Dispersion type scintillation detector for impulse gamma detection
A scintillation detector and scattering technology, applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity, large span of radiation field strength, and inability to measure pulsed gamma/X-rays accurately, so as to improve performance , Deduct the effect of interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
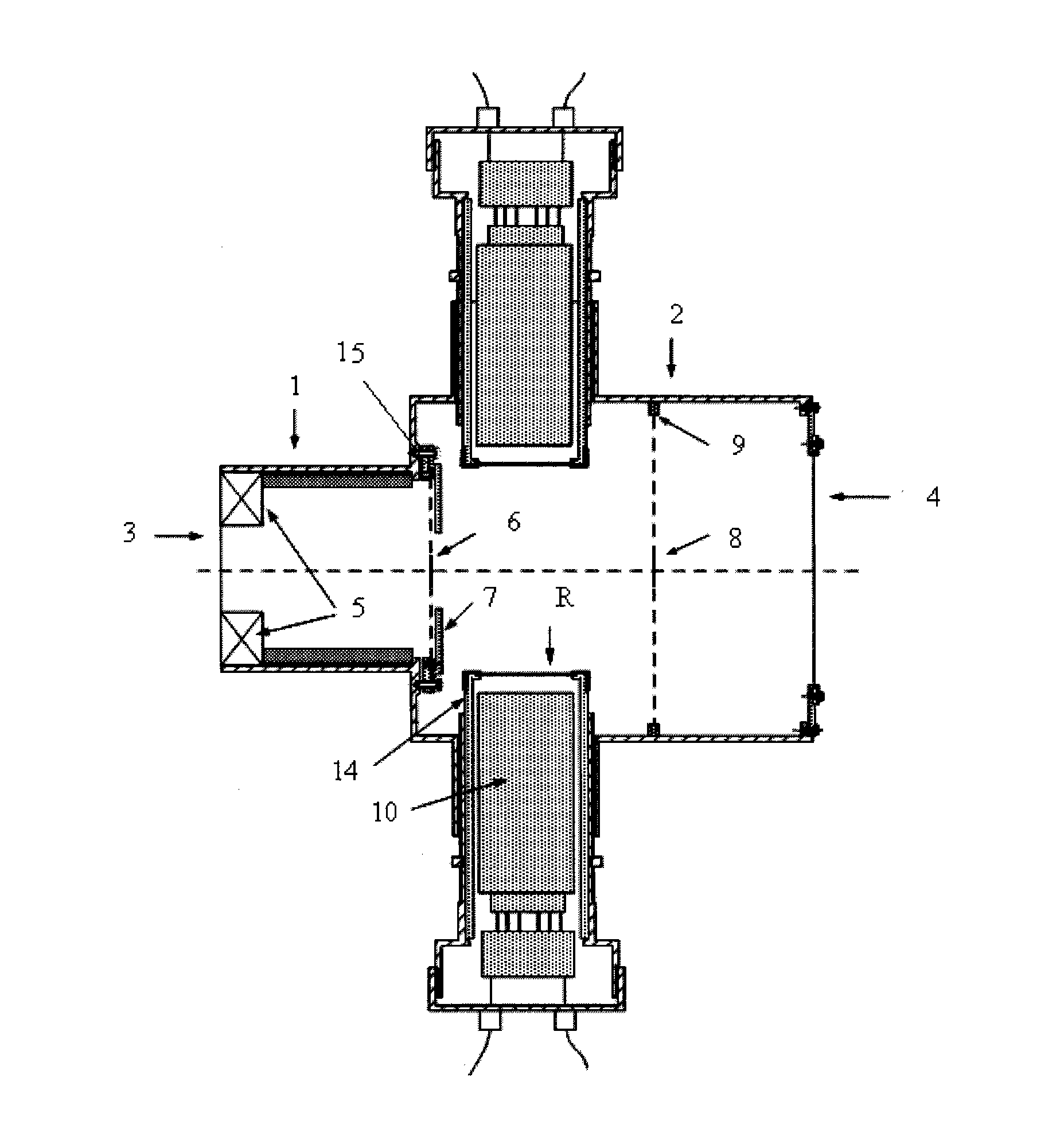
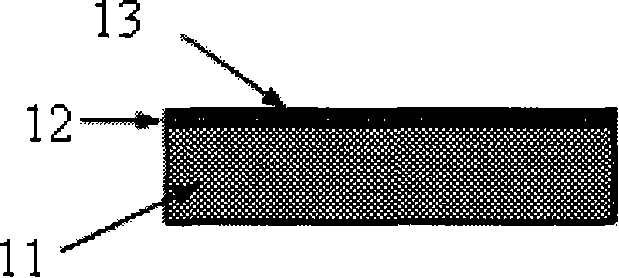
[0018] The distance between the front surface of the scintillator 11 and the central axis of the beam is 8 cm, the distance between the front target 6 and the center line of the scintillator 11 is 7 cm, and the distance between the rear target 8 and the center line of the scintillator 11 is 6 cm. The incident window 3 and the exit window 4 are 25 μm aluminum foils, which are used to seal the electrons in the space. The scintillator 11 is a ST401 plastic scintillator or a ZnO inorganic scintillator. The electronic filter 13 is 20 μm aluminum foil. The electronic aluminum retaining ring 7 is a 3mm thick aluminum sheet, and the middle expansion hole of the electronic aluminum retaining ring 7 is 50mm, and the distance between the cleaning magnet 5 and the front target 6 is 80mm. The front target 6 and the rear target 8 are Tungsten sheets of 20×0.1 mm are suspended on the front target frame 15 and the rear target frame 9 with thin wires, and the front target frame 15 and the...
Embodiment 2
[0022] In this embodiment, the distance between the front surface of the scintillator 11 and the central axis of the beam is 5 cm, the distance between the front target 6 and the center line of the scintillator 11 is 5 cm, and the distance between the rear target 8 and the center line of the scintillator 11 is 4 cm. The incident window 3 and the exit window 4 are 20 μm aluminum foil. The scintillator 11 is a ST401 plastic scintillator or a ZnO inorganic scintillator. The electronic filter 13 is 10 μm aluminum foil. The electronic aluminum retaining ring 7 is a 2mm thick aluminum sheet, and the middle expansion hole of the electronic aluminum retaining ring 7 is 40mm, the distance between the cleaning magnet 5 and the front target 6 is 60mm. The front target 6 and the rear target 8 are Tungsten sheets of 20×0.1 mm are suspended on the front target frame 15 and the rear target frame 9 with thin wires, and the front target frame 15 and the rear target frame 9 are frame struc...
Embodiment 3
[0024] In this embodiment, the distance between the front surface of the scintillator 11 and the central axis of the beam is 10 cm, the distance between the front target 6 and the center line of the scintillator 11 is 10 cm, and the distance between the rear target 8 and the center line of the scintillator 11 is 8 cm. The incident window 3 and the exit window 4 are 30 μm aluminum foil. The scintillator 11 is a ST401 plastic scintillator or a ZnO inorganic scintillator. The electronic filter 13 is 30 μm aluminum foil. The electronic aluminum retaining ring 7 is a 4mm thick aluminum sheet, and the middle expansion hole of the electronic aluminum retaining ring 7 is 60mm, and the distance between the cleaning magnet 5 and the front target 6 is 100mm. The front target 6 and the rear target 8 are Tungsten sheets of 20×0.1mm are suspended on the front target frame 7 and the rear target frame 9 with thin metal wires, and the front target frame 7 and the rear target frame 9 are f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com