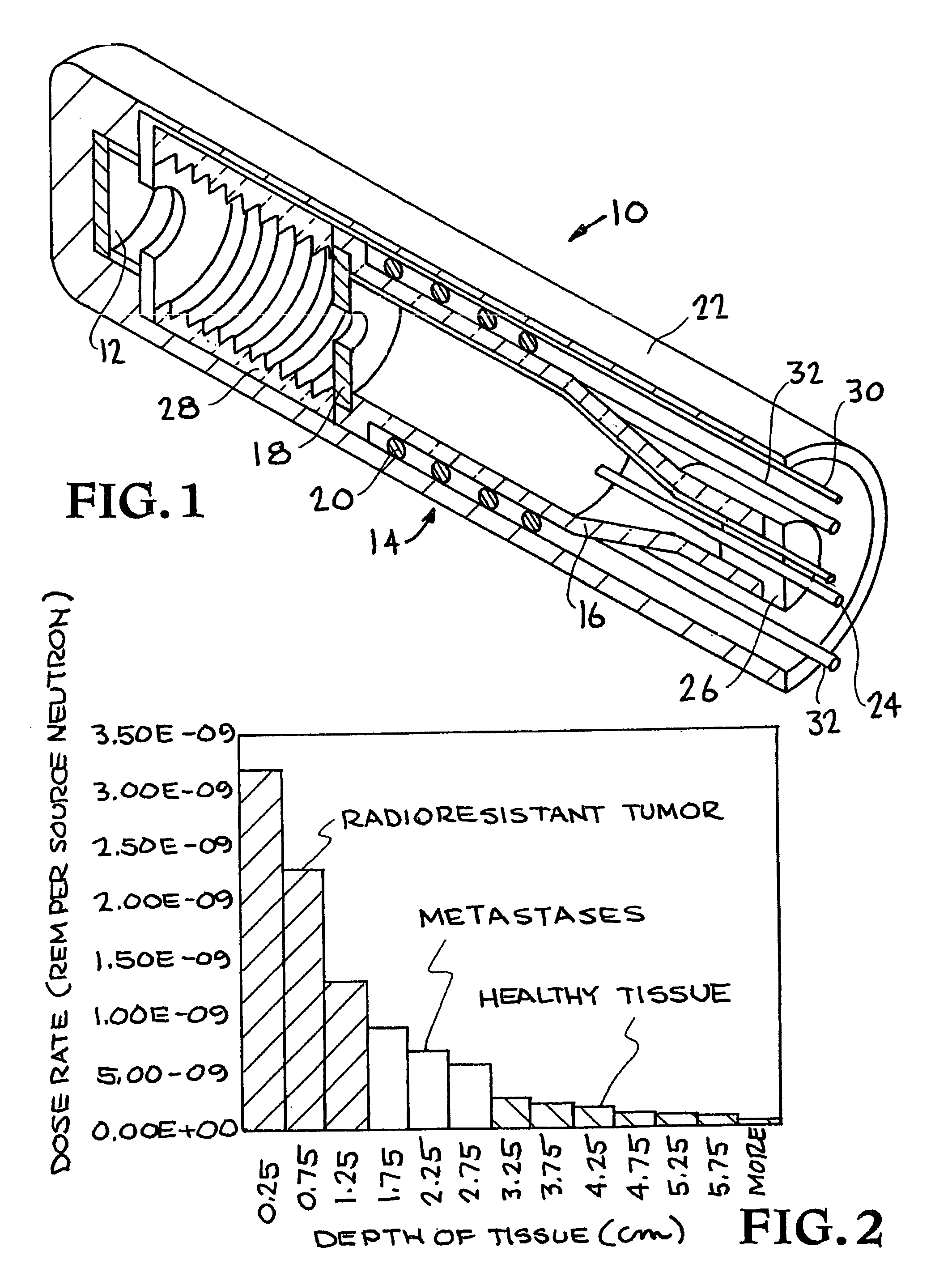
A compact neutron generator has at its outer circumference a toroidal shaped plasma chamber in which a tritium (or other) plasma is generated. A RF antenna is wrapped around the plasma chamber. A plurality of tritium ion beamlets are extracted through spaced extraction apertures of a plasma electrode on the inner surface of the toroidal plasma chamber and directed inwardly toward the center of neutron generator. The beamlets pass through spaced acceleration and focusing electrodes to a neutron generating target at the center of neutron generator. The target is typically made of titanium tubing. Water is flowed through the tubing for cooling. The beam can be pulsed rapidly to achieve ultrashort neutron bursts. The target may be moved rapidly up and down so that the average power deposited on the surface of the target may be kept at a reasonable level. The neutron generator can produce fast neutrons from a T-T reaction which can be used for luggage and cargo interrogation applications. A luggage or cargo inspection system has a pulsed T-T neutron generator or source at the center, surrounded by associated gamma detectors and other components for identifying explosives or other contraband.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
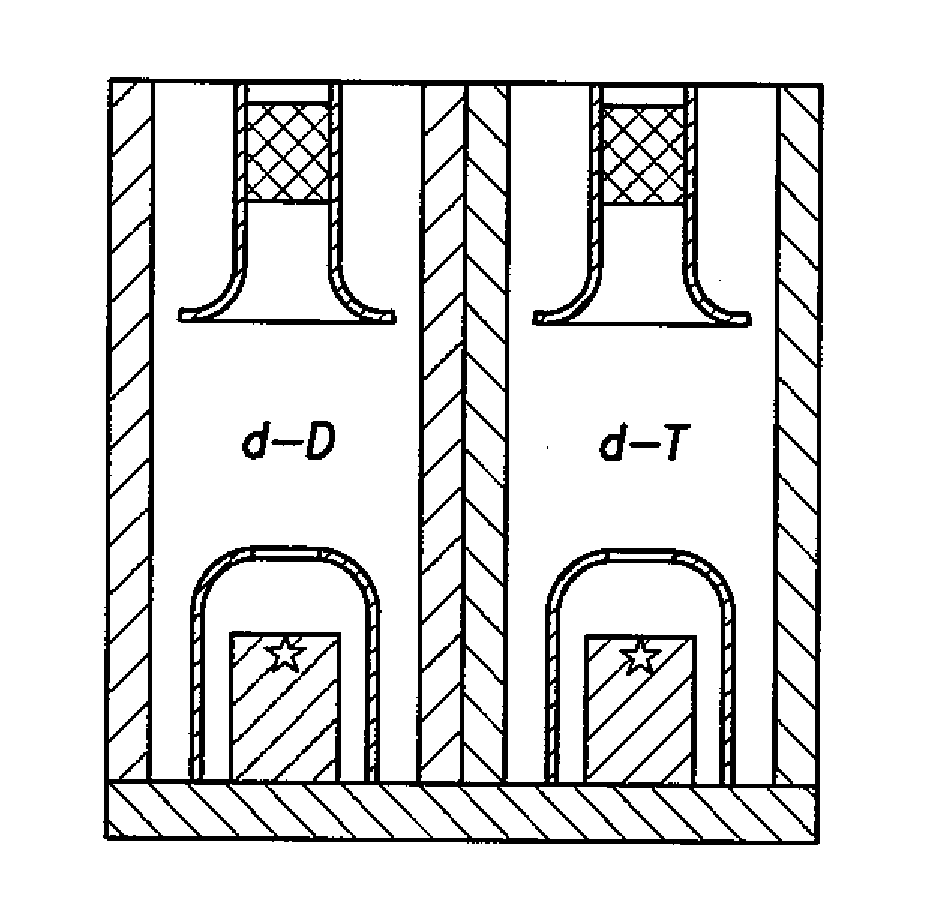
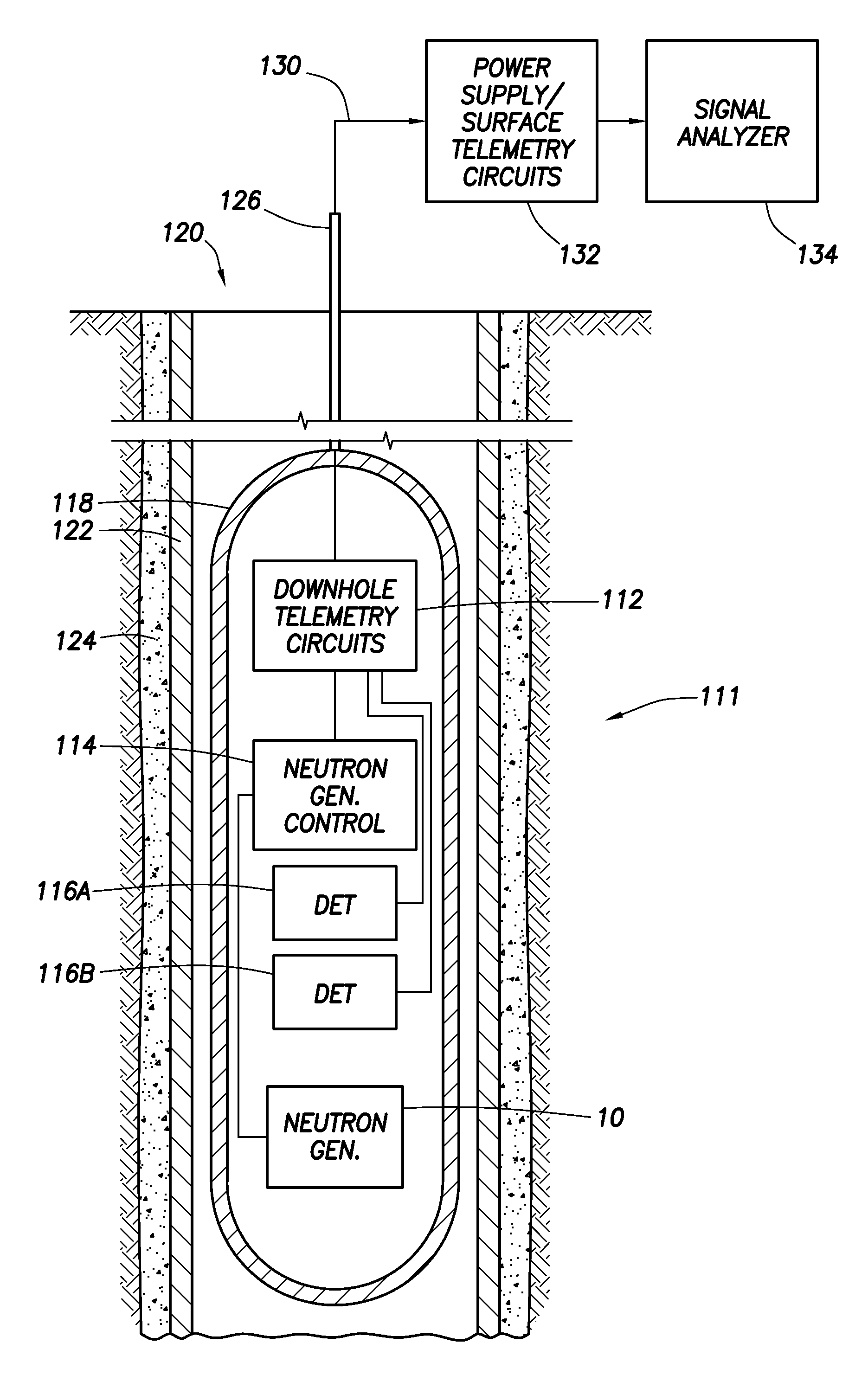
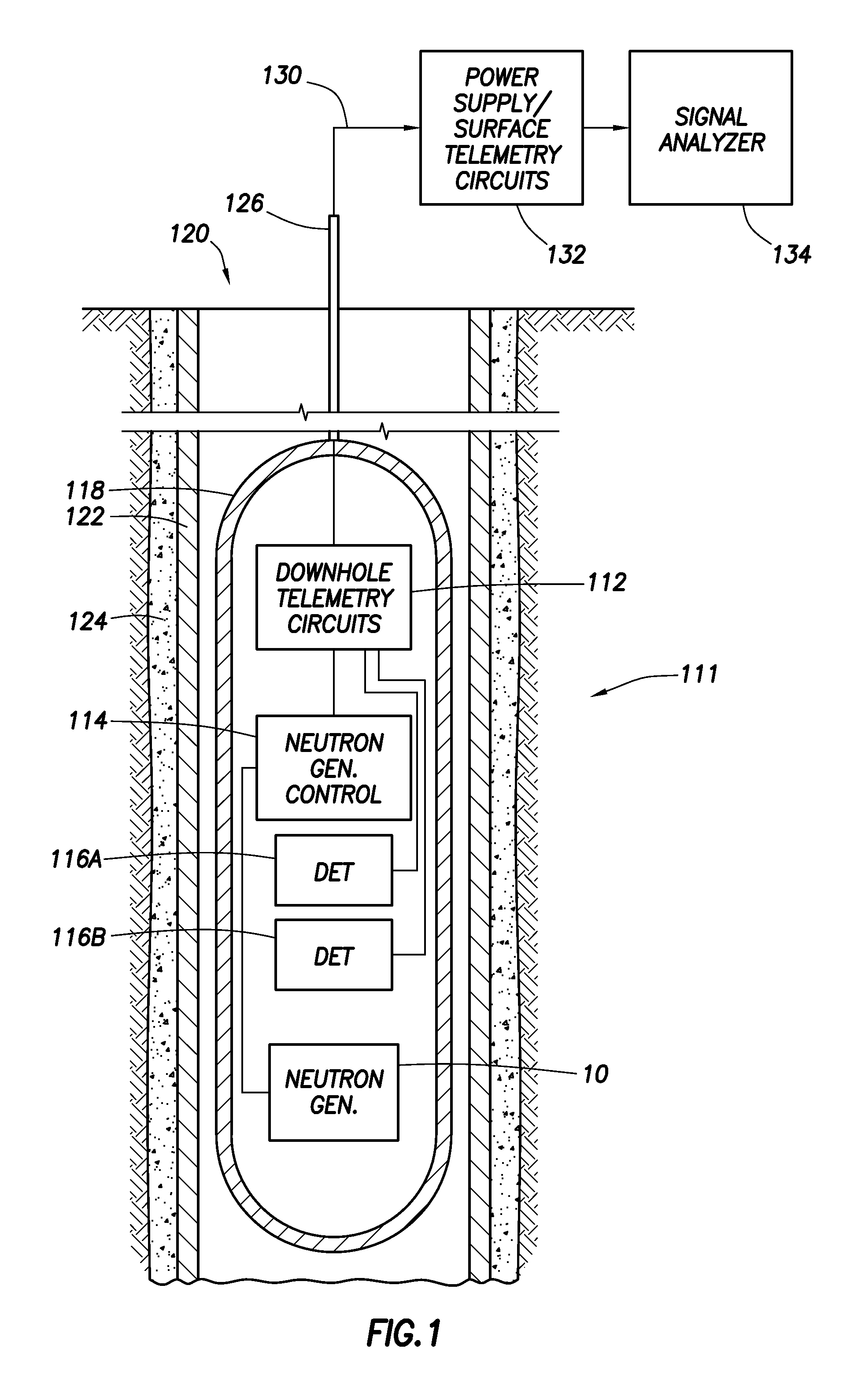
Downhole Tools Having Combined D-D and D-T Neutron Generators
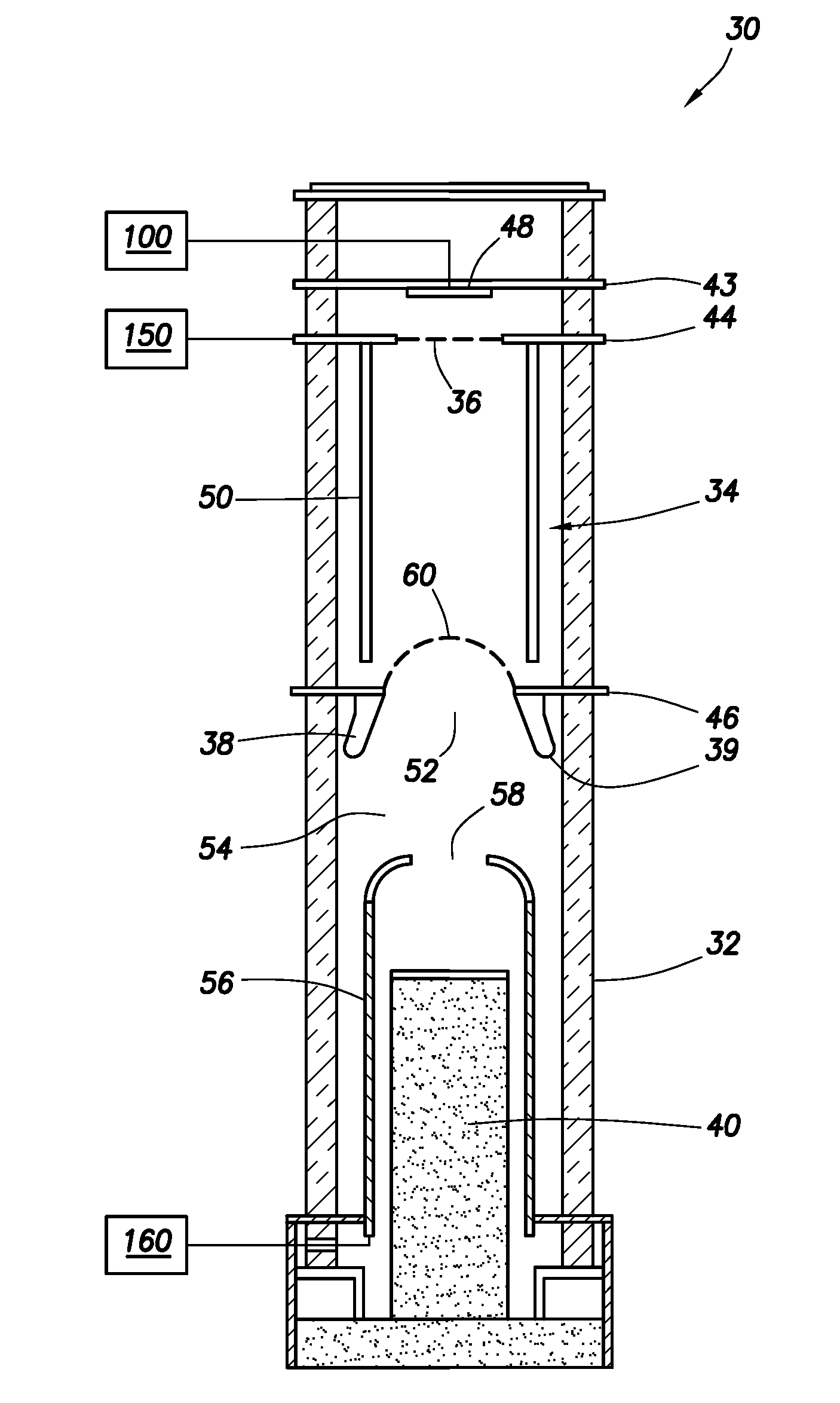
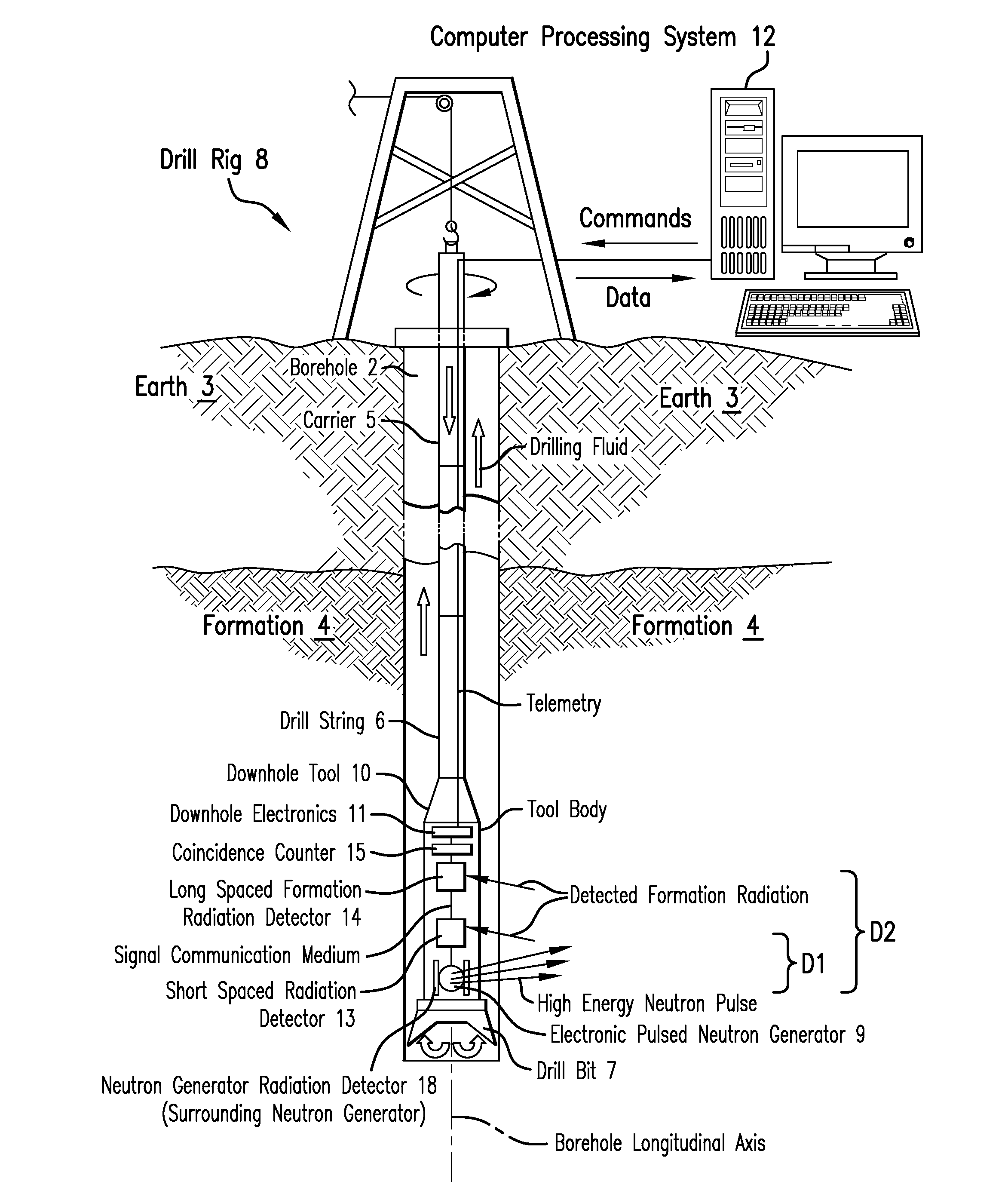
A nuclear tool includes a tool housing; a d-D neutron generator disposed in the tool housing; a d-T neutron generator disposed in the tool housing; and, optionally, a control circuit for controlling pulsing of the d-D neutron generator and the d-T neutron generator. A method for well-logging using a nuclear tool includes disposing the nuclear tool in a wellbore penetrating a formation; pulsing a d-D neutron generator to emit neutrons at a first energy level into the formation; pulsing a d-T neutron generator to emit neutrons at a second energy level into the formation; and measuring signals returning from the formation.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods and systems for determining mud flow velocity from measurement of an amplitude of an artificially induced radiation
Embodiments of the present invention relate in general to methods and apparatus for determining downhole mud flow rates and other downhole parameters. More specifically, but not by way of limitation, an embodiment of the present invention may provide a method for determining a downhole parameter that includes operating a pulsed neutron generator, detecting the activated drilling fluid at-least one known distance (d) from the pulsed neutron generator, and determining a time-of-flight (t) for the activated drilling fluid slug to travel from the pulsed neutron generator to a detection point, or between detection points
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Downhole Tools with Solid-State Neutron Monitors
ActiveUS20090057545A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesNuclear radiation detectionProximateEngineering
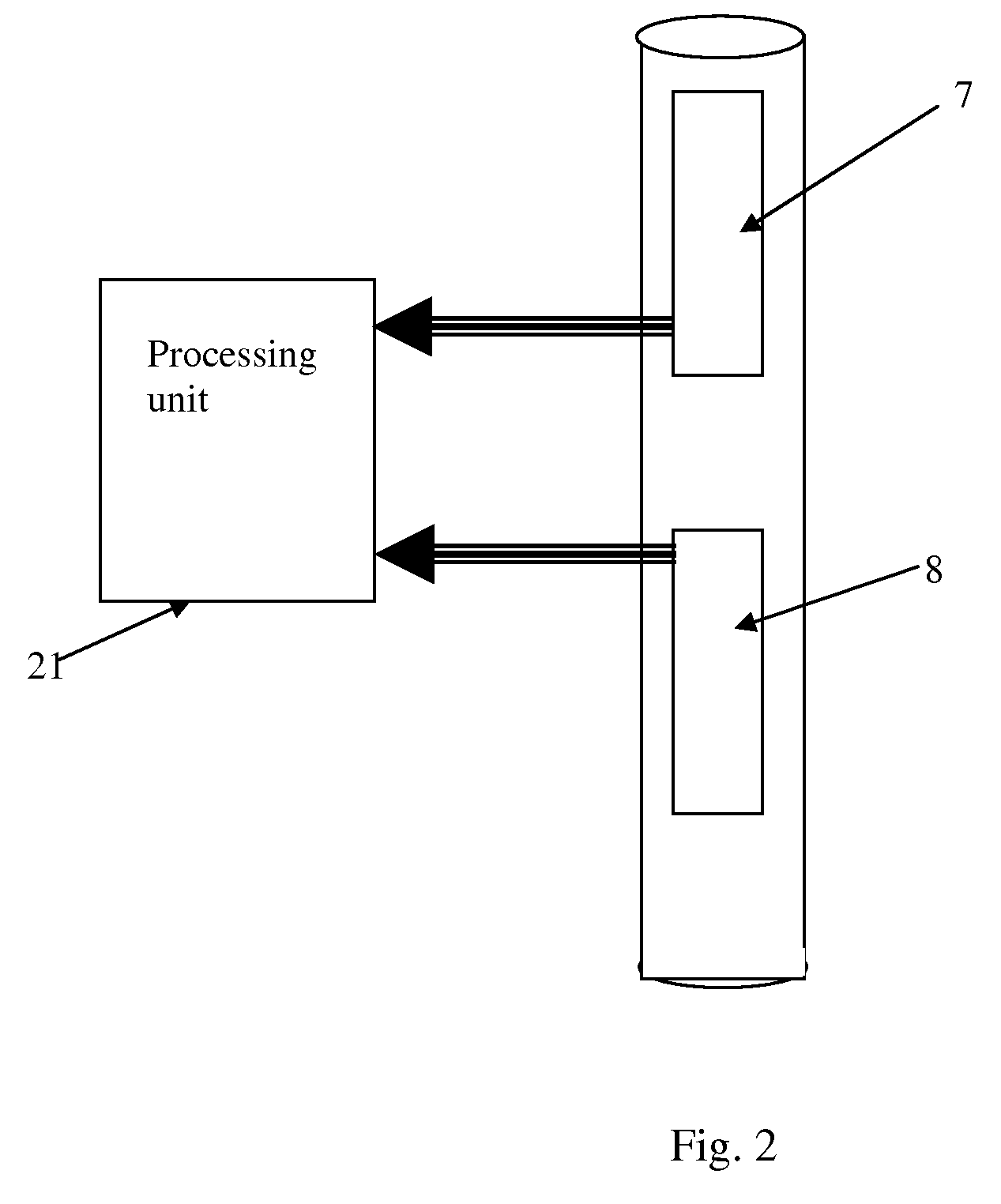
A nuclear tool includes a tool housing; a neutron generator disposed in the tool housing; and a solid-state neutron monitor disposed proximate the neutron generator for monitoring the output of the neutron generator. A method for constructing a nuclear tool includes disposing a neutron generator in a tool housing; and disposing a solid-state neutron monitor proximate the neutron generator for monitoring the output of the neutron generator. A method for logging a formation includes disposing a nuclear tool in a wellbore penetrating the formation, wherein the nuclear tool comprises a neutron generator and a solid-state neutron monitor disposed proximate the neutron generator; generating neutrons from the neutron generator; monitoring neutrons generated by the neutron generator using the solid-state neutron monitor; detecting signals generated from the neutrons traveling in the formation; and correcting the detected signals, based on signal strength detected by the solid-state neutron monitor, to produce corrected signals.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Compound isotope target assembly for production of medical and commercial isotopes by means of spectrum shaping alloys
InactiveUS20090274258A1Increase local populationLow neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron captureResonance
Owner:HOLDEN CHARLES S +1
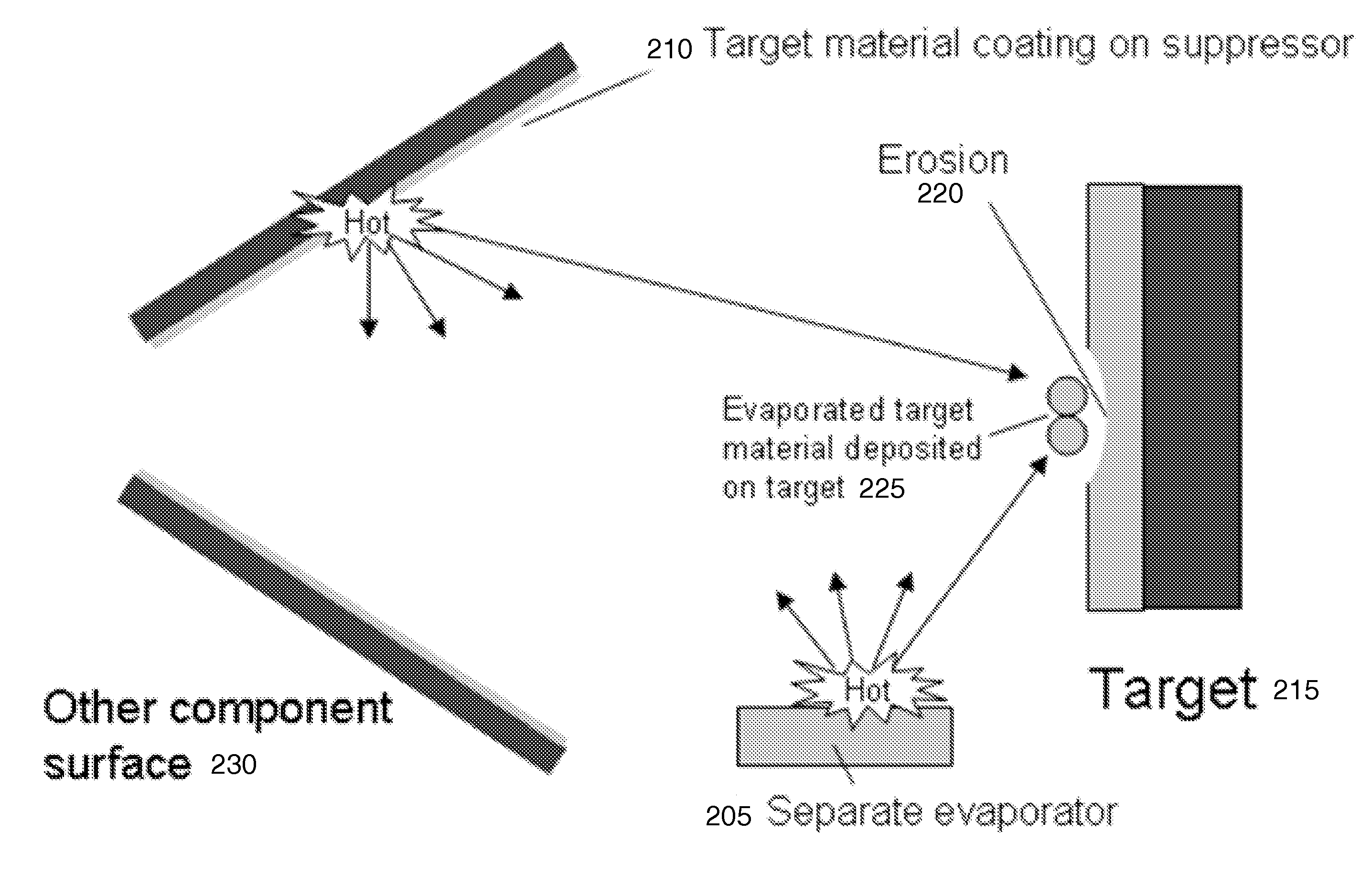
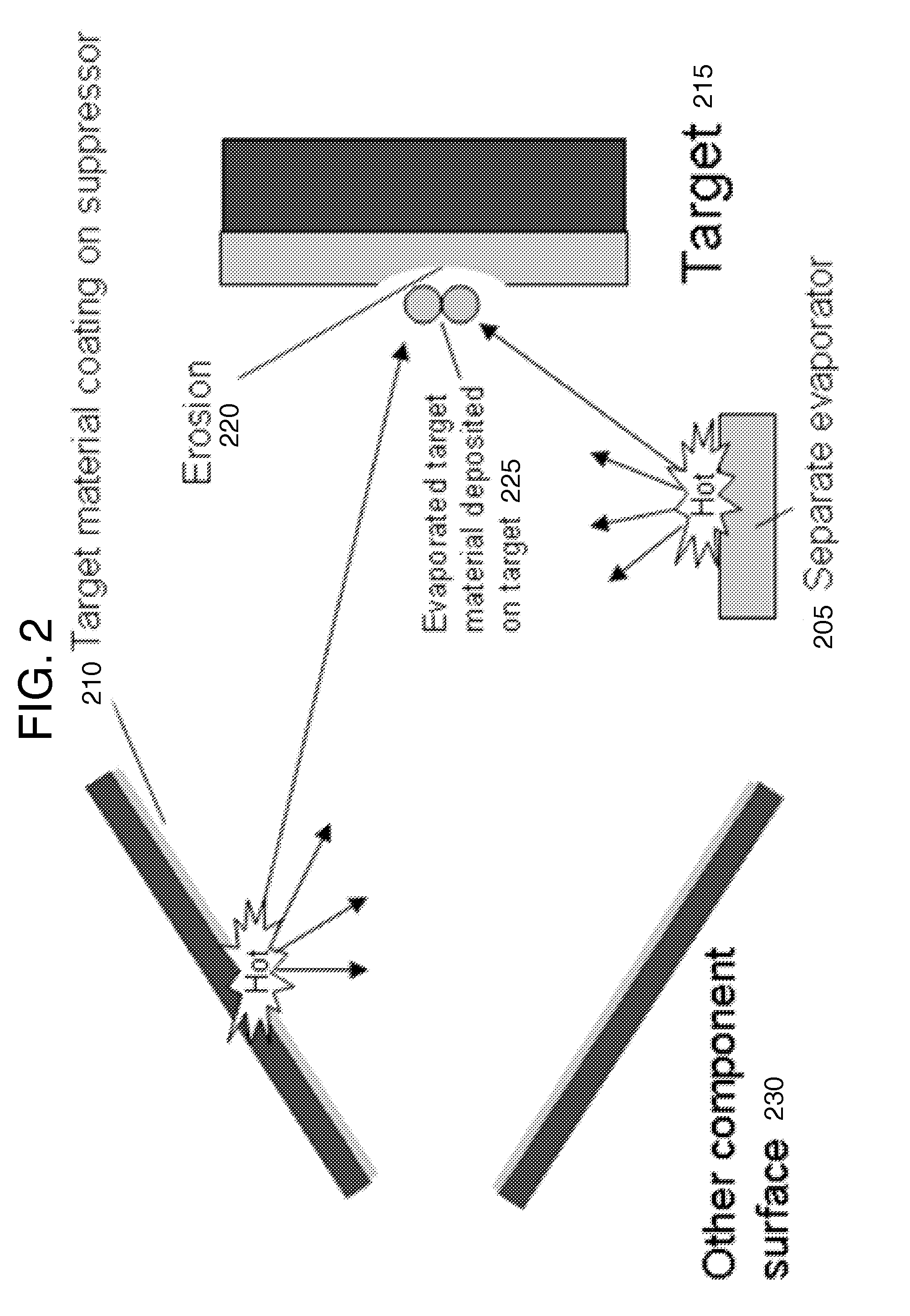
Method and system for in situ depositon and regeneration of high efficiency target materials for long life nuclear reaction devices
ActiveUS20110091000A1Maintain purityMinimize the numberNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsNeutron energy spectrumNuclear reaction
Aspects of the invention relate to several methods to deposit and regenerate target materials in neutron generators and similar nuclear reaction devices. In situ deposition and regeneration of a target material reduces tube degradation of the nuclear reaction device and covers impurities on the surface of the target material at the target location. Further aspects of the invention include a method of designing a target to generate neutrons at a high efficiency rate and at a selected neutron energy from a neutron energy spectrum.
Owner:STARFIRE IND LLC
Neutron tubes
InactiveUS7342988B2Increase surface areaHigh neutron fluxLaser detailsNuclear energy generationTarget surfaceIon beam
A neutron tube or generator is based on a RF driven plasma ion source having a quartz or other chamber surrounded by an external RF antenna. A deuterium or mixed deuterium / tritium (or even just a tritium) plasma is generated in the chamber and D or D / T (or T) ions are extracted from the plasma. A neutron generating target is positioned so that the ion beam is incident thereon and loads the target. Incident ions cause D-D or D-T (or T-T) reactions which generate neutrons. Various embodiments differ primarily in size of the chamber and position and shape of the neutron generating target. Some neutron generators are small enough for implantation in the body. The target may be at the end of a catheter-like drift tube. The target may have a tapered or conical surface to increase target surface area.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
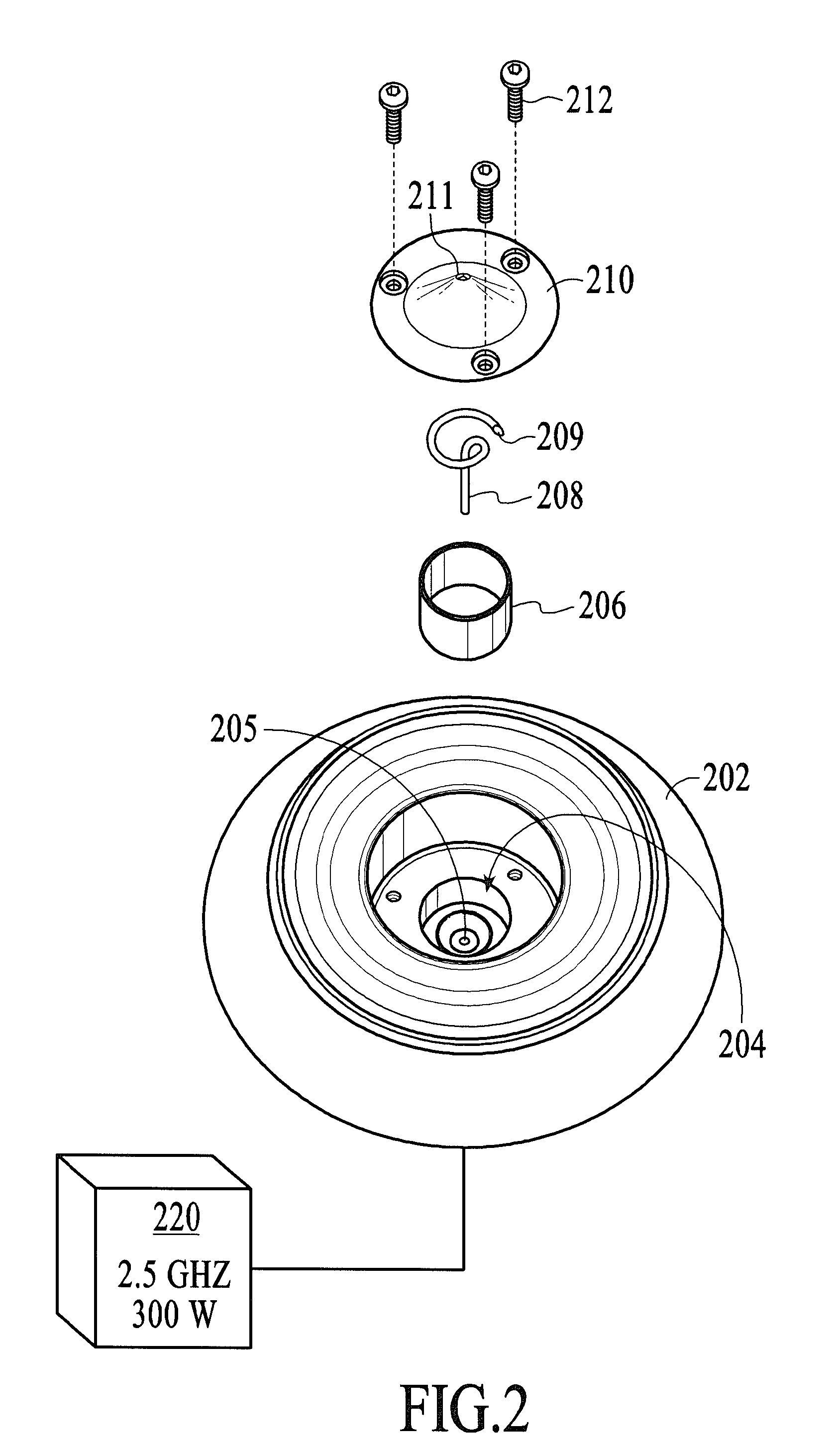
Spiral rf-induction antenna based ion source for neutron generators
InactiveUS20100066252A1Lower the volumeImprove power densityElectric arc lampsIon beam tubesHydrogenD t neutron
An ion source for the generation of hydrogen or deuterium ions is disclosed, said source suitable for the generation of D-D and D-T neutrons, wherein the body of the ion source is cylindrical, and disposed at one end of the ion source opposite the extraction plate, is a single, spiraled RF coil antenna, in which the spiraled coils are flat.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
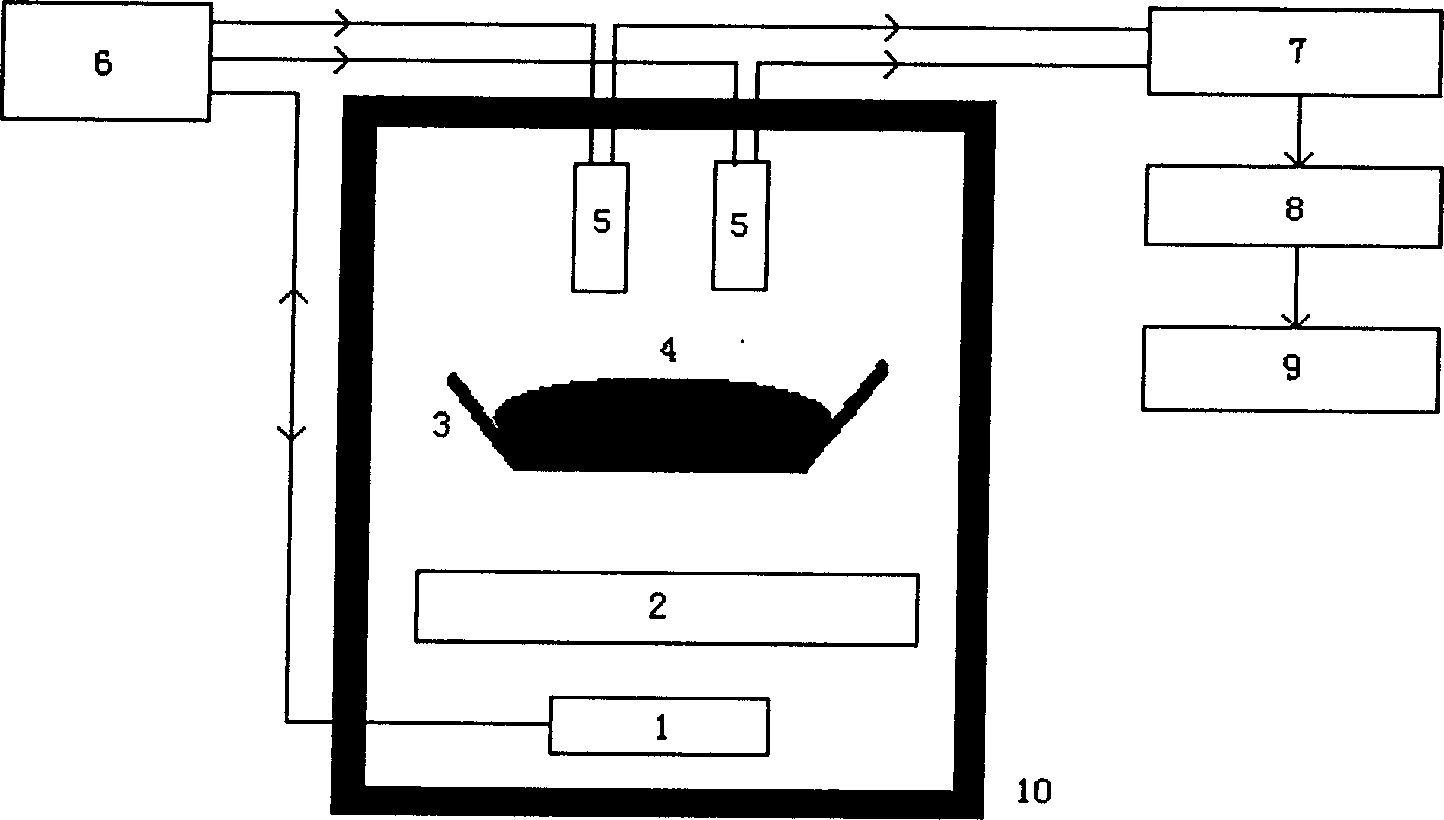
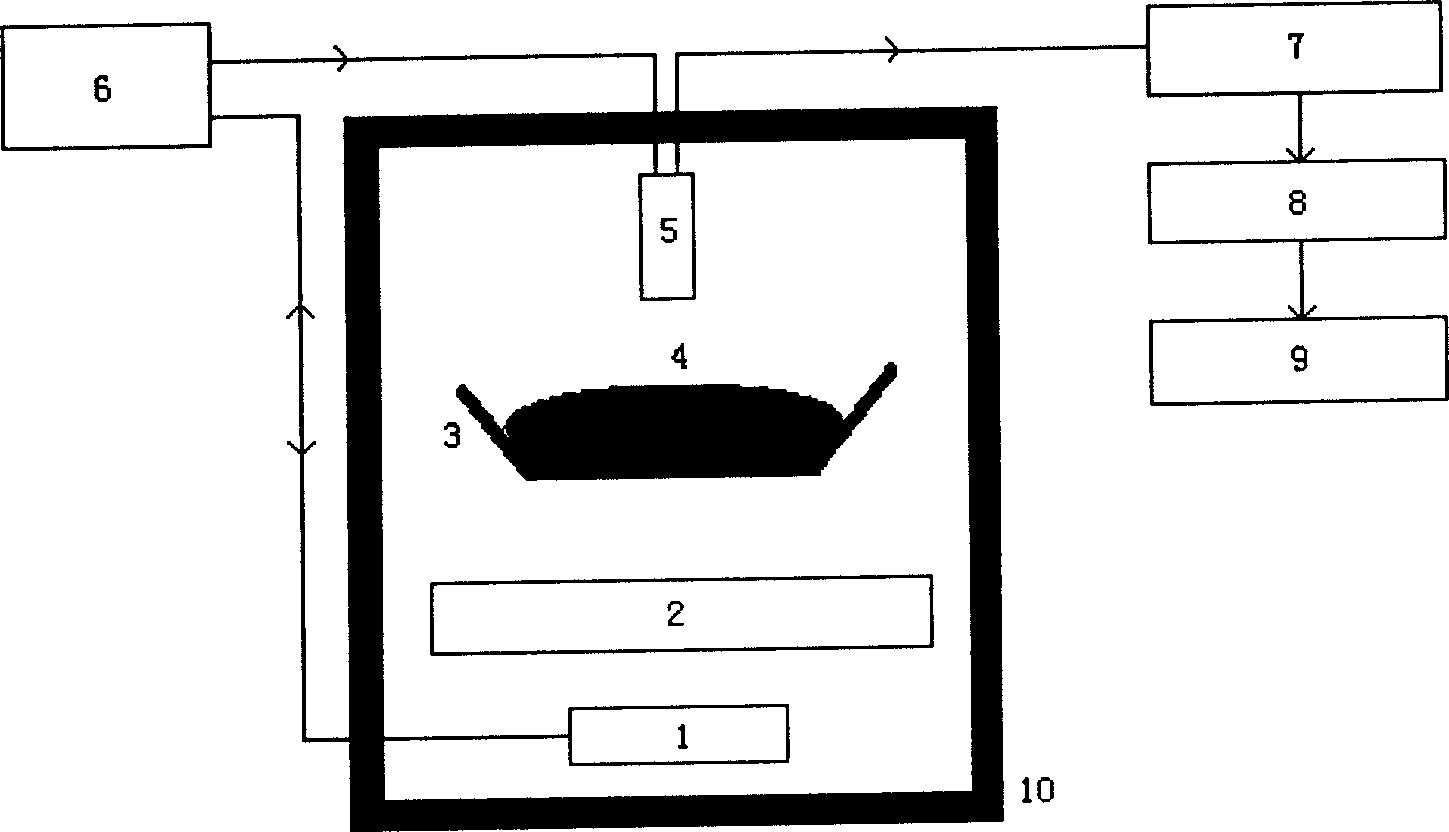
Concrete material content on-line detection system based on pulse fast heating neutron instantaneous Gamna radiation malysis tech
InactiveCN1834632AQuality improvementExtended service lifeMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationData displayData analysis system
This invention discloses pulse fast heat neutron prompt gamma cement material component online detecting system, it is aimed at status that need to online detecting cement material chemical components. It includes neutron generator, slowing down body, gamma ray detector, and complex shield safeguard system. Conveying belt crosses over the safeguard system, cement material need to be detected is on the belt, the slowing down body, neutron generator are fixed in the system and below the belt, two or more than two gamma ray detectors are fixed in the system and above the material, it is connected to digital amplifier systemthrough transmission line, the system, data getting system, data analysis system and data display system are in turn connected, so it can detect chemical components of the cement material and provide information for feed proportioning system to improve cement quality.
Owner:南京大陆中电科技股份有限公司
Methods for sourceless density downhole measurement using pulsed neutron generator
InactiveUS20130048849A1Radiation intensity measurementNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
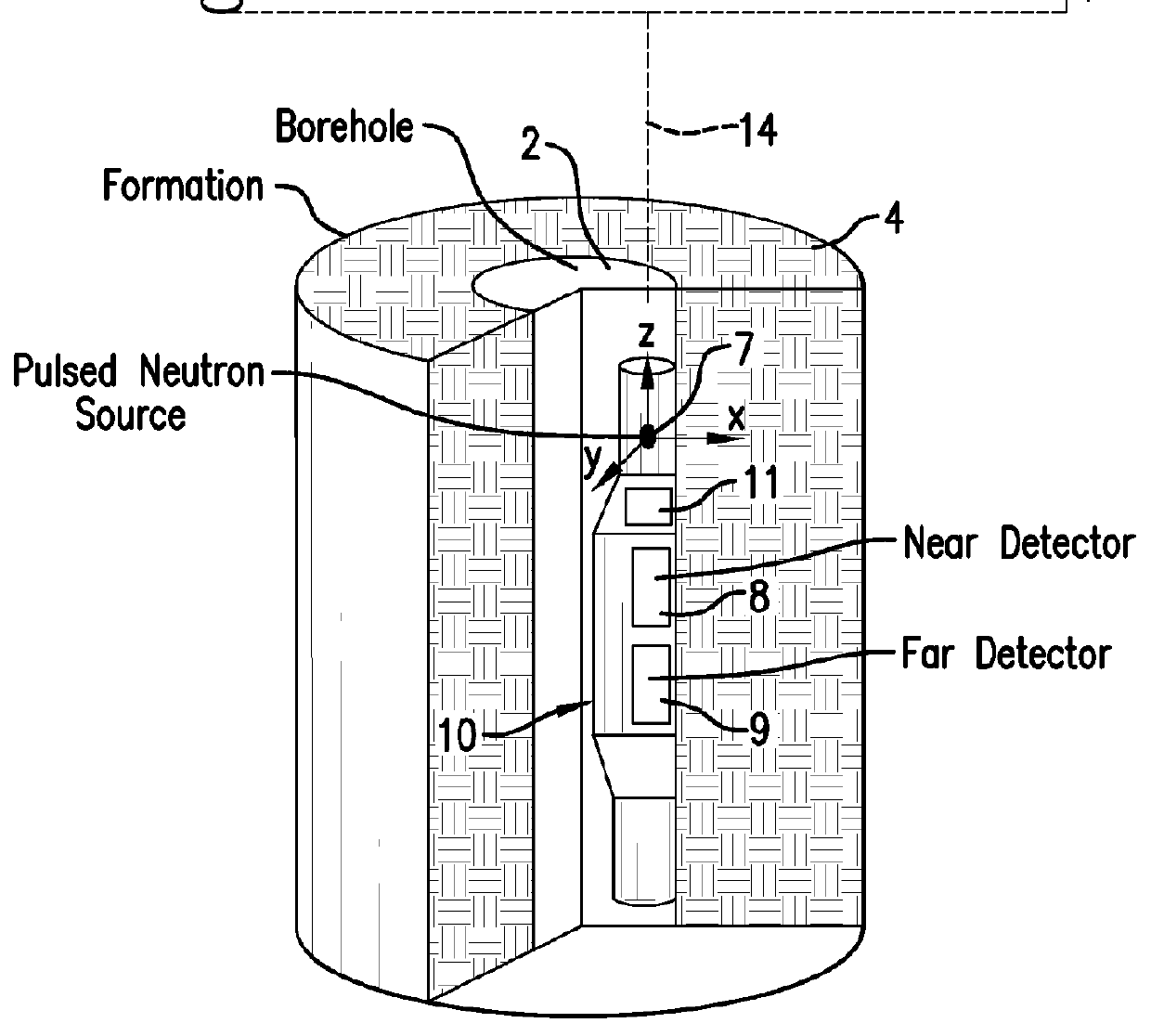
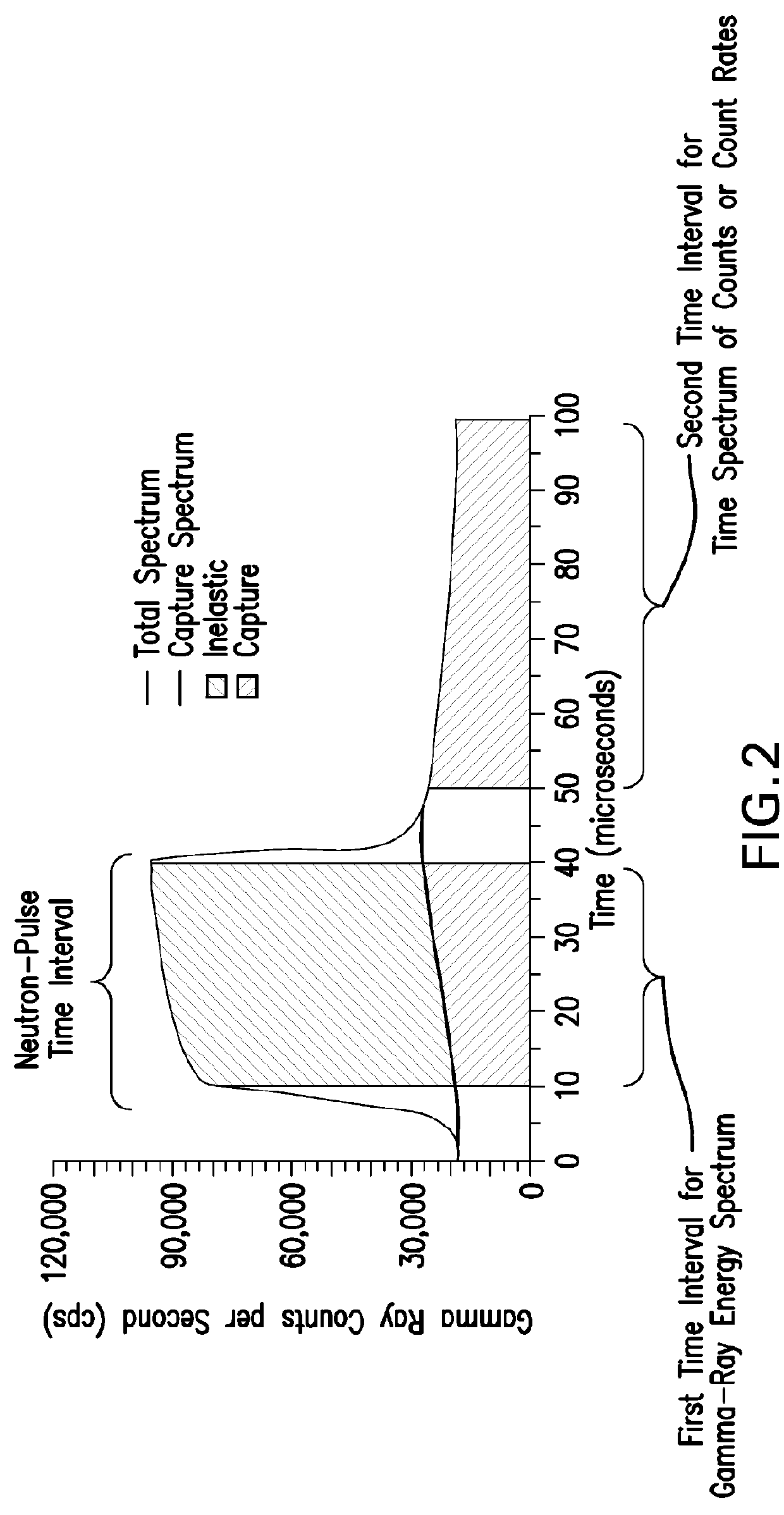
Disclosed is a method for estimating a density of an earth formation penetrated by a borehole. The method includes: emitting a pulse of fast neutrons into the formation during a neutron-pulse time interval; detecting gamma-rays due to inelastic scattering and thermal capture of the emitted neutrons in the formation to provide a gamma-ray energy spectrum due to the inelastic scattering and the thermal capture during a first time interval within the neutron-pulse time interval and to provide a time spectrum of counts or count rates due to thermal capture during a second time interval occurring after the neutron-pulse time interval; determining a macroscopic capture cross section of the formation from a decay in the time spectrum of counts or count rates; determining an elemental weight fraction from the gamma-ray energy spectrum; and estimating the density of the formation using the macroscopic capture cross section and the elemental weight fraction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
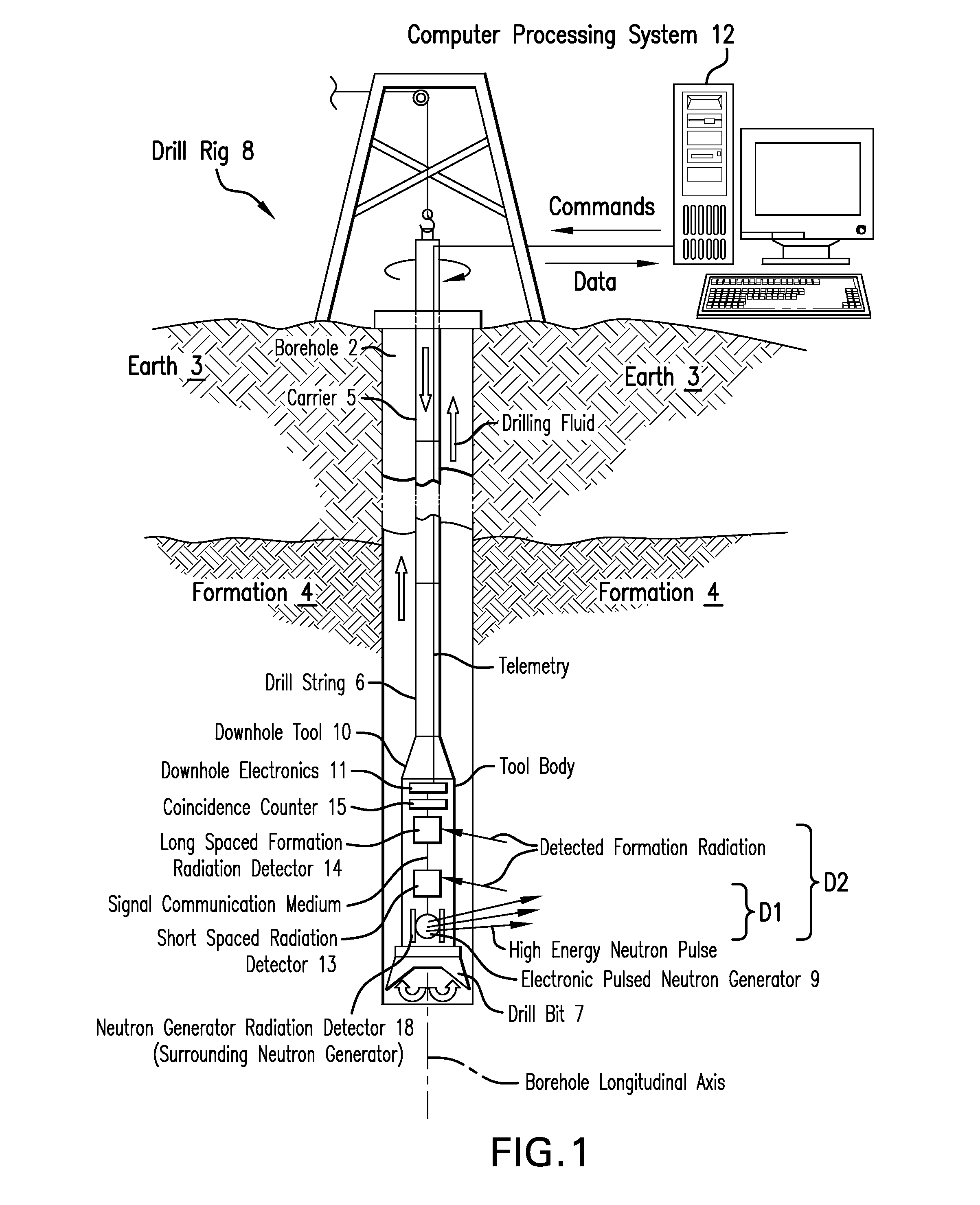
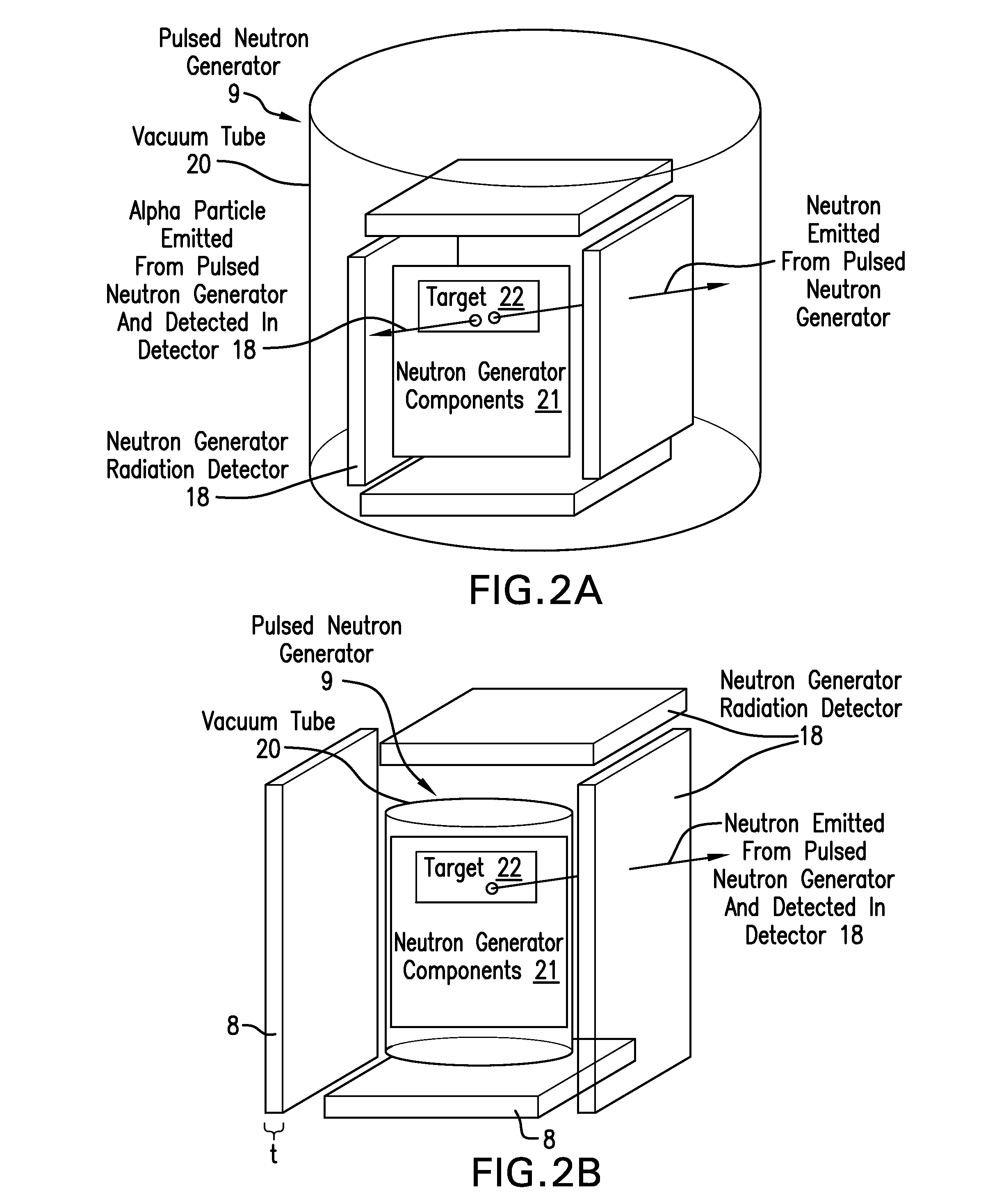
Measurement technique utilizing novel radiation detectors in and near pulsed neutron generator tubes for well logging applications using solid state materials
ActiveUS20150346382A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesNuclear radiation detectionWell loggingCrystal structure
An apparatus for estimating a property of an earth formation includes a pulsed neutron generator configured to emit a pulse of neutrons, a formation radiation detector configured to detect radiation emitted from the formation due to interactions with the pulse of neutrons, and a neutron generator radiation detector having a crystal structure and configured to detect a radiation particle emitted from the pulsed neutron generator and to provide a location within the neutron radiation detector at which the particle was detected. The crystal structure includes a plurality of detection cells, each detection cell having at least two electrically conducting columns with an applied potential difference such that electrons generated in the crystal structure by interaction with the radiation particle are collected by at least one of the electrically conducting columns to provide detection locations. A processor estimates the property using the detected formation radiation and the detection locations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
On-line detection device for component of belt transport sinted mineral material based on PGNAA technology
InactiveCN1831522AHigh speedHigh precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEngineeringThrough transmission
An on - line device for detecting composition of agglomerate material conveyed by belt based on PGNAA technique is prepared as passing the conveying belt through composite shielding protection system, setting said material on conveying belt, setting moderator and neutron generator in composite shielding protection system and under conveying belt, setting gamma ray detector in composite shielding protection system and above agglomerate material, connecting set detector to electronic amplification unit through transmission wire then connecting amplification unit to data collection unit and computer in sequence.
Owner:能能网络科技股份有限公司
Apparatus and method for generating medical isotopes
ActiveUS20130142296A1Optimize geometryImprove cooling effectFuel elementsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNeutron moderatorIsotope
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Contraband detection system
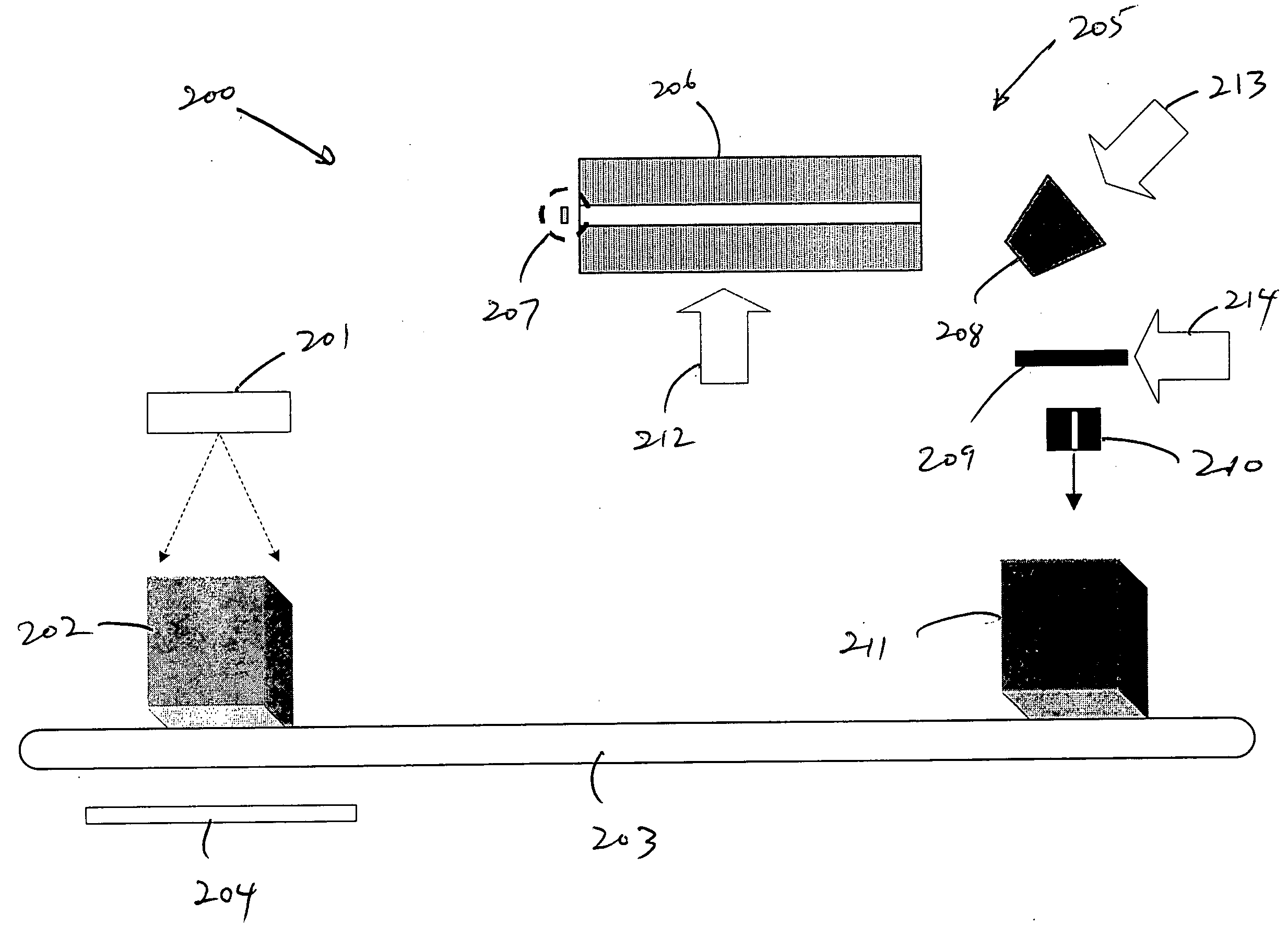
A compact contraband detection system having a radiography device which pre-screens an article subject to inspection to locate regions of interest which may then be further interrogated with a pulsed radiation generator, such as a pulsed fast neutron generator. The pulsed radiation generator includes an integrated particle generator-accelerator having a charged particle generator connected to a compact linear accelerator which produces, injects, and accelerates a charged particle beam. A beam target is provided in the path of the accelerated beam to generate a pulse of interrogating radiation which is directed to the article for interrogation.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Neutron tubes
InactiveUS20080080659A1Increase surface areaHigher neutron fluxNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsTarget surfaceIon beam
A neutron tube or generator is based on a RF driven plasma ion source having a quartz or other chamber surrounded by an external RF antenna. A deuterium or mixed deuterium / tritium (or even just a tritium) plasma is generated in the chamber and D or D / T (or T) ions are extracted from the plasma. A neutron generating target is positioned so that the ion beam is incident thereon and loads the target. Incident ions cause D-D or D-T (or T-T) reactions which generate neutrons. Various embodiments differ primarily in size of the chamber and position and shape of the neutron generating target. Some neutron generators are small enough for implantation in the body. The target may be at the end of a catheter-like drift tube. The target may have a tapered or conical surface to increase target surface area.
Owner:LEUNG KA NGO +2
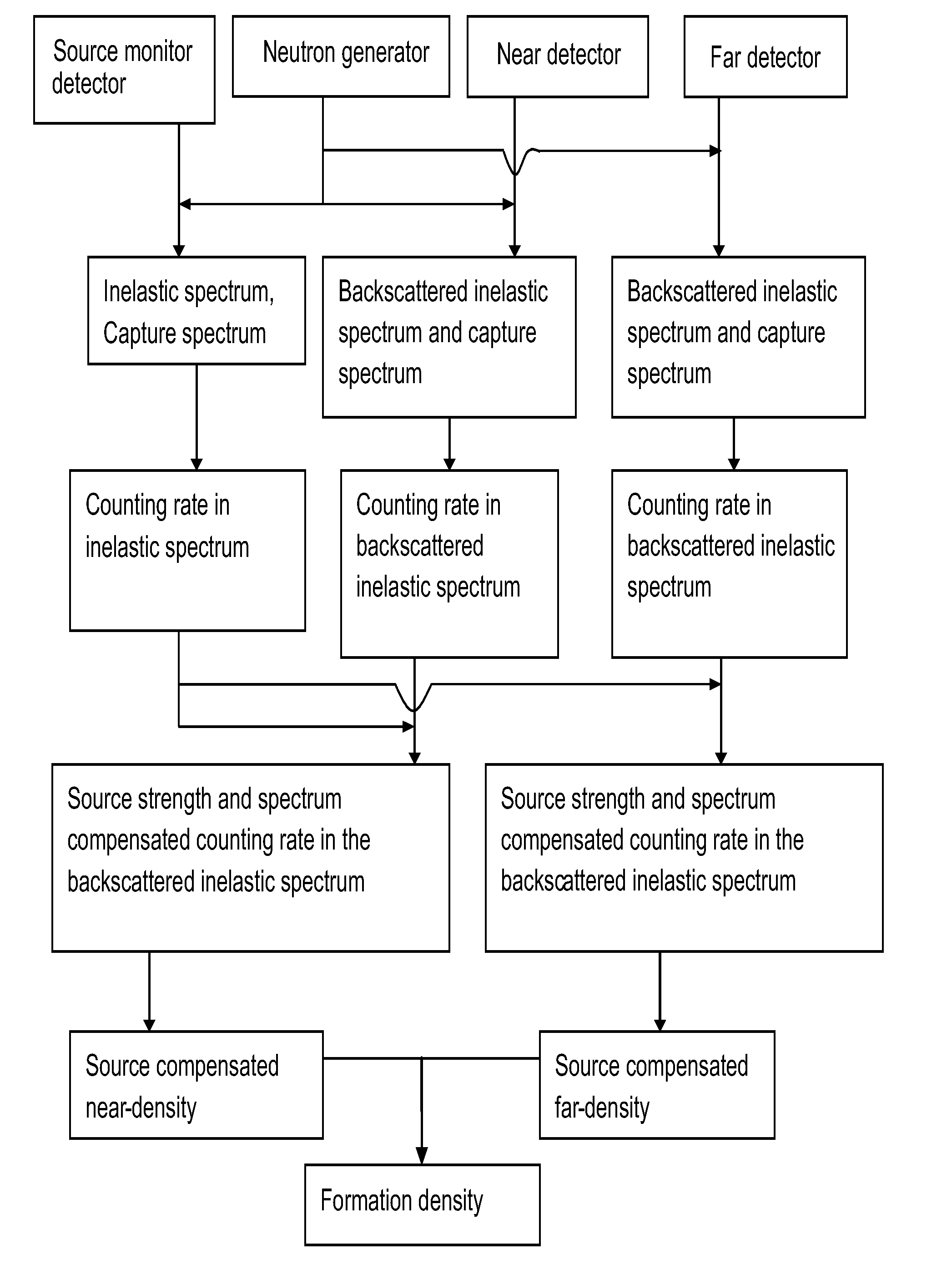
Source compensated formation density measurement method by using a pulsed neutron generator
A downhole instrument for estimating density of sub-surface materials includes: a neutron source, a source monitoring detector, a near detector and a far detector. Each of the detectors may be coupled to an electronics unit adapted for receiving a detection signal from each of the detectors and compensating the detection signal for at least one of the near detector and the far detector according to the detection signal of the source monitoring detector. A method for estimating density is provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Portable low energy neutron source for high sensitivity material characterization
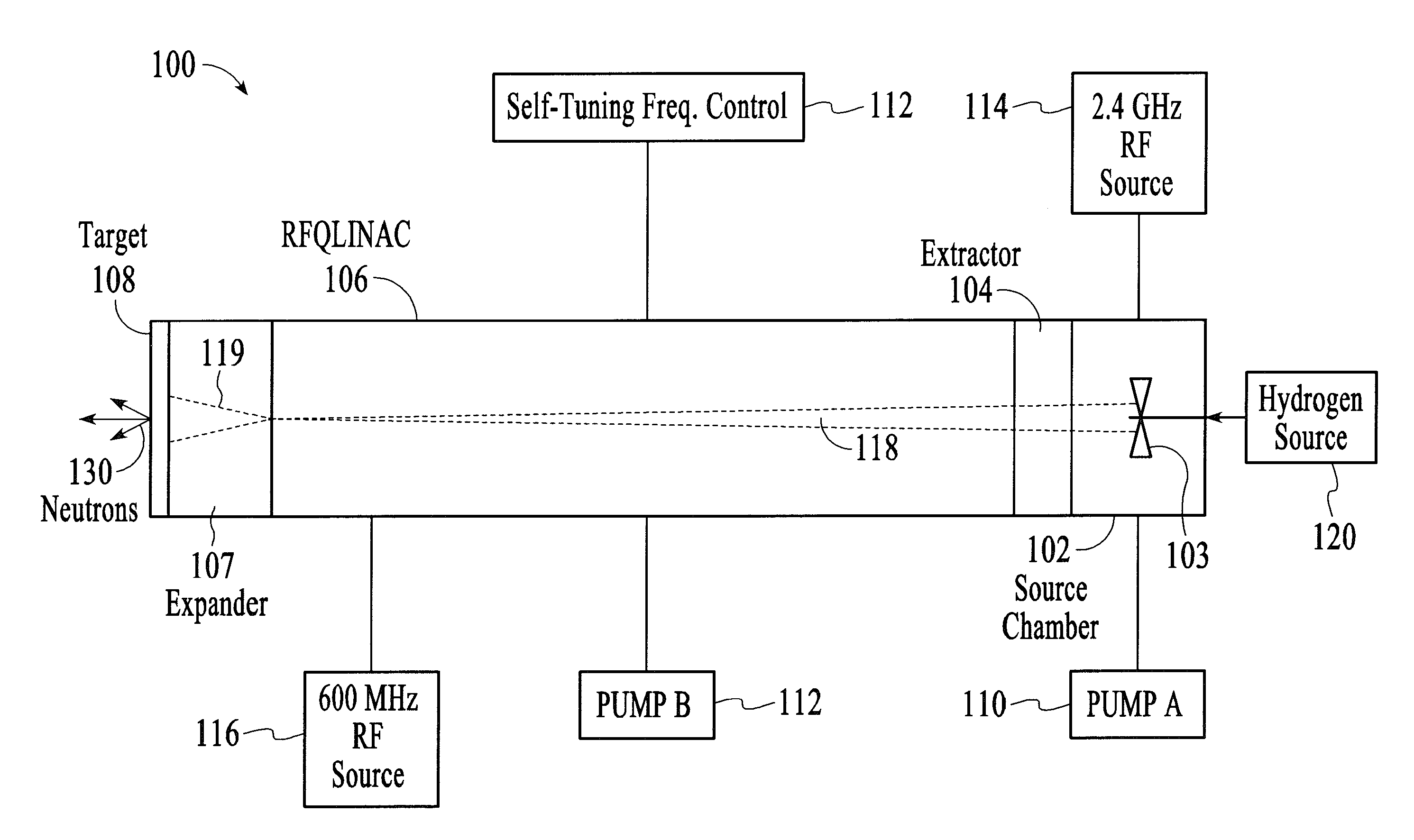
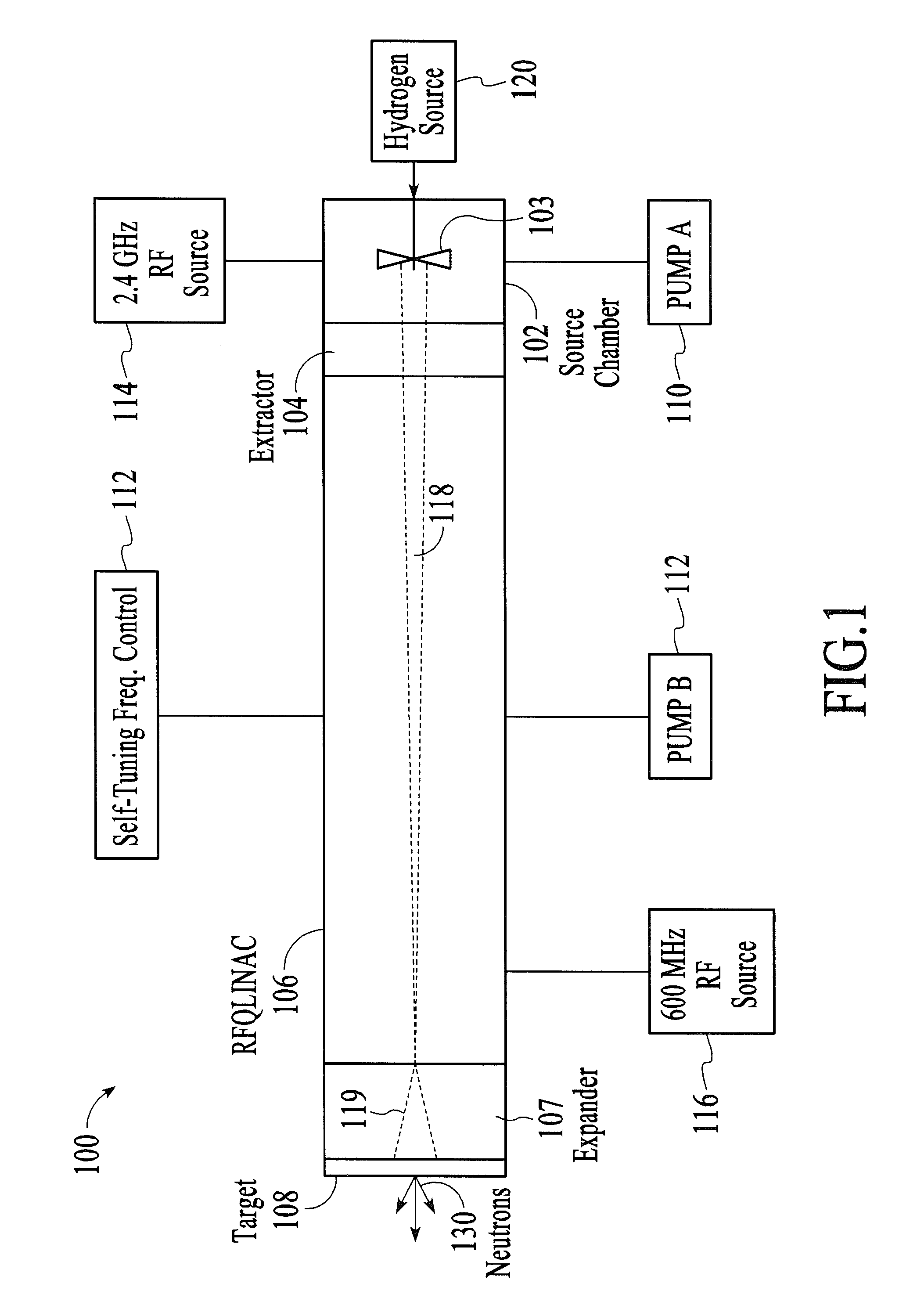
InactiveUS20110176648A1Suitable for useReduce gas loadConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsDirect voltage acceleratorsLithiumHydrogen
A portable neutron generator includes a Radio Frequency Quadrupole linear accelerator designed to accelerate charged particles of hydrogen (protons) to energies useful for producing neutrons with the (p,n) reaction on lithium. The ion source is driven by a coaxial feed and a spiral antenna to couple the microwave power into the plasma. The linear accelerator is driven by a 600 MHz pulsed RF power supply. A differential pumping scheme is used to balance the need for a high gas load on the ion source end and good vacuum on the accelerator end.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Low power neutron generators
A neutron generator and method of constructing the same. The generator includes a grid configured to produce an ionizable gas when heated by electrons impinging thereon. A cathode emits electrons to heat the grid and to collide with produced ionizable gas atoms to generate ions. Neutrons are generated from a collision of ions impinging on a target in the generator. A tool for subsurface use incorporating the neutron generator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Neutron cement multi-element analyzer
InactiveCN1632544AQuality improvementLow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationShieldingNeutron irradiationNuclear reaction
This invention relates to a cement multi-element analysis device. The neutron multi-element analysis device uses the neutron generator in the D-D reaction as neutron source and emits rapid neutrons of 2.5 Mev. The neutron reacts with the cement element to generate multi-nuclear reaction with different energy radiation gamma rays. The gamma ray detector is to detect the r rays generated by the elements in the cements. The r signals are through main amplifier and are transmitted to the micro machine for monitoring. It uses multi-path gamma spectrum device to test the area of the characteristics gamma ray peak and gives the relative nucleus content through test formula.
Owner:吉林省科仑辐射技术开发有限公司
Neutron generator
InactiveUS20110169492A1Low efficiencyLow atomic to molecular ion ratio of ionNanotechElectric discharge tubesPower gridIonization
A neutron generator includes an ion source disposed in a pressurized environment containing an ionizable gas. The ion source includes a substrate with a bundle of carbon nanotubes extending therefrom. The ends of the nanotubes are spaced from a grid. Ion source voltage supply circuitry supplies a positive voltage potential between the substrate and the grid of the ion source to cause ionization of the ionizable gas and emission of ions through the grid. An ion accelerator section is disposed between the ion source and a target. The ion accelerator section accelerates ions that pass through the grid towards the target such that collisions of the ions with the target cause the target to generate and emit neutrons therefrom. The ion source, accelerator section and target are housed in a sealed tube and preferably the carbon nanotubes of the bundle are highly ordered with at least 106 carbon nanotubes per cm2 that extend in a direction substantially parallel to the central axis of the tube. The neutron generator provides gas ionization at much higher atomic to molecular ratio that the prior art, which allows for small compact size designs suitable for logging tools that are used in space-constrained downhole environments.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Pulsed neutron generator
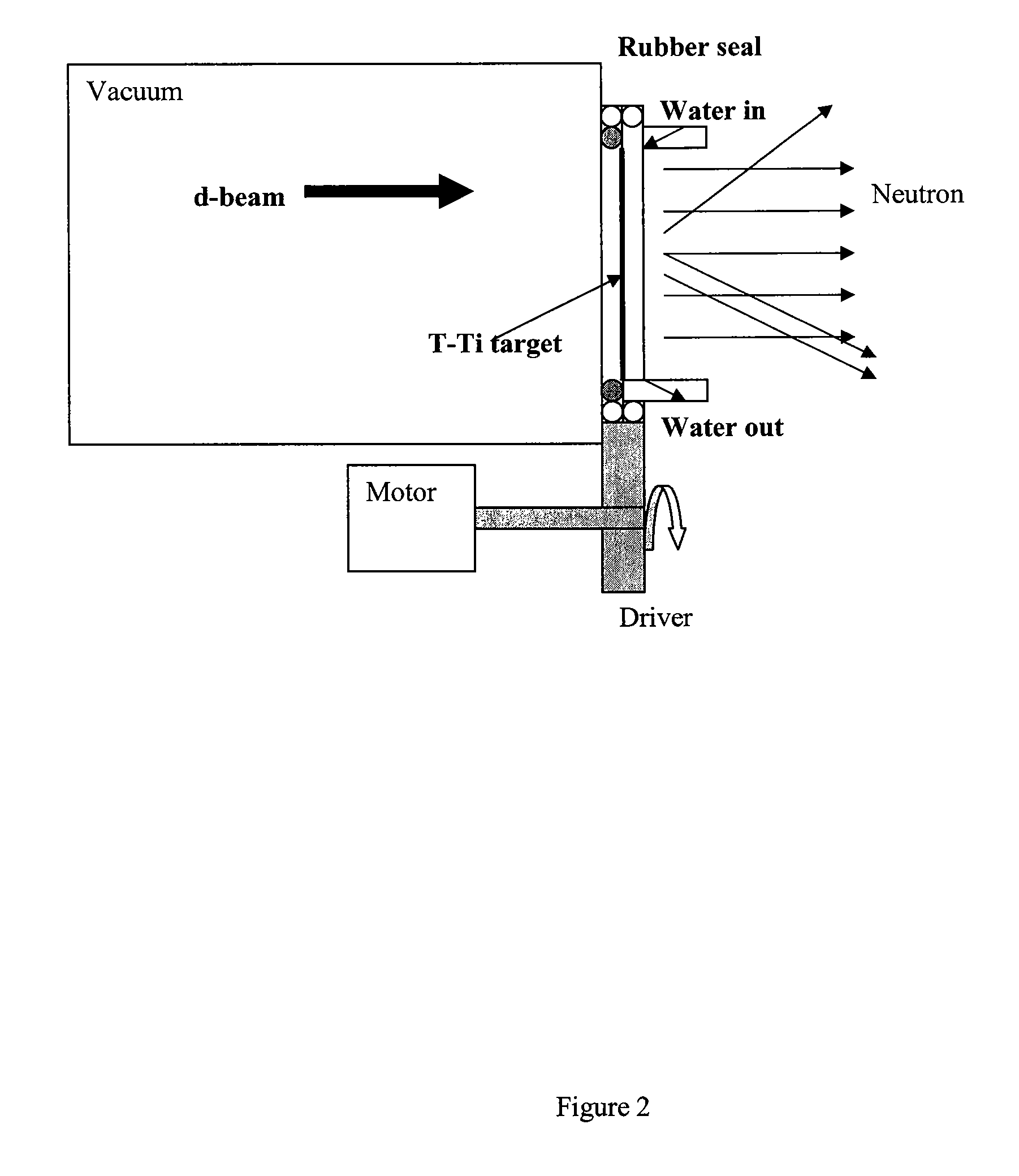
The present invention provides a pulsed neutron generator. In a high vacuum and high pressure ceramic tube, when a trigger pulse is added between the source trigger pole and cathode of vacuum arc ion, the deuterium atom is ionized and the initial plasma is diffused, such that the anode and the cathode of the ion source is conducted, the arc current is formed, and the high density plasma is generated. Under the action of accelerating the high pressure, the deuterium ion beam interacts with the tritium titanium target, the deuterium tritium reaction produces, and the pulsed neutron with the energy of 14 MeV is generated. A circular magnetic field is set up at the lead pole of the vacuum arc ion source, which can focus on the formation of the deuterium ion, increase the deuterium ion beam to the target, improve the pulsed neutron yield; The combination of a dry pump, a molecular pump, an ion pump and an air pump is used to improve the vacuum degree of the system, and reduce the loss of deuterium ion beam in the transmission process. The aluminum film with the thickness of 400 nm is coated on the surface of the tritium titanium target, which prevents the heavy ion from reaching the tritium target, and reduces the damage of the target.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
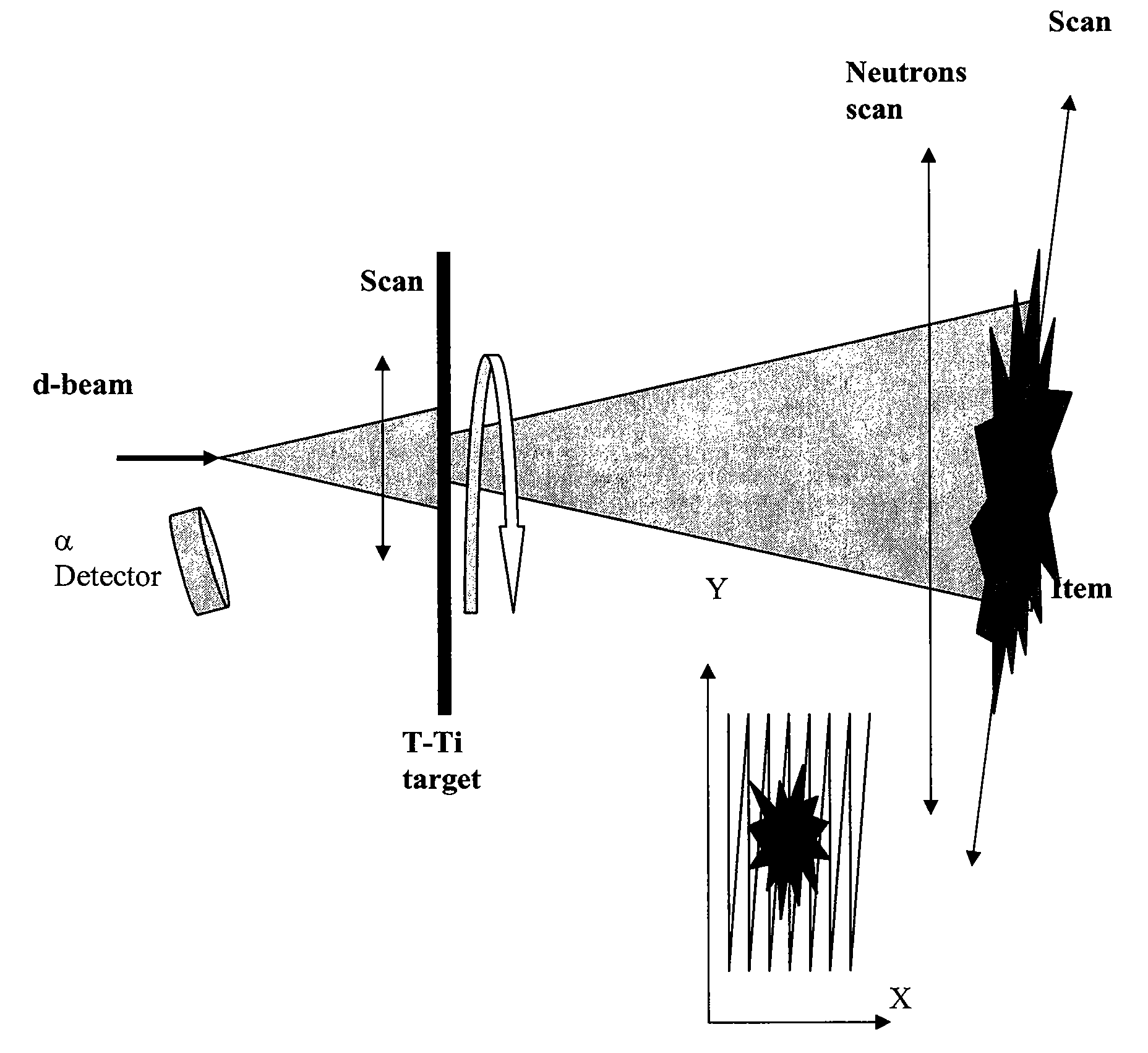
Explosives detection by directional fast neutron beams scan with associated particles
ActiveUS7420175B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsOperation modeNeutron yield
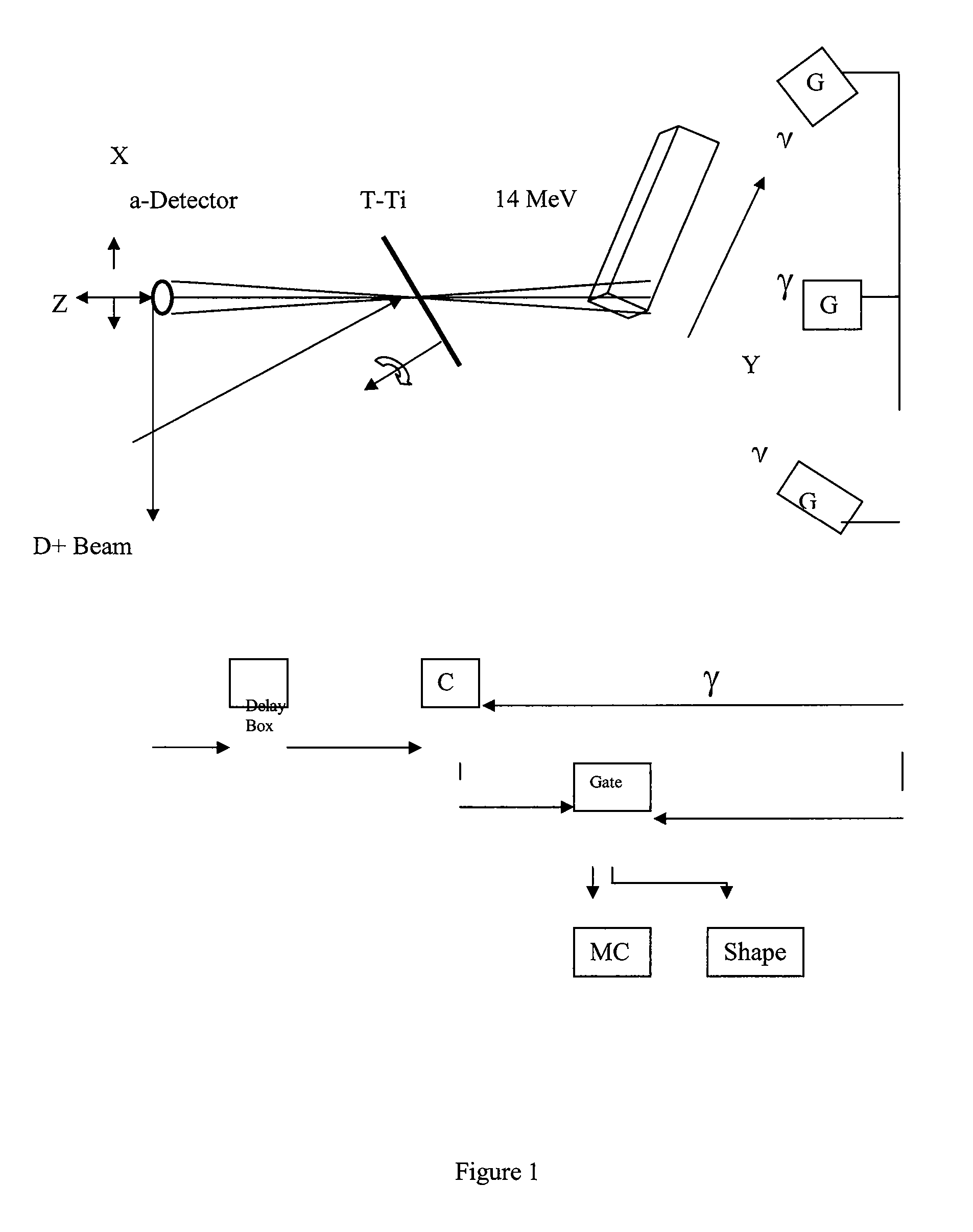
This invention is related to equipment and techniques for fast neutron activation analysis of explosives and / or other warfare agent. The techniques are based on 14 MeV fast neutrons from D-T fusion reaction, the kinematics of the nuclear reaction and fast coincidence between α-particles of the D-T reaction and γ-quanta from fast neutron induced reactions. A fast neutron generator with effective target cooling and different operation modes provides high neutron yield, long life, and simple maintenance of the equipment and good geometric resolution of the directional neutron beam. High positional resolution of the directionally scanning neutron beam, high time resolution of the coincidence and high neutron yield provide the real time robust screen of explosives with high speed and / or high sensitivity, flexibility for big and small items and overall high probability of detection (PD) and low probability of false alarms (PFA). The remote video scan device also has zooming capability to change solid angle.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Method of improving the safety of accelerator coupled hybrid nuclear systems, and device for implementing same
InactiveUS20070064859A1Reduce the required powerReduce intensityConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationOperating pointNuclear reactor
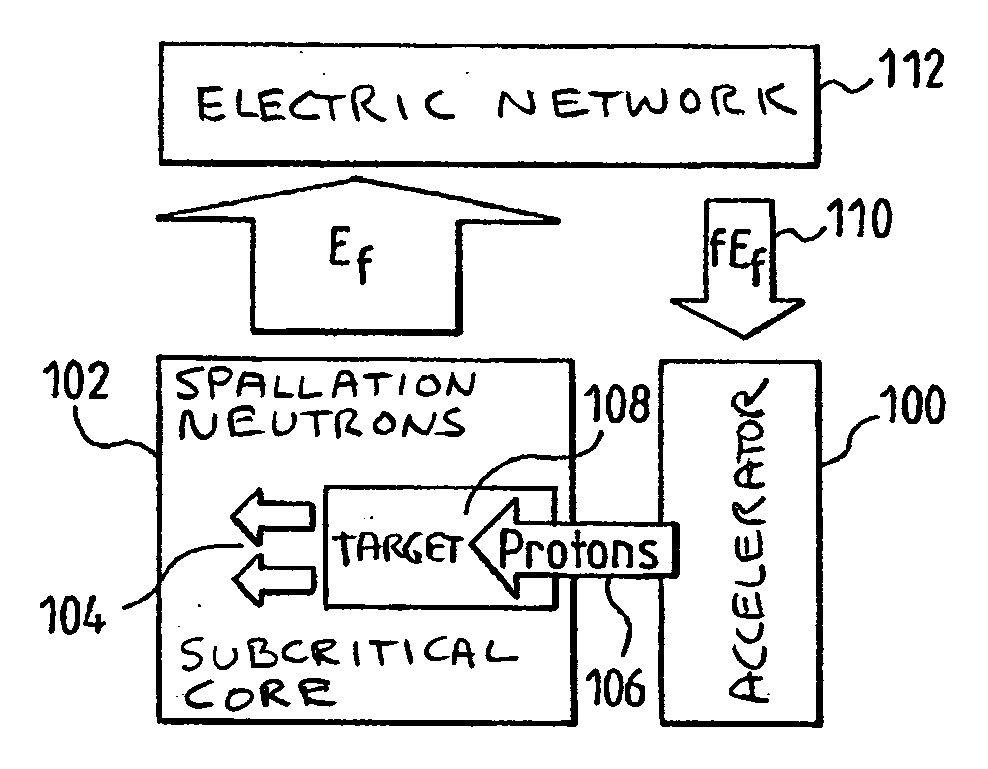
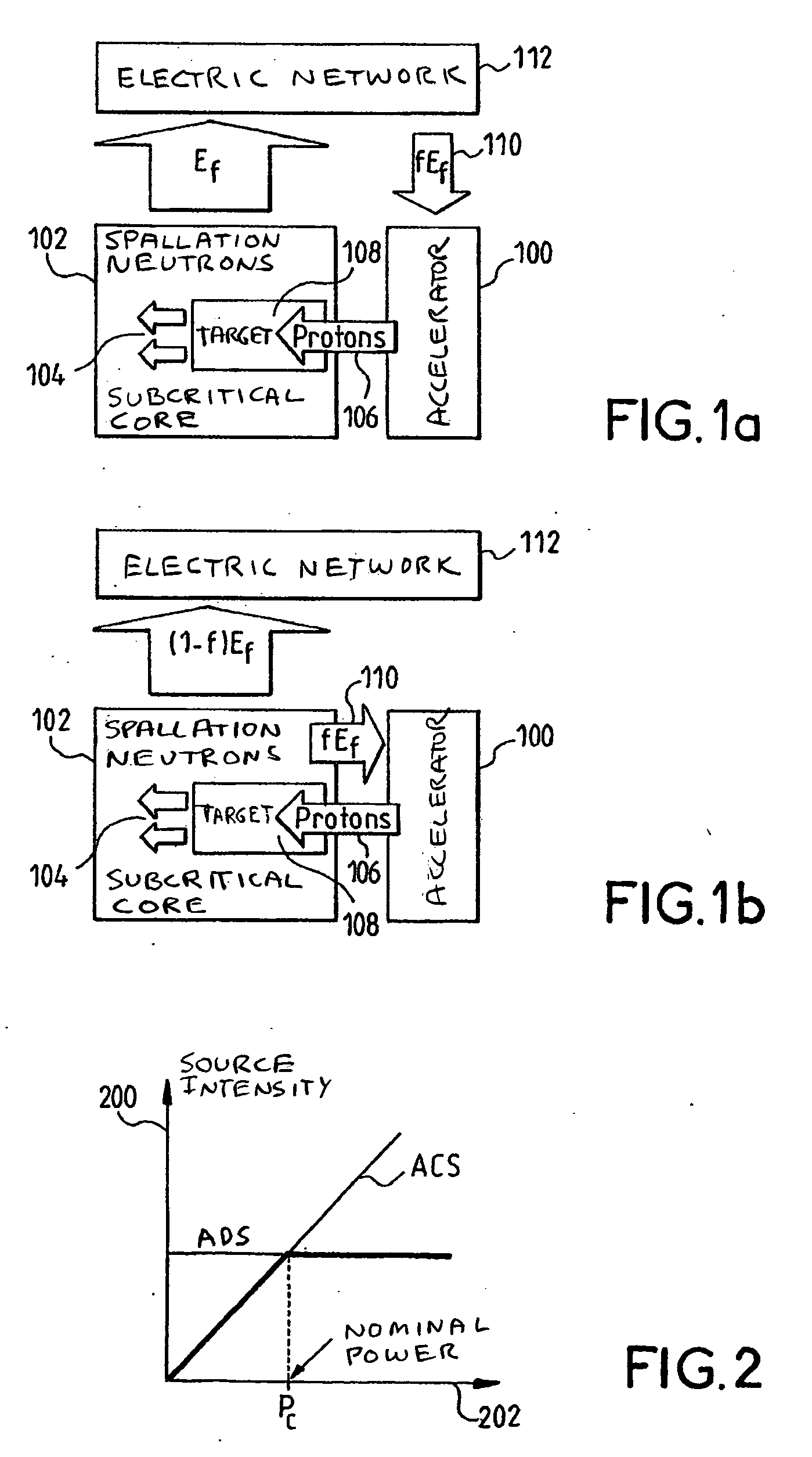
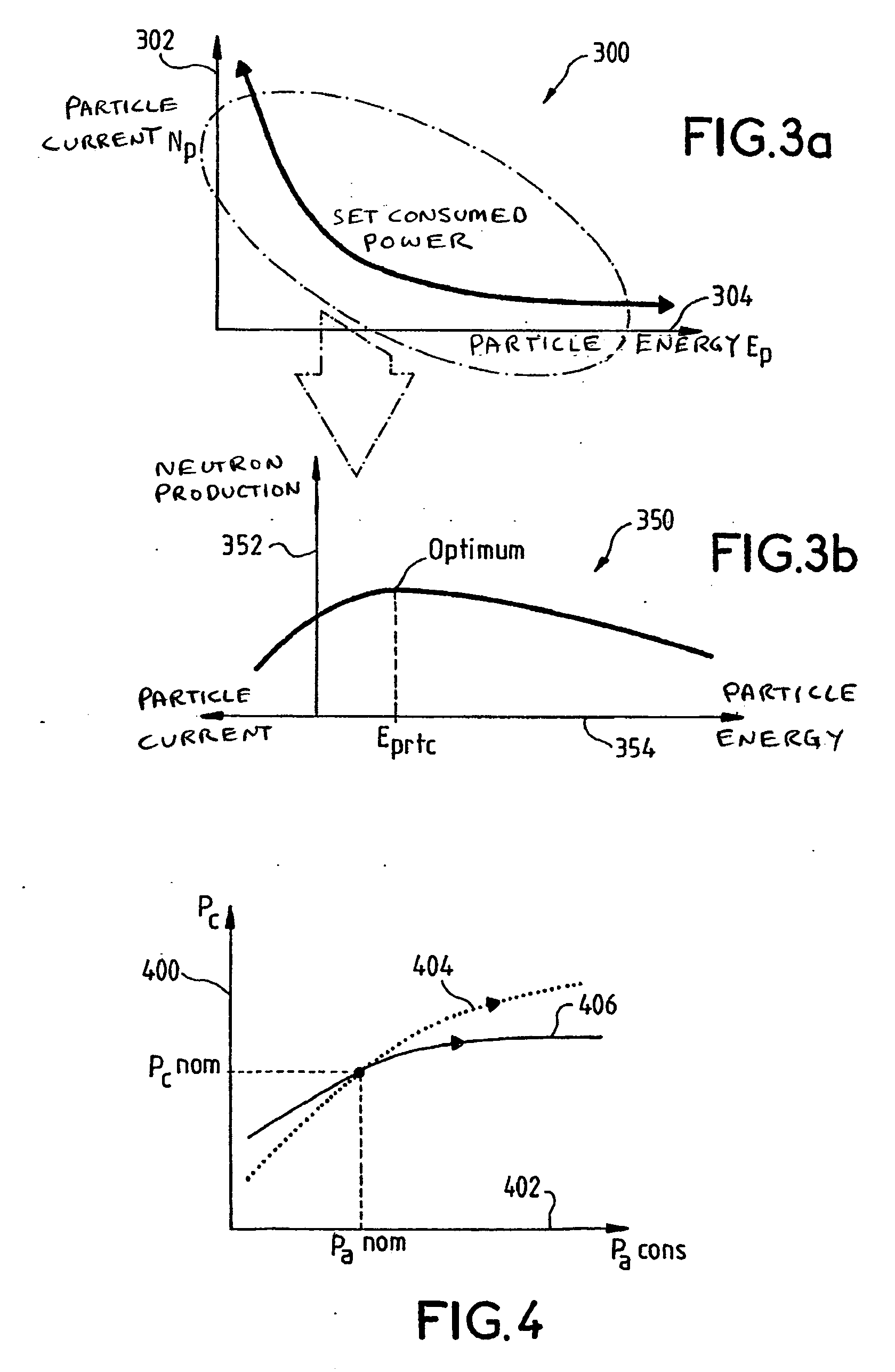
The present invention pertains to a method of controlling an accelerator coupled nuclear system comprising a nuclear reactor operating in subcritical mode and a neutron generator device using a beam of charged particles originating from an accelerator, said neutron generator supplying the quantity of neutrons necessary in order to maintain the nuclear reaction. Said method is characterized in that the operating point is determined by giving the energy Ep of the particles a value greater than or equal to the value EPMax, which maximizes the production of neutrons, and in that the number of neutrons is adjusted by acting on the energy of the particles originating from the accelerator, with constant beam intensity. The present invention also pertains to the accelerator coupled hybrid nuclear system used for same.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Neutron moderator, neutron irradiation method, and hazardous substance detector
ActiveCN101529530AStop the leakReliable removalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingNeutron irradiationHazardous substance
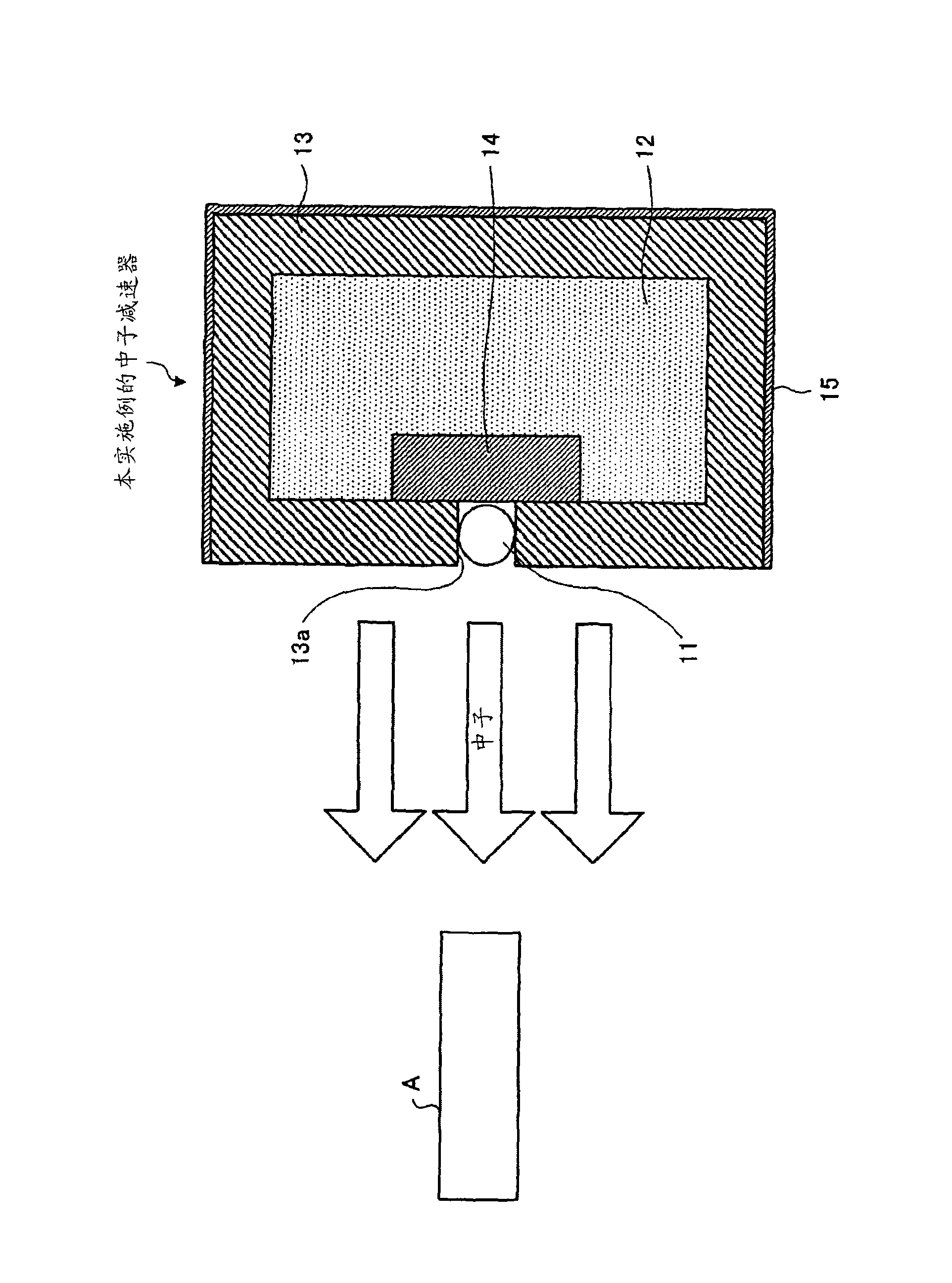
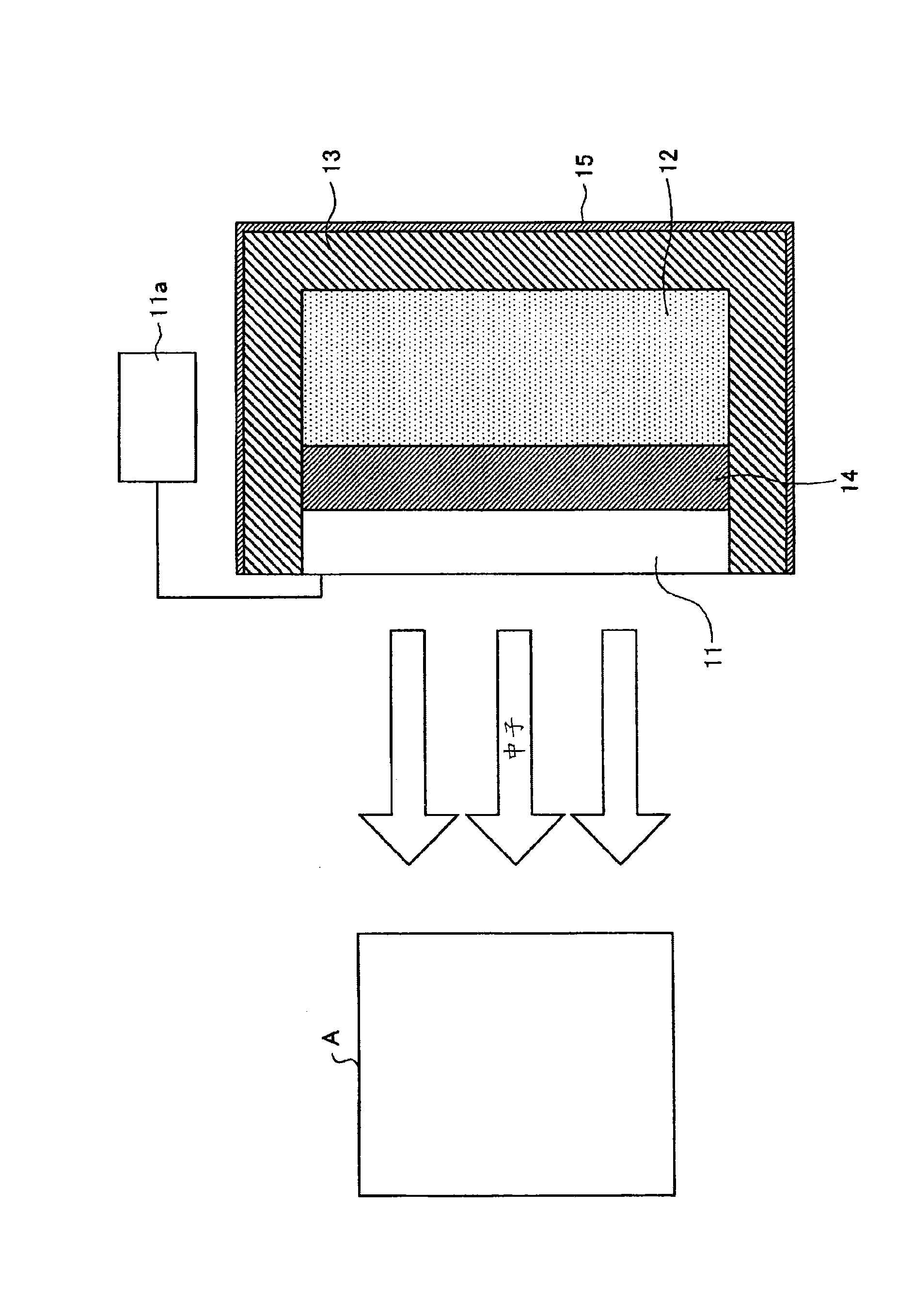
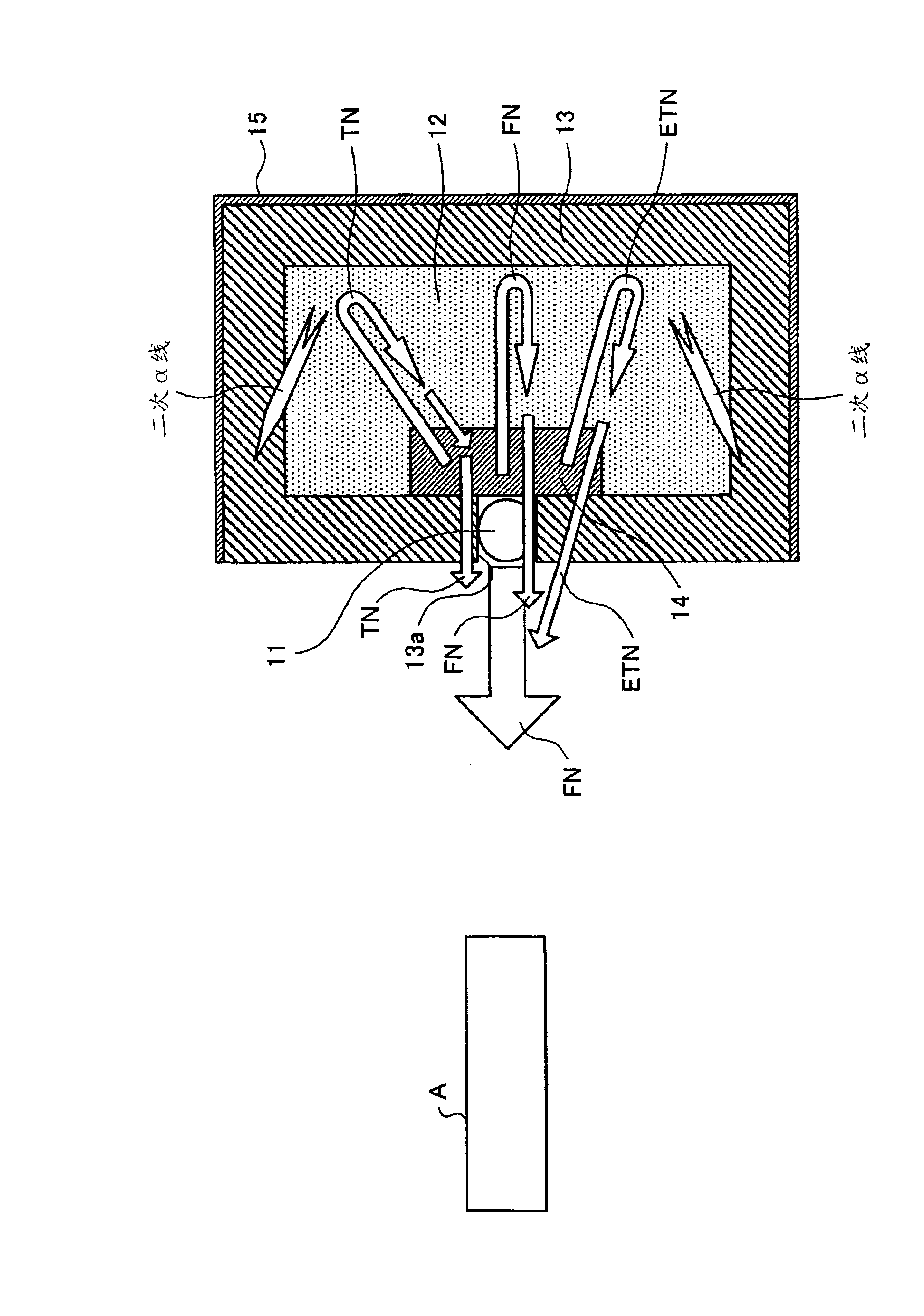
In a neutron moderator, a neutron irradiation method, and a hazardous substance detection apparatus, an inspection chamber (21) where an inspection target (A) can be inserted and removed is provided. Around this inspection chamber (21), a thermal neutron absorbing material (15) is provided. A neutron generator(11) is arranged facing the inspection target (A) in the inspection chamber (21), and a neutron moderating material (12) is arranged at an opposing side of the inspection target (A) with respect to the neutron generator (11). The external surface of the neutron moderating material (12) is covered with gamma ray shielding materials (13, 14), and a Ge detector (24) and a BGO detector (25) are provided to detect gamma ray emitted from the inspection target (A). With this configuration, necessary fast neutron and thermal neutron can be taken out, while suppressing generated secondary gamma ray. Accordingly, a hazardous substance can be detected accurately regardless of a constituent element thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com