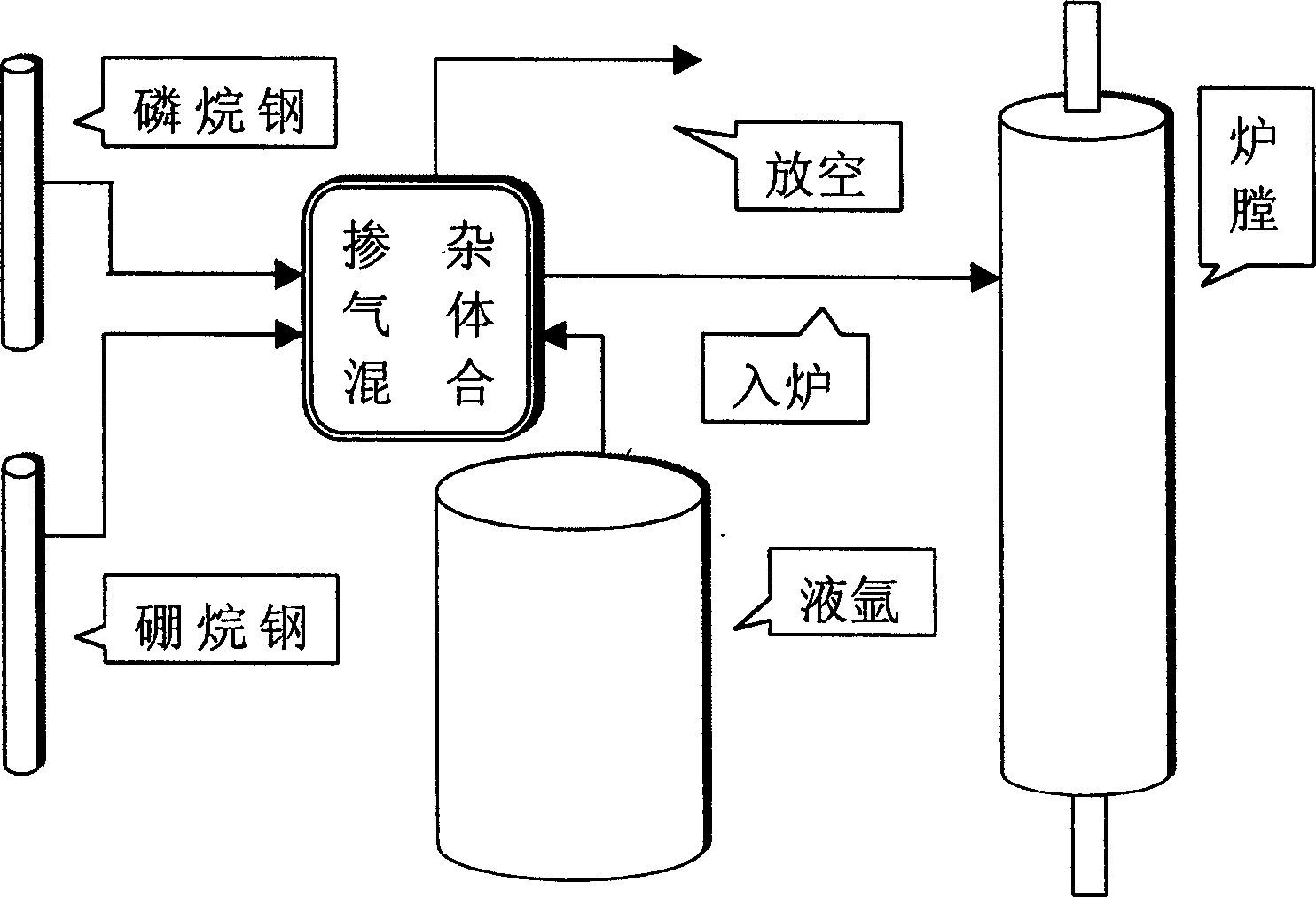
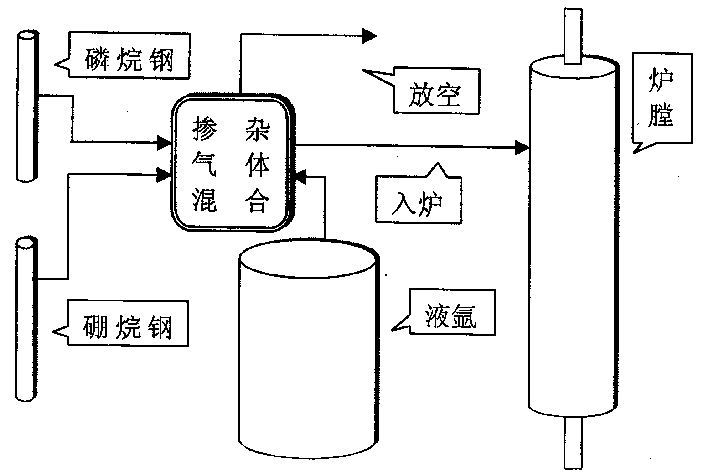
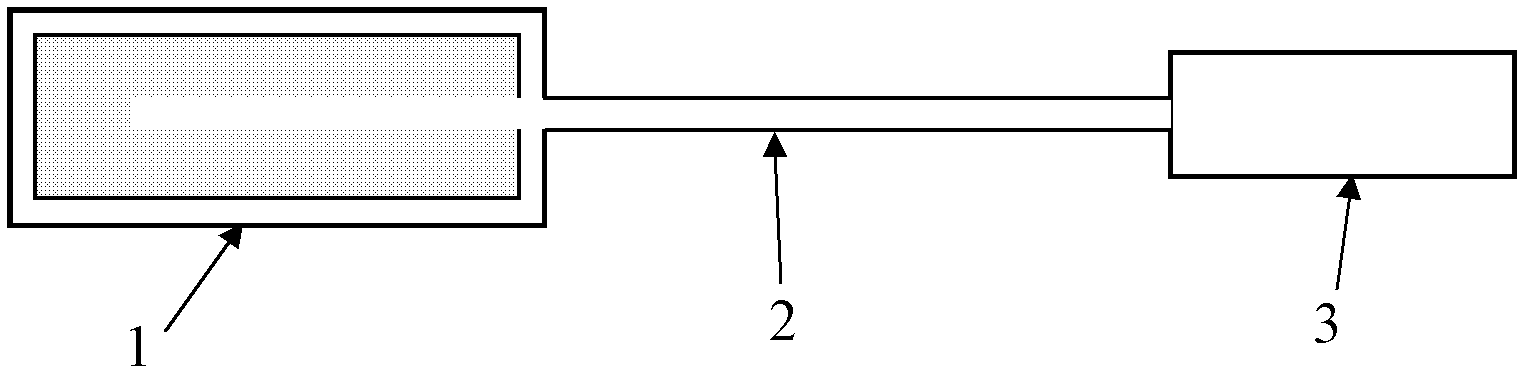
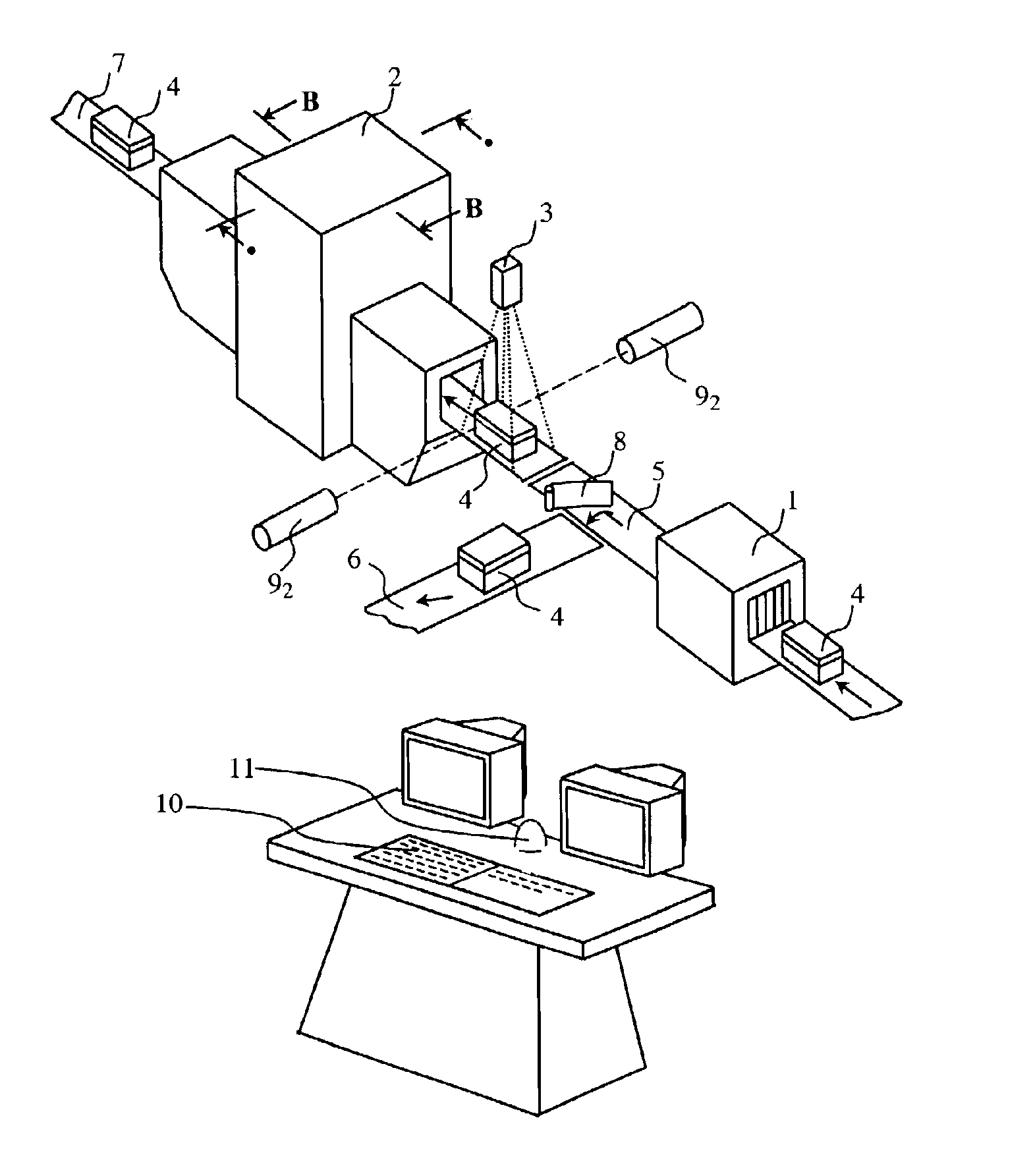
Patents
Literature
327 results about "Neutron radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
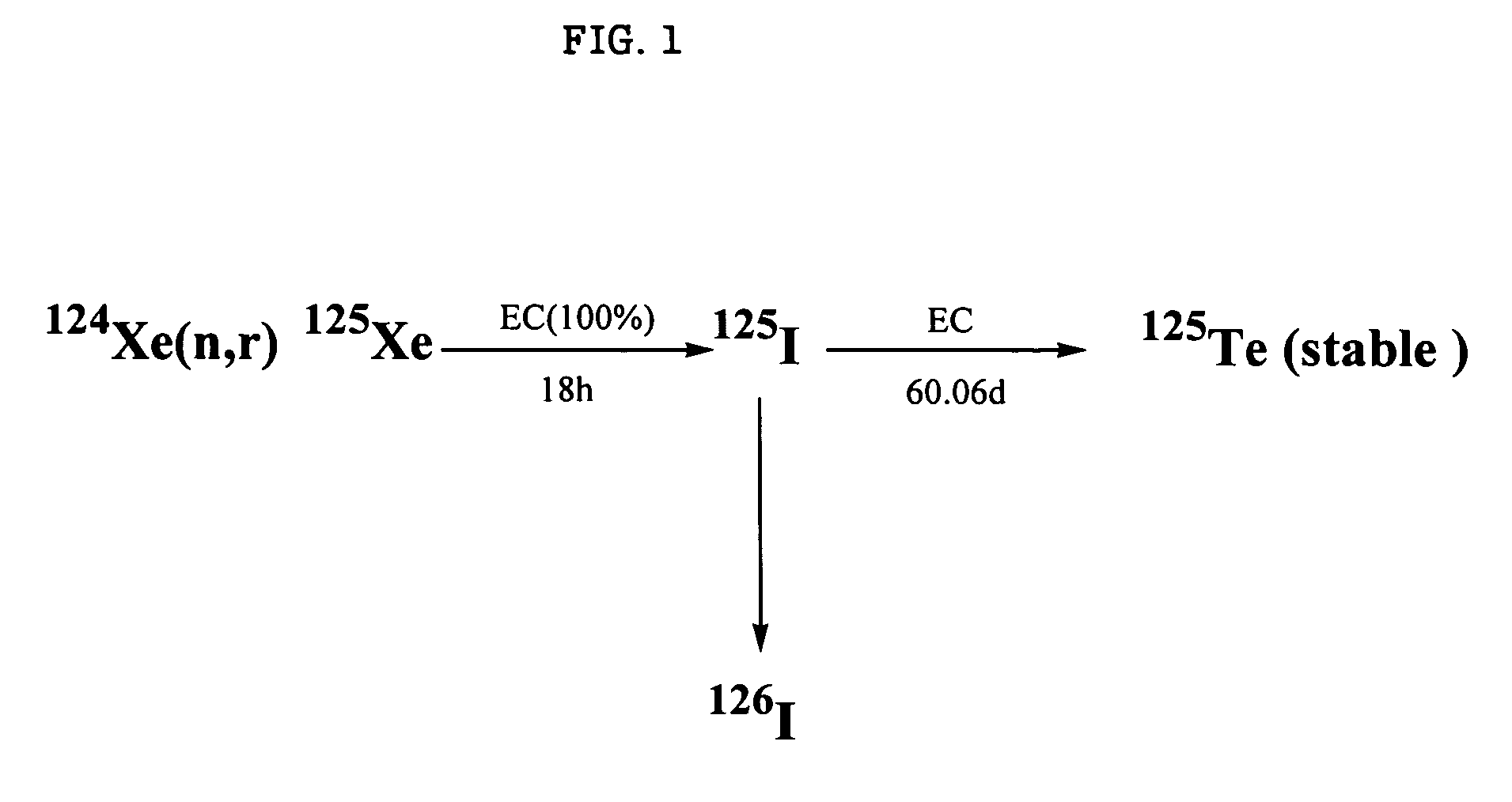
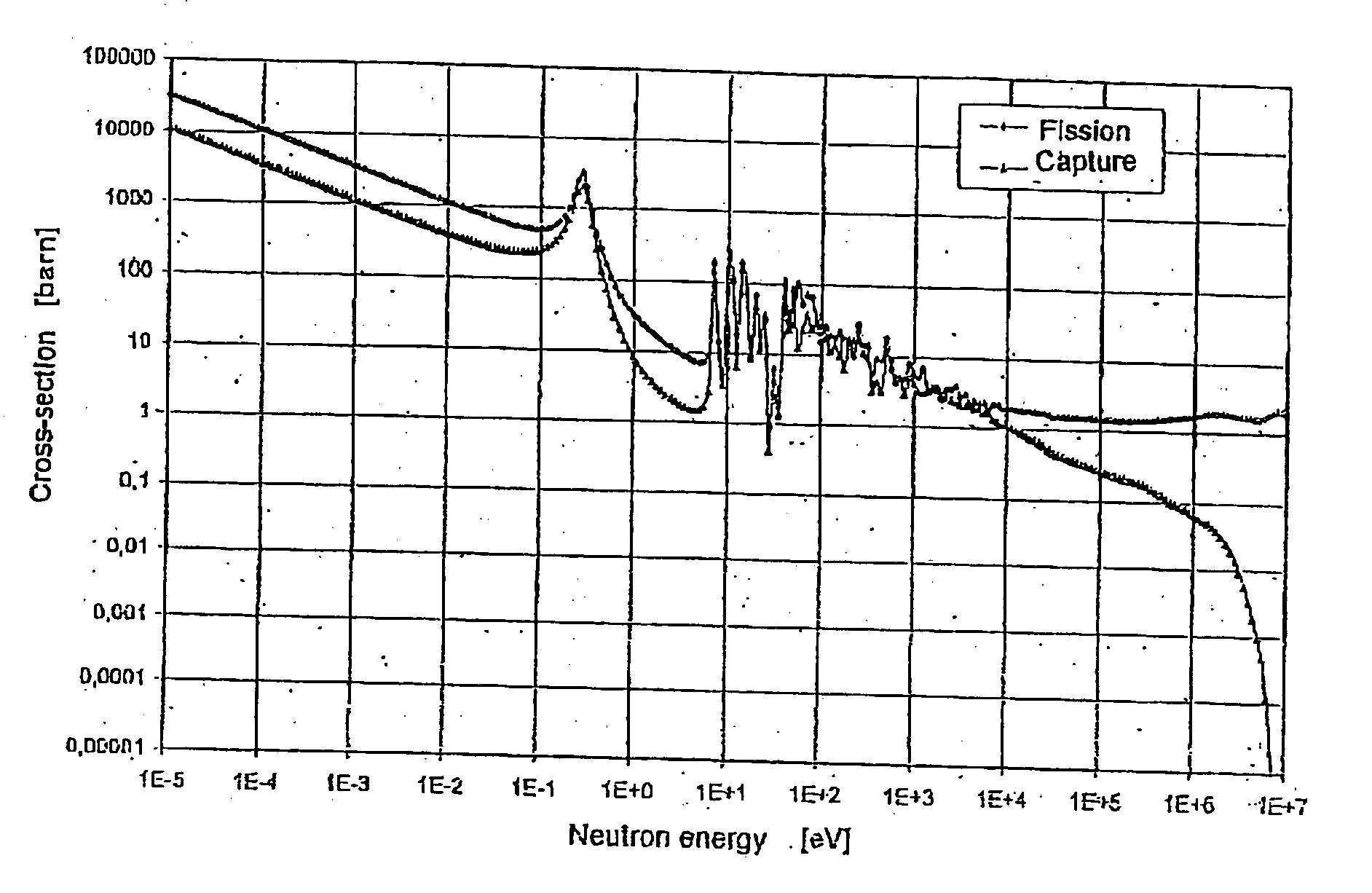
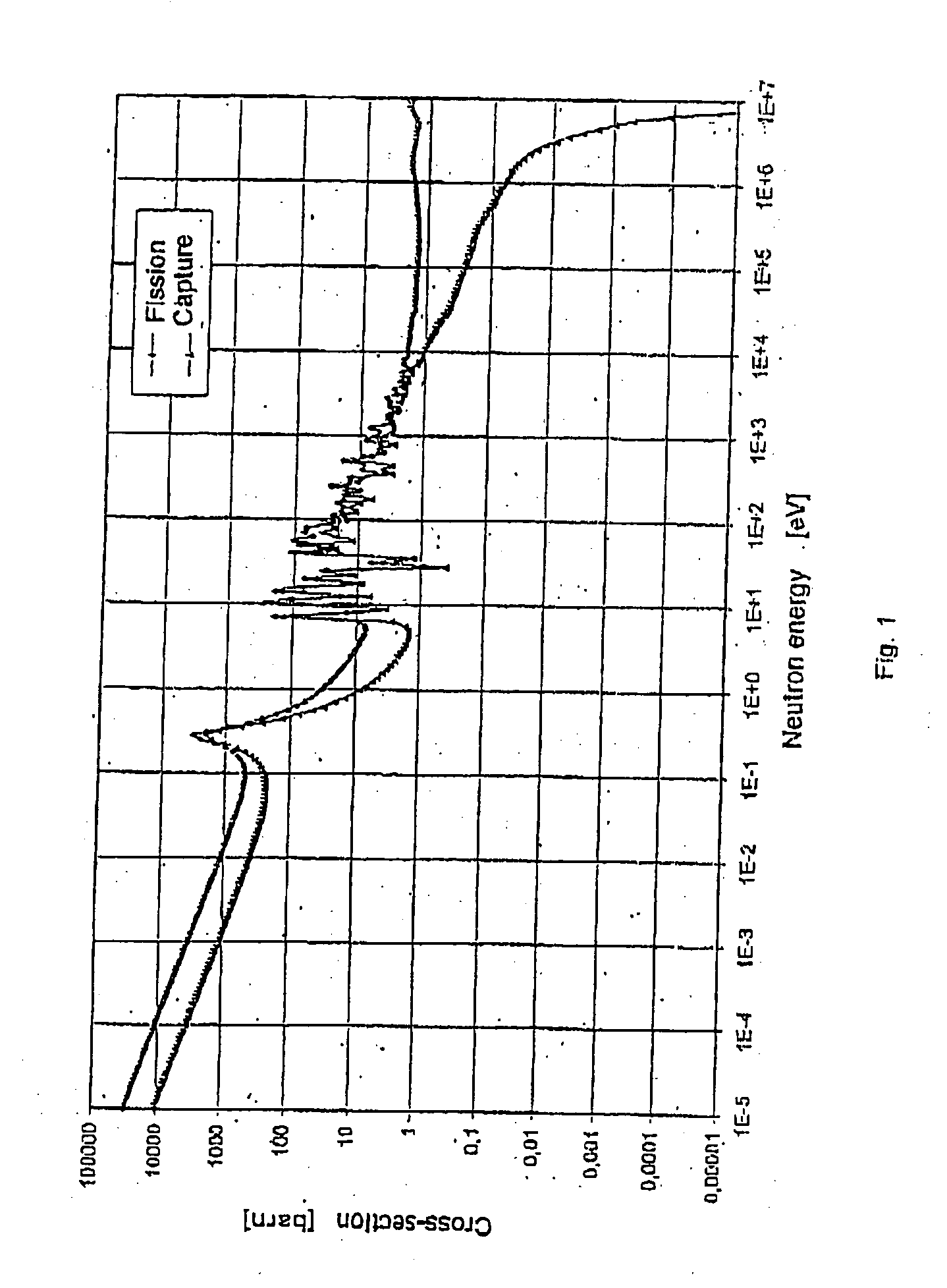
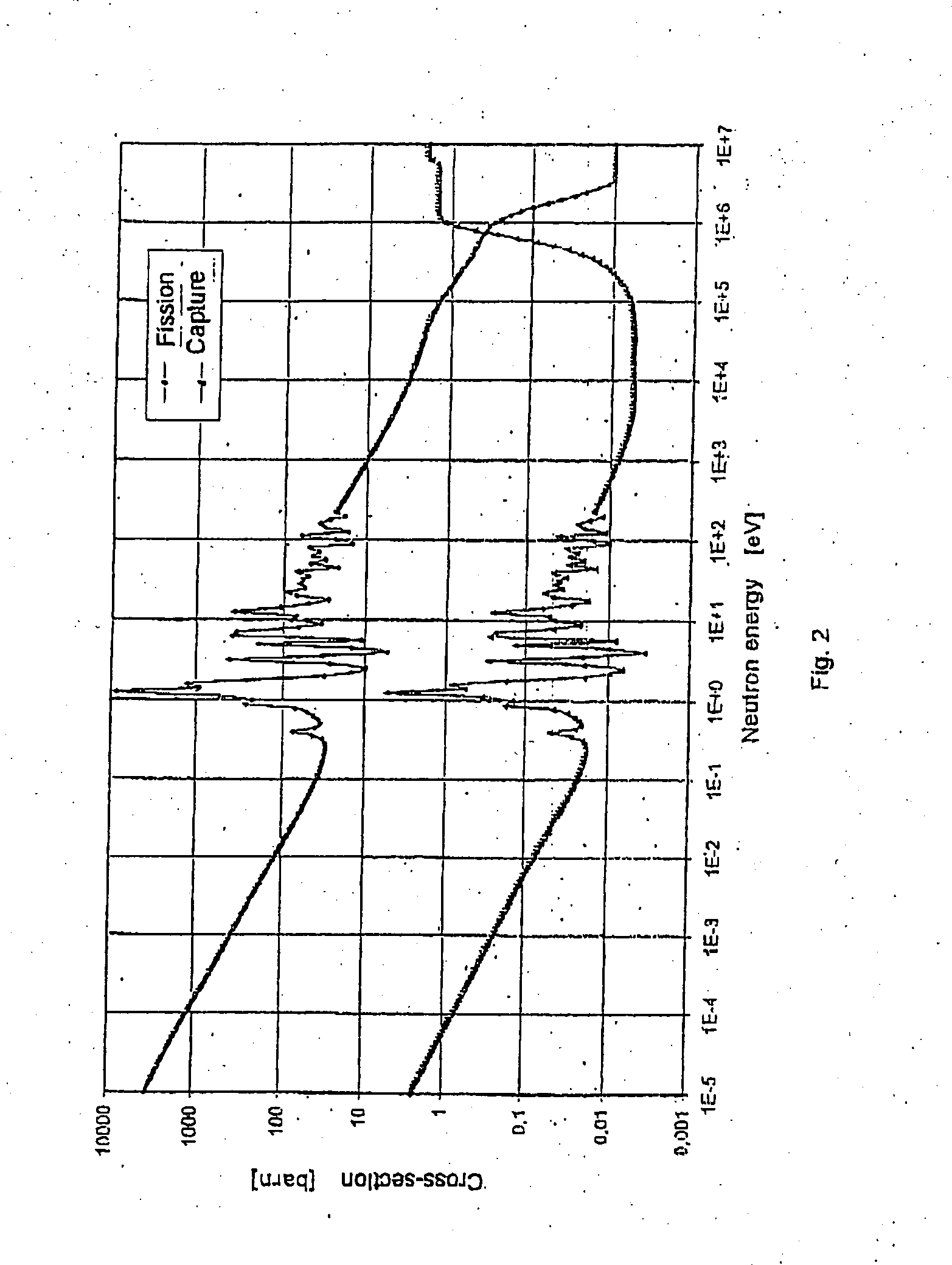
Neutron radiation is a form of ionizing radiation that presents as free neutrons. Typical phenomena are nuclear fission or nuclear fusion causing the release of free neutrons, which then react with nuclei of other atoms to form new isotopes—which, in turn, may trigger further neutron radiation. Free neutrons are unstable, decaying into a proton, an electron, plus an anti-electron-neutrino with a mean lifetime of 887 seconds (about 14 minutes, 47 seconds).
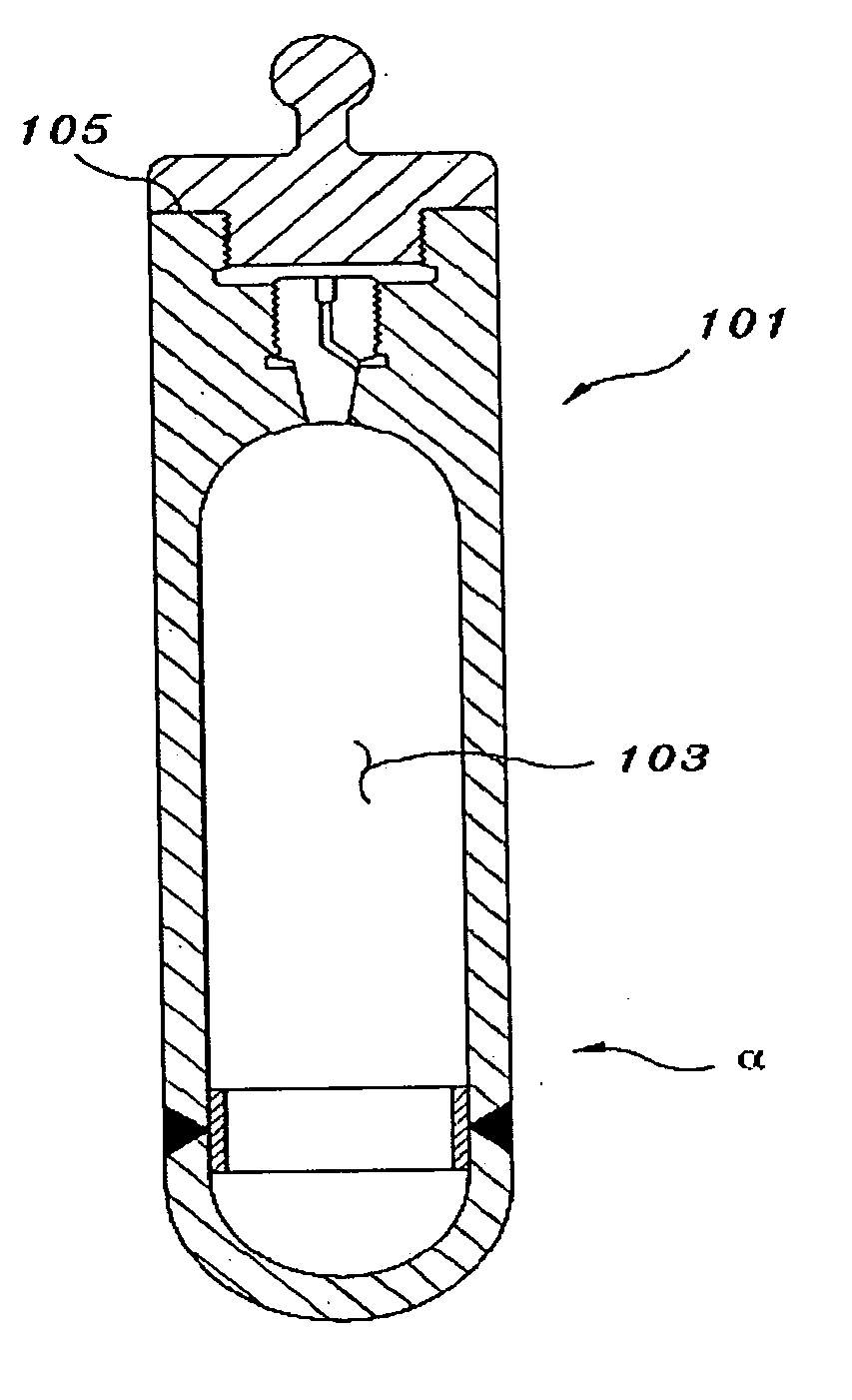
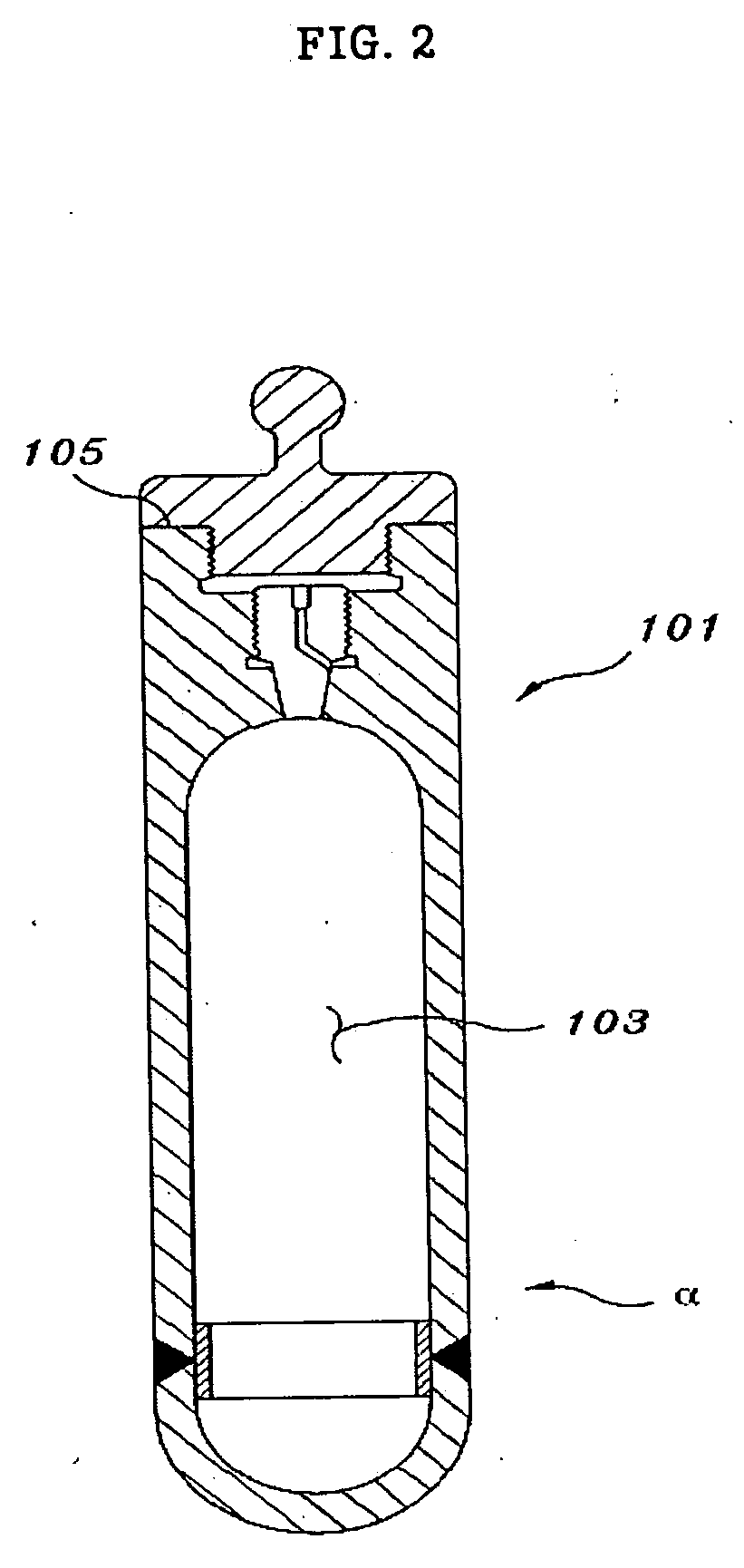
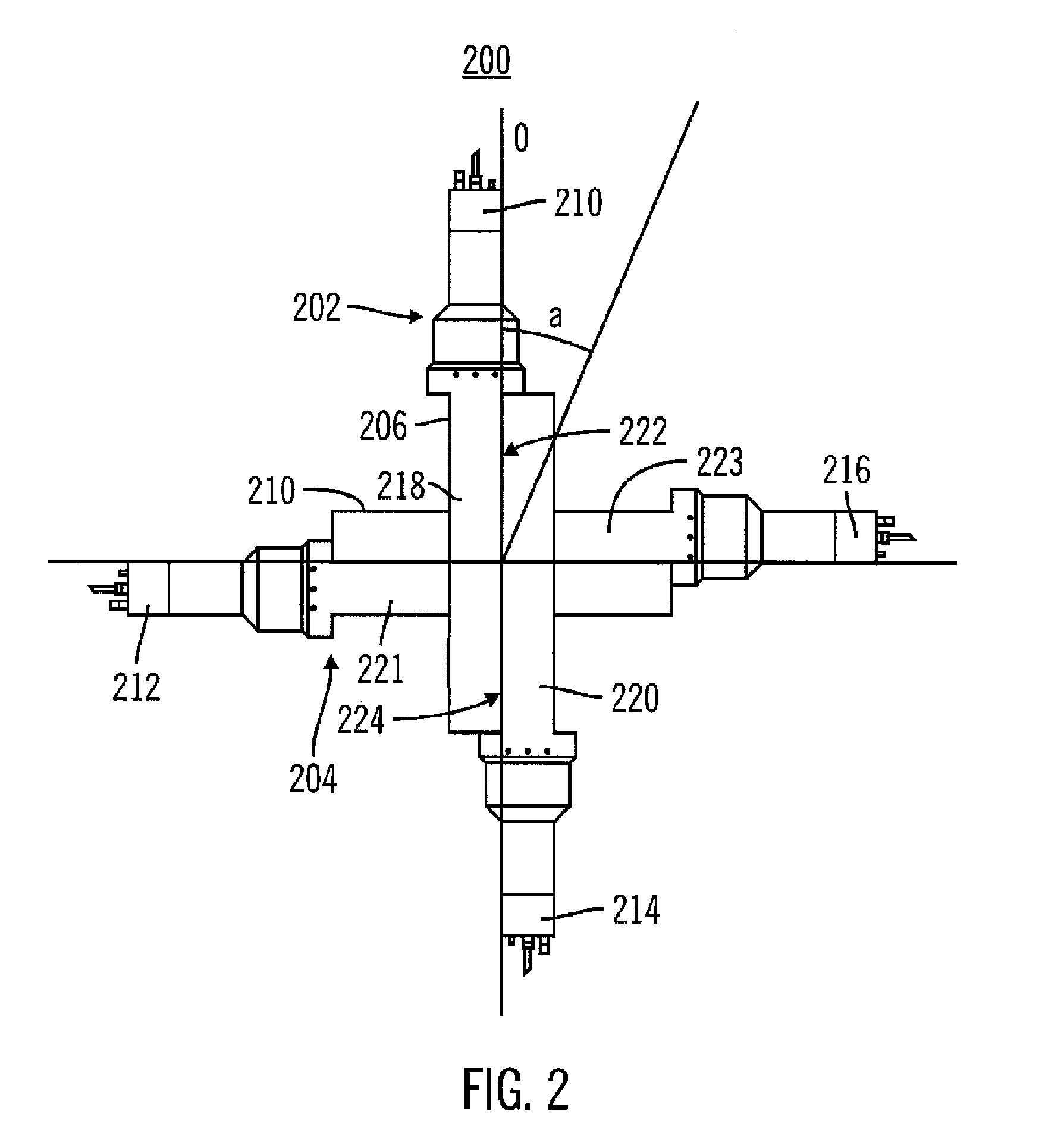
Internal circulating irradiation capsule for iodine-125 and method of producing iodine-125 using same
InactiveUS20060126774A1Reduce neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationIodine
A present invention provides an internal circulating irradiation capsule available for the production of iodine-125 and a related production method. The irradiation capsule filled with xenon gas has a lower irradiation part, an upper irradiation part, and a neutron control member. The lower irradiation part is inserted into an irradiation hole of a reactor core and irradiated with a large quantity of neutron directly. When neutron is radiated to the xenon gas, iodine-125 is produced from xenon gas. The upper irradiation part protrudes from the irradiation hole, and iodine-125 is transferred to the upper irradiation part by convection and solidified in the upper part. The neutron control member reduces neutron in the upper part to produce iodine-125 of high purity and radioactivity in a large quantity.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Neutron/gamma ray survey instrument with directional gamma ray sensitivity
ActiveUS20050121618A1High detection sensitivitySufficient thermalizationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
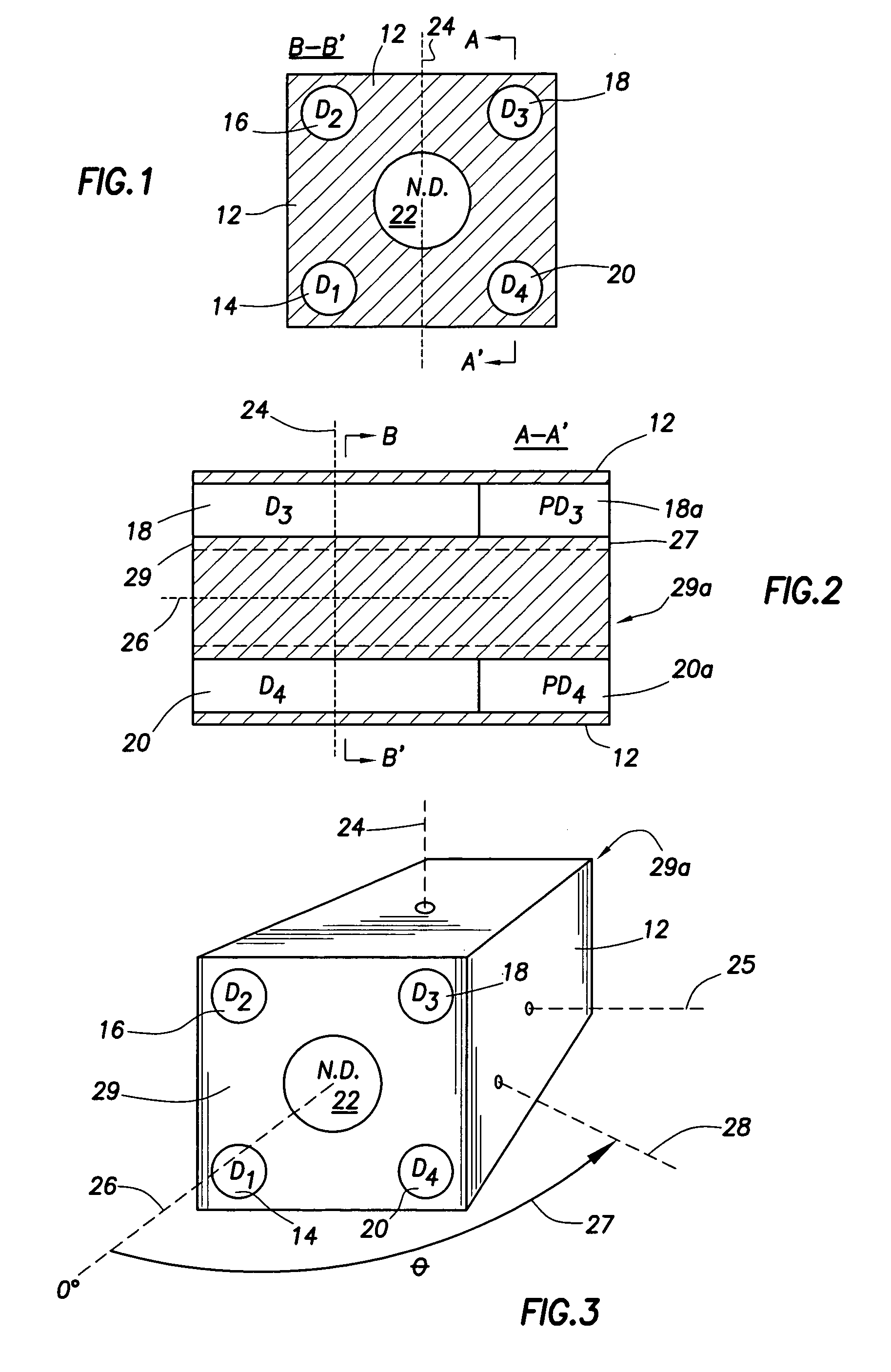
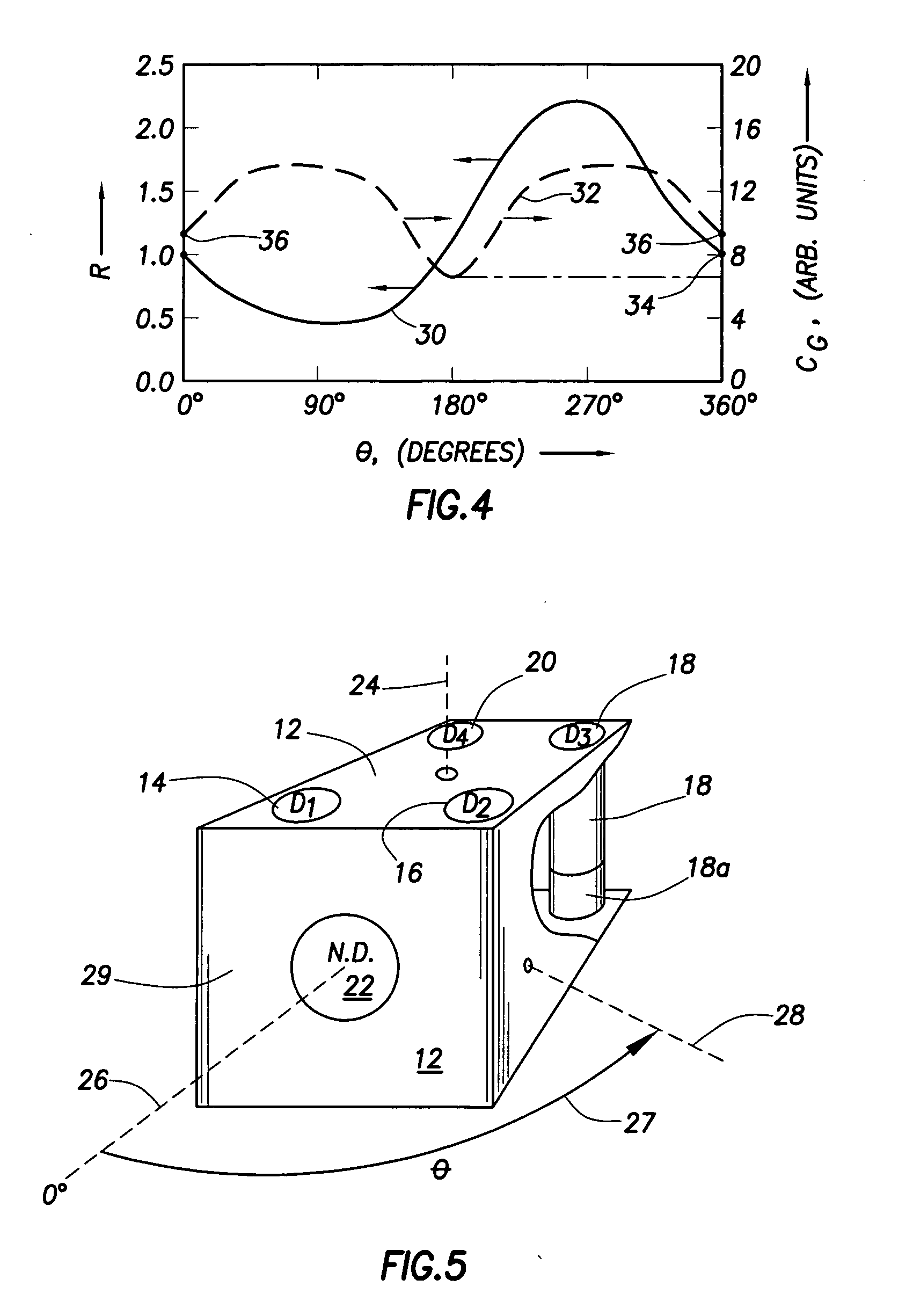
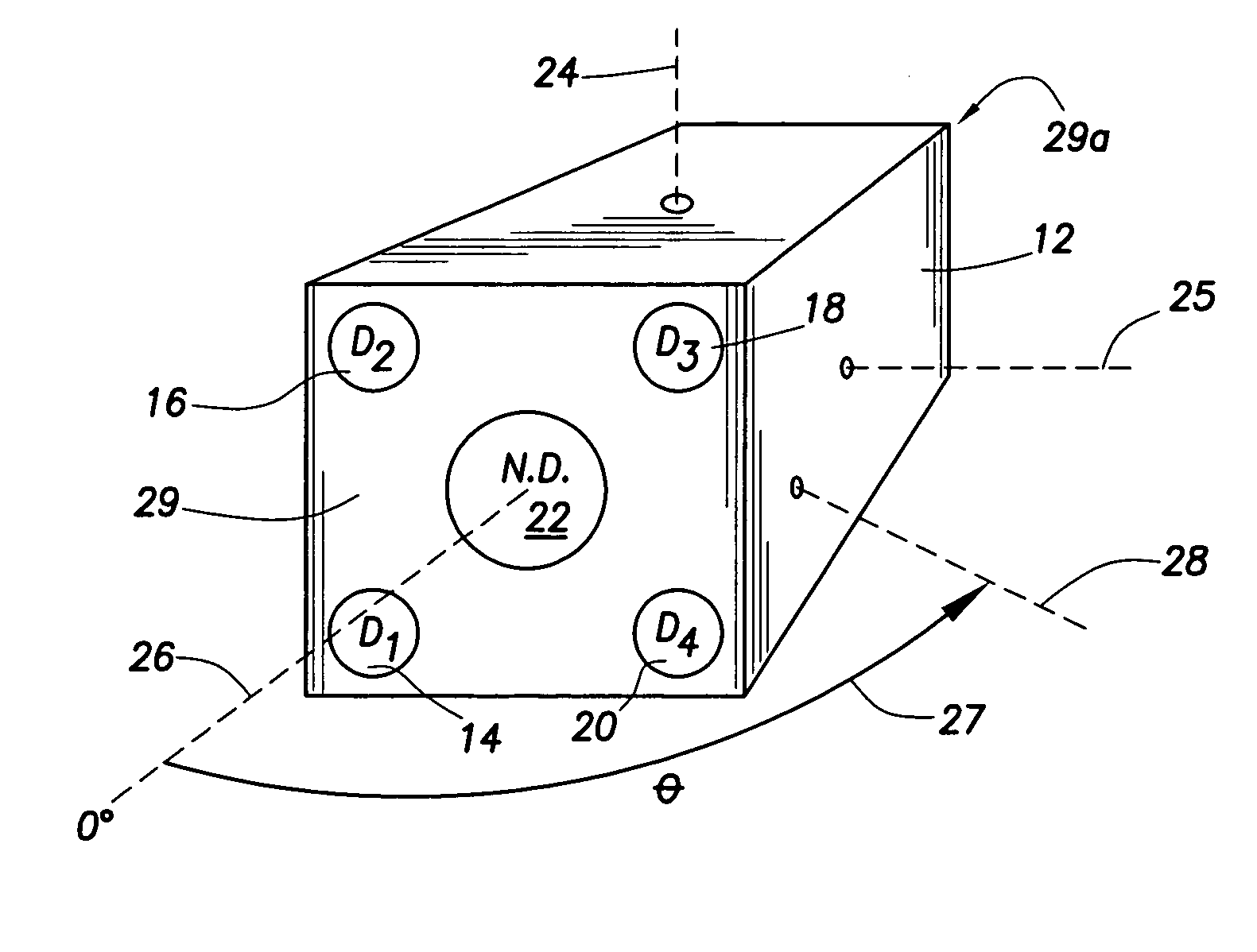
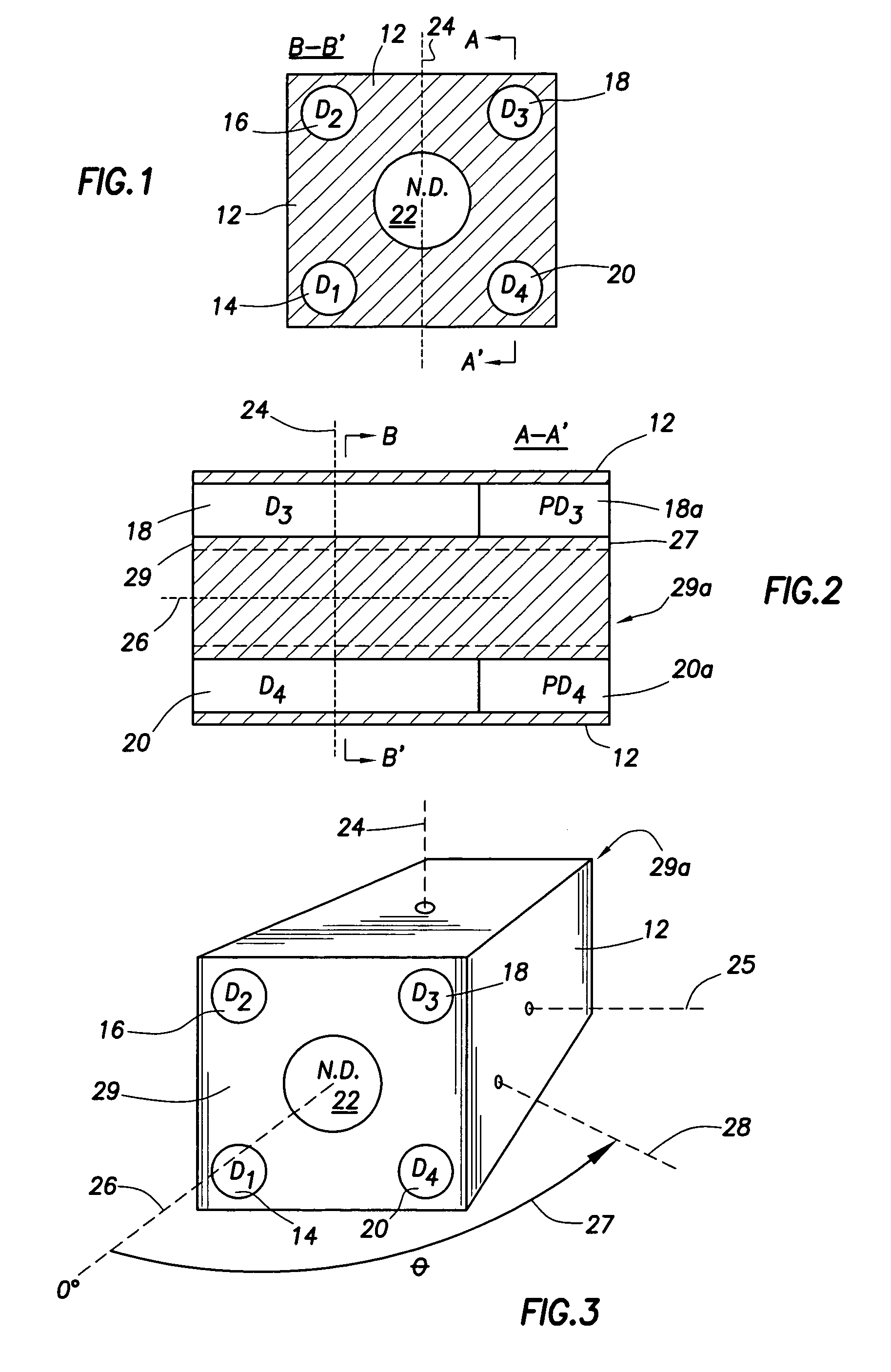
A portable survey instrument and methodology yield intensity of neutron radiation, intensity of gamma radiation, and a direction of impinging gamma radiation. The instrument uses a neutron detector surrounded by an essentially rectangular moderator with preferably four gamma ray detectors disposed symmetrically about the neutron detector and within the moderator. Material and dimensions of the moderator are selected so that the neutron-measurement is equally sensitive to fast and thermal neutrons. The moderator also induces angular responses to the gamma ray detectors. Responses of the gamma ray detectors are combined to yield a parameter indicative of the angular position of a source. The survey instrument is portable and suited for hand held use.
Owner:DELTA EPSILON INSTR
Neutron/gamma ray survey instrument with directional gamma ray sensitivity
ActiveUS7026627B2High detection sensitivityLow cross sectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsNuclear engineeringNeutron radiation
A portable survey instrument and methodology yield intensity of neutron radiation, intensity of gamma radiation, and a direction of impinging gamma radiation. The instrument uses a neutron detector surrounded by an essentially rectangular moderator with preferably four gamma ray detectors disposed symmetrically about the neutron detector and within the moderator. Material and dimensions of the moderator are selected so that the neutron measurement is equally sensitive to fast and thermal neutrons. The moderator also induces angular responses to the gamma ray detectors. Responses of the gamma ray detectors are combined to yield a parameter indicative of the angular position of a source. The survey instrument is portable and suited for hand held use.
Owner:DELTA EPSILON INSTR
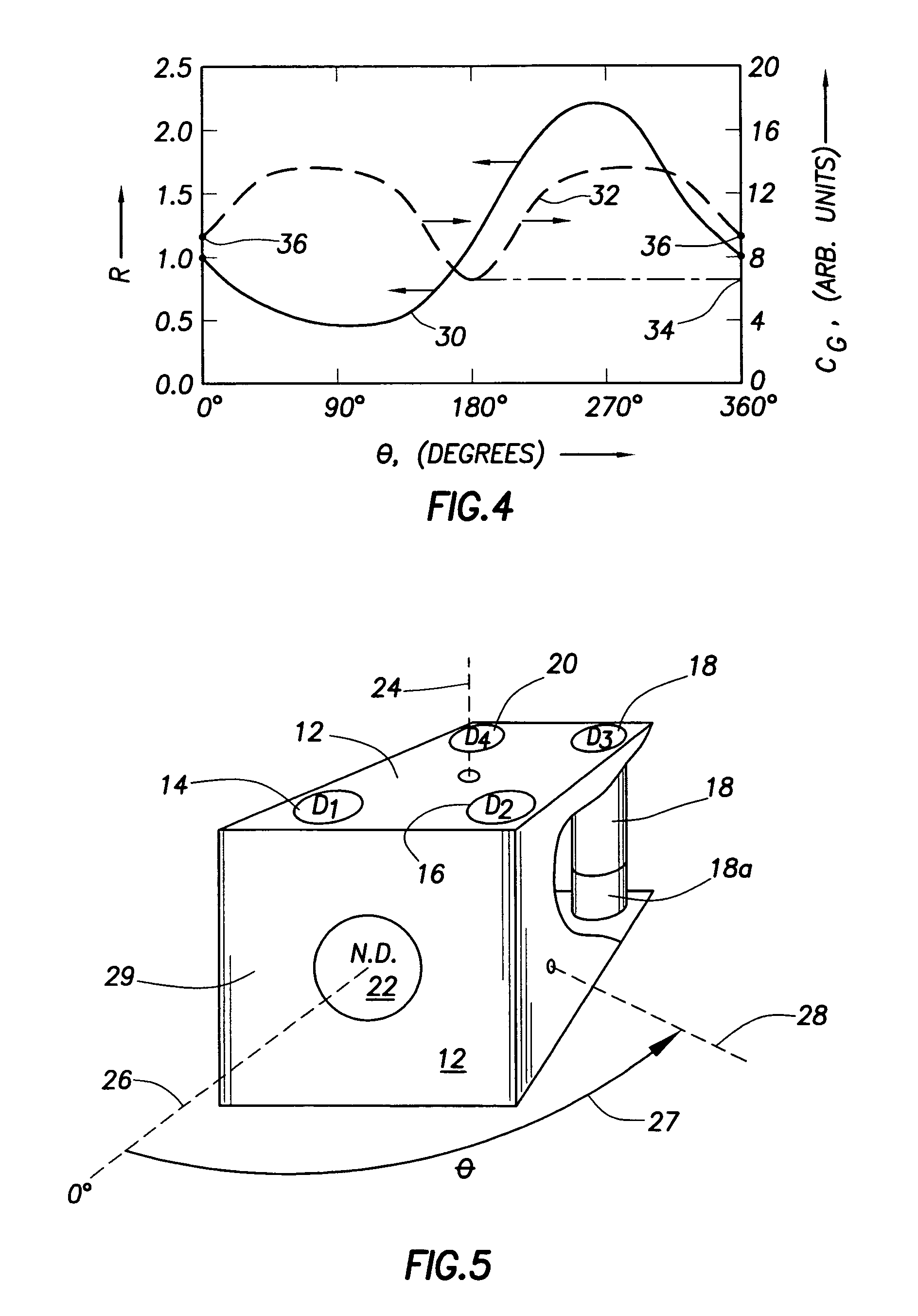
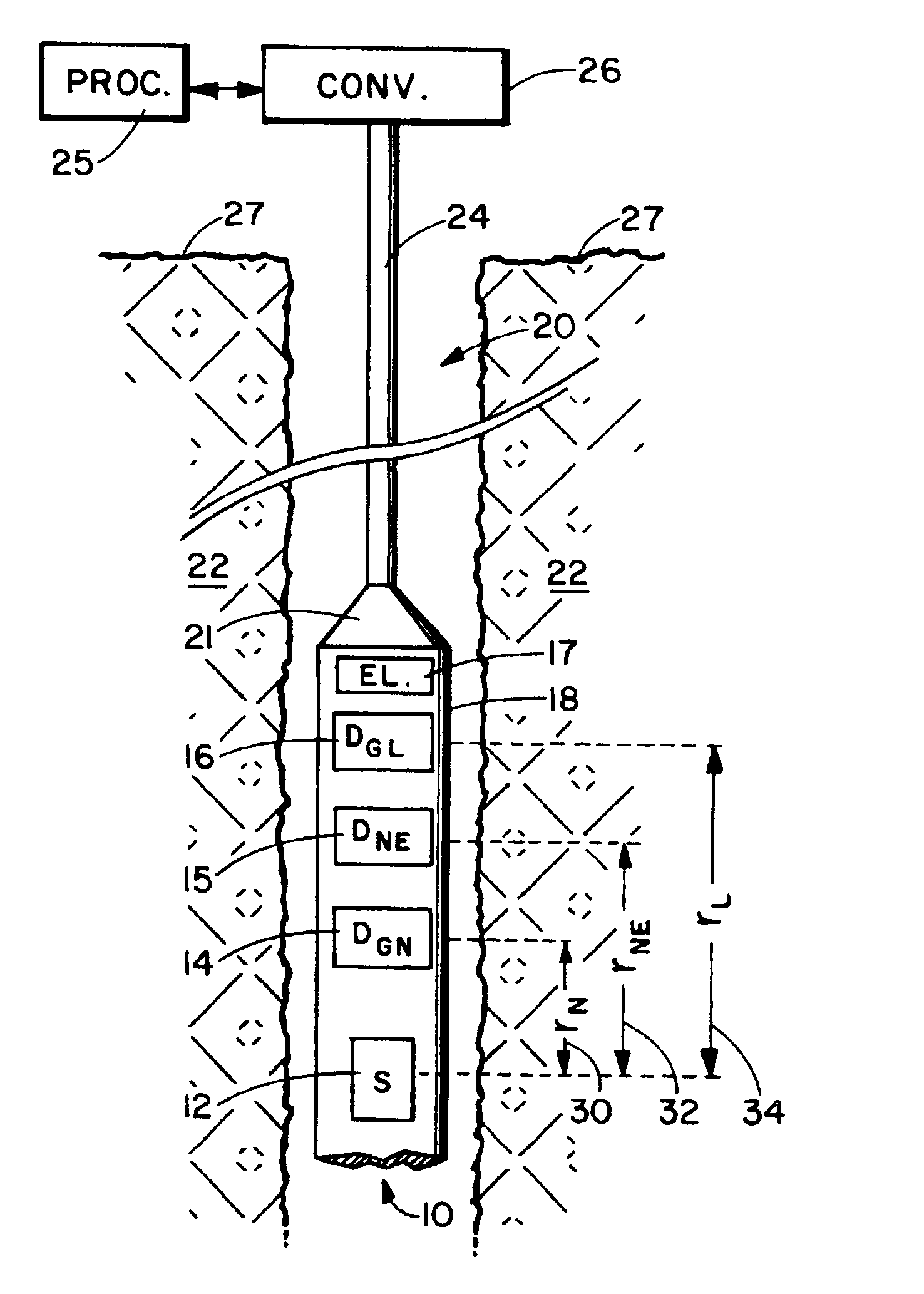
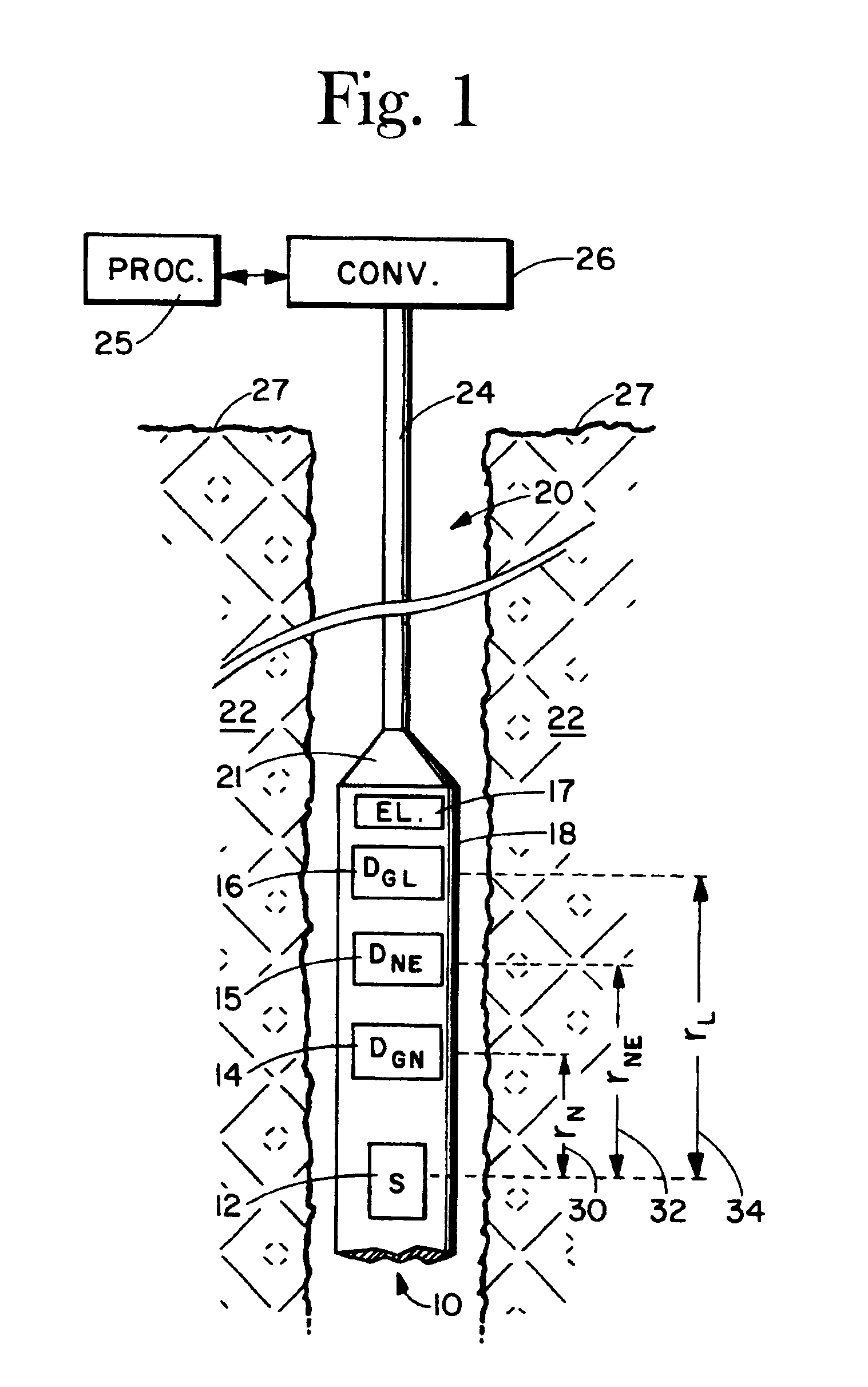
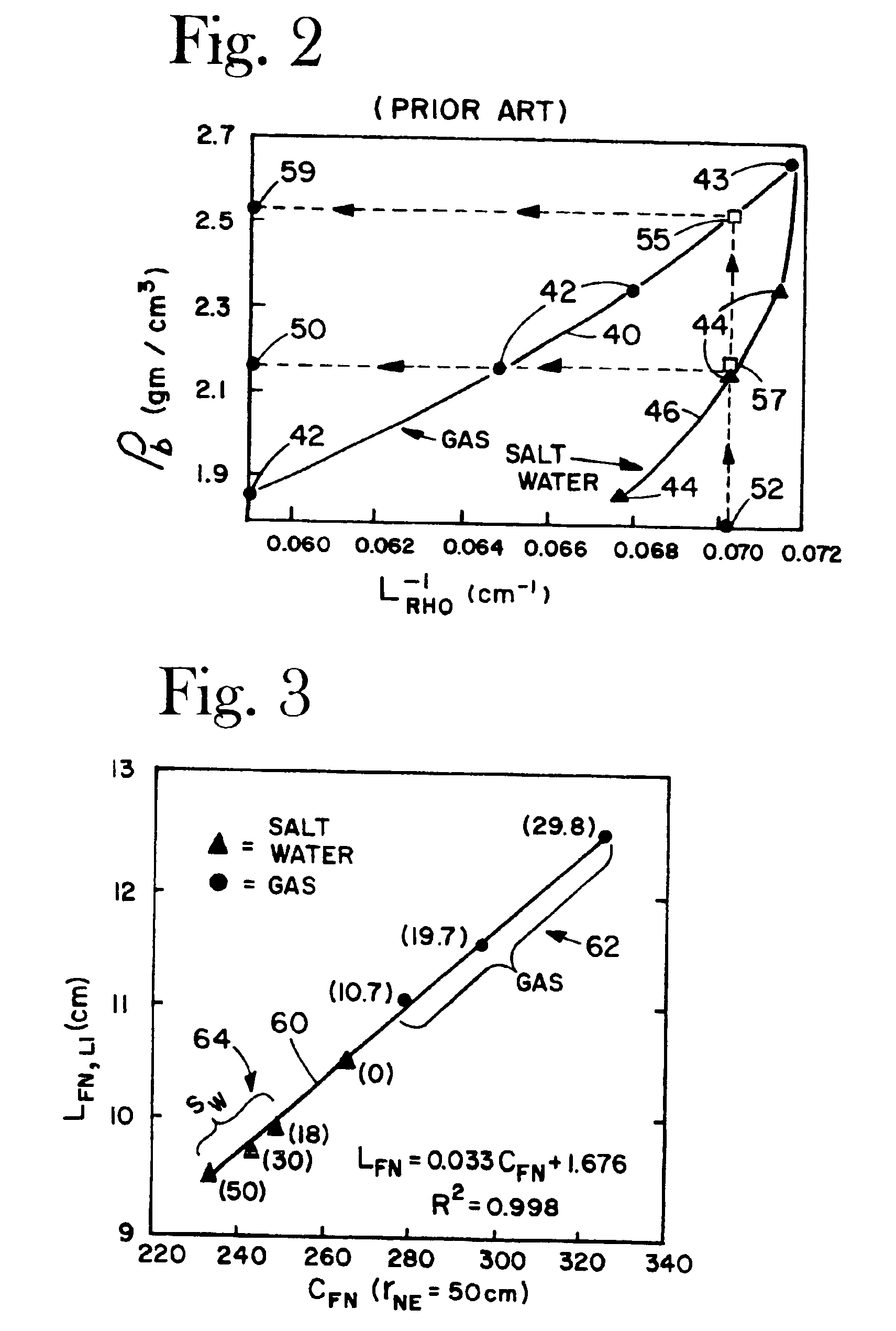
Apparatus and method for determining density, porosity and fluid saturation of formations penetrated by a borehole
InactiveUS6936812B2Reduce ambiguityMinimize adverse effectsNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringFluid saturation
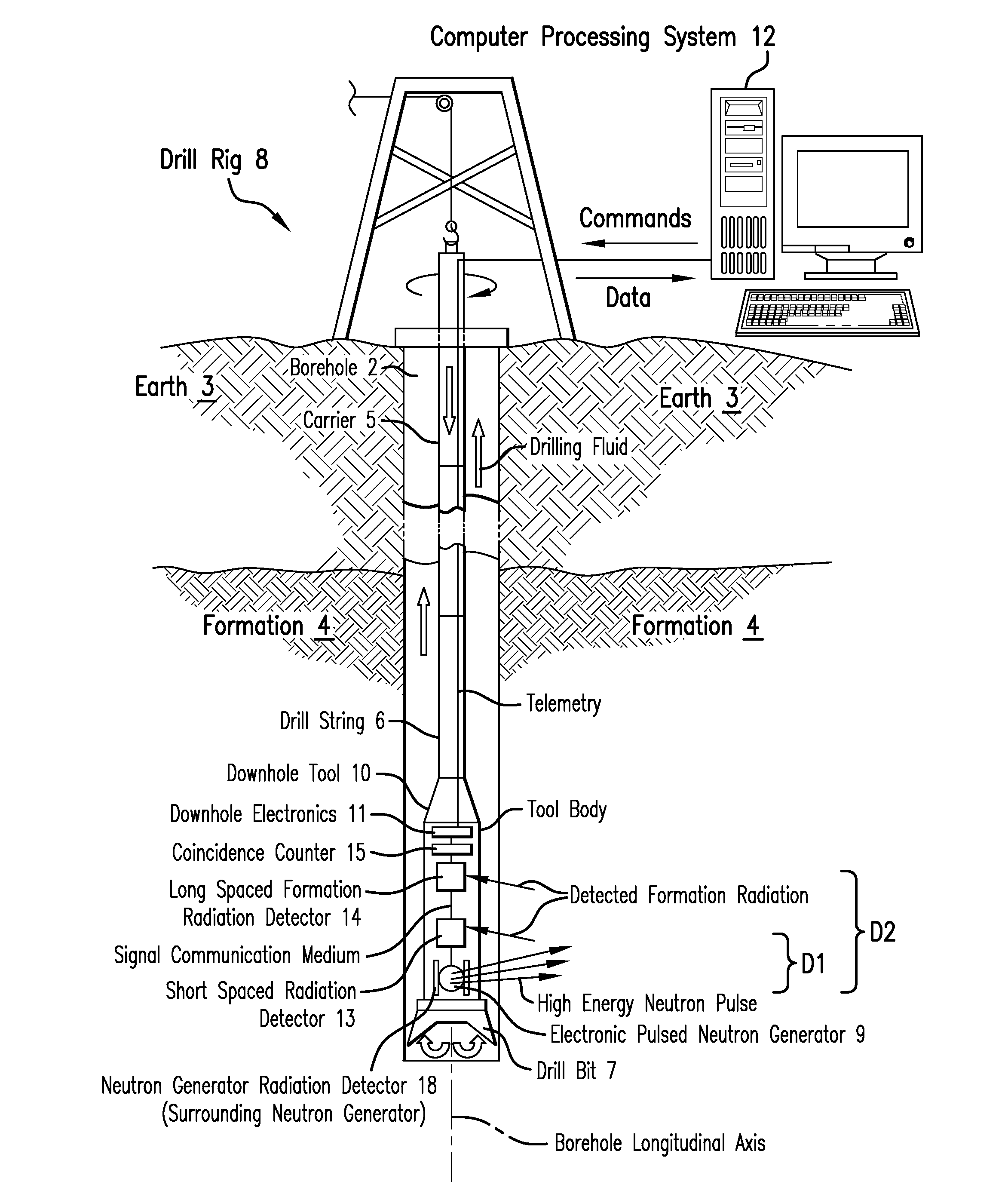
A borehole logging system for determining bulk density, porosity and formation gas / liquid fluid saturation of formation penetrated by a borehole. Measures of fast neutron radiation and inelastic scatter gamma radiation, induced by a pulsed neutron source, are combined with an iterative numerical solution of a two-group diffusion model to obtain the formation parameters of interest. Double-valued ambiguities in prior art measurements are removed by using the iterative solution of the inverted two-group diffusion model. The system requires two gamma ray detectors at different axial spacings from the source, and a single neutron detector axially spaced between the two gamma ray detectors. The system can be embodied as a wireline system or as a logging-while-drilling system.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
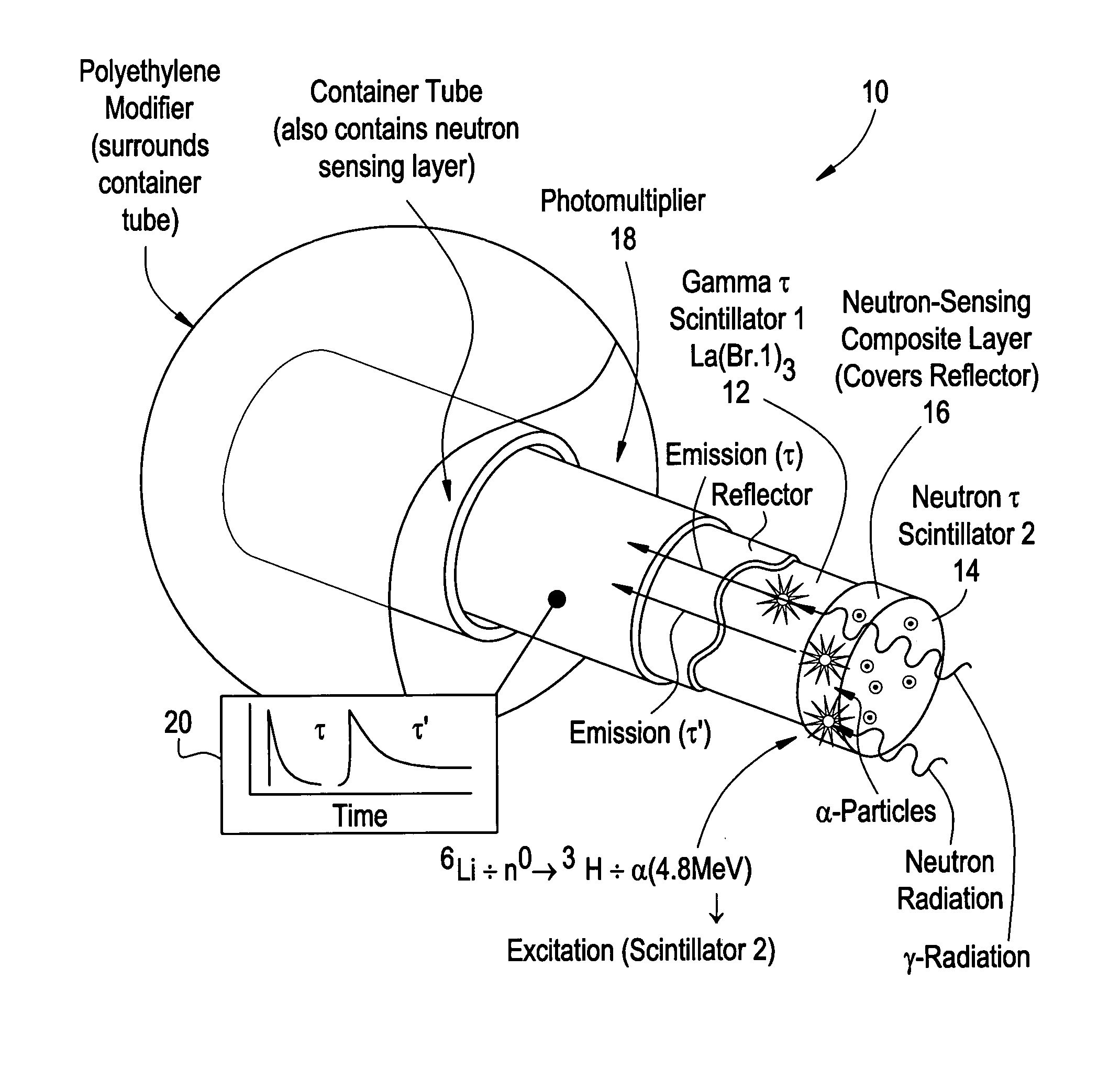
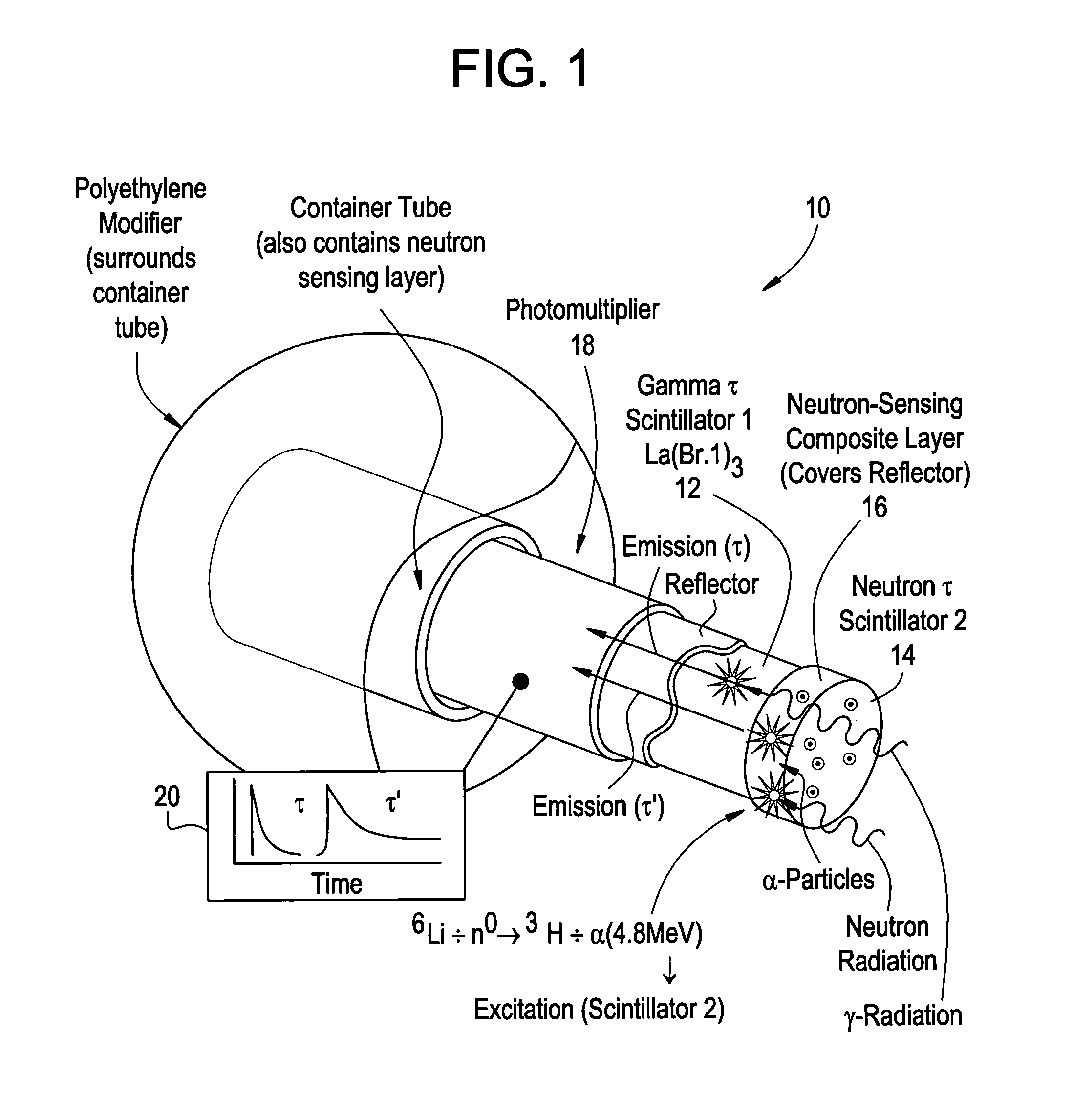
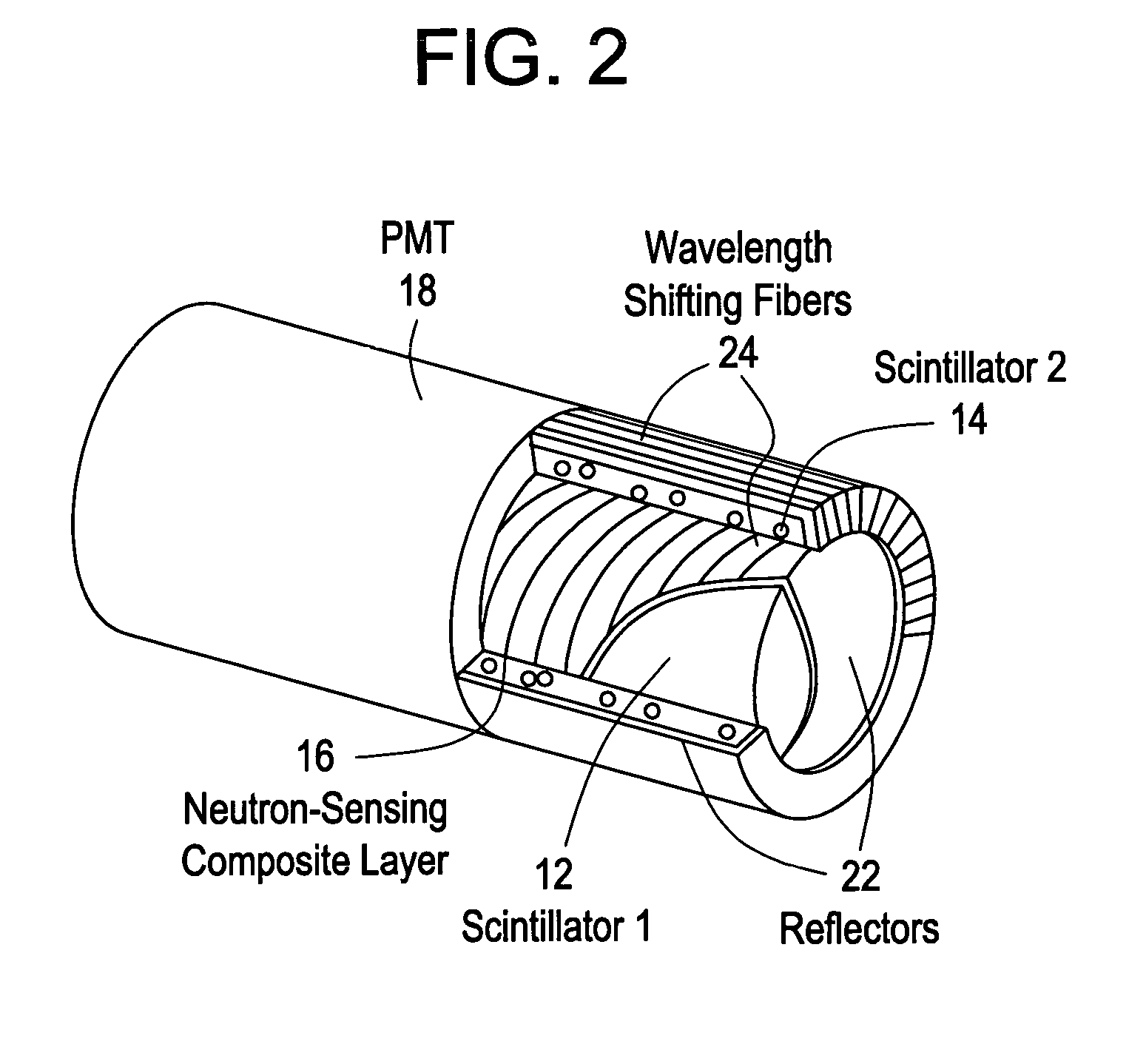
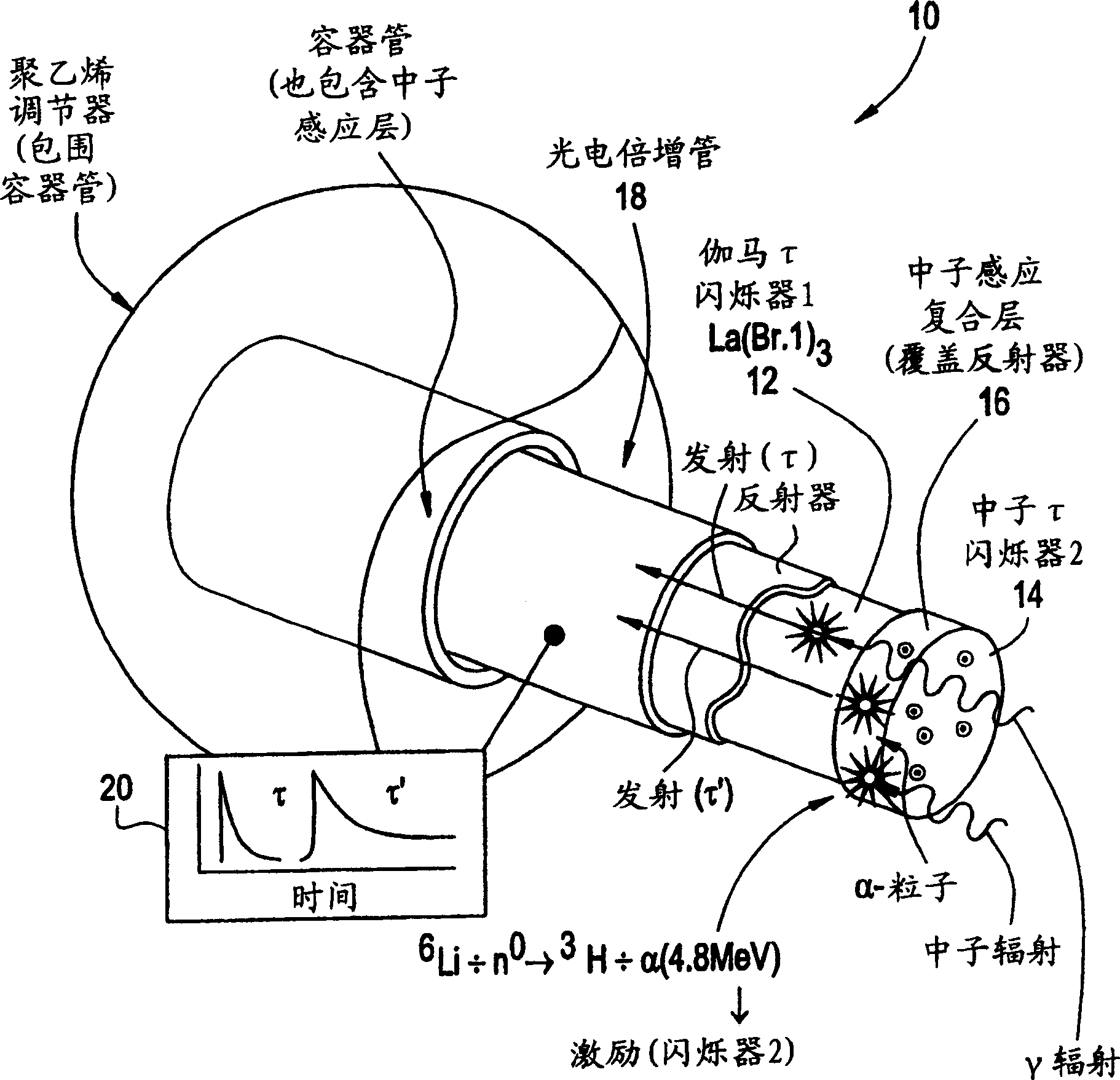
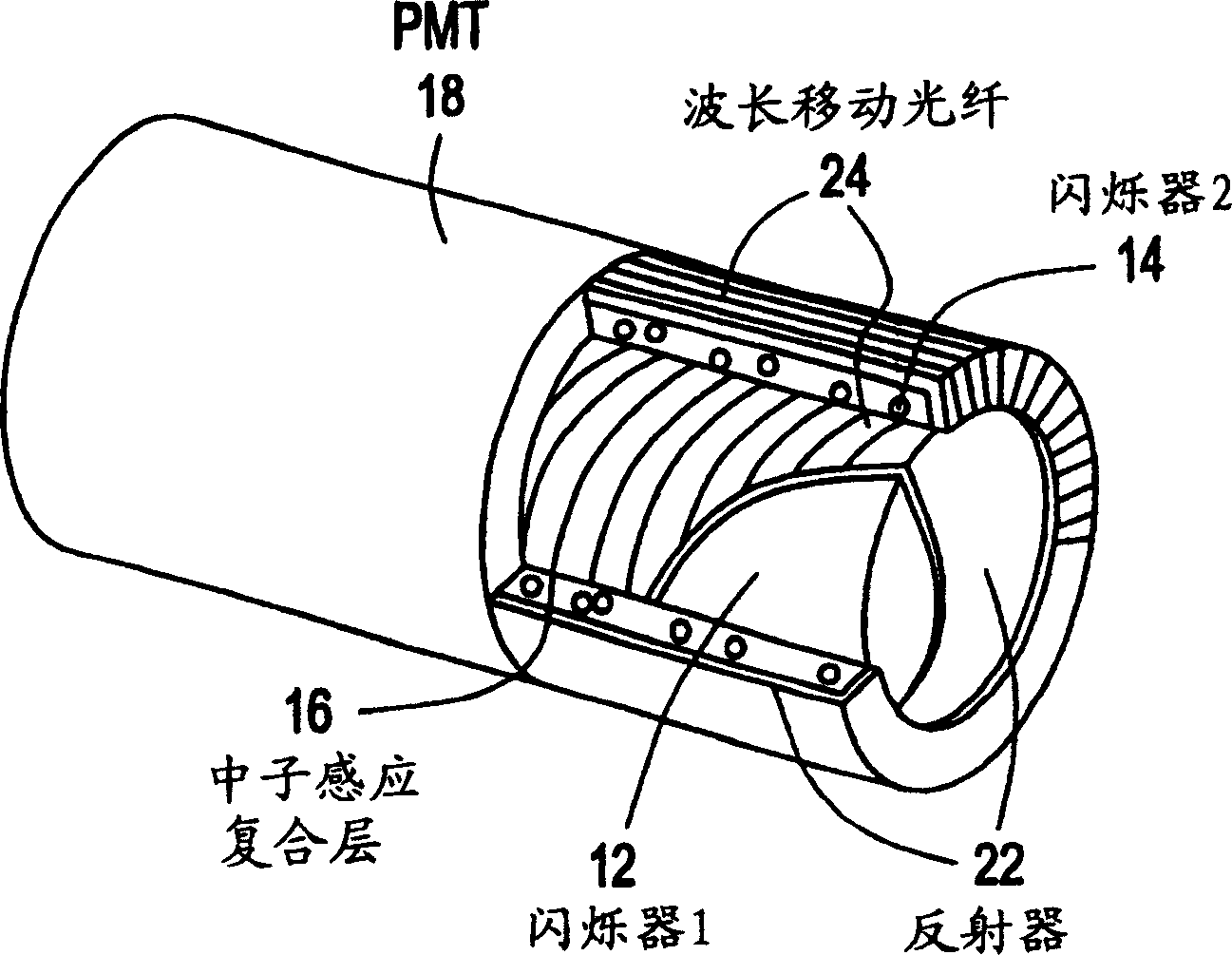
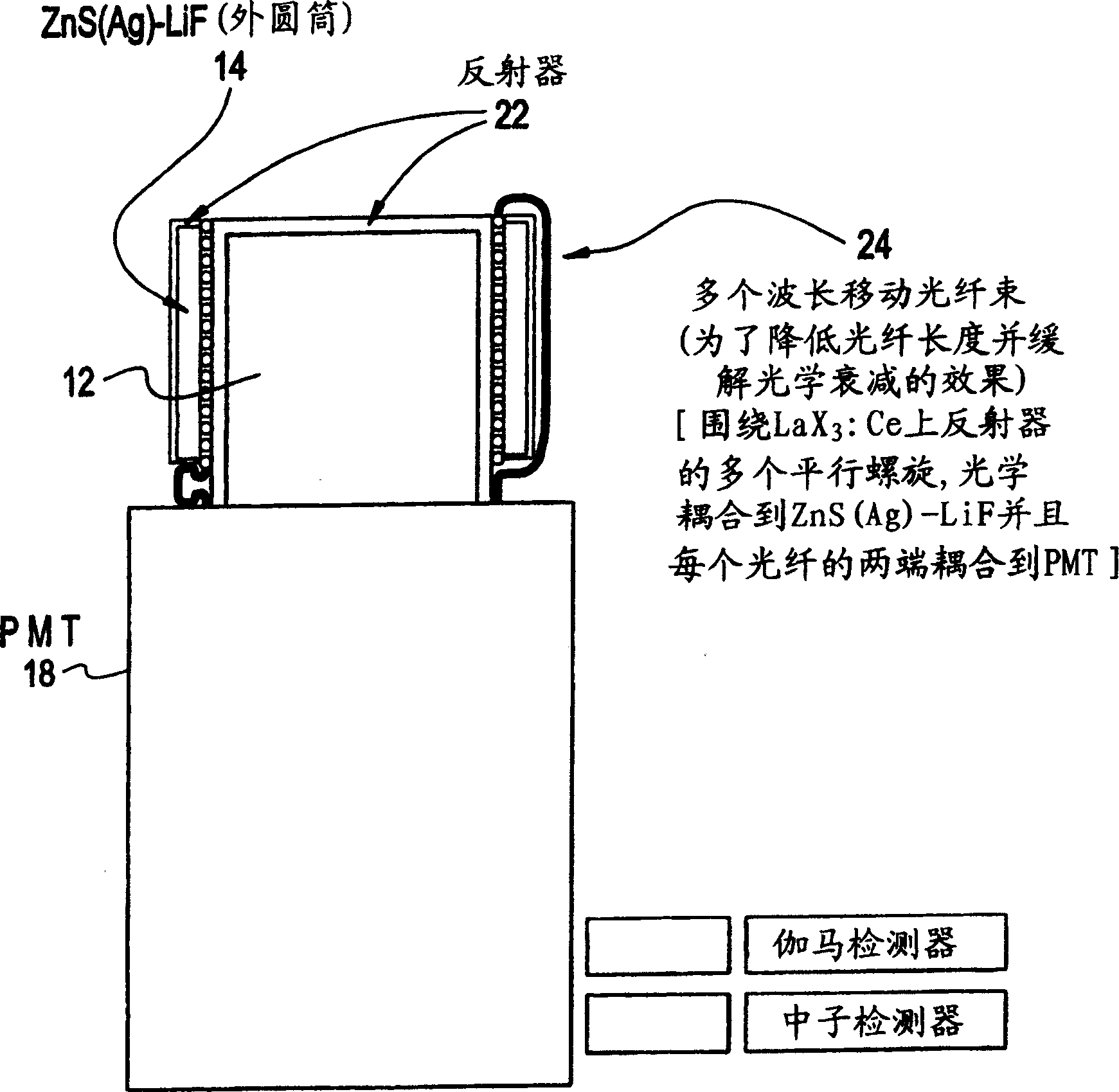
Gamma and neutron radiation detector
ActiveUS7335891B2Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillatorNeutron radiation
A sensing element or detector activated by radiation comprising a first scintillator activated by gamma radiation; and a neutron sensing layer comprising a second scintillator activated by neutron radiation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
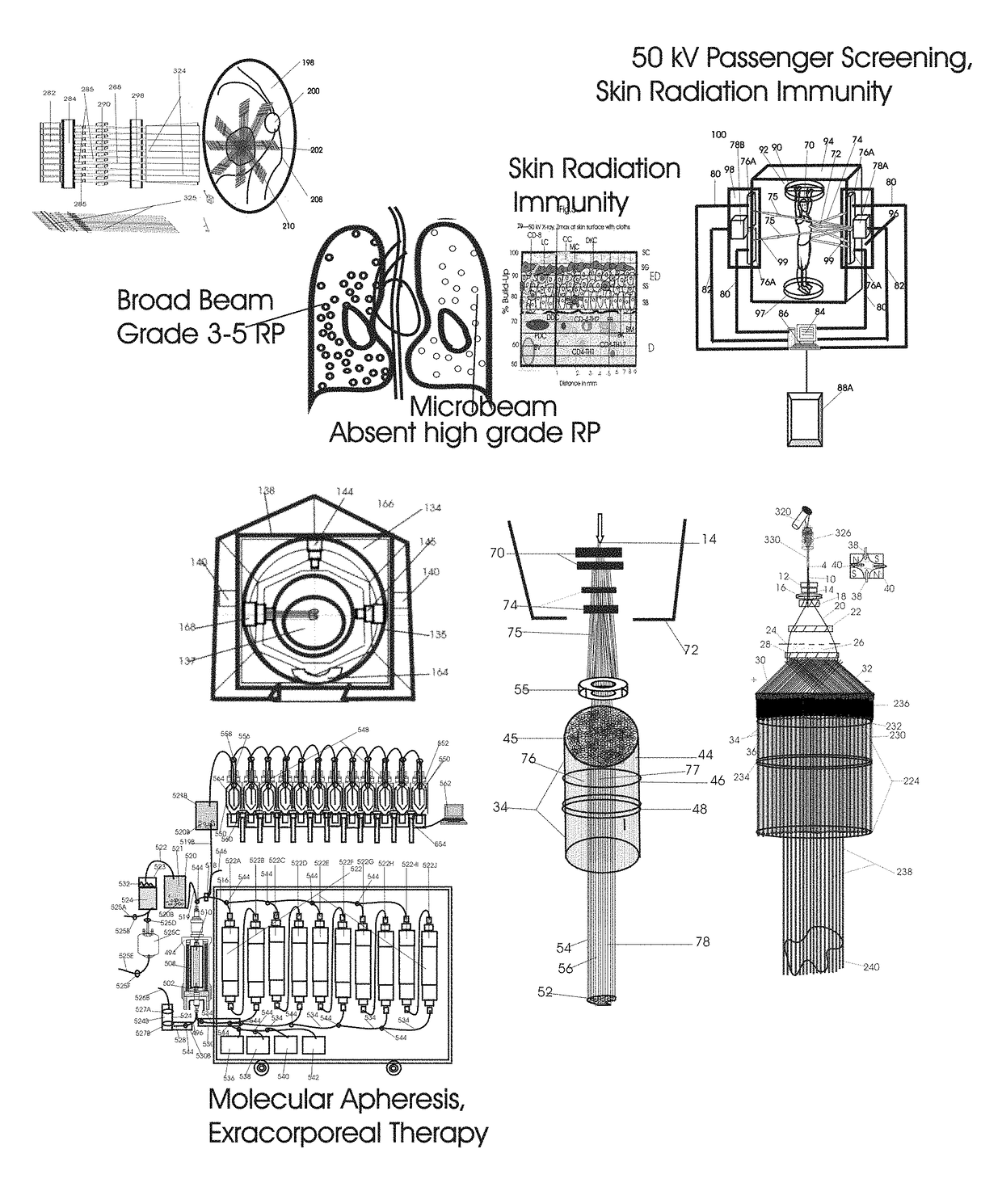
Normal Tissue Toxicity Reducing Microbeam-Broadbeam Radiotherapy, Skin's Radio-Response Immunotherapy and Mutated Molecular Apheresis Combined Cancer Treatments
InactiveUS20180154183A1Improve treatment outcomesIncreased toxicityOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationAbnormal tissue growthGamma ray
Normal tissue complications limit curative broadbeam radiotherapy to tumors including lung cancer. Radiation retinitis causing blindness limits quality of life and long term survival for patients with ocular melanoma. This invention pertains to alternative, normal tissue sparing 100 to 1,000 Gy microbeam radiations with least normal tissue complications and concomitant radio-immunotherapy by innate immune response of epidermis and dermis to low dose radiation with 50 kV X-rays. Total body skin radiation with former airport passenger screening machines with 50 kV X-ray is disclosed. Microbeams are generated without contaminating scatter and neutron radiations from collinear gamma ray and electron beam produced by inverse Compton interaction with high energy laser and electron beam and from proton and carbon ion beams in tissue equivalent cylindrical collimators. Extracorporeal immunotherapy and chemotherapy and apheresis of mutated subcellular particles released into circulation in response to cancer-therapies are by clinical continuous flow ultracentrifugation combined chromatography.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Anti-thermal neutron radiation shielding material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102708937AImprove mechanical propertiesAchieve the purpose of the inventionShieldingNeutron radiationRadiation resistance
The invention discloses an anti-thermal neutron radiation shielding material and a preparation method thereof. The anti-thermal neutron radiation shielding material is prepared by the following steps of: using rubber with radiation resistance as a matrix material; adding an anti-radiation additive which can shield thermal neutrons, a reinforced carbon black assistant and a processing assistant; and performing technical processes of a, mixing the rubber matrix, b, rolling and pre-forming the rubber matrix, c, vulcanizing and forming the rubber matrix, and the like to prepare the material. The anti-thermal neutron radiation shielding material provided by the invention has the shielding performance for the thermal neutrons, further, is good in flexibility, can be attached to the appearances of devices or apparatuses, and can be applied to surface protection of detectors such as a neutron diffraction spectrometer and the like and neutron protection of special curves.
Owner:北京富迪创业科技有限公司
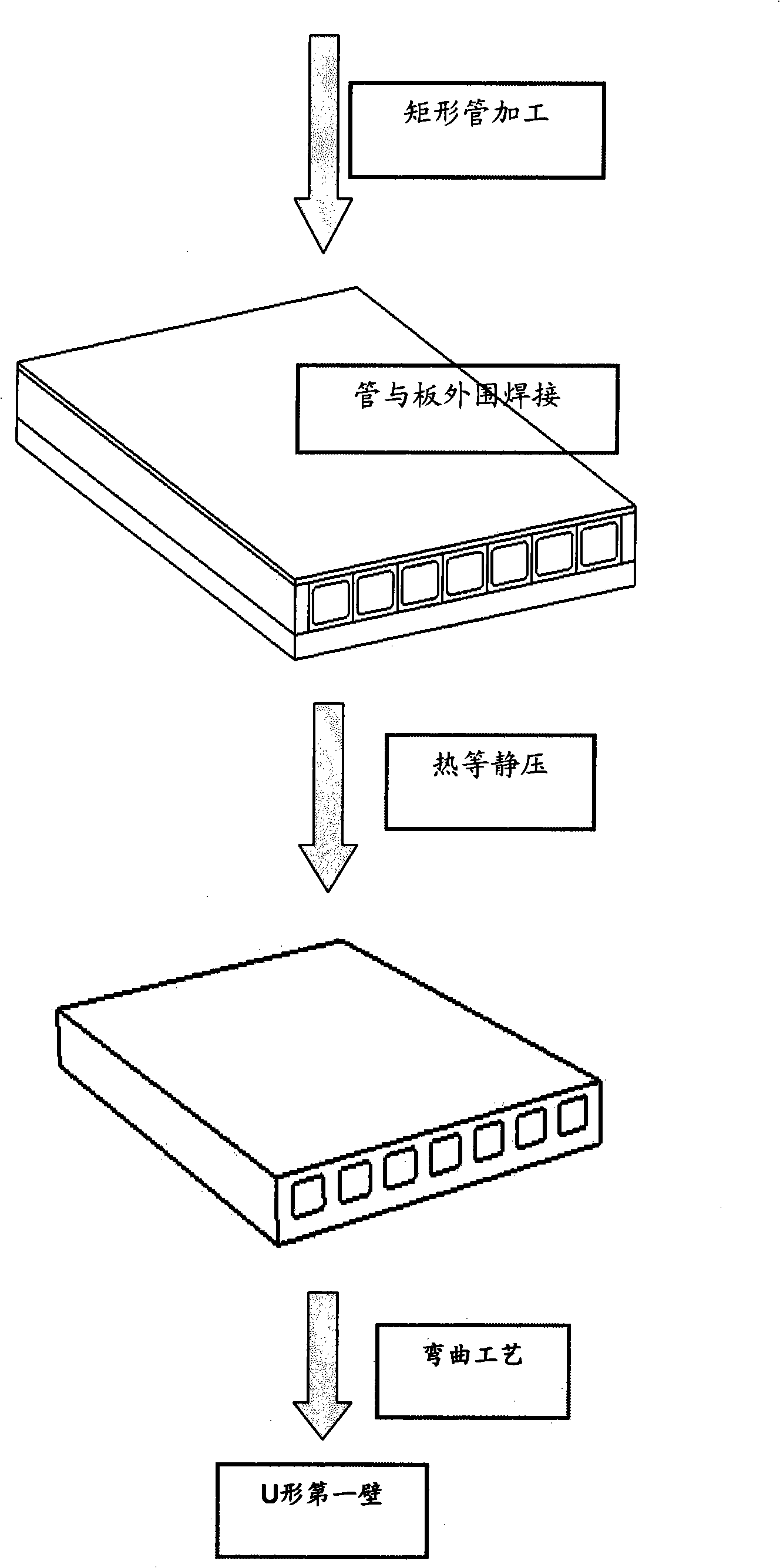
Manufacture technique for thermonuclear reactor flow-passage containing parts
InactiveCN101332557AImprove cleanlinessAvoid damageNon-electric welding apparatusAs elementHeat-affected zone
The invention discloses a production process applicable to runner-containing parts in a fusion reactor blanket. The production process includes the steps: first, a plate and a runner-containing rectangular tube are manufactured according to the design and undergo precision surface working, the roughness Ra is less than 6.3Mum; second, the runner-containing parts are cleaned and decontaminated and then heated in vacuum for degassing; third, the runner-containing parts are vacuumized in an electron beam welding machine and the periphery of the surface to be welded is hermetically welded; and then the runner-containing parts are put into a hot isostatic pressing furnace for forming by hot isostatic pressing diffusion welding; finally, bending forming, heat treatment and machining, and the like, are performed. By adopting the production process; the runner-containing parts manufactured by the production process have reliable and uniform comprehensive performance without the weak performance zones of the heat affected zone, and the like, resulting from the fusion welding process or the defects such as element segregation and air vent, and the like, existing in the similar casting parts, thereby, the production process is particularly applicable to the production of the runner-containing part with the fusion reactor blanket under the condition of intense neutron radiation.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
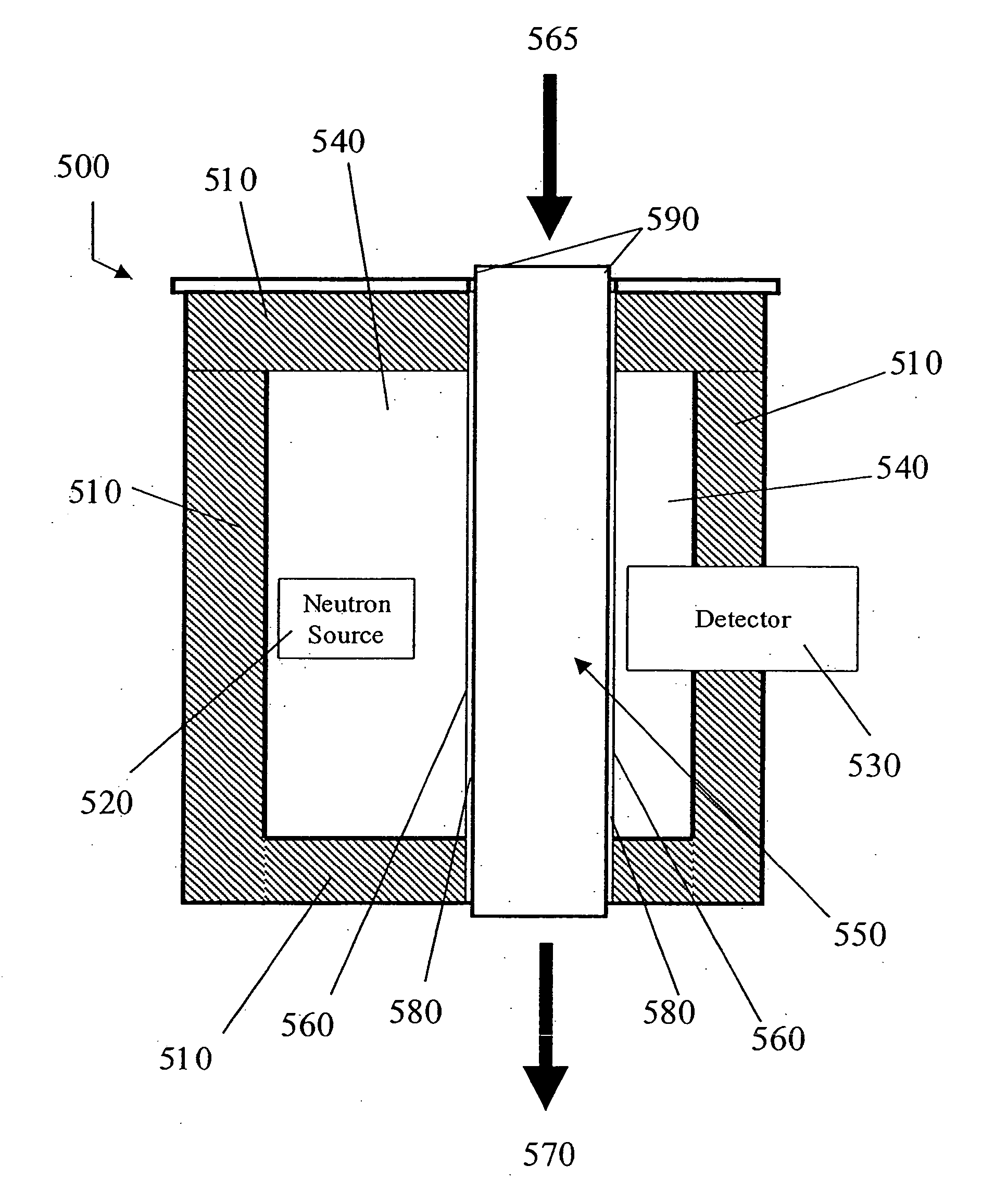
Optimized Detection of Fission Neutrons Using Boron Coated Straw Detectors Distributed in Moderator Material
InactiveUS20100301226A1Efficient detectionEasy to detectMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron radiation measurementFission neutronElectrical impulse
The present invention includes an apparatus and method for neutron radiation detection. The apparatus comprises combining thin walled, boron-coated straw tubes with a plastic moderator material interspersed around the tubes. The method involves using such an apparatus through application of voltage to a central wire running inside the tubes and collecting electrical pulses generated thereby.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
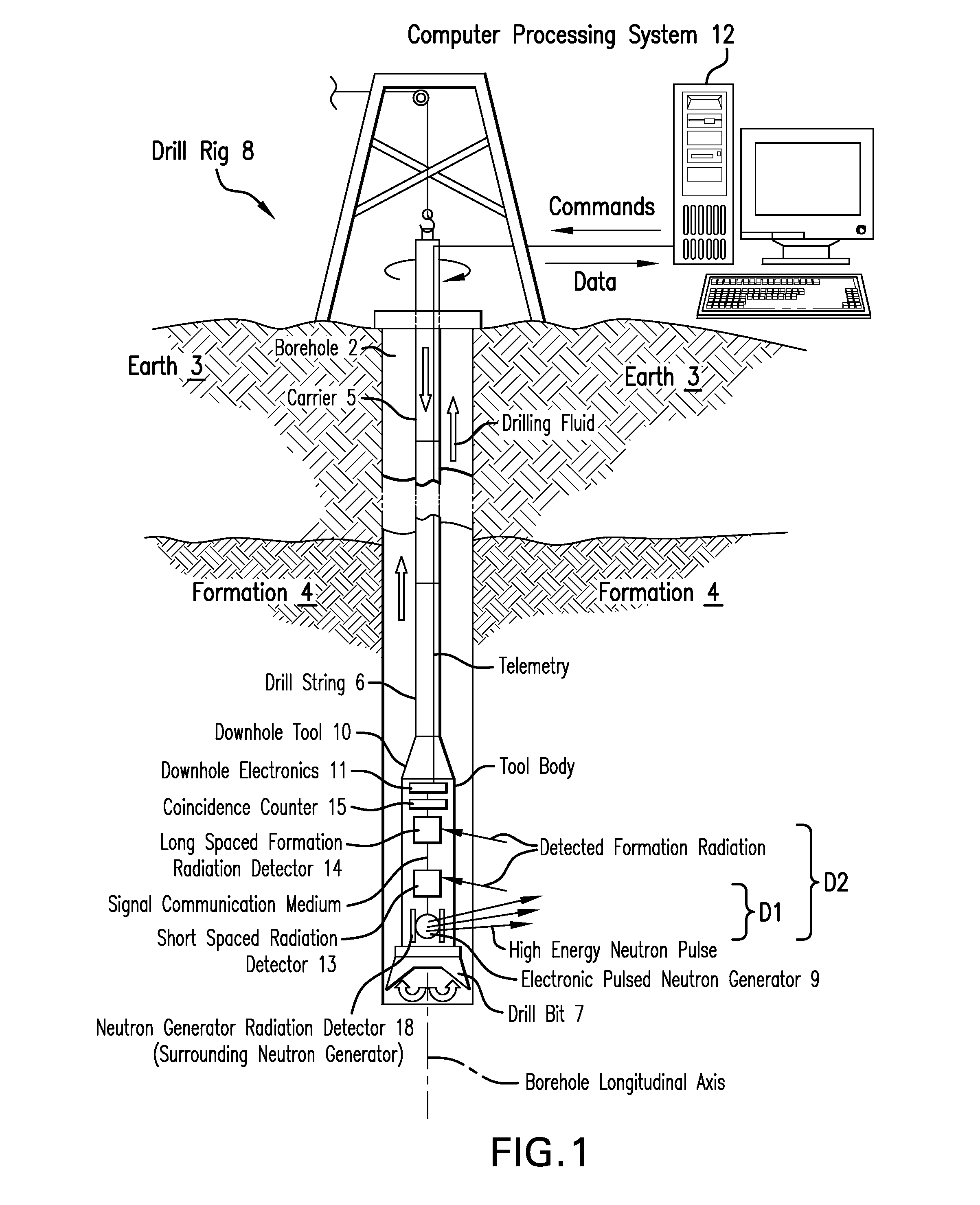
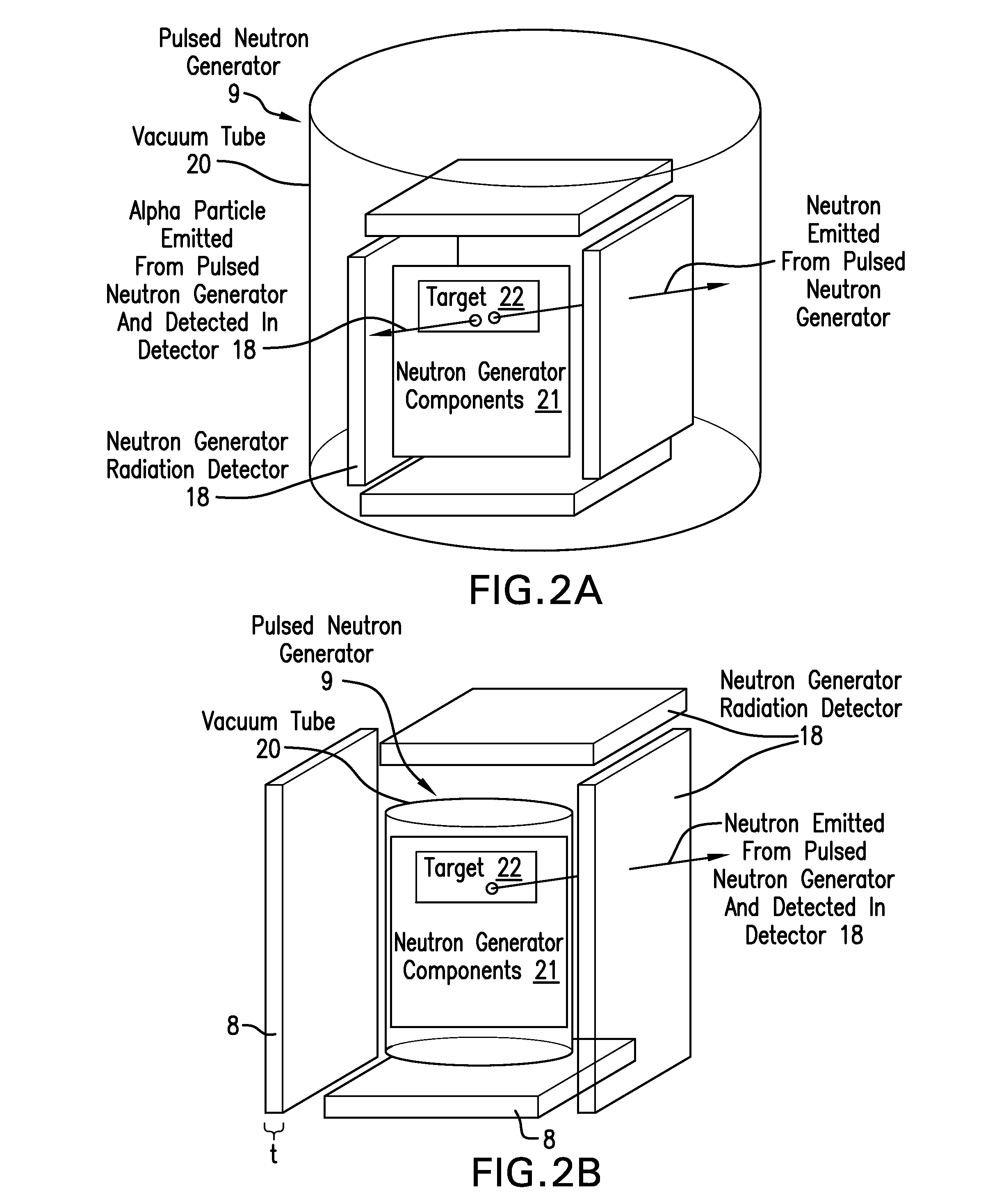
Measurement technique utilizing novel radiation detectors in and near pulsed neutron generator tubes for well logging applications using solid state materials
ActiveUS20150346382A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesNuclear radiation detectionWell loggingCrystal structure
An apparatus for estimating a property of an earth formation includes a pulsed neutron generator configured to emit a pulse of neutrons, a formation radiation detector configured to detect radiation emitted from the formation due to interactions with the pulse of neutrons, and a neutron generator radiation detector having a crystal structure and configured to detect a radiation particle emitted from the pulsed neutron generator and to provide a location within the neutron radiation detector at which the particle was detected. The crystal structure includes a plurality of detection cells, each detection cell having at least two electrically conducting columns with an applied potential difference such that electrons generated in the crystal structure by interaction with the radiation particle are collected by at least one of the electrically conducting columns to provide detection locations. A processor estimates the property using the detected formation radiation and the detection locations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
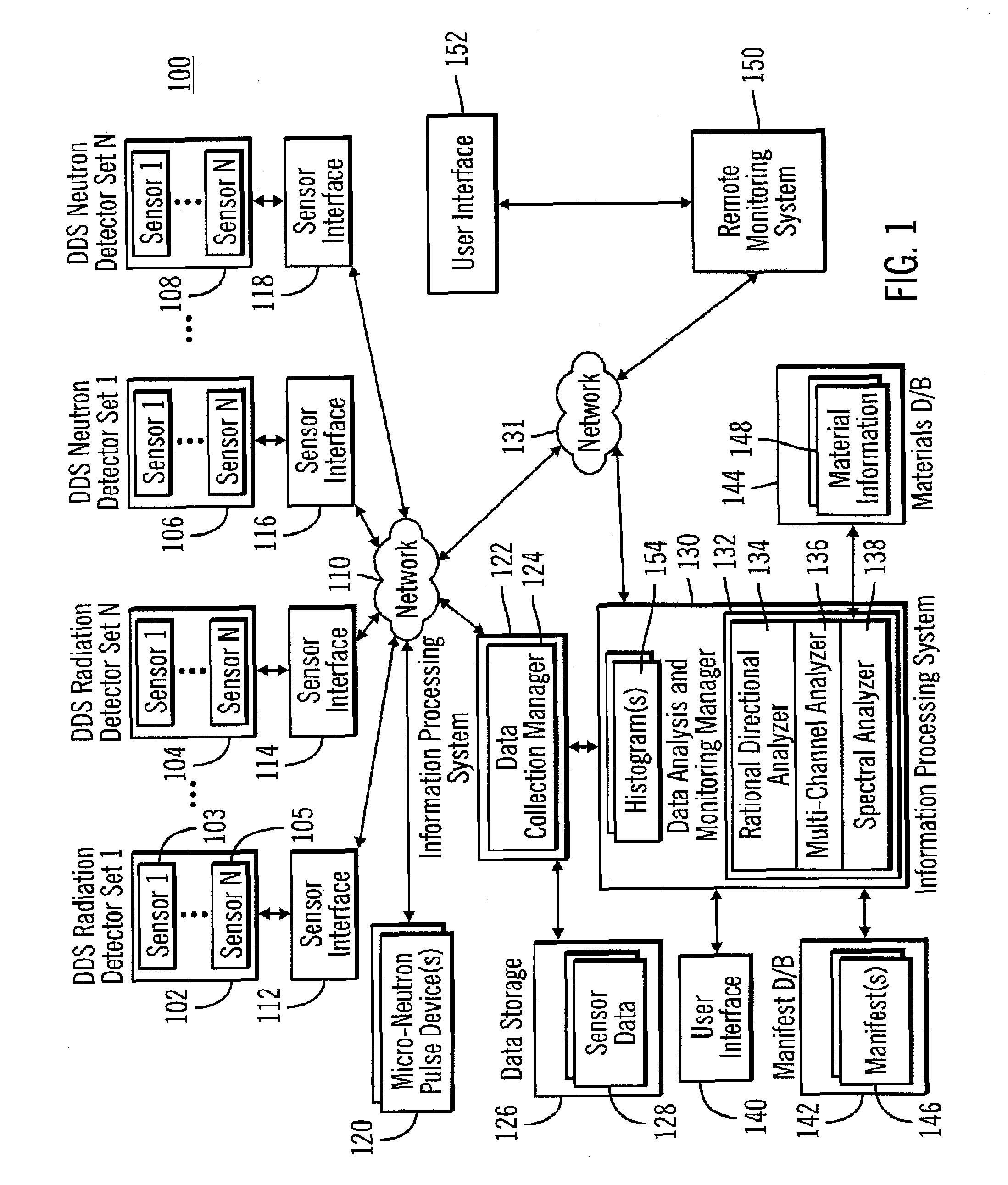
Radiation directional finder and isotope identification system
InactiveUS7994482B2Measurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesIsotopeNeutron radiation
A system and method determine a direction associated with gamma and / or neutron radiation emissions. A first radiation photon count associated with a first detector in a detector set is received from the first detector. The first radiation photon count is associated with at least one radiation source. A second radiation photon count associated with a second detector in the detector set is received from the second detector. The first radiation photon count is compared to the second radiation photon count. One of the first detector and the second detector is identified to have detected a larger number of radiation photons than the other. The at least one radiation source is determined to be substantially in a direction in which the one of the first detector and the second detector that has detected the larger number of radiation photons is facing.
Owner:ADVANCED MEASUREMENT TECH INC +2
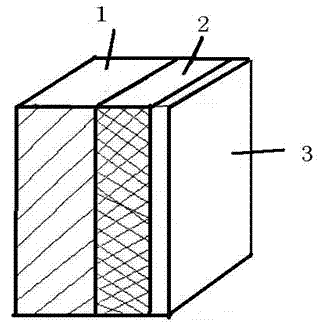
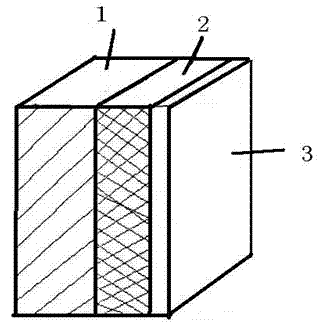
Laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102529239AFull functionHigh shielding efficiencySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationResin matrixBoron fiber
The invention discloses a laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material and a preparation method thereof; the laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material is in a three-layer composite structure, wherein a bottom layer is a polyethylene fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix, a middle layer is a boron fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix, and an upper layer is a polyethylene fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix which is grafted with acrylic lead. The epoxy resin matrixes comprise materials basically in the following weight portions: 100 portions of bisphenol A epoxy resin, 8 portions to 15 portions of imidazole curing agent and 3 portions to 7 portions of silane coupling agent. In addition, boron carbide (B4C) which occupies 5 weight percent to 20 weight percent of the total weight of the epoxy resin is added into the epoxy resin matrix on the bottom layer; and lead oxide which occupies 10 weight percent to 30 weight percent of the total weight of the epoxy resin is added into the epoxy resin matrix on the upper layer. The laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material is specially manufactured to overcome the defects of a traditional neutron radiation shielding composite material that slowing and absorption functions are not separated so that the functions of an absorbing body cannot be displayed well.
Owner:南京核安核能科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for analysis of elements in bulk substance
InactiveUS7152002B2Reduce heatReduce excitationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNeutron radiationAnalysis method
A substance analyzer utilizing Prompt Gamma Neutron Activation Analysis for identifying characteristics of a substance and method of manufacturing the same are disclosed. The analyzer is small enough to be portable and to allow its use in many applications where current analyzers cannot be utilized. The analyzer uses a neutron radiation source and a gamma-ray detector to activate the sample material and detect the prompt gamma rays emitted by the sample material. A novel housing for such an analyzer and method for making the housing are also described. Novel methods of operating such an analyzer including via a communications network are also disclosed. Also disclosed are data analysis methods that improve the accuracy and sensitivity of the results of such material analysis.
Owner:ARATAY INC
Ultra-thin neutron radiation preventive composite shielding material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102693767AThe overall thickness is thinThe thin anti-neutron radiation composite shielding material has a thin thicknessShieldingHydrogenNuclear power
The invention discloses an ultra-thin neutron radiation preventive composite shielding material and a preparation method thereof. A hydrogen-rich compound is used as a base material, a baron-containing compound is used as a neutron absorber, a small quantity of function auxiliaries are added, and the ultra-thin neutron radiation preventive composite shielding material is prepared at a certain temperature or under pressure conditions by processing technologies including quantitative weighing, heating and mixing, high-temperature mould pressing and sizing, and the like. The preparation process is simple, operation is convenient, and the prepared ultra-thin neutron radiation preventive shielding material has the advantages of thinness, high baron content and fine shielding performance, and is widely applied to the field of neutron radiation protection and research in various places such as nuclear power plants, isotope radiation sources, accelerators, medical neutron treatment equipment and radiation laboratories.
Owner:北京富迪创业科技有限公司
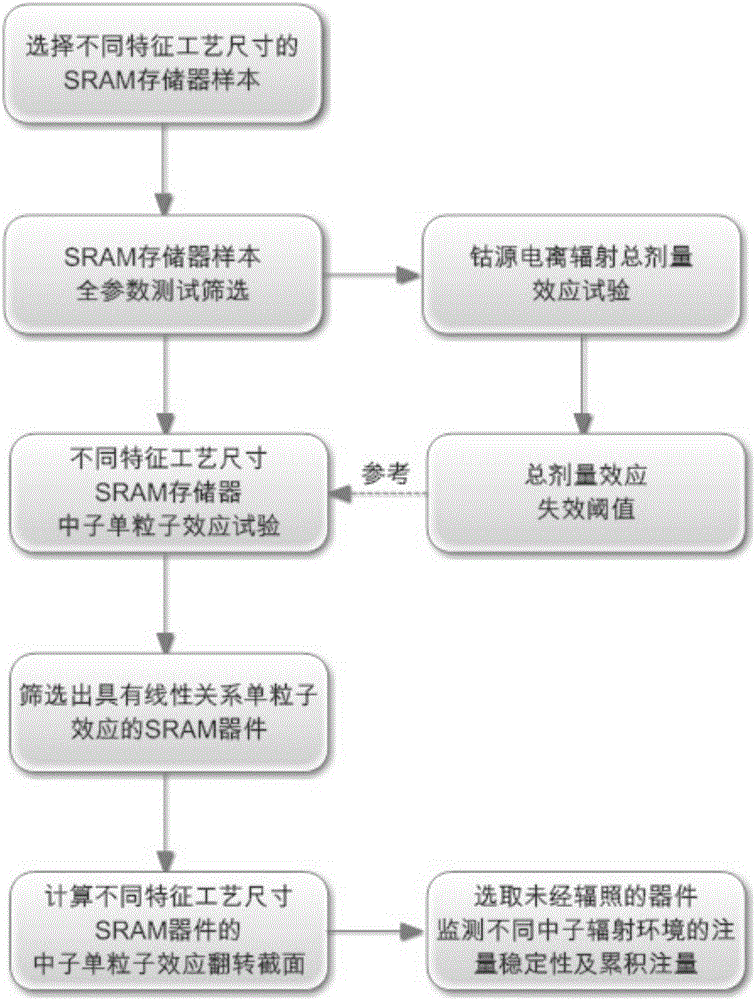
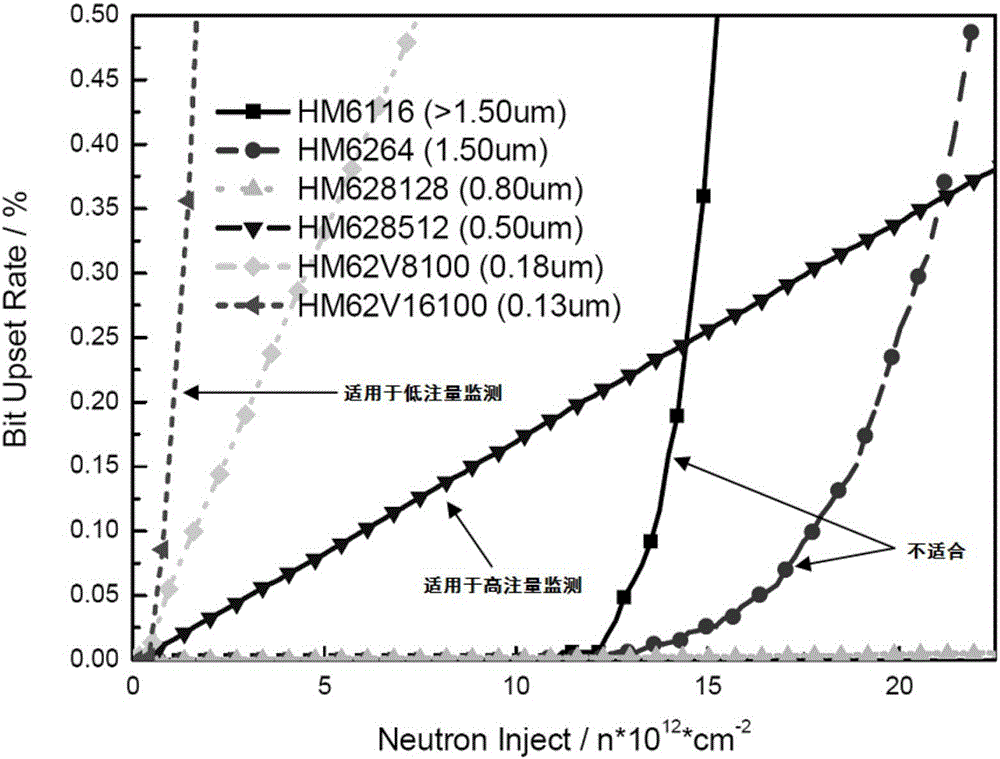
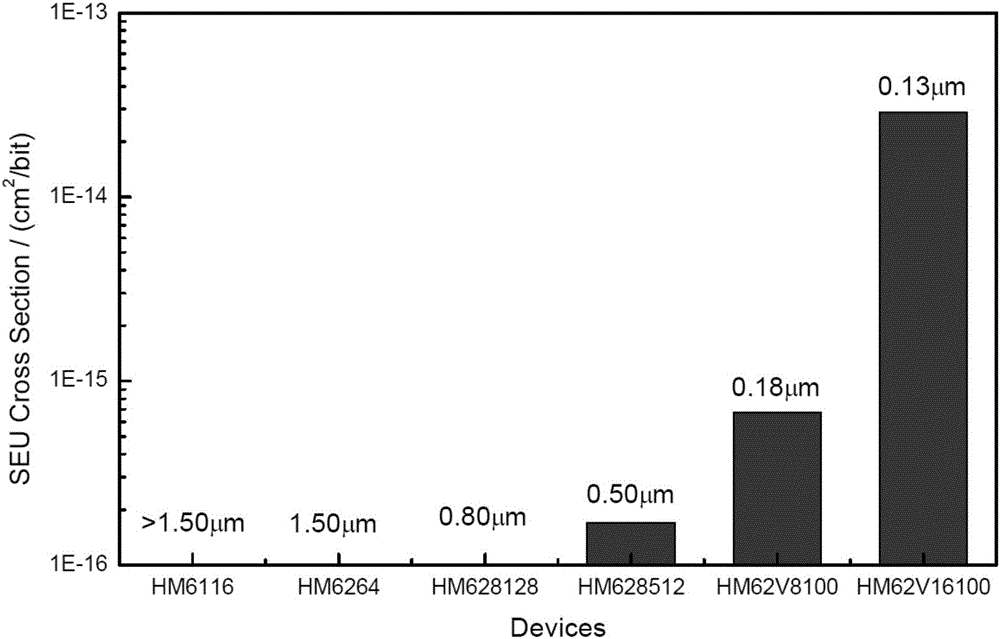
Method for monitoring neutron radiation environment by using SRAM memorizers
ActiveCN106842282ARealize fluence monitoringImprove measurement accuracyMeasurement with semiconductor devicesDigital storageNeutron radiationLinearity
The invention belongs to the field of radiation detection and relates to a method for monitoring the neutron radiation environment by using SRAM memorizers. The method includes the following steps that 1, neutron radiation calibration is conducted on SRAM memorizers different in types respectively, and a relation curve of the data flipping number and the neutron fluence are drawn; 2, the N type SRAM memorizer with the data flipping number keeping a linear relation with the neutron fluence is screened out, and the slope of the fitting curve serves as the neutron single ion effect flipping section of the N type SRAM memorizer; 3, the N type SRAM memorizer is placed in a to-be-monitored neutron radiation environment, and a relation curve of the data flipping number and the neutron fluence is drawn. According to the method, the linear and non-threshold characteristics of the neutron single ion flipping effects of the SRAM memorizers are made use of, neutron fluence monitoring in a reactor, a neutron accelerator and other neutron radiation environments is achieved, and experimental results show that the method can still maintain high measurement when the neutron fluence is very low.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Compensation type neutron dose instrument
InactiveCN102928867AIncreased fluence responseDecreased fluence responseNeutron radiation measurementNeutron doseGamma ray
The invention aims at providing a compensation type neutron dose instrument which comprises a packaging layer, a slowing-down sphere body and a heavy metal layer, wherein the slowing-down sphere body is arranged in the packaging layer, a neutron fission multiplication layer is arranged between the slowing-down sphere body and the packaging layer, the heavy metal layer is arranged in the slowing-down sphere body, a counter is arranged in the heavy metal layer, and an air rod is arranged in the slowing-down sphere body along a radial direction. According to the invention, neutron fluence response in a heat energy region can be improved, the neutron fluence response in an intermediate energy region can be correspondingly reduced, and accompanying Gamma rays in a neutron radiation field can be shielded.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Gas-phase doping-area fused silicon monocrystal production method
InactiveCN1455028ALow resistivityDoes not affect the distributionBy zone-melting liquidsVacuum pumpingGas phase
The gas phase doping zone molten-silicon monocrystal production method includes the following steps: (1) charging and vacuum-pumping; (2). preheating silicon rod; (3) melting material; (4) doping, setting gap flow control parameter on the doping gas control device; (5), joining seed crystal by fusion; (6) leading crystal; (7) growing thin nack; (8) shouldering; (9) isodiametric growing; (10) ending and draw-breaking; (11) stopping gas; and (12) stopping furnace and removing furnace. Said invention saves the neutron radiation doping process so as to shorten production period and reduce production cost, and reduce production procedure.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for fast neutron measurement
InactiveCN103163550ASimple structureReduce volumeMeasurement with scintillation detectorsScintillation counterNeutron radiation
The invention relates to the radiometric technology and in particular to an optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for fast neutron measurement. The optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for the fast neutron measurement comprises a scintillation probe which is formed by blending of fast neutron sensitive materials and scintillating mediums, a transmission optical fiber and a photovoltaic sensitive component, wherein one end of the transmission optical fiber is inserted in the middle of the scintillation probe, the other end of the transmission optical fiber is connected with the photovoltaic sensitive component, and an optical wrapping layer of one part, arranged in the scintillation probe, of the transmission optical fiber is removed. The optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for the fast neutron measurement has the advantages of being simple in structure, small in size, strong in environment adaptability, capable of achieving on line real-time monitoring and the like, and can meet the demand of fast neutron measurement under complex and severe environment.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
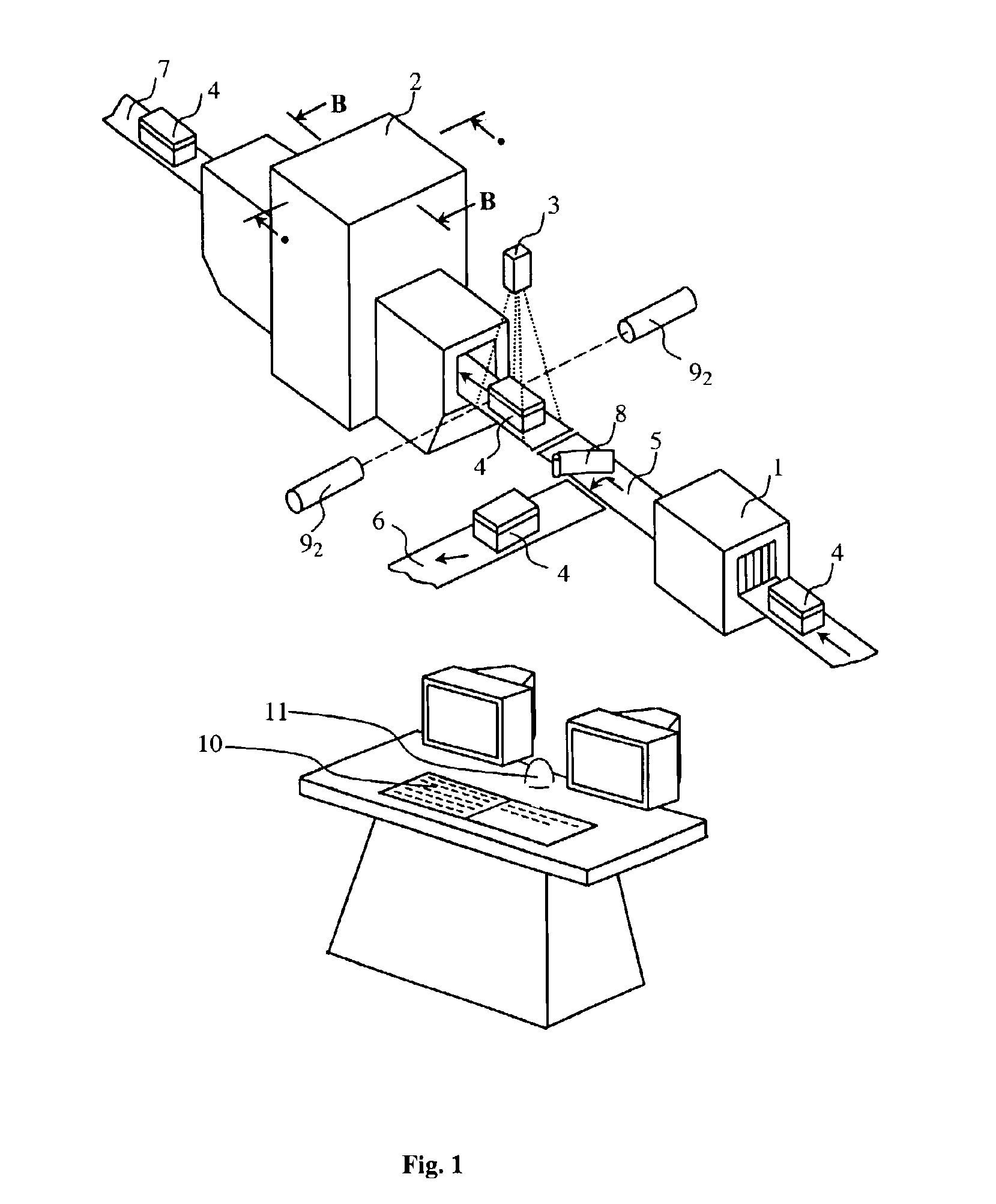
Method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation
InactiveUS6928131B2Reduce probabilityReduce false alarm rateConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsSolid-state devicesNeutron irradiationX-ray
A method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation involves the initial X-ray irradiation of the object under investigation, e.g. a piece of luggage or mailing, and forming its X-ray images; using the X-ray images to detect areas with a high density of organic materials and identifying articles therein; determining the location, dimensions and supposed mass of an unidentified article; determining and forming a directional pattern of the neutron radiator corresponding to the dimensions of the unidentified article. The method further includes subsequent thermal neutron irradiation of the area with the unidentified article; recording gamma-ray quanta having the energy of 10.8 MeV and cascade gamma-ray quanta with energies of 5.534 and 5.266 MeV by at least two gamma-ray detectors; counting of simultaneously recorded pairs of cascade gamma-ray quanta; determination of the overall gamma-ray intensity, taking into account weight factors in readings of the detectors; determination of the threshold value for the overall gamma-ray intensity basing on the supposed mass of explosive being detected; and making a decision in the event the threshold value of overall gamma-ray intensity is exceeded. When checking small-size objects, the neutron irradiation step is preceded by replacing the ambient air by a gaseous medium not containing nitrogen.
Owner:SCI & TECHN CENT RATEC
Anti-neutron size putty
ActiveCN101302367AImprove shielding effectMeet construction needsFilling pastesNeutron moderatorDrying time
The invention provides a quick dry type neutron-shielding lacquer putty and a method for preparing the same. The quick dry type neutron-shielding lacquer putty is used for filling a hole or an aperture of a neutron radiant point shielding structure in order to reduce the leakage of neutron radiation and improve the whole protective performance of a shielding system. The material is prepared by adopting a coagulant, a neutron moderator, a neutron absorber, a colorant, water and other compositions mixed together. The quick dry type neutron-shielding lacquer putty has good neutron-shielding performance, short drying time, simple structure, convenient construction, strong practicability and good economical benefit.
Owner:北京富迪创业科技有限公司 +1
Method of and apparatus for transmuting radioactive waste
InactiveUS20050013397A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationExpansion tankParticle accelerator
A radiocactive waste containing medium is circulated within two or more systems (1,2,3) separated from each other flowtechnically; and the circulated radioactive waste is exposed to neutron radiations of different energy spectrum in each system by operating a reactor physically united entirety of irradiated sections of the said systems as a nuclear reactor or an accelerator driven subcritical system. Each system (1,2,3) has a heat exchanger (9,10) and, in given cases, a circulating pump (10,21) and an expansion tank (5,16,27). The disclosed apparatus has two or more reactor regions (1,2,3) separated from each other by partitions (37,38) and, preferably, arranged coaxially within a reactor space encircled by a common shell structure (39). A particle beam (45) produced by a particle accelerator is preferably directed into the innermost reactor region (3).
Owner:BUDAPESTI MUSZAKI & GAZDASAGTUDOMANYL EGYETEM
Optimized detection of fission neutrons using boron coated straw detectors distributed in moderator material
InactiveUS8569710B2Efficient detectionEasy to detectMeasurement with semiconductor devicesDosimetersFission neutronElectrical impulse
The present invention includes an apparatus and method for neutron radiation detection. The apparatus comprises combining thin walled, boron-coated straw tubes with a plastic moderator material interspersed around the tubes. The method involves using such an apparatus through application of voltage to a central wire running inside the tubes and collecting electrical pulses generated thereby.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
Gamma and neutron radiation detector
InactiveCN1892252AMeasurement with scintillation detectorsRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorNeutron radiation
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
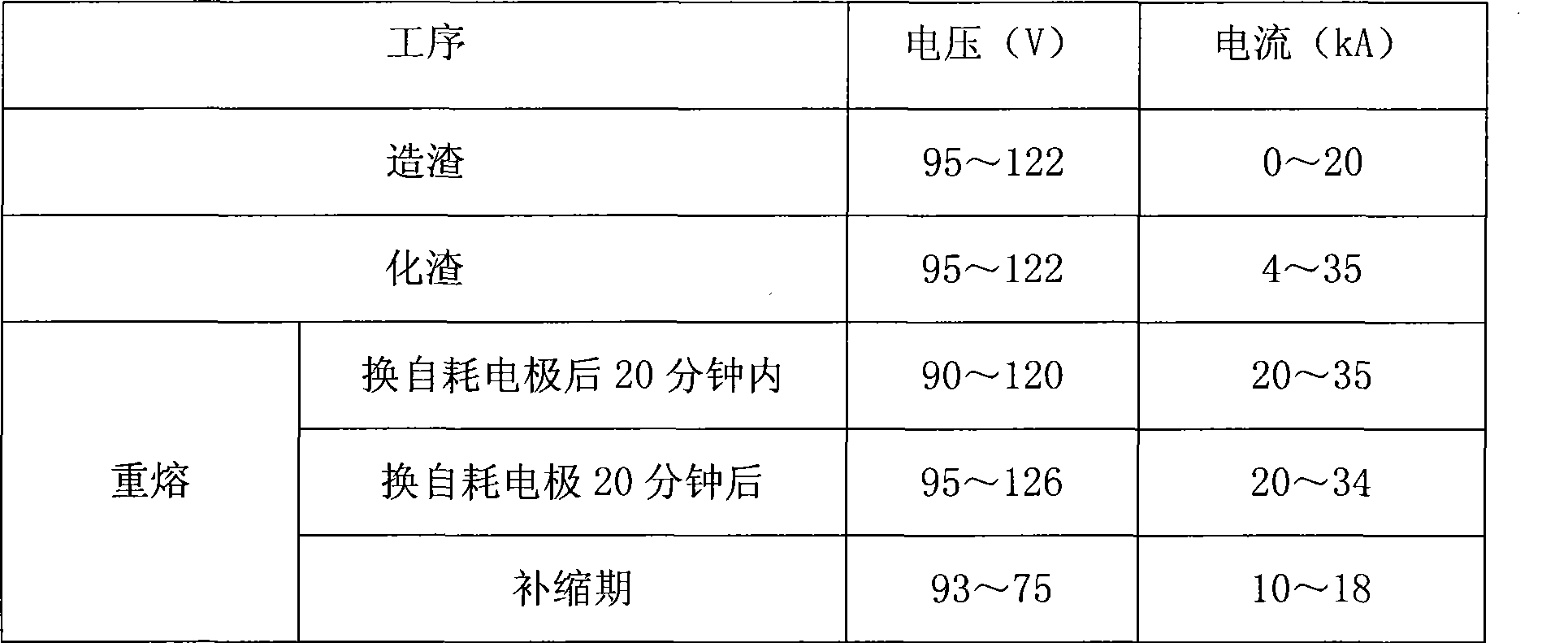
Manufacture method of steel ingot for million multikilowatt nuclear electricity pile core component
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a steel ingot used for million-kilowatt nuclear power reactor core structural component, austenitic stainless steel ingot that weighs over 25 tons is manufactured by electroslag remelting process: firstly, preparation: a single-phase bipolar series connected or triphase bipolar series connected electroslag remelting furnace is adopted; a copper wall water-cooling crystallizer and a water-cooled base plate are adopted; a consumable electrode is assembled; slag charge is matched; SiGa and Al powder are adopted for deoxidation; secondly, refinement and fusion casting: a graphite electrode is picked up and replaced by the consumable electrode to remelt the fully melted slag charge after slagging and slugging. When the actual weight of the steel ingot is 2 tons less than the preset weight, the electric power is reduced and feeding operation in telophase is carried out; thirdly, the steel ingot is stripped. The steel ingot manufactured by the invention has extremely high purity, extremely fine uniformity, excellent high temperature resistance and tarnish resistance, as well as strong anti neutron radiation embrittlement sensibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC SHMP CASTING & FORGING CO LTD +1
High-temperature resisting shielding material with neutron shielding effect
The invention relates to the field of nuclear radiation screening and protecting, and particularly relates to a high-temperature resisting shielding material with a neutron shielding effect, which is used for screening and protection of neutron radioactive sources such as isotopic neutron source, nuclear reactors, accelerators and the like. The material comprises the following components parts by weight: 40 to 50 parts of basis material, 40 to 50 parts of curing agent, 5 to 10 parts of wild phase particles, and 1 to 5 parts of modified particles. The material has a strong irradiation resisting performance, has a strong mechanical property, is used for screening and protecting to neutron radiation, and can bear the high temperature which is more than 200 DEG C.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Method and apparatus for analysis of elements in bulk substance
InactiveUS20070095157A1Reduce heatReduce excitationSamplingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAnalysis methodNeutron radiation
A substance analyzer utilizing Prompt Gamma Neutron Activation Analysis for identifying characteristics of a substance and method of manufacturing the same are disclosed. The analyzer is small enough to be portable and to allow its use in many applications where current analyzers cannot be utilized. The analyzer uses a neutron radiation source and a gamma-ray detector to activate the sample material and detect the prompt gamma rays emitted by the sample material. A novel housing for such an analyzer and method for making the housing are also described. Novel methods of operating such an analyzer including via a communications network are also disclosed. Also disclosed are data analysis methods that improve the accuracy and sensitivity of the results of such material analysis.
Owner:ARATAY INC
Method for eliminating counting loss of dose equivalent instrument around neutron
InactiveCN101082674ASimple structureHandling data is simpleNeutron radiation measurementDiscriminatorNeutron radiation
The invention discloses an eliminating method of error in omission of dosage equivalent meter around neutron in the pulse neutron radiation field or strong neutron radiation field applying technical domain, which is characterized by the following: utilizing charge quantity output by BF3 proportional pipe to be direct ratio to energy loss of electric particle in the pipe to test over two neutrons; increasing the output pulse amplitude; connecting multiple discriminators at the back of the equivalent meter to correspond to overlapped threshold of one, two and three neutrons; transmitting the output pulse of different discriminators into microprocessor; calculating the real dosage equivalent according to the probability of the overlapped energy spectrum; correcting the omission number. The invention is easy to process data with simple structure, which can correct the omission number effectively.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ambient neutron dose equivalent meter
InactiveCN102043161ALightweight instrumentEasy to carry and useMeasurement with scintillation detectorsScintillation crystalsNeutron radiation
The invention aims to disclose an ambient neutron dose equivalent meter. The ambient neutron dose equivalent meter is characterized by comprising a neutron probe, a neutron energy response adjustor and a control system, wherein a neutron detection element is arranged in the neutron probe, the neutron detection element is europium-doped lithium iodide scintillation crystal, the signal output end of the neutron probe is connected with the signal input end of the control system, and the neutron probe is placed at the position of the geometric center of the neutron energy response adjustor. Because the photomultiplier with high sensitivity is used as a photoelectric converter, the meter has light weight, portability, sensitive neutron response and good angle response, can accurately measure the ambient neutron dose equivalent level, has sound and light alarm function, is used for ambient neutron radiation monitoring of large nuclear facilities such as reactors, high-energy particle accelerators and the like, ensures neutron radiation safety of the ambient and the public, and fulfills the purpose of the invention.
Owner:上海新漫传感科技有限公司
Fast neutron spectroscopy using neutron-induced charged particle reactions
ActiveUS20110266451A1Good neutron/gamma discrimination propertyHigh energy resolution characteristicMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansPulse heightSpectroscopy
The invention provides a method of performing fast neutron detection or spectroscopy comprising selecting at least one isotope which exhibits fast neutron-induced charged particle reactions, selecting a host medium capable of performing radiation energy spectroscopy, combining the isotope and host medium into an interactive spectroscopic combination, exposing the combination structure to radiation comprising fast neutrons to provide a spectroscopic output, which includes at least one peak in the pulse-height spectrum whose height and amplitude correlate to the energy and intensity respectively of the incident neutrons; and processing the output to detect or to provide measurements of the energy and intensity of incident fast neutron radiation. The invention also provides a fast neutron spectrometer for use with the method.
Owner:BUBBLE TECH INDS
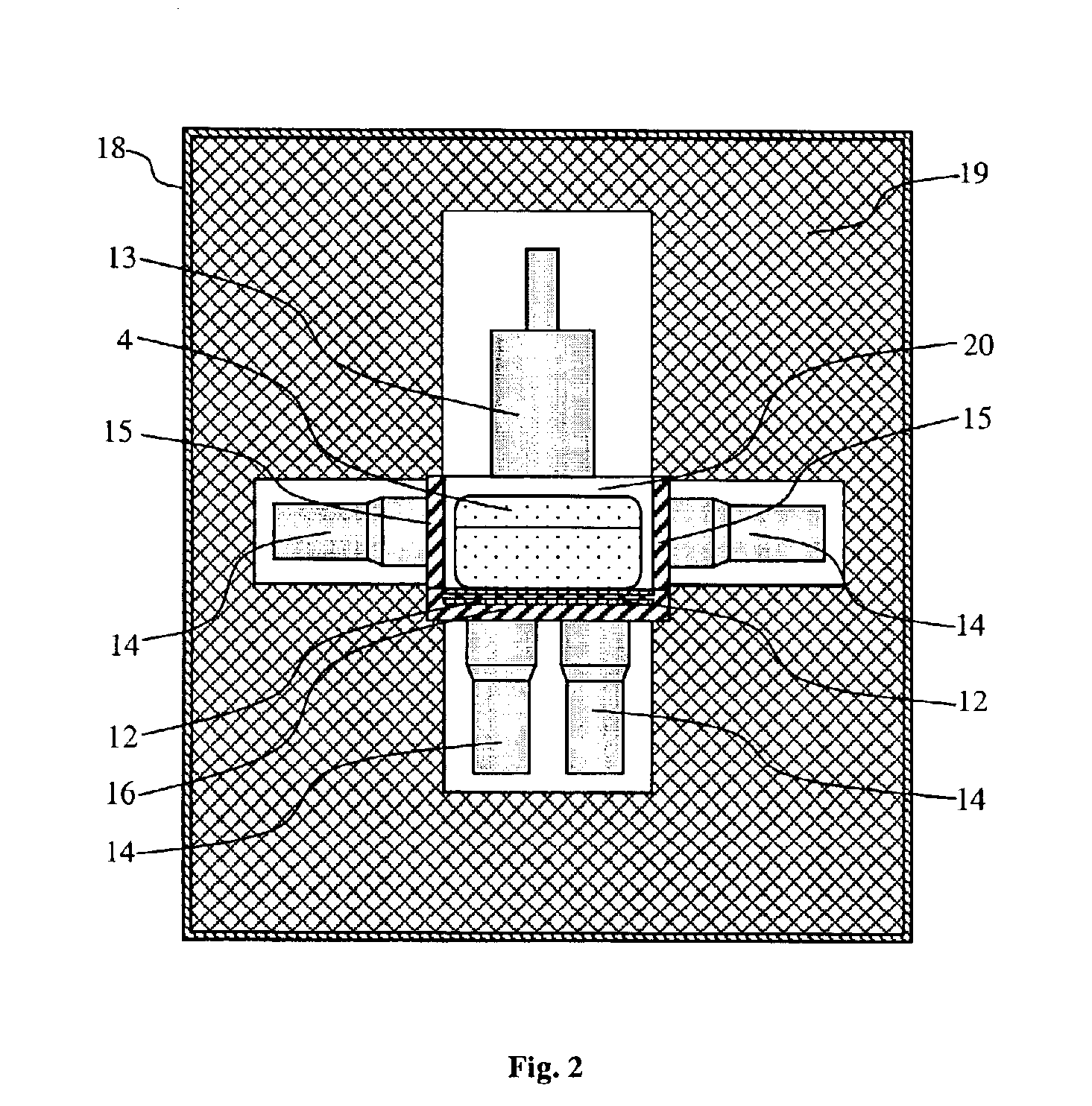
Dosimeter for the detection of neutron radiation
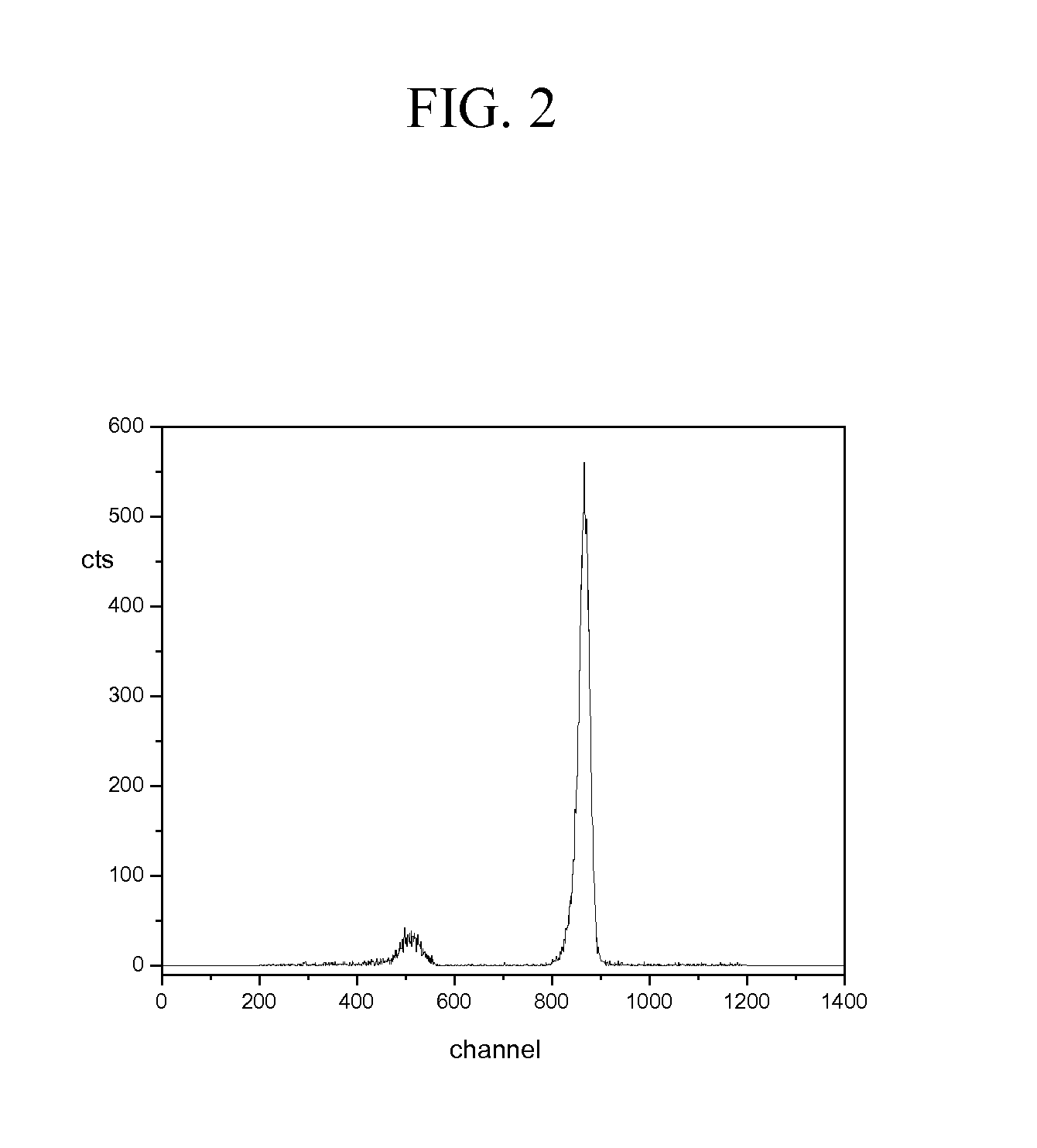
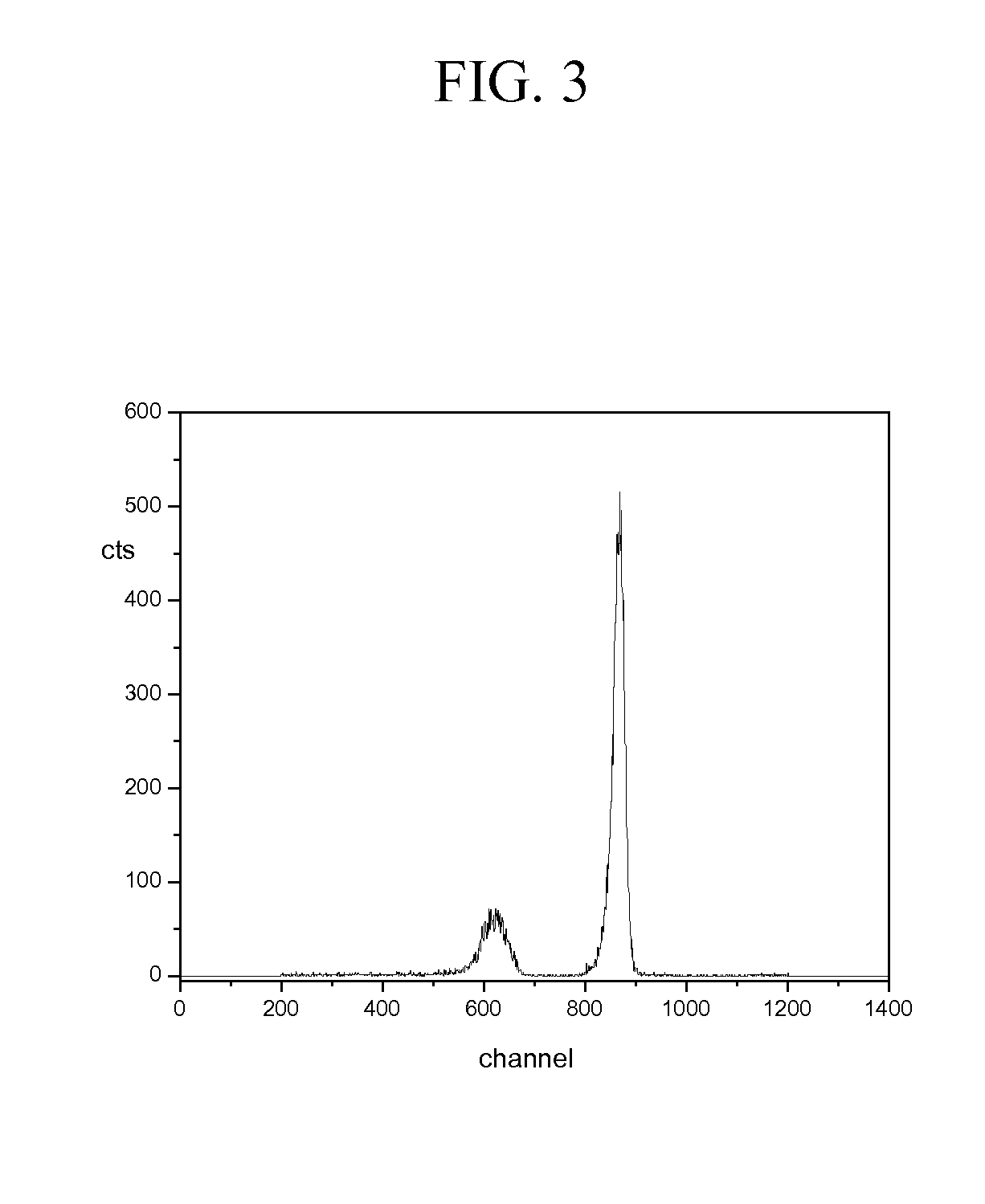
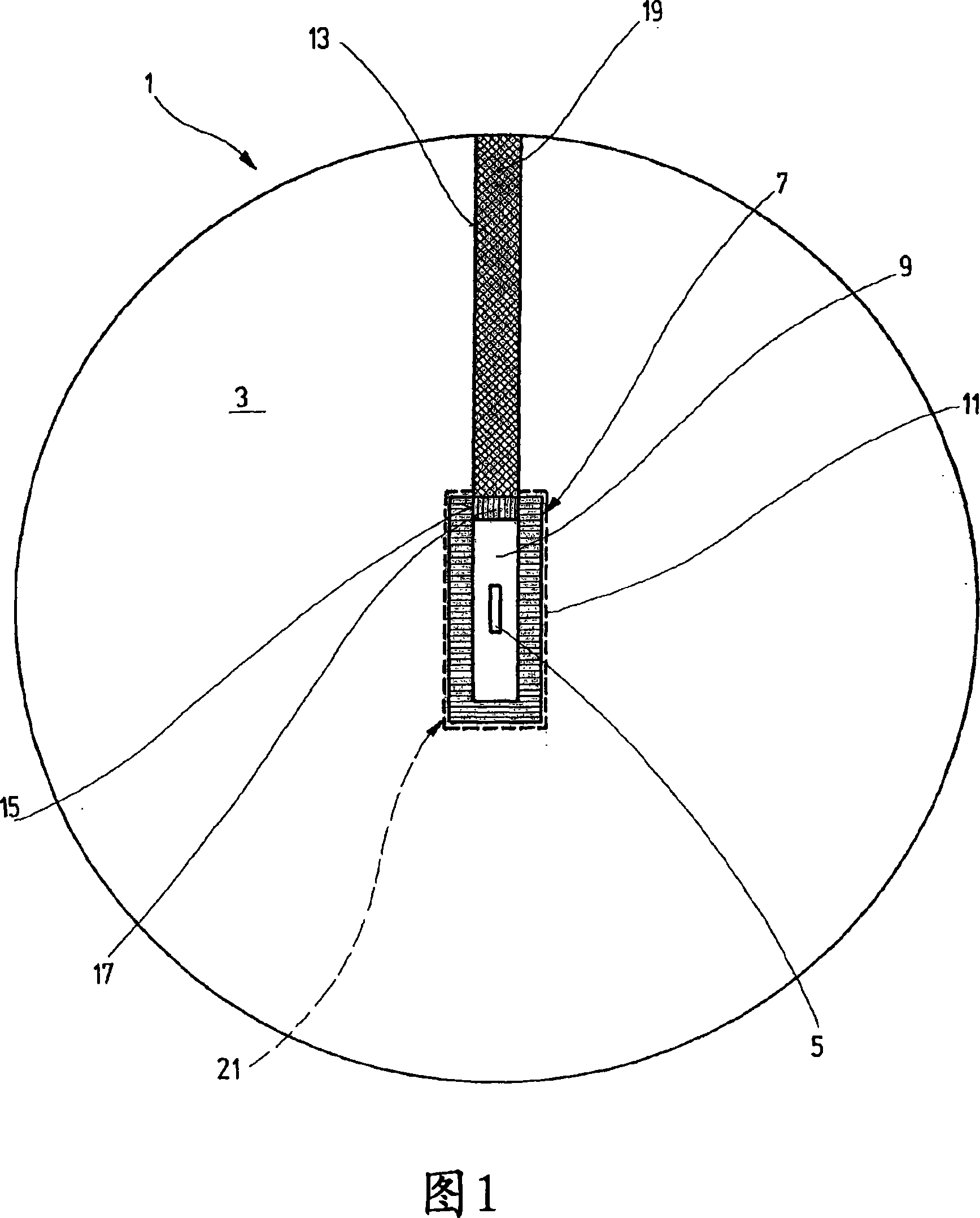
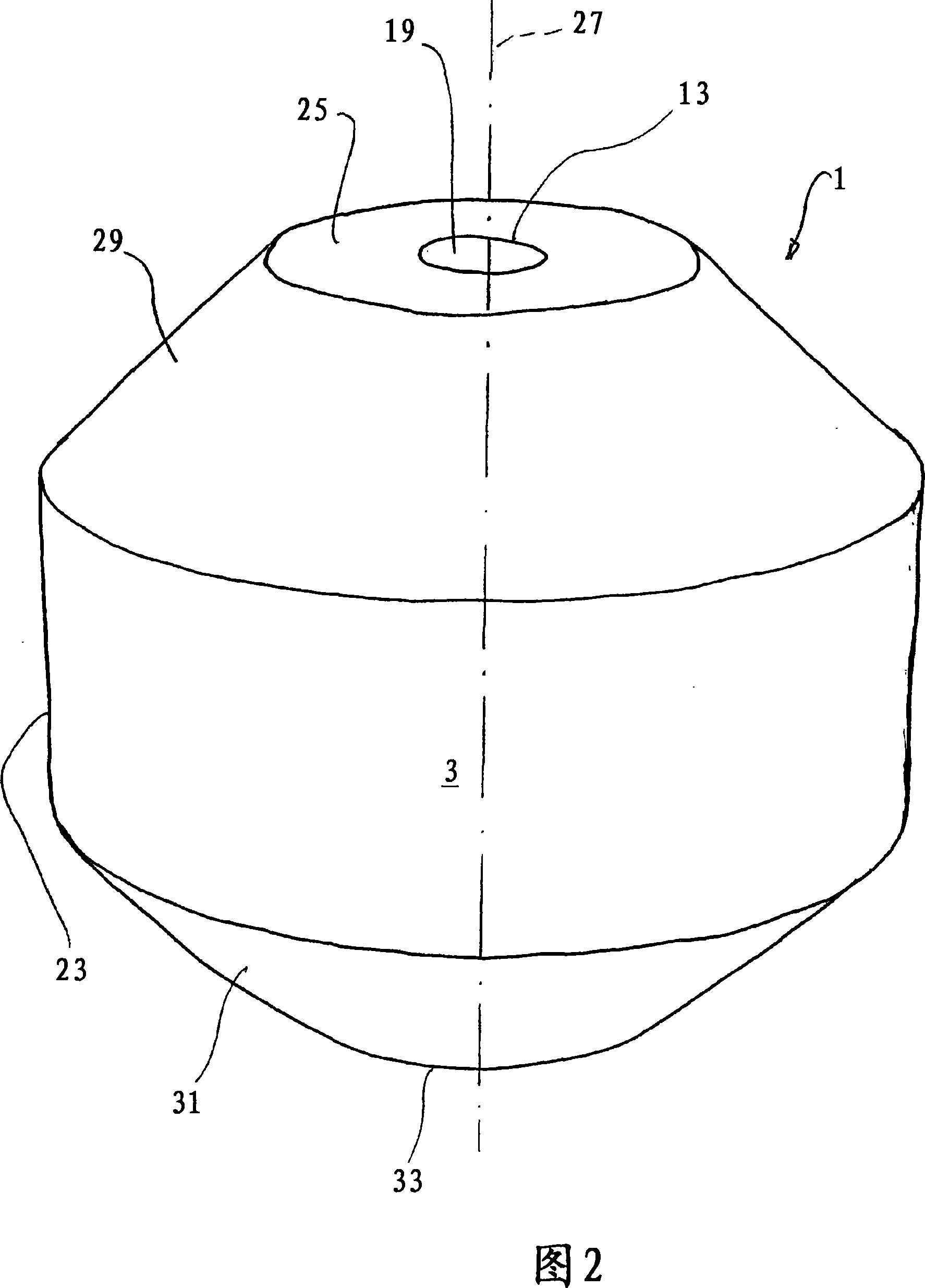
InactiveCN1981211ASimple structureEasy to reachNeutron radiation measurementNeutron converterHydrogen
Disclosed is a dosimeter (1) for the detection of neutron radiation within an energy range of 0.025 eV to several hundred GeV, comprising a substantially spherical base body (3) which is used as a moderation body and which comprises hydrogenous material, a detection element (5) which is arranged in the center of the base body (3), and a neutron converter (7) surrounding the detection element (5). The neutron converter (7) comprises metal atoms which convert the energy of the high-energy neutron radiation essentially into neutrons within a suitable energy range. The dosimeter (1) is characterized in that the base body (3) is provided with an access (19) through which the detection element (5) can be introduced into the neutron converter (7) and removed thereform, and in that the neutron converter (7) is embodied in the form of a cylinder.
Owner:GSI重离子研究亥姆霍茨中心有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com