Patents
Literature
82 results about "Scintillation counter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation by using the excitation effect of incident radiation on a scintillating material, and detecting the resultant light pulses.
Gamma-ray spectrometry
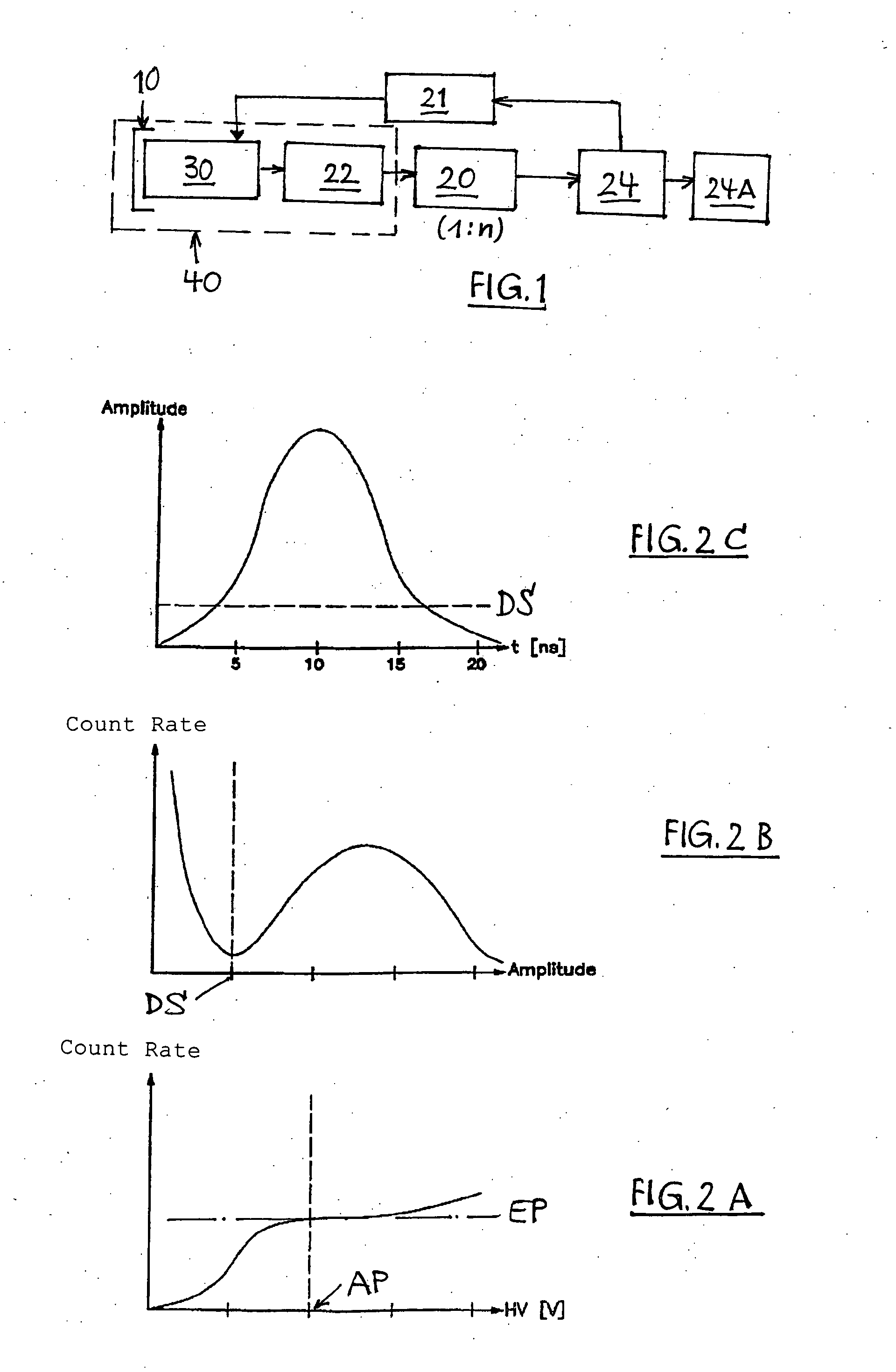
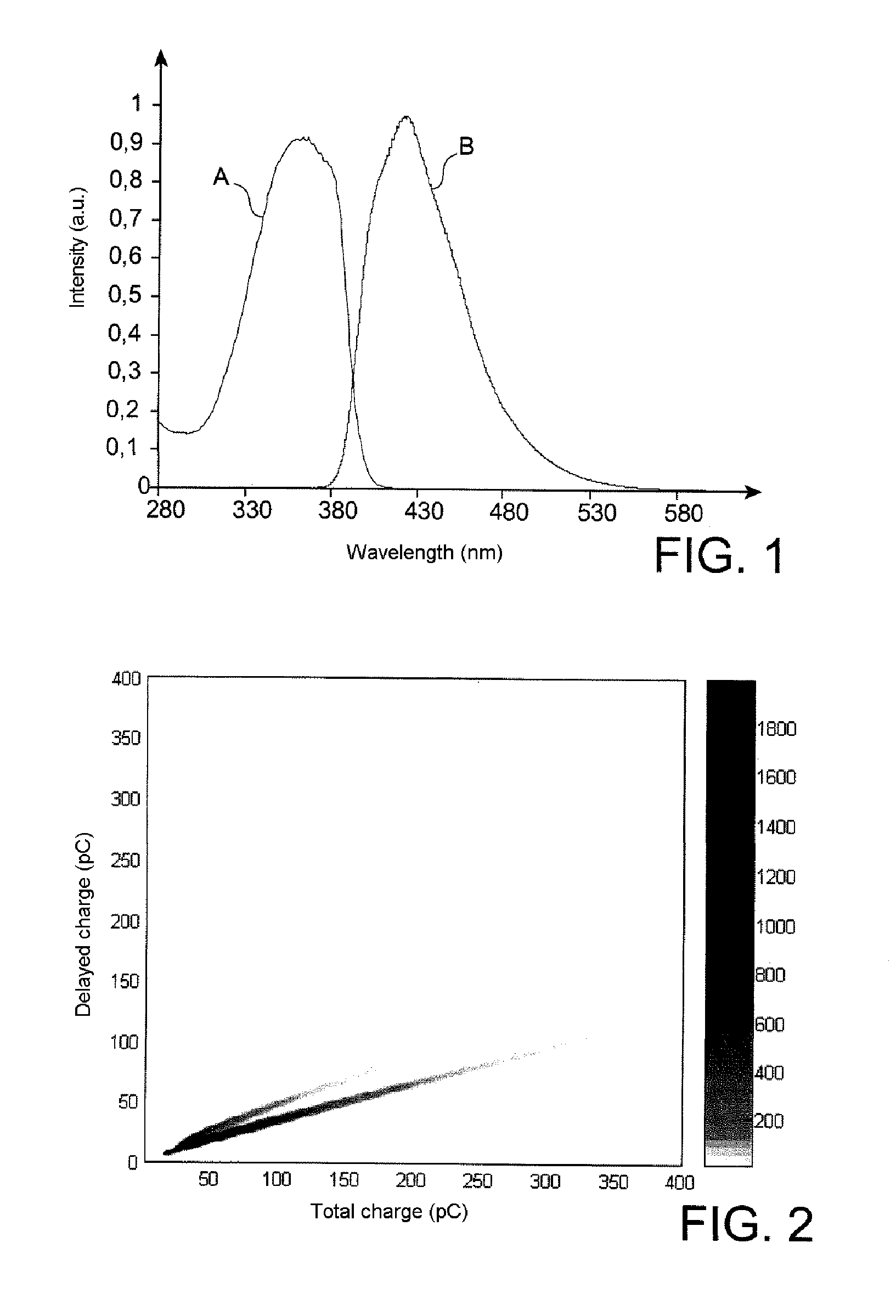
InactiveUS6940071B2Improve resolutionEnhanced signalX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansΓ ray spectrometryImage resolution
Different geometries of scintillation spectrometers are disclosed which provide improved resolution over prior art scintillation spectrometers. By ensuring that photons generated by scintillation events occurring in different locations within the scintillation material generate similar light profiles on the photo-detector, the output signal is made less sensitive to the initial interaction site. This can be achieved in a number of ways, such as: by limiting the exit window of the scintillation crystal to a smaller detector, by introducing an optical spacer (94) between the scintillation crystal and detector (99), and / or by making the crystal longer than necessary to stop the gamma rays. A principal advantage of these new geometries is that deconvolution of the raw-data is more effective, thus improving resolution.
Owner:SYMETRICA
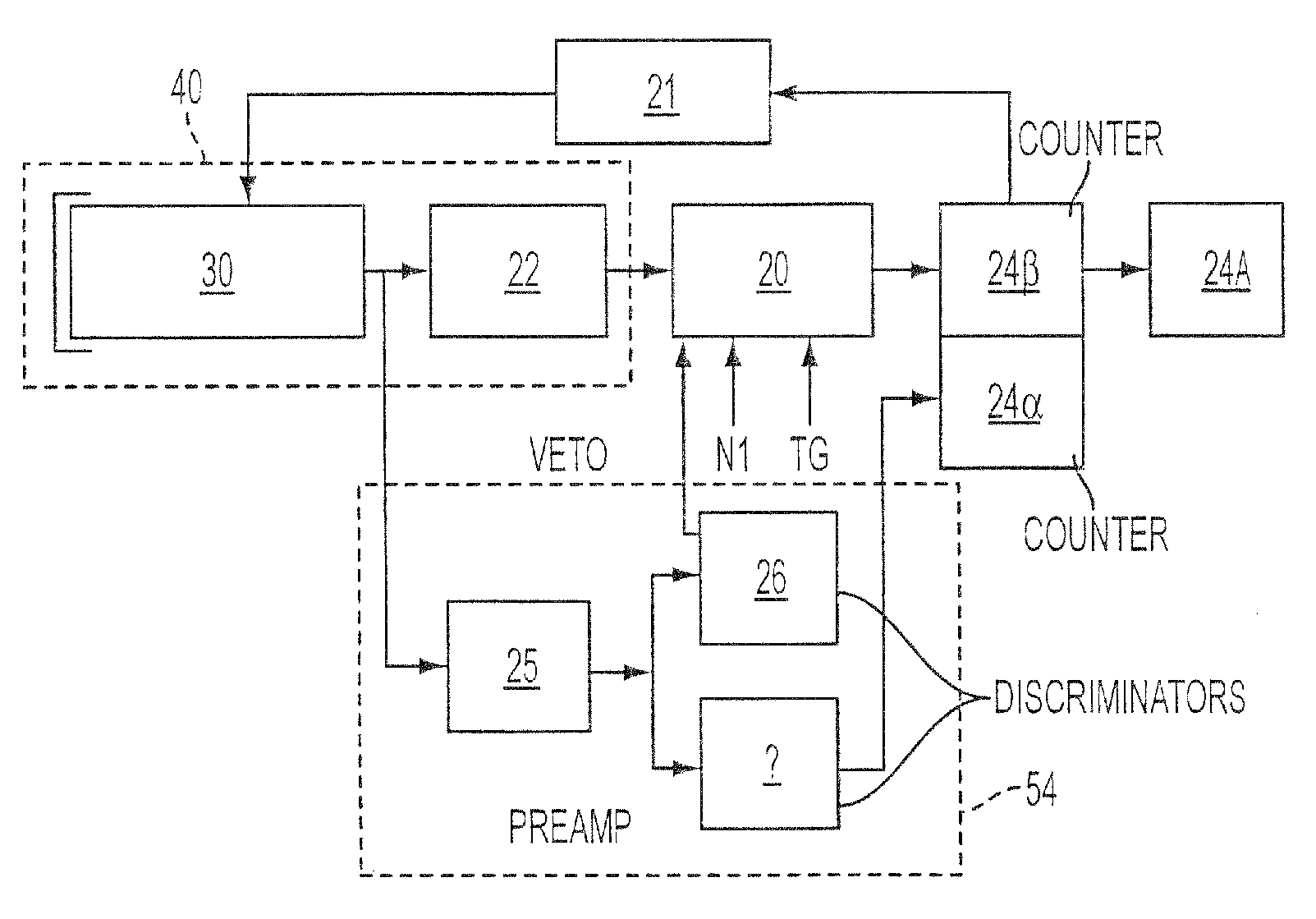
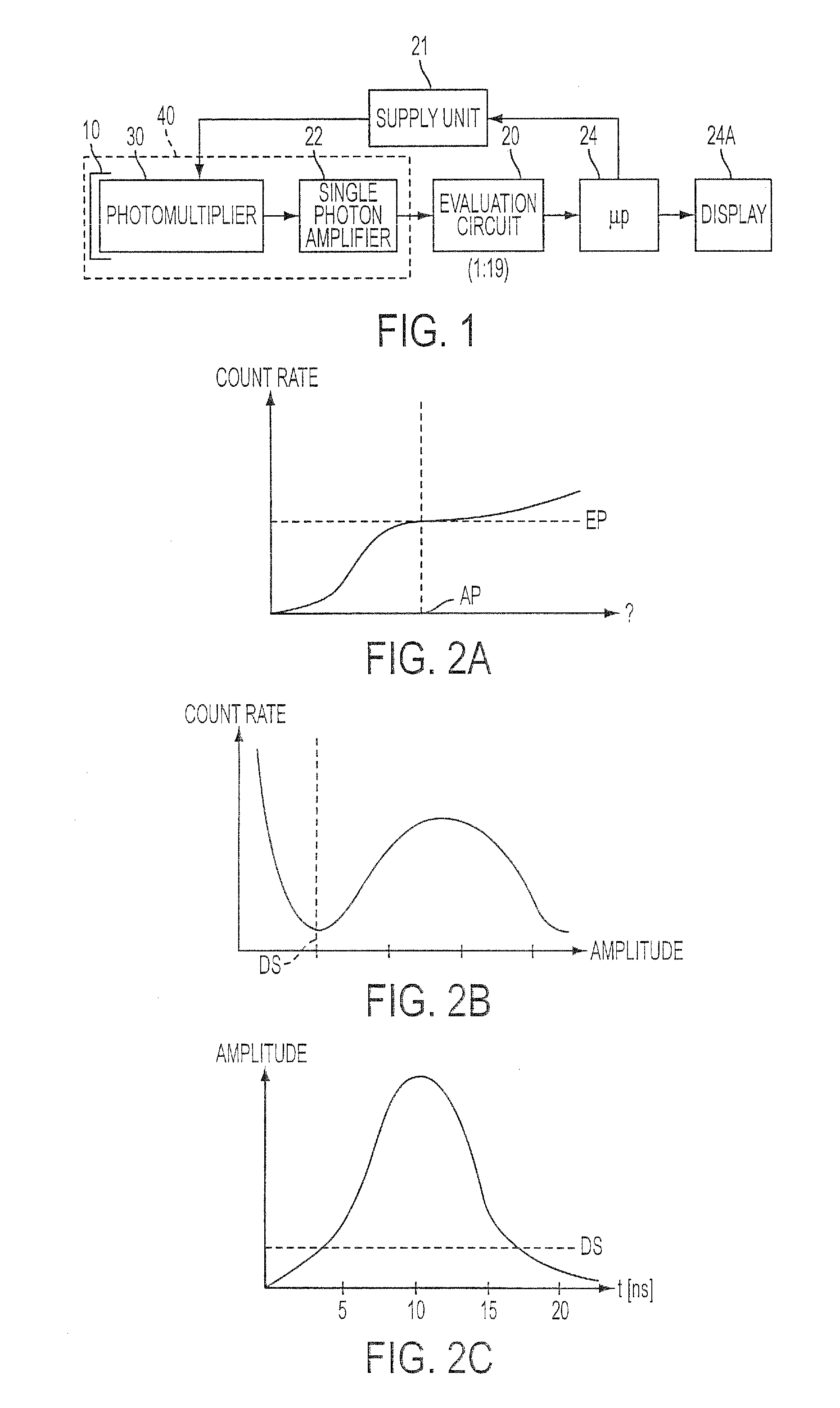
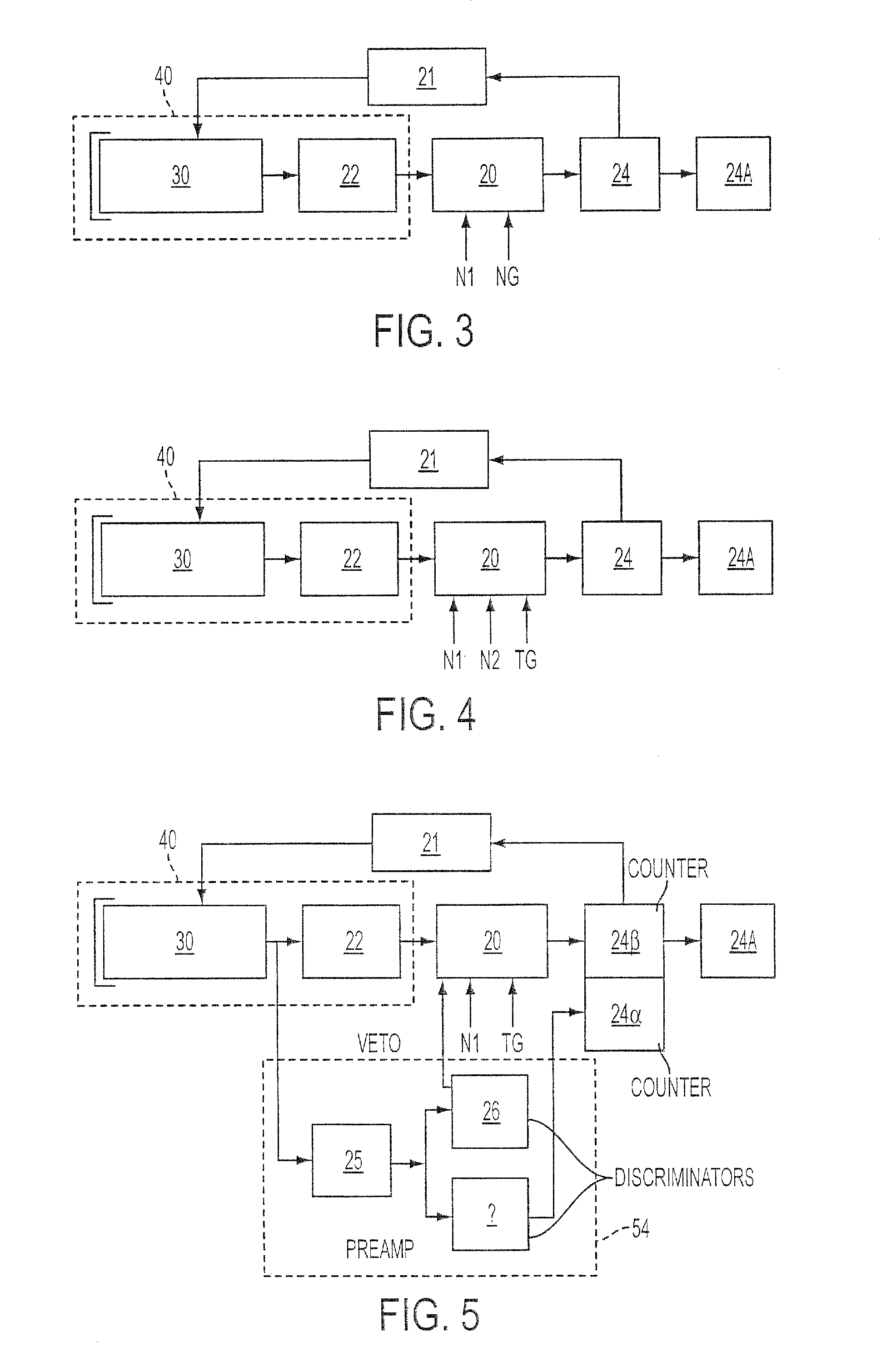
Method and apparatus for detecting ionizing radiation
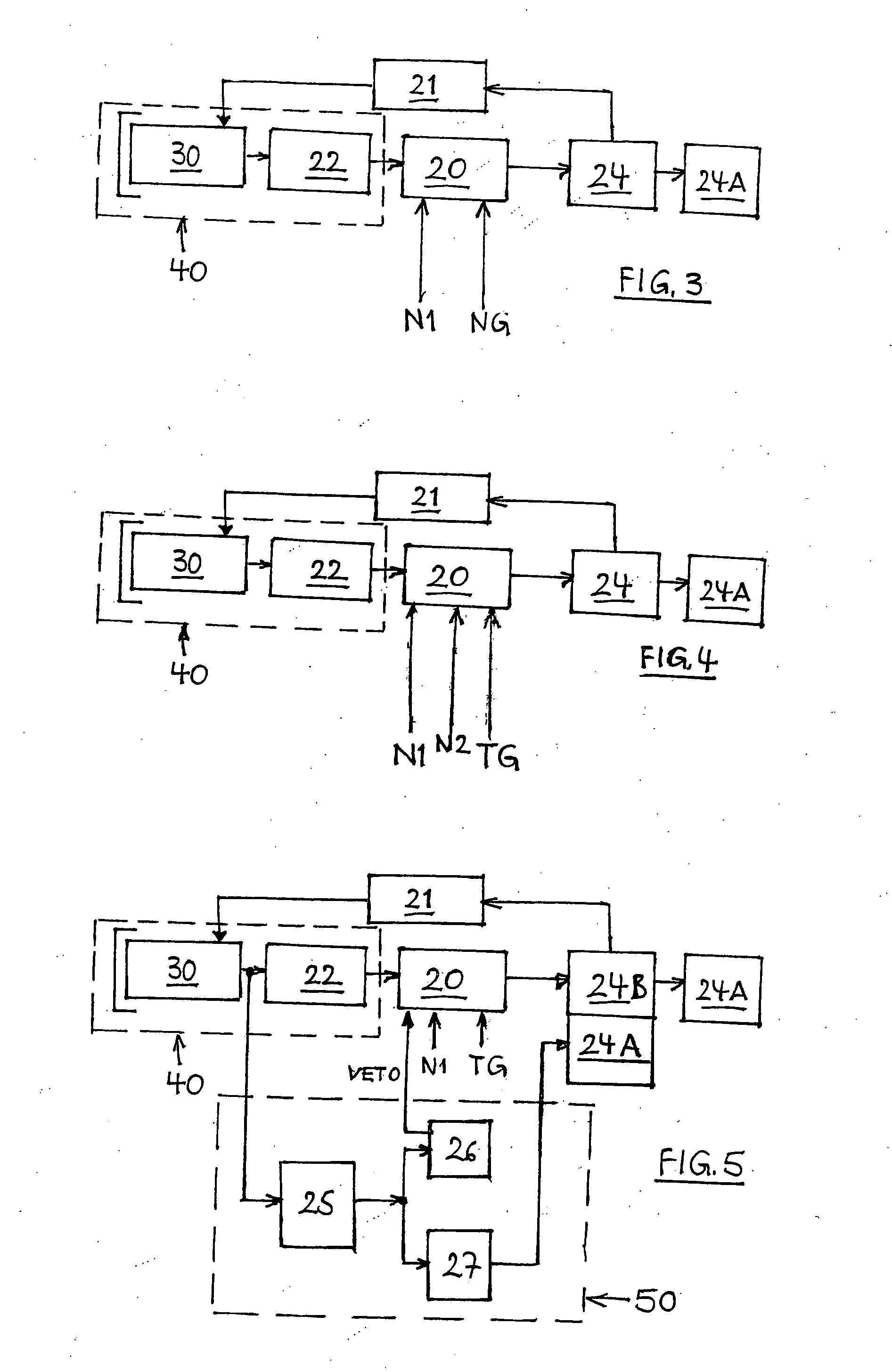
ActiveUS20060081786A1High sensitivityReduce manufacturing costMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementDiscriminatorHigh pressure
A method for detecting ionizing radiation with the aid of a scintillation counter and a photomultiplier using an inorganic solid-matter scintillator that incorporates at least one decay time component greater than 100 ns and measures the photons emitted by the scintillator with a fast single-photon counter. The single-photon counter is composed of a fast photomultiplier with high internal amplification, a stabilized high-voltage supply and a fast amplifier / discriminator with standard pulse output. With this arrangement, the measurement of all types of radiation, like alpha, beta, gamma and X radiation, can be performed, with low manufacturing costs for the detector, a high degree of sensitivity especially with regard to low beta energies, only small sensitivity changes over a large temperature range of −20 to +50 degrees C., and good long-term stability.
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
Optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for fast neutron measurement
InactiveCN103163550ASimple structureReduce volumeMeasurement with scintillation detectorsScintillation counterNeutron radiation
The invention relates to the radiometric technology and in particular to an optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for fast neutron measurement. The optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for the fast neutron measurement comprises a scintillation probe which is formed by blending of fast neutron sensitive materials and scintillating mediums, a transmission optical fiber and a photovoltaic sensitive component, wherein one end of the transmission optical fiber is inserted in the middle of the scintillation probe, the other end of the transmission optical fiber is connected with the photovoltaic sensitive component, and an optical wrapping layer of one part, arranged in the scintillation probe, of the transmission optical fiber is removed. The optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for the fast neutron measurement has the advantages of being simple in structure, small in size, strong in environment adaptability, capable of achieving on line real-time monitoring and the like, and can meet the demand of fast neutron measurement under complex and severe environment.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Scintillation camera with improved scintillation material segment interfaces
InactiveUS6015974AExpand field of viewGood energyMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementTransmittanceScintillation counter
A scintillation camera including photosensors for producing an output in response to emitted light; a scintillation material for emitting light directed to the photosensors in response to radiation absorbed by a source, the scintillation material formed in two or more segments defining an optical interface between adjacent segments; and an increased surface area at the interface for improving the transmissivity of the interface and efficiently optically coupling the adjacent sensors.
Owner:GENNA SEBASTIAN
Gamma ray scintillation detector preserving the original scintillation light distribution
InactiveUS20140175296A1Narrow downImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementGamma rayScintillation counter
An apparatus to detect gamma rays, comprising a scintillator, a position sensitive photo sensor and a scintillation-light-incidence-angle-constraining, SLIAC, element, the scintillator has faces and the position sensitive photo sensor detects scintillation photons exiting a scintillation photons transparent face of the scintillator, and a portion of a scintillator face is covered with an absorbing layer, which absorbs scintillation photons created by scintillation events due to the interaction of incoming gamma rays with the scintillator, and the SLIAC element is optically coupled between a scintillation photons transparent face of the scintillator and the position sensitive photo sensor and the SLIAC element guides the scintillation photons exiting the scintillator towards the position sensitive photo sensor, and the SLIAC element restricts the maximum allowed half light acceptance angle for the scintillation light hitting the position sensitive photo sensor to less than 45°.
Owner:GENERAL EQUIP FOR MEDICAL IMAGING SL +1
Method and device for digitalizing scintillation pulse
ActiveCN102843139AGo digitalSimple structureAnalogue-digital convertersTime-to-digital convertersLow voltageEngineering
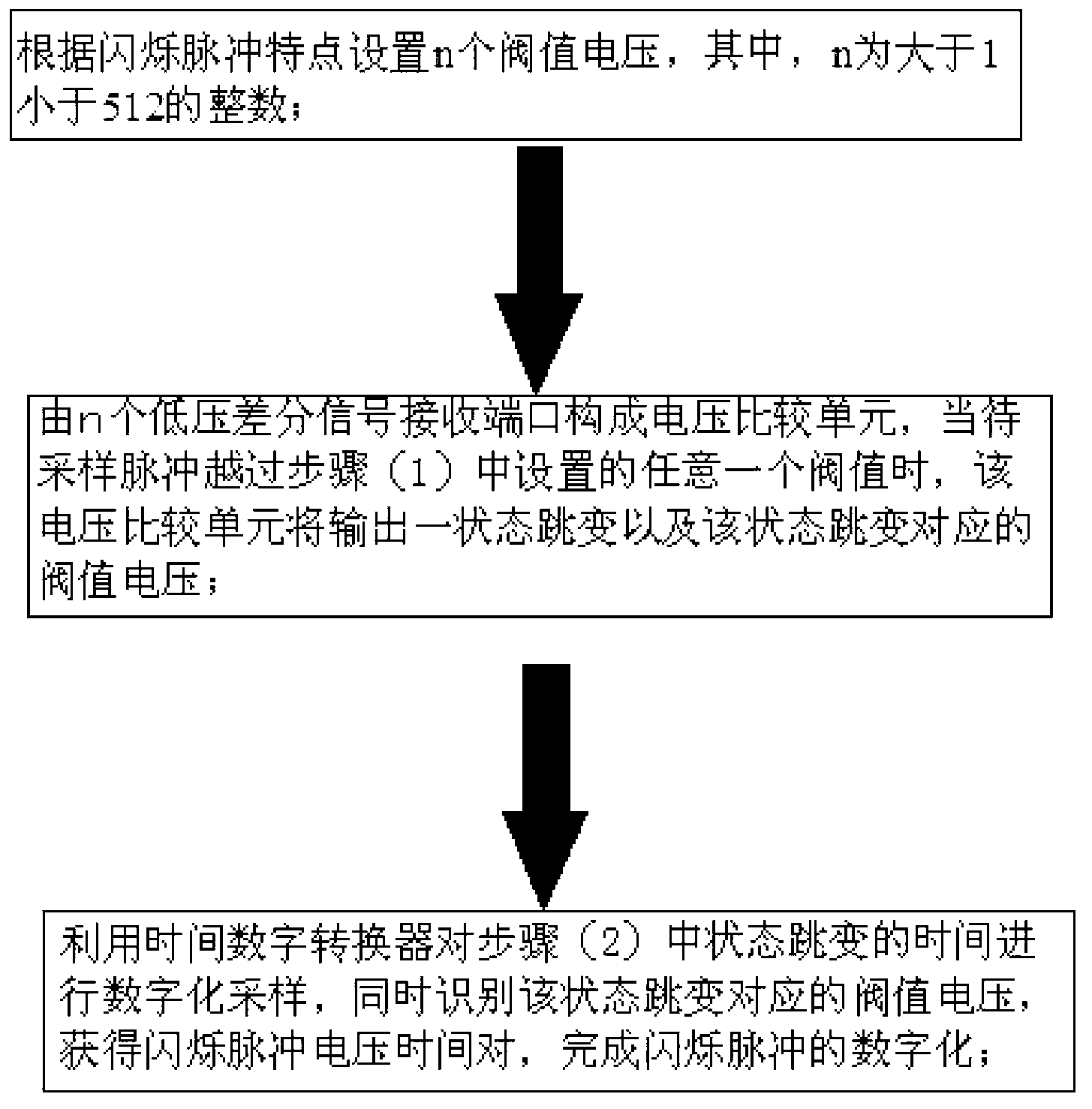
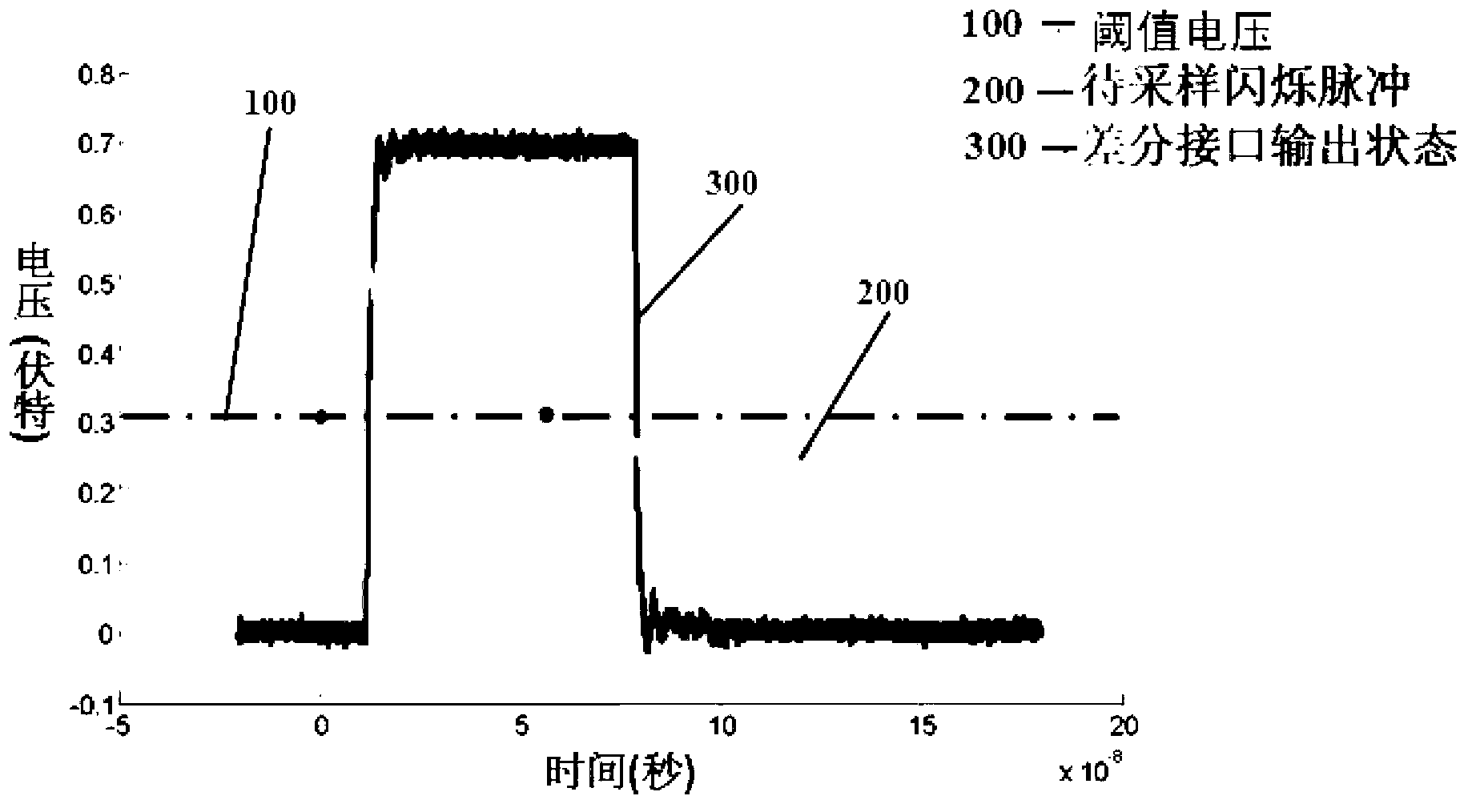
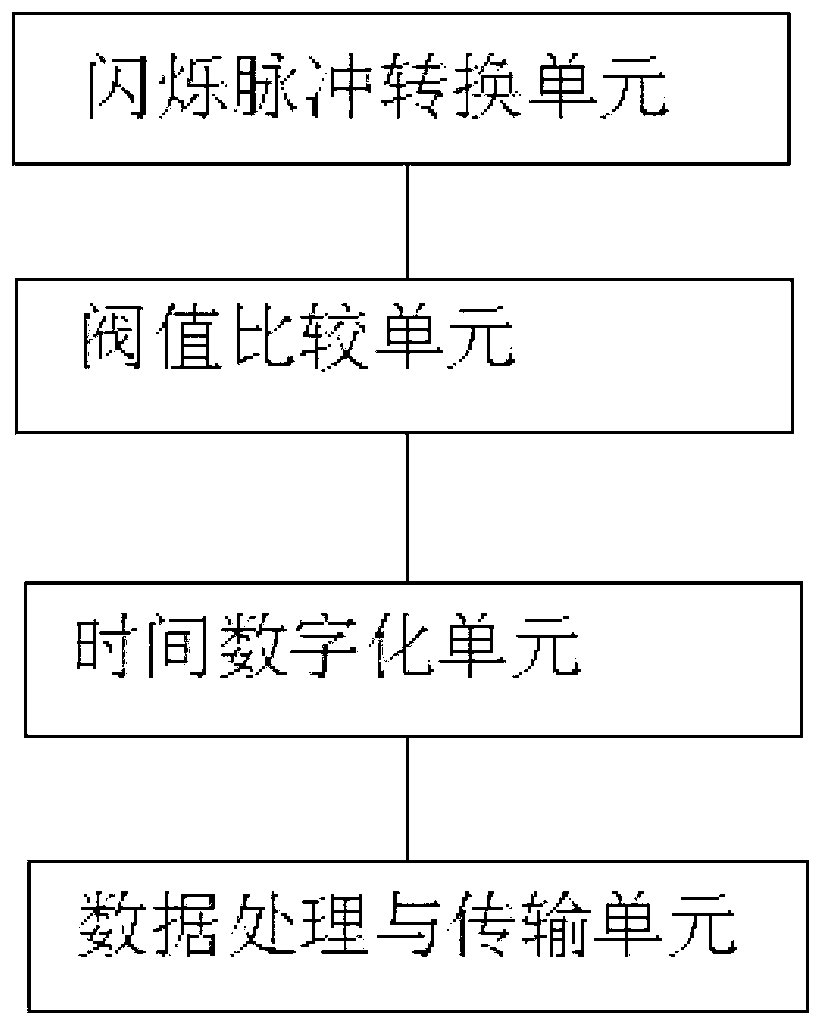
The invention provides a method for digitalizing a scintillation pulse. The method comprises the following steps of setting n threshold voltages V_th according to the characteristics of the scintillation pulse; forming a voltage comparison unit by n low voltage differential signal receiving ports, when the pulse to be sampled exceeds any threshold, the voltage comparison unit outputs a state transition and a threshold voltage corresponding to the state transition; performing digitalization sampling for the time of the state transition by a time digital converter; identifying the threshold voltage corresponding to the state transition synchronously, obtaining scintillation pulse voltage time pair and finishing digitalizing the scintillation pulse. A device for digitalizing the scintillation pulse comprises a scintillation pulse converting unit, a threshold comparison unit, a time digitalization unit and a data processing and transmitting unit. According to the method and the device provided by the invention, threshold comparison can be realized through a digital differential interface in a field programmable gate array, and the voltage time pair of the scintillation pulse can be obtained, thereby realizing digitalization of the scintillation pulse, greatly simplifying the system structure, improving integration degree of the system and reducing system power consumption.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU
Radiation tomography apparatus
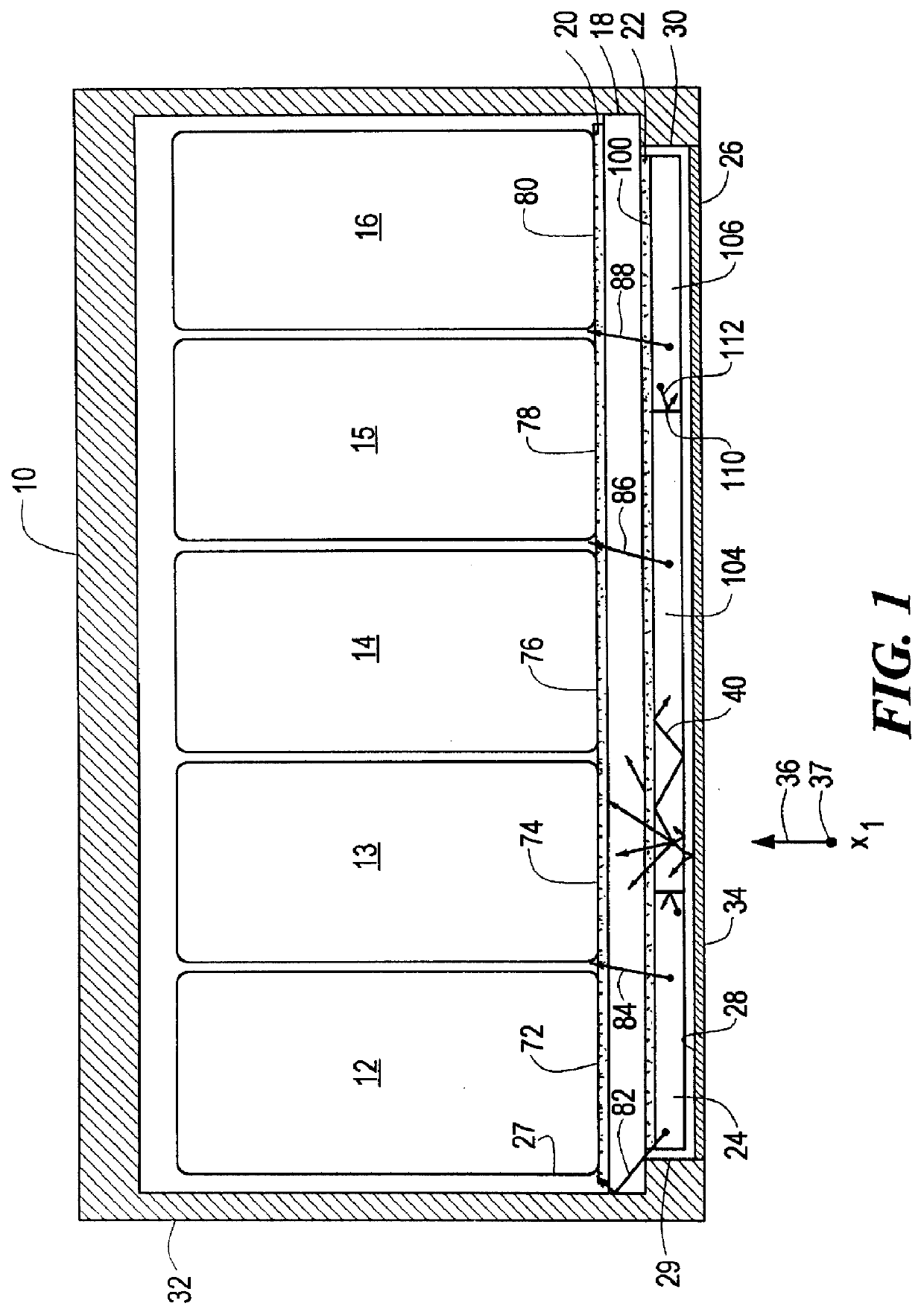
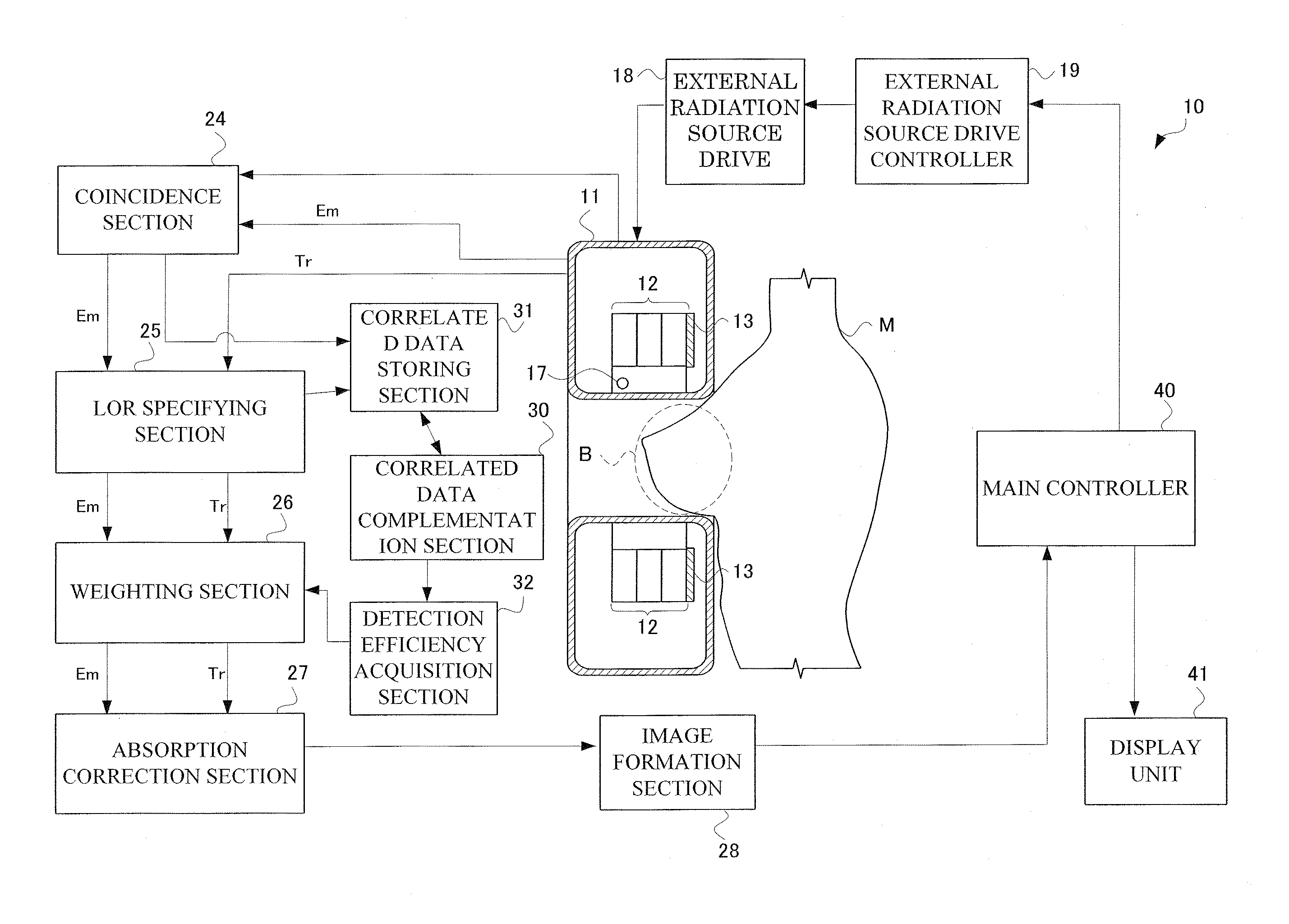
InactiveUS20110127436A1Lack of uniformityUniform shapeMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyScintillation counterData storing
A detector ring of radiation tomography apparatus according to this invention has a fracture portion having no scintillation counter crystal arranged therein. Moreover, the radiation tomography apparatus according to this invention includes a correlated data complementation section. The correlated data complementation section forms correlated data when assuming that a first scintillation counter crystal actually provided in the detector ring is in the fracture portion, and additionally stores it to a correlated data storing section, thereby complementing correlated data in the fracture portion. As noted above, the correlated data complementation section obtains positional information under assumption that the scintillation counter crystals are in the fracture portion and a corresponding number of coincident events. Consequently, this invention may realize acquisition of faithful detecting efficiencies in the scintillation counter crystals. Therefore, the radiation tomography apparatus may be provided that allows creation of radiological images suitable for diagnosis.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Fitting method for scintillation pulse digitized signals
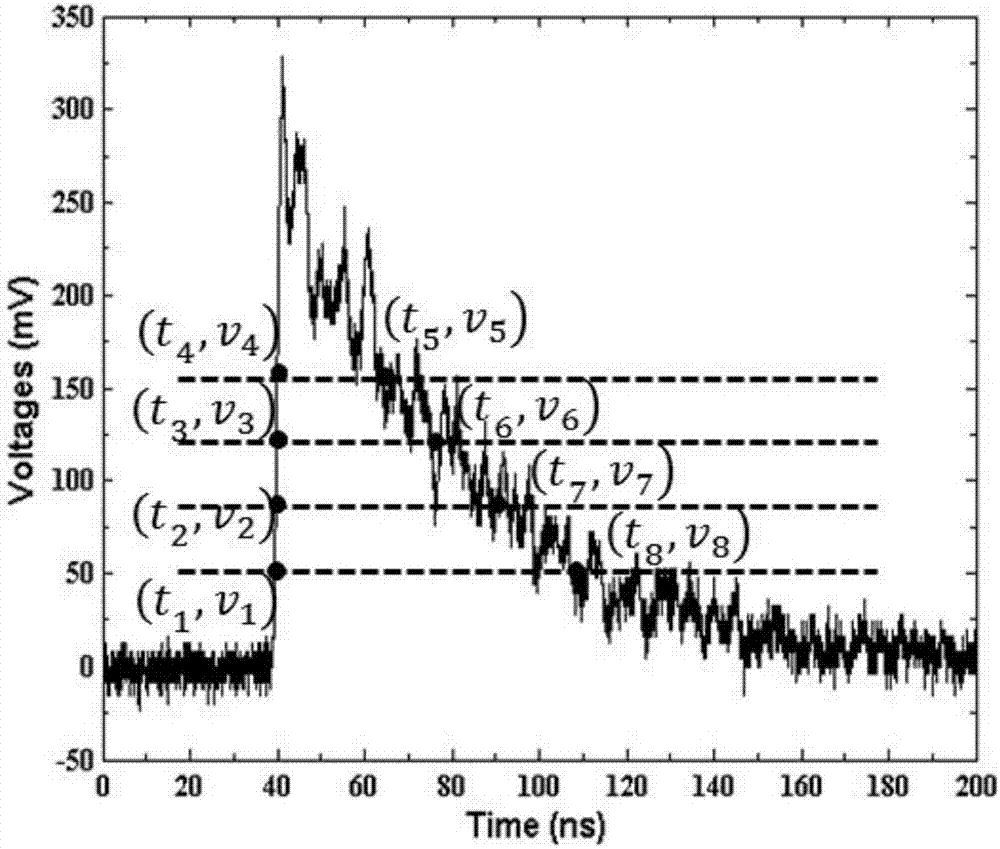
ActiveCN107024711AExtended run timeImprove convenienceRadiation intensity measurementArray data structureImage resolution
The present invention provides a fitting method for scintillation pulse digitized signals. The method comprises the steps of selecting a scintillation pulse prior model as a double-exponential model; selecting sampling points for classical pulses in a scintillation pulse database, wherein the sampling points are composed of eight voltage threshold sequences and eight time point sequences; translating the curve of the double-exponential model in the time dimension to obtain a time array; setting four initial default parameters of a target function to be 1 and storing as an initial parameter array; inputting the time array, a scintillation target function and the like into a Levenberg Marquardt Fitting function, and fitting to obtain fitting parameters; sequentially repeating each scintillation pulse in the scintillation pulse database to complete the fitting process of all scintillation pulses; integrating the fitted target function to obtain the energy value of a k pulse; solving the equation and extracting the time and energy information of the pulse. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the obtained energy resolution is remarkably improved. Therefore, the information extraction accuracy and the information extraction stability are ensured at the same time while the processing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU
Dispersion type scintillation detector for impulse gamma detection
InactiveCN101251601AHigh sensitivityImprove resolutionRadiation intensity measurementGamma detectionPhotomultiplier
The invention belongs to a radiator detecting device, in particular relating to a scattering-type scintillation detector for pulse and gamma-ray detection. An upper photoelectric device and a lower photoelectric device in the scintillation detector are respectively provided with the same electron filter, reflecting film, scintillation unit and photomultiplier which are arranged in symmetry. Therefore, the sensitivity difference between two detectors at both sides can be pre-set with the photoelectric device at one side as a background photoelectric device and the photoelectric device at the other side as a main signal detector. During measurement, a 3 millimeters thick granite sheet or aluminum sheet is added in front of the scintillation unit of the photoelectric device at one side to block electrons exiting out of a target so that the electrons are impossible to reach the scintillation unit, thus only surrounding gamma-ray and disturbance signals of neutrons are obtained. After time delay rectification and sensitivity rectification, the output signals of the two photoelectric devices are mutually deducted to obtain the true signals. Therefore, the scattering-type scintillation detector for pulse and gamma-ray detection can effectively deduct the disturbance caused by deficiency in shielding so as to improve the performance of detectors.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH +1
Method and apparatus for detecting ionizing radiation
ActiveUS7368722B2Reduce manufacturing costHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementDiscriminatorX-ray
A method for detecting ionizing radiation with the aid of a scintillation counter and a photomultiplier using an inorganic solid-matter scintillator that incorporates at least one decay time component greater than 100 ns and measures the photons emitted by the scintillator with a fast single-photon counter. The single-photon counter is composed of a fast photomultiplier with high internal amplification, a stabilized high-voltage supply and a fast amplifier / discriminator with standard pulse output. With this arrangement, the measurement of all types of radiation, like alpha, beta, gamma and X radiation, can be performed, with low manufacturing costs for the detector, a high degree of sensitivity especially with regard to low beta energies, only small sensitivity changes over a large temperature range of −20 to +50 degrees C., and good long-term stability.
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
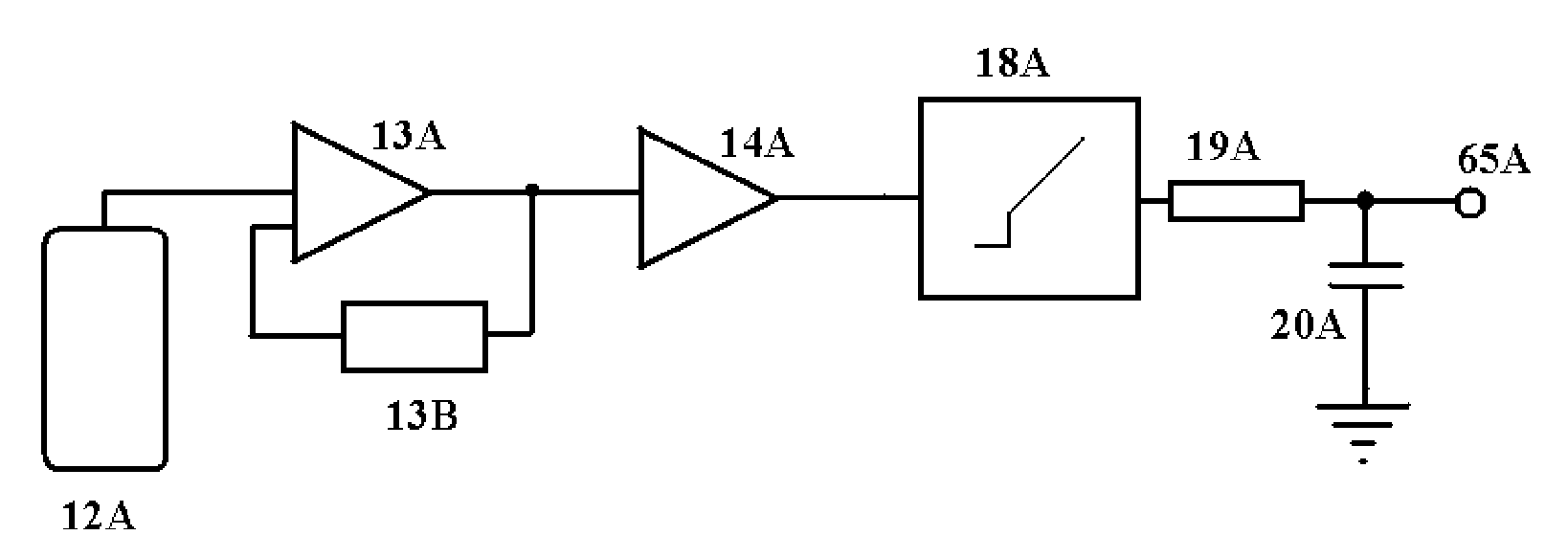
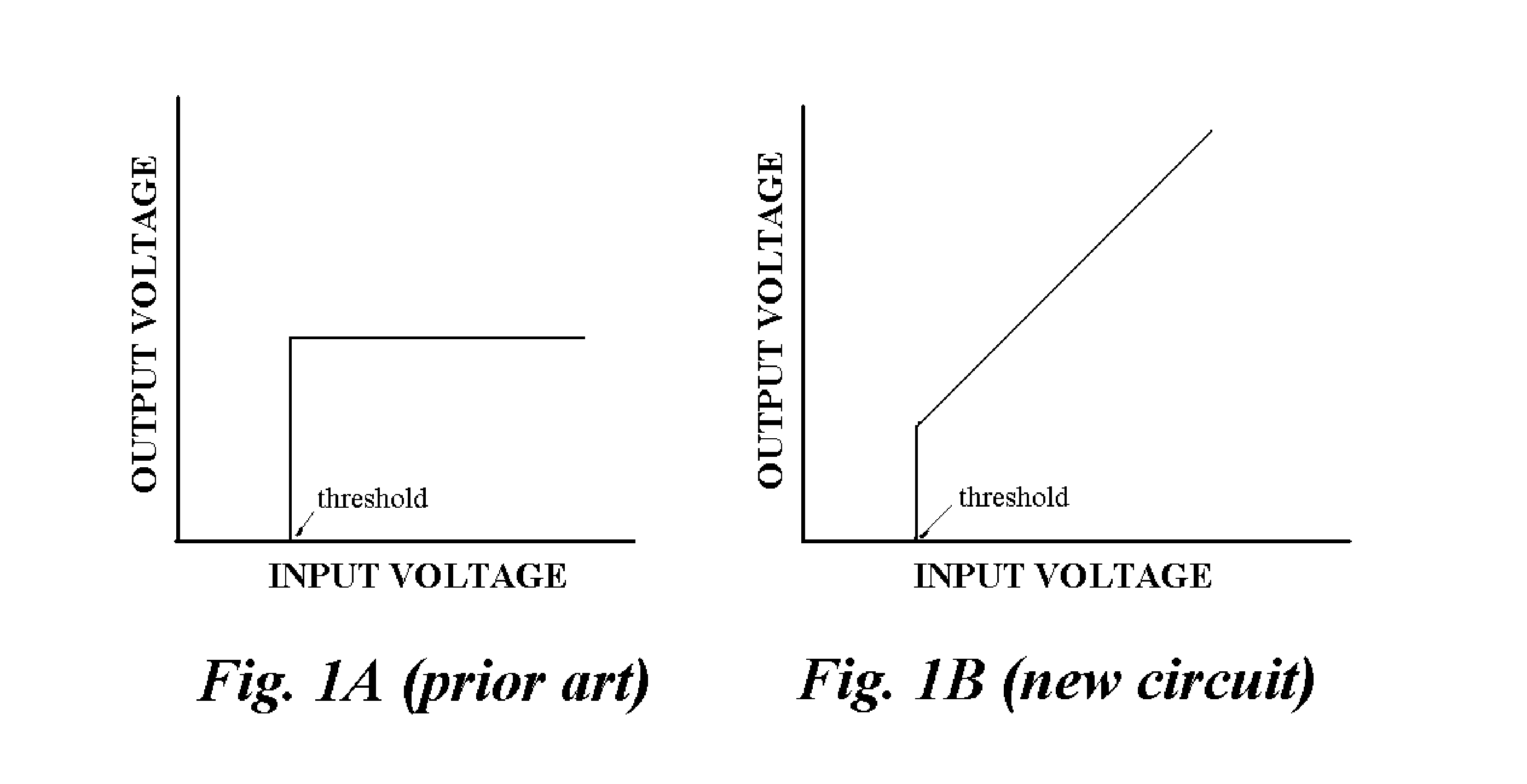
Method and Apparatus for Extending a Scintillation Counter's Dynamic Range
ActiveUS20110284753A1Enhance detector system dose-rate linearityImprove dynamic rangeMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementCounting rateDiscriminator
A semiconductor diode scintillation detector probe, in conjunction with a base-line-stabilized, wide-bandwidth first amplifying circuit DC-coupled to a constrained-bandwidth second amplifying circuit DC-coupled, in turn, to a novel analog threshold discriminator circuit, suppresses base-line fluctuation and noise at low input count-rates, while providing a linear rate-meter response for time-random input pulse rates far in excess of what would otherwise—as in the prior art—be 100% saturation.
Owner:CARROLL LEWIS RONALD
Optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for slow neutron measurement
InactiveCN103163551ASimple structureReduce volumeMeasurement with scintillation detectorsScintillation counterSlow neutron
The invention relates to the radiometric technology and in particular to an optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for slow neutron measurement. The optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for the slow neutron measurement comprises a scintillation probe which is formed by blending of slow neutron sensitive materials and scintillating mediums, a transmission optical fiber and a photovoltaic sensitive component, wherein one end of the transmission optical fiber is inserted in the middle of the scintillation probe, the other end of the transmission optical fiber is connected with the photovoltaic sensitive component, and an optical wrapping layer of one part, arranged in the scintillation probe, of the transmission optical fiber is removed. The optical fiber coupled radiation detector used for the slow neutron measurement has the advantages of being simple in structure, small in size, strong in environment adaptability, capable of achieving on line real-time monitoring and the like, and can meet the demand of slow neutron measurement under complex and severe environment.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Optical measurement apparatus and method for optical measurement
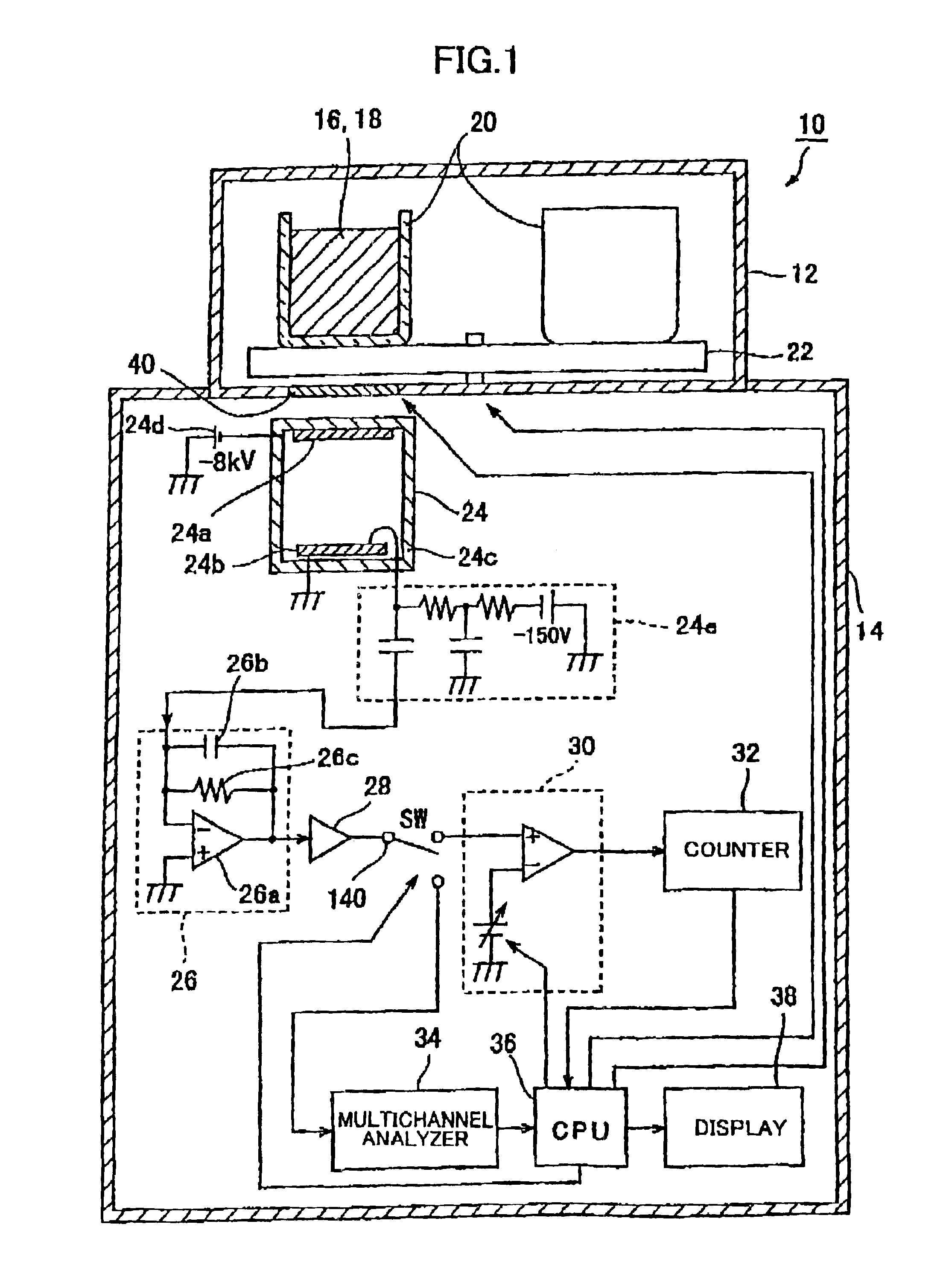
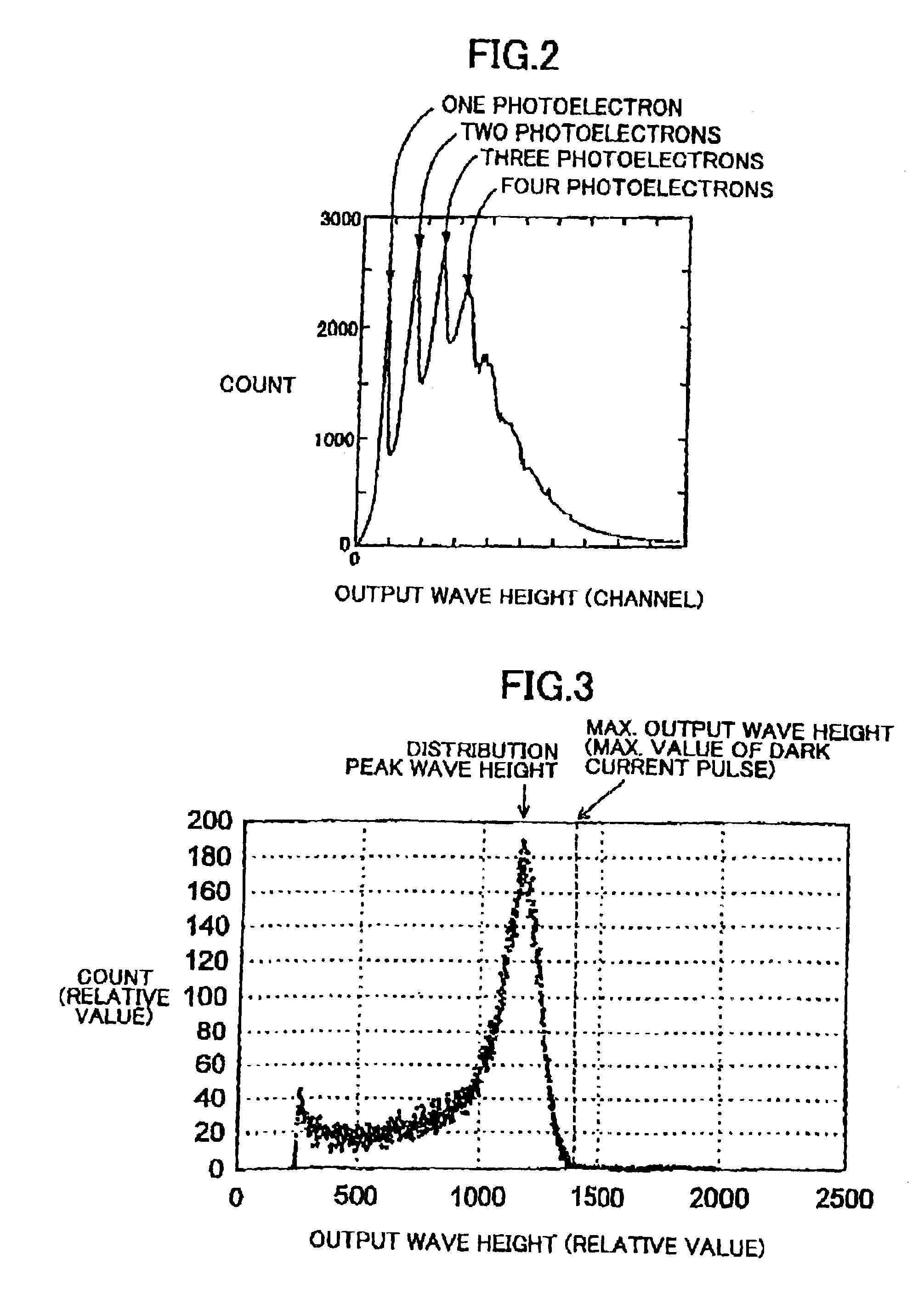
InactiveUS6960771B1Effectively eliminate dark current pulseEfficiently signaledPhotometry using reference valueIndividual particle analysisPhotocathodeDisplay device
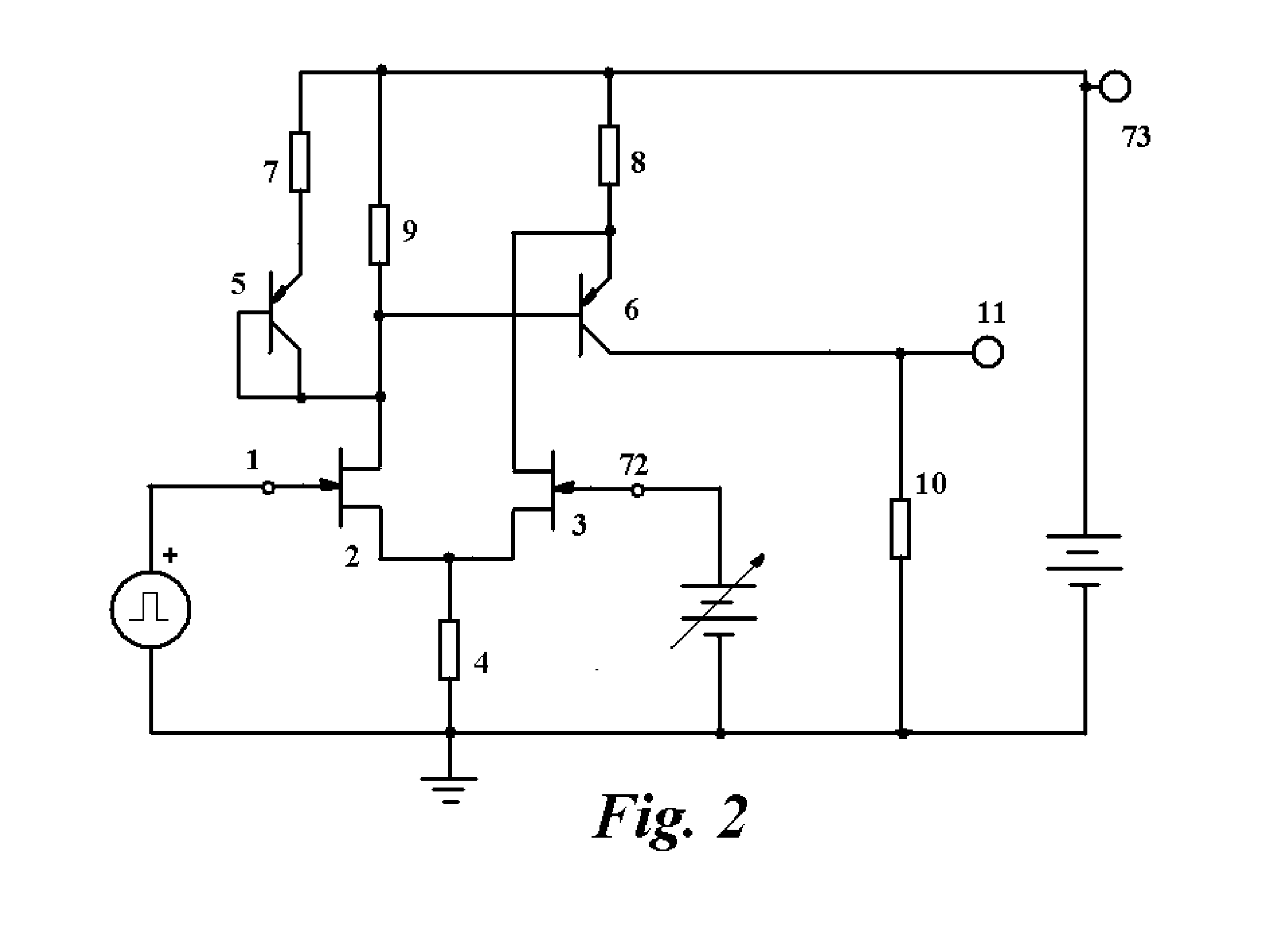
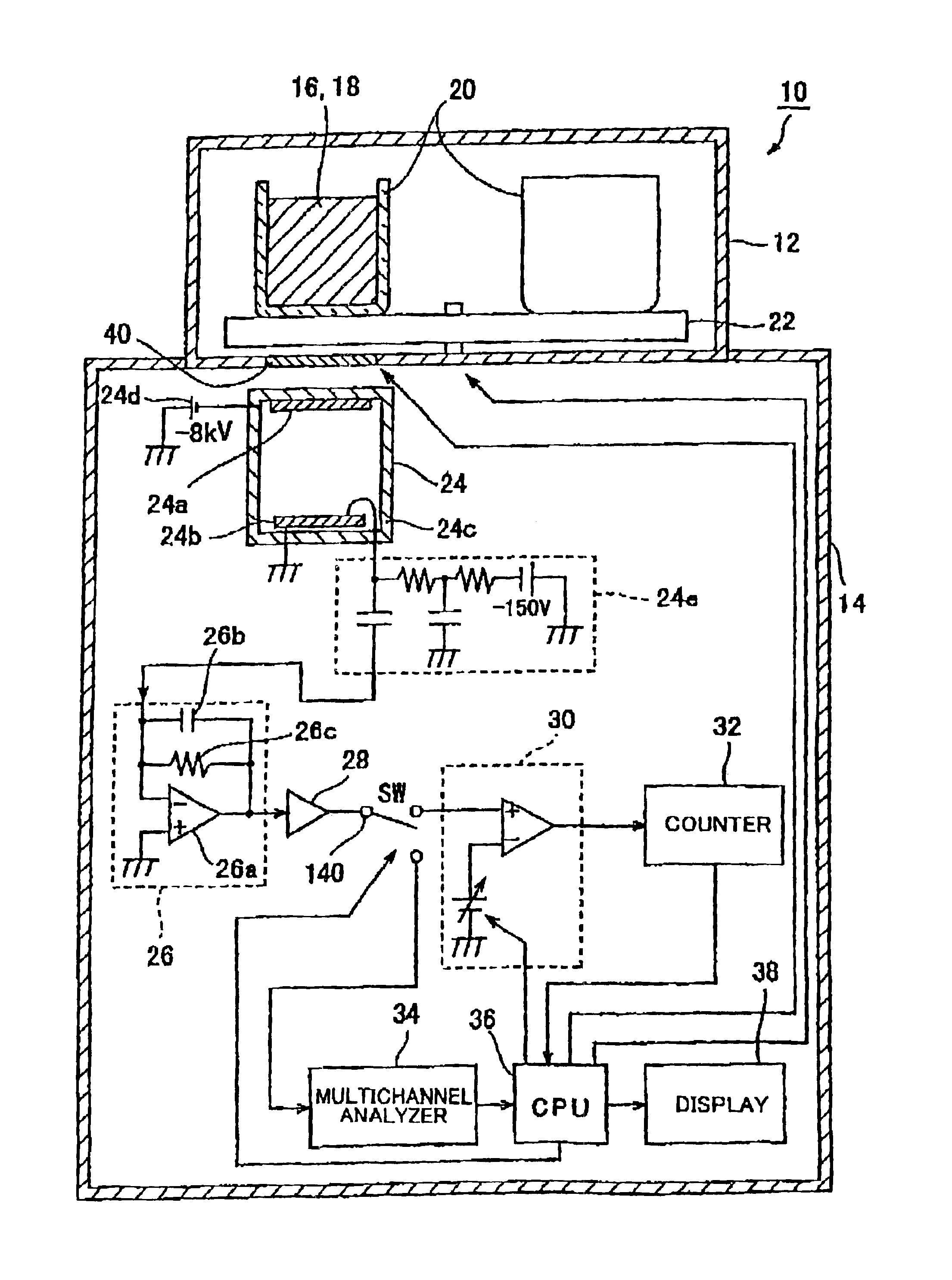
A liquid scintillation counter 10 serving as an optical measurement apparatus includes: an HPD 24, a charge amplifier 26, a voltage amplifier 28, a comparator 30, a counter 32, a multi-channel analyzer 34, a display 38, and the like. The HPD 24 has a photocathode 24a and an APD 24b for outputting a signal that corresponds to the number of incident photons. The comparator 30 outputs a logic pulse signal, serving as a comparison result signal, only when the signal outputted from the HPD 24 and amplified by the charge amplifier 26 and voltage amplifier 28 is larger than a prescribed threshold value. This threshold value is set larger than an output signal that is outputted when a single photoelectron is emitted from the photocathode 24a and smaller than another output signal that is outputted when two or more photoelectrons are emitted.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Wave spectrum and energy spectrum composite type X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer
PendingCN108508051ALarge application spaceImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFace scanningElement analysis
The invention provides a wave spectrum and energy spectrum composite type X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer. The wave spectrum and energy spectrum composite type X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer comprises an X-ray source, a light filter switching mechanism, a sample moving platform, a sample cup, a diaphragm switching mechanism, a primary collimator switching mechanism, a dispersive crystalswitching mechanism, a secondary collimator switching mechanism, a gasflow type proportional counter, a scintillation counter, an SDD detector, a main control panel and a PC machine. The wave spectrum and energy spectrum composite type X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer has the following advantages: detection or point / face scanning can be rapidly completed by using an energy spectrum function when the sample is subjected to integrated component analysis and distribution analysis, and the whole body or certain area of the sample can be subjected to element analysis and distribution analysisby a wave spectrum function, so that organic combination of the wave spectrum and energy wave spectrum functions is realized, the two functions can be applied to integrated element component analysisand distribution analysis of the sample, the characteristics of high resolution, rapidness, flexibility and combinability are achieved, the reliability of the analysis result can be improved and the detection efficiency can be improved obviously.
Owner:NAT RESERACH CENT OF GEOANALYSIS +1
Method for measuring 14C in biological sample
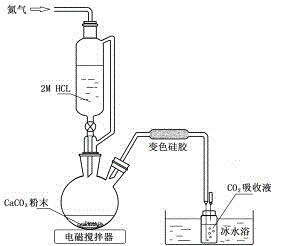
InactiveCN104062674AHigh measurement accuracyHigh measurement sensitivityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMicrobiologyLiquid scintillation counting
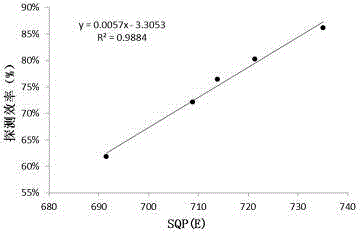
The invention discloses a method for measuring 14C in a biological sample. The method includes the following steps that (1) the biological sample is pretreated, wherein the biological sample is frozen to be in the dry state and burned and absorbs a NaOH solution and finally the biological sample is converted into CaCO3 sediment; (2) a CO2 direct absorption method is used for preparing the sample, wherein CaCO3 powder obtained in the step (1) is dissolved in HCl and a measurement bottle cooled through an ice bath and containing liquid scintillation absorption mixed liquid is used for absorbing generated CO2; (3) a low-background liquid scintillation counter is used for measurement, wherein the sample is measured, so that the counting rate is obtained, and meanwhile the value of the SQP(E) is measured; quenching correction is conducted through an SQP(E) method and the specific activity of 14C in the biological sample is calculated. The method is rapid and accurate in operation and the lower detection limit of 14C specific activity in the biological sample can reach 0.0084 Bq / gC.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
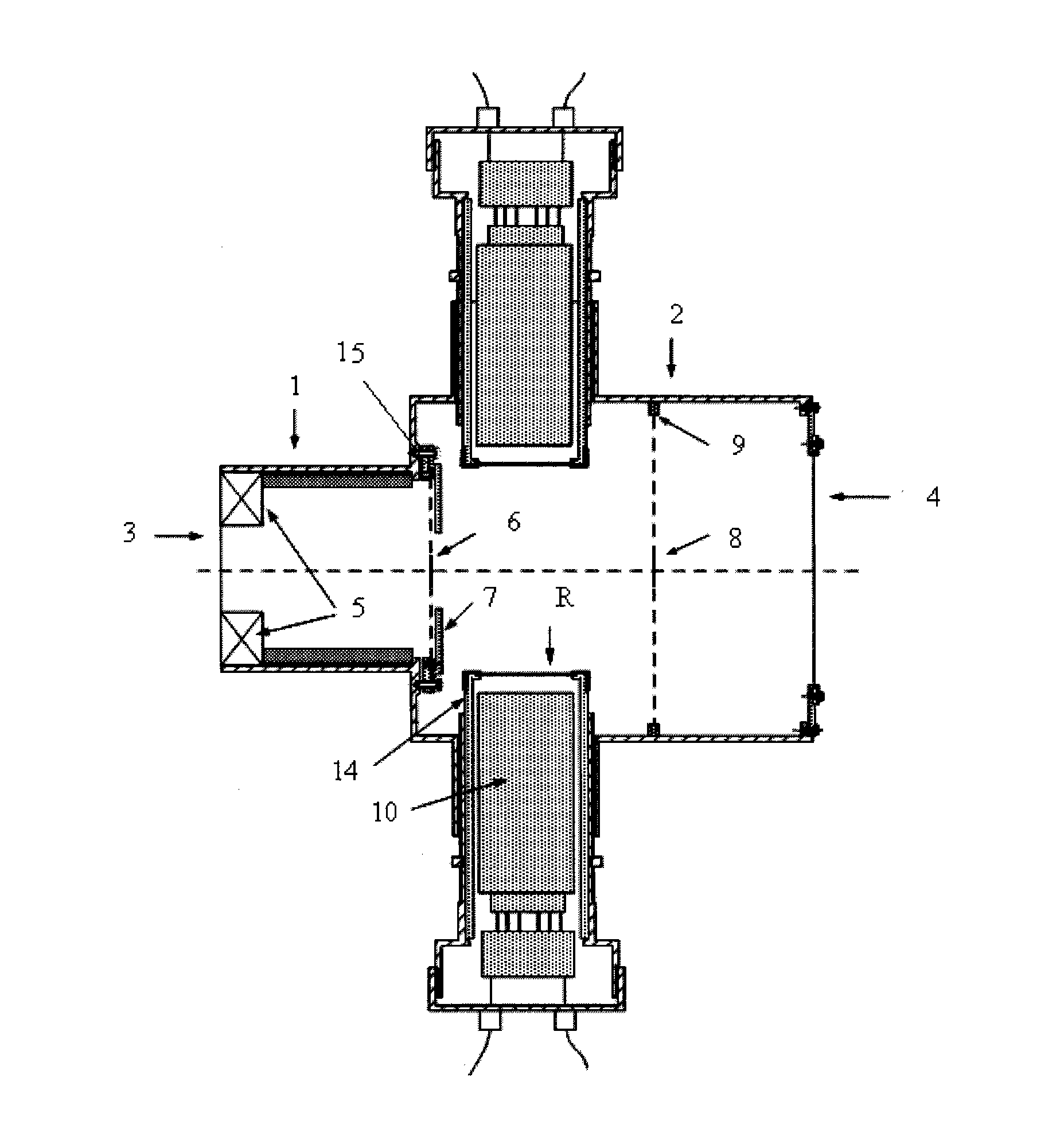
Multigrid high pressure gaseous proportional scintillation counter for detecting ionizing radiation
InactiveUS20120119095A1Improve efficiencyGood energy resolutionElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansNoble gasLepton
The present invention deals with a Multigrid High Pressure Gas Proportional Scintillation Counter for the detection of ionizing radiation such as X-rays, gamma-rays, electrons or other charged leptons, alpha-particles or other charged particles as well as neutrons, which gives information about the energy dissipated in the gas and the time of occurrence of the detection, through an electronic pulse with an amplitude approximately proportional to that energy. It is essentially characterized by:having external metallic walls (1) at ground potential,being filled at a pressure in the 1-100 atmosphere range with a pure noble gas and / or continuously purified, or in mixtures,having: a reflective CsI photocathode (7); four metallic grids: G1 (2), G2 (3), G3 (4) and G4 (5) made of thin wire and with high optical transmission, superior to 70%, defining five regions delimited by these grids (2, 3, 4, 5), by the entrance radiation window (6) and by the photocathode (7),having the high voltages of the several grids applied through feedthroughs (9), producing appropriate electric fields in the several regions of the detector, that do not vary with the time.
Owner:UNIVE DE COIMBRA
Rapid analysis method for multinuclides in radioactive contaminated soil
InactiveCN108152850AX-ray spectral distribution measurementScintillation cellsRadioactive contaminationDigestion
The invention relates to a rapid analysis method for multinuclides in a radioactive contaminated soil. The method comprises the steps that 1) drying, reducing, grinding and sieving are carried out onthe radioactive contaminated soil to acquire a radioactive contaminated soil sample; 2) 1 .0g radioactive contaminated soil is weighed for digestion; 3) after digestion is completed, liquid in a teflon tank is slowly evaporated at low temperature to nearly dry; 4) the sample is dissolved with a 10mL nitric acid solution and transferred to a centrifuge tube; 5) 0.5mL sample acquired in the step 4)is moved to a small stainless steel plate to prepare an alpha measurement source plate; 6) the total alpha and total beta of the sample are measured on the liquid scintillation counter, and the ratioof 241Am+328Pu and 239+240Pu in the total alpha is acquired; 7) the Cherenkov count of the sample is measured prior to the liquid scintillation counter, and after the end of the measurement, 137Cs and60Co in the sample are measured again on the gamma spectrum; and 8) the acidity is adjusted to 5.0 mol / L, and the U content in the sample is measured through a 30% TBP extraction spectrophotometric method. According to the invention, more than 3,000 radioactive contaminated soils in the decommissioning process of nuclear facilities are analyzed and determined.
Owner:THE 404 COMPANY LIMITED CHINA NAT NUCLEAR
Method of manufacturing radiation detector
With this invention, a light guide is placed on a scintillator while an optical adhesive for forming the scintillator does not harden. Accordingly, a method of manufacturing a radiation detector may be provided in which the step of hardening the optical adhesive that joins scintillation counter crystals to one another and the step of optically coupling the scintillator and the light guide are performed en bloc. Accordingly, the radiation detector may be manufactured with no complicated process of forming the scintillator and the light guide individually and coupling them with the optical adhesive.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Non-scintillation core-shell structure quantum dot and preparation method thereof
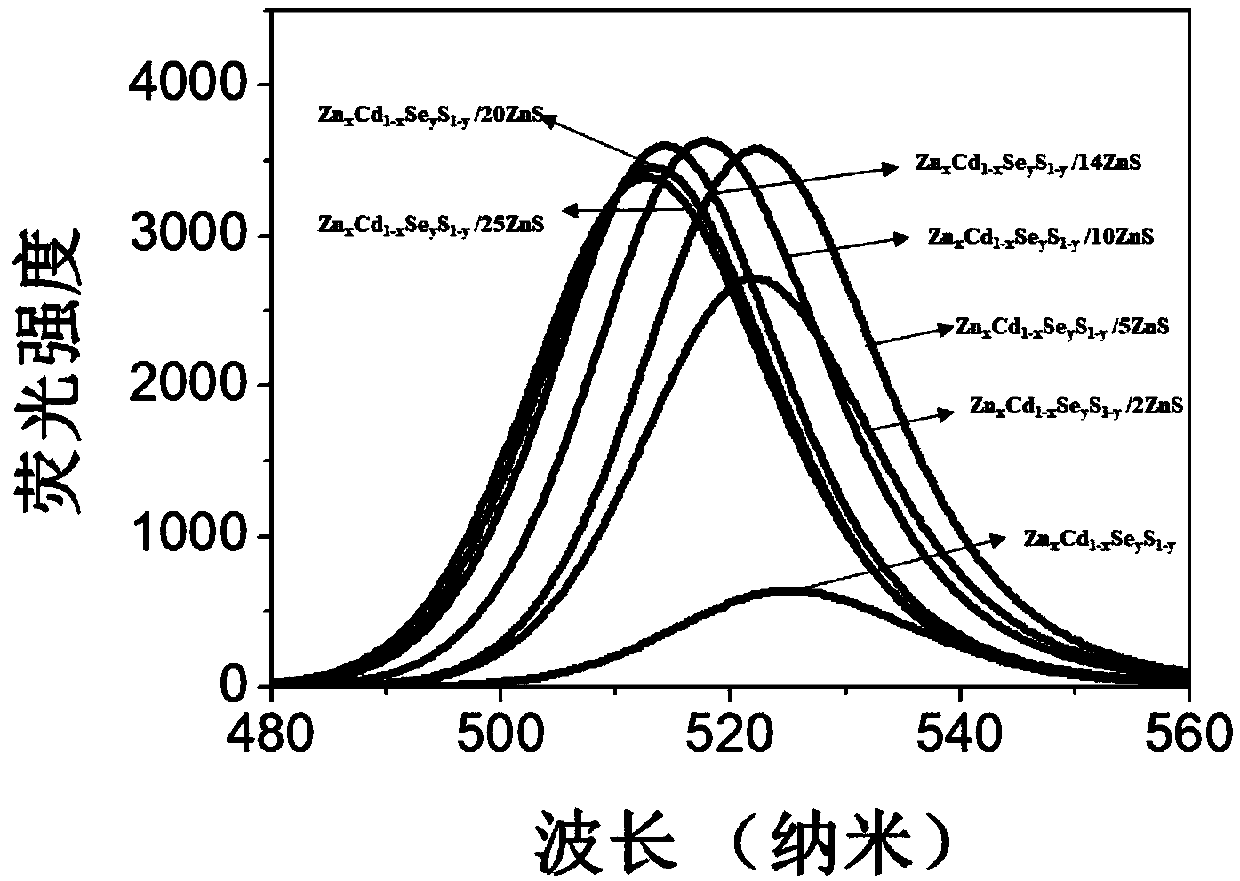
InactiveCN108048073AImprove stabilityExcellent fluorescence performanceNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldChemical composition
The invention provides a non-scintillation core-shell structure quantum dot. The non-scintillation core-shell structure quantum dot includes a core and a ZnS shell layer coated on the outer surface ofthe core; a chemical composition of the core is ZnxCd1-xSeyS1-y, wherein x is greater than 0 and smaller than 1, and y is greater than 0 and smaller than 1; the thickness of the shell layer is 0.7-10nm. The non-scintillation core-shell structure quantum dot has advantages of higher stability, higher quantum yield, good monodispersity, uniform size distribution and narrow full width at half maximum. Results of the embodiment of the non-scintillation core-shell structure quantum dot show that the quantum light state ratio of the non-scintillation core-shell structure quantum dot reaches 90-100%, the quantum yield is 60-100%, dimensional deviation can be controlled to be not more than 10%, the range of fluorescence spectrum is 480-560nm, and the full width at half maximum is 18-30nm.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method and system for discrimination pulse shape
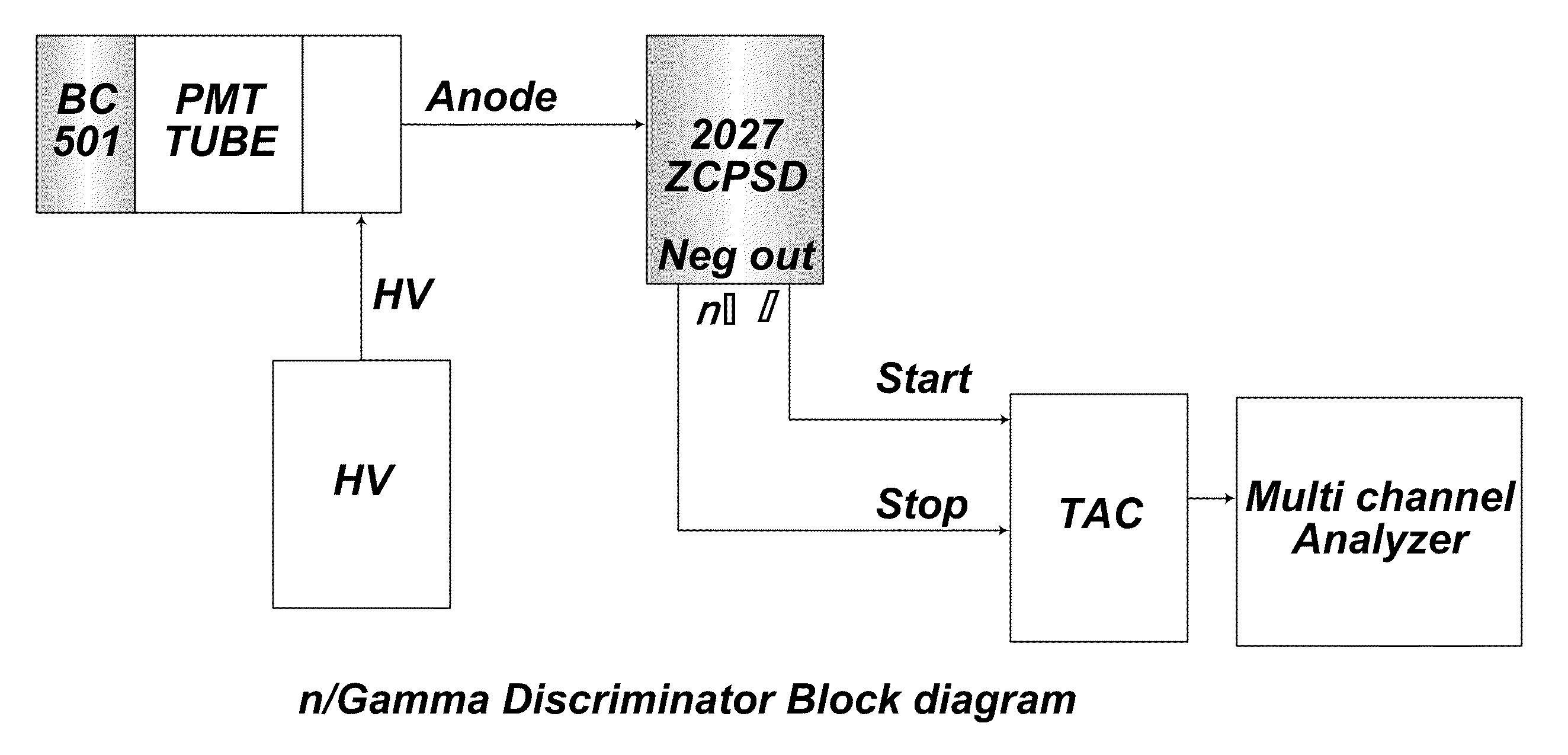
InactiveUS20100308231A1Large dynamic rangeQuickly checking system capabilityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillation counterElectron
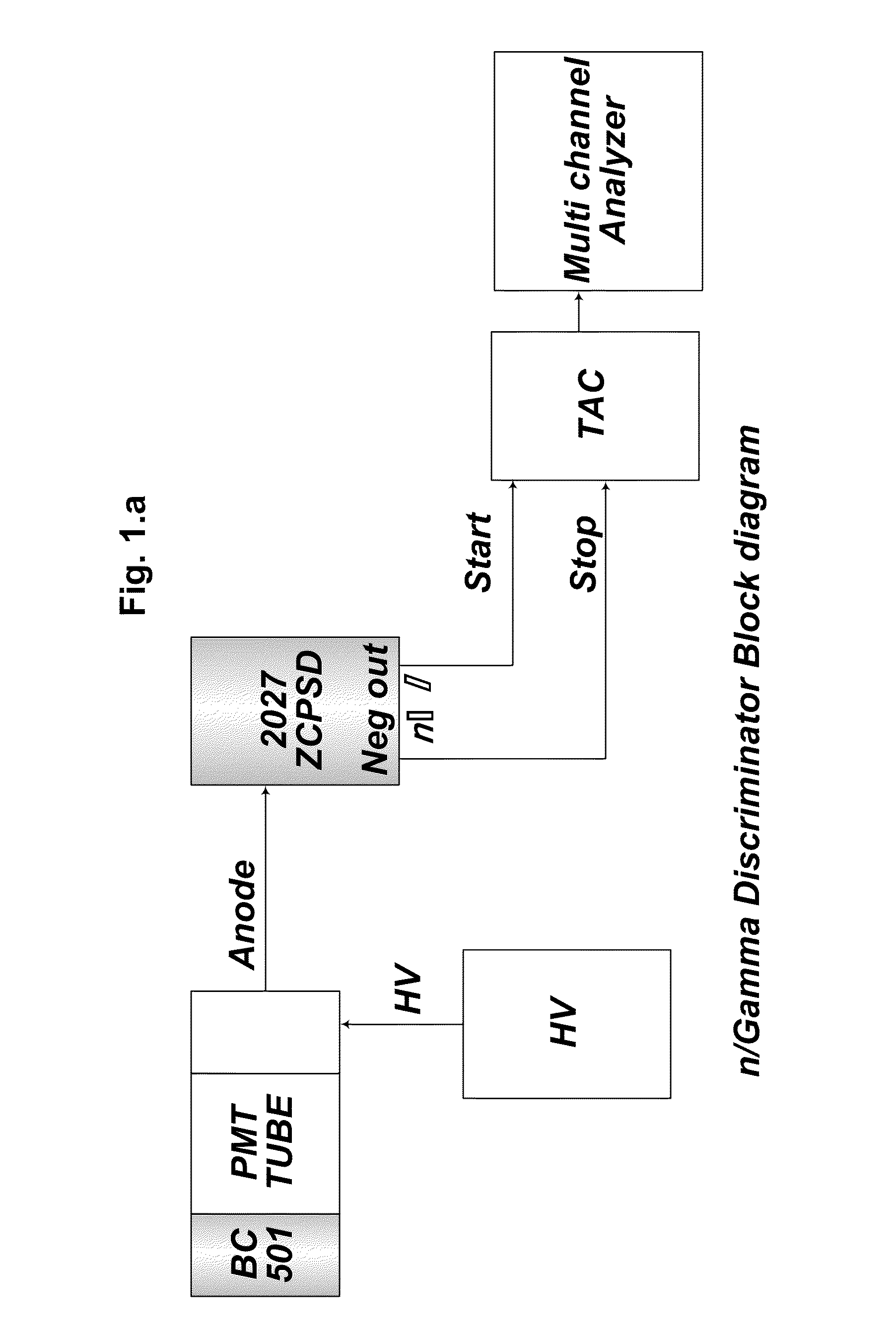
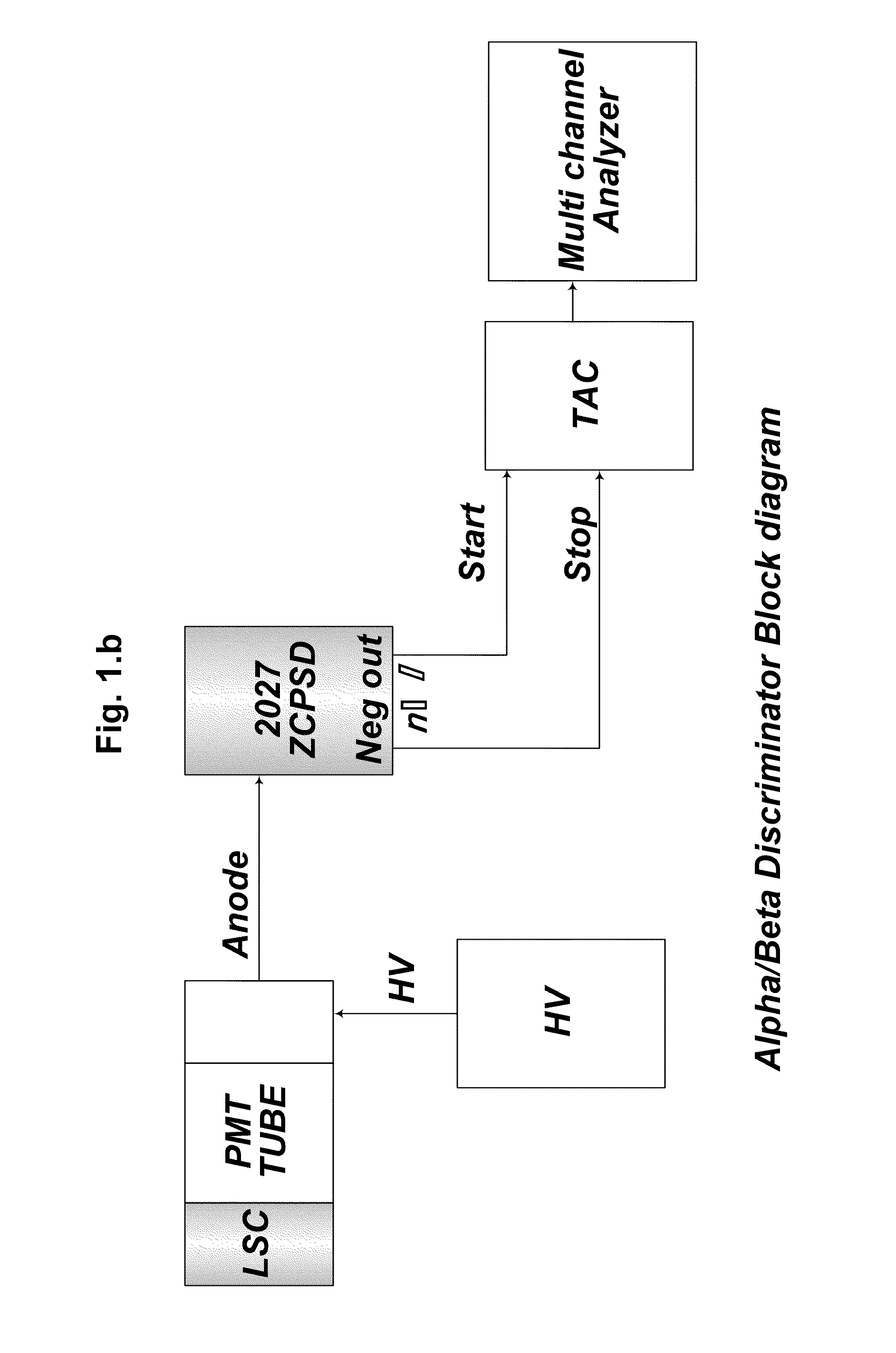
This ZCPSD Module can be used to separate neutron and gamma particles, alphas and protons, electrons and alphas etc depending on the detector used. ZCPSD provides optimum pulse shape separation for liquid scintillation counters. However the applications are not limited to n / γ separation. The ZCPSD can also be used for particle separation with inorganic scintillators, phoswitches, thick SBdetectors and proportional counters. The dc coupling allows high statistical count rate without affecting resolution, a major problem of conventional designs. The Single width NIM conforming to International Standards is easy to use, since only the anode signal is required from PM tubes. The ZCPSD can be used to generate identification spectra with a TAC and MCA or an identification signal for one species of particle.
Owner:SHARGHI IDO AMIN +1
Composition and preparation method of scintillation glass used for preparation of scintillation fiber-optic faceplate
ActiveCN105481245AEasy to adjustStrong ability to formX-ray/infra-red processesGlass furnace apparatusCrucibleScintillation counter
The invention discloses a composition and preparation method of scintillation glass used for preparation of a scintillation fiber-optic faceplate. The composition comprises, by weight, 10 to 20% of SiO2, 0 to 10% of Al2O3, 20 to 45% of B2O3, 30 to 60% of La2O3, 0 to 2% of Nb2O5, 5 to 25% of Gd2O3, 0 to 4% of Lu2O3, 0 to 5% of BaO, 0 to 2% of SnO and 0 to 5% of ZnO. The invention also provides the preparation method for the scintillation glass used for preparation of the scintillation fiber-optic faceplate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) weighing the raw materials according to the above-mentioned weight percentages, mixing all the raw materials, and grinding the raw materials until the raw materials are uniform so as to obtain a batch; (2) pouring the batch into a crucible and fusing the batch so as to prepare a glass melt; (3) casting the glass melt on a preheated heat-resistant steel die, maintaining the temperature of the die in a muffle furnace and then carrying out cooling and annealing; and (4) carrying out cutting, surface grinding and polishing so as to obtain the scintillation glass. The prepared scintillation glass has the advantages of good chemical stability, high scintillation light luminescence efficiency and capacity of realizing fiber drawing.
Owner:中建材光子科技有限公司
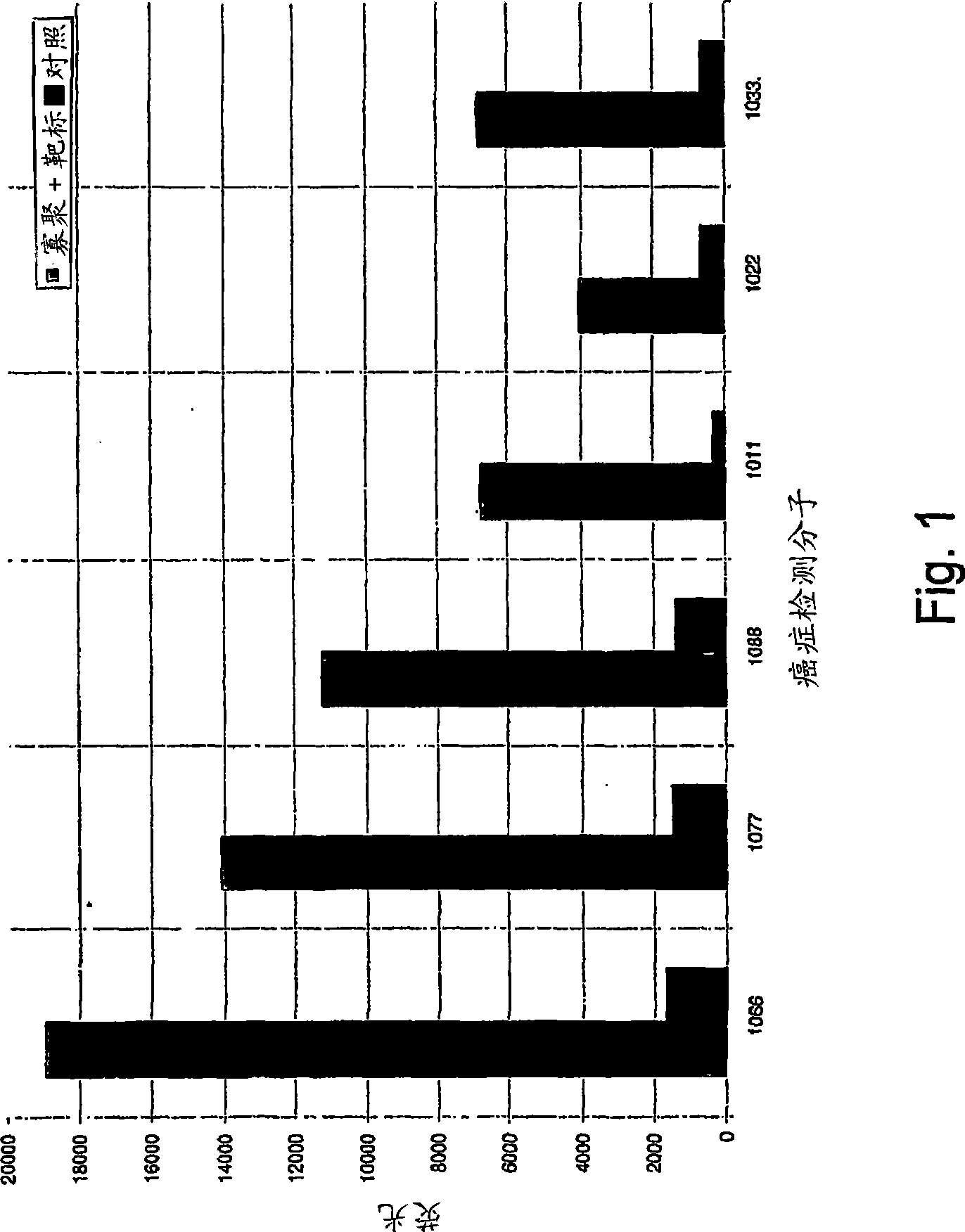
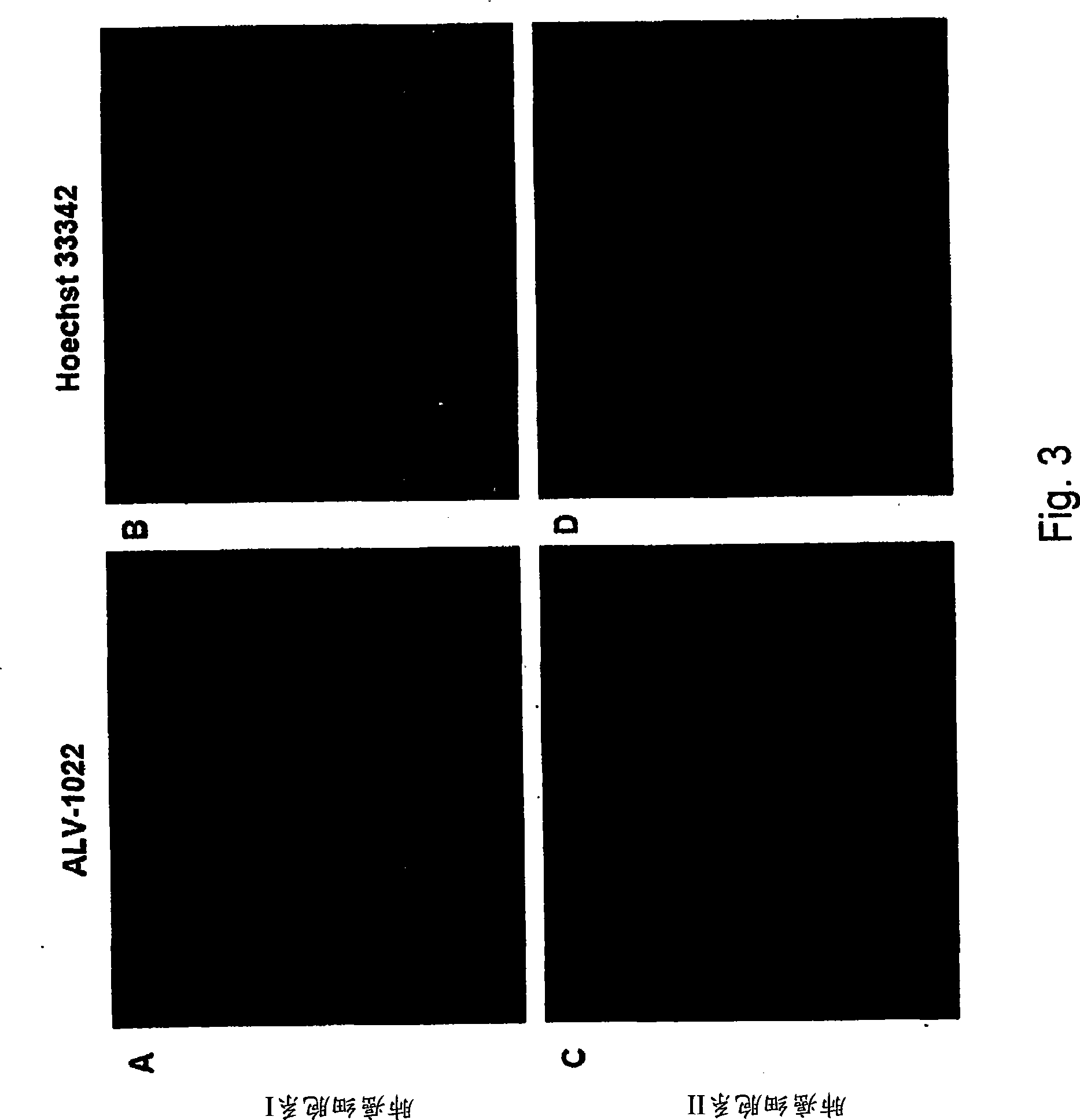
Methods and applications of molecular beacon imaging for infectious disease and cancer detection
Molecular beacon for detecting an infection and / or expression or a mutation of a disease marker for diagnostics and pharmacogenomics. The molecular beacon is capable of hybridizing a disease-related RNA or DNA of a disease marker in a specimen obtained from a living subject, thereby emitting a signal detectable without a need for signal amplification. The disease marker includes a genetic sequence specific to a pathogen including a flu virus, a cancer cell marker, and a drug resistance-related genetic mutation marker for a drug resistant cancer and infectious pathogen. To detect a disease cell, a specimen containing one or more cells is obtained from a living subject, and fixed by an organic solvent. A molecular beacon is then added to the specimen, followed by staining nuclei of the cells in the specimen. The signal is detectable with a microscope, FACS scan, ELISA plate reader, Scanner, or any combinations thereof.
Owner:ALVITAE PHARMA
PET (Positron Emission Tomography) annular detection imaging system based on scintillation fibers
ActiveCN109498044AMark accuratelyCapture comprehensiveComputerised tomographsTomographyUltrasound attenuationFiber
The invention belongs to the technical field of electron emission imaging, and discloses a PET (Positron Emission Tomography) annular detection imaging system based on scintillation fibers. The systemcomprises a plurality of detector modules which are sequentially connected along a central axis, wherein each of the detector modules consists of a scintillation fiber unit and a photosensor unit; the photosensor units are symmetrically arranged at two ends of the integral scintillation fiber unit; a plurality of photosensors are arranged on the photosensor unit at each end; and each photosensoris respectively correspondingly coupled with a plurality of scintillation fibers in the scintillation fiber unit. According to the system, the error influence caused by energy attenuation on positioning is effectively reduced, the reaction positions of the scintillation optical fibers are easily judged, missed detection cannot be caused due to splicing of a plurality of the detector modules, and detection information is more accurate and comprehensive, so that the PET annular detection imaging system has the characteristics of high efficiency, high sensitivity, high imaging resolution and morecompact devices.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Digital X-ray image detector and preparation method thereof
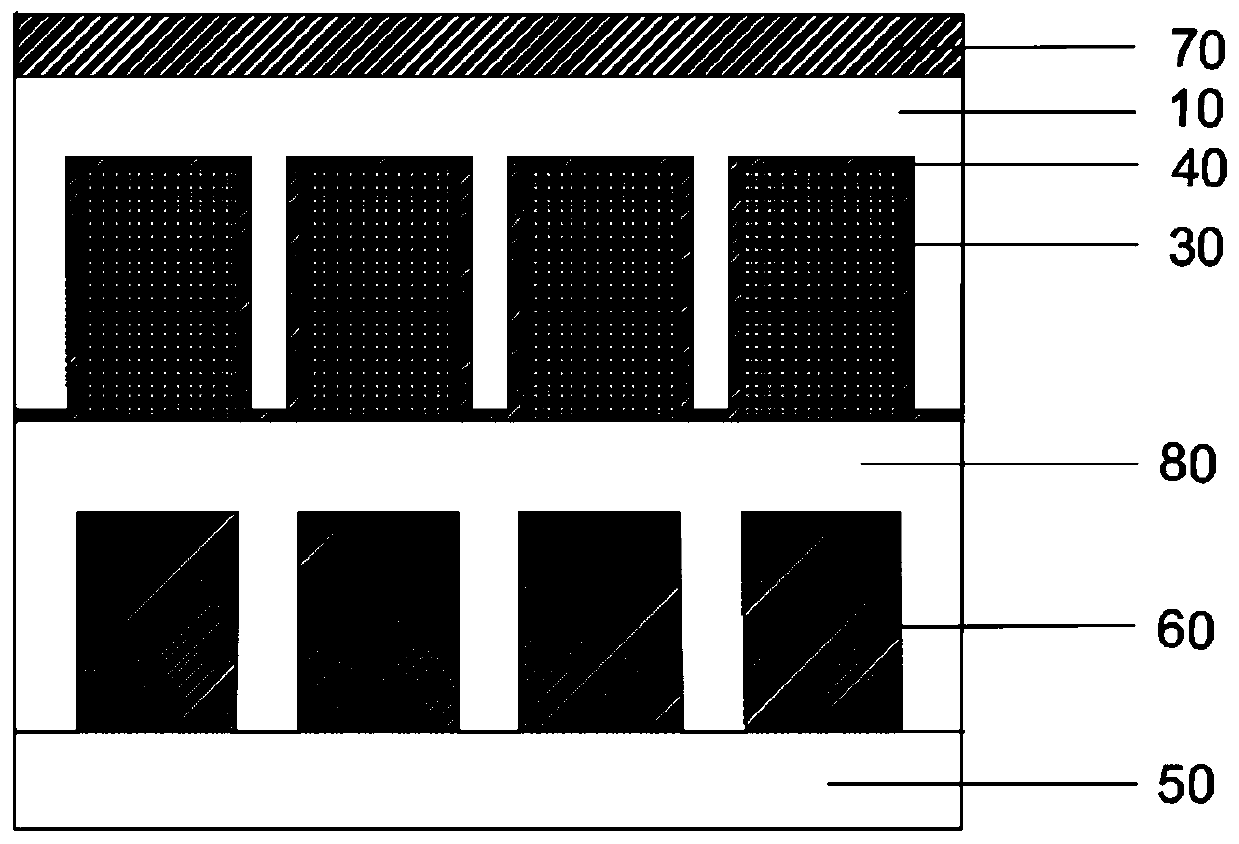
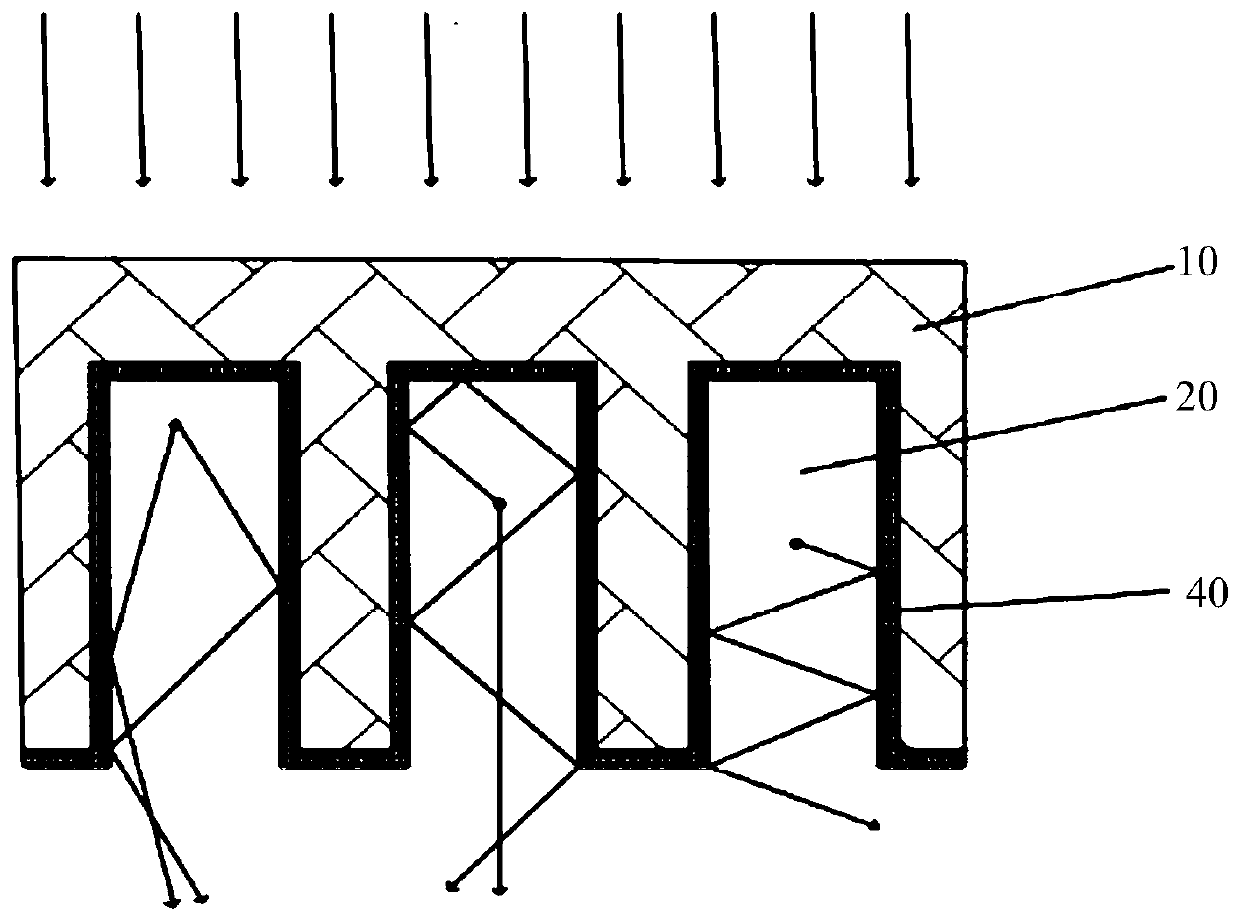
InactiveCN110416347AEliminate crosstalkImprove transmission efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesLight sensingImaging quality
The invention discloses a digital X-ray image detector and a preparation method thereof. The digital X-ray image detector comprises a first silicon wafer substrate, a deep hole structure array arranged on the lower surface of the first silicon wafer substrate, scintillation layers loaded in the deep hole structure array and a light total reflection layer arranged between the deep hole structure array and the scintillation layers, wherein the lower surface of the first silicon wafer substrate is correspondingly provided with a second silicon wafer substrate, and the second silicon wafer substrate is provided with a light sensing unit array corresponding to the deep hole structure array. According to the invention, the scintillation layers are arranged in the deep hole array structure, so that the crosstalk phenomenon of visible light between pin columns is eliminated, the generated visible light is enabled to be propagated in a total reflection mode at the interface of the scintillationlayers and the light total reflection layer, and the visible light transmission efficiency is improved. Meanwhile, the scintillation layers in the deep hole array structure are in one-to-one correspondence with the light sensing units in the light sensing unit array, so that the visible light generated by the scintillation layers is enabled to be acquired by the corresponding light sensing unitsto be greater extent, and the image quality is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
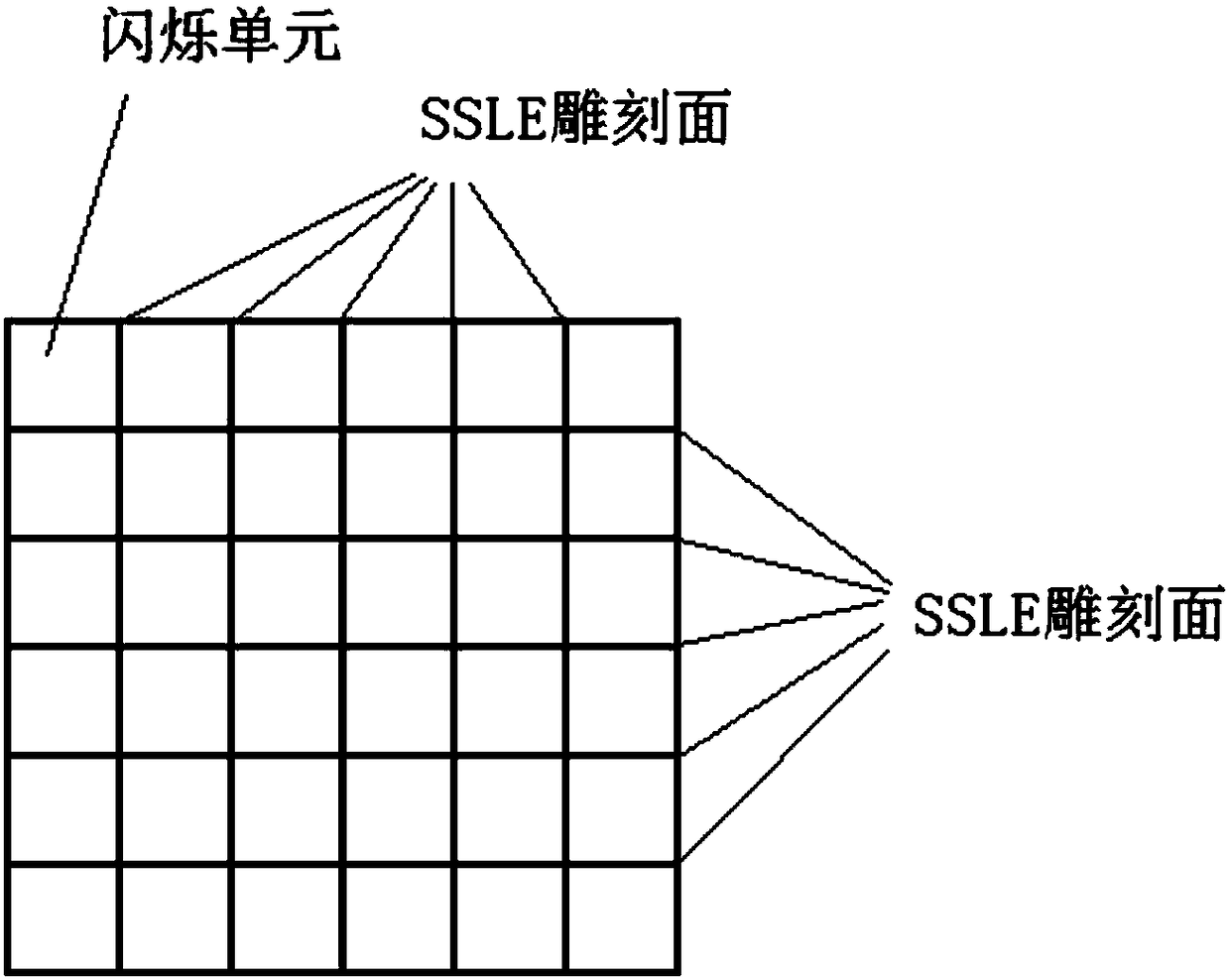
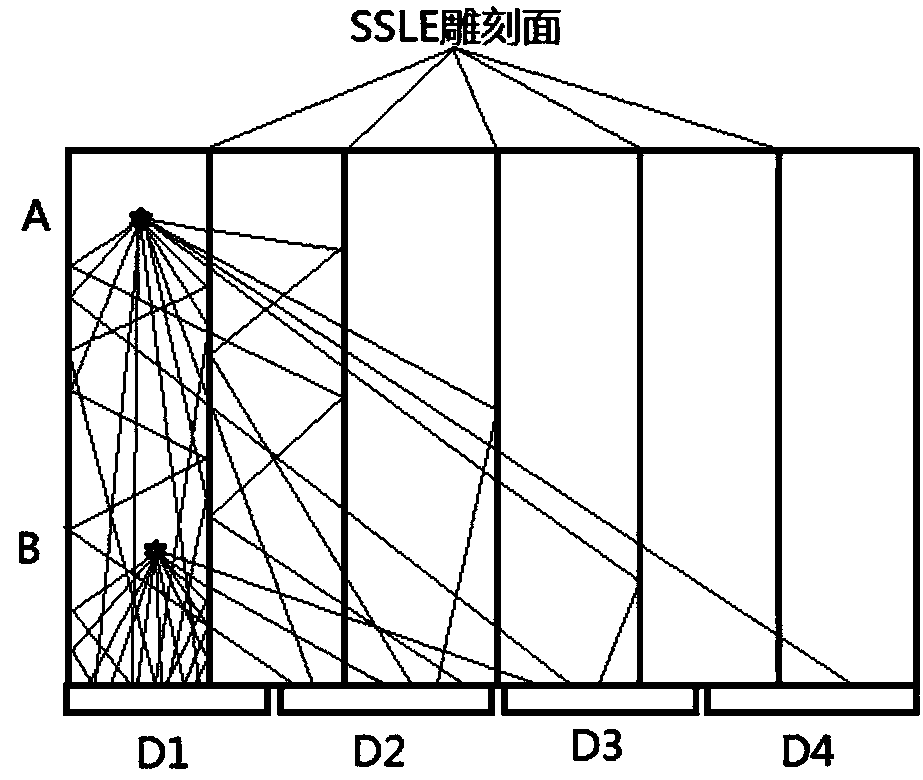
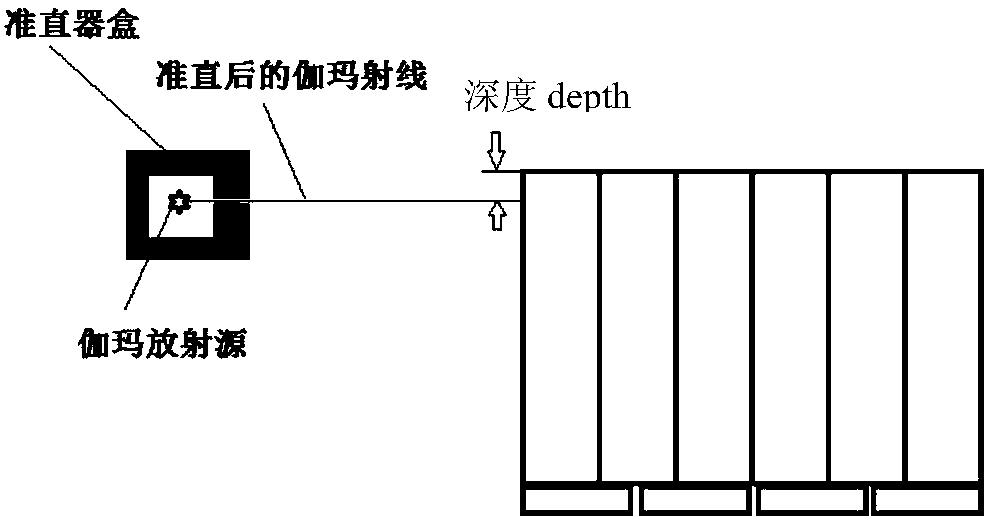
Scintillation detection method with three-dimensional recognition distinguishing capability
InactiveCN108614286ASuitable for engineeringGood energy resolutionRadiation intensity measurementScintillation counterRadioactive source
The invention discloses a scintillation detection method with the three-dimensional recognition distinguishing capability. The method comprises the steps: performing the calibration of instances at different depths in each scintillation unit of a scintillation detecting device through employing a radioactive source, and carrying out the fitting of a function of the action depth with respect to coordinates X, Y; solving the X and Y coordinates of any unknown instance detected by the scintillation detecting device through a centroid method, judging the number ij of the scintillation unit according to the range of the X and Y coordinates of the instance, selecting a corresponding function through the number ij of the scintillation unit, solving the maximum probability value of the depth of the instance, and taking the depth corresponding to the maximum probability value as the third-dimensional coordinate information of the occurrence position of the instance, wherein each scintillation unit is provided with a reflecting surface, and each reflecting surface is formed by the arrangement of a plurality of miniature burst points formed by laser inter-engraving. The method can be used forobtaining the information of the action depth, and is good in energy resolution and time resolution.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Digital X-ray flat panel detector
InactiveCN103745982AImprove imaging effectHigh resolutionX-ray/infra-red processesRadiation controlled devicesSensor arrayFlat panel detector
The invention discloses a digital X-ray flat panel detector comprising a scintillation screen and an amorphous silicon sensor array closely attached to the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen comprises a substrate, a reflection layer attached to the upper surface of the substrate, a scintillation layer deposited on the reflection layer and a waterproof thin film layer laminated on the scintillation layer, wherein the scintillation layer is an acicular-structure cesium iodide crystal array, and the thickness of the scintillation layer is 800-1000 [mu]m. The amorphous silicon sensor array is arranged on the lower surface of the substrate. With the above method, the digital X-ray flat panel detector adopts the high-resolution cesium iodide scintillation screen, and has good imaging performance.
Owner:江苏龙信电子科技有限公司
Device and method for measuring radon in scintillation chamber
ActiveCN109655874AHigh detection sensitivityIncrease count rateRadiation intensity measurementFiberSilicon photomultiplier
The invention discloses a device and method for detecting radon in a scintillation chamber, and relates to the technical field of nuclear radiation detection. The device for measuring radon in the scintillation chamber comprises a plurality of single-layer scintillation chamber bodies, wherein each single-layer scintillation chamber comprises a shell; the shells are connected together in a stackedmanner from bottom to top, and partition plates are arranged in the cavity of each shell; the corresponding partition plates divide the cavity of each shell into a plurality of sector chambers, and the inner wall surfaces of the sector chambers are coated with scintillation crystals; the distance between any two points in each sector chamber is less than the range of alpha particles produced by 222Rn decay; all the sector chambers communicate with one another in sequence, and a wavelength displacement optical fiber penetrates through the cavity of each shell; the tail ends of the wavelength displacement fibers are connected to a photomultiplier tube or a silicon photomultiplier; the photomultiplier tube or silicon photomultiplier is connected to an electronic readout system; and the wavelength-shifted fibers are used to collect flicker produced by the impact of the alpha particles on the scintillation crystals on the inner walls of the sector chambers. The concentration of the radon can be determined from the relationship between alpha particle counting and the concentration of the radon, which is identified and recorded by the electronic readout system.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
1,8-naphthalimide derivatives as scintillation agents, in particular for discriminating between fast neutrons and gamma rays
The invention relates to the use of 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives and of their salts as scintillation agents and more specifically as agents for discriminating between fast neutrons and gamma rays.It also relates to liquid scintillators comprising these scintillation agents in solution in a solvent and to novel 1,8-naphthalimide derivates of use as scintillation agents, in particular for discriminating between fast neutrons and gamma rays.Applications: all the fields of use of scintillators and in particular industry, geophysics, fundamental physics, in particular nuclear physics, the safety of goods and people, protection from radiation of workers in the industrial, nuclear and medical sectors, medical imaging, and the like.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Gamma ray scintillation detector preserving the original scintillation light distribution
InactiveUS9915739B2Improve spatial resolutionLess sensitivityRadiation intensity measurementGamma rayScintillation counter
An apparatus to detect gamma rays, comprising a scintillator, a position sensitive photo sensor and a scintillation-light-incidence-angle-constraining, SLIAC, element, the scintillator has faces and the position sensitive photo sensor detects scintillation photons exiting a scintillation photons transparent face of the scintillator, and a portion of a scintillator face is covered with an absorbing layer, which absorbs scintillation photons created by scintillation events due to the interaction of incoming gamma rays with the scintillator, and the SLIAC element is optically coupled between a scintillation photons transparent face of the scintillator and the position sensitive photo sensor and the SLIAC element guides the scintillation photons exiting the scintillator towards the position sensitive photo sensor, and the SLIAC element restricts the maximum allowed half light acceptance angle for the scintillation light hitting the position sensitive photo sensor to less than 45°.
Owner:GENERAL EQUIP FOR MEDICAL IMAGING SL +1
Scale device for fitting K value of scintillation chamber
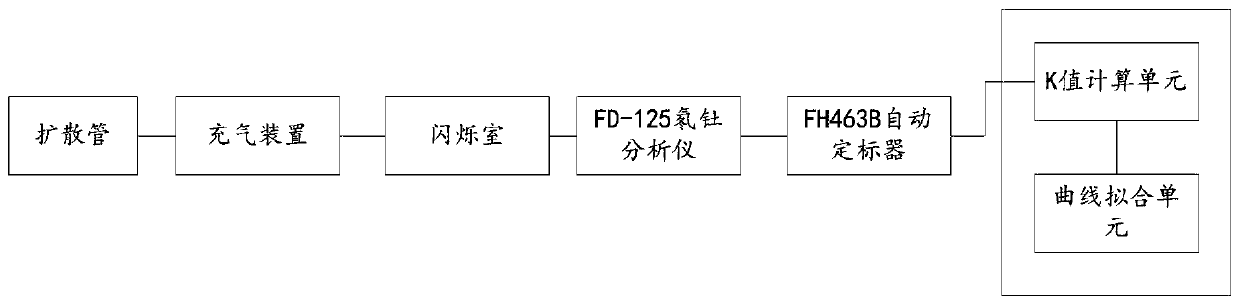
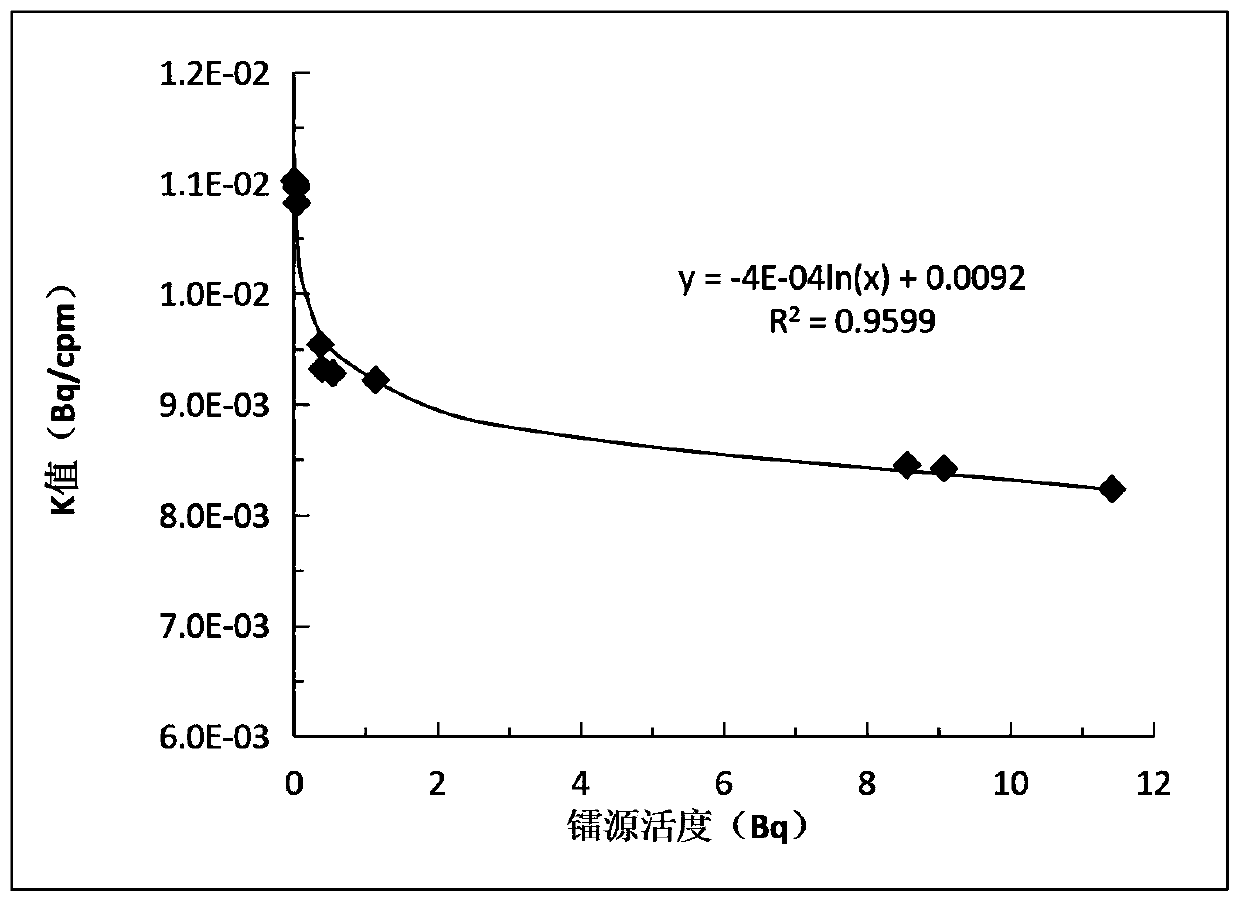
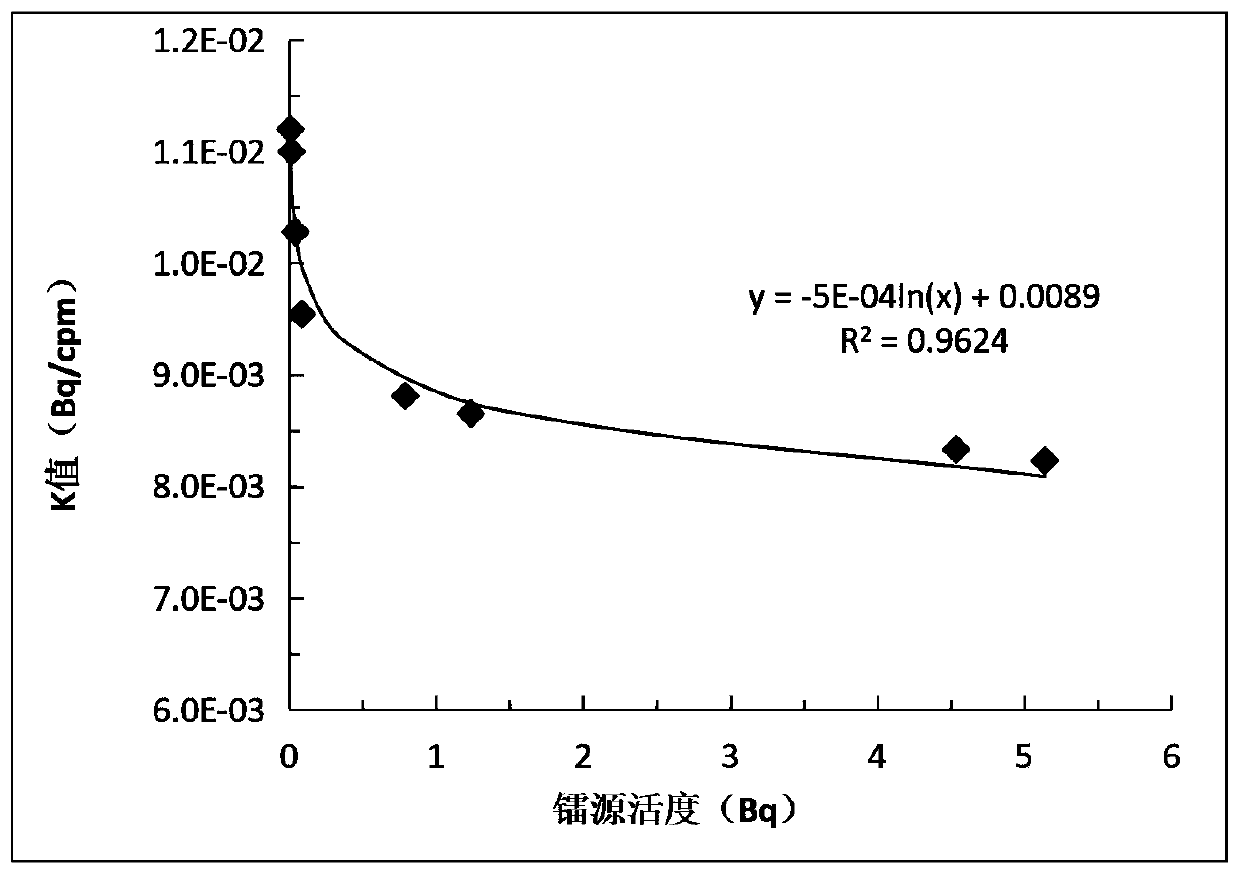
ActiveCN110082810AImprove accuracyAvoid experimental errorX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadon gasFluorescence
The invention provides a scale device for fitting the K value of a scintillation chamber, and the device comprises a diffusion tube which is used for carrying laser marking liquids with different activities and collecting radon gas in a balanced state; an inflation device which is used for inflating the radon gas in the diffusion tube into the scintillation chamber; a scintillation chamber which is used for enabling the radon gas to interact with ZnS atoms on the inner wall of the scintillation chamber to excite and emit fluorescence; an FD-125 radon thorium analyzer which is used for converting fluorescence generated by the scintillation chamber into electrons and realizing multiplication and amplification to generate an electric pulse signal; an FH463B automatic calibrator which is usedfor realizing digital recording according to the electric pulse signal output by the photomultiplier within the selected time; and a scintillation chamber K value curve model fitting device which is used for fitting to obtain a scintillation chamber K value curve according to the digital record values corresponding to the series of laser marking liquids with different activities. According to thedevice, experimental errors caused by selection of the K value of the scintillation chamber are overcome through data obtained through a scale experiment, so that the accuracy of a jet gas scintillation analysis method is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com