Patents
Literature
258 results about "Neutron irradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neutron Irradiation. Neutron irradiation is a neutron exposure process to determine the impact of radiation on materials properties and device performance.
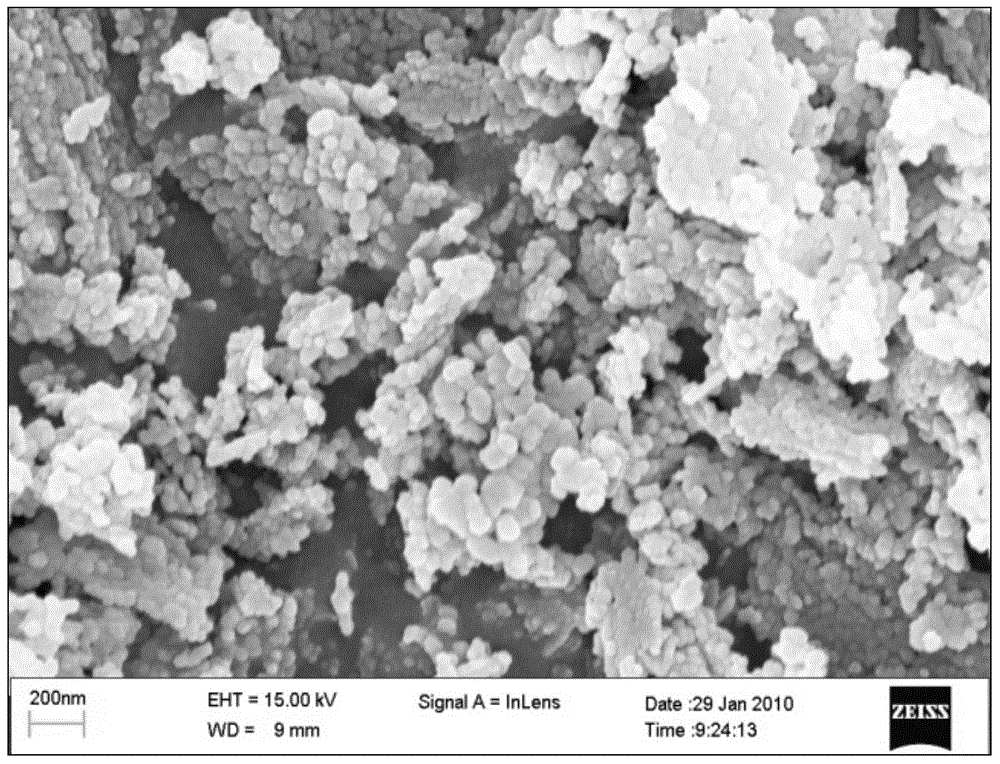
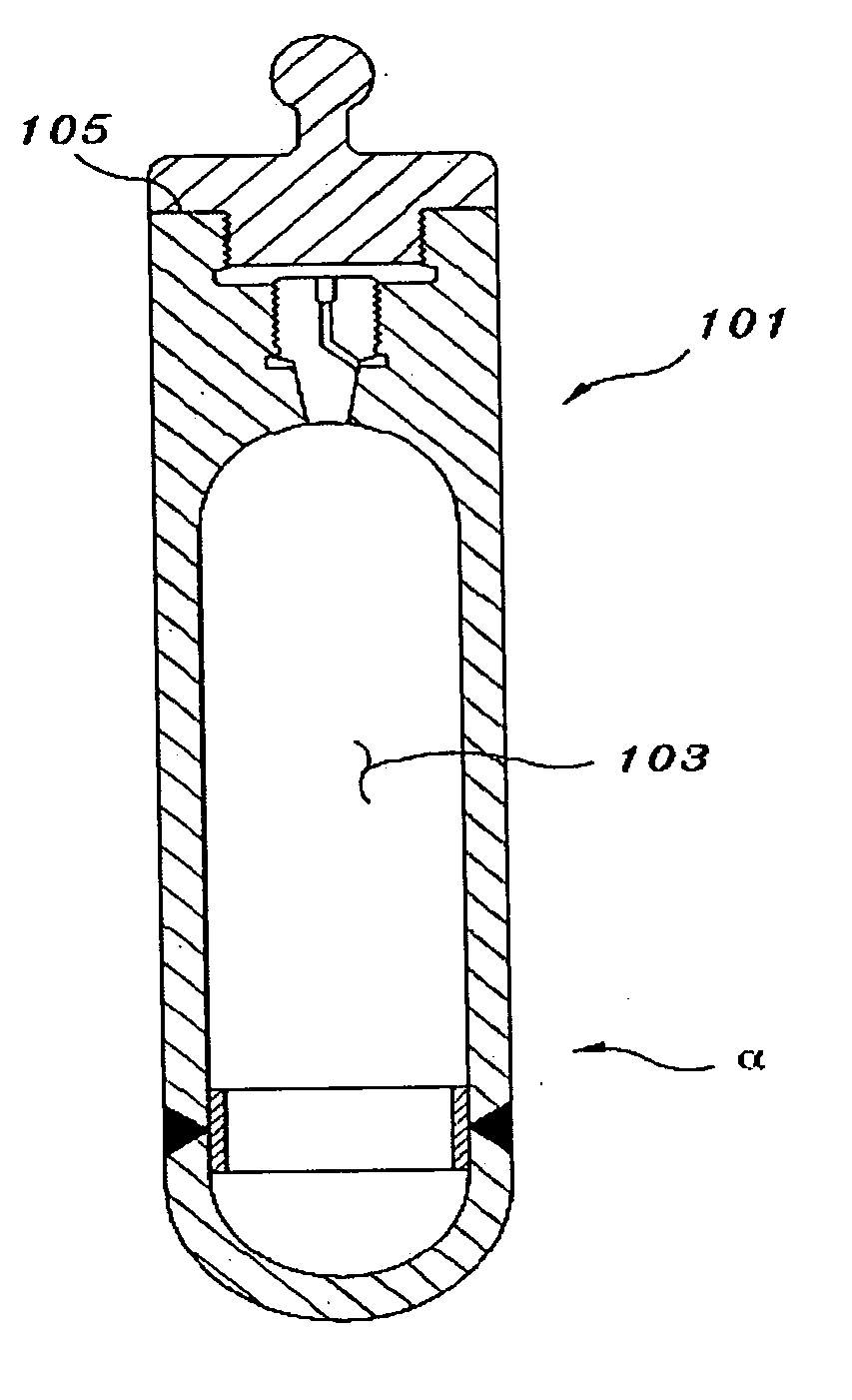
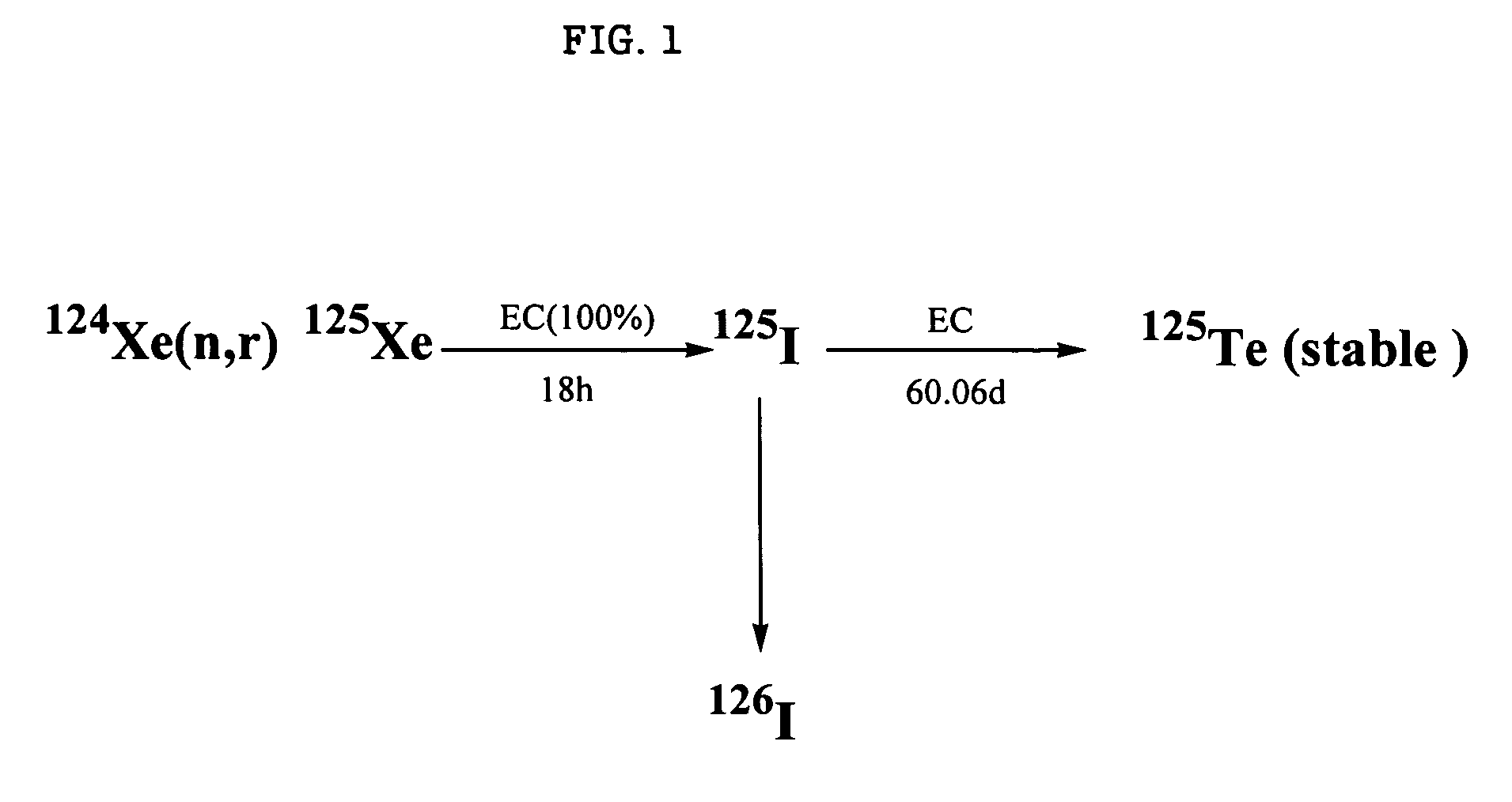
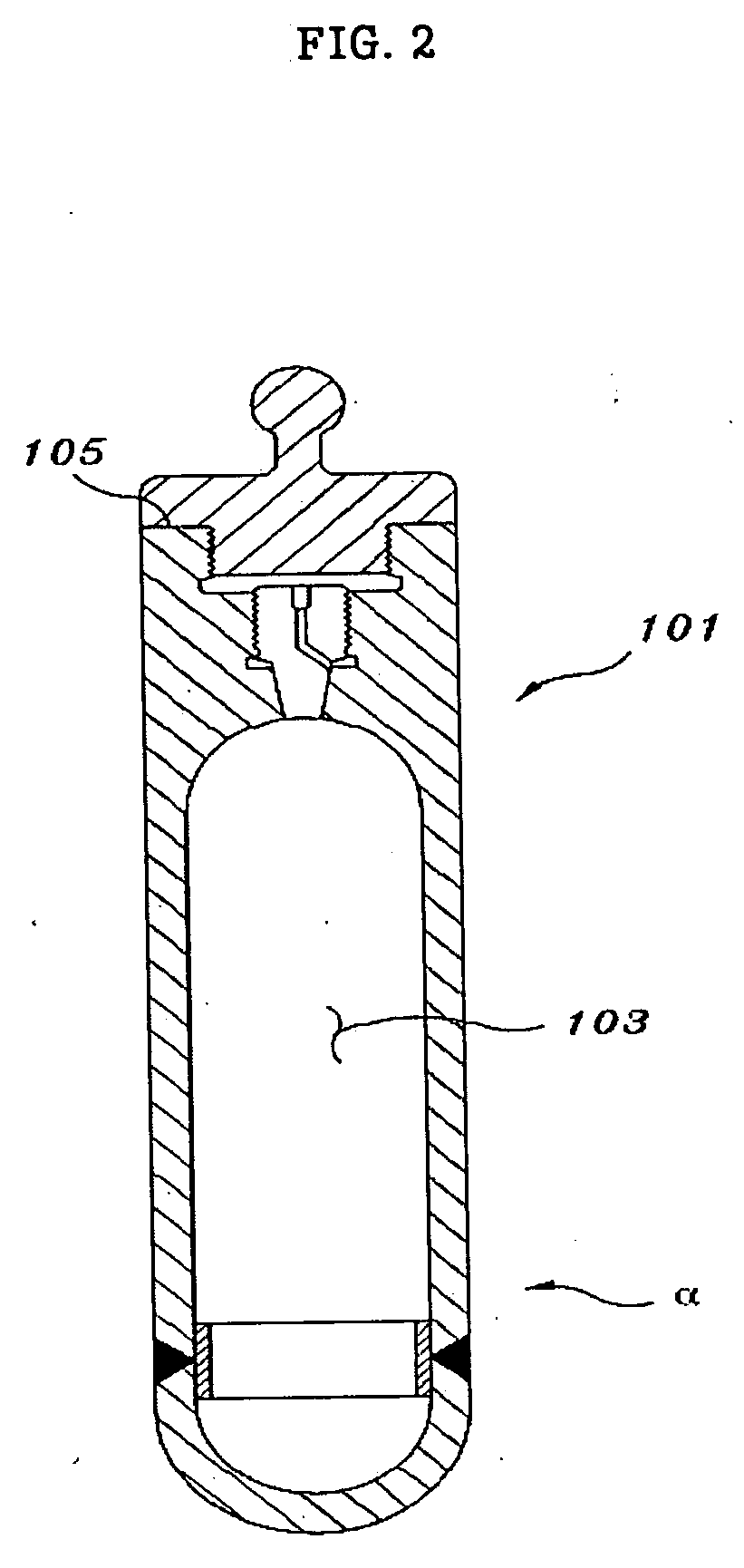
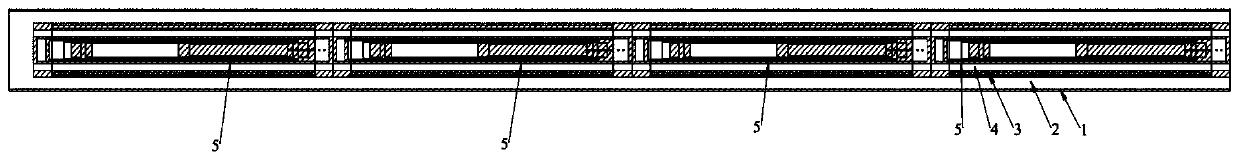
Internal circulating irradiation capsule for iodine-125 and method of producing iodine-125 using same
InactiveUS20060126774A1Reduce neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationIodine
A present invention provides an internal circulating irradiation capsule available for the production of iodine-125 and a related production method. The irradiation capsule filled with xenon gas has a lower irradiation part, an upper irradiation part, and a neutron control member. The lower irradiation part is inserted into an irradiation hole of a reactor core and irradiated with a large quantity of neutron directly. When neutron is radiated to the xenon gas, iodine-125 is produced from xenon gas. The upper irradiation part protrudes from the irradiation hole, and iodine-125 is transferred to the upper irradiation part by convection and solidified in the upper part. The neutron control member reduces neutron in the upper part to produce iodine-125 of high purity and radioactivity in a large quantity.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Method For Preparing Radioactive Film
InactiveUS20080031811A1Uniform thickness distributionLow amount of residual solventOther chemical processesRadioactive preparation formsNuclear reactorNeutron irradiation
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a radioactive film for local radioactive treatment. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a radioactive film comprising the steps of; dissolving 0.1˜14.5 weight % of a stable nuclide and 13˜32.5 weight % of a film-forming base for the total amount of a solvent in the solvent; applying a stable nuclide solution on a release paper by a coater and drying; and irradiating a stable nuclide film with neutrons in a nuclear reactor. A method for preparing a radioactive film according to the present invention provides a radioactive film having a uniform distribution of radionuclides and an even thickness. Therefore, the therapeutic efficacy of the radioactive film for selective treatment of a lesion may be maximized by attaching the radioactive film on a patient's skin or a mucous membrane and by direct radioactive radiation.
Owner:DONG WHA PHARM CO LTD +1
Method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation
InactiveUS20030147484A1Increases radiation levelReduce riskConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationX-ray
A method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation involves the initial X-ray irradiation of the object under investigation, e.g. a piece of luggage or mailing, and forming its X-ray images; using the X-ray images to detect areas with a high density of organic materials and identifying articles therein; determining the location, dimensions and supposed mass of an unidentified article; determining and forming a directional pattern of the neutron radiator corresponding to the dimensions of the unidentified article. The method further includes subsequent thermal neutron irradiation of the area with the unidentified article; recording gamma-ray quanta having the energy of 10.8 MeV and cascade gamma-ray quanta with energies of 5.534 and 5.266 MeV by at least two gamma-ray detectors; counting of simultaneously recorded pairs of cascade gamma-ray quanta; determination of the overall gamma-ray intensity, taking into account weight factors in readings of the detectors; determination of the threshold value for the overall gamma-ray intensity basing on the supposed mass of explosive being detected; and making a decision in the event the threshold value of overall gamma-ray intensity is exceeded. When checking small-size objects, the neutron irradiation step is preceded by replacing the ambient air by a gaseous medium not containing nitrogen.
Owner:SCI & TECHN CENT RATEC
Oxide dispersion strengthening low activity martensitic steel material and preparation thereof
The invention discloses an oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel. A substrate is a CLAM steel and contains 0.2 to 0.5 percent of Y2O3 and 0.10 to 0.50 percent of Ti. The method comprises the following steps that: CLAM steel powder, Y2O3 powder and Ti powder are evenly mixed and put in a sealed container for degassing, subjected to mechanical alloying, hot isostatic pressing or hot-pressing sintering and densification molding under the protection of high-purity argon gas, then subjected to hot squeezing or forging and rolling and other machining and molding processes, and the needed section material is prepared; and finally, the section material is subjected to the treatment of quenching and tempering to prepare the oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel ODS-CLAM. The oxide dispersion strengthened low-activation martensitic steel has the advantages that: the low-activation martensitic steel realizes a martensite-based alloy with oxide strengthening phases evenly dispersed and distributed and crystal grains of a reasonable size, can be used as a structural steel material, has the characteristics of strong neutron irradiation resistance, good high-temperature performance, low activation, etc. and is suitable for a fusion reactor and other environments with strong neutron irradiation and high-temperature.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
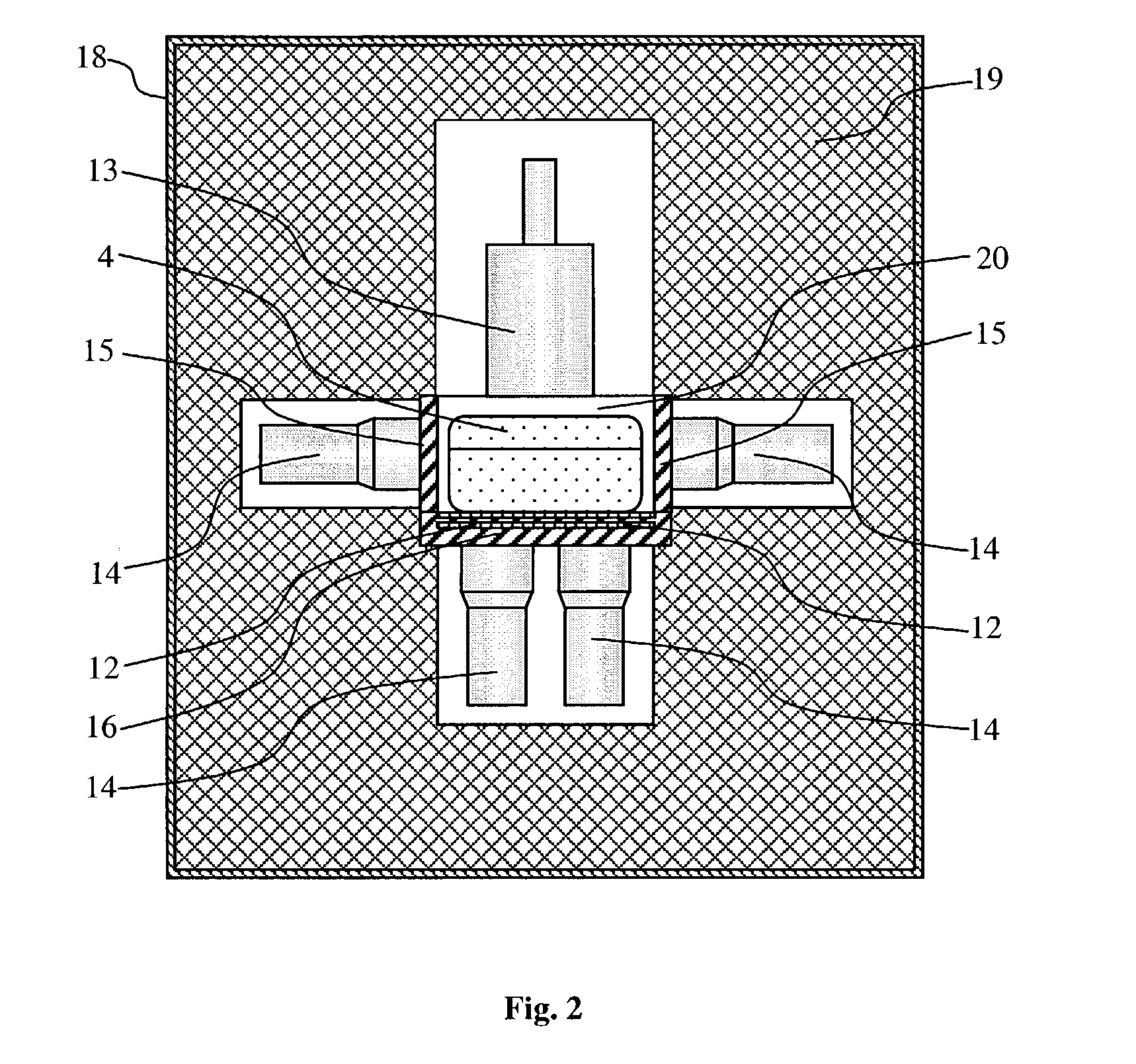
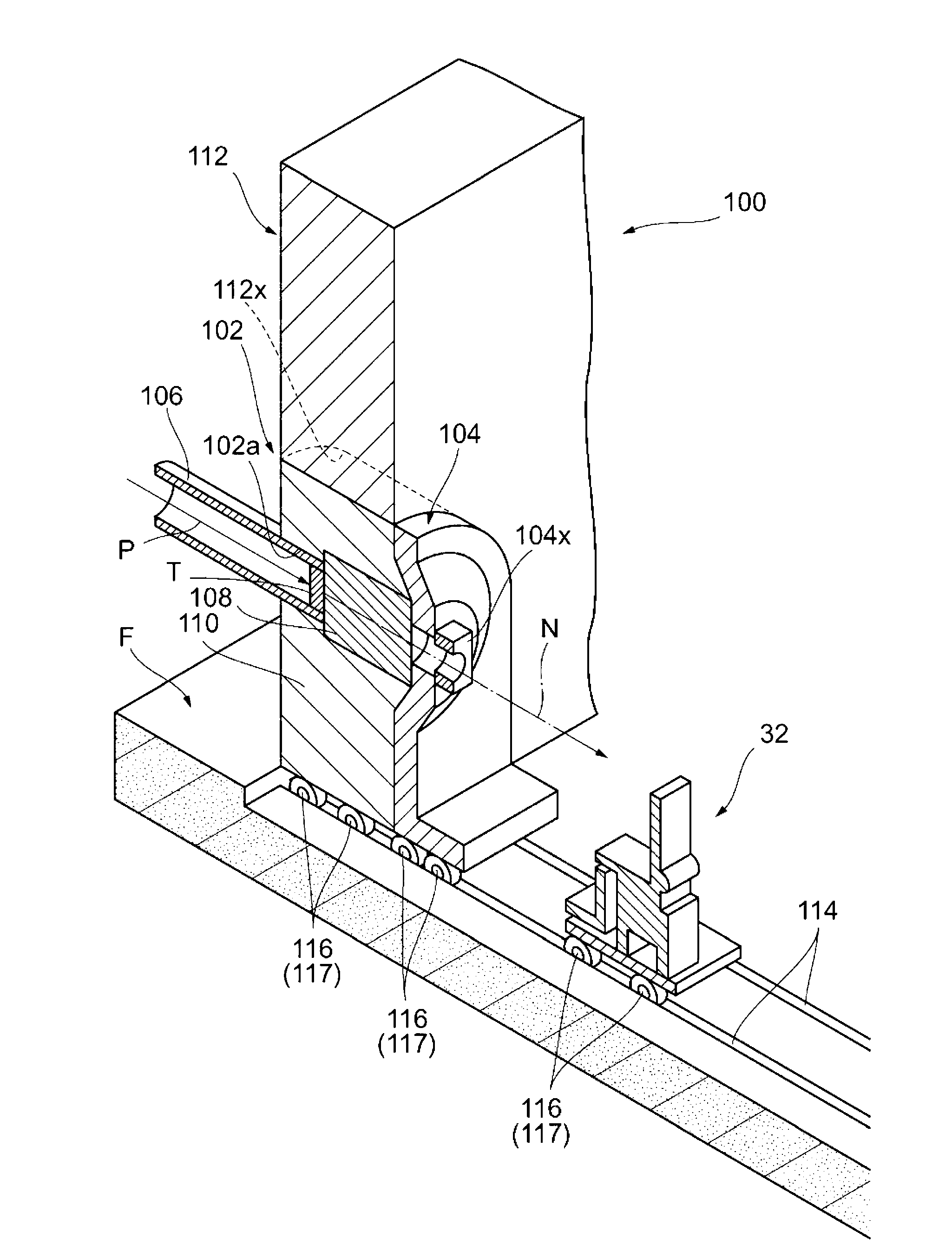
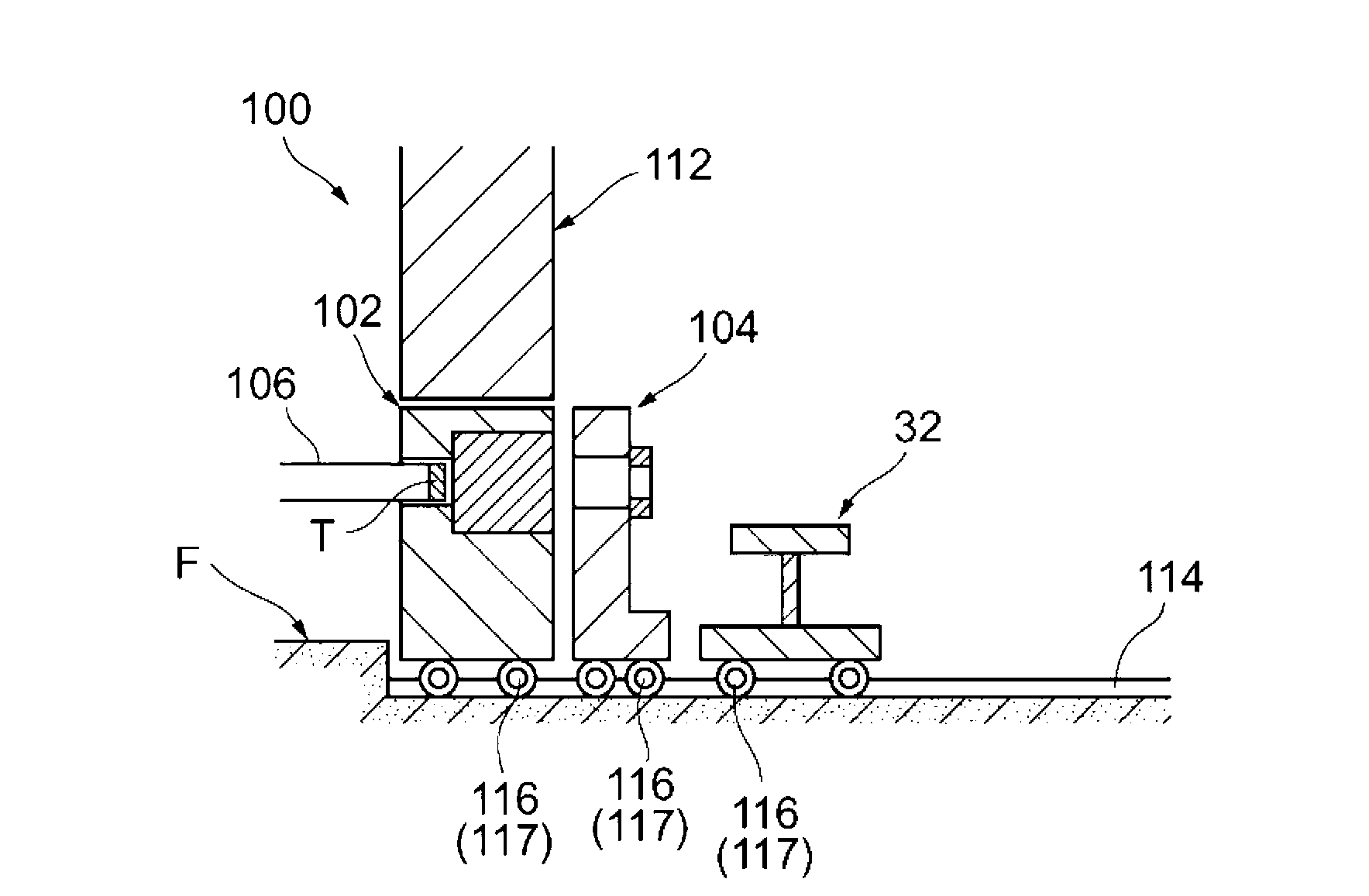
Neutron beam irradiation system
InactiveCN103052425AImprove work efficiencyRadiation/particle handlingMedical devicesNeutron irradiationCharged particle beam
A neutron beam irradiation system that irradiates an irradiation object with a neutron beam includes: a neutron beam generating section that generates a neutron beam by being irradiated with a charged particle beam; a housing section that includes at least a moderator and that houses the neutron beam generating section; a neutron beam converging section that converges the neutron beam with which the irradiation object is irradiated; a mounting stage on which the irradiation object is mounted; and a relative movement means that relatively moves the mounting stage closer to and away from the neutron beam generating section, the housing section, and the neutron beam converging section.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Method of manufacturing a ferritic-martensitic, oxide dispersion strengthened alloy
InactiveUS20030116239A1Optical rangefindersNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationOxide dispersion-strengthened alloy
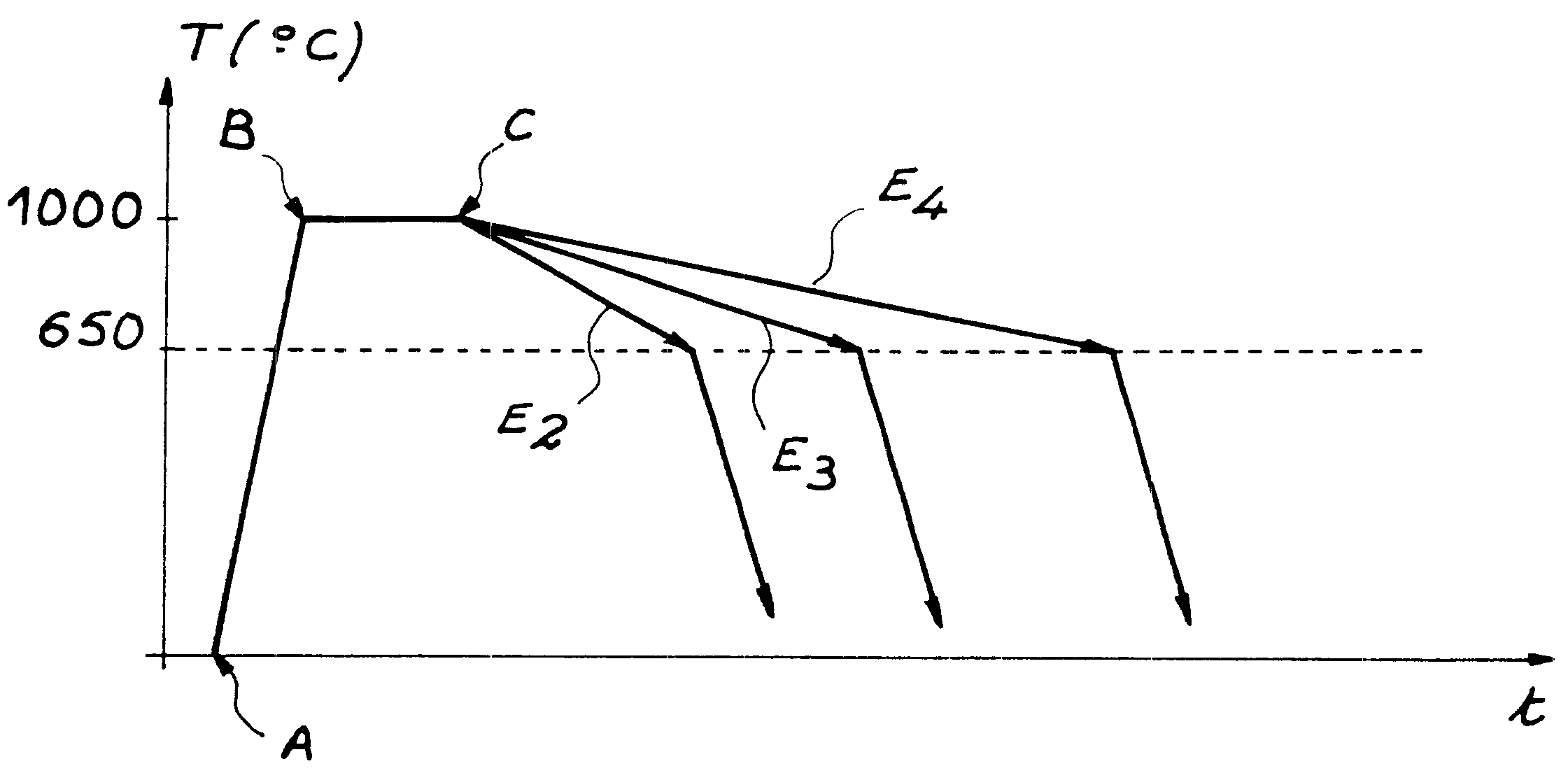
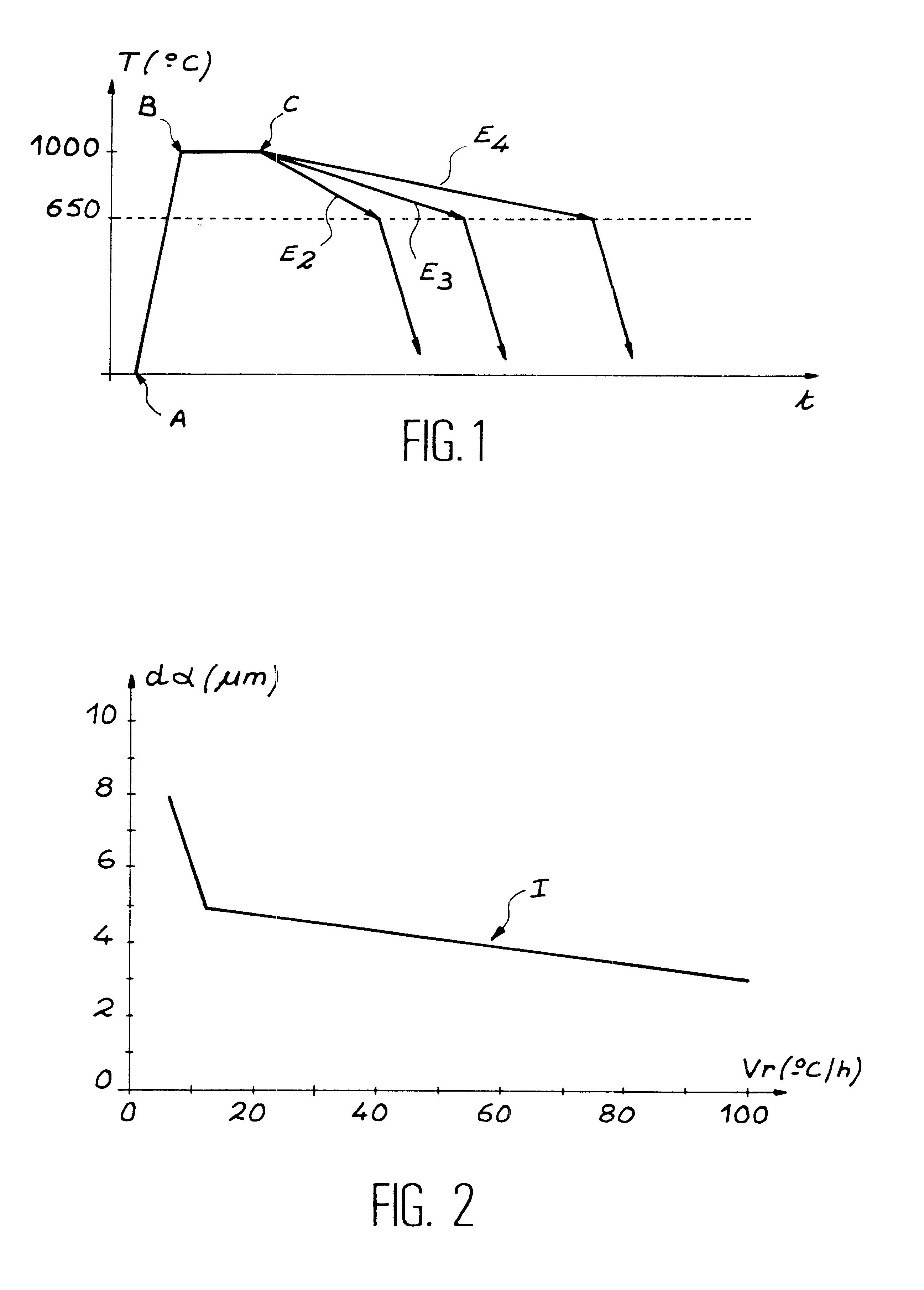
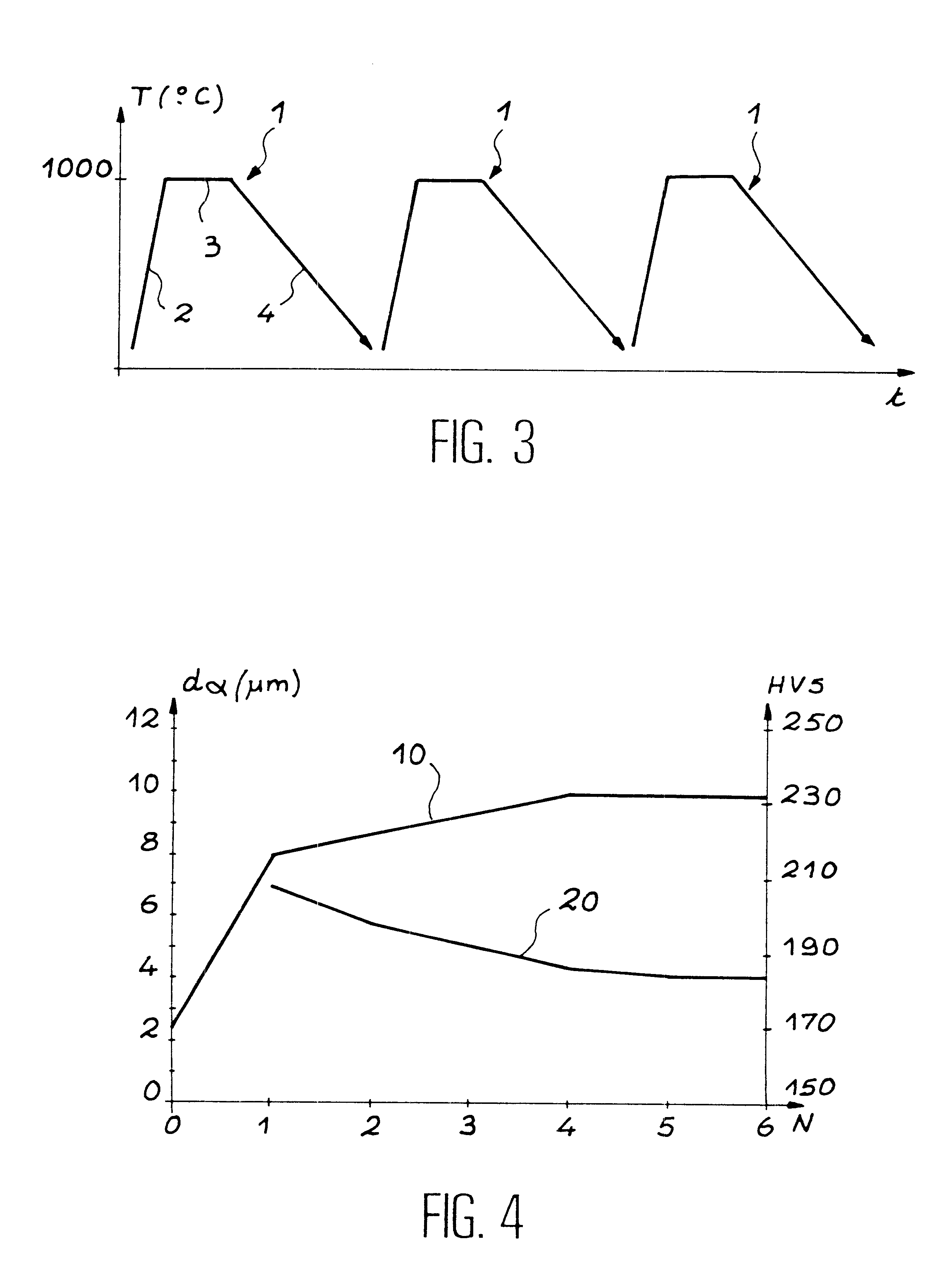
This invention relates to a method of manufacturing an improved ferritic or martensitic alloy based on iron and chromium strengthened by a dispersion of oxides, commonly called an Oxide Dispersion Strengthened or ODS alloy, and, more particularly to a method of manufacturing a ferritic or martensitic ODS alloy with large grains based on iron and chromium which has a single phase ferritic or martensitic matrix having an isotropic microstructure and a grain size that is sufficient to guarantee mechanical strength compatible with a use of this alloy at high temperature and / or under neutron irradiation. According to the invention, the method comprises slow cooling of an austenite at a cooling rate less than or equal to the critical cooling rate for transformation of this austenite into ferrite.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Neutron irradiative methods and systems
ActiveUS20080156997A1Capture cross-sectionHigh incidenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationSignal characteristic
A neutron elastic scattering detector device for non-invasively detecting the presence of at least one predetermined element of an object of interest. The detector device comprises a neutron source that simultaneously outputs, at a creation time, a neutron in a first direction and an associated baseline particle in a second direction. The first direction is opposite of the second direction. The neutron can impinge upon the predetermined element of the object of interest and scatter therefrom in a third direction. A baseline particle detector system detects the baseline particle and outputs a baseline signal characteristic thereof. A neutron detector system detects the neutron and outputs a scattering signal in characteristic thereof. The processing unit analyzes the baseline signal and the scattering signal to determine the presence of the predetermined element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Neutron irradiation preventing low-hydration-heat barite concrete
ActiveCN104529297AImprove Radiation PerformanceReduce liquiditySolid waste managementNeutron irradiationSlag
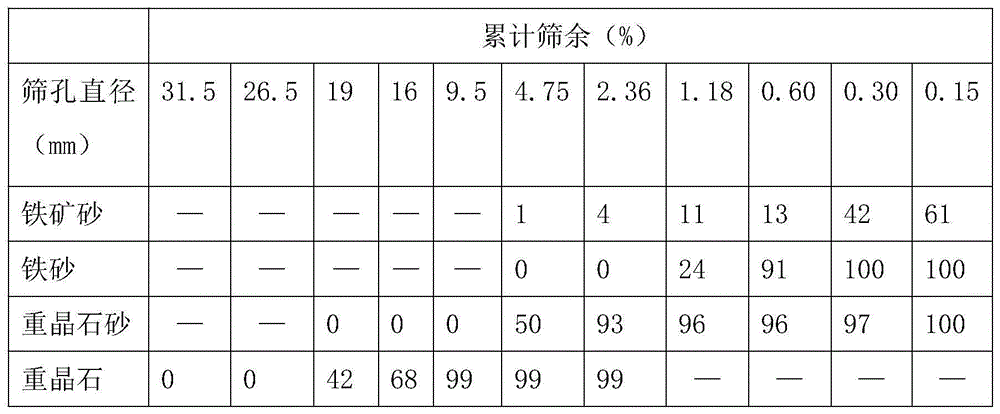
The invention relates to the technical field of concrete, and particularly relates to neutron irradiation preventing low-hydration-heat barite concrete. The neutron irradiation preventing low-hydration-heat barite concrete comprises the following components in content: 163.8-168kg / m<3> of water, 200-280kg / m<3> of cement, 90-140kg / m<3> of slag powder, 9.5-10.5kg / m<3> of boron glass powder, 850-900kg / m<3>of iron ore sand, 340-360kg / m<3> of iron sand, 1558-1600kg / m<3> of barite, 300-330kg / m<3> of barite sand, 0.85-0.95kg / m<3> of polypropylene fiber and 4% to 7% of a polycarboxylate-type water reducing agent. The neutron irradiation preventing low-hydration-heat barite concrete disclosed by the invention is larger than 3600kg / m<3> in apparent density, larger than 110kg / m<3> in retained crystal water and good in neutron irradiation prevention effect; when being applied to a large-size concrete structure of which the minimum geometric dimension is larger than 1.2m, the neutron irradiation preventing low-hydration-heat barite concrete is low in hydration heat, the internal and external temperature difference is smaller than or equal to 20 DEG C, the adiabatic temperature rise is smaller than or equal to 55 DEG C, and the neutron irradiation preventing low-hydration-heat barite concrete is applicable to a large-size radiation-proof structure. The concrete can reach relatively high requirements in aspects such as retained crystal water, fluidity, cohesiveness and water retention property and has the advantages of guaranteeing the strength and the compactness and controlling the hydration heat.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURAL ENG MACHINERY CONSTR +1
Oxide-dispersion-strengthened low-activation steel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105274445AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove purityNeutron irradiationBiological activation
The invention aims at providing oxide-dispersion-strengthened low-activation steel applicable to fusion reactor and a preparation method thereof. The technical scheme is characterized in that the low-activation steel comprises the following alloy elements in percent by mass, Fe as the matrix, 0.08%<=C<=0.15%, 8.0%<=Cr<=10.0%, 1.1%<=W<=1.55%, 0.1%<=V<=0.3%, 0.03%<=Ta<=0.2%, 0.1<=Mn<=0.6%, 0.05%<=Y2O3<=0.5%, and a little amount of impurities inevitably mixed during manufacture. The easily-activated elements and impurity elements all capable of generating radionuclides after being subjected to neutron irradiation are strictly controlled according to the following content requirements: N<0.010%, Al<0.010%, Ni<0.005%, Mo<0.005%, Nb<0.010%, Cu<0.010%, P<0.005%, and S<0.005%. The oxide-dispersion-strengthened low-activation steel is uniform in microstructure and excellent in mechanical properties.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Manufacture technique for thermonuclear reactor flow-passage containing parts
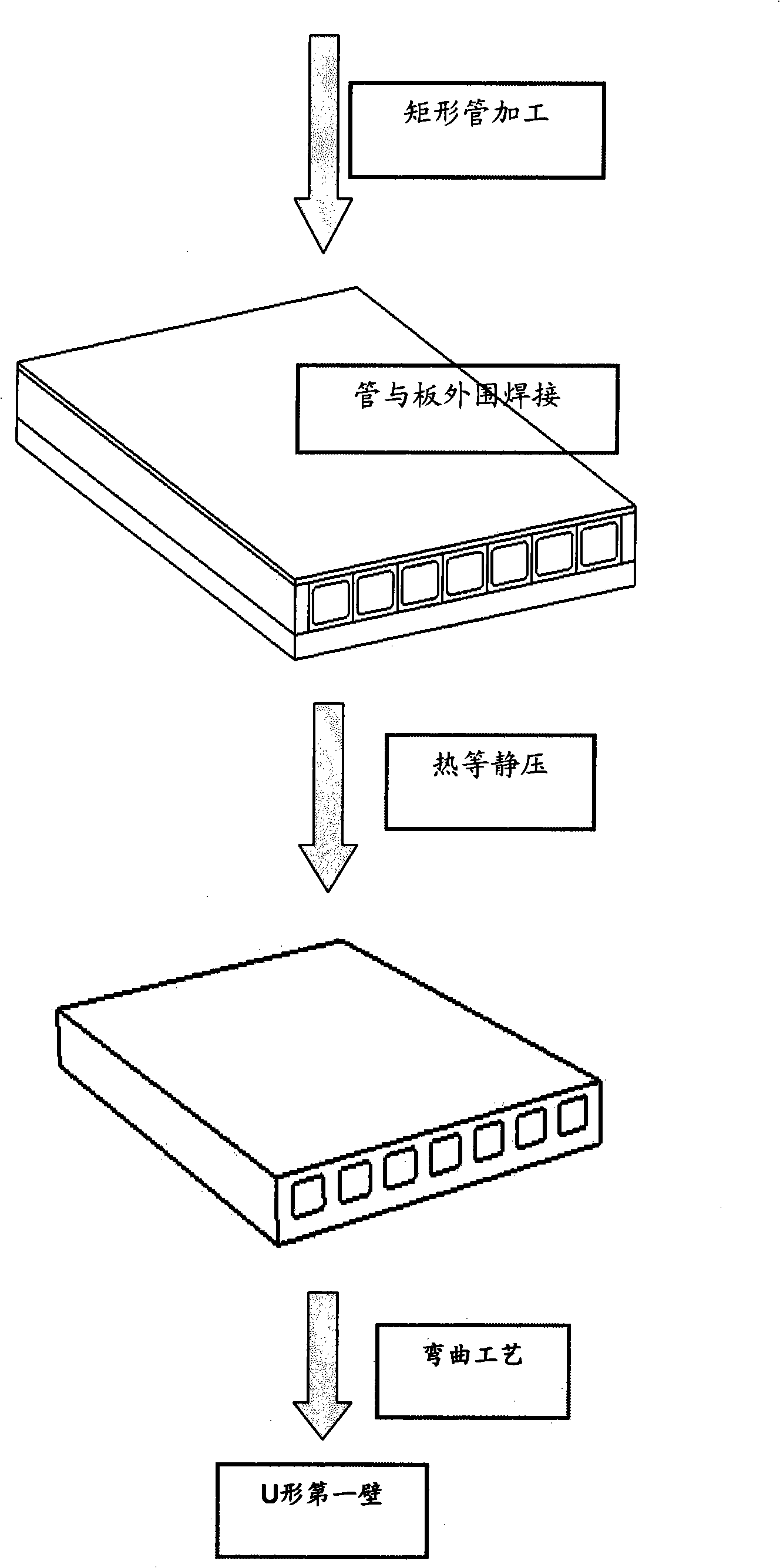
InactiveCN101332557AImprove cleanlinessAvoid damageNon-electric welding apparatusAs elementHeat-affected zone
The invention discloses a production process applicable to runner-containing parts in a fusion reactor blanket. The production process includes the steps: first, a plate and a runner-containing rectangular tube are manufactured according to the design and undergo precision surface working, the roughness Ra is less than 6.3Mum; second, the runner-containing parts are cleaned and decontaminated and then heated in vacuum for degassing; third, the runner-containing parts are vacuumized in an electron beam welding machine and the periphery of the surface to be welded is hermetically welded; and then the runner-containing parts are put into a hot isostatic pressing furnace for forming by hot isostatic pressing diffusion welding; finally, bending forming, heat treatment and machining, and the like, are performed. By adopting the production process; the runner-containing parts manufactured by the production process have reliable and uniform comprehensive performance without the weak performance zones of the heat affected zone, and the like, resulting from the fusion welding process or the defects such as element segregation and air vent, and the like, existing in the similar casting parts, thereby, the production process is particularly applicable to the production of the runner-containing part with the fusion reactor blanket under the condition of intense neutron radiation.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of manufacturing a ferritic-martensitic, oxide dispersion strengthened alloy
InactiveUS6485584B1Optical rangefindersFuel elementsNeutron irradiationOxide dispersion-strengthened alloy
This invention relates to a method of manufacturing an improved ferritic or martensitic alloy based on iron and chromium strengthened by a dispersion of oxides, commonly called an Oxide Dispersion Strengthened or ODS alloy, and, more particularly to a method of manufacturing a ferritic or martensitic ODS alloy with large grains based on iron and chromium which has a single phase ferritic or martensitic matrix having an isotropic microstructure and a grain size that is sufficient to guarantee mechanical strength compatible with a use of this alloy at high temperature and / or under neutron irradiation. According to the invention, the method comprises slow cooling of an austenite at a cooling rate less than or equal to the critical cooling rate for transformation of this austenite into ferrite.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Neutron irradiative methods and systems
ActiveUS7405409B2Fast analysisImprove personnel safetyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationSignal characteristic
A neutron elastic scattering detector device for non-invasively detecting the presence of at least one predetermined element of an object of interest. The detector device comprises a neutron source that simultaneously outputs, at a creation time, a neutron in a first direction and an associated baseline particle in a second direction. The first direction is opposite of the second direction. The neutron can impinge upon the predetermined element of the object of interest and scatter therefrom in a third direction. A baseline particle detector system detects the baseline particle and outputs a baseline signal characteristic thereof. A neutron detector system detects the neutron and outputs a scattering signal in characteristic thereof. The processing unit analyzes the baseline signal and the scattering signal to determine the presence of the predetermined element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
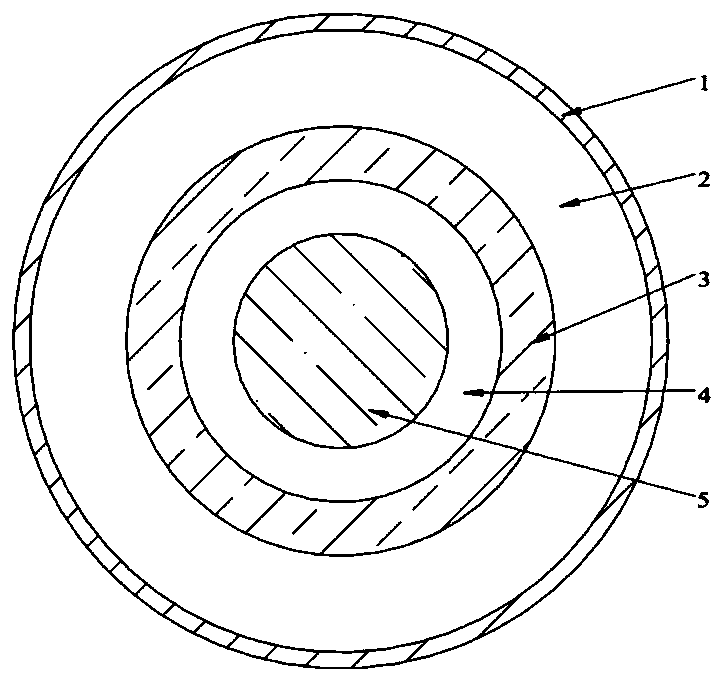
Composite structural material and process for manufacturing pipeline component using same
ActiveCN102336038ASolving Corrosion ProblemsIncrease profitMetal layered productsNeutron irradiationAlloy
The invention belongs to the field of composite material, and in particular relates to a composite structural material and a process for manufacturing a pipeline component using the same. The composite structural material is characterized by adopting a double-layer structure, wherein one layer is made of vanadium alloy material, and the other layer is made of low-activity martensite steel material. In practical application, the side in contact with liquid alkali metal is made of vanadium alloy, and the side in contact with the environment gas or other cooling agents is made of low-activity martensite steel. In the composite structural material provided by the invention, respective advantages of the vanadium alloy and low-activity martensite steel in the application to the sodium cooled fast reactor and fusion reactor liquid metal are sufficiently used, and the problems of neutron irradiation resistance and liquid metal corrosion resistance can be effectively solved. Through the manufacturing process provided by the invention, the utilization rate of material can be obviously improved, and the processing cycle can be remarkably shortened.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
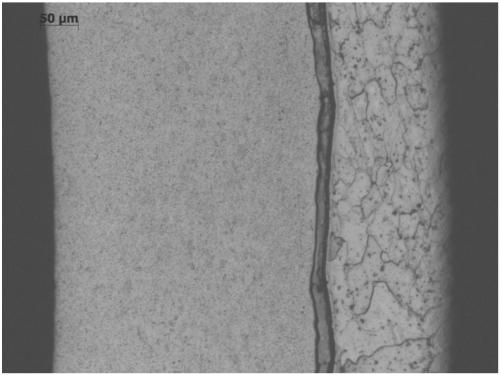
FeCrAl alloy and T91 ferrite/martensite heat-resistant steel composite tube for nuclear reactor nuclear fuel cladding and manufacturing method for FeCrAl alloy and T91 ferrite/martensite heat-resistant steel composite tube
ActiveCN109972048AImprove securityImprove reliabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNeutron irradiationNuclear reactor
The invention relates to the field of fuel cladding tubes with relatively high neutron irradiation resistance, corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance in a nuclear reactor, in particularto a FeCrAl alloy and T91 ferrite / martensite heat-resistant steel composite tube for nuclear reactor nuclear fuel cladding and a manufacturing method for the FeCrAl alloy and T91 ferrite / martensite heat-resistant steel composite tube. The inner layer is a ferrite / martensite heat-resistant steel material, the outer layer is a FeCrAl alloy material, and an iron-based material auxiliary layer is arranged between the inner layer and the outer layer. The manufacturing method for the FeCrAl alloy and T91 ferrite / martensite heat-resistant steel composite tube comprises the following steps: surface polishing of seamless composite tube blank, degassing, assembling and packaging of seamless composite tube blank, thermal deformation processing metallurgical compounding, annealing thermal treatment, cold-rolled cold-drawing and intermediate annealing, final thermal treatment, straightening, cleaning and finished product inspecting. The method is characterized in that the outer layer, an intermediate transition layer and an inner-layer tube are assembled, are assembled and packaged into seamless composite tube blank after gas exhaustion, and are sealed by a welding end head; after being heated,the metallurgical compounded seamless composite tube blank formed by thermal deformation processing is finally subjected to cold-deformation processing to form a finished product of a needed specification.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +3
Neutron cement multi-element analyzer
InactiveCN1632544AQuality improvementLow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationShieldingNeutron irradiationNuclear reaction
This invention relates to a cement multi-element analysis device. The neutron multi-element analysis device uses the neutron generator in the D-D reaction as neutron source and emits rapid neutrons of 2.5 Mev. The neutron reacts with the cement element to generate multi-nuclear reaction with different energy radiation gamma rays. The gamma ray detector is to detect the r rays generated by the elements in the cements. The r signals are through main amplifier and are transmitted to the micro machine for monitoring. It uses multi-path gamma spectrum device to test the area of the characteristics gamma ray peak and gives the relative nucleus content through test formula.
Owner:吉林省科仑辐射技术开发有限公司
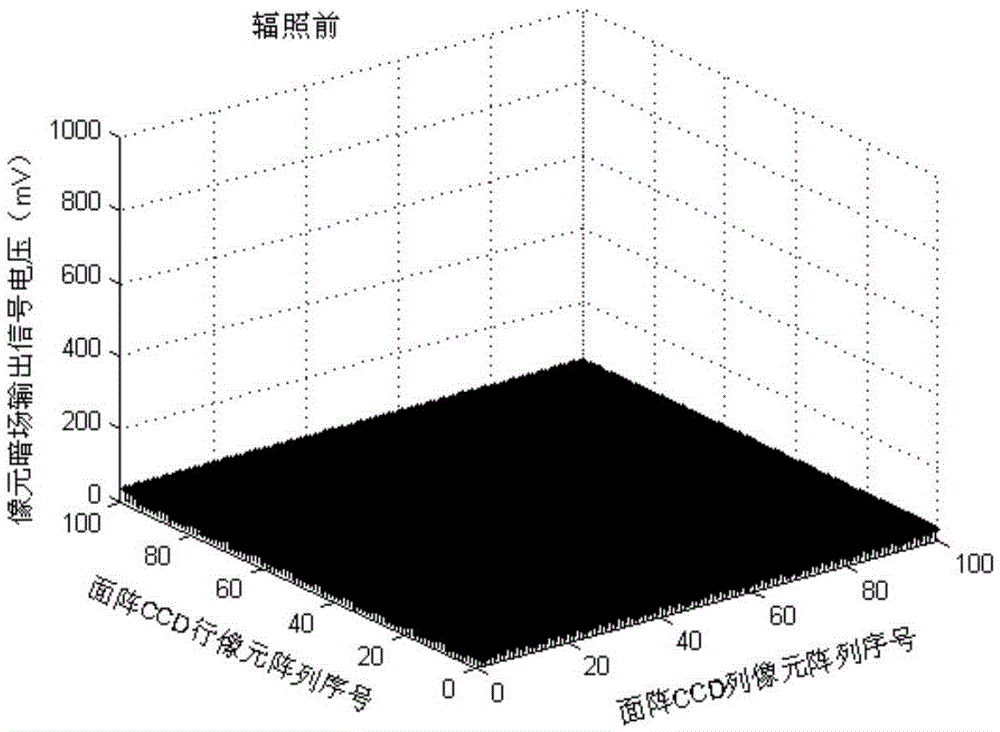
Charge transfer efficiency test method of post-neutron irradiation charge coupled device
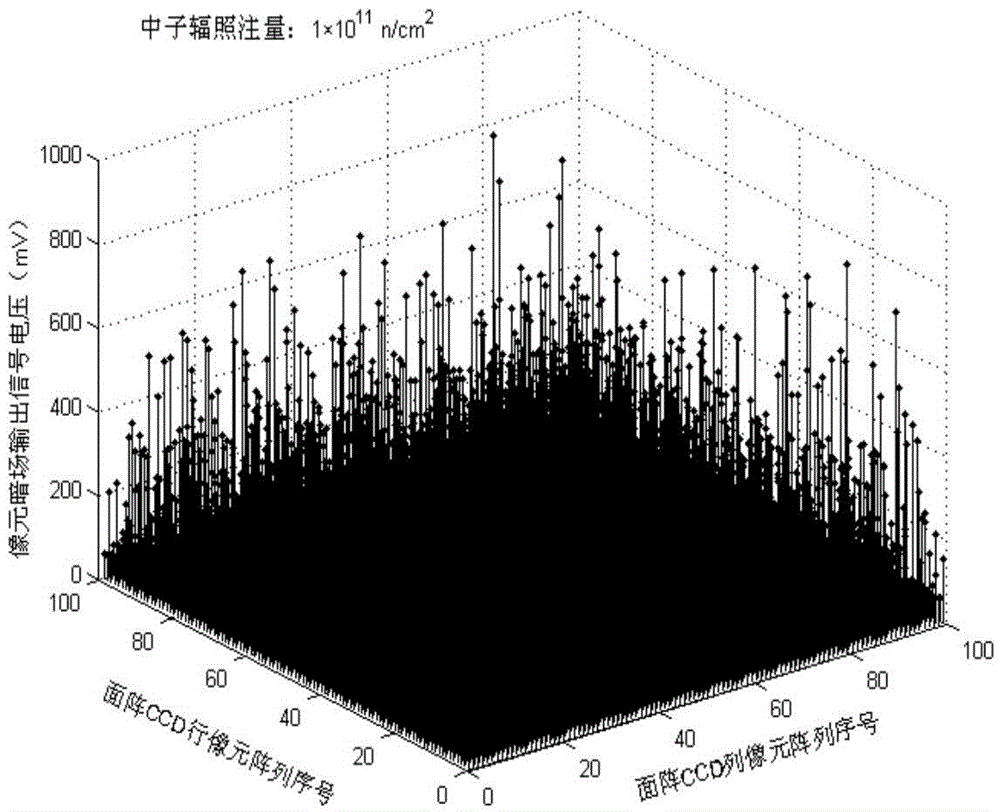
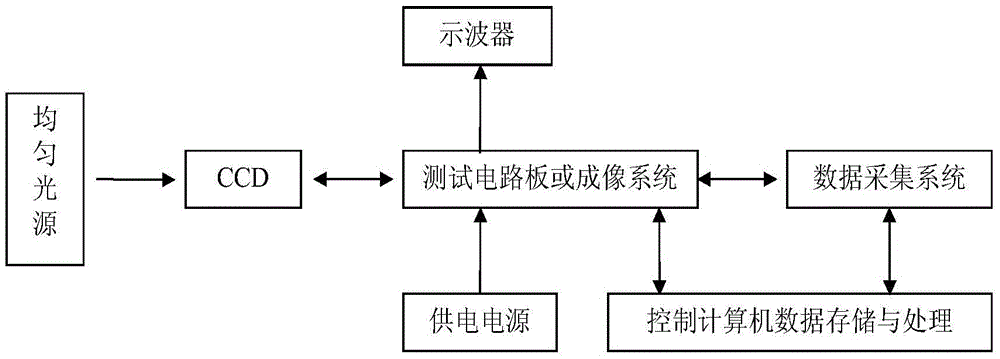
ActiveCN105572486ABig impact on degradationSaturated output has little effectElectromagentic field characteristicsNeutron irradiationCharge loss
The invention provides a charge transfer efficiency test method of a post-neutron irradiation charge coupled device. According to the method, when the readout of CCD signal charges occur, an overscanning pixel output unit is additionally adopted; defects which are generated due to the induction of neutron irradiation are made to capture CCD signal charges; captured CCD signal charges are collected in the overscanning pixel output unit; signal charge loss generated by the induction of neutron irradiation can be displayed intuitively through image output; saturated illumination is adopted to eliminate the influence of dark signal peaks on signal charge packets in a process in which the signal charge packets are sequentially transferred between CCD transfer channels; and requirements for the consistency of the size of the signal charge packets in a charge transfer efficiency test (CTE) after different neutron fluence irradiation can be satisfied. With the method adopted, the problem that a CTE test is inaccurate or even if cannot be performed existing on the post-neutron irradiation charge coupled device can be solved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation
InactiveUS6928131B2Reduce probabilityReduce false alarm rateConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsSolid-state devicesNeutron irradiationX-ray
A method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation involves the initial X-ray irradiation of the object under investigation, e.g. a piece of luggage or mailing, and forming its X-ray images; using the X-ray images to detect areas with a high density of organic materials and identifying articles therein; determining the location, dimensions and supposed mass of an unidentified article; determining and forming a directional pattern of the neutron radiator corresponding to the dimensions of the unidentified article. The method further includes subsequent thermal neutron irradiation of the area with the unidentified article; recording gamma-ray quanta having the energy of 10.8 MeV and cascade gamma-ray quanta with energies of 5.534 and 5.266 MeV by at least two gamma-ray detectors; counting of simultaneously recorded pairs of cascade gamma-ray quanta; determination of the overall gamma-ray intensity, taking into account weight factors in readings of the detectors; determination of the threshold value for the overall gamma-ray intensity basing on the supposed mass of explosive being detected; and making a decision in the event the threshold value of overall gamma-ray intensity is exceeded. When checking small-size objects, the neutron irradiation step is preceded by replacing the ambient air by a gaseous medium not containing nitrogen.
Owner:SCI & TECHN CENT RATEC
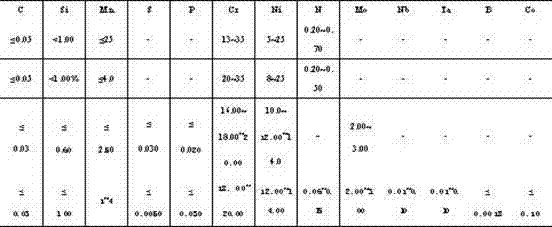
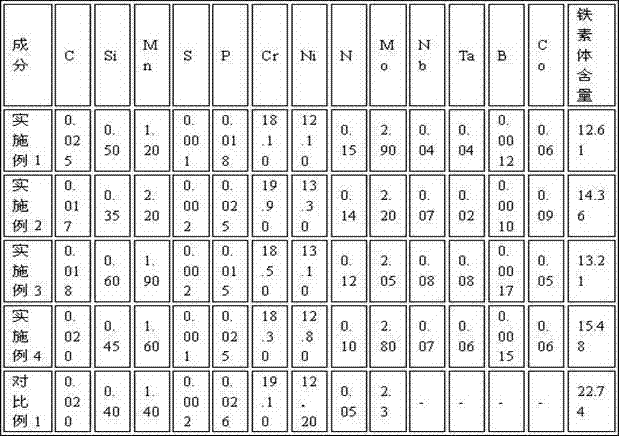
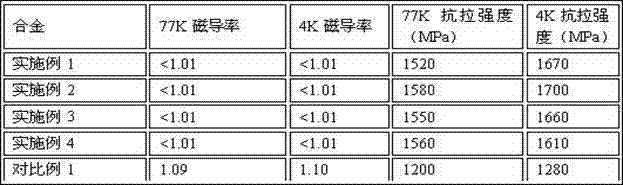
Manufacturing method of nuclear-grade austenitic stainless steel welding wire
The invention discloses a nuclear-grade austenitic stainless steel welding material. The material deposited metal has high low-temperature strength, low-temperature toughness, low-temperature non-magnetism and good neutron irradiation resistance performance, and comprises the following chemical constituents in percentage by weight: 18.00-20.0 percent of Cr, 12.00-14.00 percent of Ni, 2.00-3.00 percent of Mo, 0.06-0.15 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of C, 1.00-2.50 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 1.00 percent of Si, 0.01-0.10 percent of Nb, 0.01-0.10 percent of Ta, less than or equal to 0.10 percent of Co, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.0018 percent of B and the balance of iron and impurities generally existing in steelmaking, wherein the Val(Cr-Ni) value is less than 16. The material can be used for welding nuclear-grade materials for manufacturing forgings, plates, tubes and the like.
Owner:DANYANG HUALONG SUPERIOR STEEL
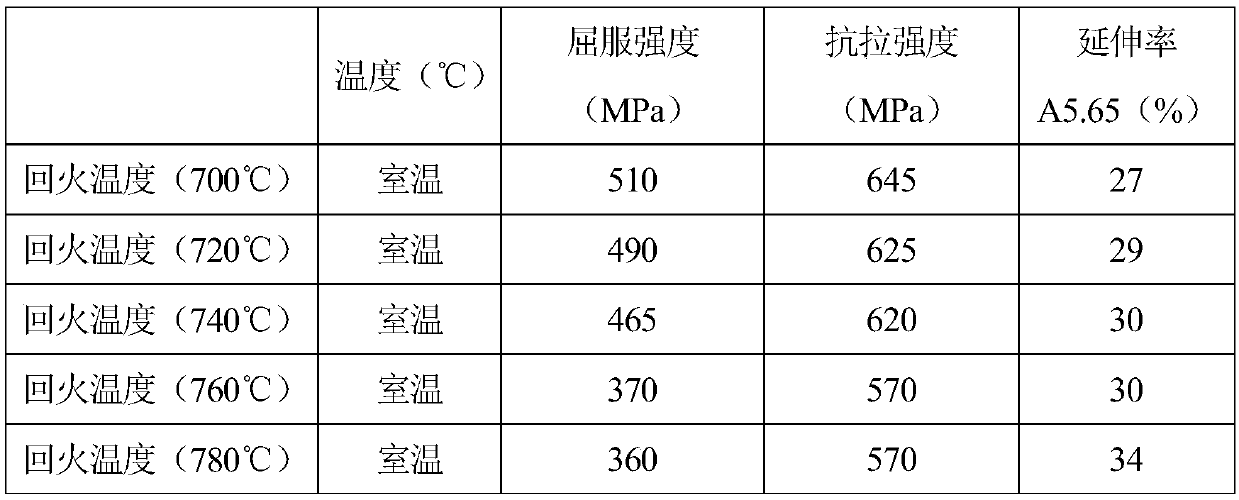
Improved structural material martensite heat-resistant steel and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN102851610AImprove high temperature performanceImprove the safety of useNeutron irradiationThermal stability
Provided are improved structural material martensite heat-resistant steel and a manufacture method thereof. The improved structural material martensite heat-resistant steel utilizes Fe to serve as a matrix, comprises 0.05-0.15% of C, 0.30-0.60% of Mn, 0.20-0.50 % of Si, 8.0-9.5% of Cr, 0.85-1.05% of Mo, 0.18-0.25% of V, 0.05-0.30% of Ta+Nb and 0.003-0.07 of N, has excellent high-temperature performance and corrosion resistance, and is resistant to strong neutron irradiation. According to the formula of the structural steel, a microalloy element Ta partially or completely replaces Nb in T / P91, refining is performed on an MX type precipitated phase, thermal stable performance of the structural steel improved, and accordingly, high-temperature performance of materials and safe reliability when the materials are used at the high temperature are further improved. Therefore, the improved structural material martensite heat-resistant steel is applicable to ammunition delivery system (ADS) reactor and other advanced reactor and applicable to other high-temperature environments simultaneously.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neutron moderator, neutron irradiation method, and hazardous substance detector
ActiveCN101529530AStop the leakReliable removalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingNeutron irradiationHazardous substance
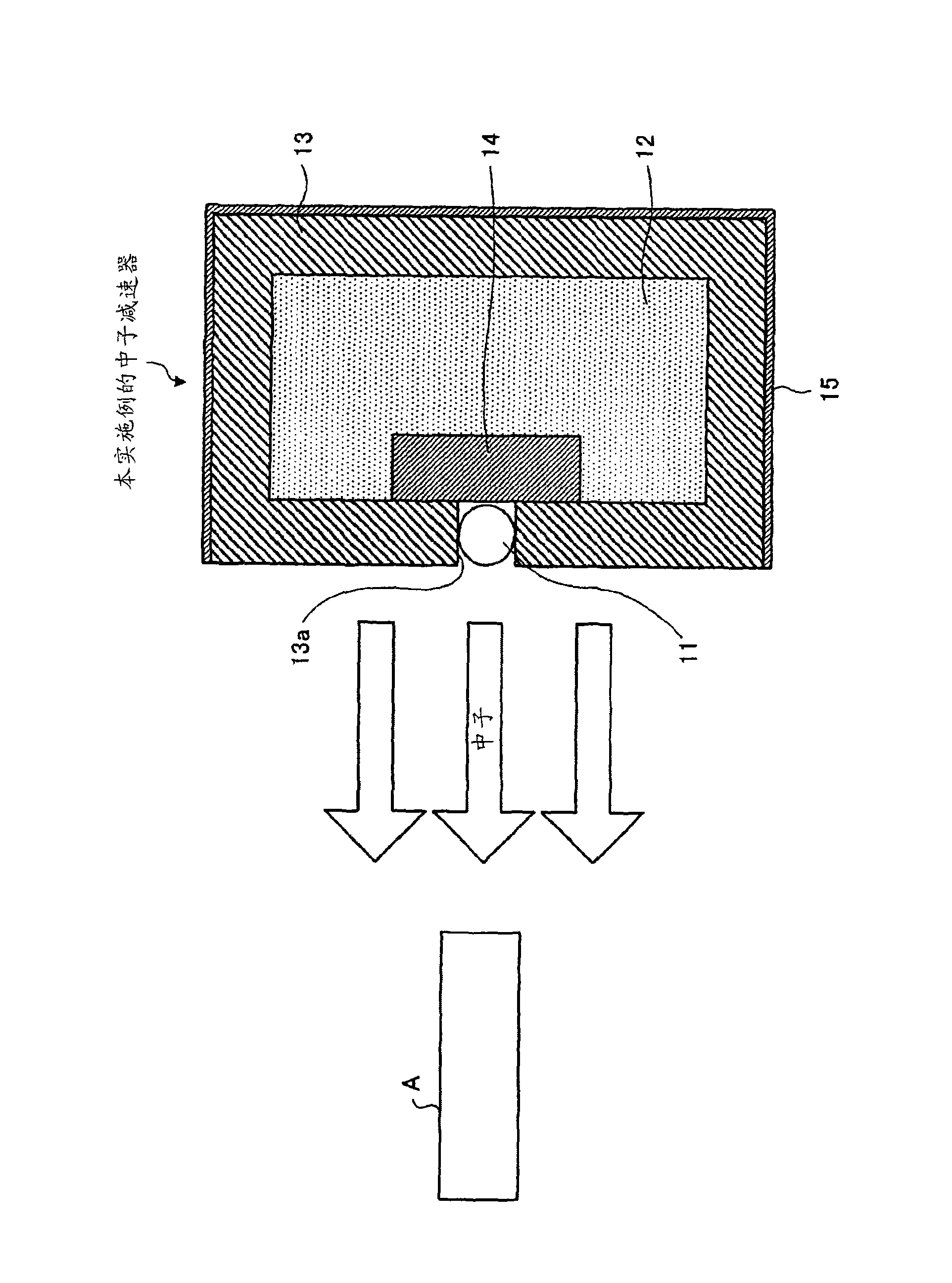
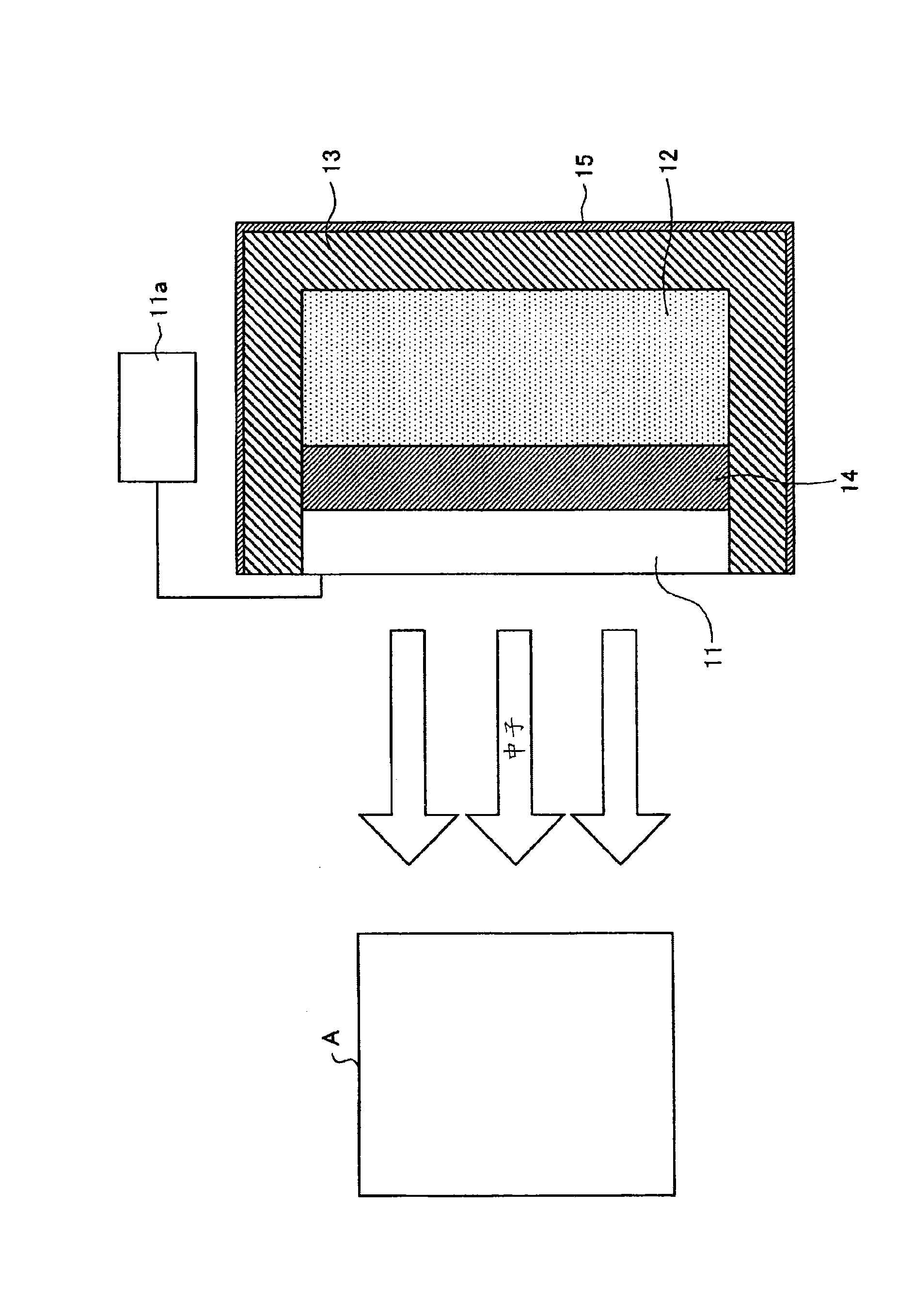
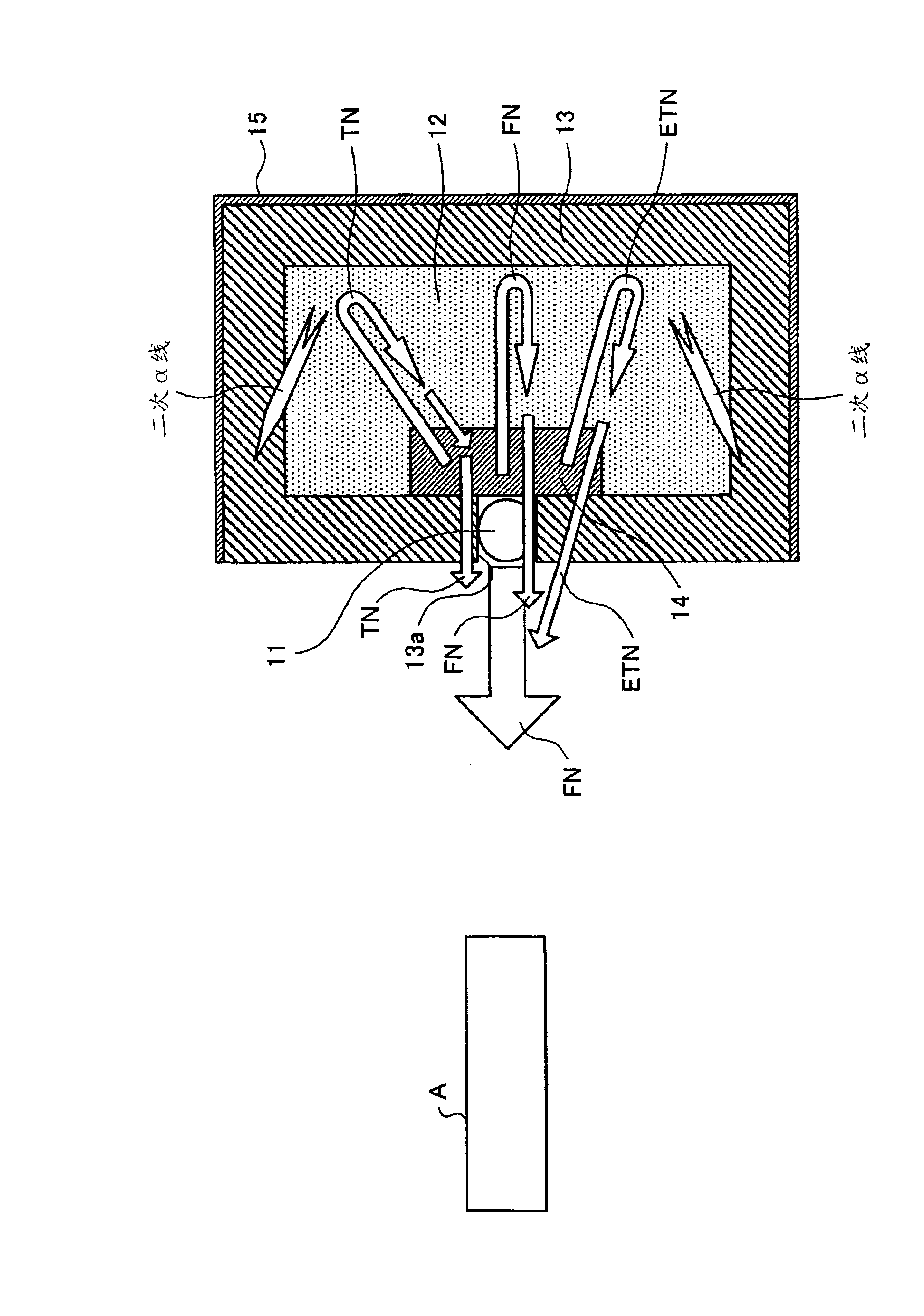
In a neutron moderator, a neutron irradiation method, and a hazardous substance detection apparatus, an inspection chamber (21) where an inspection target (A) can be inserted and removed is provided. Around this inspection chamber (21), a thermal neutron absorbing material (15) is provided. A neutron generator(11) is arranged facing the inspection target (A) in the inspection chamber (21), and a neutron moderating material (12) is arranged at an opposing side of the inspection target (A) with respect to the neutron generator (11). The external surface of the neutron moderating material (12) is covered with gamma ray shielding materials (13, 14), and a Ge detector (24) and a BGO detector (25) are provided to detect gamma ray emitted from the inspection target (A). With this configuration, necessary fast neutron and thermal neutron can be taken out, while suppressing generated secondary gamma ray. Accordingly, a hazardous substance can be detected accurately regardless of a constituent element thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
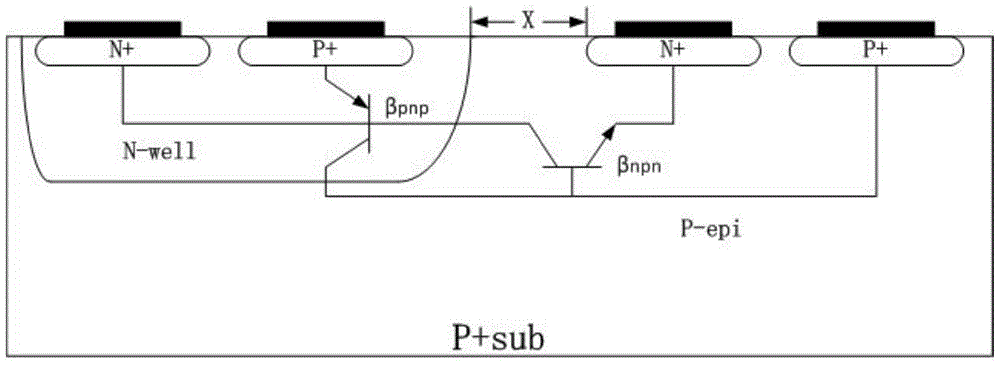
Reinforcement method for single event latchup resistance of CMOS device
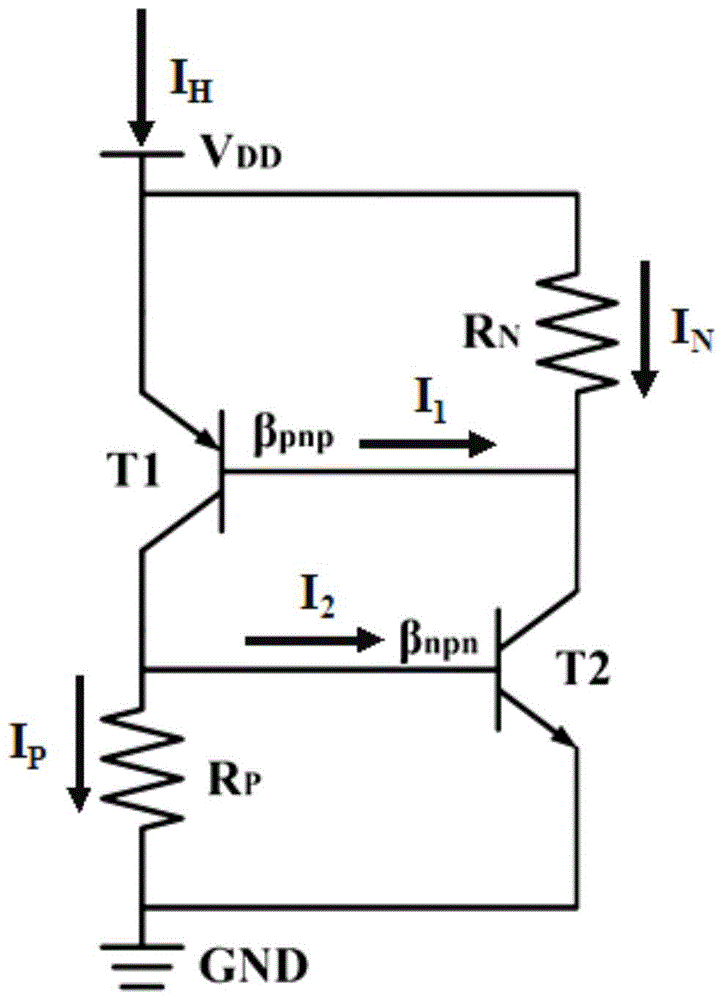
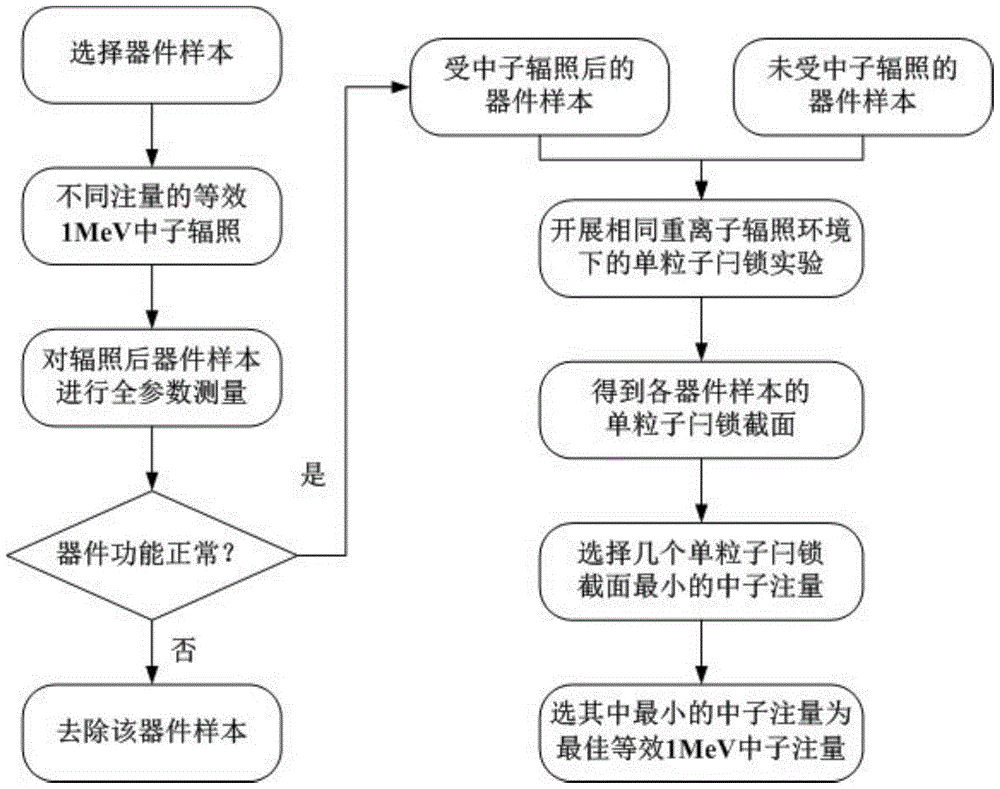
ActiveCN105679658AAvoid export restrictionsLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndividual semiconductor device testingSingle event latchupCMOS
The invention discloses a reinforcement method for the single event latchup resistance of a CMOS device. Neutron irradiation is carried out on the CMOS device; a displacement damage is introduced in the neutron irradiation; and a current gain of a parasitical bipolar transistor in an inverter of the CMOS device is reduced, so that P-N-P-N latchup is not generated. The reinforcement method is an external reinforcement method; processing steps to produce the device will not be increased; there is no need to redesign a device layout for the single event latchup effect; and complexity of an original system will not be increased. Thus, the fixed size of the device will not be changed, and a peripheral circuit will not be increased either.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Temperature measurement method taking carborundum crystals irradiated by neutrons as sensor
InactiveCN101598606ADistinctive non-intrusive measurement featuresImprove test accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesNeutron irradiationWorking temperature
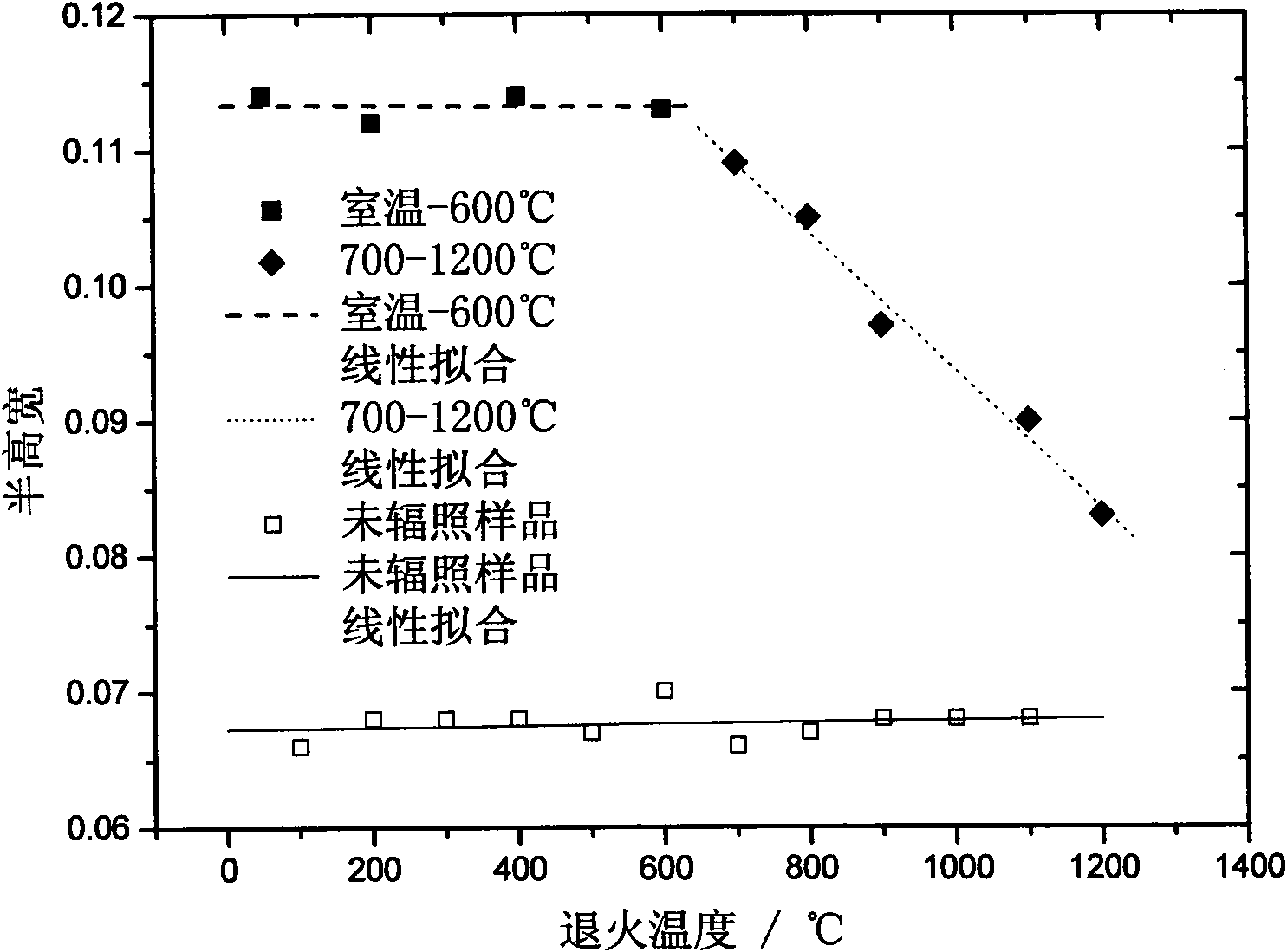
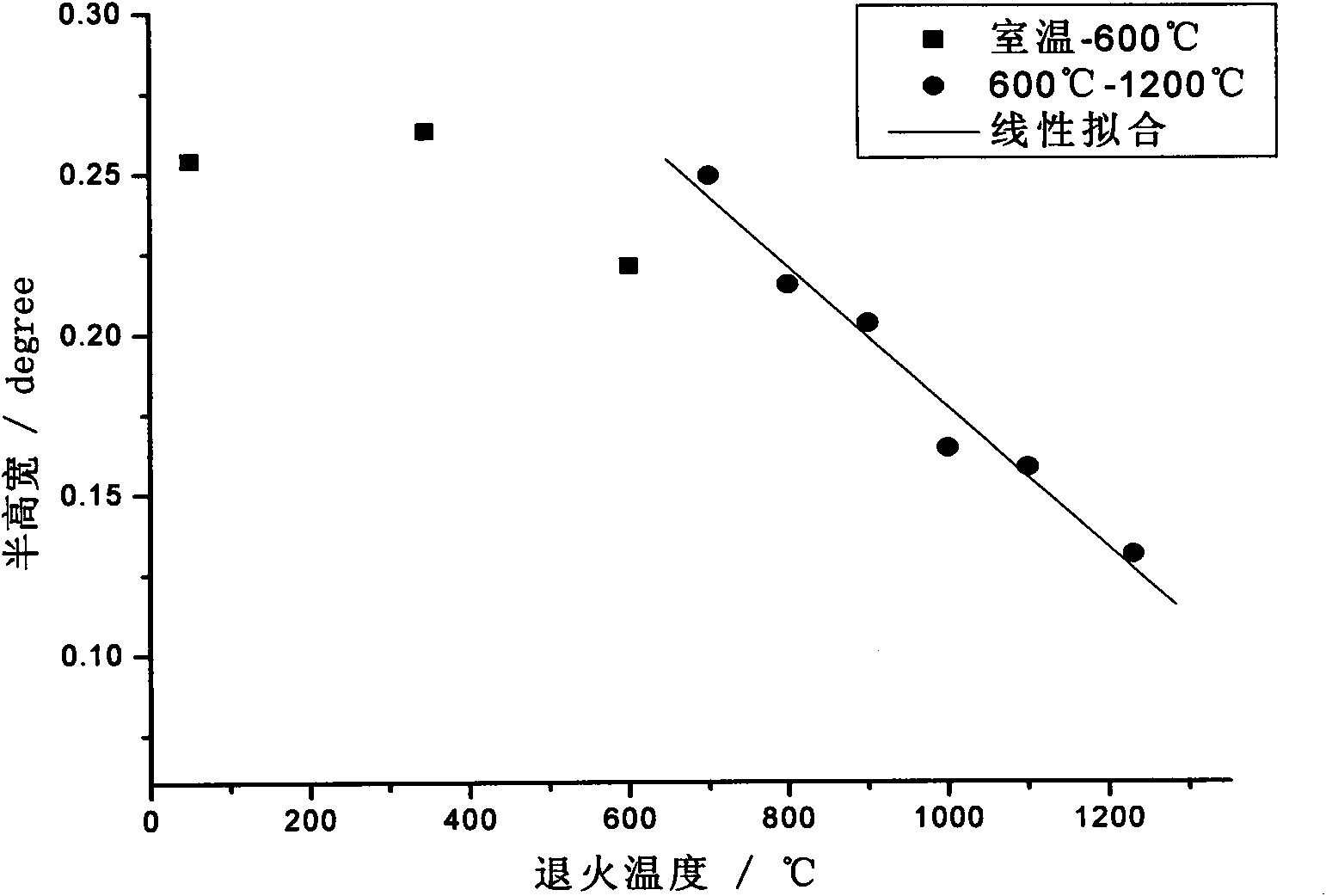
The invention relates to a temperature measurement method taking carborundum crystals irradiated by neutrons as a sensor. The temperature measurement method comprises the following steps that: a plurality of 6H-SiC crystals which are small blocks, are in the same batch and are doped with nitrogen are used as temperature measurement crystals, annealing treatment of different temperatures T is respectively carried out after neutron irradiation is carried out, then the half high width F of the X-optical diffraction peak of each temperature measurement crystal after annealing is respectively tested, the F is used as longitudinal coordinate, the T is used as horizontal coordinate, and an F-T standard curve is mapped; and the temperature measurement crystals irradiated by the neutron in the previous step are embedded into the surface layer or the surface of an article to be tested and high-temperature running is carried out along with a work system containing the article to be tested, then the temperature measurement crystals are taken out, the half full width of the temperature measurement crystals is tested, the half width is compared with the F-T standard curve to find out a temperature value corresponding to the half full width value, and the temperature is just the maximum working temperature of the article to be tested. The method has obvious non-incursion type characteristic, does not need site interpretation, can be used for the temperature test of the high-temperature work system with more than 1200 DEG C and has high testing precision and simple and convenient operation.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST +1
Safety monitor for gamma and neutron radiation in environment
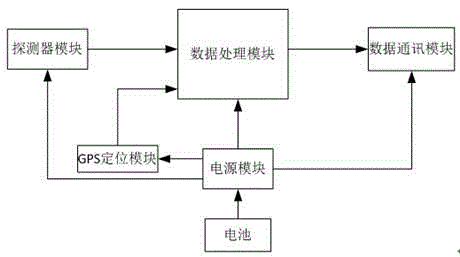
ActiveCN104656118AFunction increaseVersatilityRadiation particle trackingNeutron irradiationComputer module
The invention discloses a safety monitor for gamma and neutron radiation in the environment. The safety motor comprises a CPU, as well as a detector module, a data communication module, a power supply module and a GPS module which are connected with the CPU, wherein a time counting circuit is arranged inside the detector module which is additionally provided with a neutron / photon conversion structure; the data communication module is wirelessly connected with an external mobile phone mobile terminal or a data management center; the power supply module is connected with the detector module and the GPS module respectively, and a charging and discharging circuit and a high-voltage boosting circuit are arranged inside the power supply module. According to the safety monitor for the gamma and neutron radiation in the environment, various sources of radiation can be detected by one monitor, a warning signal is sent in real time, the size of the monitor is reduced effectively, a foundation is laid for the wide popularization and application, and the practical value of the monitor is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
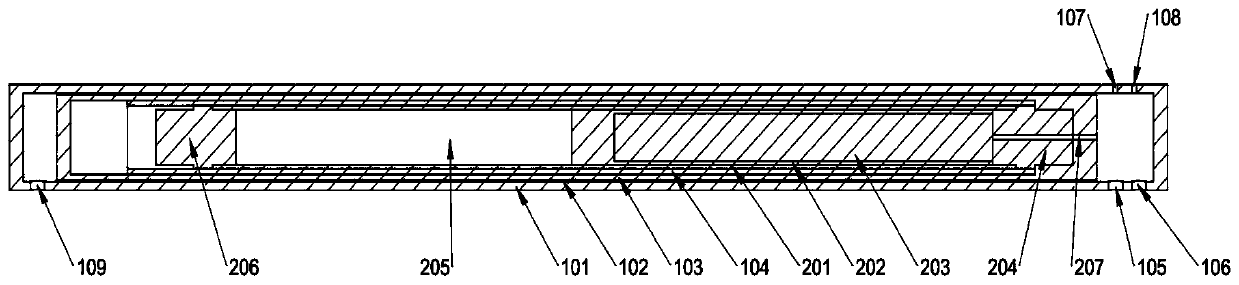
Capsule assembling apparatus for neutron re-irradiation experiments
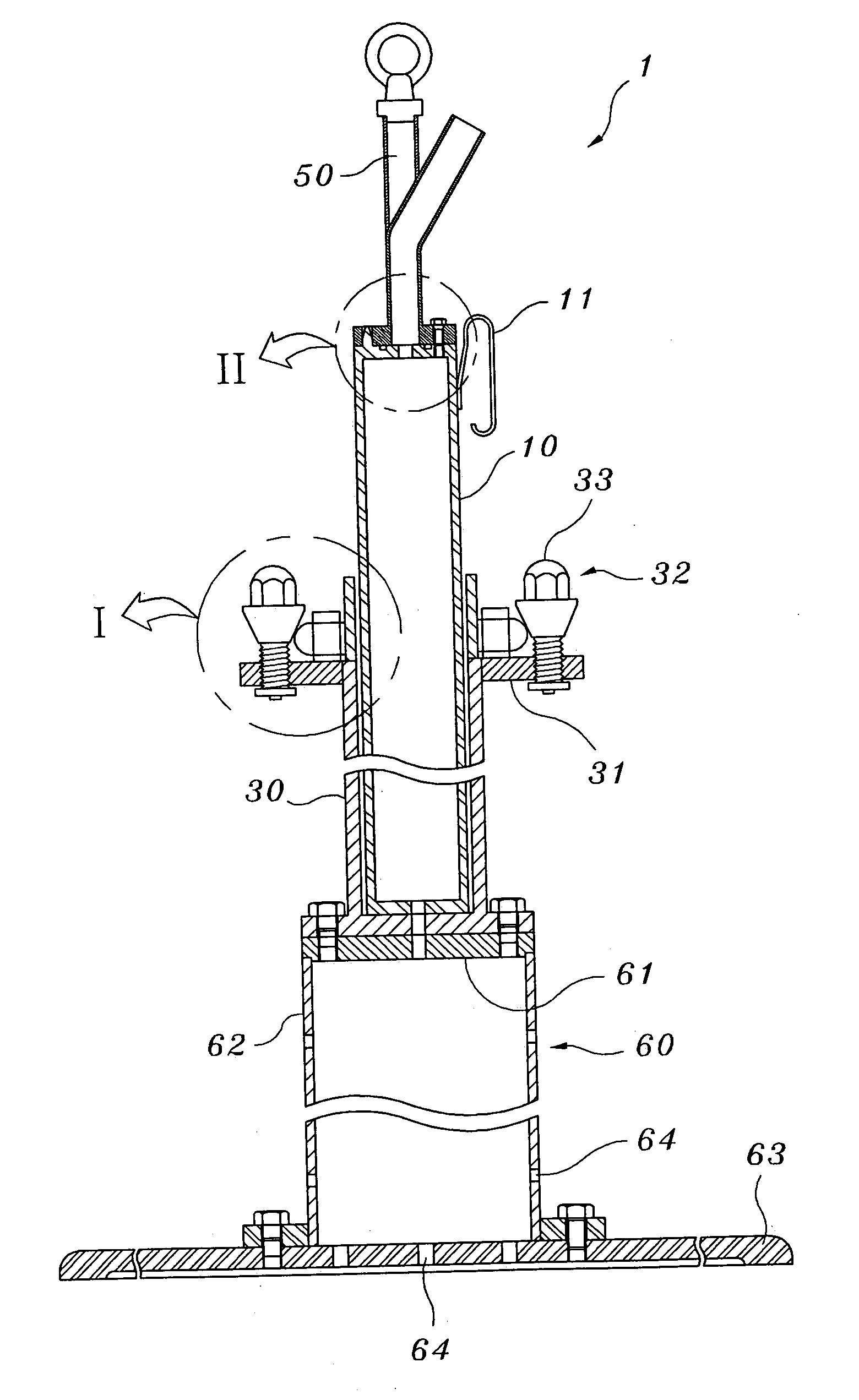
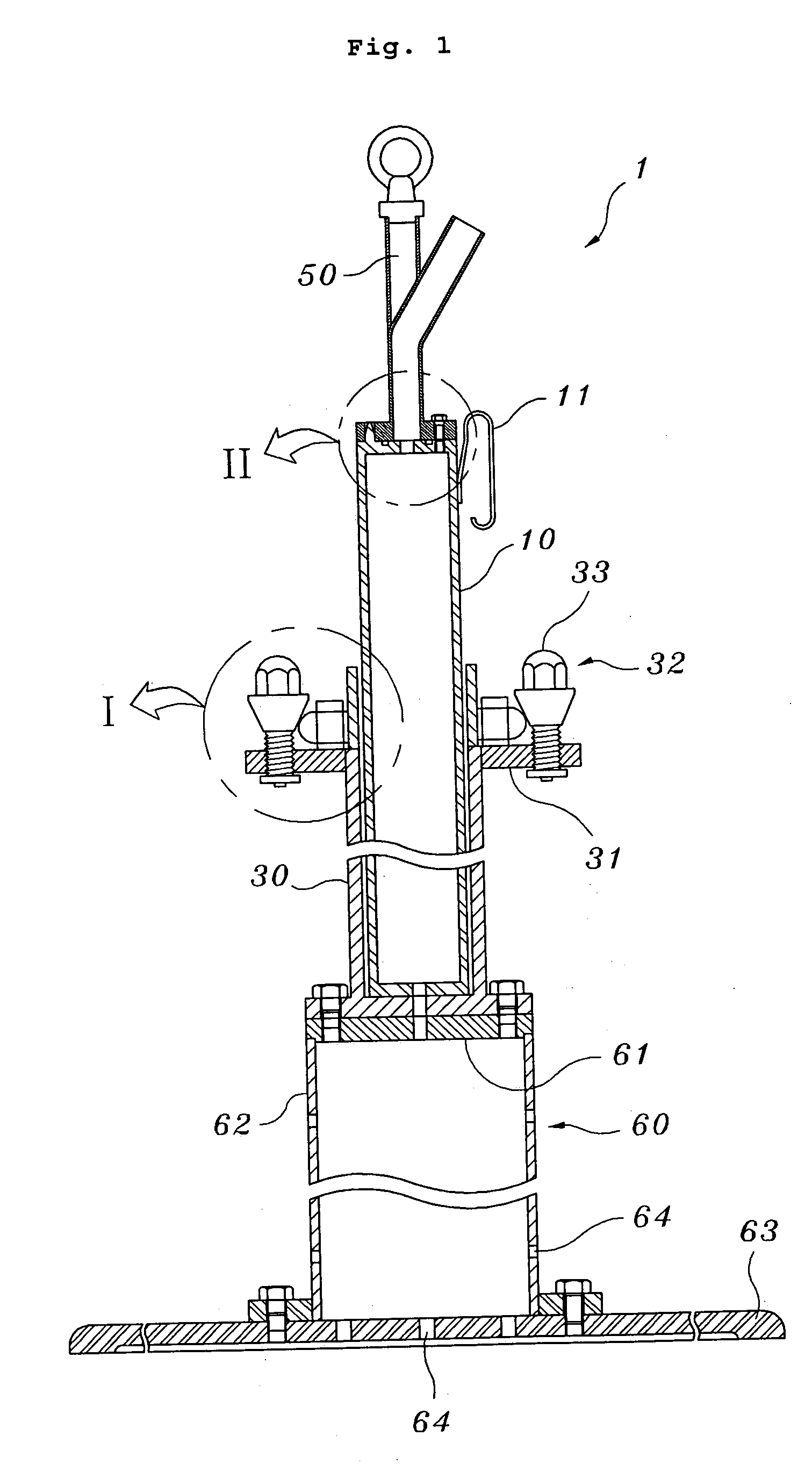
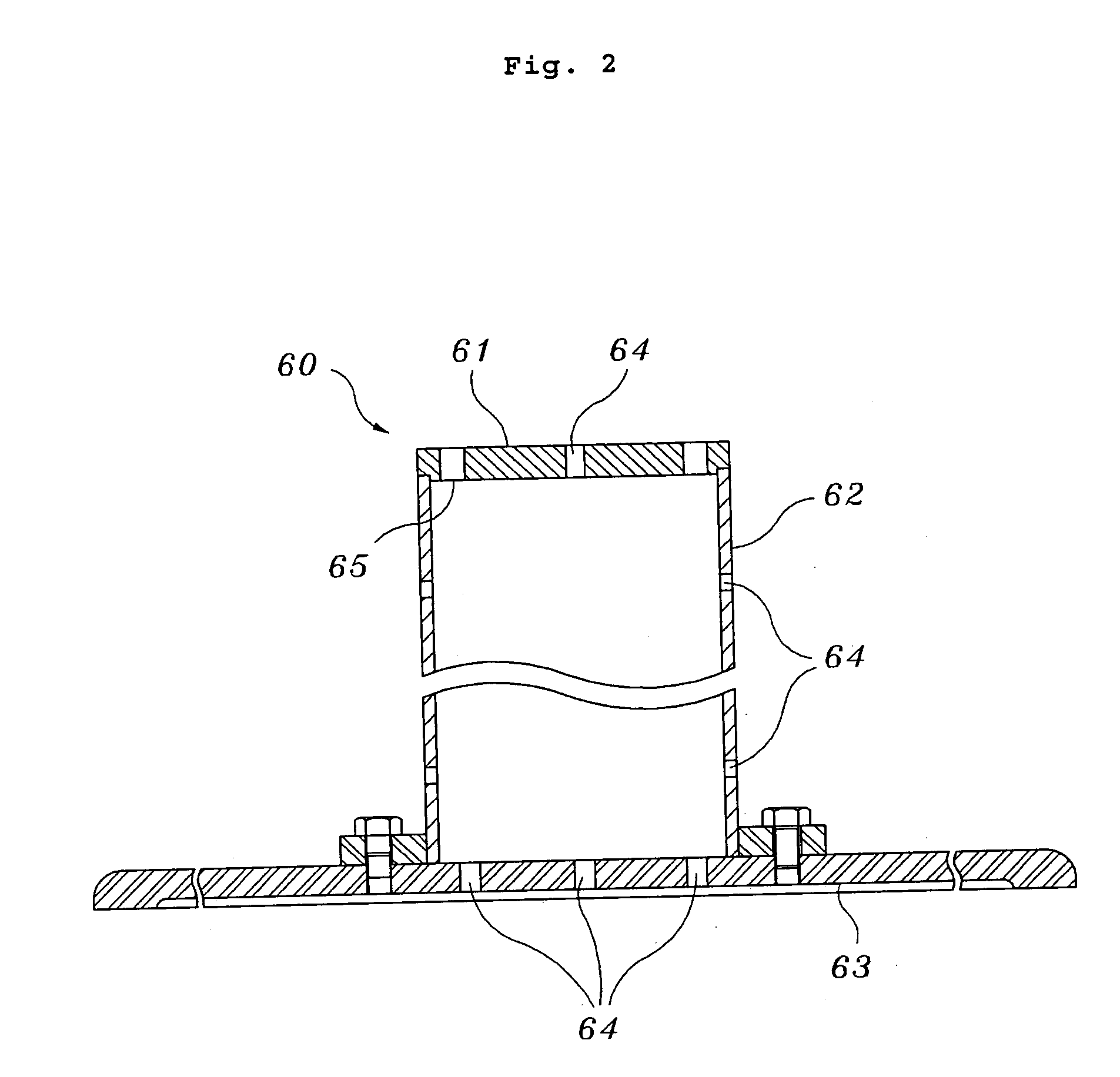
InactiveUS20050286675A1Liquid surface applicatorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates generally to an apparatus of assembling a capsule for neutron-irradiation experiments. The capsule may contain test specimens to develop nuclear fuel, and may comprise a capsule main body and protection tube that may be assembled and disassembled using separate joining means. The present invention provides a capsule assembling apparatus that may enable safe and easy assembly / disassembly of the capsule placed at a given depth in a working pool through remote working. The capsule assembling apparatus may comprise a base structure loading the capsule main body, a guiding pipe of a given length extending from the base structure to provide a pathway through which the capsule main body is loaded on the base structure, a damper fixing the capsule main body to the guiding pipe, and a coupler coupling the capsule main body with the protection tube.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
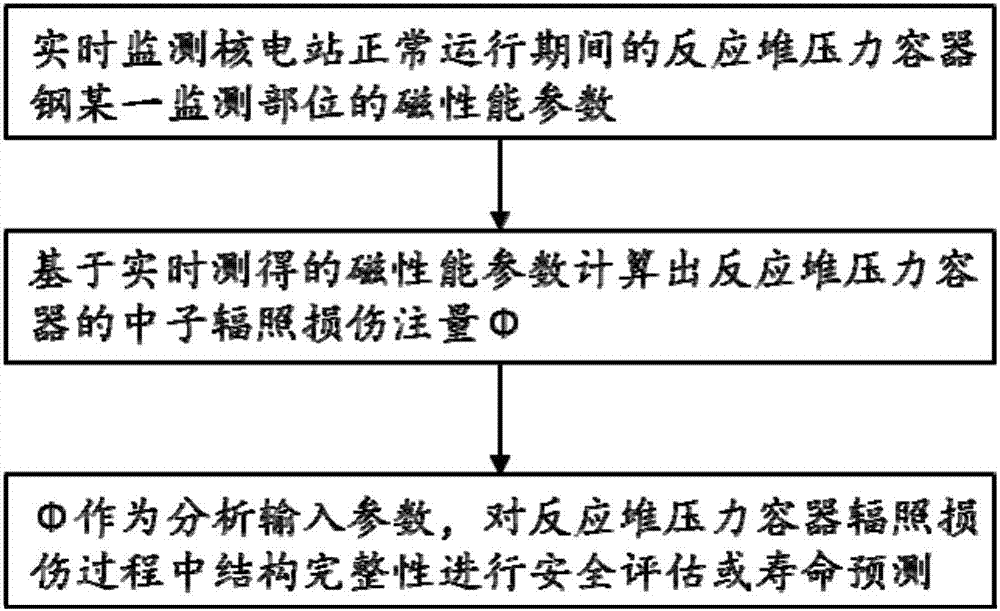
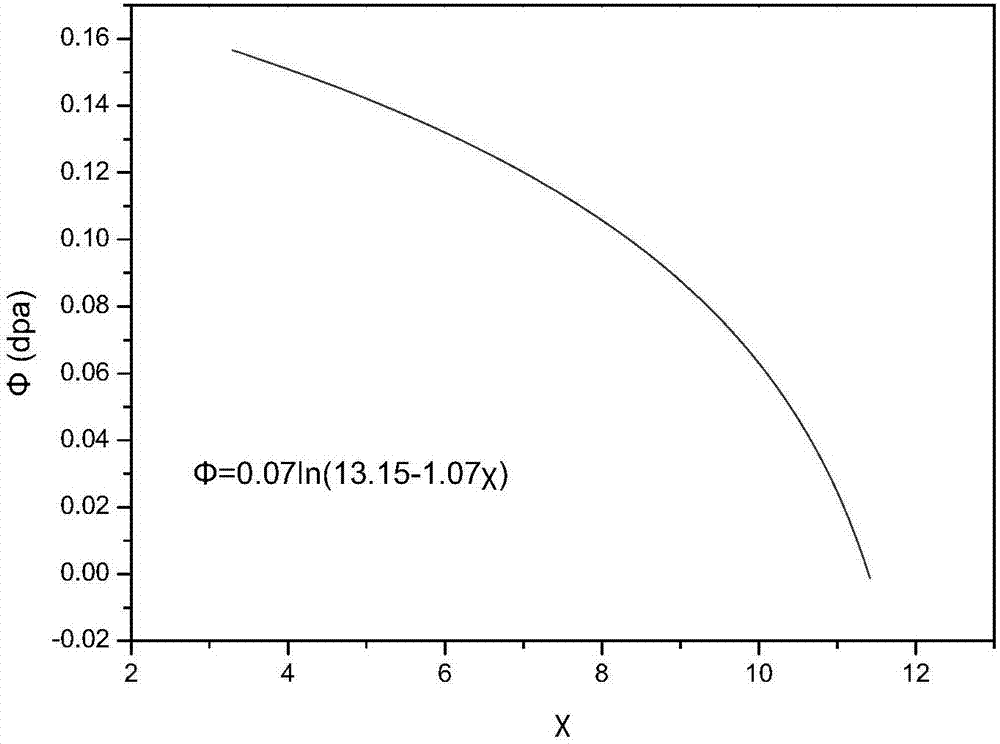
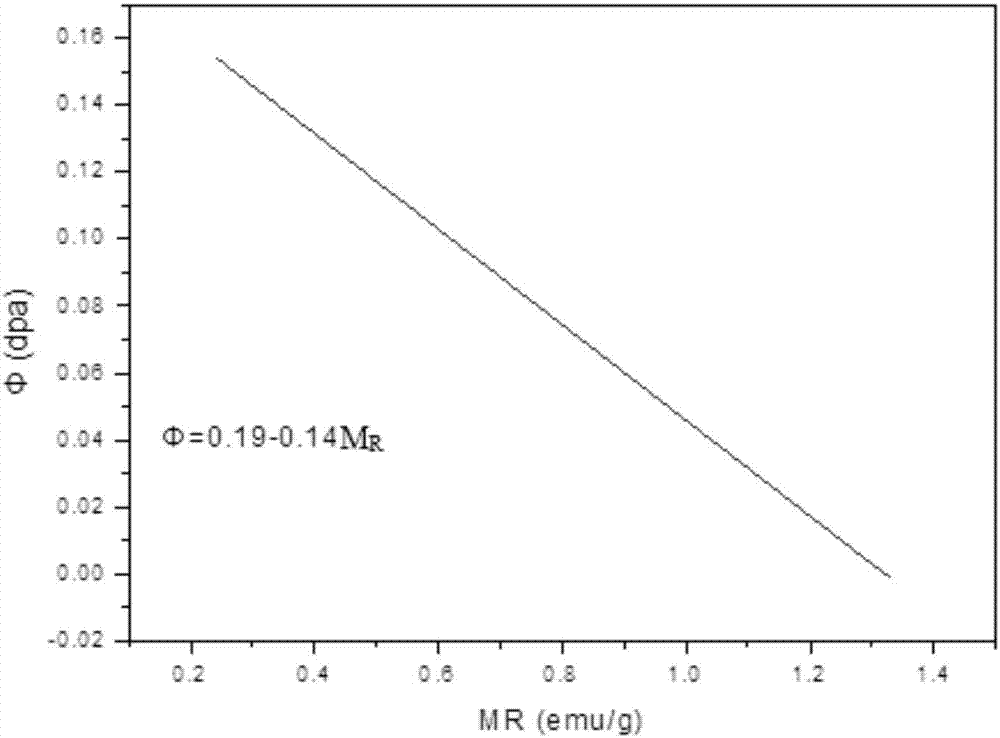
Method for monitoring neutron irradiation damage fluence of reactor pressure vessel in nuclear power plant
ActiveCN107358983AReal-time calculation of neutron radiation damage fluence dataMonitoring radiation damage fluenceNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringMagnetic susceptibilityNeutron irradiation
The invention discloses a method for monitoring neutron irradiation damage fluence of a reactor pressure vessel in a nuclear power plant. The method comprises the following steps of 1, monitoring a magnetic performance parameter of a certain monitored part of steel of the reactor pressure vessel during normal running of the nuclear power plant in real time, wherein the magnetic performance parameter is any one of magnetic susceptibility x, remanent magnetization MR and coercive force HC; calculating the neutron irradiation damage fluence phi of the reactor pressure vessel on the basis of the magnetic performance parameter obtained in real time. Compared with the prior art, through the adoption of the method for monitoring the neutron irradiation damage fluence of the reactor pressure vessel in the nuclear power plant, magnetic performance parameters of the steel of the reactor pressure vessel during normal running of the nuclear power plant can be tested in real time and continuously, neutron irradiation damage fluence data of the steel of the reactor pressure vessel is calculated and obtained in real time, and the neutron irradiation damage fluence of multiple positions of the reactor pressure vessel can be monitored simultaneously.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER DESIGN COMPANY +2
Fusion reactor tungsten divertor structure design based on high temperature fused salt cooling
InactiveCN105551530AImprove the economy of power generationEasy to handleNuclear energy generationThermonuclear fusion reactorNeutron irradiationAlloy
The present invention discloses a fusion reactor tungsten divertor structure design based on high temperature fused salt cooling. The fusion reactor tungsten divertor structure design comprises a tungsten surface pair plasma material and tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sinks. The tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sinks comprises a tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 1 and a tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 2. The tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 1 is a half pipe with a C-shaped cross section, and the tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 2 is a half pipe with a round angle and a semi-rectangle-shaped cross section. The tungsten surface pair plasma material is connected to the tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 1, and the tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 1 is connected to the tungsten and lanthanum alloy heat sink 2 to form a whole pipe. through the effective combination of tungsten and lanthanum alloy materials and a high-temperature fused salt cooling agent, the fusion reactor tungsten divertor structure design based on high temperature fused salt cooling is provided to adapt to a fusion reactor high-flux neutron irradiation environment, the heat bearing capacity can reach a 10-20MW / m2 steady-state thermal load, the structural material neutron activation is low, the , nuclear waste processing after component retirement is relatively easy, and the improvement of fusion reactor power generation economical efficiency is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of anti-irradiation low activation steel strengthened by nano-precipitation phase
ActiveCN109594009AInhibit burning lossInhibit growthFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsNeutron irradiationNuclear power
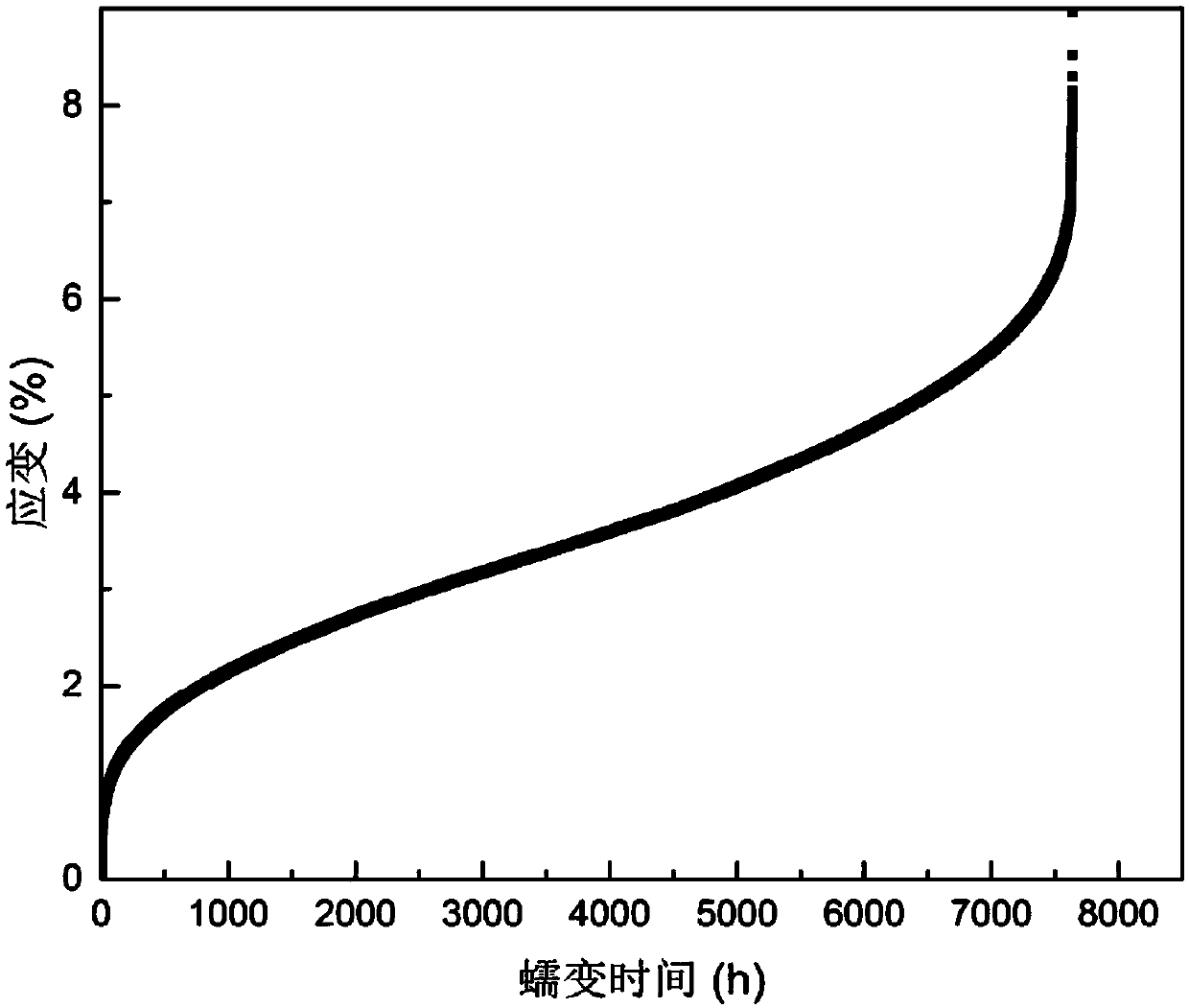
The invention relates to a preparation method of anti-irradiation low activation steel strengthened by a nano-precipitation phase, and belongs to the technical field of nuclear power steel. The methodcomprises the following steps of: firstly preparing a FeTaC intermediate alloy, and then preparing and obtaining the steel by a smelting process, a forging process, a rolling process and a heat treatment process sequentially. In the invention, a pure metal Ta is replaced by preparing the FeTaC intermediate alloy so as to avoid the burning loss of the steel caused by the high oxidation activity ofthe Ta metal during the smelting process; the burning loss of the Ta element is suppressed by the high temperature carbon deoxidation technology during the smelting process, and the Ta yield and reach more than 90%; the ultra-fine martensitic steel with excellent high-temperature creep performance and anti-neutron irradiation performance is obtained by optimizing the rolling process and promotingthe high-density uniform dispersion of the nano-precipitation phase to produce strengthening and refining grain action. The creep duration of the anti-irradiation low activation steel under the loading condition of 550 DEG C and 195MPa exceeds 5,000h.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Small high-yield deuterium-deuterium neutron generator
InactiveCN104244560AReduce exposure timeReduce volumeDirect voltage acceleratorsNeutron irradiationDeuterium ions
The invention discloses a small high-yield and deuterium-deuterium neutron generator. Modular distributed high-frequency ion sources are adopted and evenly distributed on the outer surface of a ceramic cylinder with the spherical end, and deuterium ion beams distributed evenly are output, wherein the flow intensity of the deuterium ion beams is larger than 1 A, and the single atom proportion is larger than 80%; the deuterium ion beams are accelerated in a cylindrical accelerating electric field with the spherical end and bombard a cylindrical metal or ceramic self-forming target to cause a deuterium / deuterium reaction and then generate neutrons of 2.45 MeV, and the self-forming target is located at the high-potential end and provided with the spherical end. The number of the modular distributed high-frequency ion sources and the area of the self-forming target are not limited, the yield of the neutrons of the deuterium / deuterium reaction is larger than 1011 n / s, and no radioactive pollutants are discharged. The neutron generator is suitable for commercialized application such as the fields of boron neutron capture treatment, neutron radiography, on-line material component neutron detection, neutron irradiation modification and californium neutron source substitute products.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Method for preparing boron, lead and aluminum composite board preventing X rays, gamma rays and neutron irradiation
The invention relates to a method for preparing a boron, lead and aluminum composite board preventing X rays, gamma rays and neutron irradiation to overcome the defect that a nuclear radiation and ray shielding material is single in shielding property. According to the method, aluminum powder, boron carbide powder and lead powder serve as raw materials, ball grinding, powder processing, material mixing, microwave heating, vacuum hot pressing blank stamping, and heating rolling forming are carried out, and then the boron, lead and aluminum composite board is prepared. The preparing method is advanced in technology, data are accurate and detailed, the prepared boron, lead and aluminum composite board has a good ray and neutron irradiation shielding effect, the X-ray shielding rate is larger than or equal to 95 percent, the gamma-ray shielding rate is larger than or equal to 40 percent, the neutron absorptivity is larger than or equal to 90 percent, boron carbide is evenly distributed, particles and a base body are combined tightly, high mechanical strength is achieved, the surface microhardness reaches 186.3 HV, the bending angle is larger than or equal to 15 degrees, the tensile strength is 305 MPa, the elongation after fracture is larger than or equal to 6 percent, the mechanical property and the shielding property of the boron, lead and aluminum composite board are improved, and the boron, lead and aluminum composite board can be used for single irradiation protection and can also be used for various types of radiation protection.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
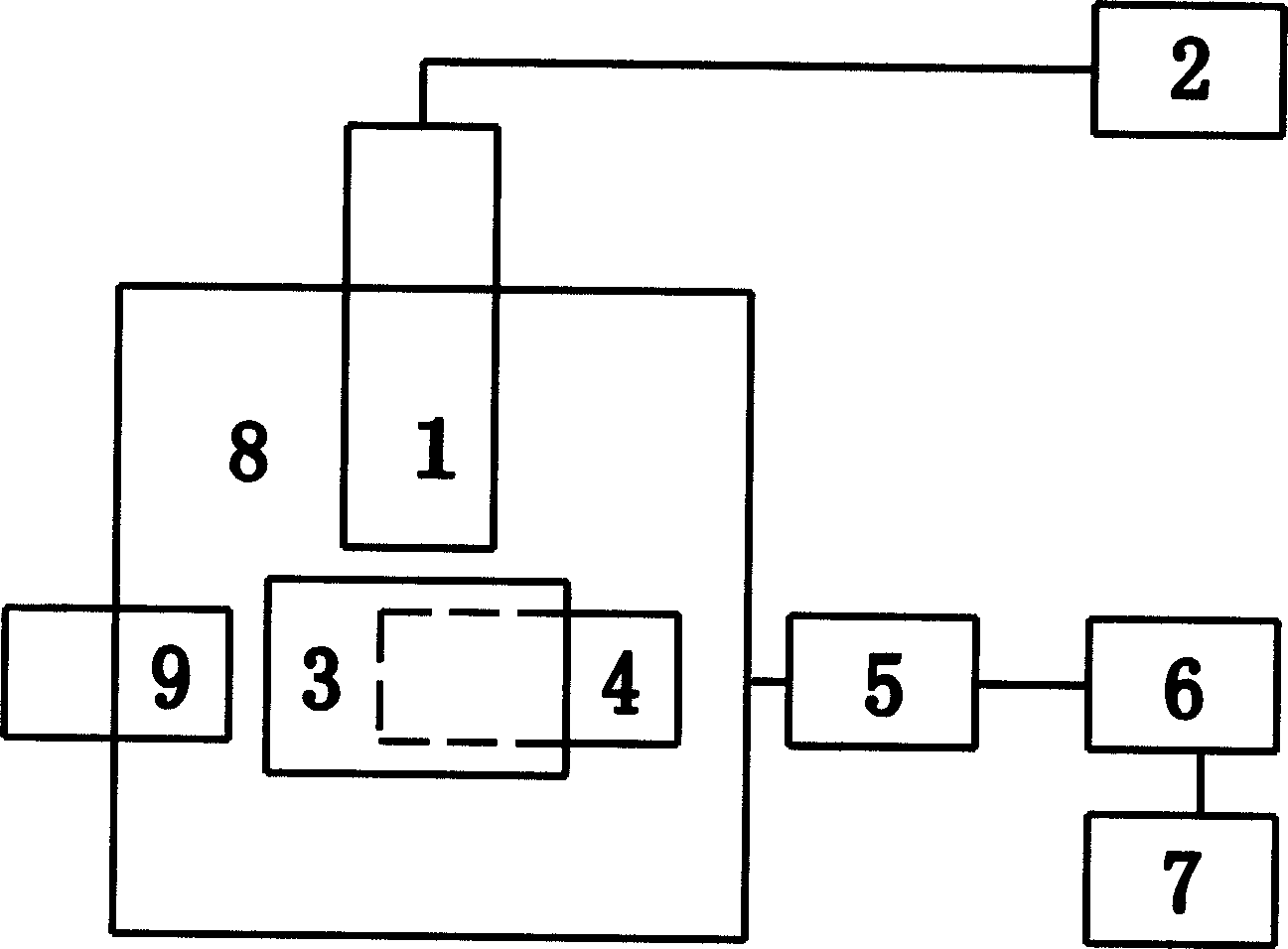
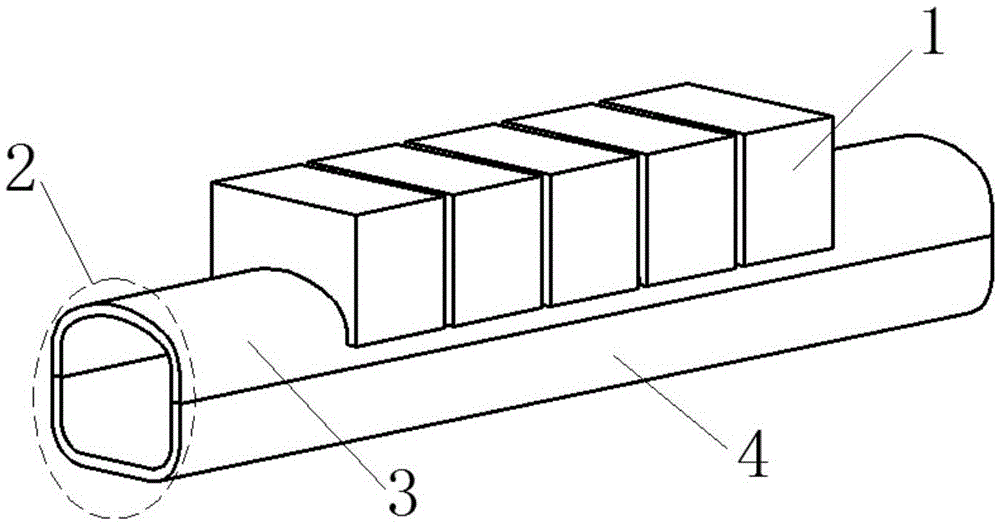
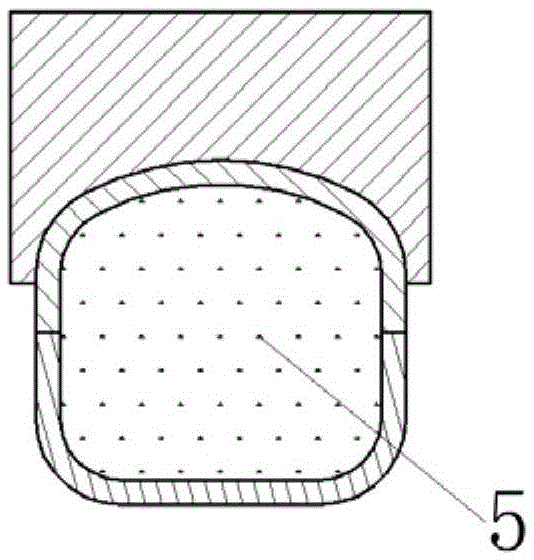
Metallic fast reactor fuel element irradiation test device
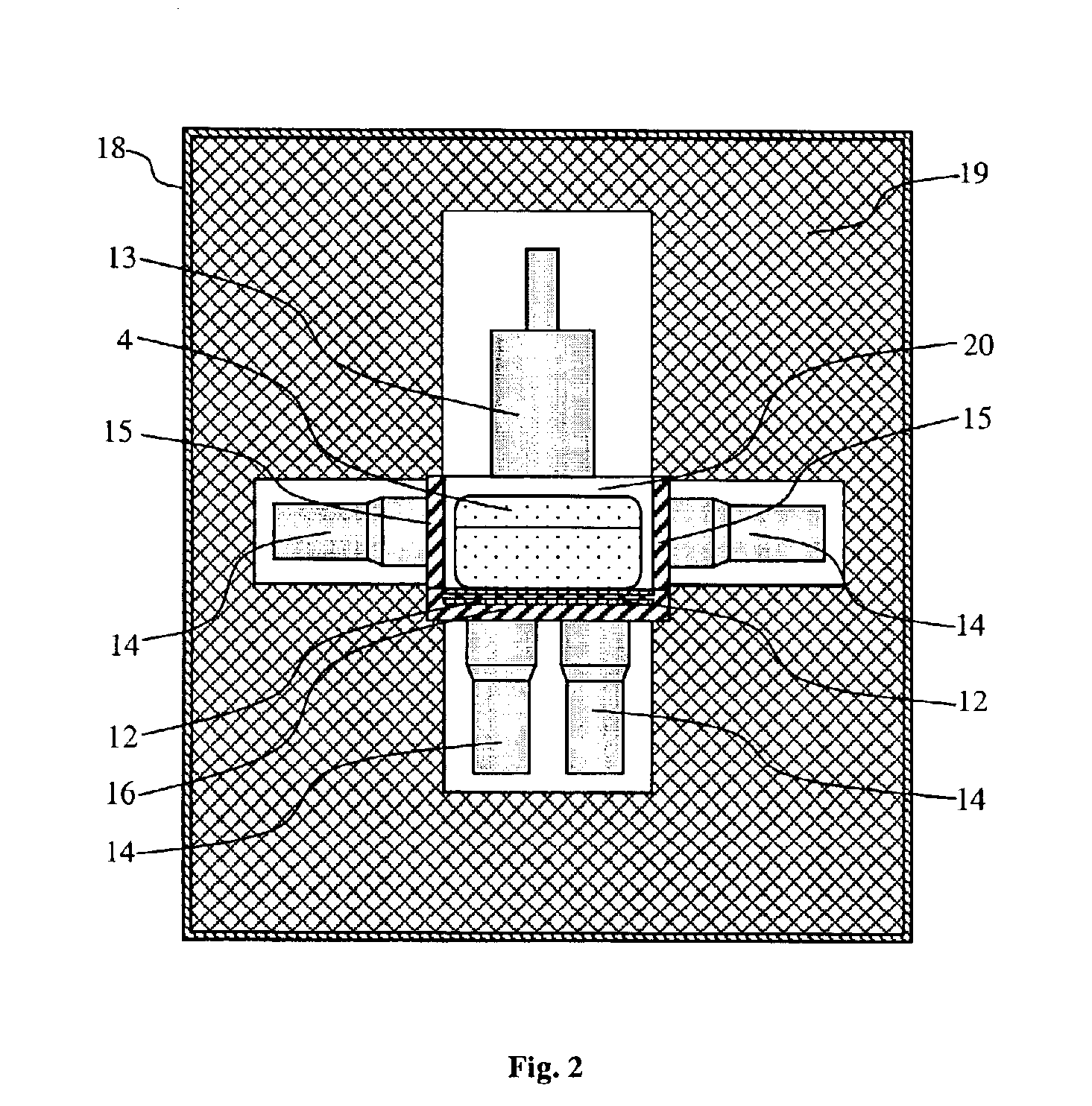
ActiveCN110600150ARegulation and control of irradiation temperatureReduce the impactNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNeutron irradiationNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a metallic fast reactor fuel element irradiation test device. The device can be used for carrying out neutron irradiation test on metallic fast reactor fuel in a thermal spectrum research reactor and has the functions of neutron spectrum hardening, metallic fuel irradiation temperature control, fuel element heat release power measurement and the like. The device comprises aprotection tube, a cadmium tube, an irradiation test piece, a related gas pipeline, a thermocouple and the like. According to the device, a cadmium metal layer is adopted to absorb thermal neutrons to reduce the thermal neutron flux rate in the device, so that the neutron energy spectrum of a test fuel element is close to that of a fast neutron reactor; and the temperature difference is established between air gaps and a liquid metal layer outside a fuel rod, and the gas components in the air gaps in each irradiation part are independently adjusted, so that the temperature of fuel core bodiesin different irradiation parts are controlled within a required temperature range.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com